Patents
Literature
47 results about "Crystal anisotropy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Anisotropic crystals are used for many optical applications, such as polarizers, optical waveplates, wedges etc. Wood and composites are the common examples of anisotropic materials. In plant cells, the interior part or cytoplasm is considered as anisotropic due to the presence of intracellular organelles.
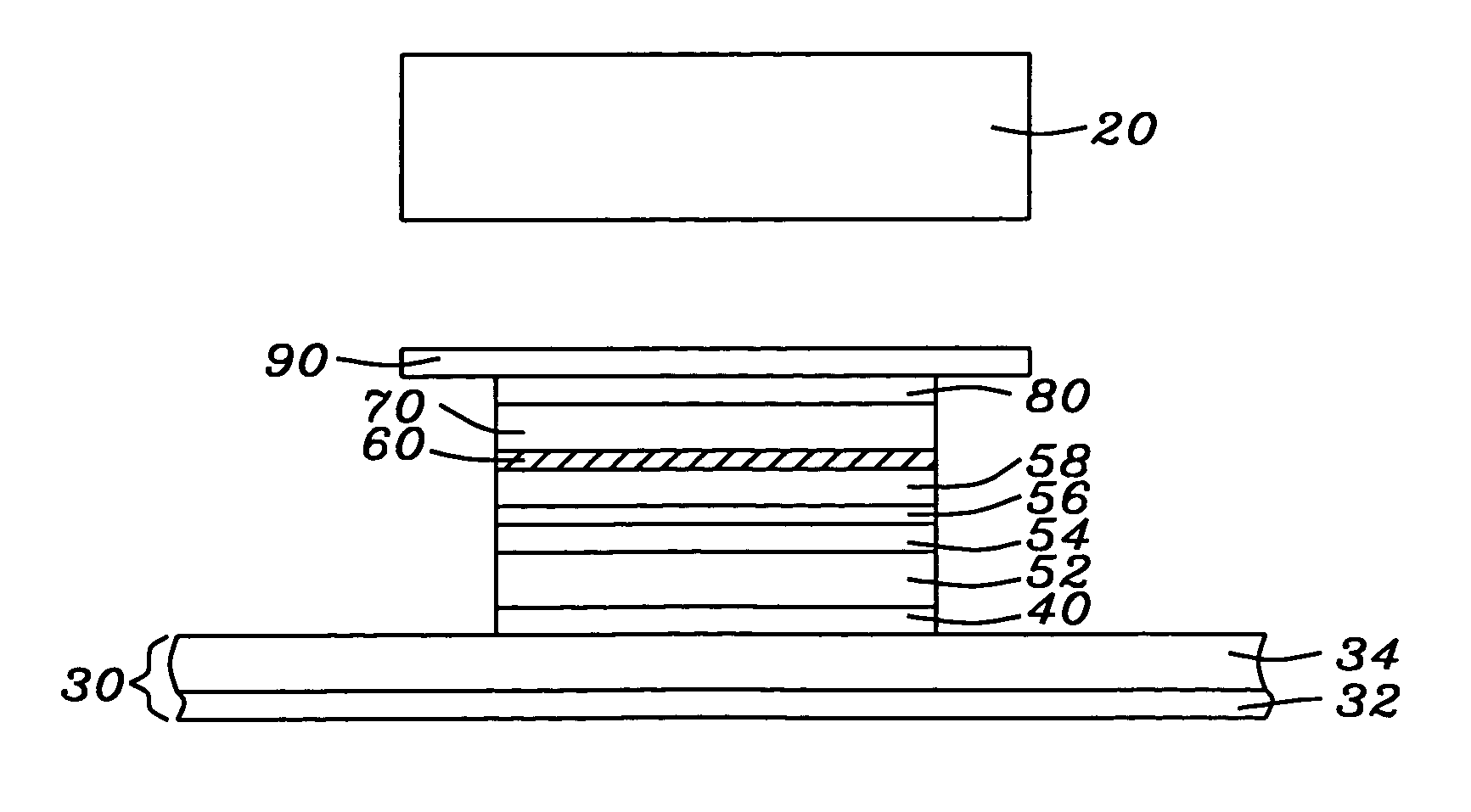
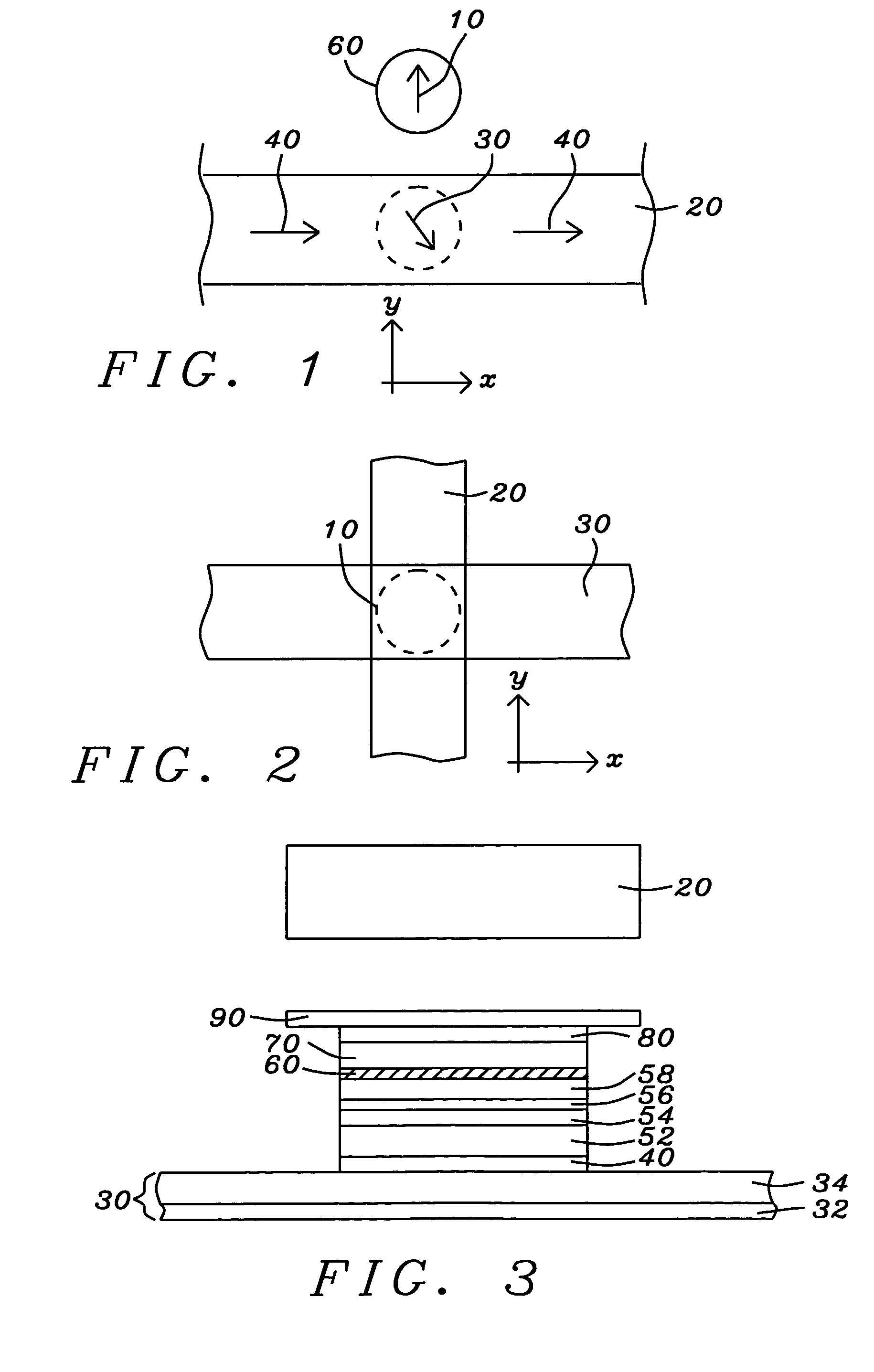
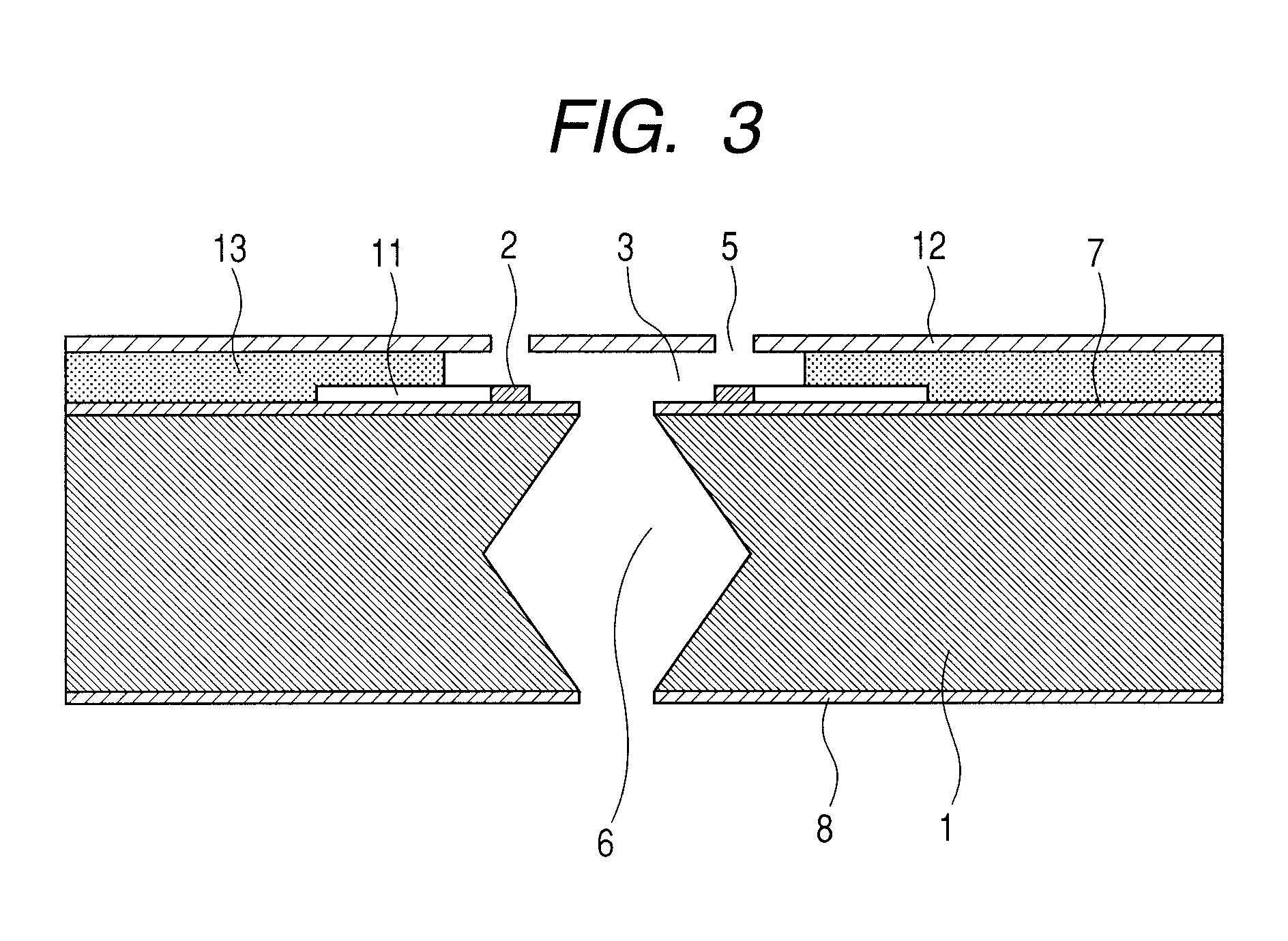
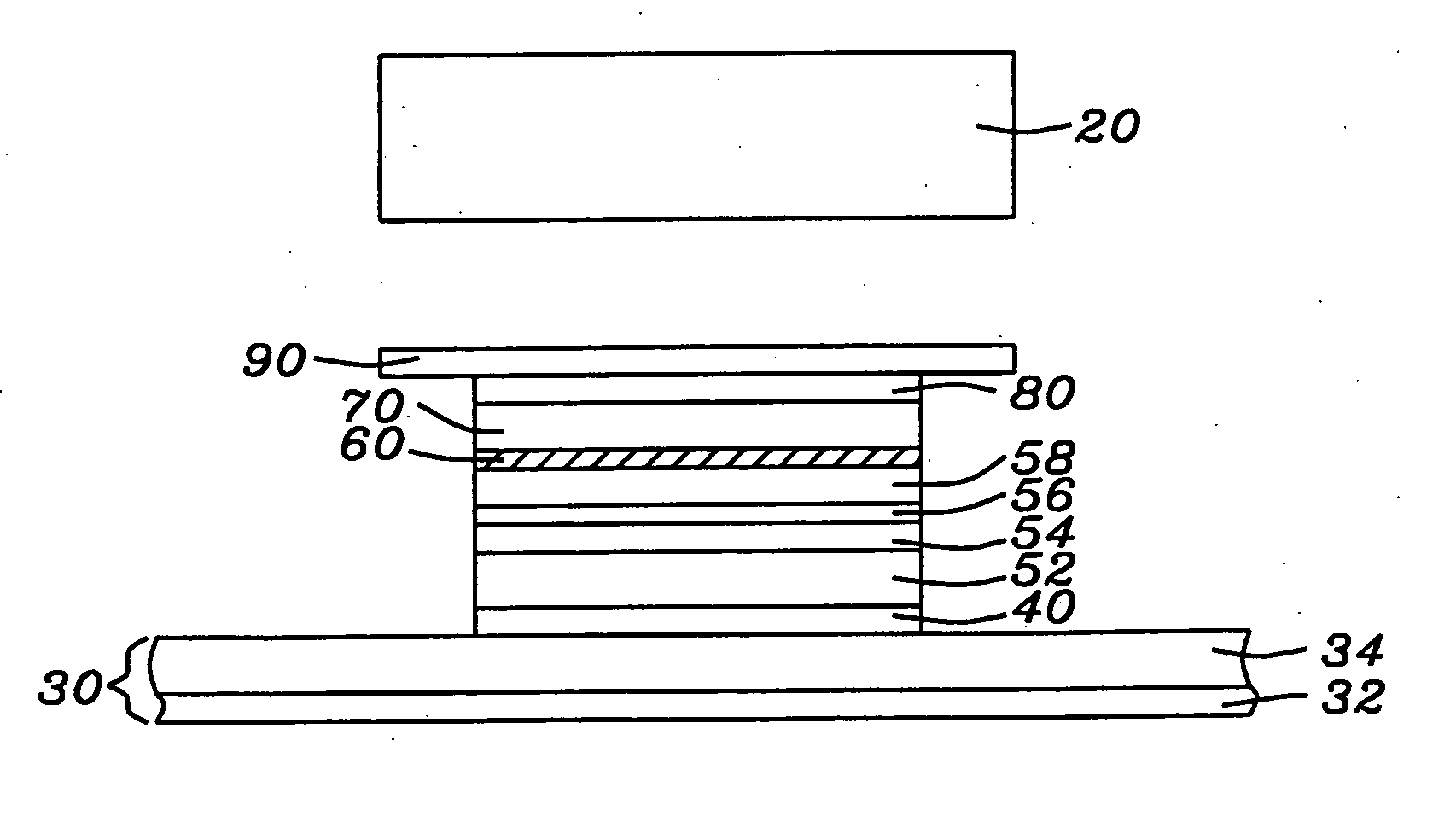
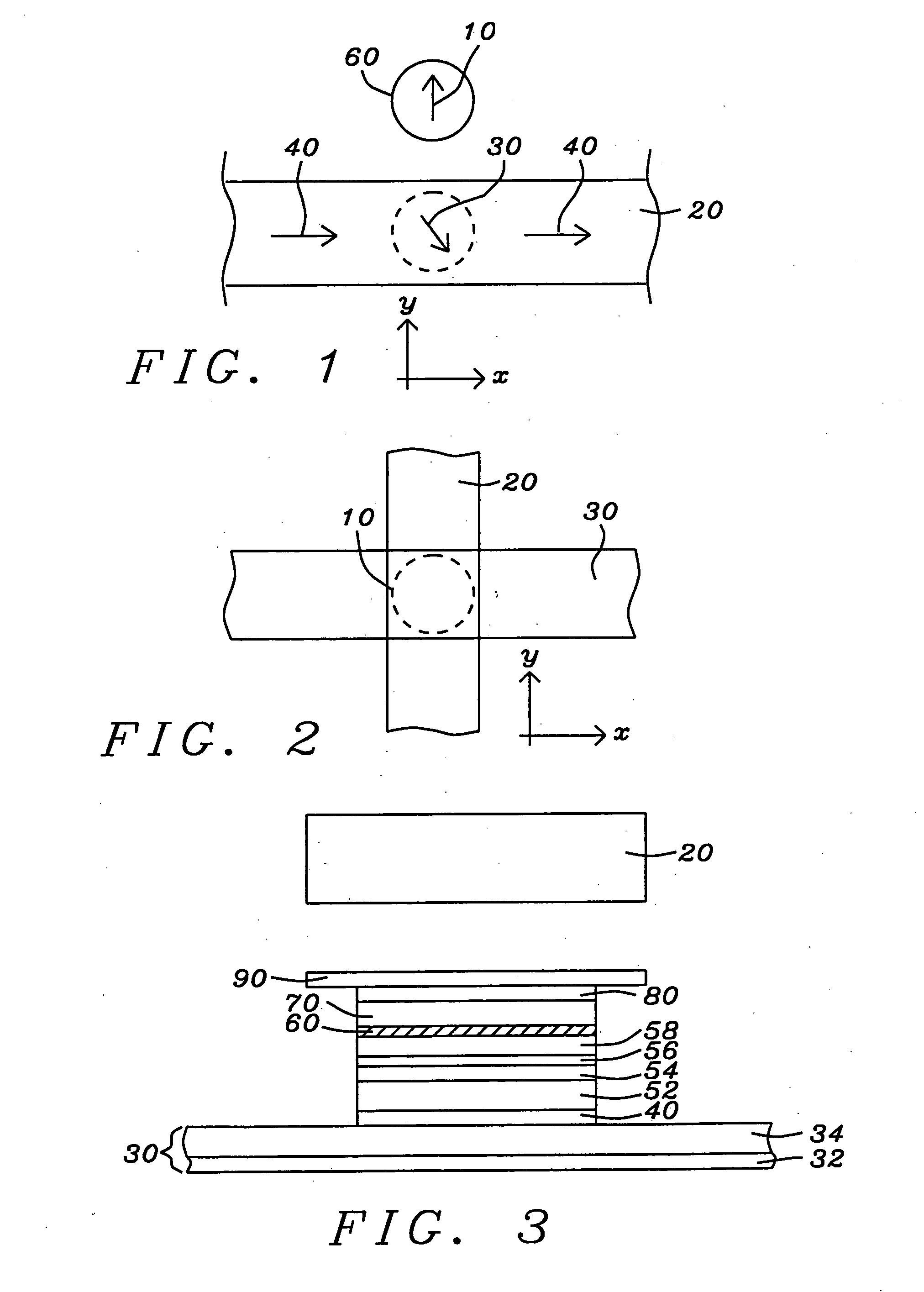
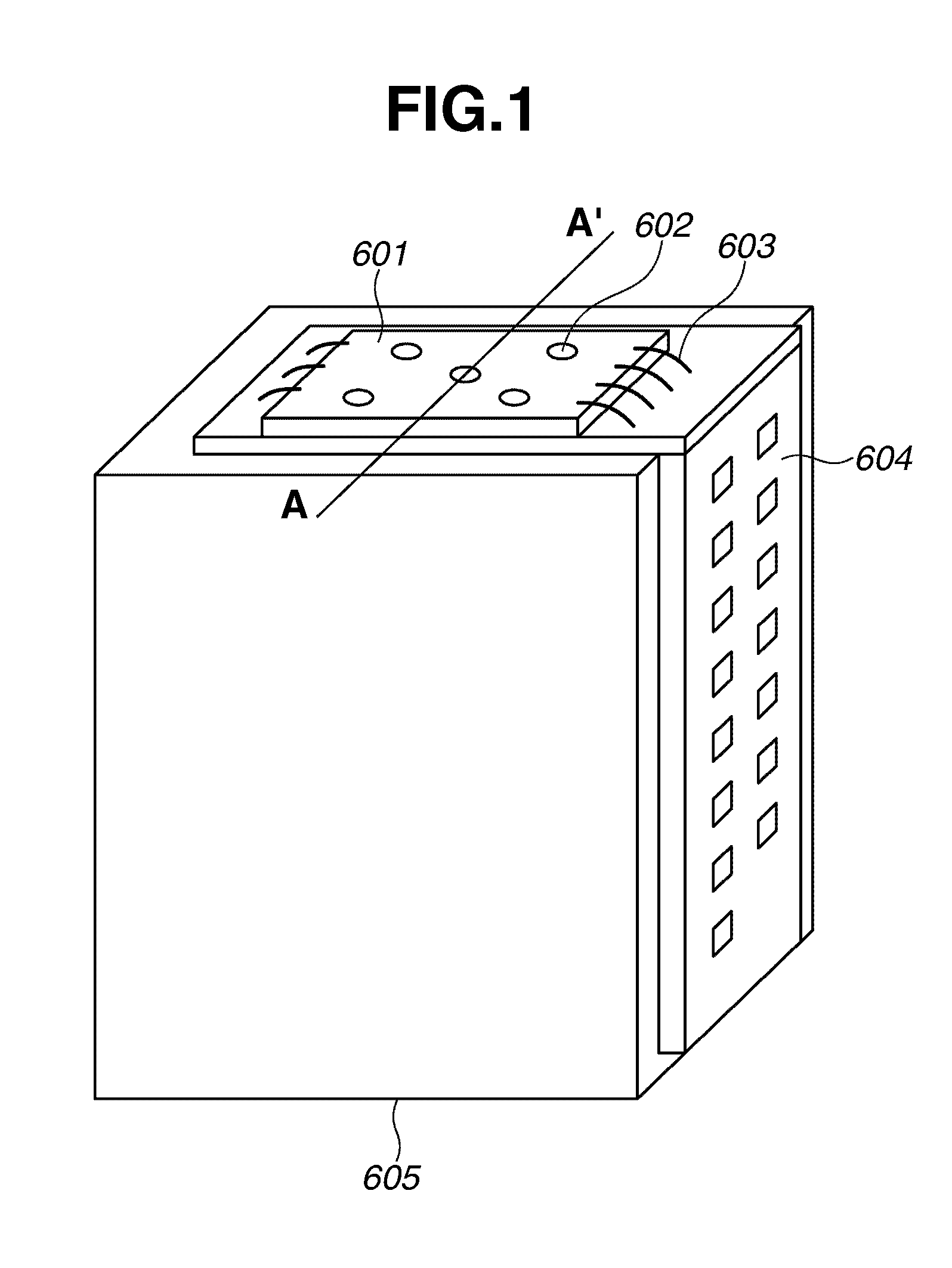
Magnetic random access memory array with coupled soft adjacent magnetic layer
InactiveUS6979586B2Data efficientReduce adverse effectsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryBit lineStatic random-access memory
An MTJ element is formed between orthogonal word and bit lines. The bit line is a composite line which includes a high conductivity layer and a soft magnetic layer under the high conductivity layer. During operation, the soft magnetic layer concentrates the magnetic field of the current and, due to its proximity to the free layer, it magnetically couples with the free layer in the MTJ. This coupling provides thermal stability to the free layer magnetization and ease of switching and the coupling may be further enhanced by inducing a shape or crystalline anisotropy into the free layer during formation.
