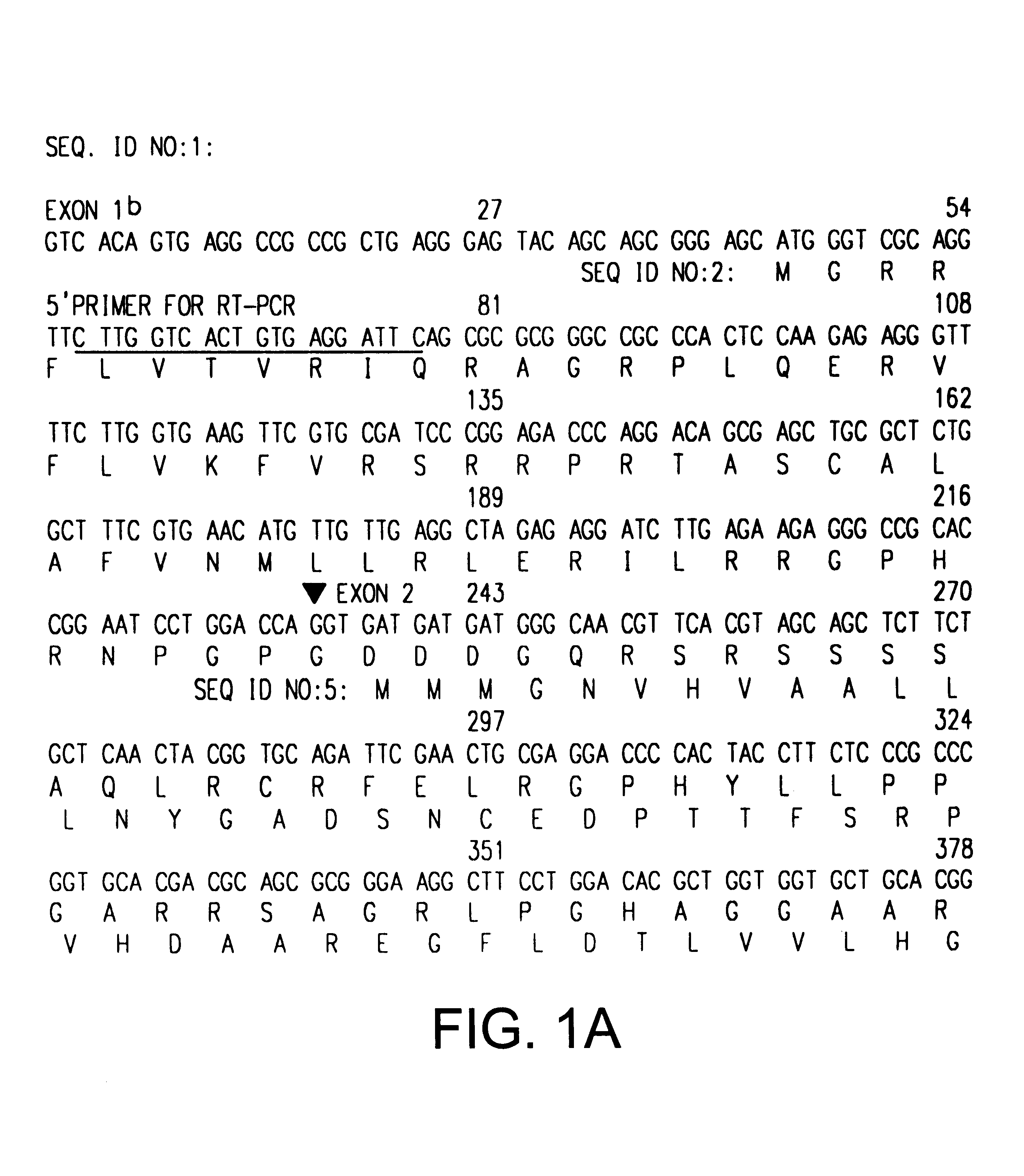
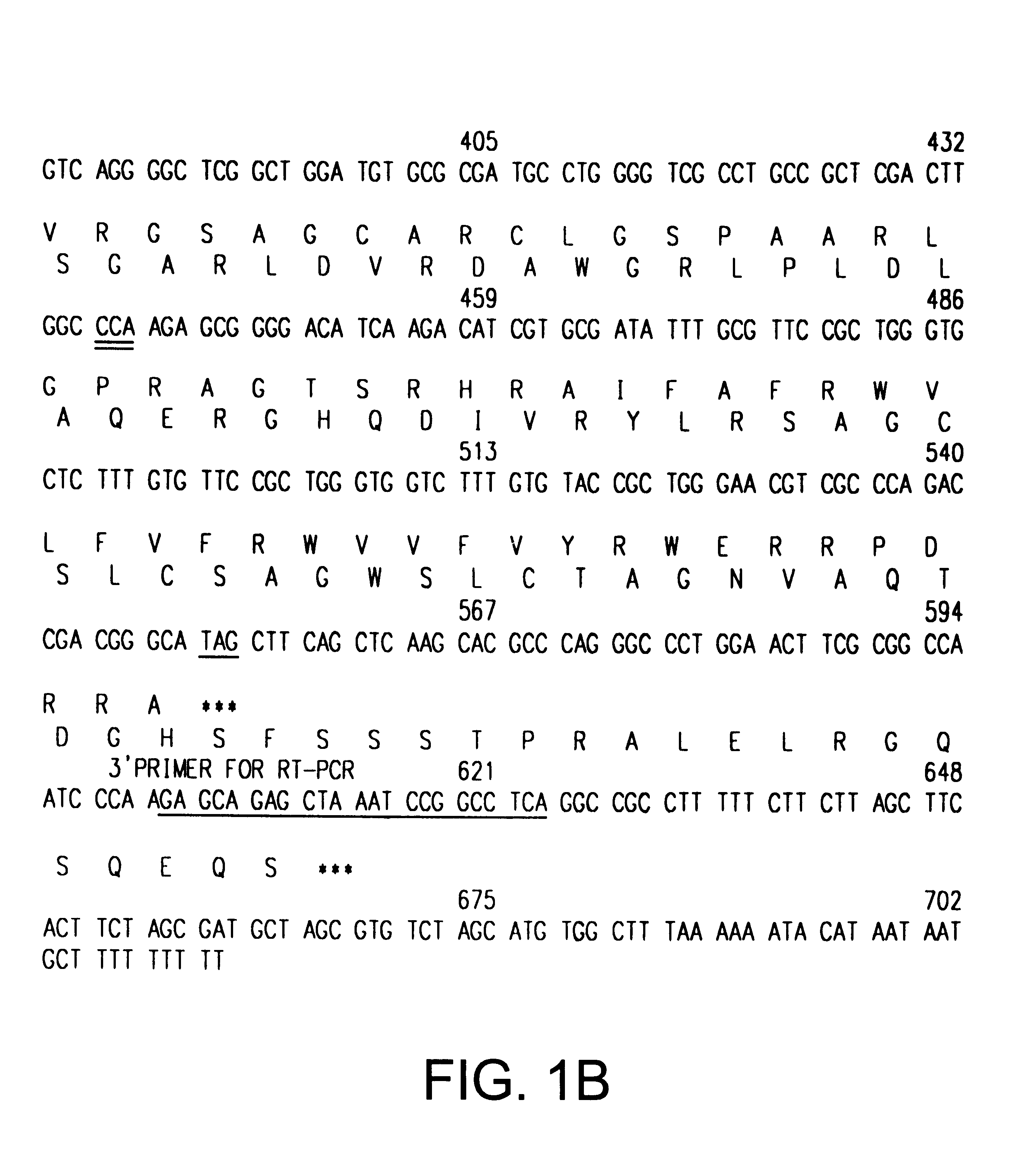
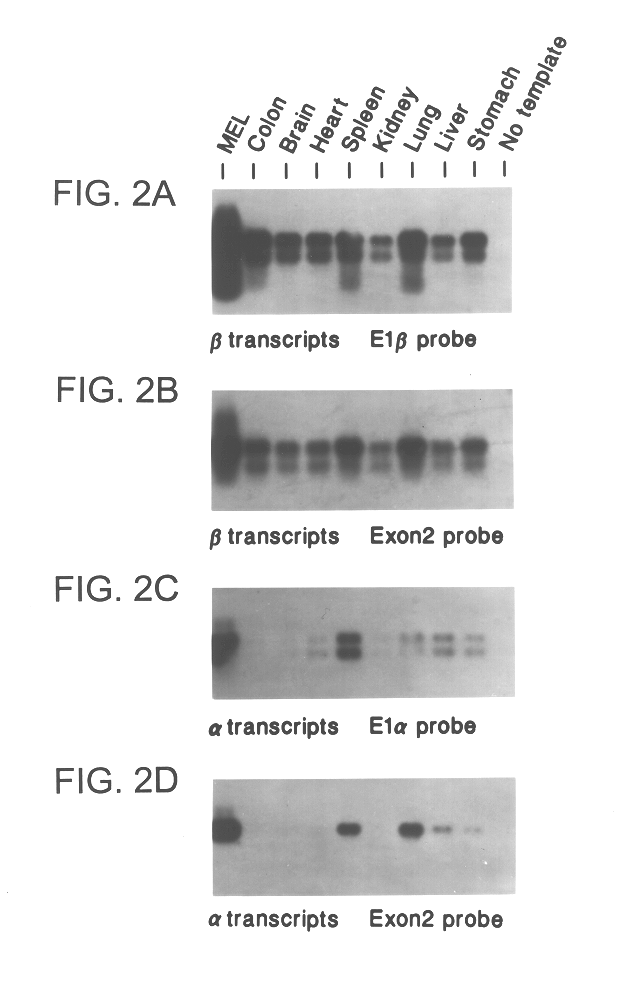
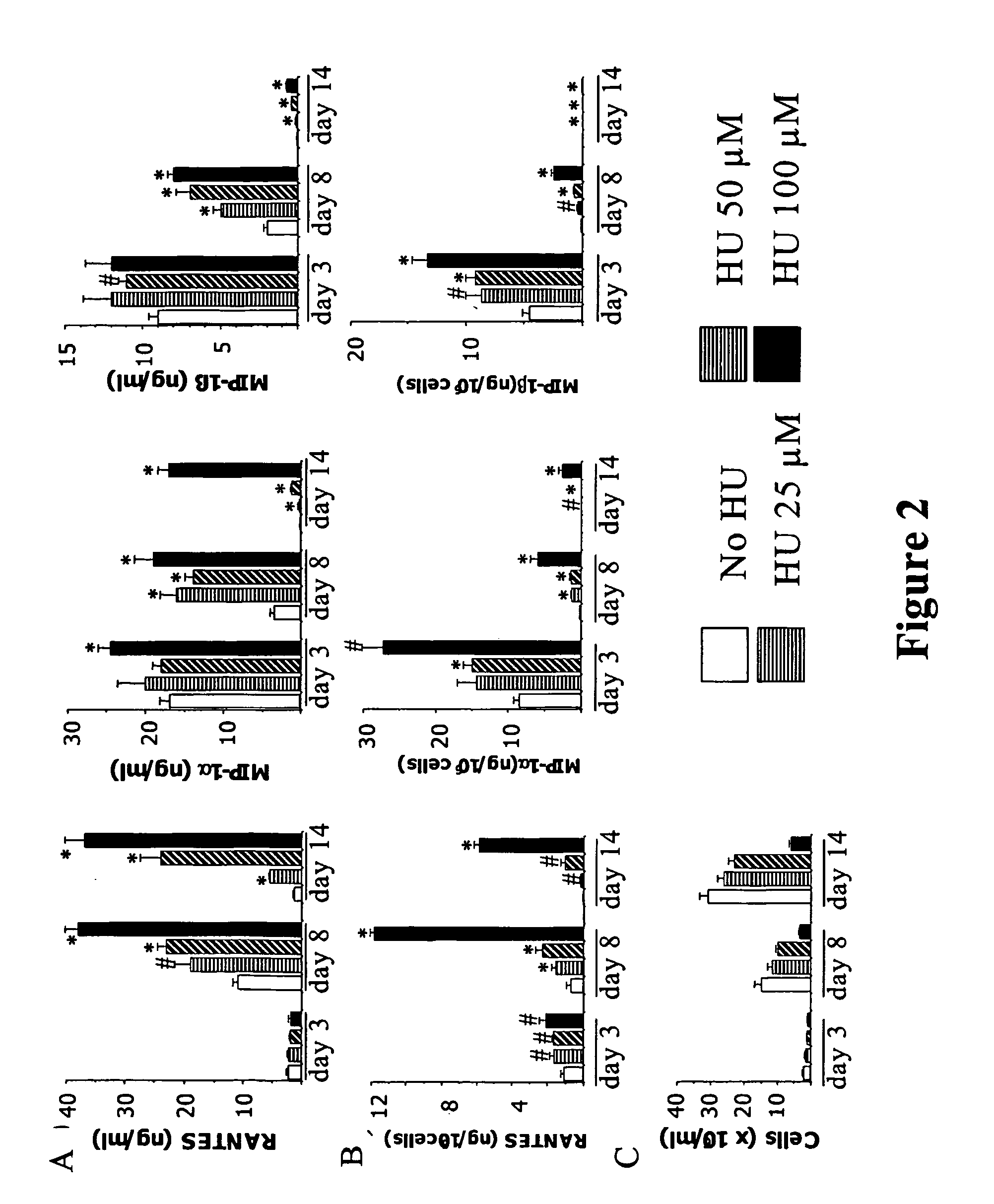
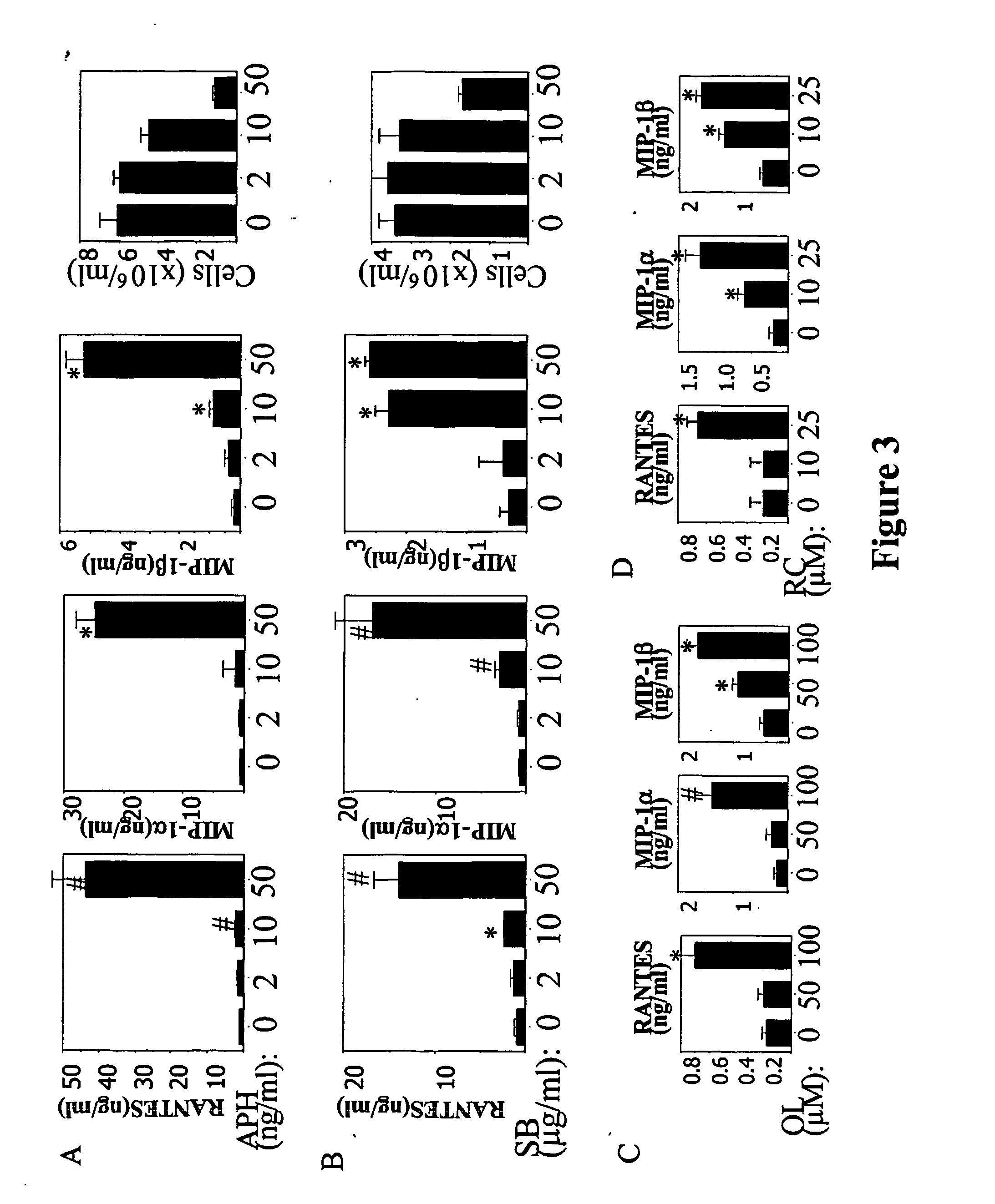
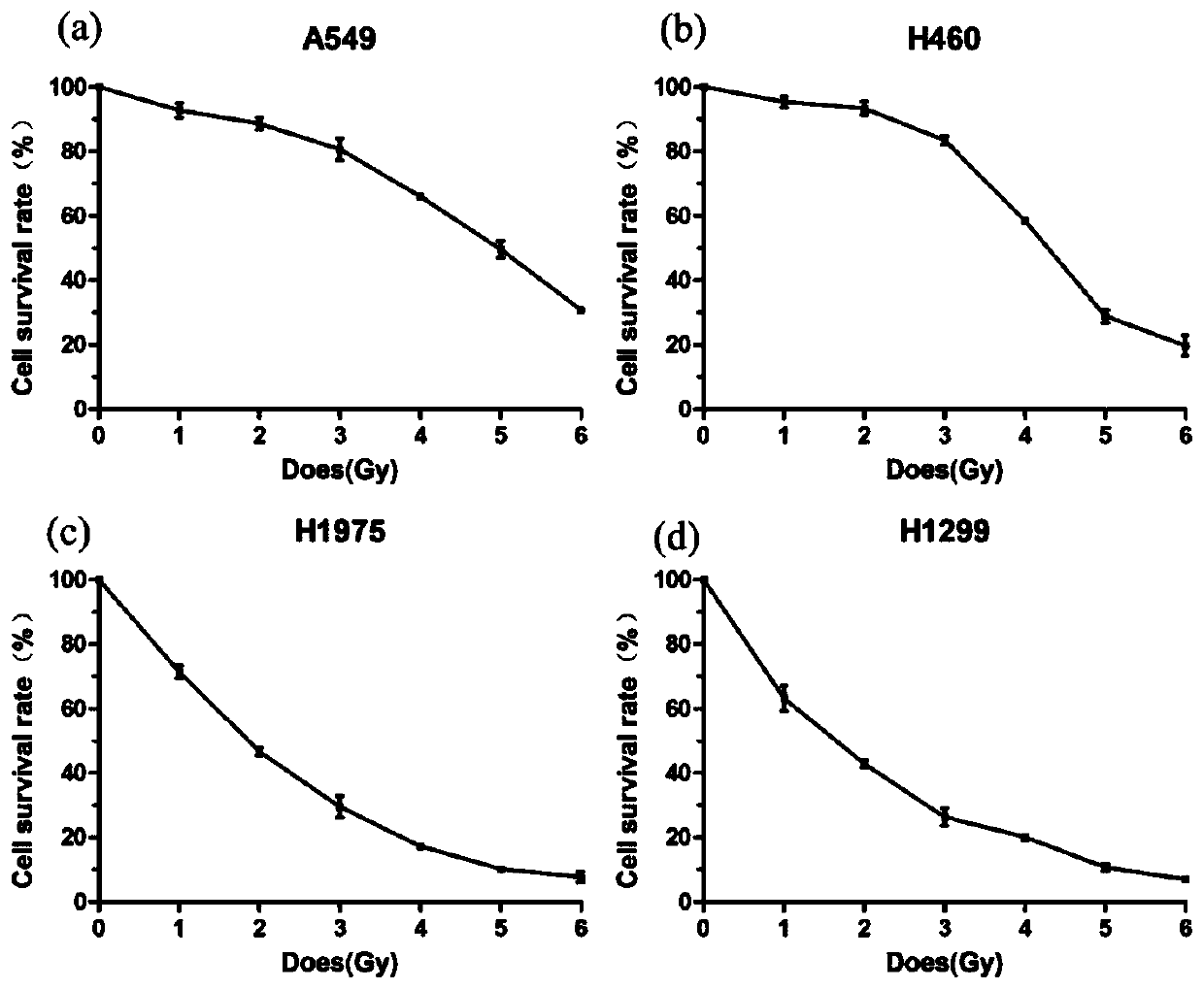
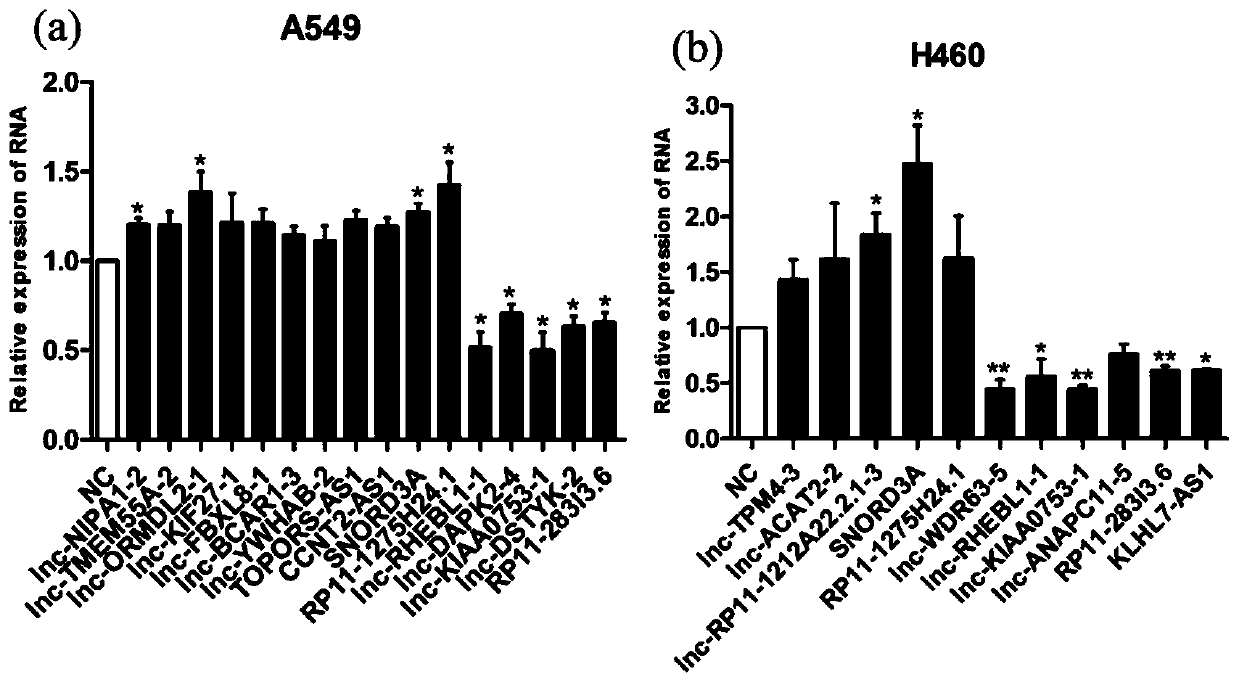
Patents
Literature
53 results about "G1 phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The g₁ phase, or Gap 1 phase, is the first of four phases of the cell cycle that takes place in eukaryotic cell division. In this part of interphase, the cell synthesizes mRNA and proteins in preparation for subsequent steps leading to mitosis. G₁ phase ends when the cell moves into the S phase of interphase.
