Patents
Literature
178 results about "Engine coolant temperature sensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
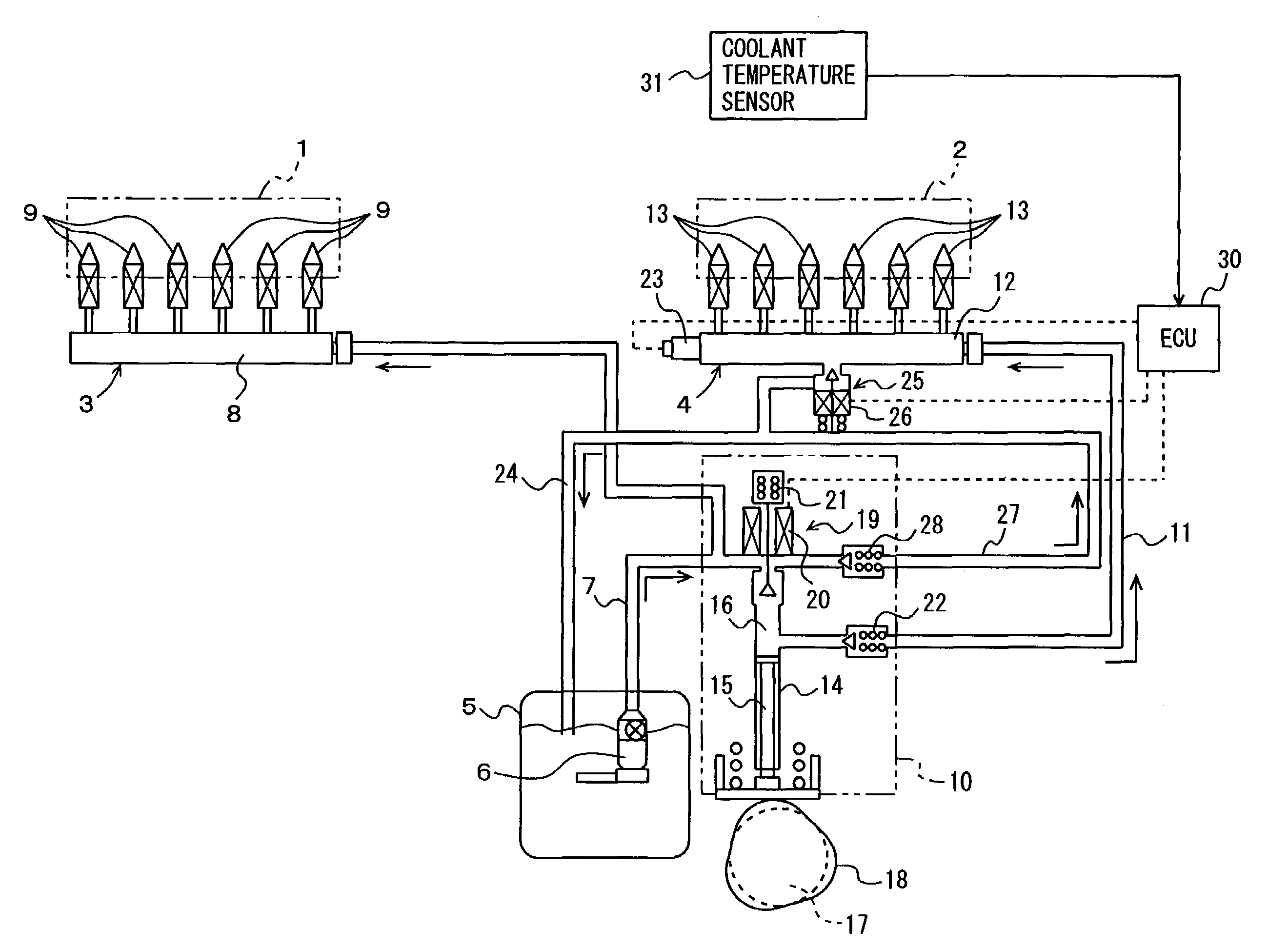
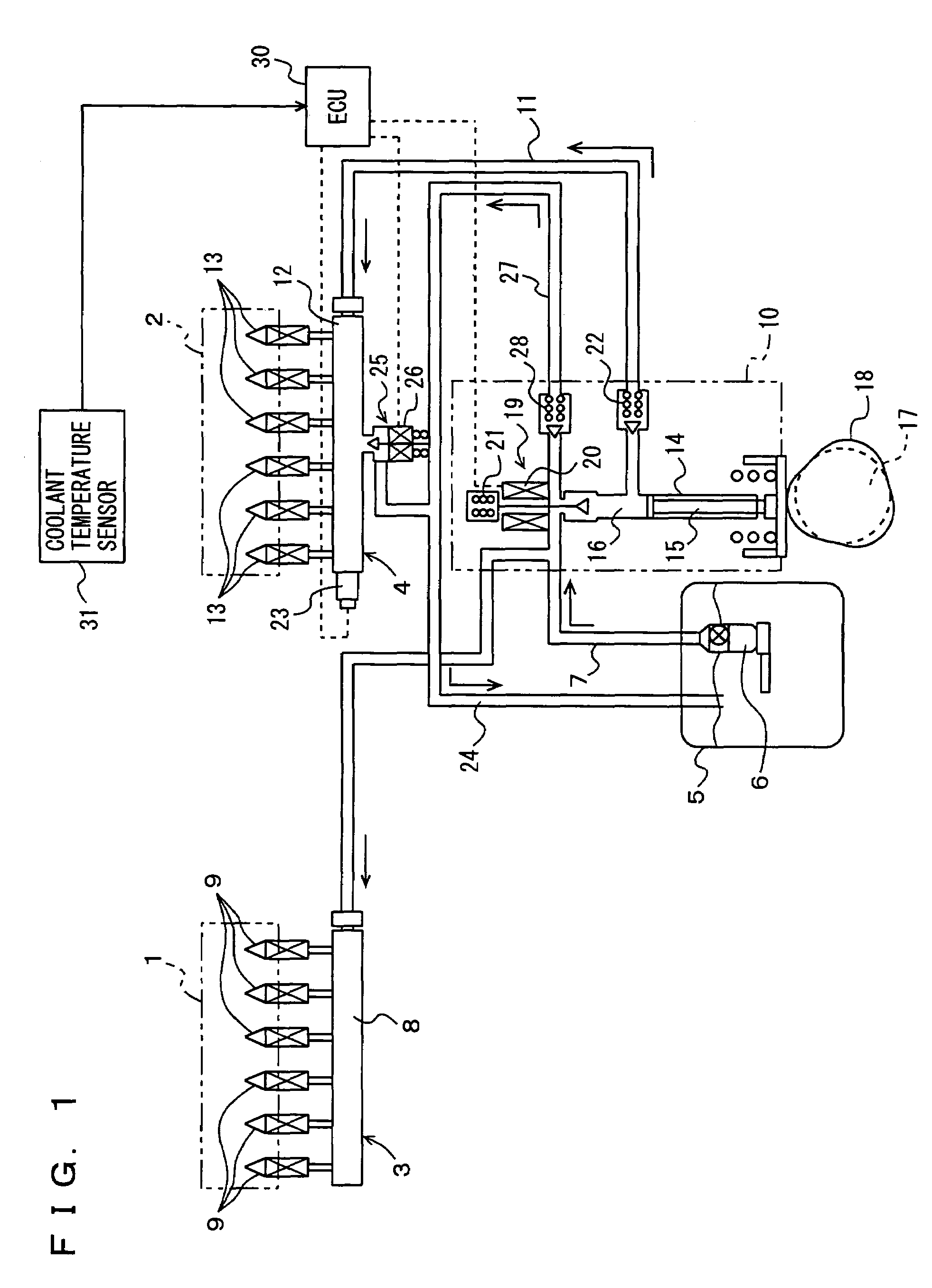
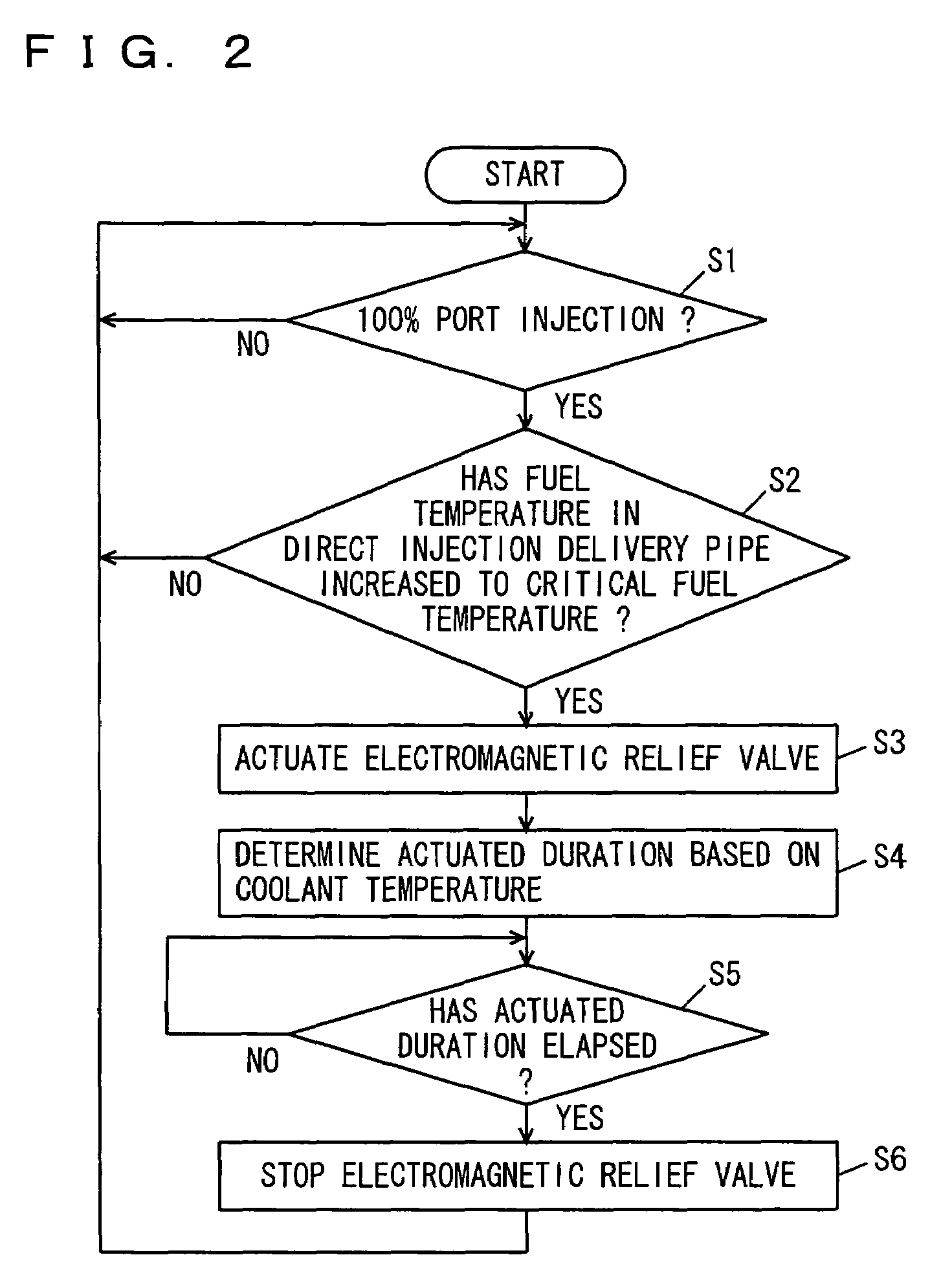
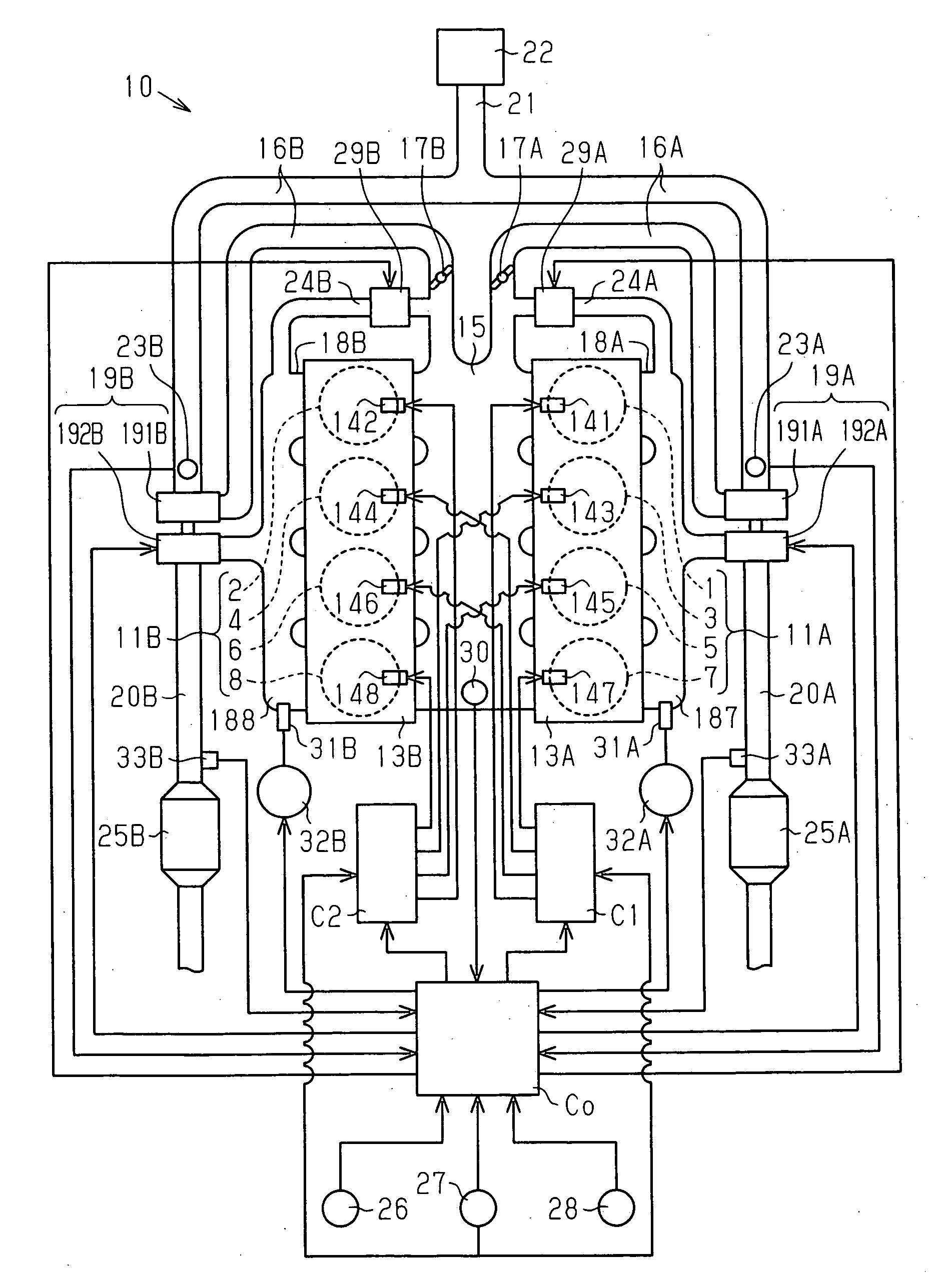
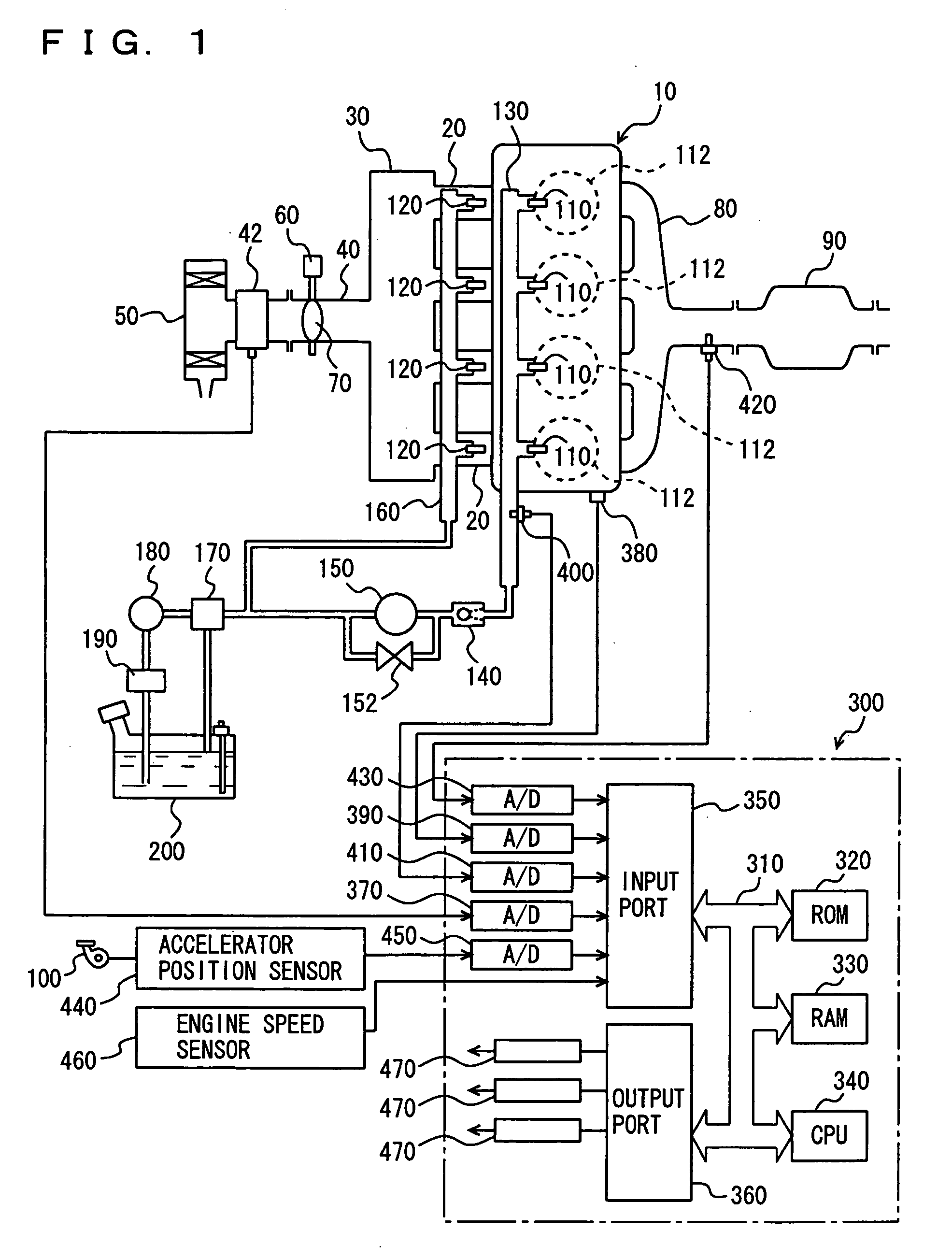
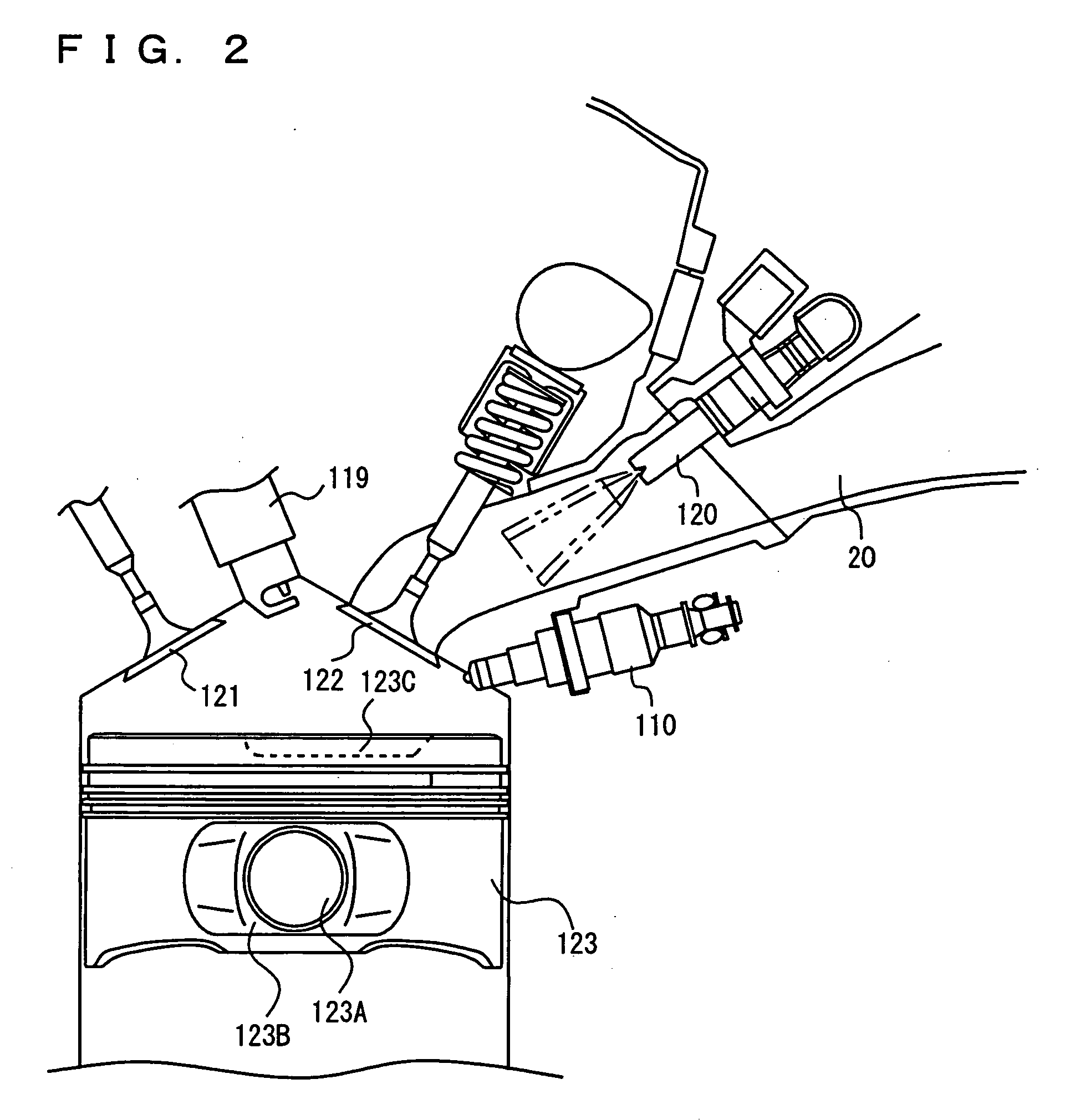
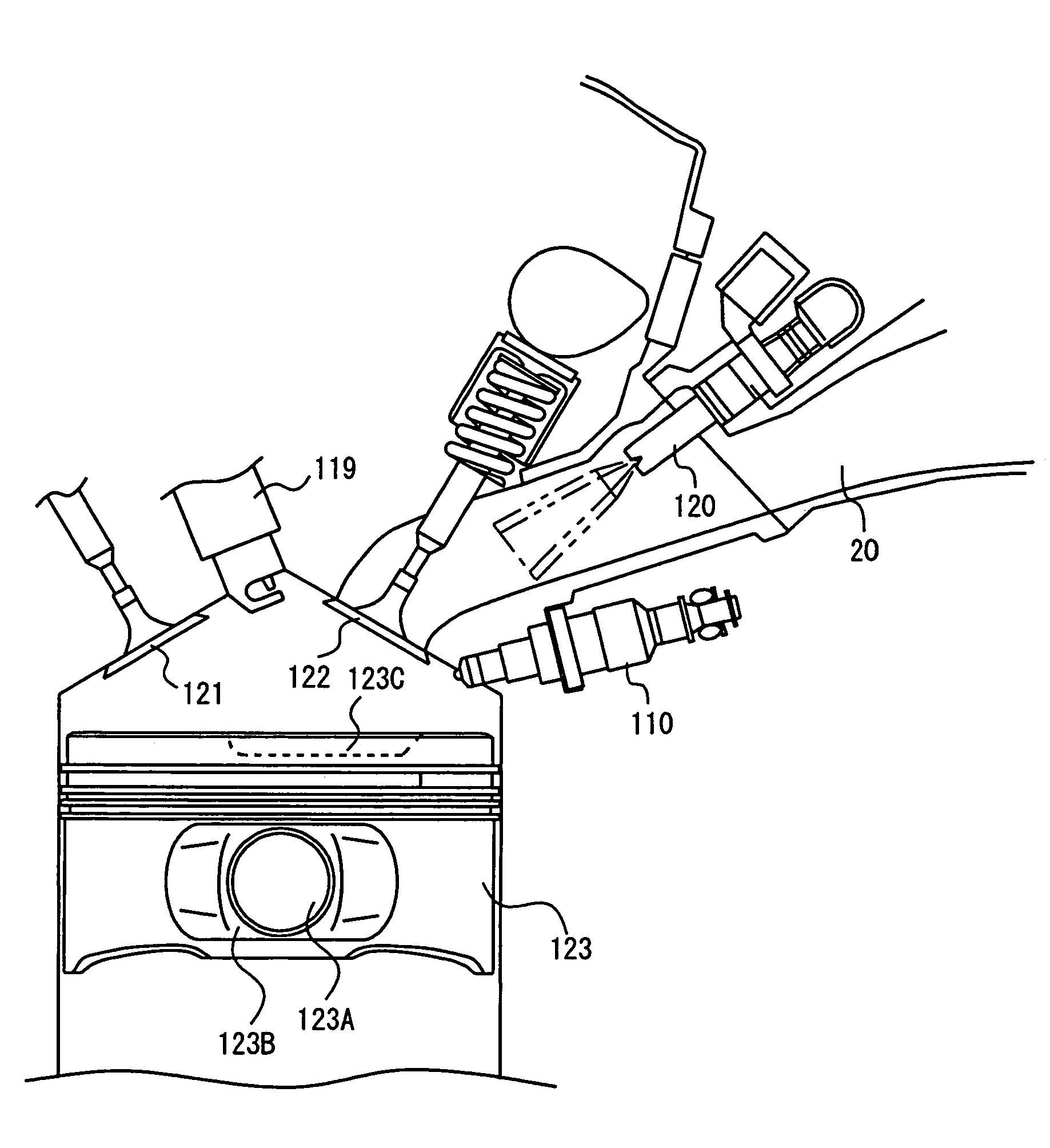
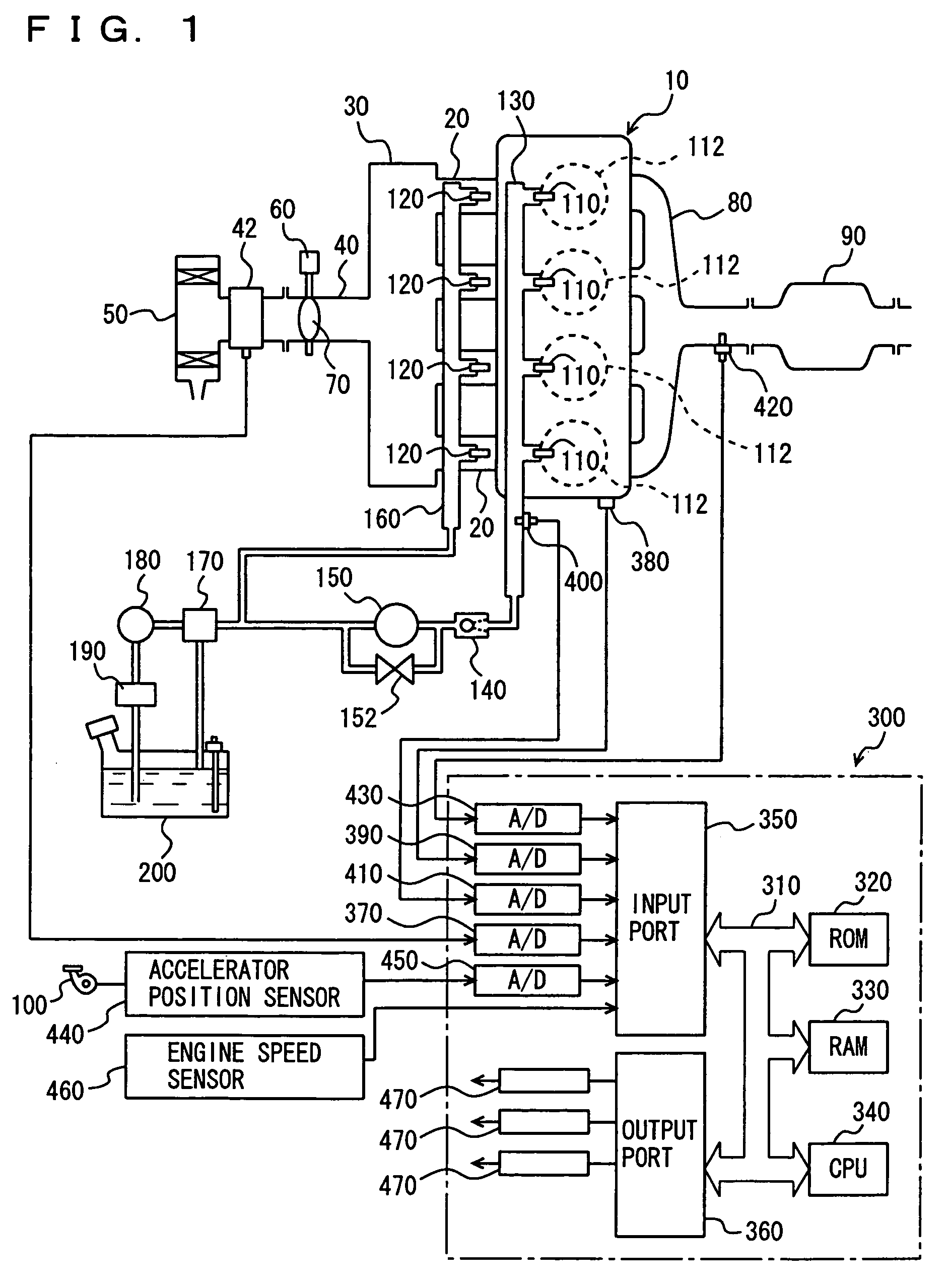
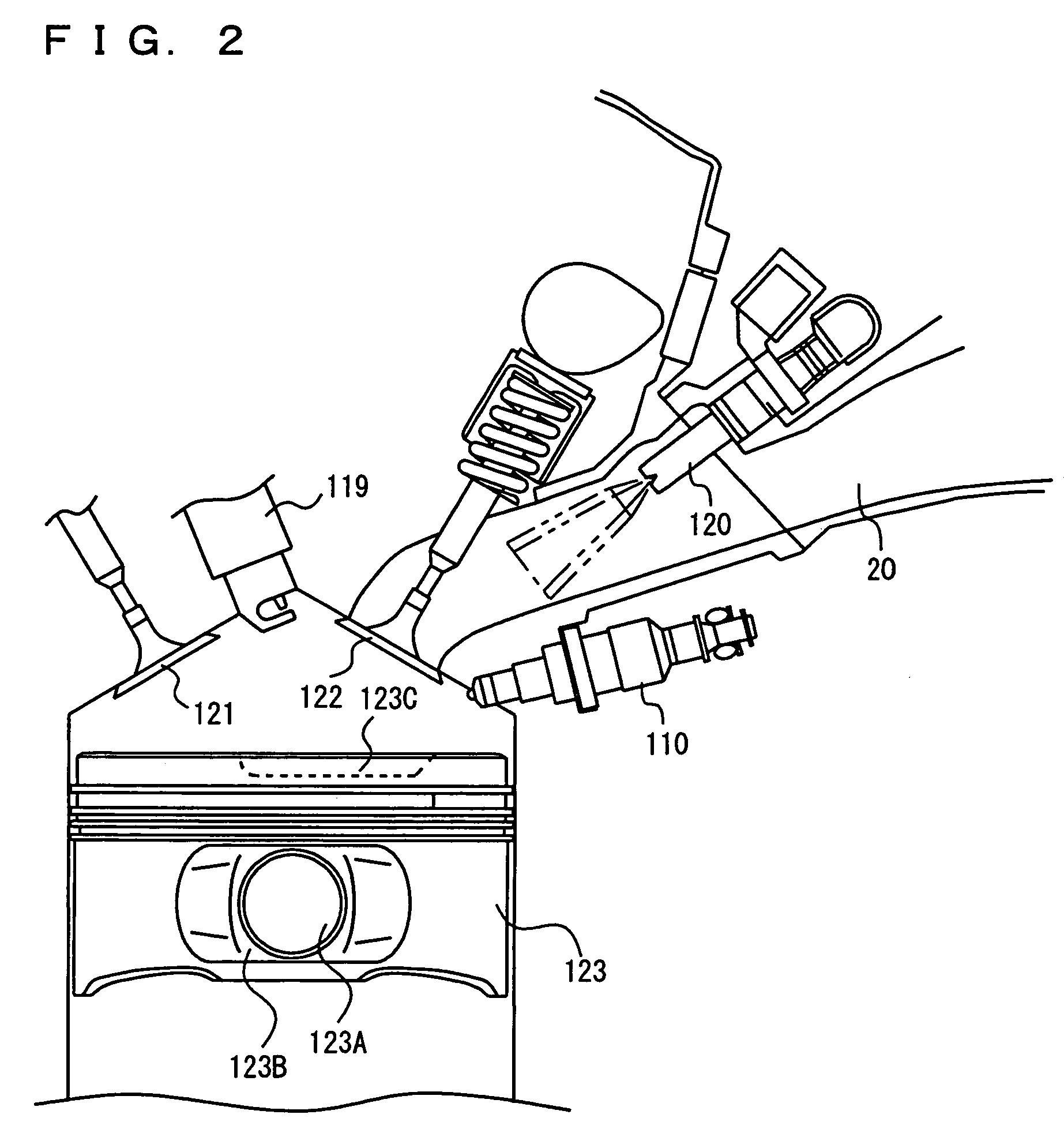
The coolant temperature sensor is used to measure the temperature of the engine coolant of an internal combustion engine. The readings from this sensor are then fed back to the Engine control unit, which uses this data to adjust the fuel injection and ignition timing. On some vehicles the sensor may also be used to switch on the electric cooling fan. The data may also be used to provide readings for a coolant temperature gauge on the dashboard.
