Patents
Literature
673results about "Other recording methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
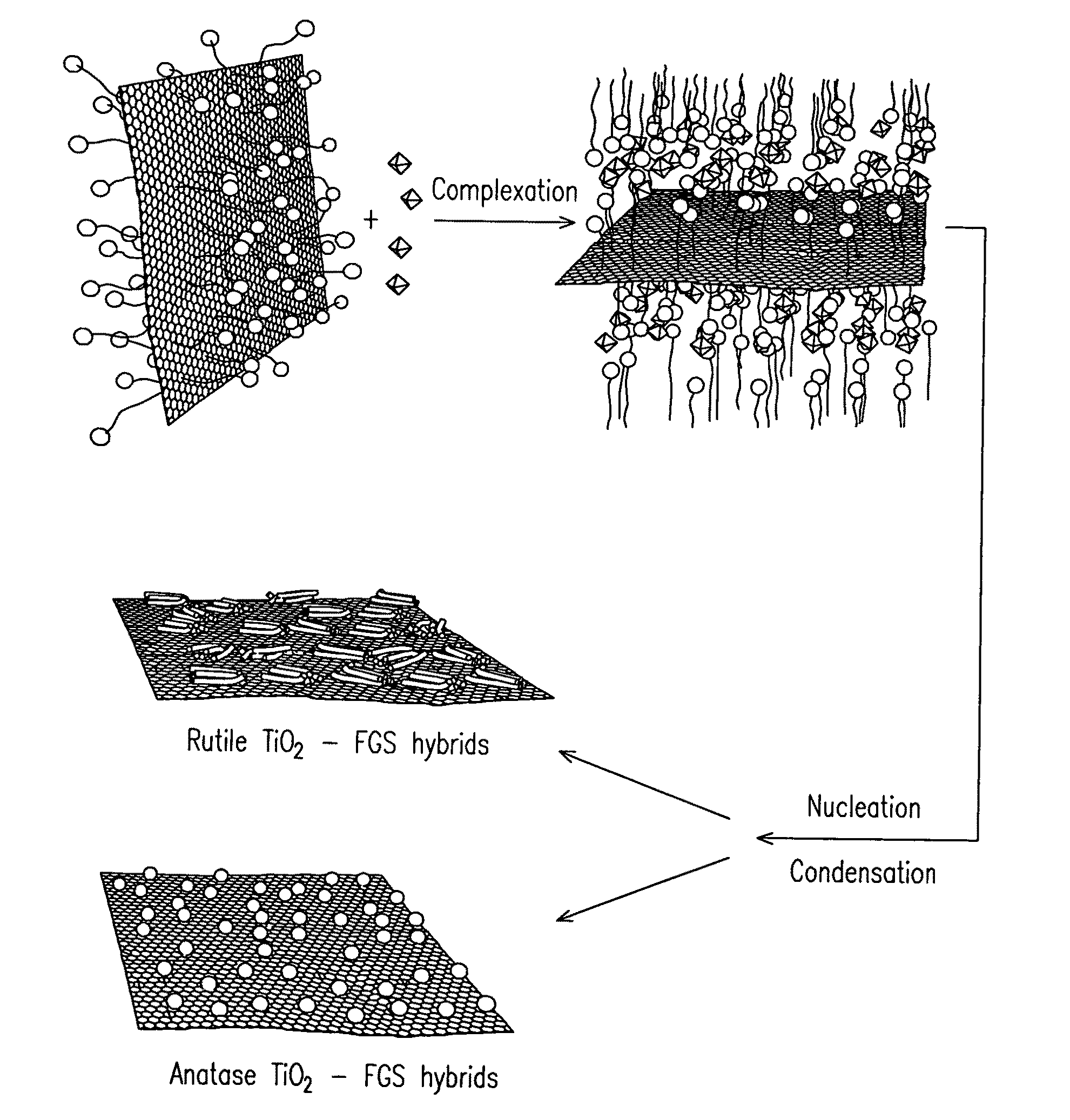
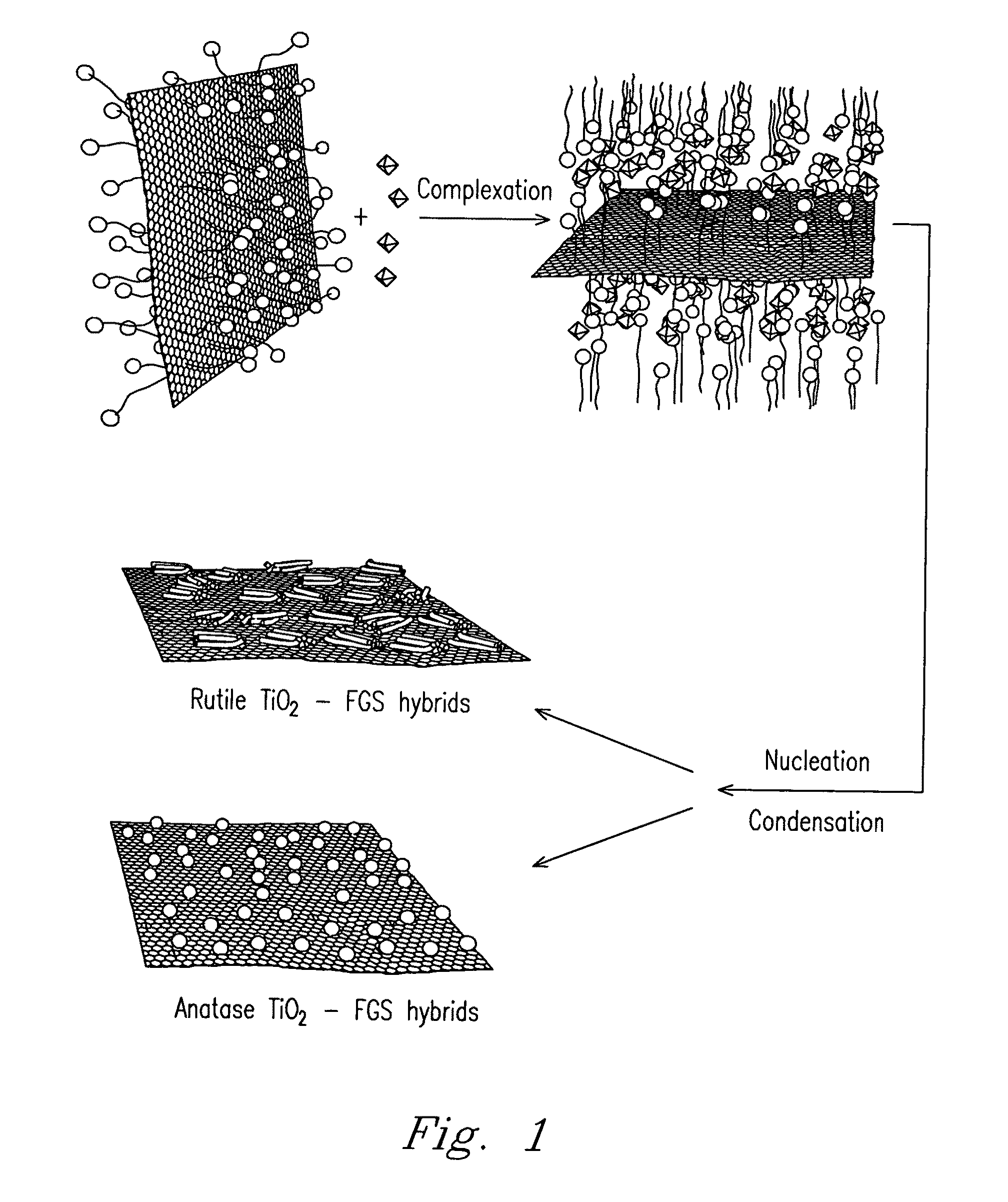
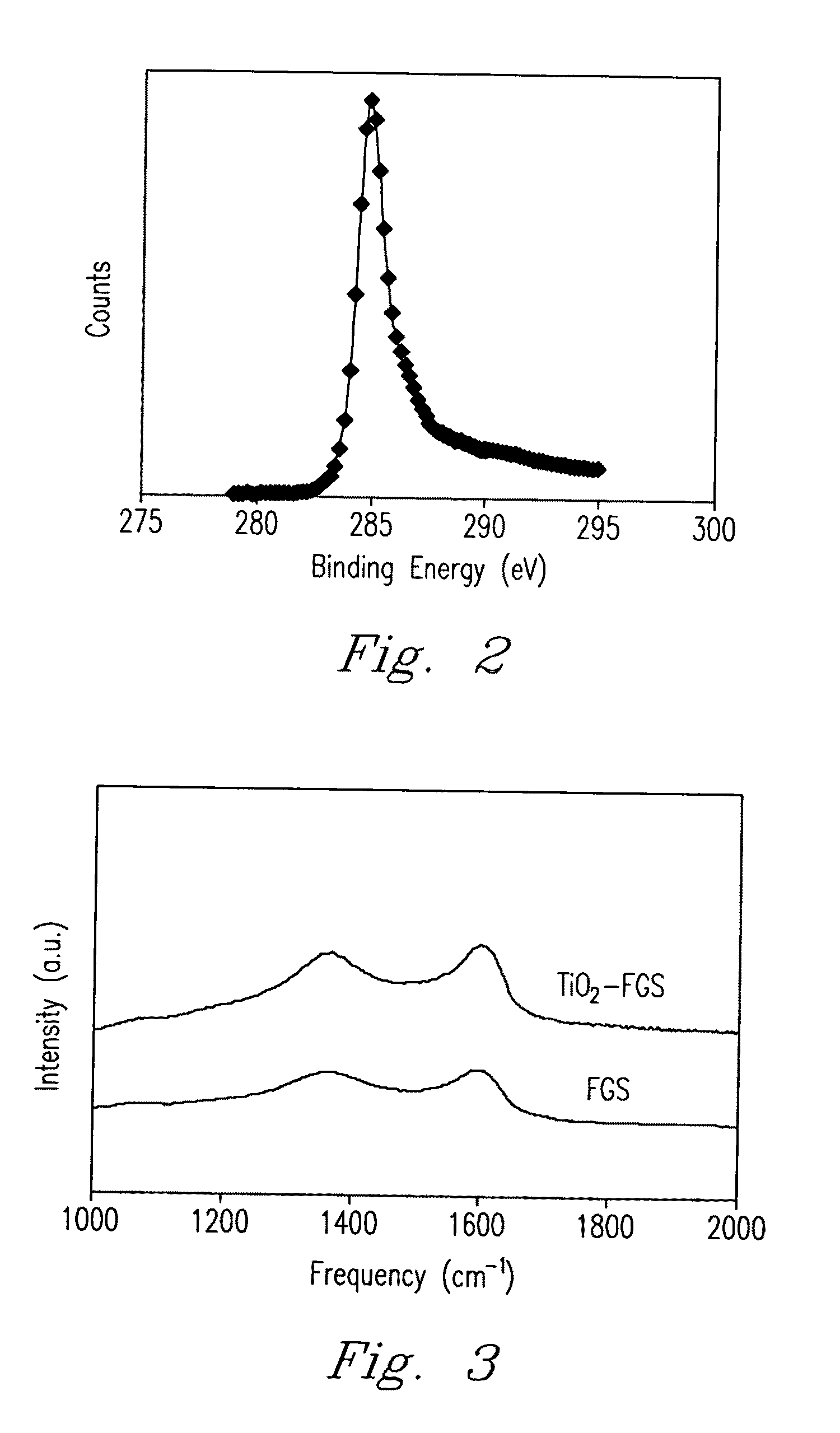
Nanocomposite of graphene and metal oxide materials
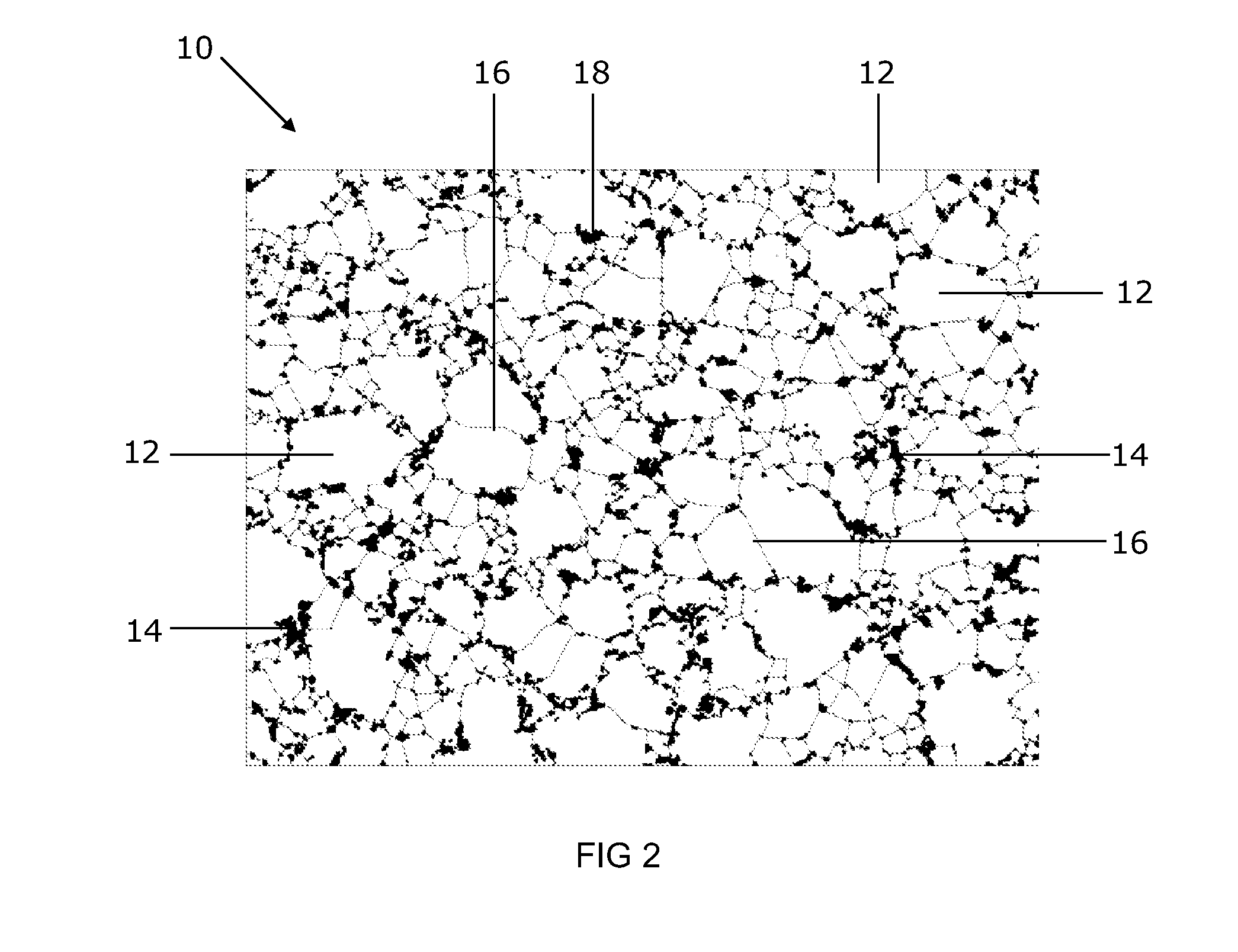
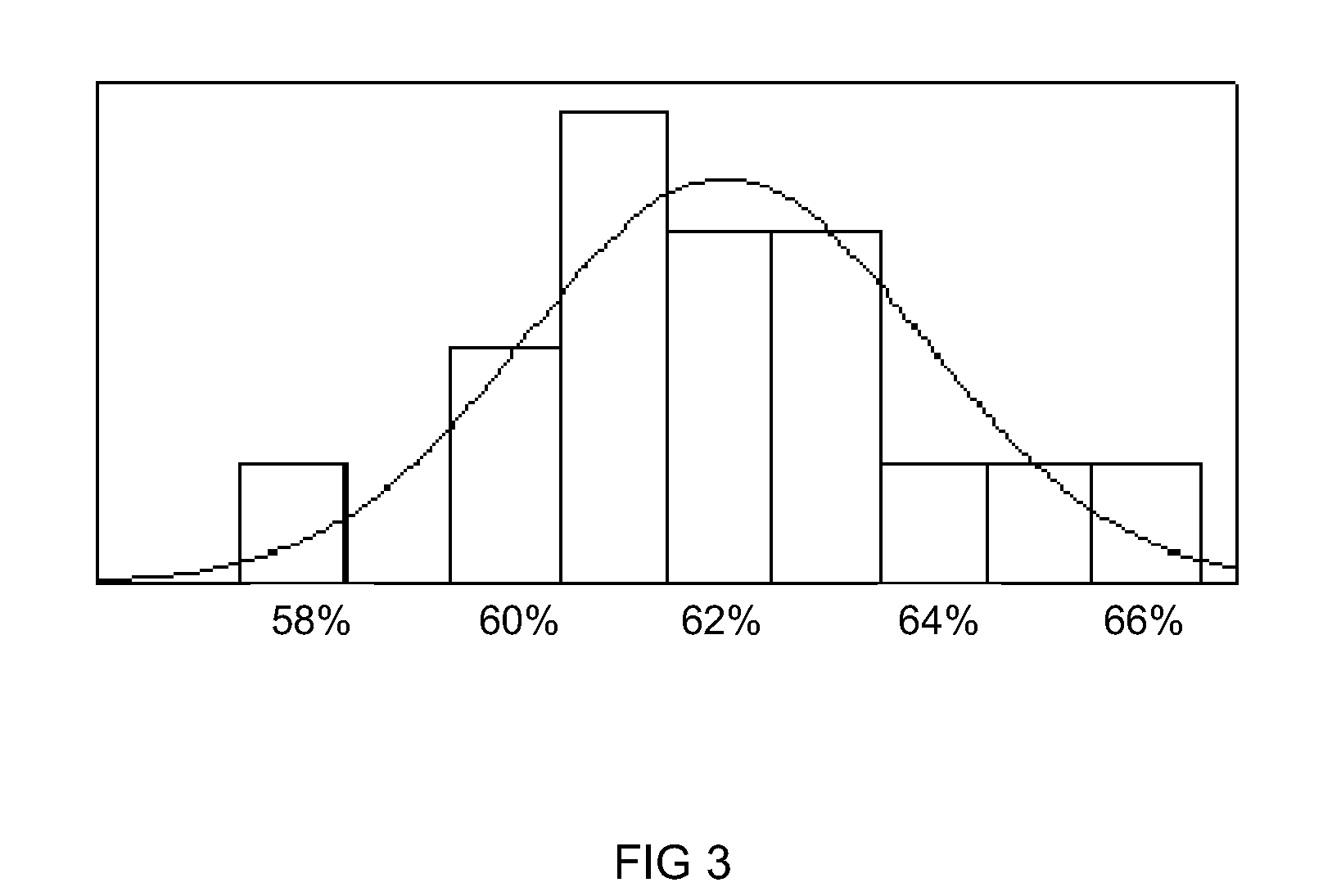
ActiveUS20100081057A1Easy to distinguishMaterial nanotechnologyRecord information storageDischarge rateCvd graphene
Nanocomposite materials comprising a metal oxide bonded to at least one graphene material. The nanocomposite materials exhibit a specific capacity of at least twice that of the metal oxide material without the graphene at a charge / discharge rate greater than about 10C.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
Foamed thermoplastic polymer and wood fiber profile and member
InactiveUS6054207AHigh compressive strengthImproved fastener retentionConstruction materialLoad-supporting elementsComposite constructionThermoplastic
Advanced structural components comprising a foamed thermoplastic that can be used in virtually any application where wooden components have a use. Such structural components can comprise sized lumber, shaped trim, posts, beams or shaped structural members. An advanced profile composite structural component comprising an exterior capping layer with an interior comprising a foamed thermoplastic can be used in the assembly of fenestration units adapted to residential and commercial structures. Preferably the profile structural component can be used in a window or door assembly. The profile member is adapted for ease of construction of the fenestration units, can be easily installed in a rough opening to framing members, and can be trimmed and adjusted on site. The profile is structurally strong, thermally stable, shrink resistant and will accept and retain the insertion of fasteners such as staples, nails and screws permanently with substantial retention and little or no damage to the units. The profile structural components possess strength that permits the manufacture of a structurally sound fenestration unit from two or more foamed profile members or other conventional members.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Fluoropolymer fine fiber
ActiveUS20090032475A1Advantageously employedHeat stableDispersed particle filtrationLiquid suspension thickening by filtrationPolymer scienceFiltration
A layer of fluoropolymer fine fiber can be made. The fine fiber can be made by electrospinning from a solvent or a solvent blend. The layers of the invention are useful in general filtration of fluid streams including gaseous and liquid streams. The fine fiber layers are also useful as hydrophobic filtration layers that can be used to separate water from a hydrocarbon stream.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Method for purification of as-produced single-wall carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20020127169A1High yieldNanostructure manufactureSpecial paperSolar cellSingle-Walled Nanotube
