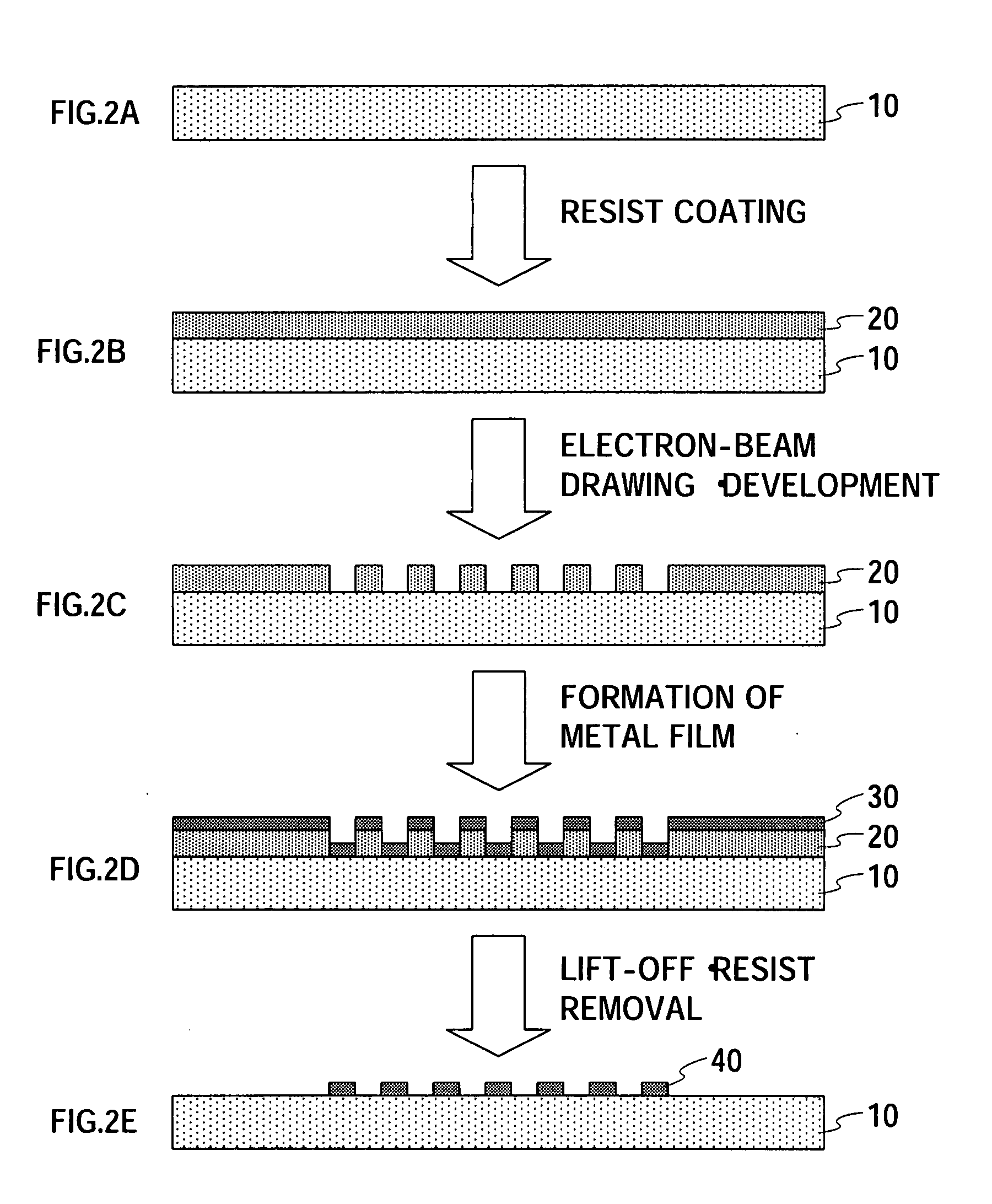
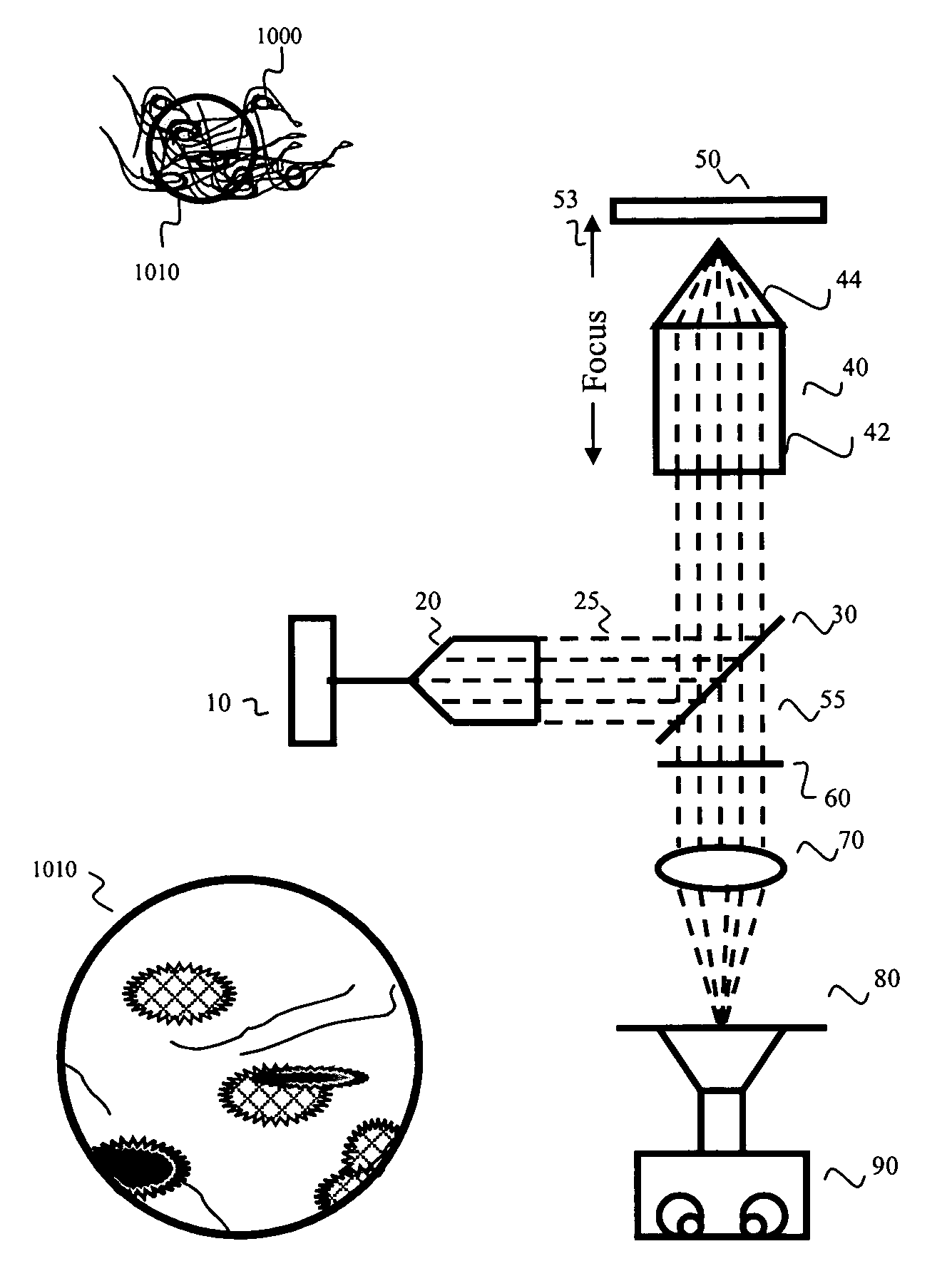
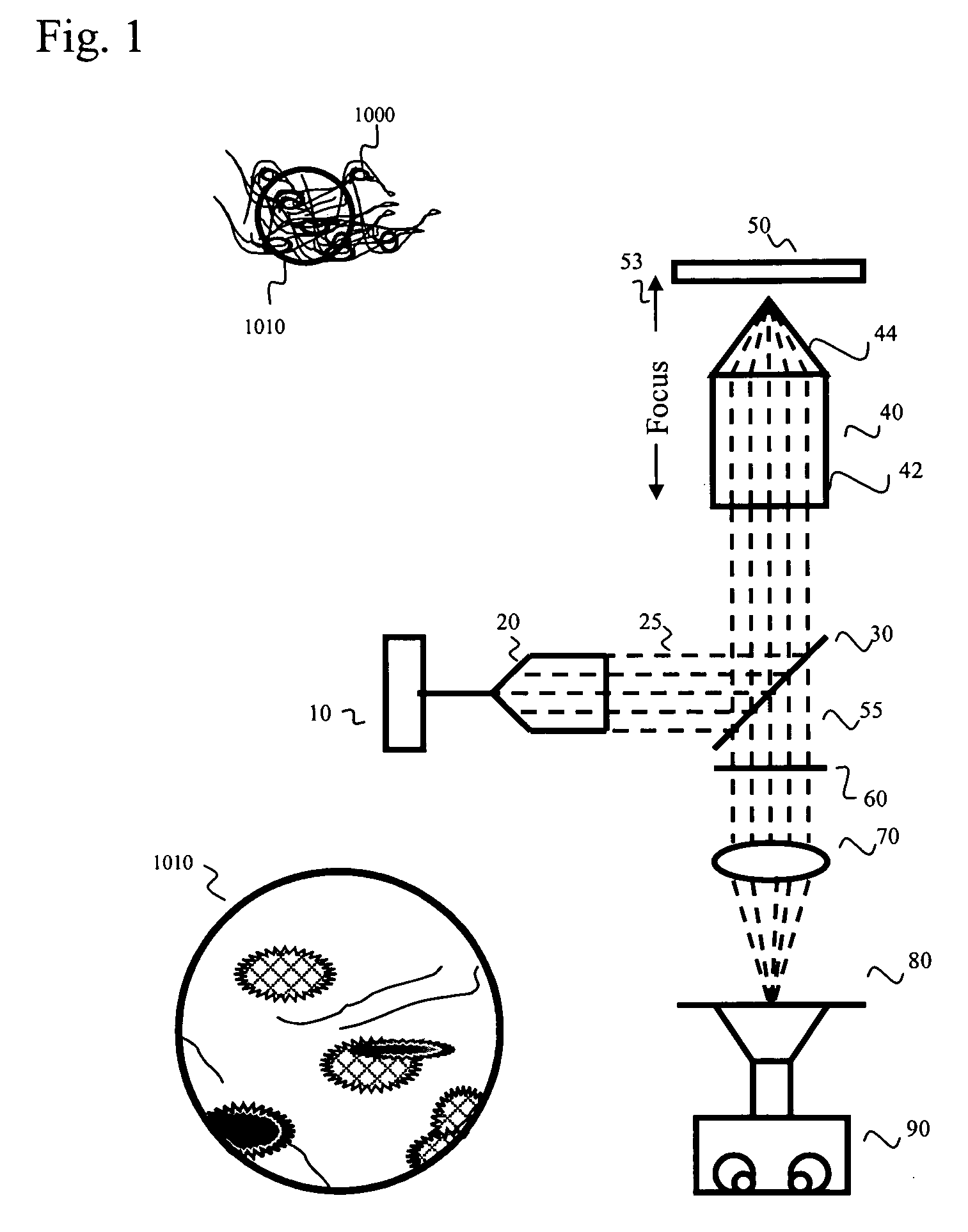
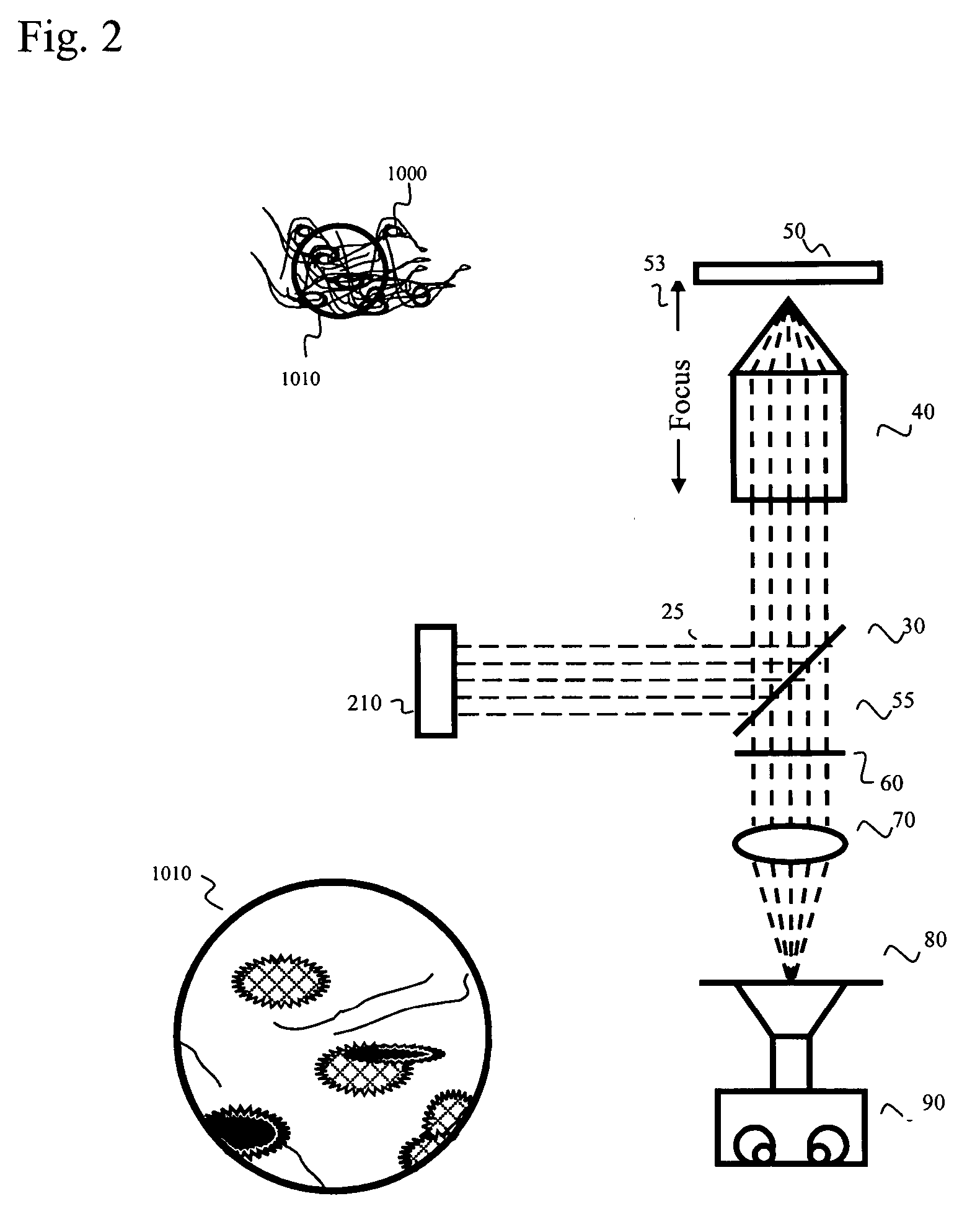
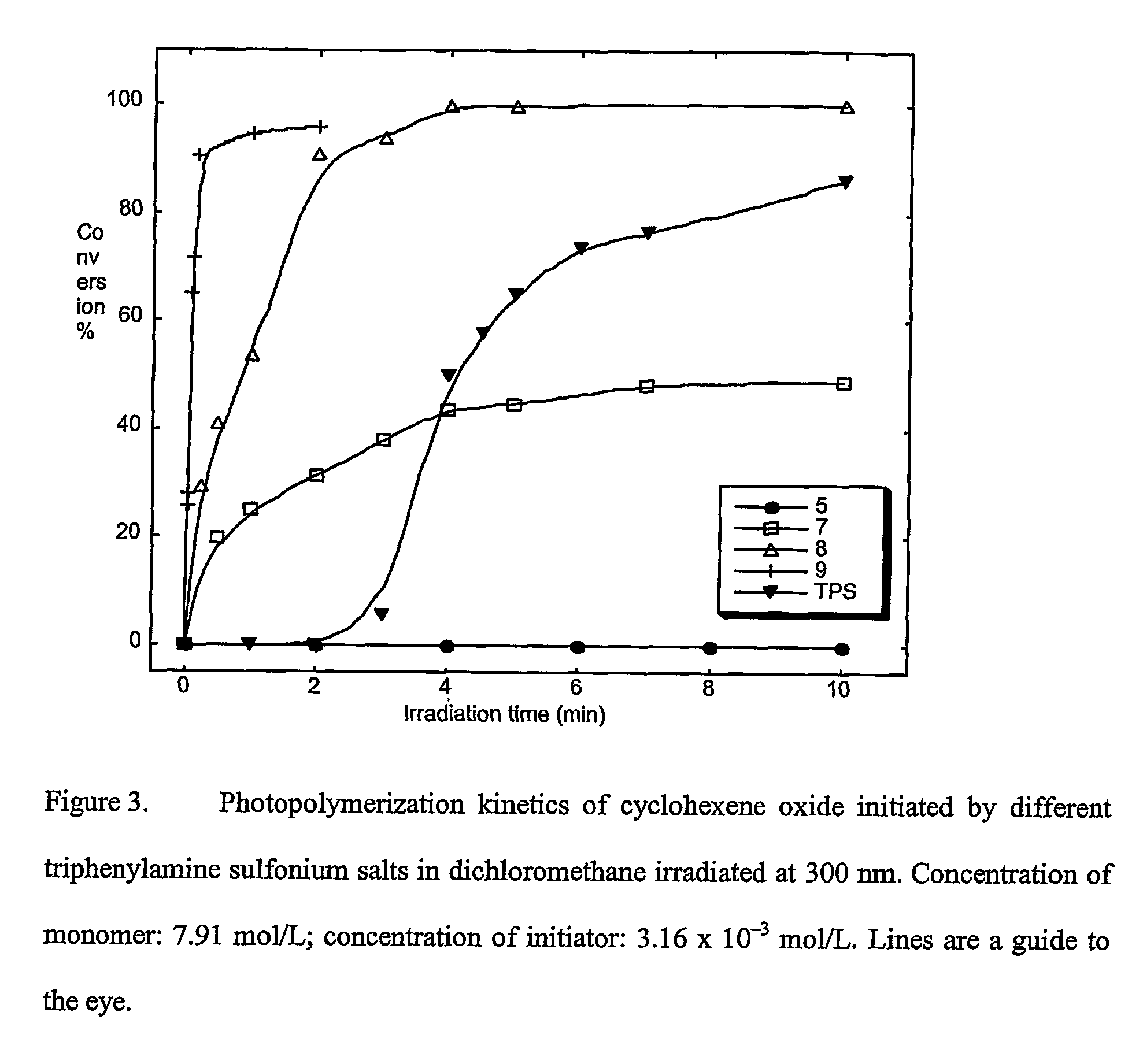
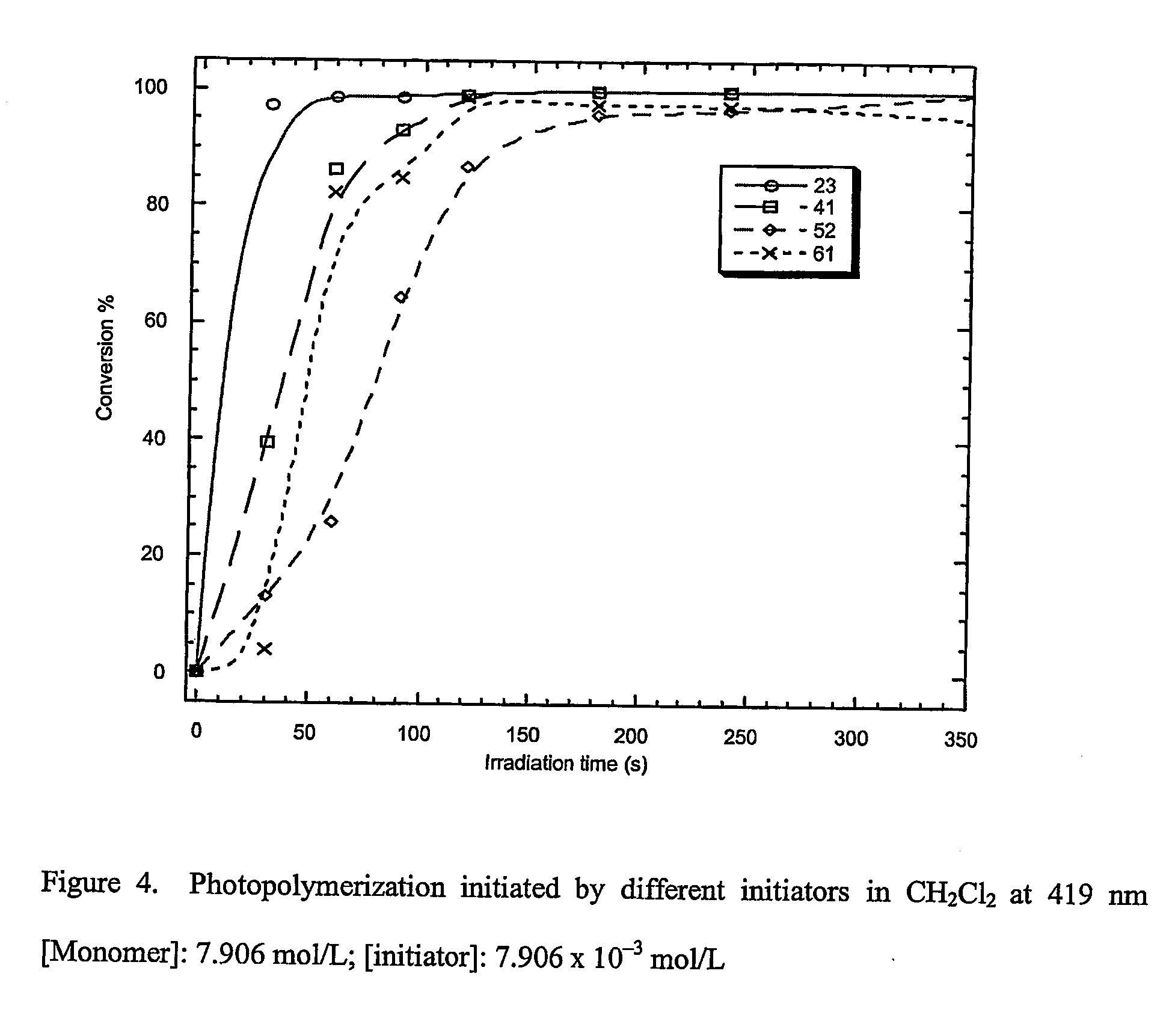
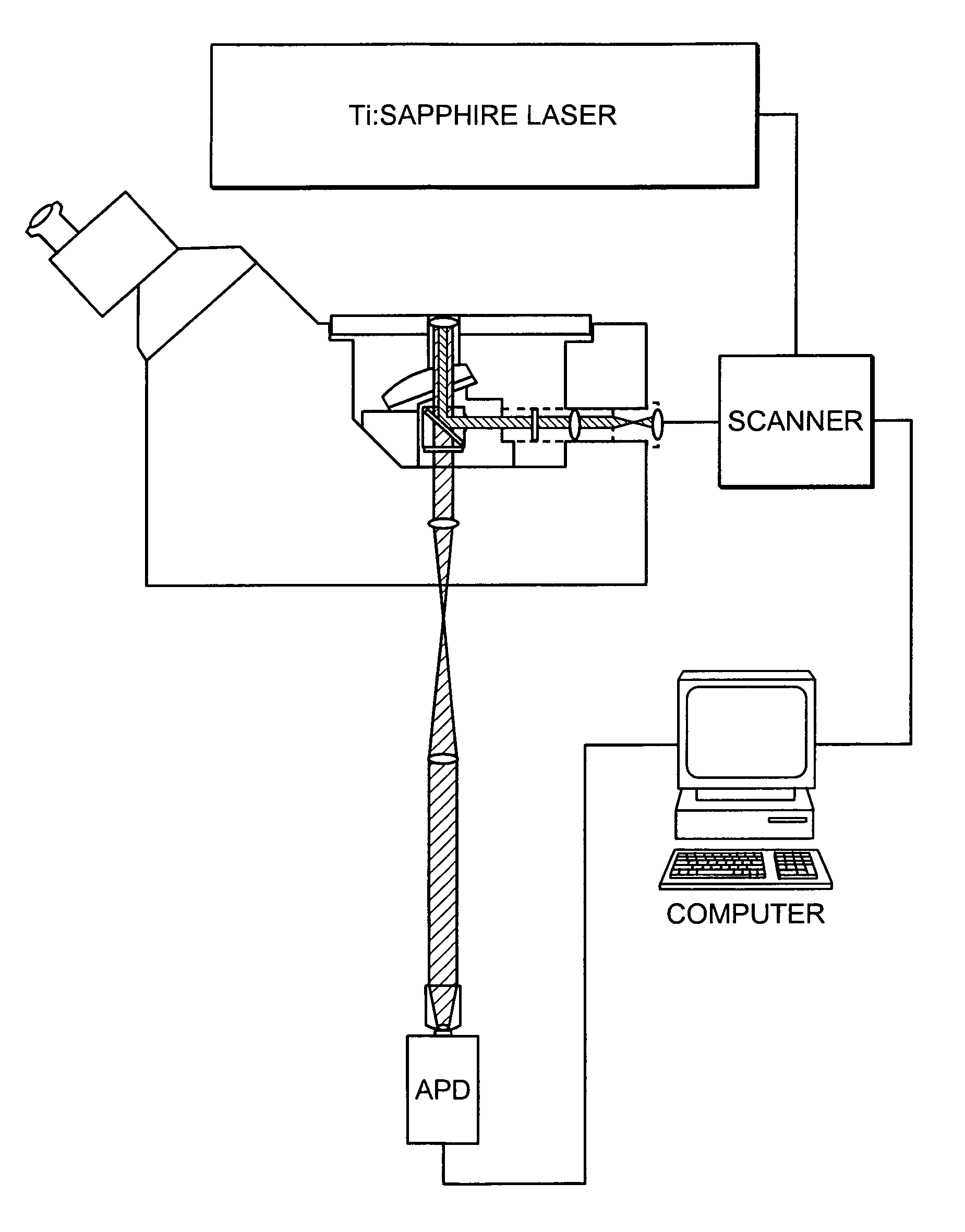
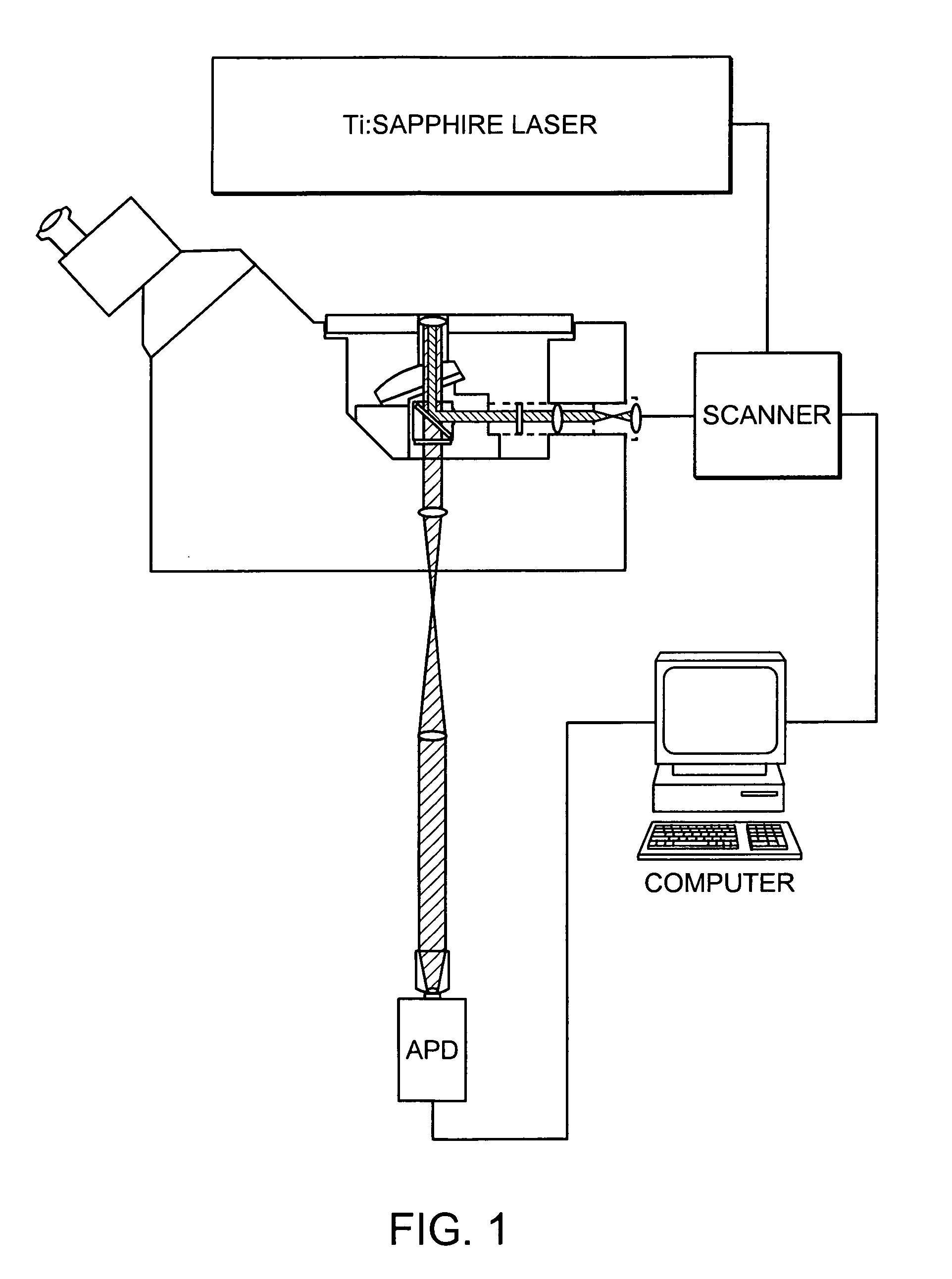
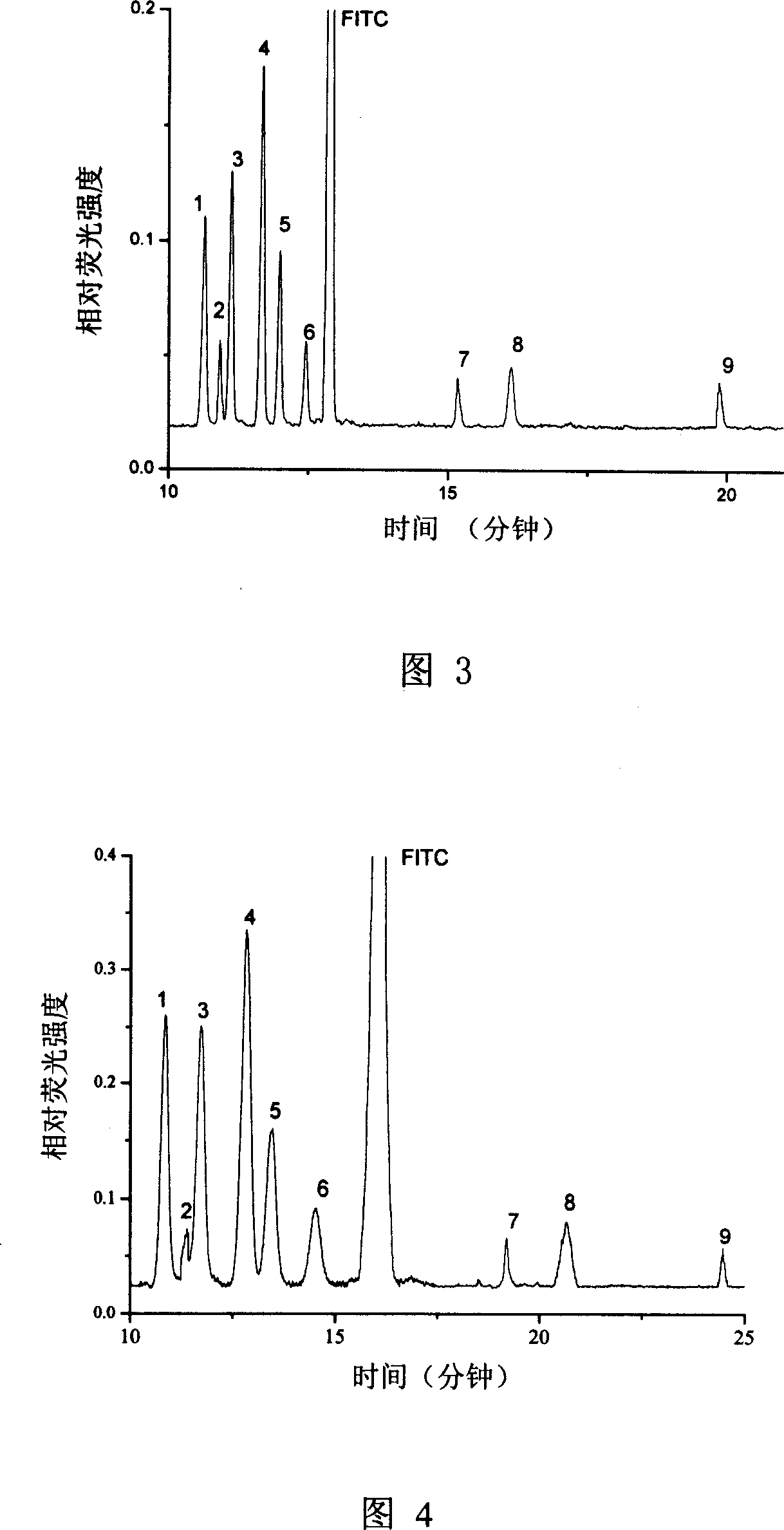
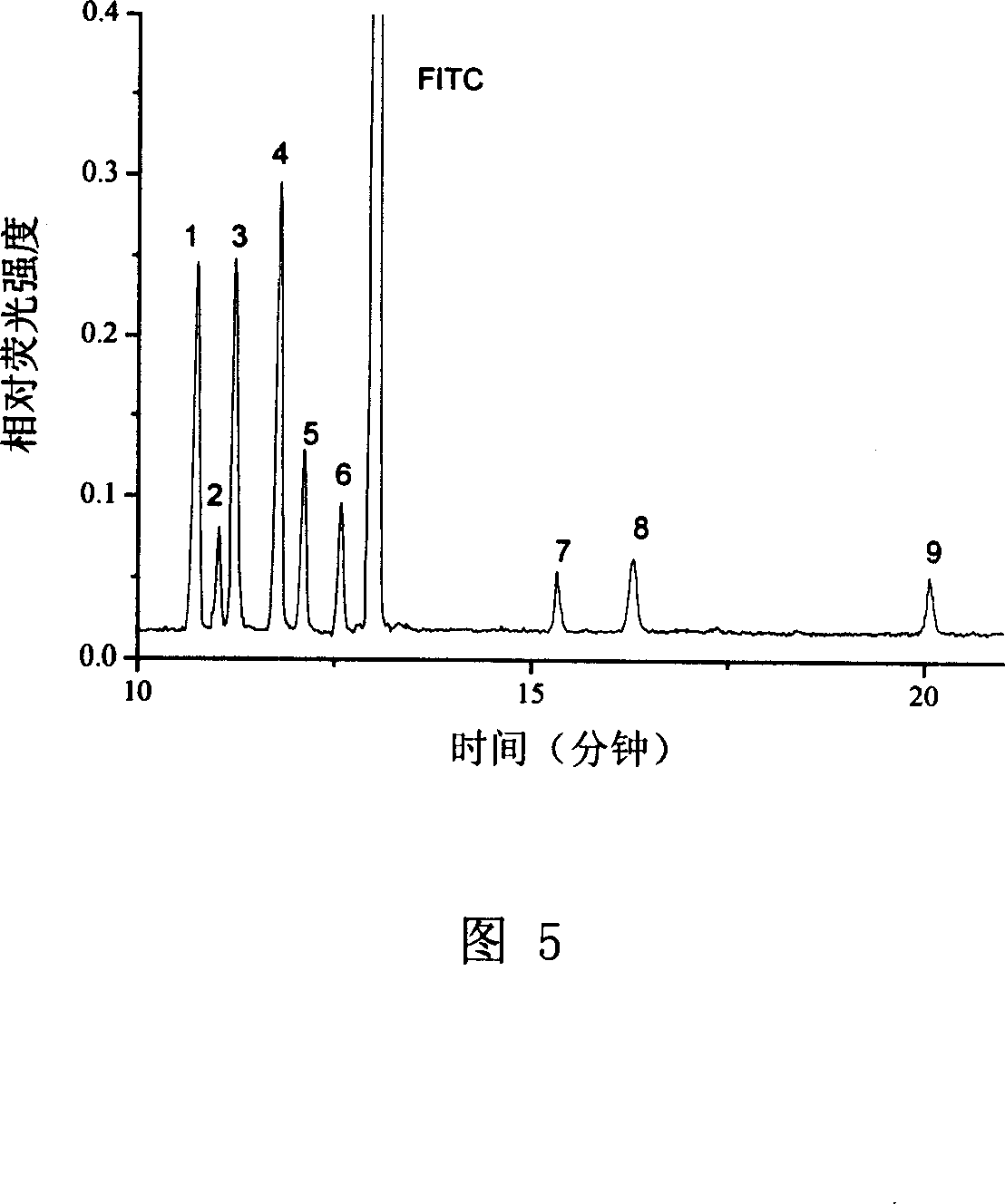
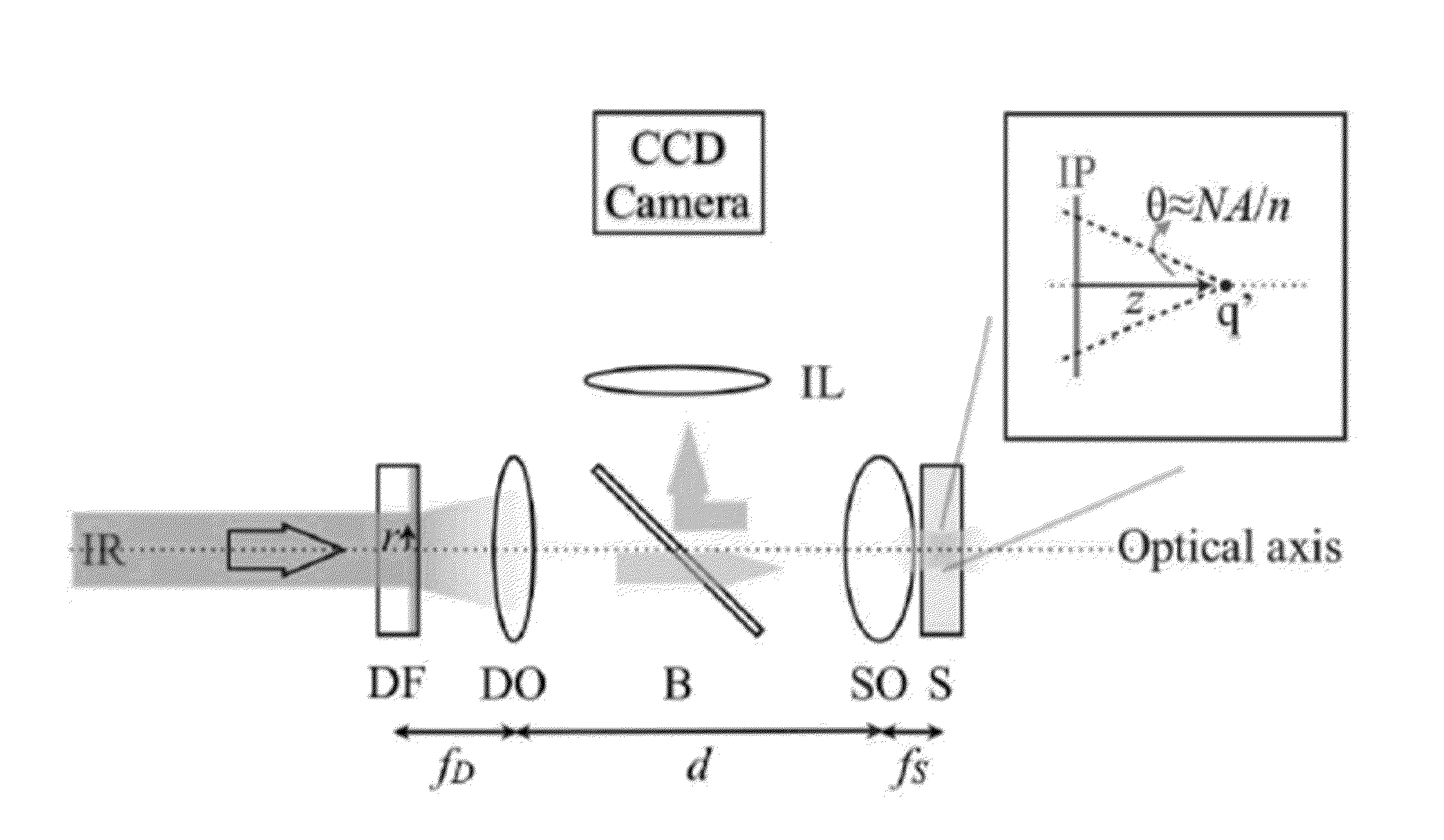
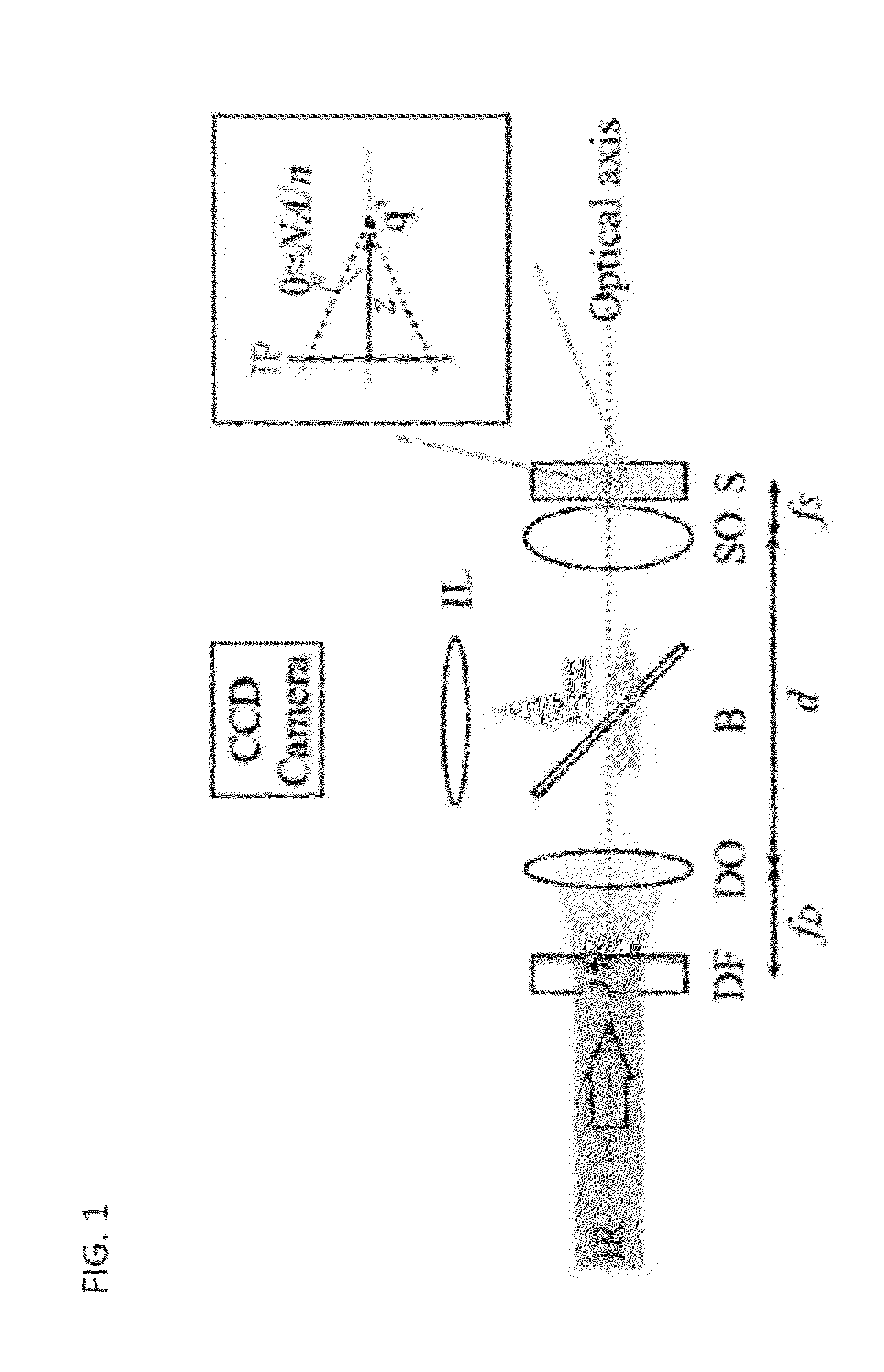
Patents
Literature
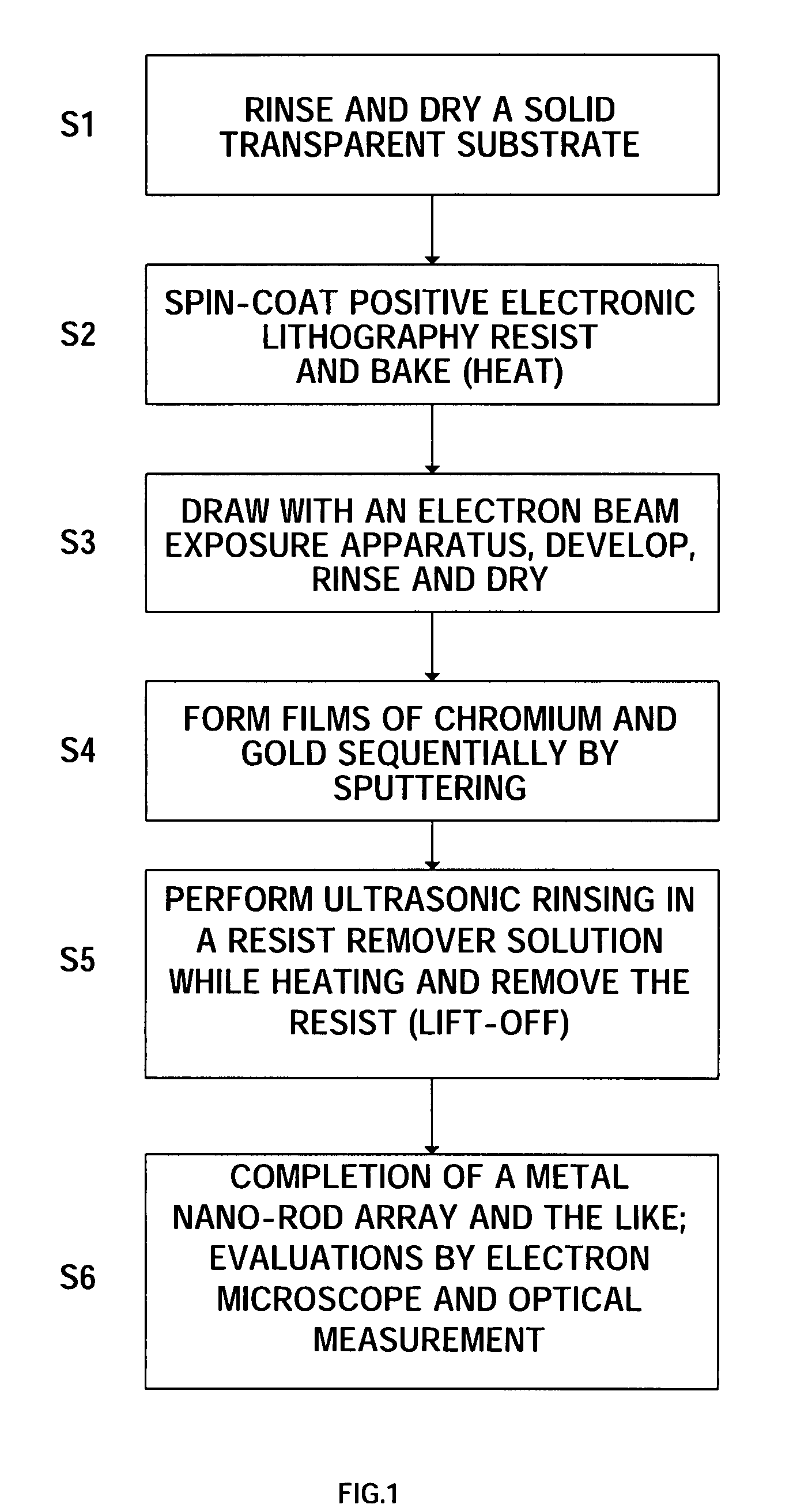
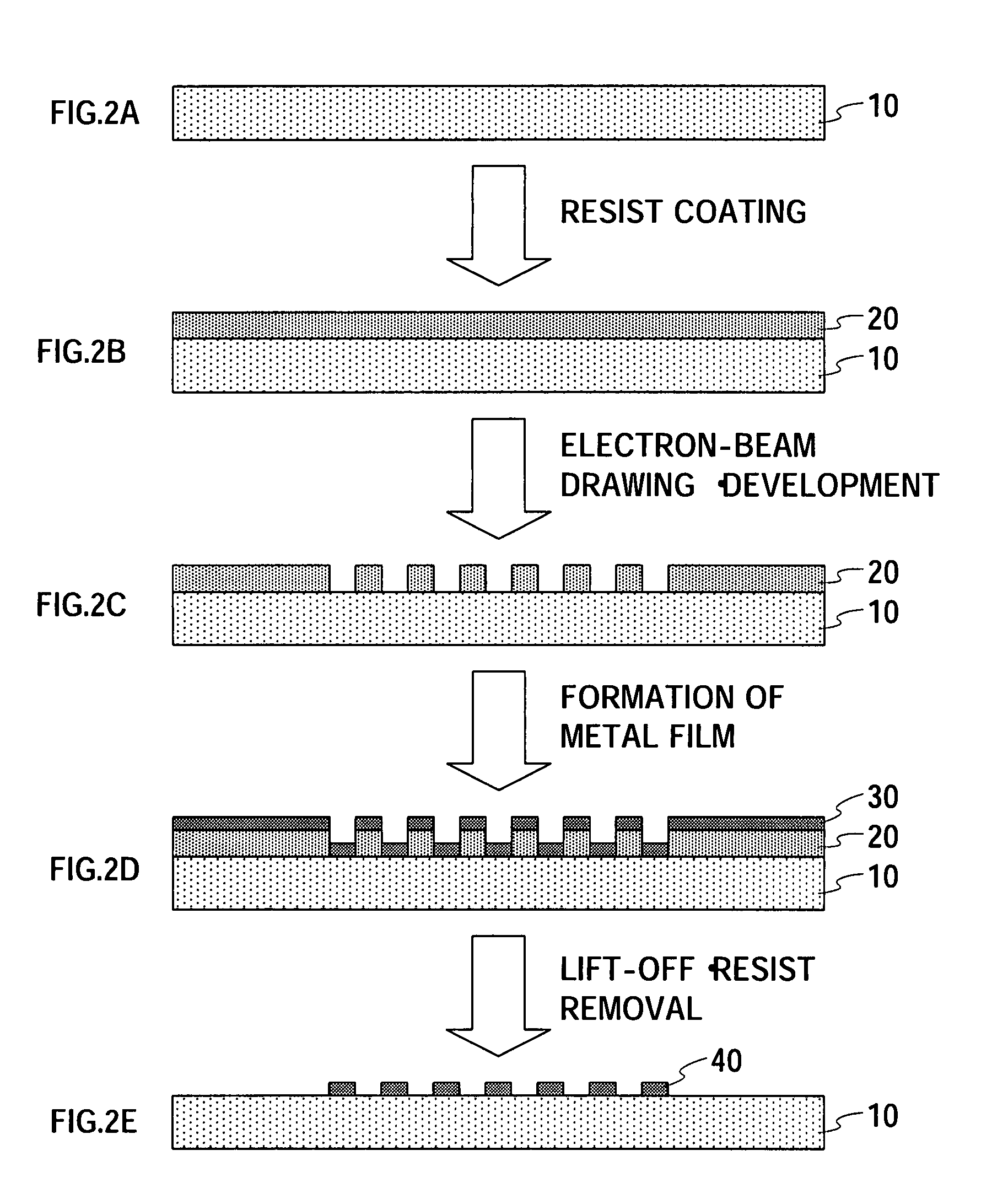
37 results about "Multi photon excitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Two-photon or higher-order absorbing optical materials and methods of use
InactiveUS6267913B1Wide bandwidthOrganic chemistryRadiation applicationsChemical compoundElectron donor
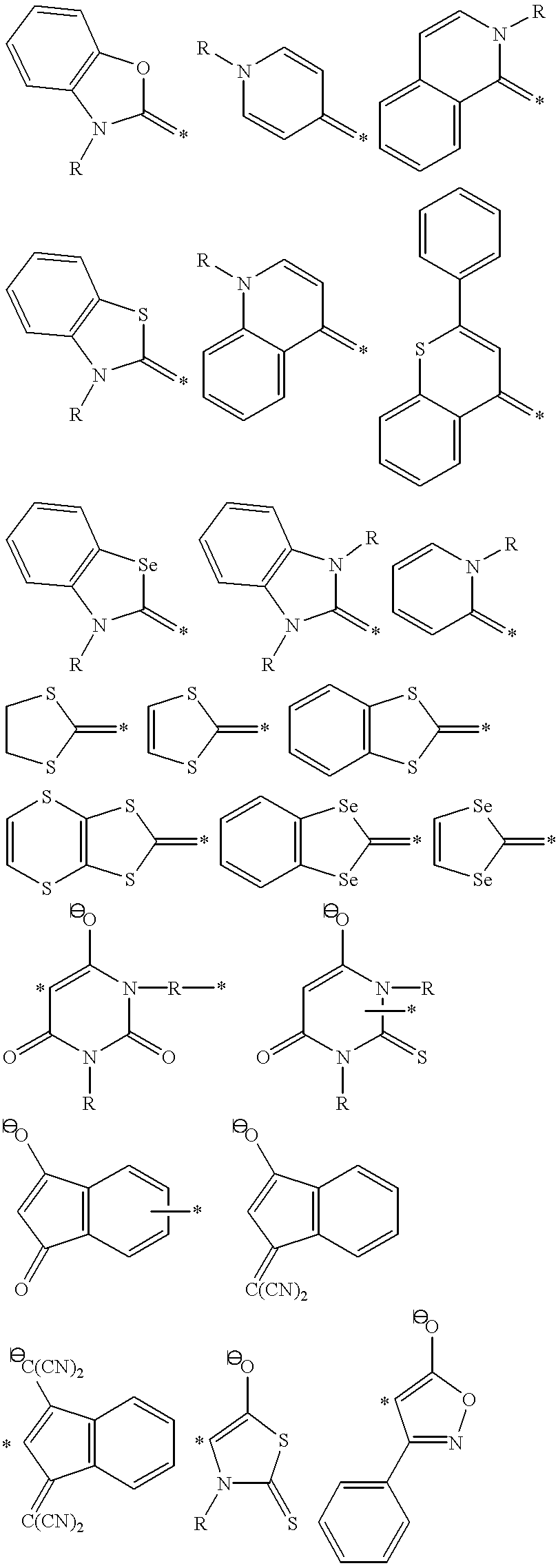
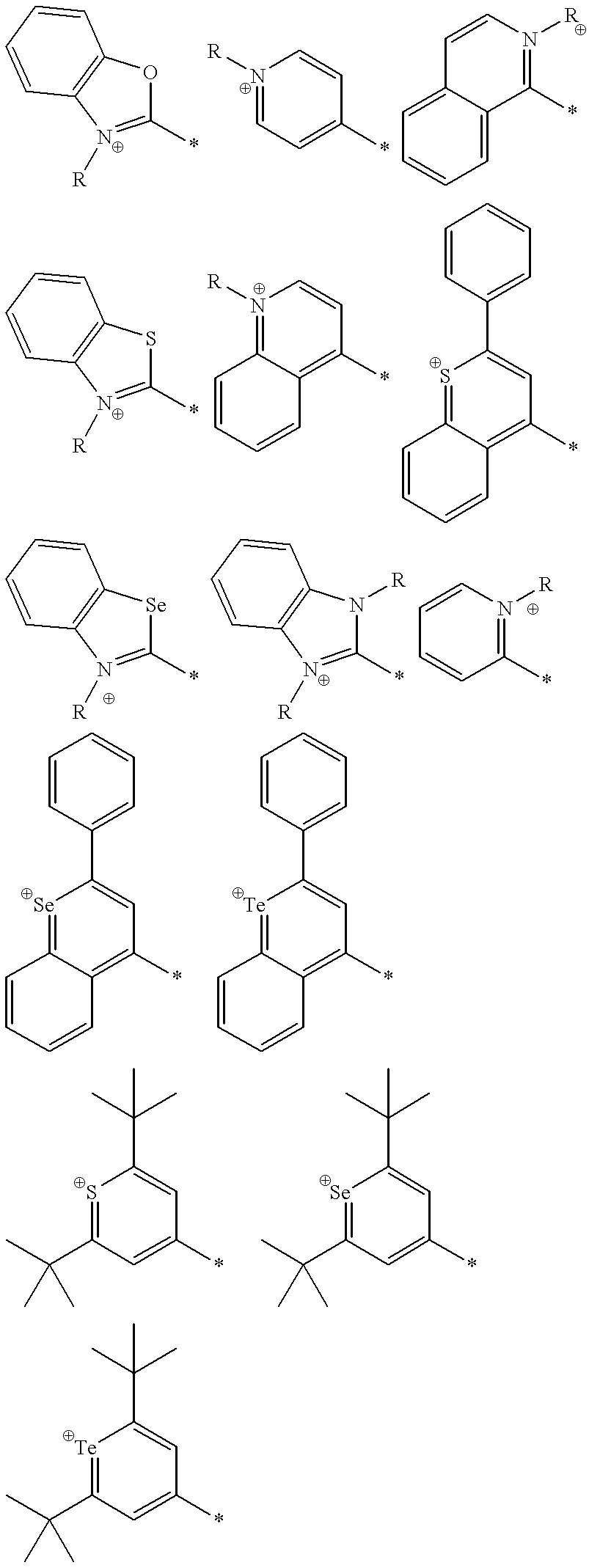
Compositions capable of simultaneous two-photon absorption and higher order absorptivities are disclosed. Many of these compositions are compounds satisfying the formulae D-Π-D, A-Π-A, D-A-D and A-D-A, wherein D is an electron donor group, A is an electron acceptor group and Π comprises a bridge of pi-conjugated bonds connecting the electron donor groups and electron acceptor groups. In A-D-A and D-A-D compounds, the pi bridge is substituted with electron donor groups and electron acceptor groups, respectively. Also disclosed are methods that generate an electronically excited state of a compound, including those satisfying one of these formulae. The electronically excited state is achieved in a method that includes irradiating the compound with light. Then, the compound is converted to a multi-photon electronically excited state upon simultaneous absorption of at least two photons of light. The sum of the energies of all of the absorbed photons is greater than or equal to the transition energy from a ground state of the compound to the multi-photon excited state. The energy of each absorbed photon is less than the transition energy between the ground state and the lowest single-photon excited state of the compound is less than the transition energy between the multi-photon excited state and the ground state.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and system for wide-field multi-photon microscopy having a confocal excitation plane
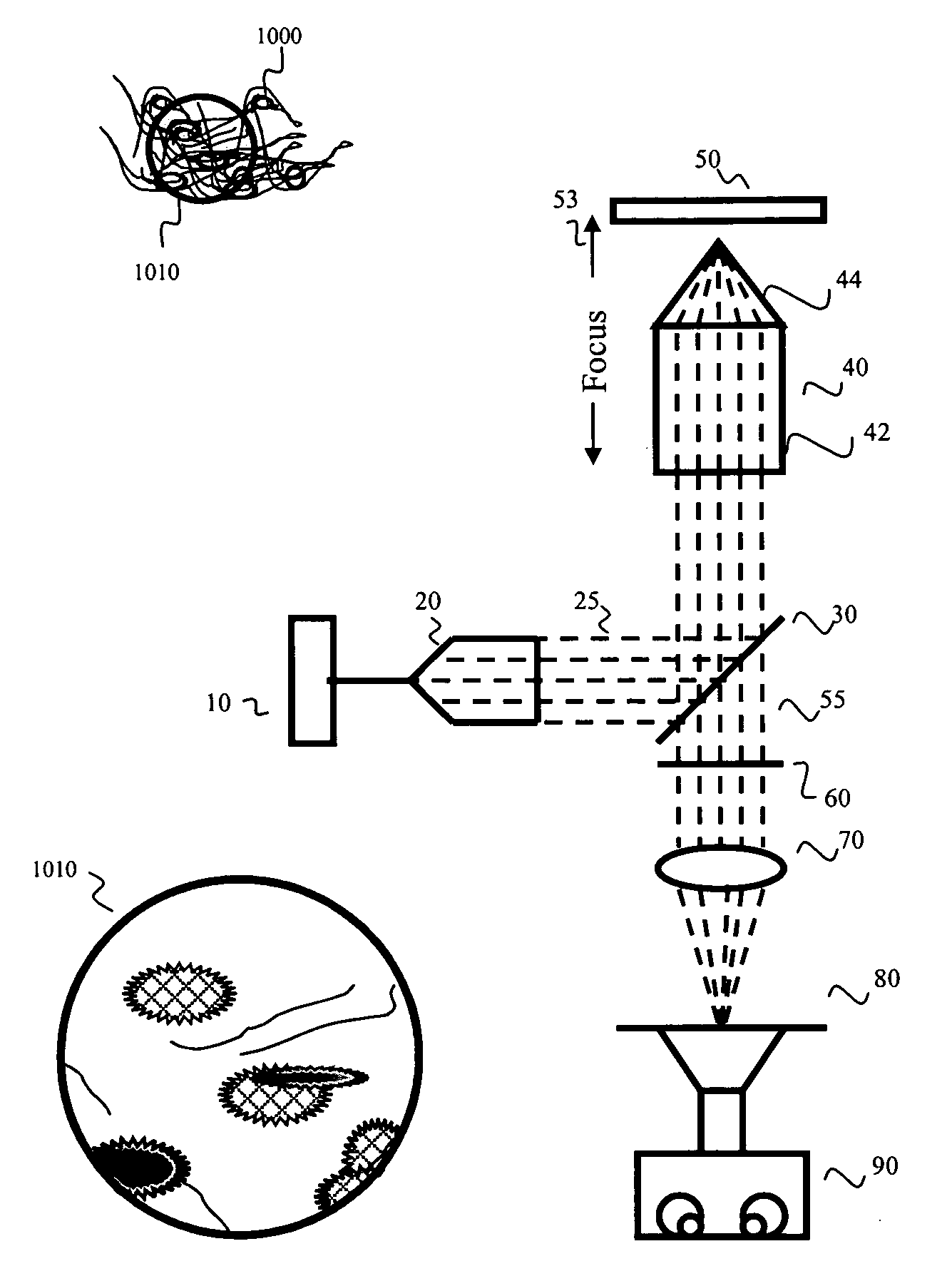
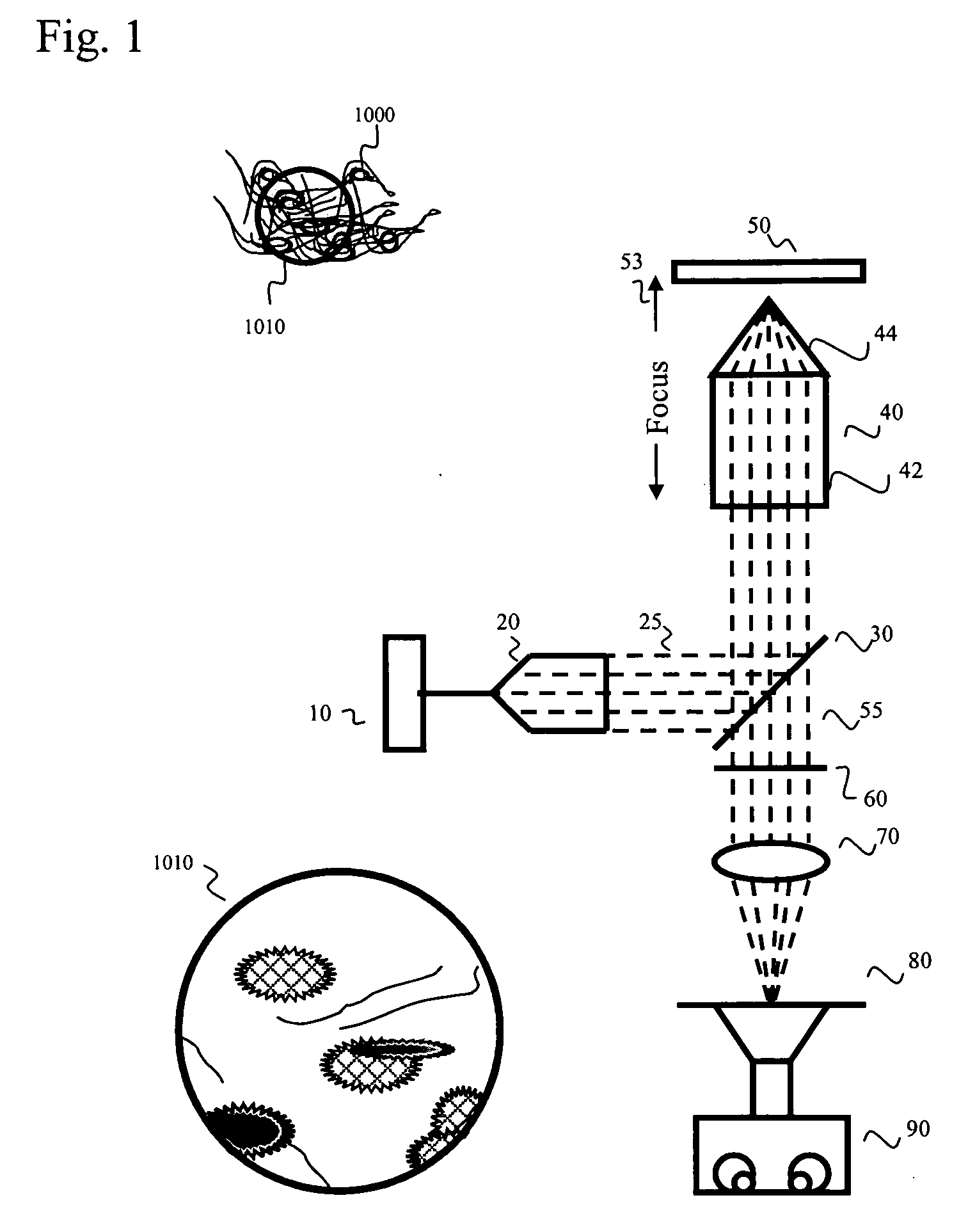
InactiveUS20080116392A1Shorten Image Acquisition TimeScanning of the excitation light source over the specimen can be reduced or eliminatedPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansWide fieldLight beam
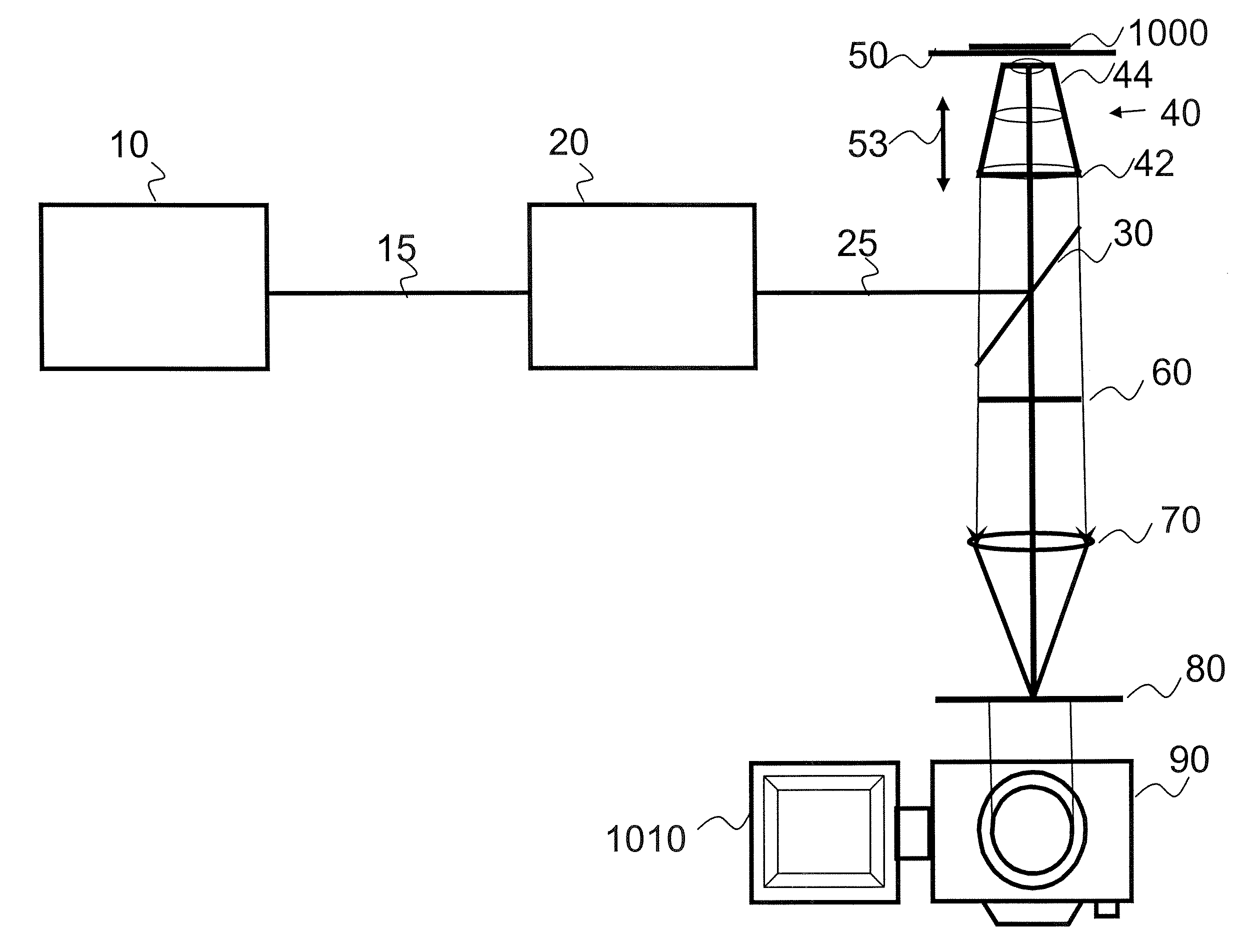
