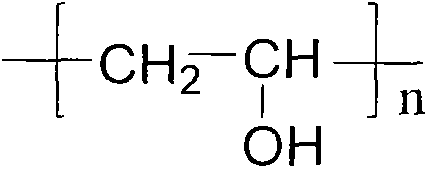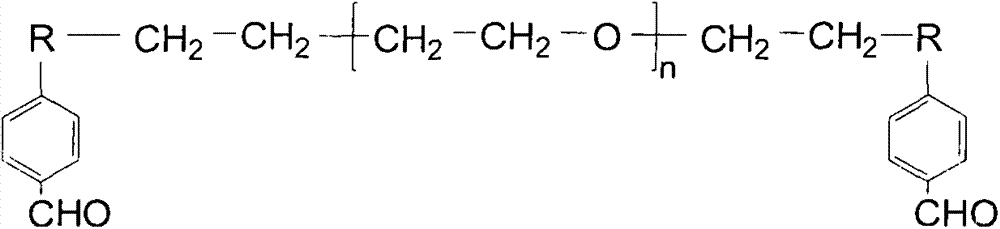Patents
Literature
77 results about "Cell encapsulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.
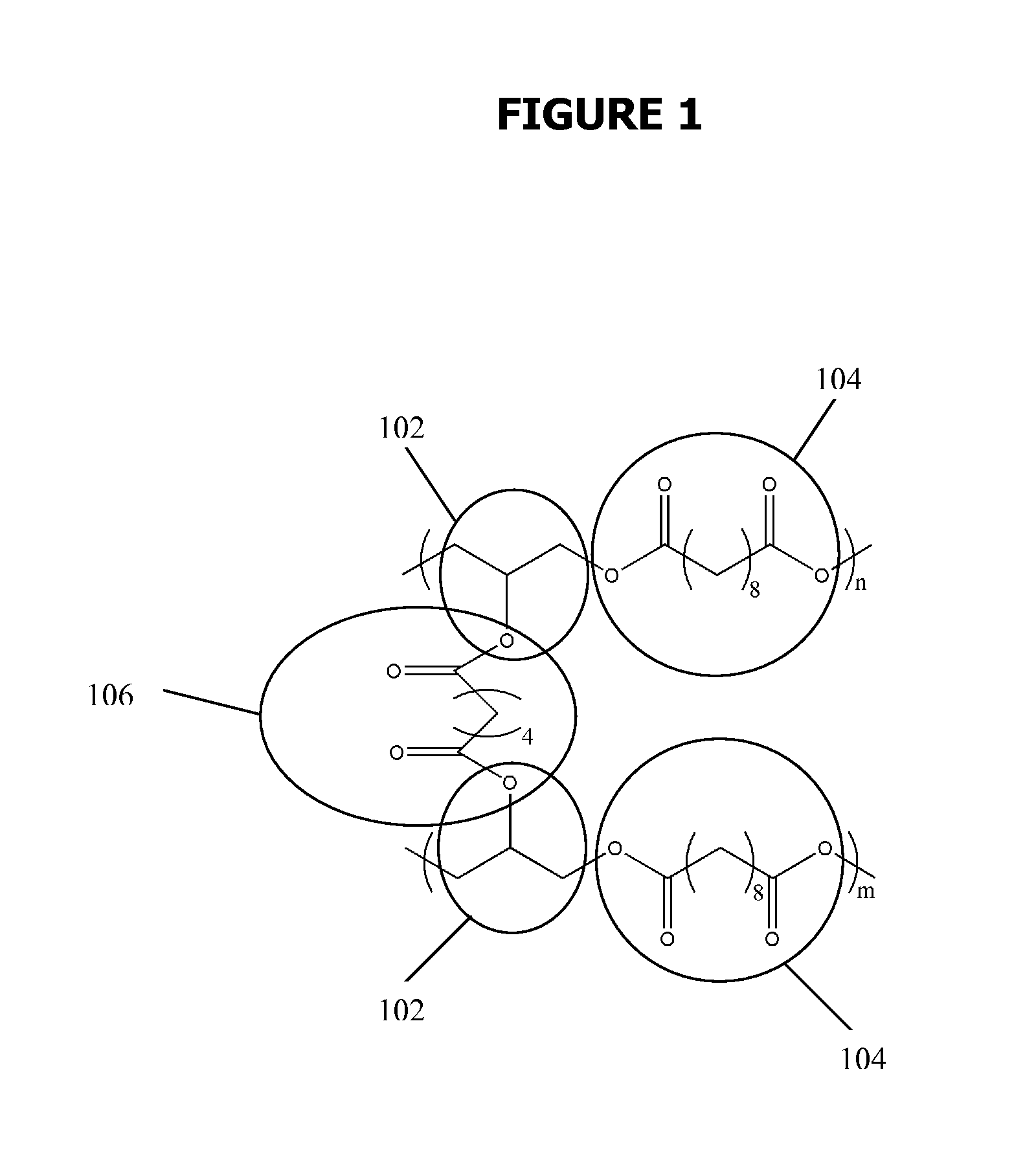
Poly(beta-amino alcohols), their preparation, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130302401A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical structureFibrosis
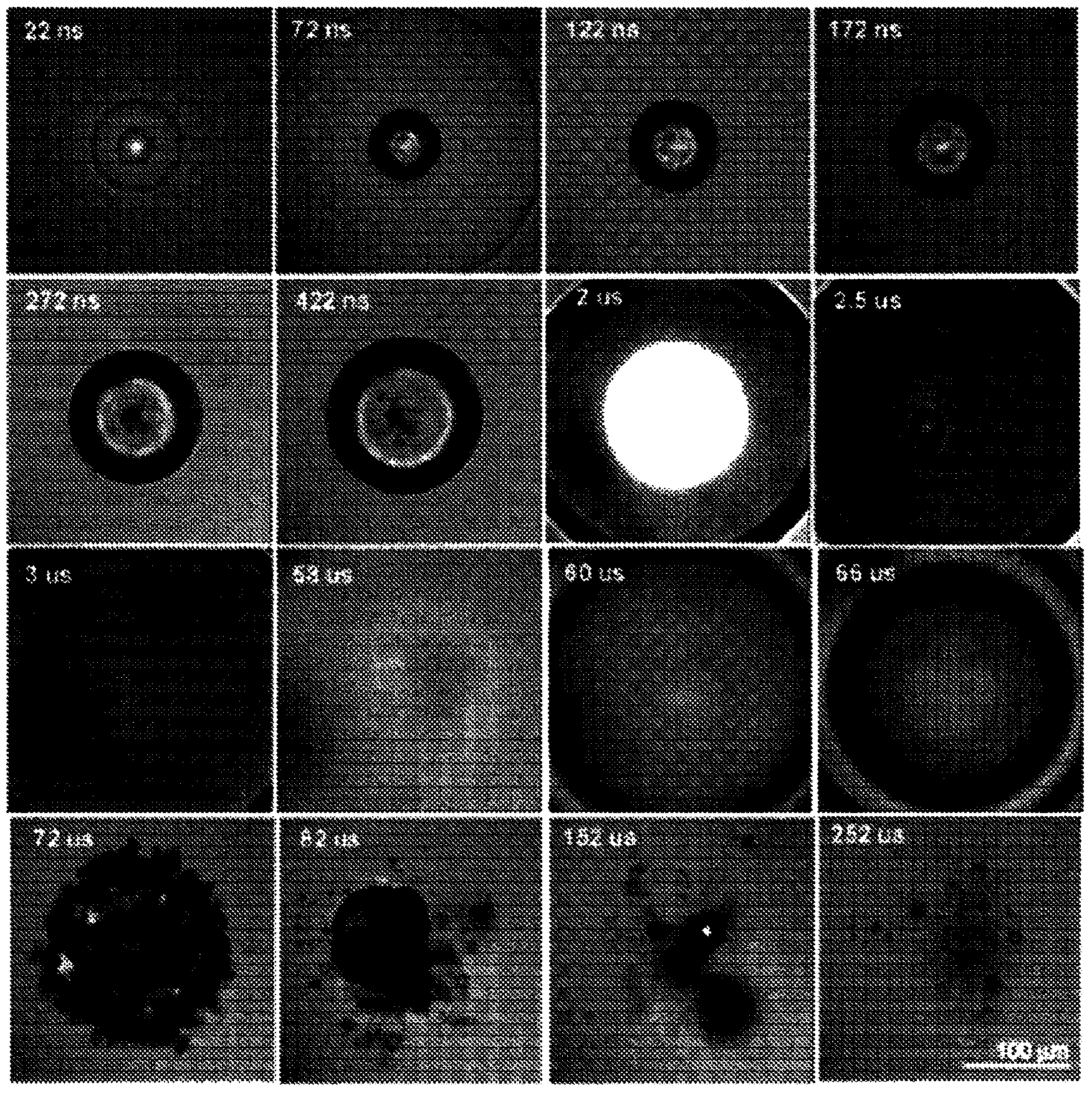
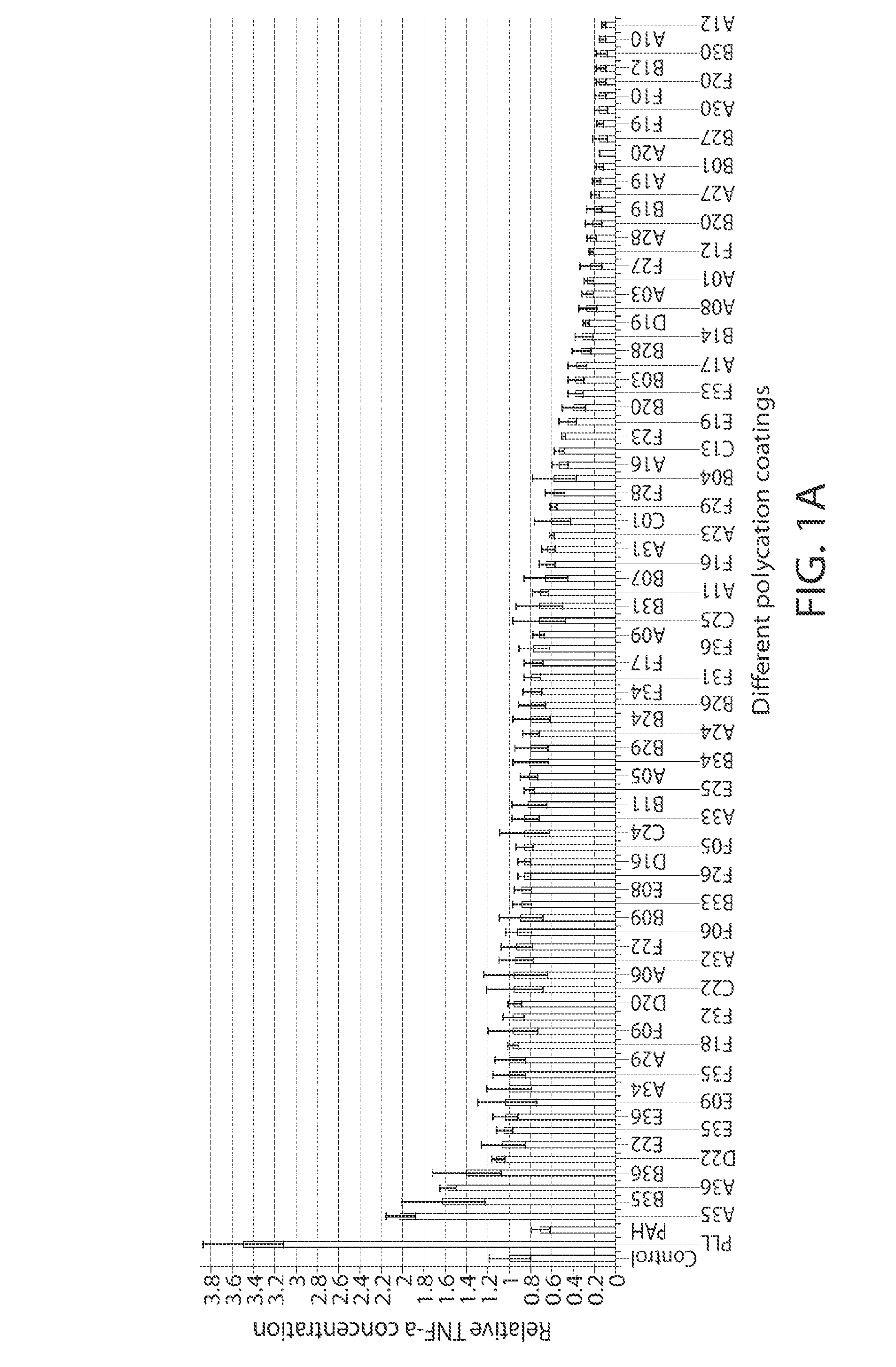
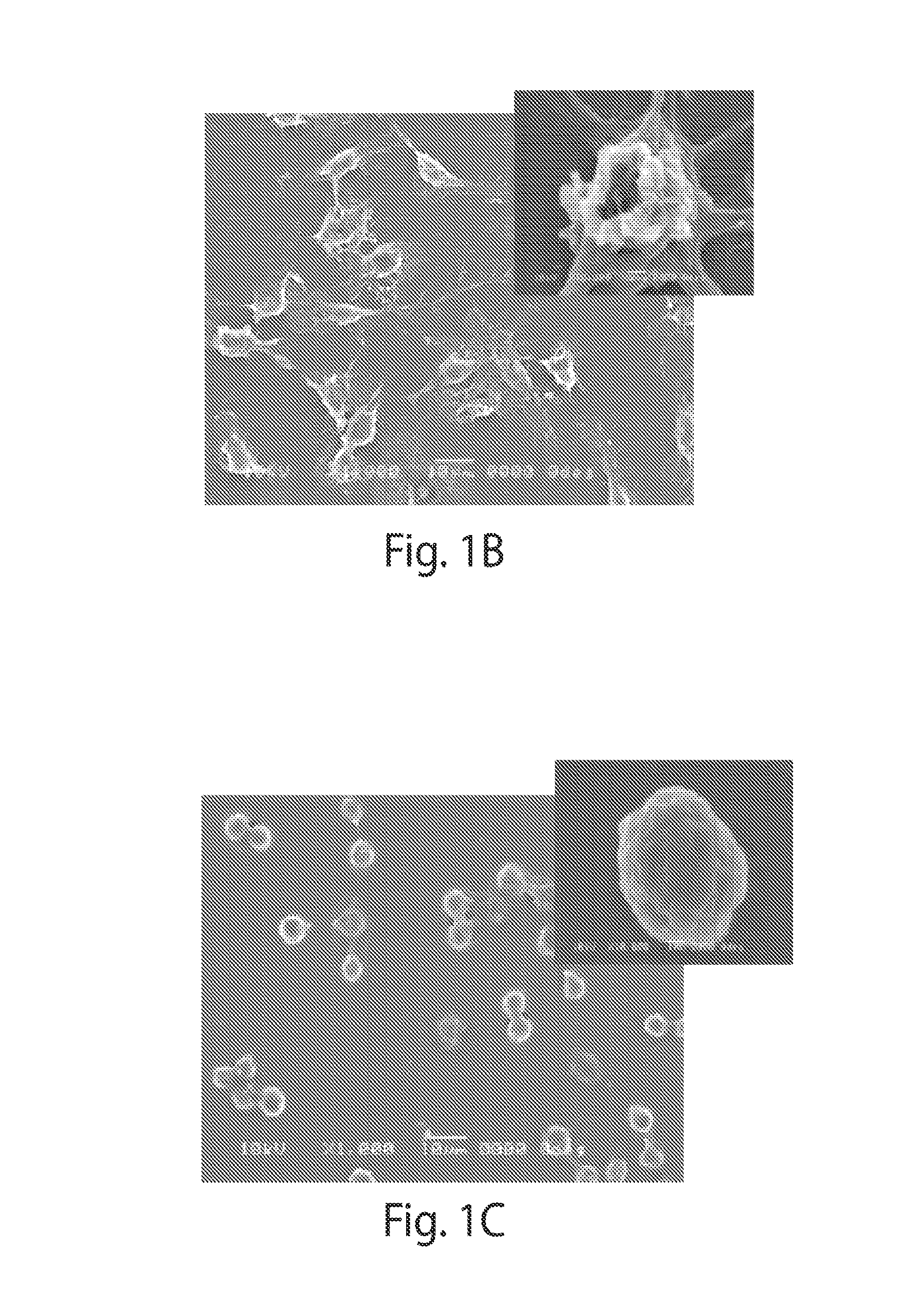
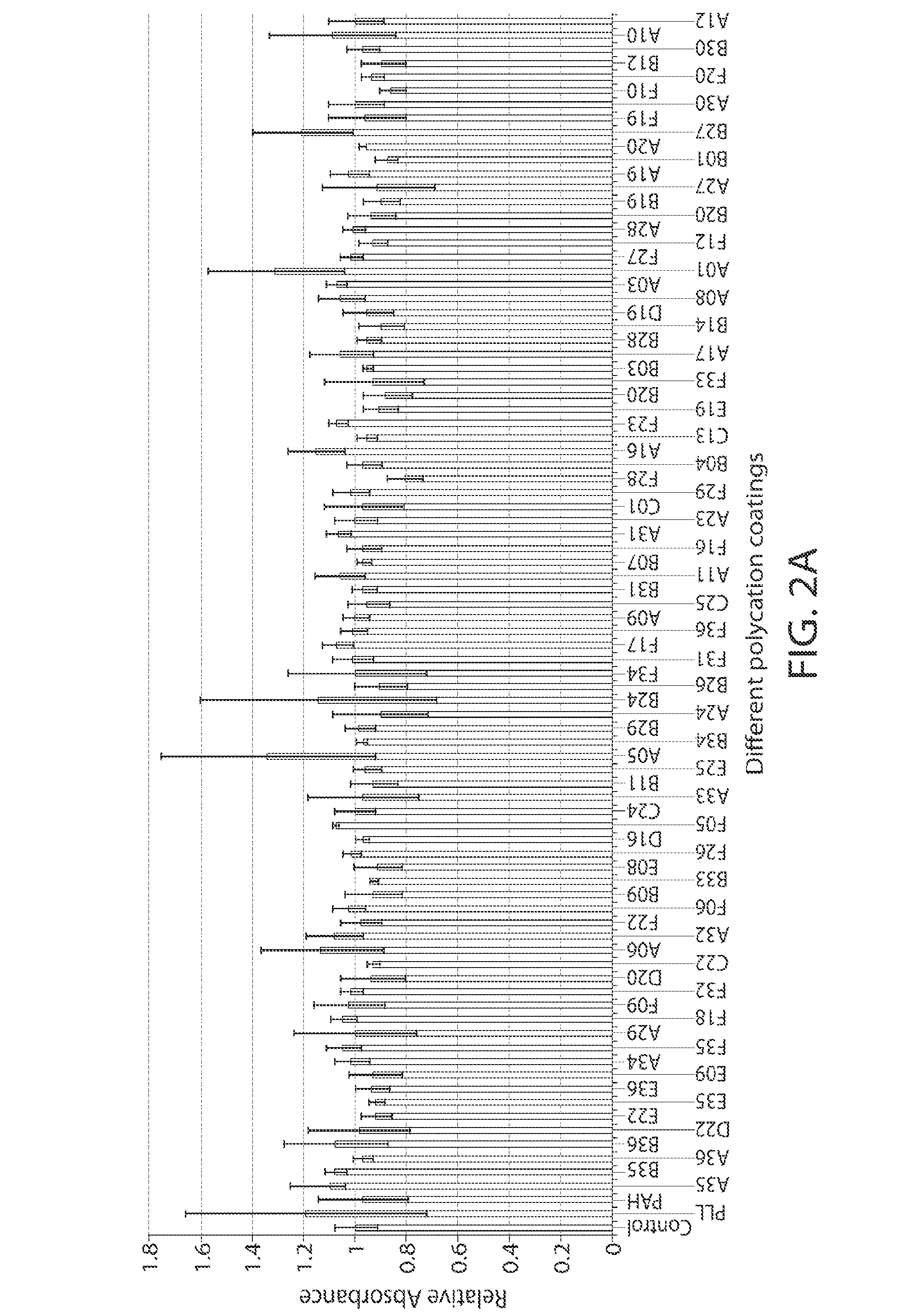
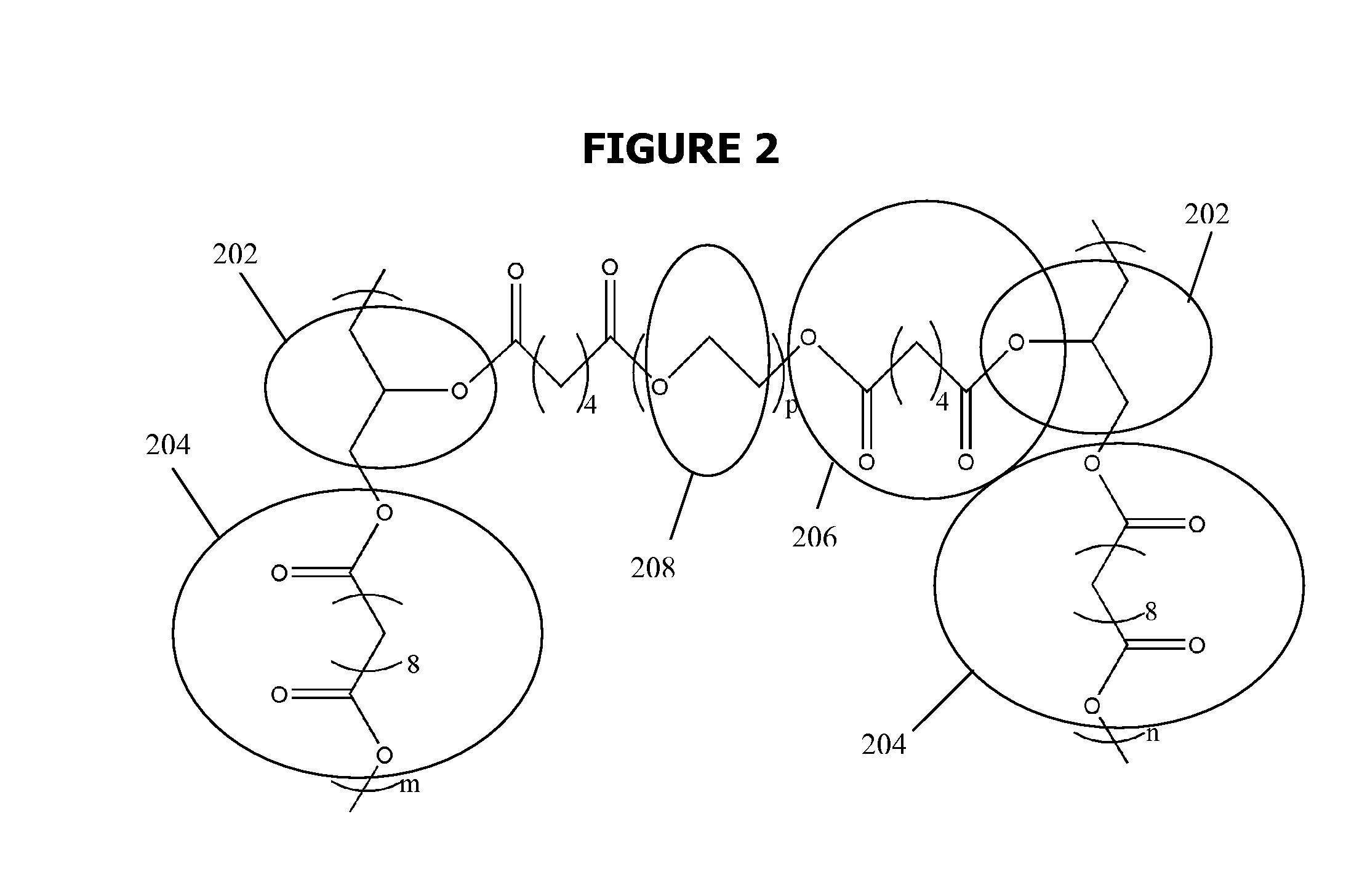
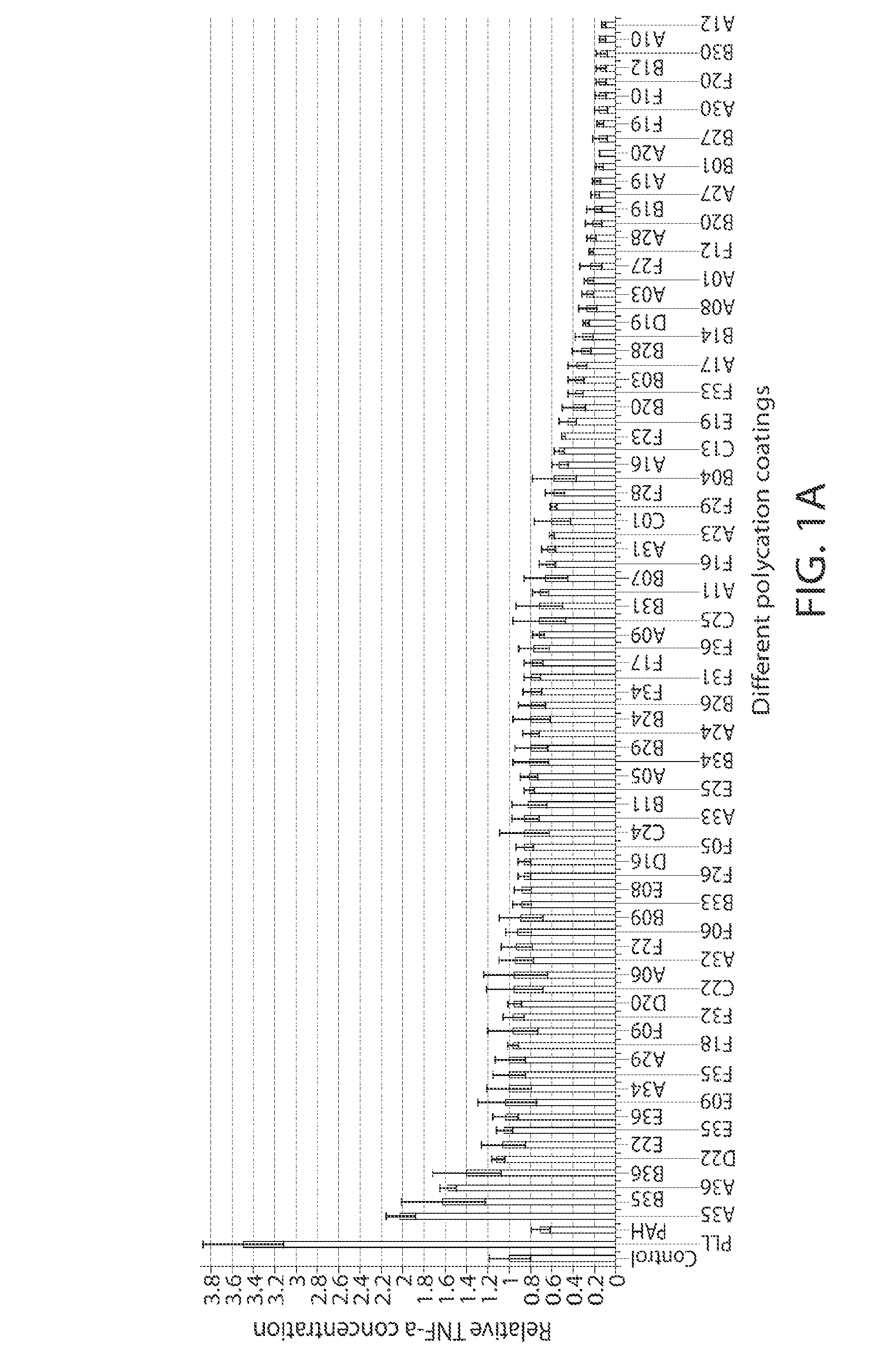
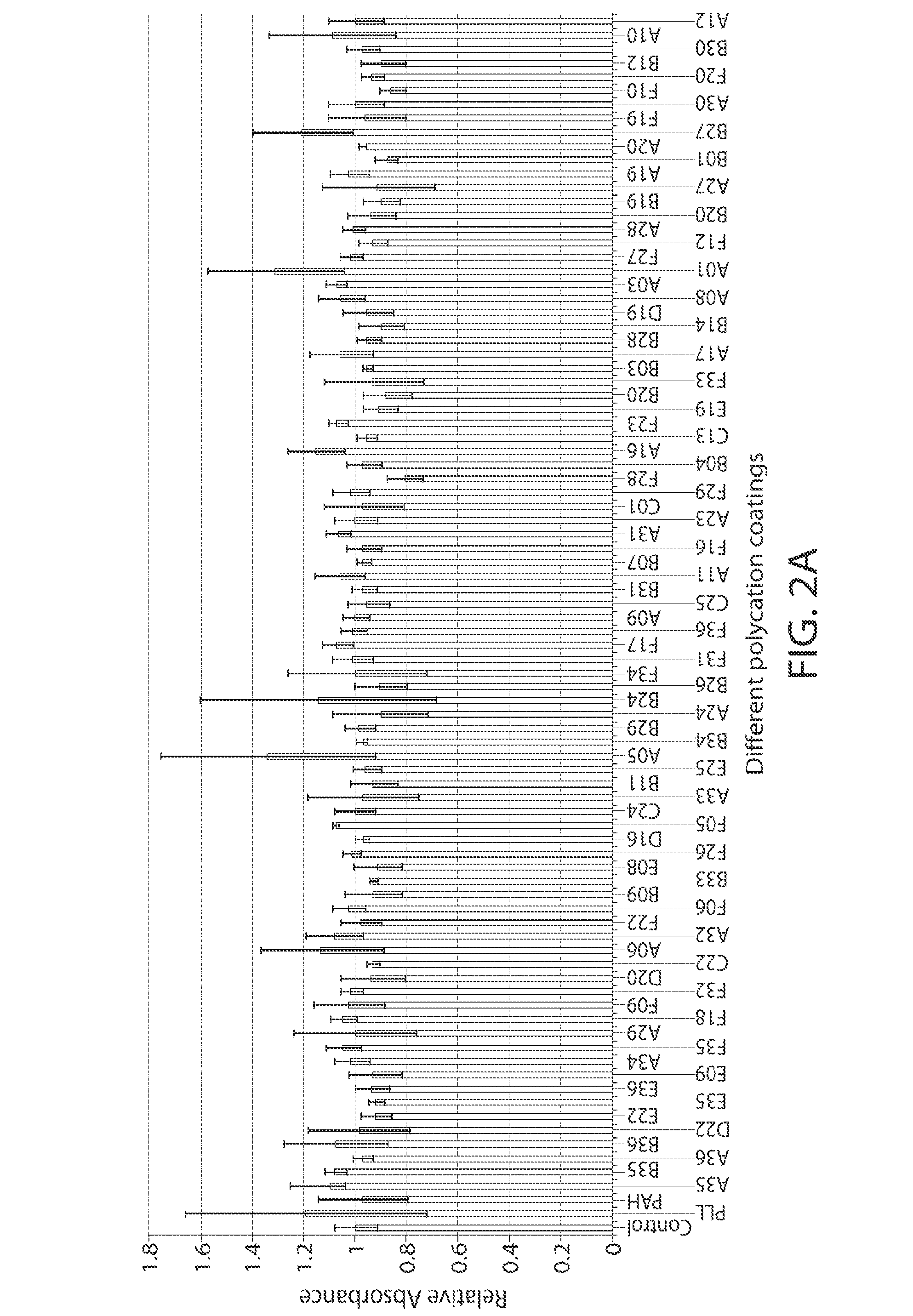
A new class of poly(beta-amino alcohols) (PBAAs) has been prepared using combinatorial polymerization. The inventive PBAAs may be used in biotechnology and biomedical applications as coatings (such as coatings of films or multilayer films for medical devices or implants), additives, materials, excipients, non-biofouling agents, micropatterning agents, and cellular encapsulation agents. When used as surface coatings, these PBAAs elicited different levels of inflammation, both in vitro and in vivo, depending on their chemical structures. The large chemical diversity of this class of materials allowed us to identify polymer coatings that inhibit macrophage activation in vitro. Furthermore, these coatings reduce the recruitment of inflammatory cells, and reduce fibrosis, following the subcutaneous implantation of carboxylated polystyrene microparticles. These polymers may be used to form polyelectrolyte complex capsules for cell encapsulation. The invention may also have many other biological applications such as antimicrobial coatings, DNA or siRNA delivery, and stem cell tissue engineering.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Bioceramic compositions
InactiveUS6972130B1Good biocompatibilityEasy to processBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsDiseaseDelivery vehicle
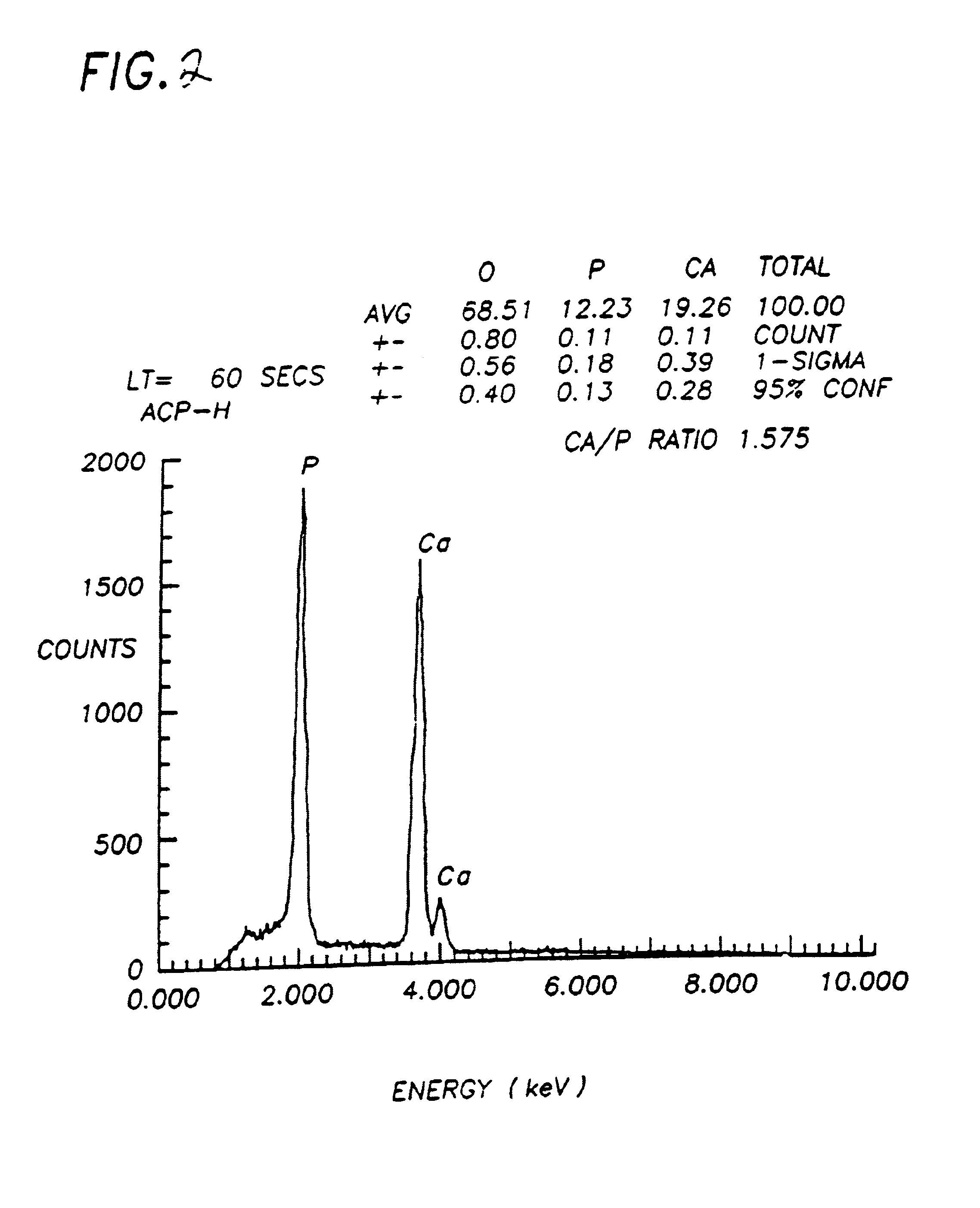
The present invention provides a synthetic, poorly crystalline apatite (PCA) calcium phosphate containing a biologically active agent and / or cells (preferably tissue-forming or tissue-degrading cells). The compositions provided by the present invention are useful for a variety of in vivo and in vitro applications, including drug delivery (for example, to bony sites, the central nervous system, intramuscular sites, subcutaneous sites, interperitoneal sites, and occular sites) tissue growth (preferably bone or cartilage) osseous augmentation, and methods of diagnosing disease states by assaying tissue forming potential of cells isolated from a host. The invention also provides methods of preparing delivery vehicles, of altering delivery vehicle characteristics, and of delivering biologically active agents to a site. The invention further provides in vitro cell culture systems and cell encapsulation materials. The invention is useful for both medical and veterinary applications.
Owner:LIFE SCI ENTERPRISES
Multi-layer cell encapsulation for tissue engineering
