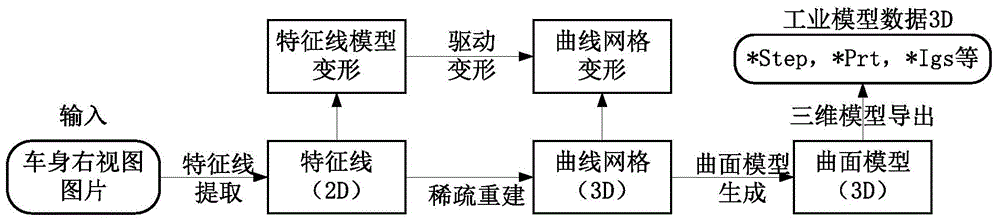
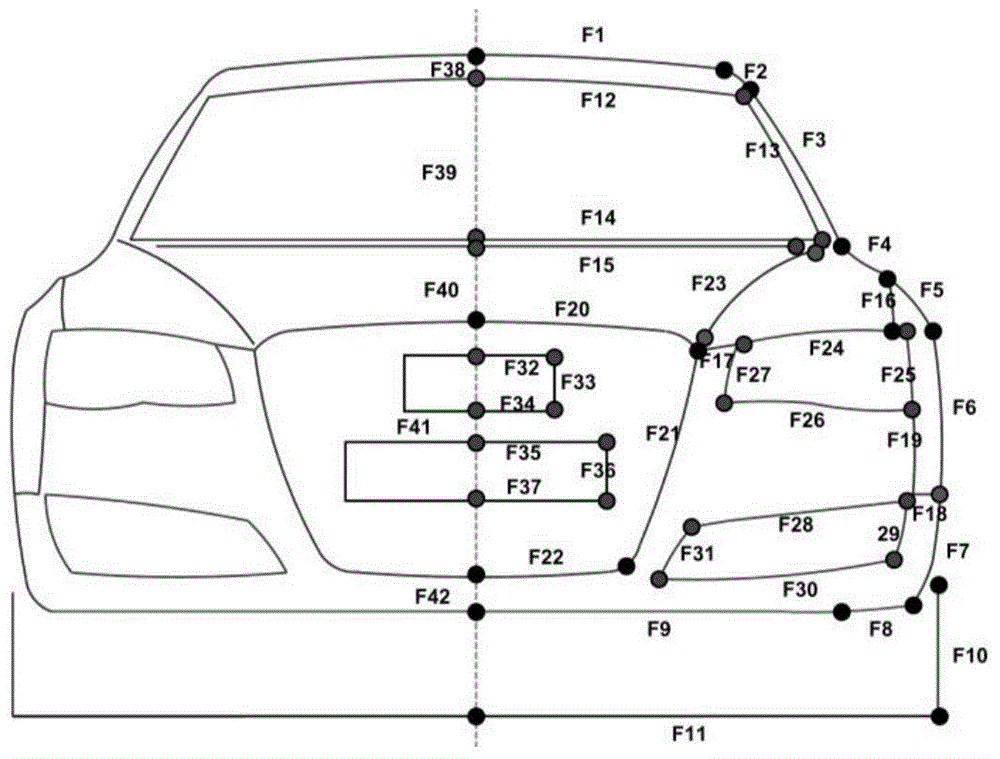
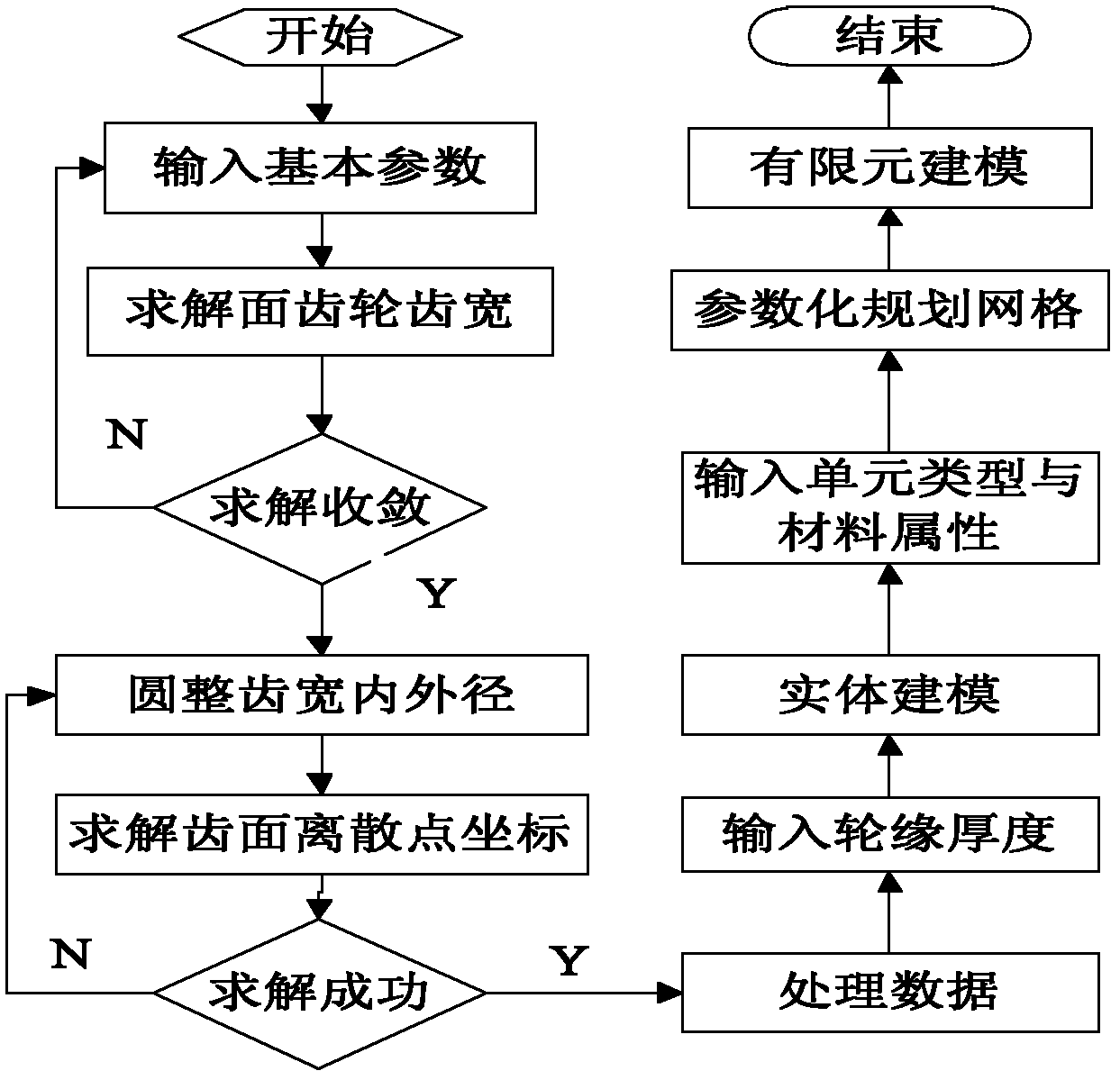
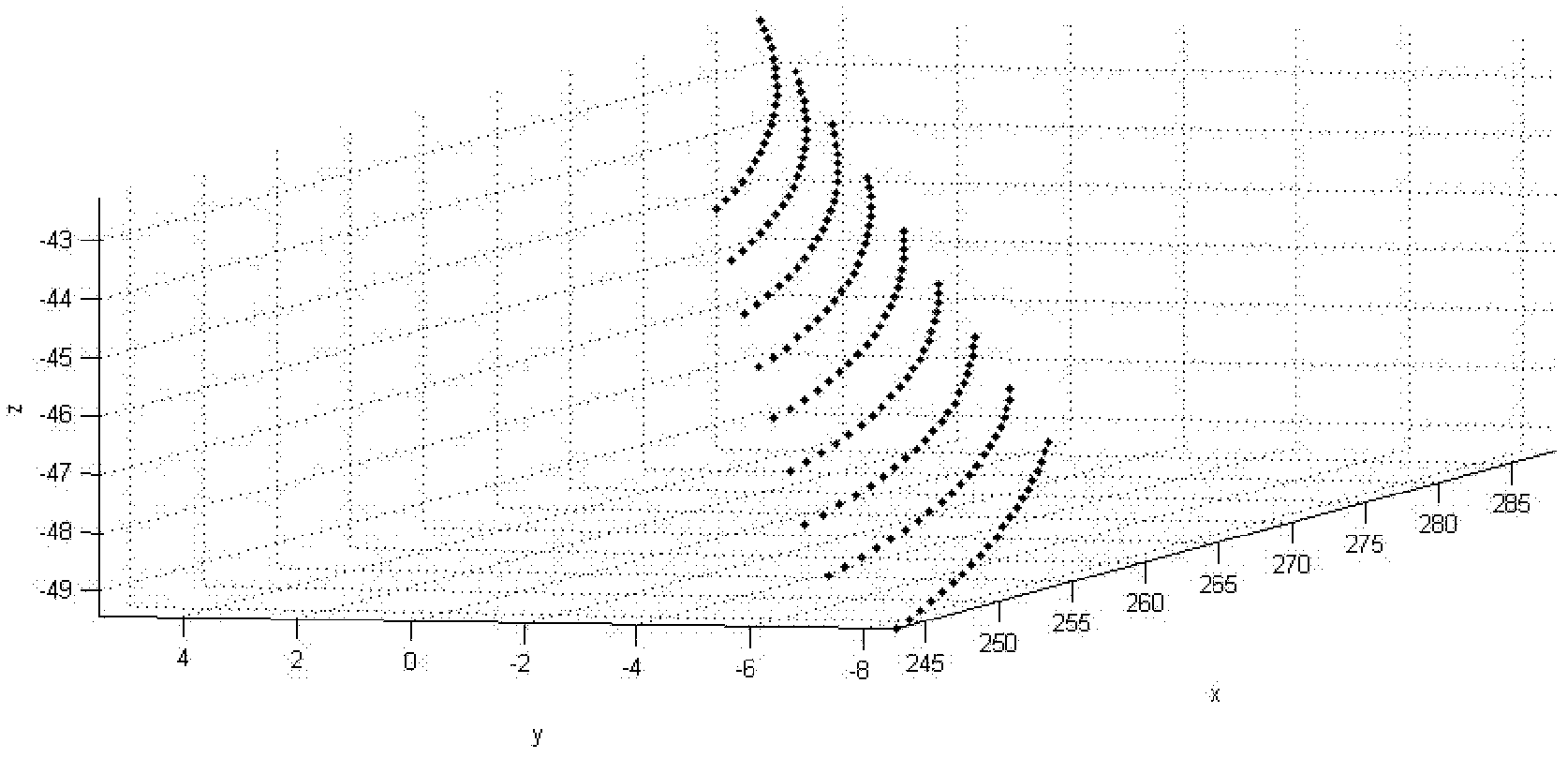
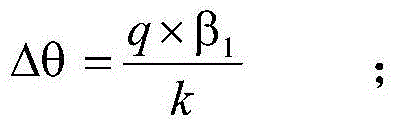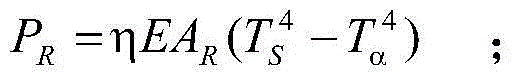Patents
Literature
129 results about "Solid modelling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solid modelling definition. A solid model is a more complete representation of a surface (or wireframe model). Furthermore, a solid model uses both geometric and topological data, which represents a solid completely. Geometric data addresses shapes, sizes and positioning in a 3D environment or coordinate system.
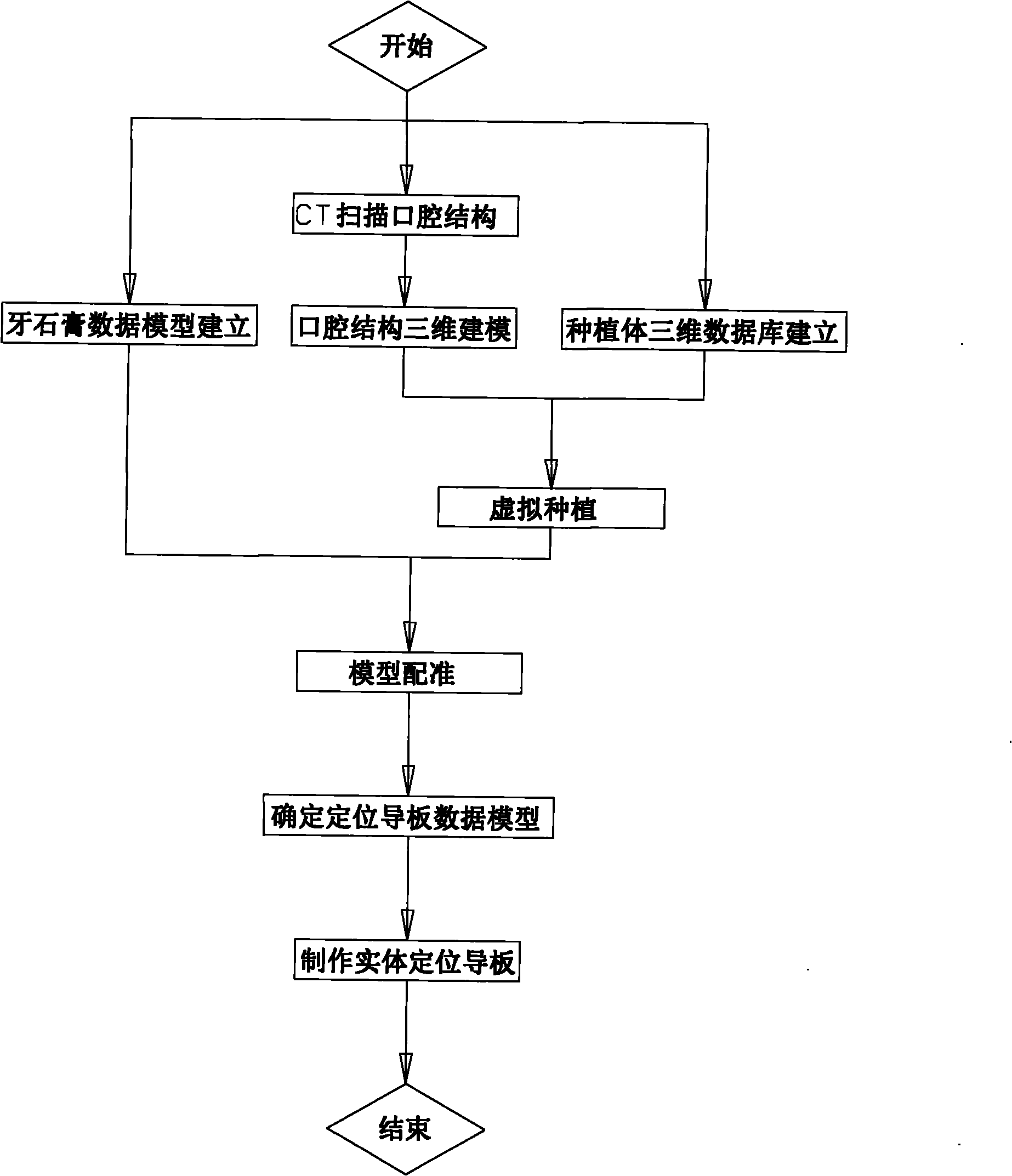
Manufacturing method of implant denture individualized positioning guide plate
InactiveCN101828974AGuaranteed manufacturing accuracyEasy to manufactureDental implantsAnatomical structuresBiomechanics
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of an implant denture individualized positioning guide plate in the technical field of tooth repair technologies, which comprises the steps of: firstly, establishing a three-dimensional model of anatomical structures of teeth, jaws, maxillary antrums, mandibular nerve conduits and the like according to oral cavity CT data of patients; secondly, carrying out virtual implanting on a solid modeled implant model, matching an implanted model with a patient oral cavity structural data model established after scanning a dental model by using an opticalscanner, determining the position of a guide hole of the positioning guide plate and the shape of a contact surface of gums, inserting a guide pipe in the guide hole; and thirdly, manufacturing a solid positioning guide plate. The solid positioning guide plate can provide optimal implanting position and direction to ensure the safety of an implanting technology and the long-term stability of an implant. The positioning guide plate can maximally utilize the bone quantity of the alveolar bone when in application. The invention can improve the efficiency and the accuracy of the implanting technology, ensure that the implanted implant accords with the biomechanical principle, and guarantee the repair aesthetic effect.