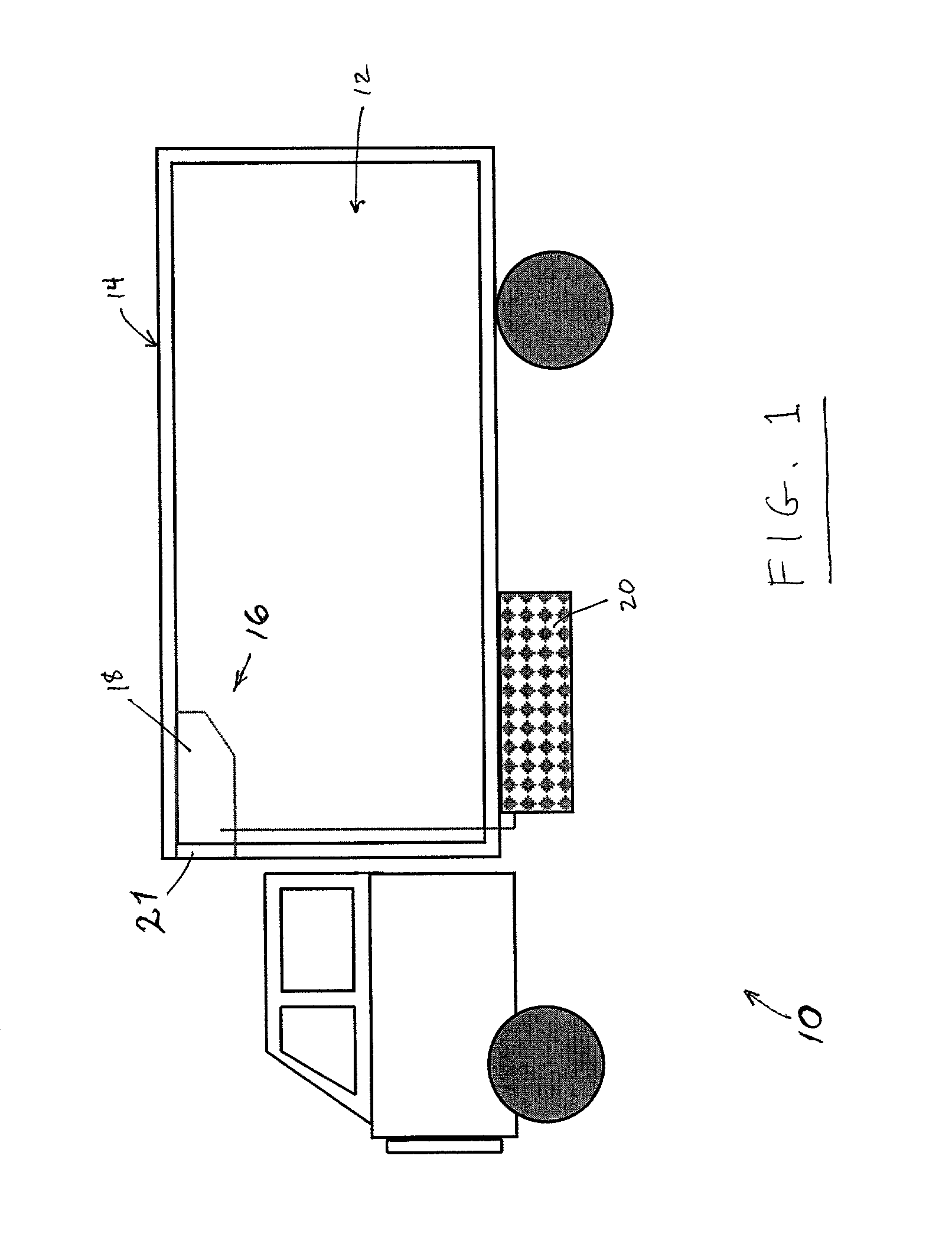
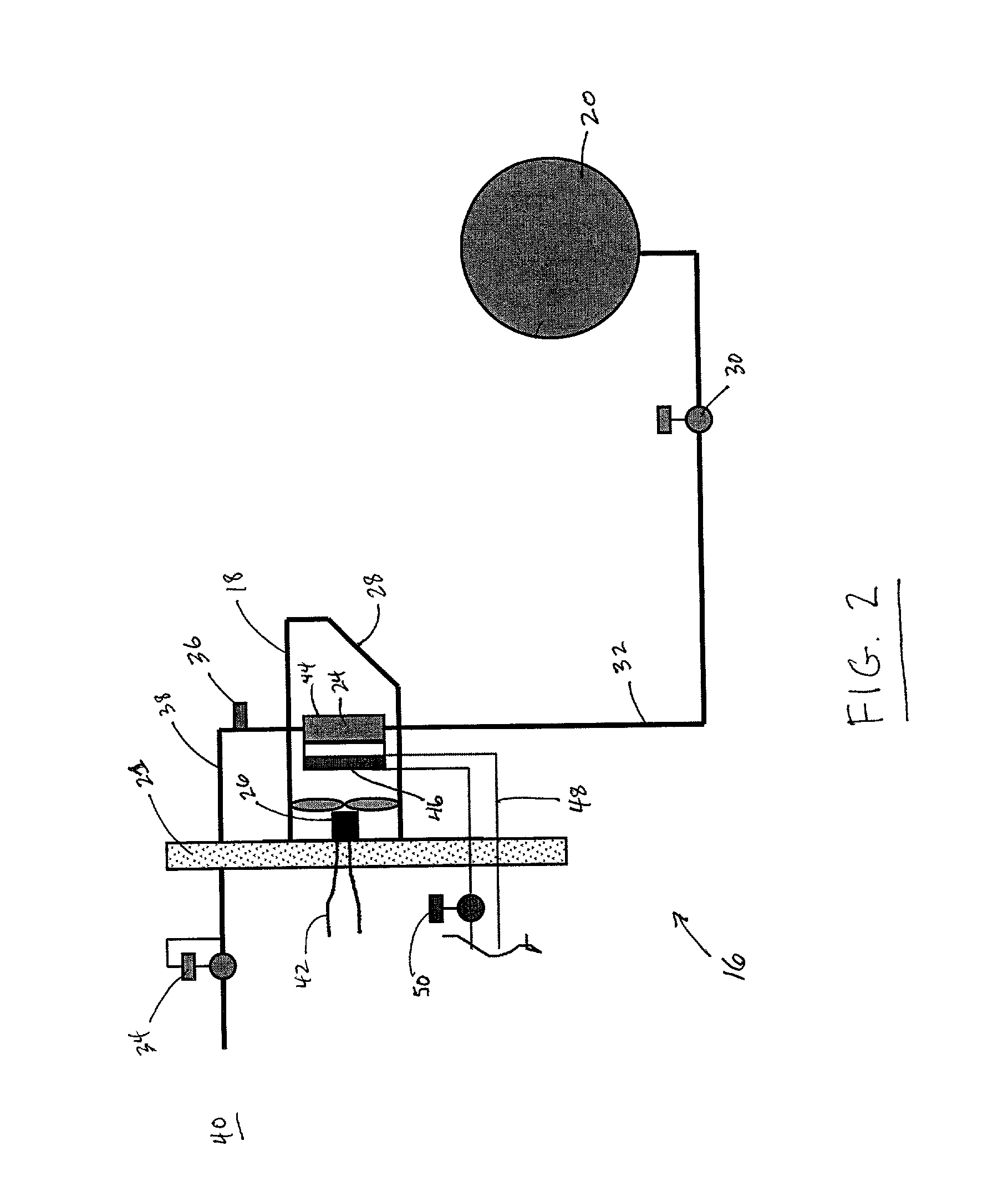
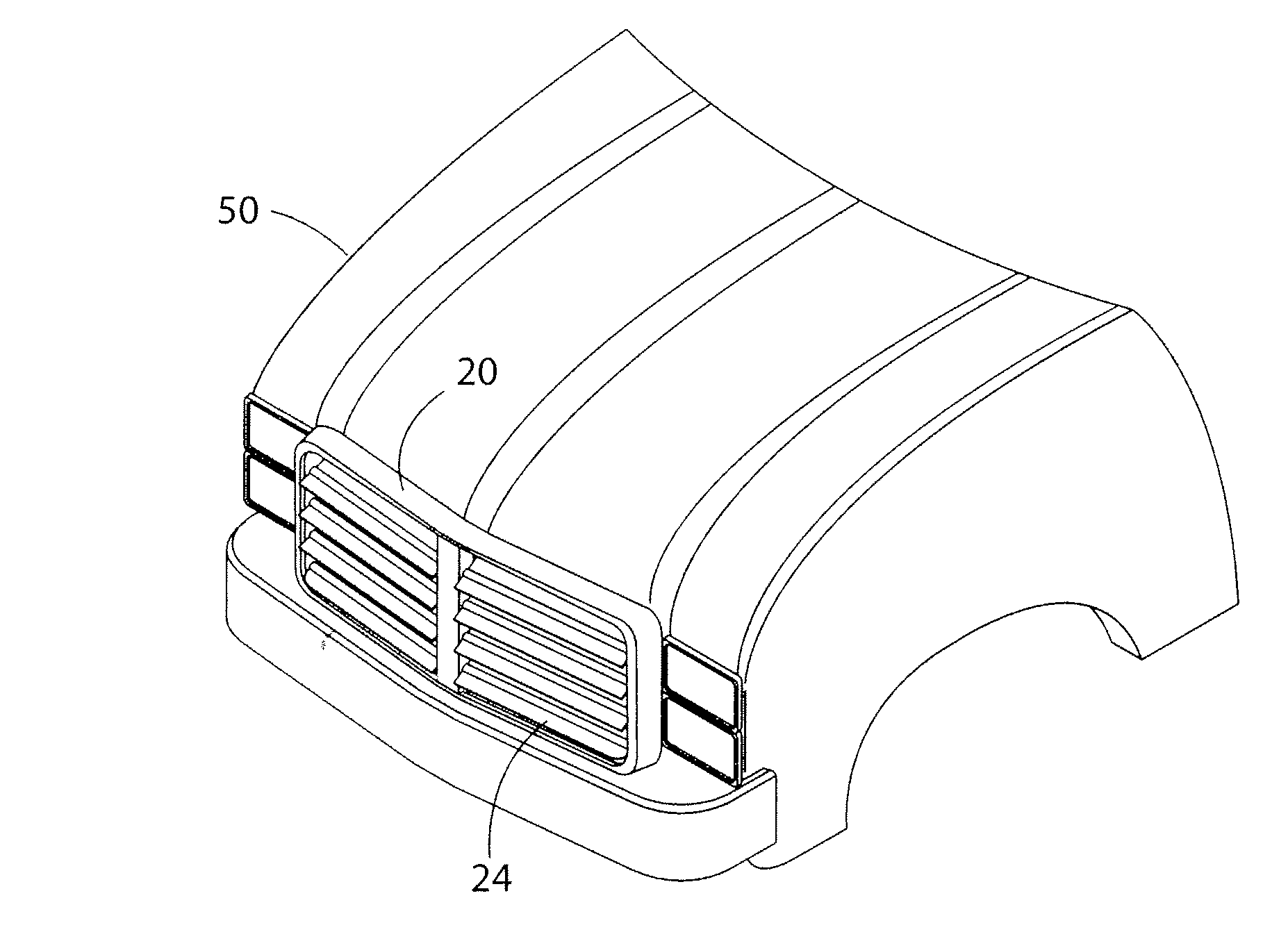
Variable vent system integrated into a vehicle front end grill
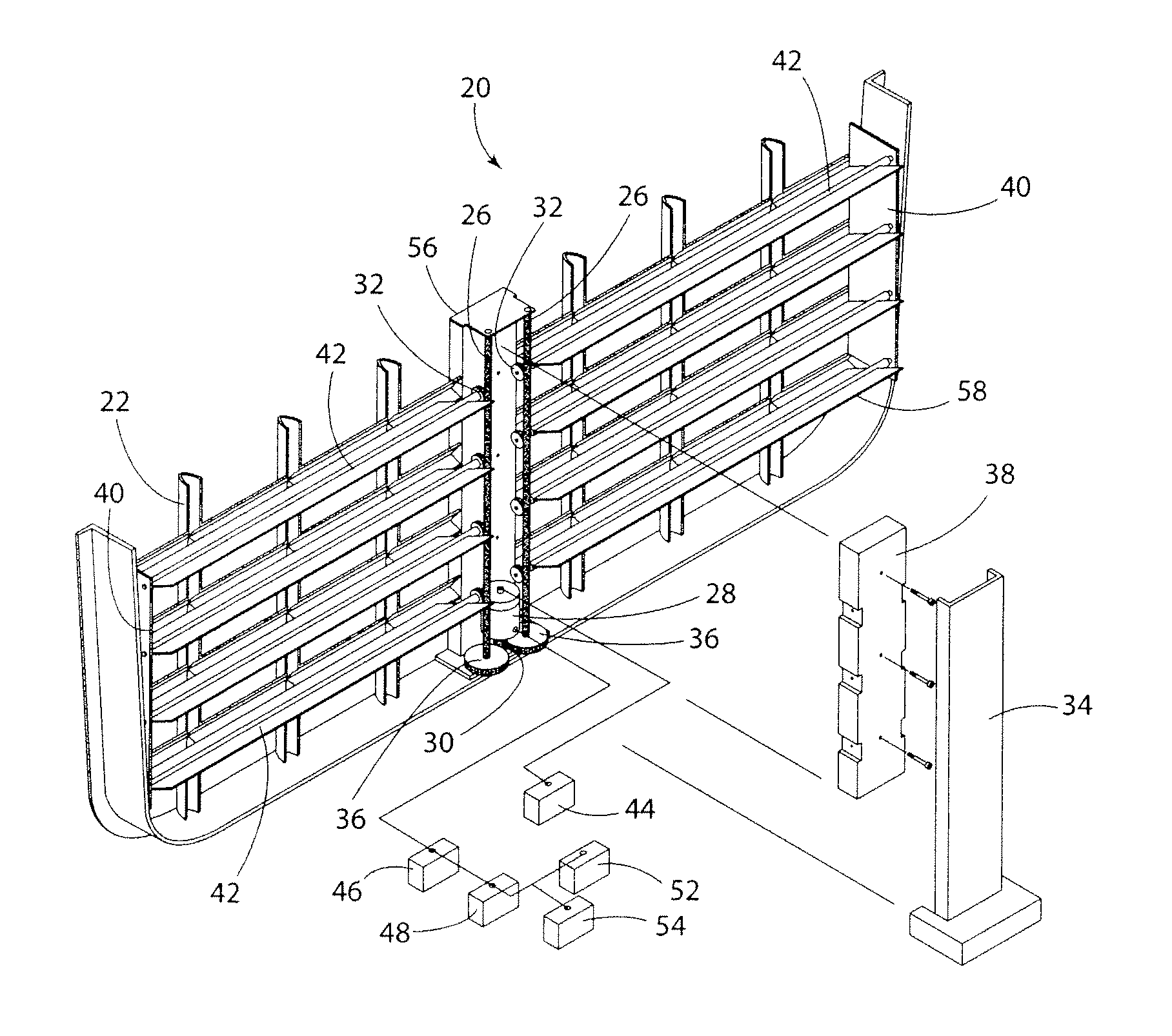
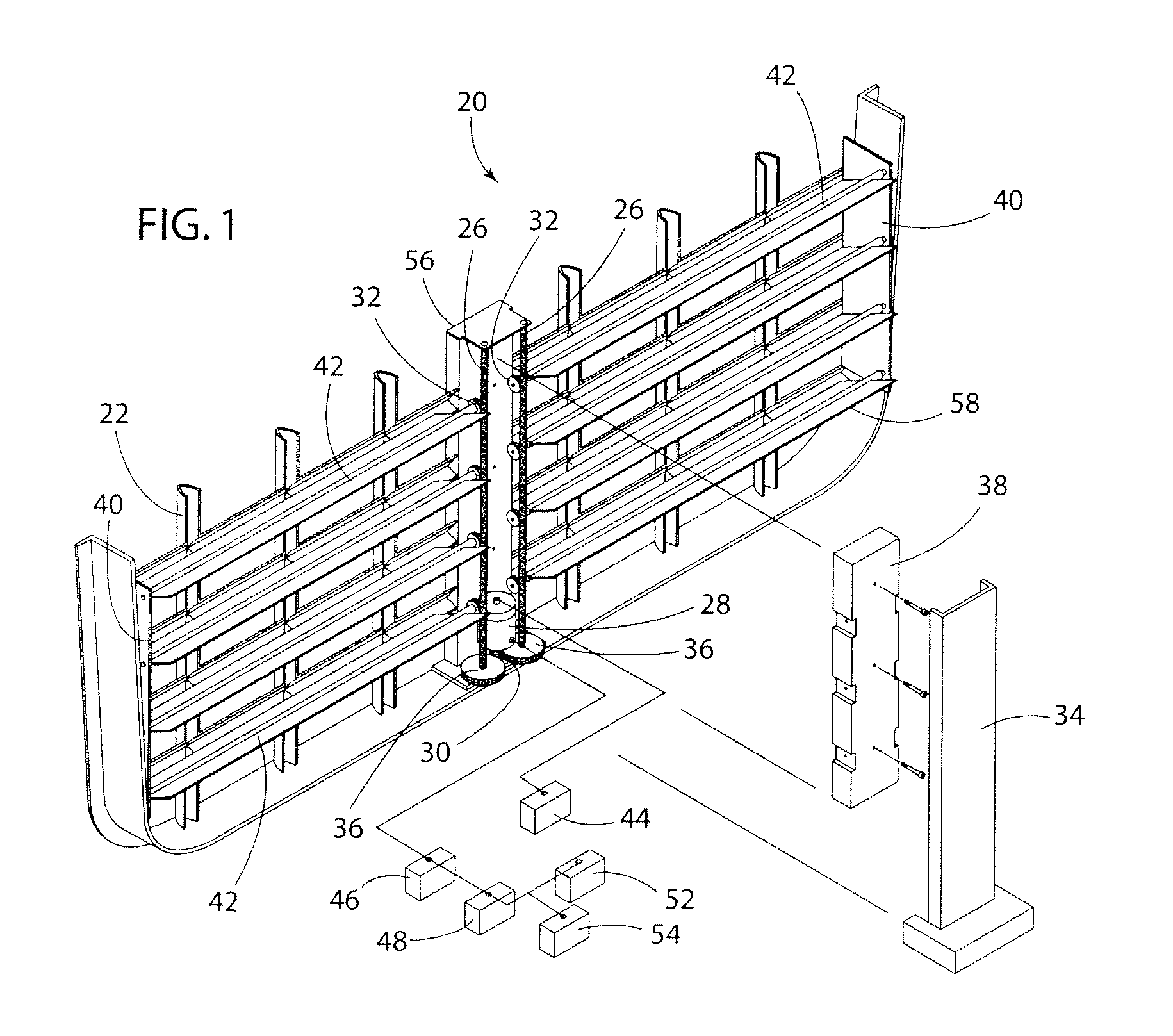
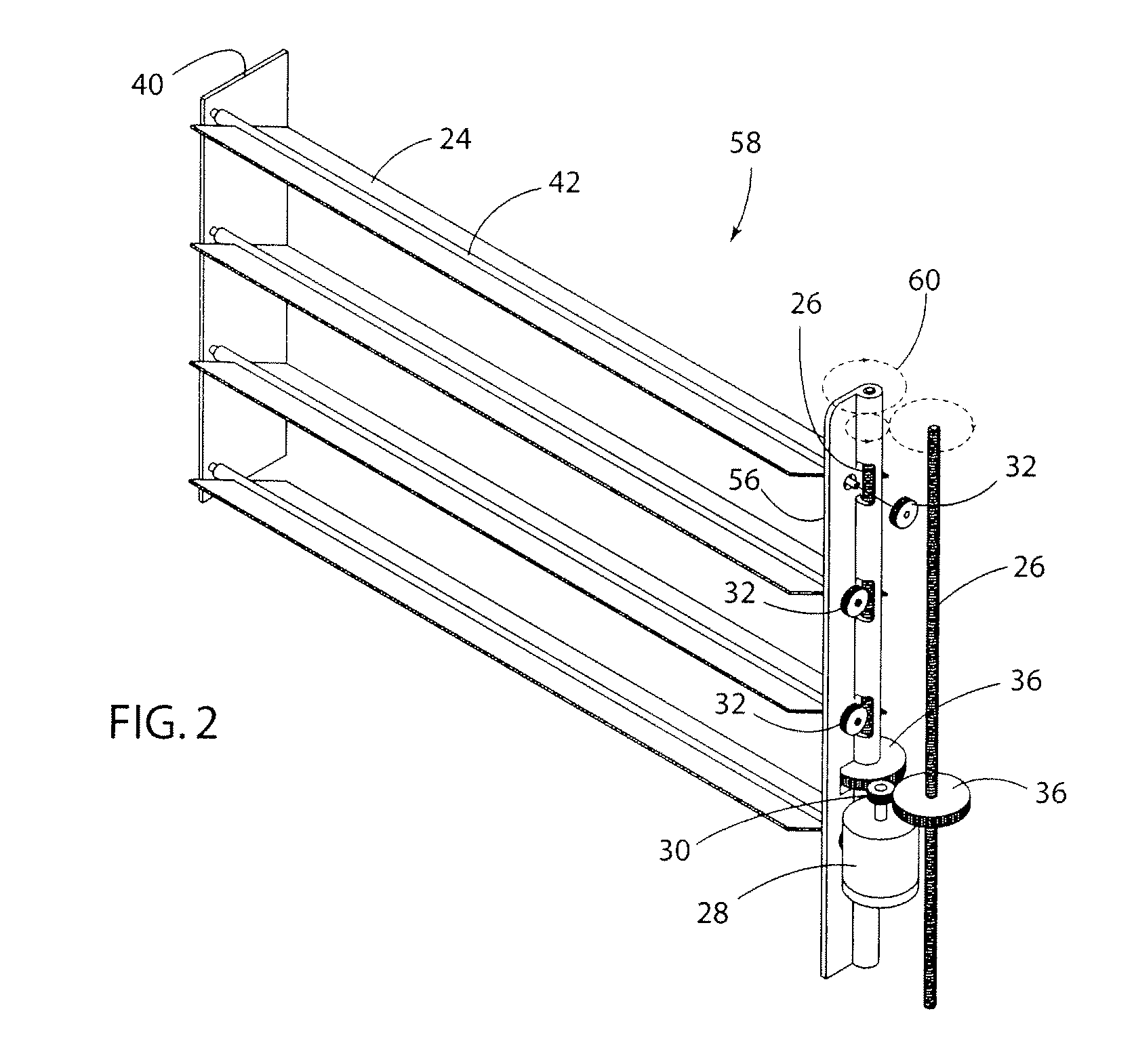
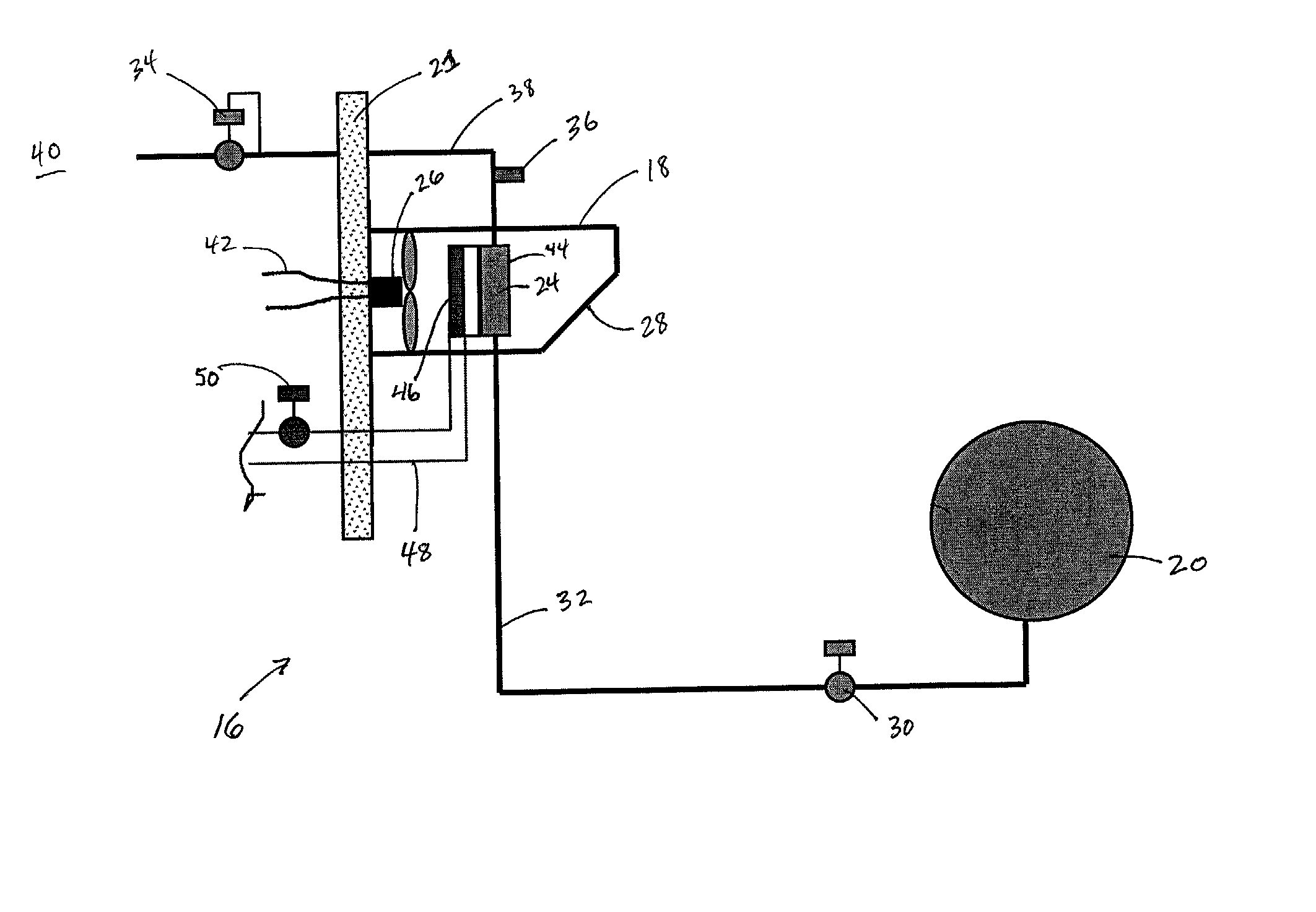
A system for variable engine compartment ventilation in a slim and compact unit with components used in non-related industries. The system can have at least one bank of movable louvers rotatably mounted within a louver frame for guiding a flow of air into a vehicle engine compartment; a motor to rotate the louvers with a motor gear formed on an output shaft rotatably connected in parallel to at least one helix cable by a helix cable drive gear and a louver pinion gear integral with each louver engaging the helix cable along its length; and a control unit for operating the assembly of movable louvers in response to an output signal from a vehicle communication bus. The output signal of the vehicle communication bus can be in response to input from an engine coolant temperature sensor or a vehicle speed sensor.
Owner:WEBASTO AG
Cryogenic refrigeration unit suited for delivery vehicles
InactiveUS20020129613A1Reduce the temperatureNot contaminate atmosphereAir-treating devicesRefrigerated goods vehicleAir cycleDelivery vehicle
An apparatus to refrigerate the cargo space of delivery vehicles. It provides an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional mechanical a / c and refrigeration units. Cooling is provided by controlled evaporation of a liquefied gas such as CO.sub.2 or nitrogen. Defrost and heating requirements, if needed, are provided by hot engine coolant or by electric heaters powered from the vehicle electrical system. Airflow for the evaporator and for circulation in the temperature controlled space is provided by a blower which is mechanically or electrically driven from vehicle power. This invention can also be applied to multi-temperature control applications. The apparatus is compact and is particularly suited for small inner city delivery vehicles. FIG. 1: The sketch shows an inner city delivery truck for which this invention is most suitable. Refrigerated goods are placed in roller cages that are designed to maximize cargo hauled by use of roller cages that extend to within 2 inches of the ceiling. The evaporator section of this invention is mounted at or near the front wall of the truck and is separated from the cargo by a vertical bulkhead. The conditioned air is delivered at the bottom of the truck to avoid top freeze of perishable cargo that is in close proximity to the ceiling. FIG. 2: This shows the piping schematic and is similar to the invention described in U.S. Application Serial No. 60 / 238,929 (the '929 application) incorporated herein by reference. FIG. 2 shows the engine coolant coil located ahead of the CO.sub.2 coil in the direction of airflow. This prevents the coldest air from coming in contact with the engine coolant--in the cooling mode the air leaving the CO.sub.2 coil can be as low as -50.degree. F. for frozen load applications and this may cause the engine coolant to start freezing. Arrangements must be made to circulate air between the two coils in defrost mode. One means to accomplish this is to place a damper at the outlet of the evaporator section and run the fans. The damper would be closed during defrost. Another method is to place the engine coolant coil on the discharge side of the CO.sub.2 coil and use a cut-out switch if the engine coolant temperature drops below a predetermined value. In this arrangement there is no need for the damper arrangement as the heat will rise to melt any frost on the CO.sub.2 coil. If electric heat is used for defrost and heating freezing of the engine coolant is not a concern and the heaters can be fastened to the discharge side of the CO.sub.2 coil. An electric stand-by mode can be provided to power the system for cooling, heating and defrost when the vehicle is parked with the engine off. A plug-in electrical cable can provide the power needed for the controls, the fans and for heating and defrost. The figure shows the electric heaters attached on the discharge side of the CO.sub.2 coil. Operation: Detailed description is in the '929 application except for the following: The evaporator section is designed for vertical installation to maximize cargo space. Air is discharged at the bottom but may be a conventional top discharge if needed for specific applications. Conventional methods can be used to provide defrost and heating. If engine coolant is used for a heat source, it is preferable to thermally isolate the CO.sub.2 coil from the engine coolant coil to avoid freezing the coolant. The evaporator blower may be located on the inlet side of the coils rather than as shown in the figures. Unique Features: 1. Absence of a conventional condensing section on the exterior of the vehicle makes this an ideal refrigeration unit for small inner city delivery vehicles. Many of the truck cabs are now almost full height (same as the truck body) and there is limited space for the condensing section. 2. Cold plates can be used and still maximize cargo cube. However, this invention has 30-40% less weight than comparable "cold plate" systems. 3. Other features are described in the '929 application.]
Owner:THERMO KING CORP
Variable vent system integrated into a vehicle front end grill
A system for variable engine compartment ventilation in a slim and compact unit with components used in non-related industries. The system can have at least one bank of movable louvers rotatably mounted within a louver frame for guiding a flow of air into a vehicle engine compartment; a motor to rotate the louvers with a motor gear formed on an output shaft rotatably connected in parallel to at least one helix cable by a helix cable drive gear and a louver pinion gear integral with each louver engaging the helix cable along its length; and a control unit for operating the assembly of movable louvers in response to an output signal from a vehicle communication bus. The output signal of the vehicle communication bus can be in response to input from an engine coolant temperature sensor or a vehicle speed sensor.
Owner:WEBASTO AG
Electric-controlled petrol engine work system
InactiveCN101363380ARich control functionsGood control function integration performanceElectrical controlMachines/enginesIdle speed controlIgnition coil
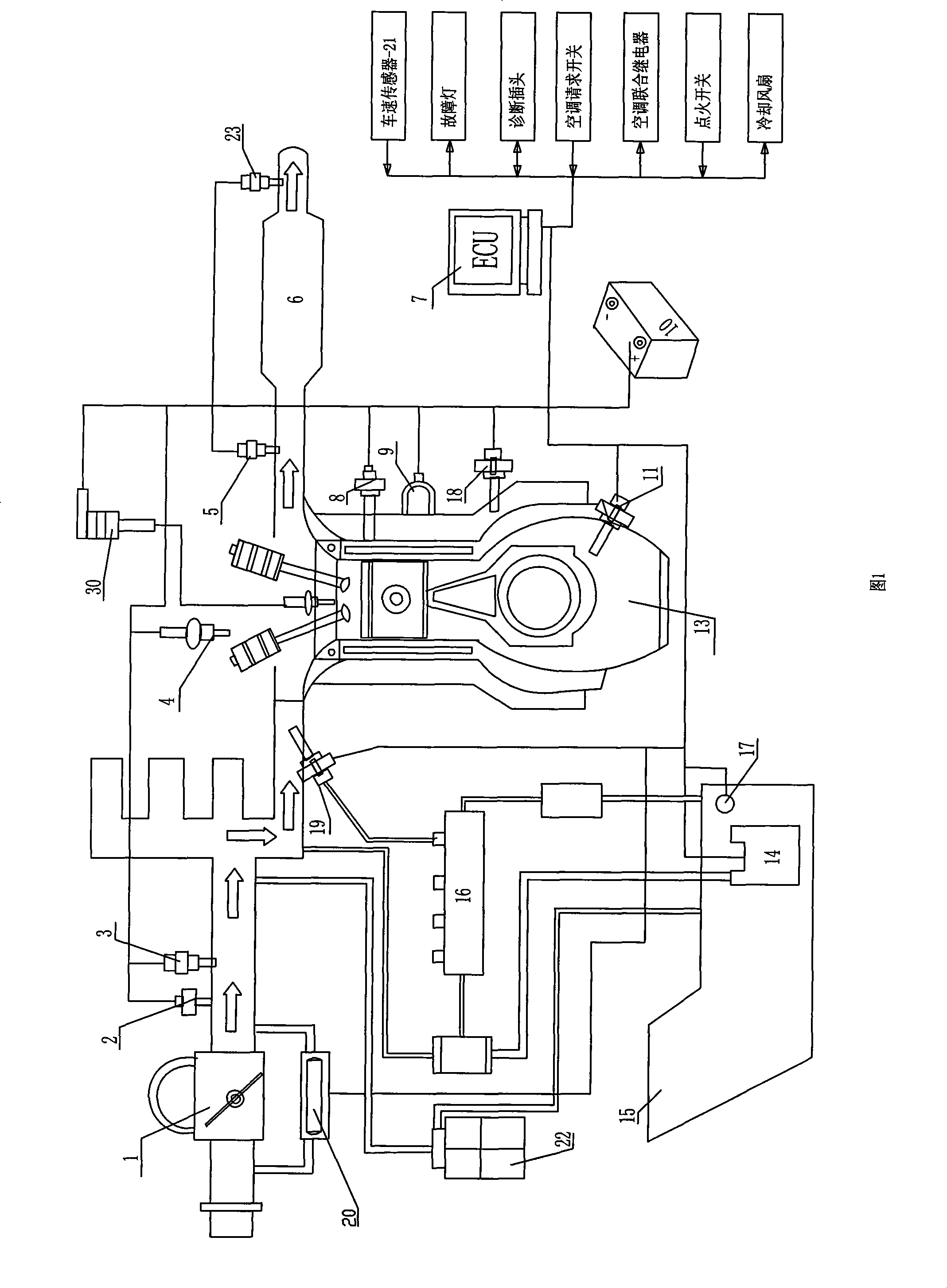
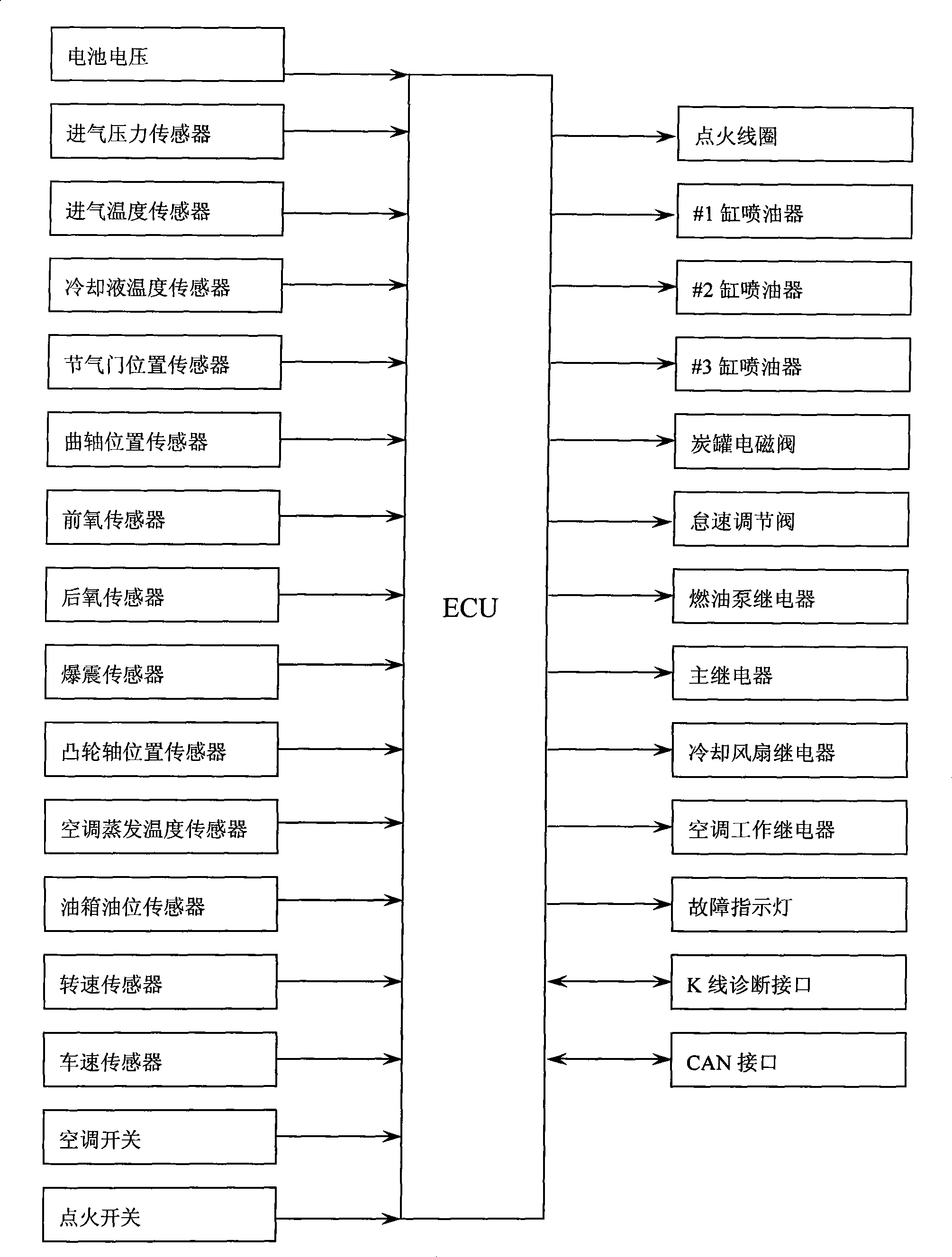
The invention provides a work system of an electronically controlled gasoline engine, comprising an air intake system, a fuel oil supply system, an ignition system as well as an electronic control system; the electronic control system consists of a sensor section, an electronic control unit ECU and an actuator section, wherein, the sensor section includes a throttle position sensor, an intake pressure and temperature sensor and an intake temperature sensor which are arranged on an intake pipe of an intake system, a camshaft position sensor, a coolant temperature sensor and a crankshaft position sensor which are arranged on the engine, a front oxygen sensor arranged in front of a three-way catalyst converter on an exhaust pipe of the engine, and the components of the sensor section are all connected with the ECU, and the actuator section consists of an electric fuel pump, an oil sprayer, an idle speed regulating valve and an ignition coil; the components of the actuator section are all connected with the ECU, and the ECU includes a fuel injection control program, an ignition control program and an idle speed control program; the system adopts reasonable control strategy and has comprehensive control function, good integrated performance of control function and fine system portability.