Owner:APPLIED SPINTRONICS +1
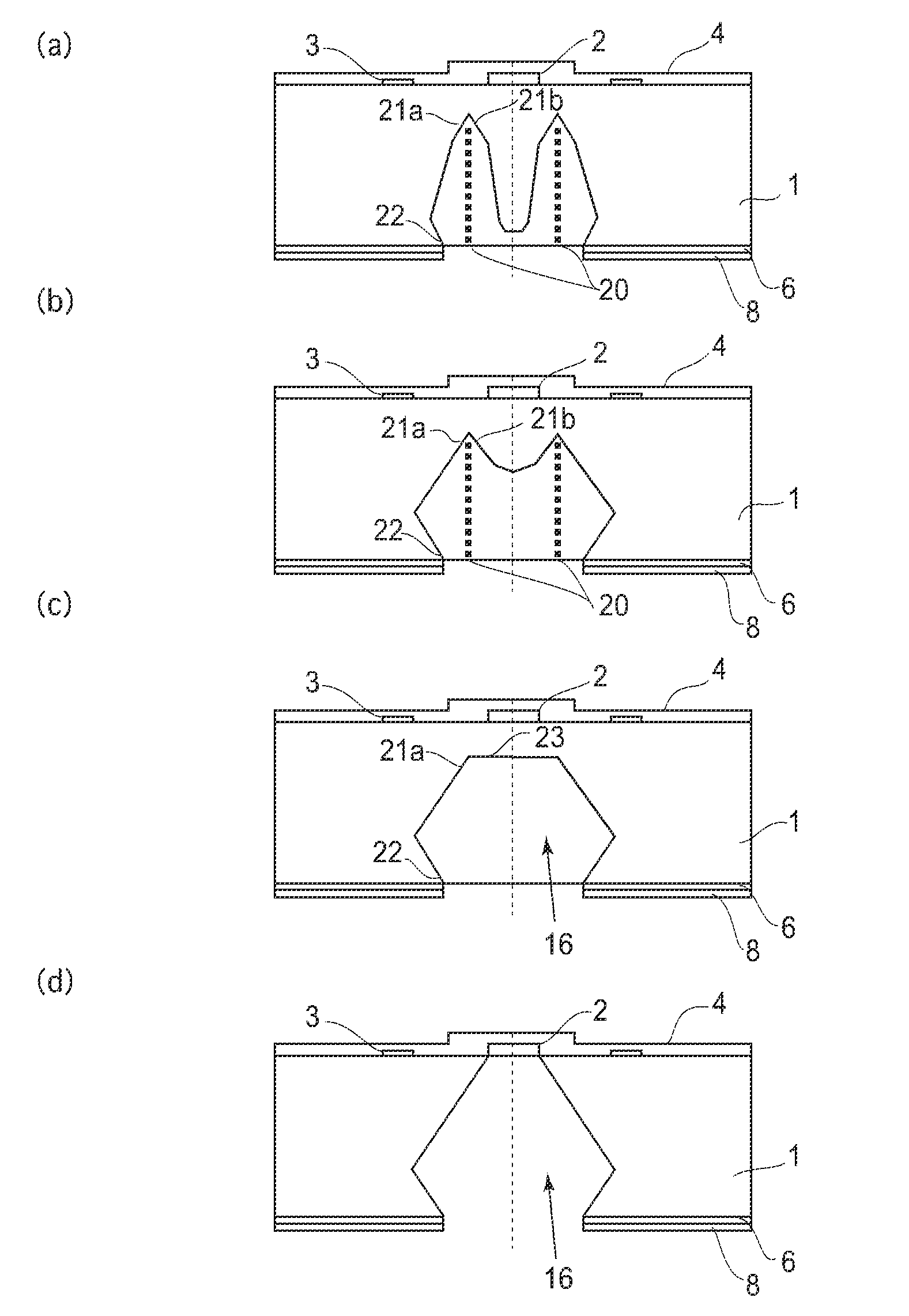
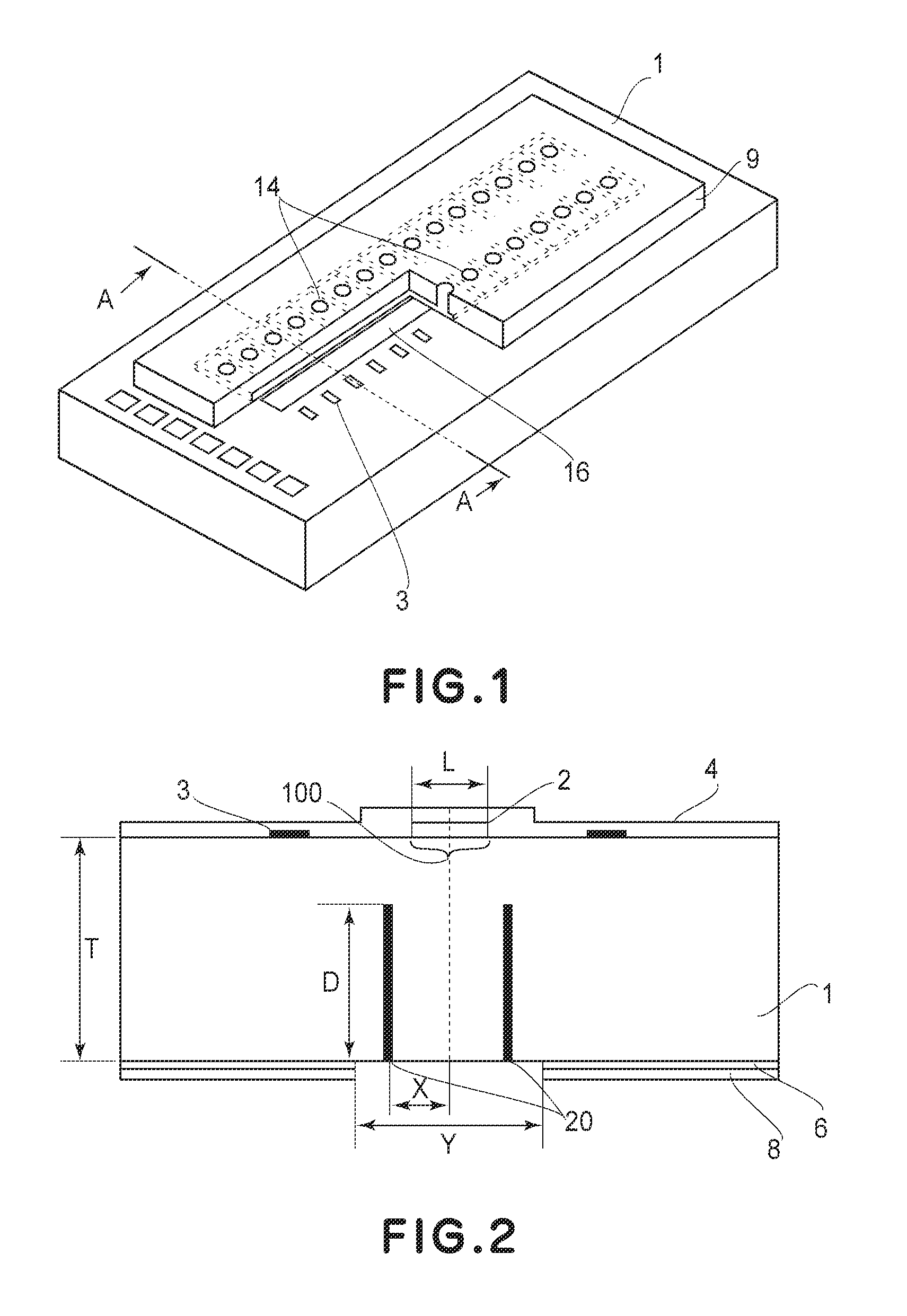
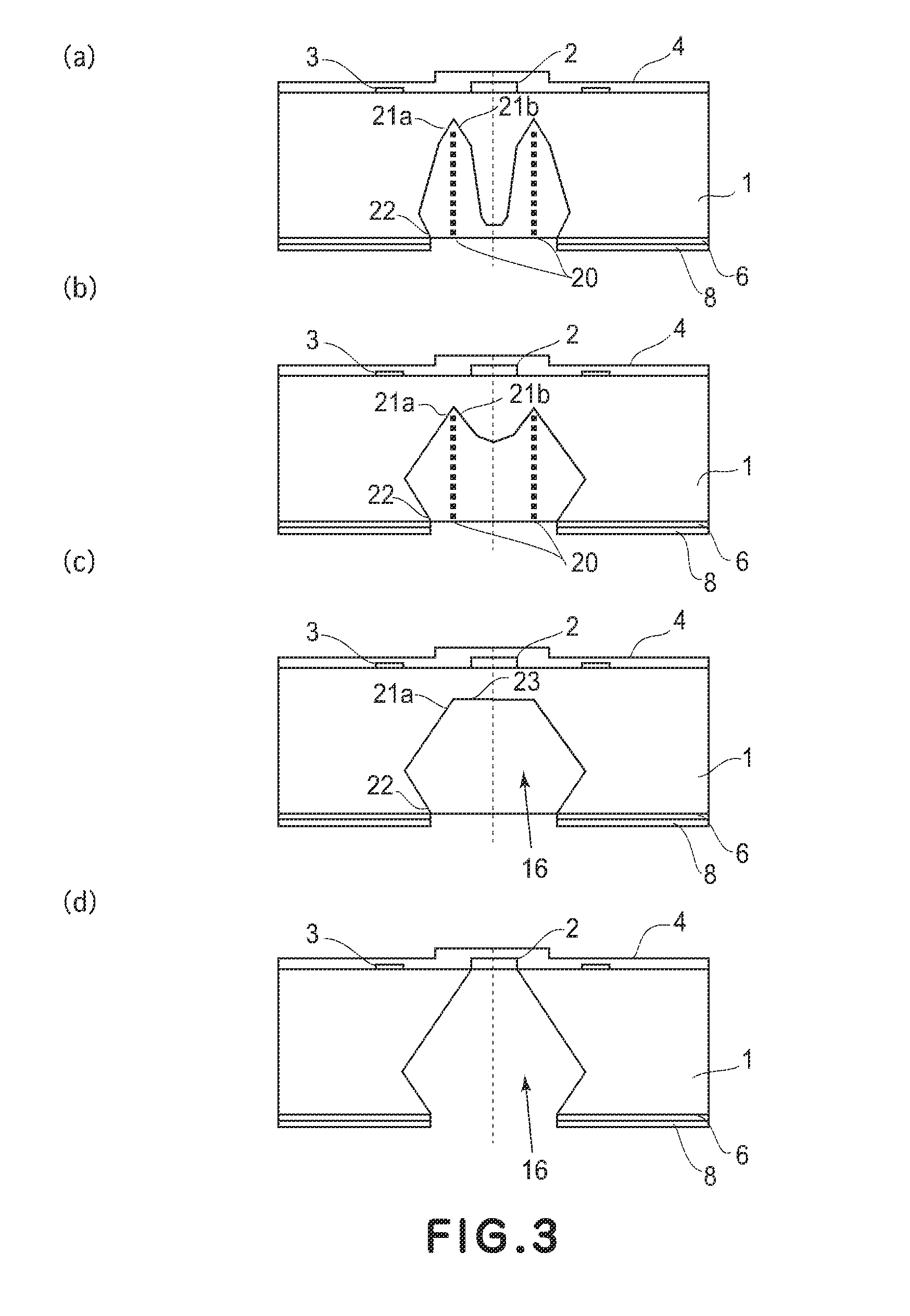
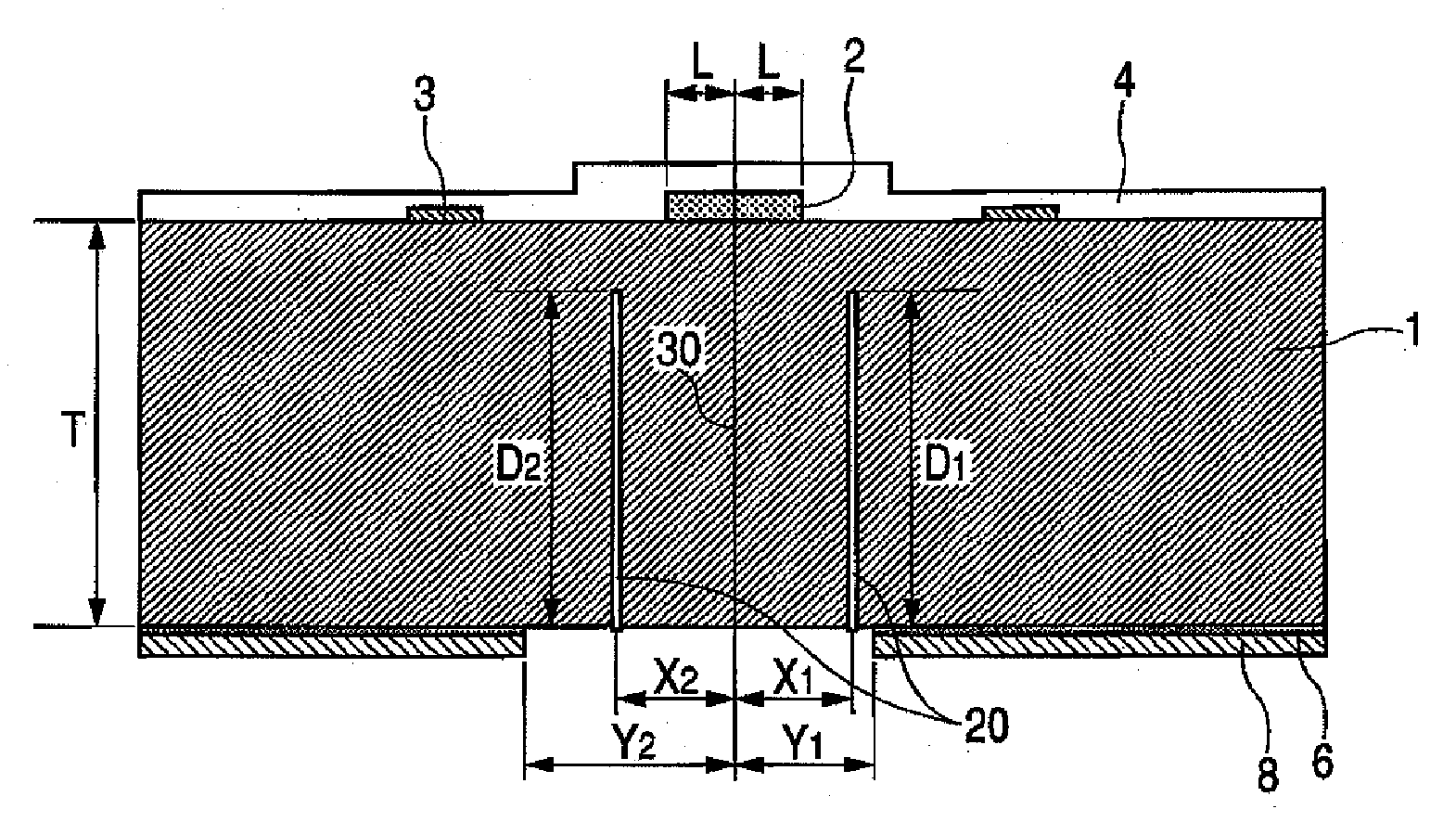
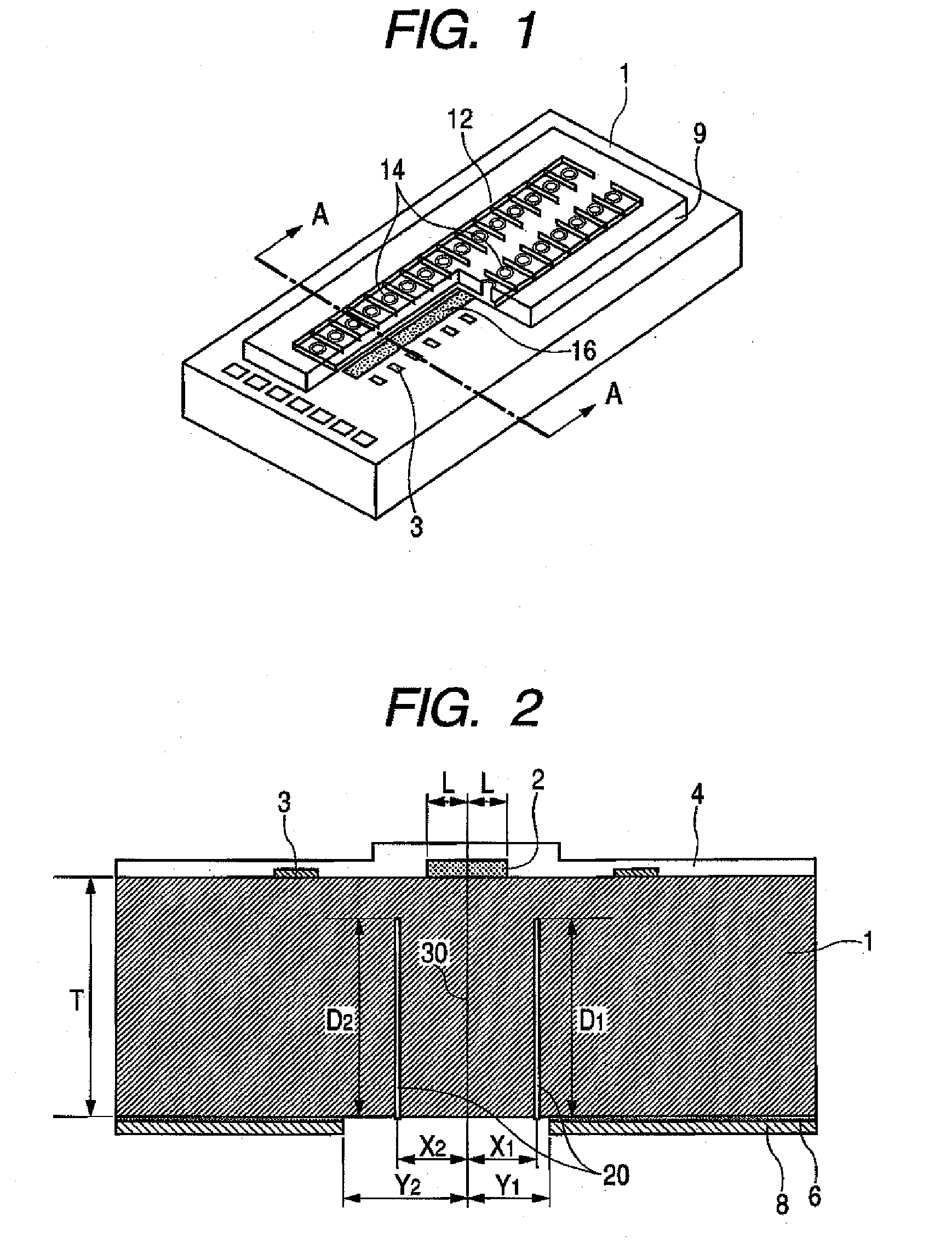
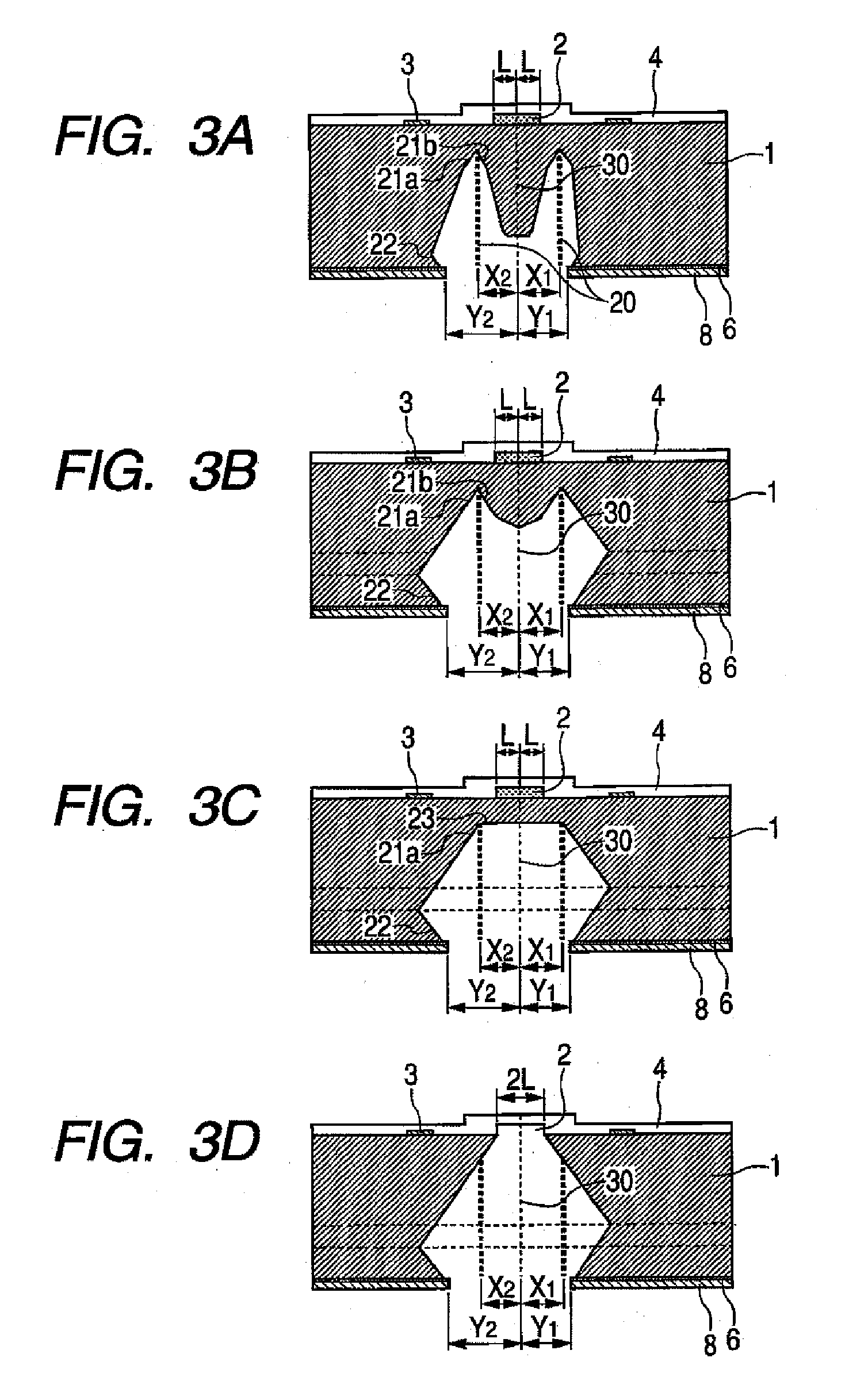
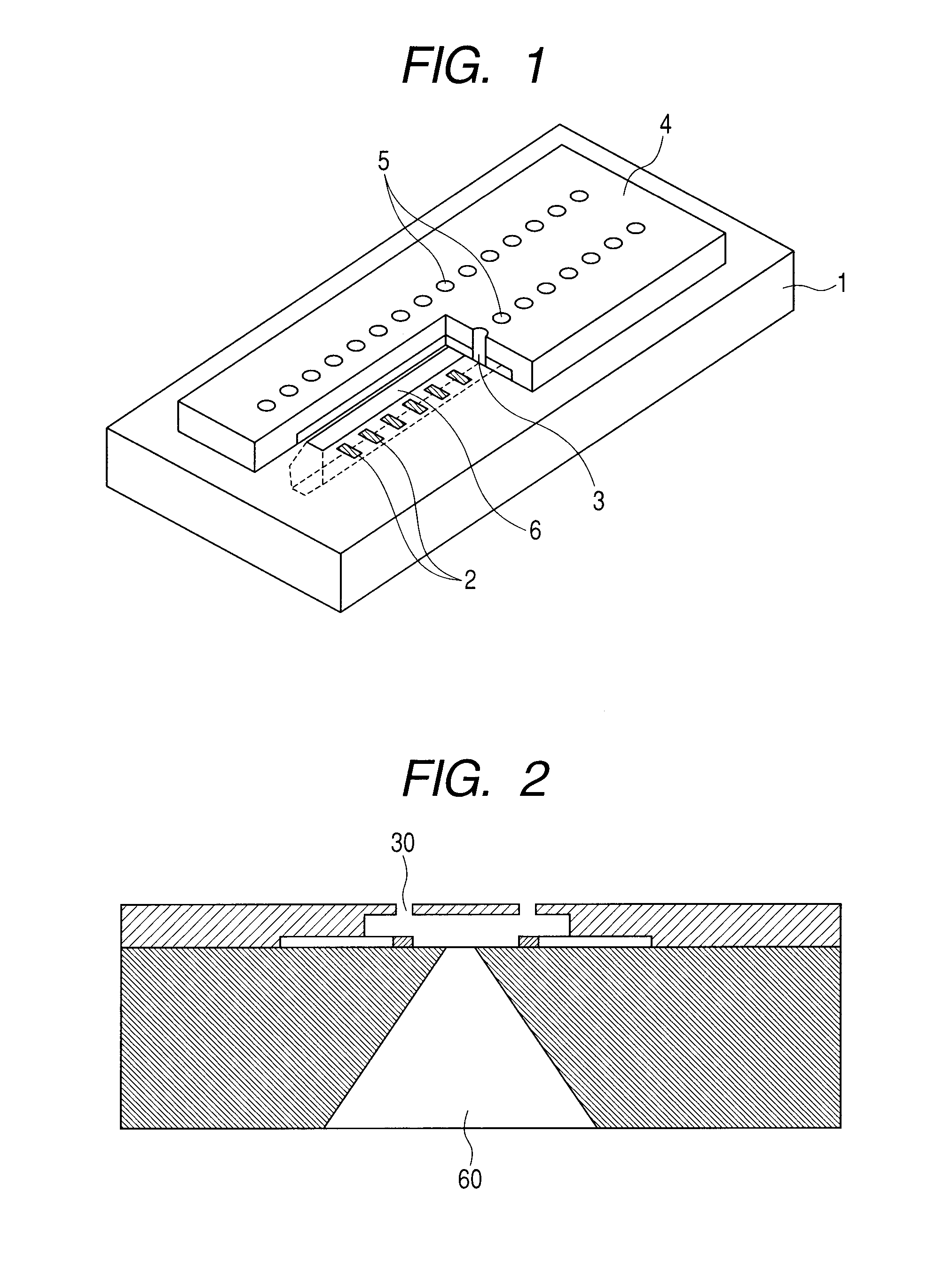
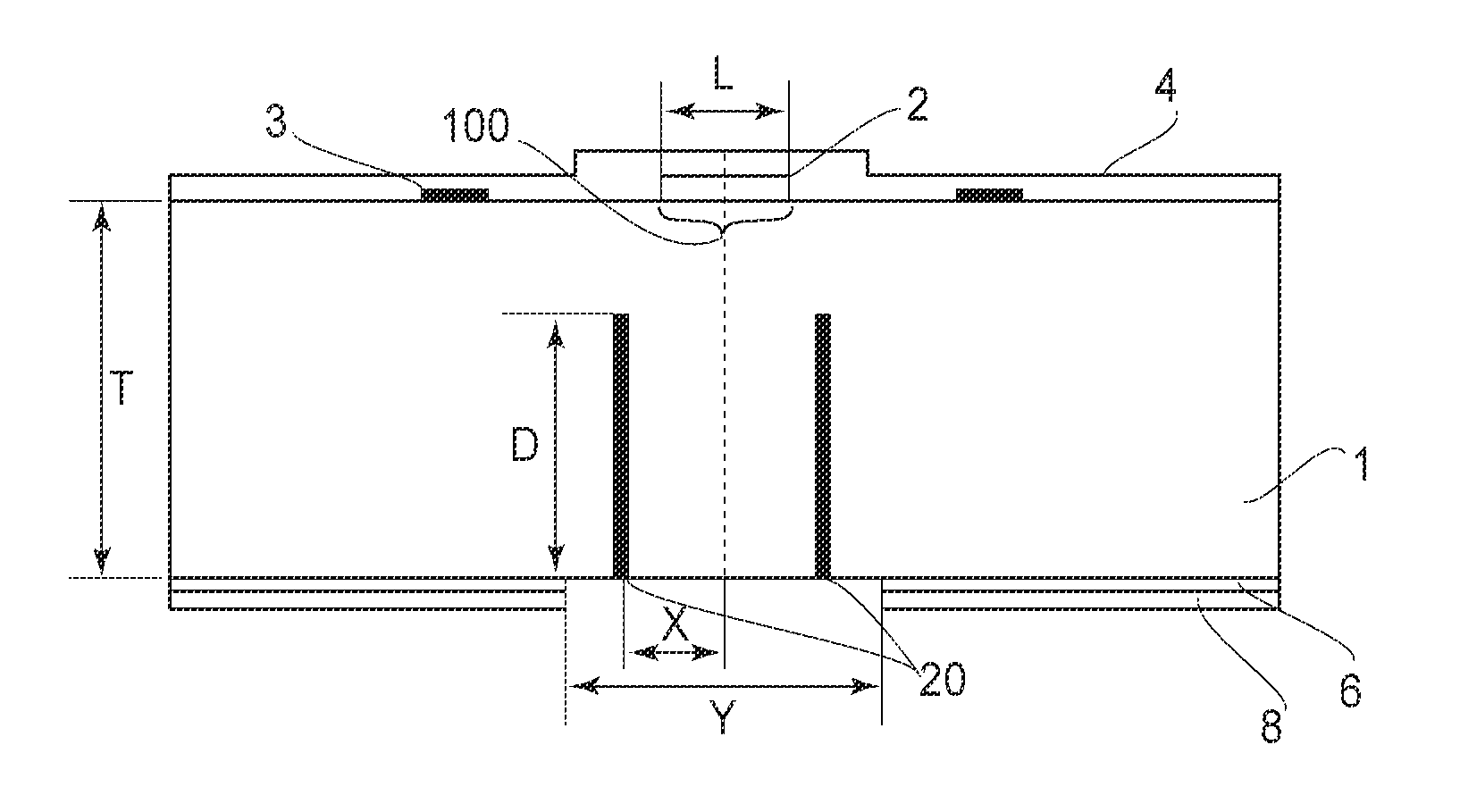
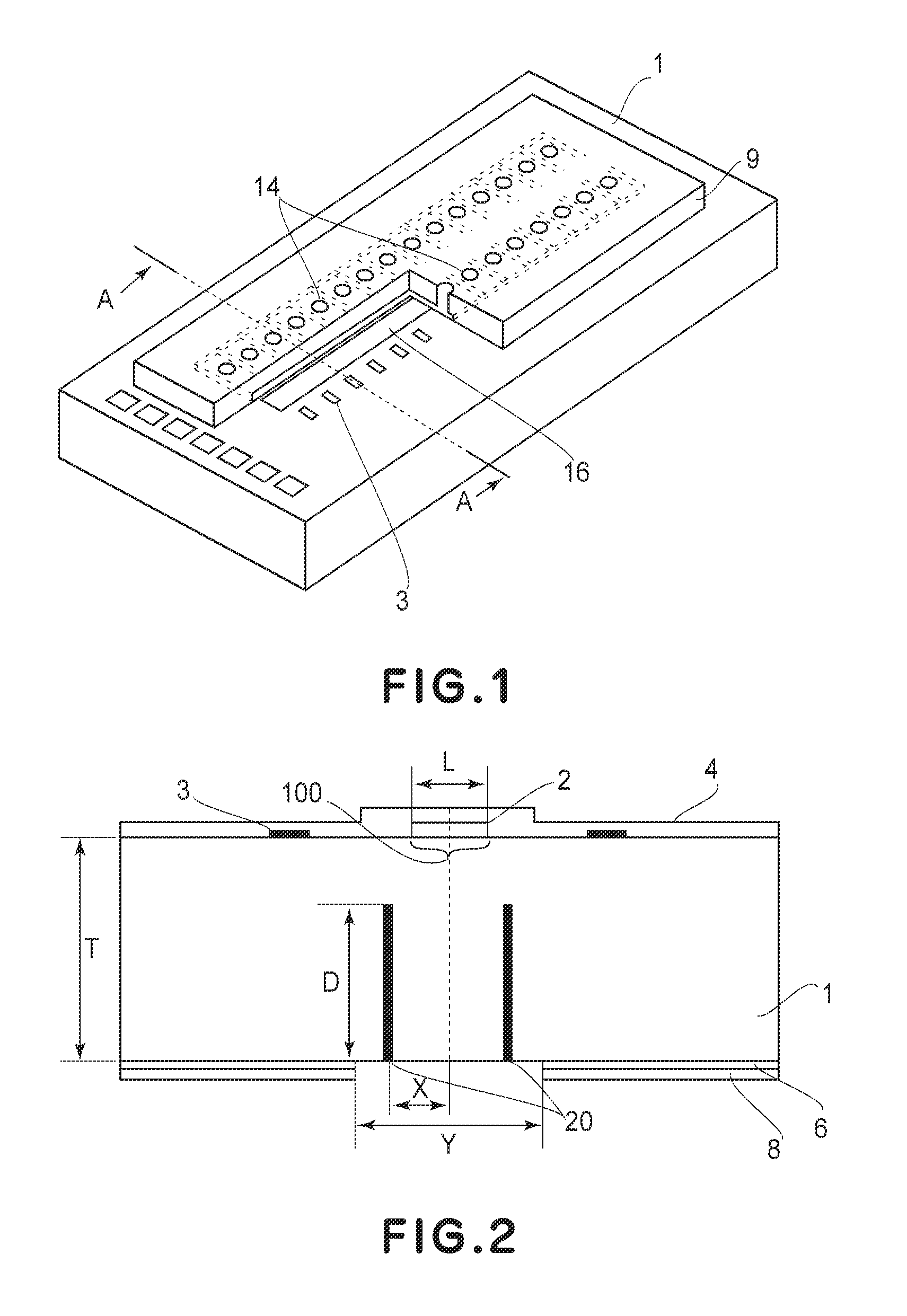
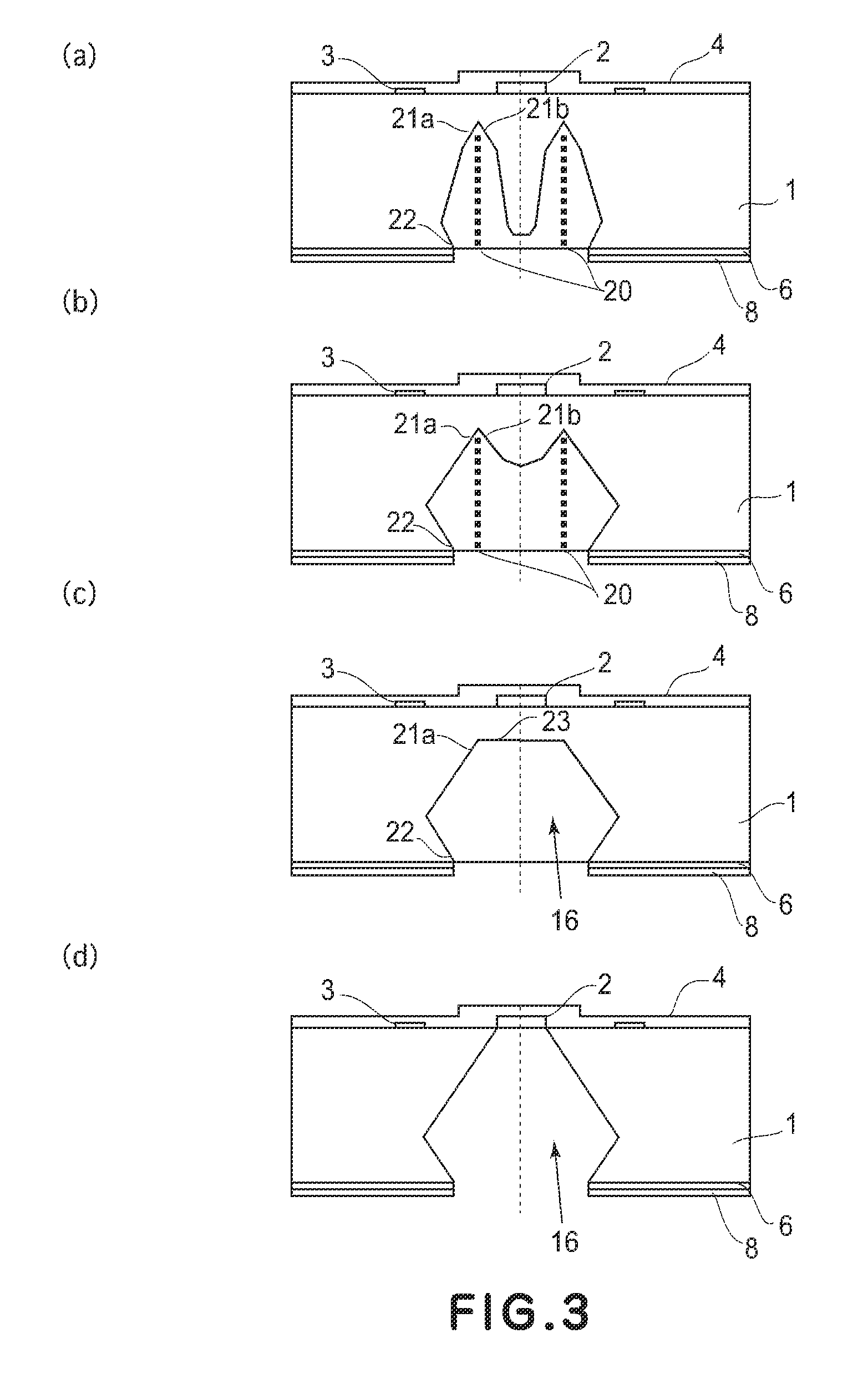
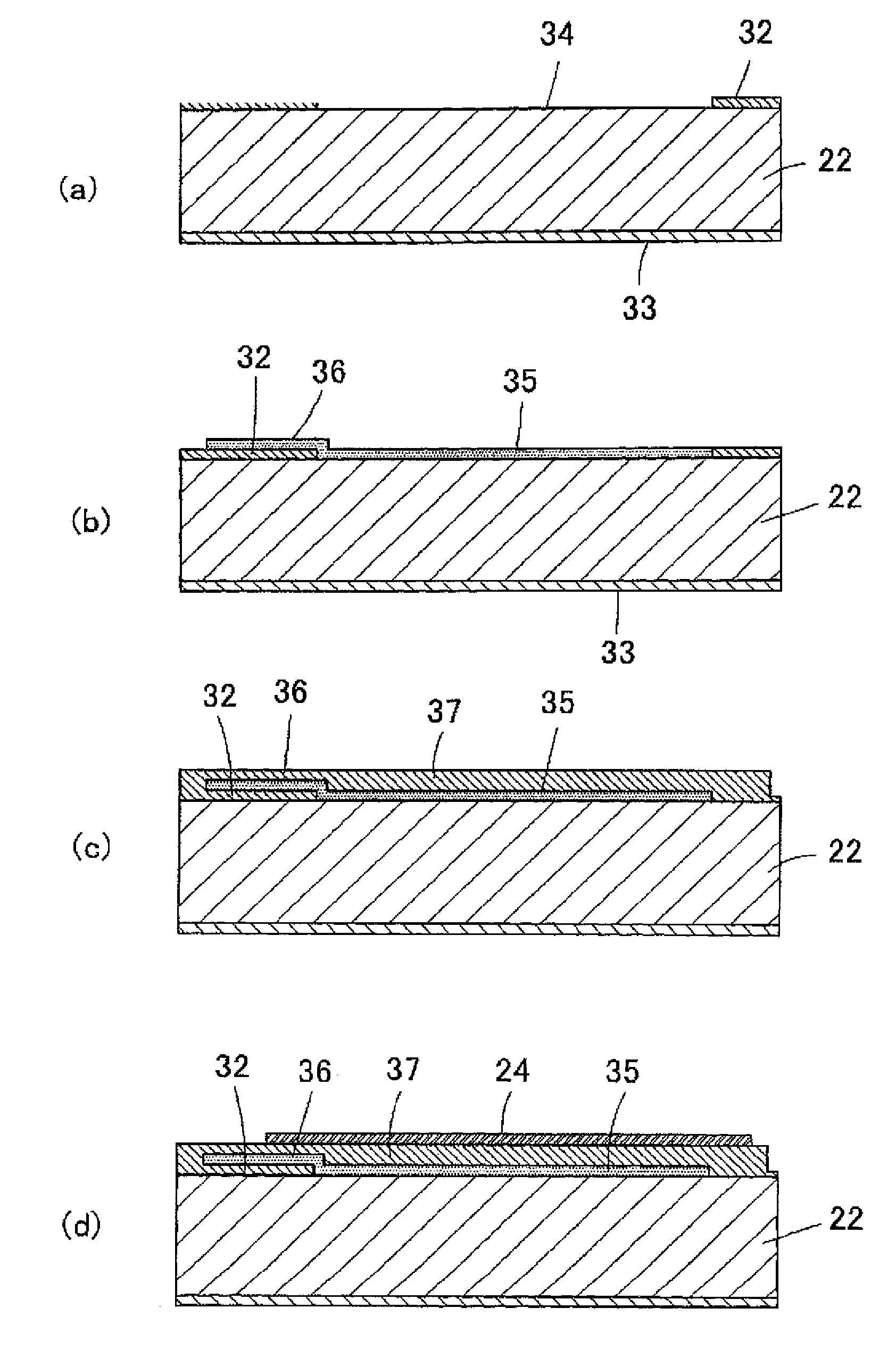
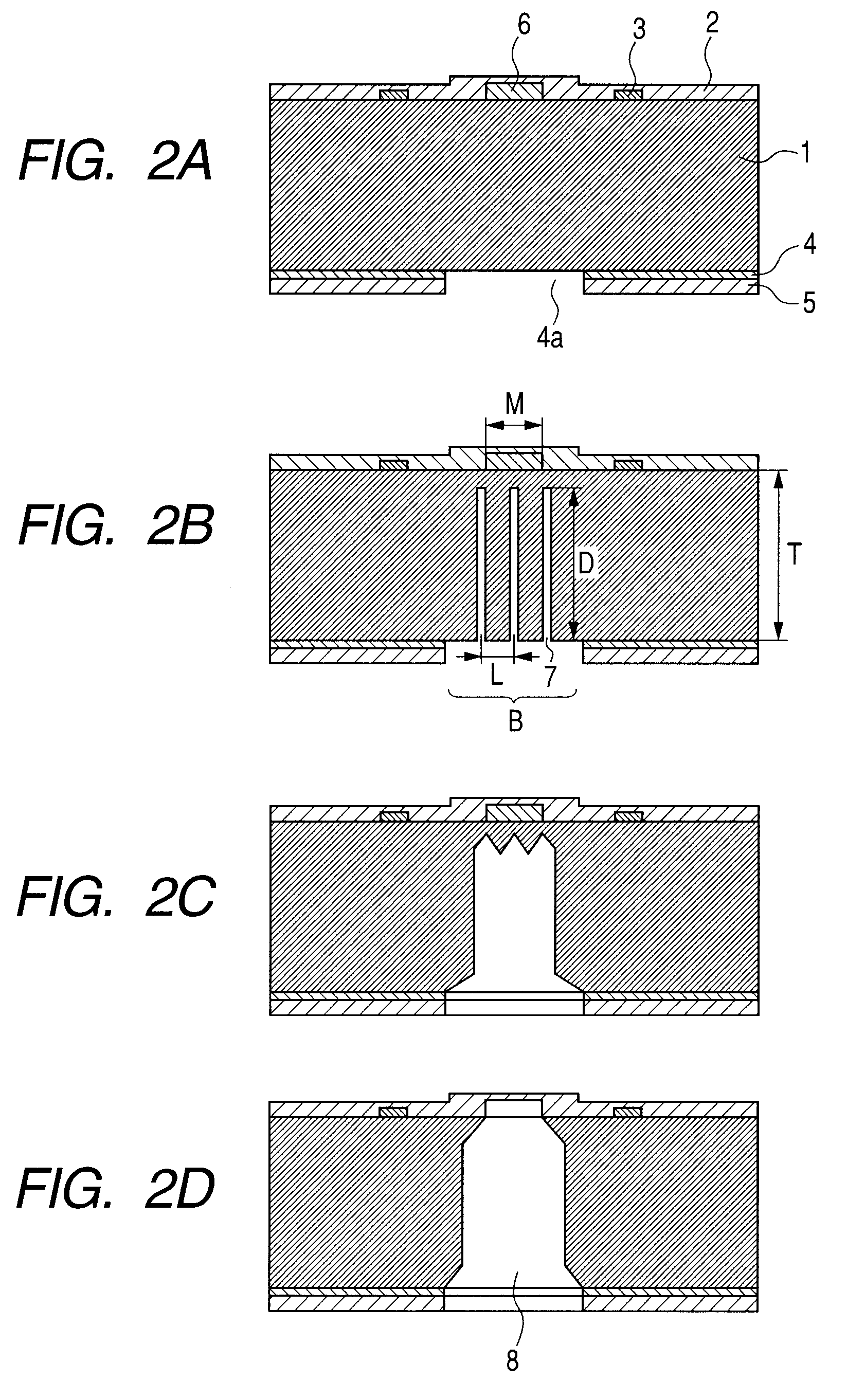
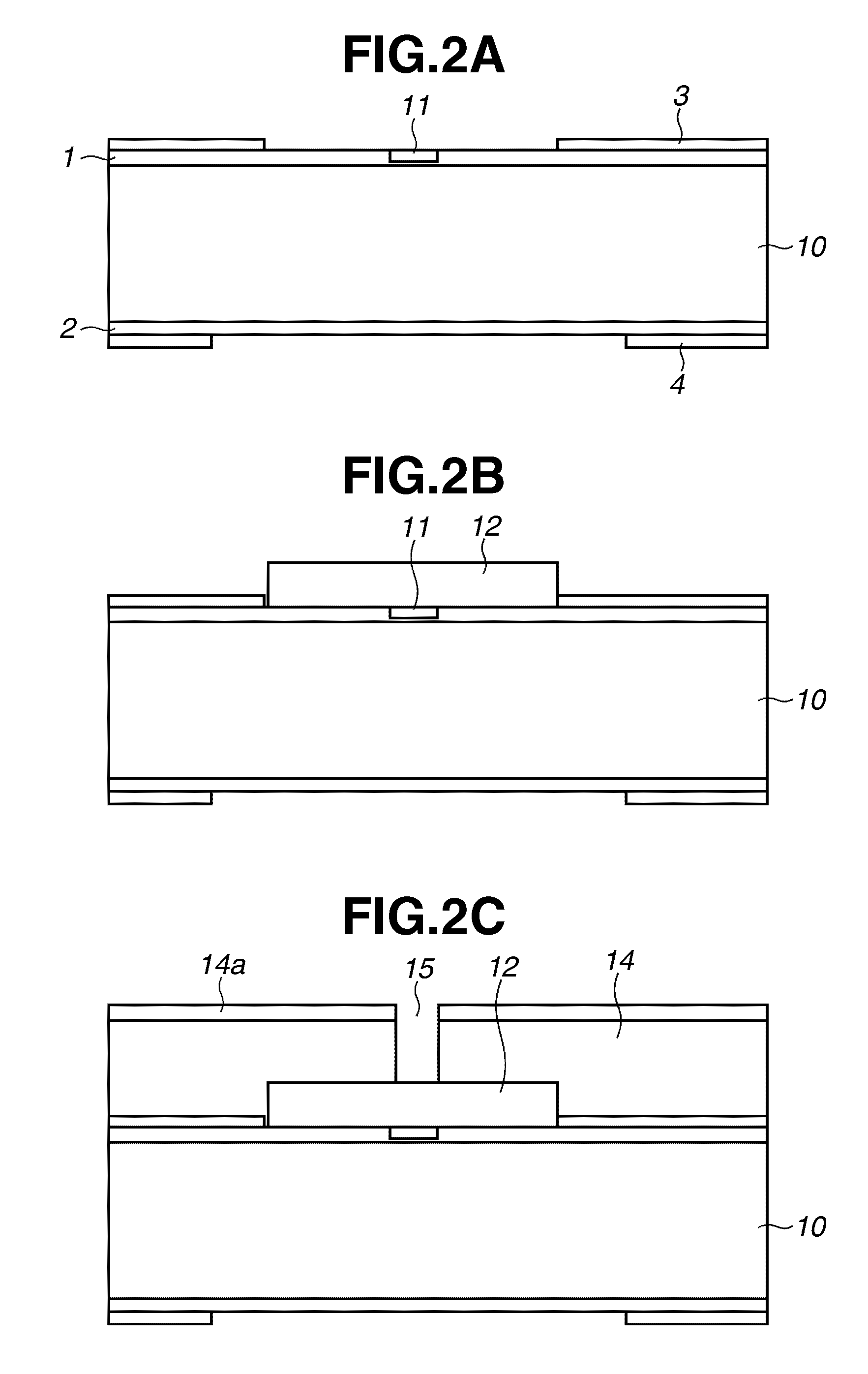
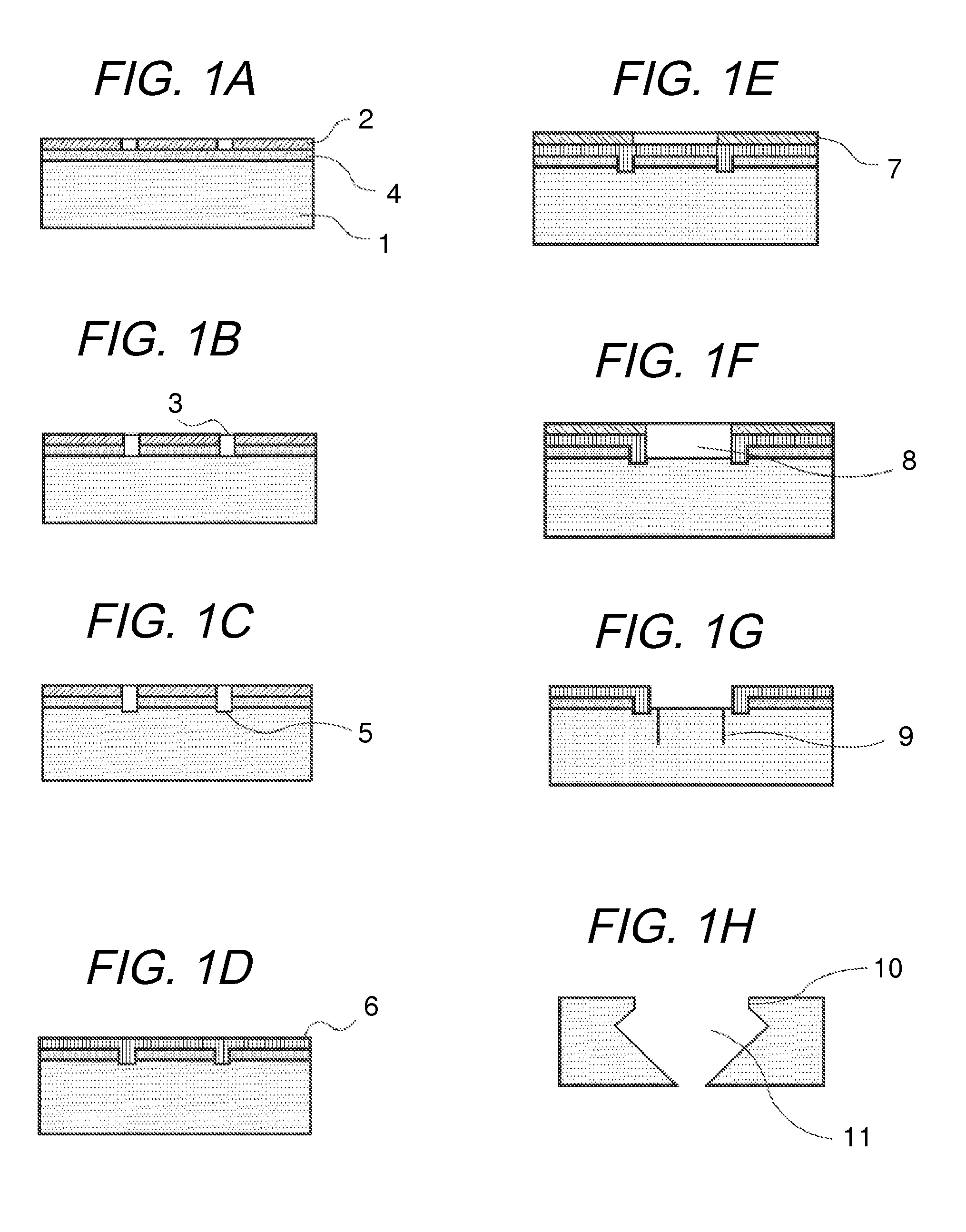
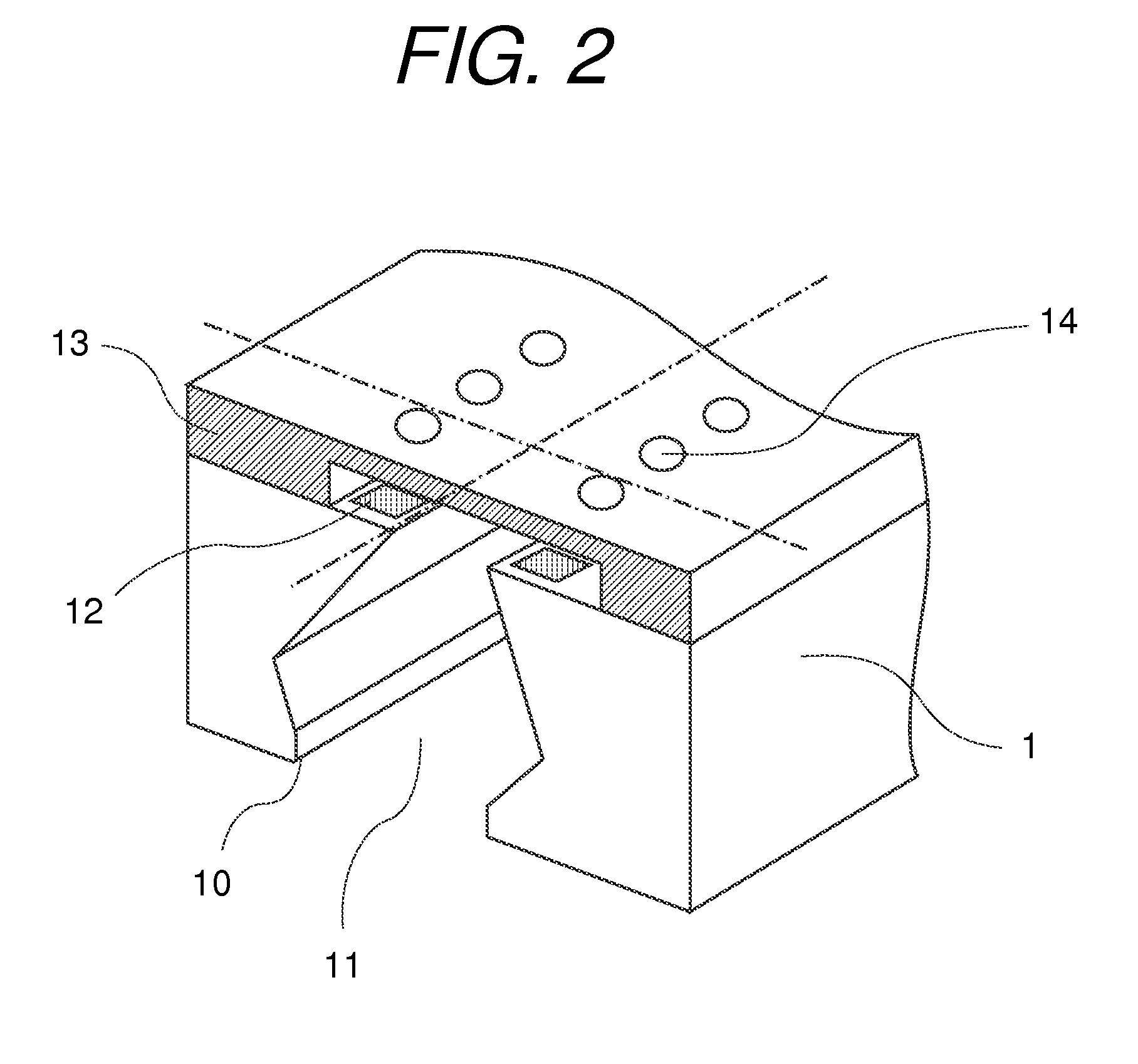
Manufacturing method for ink jet recording head chip, and manufacturing method for ink jet recording head