Formulations for cell-schedule dependent anticancer agents
InactiveUS20060121085A1Strong specificityEliminate side effectsPowder deliveryBiocideMetaboliteAnticarcinogen
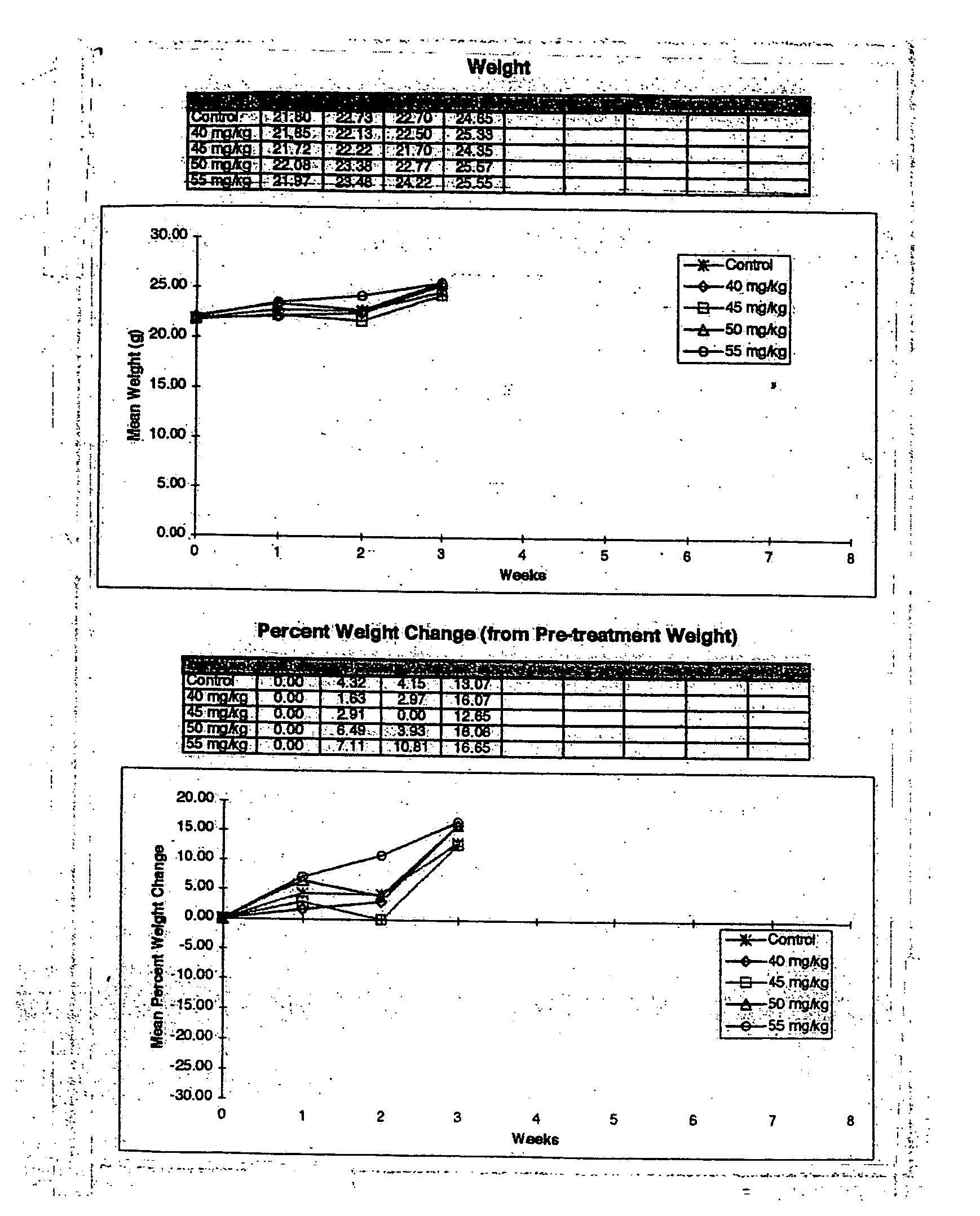
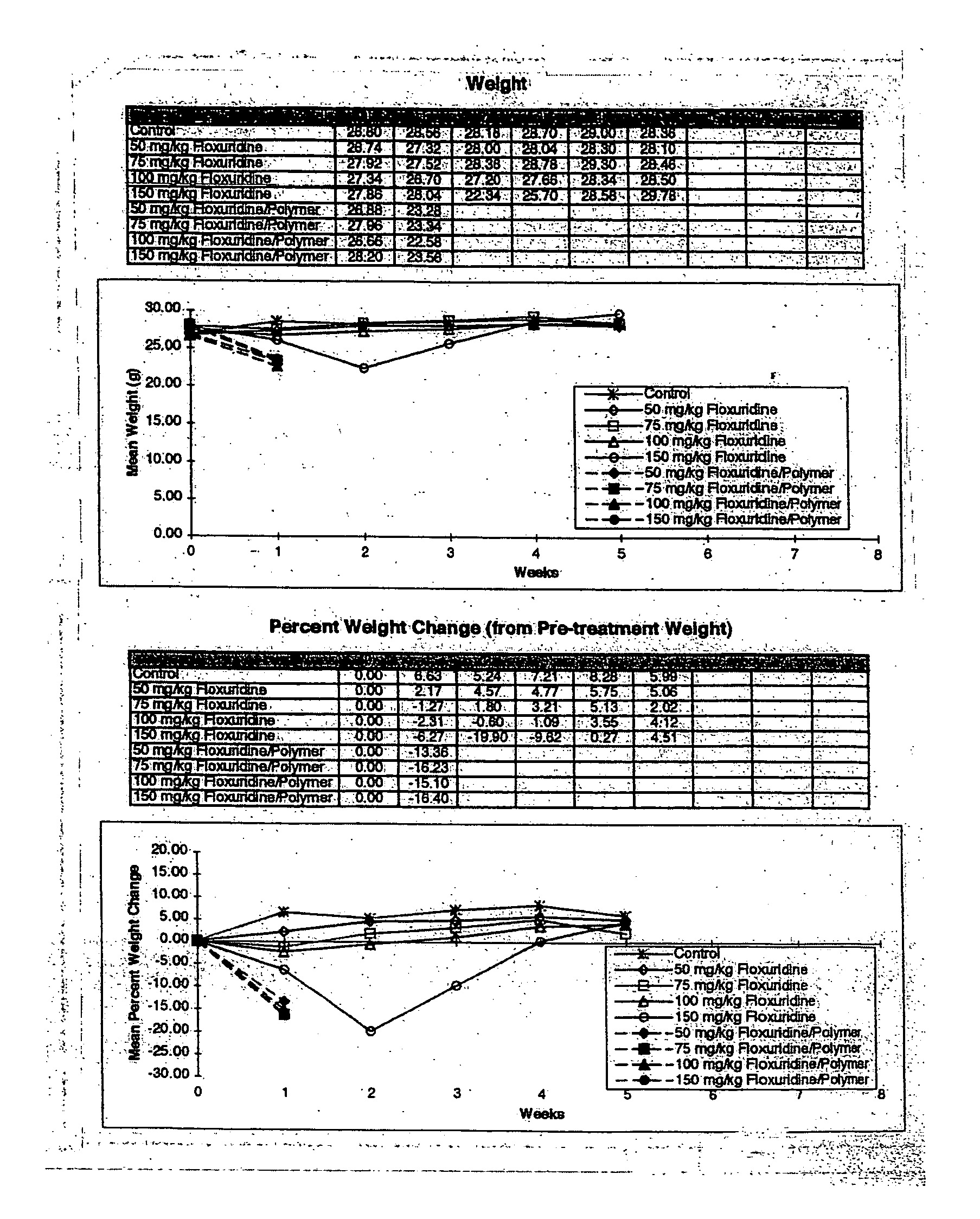
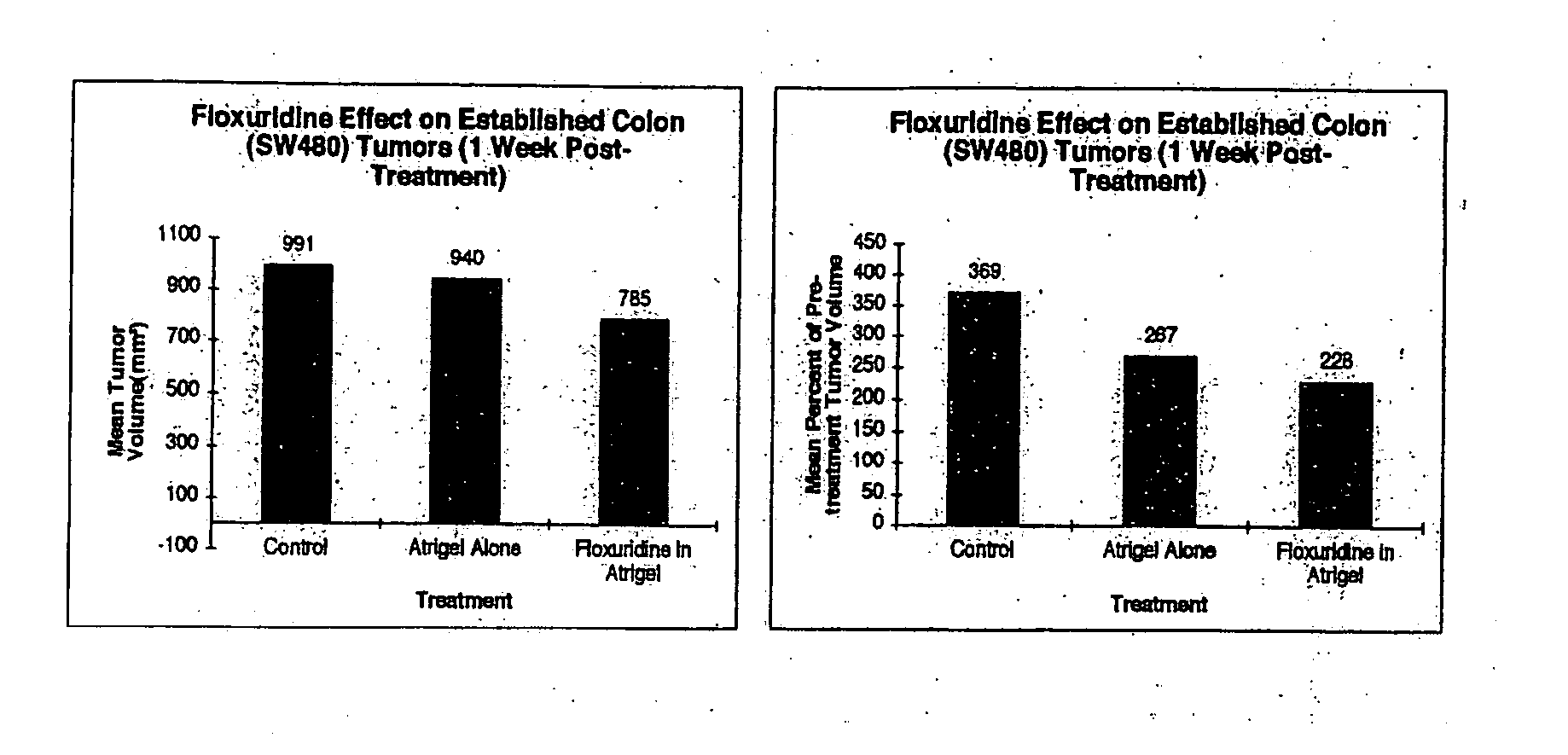
The present invention provides a flowable composition suitable for use as a controlled release implant. The composition includes: (a) a biodegradable, biocompatible thermoplastic polymer that is at least substantially insoluble in aqueous medium, water or body fluid; (b) a cell-cycle dependent biological agent, a schedule-dependent biological agent, a metabolite thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a prodrug thereof; and (c) a biocompatible organic liquid, at standard temperature and pressure, in which the thermoplastic polymer is soluble. The present invention also provides a method of treating cancer in a mammal. The present invention also provides a method of blocking, impeding, or otherwise interfering with cell cycle progression at the G1-phase, G1 / S interphase, S-phase, G2 / M interface or M-phase of the cell cycle in a mammal. The methods includes administering to a mammal an effective amount of a flowable composition of the present invention.
Owner:QLT USA INC
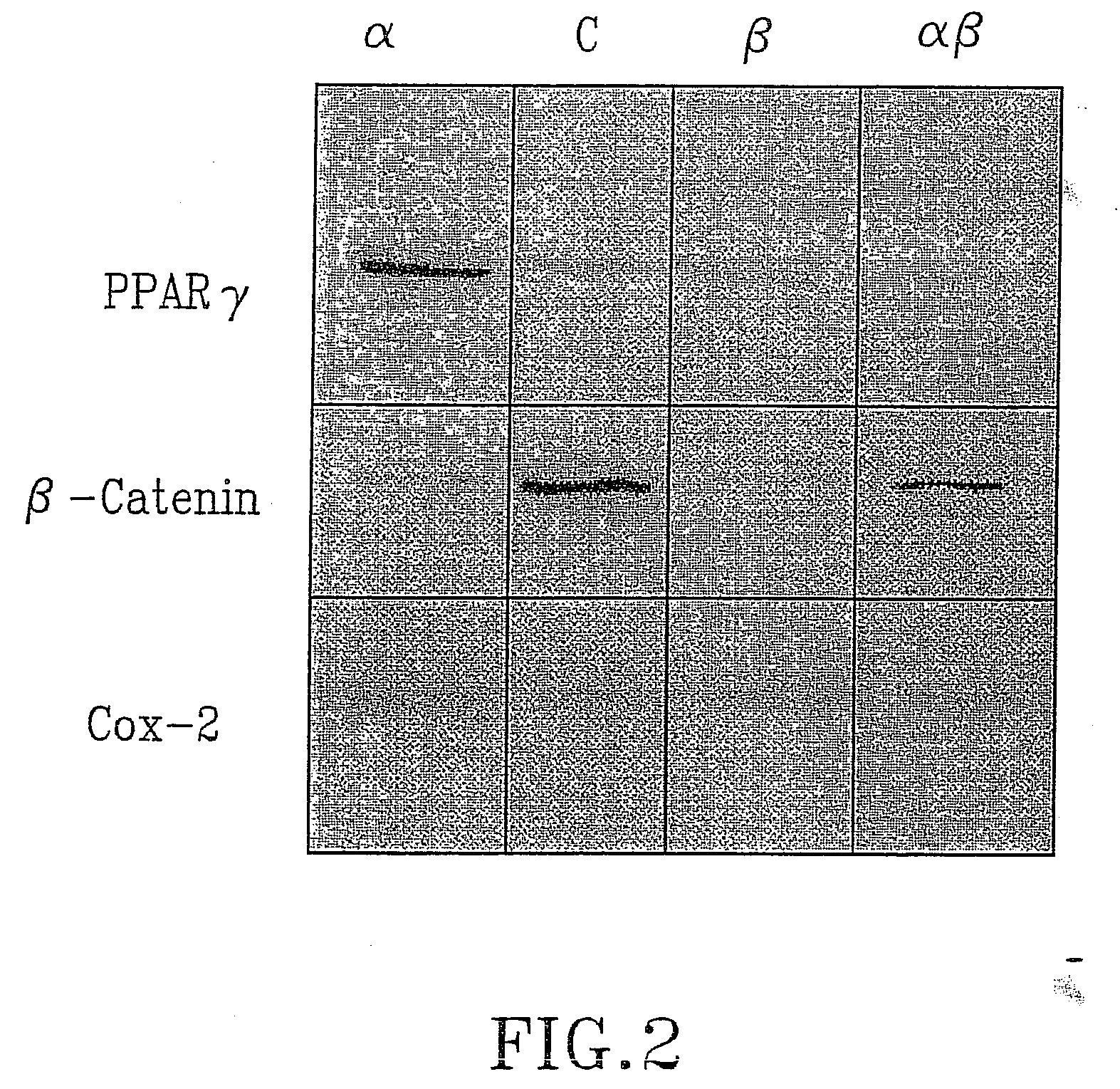
Treatment of tumours
InactiveUS20050192262A1Good curative effectSquelching unwanted PPARγ-activityOrganic active ingredientsSteroidsDiseaseAndrostane
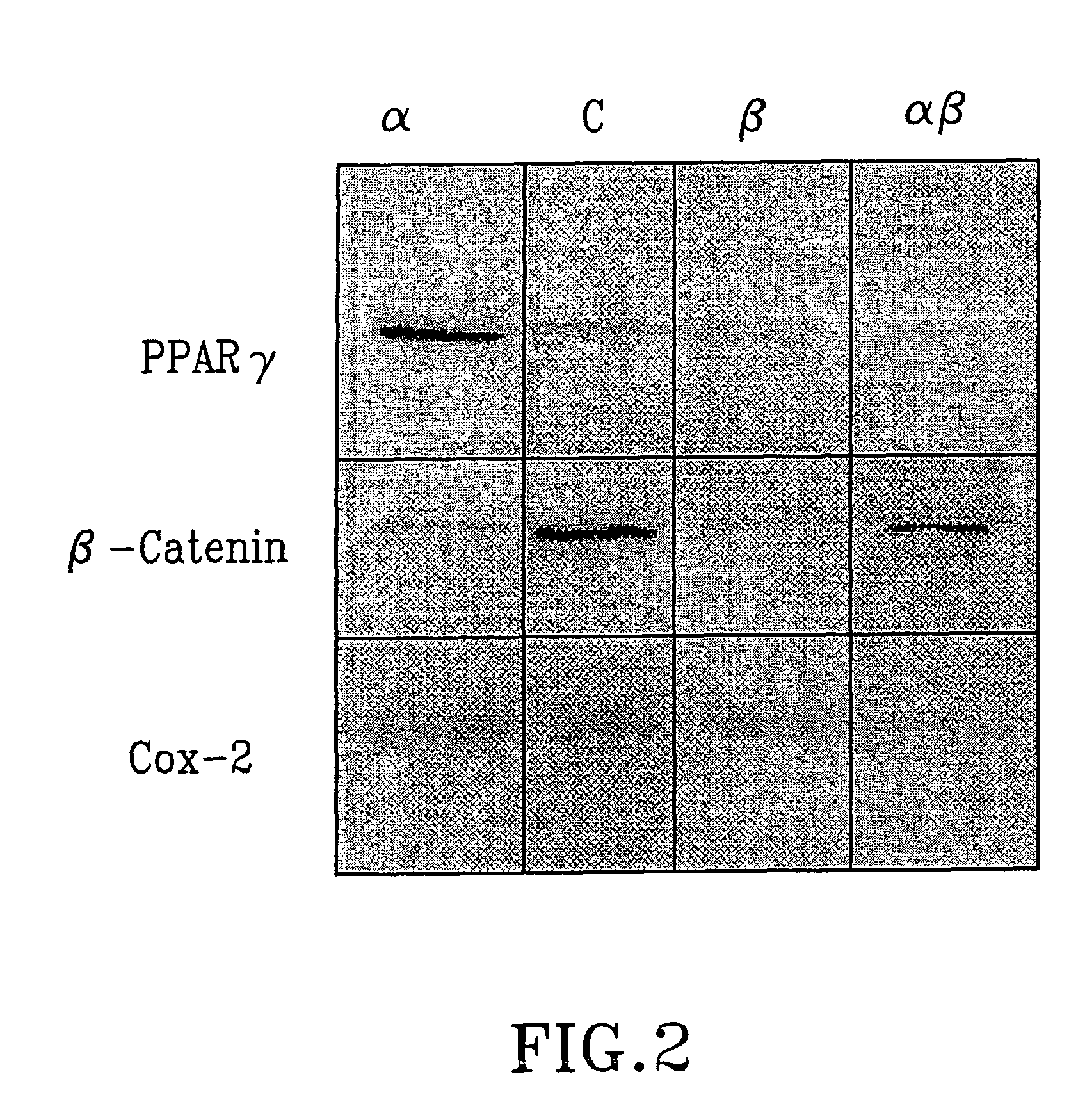
The present invention refers to steroid derivatives for use as medicaments. More specifically, the invention also relates to the use of a steroid derivative of 5-androstene-, 5-pregnenolone or corresponding saturated derivatives (androstane- or pregnane-) in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a benign and / or malignant tumour, which medicament is capable of interrupting disturbances in Wnt-signaling, such as cell-cycle arrest in G1-phase, and / or providing an angiostatic effect. Examples of such steroid derivatives are -5-androstene-17-ol, androstane-17-ol-pregnane-17-ol or pregnane-17-ol derivatives. In a further aspect, the invention relates to a method of producing a medicament for the treatment of a benign and / or malignant tumour and / or an inflammatory condition comprising the steps of contacting 5-androstane-3β,17-diol or androstane-3β-diol, an enzyme and a sulfotransferase to provide 5-androstene-17-ol-3β-sulfate or corresponding andros tane derivative (17-AEDS or 17-AADS); and mixing the 17-AEDS or 17-AADS so produced with a suitable carrier; whereby a medicament which is capable of acting as a ligand to peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-(PPAR) is produced.