Owner:AFFILIATED STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
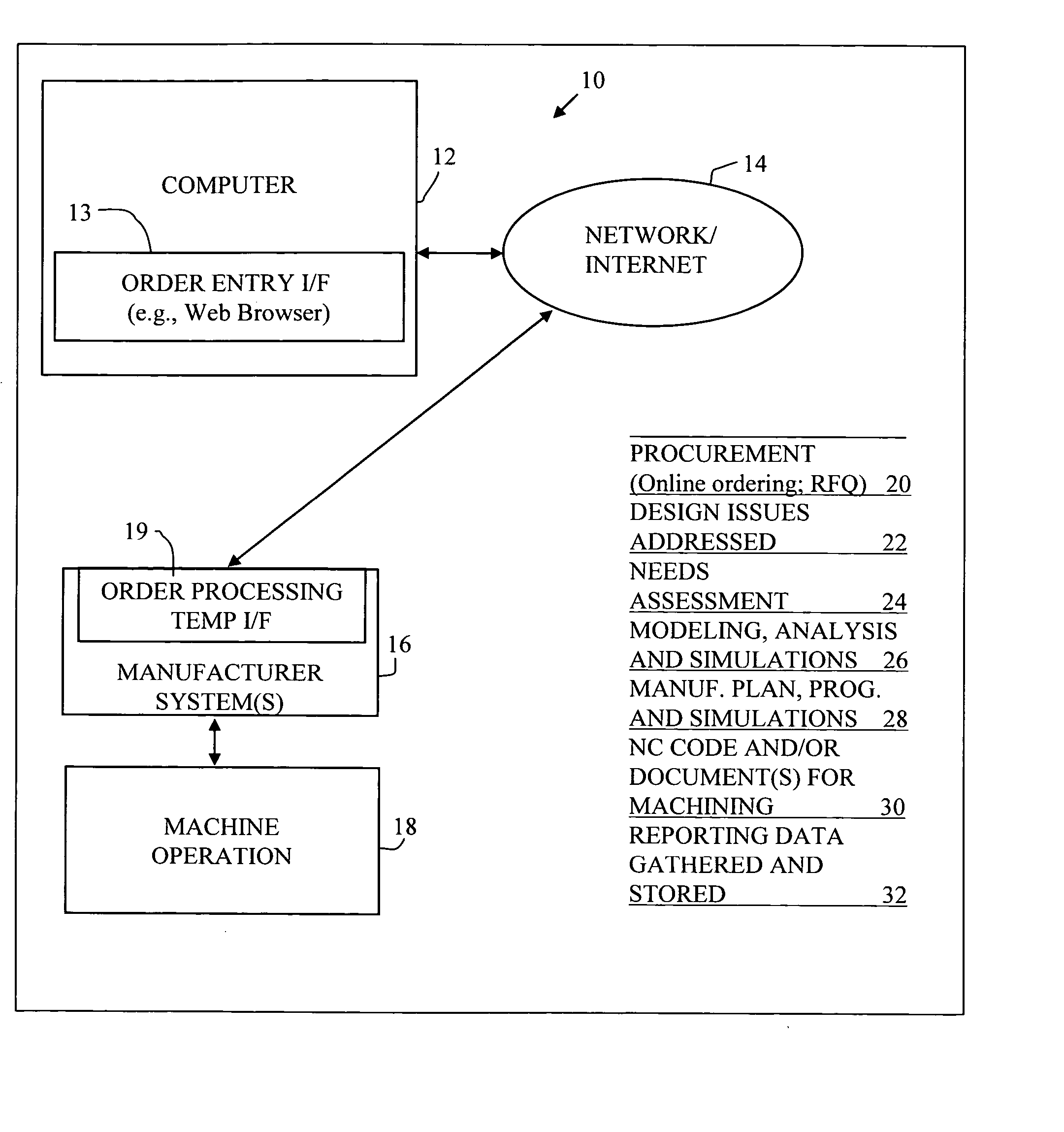
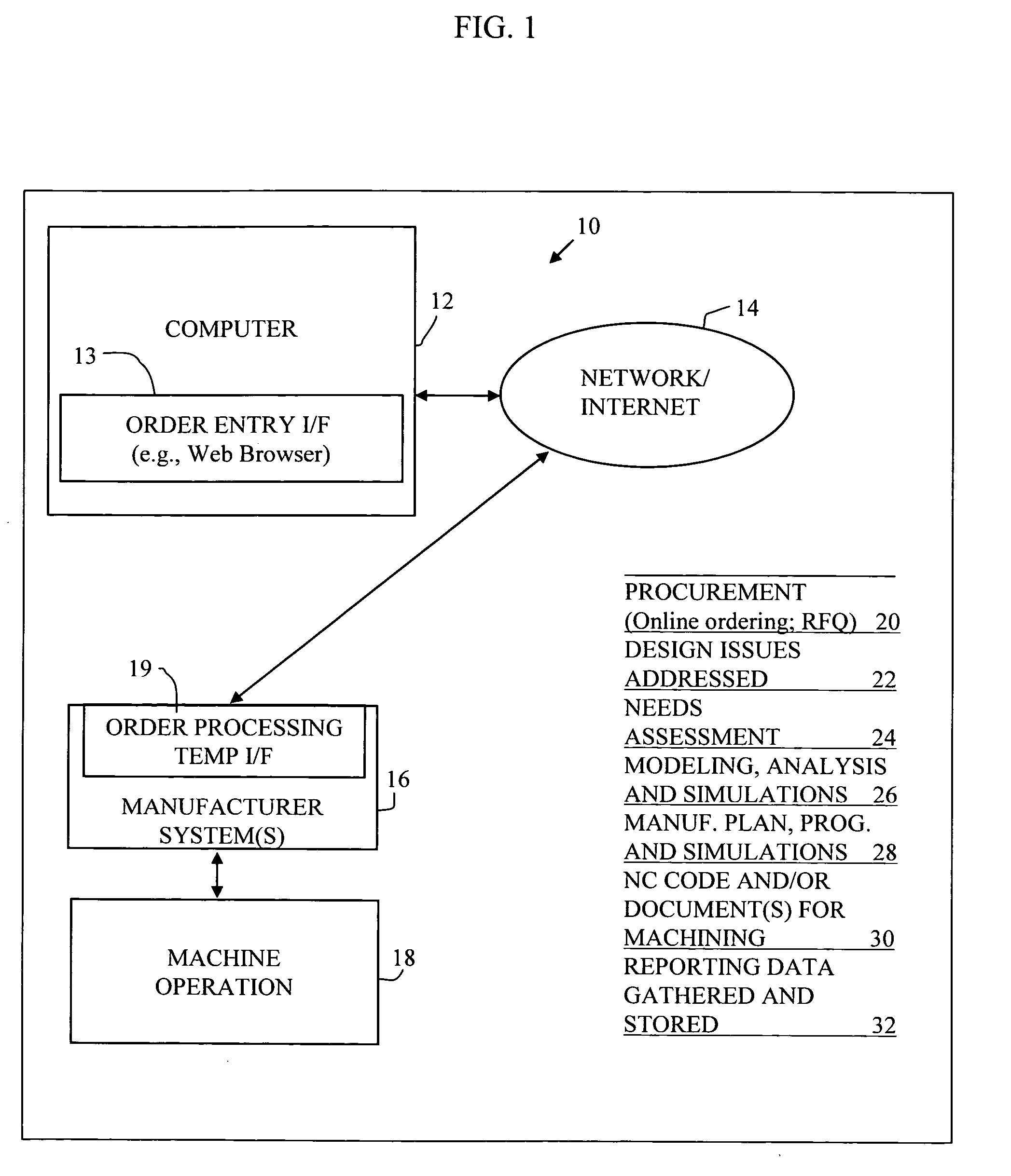
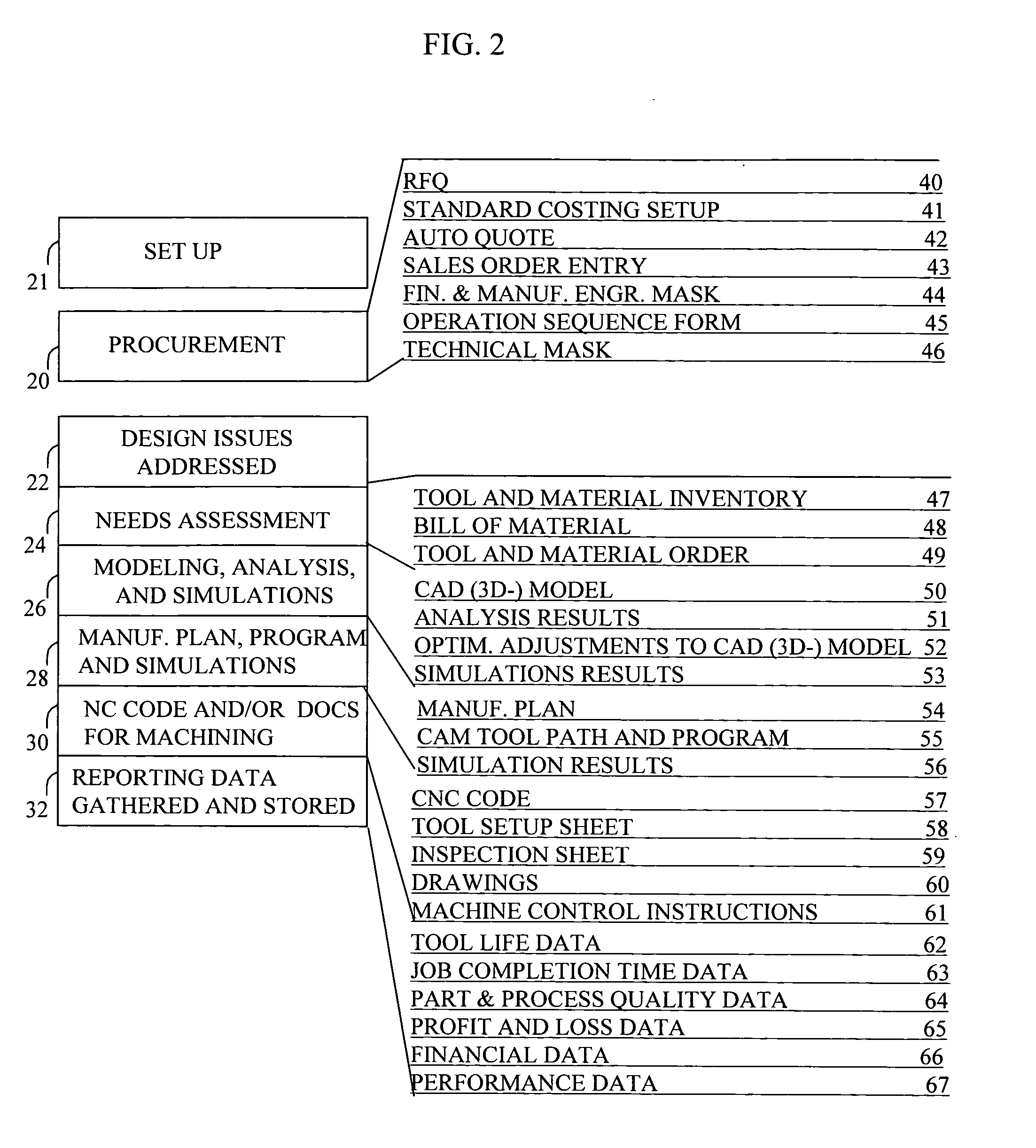
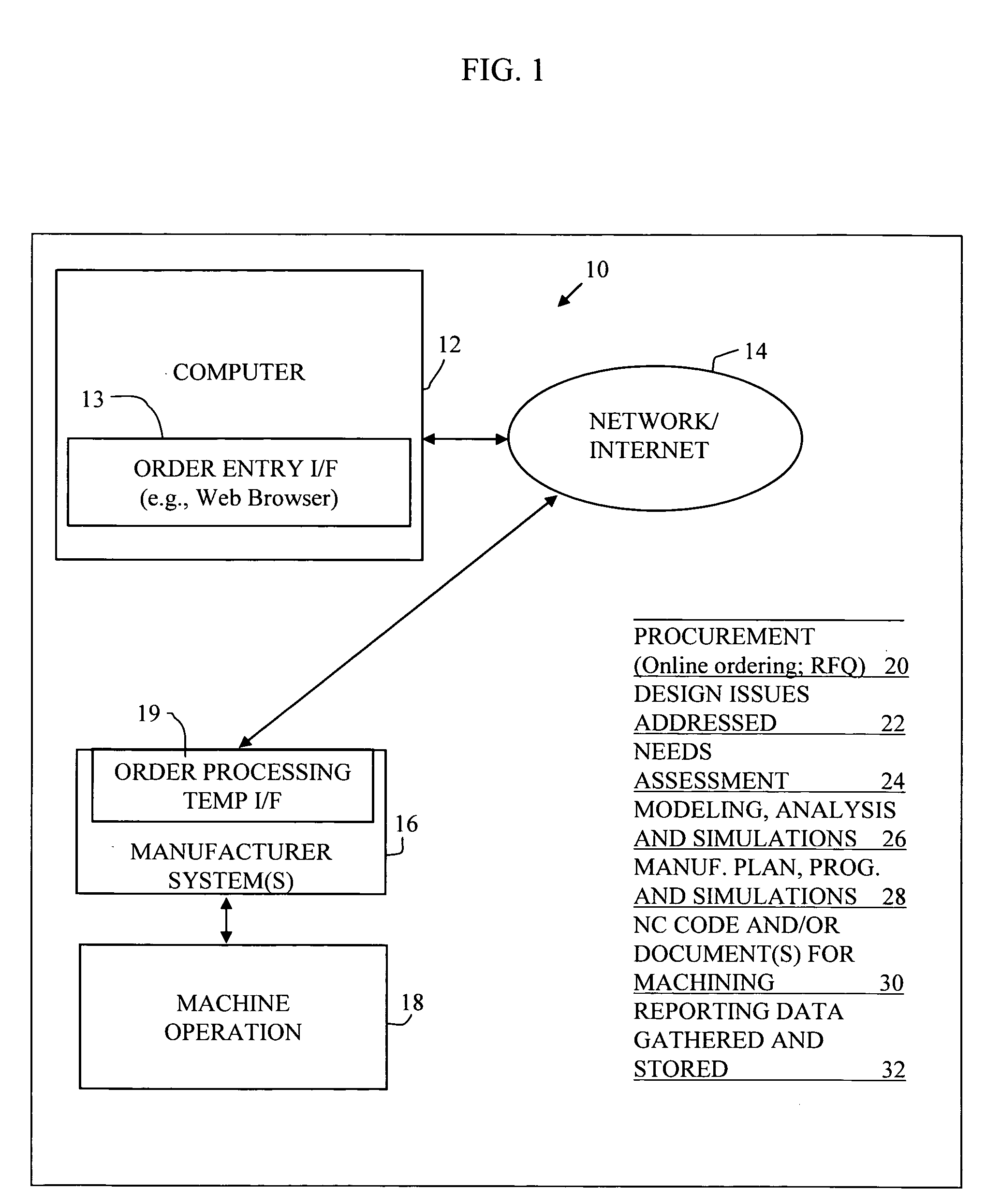
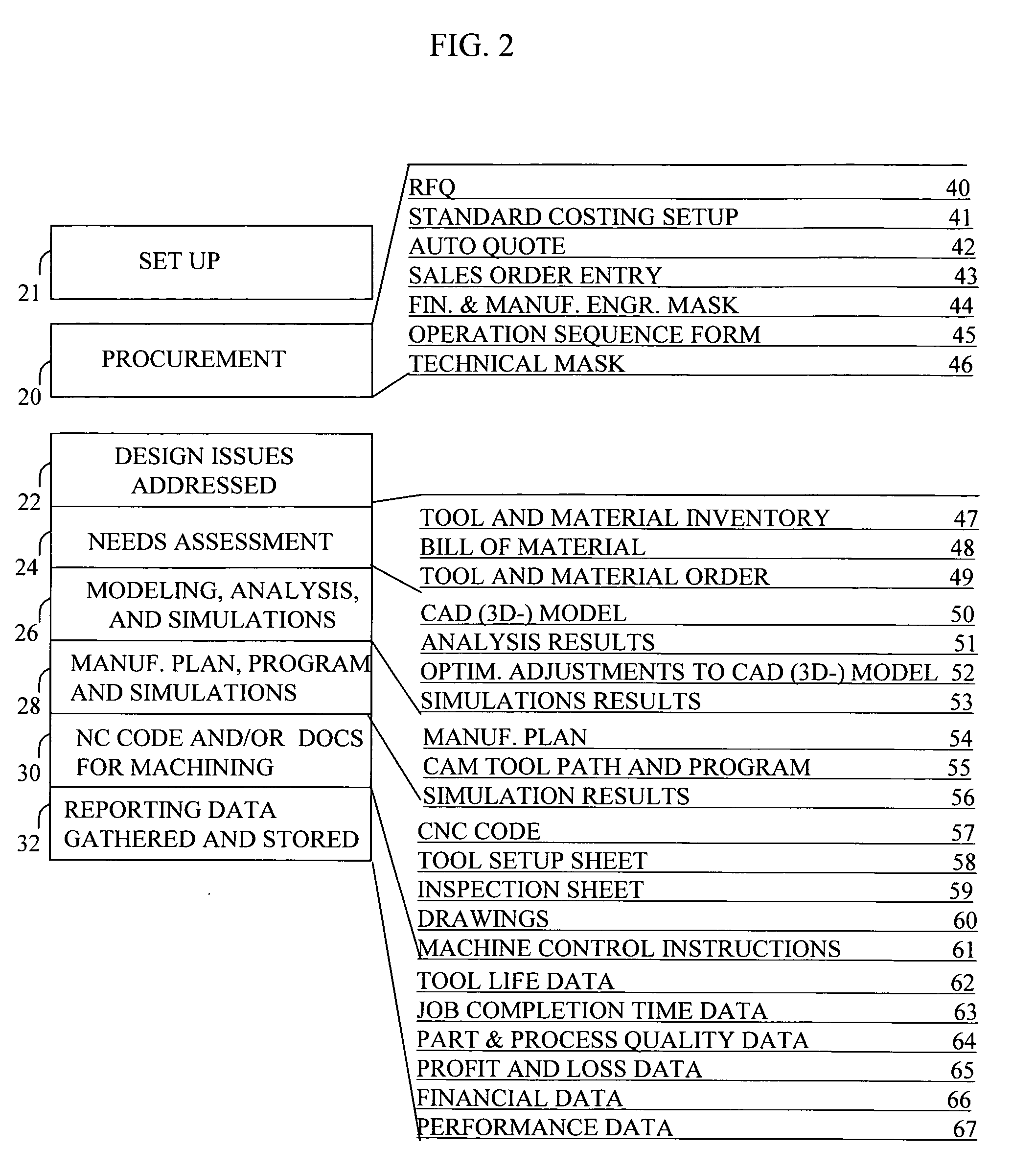
Automated planning and manufacturing systems
InactiveUS20060129462A1Increased riskImprove product qualityBuying/selling/leasing transactionsOrder formOrder processing
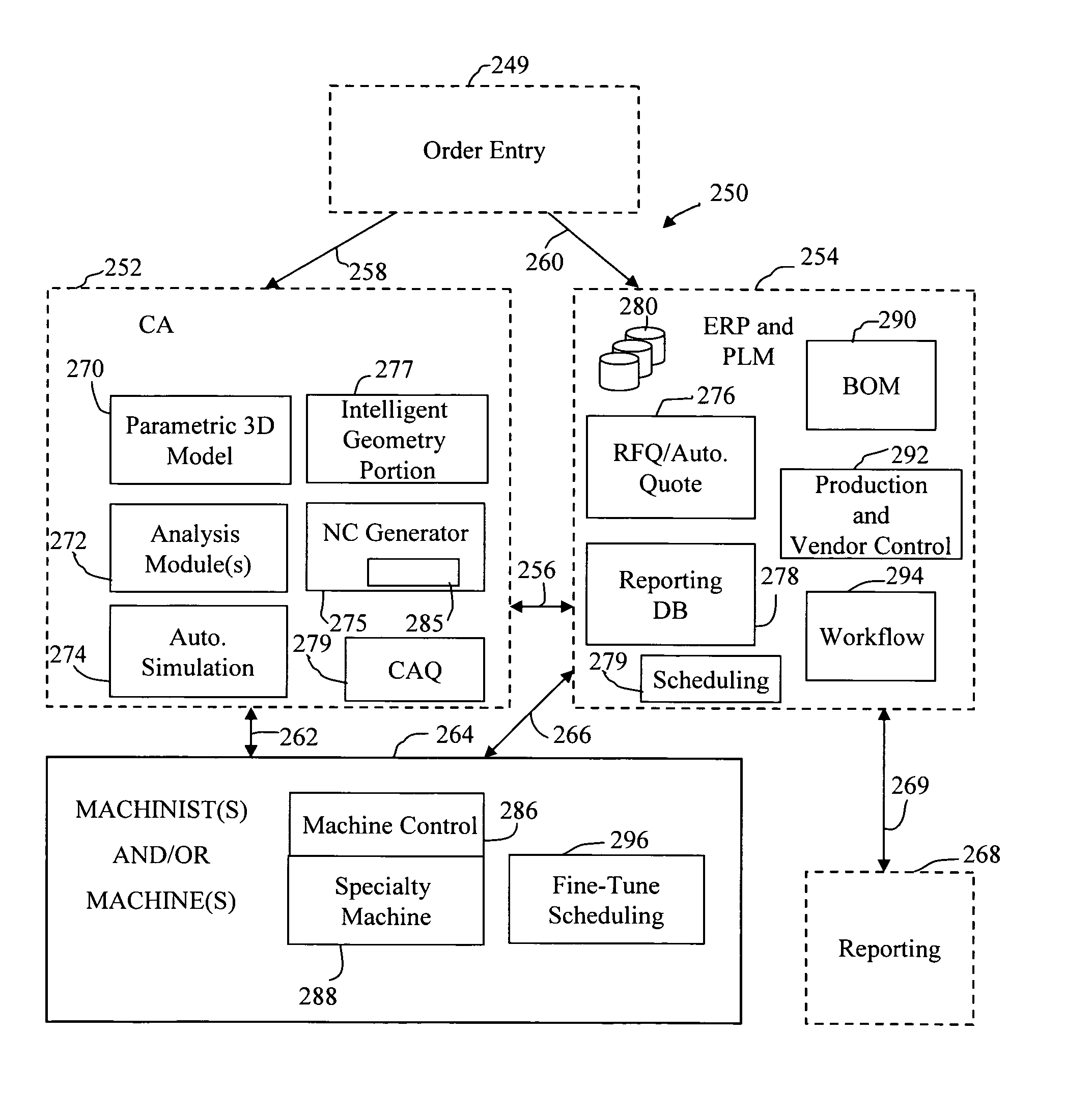
A system is provided for part ordering, design, and manufacturing. A manufacturer computer system is provided which comprises a parametric design mechanism to specify geometries of the part with parameters, an intelligent geometry portion, a 3D solid modeling function, and one or more simulation components. The intelligent geometry portion determines machining cycles to manufacture the part. Part-related databases are provided, and order processing components are provided. Such part-related databases and order processing components may form part of one or both of an ERP and PLM computer system. An order processing template is provided to facilitate sales and order processing, tool planning, CA parametric modeling, computer simulation, and the generation of a factory machine program. The order processing template comprises financial and manufacturing engineering planning fields and technical fields. An order template interface, or a set of order template interfaces, is provided. This interface or set of interfaces provides, for a given ordered part, from the order template, CA-specific information to the manufacturer computer system before the manufacturer computer system performs any CAD modeling or CAE calculation of the part. The interface or set of interfaces further provides, for the given ordered part, from the order template, ERP-specific information to the ERP system before the ERP system performs any scheduling of machines and resources, material reservation, or RFQ calculations.
