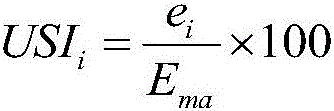Patents
Literature
50 results about "Electroanalytical method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electroanalytical methods are a class of techniques in analytical chemistry which study an analyte by measuring the potential (volts) and/or current (amperes) in an electrochemical cell containing the analyte. These methods can be broken down into several categories depending on which aspects of the cell are controlled and which are measured. The three main categories are potentiometry (the difference in electrode potentials is measured), coulometry (the cell's current is measured over time), and voltammetry (the cell's current is measured while actively altering the cell's potential).
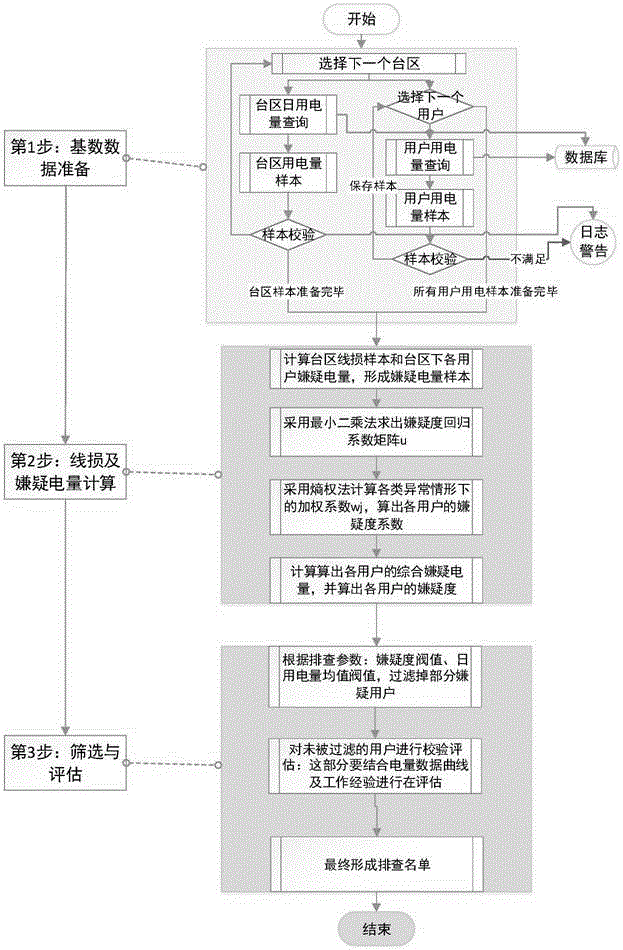
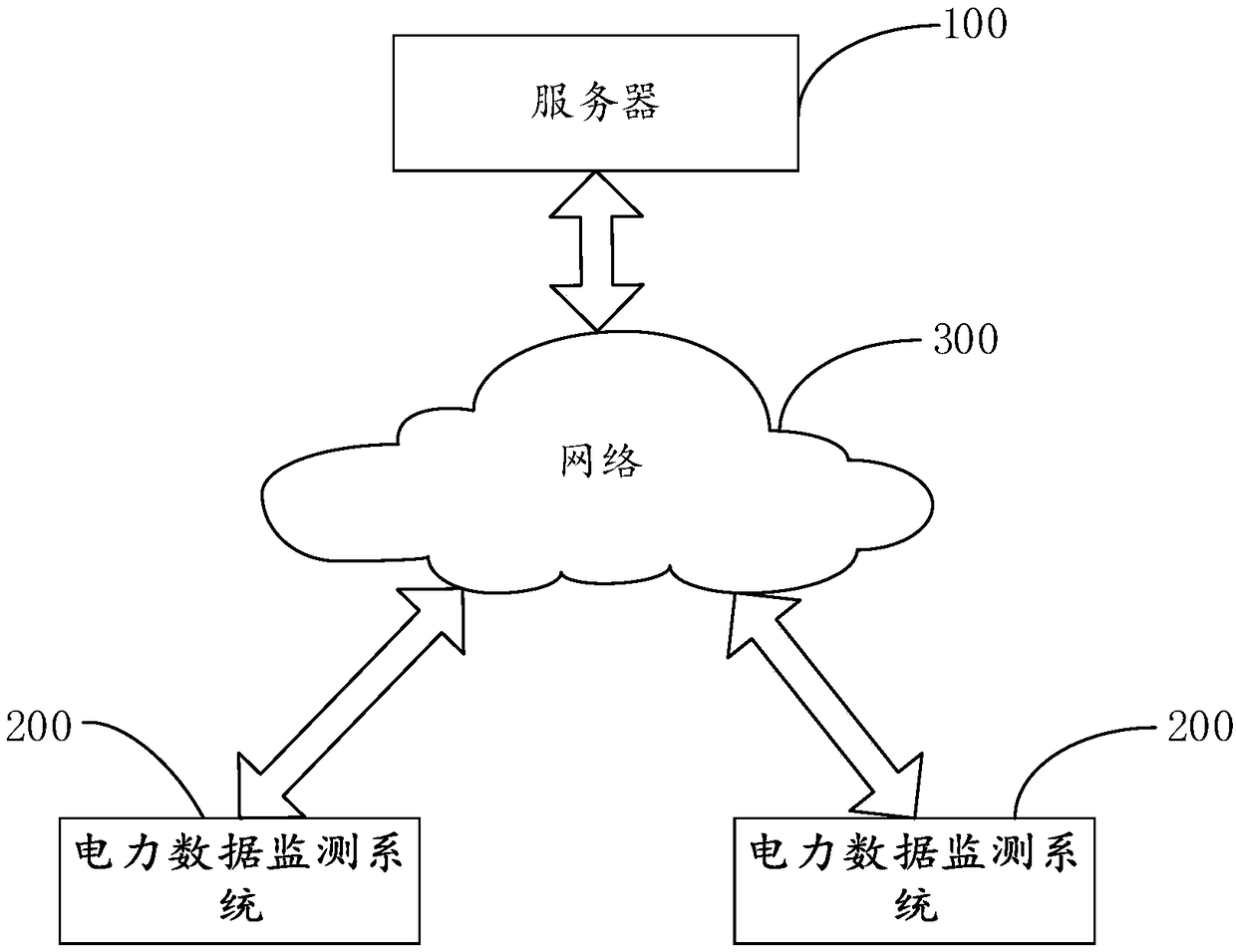
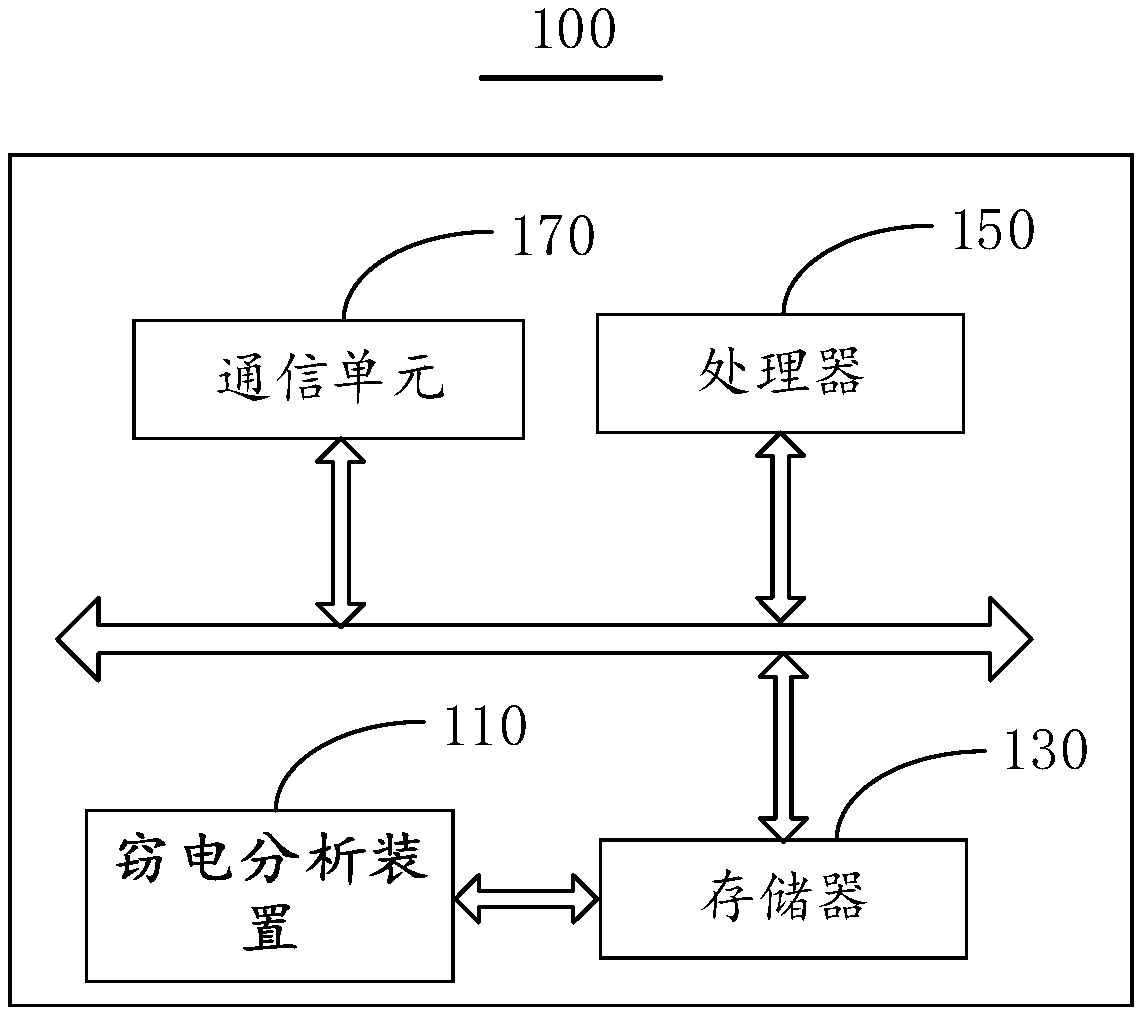
Electricity stealing analysis method and device
InactiveCN107492043AImprove analysis efficiencyImprove analytical accuracyData processing applicationsMachine learningElectricityData mining
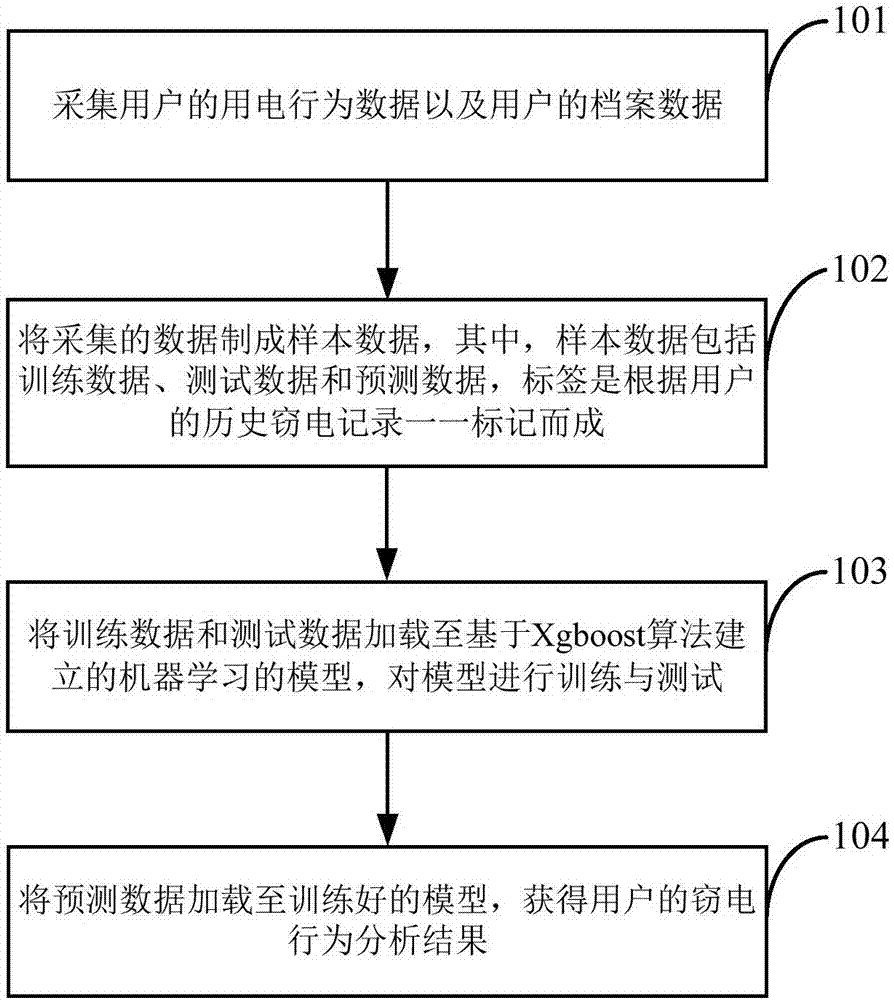
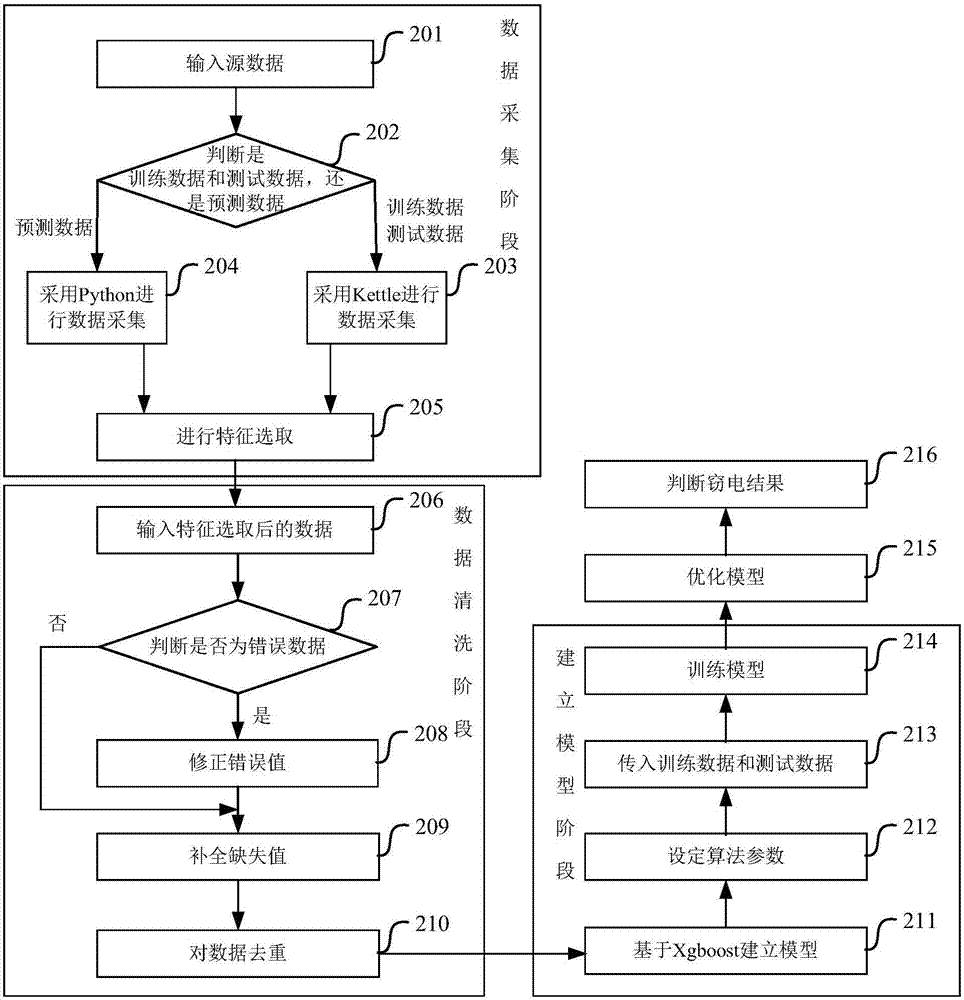
The invention discloses an electricity stealing analysis method and device. The method comprises steps that electricity behavior data of a user and archive data of the user are acquired; the acquired data is made to be sample data, the sample data comprises training data, test data and prediction data, the training data and the test data have labels, and the labels are made through marking historical electricity stealing records of the user one by one; the training data and the test data are loaded to a machine learning model established based on an Xgboost algorithm, and the model is trained and tested; the prediction data is loaded to the trained model, and the electricity stealing behavior analysis result of the user is acquired. The method is advantaged in that high-efficiency and accurate electricity stealing suspicion analysis can be realized.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST STATE GRID JIBEI ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +3
Power utilization analysis method based on acquisition data of power utilization information
InactiveCN106447206APrecise positioningAccurate and accurate investigationResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsElectricity marketTime-sharing
The invention relates to a power utilization analysis method based on acquisition data of power utilization information, and relates to a power utilization analysis method. At present, power utilization is difficult to be analyzed and monitored, and the accuracy is low. The power utilization analysis method comprises the steps of 1) acquiring daily time-sharing load statistic data details of users; 2) grouping the detail data according to users and industries; 3) performing normalization processing; 4) performing k-means clustering calculation to acquire characteristic load curves of each industry and each user; 5) adjusting the number of the generated curves, acquiring obviously characterized curves, labeling the acquired curves, and corresponding each industry and each user to the respective characteristic load curves; and 6) extracting characteristic users according to the characteristic load curves, and performing comparative analysis on the characteristic load curves. The technical scheme provided by the invention improves the accuracy of a power utilization information acquisition system, and provides basic guarantee for supporting execution of tiered pricing for electricity, reinforcing lean management, improving the high-quality service level, extending the power market and innovating the transaction platform.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +2
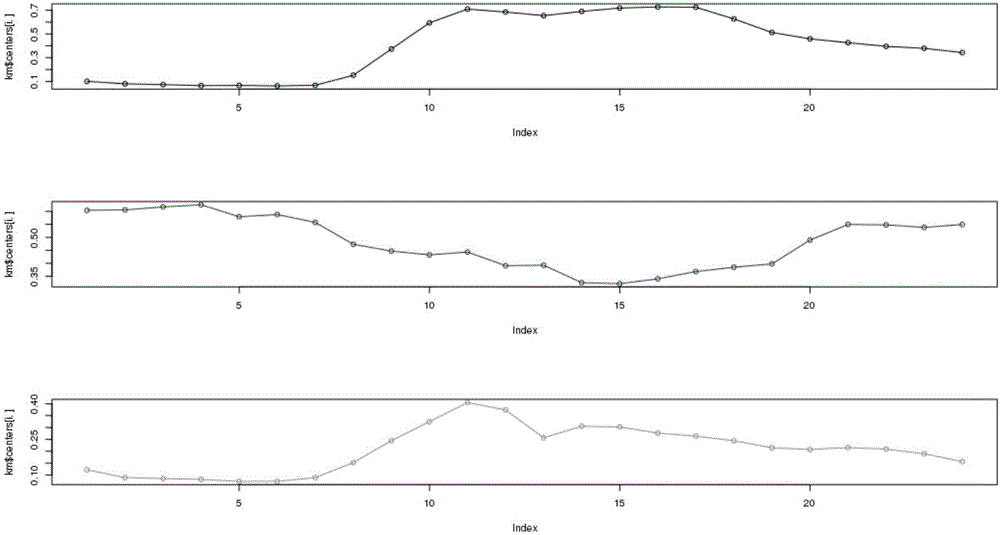
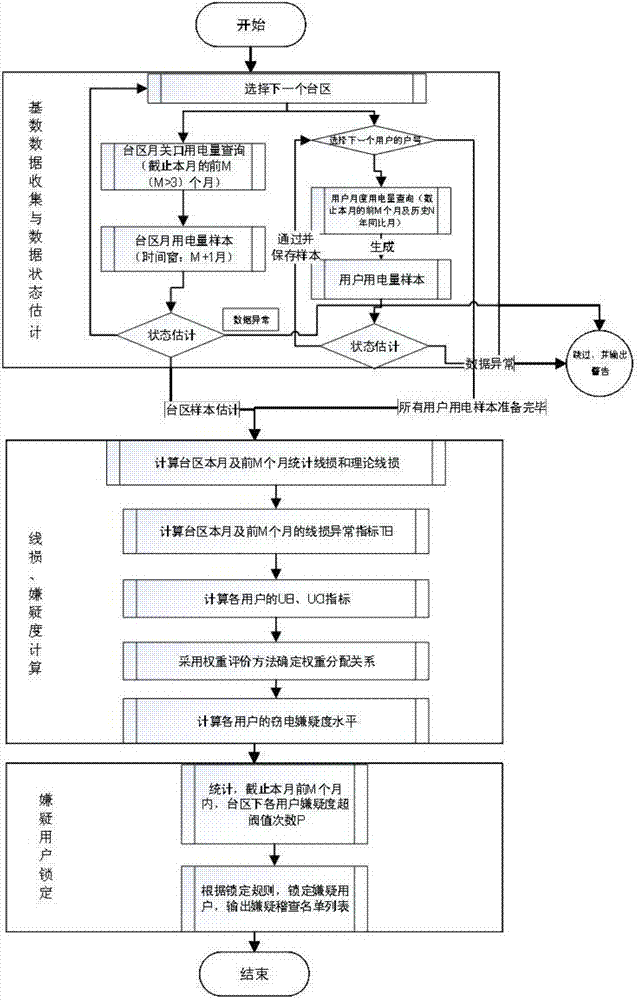
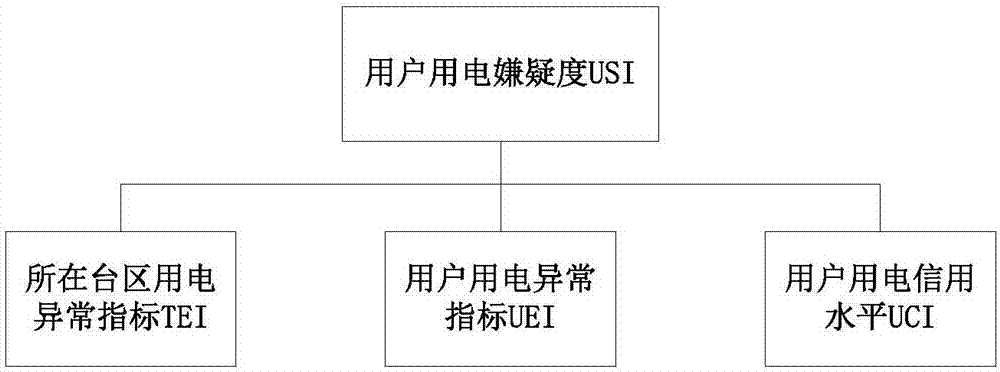
Anti-stealing electricity analysis method based on quantitative evaluation model sealing electricity suspicion analysis algorithm
InactiveCN107221927AHigh locking precisionImprove work efficiencyAc network circuit arrangementsElectricityLow voltage
The invention provides an anti-stealing electricity analysis method based on a quantitative evaluation model sealing electricity suspicion analysis algorithm. The anti-stealing electricity analysis method is characterized by comprising the following steps of S1, collecting basic data; S2, estimating a basic data state; S3, calculating loss line of a zone area; S4, calculating a stealing electricity suspicion level of each user in a month under the zone area by employing the quantitative evaluation model sealing electricity suspicion analysis algorithm; and S5, locking a suspicion stealing electricity user. The anti-stealing electricity analysis method has the beneficial effects that the locking accuracy of the stealing electricity user in a low-voltage power supply zone area is improved, the marketing management line loss level is reduced, so that the working efficiency of an audit department is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU TONGCHI POWER AUTOMATION
Loss allocation suspicion analysis-based anti-electricity stealing analysis method
InactiveCN106066423AHigh locking precisionData processing applicationsElectrical measurementsElectricityPower user
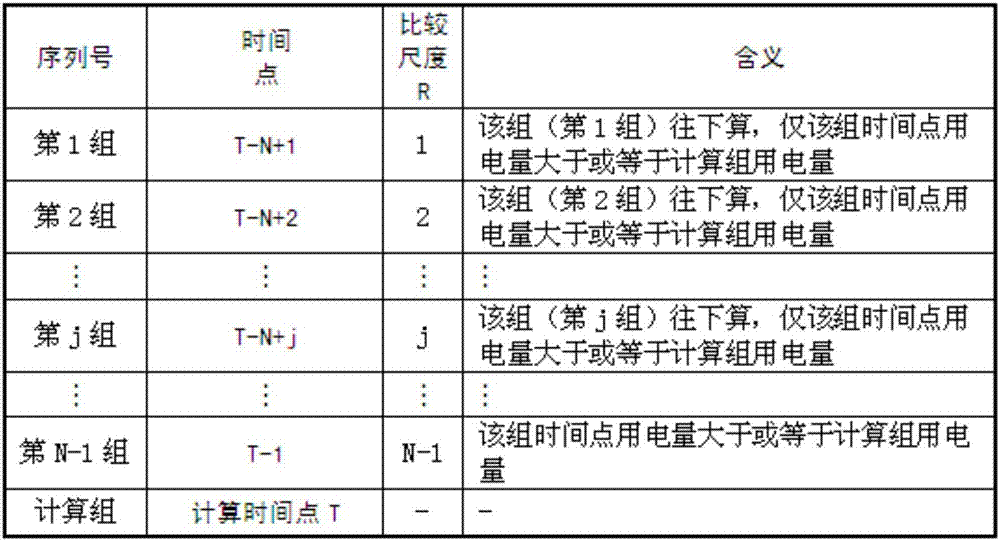
The invention relates to a loss allocation suspicion analysis-based anti-electricity stealing analysis method. The loss allocation suspicion analysis-based anti-electricity stealing analysis method is put forward based on analysis on different line loss and power consumption anomaly and by means of suspected power consumption calculation. With the loss allocation suspicion analysis-based anti-electricity stealing analysis method adopted, the electricity stealing behaviors of users are ultimately reflected by the anomaly of measured power consumption of the users. The objective of the invention is to approximately calculate power consumption of the users in a transformer area which are not measured actually so as to determine suspected power users. According to the loss allocation suspicion analysis-based anti-electricity stealing analysis method of the invention, line loss calculation is divided into statistical line loss calculation, theoretical line loss calculation and management line loss calculation; and calculation methods of different lines are put forward; loss-counted power consumption abnormal conditions are calculated in different aspects; suspected power consumption is analyzed; suspected power consumption is compared and distinguished according to a plurality of power consumption abnormal conditions, so that the suspected power consumption of the users can be analyzed quantitatively; a specific power consumption suspicion degree method is put forward; the suspicion degrees of the users are calculated; thresholds are screened based on the suspicion degrees; required target users are filtered out; and an investigation list is formed.