A multi-layered microcapsule has an inner extracellular matrix and an outer shell. The inner extracellular matrix includes a first inner layer of biopolymer and a second intermediate layer of polymer that provides partial immune-protection and holds the first layer in place. The outer shell can form an exoskeleton to provide mechanical stability. Each of the individual layers can be varied to optimize mechanical stability, cell function, and immuno-protection.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
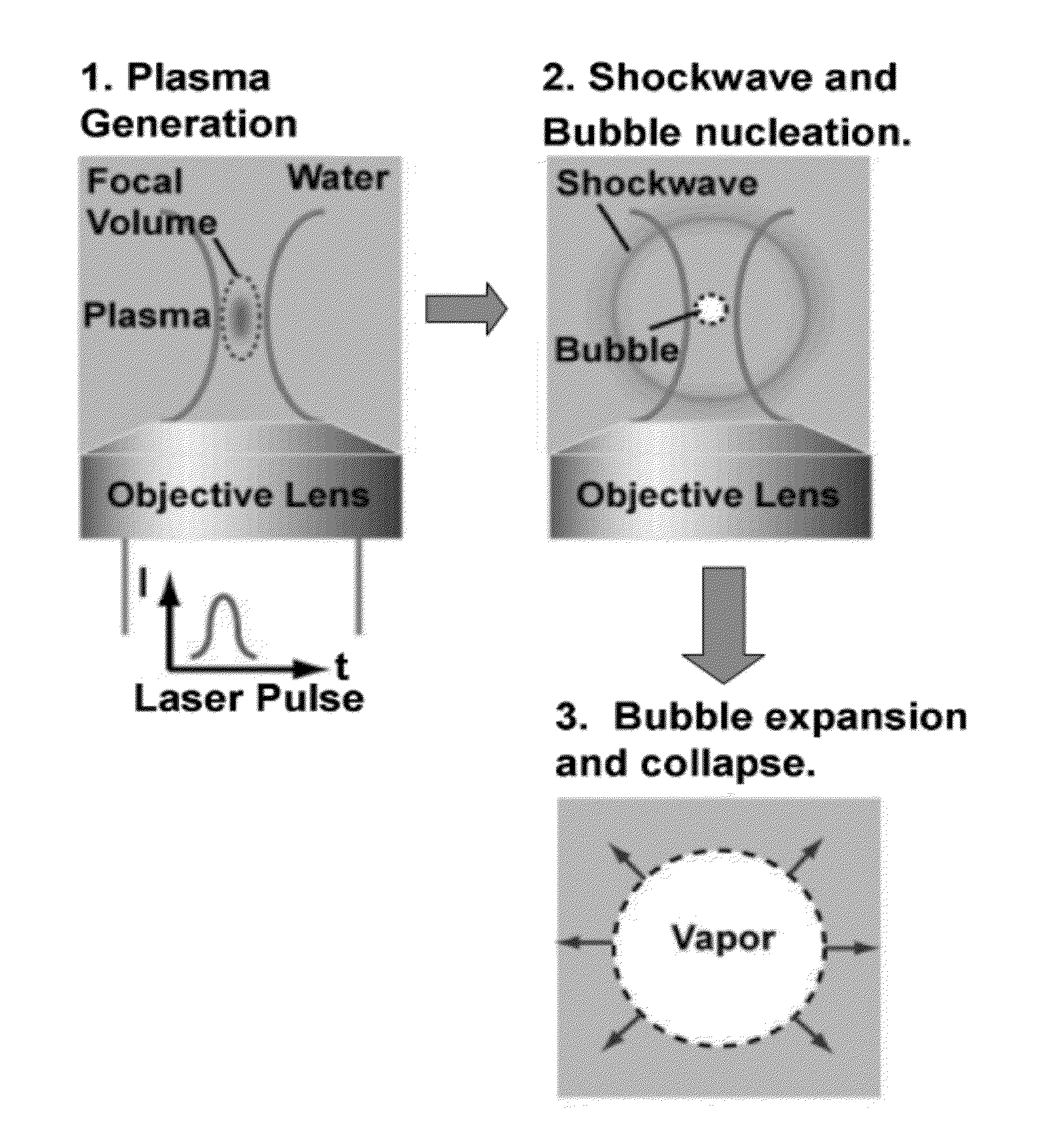
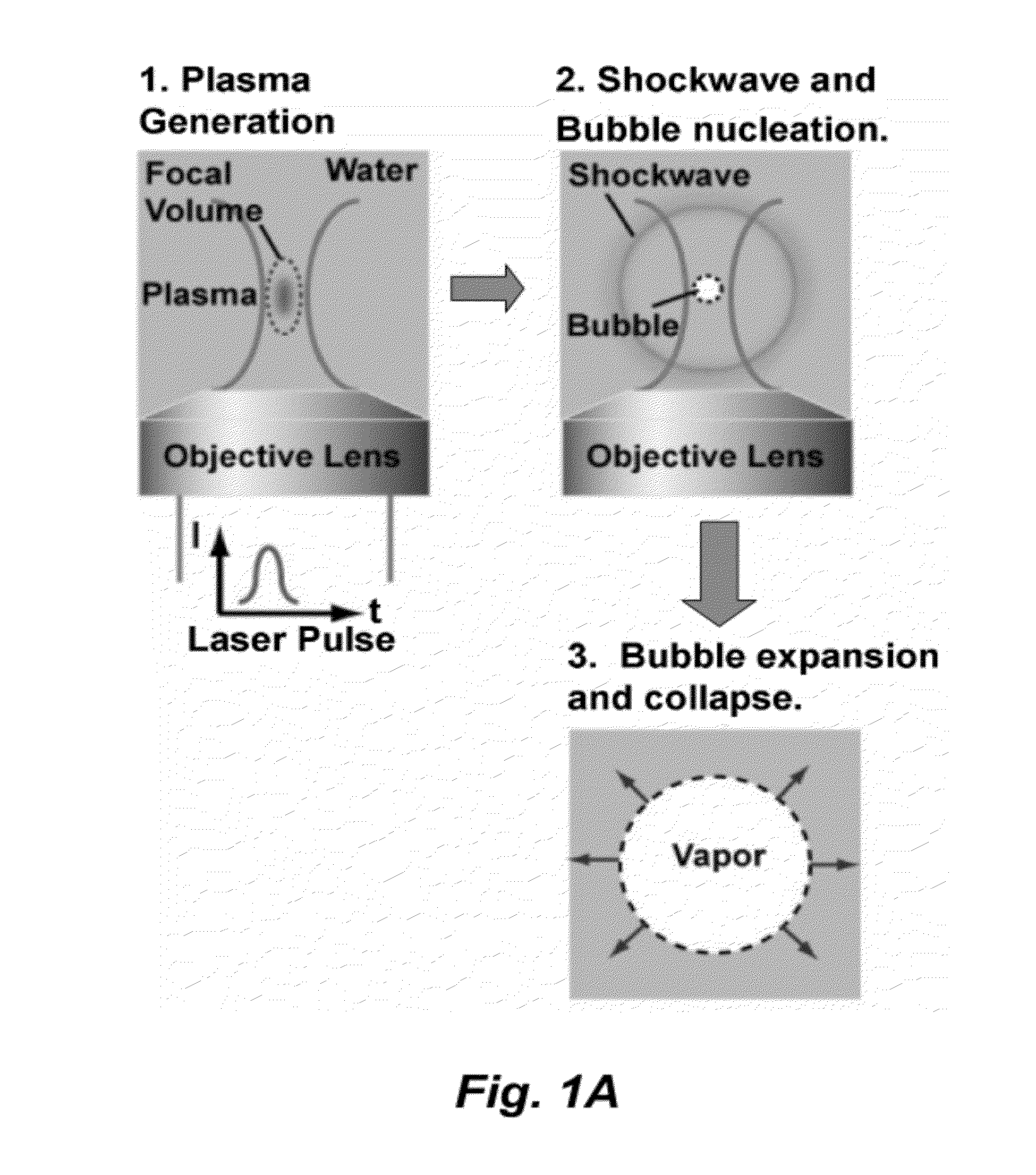
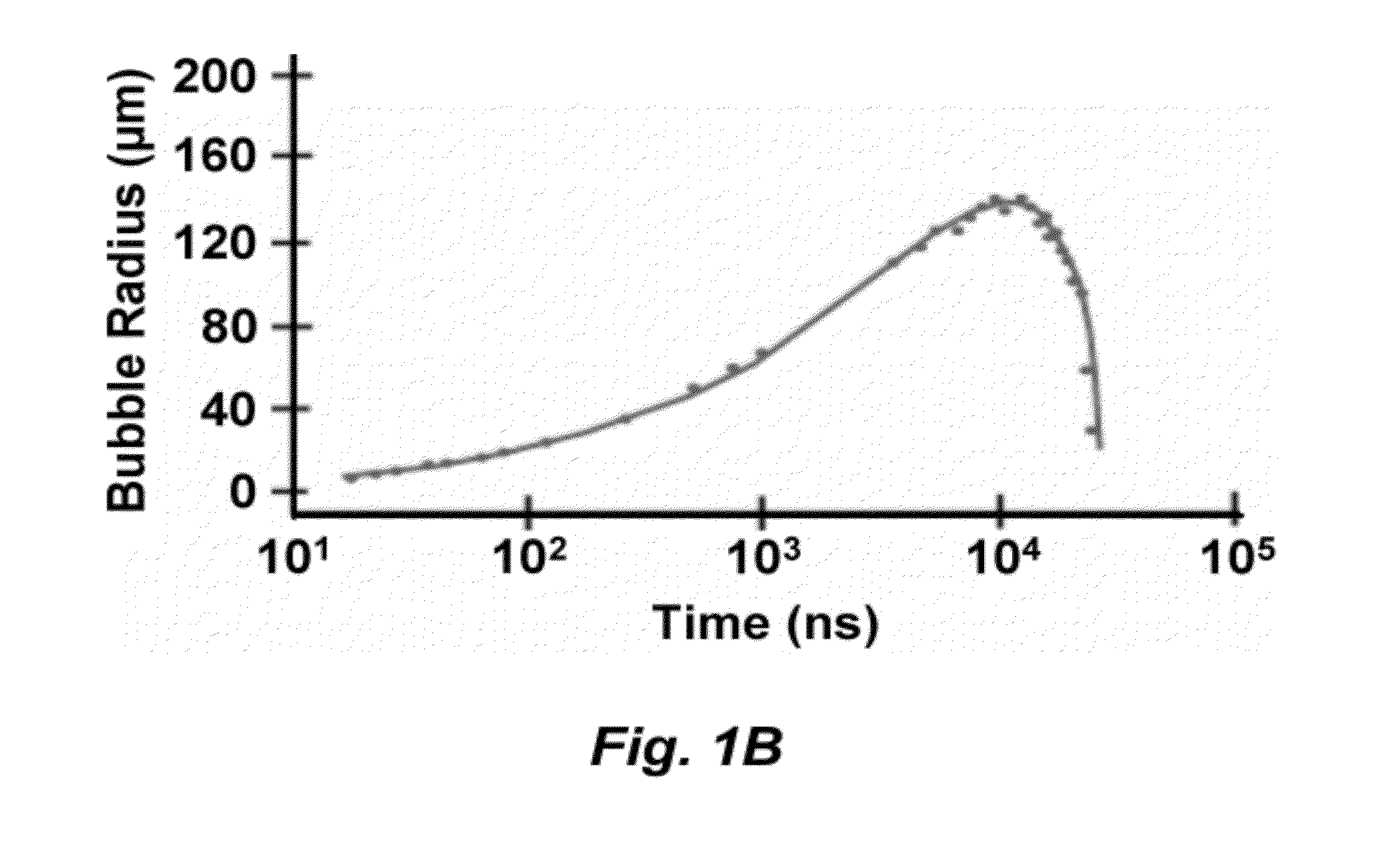
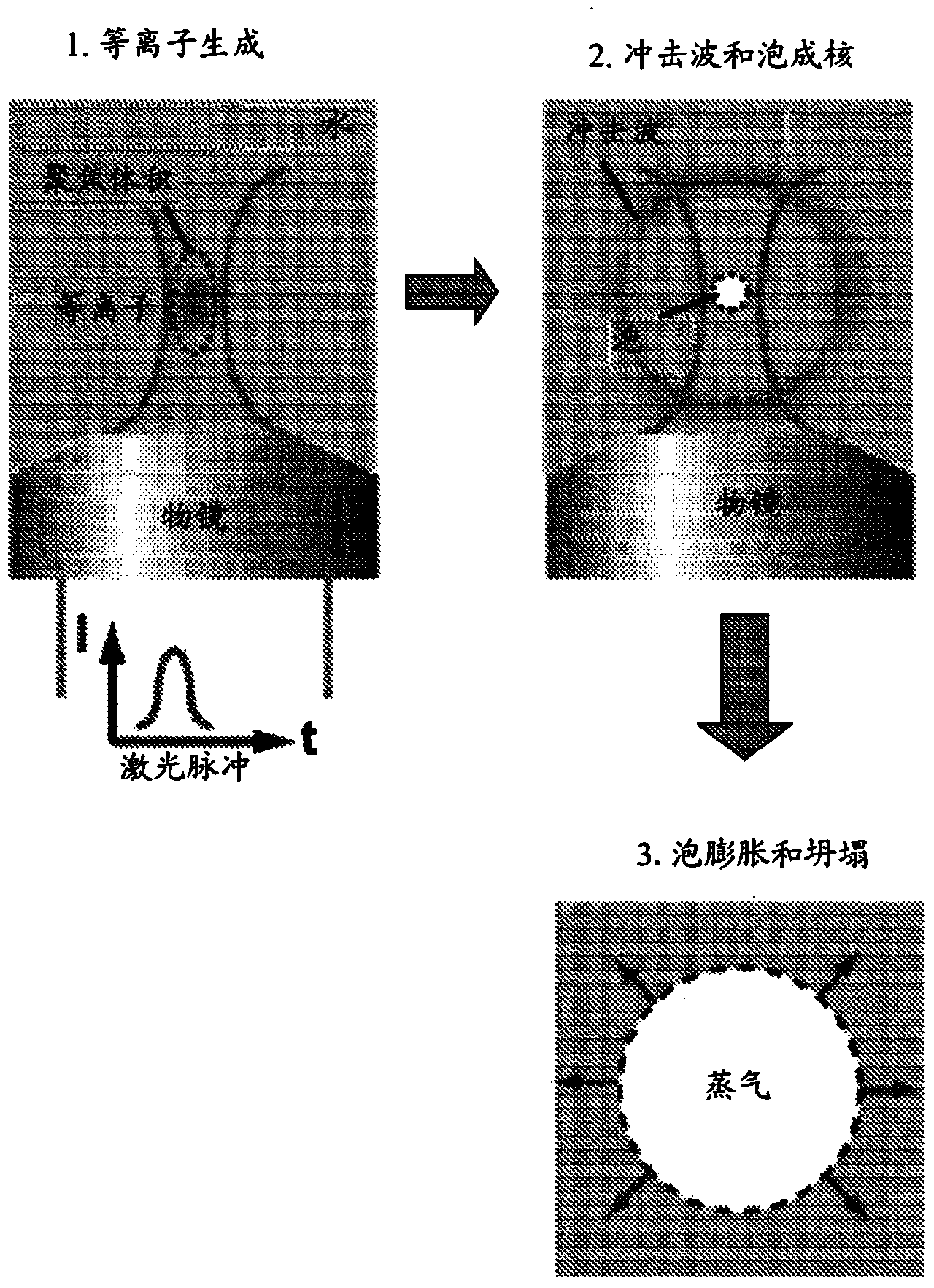
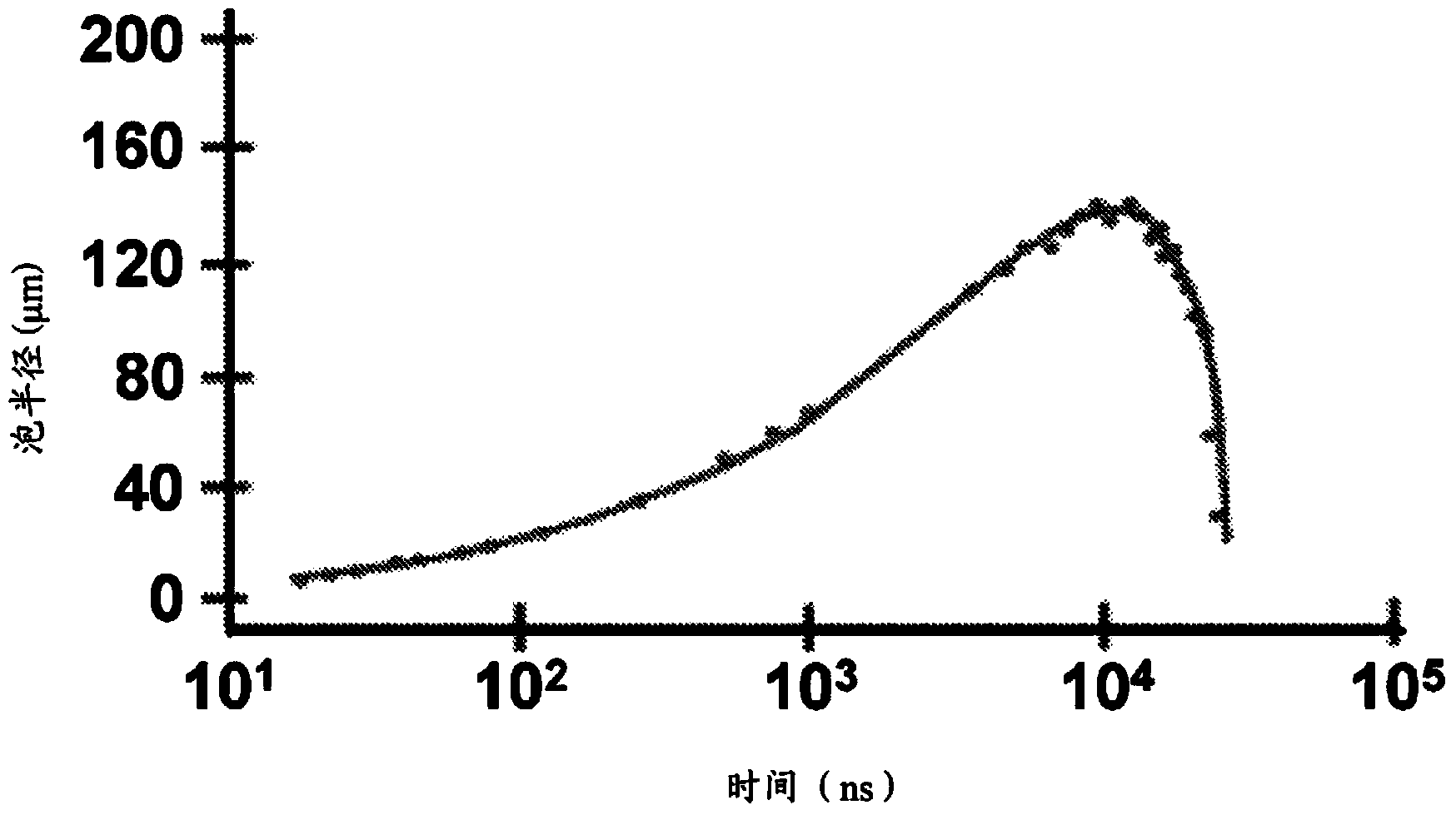
High-speed on demand droplet generation and single cell encapsulation driven by induced cavitation
ActiveUS20120236299A1Vibration measurement in solidsOptical radiation measurementCavitationChemical physics
Methods and devices for the formation of droplets of a first fluid in a second fluid and the encapsulation of particles or cells within such droplets are disclosed. Impetus for droplet formation is provided by the creation of a transient bubble, which may be induced using a pulsed laser. Droplet volume and the frequency at which droplets are formed can be controlled by modulation of the pulsed laser. The disclosed methods and devices are particularly suitable for use in microfluidic devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biodegradable Elastomers
The present inventions in various aspects provide elastic polymers compositions for encapsulation of cells. In various embodiments, the polymers are formed by the reaction of a multifunctional alcohol or ether and a difunctional or higher order acid to form a pre-polymer, which is cross-linked in the presence of glycerol and a population of cells to form elastic porous polymer scaffolds suitable for cell encapsulation and / or proliferation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Modified alginates for cell encapsulation and cell therapy
ActiveUS20120308650A1Avoid encapsulationImprove propertiesPowder deliveryBiocideBiocompatibility TestingBiochemistry
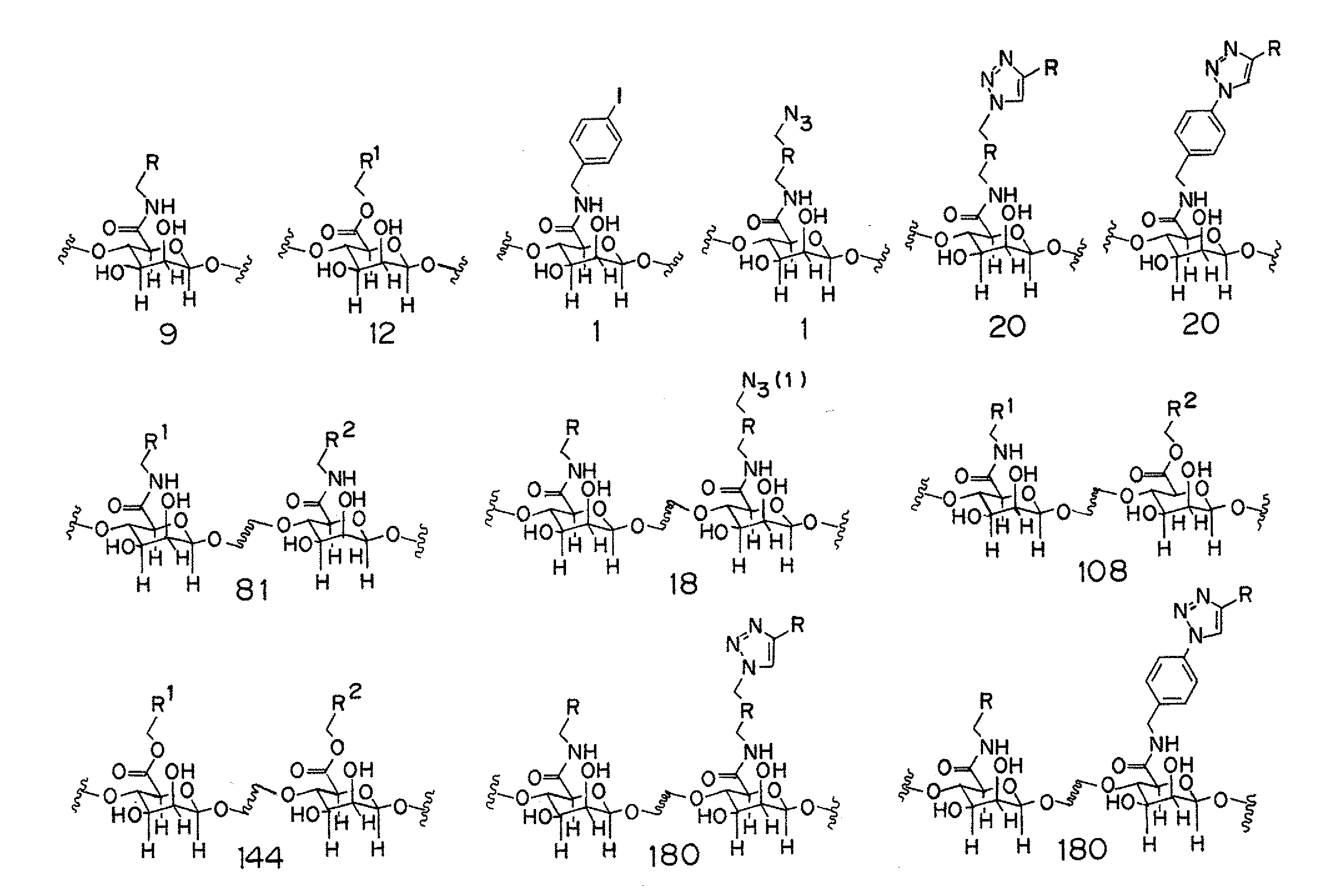
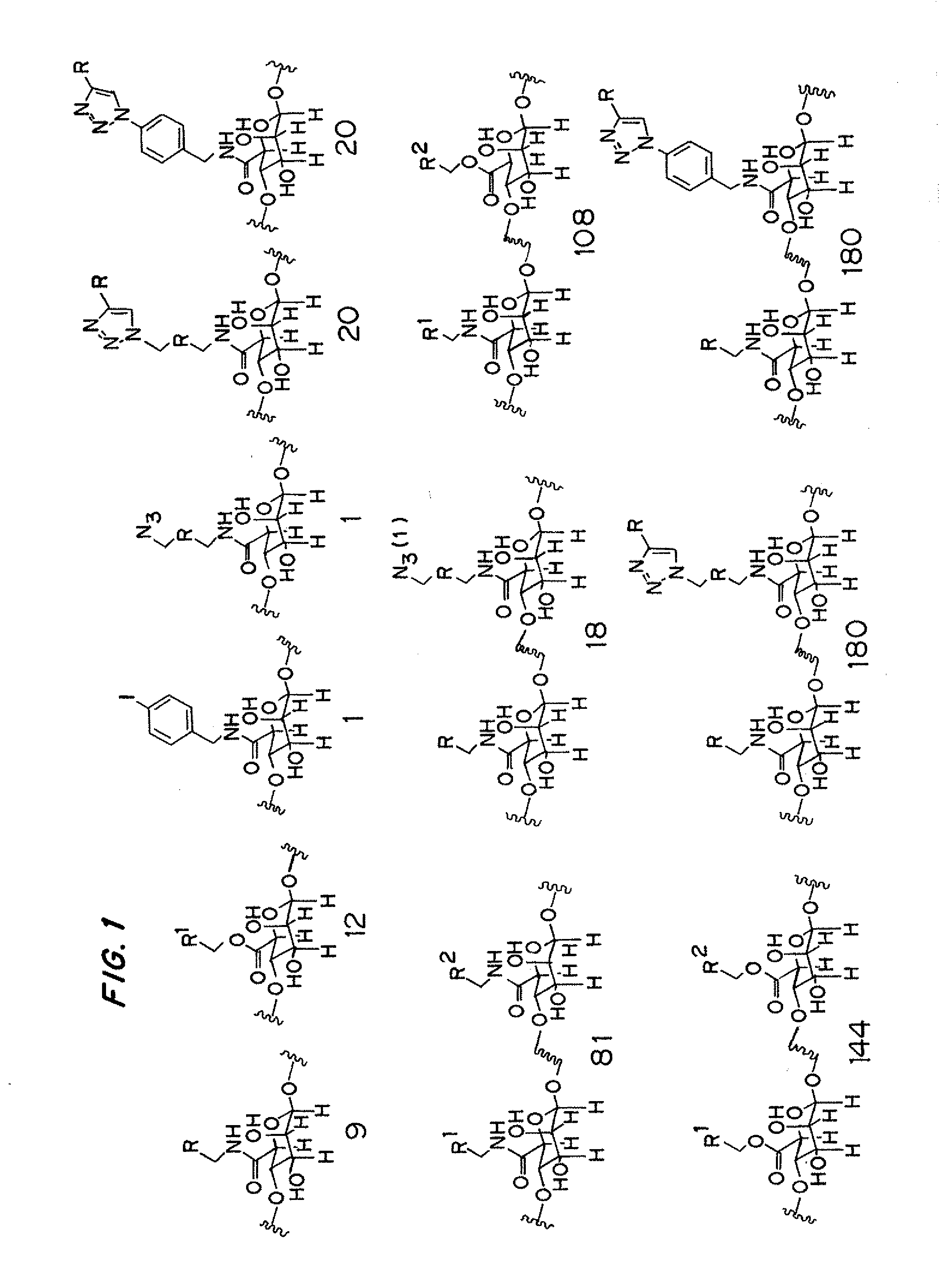
Covalently modified alginate polymers, possessing enhanced biocompatibility and tailored physiochemical properties, as well as methods of making and use thereof, are disclosed herein. The covalently modified alginates are useful as a matrix for the encapsulation and transplantation of cells. Also disclosed are high throughput methods for the characterizing the biocompatibility and physiochemical properties of modified alginate polymers.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Single-cell encapsulation and flexible-format module architecture for photovoltaic power generation and method for constructing the same
InactiveUS20140000683A1Reduce cell damageOvercome disadvantagesPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer architectureEmbedded system
A method for encapsulating photovoltaic cells into single functional units is described. These units share the mechanical and electric properties of the encapsulation layers and allow for flexible module architecture to be implemented at the cell level. This enables cost reduction and improved performance of photovoltaic power generation.
Owner:TESSOLAR
Poly(beta-amino alcohols), their preparation, and uses thereof
