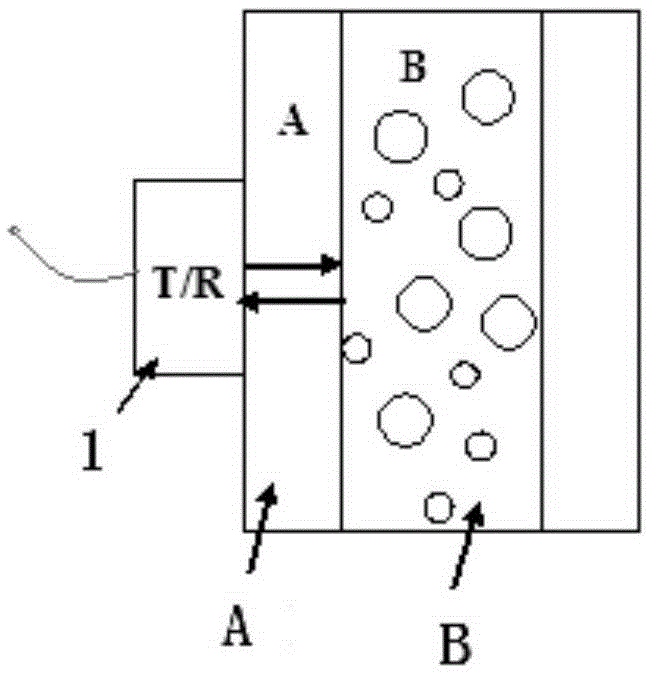
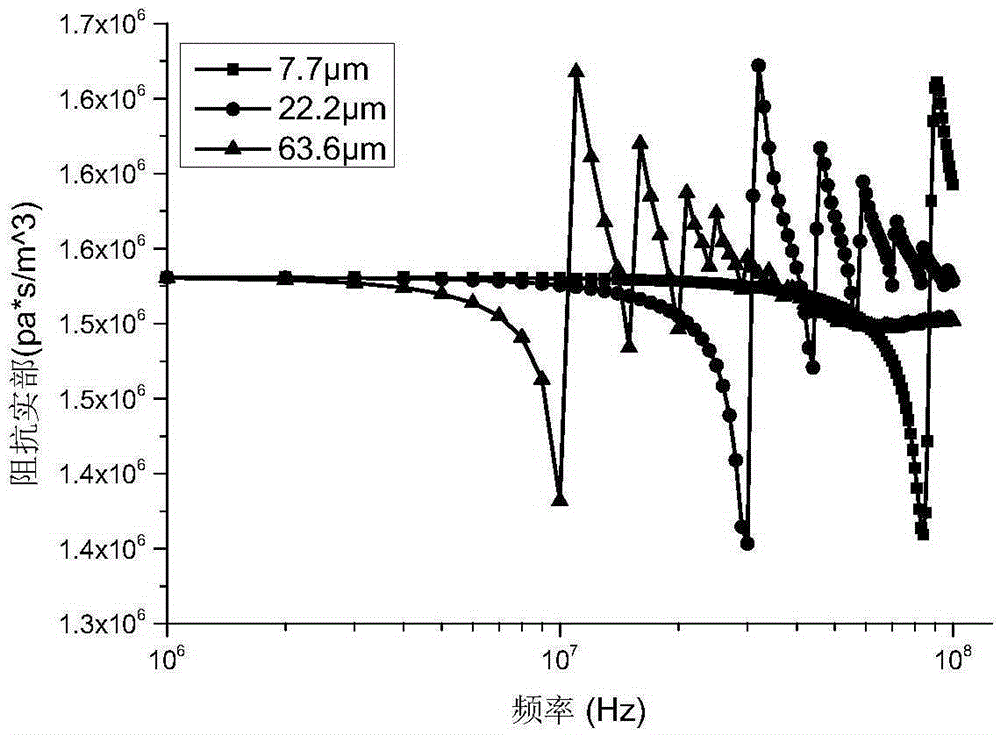
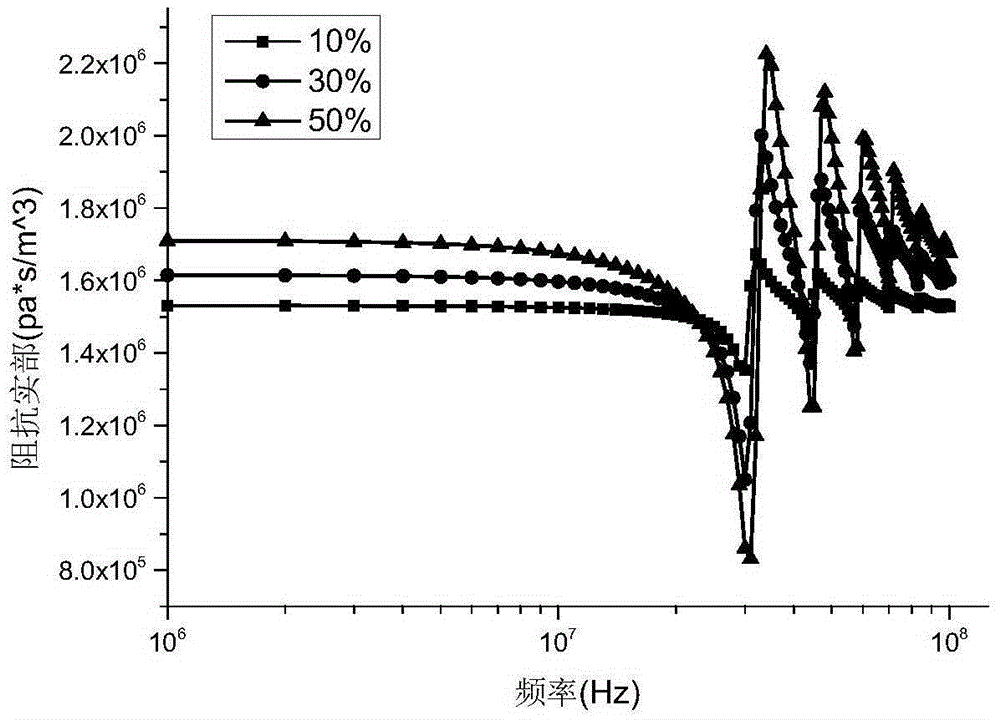
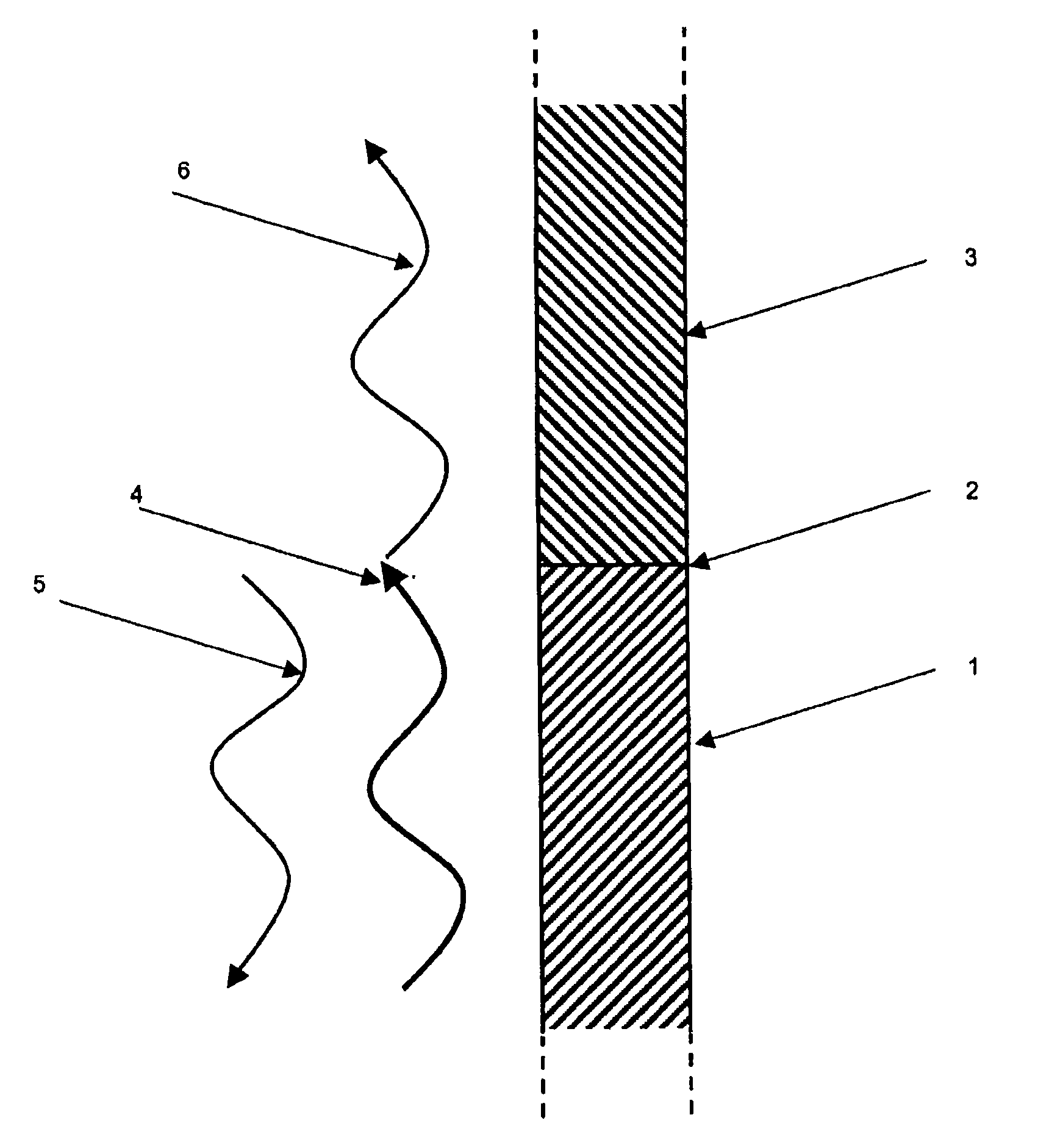
Patents
Literature
202 results about "Acoustical impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
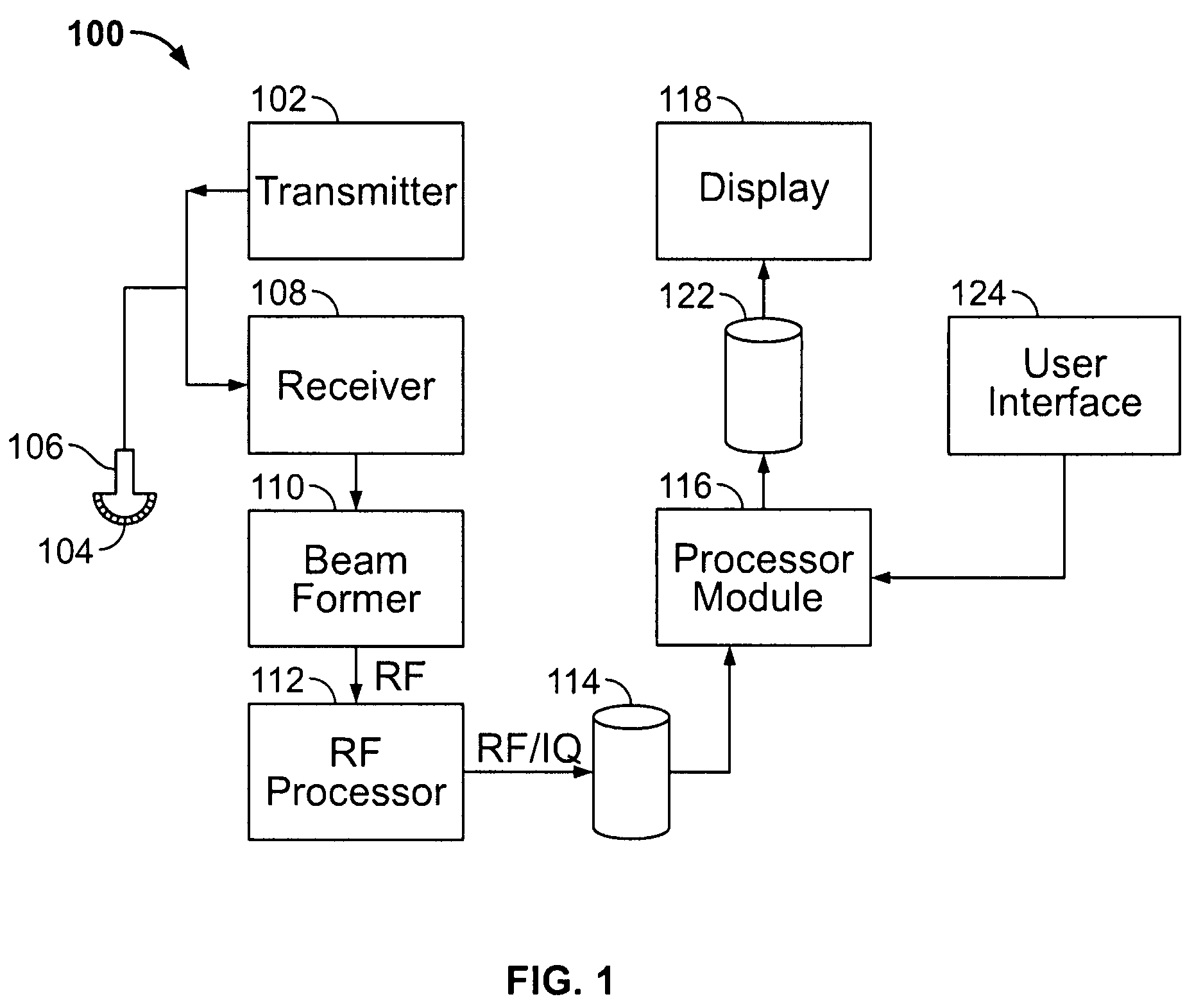
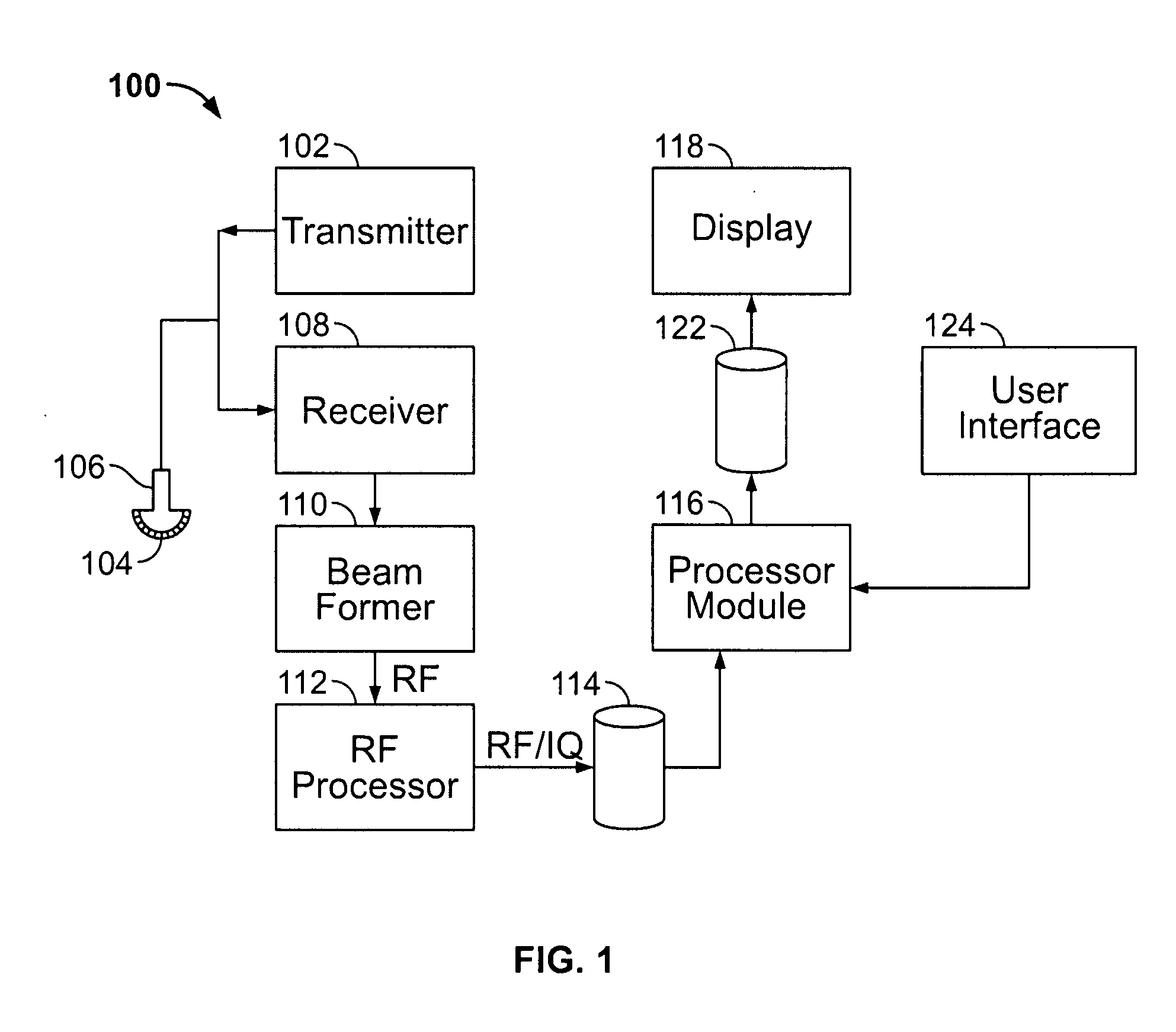
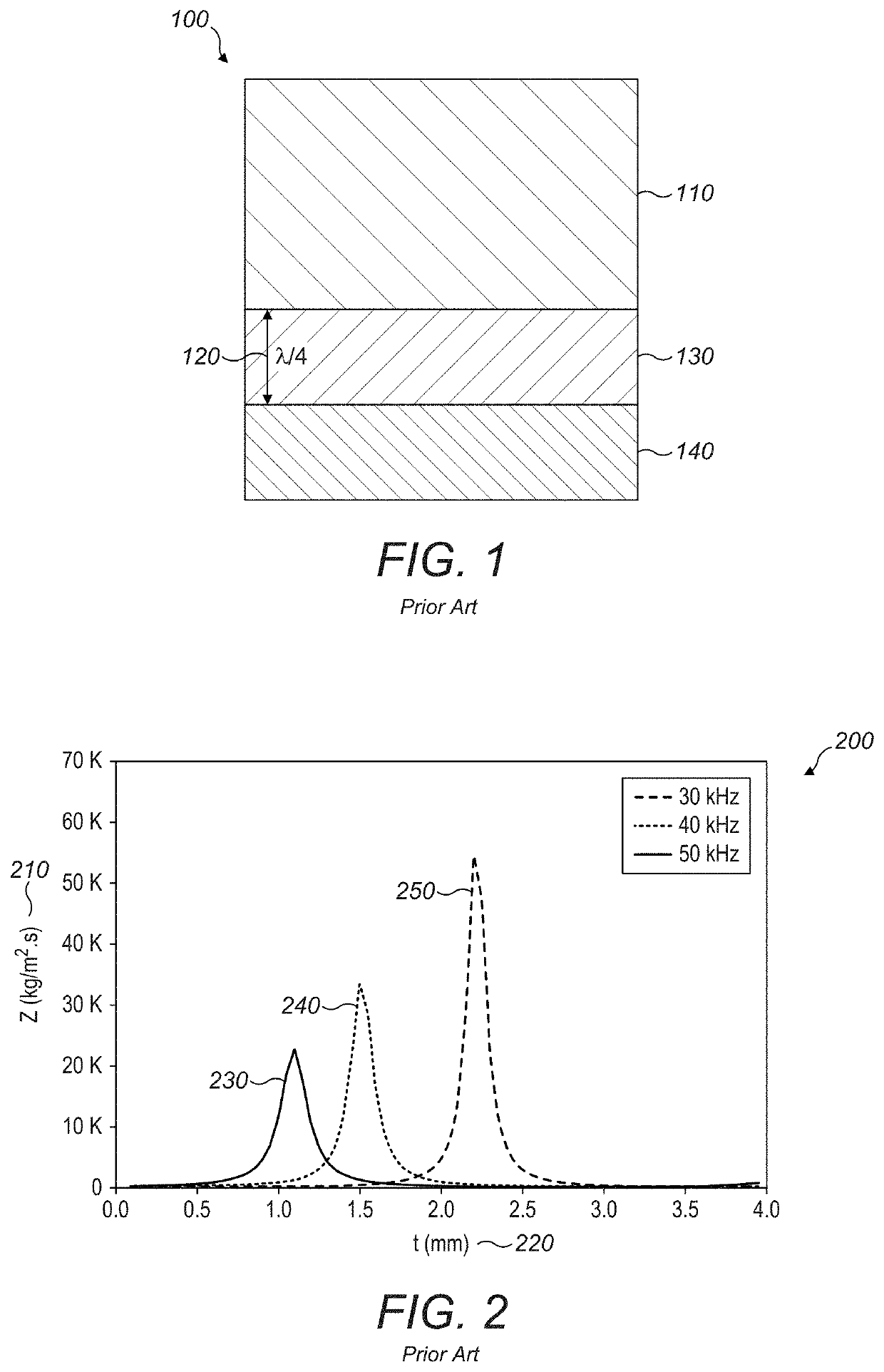
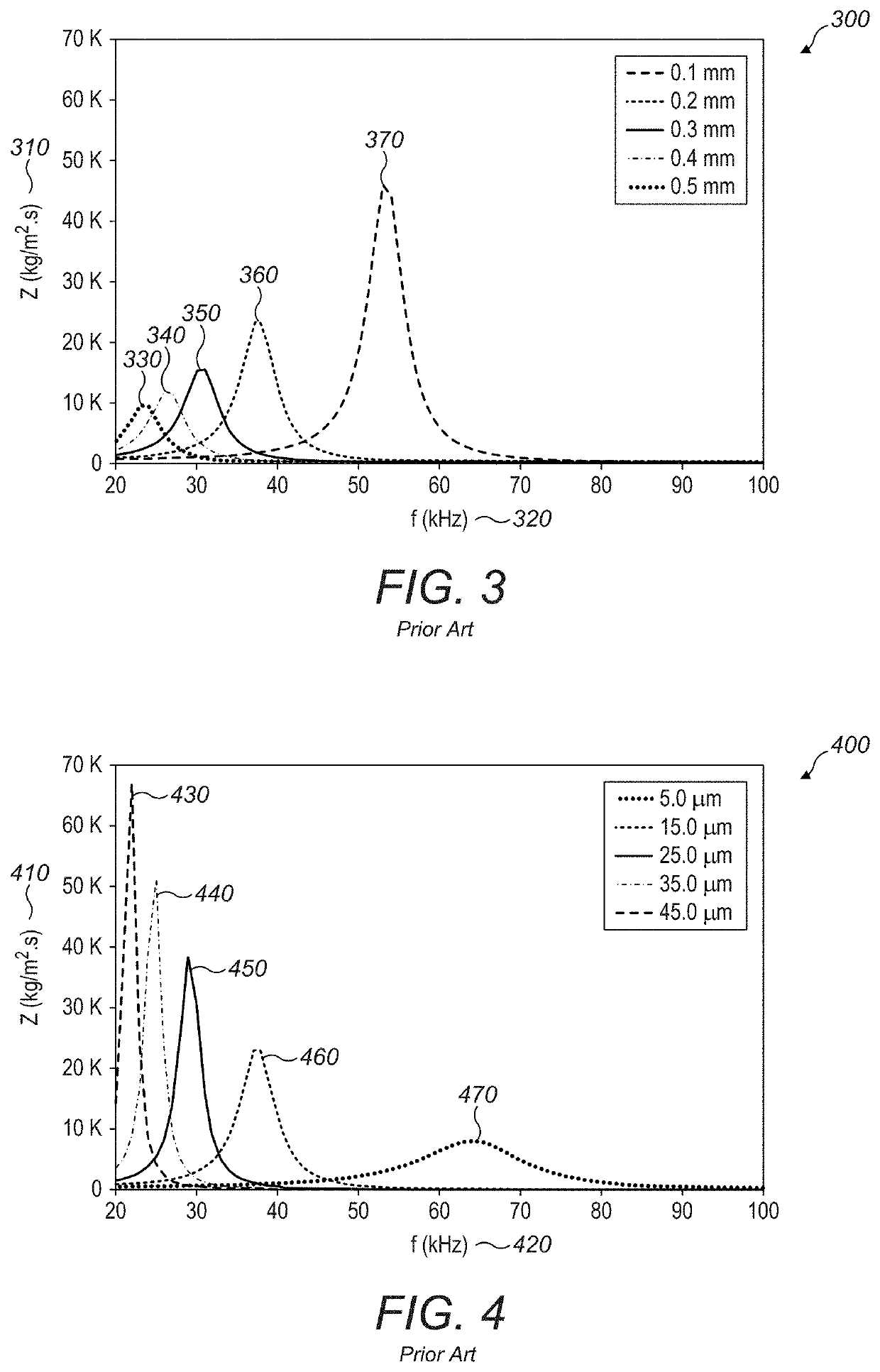
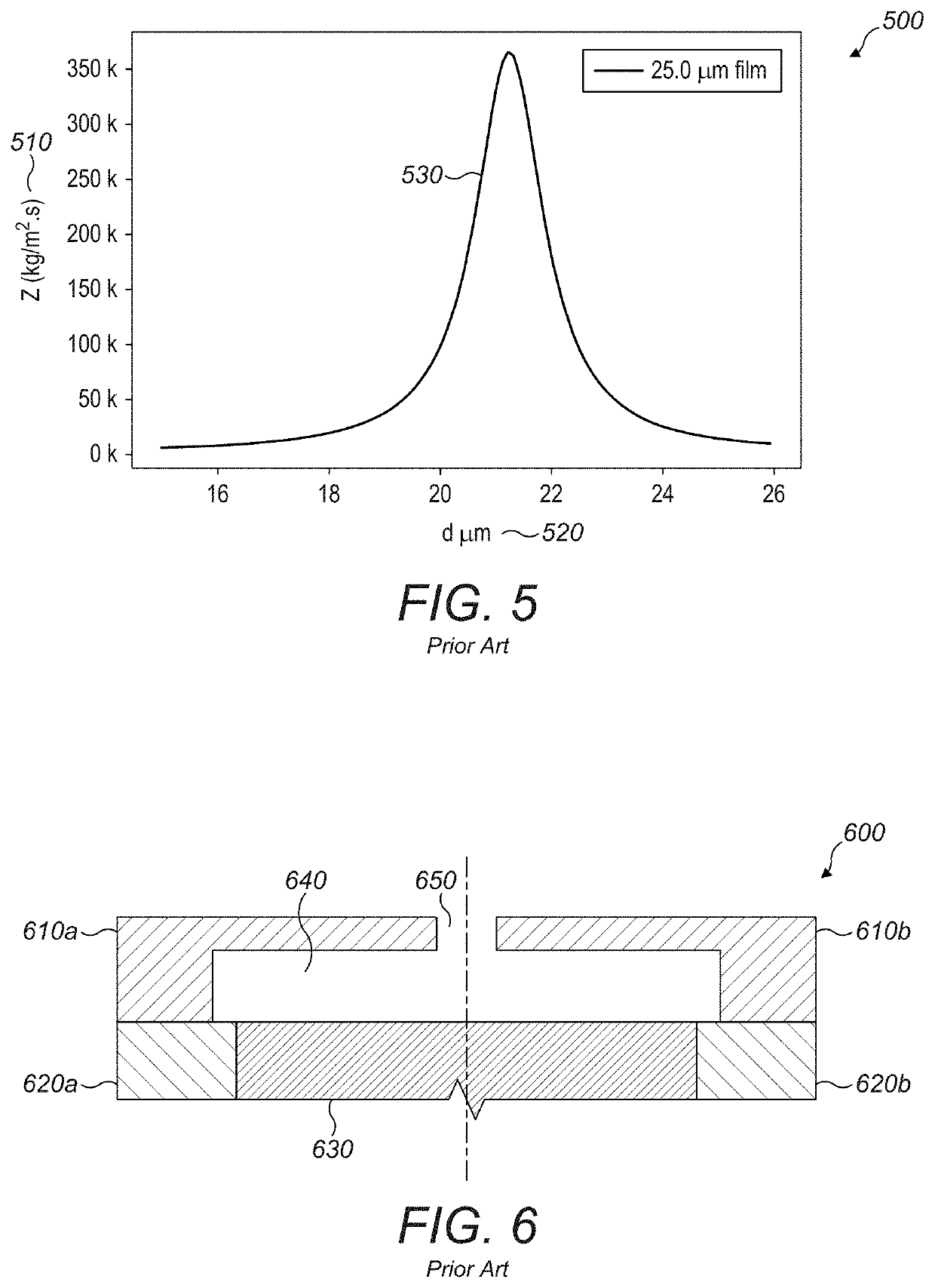
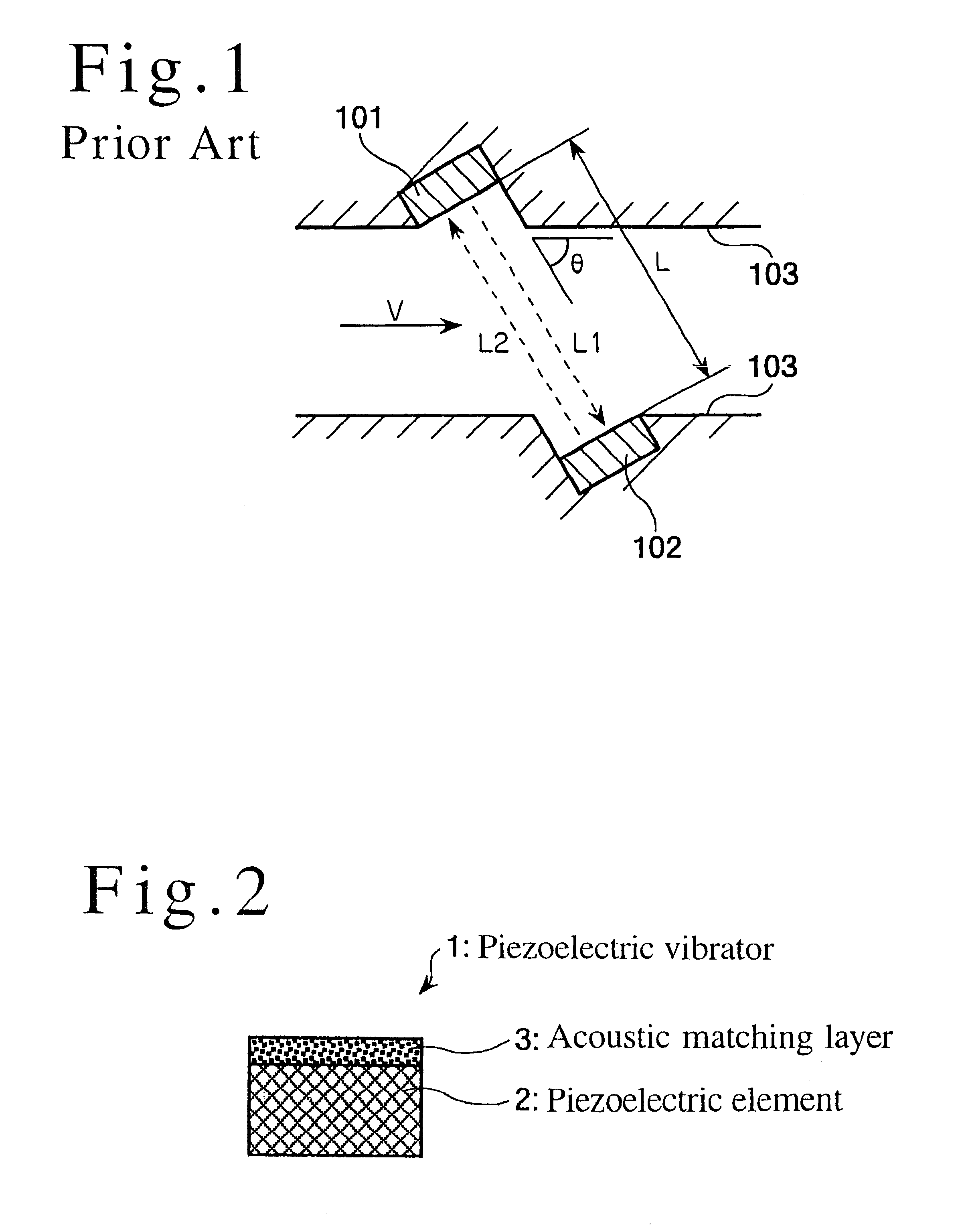
Acoustic impedance ( Z) is a physical property of tissue. It describes how much resistance an ultrasound beam encounters as it passes through a tissue. Acoustic impedance depends on: the density of the tissue (d, in kg/m 3)
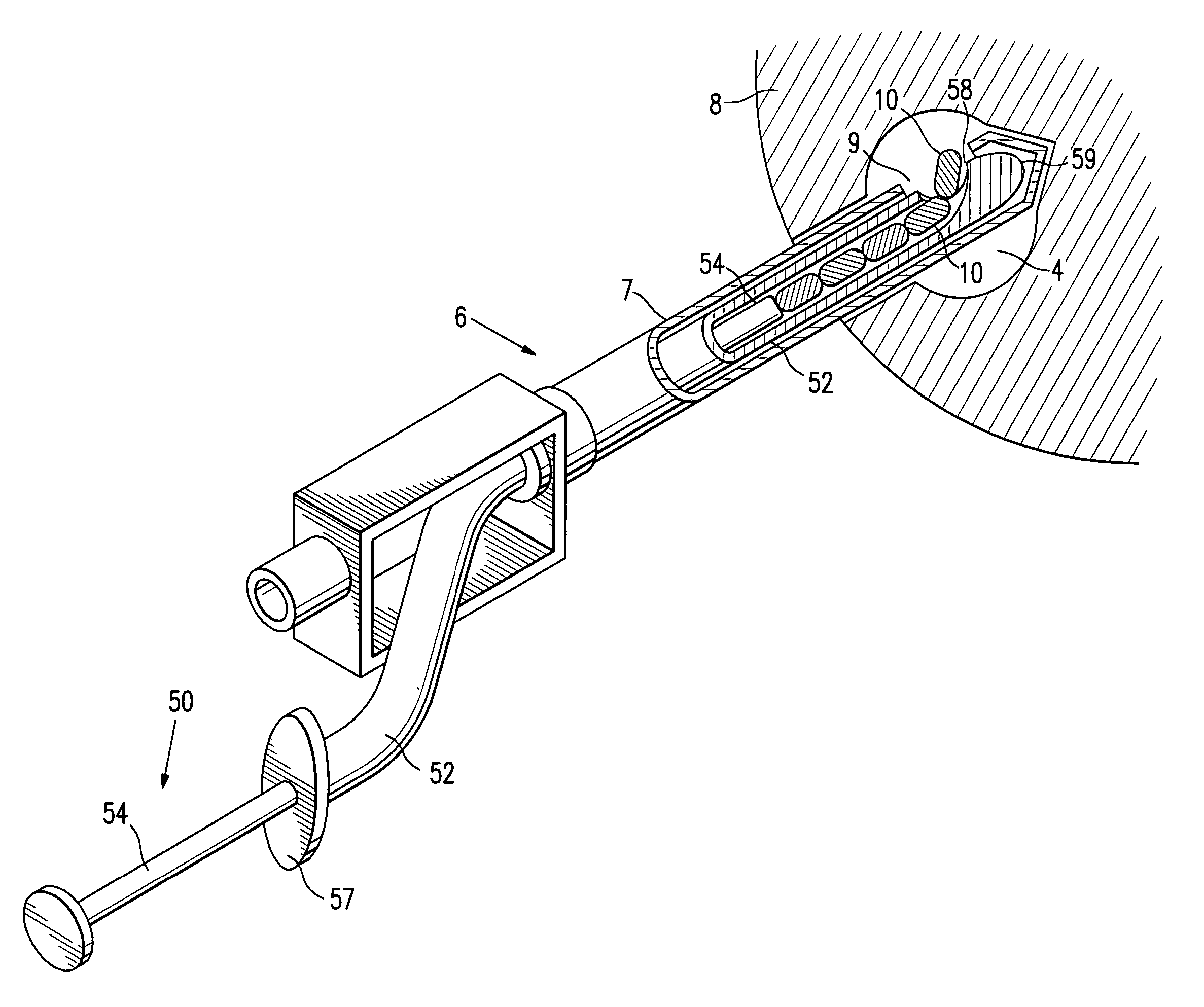
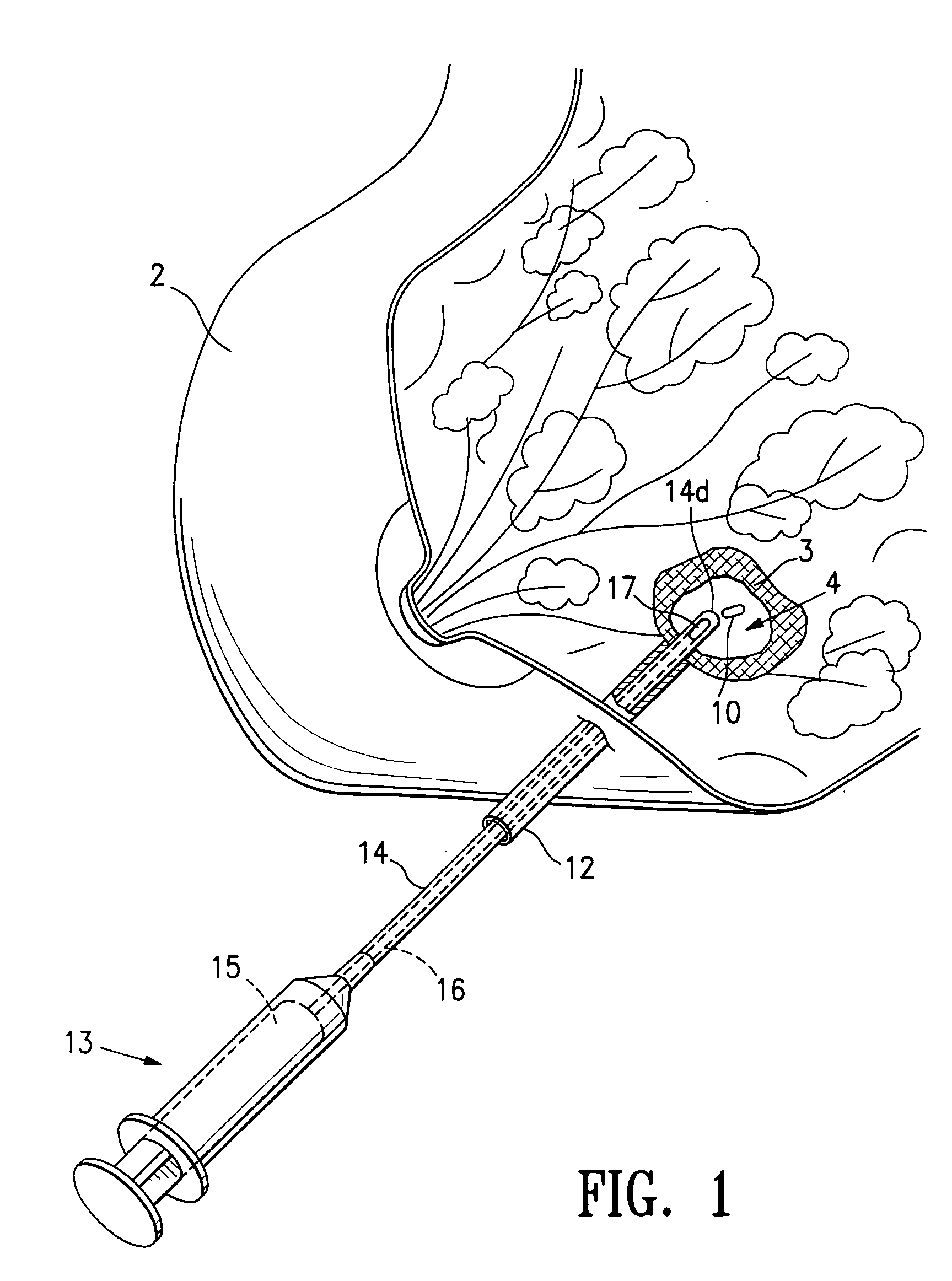
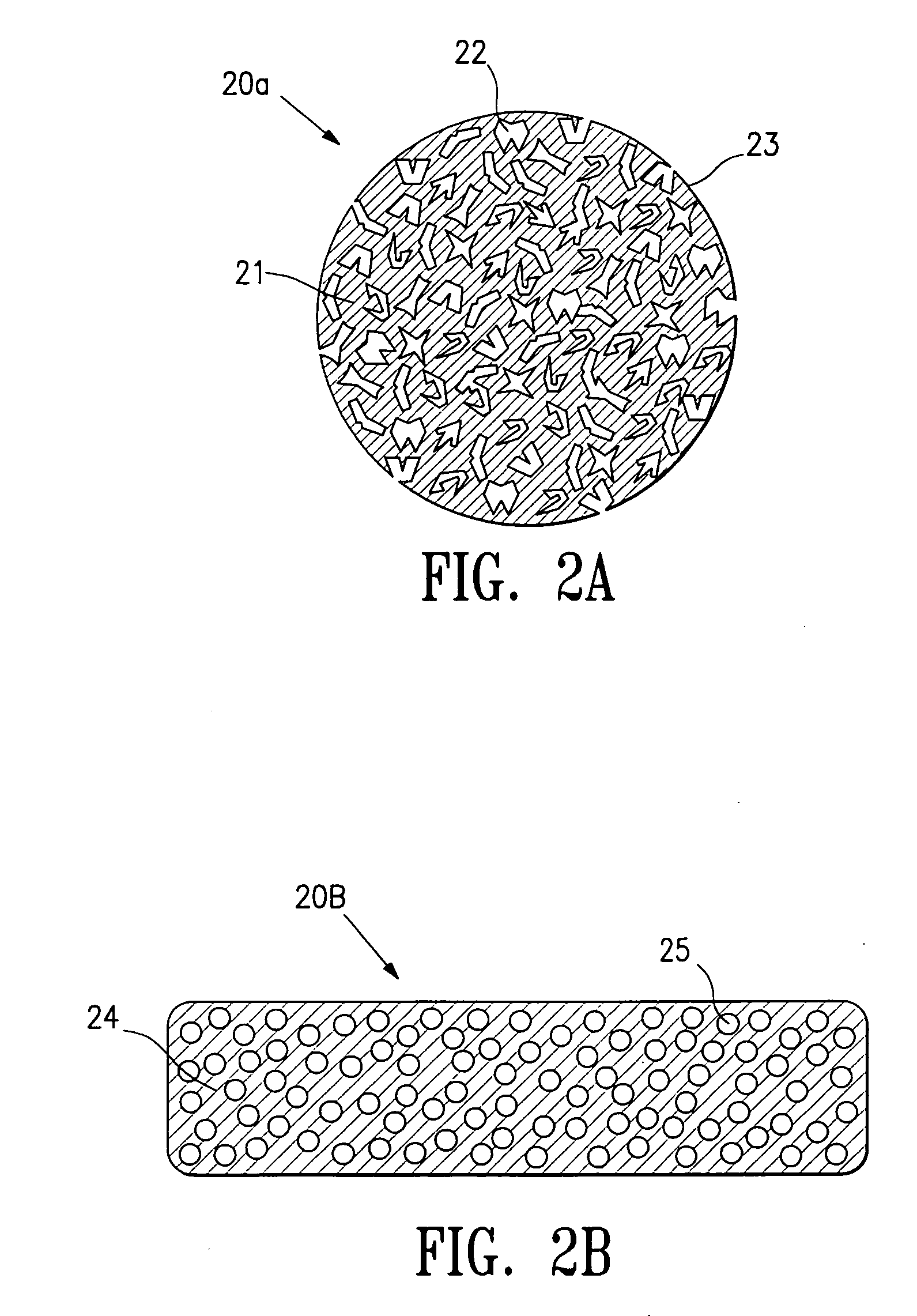
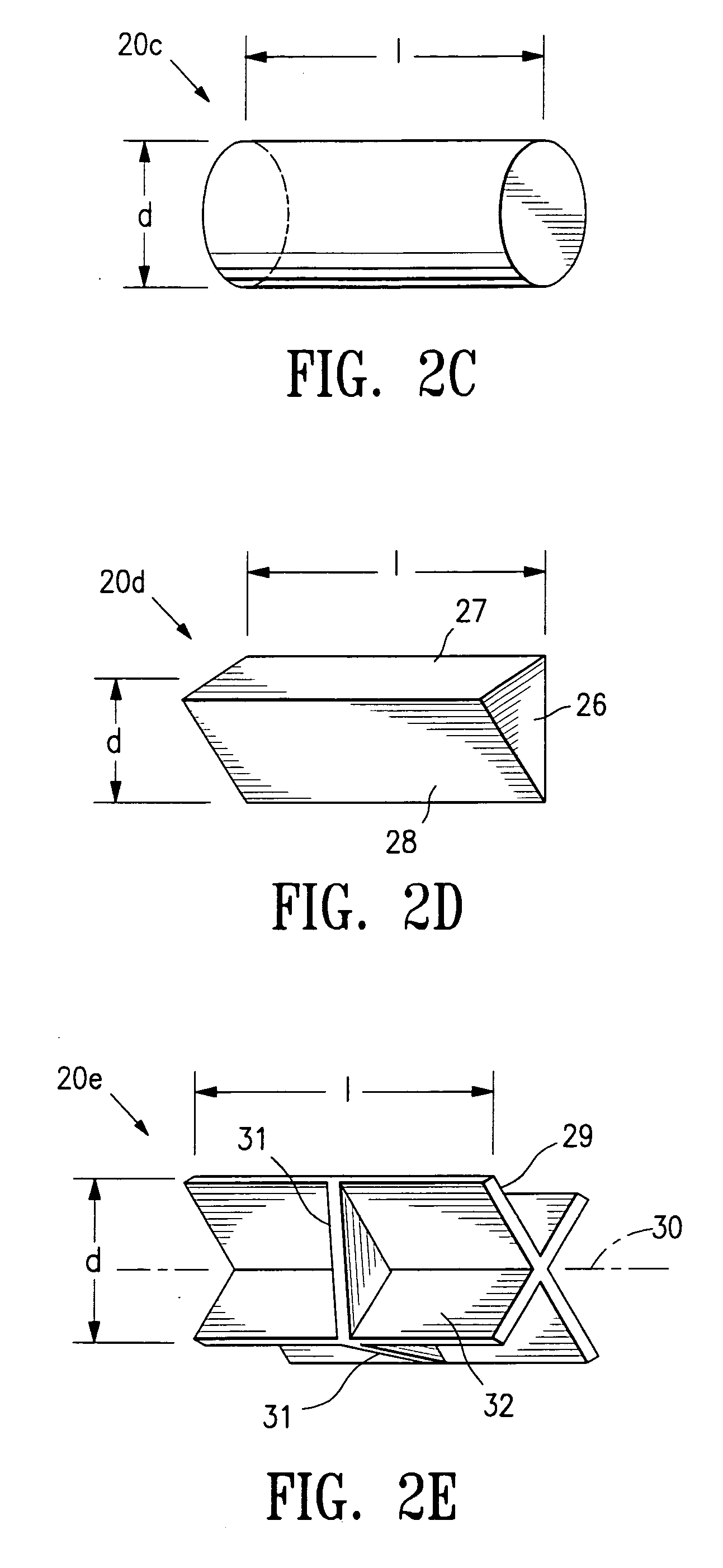
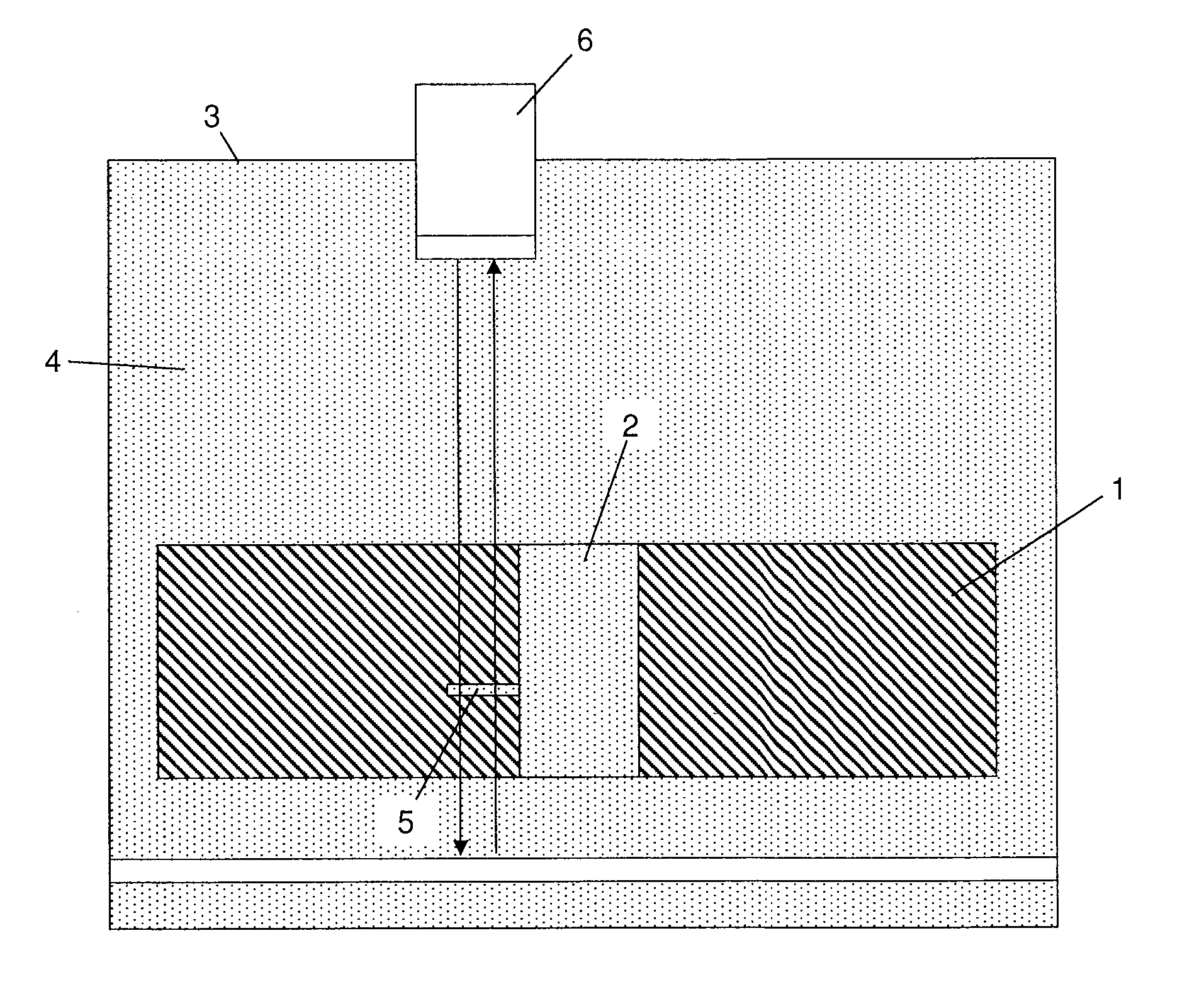
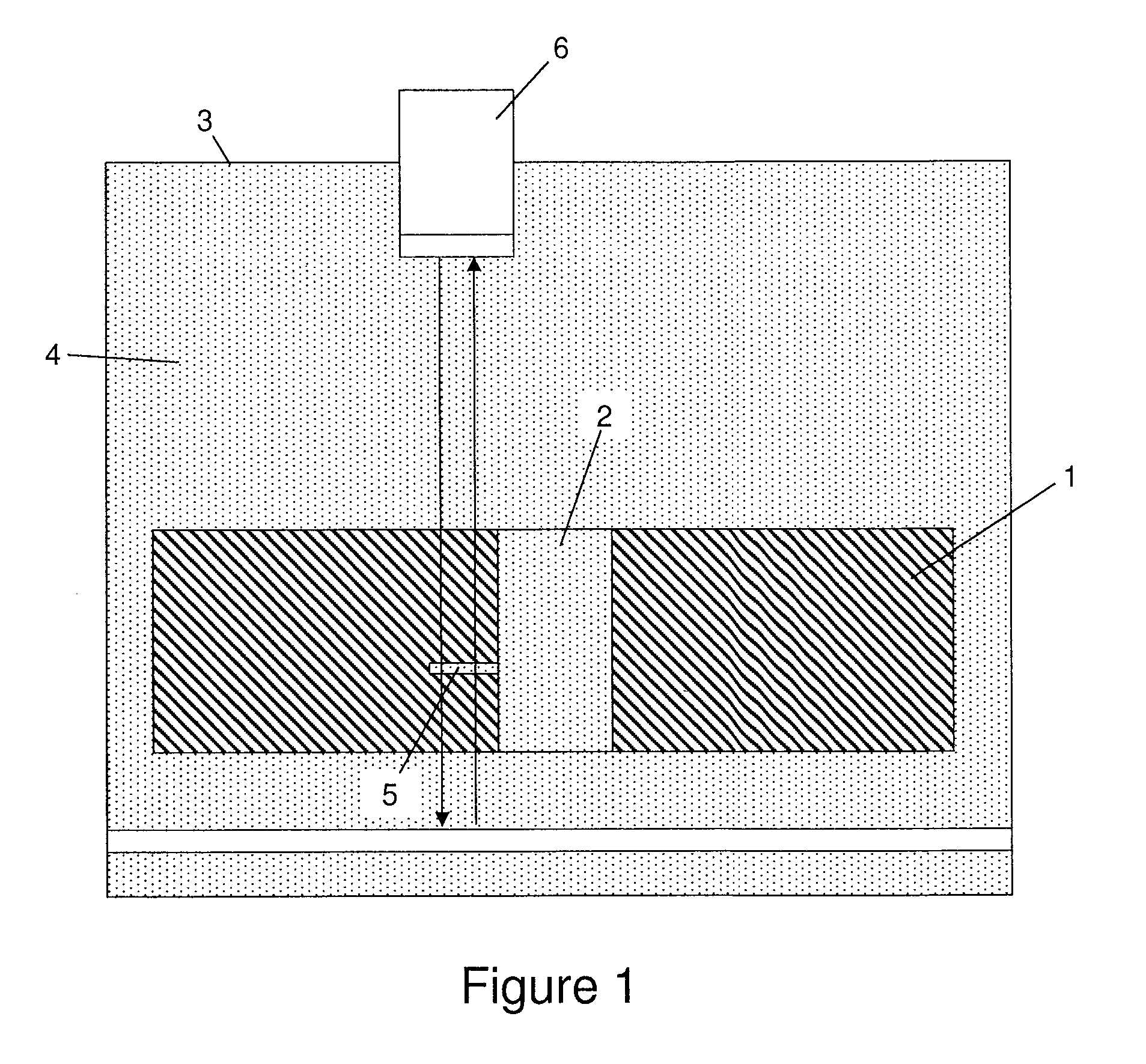
Tissue site markers for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS6993375B2Enhance acoustical reflective signature and signalEasy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesContrast levelIn vivo
Owner:SENORX
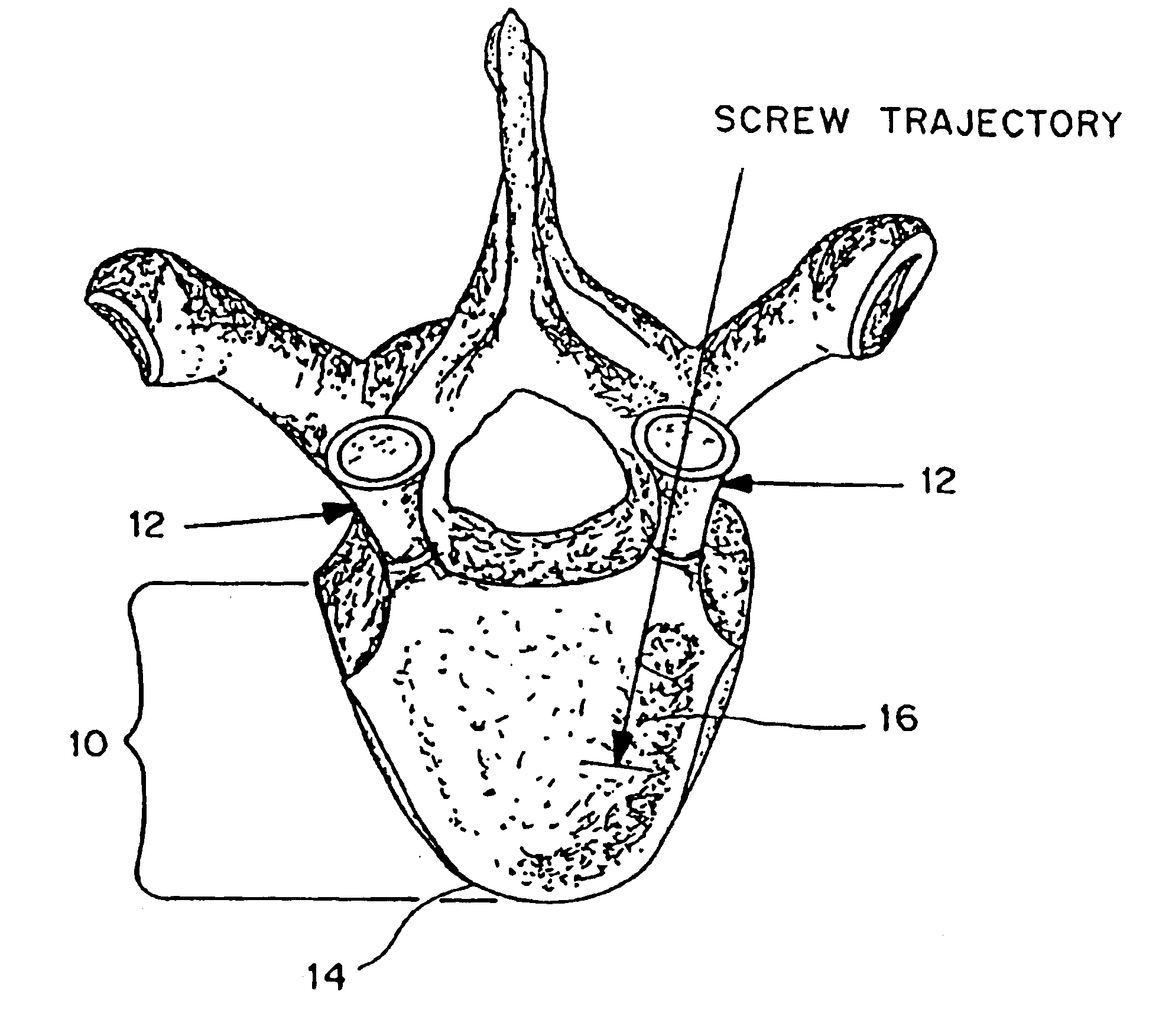
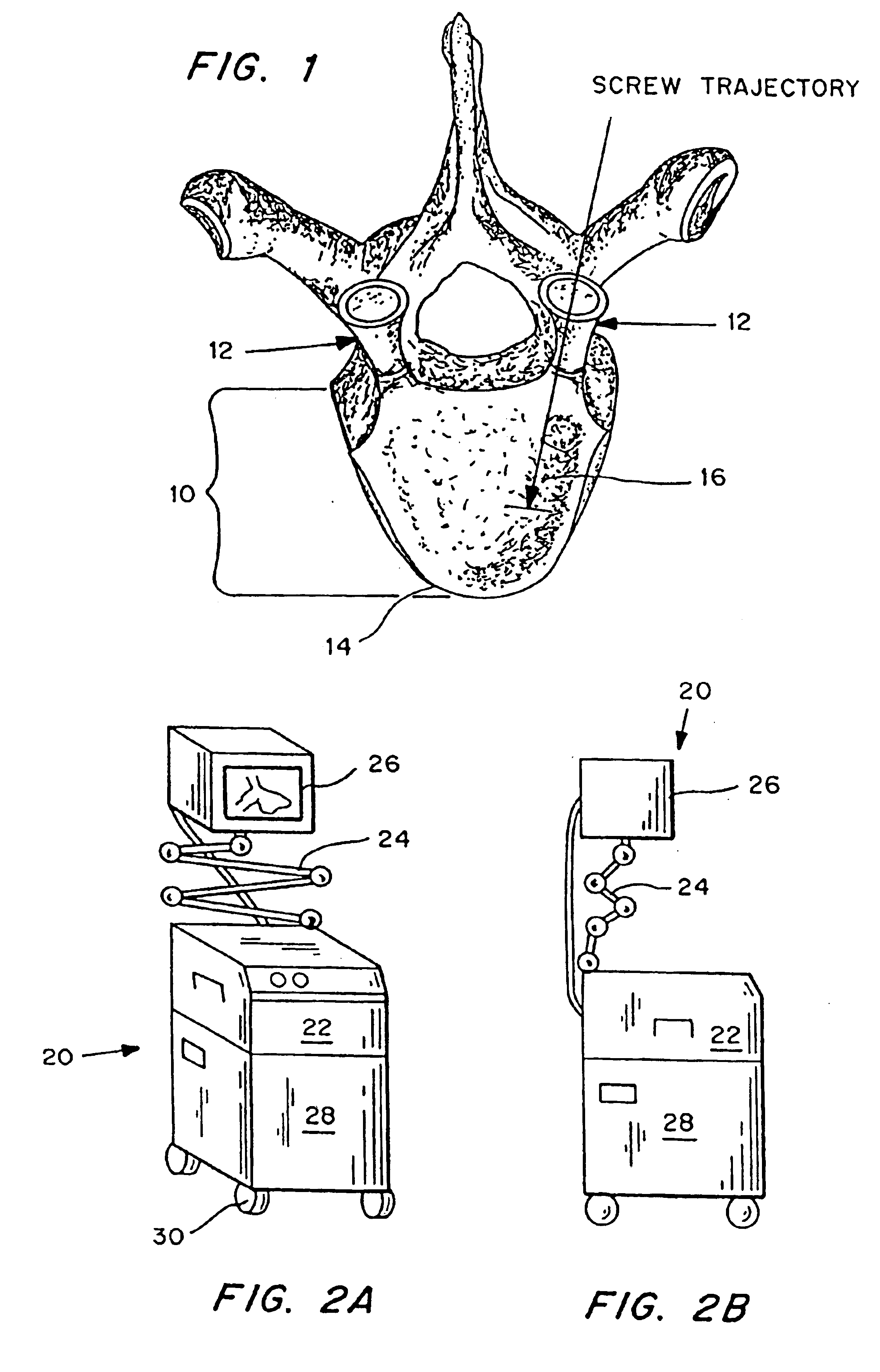
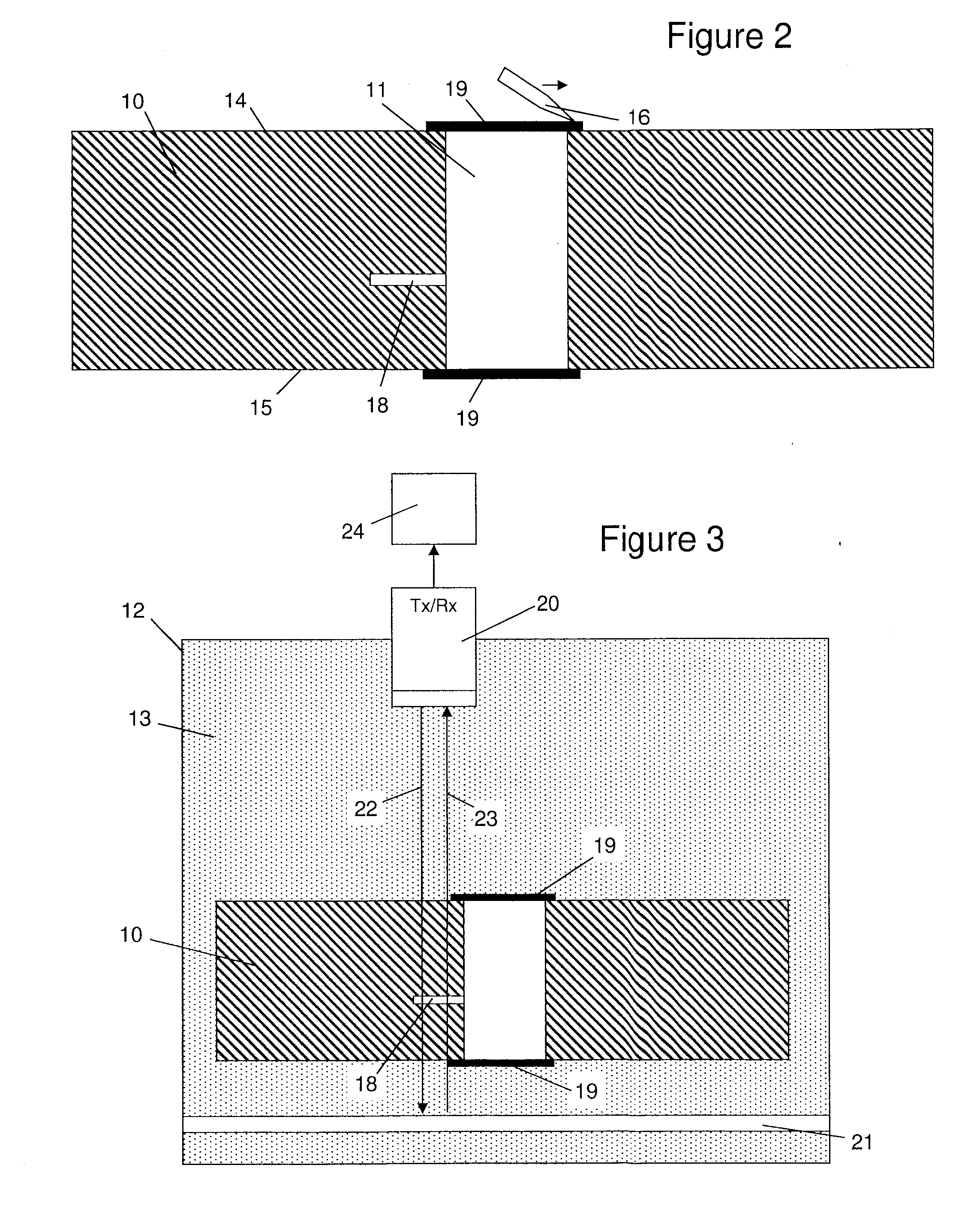
Intraosteal ultrasound during surgical implantation
IntraOsteal UltraSound (IOUS) is the use of acoustical energy to facilitate “real-time” manipulation and navigation of a device for intraosseous placement of synthetic or biologic implants and to diagnose the condition of the tissue into which the implant is being placed. Representative applications include placement of synthetic or biologic implants, such as bone screws, through vertebral pedicles during spinal fusion surgery. Devices for use in the placement of the implants include a means for creating a lumen or channel into the bone at the desired site in combination with a probe for providing realtime feedback of differences in density of the tissue, typically differences in acoustical impedance between cancellous and cortical bone. The devices will also typically include means for monitoring the feedback such as a screen creating an image for the surgeon as he creates the channel, and / or an audible signal which different tissues are present. The system can also be used for diagnostic applications.
