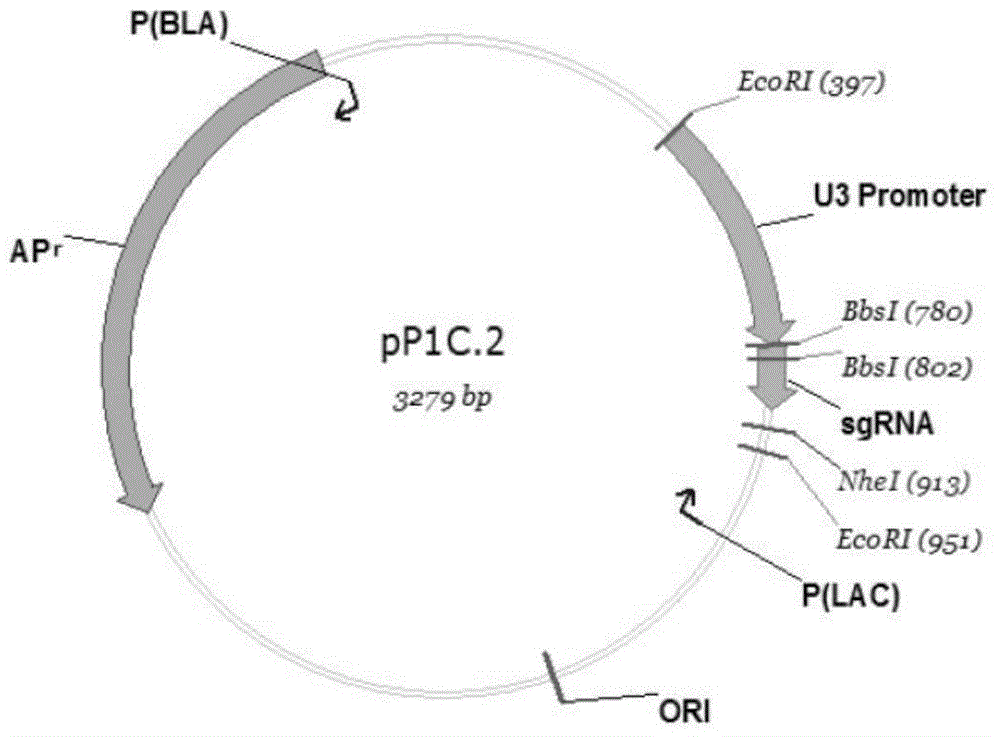
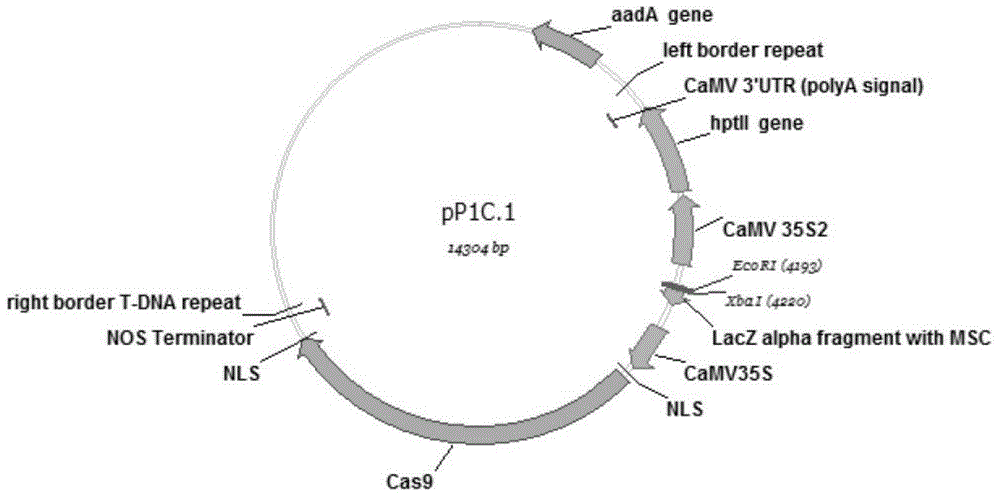
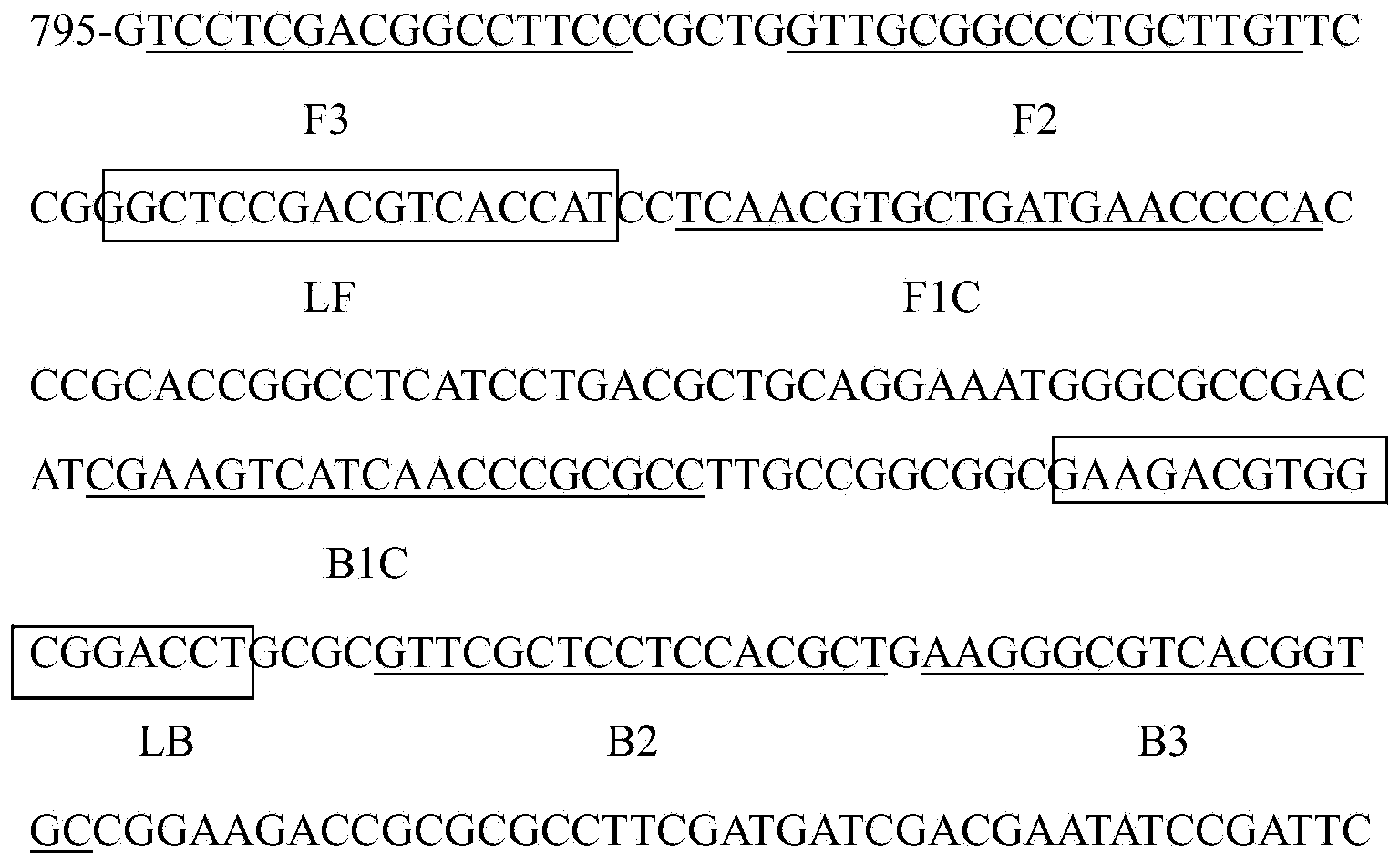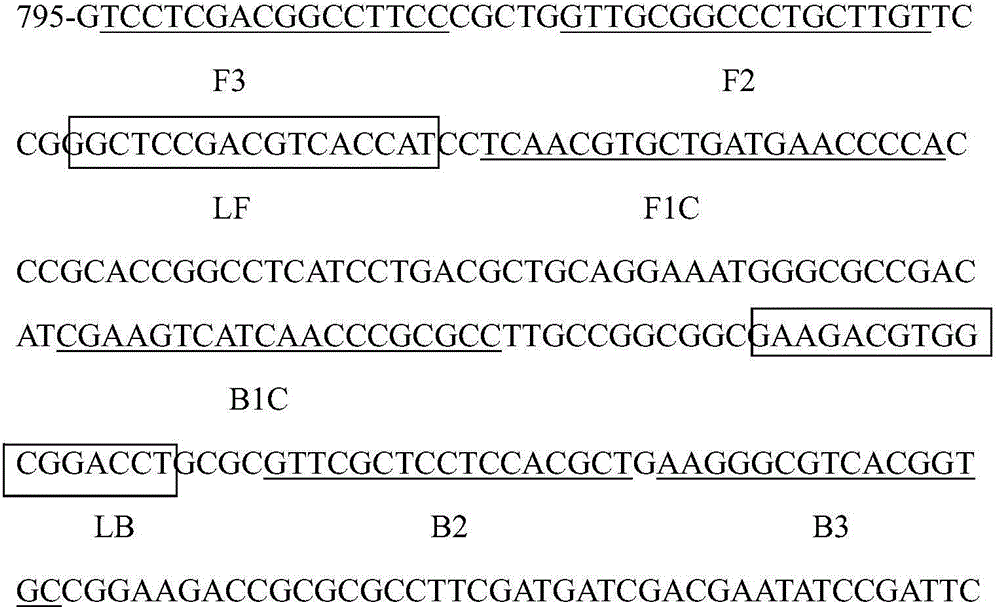Patents
Literature
31 results about "Gene flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations are considered to have equivalent allele frequencies and therefore effectively be a single population. It has been shown that it takes only "One migrant per generation" to prevent populations from diverging due to drift. Gene flow is an important mechanism for transferring genetic diversity among populations. Migrants change the distribution of genetic diversity within the populations, by modifying the allele frequencies (the proportion of members carrying a particular variant of a gene). High rates of gene flow can reduce the genetic differentiation between the two groups, increasing homogeneity. For this reason, gene flow has been thought to constrain speciation by combining the gene pools of the groups, thus preventing the development of differences in genetic variation that would have led to full speciation. In some cases migration may also result in the addition of novel genetic variants to the gene pool of a species or population.