ActiveUS9193827B2Organic active ingredientsAntifouling/underwater paintsChemical structurePolystyrene
A new class of poly(beta-amino alcohols) (PBAAs) has been prepared using combinatorial polymerization. The inventive PBAAs may be used in biotechnology and biomedical applications as coatings (such as coatings of films or multilayer films for medical devices or implants), additives, materials, excipients, non-biofouling agents, micropatterning agents, and cellular encapsulation agents. When used as surface coatings, these PBAAs elicited different levels of inflammation, both in vitro and in vivo, depending on their chemical structures. The large chemical diversity of this class of materials allowed us to identify polymer coatings that inhibit macrophage activation in vitro. Furthermore, these coatings reduce the recruitment of inflammatory cells, and reduce fibrosis, following the subcutaneous implantation of carboxylated polystyrene microparticles. These polymers may be used to form polyelectrolyte complex capsules for cell encapsulation. The invention may also have many other biological applications such as antimicrobial coatings, DNA or siRNA delivery, and stem cell tissue engineering.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Preparation and application of pH glucose dual sensitive hydrogel
InactiveCN104758939ABiocompatibleHas pHMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPhenylboronic acidDiabrezide
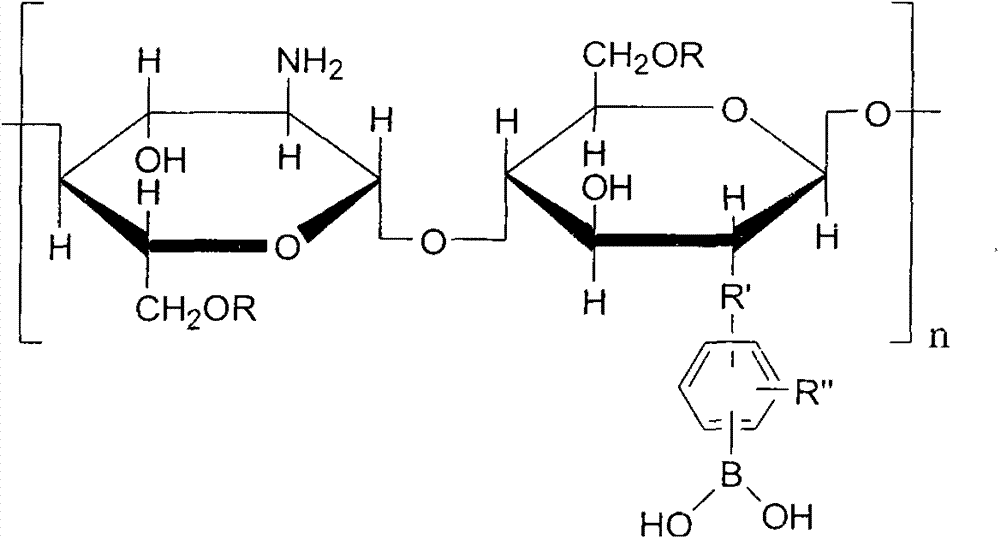
The invention discloses preparation and application of a pH glucose dual sensitive hydrogel. The hydrogel is formed by crosslinking of phenylboronic acid modified chitosan and an active functional group equipped crosslinking agent through imine bond and phenylboronic acid ester two dynamic covalent bonds, and has injectability and self-repairing performance. The imine bond is stable under normal physiological pH value, can hydrolyze under slightly acidic pH value, and is sensitive to the pH value change. Phenylboronic acid ester can undergo competing reaction in the presence of glucose, so that hydrogel can have network structure change so as to have glucose responsiveness. By regulating the structure, composition and functional groups of phenylboronic acid modified chitosan and the crosslinking agent, the rheological properties of the hydrogel can be adjusted, and activity release of the hydrogel to a substrate can be controlled. The system can be used as a drug carrier to convey various antitumor and diabetes drugs, also can be applied as a tissue engineering scaffold material to cell encapsulation and culture, thus realizing synergic treatment on the drug and cell level.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
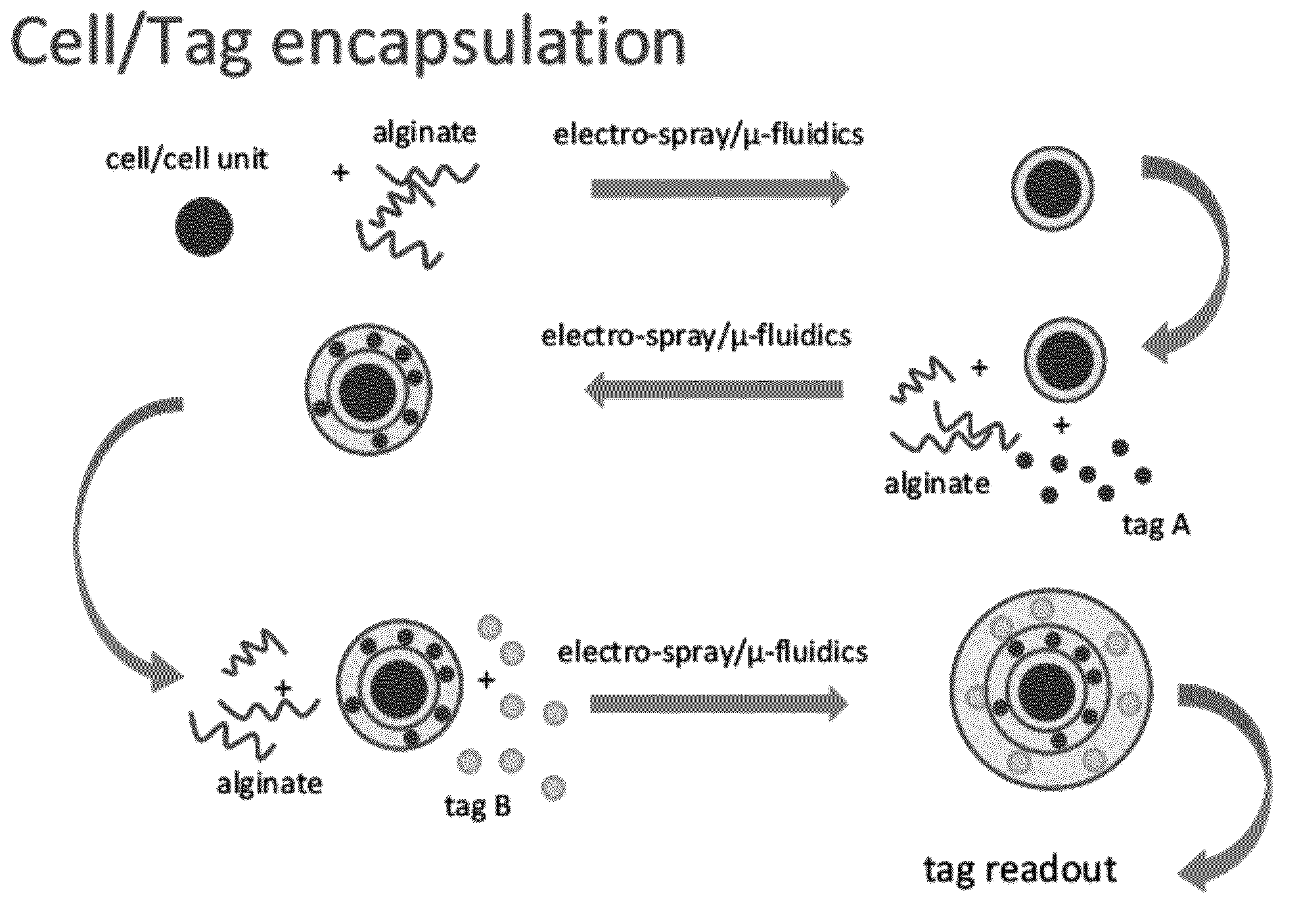
Nested cell encapsulation
InactiveUS20120270295A1Other foreign material introduction processesGranular deliveryLiving cellCell encapsulation
The invention relates to a method for encapsulating living cells and labels, as well as encapsulated labelled cells and kits for performing such encapsulation. The encapsulated cells may be useful in multiple parallel tissue culture experiments, where the labels in each microcapsule may be used to decipher a cells path through a series of culturing steps.