ActiveUS20070212890A1Improve efficiencyHigh precisionRecording apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnisotropic etchingCrystal anisotropy
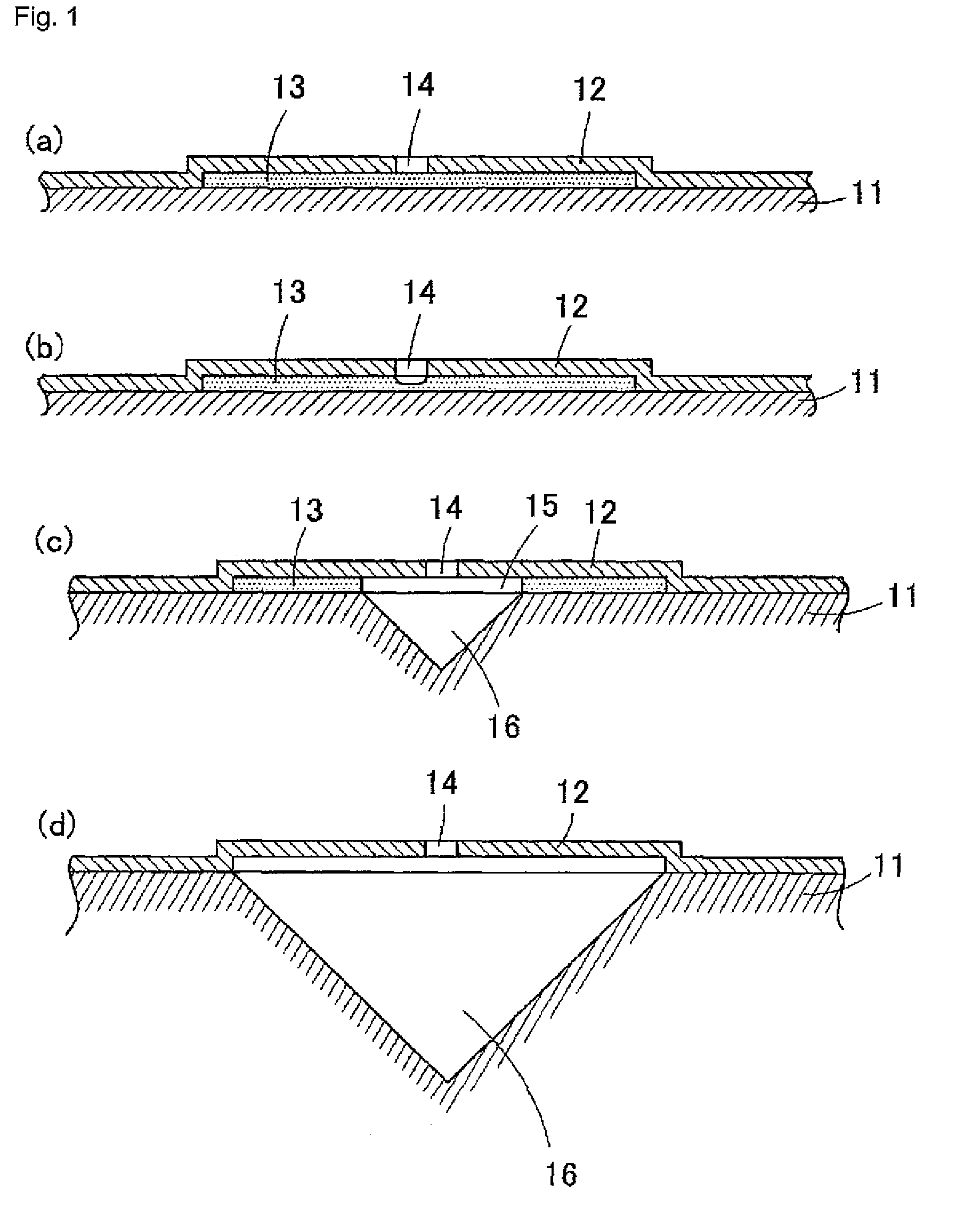
A manufacturing method for a substrate for an ink jet head, including formation of an ink supply port in a silicon substrate, the method includes a step of forming, on one side of the substrate, an etching mask layer having an opening at a position corresponding ink supply port; a step of forming unpenetrated holes through the opening of the etching mask layer in at least two rows in a longitudinal direction of the opening; and a step of forming the ink supply port by crystal anisotropic etching of the substrate in the opening.
