Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Reduce gate size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
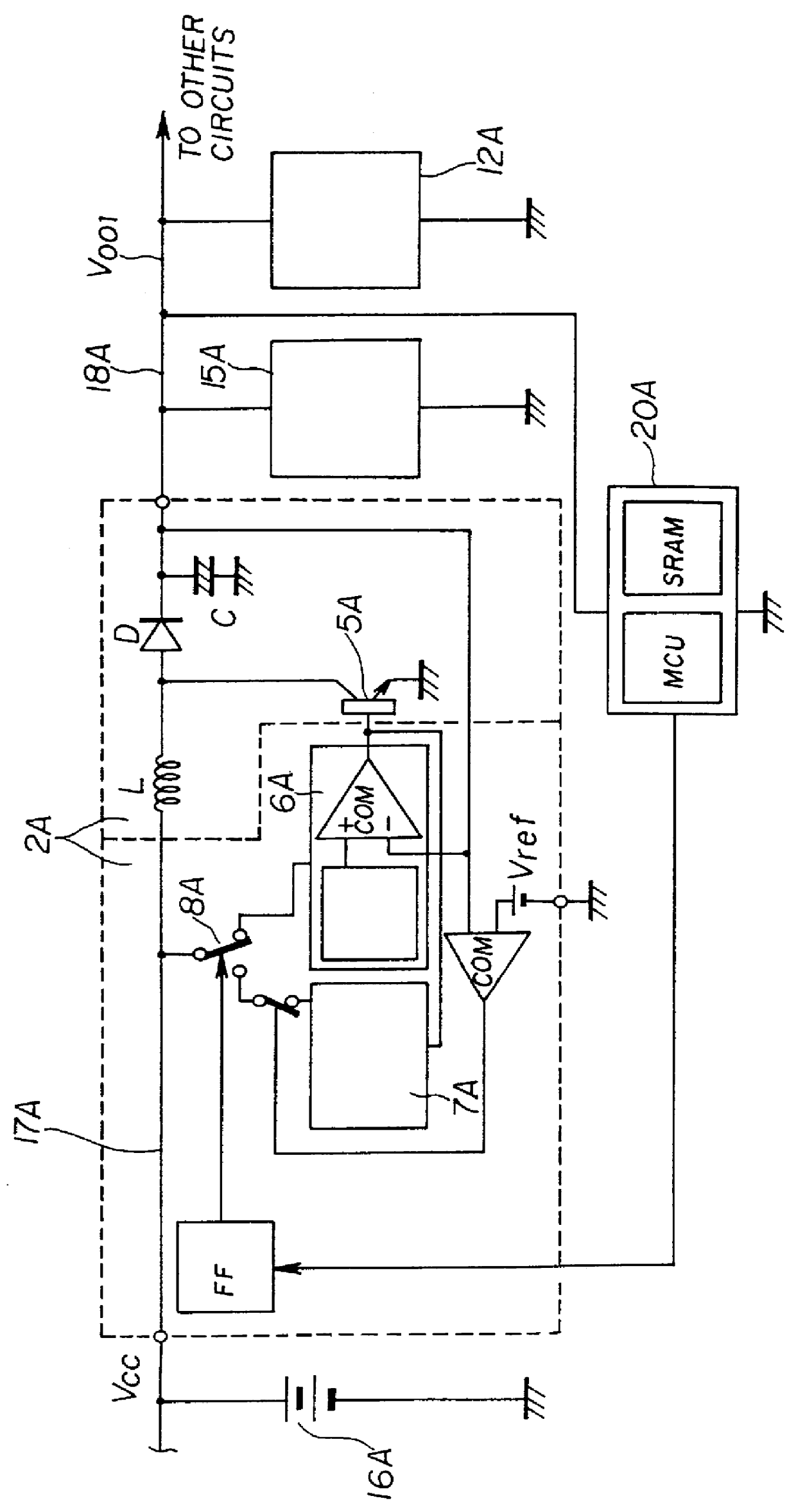
DC-DC converter
InactiveUS6154015AReduce in quantityConvenient power supplyEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionEngineeringDc converter
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
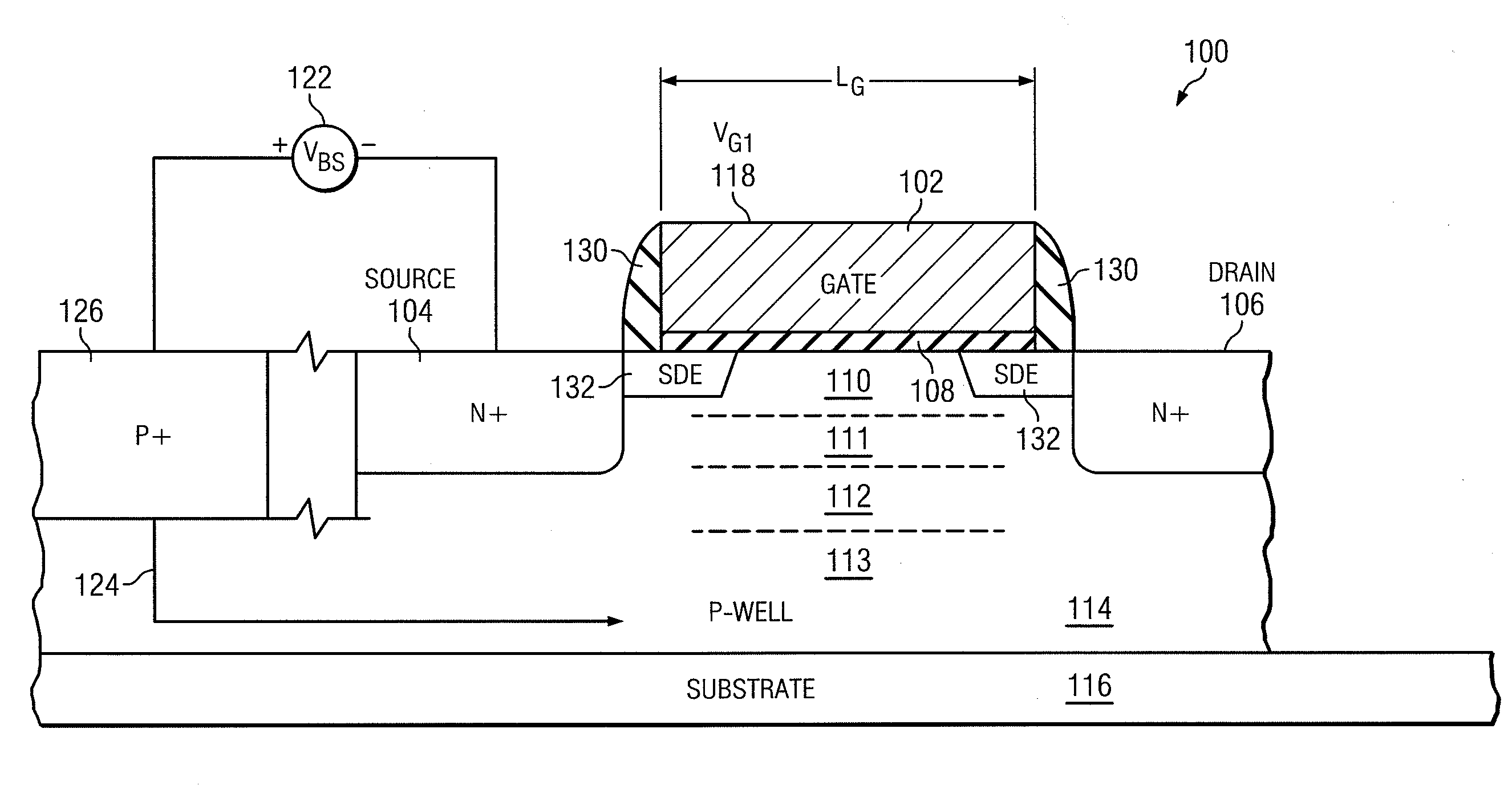
Advanced transistors with punch through suppression
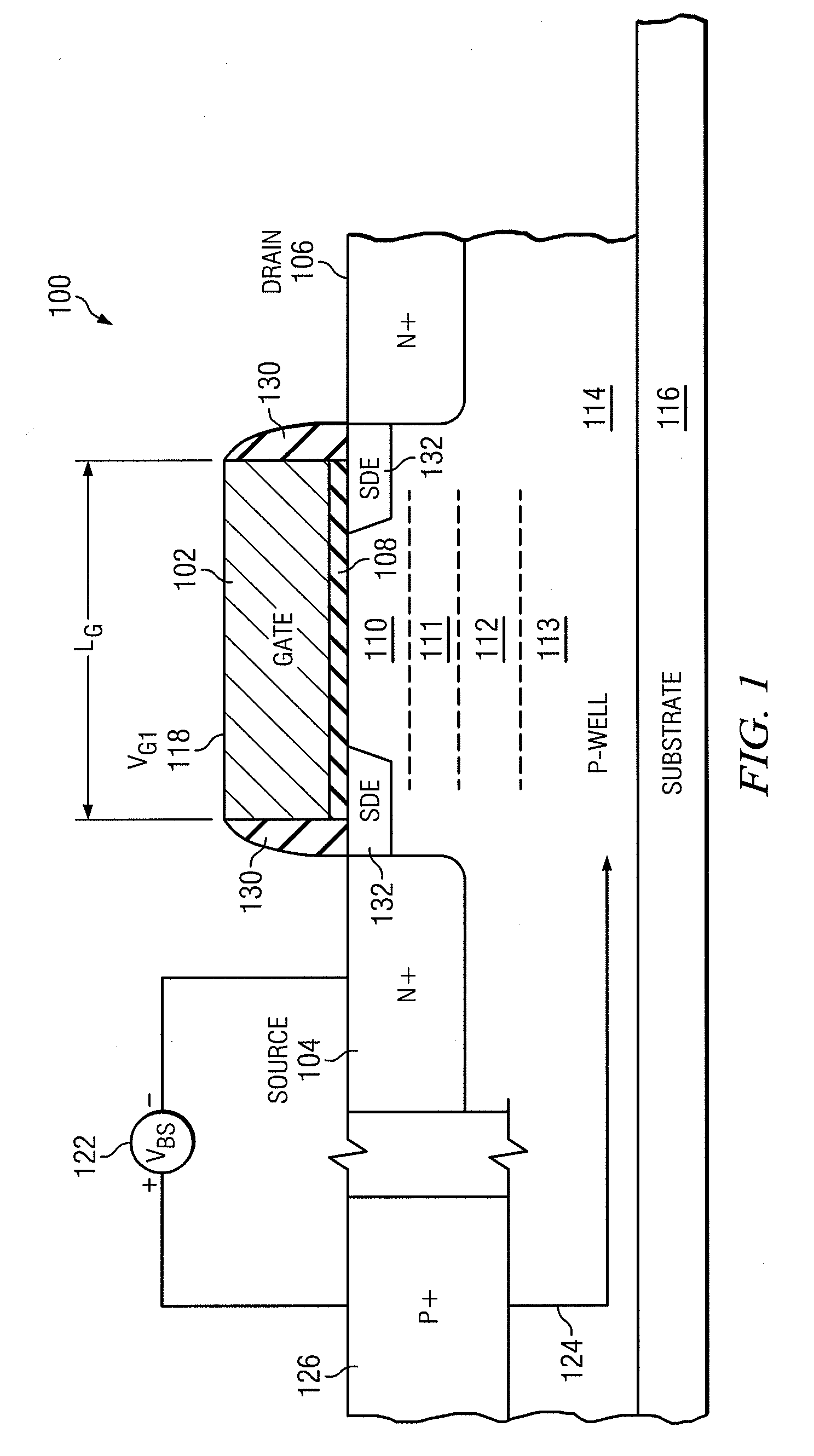
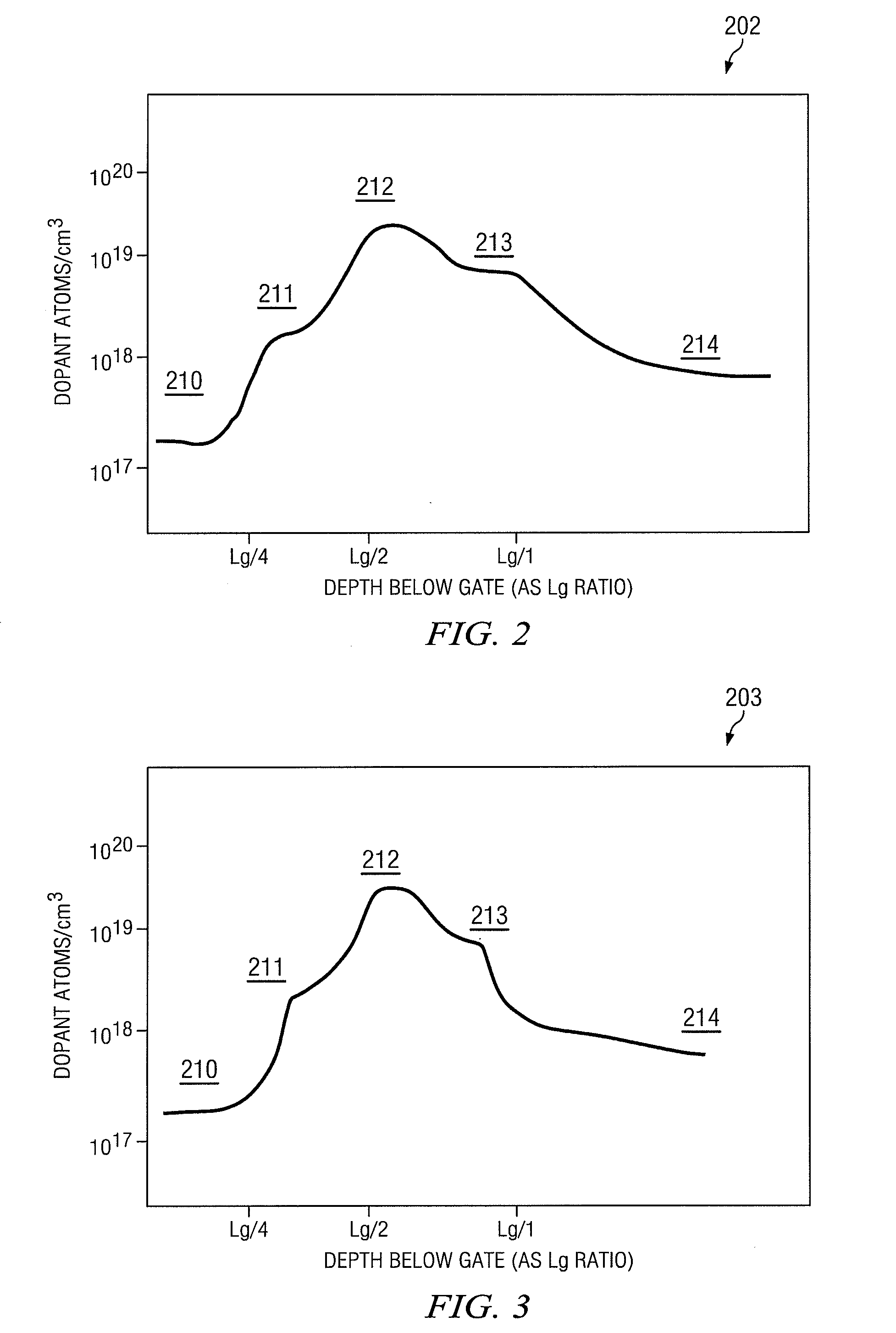
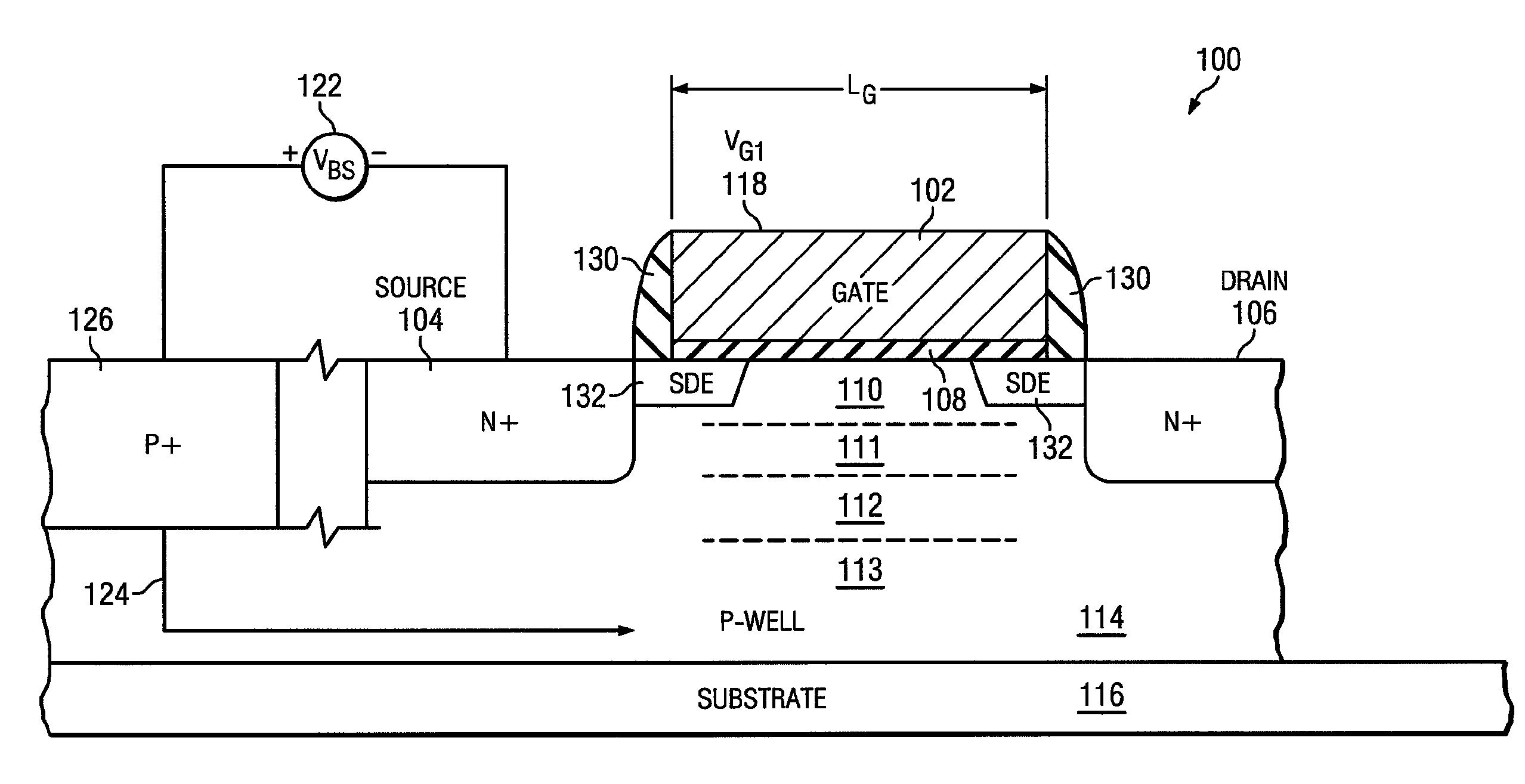
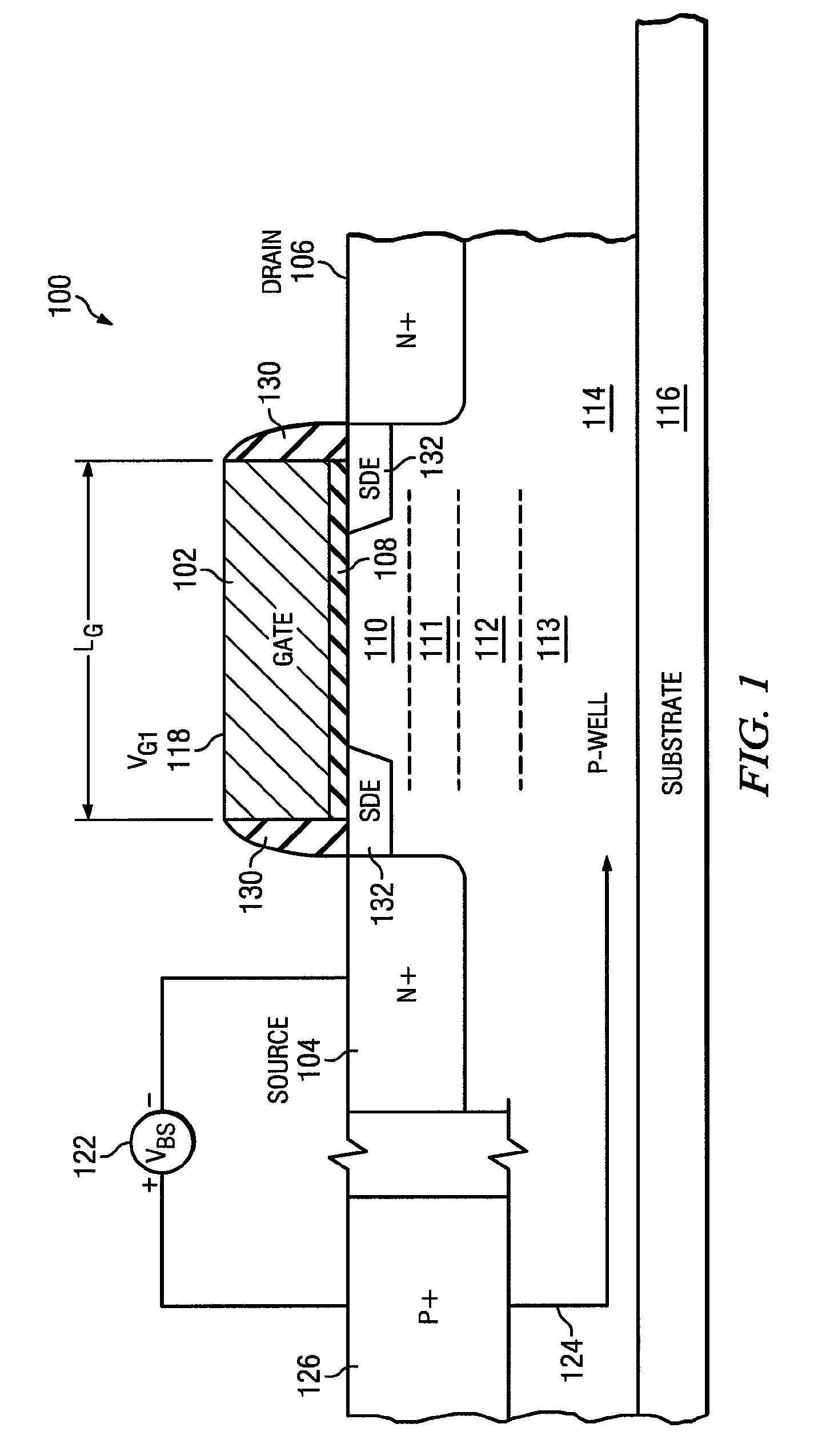
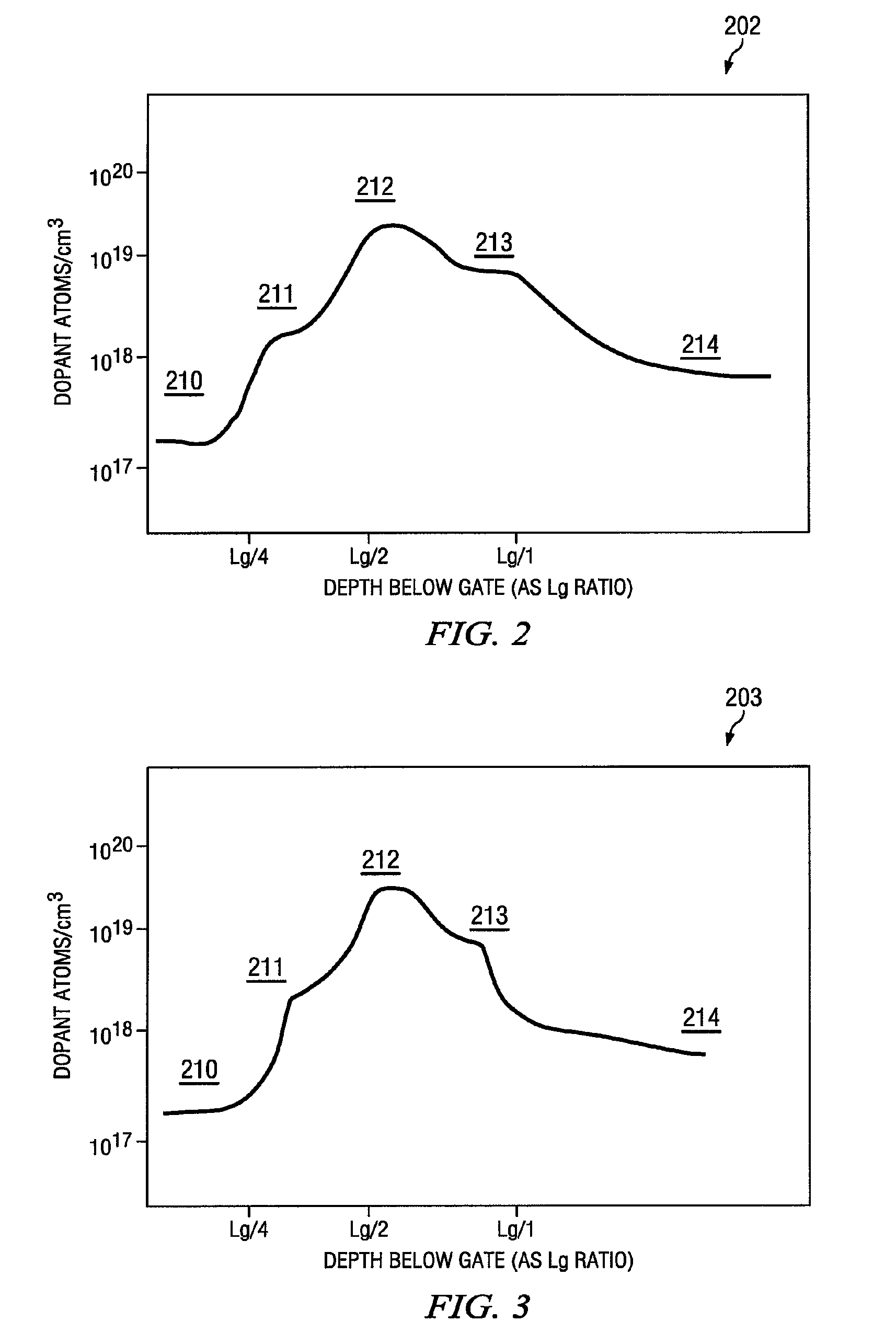
An advanced transistor with punch through suppression includes a gate with length Lg, a well doped to have a first concentration of a dopant, and a screening region positioned under the gate and having a second concentration of dopant. The second concentration of dopant may be greater than 5×1018 dopant atoms per cm3. At least one punch through suppression region is disposed under the gate between the screening region and the well. The punch through suppression region has a third concentration of a dopant intermediate between the first concentration and the second concentration of dopant. A bias voltage may be applied to the well region to adjust a threshold voltage of the transistor.
Owner:MIE FUJITSU SEMICON
Cryptographic processing apparatus
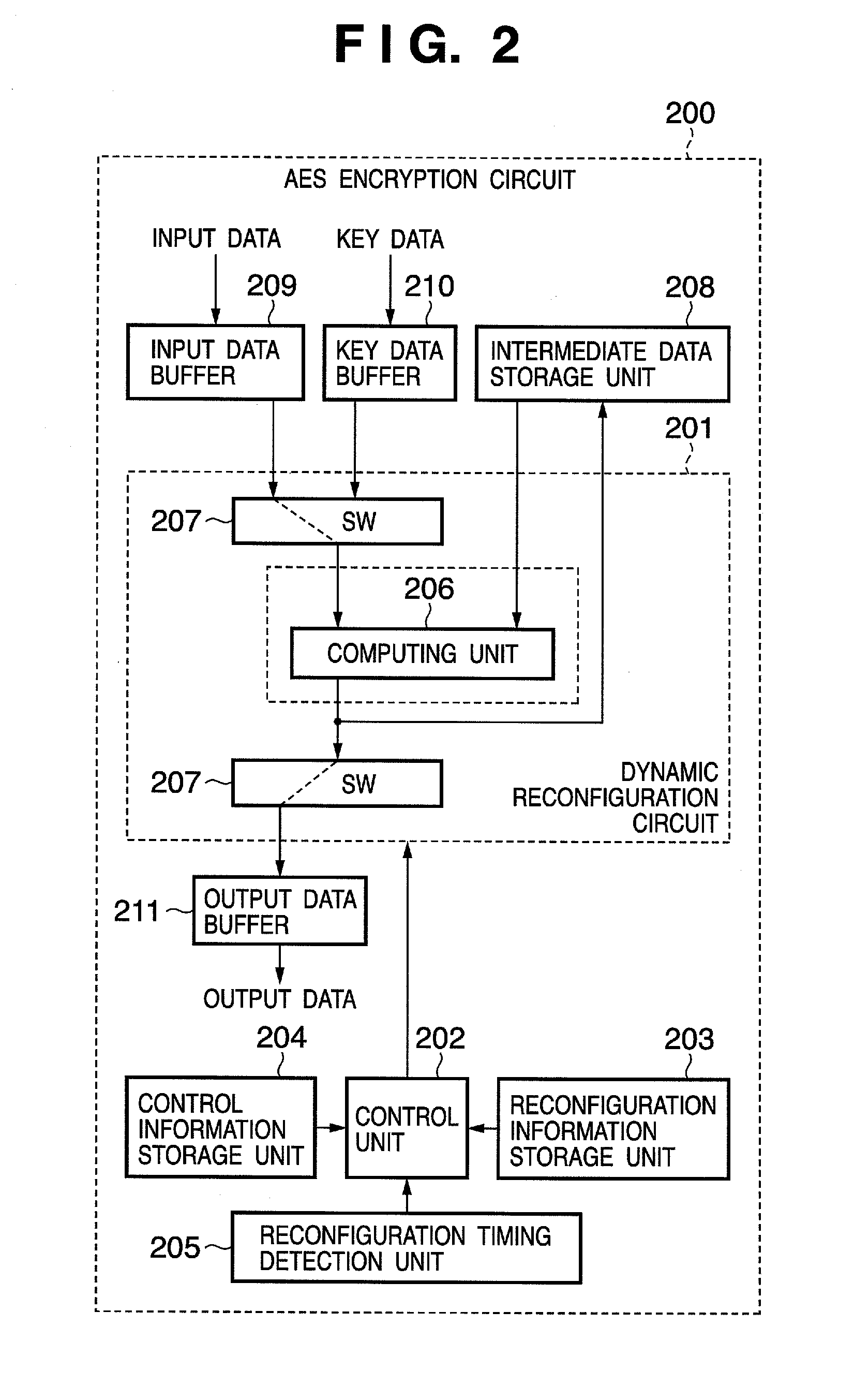
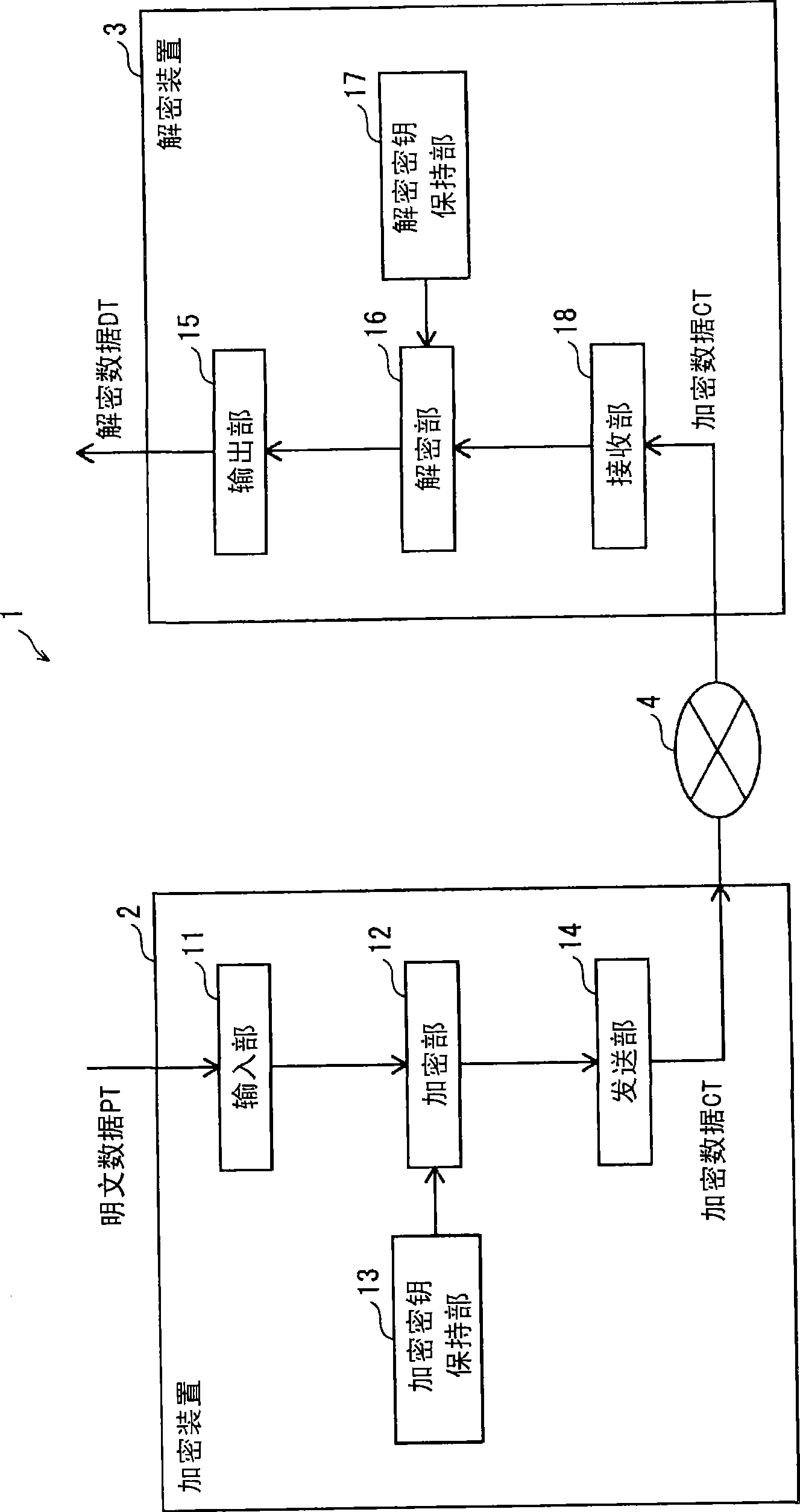