Owner:HAGSTROM TOMAS
ARF-P19, a novel regulator of the mammalian cell cycle
InactiveUS6407062B1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
The INK4A (MTS1, CDKN2) gene encodes a specific inhibitor (InK4a-p16) of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. InK4a-p16 can block these kinase from phosphorylating the retinoblastoma protein (pRb), preventing exit from the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Deletions and mutations involving the gene encoding InK4a-p16, INK4A, occur frequently in cancer cells, implying that INK4a-p16, like pRb, suppresses tumor formulation. However, a completely unrelated protein (ARF-p19) arises in major part from an alternative reading frame of the mouse INK4A gene. Expression of an ARF-p19 cDNA (SEQ ID NO:1) in rodent fibroblasts induces both G1 and G2 phase arrest. Economical reutilization of protein coding sequences in this manner is without precedent in mammalian genomes, and the unitary inheritance of INK4a-p16 and ARF-p19 may reflect a dual requirement for both proteins in cell cycle control.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
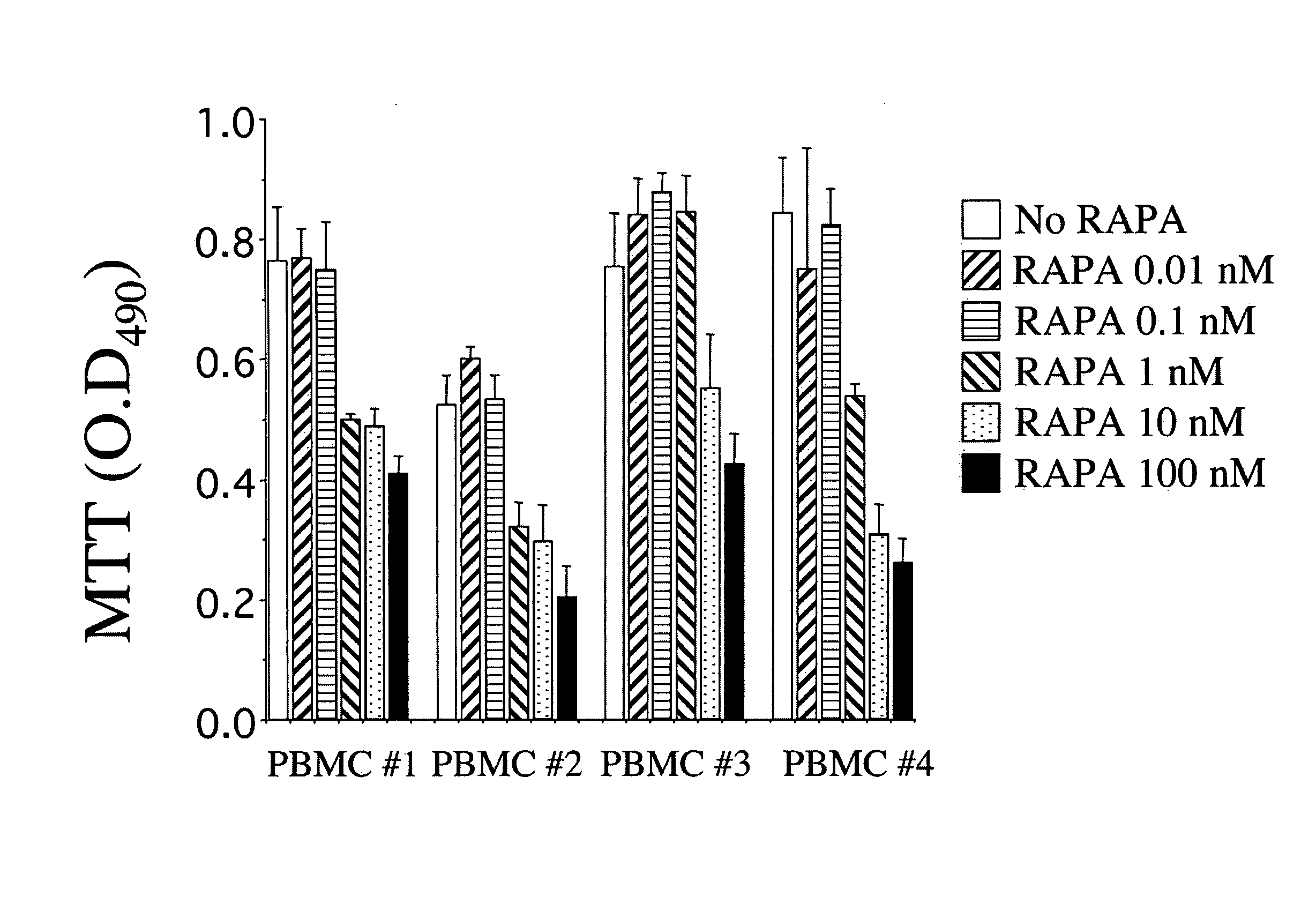
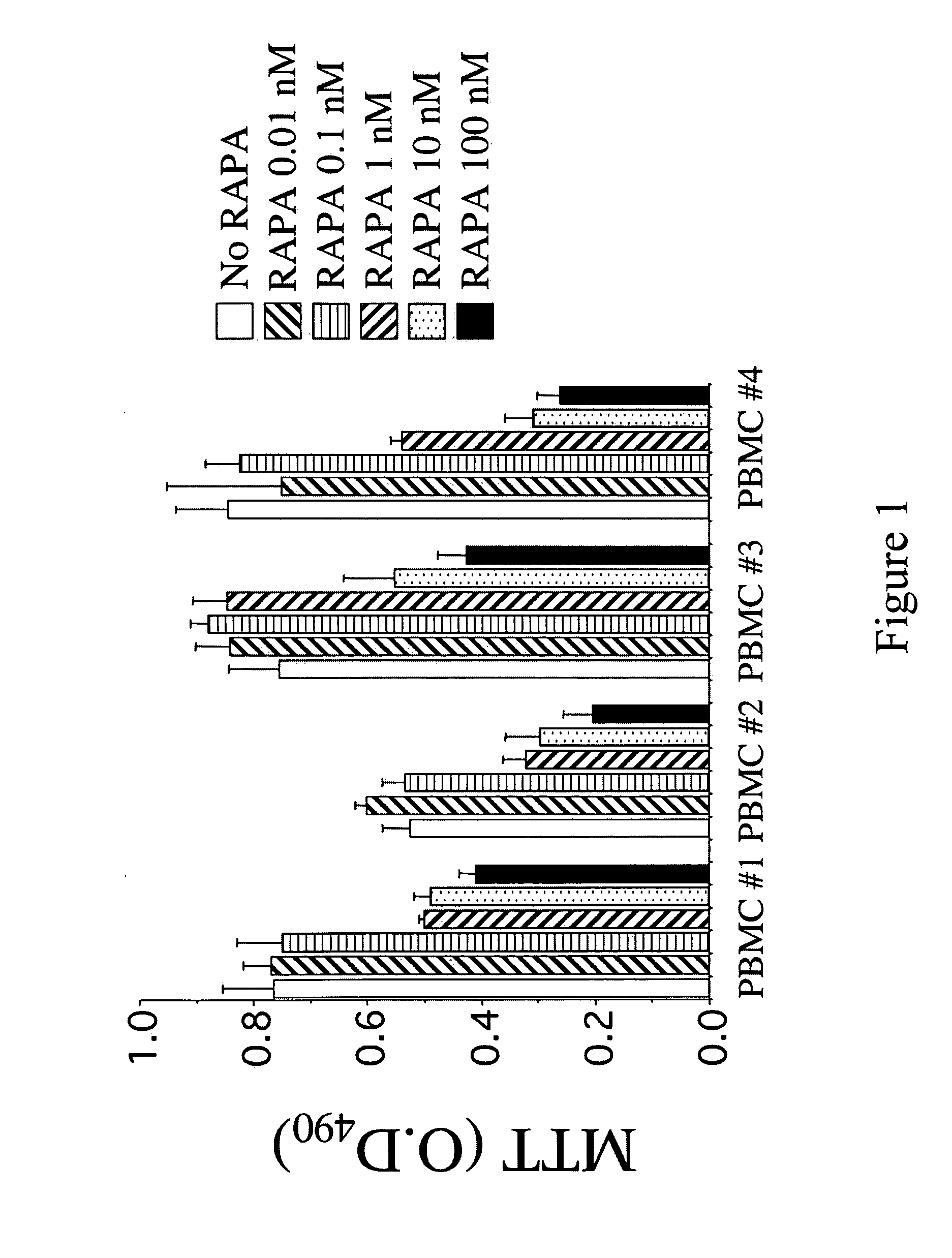
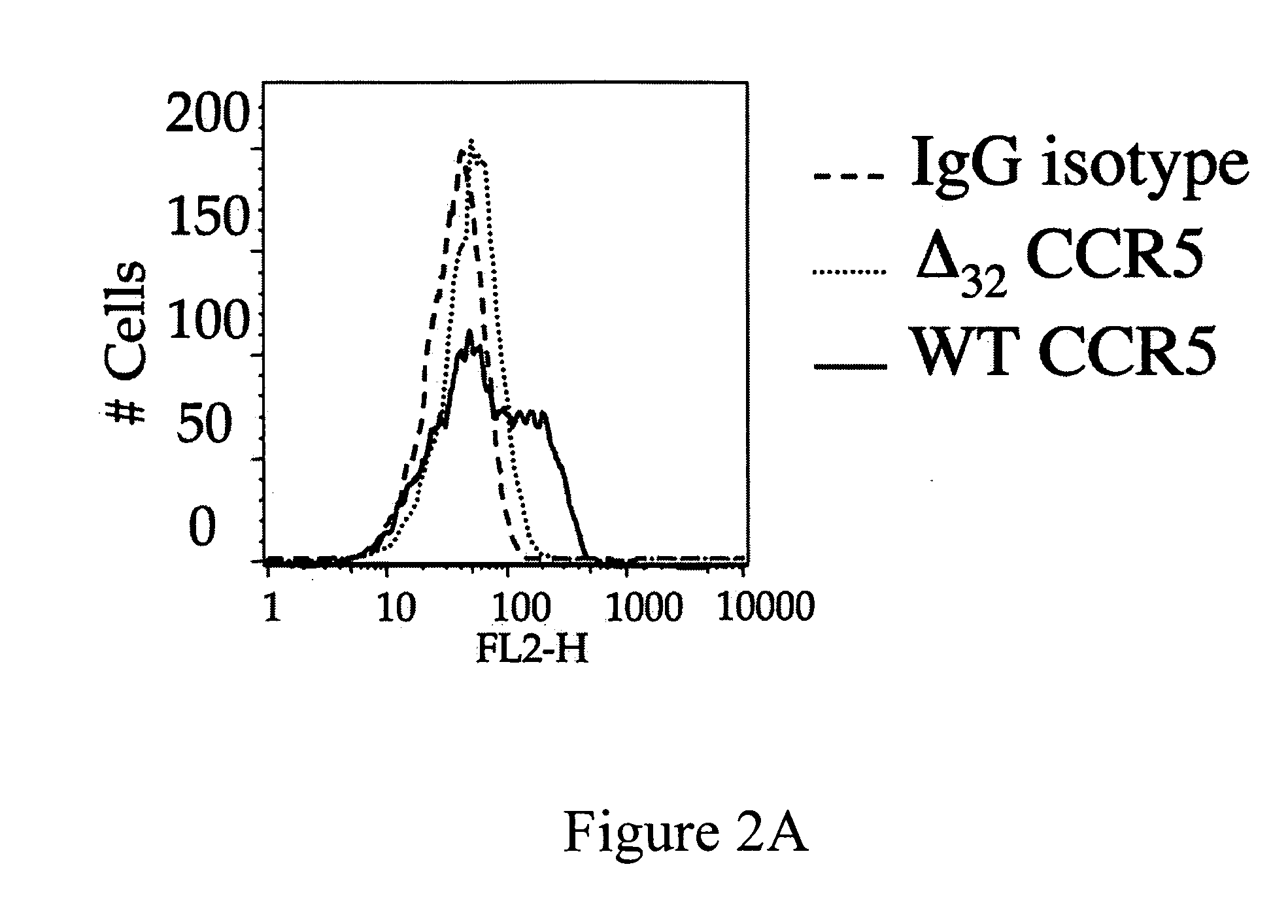
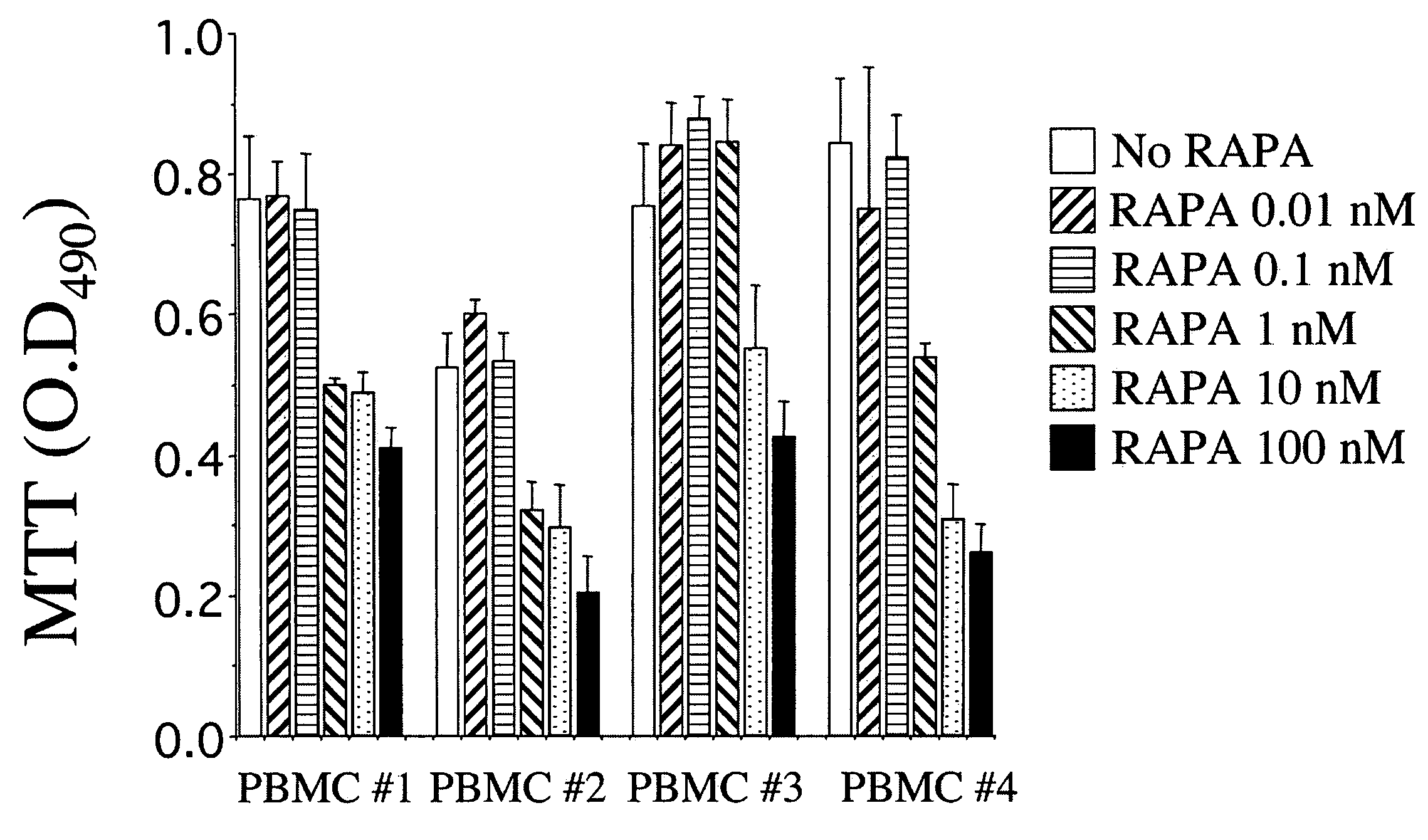
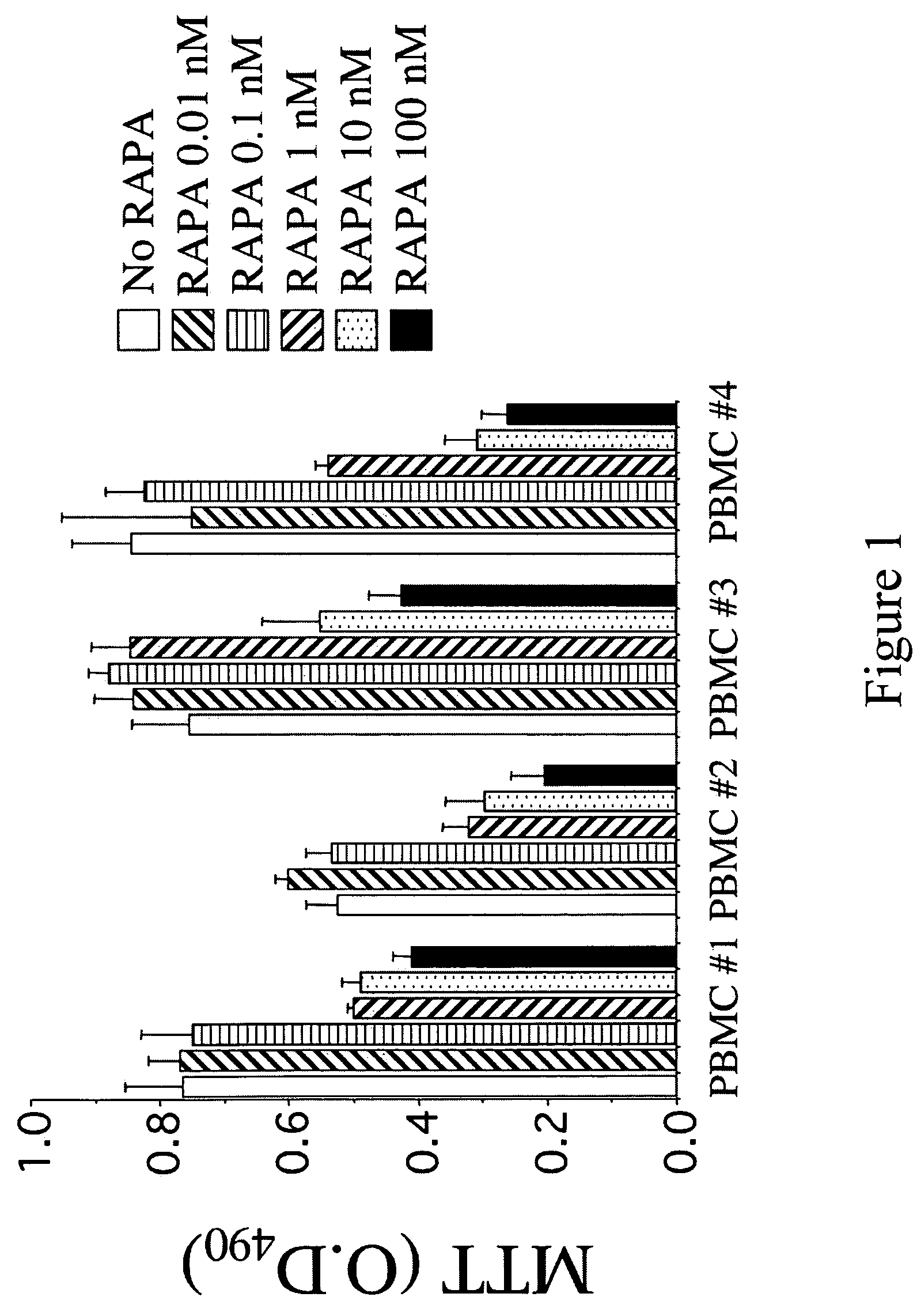
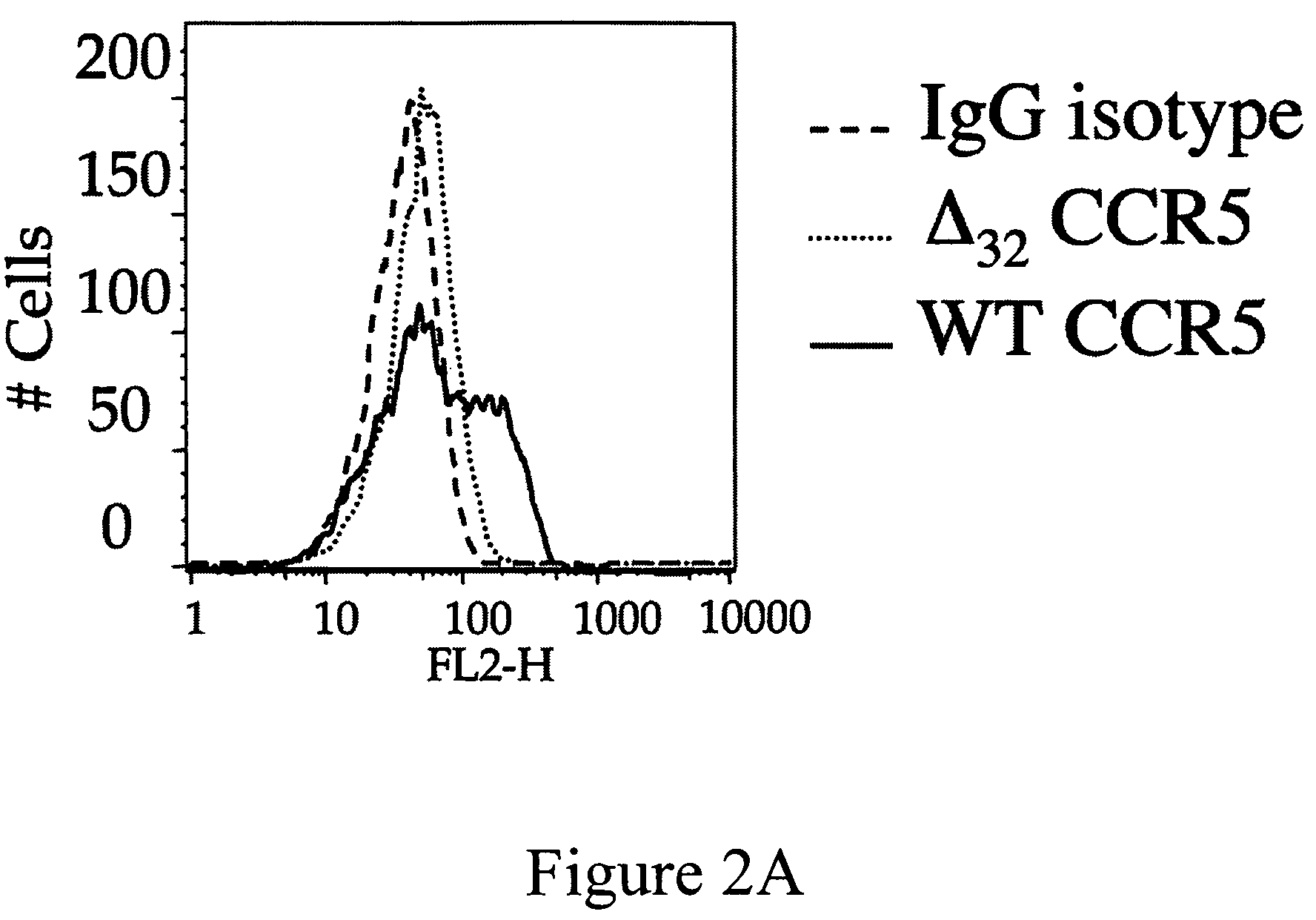
Compositions for down-regulation of CCR5 expression and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060154857A1Reduces receptor sitesSuppressing transcriptionBiocideAntiviralsG1/S checkpointHIV receptor
The present invention relates to the downregulation of surface receptor CCR5 expression through manipulation of the cell cycle in activated lymphocytes by administering a composition that arrests the G1 phase of the cell cycle, thereby reducing receptor sites for entry of HIV into T cells, and thus, the effects of HIV. Further, compositions are disclosed that include at least one G1 phase arresting agent and at least one antiviral agent, wherein the combination of agents synergistically enhances the activity of the antiviral agent.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
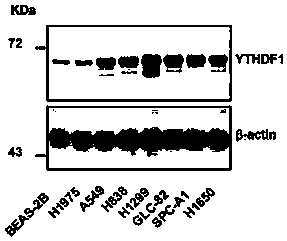
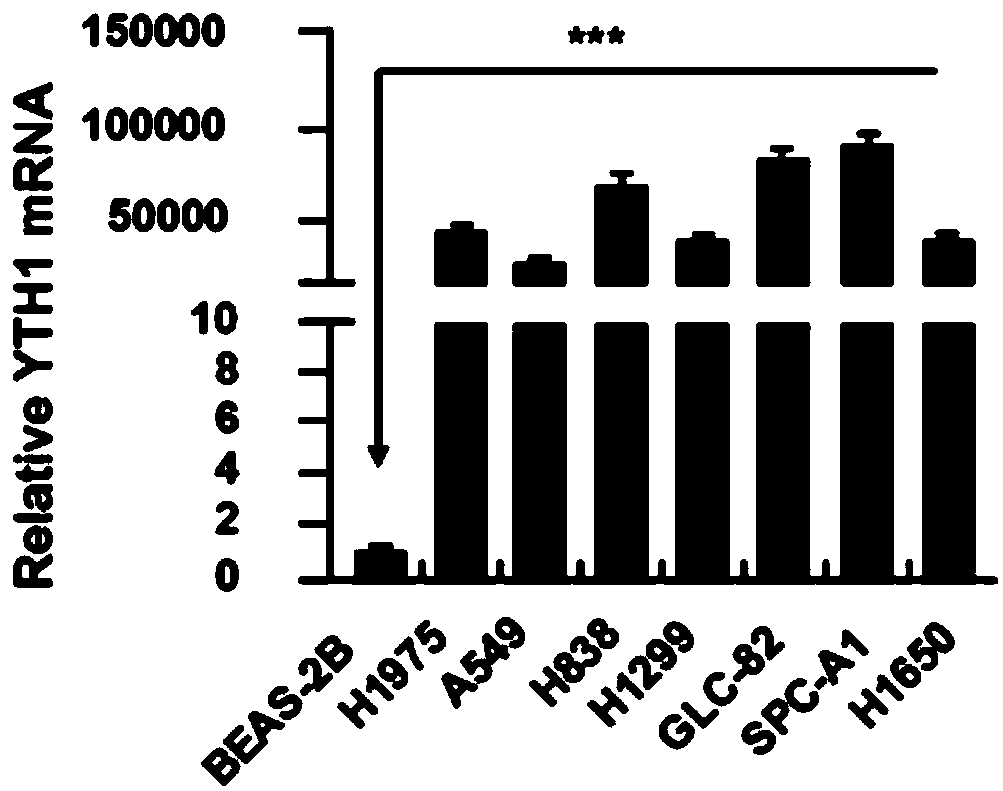
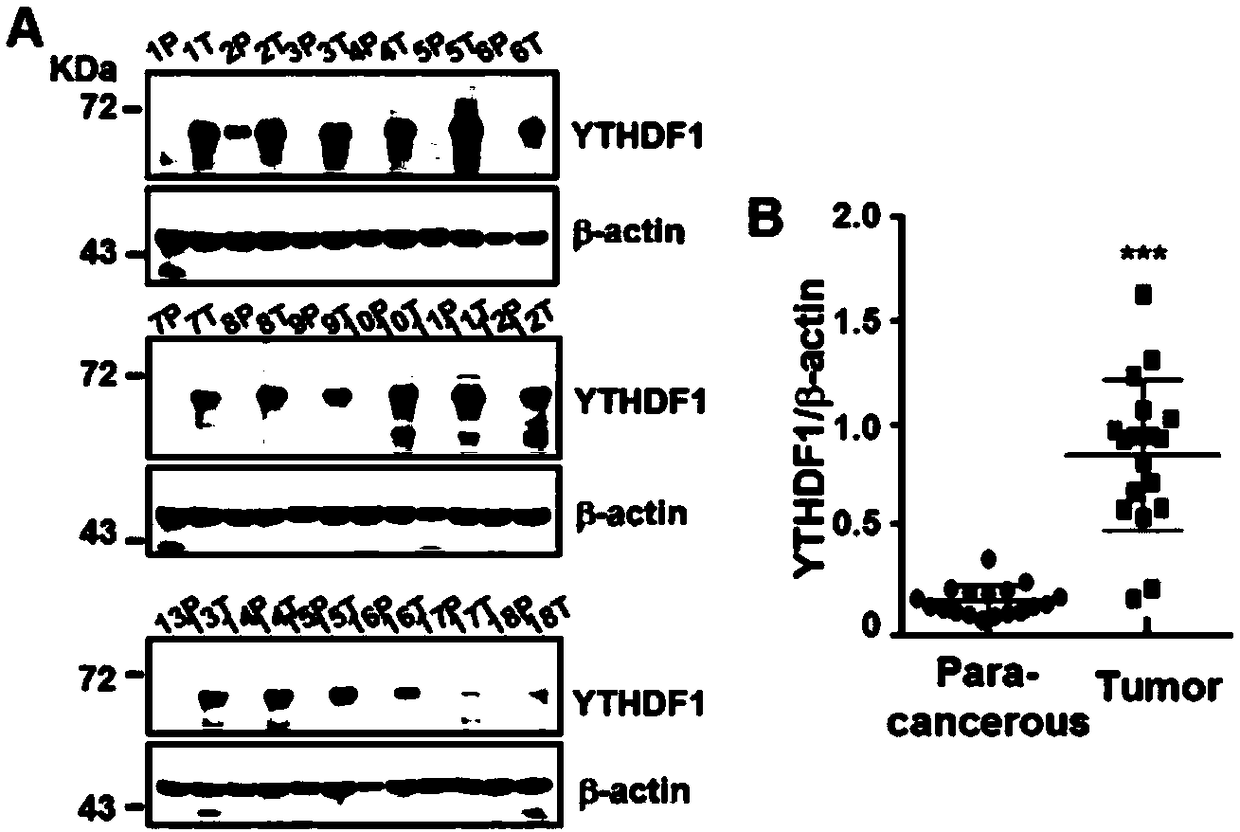
Application of human YTHDF1 (Youth-Tech-Health Domain Family Member 1) gene
ActiveCN109337980APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellKnockout animal
The invention discloses novel application of a human YTHDF1 (Youth-Tech-Health Domain Family Member 1) gene, that is, a human YTHDF1 gene expression amount detection reagent is applied to preparationof lung cancer clinical diagnosis reagents, a human YTHDF1 gene is applied to preparation of lung cancer medicines, compared with normal pulmonary epithelial cells, the YTHDF1 gene is highly expressed in lung cancer cells, RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) designed according to the YTHDF1 gene is capable of interfering slow viruses, inhibiting expression of YTHDF1, remarkably inhibiting proliferation of thelung cancer cells, retarding tumor cell division at a G0 / G1 phase and promoting cell apoptosis, inhibiting formation of nude mouse transplanted tumour, and furthermore the purpose of treating lung cancer can be achieved; YTHDF1 gene knockout mouse tumor formation capability detection shows that cell proliferation is remarkably inhibited, and cell apoptosis is remarkably increased; the results show that the YTHDF1 gene can be used as a target for lung cancer treatment, and wide prospects are provided for development of lung cancer treatment medicines based on YTHDF1 genes in future.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of 2,3-indolediketone-3-oxime and application in prevention and control of cancer
InactiveCN101816649AGenotoxicIncreased drug resistanceOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCancer preventionCancer cell
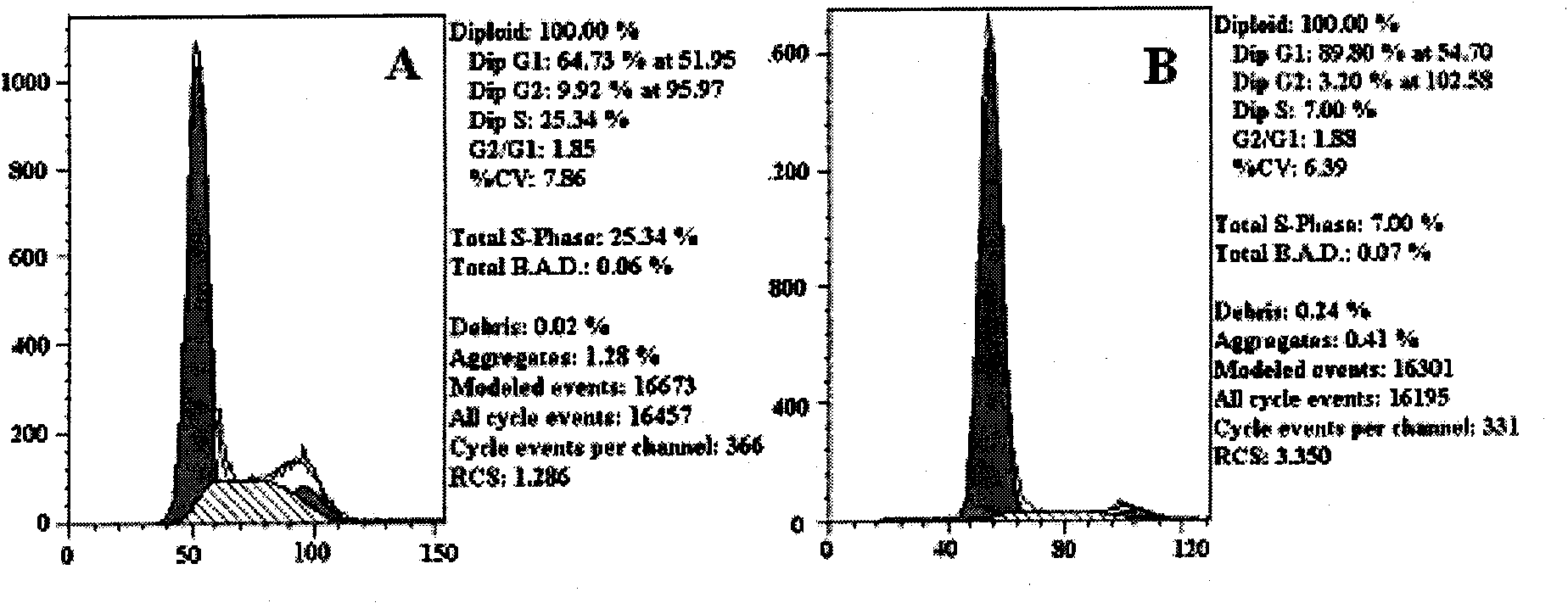
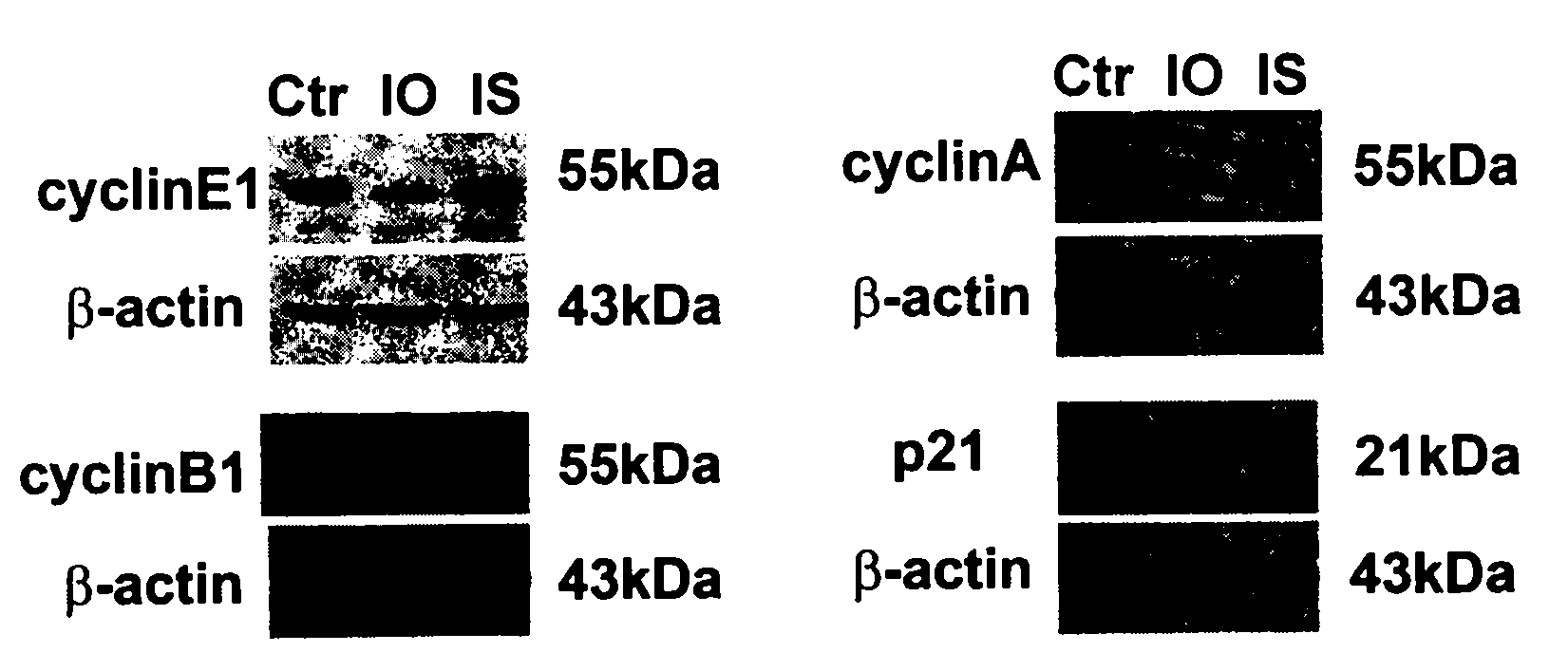