Hydro-fluctuation belt wetland vegetation restoration proper species screening method
InactiveCN106472134ALess prone to intrusionPrevent genetic driftInvasive species monitoringHorticulture methodsRevegetationTidal flat
The invention discloses a hydro-fluctuation belt wetland vegetation restoration proper species screening method. The method includes: investigating region vegetation, and preliminarily selecting species suitable for region vegetation restoration from the aspects of life form and growth form of species; adopting a soil seed bank germination experiment to screen to obtain omissive proper plants; inferring proper plants for vegetation restoration of a hydro-fluctuation belt according to vegetation investigation on the hydro-fluctuation belt and the soil seed bank germination experiment of the same; performing a waterlogging tolerance experiment on the proper plants, and screening proper species for region vegetation restoration; according to waterlogging tolerance and region hydrologic changing characteristics, arranging the proper species obtained by screening, and conducting practice demonstration of vegetation restoration. The method is conducive to preventing genetic drift caused by gene flow and maintaining a gene bank of local species stable, less prone to causing intrusion of foreign species and provides technical support and scientific guidance for large-area demonstration and popularization of vegetation restoration in regions like reservoir hydro-fluctuation belts, riparian zones and tidal flat wetland.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for determining genetic affiliation, substructure and gene flow within human populations
InactiveUS6929911B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA paternity testingPresent method
The present invention provides novel polymorphisms on the Y chromosome and methods of using these polymorphisms as well as known polymorphisms on the Y chromosome as indicators of evolutionary heritage. The polymorphisms of the present invention clustered to specific regions of the Y chromosome, and polymorphisms of particular use to the present methods are found in the non-recombining region of the human Y chromosome (NRY). These polymorphisms, including SNPs, insertions, and deletions, may be useful for numerous applications, including forensics, paternity testing, diagnosis and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for creating rice engineering maintainer lines preventive against gene flow and application of rice engineering maintainer lines
InactiveCN105063083AAvoid Ecological Security RisksAvoid Ecological PollutionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceMutant line
The invention discloses a method for creating rice engineering maintainer lines preventive against gene flow. The method includes the steps of 1, site-specifically inserting an exogenous reporter gene and a pollen lethal gene into a flanking sequence of a fertility control gene of a wild rice chromosome so as to obtain a transgenic line containing the exogenous reporter gene and the pollen lethal gene, wherein the exogenous reporter gene, the pollen lethal gene and the fertility control gene are able to closely link and inherit; 2, hybridizing wild rice and homozygous recessive rice common genic male sterile lines to obtain F1-generation plants, hybridizing the F1-generation plants as male parents to the transgenic line to obtain a generation F2, screening the generation F2 to obtain hybrid lines containing the exogenous reporter gene, namely rice engineering maintainer lines required, wherein the homozygous recessive rice common genic male sterile lines are mutant lines with the sterility control gene. The invention further discloses application of the rice engineering maintainer lines preventive against gene flow in rice breeding.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) rapid detection method and application of glyphosate-resist transgenic soybean