A wide field microscope includes a stage configured to hold a specimen having a fluorescent material therein, and a multi-photon excitation light source configured to produce excitation light having a single photon energy less than an absorption energy required for single photon excitation of said fluorescent material. A beam expansion unit is optically coupled to the light source and configured to expand the excitation light with reduced pulse spreading characteristics, and an infinity corrected objective optically coupled to the expansion unit and configured to focus the excitation light onto the specimen such that multi-photon excitation of the fluorescent material simultaneously occurs over a predetermined area of the specimen. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from said predetermined area of the specimen onto at least two pixels of an image detector simultaneously.
Owner:CELLOPTIC
In vivo flow cytometry based on cellular autofluorescence
InactiveUS20110044910A1Avoid damageOptical radiation measurementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFluenceFluorophore
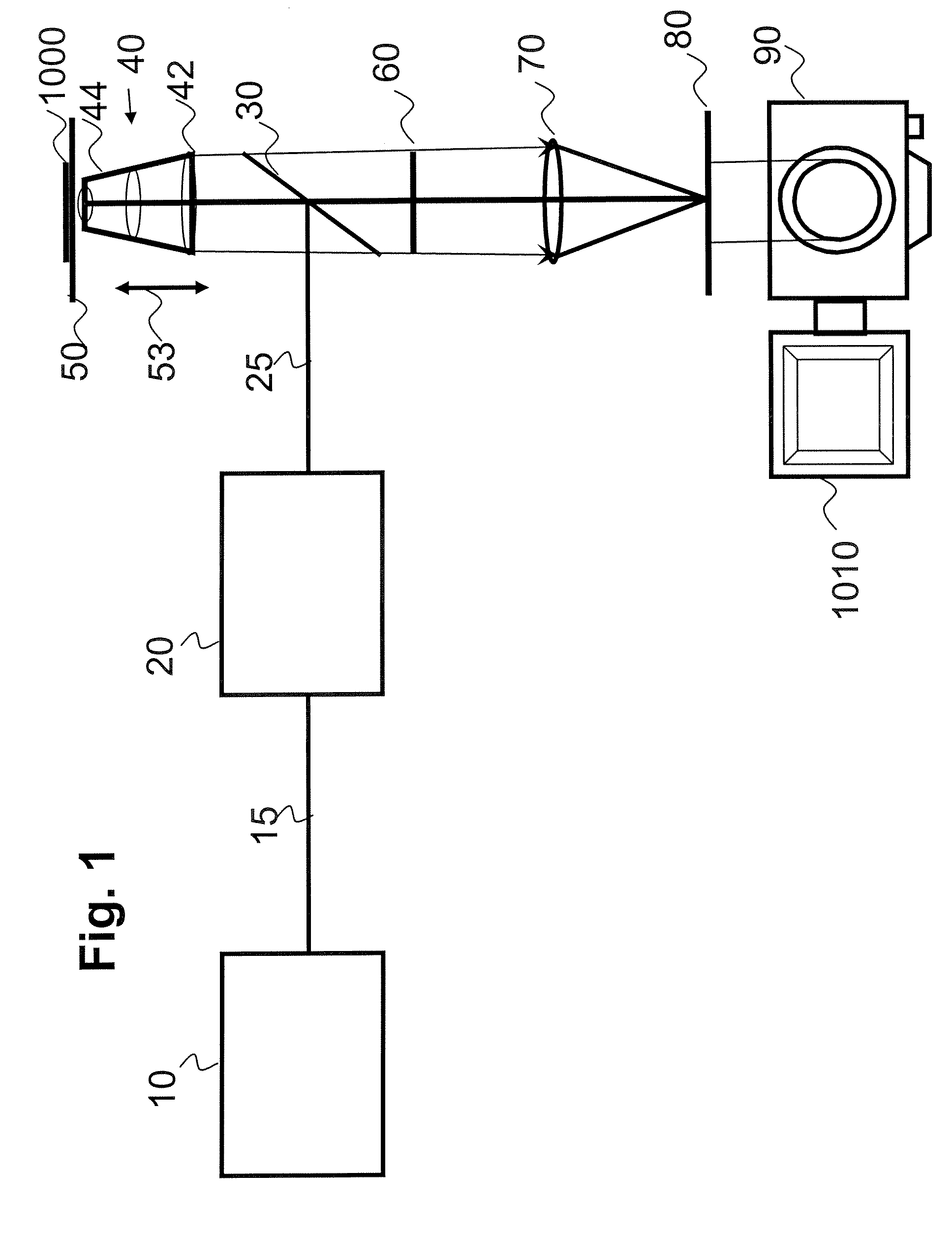
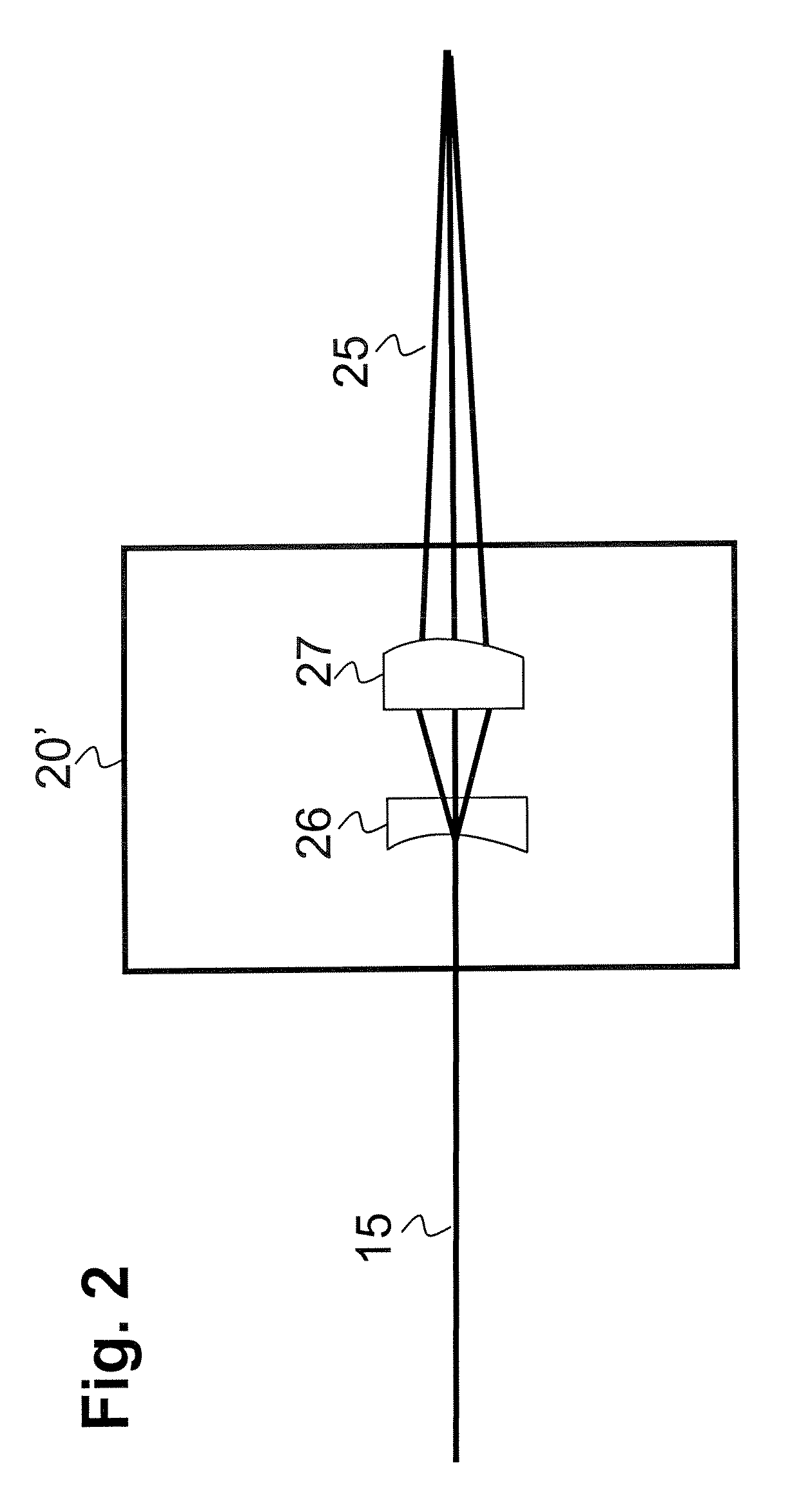
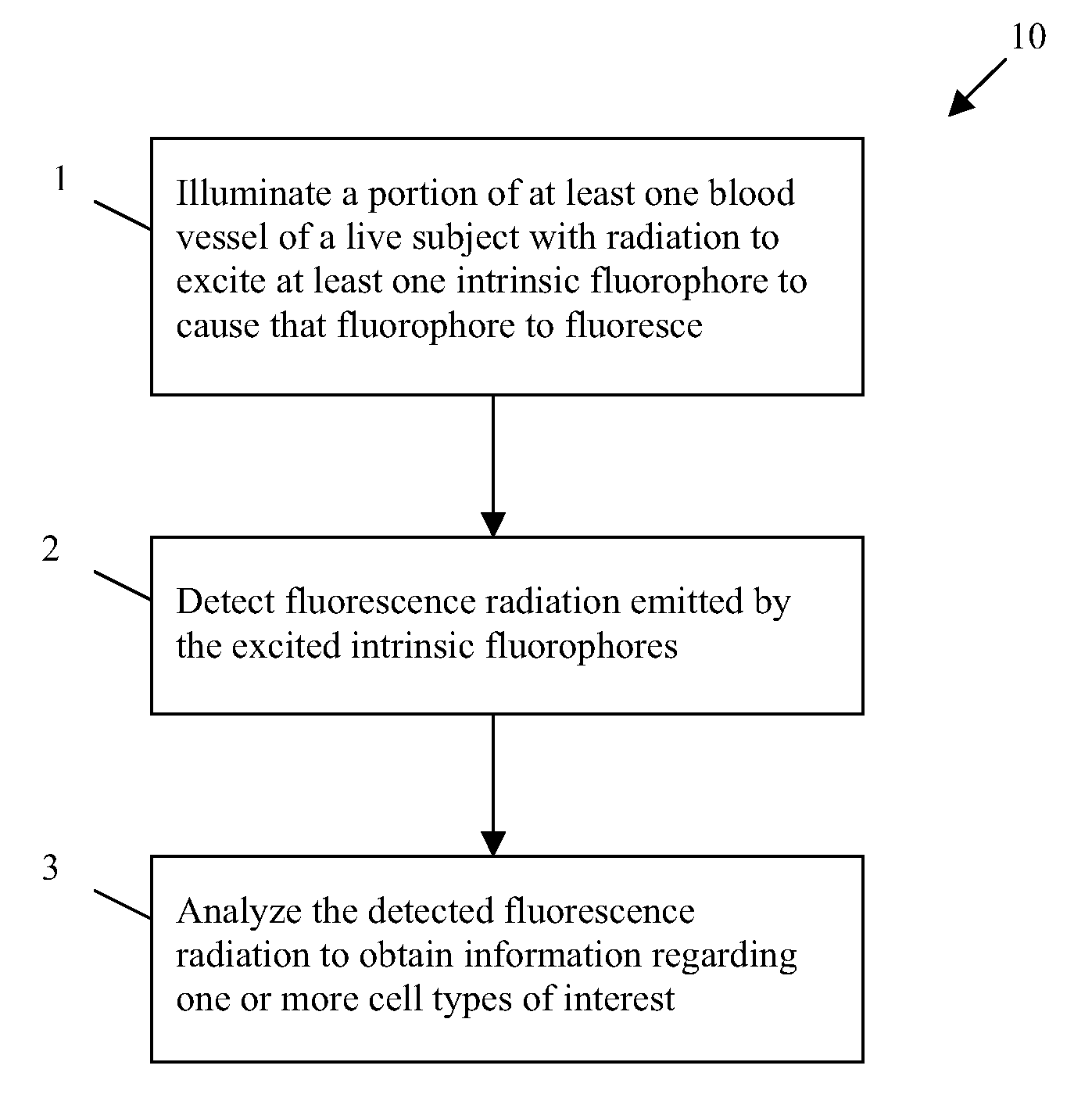
The present invention generally provides methods and systems for performing in vivo flow cytometry by using blood vessels as flow chambers through which flowing cells can be monitored in a live subject in vivo without the need for withdrawing a blood sample. In some embodiments, one or more blood vessels are illuminated with radiation so as to cause a multi-photon excitation of an exogenous fluorophore that was previously introduced into the subject to label one or more cell types of interest. In some other embodiments, rather than utilizing an exogenous fluorophore, endogenous (intrinsic) cellular fluorescence can be employed for in vivo flow cytometry. The emission of fluorescence radiation from such fluorophores in response to the excitation can be detected and analyzed to obtain information regarding a cell type of interest.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
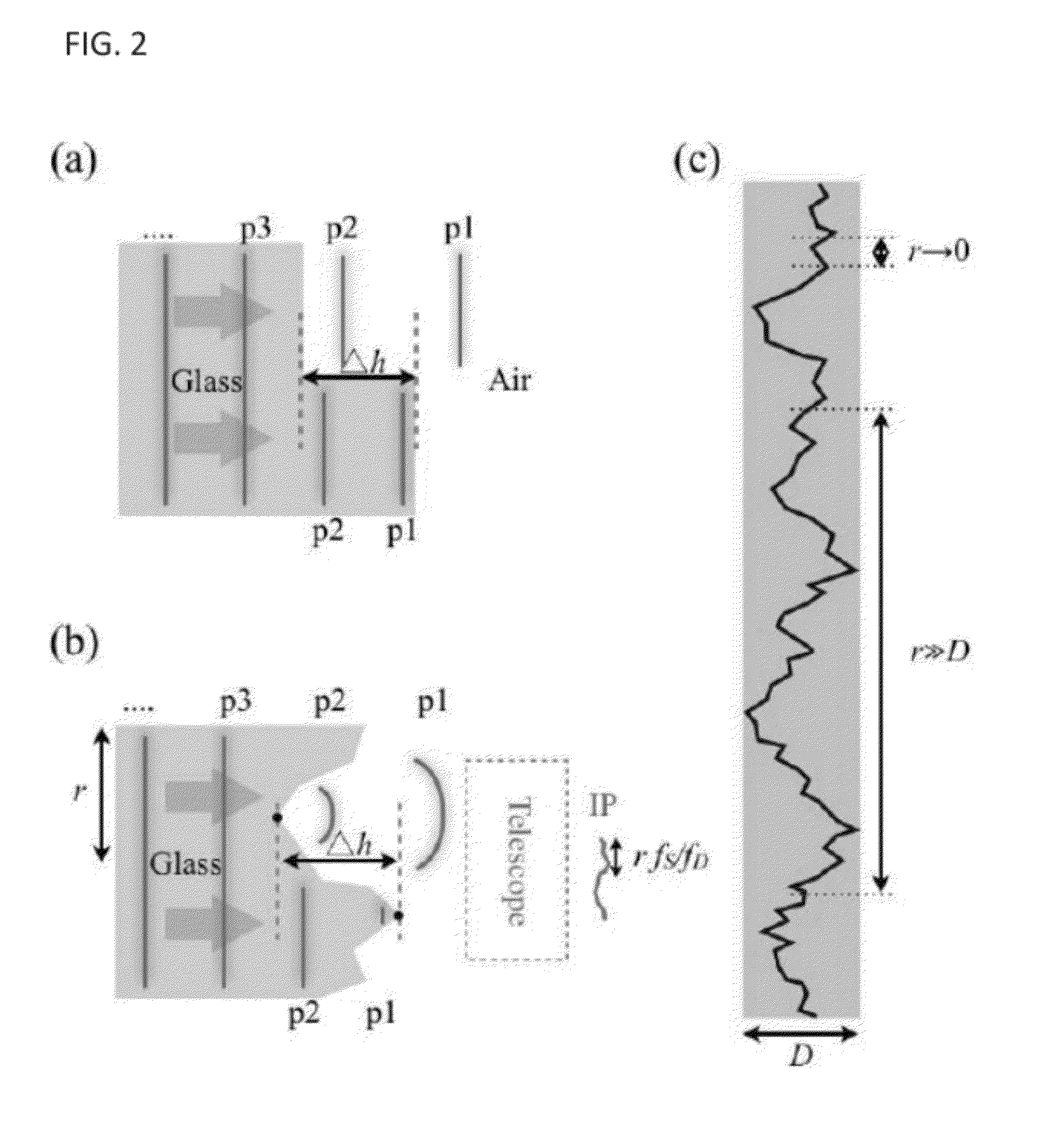
High-Resolution Microscope and Method for Determining the Two- or Three-Dimensional Positions of Objects
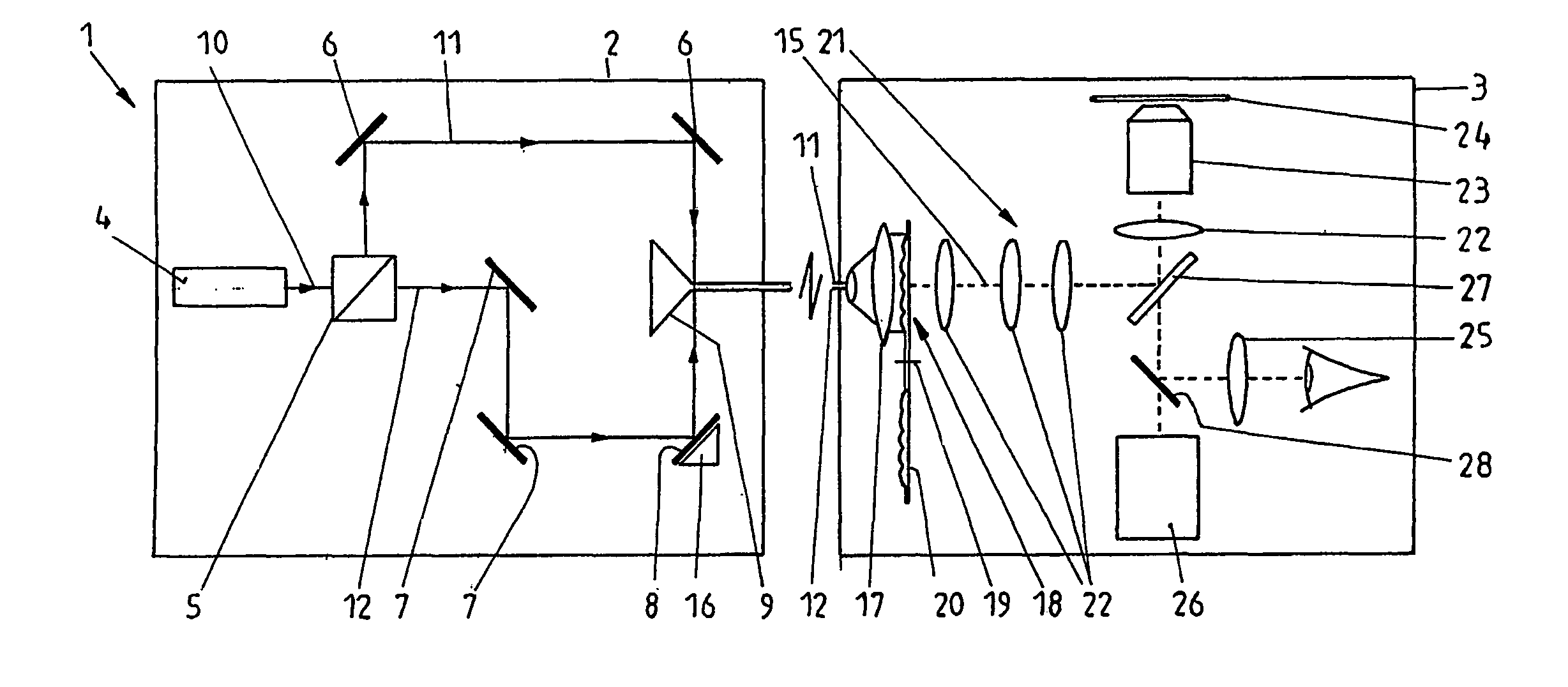
ActiveUS20130010098A1High resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsGratingControl selection
The invention relates to a high-resolution microscope and to a method for determining the two- or three-dimensional positions of objects. The microscope and method includes the following: (a) The vertical (Z) position of imaged particles or molecules being determined from the orientation and shape thereof by means of an anamorphic lens, preferably a cylindrical lens, in the imaging, (b) the detection beam path being split into at least two partial detection beam paths having different