Owner:PANKL GEROLD +1
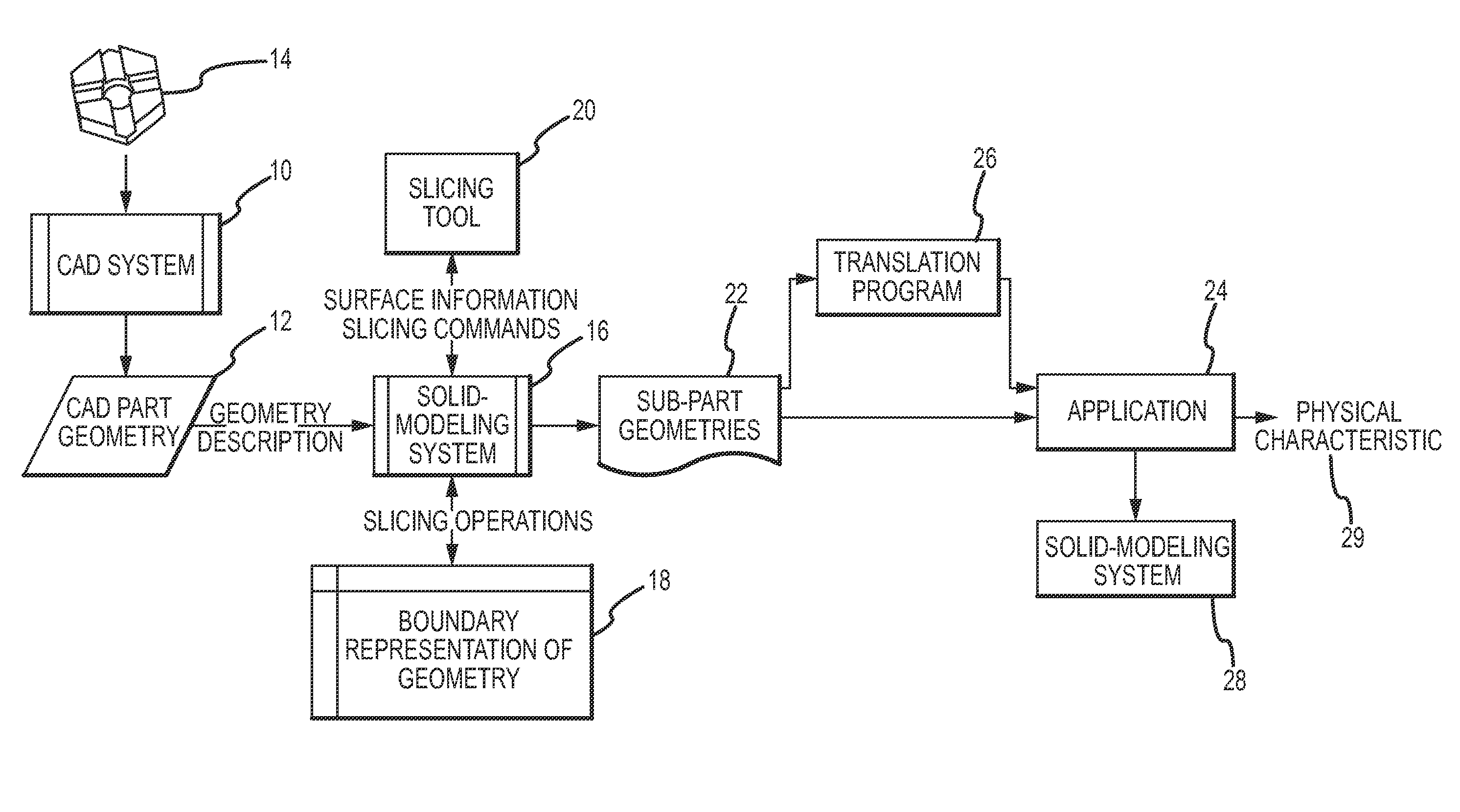
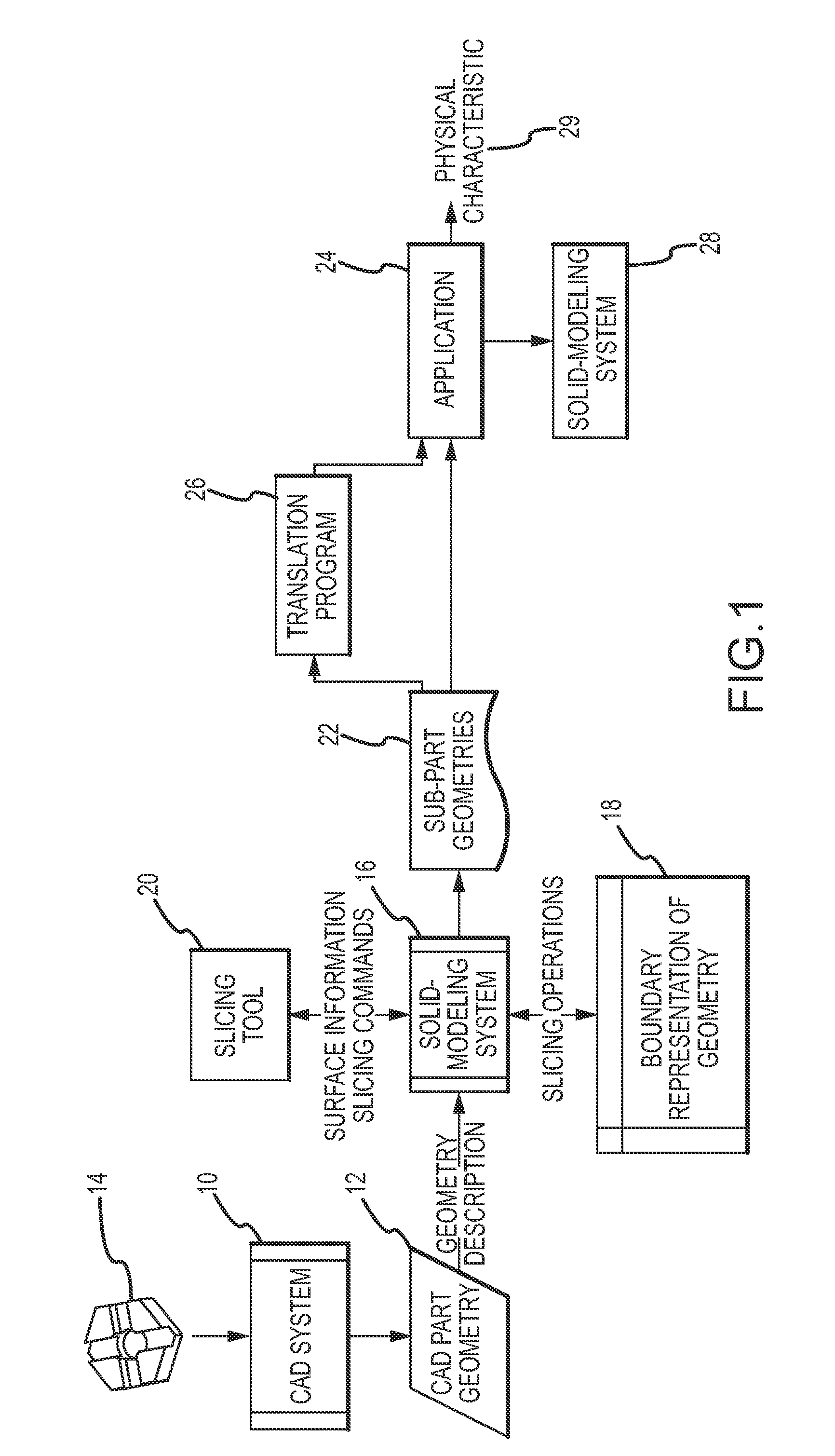
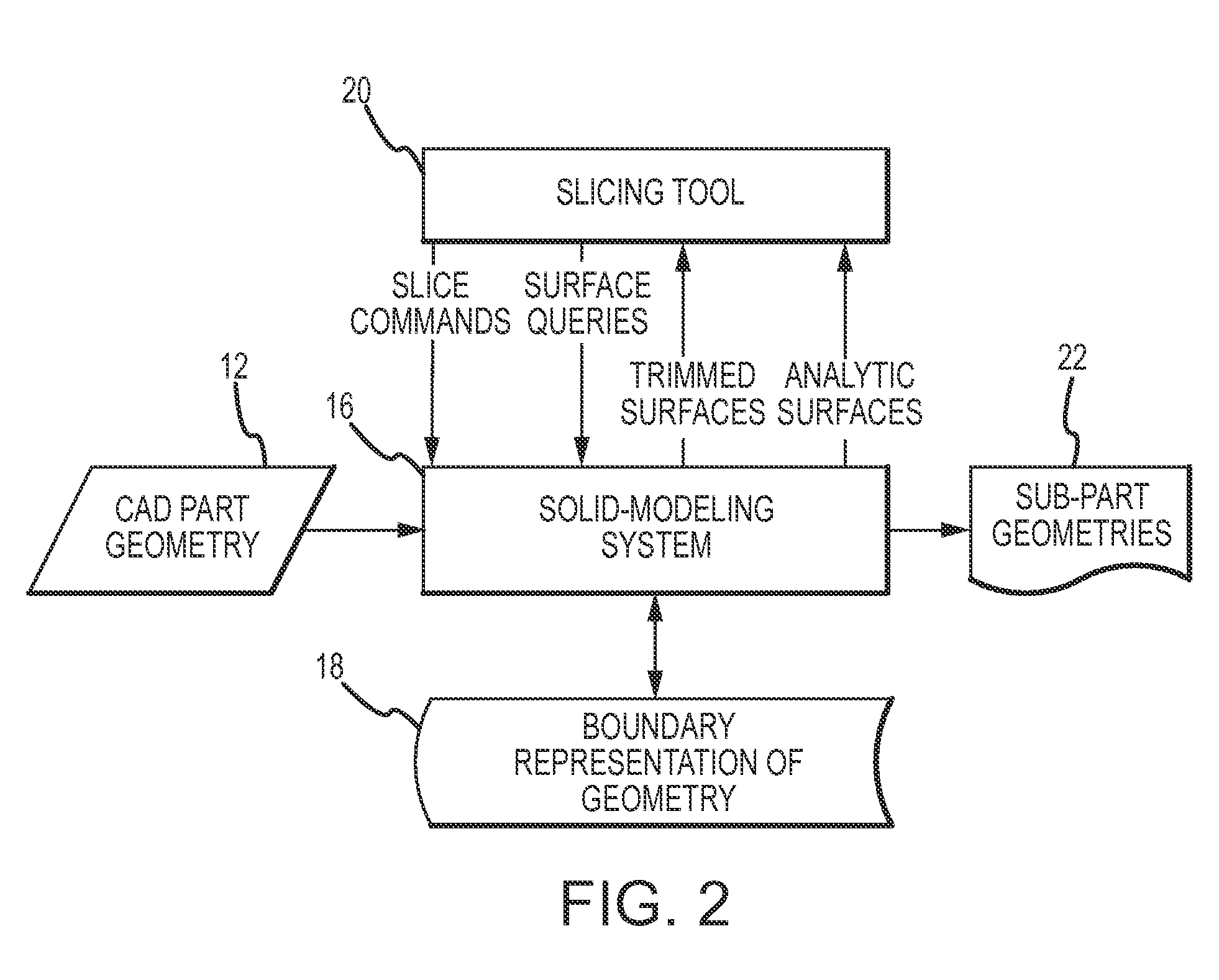
System and method for partitioning CAD models of parts into simpler sub-parts for analysis of physical characteristics of the parts
ActiveUS7733339B2Reduce complexityConstraint-based CADSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
A slicing tool works with a solid modeling system to partition the geometric representation of a three-dimensional part into a series of simpler sub-parts the union of which replicates the original part in a manner that introduces a minimal number of new surfaces in each sub-part and in total. This approach uses the existing analytic surfaces that define the part geometry to partition the part and selects a partition from a quality metric based on the number of trimmed surfaces of the part being partitioned and the candidate sub-parts. This approach greatly reduces the complexity of any downstream solid modeling applications that perform combinatorial surface operations on the geometric representation of the series of sub-parts to analyze physical characteristics such as radiation, mechanical, optical, thermal, structural or biological of the original part.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
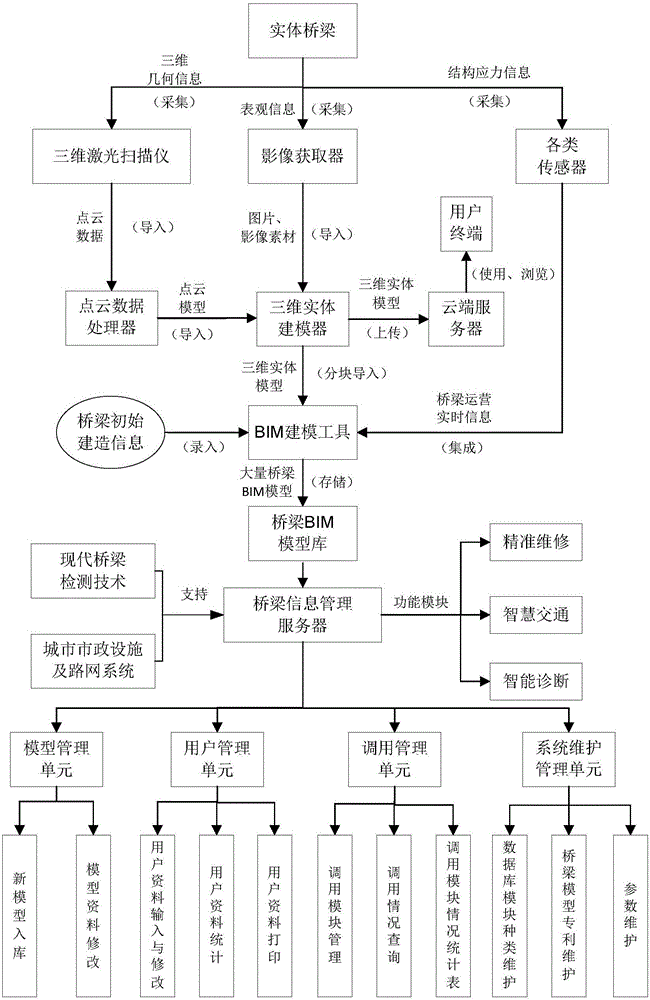
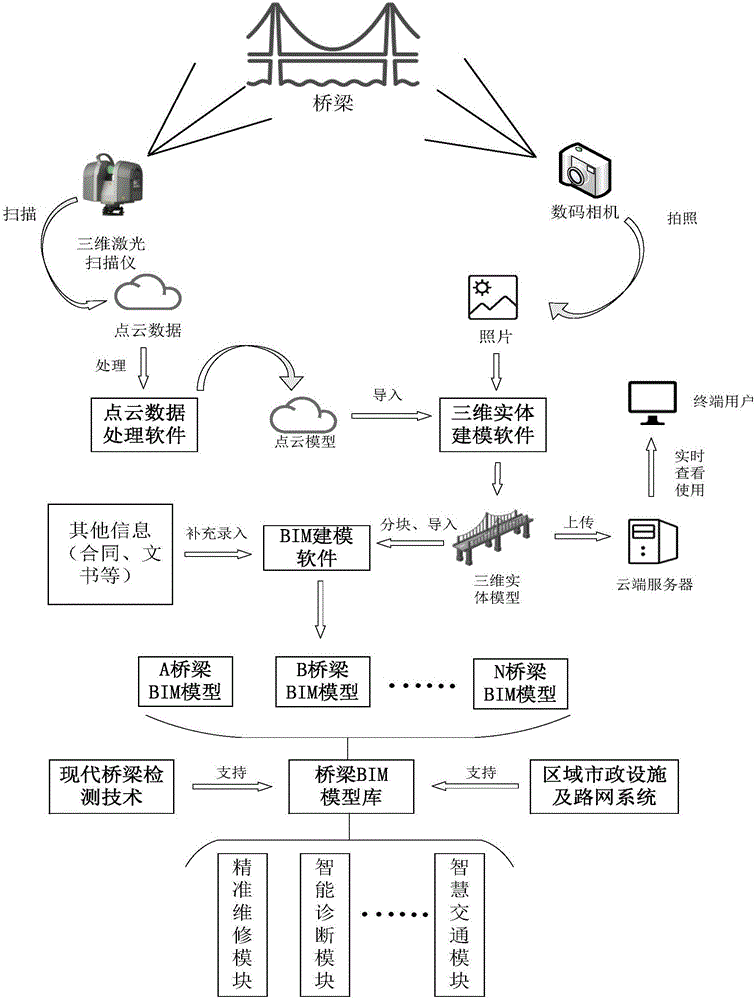
Existing bridge quick BIM modeling system and method
PendingCN106777680AOvercome limitationsImprove efficiencyGeometric CADImage data processingPoint cloudModeling software
The invention discloses an existing bridge quick BIM modeling system and method. The three-dimensional laser scanning technology serves as a bridge three-dimensional geometric data acquisition tool, and the limitation of passive ranging in traditional close-range photogrammetry, namely limitation of natural light conditions, is overcome. In actual application examples, by comparing a BIM model built through three-dimensional scanning and an actual building, it is found that the similarity between the BIM model and the actual building can reach 90% or above. A full-color-point cloud model is obtained through the three-dimensional scanning technology, a vivid and fine virtual model can be generated through three-dimensional entity modeling software processing, the method can be used for webpage real-time publish and sharing, and the cooperative work efficiency is improved. The whole BIM modeling process is convenient, quick and precise, as for small-and-medium-sized bridges, it takes a few hours from field work scanning to building of the whole BIM model, and model errors can be controlled at the millimeter level.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
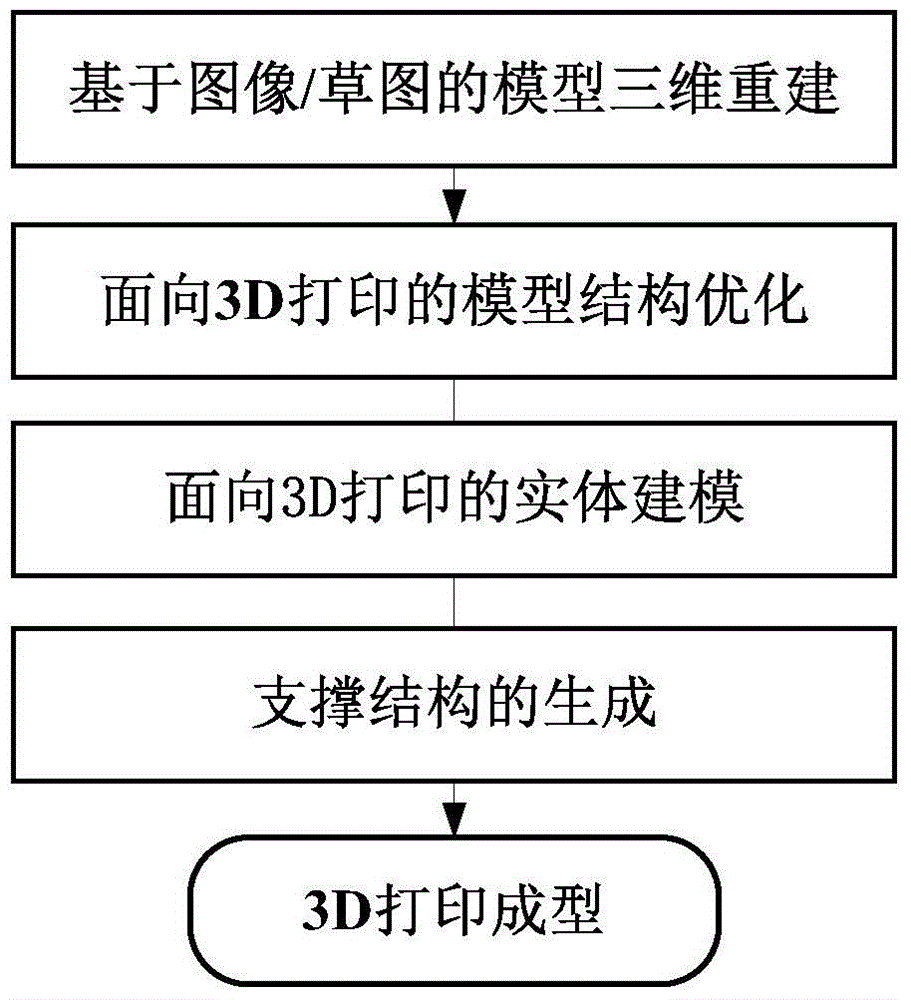
3D (three-dimensional) printing based processing technique of automobile styling concept model
ActiveCN104881513AReduce processing costsImprove processing efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusSpecial data processing applicationsDesign phaseEngineering
The invention provides a 3D (three-dimensional) printing based processing technique of an automobile styling concept model and belongs to the field of automobile styling concept design. The technique includes the steps of 1, performing three-dimensional model reconstruction based on an image / draft; 2, performing 3D printing oriented model structural optimization; 3, performing 3D printing oriented solid modeling; 4, generating a support structure; and 5, performing 3D printing. The technique has the advantages that quick expression of an automobile solid model from an automobile image / draft is achieved, model processing cost is lowered at the premise of quickly implementing a personalized solid model, processing efficiency is improved, operating is simple, and the technique is reliably applied to the automobile concept design phase for automobile styling engineers.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Parametric modeling method of face gear teeth
InactiveCN102567596AQuality improvementReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelPhysical model
The invention discloses a parametric modeling method of face gear teeth, comprising the following steps: first, calculating tooth surface numerical value of a face gear; then processing tooth surface discrete points coordinate data to directly read in the data to ANSYS environment; and parametrically establishing a gear tooth finite element model after parametrically establishing a gear tooth physical model, thereby obtaining a parametric finite element model. By mixed programming of Matlab and APDL (parametric design language), the method combines functions of face gear teeth width design, tooth surface stimulation, physical modeling, finite element modeling and the like, and realizes parameterization and intellectualization of face gear teeth design and modeling, high quality of finite element model, reduction of workload of designers and improvement of work efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
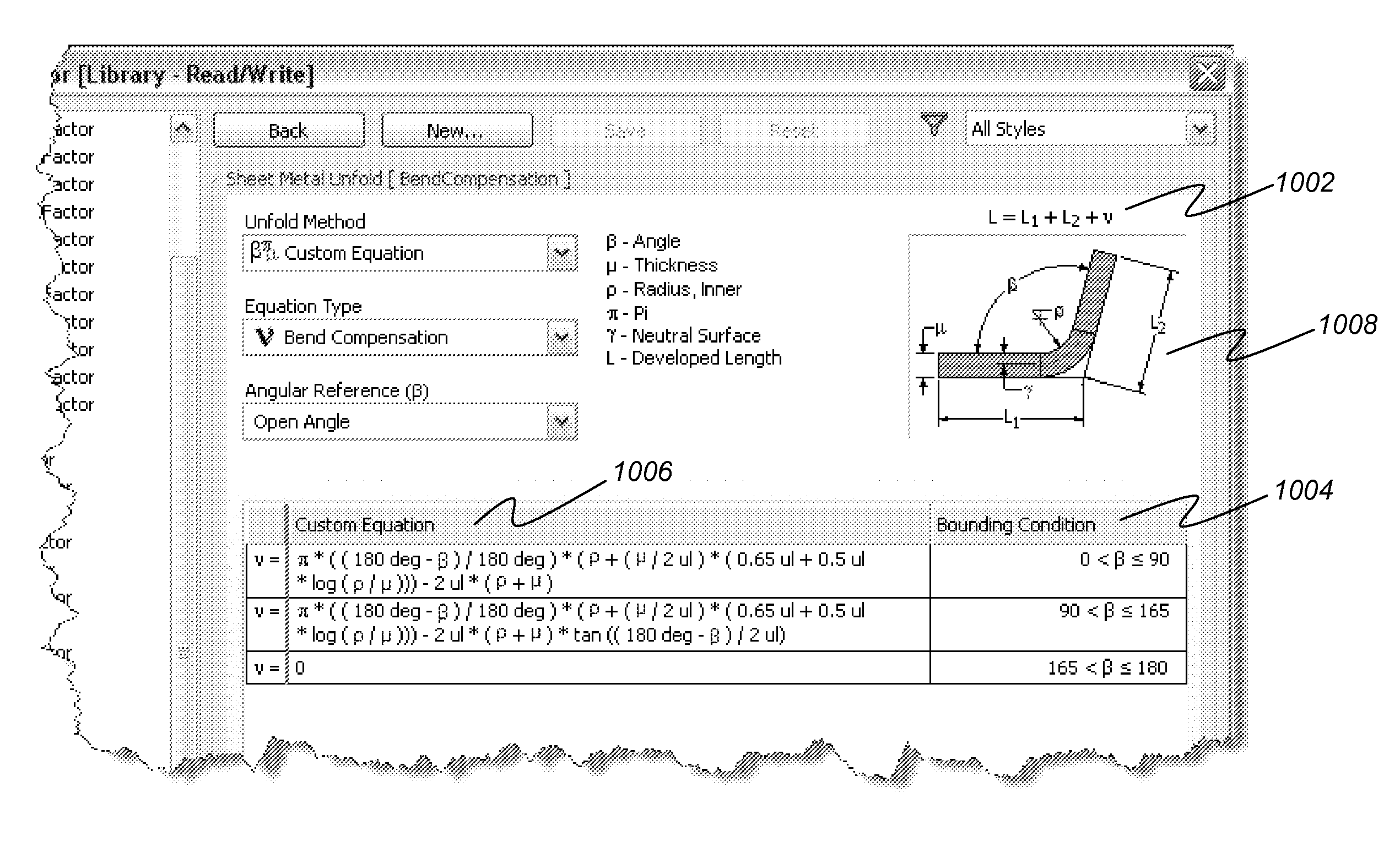
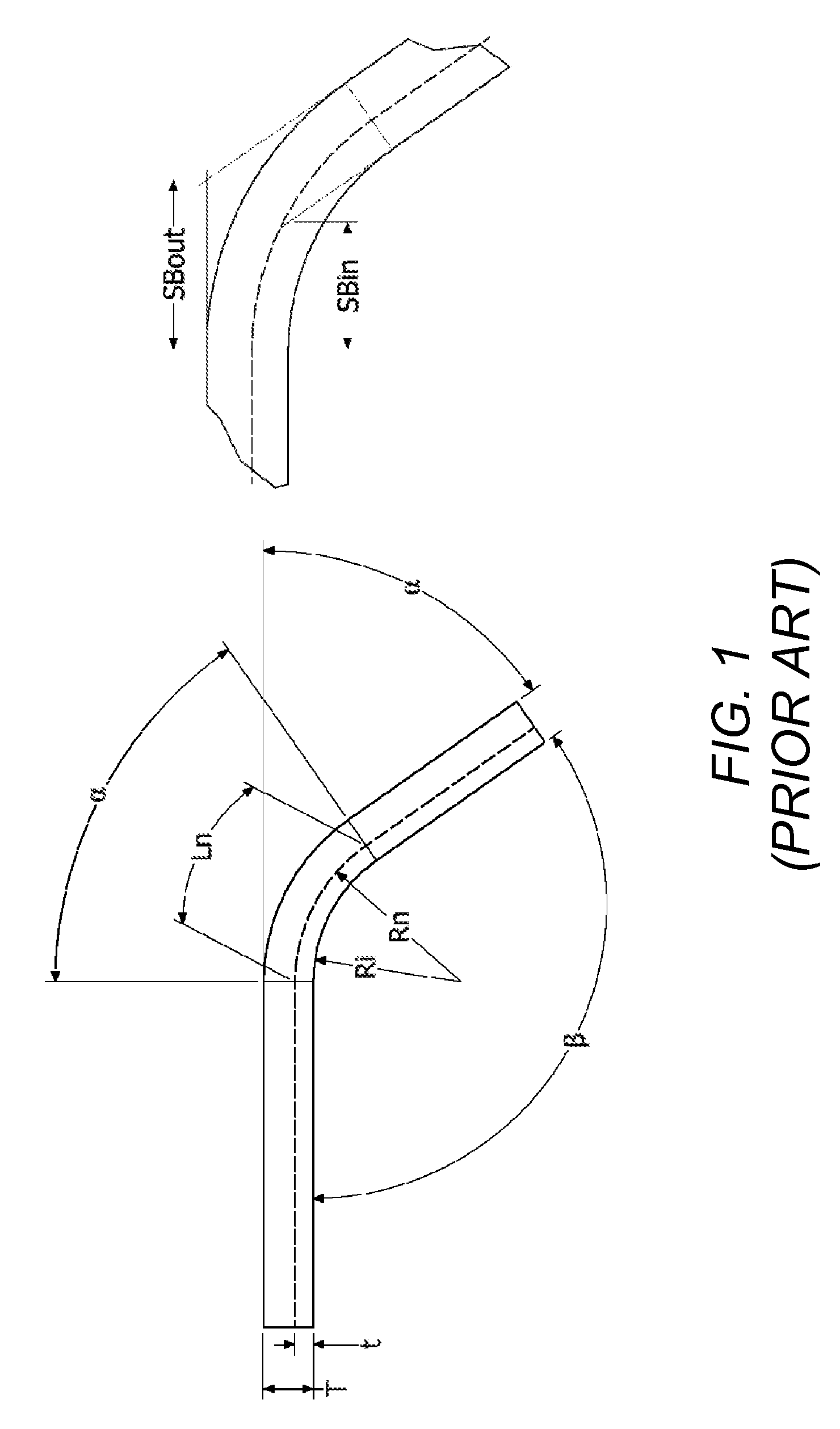
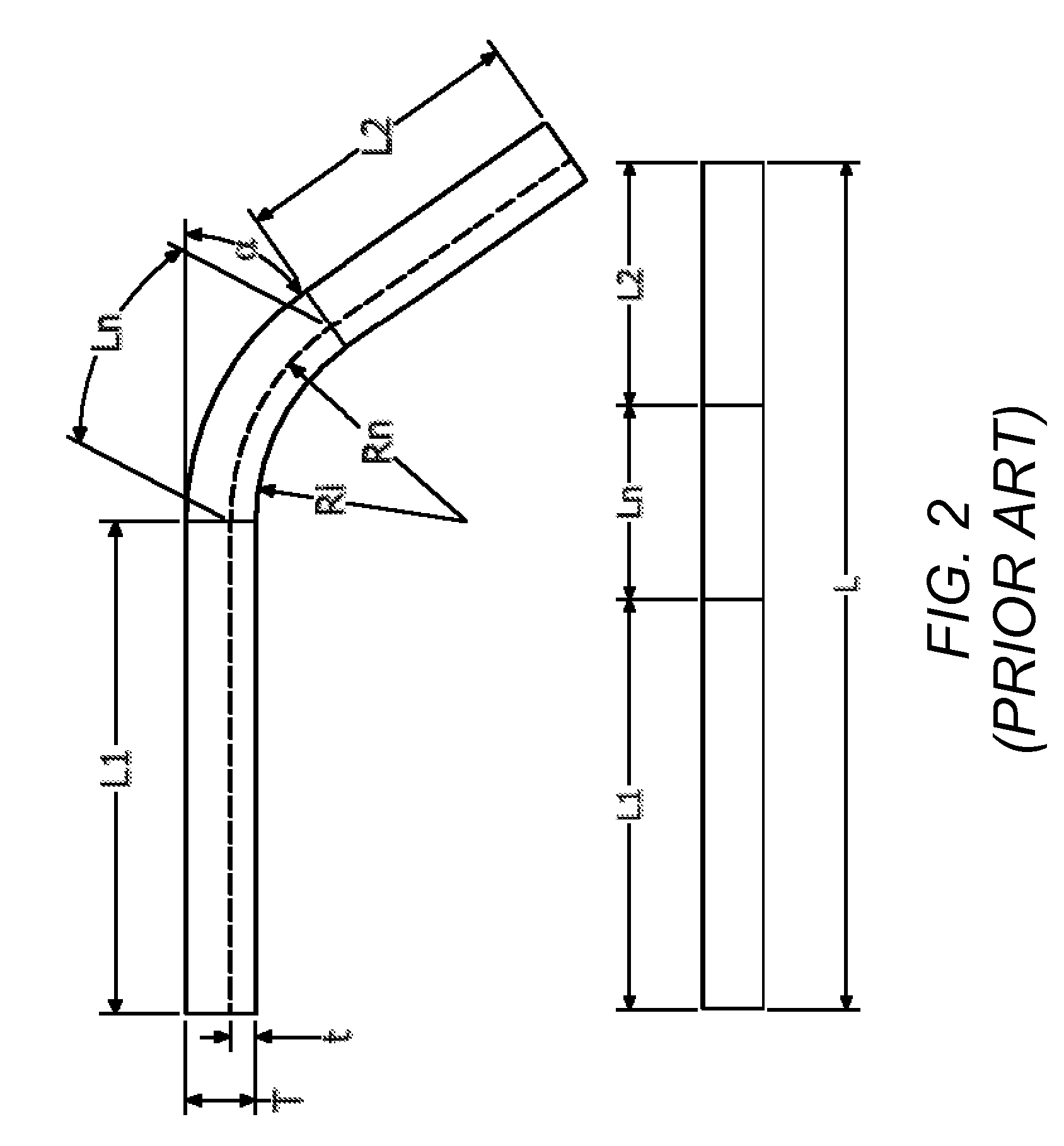
Custom equations for the unfolding of sheet metal
ActiveUS20100106463A1Easy to controlComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designObject basedUser input