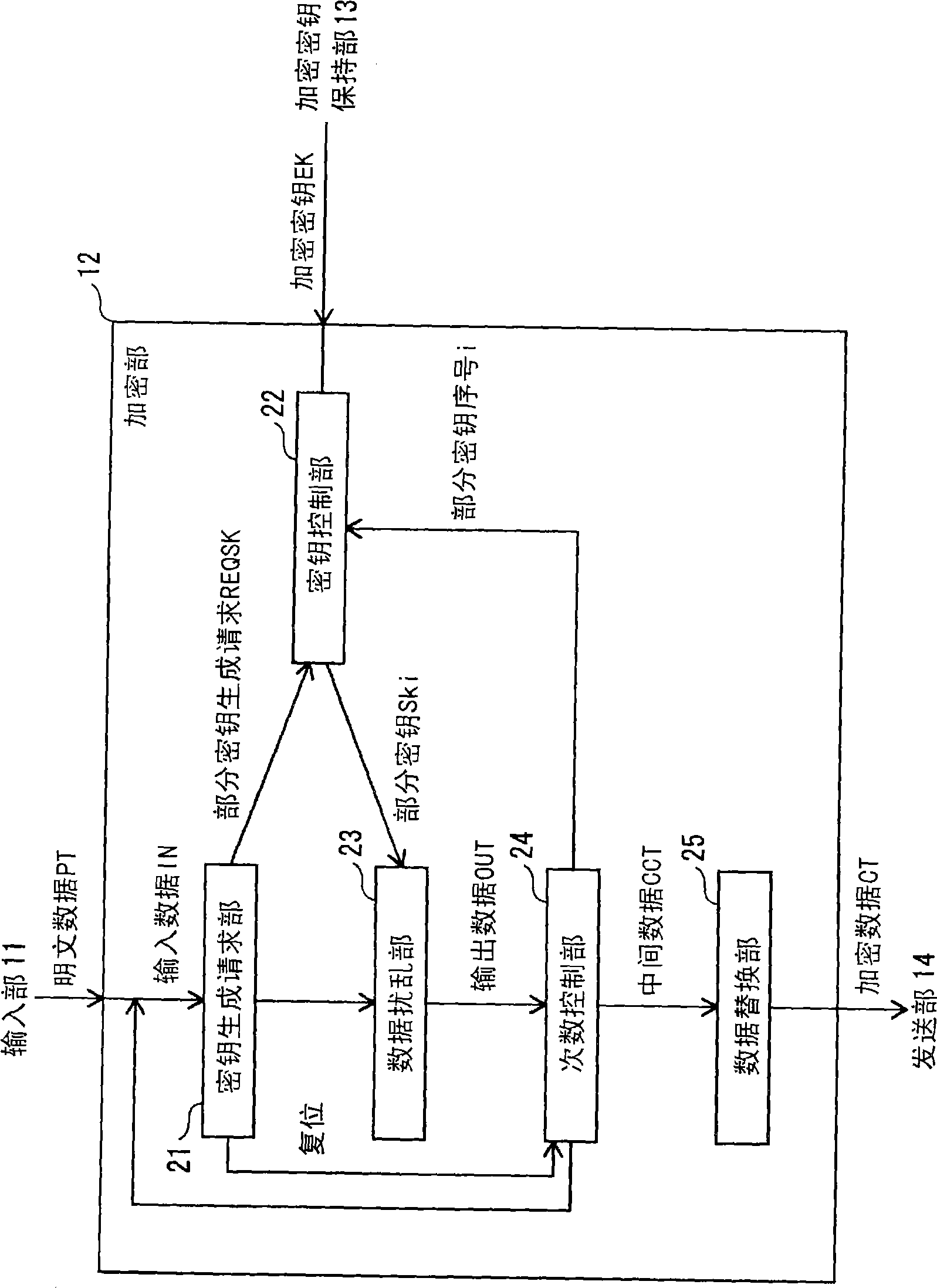
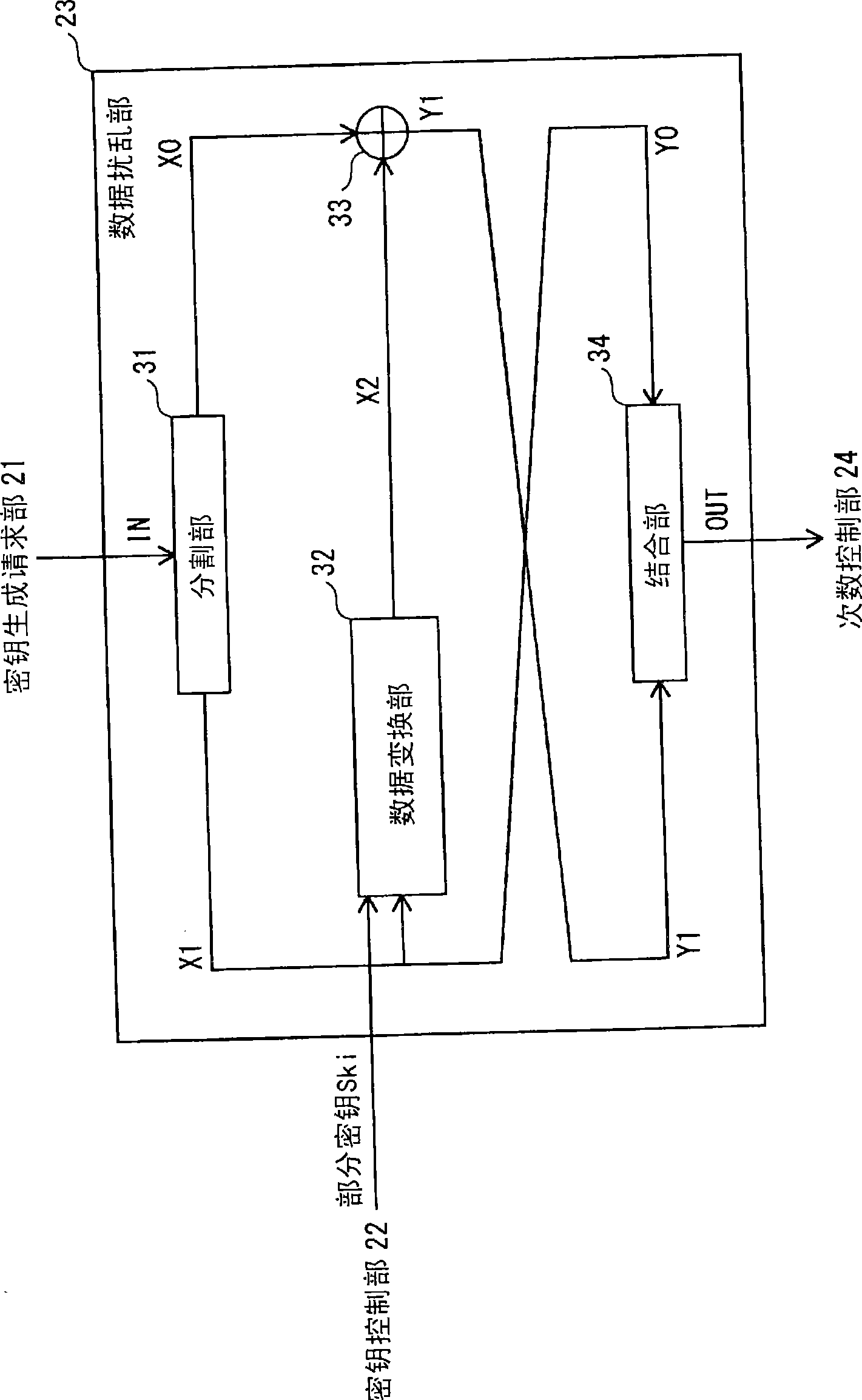
InactiveUS20070098153A1Reduce power consumptionReduce gate sizePublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareControl unit
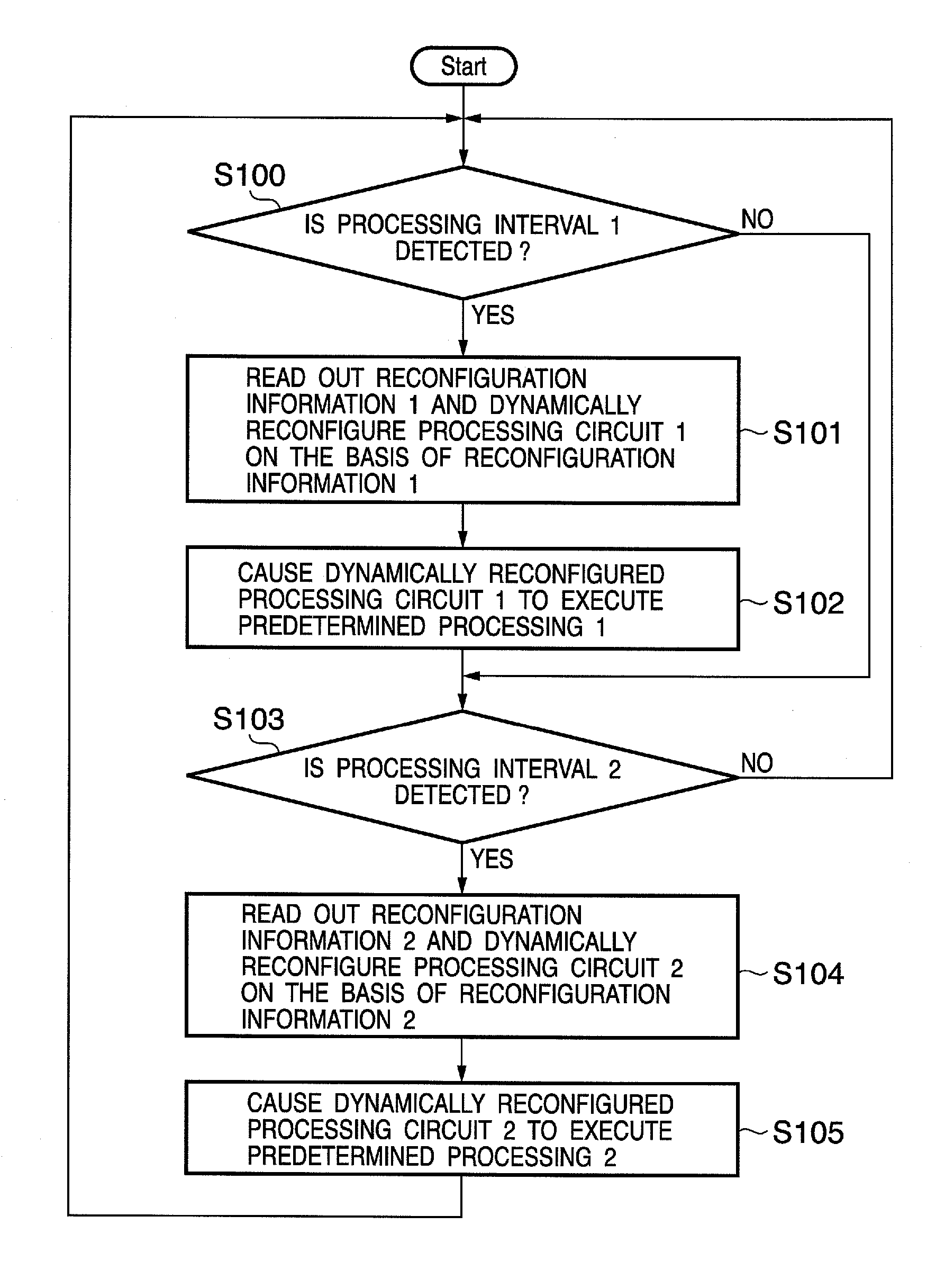
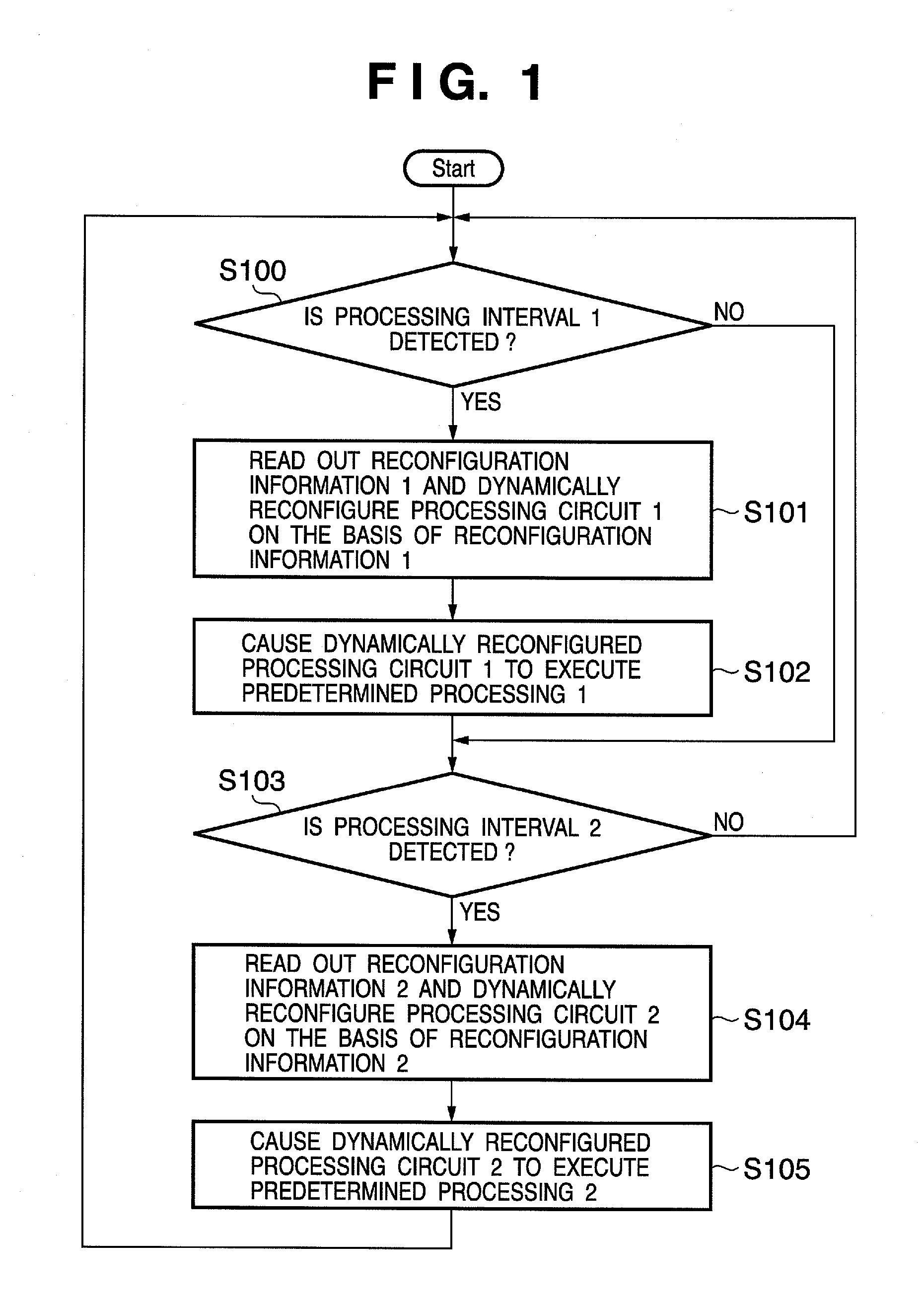
A cryptographic processing apparatus includes a holding unit adapted to hold data of a processing target, an intermediate data holding unit adapted to hold information generated during the cryptographic processing as intermediate data, a circuit reconfiguration processor which reconfigures a first circuit which generates round key information on the basis of the intermediate data and / or the key information, in accordance with input of first control information, and reconfigures a second circuit which performs operation processing on the basis of the data and / or the intermediate data and the round key information, in accordance with input of second control information, and a control unit adapted to output the first control information to the circuit reconfiguration processor at a first timing, and output the second control information to the circuit reconfiguration processor at a second timing.
Owner:CANON KK
Advanced transistors with punch through suppression
An advanced transistor with punch through suppression includes a gate with length Lg, a well doped to have a first concentration of a dopant, and a screening region positioned under the gate and having a second concentration of dopant. The