The invention discloses a preparation method of 2,3-indolediketone-3-oxime or isatin-3-oxime and discloses application of the 2,3-indolediketone-3-oxime in preparing cancer prevention or control drugs. The application of the 2,3-indolediketone-3-oxime in prevention and control of cancer or other malignant tumours is characterized in that the substance has obvious growth inhibition action on various tumour cells, has specific G1-phase blocking action on cell generation cycle, i.e. the substance can stop the tumour cells carrying out DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) replication, and has obvious down regulation action on the expression of cycle proteins cyclin E, cyclin B and cyclin A, obvious up regulation action on the expression of a cell cycle inhibiting factor p21, induction action on cancer cells or precancerosis cells and sensitization action on gene toxic chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
ARF-P19, a novel regulator of the mammalian cell cycle
The INK4A (MTS1, CDKN2) gene encodes a specific inhibitor (InK4a-p16) of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. InK4a-p16 can block these kinase from phosphorylating the retinoblastoma protein (pRb), preventing exit from the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Deletions and mutations involving the gene encoding InK4a-p16, INK4A, occur frequently in cancer cells, implying that INK4a-p16, like pRb, suppresses tumor formulation. However, a completely unrelated protein (ARF-p19) arises in major part from an alternative reading frame of the mouse INK4A gene. Expression of an ARF-p19 cDNA (SEQ ID NO:1) in rodent fibroblasts induces both G1 and G2 phase arrest. Economical reutilization of protein coding sequences in this manner is without precedent in mammalian genomes, and the unitary inheritance of INK4a-p16 and ARF-p19 may reflect a dual requirement for both proteins in cell cycle control.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
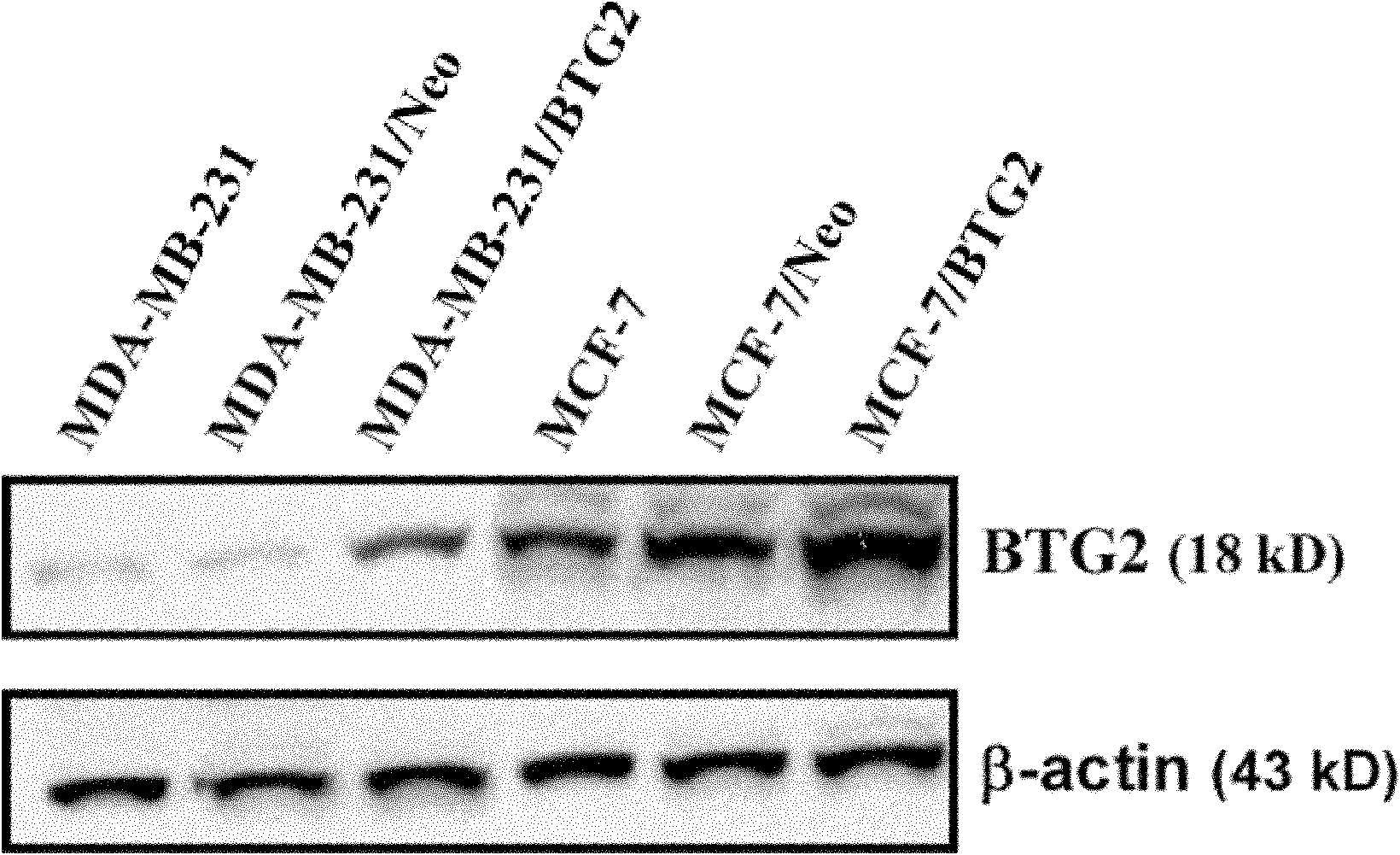
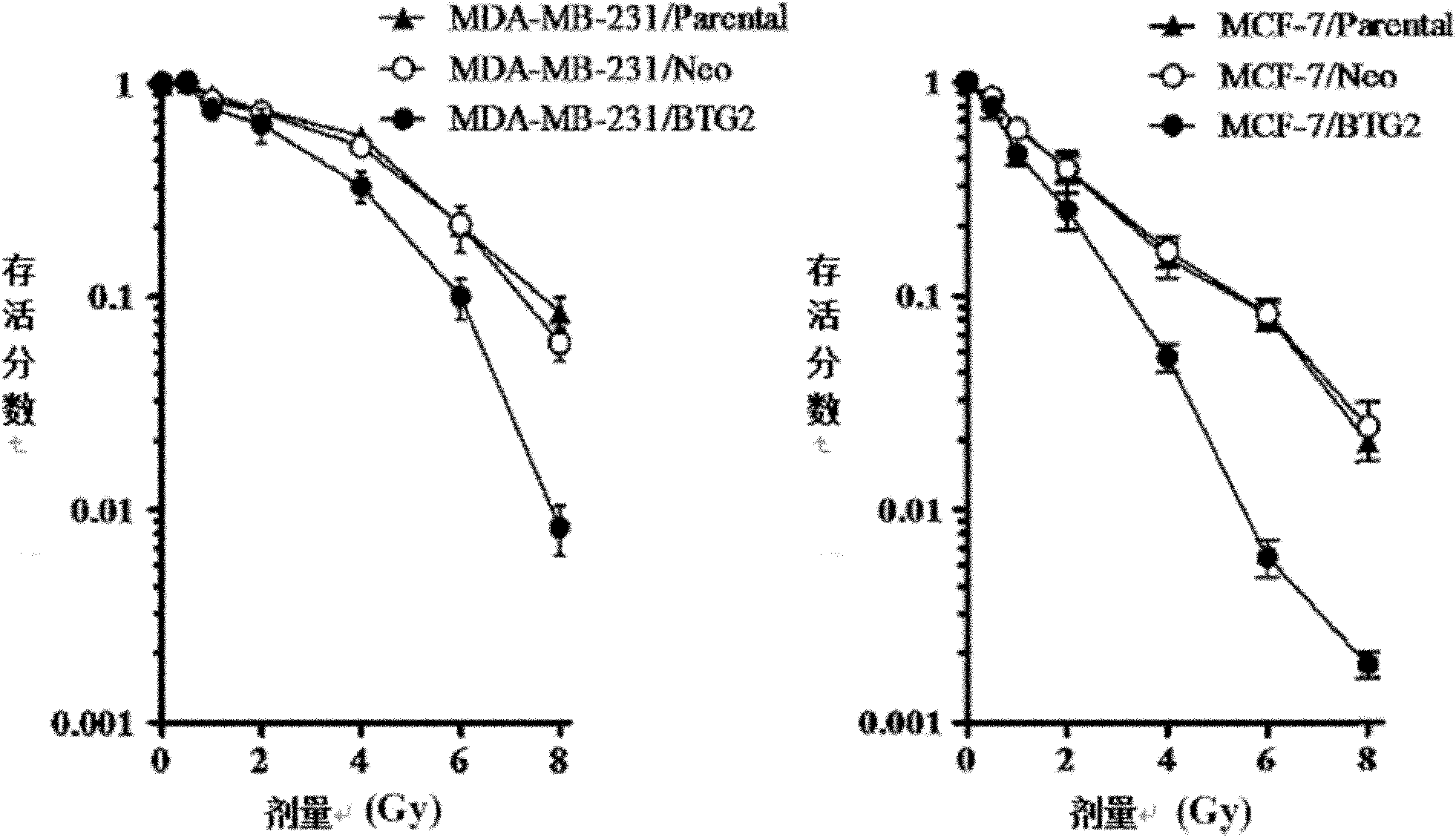
Application of BTG2 (B cell translocation gene 2) in preparing radiation sensitizing agent
InactiveCN102028957APromote apoptosisIncreased sensitivityGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCyclin D1Mda mb 231
The invention belongs to the field of radiation sensitizing agents, in particular to an application of BTG2 (B cell translocation gene 2) in preparing a tumor radiation sensitizing agent for ionizing radiation including X-rays. The invention discloses an application of liposome mediated eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA3-BTG2 in preparing the radiation sensitizing agent, wherein the liposome mediated eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA3-BTG2 is transfected to MCF-7 (macrophage chemotactic factor-7) breast cancer cells and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells and expressed successfully, and the BTG2 protein can up-regulate the proapoptosis Bax protein and down-regulate the cell cycle regulatory protein Cyclin D1, and by promoting the cell apoptosis, G0 / G1 phase arrest of the cells is promoted, thereby increasing the sensitivity of the breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation including the X-rays.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
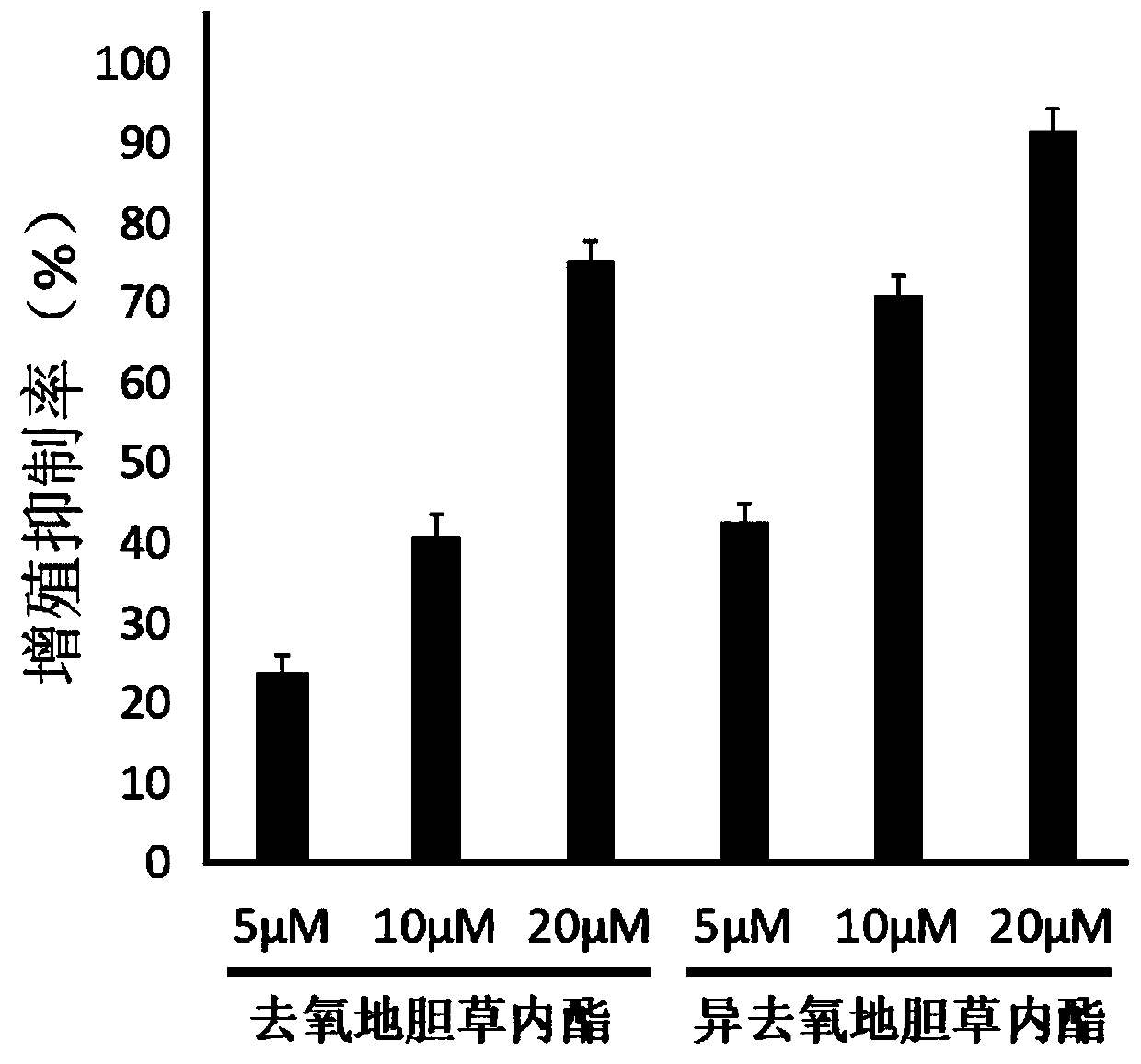
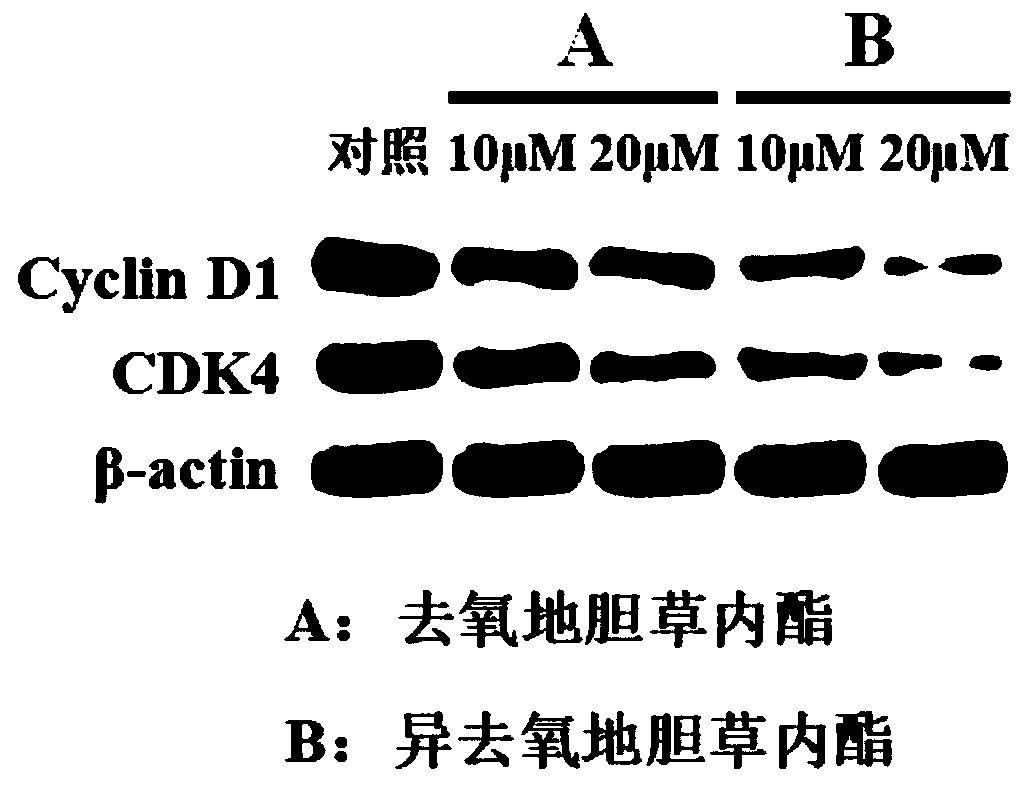
Application of deoxyelephantolide or isodeoxyelephantolide in preparation of a medicine used for resisting lung fibrosis
ActiveCN111084773ADivide and proliferateProliferation inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderCell divisionCyclin D1
The invention discloses an application of deoxyelephantolide or isodeoxyelephantolide in preparation of a medicine used for resisting lung fibrosis. Researches find that the deoxyelephantolide or theisodeoxyelephantolide can be used for effectively inhibiting the proliferation of human embryonic lung fibroblasts HFL1. Western Blot results show that the proliferation inhibition effect of the deoxyelephantolide or the isodeoxyelephantolide on human embryonic lung fibroblasts HFL1 is likely to be related with the situation that the human embryonic lung fibroblasts is blocked in a G1 phase and can not realize cell division and proliferation through down regulation of the expression of cyclin D1 and CDK4. Therefore, the deoxyelephantolide or the isodeoxyelephantolide has the prospect of beingdeveloped into the medicine used for resisting the lung fibrosis.
