Patents
Literature
34 results about "Colorectal tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Brain endothelial cell expression patterns
InactiveUS20060127902A1Auxiliary diagnosisCompound screeningNervous disorderAbnormal tissue growthBrain tumor
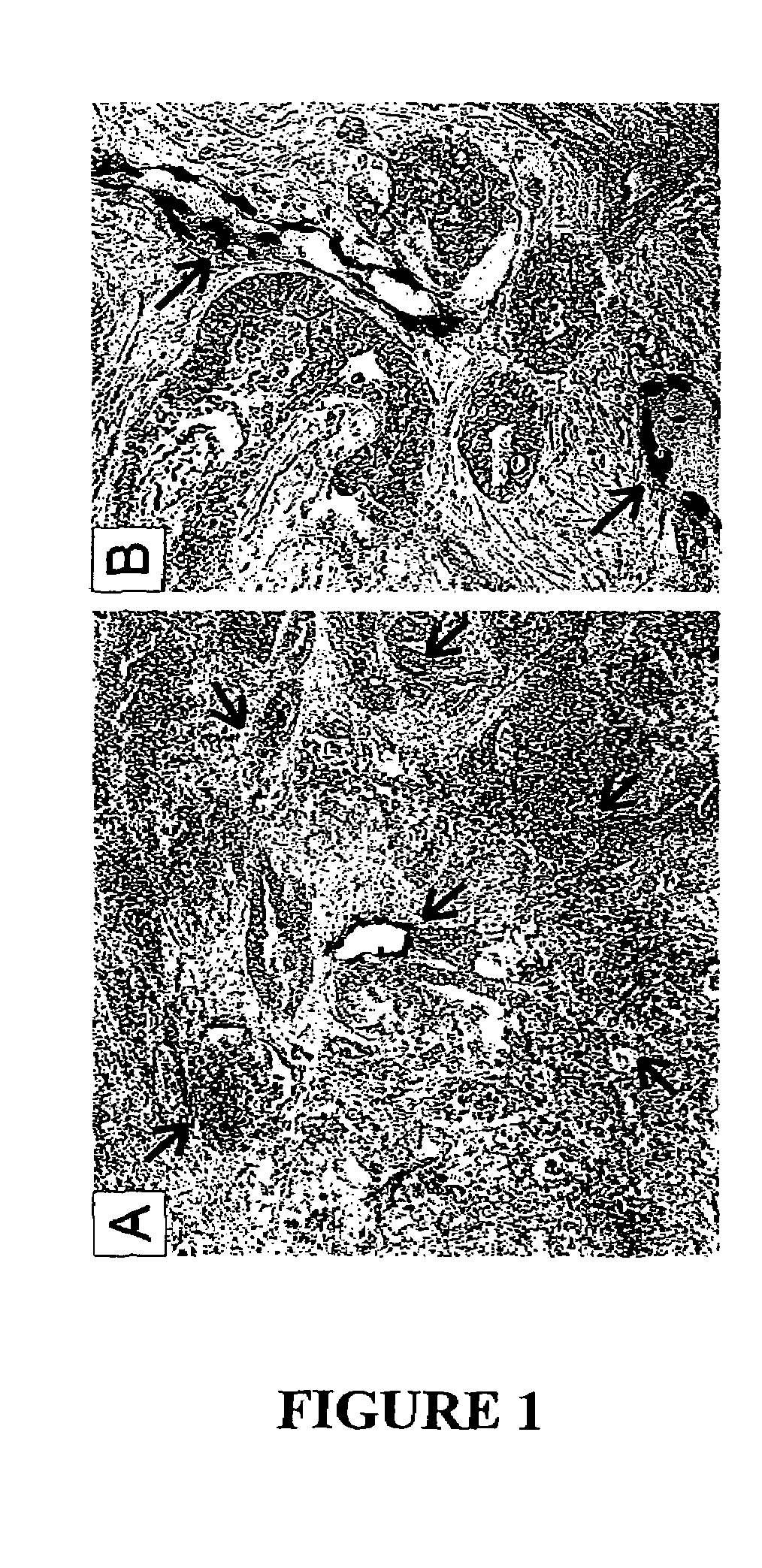
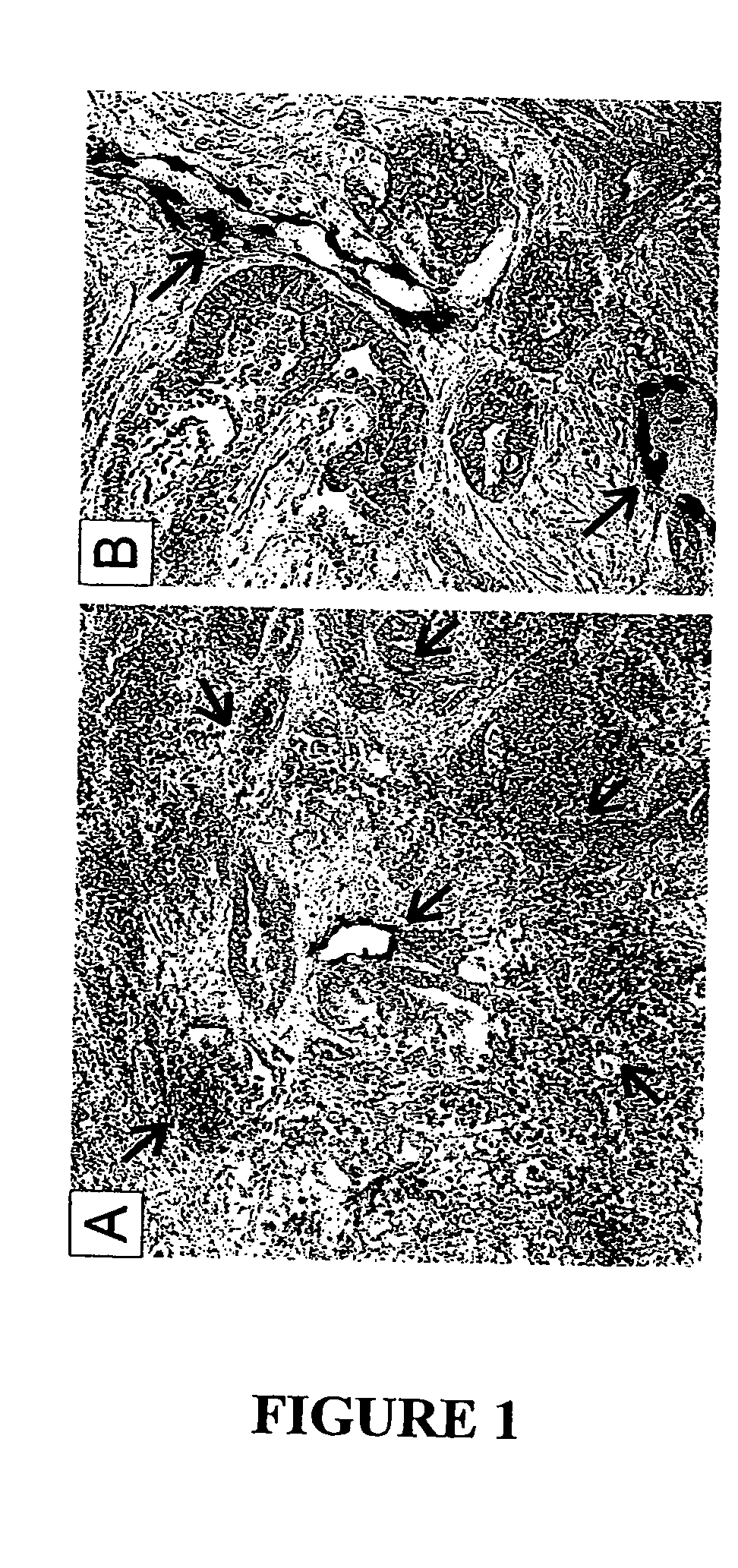
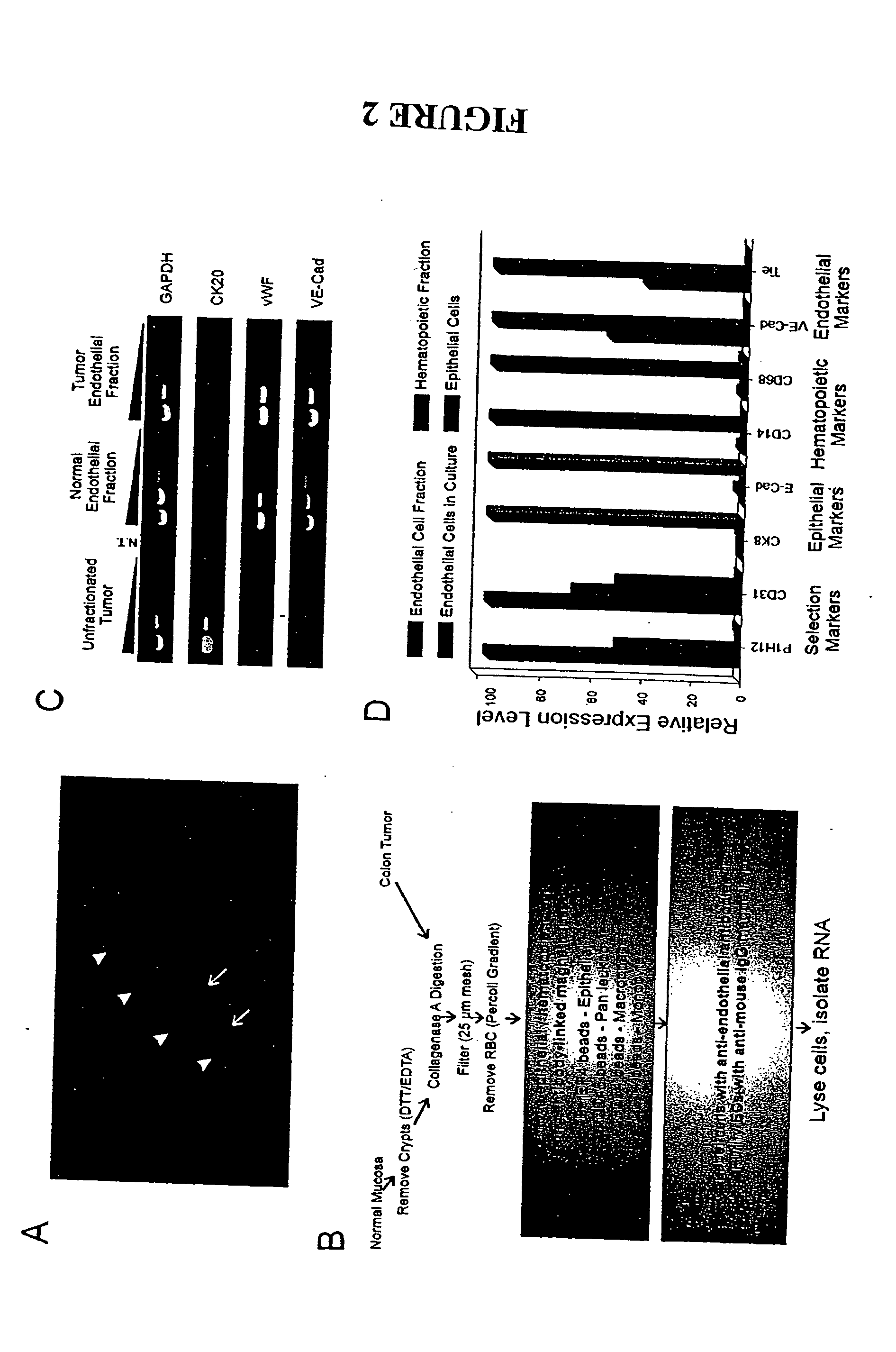
To gain a better understanding of brain tumor angiogenesis, new techniques for isolating brain endothelial cells (ECs) and evaluating gene expression patterns were developed. When transcripts from brain ECs derived from normal and malignant colorectal tissues were compared with transcripts from non-endothelial cells, genes predominantly expressed in the endothelium were identified. Comparison between normal- and tumor-derived endothelium revealed genes that were specifically elevated in tumor-associated brain endothelium. These results confirm that neoplastic and normal endothelium in human brains are distinct at the molecular level, and have significant implications for the development of anti-angiogenic therapies in the future.
Owner:GENZYME CORP +1
Endothelial cell expression patterns
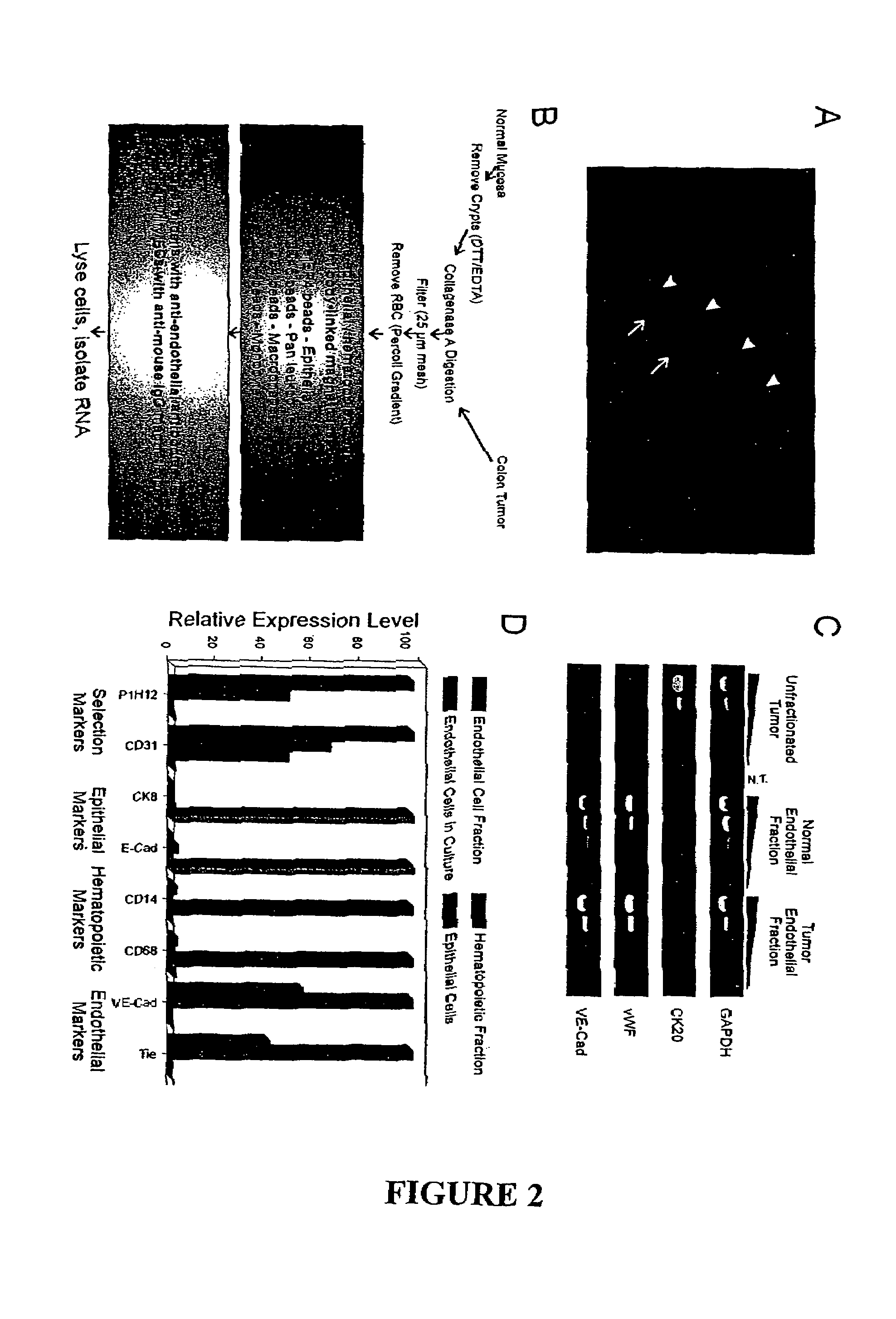
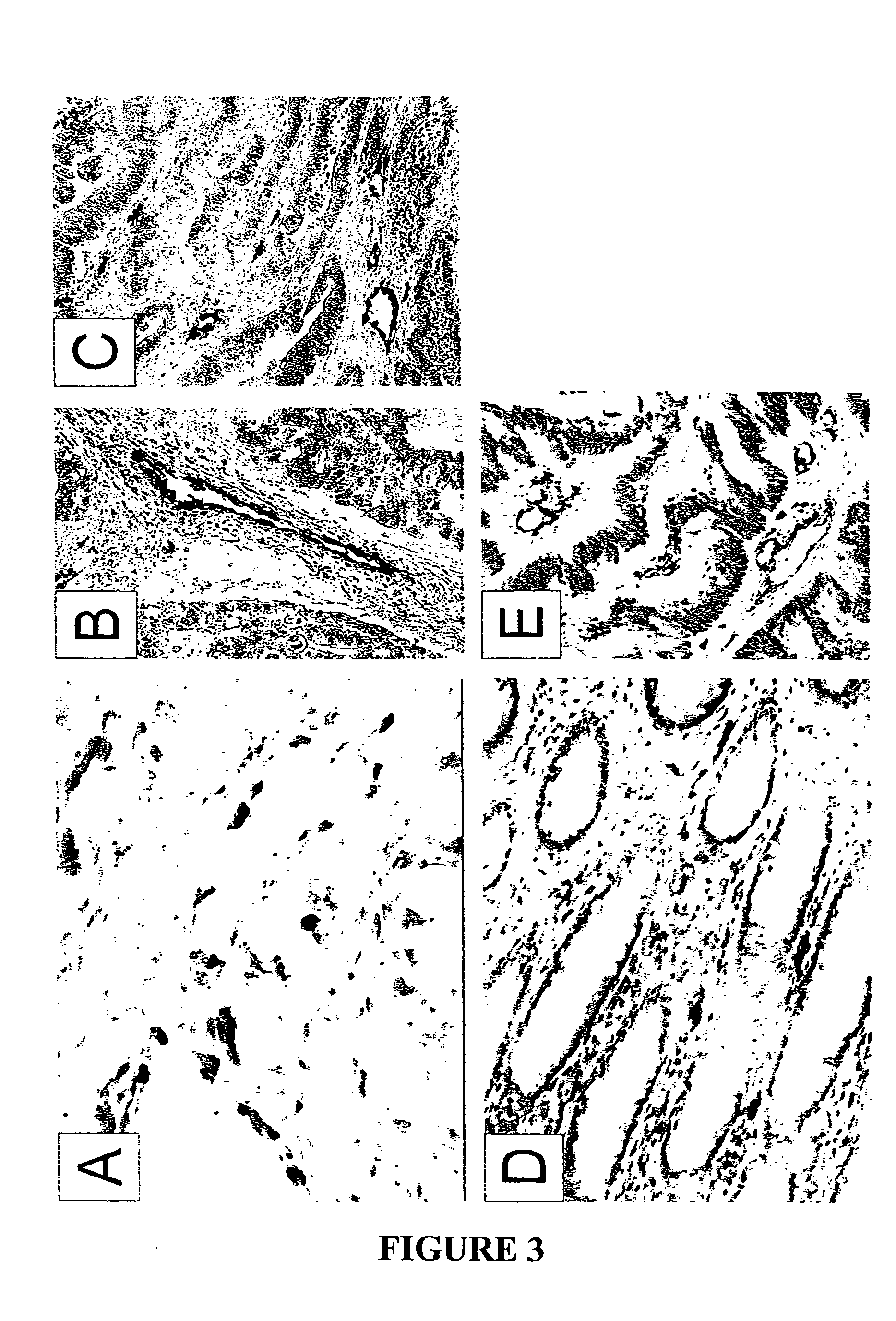
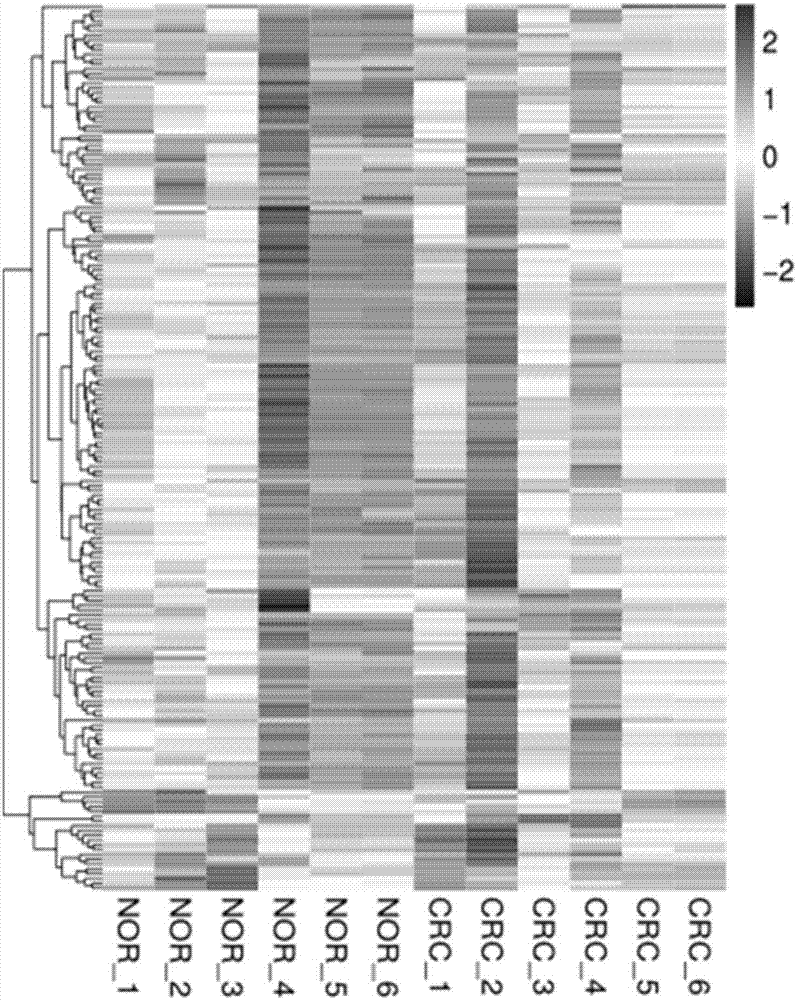
To gain a better understanding of tumor angiogenesis, new techniques for isolating endothelial cells (ECs) and evaluating gene expression patterns were developed. When transcripts from ECs derived from normal and malignant colorectal tissues were compared with transcripts from non-endothelial cells, over 170 genes predominantly expressed in the endothelium were identified. Comparison between normal- and tumor-derived endothelium revealed 79 differentially expressed genes, including 46 that were specifically elevated in tumor-associated endothelium. Experiments with representative genes from this group demonstrated that most were similarly expressed in the endothelium of primary lung, breast, brain, and pancreatic cancers as well as in metastatic lesions of the liver. These results demonstrate that neoplastic and normal endothelium in humans are distinct at the molecular level, and have significant implications for the development of anti-angiogenic therapies in the future.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Endothelial cell expression patterns
InactiveUS20050142138A1Reduced activityHigh activitySenses disorderAntipyreticAbnormal tissue growthMolecular level
To gain a better understanding of tumor angiogenesis, new techniques for isolating endothelial cells (ECs) and evaluating gene expression patterns were developed. When transcripts from ECs derived from normal and malignant colorectal tissues were compared with transcripts from non-endothelial cells, over 170 genes predominantly expressed in the endothelium were identified. Comparison between normal- and tumor-derived endothelium revealed 79 differentially expressed genes, including 46 that were specifically elevated in tumor-associated endothelium. Experiments with representative genes from this group demonstrated that most were similarly expressed in the endothelium of primary lung, breast, brain, and pancreatic cancers as well as in metastatic lesions of the liver. These results demonstrate that neoplastic and normal endothelium in humans are distinct at the molecular level, and have significant implications for the development of anti-angiogenic therapies in the future.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Colorectal cancer diagnostic biomarker and application thereof
ActiveCN107447033AAccurate judgmentQuick judgmentNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurement5 year survival rateMortality rate
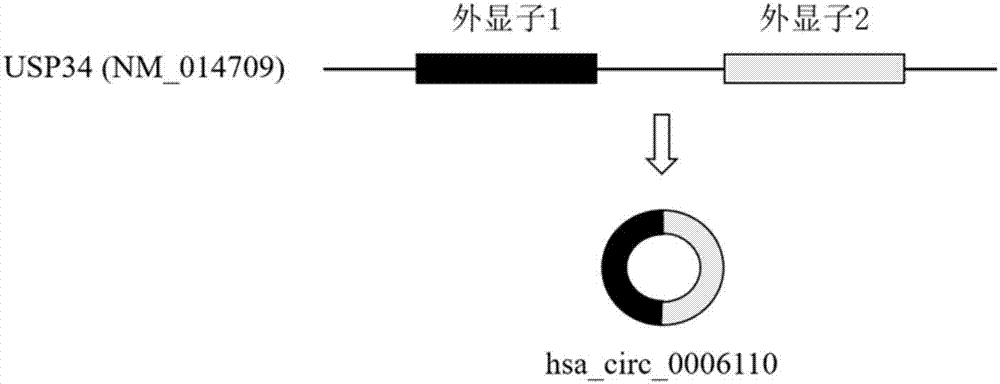
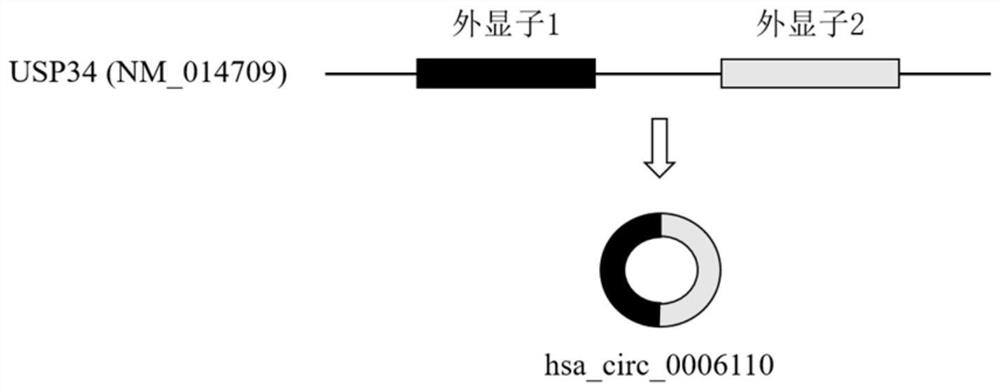