InactiveCN103642918AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementResistGene flow
The invention relates to an LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) rapid detection method and application of a glyphosate-resist transgenic soybean. The method comprises the following steps: designing and selecting 6 LAMP primers F3, B3, FIP, BIP, LB and LF according to the specificity of a CP4-EPSPS gene sequence; and preparing and optimizing an LAMP reaction system. The glyphosate-resist transgenic soybean can be rapidly detected through DNA extraction of the glyphosate-resist transgenic soybean, loop-mediated isothermal amplification, amplification output color development and observation. According to the detection method, the specificity is strong, the sensitivity is high, the detection is rapid, the cost is low, the operation is convenient, and application values in rapid detection of transgenic soybean and processed goods and field monitoring of gene flow of the transgenic soybean are high.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
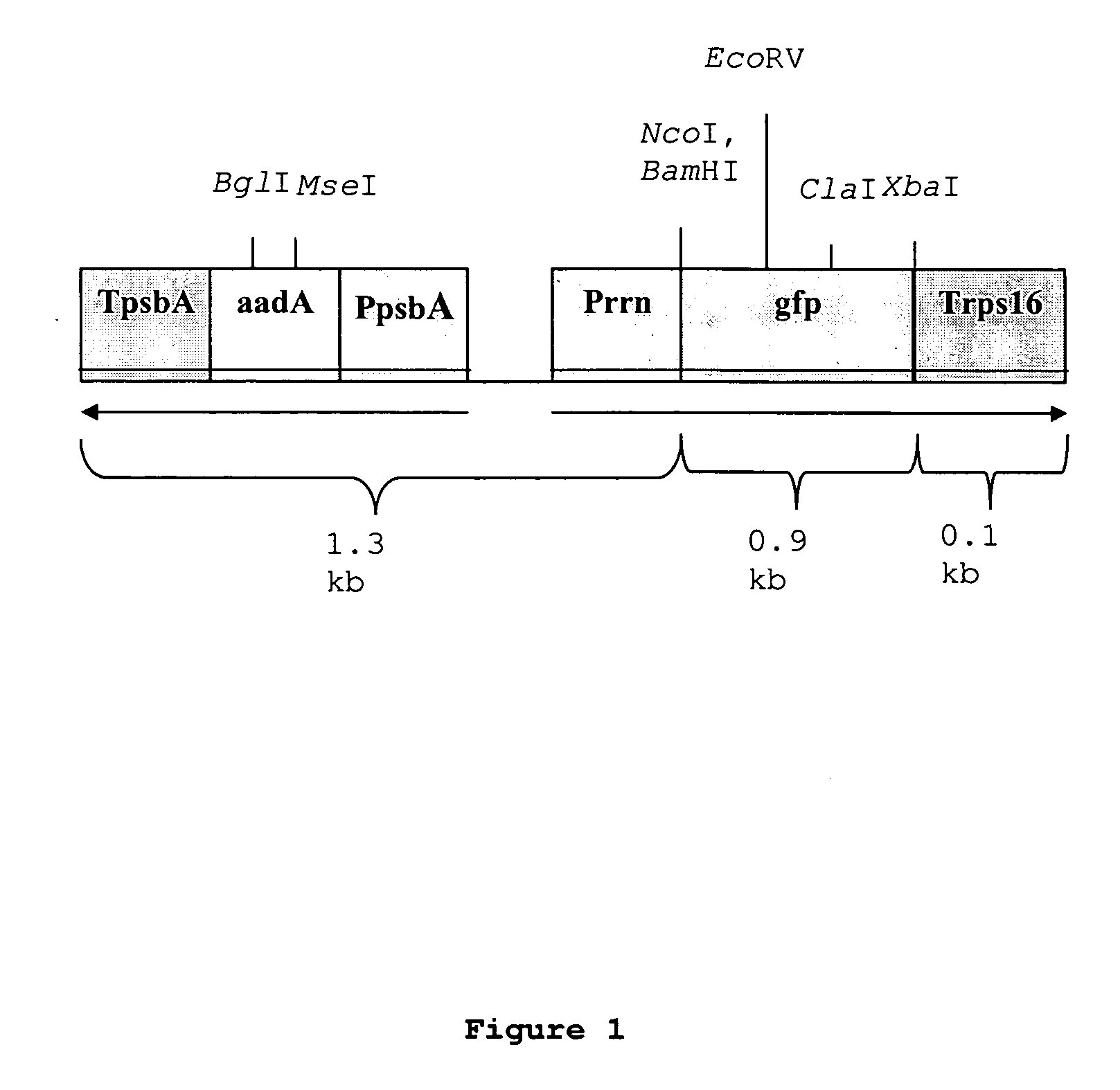
Chloroplast transgenesis of monocots: bioconfined genetically engineered monocot crops that will eliminate transgene flow
The present invention discloses transgenic monocot plants in which the plastid genome has been genetically engineered. The bioconfined genetically engineered monocot crops have transgene-free pollen grains which eliminate or dramatically reduce transgene flow. The present invention discloses plastid transgenesis technology having the additional advantages of the absence of gene silencing and position effect variation, the ability to express polycistronic messages from a single promoter, integration via a homologous recombination process that facilitates targeted gene replacement and precise transgene control, and sequestration of foreign proteins in the organelle which prevents adverse interaction with the cytoplasmic environment.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
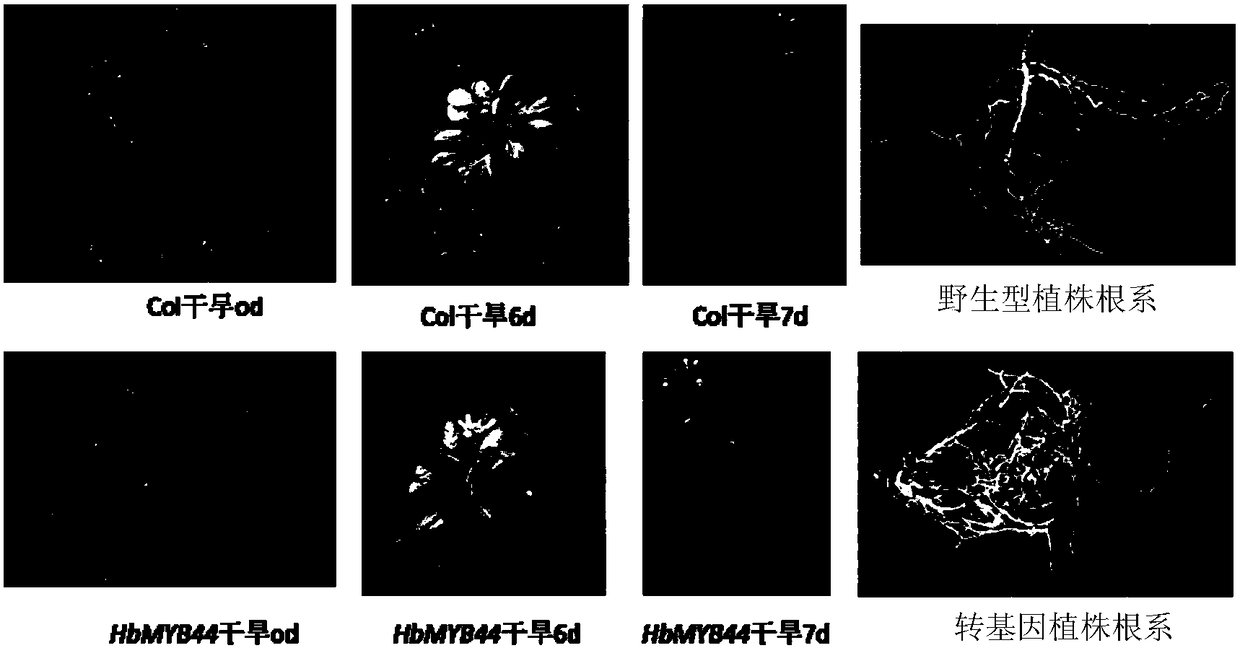
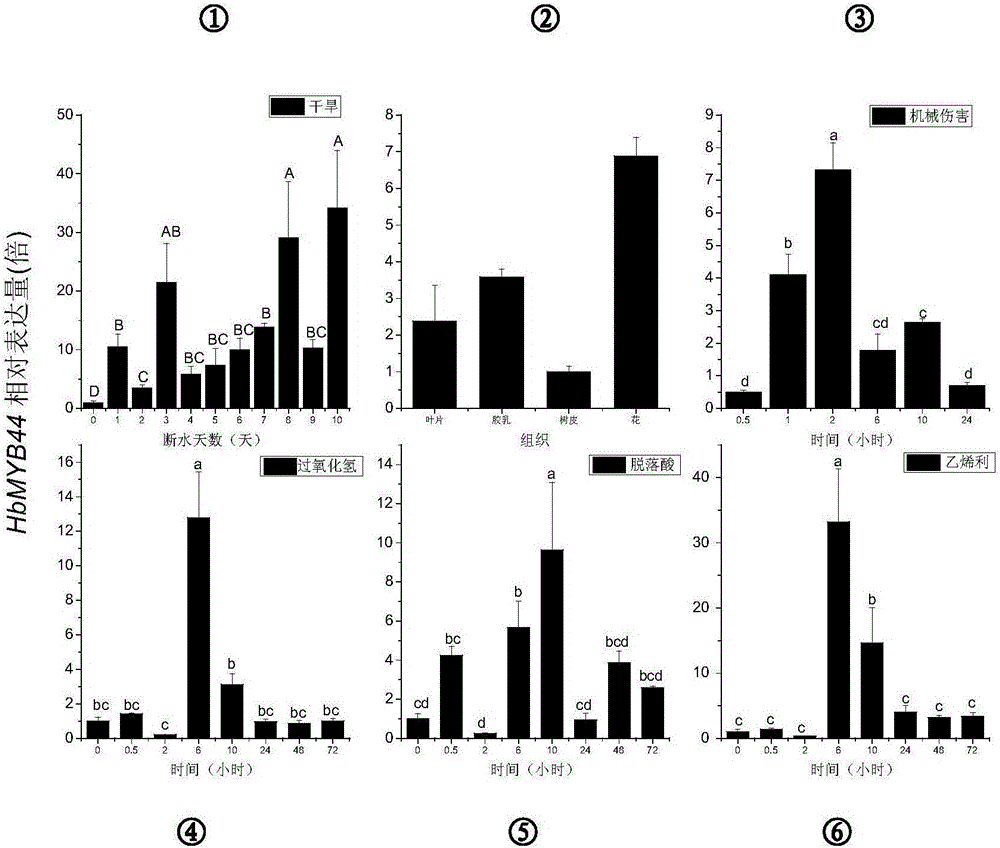
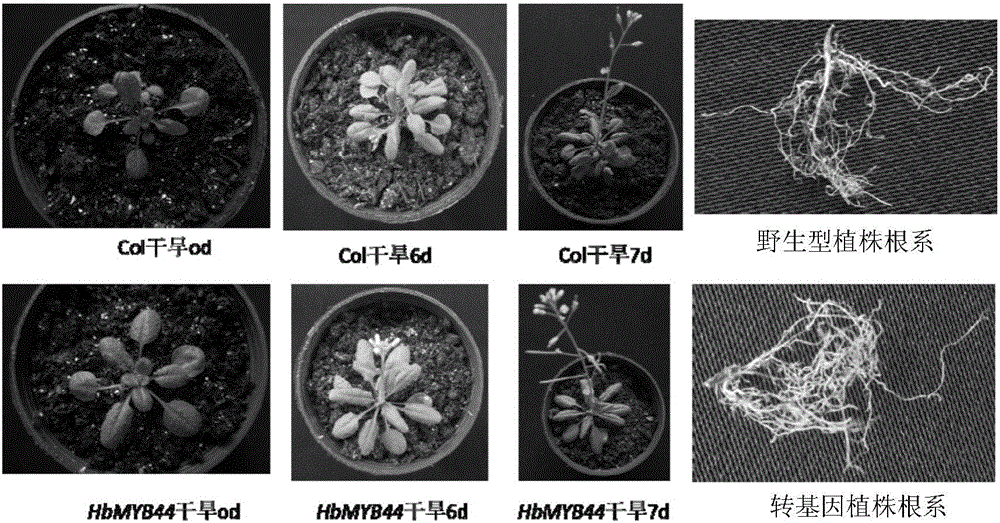
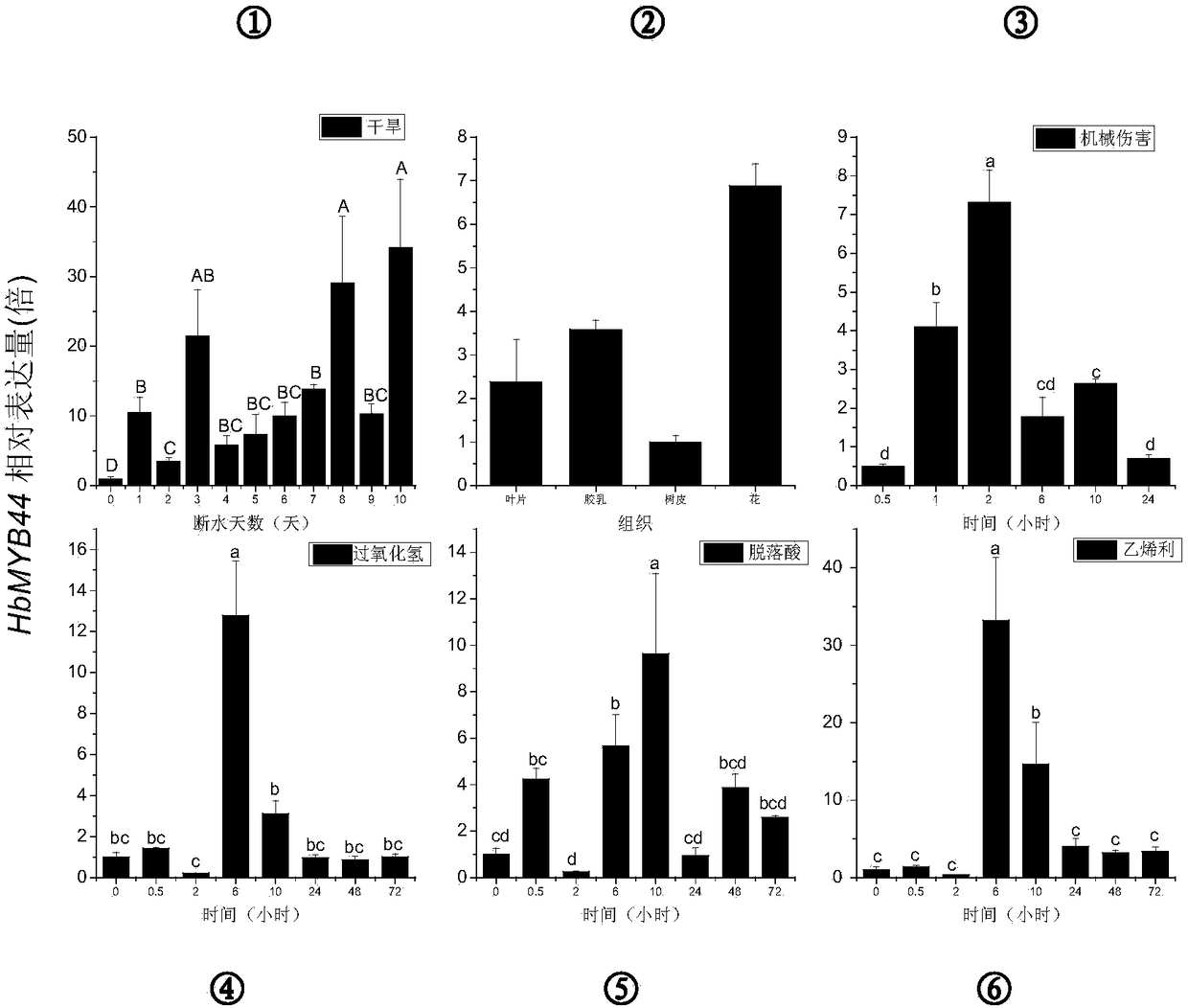
Rubber tree transcription factor HbMYB44 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105861519AImprove drought resistanceReduce the impactMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesEndurance capacityGene flow
The invention relates to a rubber tree transcription factor HbMYB44 gene and the application thereof. The transcription factor HbMYB44 gene relevant to drought resistance of rubber trees is provided, function study of the gene is conducted through arabidopsis thaliana transformation of the HbMYB44 gene, and the drought stress endurance capacity of transgenic arabidopsis is improved. The gene can be used for drought resisting transgenosis research of rubber trees and other crops. The transcription factor HbMYB44 gene relevant to drought resistance of rubber trees comes from rubber trees, gene flow is avoided, influences on the environment are small, and a new gene resource is provided for improving the drought resistance of plants.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
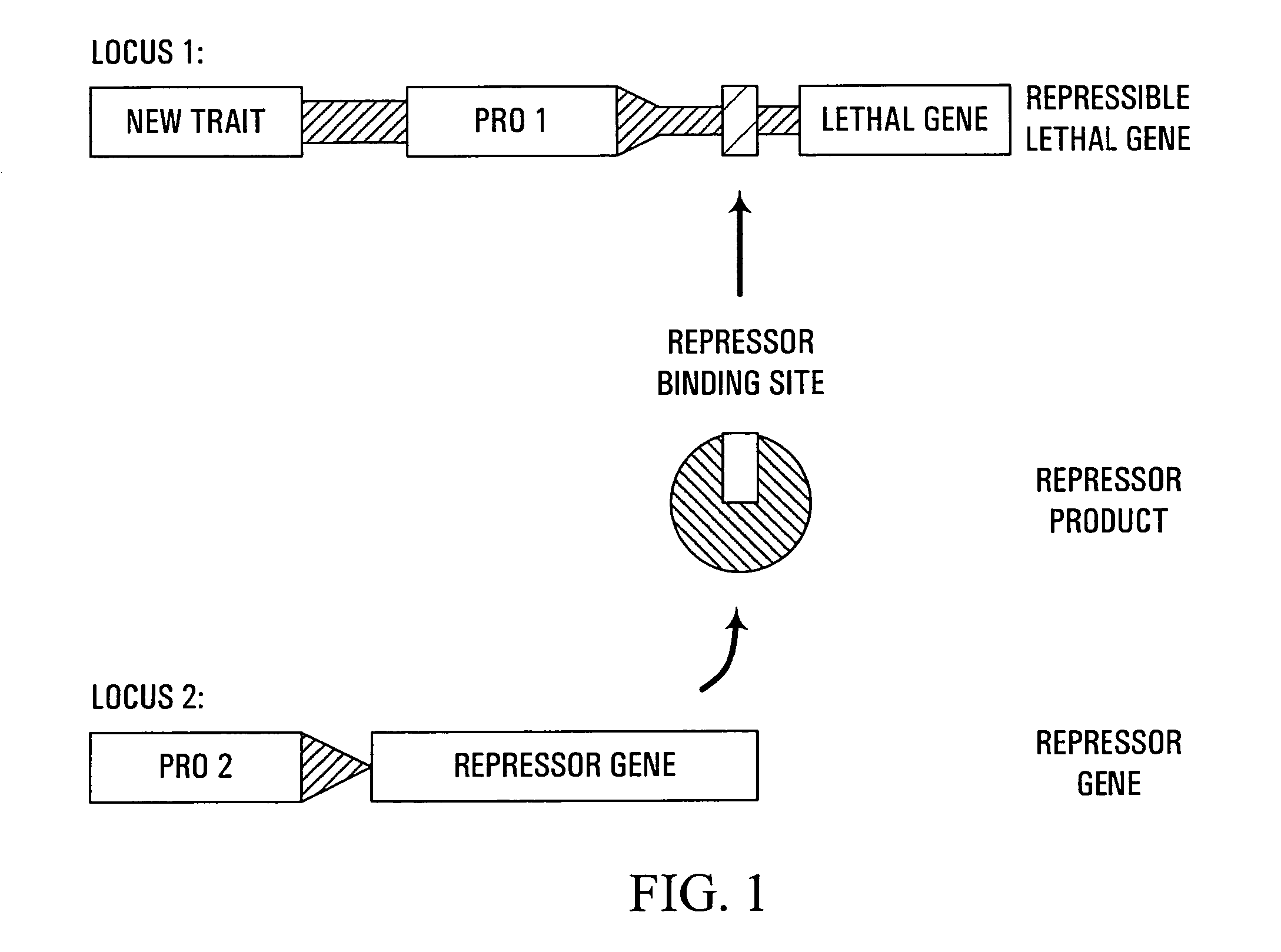
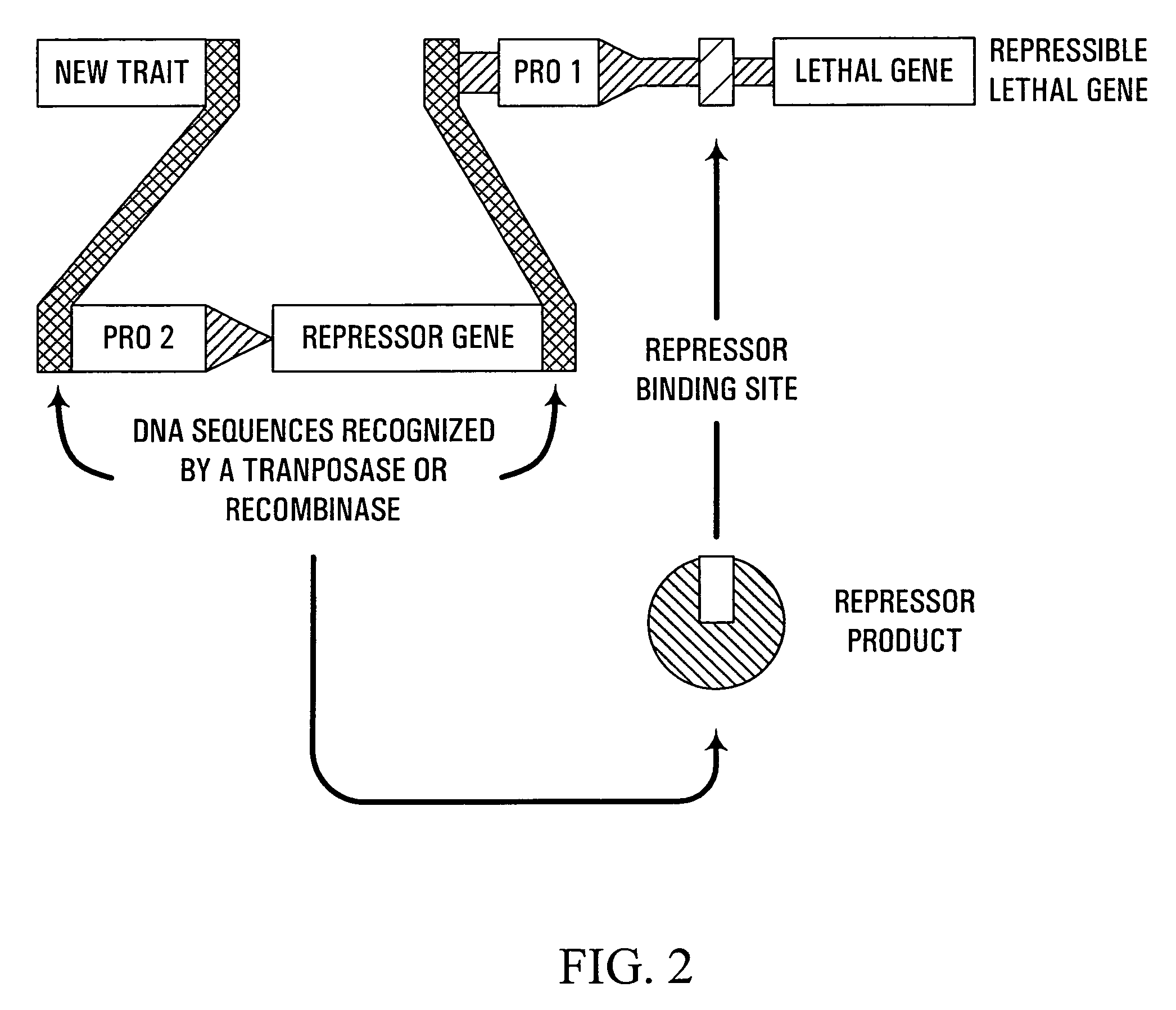
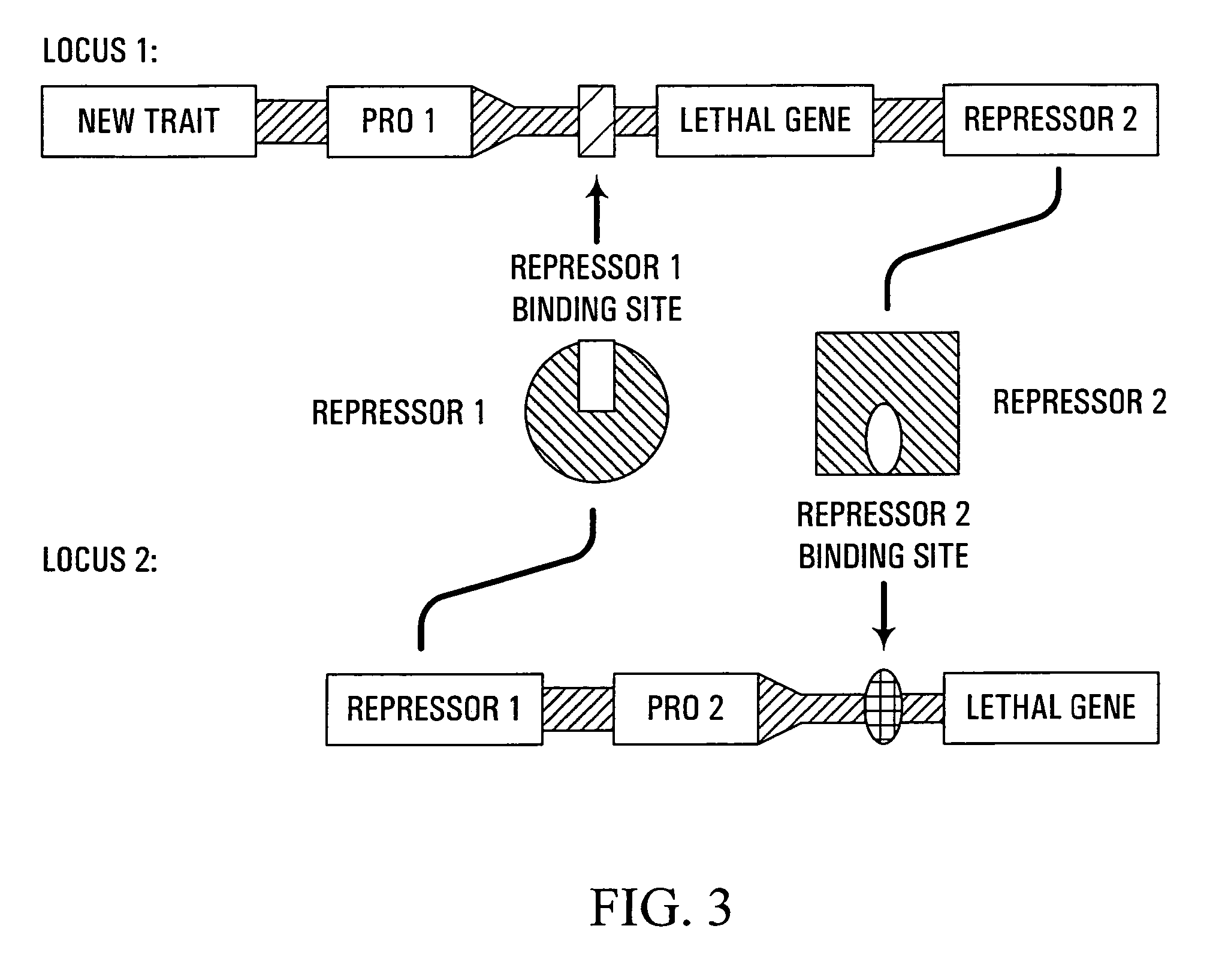
Methods and genetic compositions to limit outcrossing and undesired gene flow in crop plants
InactiveUS7671253B2Avoid spreadingAvoid persistenceSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesMeiosisRecombinant DNA
