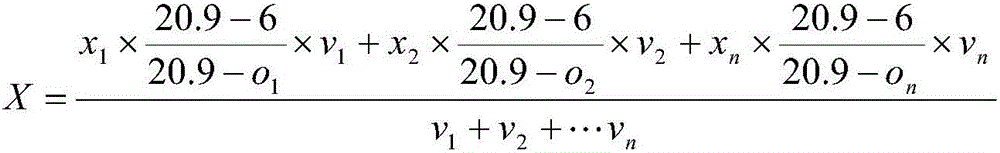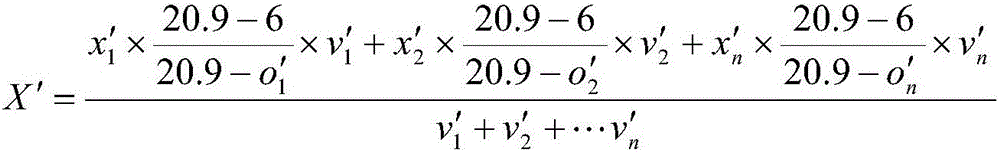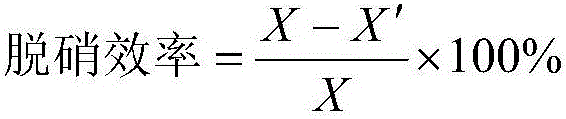Patents
Literature
69 results about "Limiting oxygen concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
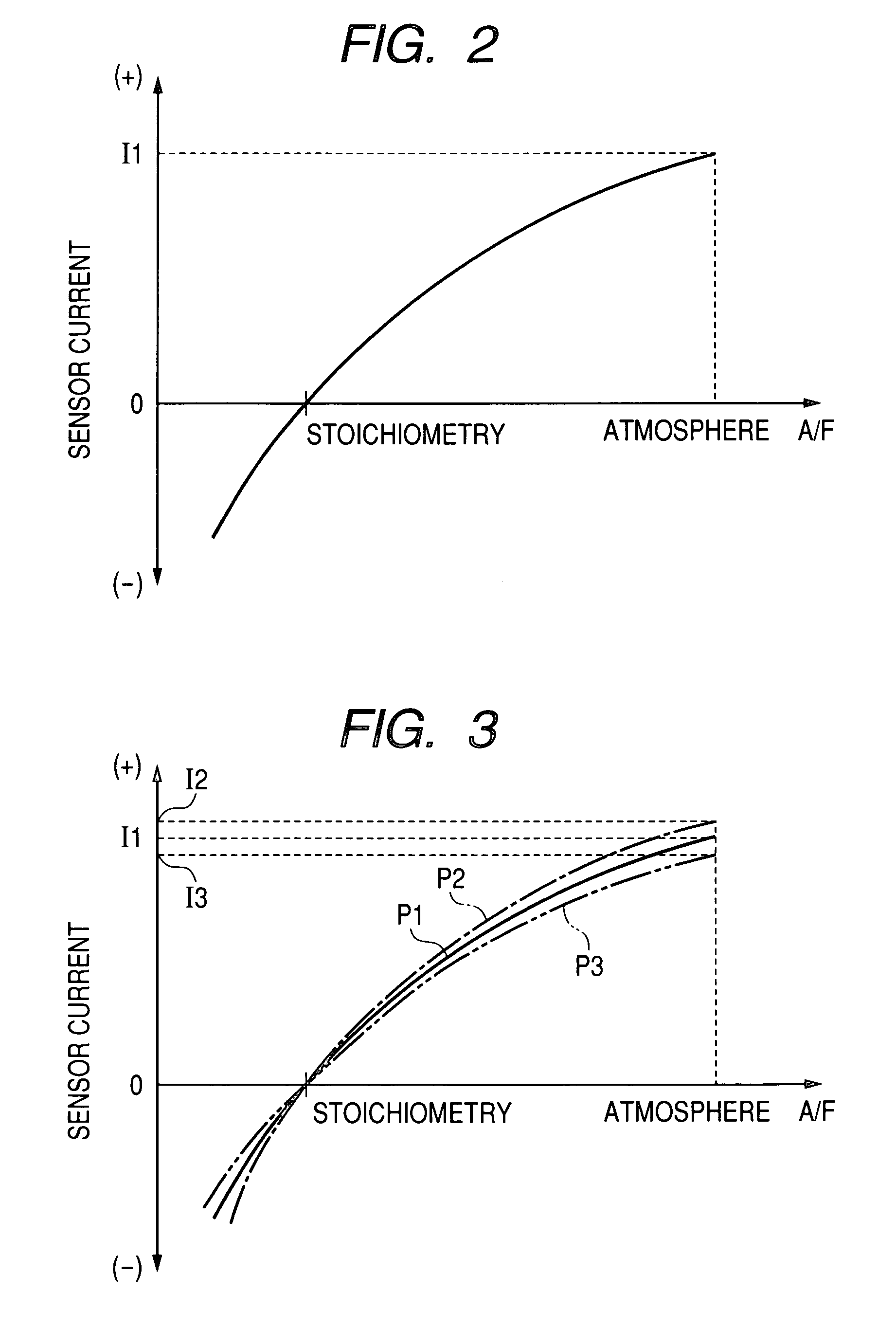
The limiting oxygen concentration, (LOC), also known as the minimum oxygen concentration, (MOC), is defined as the limiting concentration of oxygen below which combustion is not possible, independent of the concentration of fuel. It is expressed in units of volume percent of oxygen. The LOC varies with pressure and temperature. It is also dependent on the type of inert (non-flammable) gas.
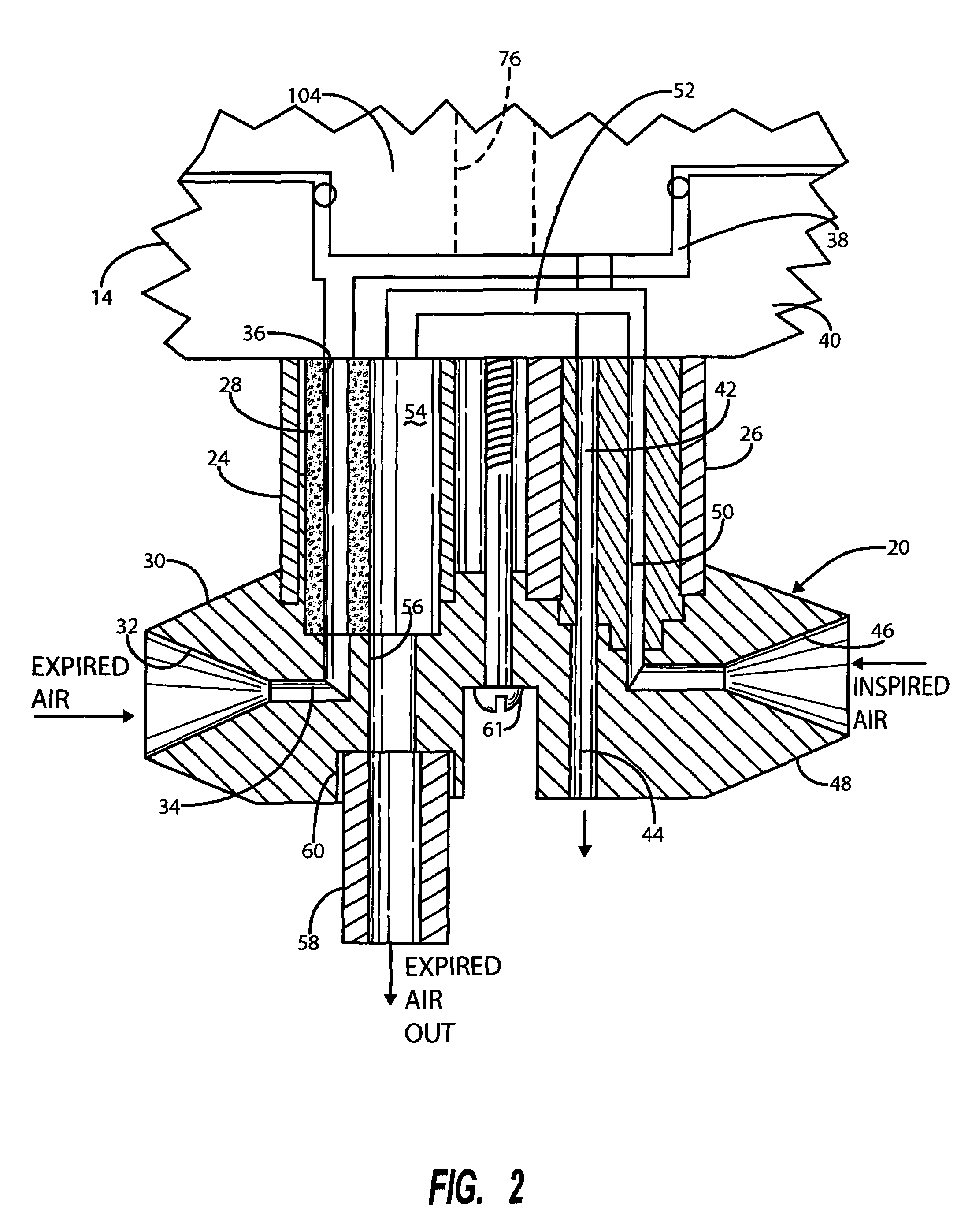
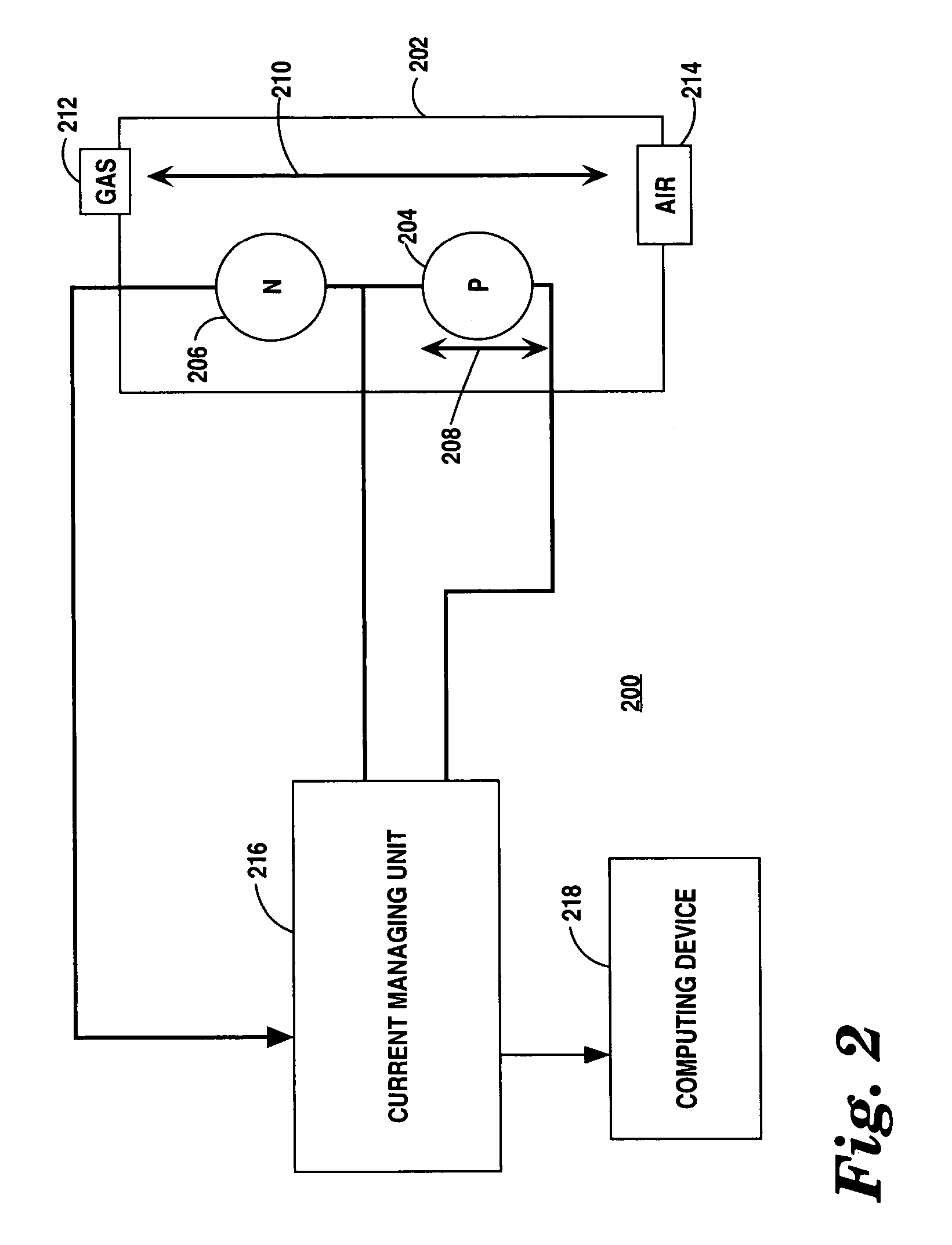
Reduced-oxygen breathing device
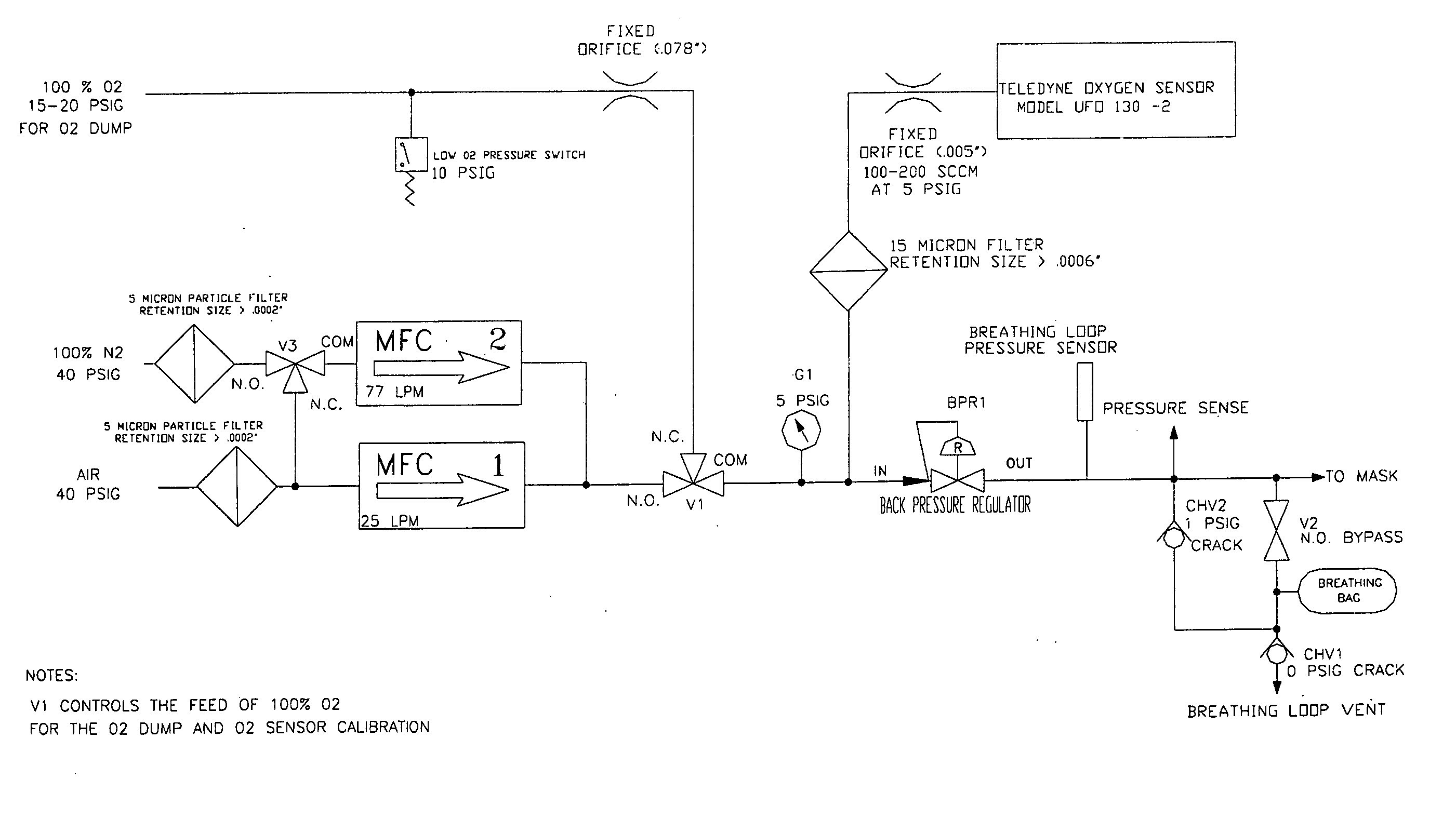
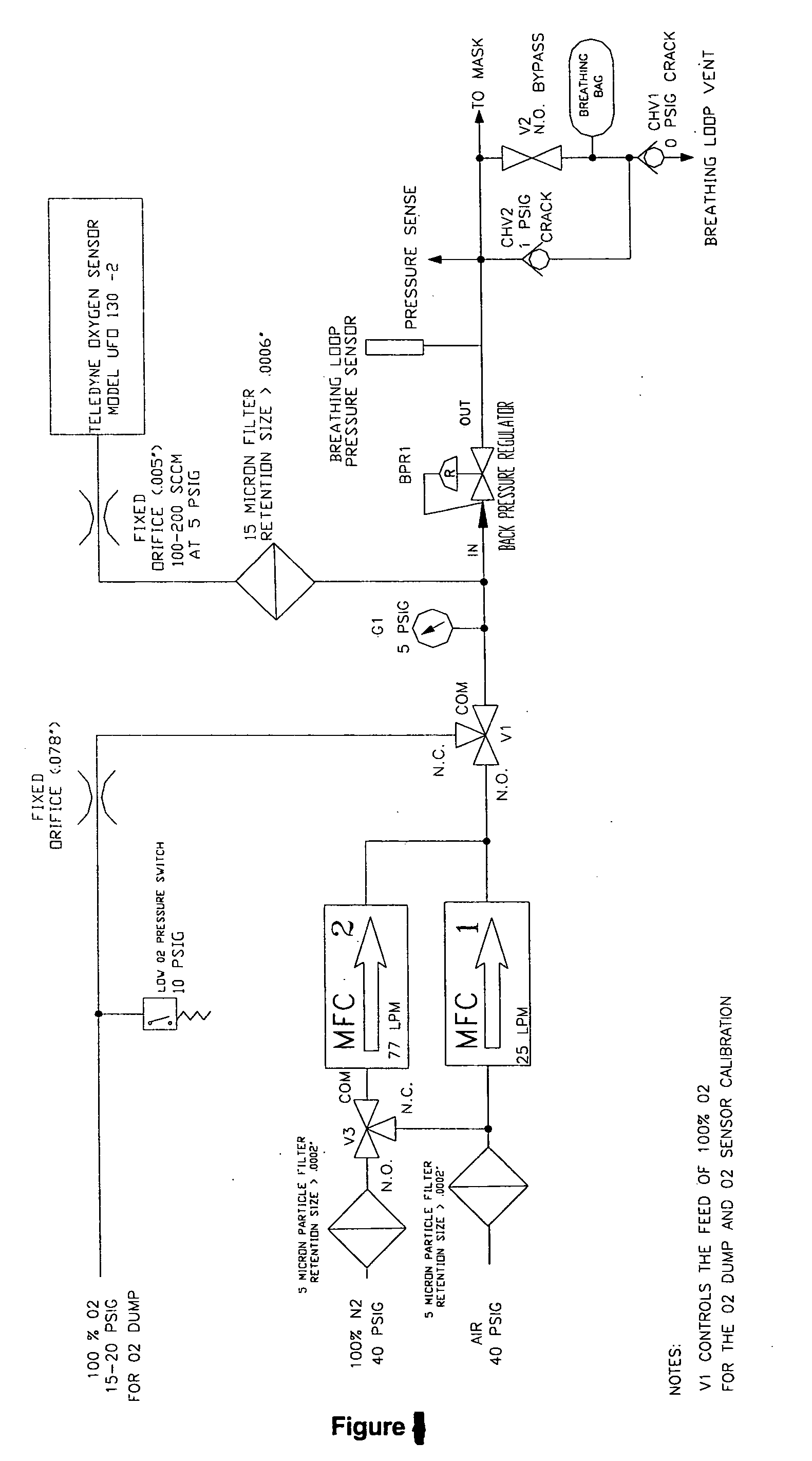
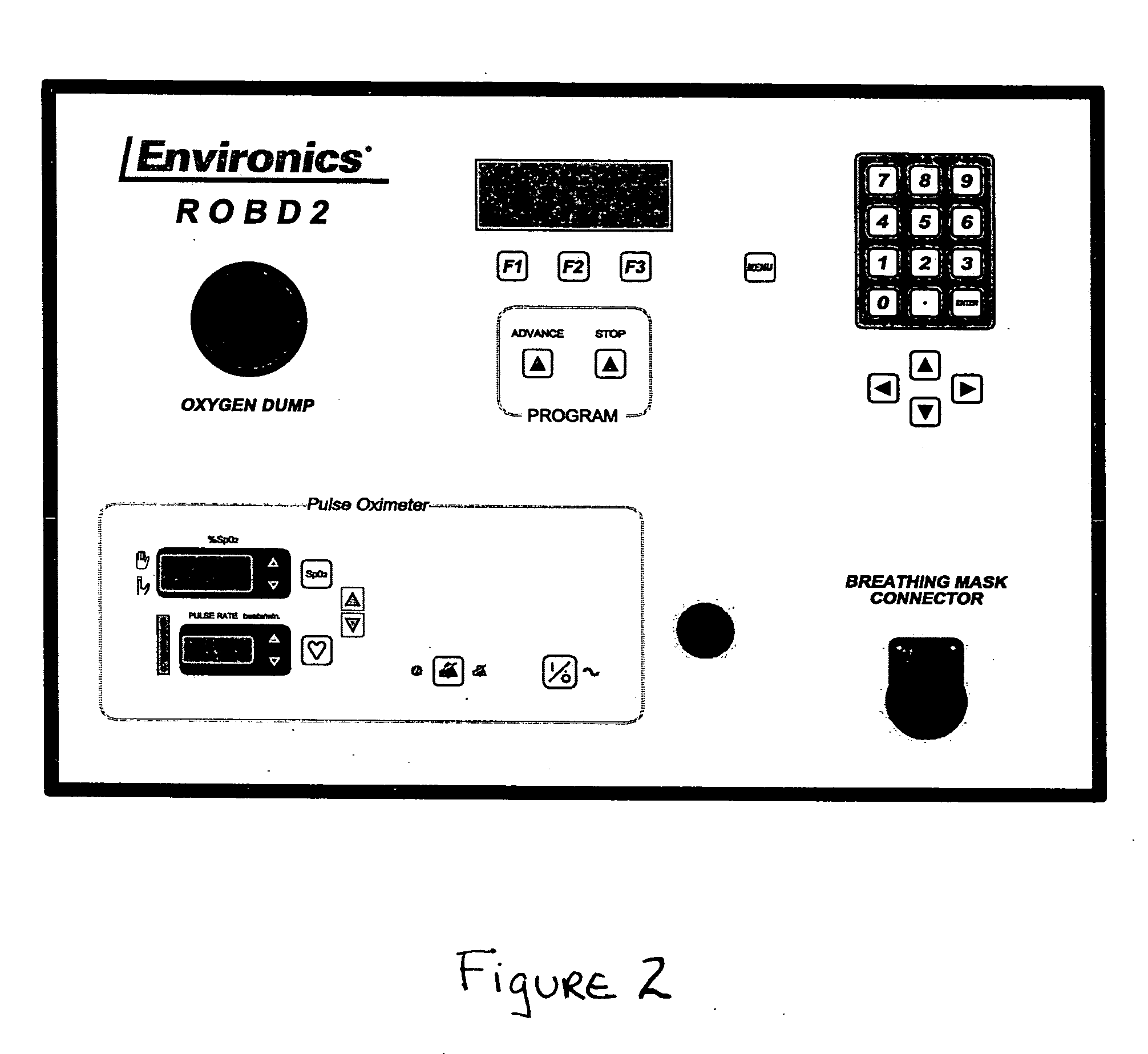
The Reduced Oxygen Breathing Device (ROBD2) is an apparatus that dilutes the oxygen present in air to concentrations below 21% by mixing the air with nitrogen. The purpose of this dilution is to simulate the reduced oxygen concentration available as one ascends in altitude. The ROBD2 is unique and different from previous devices that reduce the concentration of oxygen in room air via dilution with nitrogen gas in that it uses sophisticated gas regulating devices known as mass flow controllers. The ROBD also employs a gas extraction device as an independent component of the system that can separate nitrogen gas from air for use in the device.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
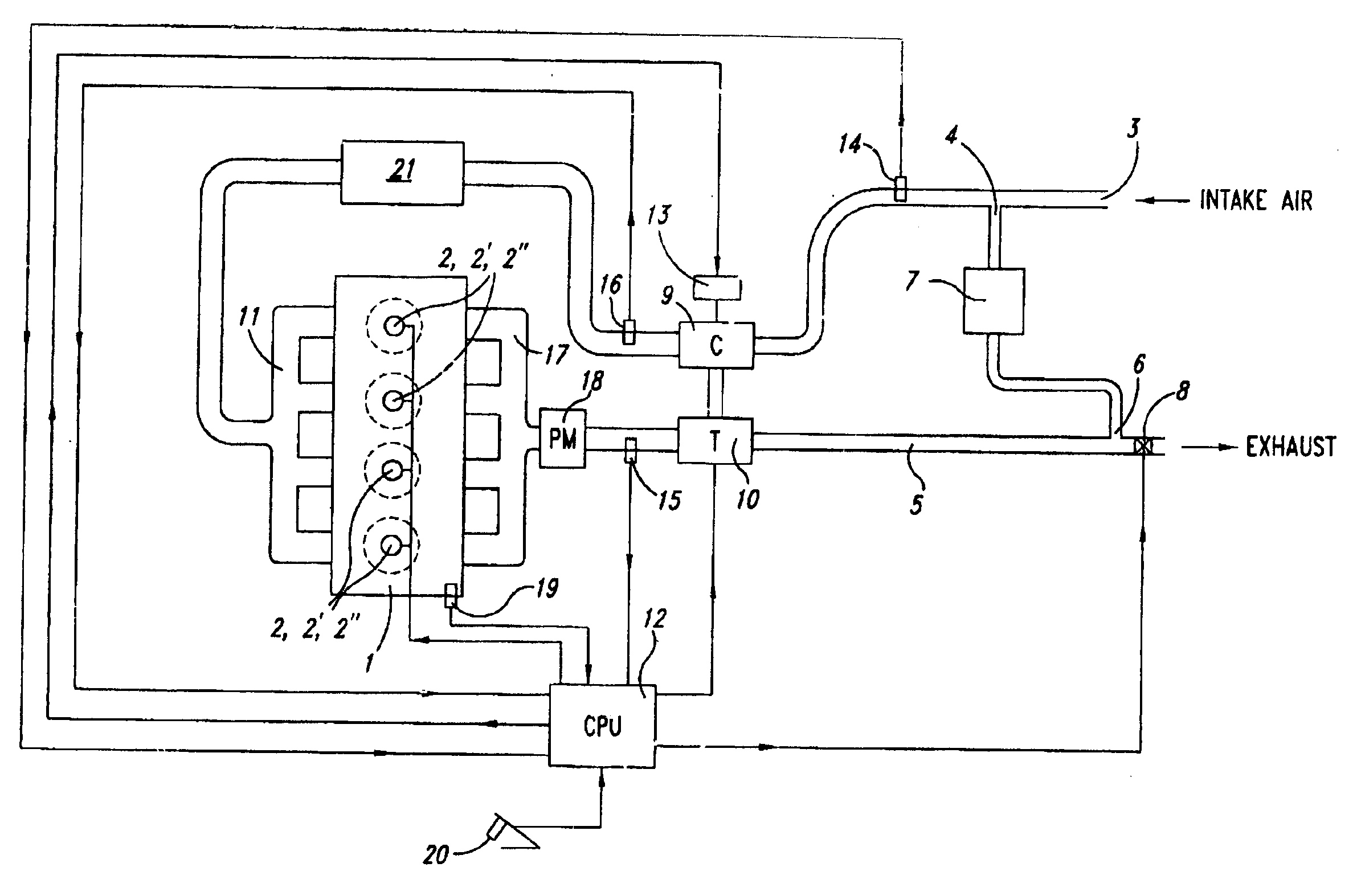
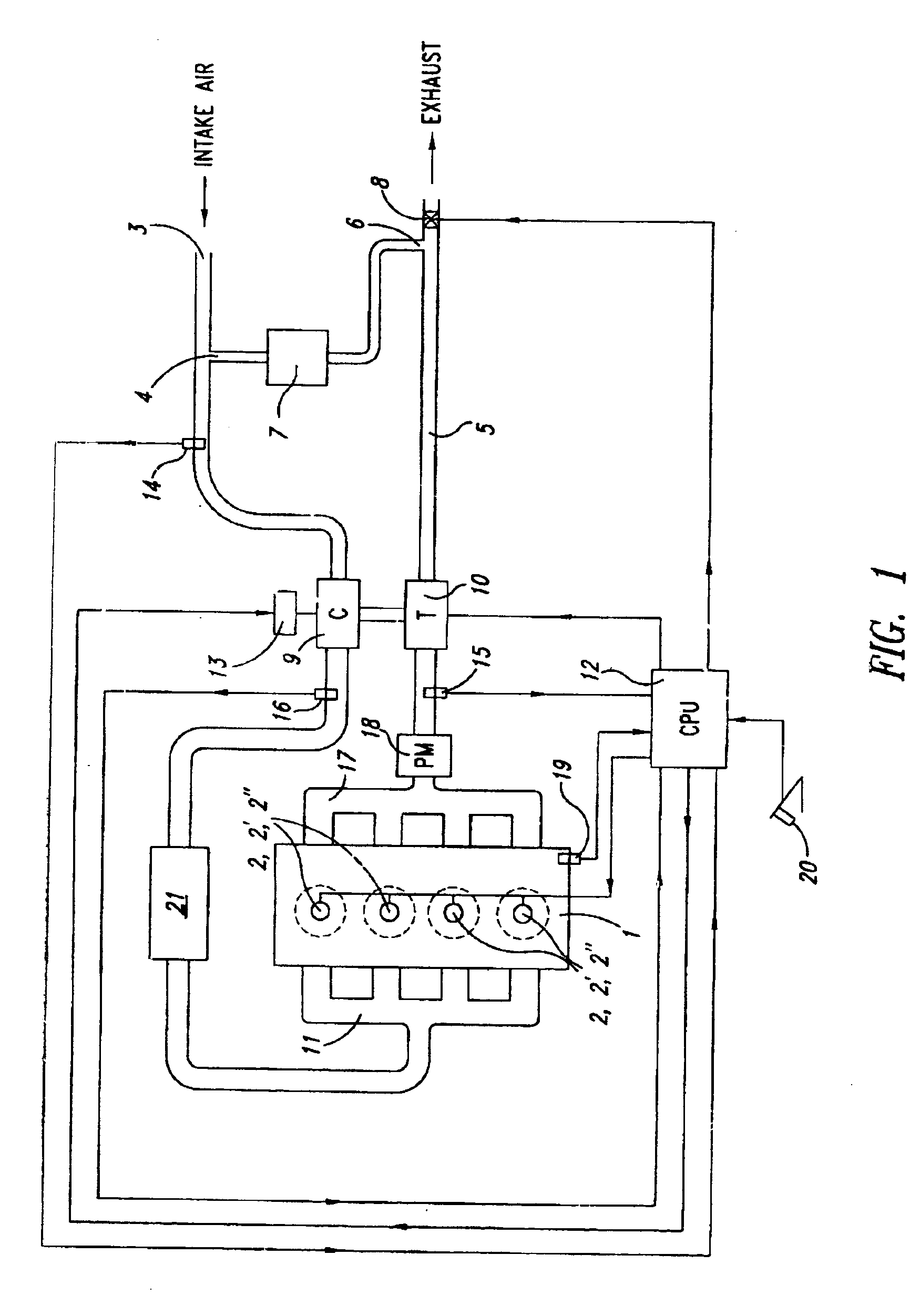
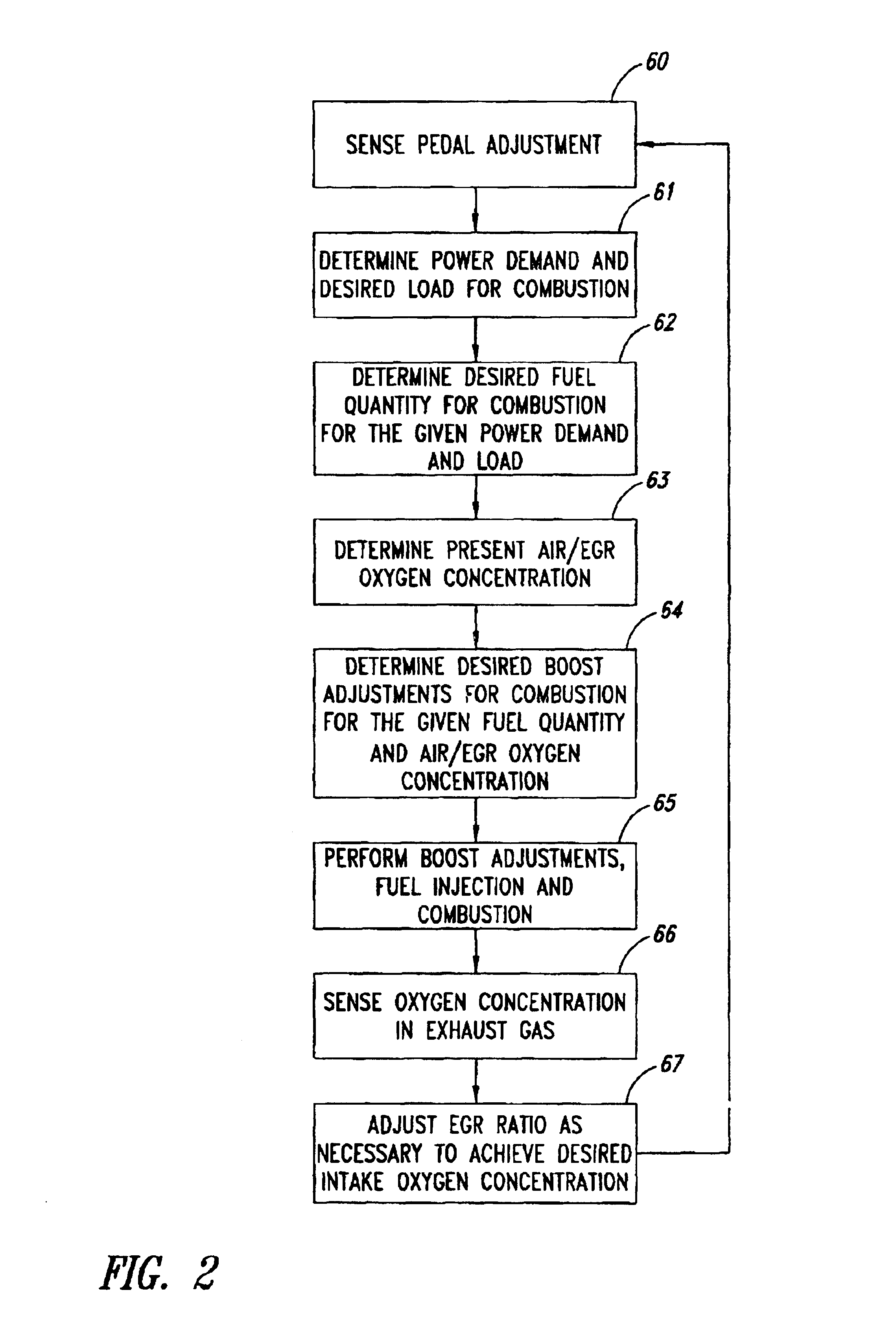
Low emission diesel combustion system with low charge-air oxygen concentration levels and high fuel injection pressures
InactiveUS6857263B2Cost effectiveLower Level RequirementsLiquid coolingEngine sealsLow loadMass ratio
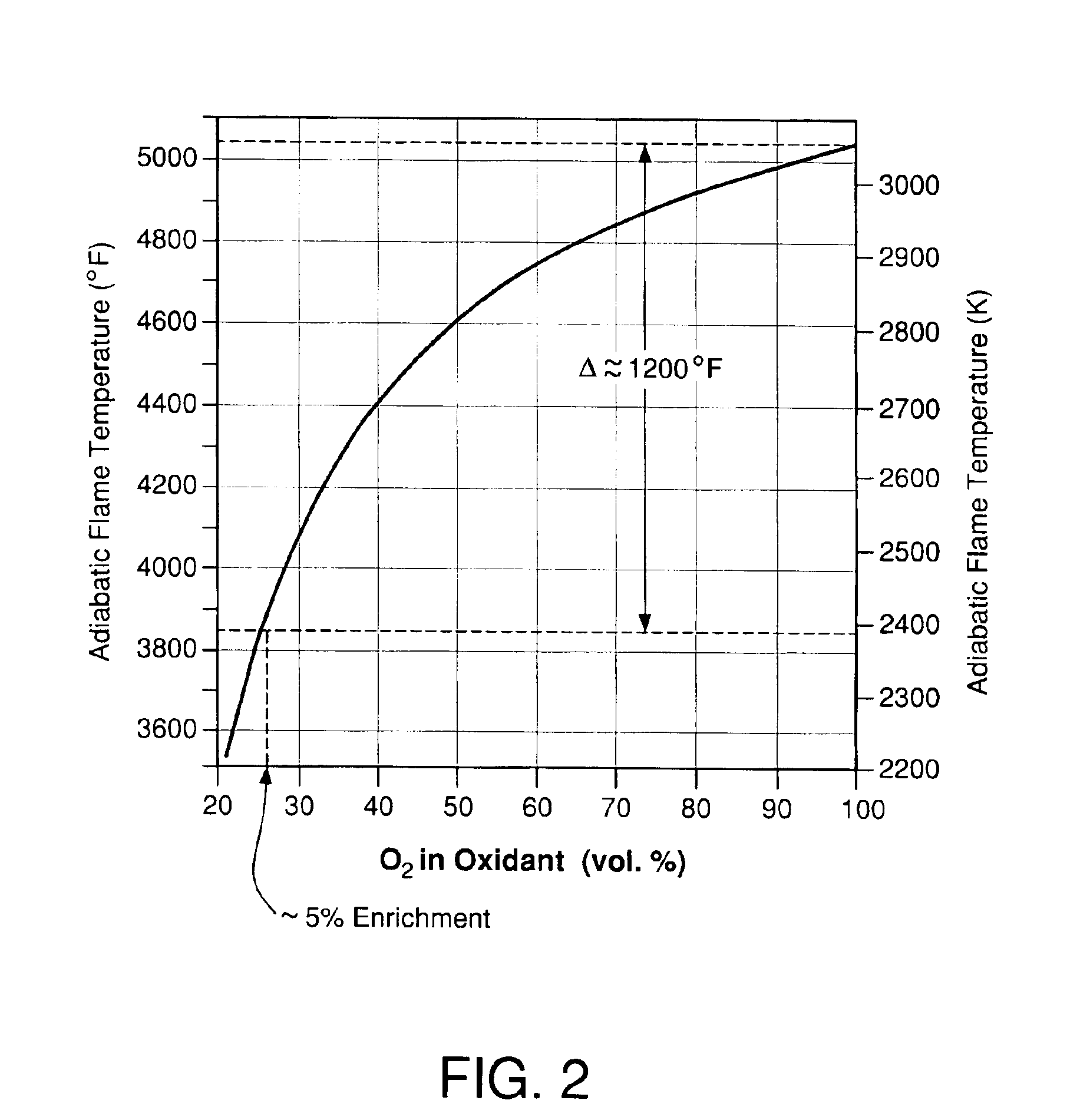
This invention sets forth a commercially viable diesel combustion system that meets environmentally acceptable levels of NOx emissions (i.e. 0.2 g / bhp-hr or lower across a full map of engine speeds and loads) without the need for use of NOx aftertreatments, and simultaneously maintains engine-out PM emissions relatively close (e.g. with smoke levels at or below 3 BSN) to environmentally acceptable PM post-aftertreatment levels. The invention achieves these results by operating within a unique combination of parameters. These parameters comprise: (1) charge-air oxygen concentration below 16%, preferably between 10% and 15%, more preferably between 11% and 14%, and most preferably between 12% and 13.5% for virtually all engine operating conditions (but not necessarily at no-load or low load conditions), (2) fuel injection pressures at or exceeding 1800 bar, preferably exceeding 2100 bar, more preferably exceeding 2300 bar, and most preferably exceeding 2500 bar, at most engine speeds and loads, and (3) charge-air mass / fuel mass ratio between 25:1 and 45:1 for medium and high loads. Furthermore, the system is preferably run continuously slightly lean of stoichiometry, providing just enough excess oxygen to facilitate completeness of combustion and to maintain an exhaust oxygen level sufficient for continuous trap regeneration at a balance point in operation.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