optical path lengths, which are detected at an offset on a detector, (c) activation or switchover being performed by means of a multi-photon excitation process, preferably two-photon excitation. The following are also included: (d) a point-scanning activation or switchover, (e) a line-scanning activation or switchover, (f) the sample is excited and the sample light is detected in the wide-field mode, (g) manually or automatically predetermined sample regions are activated or switched over, (h) the activation or switchover is performed by means of AOTF or SLM or DMD, (i) laser pulses for activating or switching are spectrally split by means of a spectrally splitting element, preferably a grating, (j) an SLM or DMD in the beam path after the grating performs a controlled selection of split laser pulse fractions, (k) the laser wide-field excitation is guided by SLM or DMD, (l) ROIs are selected by SLM or DMD, (m) a multi-photon switching or activation is performed by means of a microlens array, preferably a cylindrical lens array, n) switching and / or excitation is performed by means of a line scanner, and (o) a line detection is performed by means of a spatially resolved sensor, wherein at least two sensor rows, each comprising a plurality of sensors, are illuminated with sample light by means of a slit diaphragm position.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Method and system for wide-field multi-photon microscopy having a confocal excitation plane
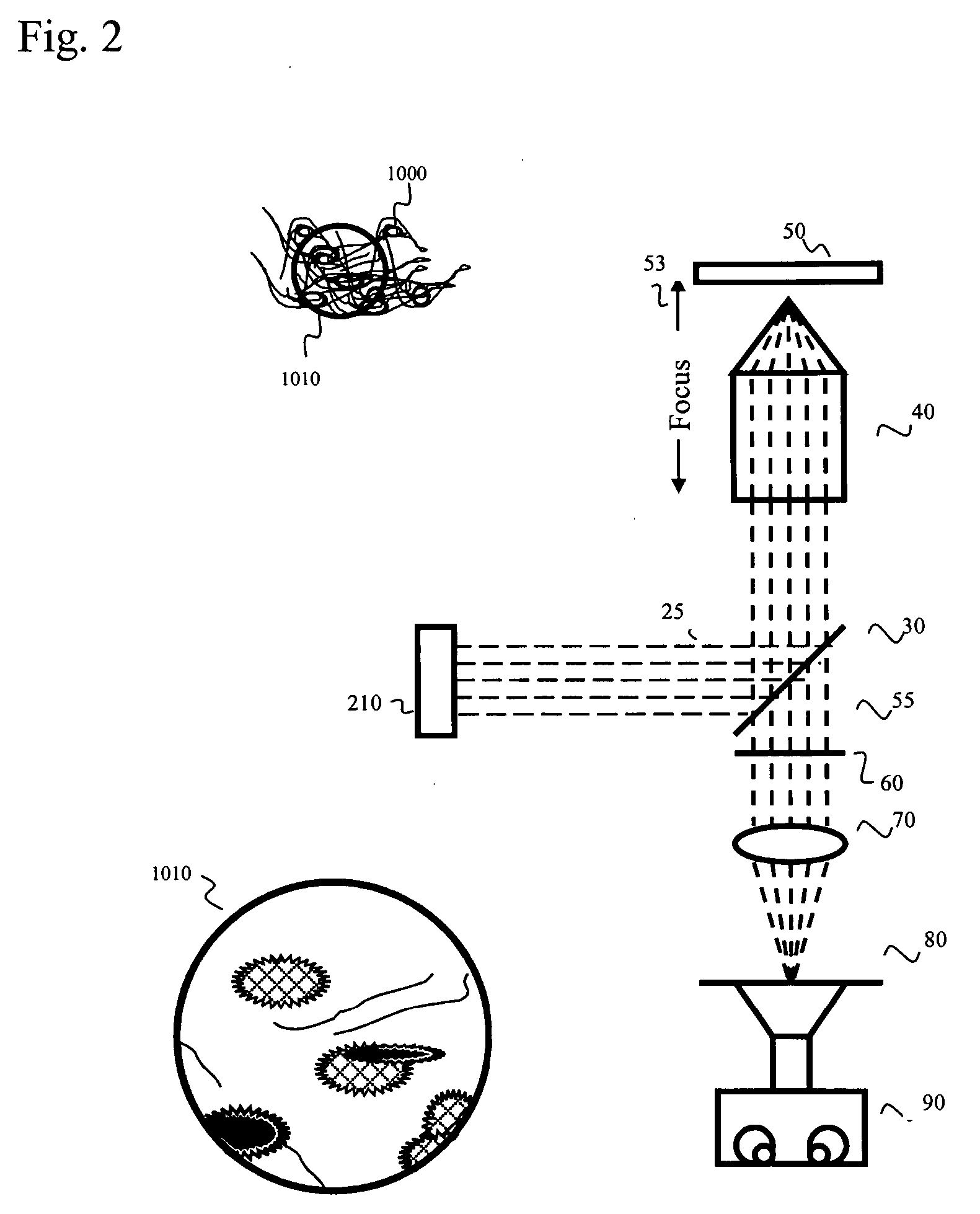
ActiveUS20050259319A1Shorten Image Acquisition TimeScanning of the excitation light source over the specimen can be reduced or eliminatedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersEyepieceImage plane
According to one aspect of the invention, a wide-field microscope includes a stage configured to hold a specimen having a fluorescent material therein, and a multi-photon excitation light source configured to produce a substantially parallel beam of excitation light having a single photon energy less than an absorption energy required for single photon excitation of the fluorescent material. An infinity corrected objective is optically coupled to the multi-photon excitation light source and configured to focus the substantially parallel beam of excitation light onto the specimen such that multi-photon excitation of the fluorescent material simultaneously occurs over a predetermined area of the specimen. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from the predetermined area of the specimen onto at least two pixels of an image detector simultaneously. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from the predetermined area of the specimen onto an image plane, such that the image plane can be viewed through a binocular eyepiece or an imaging array detector.