Owner:SHANGHAI PROINVENT INFORMATION TECH
Microfluidic cartridge and reader device, system, and method of use
InactiveUS20170014822A1Promoting amountReduce electrode costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresMedical recordChemical reaction
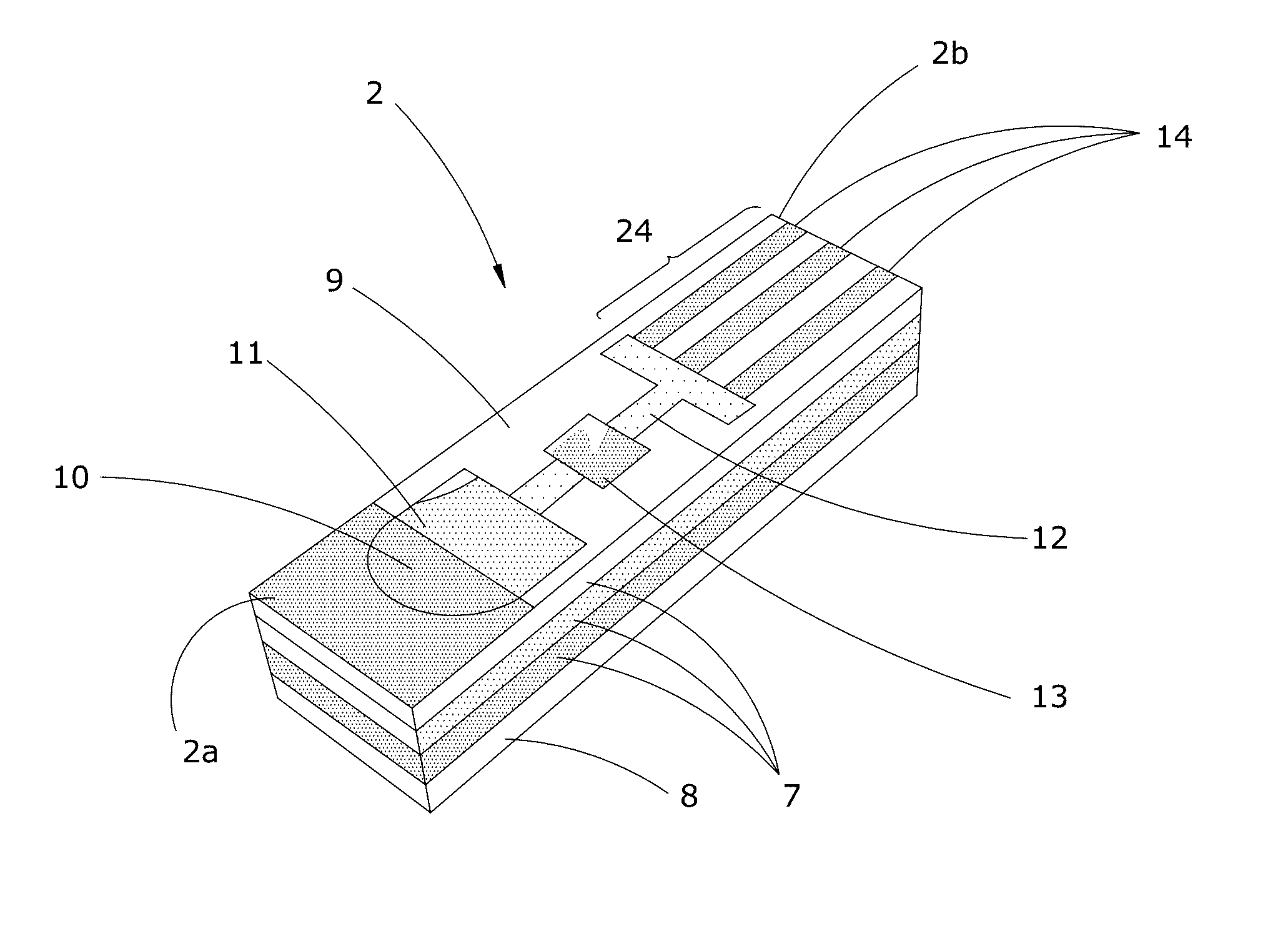
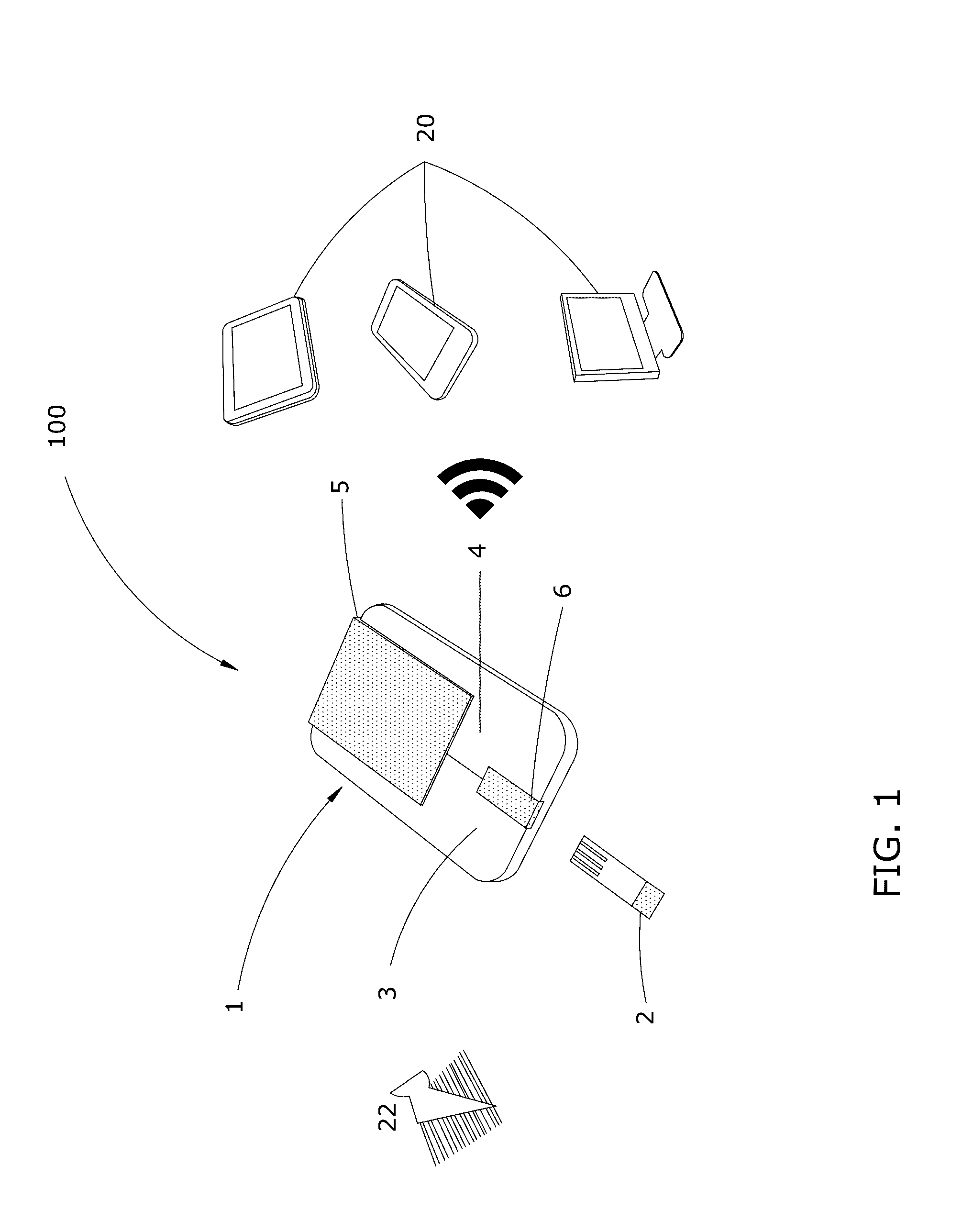
Disposable microfluidic cartridges, potentiostat reader devices, systems, kits, and methods to determine the concentration of analyte reaction products in a patient's specimen, such as: blood, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, joint fluid or tears. The microfluidic cartridges are disposable, paper-based strips comprising multiple assay layers, each layer comprising: a drop zone for receiving a patient specimen; a filter to remove contaminates, and / or isolate assay reactants; a hydrophilic microfluidic channel to direct movement of the specimen down the cartridge; a centered reaction chamber comprising impregnated enzymes and reagents to chemically react with the filtered specimen to produce an analyte; and a detector mechanism. Multiple analytes can be produced in parallel (e.g. one per layer), or sequentially along one layer. The detector mechanism utilizes electro-analytic methods to facilitate the reader device in quantifying each analyte, and each analyte concentration is wirelessly transmitted to an electronic computing device for storage in a patient's medical record.
Owner:KER JUSTIN R DR
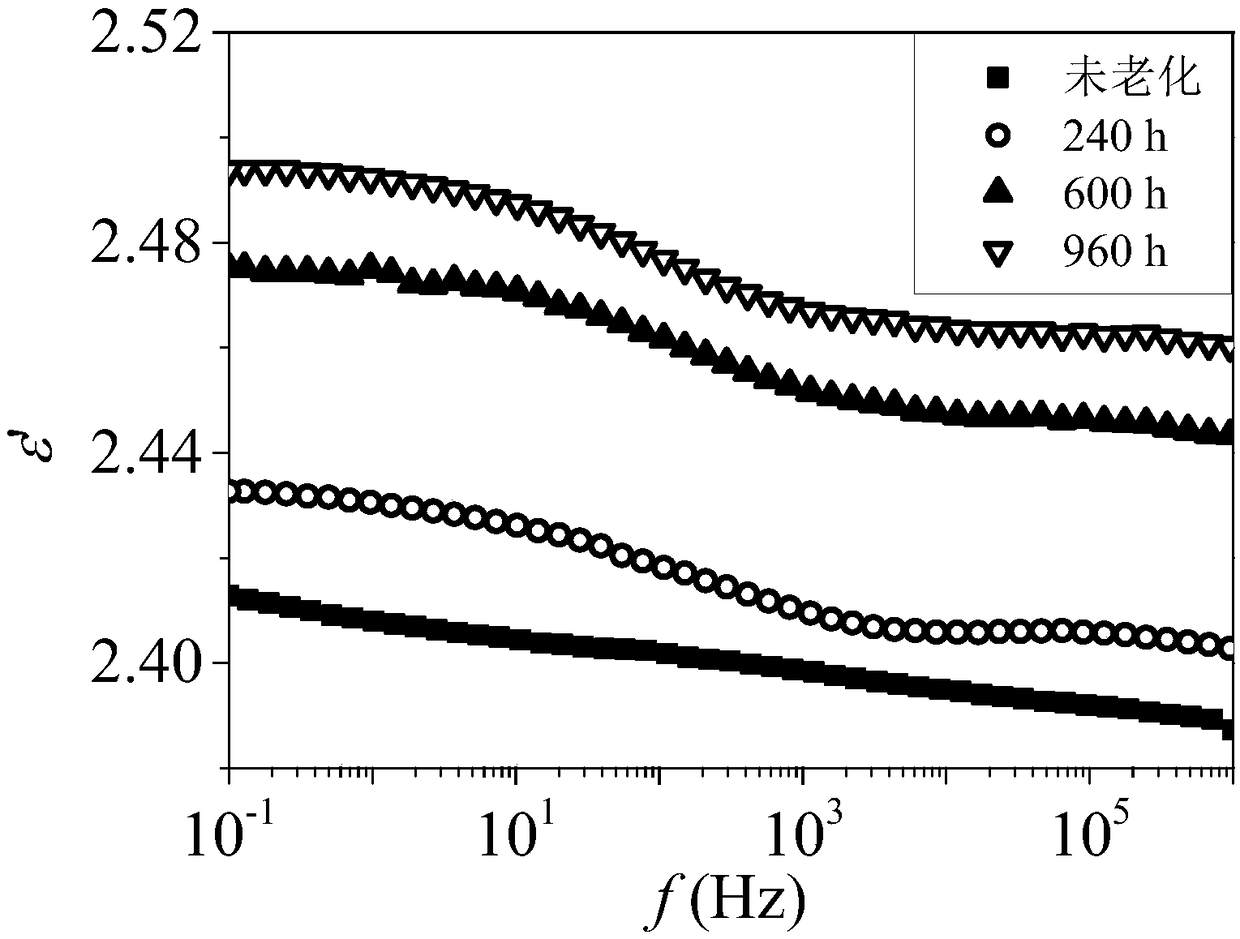
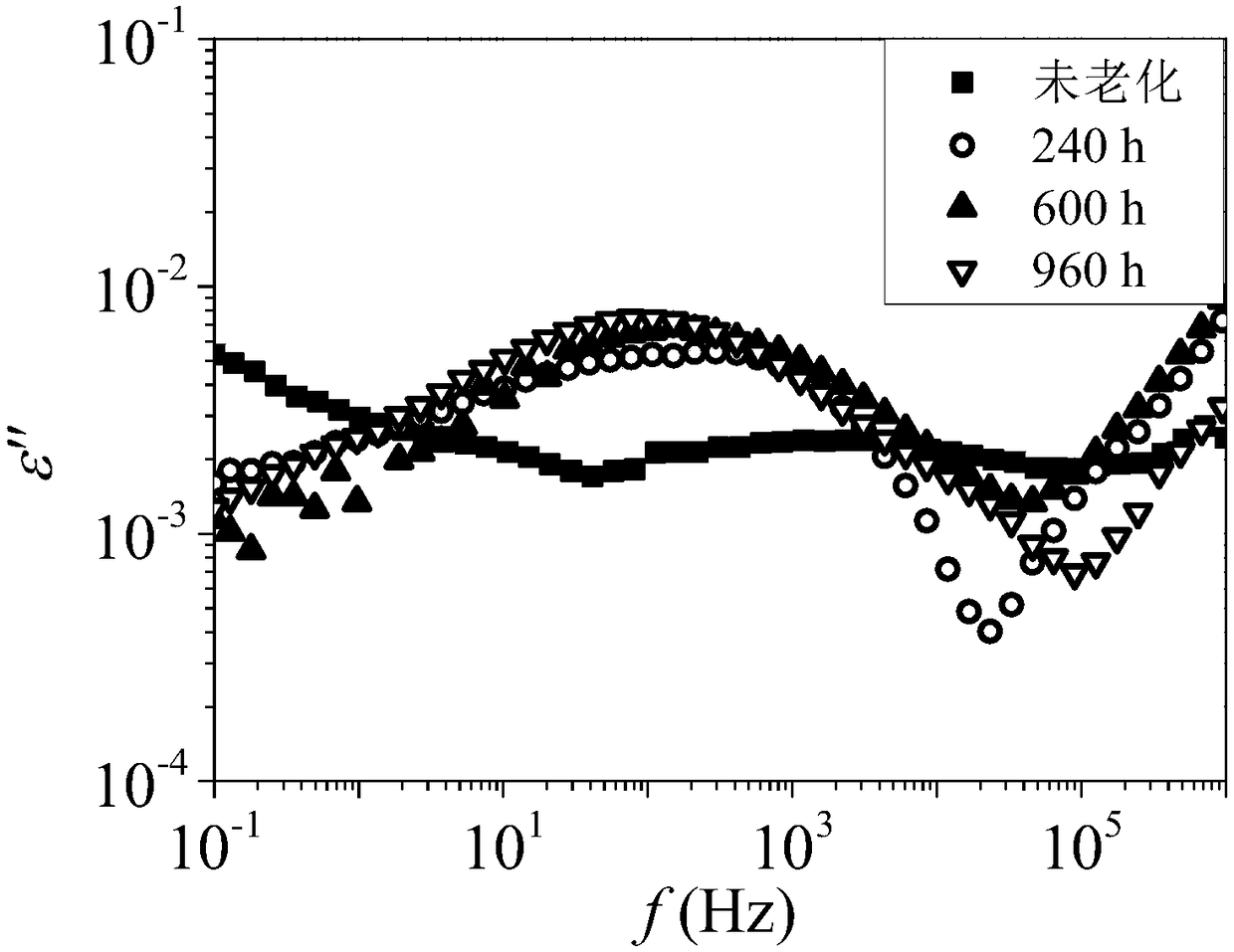
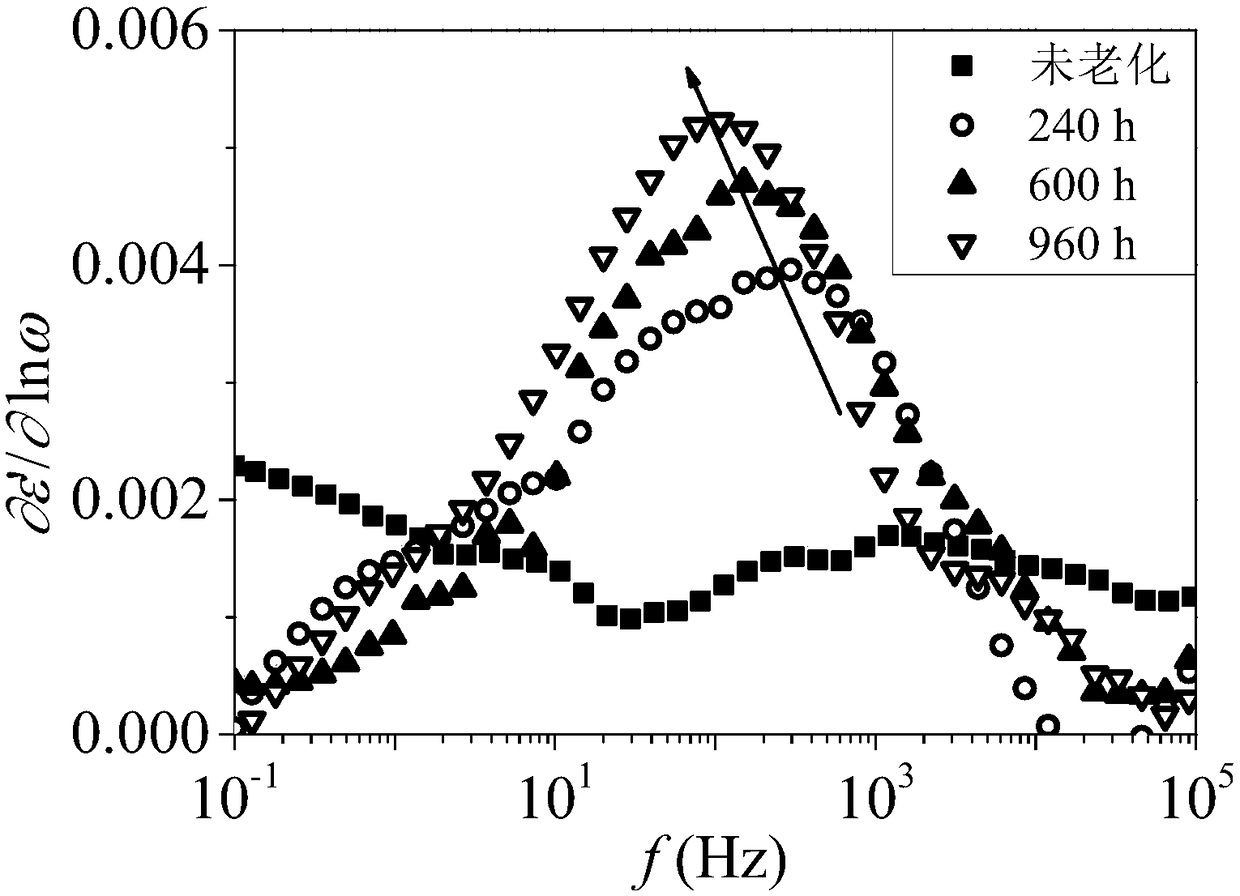
Dielectric analysis method for evaluating insulation aging state of XLPE cable
ActiveCN108508337AClear indication of aging statusDielectric property measurementsTesting dielectric strengthElectricityDielectric
The invention relates to a dielectric analysis method for evaluating insulation aging state of XLPE cables, which comprises the following steps of: step 1, measuring the frequency spectrum of the complex dielectric constant of XLPE cable insulation at a set temperature, and obtaining the change curve of a dielectric constant real part epsilon' and a dielectric constant imaginary part epsilon' following frequency; step 2, performing mathematical change on the dielectric constant real part epsilon' to obtain the change curve of mathematical formula with a dielectric constant real part epsilon' following the frequency; step 3, analyzing the insulation aging state of XLPE cable according to the change curve of step 2. Compared with the prior art, the dielectric analysis method for evaluating insulation aging state of XLPE cables has the advantages that the method is simple and feasible, and has certain engineering application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
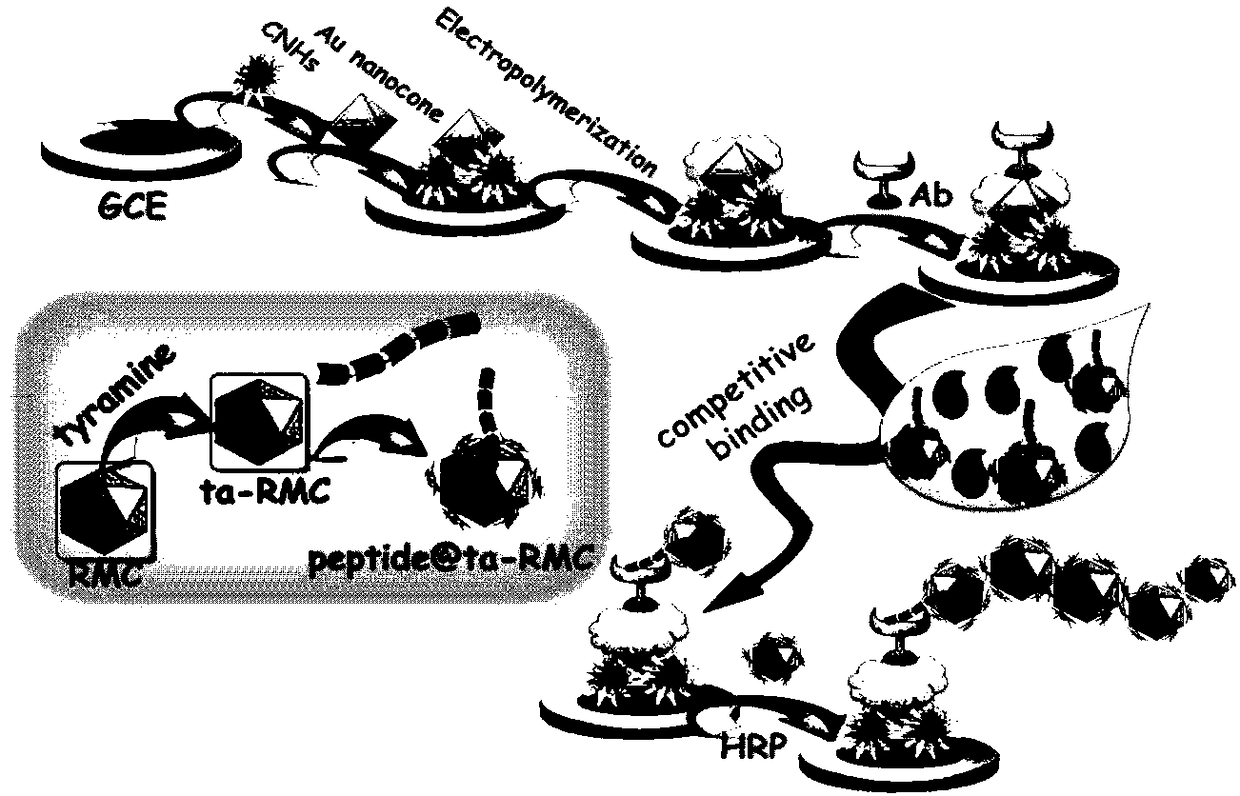
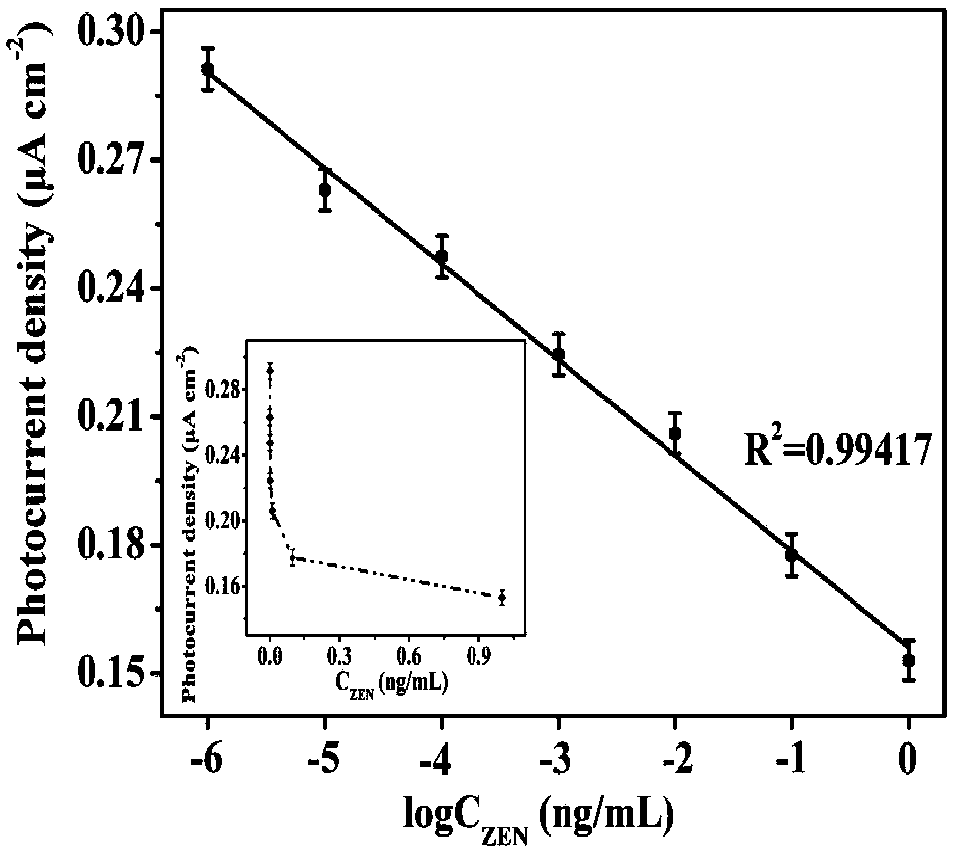
Non-toxic photoelectrochemistry competition immunoassay method of zearalenone based on peptide sensor
InactiveCN108535345AHigh porosityFast transmissionBiological material analysisBiological testingCysteaminePhotoelectrochemistry
The invention discloses a non-toxic photoelectrochemistry competition immunoassay method of zearalenone based on a peptide sensor. According to a sensing interface building method, carbon nanohorns, cysteamine functional golden cone and polyglycine are used as substrates; corn zeranol antibodies (Ab) are further immobilized; tyramine functionalized nanometer rutile type TiO2 mesoscopic crystals are used for immobilizing peptide chains with the specific sequences as a photoelectric probe; the peptide chain has the effect of simulating the zearalenone, the zearalenone can compete with the markedphotoelectric probe to combine the corn zeranol antibodies immobilized on the sensing interface. The photoelectric probe combined onto the sensing interface can further combine with tyramine-Rutile TiO2 mesoscopic crystal compounds under the catalysis effect of horseradish peroxidase; optoelectronic signals can be further amplified. On the basis, the non-toxic photoelectrochemistry competition immunoassay method on the corn zeranol can be built.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
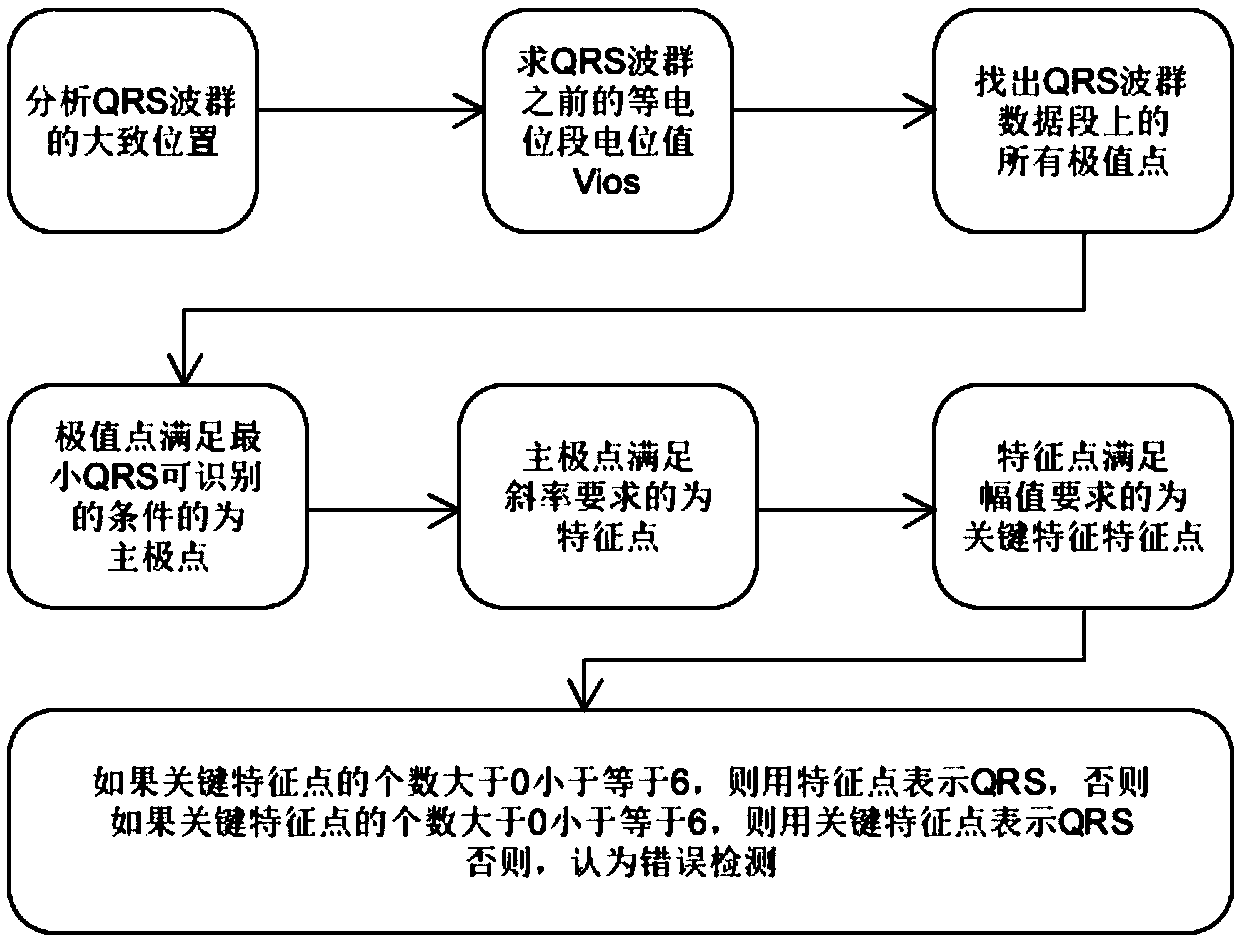
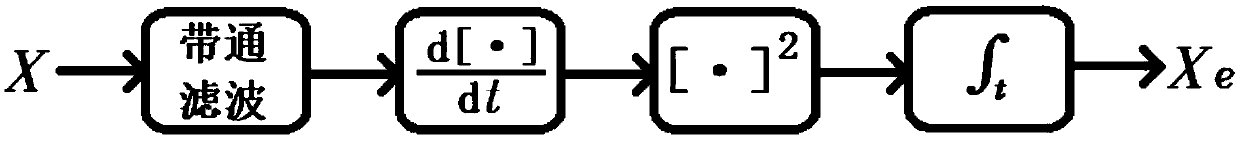
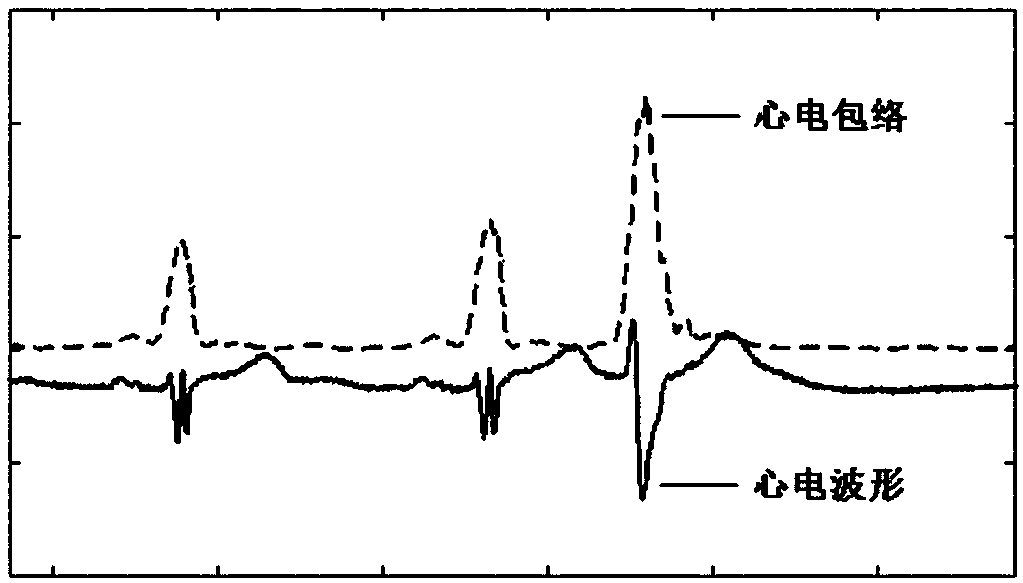
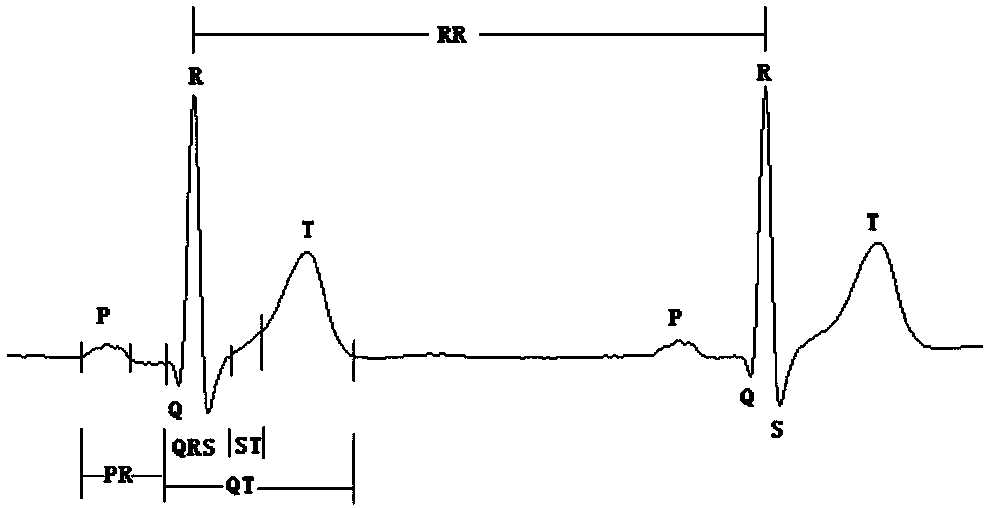