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and article of manufacture provide the ability to utilize custom equations for the unfolding of sheet metal in a solid modeling application. A drawing model is obtained and defines a sheet metal object in the solid modeling application. User input is accepted that defines a custom equation for a first variable that is directly used to calculate a developed length for a bend in the sheet metal object. The custom equation is converted into a standard equation that produces the developed length and is accepted by a modeling kernel of the solid modeling application. The modeling kernel dynamically displays an unfolded version of the sheet metal object based on the standard equation and the calculated developed length without exposing the standard equation to the user.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Transient temperature field simulation method based on multiple commutation failures of smoothing reactor
ActiveCN104834781ASpecial data processing applicationsSteady state temperatureFinite element software
The invention discloses a transient temperature field simulation method based on multiple commutation failures of a smoothing reactor. The method comprises the following steps that A, an oil immersed type smoothing reactor three-dimensional geometrical model is built in a solid modeling mode on the basis of ANSYS finite element software; B, an oil immersed type smoothing reactor is subjected to heat generating analysis; C, the oil immersed type smoothing reactor is subjected to heat radiation analysis; D, the boundary conditions of temperature field simulation calculation are determined; E, the steady temperature field of the smoothing reactor under the normal work condition is calculated; F, the obtained steady temperature field result is used as an initial value of a failure transient model, then, the failure current is loaded, a step-length method is adopted, the distribution of the temperature field along with time after the failure is calculated, and the transient temperature field simulation method based on multiple commutation failures of the smoothing reactor is completed. The method has the advantage that basis is provided for checking the maloperation reason of a smoothing reactor gas relay and setting the gas checking setting valve of the smoothing reactor.
Owner:STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST +1
Processes and systems for creation of machine control for specialty machines requiring manual input
InactiveUS20060129270A1Increased riskImprove product qualityComputer controlSimulator controlComputer architectureMachine control
A system is provided for creating specialty machine control programs for manufacturing a part. A CA (computer aided) computer system is provided. The CA system may comprise a computer aided design and computer aided manufacture (CAD / CAM) computer system. The CA computer system may further comprise a computer aided engineering (CAE) computer system. The CA computer system may further comprise a computer aided quality (CAQ) computer system. The CA computer system comprises a parametric design mechanism to specify geometries of the part with parameters. In addition, an intelligent geometry portion is provided to determine machining cycles to manufacture the part. A 3D solid modeling function is provided, and one or more simulation components are provided. A human-readable control program generator is provided to generate from the CA computer system a human-readable control program including instructions for a human to carry out.
Owner:PANKL GEROLD +1
Geometric design method for cross shaft straight-teeth conical gear pair with changeable transmission ratio
InactiveCN1752486AImprove performanceSimple transmission structurePortable liftingToothed gearingsKinematicsGear wheel
The present invention relates to a variable transmission ratio concurrent axis coniflex gear pair geometrical designing method. Based on spherical engagement theory research said method can implement parameter design of given transmission ratio relationship and concurrent axis coniflex gear pair of interaxial included angle. Tooth profile calculation and solid model creation, and utilizes given transmission relationship and interaxial included angle to define parameter equation of a pair of pitch cone faces and utilizes the kinematics relationship of spherical engagement and CAD software to form non-cone gear solid model. Said non-cone gear pair can simplify existent variable transmission ratio transmission mechanism and can be substituted for combination of several pairs of gear pairs, so that it has extensive universality.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for carrying out stress analysis on first-class nuclear reactors through using ANSYS software
ActiveCN102184289AShorten design timeSave design costSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelDesign specification
The invention discloses a method for carrying out stress analysis on first-class nuclear reactors through using ANSYS software, belonging to the technical field of analysis and design methods for first-class nuclear reactors. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, after carrying out routine design according to a design specification, thus obtaining a design drawing; establishing a geometric model and a finite element model by using a simulation device in an ANSYS; carrying out analysis and calculation on all nuclear parts; extracting a stress analysis result; and carrying out strength assessment according to the specifications stipulated in subsections NB and NF of section III of ASME (American society of mechanical engineers), then obtaining a detailed design report. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention summarizes and improves a method for carrying out analysis and design on first-class nuclear reactors through using ANSYS software; compared with an analytical method and a test method, by using the method disclosed by the invention, the design time is greatly shortened, the design expense is reduced, the analysis efficiency is greatly improved, and the analysis cost is reduced; and in the process of analysis, an entity is adopted for modeling a hexahedron unit, thereby improving the calculation accuracy.