A method for purifying a mixture comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes and amorphous carbon contaminate is disclosed. The method includes the steps of heating the mixture under oxidizing conditions sufficient to remove the amorphous carbon, followed by recovering a product comprising at least about 80% by weight of single-wall carbon nanotubes. A method for producing tubular carbon molecules of about 5 to 500 nm in length is also disclosed. The method includes the steps of cutting single-wall nanotube containing-material to form a mixture of tubular carbon molecules having lengths in the range of 5-500 nm and isolating a fraction of the molecules having substantially equal lengths. The nanotubes may be used, singularly or in multiples, in power transmission cables, in solar cells, in batteries, as antennas, as molecular electronics, as probes and manipulators, and in composites.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing with a probe on erasable magnetic media
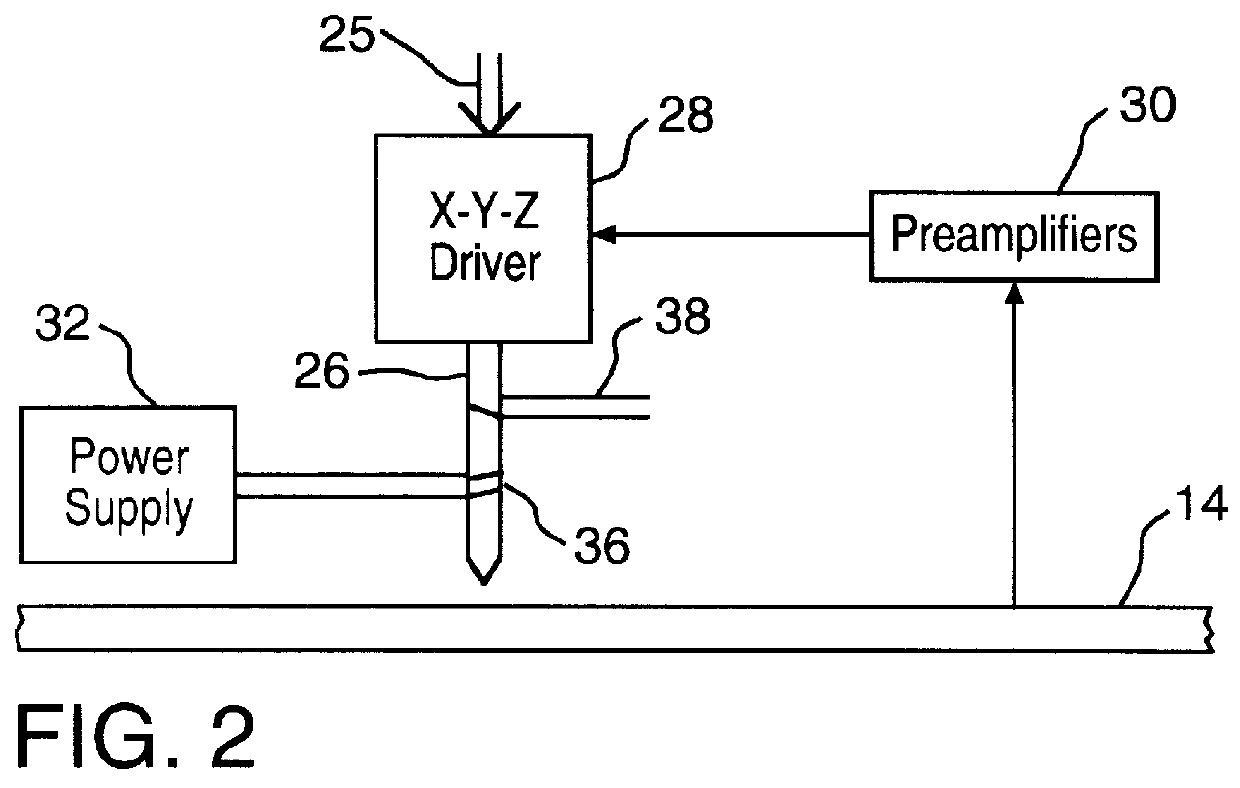
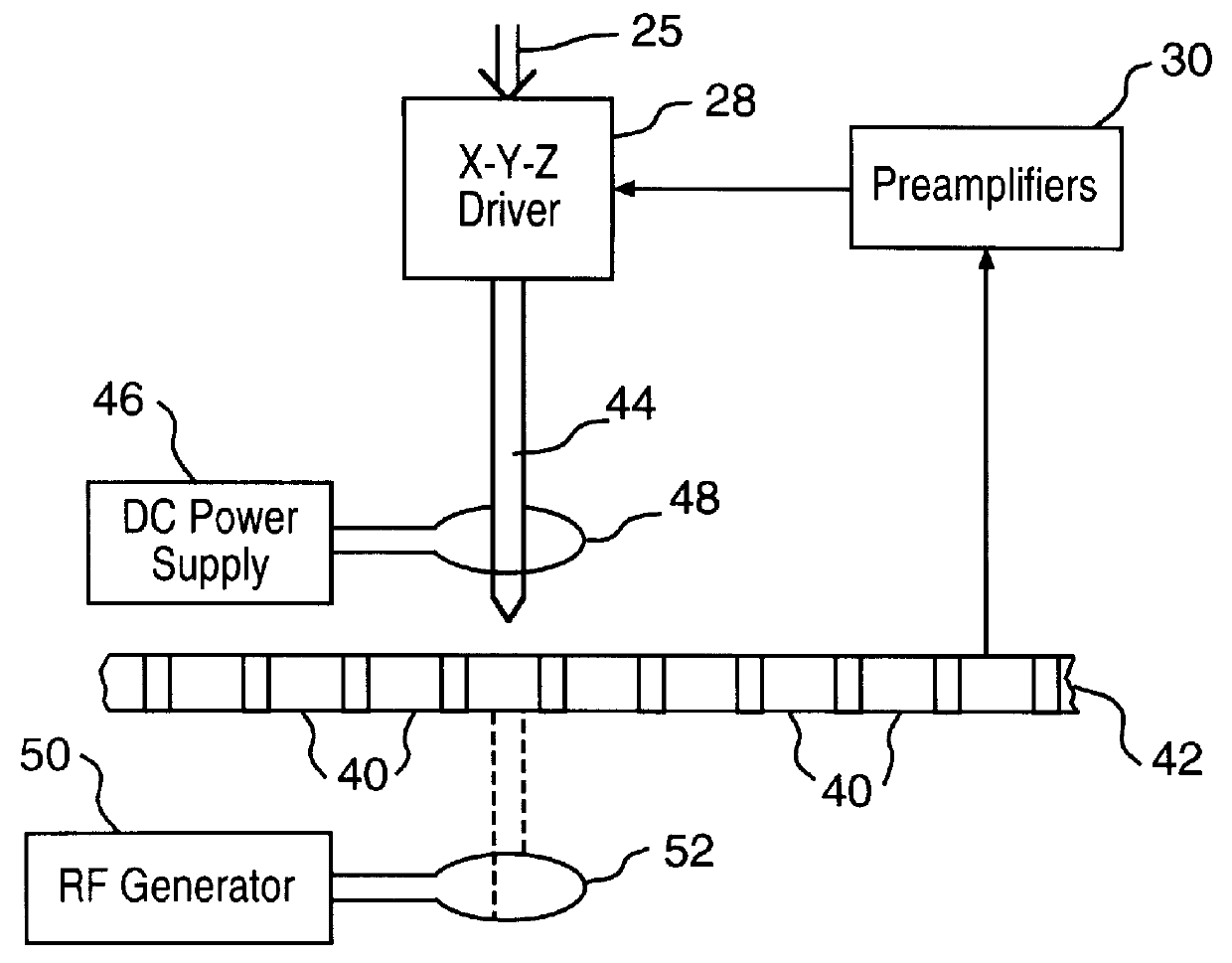
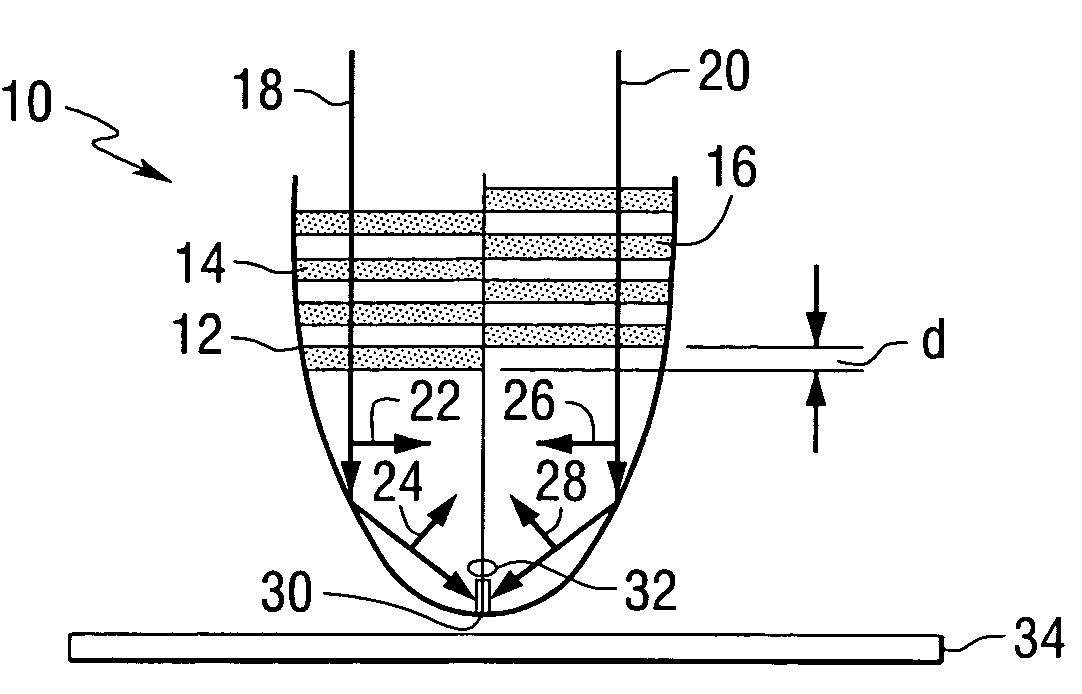
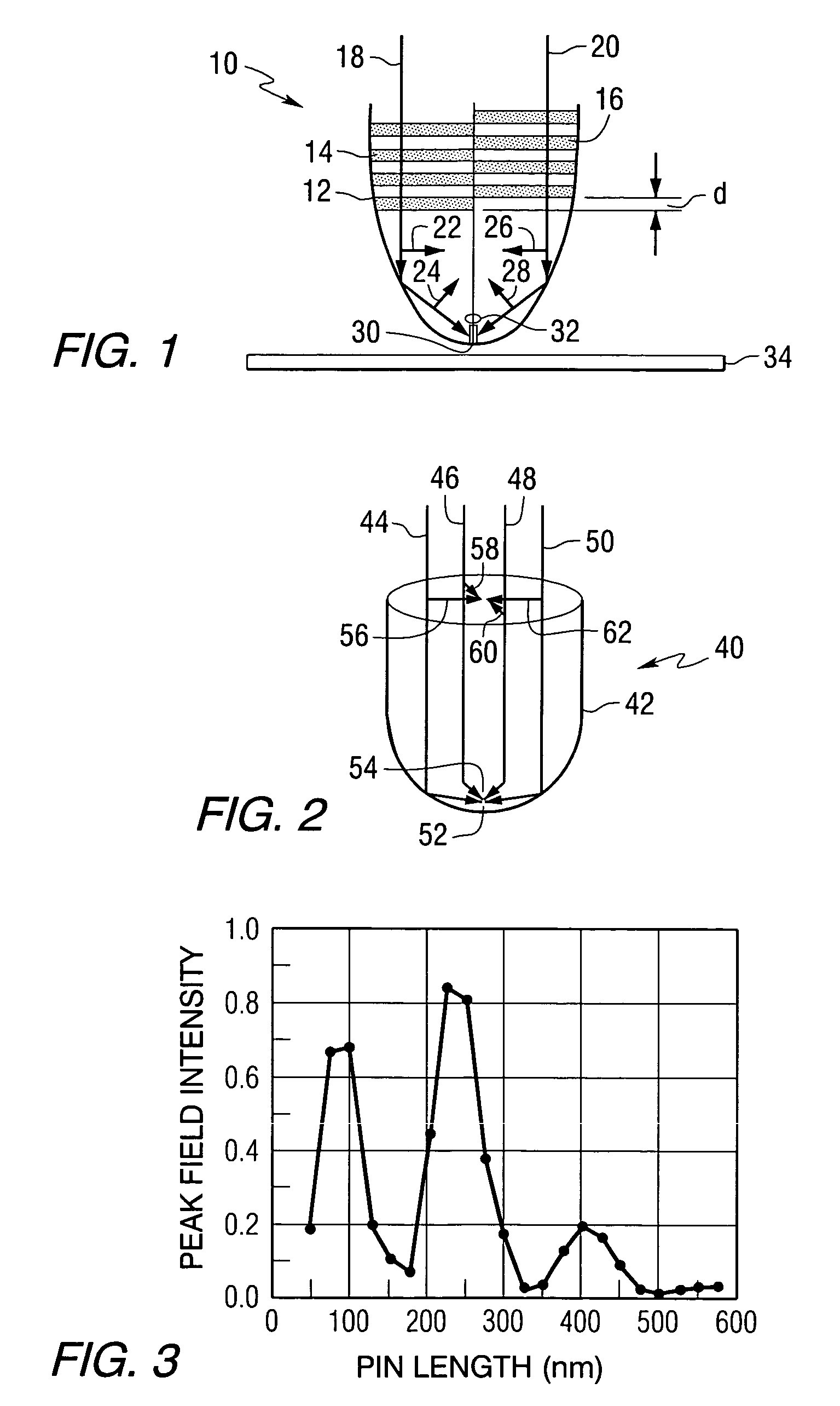
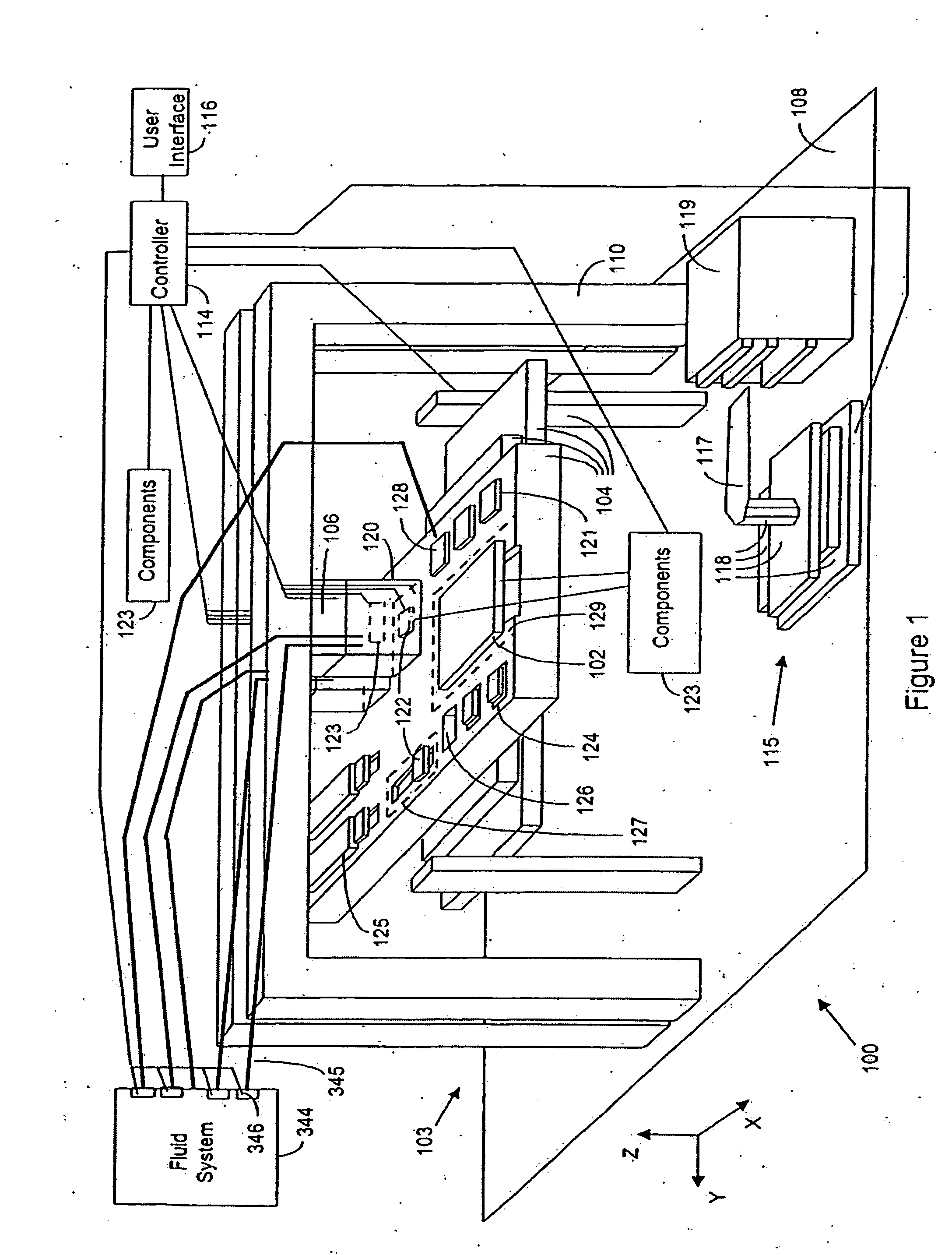
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing on an erasable magnetic medium include using a micromachined mechanism having two probes for writing to the medium. Use of the two probe embodiment eliminates the need to change the magnetic orientation of the probe. In another embodiment, a single probe is provided which is heated to the vicinity of its Curie temperature to enable the magnetic orientation of the probe to be switched. The probe may be heated to its Curie temperature through the use of a heating element or a focused laser. In another embodiment of the present invention, either the magnetic orientation of the probe or the magnetic orientation of the medium may be switched through the combination of a static magnetic field, a radio frequency magnetic field and, under certain circumstances, the magnetic field of the probe. In all cases, the writing techniques enable information to be written to a magnetic medium in a manner which enables the information to be erased and the medium rewritten.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Low density lightning strike protection for use in airplanes
ActiveUS20090227162A1Minimize micro-crackingWeight optimizationConductive materialWarp knittingFiberEpoxy
Surface films, paints, or primers can be used in preparing aircraft structural composites that may be exposed to lightning strikes. Methods for making and using these films, paints or primers are also disclosed. The surface film can include a thermoset resin or polymer, e.g., an epoxy resin and / or a thermoplastic polymer, which can be cured, bonded, or painted on the composite structure. Low-density electrically conductive materials are disclosed, such as carbon nanofiber, copper powder, metal coated microspheres, metal-coated carbon nanotubes, single wall carbon nanotubes, graphite nanoplatelets and the like, that can be uniformly dispersed throughout or on the film. Low density conductive materials can include metal screens, optionally in combination with carbon nanofibers.
Owner:ROHR INC +1
Coatings, materials, articles, and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS20040229031A1Low costSufficient powerMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsHot zoneMaterials science