Owner:CANON KK
Manufacturing method of substrate for ink jet head and manufacturing method of ink jet recording head
InactiveUS20070212891A1Improve accuracyShort timeRecording apparatusDecorative surface effectsEngineeringAnisotropic etching
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of a substrate for an ink jet head including forming an ink supply opening to a silicon substrate, including (a) forming, at the back surface of the silicon substrate, an etching mask layer, which has an opening that is asymmetric with a center line, extending in the longitudinal direction, of an area on the surface of the silicon substrate where the ink supply opening is to be formed; (b) forming a non-through hole on the silicon substrate via the opening on the etching mask layer; and (c) forming the ink supply opening by performing a crystal anisotropic etching to the silicon substrate from the opening.
Owner:CANON KK
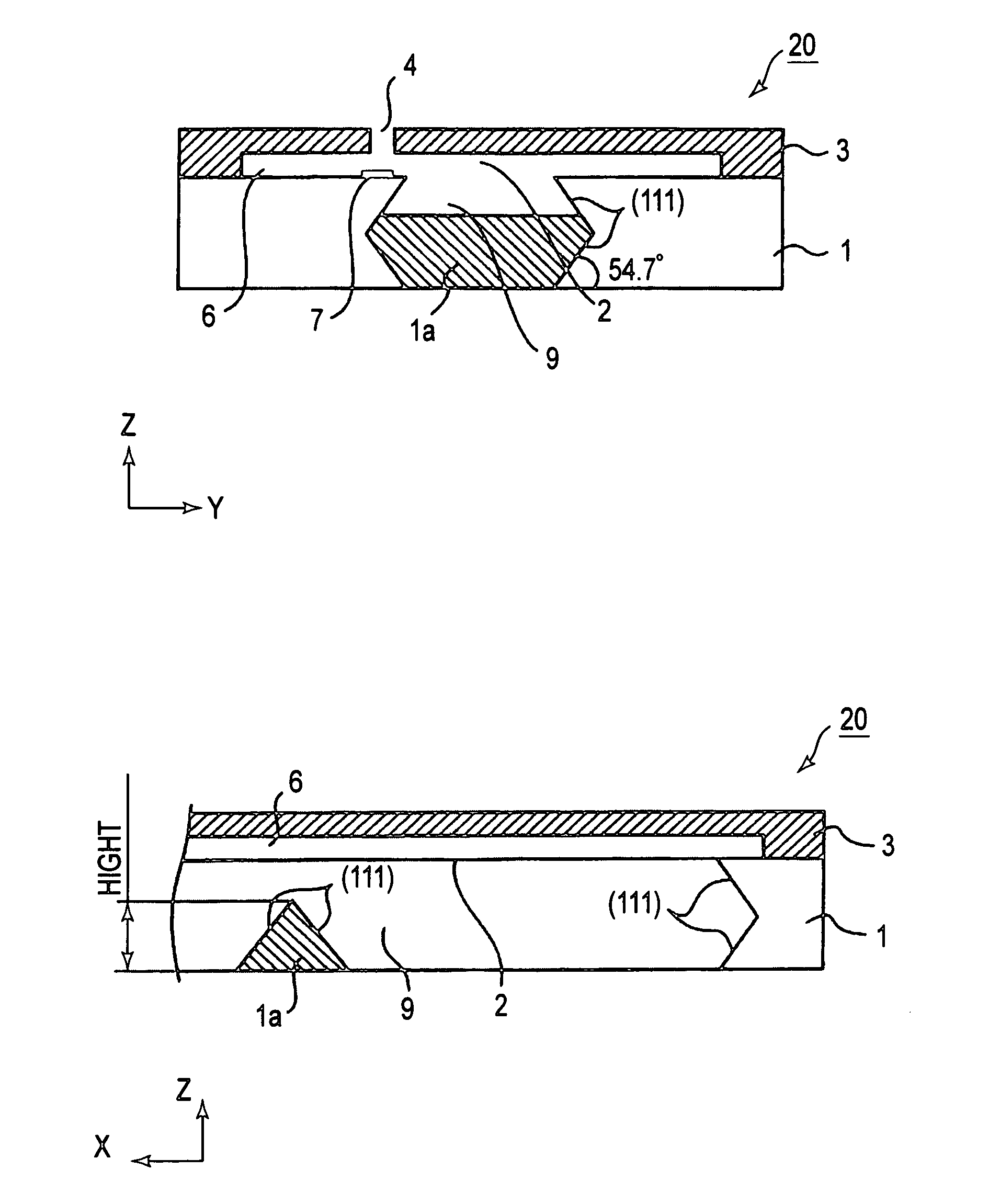
Optical element module and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100142886A1Inhibition effectProblem in costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer moduleEngineering
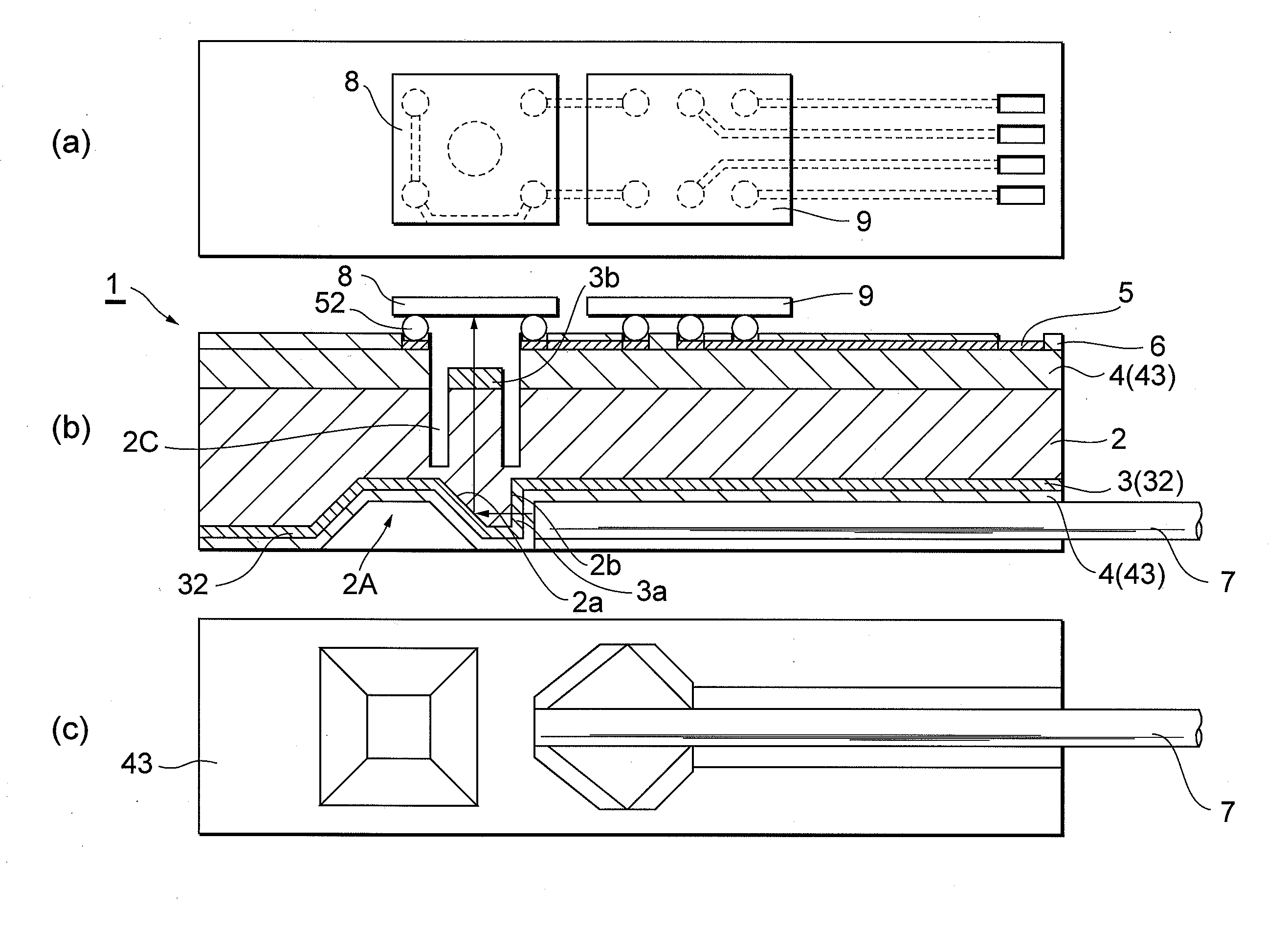
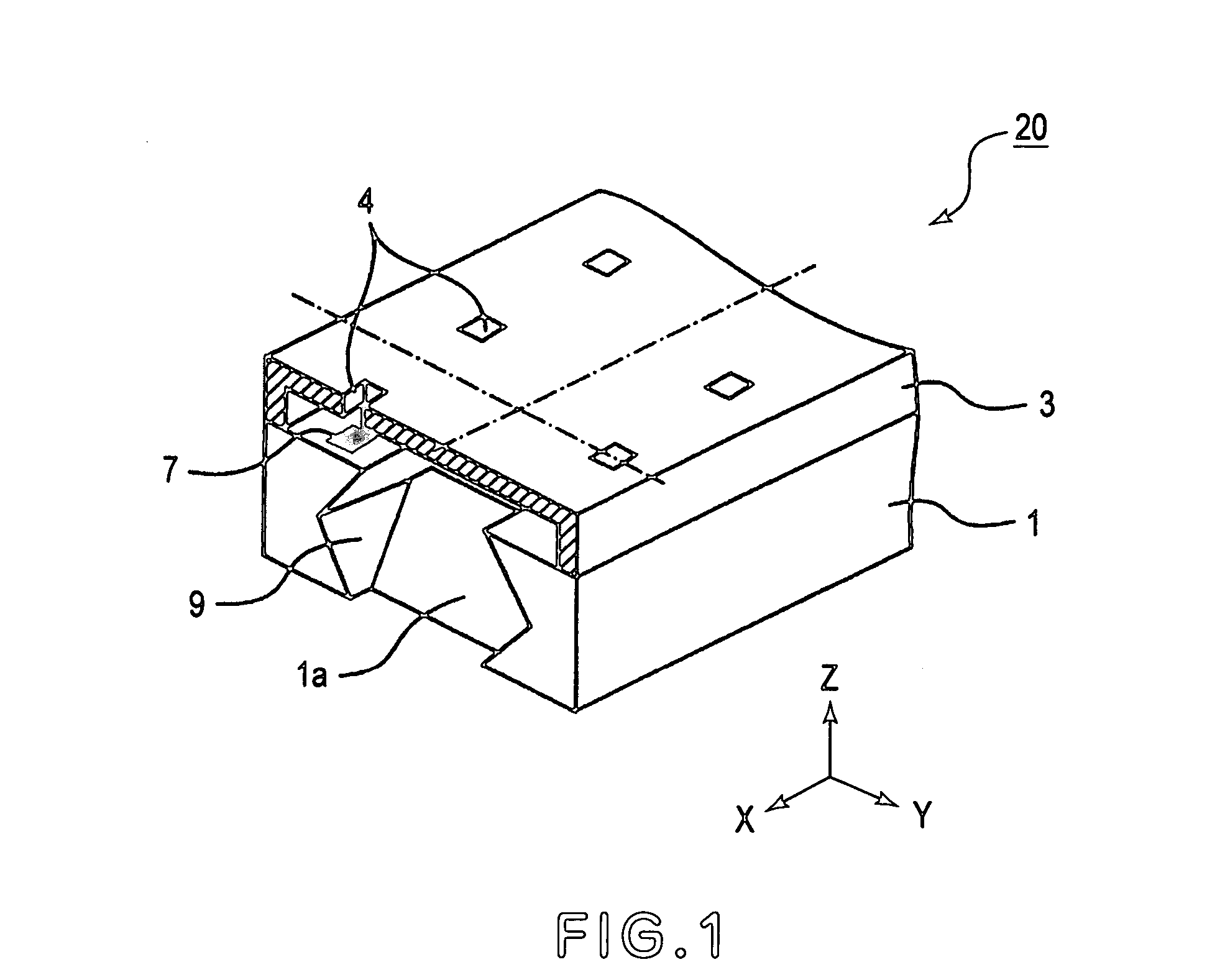
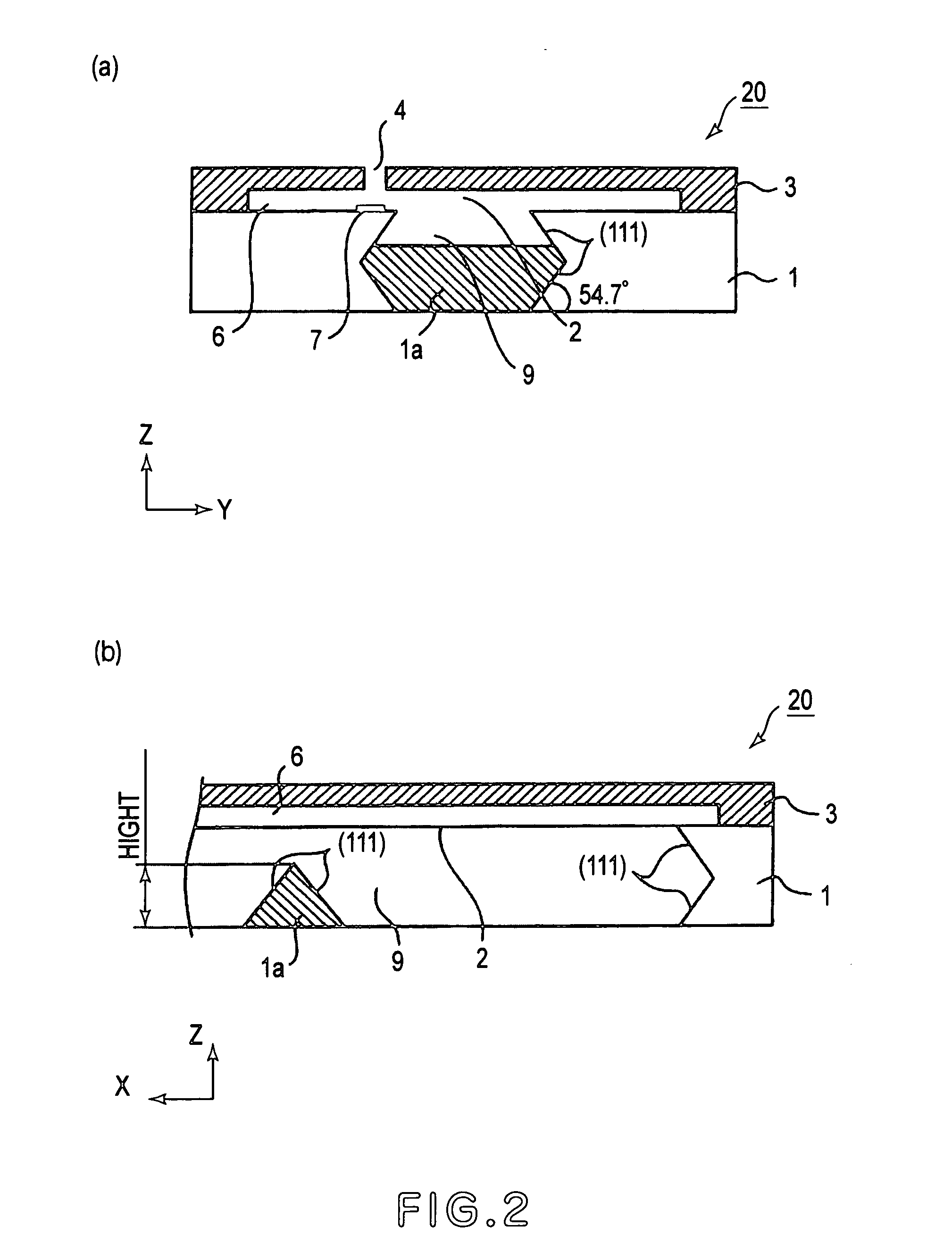
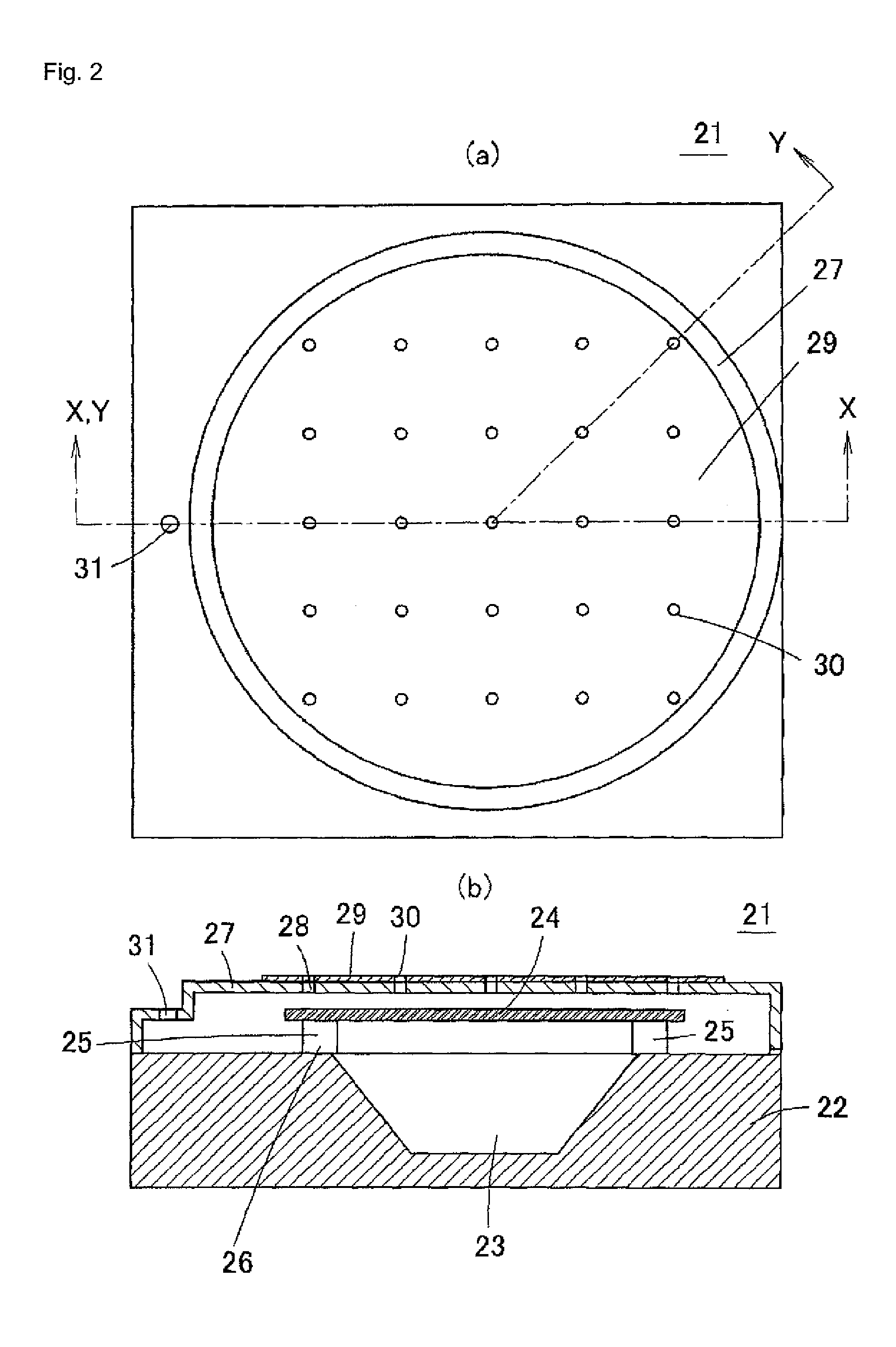
A method of manufacturing an optical element module 1 in which an optical element 8 and a semiconductor circuit element 9 are mounted on one surface of a silicon substrate 2, a mirror surface 2a inclined at approximately 45 degrees is formed on the other surface, and an optical fiber 7 facing the mirror surface is disposed in a V groove formed along the other surface, the method of manufacturing includes the steps of forming the mirror surface 2a and V-shaped side surfaces of the V groove simultaneously by first crystal anisotropic etching on the other surface, and forming an attaching surface 2b substantially perpendicular to the one surface and the other surface, which is formed at an end side of the V groove, and for attaching an end of the optical fiber 7, by second crystal anisotropic etching in a crystal plane orientation different from that of the first crystal anisotropic etching. Thereby, it is possible to realize an optical element module including an optical element that receives light or emits light, a semiconductor circuit element, and an optical fiber optically connected to the optical element, the optical element module highly-functionally performs an optical connection between the optical element and the optical fiber, and realize a method of efficiently manufacturing the optical element module.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Method for manufacturing liquid discharge head
InactiveUS20090095708A1High shape accuracyFavorable supply characteristicRecording apparatusRecord information storageAnisotropic etchingMechanical engineering
A method for manufacturing a liquid discharge head including a substrate on which supply ports for supplying a liquid are provided, includes forming a first supply port among the supply ports by performing crystal anisotropic etching on the substrate from one surface of the substrate, and forming a plurality of second supply ports among the supply ports by performing dry etching on the substrate using a crystal anisotropic etching method from a surface exposed toward the one surface of the substrate to a rear surface so that the independent second supply ports are respectively opened on the rear surface.