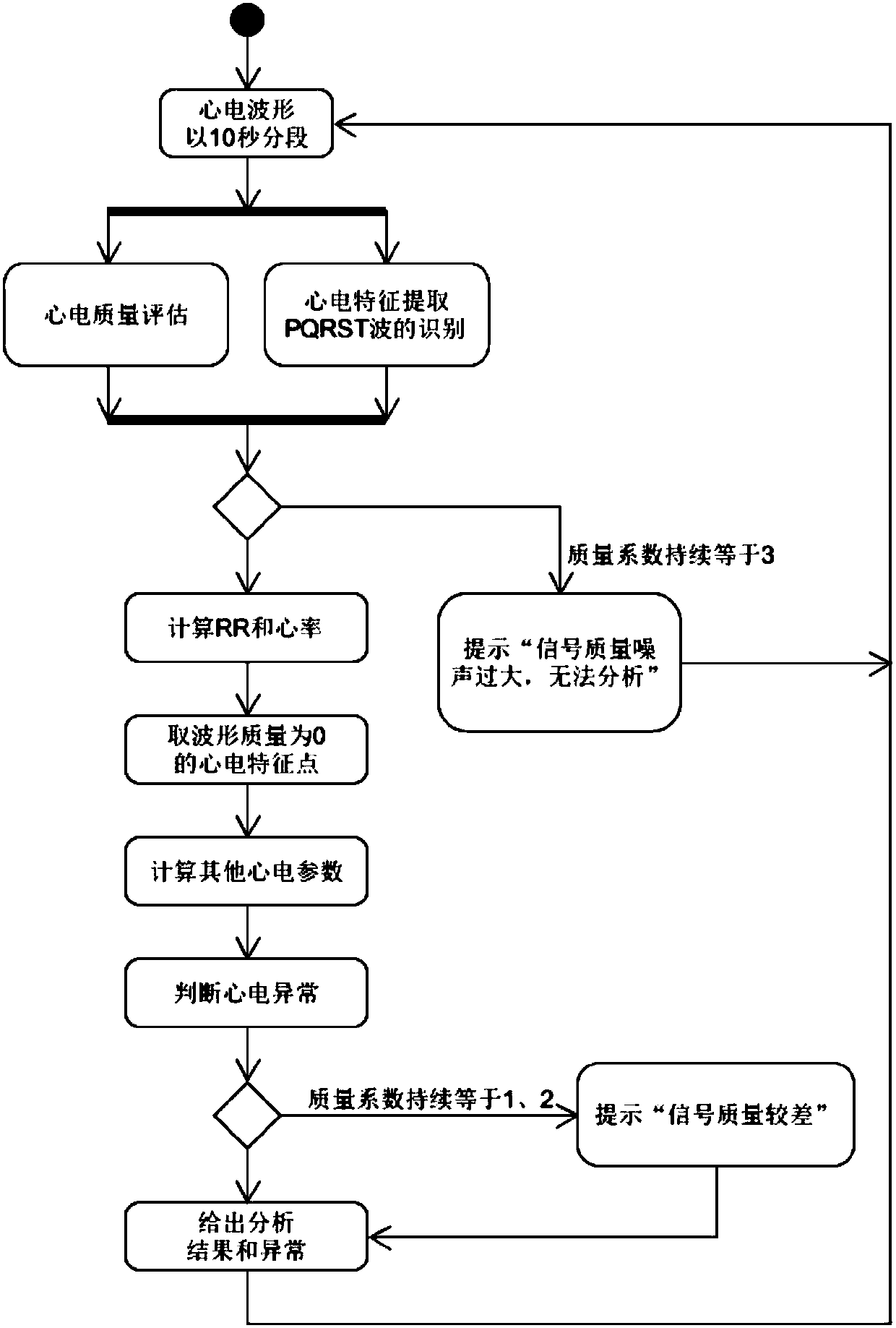
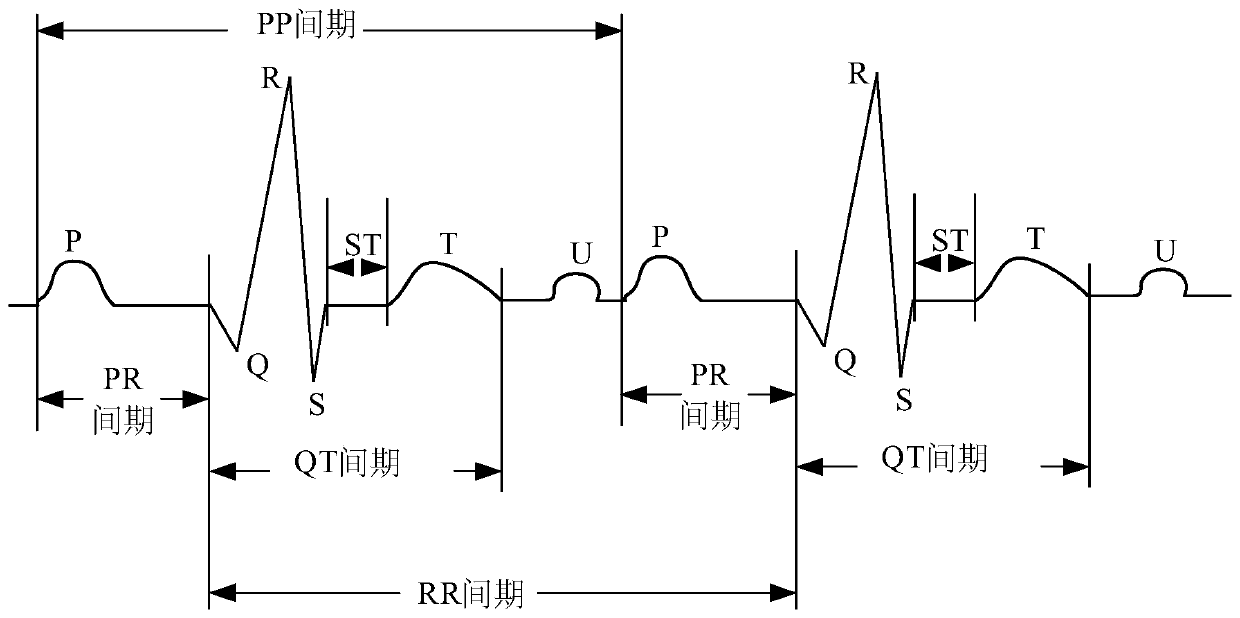
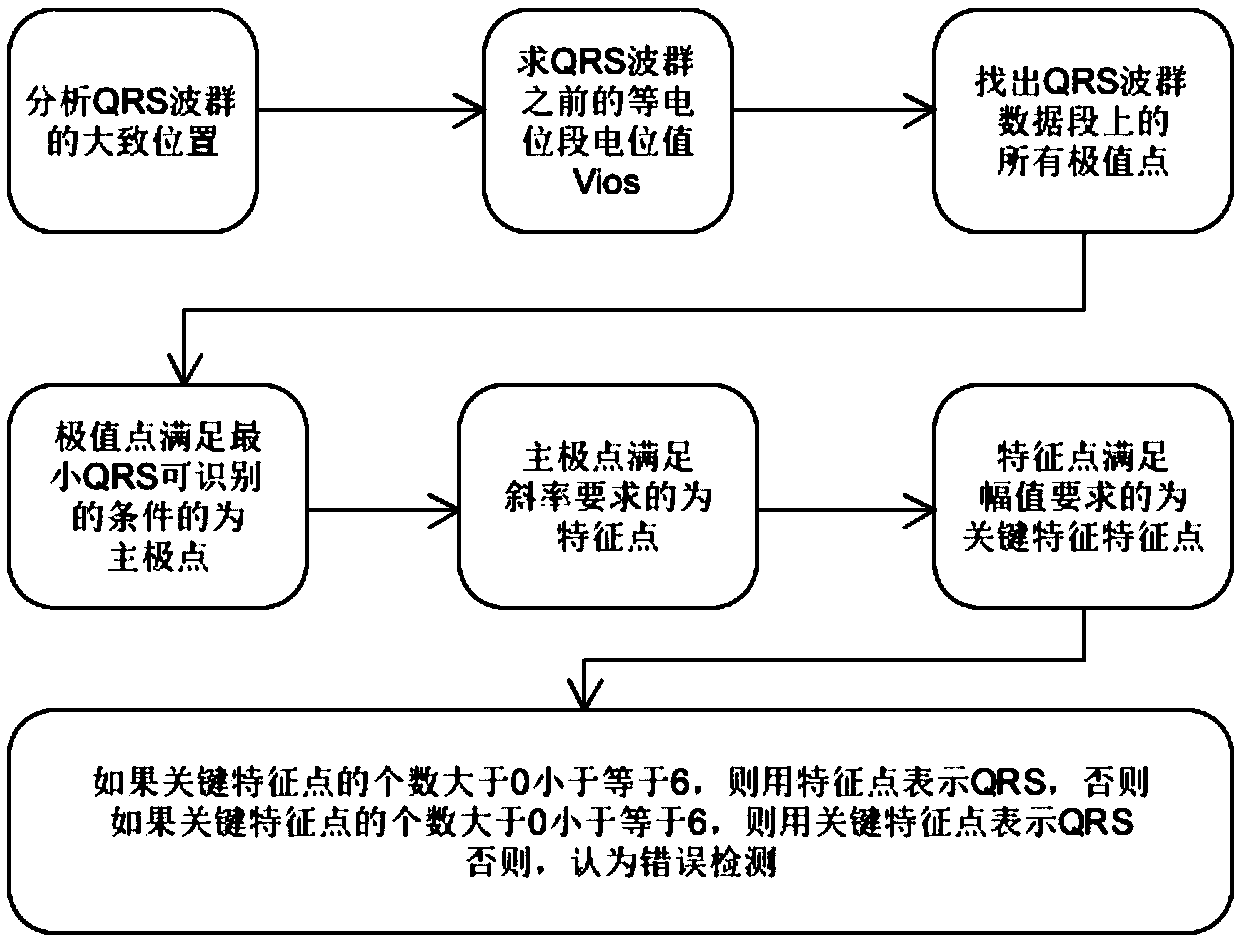
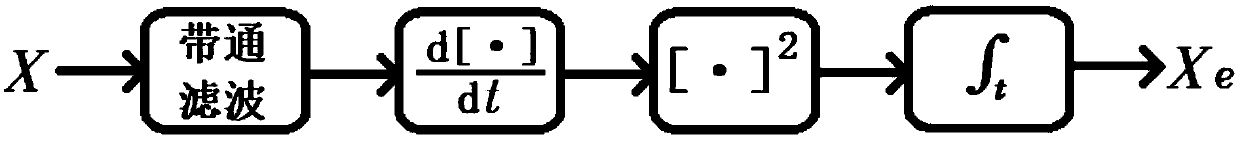
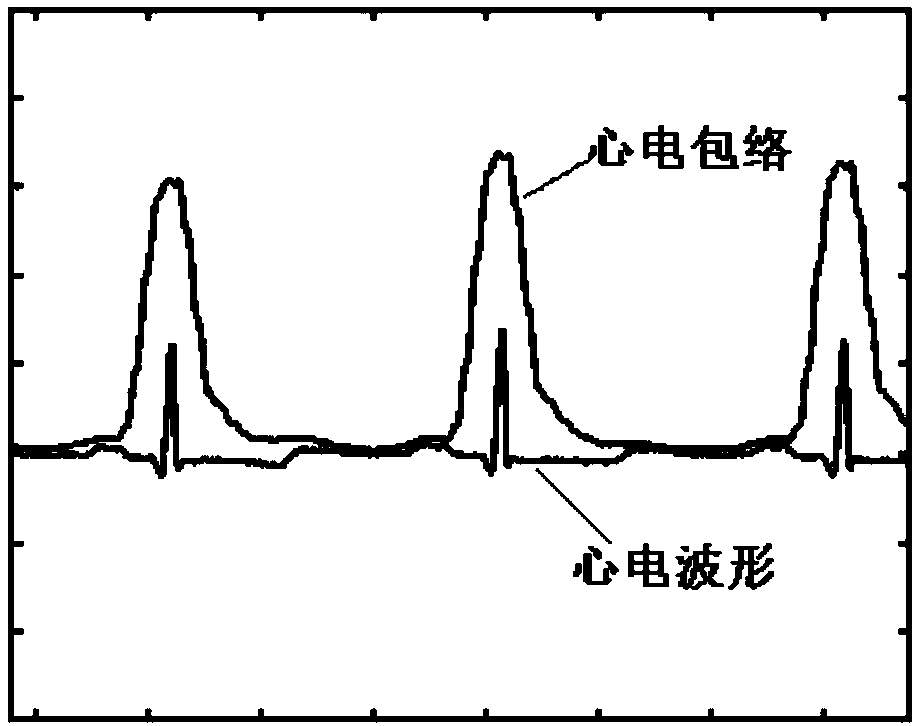
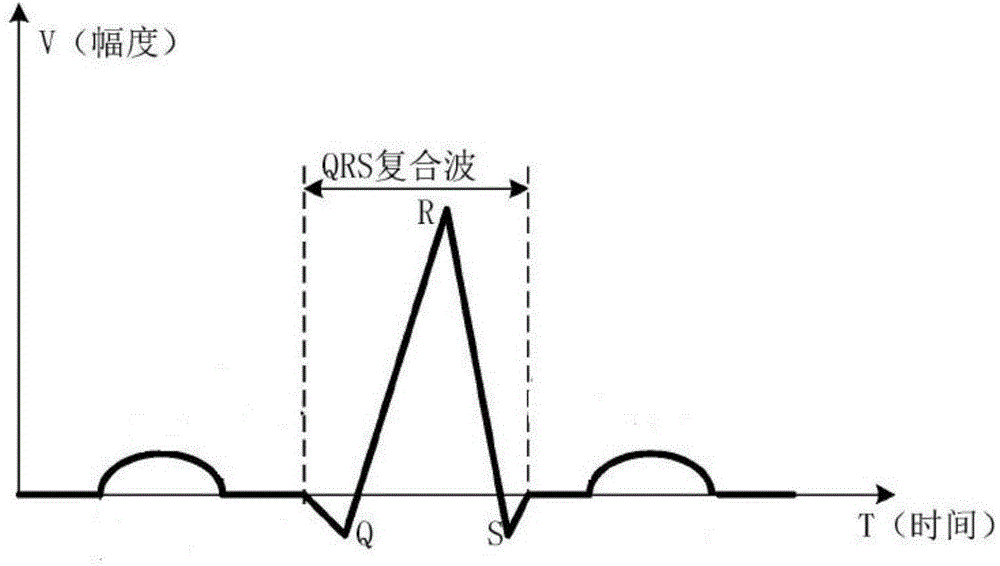
Method for detecting electrocardiogram QRS wave group and electrocardiogram analysis method thereof
ActiveCN108814590AImprove accuracyAccurately outline the morphological featuresDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRR intervalElectrocardiogram analysis
The invention discloses a method for detecting an electrocardiogram QRS wave group. The method comprises the steps of using an extremum method to find peaks and troughs in a QRS wave, according to anextremum point found, and combining an equipotential step potential value and amplitude information to detect each sub-waveform in the QRS wave group so as to determine the time position of the QRS wave group so that QRS wave group forms can be clearly displayed and the heart rate can be calculated; the accurate detection of the QRS wave group is the basis for the automatic diagnosis of an electrocardiogram. After the detection of the QRS wave group is determined, it is possible to calculate the heart rate, that is, the number of heart beats per minute, heart rate variability and other electrocardiogram time interval measurement and amplitude measurement.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAKANG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
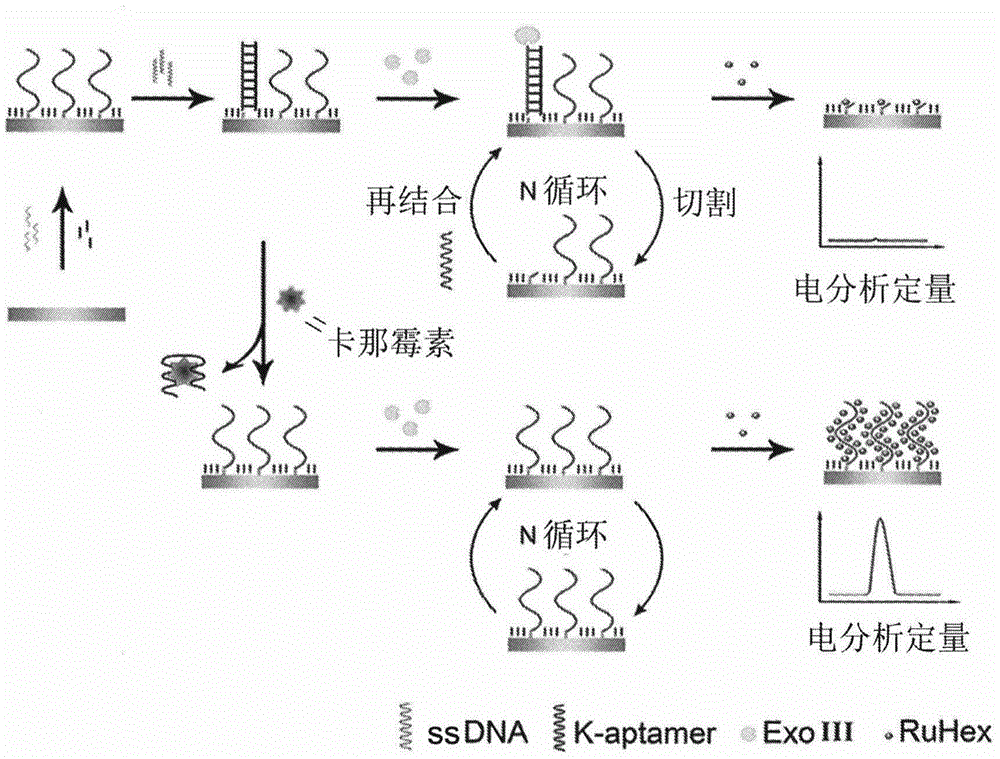
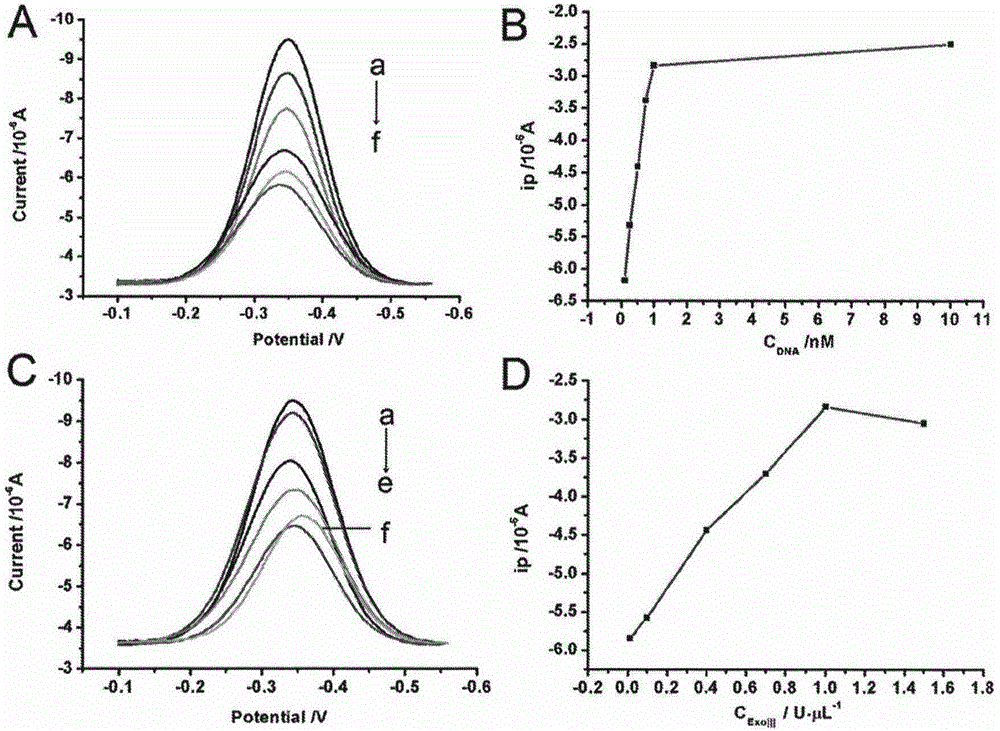
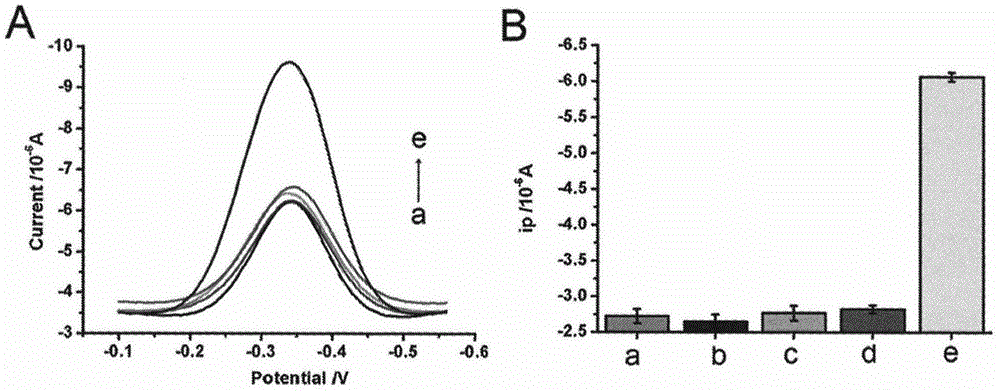
Method for detecting residual kanamycin
InactiveCN105651850ASensitive detectionRealize detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesKanamycinEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a method for detecting residual kanamycin and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of analysis chemistry, wherein the detection method is based on aptamer initiated cyclic enzyme digestion of exonuclease III (Exo III). According the method, mercapto self-assembly is utilized, single stranded DNA (ssDNA) that is complementary with kanamycin aptamer (K-aptamer) is grafted on the surface of a gold electrode, then a little amount of K-aptamer is added, and the K-aptamer is matched with ssDNA to form a little amount of double stranded DNA (dsDNA). Then Exo III is added, the ssDNA in dsDNA can be specifically digested by Exo III, thus the residual aptamers are released, the released aptamers can combine with ssDNA to form dsDNA, another enzyme digestion is triggered then, and after several circulations, the modified ssDNA is completely digested by enzymes. Kanamycin exists in the system, through the combination between kanamycin and aptamers, the circulation enzyme digestion is inhibited, thus ssDNA is preserved, and the amount of preserved ssDNA is related with the concentration of kanamycin. An electro-analysis method is used to absorb electrical signal molecules namely hexaammine ruthenium (RuHeX) through static electricity absorption so as to quantitatively detect residual kanamycin; and the method has high sensitivity and can sensitively detect residual kanamycin in milk.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
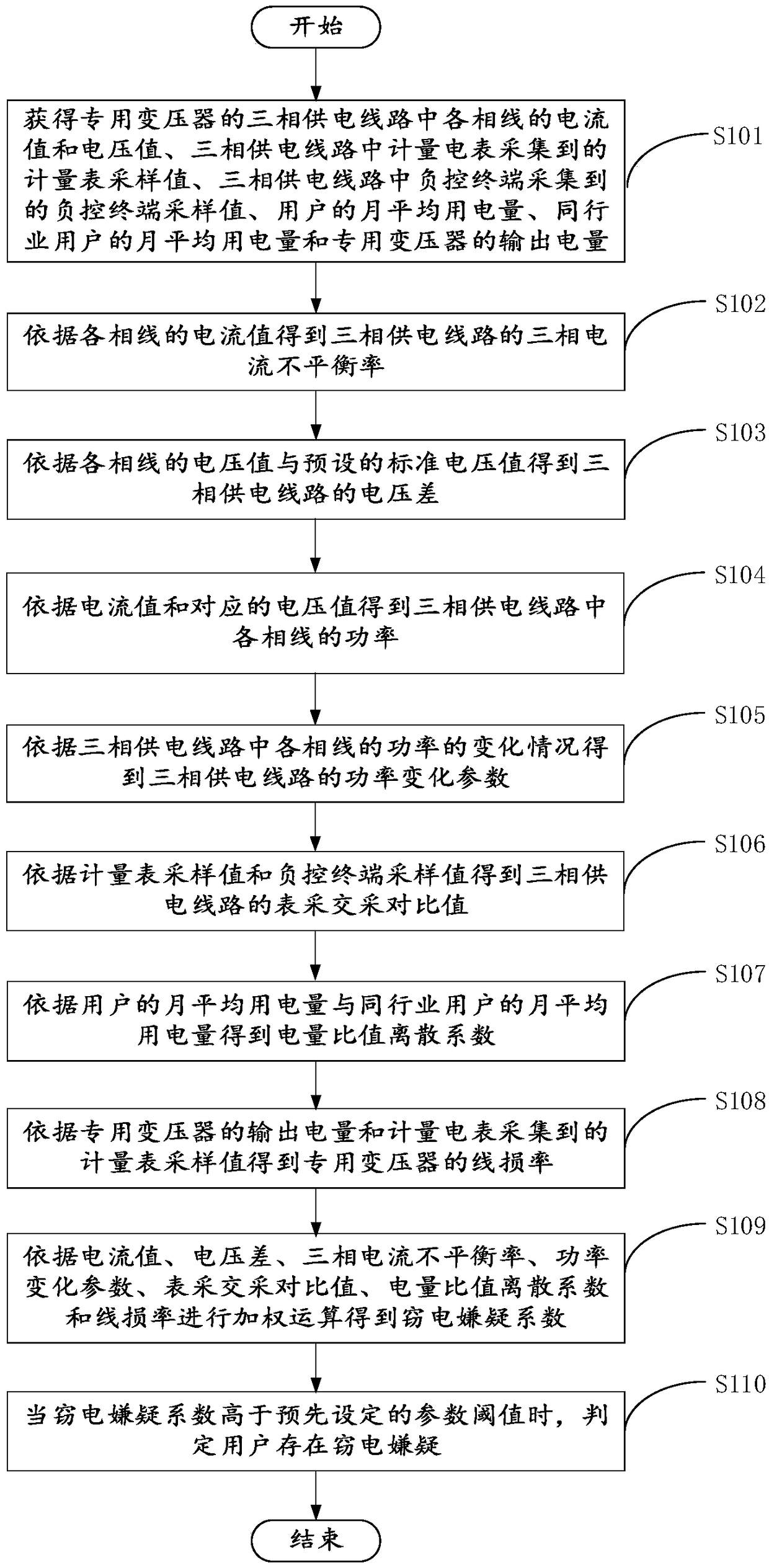
Electricity stealing analysis method, device and server
ActiveCN109116072AIntelligent abnormal monitoringIntelligent positioningTime integral measurementElectricityPower analysis
The invention provides an electricity stealing analysis method, device and server, which relate to the field of power analysis. The electricity stealing analysis method is applicable to the server forcarrying out electricity stealing analysis on a user accessed to a special transformer. The method comprises steps: According to a current value, a voltage difference, a three-phase current unbalancerate, a power change parameter, a meter acquisition and AC acquisition comparison value, an electric quantity ratio discrete coefficient and a line loss rate, an electricity stealing suspicion coefficient is obtained by weighting calculation; and when the electricity stealing suspicion coefficient is higher than a preset parameter threshold, the user is judged to have electricity stealing suspicion. According to the electricity stealing analysis method, the device and the server provided in the invention, according to the monitored electricity consumption operation data of the user, the electricity stealing suspicion coefficient of each user is calculated automatically, and when the electricity stealing suspicion coefficient is higher than the preset parameter threshold, the user is judged to have electricity stealing suspicion, and an inspector can perform on-site investigation to detect whether a suspicious user has an electricity stealing behavior.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