The invention relates to a colorectal cancer diagnostic biomarker and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The colorectal cancer diagnostic biomarker provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that hsa_circ_0006110 gene expression is discovered to be closely related to a colorectal cancer for the first time; through detecting the expression of hsa_circ_0006110 in a subject colorectal tissue, whether a subject suffers from the colorectal cancer or the risk of the colorectal cancer exists or not can be more accurately and quickly judged, so that a prevention or treatment scheme is provided for a clinician. A target gene as a drug for treating the colorectal cancer provides a new treatment targets and treatment approach for colorectal cancer treatment; compared with a traditional detection means, the diagnostic biomarker is more timely and more specific to diagnose, so that the five-year survival rate of a colorectal cancer patient is improved, and the death rate is reduced, therefore, the application prospect is wide.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Secreted and cytoplasmic tumor endothelial markers
InactiveUS20090233270A9Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthHuman tumor
To gain a better understanding of tumor angiogenesis, new techniques for isolating endothelial cells (ECs) and evaluating gene expression patterns were developed. When transcripts from ECs derived from normal and malignant colorectal tissues were compared with transcripts from non-endothelial cells, over 170 genes predominantly expressed in the endothelium were identified. Comparison between normal- and tumor-derived endothelium revealed many differentially expressed genes, including a large nujber of genes that were specifically elevated in tumor-associated endothelium. Experiments with representative genes from this group demonstrated that most were similarly expressed in the endothelium of primary lung, breast, brain, and pancreatic cancers as well as in metastatic lesions fo the liver. Theses results demonstrate that neoplastic and normal endothelium in humans are distinct at the molecular level, and have significant implications for the development of anti-angiogenic.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Endothelial cell expression patterns
To gain a better understanding of tumor angiogenesis, new techniques for isolating endothelial cells (ECs) and evaluating gene expression patterns were developed. When transcripts from ECs derived from normal and malignant colorectal tissues were compared with transcripts from non-endothelial cells, over 170 genes predominantly expressed in the endothelium were identified. Comparison between normal- and tumor-derived endothelium revealed 79 differentially expressed genes, including 46 that were specifically elevated in tumor-associated endothelium. Experiments with representative genes from this group demonstrated that most were similarly expressed in the endothelium of primary lung, breast, brain, and pancreatic cancers as well as in metastatic lesions of the liver. These results demonstrate that neoplastic and normal endothelium in humans are distinct at the molecular level, and have significant implications for the development of anti-angiogenic therapies in the future.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Membrane Associated Tumor Endothelium Markers
InactiveUS20110104059A1Reduced activityHigh activitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMolecular levelFhit gene
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis for regulating signal path of colon tumor and application thereof
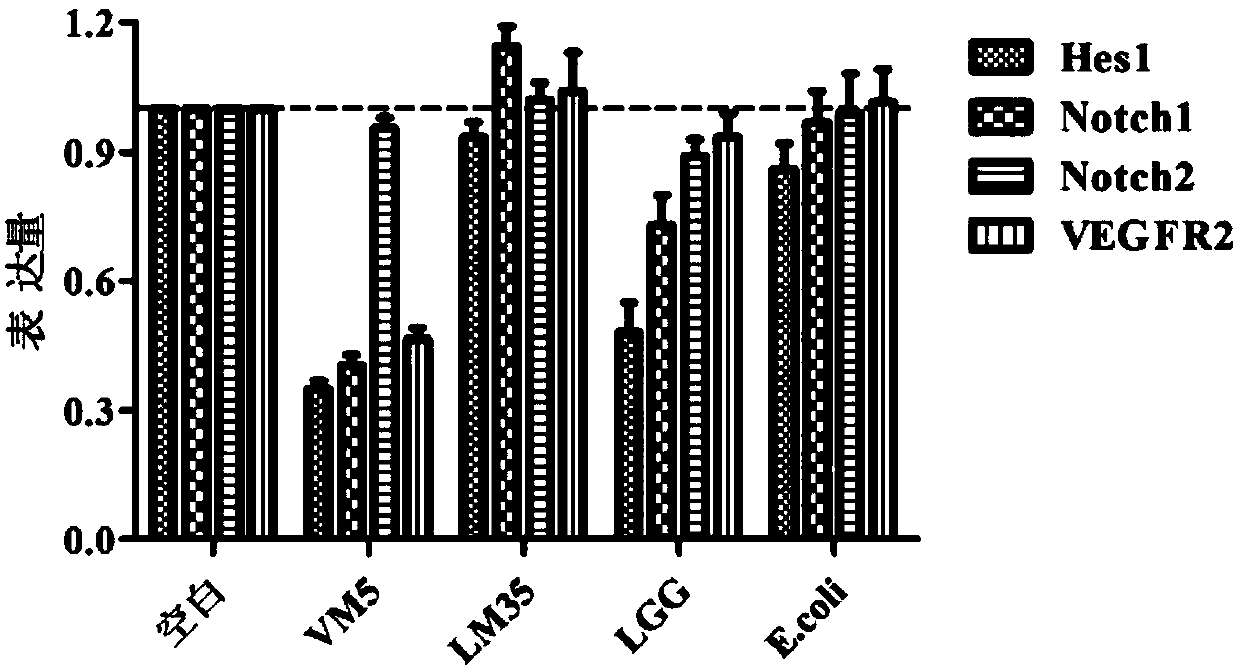
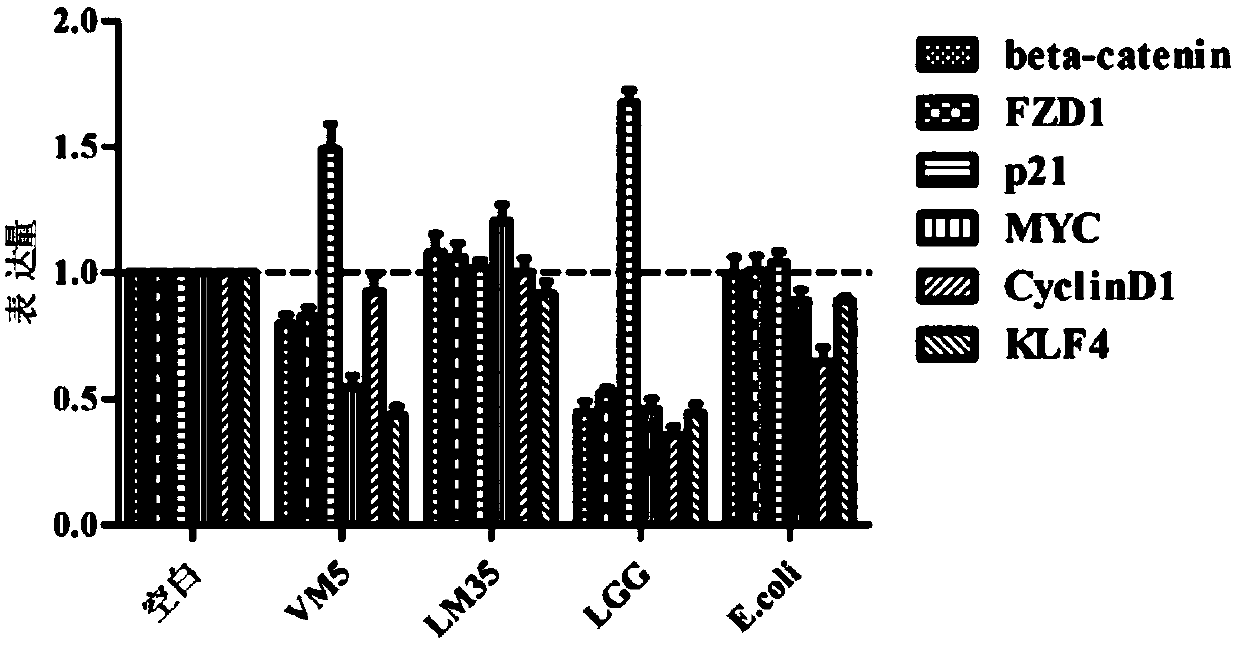
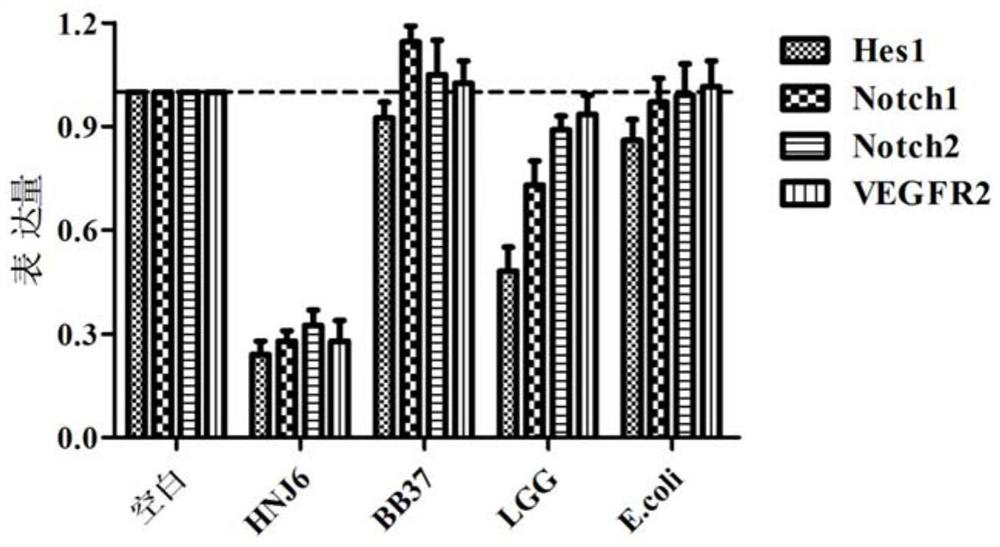
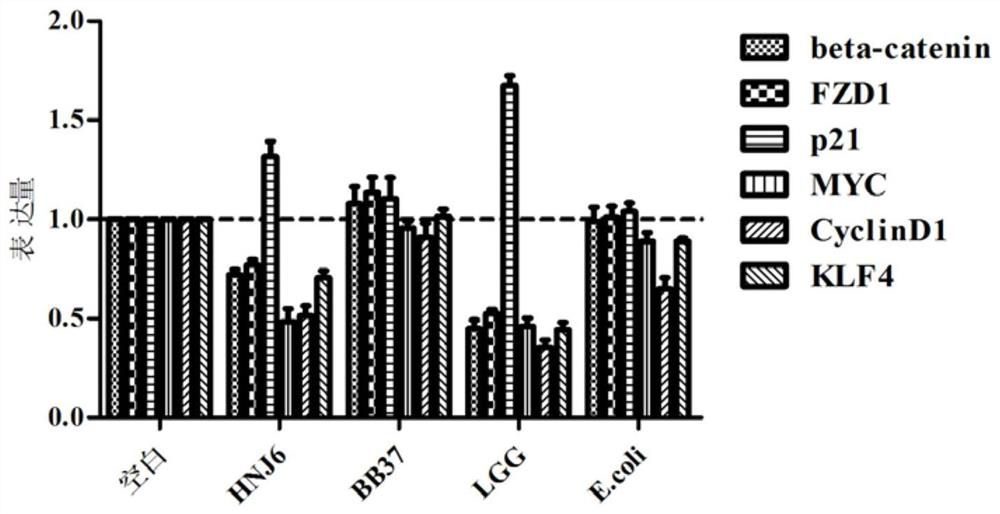
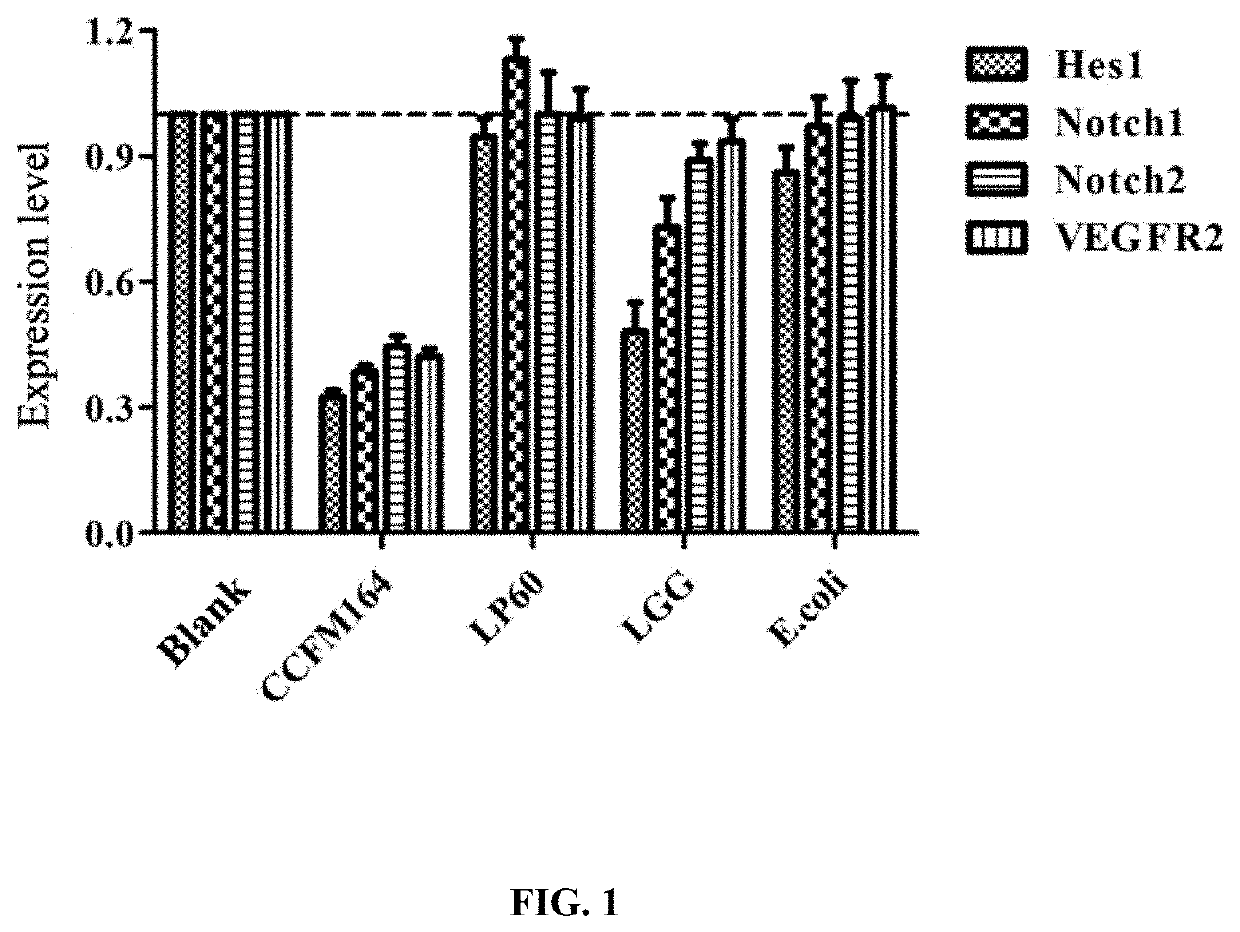
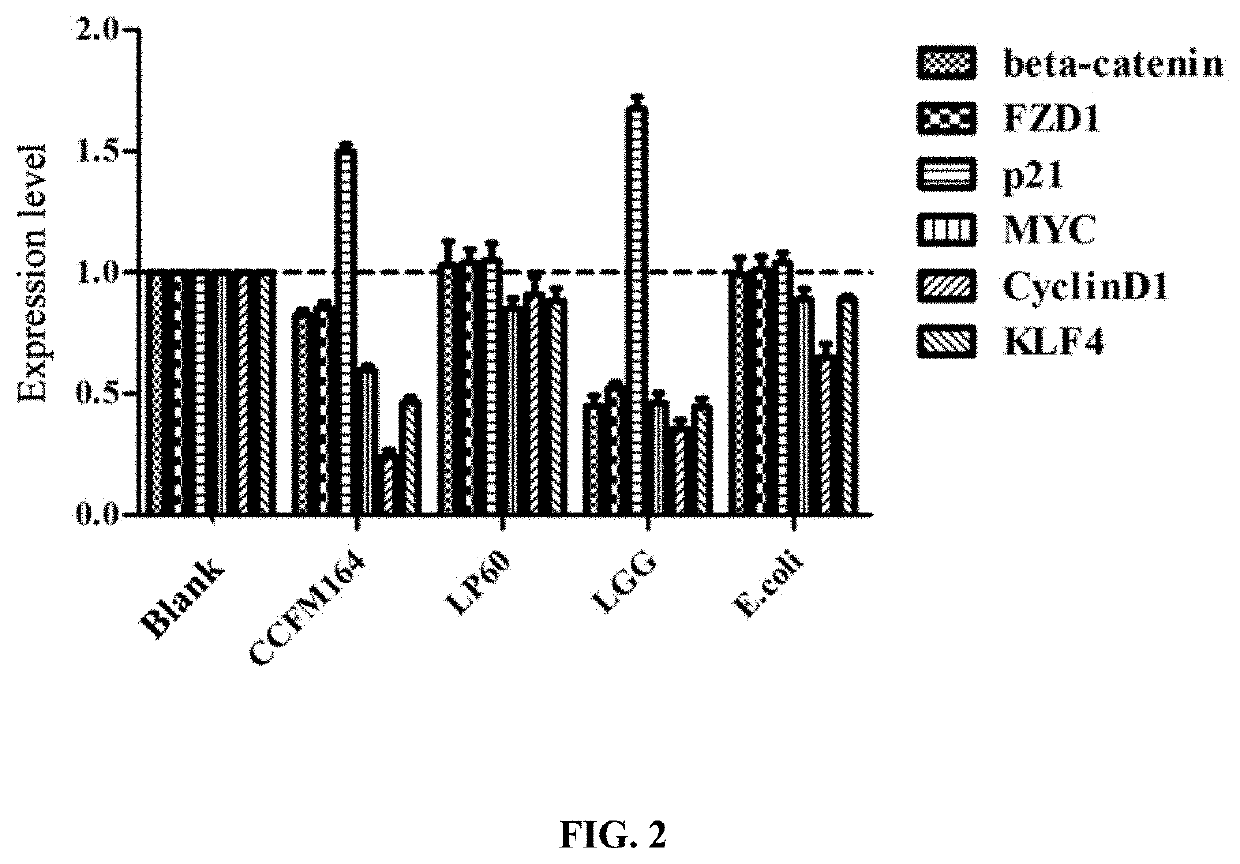
