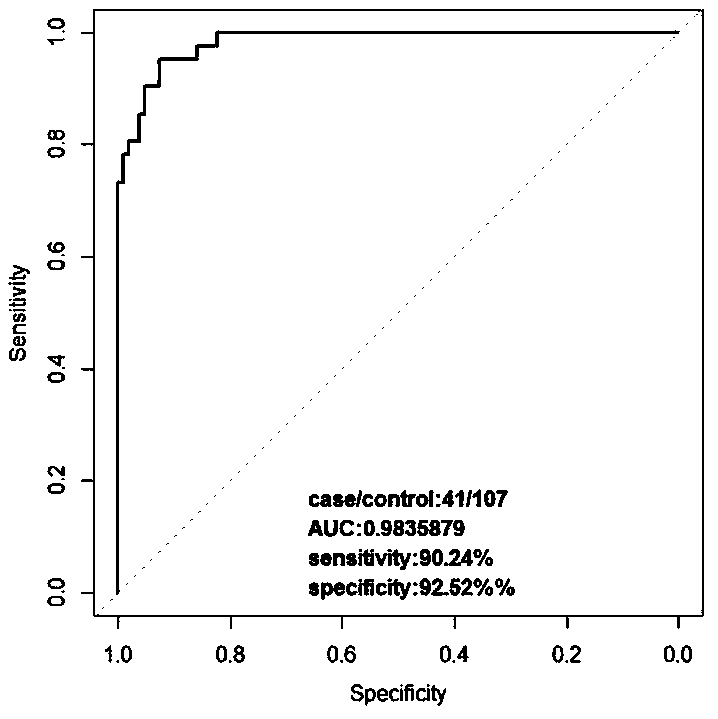
Patents
Literature
84 results about "Leucine-rich repeat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
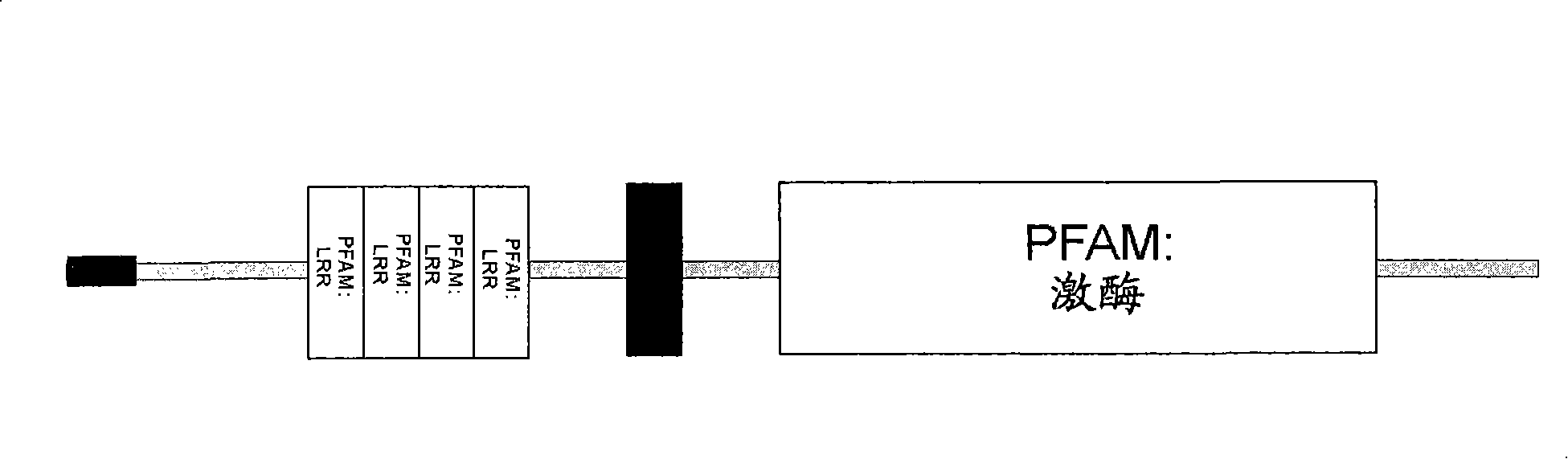
A leucine-rich repeat (LRR) is a protein structural motif that forms an α/β horseshoe fold. It is composed of repeating 20–30 amino acid stretches that are unusually rich in the hydrophobic amino acid leucine. These tandem repeats commonly fold together to form a solenoid protein domain, termed leucine-rich repeat domain. Typically, each repeat unit has beta strand-turn-alpha helix structure, and the assembled domain, composed of many such repeats, has a horseshoe shape with an interior parallel beta sheet and an exterior array of helices. One face of the beta sheet and one side of the helix array are exposed to solvent and are therefore dominated by hydrophilic residues. The region between the helices and sheets is the protein's hydrophobic core and is tightly sterically packed with leucine residues.
Immunostimulatory Combinations for Vaccine Adjuvants
This invention discloses immunostimulatory combinations of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily (TN-FRSF) agonists, Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) agonists, “domain present in NAIP, CIITA, HET-E, TP-I (NACHT)-Leucine Rich Repeat (LRR)” or “NLR” agonists, RIG-I-Like Helicase or “RLH” agonists, purinergic receptor agonists and cytokine / chemokine receptor agonists, together with delivery methods. The combinations, when used alone at the site of pathology, provide immunostimulation that induces host humoral and cellular immunologic responses to eliminate pathogens or neoplasms. Alternatively, when the combinations are used with a defined antigens, these combinations can induce focused humoral and cellular immunologic responses useful as prophylactic and / or ameliorative therapeutic modalities for infections and the treatment of neoplastic disorders.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Composition for stabilizing corneal tissue during or after orthokeratology lens wear
Two types of compositions having an eye-drop delivery system are used during or after an orthokeratology procedure to prevent or retard relaxation of corneal tissue back to the original anterior curvature of the cornea. Each composition functions independently from the others and is a different approach of preparing a stabilizing agent. The first composition is directed to a biologically compatible composition comprising fibril associated collagens with interrupted triple helices (FACITs) and / or small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans (SLRPs). The fibril associated collagen family includes various types of collagens, such as type VI, type XX, type XII, and type XIV. The small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans family includes decorin, keratocan, biglycan, epiphycan, lumican, mimecan, and fibromodulin. The second composition includes the enzyme found as a normal component of tissues, plasma, or epidermis, such as transglutaminase.
Owner:EUCLID SYST CORP +2
Brown planthopper resistant rice gene Bph9 as well as molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN103667309AClear functionGood effectBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteProtein
The invention provides a brown planthopper resistant rice gene Bph9 as well as a molecular marker and application thereof. The brown planthopper resistant rice gene Bph9 has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and a cDNA (complementary Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2. The Bph9 gene is located between molecular markers InD2 and RM28466. The molecular markers closely linked with the gene also includes one of RM28438, InD28450, InD28453, InD14, InD28432, RM28481 and RM28486 which can be used for sieving the rice containing the brown planthopper resistant gene Bph9. The Bph9 gene belongs to the NBS-LRR (Nucleotide Binding Site-Leucine Rich Repeat) gene family; the encoded protein is related to the plant disease resistance; the Bph9 gene is transferred into common rice by virtue of genetic transformation and hybridization, and thus the resistance of rice to brown planthopper can be improved, so that the damage of brown planthopper is decreased, and the purposes of yield increase and yield stabilization are realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
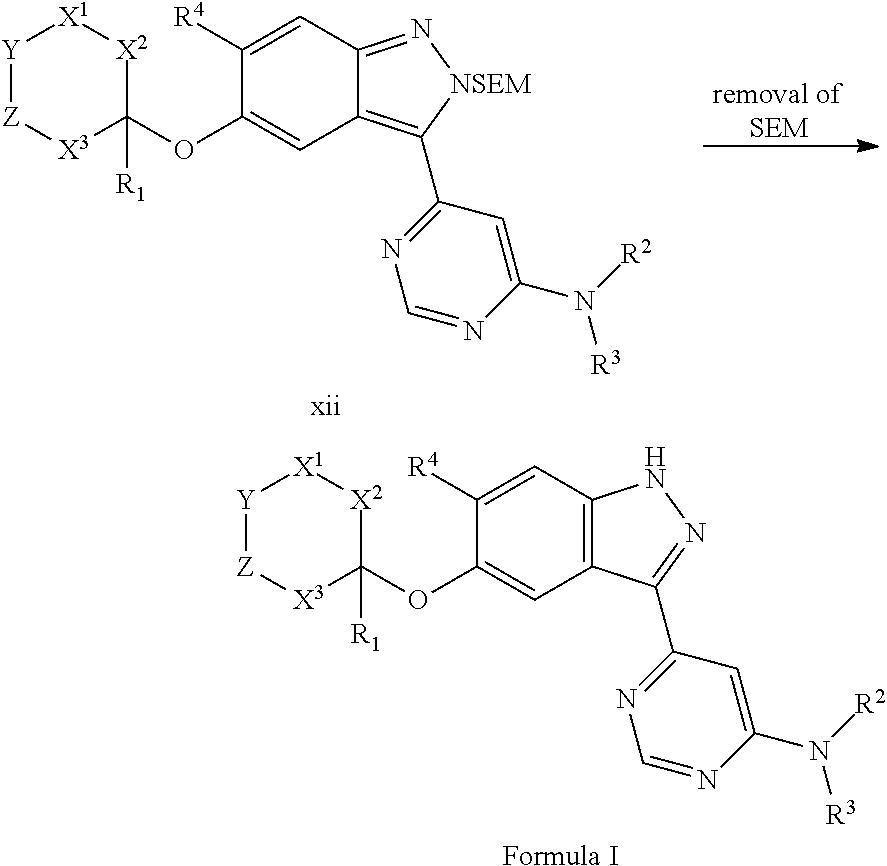
Novel kinase inhibitors
ActiveUS20120329780A1Improve propertiesReduce formationBiocideSenses disorderAutoimmune responsesAutoimmune disease
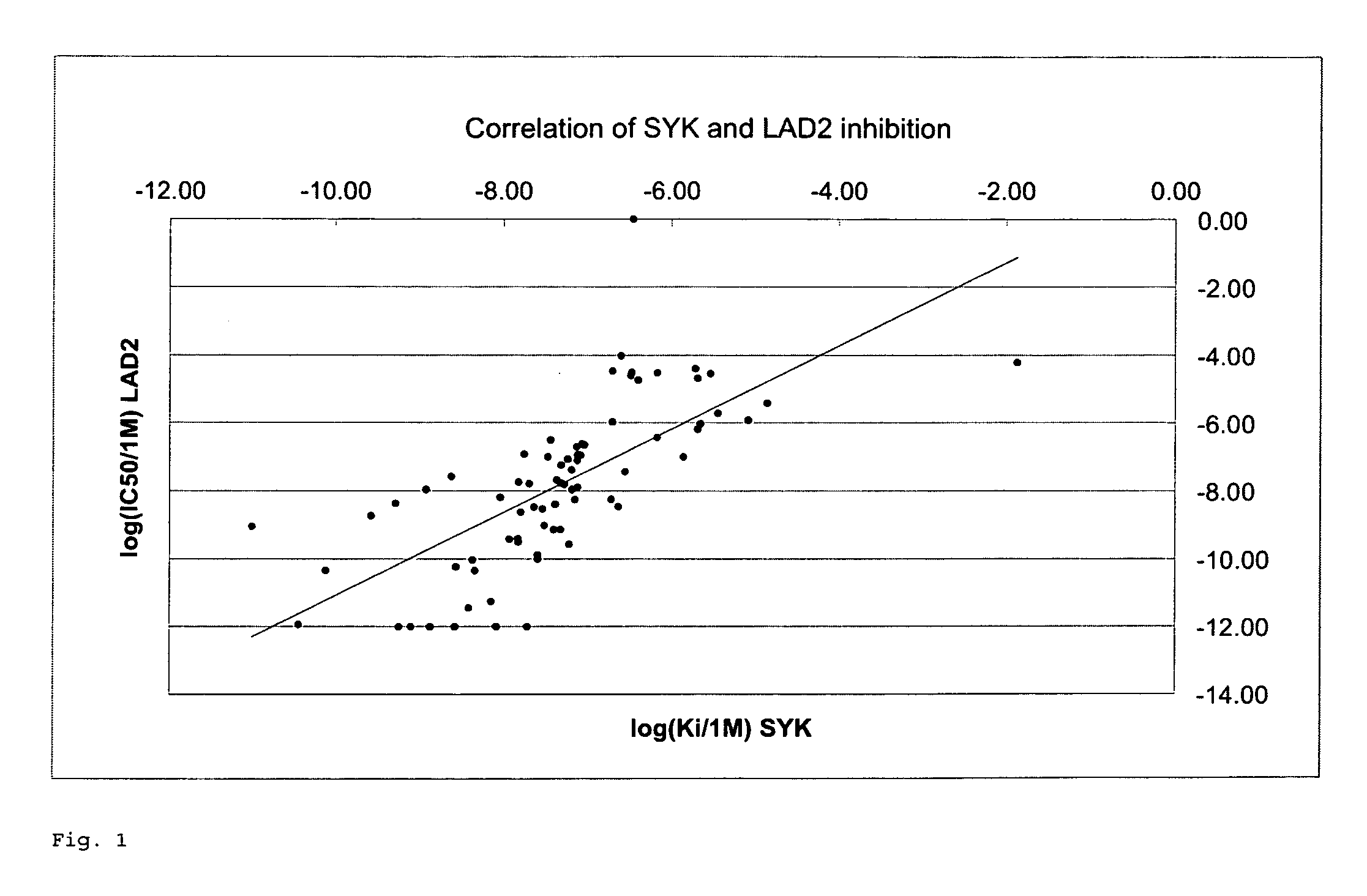
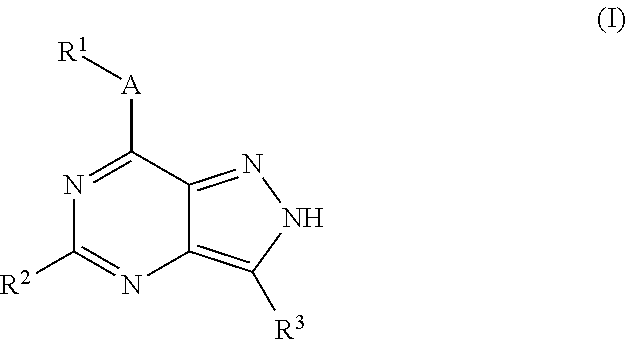
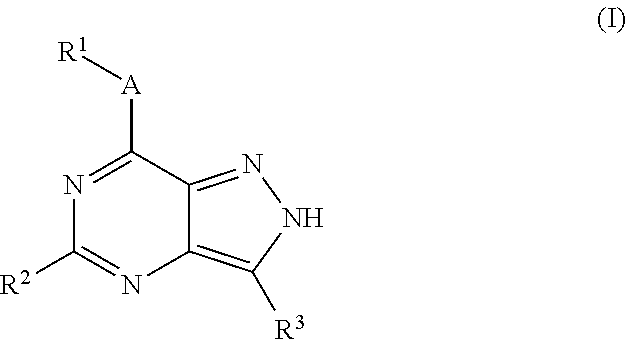
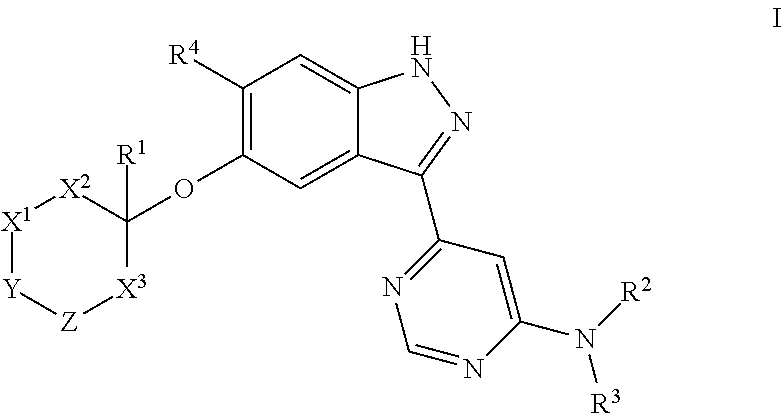
The present invention relates to novel compounds of formula (I)that are capable of inhibiting one or more kinases, especially SYK (Spleen Tyrosine Kinase), LRRK2 (Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2) and / or MYLK (Myosin light chain kinase) or mutants thereof. The compounds find applications in the treatment of a variety of diseases. These diseases include autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases, bone diseases, metabolic diseases, neurological and neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, allergies, asthma, alzheimer's disease, parkinson's disease, skin disorders, eye diseases, infectious diseases and hormone-related diseases.