second concentration of dopant may be greater than 5×1018 dopant atoms per cm3. At least one punch through suppression region is disposed under the gate between the screening region and the well. The punch through suppression region has a third concentration of a dopant intermediate between the first concentration and the second concentration of dopant. A bias voltage may be applied to the well region to adjust a threshold voltage of the transistor.
Owner:MIE FUJITSU SEMICON
Semiconductor device with a vertical MOSFET and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080073710A1Reduce gate sizeIncrease widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETActive cell
The size of a gate contact region is decreased by connecting a gate connection electrode embedded in a trench and a gate wiring formed over the gate connection electrode, without forming another conductive film different from the gate connection electrode or the gate wiring. The semiconductor body includes an active cell region and a gate contact region. The active cell region includes a vertical MOSFET with a gate electrode disposed in a first trench. The gate contact region includes the gate connection electrode disposed in a second trench and formed of a same conductive material with the gate electrode. The gate connection electrode includes an embedded part formed in the second trench and an extended part extended therefrom and formed outside the second trench. An interlayer insulation film formed on the gate connection electrode and having a via hole exposing at least a portion of the embedded part of the gate connection electrode.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor memory device
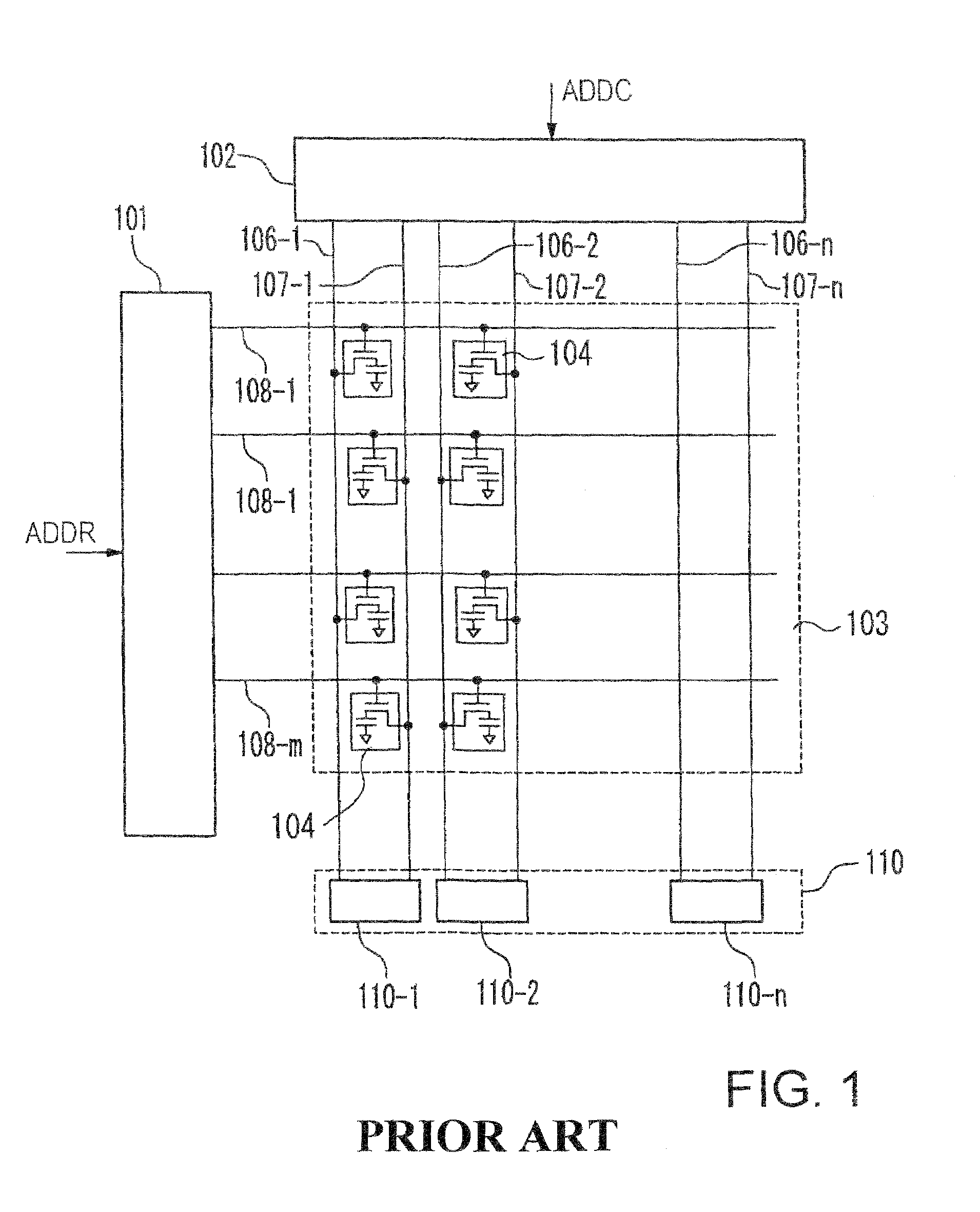
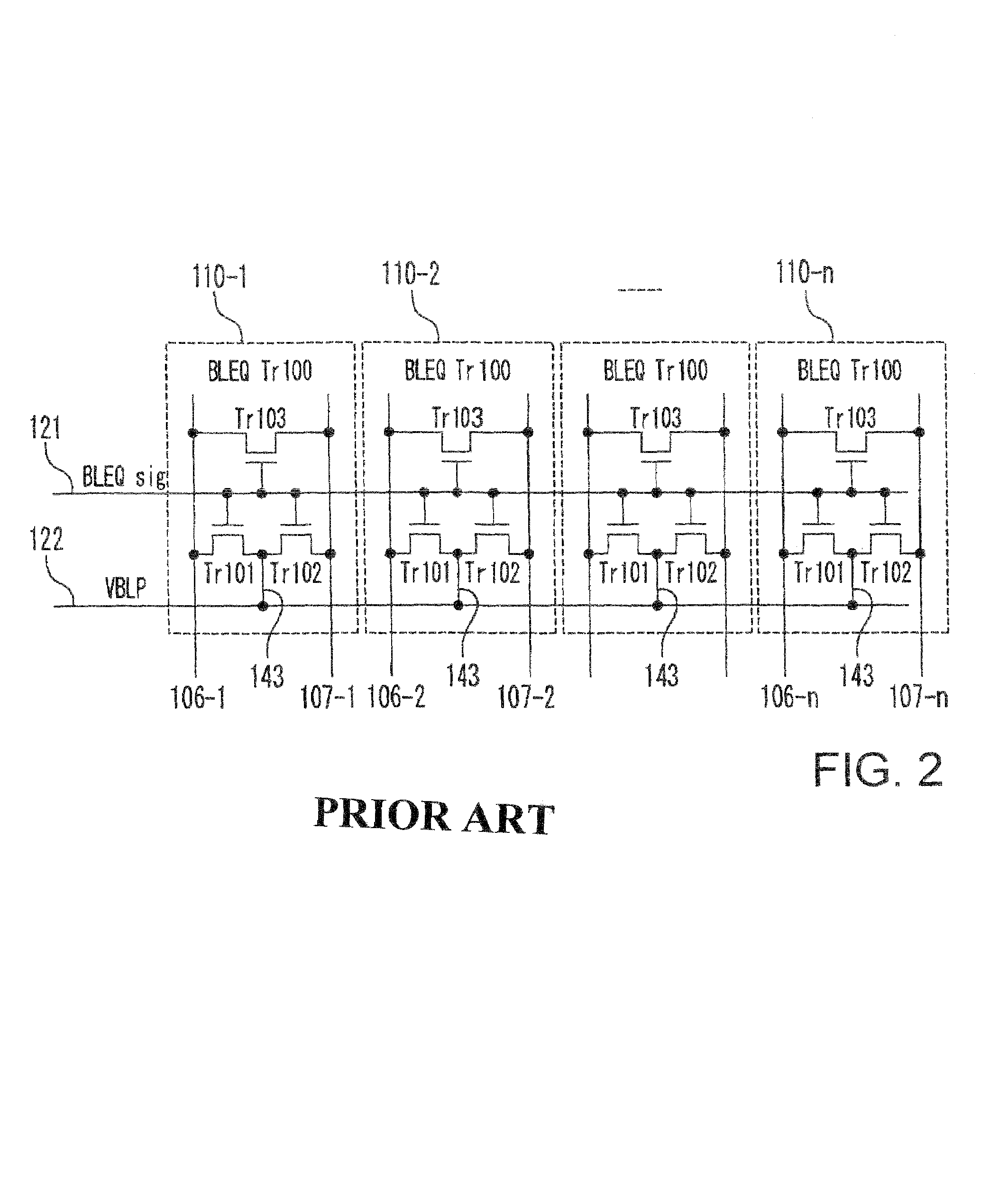
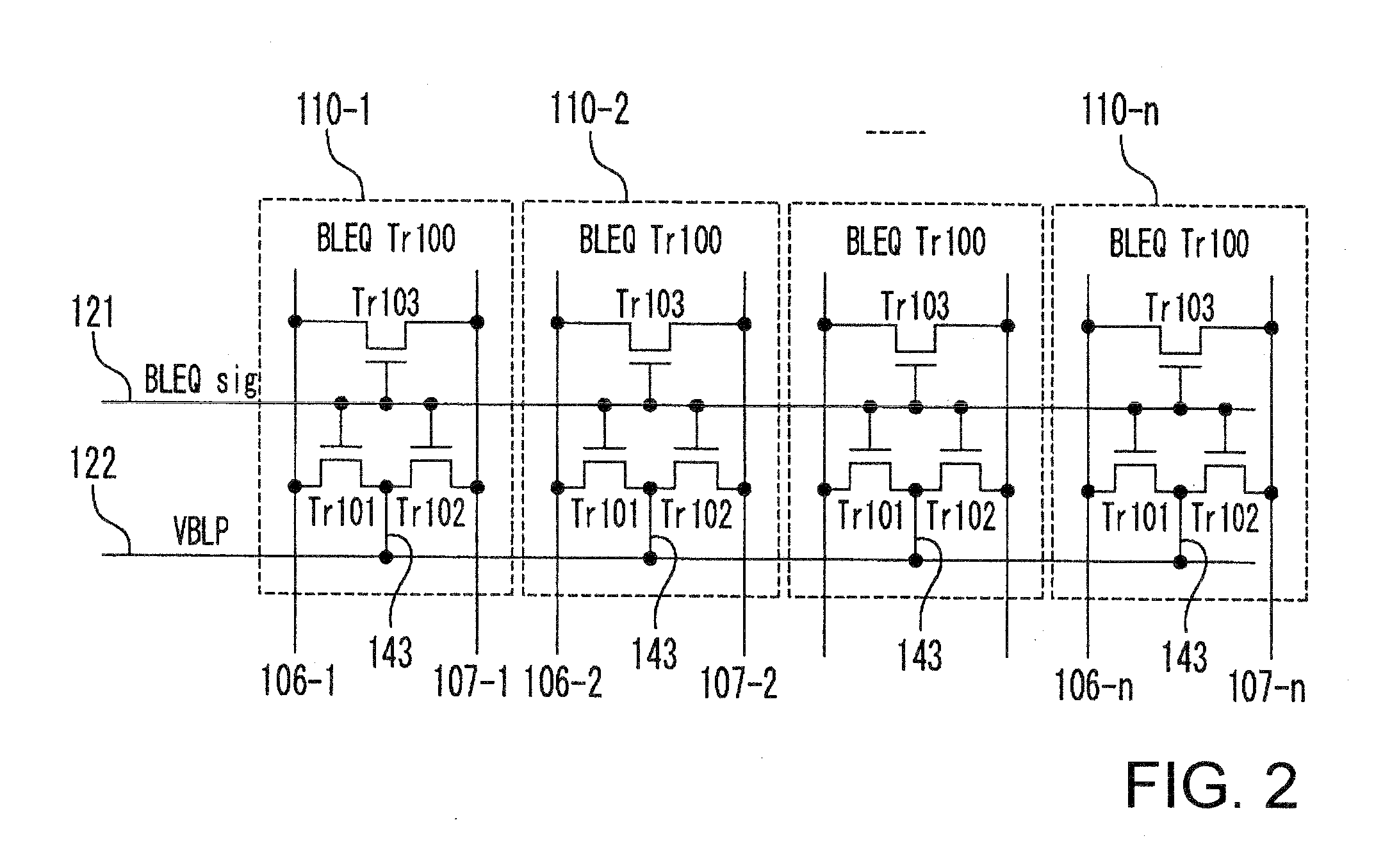
InactiveUS7583550B2Small sizeReduce gate sizeSolid-state devicesDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Semiconductor memory device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20060022243A1Reduce gate resistance valueReduce gate sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesImpurity diffusionEngineering
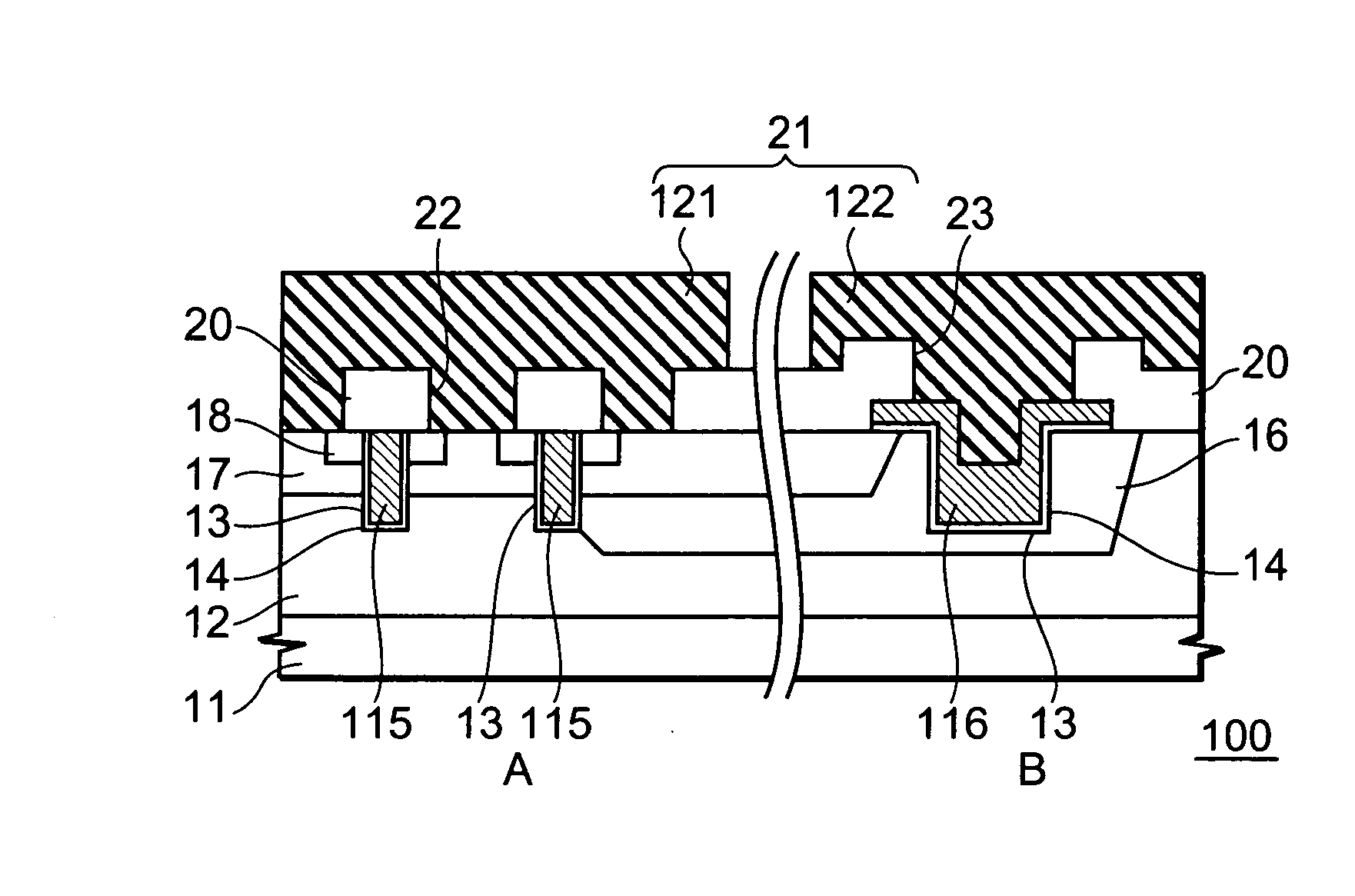
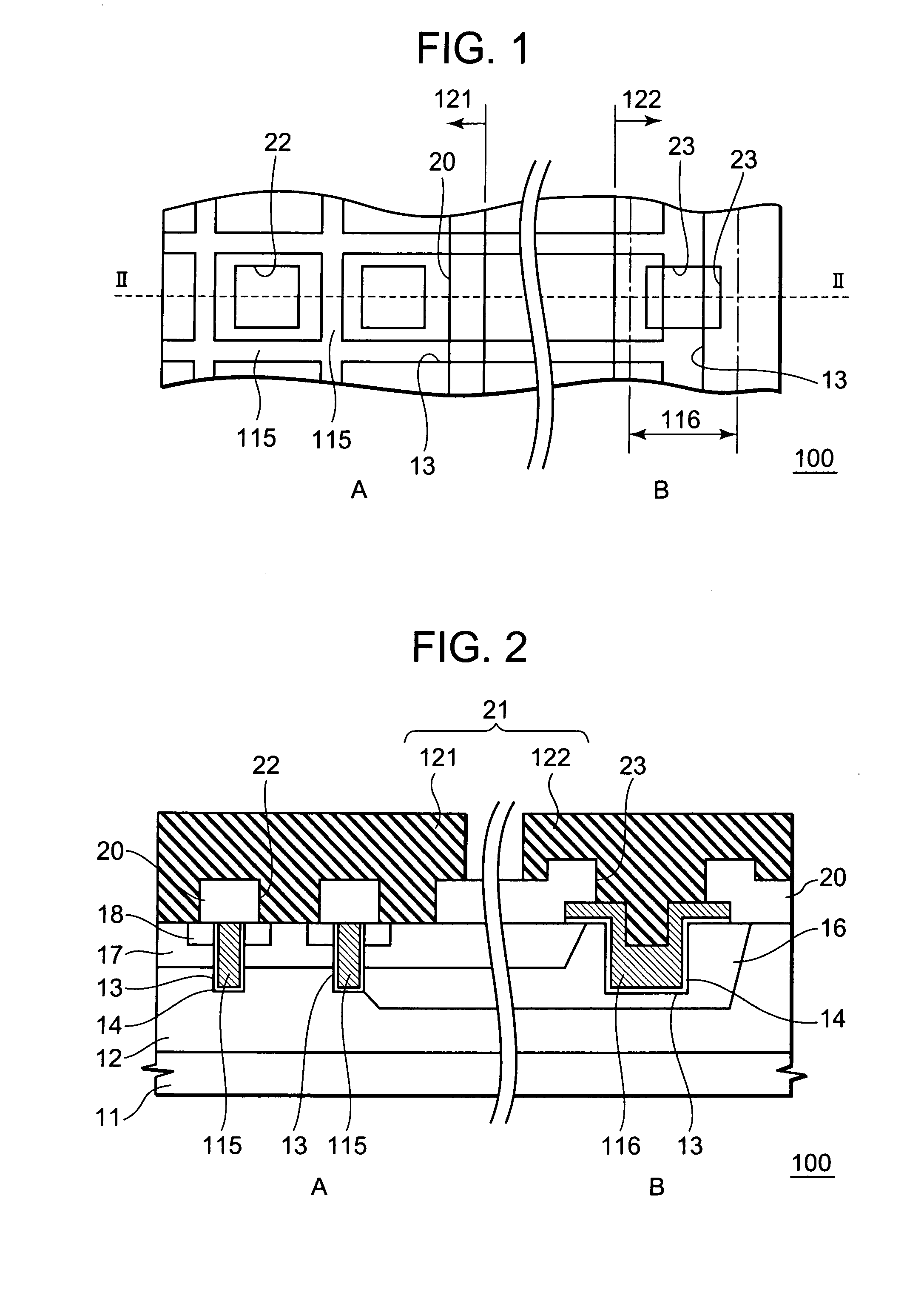
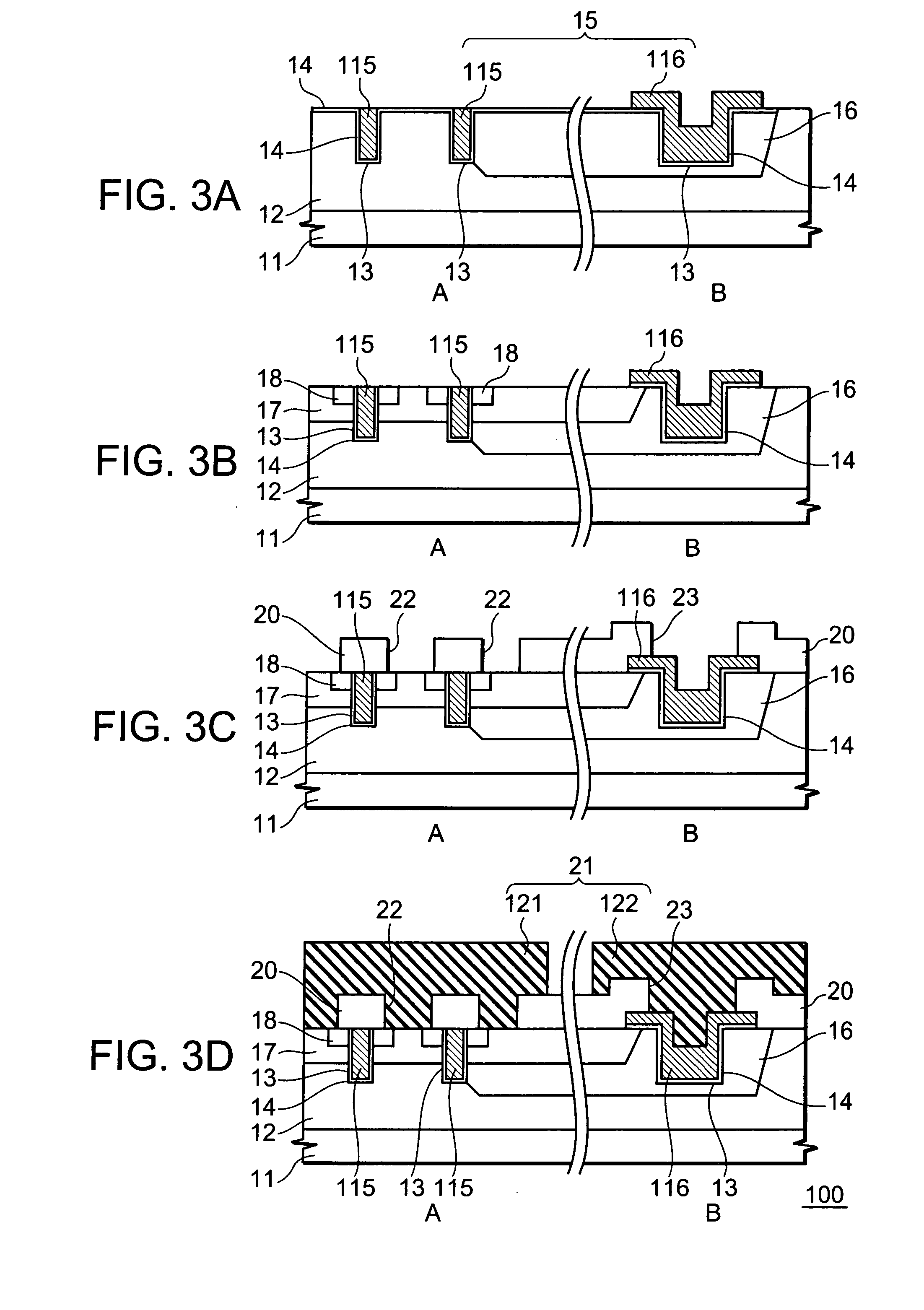
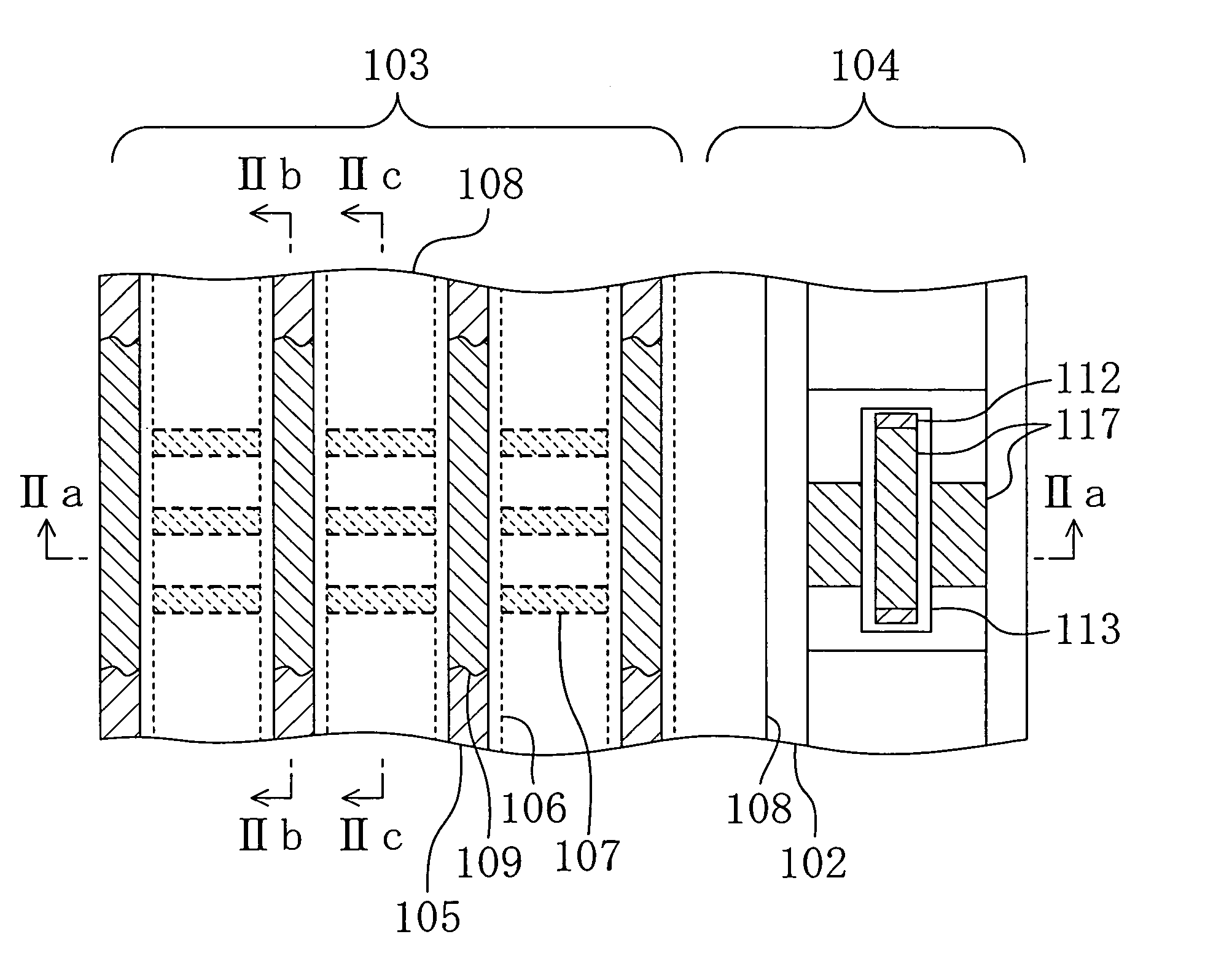
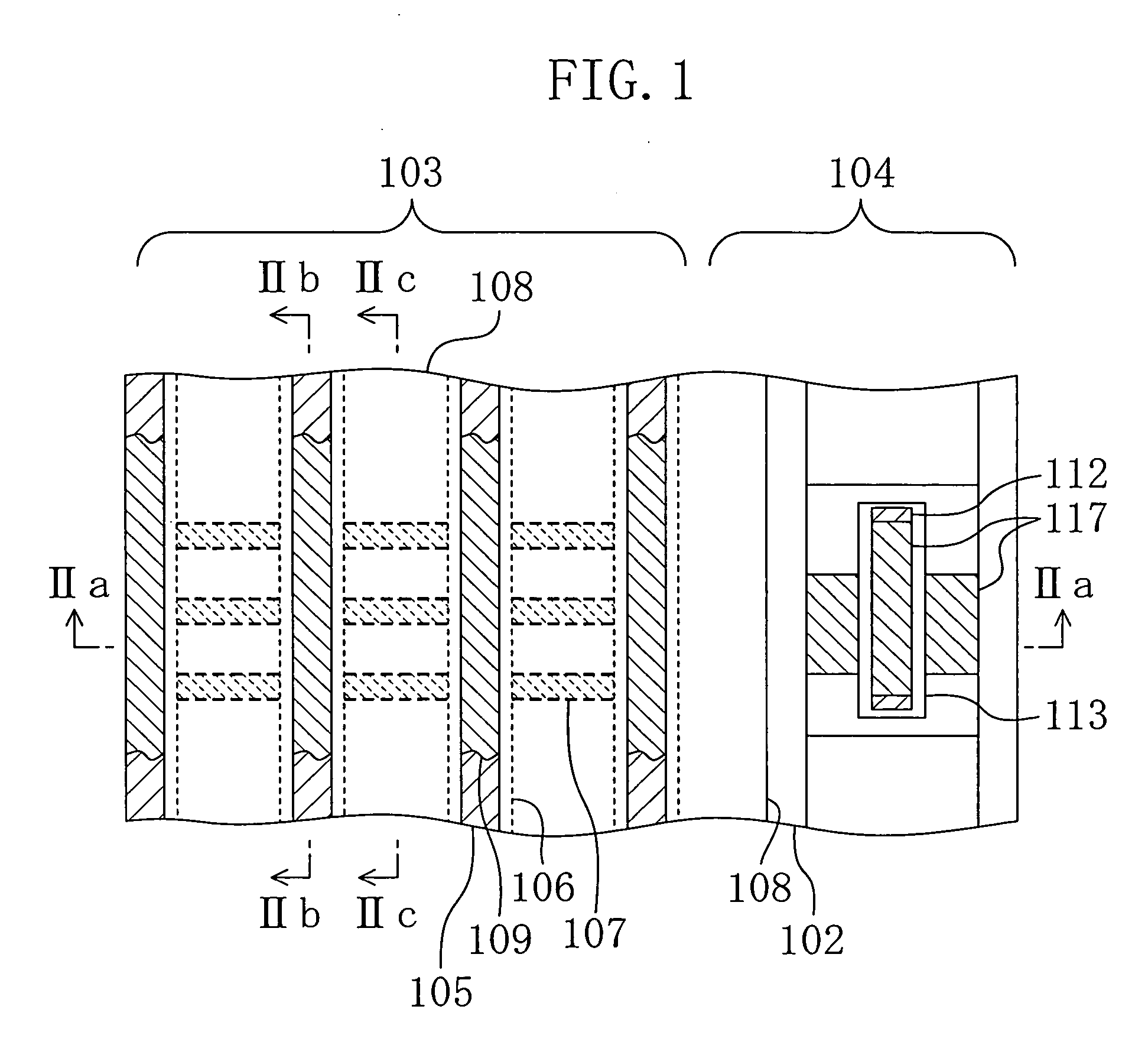
A semiconductor memory device has a memory region which is formed on a semiconductor substrate and in which a plurality of memory cells each including a memory transistor are arranged as a matrix using a plurality of impurity diffusion layers (bit lines) and a plurality of gate electrodes (word lines) intersecting each other. The gate electrode of each of the memory transistors has an upper surface thereof formed into a protruding portion which is higher in level at the middle portion than at the edge portions. A silicide layer is formed on the upper surface of the protruding portion of the gate electrode of each of the memory transistors.