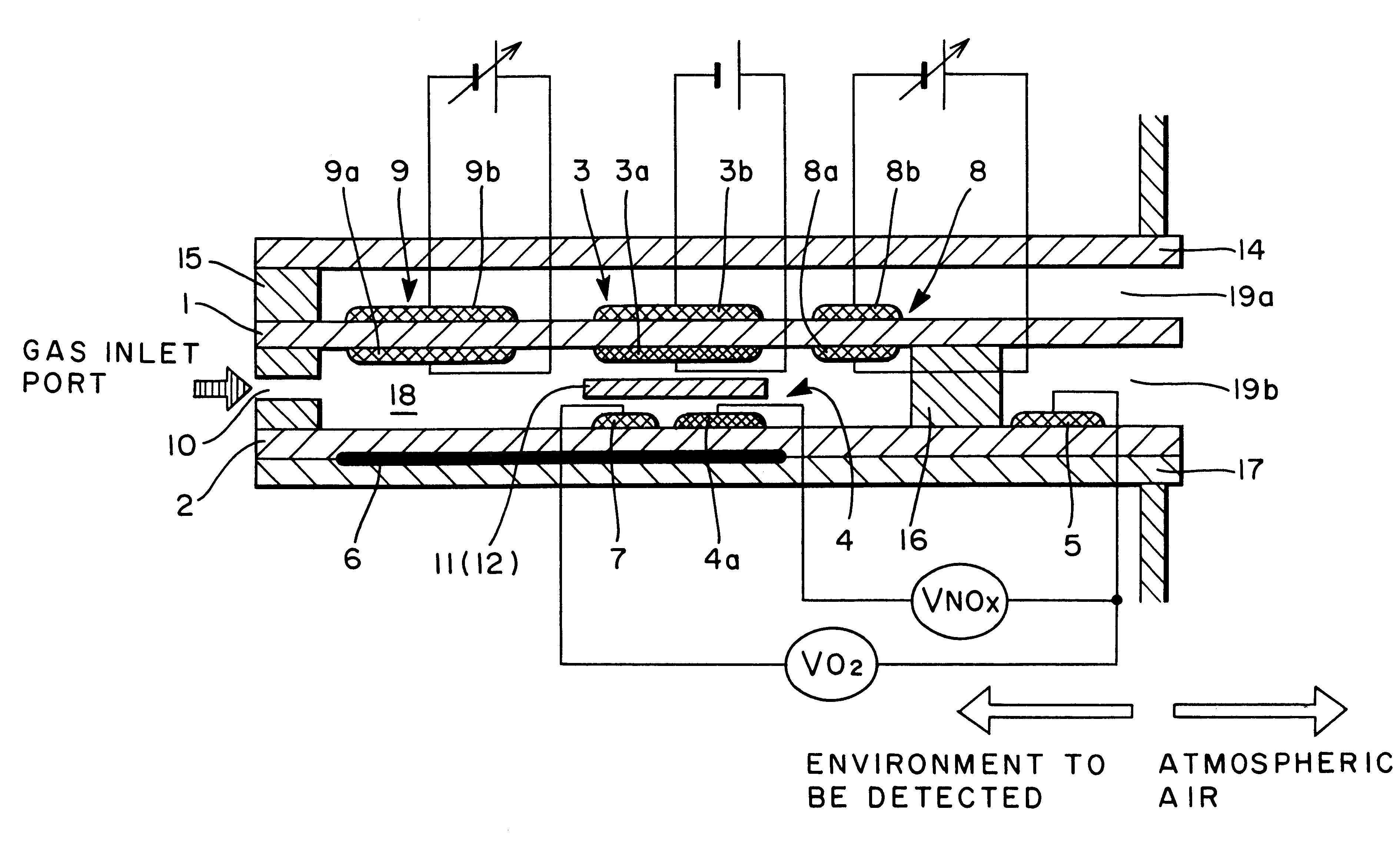
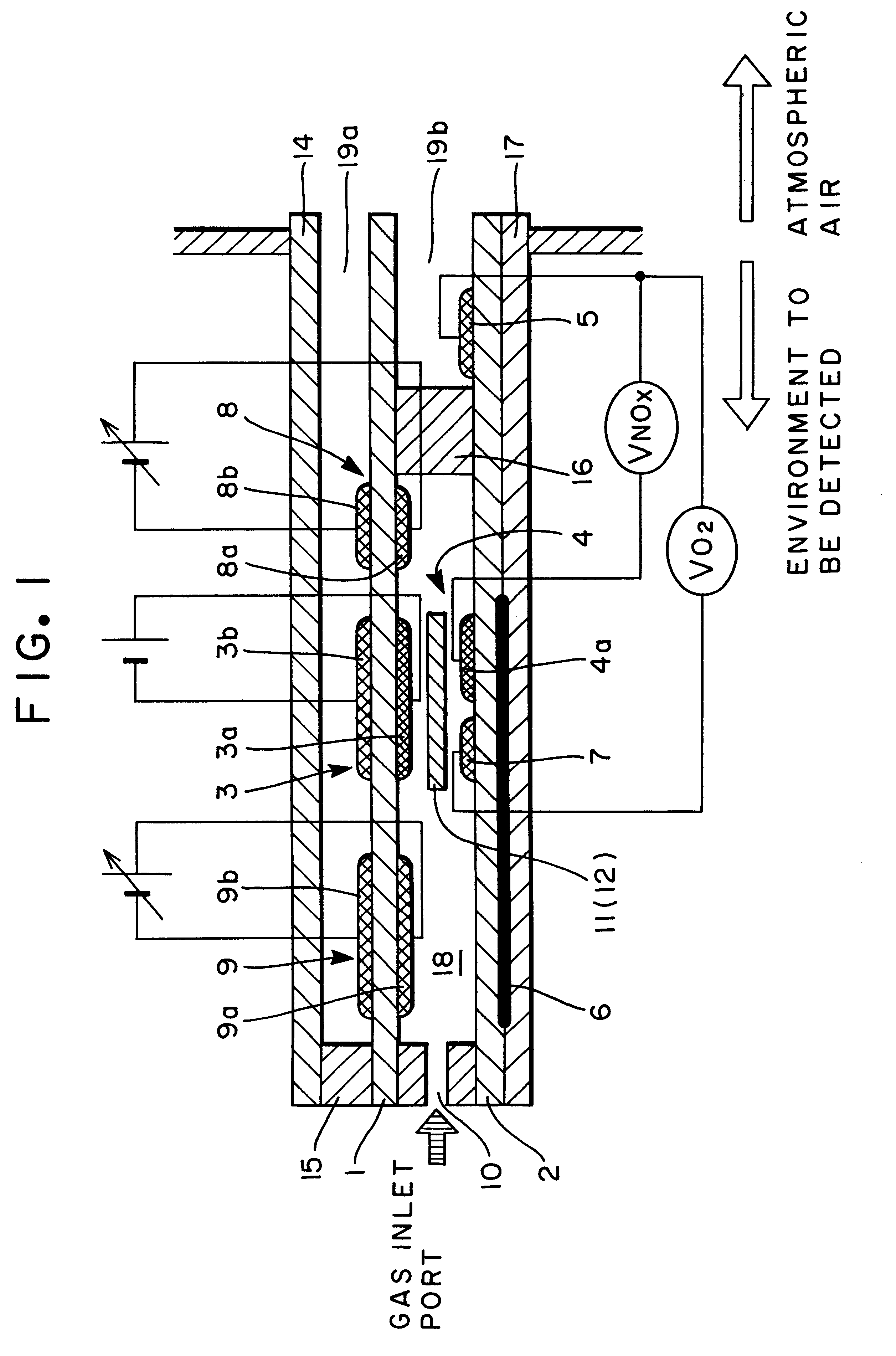
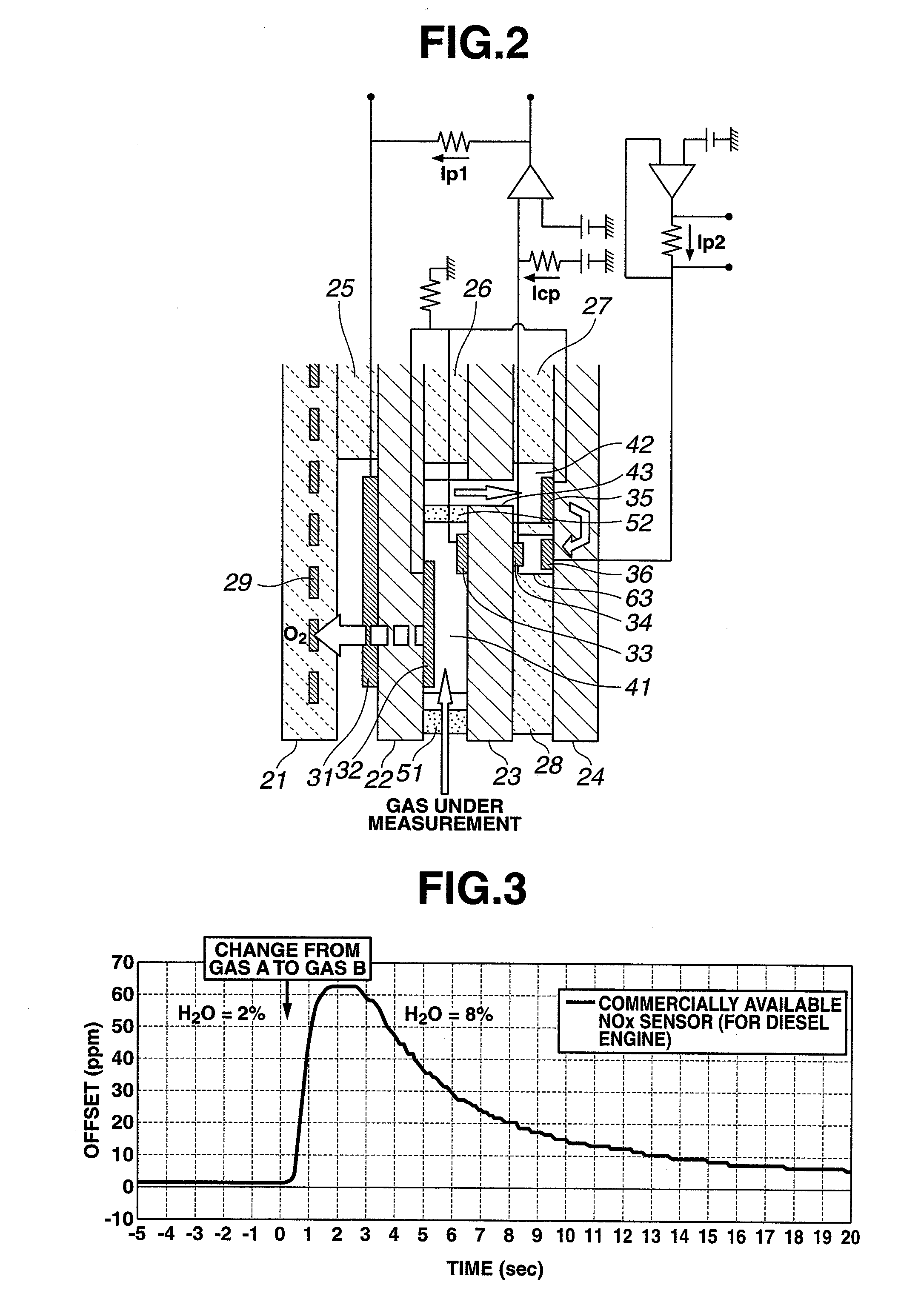
Nitrogen oxide sensor
InactiveUS6319377B1Improve abilitiesHigh and stable sensor outputMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAir quality improvementNitrogen oxide sensorGas chamber
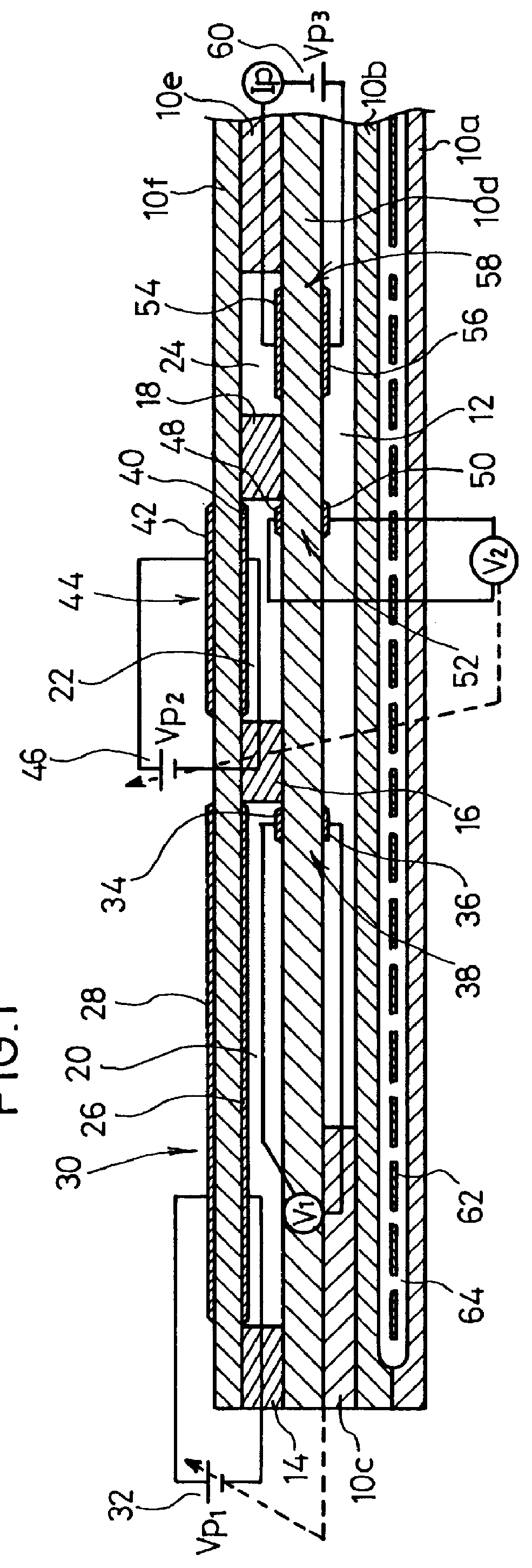
A nitrogen oxide sensor enabled to enhance the measurement concentration of a total of nitrogen oxides by oxidizing or reducing the nitrogen oxides on the surfaces of electrodes in addition to the control of an oxygen concentration by an oxygen pump. An electrode (3a) in a gas chamber (18) constructing an oxygen pumping portion (3) is made of a material (e.g., Pt-3 wt % Rh) having a function to oxidize a nitrogen oxide gas.
Owner:RIKEN CO LTD
Low emission diesel combustion system with low charge-air oxygen concentration levels and high fuel injection pressures
InactiveUS20040055282A1Lower levelReduce the temperatureLiquid coolingEngine sealsLow loadMass ratio
This invention sets forth a commercially viable diesel combustion system that meets environmentally acceptable levels of NOx emissions (i.e. 0.2 g / bhp-hr or lower across a full map of engine speeds and loads) without the need for use of NOx aftertreatments, and simultaneously maintains engine-out PM emissions relatively close (e.g. with smoke levels at or below 3 BSN) to environmentally acceptable PM post-aftertreatment levels. The invention achieves these results by operating within a unique combination of parameters. These parameters comprise: (1) charge-air oxygen concentration below 16%, preferably between 10% and 15%, more preferably between 11% and 14%, and most preferably between 12% and 13.5% for virtually all engine operating conditions (but not necessarily at no-load or low load conditions), (2) fuel injection pressures at or exceeding 1800 bar, preferably exceeding 2100 bar, more preferably exceeding 2300 bar, and most preferably exceeding 2500 bar, at most engine speeds and loads, and (3) charge-air mass / fuel mass ratio between 25:1 and 45:1 for medium and high loads. Furthermore, the system is preferably run continuously slightly lean of stoichiometry, providing just enough excess oxygen to facilitate completeness of combustion and to maintain an exhaust oxygen level sufficient for continuous trap regeneration at a balance point in operation.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
Gas sensor
InactiveUS6045673AEasy to controlSlow changeWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementDiffusionElectricity
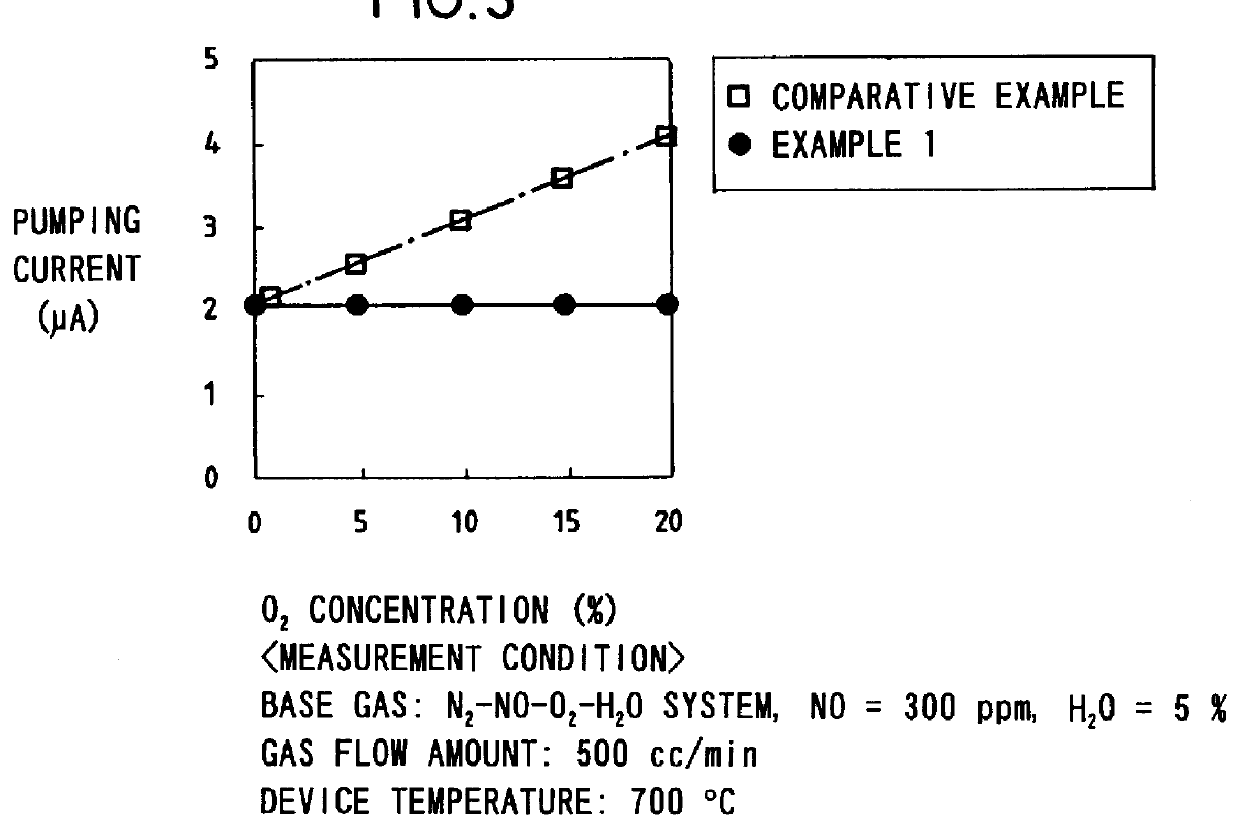
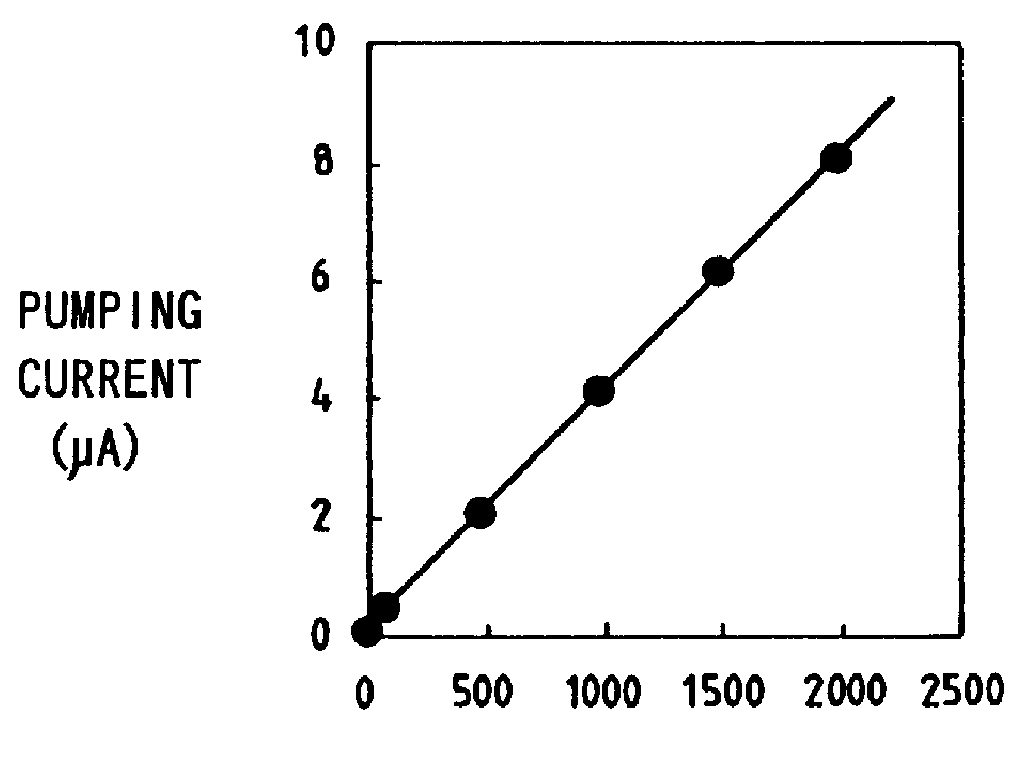