Owner:ORIGENIS
Compounds inhibiting leucine-rich repeat kinase enzyme activity
The present invention is directed to azaindazole compounds which are potent inhibitors of LRRK2 kinase and useful in the treatment or prevention of diseases in which the LRRK2 kinase is involved, such as Parkinson's Disease. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and the use of these compounds and compositions in the prevention or treatment of such diseases in which LRRK-2 kinase is involved.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Compositions and methods for treatment of neurogenerative diseases
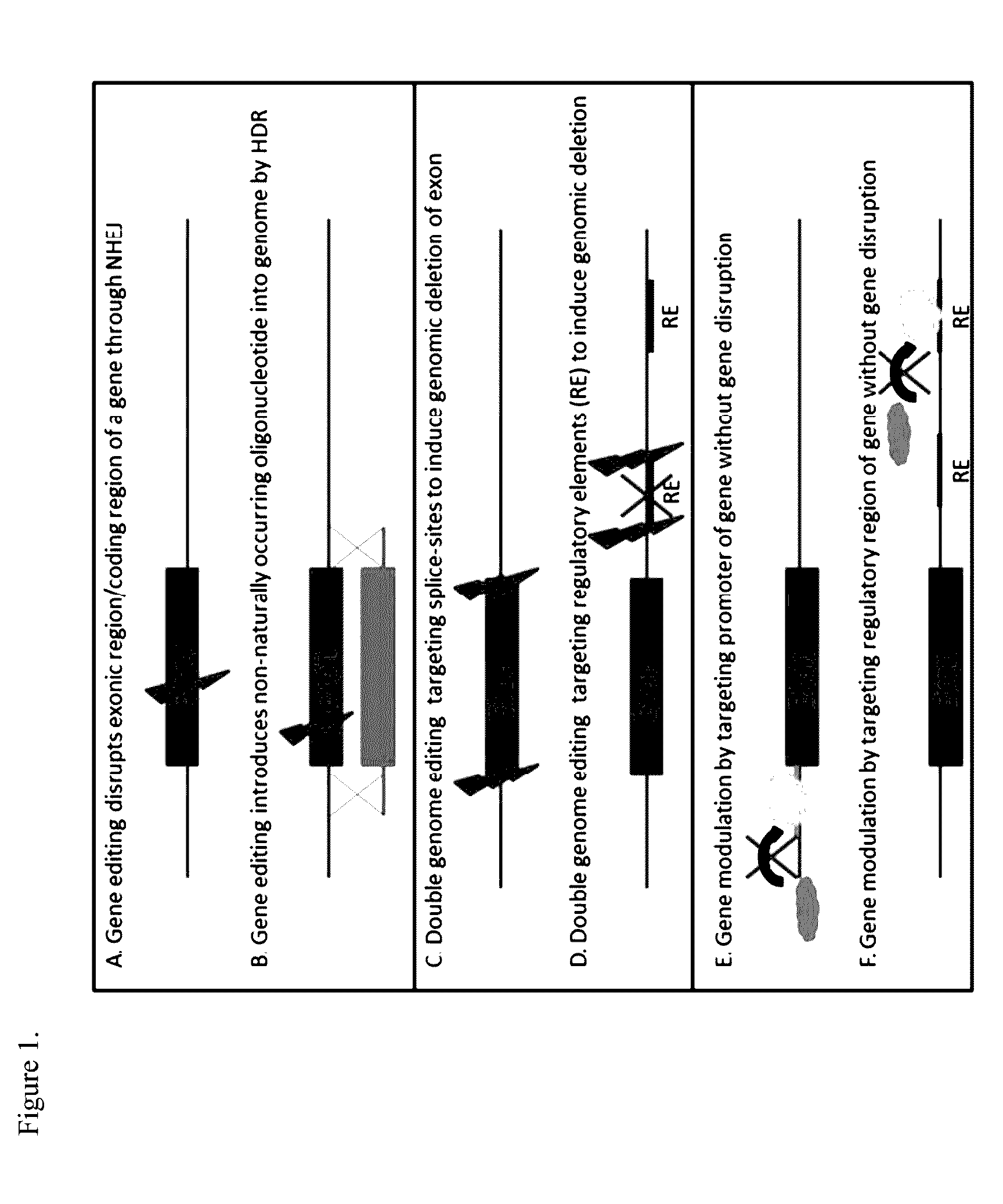
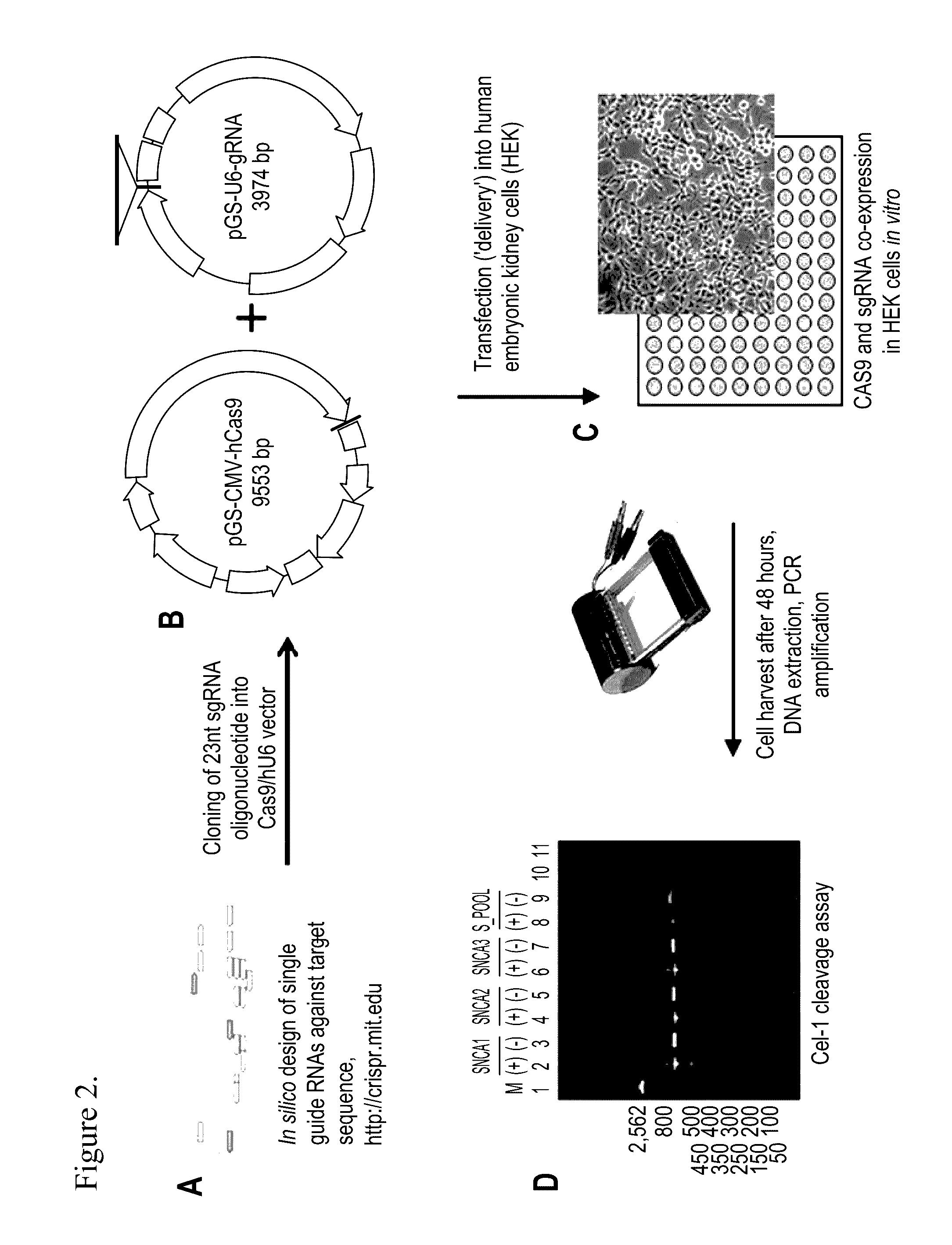
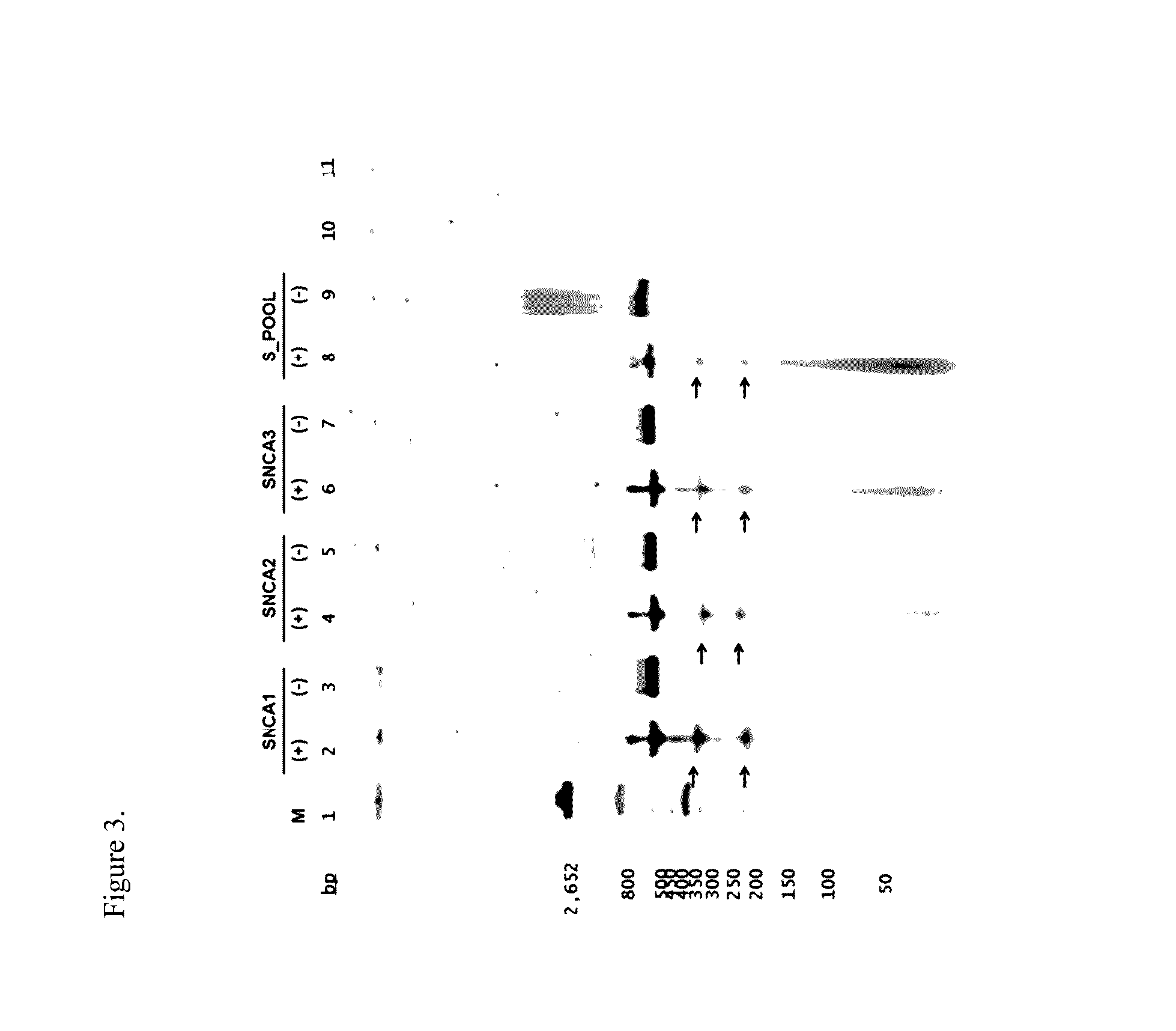
Medical compositions and methods of treating or preventing neurodegeneration in a human suffering from or that is at risk of or susceptible to neurodegeneration or cellular dysfunction associated with expression or impaired cellular function of a neuronal protein encoded by one or more genes that code for alpha-synuclein (SNCA), Parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase, (PARK2), Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), PTEN-induced putative kinase / (PINK1), Daisuke-Junko 1, (DJ-1) and ATPase type 13A2 (ATP13A2), are disclosed. Methods of treatment for these disorders is also provided, comprising administering a vector into a cell, wherein the vector facilitates expression of a molecular component that alters one of the aforementioned genes in the cell or expression of the gene in the cell, the gene being implicated in an etiology of the neurological deficit.