Owner:大连船舶重工集团装备制造有限公司
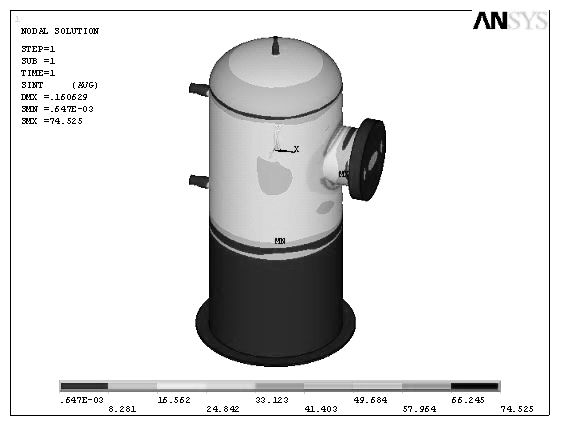
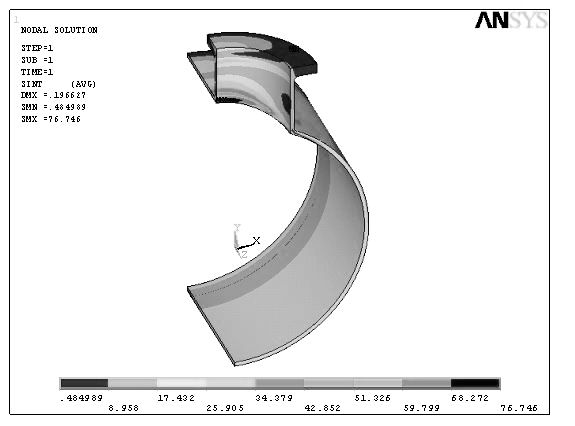
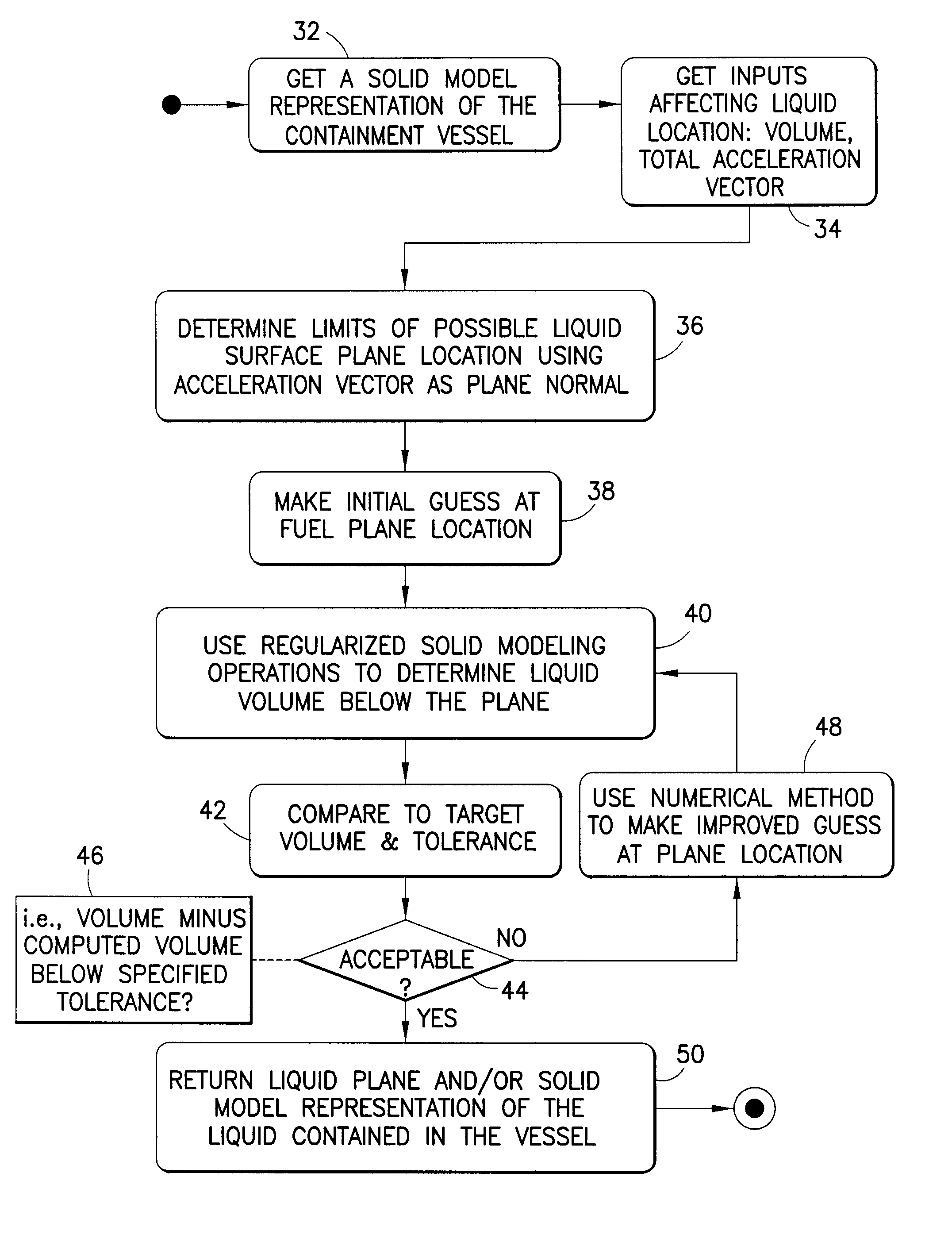
Calculating Liquid Levels in Arbitrarily Shaped Containment Vessels Using Solid Modeling
ActiveUS20120150517A1Reduce the amount requiredSimple calculationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringSolid modeling
Systems and method for simulating liquid containment behavior. The system comprises a solid modeler and a nonlinear equation solver. The nonlinear equation solver takes as input the solid model representation of the containment vessel from the solid modeler, a desired orientation in space, dynamic conditions (e.g., lateral acceleration) and an amount of liquid. To find the level of liquid in the vessel, the system solver iteratively performs successive Boolean subtractions using an infinite horizontal half-space that represents the liquid level of the vessel. The resulting sliced solid model is used to compute the volume of the liquid at that level. The iterative system solver terminates when the computed volume of the sliced containment vessel matches the specified volume of liquid (e.g., fuel) within a given tolerance. To accommodate dynamic situations, e.g., when acceleration is present, the horizontal liquid plane is replaced with a plane at an angle that corresponds to the total acceleration.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Generating method of finite element mesh in thin-wall curved surface structure
InactiveCN101840453ARealize generationSimple designSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelTopology information
The invention discloses a generating method of a finite element mesh in a thin-wall curved surface structure, aiming to solve the technical problem of great equivalent stress of a traditional design method of a finite element model in a perforated thin-wall conical curved surface structure. The technical scheme comprises the following steps of: firstly, generating a plane finite element mesh on a parameter plane by adopting a solid modeling method; then, generating network nodes in a space thin-wall curved surface structure through a parametric mapping relation by adopting a direct generating method; and generating a finite element mesh in the space thin-wall curved surface structure by utilizing corresponding unit topology information on the parameter plane. Compared with the prior art, the maximum equivalent stress of the finite element model in the perforated thin-wall conical curved surface structure in the same size is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANTONG HENGDA MACHINERY MFG +1
Efficient computation of Voronoi diagrams of general generators in general spaces and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100036647A1Character and pattern recognitionComputation using non-denominational number representationData compressionCollision detection
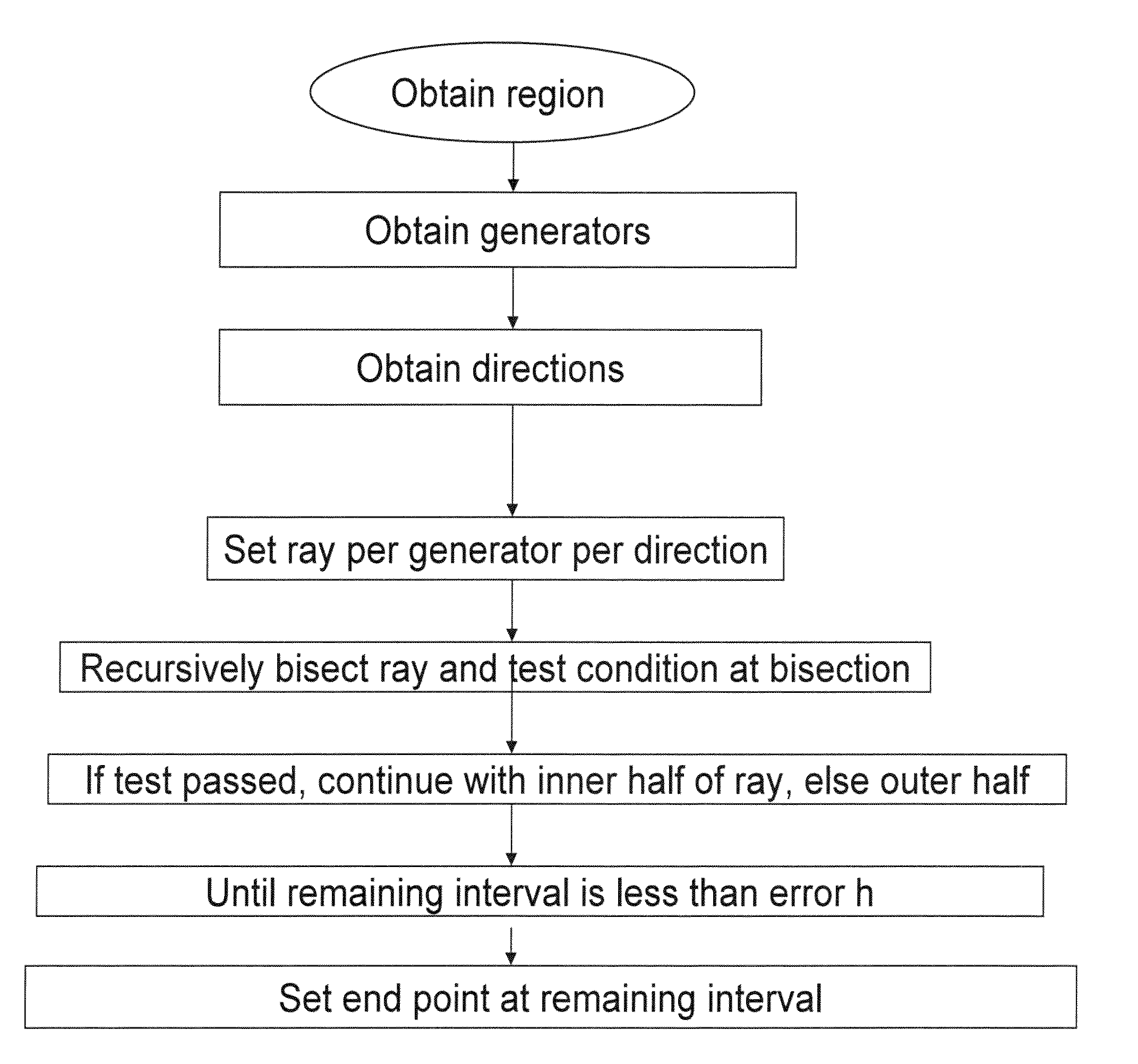
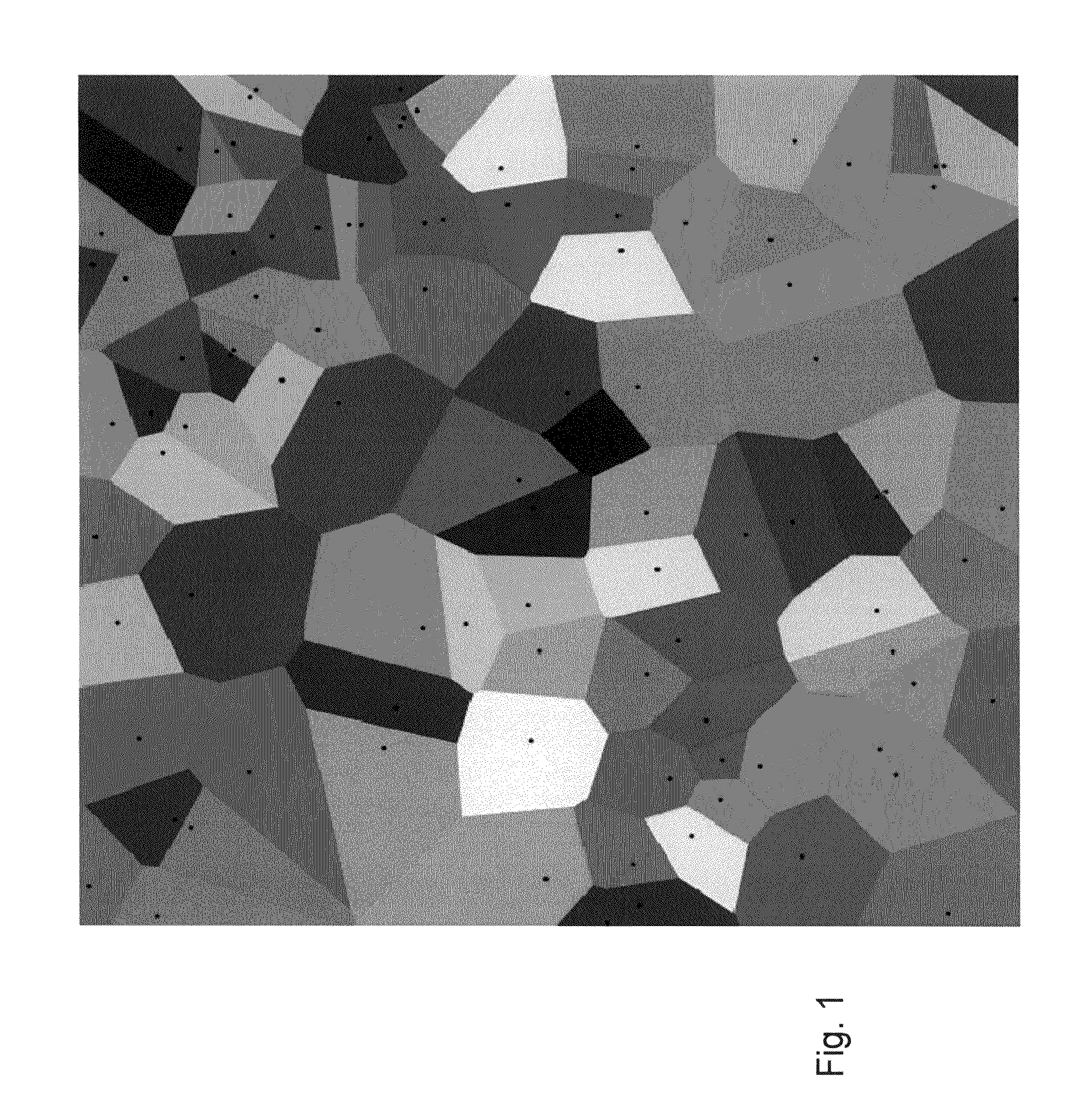
A computerized method of computing the Voronoi diagram has applications including communications networks, robotics, three-dimensional networks, materials science, searching image processing, data clustering, data compression, control of a groups of methods for image processing and the like, design of electronic circuits, geographic information systems, solutions of the efficient location problem, face recognition, mesh generation and re-meshing, curve and surface generation / reconstruction, solid modeling, collision detection, controlling motion of vehicles, navigation, accident prevention, data clustering and data processing, proximity operations, nearest neighbor search, numerical simulations, weather prediction, analyzing and modeling proteins and other biological structures, designing drugs, finding shortest paths, pattern recognition and as an artistic tool. The Voronoi diagram is a decomposed region X made into cells, the decomposition being induced by a set of generators (Pk)k-K, and a distance function, and involves finding for each generator Pk a cell, which is a set of all the points in X satisfying the condition that the distance to the current generator P=Pk is not greater than the distance thereof to the union A of the other generators, The method comprising: for each generator, and for each point p in this generator, selecting a set of directions, then for each direction recursively testing a ray in that direction, until a certain interval on the ray is of length less than or equal to a given error parameter. A point corresponding to the interval on the ray is then selected as an end point, the cells are defined from the end points, thus forming the Voronoi diagram.