Owner:CUTTING EDGE SURGICAL
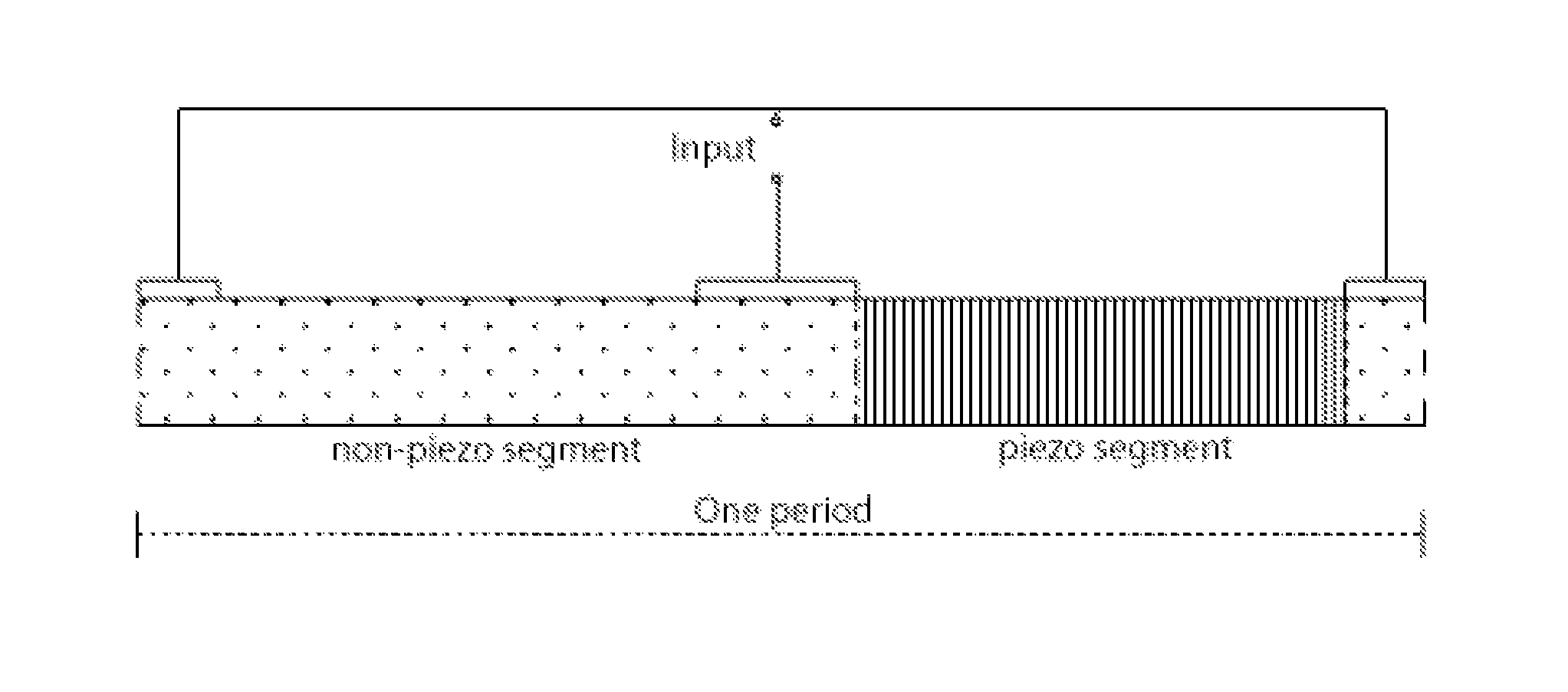
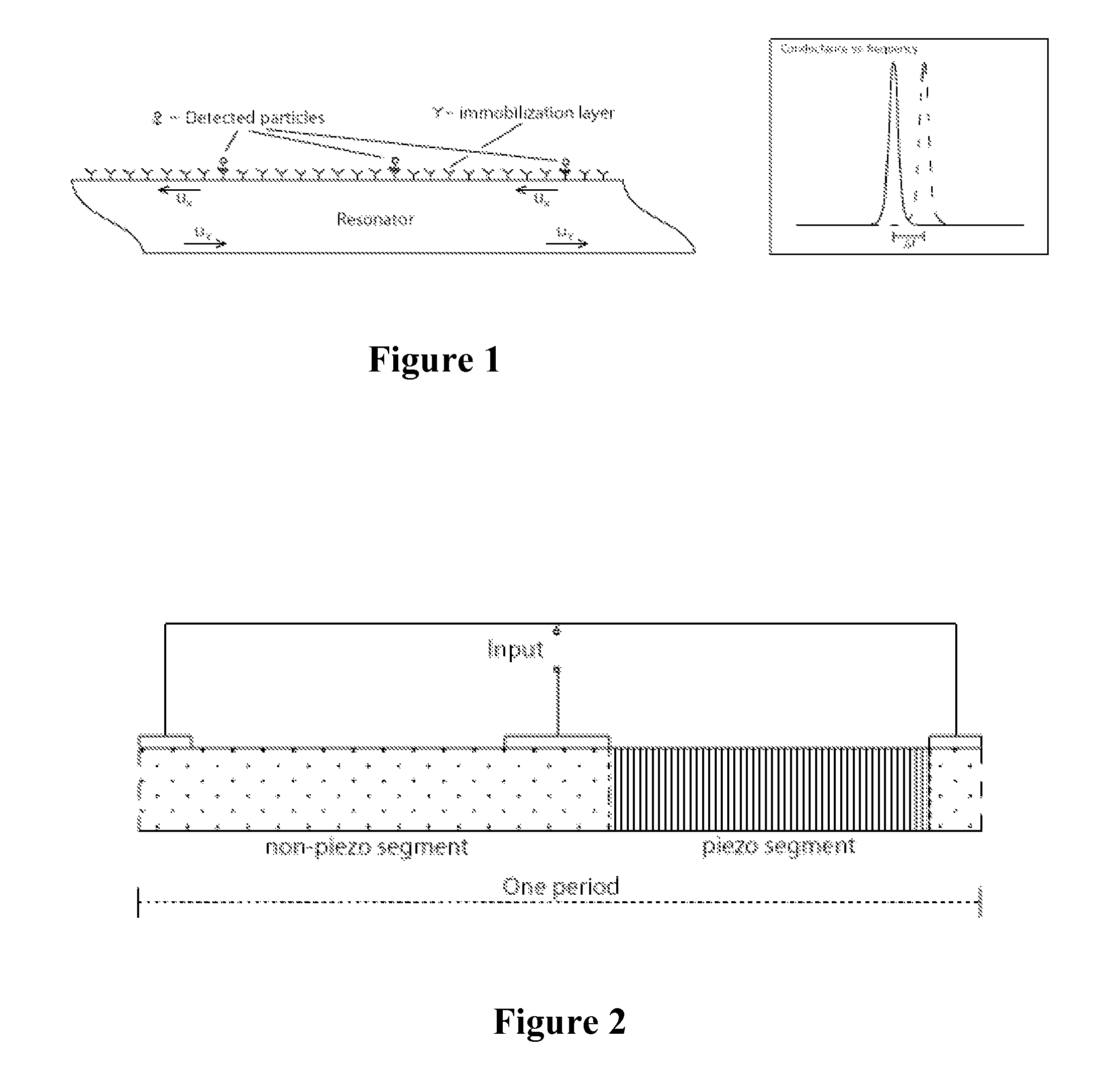
Piezoelectric resonator operating in thickness shear mode
InactiveUS8829766B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksElectrical polarityAcoustic wave
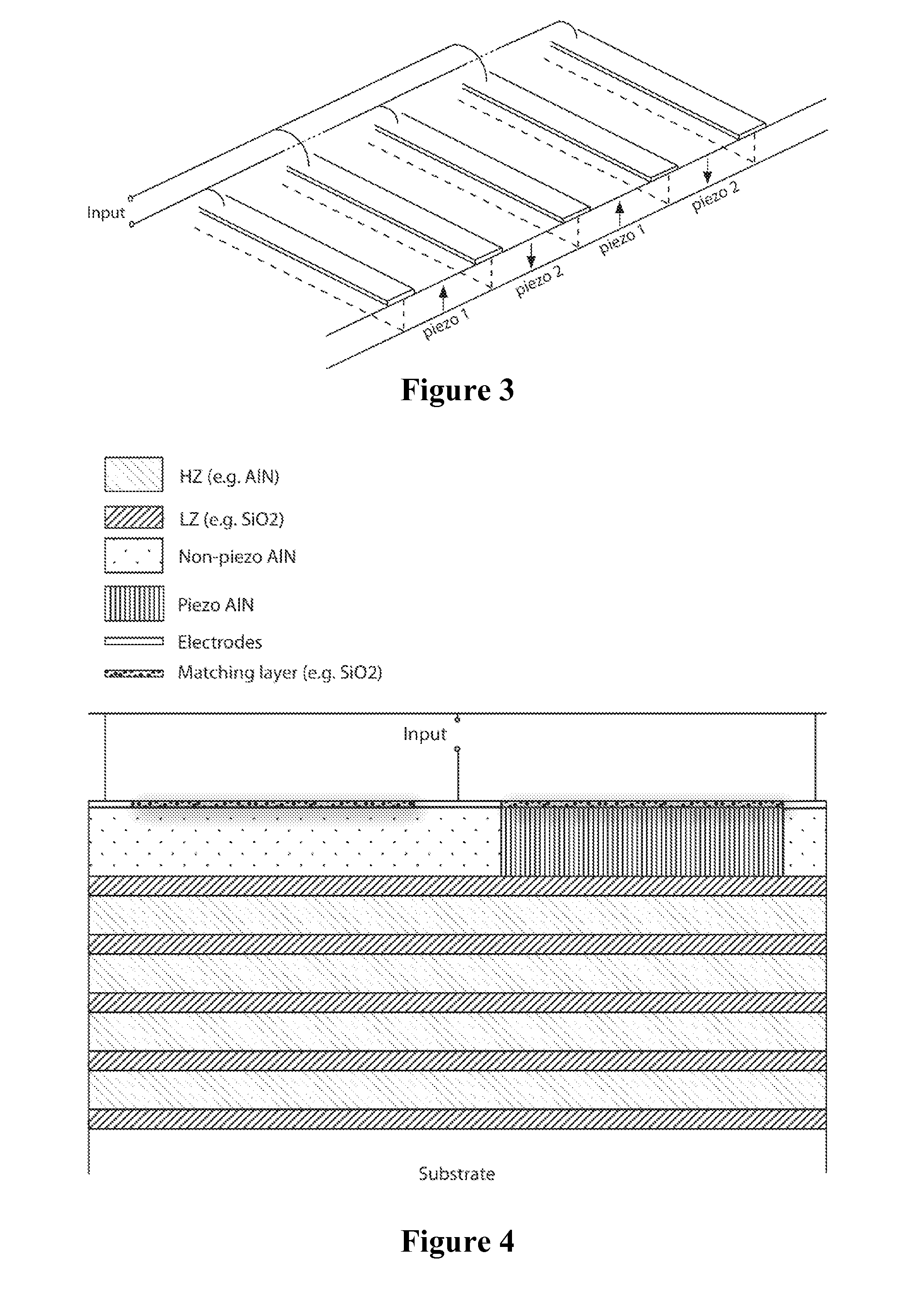
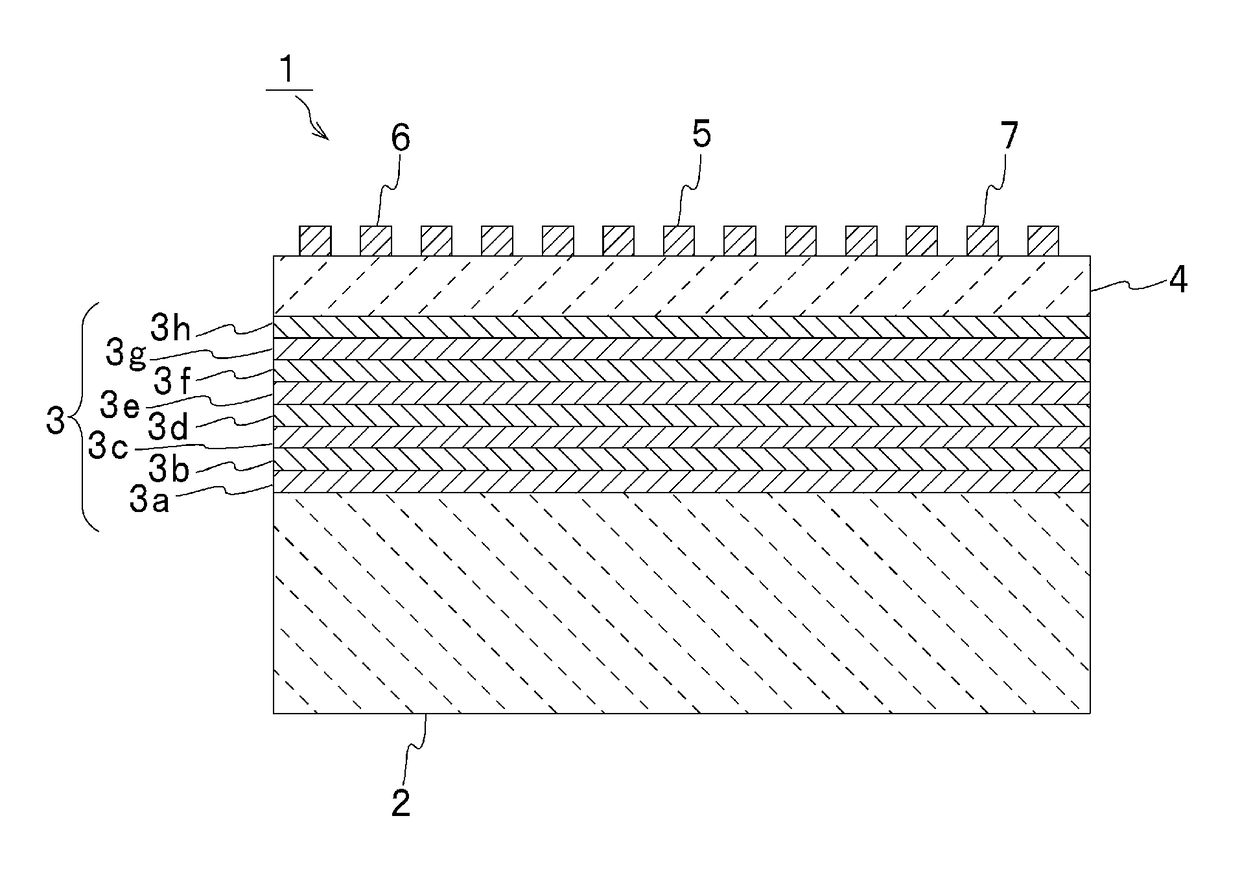
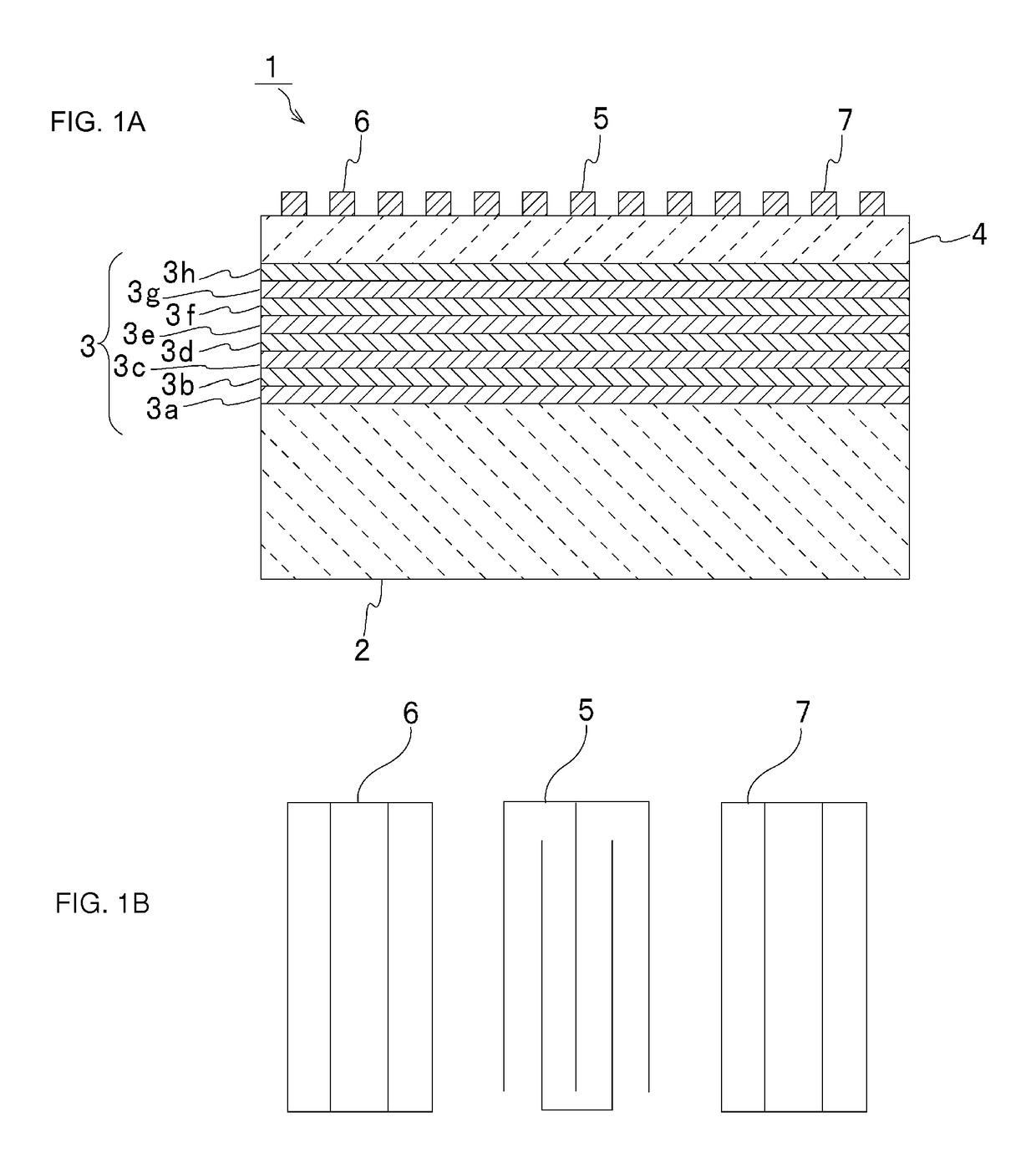
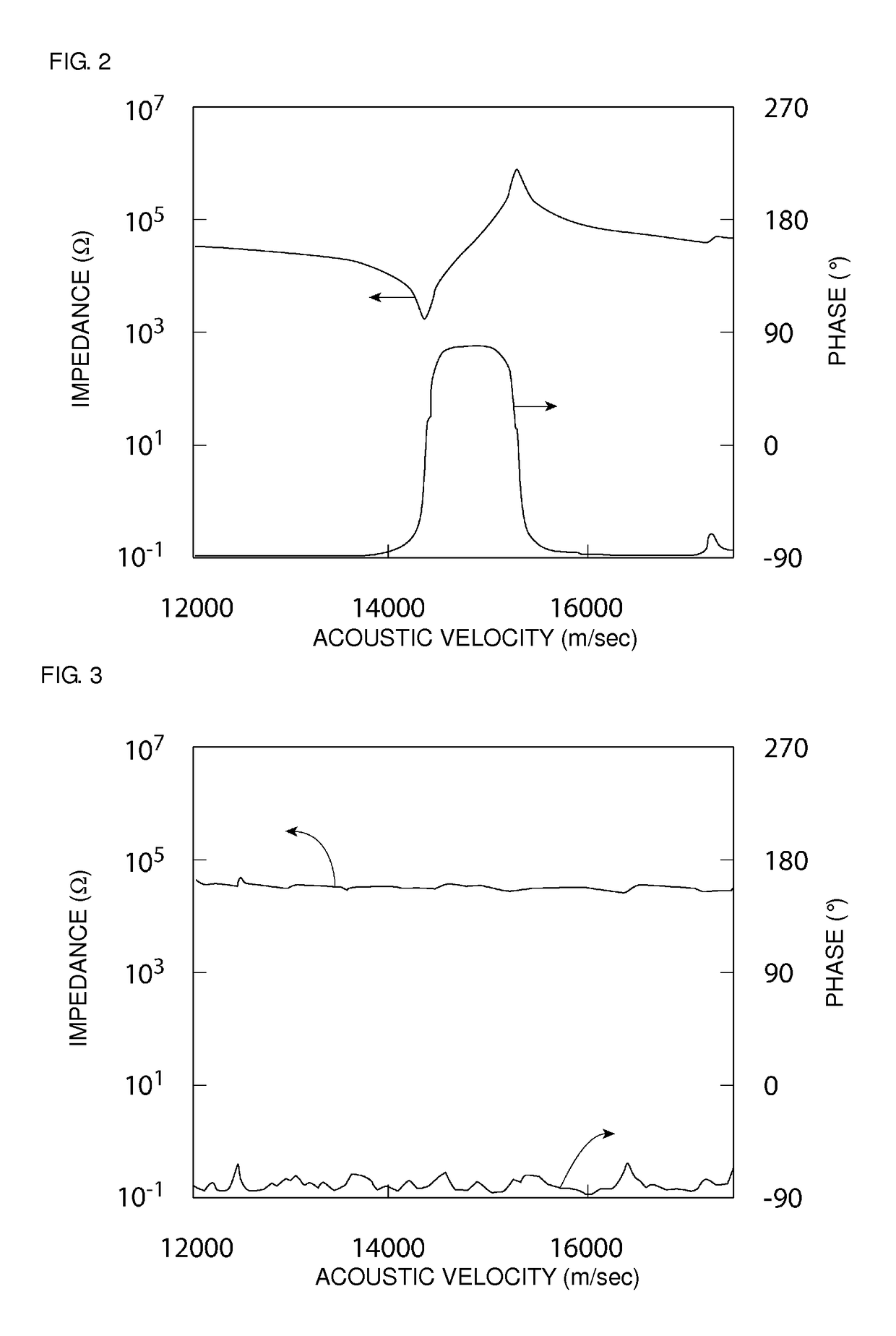
An acoustic wave resonator device comprising a resonant layer that comprises a series of side-by-side areas of first and second dielectric materials. In one embodiment the first dielectric material is a piezoelectric, in particular the first dielectric material can be a piezoelectric and the second dielectric material can be non-piezoelectric. In another embodiment, the first dielectric material is a piezoelectric of first polarity and the second dielectric material is a piezoelectric of opposite polarity or different polarity. Where needed, the resonant layer is supported on a reflector composed of series of layers of high acoustic impedance material(s) alternating with layers of low acoustic impedance material(s). For example, the reflector comprises AlN, Al2O3, Ta2O5, HfO2 or W as high impedance material and SiO2 as low impedance material.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Elastic wave device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9780759B2Good general characteristicGood temperature characteristicsImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionAcoustic impedanceAcoustic reflection
An elastic wave device propagating plate waves includes a stack of an acoustic reflection layer, a piezoelectric layer, and IDT electrode on a supporting substrate. The piezoelectric layer is thinner than a period of fingers of the IDT electrode. The acoustic reflection layer includes low-acoustic-impedance layers and high-acoustic-impedance layers. The low-acoustic-impedance layers are made of SiO2, and the high-acoustic-impedance layers are made of at least one material selected from the group consisting of W, LiTaO3, Al2O3, AlN, LiNbO3, SiN, and ZnO.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