Owner:FLYNN ALEXANDER C
Compounds inhibiting leucine-rich repeat kinase enzyme activity
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Compositions and methods for producing bioactive fusion proteins
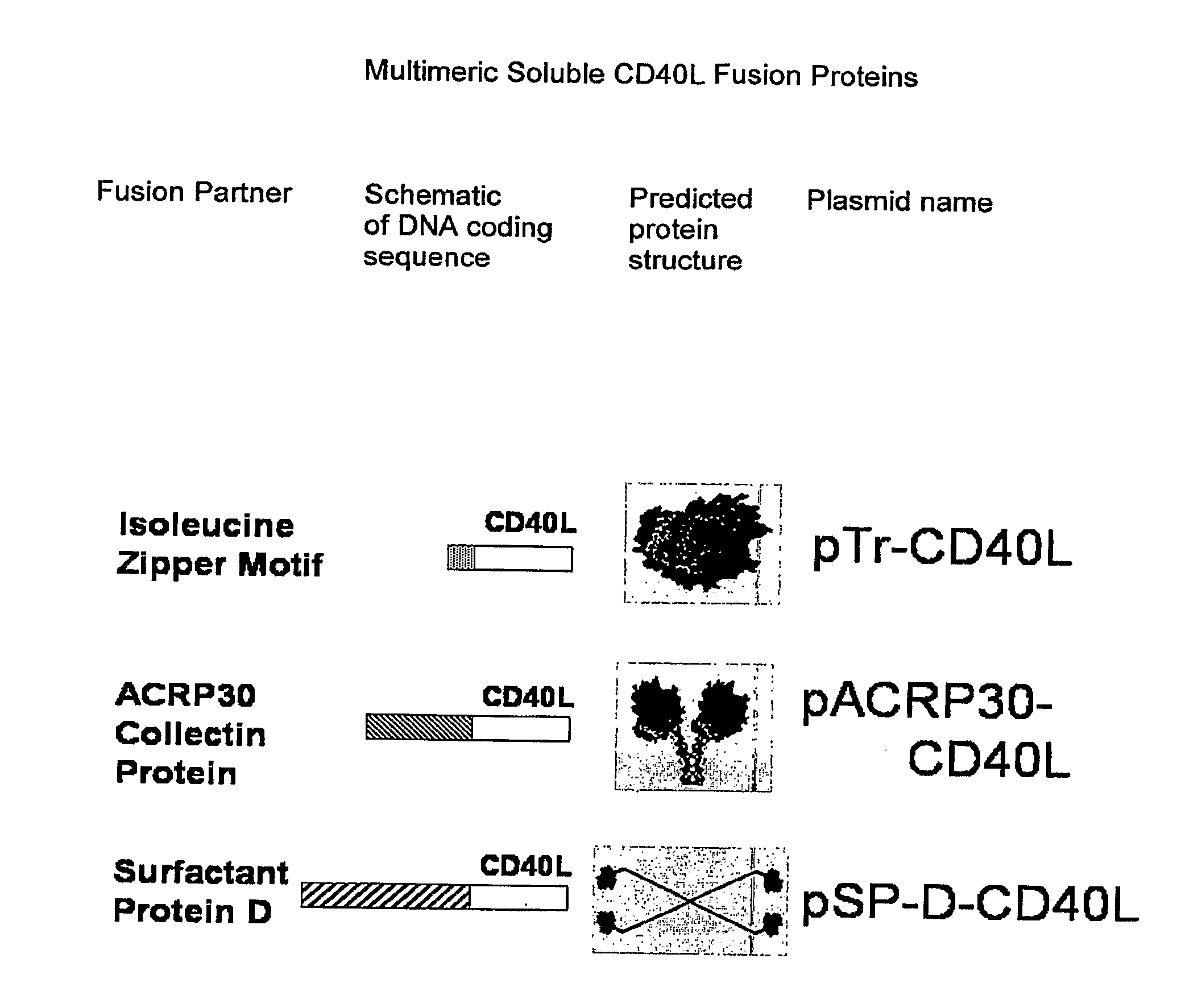
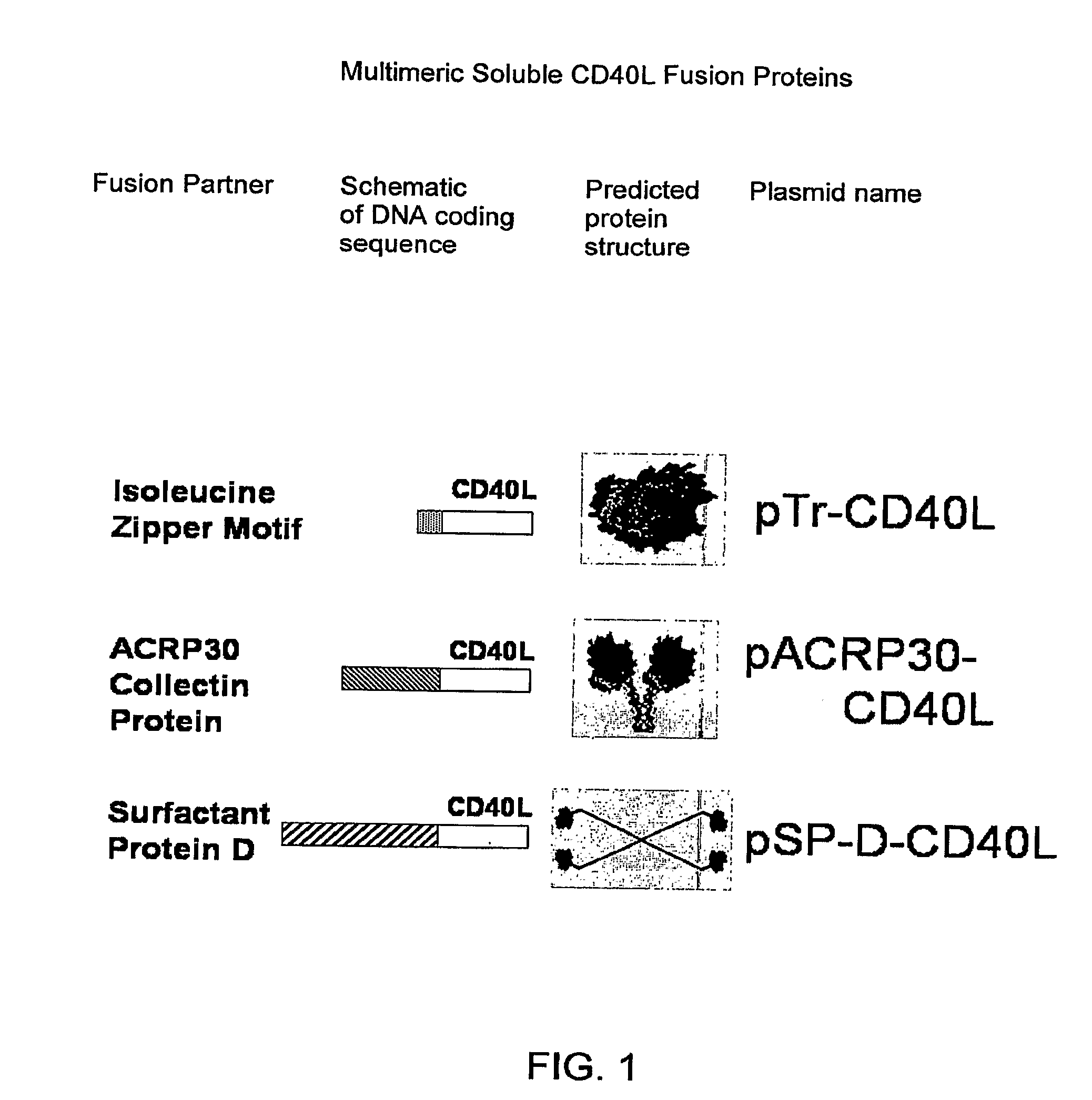
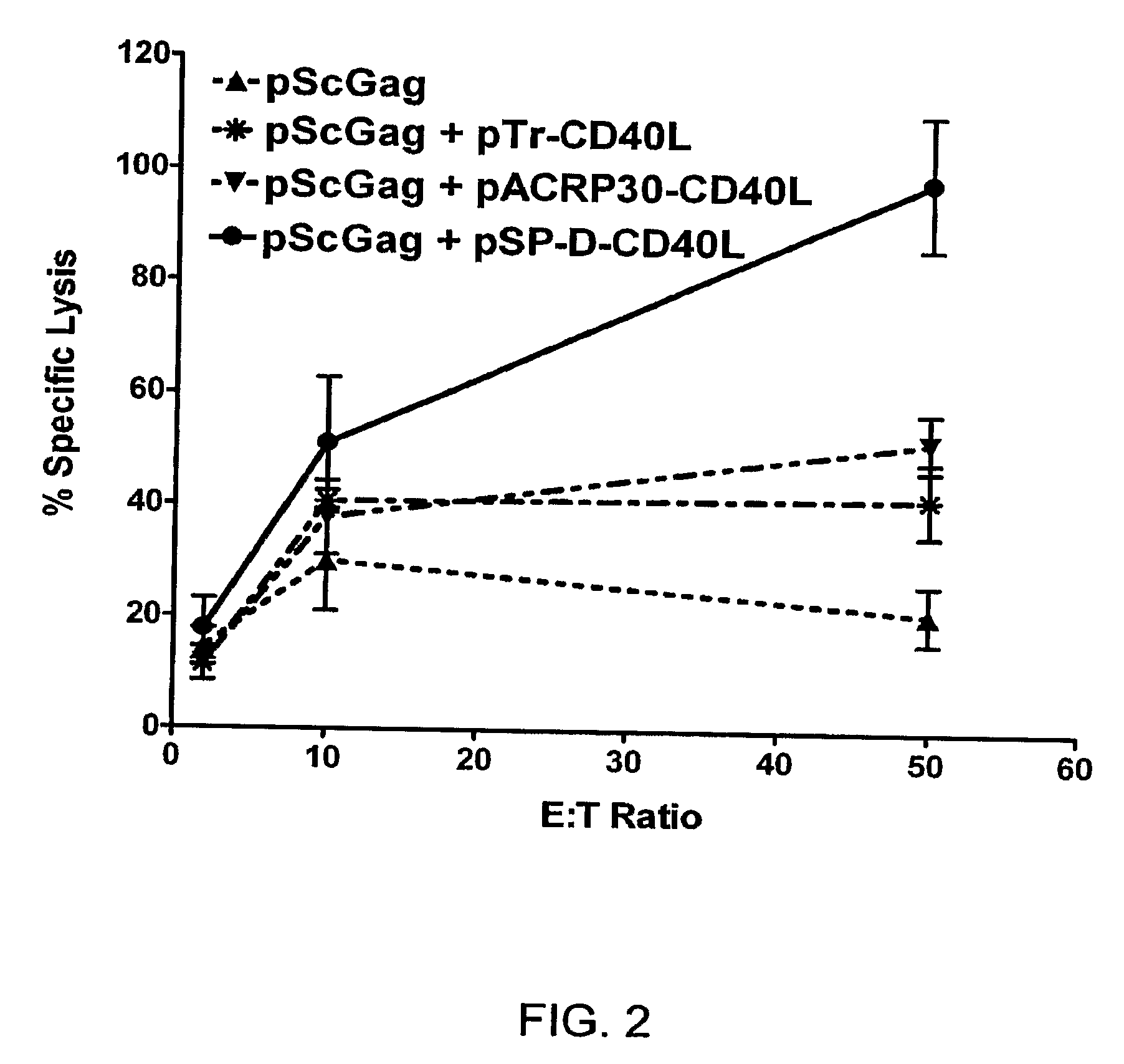
Disclosed is a composition of matter involving a recombinant fusion protein comprising a a pharmacologically active protein partner, and a small pharmacologically inactive protein domain partner of human origin, such as but not limited to, a 10th fibronectin III domain, a SH3 domain, a SH2 domain, a CH2 domain of IgG1, a PDZ domain, a thrombospondin repeat domain, an ubiquitin domain, a leucine-rich repeat domain, a villin headpiece HP35 domain, a villin headpiece HP76 domain, or a fragment or modification of any of these. Also disclosed are nucleic acids (e.g., DNA constructs) encoding the fusion protein, expression vectors and recombinant host cells for expression of the fusion protein, and pharmaceutical compositions containing the recombinant fusion protein and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and method of producing a pharmacologically active recombinant fusion protein.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Fusion protein containing leucine-rich repetitive sequence, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104119445AEfficient and convenient productionFermentationHybrid peptidesSlit2 proteinTert-leucine
The invention discloses fusion protein containing a leucine-rich repetitive sequence, and a preparation method and application thereof. Concretely, the invention relates to fusion protein, and the fusion protein possesses the following structure from N terminal to C terminal: A-X-E-Y1-Y2 (formula Ia) or A-Y2-Y1-E-X (formula Ib), wherein A is an optional secretion signal peptide, X is a member rich in leucine repetitive sequence 1-2 (LRRs1-2) of Slit2 protein (neuronal guidance factor 2), E is a restriction enzyme cutting site, Y1 is a first tag peptide member, Y2 is a second tag short peptide member and the second tag short peptide member is His tag member, and '-' represents a peptide bond or a peptide joint for connecting the above members. The fusion protein is beneficial for correct folding of LRR (leucine-rich repeat) and forming active functional polypeptide, and is capable of simply removing two tag members through once resection enzyme cutting, thereby preparing high-purity high-activity LRR sequence.
Owner:李华顺
LRR-RLK (leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase) gene in arachis hypogaea.L and application thereof to bacterial wilt resistance of tobaccos