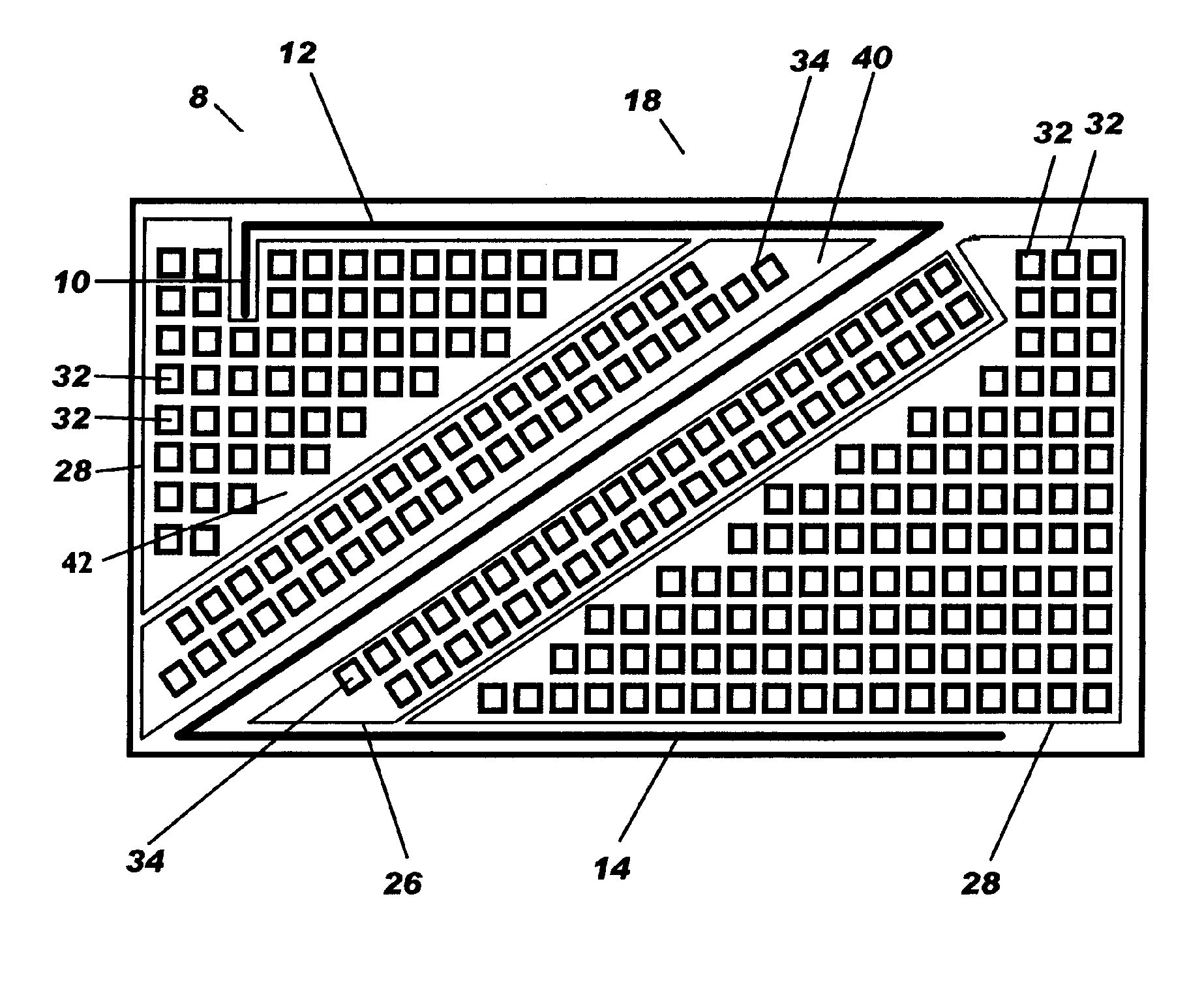
IC tiling pattern method, IC so formed and analysis method
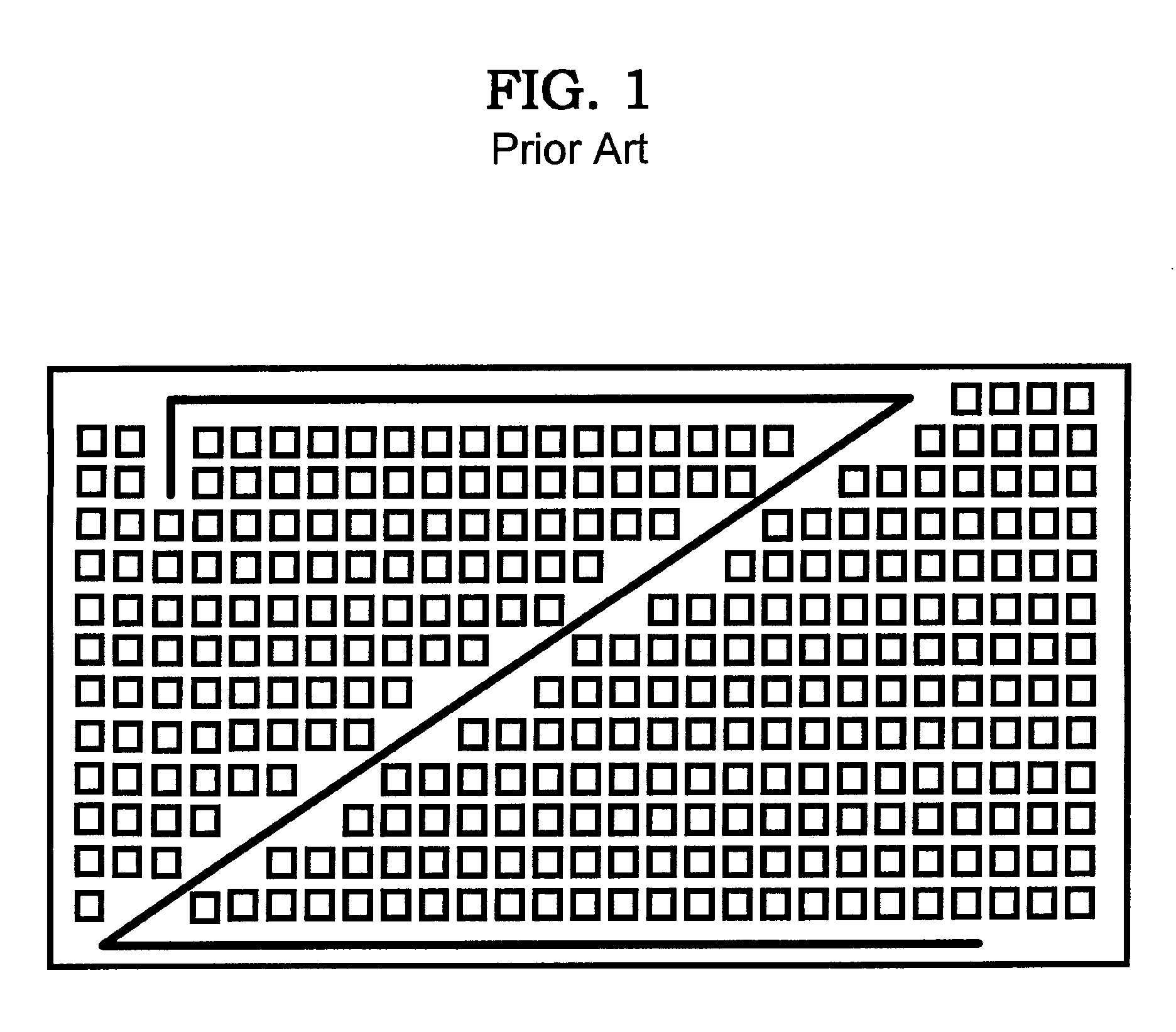
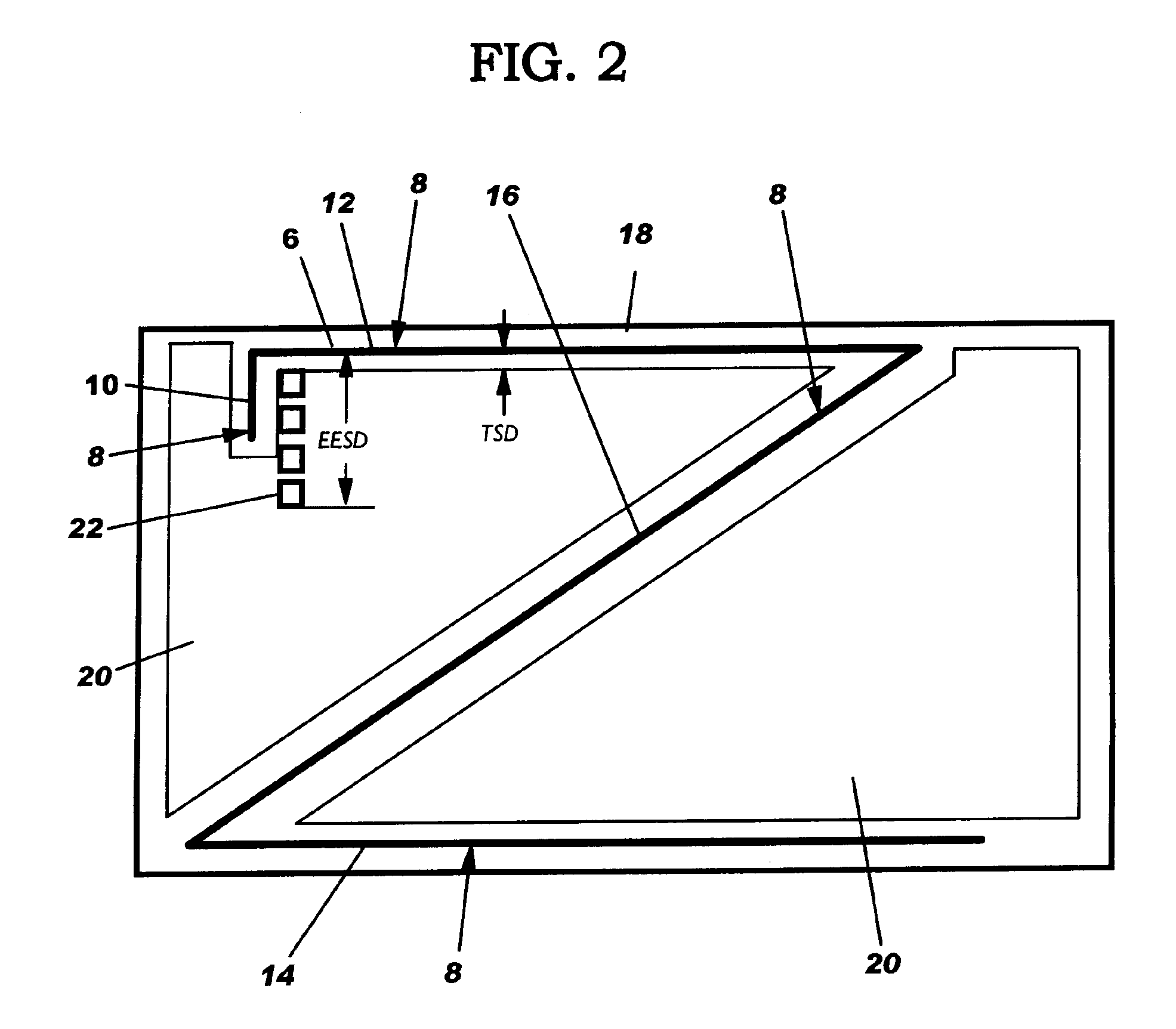
InactiveUS20050273744A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsDetecting faulty computer hardwareAnalysis methodIntegrated circuit
The invention provides a method for providing an integrated circuit (6) having a substantially uniform density between parts (10, 12, 14 and 16) of the IC that are non-orthogonally angled. In particular, the invention provides fill tiling patterns (32, 34) oriented substantially parallel to electrical structure regardless of their angle. A method of electrical analysis based on this provision is also provided as is a related program product.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
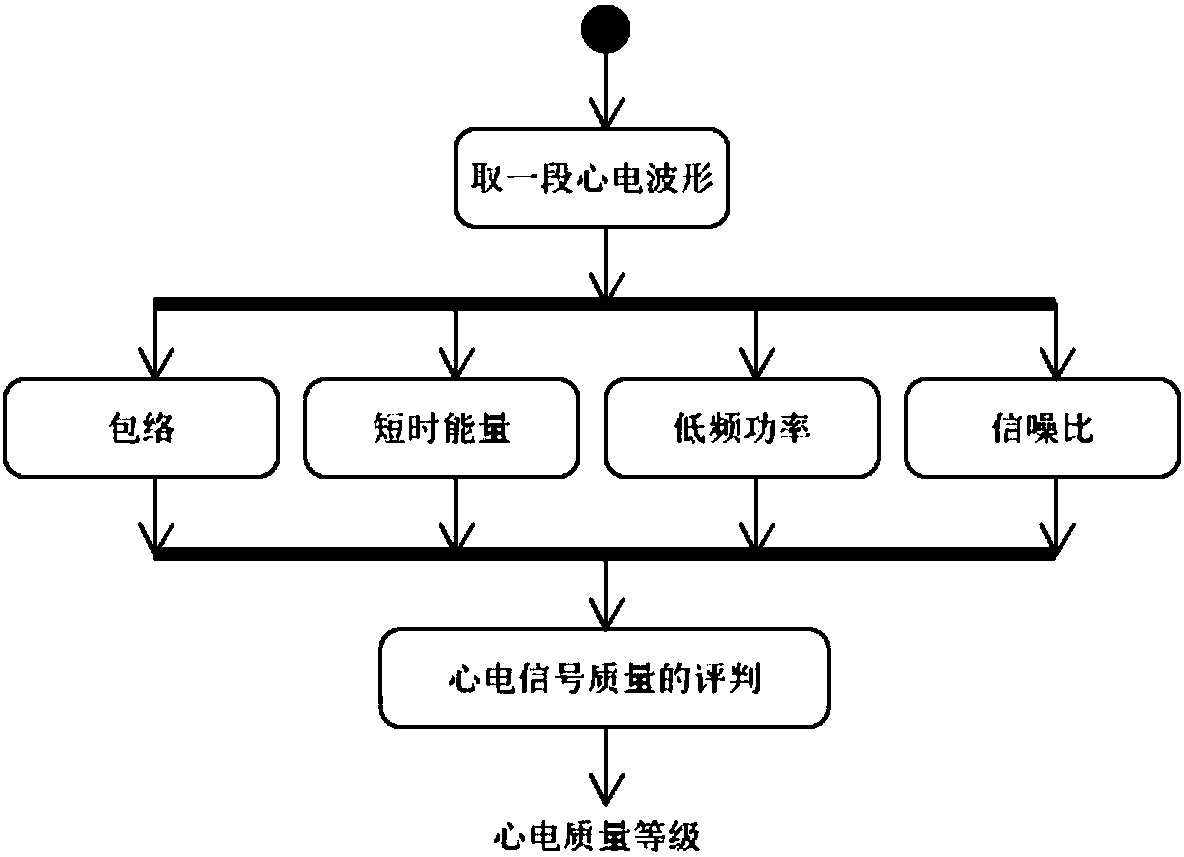
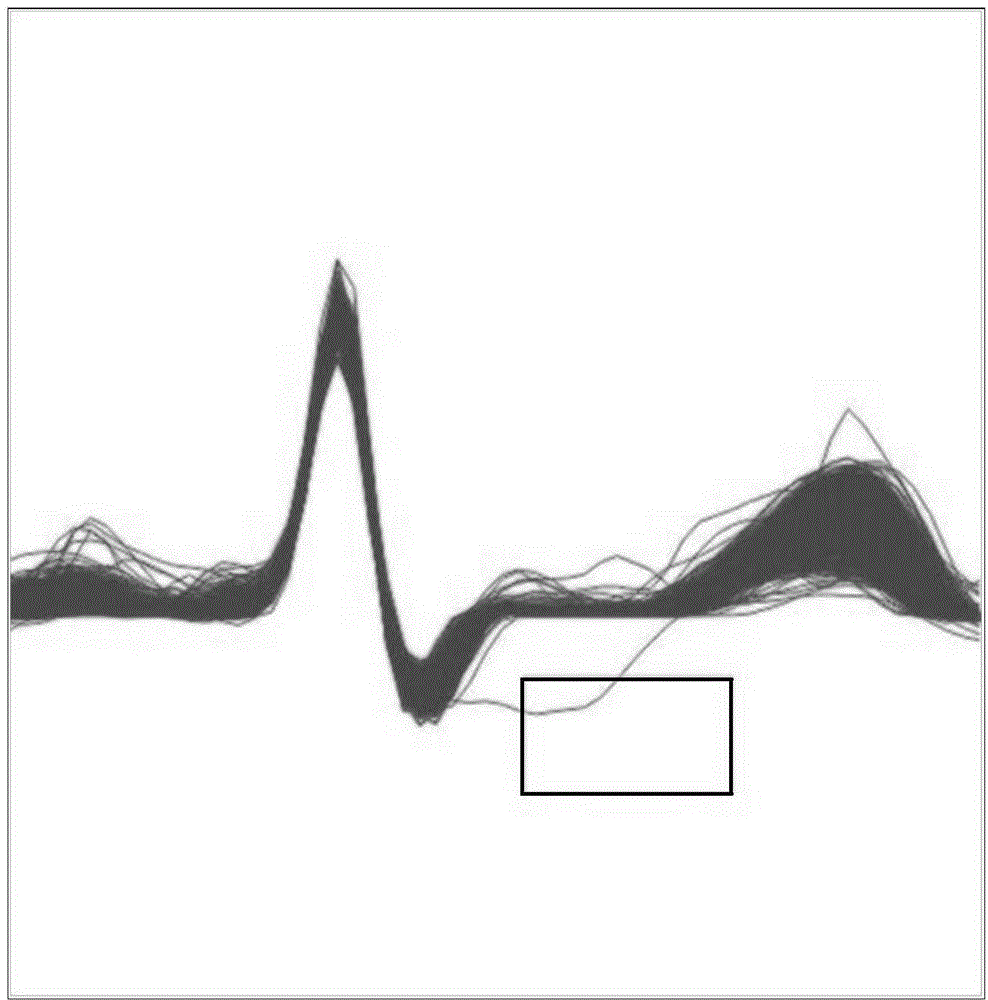
Electrocardiosignal quality identification method and electrocardiogram analysis method
ActiveCN108523877AIncrease credibilityImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses an electrocardiosignal quality identification method. The electrocardiosignal quality identification method comprises the steps of S1, acquiring original electrocardiogram waveform amplitude data; S2, carrying out fragment segmentation on the electrocardiosignal by taking 1 second as a unit; S3, taking out the maximum value and the minimum value of the amplitude of each fragment to form an envelope point, and comparing all the envelope points so as to obtain envelope difference; S4, acquiring the amplitude variance yield of each segmentation section; S5, converting a time domain signal of an electrocardiogram fragment signal into a frequency domain signal, namely a power spectrum signal by utilizing fast Fourier transform, and integrating the amplitude of 1-5 Hz soas to obtain the power; S6, after acquiring a power spectrum signal of the electrocardiogram fragment signal in the step S5, integrating the amplitude of 5-40 Hz and the amplitude of 40-100 Hz separately so as to obtain the corresponding power, and calculating the signal-to-noise ratio of the two kinds of power; and S7, grading the quality of the electrocardiogram waveform according to the parameter envelope difference, the variance yields, the power of the signals with 1-5 Hz and the qualified condition of the signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE +2
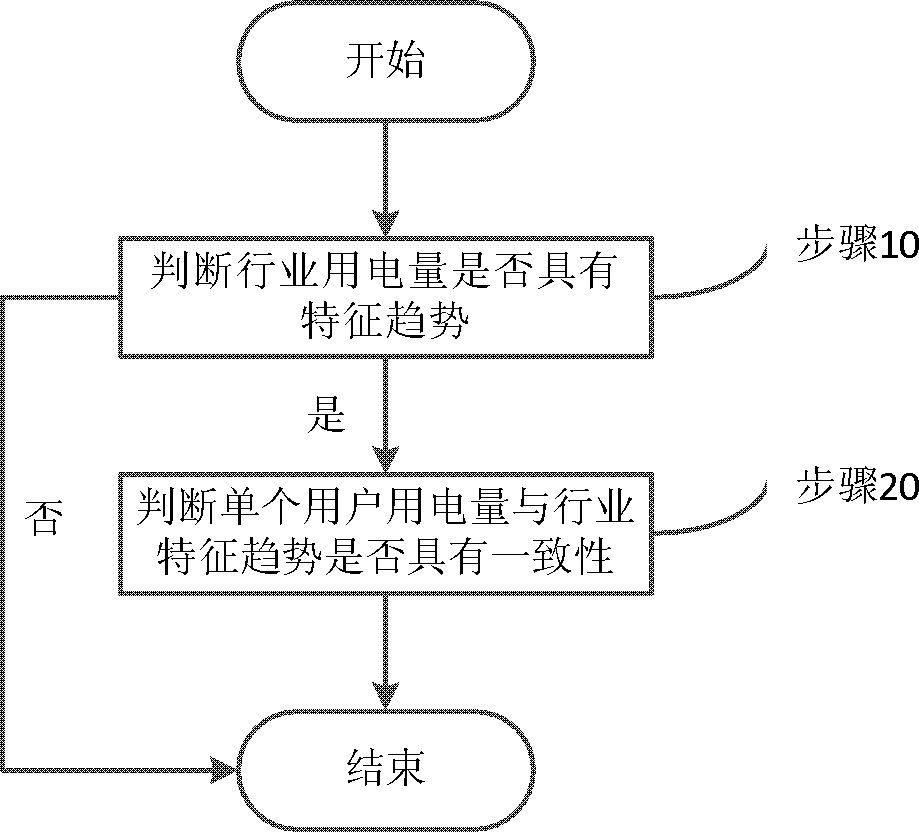
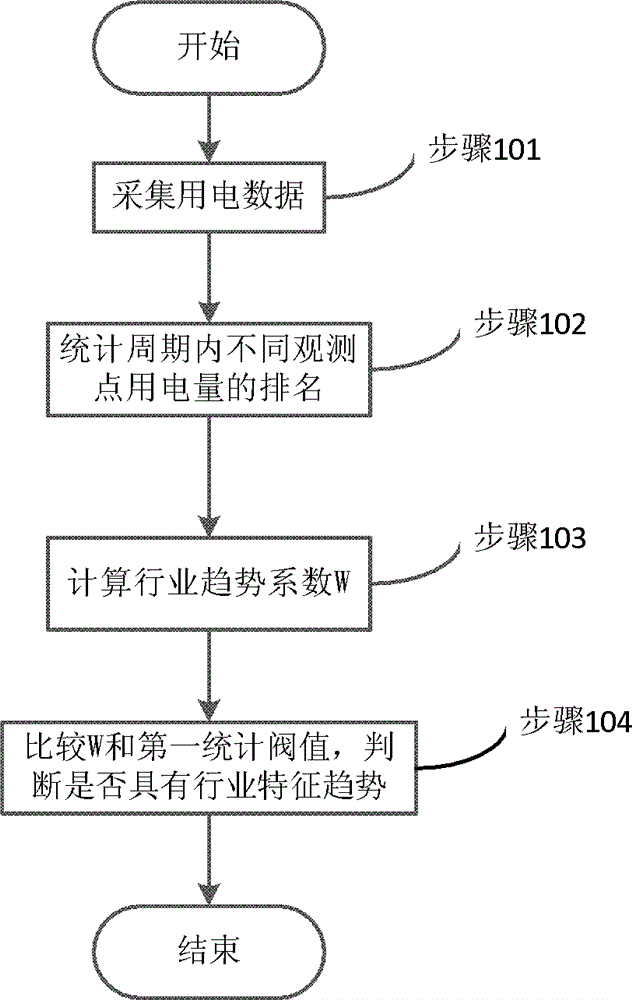
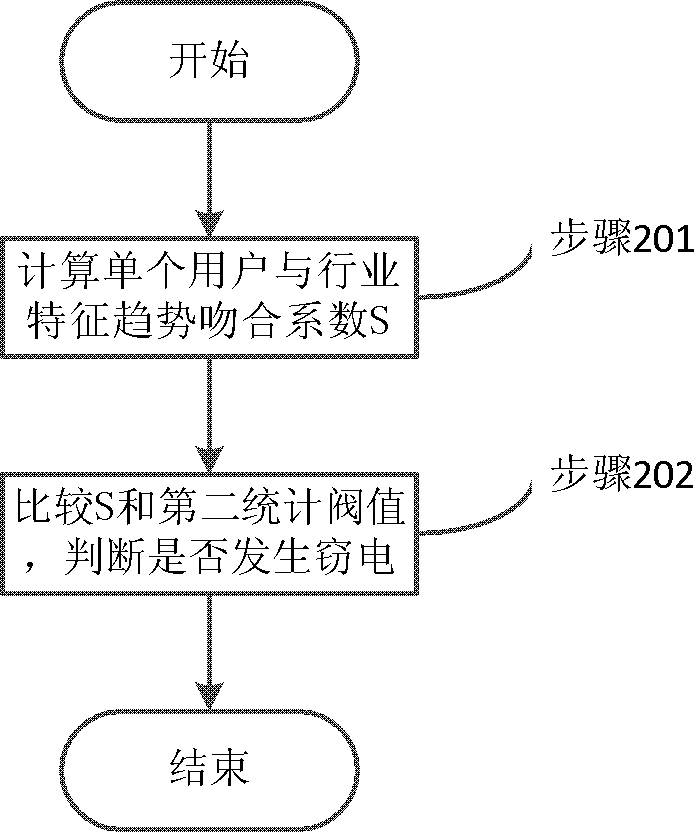
Electricity theft analyzing method and system
ActiveCN104951989AImprove effectivenessImprove targetingData processing applicationsEnergy efficient computingCollection systemElectricity market
The invention discloses an electricity theft analyzing method and system. The method includes calculating industry power consumption amount trend coefficient and judging whether the industry power consumption amount trend is greater than a first statistical threshold value or not; if the industry power consumption amount trend is greater than the first statistical threshold value, calculating the matching coefficient of a single user and the industry characteristic trend and judging whether the matching coefficient of the single user and the industry characteristic trend is greater than a second statistic threshold value or not. If the matching coefficient of the single user and the industry characteristic trend is greater than the second statistic threshold value, no electricity theft occurs; if the matching coefficient of the single user and the industry characteristic trend is not greater than a second statistic threshold value, electricity theft may occur. According to the invention, through studying current information of a power consumption information collecting system and through deep digging and effective use of mass data, industry power consumption trend and power consumption trend of users in the industry can be analyzed and the matching degree can be judged, so that whether electricity theft occurs or not can be judged. Therefore, effectiveness and pointedness of the collection system in aspects of electricity theft prevention and investigation are improved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