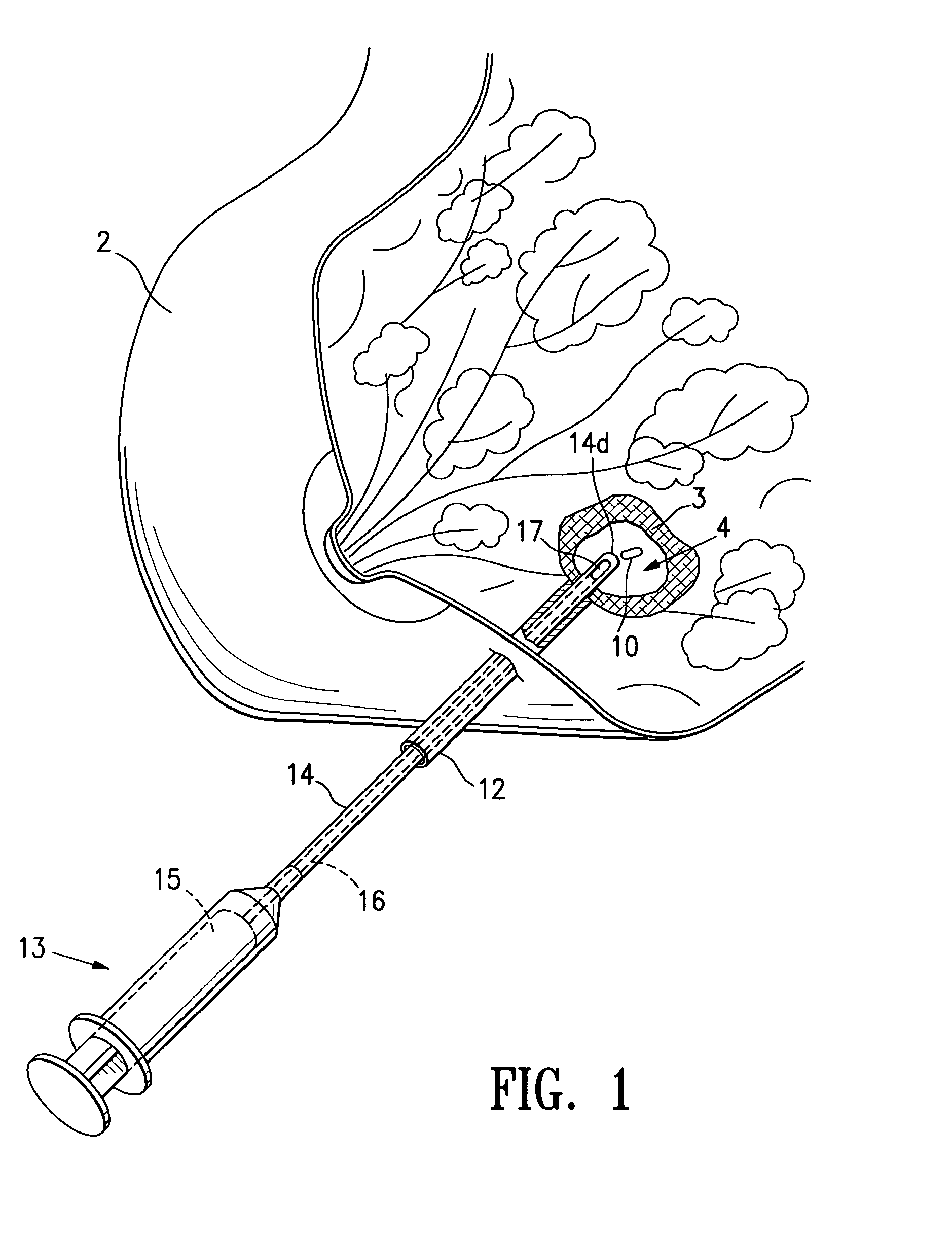
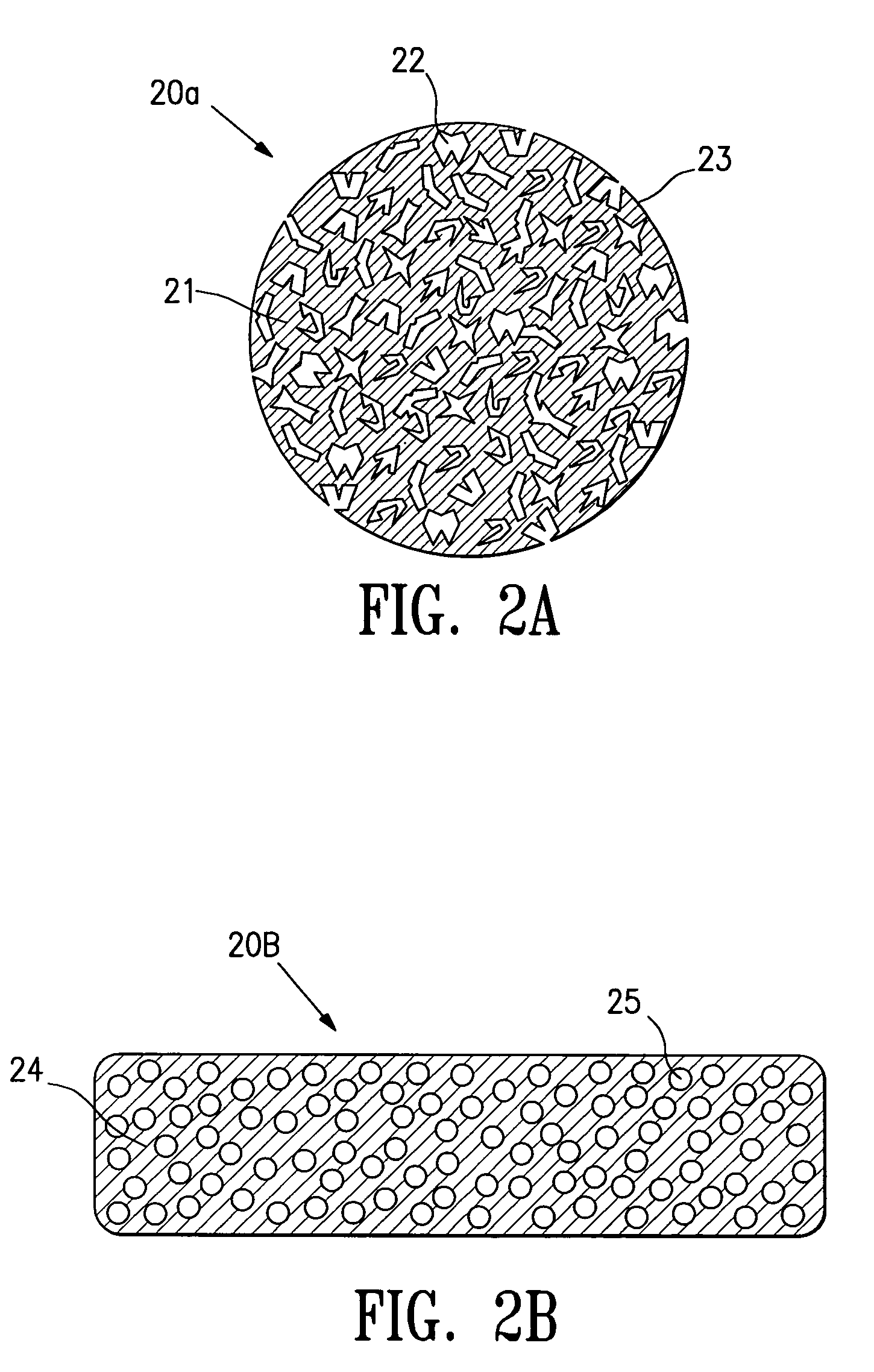
Tissue site markers for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS20050063908A1Small volumeImprove reflectivityLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesContrast levelIn vivo
The invention is directed biopsy site markers and methods of marking a biopsy site, so that the location of the biopsy cavity is readily visible by conventional imaging methods, particularly by ultrasonic imaging. The biopsy site markers of the invention have high ultrasound reflectivity, presenting a substantial acoustic signature from a small marker, so as to avoid obscuring diagnostic tissue features in subsequent imaging studies, and can be readily distinguished from biological features. The several disclosed embodiments of the biopsy site marker of the invention have a high contrast of acoustic impedance as placed in a tissue site, so as to efficiently reflect and scatter ultrasonic energy, and preferably include gas-filled internal pores. The markers may have a non-uniform surface contour to enhance the acoustic signature. The markers have a characteristic form which is recognizably artificial during medical imaging. The biopsy site marker may be accurately fixed to the biopsy site so as to resist migration from the biopsy cavity when a placement instrument is withdrawn, and when the marked tissue is subsequently moved or manipulated.
Owner:SENORX
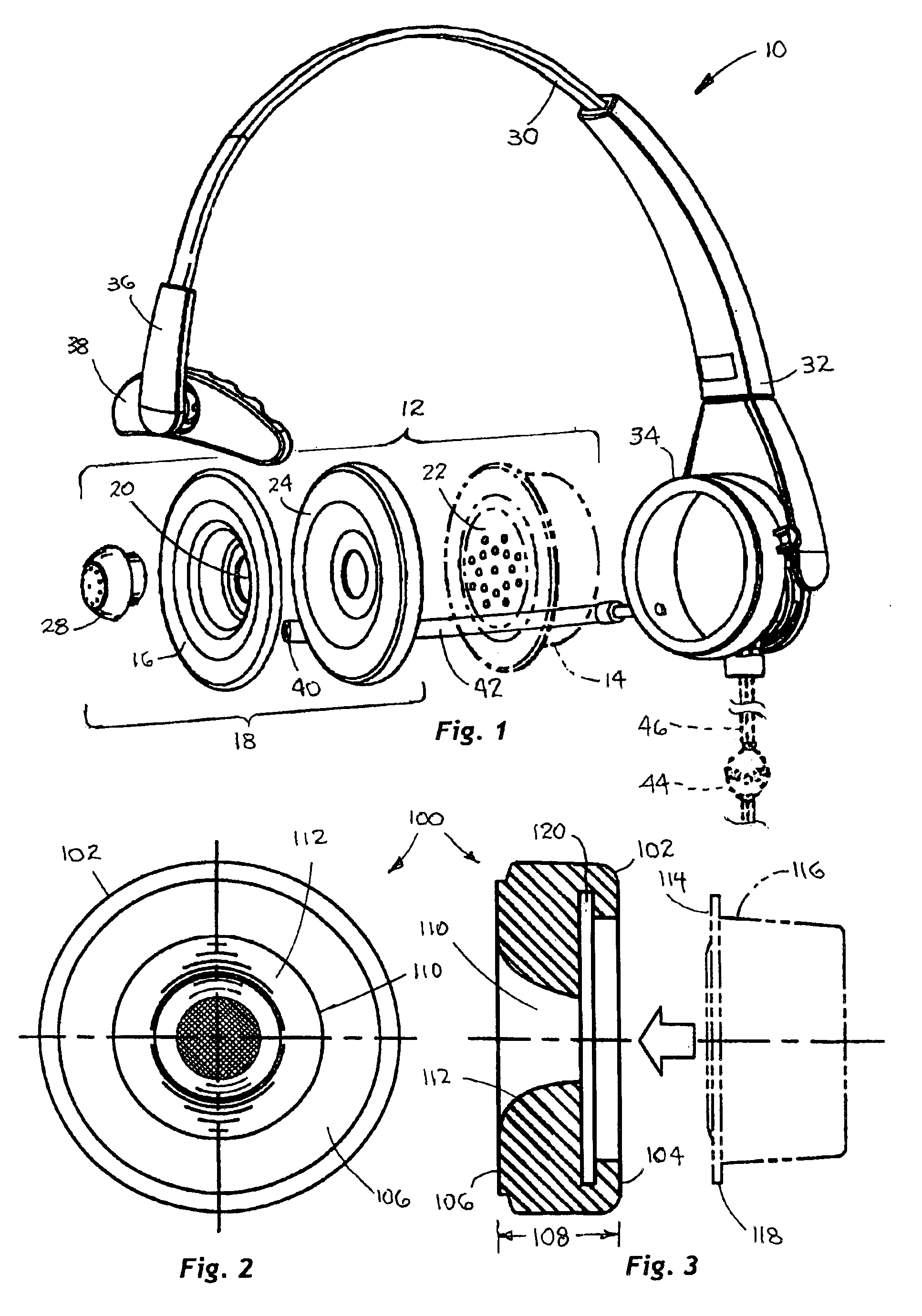
Comfortable earphone cushions
InactiveUS6856690B1Improved and long-term wearing comfortImprove cooling effectPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesElastomerTransducer
A cushion for a headset earphone comprises a resilient ring having opposite input and output faces, and a through-opening defining an interior surface between the two faces. The input face has structure for acoustically coupling the opening to an output face of an audio speaker, and the output face is resiliently conformable to a lateral face of an external ear of a listener, thereby acoustically coupling the opening, and hence, the speaker, to the listener's ear. The interior surface of the cushion can be configured to effectively match the acoustical impedance at the output face of the speaker to the acoustical impedance at the entrance of the listener's ear. In one possible embodiment, the ring is formed of an elastomer filled with microcapsules containing a material capable of an endothermic phase changes at a constant temperature, such that the cushion more effectively conducts heat away from the ear, thereby providing long term listening comfort. In another embodiment, the through-opening is acoustically coupled to the output of the transducer with an acoustic plug such that the cushion is flexibly articulated about the plug relative to the speaker, thereby enabling the cushion to comply more easily to the listener's ear using lower contact forces between the cushion and the ear.
Owner:PLANTRONICS
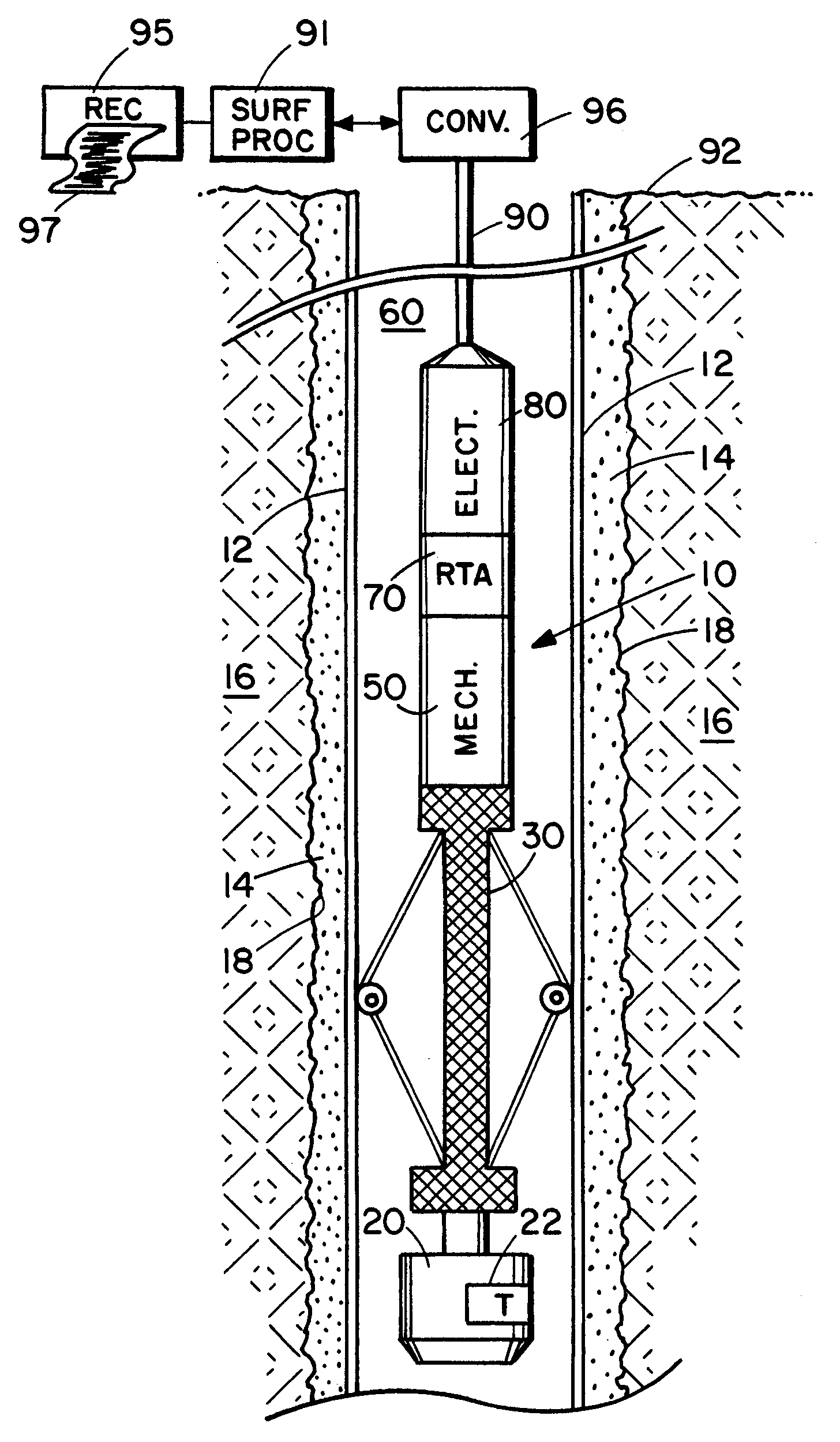
Ultrasonic cement scanner
InactiveUS20060067162A1Minimizing telemetry band width requirementMinimization requirementsConstructionsSeismology for water-loggingSystematic variationFull wave
An acoustic borehole logging system for parameters of a well borehole environs. Full wave acoustic response of a scanning transducer is used to measure parameters indicative of condition of a tubular lining the well borehole, the bonding of the tubular to material filling an annulus formed by the outside surface of the tubular and the wall of the borehole, the distribution of the material filling the annulus, and thickness of the tubular. A reference transducer is used to correct measured parameters for variations in acoustic impedance of fluid filling the borehole, and for systematic variations in the response of the scanning transducer. Corrections are made in real time. The downhole tool portion of the logging system is operated essentially centralized in the borehole using a centralizer that can be adjusted for operation in a wide range of borehole sizes.