Owner:CANON KK
POLYCRYSTALLINE MgO SINTERED BODY, PRODUCTION METHOD THEREFOR, AND MgO SPUTTERING TARGET
ActiveUS20100294657A1Increase chanceShrink poresLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringHigh rate
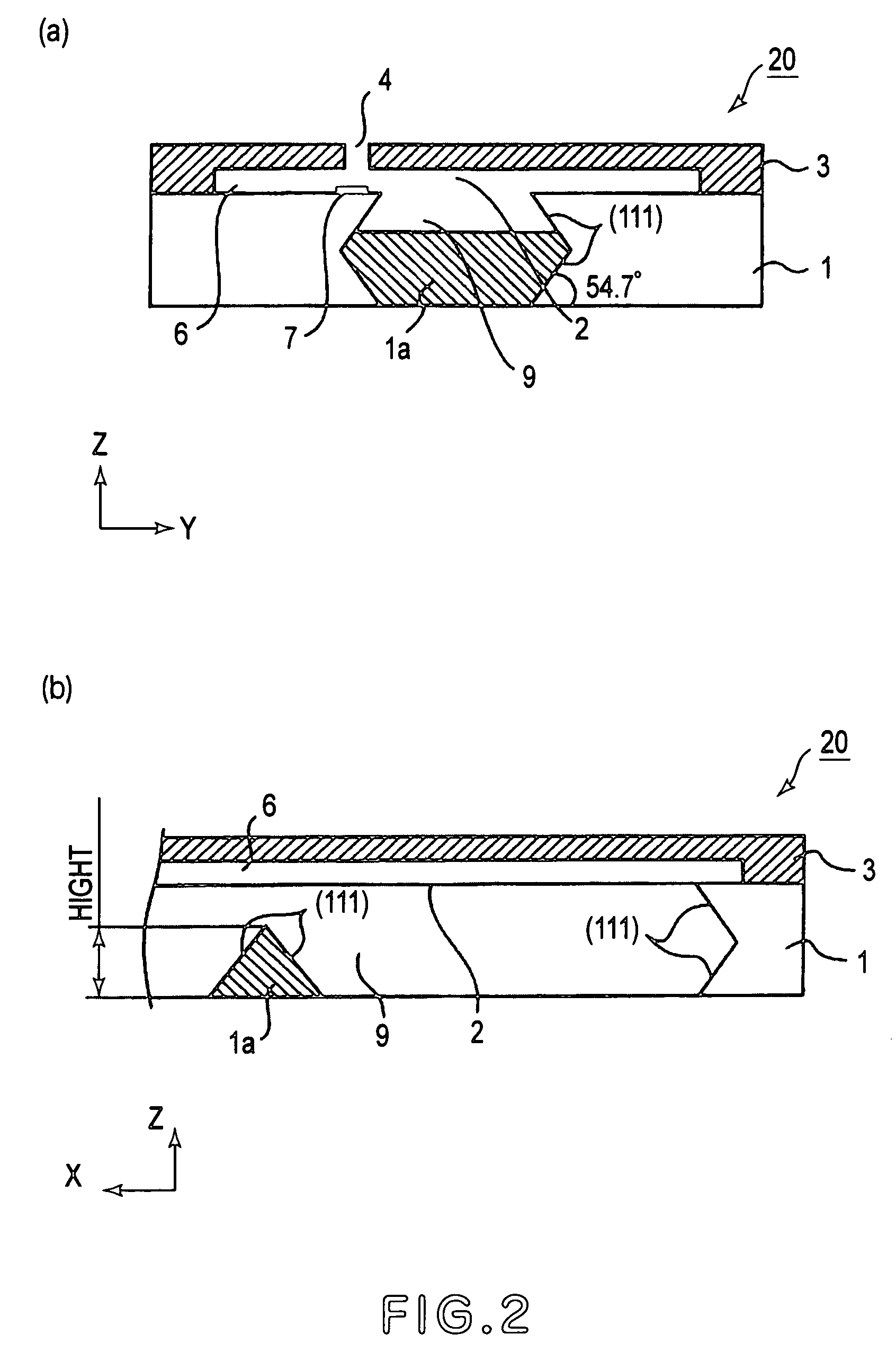
Provided is a polycrystal MgO sintered body which is capable of having a sintered density close to a theoretical density thereof, and exhibiting excellent mechanical properties and heat conductivity, while reducing contamination of an atmosphere due to gas generation, and a production method for the sintered body. The polycrystal MgO sintered body has a unique crystalline anisotropy in which (111) faces are oriented along a surface applied with a uniaxial pressure at a high rate. The polycrystalline MgO sintered body is obtained by a method which comprises the steps of: sintering an MgO raw material powder having a particle size of 1 μm or less, under a uniaxial pressure; and then subjecting the sintered powder to a heat treatment under an atmosphere containing 0.05 volume % or more of oxygen, at a temperature of 1273 K or more for 1 minute or more.
Owner:NIPPON TUNGSTEN CORP +1
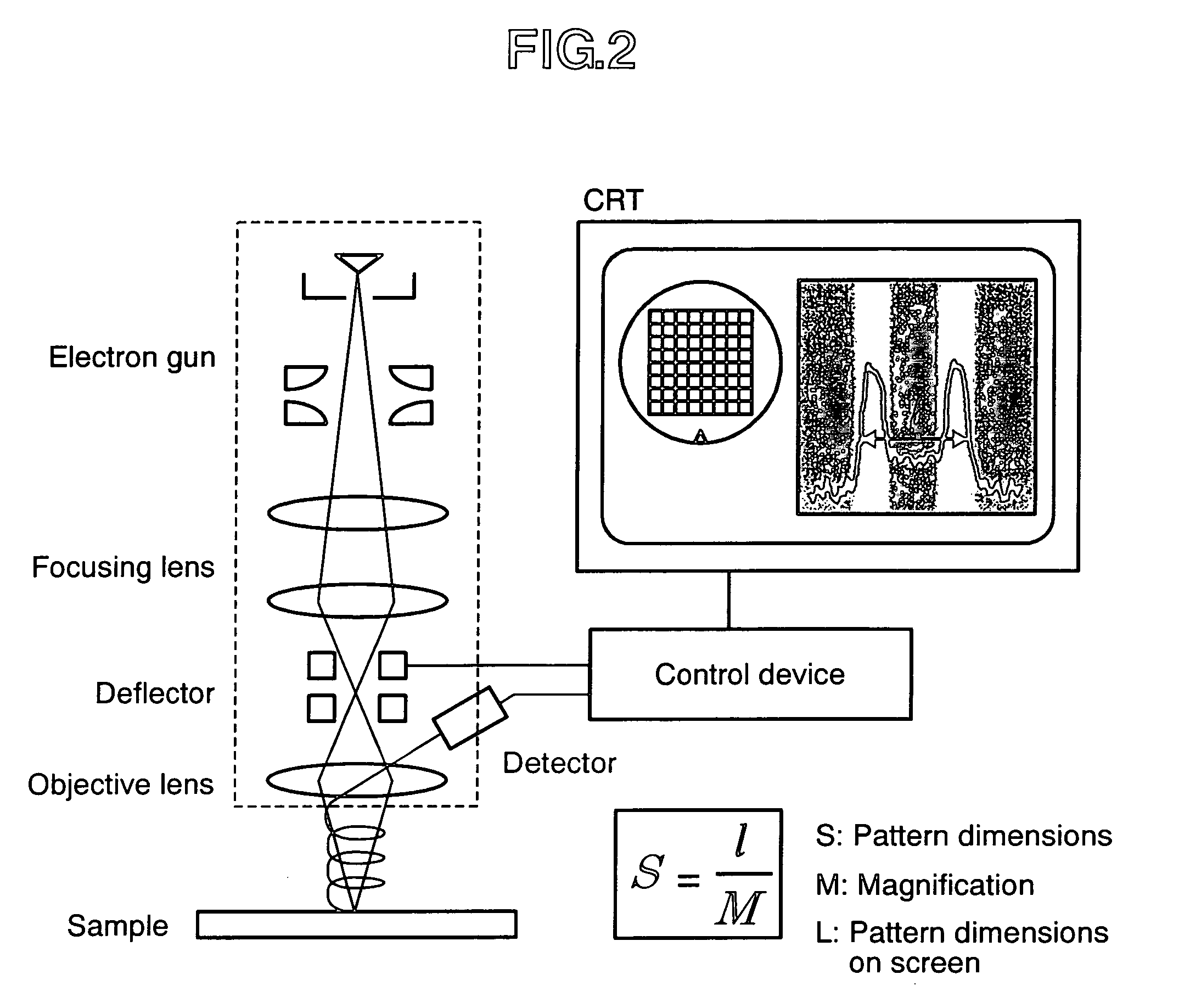
Charged particle beam apparatus and methods for capturing images using the same
ActiveUS20070164219A1Eliminate variationEliminate errorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLight beamAnisotropic etching
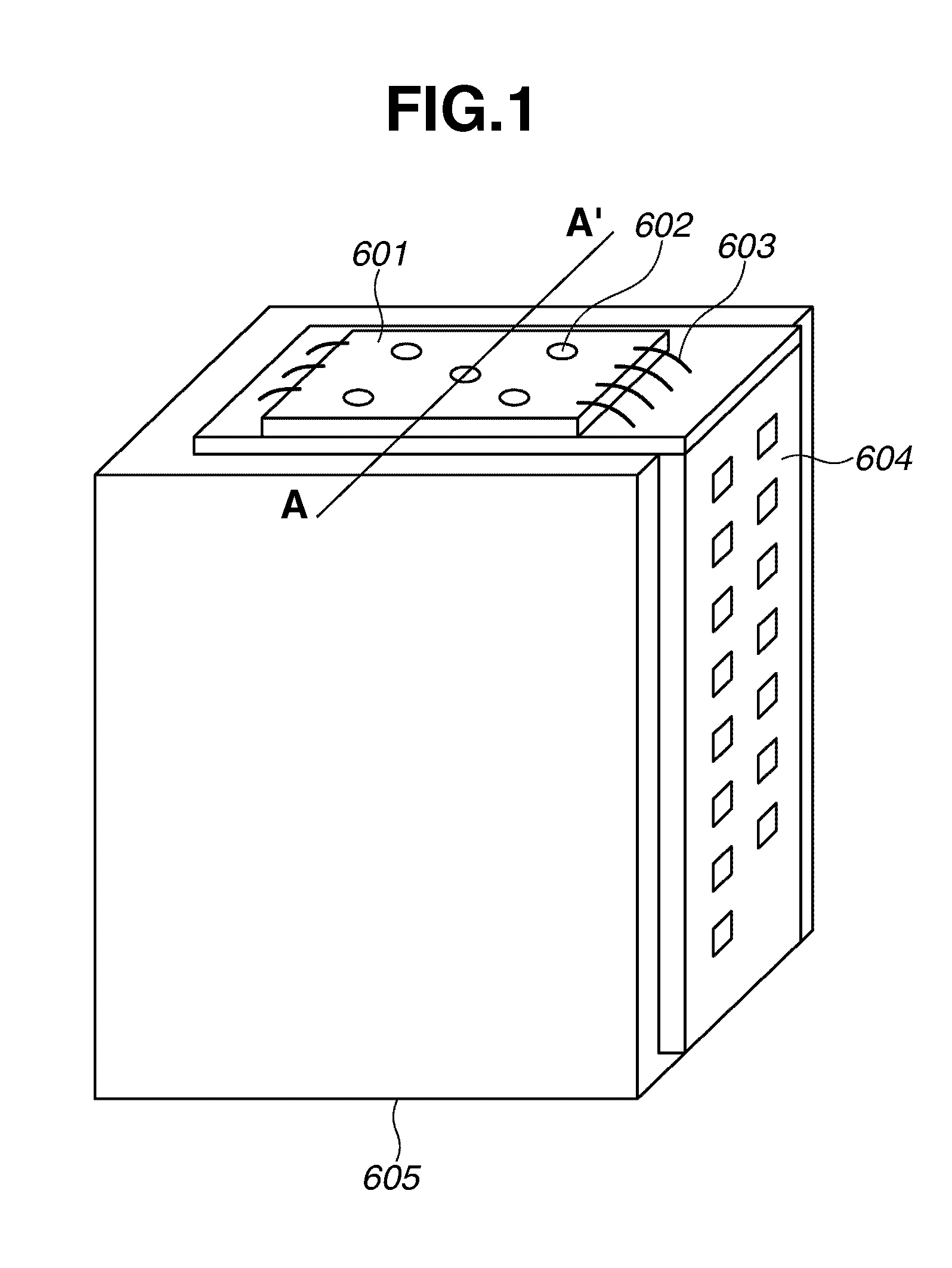
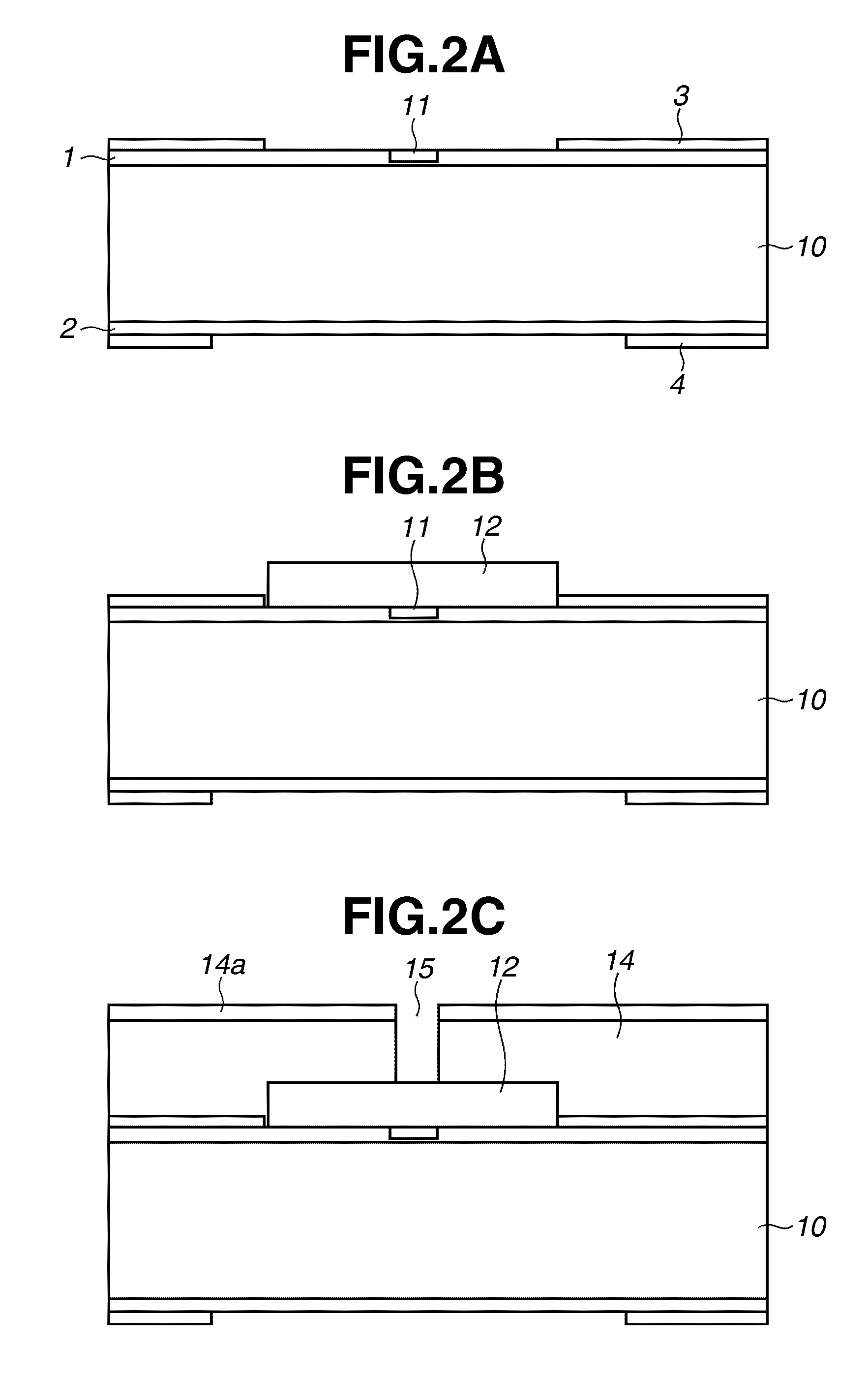
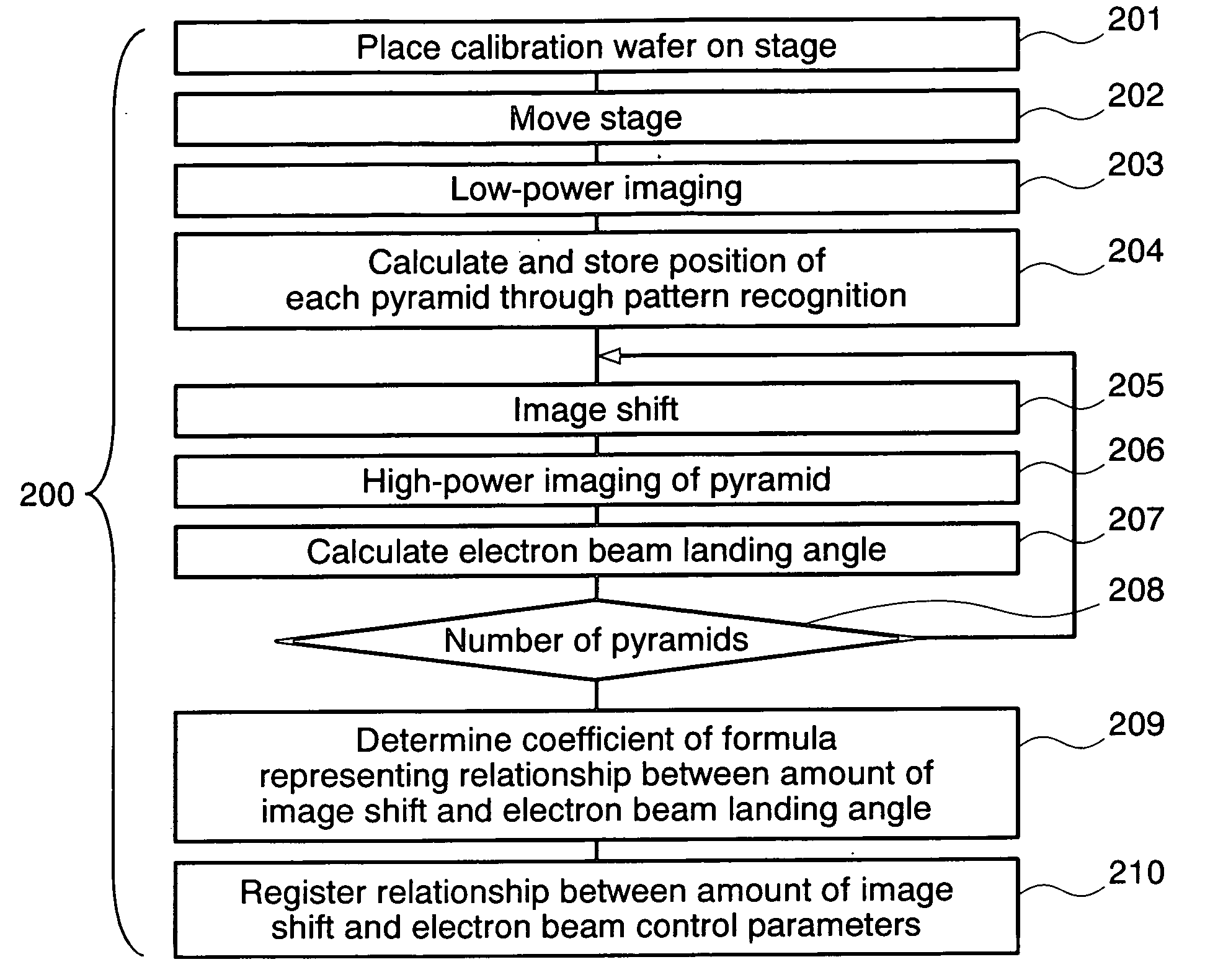
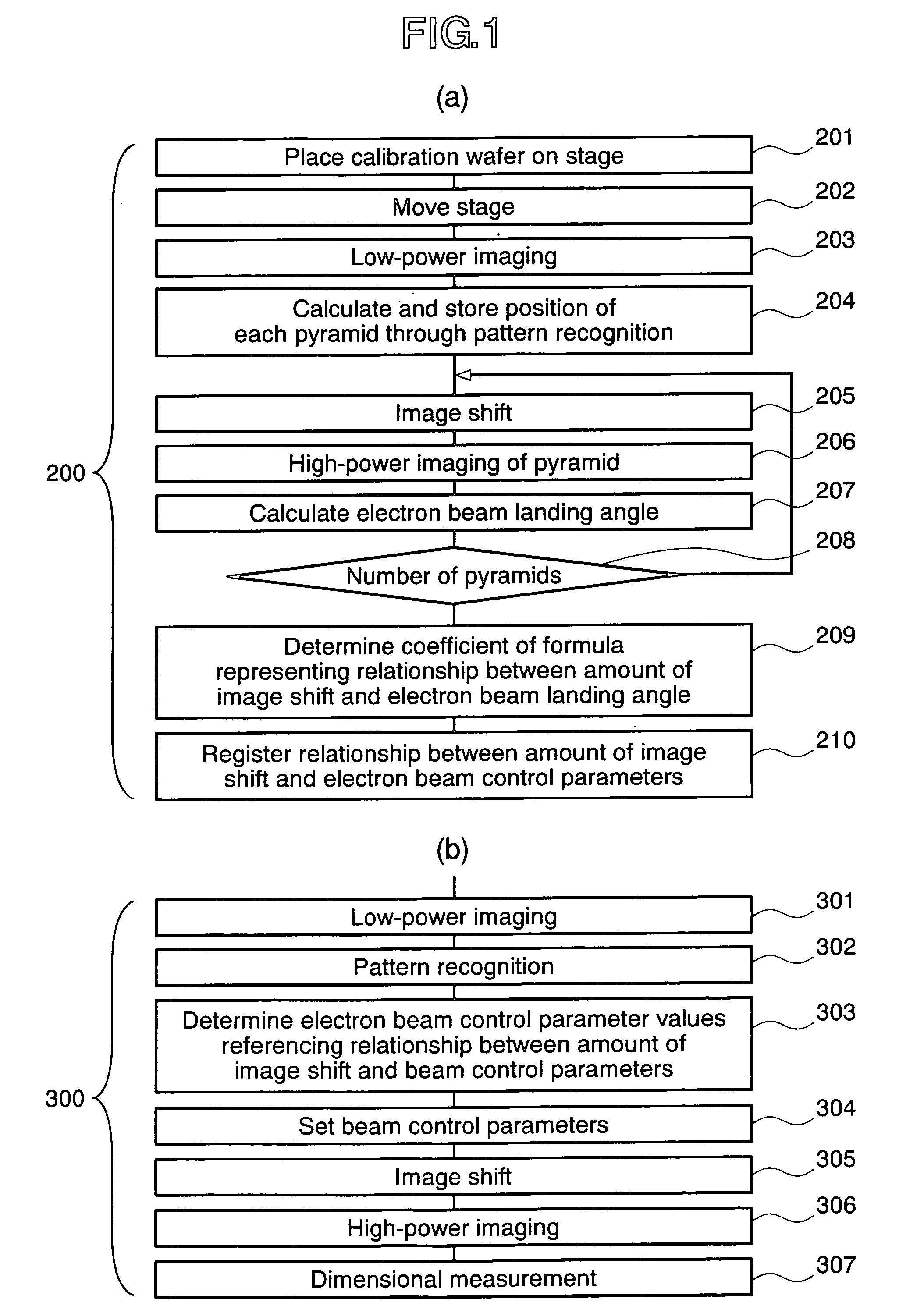
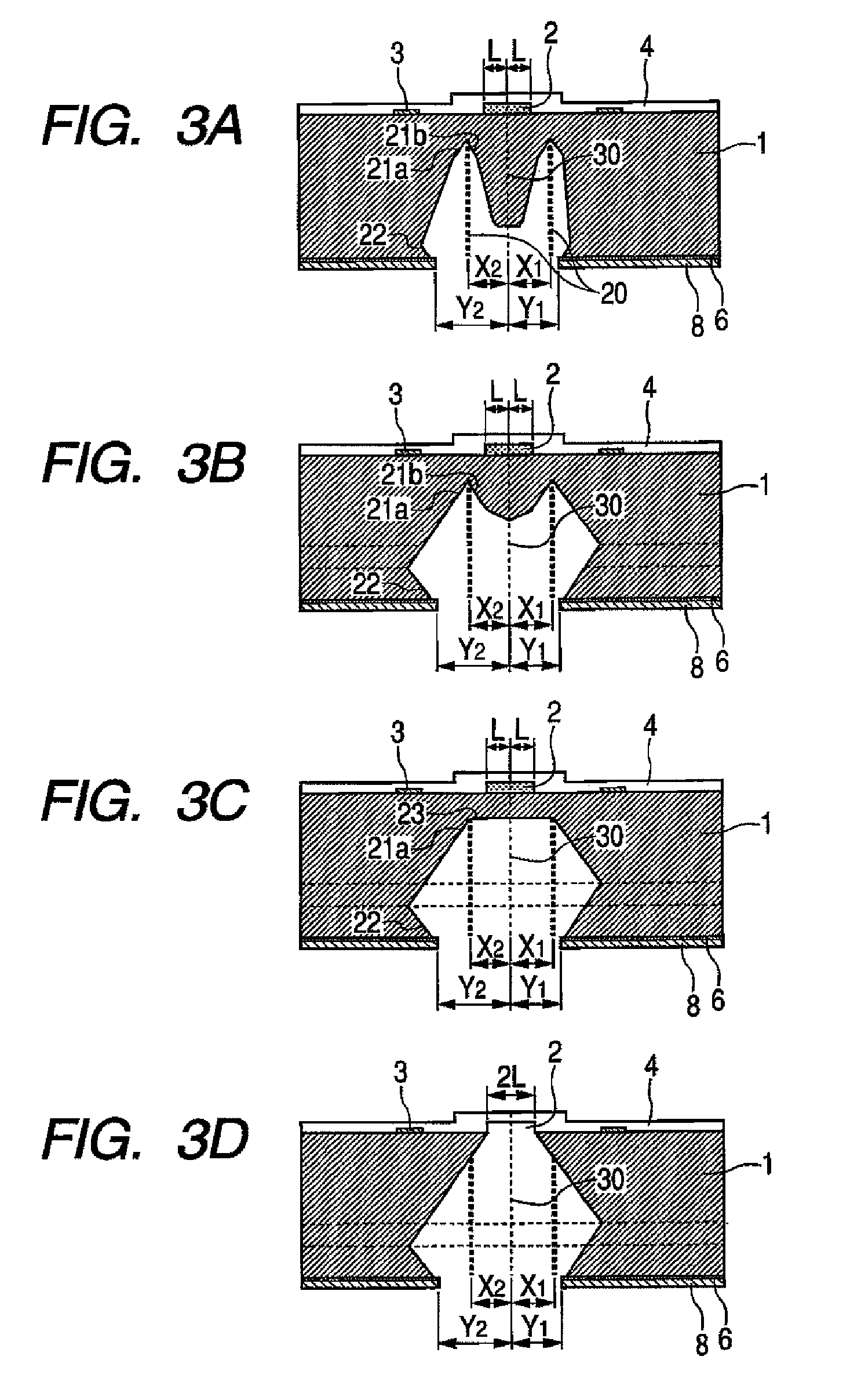
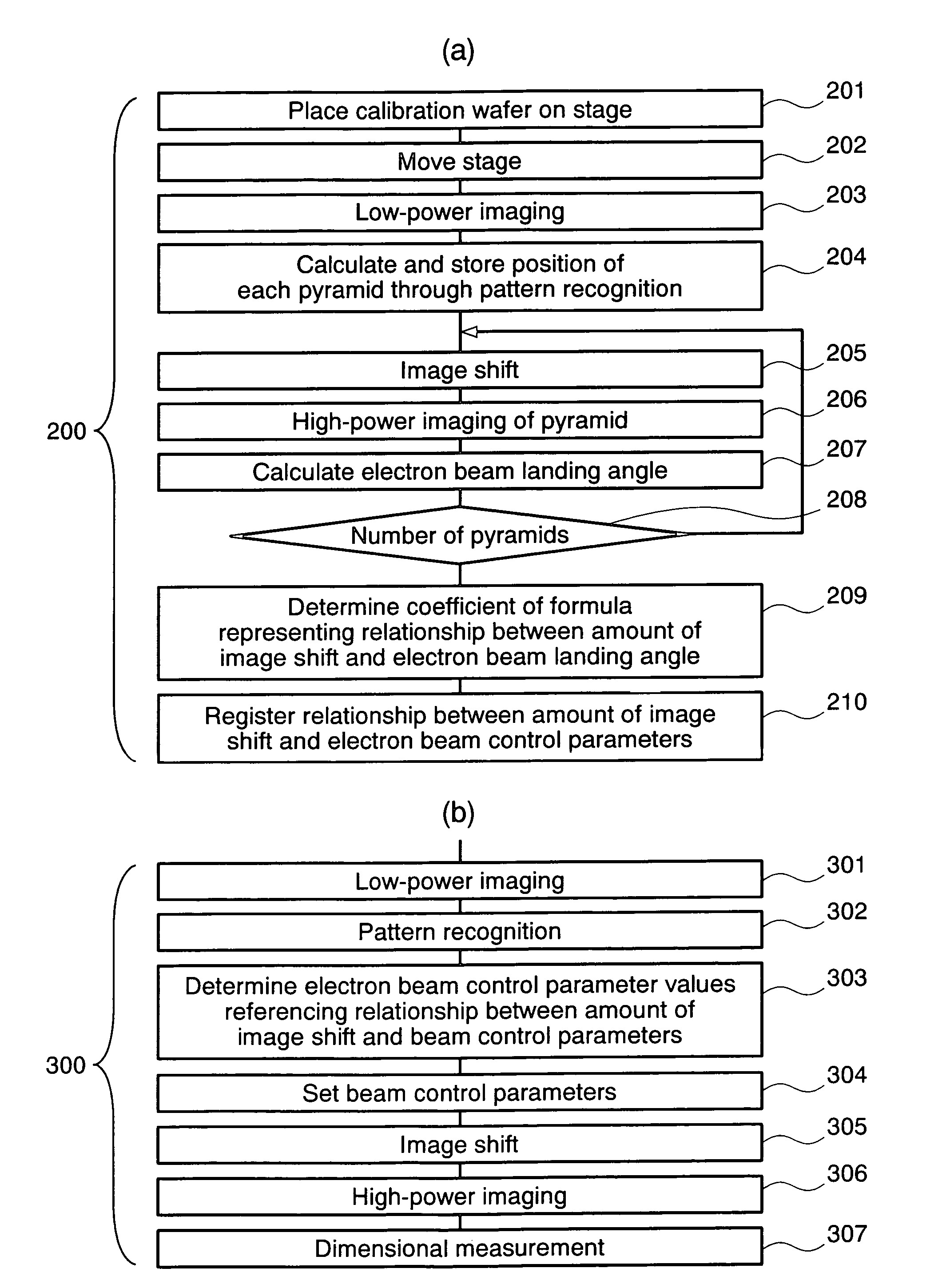
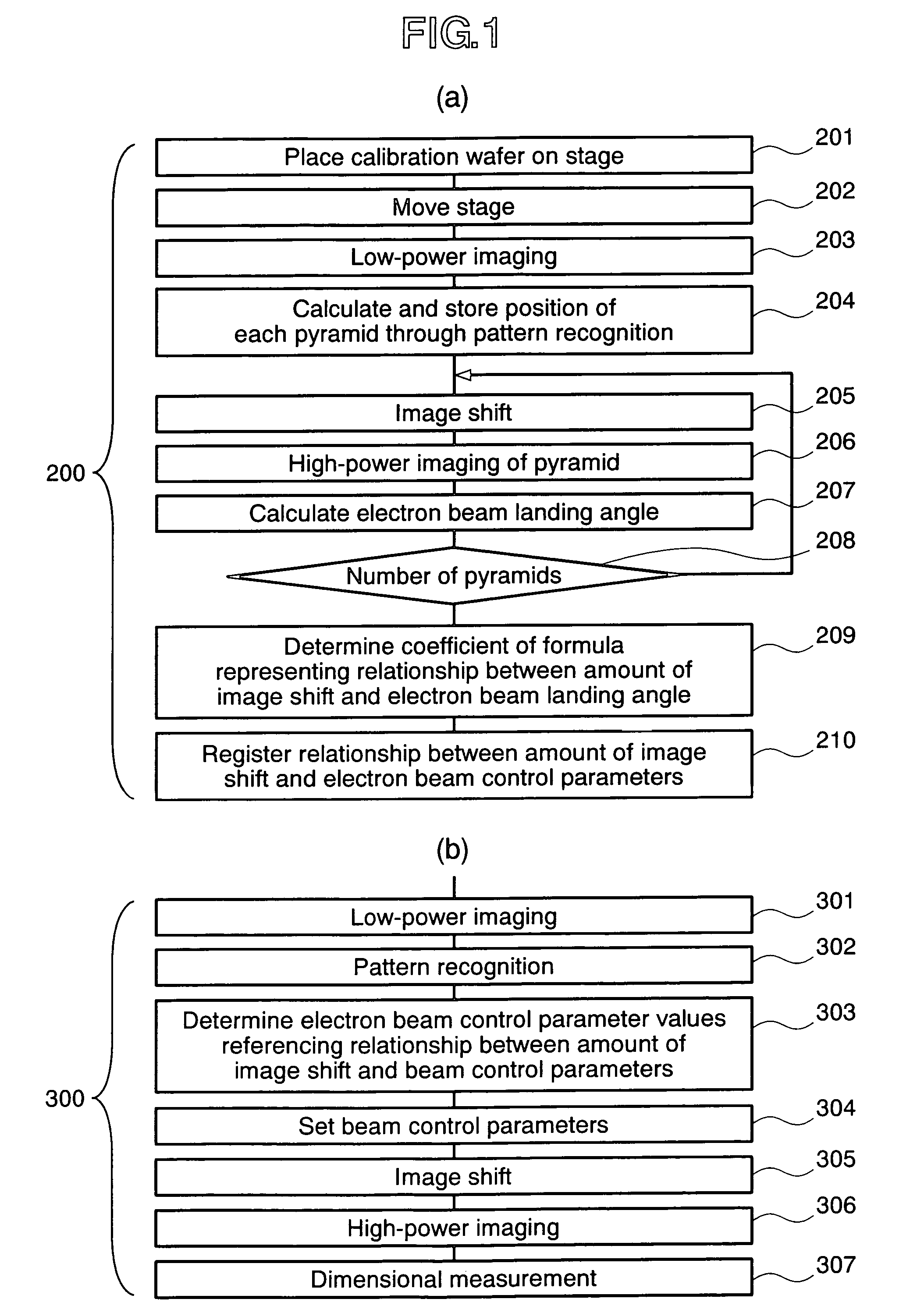
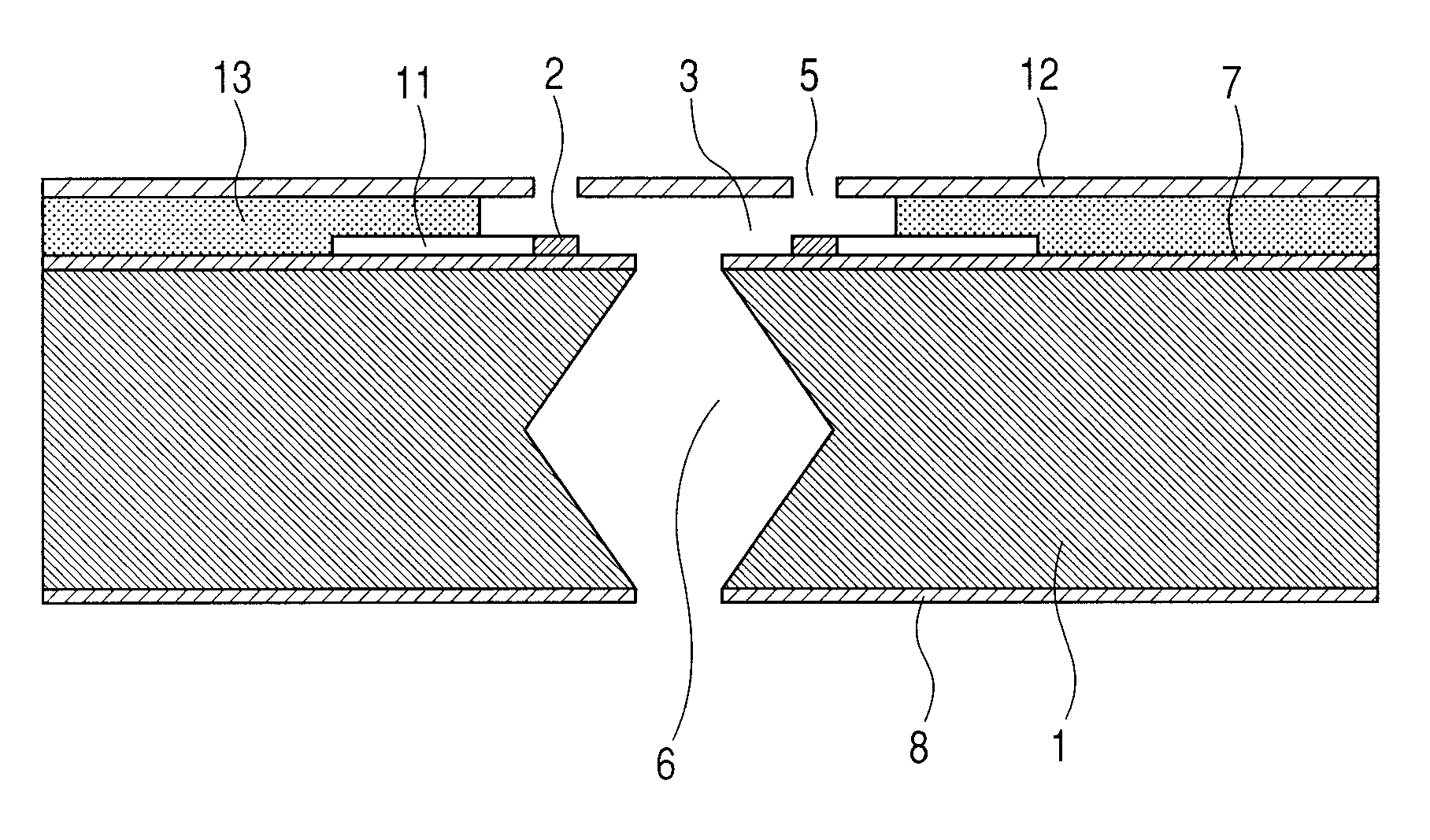
The present invention provides a charged particle beam apparatus used to measure micro-dimensions (CD value) of a semiconductor apparatus or the like which captures images for measurement. For the present invention, a sample for calibration, on which a plurality of polyhedral structural objects with known angles on surfaces produced by the crystal anisotropic etching technology are arranged in a viewing field, is used. A beam landing angle at each position within a viewing field is calculated based on geometric deformation on an image of each polyhedral structural object. Beam control parameters for equalizing the beam landing angle at each position within the viewing field are pre-registered. The registered beam control parameters are applied according to the position of the pattern to be measured within the viewing field when performing dimensional measurement. Accordingly, the present invention provides methods for reducing the variation in the CD value caused by the variation in the electron beam landing angle with respect to the sample with an equal beam landing angle and methods for reducing the instrumental error caused by the difference in the electron beam landing angle between apparatuses.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