Owner:仁合熙德隆药业有限公司
Effective nuclear reprogramming in mammals using CDK2 inhibitors
InactiveUS6906238B2Convenient timeOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureMammalGenetic Materials
The present invention provides methods of producing a cloned non-human mammalian nuclear transfer (NT) embryo and methods for producing a cloned non-human mammal. Embodiments of the methods include introducing donor genetic material into a metaphase I oocyte; introducing donor genetic material into a non-enucleated oocyte; introducing donor genetic material obtained from a donor cell that is at metaphase into an oocyte; introducing donor genetic material into an oocyte, and naturally activating the oocyte or the NT embryo; and introducing donor genetic material obtained from a donor cell that is at late G1 phase into an oocyte.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Compositions for inducing increased levels of beta-chemokines and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS20060099170A1Improve the level ofImprove availabilityBiocideAntiviralsViral ReceptorG1/S checkpoint
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for inducing increased levels and availability of β-chemokines by administering to a subject at least one G1 phase arresting compound, wherein the increased levels and availability of β-chemokines block chemokine / viral receptors thereby preventing or treating viral infections.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BIOTECH INST
Application of long-chain non-coding RNA lncLCIR-1 as lung cancer molecular marker
ActiveCN110066875APrevent proliferationInhibition of invasion and metastasisOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceG1/S checkpoint
The invention relates to an application of long-chain non-coding RNA lncLCIR-1 as a lung cancer molecular marker. According to the invention, stable high expression of the lncLCIR-1 in lung cancer tissues is found for the first time, and the level of the lncLCIR-1 is reduced after radiotherapy, so that the lncLCIR-1 in the lung cancer is a potential index for predicting the curative effect of theradiotherapy, and is a novel lung cancer molecular marker. The application of the lncLCIR-1 detection reagent in preparing a reagent for diagnosing the prognosis of a lung cancer patient mainly uses the lncLCIR-1 as a detection marker to prepare a corresponding fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit for detecting the prognosis of the lung cancer patient in radiotherapy. In addition, the siRNAcan inhibit the expression of lncLCIR-1, so that the cell cycle of the lung cancer is regulated, the G1 phase block of the lung cancer cell is caused, the proliferation of the lung cancer cell is inhibited, and the siRNA has important significance in the preparation of a medicament for treating the lung cancer.
Owner:SHANDONG RES INST OF TUMOUR PREVENTION TREATMENT
Compositions for down-regulation of CCR5 expression and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7863242B2Reduces receptor sitesSuppressing transcriptionBiocideAntiviralsG1/S checkpointHIV receptor
The present invention relates to the downregulation of surface receptor CCR5 expression through manipulation of the cell cycle in activated lymphocytes by administering a composition that arrests the G1 phase of the cell cycle, thereby reducing receptor sites for entry of HIV into T cells, and thus, the effects of HIV. Further, compositions are disclosed that include at least one G1 phase arresting agent and at least one antiviral agent, wherein the combination of agents synergistically enhances the activity of the antiviral agent.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Treatment of tumours
InactiveUS20070111973A1Good curative effectSquelching unwanted PPARγ-activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseAndrostane
The present invention refers to steroid derivatives for use as medicaments. More specifically, the invention also relates to the use of a steroid derivative of 5-androstene-, 5-pregnenolone or corresponding saturated derivatives (androstane- or pregnane-) in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a benign and / or malignant tumour, which medicament is capable of interrupting disturbances in Wut-signaling, such as cell-cycle arrest in G1-phase, and / or providing an angiostatic effect. Examples of such steroid derivatives are -5-androstene-17-ol, androstane-17-ol-pregnane-17-ol or pregnane-17-ol derivatives. In a further aspect, the invention relates to a method of producing a medicament for the treatment of a benign and / or malignant tumour and / or an inflammatory condition comprising the steps of contacting 5-androstane-3B,17-dio 1 or androstane-3B-diol, an enzyme and a sulfotransferase to provide 5-androstene-17-ol-3B-sulfate or corresponding andros tane derivative (17-AEDS or 17-AADS); and mixing the 17-AEDS or 17-AADS so produced with a suitable carrier; whereby a medicament which is capable of acting as a ligand to peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor—(PPAR) is produced.
Owner:HAGSTROM TOMAS +2
Application of miR-486-5p in non-small cell lung carcinoma cell line
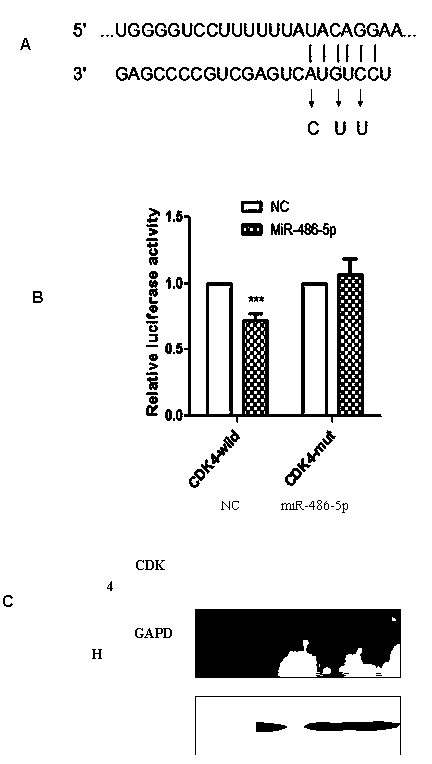
InactiveCN104069506AInhibition of translationAvoid degradationGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsH1299 cellDrug target
The invention relates to application of miR-486-5p in a non-small cell lung carcinoma cell line. The miR-486-5p performs specific low-expression in a non-small cell lung carcinoma cell and a series of lung carcinoma tissue clinical specimen; in an H1299 cell, the over-expressed miR-486a-5p can inhibit cell proliferation of H1299 and inhibit G1 / S conversion to block the cell in the G1 phase. Experiments based on bioinformatics analysis discovers that the miR-486a-5p is complementary with 3'-UTR () of a target gene mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid), so that translation of the mRNA of the target gene can be inhibited or the mRNA of the target gene can be directly degraded; furthermore, western blotting and other experiments prove that the CDK4 gene is the target gene of the miR-486a-5p. The experiment first proves that the CDK4 gene is the garget gene of miR-486a-5p, and the miRNA is utilized to diagnose and treat non-small cell lung carcinoma in clinical application, and a certain application value is created for providing the aspect of drug targets.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Valinomycin B, preparation method and medical purpose thereof