Owner:CELLOPTIC
Method and device for multi photon excitation of a sample
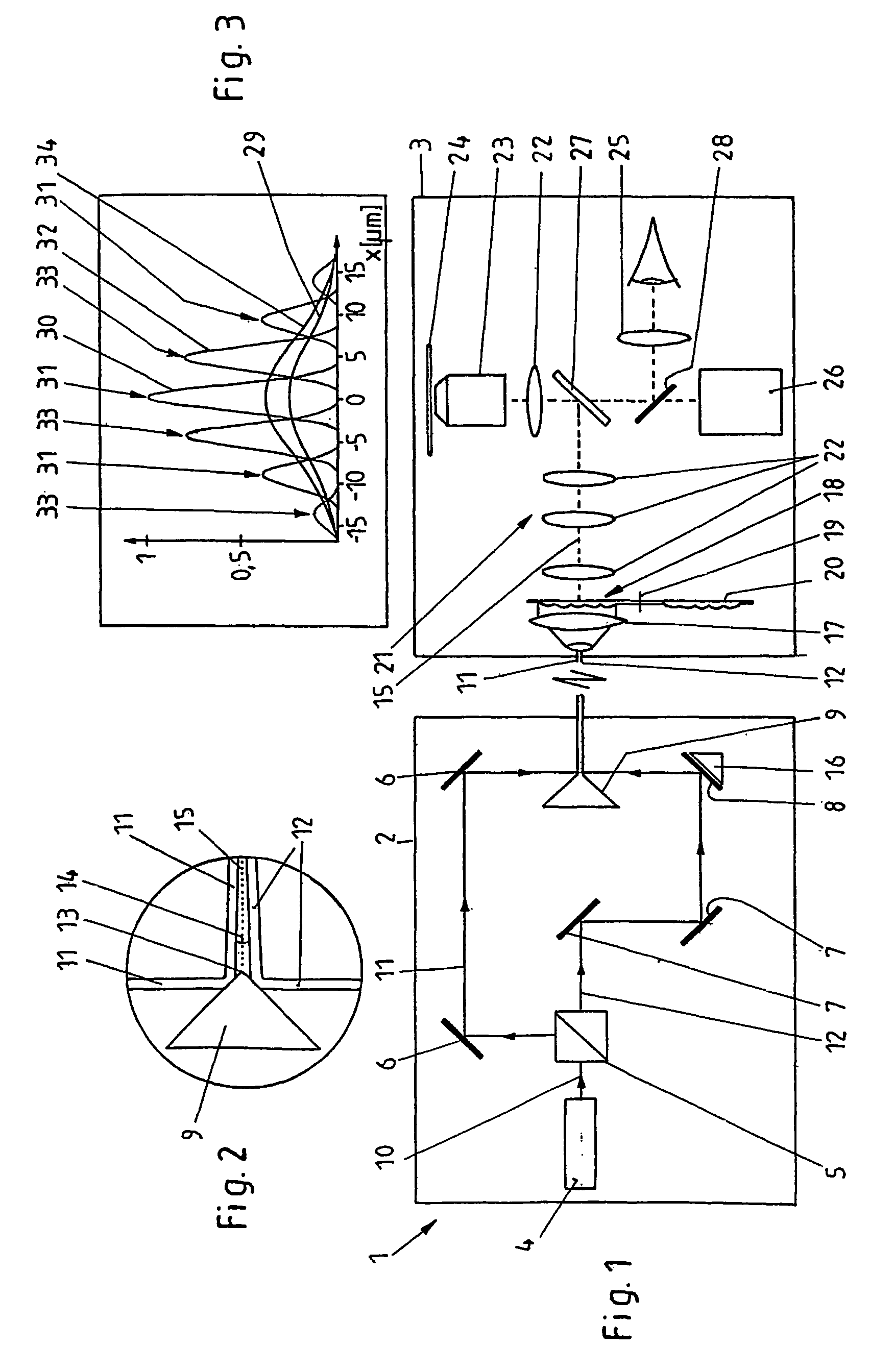
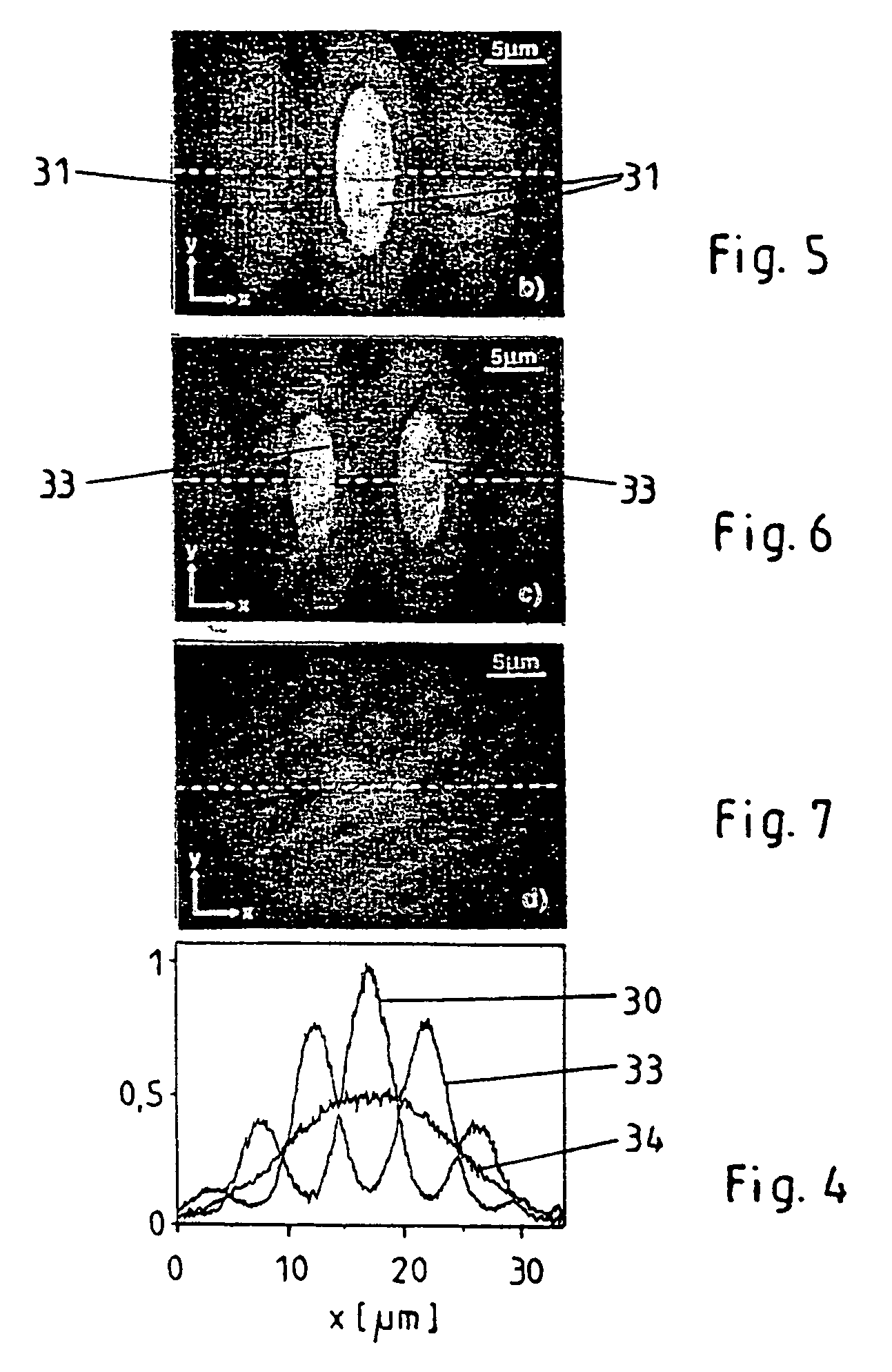
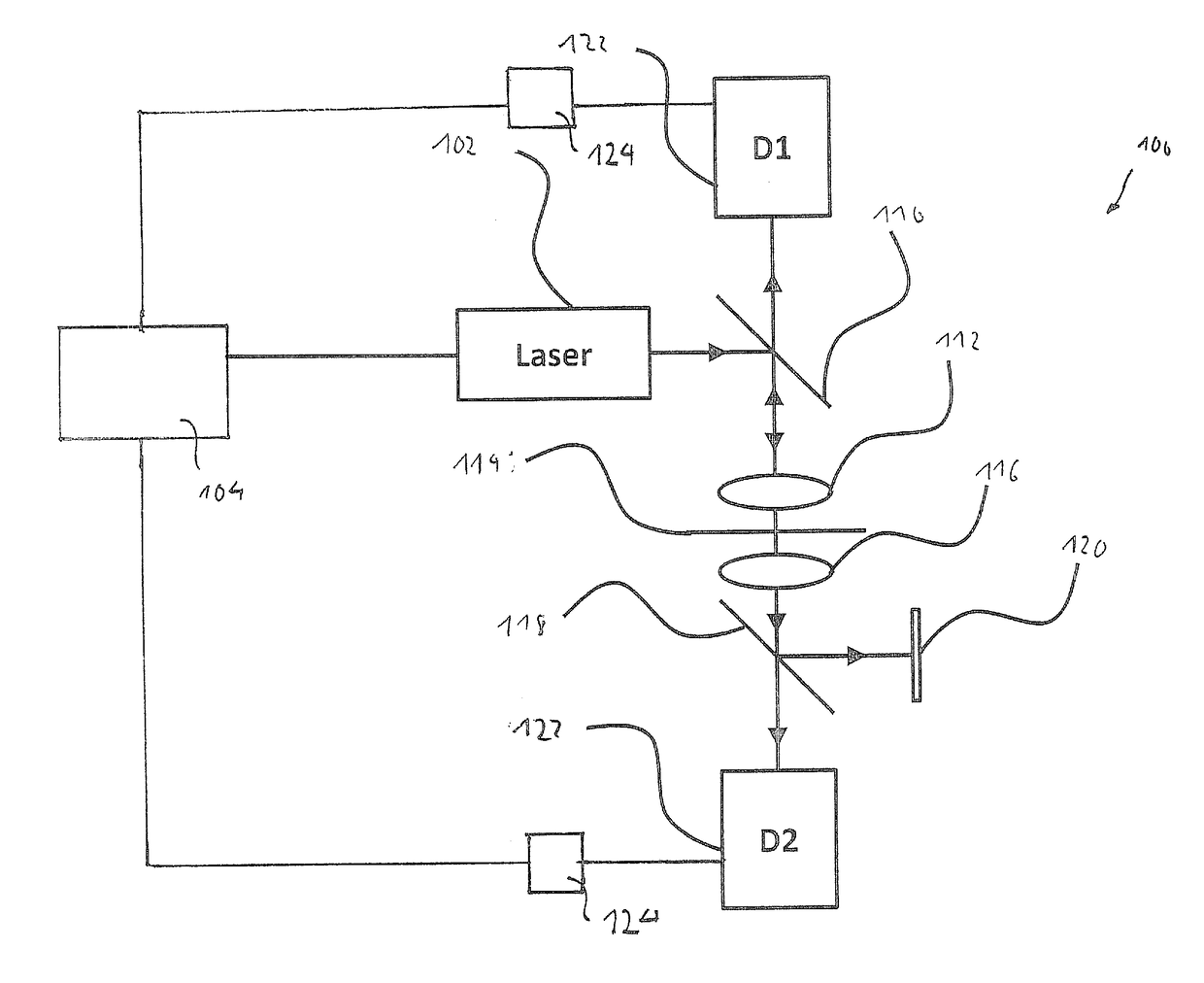
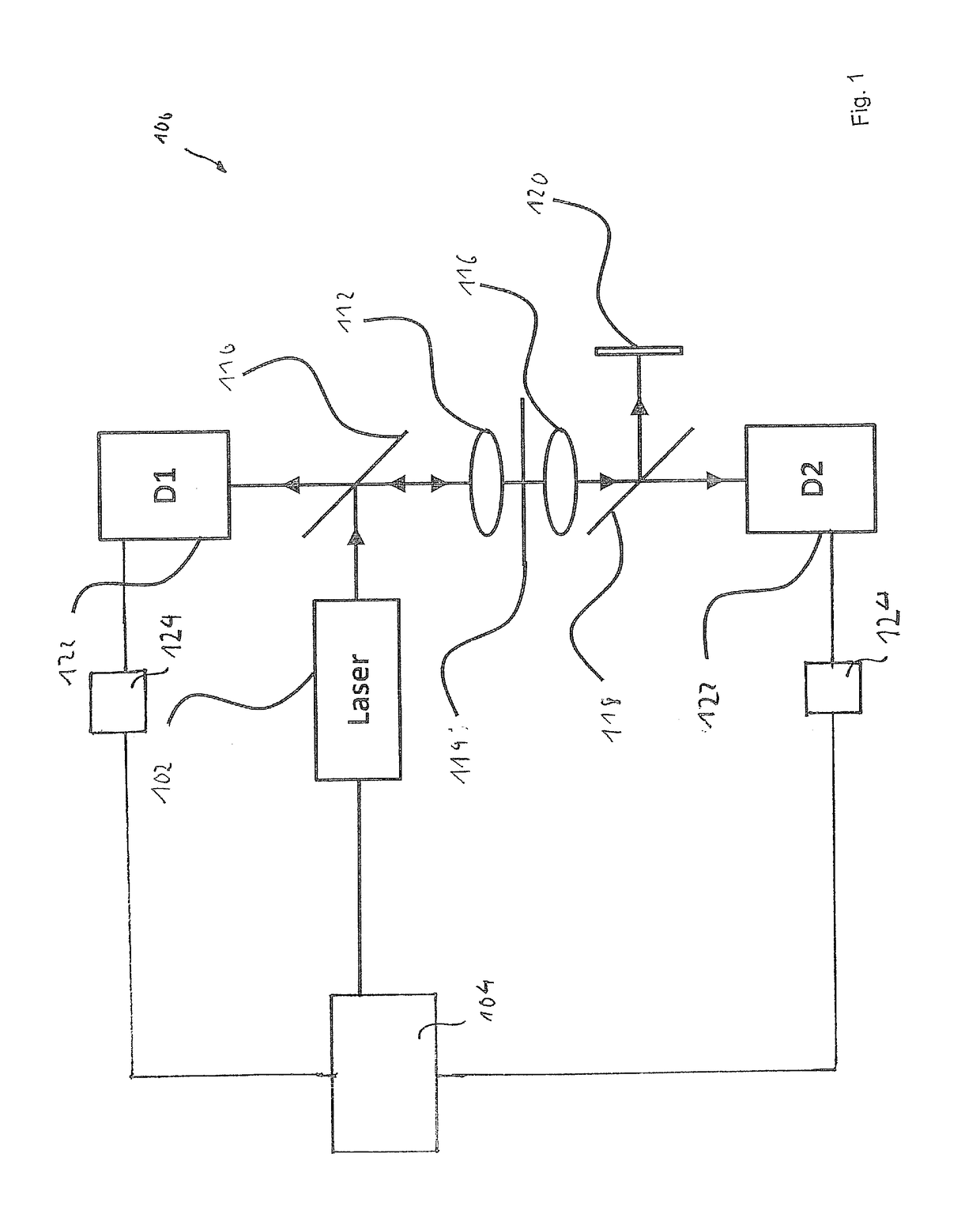
InactiveUS7115885B2Uniform intensity distributionIncrease productionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical axisLight beam
In a method for multi photon excitation of a sample a laser beam is split into at least two coherent partial beams each having a beam axis and a same intensity distribution about its beam axis. The partial beams are directed from different directions towards a common measuring plane running transversely to the beam axes at an inclination angle <1 between the beam axes of the partial beams; and the partial beams are projected onto the measuring plane by means of a common lens system. Thus, an interference pattern formed by the coherent partial beams within the measuring plane provides areas of maximum light intensity adjacent to areas of minimum light intensity.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Sensing Device, Sensing Apparatus, and Sensing Method
There are provided a sensing device, a sensing apparatus, and a sensing method capable of realizing effective multi-photon absorption and local plasmon enhancement function. The sensing device can realize a high multi-photon excitation efficiency and selectivity by accurately controlling the material, shape, size, interval, and direction of metal particles arranged on a substrate. By employing the sensing device in various sensing apparatuses such as a fluorescent sensing apparatus, it is possible to realize sensing of detection object material with a high sensibility.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY
Method and system for wide-field multi-photon microscopy having a confocal excitation plane
ActiveUS7170675B2Scanning of the excitation light source over the specimen can be reduced or eliminatedShorten Image Acquisition TimePhotometryLuminescent dosimetersEyepieceImage plane
According to one aspect of the invention, a wide-field microscope includes a stage configured to hold a specimen having a fluorescent material therein, and a multi-photon excitation light source configured to produce a substantially parallel beam of excitation light having a single photon energy less than an absorption energy required for single photon excitation of the fluorescent material. An infinity corrected objective is optically coupled to the multi-photon excitation light source and configured to focus the substantially parallel beam of excitation light onto the specimen such that multi-photon excitation of the fluorescent material simultaneously occurs over a predetermined area of the specimen. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from the predetermined area of the specimen onto at least two pixels of an image detector simultaneously. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from the predetermined area of the specimen onto an image plane, such that the image plane can be viewed through a binocular eyepiece or an imaging array detector.