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
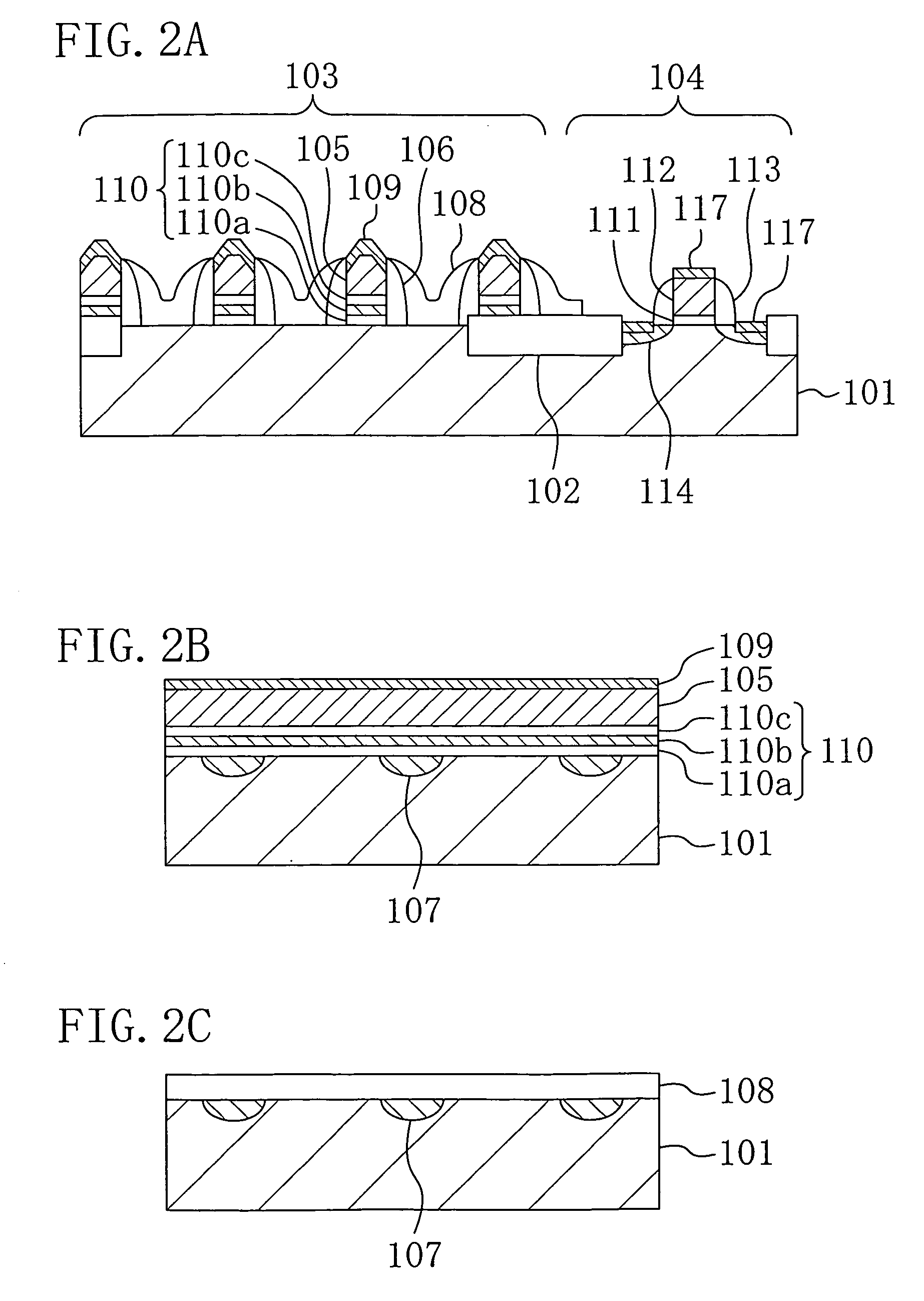
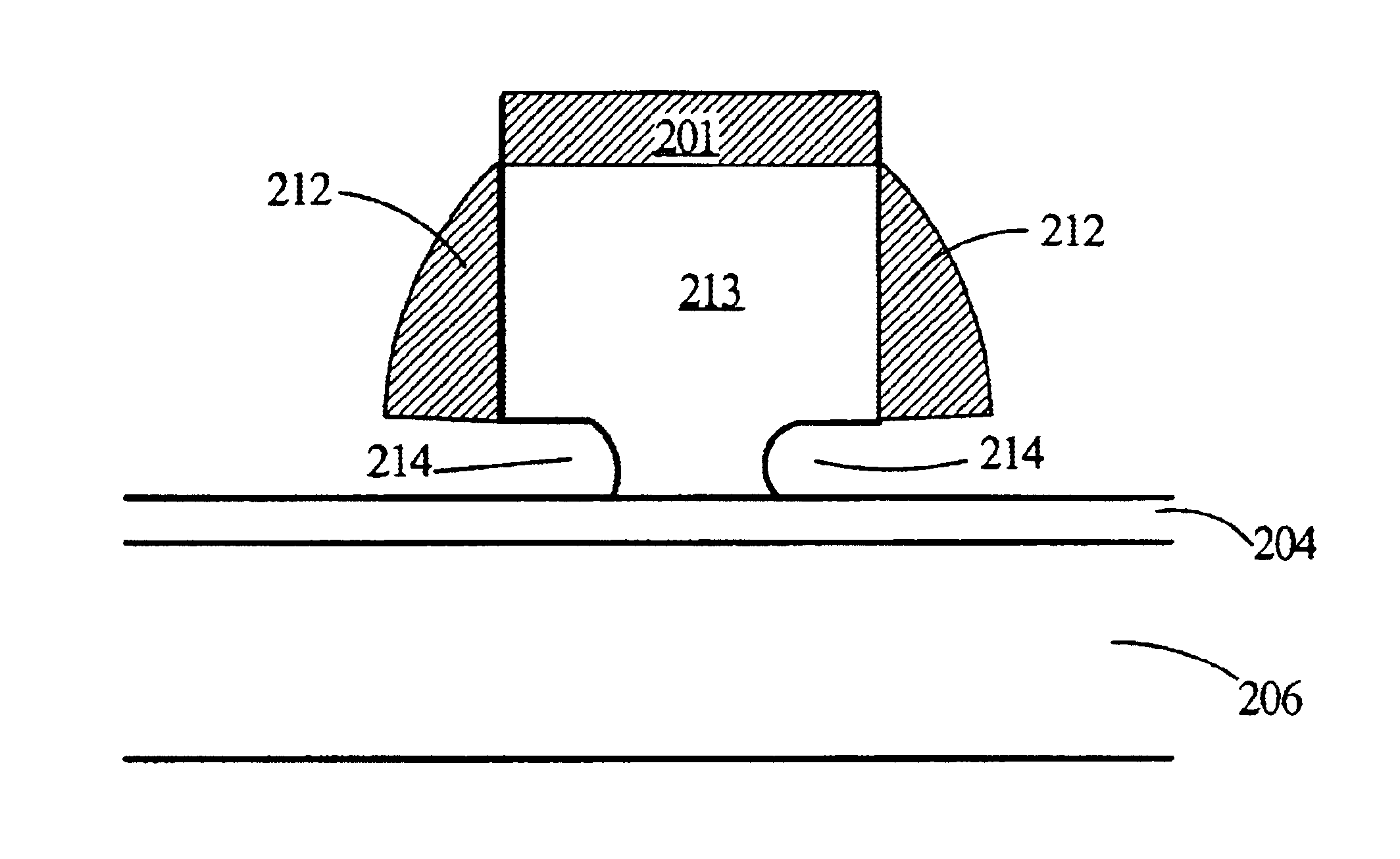
Notched gate structure fabrication
InactiveUS6875668B2Large enough print sizeReduce gate sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringConductive materials
Aspects for notched gate structure fabrication are described. The notched gate fabrication includes forming spacers of hard mask material on a gate conductor, and utilizing the spacers during etching to form notches in the gate conductor and provide a notched gate structure. In a further aspect, notched gate fabrication includes performing a timed etch of masked gate conductive material to maintain a portion of a gate conductive layer and provide gate structure areas in the gate conductive layer. Anisotropically etching the gate structure areas provides spacers on the gate structure areas. Isotropically etching the portion of the gate conductive layer provides notched gates in the gate structure areas.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor memory device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS7446381B2Reduce the valueReduce gate sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineImpurity diffusion
A semiconductor memory device has a memory region which is formed on a semiconductor substrate and in which a plurality of memory cells each including a memory transistor are arranged as a matrix using a plurality of impurity diffusion layers (bit lines) and a plurality of gate electrodes (word lines) intersecting each other. The gate electrode of each of the memory transistors has an upper surface thereof formed into a protruding portion which is higher in level at the middle portion than at the edge portions. A silicide layer is formed on the upper surface of the protruding portion of the gate electrode of each of the memory transistors.
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
Communication apparatus
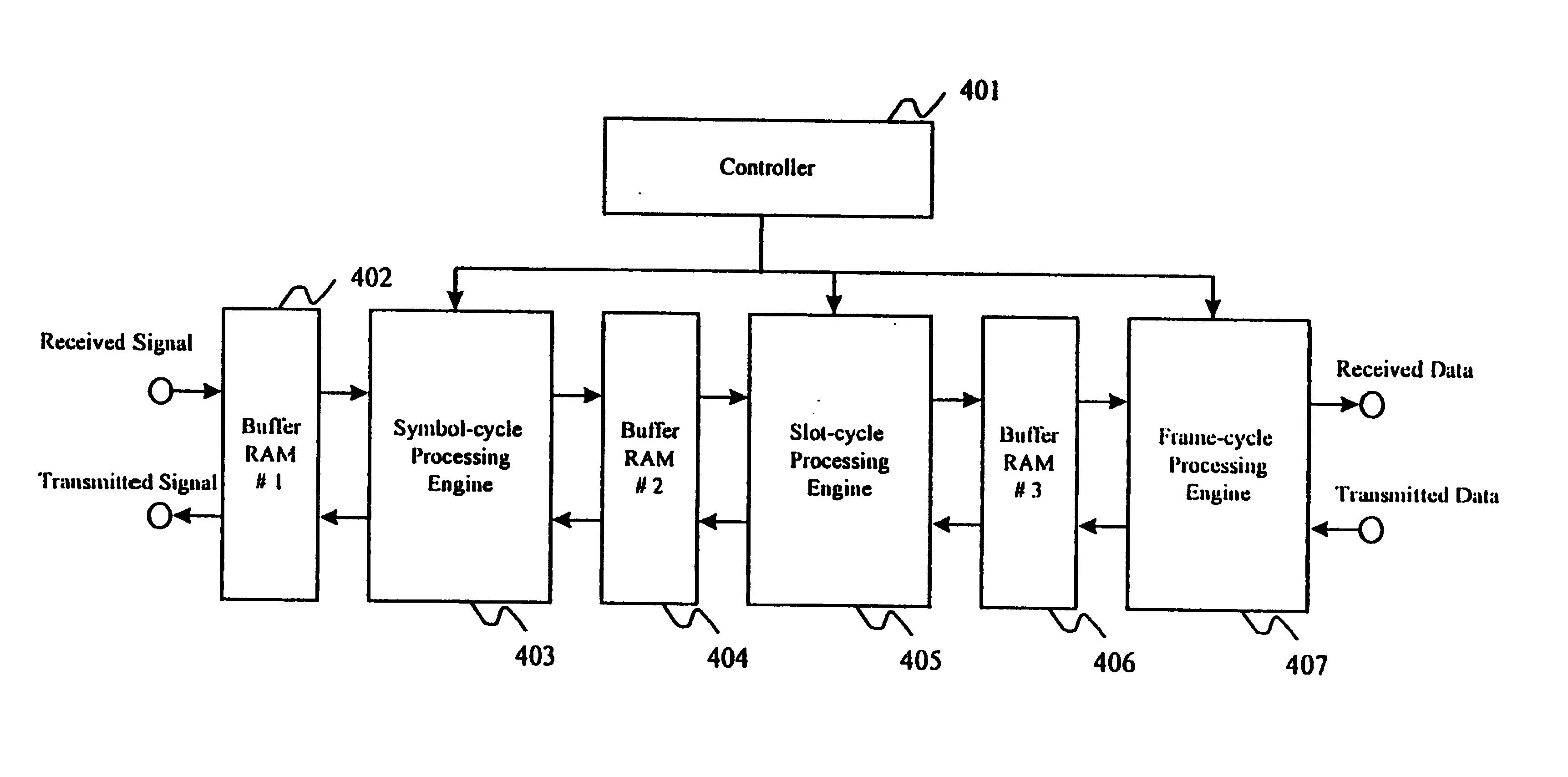
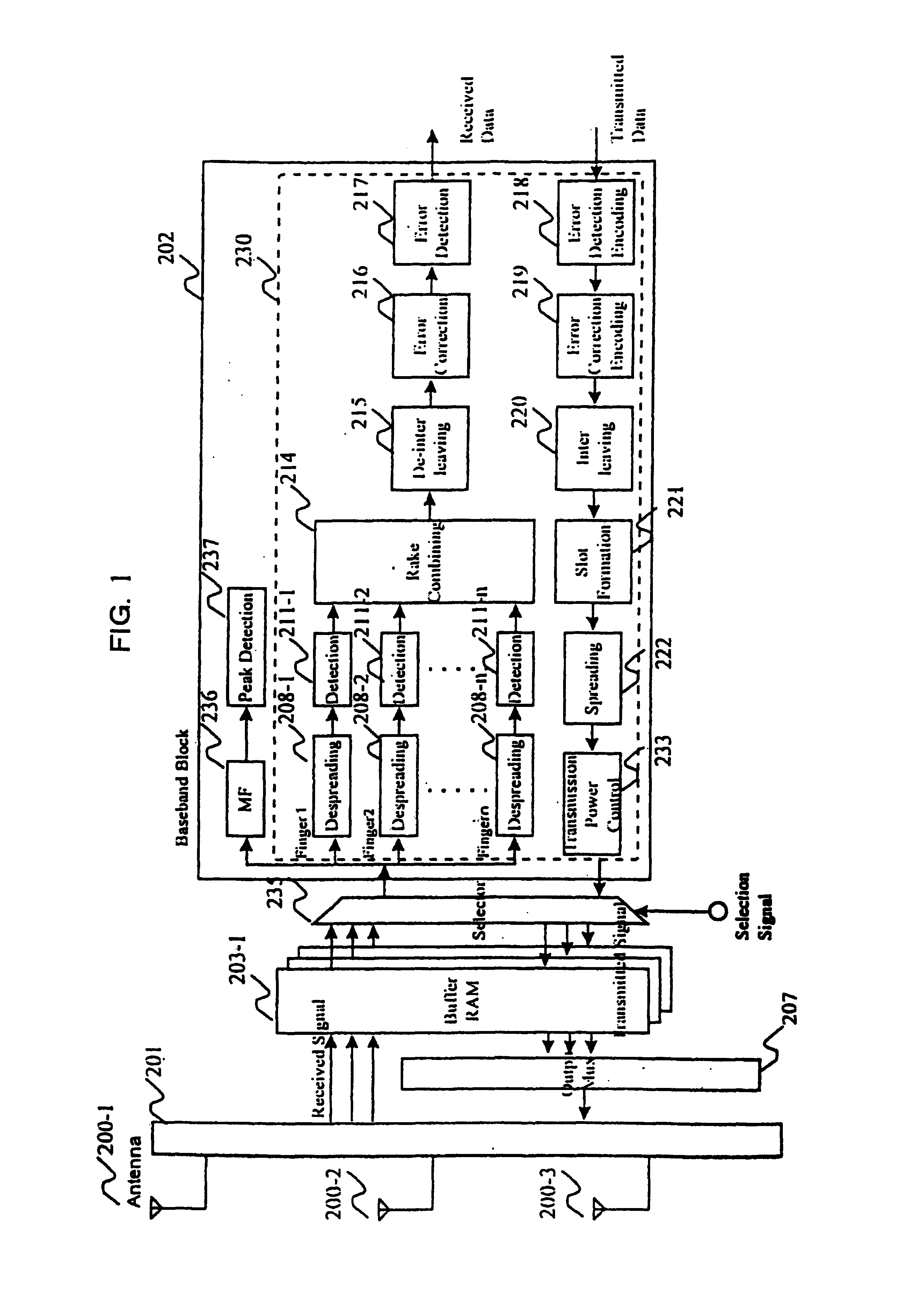
InactiveUS7088696B1Reduce gate sizeEasy to readConnection managementCode division multiplexStatistical time division multiplexingCommunications system
The hardware configuration of a baseband block in a radio communication system is reduced in gate size. Modulation / demodulation processing in a baseband block is divided into a plurality of processing units, which are connected to one another by buffer memories. The hardware gate sizes are reduced by performing processing on a plurality of channels by time division multiplexing at a speed higher than the speed at which received signals are written into the buffer memories.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20080165563A1Small sizeReduce gate sizeSolid-state devicesDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
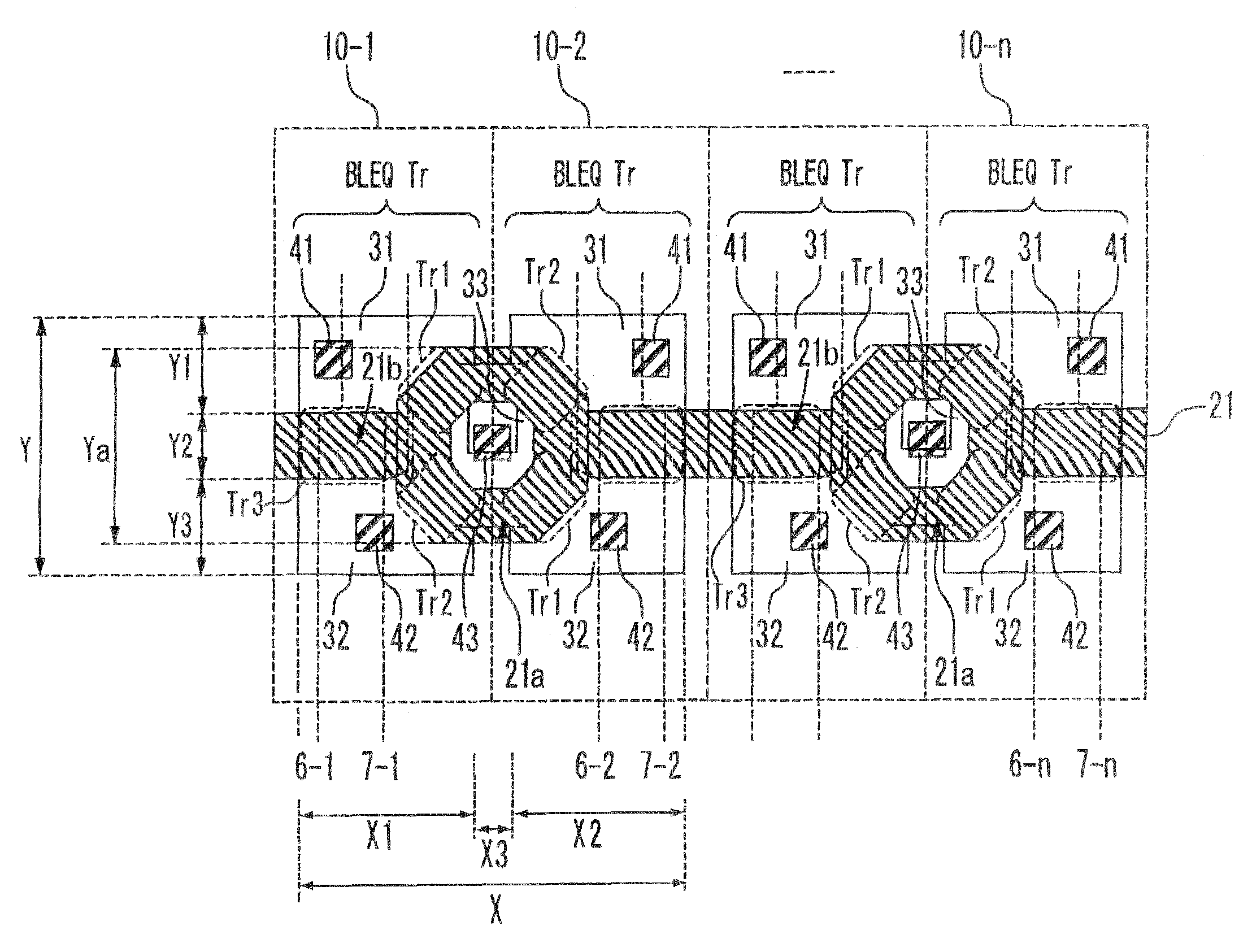
In a sense amplifier circuit having a plurality of sense amplifier portions arranged in order, each of the sense amplifier portions includes a transistor that supplies a bit line potential to a bit line pair in a corresponding column of a memory cell array and a gate electrode for supplying a precharge signal to a gate of the transistor. The gate electrode of the plurality of sense amplifier portions is provided as one piece as a whole and extends in a direction parallel to a row direction in the memory cell array. A gate electrode portion which is a connected portion between the gate electrode in a k-th sense amplifier portion and the gate electrode in a (k+1)-th sense amplifier portion is ring-shaped, where k is an odd number.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Junctionless semiconductor channel gate array storage structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108257968AImprove capture abilityImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesInsulation layerSemiconductor materials
The present invention provides a junctionless semiconductor channel gate array storage structure and a preparation method thereof. The structure comprises: a semiconductor substrate; an insulation layer located on the semiconductor substrate; a carbon nano tube gate array located on the insulation layer; a gate charge trapping structure located on the carbon nano tube gate array; a semiconductor channel, employing two-dimensional semiconductor materials, located on the gate charge trapping structure; and a source contact electrode and a drain contact electrode respectively located at two endsof the carbon nano tube gate array and connected with the semiconductor channel. The storage structure employs two-dimensional semiconductor material channel to replace a traditional silicon-doping channel and employs the metal carbon nano tube gate array to improve the gate charge tripping performance, simplify the device structure and further improve the storage array density.