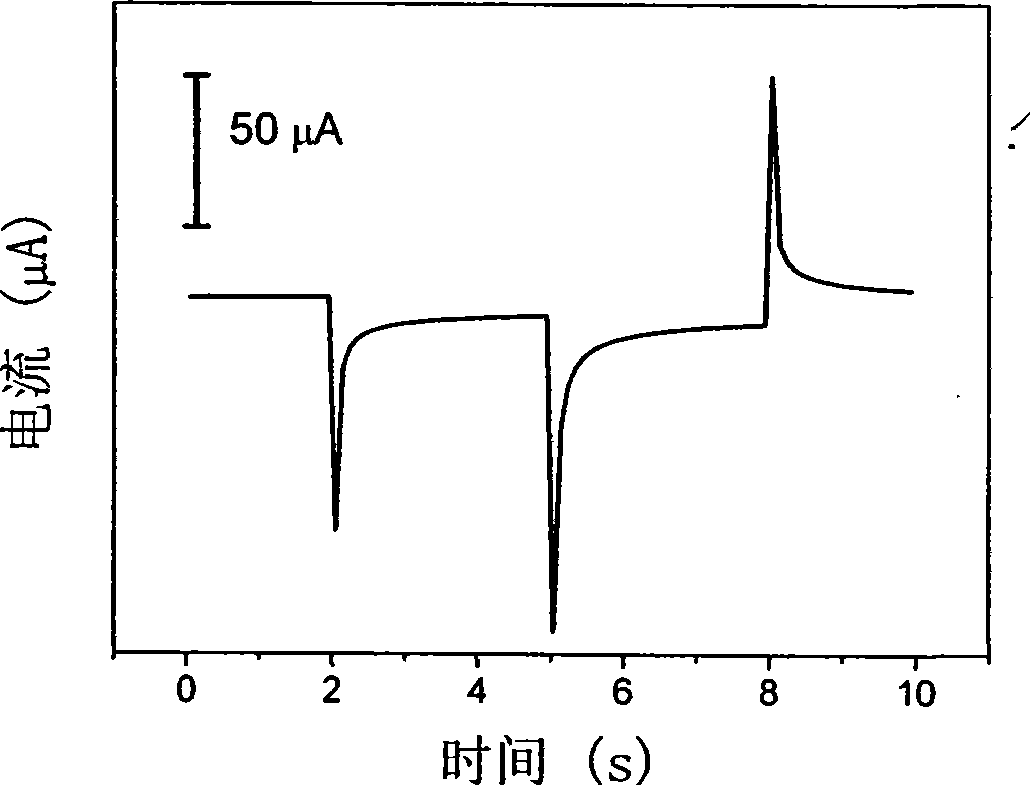
Fast quantifying electrolysis method
ActiveCN101377473ALow costThe pre-processing process is simpleMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrolysisLinear relationship
The invention discloses a quantitive electrochemical analysis method for fast analyzing substance concentration, which utilizes different electrode systems aiming at different substances. The method determines potential interval between reduction (or oxidization) peaks of the to-be-tested substance by the means of cyclic voltammetry; and based on the interval, the method determines the potential step intervals for three times of potential steps; current-time data is recorded during the three times of potential steps; electric quantity is obtained by integral upon the time with the current peak corresponding to the second potential step interval; the electric quantity is in linear relationship with the concentration of the to-be-detected substance, which can prove the quantitive characteristic. The invention has fast analysis speed and simple operation.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
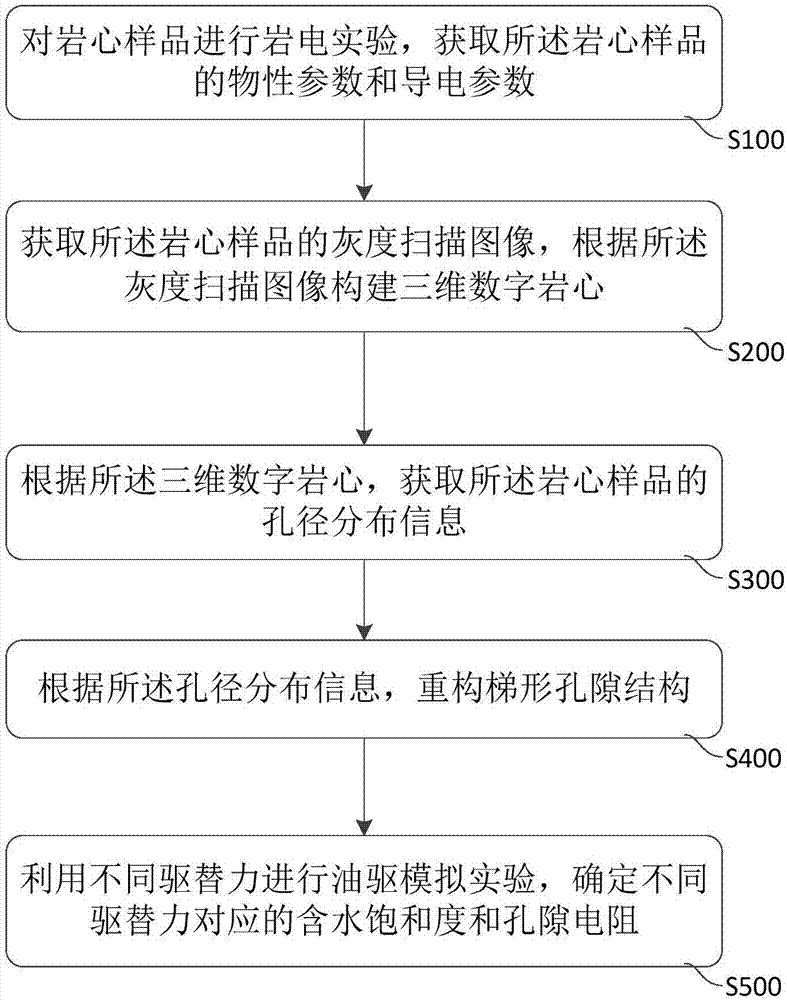
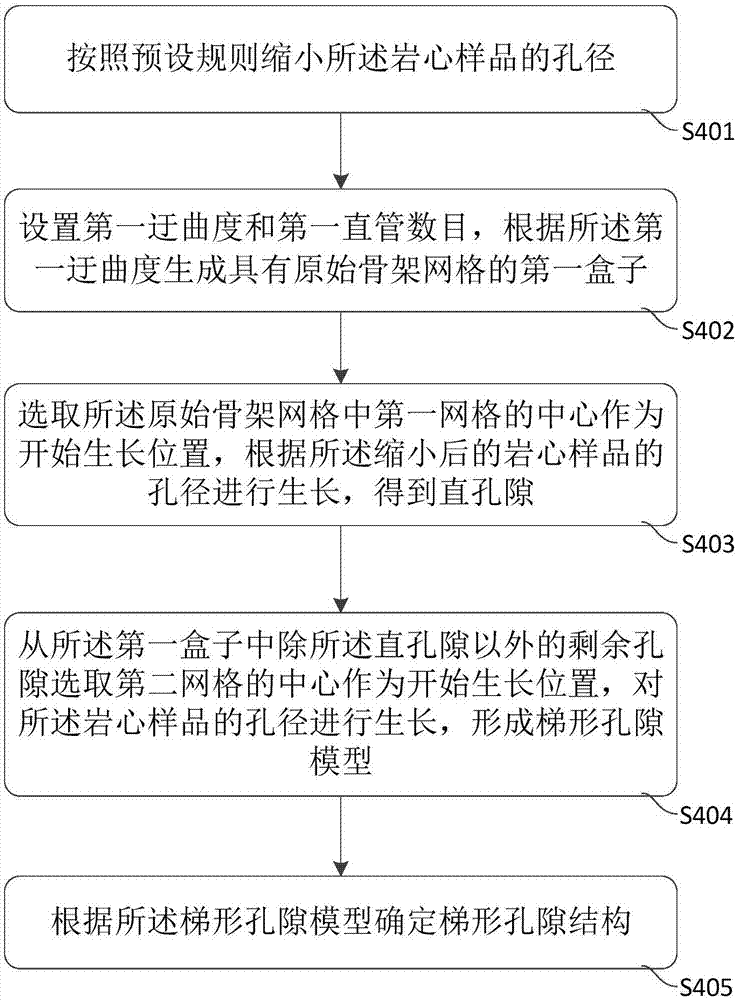
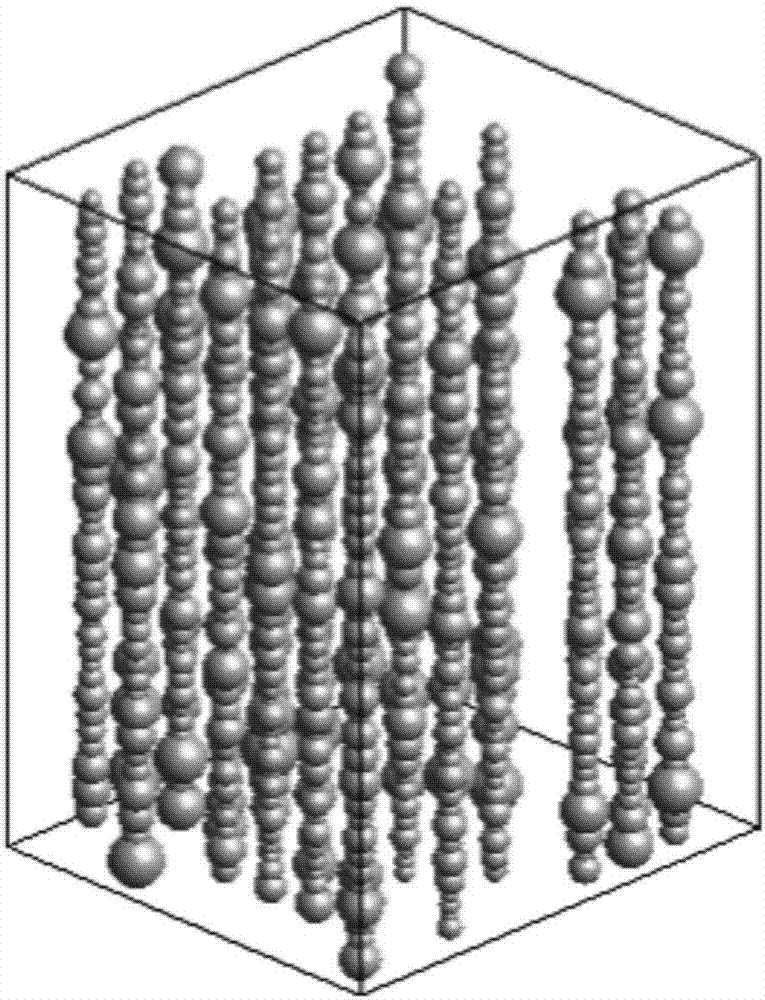
Dense sand rock conductivity analysis method and system
ActiveCN107300519AFast for conductivity analysisConductive analysis is accuratePermeability/surface area analysisElectricityRock core
The embodiment of the invention discloses a dense sand rock conductivity analysis method and system. The method comprises the following steps: performing rock electricity testing on a rock core sample, and acquiring physical parameters and conductive parameters of the rock core sample; acquiring a gray scanning image of the rock core sample, and establishing a three-dimensional digital rock core according to the gray scanning image; according to the three-dimensional digital rock core, acquiring aperture distribution information of the rock core sample; according to the aperture distribution information, reestablishing a trapezoid pore structure; and performing oil-driving simulation experiments with different displacement forces, and confirming water saturation and pore resistance corresponding to different displacement forces. By adopting the dense sand rock conductivity analysis method and system disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, rapid and accurate dense sand rock conductivity analysis can be achieved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
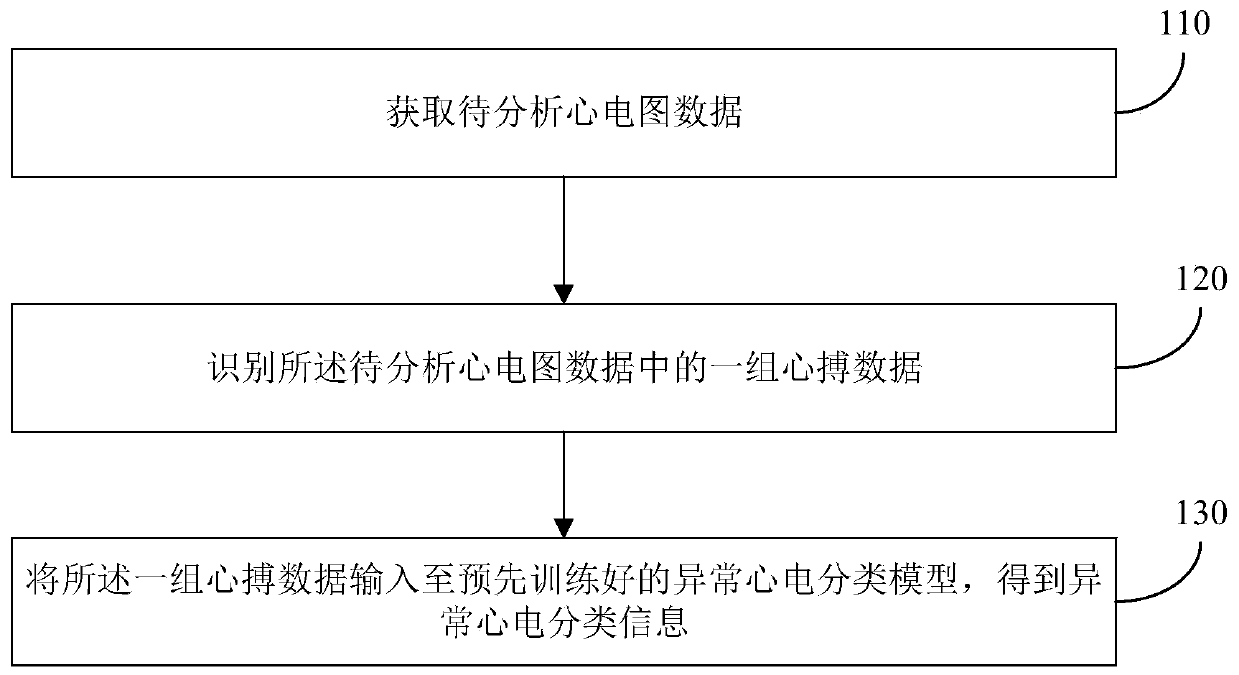
Electrocardio analysis method and device based on picture and heart beat information, equipment and medium
ActiveCN110495872ARealize intelligent analysisReduce the complexity of acquisitionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnalysis methodComputer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses an electrocardio analysis method and device based on picture and heart beat information, equipment and a medium. The electrocardio analysis method comprises the steps that to-be-analyzed electrocardiogram data are obtained; one group of heart beat data in the to-be-analyzed electrocardiogram data is identified; the group of the heart beat data isinput intoa pre-trained abnormal electrocardio classification model to obtain abnormal electrocardio classification information; the to-be-analyzed electrocardiogram data are electrocardiogram data with aset number of leads, and the group of the heart beat data comprise heart beat cycle data corresponding to the set number of leads correspondingly. According to the technical scheme, the intelligent analysis of the electrocardiogram is achieved, meanwhile the acquisition complexity of training sample data is lowered, and the demanded quantity of the training sample data is decreased.