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT +2
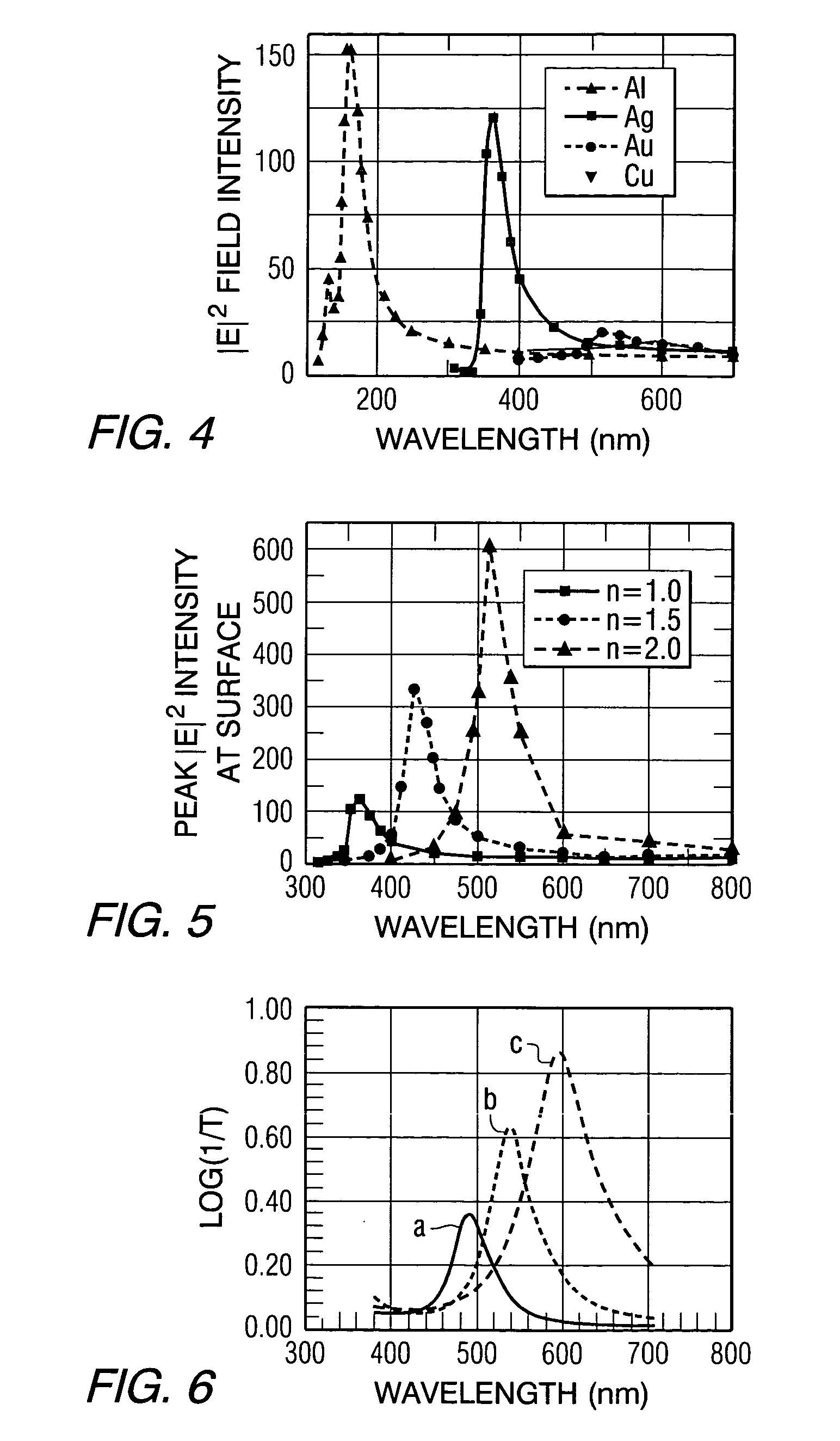
Transducer for heat assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS7272079B2Combination recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic storage
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
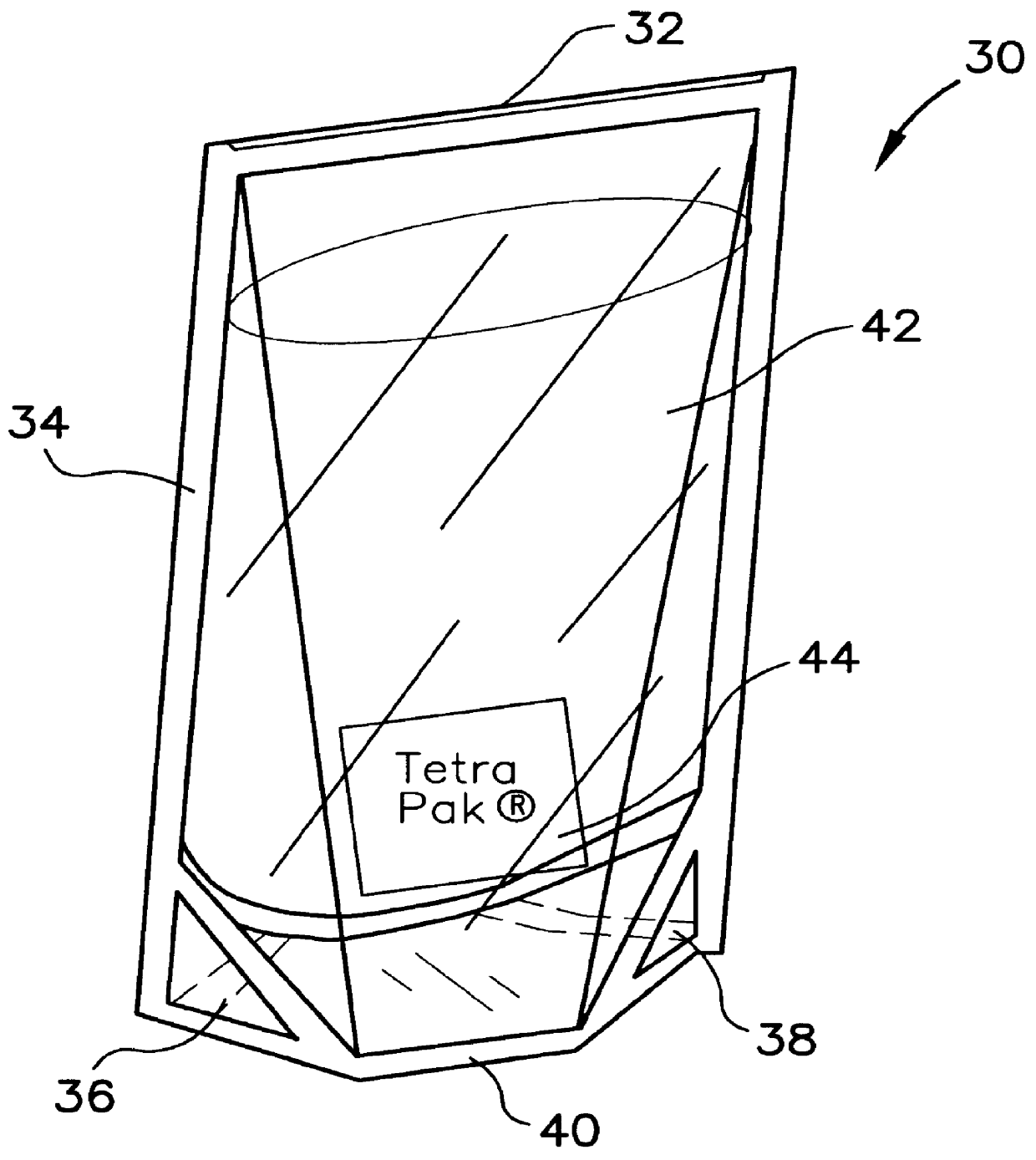
Polyolefin material integrated with nanophase particles
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
Method for growing continuous fiber
This invention relates generally to a method for growing carbon fiber from single-wall carbon nanotube (SWNT) molecular arrays. In one embodiment, the present invention involves a macroscopic molecular array of at least about 106 tubular carbon molecules in generally parallel orientation and having substantially similar lengths in the range of from about 50 to about 500 nanometers. The hemispheric fullerene cap is removed from the upper ends of the tubular carbon molecules in the array. The upper ends of the tubular carbon molecules in the array are then contacted with a catalytic metal. A gaseous source of carbon is supplied to the end of the array while localized energy is applied to the end of the array in order to heat the end to a temperature in the range of about 500° C. to about 1300° C. The growing carbon fiber is continuously recovered.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Carbon nanotube composite and method for fabricating the same
A carbon nanotube composite includes a carbon nanotube structure and a number of nanoparticles. The carbon nanotube structure includes a plurality of carbon nanotubes connected to each other via van der Waals force. The nanoparticles are distributed in the carbon nanotube structure. The carbon nanotubes in the carbon nanotube composite are connected to each other to form a carbon nanotube structure and are arranged in an orderly or disorderly fashion.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Fibrous structures
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Continuous fiber of single-wall carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20020127162A1High yieldCarbon compoundsElectrolytic capacitorsFiberElectric power transmission
A method for purifying a mixture comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes and amorphous carbon contaminate is disclosed. The method includes the steps of heating the mixture under oxidizing conditions sufficient to remove the amorphous carbon, followed by recovering a product comprising at least about 80% by weight of single-wall carbon nanotubes. A method for producing tubular carbon molecules of about 5 to 500 nm in length is also disclosed. The method includes the steps of cutting single-wall nanotube containing-material to form a mixture of tubular carbon molecules having lengths in the range of 5-500 nm and isolating a fraction of the molecules having substantially equal lengths The nanotubes may be used, singularly or in multiples, in power transmission cables, in solar cells, in batteries, as antennas, as molecular electronics, as probes and manipulators, and in composites.