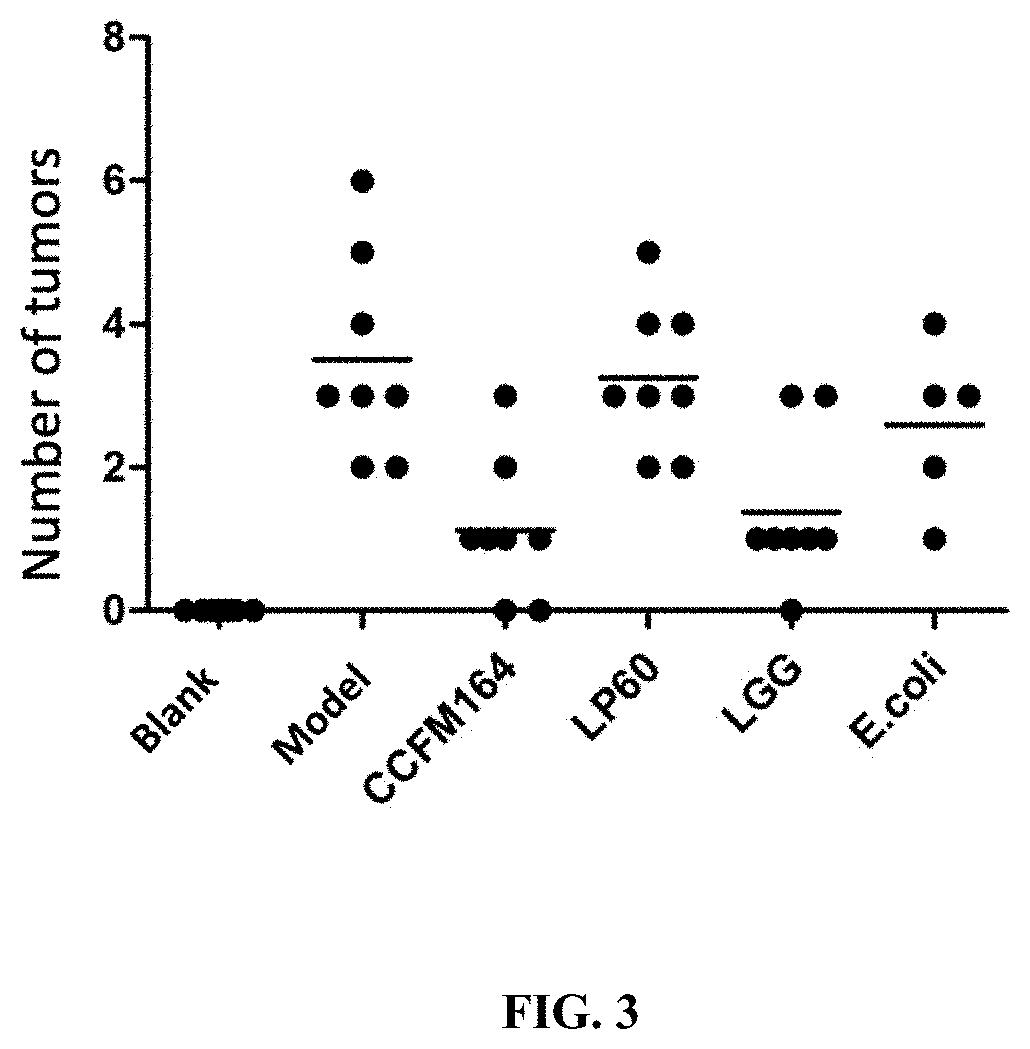
The invention discloses a lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis for regulating a signal path of colon tumor and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The lactococcuslactis subsp. lactis VM5 provided by the invention is preserved with the preservation number of GDMCC No.60256, is capable of enduring gastric acid and cholate, is capable of obviously relieving the inflammatory response of the colorectal part of a colorectal cancer model rat and is capable of reducing the tumor quantity on the colorectal parts of the model rat in the manner of regulating the expression of Notch1 signal path and VEGFR2 molecule in the colorectal tissue. Besides, the lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis VM5 is capable of improving the short chain fatty acid level in intestinal flora structures and intestinal tracts. The lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis VM5 is used for preparing the fermented food for restraining the happening of colorectal cancer and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV YANGZHOU FOOD BIOTECH INST +1
Lactobacillus plantarum with colorectal cancer inhibition function and application of Lactobacillus plantarum
ActiveCN107629987AGood resistance to gastric acid and bile saltsAchieve inhibitionMilk preparationBacteriaMicroorganismGut flora
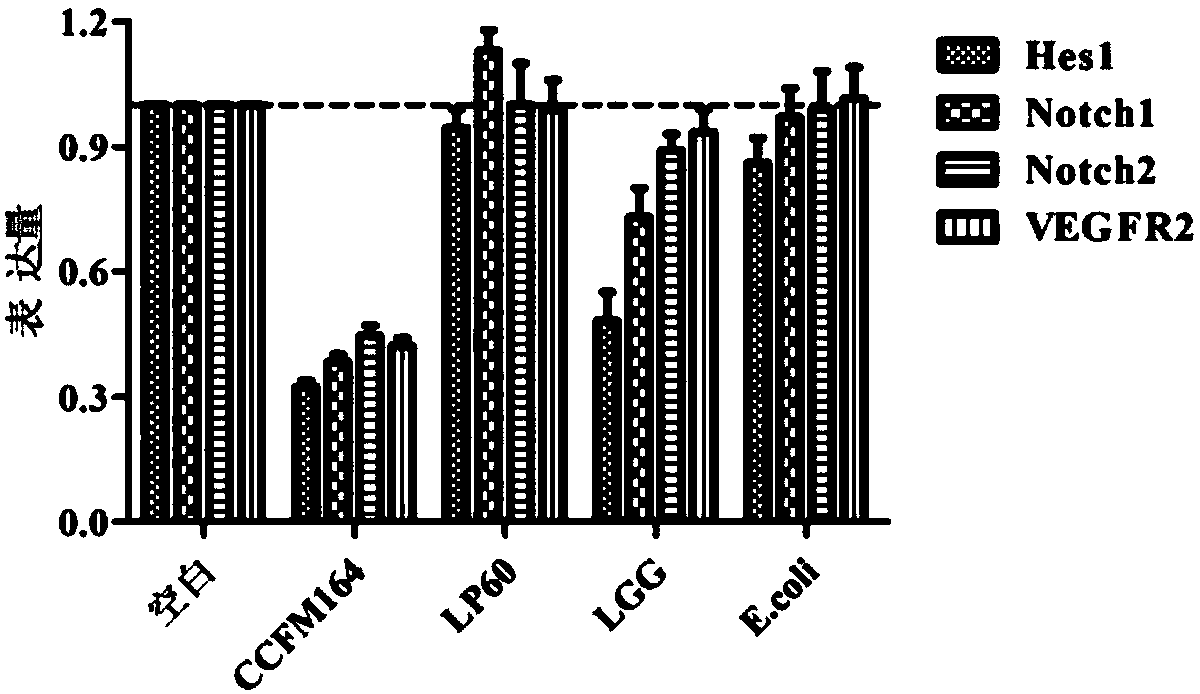
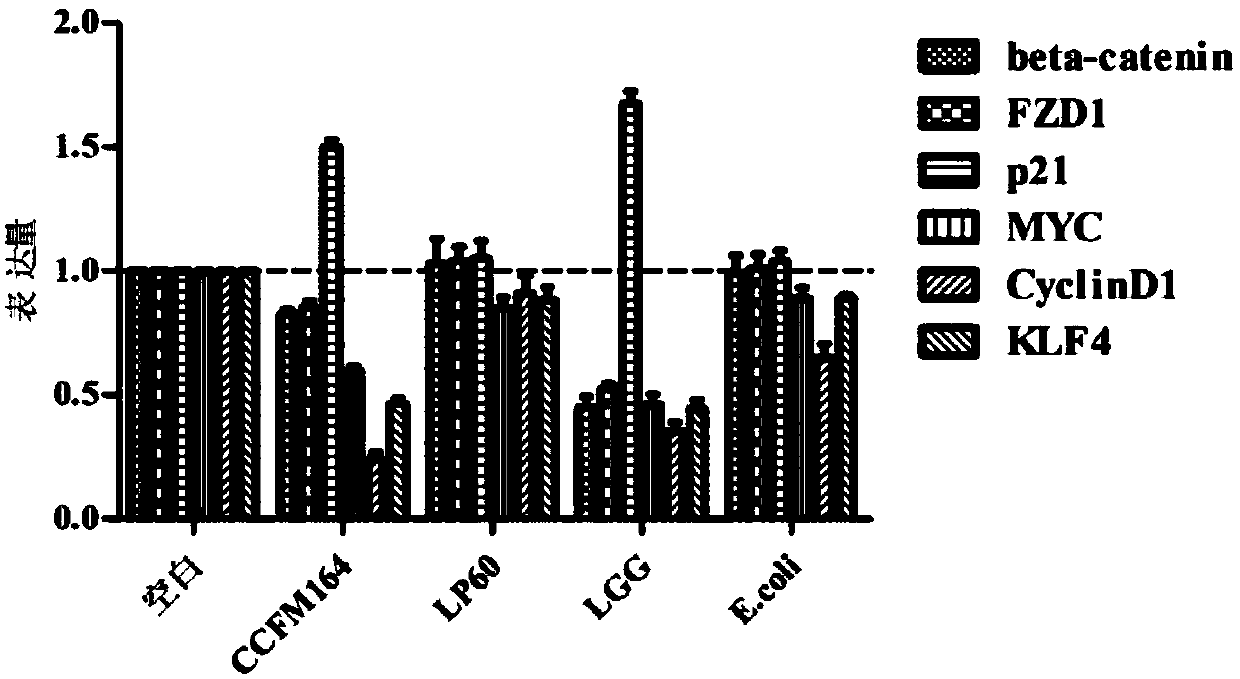
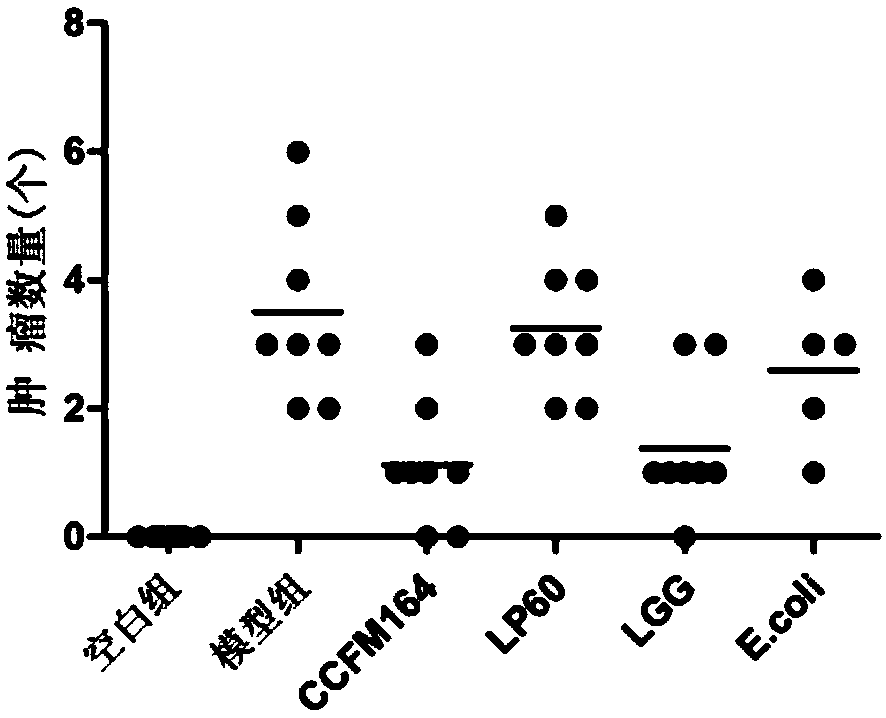
The invention discloses Lactobacillus plantarum with a colorectal cancer inhibition function and an application of the Lactobacillus plantarum and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. TheLactobacillus plantarum CCFM164 with the preservation number being CGMCC No.14520 can tolerate gastric acid and cholate, remarkably relieve inflammatory response at a colorectal part of a colorectalcancer model mouse, and tumor quantity of the colorectal part of the model mouse is reduced by regulating Notch1 and Notch2 signaling pathways in colorectal tissue and expression of VEGFR2 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2) molecules. Besides, the Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM164 can improve intestinal flora structure and short-chain fatty acid level in the intestinal tract. The Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM164 can be used for preparing fermented food capable of inhibiting colorectal cancer and has quite extensive application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Use of set of biomarkers in preparation of colorectal cancer diagnostic reagents
InactiveCN106468714AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresOmicsBiological testingDiagnosis earlyTest sample
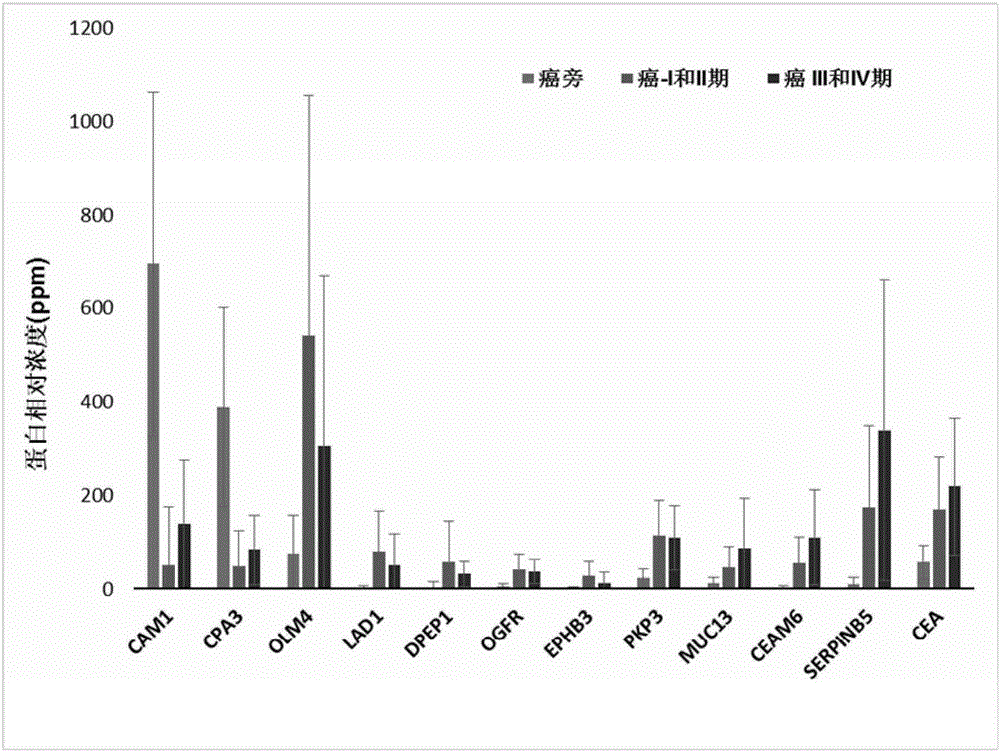
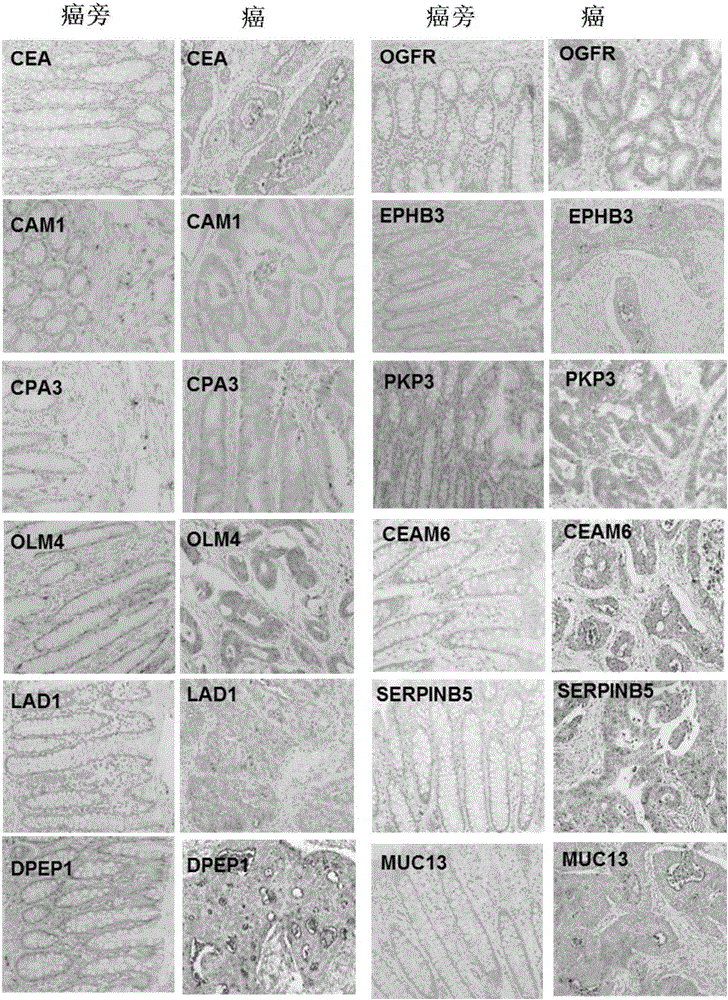
The invention discloses the use of a set of biomarkers in the preparation of colorectal cancer diagnostic reagents, and further proposes a method of using biomarkers for distinguishing between normal intestinal cells and colorectal cancer cells. The method comprises: a) separating a test sample from a biopsy specimen of a subject; b) separating biological samples containing normal colorectal tissue cells or tissues from the biopsy specimens or the subject or family members thereof; c) analyzing the content of biomarker proteins of the above samples in a) and b); and d) comparing the content of biomarker proteins in normal and colorectal cancer cells or tissues. The invention also discloses a kit for detecting the level of biomarkers in a specimen. The method of the invention can be combined with other diagnostic methods to detect colorectal adenoma / colorectal cancer and improve the overall sensitivity and specificity, and can be also applied to early diagnosis and monitoring.