Owner:ZING SEMICON CORP
Gate driver circuit and display device including the same
ActiveUS20220199034A1Reduce in quantityLarge display sizeStatic indicating devicesDigital storageDriver circuitDisplay device
A gate driver circuit can include a plurality of stage circuits, in which each of the plurality of stage circuits supplies a gate signal to gate lines arranged in a display panel, and includes an M node, a Q1 node, a Q2 node, a QB node, a line selector, a Q1 node controller, a Q1 node stabilizer, an inverter, a QB node stabilizer, a carry signal output circuit portion, and a gate signal output circuit portion, in which a first low-potential voltage level, a third low-potential voltage level, and a fourth low-potential voltage level for operating the gate driver circuit are set to different values, and the gate driver circuit can have a reduced size and better prevent leakage current while also providing more stable gate signals.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Gate driver circuit and display device including the same
ActiveUS20220208113A1Reduce gate sizeIncrease in sizeStatic indicating devicesDigital storageDriver circuitDisplay device
Disclosed are a gate driver circuit having a reduced size, and a display device including the same. The gate driver circuit includes a plurality of stage blocks for outputting n gate signals (n is a positive integer). Each stage block includes each start stage circuit including a blank start circuit for receiving a block selection signal, and a signal output circuit for outputting a carry signal and a gate signal; and a plurality of normal stage circuits connected to each start stage circuit.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Cipher processing apparatus, data converting method, data converting program, recording medium and integrated circuit
ActiveCN101479774AReduce gate sizeEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCoding/ciphering apparatusExclusive orComputer science
A cipher processing apparatus wherein the gate scale of hardware has been reduced as compared with a conventional one using a substitution cipher table and wherein a high misleading characteristic has been achieved. A data converting part included in an encrypting apparatus divides an input data of 256 bits into block data A1, B1, A2 and B2 of 32 bits each. A first fusing part (43) provides an exclusive-OR of A1 and B1 and also provides an exclusive-OR of A2 and B2. A first misleading part (44) branches each of A1, A2 and the results of exclusive-OR (C1,C2) into three block data, and cyclically shifts two of those three block data and then fuses all of the block data. A second fusing part (45) provides an exclusive-OR of D1 and E2, which are results from the first misleading part (44), and also provides an exclusive-OR of E1 and D2 that are also results from the first misleading part (44). A block coupling part (46) couples the calculation results of the second fusing part (45). A second misleading part (47) branches each of the coupled data into three block data, and cyclically shifts two of those three block data and then fuses all of the block data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
NAND gate flash memory without junction in rear grid and manufacturing method of flash memory
ActiveCN108305877ASimple structureHigh densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsCarbon nanotube
The invention provides an NAND gate flash memory without a junction in a rear grid and a manufacturing method of the flash memory. The memory comprises a substrate, an insulating layer, a 2D semiconductor material channel layer, a carbon nanotube grid array, a grid trap structure, a protective layer, a source contact electrode and a drain contact electrode; the grid trap structure comprises a tunnel layer, a charge trap layer and a barrier layer, the tunnel layer is positioned on the channel layer, the barrier layer surrounds outer side surfaces of carbon nanotubes in the carbon nanotube gridarray, and the charge trap layer comprises a first part surrounding the outer side of the barrier layer and a second part positioned on the tunnel layer and making contact with the first part. The NAND gate flash memory without junction in the rear grid uses a horizontal channel of a 2D semiconductor material, the metallic carbon nanotube grid array is used, the barrier layer and the charge trap layer surround the carbon nanotube grid, the device structure is simplified, the density of storage units is improved, and a higher grid charge trap performance can be obtained.
Owner:ZING SEMICON CORP
Static random access memory
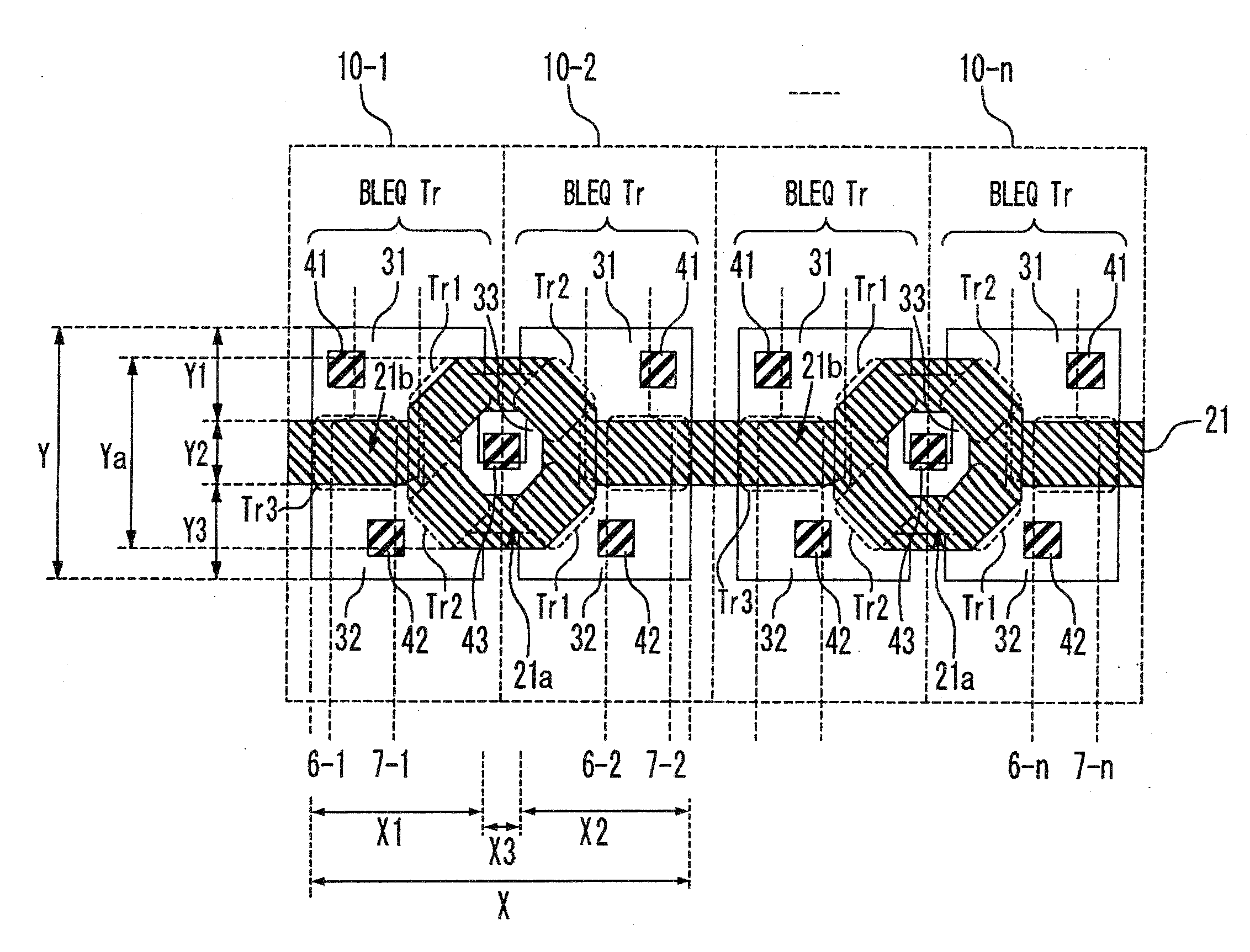
ActiveCN106653755AReduce gate sizeSmall sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
The present invention discloses a static random access memory comprising at least one static random access memory unit. The gate layout of the static random access memory unit includes first to fourth strip-like doped regions, a concave gate line, a first gate line, and a second gate line. The first to fourth strip-like doped regions are sequentially disposed in the substrate and separated from each other. The concave gate lines intersect the first to fourth strip-like doped regions. The first to fourth strip-like doped regions are disconnected from the intersection of the concave gate lines. The first gate line intersects the first strip-like doped region and the second stripe-like doped region. The first strip-like doped region and the second strip-like doped region are disconnected from the intersection of the first gate line. The second gate line intersects the third strip-like doped region and the fourth strip-like doped region. The third strip-like doped region and the fourth strip-like doped region are disconnected from the intersection of the second gate line.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Fabrication method of flash memory
InactiveUS20070032006A1Contact resistanceReduce gate sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricCell region
A fabrication method of a flash memory is provided. The substrate having a cell region and a peripheral circuitry region is provided. A patterned dielectric layer and a patterned conductive layer are formed on the substrate, and isolation structures are formed in the substrate. An inter gate dielectric layer and a poly layer are formed sequentially over the substrate. The poly layer and the inter gate dielectric in peripheral circuitry region are removed. After forming a second conductive layer and a mask layer over substrate, memory cells are formed in the cell region and a gate structure is formed in the peripheral circuitry region. A conductive plug is formed above the gate structure for electrically connecting the second conductive layer. Since the inter gate dielectric layer in the peripheral circuitry region is removed, the fabrication of the conductive plug can be simpler and the process window thereof can be improved.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
CDMA modulation method and device thereof
InactiveCN1192509CEasy to operateSimple methodMultiplex code generationPhase-modulated carrier systemsDigital dataCode division multiple access
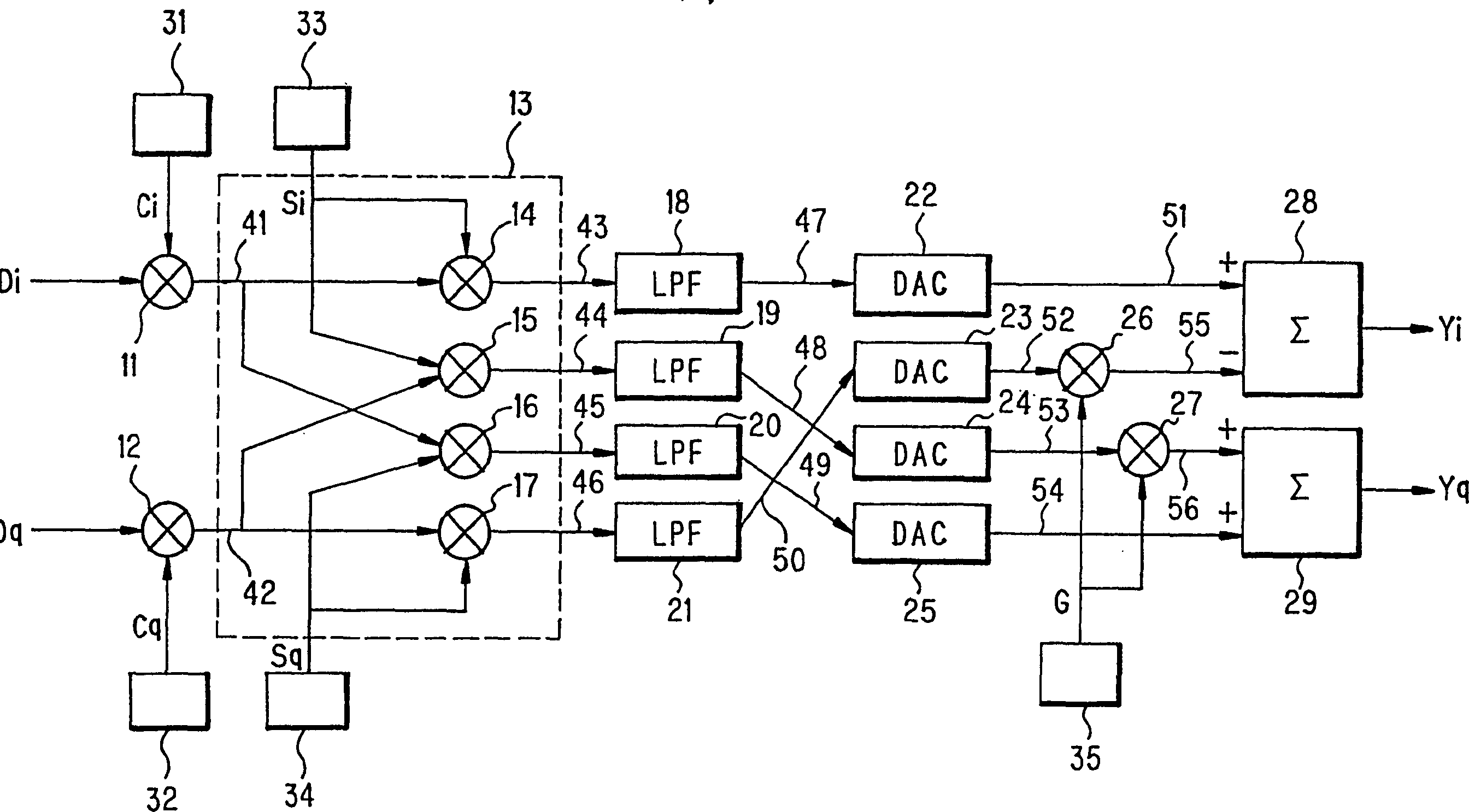
CDMA complex QPSK spread modulation for reducing the scale of the gate and power consumption. Digital data signals (Di, Dq) are spread-modulated by multipliers (11, 12) with first spread codes (Ci, Cq) generated by spread code generators (31, 32), and a spread modulating signal (Di.Ci) (41) and a spread modulating signal (Dq.Cq) (42) are generated. The signals (41, 42) are inputted to a complex QPSK operation unit (13), subjected to a complex QPSK operation with second spread codes (Si, Sq) generated by spread code generators (33, 34), and filtered by LPFs (18-21). Multipliers (26, 27) apply the weight of the gain factor G from a gain factor controller (63) to signals (44, 45) converted into analog values (51-54) by DAC (22-25) and including an ICH data signal (Dq).
Owner:SHARP KK
Gate Driver Circuit and Display Device Including the Same
ActiveUS20220208104A1Small sizeReduce in quantityStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceHemt circuits
Disclosed are a gate driver circuit having a reduced size, and a display device including the same. The gate driver circuit includes a plurality of stage circuits. Each stage circuit supplies a gate signal to each of gate lines arranged in a display panel, and includes a M node, a Q node, a QH node, and a QB node. Each stage circuit includes a gate signal output module configured to operate based on a voltage level of the Q node or a voltage level of the QB node to output first to j-th gate signals based on first to j-th scan clock signals or a first low-potential voltage.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Static random access memory
ActiveUS9484349B1Small sizeEasier optical proximity correction (OPC)TransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
A static random access memory (SRAM) including at least a SRAM cell is provided. A gate layout of the SRAM cell includes first to fourth strip doped regions, a recessed gate line and first and second gate lines. The first to fourth strip doped regions are disposed in the substrate in order and separated from each other. The recessed gate line intersects the first to fourth strip doped regions. The first to fourth strip doped regions are disconnected at intersections with the recessed gate line. The first gate line intersects the first and the second strip doped regions. The first and the second strip doped regions are disconnected at intersections with the first gate line. The second gate line intersects the third the fourth strip doped regions. The third and the fourth strip dopeds region are disconnected at intersections with the second gate line.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Planar mono-silicon double-metal layer power device and its production
InactiveCN1897304ALow costCapacitor fastSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceGate oxide
A plane single silicon bimetal layer power parts and the manufacture method, the power parts includes: the silicon underlay; the two oxidation layers that forms at the trap area in the silicon underlay and the front surface of the silicon underlay; the leaking pole metal, the source pole metal and the grid metal that are located at the front surface of the two oxidation layers; the trap touching area, the source area, the leaking area and the channel area that is established in the silicon underlay; forms a grid oxidation layer at the front surface of the silicon underlay; the multi-crystal grid located on the oxidation layer; the two oxidation layers with several holes respectively; the filling holes of the leaking pole metal, the source pole metal and the grid metal on the front surface of the two oxidation layers connect with the leaking area, the trap touching area, the source area and the multi-crystal silicon grid. The manufacture method includes the grid oxidation layer, the trap area, the channel area, the multi-crystal silicon grid, the trap touching area, the source area, the leaking area, the oxidation layer and the metal layer. The invention is low cost, small engrossing area, small grid capacitance, and easy integration.