Owner:RICE UNIV
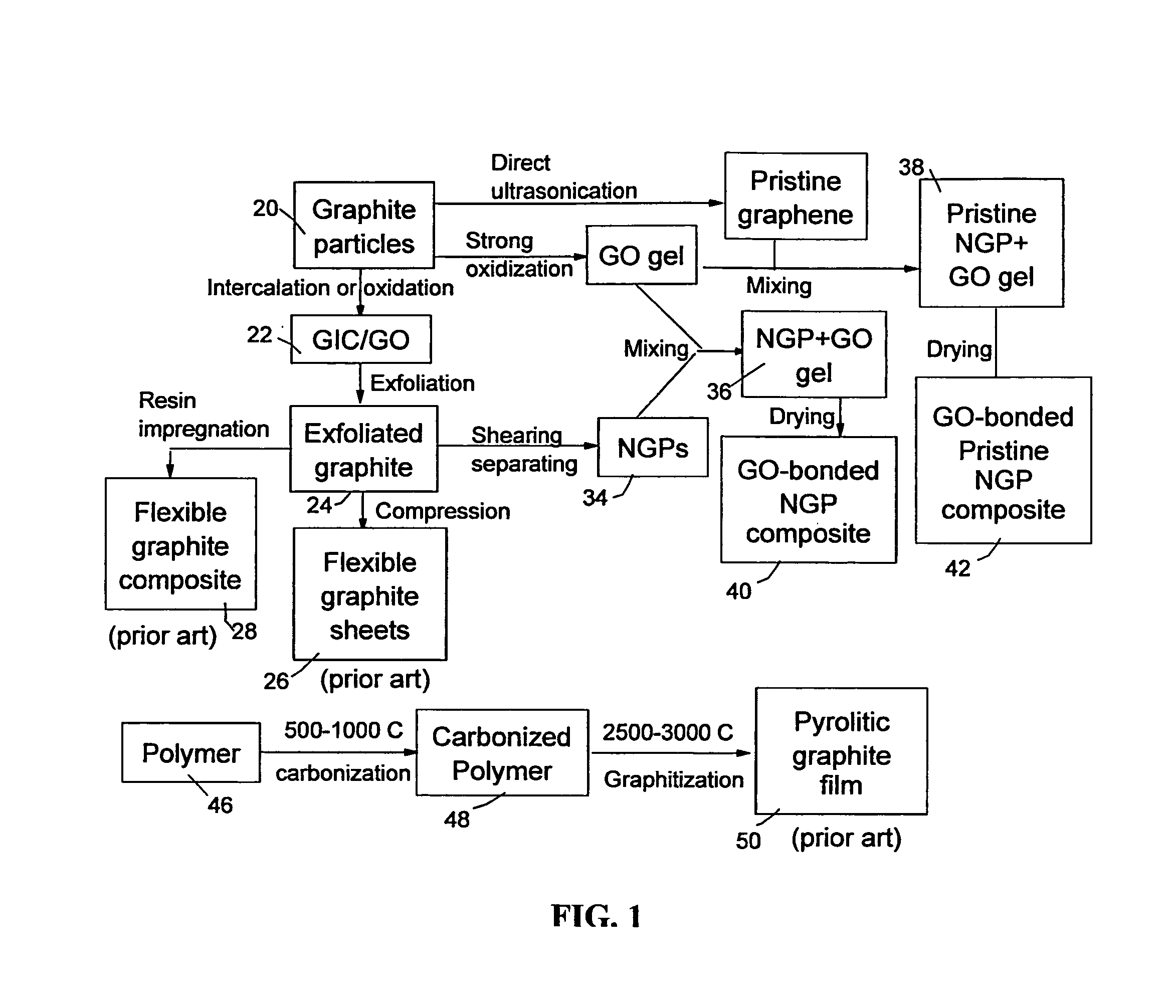
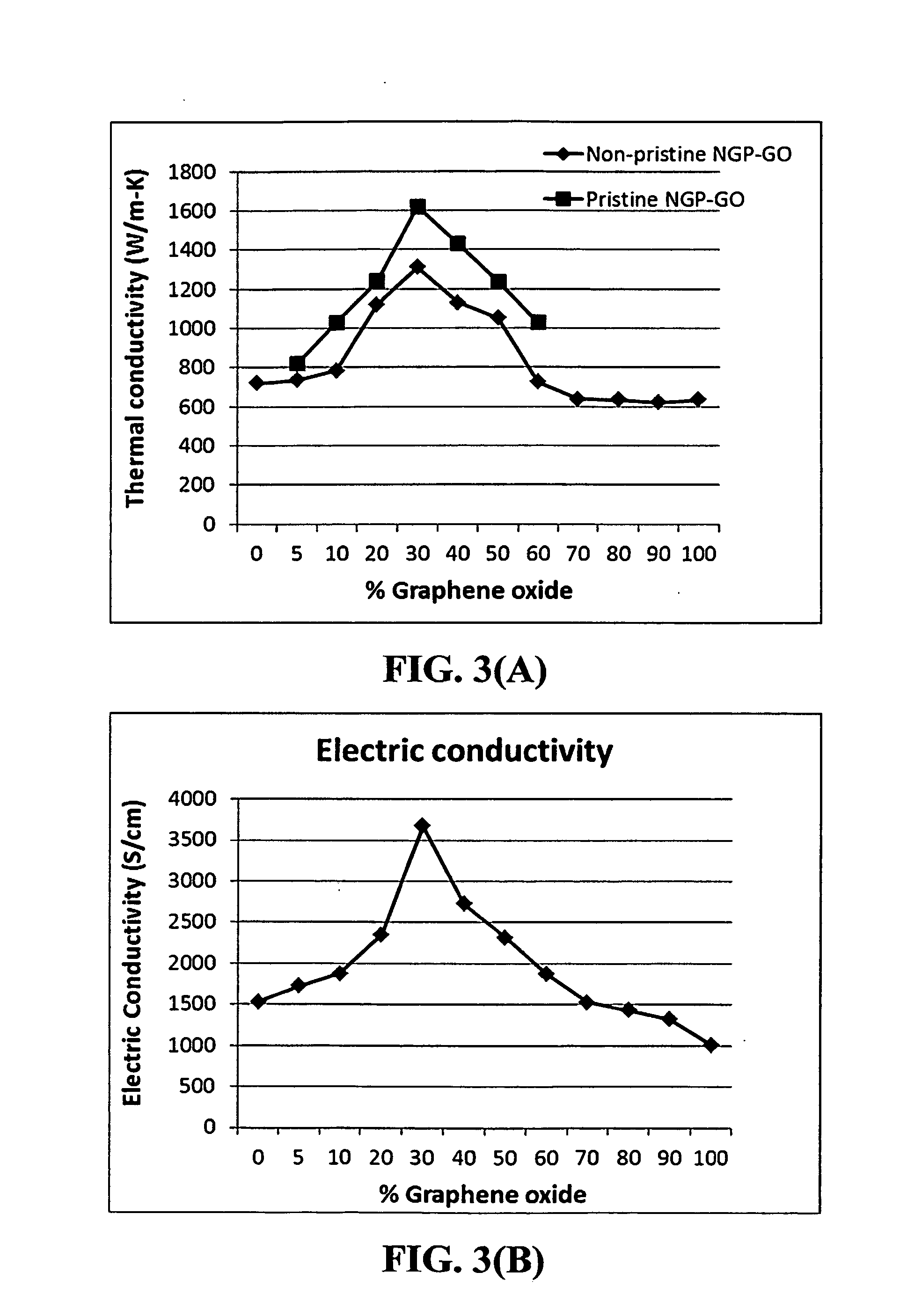
Graphene oxide gel bonded graphene composite films and processes for producing same
ActiveUS20130236715A1Low densityThermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyNon-metal conductorsPhysical chemistryThin membrane
Disclosed is a graphene composite thin film composition composed of nano graphene platelets (NGPs) bonded by a graphene oxide binder, wherein the NGPs contain single-layer graphene or multi-layer graphene sheets having a thickness from 0.335 nm to 100 nm. The NGPs occupy a weight fraction of 1% to 99.9% of the total composite weight. The graphene oxide binder, having an oxygen content of 1-40% (preferably <10%) by weight based on the total graphene oxide weight, is obtained from a graphene oxide gel. The composite forms a thin film with a thickness no greater than 1 mm, but preferably no greater than 100 μm and no less than 10 μm. This composition has a combination of exceptional thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength unmatched by any thin-film material of comparable thickness range.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
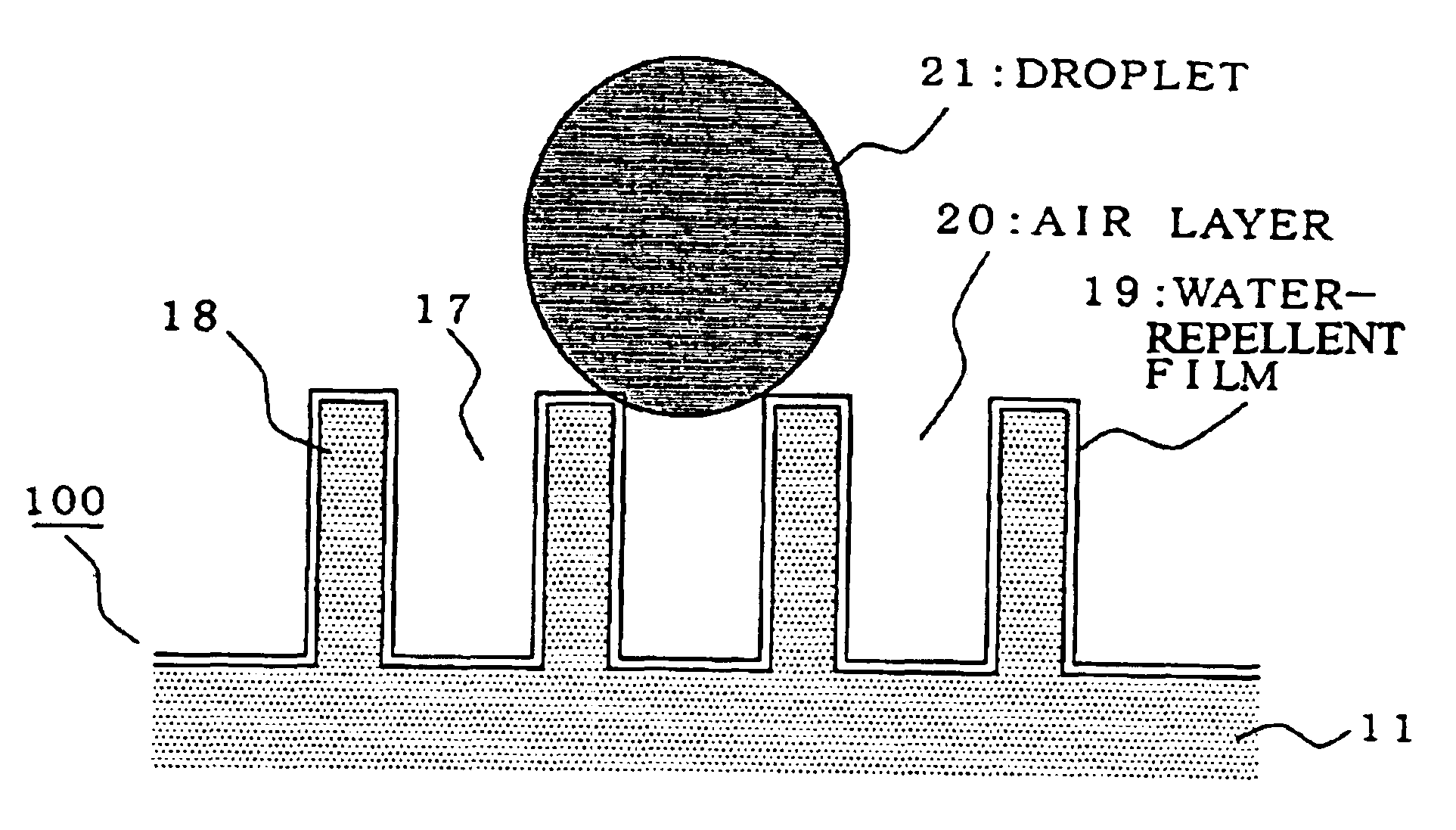
Structural member superior in water repellency and method for manufacturing the same
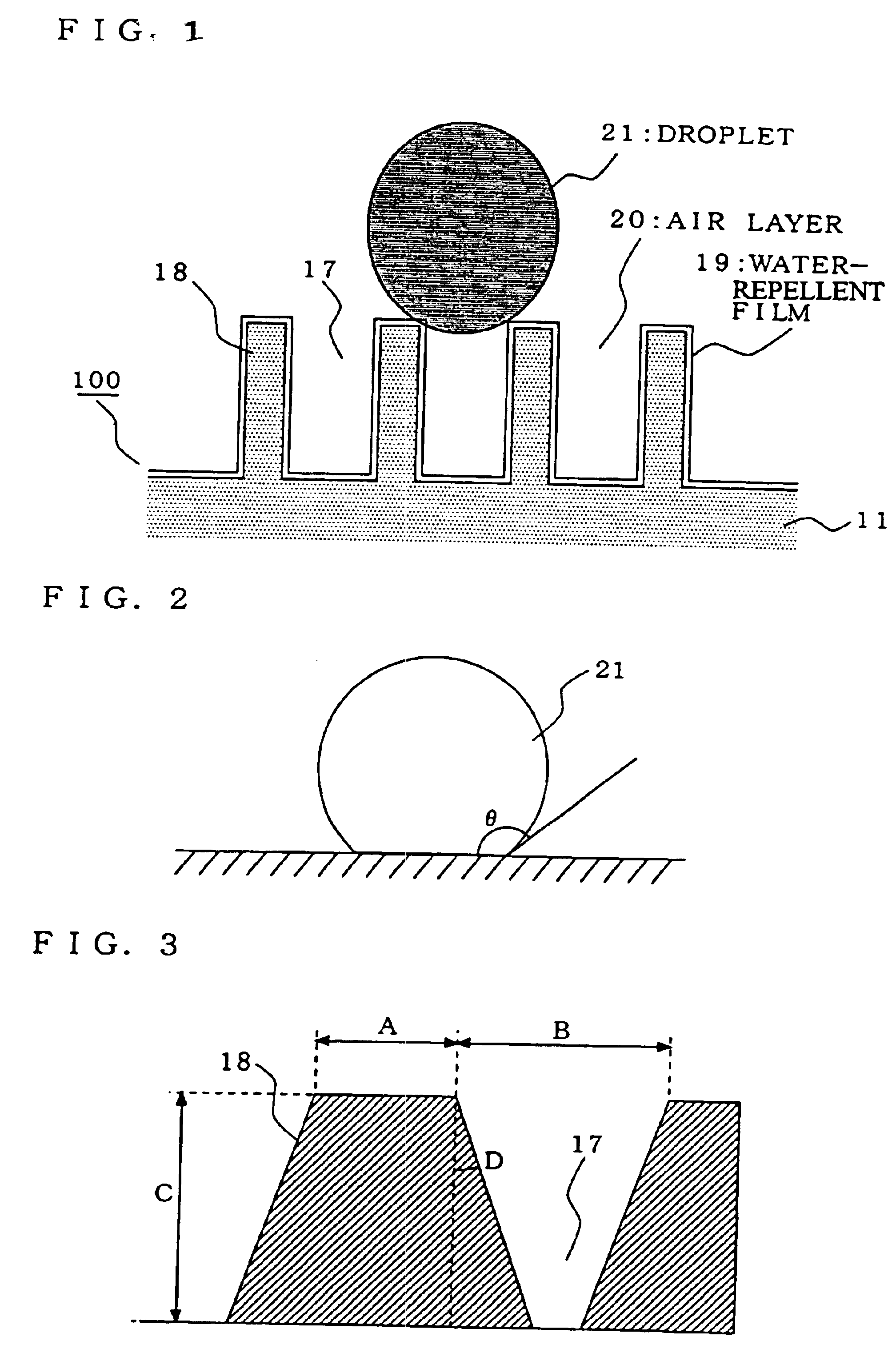
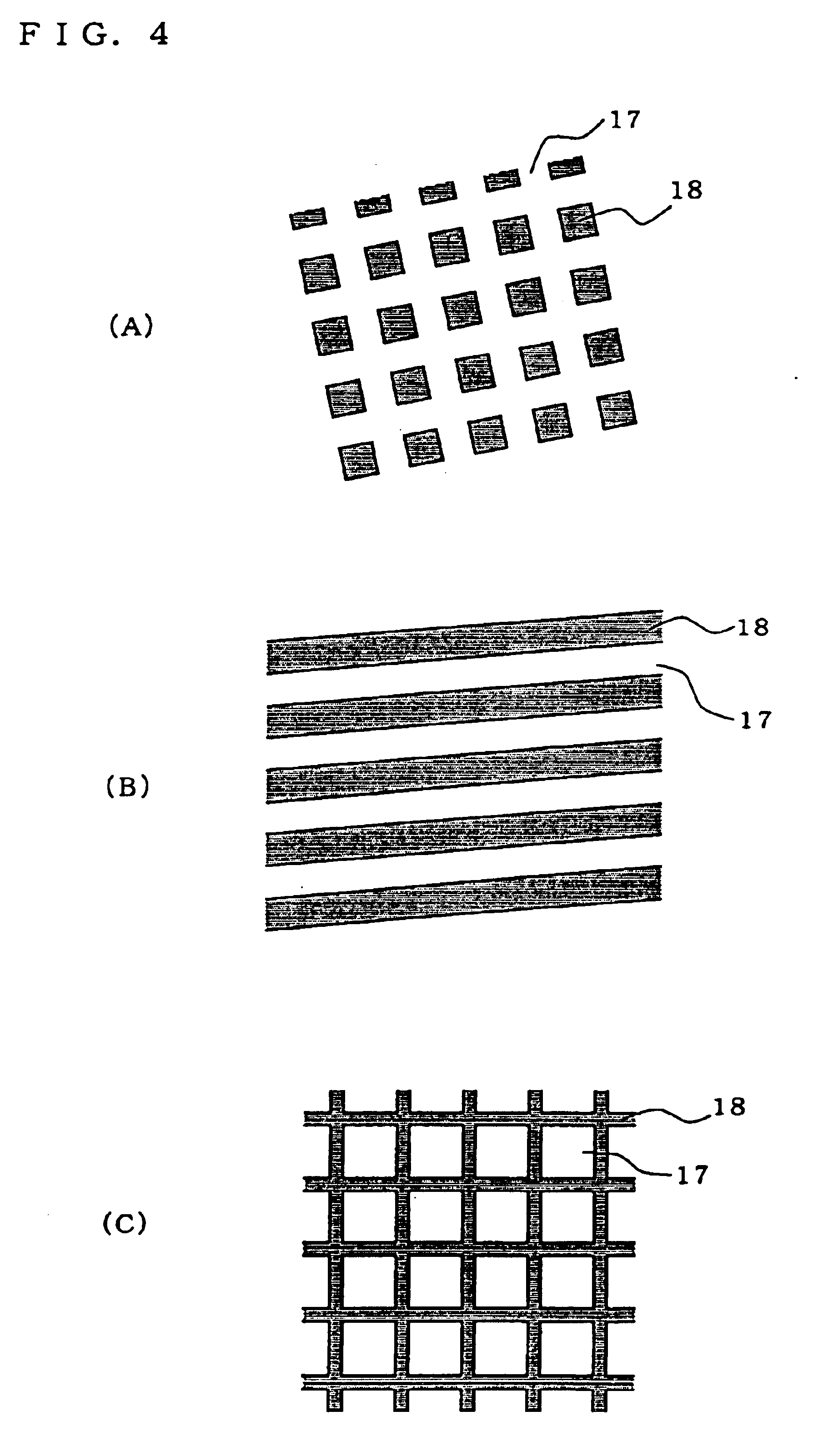
InactiveUS6764745B1Synthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageBiomedical engineeringWater repellent
A structural member in which a super water-repellent function and high durability and scratch assistance can be obtained; and a method of manufacturing such a structural member. A water-repellent structure (100) consisting of appropriate irregularities comprising protrusion portions (18) uniform in height is formed on an external surface. The irregularities (17 and 18) have such dimensions that any droplet should not fall in a recess portion and the droplet is in contact with an air layer (20) in the recess portion (17).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Thermoplastic film structures having improved barrier and mechanical properties