Owner:REICH SIMEON +1
Fully integrated machinable profile based parametric solid modeler
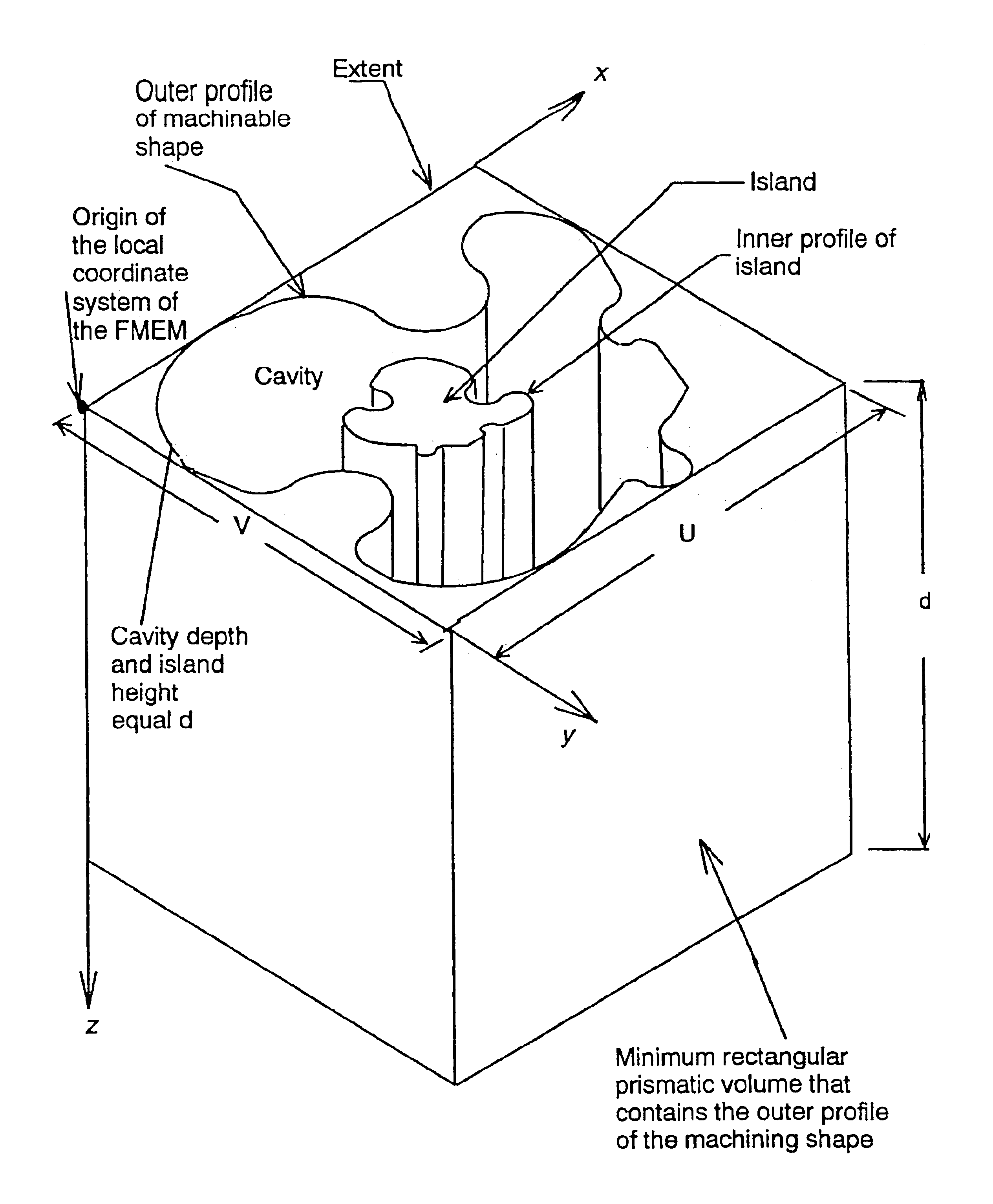
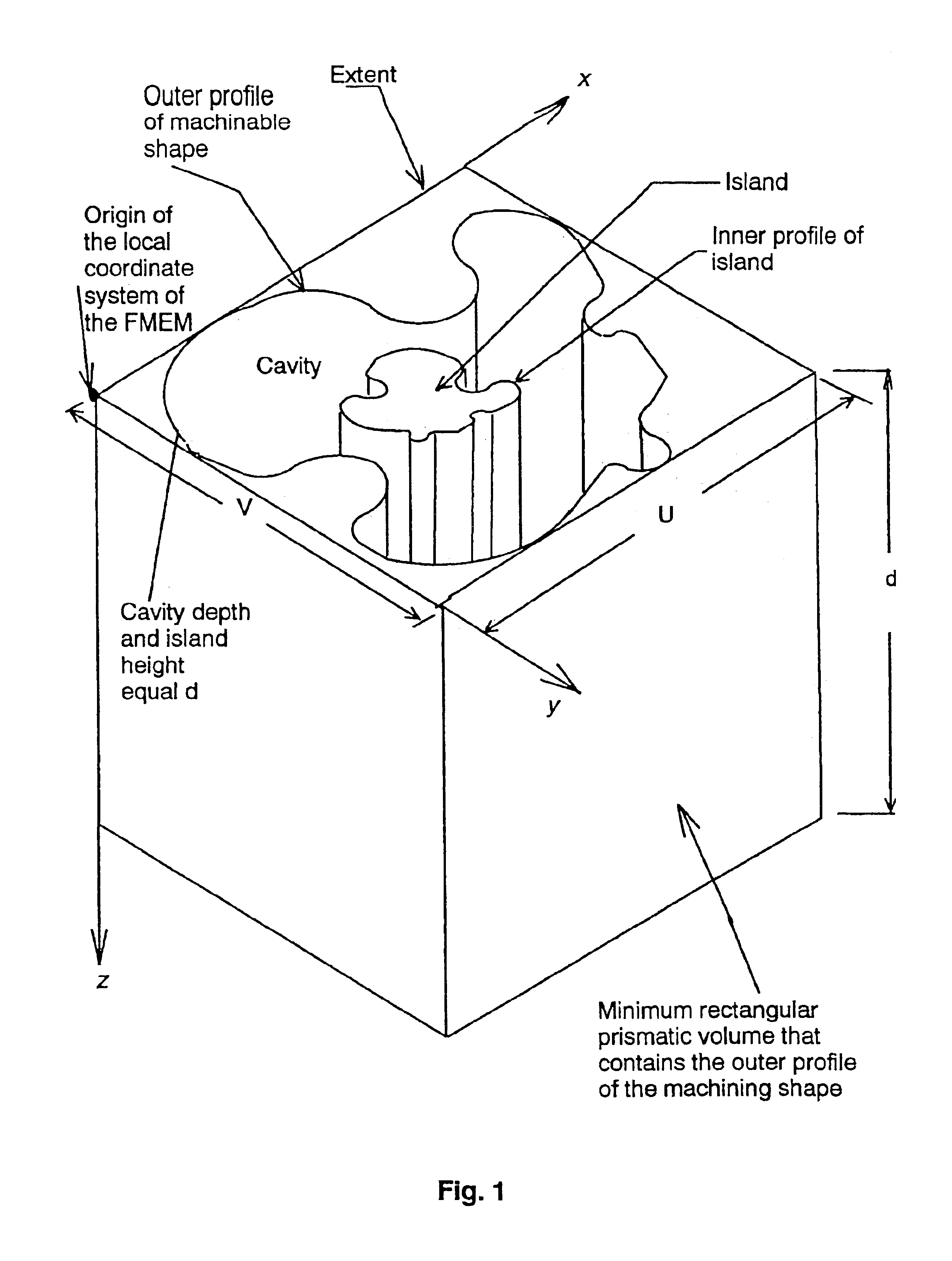
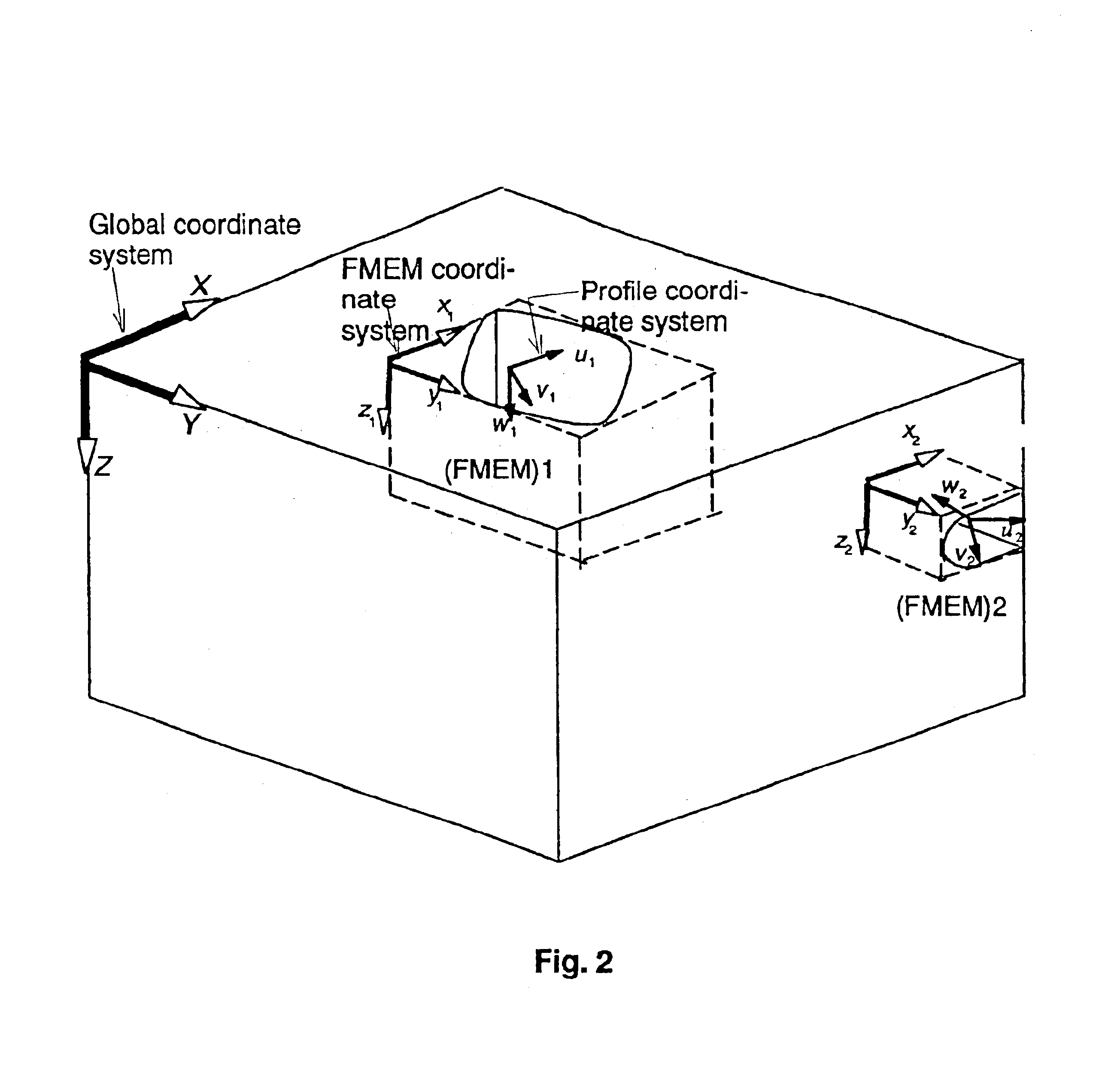
InactiveUS6862023B1Remove restrictionsOperational constraintDrawing from basic elements3D modellingMaterial removalEngineering
A solid modeler is provided which is specifically tailored for the material removal process associated with milling procedure. The solid modeler permits a part to be designed using only machinable profiles thereby constraining the designer to real world machinable operations. The method utilized by this solid modeler allows design manipulation of the edges and curves of a very general feature profile, thereby representing the milling process with the same degree of flexibility that the actual milling process has, and provides a means to create and store for use in the generation of other parts any combination of 2D and 3D features.
Owner:SHAIKH MOHAMMAD SALIM
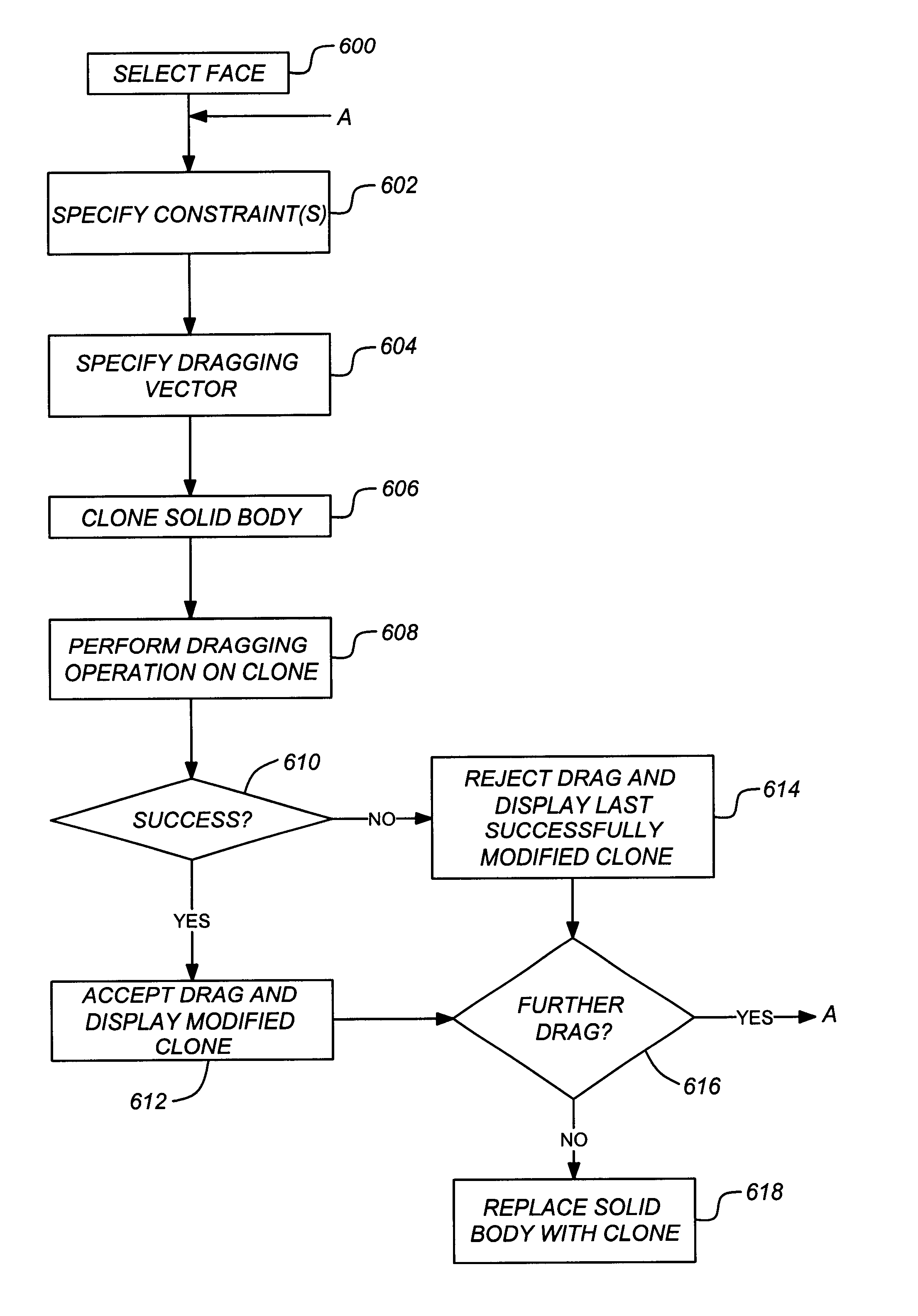
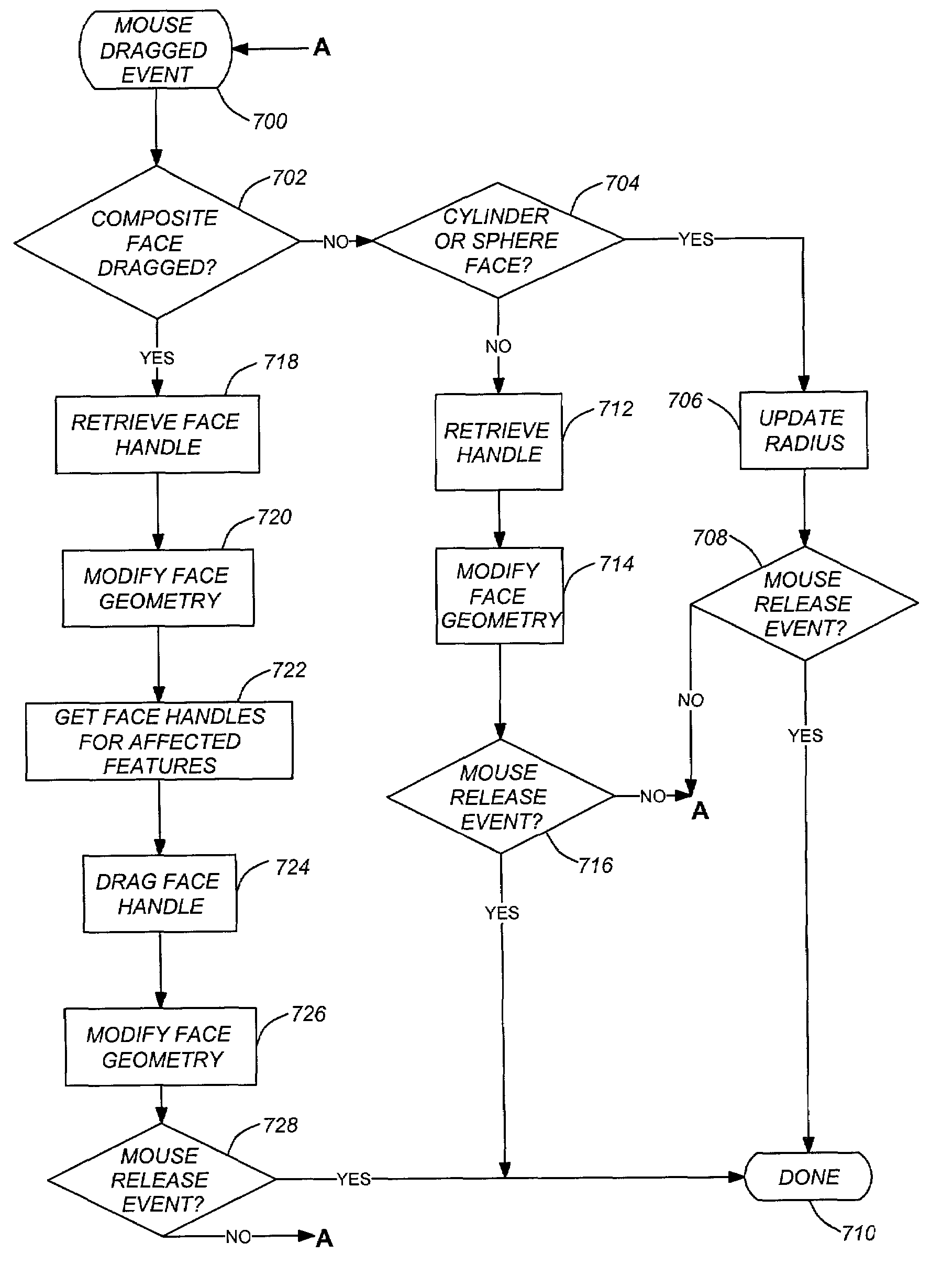
Controlled face dragging in solid models
One or more embodiments of the invention provide a method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for modifying a three-dimensional model. A three-dimensional model is displayed in a computer implemented solid modeling system. A first face of the three-dimensional model is then selected. A first constraint that controls a behavior of a repositioning operation for the first face is specified. Once the face and constraint have been selected / specified, the three-dimensional model is modified by repositioning the selected first face, wherein the repositioning operation is constrained in accordance with the specified first constraint.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Rotor Assembly System and Method
A system for assembling a rotor stack having a plurality of rotor disks may include a measurement system for measuring characteristics of the rotor disks, a computer electronically connected to the measurement system for capturing data from the measurement system, and solid modeling software for creating a virtual stack of the rotor disks optimized for concentricity.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for hybrid solid and surface modeling for computer-aided design environments
Systems and methods for modeling computer-aided design (CAD) environments and objects are disclosed. The systems and methods provided herein comprise a hybrid between solid modeling and surface modeling. The methods and systems are directed to structures that represent objects and rendering of the objects. The hybrid solution combines the modeling features and rules of solid modeling and the performance abilities provided by surface modeling. This provides efficient memory usage and advantageous run time performance.
Owner:CCT INT
System and method for solid modeling
InactiveUS6748419B2Improve processing efficiencyAdd optionsMultiple digital computer combinationsAerodynamics improvementData storeUser interface
Modeling three-dimensional objects on a computer system via a high bandwidth distributed network, facilitating the computing of intensive computer-aided design (CAD) tasks to take place on a series of servers. A multi-tiered distributed processing architecture, which separates client user interface, multiple application servers and database servers is employed, resulting in the separation of server computing and data storage from the client control device. Computing for CAD tasks is directed to the client device or to an application server, as is appropriate for the complexity of tasks being performed.