Owner:POOCHON SCI LLC
Brain Endothelial Cell Expression Patterns
To gain a better understanding of brain tumor angiogenesis, new techniques for isolating brain endothelial cells (ECs) and evaluating gene expression patterns were developed. When transcripts from brain ECS derived from normal and malignant colorectal tissues were compared with transcripts from non-endothelial cells, genes predominantly expressed in the endothelium were identified. Comparison between normal- and tumor-derived endothelium revealed genes that were specifically elevated in tumor-associated brain endothelium. These results confirm that neoplastic and normal endothelium in human brains are distinct at the molecular level, and have significant implications for the development of anti-angiogenic therapies in the future.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method of examining colon cancer and colon adenoma
InactiveUS20070196874A1Biological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsNon cancerIsozyme
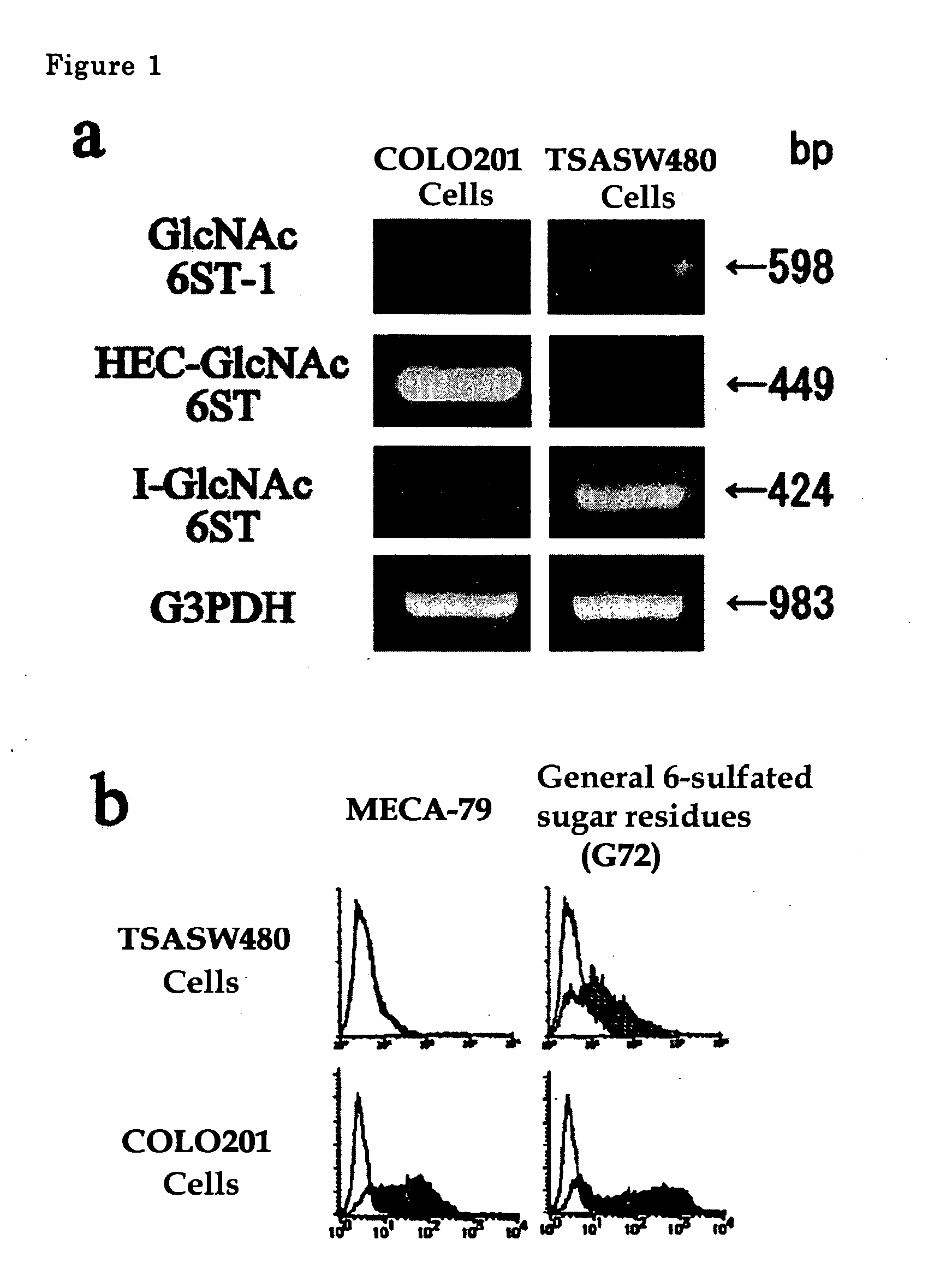
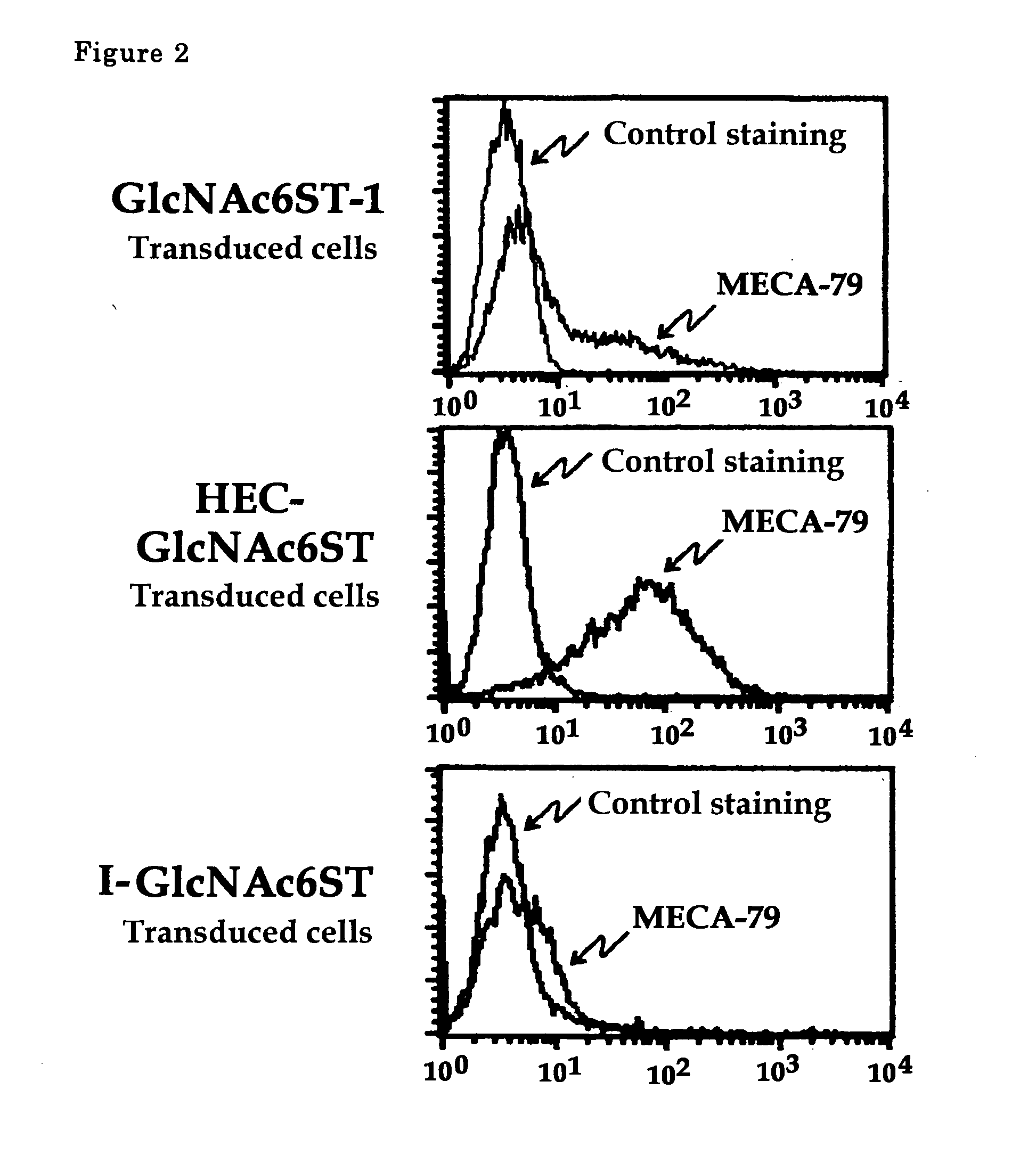
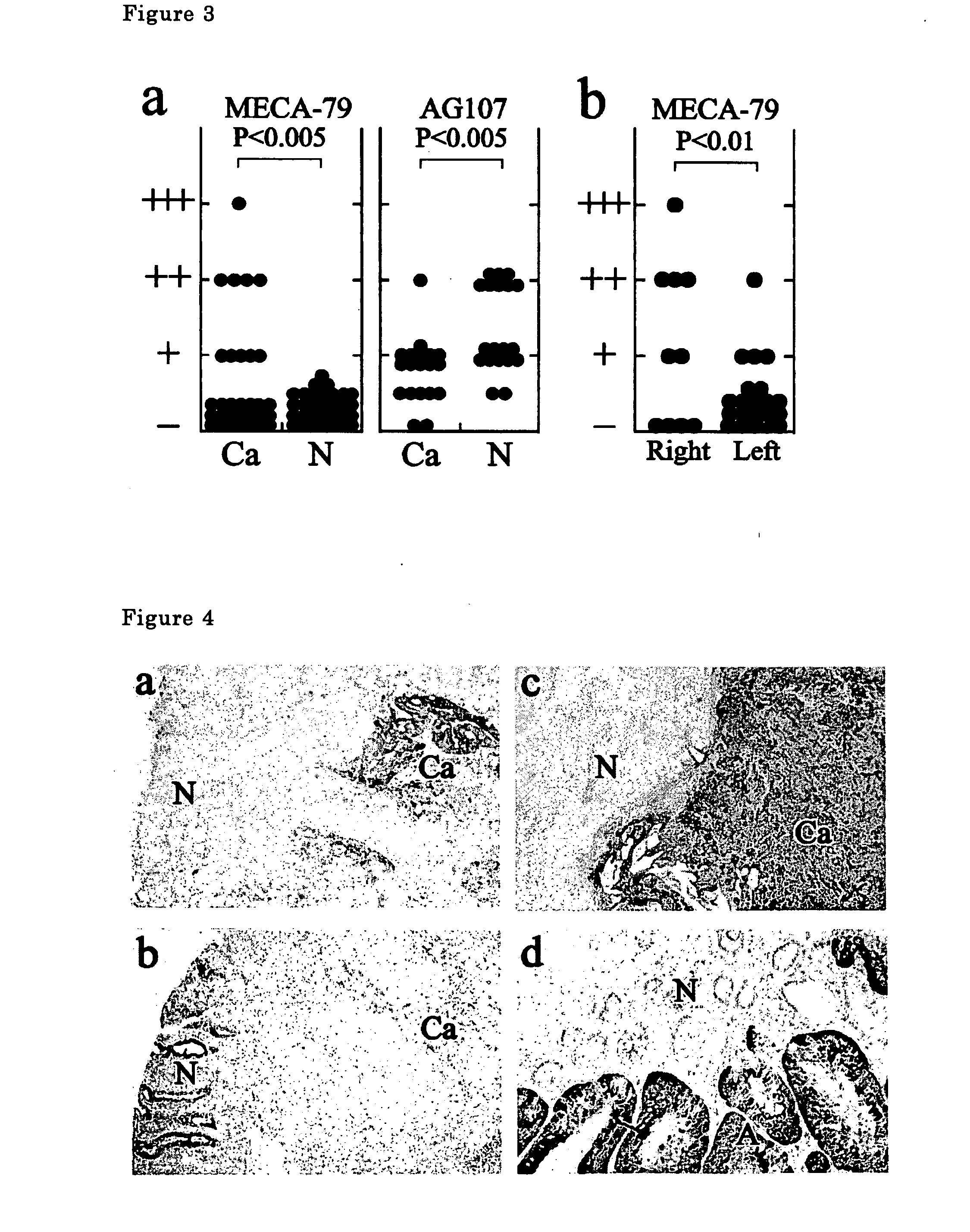
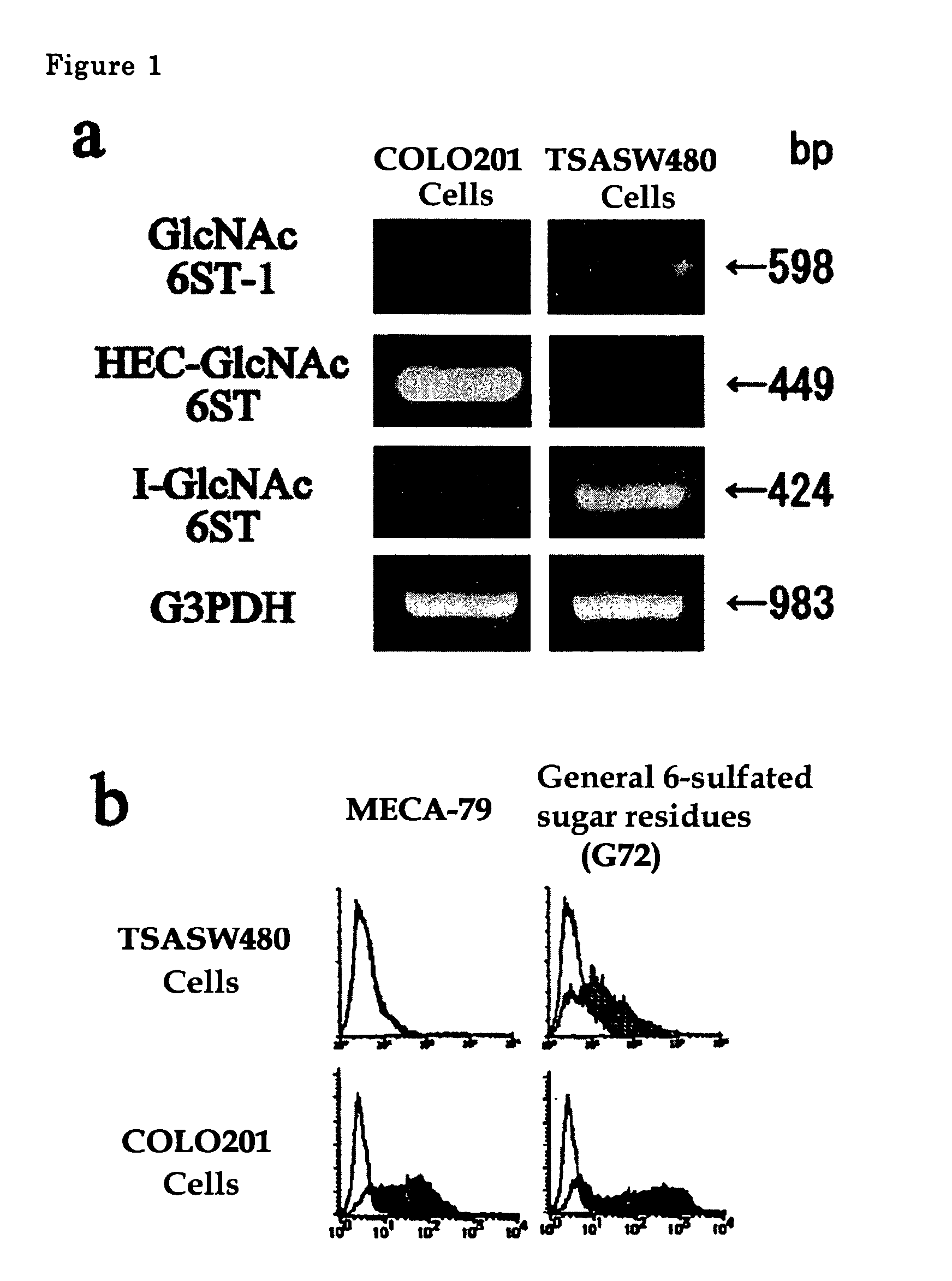
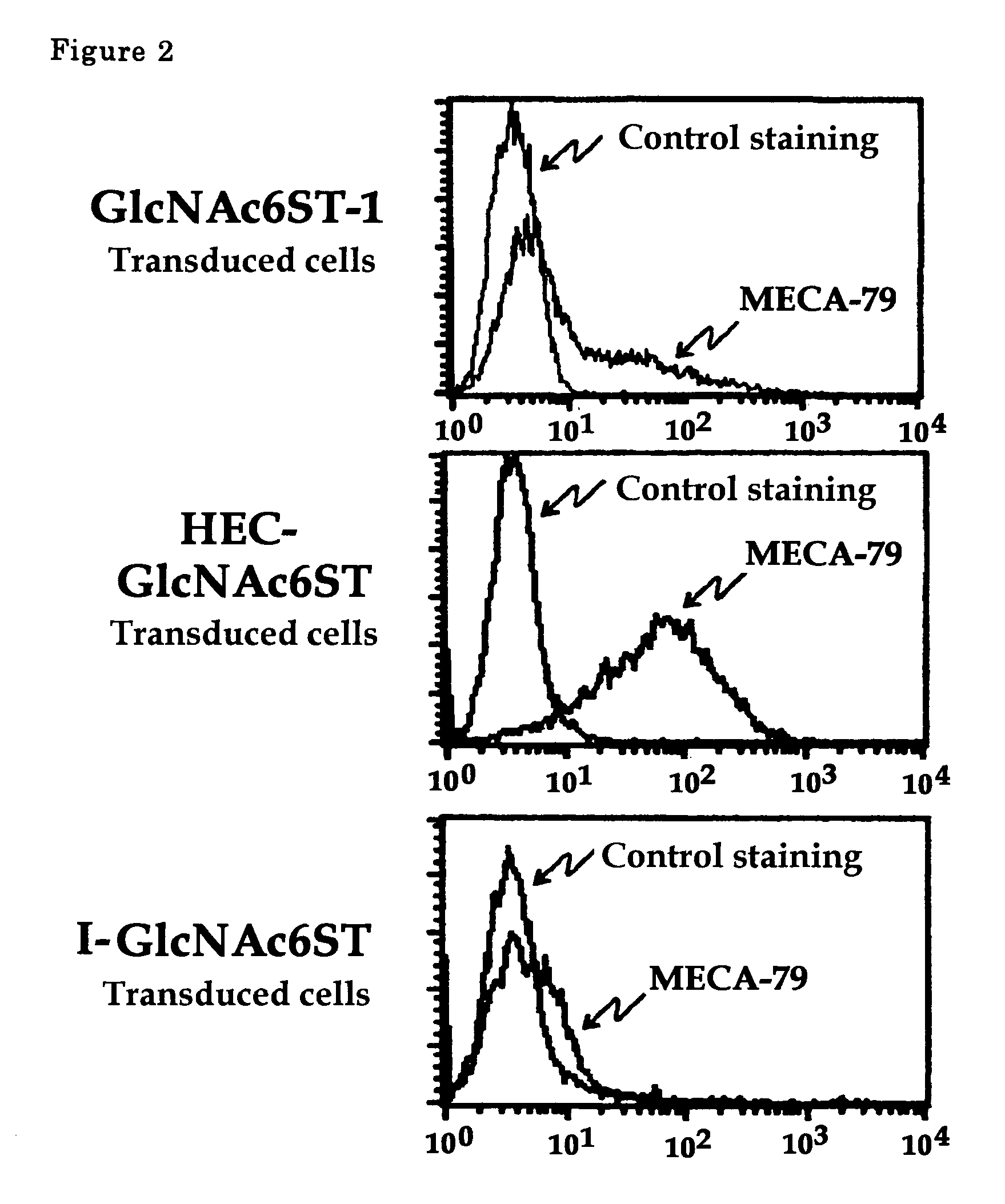
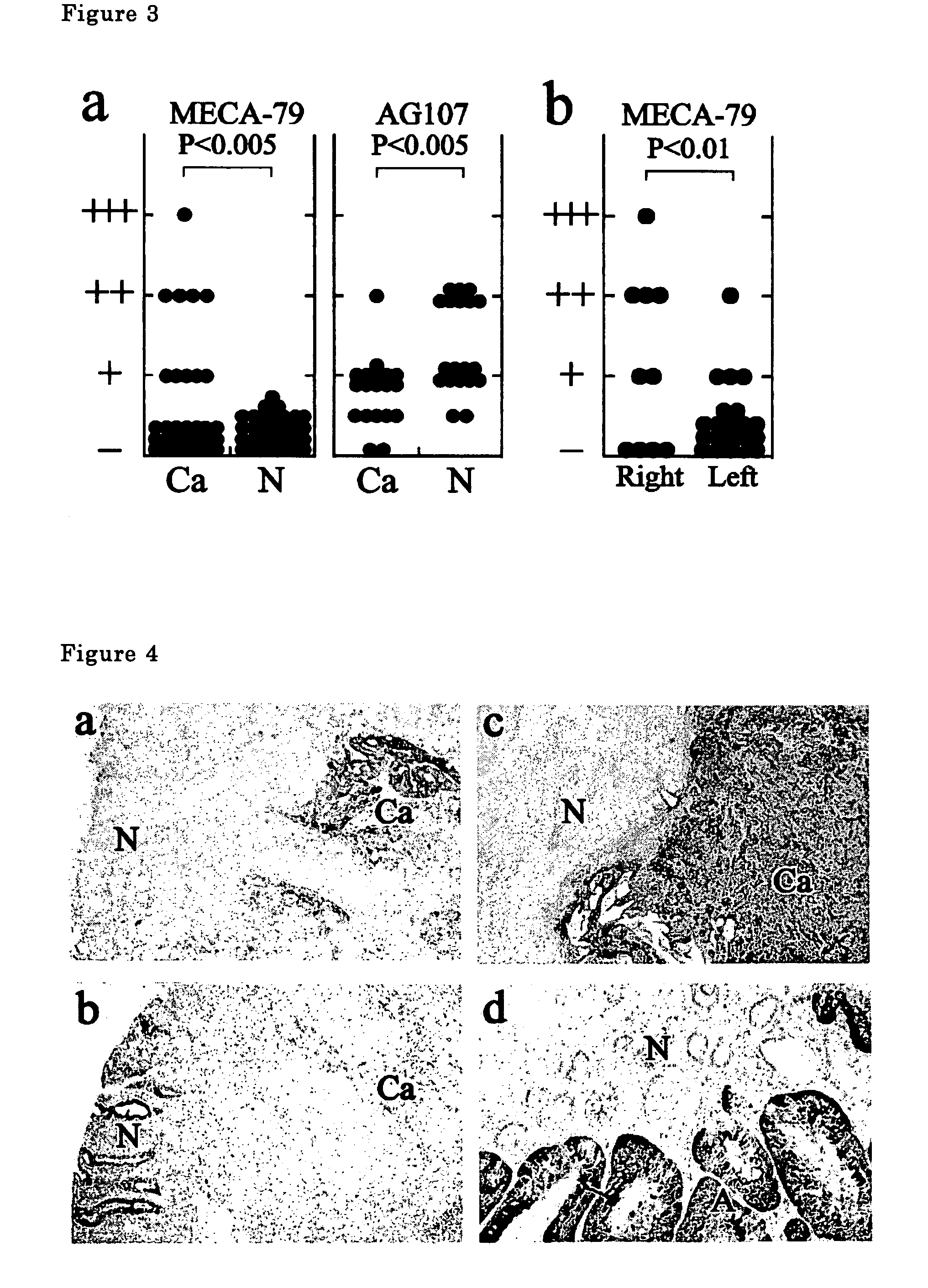
The present invention provides a method for examining colorectal cancer and colorectal adenoma, which enables to detect colorectal cancer patients and patients at high risk of colorectal cancer at a high probability and is useful for diagnosis of colorectal cancer and colorectal adenoma, and provides the examination reagents thereof. The present inventors discovered that there are significant differences in the distribution of GlcNAc-6-sulfotransferase isozymes, sulfation enzymes of sugar residues, among non-cancer colorectal tissues, colorectal cancer tissues and colorectal adenoma tissues. Furthermore the inventors applied the discovery to diagnosis and found that colorectal cancers and adenomas are detected specifically by assaying a definite range of GlcNAc-6-sulfated sugar residues in tissues from patients or feces samples. MECA-79 antibody (Pharmingen, catalog No. 09961D, Distributor: Becton Dickinson), reacting with GlcNAc-6-sulfated sugar residues, which are produced specifically by the enzyme present in colorectal cancer and colorectal adenoma tissues could be used for the examination of colorectal cancers and colorectal adenomas.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +2
Method of examining colon cancer and colon adenoma
The present invention provides a method for examining colorectal cancer and colorectal adenoma, which enables to detect colorectal cancer patients and patients at high risk of colorectal cancer at a high probability and is useful for diagnosis of colorectal cancer and colorectal adenoma, and provides the examination reagents thereof. The present inventors discovered that there are significant differences in the distribution of GlcNAc-6-sulfotransferase isozymes, sulfation enzymes of sugar residues, among non-cancer colorectal tissues, colorectal cancer tissues and colorectal adenoma tissues. Furthermore the inventors applied the discovery to diagnosis and found that colorectal cancers and adenomas are detected specifically by assaying a definite range of GlcNAc-6-sulfated sugar residues in tissues from patients or feces samples. MECA-79 antibody (Pharmingen, catalog No. 09961D, Distributor: Becton Dickinson), reacting with GlcNAc-6-sulfated sugar residues, which are produced specifically by the enzyme present in colorectal cancer and colorectal adenoma tissues could be used for the examination of colorectal cancers and colorectal adenomas.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +2
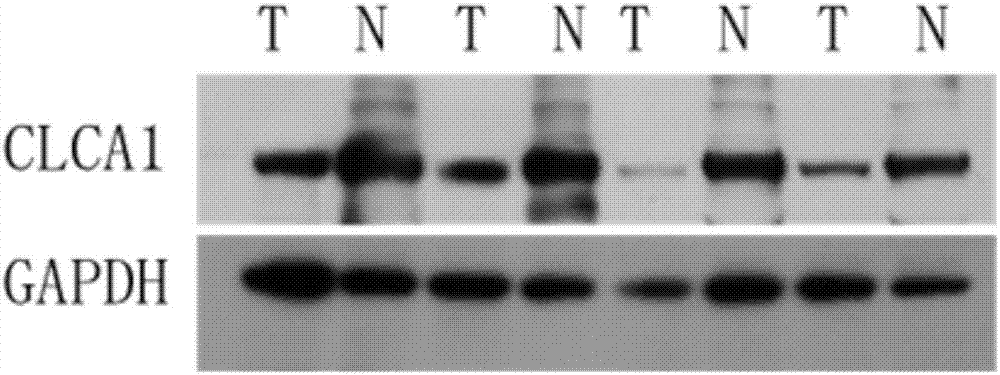
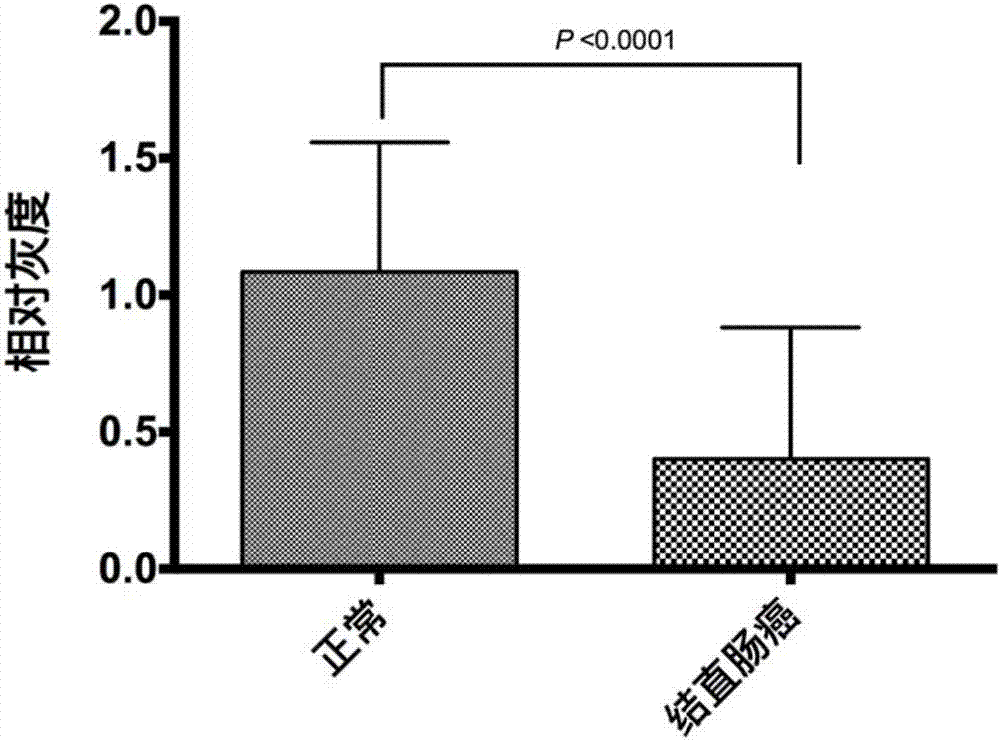
Human colorectal cancer protein mark CLCA1 (calcium-activated chloride channel 1) kit and application thereof
InactiveCN107015002ALow costDisease diagnosisBiological testingEthylene diamineChloride channel blocker
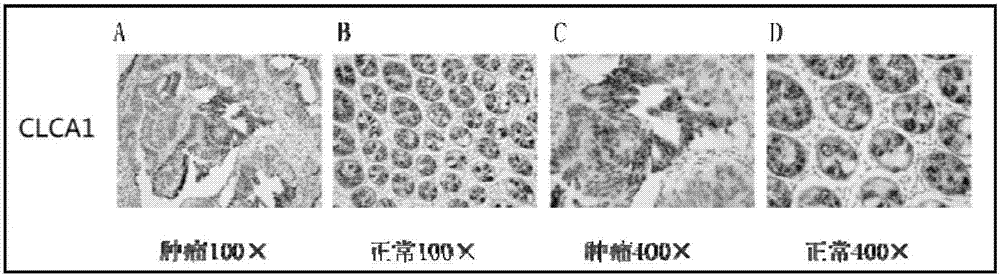
The invention provides a human colorectal cancer protein mark CLCA1 (calcium-activated chloride channel 1) kit, which comprises a specific antibody aiming at CLCA1, an EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) antigen restoration solution, an endogenous peroxidase blocker, goat serum, second antibodies, a PBS buffer solution, hematoxylin and a DAB color developing solution. Study results show that the expression quantity of the CLCA1 in the normal colorectal tissues is obviously higher than that in the colorectal cancer tissues; the content of the CLCA1 in the health people blood is obviously higher than the content in the blood of the colorectal cancer patient; in addition, the lifetime of the colorectal cancer patients with high CLCA1 expression is obviously longer than the patient with low CLCA1 expression; the scientific basis is provided for effectively judging the colorectal cancer canceration progress, detecting the human colorectal cancer in the early stage and judging the prognosis. Therefore the kit provided by the invention is used for preparing a preparation for screening, diagnosing or predicting the human colorectal cancer, can be used for screening anti-colorectal-cancer medicine targets, and are also used for preparing medicine for relieving or treating the human colorectal cancer. The kit provided by the invention is efficient and convenient, and the cost is lower.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kind of Bifidobacterium bifidum capable of alleviating colorectal cancer and its application
ActiveCN107629988BGood resistance to gastric acid and bile saltsAchieve inhibitionMilk preparationBacteriaGut floraBacterosira
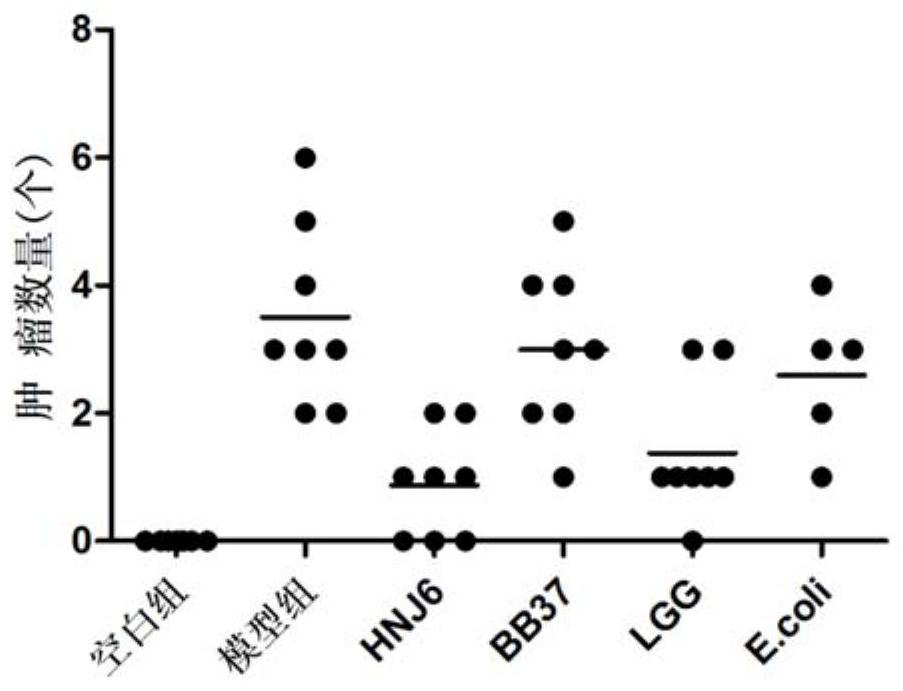