ActiveCN105968067APrevent proliferationReduce protein expressionOrganic chemistryBacteriaPharmaceutical SubstancesCell cycle
The invention provides a compound valinomycin B having glioma activity resistance, provides an active substance producing strain streptomyces parvus separated and cultured from sea mud, and the active substance valinomycin B can be prepared. The streptomyces parvus is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection and named as P11-23B (Streptomyces parvus P11-23B) with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2015675 on Nov, 12th, 2015. The valinomycin B has features of obviously inhibiting multiplication of various kinds of glioma cells, obviously inhibiting glioma cell cycle at G0 / G1 phase, and reducing the protein level expression of several key enzymes with different metabolism approaches of glioma cells, and has unique anti-tumor effect. The valinomycin B can be used for preparing medicines for treating glioma. The chemical structural formula of the valinomycin B is as shown in the specification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Composition for inhibiting glioma growth and application thereof
InactiveCN103784962ADown-regulation of AKT phosphorylation levelsRaise the ratioGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAfter treatmentPhosphorylation
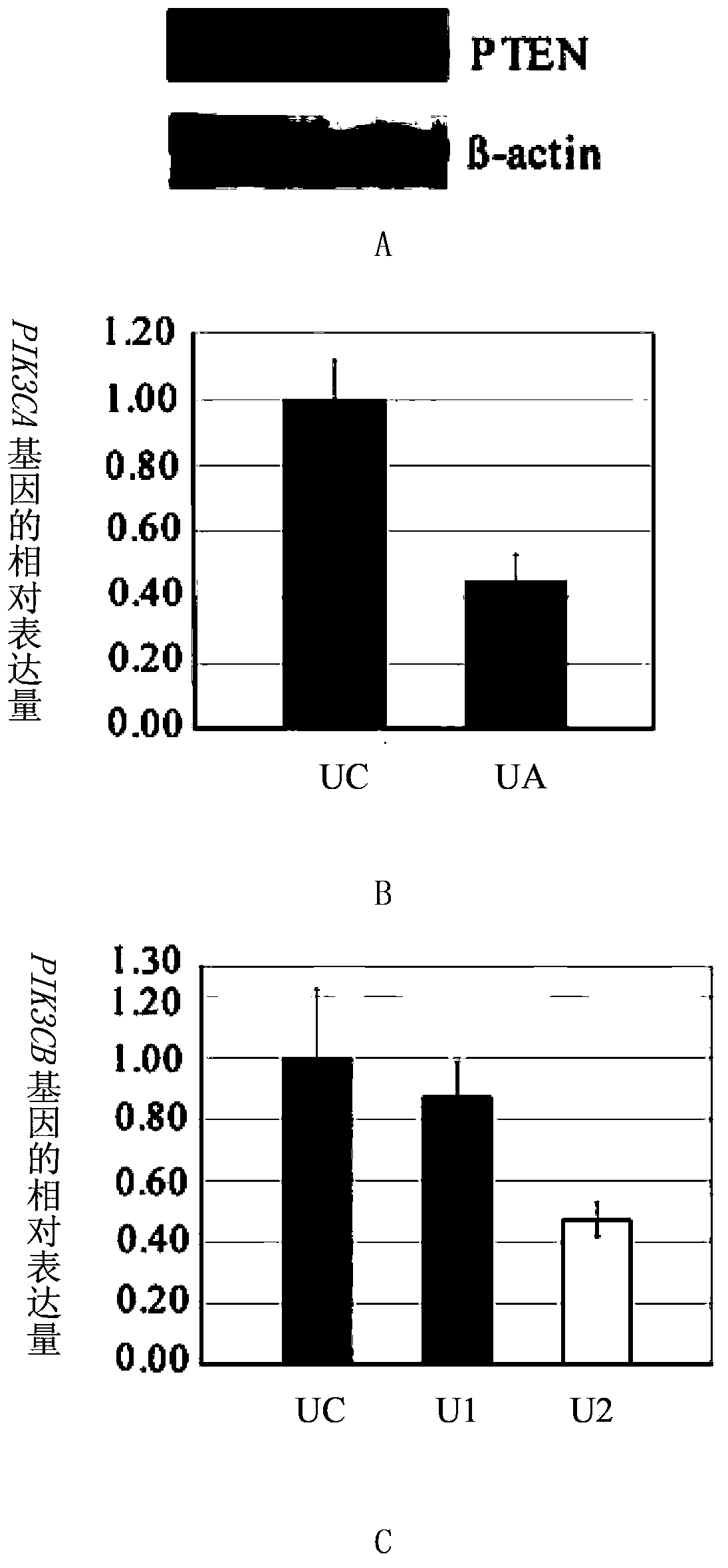
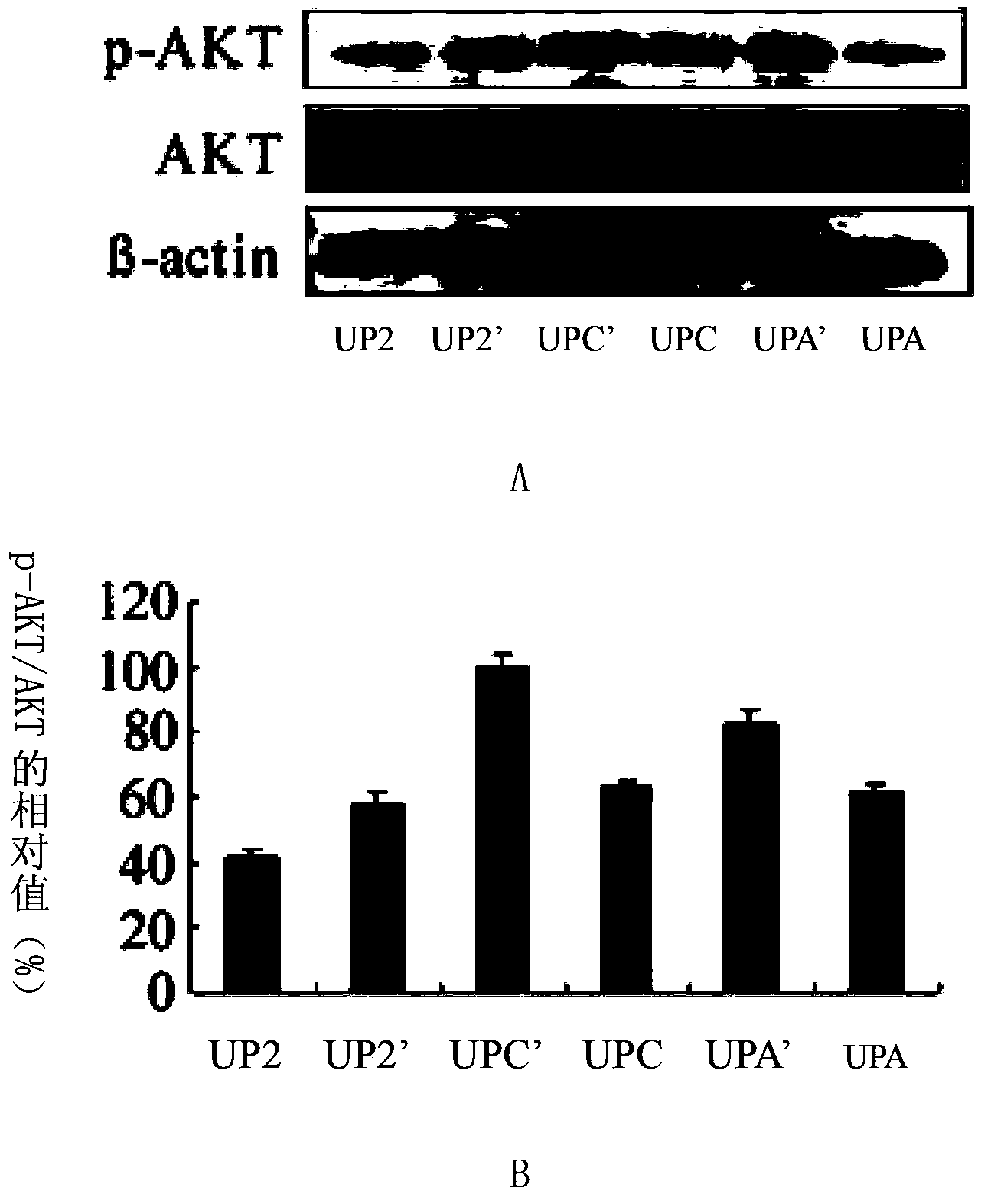
The invention discloses a composition for inhibiting glioma growth and an application thereof. The composition comprises a substance for improving the expression of protein (PTEN) as shown in sequence 1 of the sequence table, and a substance for inhibiting the expression of protein (B) as shown in sequence 3 of the sequence table. Experiments demonstrate that when the combination of recovering the expression of protein PTEN with inhibiting the expression of protein B is compared with only recovery of the expression of protein PTEN or only inhibition of expression of protein B, the AKT phosphorylation level of recombinant glioma cell lines is significantly decreased, cell proliferation and colony formation are significantly inhibited, and the proportion of cells stopping at the G0 / G1 phase and the cell apoptosis rate are significantly increased; Glioma in transplanted mouse body has no increase in size at 20-48 days after treatment by recovering the expression of protein PTEN combined with inhibiting the expression of protein B, and the tumor weight is almost zero at the 48th day after the treatment. The invention provides a new and effective combination therapy scheme for glioma, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
mir-2 small molecule and application
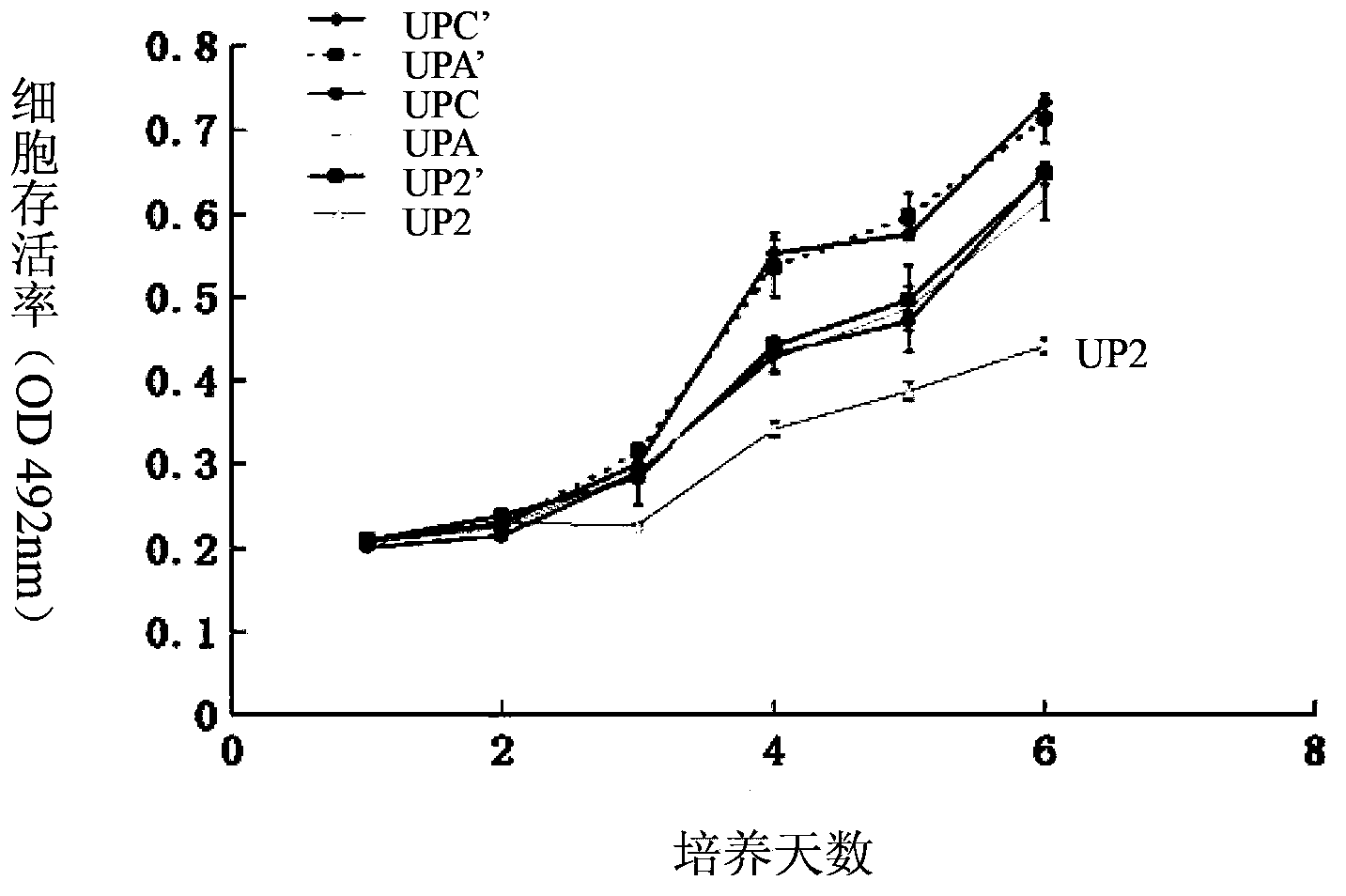
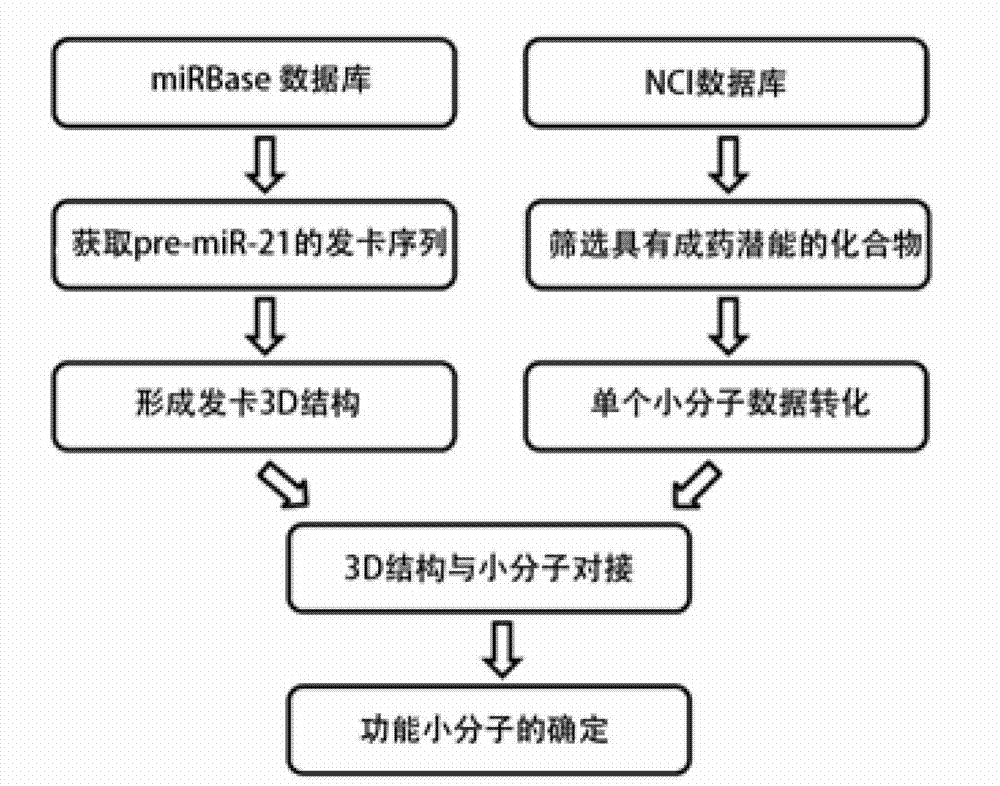
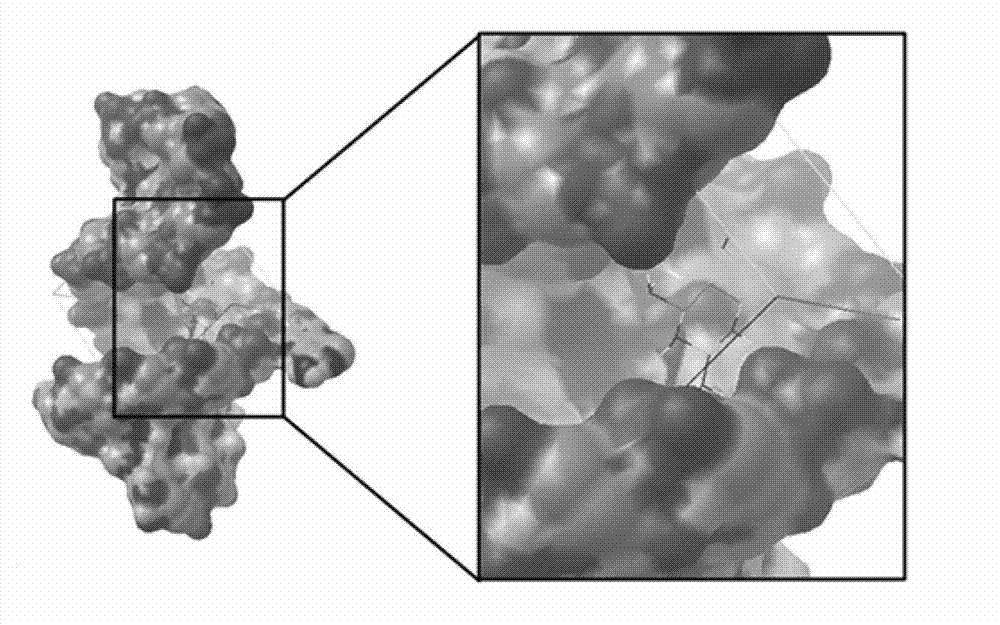
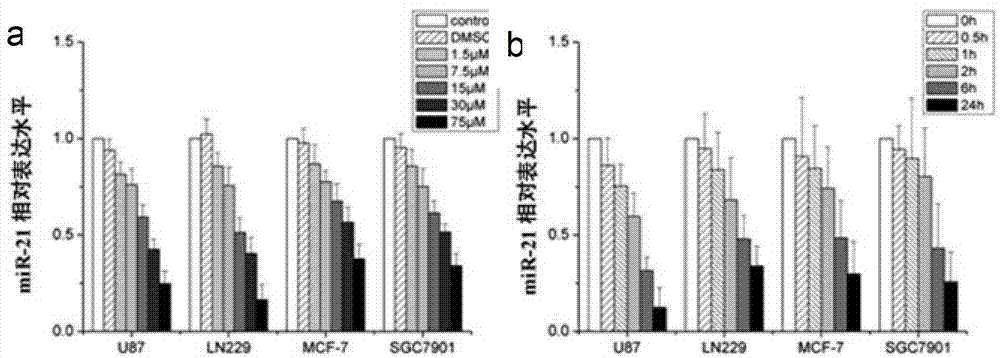
ActiveCN103044338AEffectively induce apoptosisPlay an antitumor roleOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryG1/S checkpointColloid
The invention relates to an miR-21 small molecule inhibitor and an application The medicament of the invention can specifically inhibiting the expression of miR-21, thereby promoting a compound 2,4-diamino-1,3-diazacyclohexane-5-nitrile which can induce various tumor cell apoptosis. The binding capability of 2,4-diamino-1,3-diazacyclohexane-5-nitrile is that: Ki=1.49nM, deltaG=-12.04kcal / mol. The preparation method comprises: dissolving 2,4-diamino-1,3-diazacyclohexane-5-nitrile in deionized water to prepare mother solution, adding the mother solution into a tumor cell (colloid tumor, stomach cancer and breast cancer) culturing system according to a certain proportion. The medicament can specifically inhibit the expression of miR-21 without affecting the expression of miRNA. The cell cycle appearances G0 / G1 phase arrest, the cell apoptosis proportion is obviously increased, and more effective inhibition to tumour can be implemented.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
P53 messenger RNA nanoparticles, preparation method thereof and application thereof in preparing drug for treating tumors
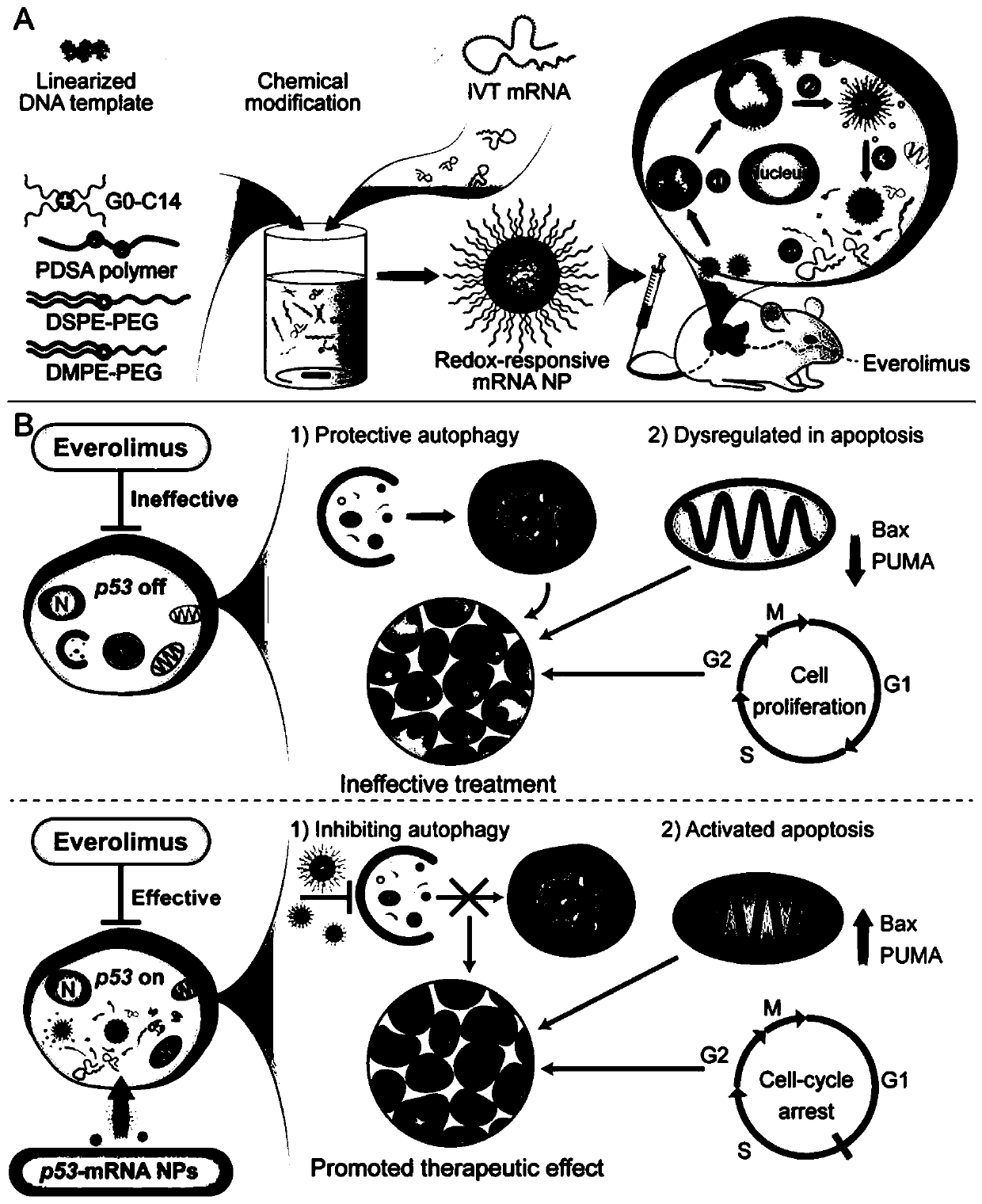
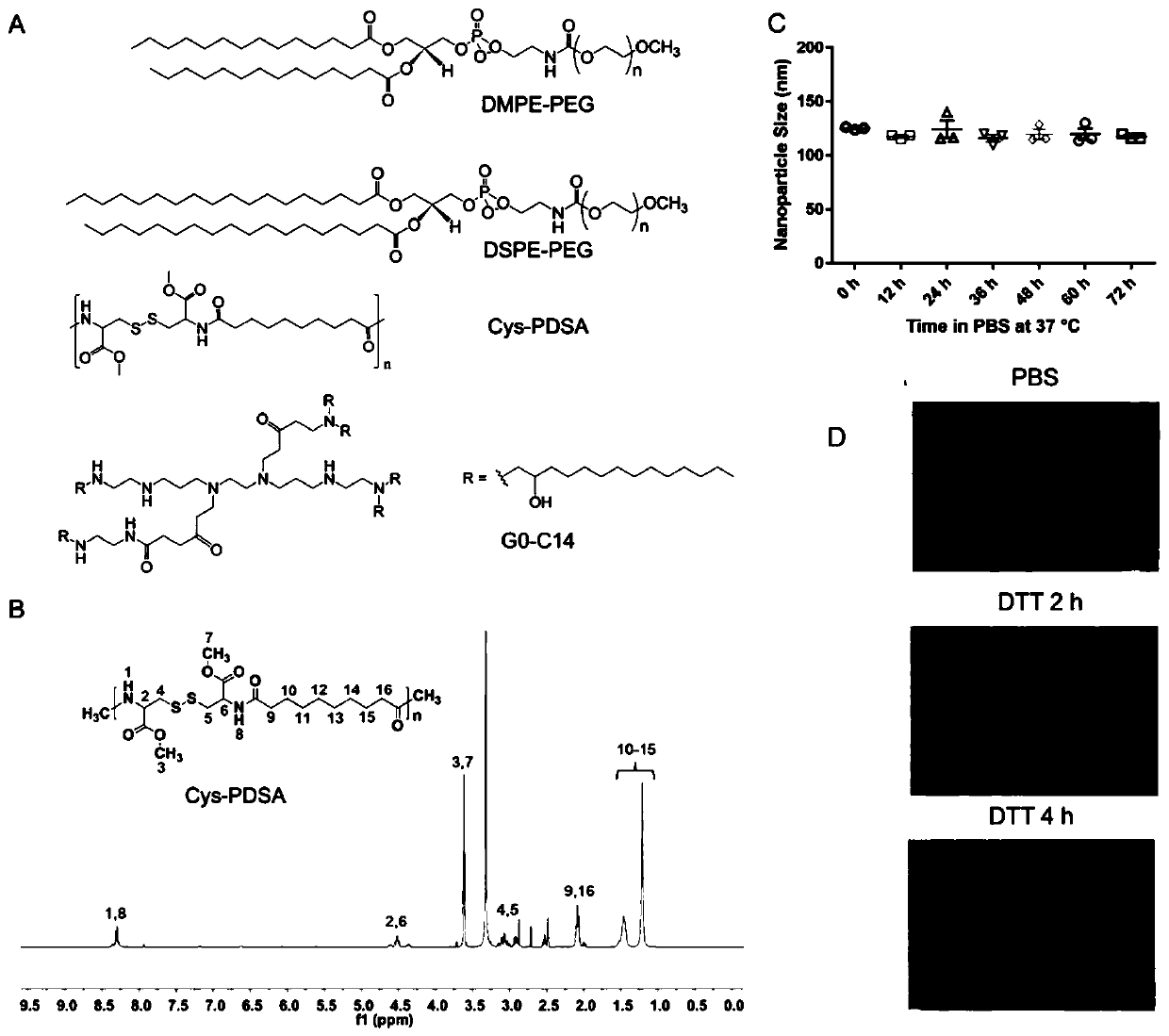
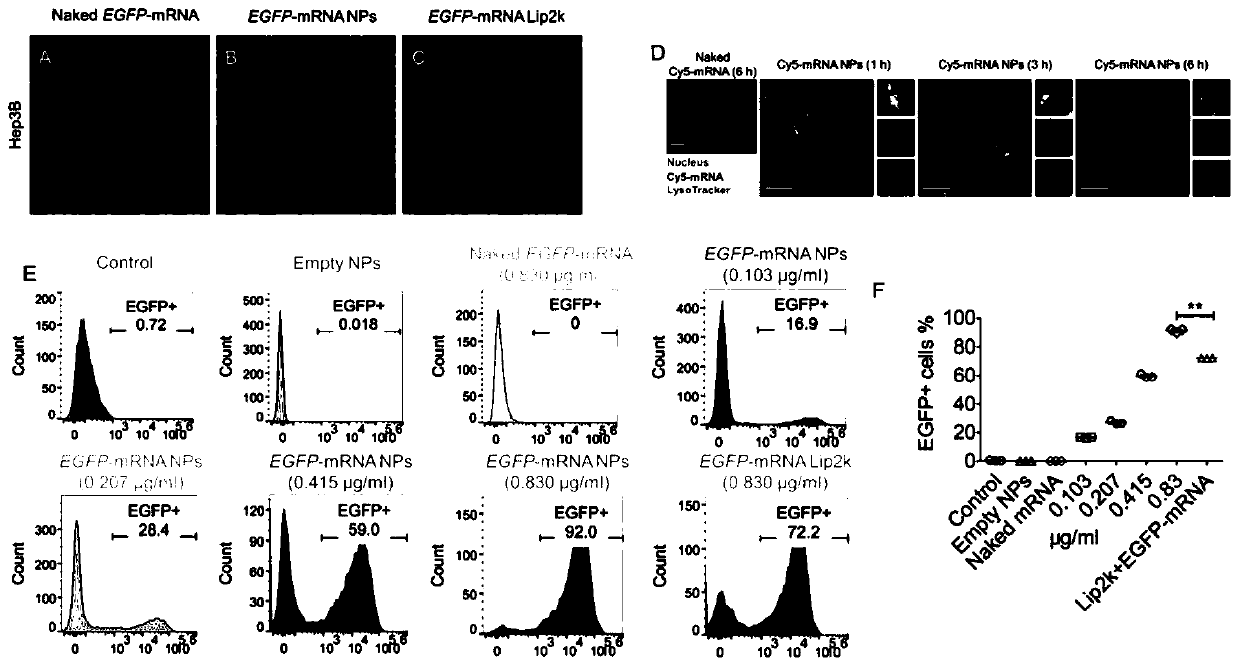
InactiveCN110974804AInduce apoptosisInduced cycle arrestOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsEverolimusMessenger RNA
The p53 messenger RNA nanoparticles, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof in preparing a drug for treating tumors belong to the technical field of genetic engineering. The p53 messenger RNA nanoparticles are prepared by the following method: 1, chemically modified p53mRNA is synthesized in vitro; and 2, a nano-system is prepared by a self-assembly method to deliver the p53 messenger RNA in vivo. The p53 messenger RNA nanoparticles play an anti-tumor and chemosensitivity-enhancing therapeutic role by restoring the anti-tumor function of p53. The advantages of the invention are as follows: 1, the p53 messenger RNA in the invention is successfully delivered to the p53 inactivated liver cancer and lung cancer tumor cells through the nano-system to effectively and rapidly induce cell apoptosis and G1 phase cell cycle arrest in vivo and in vitro, thus significantly inhibiting the growth of tumor cells; and 2, the p53 messenger RNA delivered by the nanoparticles can enhancethe anti-tumor effect of a mTOR inhibitor everolimus by supplementing the tumor suppressor p53 deleted in the tumor.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Ouiescent cell populations for nuclear transfer
InactiveCN1769432AHybrid cell preparationMammal material medical ingredientsSomatic cellResting Cell
Methods for reconstituting animal embryos involve transferring the nuclei of quiescent donor cells into appropriate recipient cells. The donor cells are quiescent in that they exit the growth and division cycle in the G1 phase and cease in the G0 state. Nuclear transfer can be performed by cell fusion. The recombinant embryo can then produce one or more animals. The present invention can be used for the production of transgenic as well as non-transgenic animals with high genetic value.
Owner:ROSLIN INST (EDINBURGH) ET AL +2