Owner:ALIBRE
CPS physical solid formalized modeling method based on blend space-time Petri net model
InactiveCN105653577AGuaranteed real-timeRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsPhysical entityPetri net
The invention provides a CPS physical solid formalized modeling method based on blend space-time Petri net model. First, a rational system structure map is provided after Cyber-physical System (CPS) features are analyzed; a new event presentation is designed for space-time features of the CPS event message and physical solid dynamic changes; space-time factors and continuous variables are introduced on the basis of the Petri net to construct a blend space-time Petri net model; physical solid logic and time hierarchal behaviors can be described and state changes due to changes of physical solid position changes can be described. The CPS physical solid formalized modeling method based on a blend space-time Petri net model can be applied to real-time event CPS model design, so a new CPS physical solid modeling method can be achieved. Consistency between real-time property and space-time can be achieved for the CPS by the use of the method; continuous variables are introduced in consideration of physical environment dynamic property, so the method is suitable for all environments; and foundation is laid for the development of CPS.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
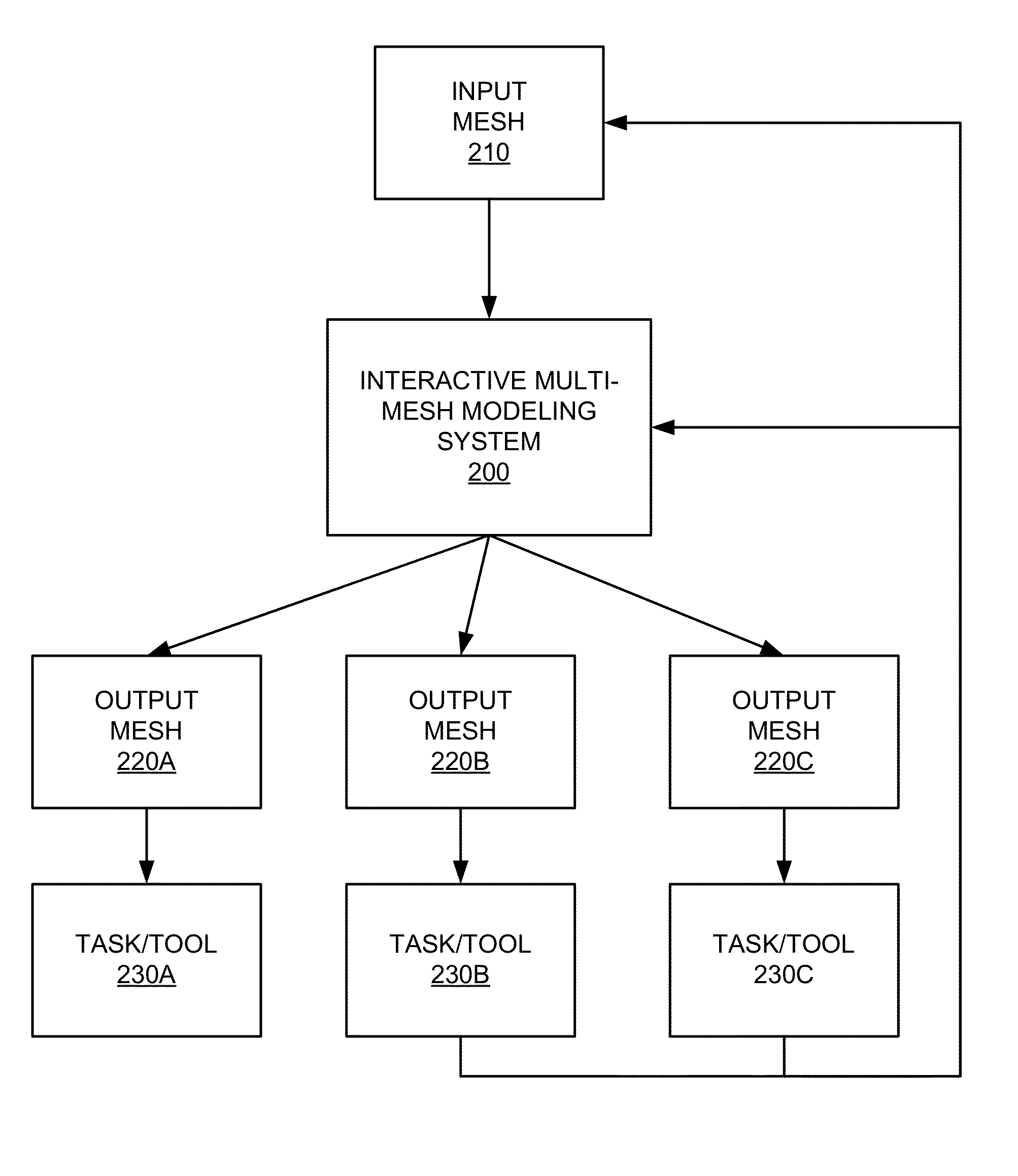
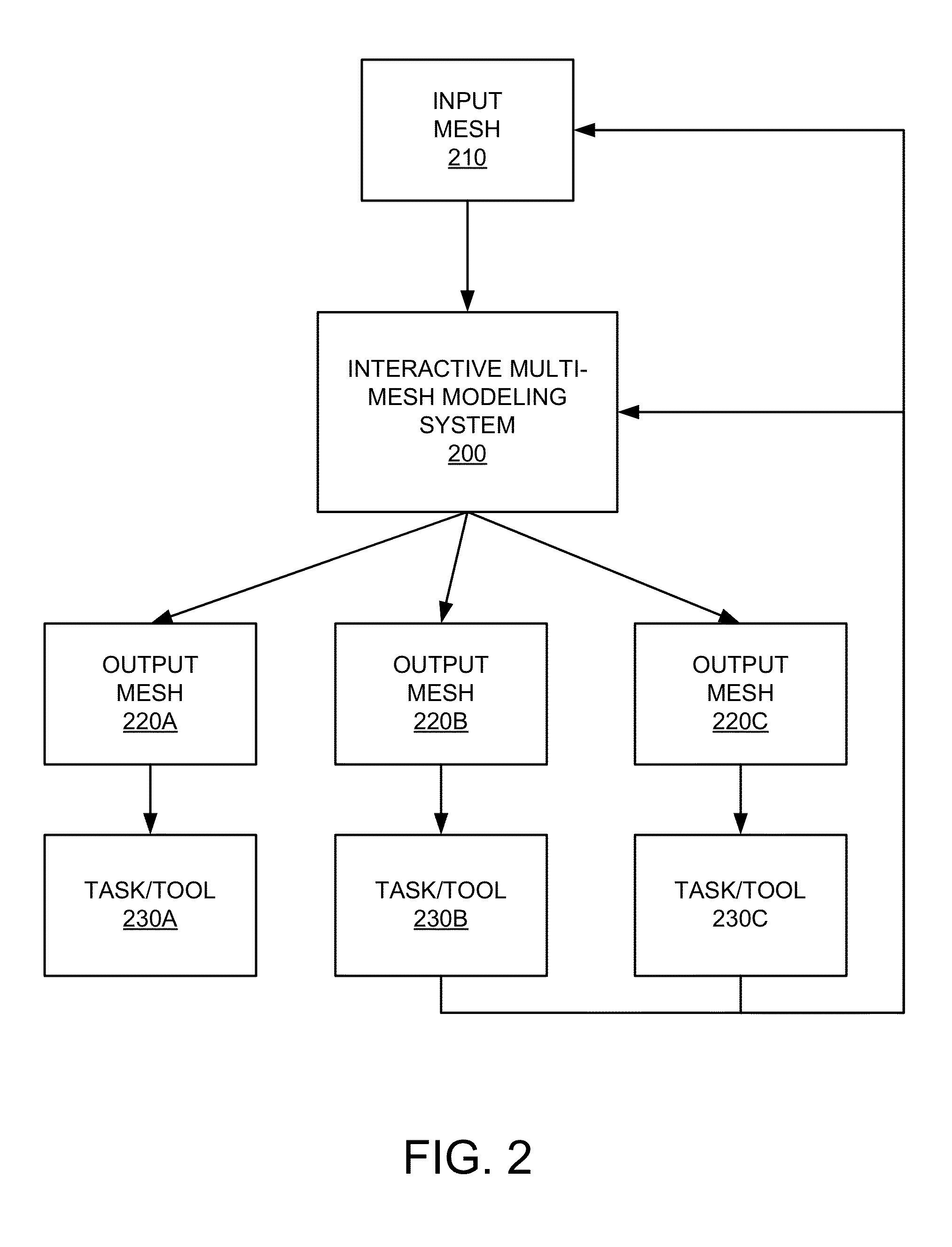
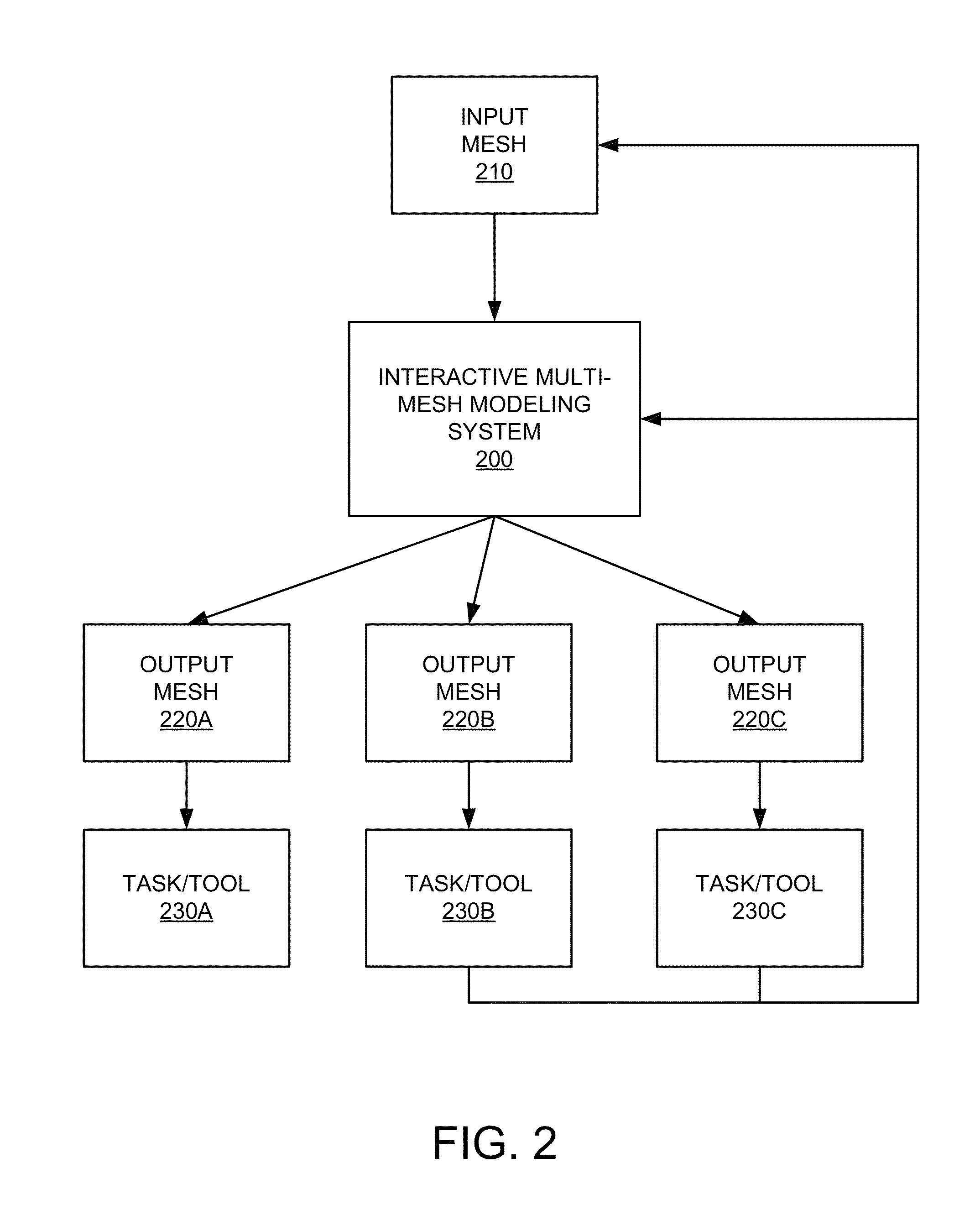
Interactive multi-mesh modeling system
An interactive multi-mesh modeling system allows users to employ a variety of modeling techniques to interactively create objects for a variety of different tasks or tools. Some of these different tasks or tools can have requirements for computer-generated representations of objects on which they operate. These requirements may differ from how some computer-generated representations were originally created (e.g., 3D solid objects output using solid modeling techniques vs. 2D flat “panel constructed” objects required for some computer simulations). Thus, the interactive multi-mesh modeling system may further employ a variety of techniques for taking a source computer-generated representation of an object and providing the automatic creation, management, and maintenance of instances or versions of the source. The interactive multi-mesh modeling system may further employ a variety of techniques for the automatic management and transfer of information defined thereon or associated with these meshes.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
Face modification tool
ActiveUS7092859B2Avoiding adding new operationComputation using non-denominational number representationInput/output processes for data processingComputational scienceBoundary representation
One or more embodiments of the invention provide a method, apparatus, system, and article of manufacture for modifying a three-dimensional model. A composite three-dimensional model is displayed in a computer implemented solid modeling system. The composite model comprises a first primitive and a second primitive. A first face of the first primitive is selected. Once selected, a first boundary representation of the first primitive is modified using the selected first face. Thereafter, a second boundary representation of the second primitive is automatically modified based on the modification to the first boundary representation.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Method for enhancing typhoon protection capacity of buildings
ActiveCN106844983AEasy accessEfficient acquisitionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationPoint cloudComputer science
The invention discloses a method for enhancing typhoon protection capacity of buildings. The method includes the following steps: firstly, structuring a two-dimensional line drawing and a three-dimensional model of a typhoon damaged building; to be more specific, a, acquiring laser point cloud data of the disaster damaged building; b, performing registration and splicing on the point cloud data so as to obtain the two-dimensional line drawing; c, performing solid modeling through the two-dimensional line drawing matching with the point cloud data so as to obtain the three-dimensional model of the building; secondly, computing disaster damage according to the two-dimensional line drawing of the building, judging disaster damage types of the building structure according to the three-dimensional model, and adopting different design schemes on different structures of the building according to the disaster damage types. Through the method, the three-dimensional model of the typhoon damaged building can be structured, and theoretical guidance is provided for the anti-typhoon structure of the buildings according to the three-dimensional model.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV OF TECH
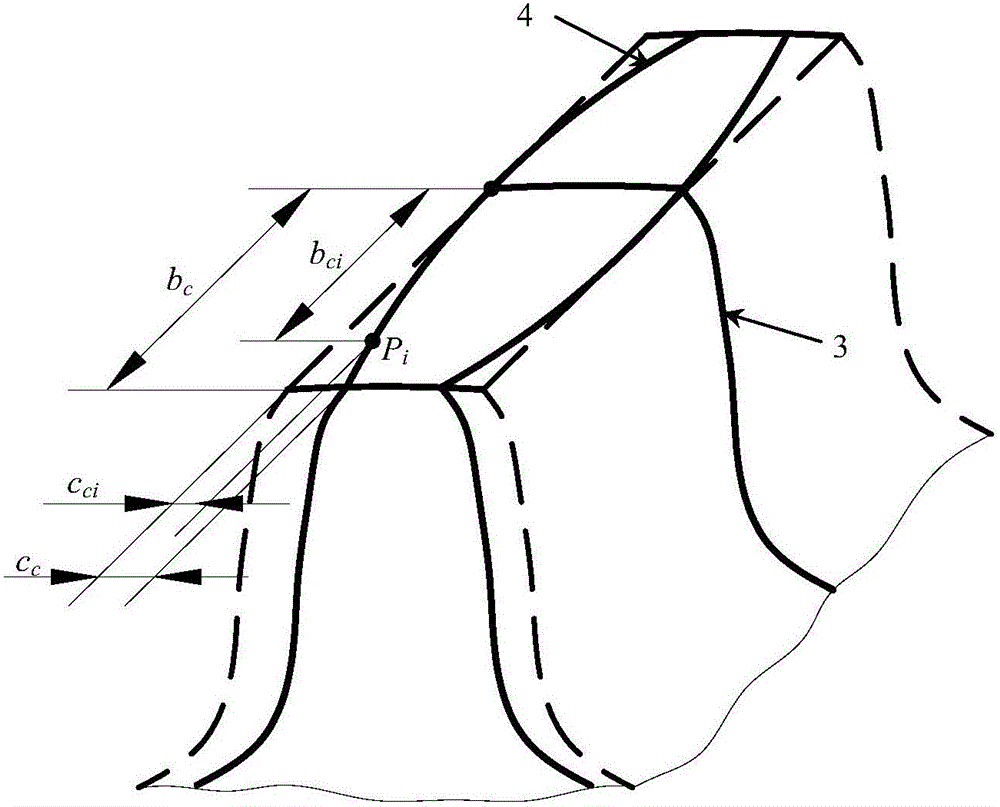
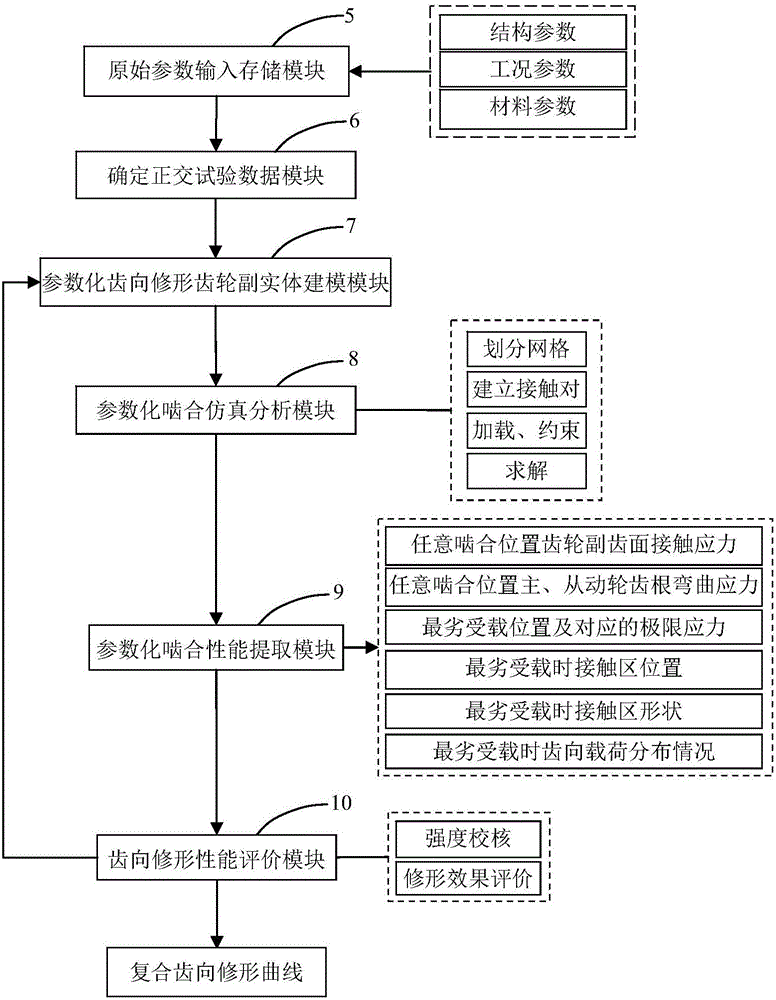
Axial modification method of involute straight toothed spur gear pair and special parametric CAD (computer aided design) system matched with axial modification method
ActiveCN106202732AExtended service lifeAccurate calculation of strengthGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputer Aided DesignEngineering
The invention discloses an axial modification method of an involute straight toothed spur gear pair and a special parametric CAD (computer aided design) system matched with the axial modification method. The axial modification method of the involute straight toothed spur gear pair comprises main steps as follows: universal composite axial modification curves are established, simulated axial modification of gears is performed by means of the obtained multiple composite axial modification curves one by one with an orthogonal test method, and a simulation transmission test is performed, so that the composite axial modification curve corresponding to the optimal simulation transmission test result is screened out. According to the special parametric CAD system matched with the axial modification method, the involute straight toothed spur gear pair after axial modification is treated in processes including solid modeling, meshing simulation analysis, extraction of meshing performance of an axial modification gear pair and the like and then is blended into the system, and the system has complete functions, is convenient to use and can be efficiently used for aided design for research and development of the gears. The axial modification method is high in universality and stable and reliable in modification quality; the CAD system has the complete functions and is simple to operate.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
True three-dimensional mining blast unit body modeling method
ActiveCN103218850ARealize automatic statisticsHigh precisionSpecial data processing applications3D modellingGraphicsDimensional modeling
The invention discloses a true three-dimensional mining blast unit body modeling method which is applied to a subsection caving mining method without sill pillars. The computer three-dimensional modeling technique is utilized to model a mining blast unit body so as to achieve true expression and independent and omnibearing three-dimensional display of the blast unit body. The purpose of cognitive comprehensiveness and management refine on the blast unit body is achieved. The true three-dimensional mining blast unit body modeling method comprises the following steps of designing distance according to extraction approaches, generating all central lines of the distance of the extraction approaches a main layer and an upper layer on the XY plane, forming line files to be stored, simultaneously cutting extraction approaches of a blast unit body to be built and two layered extraction approaches on the blast unit body to be built according to caving step pitch, generating a central line of a main layer extraction approach in the Z direction, opening the central line file of the main layer and the upper layer and section patterns of extraction approaches of the blast unit body to be built in a software pattern window, inputting parameter, choosing space objects and operating algorithm to model solidly.