The invention discloses a Bifidobacterium bifidum capable of significantly inhibiting the occurrence of colorectal cancer and its use, belonging to the technical field of microbes. Bifidobacterium bifidum HNJ6 provided by the present invention has a preservation number of GDMCC No.60255, can tolerate gastric acid and bile salts, and can significantly reduce the inflammatory response in the colorectal part of colorectal cancer model mice, by regulating colorectal tissue The expression of Notch1 and Notch2 signaling pathways and VEGFR2 molecules in the tumor can reduce the number of tumors in the nodal and rectal regions of model mice. In addition, Bifidobacterium bifidum HNJ6 can also improve the structure of intestinal flora and the level of short-chain fatty acids in the intestine. The bifidobacterium bifidum HNJ6 is used to prepare fermented food that inhibits the occurrence of colorectal cancer, and has very broad application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV YANGZHOU FOOD BIOTECH INST +1
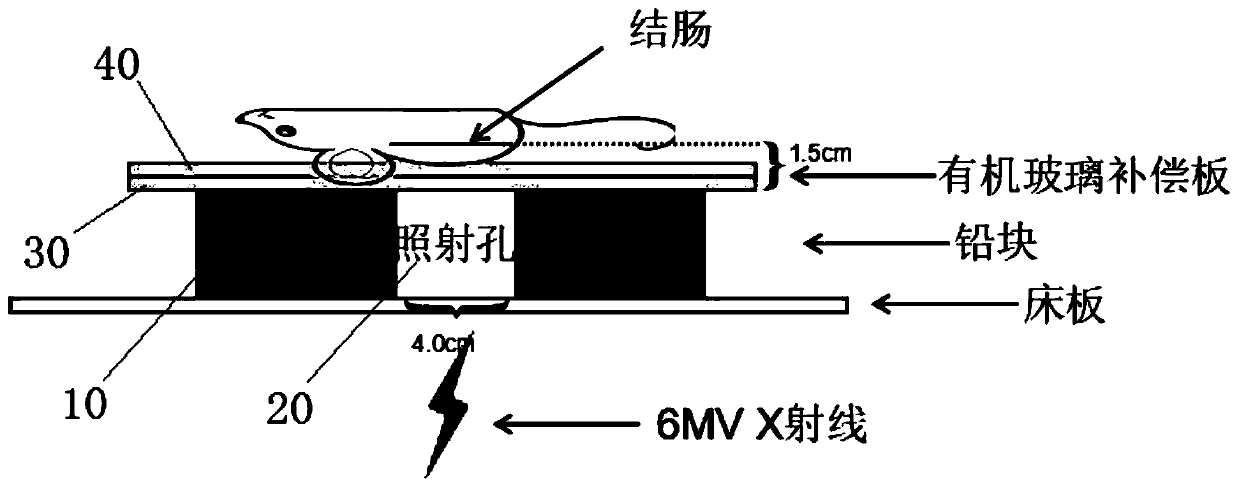
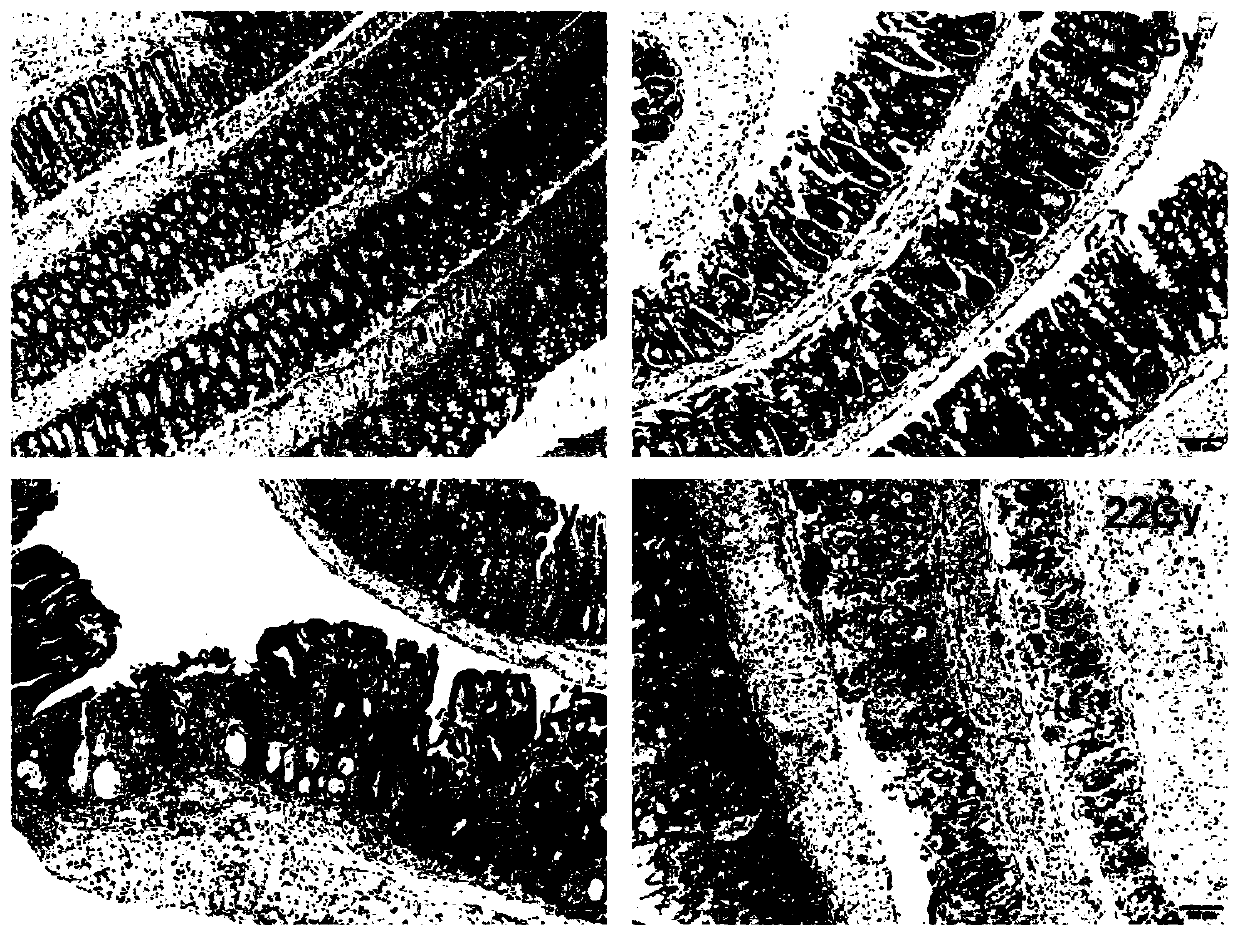
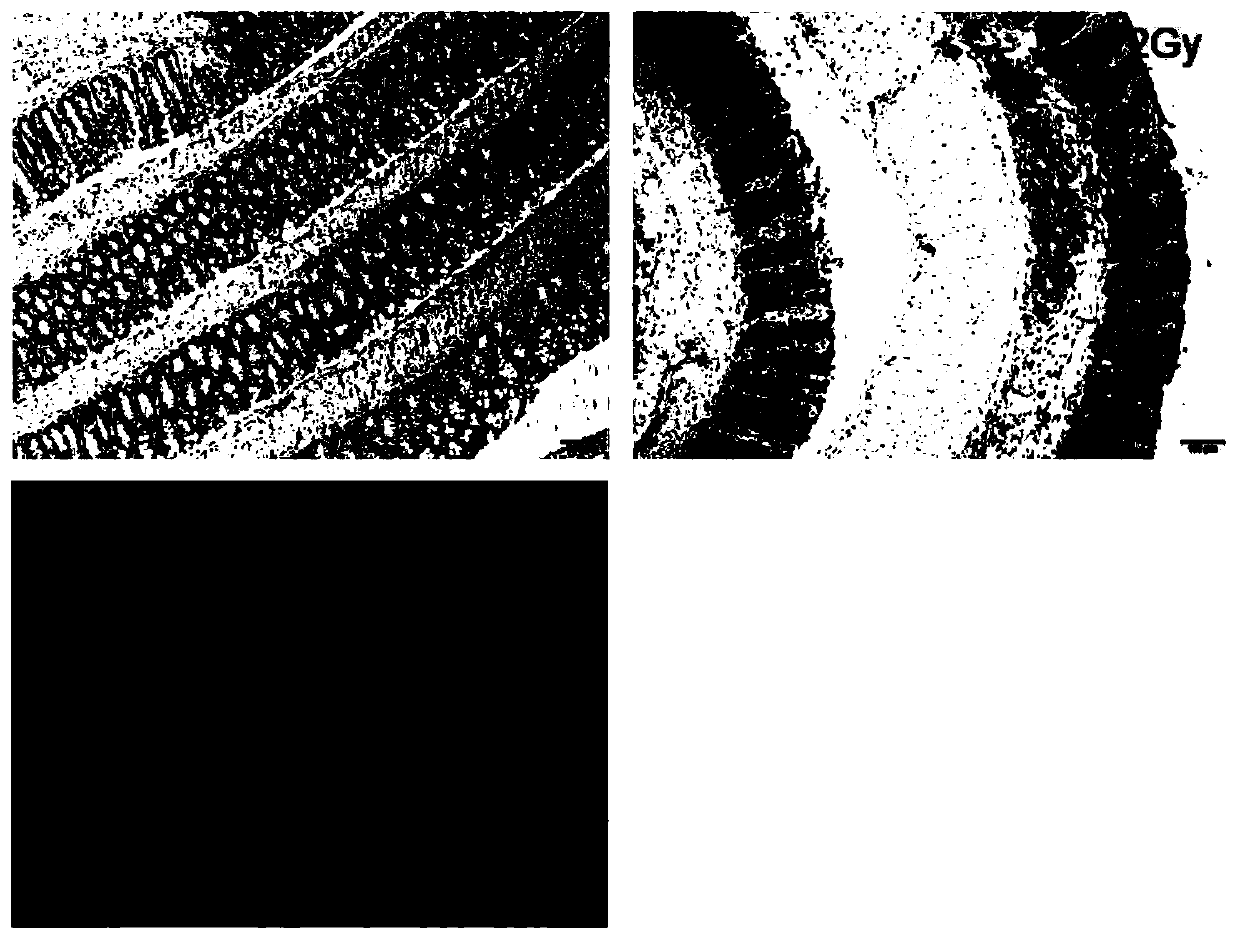
Method for establishing animal model of radiation-induced colorectal inflammation
InactiveCN110013345AAdapt to the living environmentReduce mortalityPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansLarge doseX-ray
The present invention provides a method for establishing an animal model of radiation-induced colorectal inflammation. The method comprises the following steps: mice are randomly divided into two large groups; the mice are normal fed for 1-2 weeks to enable the mice to be adapted to a new living environment; body positions of the mice during irradiation are simulated and an average value is taken;a radiotherapy plan is developed; depending on different group designs, a single large dose radiation is conducted using different doses of gradient rays; and severity of colorectal tissue lesions isassessed. Combining clinical practices, a common therapeutic ray (6MV X ray) used by a medical linear accelerator can better simulate radioactive colorectal injury lesion process of clinical radiotherapy side reactions, and besides, the method is low in animal mortality and simple and easy to repeat, provides an experimental basis for studying the radioactive colorectal injury, is convenient forfurther studying mechanism of the radioactive colorectal injury and guiding clinical medication, closer to clinical practice and more conducive to studying course mechanism of radiation enteritis anddrug development, and can also further expand use of a prevention and treatment technology applied in the radiation enteritis.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Application of target gene DNA methylation as molecular markers in preparation of kit for distinguishing colorectal tissue canceration progress
ActiveCN110283910AImprove diagnostic efficiencyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAdenocarcinoma polypsDNA methylation
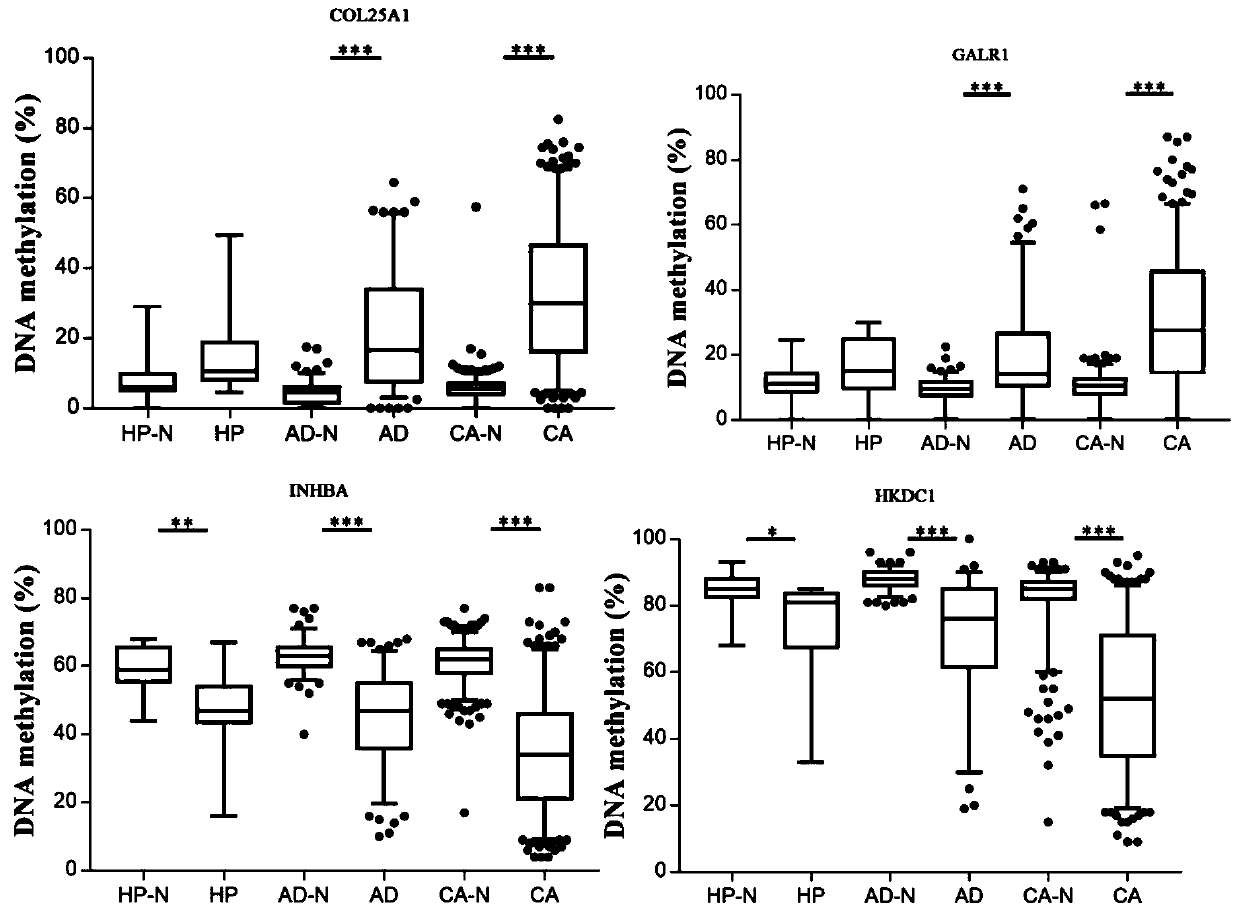
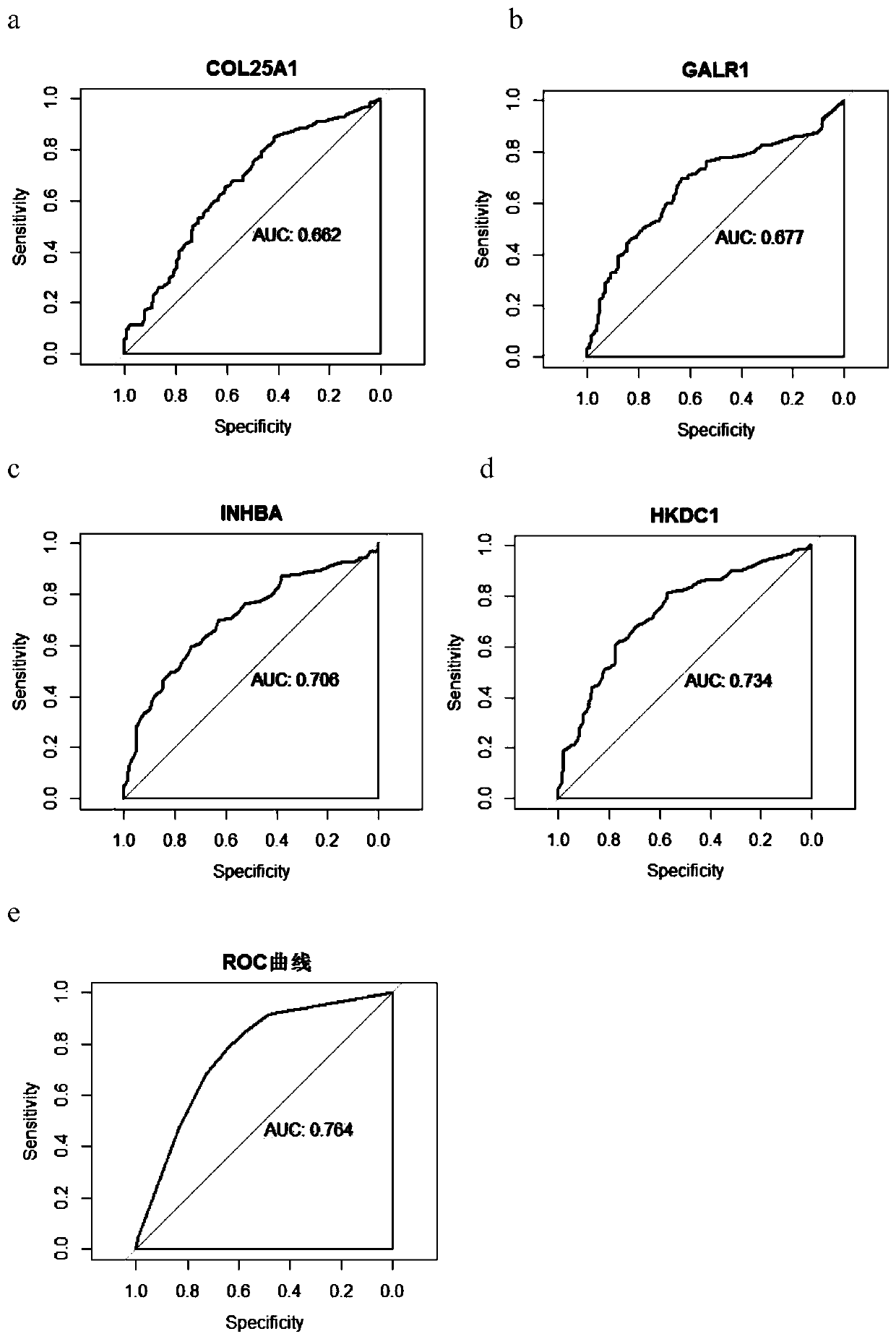
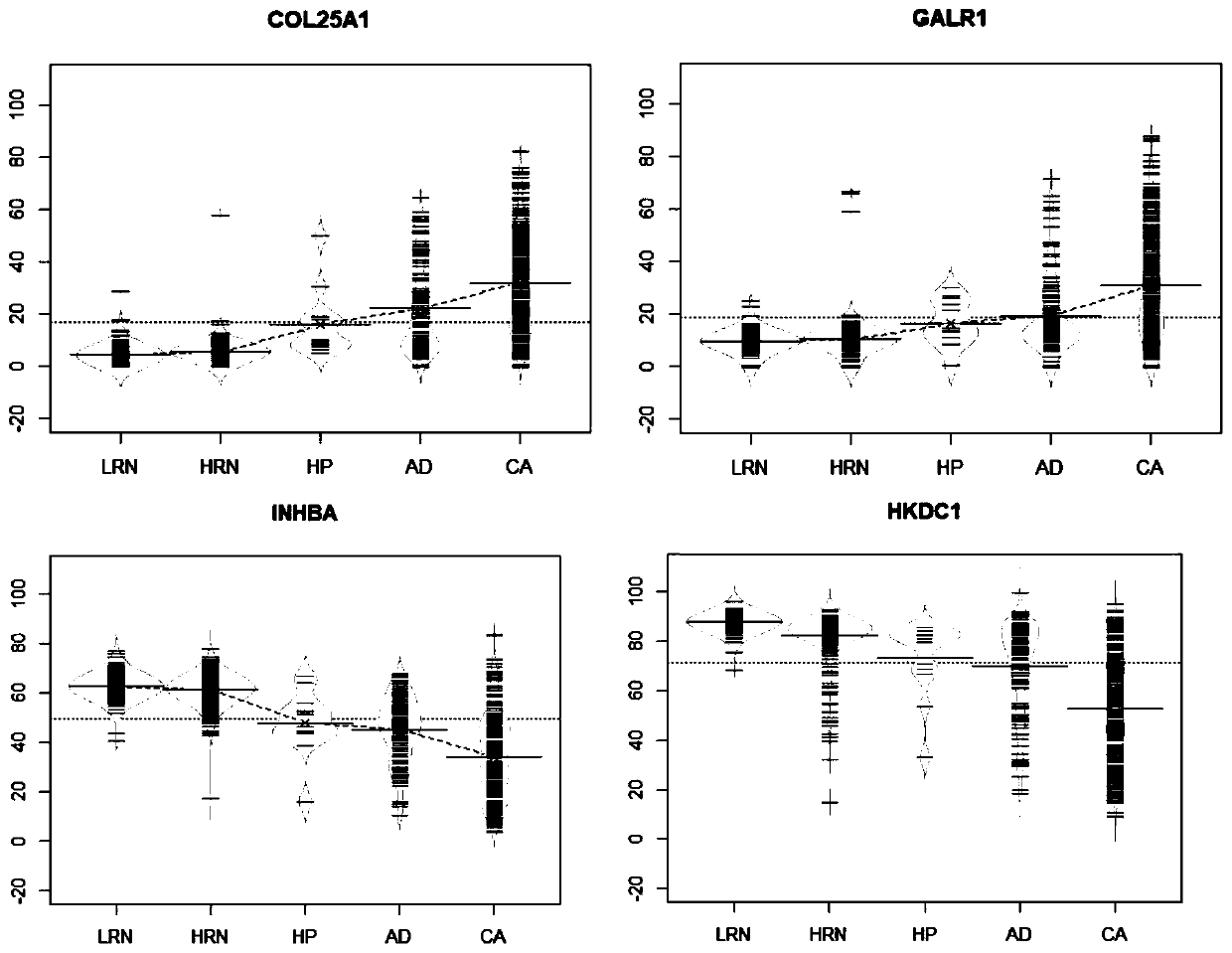
The invention discloses an application of target gene DNA methylation as molecular markers in preparation of a kit for distinguishing colorectal tissue canceration progress. The target gene DNA methylation is one or more of COL25A1, GALR1, INHBA and HKDC1 genes. The invention finds for the first time that the DNA methylation molecular markers shown in SEQ ID NO.1-4 can be used for distinguishing the colorectal tissue canceration progress, an obtained model has better identification and diagnosis efficiency, and AUC is 0.662-0.734. The AUC of the model is 0.764 after four target gene DNA methylation markers are combined. The DNA methylation molecular markers have the characteristics of high sensitivity and high specificity when distinguishing rectal polyp and colorectal cancer and can assist in monitoring the process of rectal polyp to colorectal cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for predicting colorectal cancer mismatch repair function
InactiveCN113361580AReduce dependenceImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisStainingTumor region
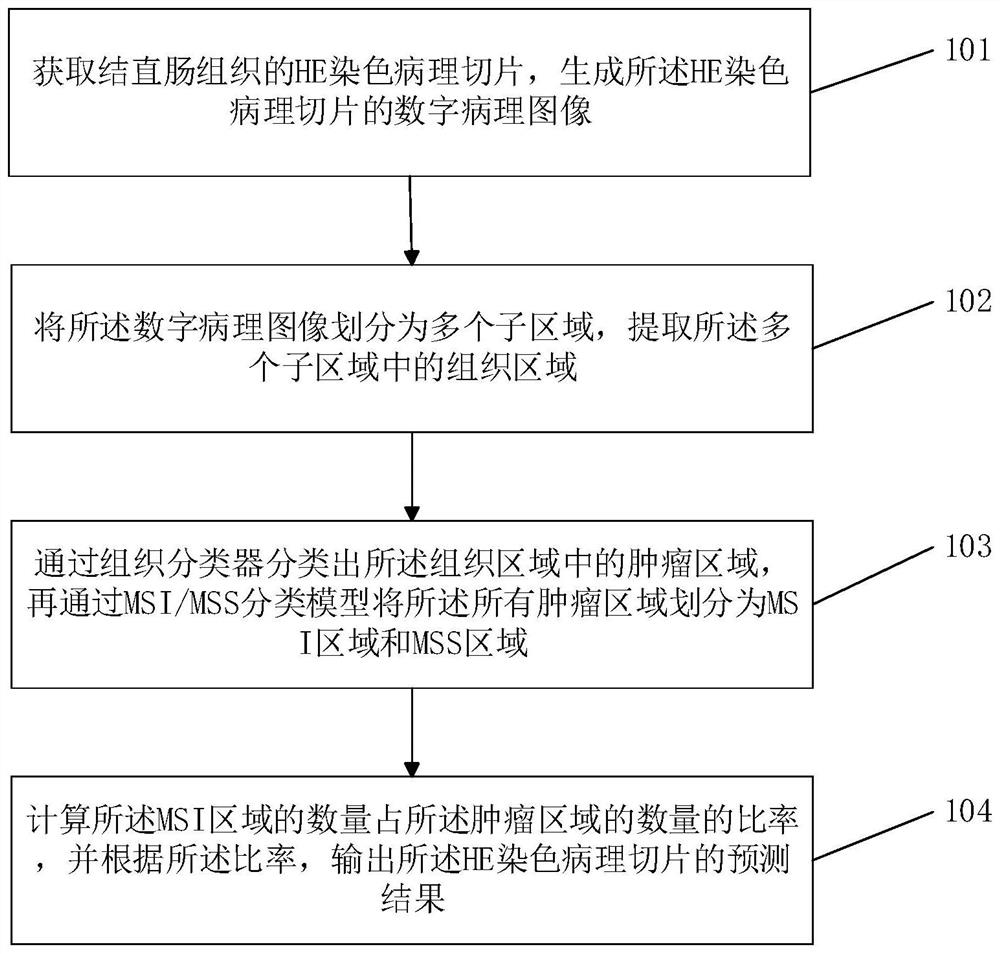
The invention discloses a colorectal cancer mismatch repair function prediction method and device, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an HE staining pathological section of a colorectal tissue, generating a digital pathological image of the HE staining pathological section, dividing the digital pathological image into a plurality of sub-regions, extracting tissue regions in the plurality of sub-regions, classifying tumor areas in a tissue area through a tissue classifier, dividing all tumor areas into MSI areas and MSS areas through an MSI / MSS classification model, calculating the ratio of the number of the MSI areas to the number of the tumor areas, and outputting a prediction result of an HE staining pathological section according to the ratio. Compared with the prior art, the method and the device for predicting the colorectal cancer mismatch repair function have the advantages that the dependence on manpower is reduced, and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
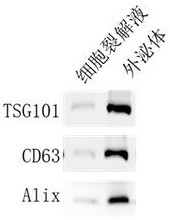
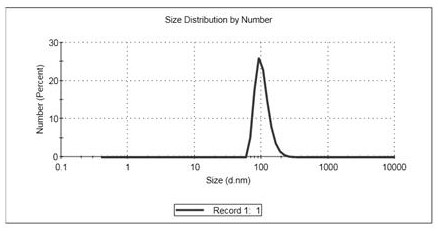
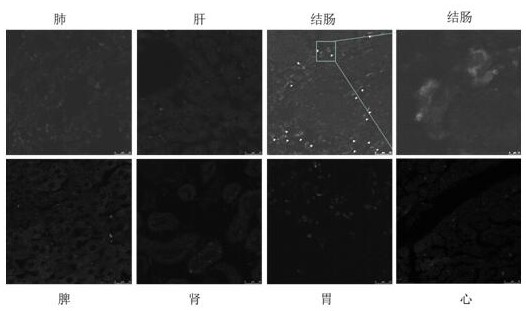
Colorectum-targeted drug-loaded exosome and application thereof, and drug for treating colorectal diseases
InactiveCN113528427ASolve outputGood treatment effectArtificial cell constructsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPneumonocyteDisease
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicine, and provides a colorectum-targeted drug-loaded exosome and application thereof, and a medicine for treating colorectal diseases. The colorectum-targeted drug-loaded exosome is obtained by introducing the medicine for treating the colorectal diseases into an exosome with a colorectal tissue targeting property; and the exosome with colorectal tissue targeting property is derived from lung cells. A colorectal tumor treatment drug contains the colorectum-targeted drug-loading exosome. Compared with the prior art, the exosome secreted by the lung cells can be enriched in the colorectum without any modification, the exosome derived from the lung cells is used, the problem of exosome yield is solved, and good application prospect is obtained; and different drugs or active molecules can be loaded by using the lung cell-derived exosome, and the treatment effect of colorectal diseases is improved and toxic and side effects of the drugs are reduced through targeted colorectal tissue administration.