Owner:张和君 +1
Fuel supply apparatus for internal combustion engine
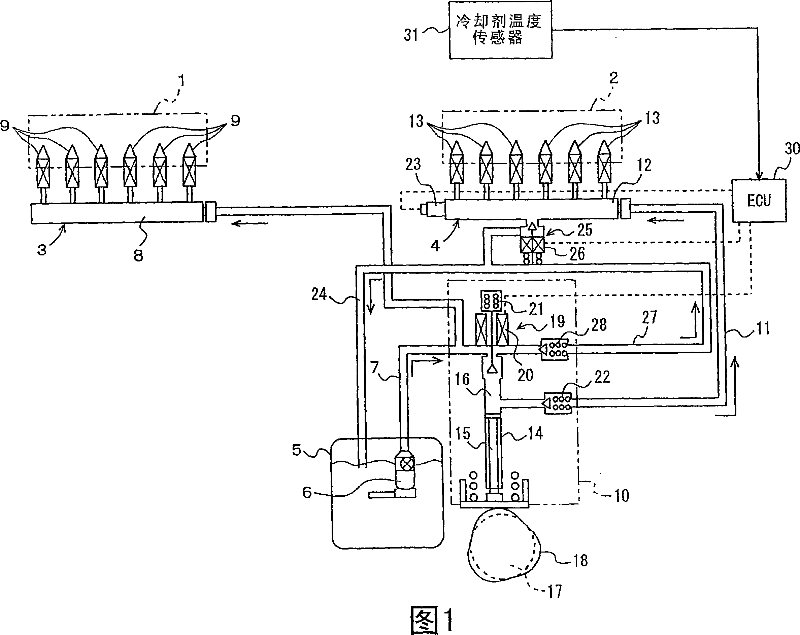
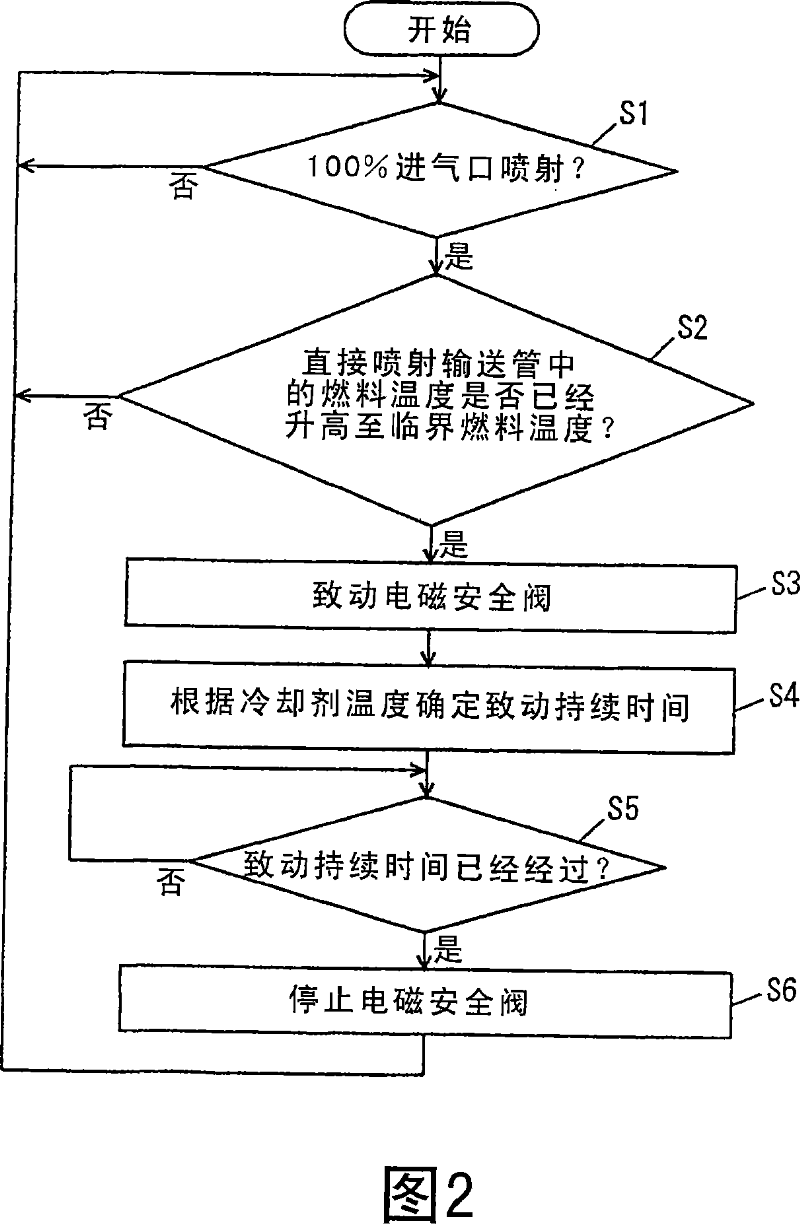
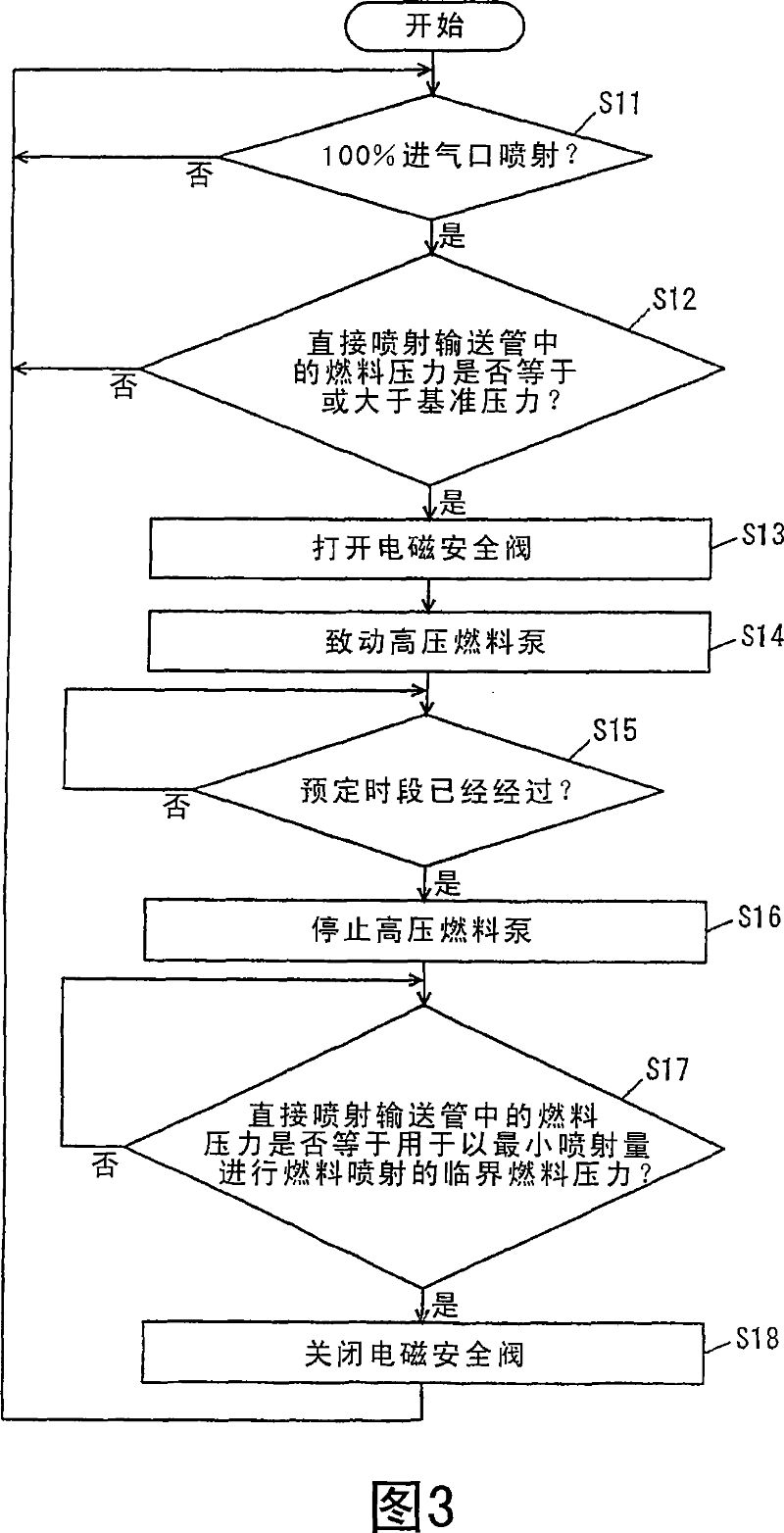
InactiveUS7263973B2Suppress mutationImprove the state of combustionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineHigh pressure
The engine ECU executes a program including the step of detecting an engine coolant temperature, the step of detecting an engine speed and an engine load, the step of estimating a temperature at a tip end of an in-cylinder injector based on the engine coolant temperature, the engine speed and the engine load, and, when the temperature at the tip end is greater than a guaranteed temperature, the step of calculating a drive duty of a high-pressure fuel pump that ensures a decrease of the temperature at the tip end of the in-cylinder injector to the guaranteed temperature, and the step of controlling the high-pressure fuel pump using the drive duty.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Exhaust gas purifying apparatus for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20060218899A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineExhaust fumes
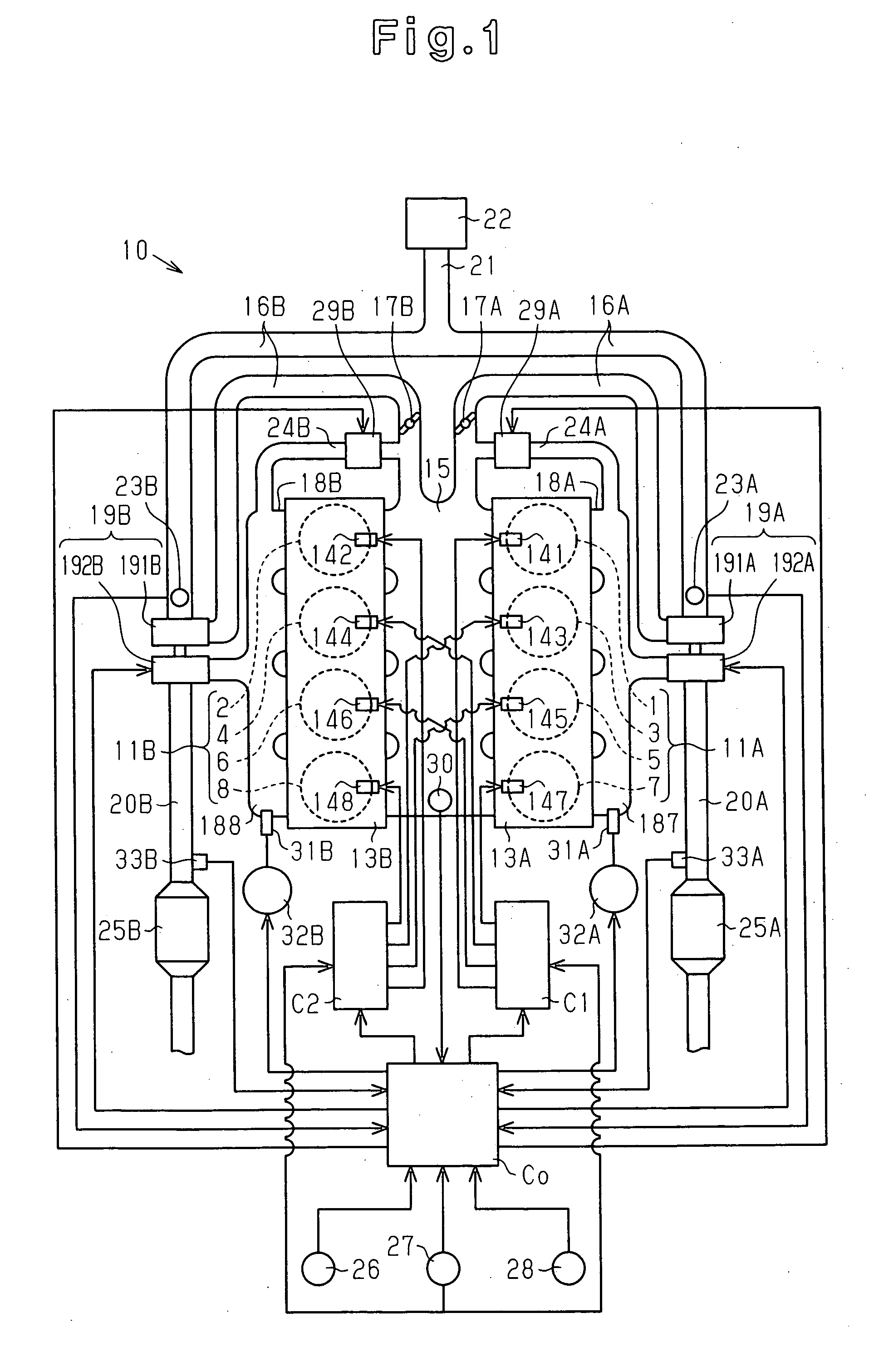
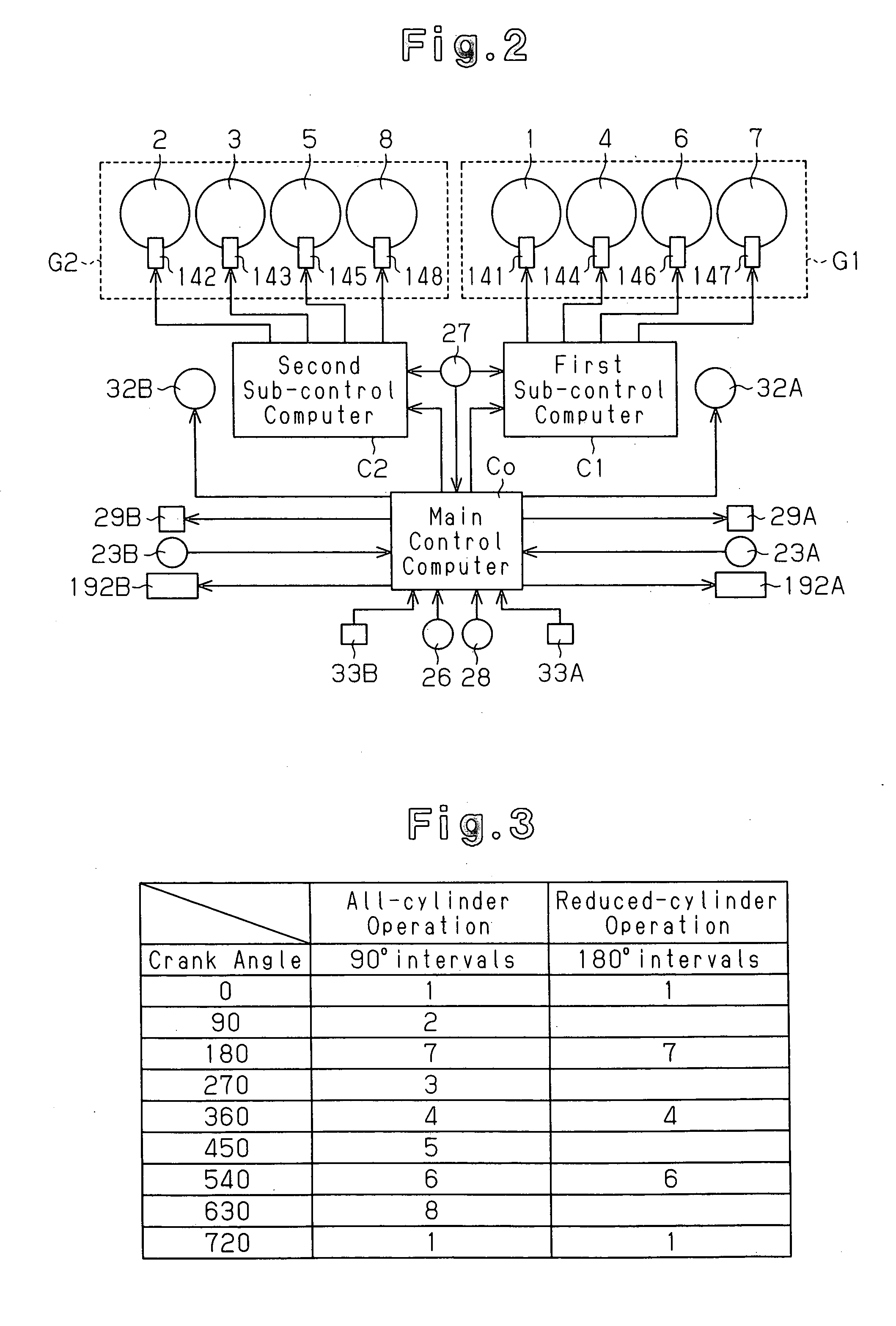
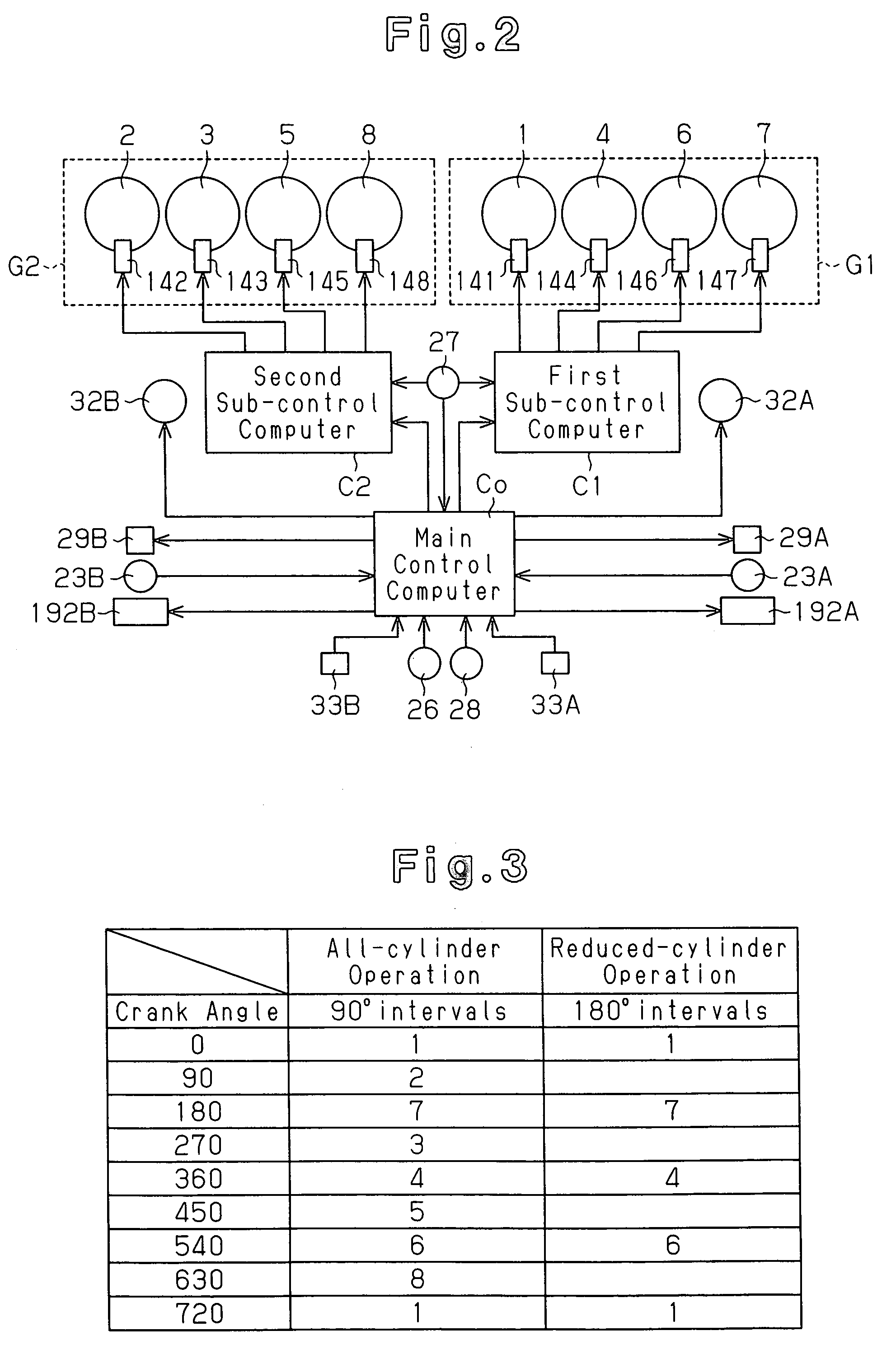
A main control computer commands a second sub-control computer to perform a reduced-cylinder operation when the coolant temperature detected by a coolant temperature sensor is greater than or equal to a reference temperature, and the exhaust temperature detected by a temperature sensor is less than a reference exhaust temperature and is within a reduced-cylinder operation allowable range in which a combination of the engine speed and the engine load is set in advance. The second sub-control computer deactivates a second cylinder group based on a command of the reduced-cylinder operation. The main control computer commands a first sub-control computer and the second sub-control computer to perform an all-cylinder operation when the coolant temperature detected by the coolant temperature sensor is less than the reference temperature, and the exhaust temperature detected by the temperature sensor is greater than or equal to the reference exhaust temperature or is out of the reduced-cylinder operation allowable range in which a combination of the engine speed and the engine load is set in advance.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP +1
Control device for vehicle
ActiveUS20120074238A1High calorific valueEfficient and adequate supplyLiquid coolingAir-treating devicesCoolant temperatureHeater core
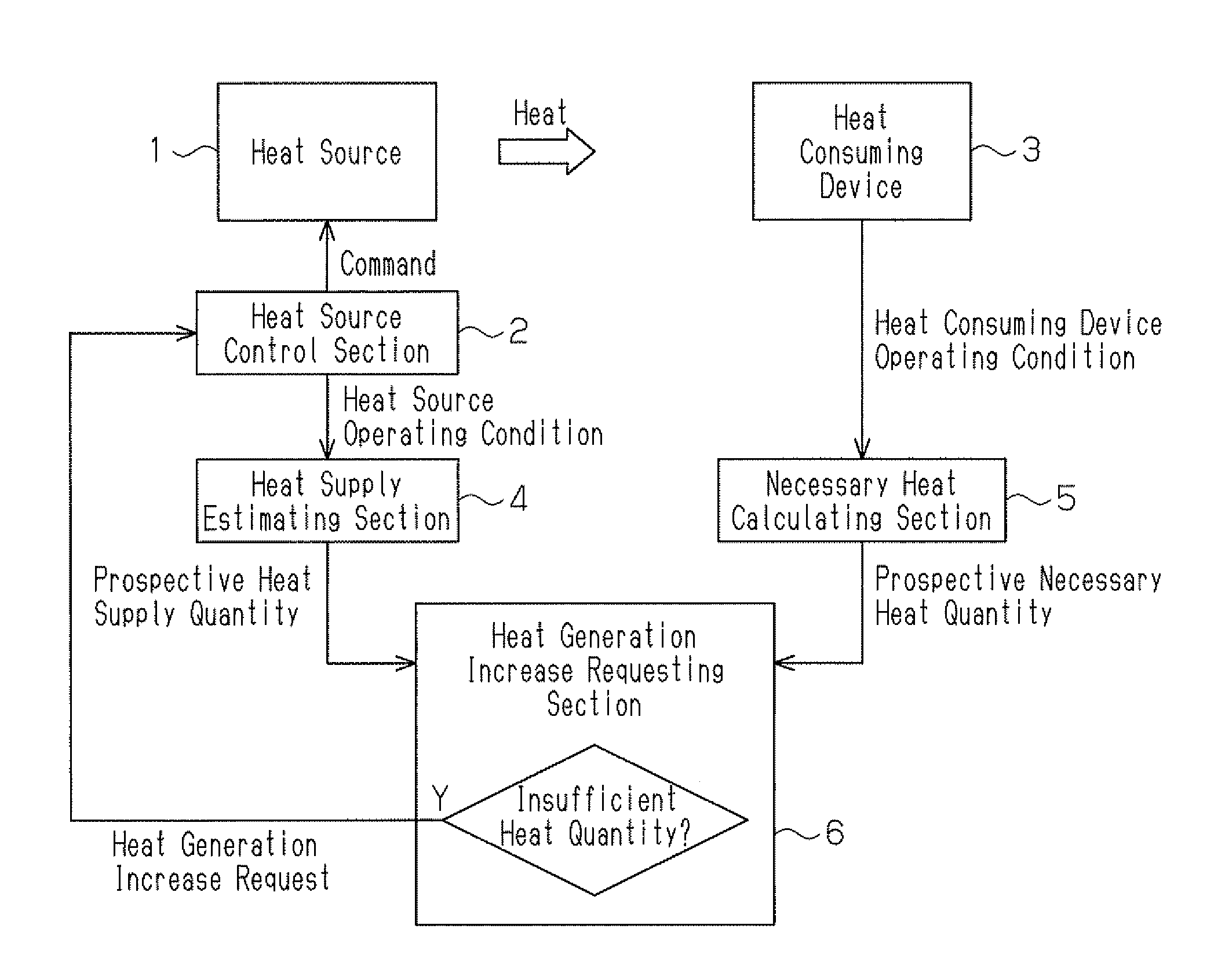
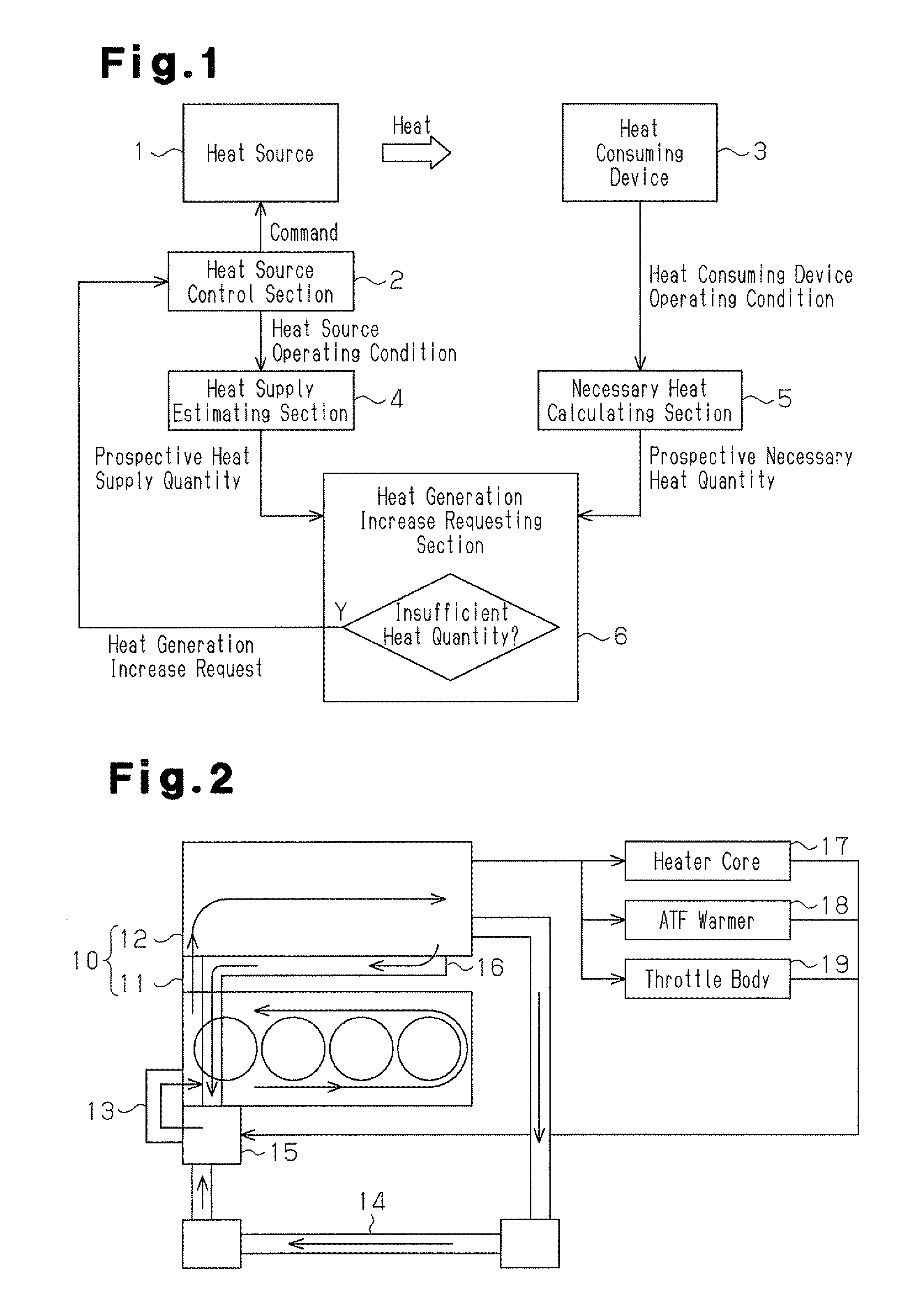
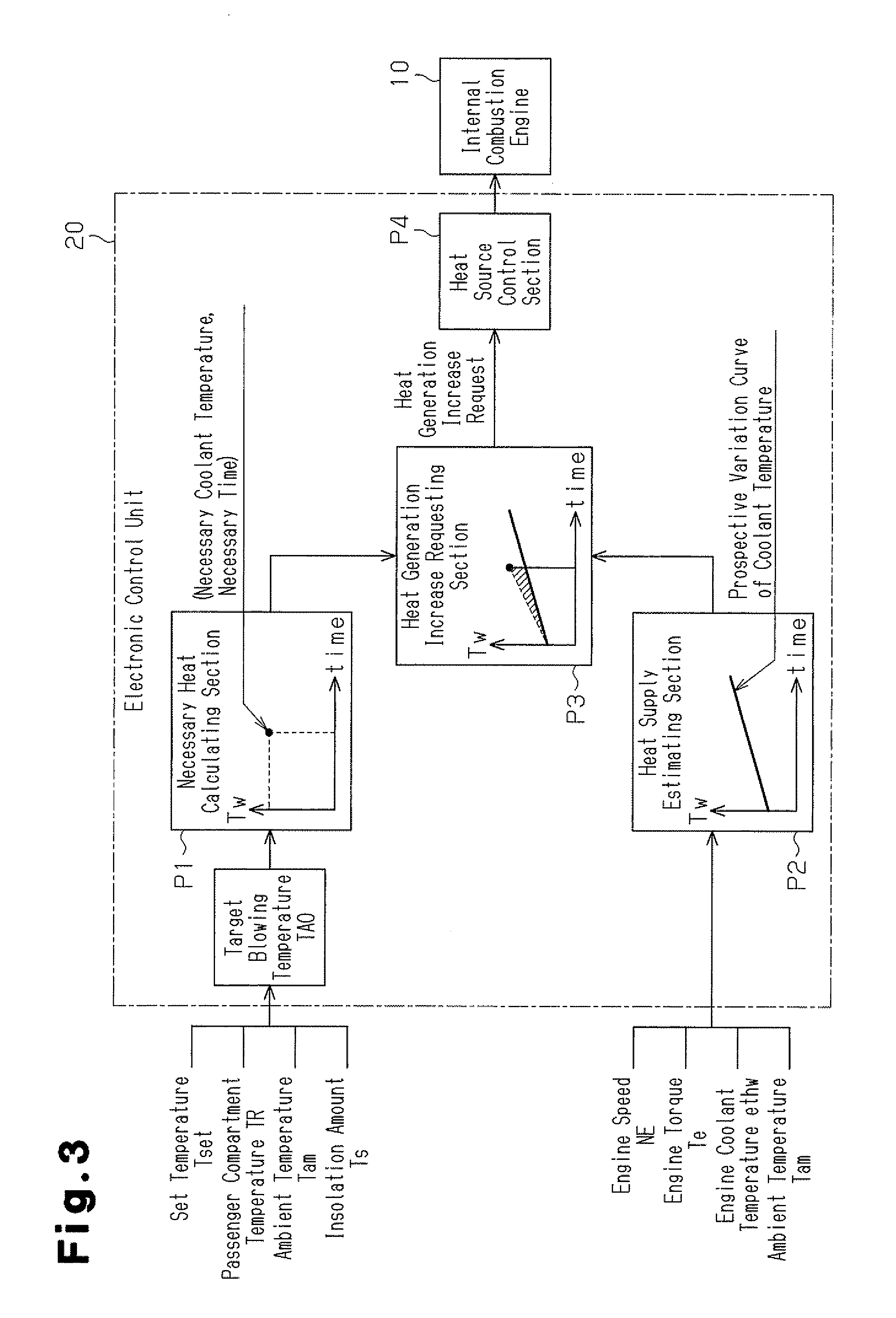
By employing a heat source control section that controls the operating state of an internal combustion engine mounted in a vehicle, a necessary heat calculating section that calculates the engine coolant temperature needed by a heater core, which consumes the heat supplied from the engine through engine coolant water, and the time at which this engine coolant temperature becomes necessary, a heat supply estimating section that estimates engine coolant temperature at the aforementioned time in a case in which the engine is operated continuously in the current operating state, and a heat generation increase requesting section that requests the heat source control section to increase heat generation quantity of the engine when the engine coolant temperature estimated by the heat supply estimating section is less than the engine coolant temperature calculated by the necessary heat calculating section the heat necessary for the heater core is supplied more efficiently and adequately.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
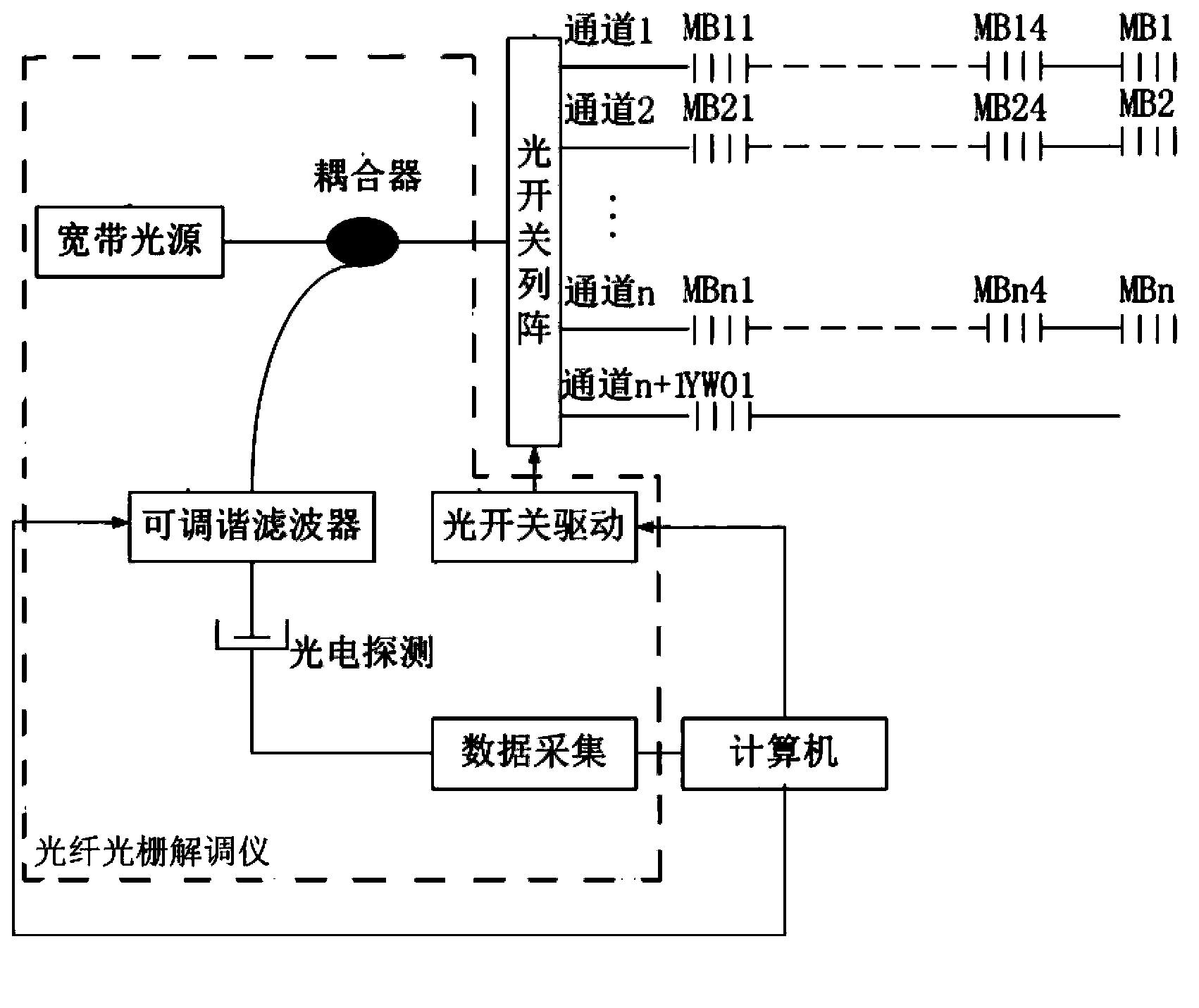
Inner surface stress and temperature monitoring method of internal combustion engine main bearing based on fiber bragg grating
ActiveCN103411550ASimultaneously monitor temperatureSimultaneous monitoring of strain changesThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFiberGrating
The invention provides an inner surface stress and temperature monitoring method of an internal combustion engine main bearing based on a fiber bragg grating. Fiber bragg grating strain sensors and fiber bragg grating temperature sensors for temperature compensation are respectively arranged on an internal surface of a to-be-tested main bearing so as to obtain strain changes of a bearing working surface; the fiber bragg grating strain sensors are arranged at all directions of the inner surface of a bearing so as to obtain the strain changes of the bearing at each direction; an engine oil temperature sensor is arranged in a waste engine oil pipe of the internal combustion engine so as to obtain engine oil temperature data; a fiber Bragg grating demodulation instrument is used to obtain center wavelength changes of the engine oil temperature sensor, and to convert the center wavelength changes into electrical signals; and engine oil temperature changes when the internal combustion engine works can be calculated. With the use of characteristics that the fiber bragg grating can simultaneously measure the strain and temperature and is small-sized and one-line-multi-point, the inner surface stress and temperature monitoring method of the internal combustion engine main bearing based on the fiber bragg grating can simultaneously monitor the temperature and strain distribution of the main bearing working when the internal combustion engine works, so as to provide accurate data to support optimization of the structural design of the internal combustion engine main bearing.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Control device of internal combustion engine
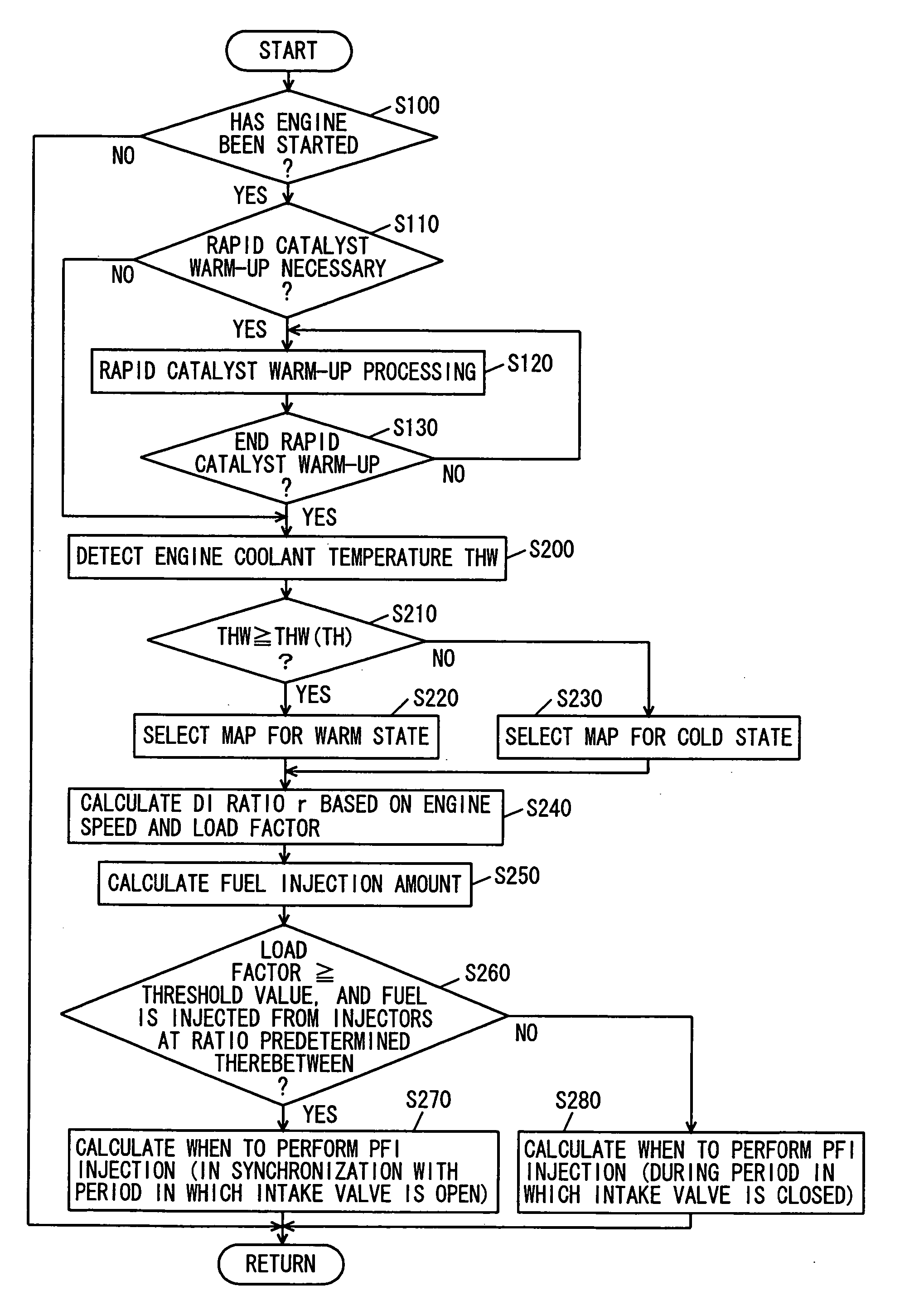
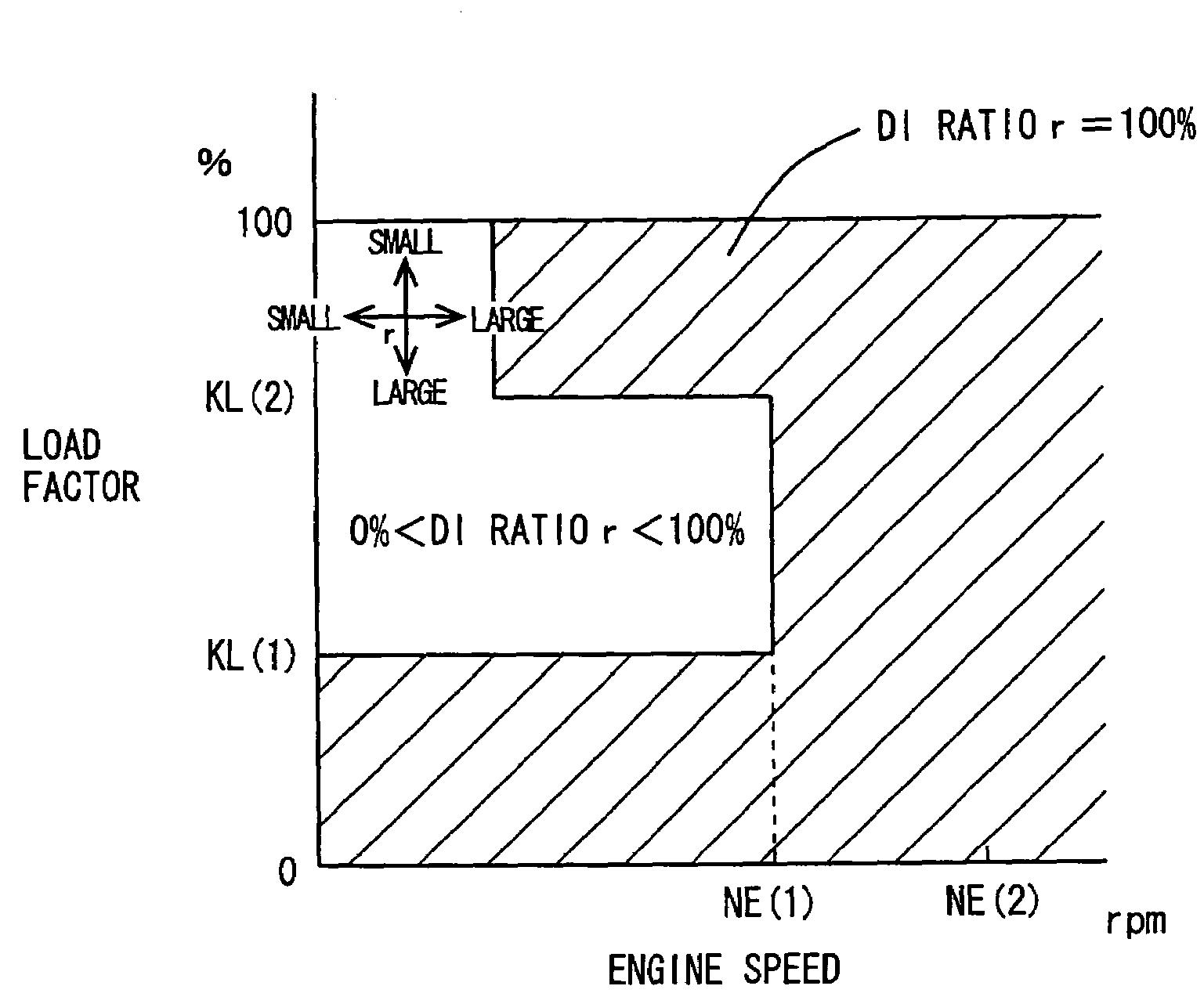
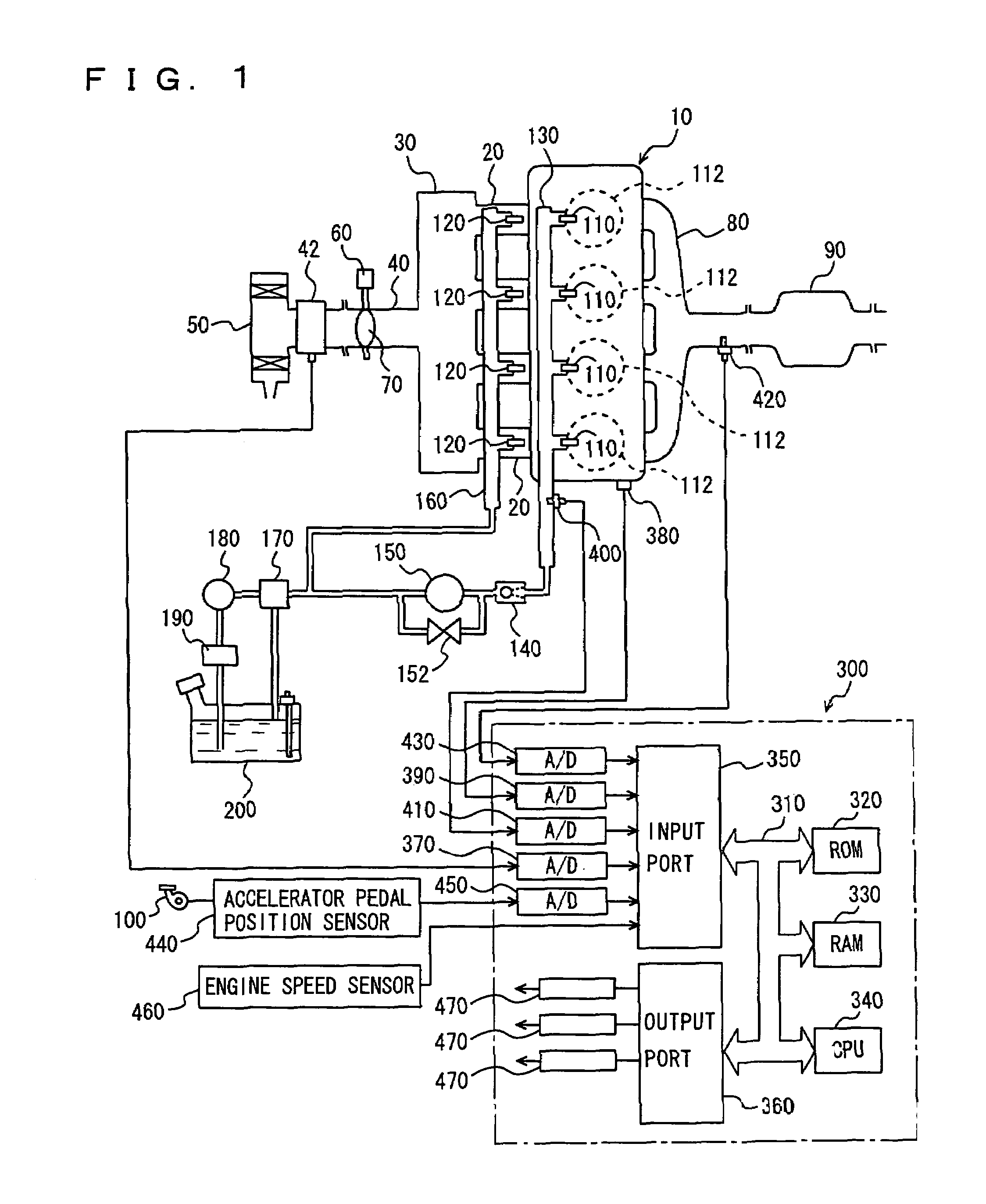
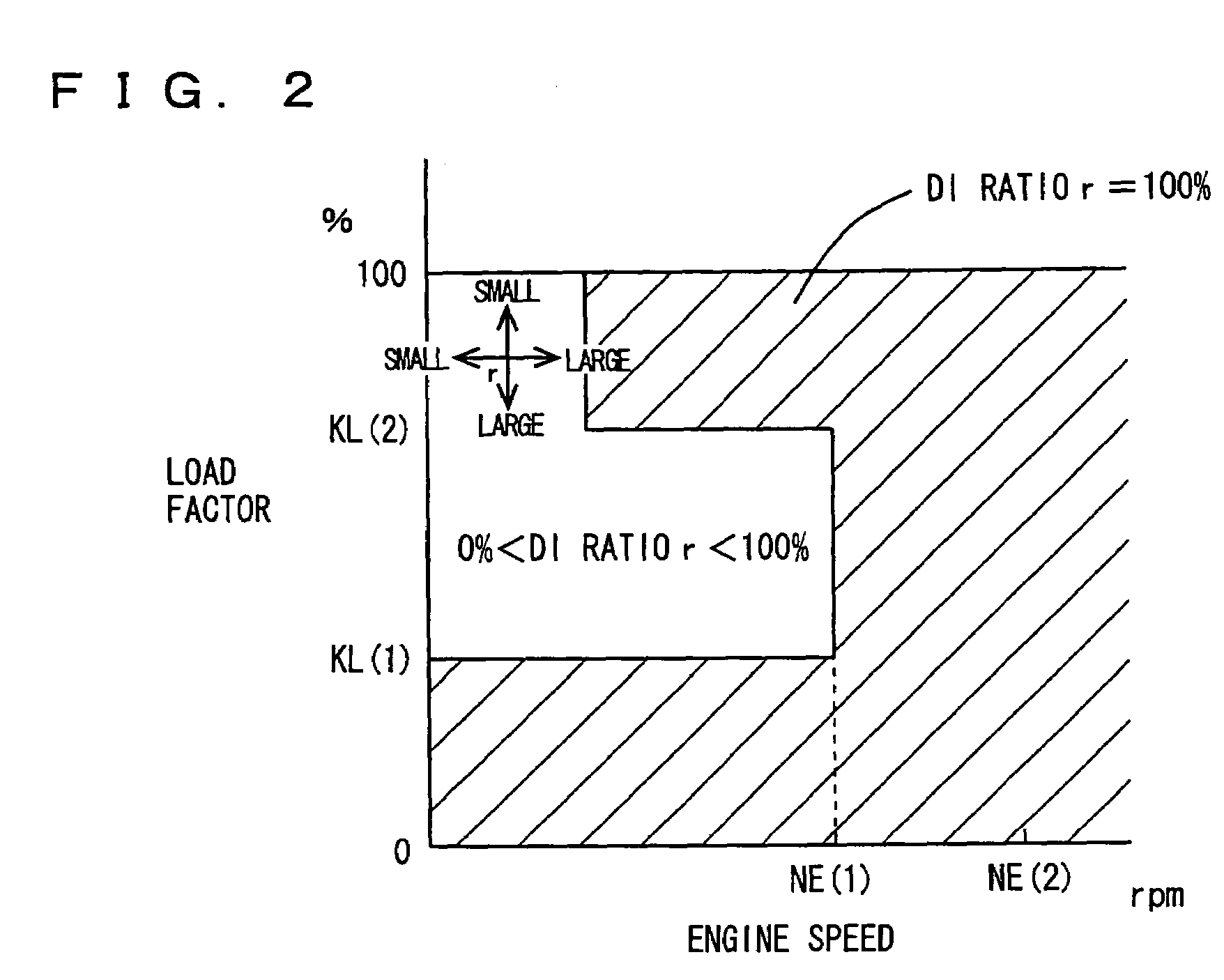
InactiveUS20060225703A1Improve homogeneityDiffuse fullyValve arrangementsElectrical controlInlet valveCoolant temperature