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
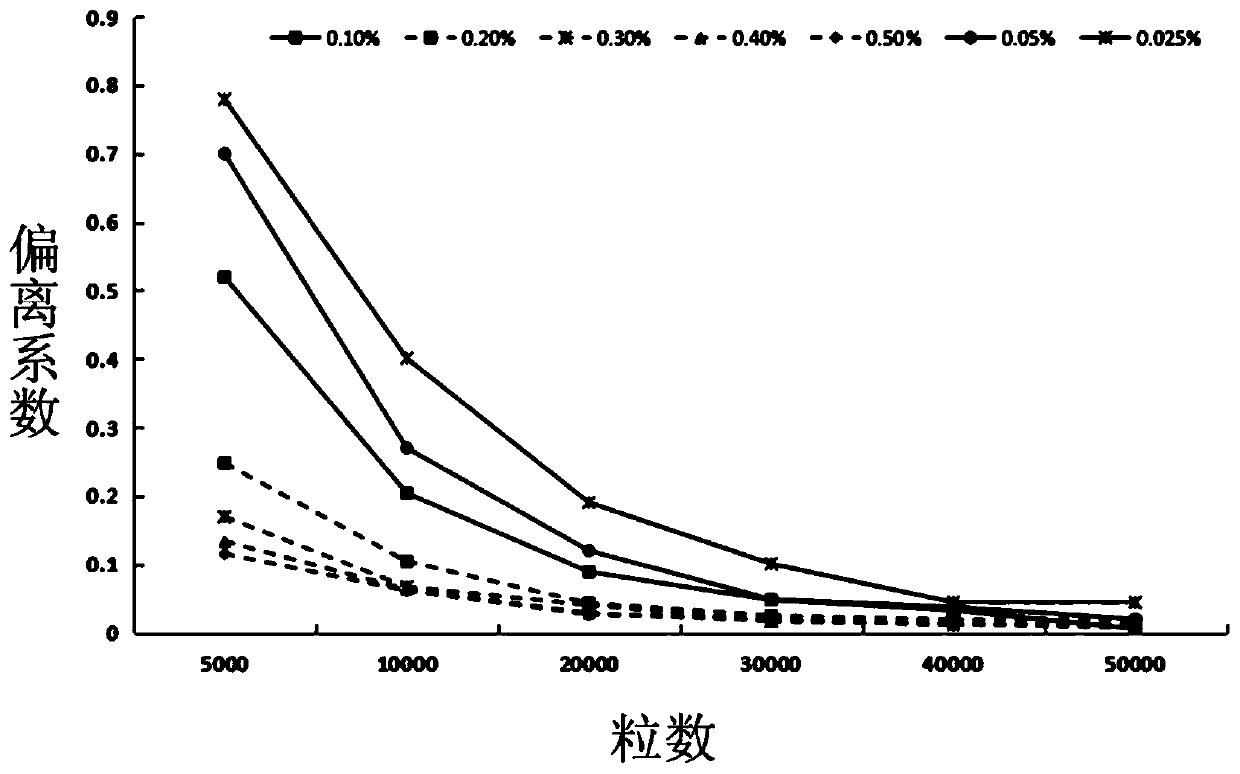
Method for evaluating influence of environmental single factor on transgene plant gene flow
InactiveCN102373268AEliminate the possibility of spreadingImprove securityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGene flowRoom temperature
The invention provides a method for evaluating the influence of an environmental single factor on transgene plant gene flow. According to the method, factors which may influence the gene flow are extracted from natural environment by manual simulation at room temperature. The natural environment is separated and the gene flow test is carried out under a single factor so as to determine the influence of the single factor on the gene flow. With the combination of real measured values under different regional and environmental factors, main factors which influence the gene flow in the locality can be better determined and an effective predetermined plan for the planting of transgene plants is made, so as to minimize test repetitions to some extent and save test cost. In addition, different from wagon-wheel bulk sampling point F1 sampling analysis, the method provided by the invention requires less occupation space, and can be used to reduce F1 sampling amount and greatly decrease the workload of test post-detection and analysis.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Camphor free whole genome SSR molecular marker, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108823327AAvoid missingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMarker-assisted selectionGene flow
The invention discloses a camphor free whole genome SSR molecular marker, a preparation method and application thereof. A camphor tree microsatellite molecular marker can be applied to population genetic diversity detection and genetic relationship analysis of ancient camphor trees, provides a bath of novel microsatellite molecular markers for lauraceae, and further provides a novel tool for researches on population genetic differentiation and structure and population genetic diversity level, gene flow and mating system among populations, speciational evolution and marker assisted selection oflauraceae.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF FORESTRY
Genetic diversity analysis method for inbreeding male giant freshwater prawn
InactiveCN108642187AQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFresh water organismAllele frequency
The invention discloses a genetic diversity analysis method for a inbreeding male giant freshwater prawn, which comprises the following steps of: step 1, acquiring inbreeding giant freshwater prawn samples with different traits, and extracting the DNA; step 2, selecting a microsatellite marker combination and designing a specific PCR primer set for amplification; step 3, evaluating the number of PCR products and observing the genotype and size of the alleles; step 4, recording the allele number A, the allele duplication number G, the observed heterozygosity Ho, the desired heterozygosity He, and the accuracy deviation value P based on the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium law of each prawn, and analyzing the difference of the microsatellite sites; calculating the gene flow Nm according to the frequency parameters of the population allele; gene spacing is determined by using the gene Nei coefficient method. According to the invention, based on the microsatellite analysis method, the method provides a genetic diversity analysis method for a inbreeding male giant freshwater prawn, which is very suitable for researching the genetic structure of different near-parent male prawn groups, and provides a high-quality male parent for the giant freshwater prawns.