Owner:CAS & MEDICALSYSTEM AI RES LAB SUZHOU CO LTD
Method for detecting electrocardiogram QRS wave group width and electrocardiogram analysis method thereof
ActiveCN108814591AImprove accuracyAccurately outline the morphological featuresDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrocardiogram analysisComputer science
The invention discloses a method for detecting an electrocardiogram QRS wave group width. The method comprises the steps of searching for peaks and troughs in a QRS wave by using an extremum method, and according to an extremum point found, the combined gradient, a triangle method, an equipotential section potential value and amplitude information, determining the start and end points of the QRS wave group, wherein the start and end points of the QRS wave group are the width of the QRS wave group. Accurate detection of the width of the electrocardiogram QRS wave group has significant effect oncardiac function tests and diagnosis and prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +2
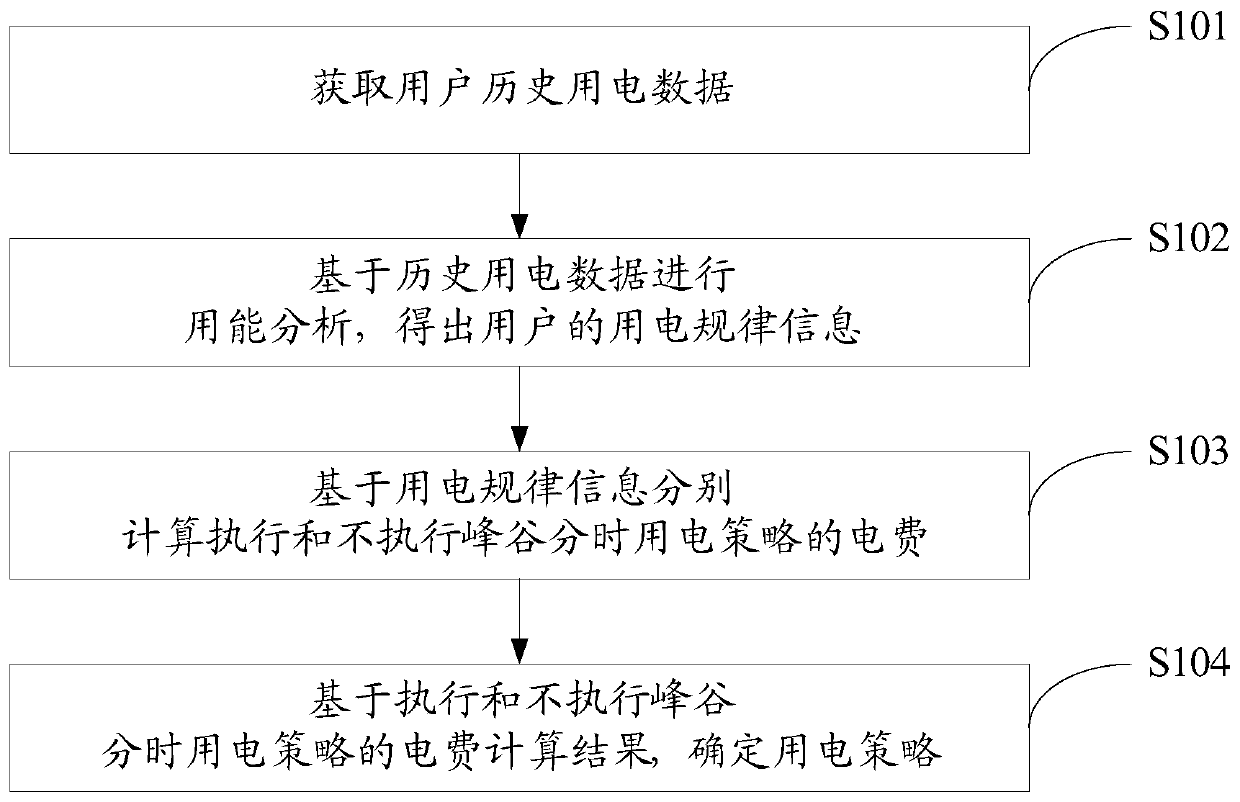
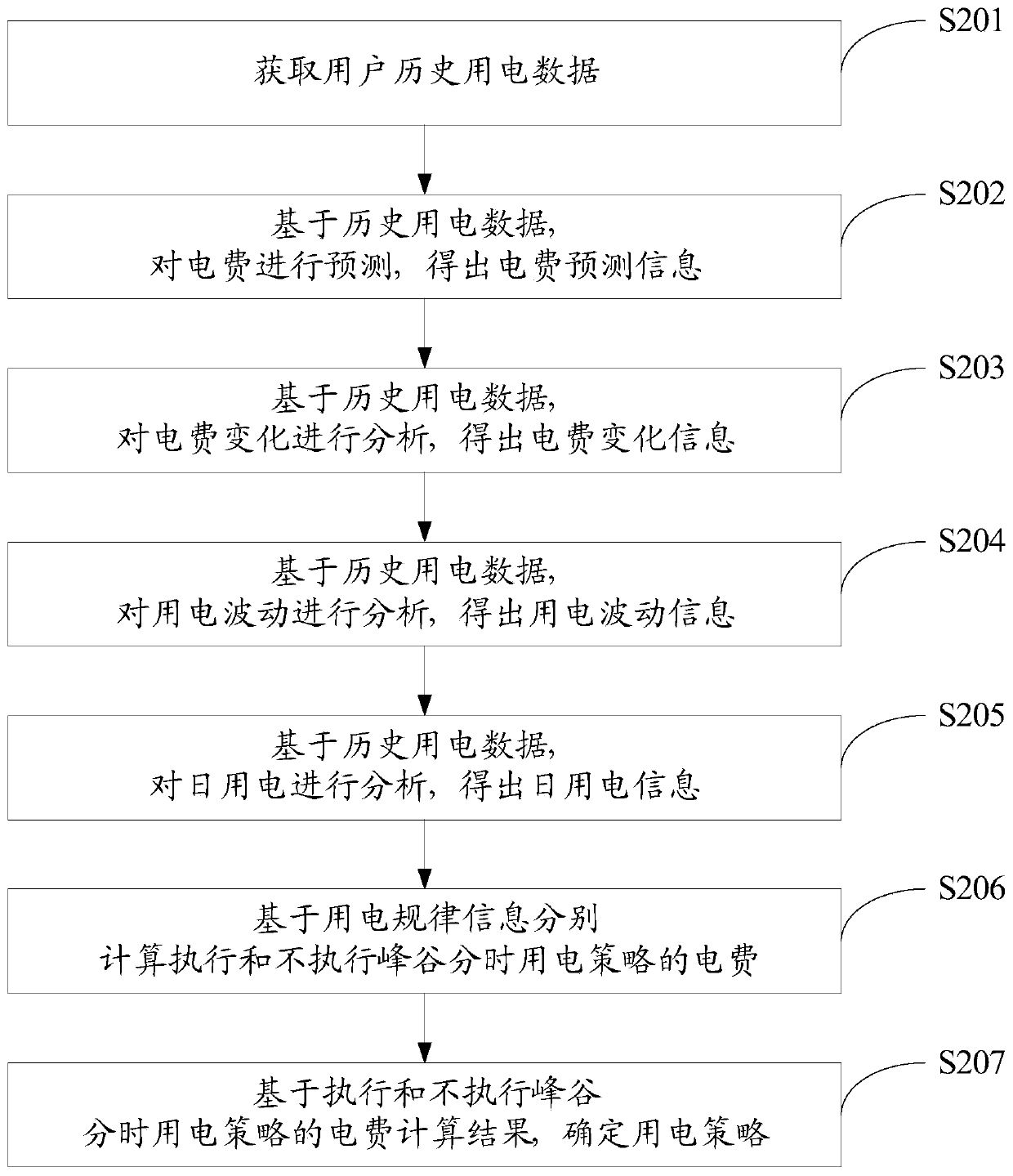
Intelligent power utilization analysis method and system based on cloud computing
InactiveCN110599042ALower electricity billsImprove power utilizationTechnology managementResourcesTime-sharingAnalysis method
The invention discloses an intelligent power utilization analysis method and system based on cloud computing, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the historical power utilization data of a user, carrying out the energy utilization analysis based on the historical power utilization data, and obtaining the power utilization rule information of the user; and based on the power utilization rule information, respectively calculating the electric charge of executing and not executing the peak-valley time-sharing power utilization strategy, and based on the electric charge calculation result of executing and not executing the peak-valley time-sharing power utilization strategy, determining the power utilization strategy. According to the invention, the electric charge of executing or not executing the peak-valley time-sharing power utilization strategy can be calculated in combination with the historical power utilization data of the user, and the corresponding power supply strategyis provided for the user according to the calculation result, so that the purposes of reducing the power utilization cost of the user and improving the electric energy utilization rate are achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID E COMMERCE CO LTD +1
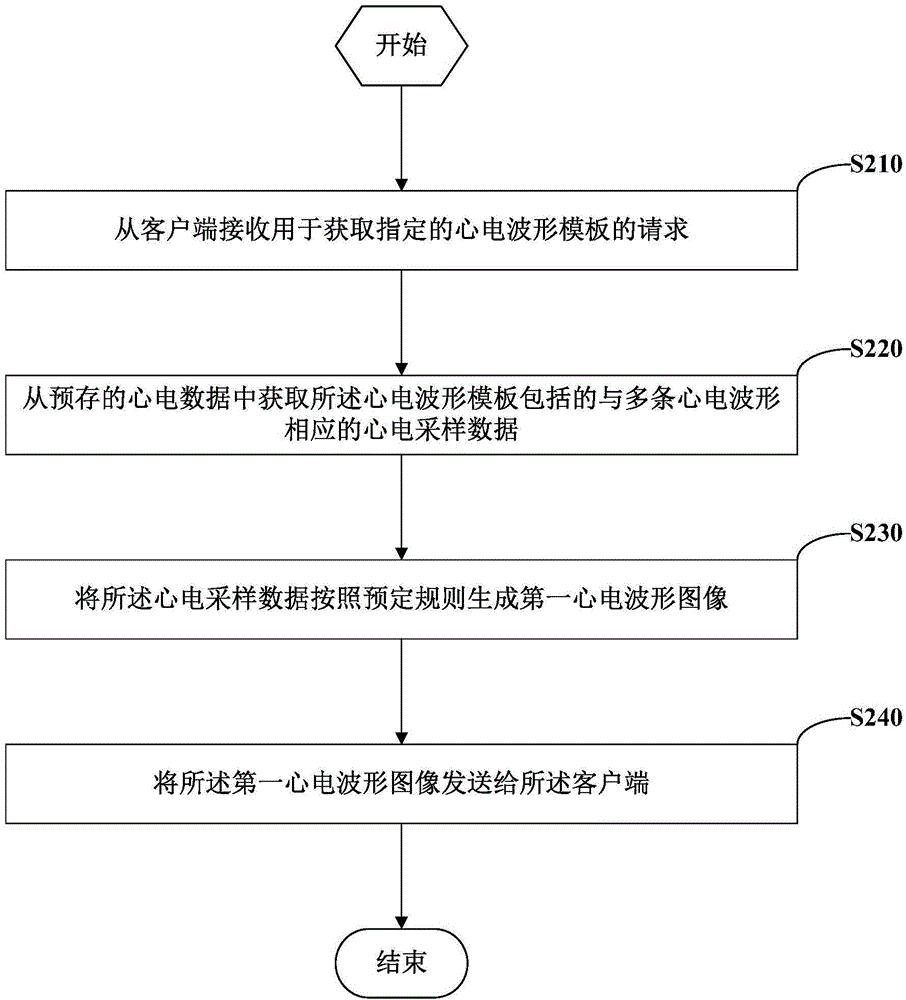
Image-based ECG analysis method and apparatus
InactiveCN104866724AECG analysis is convenientECG analysis is flexibleSpecial data processing applicationsLong term dataData mining
Embodiments of the present invention provide an image-based ECG analysis method and apparatus. The method comprises: receiving from a client a request for acquiring a designated ECG waveform template; acquiring from prestored ECG data ECG sampling data corresponding to a plurality of ECG waveforms included in the ECG waveform template; generating the ECG sampling data into a first ECG waveform image according to a predetermined rule; and sending the first ECG waveform image to the client. The image-based ECG analysis method and apparatus provided in the embodiments of the present invention can separate display of the ECG data from analysis of the ECG data, implement long-term data collection and analysis, and hence achieve more convenient and flexible ECG analysis.
Owner:北京海思敏医疗技术有限公司
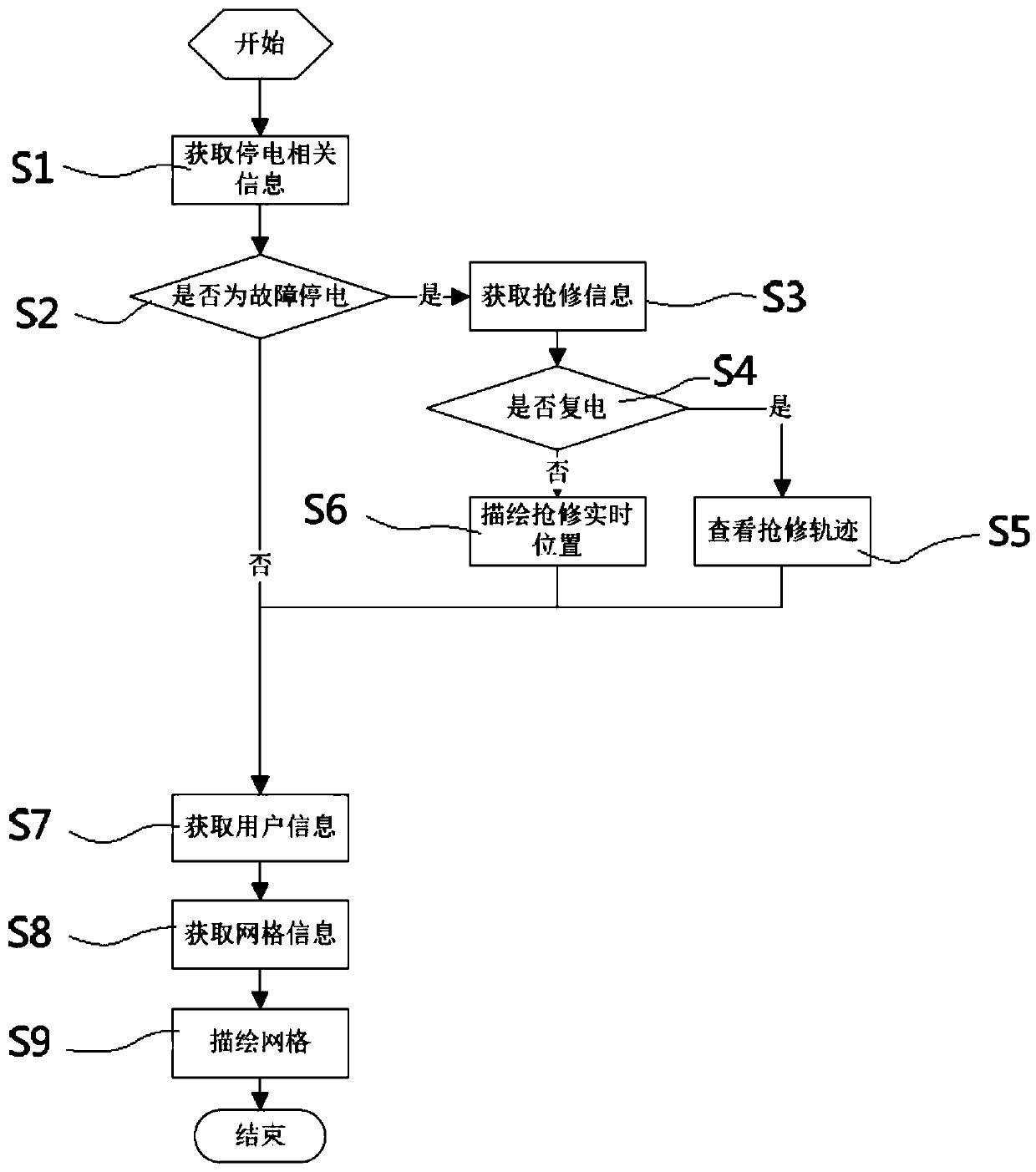
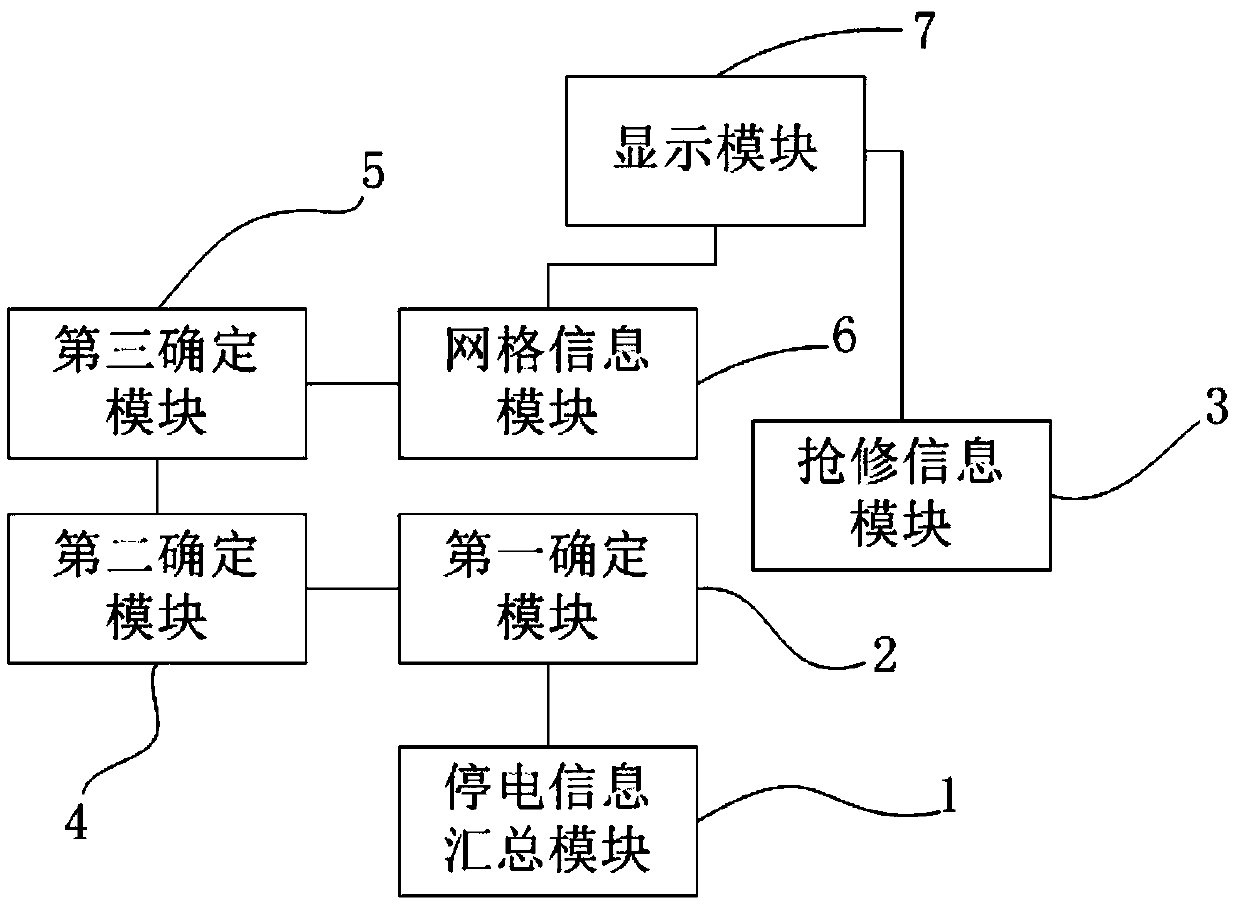
A grid-based blackout analysis method and system
The invention provides a grid-based power outage analysis method and a system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining power outage related information; determining whether a power outageevent is a fault power outage according to the power outage event information; Acquiring rush repair process information of the power outage event, wherein the rush repair process information at leastcomprises a power recovery state, historical position information and real-time position information of a rush repair person or a rush repair vehicle; Determining a rush repair trajectory of the rushrepair process according to the historical coordinate information, and replaying and displaying the rush repair trajectory and the real-time position information on a map; Determining blackout user information affected by the blackout event according to the blackout event information; Determining corresponding grid information according to the power outage user information; The corresponding mapgrid information is obtained according to the grid information, and the grid information is displayed on the map according to the map grid information. The invention well meets the service requirements of monitoring and managing personnel for monitoring the power outage and rush repair and viewing the rush repair trajectory.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
Detection method of poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase
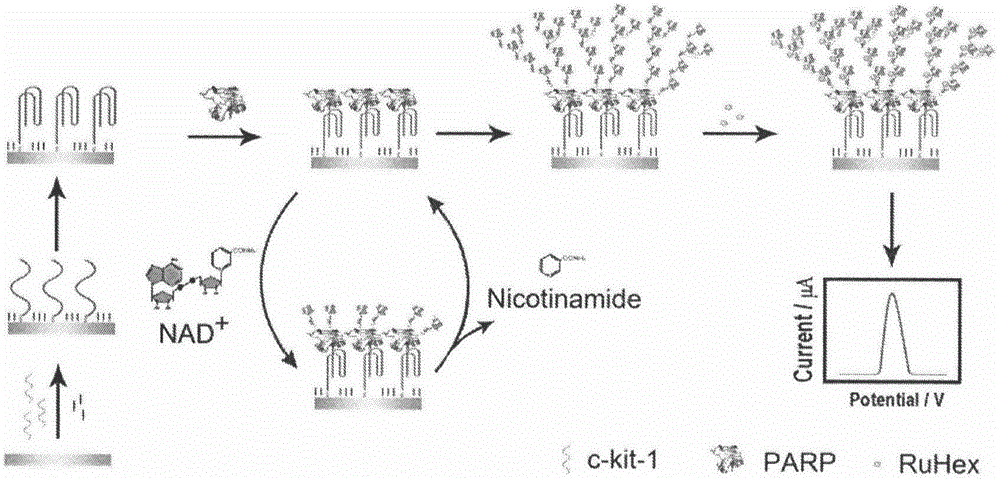
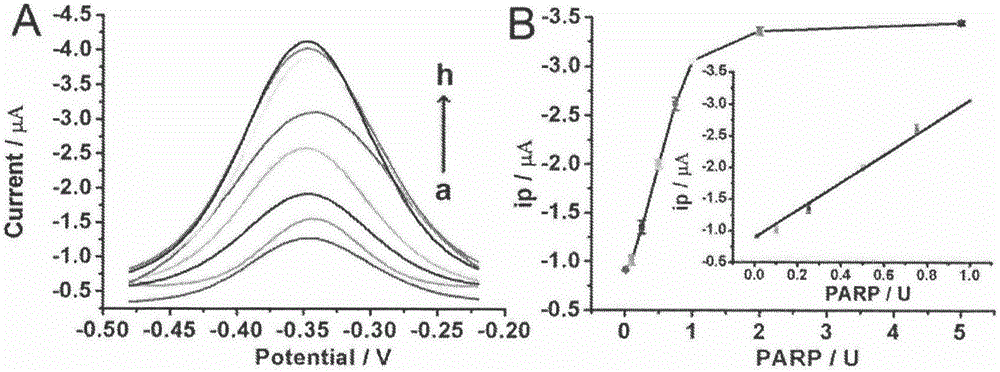
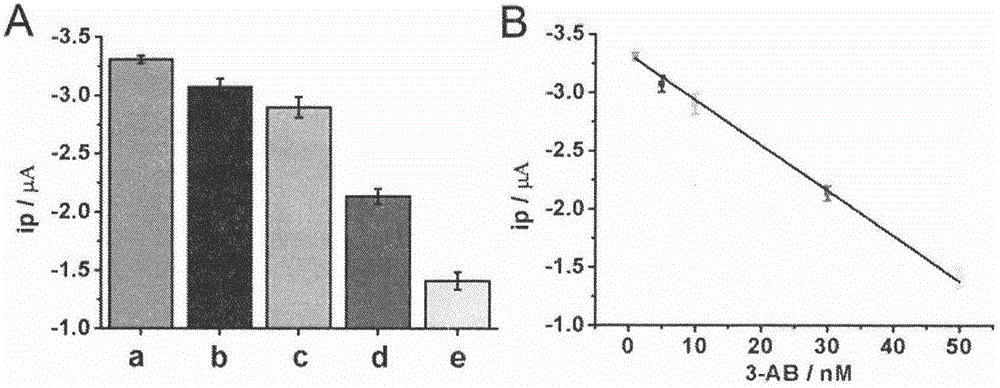
InactiveCN105606671AEnable label-free detectionSimple methodMaterial electrochemical variablesSignalling moleculesPolyadenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase
The invention belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry and relates to a detection method and application of PARP [poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase]. The detection method mainly includes: modifying a single-stranded DNA (c-kit-1) capable of specifically binding with the PARP on the surface of a gold electrode in a classical mercapto self-assembly mode and enabling c-kit-1 to form a tetramer configuration through treatment; after the tetramer configuration is incubated with the PARP, adding a specific catalytic substrate, namely NAD (nicotinamide ademinedinucleotide) of the PARP, to enable the PARP to self-catalyze to produce PAR with high negative charges; using the negative charges of the PAR for adsorbing electrical signal molecules RuHex with positive charges, quantifying the RuHex adsorbed on the surface of the electrode through an electroanalysis method, and drawing a standard curve according to a relation between electrochemical signals and PARP concentration so as to achieve sensitive PARP detection by measuring the electrochemical signals of to-be-detected samples and calculating. The detection method is high in repeatability and sensitivity and can be applied to detection of the PARP and an inhibitor 3-AB (3-aminobenzamide) thereof.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Power failure analytical method based on topological island analysis
InactiveCN104112240AImprove analysis efficiencyNarrow searchData processing applicationsEnergy efficient computingNODALTopological order
The invention discloses a power failure analytical method based on topological island analysis. The power failure analytical method based on topological island analysis includes acquiring all connection nodes which are connected with two ends of a deflection switch through other closed switches, and relevant equipment information; judging whether deflection of the switch causes changes of the quantity of topological nodes according to the information in the last step, and finishing revision if the topological nodes are not affected; further performing analysis revision on a topological island if the quantity of the topological nodes is changed. According to the power failure analytical method based on topological island analysis, on the basis of equipment in connection with the topological island for power failure analysis, topological local revision is performed according to a hierarchical search strategy, and efficiency of power failure topology analysis is improved; great values are achieved on optimization of load transfer and power failure operation plans of a power distribution network under emergency conditions.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