Disclosed is a gas sensor comprising a first internal space for making communication with the external space via a first diffusion rate-determining section, a first electrochemical pumping cell for controlling the oxygen concentration in the atmosphere in the first internal space to have a predetermined value, a second internal space for making communication with the first internal space via a second diffusion rate-determining section, a second electrochemical pumping cell for finely adjusting the oxygen concentration in the atmosphere in the second internal space to have a predetermined value, a third internal space for making communication with the second internal space via a third diffusion rate-determining section, a third electrochemical pumping cell for pumping out oxygen produced by reduction or decomposition of a component having bound oxygen in the measurement gas in the third internal space, and an ammeter Ip for detecting a pumping current which is allowed to flow in accordance with the pumping operation effected by the third electrochemical pumping cell. Accordingly, it is possible to avoid interference exerted on the sensitivity for NO by the change in oxygen concentration in exhaust gas, and improve the measurement accuracy for the measurement gas component.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
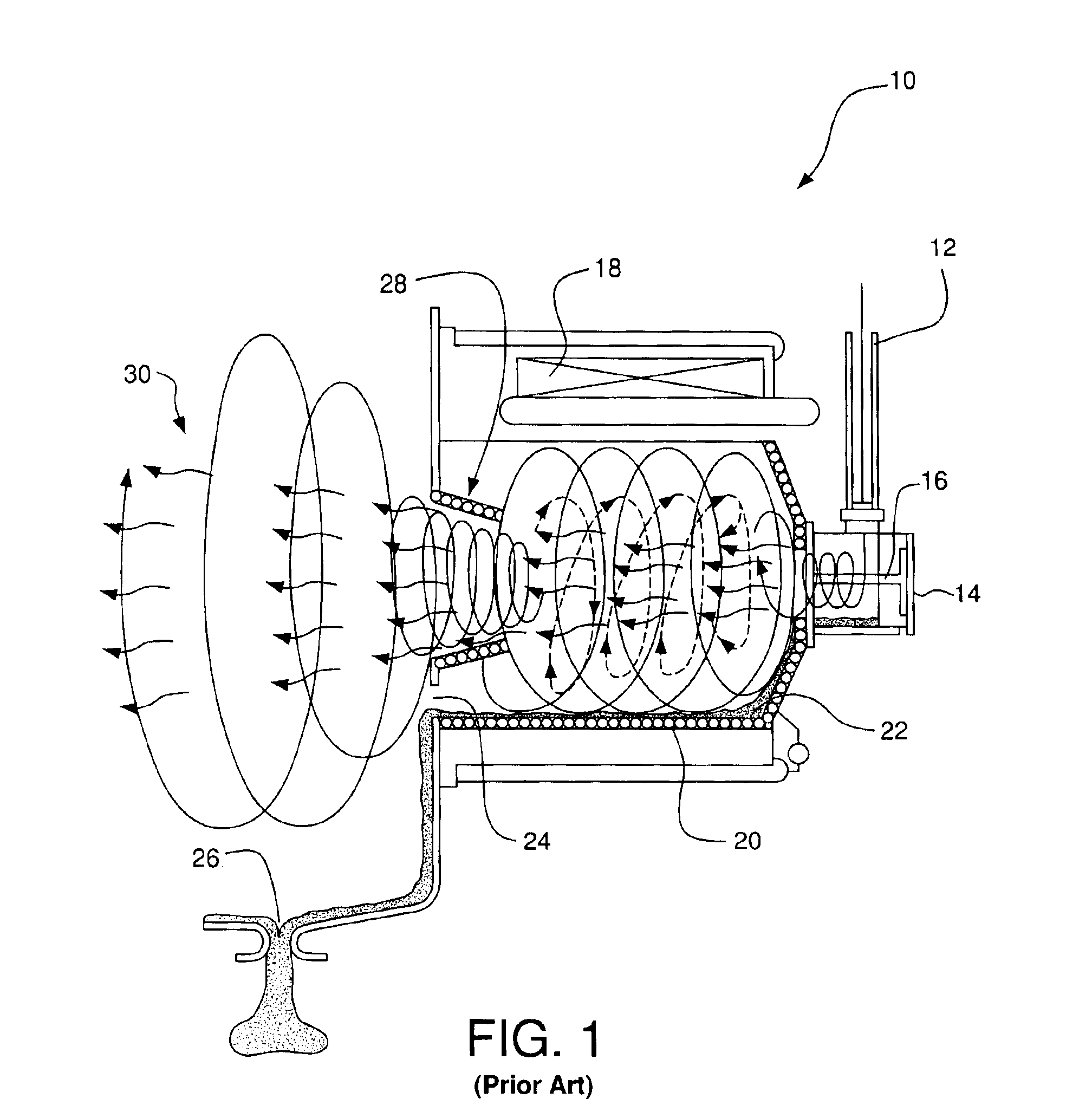
Selective oxygen enrichment in slagging cyclone combustors
InactiveUS6910432B2Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsIncrease rangePulverulent fuel combustion burnersIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationCycloneCombustor
A method for combusting a fuel in a cyclone combustor having a burner and a barrel includes: feeding a stream of the fuel into the barrel at the burner end of the barrel; feeding a stream(s) of a first oxidant (e.g., air) having a first oxygen concentration into the barrel at a first flowrate, the stream(s) of the first oxidant including a predominant stream; feeding a stream(s) of a second oxidant (e.g., oxygen) having a second oxygen concentration into the barrel at a second flowrate and in a selective manner, whereby a portion of the first oxidant combines with a portion of the second oxidant, thereby forming a combined oxidant having a combined oxygen concentration, and a portion of the first oxidant from the predominant stream continues having the first oxygen concentration; and combusting a portion of the fuel with a portion of the combined oxidant in the barrel.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
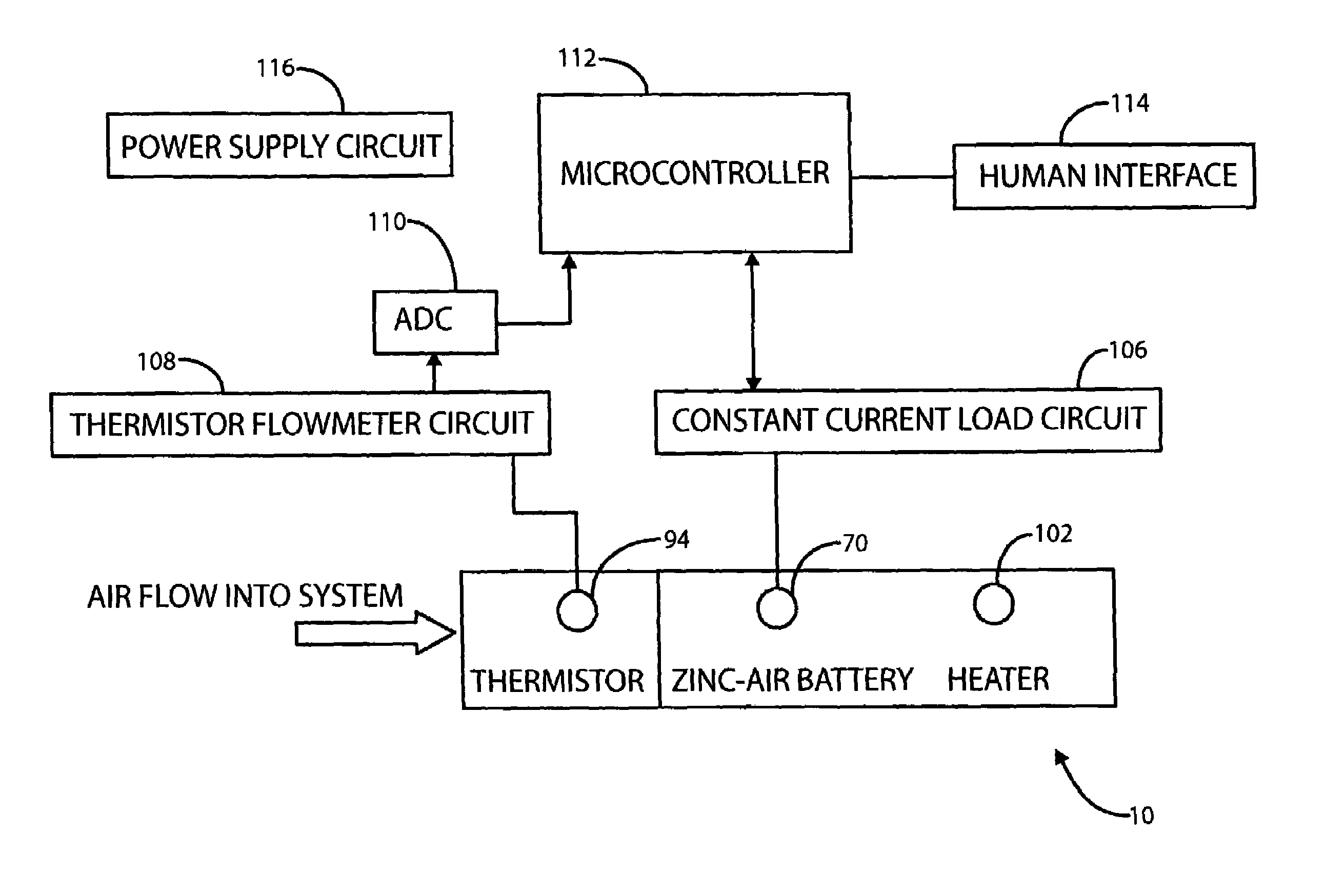
Respiratory exchange ratio sensor
A device for directly measuring a person's respiratory exchange ratio (RER) utilizes a Zn-air battery cell and a constant current load circuit as an O2 pump capable of drawing oxygen from expired air. A thermistor located in the flow path forms a leg of a bridge circuit whose output is proportional to oxygen concentration in the expired air and, therefore, to oxygen uptake. The thermistor flowmeter circuit utilizes the thermal conductivity differences between O2 and CO2 to provide a measure at the relative ratio of the two gases present.