Owner:姜海涛
A diagnostic biomarker for colorectal cancer and its application
ActiveCN107447033BAccurate judgmentQuick judgmentNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideTreatment targets
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Antihuman Reg4 monoclone antibody, preparation, application and hybrid tumor cell strain
InactiveCN101270161AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTissue cultureNucleotide sequencingCell strain
The present invention provides an anti-human regenrating gene 4 monoclonal antibody, a preparation method and applications thereof as well as a hybridoma cell line producing the monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody has specificity in respect to the 333th to 743th nucleotide (that is, the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.3) encoded polypeptides of the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1. The present invention is mainly characterized in providing the anti-human regenrating gene 4 monoclonal antibody, the preparation method and applications thereof as well as the hybridoma cell line producing the monoclonal antibody, laying a foundation for further crystalizing the expression of Reg 4 in colorectal tissues, and the anti-human regenrating gene 4 monoclonal antibody can be used for the preparation of the early detection kit of colorectal cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of stem cell exosome in preparation of drug for resisting colitis deterioration
PendingCN111759862AInhibits progression of colitisDelay or inhibit the progression of colitisAntipyreticAnalgesicsMesenchymal stem cellPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides application of a stem cell exosome in preparation of a drug for resisting colitis deterioration. A mouse colorectal cancer (CRC) model is induced in an AOM / DSS combined induction manner, the mouse weight, disease activity index (DAI), colorectal tissue pathologic structure and colorectal tissue deterioration degree are detected, and results show that the exosome derived fromhuman umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hucMSCs) can inhibit the colorectal deterioration process. The invention belongs to biotherapy, and the exosome delays or inhibits the colitis deterioration process of a model animal by inhibiting expression of SUMO1 protein, has the characteristics of low immunogenicity, source convenience and the like and has good application prospects in resisting the colitis deterioration process.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Probe related to colorectal cancer and application thereof
InactiveCN105734126AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationColorectal tissueCarcinoma
The invention discloses a probe related to colorectal cancer and application thereof. The probe has a sequence of GACGACGCTGACCGTCCTGCCCCAC and can be hybridized with hsa-circ-0003098. Because expression of the hsa-circ-0003098 in colorectal cancer tissues is higher than that in normal colorectal tissues, the probe has high application value on early diagnosis of the colorectal cancer and provides a support for early diagnosis and early treatment of the colorectal cancer clinically.
Owner:JIANGSU CANCER HOSPITAL +1
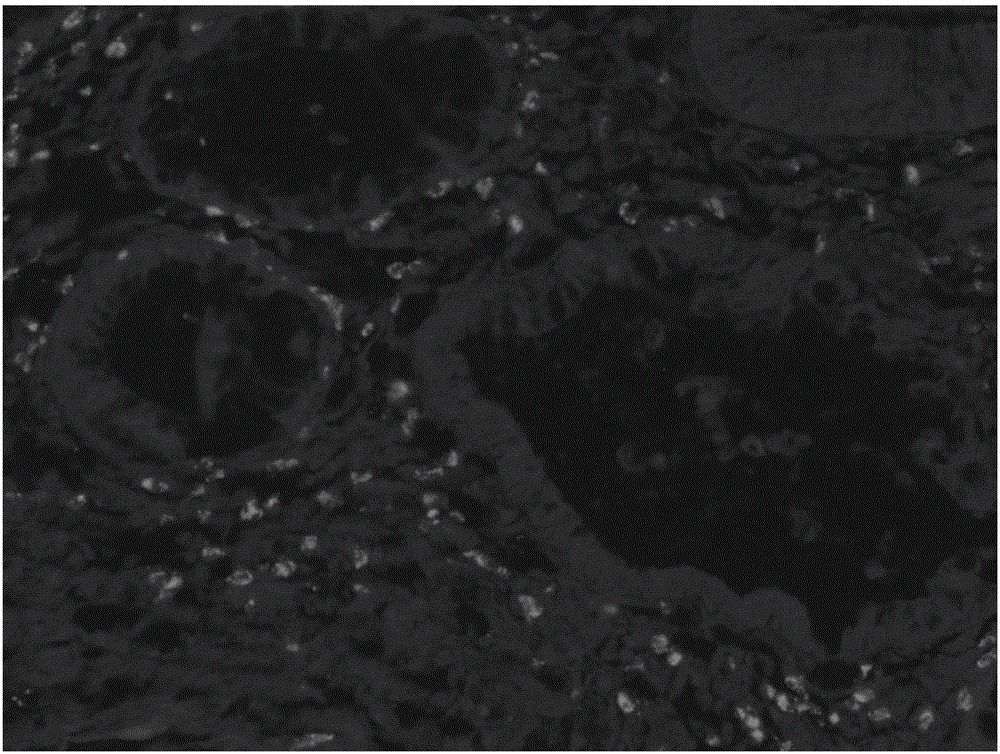
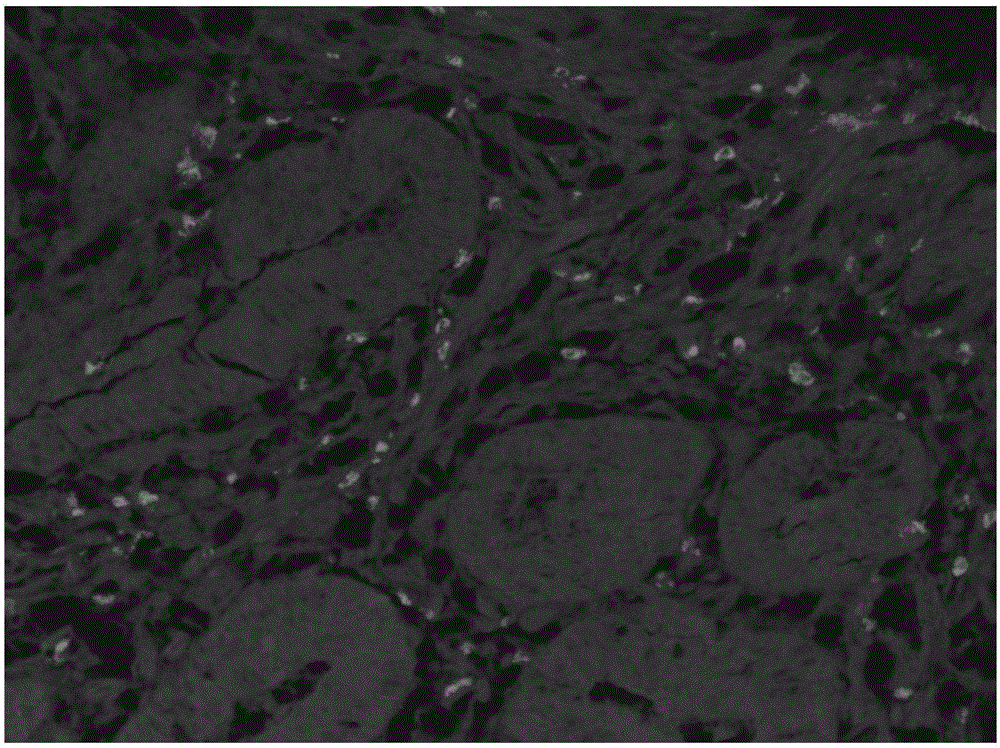
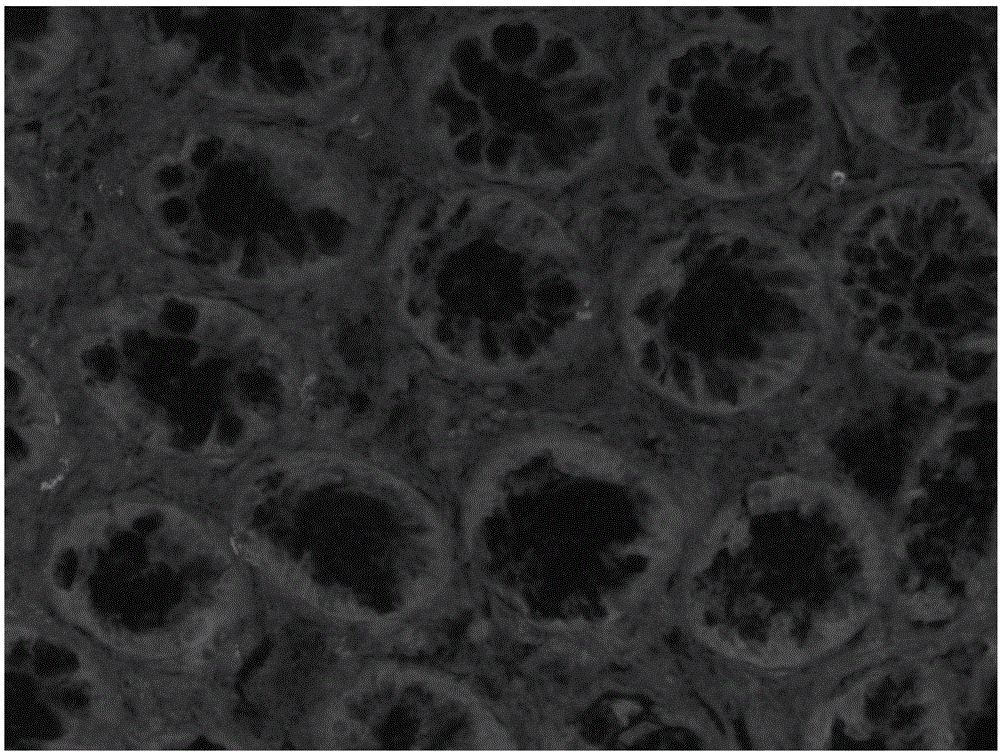
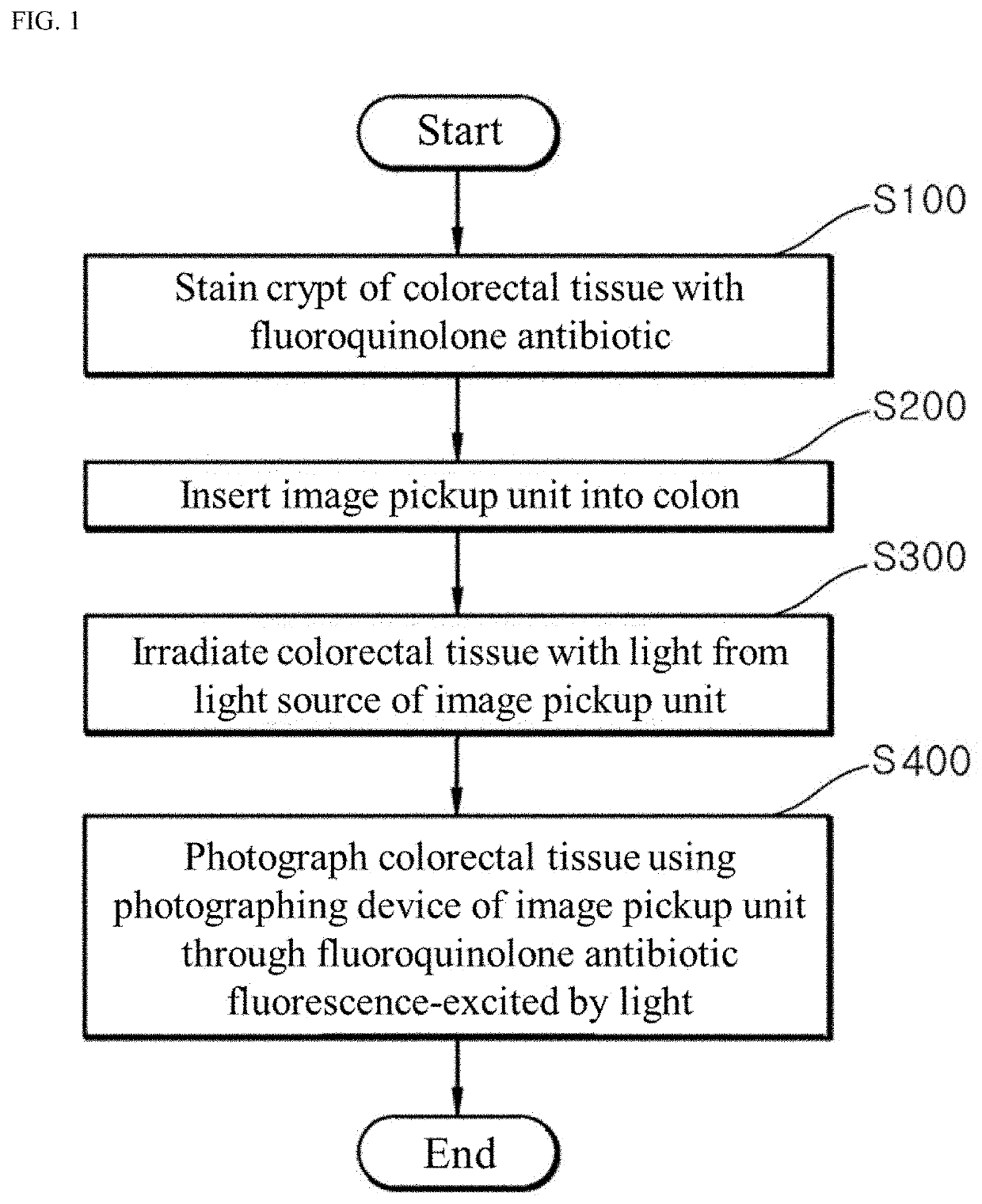
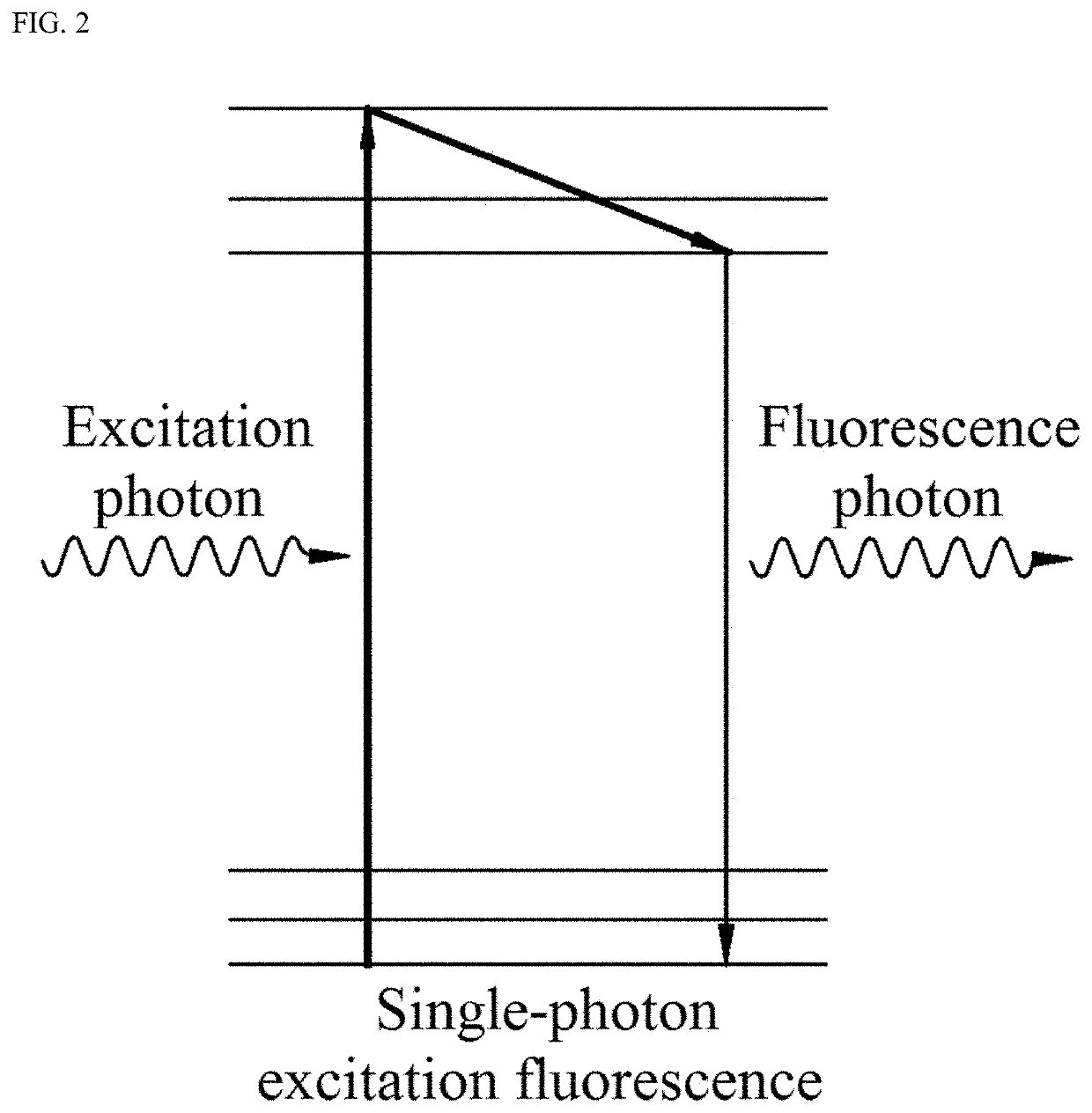
Fluorescence endoscopic method for visualization of colorectal tissue using fluoroquinolone antibiotics and method for diagnosis of lesions of colorectal tissue using the same
A fluorescence endoscopic method for visualization of colorectal tissue using a fluoroquinolone antibiotic and a method for diagnosis of lesions of colorectal tissue using the same. The fluorescence endoscopic method for visualization of colorectal tissue includes staining goblet cells of the colorectal tissue with moxifloxacin, which is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, and exciting the stained goblet cells with single photons in the near UV region or in the visible region, followed by fluorescence endoscopic photographing of the goblet cells, thereby enabling acquisition of morphological information on living tissue without damage to or destruction of the colorectal tissue, while allowing diagnosis of lesions of the colon based on the morphological information on living tissue such as information on the distribution of the goblet cells. Specifically, the fluorescence endoscopic method includes: a colorectal tissue staining step in which the crypt of the colorectal tissue is stained with a fluoroquinolone antibiotic; an image pickup unit insertion step in which an image pickup unit is inserted into the colon; a light irradiation step in which the colorectal tissue is irradiated with excitation light from a light source of the image pickup unit; a colorectal tissue photographing step in which the colorectal tissue is photographed using a photographing device of the image pickup unit through the fluoroquinolone antibiotic fluorescence-excited by light in the light irradiation step, wherein, in the colorectal tissue staining step, goblet cells of the crypt are stained with the fluoroquinolone antibiotic; in the light irradiation step, the light source emits single photons as excitation light inducing fluorescence of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic, the excitation light from the light source having a wavelength band within the near UV and visible regions; and, in the image pickup unit insertion step, the image pickup unit is a general fluorescence endoscope or a confocal endoscopic microscope.