Owner:NANKER GUANGZHOU SEMICON MFG
Forming method of CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) transistor
InactiveCN104681489AGood removal effectQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSP channel
The invention provides a forming method of a CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) transistor. The forming method comprises the following steps that a semiconductor substrate is provided, and the semiconductor substrate comprises an NMOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor) region, a PMOS (P-channel metal oxide semiconductor) region, a first groove positioned in the surface of the NMOS region and a second groove positioned in the surface of the PMOS region; a grid dielectric material layer, a first metal layer, a second metal layer and a third metal layer are sequentially formed on the surfaces of the inner walls of the first groove and the second groove and the surface of a dielectric layer; covering material layers filling into the first groove and the second groove are formed, the materials of the covering material layers are insulation dielectric materials; the covering material layer on the NMOS region is removed; the covering material layer at partial thickness in the second groove is removed for forming a covering layer; a third metal layer and a second metal layer in the first groove, above the dielectric layer as well as above the covering layer and in the second groove are removed; the covering layer is removed; a first grid electrode and a second grid electrode are formed in the first groove and the second groove. The forming method of the CMOS transistor has the advantage that the performance of the CMOS transistor can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Gate voltage control device
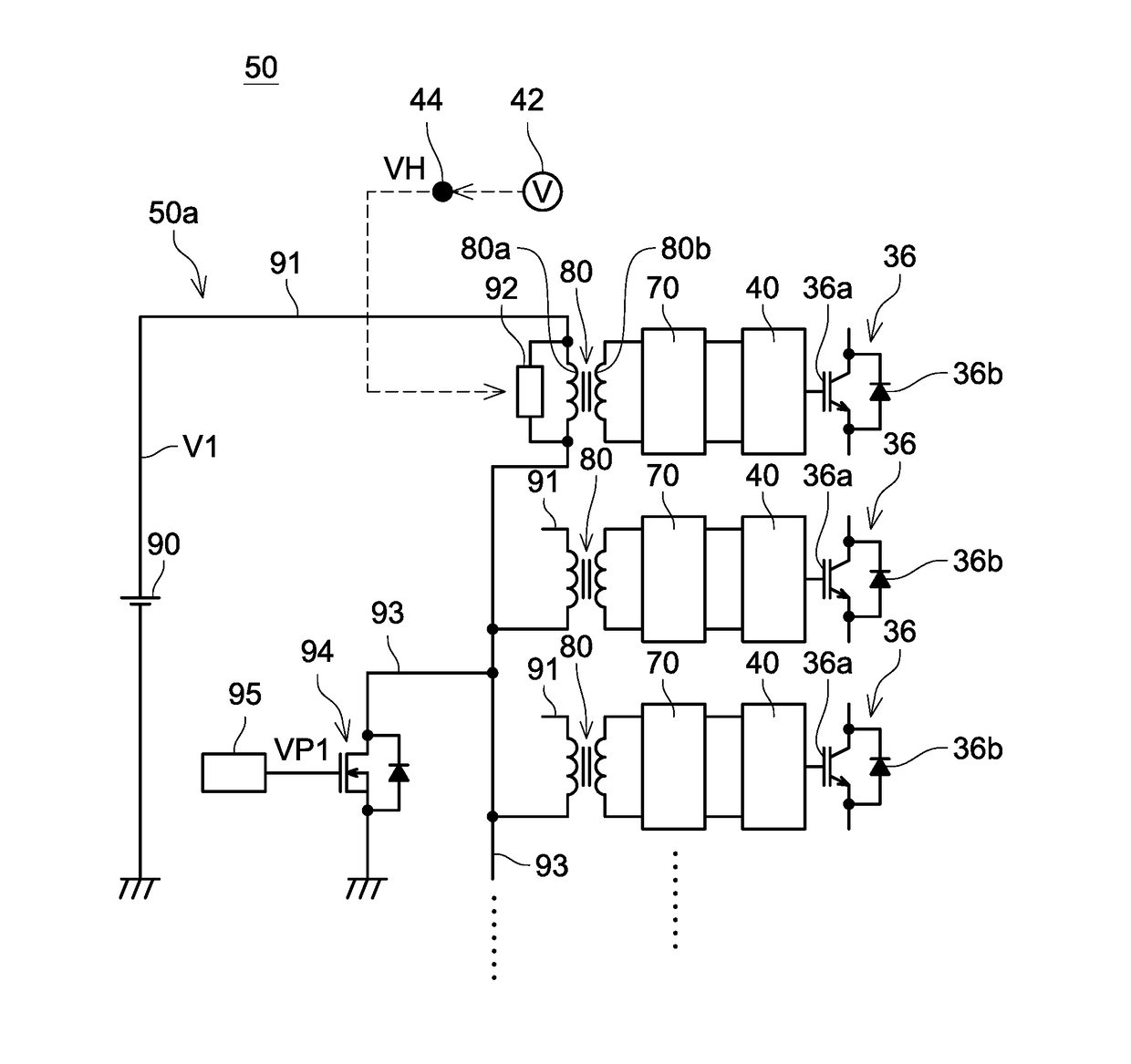
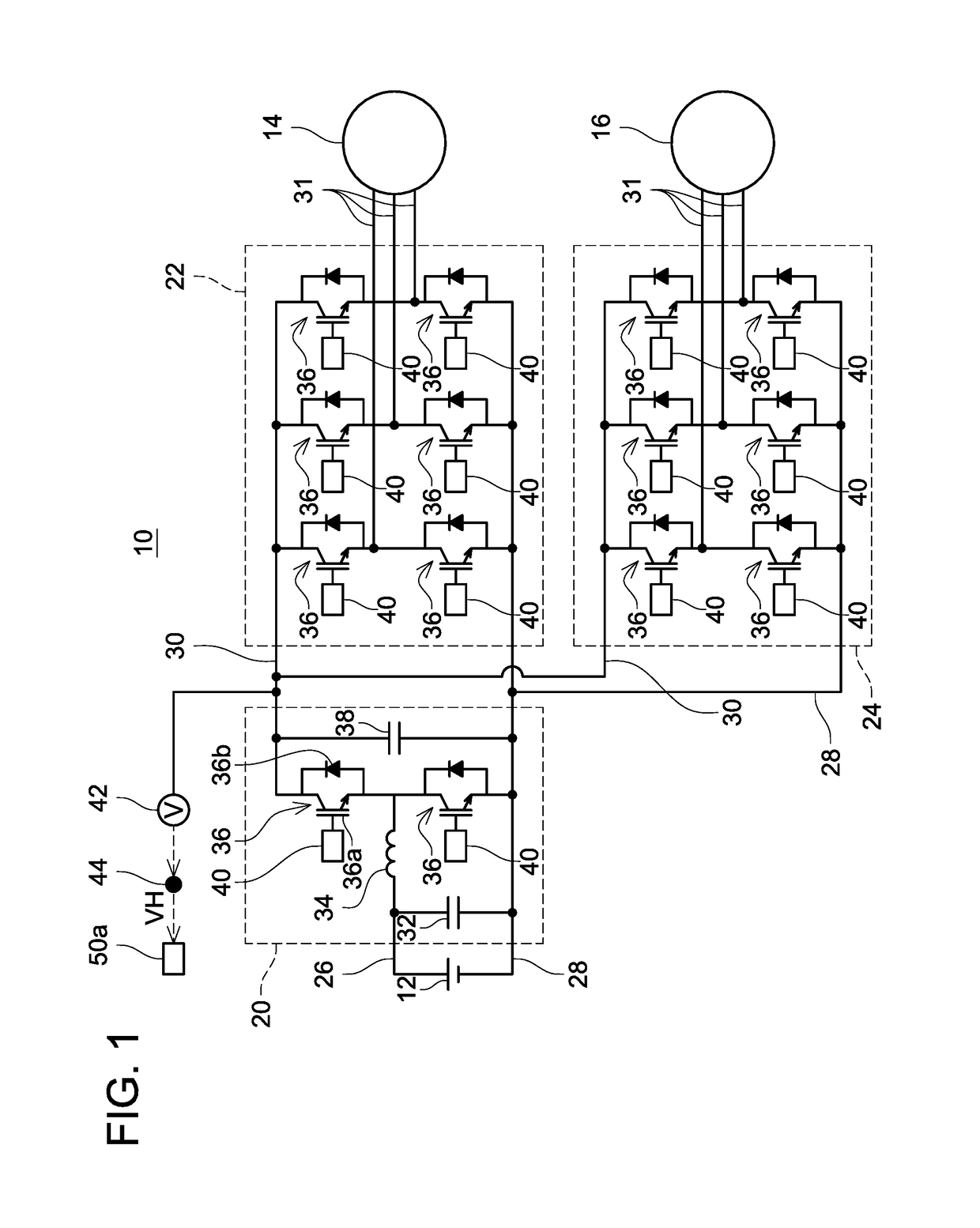
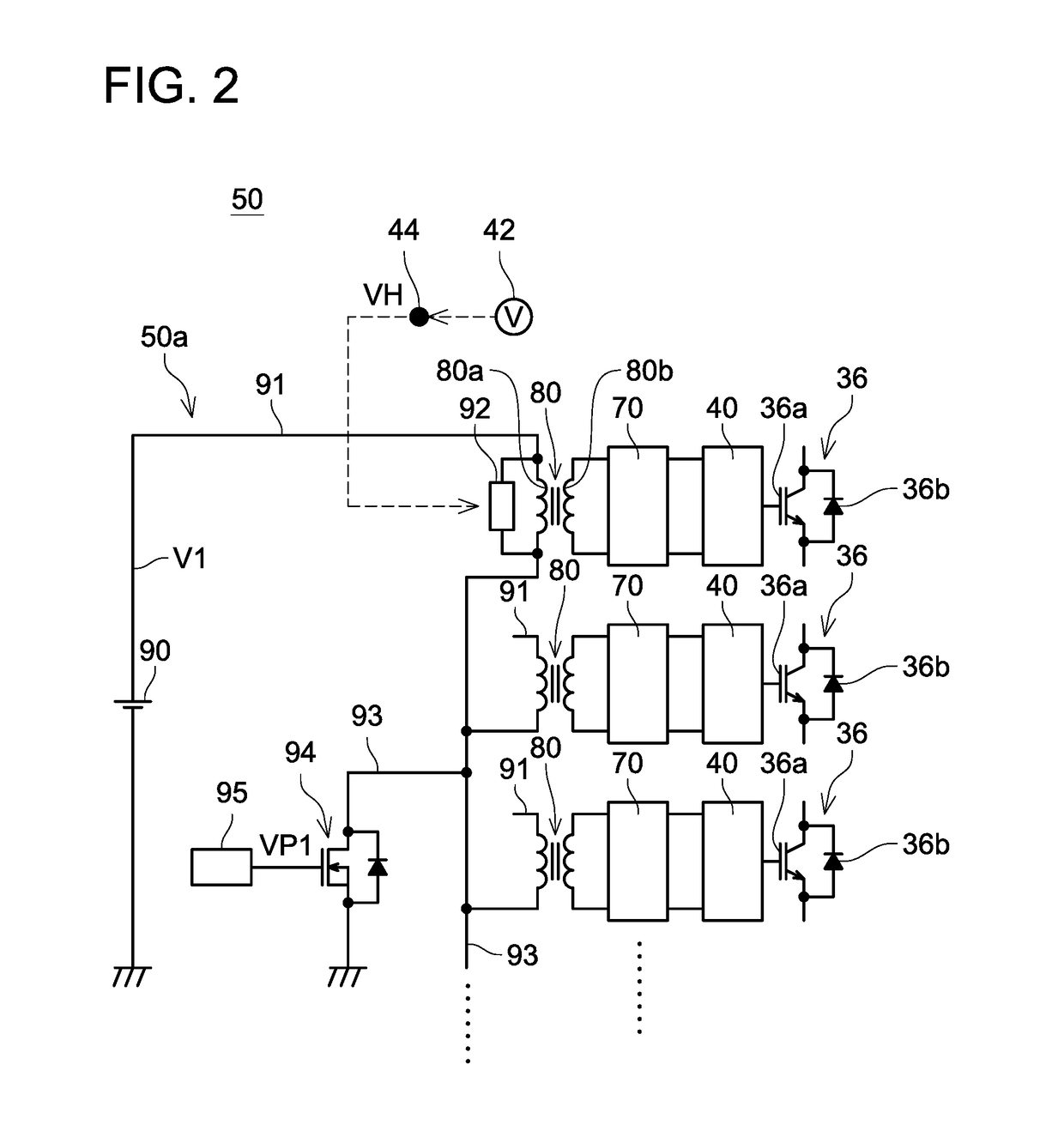
ActiveUS20170257020A1Reduce gate sizeSmall sizeAC motor controlEfficient power electronics conversionWave shapeVoltage regulation
A gate voltage control device includes a detection circuit, a plurality of isolation transformers including primary coils and secondary coils, a primary circuit connected to the primary coils, secondary circuits connected to the secondary coils, and voltage regulator circuits connected to the secondary circuits and gates. The detection circuit transmits signal corresponding to detected physical quantity to the primary circuit. The primary circuit cyclically performs applying a variable voltage in a waveform that corresponds to the signal transmitted from the detection circuit between both ends of each primary coil. Each secondary circuit converts the variable voltage generated in the corresponding secondary coil to a direct voltage. Each voltage regulator circuit is powered by the direct voltage converted by the corresponding secondary circuit as a power source, and changes a change-pattern of the corresponding gate voltage according to a waveform of the variable voltage generated in the corresponding secondary coil.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
SRAM
ActiveCN106653755BReduce gate sizeSmall sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
The invention discloses a static random access memory, which includes at least one static random access storage unit. The gate layout of the static random access memory unit includes first to fourth strip-shaped doped regions, a recessed gate line, a first gate line and a second gate line. The first to fourth strip-shaped doped regions are sequentially arranged in the substrate and separated from each other. The concave gate line intersects the first to the fourth strip doped regions. The first to fourth strip-shaped doped regions are disconnected at intersections with the recessed gate lines. The first gate line intersects the first strip-shaped doped region and the second strip-shaped doped region. The first strip-shaped doped region is disconnected from the second strip-shaped doped region at the intersection with the first gate line. The second gate line intersects the third strip-shaped doped region and the fourth strip-shaped doped region. The third strip-shaped doped region is disconnected from the fourth strip-shaped doped region at the intersection with the second gate line.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
A method for preparing 10nm T-grid by electron beam exposure
InactiveCN105047548BImprove stabilityReduce experimental errorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMetal electrodesReactive-ion etching
The present invention belongs to the technical field of micro-electronic components, and especially provides a method for manufacturing a 10-nanometer T-shaped gate through electron beam lithography. The method adopts the technology combining electron beam overlap lithography with reactive ion etching, and comprises the steps of applying electron beam photoresist to the surface of an epitaxial layer of a device substrate in a spin coating way, designing a layout through electron beam lithography, performing metal evaporation, stripping the evaporated metal, then performing reactive ion etching to form a table top, applying the electron beam photoresist to a sample with the etched table top in a spin coating way, utilizing the precise electron beam overlap lithography to form a T-shaped morphology, performing metal evaporation again, and stripping the evaporated metal to form a T-shaped metal electrode, thereby manufacturing a 10-nanometer T-shaped gate between a source electrode and a drain electrode of the device through the electron beam lithography. The method of the present invention not only can greatly reduce the foot size of the T-shaped gate, but also can manufacture the T-shaped gate having a very wide head, thereby reducing gate resistance of the device and raising cut-off frequency of the device, therefore, the method has important significance in a process for manufacturing GaN-based and InP-based high-electron-mobility transistors.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
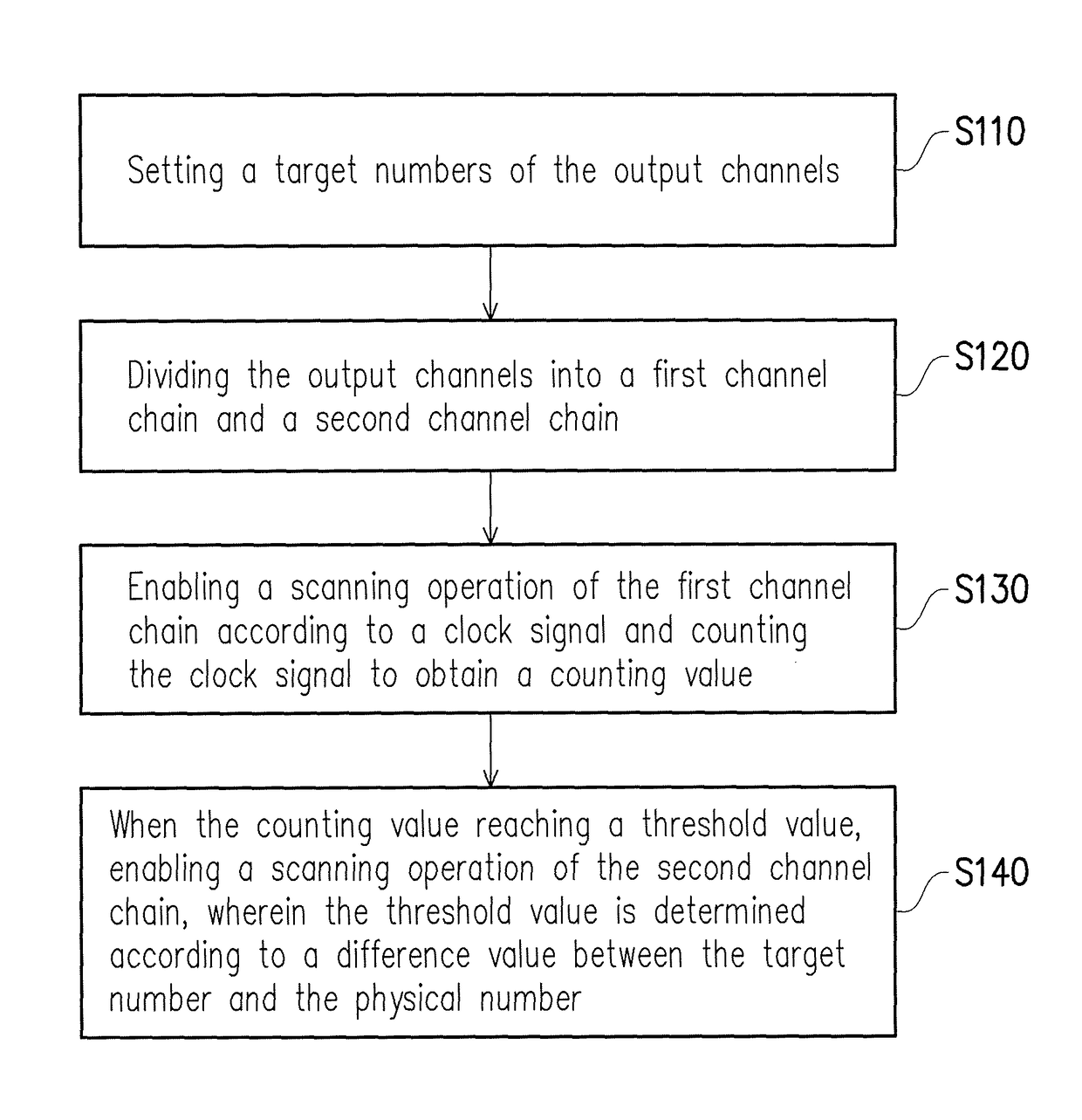
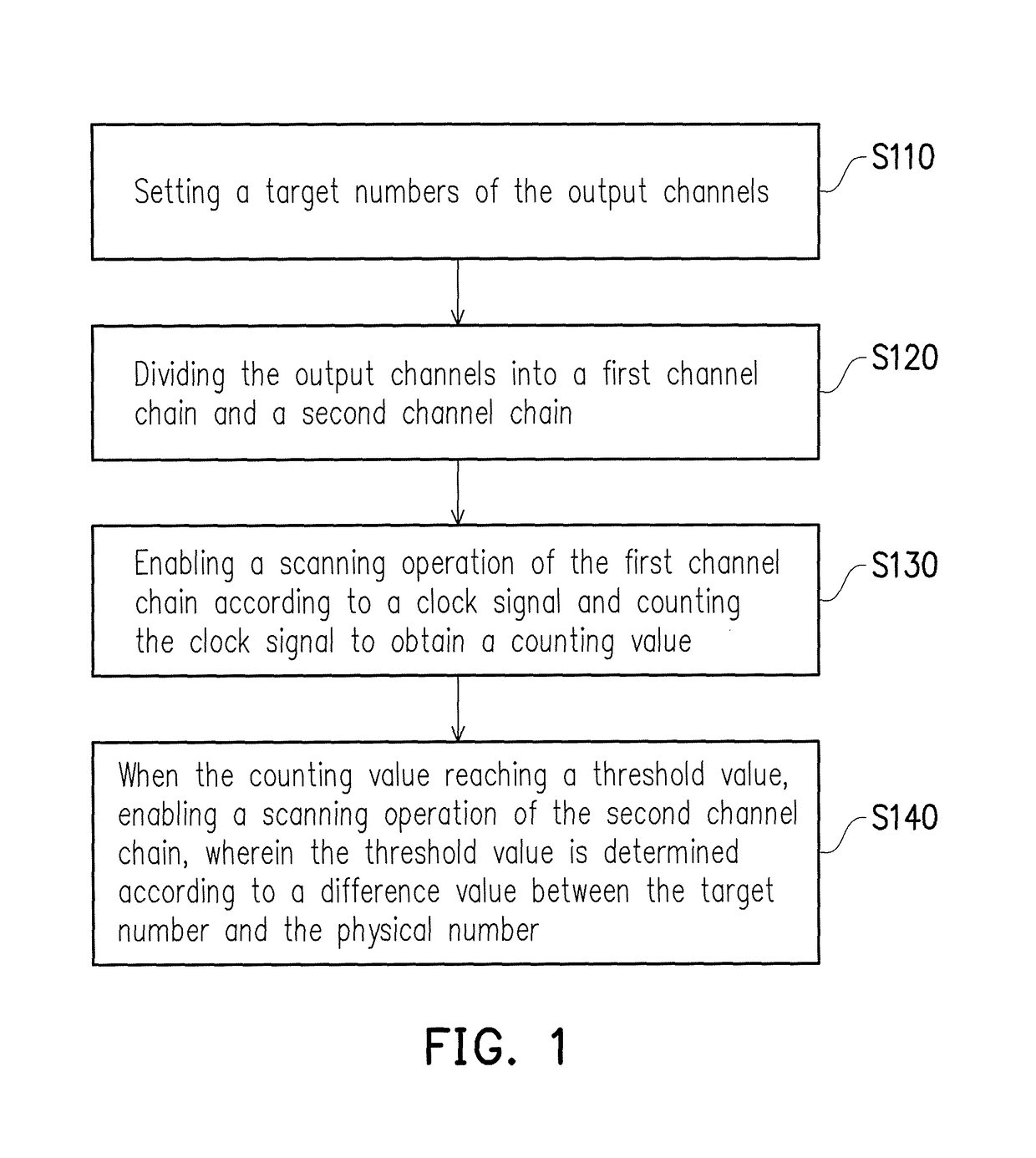
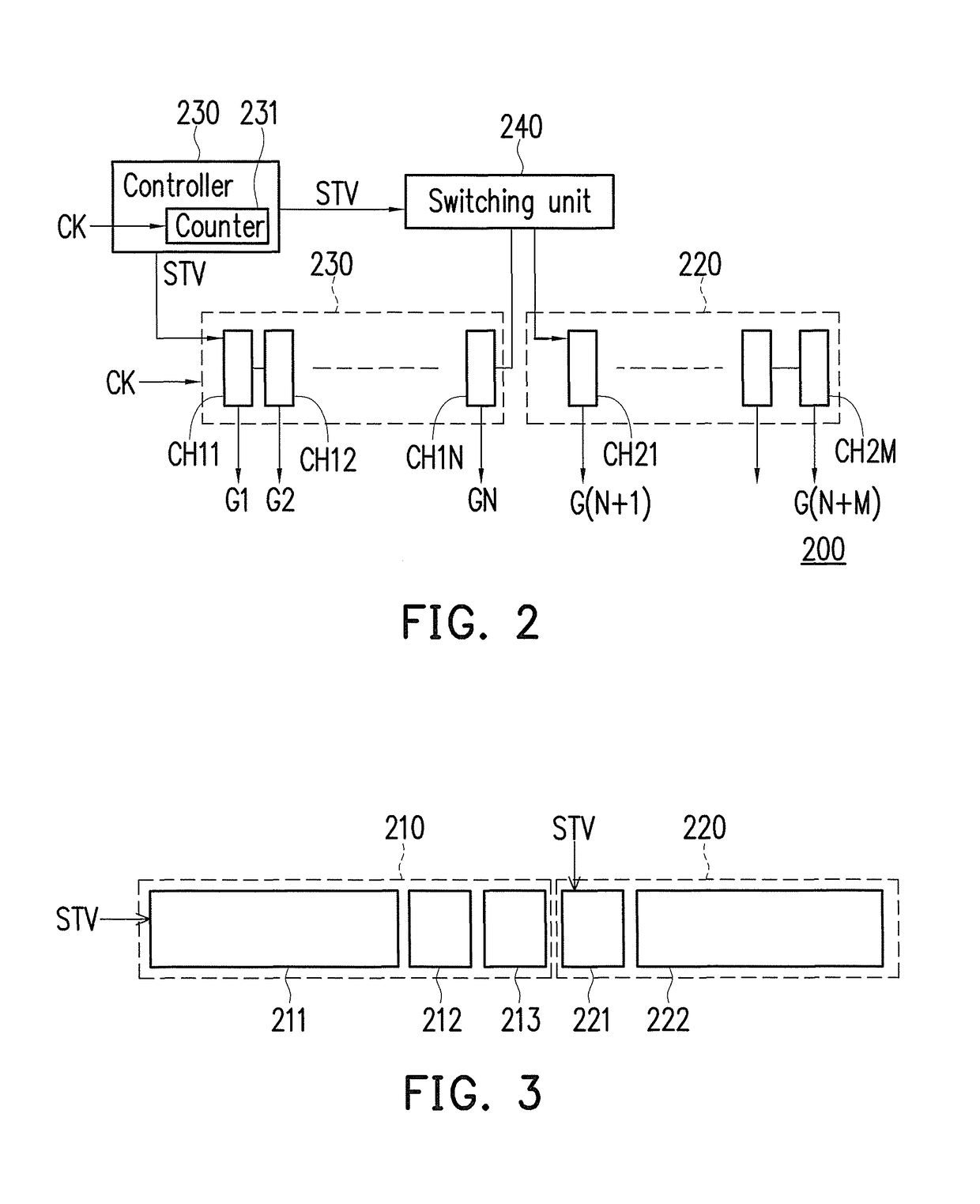
Gate driver and method for adjusting output channels thereof
A gate driver and a method for adjusting output channels thereof are provided. The method includes: setting a target number of the output channels; dividing the output channels into a first channel chain and a second channel chain; enabling a scanning operation of the first channel chain according to a clock signal and counting the clock signal to obtain a counting value; and when the counting value reaching a threshold value, enabling a scanning operation of the second channel chain, wherein the threshold value is determined according to a difference value between the target number and the physical number.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
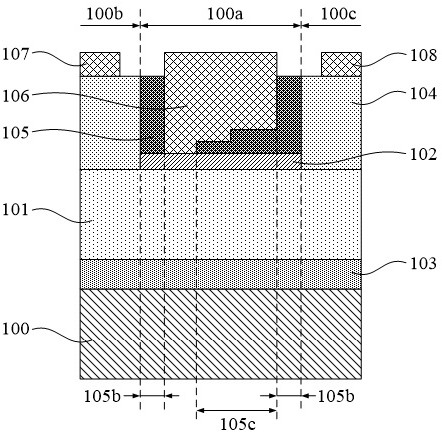
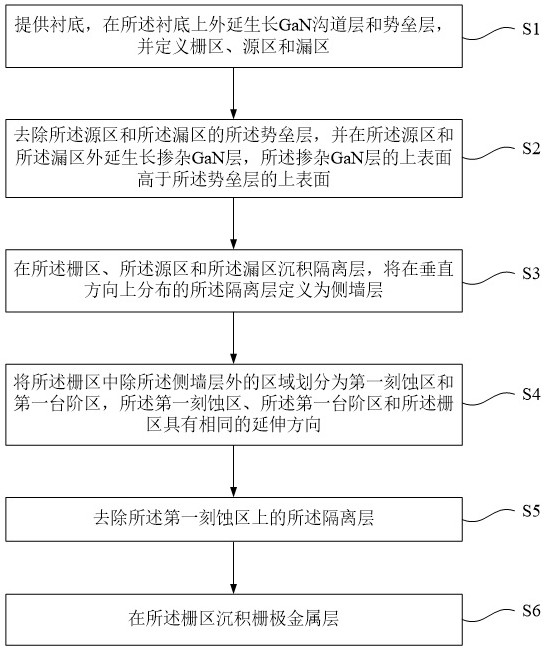
Step-type gan gate device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111508840BImprove pressure resistanceReduced precision requirementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIsolation layerEngineering
The invention provides a stepped GaN gate device and its preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: providing a substrate, growing a GaN channel layer and a barrier layer, defining gate, source, and drain regions; removing the source-drain region barrier layer, and grow a doped GaN layer in the source and drain regions, and the upper surface of the doped GaN layer is higher than the barrier layer; deposit an isolation layer, and define the isolation layer in the vertical direction as a side wall layer; except the side wall layer in the gate area The area is divided into a zero etching area and a zero step area, and the zero etching area, the step area and the gate area have the same extension direction; the isolation layer of the zero etching area is removed; and a gate metal layer is deposited in the gate area. The present invention forms the step-type field plate of the grid through the isolation sidewall process, and at the same time reduces the size of the grid, and also improves the withstand voltage performance of the device by using the step-type field plate. The size of the grid in the invention is controllable, and the precision of the photolithography equipment is not high; the stepped field plate structure and the grid structure are formed together, and the process conditions are simple and feasible, and the repeatability is high.