An engine ECU executes a program including the steps of: selecting a map for a warm state or a map for a cold state based on an engine coolant temperature after an engine is started and rapid catalyst warm-up ends; calculating DI ratio r; calculating when to inject fuel from an intake manifold injector as time in synchronization with air intake if a load factor is equal to or greater than a threshold value and fuel is injected from injectors at a ratio predetermined therebetween; and otherwise calculating when to inject fuel from the intake manifold injector as during a period in which an intake valve is closed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control device of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7198031B2Improve homogeneityValve arrangementsElectrical controlExternal combustion engineInlet valve
An engine ECU executes a program including the steps of: selecting a map for a warm state or a map for a cold state based on an engine coolant temperature after an engine is started and rapid catalyst warm-up ends; calculating DI ratio r; calculating when to inject fuel from an intake manifold injector as time in synchronization with air intake if a load factor is equal to or greater than a threshold value and fuel is injected from injectors at a ratio predetermined therebetween; and otherwise calculating when to inject fuel from the intake manifold injector as during a period in which an intake valve is closed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Engine electric control auxiliary cooling system freeing from engine rotational speed influence
InactiveCN102230417AReduce volumeSmall footprintAir-treating devicesCoolant flow controlLiquid temperatureOperation mode
The invention discloses an engine electric control auxiliary cooling system freeing from an engine rotational speed influence. The engine electric control auxiliary cooling system comprises an electronic water pump which is sequentially connected in series with an engine, a thermolator, a heat radiator and an air heating core and is connected in parallel with a mechanical water pump; the outlet of the electronic water pump and the inlet of the mechanical water pump are respectively provided with a one-way valve; the electronic water pump is provided with an electronic water pump controller; the signal input end of the electronic water pump controller is respectively connected with an engine cooling liquid temperature sensor on the water outlet of the engine and an engine controller; and the signal output end of the electronic water pump controller is connected with the electronic water pump. According to the engine electronic control auxiliary cooling system provided by the invention, the power requirement on the mechanical water pump from the cooling system is reduced, thereby the volume and layout requirements of the mechanical water pump are reduced; the application of the engine cooling system provided by the invention adopts an operation mode of mainly relying on the mechanical water pump supplemented by the electronic water pump, and has the advantages of convenience for operation, high reliability, low cost, good applicability and easiness for popularization.
Owner:CATARC TIANJIN AUTOMOTIVE ENG RES INST CO LTD
Fuel supply apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveCN101040111ATemperature monitoringSimple structureElectrical controlFuel injection apparatusEngineeringHigh pressure
The engine ECU executes a program including the step (S100) of detecting an engine coolant temperature, the step (S110) of detecting an engine speed and an engine load, the step (S120) of estimating a temperature at a tip end of an in-cylinder injector based on the engine coolant temperature, the engine speed and the engine load, and, when the temperature at the tip end is greater than a guaranteed temperature (YES in S130), the step (S140) of calculating a drive duty of a high-pressure fuel pump that ensures a decrease of the temperature at the tip end of the in-cylinder injector to the guaranteed temperature, and the step (S160) of controlling the high-pressure fuel pump using the drive duty.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Actuator control apparatus
InactiveUS20080289605A1Improve diagnostic accuracyMinimize the possibilityValve arrangementsElectrical controlExternal combustion engineCoolant temperature
An actuator control apparatus is provided which has: an actuator provided in an internal combustion engine at a position distant from combustion chambers to change an engine state amount; a sensor that detects the actual operation position of the actuator; a controller that controls the actuator to bring the actual operation position to a target operation position set based on the engine operation state; a diagnosis portion that diagnoses the actuator to be in an abnormal state when the deviation of the actual operation position from the target operation position has been larger than a reference amount for a reference time; and a setting portion that sets, upon the diagnosis by the diagnosis portion, the reference time such that the lower the engine coolant temperature, the longer the reference time, and the lower the ambient temperature, the longer the reference time corresponding to the engine coolant temperature.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
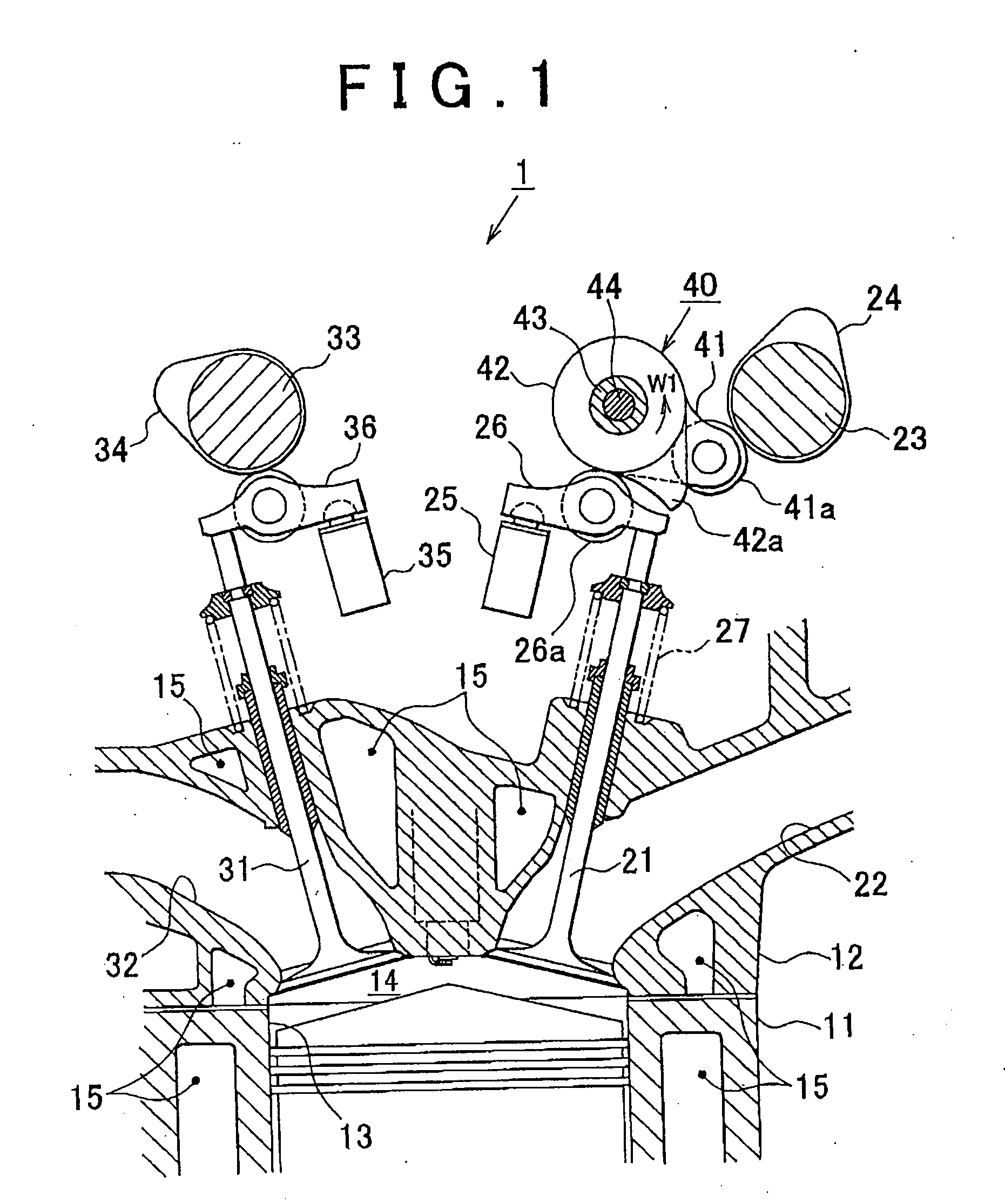
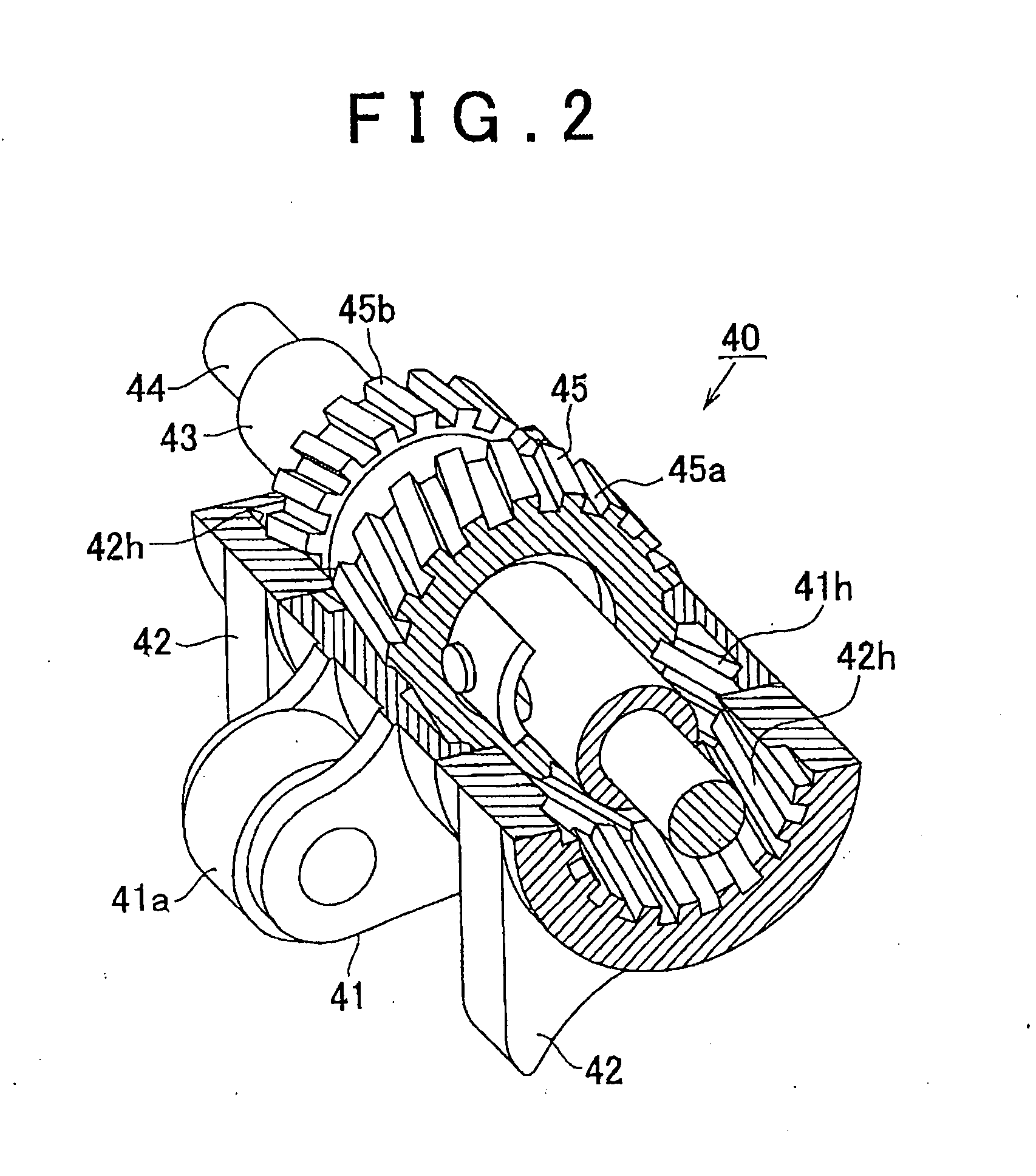
Valve timing control for marine engine
InactiveUS6957635B2Accurately follow commandLow viscosityCamsValve arrangementsExhaust valveCombustion chamber
An engine for a marine drive has a combustion chamber. An engine body of the engine defines intake and exhaust ports communicating with the combustion chamber. An air induction system communicates with the combustion chamber through intake ports. An exhaust system communicates with the combustion chamber through the exhaust ports. Intake valves move between an opening position and a closing position of the intake ports. Exhaust valves move between an opening position and a closing position of the exhaust ports. Camshafts actuate the intake and the exhaust valves. A hydraulic VVT mechanism changes an actuating timing of the camshaft at which the camshaft actuates the intake valves or the exhaust valves. An ECU controls the VVT mechanism based upon a control characteristic. A temperature sensor, such as an oil temperature sensor, a water temperature sensor and an engine body temperature sensor, senses a temperature of oil of the VVT or a temperature relating to the temperature of the oil and sends a temperature signal to the ECU. The ECU adjusts the control characteristic when the temperature is lower than a preset temperature.