Owner:CELLOPTIC
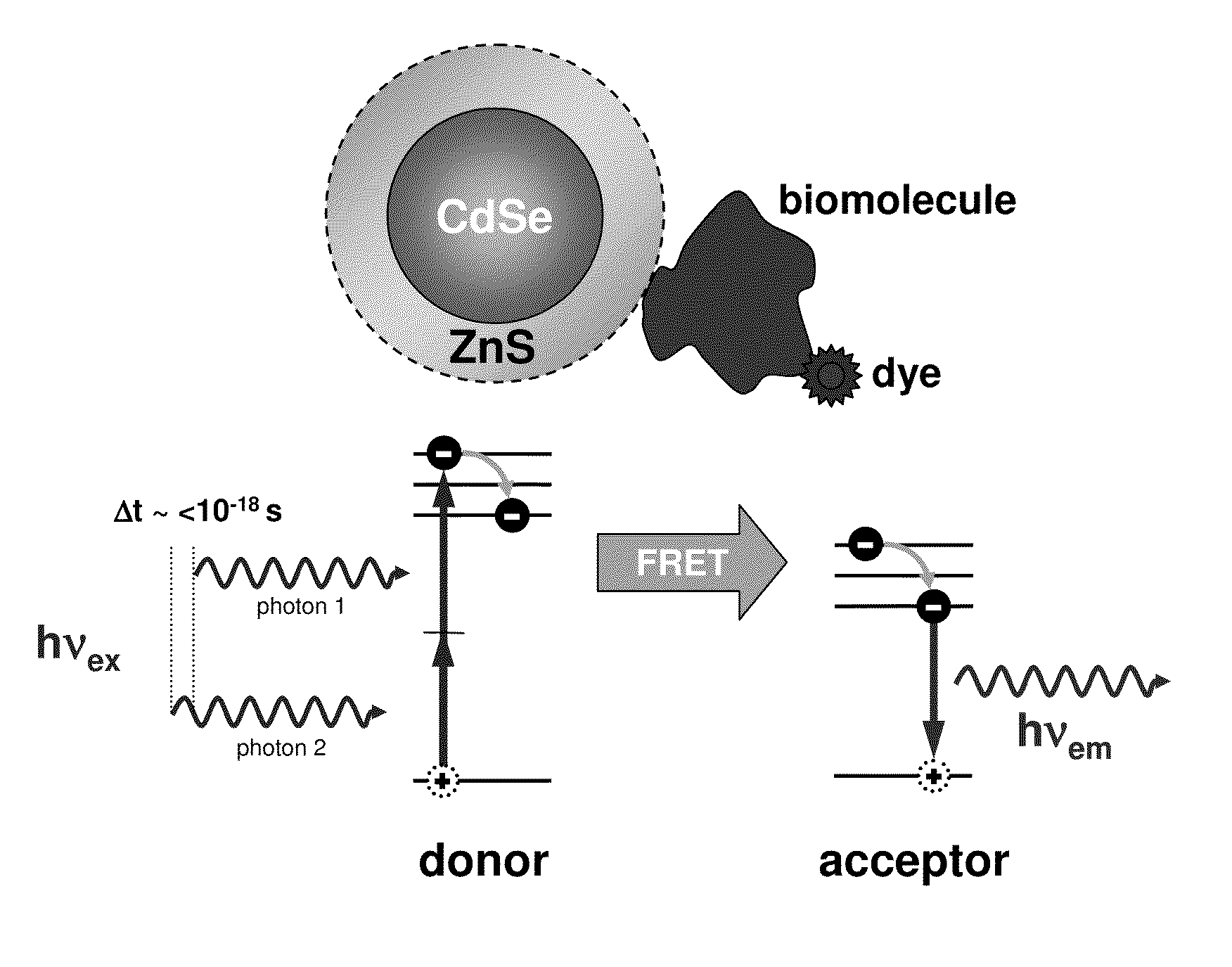
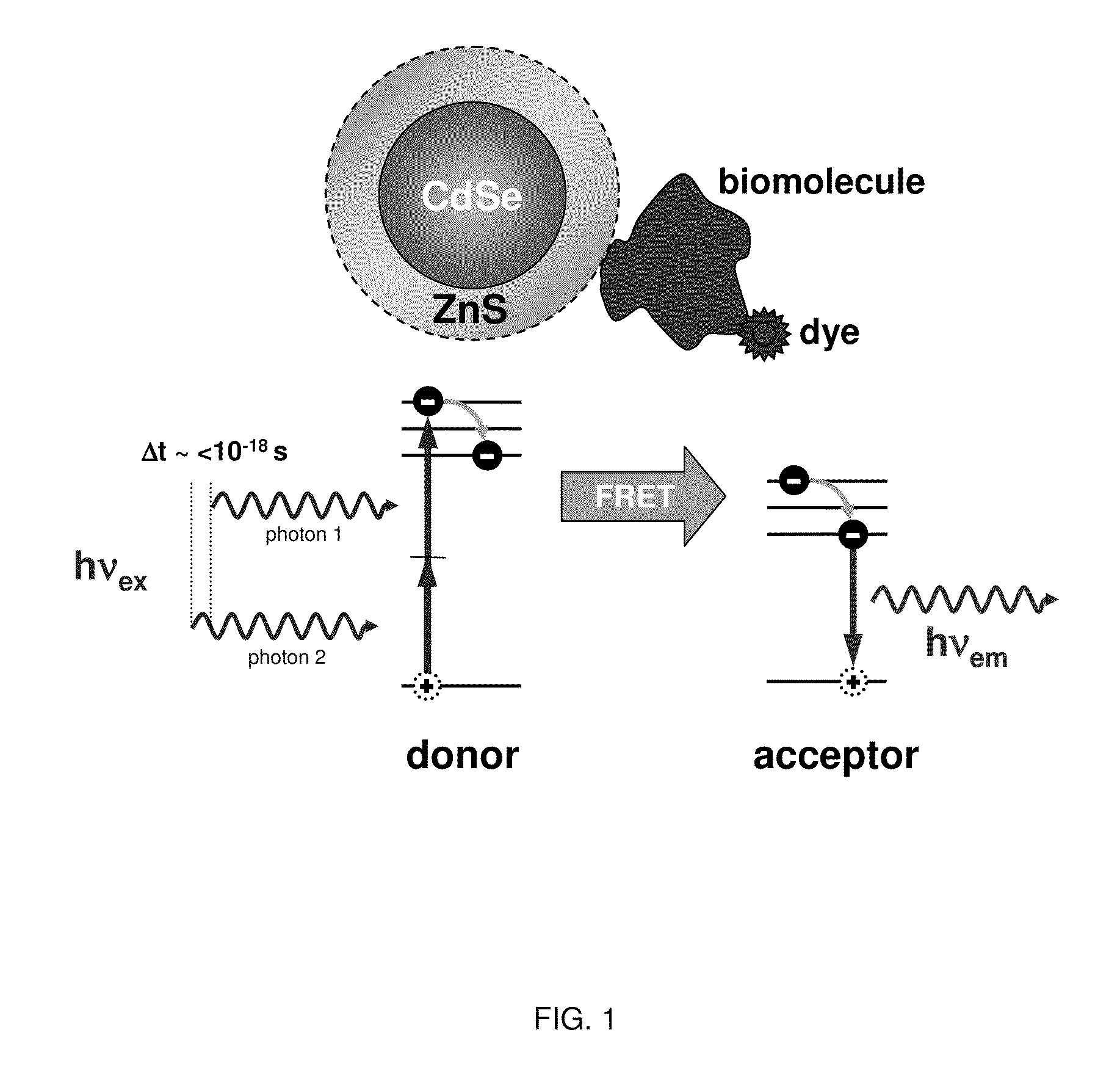
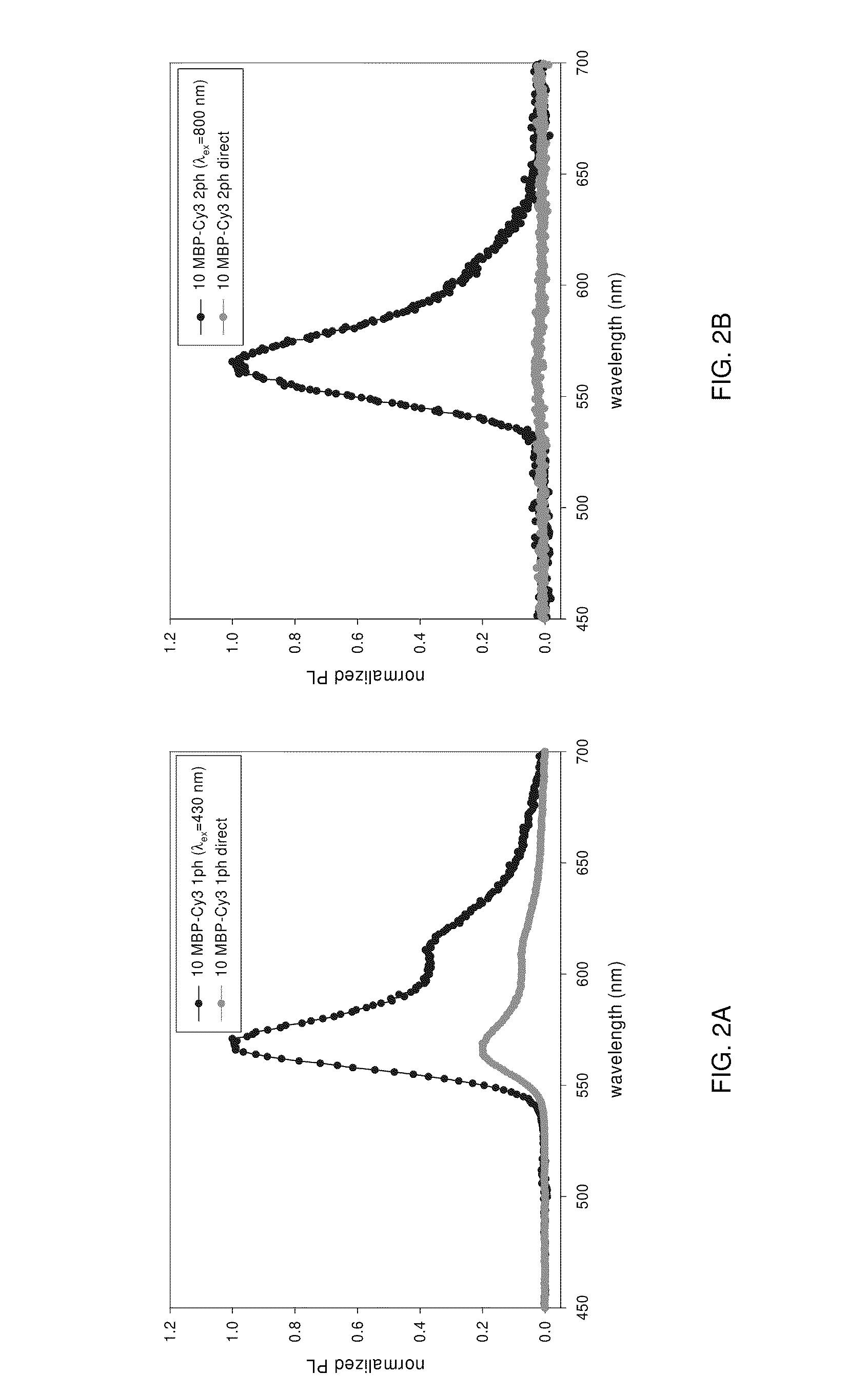
Methods of generating florescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between semiconductor quantum dots and fluorescent dyes/proteins via multi-photon excitation, achieving zero background or direct excitation contributions to the fret signature
InactiveUS20100075361A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnalysis by material excitationSemiconductor quantum dotsBiomolecule
A system and method of sensing physiological conditions in biological applications includes a laser source for optically exciting a plurality of luminescent quantum dots and a plurality of biomolecules in a nanoscale sensing system having a nanocrystal structure, where the plurality of biomolecules is stained with dye. In a multi-photon excitation process, a laser system optically excites, the plurality of luminescent quantum dots and the plurality of biomolecules in the nanoscale sensing system, where fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) occurs between the plurality of quantum dots and the plurality of biomolecules. Stability of self assembly of quantum dot peptide conjugates within the plurality of biomolecules is investigated. Physiological conditions at the cellular level are determined, using a spectrometer to sense fluorosence spectra. The sensing of physiological conditions includes transducing signals into immunoassays, clinical diagnostics and cellular imaging to provide treatment to biological subjects including human patients.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA GOVT REPRESENTED BY THE SECRDETARY OF THE NAVY CHIEF OF NAVAL RES ONR NRL
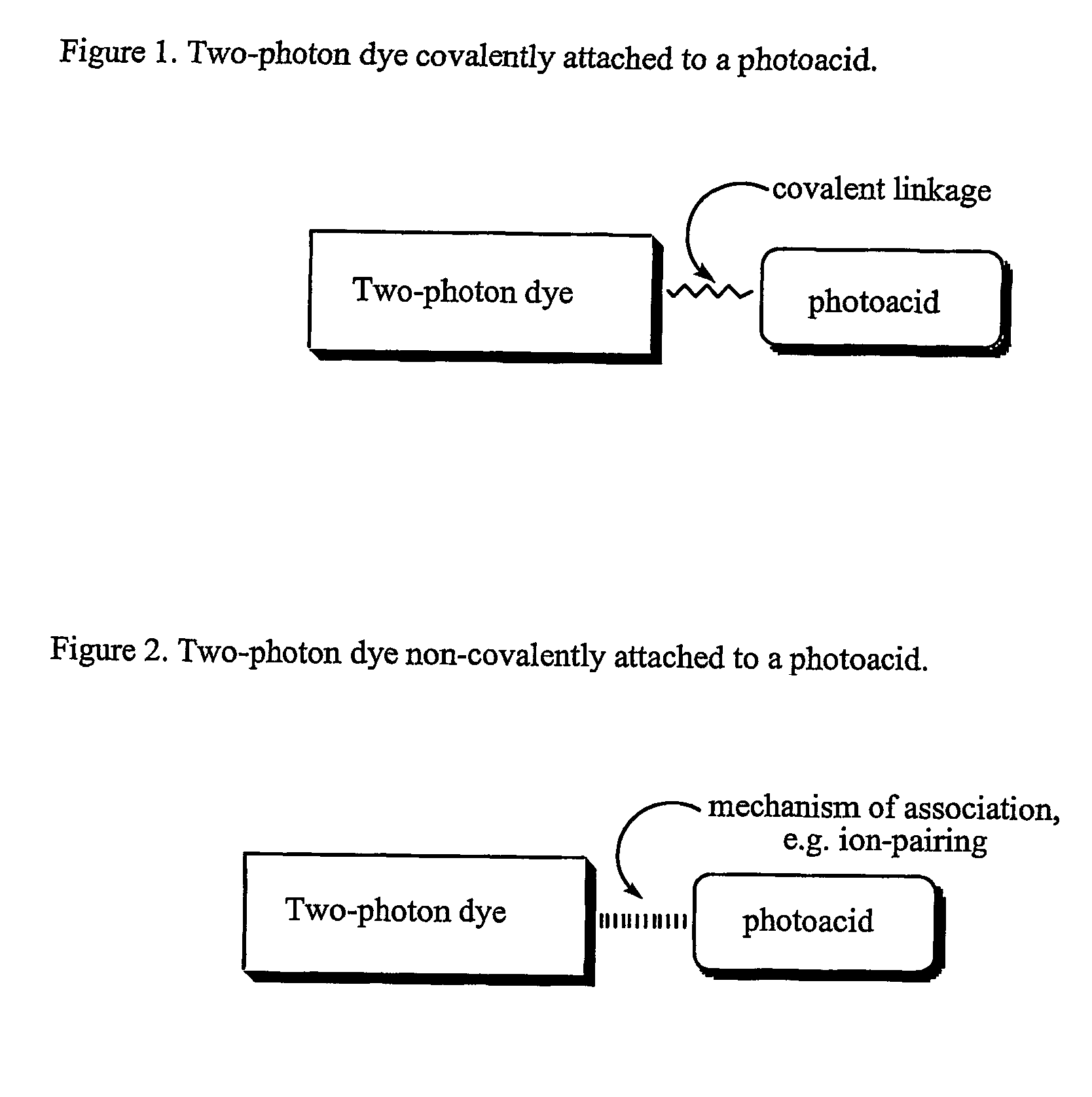
Materials, methods, and uses for photochemical generation of acids and/or radical species
InactiveUS7459106B2Efficiently photoactivatedOvercome limitationsOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsChemical compoundChromophore
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
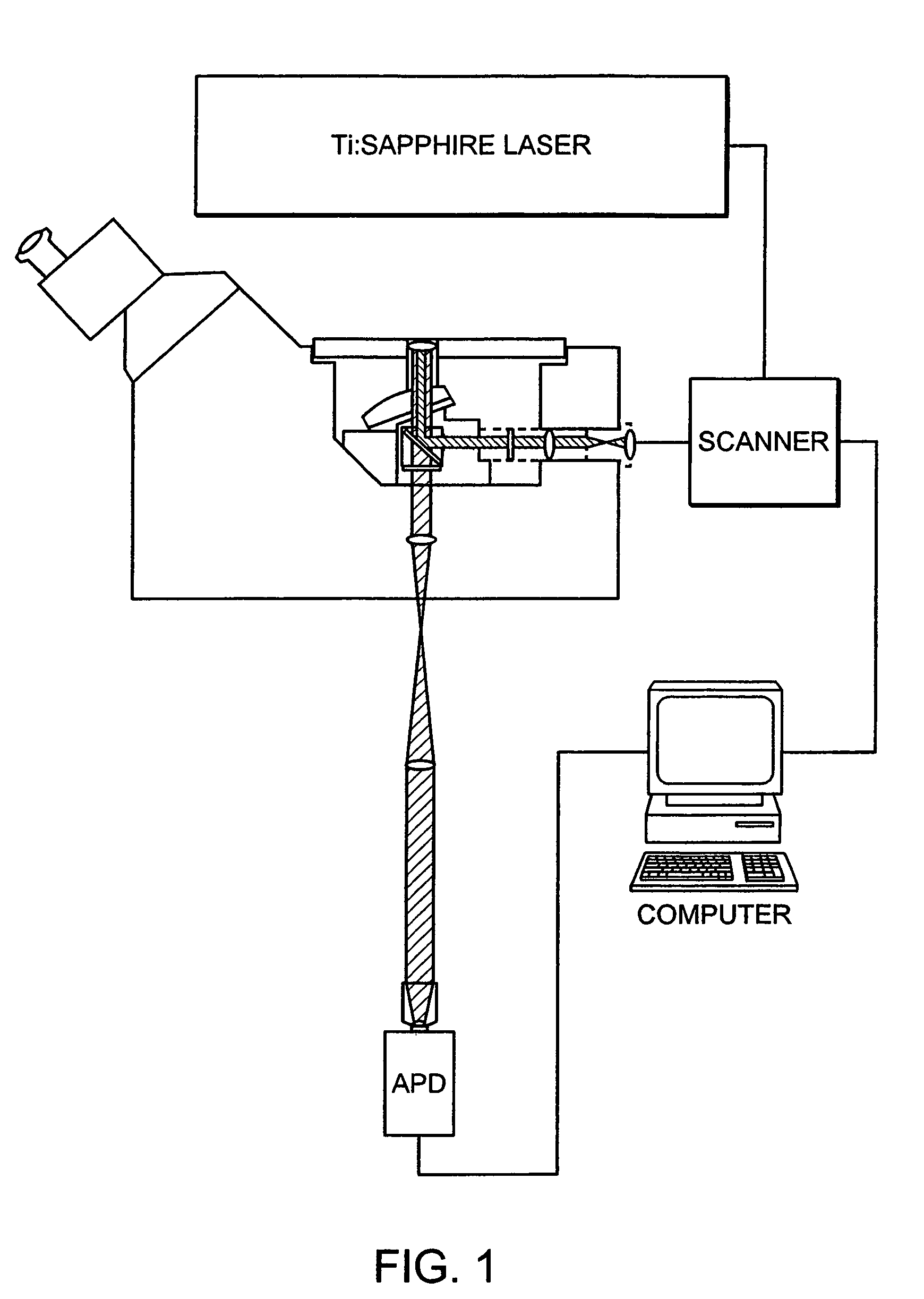
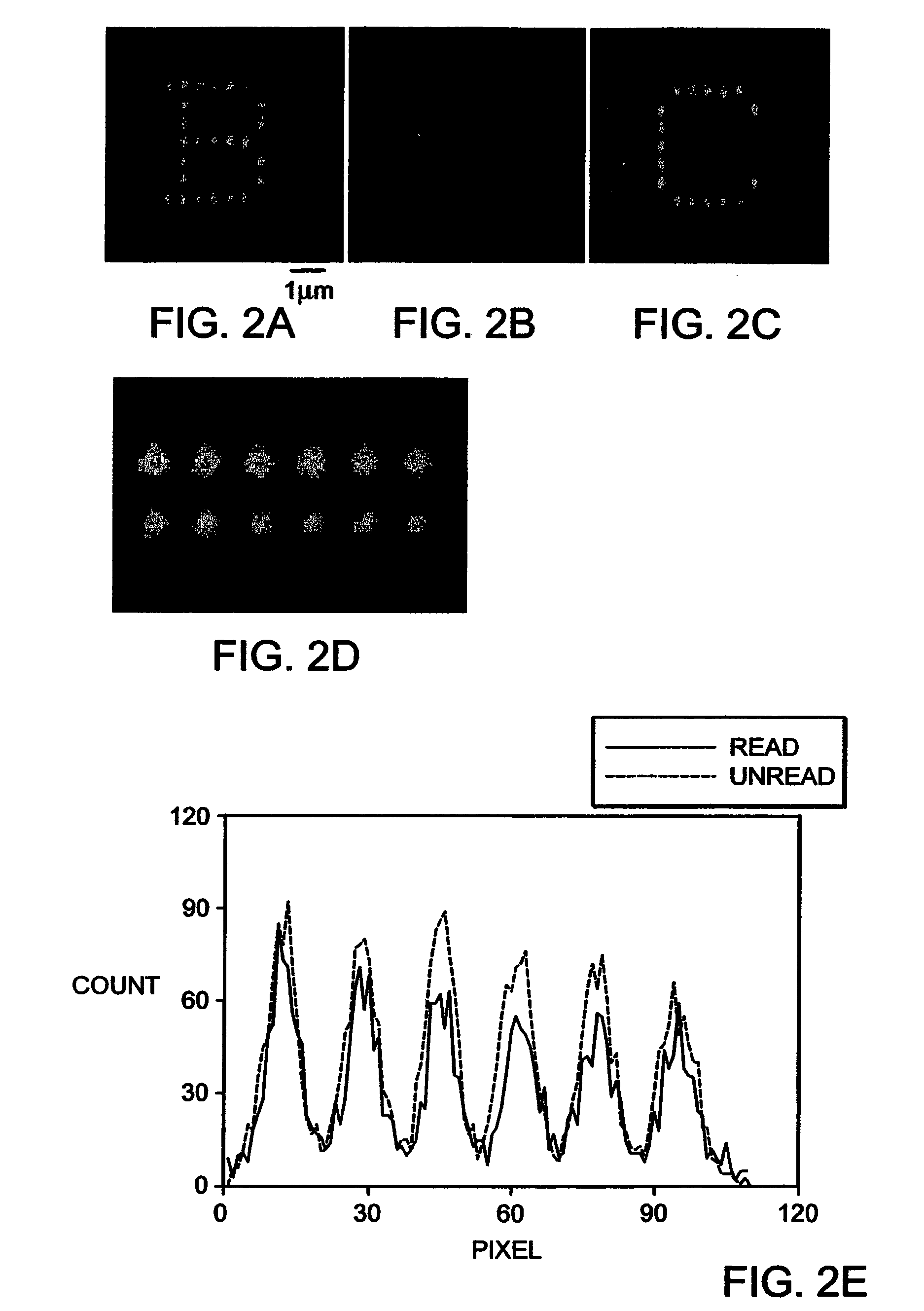
Methods for three-dimensional optical data storage and retrieval
InactiveUS6998214B2Increase memory capacityImprove optical qualityOrganic chemistryPhotography auxillary processesData recordingData storing
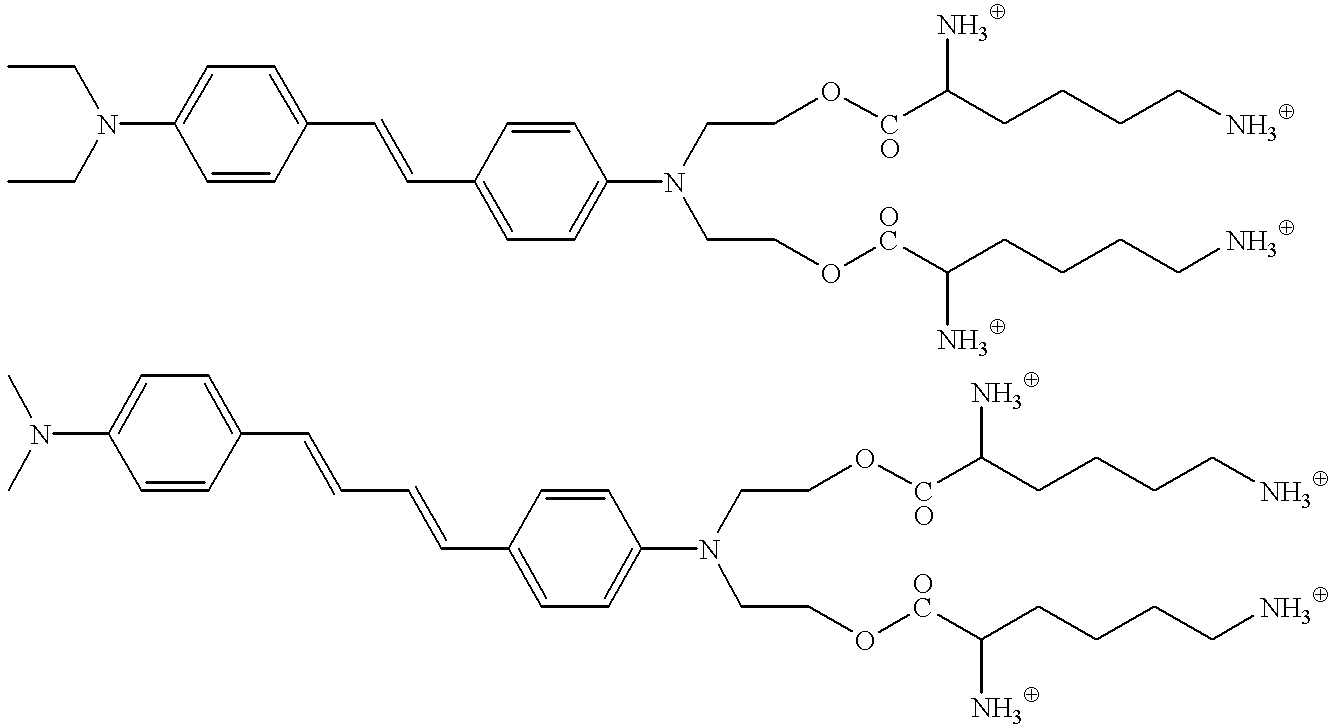
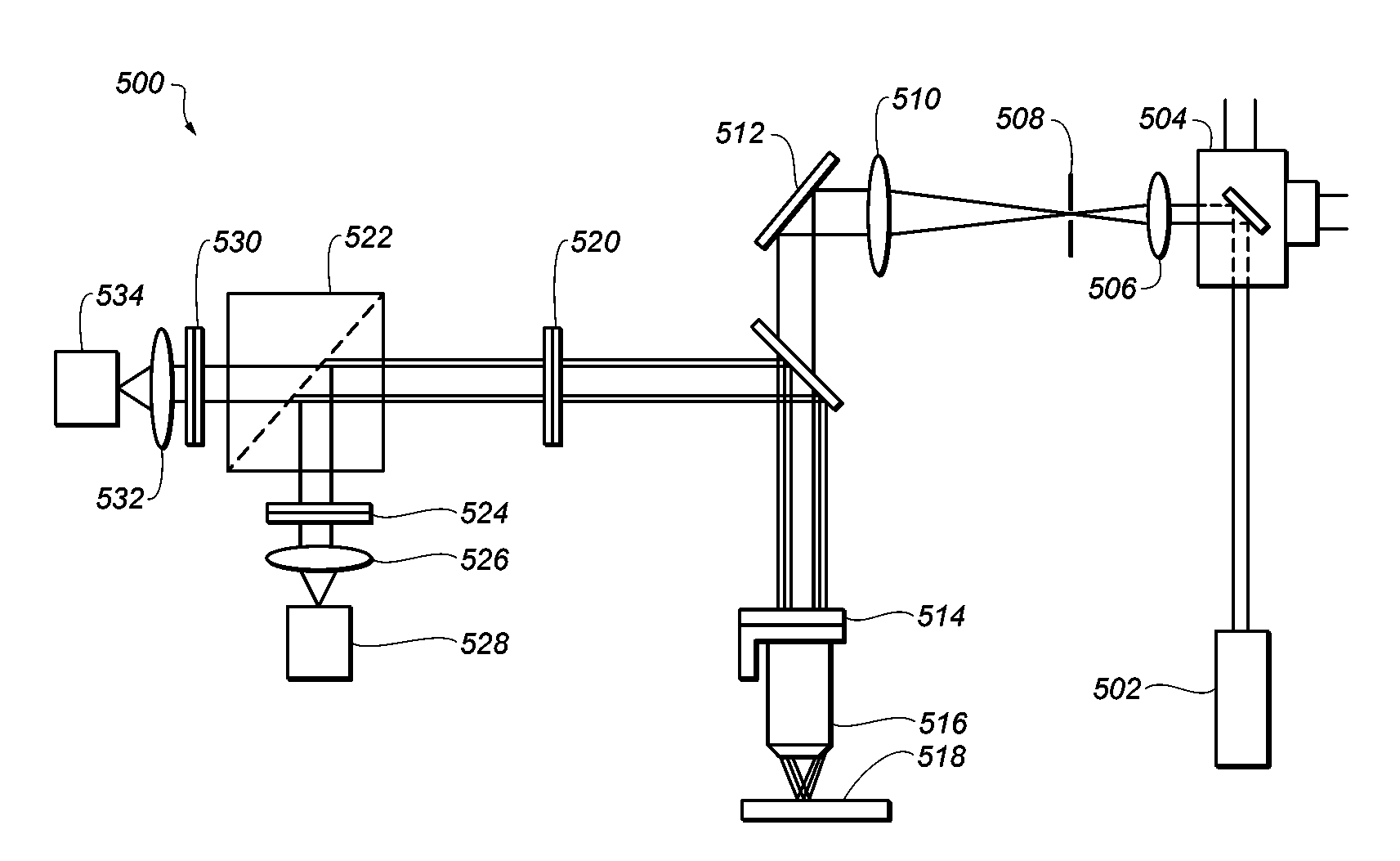
A three dimensional optical data storage and retrieval system that includes a three dimensional optical data storage medium and an apparatus for providing access to data stored on the medium. The data storage medium includes an optical data storage material which either a low molecular weight or polymeric glassy solid that are capable of undergoing multi-photon excitation that are energetically different in the write and read cycles. The optical data storage materials provide substantially higher storage capacities relative to conventional materials, and show high robustness in that written and stored data can undergo multiple read cycles without erasure or overwriting. An apparatus for data recording and accessing stored data on the medium includes a controllable variable energy photo-emitting excitation source and an emission photo-detector.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
Method of deep tissue imaging using multi-photon excitation of a fluorophore
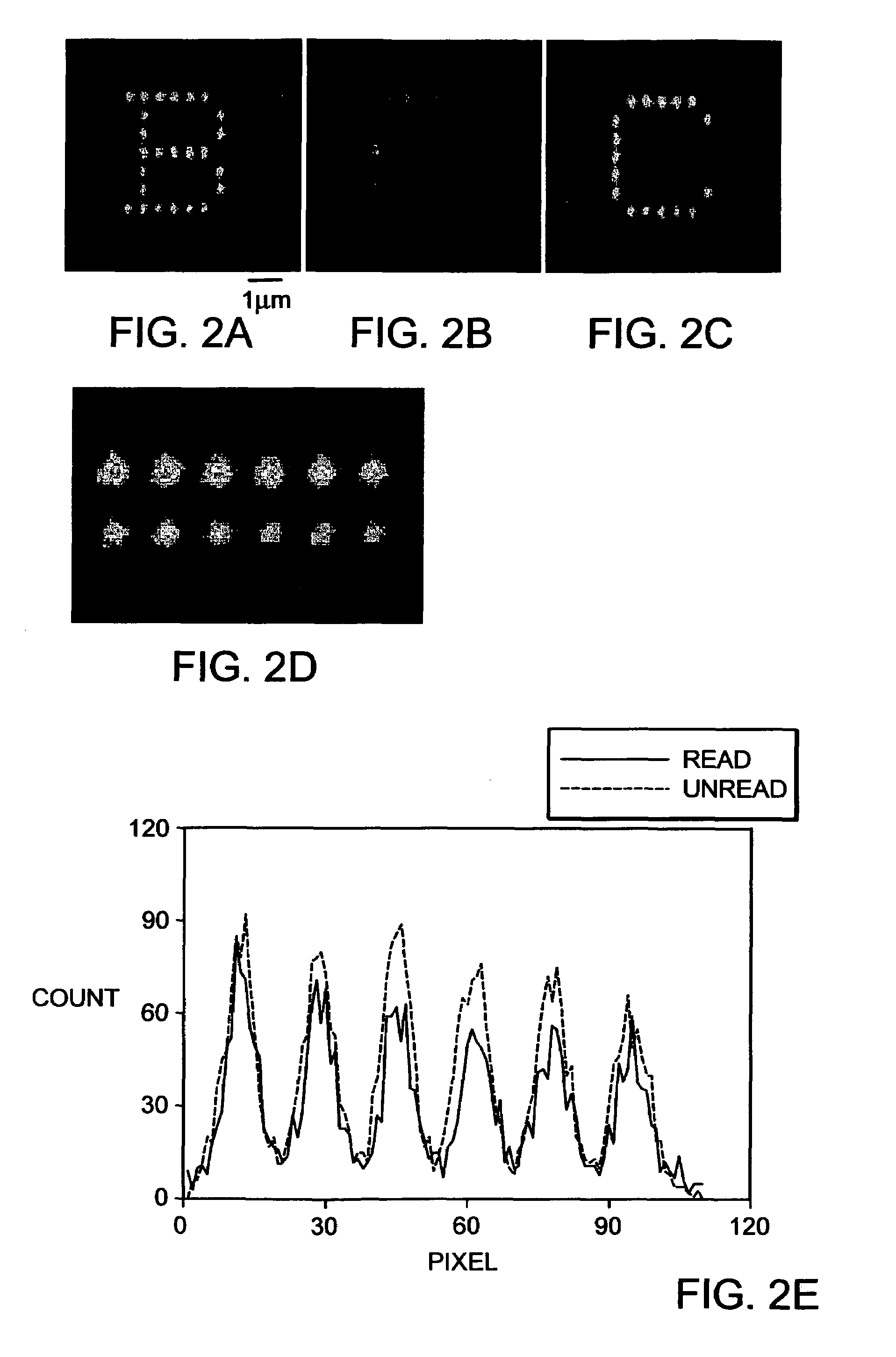
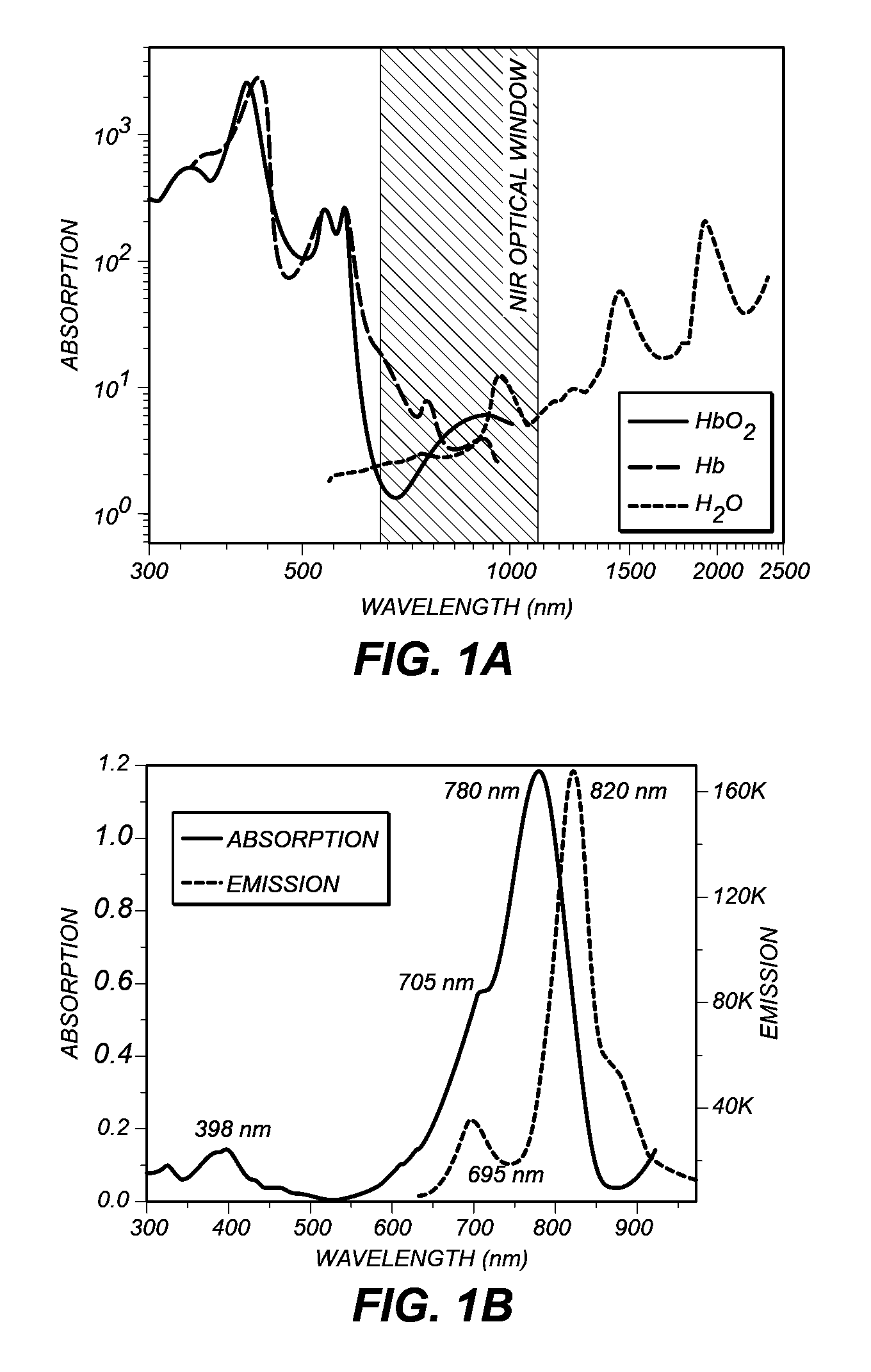
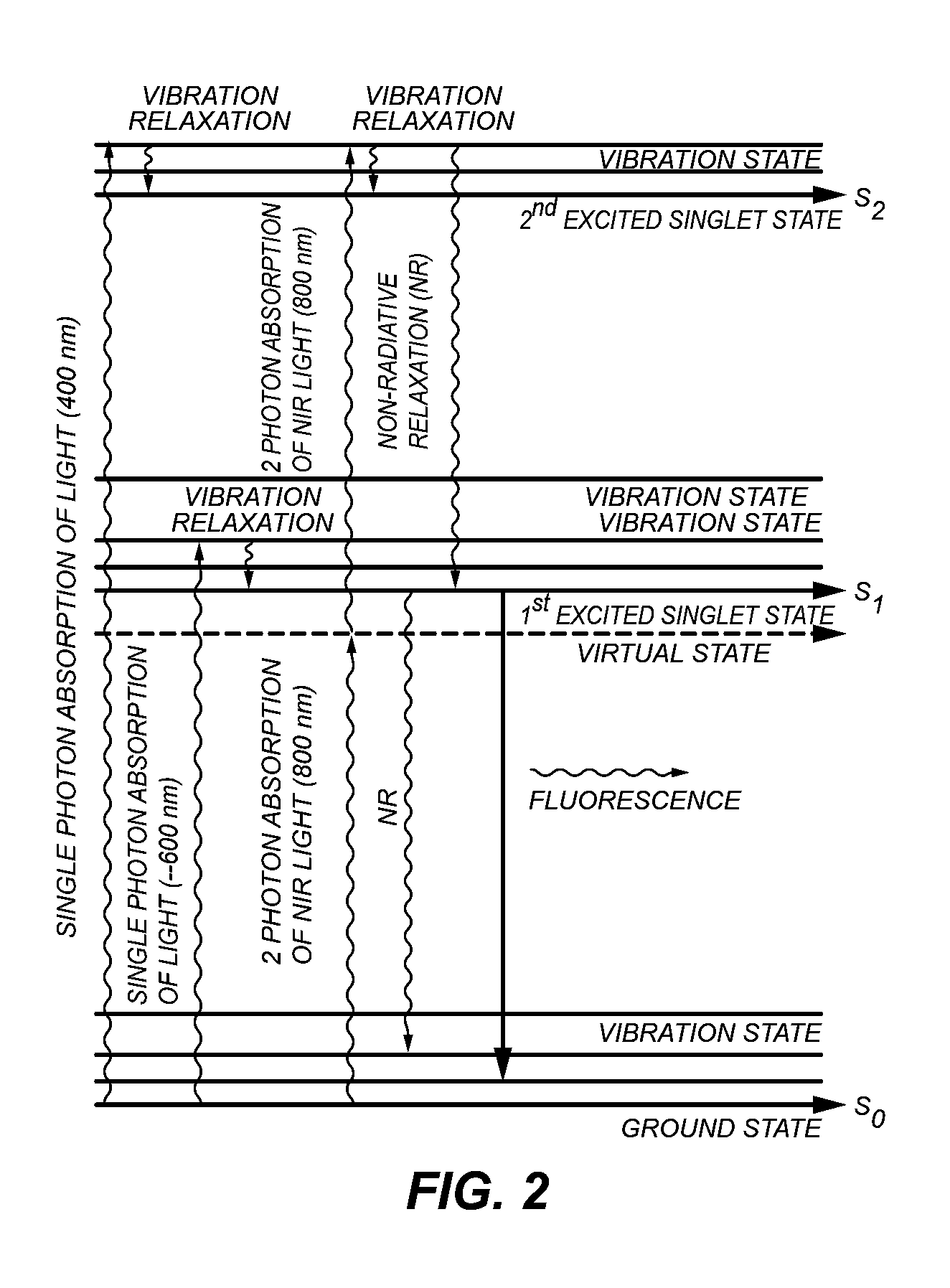
A method is provided for deep tissue imaging using multi-photon excitation of a fluorescent agent. The fluorescent agent is irradiated with an ultrafast laser to produce an excited singlet state (Sn) which subsequently undergoes non-radiative relaxation to a first singlet state (S1). The S1 state undergoes fluorescence to the ground state S0 to produce an emission wavelength. Both the excitation and emission wavelengths are within the near infrared optical window, thereby permitting deep tissue penetration for both the incoming and outgoing signals.