Owner:PLASTICELL LTD
Biocompatible coatings and hydrogels for reducing foreign body response and fibrosis
ActiveUS20170355799A1Good biocompatibilityLow cytotoxicitySurgeryMammal material medical ingredientsCross-linkHydrophilic monomer
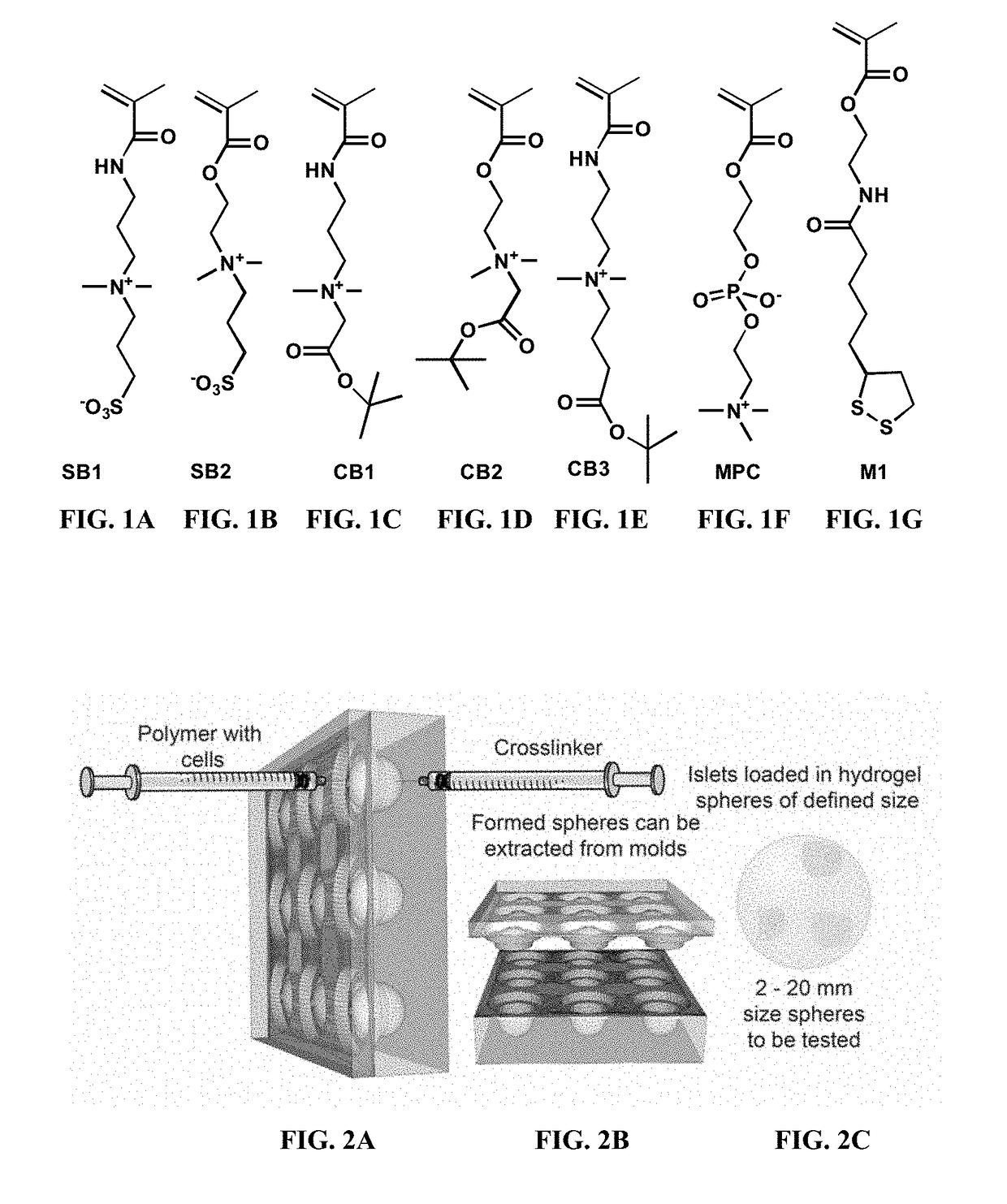
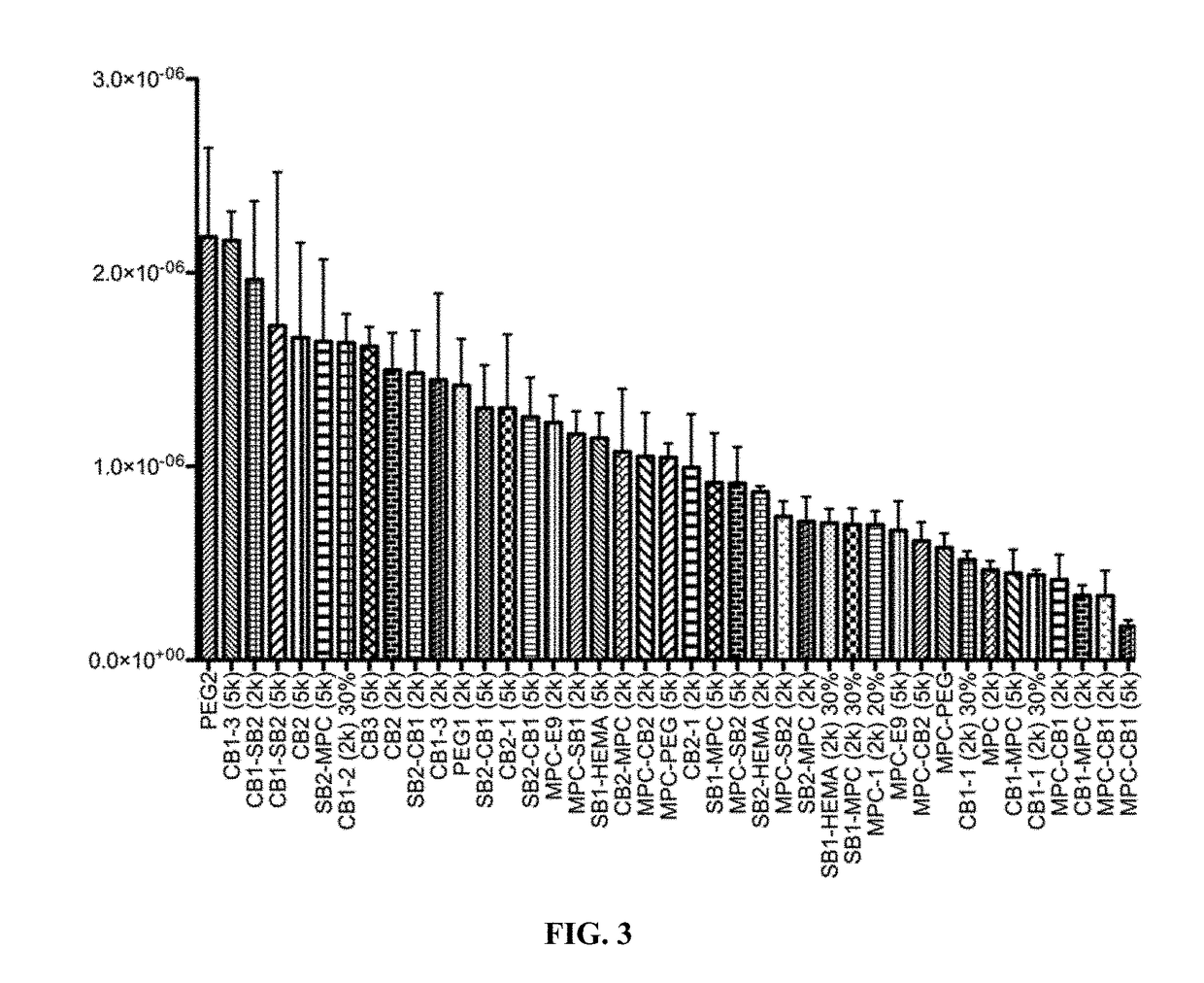
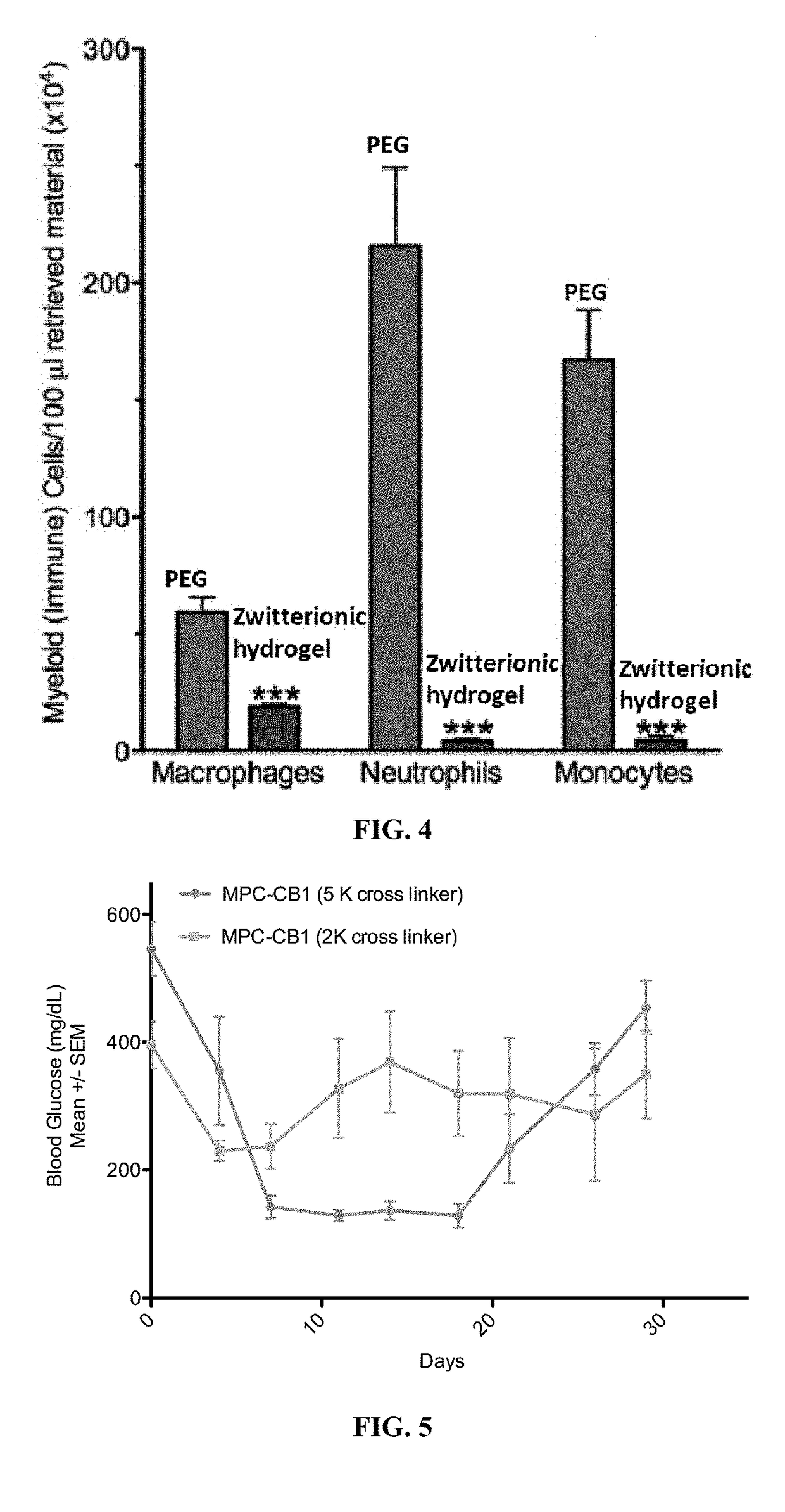
Zwitterionic polymers or biocompatible polymers with improved properties for cell encapsulation, coating of devices, or a combination thereof are described. The biocompatible polymer contains a zwitterionic monomer, a monomer with a reactive side chain, and optionally another hydrophobic monomer or a neutral hydrophilic monomer. The zwitterionic polymers are cross-linked with a cross-linker via covalent bond to form a zwitterionic hydrogel in the presence of cells. Also provided, are methods of making and using the zwitterionic polymers.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
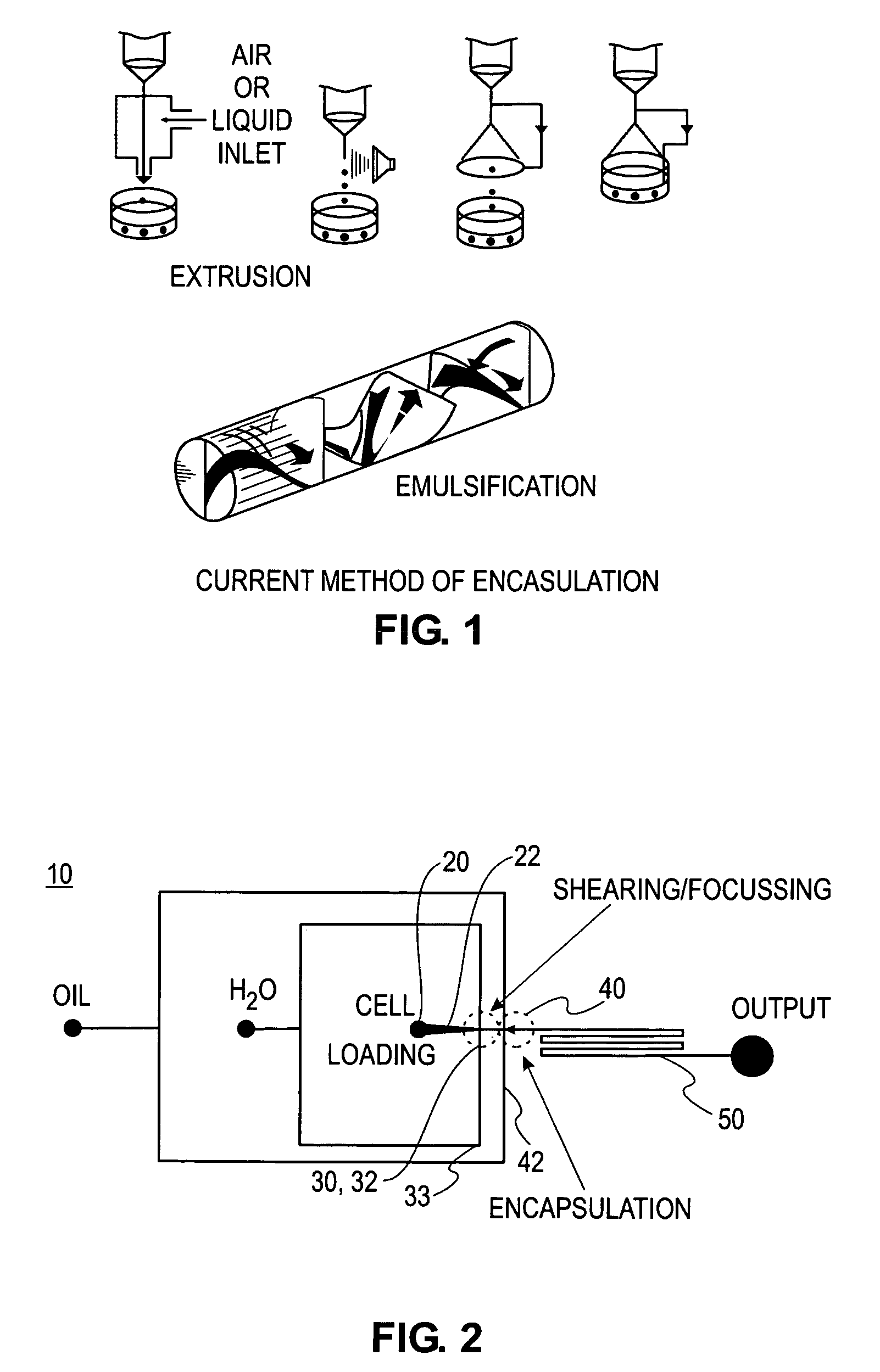
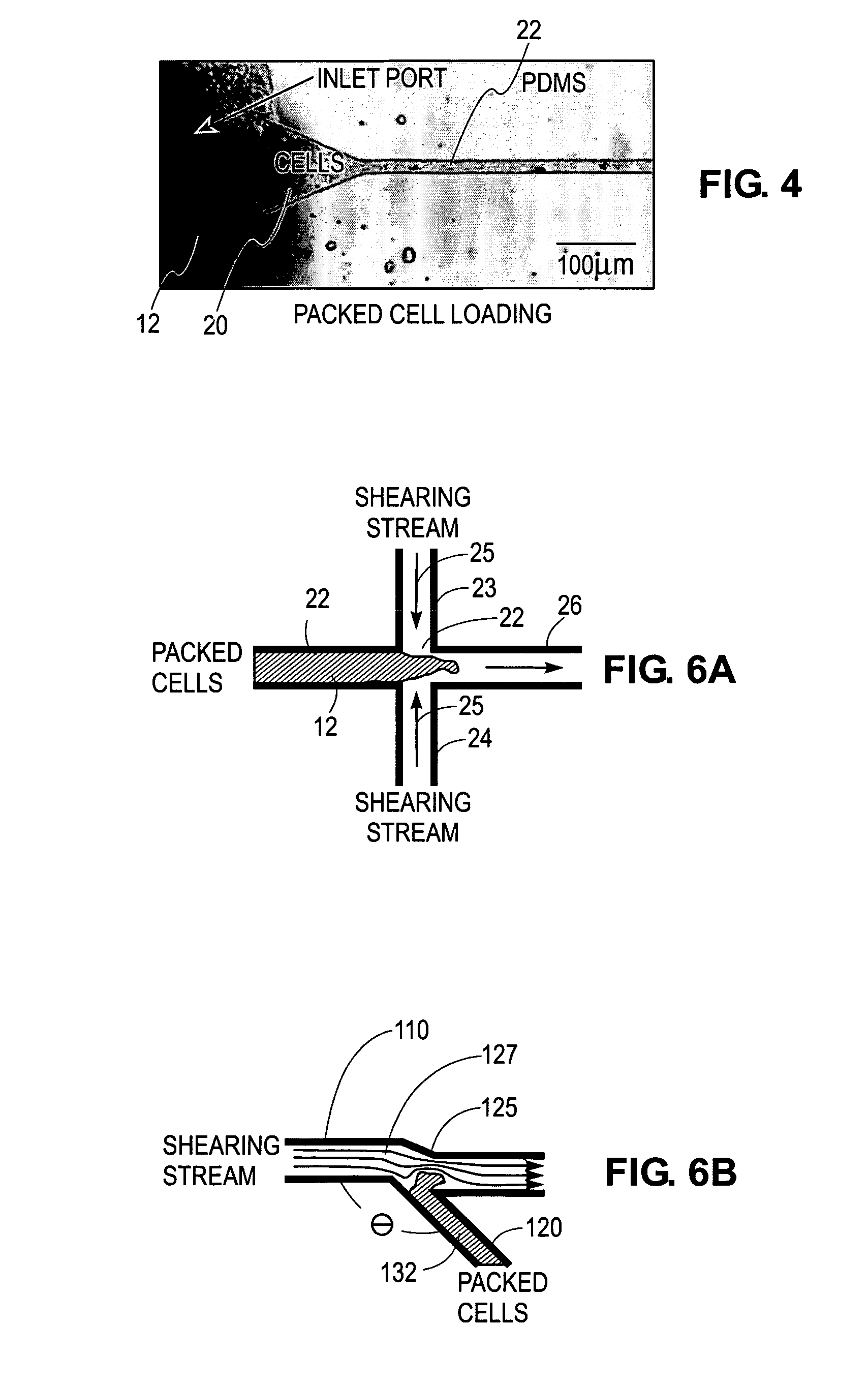
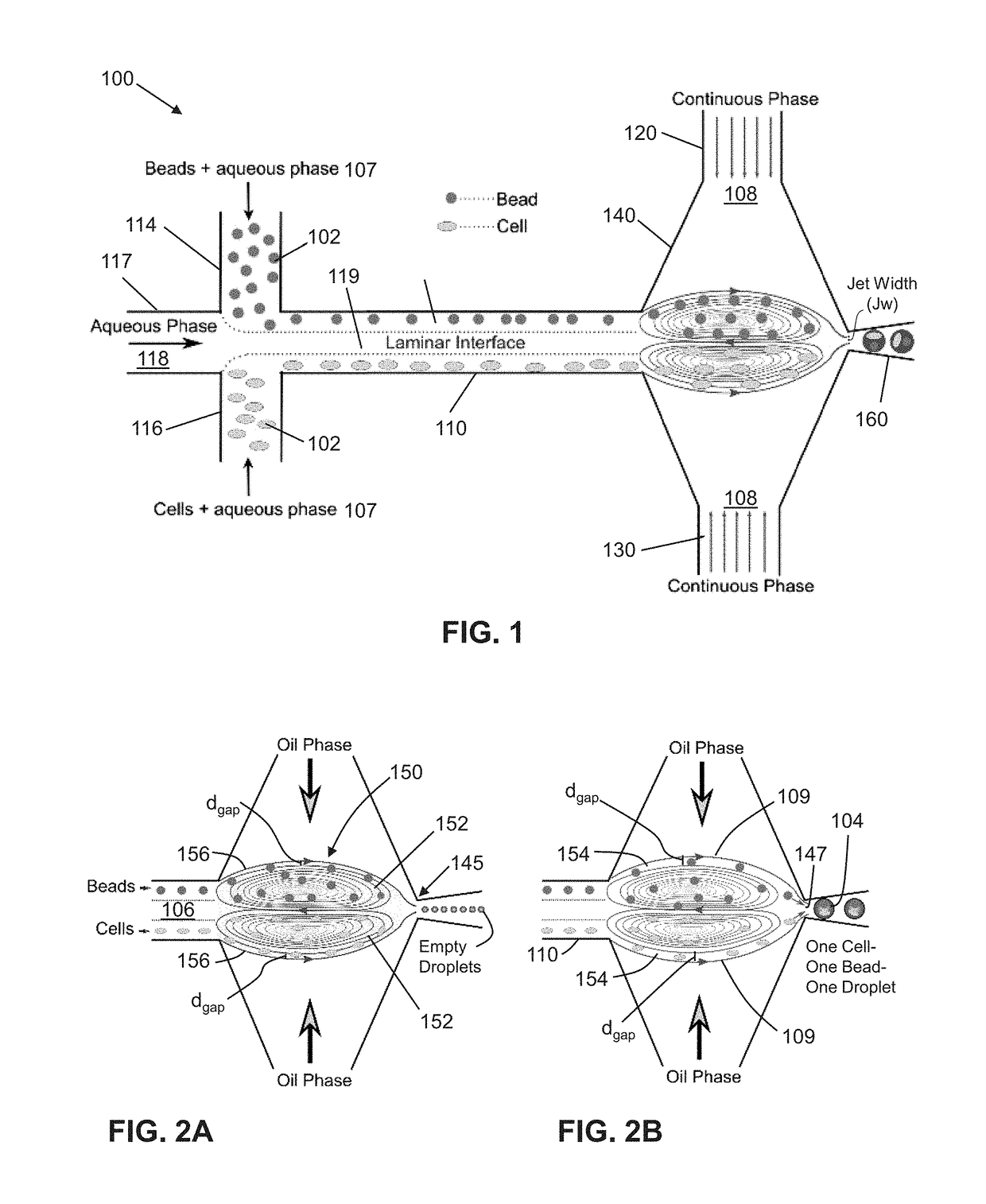
Cell encapsulation microfluidic device
ActiveUS7759111B2Small droplet sizeUniform polymerization timeBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEngineeringCell encapsulation
Devices and methods for the encapsulation of cells on microfluidic platforms are disclosed. The microfluidic device generally includes a plurality of functional regions to shear, focus, and encapsulate a desired cell or group of cells into a droplet. The microfluidic device can further comprise a polymerization zone to form a polymer bead around the droplet.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
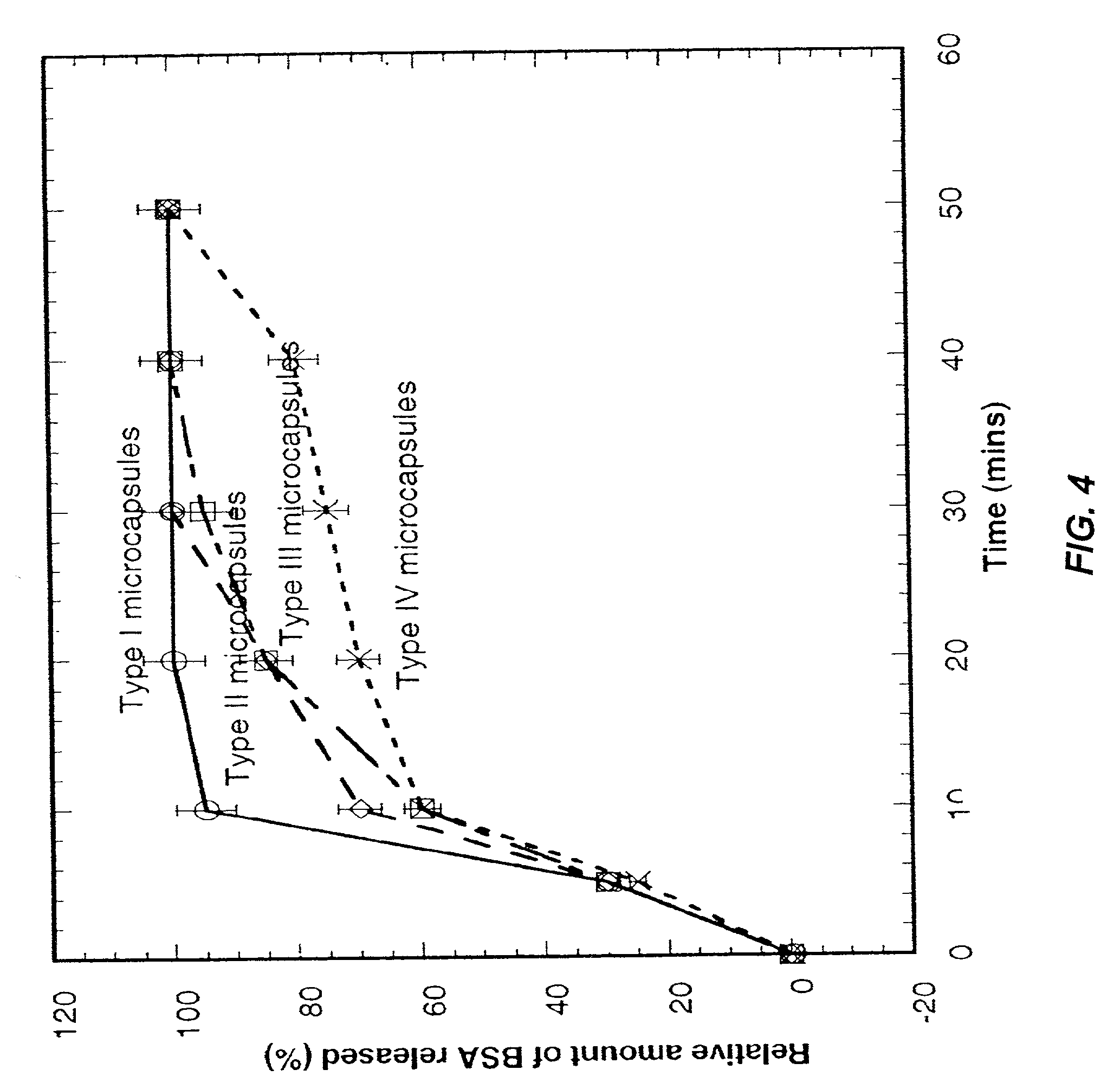
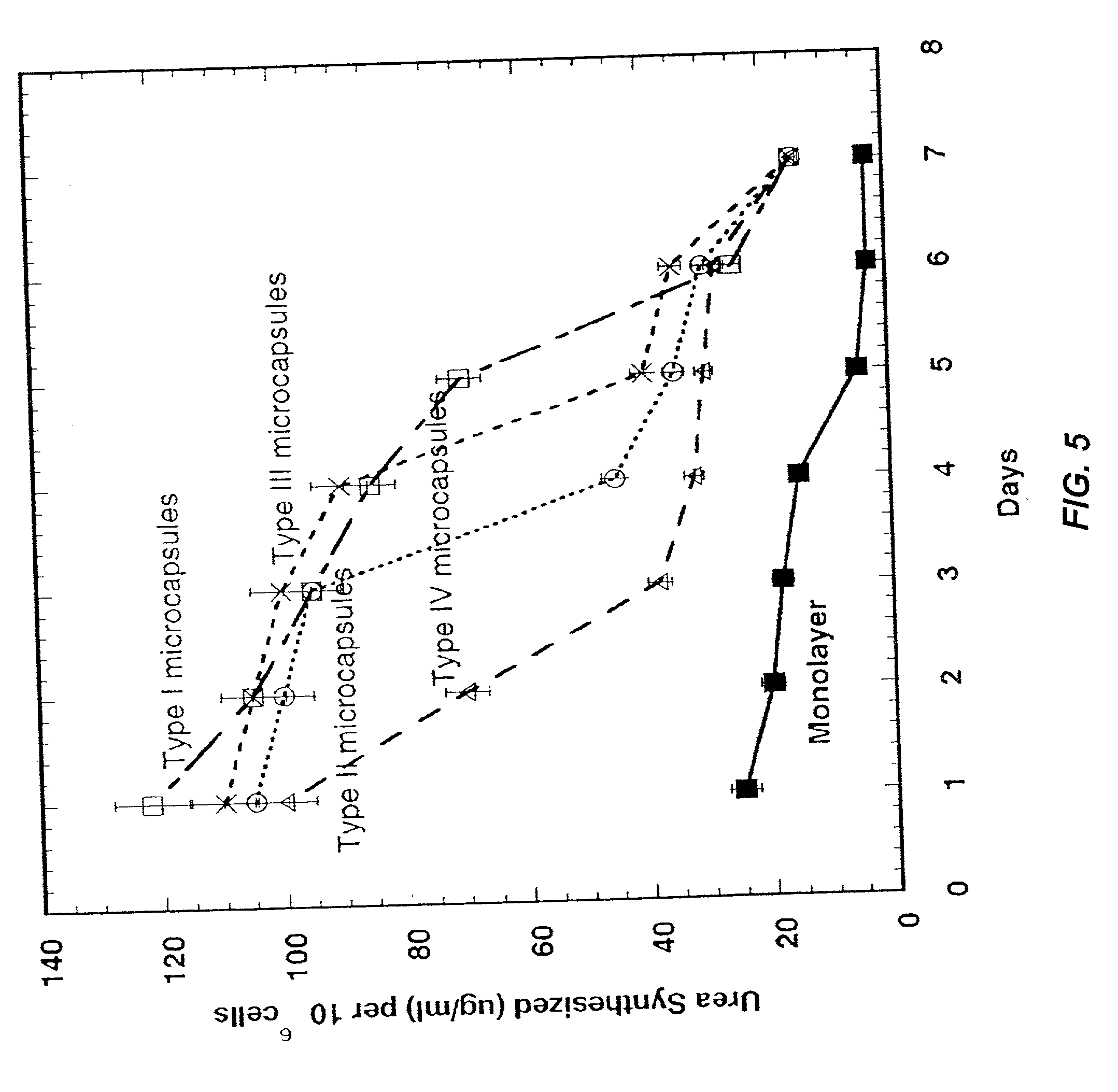
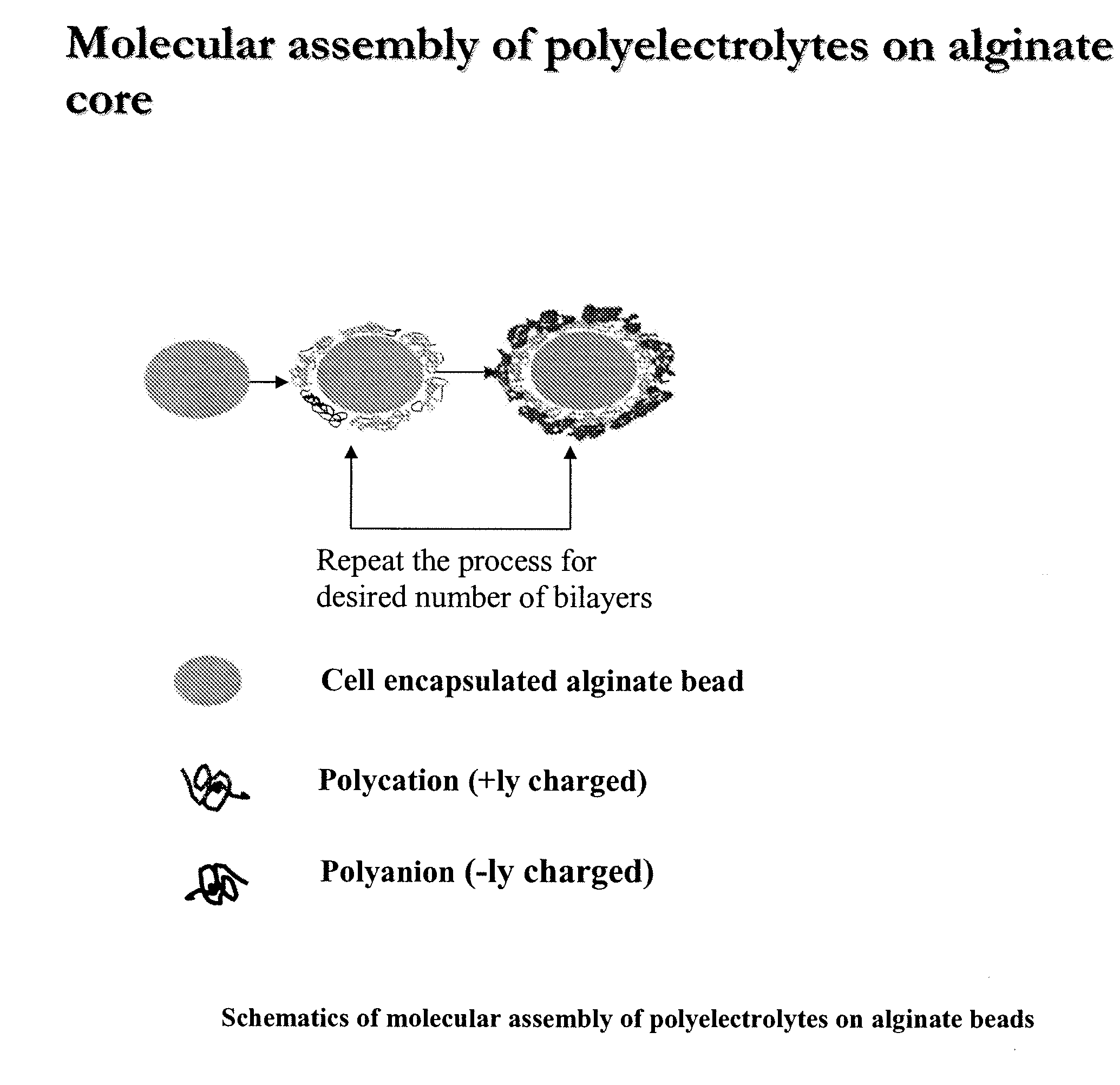
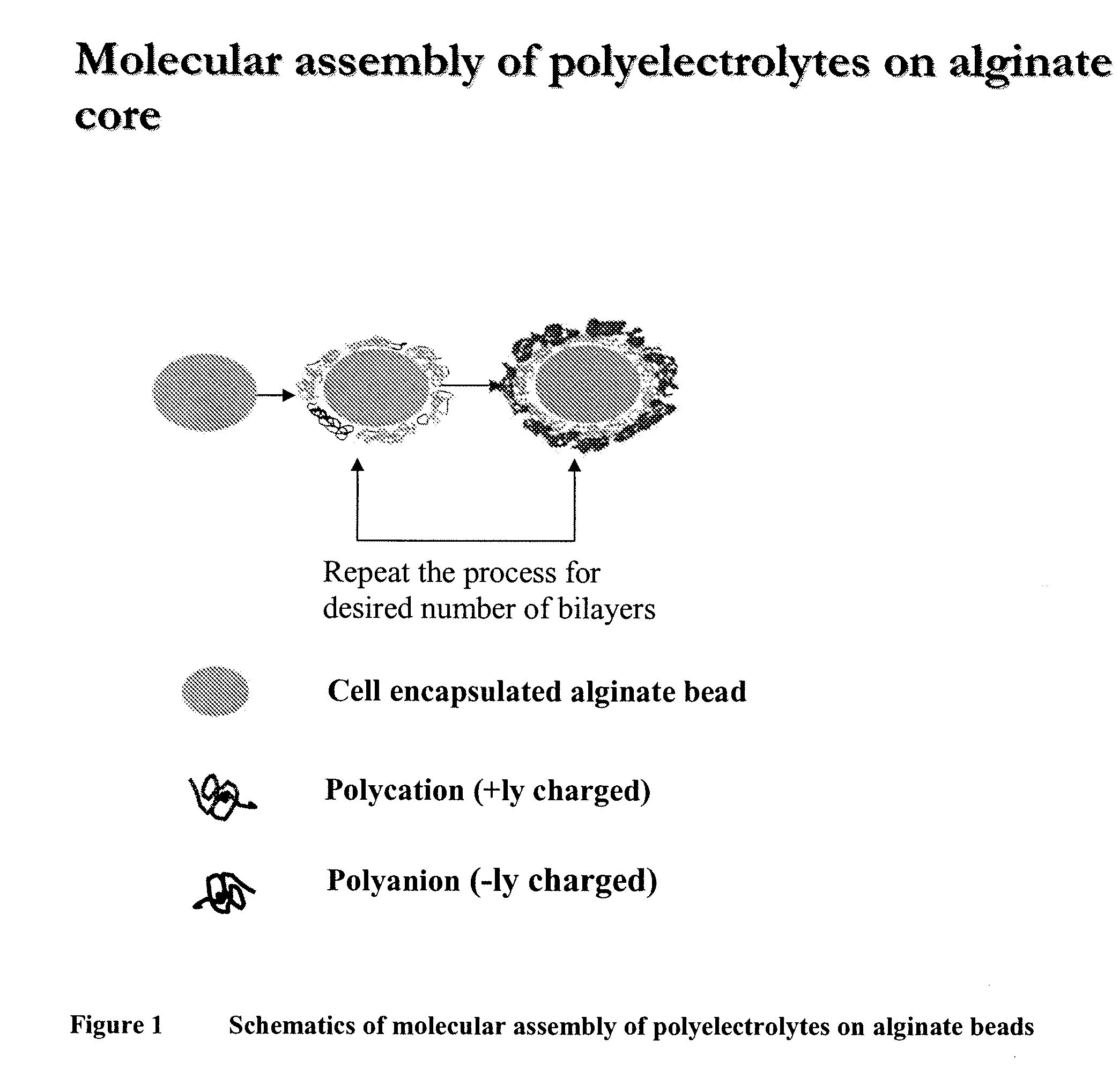
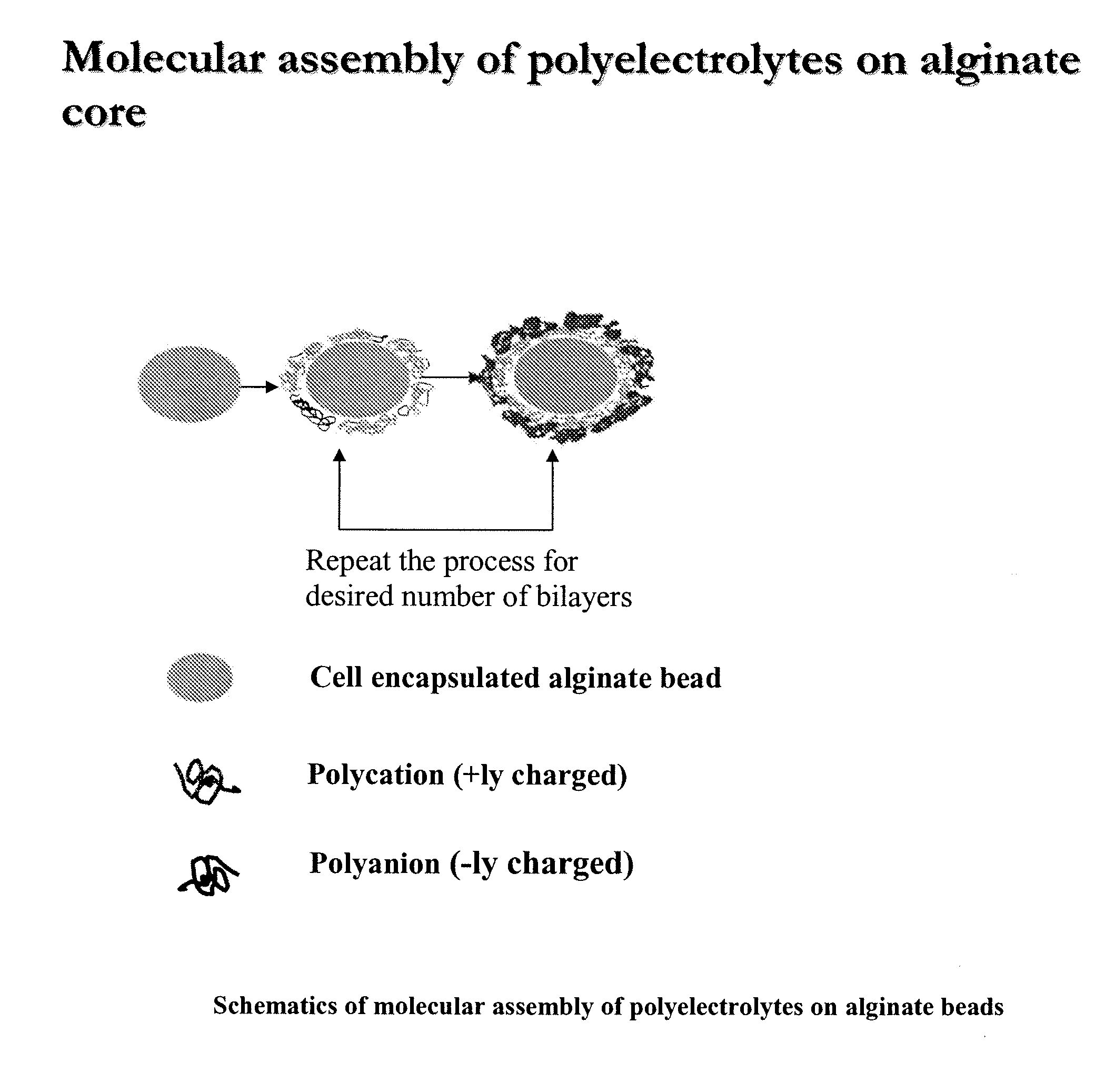
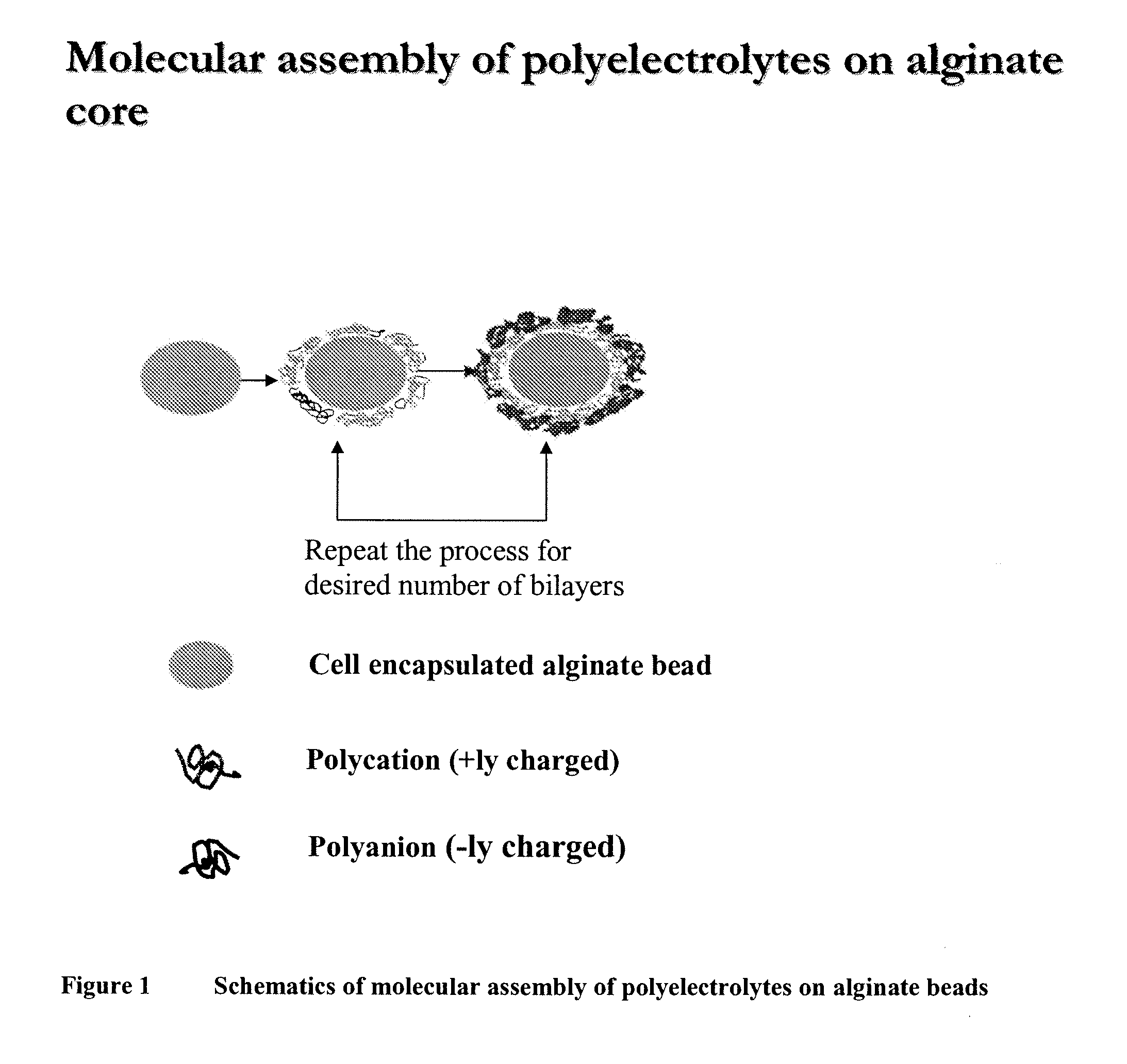
Multilayered polyelectrolyte-based capsules for cell encapsulation and delivery of therapeutic compositions
The present invention provides novel, biocompatible matrices for cell encapsulation and transplantation. It further provides methods for delivering agents to encapsulated cells and to the local environment of a host system. The invention also provides methods for targeting and manipulating particular cells and / or proteins of the host system. In a composition aspect of the invention, a composition including a collection of capsules is provided. The capsules comprise an inner core, and the inner core is covered by an outer shell composed of a positive polyelectrolyte and a negative polyelectrolyte. The inner core of the capsules contains at least one cell.
Owner:ISLET SCI
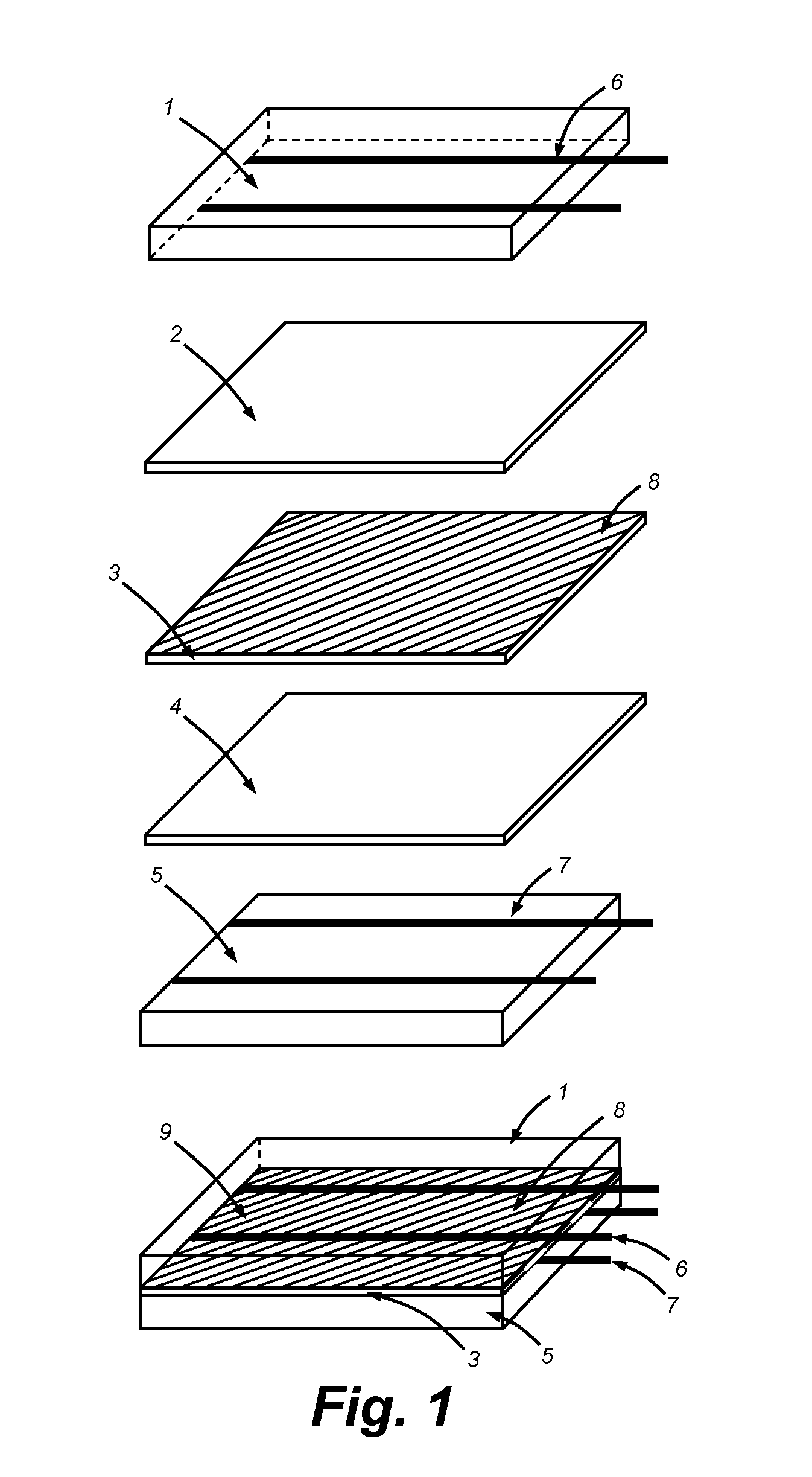
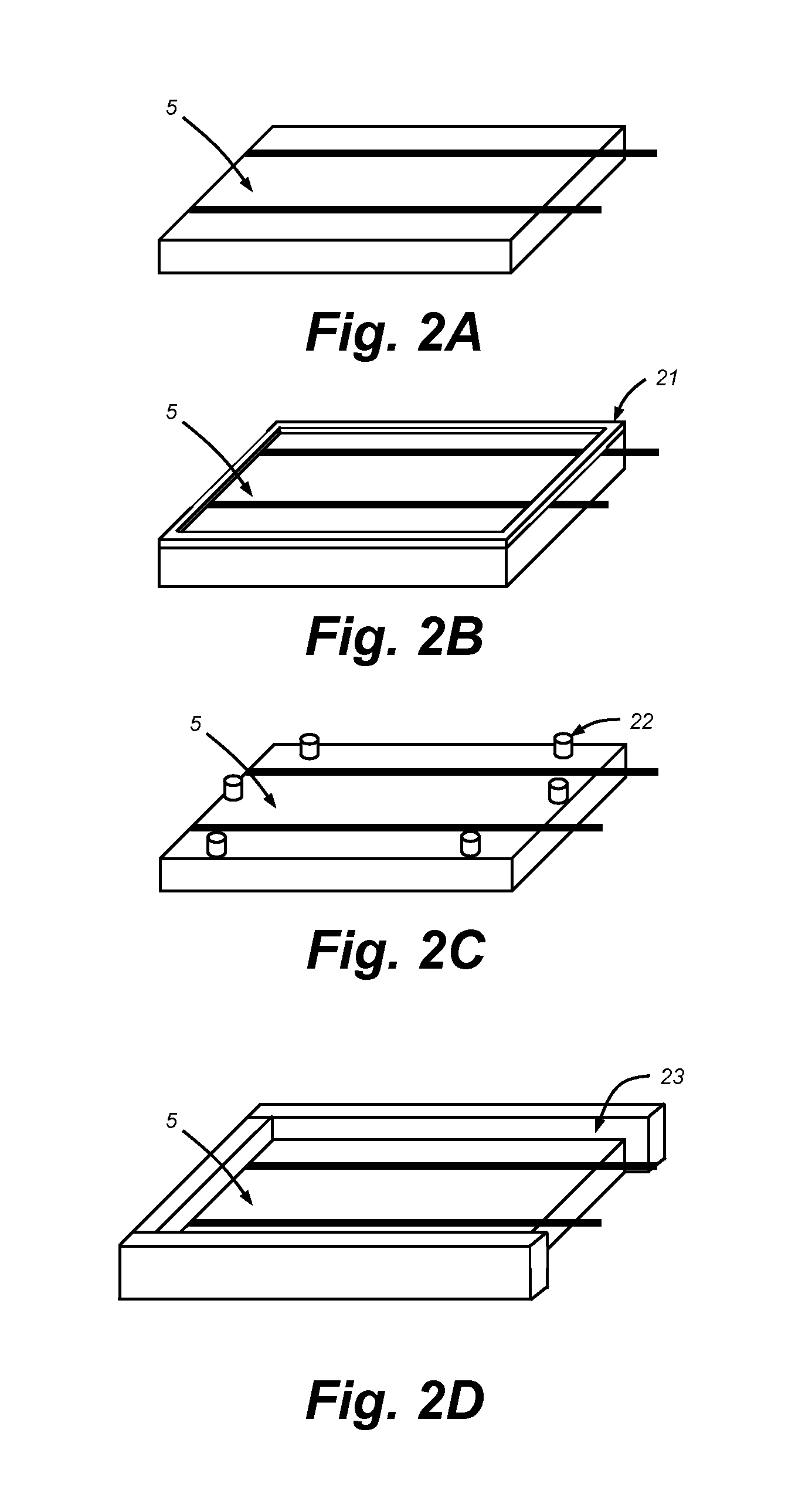
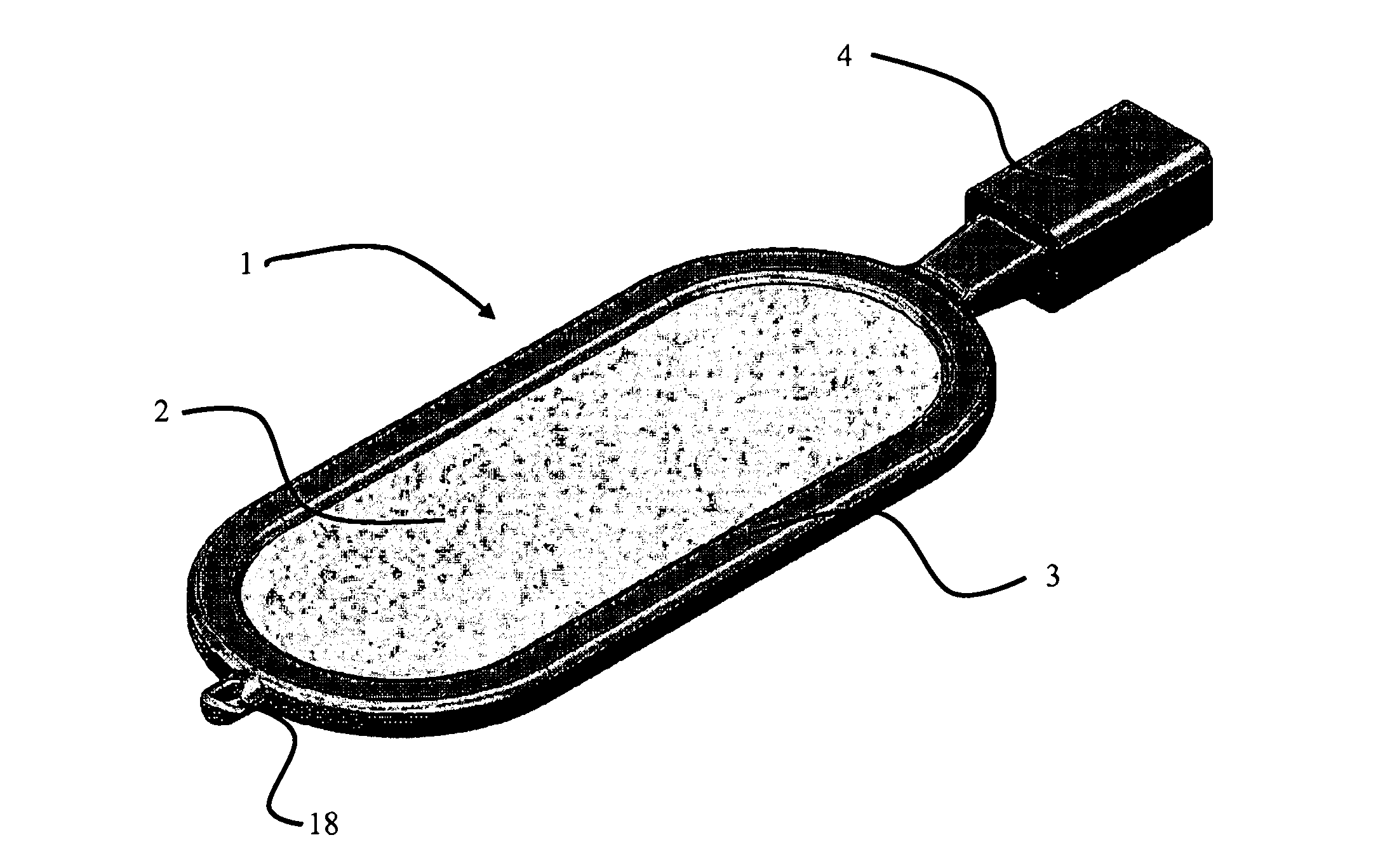
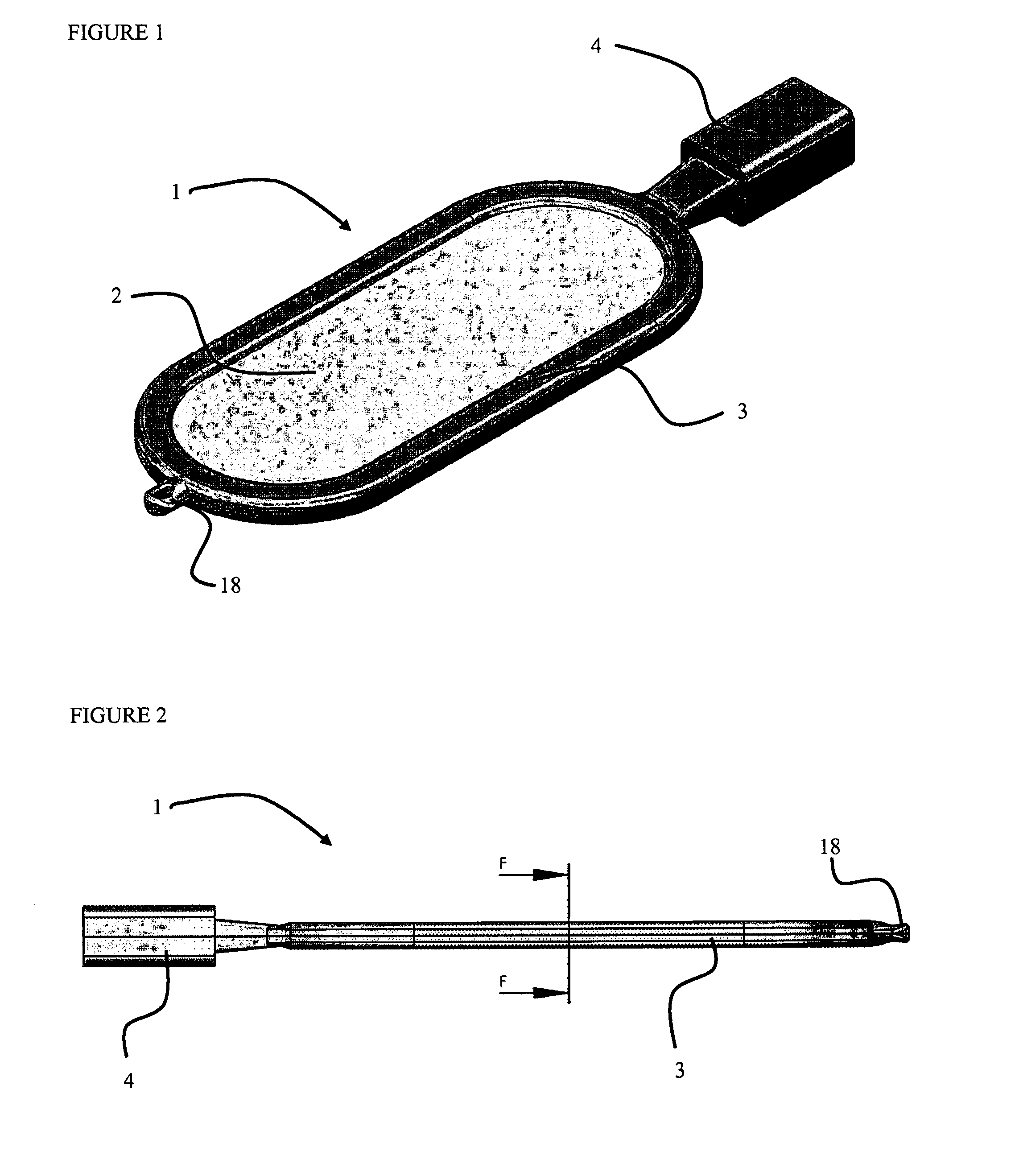
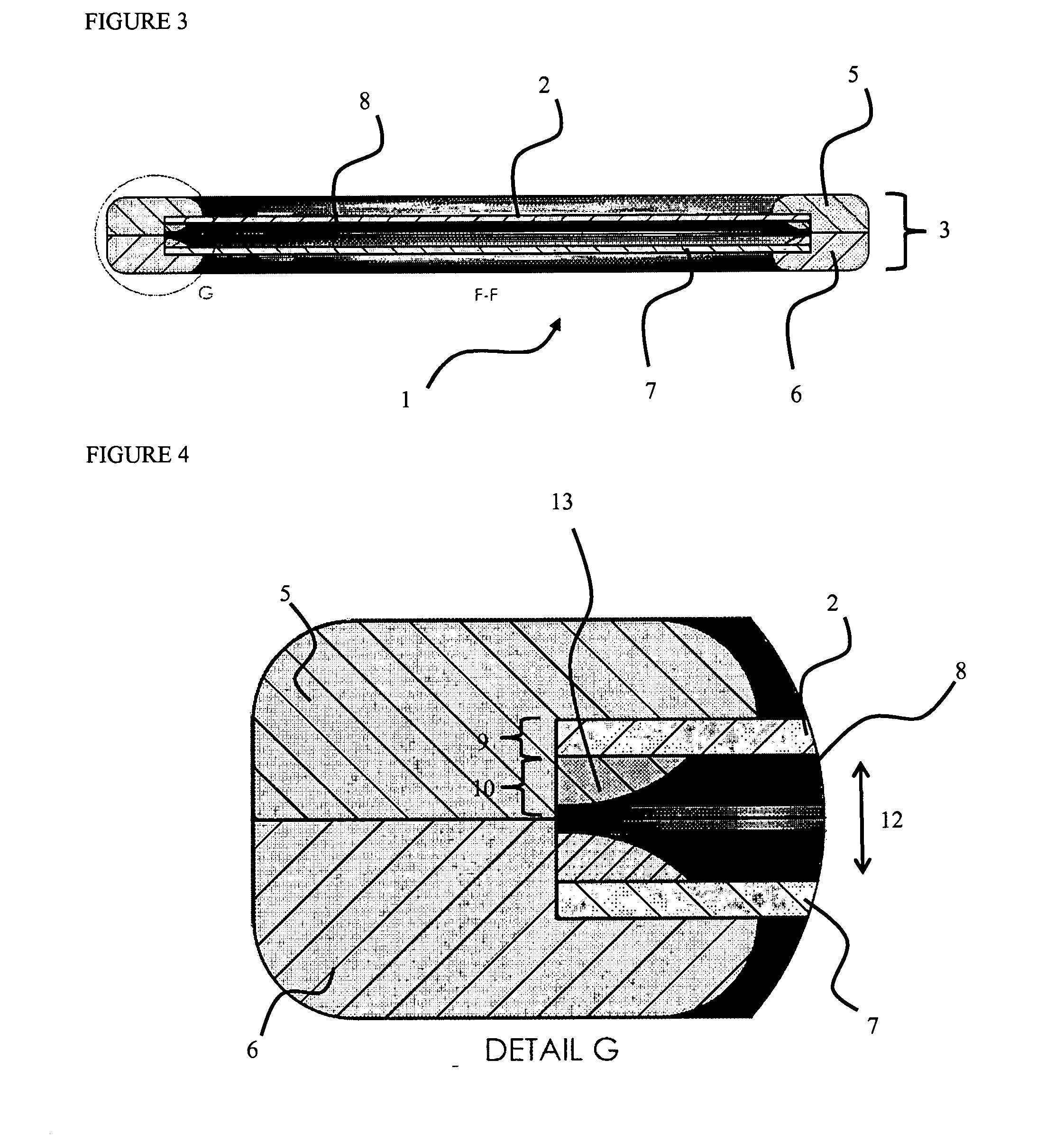
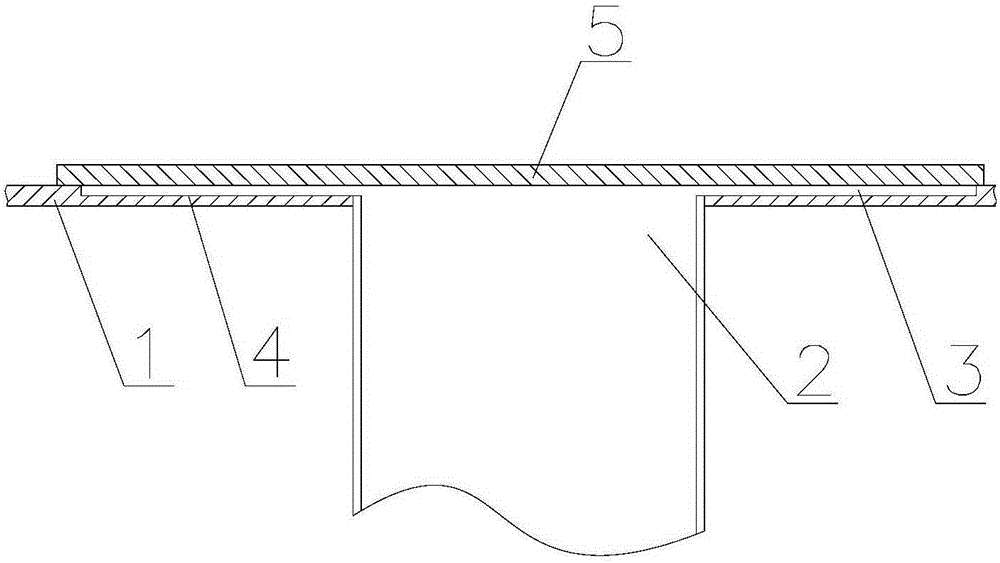
Encapsulation device
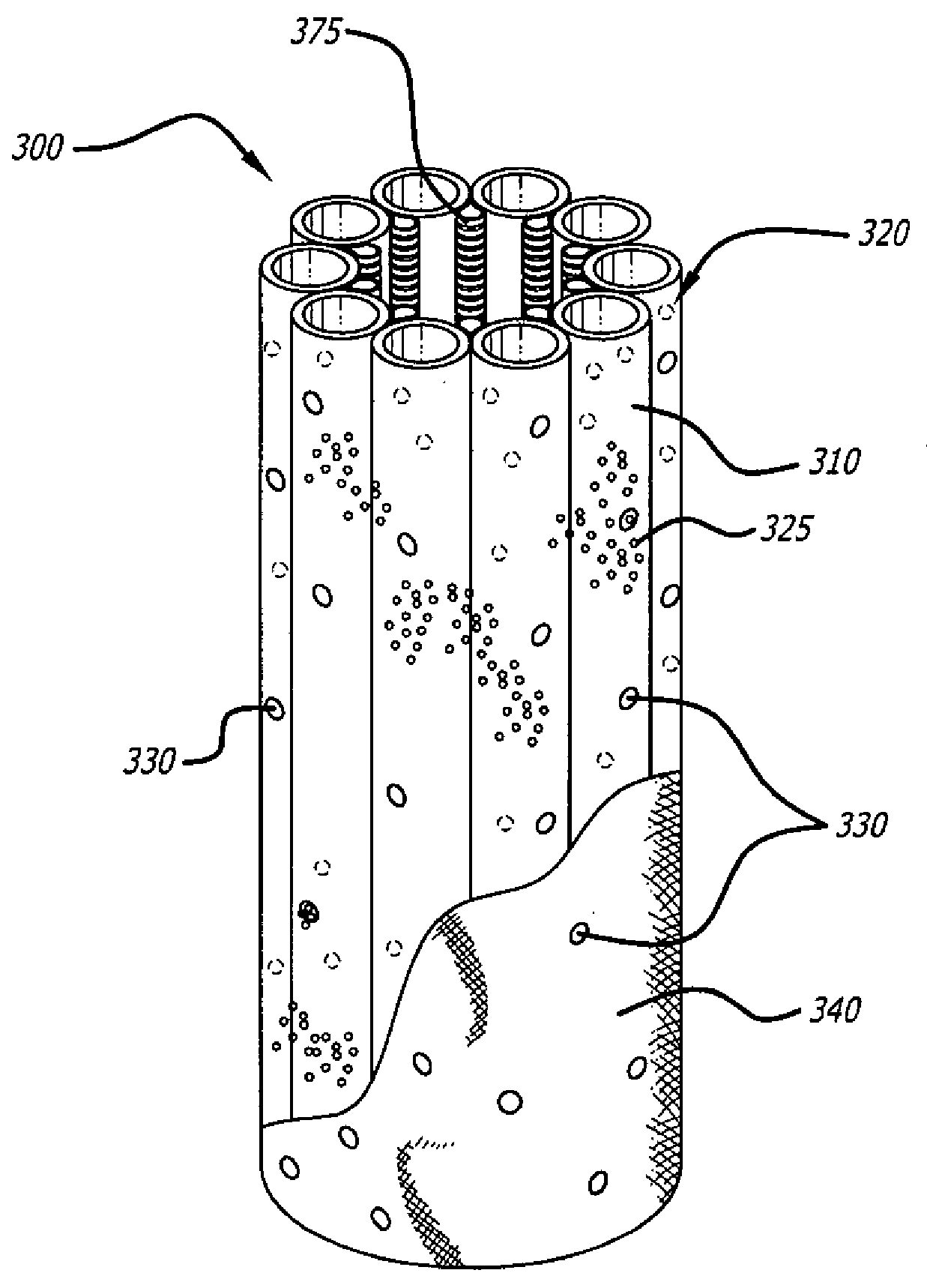
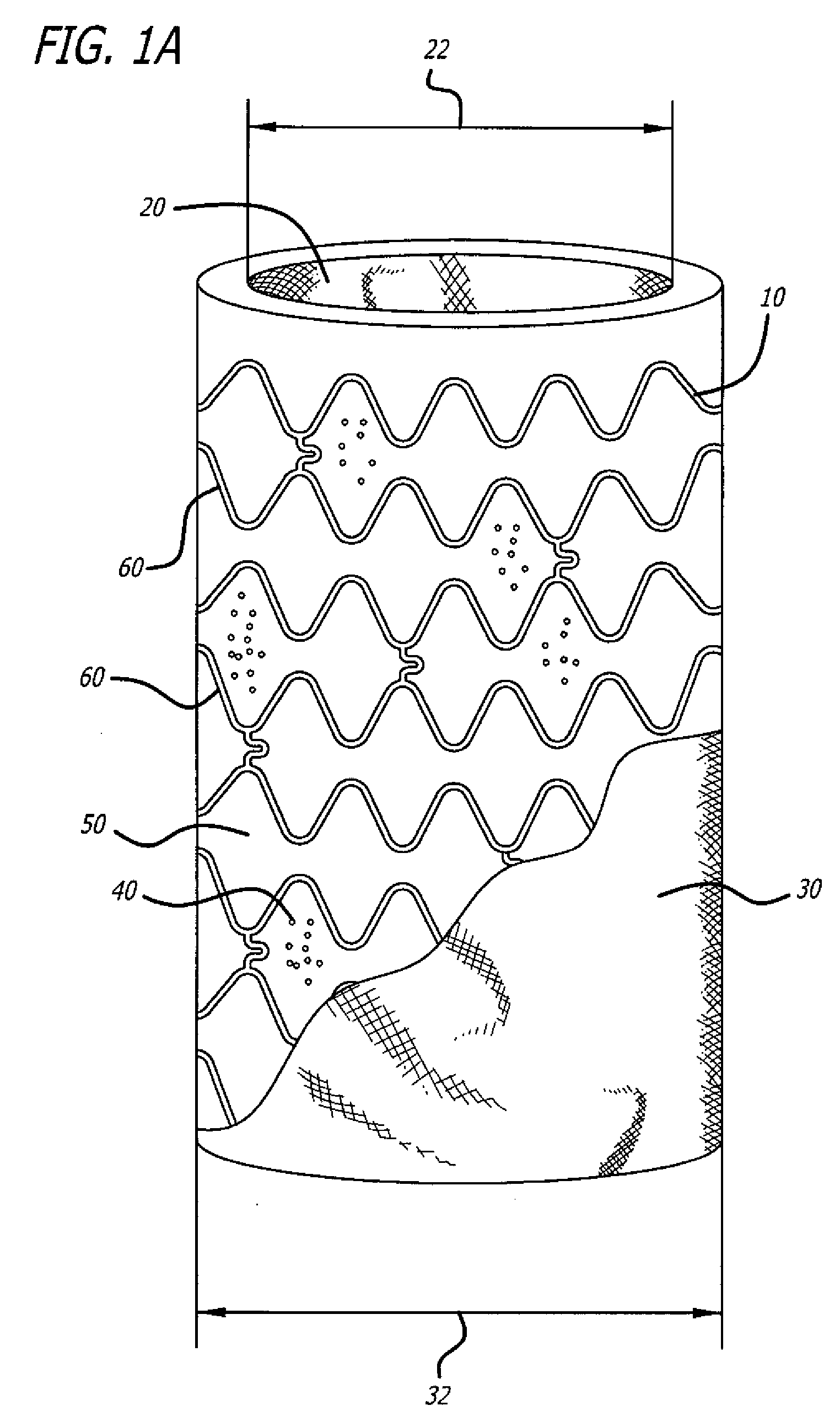
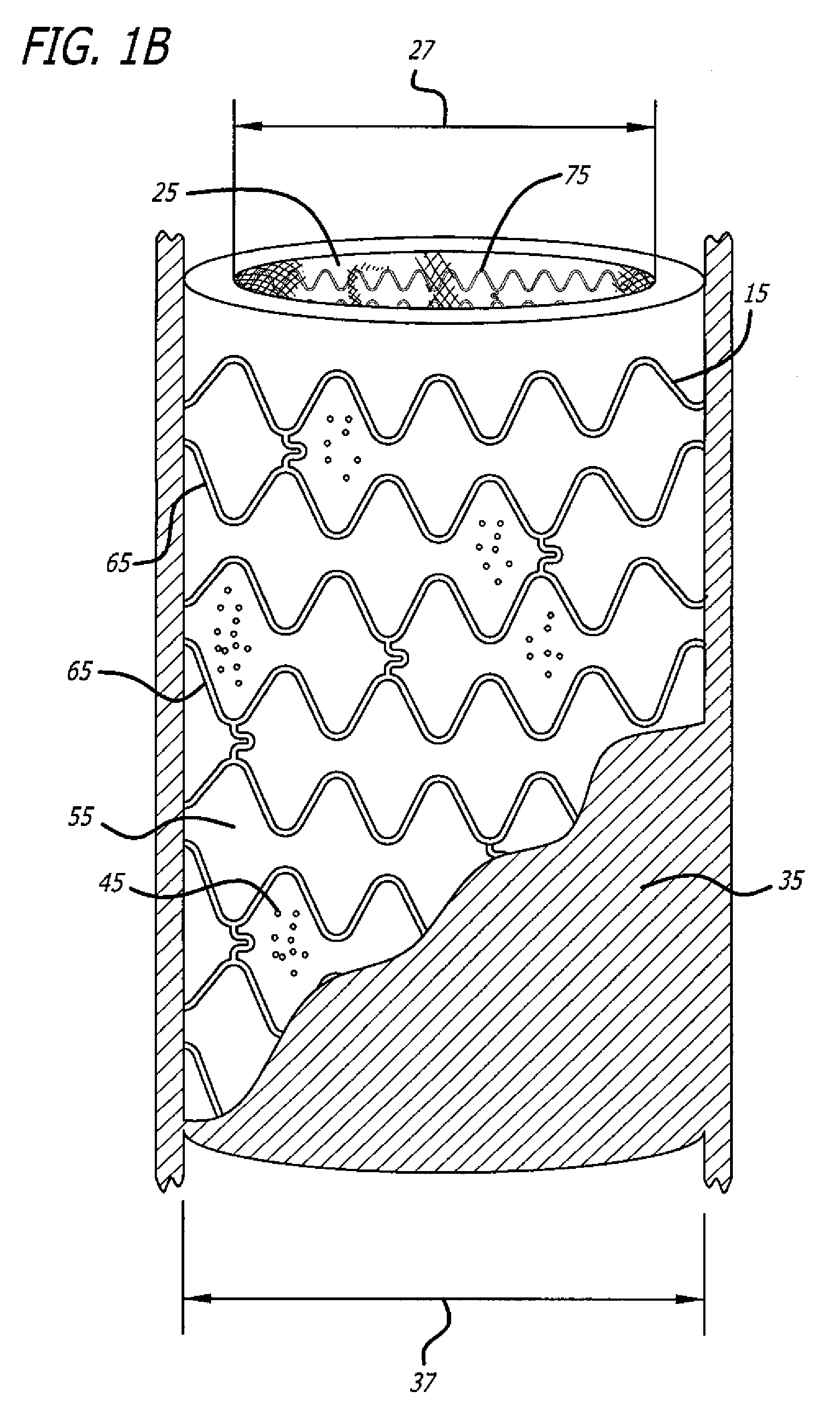
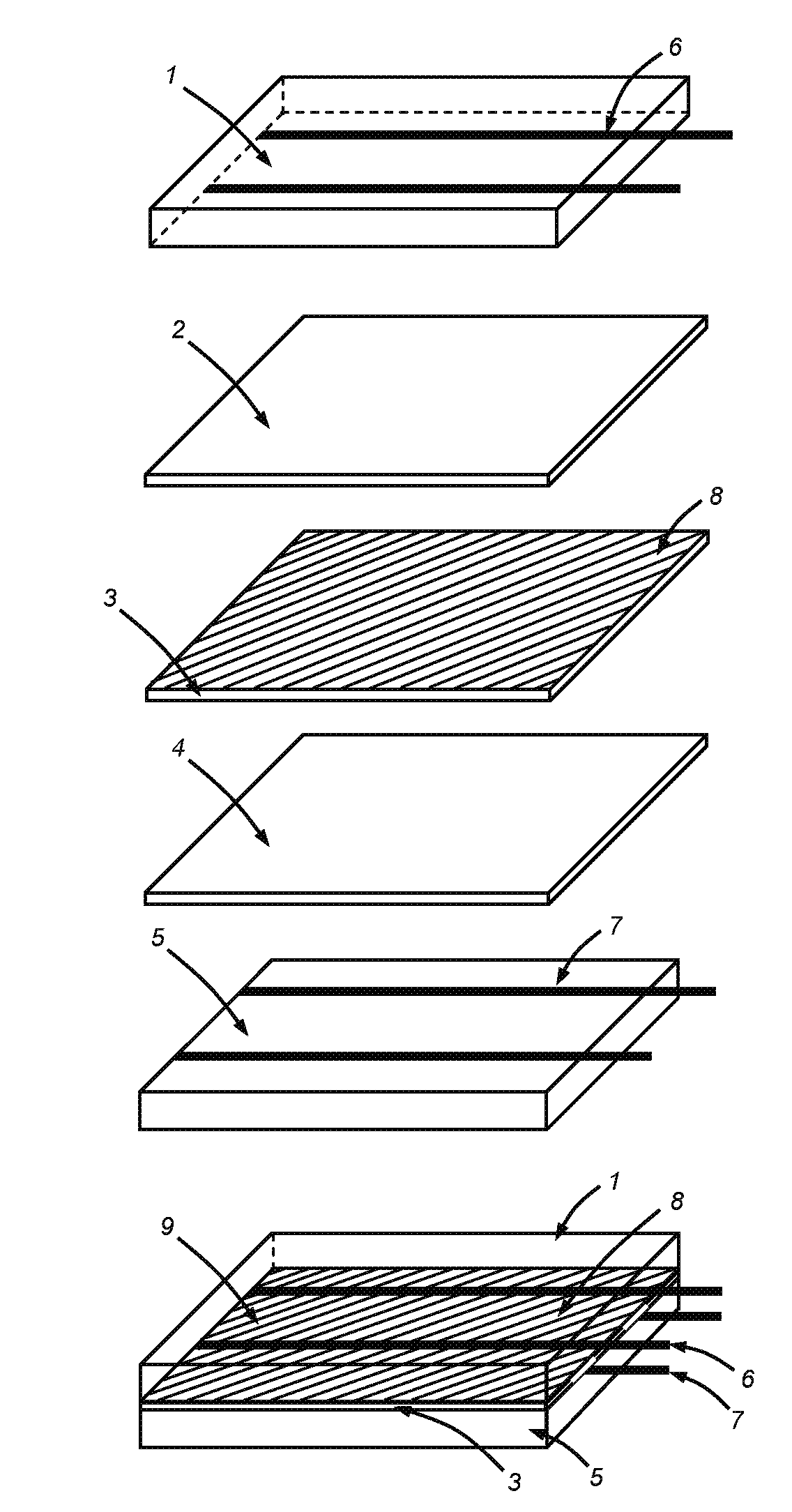
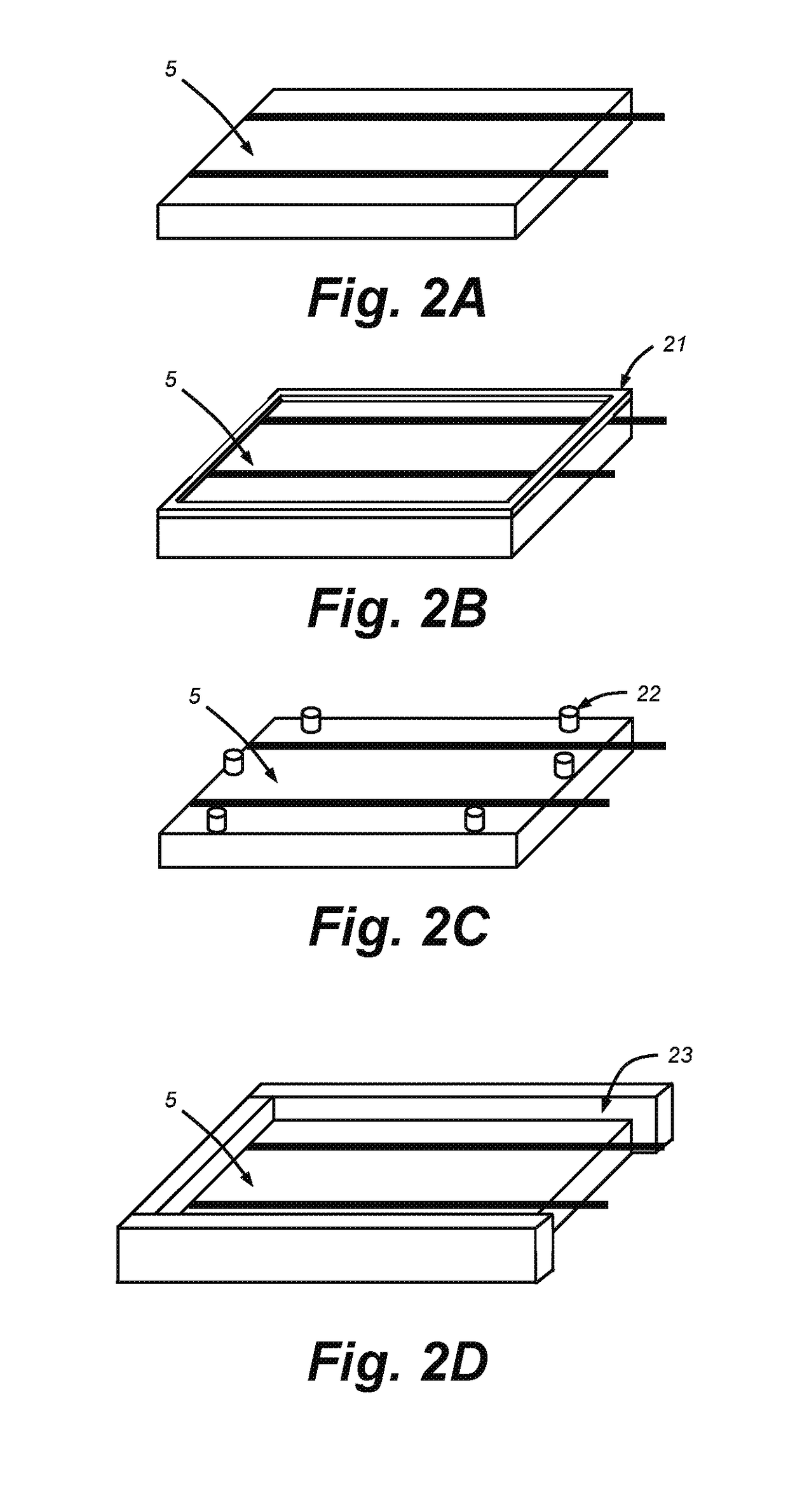
Provided herein is a cell encapsulation device comprising an internal chamber suitable for holding biological agents, wherein the internal chamber is disposed between a first semipermeable layer and a second semi-permeable layer, and the first and second semi-permeable layers are mounted on a supporting frame surrounding a perimeter of the internal chamber; wherein the supporting frame comprises a first frame element and a second frame element, and the first and second frame elements co-operate to position the first and second semipermeable layers at a predetermined separation distance between the layers.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA +1