InactiveCN104480118AIncreased bacterial wilt disease resistanceImprove disease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to an LRR-RLK (leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase) gene AhRLK6 associated with bacterial wilt resistance of arachis hypogaea.L and a construction method of an over-expression vector of the gene and in particular relates to an application of the gene AhRLK6 in arachis hypogaea.L to tobacco bacterial wilt resistant gene engineering, belonging to the technical field of plant gene engineering. The gene contains nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID No.1. The over-expression vector is constructed to transform Cuibi-1 tobaccos, the transgenic plants are inoculated with ralstonia solanacearum through molecular detection, and over-expression of the over-expression vector in the tobaccos can conduce to obviously improving the resistance of the transgenic tobaccos to bacterial wilt, thereby indicating that AhRLK6 possibly participates in the defence reaction of the plants to ralstonia solanacearum, which lays the foundation for bacterial wilt resistant genetic breeding of the plants and strongly promotes the development and application of the tobacco bacterial wilt resistant gene engineering.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Compositions and methods for producing bioactive fusion proteins
InactiveUS20090118181A1Low immunogenic riskReduce riskBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA constructActive protein
Disclosed is a composition of matter involving a recombinant fusion protein comprising a a pharmacologically active protein partner, and a small pharmacologically inactive protein domain partner of human origin, such as but not limited to, a 10th fibronectin III domain, a SH3 domain, a SH2 domain, a CH2 domain of IgG1, a PDZ domain, a thrombospondin repeat domain, an ubiquitin domain, a leucine-rich repeat domain, a villin headpiece HP35 domain, a villin headpiece HP76 domain, or a fragment or modification of any of these. Also disclosed are nucleic acids (e.g., DNA constructs) encoding the fusion protein, expression vectors and recombinant host cells for expression of the fusion protein, and pharmaceutical compositions containing the recombinant fusion protein and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and method of producing a pharmacologically active recombinant fusion protein.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Compositions and systems for conferring disease resistance in plants and methods of use thereof
Compositions, systems and methods are provided for conferring disease resistance to plant pathogens that use proteases to target plant substrate proteins inside plant cells. Briefly, the compositions, systems and methods are based upon plant substrate proteins that are targeted by pathogen-specific proteases and that activate nucleotide binding site-leucine rich repeat (NB-LRR) disease resistance proteins when cleaved by the protease. These substrate proteins are modified such that the endogenous protease recognition sequence is replaced by a protease recognition sequence specific to a different pathogen protease (i.e., a heterologous protease recognition sequence). The modified plant substrate protein therefore can be used in connection with its corresponding NB-LRR protein to activate resistance in response to cleavage by the heterologous pathogen-specific protease. When activated by the plant pathogen-specific protease, the pair initiates host defense responses thereto, including programmed cell death.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