Owner:YAMAHA MARINE KK
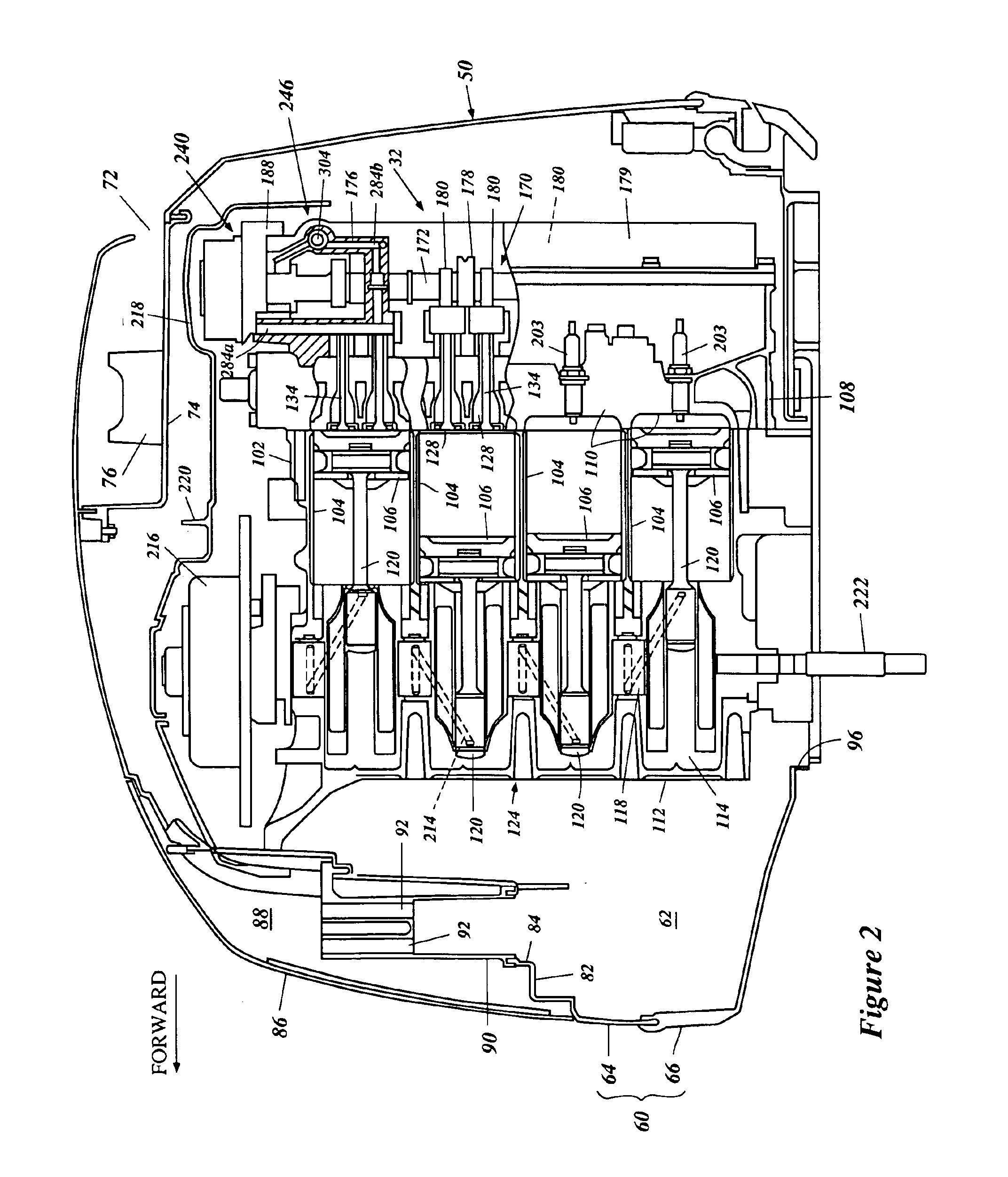
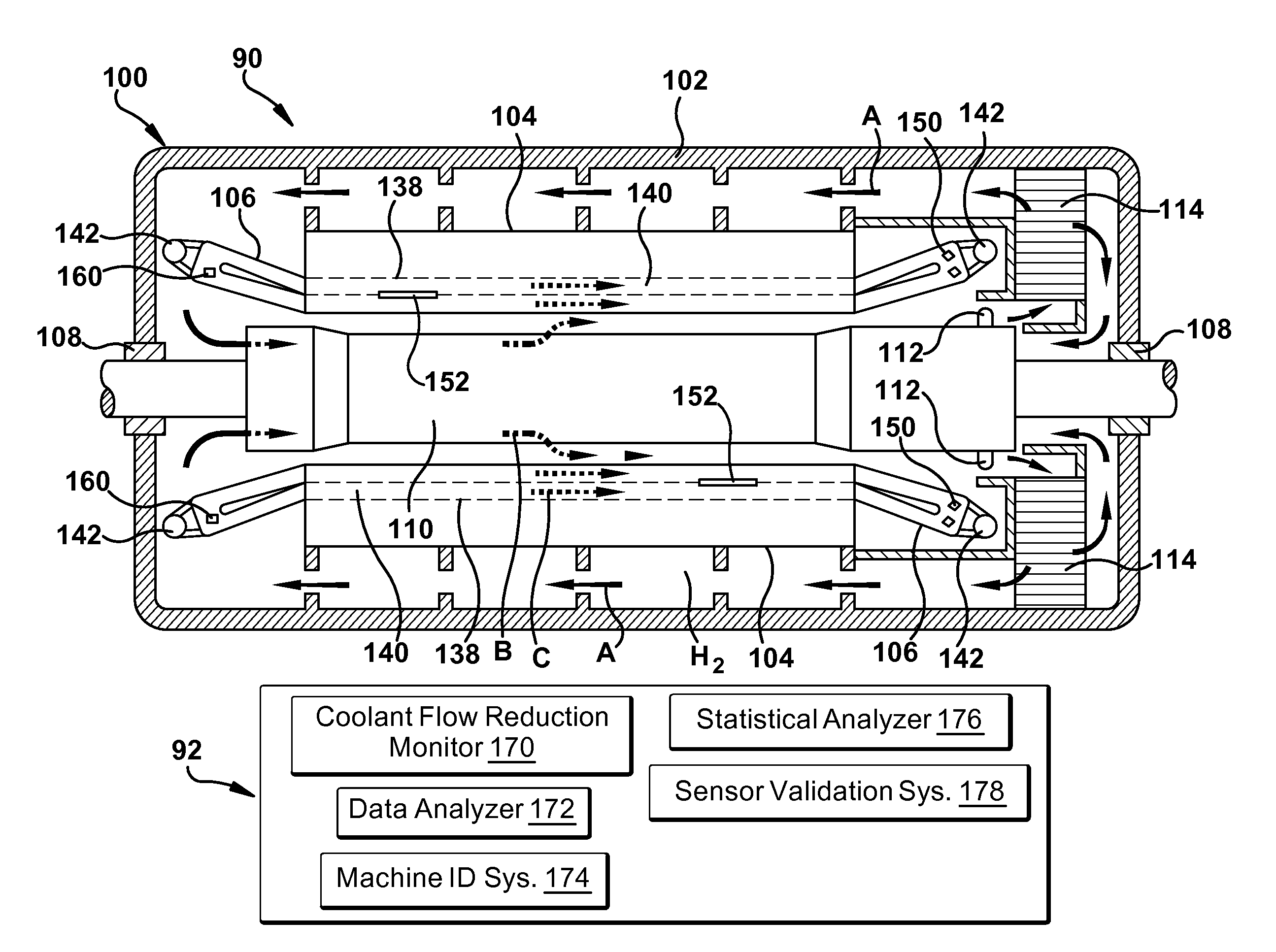
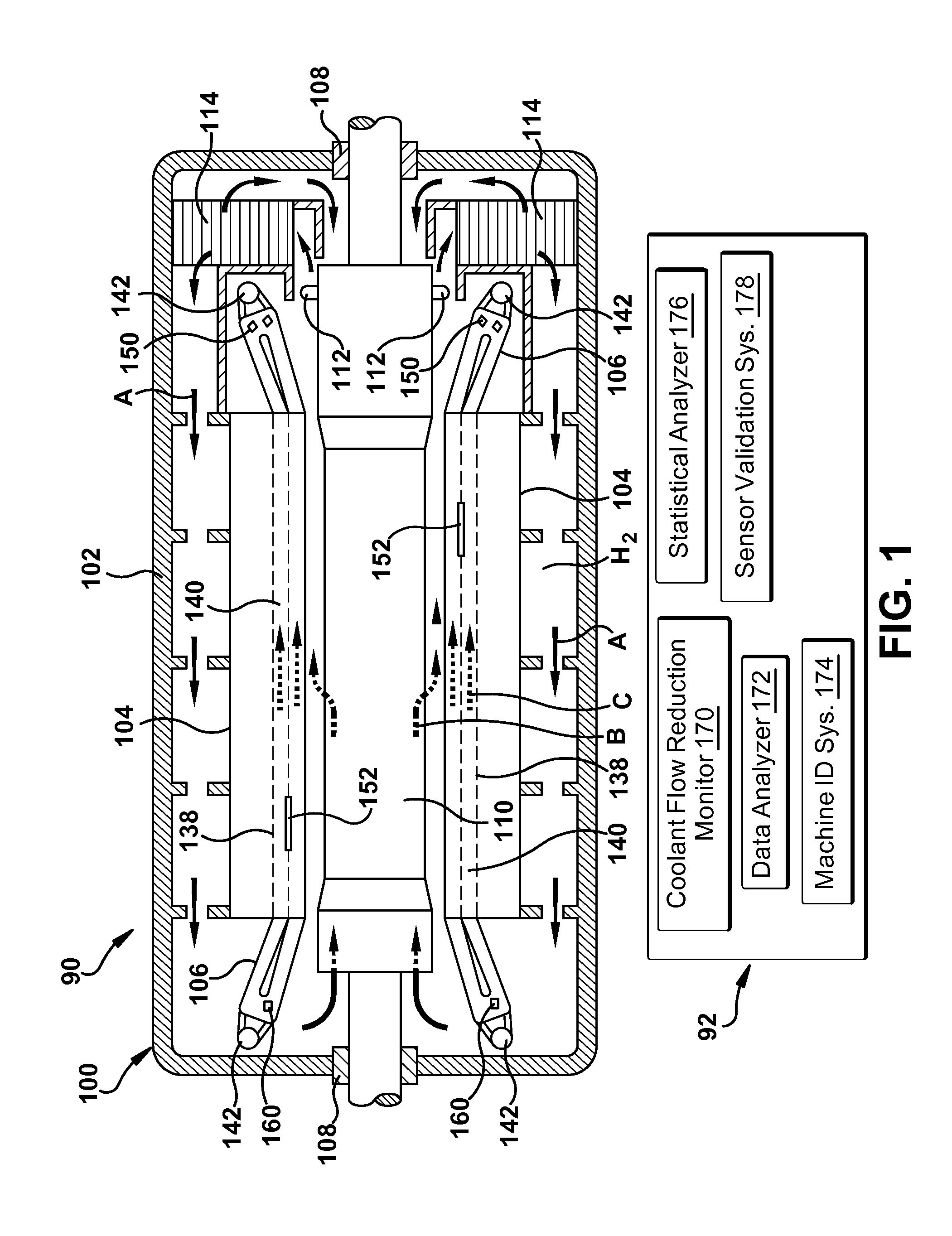
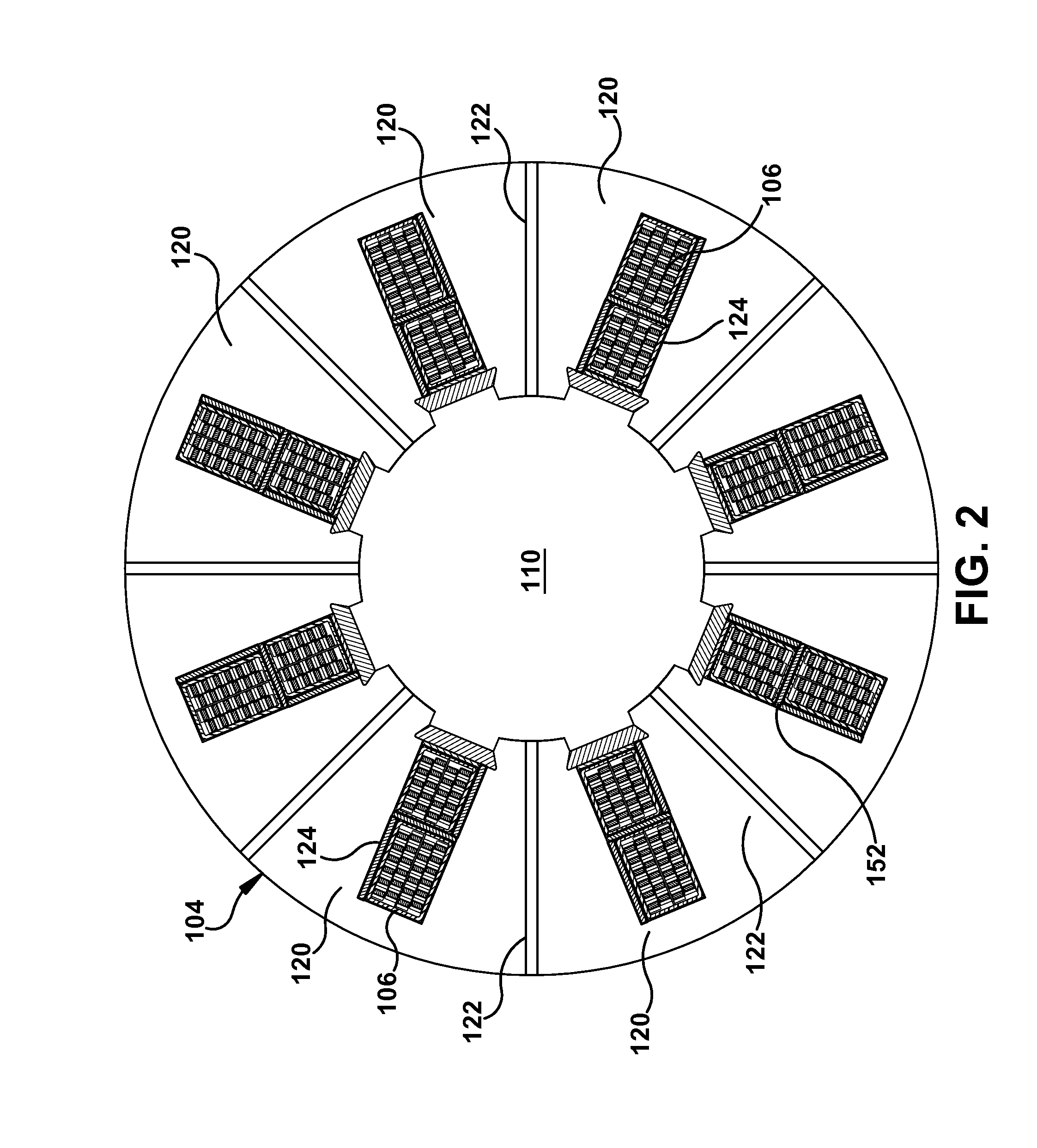
Stator coil coolant flow reduction monitoring
A coolant flow reduction monitoring system for a rotary electric machine having stator coils within a plurality of slots of a stator thereof is provided. The stator coils are cooled by a coolant flowing in a plurality of passages provided in the stator coils. The system includes an outlet temperature sensor for measuring a coolant outlet temperature of the coolant in an outlet of at least one of the plurality of passages, a slot temperature sensor for measuring a temperature in at least one slot at a location along a length of each slot and outside of the stator coils, and an inlet temperature sensor for measuring a coolant inlet temperature of the coolant. A coolant flow reduction monitor generates an alarm indicating a coolant flow reduction based on the at least one coolant outlet temperature, the at least one slot temperature and the coolant inlet temperature.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
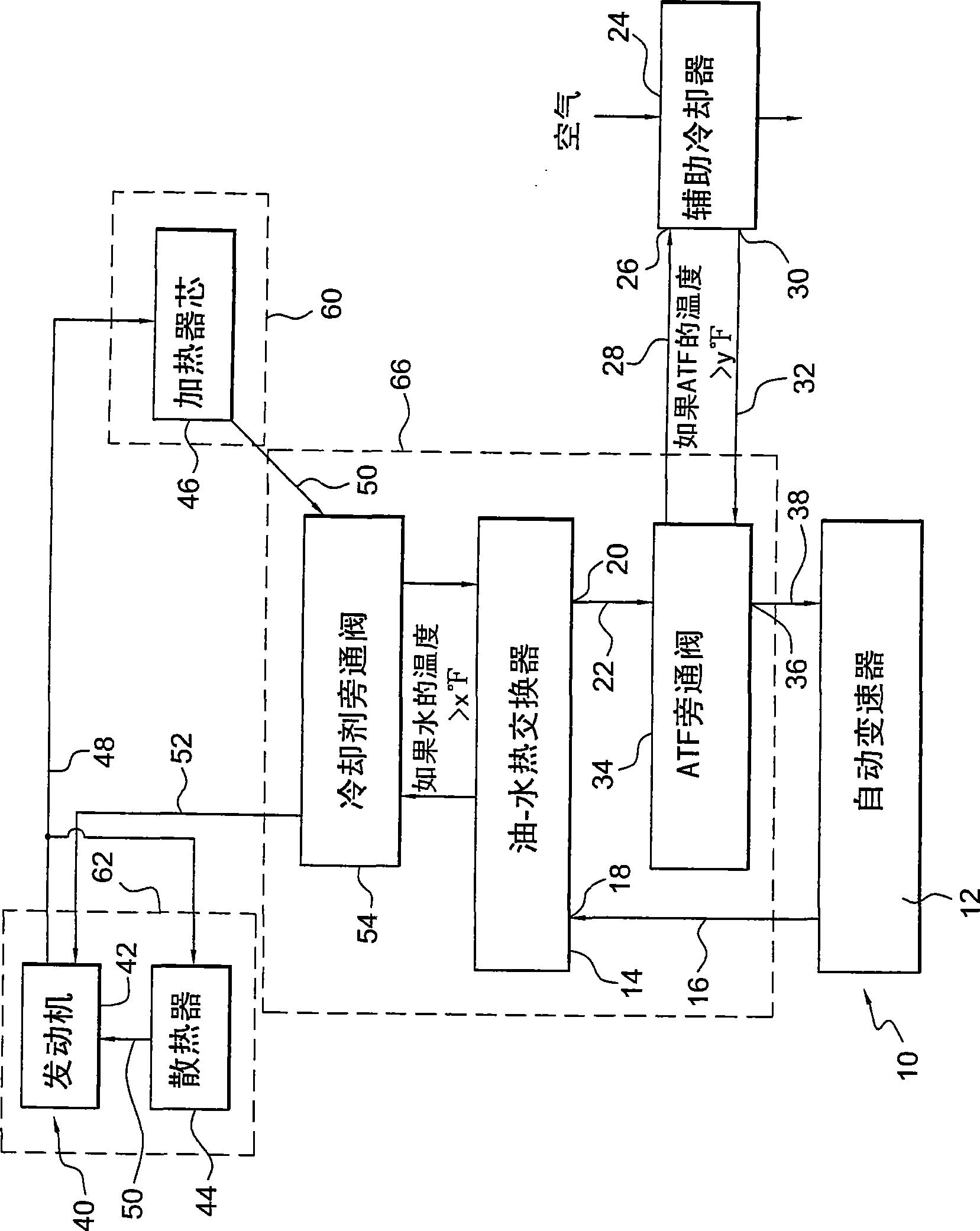
Regulating transmission fluid and engine coolant temperatures in a motor vehicle
InactiveCN101417608AAllowed to enterLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlEngineeringCoolant temperature
A system for controlling the temperature of a transmission fluid includes a first heat exchanger communicating with a source of engine coolant for transferring heat between the engine coolant and the transmission fluid and including a first outlet through which transmission fluid exits the first heat exchanger, a second heat exchanger through which air may flow for transferring heat between the transmission fluid and the air and including a second inlet through which transmission fluid enters the second heat exchanger, and second outlet through which transmission fluid exits the second heat exchanger, and a first bypass valve for alternately opening and closing the second inlet and the second outlet when a temperature of transmission fluid exiting the first outlet is greater than a first reference temperature, and for bypassing the second heat exchanger when the temperature of transmission fluid exiting the first outlet is less than the second reference temperature.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
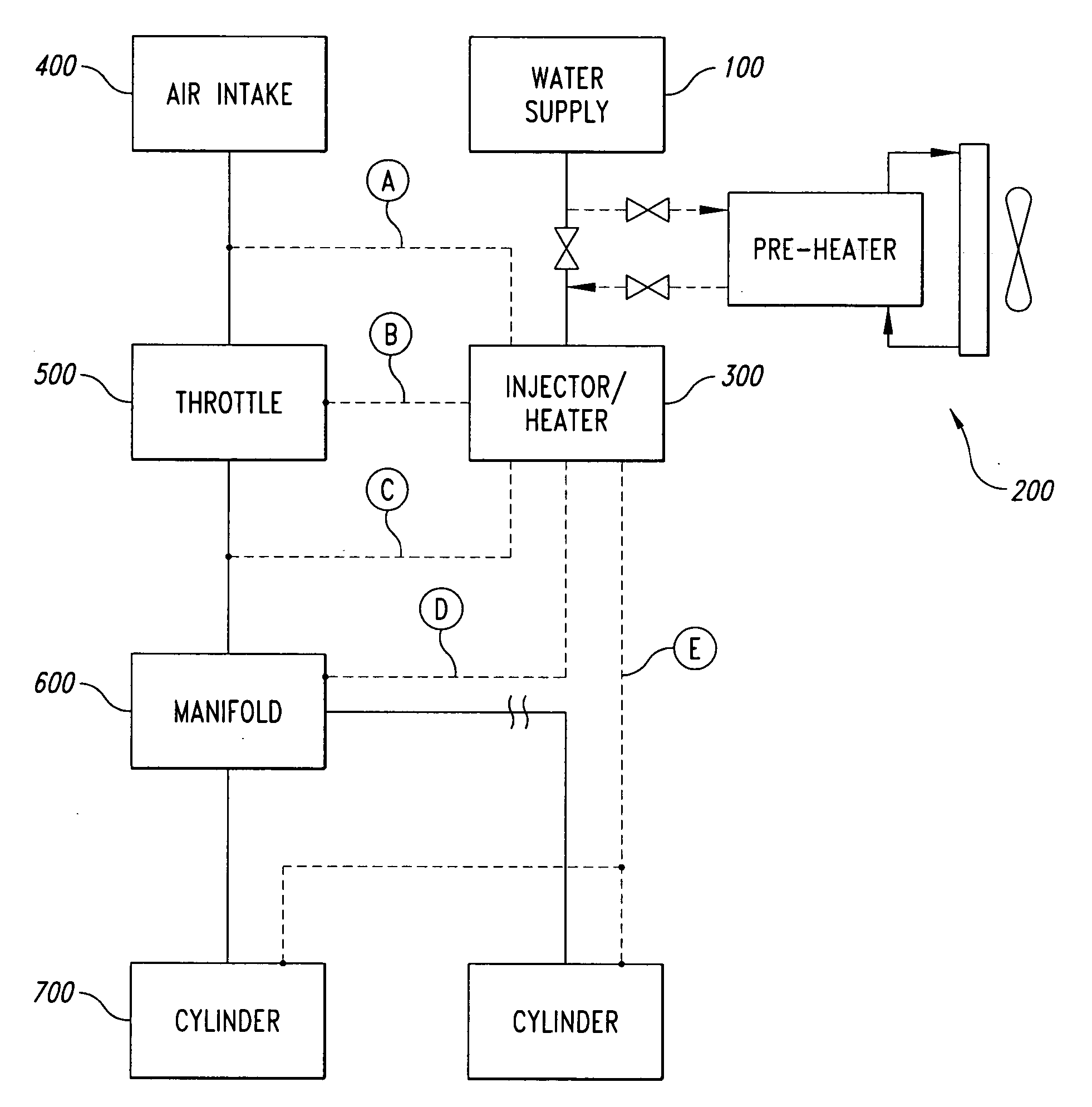
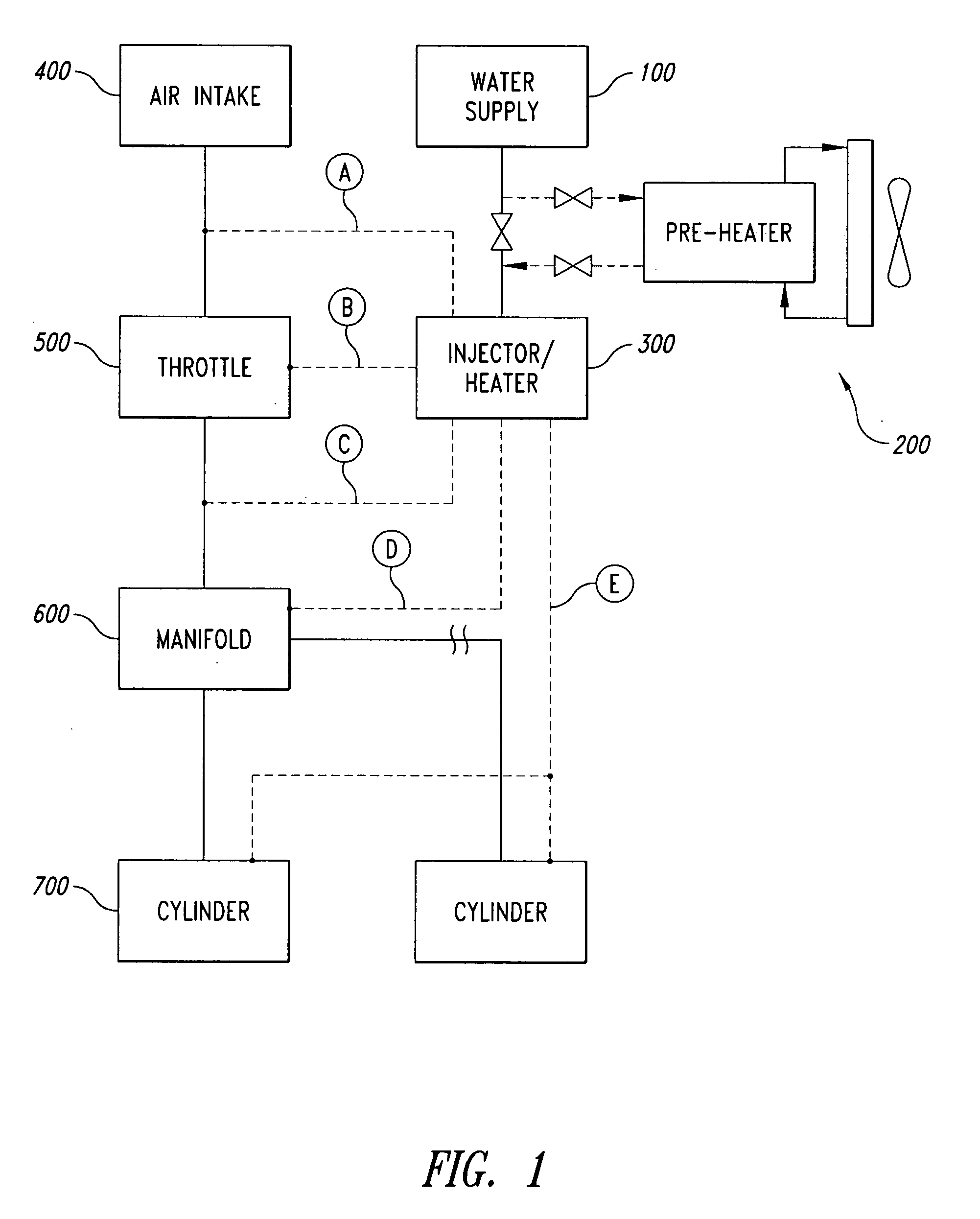
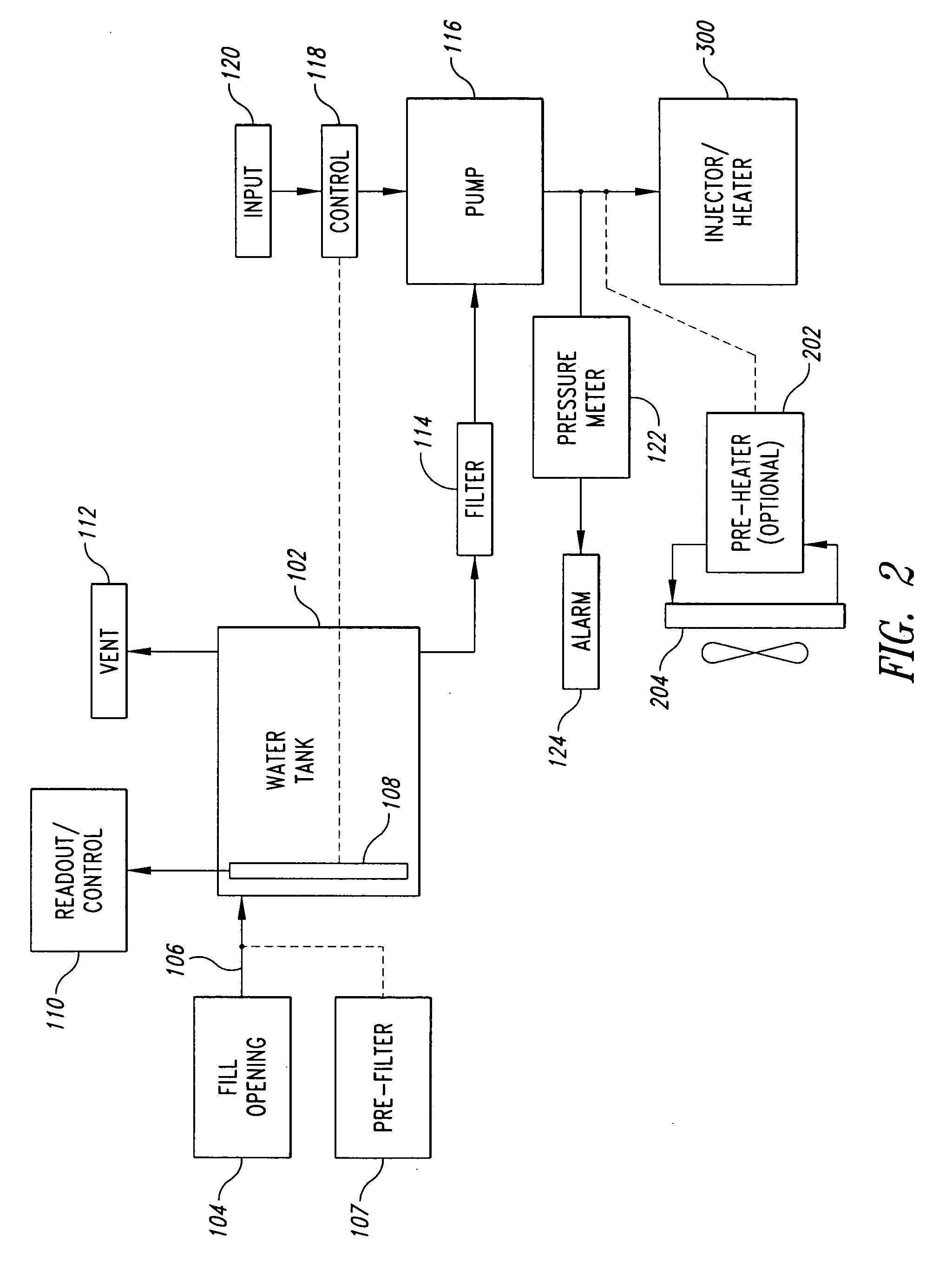
Devices, systems and methods for controlling introduction of additives into an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060249102A1Internal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExternal combustion engineControl signal
A water injection control system includes a control unit adapted to receive one or more of a plurality of sensor signals from sensors provided as standard equipment in a vehicle, and to provide one or more control signals configured to control the operation of a water injection system associated with an engine of the vehicle. The received sensor signals may include signals from sensors such as an O2 sensor, an engine coolant temperature sensor, a mass air flow sensor, a manifold absolute pressure sensor, a crankshaft position sensor, a vehicle speed sensor, an intake air temperature sensor, and a throttle position sensor. The control signals provided by the controller may include signals for controlling functions such as water injector pulse rate and pulse width, water pump operation, water heater power, dashboard indicators, and PCU O2 sensor input.