Owner:PRECISION DRILLING TECH SERVICES GROUP +1
Method of forming a model representative of the distribution of a physical quantity in an underground zone, free of the effect of correlated noises contained in exploration data
InactiveUS7092823B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingData spaceSynthetic data
The invention is a method of estimating, from data obtained by exploration of a zone of a heterogeneous medium, a model representative of a distribution, in the zone, of at least one physical quantity, the model being free of a presence of correlated noises that may be contained in the data which has application to determining the distribution in an underground zone of acoustic impedance, propagation velocities and permeabilities, etc. The method includes acquiring measurements giving information about physical characteristics of the zone; specifying a noise modelling operator which associates, with a model of each physical quantity, synthetic data that constitute a response of the model; selecting a noise modelling operator which associates a correlated noise with a noise-generating function belonging to a predetermined space of the noise-generating functions; specifying a norm or of a semi-norm in the data space; specifying a semi-norm in the space of the noise-generating functions; defining a cost function; and adjusting the model and of the noise-generating functions.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
3-d quantitative-imaging ultrasonic method for bone inspections and device for its implementation
InactiveUS20110112404A1Enabling useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsPorositySonification
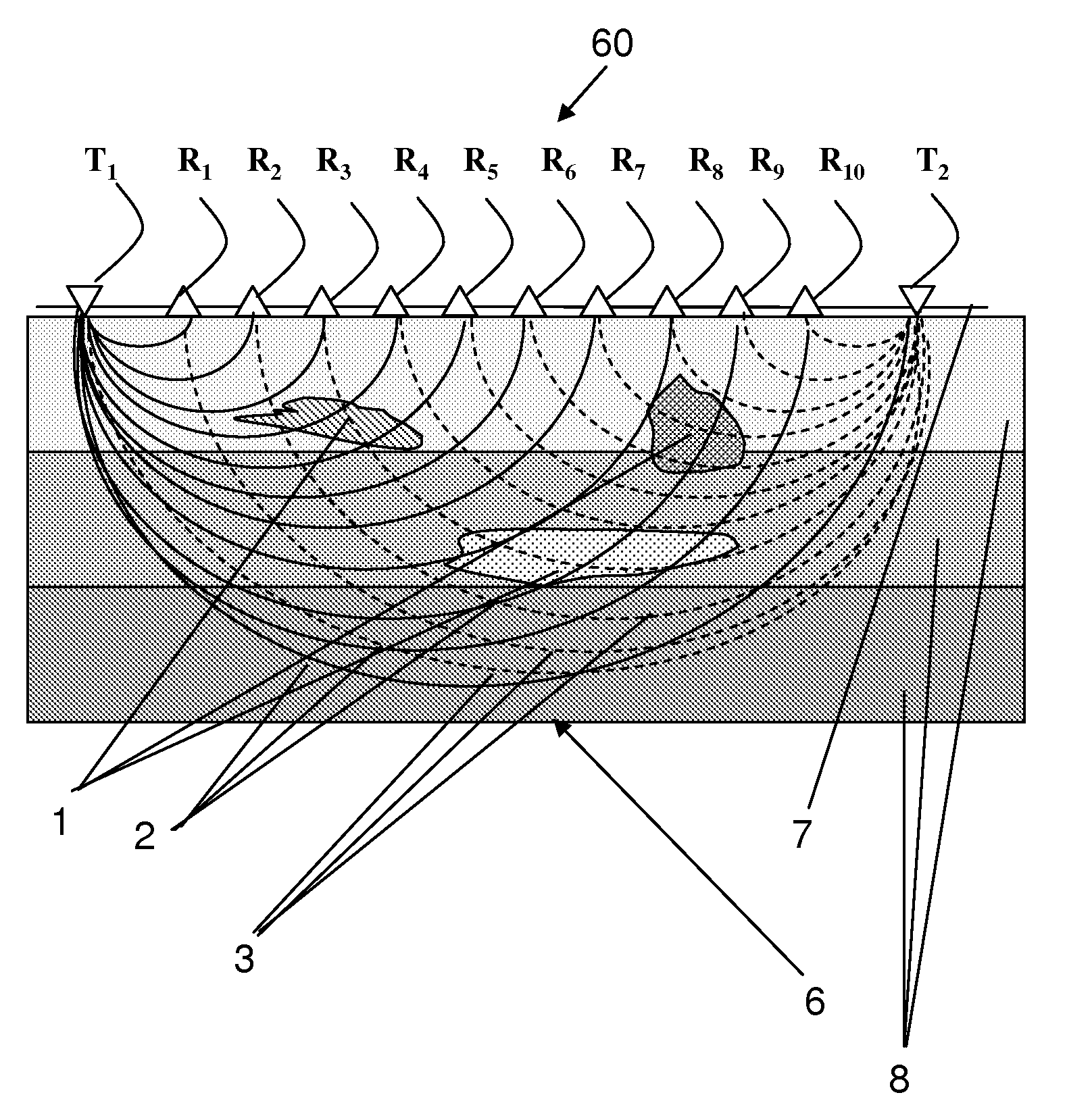
The invention is a differential 3D Quantitative-Imaging Ultrasonic Tomography method for inspecting a layered system that is comprised of a heterogeneous object embedded in a volume of space that comprises layers having an acoustic impedance gradient between the layers providing non-linear beams travels. A transducer grid is attached to the surface of the layered system in a unilateral manner. By sequentially changing the distance between transmitter and receiver the fastest travel times of the ultrasonic oscillations are measured. A differential approach provides from the data the longitudinal wave velocities values for each elementary volume that make up an inspected volume. These values are used to construct two and three-dimensional maps of the longitudinal wave velocity values distribution in the inspected volume and the porosity values distribution in the heterogeneous object. By applying statistical treatment to the obtained data the longitudinal wave velocity in the inspected material matrix part is estimated.
Owner:GOUREVITCH ALLA
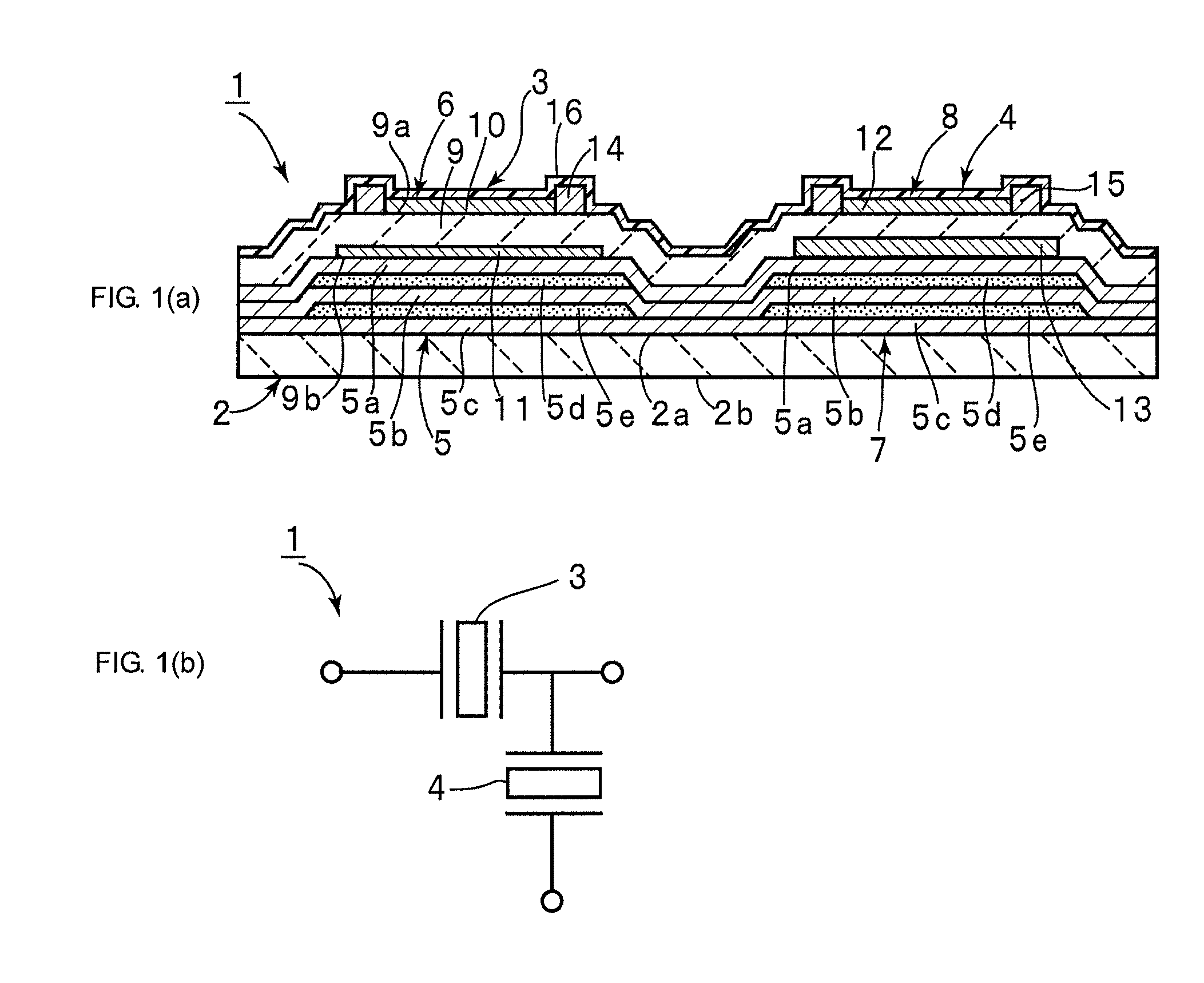
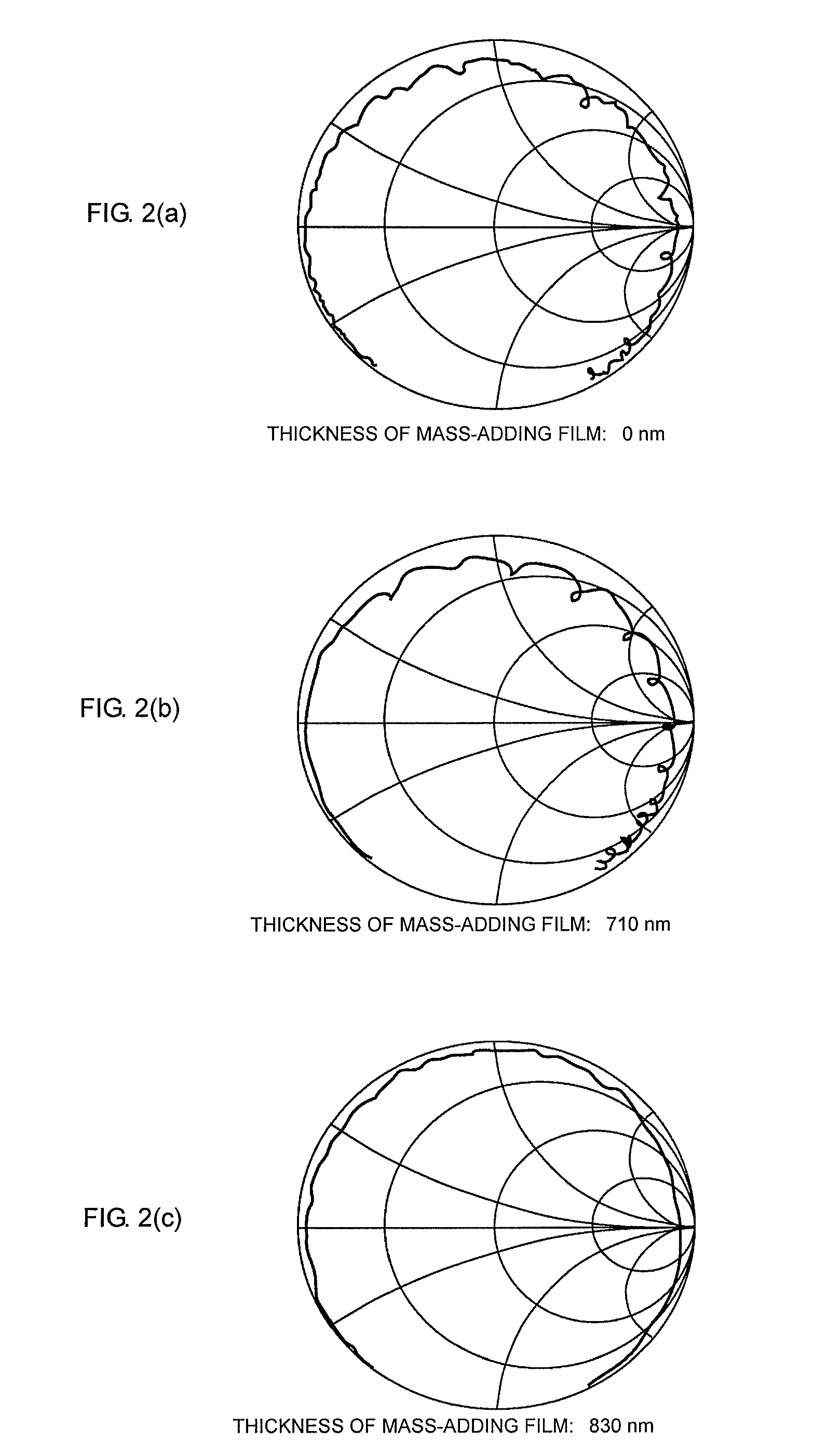
Piezoelectric Resonator and Piezoelectric Filter Device
InactiveUS20100134210A1Improve insertion lossReduce resistanceImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyThin membraneReflective layer
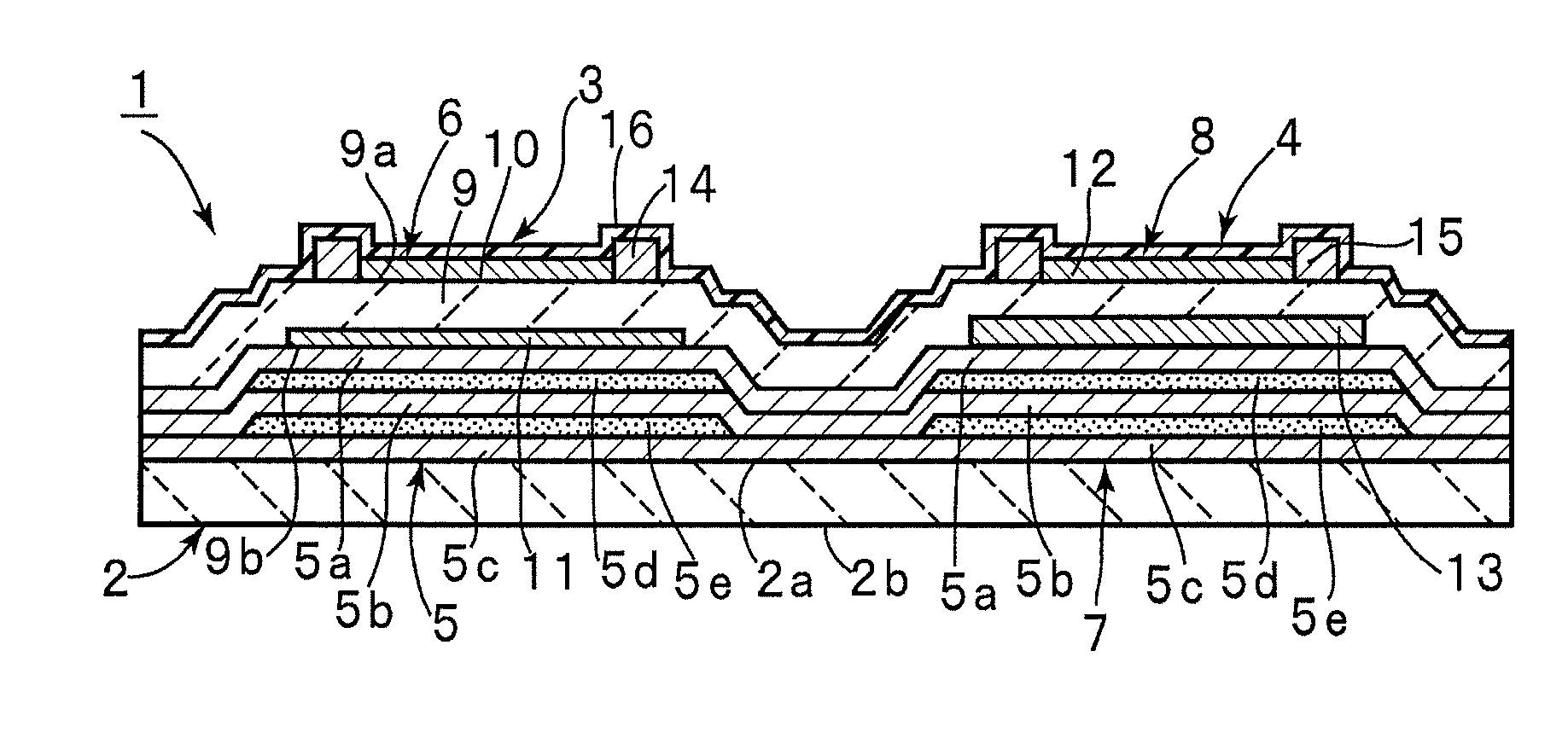
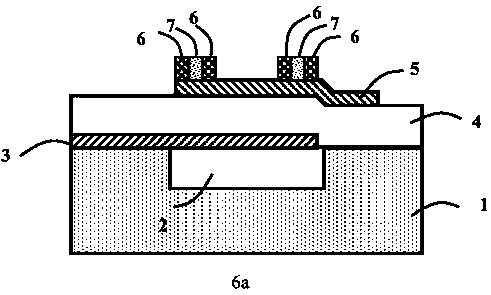
A piezoelectric resonator includes an acoustic reflective layer including first acoustic impedance sub-layers made of a material with relatively low acoustic impedance and second acoustic impedance sub-layers made of a material with relatively high acoustic impedance. A thin-film laminate is disposed on the acoustic reflective layer. The thin-film laminate includes a piezoelectric thin-film, a first electrode, a second electrode greater than the first electrode, and a mass-adding film. The second electrode is disposed on the acoustic reflective layer. The mass-adding film is disposed in at least one portion of a region outside a piezoelectric vibrational section and extends around the first electrode. The second electrode extends over the piezoelectric vibrational section to a region containing the mass-adding film.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
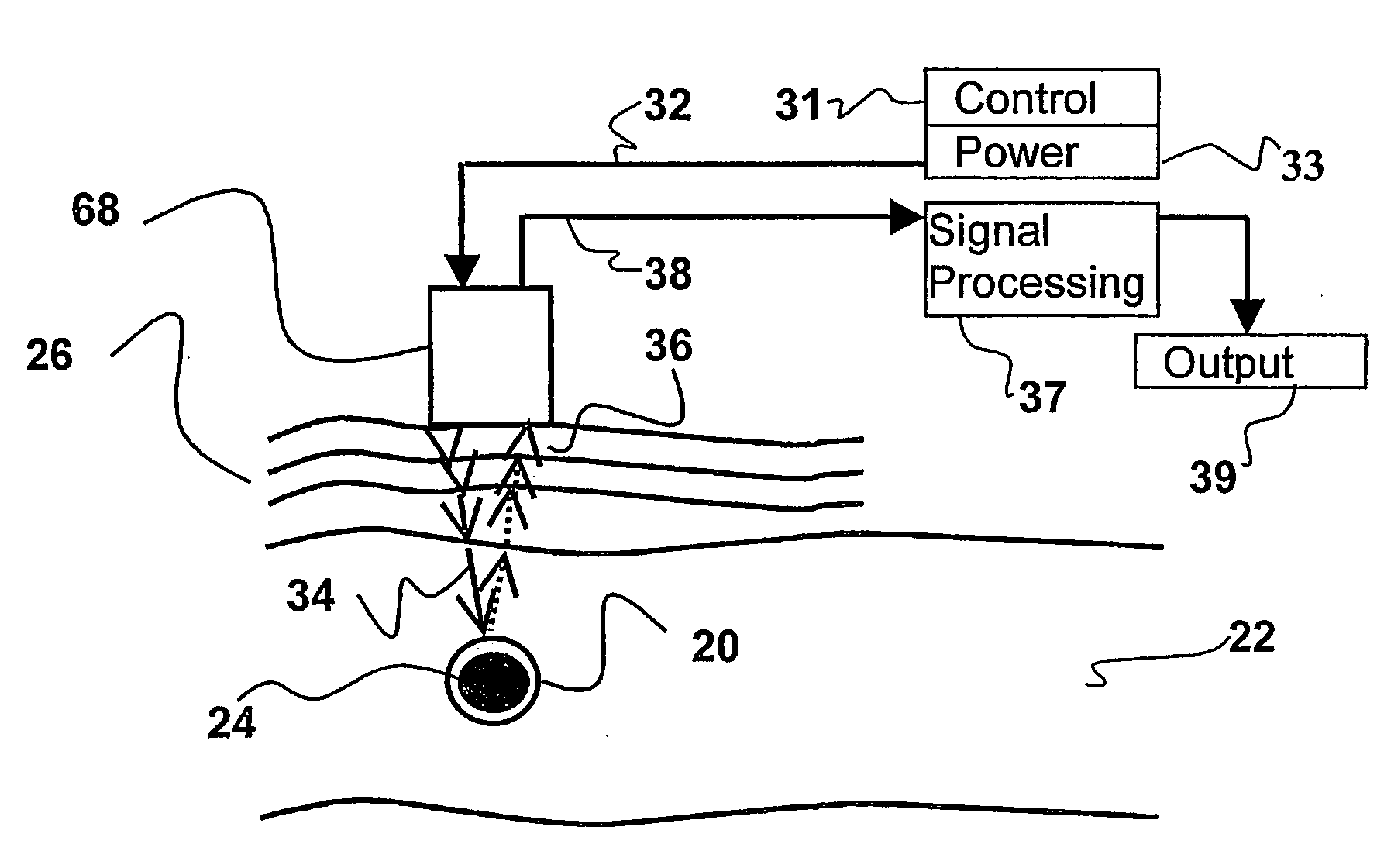
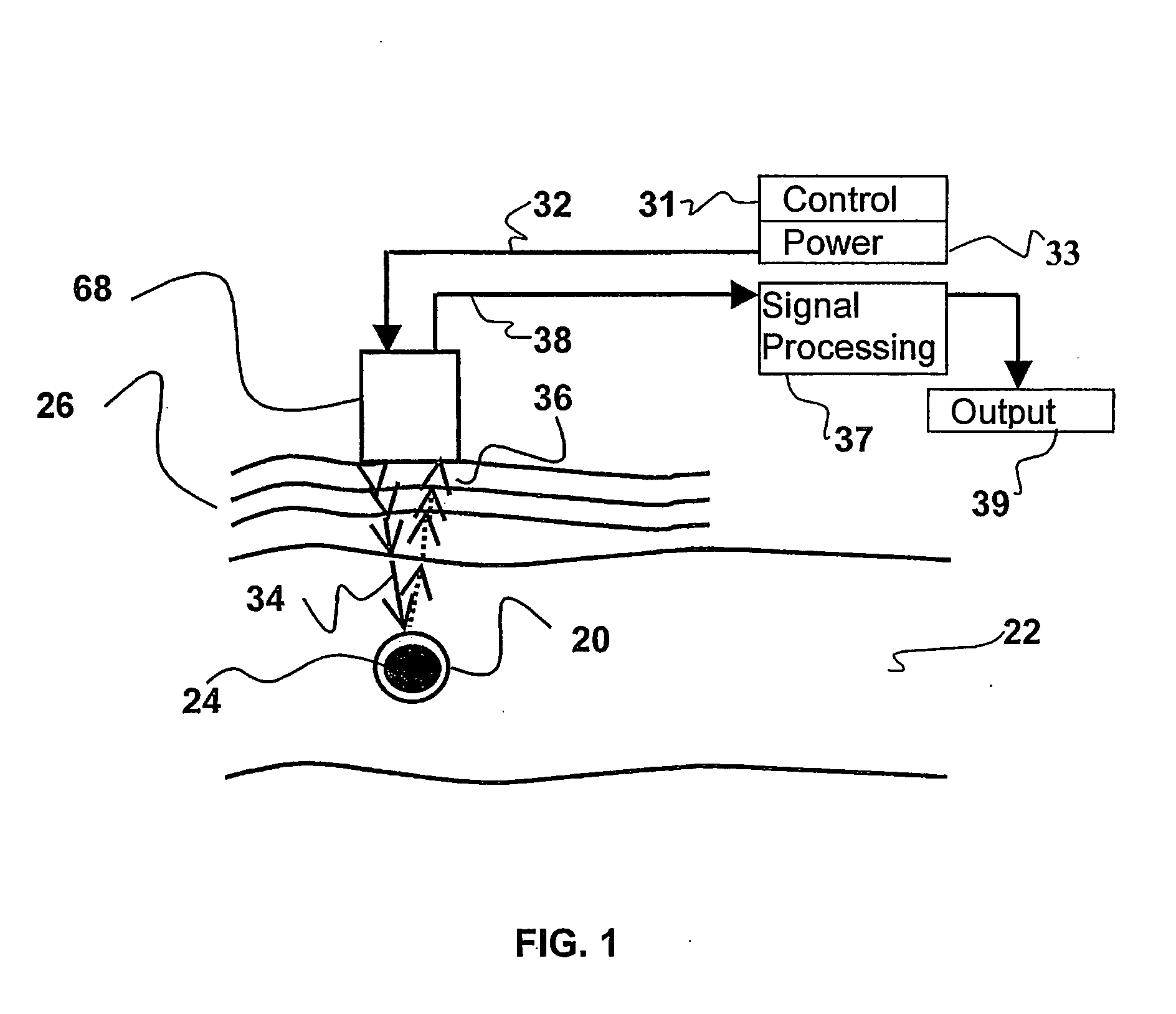
Interactive Ultrasound-Based Depth Measurement For Medical Applications
InactiveUS20080234579A1Small dimensionControl volumeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLiquid jetBone structures
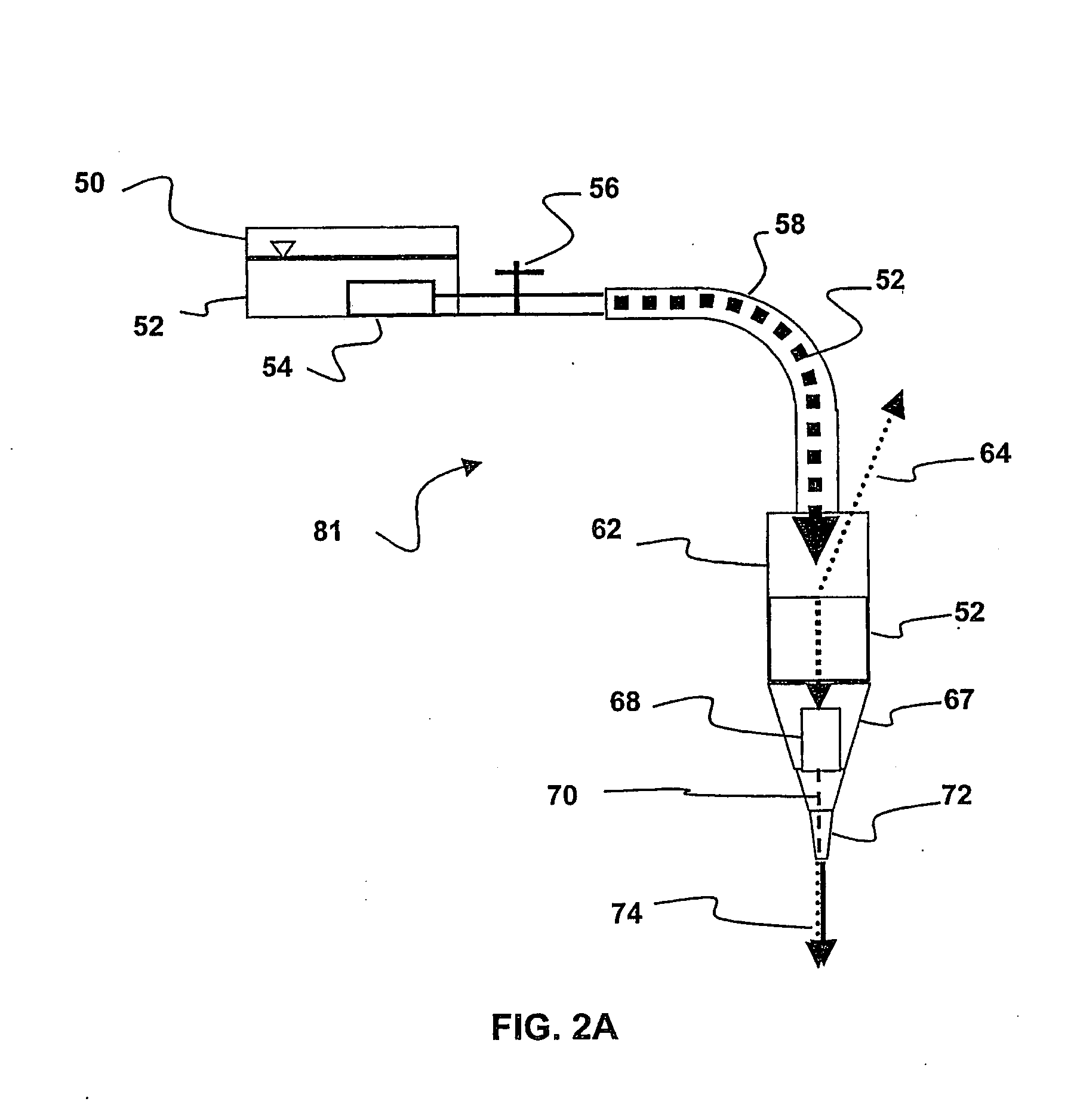
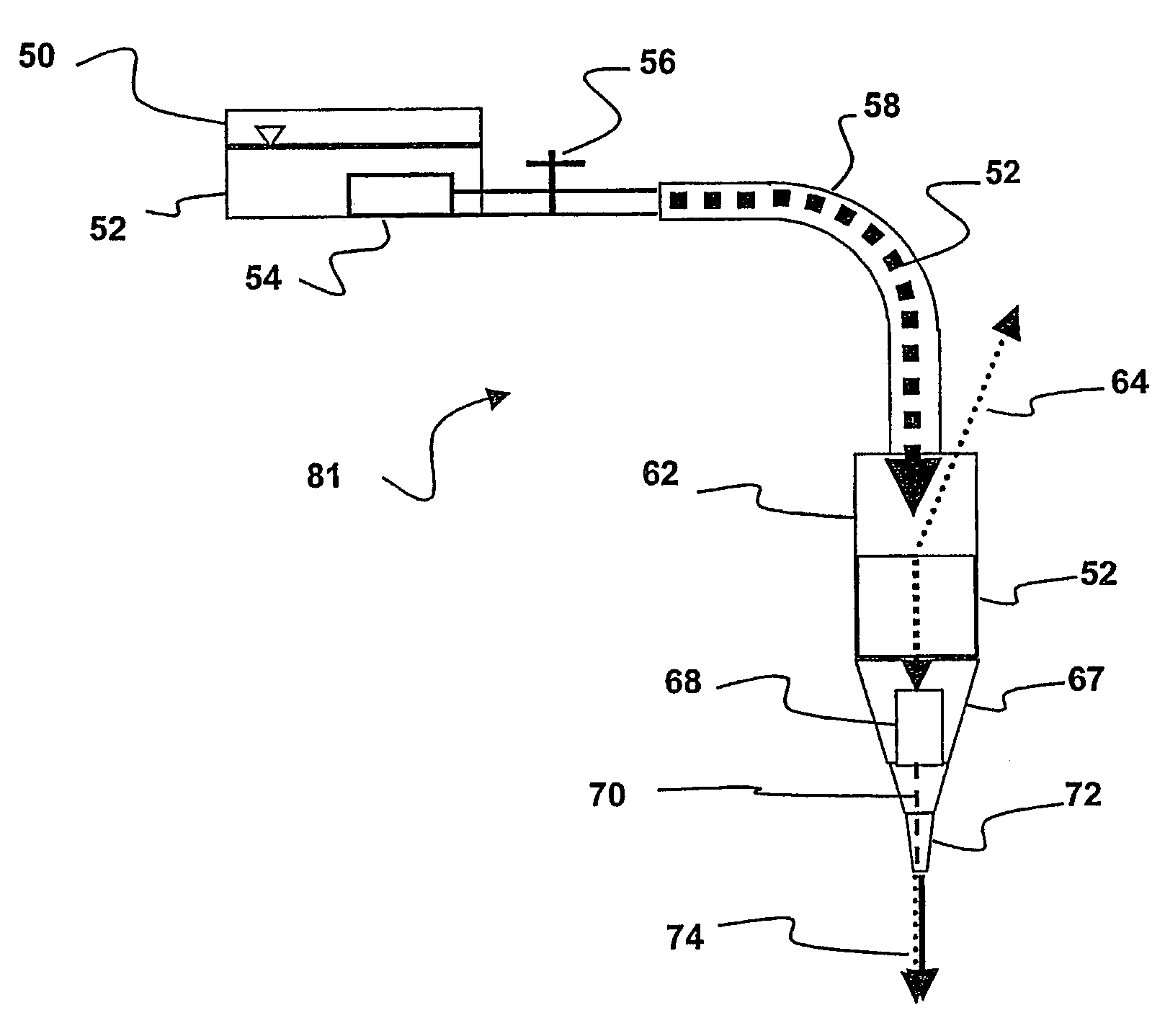
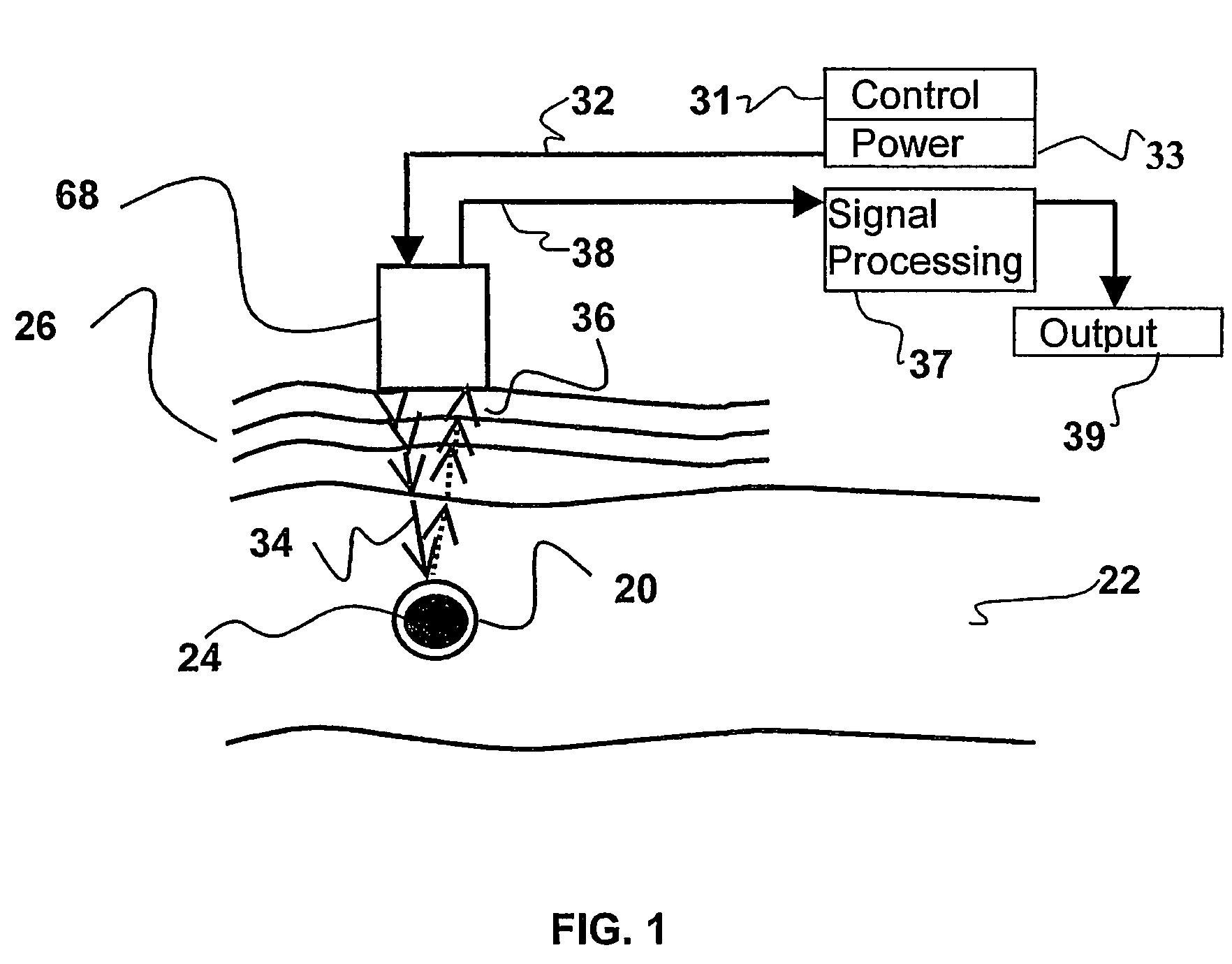
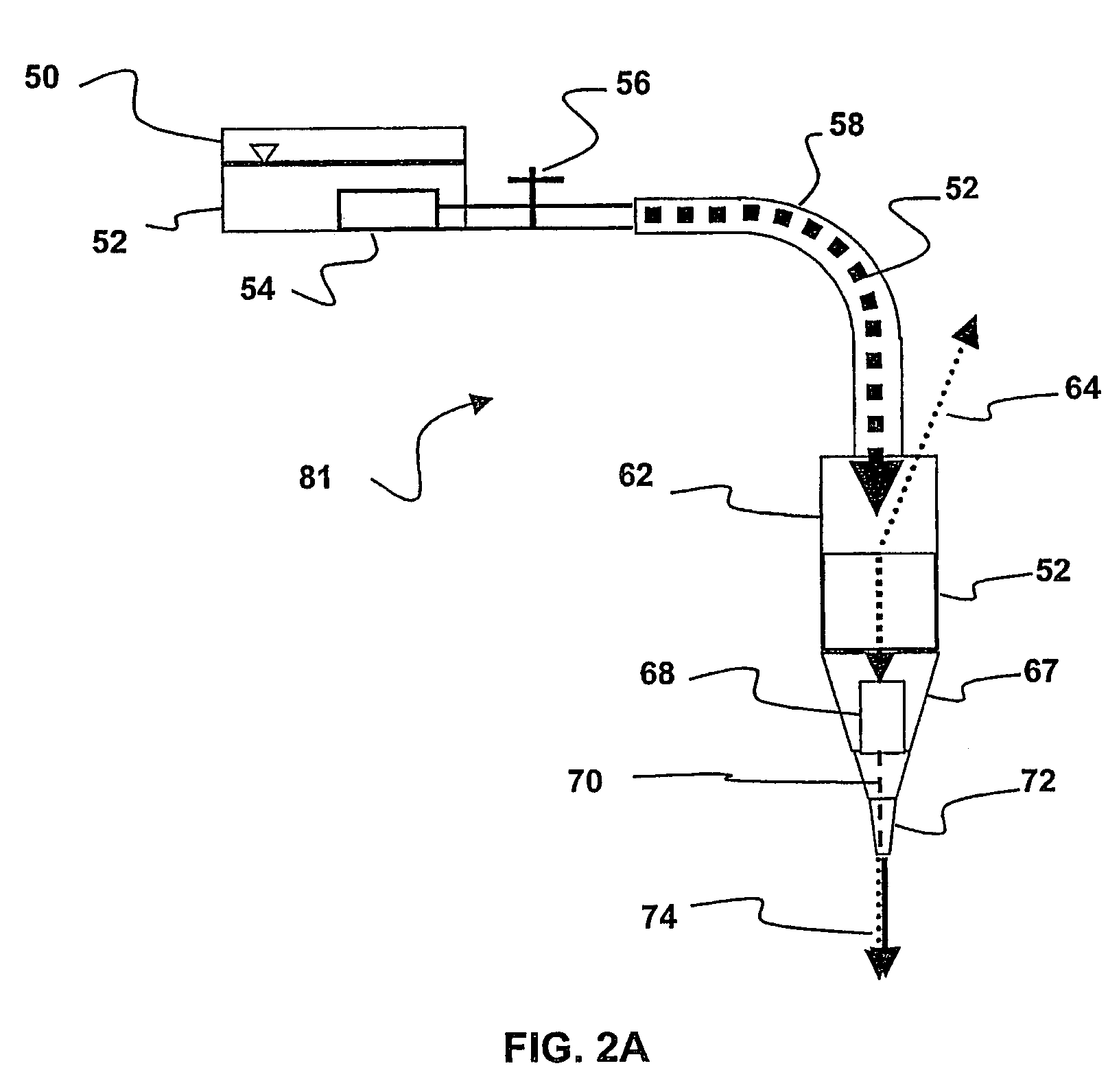
A device for determining the internal structure of a bone along a path directed into the bone (or other tissue) is disclosed. The device comprises a nozzle fluidically connected to a liquid reservoir for providing a liquid jet directed at the bone in the direction of the path; an ultrasonic transducer for generating ultrasonic waves through the liquid jet and for detecting echoes of the ultrasonic waves caused by changes in the acoustical impedance in the bone characterizing changes in the structure of the bone along the path; and an analyzer for interpreting the echoes into meaningful information relating to the location of the structural changes along the path.
Owner:JETGUIDE
P-wave anisotropy evaluation by measuring acoustic impedance of the rock by beam-steering from within the borehole at different angles
A phased array of transducers is used to generate elastic waves into the earth formation in a selected direction. The impedance measured at the input to the transducer array is indicative of the elastic impedance of the earth formation in the selected direction.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
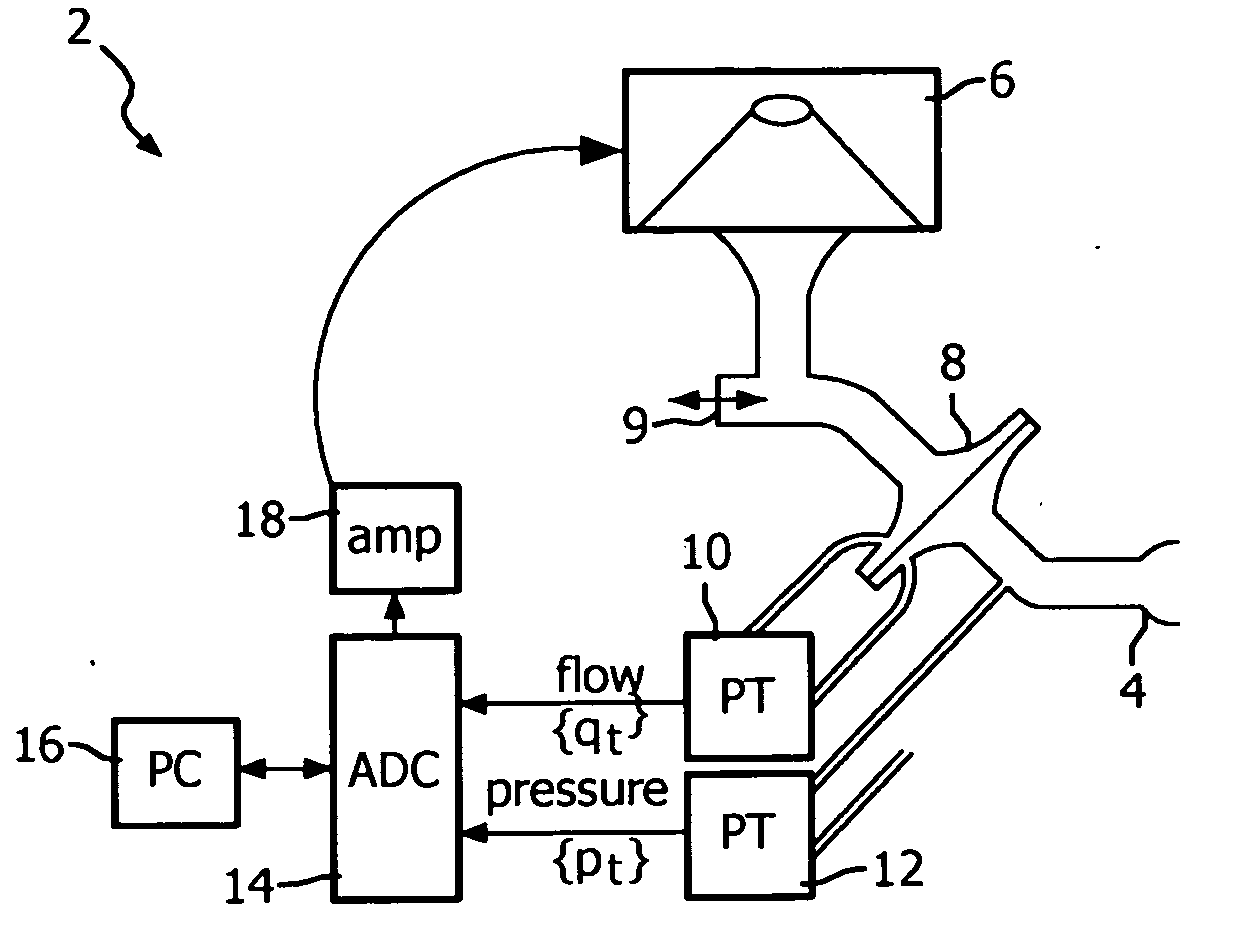
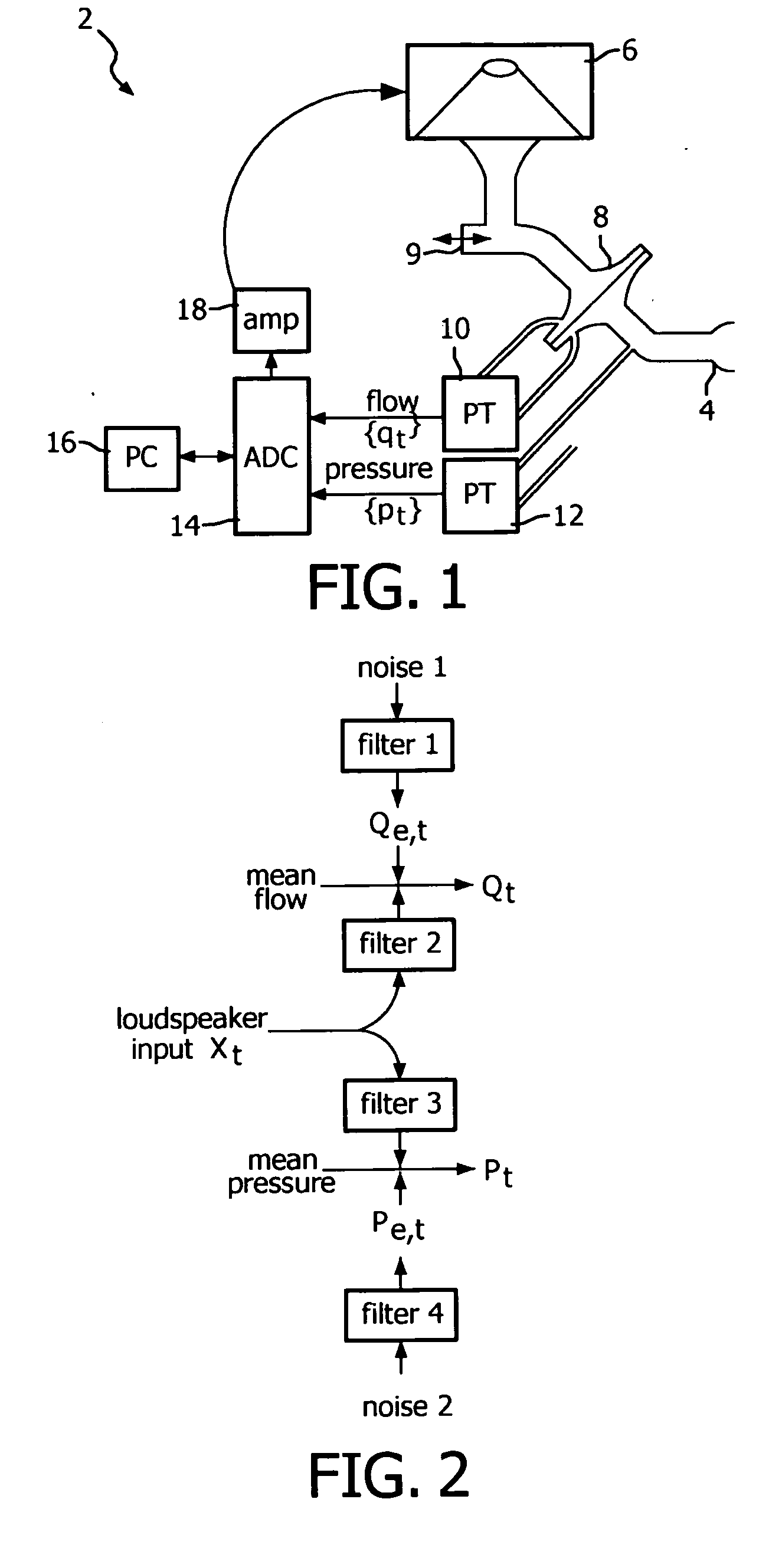
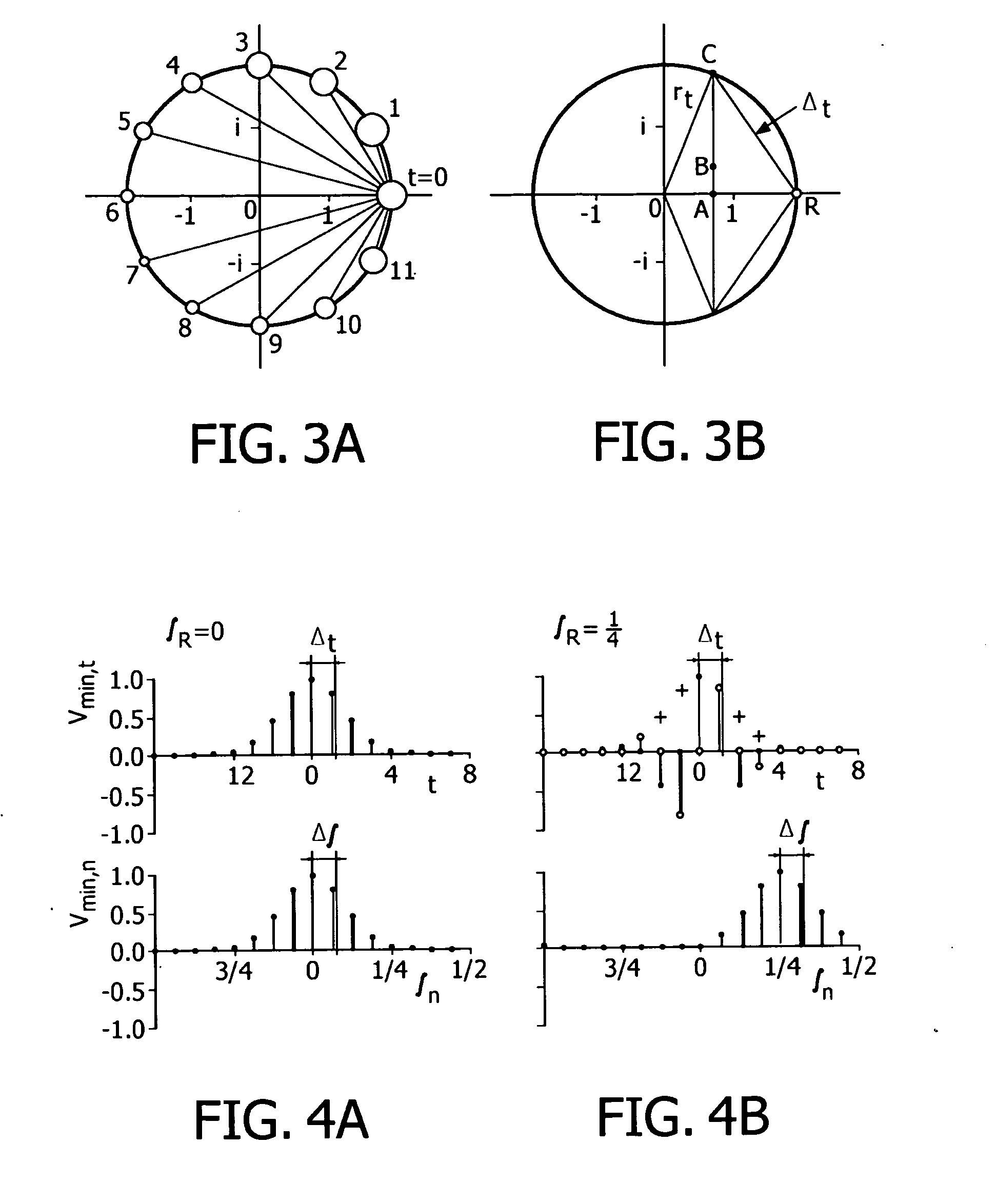