Owner:GUANGXI ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
Method for assessing weedization gene flow risk of transgenic rice and application thereof
ActiveCN111139311AImprove concealmentEvaluate scientifically and accuratelyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
The invention discloses a method for assessing a weedization gene flow risk of transgenic rice and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: performing mixed cropping by intercropping or surrounding cropping, respectively harvesting offspring seeds of transgenic rice and weedy rice, performing forward flow detection and seedling resistance screening, and detecting a resistancegene of surviving plants; and performing reverse flow detection on a red husk Rc gene in seeds. According to detection rates of the resistance gene and the Rc gene, a gene flow rate of the transgenicrice is calculated, and a gene flow risk is assessed. The method overcomes the defect that the actual flow risk is underestimated in the past since only the forward flow risk is considered and the reverse flow risk is ignored, and thus, the pollen-mediated gene flow risk of the transgenic rice can be assessed more accurately, thereby providing technical supports for environmental safety evaluation and management in the transgenic rice commercialization process.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
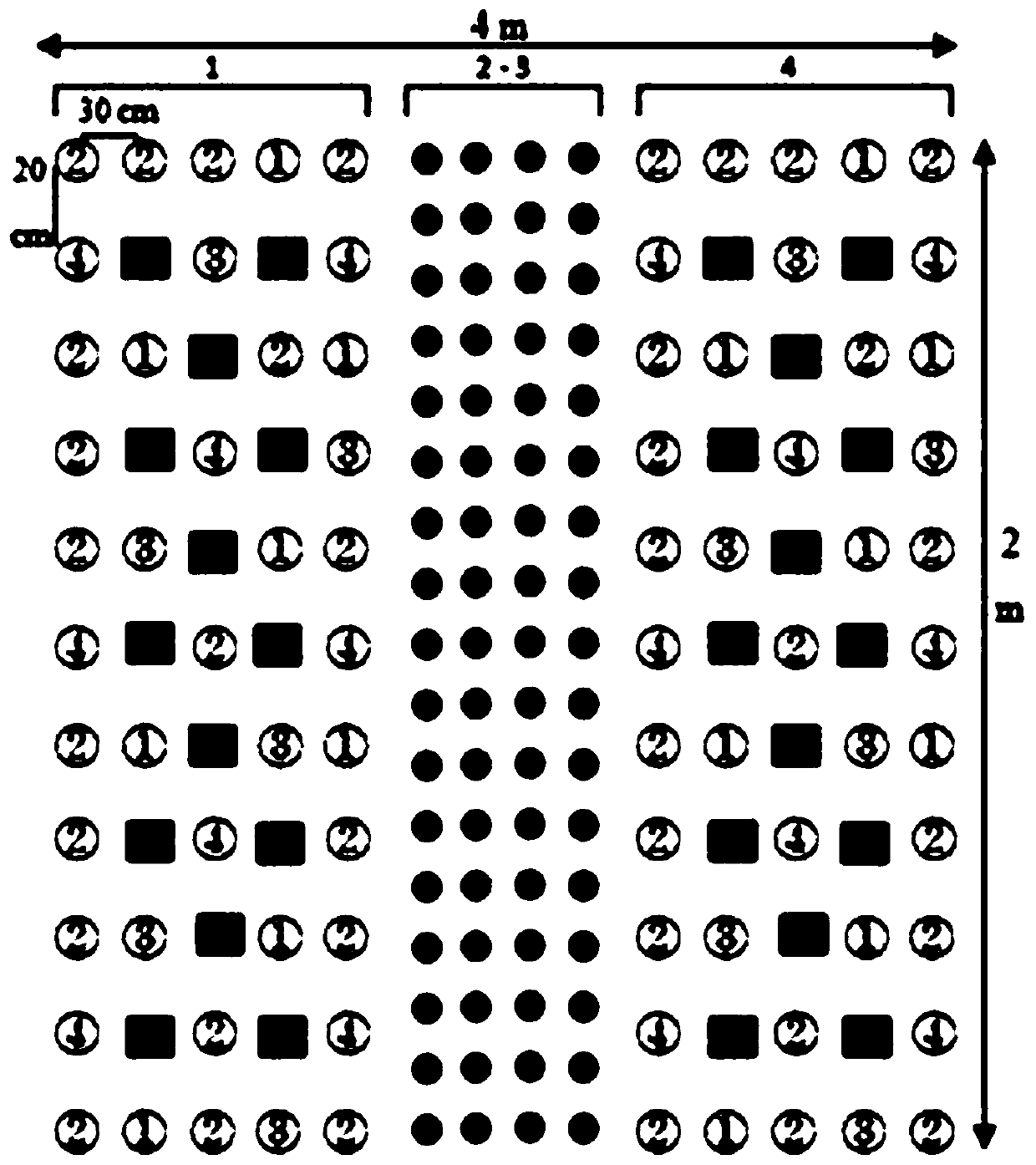
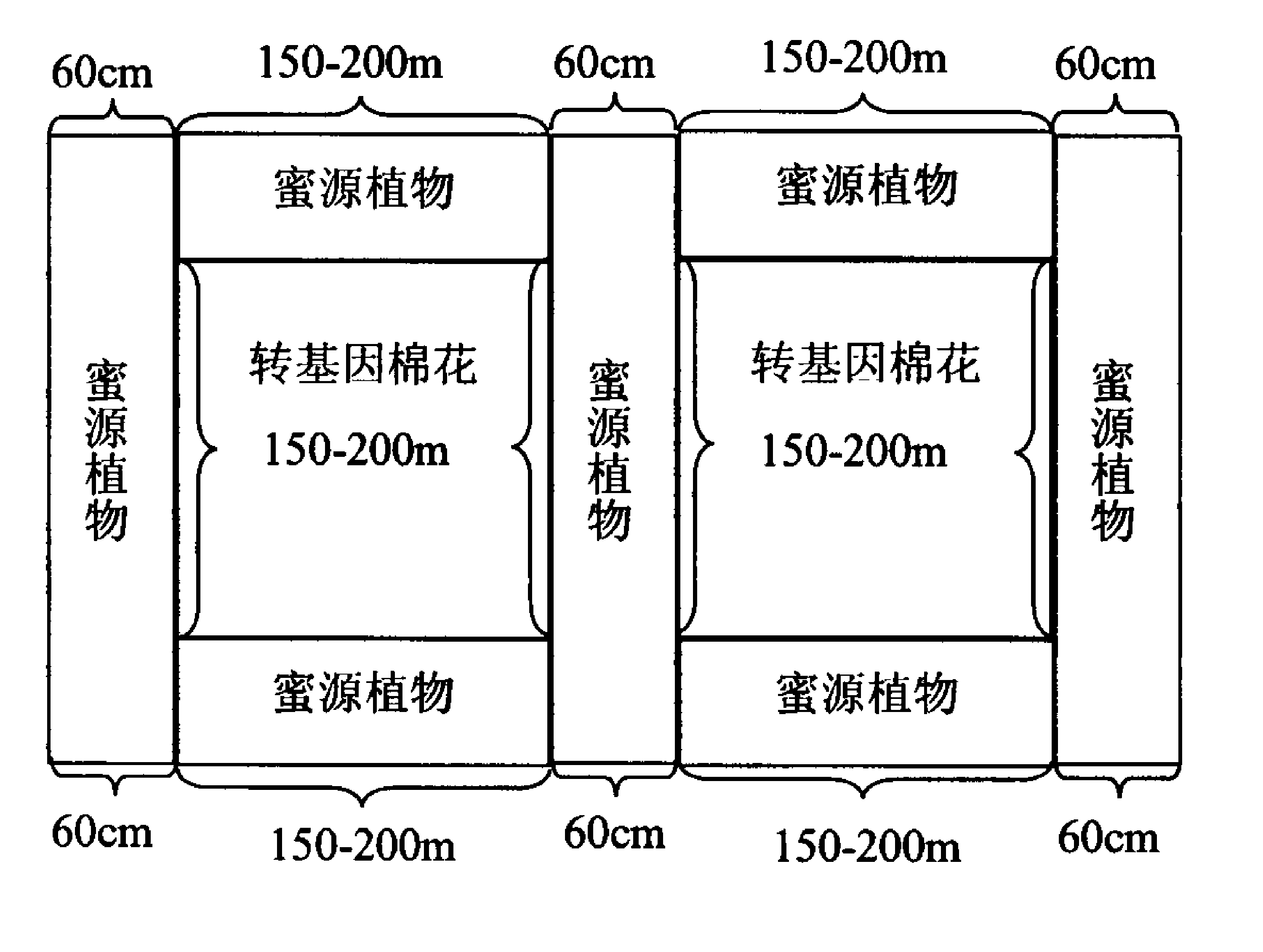
Method for preventing transgenic cotton from gene flow by using nectariferous plant
ActiveCN103891593APrevent outcrossing ratePrevent genetic contaminationAnimal huntingPlant genotype modificationAgricultural sciencePollen
The method relates to an effective method for measuring a pollen gene drift distance of a transgenic cotton, and the method is simple and practical, and has strong maneuverability. A sterile line of cotton used in production is planted at different positions surrounding the transgenic cotton, to form a drift region of transgenic cotton pollens. If the sterile line of cotton sends up boll and goes to seed normally, it can be confirmed as outcrossing; and then the rate of transgenic cotton is further analyzed. The method is easy for assessment of pollination rate and pollination source of cotton, avoids high frequencies of field monitoring and reduces the workload of cotton leaf DNA extraction and exogenous gene detection in laboratory. The method has the main characteristics of fastness, accuracy and strong operability.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SSR primer of endangered species thuja sutchuenensis and application of SSR primer
ActiveCN112226531AReveal the Law of Genetic VariationElucidating phylogenetic evolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpecific populationGenetics
The invention belongs to the field of thuja sutchuenensis research, and discloses a specific SSR primer of an endangered species thuja sutchuenensis and application of the specific SSR primer in the aspects of population genetic diversity analysis, population genetic structure analysis, population genetic differentiation analysis and the like of the endangered species thuja sutchuenensis. Geneticdifferentiation and gene flow conditions of different populations and phylogenetics and evolution relations of the populations are clarified, so that genetic variation rules of the thuja sutchuenensispopulations can be revealed, and phylogenetic evolution and geographical differentiation of the thuja sutchuenensis populations are illustrated; and therefore, very important theoretical and practical significance is achieved for mastering sources and population differentiation conditions of the thuja sutchuenensis and developing and utilizing the thuja sutchuenensis.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Quick detection method of exogenous herbicide resistance gene flow on soybean plant
PendingCN110244005AGuaranteed purityReduce testing costsTesting plants/treesGerm plasmHerbicide resistance
The invention discloses a quick detection method of exogenous herbicide resistance gene flow on soybean plant. The method comprises the following operation steps: (1) cutting off leaves of a to-be-detected soybean plant, positive reference plants and negative reference plants at the leaf stalks, wherein the number of each of the negative reference material and the positive reference material is two; (2) inserting the obtained leaves into centrifugal tubes to perform water planting; (3) placing the centrifugal tubes filled with the water-planting blades in a greenhouse to culture, spraying herbicide on the to-be-detected water-planting leave, the negative reference material CK3 and the positive reference material CK4, wherein the negative reference material CK1 and the positive reference material CK2 blades are blank control and free from spraying herbicide; and (4) observing after 5-7 days. The method provided by the invention is simple and quick in detection and low in cost, and a detection result is highly consistent with the traditional PCR detection and protein test strip detection result, and free from significant difference. The quick detection method disclosed by the invention can be used as a high-throughput method for important genetic or breeding material gene flow screening. And the method can provide technical support for protecting the import genetic germ plasm purity and genetic integrity.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Camphor tree whole genome ssr molecular marker and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108823327BAvoid missingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGene flow
The invention discloses a whole genome SSR molecular marker of camphor tree and its preparation method and application. The camphor tree microsatellite molecular markers developed by the present invention can be applied to the population genetic diversity detection and kinship analysis of ancient camphor trees, providing a new batch of microsatellite molecular markers for Lauraceae plants, and also for the population genetic differentiation of Lauraceae plants New tools are provided for the study of genetic diversity and structure, the level of genetic diversity of populations, the gene flow and mating system between populations, species evolution, and molecular assisted breeding.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF FORESTRY
LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) rapid detection method and application of glyphosate-resist transgenic soybean
InactiveCN103642918BWide applicabilityHigh detection detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGene flow
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Specific primers and detection methods of microsatellite markers from Castanopsis similarius and Castanopsis militaris
ActiveCN105087801BLow costIncrease the number of pointsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyCastanopsis
The invention discloses specific primers and a detection method of Castanopsis fargesii and Castanopsis carlesii microsatellite markers. Eight pair of specific primers, of Castanopsis fargesii microsatellite molecular markers, suitable for Castanopsis carlesii are developed by utilizing an existing Castanopsis fargesii nucleotide sequence in a common database, applying a bioinformatics method and performing experimental verification, and base sequences are shown as SEQ ID NO.1-16. The invention further provides a detection method of EST-SSR molecular markers of Castanopsis fargesii and Castanopsis carlesii. The detection method of the EST-SSR molecular markers has the advantages of quickness, simplicity, stability and low cost, and a reference is provided for developing of EST-SSR molecular markers of other Castanopsis plants. By the specific primers and the microsatellite marker detection method, novel tools are provided for study on population genetic differentiation and structure, genetic diversity level of populations, gene flow among the populations and mating systems of the Castanopsis plants like Castanopsis fargesii and Castanopsis carlesii and study on molecular assisted selection of the Castanopsis plants.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF FORESTRY
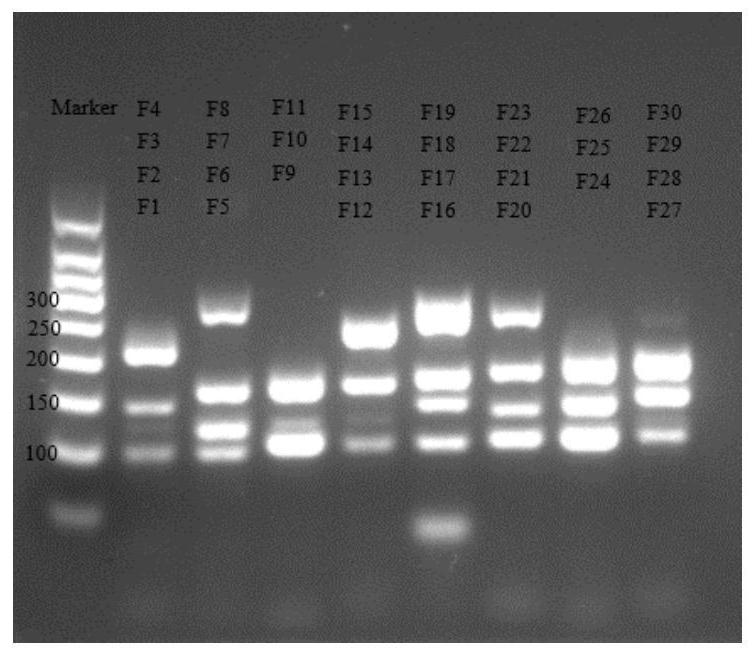
Soybean cleistogamous flower molecular marker and application thereof
InactiveCN111663000AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGene flow
The invention discloses a soybean cleistogamous flower molecular marker. The molecular marker comprises a DNA molecule SNP2 obtained by using soybean genome DNA as a template and performing amplification by using a SNP2 primer pair, and a DNA molecule SNP3 obtained by using the soybean genome DNA as a template and performing amplification by using a SNP3 primer pair, wherein the SNP2 primer pair and the SNP3 primer pair are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.4. A method of map-based cloning is used to locate a cleistogamous flower trait decisive base sequence in cleistogamous flower soybean genome, and perform cloning, according to the cloning result, whether the trait of soybean is the cleistogamous flower is determined, and then the soybean is planted, so that the plant maintains a pure breed by avoiding the interference of foreign pollens, and the gene flow is controlled.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for domesticating desert plant agriophyllum squarrosum from beginning based on population polymorphism