Owner:MEDICAL GRAPHICS CORP A CORP OF MN
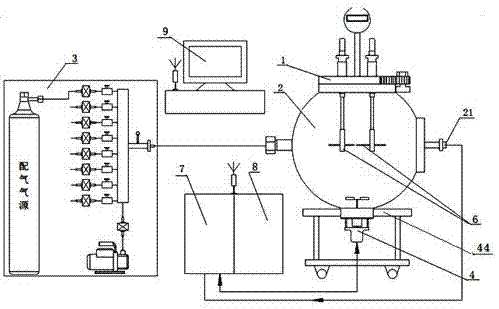
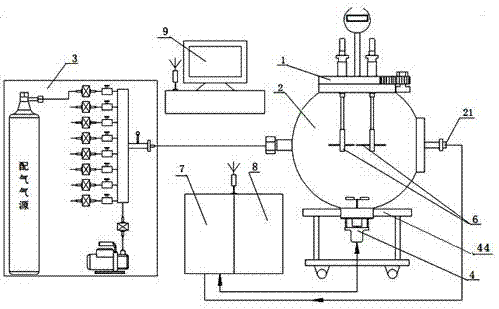
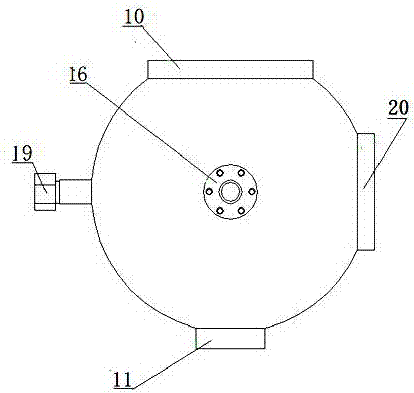
Device for measuring limit oxygen concentration parameter of combustible gas and operating method
The invention relates to a device for measuring a limit oxygen concentration parameter of combustible gas and an operating method. The device comprises a quick sealing screw cover, an explosion experiment container tank, a multi-path precision proportional gas distribution device, a gas stirrer device, an oxygen concentration detection device, an igniting device, a control unit, a data acquisition unit, a computer wireless monitoring system and a base, wherein the multi-path precision proportional gas distribution system achieves gas distribution and sample injection so as to achieve measurement of the limit oxygen concentration of the combustible gas at normal temperature and under normal pressure; the gas stirring system is mounted at the inner bottom of the explosion container so as to achieve rapid uniform mixing of the combustible gas in the explosion experiment container tank; the quick sealing screw cover achieves rapid sealing; through increase of the volume fraction of inert gas, the limit air concentration LAC of the combustible gas is measured, and the limit oxygen concentration LOC of the combustible gas to be measured is calculated. The device has the technical effects as follows: the device adopts a modular design, is stable in performance, reasonable in structure, convenient and fast to operate, safe and reliable, and can simultaneously achieve measurement of a variety of explosion parameters.
Owner:应急管理部天津消防研究所 +1
Exhaust gas purifying method and exhaust gas purifying system
ActiveUS7191590B2Accurate detectionReduced stateElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelSulfurExhaust fumes
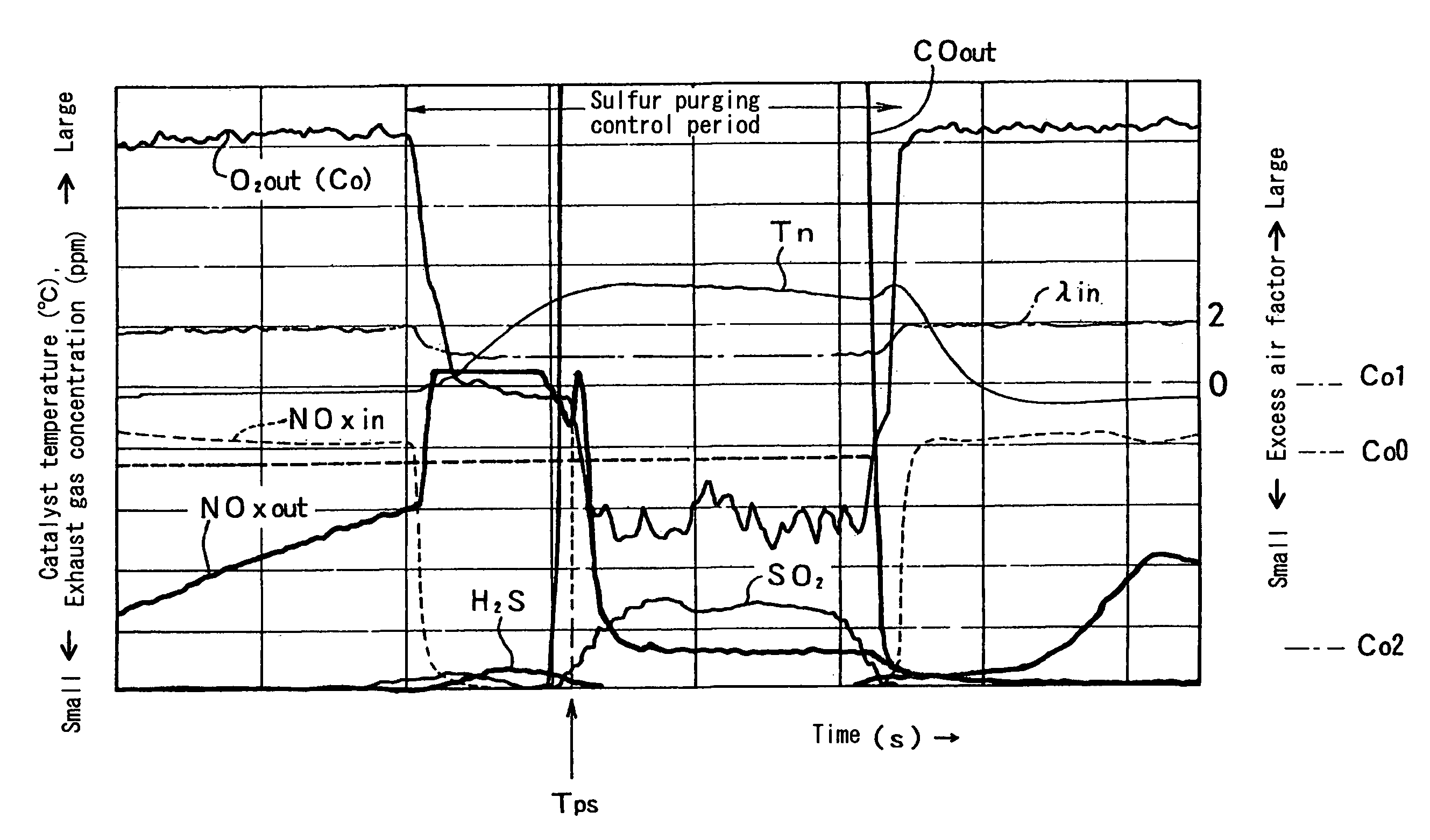
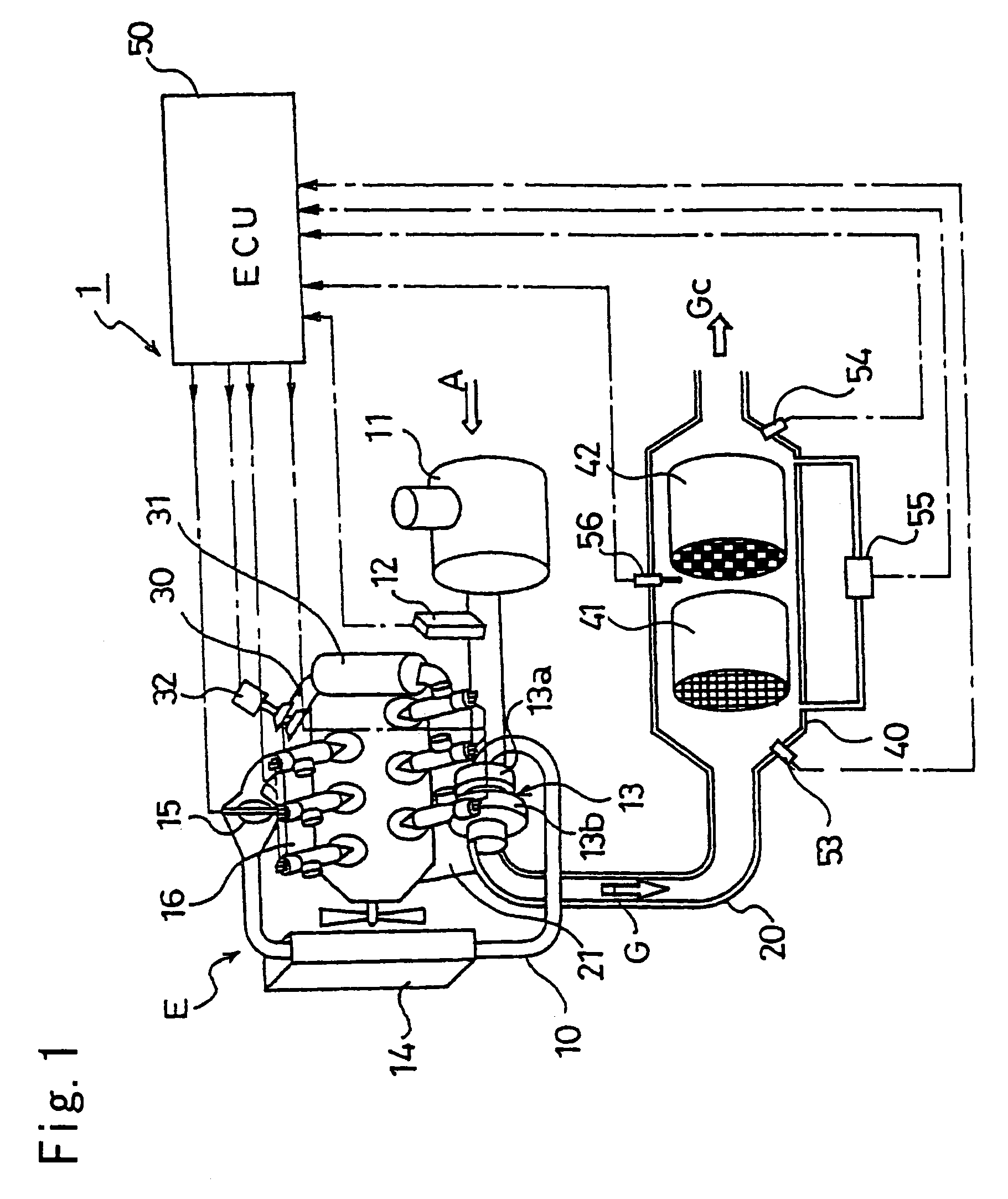
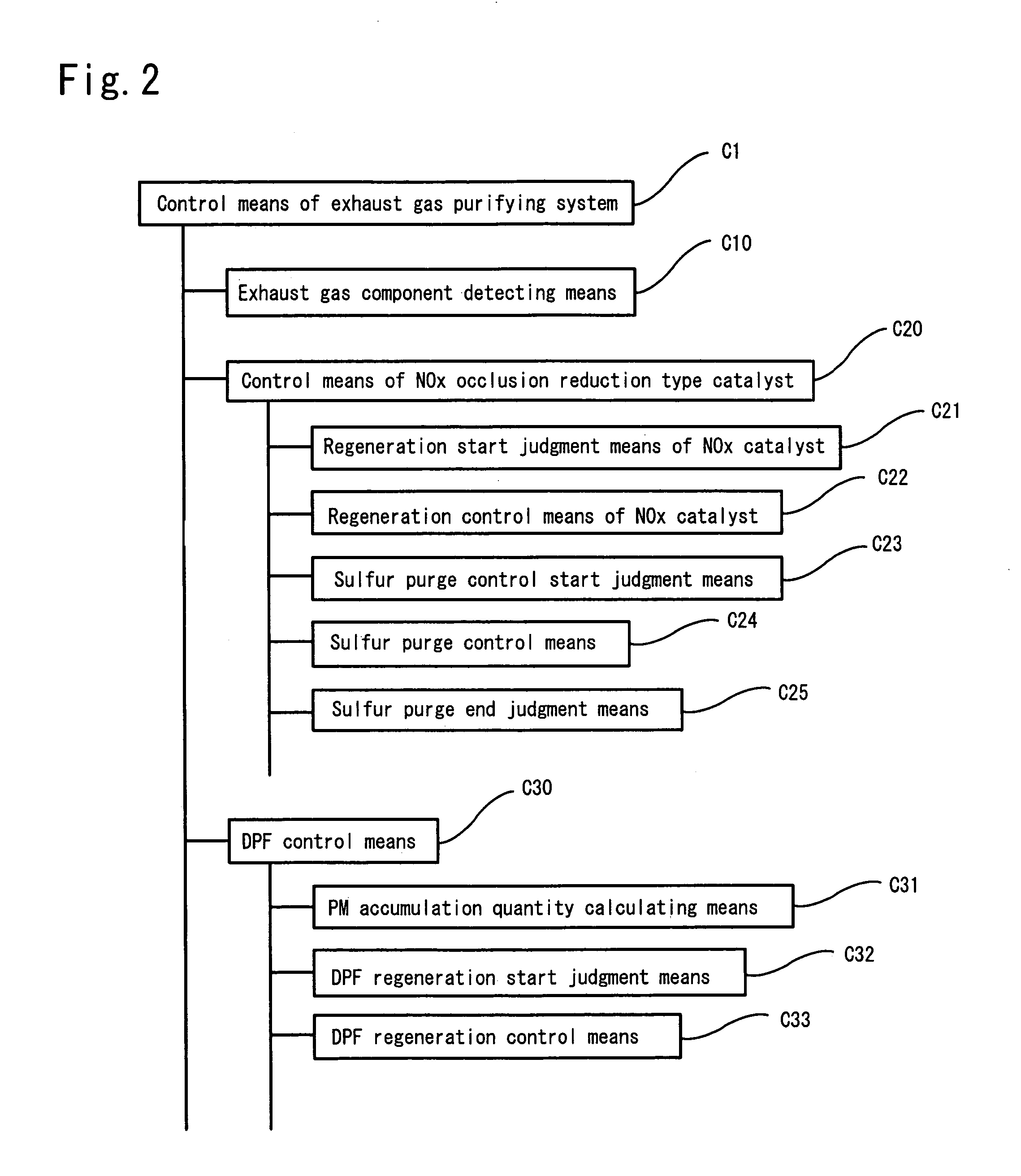
In an exhaust gas purifying system (b 1) that purifies NOx for the exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine (E) through sulfur purging control by a NOx occlusion reduction type catalyst (41), sulfur purging is judged to have started when the oxygen concentration (Co) detected by an oxygen concentration detector (54) disposed downstream of the NOx occlusion reduction type catalyst (41) drops from a first predetermined oxygen concentration indicating that the NOx discharge condition to a second predetermined oxygen concentration indicating that NOx discharge has ended and that Sox discharge has started. Accordingly, during sulfur purging control by the NOx occlusion reduction type catalyst (41), consideration is given to the discharge of NOx without sulfur purging at the start of sulfur purging control; furthermore, this timing is judged by monitoring the concentration of oxygen downstream of the NOx occlusion reduction type catalyst (41), thus optimizing sulfur purging control.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Metal crown lid internal gasket sealing material with oxygen absorbing function
The invention relates to a metal crown lid internal gasket sealing material with an oxygen absorbing function. The metal crown lid internal gasket sealing material is prepared by respectively adding 2-30 parts by weight of single-components of different types or an oxygen absorbent of a compound component by taking a thermoplastic elastomer as a base material. The metal crown lid internal gasket sealing material can be processed into a metal crown lid gasket by adopting an existing non-oxygen absorbing gasket machining process, can absorb residual oxygen of a headspace in an absorbing bottle while keeping the original machining and sealing property of the gasket, and ensures that the oxygen concentration is reduced to a limit oxygen concentration of 0.5ml / l from 210ml / l, thereby prolonging the quality guarantee period.