Method and apparatus for estimating respiratory impedance
The acoustic impedance of the respiratory system can be inferred from oscillations that are generated in an airway of a subject. The impedance describes the frequency-dependent relation between the resulting oscillations in flow and pressure. When the impedance varies from inspiration to expiration, it has to be estimated with a high time resolution. A method is provided that reliably estimates the impedance in time intervals that are short enough for physiological purposes. A simple version of the uncertainty principle has been derived for discrete time and frequency. A discrete time-frequency transform has been developed that gives an optimal time-frequency resolution according to this principle. The transform is orthonormal, which permits an analysis of variance in the discrete time-frequency domain. The impedance follows from bivariate least-squares analysis in the time-frequency domain, under the assumption that noise is present in both flow and pressure.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
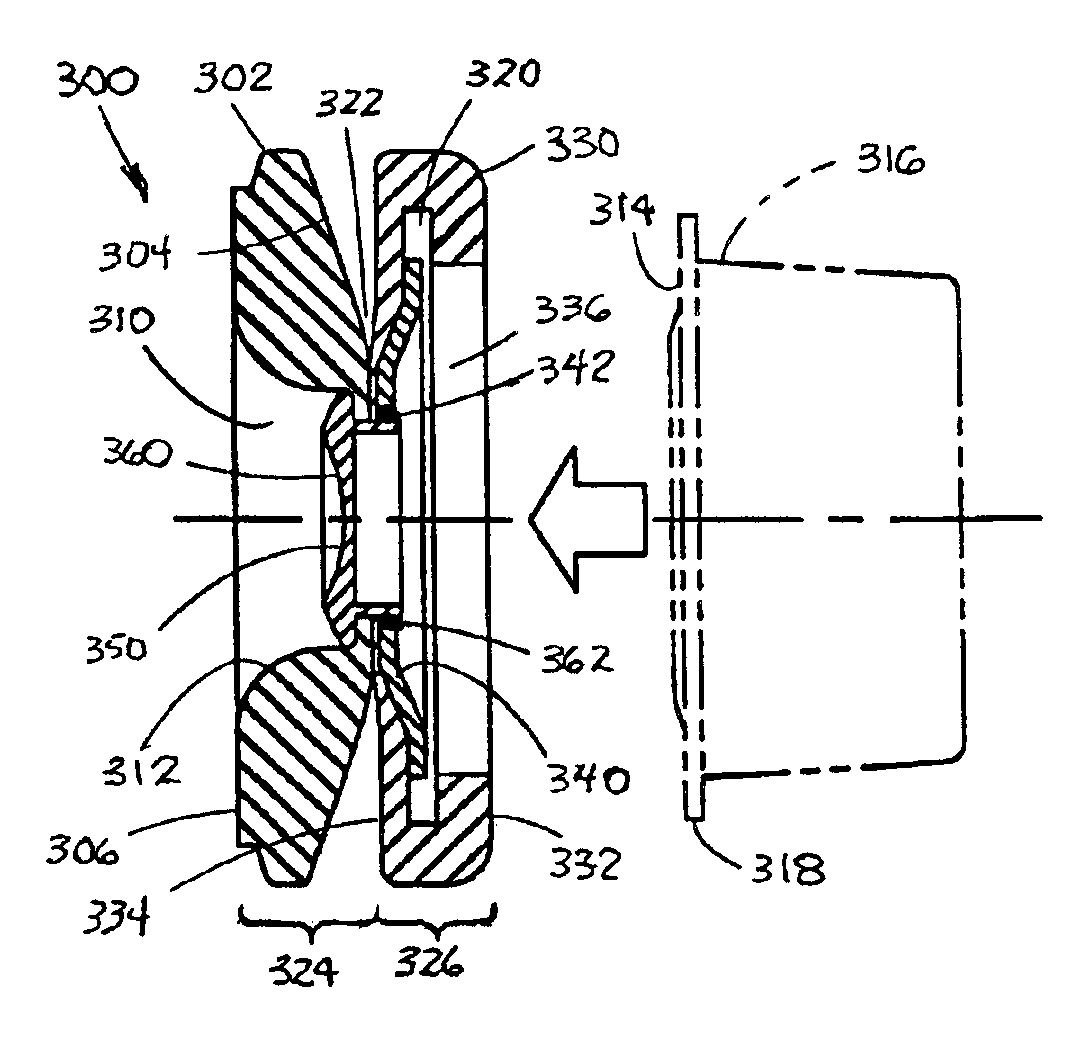
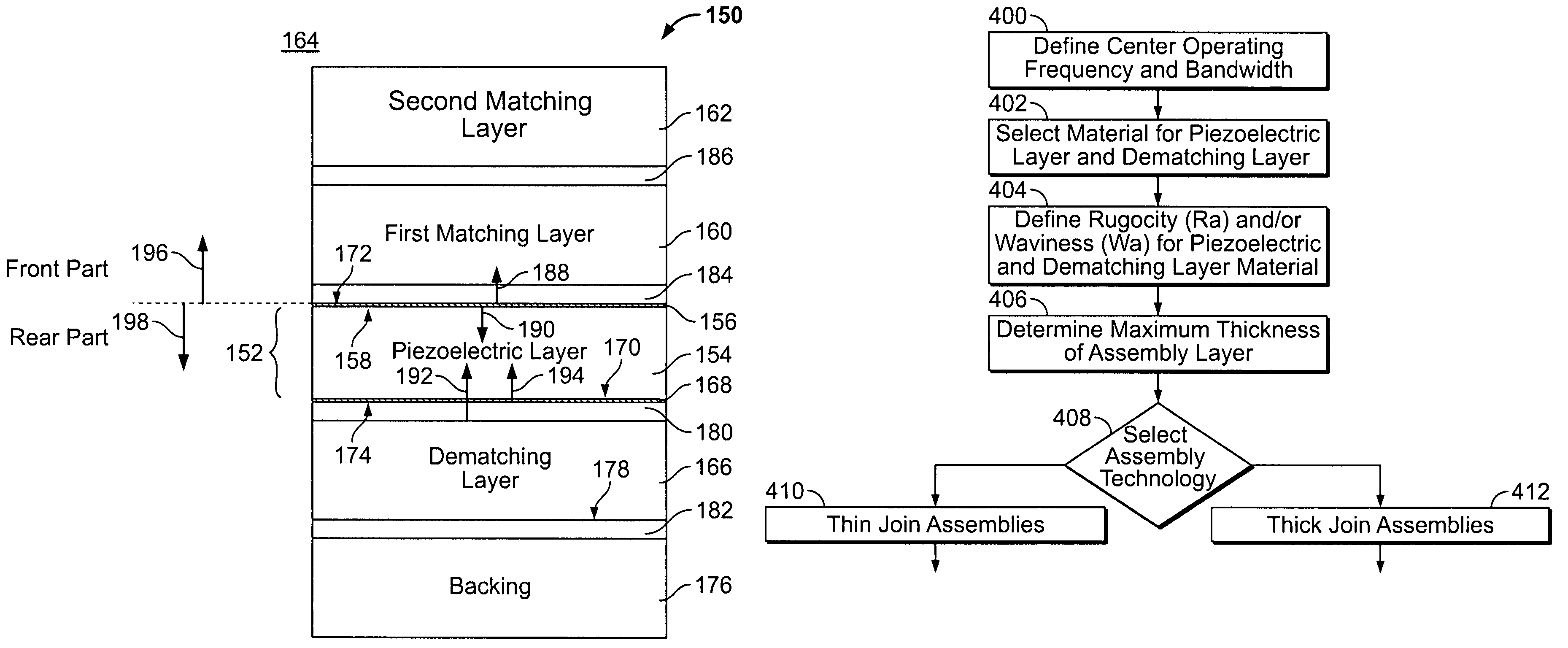
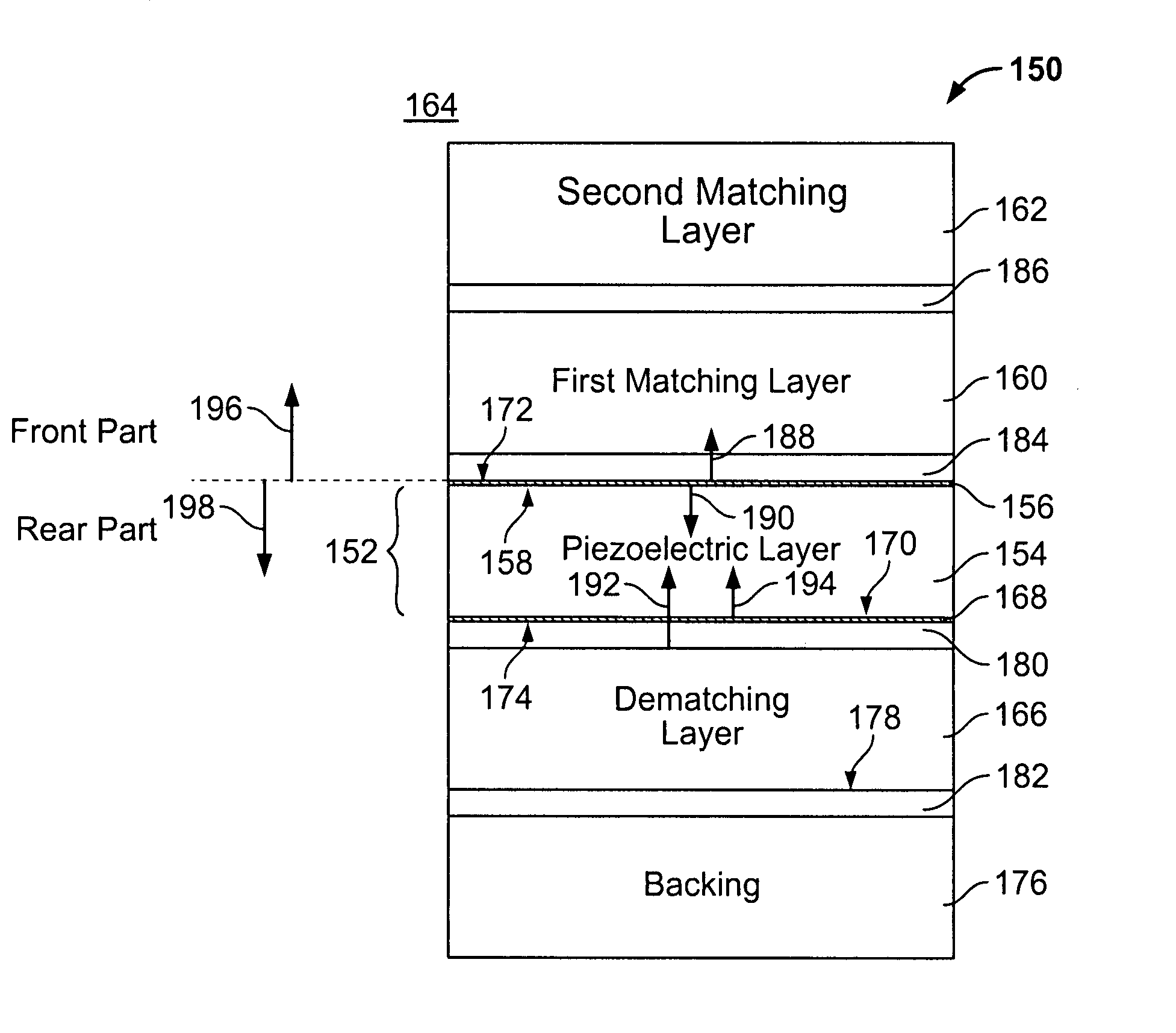
Method for optimized dematching layer assembly in an ultrasound transducer
ActiveUS7621028B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerEngineering
A method for manufacturing an acoustical stack for use within an ultrasound transducer comprises using a user defined center operating frequency of an ultrasound transducer that is at least about 2.9 MHz. A piezoelectric material and a dematching material are joined with an assembly material to form an acoustical connection therebetween. The piezoelectric material has a first acoustical impedance and *at least one of* an associated piezoelectric rugosity (Ra) and piezoelectric waviness (Wa). The dematching material has a second acoustical impedance that is different than the first acoustical impedance and at least one of an associated dematching Ra and dematching Wa. The piezoelectric and dematching materials have an impedance ratio of at least 2. The assembly material has a thickness that is based on the center operating frequency and at least one of the piezoelectric Ra, piezoelectric Wa, dematching Ra and dematching Wa.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for optimized dematching layer assembly in an ultrasound transducer
ActiveUS20090072668A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerEngineering
A method for manufacturing an acoustical stack for use within an ultrasound transducer comprises using a user defined center operating frequency of an ultrasound transducer that is at least about 2.9 MHz. A piezoelectric material and a dematching material are joined with an assembly material to form an acoustical connection therebetween. The piezoelectric material has a first acoustical impedance and *at least one of* an associated piezoelectric rugosity (Ra) and piezoelectric waviness (Wa). The dematching material has a second acoustical impedance that is different than the first acoustical impedance and at least one of an associated dematching Ra and dematching Wa. The piezoelectric and dematching materials have an impedance ratio of at least 2. The assembly material has a thickness that is based on the center operating frequency and at least one of the piezoelectric Ra, piezoelectric Wa, dematching Ra and dematching Wa.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multiple-use acoustic port
Two or more acoustic transducers share the same acoustic port in a device. The acoustic properties—such as acoustic impedance and frequency response—of the shared acoustic port are matched to each of the two or more acoustic transducers. To accomplish acoustic impedance matching, a separate back volume is provided for each of the acoustic transducers, matched to that transducer. Frequency response matching can be accomplished by the design of the transducer itself, but also by providing an adjacent element in the acoustic system of the transducer. One transducer may serve as an element in the acoustic system of another transducer. Frequency response adjustment of an individual element may also affect acoustic impedance of the entire port-transducer system.
Owner:APPLE INC
Blocking Plate Structure for Improved Acoustic Transmission Efficiency
ActiveUS20210170447A1Improve transmission efficiencyIncreased Radiation PowerLoudspeaker transducer fixingFlexible member pumpsAcoustic transmissionAcoustic medium
An acoustic matching structure is used to increase the power radiated from a transducing element with a higher impedance into a surrounding acoustic medium with a lower acoustic impedance. The acoustic matching structure consists of a thin, substantially planar cavity bounded by a two end walls and a side wall. The end walls of the cavity are formed by a blocking plate wall and a transducing element wall separated by a short distance (less than one quarter of the wavelength of acoustic waves in the surrounding medium at the operating frequency). The end walls and side wall bound a cavity with diameter approximately equal to half of the wavelength of acoustic waves in the surrounding medium. In operation, a transducing element generates acoustic oscillations in the fluid in the cavity. The transducing element may be an actuator which generates motion of an end wall in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the cavity to excite acoustic oscillations in the fluid in the cavity, and the cavity geometry and resonant amplification increase the amplitude of the resulting pressure oscillation. The cavity side wall or end walls contain at least one aperture positioned away from the center of the cavity to allow pressure waves to propagate into the surrounding acoustic medium.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Ultrasonic transducer and ultrasonic flowmeter using same