Owner:NANJING MEISHAN METALLURGY DEV
Method for transformer fault graphic early warning
ActiveCN103091610ASimple modelReduce data volumeTesting dielectric strengthGraphicsEarly warning system
The invention relates to a method for transformer fault graphic early warning. The method is a wireframe model method. When a wireframe model is adopted to extract data, a top point and seamed edges of only an entity need to be recorded. Compared with surface modeling and entity modeling, the entity modeling is simpler. Due to the fact that the method is different from an existing three-dimensional model method which needs to record all points, lines and surfaces in a three-dimensional model entity, the method only needs to record the top point and the seamed edges, the data size which needs to be calculated is smaller, and the calculating speed is faster. The method solves the problem that a transformer fault graphic early warning system is slow in real-time response.
Owner:CHAOYANG POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY +3
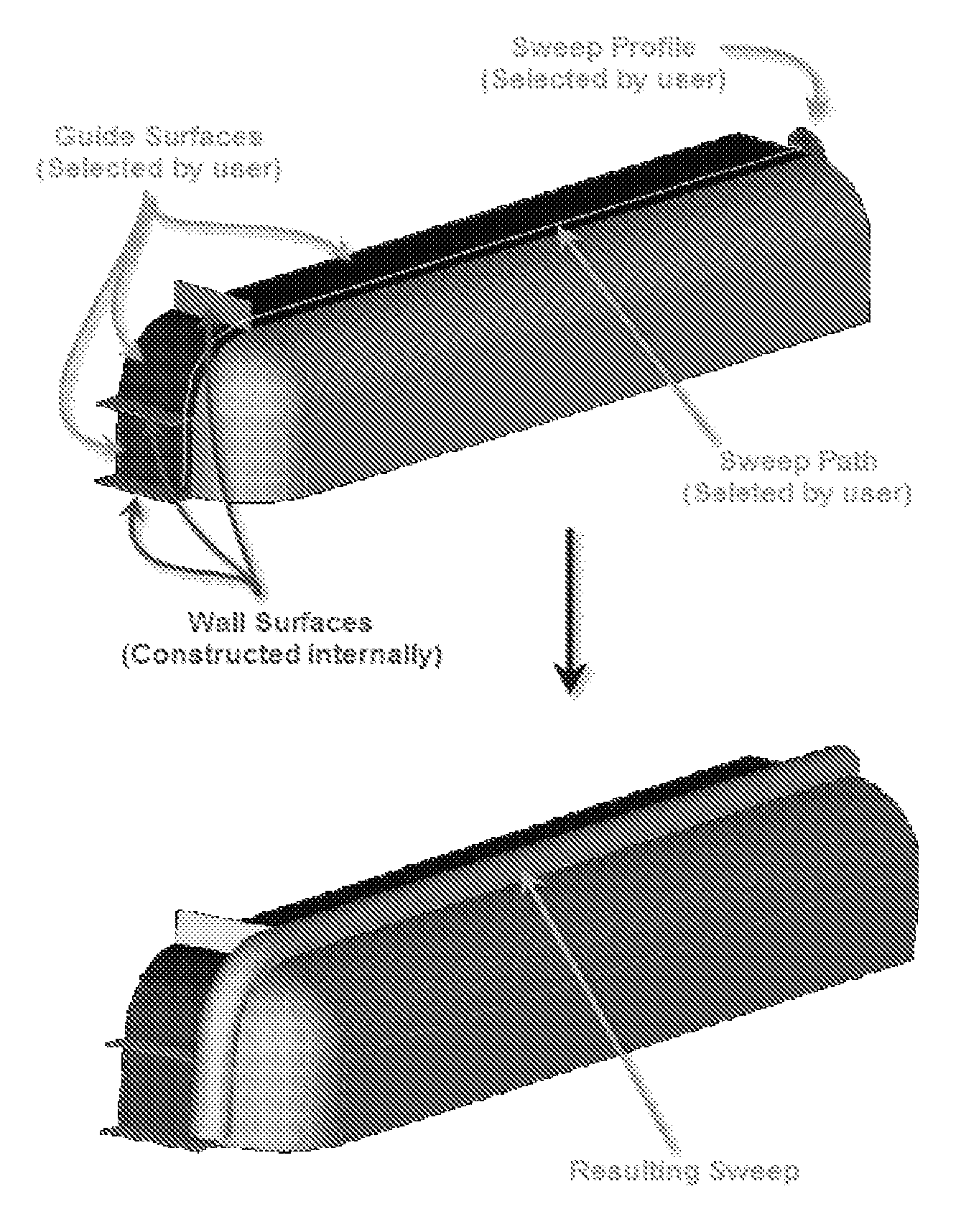
Sweep with guide surface
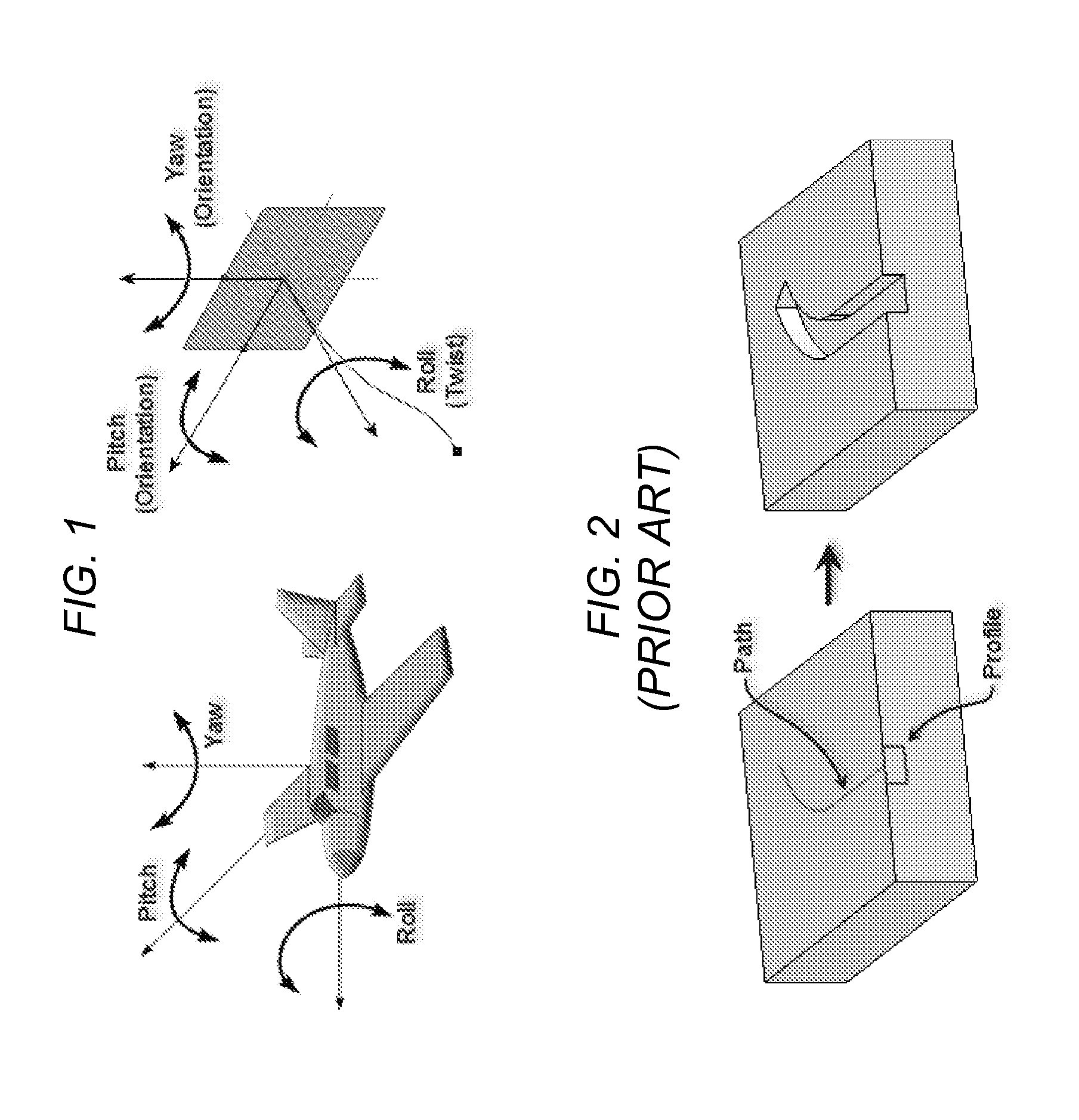
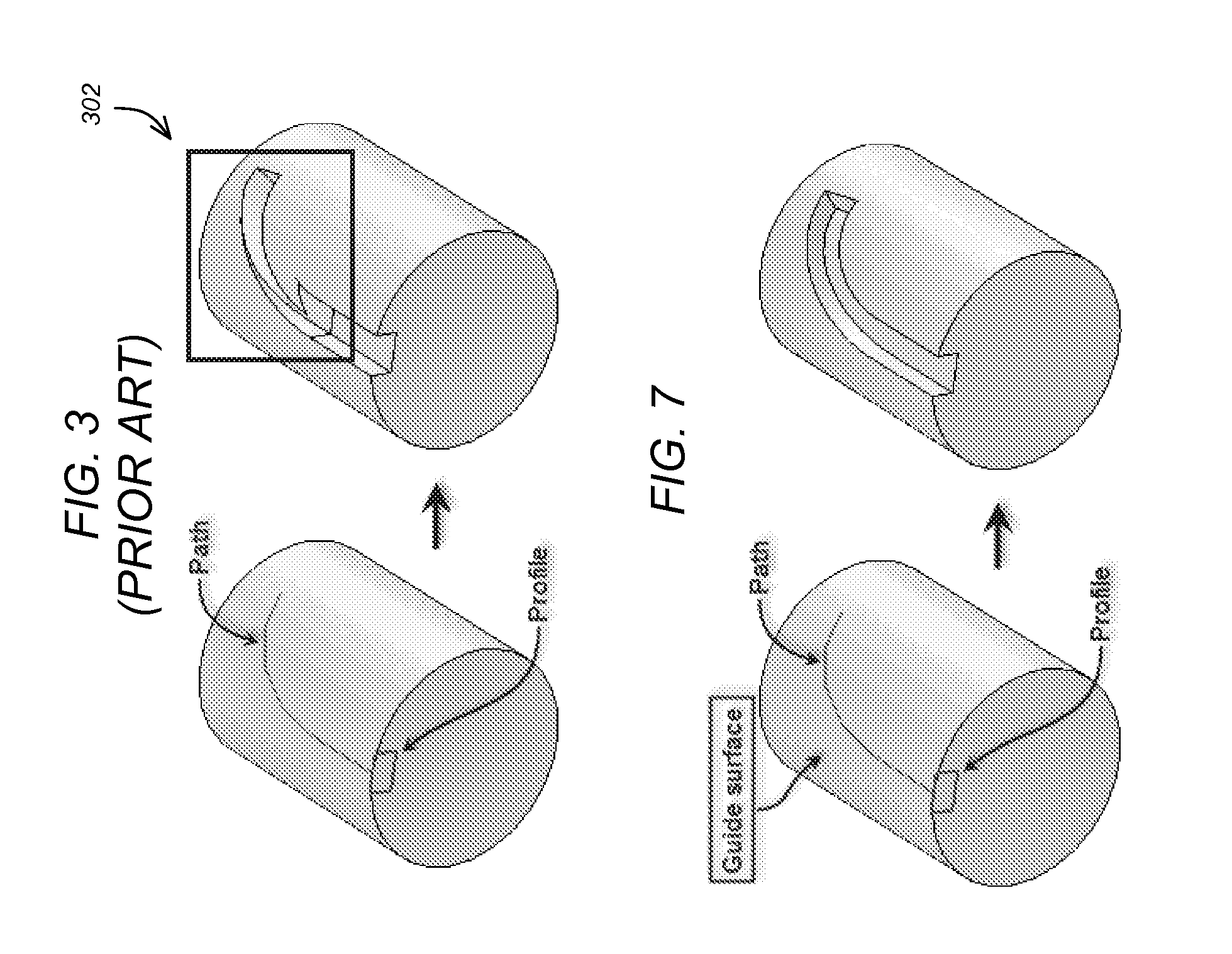
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture provide the ability to conduct a sweep operation in a computer-implemented solid modeling system, A 3D non-planar surface is created. A path for a sweep operation is created. A profile for the sweep operation is created. The 3D surface is selected for use as a guide. An angle between the profile and the 3D non-planar surface is calculated. A sweep operation is conducted wherein a twist of the profile is maintained within a pre-defined range of the angle.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Fractured texture coordinates
InactiveUS8681147B1Reduce distortion problemsCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingUV mappingMulti mesh
In various embodiments, an interactive multi-mesh garment modeling system may allow a user to employ solid modeling techniques to create one or more representations of garment objects whose motions are typically determined by computer simulations. Accordingly, in one aspect, the interactive multi-mesh garment modeling system may automatically generate one or more meshes that satisfy the requirements for computer simulations from a source mesh modeled by a user using solid modeling techniques. For each polygon associated with a UV mapping of one of these meshes, gradients of U and V for the polygon can be determined with respect to a 3D representation of an object that are substantially orthogonal and of uniform magnitude and that approximate the original gradients of U and V for the polygon. In another aspect, each polygon in a plurality of polygons of a 2D parameterization of an object can be reshaped based on individually corresponding polygons in a 3D representation of the object.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
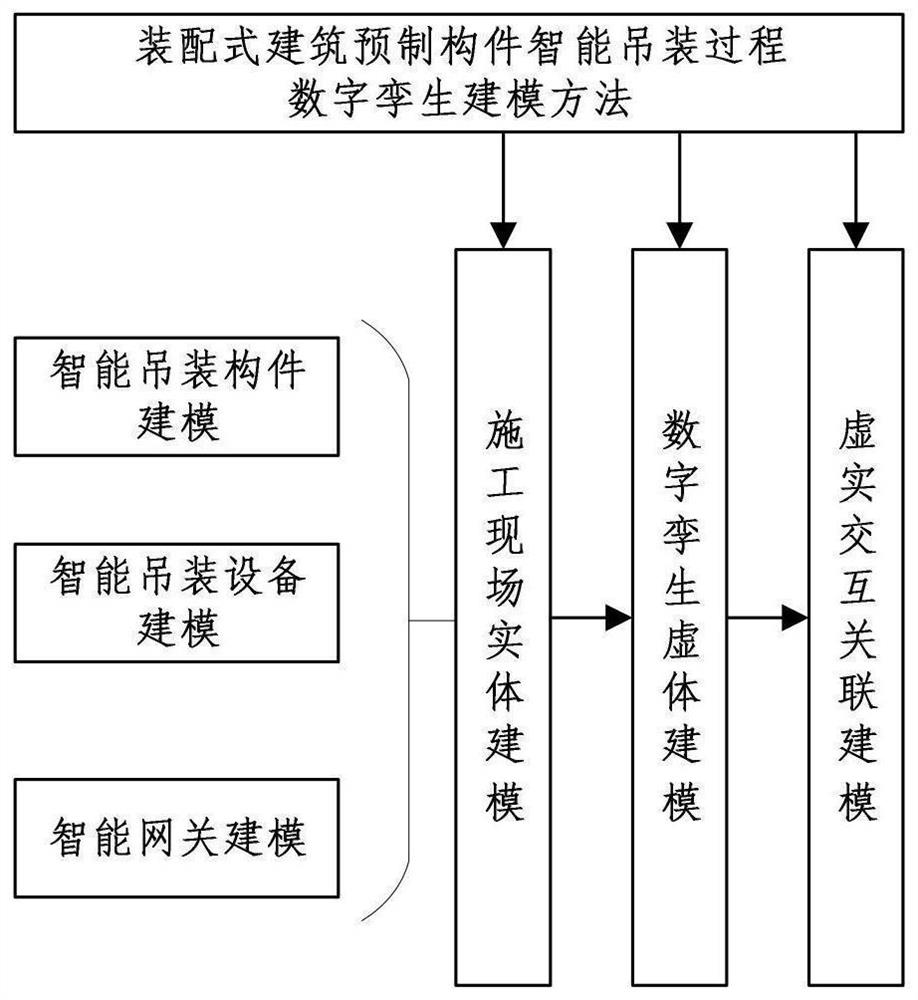
Digital twin modeling method for intelligent hoisting process of prefabricated parts of fabricated building
PendingCN112084550AEasy to controlImprove construction efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationInformatizationSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a digital twin modeling method for an intelligent hoisting process of prefabricated parts of a fabricated building. The method mainly comprises the steps of fabricated buildingconstruction site solid modeling, digital twinning virtual body modeling and virtual-real interaction association modeling. The construction site entity modeling is composed of intelligent hoisting component modeling, intelligent hoisting equipment modeling and intelligent gateway modeling, and construction site data acquisition is achieved. The digital twin virtual body modeling carries out analog simulation on a construction site from four aspects of geometry, physics, behaviors and rules; according to virtual-real interaction association modeling, synchronous simulation of construction site solid modeling and digital twin virtual body modeling is achieved through a data transmission protocol, and prediction and optimization of model driving are achieved. According to the invention, theproblems that in the hoisting process of prefabricated components of a traditional fabricated building, data are difficult to map, information is redundant and not visual enough, and searching is difficult can be solved, control over the fabricated construction process is enhanced, the construction efficiency is improved, and the informatization level of the fabricated hoisting process is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Implicit feature recognition for a solid modeling system
ActiveUS7643027B2Drawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer Aided DesignAlgorithm
Owner:DASSAULT SYST SOLIDWORKS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com