Owner:SHANGHAI FRONTIER ELASTOMER
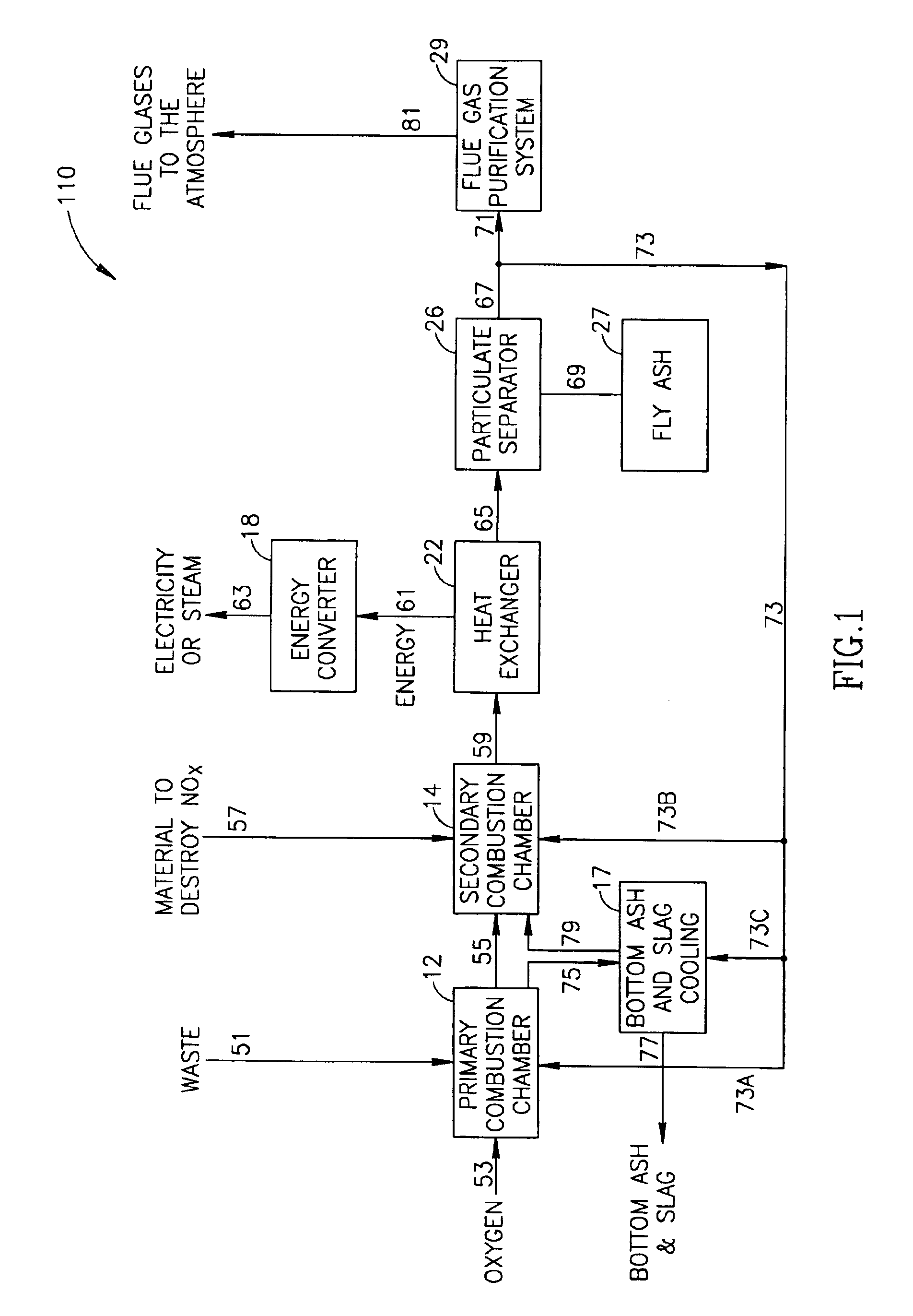
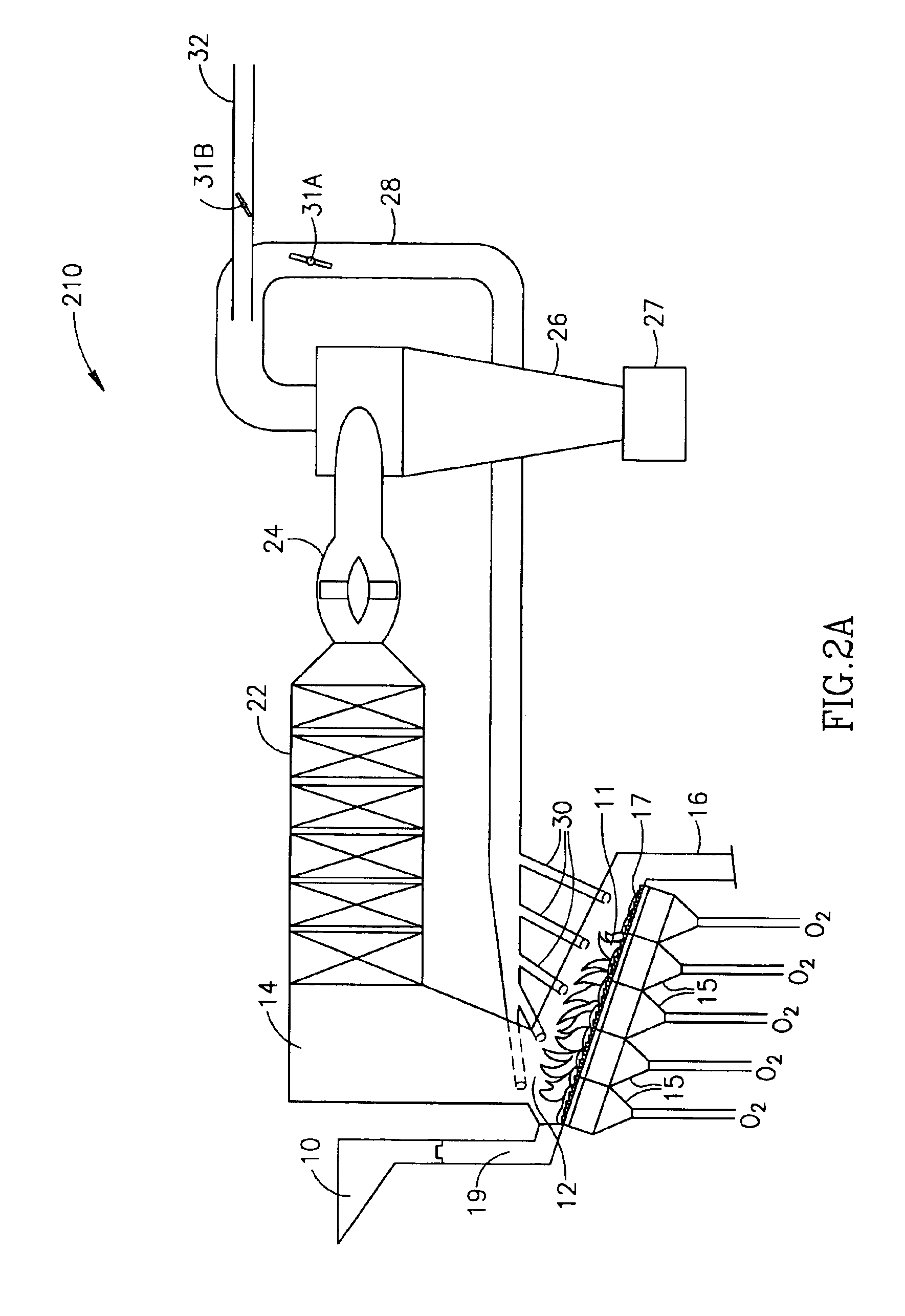
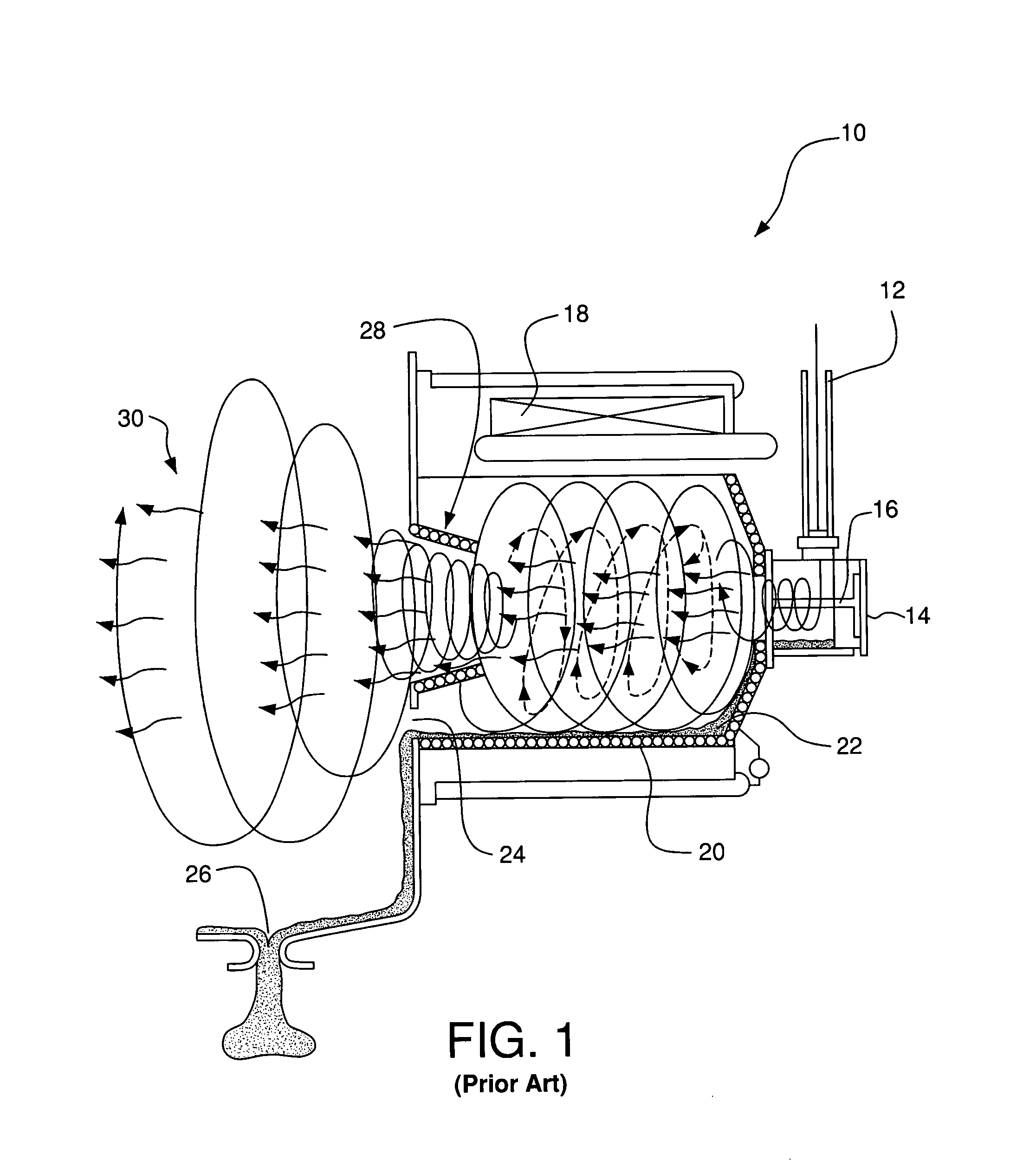
Incineration process using high oxygen concentrations
InactiveUS6952997B2Maximize throughputMinimizing gas emissionFurnace componentsEmission preventionParticulatesCombustion chamber
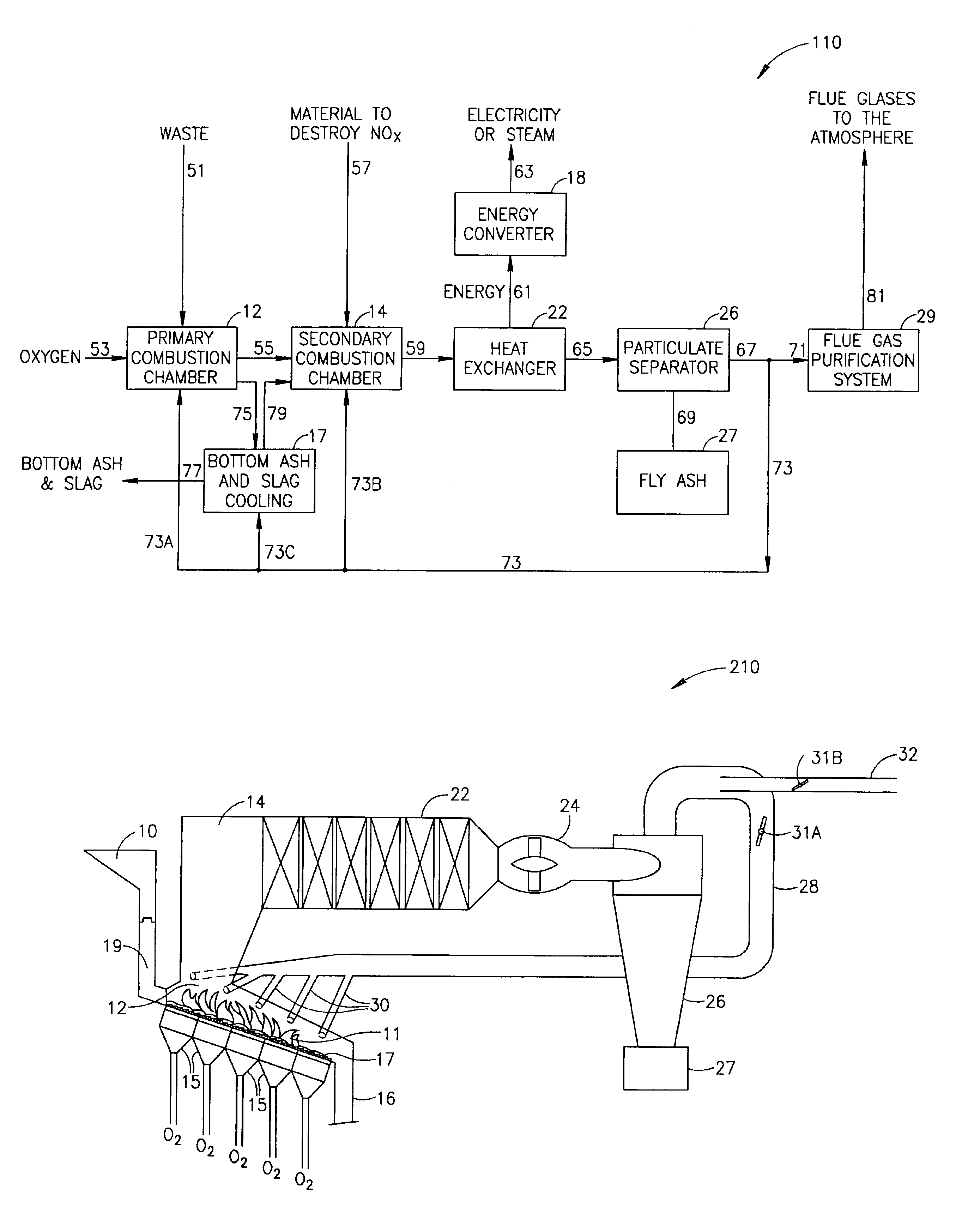
A process for incinerating combustible materials including the steps of: delivering combustible material and inlet gases to a primary combustion chamber, the inlet gases having an oxygen content of at least 50 vol %; burning the combustible material with the oxygen of the inlet gases in the primary combustion chamber producing flue gases and solid particulates as thermal decomposition products of the burnt combustible material; passing the flue gases and particulates to a secondary combustion chamber where further combustion occurs; cooling the flue gases exiting the secondary combustion chamber; returning a portion of the cooled flue gases to at least one of the combustion chambers where the cooled gases moderate the temperature in the at least one chamber; and passing the remaining portion of cooled flue gases on to a flue gas purification system where pollutants in the flue gases and particulates are substantially converted to benign compounds or removed entirely before the flue gases are emitted into the atmosphere.