The present invention relates to thermoplastic film structures having improved barrier and / or mechanical properties and methods for making the film structures. These improvements are achieved by incorporating into the thermoplastic film structures a polymeric nanocomposite comprising a polymer and nanosize particles of a modified clay.
Owner:BEMIS COMPANY INC +1
High density data storage medium
InactiveUS20050050258A1Toughening of surfaceImprove wearing rateNanoinformaticsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationAtomic force microscopyCross-link
An approach is presented for designing the polymeric recording layer for nanometer scale thermomechanical storage devices. Cross linked polymers are used as the recording layers in atomic force microscopy data storage devices, giving significantly improved performance when compared to the previously reported linear polymers. This results in superior wear resistance and enhanced erasing, critical features for the long-term multiple read-write cycles of such thermomechanical storage devices. In addition, this ability to introduce a predetermined extent of cross linking allows fine tuning of the thermal and force parameters in the R / W / E (read-write-erase) cycles.
Owner:IBM CORP
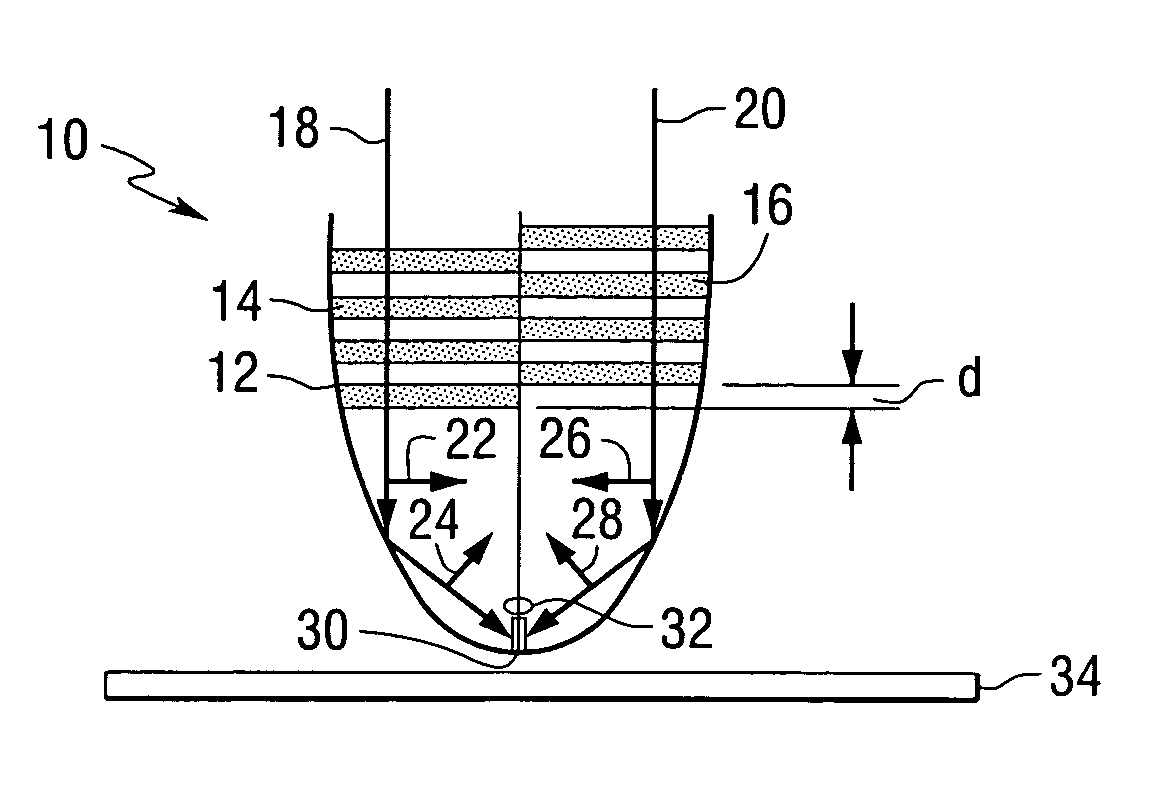
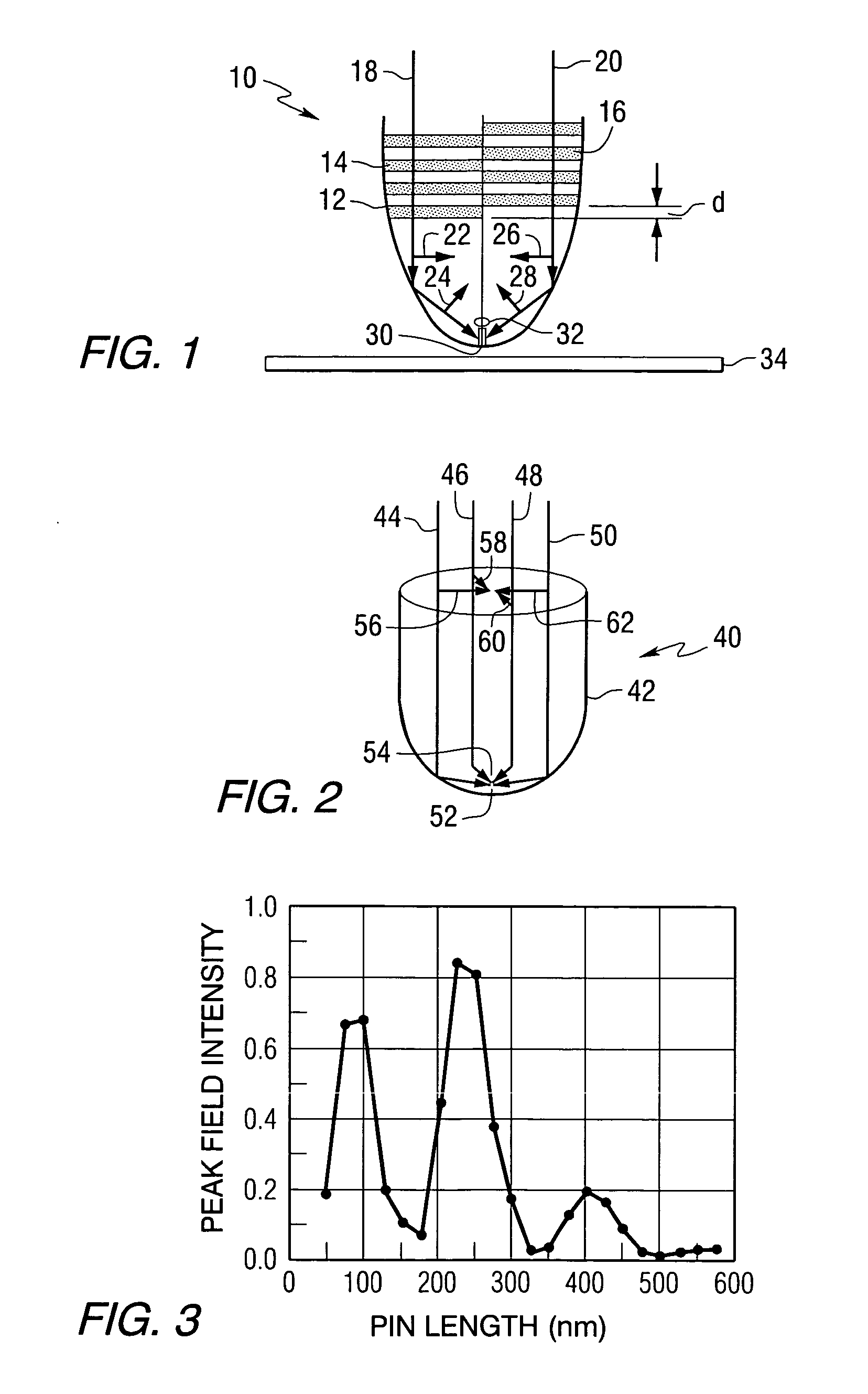
Optical recording systems
InactiveUS6094413AIncrease contrastImprove signal-to-noise ratioNanoinformaticsOptical beam sourcesOptical storageOptical recording
An optical storage system suitable for optical storage and retrieval of information using a storage medium comprising a substrate, an active layer for retention of the data, and an overlying optical layer, or layers for double-sided. The optical layer serves to produce an evanescent field in or adjacent to the active layer in response to an incident beam of radiation. The evanescent field is frustrated or attenuated by the data in the active layer and produces a signal.