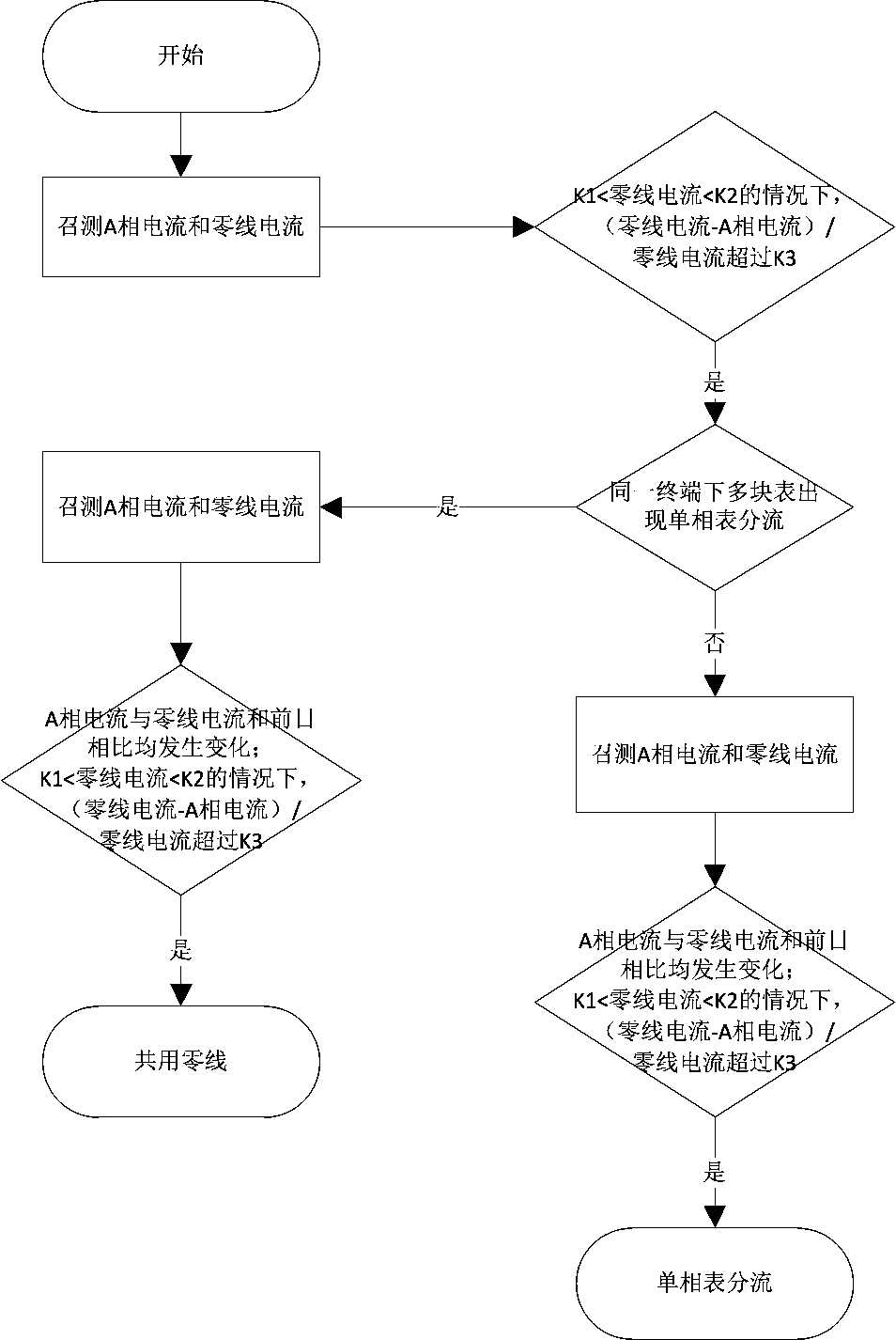
Single-phase meter shunting accurate judgment method for analyzing electricity stealing
ActiveCN107621562AImprove accuracyImprove comprehensivenessTime integral measurementPhase currentsElectricity
The invention discloses a single-phase meter shunt accurate judging method for analyzing electricity stealing, which relates to an electricity stealing analysis method. At present, the electricity theft analysis is not comprehensive, and there are misjudgments and misjudgments of sharing the neutral line. The present invention includes the following steps: 1) calling the A-phase current and zero line current of the low-voltage single-phase user smart meter once a month; 2) judging whether the single-phase meter is shunting; If it is suspected that there is a shared neutral line, it will not be generated as an exception; 4) For all users who suspect that there is a shared neutral line, call again on the next day. If there are changes compared with the previous day and still meet the diversion Judgment conditions, judge again whether there is a shared neutral line; 5) For electric energy meters that do not have a shared neutral line, call through again after a period of time. An exception is generated. The technical solution removes the situation of sharing the zero line, and prevents misjudgment and misjudgment.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +2
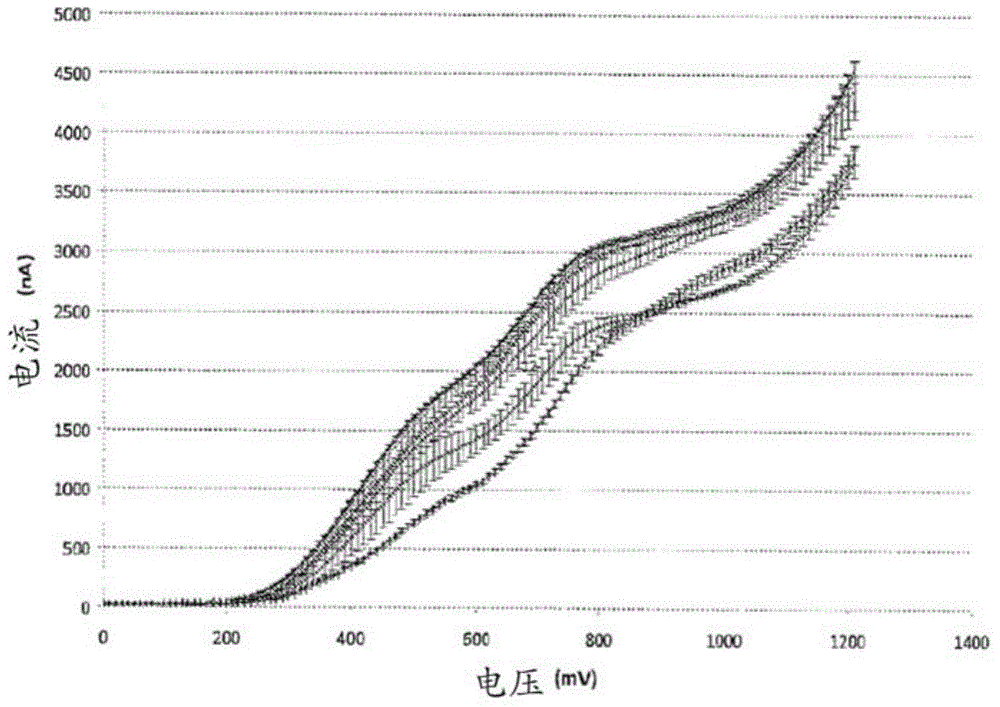
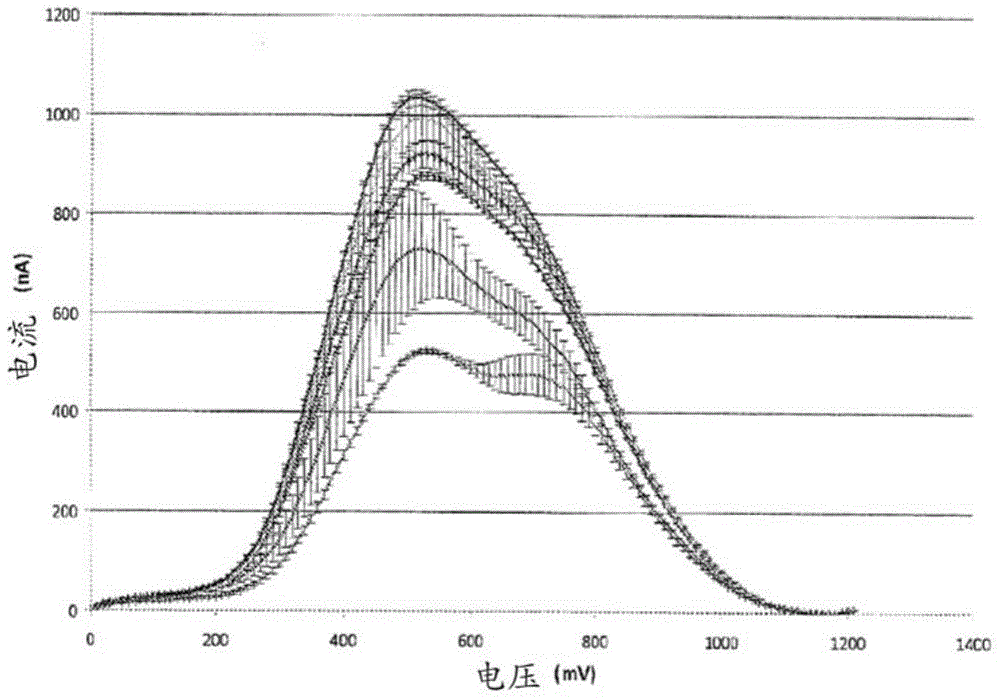
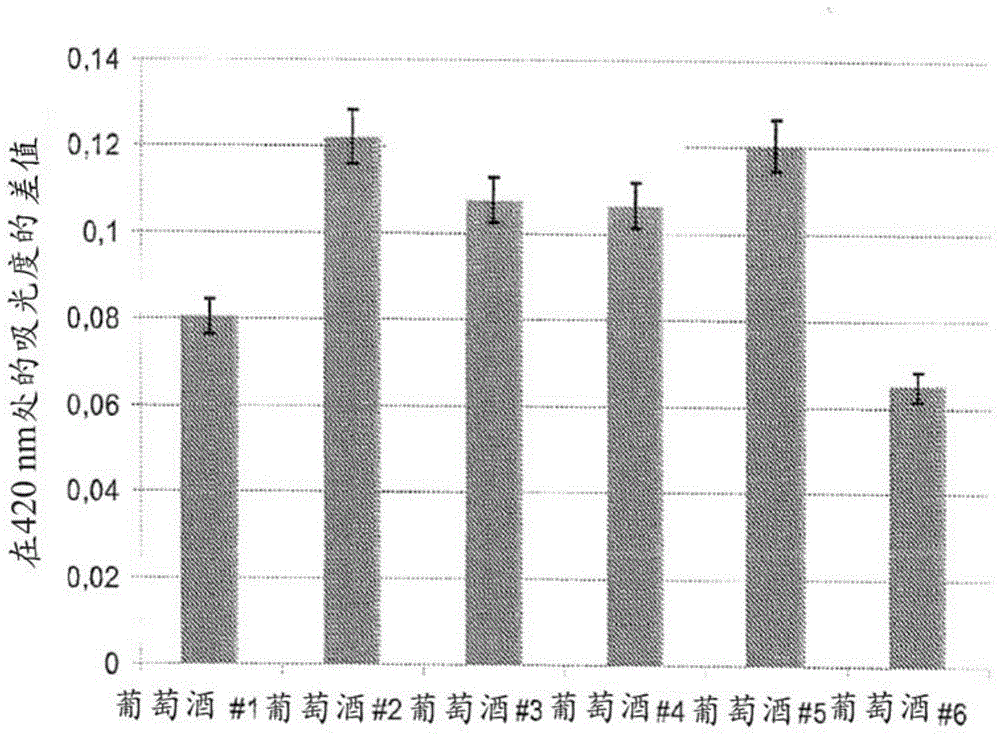
Electroanalytical methods for predicting the oxidability of a wine or a grape must and related systems
An electroanalytical method for predicting the oxidability of a wine or a grape must is disclosed. This example includes recording an electrochemical signal of a sample of the wine or grape must; comparing an electrochemical signature of the electrochemical signal obtained in a) with reference curves of voltammograms obtained from wines or grape musts with known oxidability; and predicting the oxidability of the sample tested based on the comparison. Markers for predicting the oxidability of a wine or a grape must and the use of electrochemistry for predicting the oxidability of a wine or a grape must are also disclosed. A method for predicting the optimal total oxygen supply for storing a wine or a grape must in a container; a method for wine maturation and / or ageing and; a method for selecting an optimal closure for storing a wine or a grape must in a container are also disclosed.
Owner:VINVENTIONS USA LLC
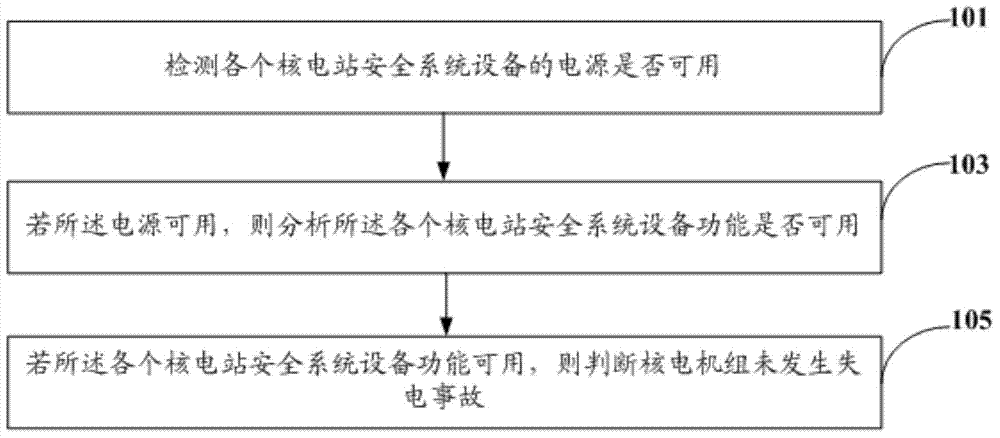
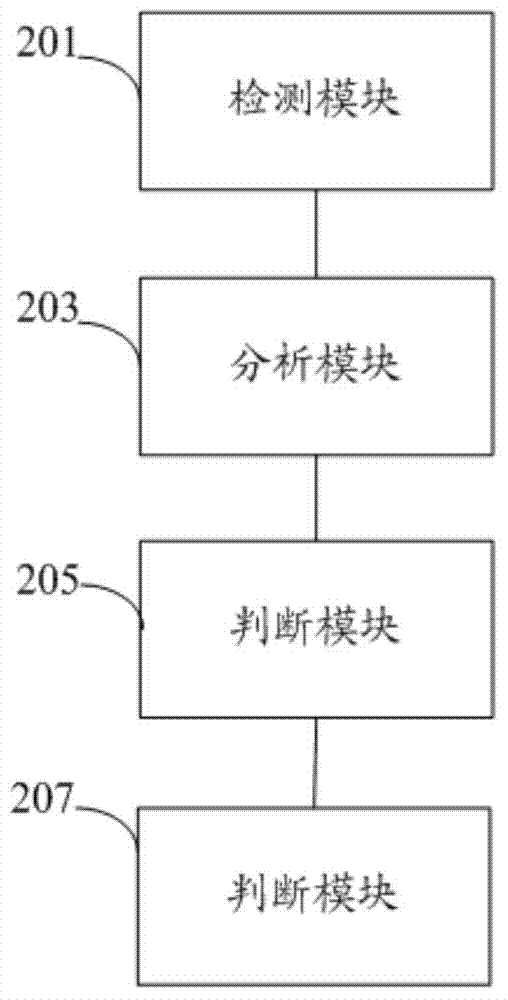
Nuclear power station power-losing accident analysis method and system
ActiveCN103578590AMeet the requirements of security protectionMeet the needs of nuclear power engineering sitesPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear engineeringNuclear power
The invention discloses a nuclear power station power-losing accident analysis method and system. The nuclear power station power-losing accident analysis method includes the steps of detecting whether a power source of each nuclear power station safety system device is available or not, analyzing whether each nuclear power station safety system device is available or not if the power source of each nuclear power station safety system device is available, and judging that a nuclear power unit does not have power-losing accidents if each nuclear power station safety system device is available. According to the nuclear power station power-losing accident analysis method, whether the power source and the functions of each nuclear power station safety system device are available or not is detected to further judge whether the nuclear power unit has the power-losing accidents or not, nuclear power station safety protection requirements are effectively met, and the defect that the method that a manual failure tree is used for conducting accident analysis is low in efficiency is solved. In addition, the invention further discloses the nuclear power station power-losing accident analysis system.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Dislocation type electric leakage analysis method in grooved MOS device
ActiveCN103913687APrecise positioningRapid positioningIndividual semiconductor device testingEngineeringTem analysis
The invention discloses a dislocation type electric leakage analysis method in a grooved MOS device. The method comprises the steps of obtaining defect positions corresponding to light emitting points through an EMMI analysis method, controlling EMMI analysis conditions to enable the diameters of the light emitting points to be smaller than or equal to 1.5 microns, preparing TEM samples at the defect positions through an FIB method, and carrying out TEM analysis on the TEM samples, wherein the centers of the TEM samples and the centers of the defect positions coincide, and the thickness of the TEM samples is larger than or equal to the diameter of the light emitting points at the defect positions. The method can be used for quickly and accurately locating, analyzing and determining electric leakage failure caused by dislocation.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Unit discharge analysis method and system of neuron information
ActiveCN101908099AReal-time processingEasy to handleDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInformation processingPattern recognition
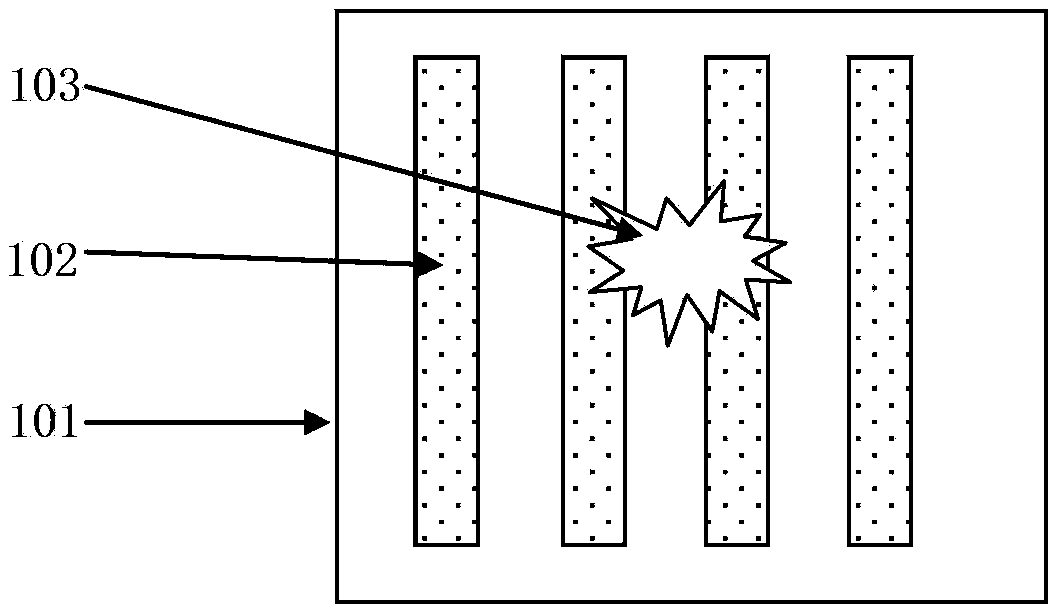
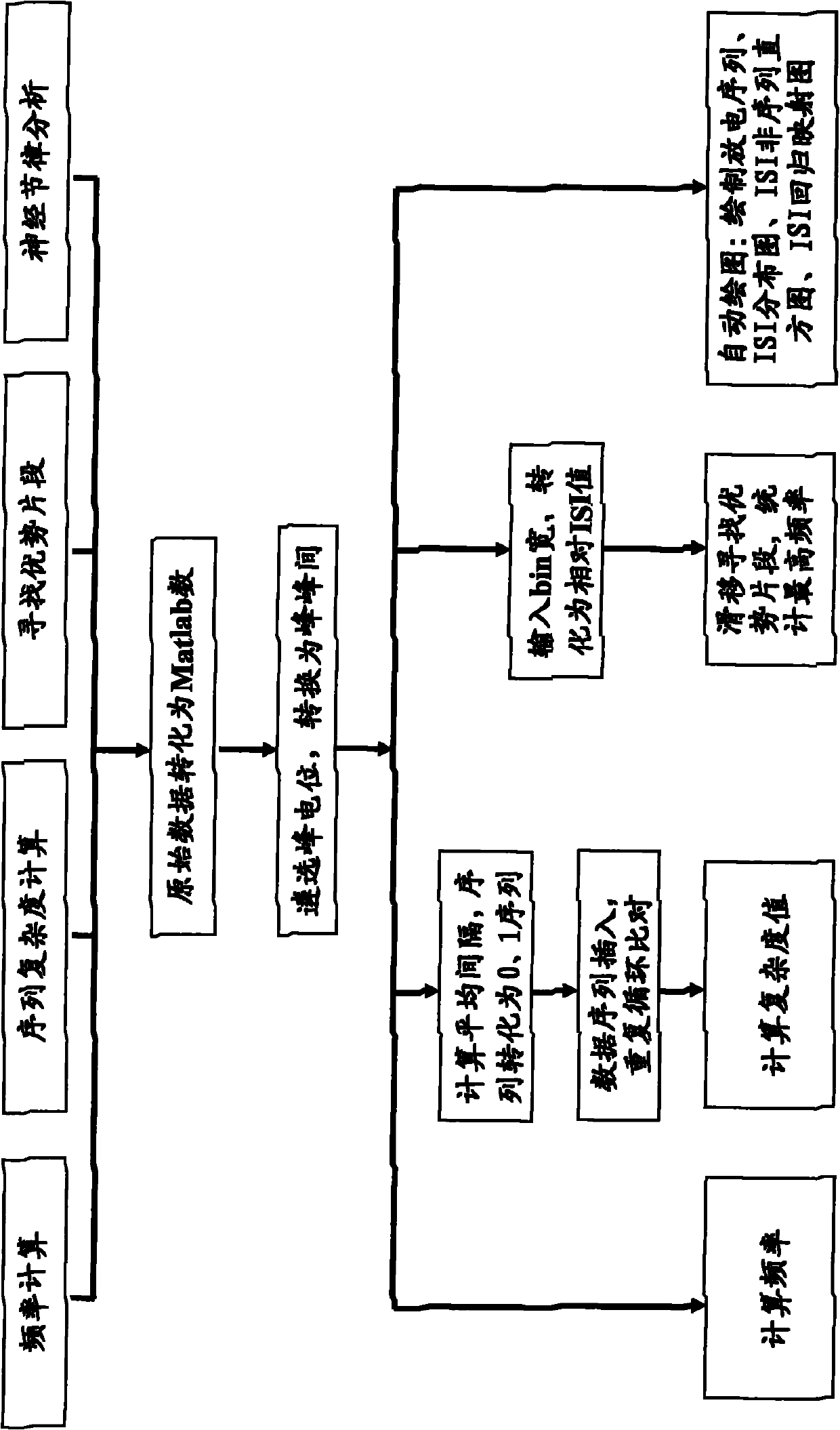
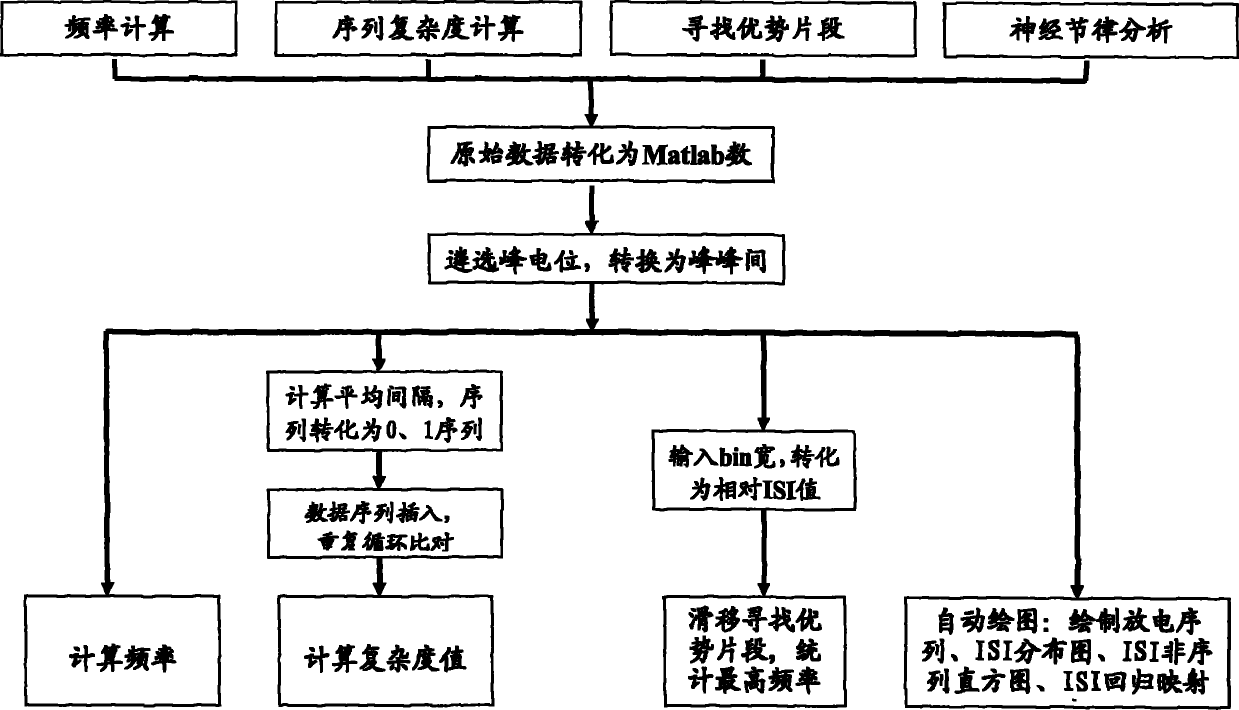
The invention discloses unit discharge analysis system and method, relating to the technical field of information processing. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting neuron peak potentials from superior segments through a peak selection unit, and determining the peak-peak interval of neurons; extracting the time interval of peak potentials of adjacent action potentials through the conversion of original data so as to carry out data conversion, respectively acquiring statistical values: frequency, complexity and superior segments according to different requirements, drawing a nerve rhythm feature multi-analysis diagram and judging the rhythm characteristics of the neutrons.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
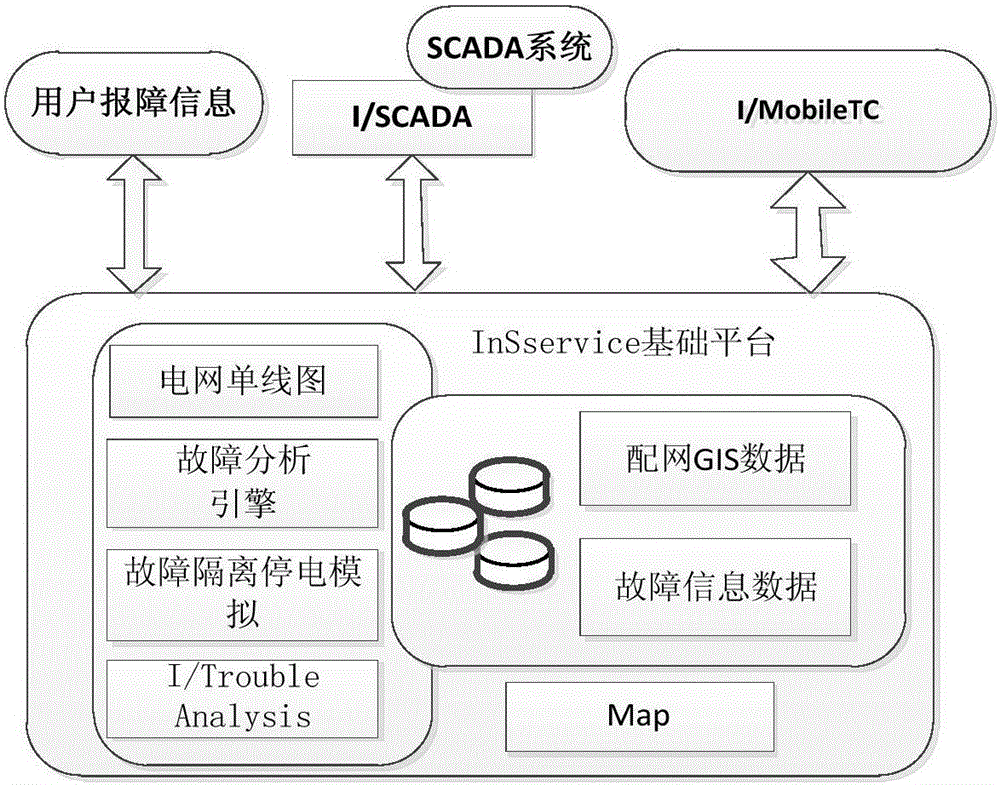
Power failure analysis method based on single line diagram of distribution network GIS power grid
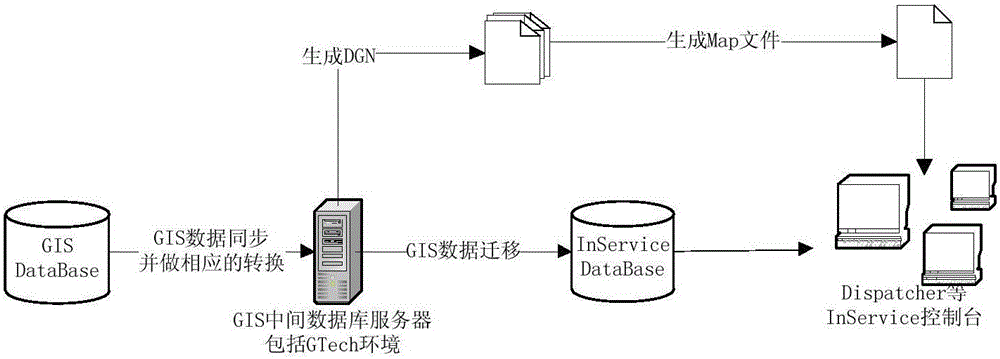
InactiveCN105977971AAvoid duplicationReduce the impactData processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsData synchronizationGraphics
The invention discloses a power failure analysis method based on a single line diagram of a distribution network GIS power grid. According to the system of the invention, the InService from the Intergraph Corporation is used as the basic development platform; the data of the currently-operated GIS system is subjected to certain processing to be synchronized to the database of the InService at a certain time to allow the InService platform to use the data; the graphic data in the GIS is converted into map files and the single line diagram of the distribution network GIS power grid which can be recognized by the InService; the data synchronization mode is timing synchronization based on rules; an intermediate server is required in the overall data migration process to be used as transfer of the GIS data; and the model of the GIS data in the intermediate server needs to be correspondingly corrected and modified to enable the GIS data model to satisfy the related requirements of the data migration from the GIS data to the InService and to generate the single line diagram of the distribution network GIS power grid. The power failure analysis method based on the single line diagram of the distribution network GIS power grid has the advantages of saving rush-repairing resource of power failure, accurate fault positioning, reasonable fault isolation, high working efficiency, and high power-supply reliability.