Owner:PURE FIRE TECH
Selective oxygen enrichment in slagging cyclone combustors
InactiveUS20050039654A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsIncrease rangePulverulent fuel combustion burnersIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationCycloneCombustor
A method for combusting a fuel in a cyclone combustor having a burner and a barrel includes: feeding a stream of the fuel into the barrel at the burner end of the barrel; feeding a stream(s) of a first oxidant (e.g., air) having a first oxygen concentration into the barrel at a first flowrate, the stream(s) of the first oxidant including a predominant stream; feeding a stream(s) of a second oxidant (e.g., oxygen) having a second oxygen concentration into the barrel at a second flowrate and in a selective manner, whereby a portion of the first oxidant combines with a portion of the second oxidant, thereby forming a combined oxidant having a combined oxygen concentration, and a portion of the first oxidant from the predominant stream continues having the first oxygen concentration; and combusting a portion of the fuel with a portion of the combined oxidant in the barrel.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Exhaust gas purifying system
ActiveUS20100199635A1Reduced fuel efficiencyEnsure compatibilityElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelTrappingExhaust fumes
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
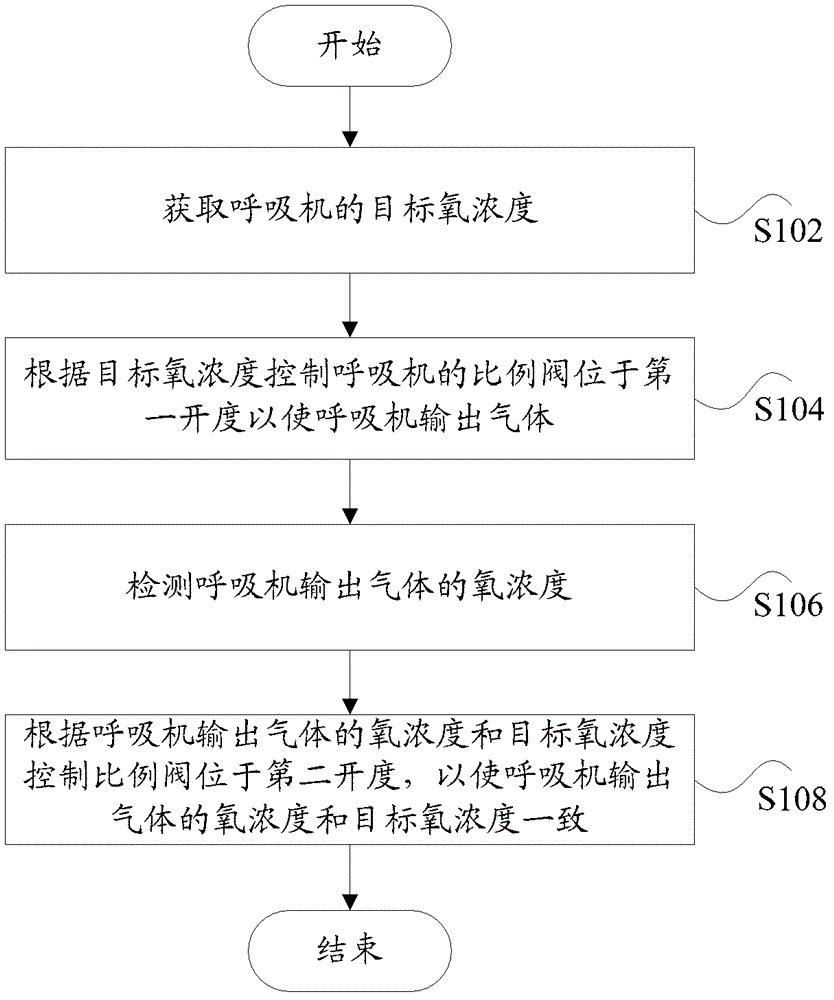
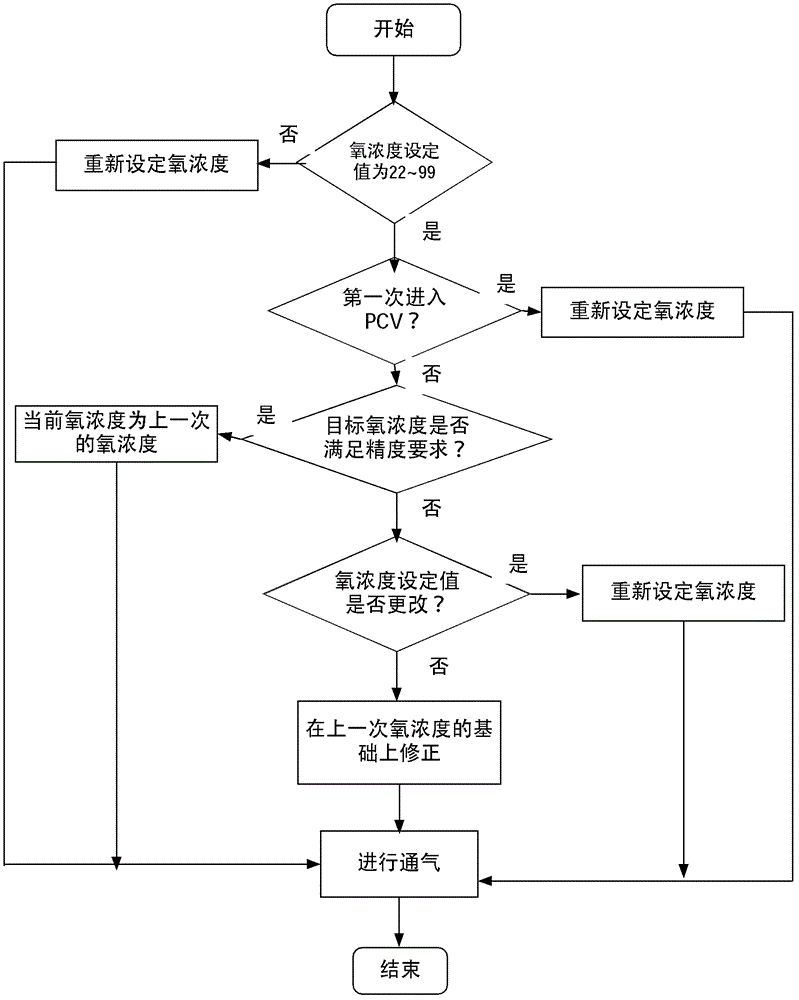
Control method and control device for breathing machine oxygen concentration
ActiveCN103055397ASolve the problem of poor oxygen concentration control effectImprove the accuracy of oxygen concentration controlRespiratorsEngineeringProduct gas
The invention discloses a control method and a control device for breathing machine oxygen concentration. The control method for the breathing machine oxygen concentration comprises the steps of obtaining target oxygen concentration of a breathing machine, controlling a proportional valve of the breathing machine to be at a first opening degree according to the target oxygen concentration so as to enable the breathing machine to output gas, detecting the oxygen concentration of the gas output by the breathing machine, and controlling the proportional valve to be at a second opening degree according to the oxygen concentration of the gas output by the breathing machine and the target oxygen concentration so as to enable the oxygen concentration of the gas output by the breathing machine to accord with the target oxygen concentration. The control method and the control device for the breathing machine oxygen concentration are capable of improving control effect of the oxygen concentration of the breathing machine.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
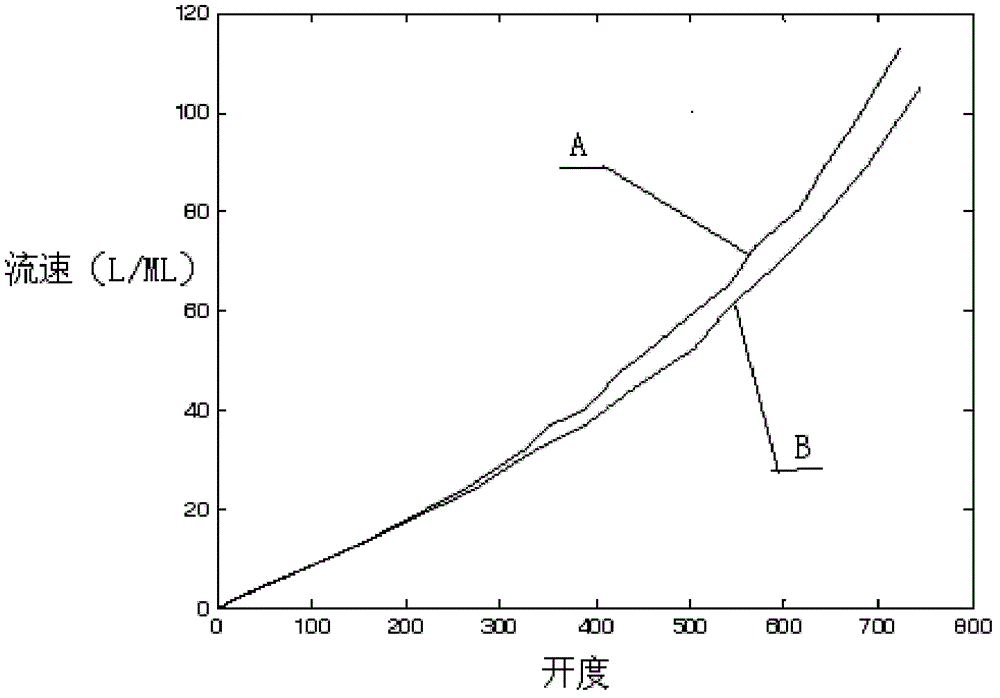
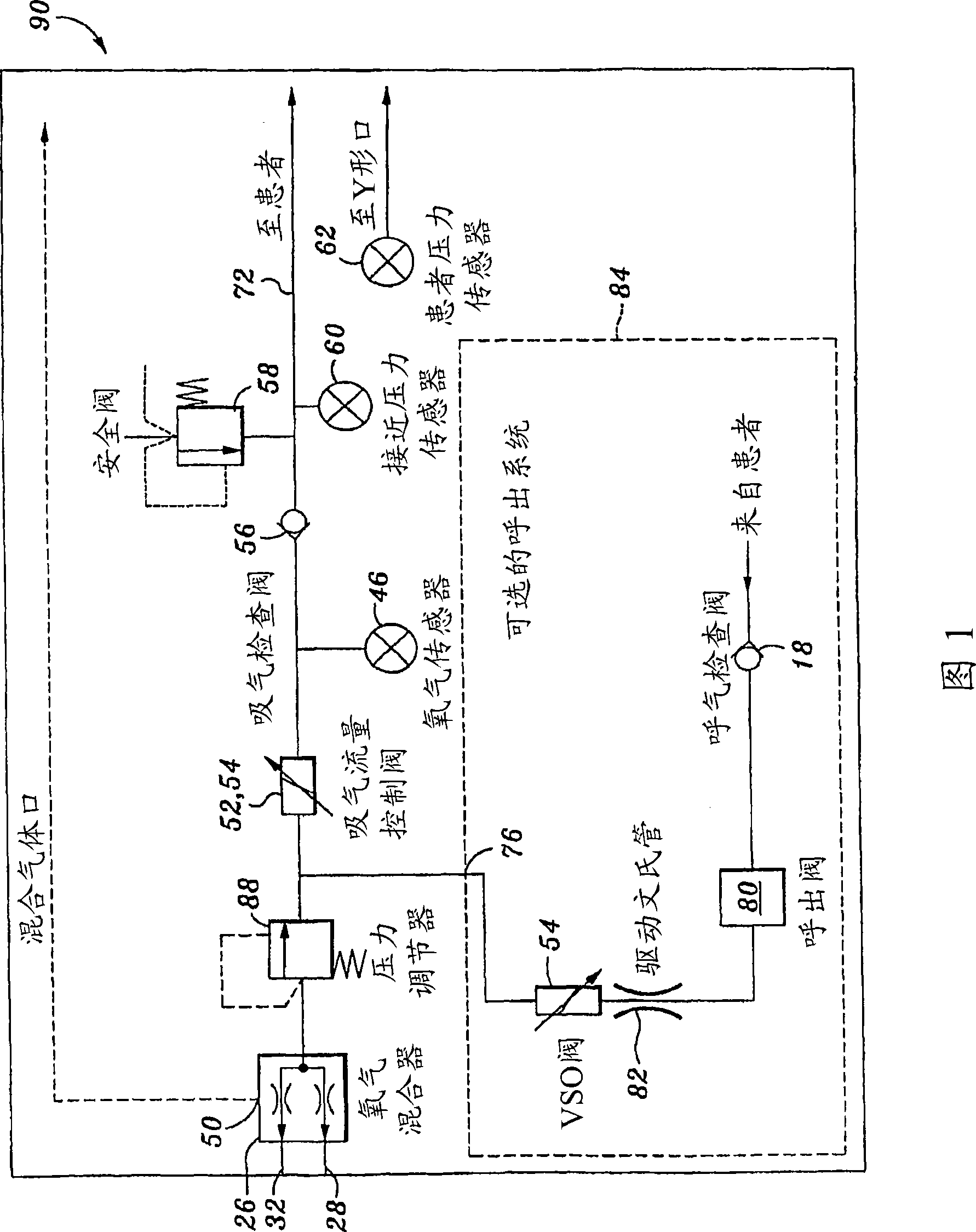
Hardware configuration for pressure driver
A pressure driver for a ventilation system comprises a gas source, an inspiration flow control valve and a patient pressure sensor to form a closed loop control system. The inspiration flow control valve may be mounted within a housing and is operative to open and close in response to patient pressure measurements in order to produce a desired pressure at the patient. The pressure driver may further include a mixture control for allowing selective adjustment of the oxygen concentration in pressurized gas delivered to the patient. An oxygen mixer is connected between the gas source and the mixture control and is operative to deliver the desired mixture of oxygen and air to the inspiration flow control valve for delivery to the patient. An oxygen sensor monitors the oxygen concentration in the gas provided by the oxygen mixer.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 211 INC
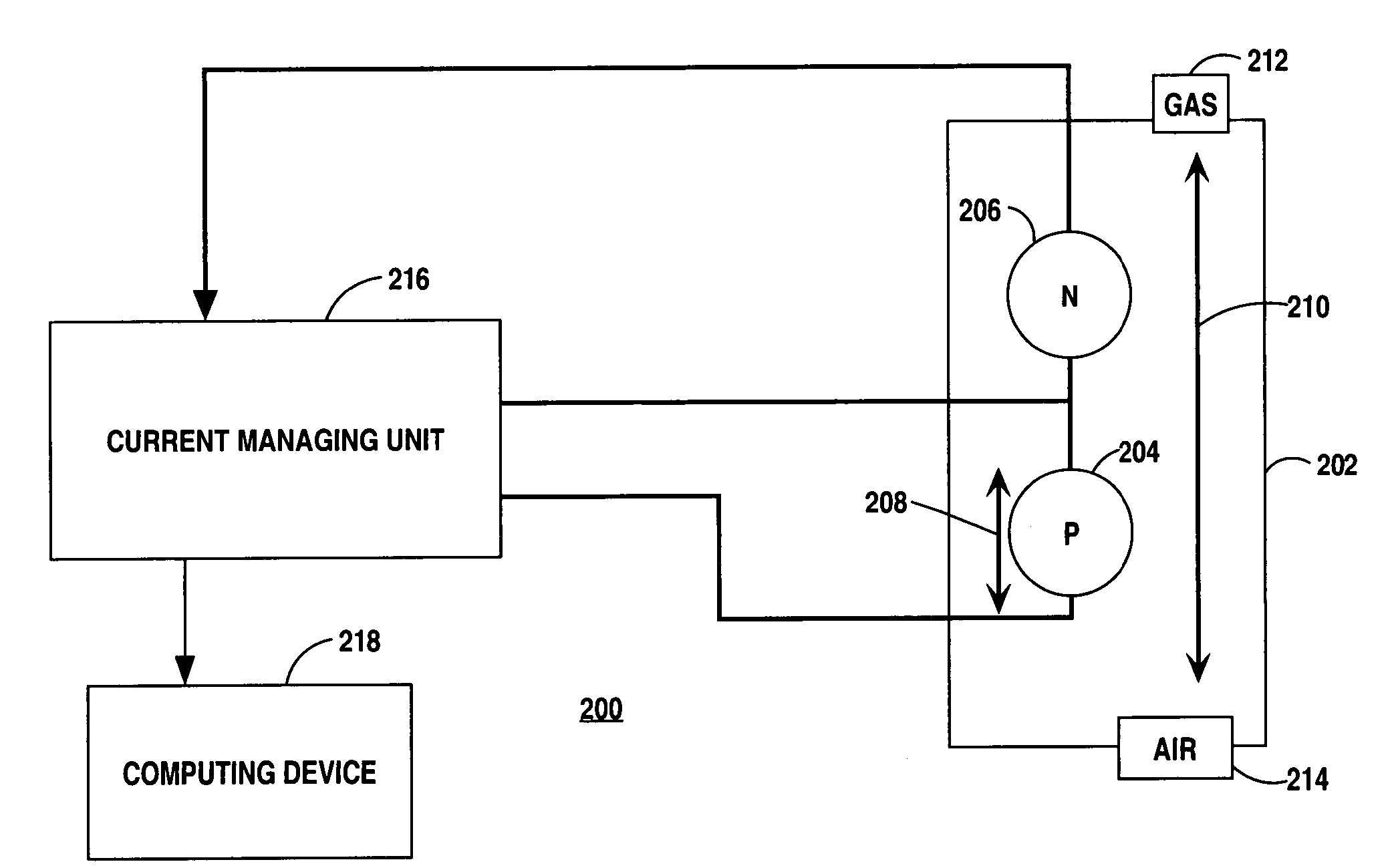
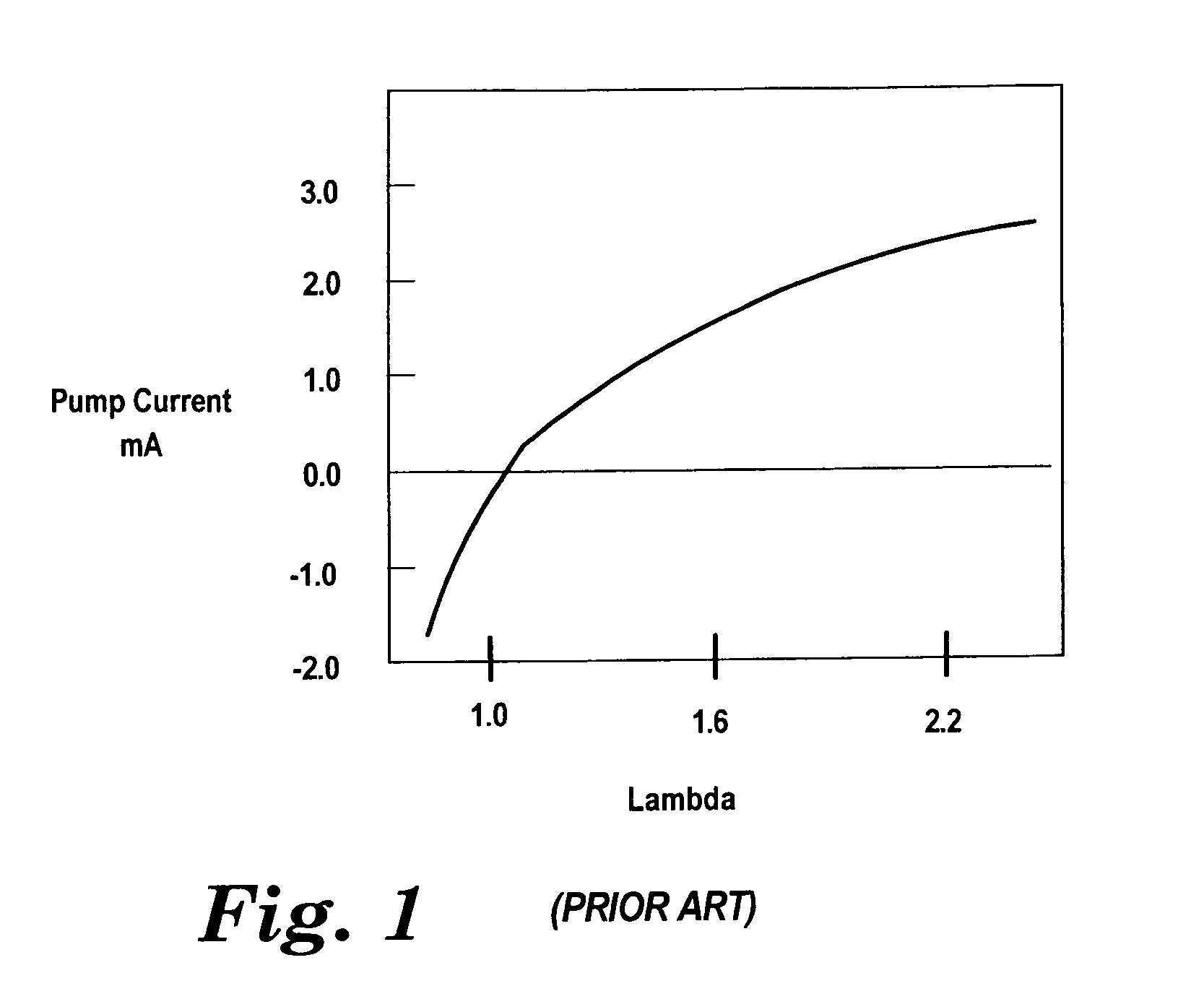
System, apparatus, and method for measuring an oxygen concentration of a gas
An apparatus, system and method maximizes efficiency and accuracy of measuring an oxygen concentration of a measured gas by varying a flow of oxygen ions within a measuring cell (202) in accordance with an output signal of an oxygen sensor cell (206). The pump current (208) through a pump cell (204) is switched between a constant positive current and a constant negative current when upper and lower thresholds of the output signal are reached. The pulse width ratio of the square wave produced by the varying current is compared to a pulse width ratio function derived from a calibration procedure to determine the oxygen concentration of the measured gas.
Owner:EMISENSE TECH
Oxygen uptake instrument
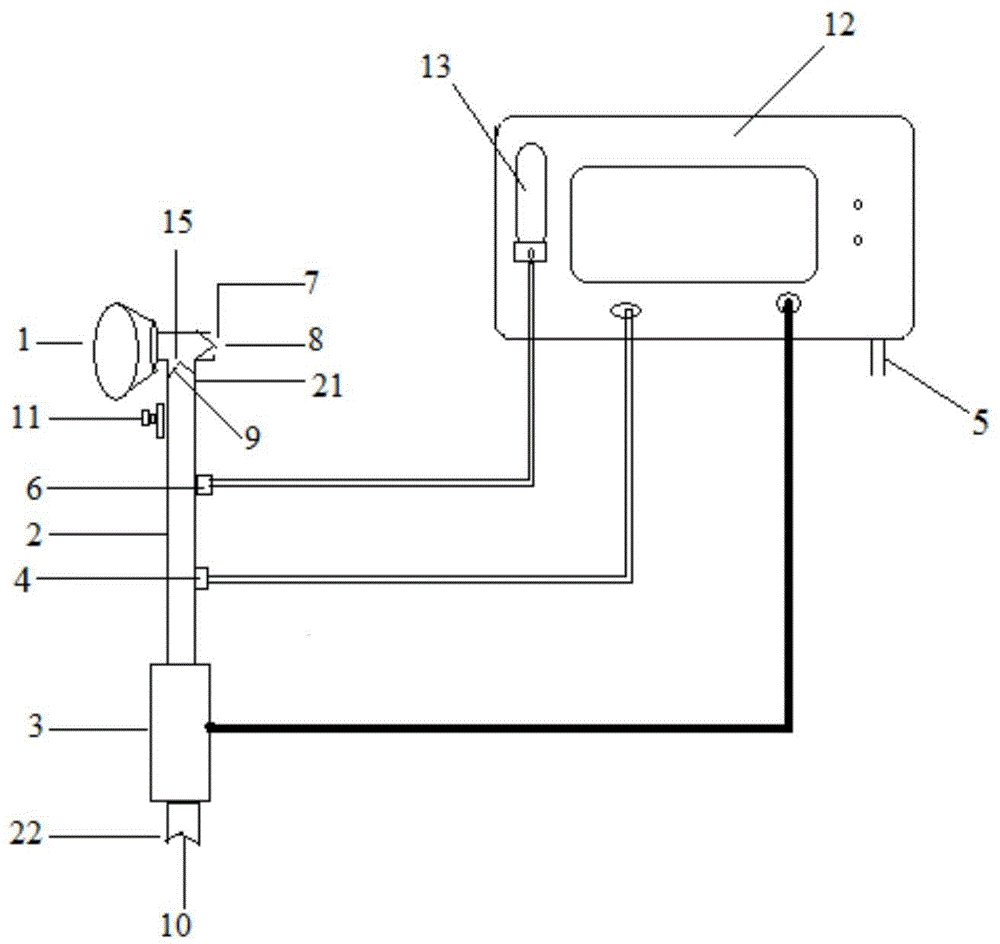
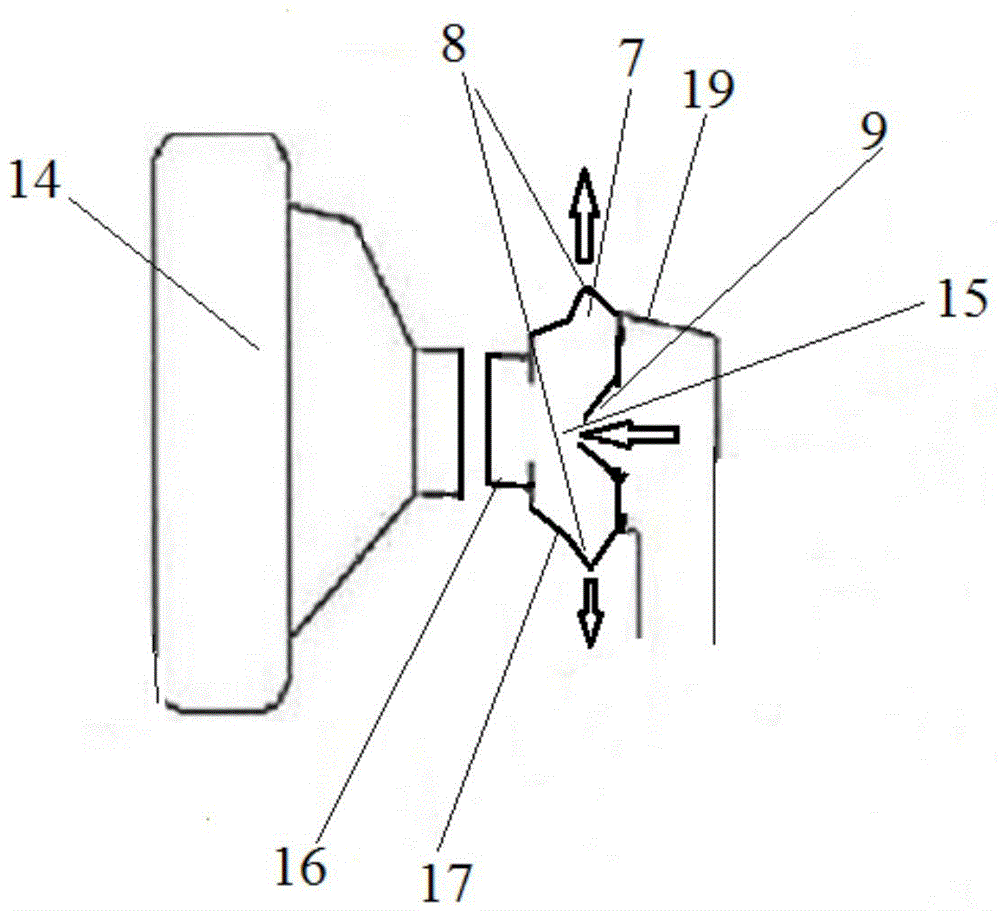
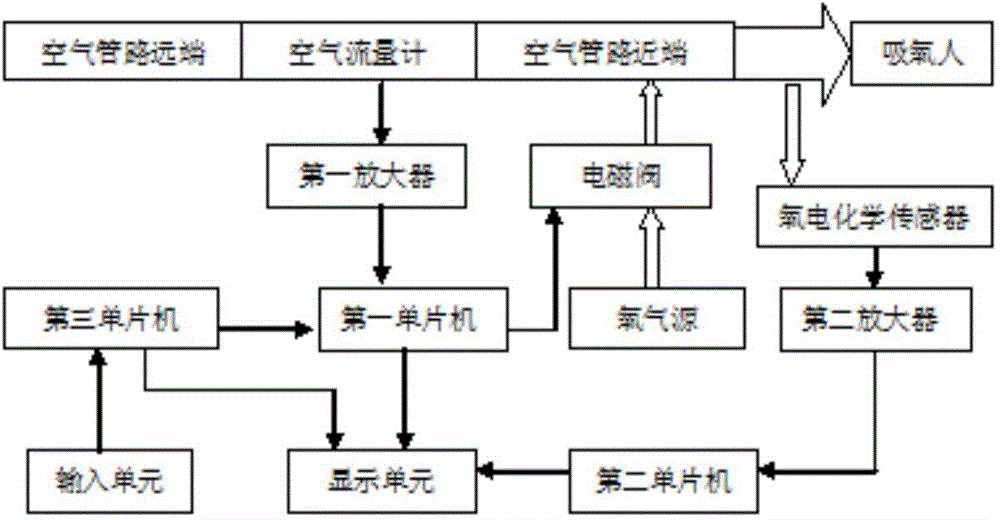
The invention discloses an oxygen uptake instrument which comprises a sealing mask assembly, an air pipeline, an oxygen branch pipeline, an air flowmeter and a control device, wherein the sealing mask assembly is provided with an expiration hole and an admission hole; an expiration one-way valve which is communicated with the atmosphere is arranged at the expiration hole of the sealing mask assembly; an admission one-way valve is arranged at the admission hole; the air pipeline is provided with a first end and a second end; the first end of the air pipeline is communicated with the expiration hole of the sealing mask assembly in an airtight manner; an air inlet one-way valve which is communicated with the atmosphere is arranged at the second end of the air pipeline; the oxygen branch pipeline is communicated with the air pipeline in an airtight manner; the oxygen branch pipeline can be connected with an oxygen supply source through a solenoid valve; the air flowmeter is arranged in the air pipeline; the control device is connected with the air flowmeter and the solenoid valve and is used for controlling the oxygen flow inside the oxygen branch pipeline according to individual air expiration amount detected by the air flowmeter, of an oxygen taker. By adopting the oxygen uptake instrument disclosed by the invention, not only is the taken oxygen concentration automatically and accurately controlled and monitored, but also a great deal of oxygen is saved, and the comfort in oxygen taking is improved.