Owner:UNIV OF ULSAN FOUND FOR IND COOPERATION +3
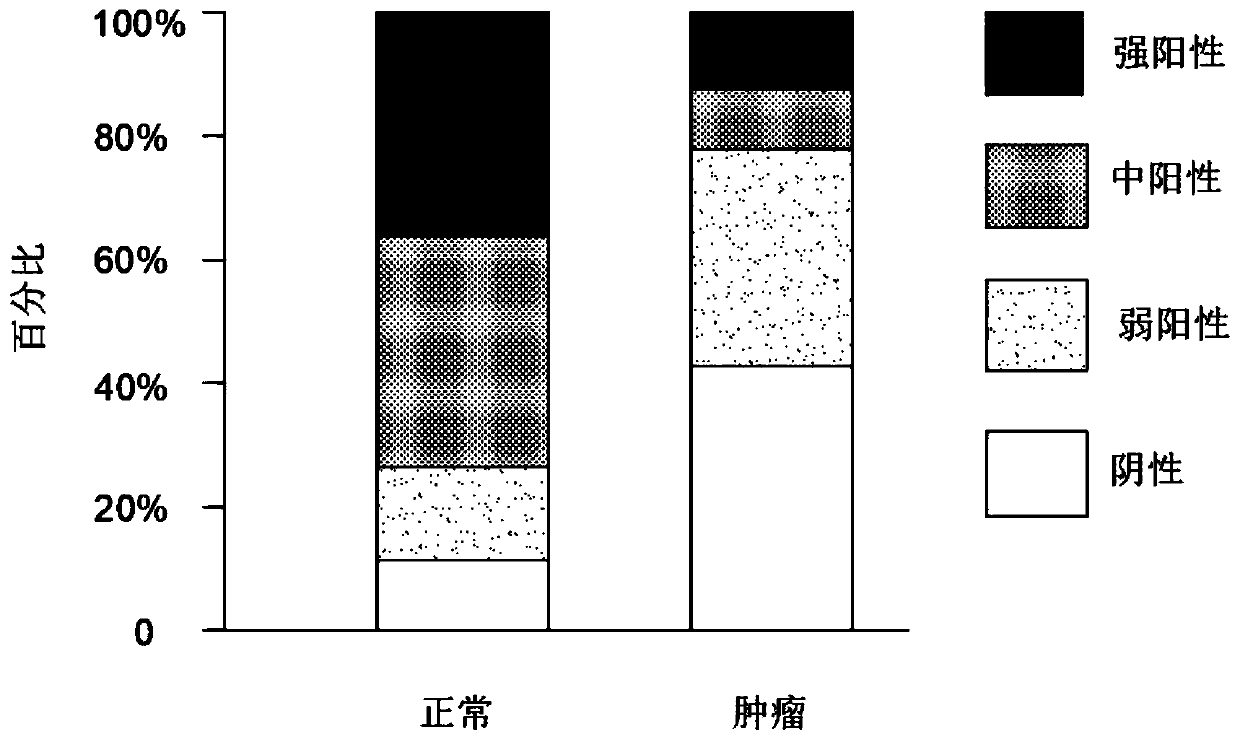
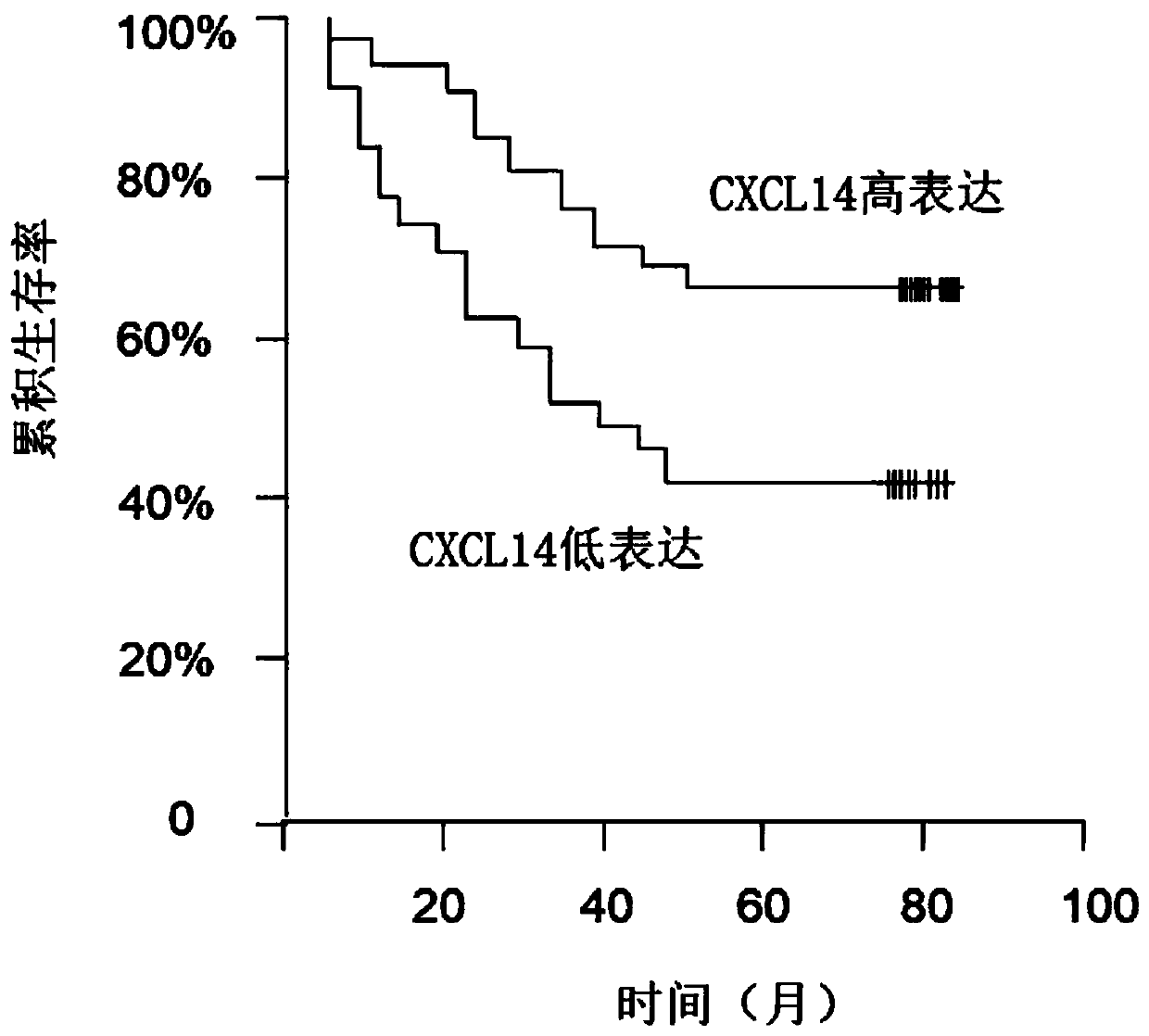
Application of chemokine CXCL14 in predicting prognosis of colon cancer
PendingCN110488015ASignificant predictive valueImproving Poor Treatment OutcomesPreparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisQuality of lifeOncology
The invention discloses the application of chemokine CXCL14 in predicting the prognosis of colon cancer, and the application of a reagent for detecting the chemokine CXCL14 in the preparation of a tool for predicting the prognosis of colorectal cancer is included. The invention particularly discloses a method for quantitatively detecting the expression of CXCL14 protein in colorectal tissues through an immunological method to predict the prognosis of the colon cancer. The method has a significant predictive value for the prognosis of the total survival time of a patient with an III-IV colorectal cancer, therefore, the poor treatment prognosis can be improved in a targeted manner, the medical level is improved, and the quality of life is improved.
Owner:成都和同易创生物科技有限公司
Method for detecting expression quantity of tumor-related gene spectrum and application of method
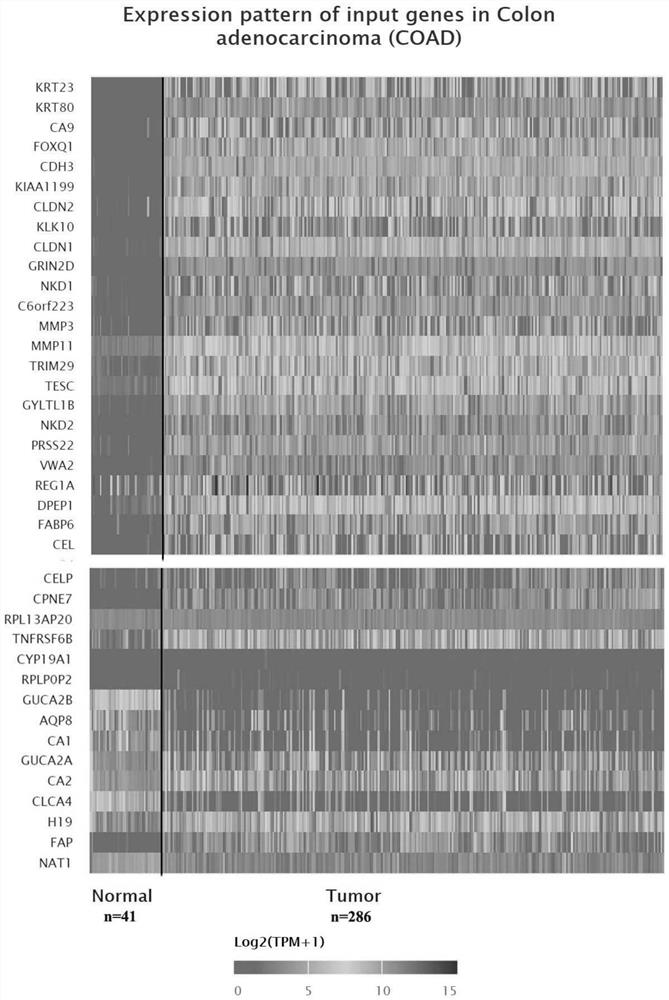
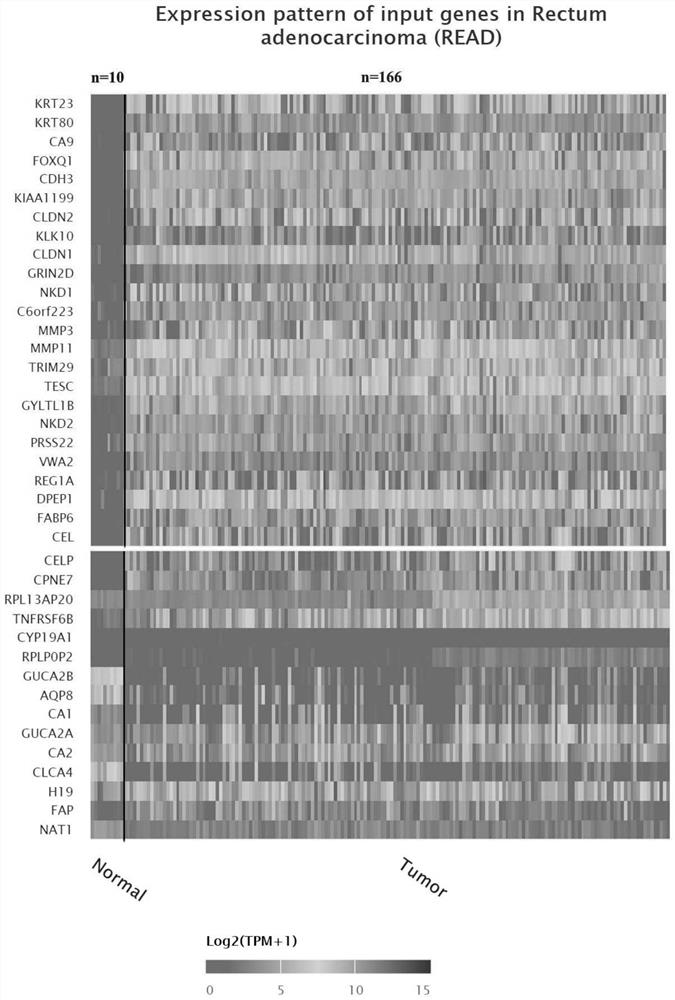
PendingCN114672554AStrong subjectivityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVWA2PRSS22
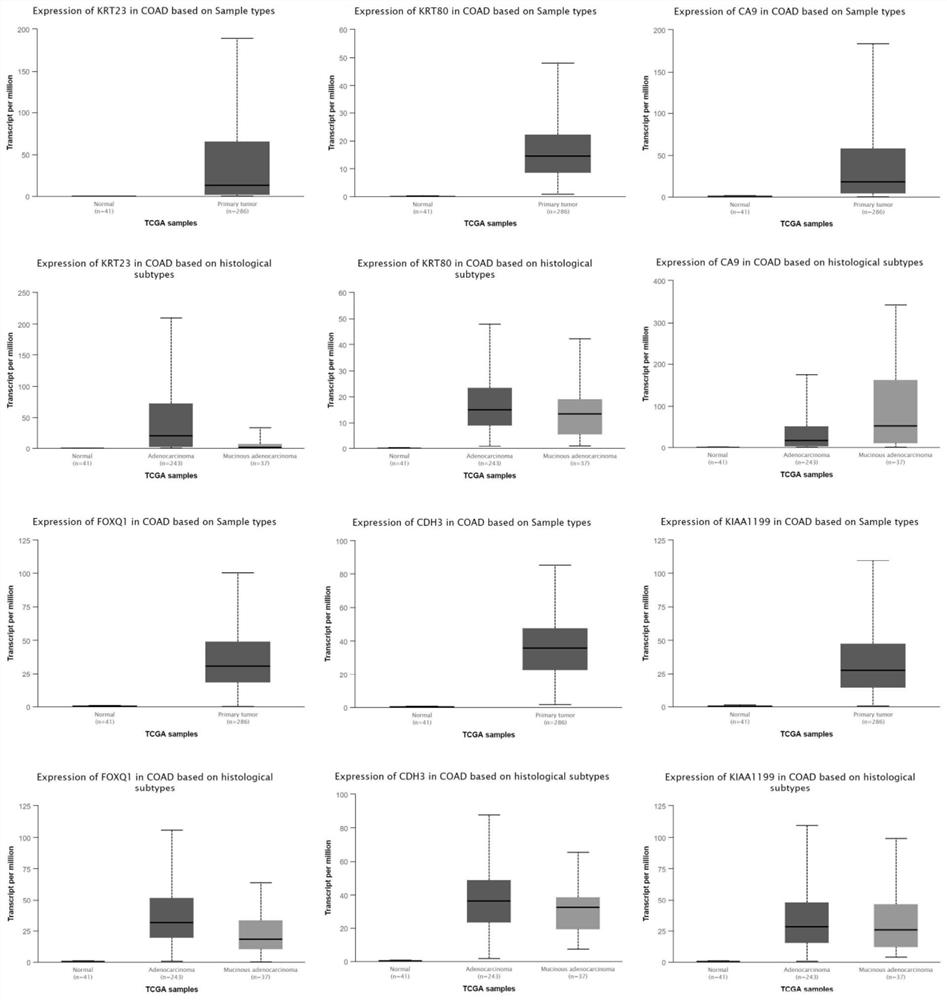
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological and medical examination, and relates to a molecular biological method for detecting the expression quantity of tumor-related gene products, and the method can be used for providing references for identification of colorectal cancer change, colorectal cancer classification / type, prognosis evaluation and the like. The related genes comprise: KRT23, KRT80, CA9, FOXQ1, CDH3, KIAA1199, CLDN2, KLK10, CLDN1, GRIN2D, NKD1, C6ORF223, MMP3, MMP11, TRIM29, TESC, GYLTL1B, NKD2, PRSS22, VWA2, REG1A, DPEP1, FABP6, CEL, CELP, CPNE7, RPL13AP20, TNFRSF6B, CYP19A1, RPLP0P2, GUCA2B, AQP8, CA1, GUCA2A, CA2, CLCA4, H19, FAP, NAT1 and the like. The combined application of the genes (single or any combination) is beneficial to providing references for identification, classification / type, prognosis evaluation and the like of the colorectal cancer; when the genes are jointly applied to identify colorectal cancer and normal colorectal tissues, the sensitivity can reach 97% when the specificity is 100%.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Lactobacillus plantarum with colorectal cancer inhibition function and use thereof
ActiveUS20220096570A1Improve abilitiesAvoid it happening againMilk preparationBacteriaGut floraFatty acid
The present invention relates to the technical field of microbes, in particular to a Lactobacillus plantarum which can significantly inhibit the occurrence of colorectal cancer, and its use thereof. The Lactobacillus plantarum strain CCFM164 has a deposit number CGMCC No. 14520, which has a good tolerance to gastric acid and bile salts, significantly alleviate the level of colorectal inflammation in colorectal cancer model mice, and can reduce the number of tumors in the colon and rectum of the model mice by regulating the Notch1, Notch2 signaling pathway and the expression of VEGFR2 molecule in colorectal tissue. In addition, the Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM164 can also improve the intestinal flora population and short-chain fatty acid levels in the intestine. The Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM164 is used to prepare a fermented food for the inhibition of the occurrence of colorectal cancer with wild applications.