InactiveCN112205247AImprove adaptabilitySpeed up gene flowSeed and root treatmentCultivating equipmentsSoil typeGene flow
The invention relates to the technical field of domesticating desert plants from the beginning, in particular to a method for domesticating desert plant agriophyllum squarrosum from the beginning based on population polymorphism. The method comprises the steps that phenotypic variation caused by soil type, slope, climate and hydrological environment difference is excluded through homogeneous garden experiments; morphological or phenotypic differences formed by genetic differentiation is screened out through phenotypic data determination of wild agriophyllum squarrosum; the optimal natural growth condition influencing the heritable phenotype of the agriophyllum squarrosum is determined by combining the meteorological factor data of the agriophyllum squarrosum group of the origin; and groupgenetic evaluation is carried out on domesticated high-quality germplasm resources, and large-area popularization and demonstration of the germplasm resources are determined. According to the method for domesticating the desert plant agriophyllum squarrosum from the beginning based on population polymorphism, a genetic database of germplasm resource populations is constructed for the first time, gene flow among the populations is accelerated through the homogeneous garden experiments, and the adaptability of crop target phenotypes to the climate is improved; and the traditional time-consumingand labor-consuming artificial hybridization process is changed, and various risks caused by a transgenic technology are further avoided.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
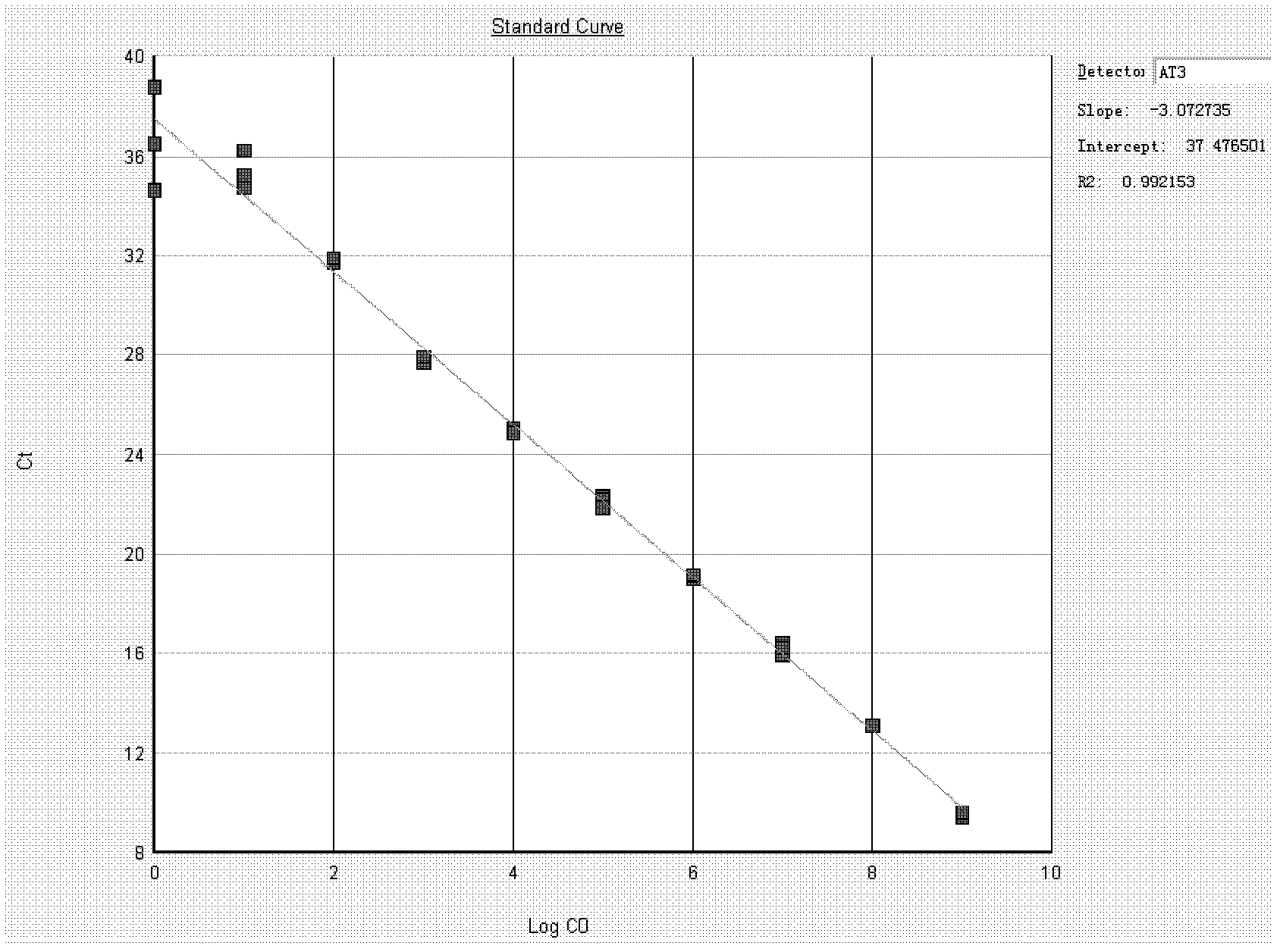
Method for analyzing exogenous gene flow risk of human antithrombinIII transgenic sheep
ActiveCN102321761AHigh detection specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementGene flowAnalysis method
The invention provides a method for analyzing the exogenous gene flow risk of human antithrombinIII transgenic sheep. The method comprises the following steps: designing a primer and a Taqman probe, preparing blood genome DNA, amplifying ATIII gene, cloning AT111 gene, performing a fluorescent quantitative PCR detection, sensitivity evaluation and quantitative analysis. Aiming at sensitively detecting the micro AT111 gene, a technical method for detecting humanATIII gene by sensitive and specific real time fluorescent quantification PCR can be established by researches, the AT111 gene of 1copy can be detected at least, and the detected specificity is high. A primary research on security assessment of environment of antithrombinIII transgenic sheep is developed on the basis. The detection works (57 samples in total) of AT111 gene in homologous and heterologous animal blood genome which is closely contacted with ATIII transgenic sheep are completed. The results show that humanATIII genedose not flow between the transgenic sheep and non-transgenic sheep or other animals, and prompts that the transgenic sheep is safe to the environment.
Owner:青岛森淼生物技术有限公司
Hevea transcription factor hbmyb44 gene and its application
ActiveCN105861519BImprove drought resistanceImprove toleranceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesGene flowEndurance capacity
The invention relates to a rubber tree transcription factor HbMYB44 gene and an application thereof. The transcription factor gene HbMYB44 related to the drought resistance of the rubber tree provided by the present invention, through transforming the Arabidopsis thaliana with the HbMYB44 gene to carry out functional research on the gene, verifies that the drought stress tolerance of the transgenic Arabidopsis is improved. The gene can be used in drought-resistant transgenic research of rubber trees and other crops. The transcription factor gene HbMYB44 related to the drought resistance of the rubber tree in the invention is from the rubber tree, does not generate gene drift, has little impact on the environment, and provides new gene resources for improving the drought resistance of plants.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Specific primers and detection method of Castanopsis fargesii and Castanopsis carlesii microsatellite markers
ActiveCN105087801ALow costIncrease the number of pointsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCastanopsisMicrosatellite
The invention discloses specific primers and a detection method of Castanopsis fargesii and Castanopsis carlesii microsatellite markers. Eight pair of specific primers, of Castanopsis fargesii microsatellite molecular markers, suitable for Castanopsis carlesii are developed by utilizing an existing Castanopsis fargesii nucleotide sequence in a common database, applying a bioinformatics method and performing experimental verification, and base sequences are shown as SEQ ID NO.1-16. The invention further provides a detection method of EST-SSR molecular markers of Castanopsis fargesii and Castanopsis carlesii. The detection method of the EST-SSR molecular markers has the advantages of quickness, simplicity, stability and low cost, and a reference is provided for developing of EST-SSR molecular markers of other Castanopsis plants. By the specific primers and the microsatellite marker detection method, novel tools are provided for study on population genetic differentiation and structure, genetic diversity level of populations, gene flow among the populations and mating systems of the Castanopsis plants like Castanopsis fargesii and Castanopsis carlesii and study on molecular assisted selection of the Castanopsis plants.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF FORESTRY
Polymorphic primers of cinnamomum camphora chloroplast SNP molecular markers and application of polymorphic primers
ActiveCN110760610AFully reveal the true levelGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCinnamomum camphoraGene flow
The invention discloses polymorphic primers of cinnamomum camphora chloroplast SNP molecular markers and application of the polymorphic primers, and belongs to the technical field of forestry molecular biology. 11 pairs of polymorphic primers of the cinnamomum camphora chloroplast SNP molecular markers are screened and applied to ancient cinnamomum camphora genetic diversity analysis and ancient cinnamomum camphora pedigree analysis, and on the basis of chloroplast haplotype analysis, results are shown that different haplotypes have obvious distribution differences, most haplotypes only existin specific populations, and only few haplotypes are shared haplotypes; and thus a fact is indicated that certain geographic differentiation exists among the haplotypes. A genetic differentiation coefficient Fst of 18 cinnamomum camphora populations is 0.212, gene flow Nm of the cinnamomum camphora populations is 0.929, and a result is shown that middle gene flow exists among the cinnamomum camphora populations. By adopting the polymorphic primers, the SNP molecular markers have good repeatability, a true level of cinnamomum camphora genetic diversity can be revealed completely, and theoretical foundations are provided for wild cinnamomum camphora resource protection and utilization.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV +1
Method for lowering seed shattering of hybrid progeny of cultivated rice and weedy rice by using SH4 gene silencing
ActiveCN107090469ADecreased shatteringReduce the risk of proliferationPlant peptidesFermentationOryzaAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioenvironmental safety detection, and particularly relates to a method for lowering seed shattering of a hybrid progeny of cultivated rice and weedy rice by using a SH4 gene silencing. According to the method, a gene silencing technology is applied to make the function of the seed shattering gene SH4 of the cultivated rice loss, once cultivated rice transgenes which contain SH4 gene silencing elements are transferred to a weedy rice colony through gene flow, the risk of transgene diffusion can be lowered since the seed shattering is lowered; meanwhile, the seed shattering and diffusibility of the weedy rice colony which contains the SH4 gene silencing elements can be lowered greatly, accordingly through the gene flow from the cultivated rice to the weedy rice, characteristics of seed shattering lowering can be transferred to the weedy rice colony, and the purposes of controlling the diffusion of the weedy rice colony and lowering the risk of the weedy rice are achieved. The method can greatly lower the environmental safety risk which can be caused after the transgenes escape to the weedy rice, lower the weedy rice diffusion and endanger and avoid economic loss, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for evaluating fitness of hybridization or backcrossing offspring of Glycine max and Glycine soja Sieb.et Zucc.