Owner:昌克勤 +1
Limiting current type oxygen sensor and method of sensing and measuring oxygen concentrations using the same
InactiveCN101097209AEasy to processAccurate sensingSpecial data processing applicationsMaterial electrochemical variablesDiffusionInterior space
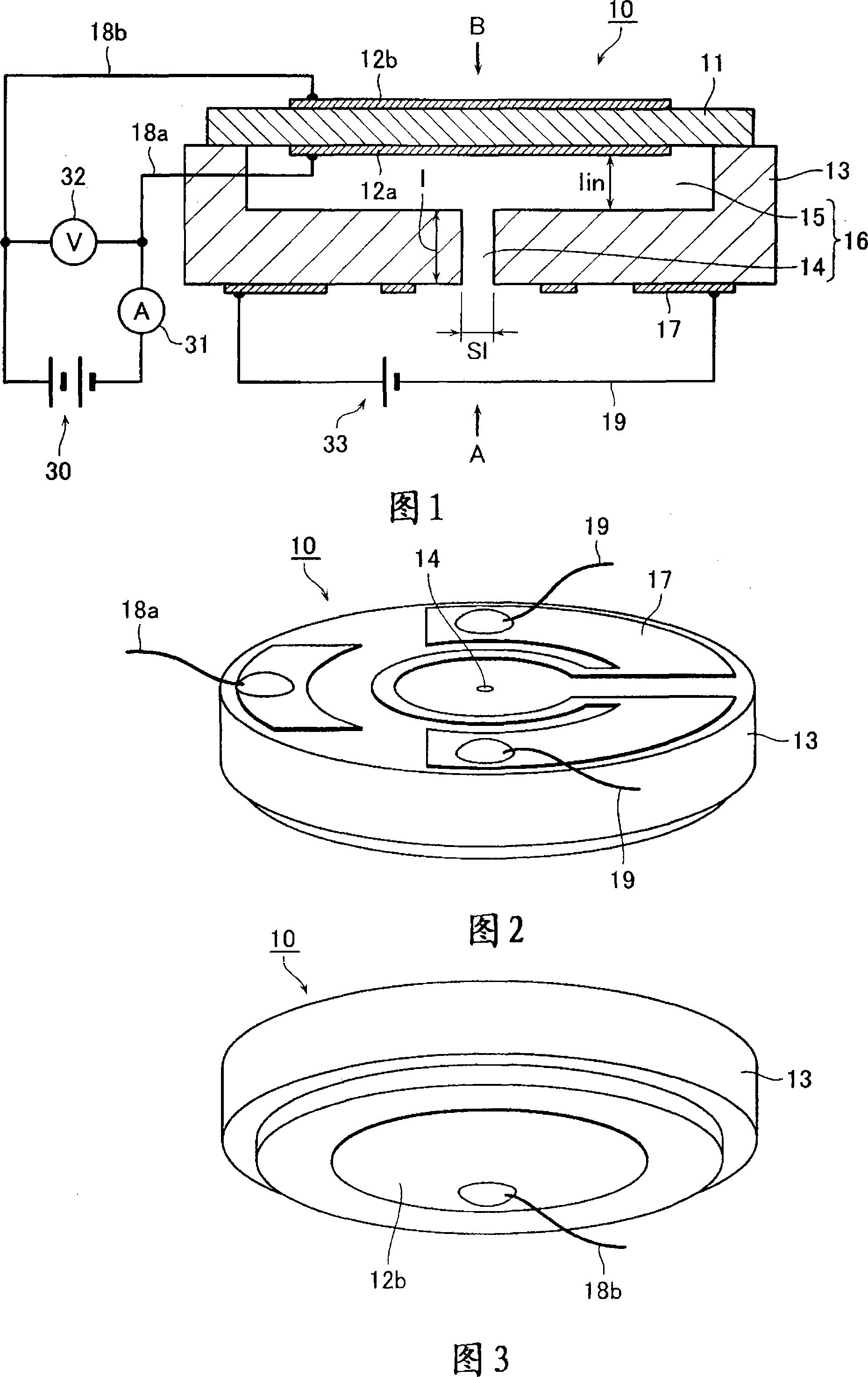
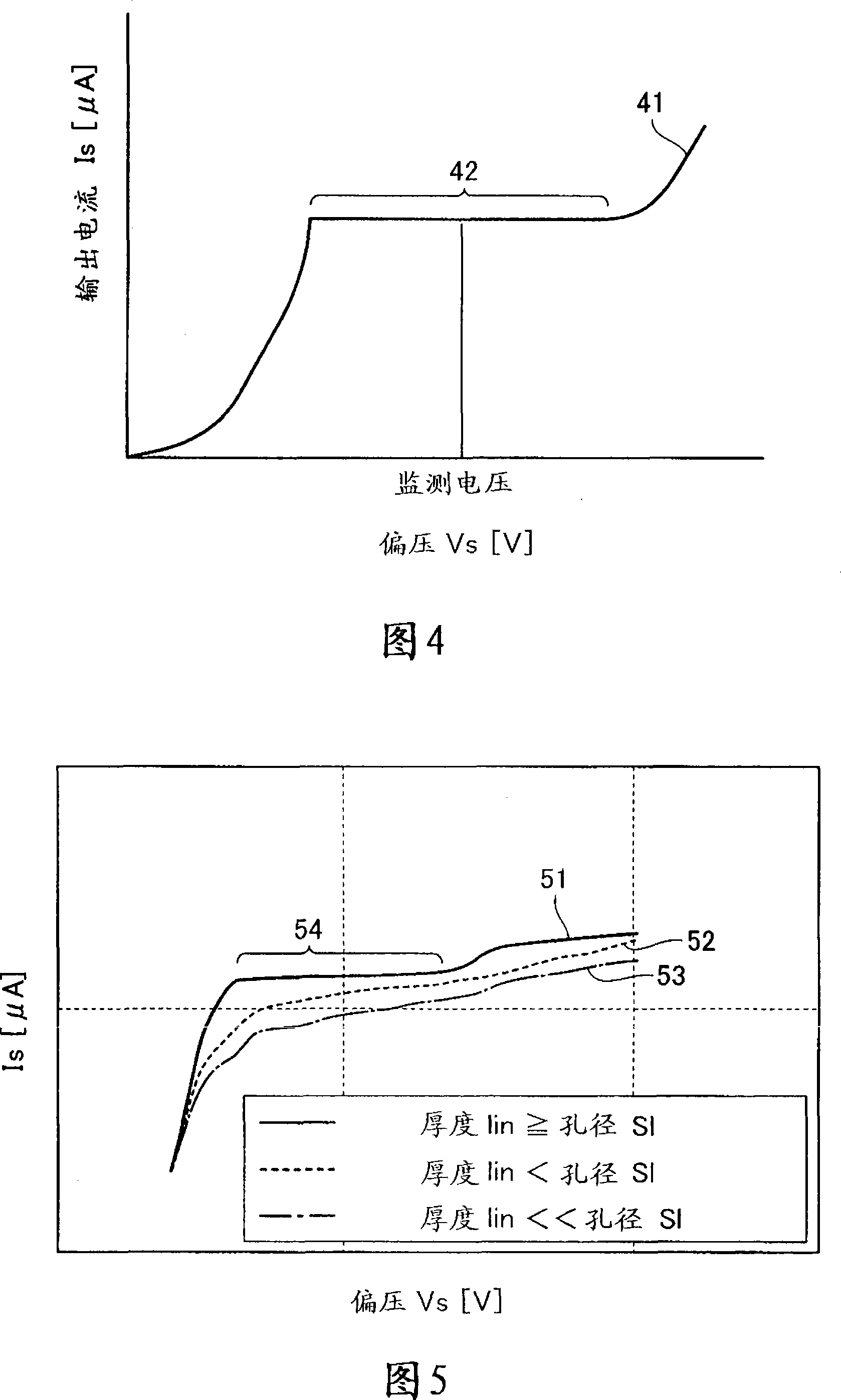
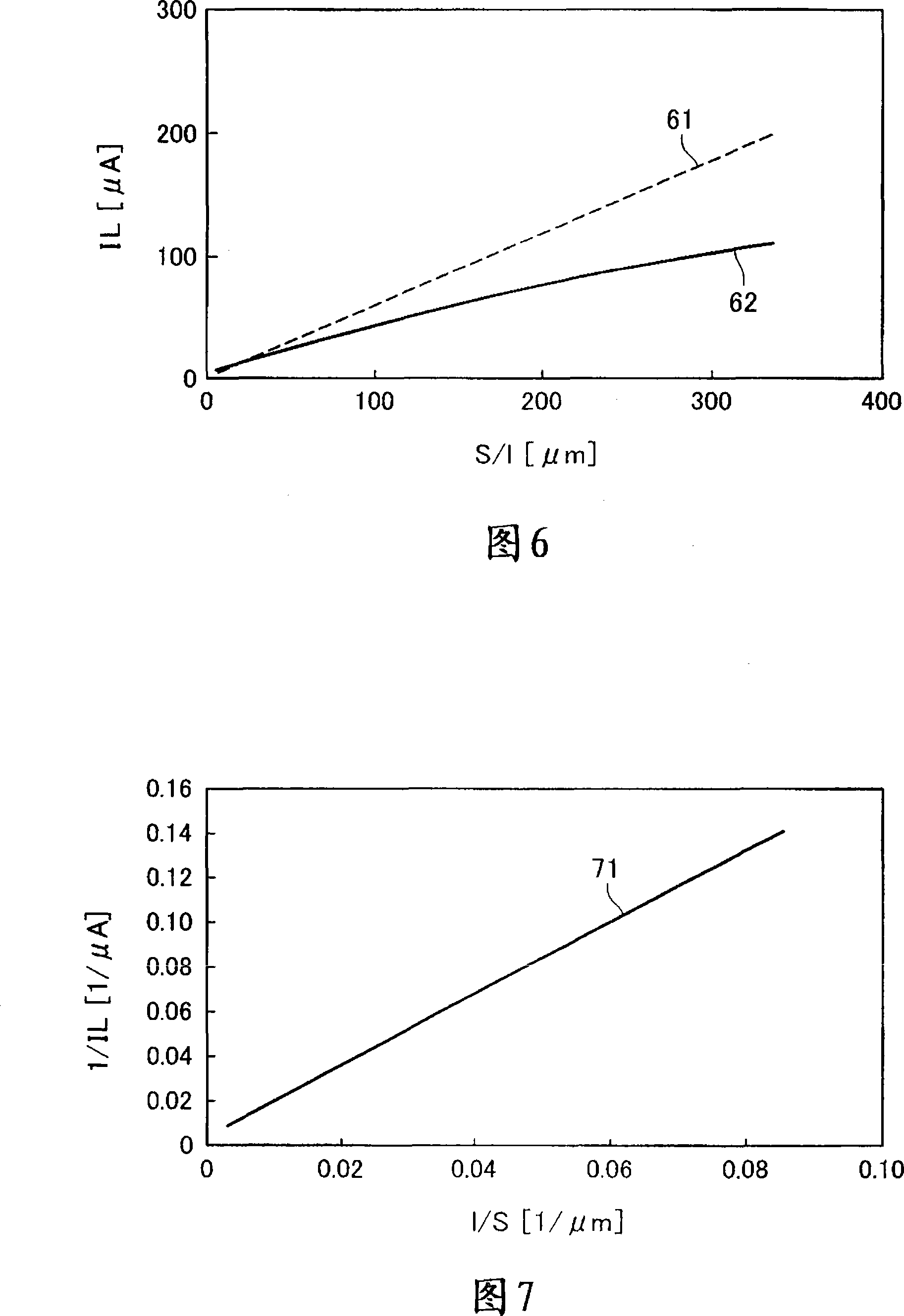
A limiting current type oxygen sensor comprises an ion conductor, a pair of electrodes, a gas diffusion mechanism for supplying a diffusion-rate-determined gas, and a heater for heating the ion conductor. The gas diffusion mechanism includes a gas diffusion bore and an internal space communicating with the gas diffusion bore. In a first embodiment, the gas diffusion mechanism is configured such that the thickness (lin) of the internal space is formed equal to or larger than the bore diameter (S1) of the gas diffusion bore. This makes it possible to dominate diffusion-rate-determinateness in the gas diffusion bore and minimize the influence of diffusion-rate-determinateness in the internal space, thereby sensing the limiting current value accurately. In a second embodiment, the gas diffusion mechanism is configured such that an oxygen concentration gradient within the internal space satisfies the following expression: 1 / I lim = (1 / 4FDC o2 ){(l / S) + (l in / S in which is based on a relationship between the Faraday constant (F); a diffusion coefficient (D); an oxygen concentration (C o2 ); a bore area (S) of the gas diffusion bore; a bore length (1) in the axial direction of the gas diffusion bore; a distance (l in ) in the internal space between the first elextrode and the inner surface opposed thereto; an effective cross section (S in ) of the internal space; and an output current value (I lim ).
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Ventilator
ActiveCN108348715ASolution to short lifeSave construction spaceRespiratorsMedical devicesOxygen sensorEngineering
A ventilator (1) comprises a gas pipe system for supplying respiratory gas to a patient; at least one monitoring device is provided for monitoring the oxygen concentration in the respiratory gas; saidmonitoring device includes at least one receptacle (5) for an oxygen sensor (12, 15); a galvanic oxygen sensor (12) or a paramagnetic oxygen sensor (15) can be selectively inserted into the receptacle (5).
Owner:欧根卡根
Efficiency calculation method for novel SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) denitration device
ActiveCN105866338AConcentration Accurate and ScientificIn line with actual operating conditionsAnalysing gaseous mixturesFlue gasNitric oxide
The invention relates to an efficiency calculation method for a novel SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) denitration device. The efficiency calculation method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting and sampling a sampling measuring point in the manner as specified in GB / T16157-1996 Method for Determining Particulate Matters in Stationary Pollution Source Exhaust Gas and Sampling Gaseous Pollutants 4.2; and (2) performing sampling measurement for flue gas flow speed, oxygen concentration and nitric oxide concentration at each sampling point at the inlet and outlet of the SCR denitration device, adding the flue gas flow speed and calculating nitric oxide concentration and efficiency in the flue gas. According to the efficiency calculation method, the flue gas flow speed is added as the factor participating into the calculation in a detection process, the calculated nitric oxide concentration is more accurate and scientific, and the calculated denitration efficiency more conforms to the practical operation condition of the equipment.