Owner:S I S POWER
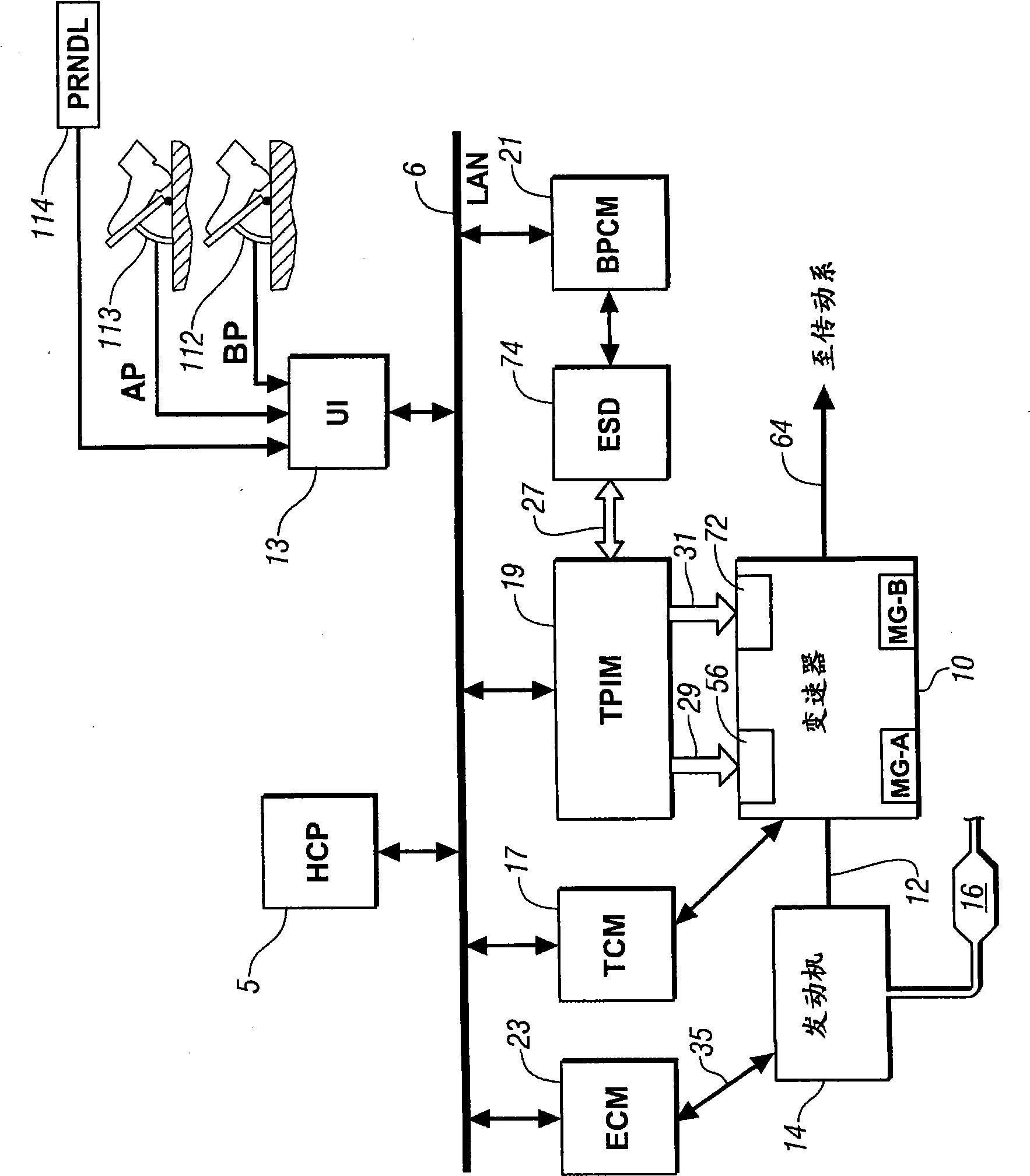
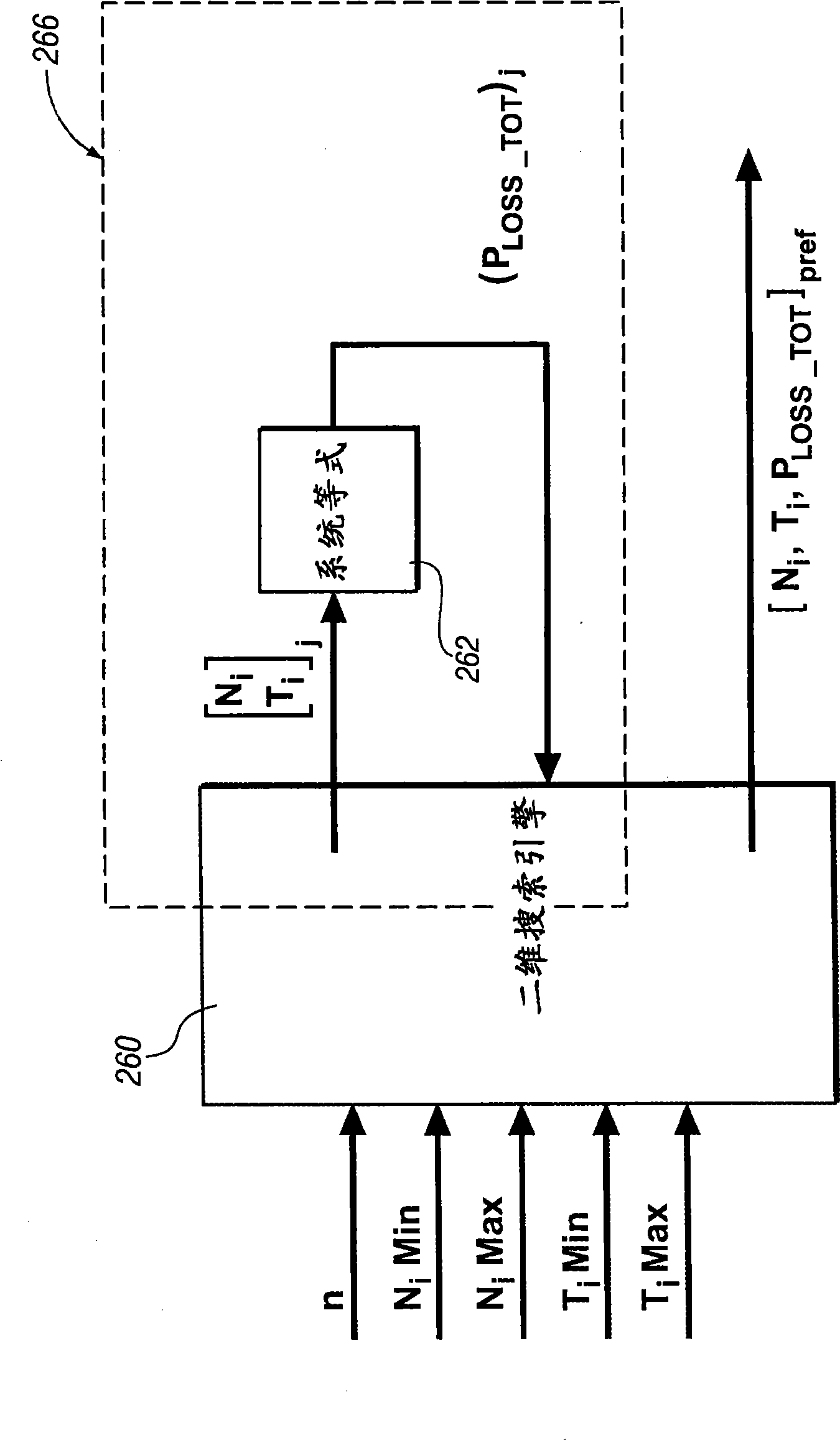
Method and apparatus to control engine temperature for a hybrid powertrain
ActiveCN101519070AElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCoolant temperatureEngine power
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus to control engine temperature for a hybrid powertrain. An internal combustion engine is connected to a transmission to transmit tractive power to a driveline. Engine coolant temperature is determined, and power output of the engine is adjusted based upon the coolant temperature and preferred coolant temperature range. The transmission is controlled to transmit tractive power to the driveline to meet an operator torque request based upon the adjusted power output of the engine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
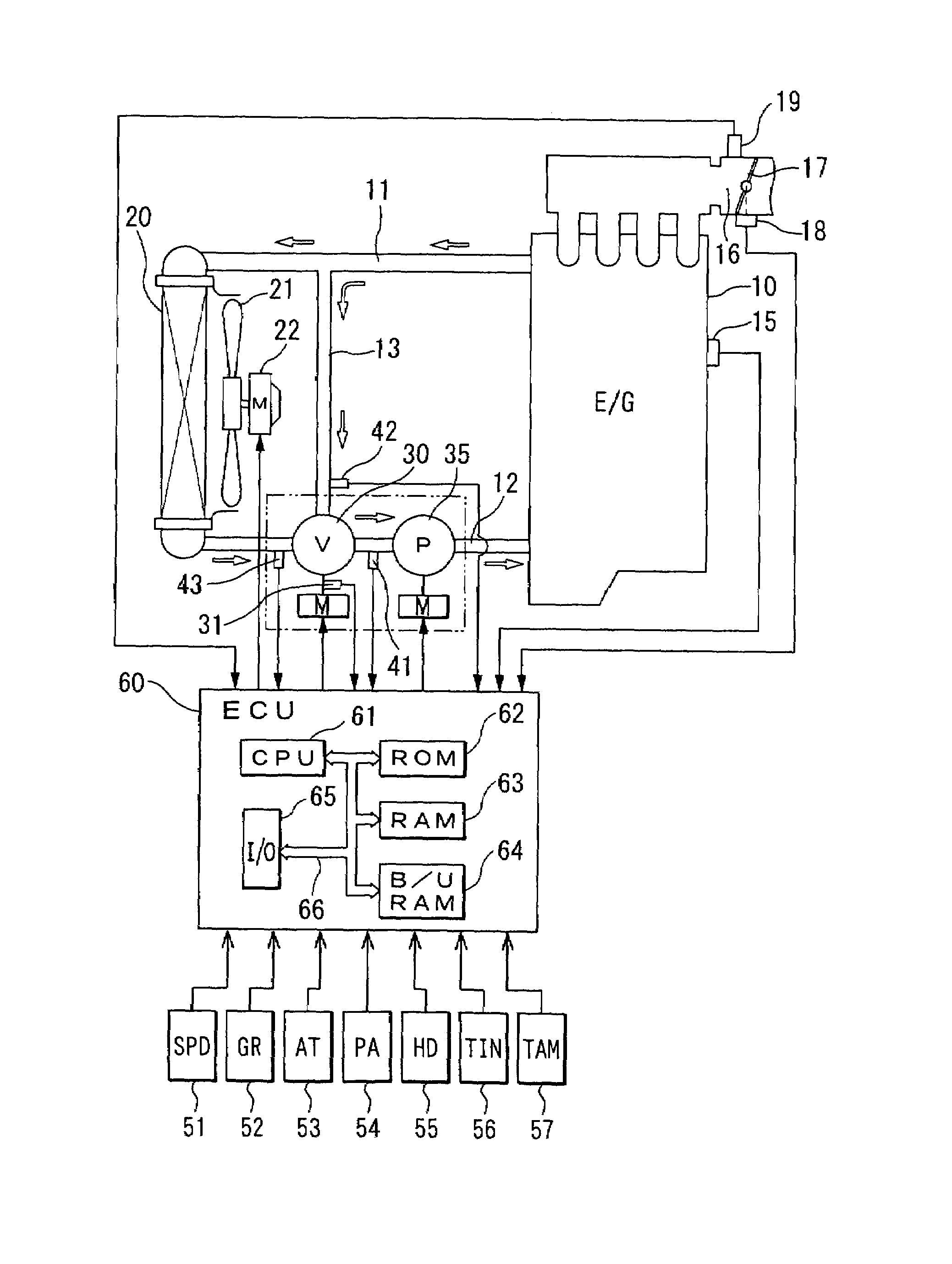
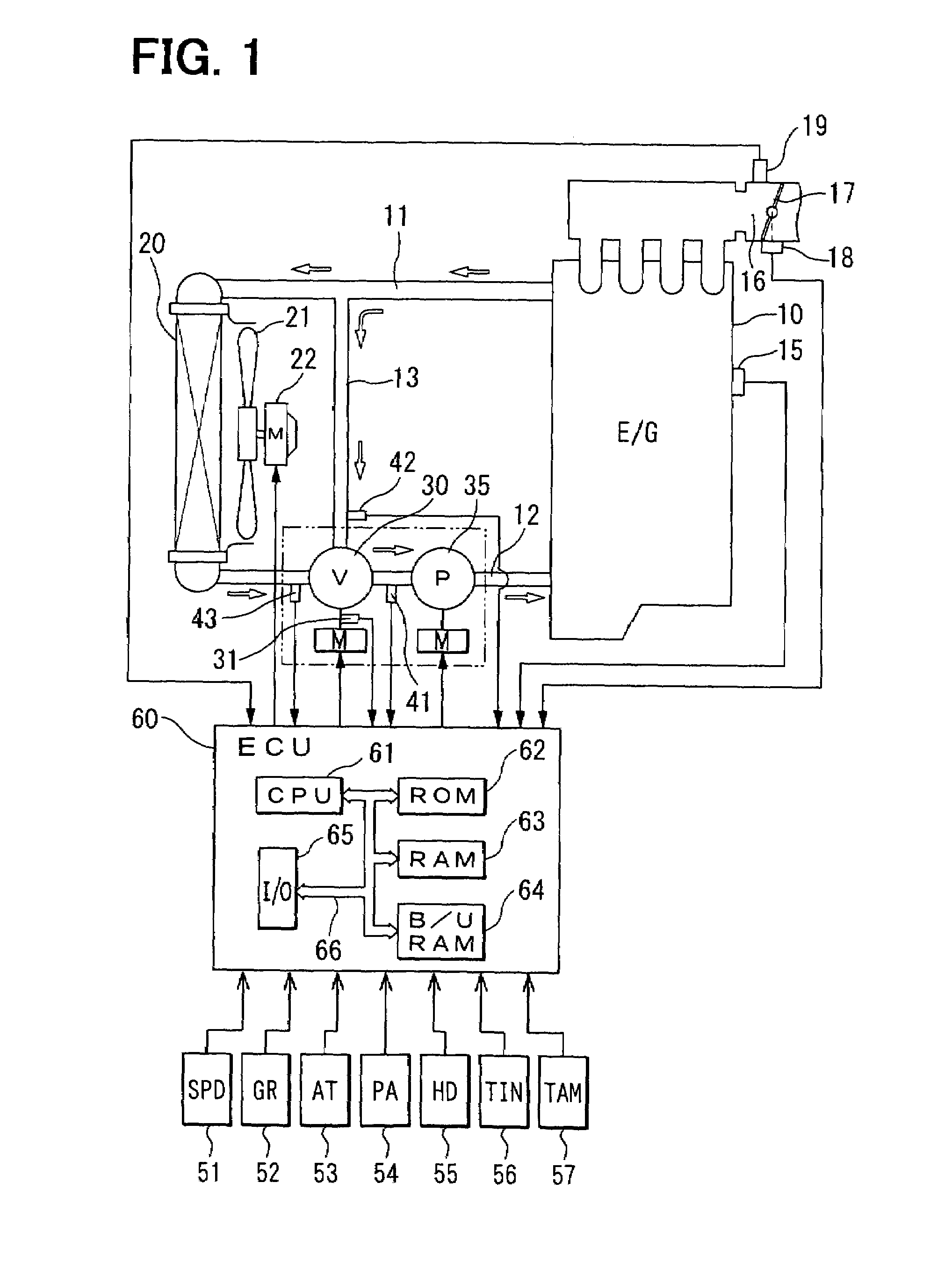
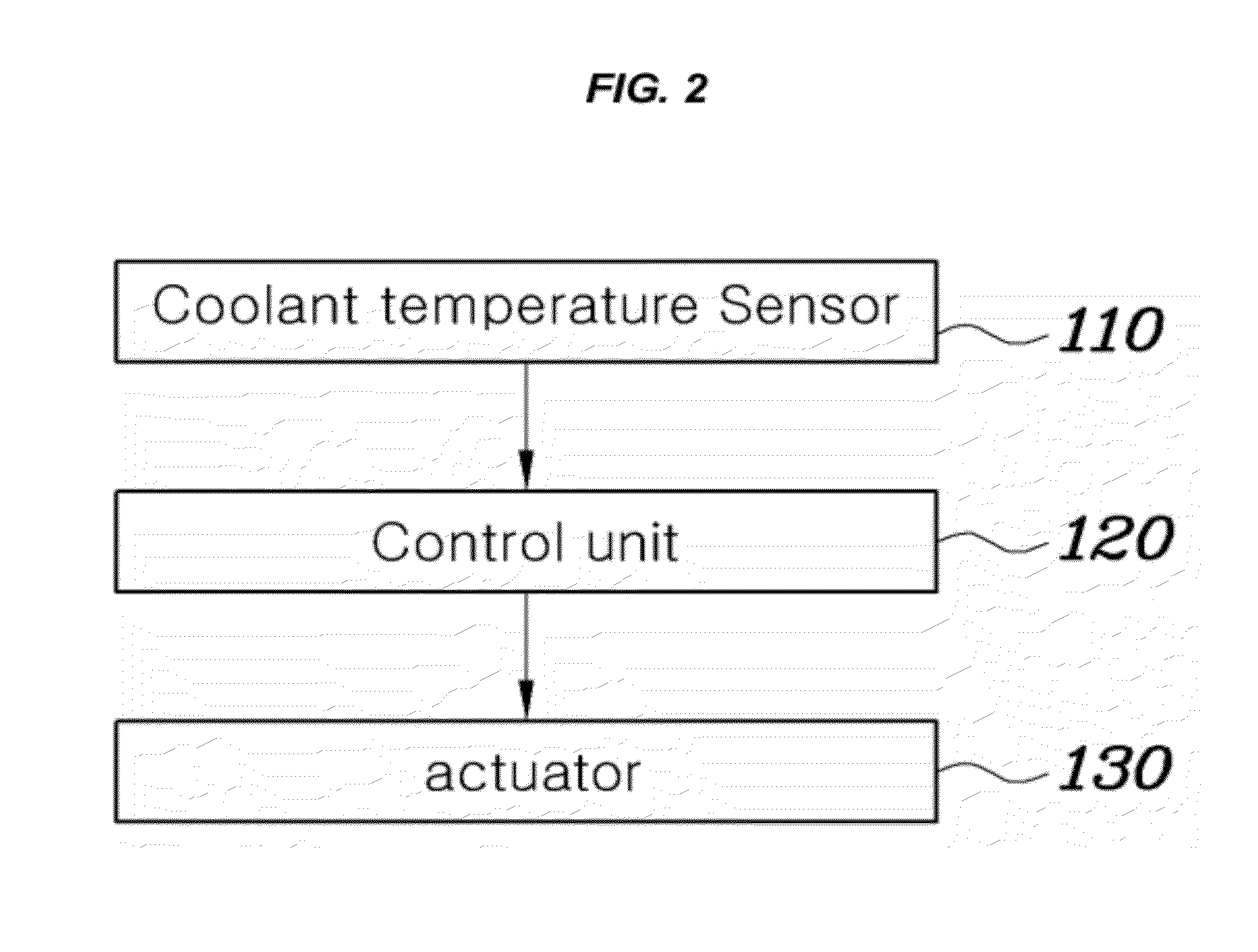
Abnormality diagnosis apparatus and engine cooling system having the same
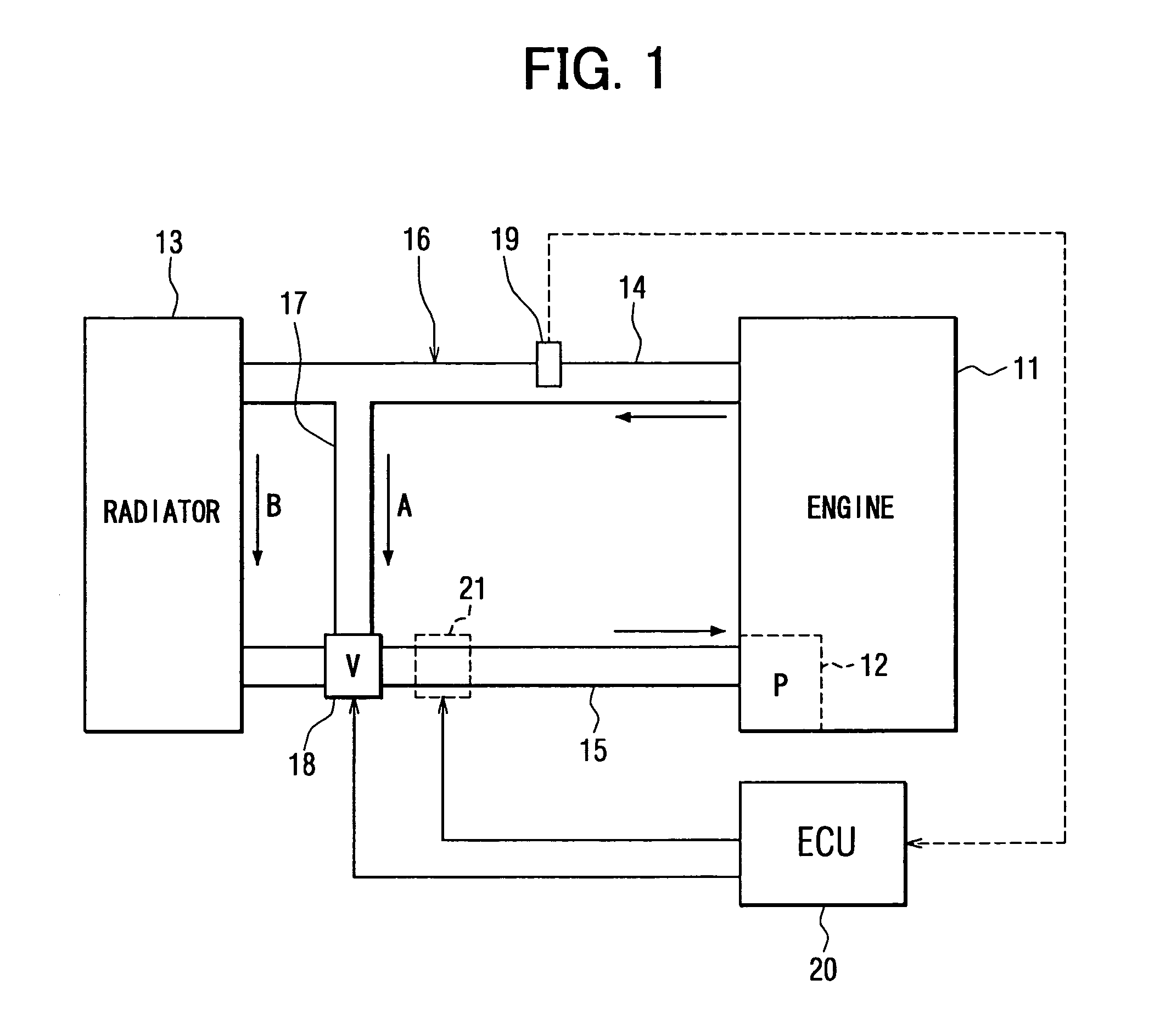
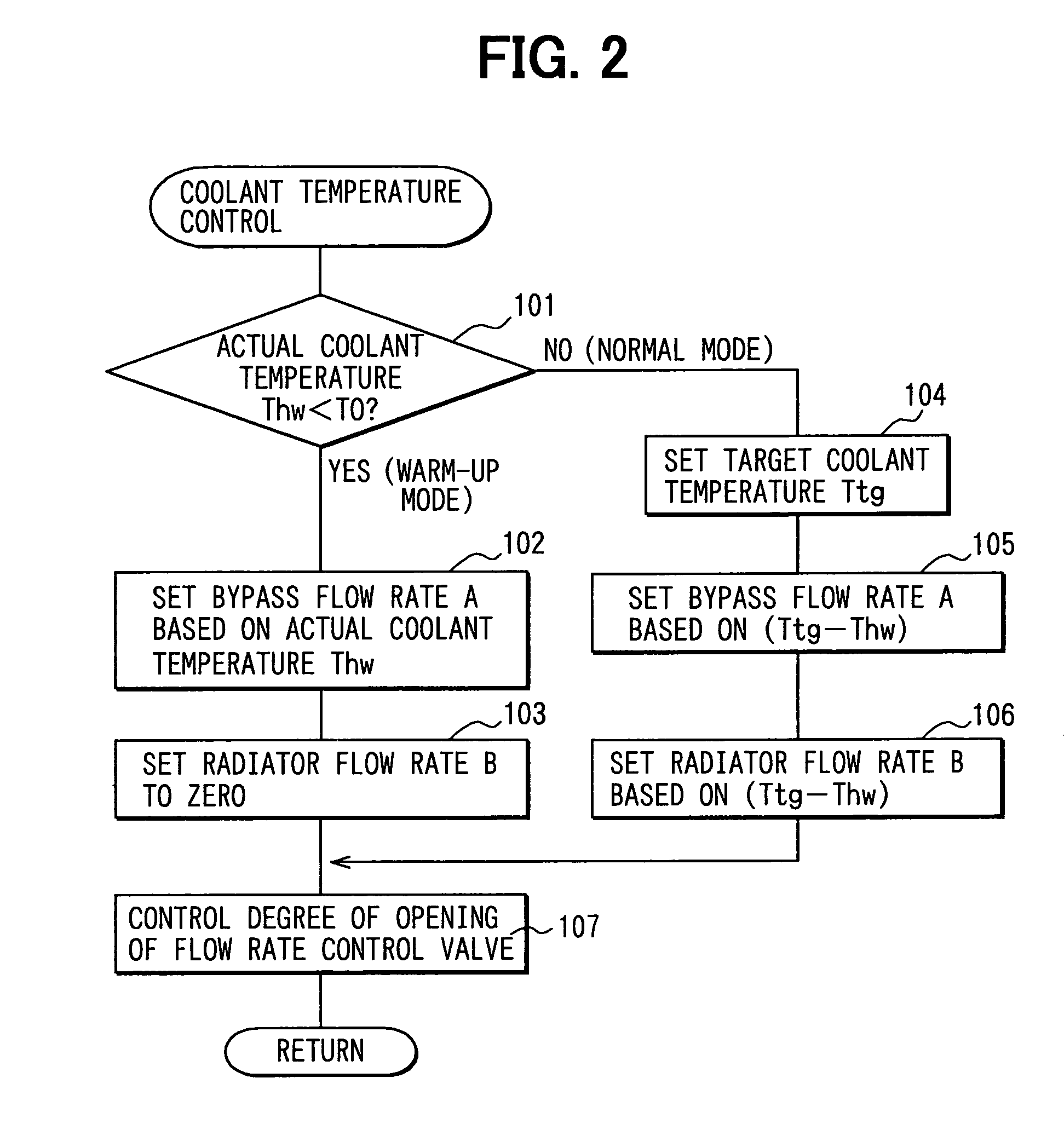
A coolant temperature of coolant in a circulation line system is measured through a coolant temperature sensor and is controlled by controlling a flow rate control valve. The flow rate control valve is diagnosed to determine whether abnormality of the flow rate control valve exists based on behavior of the measured coolant temperature, which is measured through the coolant temperature sensor during a warm-up period of an internal combustion engine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Exhaust gas purifying apparatus for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7360356B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineExhaust fumes
A main control computer commands a second sub-control computer to perform a reduced-cylinder operation when the coolant temperature detected by a coolant temperature sensor is greater than or equal to a reference temperature, and the exhaust temperature detected by a temperature sensor is less than a reference exhaust temperature and is within a reduced-cylinder operation allowable range in which a combination of the engine speed and the engine load is set in advance. The second sub-control computer deactivates a second cylinder group based on a command of the reduced-cylinder operation. The main control computer commands a first sub-control computer and the second sub-control computer to perform an all-cylinder operation when the coolant temperature detected by the coolant temperature sensor is less than the reference temperature, and the exhaust temperature detected by the temperature sensor is greater than or equal to the reference exhaust temperature or is out of the reduced-cylinder operation allowable range in which a combination of the engine speed and the engine load is set in advance.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP +1
Gear-shift control device and gear-shift control method for automatic transmission
InactiveUS6915681B2Machine gearing/transmission testingEngine testingAutomatic transmissionHydraulic fluid
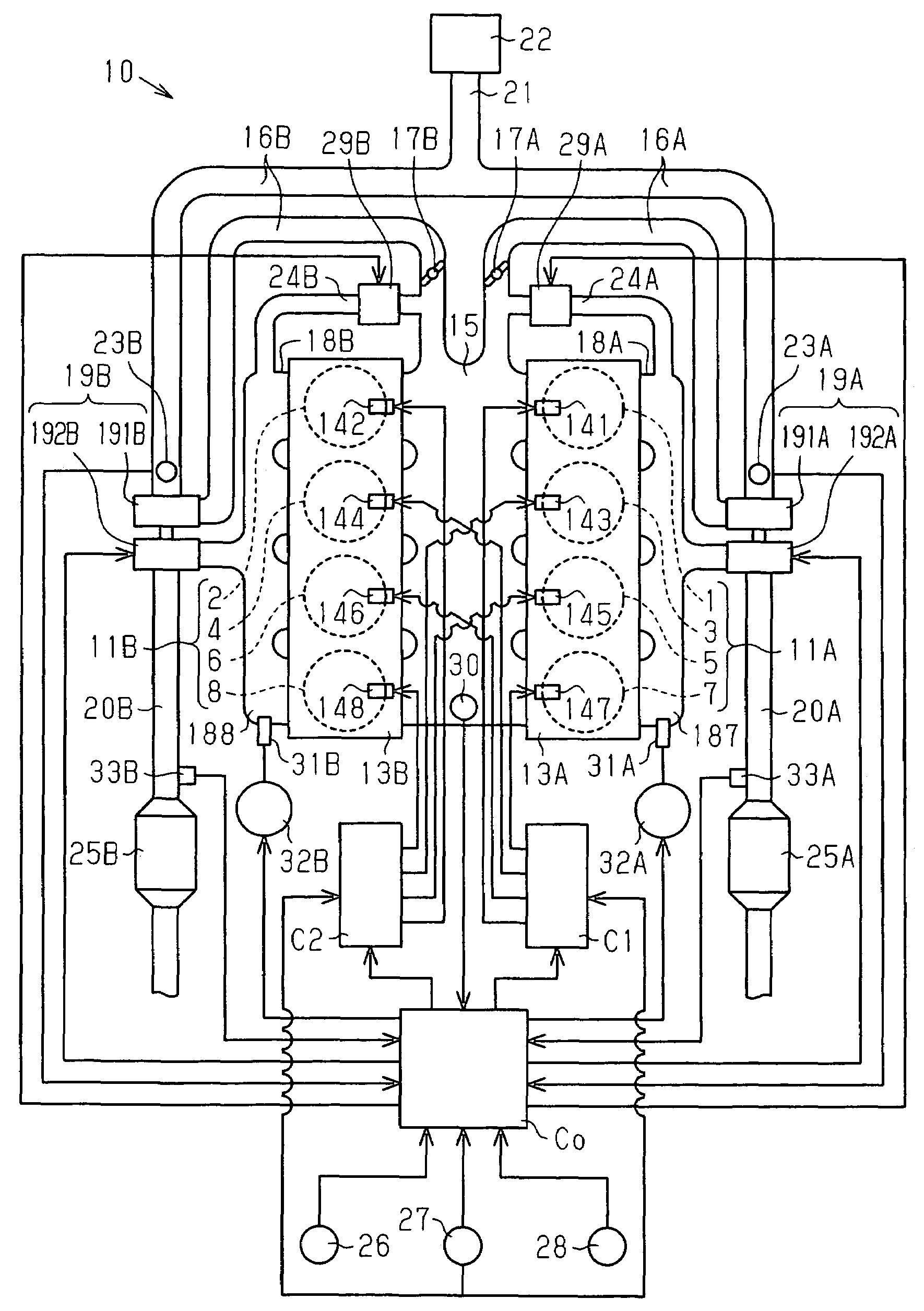
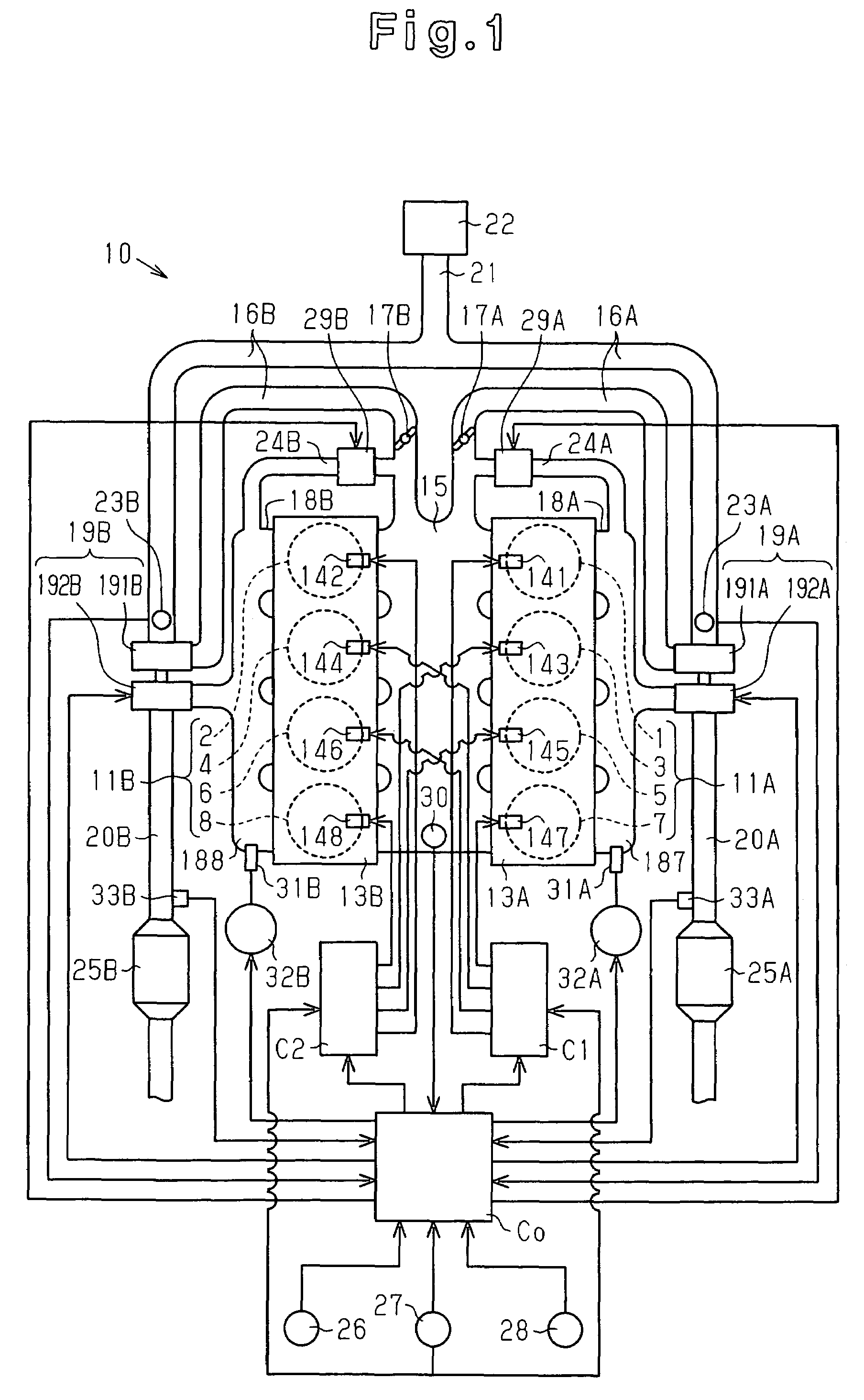
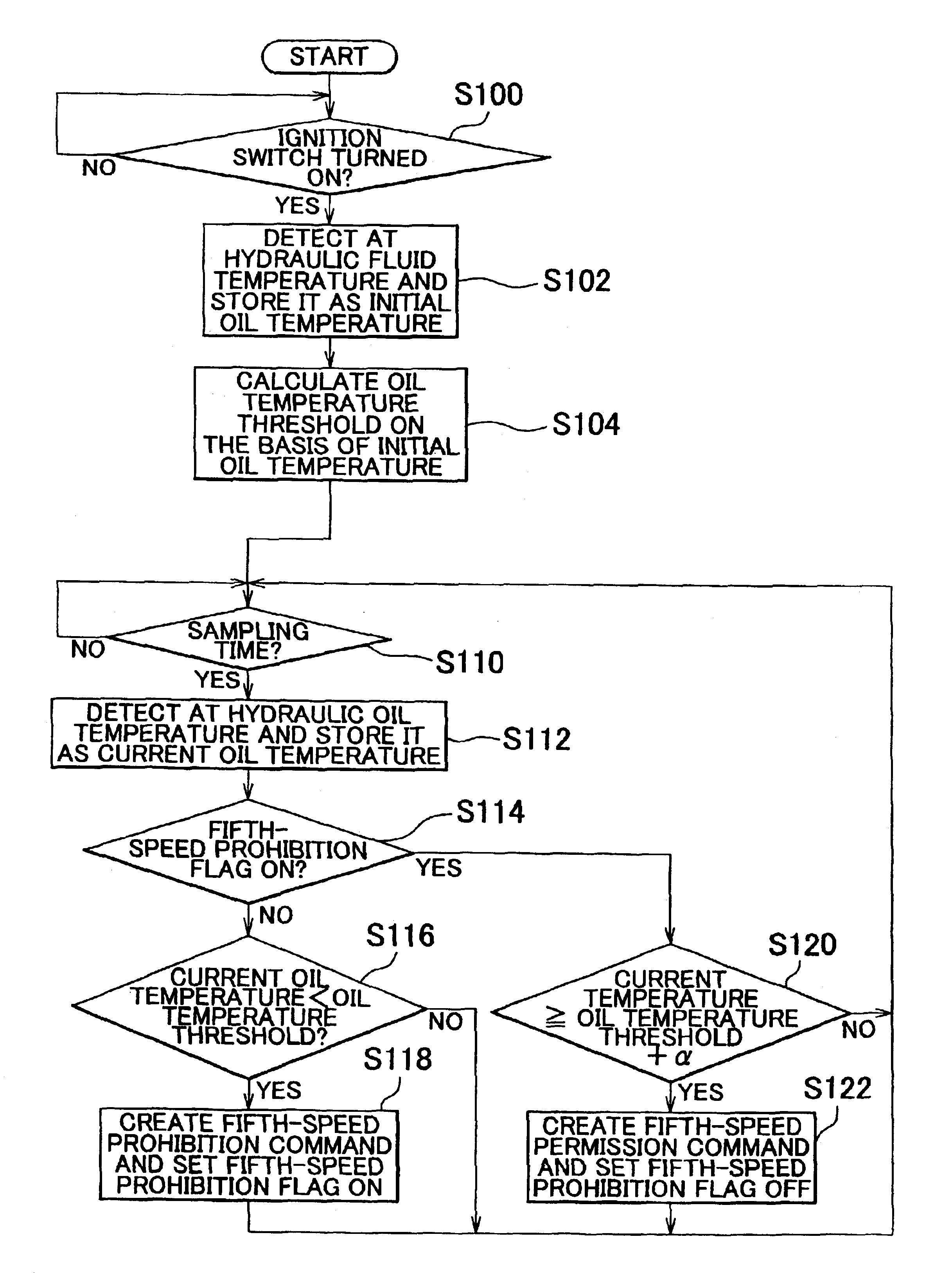
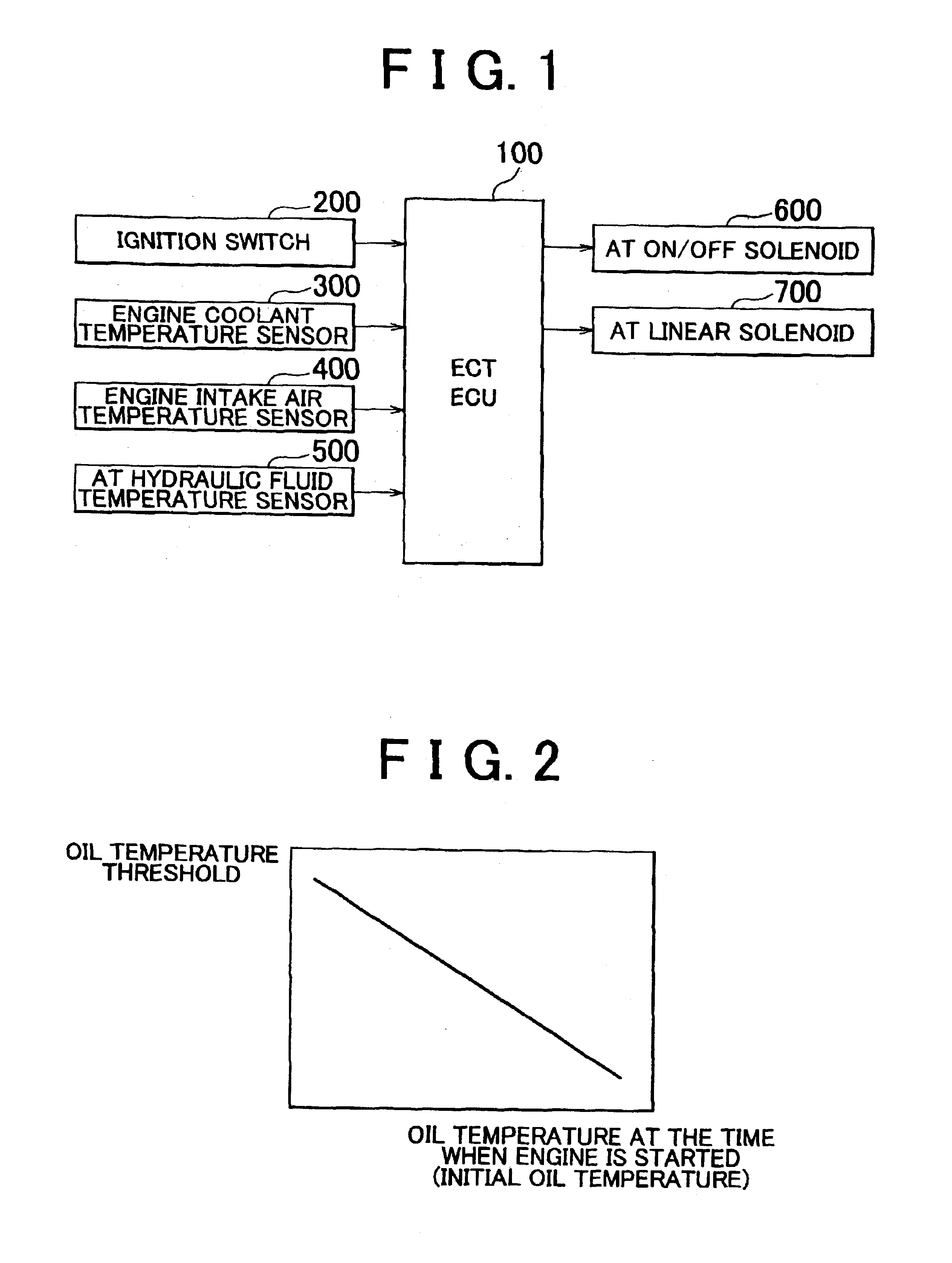
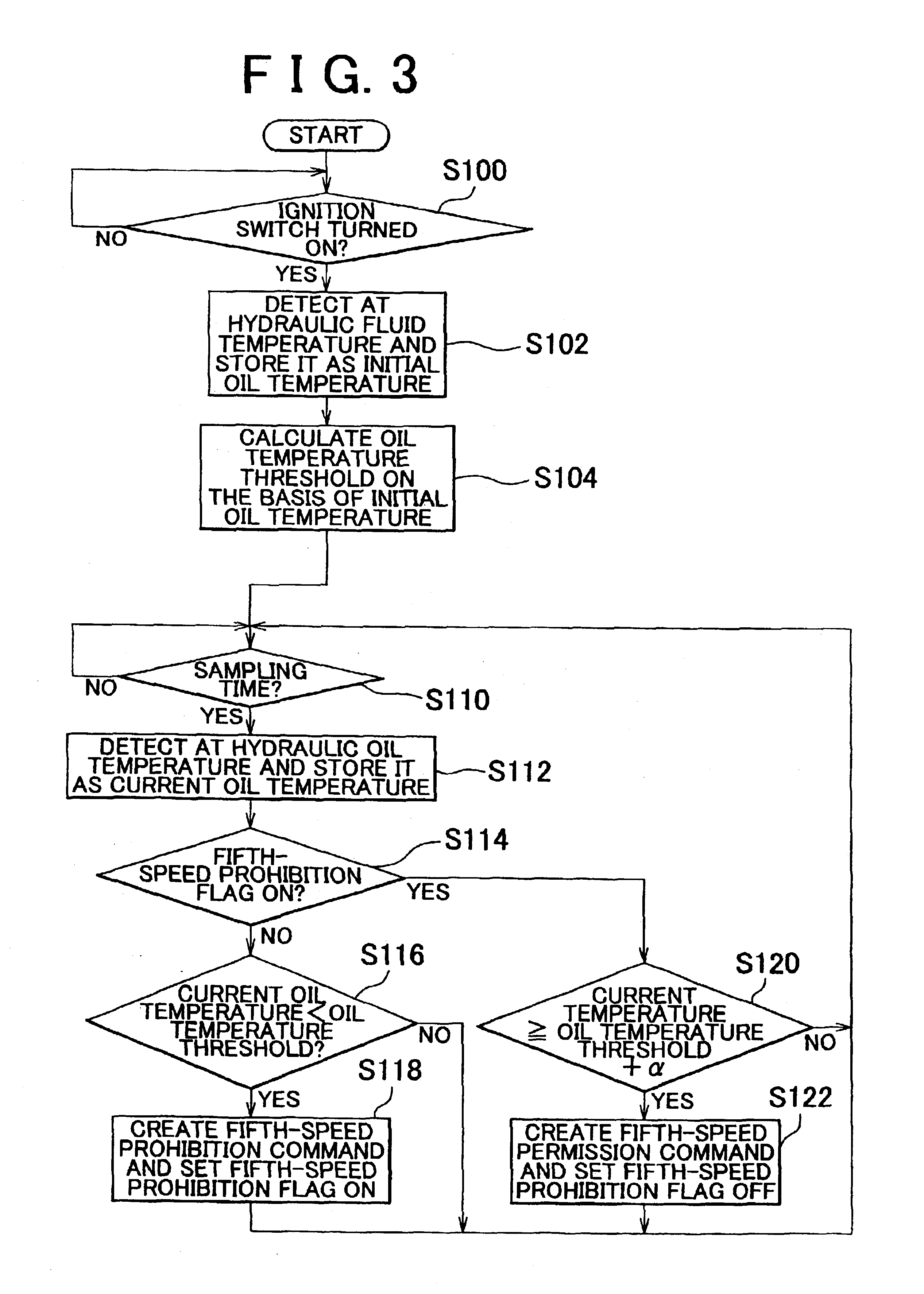
An ECT-ECU includes a circuit that calculates an oil temperature threshold on the basis of a signal input from one of an engine coolant temperature sensor, an engine intake air temperature sensor, and an AT hydraulic fluid temperature sensor if a signal for starting an engine of a vehicle is input thereto from an ignition switch, a circuit that detects an oil temperature on the basis of a signal input from the AT hydraulic fluid temperature sensor at intervals of a predetermined sampling time while the vehicle is running, and a circuit that controls an automatic transmission to prohibit a gear shift from fourth speed to fifth speed if a detected oil temperature is lower than the oil temperature threshold.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Automatic protection device of anti-explosive diesel engine
InactiveCN102720594AReal-time monitoring of surface temperatureReal-time monitoring of exhaust temperatureElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFuel oilLimit value
The invention discloses an automatic protection device of anti-explosive diesel engine. The automatic protection device comprises an infrared temperature measurement device, a water coolant temperature sensor, a water coolant level sensor, an air exhaust temperature sensor, an engine oil pressure sensor, a combustible gas detector, an electronic control unit (ECU), a fuel oil shutoff valve and an automatic fire extinguishing device, wherein the infrared temperature measurement device, the water coolant temperature sensor, the water coolant level sensor, the air exhaust temperature sensor, the engine oil pressure sensor and the combustible gas detector are connected with the ECU through a bus. By the automatic protection device, the surface temperature, the air exhaust temperature, the water coolant temperature and level, the engine oil pressure, and the combustible gas content in an environment can be monitored in real time; and when the monitoring parameter exceeds a limit value, an alarm can be automatically sounded, and protective measures can be taken; and therefore, accidents can be prevented.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