PendingCN111387050AResponse fitness effectFabaceae cultivationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGene flow
The invention belongs to the field of ecological safety evaluation of Glycine max, and particularly relates to a method for evaluating the fitness of the hybridization or backcrossing offspring of Glycine max and Glycine soja Sieb.et Zucc.. The characters, which most favorably reflect viability and fertility of a hybridization or backcrossing offspring of the Glycine max and Glycine soja Sieb.et Zucc. in a whole life history period, can be calculated and measured, and finally, total fitness can be used for clearly obtaining the fitness of the hybridization or backcrossing offspring of the Glycine max and the Glycine soja Sieb.et Zucc., wherein the characters include four characters of a vegetative period and eight characters of a reproductive period. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the problem that no methods for evaluating the fitness of the hybridization or backcrossing offspring of the Glycine max and the Glycine soja Sieb.et Zucc. are provided are present can besolved. The method has an important function for scientifically evaluating the fitness of the hybridization or backcrossing offspring of the Glycine max and the Glycine soja Sieb.et Zucc.. The evaluation of the fitness is an important link for safely releasing the Glycine max, and after the Glycine max is subjected to gene flow to the Glycine soja Sieb.et Zucc., gene flow prevention work is carried out on an influence on the fitness of the Glycine soja Sieb.et Zucc. in advance.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for analyzing exogenous gene flow risk of human antithrombinIII transgenic sheep
ActiveCN102321761BHigh detection specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementGene flowAnalysis method
Owner:青岛森淼生物技术有限公司
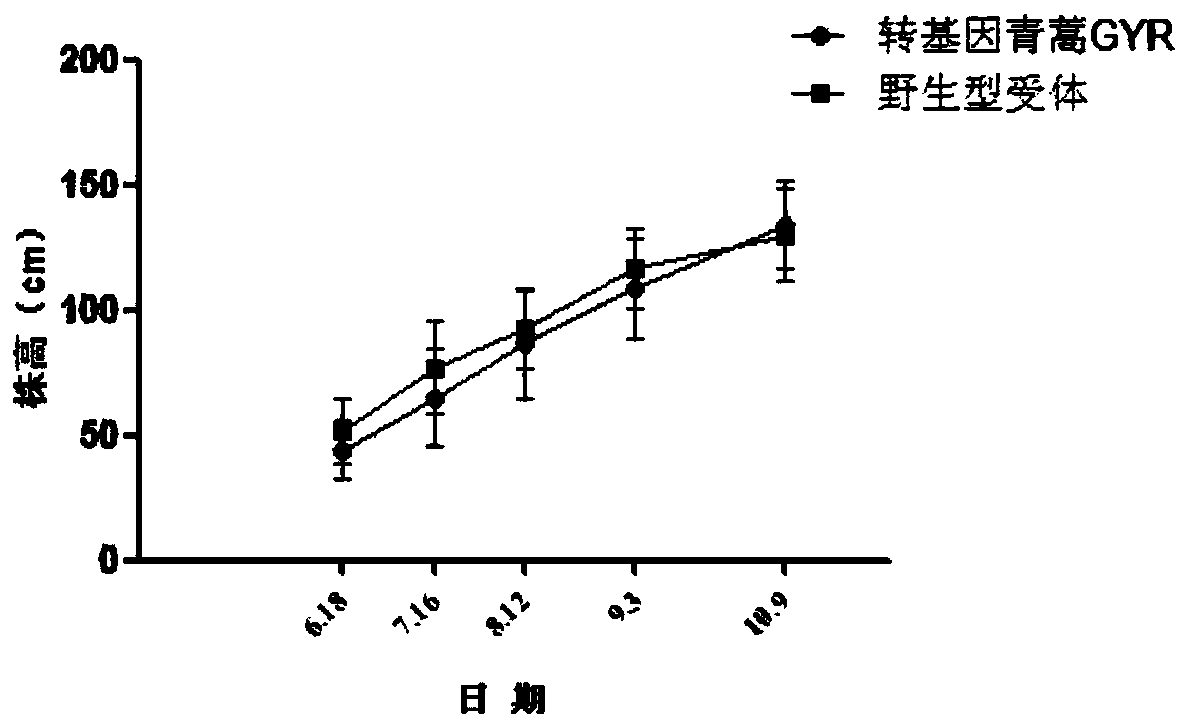
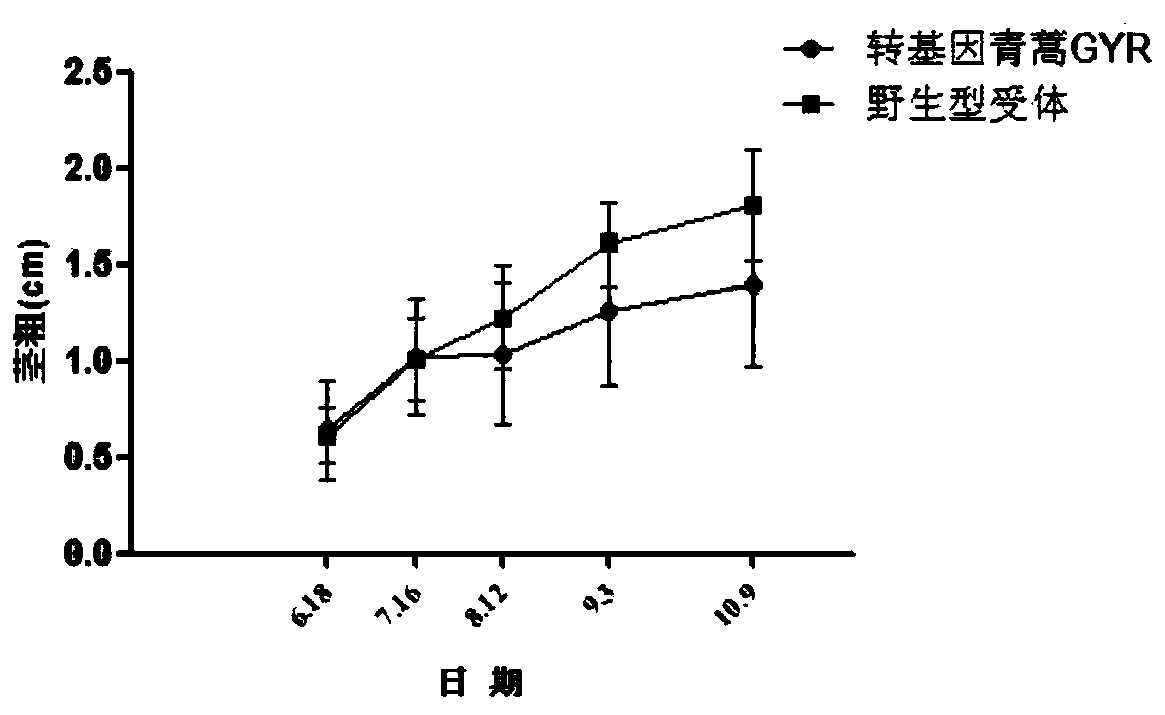
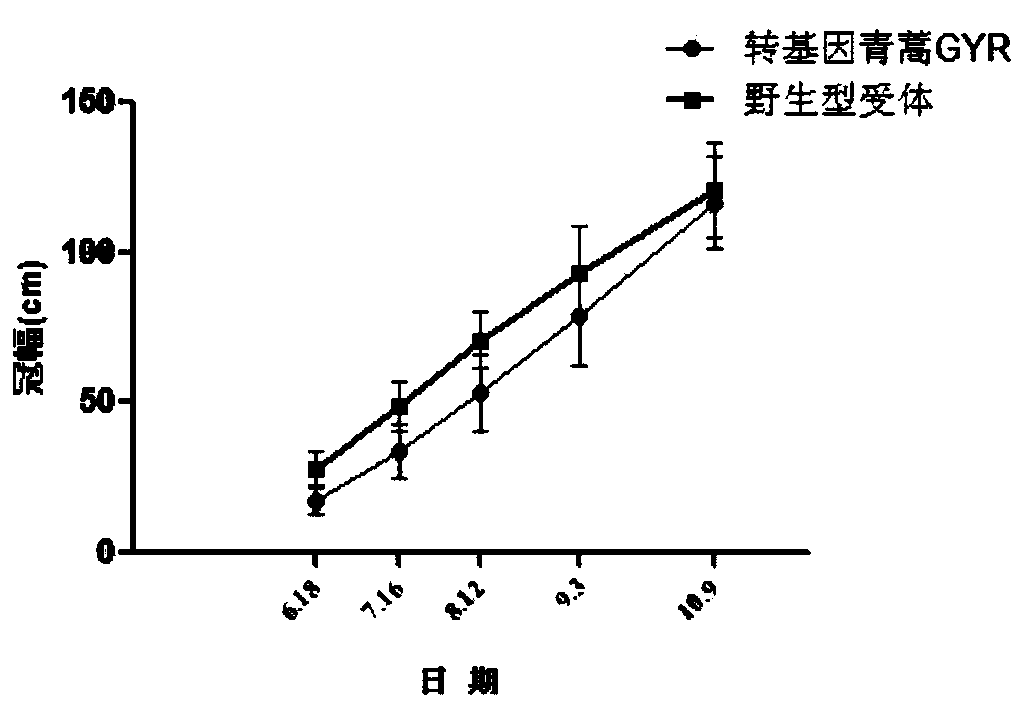
A method for environmental safety assessment of transgenic Artemisia annua
The invention provides an environmental safety evaluation method of transgenic shoots. The method is characterized in that the agronomic characters, the stress resistance and the gene flow of the transgenic shoots are tested; meanwhile, wild type receptor shoots are treated as the contrast; the parameters set in the evaluation cover various indexes of difference of the transgenic shoots and the wild type receptor shoots; on this basis, a model is built for the environmental release of the transgenic shoots, and the important demonstration significance on explaining the substantial equivalence is brought. According to the method, an evaluation system built based on the abovementioned three parts is simple to operate, easy to achieve, and high in intuition and result accuracy. The method provides testing indexes for the environmental safety evaluation of the transgenic shoots and also provides the technical support for the commercial risk evaluation of the transgenic shoot varieties.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Polymorphic primers for chloroplast SNP molecular markers of Cinnamomum camphora and its application