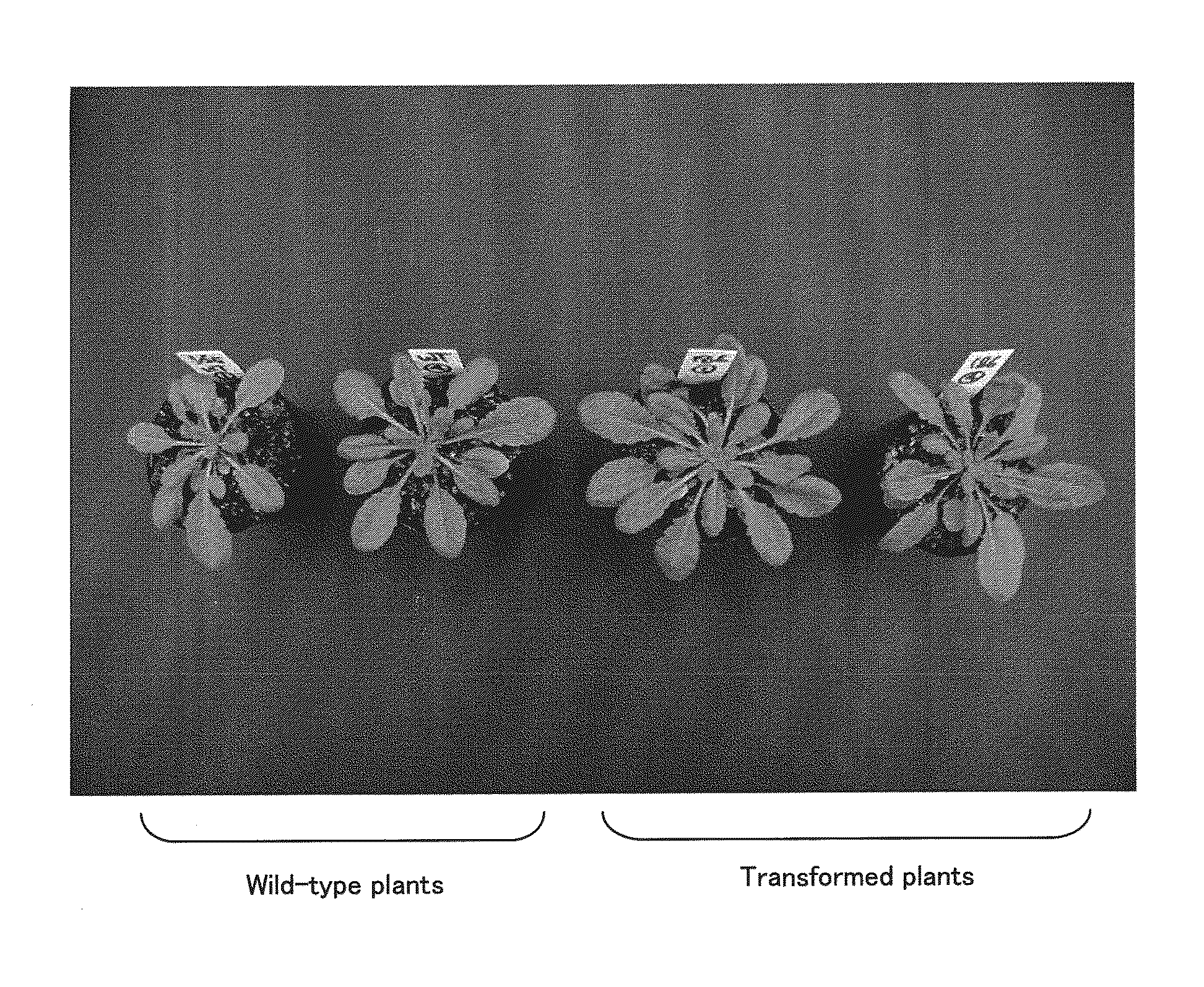
Plants having improved growth characteristics and method for making the same
InactiveCN101189342AImprove growth characteristicsHigh yieldClimate change adaptationEnzymesLeucine-rich repeatWild type
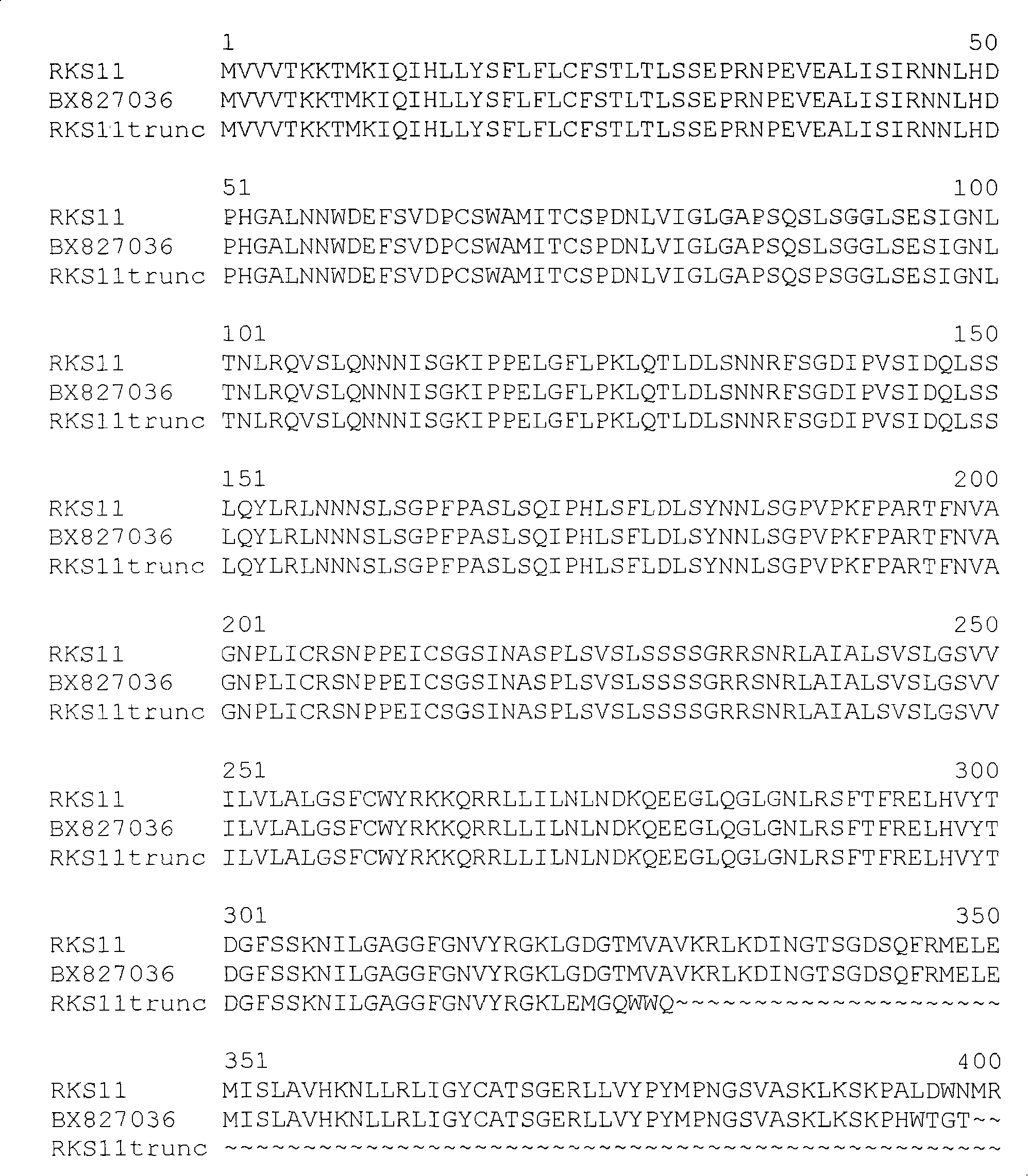
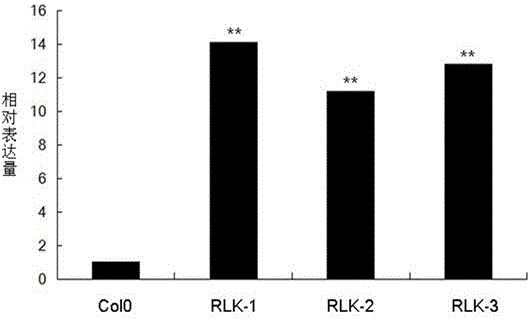
The present invention concerns a method for improving the growth characteristics of plants by increasing expression of at least part of a Leucine Rich Repeat Receptor-Like Kinase (RKS11, RKS4 or an orthologue of these). One such method comprises introducing into a plant a nucleic acid encoding at least part of a Leucine Rich Repeat Receptor-Like Kinase (RKS11 or RKS4 or an orthologue thereof). The invention also relates to transgenic plants having introduced therein a nucleic acid or variant thereof encoding at least part of a Leucine Rich Repeat Receptor-Like Kinase (RKS11 or RKS4 or an orthologue thereof), which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. The present invention also concerns constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
LRR-RLK (leucine-rich repeats-receptor-like kinase) in arabidopsis thaliana and application thereof
InactiveCN105039280AGrowth does not affectReduce damageTransferasesFermentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
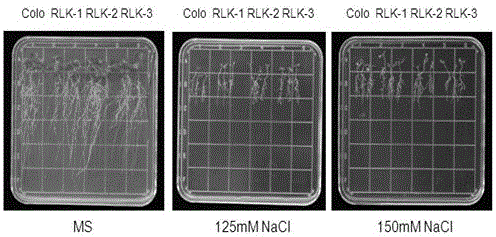
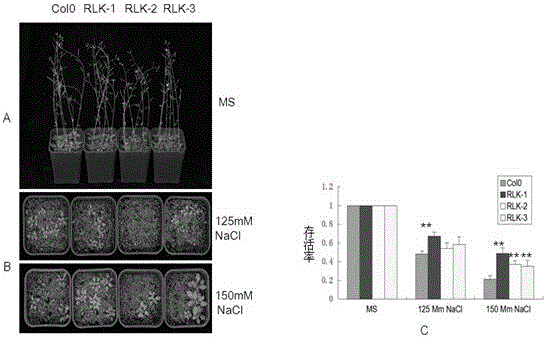
The invention relates to salt tolerance related LRR-RLK (leucine-rich repeats-receptor-like kinase) in arabidopsis thaliana and an application thereof to cultivation of salt tolerant transgenic plants. The amino acid sequence of LRR-RLK of a protein is shown in SEQ ID No.2 and a coded nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The protein related to salt tolerance of plants and a coding gene thereof, which are provided by the invention, have important significance in improving and reinforcing the stress resistance of arabidopsis thaliana and then accelerating the stress resistant molecular breeding process and have realistic application values in agricultural production in China.
Owner:WUHAN BINGGANG BIOTECH CO LTD
Human leucine-rich repeat containing protein expressed predominately in small intestine, HLRRSI1
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Compounds inhibiting leucine-rich repeat kinase enzyme activity
ActiveUS20160009689A1Useful in treatmentReduce usageNervous disorderOrganic chemistryDiseaseKinase activity
The present invention is directed to indazole compounds which are potent inhibitors of LRRK2 kinase and useful in the treatment or prevention of diseases in which the LRRK2 kinase is involved, such as Parkinson's Disease. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and the use of these compounds and compositions in the prevention or treatment of such diseases in which LRRK-2 kinase is involved.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Anti-bacterial compositions