Owner:ALFANO ROBERT R
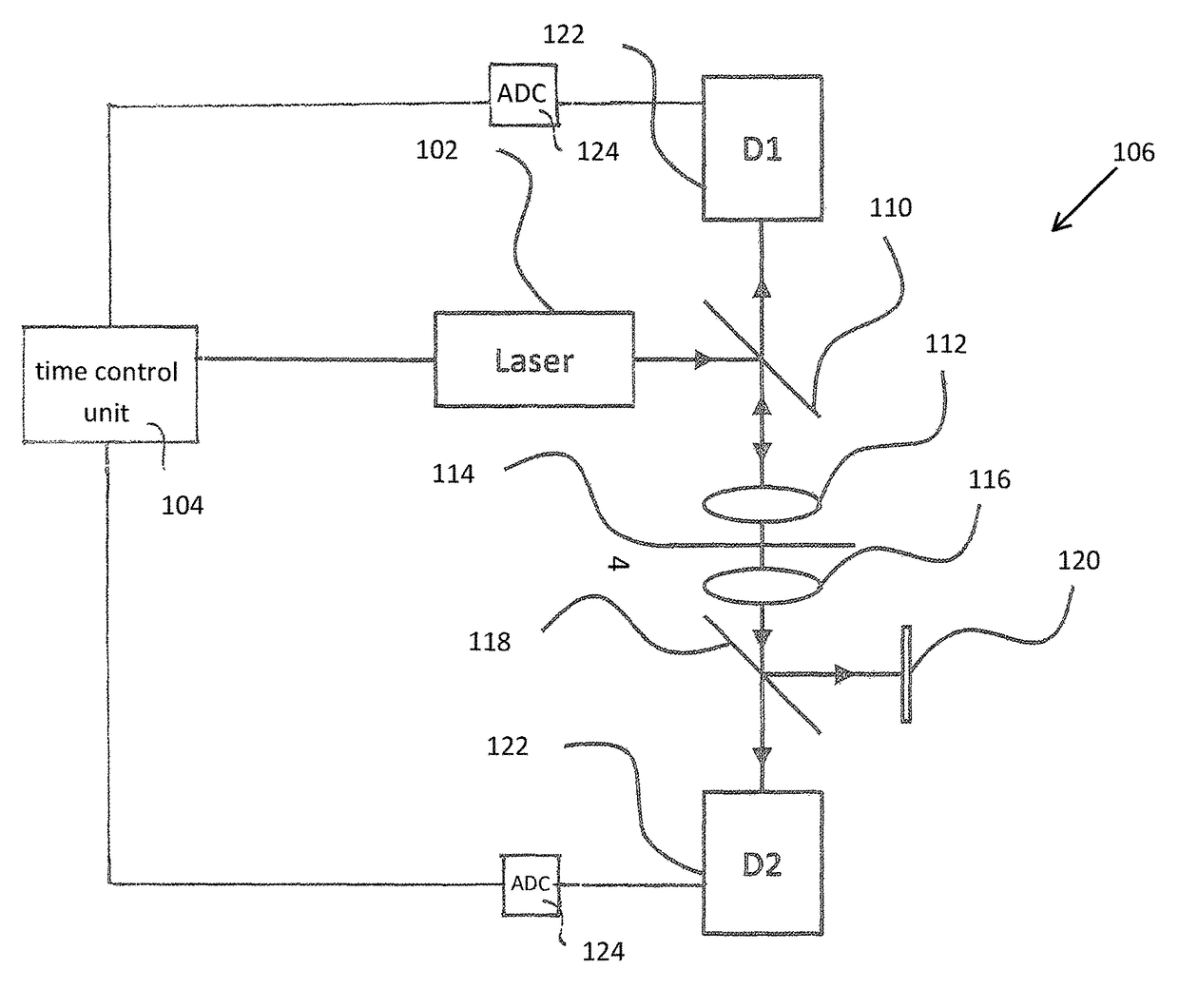
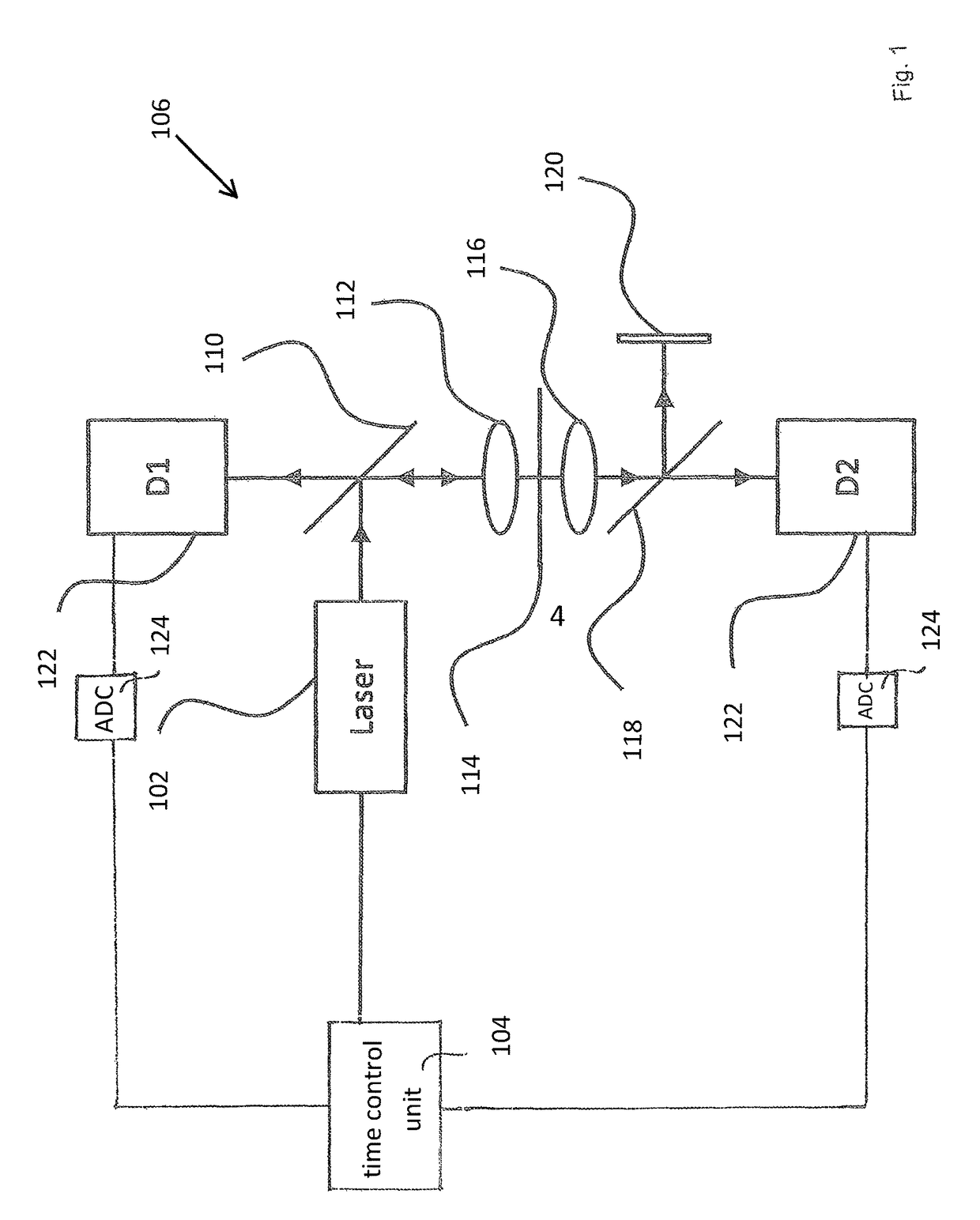
A System and Method for Inducing and Detecting Multi-Photon Processes in a Sample
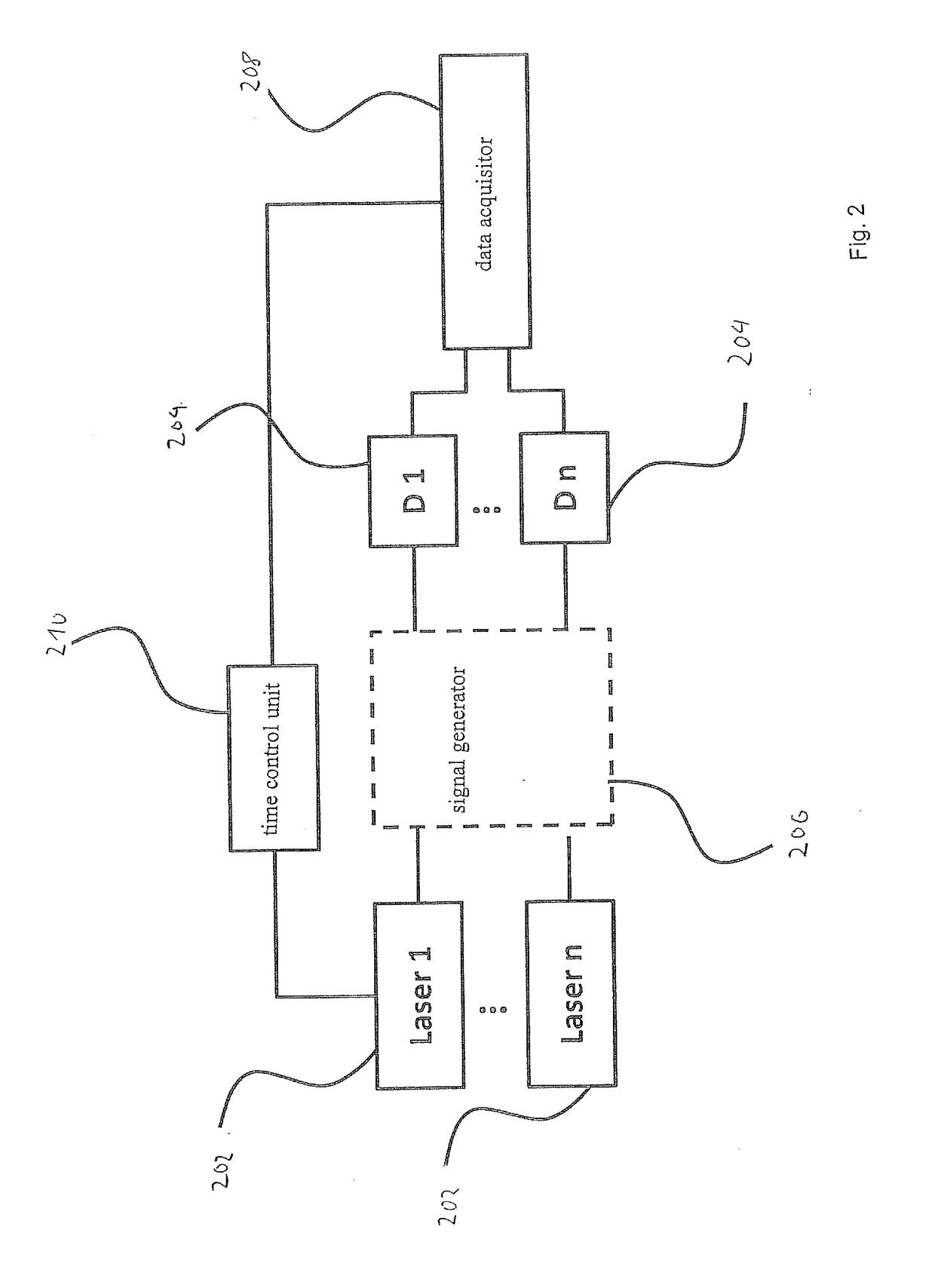
ActiveUS20170146458A1High strengthAvoid pollutionLaser detailsRaman/scattering spectroscopyFluorescenceBeam delivery
Described is a system for inducing and detecting multi-photon processes, in particular multi-photon fluorescence or higher harmonic generation in a sample. The system comprises a dynamically-controllable light source, said dynamically-controllable light source comprising a first sub-light source, said first sub-light source being electrically controllable such as to generate controllable time-dependent intensity patterns of light having a first wavelength, and at least one optical amplifier, thereby allowing for active time-control of creation of multi-photon-excitation. The system further comprises a beam delivery unit for delivering light generated by said dynamically-controllable light source to a sample site, and a detector unit or detector assembly for detecting signals indicative of said multi-photon process, in particular multi-photon fluorescence signals or higher harmonics signals.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHES LASERZENTRUM LUEBECK GMBH
Multi-mode array type scanning imaging device combined with multi-photon excitation
InactiveCN110941100AFast scanningMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam splitterImaging quality
The invention discloses a multi-mode array type scanning imaging device combined with multi-photon excitation, and belongs to the field of optical microscopic measurement. Aiming at different imagingrequirements of a transparent thin sample and a thick scattering sample, the multi-mode imaging device combining multi-photon excitation imaging and common wide-field fluorescence imaging is designedthrough selection of different light sources, and the two light sources can realize switching of multiple modes through combination of a beam splitter. A fixed micro-lens array is used for accuratelycontrolling an illumination mode and the position of an excitation point so as to generate sparse focus illumination, rapid scanning of a sample is completed, rapid double-resolution imaging of a transparent sample and a thick sample is achieved, and meanwhile the image contrast of the thick scattering sample is improved. Moreover, an adaptive aberration correction unit is introduced into the imaging system, so that the aberration of the system is reduced or eliminated, and the imaging depth and the imaging quality in a multi-photon imaging mode are improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multi-photon fluorescence microscopic imaging system with ultra-fast time resolution and low excitation threshold
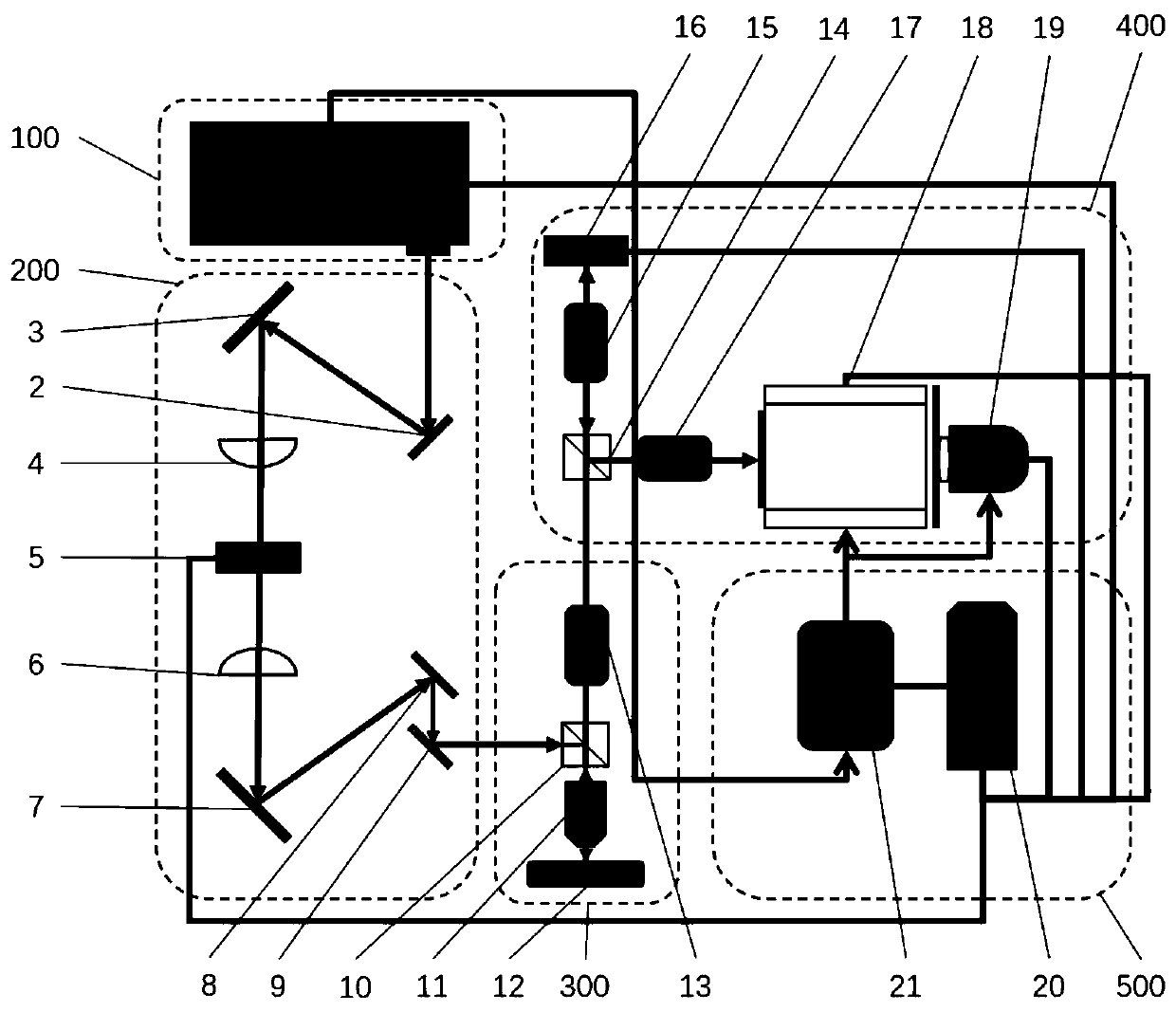
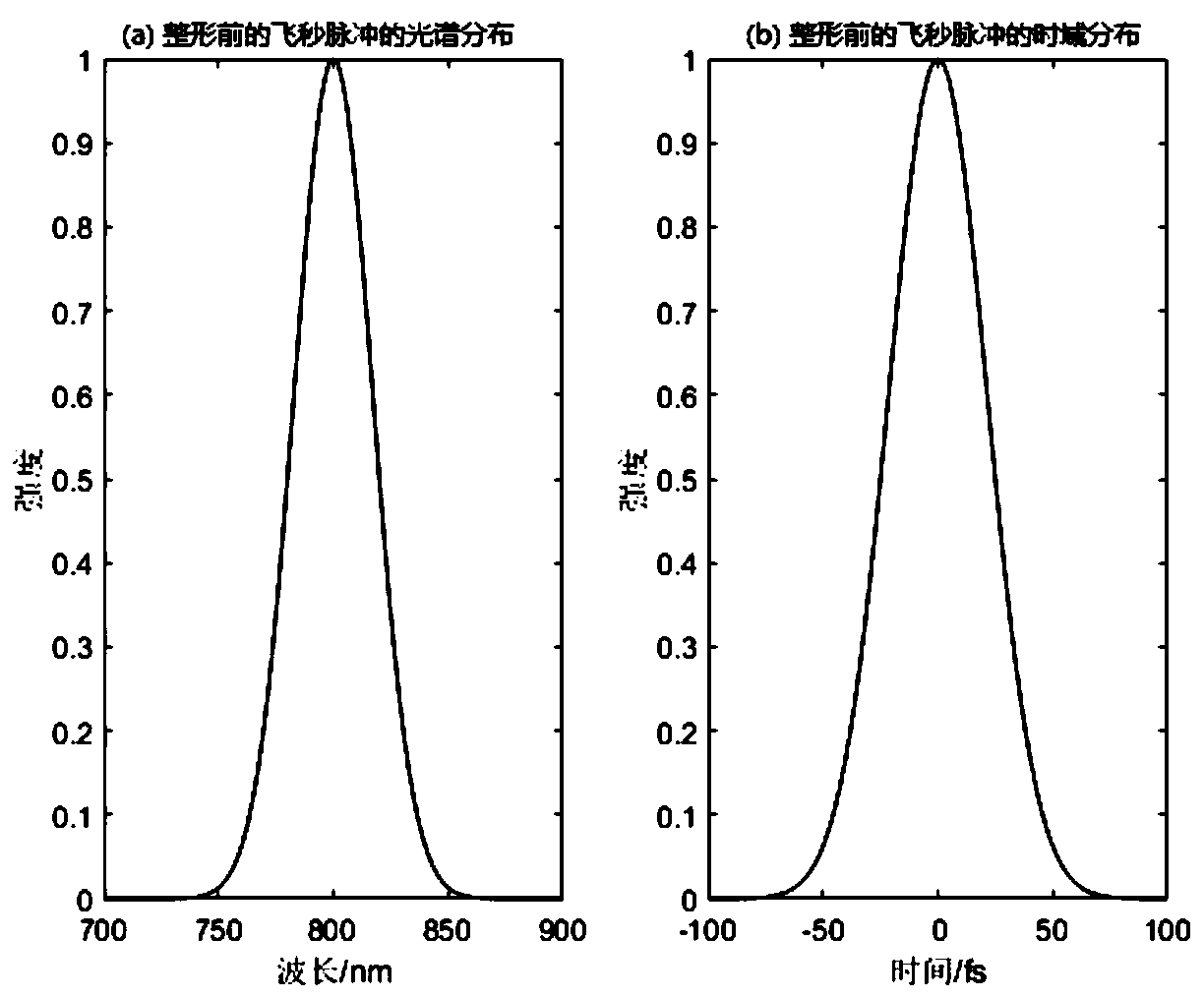
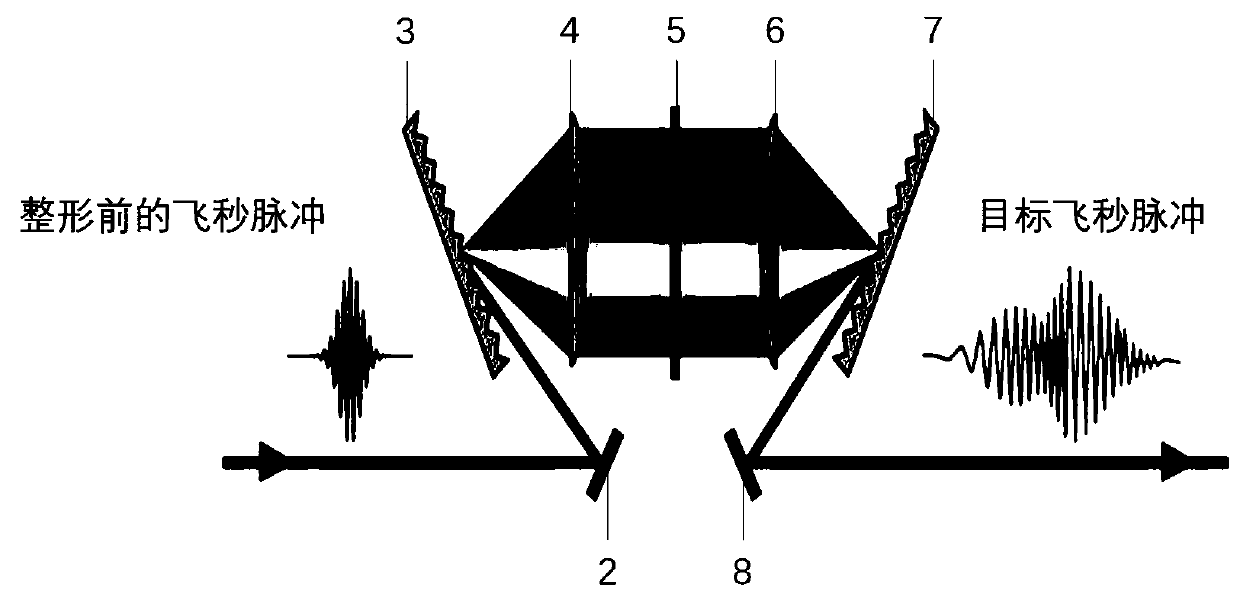
ActiveCN111537477ALow multiphoton excitation threshold propertiesLow fluorescence efficiencyMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageMicro imaging
The invention discloses a multi-photon fluorescence microscopic imaging system with ultra-fast time resolution and a low excitation threshold. The multi-photon fluorescence microscopic imaging systemcomprises a femtosecond laser, an adaptive femtosecond pulse shaping module, a fluorescence microscopic imaging module, a compressed sensing ultra-fast imaging module and a computing communication module. According to the invention, a target femtosecond pulse after time domain shaping is obtained through the femtosecond laser and the adaptive femtosecond pulse shaping module; a fluorescence microscopic signal is obtained by the fluorescence microscopic imaging module, sparse coding two-dimensional digital image data are generated by the compressed sensing ultra-fast imaging module, and targetsignal reconstruction is carried out on the sparse coding two-dimensional digital image data by the computing communication module. According to the invention, the femtosecond laser pulse is subjectedto waveform shaping, phase modulation and sparse coding of fluorescence information, so that the excitation threshold of a multi-photon fluorescence process is reduced; and the fluorescence lifetimeis estimated by using a sparse coding model, so that single-pulse fluorescence microscopic imaging with a low multi-photon excitation threshold characteristic and ultra-fast time resolution of a single pulse is realized.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Sensing device, sensing apparatus, and sensing method
There are provided a sensing device, a sensing apparatus, and a sensing method capable of realizing effective multi-photon absorption and local plasmon enhancement function. The sensing device can realize a high multi-photon excitation efficiency and selectivity by accurately controlling the material, shape, size, interval, and direction of metal particles arranged on a substrate. By employing the sensing device in various sensing apparatuses such as a fluorescent sensing apparatus, it is possible to realize sensing of detection object material with a high sensibility.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY
Sensor, sensing apparatus and sensing method
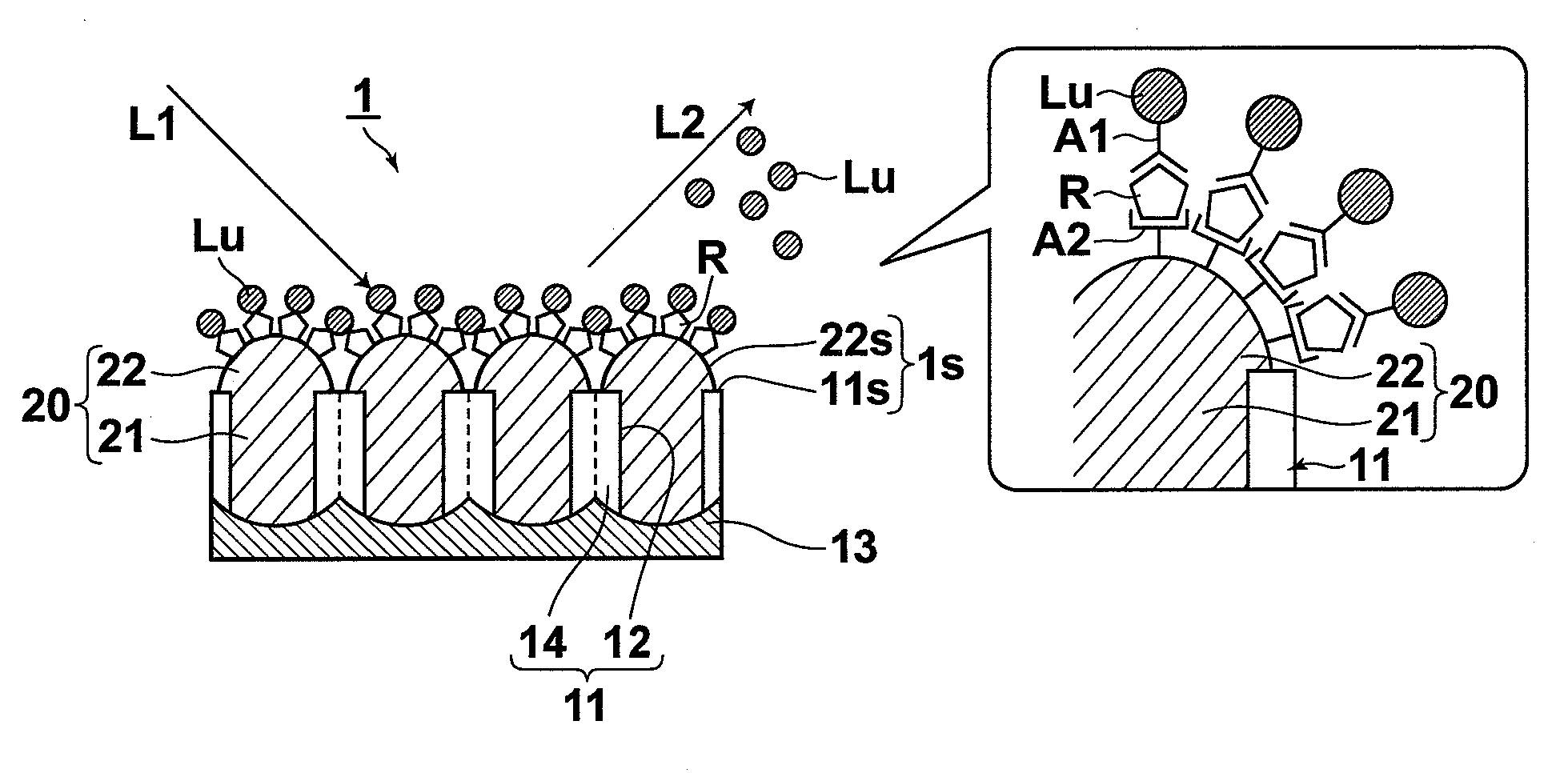
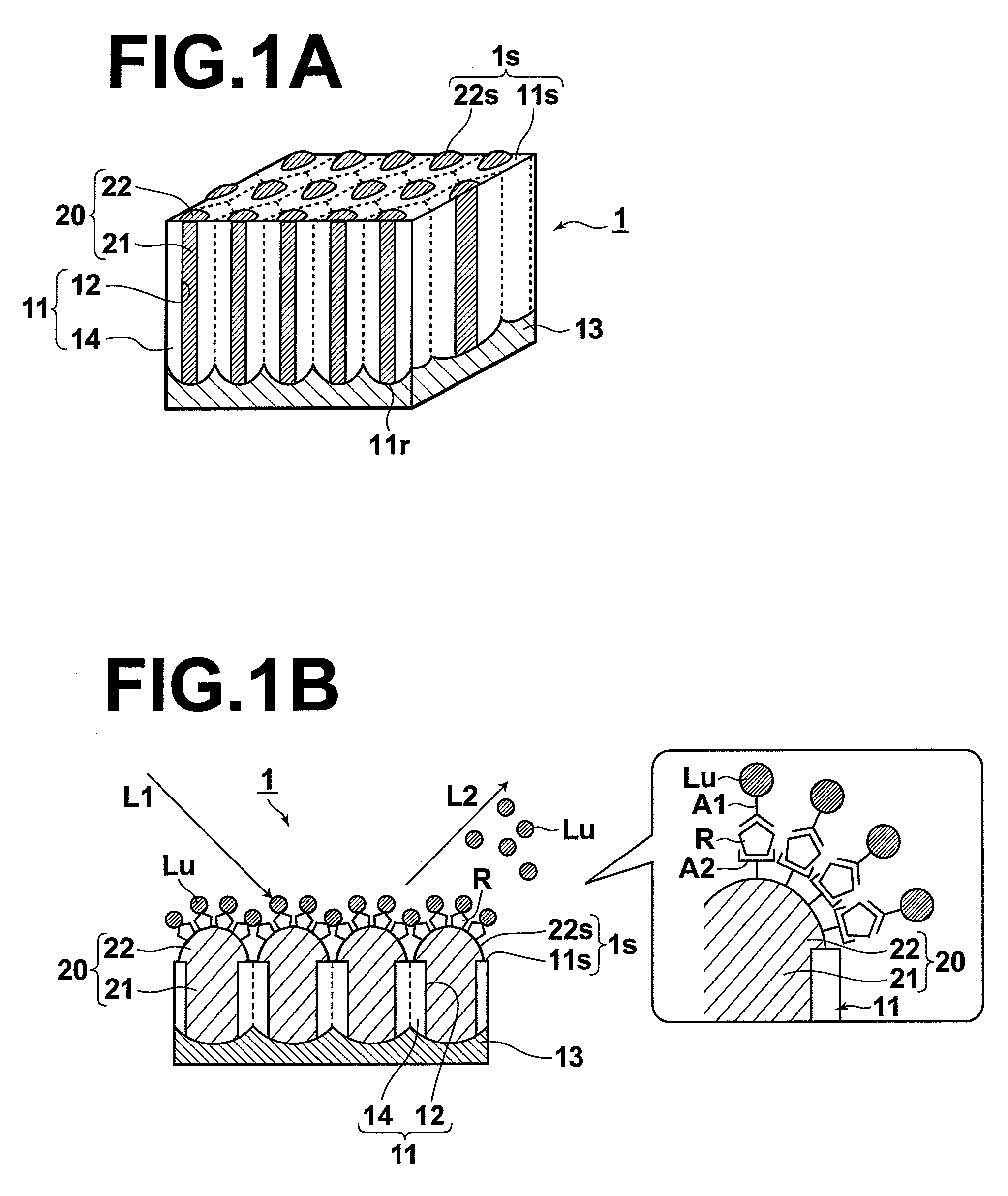
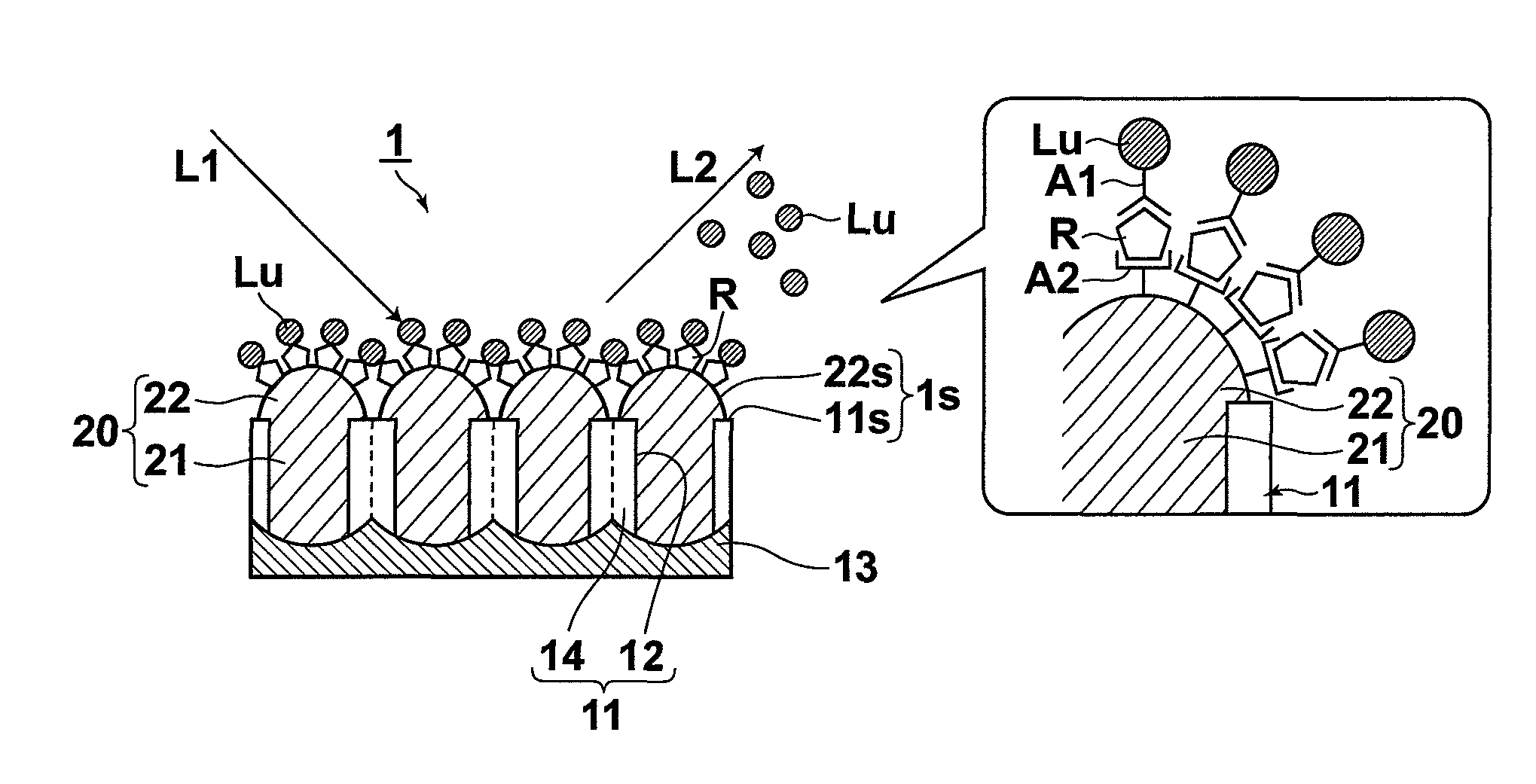
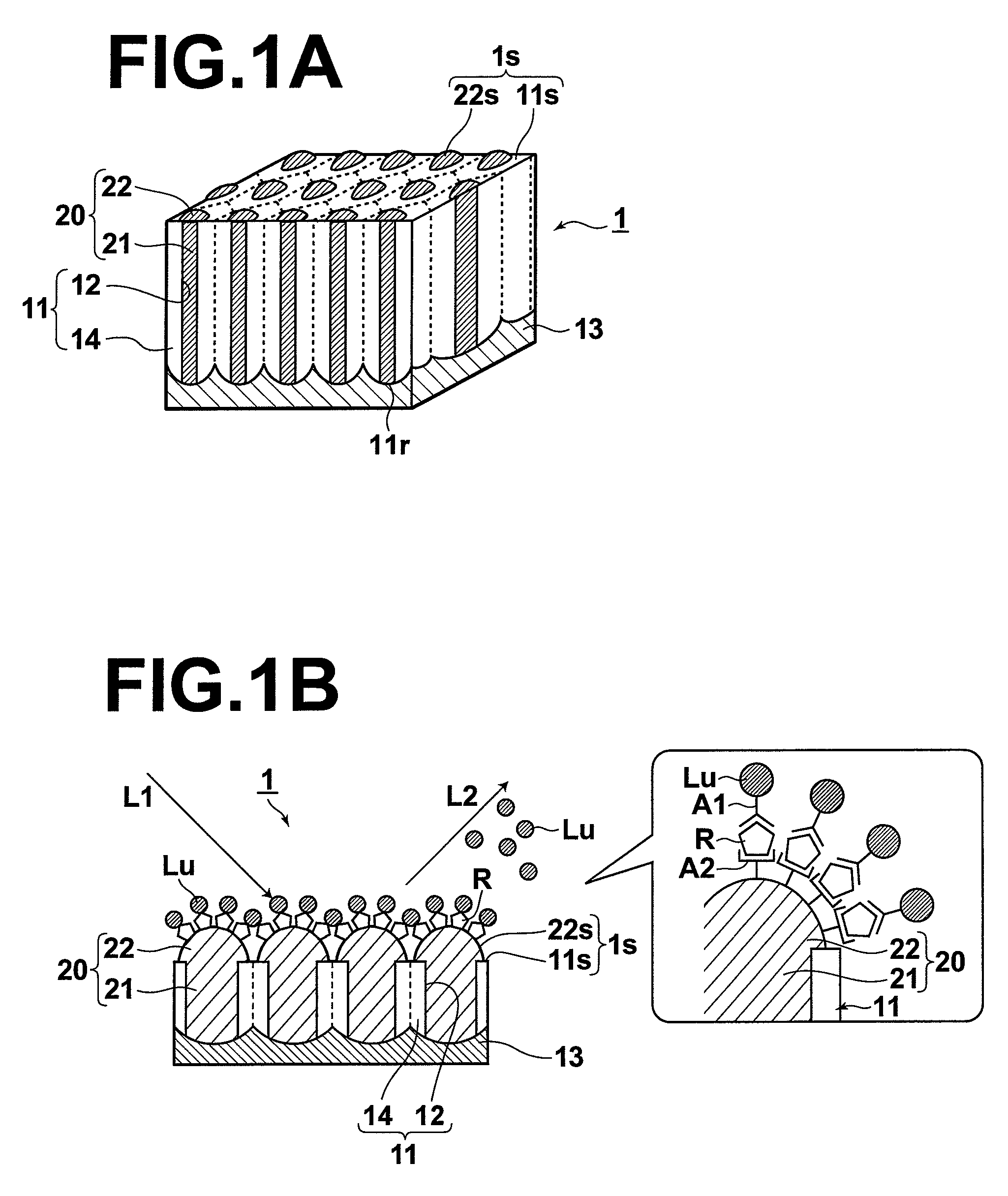
InactiveUS20080137063A1Power of measurement is increasedHigh fluorescence efficiencyRadiation pyrometrySamplingLength waveSurface binding
A sensor has a sensing surface, to which a specific substance R to be detected can bind. Further, the sensor has a metal portion, at least a portion of which is exposed at the sensing surface, and in which localized plasmons can be excited. The sensor is used in sensing, in which the substance R to be detected is marked with a fluorescent marker Lu that selectively binds to the substance R to be detected and one of two-photon excitation fluorescence and multi-photon excitation fluorescence of the fluorescent marker Lu is detected. Further, the sensing surface is illuminated with measurement light L1 having a wavelength that can excite localized plasmons in the metal portion and that is an absorption wavelength of the fluorescent marker Lu, at which the fluorescent marker Lu emits one of the two-photon excitation fluorescence and the multi-photon excitation fluorescence.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
High-resolution microscope and method for determining the two- or three-dimensional positions of objects
ActiveUS9234846B2High resolutionColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsGratingControl selection