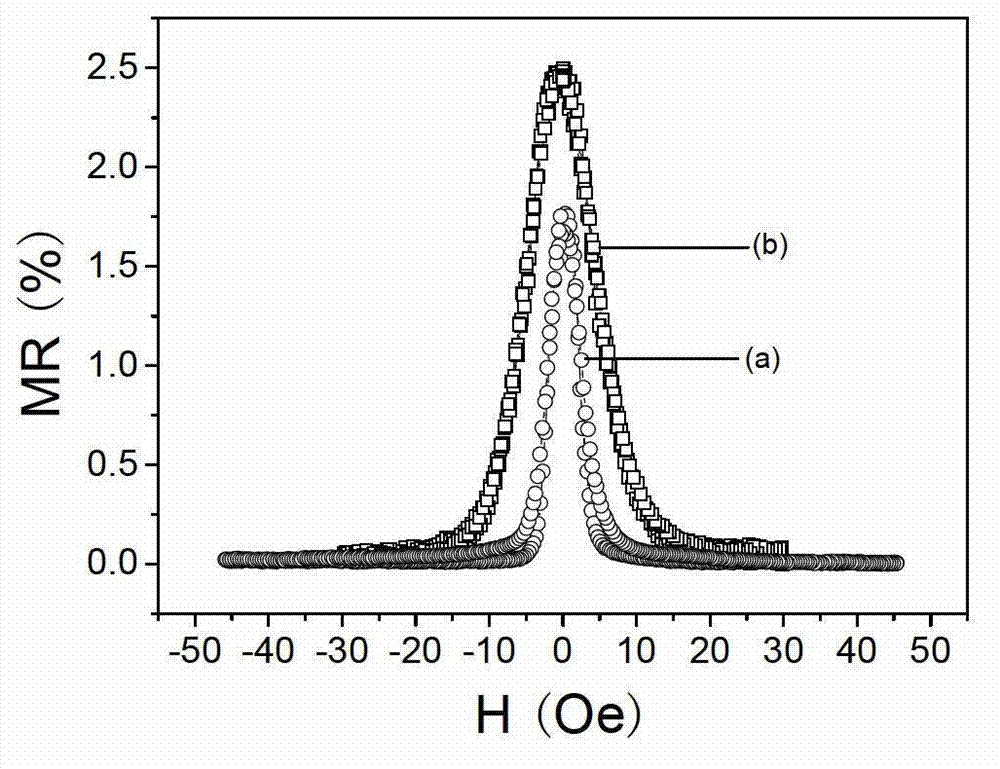
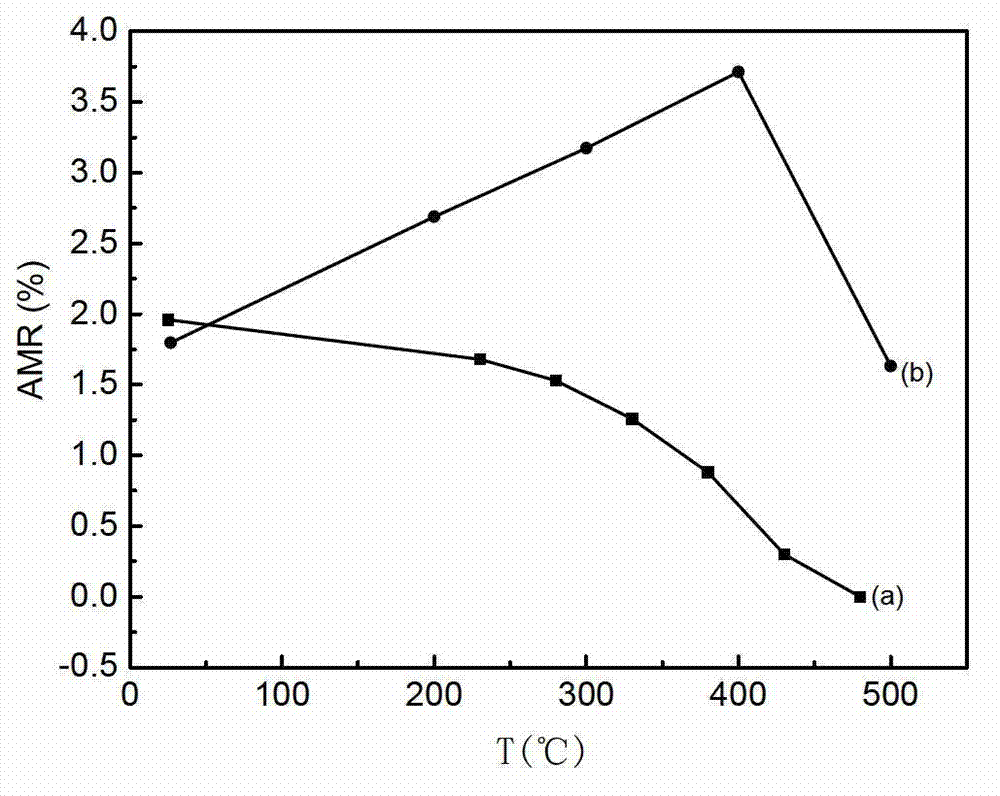
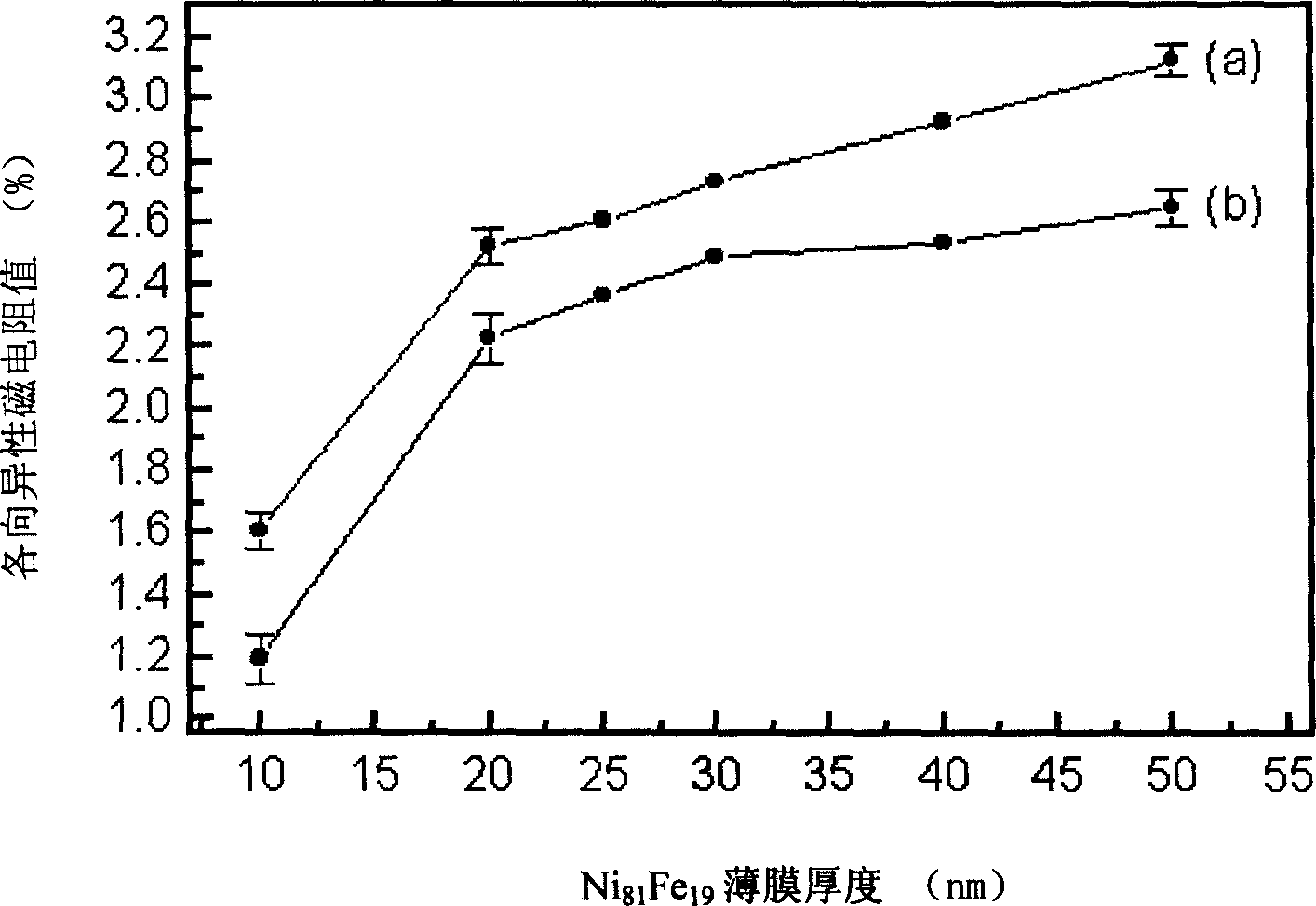
Method for improving thermostability of anisotropic magnetoresistance permalloy film
InactiveCN102867645AHigh AMR valueAMR value increasedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringPermalloy
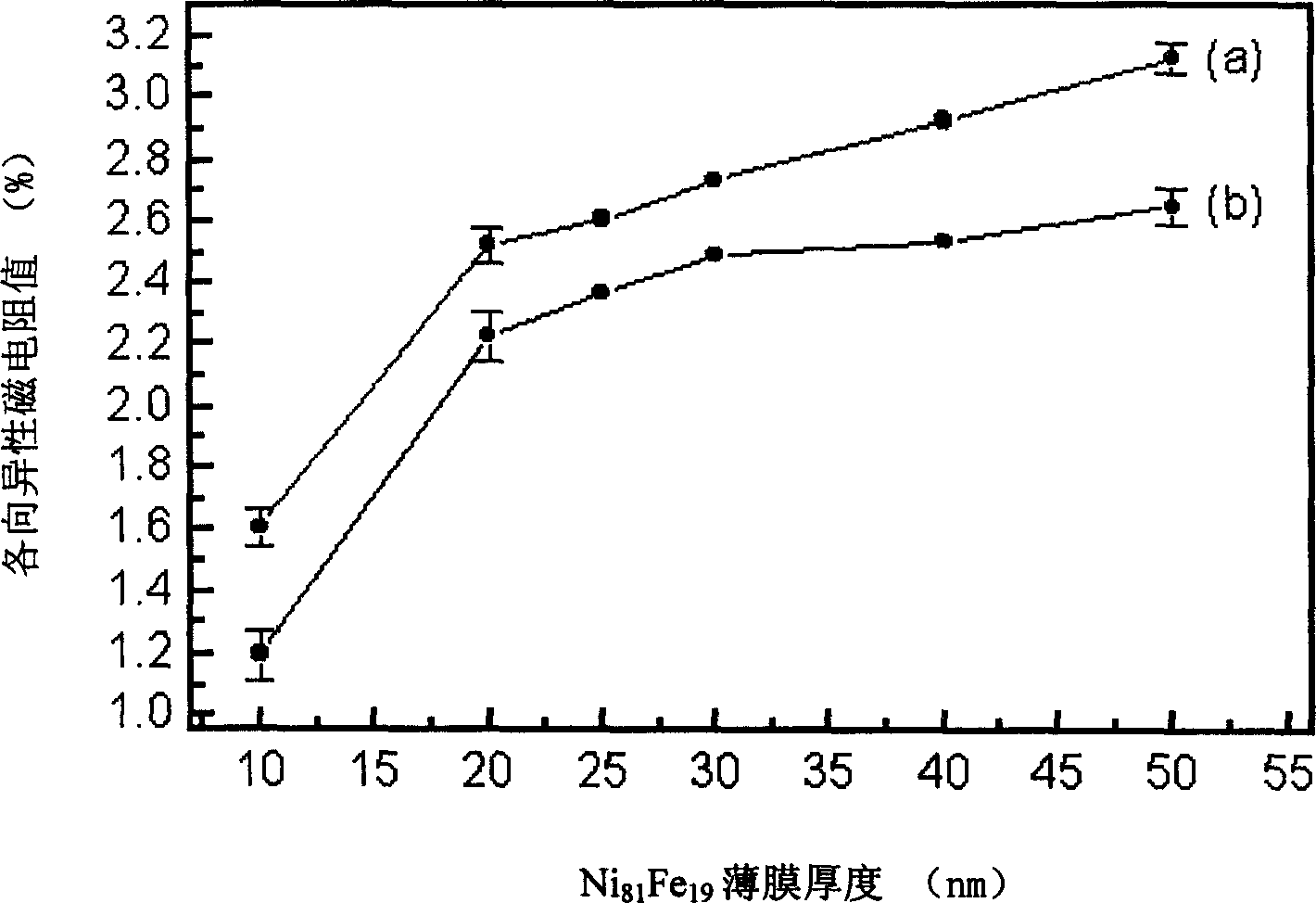
The invention relates to a method for improving thermostability of an anisotropic magnetoresistance permalloy film. The method adopts a magnetron sputtering process, where the vacuum degree of a sputtering chamber background is 1*10-5 to 9*10-5Pa; argon gas with purity of 99.99% is introduced before sputtering; the argon gas pressure in sputtering is 0.4-2.7Pa; a 150-300Oe magnetic field is applied in the direction parallel to a substrate; the substrate rotates at the speed of 8-30 turns per minutes all the time; a buffer layer Ta, a CoFeB layer, a magnetic layer NiFe, a CoFeB layer and a protective layer Ta are successively deposited on a glass or silicon substrate which is washed clean; and the thickness of the CoFeB layer is 1.0-20.0nm. The film material prepared by the method provided by the invention has the advantage that when the film is very thin, the film material has the combination properties of high anisotropic magnetoresistance value and weak coercive force, low crystal anisotropy, good thermostability and the like so as to meet requirements of performances and products of magnetic sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Beam, ink jet recording head having beams, and method for manufacturing ink jet recording head having beams
InactiveUS20050140737A1Easy to changeEasy to useSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsLight beamEngineering
A beam having a base material of silicon monocrystal and at least one projection which is integrally formed so as to be supported at least at one end thereof and which has two surfaces having an orientation plane (111), includes a bottom surface in a plane which is common with a plane of the base material; a groove penetrating from the bottom surface to a top of the projection; and a protecting member having a resistance property against a crystal anisotropic etching liquid and covering an inner wall of the groove.