InactiveCN102037006AAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsLeucine-rich repeatAnti bacterial
An isolated protein for use as an antimicrobial agent comprises a plurality of LRR (leucine rich repeat) domains, each LRR domain independently comprising an amino acid sequence of formula (I): (F1LxxLxL(xxZ)YF2) wherein: F1 and F2 are independently, a contiguous amino acid sequence of between 1 and 30 residues; x can be any amino acid; L can be Leu, Ile, VaI or Phe; Z can be NxL or CxxL; N is Asn, Thr, Ser or Cys; C is Cys or Ser; and Y = 0 or 1.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Leucine-rich repeat kinase (LRRK2) drosophila model for parkinson's disease: wildtype1 (WT1) and G2019S mutant flies
InactiveUS20100175140A1Effective preventionEffective treatmentCompounds screening/testingGenetic engineeringNeuronal degenerationWild type
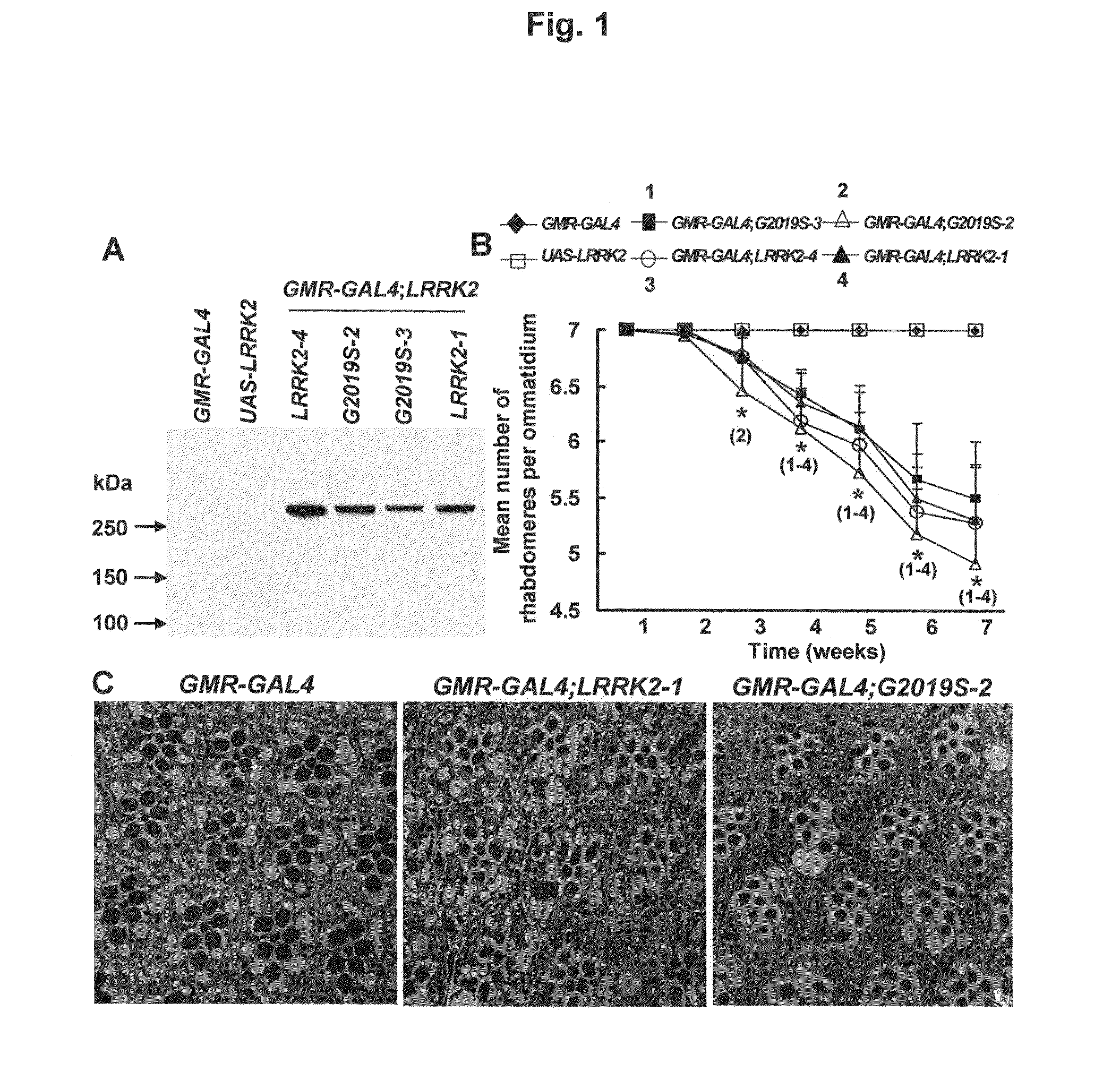
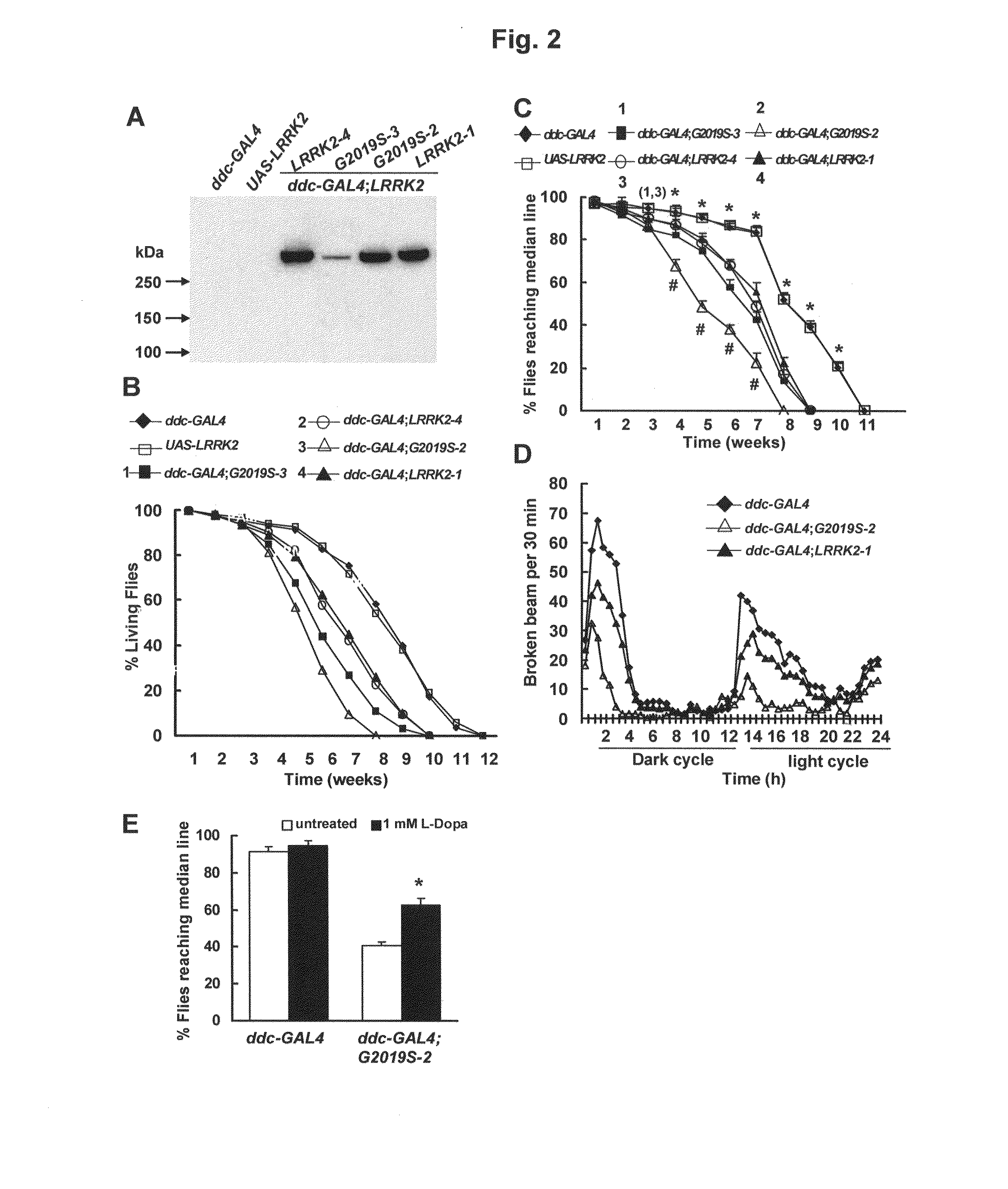
Mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase (LRRK2) gene cause late-onset autosomal dominant Parkinson's disease (PD) with pleiomorphic pathology. Previously, we and others found that expression of mutant LRRK2 causes neuronal degeneration in cell culture. Here we used the GAL4 / UAS system to generate transgenic Drosophila expressing either wild-type (WT1) human LRRK2 or LRRK2-G2019S, the most common mutation associated with PD. Expression of either WT1 human LRRK2 or LRRK2-G2019S in the photoreceptor cells caused retinal degeneration. Expression of WT1 LRRK2 or LRRK2-G2019S in neurons produced adult-onset selective loss of dopaminergic neurons, locomotor dysfunction, and early mortality. Expression of mutant G2019S-LRRK2 caused a more severe parkinsonism-like phenotype than expression of equivalent levels of WT1 LRRK2. Treatment with L-DOPA improved mutant LRRK2-induced locomotor impairment but did not prevent the loss of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive neurons. To our knowledge, this is the first in vivo “gain-of-function” model which recapitulates several key features of LRRK2-linked human parkinsonism. These flies may provide a useful model for studying LRRK2-linked pathogenesis and for future therapeutic screens for PD intervention.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
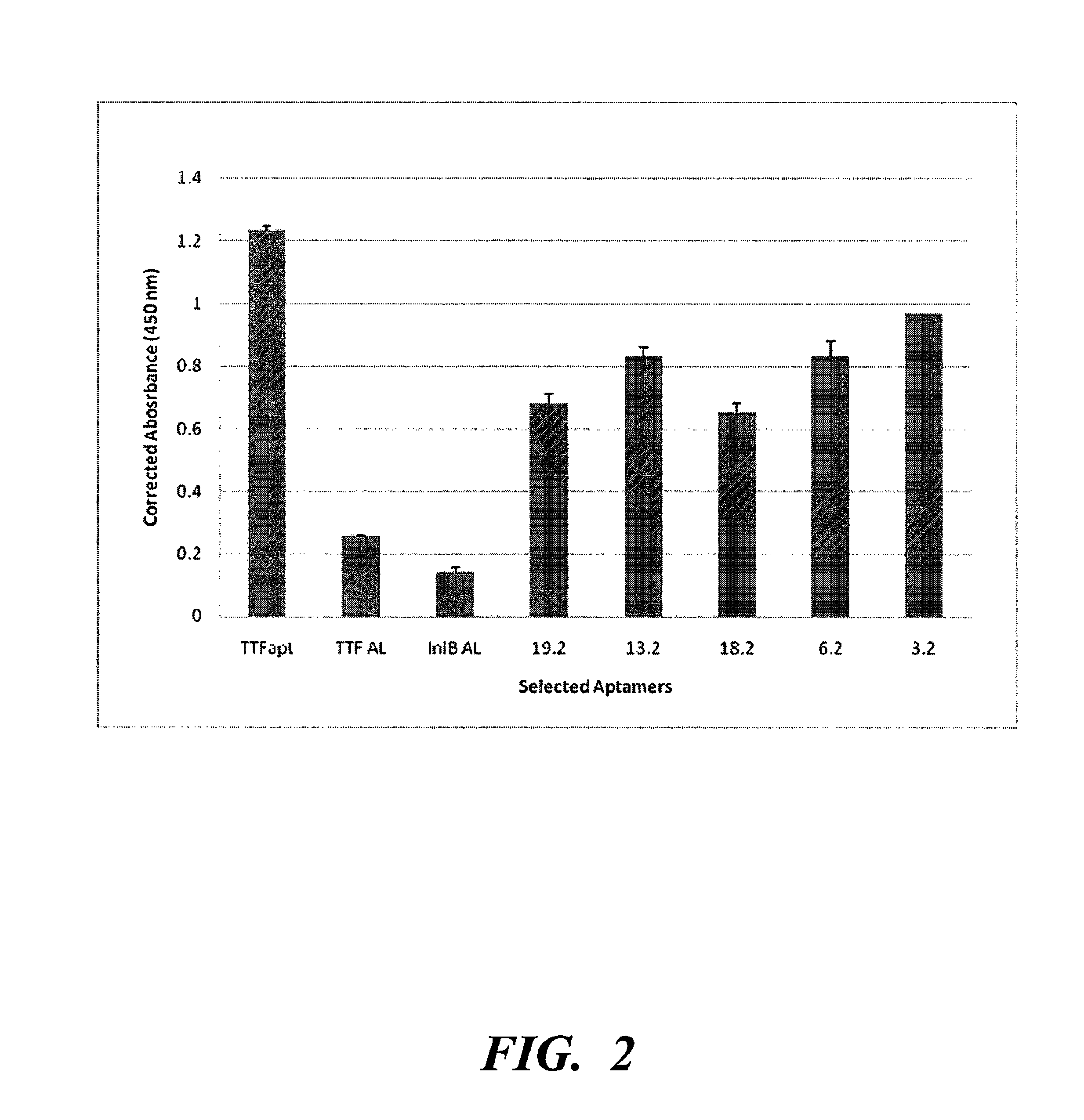
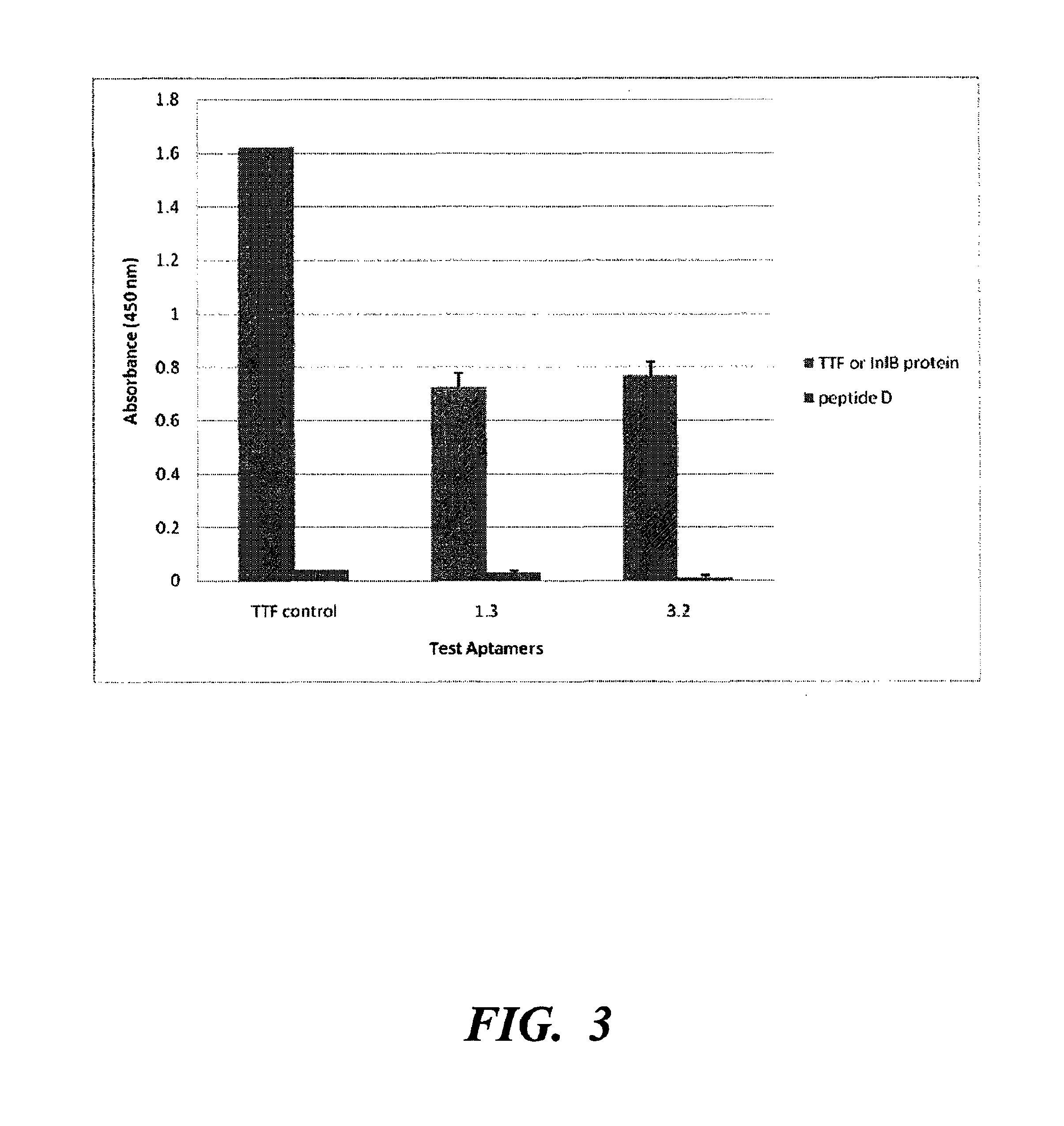
Nucleic acid ligands capable of binding to internalin B or internalin A