Method for promoting secretory expression of rhIL-24 by engineering cell strain by using sodium butyrate
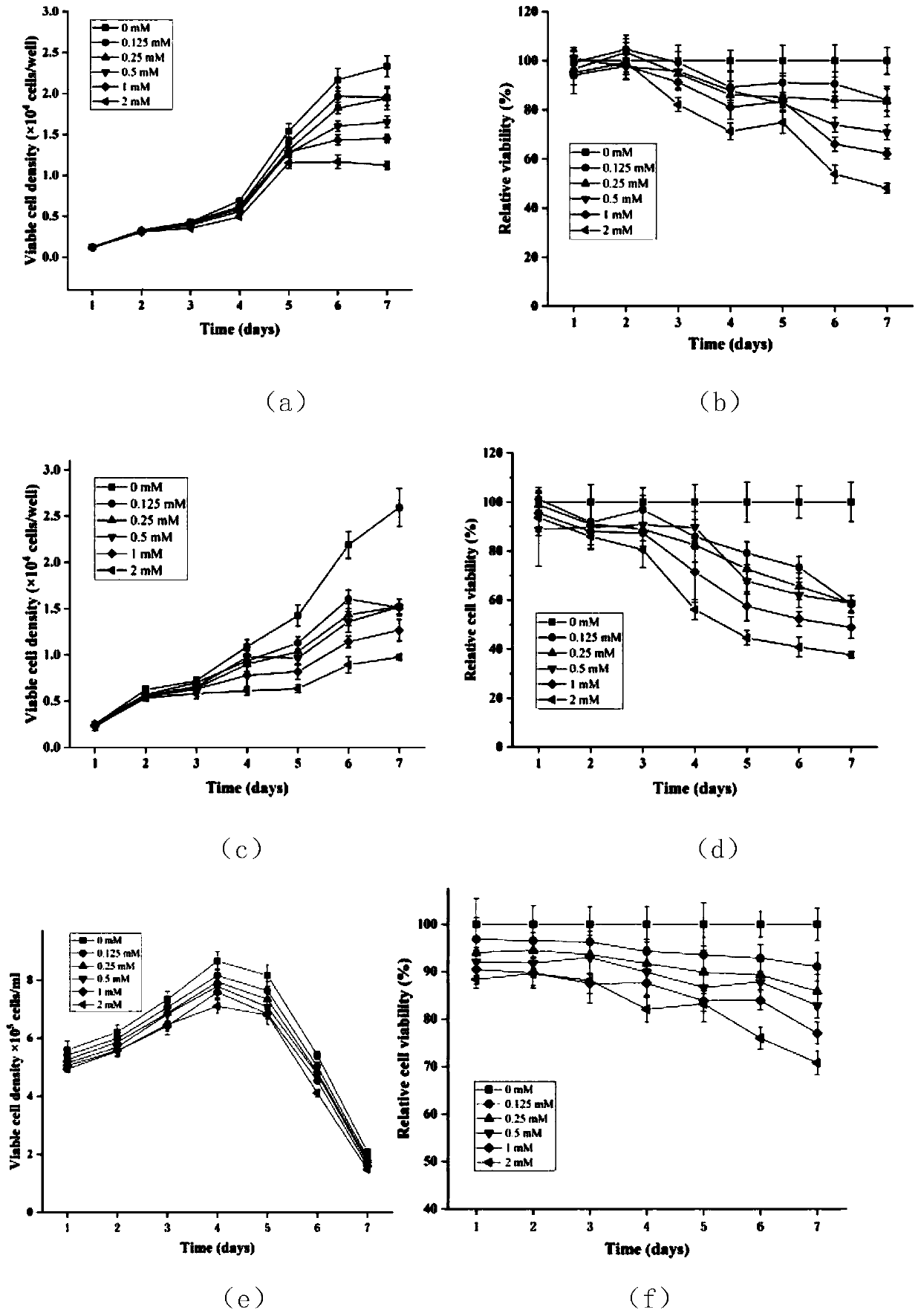
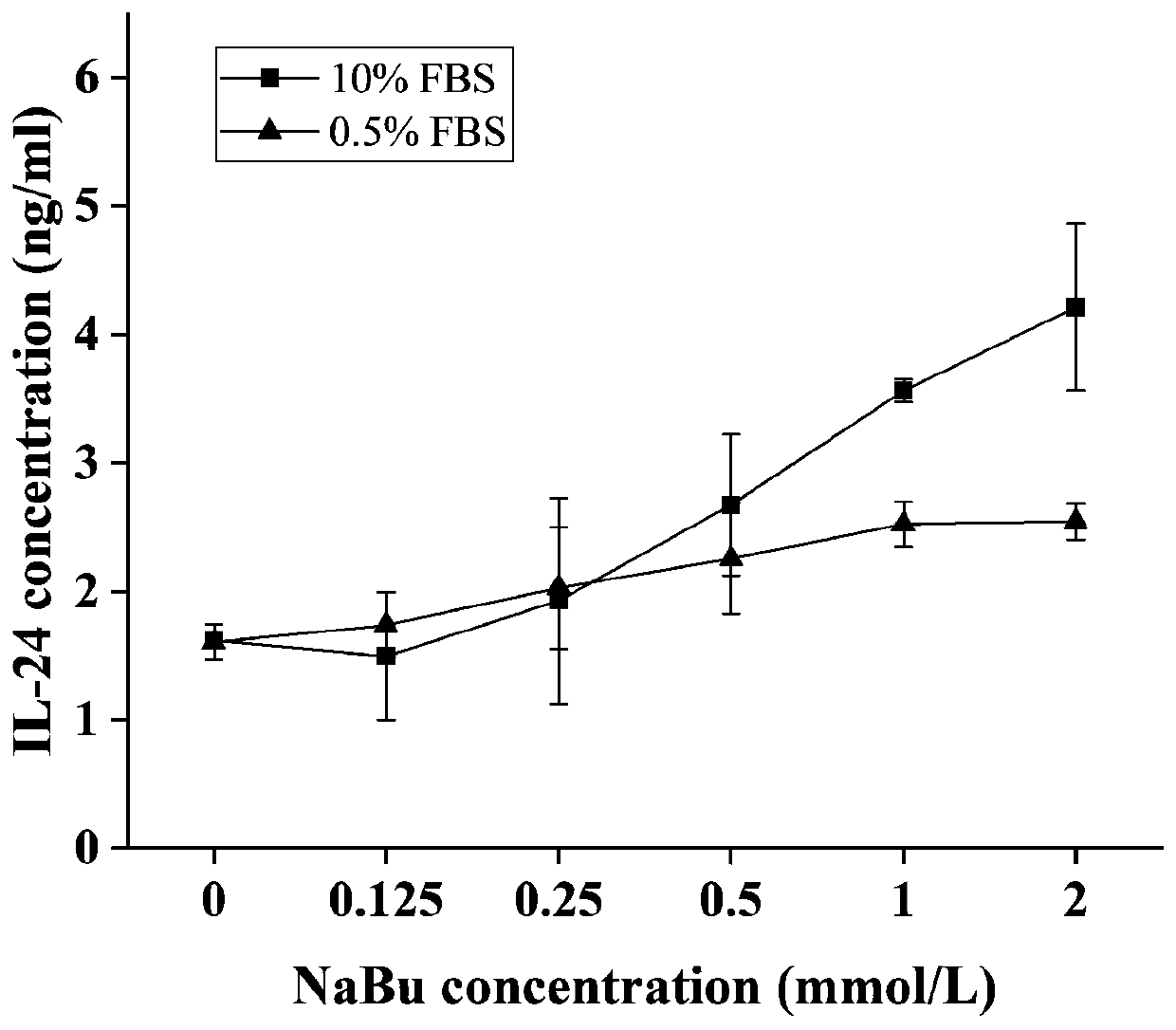
InactiveCN111233996AImprove the level ofMay alter metabolic activityGenetically modified cellsCulture processGenetic engineeringCulture mediums
The invention provides a method for promoting secretory expression of rhIL-24 by an engineering cell strain by using sodium butyrate, belonging to the technical field of gene expression. On the basisthat a site-specific integrated engineering cell strain FCHO / IL-24 for secretory expression of the rhIL-24 is subjected to adherent culture with a culture medium containing 10% of serum, adherent culture with a culture medium containing 0.5% of serum adherence and suspension culture with a culture medium containing 0.5% of serum, the cell strain is treated by using sodium butyrate with different final concentrations (0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1 and 2 mmol / L). According to the invention, NaBu can improve the secretory expression level of foreign protein by CHO cells, promotes the secretory expression level of rhIL-24 by engineering cells, promotes generation of G0 / G1 phase arrest of the engineering cells, and can change the metabolic activity of the cells under adherent culture conditions; and by using of the NaBu as an additive of a serum-free culture medium of the cell strain, the secretory expression level of the rhIL-24 by the cell strain is improved in high-density suspension culture, so experimental data is provided for large-scale culture of FCHO / IL-24 cells, and a reference can be provided for expressing gene engineering proteins by using mammalian cells at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
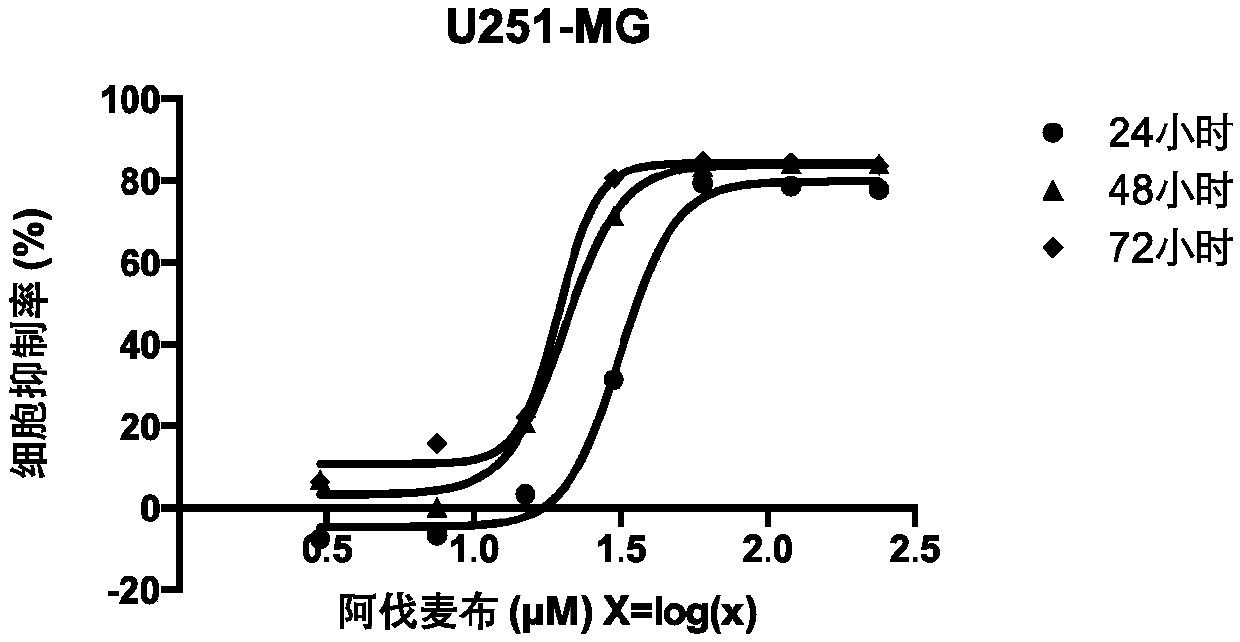
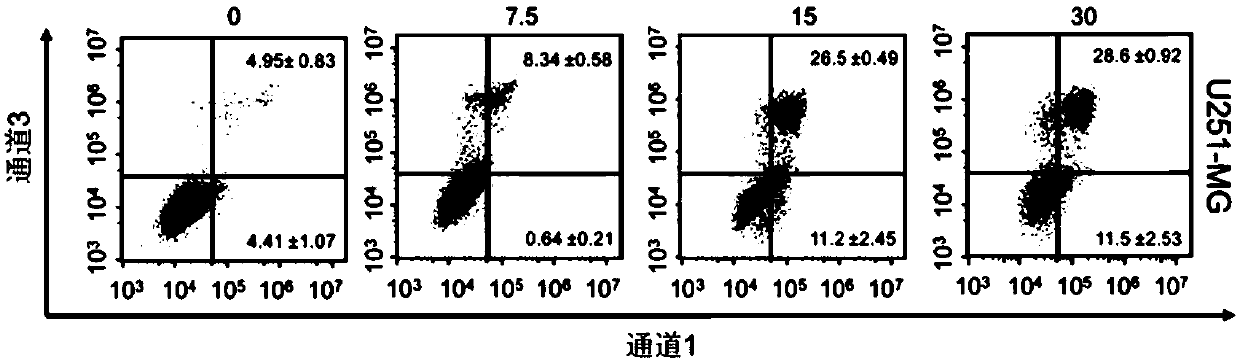
Application of avasimibe in preparation of medicine for preventing or treating glioblastoma
InactiveCN111084767AHigh degree of malignancyAggressiveAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsBlastomaGlioblastoma
The invention relates to an anti-tumor medicine for treating glioblastoma, wherein the medicine is avasimibe. The medicine provided by the invention induces apoptosis through a mitochondrial pathway to realize the activity against the glioblastoma; the medicine provided by the invention induces the apoptosis by non-specifically blocking a cell cycle; and the medicine provided by the invention induces the cell cycle to be blocked in a G0 / G1 phase and a G2 / M phase through a p53-dependent pathway.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for culturing islet cells suitable for clinical application
PendingCN114276980AImprove stabilityNo residueMetabolism disorderArtificial cell constructsIslet cellsMesenchymal stem cell
According to the method, the islet cells are obtained through induced differentiation by taking mesenchymal stem cells as an initial raw material, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out starvation culture on the mesenchymal stem cells, so that the cell cycle is retarded in a G0 / G1 phase; step S2, carrying out first-stage induction culture so as to generate islet-like bulk cells; s3, carrying out second-stage induction culture, so that the ratio of the insulin positive cells to the nest protein positive cells reaches a preset value; and S4, carrying out third-stage induction culture to obtain mature islet cells. The islet cells prepared by the method can be used for preventing, relieving and treating type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Owner:王意忠
Human PKMYT1AR gene and application thereof
ActiveCN114231529APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryNucleotideOncology
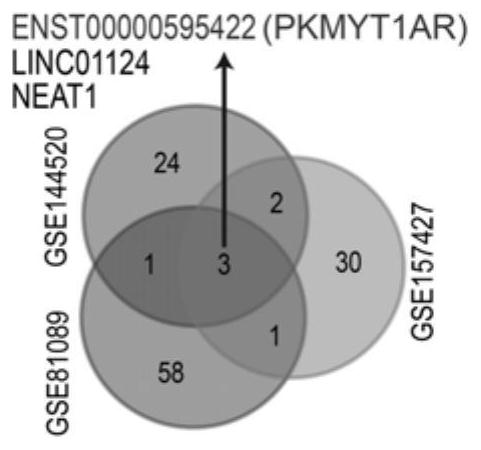
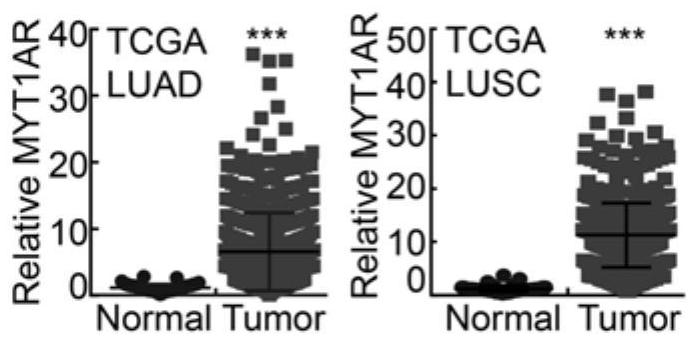
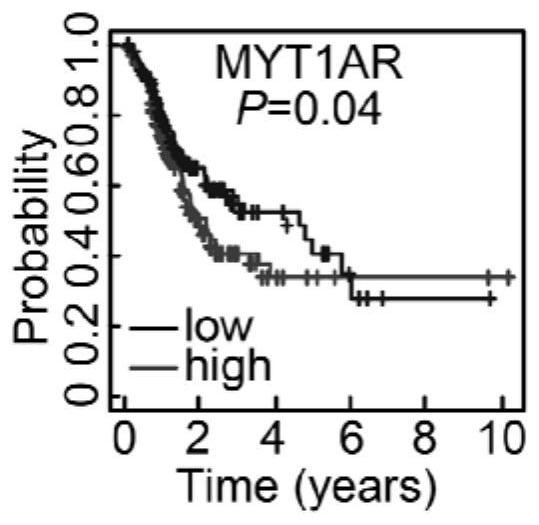
The invention discloses a human PKMYT1AR gene. The nucleotide sequence of the human PKMYT1AR gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; the reagent for detecting the expression quantity of the human PKMYT1AR gene is applied to preparation of the non-small cell lung cancer clinical diagnosis reagent, the expression level of the human PKMYT1AR gene is in negative correlation with clinical prognosis of the non-small cell lung cancer, and experimental results show that the expression of the human PKMYT1AR gene in a non-small cell lung cancer cell line is higher than that of normal pulmonary epithelial cells; after the PKMYT1AR gene is knocked down, the proliferation of a non-small cell lung cancer cell line is obviously inhibited, and the cell cycle is retarded in a G0 / G1 phase; the killing effect of clinical platinum chemotherapeutic drugs for non-small cell lung cancer on tumor cells can be obviously improved; the invention reveals that the PKMYT1AR gene is a potential risk gene of the non-small cell lung cancer, and PKMYT1AR expression inhibition is combined with a radiotherapy or chemotherapy drug DDP for use, so that the clinical treatment effect of the non-small cell lung cancer is enhanced.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
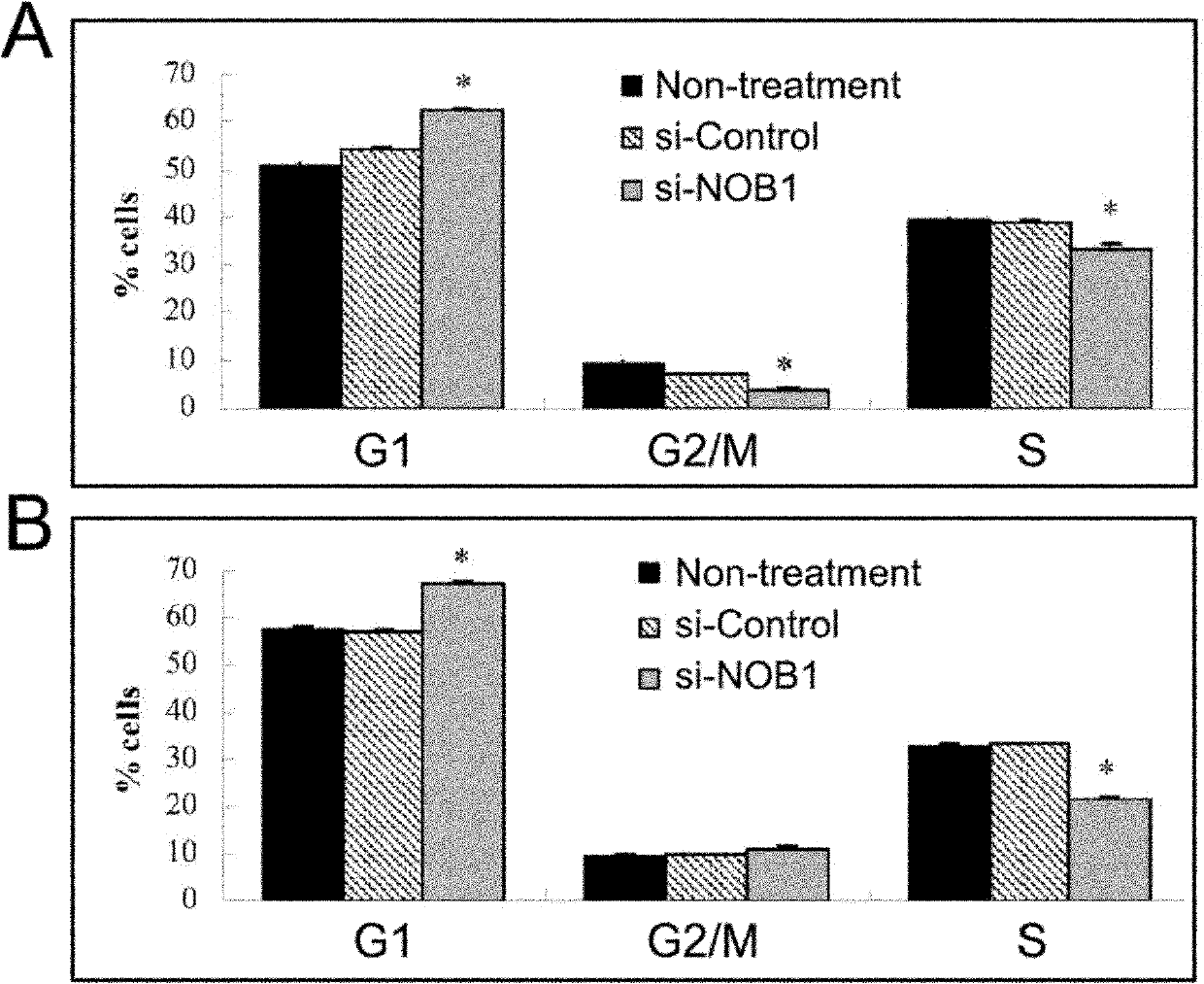
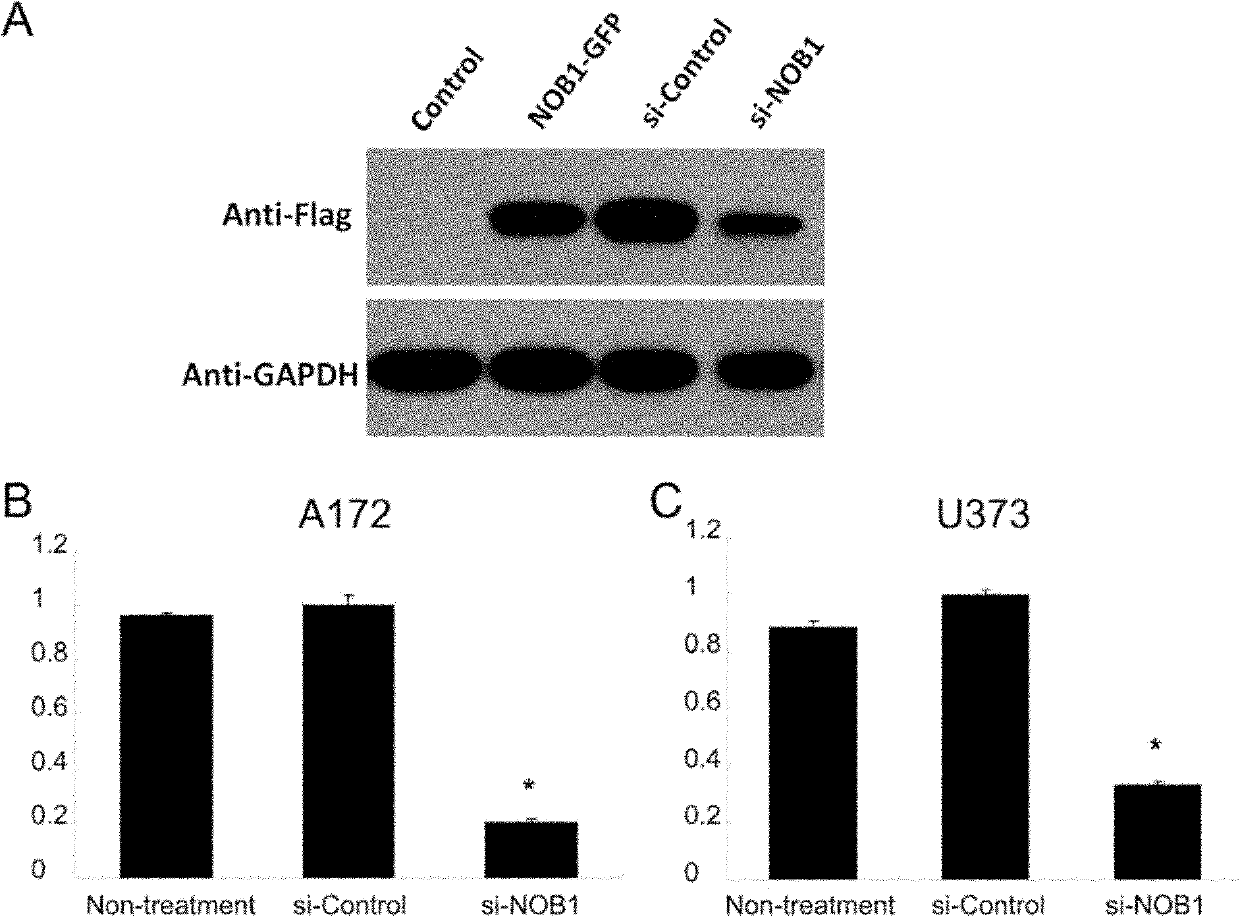
Application of NOB1 gene in treating brain glioma disease
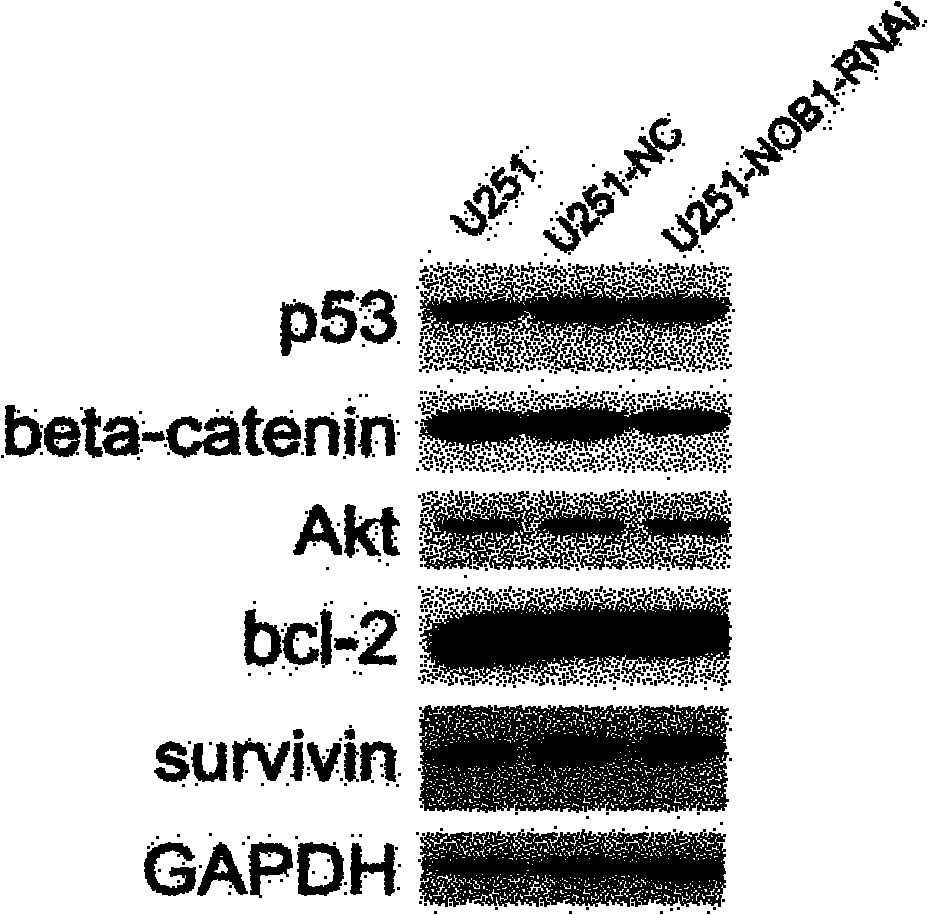
The invention relates to an application of NOB1 gene in treating a brain glioma disease. NOB1 gene can regulate and control cell cycle of human glioma to reduce G1 phase stagnation in the cell cycle caused by NBO1 level; in addition, the NOB1 gene can regulate and control proliferation of human glioma cells to inhibit growth retardation of the glioma cells caused by the NOB1; moreover, the reduction of the NOB1 can prevent occurrence of the human glioma cell tumor. The study finds the NOB1 of the invention is necessary to inhibiting the occurrence of brain glioma in vivo or in vitro; in addition, according to the expression result of the NOB1 gene in the brain glioma tissue, the NOB1 gene provides powerful means for biological targeted therapy of the glioma in the future.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
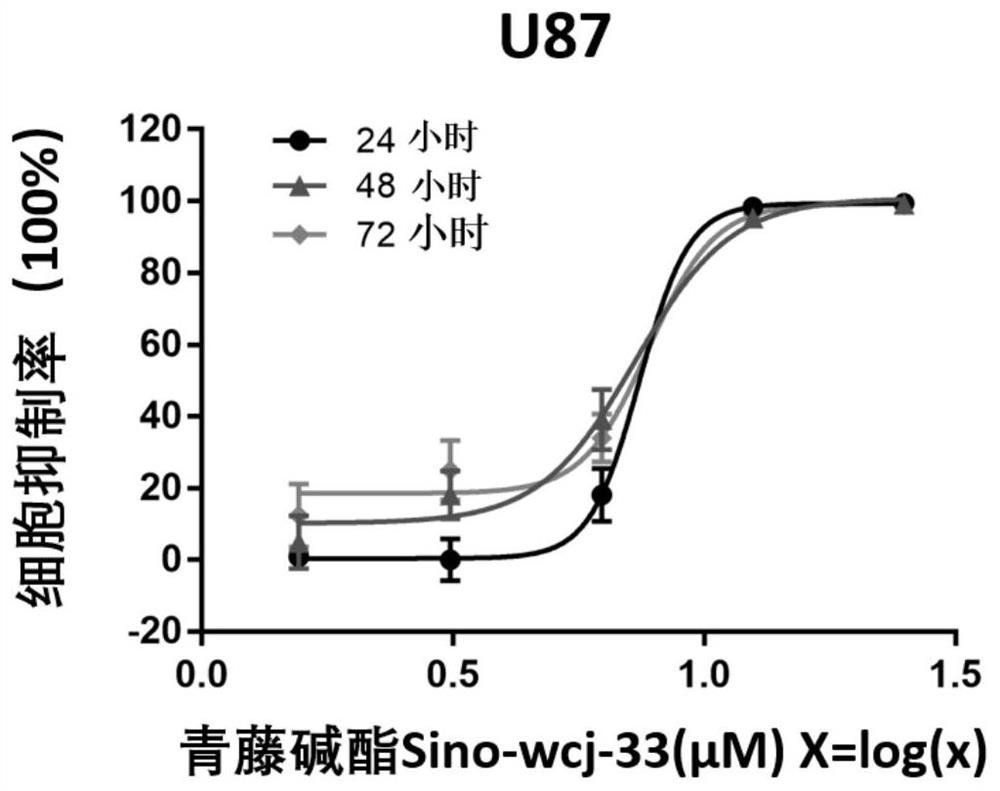
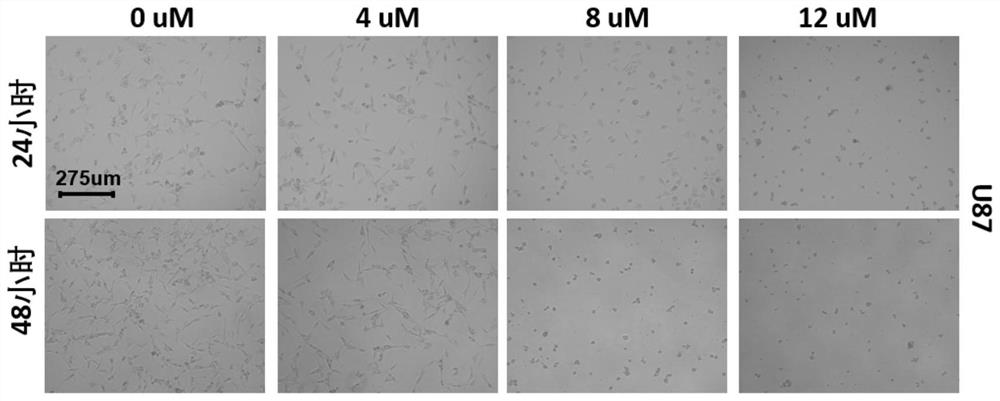
Application of sinomenine compound to preparation of medicines for preventing or treating glioma
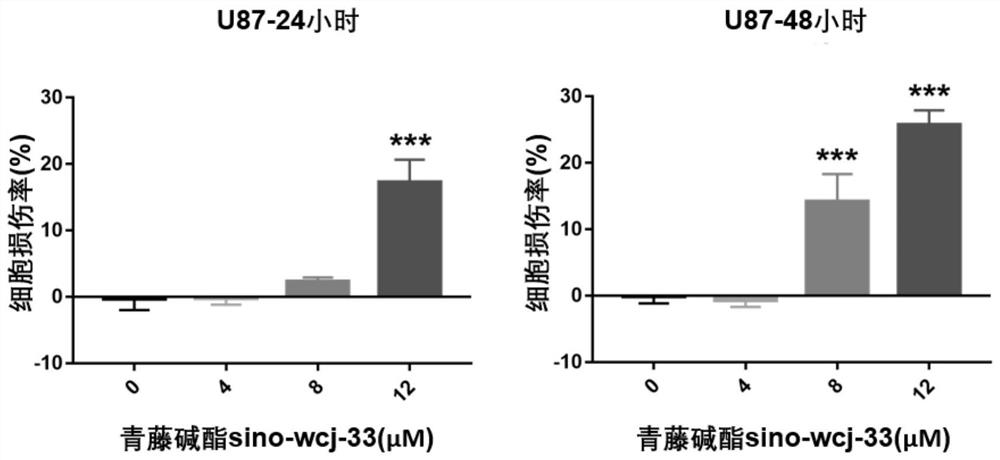