The invention relates to a high-resolution microscope and to a method for determining the two- or three-dimensional positions of objects. The microscope and method includes the following: (a) The vertical (Z) position of imaged particles or molecules being determined from the orientation and shape thereof by means of an anamorphic lens, preferably a cylindrical lens, in the imaging, (b) the detection beam path being split into at least two partial detection beam paths having different optical path lengths, which are detected at an offset on a detector, (c) activation or switchover being performed by means of a multi-photon excitation process, preferably two-photon excitation. The following are also included: (d) a point-scanning activation or switchover, (e) a line-scanning activation or switchover, (f) the sample is excited and the sample light is detected in the wide-field mode, (g) manually or automatically predetermined sample regions are activated or switched over, (h) the activation or switchover is performed by means of AOTF or SLM or DMD, (i) laser pulses for activating or switching are spectrally split by means of a spectrally splitting element, preferably a grating, (j) an SLM or DMD in the beam path after the grating performs a controlled selection of split laser pulse fractions, (k) the laser wide-field excitation is guided by SLM or DMD, (l) ROIs are selected by SLM or DMD, (m) a multi-photon switching or activation is performed by means of a microlens array, preferably a cylindrical lens array, n) switching and / or excitation is performed by means of a line scanner, and (o) a line detection is performed by means of a spatially resolved sensor, wherein at least two sensor rows, each comprising a plurality of sensors, are illuminated with sample light by means of a slit diaphragm position.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
System and method for inducing and detecting multi-photon processes in a sample
Described is a system for inducing and detecting multi-photon processes, in particular multi-photon fluorescence or higher harmonic generation in a sample. The system comprises a dynamically-controllable light source, said dynamically-controllable light source comprising a first sub-light source, said first sub-light source being electrically controllable such as to generate controllable time-dependent intensity patterns of light having a first wavelength, and at least one optical amplifier, thereby allowing for active time-control of creation of multi-photon-excitation. The system further comprises a beam delivery unit for delivering light generated by said dynamically-controllable light source to a sample site, and a detector unit or detector assembly for detecting signals indicative of said multi-photon process, in particular multi-photon fluorescence signals or higher harmonics signals.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHES LASERZENTRUM LUEBECK GMBH
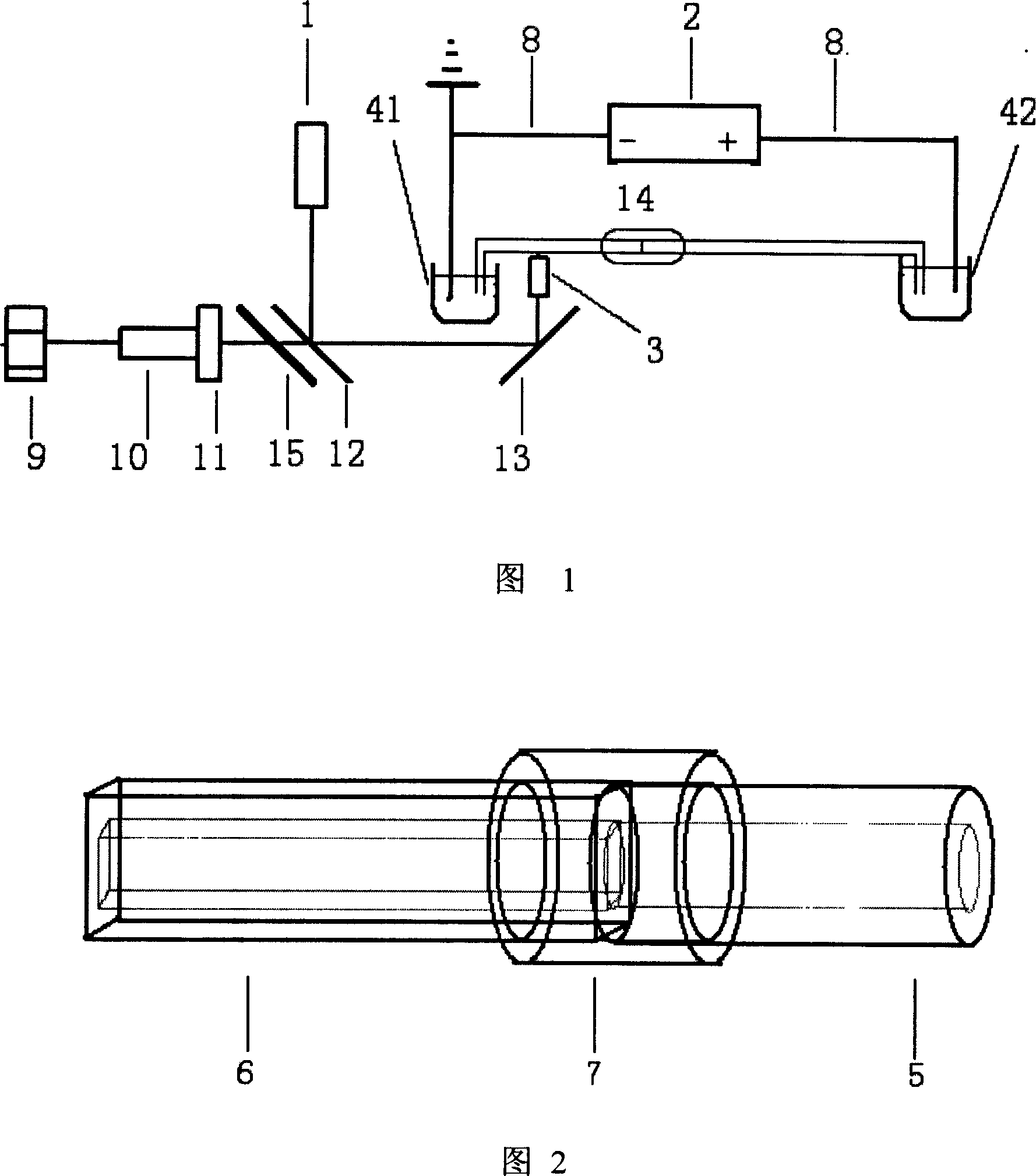
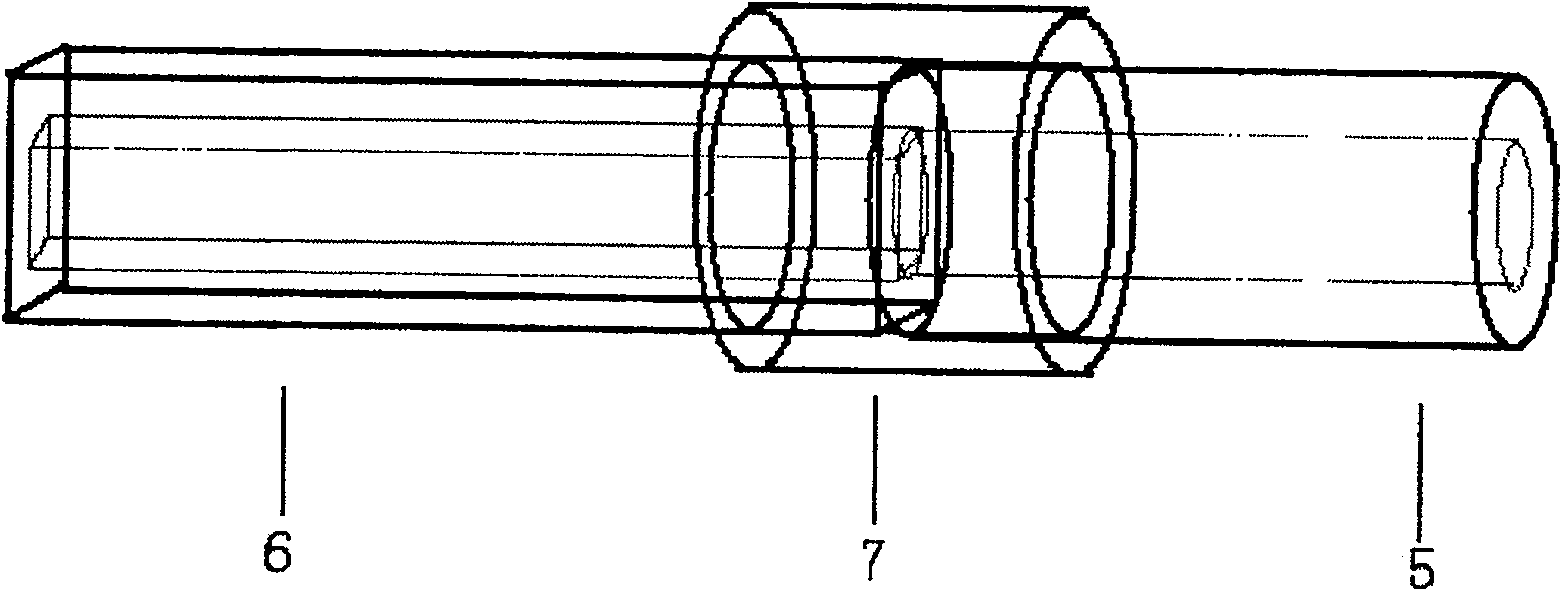
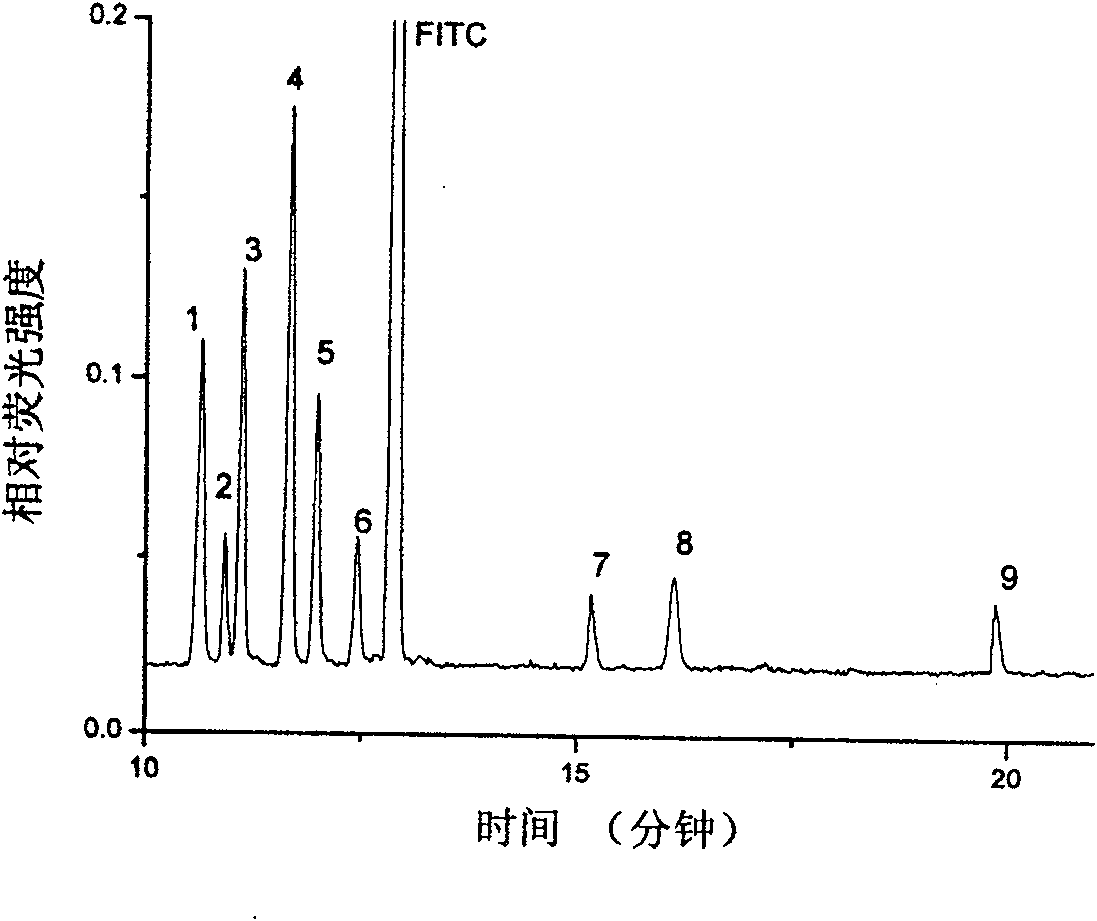
Detecting instrument on capillary cataphoretic-multi-photon excitation fluorescent column
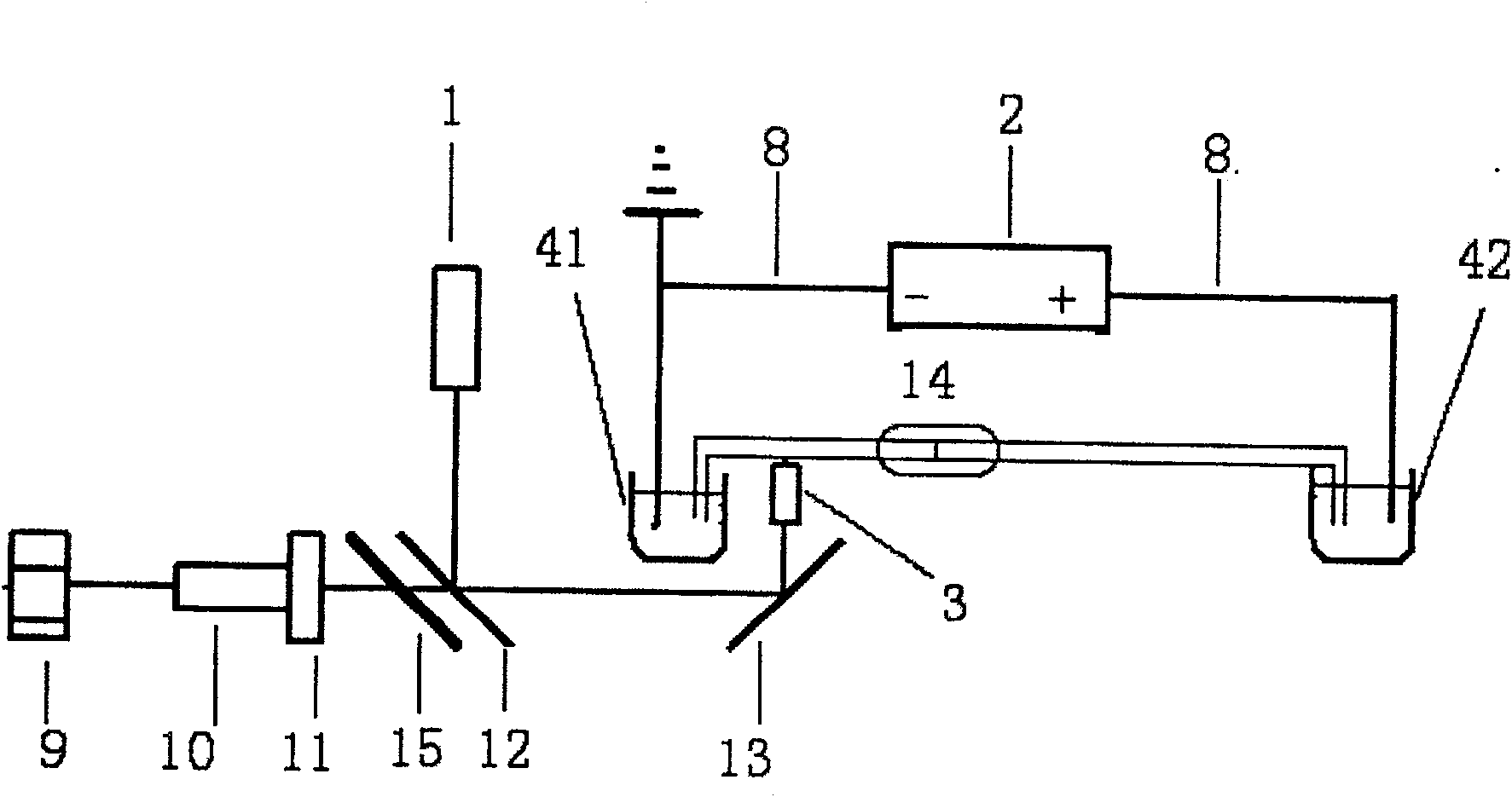
InactiveCN101021476APreserve separation effectSimplify post-column testingDispersed particle separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFluorescenceBand-pass filter
The invention discloses a column detector of capillary electrophoresis-multiphoton exciting fluorescence. It contains semiconductor laser, objective lens, computer, collecting card, electron-multiplier phototube, dichroscope, band-pass filter, all mirror, platinum electrode, constant-current high-voltage power, first buffer pool, second buffer pool and column detector. Connects square and round capillaries, in which round capillary is used for division (according to experiments, division effect of round capillary is batter than that of squire capillary) and squire capillary is used for column detecting. The combination of squire and round capillaries not only simplifies experimental devices, lowers cost and simplifies complex post column detection, but also improves detecting sensitivity.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Plane-projection multi-photon microscopy
ActiveUS20120182413A1Uniform sizeLarge numerical apertureColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsWide fieldLaser light
A novel method and system for conducting wide-field multi-photon microscopy through plane-projection are provided. It has been discovered that the limitations of conventional temporal-focusing techniques, such as single excitation wavelength and low acquisition rates can be resolved utilizing a novel optical set-up in which an optical diffuser is used as the scatterer. The use of such an optical arrangement enables temporal focusing regardless of the central wavelength of laser pukes. In addition, the optical sectioning possible using the disclosed microscopy is comparable to confocal microscopy, and can be robustly achieved by both moderate and high NA objectives at 100-fs puke width. Moreover, the multi-photon excitation efficiency of the disclosed system can be enhanced by lowering the repetition rate of the ultrafast laser light source at constant pulse width and average power.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
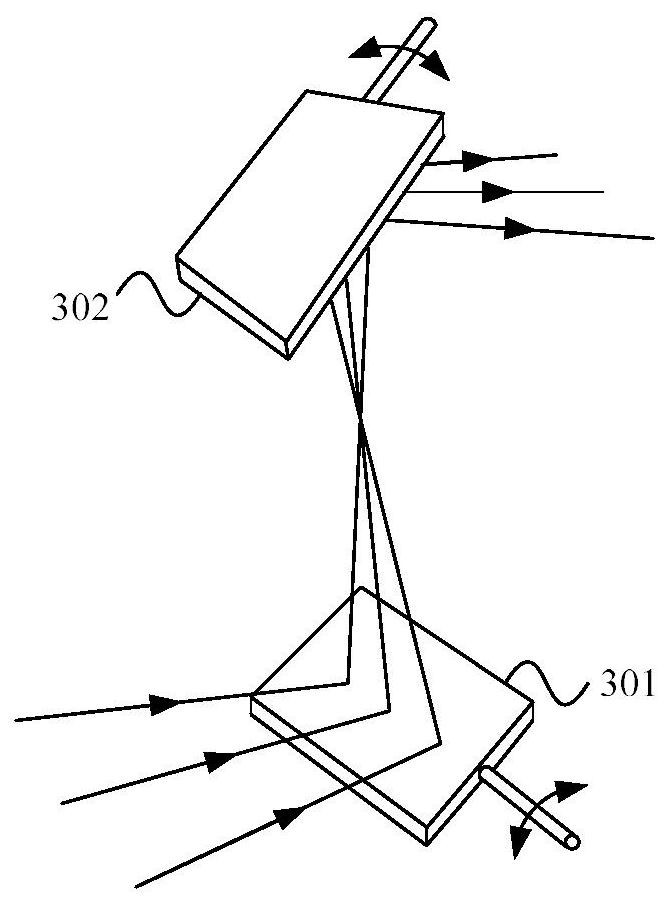
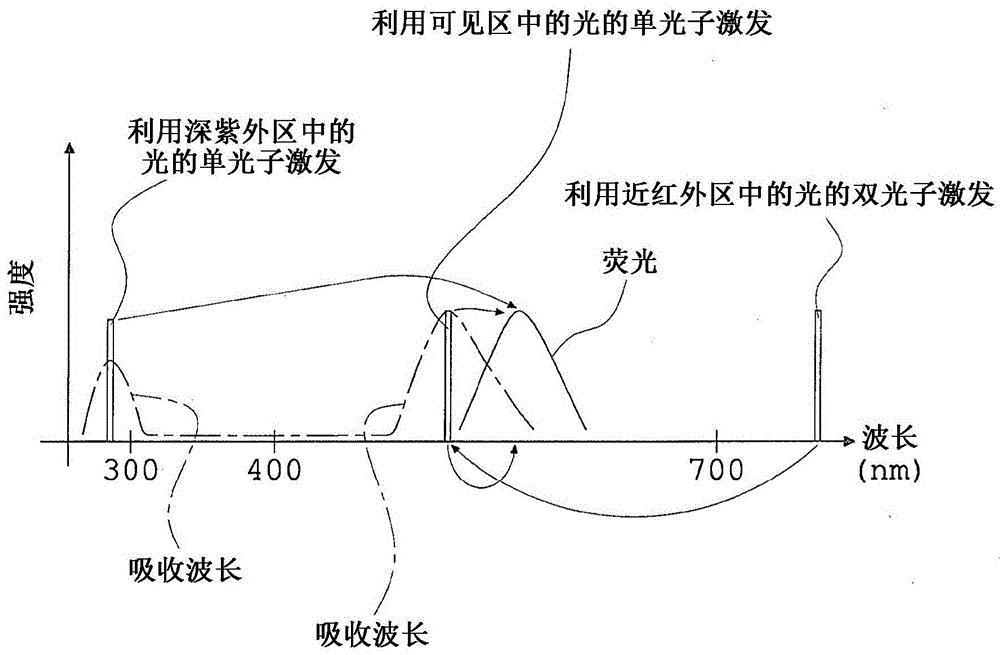
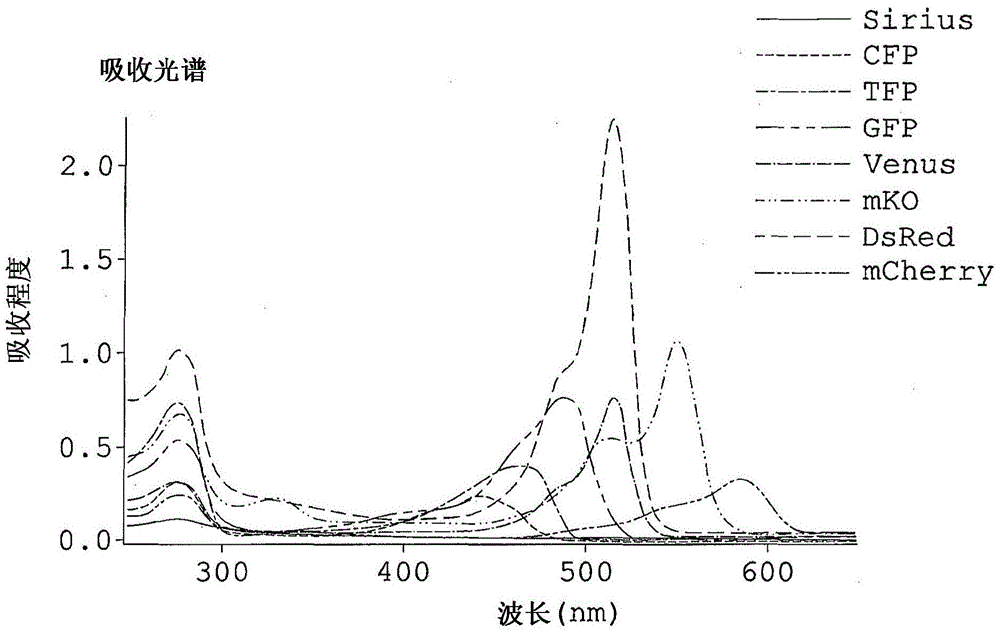
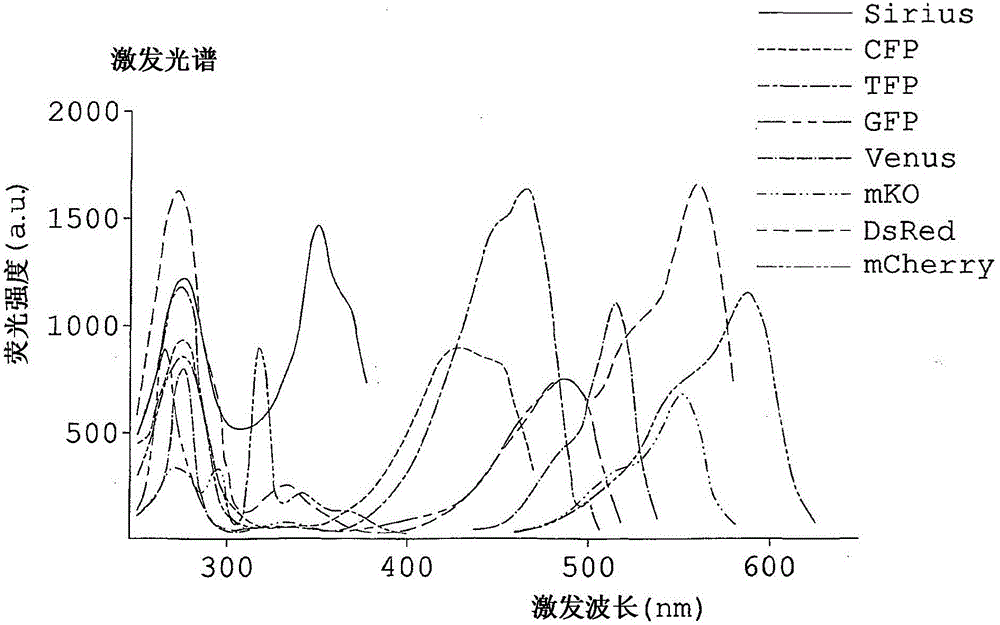
Fluorescece obsevation method and fluorescence obsevation apparatus
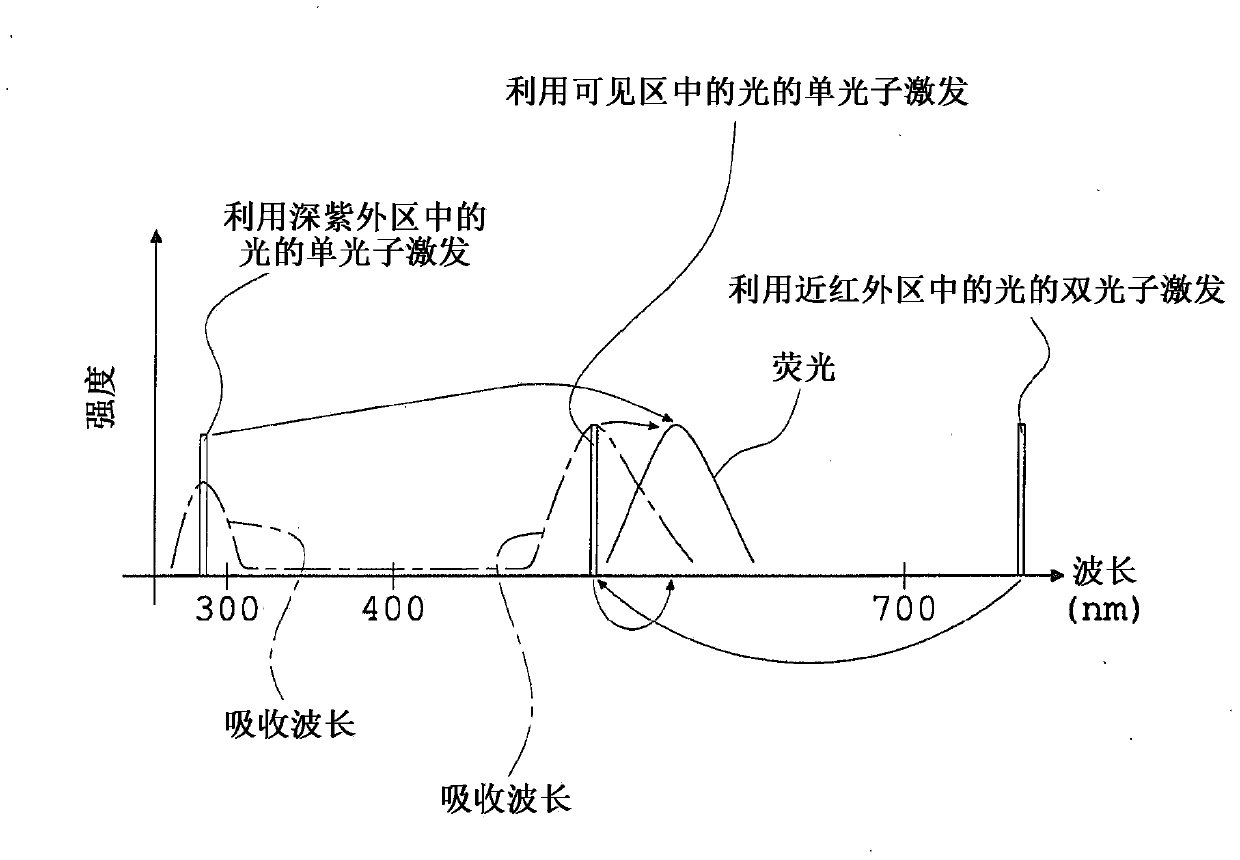
A fluorescence observation method in which it is possible to observe plural types of fluorescence emitted from plural kinds of fluorescent molecules simultaneously without the necessity of plural kinds of exciting wavelengths and with a simple optical structure, an observed object for which a fluorescent molecule is used as a fluorescent label suffers little damage, and it is possible to use glass that is in common use as an optical material used for fluorescence observation, and a fluorescence observation apparatus are offered. A fluorescence observation method of the present invention for detecting plural types of fluorescence emitted from two or more kinds of fluorescent molecules includes: subjecting each of the two or more kinds of fluorescent molecules to multi-photon excitation by exciting light having an exciting wavelength equal to or shorter than 700nm in a visible region, to generate fluorescence upon making use of an absorption wavelength band in a deep ultraviolet region of each of the two or more kinds of fluorescent molecules; and simultaneously detecting plural types of fluorescence generated on a shorter-wavelength side or on both of the shorter-wavelength side and a longer-wavelength side of the exciting wavelength of the exciting light.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Near-infrared fluorescent molecule with double (multi) photon excitation and synthesis method of near-infrared fluorescent molecule
PendingCN113549090AStrong absorption capacityStrong launching abilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical compoundPhenyl group
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Apparatus for three-dimensional optical data storage and retrieval