Owner:CANON KK
Manufacturing method of substrate for ink jet head and manufacturing method of ink jet recording head
InactiveUS7727411B2Improve accuracyShort timeRecording apparatusDecorative surface effectsEngineeringAnisotropic etching
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of a substrate for an ink jet head including forming an ink supply opening to a silicon substrate, including (a) forming, at the back surface of the silicon substrate, an etching mask layer, which has an opening that is asymmetric with a center line, extending in the longitudinal direction, of an area on the surface of the silicon substrate where the ink supply opening is to be formed; (b) forming a non-through hole on the silicon substrate via the opening on the etching mask layer; and (c) forming the ink supply opening by performing a crystal anisotropic etching to the silicon substrate from the opening.
Owner:CANON KK
Charged particle beam apparatus and methods for capturing images using the same
ActiveUS7807980B2Improve measurement repeatabilityReduce the differenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesDimension measurementLight beam
The present invention provides a charged particle beam apparatus used to measure micro-dimensions (CD value) of a semiconductor apparatus or the like which captures images for measurement. For the present invention, a sample for calibration, on which a plurality of polyhedral structural objects with known angles on surfaces produced by the crystal anisotropic etching technology are arranged in a viewing field, is used. A beam landing angle at each position within a viewing field is calculated based on geometric deformation on an image of each polyhedral structural object. Beam control parameters for equalizing the beam landing angle at each position within the viewing field are pre-registered. The registered beam control parameters are applied according to the position of the pattern to be measured within the viewing field when performing dimensional measurement. Accordingly, the present invention provides methods for reducing the variation in the CD value caused by the variation in the electron beam landing angle with respect to the sample with an equal beam landing angle and methods for reducing the instrumental error caused by the difference in the electron beam landing angle between apparatuses.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method of manufacturing substrate for liquid discharge head
InactiveUS20100255616A1Shorten production timeSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrintingEngineeringAnisotropic etching
A method of manufacturing a substrate for a liquid discharge head having a supply port passing through a silicon substrate provided with an energy-generating element generating the energy used to discharge a liquid and allowing liquid to be supplied to the energy-generating element, includes preparing a silicon substrate in which a first etching mask having a first opening is provided on a first face, and a second etching mask having a second opening is provided on a second face that is the rear face of the first face; forming a first recess towards the second face from the first face within the first opening, and forming a second recess towards the first face from the second face within in the second opening; and performing crystalline anisotropic etching using the first and second etching masks as masks from both of the first and second faces, to form the supply port.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic random access memory array with coupled soft adjacent magnetic layer
InactiveUS20050280960A1Easy to repositionIncreases magnetic switching volume of cellOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryBit lineCoupling
An MTJ element is formed between orthogonal word and bit lines. The bit line is a composite line which includes a high conductivity layer and a soft magnetic layer under the high conductivity layer. During operation, the soft magnetic layer concentrates the magnetic field of the current and, due to its proximity to the free layer, it magnetically couples with the free layer in the MTJ. This coupling provides thermal stability to the free layer magnetization and ease of switching and the coupling may be further enhanced by inducing a shape or crystalline anisotropy into the free layer during formation.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Preparation method of lithium triborate crystal high-laser-damaged-threshold antireflection film
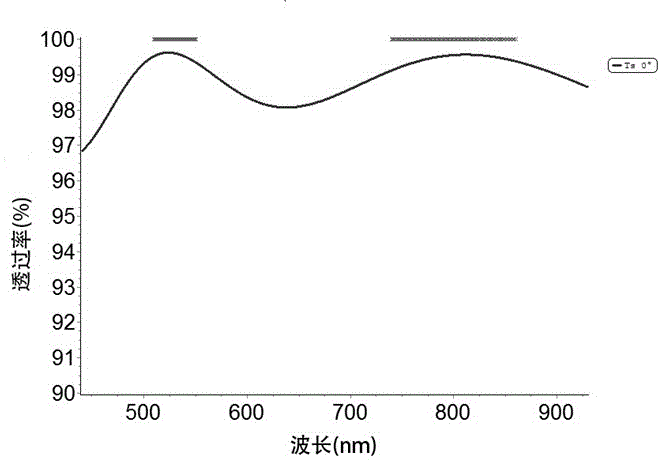
InactiveCN106435487AHas a waterproof effectReduce deliquescenceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh power lasersOptical property
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nonlinear crystal lithium triborate crystal surface high-laser-damaged-threshold antireflection film. Aiming at high LBO crystal anisotropy and the damage mechanism of the antireflection film, the method includes the steps that the surface of an LBO crystal is plated with a SiO2 film through an IAD process, and the film with which the surface of the LBO crystal is plated through the IAD process carries out plating through a sol-gel method. The LBO antireflection film prepared through the method has excellent optical properties, the high damage threshold and good environmental stability, and can be compatible with existing substrate machining, cleaning and film preparation processes. The preparation method has the beneficial effects of being high in process repeatability, high in controllability, easy to popularize and the like, and has wide application prospects in the field of high-power laser films in future.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
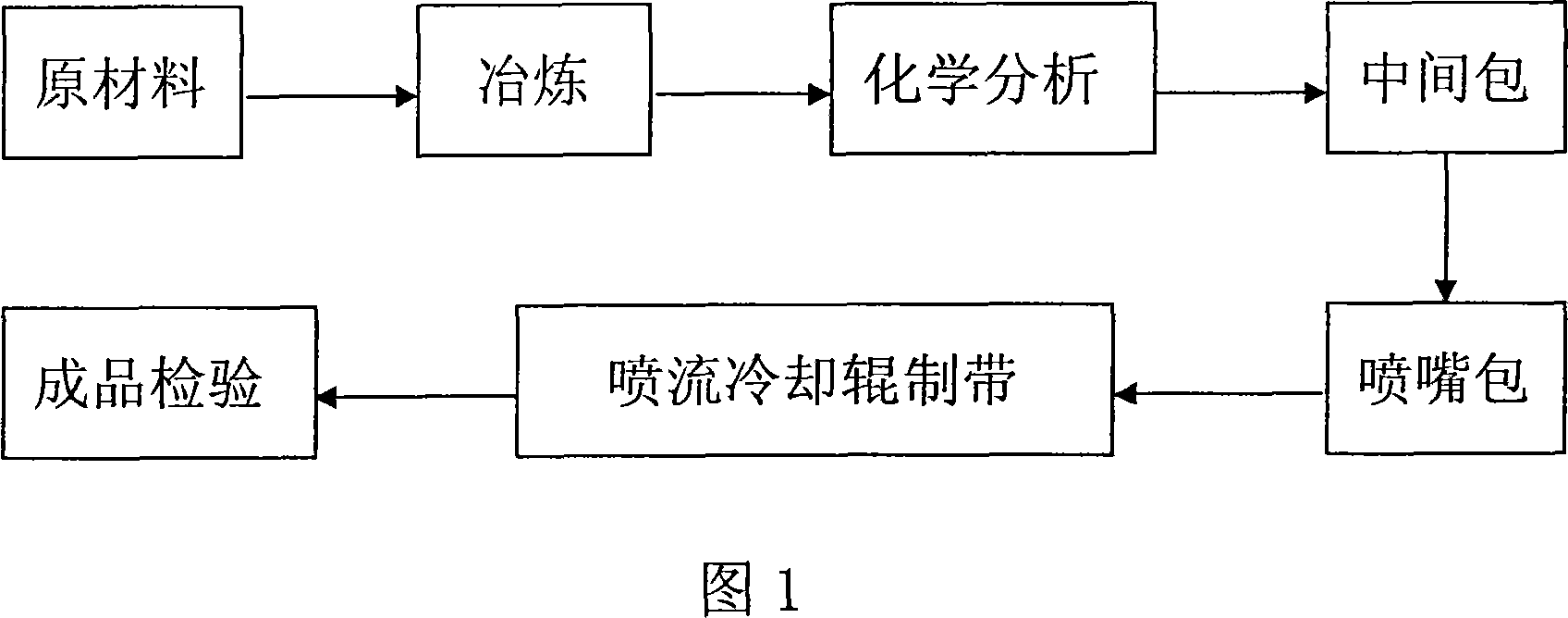
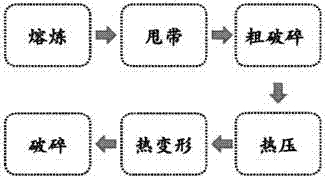
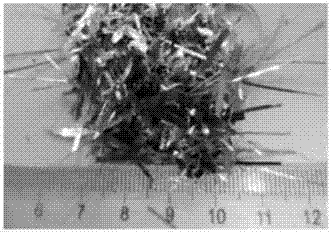
Amorphous mobile tape-making production process
The moving process of producing amorphous belt includes the following steps: smelting alloy ingot with amorphous iron-base material, chemical analysis, pouring molten steel into pouring basket, making molten steel enter to nozzle ladle, making molten steel flow to cooling roll in high speed rotation for chilling to form thin amorphous belt, and product inspection. The amorphous belt has no crystal, excellent magnetic, electric, chemical and mechanical performance, short production process, low production cost and other advantages.
Owner:上海安泰至高非晶金属有限公司
Method for preparing aeolotropic magneto resistor permalloy thin film
InactiveCN1632965AHigh anisotropic magnetoresistance valueMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsVacuum evaporation coatingPermalloyAlloy
It is an anisotropism magnetic resistance permalloy film process method, which comprises the following steps: to adopt magnetic control splash method and to select different contents Ni#-[x]Fe#-[1-x] alloy target, wherein x is between 78 to 85; to go to the coating chamber with 99.99 úÑ argon gas for 0.5 to 1 hour before splash; to sustain the gas pressure as 0.1 to 0.5 Pa; to control the thin film impurity content less than 0.1 percent; to process the Ni#-[81]Fe#-[19] thin film with accurate content.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
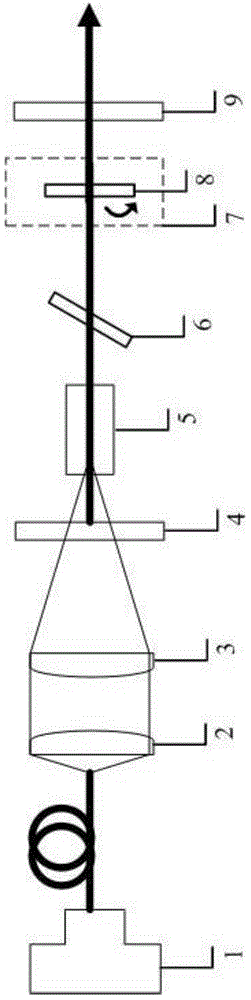
Laser device and method for adjusting and controlling passively Q-switched laser output characteristics through Cr<4>+: YAG crystal anisotropy characteristics
InactiveCN103986061ARealize regulationAchieve anisotropic changeLaser output parameters controlOptical pumpingTransmittance
Disclosed are a laser device and method for adjusting and controlling passively Q-switched laser output characteristics through Cr<4>+: YAG crystal anisotropy characteristics. The device comprises a semiconductor laser pumping source (1), a first aspherical lens (2), a second aspherical lens (3), a laser front cavity mirror (4), a laser crystal (5), an adjusting frame (7) with a rotary adjusting function, a Cr<4>+: YAG crystal (8) and a laser output mirror (9), wherein the semiconductor laser pumping source (1), the first aspherical lens (2), the second aspherical lens (3), the laser front cavity mirror (4), the laser crystal (5), the adjusting frame (7), the Cr<4>+: YAG crystal (8) and the laser output mirror (9) are arranged in sequence in the beam propagation direction. The method comprises the first step of constructing Cr<4>+: YAG crystal passively Q-switched laser output, and the second step of rotating and adjusting the adjusting frame to achieve anisotropy changes of Cr<4>+: YAG crystal energy transmittance in a laser resonance cavity, and finally adjusting and controlling the passively Q-switched laser output performance. According to the device and method, the passively Q-switched laser output performance is controlled through the Cr<4>+: YAG crystal anisotropy energy transmittance, and the method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Beam, ink jet recording head having beams, and method for manufacturing ink jet recording head having beams
InactiveUS7275813B2Easy to changeImprove corrosion resistanceSemi-permeable membranesFixed microstructural devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceLight beam
A beam having a base material of silicon monocrystal and at least one projection which is integrally formed so as to be supported at least at one end thereof and which has two surfaces having an orientation plane (111), includes a bottom surface in a plane which is common with a plane of the base material; a groove penetrating from the bottom surface to a top of the projection; and a protecting member having a resistance property against a crystal anisotropic etching liquid and covering an inner wall of the groove.
Owner:CANON KK
Silicon processing method and silicon substrate with etching mask
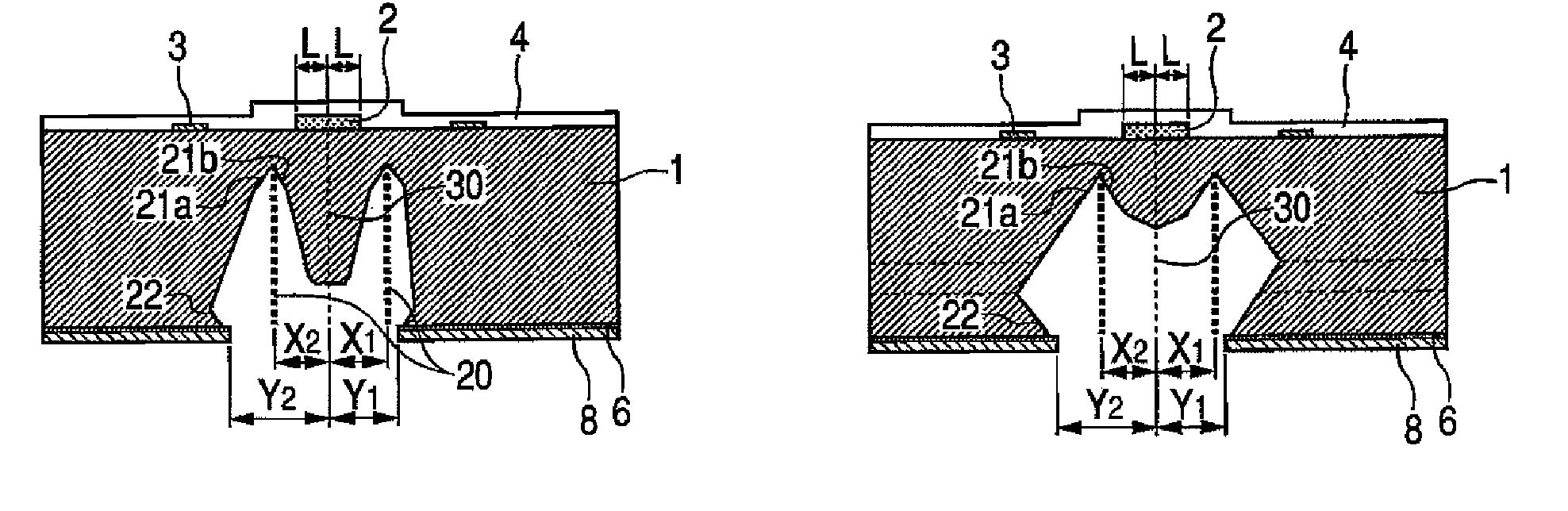
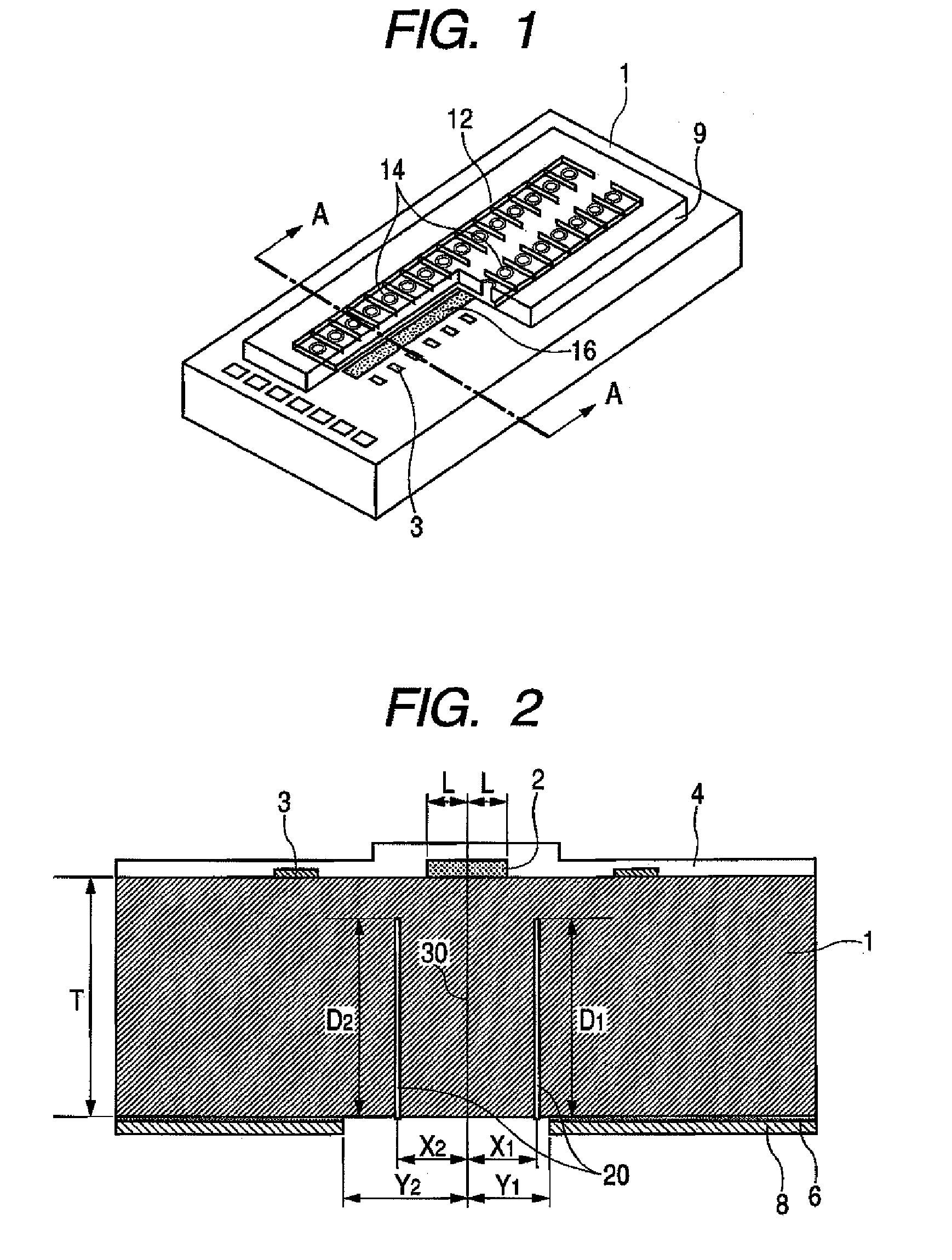
InactiveUS20100051944A1Less processing dimension errorGain is not constantSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDecorative surface effectsAnisotropic etchingCrystal anisotropy
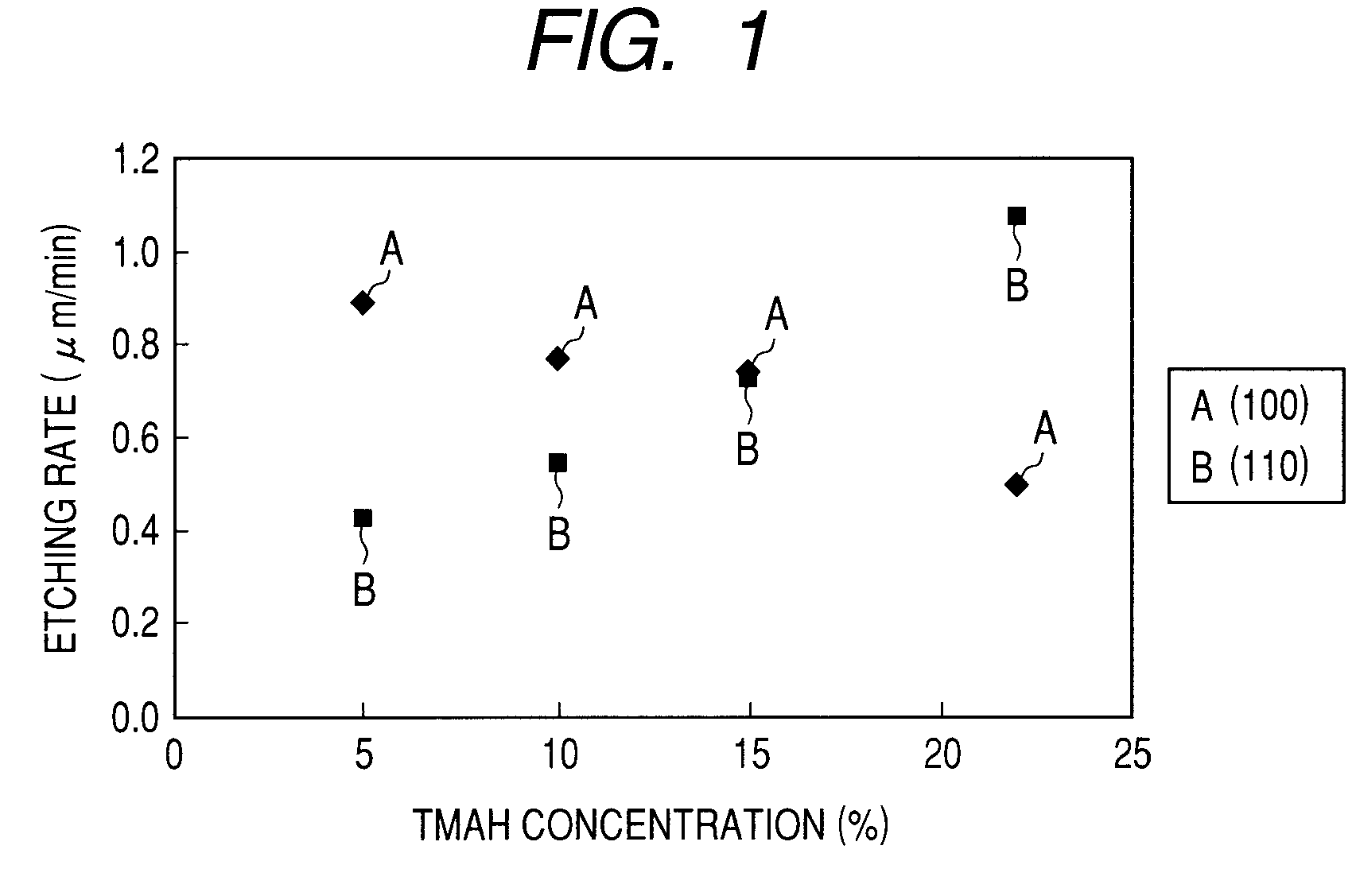
A silicon processing method includes: forming a mask pattern on a principal plane of a single-crystal silicon substrate; and applying crystal anisotropic etching to the principal surface to form a structure including a (111) surface and a crystal surface equivalent thereto and having width W1 and length L1. The principal plane includes a (100) surface and a crystal surface equivalent thereto or a (110) surface and a crystal surface equivalent thereto. A determining section for determining the width W1 of the structure is formed in the mask pattern. The width of the determining section for the width W1 of the mask pattern is width W2. The width of the mask pattern other than the determining section is larger than the width W2 over a length direction of the mask pattern.