The invention relates to application of a sinomenine compound in preparation of a medicine for preventing or treating glioma. The sinomenine compound is sino-wcj-33. The sino-wcj-33 disclosed by the invention can be used for inhibiting the proliferation of glioma cells. The sino-wcj-33 disclosed by the invention realizes an anti-tumor effect by inducing cell apoptosis. The sino-wcj-33 provided bythe invention inhibits tumor by inhibiting migration and invasion of glioma cells. The sino-wcj-33 provided by the invention blocks the cell cycle tissue in a G0 / G1 phase.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
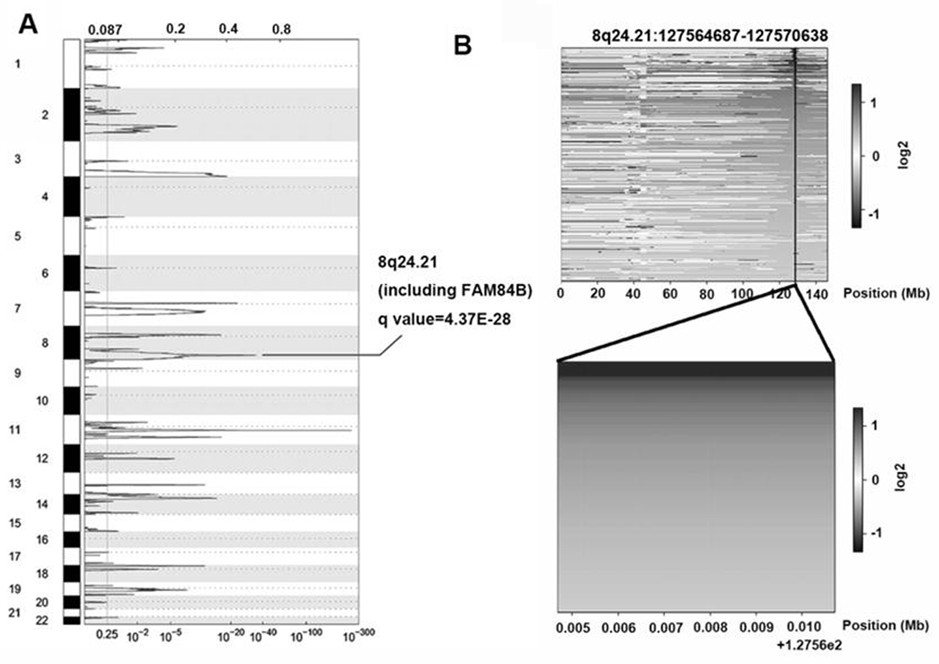
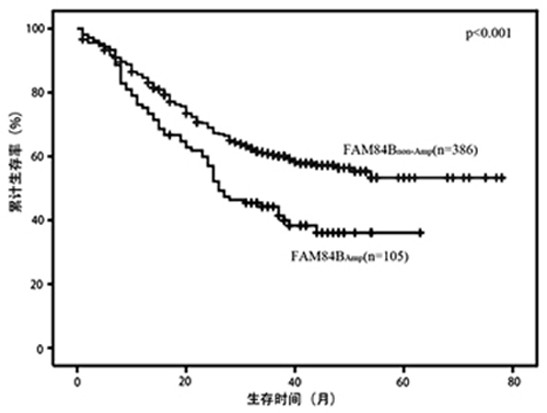
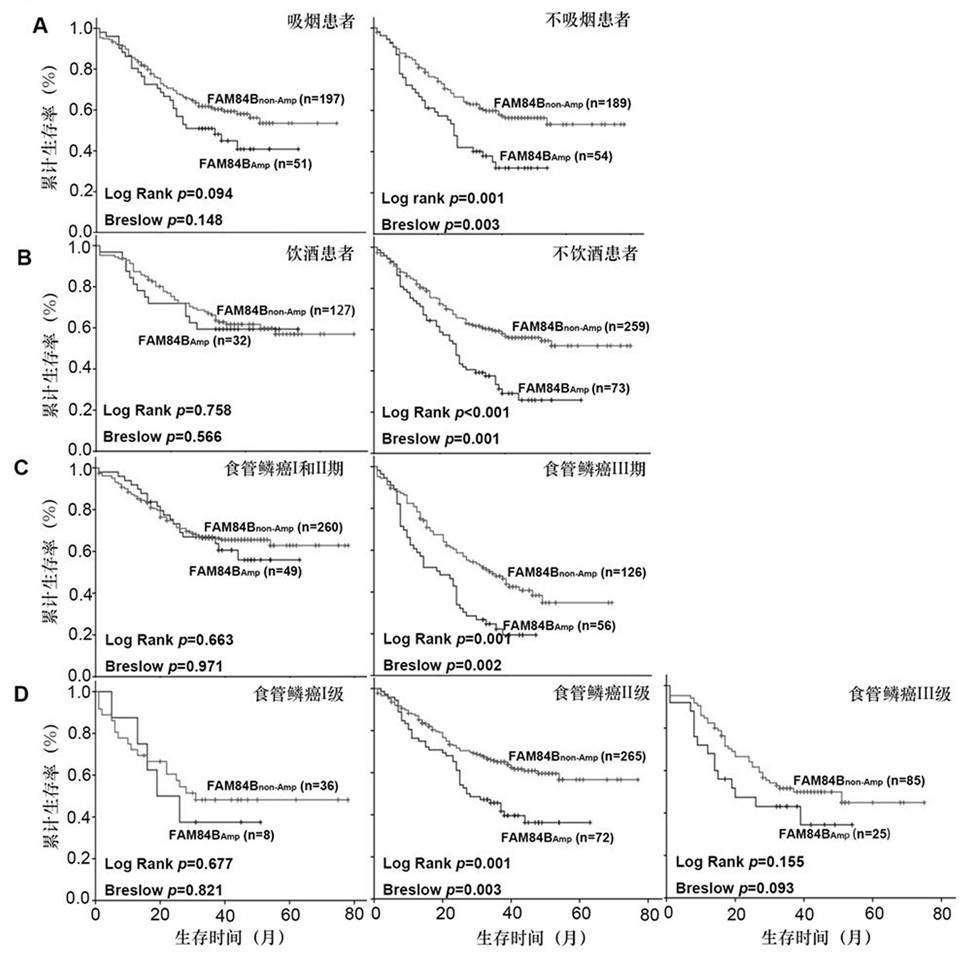
Application of FAM84B in preparation of reagent for prognosis evaluation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and in screening of drugs for targeted treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN113265463AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMechanism of actionOncology
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicines, aims to clarify a relationship between FAM84B copy number change and prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and demonstrate an action mechanism of FAM84B in occurrence and development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and an effect of FAM84B in screening of drugs for targeted treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and provides application of FAM84B in preparation of a reagent for prognosis evaluation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and screening of the drugs for targeted treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The invention discloses application of copy number amplification and high expression of the FAM84B gene in preparation of the reagent for prognosis evaluation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The copy number amplification of the FAM84B gene becomes a new index for the prognosis of the patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The amplification of the copy number of the FAM84B gene causes the increase of the expression of the esophageal squamous carcinoma FAM84B, and the high expression of the FAM84B can promote the proliferation and cycle of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells; and the low expression of the FAM84B can inhibit the proliferation and cycle of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells and block the cells in a G1 phase.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Application of histone methylation h3k4me3 in porcine ovarian granulosa cells
ActiveCN109852662BSimple designReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementHistone methylationH3K4me3
The invention discloses an application of histone methylation H3K4me3 in pig ovary granulosa cells, and belongs to the technical fields of cell engineering and genetic engineering. The invention takes H3K4me3 as an entry point, and uses cell biology methods to study its influence on the function of porcine ovary granulosa cells. The technical scheme of the invention is carefully designed and the result is reliable. In order to confirm the influence of H3K4me3 on the function of porcine ovary granulosa cells, the present invention verifies from multi-level and multi-angle, at cell level and protein level. The present invention clarifies the influence of H3K4me3 on the function of porcine ovarian granulosa cells: H3K4me3 can promote the proliferation of porcine ovarian granulosa cells, inhibit the apoptosis of porcine ovarian granulosa cells, and reduce the proportion of porcine ovarian granulosa cells blocked in the GO / G1 phase; It is of great application value to study the mechanism of histone methylation on the development of ovarian follicles and the reproductive performance of sows.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
New application of doublecortin-like kinase 1
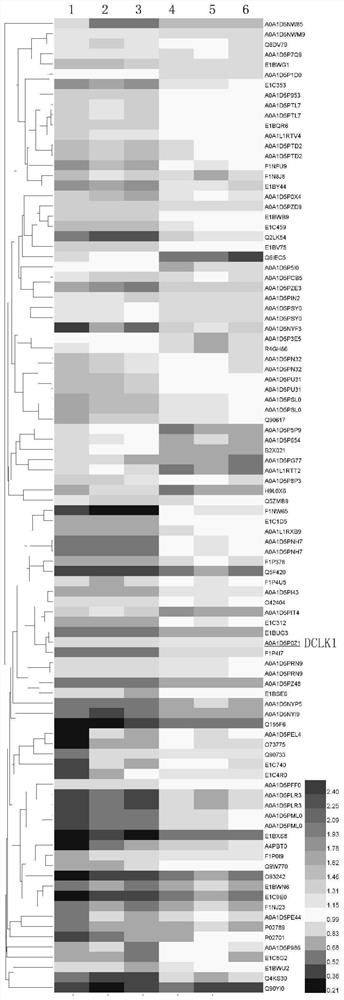
ActiveCN114032216AIncrease capacityEasy to copyTransferasesMicroorganism based processesLeucosisAvian leukosis viruses
The invention relates to the field of virology, in particular to novel application of doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1), wherein the application is to prepare a J subgroup avian leukosis virus replication enhancer. According to the invention, it is found that the DCLK1 can interact with ALV-J SU protein and promote a cell cycle to be converted from the G1 phase to the S phase so as to remarkably increase the ALV-J replication amount, and on this basis, the ALV-J replication amount is remarkably increased. a DCLK1 overexpression plasmid pcDNA3.1-DCLK1 transfected DF-1 cell is constructed, so that the DCLK1 is highly expressed in the cell, ALV-J replication is remarkably promoted, the virus yield is improved, the DCLK1 has no toxic or side effect on the cell, and the DCLK1 can be used as a virus replication enhancer to be applied to culture of ALV-J.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Synthetic peptide sp4 and use thereof
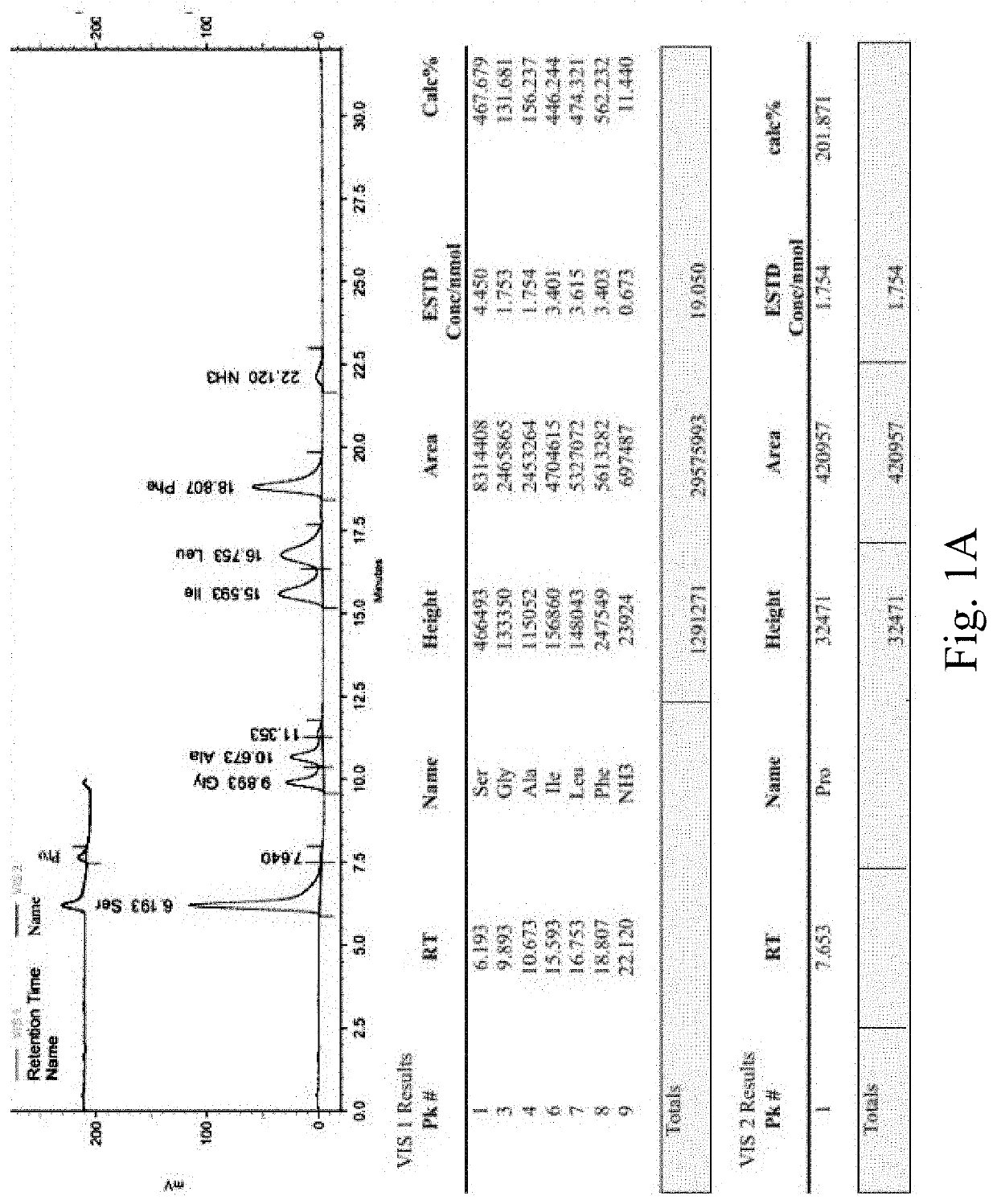
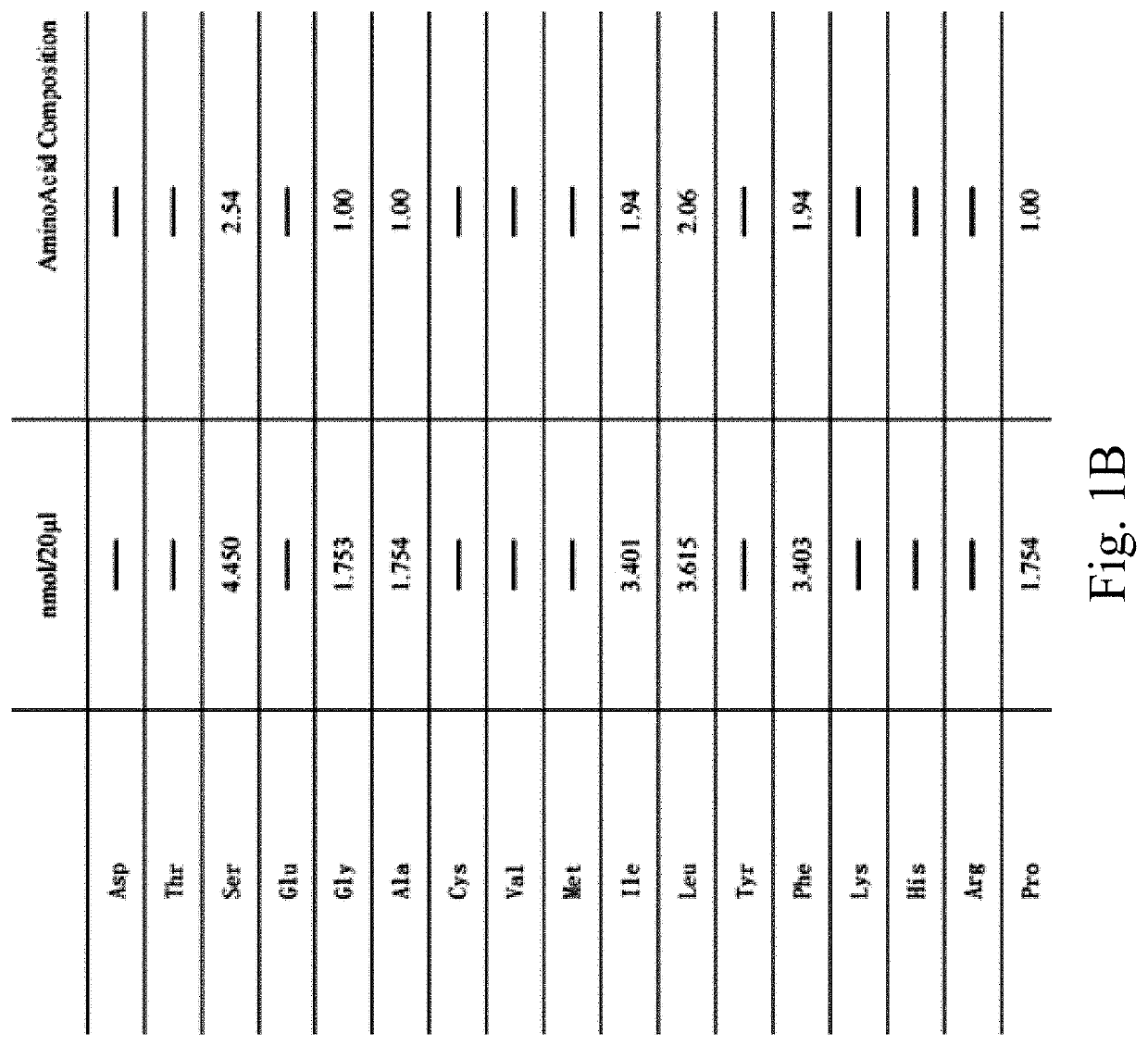
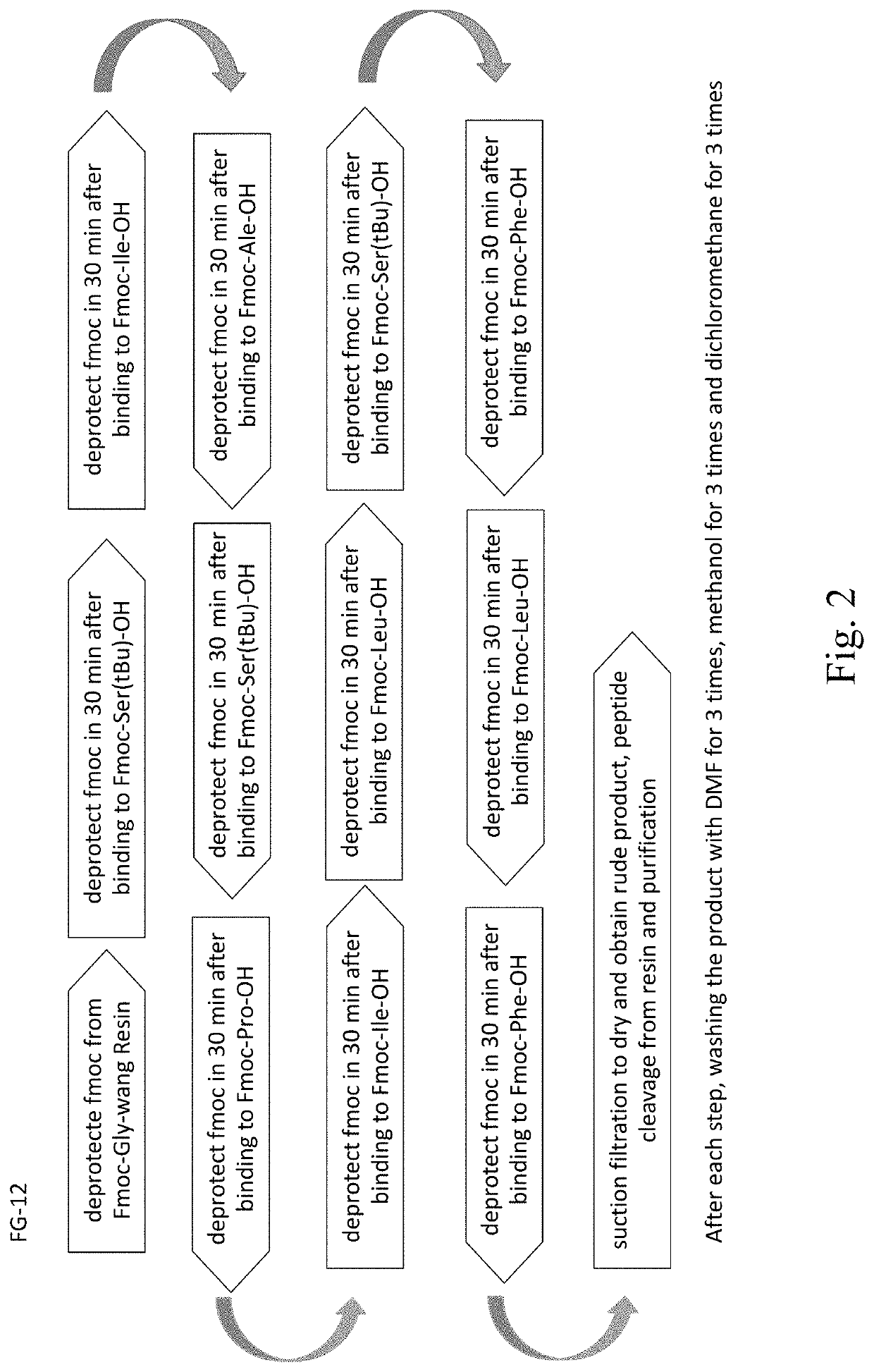
InactiveUS20210179664A1Maintain cell divisionStrong inhibitory activityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesTelomeraseEfficacy
A synthetic peptide sp4 has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. As the sole effective ingredient in the antitumor efficacy test, it has a significant inhibitory effect on both the tumor volume and tumor weight of human osteosarcoma MG-63 in nude mice and has a significant dose-effect and time-effect relationship. There is no difference between the relative tumor growth rate T / C (%) of sp4 and that of the positive control group of Paclitaxel. The safety of sp4 is that its maximal tolerated dose for intravenous administration is 700 mg / kgBW. Sp4 has clear targets of pharmacological effects, while having efficacy in vivo, it also has an inhibitory effect on tumor telomerase, has an arrest on G1 phase of the tumor cell cycle, and inhibits the high expressions of tumor PD-L1 and CD47. The present disclosure relates to multiple uses of sp4, especially in the preparation of a class of antitumor drugs.
Owner:TAIAN CITY QIHANG BIOTECH CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com