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Schiff method for dyeing intestinal mucous cell of yellow-feather quail
InactiveCN107014660AGood colorGood coloring effectPreparing sample for investigationGoblet cellMucous cell
The invention discloses a Schiff method for dyeing an intestinal mucous cell of a yellow-feather quail. The method comprises the steps of completing Schiff dye liquor preparation, selecting 1cm tissue samples of middle segments of the duodenum, the jejunum, the ileum, the cecum and the colorectum of the quail, immobilizing the tissue samples into a Bouin liquid and slicing conventional paraffin for washing; dyeing a Schiff dye liquor for 40min and washing for 10min; redyeing by using hematoxylin for 1min and carrying out differentiation and blueing; and finally carrying out washing, dehydration, transparency and mounting, wherein the dyeing result is that a goblet cell is red. The Schiff method is easy to color and stable in coloring effect.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
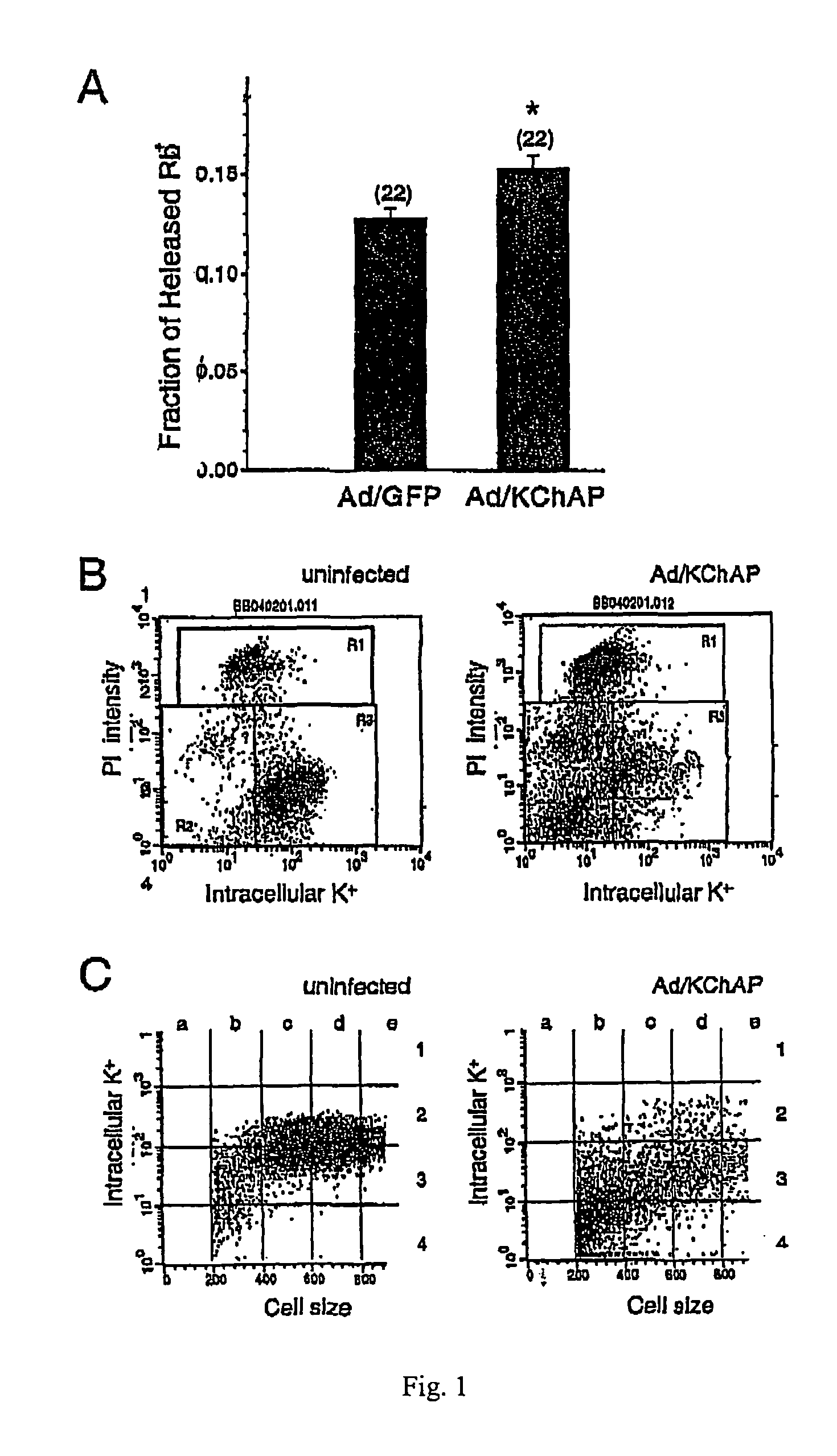
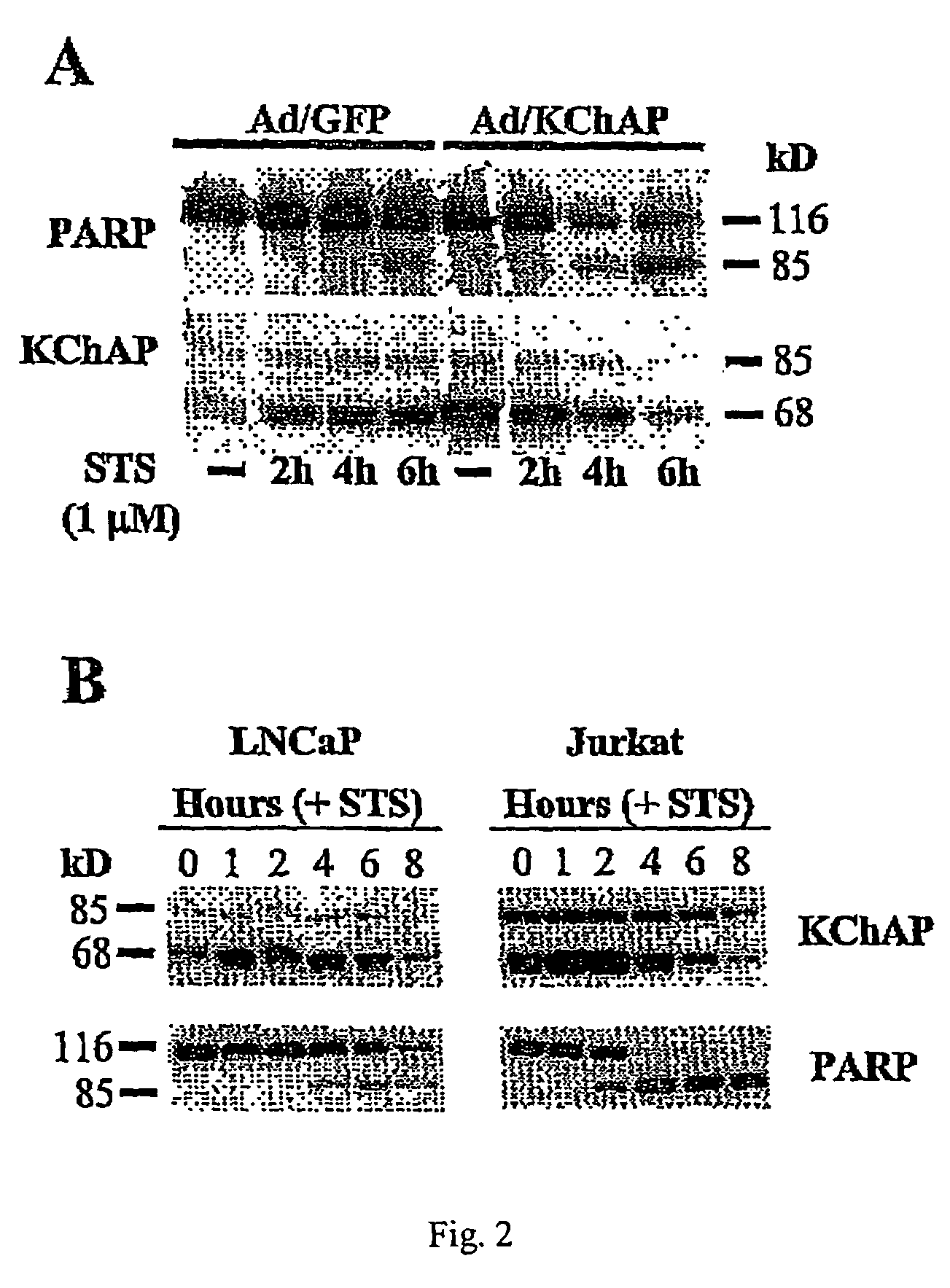
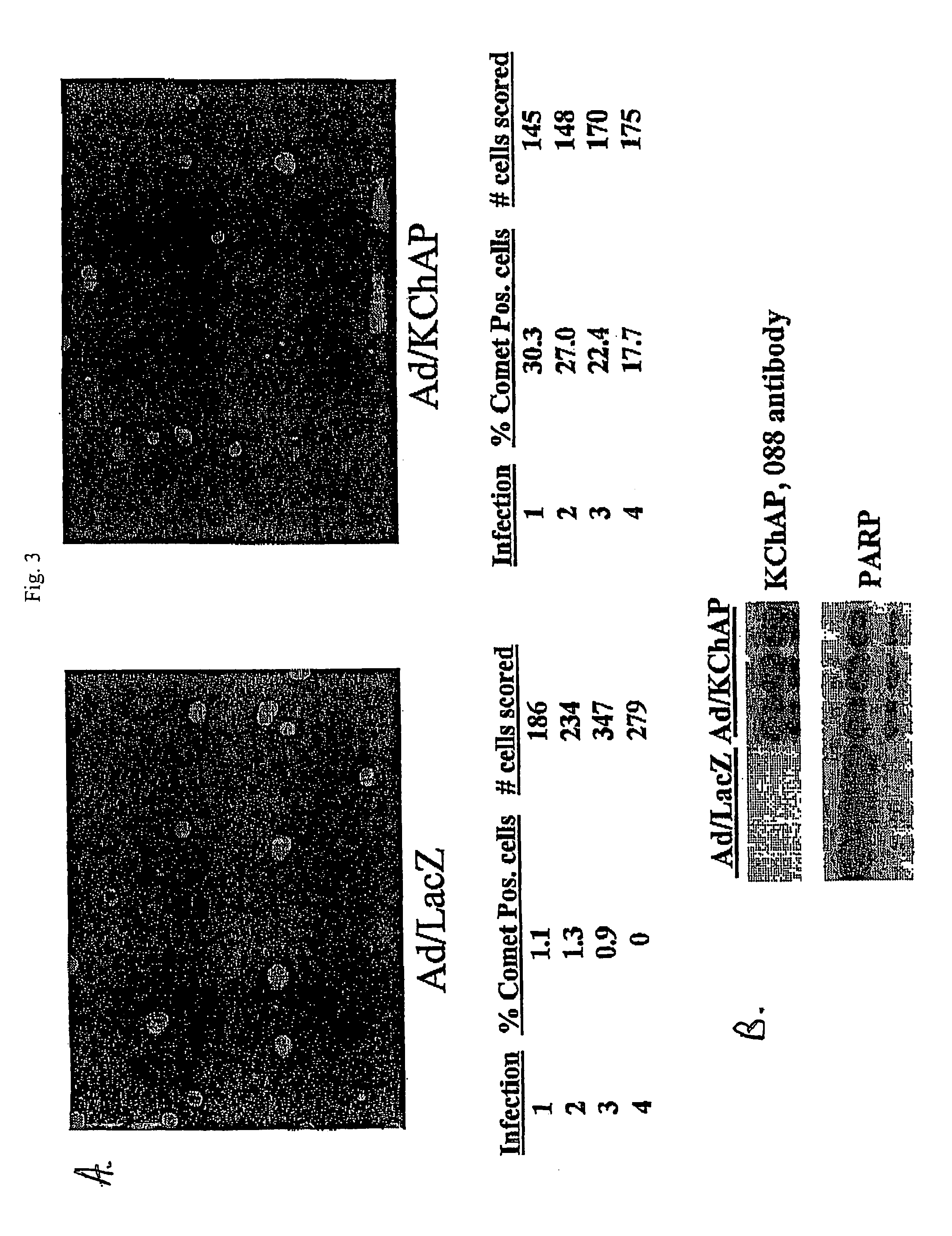
Methods of inducing apoptosis in hyperproliferative cells
Methods of inducing apoptosis in hyperproliferative cells, particularly cancer cells are provided. Such method involves increasing the levels of a potassium channel modulatory protein in the cell. Examples of such proteins are native KChAP protein, a biologically active variant of native KChAP protein, or a biologically active KChAP-related protein (collectively referred to hereinafter as “KChAP protein”). In one embodiment, the cells are contacted with the KChAP protein under conditions permitting uptake of the protein by the cells. In another embodiment, the cells are contacted with (i) a nucleic acid encoding the KChAP protein, and (ii) a promoter active in the cancer cell, wherein the promoter is operably linked to the region encoding the KChAP protein, under conditions permitting the uptake of the nucleic acid by the cancer cell. Methods of detecting cancerous cells in a biological sample selected from the group consisting of a colorectal tissue sample or brain tissue sample are also provided. Such method comprises assaying for the presence of elevated levels of KChAP mRNA or KChAP protein in the sample.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method for detecting and treating colon cancer by measuring heavy metal concentrations
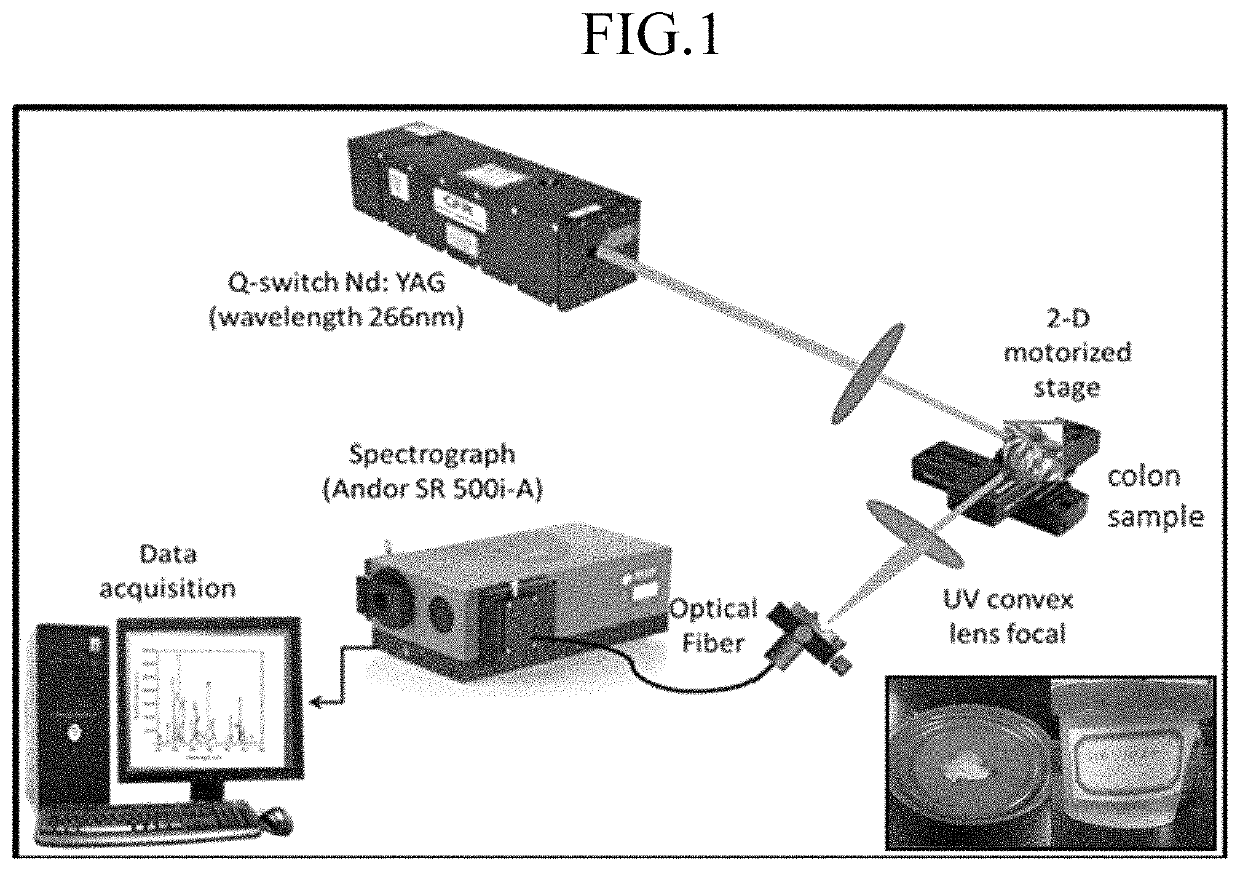
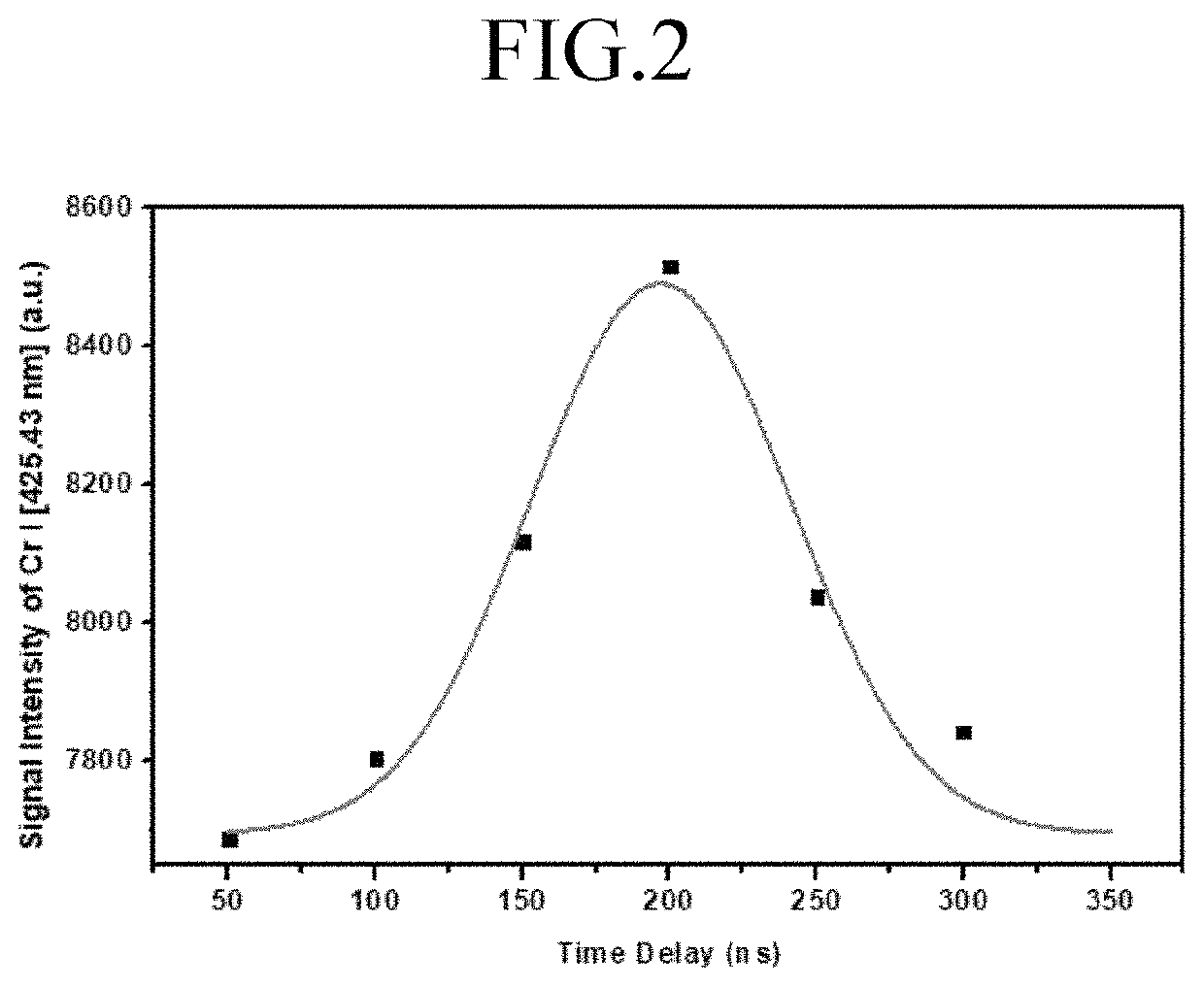
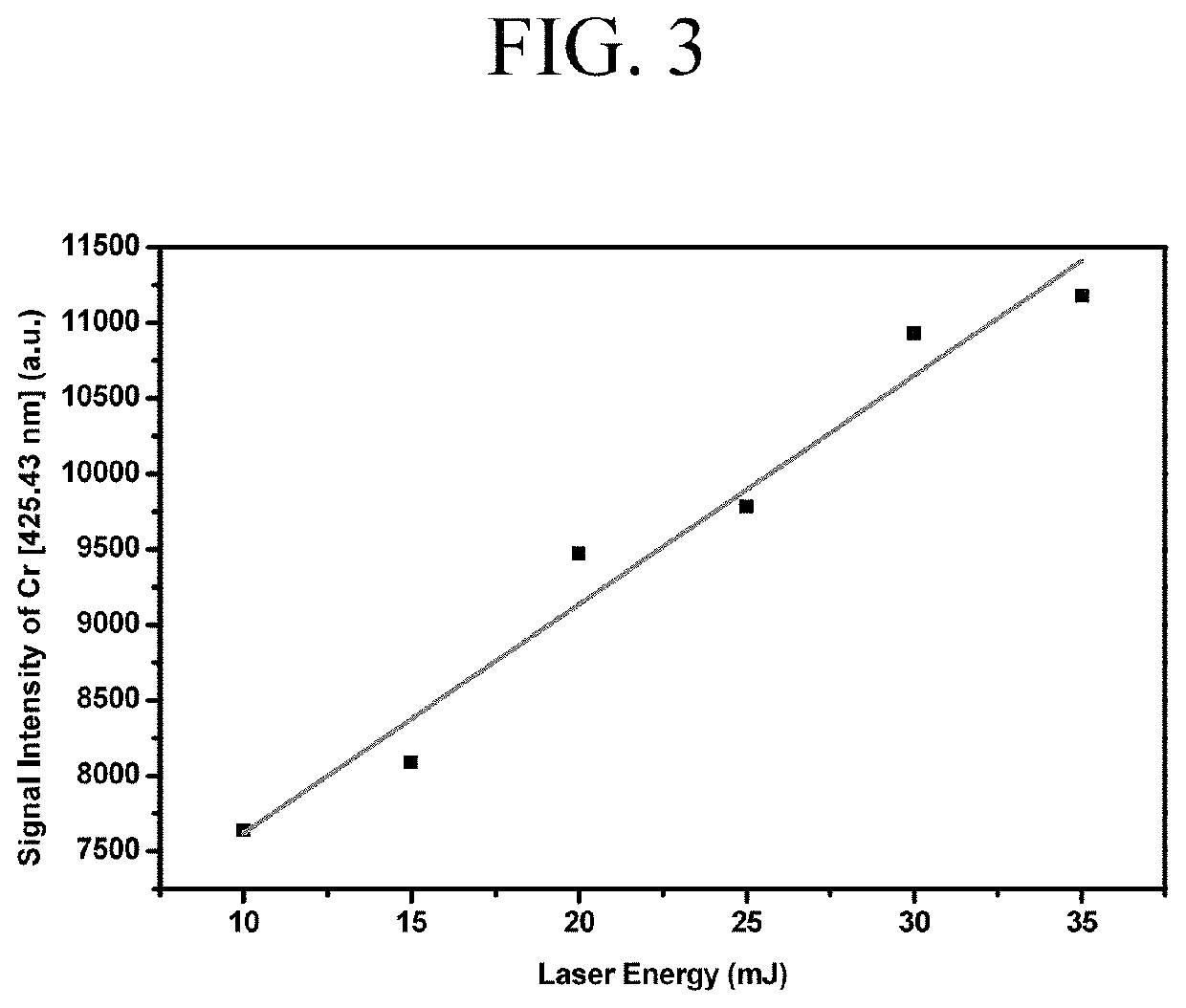
ActiveUS11415582B2Reduce noiseColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopyOncology
Method for detecting colon or colorectal cancer by measuring heavy metal concentrations in colon or colorectal tissue using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS).
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com