The present disclosure relates to the isolation of a novel reagent selected for its binding characteristics to the proteins internalin B or internalin A. InIB is a surface-localized protein of Listeria monocytogenes that binds and activates the receptor tyrosine kinase Met. InIB promotes invasion of a number of cells including hepatocytes, endothelial and epithelial cell lines and causes activation of the actin-mediated internalization of the bacterium. InIA belongs to a large group of surface-localized leucine-rich repeat (LRR) proteins identified in the Listeria genome. InIA enables Listeria monocytogenes to invade non-phagocytic cells such as those of the human intestinal epithelium and is sufficient for adhesion to and inducing uptake into epithelial cells. The disclosed nucleic acid ligands to internalin B and internalin A may be useful for determining the presence or absence of internalin B, internalin A, or Listeria in food, clinical or environmental samples; they may also be useful as an agent for combating Listeria infection by binding to and inactivating the infection-promoting inlB or inlA proteins. One object is to incorporate these nucleic acid ligands into an in vitro diagnostic or biosensor platform designed to detect the presence or absence of internalin B, internalin A, or Listeria in food, clinical or environmental samples. Another object is to employ these nucleic acid ligands in methods for treating or preventing Listeria infection.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION +1
Master activators of pathogen responsive genes
InactiveUS20050262584A1Increase productivityQuality improvementTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesConstitutively activeLeucine-rich repeat
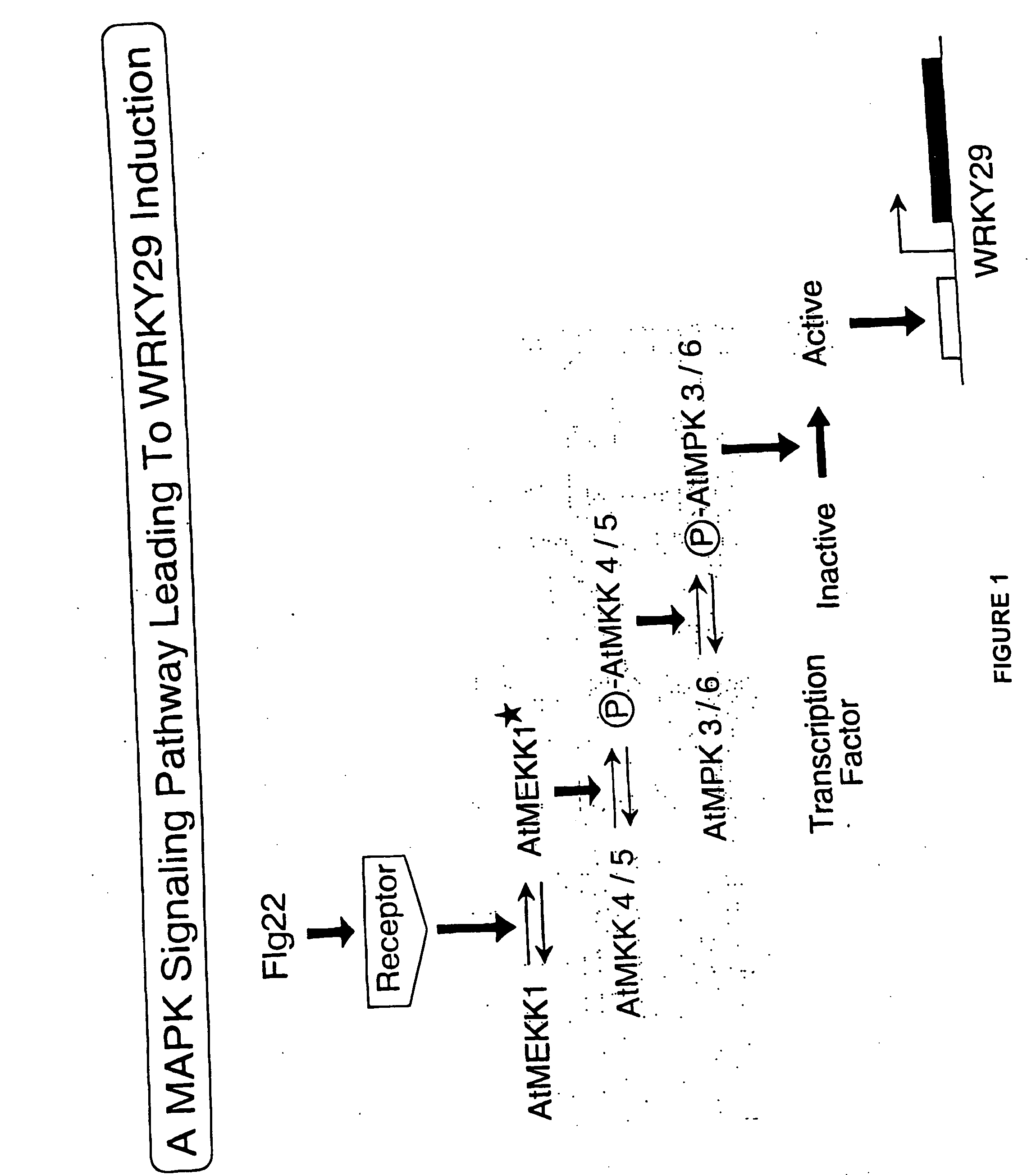
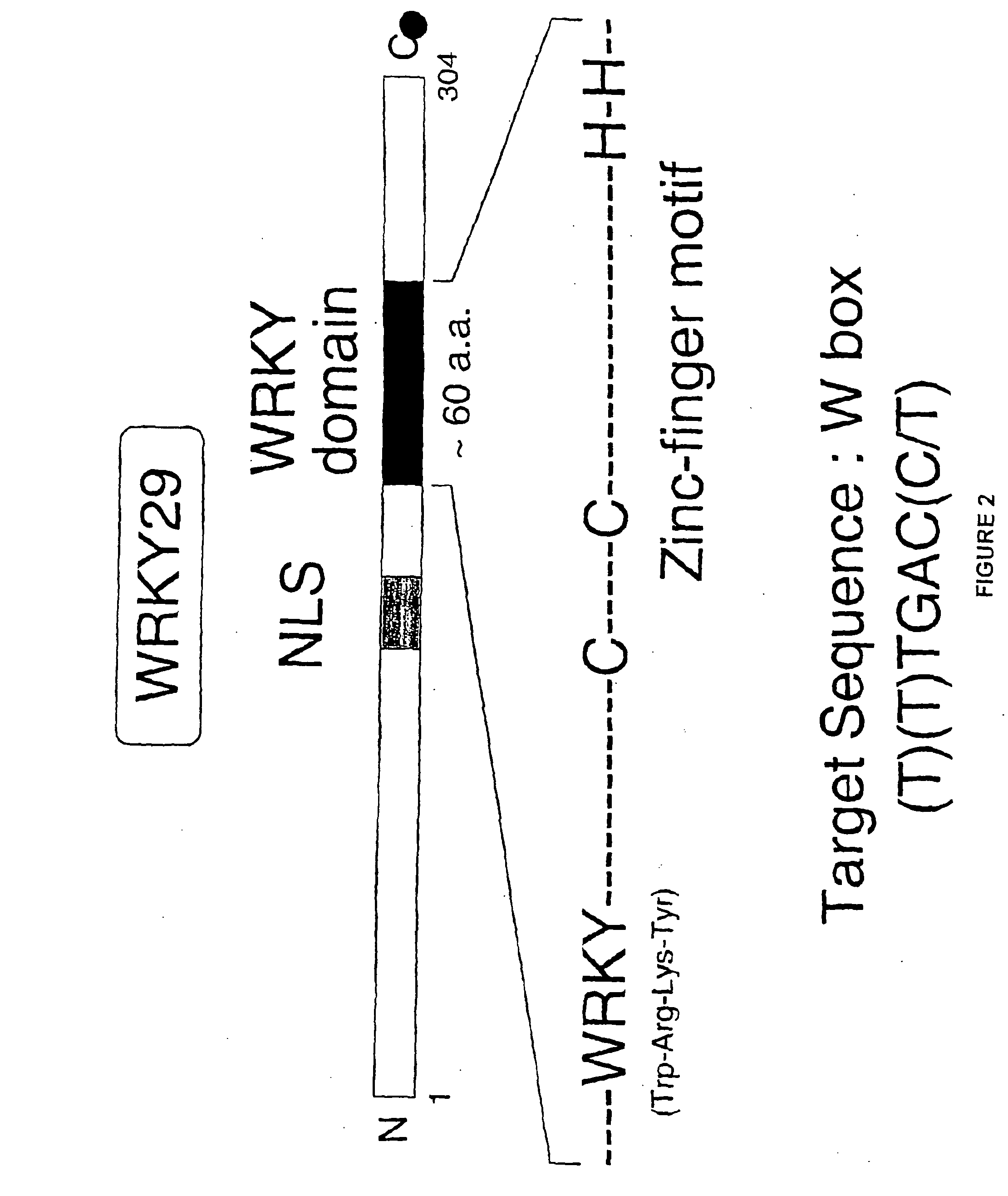
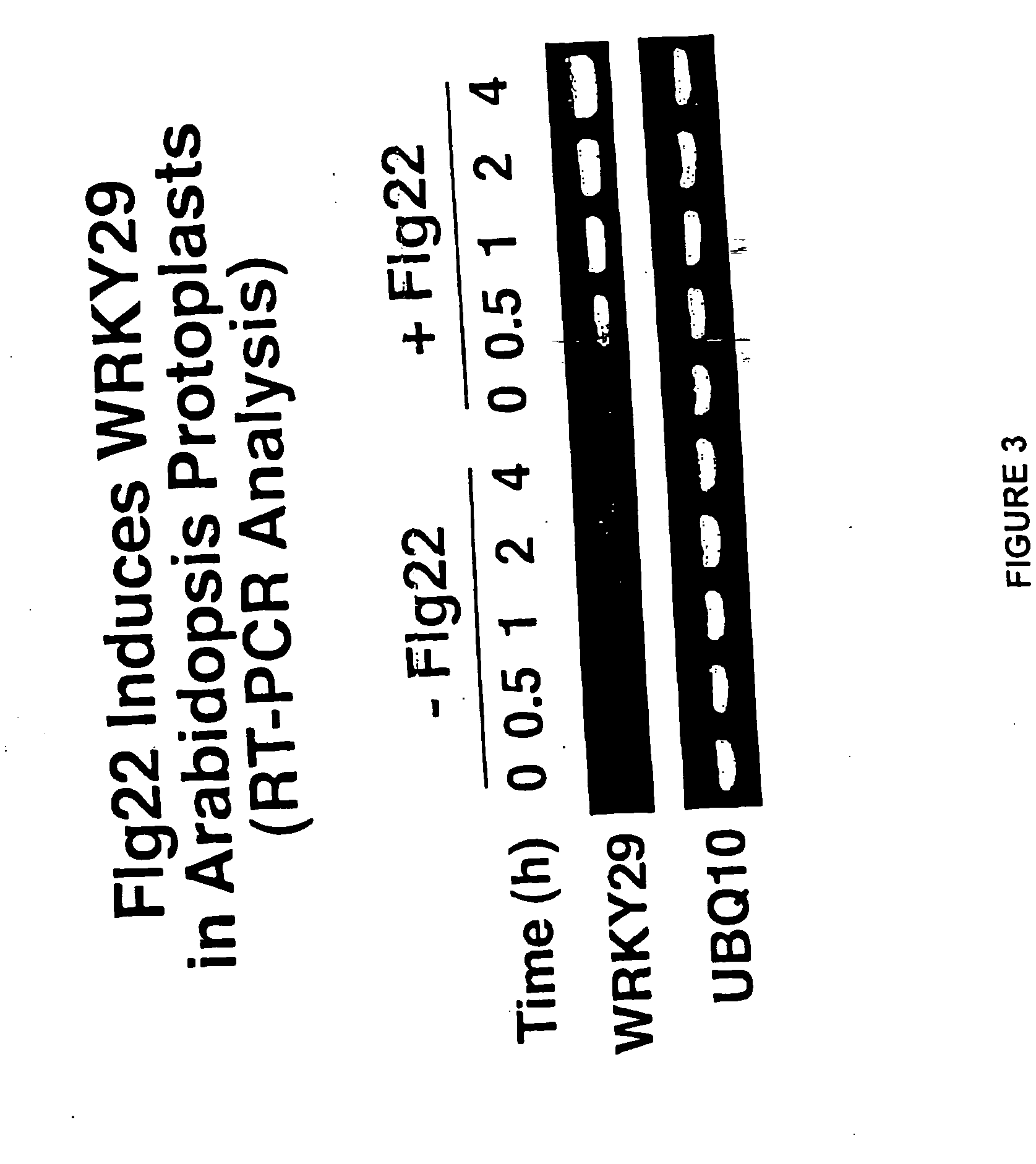
Disclosed is a complete plant MAP kinase cascade (e.g., MEKK1, MKK4 / MKK5, and MPK3 / MPK6) and WRKY22 / WRKY29 transcription factors that function downstream of the flagellin receptor FLS2, a leucine-rich-repeat (LRR) receptor kinase. Activation of such a MAPK cascade confers resistance to both bacterial and fungal pathogens. Also disclosed are disease-resistant plants expressing one or more members of this MAP kinase signaling cascade. Such members include constitutively active MEKK1 (ΔMEKK1), MKK4 (MKK4a), and MKK5 (MKK5a) or wild-type WRKY29.
Owner:SHEEN JEN +3
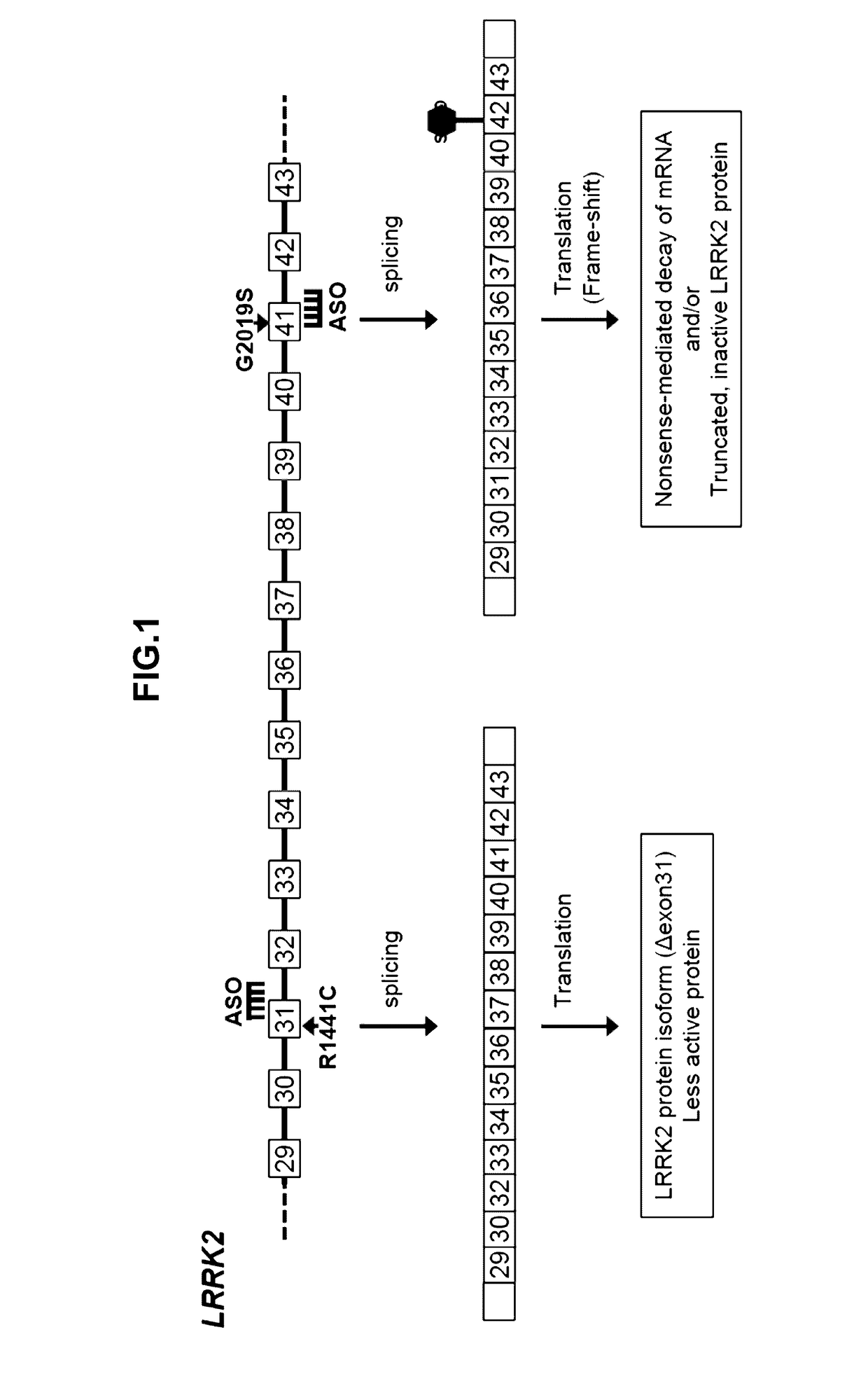
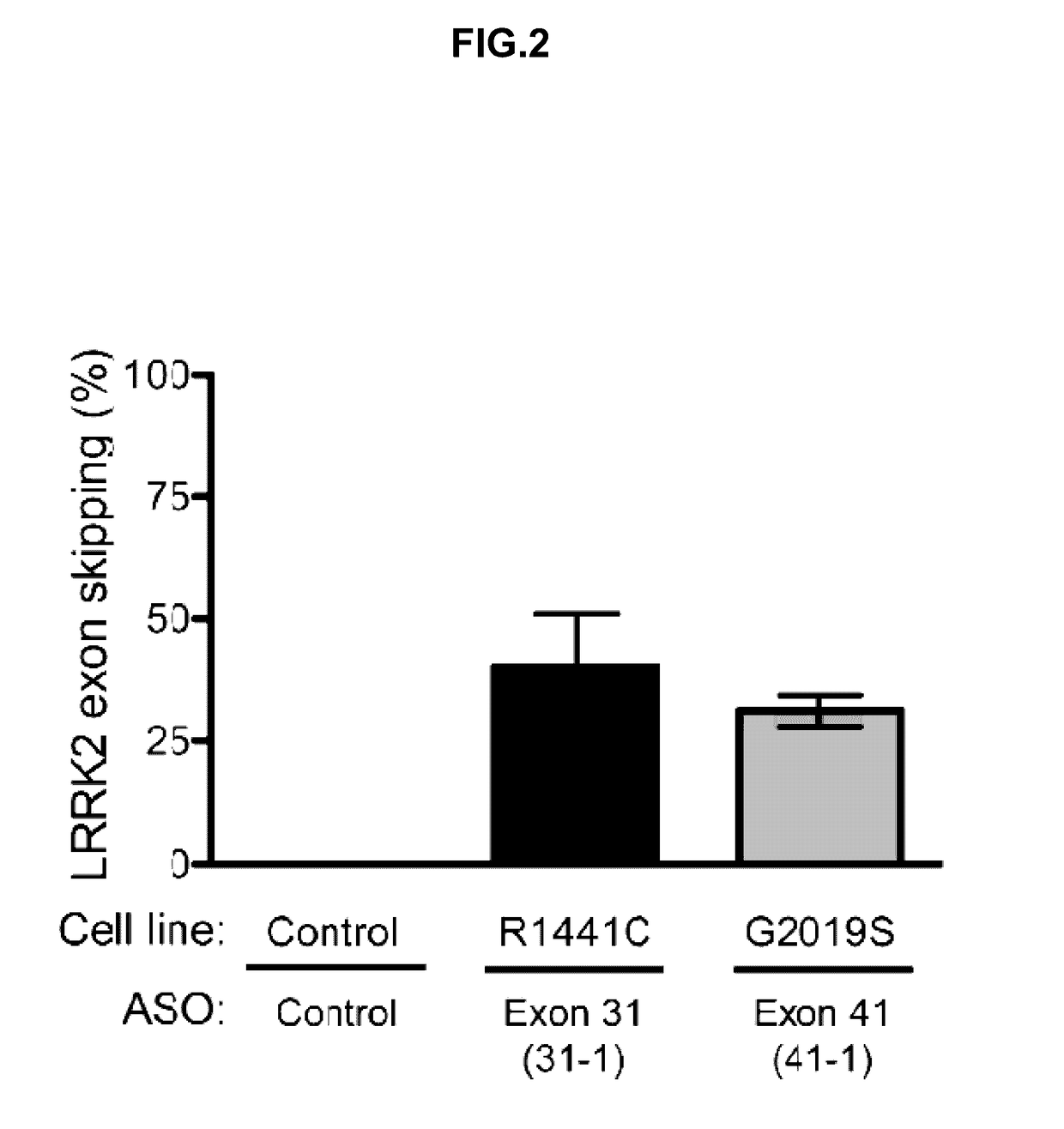
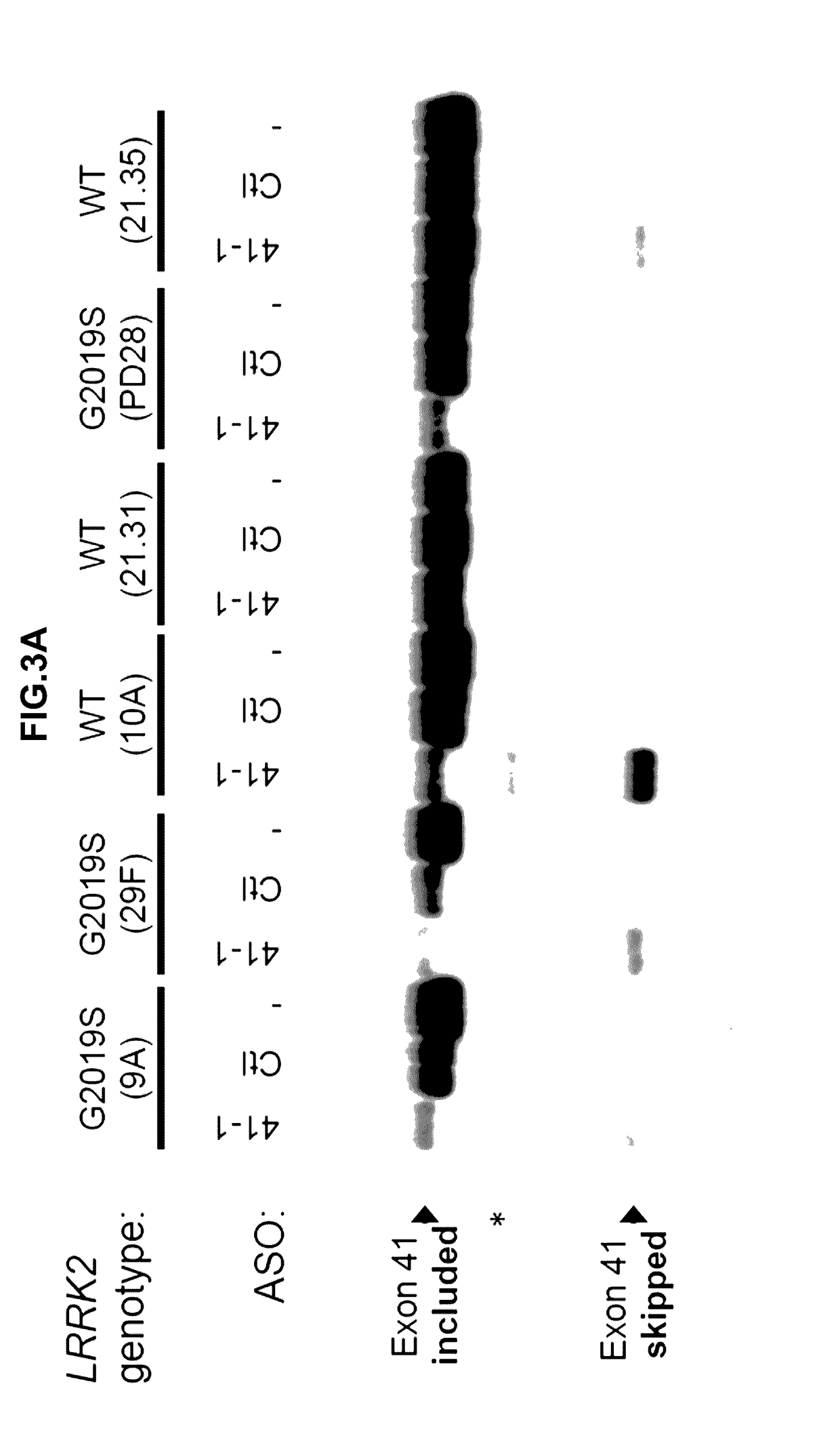
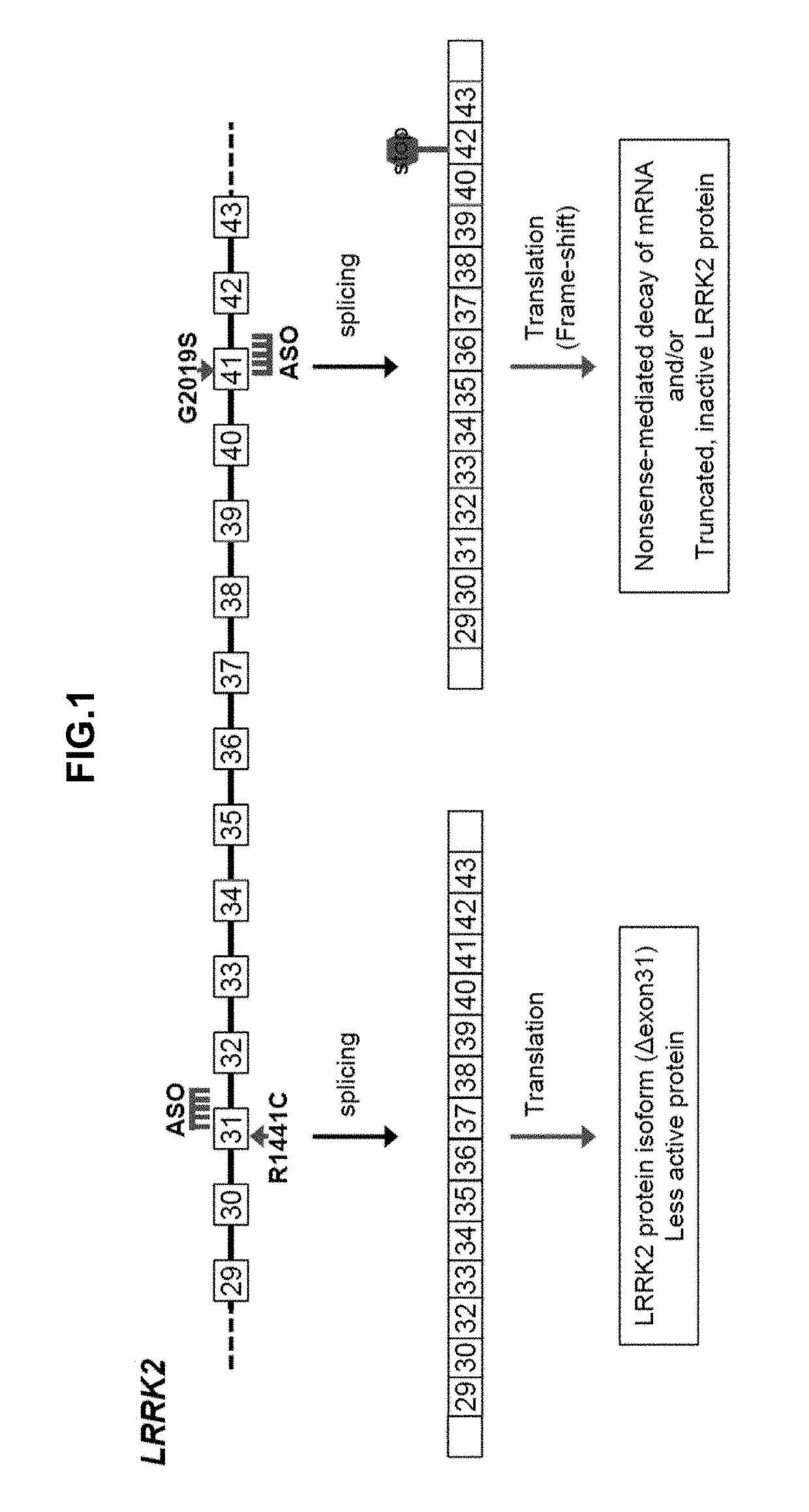
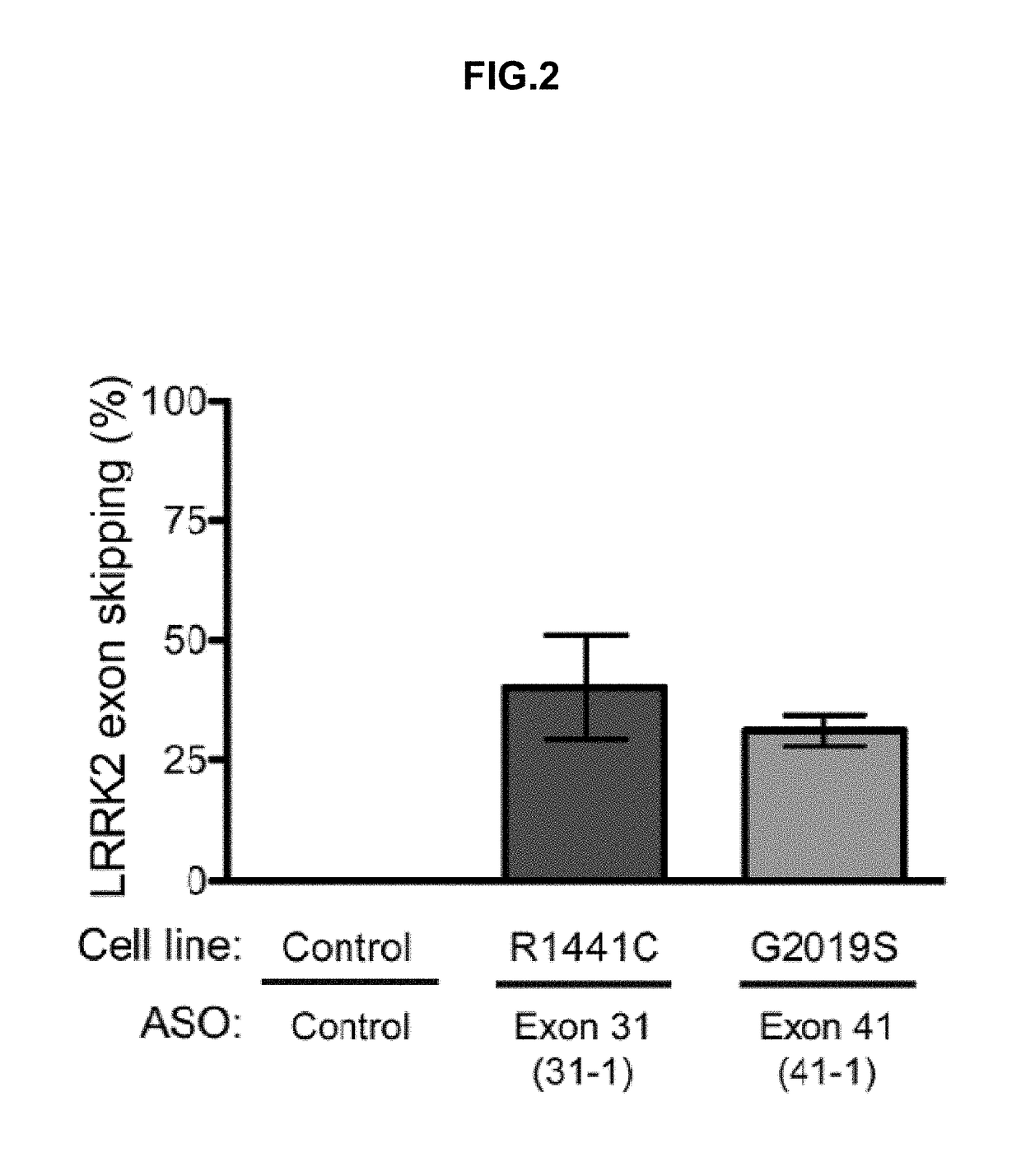
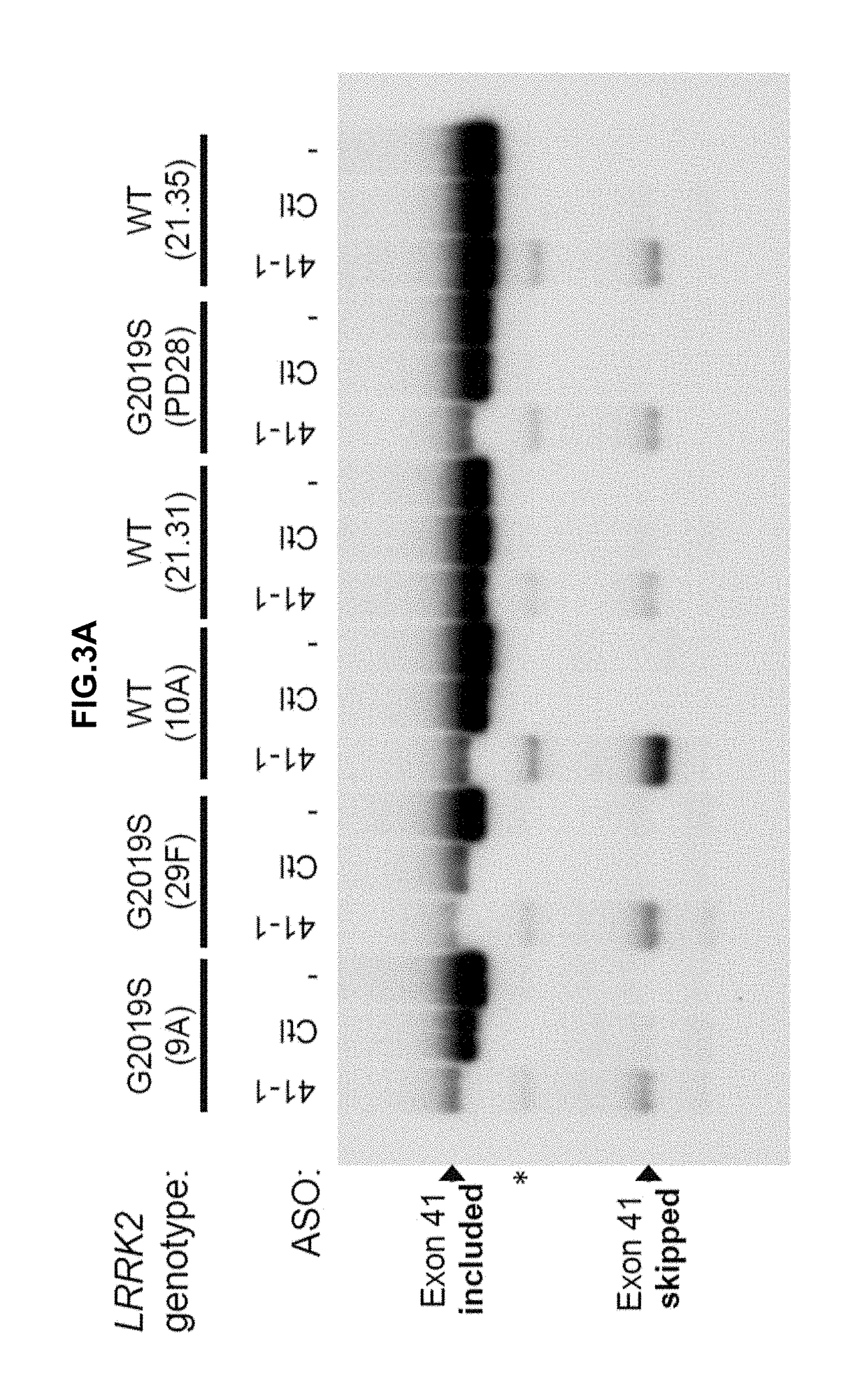
Antisense Compounds Targeting Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (LRRK2) For The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
The present disclosure relates generally to compounds comprising oligonucleotides complementary to a Leucine-Rich-Repeat-Kinase (LRRK2) RNA transcript. Certain such compounds are useful for hybridizing to a LRRK2 RNA transcript, including but not limited to a LRRK2 RNA transcript in a cell. In certain embodiments, such hybridization results in modulation of splicing of the LRRK2 transcript. In certain embodiments, such compounds are used to treat one or more symptoms associated with Parkinson's disease.