Owner:浙江集迈科微电子有限公司
Decoder, data driver and display device
ActiveCN102163400BReduce gate sizeWide voltage rangeStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Image display device and manufacturing method thereof
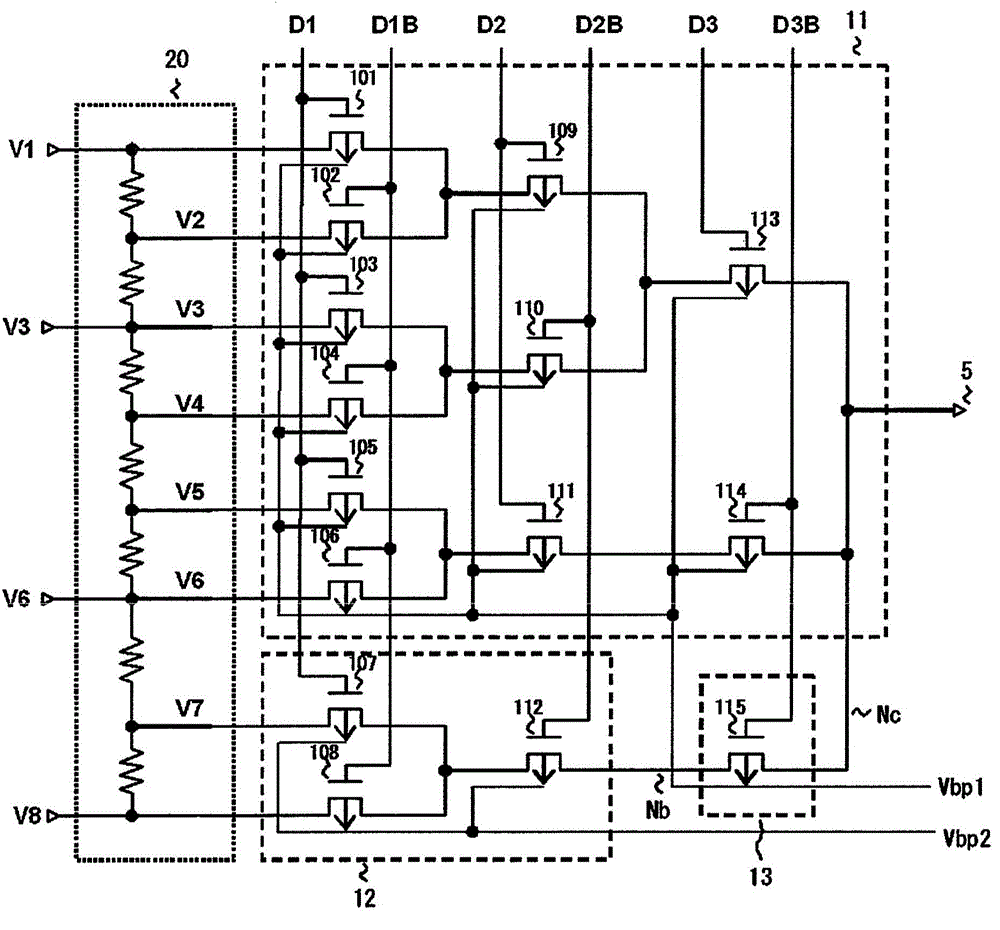
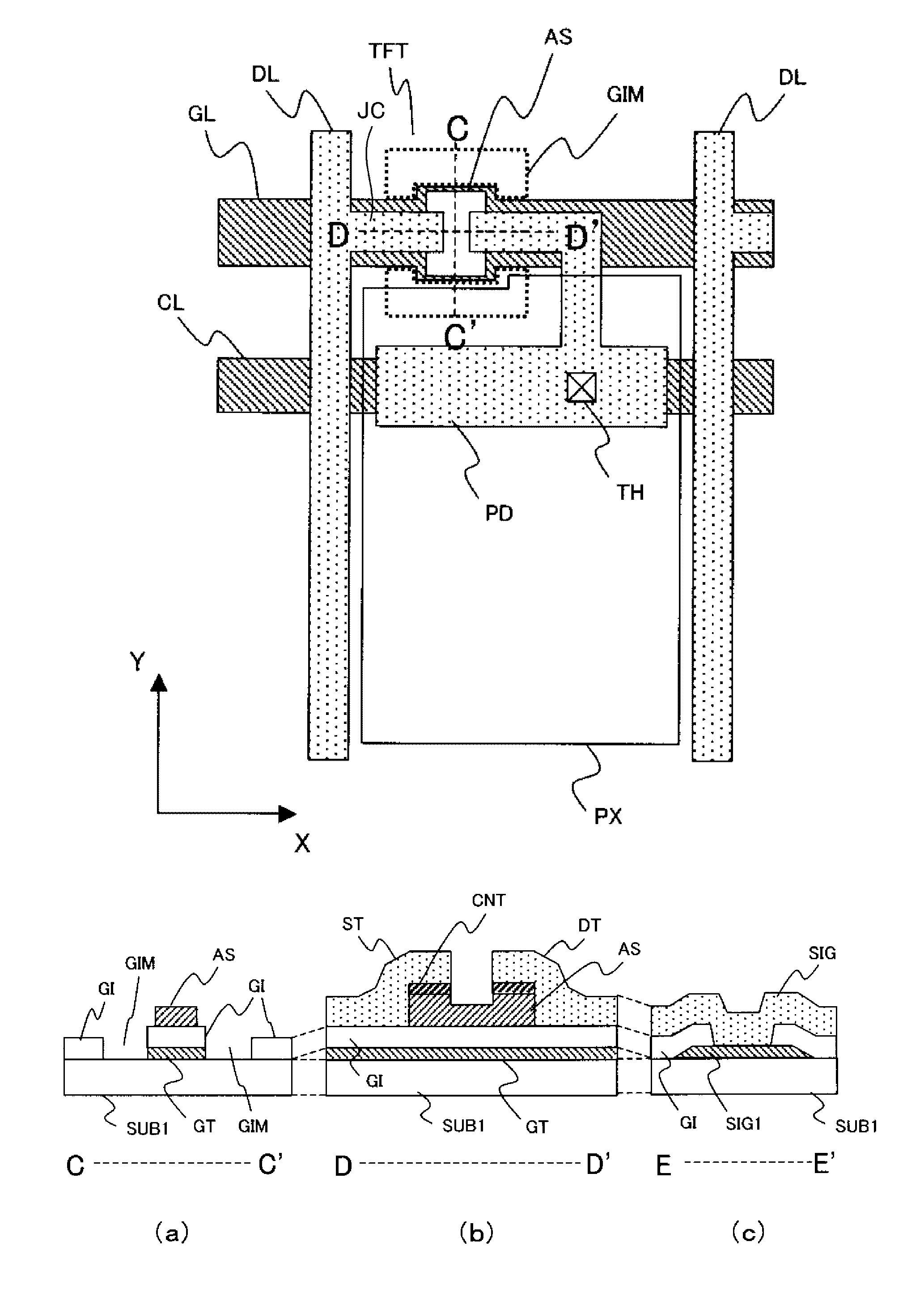
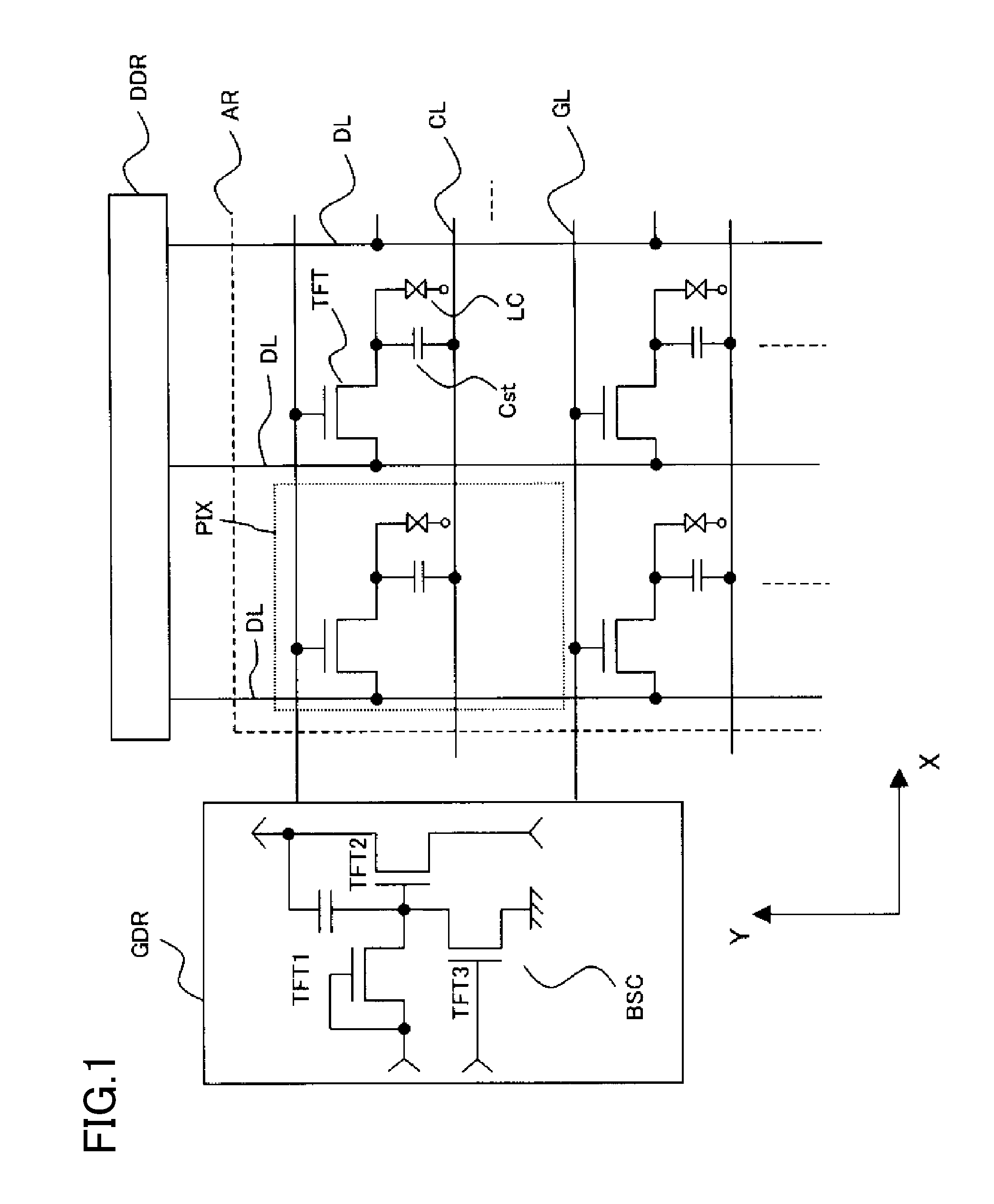
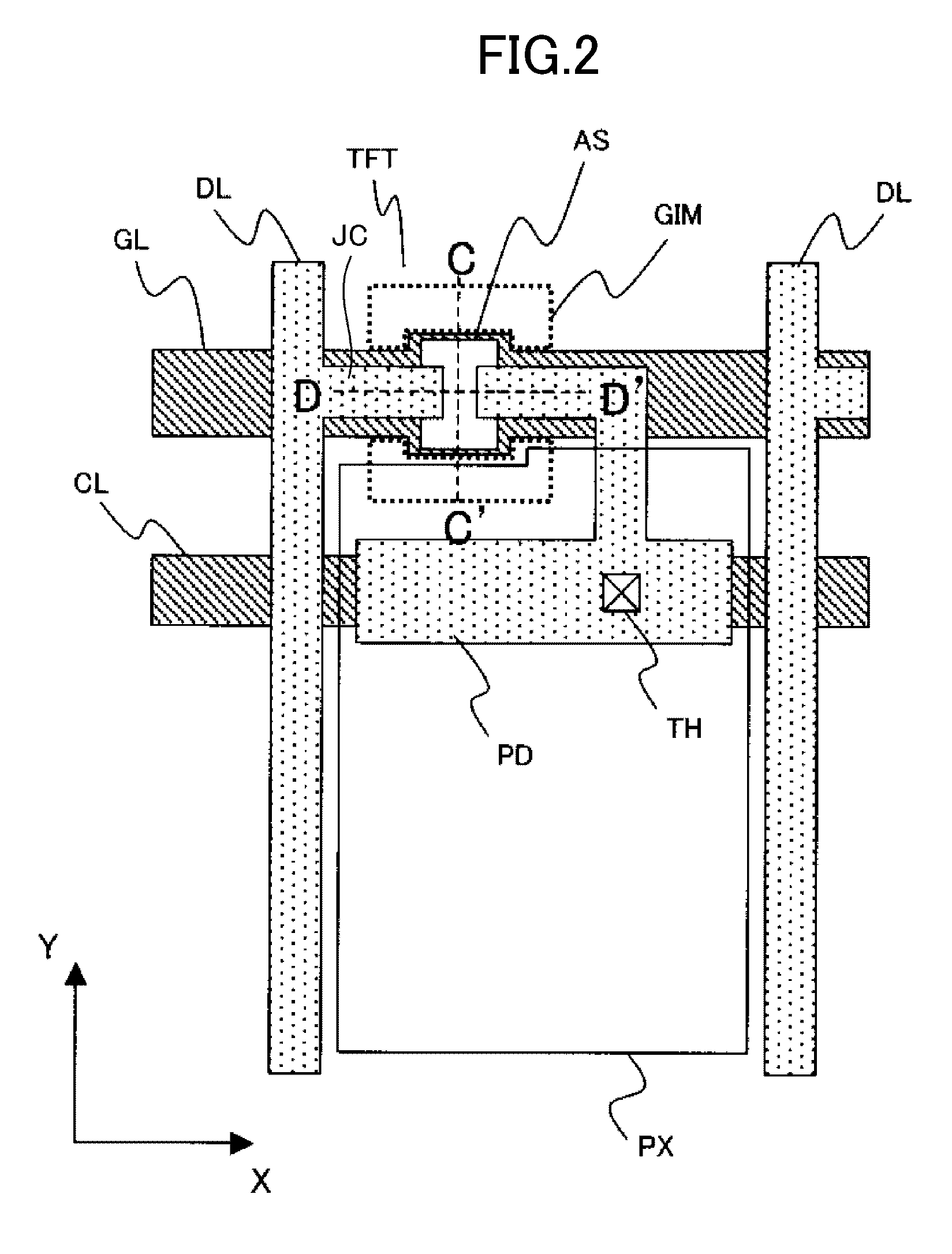
ActiveUS8436358B2Total current dropIncrease the aperture ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceChannel width
Provided is an image display device including thin film transistors on a substrate, including: gate lines and drain lines intersecting the gate lines, each thin film transistor having, in a channel region, a laminate structure in which a gate electrode, a gate insulating film, and a semiconductor layer are laminated in the stated order from the substrate side; and a pair of removal regions in which parts of the gate insulating film are removed, which are formed on both sides of the gate electrode and formed in a channel width direction of the channel region, in which when W represents a width of the gate electrode in the channel width direction of the channel region, and R represents a width of the gate insulating film in the channel width direction, which is sandwiched between the pair of removal regions, R≧W is satisfied.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com