Owner:SENSHIN CAPITAL +1
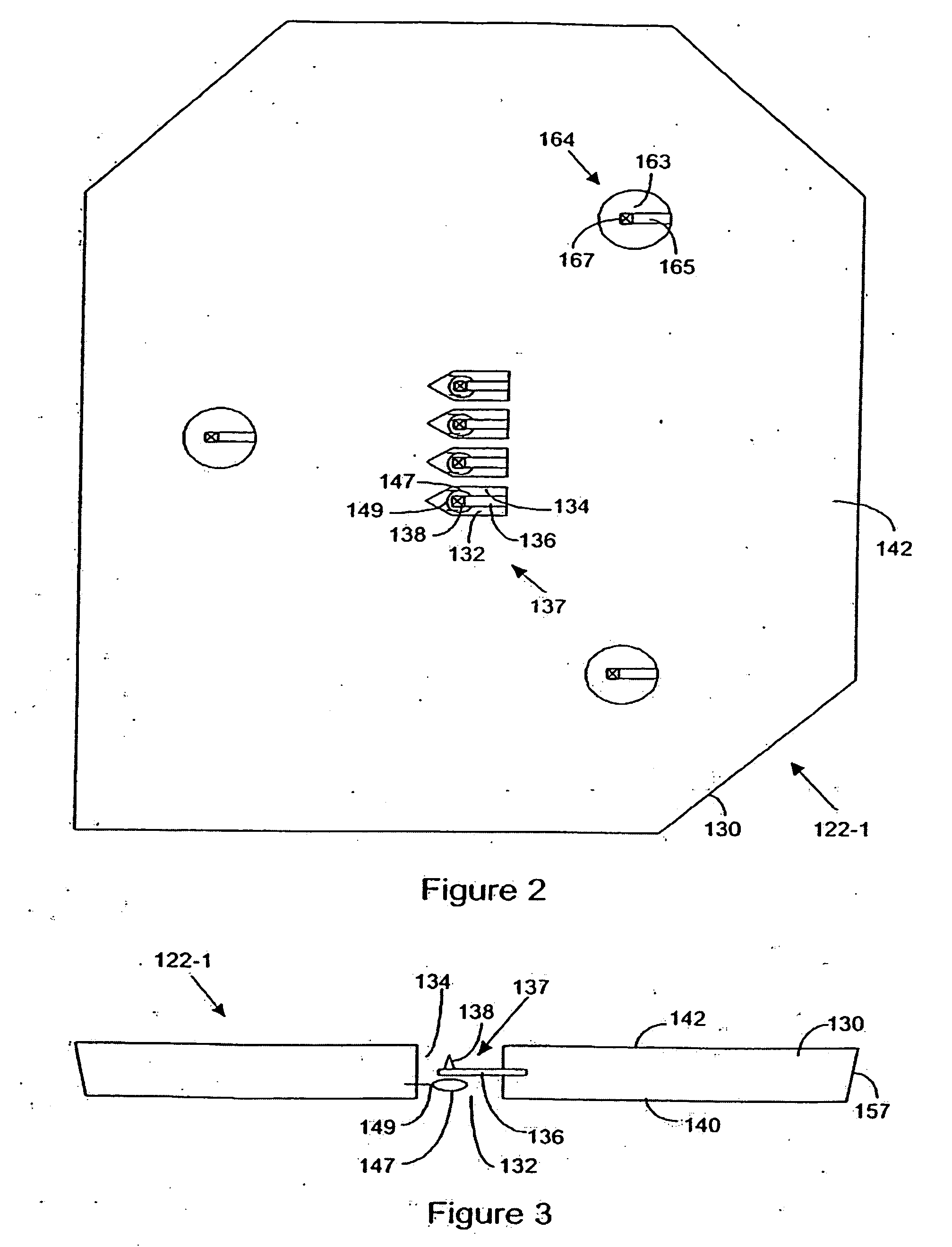
Scanning probe microscopy inspection and modification system
InactiveUS20080315092A1Manufacture head surfaceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEngineeringScanning probe microscopy
A scanning probe microscopy (SPM) inspection and / or modification system which uses SPM technology and techniques. The system includes various types of microstructured SPM probes for inspection and / or modification of the object. The components of the SPM system include microstructured calibration structures. A probe may be defective because of wear or because of fabrication errors. Various types of reference measurements of the calibration structure are made with the probe or vice versa to calibrate it. The components of the SPM system further include one or more tip machining structures. At these structures, material of the tips of the SPM probes may be machined by abrasively lapping and chemically lapping the material of the tip with the tip machining structures.
Owner:GEN NANOTECH L L C +1
Transducer for heat assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS20050289576A1Combination recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic storage
An apparatus for concentrating electromagnetic energy comprises a metallic transducer including a first section and a second section, wherein the first section is wider than the second section and has a width to length aspect ratio greater than or equal to a width to length aspect ratio of the second section, and a condenser for directing electromagnetic radiation onto the transducer. A magnetic storage device that includes the apparatus is also provided.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Functionalized substrates comprising perfume microcapsules
ActiveUS7786027B2Synthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsCelluloseWater dispersible
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
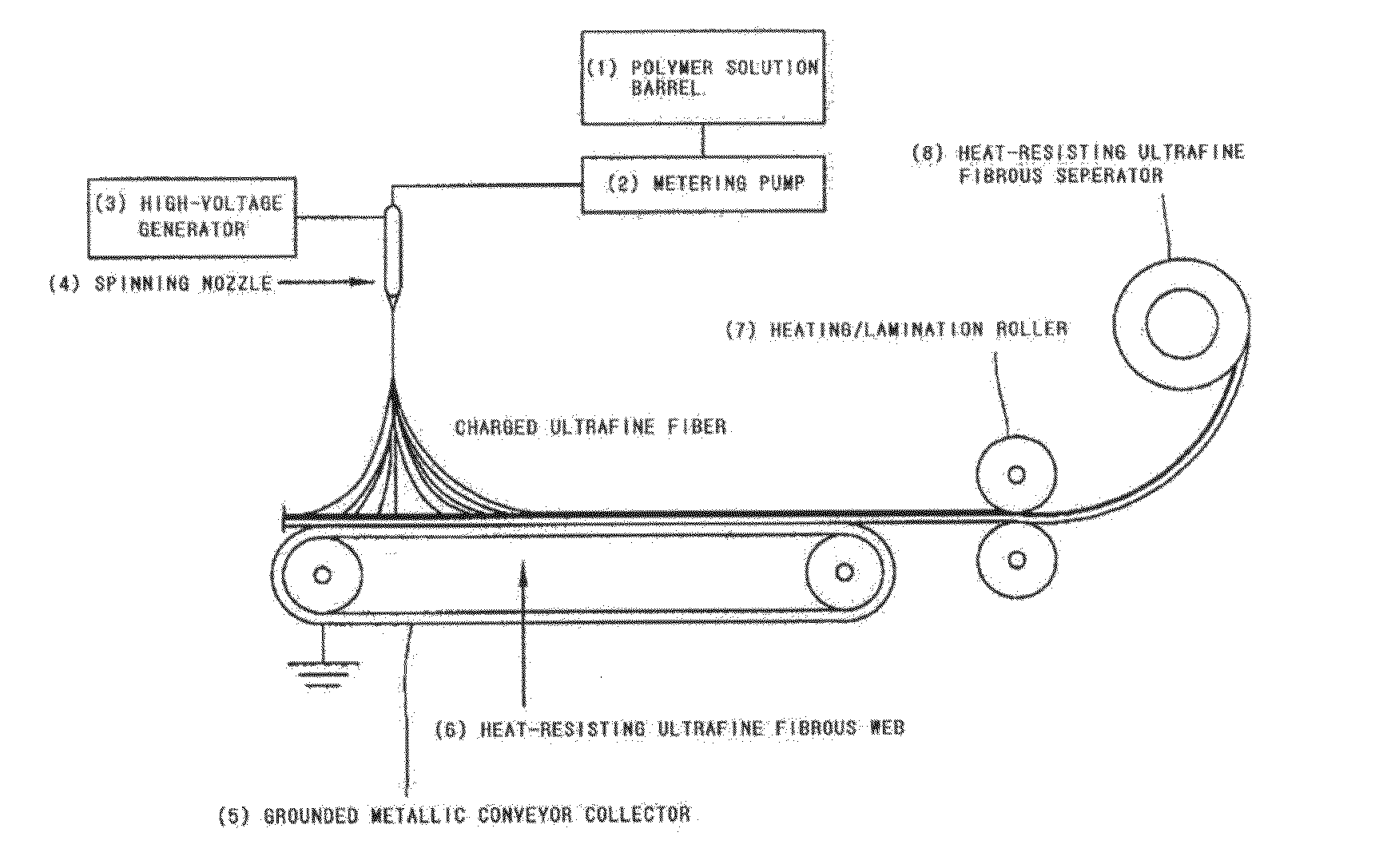
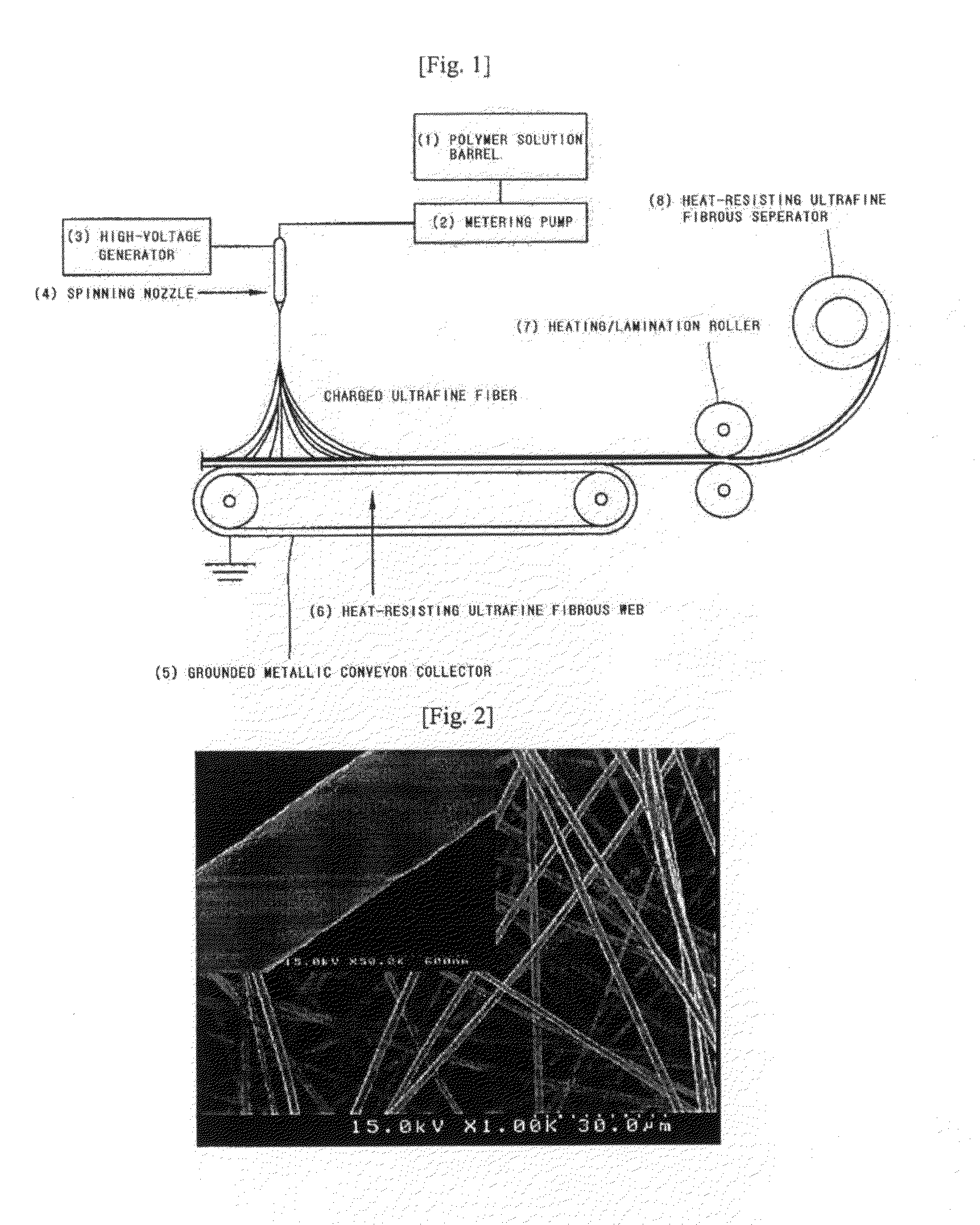
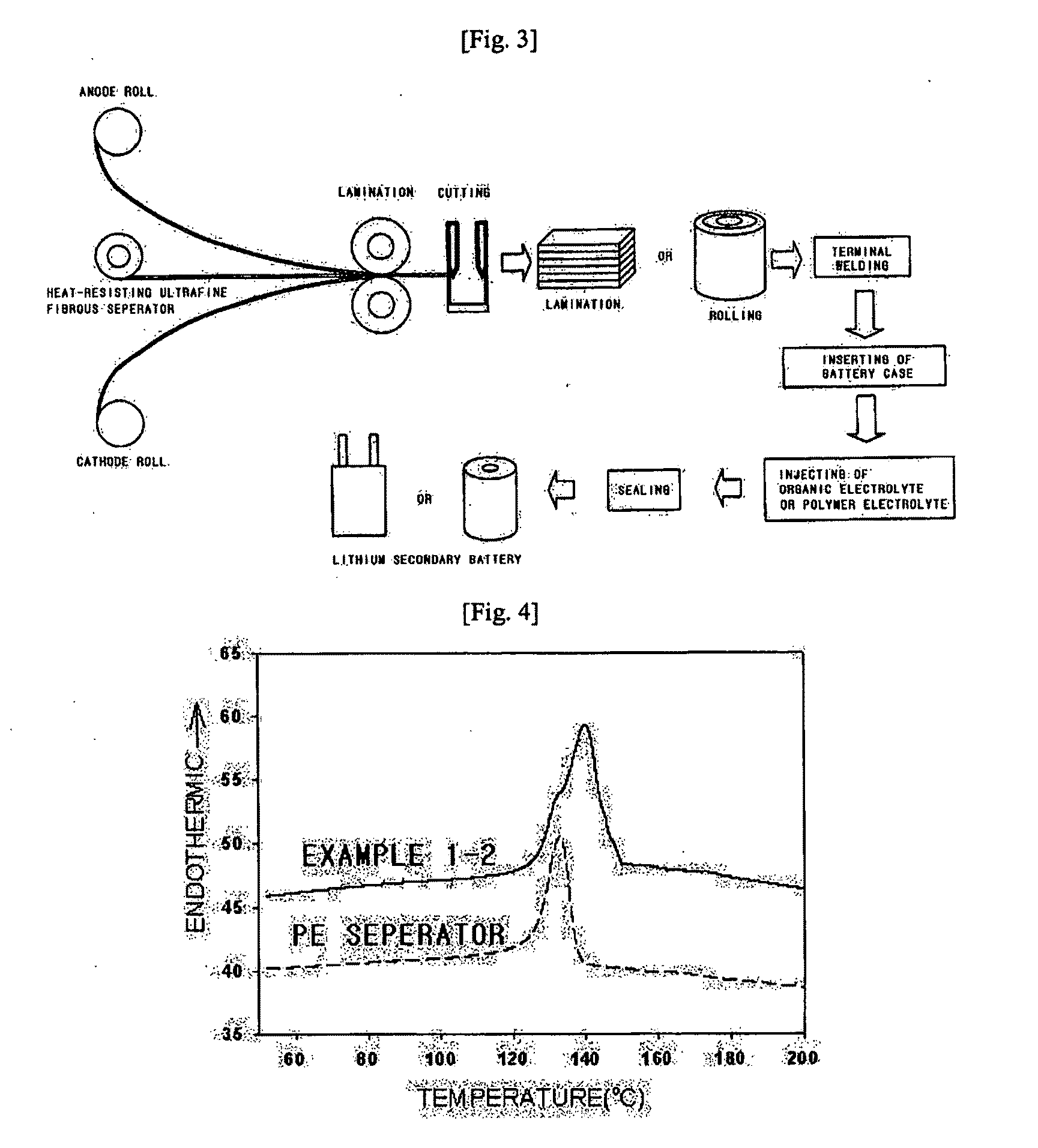
Heat resisting ultrafine fibrous separator and secondary battery using the same
ActiveUS20100233523A1Simple and easy processLow thermal contractionCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufactureFiberPolymer science
A heat-resisting ultrafine fibrous separator of the present invention is prepared by an electrospinning process, formed of ultrafine fibers of heat-resisting polymer resin having a melting point more than 1800 C or not having the melting point, or ultrafine fibers of polymer resin capable of swelling in an electrolyte, together with the ultrafine fibers of heat-resisting polymer resin. Also, polyolefine fine particles providing a shutdown function are dispersed in the heat-resisting resin or the polymer resin capable of swelling in the electrolyte. The heat-resisting ultrafine fibrous separator of the present invention has the shutdown function, low thermal contraction, thermal endurance, excellent ionic conductivity and excellent adhesive property with an electrode, so a battery having excellent cycling characteristics, and having high-energy density and high capacity can be prepared.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Polycrystalline diamond
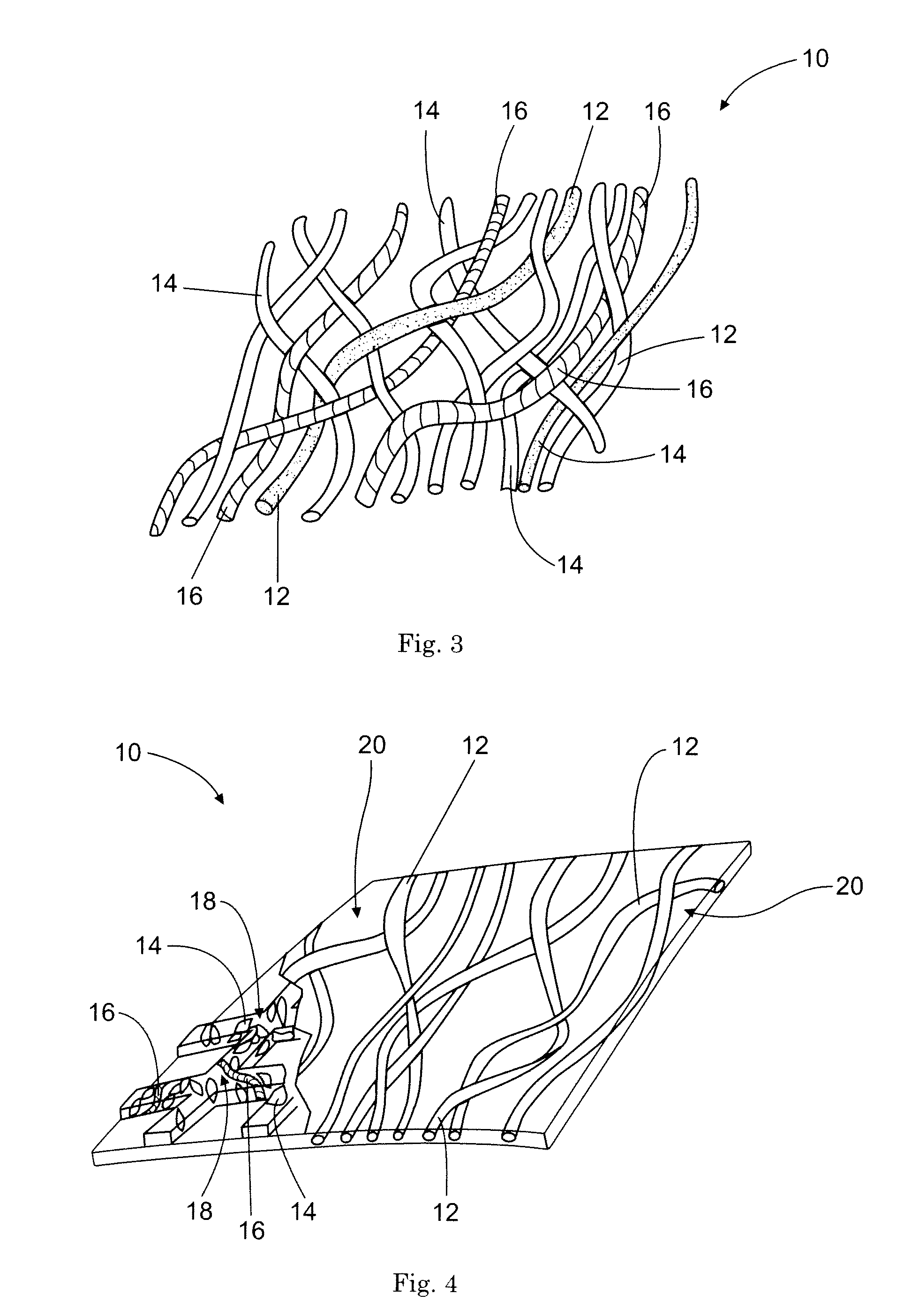
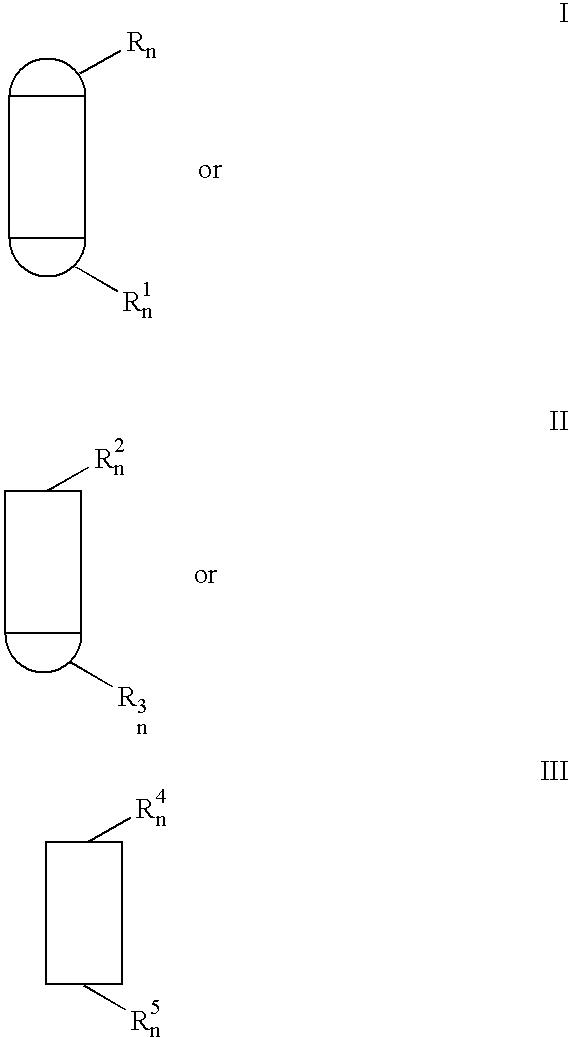
A polycrystalline diamond (PCD) material 10 comprising at least 88 volume percent and at most 99 volume percent diamond grains 12, the mean diamond grain contiguity being greater than 60.5 percent. The PCD material 10 is particularly but not exclusively for use in boring into the earth.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX ABRASIVES