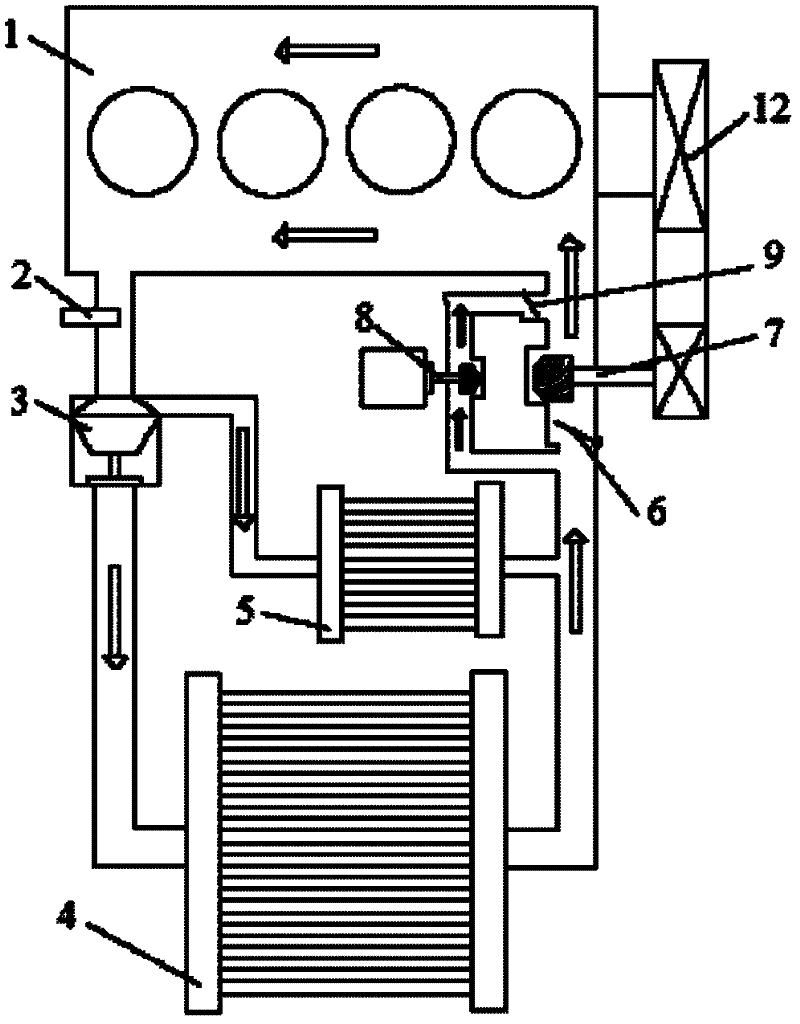
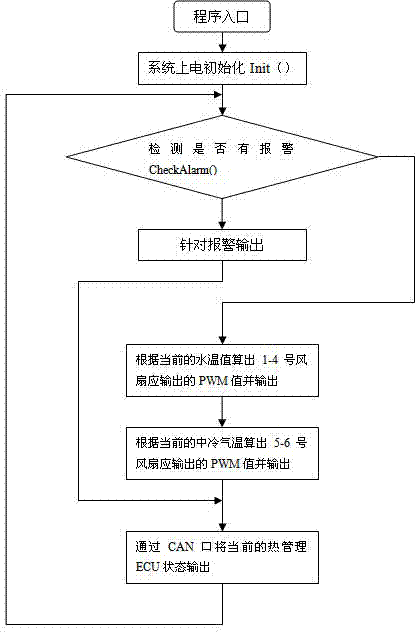
Engine thermal management system
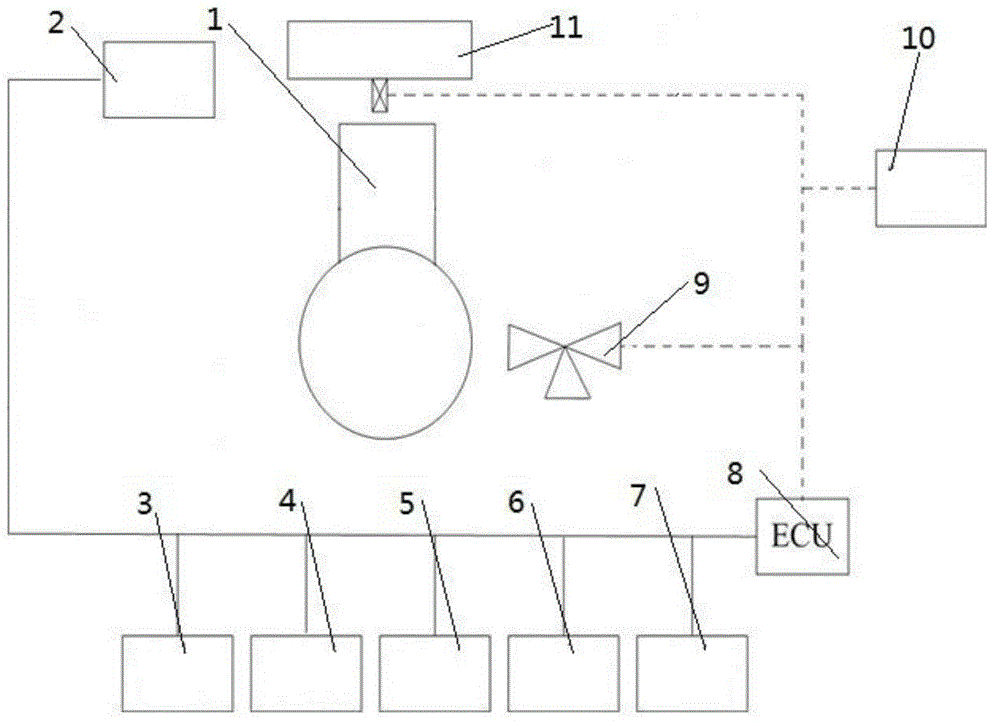
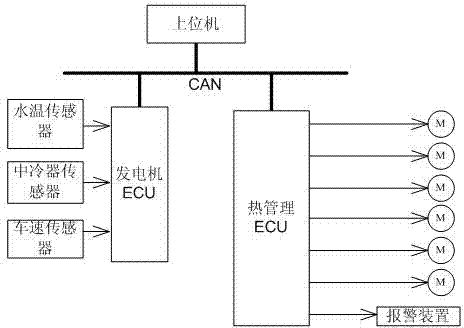
ActiveCN102817692AReduce volumeSave spaceCoolant flow controlMachines/enginesArea networkWorking temperature
The invention relates to an engine thermal management system. The system comprises an upper computer and an engine electronic control unit (ECU), the upper computer is connected with an in-vehicle controller area network (CAN) bus, the engine ECU is connected with an engine water temperature sensor, an intercooler sensor and a vehicle speed sensor in a sampling mode, the engine thermal management system further comprises a thermal management ECU which is connected with the in-vehicle CAN bus, the thermal management ECU outputs a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal to be connected with a group of cooling fans in a driving mode, the group of cooling fans is used for cooling engine water temperature and an intercooler, and the thermal management ECU is further connected with an alarm device in a drive control mode. According to the engine thermal management system, the heat-dissipating mode of the vehicle intercooler is changed from mechanical power type to electronic type, the operation of the cooling fans can be automatically controlled according to the temperature information of the engine, and the engine is maintained in the optimum working temperature.
Owner:CAMALUOYANGELECTROMECHANIC
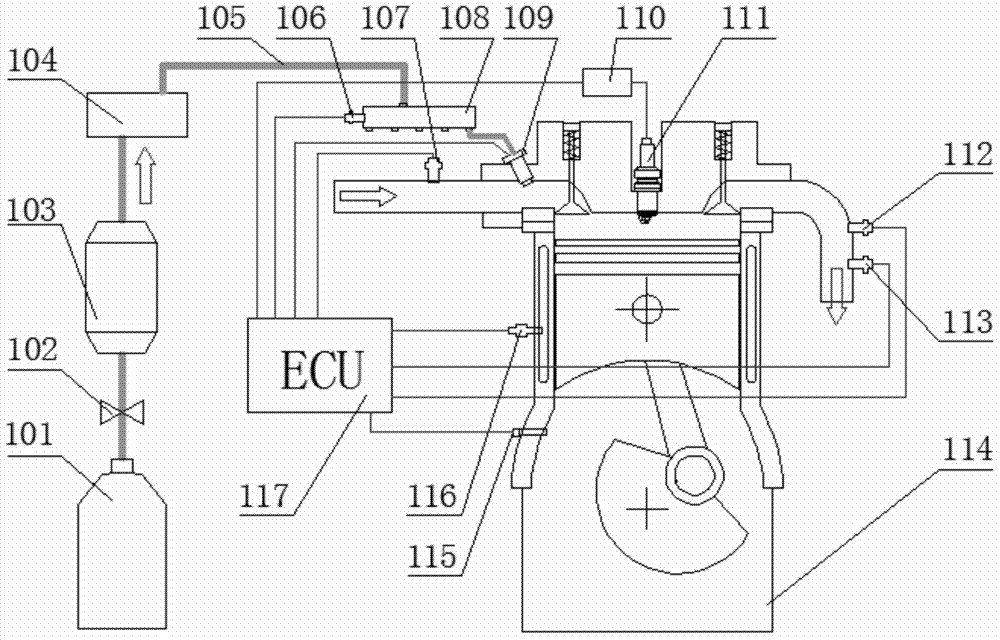
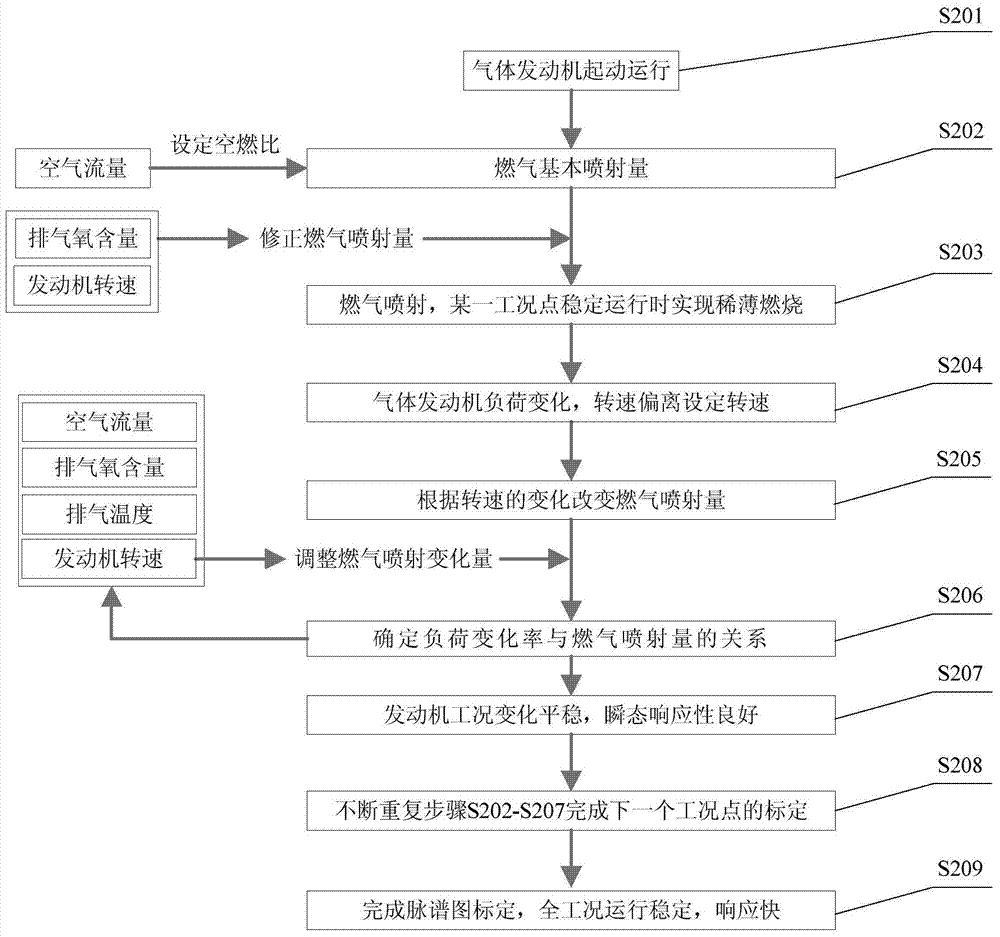
Control system and control method for improving transient response of gas engine
ActiveCN104775941AReasonable structureQuick responseInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusElectronic controllerFuel supply
The invention discloses a control system and a control method for improving the transient response of a gas engine. The control system comprises the gas engine, a fuel supply system, an ignition control system and a working state monitoring and feedback system, the fuel supply system comprises a fuel storage device, a gas line, a gas track and a gas injection valve, the ignition control system comprises an ignition module and an electronic controller, and the working state monitoring and feedback system comprises an engine speed sensor, an engine water temperature sensor, a gas track pressure sensor, an airflow sensor, an exhaust temperature sensor and an exhaust oxygen sensor. The invention utilizes the fuel storage device to increase the amount of stored gas and ensure the stability of pressure in the process of supplying gas; by acquiring information such as airflow, exhaust oxygen content, exhaust temperature and engine speed, the invention regulates the change of gas injection, and consequently, not only can the transient response of the gas engine be improved, but also the operating sensitivity of the gas engine as a power device of power source can be increased.
Owner:JINAN RICHNES ELECTRONICS CO LTD
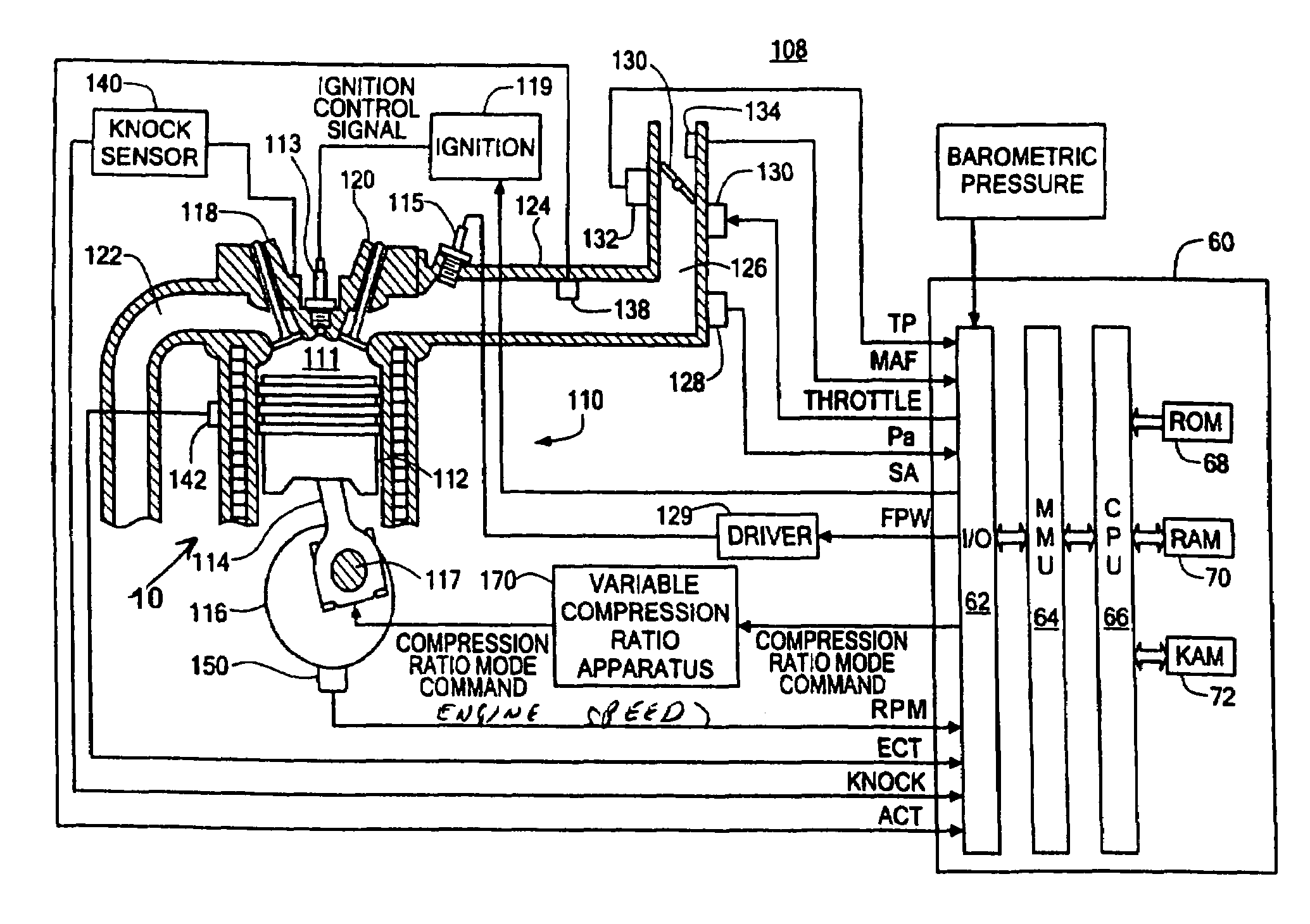
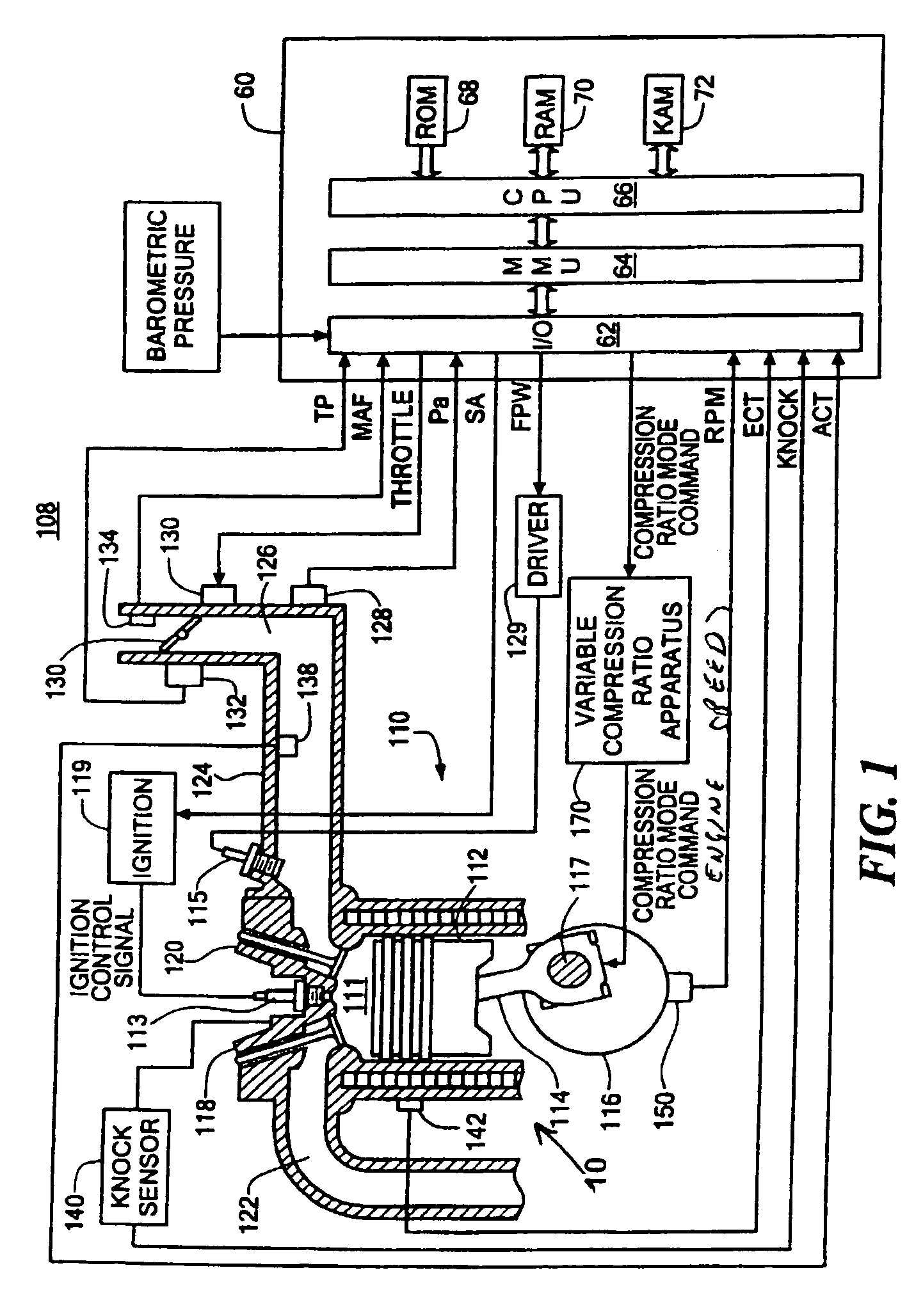
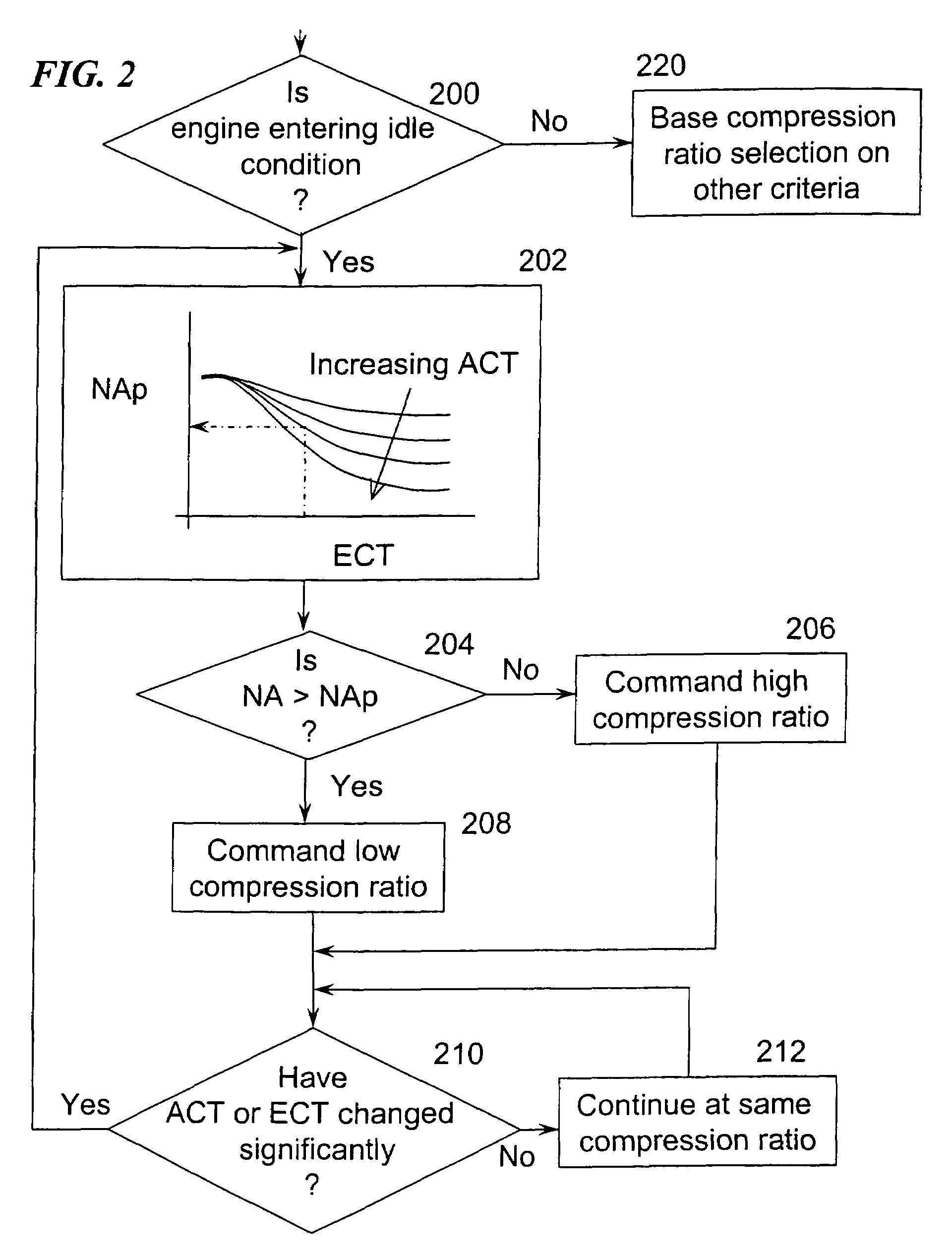
Variable compression ratio scheduling at idle speed conditions
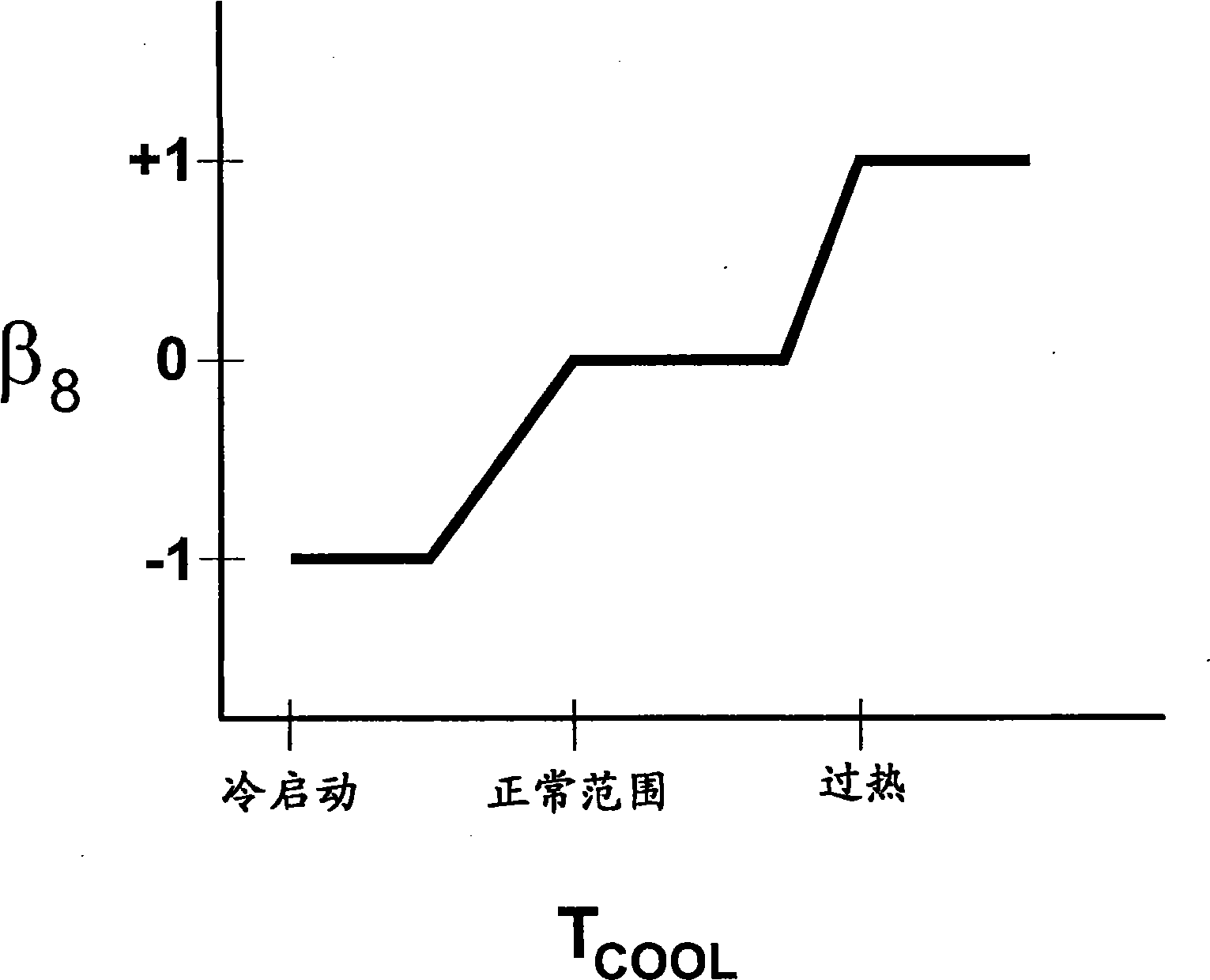
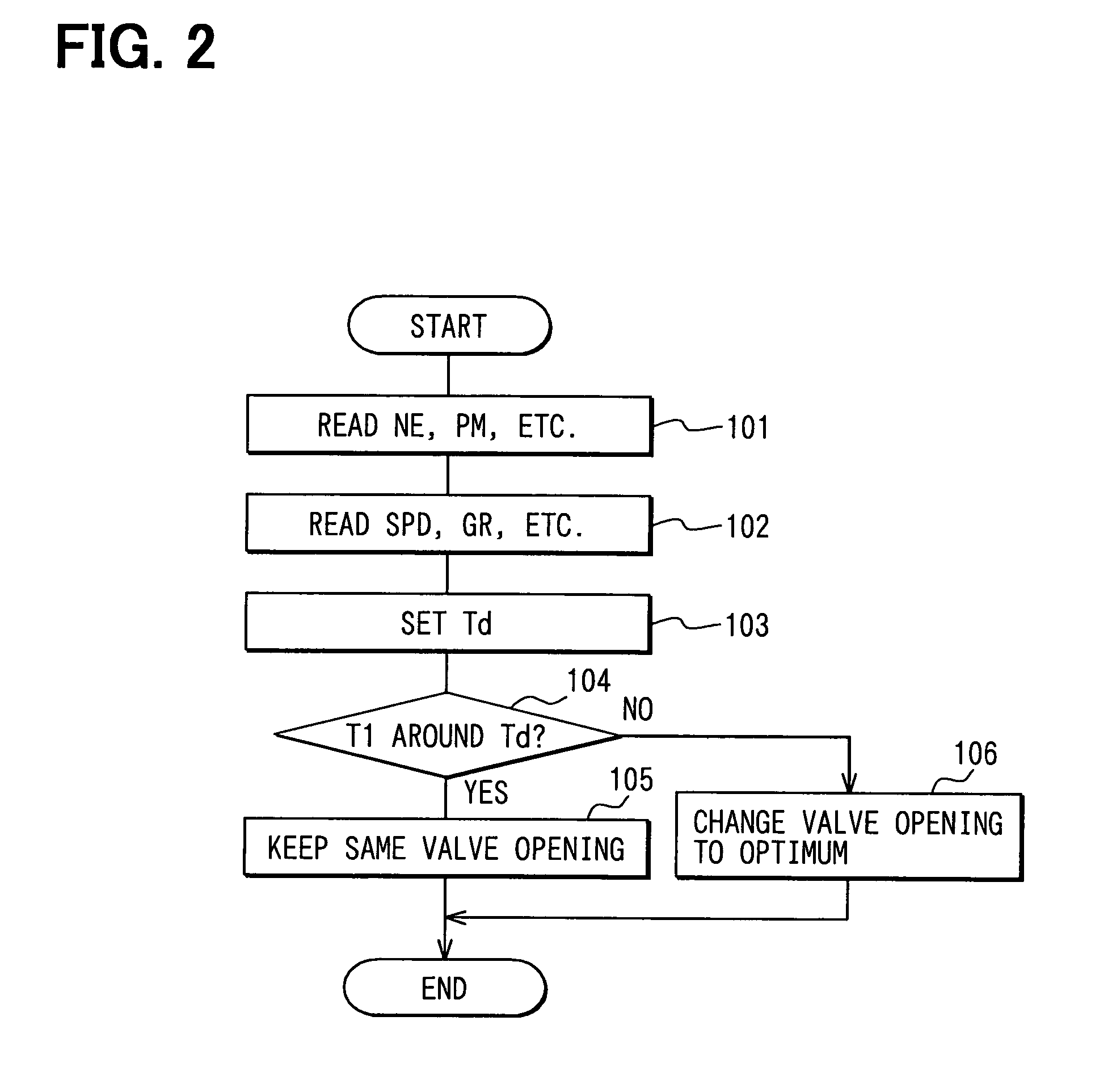
A method for selecting compression ratio of a variable compression ratio internal combustion engine when such engine is operating under an idle condition is disclosed. The compression ratio is selected to avoid engine knock, an undesirable phenomenon which is more likely at higher temperatures, higher compression ratios, lower engine speeds, and higher engine torques. The selected compression ratio is based on one or more of engine torque required to drive engine accessories, engine coolant temperature, engine air temperature, and transmission status (neutral idle or drive idle). A normalized airflow parameter is computed or found in a lookup table based on engine coolant temperature and engine air temperature. When actual normalized airflow (that which provides necessary engine torque to drive engine accessories and overcome engine friction) exceeds normalized airflow parameter exceeds, a higher compression ratio is selected.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control apparatus for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7302928B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineEngineering
An engine ECU executes a program including the step of detecting an engine coolant temperature (THW), the step of selecting a map for a warm state as the map for calculating a fuel injection ratio (or a DI ratio) r when the engine coolant temperature (THW) is equal to or higher than a temperature threshold value (THW(TH)) (YES in S110), the step of selecting a map for a cold state as the map for calculating the fuel injection ratio (or the DI ratio) r when the engine coolant temperature (THW) is lower than the temperature threshold value (THW(TH)) (NO in S110), and the step of calculating the fuel injection ratio between the in-cylinder injector and the intake manifold injector (or the DI ratio) r based on the engine speed, load factor, and the selected map.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