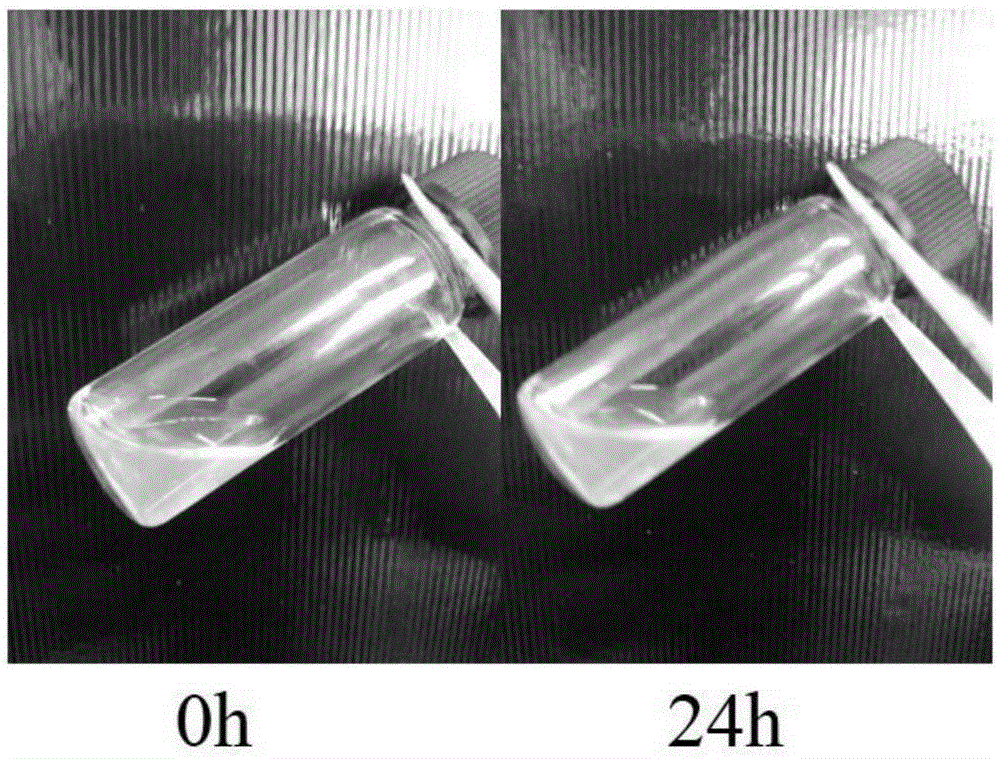
Dipeptide hydrogel, and preparation method and application thereof
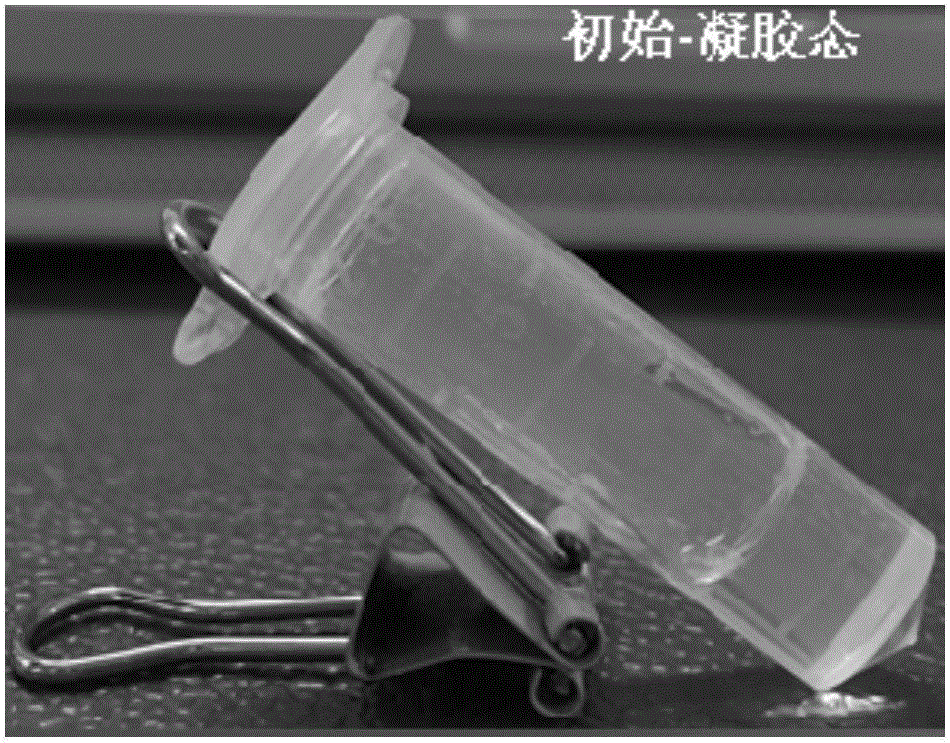
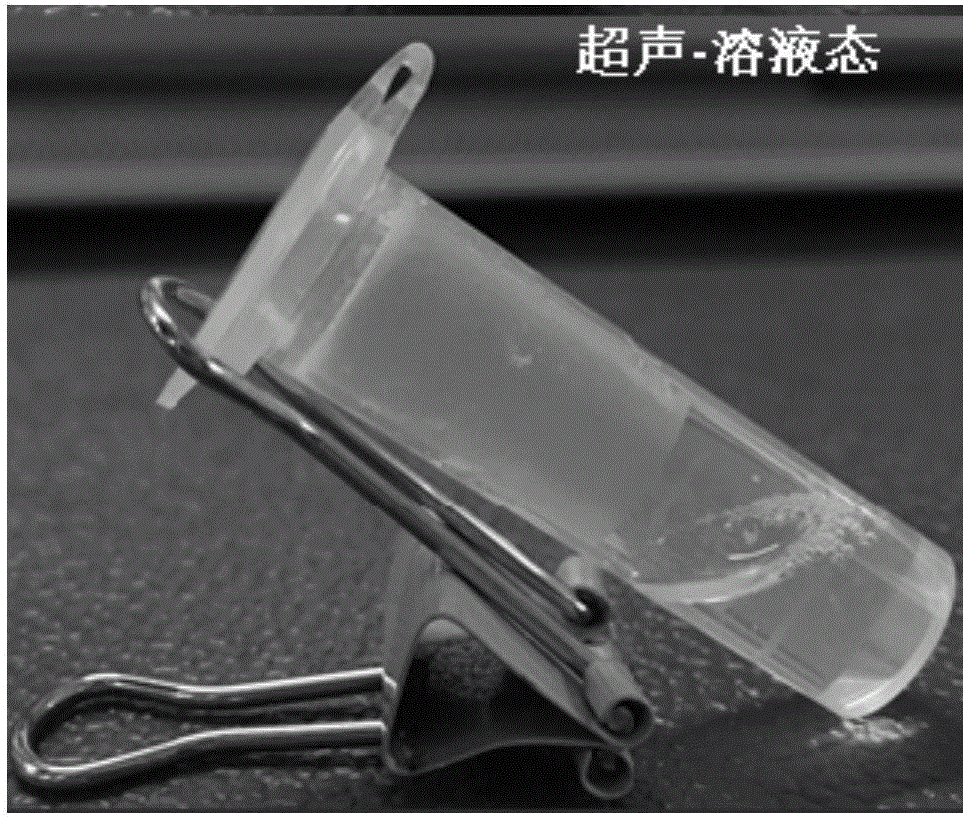
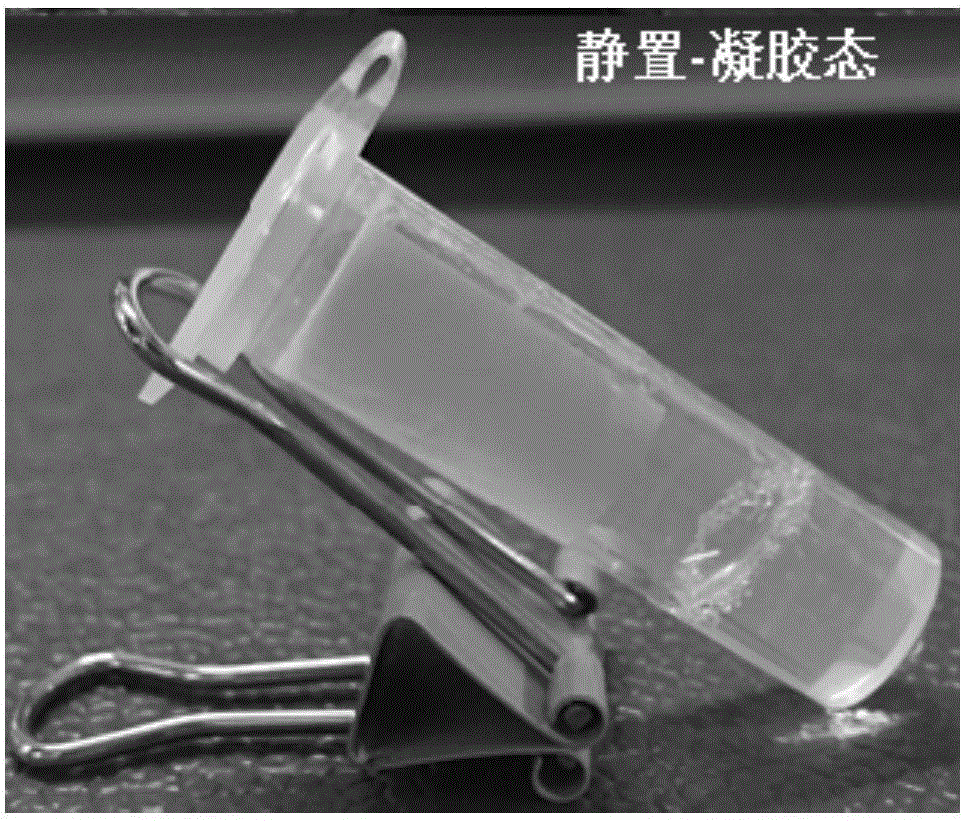
ActiveCN106333922AUniform and transparent appearanceGood ultrasonic responsivenessOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryTissue repairDipeptide
The invention relates to the field of responding type injectable hydrogels, in particular to a dipeptide hydrogel, a preparation method and application thereof. A dipeptide molecule is of an XY structure, wherein X is selected from tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan or histidine; Y is selected from aspartic acid, asparagine, glutamic acid or glutamine. The hydrogel has a quick ultrasonic response characteristic, can be quickly recovered to a gel state after stimulating response, is stable and uniform in properties, and can be applied to the fields of biological nano-materials, medicament controlled-release, medicament delivery, cell encapsulation and tissue repair.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
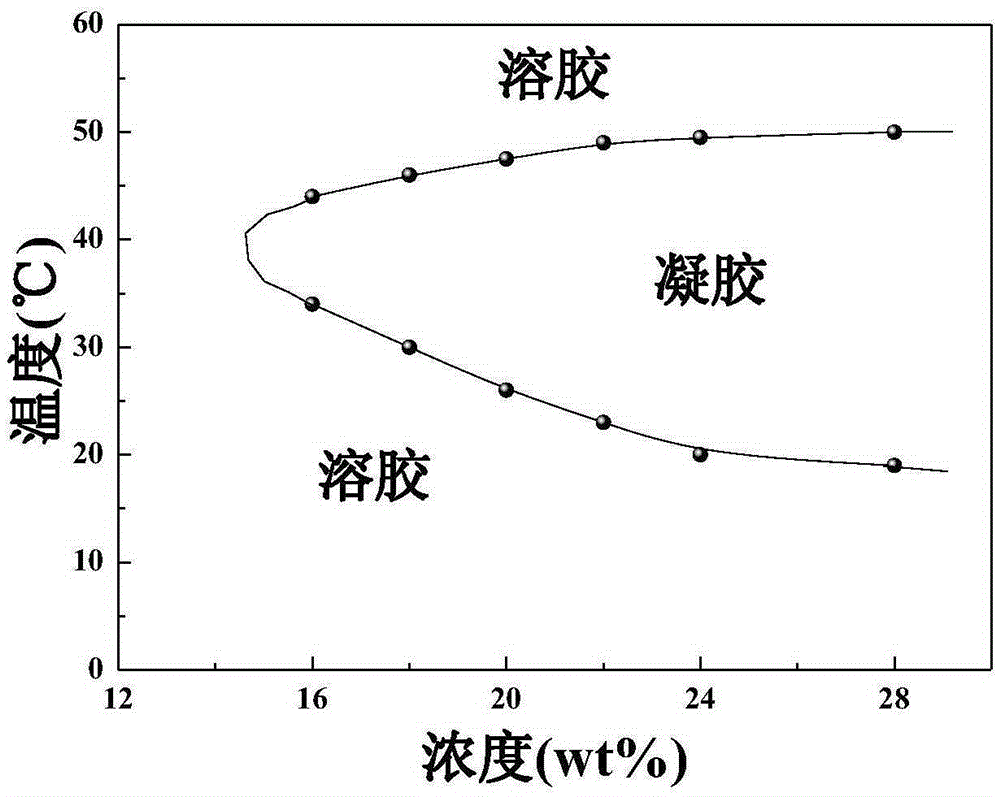
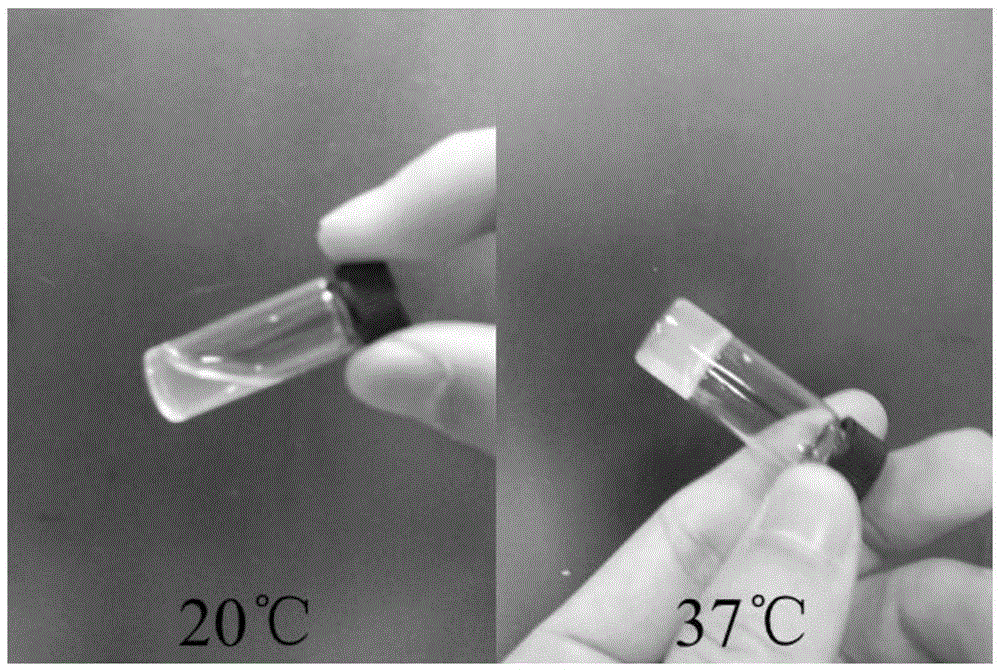
Injectable thermosensitive physical hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105396137AAdjust modulusRegulation of degradation rateAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryTissue repairPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical polymer materials, in particular to injectable thermosensitive physical hydrogel with functional side groups and a preparation method thereof. Polyethylene glycol serves as a hydrophilic block (B), polycaprolactone serves as a hydrophobic block (A), a polymer composition with the functional side groups is connected, an aqueous solution, with a certain mass percentage, of the composition is in a free flowing sol state when the temperature of the aqueous solution is lower than that of a human body and is in a non-flowing gel state when the temperature of the aqueous solution is equal to that of the human body, and conversion from sol to gel is achieved when the low temperature is raised to the high temperature. The hydrogel is injectable and biodegradable, has good biocompatibility and can be widely applied to medicine conveying, cell encapsulation and tissue repair.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Modified alginates for cell encapsulation and cell therapy
ActiveUS9422373B2Avoid encapsulationImprove propertiesMetabolism disorderUnknown materialsBiocompatibility TestingBiochemistry
Covalently modified alginate polymers, possessing enhanced biocompatibility and tailored physiochemical properties, as well as methods of making and use thereof, are disclosed herein. The covalently modified alginates are useful as a matrix for the encapsulation and transplantation of cells. Also disclosed are high throughput methods for the characterizing the biocompatibility and physiochemical properties of modified alginate polymers.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
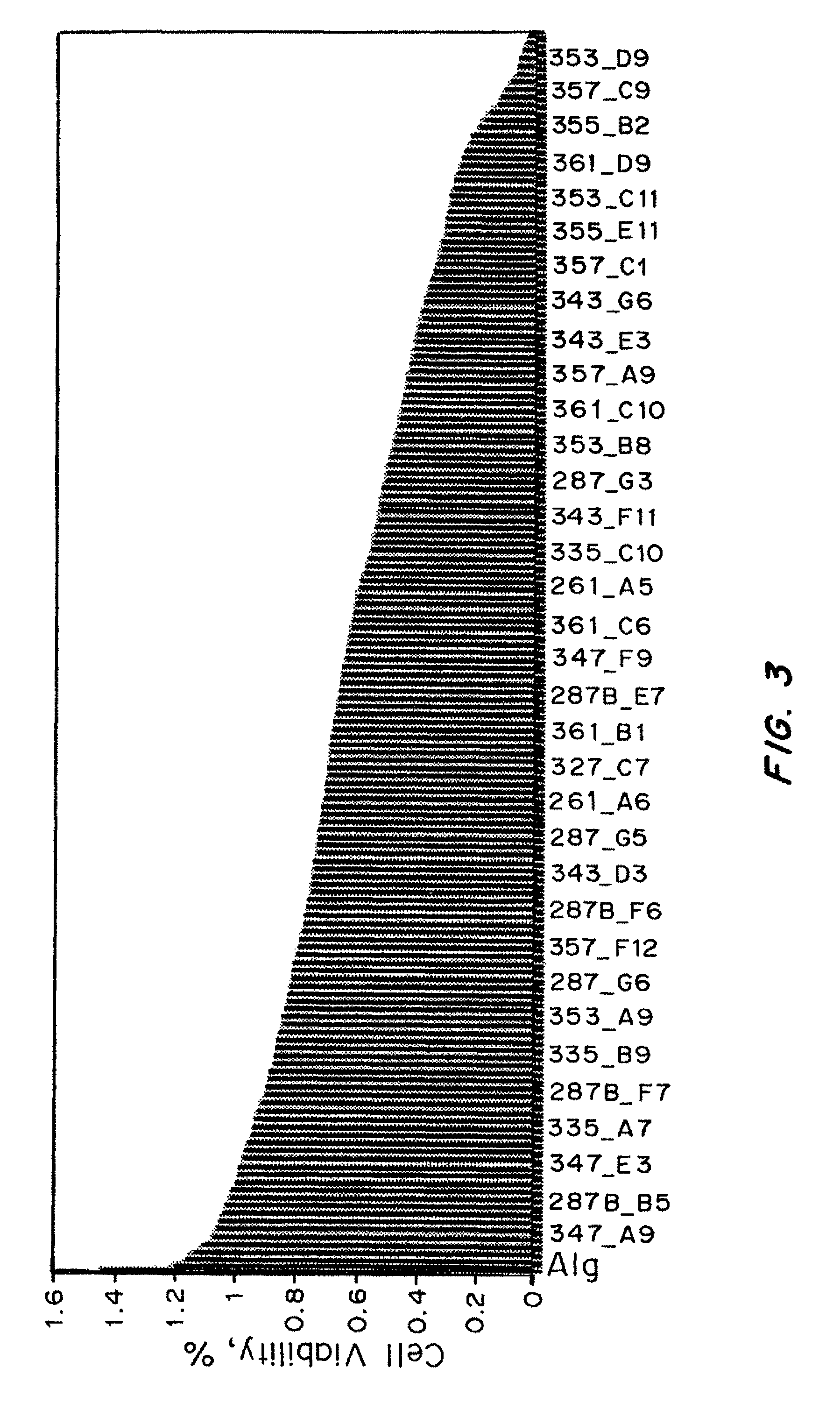
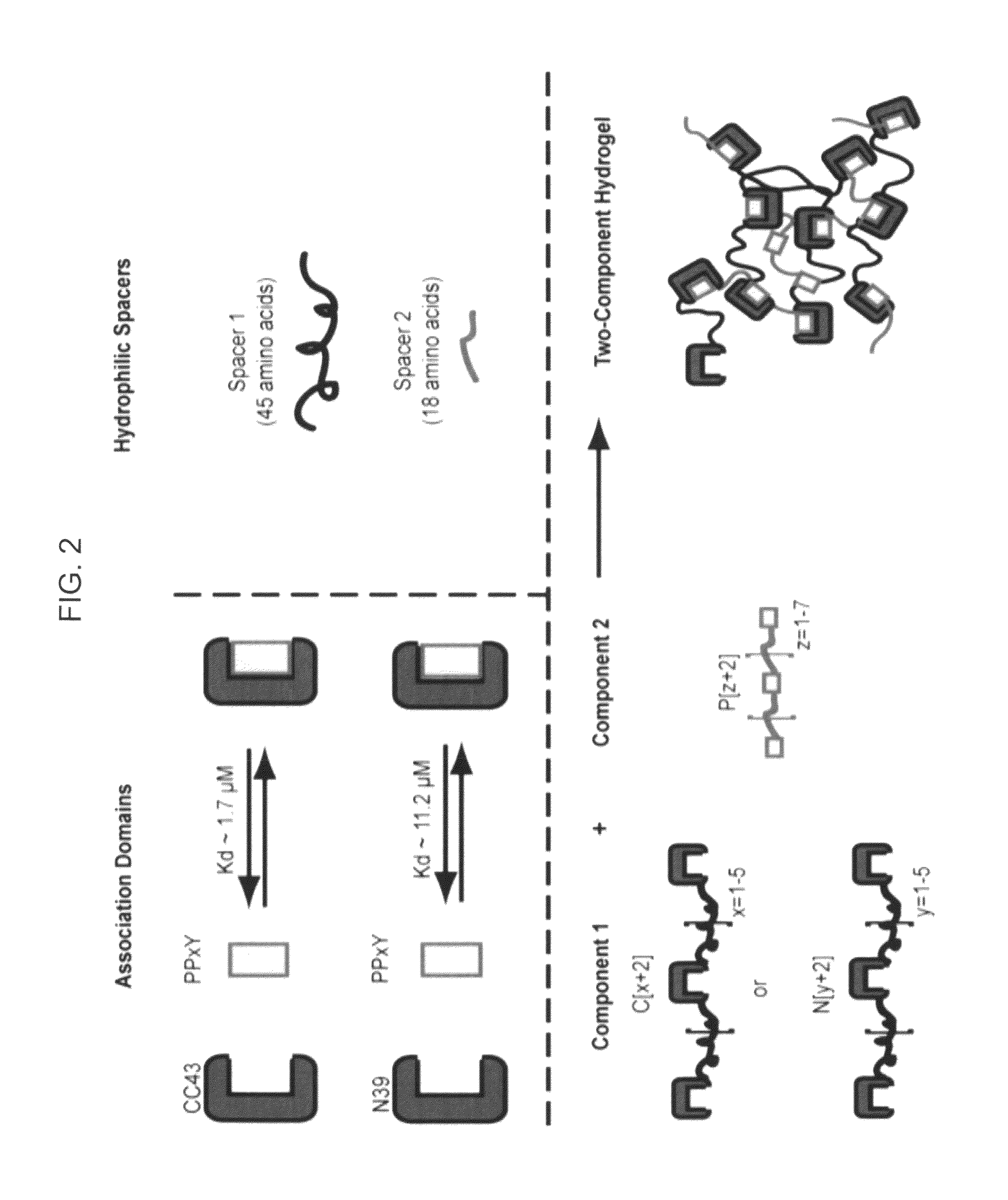
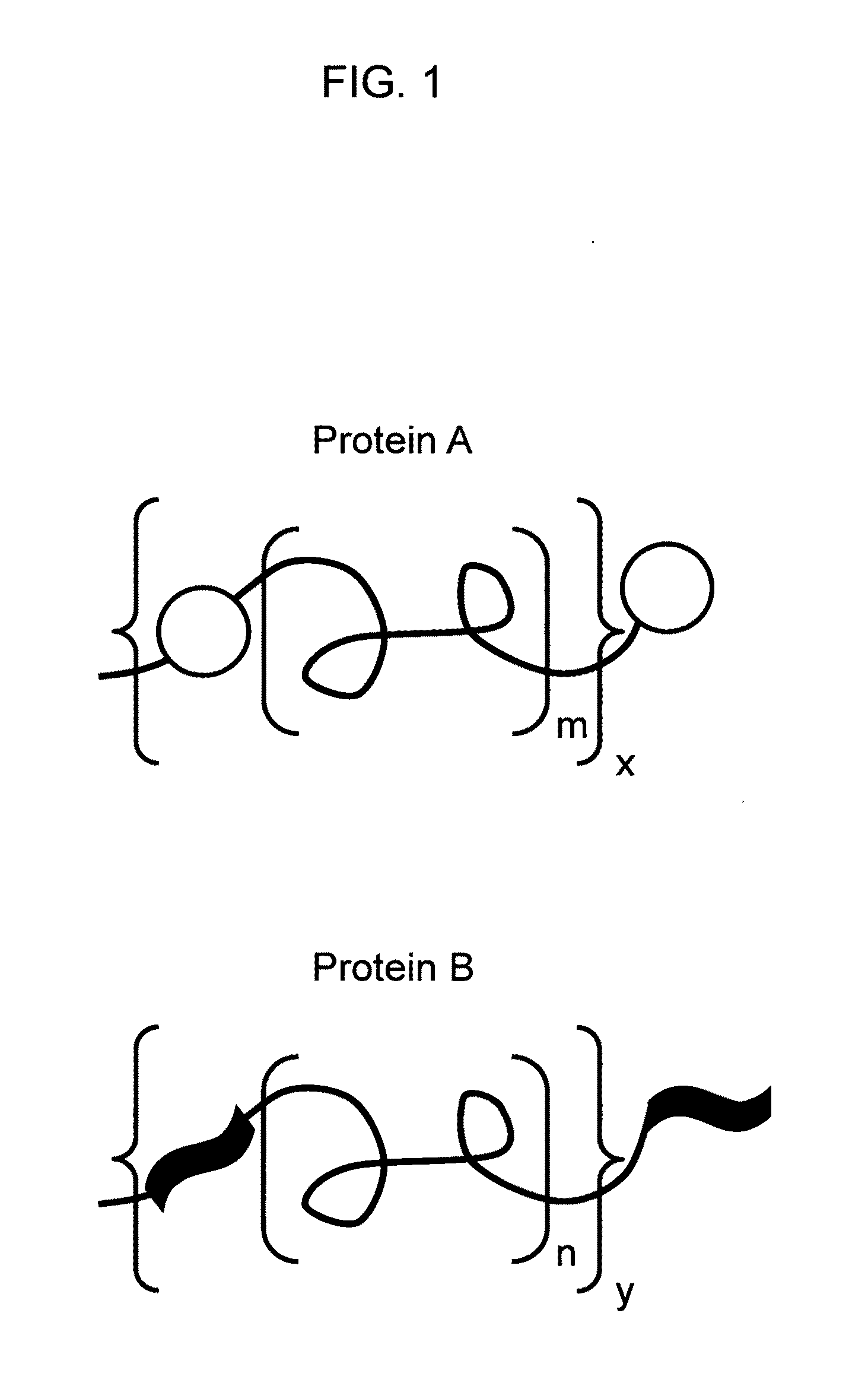
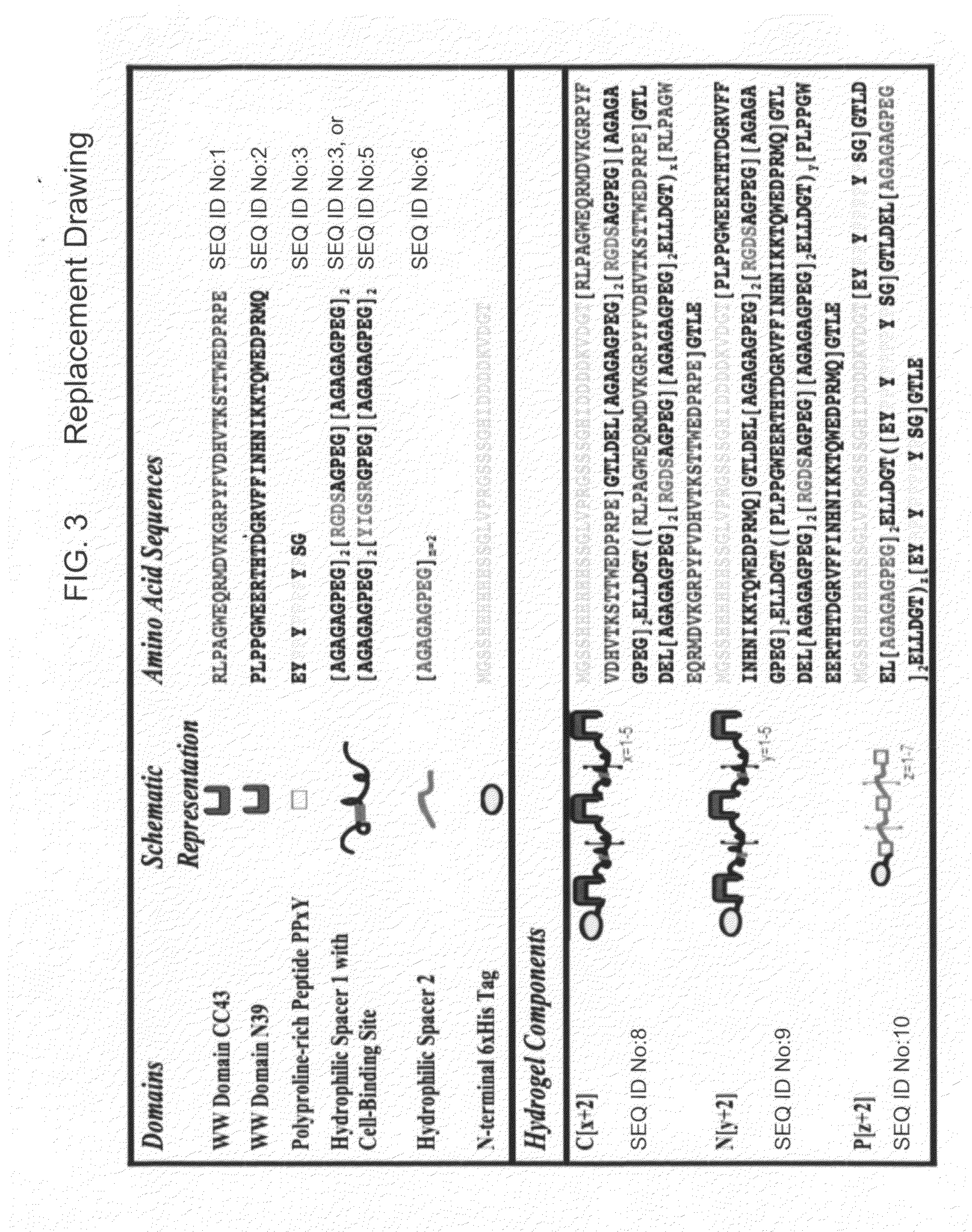