InactiveUS20060057497A1Increase memory capacityImprove optical qualityOrganic chemistryPhotography auxillary processesData recordingData storing
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
Surface plasmon sensor, sensing apparatus and sensing method
InactiveUS7898659B2Simple structureHigh fluorescence efficiencyRadiation pyrometrySamplingFluorescenceSurface plasmon
A sensor has a sensing surface, to which a specific substance R to be detected can bind. Further, the sensor has a metal portion, at least a portion of which is exposed at the sensing surface, and in which localized plasmons can be excited. The sensor is used in sensing, in which the substance R to be detected is marked with a fluorescent marker Lu that selectively binds to the substance R to be detected and one of two-photon excitation fluorescence and multi-photon excitation fluorescence of the fluorescent marker Lu is detected. Further, the sensing surface is illuminated with measurement light L1 having a wavelength that can excite localized plasmons in the metal portion and that is an absorption wavelength of the fluorescent marker Lu, at which the fluorescent marker Lu emits one of the two-photon excitation fluorescence and the multi-photon excitation fluorescence.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for detecting biological molecules based on upconversion luminescent material and detection system implementing same
ActiveCN104345048AEliminate distractionsAvoid strong scatteringMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by material excitationUpconversion luminescenceReaction system
The invention provides a method for detecting biological molecules based on an upconversion luminescent material. The method comprises the following steps: 1) combining the to-be-detected biological molecules with markers, wherein the markers are prepared by using the upconversion luminescent material; and then removing uncombined excess markers; 2) adding a dissociation agent into the reaction system of the step 1), and making the upconversion luminescent material dissociated to a liquid phase; and 3) detecting the presence or the amount of the markers or the upconversion luminescent material in the reaction system of the step 2). The method is a multi-photon excitation upconversion luminescent mark liquid phase detection technology suitable for quantitative or qualitative detection of the biological molecules. The invention also provides a detection system for implementing the method.
Owner:杨晓林 +2
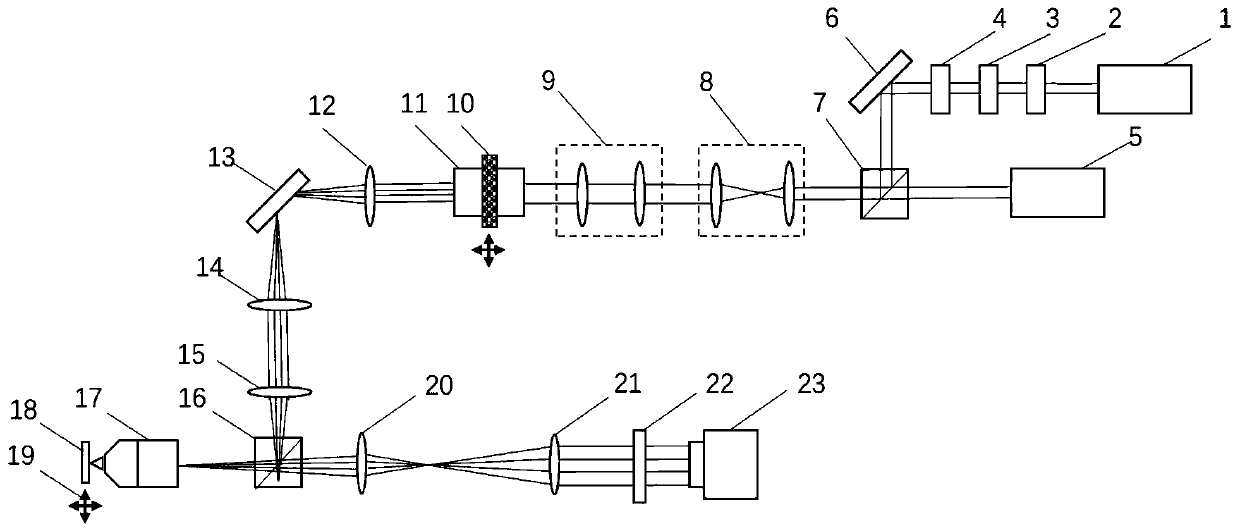
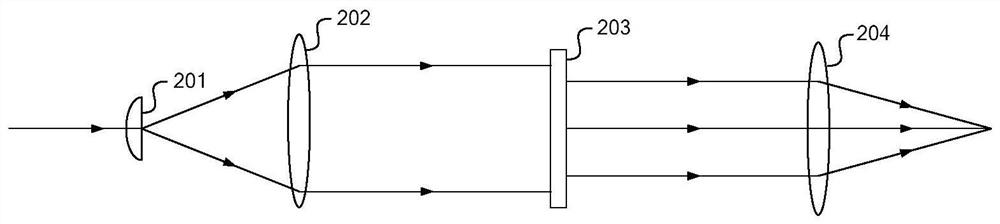
Method for inspecting an article and apparatus for measuring the article by multi-photon excitation technique
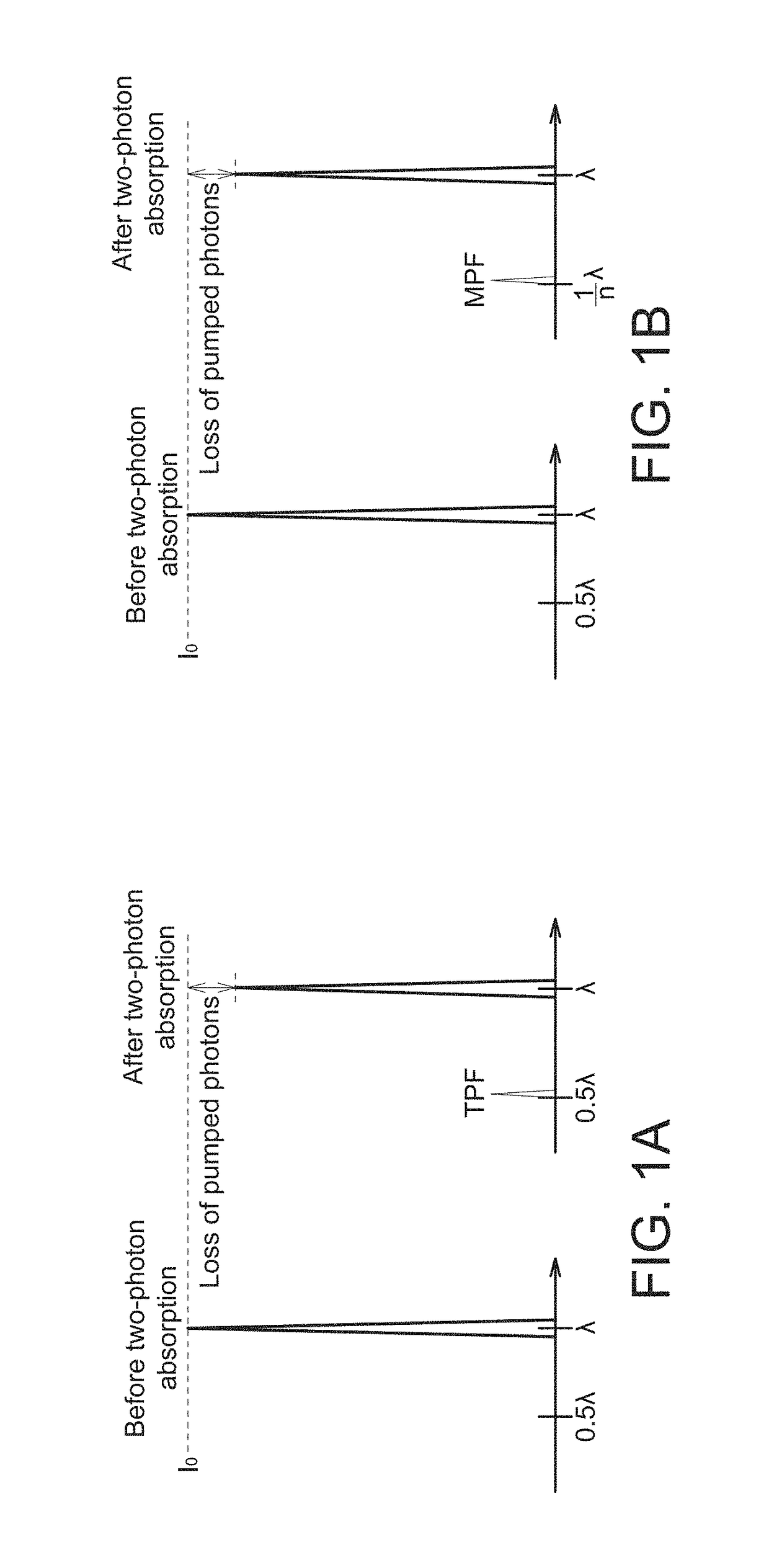
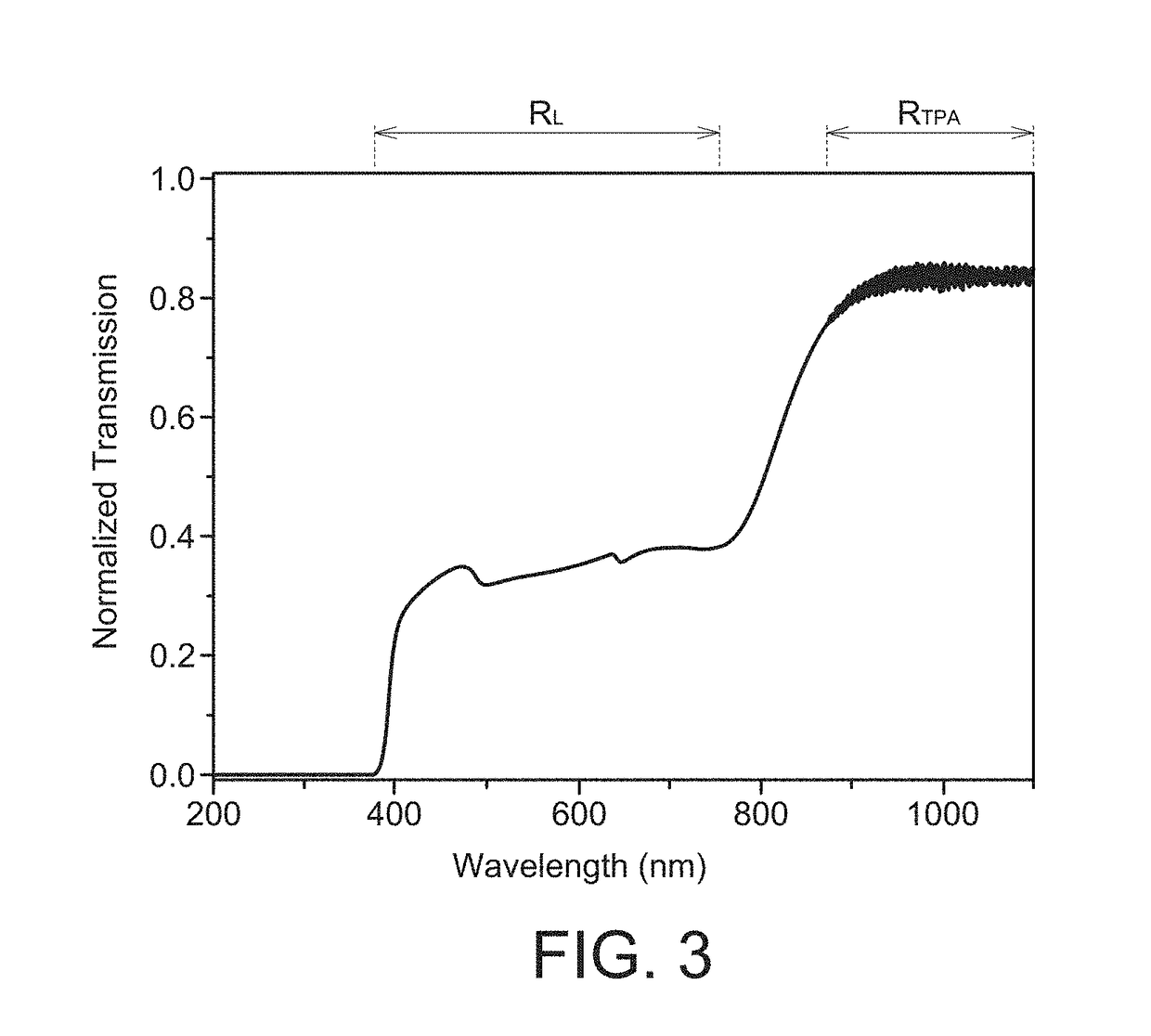
A method for inspecting an article containing a target material is provided. A sampling position of the article is illuminated by a beam of laser light having a wavelength λ. Illumination focus to a focal point at the sampling position of the article to produce molecular excitation of the target material by simultaneous absorption of n incident photons of the beam of laser light, wherein n is equal to or greater than two. An output light exited from the article is analyzed by a detector, wherein the output light is of a wavelength range between 0.8λ and 1.2λ.
Owner:CM VISUAL TECH CORP
Detecting instrument on capillary electrophoresis-multi-photon excitation fluorescent column
InactiveCN100573107CPreserve separation effectSimplify post-column testingDispersed particle separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBandpass filteringFluorescence
The invention discloses a detector on a capillary electrophoresis-multiphoton excitation fluorescent column, which includes a semiconductor laser, an objective lens, a computer, an acquisition card, a photomultiplier tube, a dichroic mirror, a band-pass filter, and a total reflection mirror , platinum electrode, DC high voltage power supply, first and second buffer pools and column detector. The on-column detector uses a Teflon tube to connect the square capillary and the circular capillary, wherein the circular capillary is used for separation (experiments have proved that the separation effect of the square capillary is not as good as the circular one), while the square capillary is used for on-column detection. The square capillary detected on the fluorescent column is combined with the circular capillary used for separation to realize on-column detection, which not only simplifies the traditional experimental equipment, reduces the cost of experimental equipment, simplifies the post-column detection method of complex operations, but also improves the detection sensitivity .
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
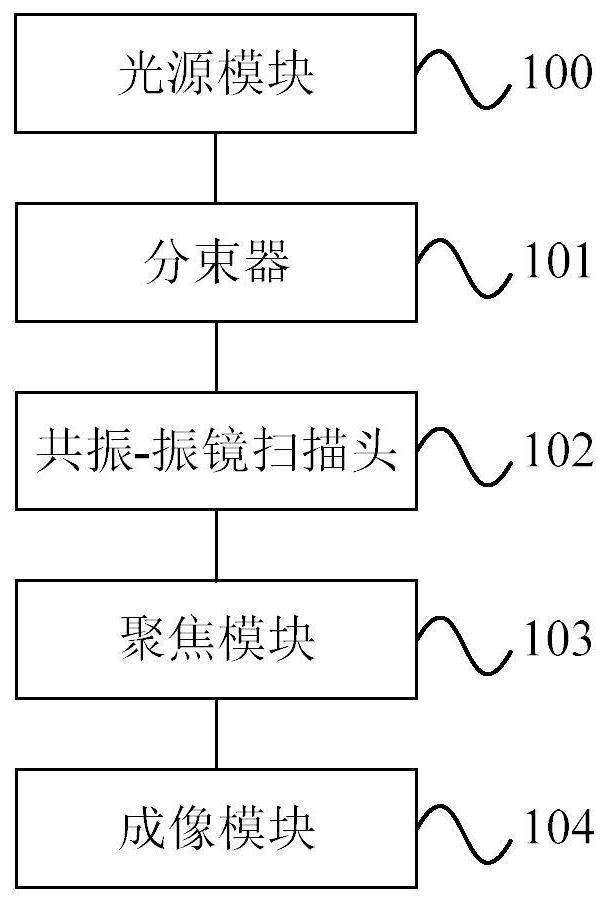
Multi-beam multi-photon microscopy imaging device
The invention provides a multi-beam multi-photon microscopic imaging device, comprising: a light source module, used to generate laser light that can be used for multi-photon excitation; a beam splitter, used to generate multiple beams distributed on a straight line with equiangular intervals laser; the resonant-galvanometer scanning head, the scanning direction of the resonant scanning head and the galvanometer scanning head are perpendicular to each other and the arrangement direction of the multi-beam laser is consistent with the scanning direction of the galvanometer scanning head; the focusing module is used to combine the resonant-vibration The laser light emitted by the mirror scanning head is converted into equidistant focused light spots to irradiate the sample to excite fluorescence or multi-photon higher-order harmonic signals; the imaging module is used to collect fluorescence or multi-photon higher-order harmonic signals for imaging. A multi-beam multi-photon microscopic imaging device provided by the present invention adopts multi-beam lasers distributed on a straight line, and the arrangement direction of the multi-beam lasers is consistent with the scanning direction of the galvanometer scanning head, so that the multi-beams can scan the sample at the same time Scanning, improved imaging speed.
Owner:北京卓奥友科技有限公司
Fluorescence observation method and fluorescence observation equipment
A fluorescence observation method of the present invention for detecting plural types of fluorescence emitted from two or more kinds of fluorescent molecules includes: subjecting each of the two or more kinds of fluorescent molecules to multi-photon excitation by exciting light having an exciting wavelength equal to or shorter than 700 nm in a visible region, to generate fluorescence upon making use of an absorption wavelength band in a deep ultraviolet region of each of the two or more kinds of fluorescent molecules; and simultaneously detecting plural types of fluorescence generated on a shorter-wavelength side or on both of the shorter-wavelength side and a longer-wavelength side of the exciting wavelength of the exciting light.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com