Owner:CANON KK
Manufacturing method for ink jet recording head chip, and manufacturing method for ink jet recording head
ActiveUS7824560B2High precisionIncreased accuracy levelRecording apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnisotropic etchingCrystal anisotropy
A manufacturing method for a substrate for an ink jet head, including formation of an ink supply port in a silicon substrate, the method includes a step of forming, on one side of the substrate, an etching mask layer having an opening at a position corresponding ink supply port; a step of forming unpenetrated holes through the opening of the etching mask layer in at least two rows in a longitudinal direction of the opening; and a step of forming the ink supply port by crystal anisotropic etching of the substrate in the opening.
Owner:CANON KK
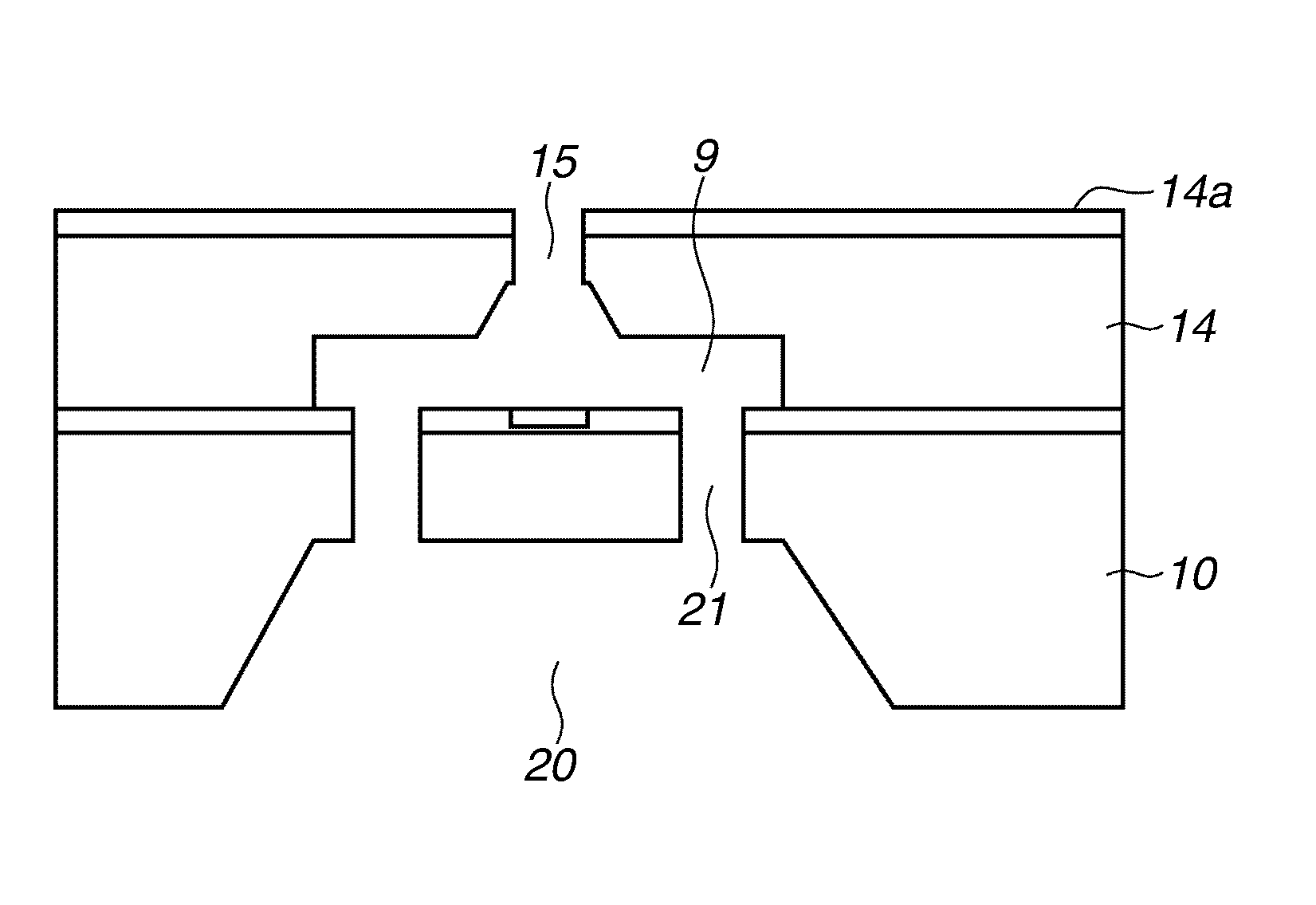
Microphone manufacturing method
ActiveUS7849583B2Large resistanceImprove low frequency characteristicsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesWave amplification devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
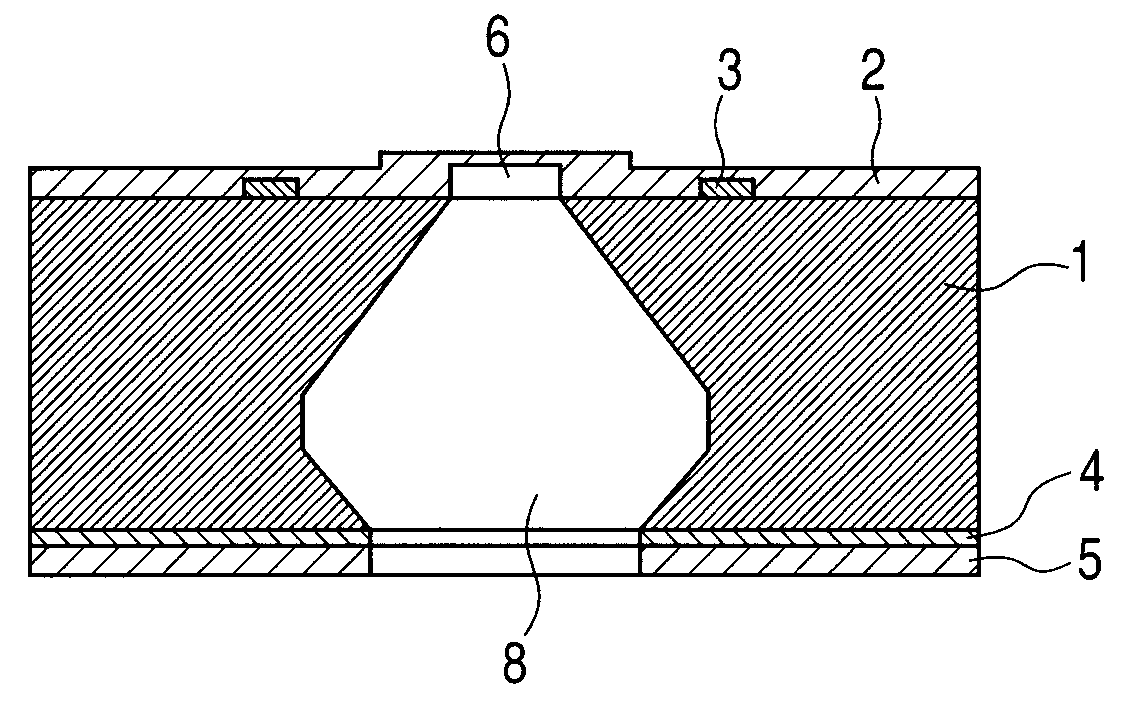
A microphone manufacturing method that includes forming an etching protective film on a surface of a semiconductor substrate, opening an etching window through the etching protective film, and forming a sacrifice layer in the etching window and also on an upper face of the etching protective film. The method includes forming a vibration film above said sacrifice layer and starting an etching process of said sacrifice layer through a preformed port at a location wherein said sacrifice layer is sandwiched by said vibration film and the etching protective film and located apart from the etching window. The etching process uses an etchant to which the etching protective film is resistant, to open the etching window. The method includes crystal anisotropically etching said semiconductor substrate through the port and the etching window by using an etchant to which the etching protective film is resistant so that a cavity is formed.
Owner:MMI SEMICON CO LTD
Polycrystalline magnesium oxide (MgO) sintered body and MgO sputtering target
ActiveUS8454933B2Increase chanceShrink poresLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringHigh rate
The invention provides a polycrystal magnesium oxide (MgO) sintered body which is capable of having a sintered density close to a theoretical density thereof. The MgO sintered body exhibits excellent mechanical properties and heat conductivity, while reducing contamination of an atmosphere due to gas generation. The invention also provides a production method for the sintered body. The polycrystal MgO sintered body has a unique crystalline anisotropy in which (111) faces are oriented along a surface applied with a uniaxial pressure at a high rate. The polycrystalline MgO sintered body is obtained by a method which includes the steps of: sintering an MgO raw material powder, having a particle size of 1 μm or less, under a uniaxial pressure and then subjecting the sintered powder to a heat treatment under an atmosphere containing 0.05 volume % or more of oxygen, at a temperature of 1273 K or more for 1 minute or more.
Owner:NIPPON TUNGSTEN CORP +1
Method of processing silicon substrate and method of manufacturing substrate for liquid discharge head
InactiveUS8287747B2Small widthEfficiently formedRecording apparatusDecorative surface effectsPlane orientationAnisotropic etching
Owner:CANON KK
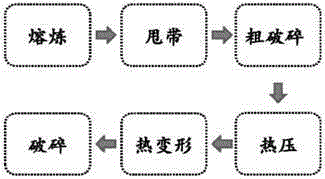
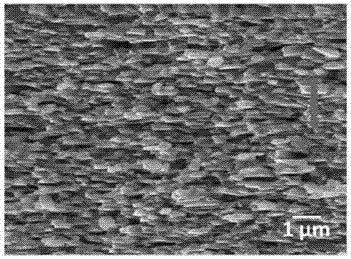
Anisotropic high-frequency microwave magnetic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105280320AExcellent high-frequency microwave magnetic propertiesAchieve overlayInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsMicrowaveRare earth
The invention belongs to the field of magnetic materials, and particularly to an anisotropic high-frequency microwave magnetic material and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the magnetic material is RxFe100-x-yBy (at%), wherein 11.76<x<=15, 5.88<=y<=7.0, and R is selected from Sm, Er and Tm. The magnetic material has magnetic crystal anisotropy, wherein an easily magnetized surface is vertical with a C axis. The magnetic material is prepared through processes of melting, preparing to a belt, rough crushing, hot pressing, heat deforming and crushing. The anisotropic high-frequency microwave magnetic material which is made of one compound of a metal selected from rare earth intermetallics according to the invention realizes superposing of a magnetic crystal anisotropic field and a shape anisotropic field, so that the material has better high-frequency characteristic.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Method for manufacturing liquid discharge head
InactiveUS8778200B2High shape accuracyFavorable supply characteristicRecording apparatusDecorative surface effectsAnisotropic etchingMechanical engineering
Owner:CANON KK
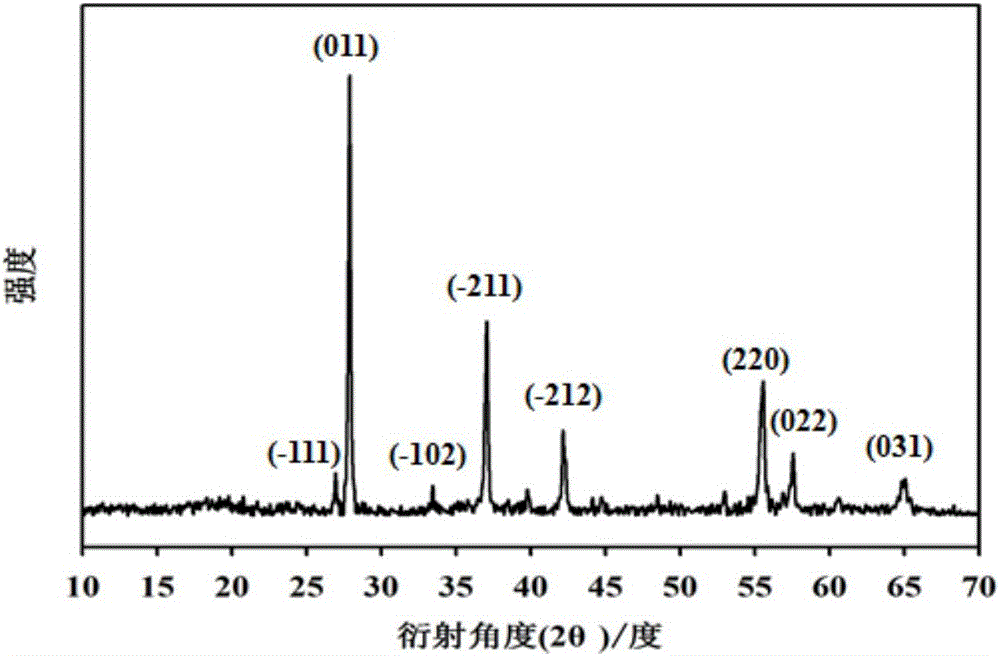
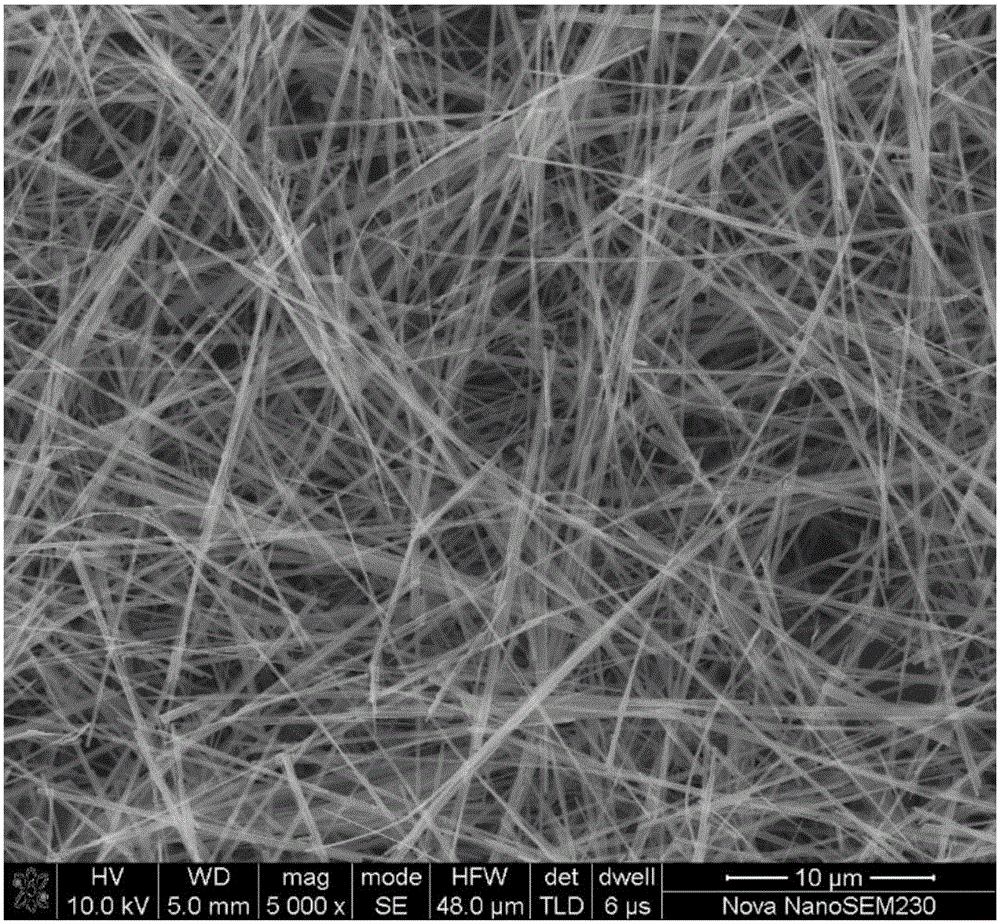
Monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106395901AEvenly distributedHigh crystallinityNanotechnologyVanadium oxidesVanadium dioxideNanowire
The invention discloses a method for preparing a monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a vanadium source, stearic acid and water, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction on the obtained mixed solution, sequentially centrifuging, washing and drying the obtained product after the hydrothermal reaction is completed, thereby obtaining the monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire. By utilizing the dual effects of inducing anisotropic growth of crystals through a reducing agent and a surfactant in the stearic acid, the monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire with thermal induced phase transition property can be prepared in a one-step process, the preparation process is simple, complicated equipment is not needed, the production cost is low, the reaction conditions are easy to control, and large-scale industrial production is easily realized; and moreover, the monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire is uniform in distribution and high in crystallinity and can be applied to the fields of smart windows, photoelectric switches, camouflage and stealth, infrared detection devices and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for preparing aeolotropic magneto resistor permalloy thin film
InactiveCN100352076CHigh anisotropic magnetoresistance valueMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical resistance and conductancePermalloy
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method of preparing Cr<3+>-doped CoFe2O4 high-density magnetic-recording material
ActiveCN105129868AImprove coercive forceThe method is economical and convenientCobalt compoundsMagnetic mediaPeak value
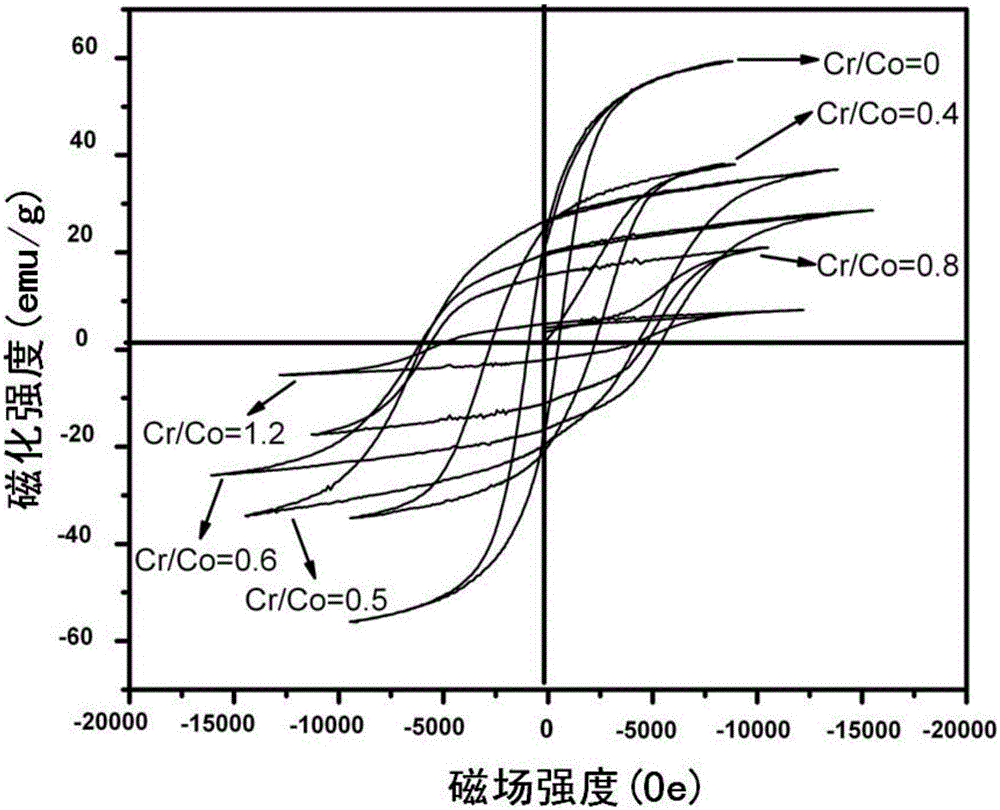
A method of preparing a Cr<3+>-doped CoFe2O4 high-density magnetic-recording material belongs to the technical field of preparation of magnetic-recording materials. In the method, Cr<3+> is doped into metal oxides through a hydrothermal method, so that size of product particles is changed. In a spinel ferrite structure, iron ions are subjected to crystal field to cause quenching of orbital angular momentum, which leads to low magnetic crystal anisotropy and a low coercive force. As a result, by means of the Cr<3+>, of which the orbital angular momentum is not quenched, for doping the CoFe2O4, the CoFe2O4 is improved in magnetic crystal anisotropy. By means of the hydrothermal method, the Cr<3+> is doped with the CoFe2O4, so that two methods of size controlling and element doping are combined, thereby further increasing the coercive force of the magnetic medium. During the process of doping the Cr<3+>, with increase of the doping amount of the Cr<3+>, the product is gradually increased in magnetic crystal anisotropy, and meanwhile, the size of the particles is gradually changed, and when the size is in single-domain critical size range (about 40-100 nm), the product reaches a peak value in the coercive force. The method can further increase the coercive force of the magnetic medium, and is economical and convenient and is easy to popularize.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
A kind of easy-face anisotropic high-frequency microwave magnetic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105280320BExcellent high-frequency microwave magnetic propertiesAchieve overlayInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare earth metal compoundsThermal deformation
The invention belongs to the field of magnetic materials, in particular to an anisotropic high-frequency microwave magnetic material with easy surface and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the magnetic material is expressed according to the atomic ratio: RxFe100‑x‑yBy (at%), wherein, 11.76<x≤15, 5.88≤y≤7.0, R is one of Sm, Er, Tm; the magnetic material It has easy-plane magnetic crystal anisotropy, and its easy-magnetization plane is perpendicular to the C-axis; the magnetic material is prepared by smelting→spinning→coarse crushing→hot pressing→hot deformation→crushing. The high-frequency microwave magnetic micropowder of the easy-plane anisotropic rare earth intermetallic compound obtained by the invention realizes the superposition of the magnetic crystal anisotropy field and the shape anisotropy field, so that the material has more excellent high-frequency characteristics.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Method of manufacturing a substrate for liquid ejection head
InactiveUS8435805B2Improve opening accuracyInhibition effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrintingEngineeringProtection layer
Provided is a method of manufacturing a substrate for liquid ejection head, including: forming a groove portion by etching on one surface side of a silicon substrate, the groove portion being formed so as to surround a portion at which a liquid supply port is to be formed on an inner side of the groove portion; forming a protective layer on the one surface side of the silicon substrate, the protective layer being formed inside the groove portion and on an outer side of the groove portion; and forming the liquid supply port by subjecting the silicon substrate to crystal anisotropic etching treatment with use of the protective layer as a mask.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com