Owner:ROSALIND FRANKLIN UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE +1
Application of NtRLK2 gene to resistance of tobacco to bacterial wilt
The invention relates to a sequence and functional application of an LRR (Leucine-Rich Repeat) acceptor protein kinase gene NtRLK2 related to the resistance of tobacco to bacterial wilt, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. According to the sequence and the functional application, through the analysis of a gene chip, a partial segment of one LRR acceptor protein kinase gene NtRLK2 of which the expression is up-regulated by 2 times when being induced by ralstonia solanacearum is obtained; a full-length cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence of the LRR acceptor protein kinase gene NtRLK2 is obtained through an RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA end) technique; the gene is cloned from a high-bacterial-wilt-resistance variety line 3 of the tobacco, is used for constructing over-expression and RNAi (Ribonucleic Acid interference) expression vectors, and is transferred into a bacterial wilt infected variety Cuibi 1# in the tobacco; indicated by inoculation identification, the RANi of the gene obviously enhances the disease resistance of a tobacco plant to the bacterial wilt; preliminarily predicted, the gene is possibly an interacting gene of an endogenous disease-resistant gene; the expression of the disease-resistant gene is inhibited. According to the application, a foundation is about to be laid for the bacterial-wilt disease-resistant genetic breeding of the tobacco.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
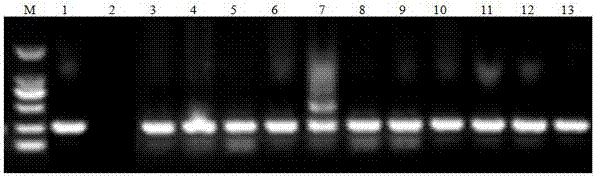
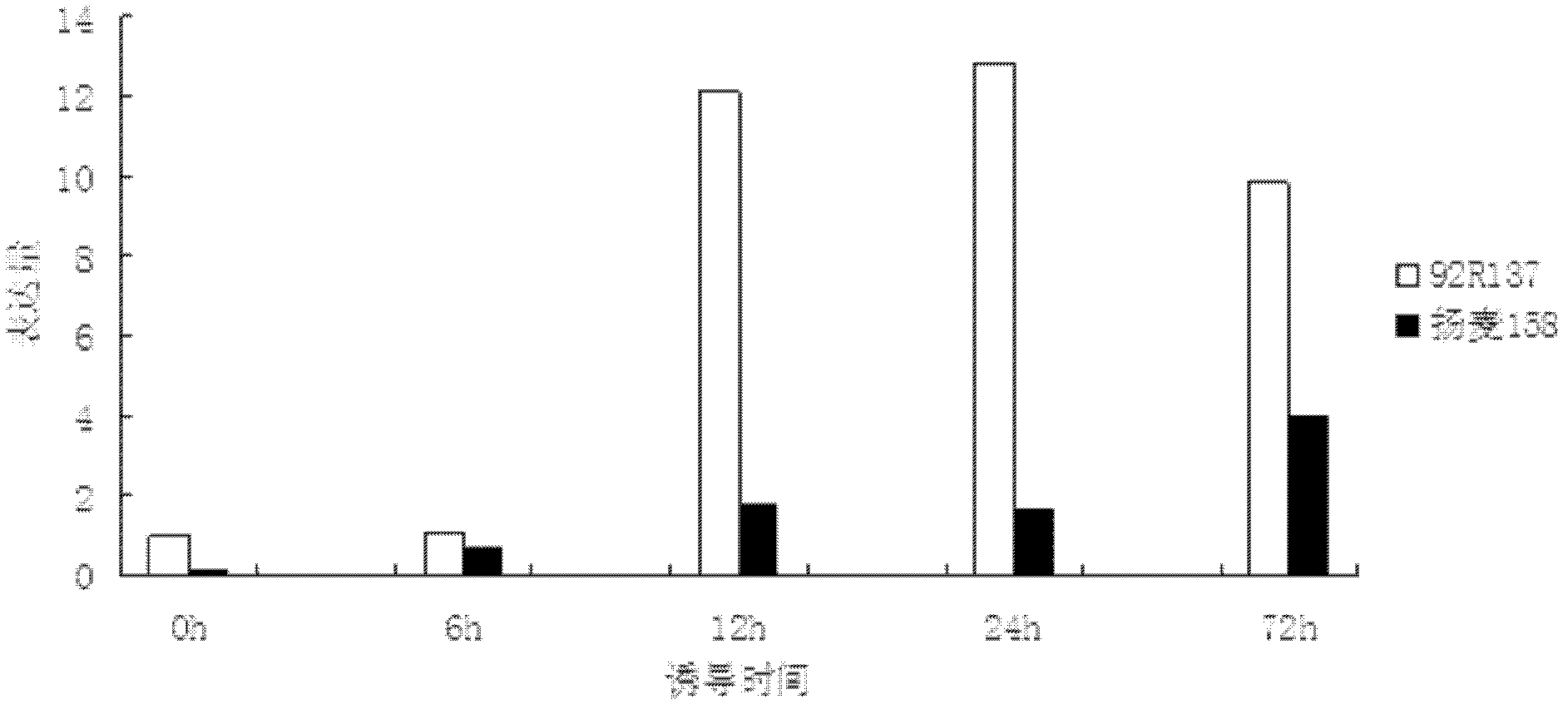
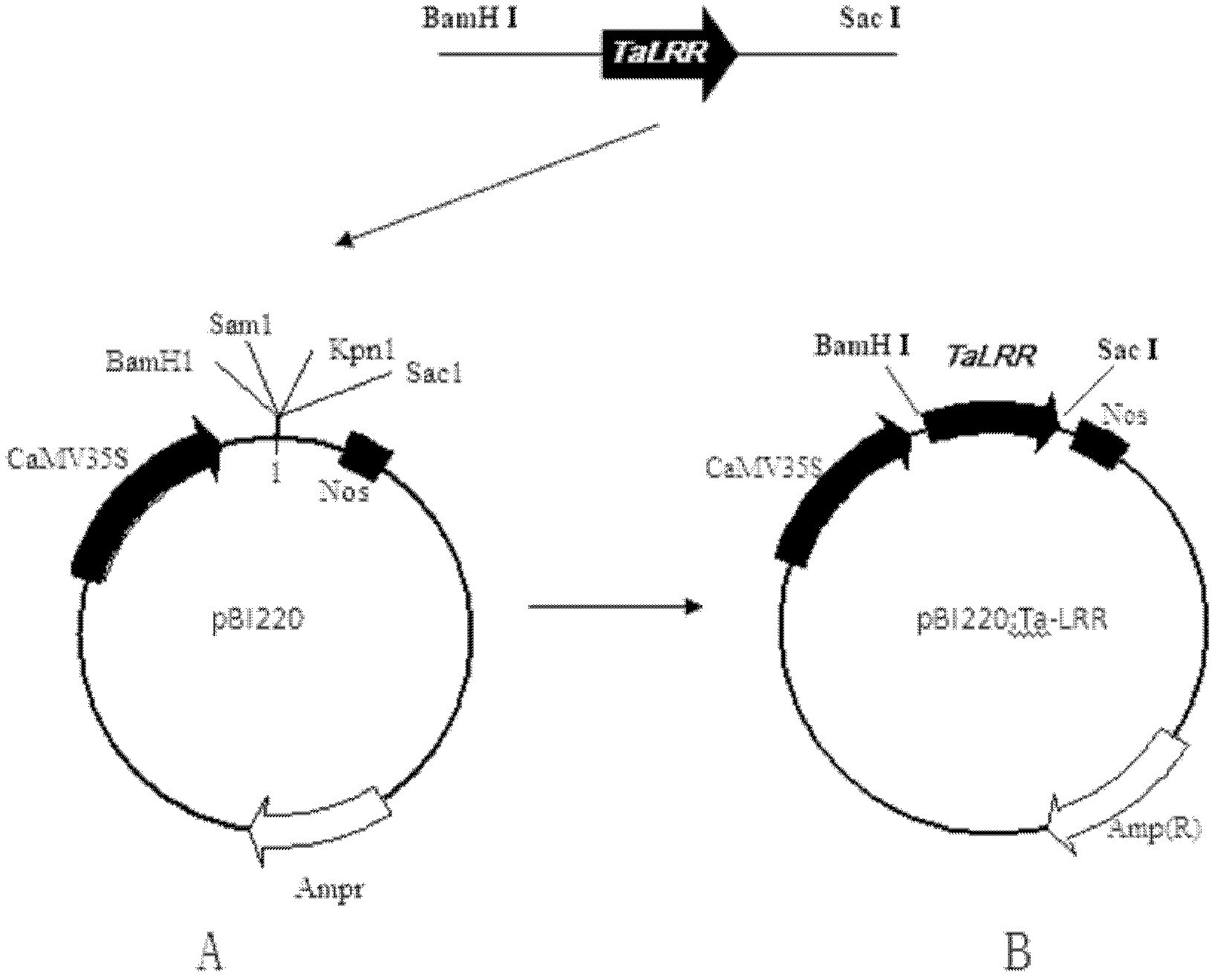
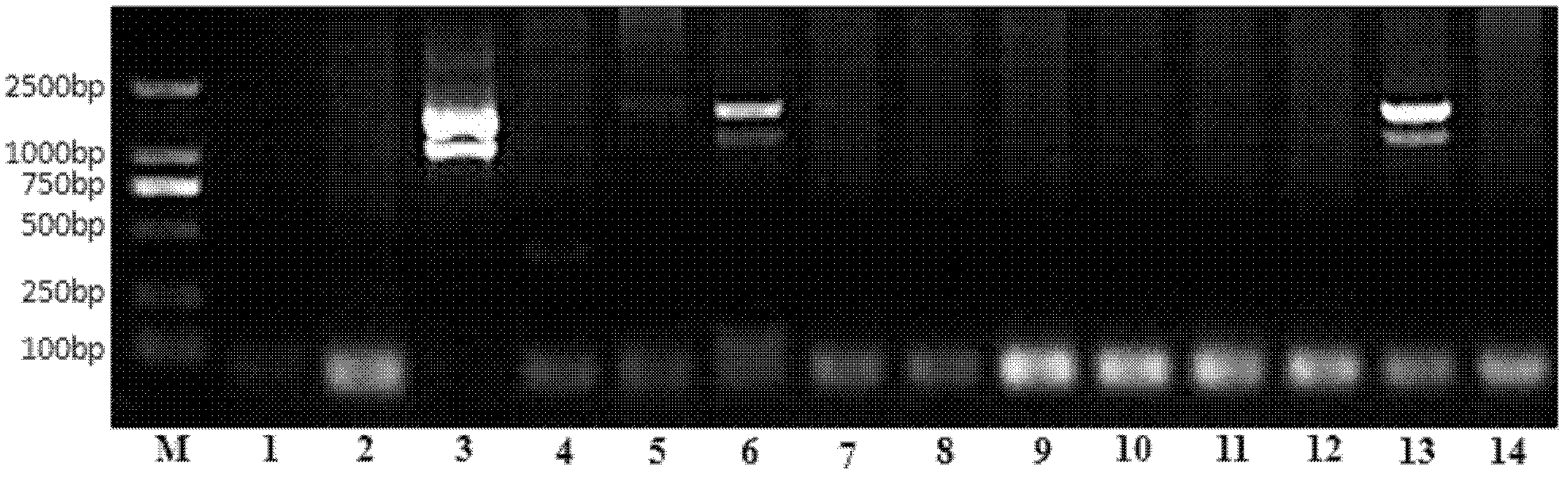
Transmembrane protein gene triticum asetivum leucine rich repeat 3 (TaLRR3) with leucine rich repeat (LRR) structure domain as well as expression vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a transmembrane protein gene triticum asetivum leucine rich repeat 3 (TaLRR3) with a leucine rich repeat (LRR) structure domain as well as an expression vector and an application thereof and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) sequence of the transmembrane protein gene TaLRR3 with the LRR structure domain is SEQ ID NO.1,and the coded amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.2. The gene is from ordinary wheat (Triticum asetivum L.) 92R137 and is reported in the wheat for the first time. The TaLRR3 is induced by stripe rust in a stripe rust resistant wheat variety 92R137, the expression is enhanced, and in addition, the expression level is much higher than the expression level in the disease susceptible variety Yangmai 158. The gene is inserted into pBI220 to obtain an over-expression vector, in addition, the susceptible stripe rust wheat variety Yangmai 158 is converted, and T0-generation stripe rust qualification results show that the over-expression of the TaLRR3 can improve the stripe rust resistance of the susceptible stripe rust wheat variety.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Composition for stabilizing corneal tissue during or after orthokeratology lens wear
Two types of compositions having an eye-drop delivery system are used during or after an orthokeratology procedure to prevent or retard relaxation of corneal tissue back to the original anterior curvature of the cornea. Each composition functions independently from the others and is a different approach of preparing a stabilizing agent. The first composition is directed to a biologically compatible composition comprising fibril associated collagens with interrupted triple helices (FACITs) and / or small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans (SLRPs). The fibril associated collagen family includes various types of collagens, such as type VI, type XX, type XII, and type XIV. The small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans family includes decorin, keratocan, biglycan, epiphycan, lumican, mimecan, and fibromodulin. The second composition includes the enzyme found as a normal component of tissues, plasma, or epidermis, such as transglutaminase.
Owner:EUCLID SYST CORP
Fusion protein containing leucine-rich repetitive sequence, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104119447AEfficient and convenient productionMicroorganism based processesArtificial cell constructsSlit2 proteinTert-leucine
The invention discloses fusion protein containing a leucine-rich repetitive sequence, and a preparation method and application thereof. Concretely, the invention relates to fusion protein, and the fusion protein possesses the following structure from N terminal to C terminal: A-X-E-Y1-Y2 (formula Ia) or A-Y2-Y1-E-X (formula Ib), wherein A is an optional secretion signal peptide, X is a member rich in leucine repetitive sequence 2 (LRRs2) of Slit2 protein (neuronal guidance factor 2), E is a restriction enzyme cutting site, Y1 is a first tag peptide member, Y2 is a second tag short peptide member and the second tag short peptide member is His tag member, and '-' represents a peptide bond or a peptide joint for connecting the above members. The fusion protein is beneficial for correct folding of LRR (leucine-rich repeat) and forming active functional polypeptide, and is capable of simply removing two tag members through once resection enzyme cutting, thereby preparing high-purity high-activity LRR sequence.
Owner:李华顺
Gene marker for detecting esophageal cancer and use thereof and detection method
PendingCN108103196AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphodiesteraseLymphatic Spread
The invention discloses a gene marker for detecting esophageal cancer and a use thereof and a detection method. The gene marker comprises one or more of genes of a phospholipid inositol phosphatase CXdomain containing protein 3, a sulfatase 1, a F-Box and leucine-rich repeat protein 7, a Tolloid-like protein 1, a RNA binding template single-stranded function protein 3, an ADAMTS-like protein 1, phosphodiesterase 10A, a LIM-domain ligase 2, a gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor protein in the gamma 3 subfamily and a sequence similar 155 family protein A. The gene marker is used for detecting esophageal cancer. The gene marker is suitable for a more extensive source of DNA samples, the detection is safe and non-invasive, the asymptomatic people have high acceptance to detection, the accuracy is high, the gene marker has high sensitivity and specificity to the early esophageal cancer, the operation is convenient, the user experience is good and the dynamic monitoring of the recurrence and metastasis of esophageal cancer is easy.
Owner:SHANGHAI EPICAN BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Gene capable of increasing amount of plant biomass, and method for utilizing same
InactiveCN102165063AIncrease biomassLarge biomassClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBinding siteLeucine-rich repeat
Disclosed is a technique for largely increasing the amount of a plant biomass and imparting salt stress tolerance. A gene encoding a protein is introduced, wherein the protein contains a consensus sequence comprising the amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:3 and a consensus sequence comprising the amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:2 in this order from the N-terminal side, and has a coiled-coil structure, a nucleic acid-binding site, and a leucine-rich repeat structure. Alternatively, an expression control region for the gene which is present endogenously is modified.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Application of chlamydomonas reinhardtii LRR (Leucine Rich Repeat) gene in regulating and controlling cadmium resistance of chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN107760693ASimple methodImprove efficiencyUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses application of a chlamydomonas reinhardtii LRR (Leucine Rich Repeat) gene in regulating and controlling cadmium resistance of chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and belongs to the technical field of biologics and the field of environmental pollution improvement. According to the application, an aphVIII fragment with a paromomycin resistance gene is randomly inserted into chlamydomonas, then a chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant alga strain which is remarkable in cadmium chloride resistance is cultured, and further identification shows that the cadmium sensitivity of the mutant alga strain is caused since the aphVIII (SEQ ID NO:3) fragment is inserted into an LRR gene (a CDS (Cadmium Sulfide) sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in the specification). By reducing expression of thechlamydomonas reinhardtii LRR gene, deactivating the LRR gene or by deleting the LRR gene, the cadmium resistance of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii can be improved; a cadmium resistance improved chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain obtained by means of genetic engineering can be applied to monitoring and improvement of cadmium polluted water areas, cadmium polluted water environments can be treated with the cadmium resistance improved chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain, the operation is simple and feasible, and the cost is low.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Antisense compounds targeting leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) for the treatment of parkinsons disease
The present disclosure relates generally to compounds comprising oligonucleotides complementary to a Leucine-Rich-Repeat-Kinase (LRRK2) RNA transcript. Certain such compounds are useful for hybridizing to a LRRK2 RNA transcript, including but not limited to a LRRK2 RNA transcript in a cell. In certain embodiments, such hybridization results in modulation of splicing of the LRRK2 transcript. In certain embodiments, such compounds are used to treat one or more symptoms associated with Parkinson's disease.
Owner:ROSALIND FRANKLIN UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE +1
Gene capable of increasing the production of plant biomass and method for using the same
InactiveUS20110239330A1Reduce the amount of solutionIncreased biomass productionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBinding siteLeucine-rich repeat
According to the present invention, a technique with which the production of plant biomass can be drastically increased and salt stress resistance can be imparted to a plant is provided.A gene encoding a protein comprising a common sequence consisting of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 and a common sequence consisting of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 in such order from the N-terminal side and having a coiled-coil structure, a nucleic acid binding site, and a leucine rich repeat structure has been introduced or an expression control region of the gene that is endogenously presented has been altered.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com