Touch panel and display device using the same
ActiveUS20090160796A1Alternating current plasma display panelsThermionic cathodesCarbon nanotubeTouchpad
A touch panel includes a first conductive layer, a second conductive layer and a capacitive sensing member. The first conductive layer includes a plurality of first conductive lines. The second conductive layer separated from the first conductive layer includes a plurality of second conductive lines. One of the plurality of conductive lines is located above the other plurality of conductive lines. The capacitive sensing member is connected to the first conductive lines. At least one of the first and second pluralities of conductive lines includes carbon nanotube wires. The carbon nanotube wires each include a plurality of carbon nanotubes. Further, a display device using the above-described touch panel is also included.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Films, articles prepared therefrom, and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20100040875A1Synthetic resin layered productsRecord information storagePolyolefinPolymer science
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Transparent polymer nanocomposites containing nanoparticles and method of making same
InactiveUS20090233090A1High transparencyIncrease contentMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentMetal oxide nanoparticlesThermal stability
The present invention relates to transparent nanocomposites comprising of metal oxide nanoparticles dispersed in polymer matrix. The nanoparticles have capping agents attached onto the nanoparticle surfaces and a precursor solution of capped nanoparticles and polymer is prepared and dried to obtain the nanocomposites. The nanocomposites exhibit UV absorption, low haze, and improved thermal stability. The present invention also relates to the methods associated with the preparation of capped nanoparticles, precursor solution and nanocomposites.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Biaxially oriented thermoplastic resin film
InactiveUS20050020803A1High modulusHigh melting pointFixed capacitor dielectricSynthetic resin layered productsPlane orientationPeak value
In order to provide a film having excellent heat resistance, thermal dimensional stability, and mechanical properties, in particular, a film capable of satisfying required properties, e.g., higher strength in accordance with the reduction in thickness of a base film, improved thermal dimensional stability and mechanical properties in a use environment, and higher heat resistance and improved thermal dimensional stability in accordance with the needs for miniaturization and more functionality in electrical and electronic areas, a thermoplastic resin is allowed to contain transition metal oxide particles, and is formed into a biaxially oriented thermoplastic resin film, wherein the melting point of the film is allowed to become higher than the melting point of the thermoplastic resin to be used. Preferably, the difference between a peak temperature (melting point T1) of the heat of fusion in the first run of the measurement of the biaxially oriented thermoplastic resin film with a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) and a peak temperature (melting point T2) of the heat of fusion in the second run is allowed to satisfy the following Formula. 2° C.≦T1−T2≦30°C. Alternatively, the plane orientation factor of the biaxially oriented thermoplastic resin film containing the transition metal oxide particles is controlled at 0.120 or more and less than 0.280.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Heat assisted magnetic recording head