Owner:YUXI POWER SUPPLY BUREAU OF YUNNAN POWER GRID +1
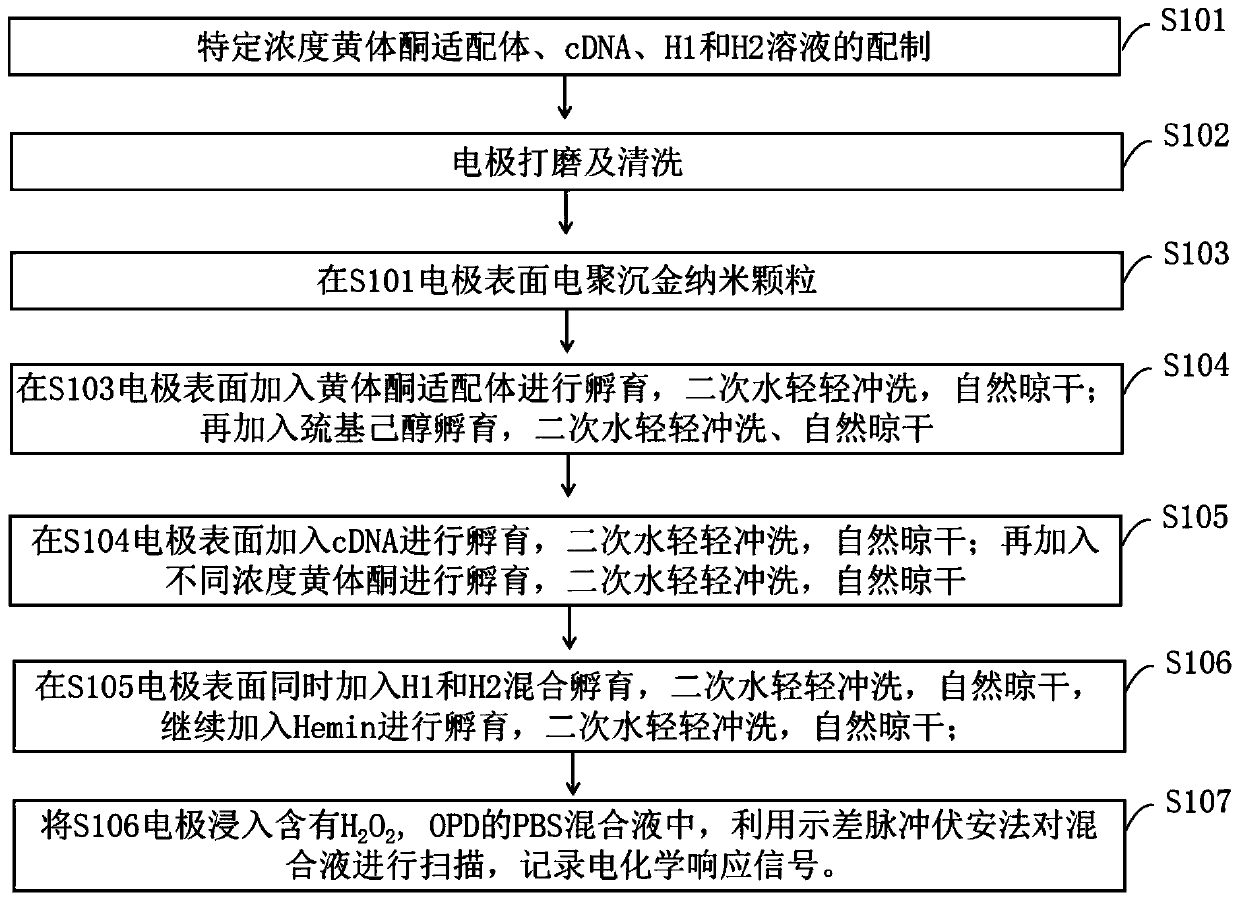
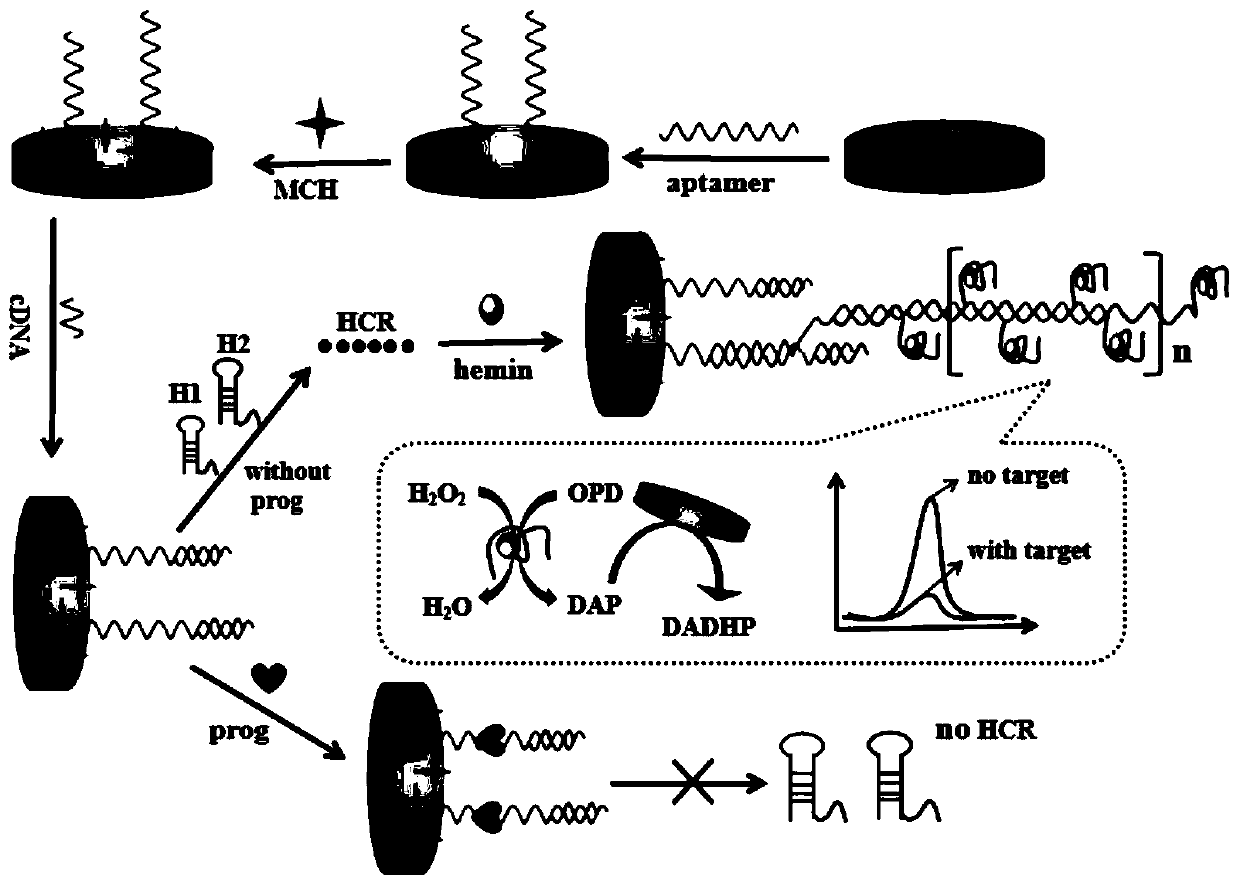
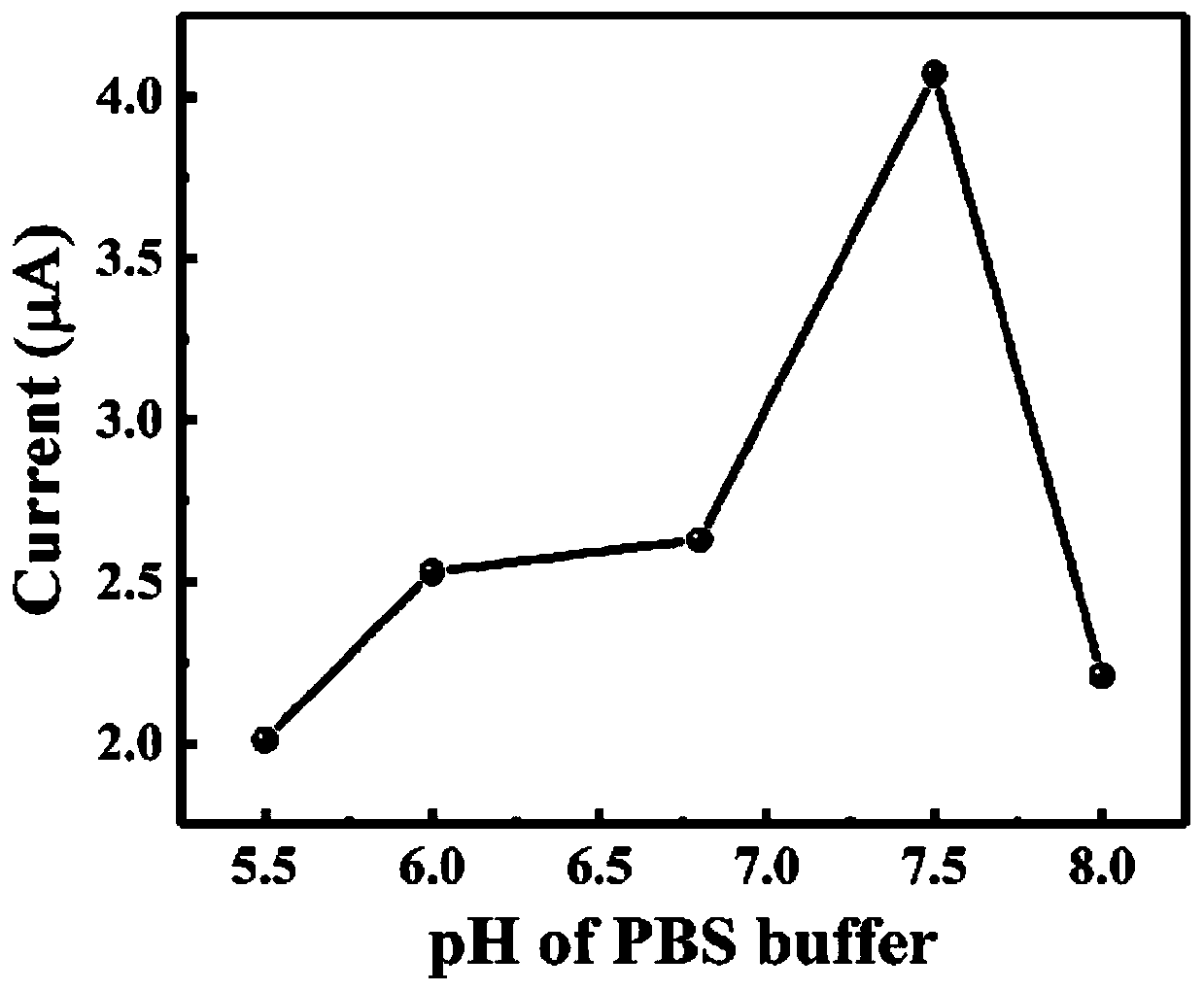
G-quadruplet DNAzyme signal amplification strategy-based progesterone detection method for aptamer sensors
ActiveCN109991297AHigh sensitivityImprove catalytic abilityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityCost effectiveness
The invention discloses a G-quadruplet DNAzyme signal amplification strategy-based progesterone detection method for aptamer sensors. Compared with the traditional progesterone detection method, the method provided by the invention is capable of avoiding the establishment of an analysis method for precious instruments; and a nucleic acid aptamer is used as a recognition element, so that the selectivity and stability of target detection are improved. A signal amplification strategy and an electric analysis method are combined to construct an electrochemical sensing new method and new technologytaking progesterone as a detection object, so that the analysis sensitivity is improved. The progesterone detection method provided by the invention is more convenient, more sensitive and higher in selectivity and cost benefit, and has important practical significance and development prospect in the analysis of trace small biological molecules.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Power supply transfer check analysis method and system for power distribution network
ActiveCN109888778AEliminate the effects of planned outagesImprove power supply reliabilityInformation technology support systemAc network circuit arrangementsAnalysis methodComputer science
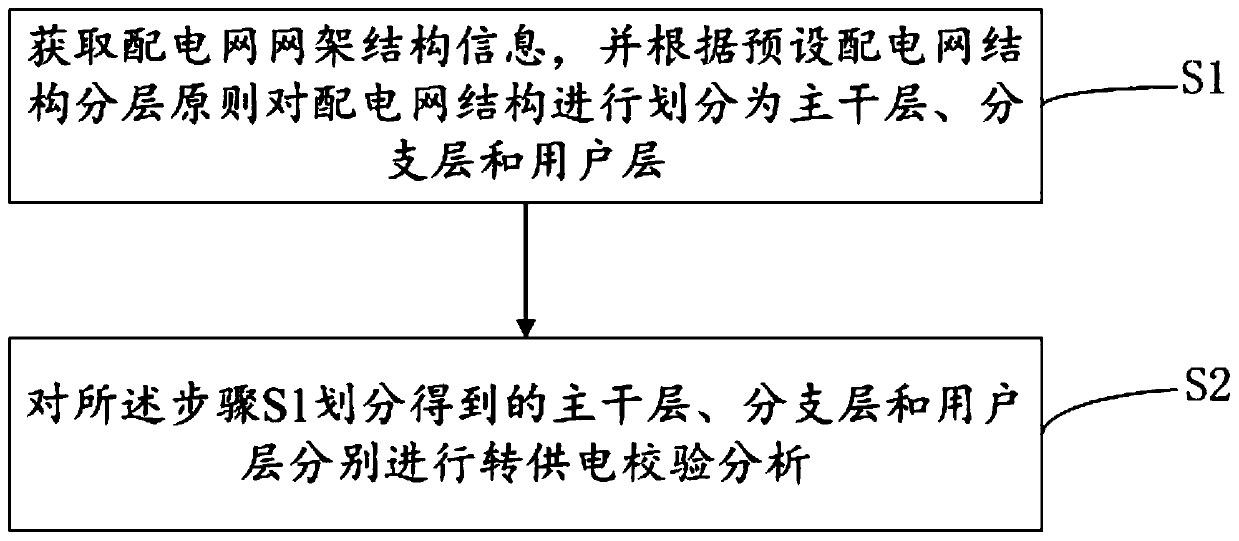
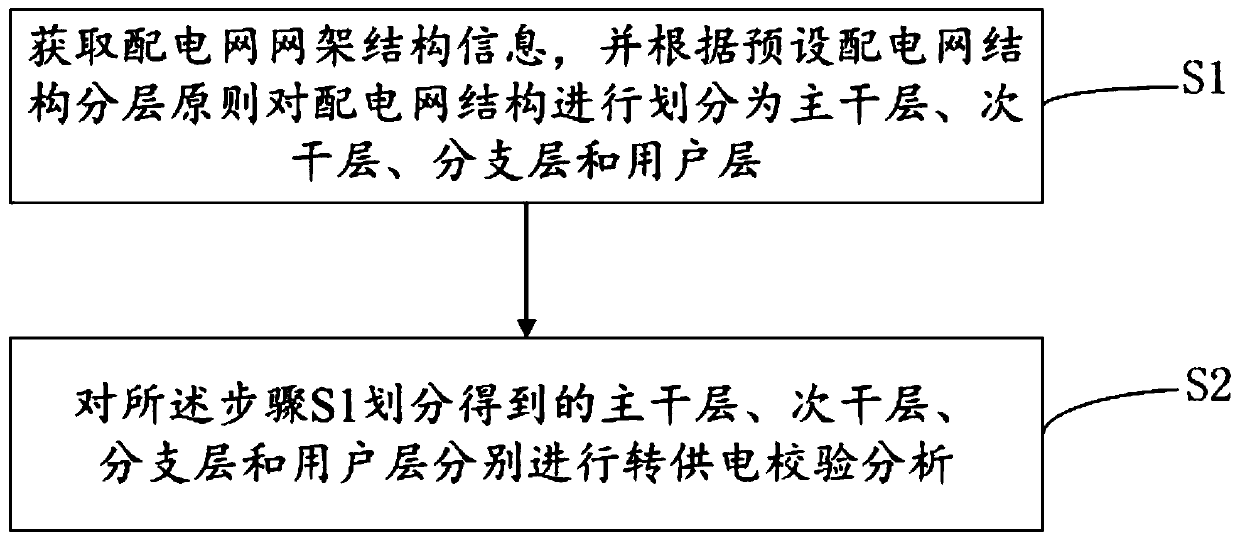
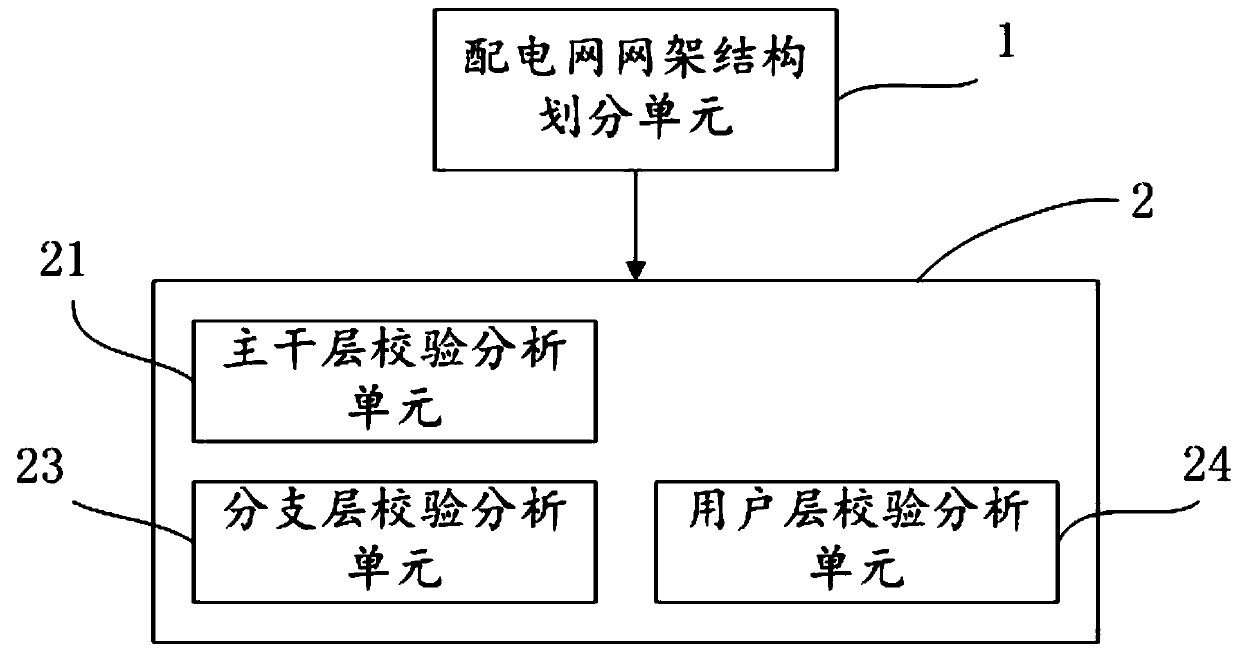
The invention provides a power supply transfer check analysis method and system for a power distribution network. The method comprises the steps of S1, acquiring network framework structure information of the power distribution network, and dividing a power distribution network structure according to a preset power distribution network structure layering principle, specifically, dividing the network framework structure of the power distribution network into a trunk layer, a branch layer and a user layer, wherein the trunk layer comprises a 10kV overhead or cable line part which is fed out froma transformer substation or a switching station and undertakes a main electric energy transmission and distribution function, and a line section part with a contact function; the branch layer comprises a 10kV line part which is led out from a 10kV trunk line, except the trunk layer; the user layer comprises a distribution transform part for directly supplying power to a user; and S2, conducting power supply transfer check analysis on the trunk layer, the branch layer and the user layer obtained by division in the step S1. The system is used for realizing the method. A check analysis result can be used as a basis of a processing mode for eliminating the influence of scheduled outage.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com