Hetero-assembled hydrogels
A two-component, molecular-recognition gelation strategy that enables cell encapsulation without the need for environmental triggers is provided. The two components, which in one example contain WW and polyproline-rich peptide domains that interact via hydrogen bonds, undergo a sol-gel phase transition upon simple mixing. Hence, physical gelation is induced by the mixing of two components at constant environmental conditions, analogous to the formation of chemically crosslinked epoxies by the mixing of two components. Variations in the molecular-level design of the two components are used to predictably tune the association energy and hydrogel viscoelasticity. These hetero-assembly physical hydrogels encapsulate neural progenitor cells at constant physiological conditions within 10 seconds to create uniform 3D cell suspensions that continue to proliferate, differentiate, and adopt well-spread morphologies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Sealing cell and method for encapsulating a microelectronic component with such a sealing cell
ActiveUS20180309097A1Components is relatively effectiveEfficient packagingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPeripheral zone
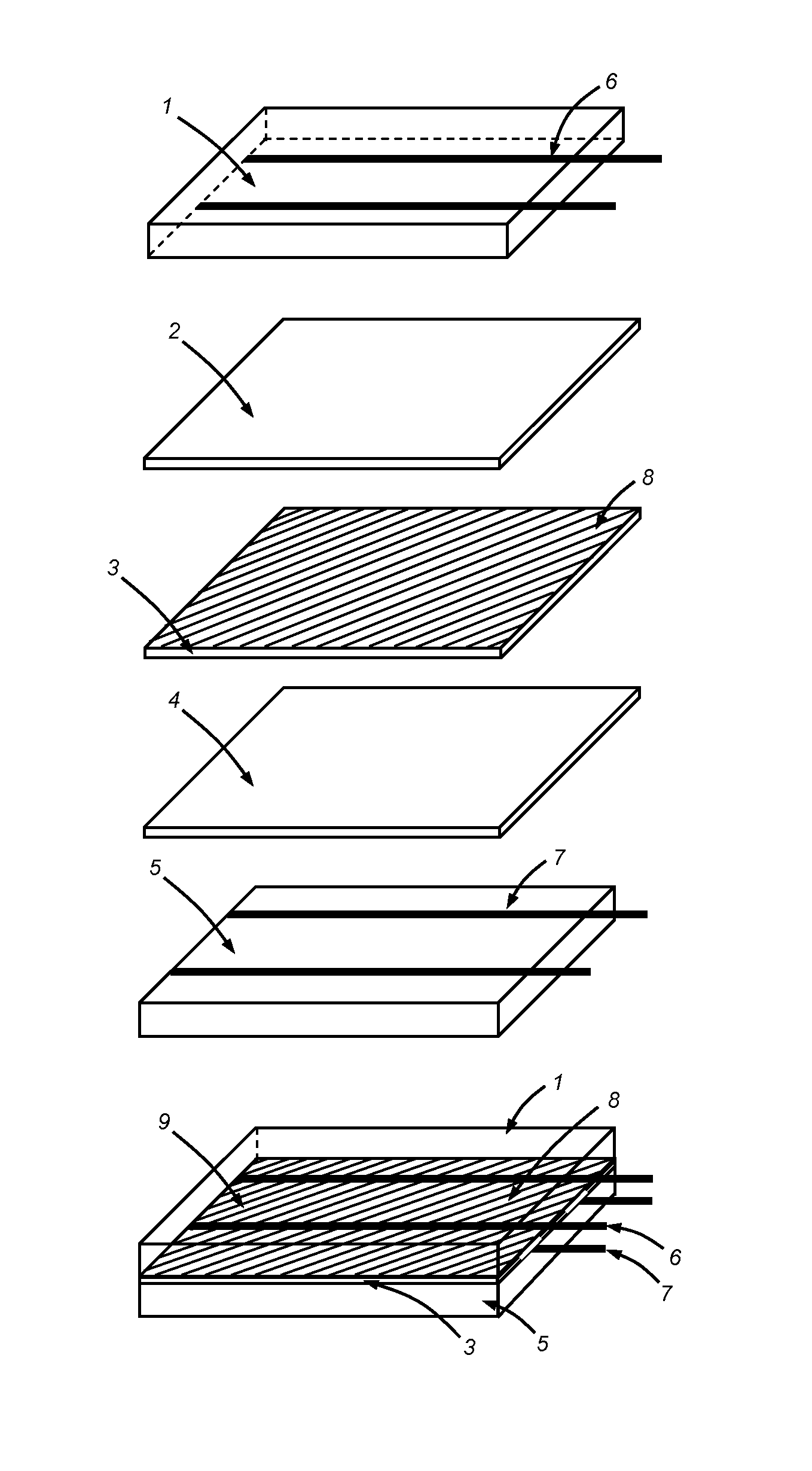
Sealing cell for encapsulating a microelectronic component arranged on a substrate, with a cap, said sealing cell including: a bottom including a receiving zone for the substrate and a peripheral zone surrounding the receiving zone, a side wall formed of an internal face, an external face and an upper face, the upper face being configured to support the cap facing the receiving zone, an opening, arranged in the bottom of the cell, in the side wall, or in the cap, the opening being configured to be connected to a pumping system, in such a way as to be able to place under controlled atmosphere a cavity delimited by the side wall, the bottom and the cap.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
High-speed on demand droplet generation and single cell encapsulation driven by induced cavitation
ActiveCN104321652AMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsTransient stateChemical physics
Methods and devices for the formation of droplets of a first fluid in a second fluid and the encapsulation of particles or cells within such droplets are disclosed. Impetus for droplet formation is provided by the creation of a transient bubble, which may be induced using a pulsed laser. Droplet volume and the frequency at which droplets are formed can be controlled by modulation of the pulsed laser. The disclosed methods and devices are particularly suitable for use in microfluidic devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multilayered polyelectrolyte-based capsules for cell encapsulation and delivery of therapeutic compositions
The present invention provides novel, biocompatible matrices for cell encapsulation and transplantation. If further provides methods for delivering agents to encapsulate cells and to the local environment of a host system. The invention also provides methods for targeting and manipulating particular cells and / or proteins of the host system. In a composition aspect of the invention, a composition including a collection of capsules is provided. The capsules comprise an inner core, and the inner core is covered by an outer shell composed of a positive polyelectrolyte and a negative polyelectrolyte. The inner core of the capsules contains at least one cell.
Owner:STEEL JOHN