InactiveUS6776051B2Volume/mass flow measurementPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersOrganic OxideEngineering
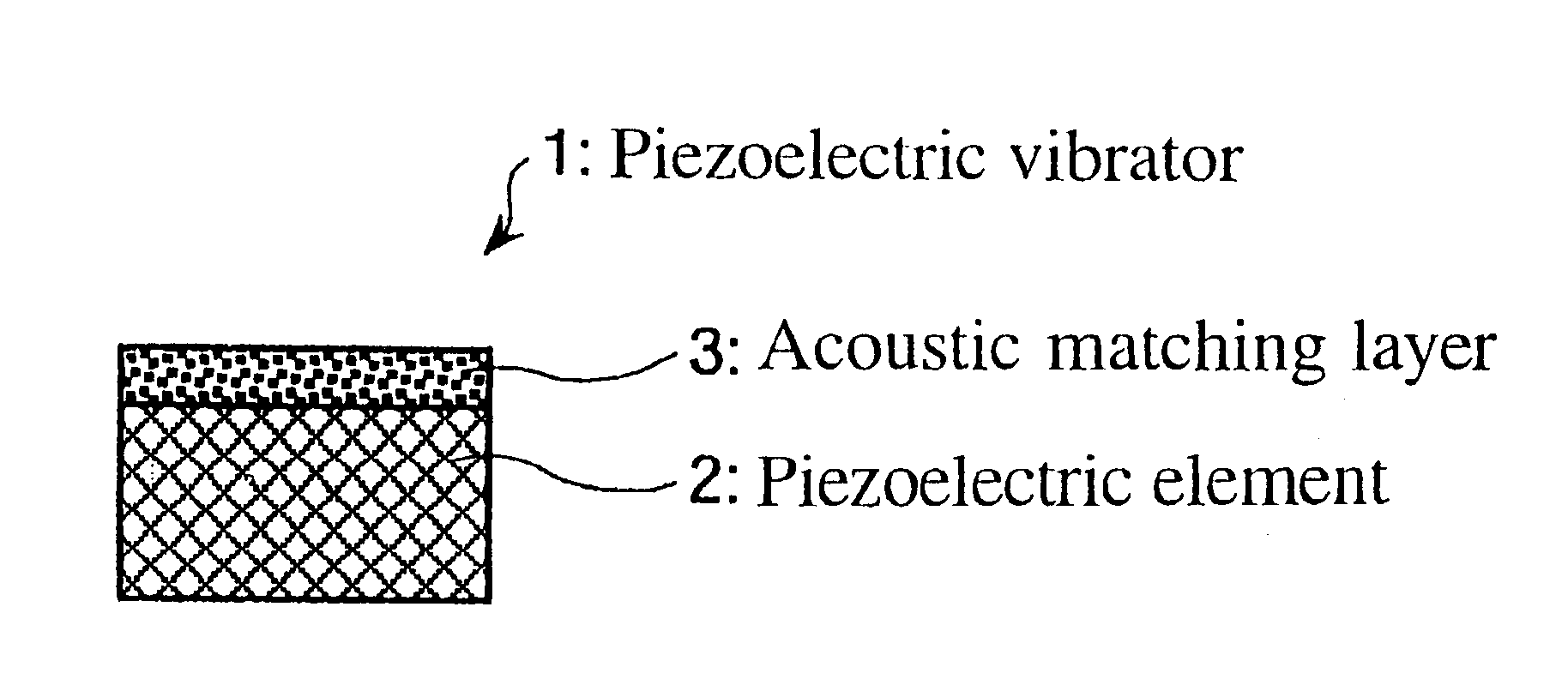
It is an object of the present invention to provide an ultrasonic transducer, which is so configured as to reduce the variations in characteristics, thereby to enable the stabilization of the precision, as well as to enable the improvement of the durability, and the like, a method for manufacturing the ultrasonic transducer, and an ultrasonic flowmeter. In order to attain this object, in accordance with the present invention, the ultrasonic transducer is so configured as to include a piezoelectric element and an acoustic matching layer, wherein the acoustic matching layer is made of a dry gel of an inorganic oxide or an organic polymer, and a solid skeletal part of the dry gel has been rendered hydrophobic. With this configuration, it is possible to obtain the ultrasonic transducer having an acoustic matching layer 3 which is very lightweight and has a small acoustic impedance due to the solid skeletal part of the dry gel which has been rendered hydrophobic. Further, it is also possible to obtain the ultrasonic transducer which shows a narrow range of characteristic variations, and is stable due to the high homogeneity of the dry gel.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High-Q-value bulk acoustic wave resonator
Disclosed is a high Q-value bulk acoustic wave resonator, and the wave resonator comprises a substrate; a piezoelectric stack structure which is located on the substrate, wherein an acoustic reflection structure is arranged between the piezoelectric stack structure and the substrate; one or more high acoustic impedance annular convex structures; one or more low acoustic impedance annular convex structures; wherein the high-acoustic-impedance annular bulge structures and the low-acoustic-impedance annular bulge structures alternately surround the boundary of the piezoelectric stack structure top electrode. According to the invention, through arranging the multiple circles of annular projection structures on the boundary of the top electrode, the transverse leakage of sound waves can be effectively reduced, thereby improving the Q value of the bulk acoustic wave resonator.
Owner:武汉敏声新技术有限公司
Interactive ultrasound-based depth measurement for medical applications
InactiveUS7748273B2Small dimensionControl volumeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLiquid jetBone structures
A device for determining the internal structure of a bone along a path directed into the bone (or other tissue) is disclosed. The device comprises a nozzle fluidically connected to a liquid reservoir for providing a liquid jet directed at the bone in the direction of the path; an ultrasonic transducer for generating ultrasonic waves through the liquid jet and for detecting echoes of the ultrasonic waves caused by changes in the acoustical impedance in the bone characterizing changes in the structure of the bone along the path; and an analyzer for interpreting the echoes into meaningful information relating to the location of the structural changes along the path.
Owner:JETGUIDE
Ultrasound inspection method and apparatus
InactiveUS20110030477A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic tapeCoupling
A method of inspecting a component, the component comprising a hole with an entrance. The method comprises: directing ultrasound into the component via a liquid coupling medium; receiving ultrasound from the component via the liquid coupling medium; and processing the received ultrasound to determine a property of the component. The entrance of the hole is sealed with tape to prevent the liquid coupling medium from flowing into the entrance of the hole.The tape has an acoustic impedance within 40% of the acoustic impedance of the liquid coupling medium. By selecting a tape with an acoustic impedance relatively close to that of the liquid coupling medium (which in most cases will be water) the tape is relatively transparent to ultrasound and thus enables at least the presence or absence of a defect in a wall of the hole to be determined.
Owner:AIRBUS UK
Substrate process tank with acoustical source transmission and method of processing substrates
ActiveUS6955727B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove energy transfer efficiencyElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistSound energy
Owner:AKRION TECH
Optimizing acoustic efficiency of a sonic filter or separator
ActiveUS20140301902A1Operation efficiency can be improvedEasy to operateMechanical vibrations separationFlotationEngineeringAcoustic wave
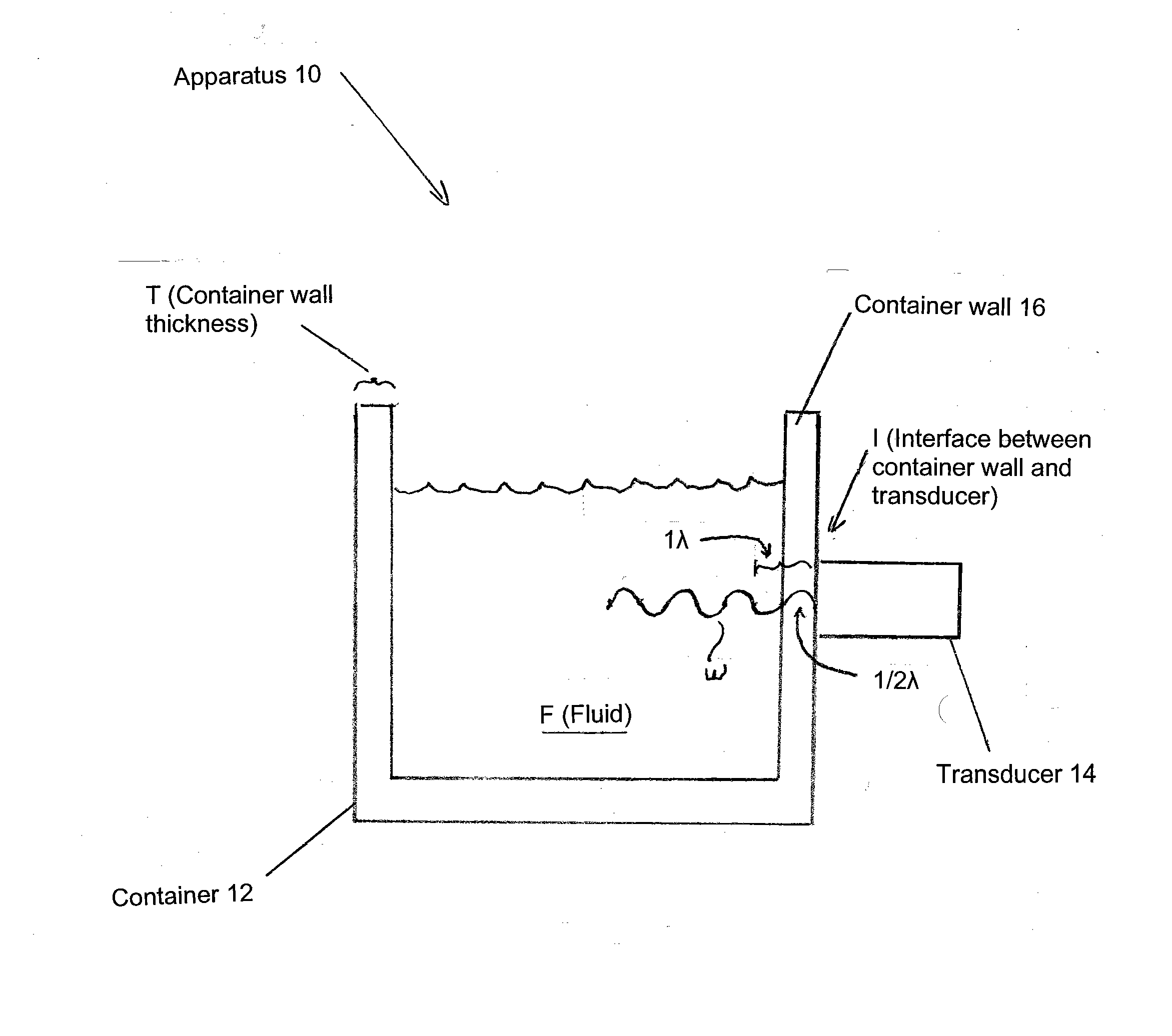
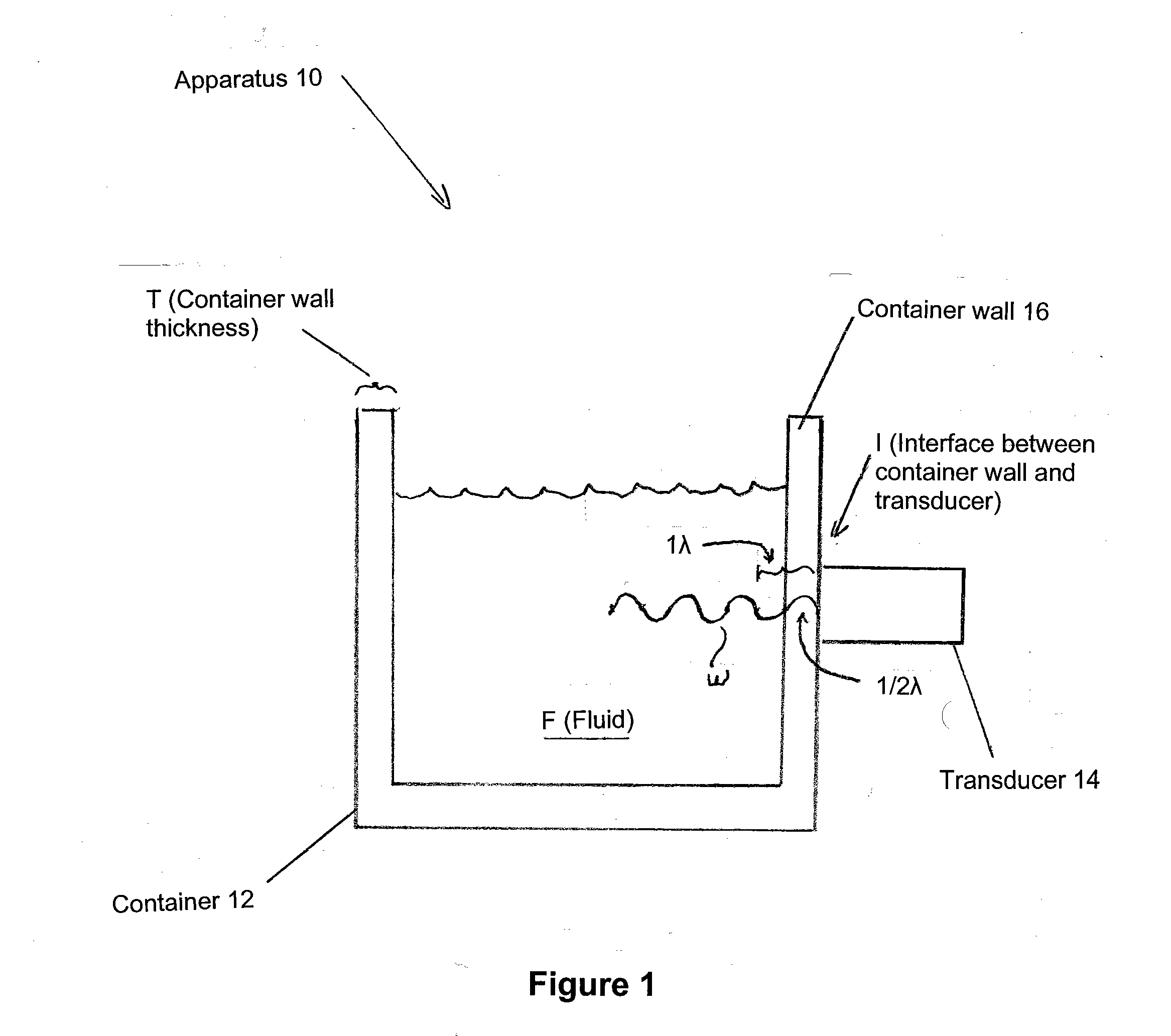
Apparatus features a container and a transducer. The container is made of a selected material and has a container wall with a selected thickness, and configured to hold a fluid therein. The transducer is configured on the outside of the container wall, and is also configured to provide a standing wave into the fluid. The selected thickness and material of the container wall is chosen to ensure about a ½ wavelength of a desired frequency exists within the container wall, so as to substantially reduce back reflections toward the transducer due to any mismatch in acoustic impedance at the interface between the container wall and the fluid, and so as to substantially maximize the amount of energy delivered to the fluid, thus improving the operating efficiency of the apparatus.