InactiveUS20070165495A1Easy to manufactureImprove power generation efficiencyCombination recordingManufacture head surfaceHeat-assisted magnetic recordingWaveguide
A heat assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) head is provided. The HAMR head is mounted in a slider having an ABS that faces a recording medium and illuminates light on the local area of the recording medium, and includes a recording unit that performs recording and a near field light emitter that illuminates near field light onto the local area of the recording medium, the near field light emitter including a light source, a waveguide, and a near field light emission (NFE) pole located between the recording unit and the waveguide, and which generates near field light that is illuminated on the recording medium using light transmitted through the waveguide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of patterning magnetic products using chemical reactions
InactiveUS6841224B2Improve productivityFlat surfaceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesHalogenChemical reaction
A method of patterning magnetic material includes forming a ferromagnetic material layer containing one element selected from the group consisting of Fe, Co and Ni on a substrate, selectively masking a surface of the ferromagnetic material layer, and making nonferromagnetic. The making nonferromagnetic step includes exposing an exposed portion in halogen-containing reaction gas, changing magnetism of the exposed portion and a lower layer thereof by chemical reaction, and making the exposed portion a nonferromagnetic material region. A magnetic recording medium is fabricated by using the magnetic material patterning method and includes a plurality of recording regions made of ferromagnetic materials, each containing at least one element selected from the group consisting of Fe, Co and Ni, and a nonferromagnetic material region for separating the recording regions from each other. The nonferromagnetic material region is a compound region of the ferromagnetic material and halogen.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
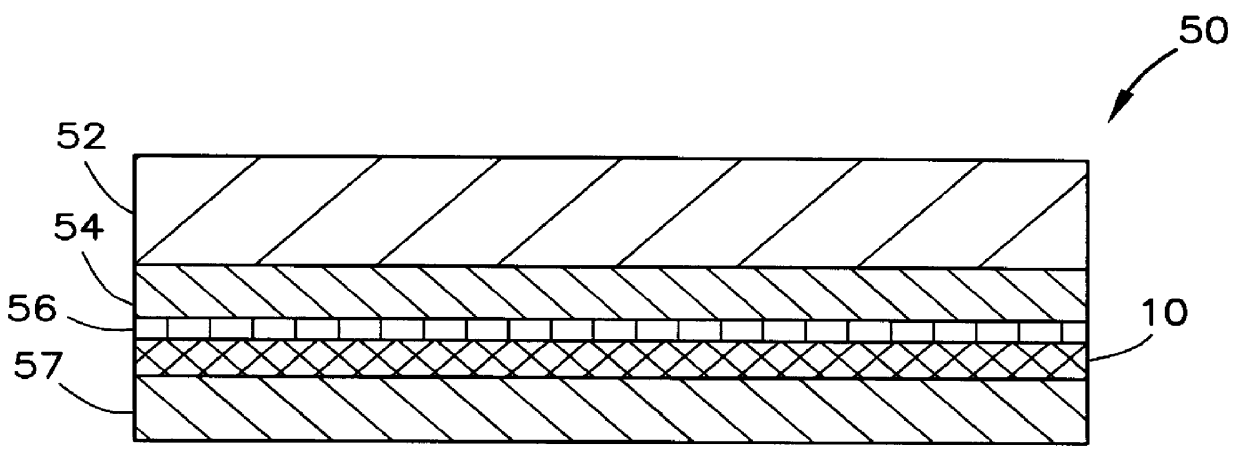
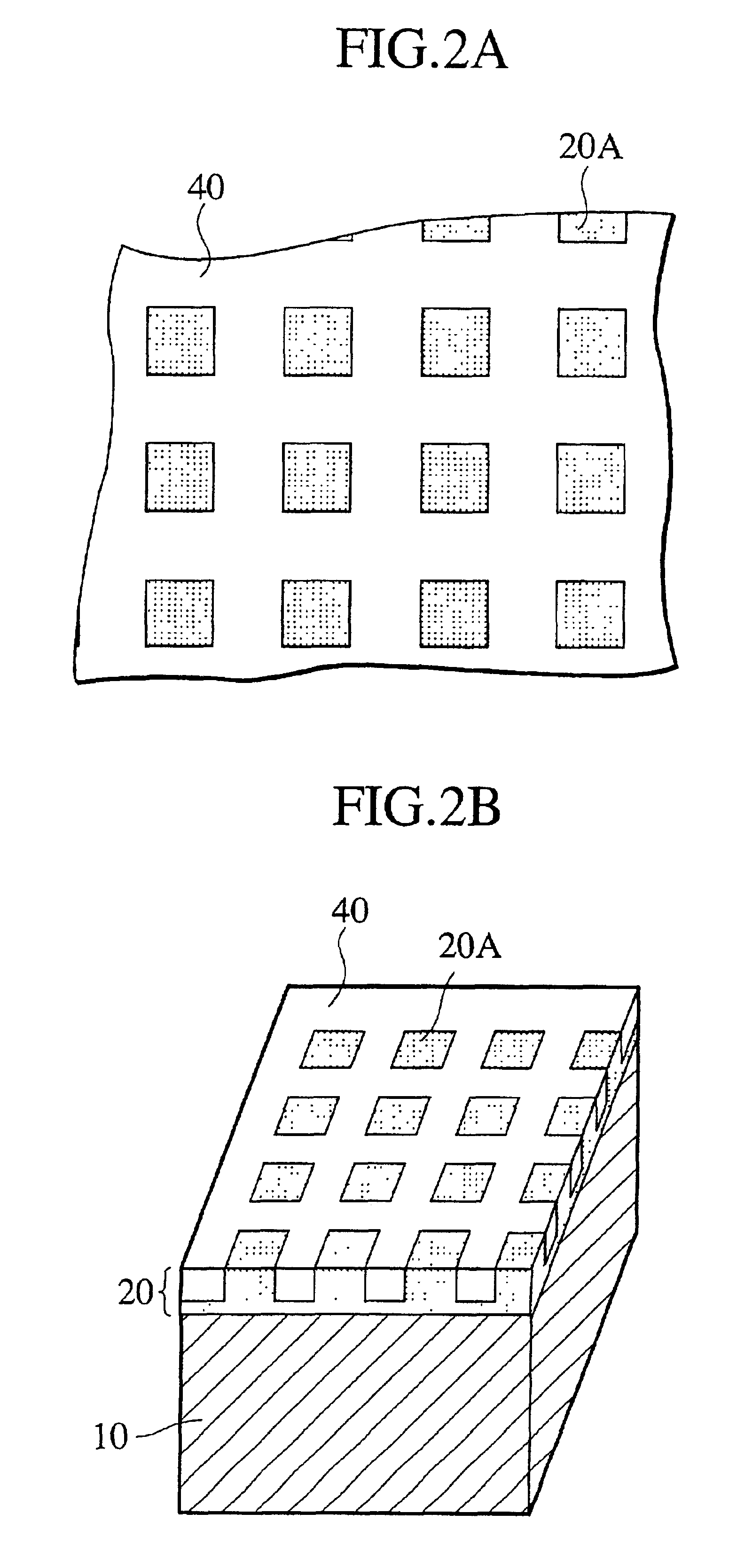
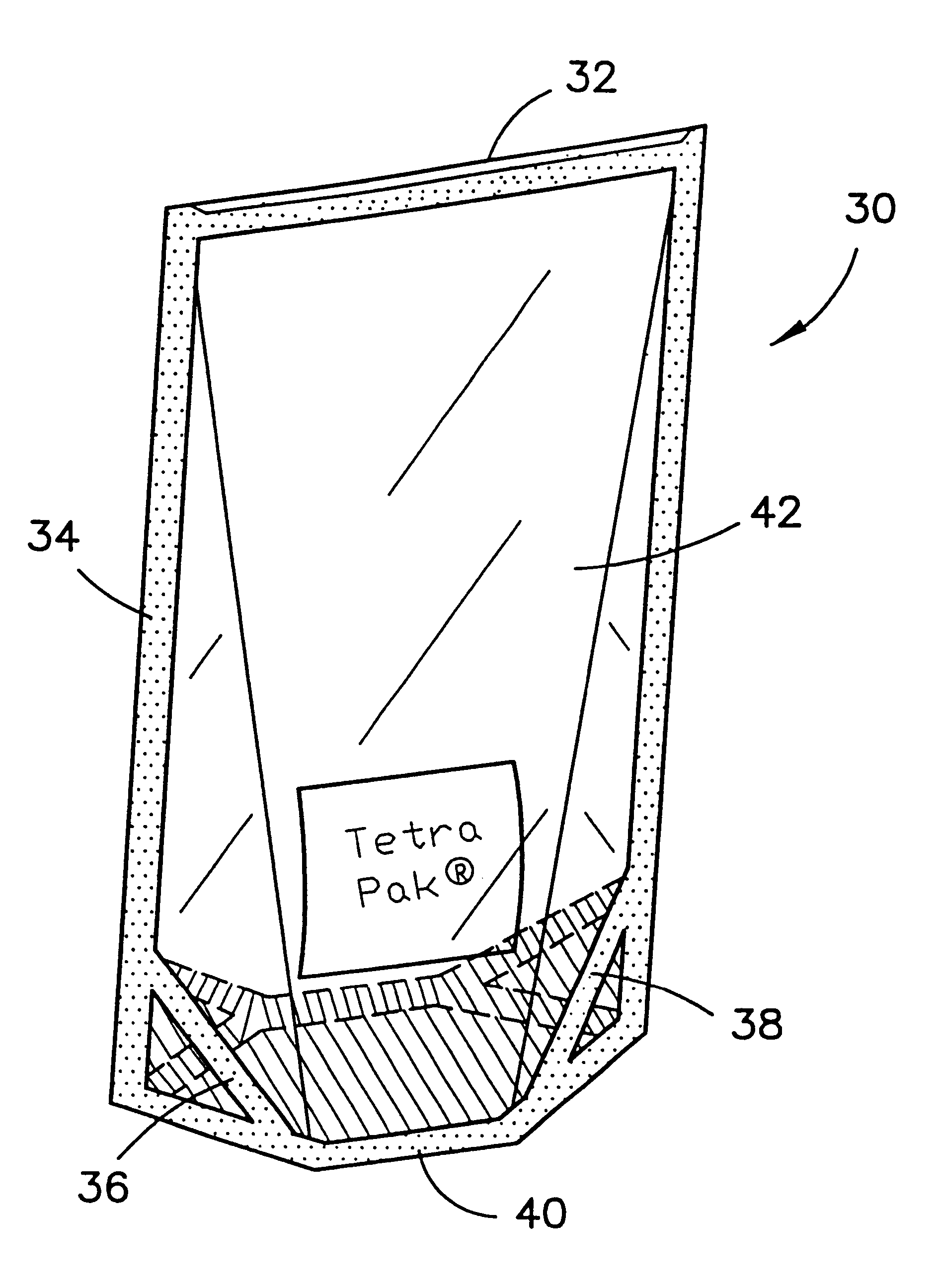
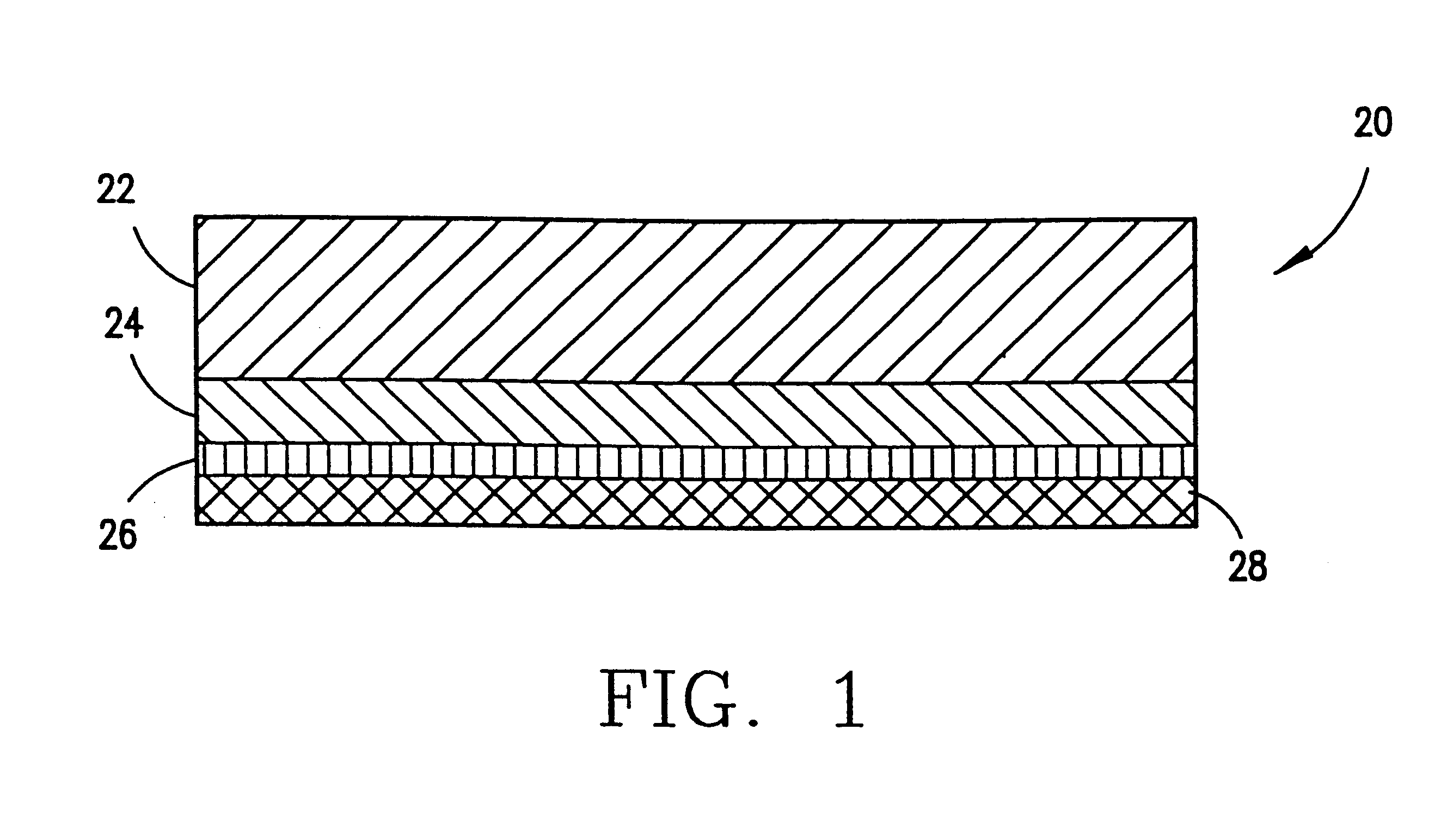
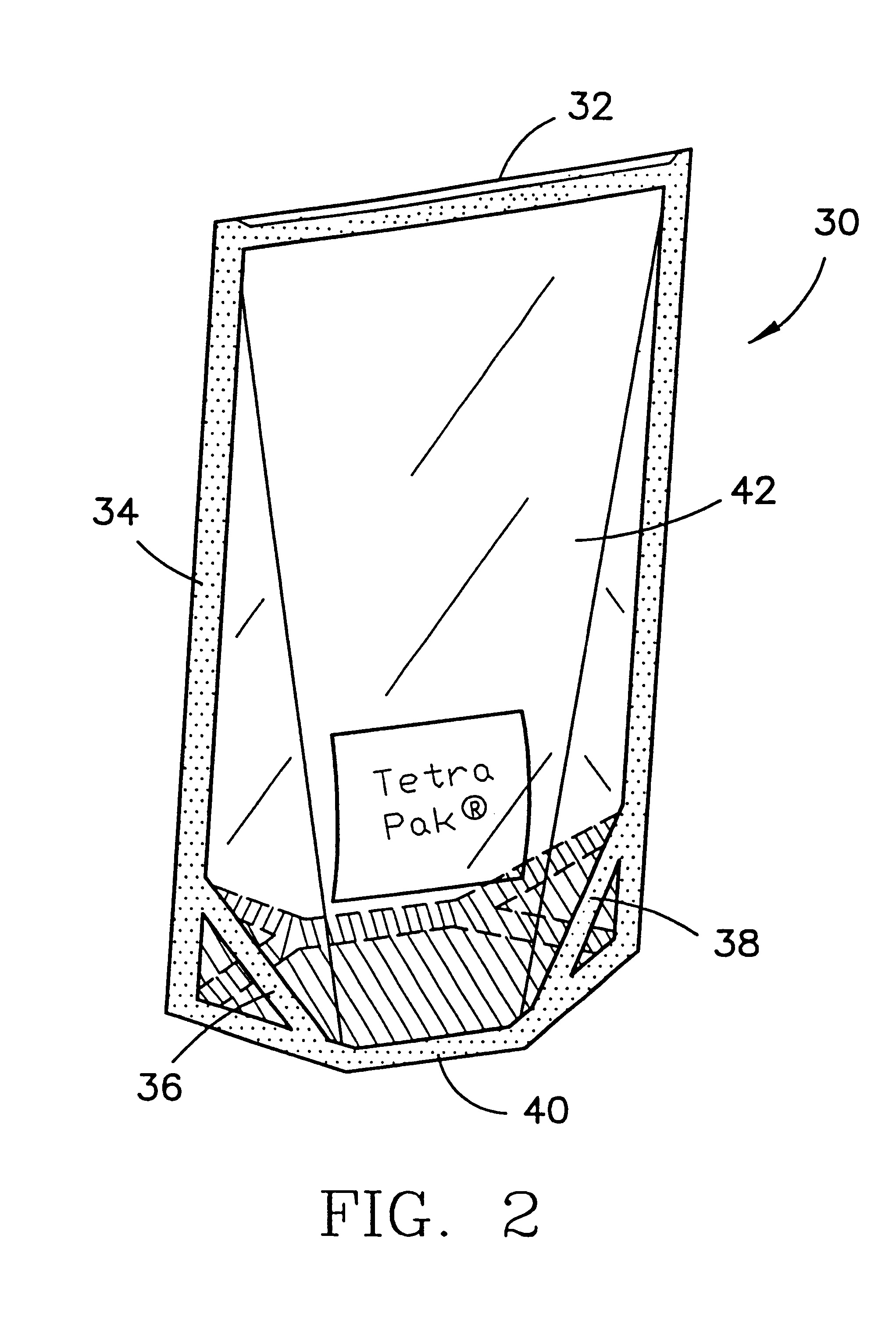
Transparent high barrier multilayer structure
A transparent multilayer structure is disclosed such as a flexible self-supporting container for a flowable food product such as fruit juice. The transparent multilayer structure possesses superior barrier properties to oxygen, water vapor and aromatic gases. The multilayer structure may include an exterior layer having a metal oxide deposition laminated to an interior layer through use of an adhesive. In one embodiment, the metal oxide is SiOx where x has a value between 1.5 and 2.2 thereby allowing for a transparent multilayer structure. The metal oxide may be deposited on the exterior layer through a number of various methods. An exemplary method is plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. The exterior layer may be composed of a polymer material integrated with a clay mineral between 0.1% and 10% weight of the polymer material. The polymer material may be selected from the group consisting of polyamide, polyethylene terephthalate, copolymers of polyethylene terephthalate and mixtures thereof.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com