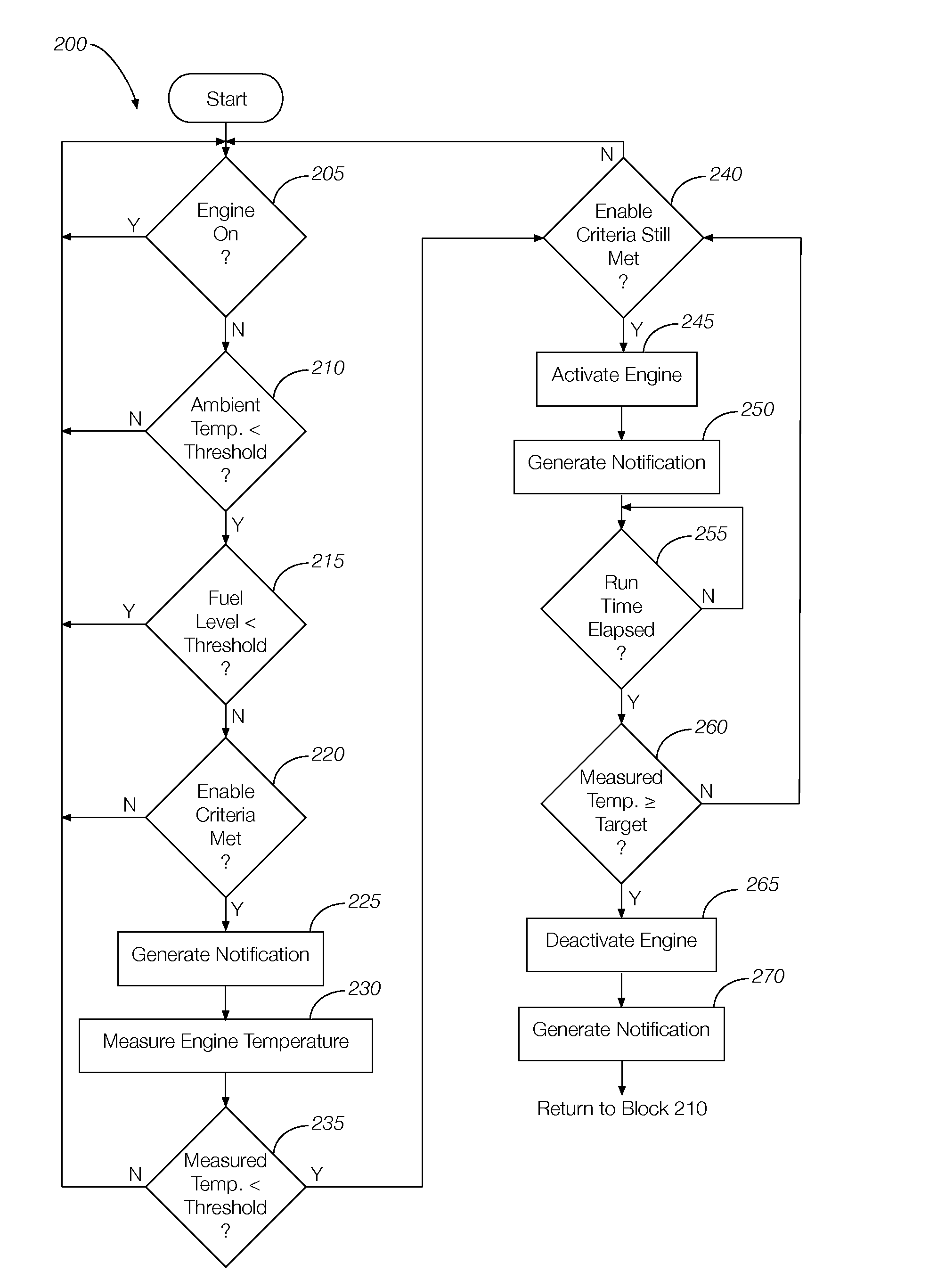
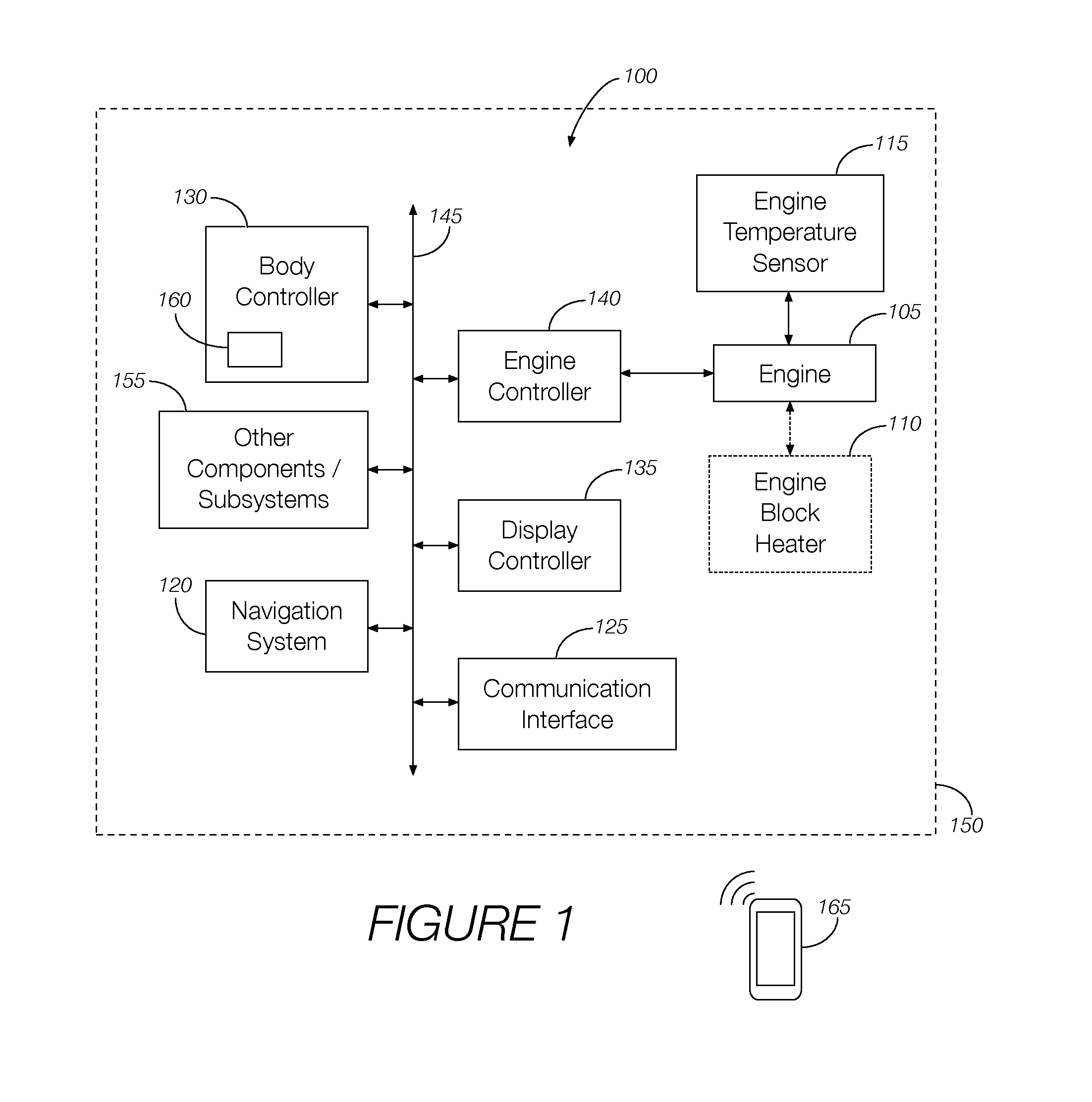
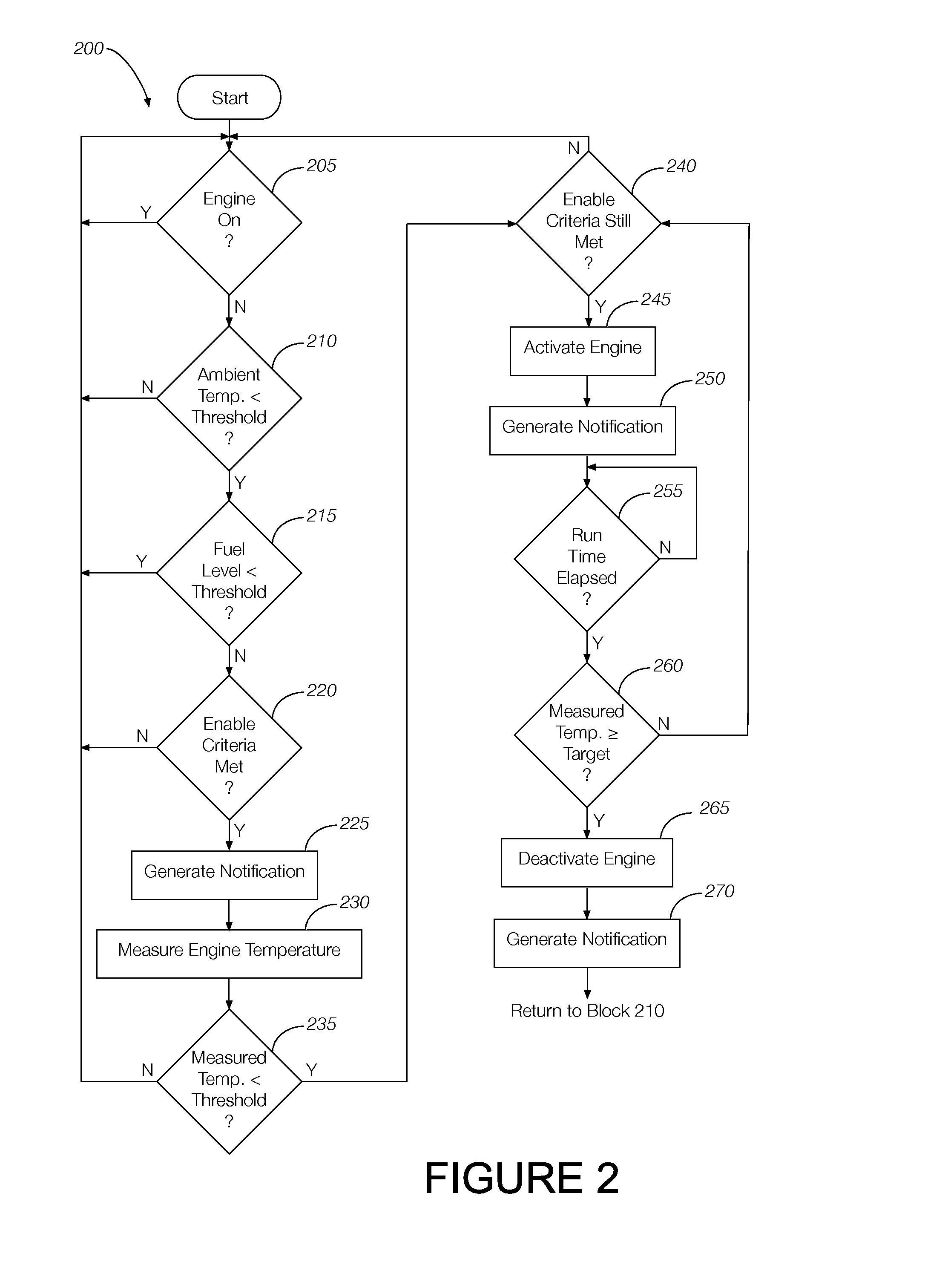
Engine off temperature management
InactiveUS20150159615A1Analogue computers for vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesEngine control unitEngine coolant temperature sensor
A vehicle system includes an engine temperature sensor configured to measure a temperature of a vehicle engine and a remote engine controller system configured to compare the measured engine temperature to a predetermined threshold. The engine controller selectively activates the engine based on the measured engine temperature relative to the predetermined threshold to prioritize the heating of the engine block over heating of the vehicle cabin. In some implementations, the remote engine controller system selectively activates the engine when the measured temperature is below a minimum temperature and deactivates the engine when the measured temperature is equal to or greater than a target temperature.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
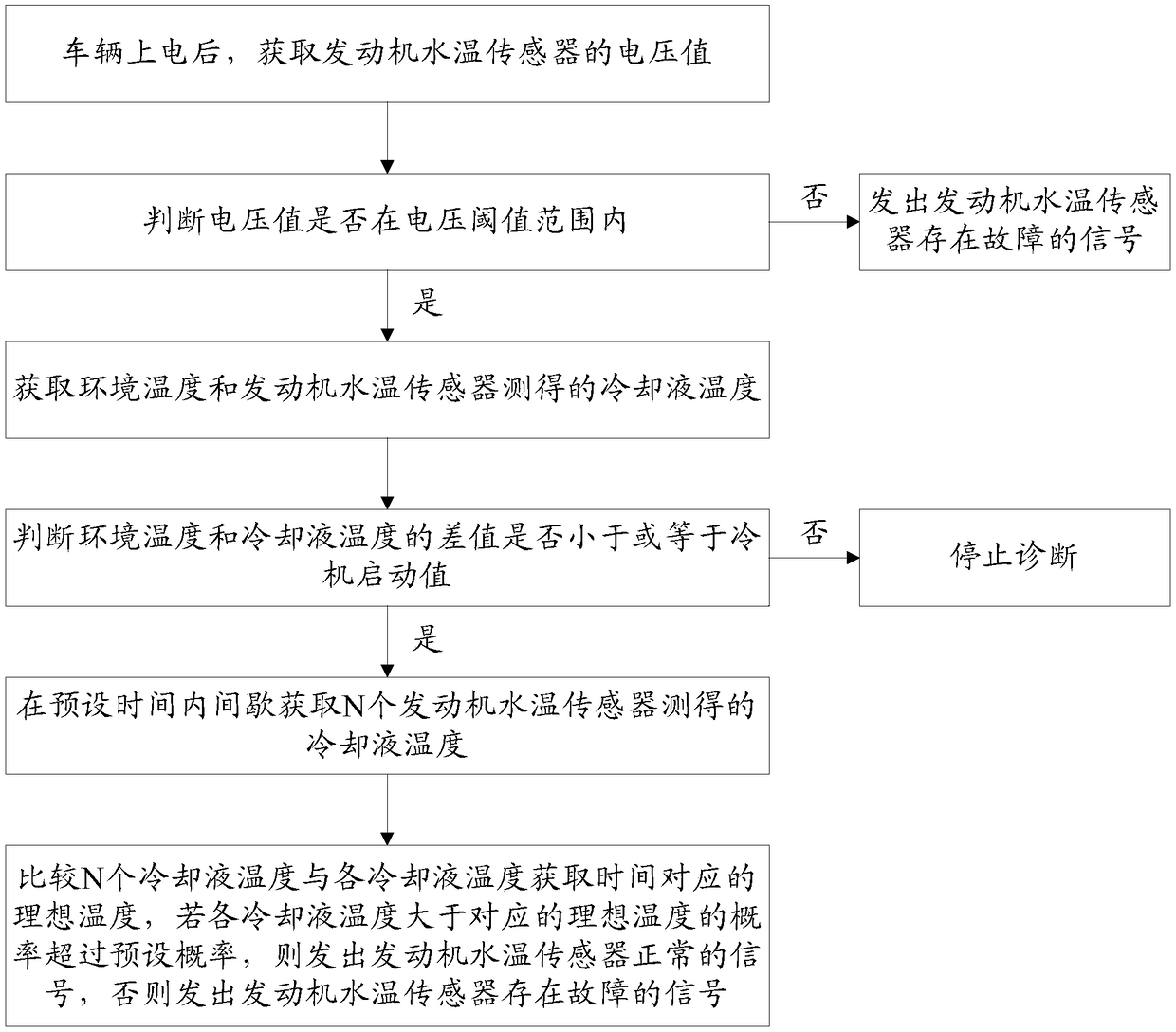
Diagnosis method and module for engine water temperature sensor
ActiveCN109386374AReliable diagnosisMachines/enginesEngine cooling apparatusDiagnosis methodsComputer module
The invention discloses a diagnosis method and module for an engine water temperature sensor. The method comprises the steps of S01, obtaining a voltage value of the engine water temperature sensor; S02, judging whether the voltage value is within the range of a voltage threshold value or not, and if yes, executing S03; S03, obtaining environment temperature and coolant temperature; S04, judging whether the difference value of the environment temperature and the coolant temperature is smaller than or equal to a refrigerator starting value or not, and if yes, executing S05; S05, intermittentlyobtaining N coolant temperatures within a preset time; S06, comparing the N coolant temperatures with ideal temperatures corresponding to obtaining times of all the coolant temperatures, and if the probability that all the coolant temperatures are larger than the corresponding ideal temperatures exceeds preset probability, sending out signals that the engine water temperature sensor is normal. Bymeans of the diagnosis method for the engine water temperature sensor, after the engine water temperature sensor is diagnosed multiple times, whether the engine water temperature sensor breaks down ornot is judged, and the engine water temperature sensor is more accurately and reliably diagnosed.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Internal combustion engine cooling system
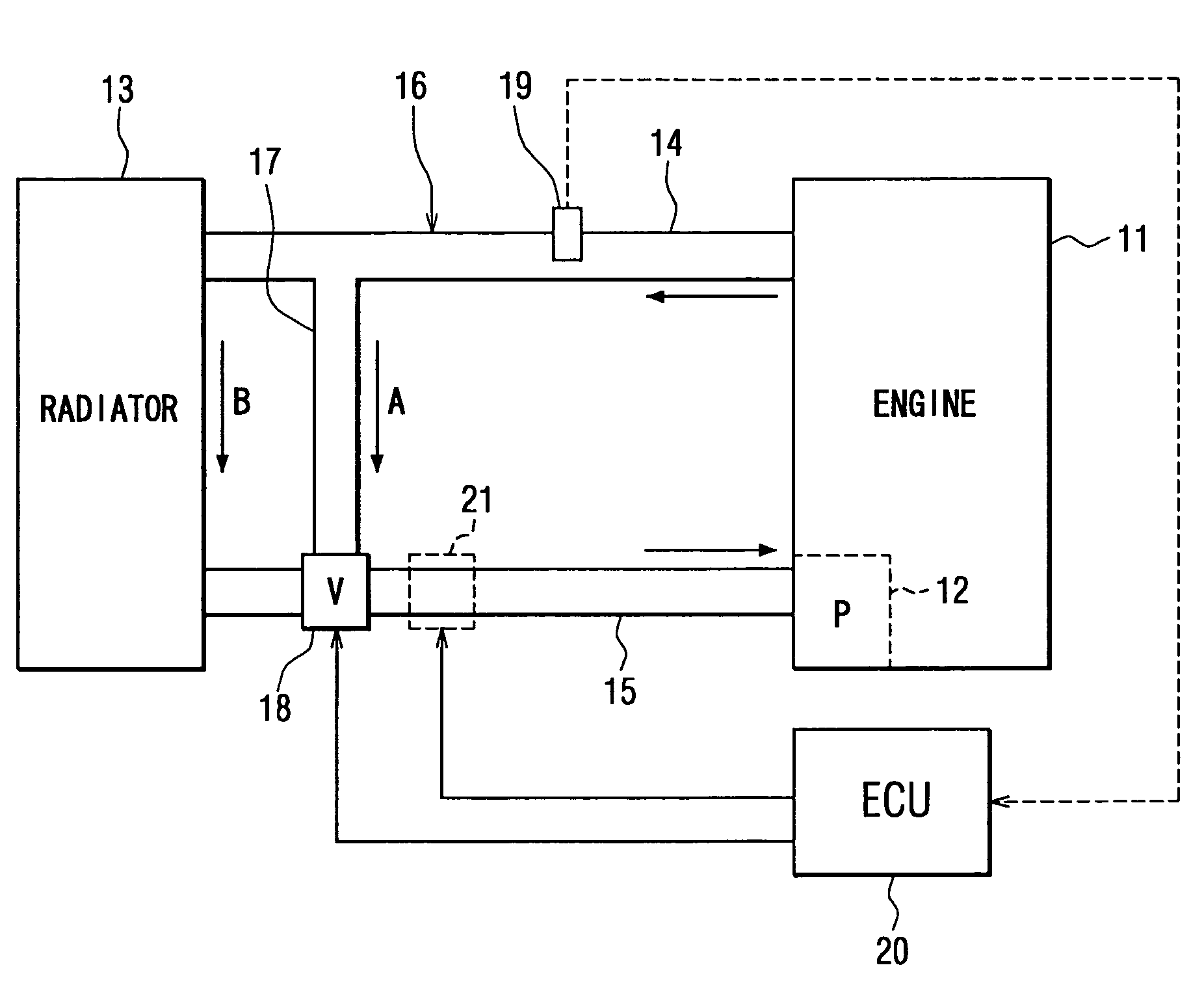
InactiveUS7182048B2Reduce fuel consumptionEffective temperatureCoolant flow controlMeasurement deviceDetonationExternal combustion engine
In a cooling system of an internal combustion engine, coolant flowing through a radiator and bypassing the radiator are mixed in a flow control valve controlled by ECU on the basis of signals provided by sensors such as a coolant temperature sensor, so that the coolant is circulated by an electric pump to control the coolant temperature for the internal combustion engine. A desired coolant temperature is changed according to the operating condition of the internal combustion engine, the traveling condition of a vehicle and the ambient condition. Thus, the temperature of the coolant flowing into the internal combustion engine is changed properly so that frictional resistance in the engine and exhaust gas may be reduced and the internal combustion engine may be kept at its most efficient temperature near a detonation limit temperature.
Owner:DENSO CORP
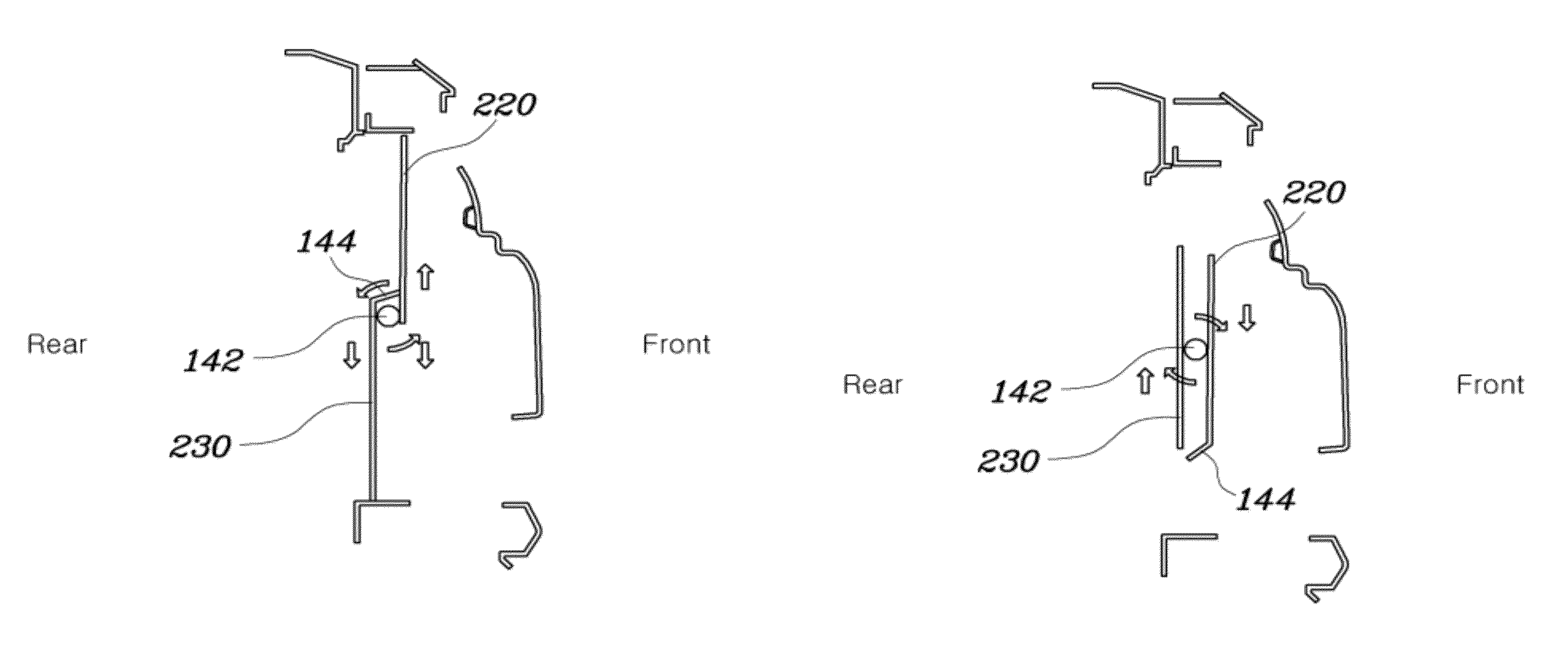
Apparatus for opening and closing air flap for vehicle
ActiveUS8302715B2Improve aerodynamic performanceShortening the time required to warm up the engineCoolant flow controlAir coolingControl signalComputer module
Disclosed herein is an apparatus for opening and closing an air flap for a vehicle. The apparatus for opening and closing an air flap may include a coolant temperature sensor provided at an engine to measure a coolant temperature of the engine, a control unit comparing a measurement value input from the coolant temperature sensor with a reference value stored therein, thus outputting a control signal, an actuator rotating in response to the control signal of the control unit, a power transmission unit connected to the actuator to transmit rotating force of the actuator, and a flap unit installed in an opening of a front end module carrier, and being selectively movable in a vertical direction in the opening by power transmitted from the power transmission unit to the flap unit to open or close the opening, thus permitting or preventing an inflow of air into the cooling module.
Owner:KIA MOTORS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com