Method for encapsulation of cellular material using a charged initiator polymer
ActiveUS7585499B2Promote aggregationImprove solubilityBiocidePreparing sample for investigationMacromonomerCellular material
Positively-charged initiator polymers having a polymerization initiator group and a cationic portion are provided. The initiator polymers can be used with a polymerizable material for the formation of a polymeric matrix on a surface. The initiator polymers are particularly useful for cell encapsulation using macromers.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Single-cell encapsulation and flexible-format module architecture and mounting assembly for photovoltaic power generation and method for constructing, inspecting and qualifying the same
InactiveUS20180138338A1Overcome disadvantagesPreparation automationPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesEngineeringElectric properties
A method for encapsulating photovoltaic cells into single functional units is described. These units share the mechanical and electric properties of the encapsulation layers and allow for flexible module architecture to be implemented at the cell level. This enables cost reduction and improved performance of photovoltaic power generation.
Owner:TESSOLAR
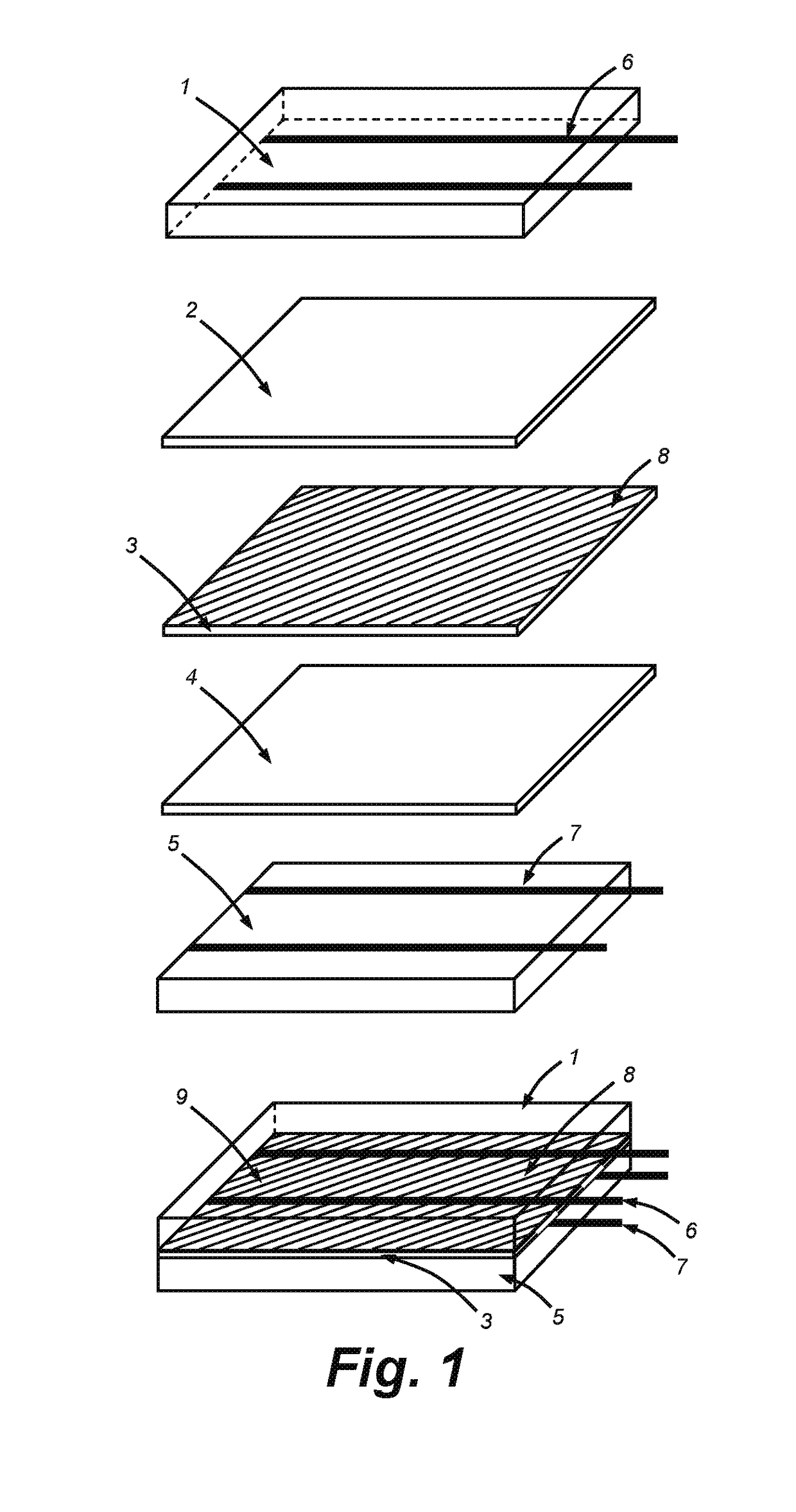
Thin film cell encapsulation devices
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Photoresponsive protein hydrogels and methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190345227A1Cell dissociation methodsConnective tissue peptidesCell encapsulationLight sensitive
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lithium battery cell encapsulation aluminum shell feeding device
InactiveCN108539245AEasy loadingIntelligent productionConveyorsAssembling battery machinesNew energyBiochemical engineering
The invention relates to the field of new energy source lithium battery production, in particular to a square lithium battery cell encapsulation aluminum shell device. The square lithium battery cellencapsulation aluminum shell device comprises a machine frame assembly, a second work table, an aluminum shell feeding device and an aluminum shell carrying device, wherein the second work table is fixedly arranged on the machine frame assembly; a work procedure for completing the battery cell and aluminum shell compression is completed in the second work table; the aluminum shell feeding device is fixedly arranged on the machine frame assembly, is arranged beside the second work table and is used for conveying an aluminum shell to be processed; the aluminum shell carrying device is fixedly arranged on the second work table and can leftwards and rightwards move; the aluminum shell on the aluminum shell feeding device is carried on the second work table for processing. The square lithium battery cell encapsulation aluminum shell device has the advantages that the operation of charging a battery cell into the aluminum shell is completed; the automation level is improved; the square lithium battery production is more intelligentized.
Owner:吴崇清
High-efficiency encapsulation in droplets based on hydrodynamic vortices control
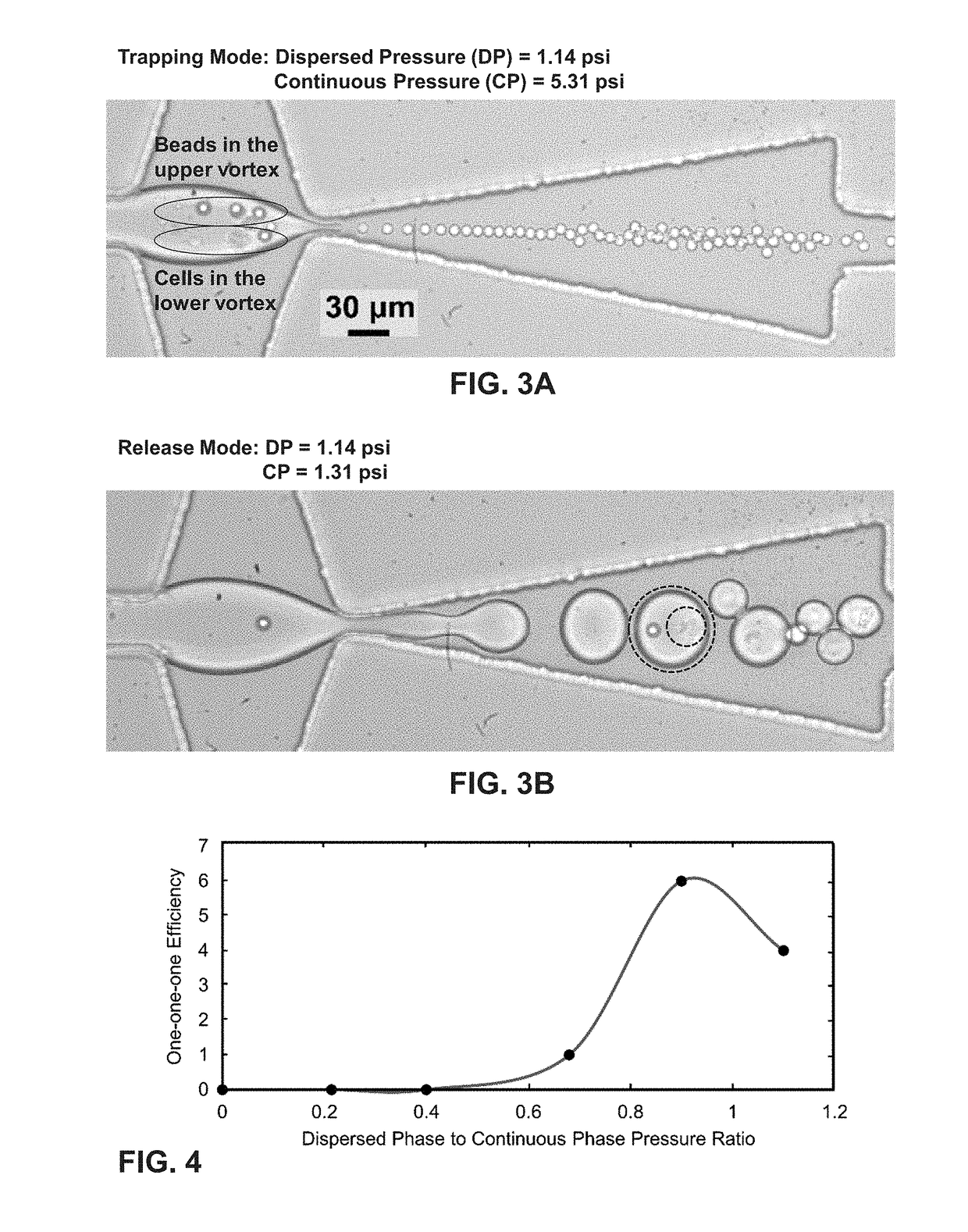
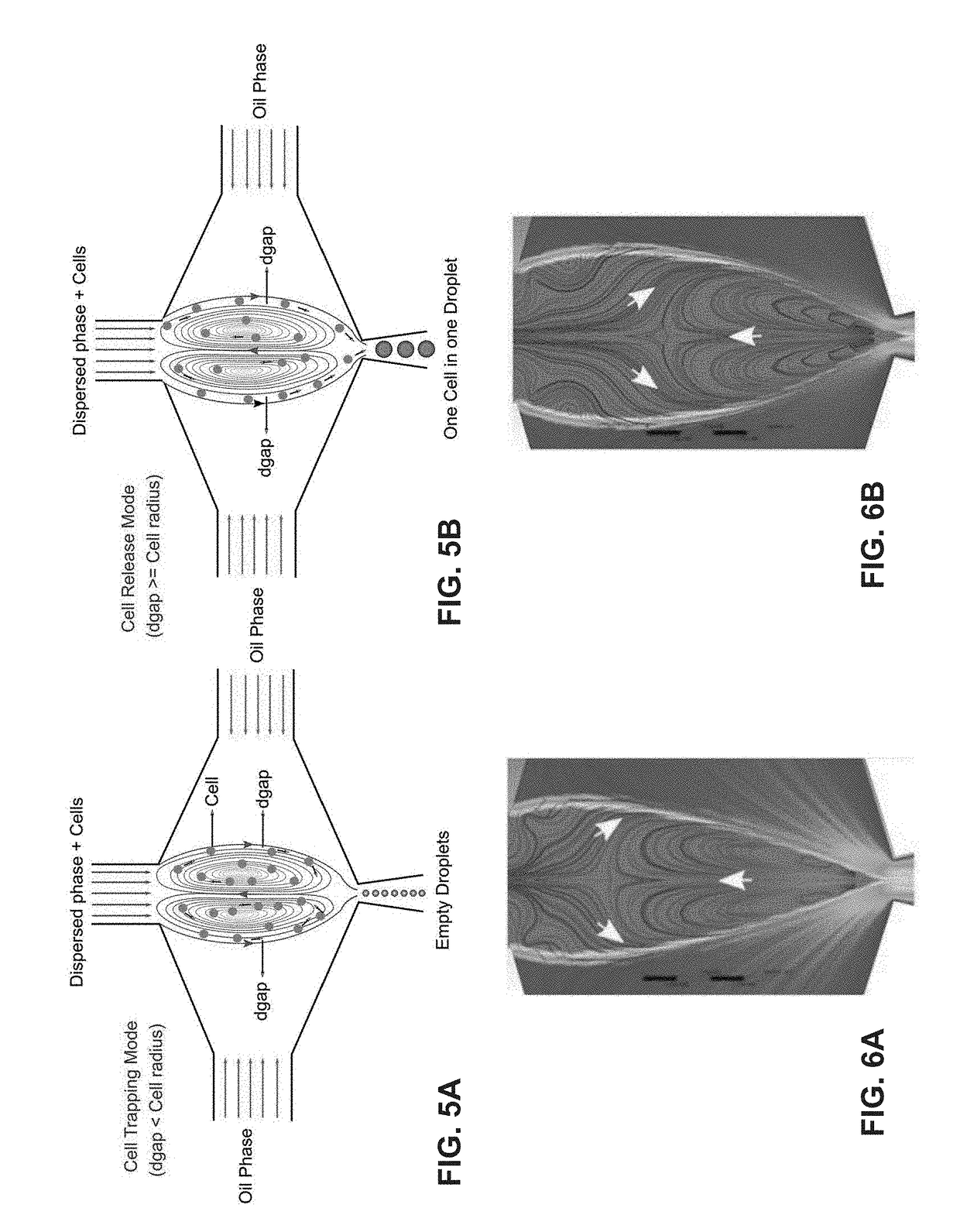
ActiveUS20180353963A1Maximum encapsulation efficiencyImprove efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresGenomicsTrapping
An interfacial technique utilizes hydrodynamic micro-vortices to perform (i) high efficiency single cell encapsulation and (ii) size-selective capturing of cells based on their sizes in a single microfluidic device. A notable feature of this technique is that it can perform high efficiency single cell encapsulation at low cell concentrations, and this technique is all passive, controlled only by the flow rates of the two phases and does not require complex structures or on-chip active devices. Single bead / cell encapsulation was demonstrated at 50% efficiency, which is at least 10 times greater than the random encapsulations at the introduced cell concentrations. Also demonstrated is the selective trapping of cells based on their sizes. This present technique expands the capabilities of droplet microfluidics for applications ranging from single cell genomics, proteomic assays to sample preparation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Ejector pin structure of laminating machine
InactiveCN105206712AGuaranteed degree of cross-linkingConsistent degree of crosslinkingFinal product manufactureLaminationEngineeringSolar battery
The invention relates to the technical field of solar battery cell encapsulation, particularly to an ejector pin structure of a laminating machine. The laminating machine comprises a heating plate, wherein a guide hole is formed in the heating plate; the upper surface of the heating plate is a plane. The ejector pin structure comprises an ejector pin body matched with the guide hole and a platform covering the top of the ejector pin body, wherein the upper surface the platform is a plane; the ejector pin body is inserted in the guide hole; a sunken part matched with the platform is arranged at the part, right below the platform, of the heating plate; when the lower surface of the platform is in contact with the bottom surface of the sunken part, the upper surface of the platform and the upper surface of the heating plate are level. According to the ejector pin structure of the laminating machine provided by the invention, the materials of the ejector pin body, the platform and the heating plate are the same, so that consistency of heat transfer among the ejector pin part and other parts of the heating plate is guaranteed when the heating plate is heated; the platform is added at the top of the ejector pin body, so that pieces to be subjected to lamination are uniformly heated when the laminating machine is heated, consistency of EVA crosslinking degree in the pieces to be subjected to lamination is guaranteed, and the properties of a solar component are guaranteed.
Owner:EGING PHOTOVOLTAIC TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Hetero-assembled hydrogels
A two-component, molecular-recognition gelation strategy that enables cell encapsulation without the need for environmental triggers is provided. The two components, which in one example contain WW and polyproline-rich peptide domains that interact via hydrogen bonds, undergo a sol-gel phase transition upon simple mixing. Hence, physical gelation is induced by the mixing of two components at constant environmental conditions, analogous to the formation of chemically crosslinked epoxies by the mixing of two components. Variations in the molecular-level design of the two components are used to predictably tune the association energy and hydrogel viscoelasticity. These hetero-assembly physical hydrogels encapsulate neural progenitor cells at constant physiological conditions within 10 seconds to create uniform 3D cell suspensions that continue to proliferate, differentiate, and adopt well-spread morphologies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com