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
Method for measuring particle concentration and sizes on basis of ultraphonic impedance spectrum
ActiveCN105300856AConducive to online real-time measurement applicationsSimple structureParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisHigh concentrationUltrasonic attenuation
The invention relates to a method for measuring particle concentration and sizes on the basis of an ultraphonic impedance spectrum. The method comprises that steps that 1, a theoretical impedance real component spectrum is obtained through an ECAH model and theory; 2, a theoretical curve of particle size-resonant frequency and a theoretical curve of a concentration-resonant amplitude are obtained; 3, an acoustic impedance spectrum is obtained from experiments according to an ultrasonic transducer and calculation, a real time component is taken from the acoustic impedance spectrum, and an experimental impedance real component spectrum is obtained; treatment is conducted on signals obtained from the experiments through a formula in the third step, resonant frequency for measuring the object impedance real component spectrum can be obtained, the resonant frequency fR is extracted, and the concentration and the particle size of a measured object can be obtained from the curves of the particle size-resonant frequency and the concentration-resonant amplitude determined in the second step. According to the method for measuring the particle concentration and sizes on the basis of the ultraphonic impedance spectrum, a system is simple in structure and low in cost, online measurement can be achieved, and the method can be used for the laboratory science research; compared with utilizing the ultrasonic attenuation and phase velocity, the method is more suitable for measurement of particles in a high concentration two-phase mixture.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Acoustic isolator
ActiveUS20100157741A1Mitigate reflectionReduce reflectionSurveyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersAcoustic waveTransmitter
An acoustic isolator for use with tubular assemblies such as drillpipe or production tubing comprising an acoustic wave transmitter, the acoustic isolator comprising, in series connection, an odd integer λ / 4 multiple tuning bar of first acoustic impedance adjacent the acoustic wave transmitter, an odd integer λ / 4 multiple reflector tube of second acoustic impedance, and a snubber of third acoustic impedance, wherein there is an acoustic impedance mismatch between the odd integer λ / 4 multiple tuning bar and the odd integer λ / 4 multiple reflector tube and an acoustic impedance mismatch between the odd integer λ / 4 multiple reflector tube and snubber, such that a ‘down’ wave propagated toward the isolator is reflected back substantially in phase with an ‘up’ wave propagated from the acoustic wave source away from the isolator. Furthermore, the acoustic isolator is similarly effective in reflecting ‘up’ propagating waves originating from below the isolator, hence further protecting the acoustic wave source from possible deleterious interference.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC
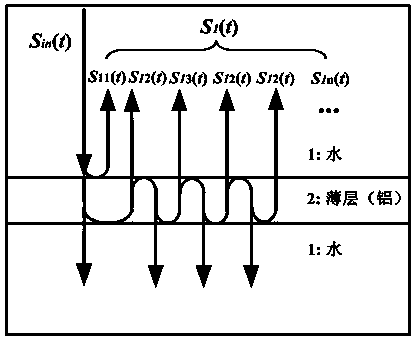
Method for simultaneously measuring multiple parameters of linear visco-elastic thin layer material by employing ultrasonic flat probe
InactiveCN103616439ASolve the problem of signal aliasingAvoid initial guess selection conundrumsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesThin layerComputational physics
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously measuring multiple parameters of a linear visco-elastic thin layer material by employing an ultrasonic flat probe. The method comprises the steps: 1) immersing a referred base material and the linear visco-elastic thin layer material in water, placing the ultrasonic flat probe respectively right above the referred base material and the linear visco-elastic thin layer material to measure and obtain reflection echo s0(t) and s1(t); 2) performing low-pass filtering on s0(t) and s1(t); 3) performing optimum estimate on echo s11(t) which belongs to s1(t) and comes from the upper surface of the linear visco-elastic thin layer material, so as to obtain an optimum measured value Zm2 of acoustic impedance, and subtracting a corresponding s11(t) from s1(t) when the acoustic impedance is equal to Zm2; and 4) performing optimum estimate on echo s12(t) which belongs to s1(t) and comes from the lower surface of the linear visco-elastic thin layer material, so as to obtain optimum measured values delta tm2 and alpha m2 of transit time and attenuation coefficient. The method helps to avoid the fitting convergence domain problem frequently appeared in conventional measuring methods based on reflection coefficient spectrum fitting, and is suitable for measuring acoustics characteristics of thin layer materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
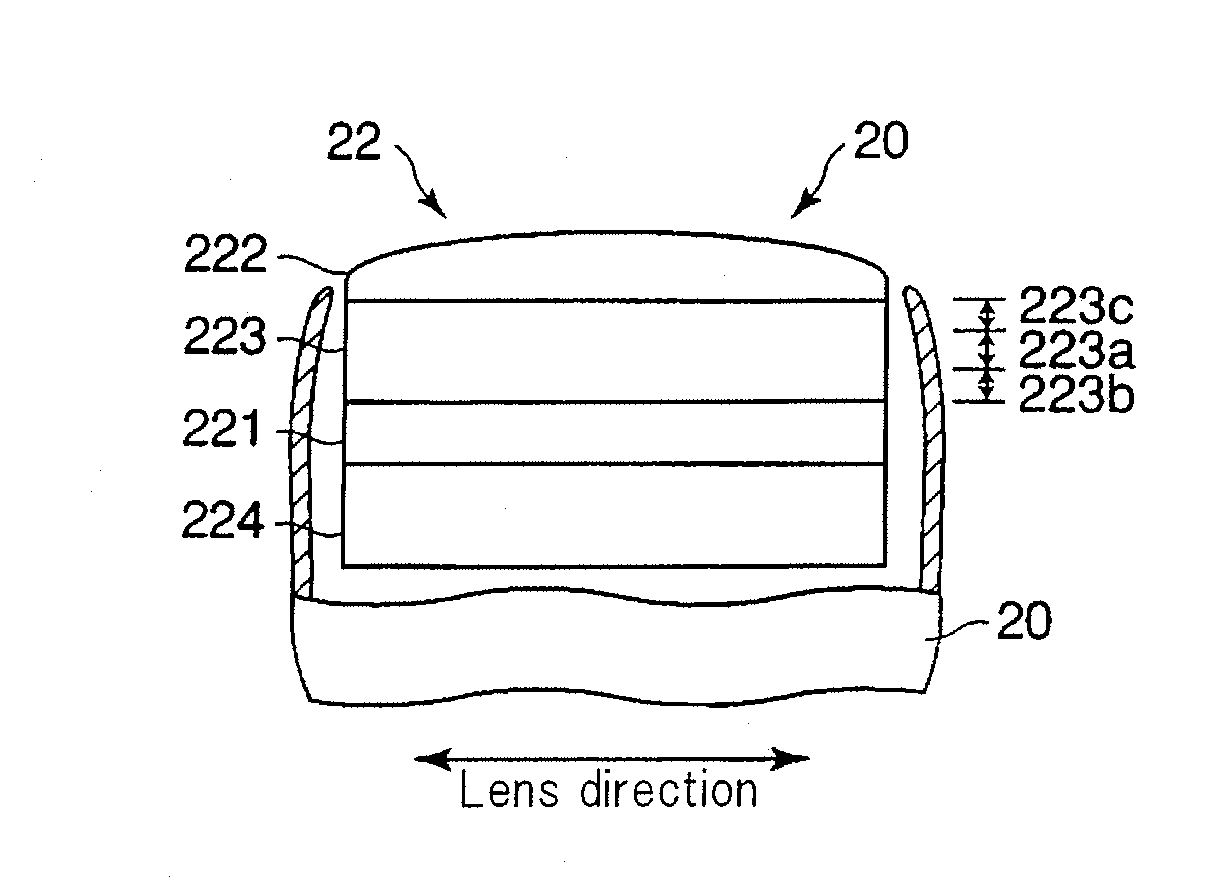
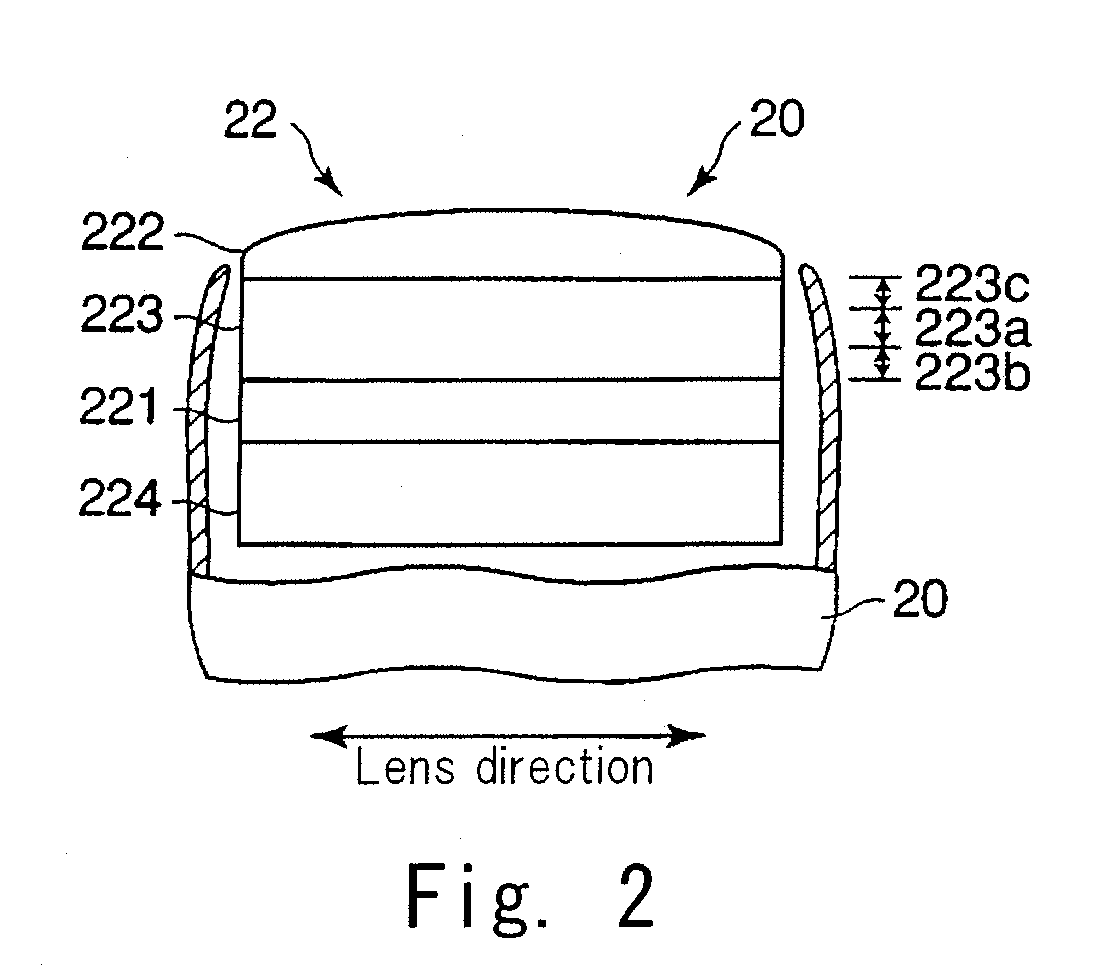
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus and ultrasonic probe
InactiveUS20070108872A1Improve efficiencyEfficient disseminationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical vibrations separationFocus ultrasoundAcoustics
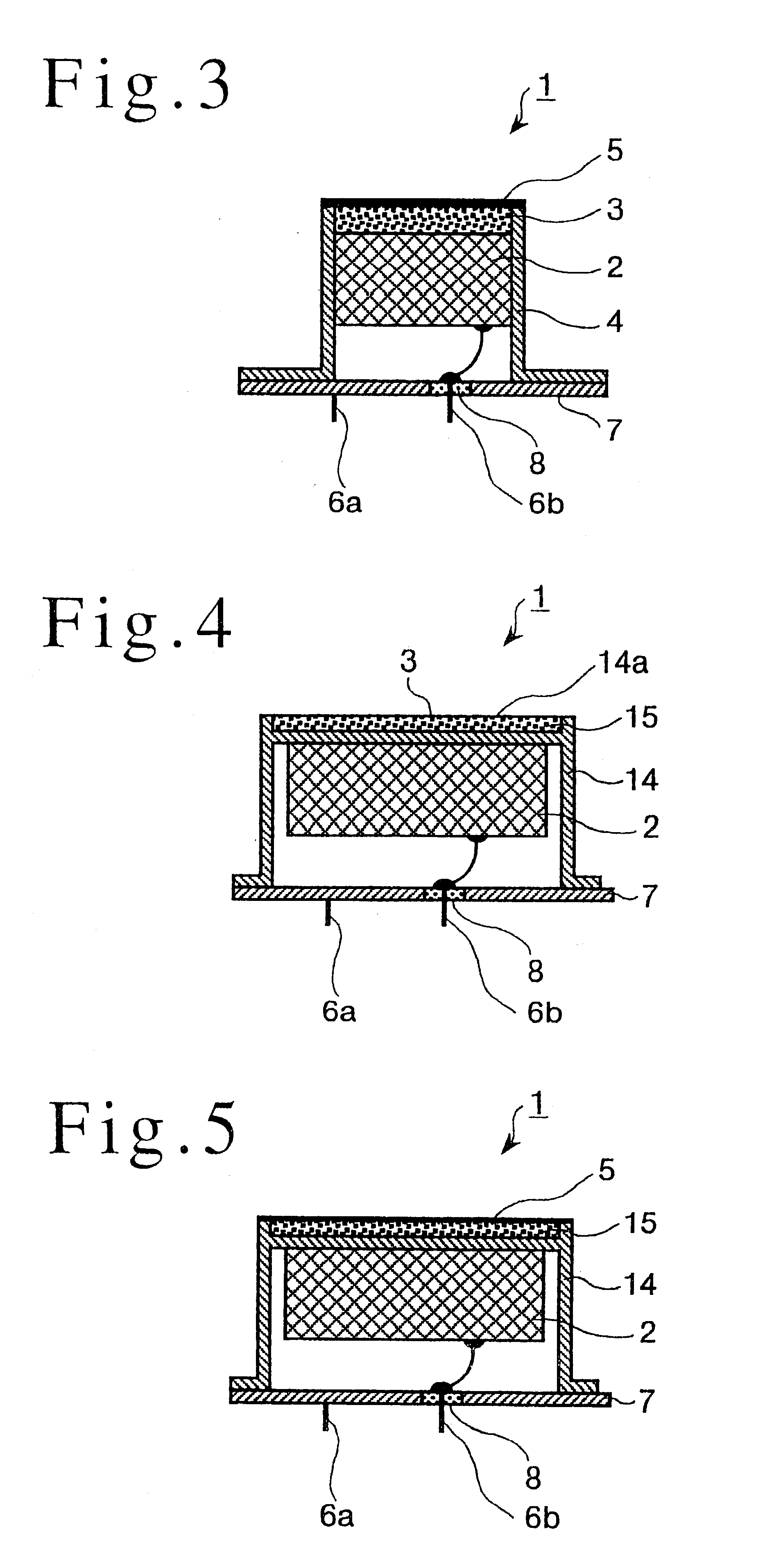
An ultrasonic probe including a piezoelectric vibrator configured to transmit and receive ultrasonic waves, an acoustic lens configured to focus the ultrasonic waves and an acoustic matching layer arranged between the piezoelectric vibrator and the acoustic lens and configured to modify acoustic impedance from the piezoelectric vibrator to the acoustic lens. The acoustic matching layer includes a first region arranged at center areas along a direction of transmitting and receiving of the ultrasonic waves, a second region arranged between the first region and the piezoelectric vibrator and having a rate of change of acoustic impedance which is less than rate of change of acoustic impedance of the first region and a third region arranged between the first region and the acoustic lens, and having a rate of change of acoustic impedance which is less than a rate of change of acoustic impedance of the first region.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Ultrasonic endoscopic image intelligent segmentation and quantification method and system based on deep learning
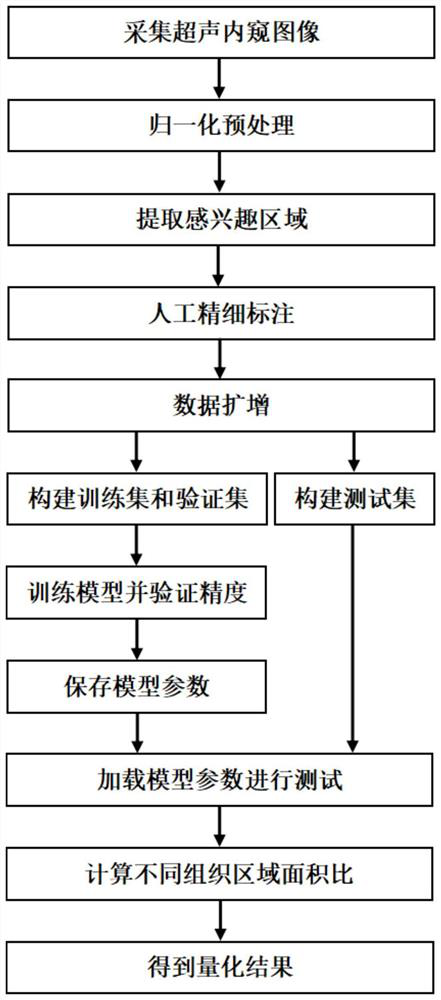
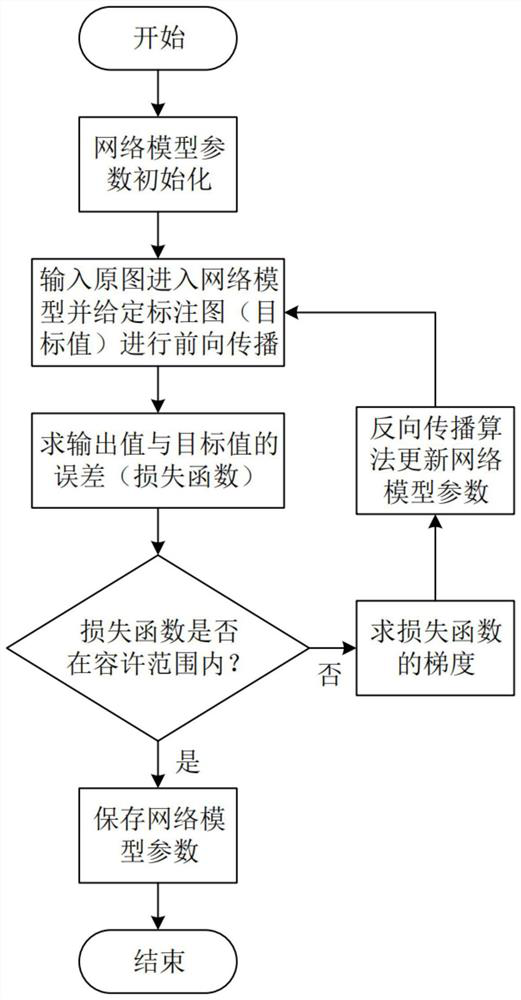
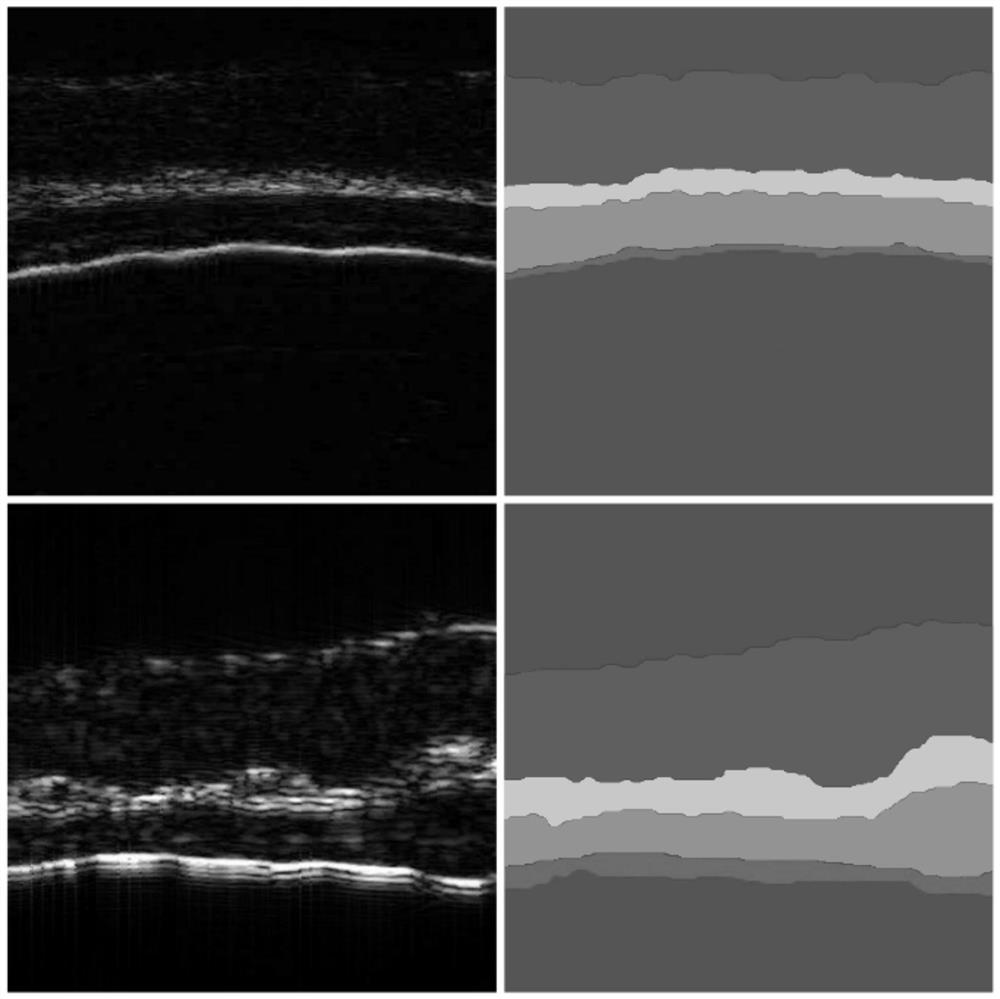
ActiveCN111784721AImprove accuracyOvercome the difficulty of getting accurate segmentation resultsImage analysisNeural architecturesNetwork modelTest set
The invention discloses an ultrasonic endoscopic image intelligent segmentation and quantification method and system based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out image normalization preprocessing; extracting a region of interest; carrying out artificial fine labeling on different acoustic impedance layers; performing data amplification to obtain more images, and dividing the images and the corresponding manually labeled images into a training set, a verification set and a test set; constructing a full convolutional neural network model; sending the training set into a network model for training to obtain a segmentation model; verifying the segmentation precision of the trained model for the verification set; and calculating the relative area ratio of the acoustic impedance layers of different tissues after segmentation to obtain a quantification result. Based on the method, a fine acoustic impedance layered segmentation image and accurate quantizationparameters can be obtained, labor cost is reduced, and the method is expected to be applied to the fields of medical image analysis and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Sound absorption unit and sound absorption device
PendingCN112435647AReduce manufacturing costImprove elimination effectSound producing devicesHelmholtz resonatorLow frequency band
The invention provides a sound absorption unit and a sound absorption device. The sound absorption unit comprises at least one quarter-wavelength tube bank body and at least one Helmholtz resonator row body which are arranged in a stacked mode in the preset direction; the quarter-wave tube bank body comprises a plurality of quarter-wave tubes arranged side by side, and each quarter-wave tube is provided with a first open end and a first closed end which are oppositely arranged; the Helmholtz resonator row body comprises a plurality of Helmholtz resonators arranged side by side, and each Helmholtz resonator is provided with a second open end and a second closed end which are oppositely arranged; the first open ends and the second open ends are adopted to jointly form a sound wave incident surface of the sound absorption unit; and in the preset frequency band, the overall acoustic impedance of the sound absorption unit is matched with the acoustic impedance of the air. The sound absorption unit can achieve a good sound absorption effect at a low frequency band, space can be saved, the preparation cost is reduced, and environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:南京光声超构材料研究院有限公司 +1
Ultrasonic transmitter-receiver and ultrasonic flowmeter
InactiveCN1578900AVolume/mass flow measurementSound producing devicesEngineeringUltrasonic vibration
An ultrasonic transducer according to the present invention includes: a piezoelectric body 4 to set up ultrasonic vibrations; an acoustic matching layer 3 made of a material with a density of 50kg / m3 to 1,000 kg / m3;and an acoustic impedance of 2.5x103kg / m2 / s to 1.0x106kg / m2 / s ; a lower acoustic matching layer 9 provided between the piezoelectric body 4 and the acoustic matching layer 3; and a structure supporting member 6 that supports the lower acoustic matching layer 9 and the piezoelectric body 4 thereon and shields the piezoelectric body 4 from a fluid that propagates the ultrasonic vibrations. The ultrasonic transducer includes a protective portion, which contacts with at least a portion of a side surface of the acoustic matching layer 4. This protective portion is defined by a portion of the lower acoustic matching layer 9 and forms an integral part of the lower acoustic matching layer 9.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com