ActiveCN110760610BFully reveal the true levelGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCinnamomum camphoraGene flow
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV +1
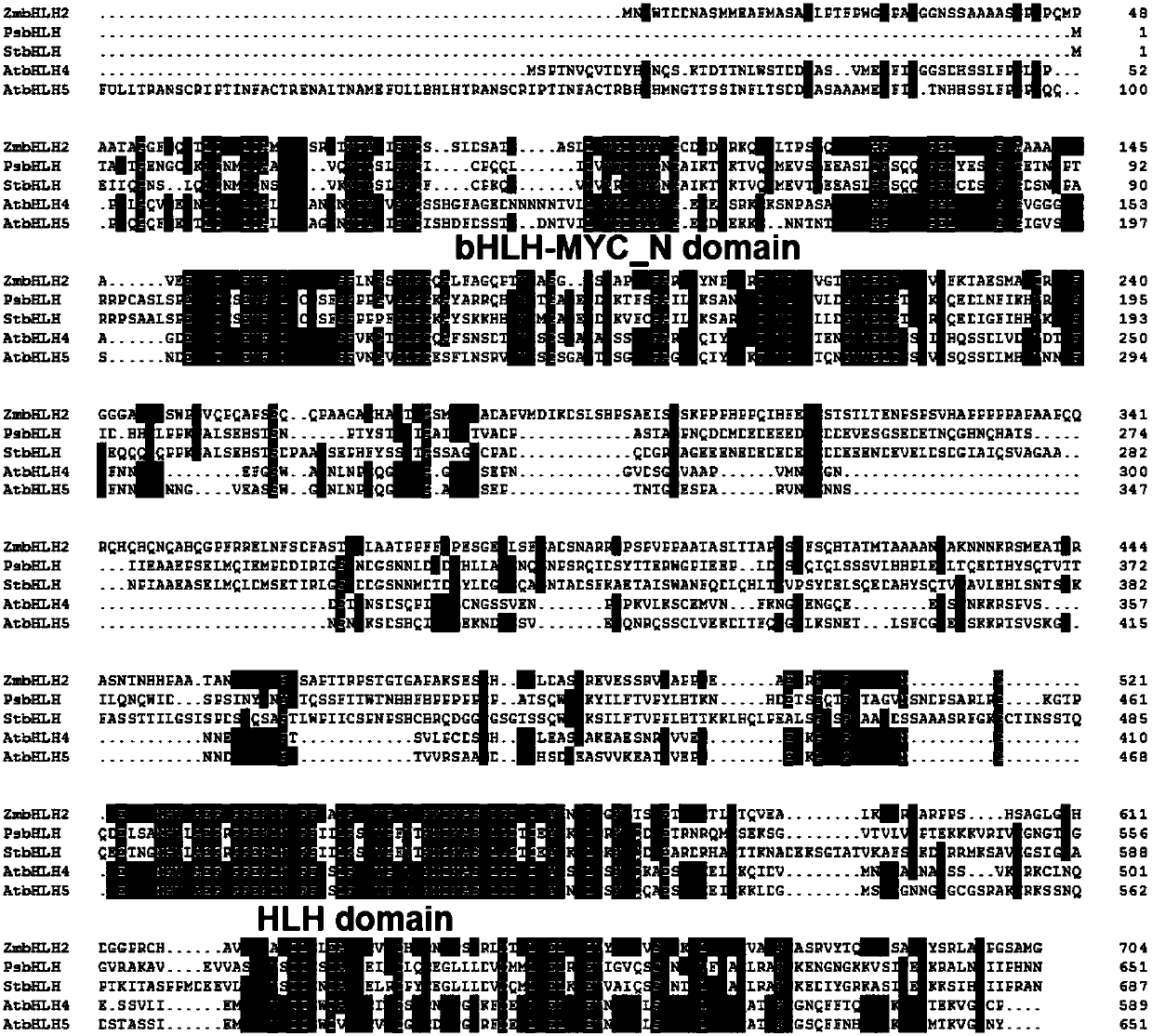
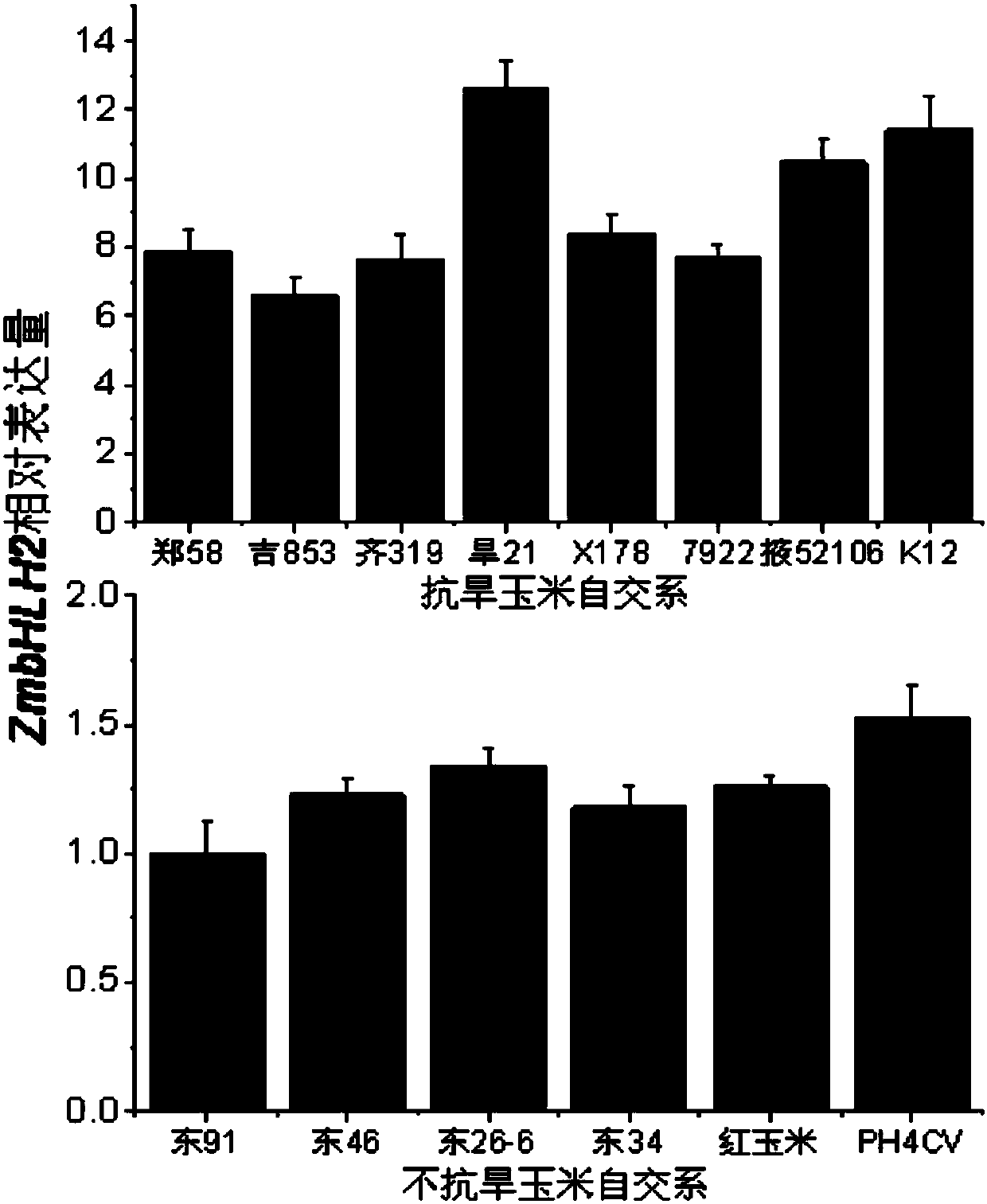
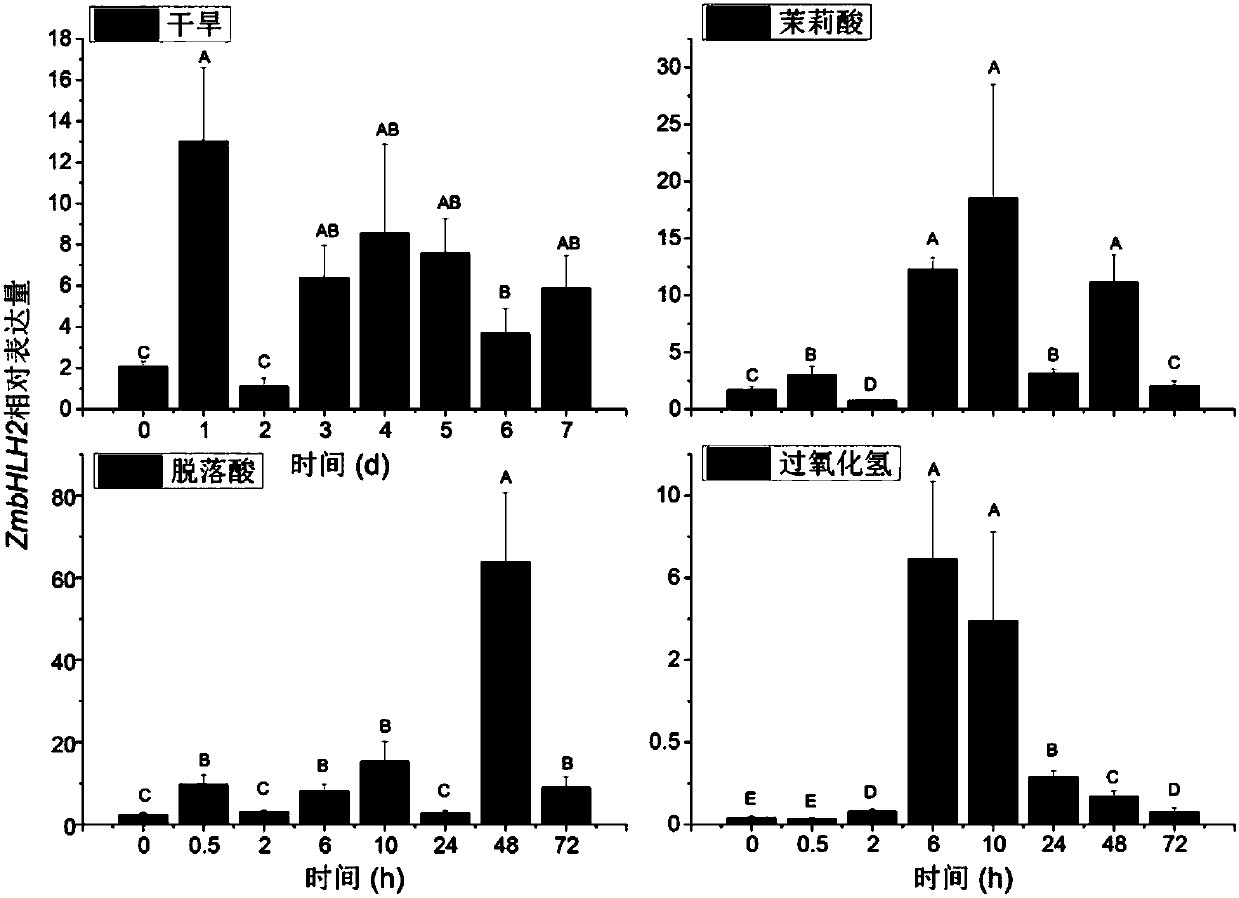
Maize transcription factor zmbhlh2 and its application
ActiveCN106282201BImprove drought resistanceImprove toleranceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesAgricultural scienceGene flow
The invention relates to a corn transcription factor ZmbHLH2 and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the corn transcription factor ZmbHLH2 is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1. The transcription factor is related to drought resisting of corn. By conducting drought resisting function verification of the gene on ZmbHLH2 gene-modified arabidopsis thaliana, it is proved that the endurance capacity of the ZmbHLH2 gene-modified arabidopsis thaliana to drought stress is improved. The gene can be applied to drought-resisting transgene study on the corn and other crops. The corn transcription factor ZmbHLH2 comes from the corn, gene flow cannot be generated, and a new gene resource is provided for improving the drought resistance of plants.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for evaluating influence of environmental single factor on transgene plant gene flow
InactiveCN102373268BEliminate the possibility of spreadingImprove securityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGreenhouseGene flow
The invention provides a method for evaluating the influence of an environmental single factor on transgene plant gene flow. According to the method, factors which may influence the gene flow are extracted from natural environment by manual simulation at room temperature. The natural environment is separated and the gene flow test is carried out under a single factor so as to determine the influence of the single factor on the gene flow. With the combination of real measured values under different regional and environmental factors, main factors which influence the gene flow in the locality can be better determined and an effective predetermined plan for the planting of transgene plants is made, so as to minimize test repetitions to some extent and save test cost. In addition, different from wagon-wheel bulk sampling point F1 sampling analysis, the method provided by the invention requires less occupation space, and can be used to reduce F1 sampling amount and greatly decrease the workload of test post-detection and analysis.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com