Owner:STATE GRID TIANJIN ELECTRIC POWER +1
Method for starting up reactor
InactiveUS7326810B2Reduce the amount requiredReducing duration of operationOrganic oxidationOrganic compound preparationGas phaseProduct gas
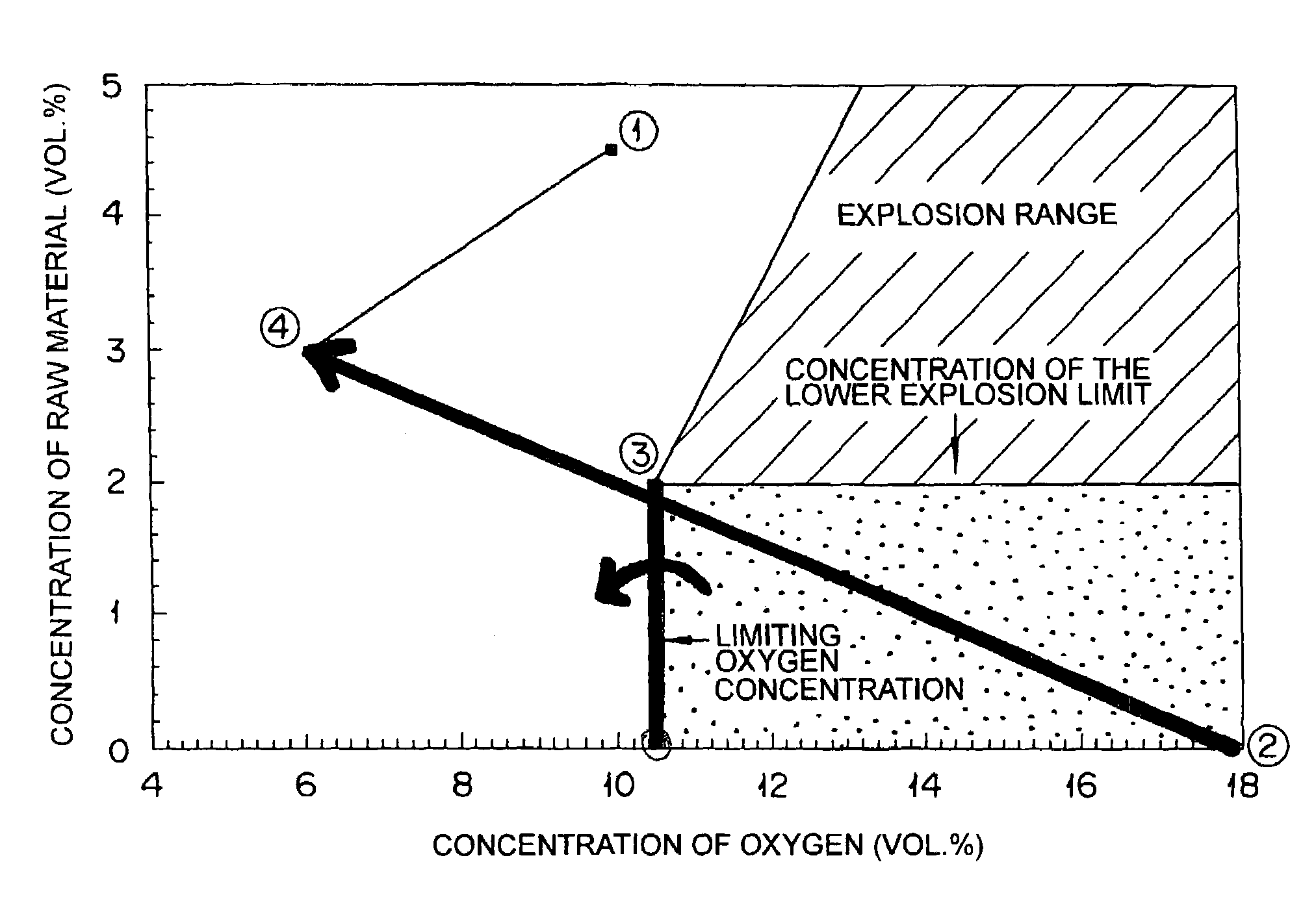
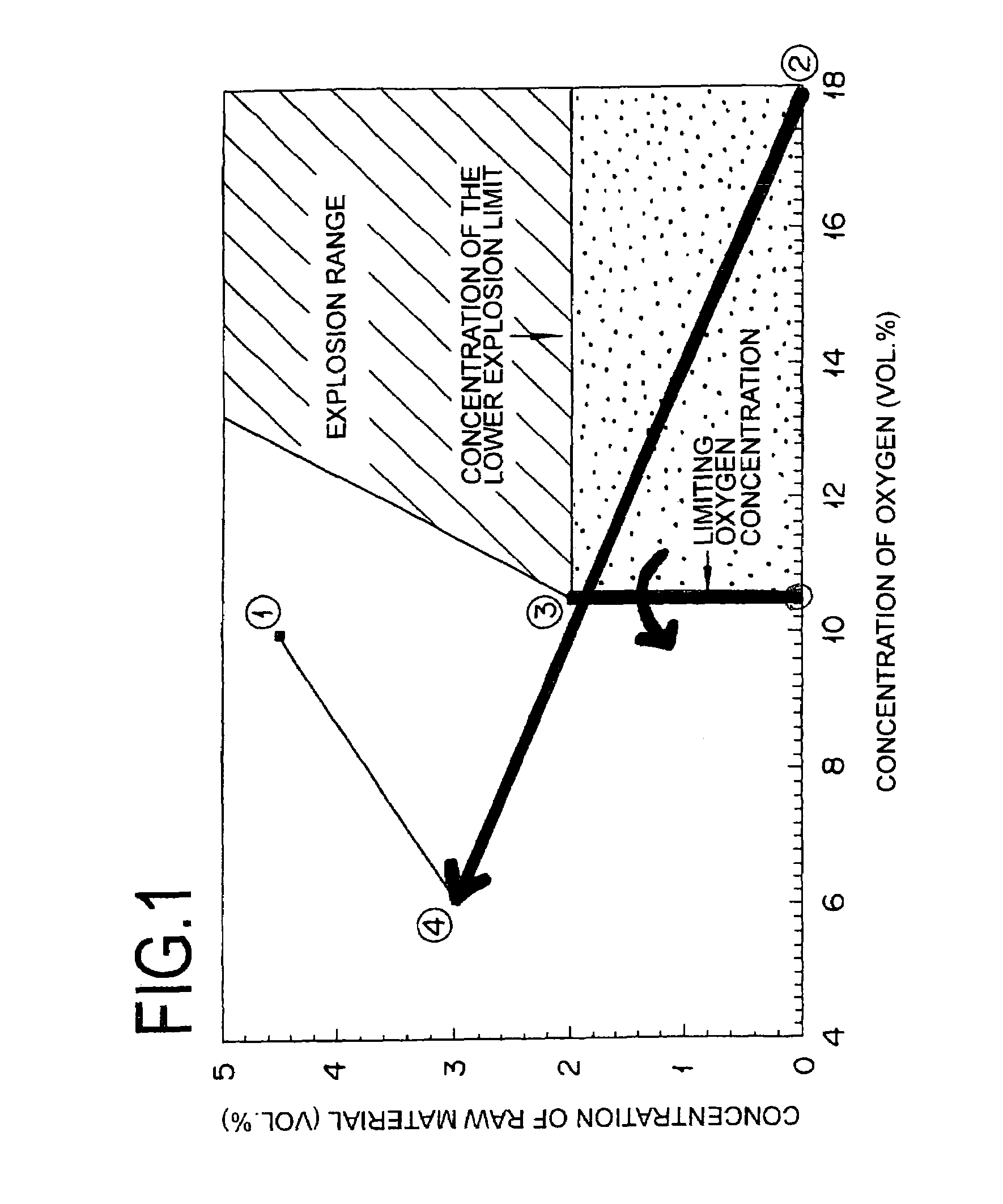
In the reaction of catalytic gas phase oxidation induced by the supply of at least a raw material to be oxidized and a molecular oxygen-containing gas to a reactor for catalytic gas phase oxidation, a method for starting up the reactor for catalytic gas phase oxidation is disclosed which is characterized by causing the raw material and the molecular oxygen-containing gas to pass a range in which the concentration of the raw material is less than the lower explosion limit of the raw material and the concentration of oxygen is not less than the limiting oxygen concentration, but excluding the concentration of the raw material of 0 vol. %. The method enables the reactor to be started up economically and safely by avoiding the explosion range induced by the composition of a raw material and a molecular oxygen-containing gas supplied to the reactor and decreasing the amount of a diluting gas to be supplied.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Gas sensor controller
InactiveUS7743759B2Reduce exhaust emissionsAvoid crackingElectrical controlExhaust apparatusEngineeringInternal combustion engine
An ECU controls an A / F sensor that is provided in an exhaust system of an internal combustion engine and produces current outputs corresponding to the concentration of oxygen in exhaust gas by being supplied with voltage and produces voltage outputs corresponding to the concentration of oxygen in exhaust gas according to the difference between the oxygen concentration around one of a pair of electrodes of the A / F sensor and the oxygen concentration around the other electrode. The ECU has: an energization limitation portion that, when moisture content is adhering on an inner face of an exhaust passage near the A / F sensor, energizes a heater of the A / F sensor while limiting the amount of power supplied thereto; and a specific output obtaining portion that obtains voltage outputs from the A / F sensor at least when the energization limitation portion is energizing the heater while limiting the amount of power supplied thereto.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
On-Site Generation of a Fracturing Fluid Stream and Systems and Methods Utilizing the Same
ActiveUS20140367109A1Increase productionFluid removalSealing/packingFracturing fluidFlammability limit
On-site generation of a fracturing fluid stream system includes a fracturing fluid generation assembly and a fracturing fluid supply assembly. The fracturing fluid generation assembly is configured to receive a hydrocarbon stream and to generate a fracturing fluid stream from the hydrocarbon stream. The fracturing fluid stream has an oxygen concentration, which is less than a limiting oxygen concentration for supporting combustion of a combustible fluid that is present within a subterranean formation. The fracturing fluid stream also has a combustible portion, which defines a concentration that is below a lower flammability limit of the combustible portion in the fracturing fluid stream. The fracturing fluid supply assembly is configured to receive the fracturing fluid stream and to convey the fracturing fluid stream to the subterranean formation to fracture the subterranean formation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
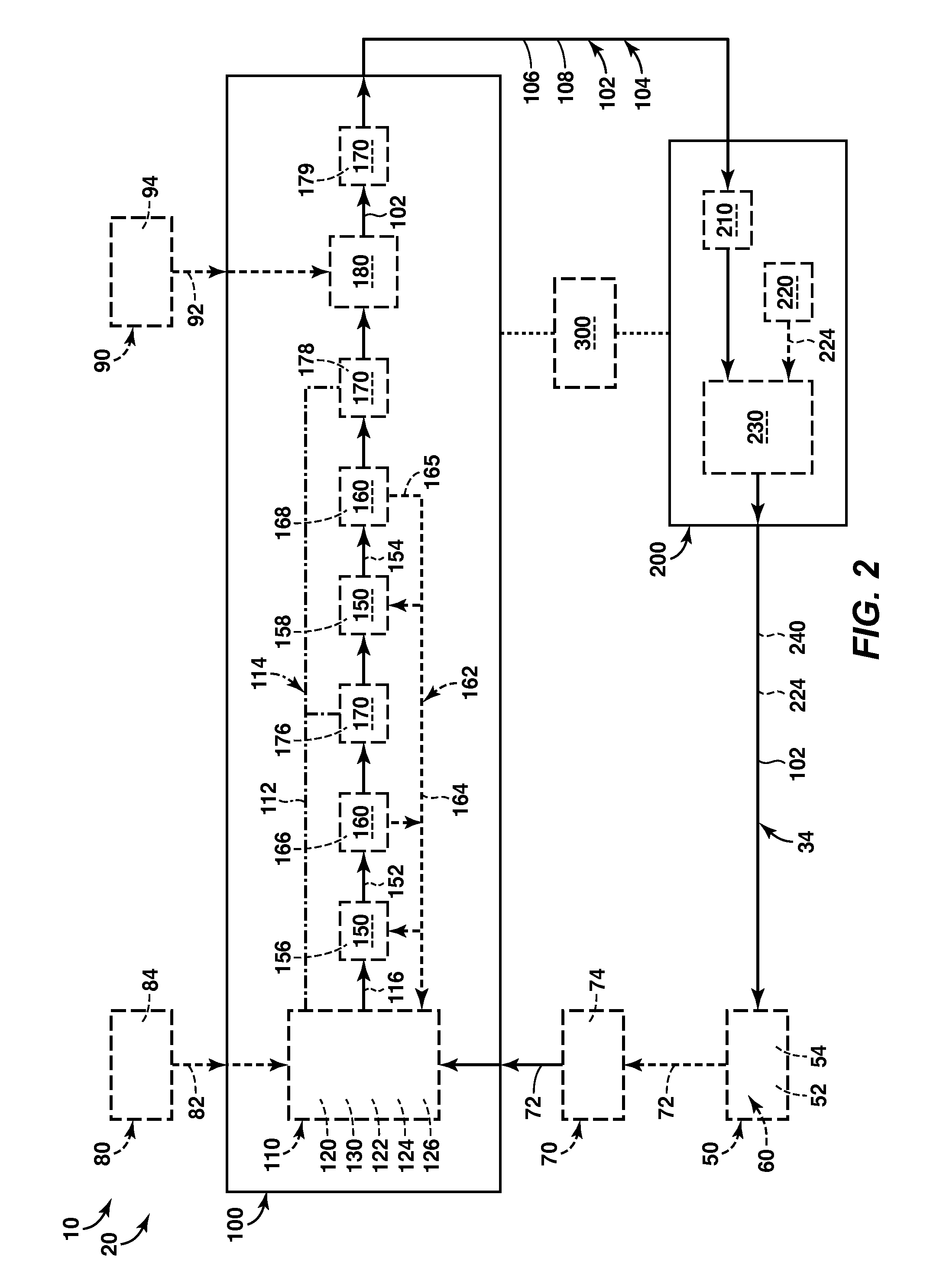
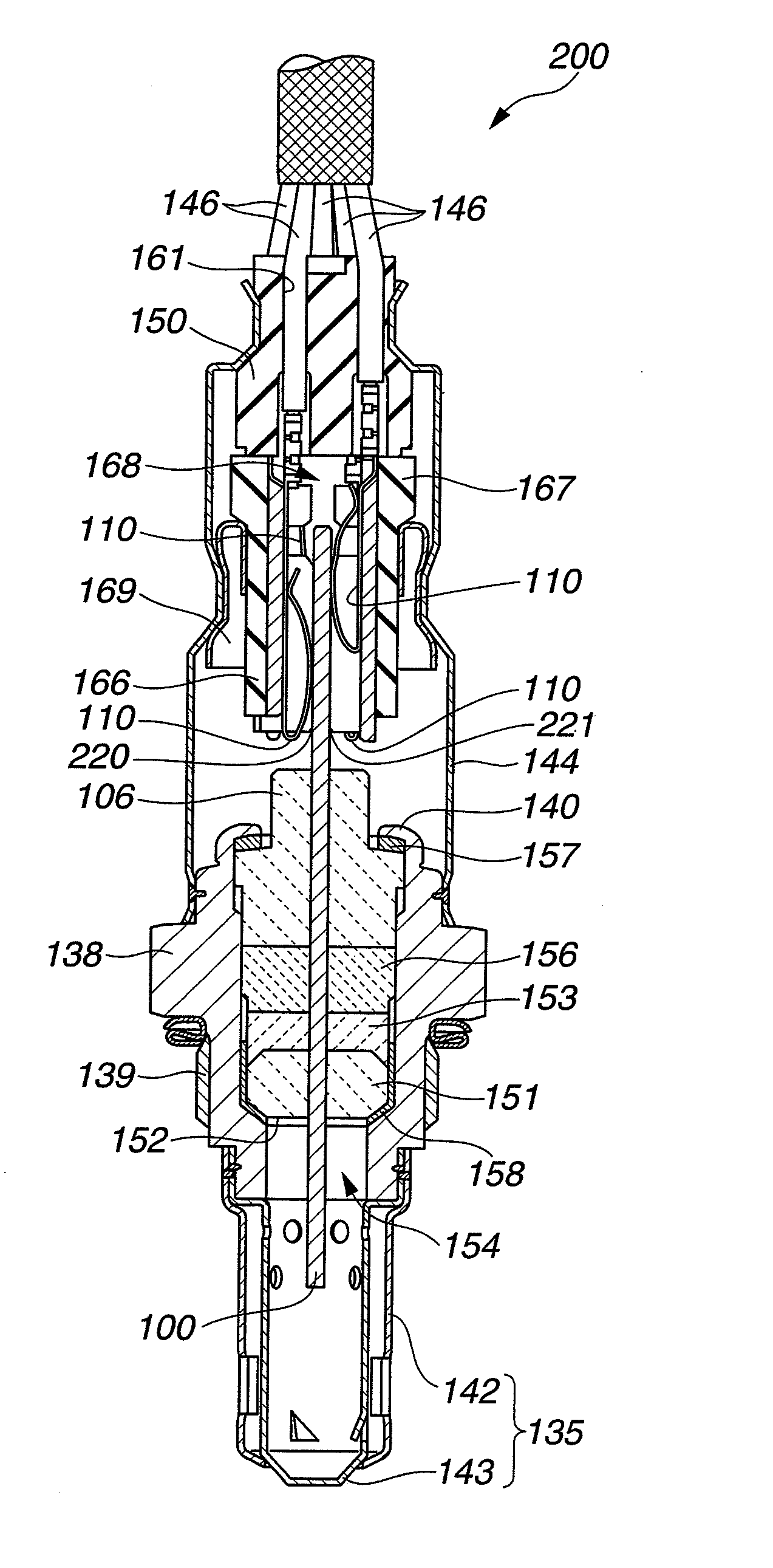
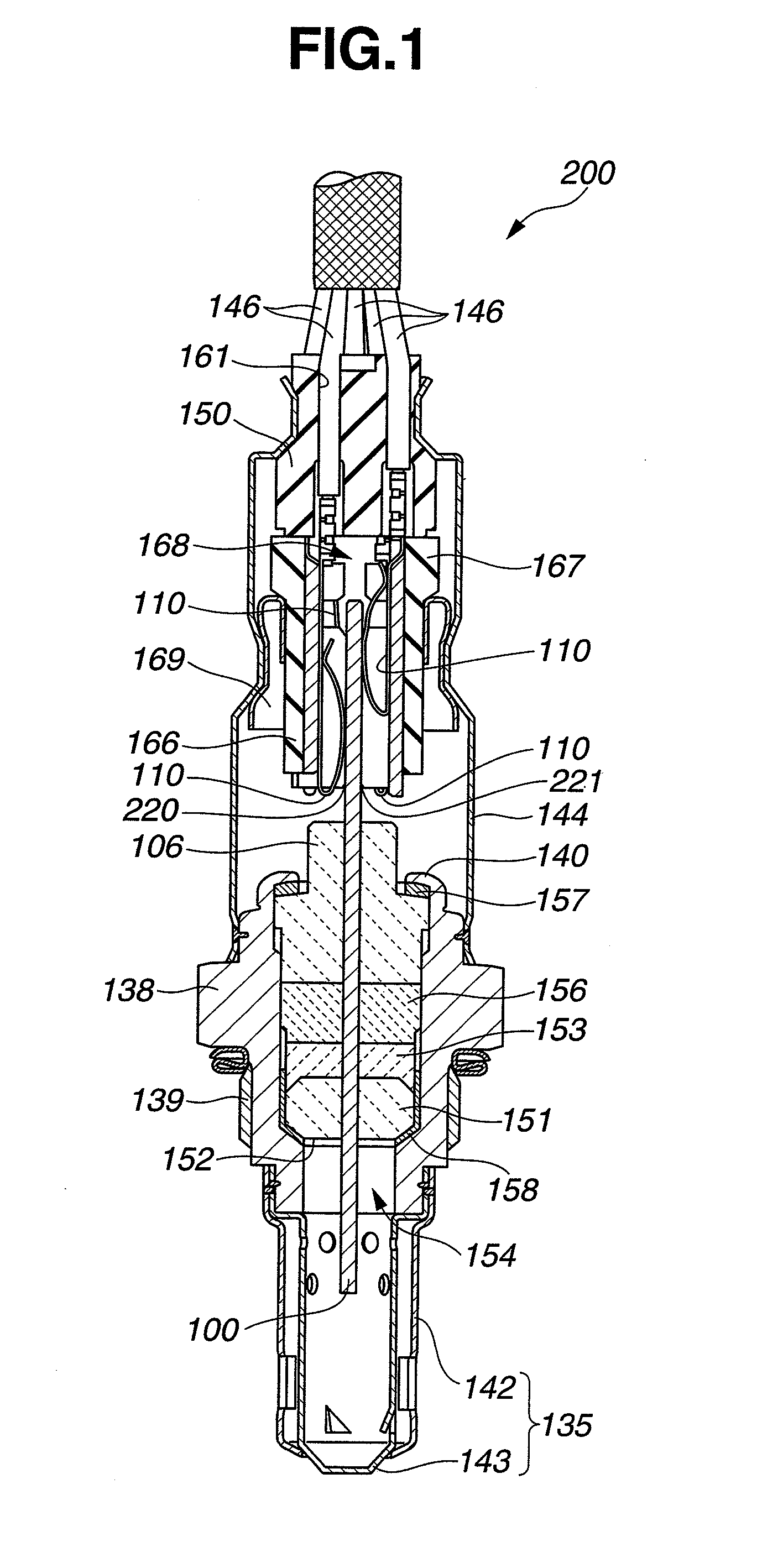
NOx SENSOR AND PRODUCTION METHOD THEREOF
ActiveUS20090188813A1Accurate detectionWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementPeak valueEngineering
A NOx sensor includes a sensor element equipped with first and second pumping cells to define first and second measurement chambers. The first pumping cell exerts an oxygen pumping action against the first measurement chamber to adjust the oxygen concentration in the gas under measurement within the first measurement chamber to a given level. The second pumping cell exerts an oxygen pumping action against the second measurement chamber to produce a pumping cell current according to the NOx concentration in the gas under measurement. When the moisture content of the gas under measurement changes from 2 vol % to 8 vol %, the NOx sensor allows a variation of NOx concentration detection value based on the pumping cell current in such a manner that the NOx concentration detection value reaches a transient peak value of 20 ppm or smaller and converges to ±5 ppm of a reference value within 5 seconds.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Combustible Gas Limiting Oxygen Concentration Parameter Measuring Device and Operation Method
Owner:应急管理部天津消防研究所 +1
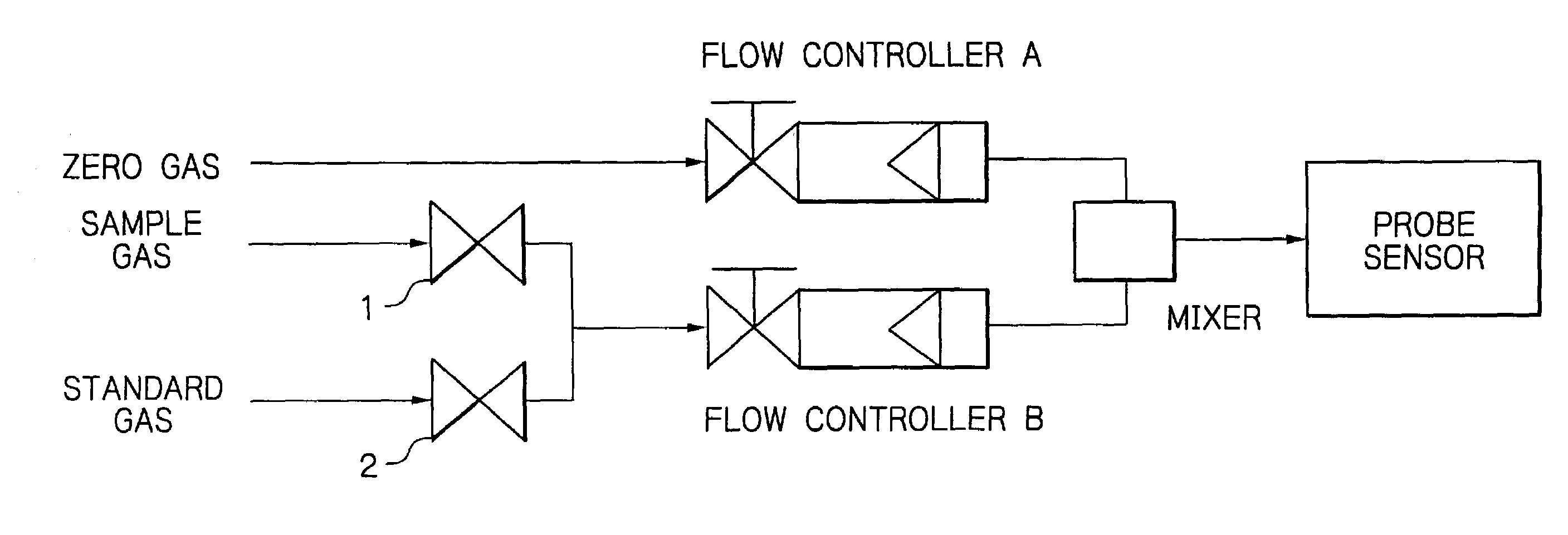
Method for analyzing the oxygen concentration of a gas
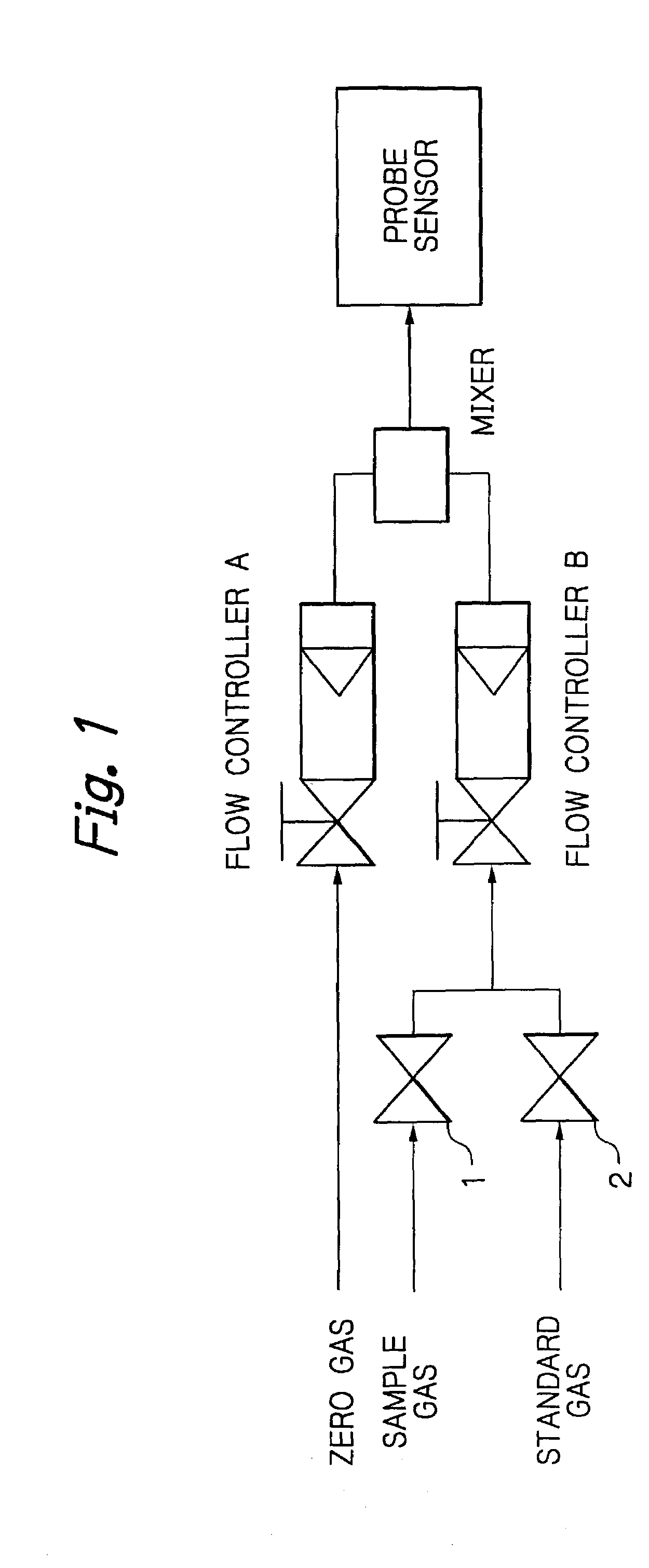
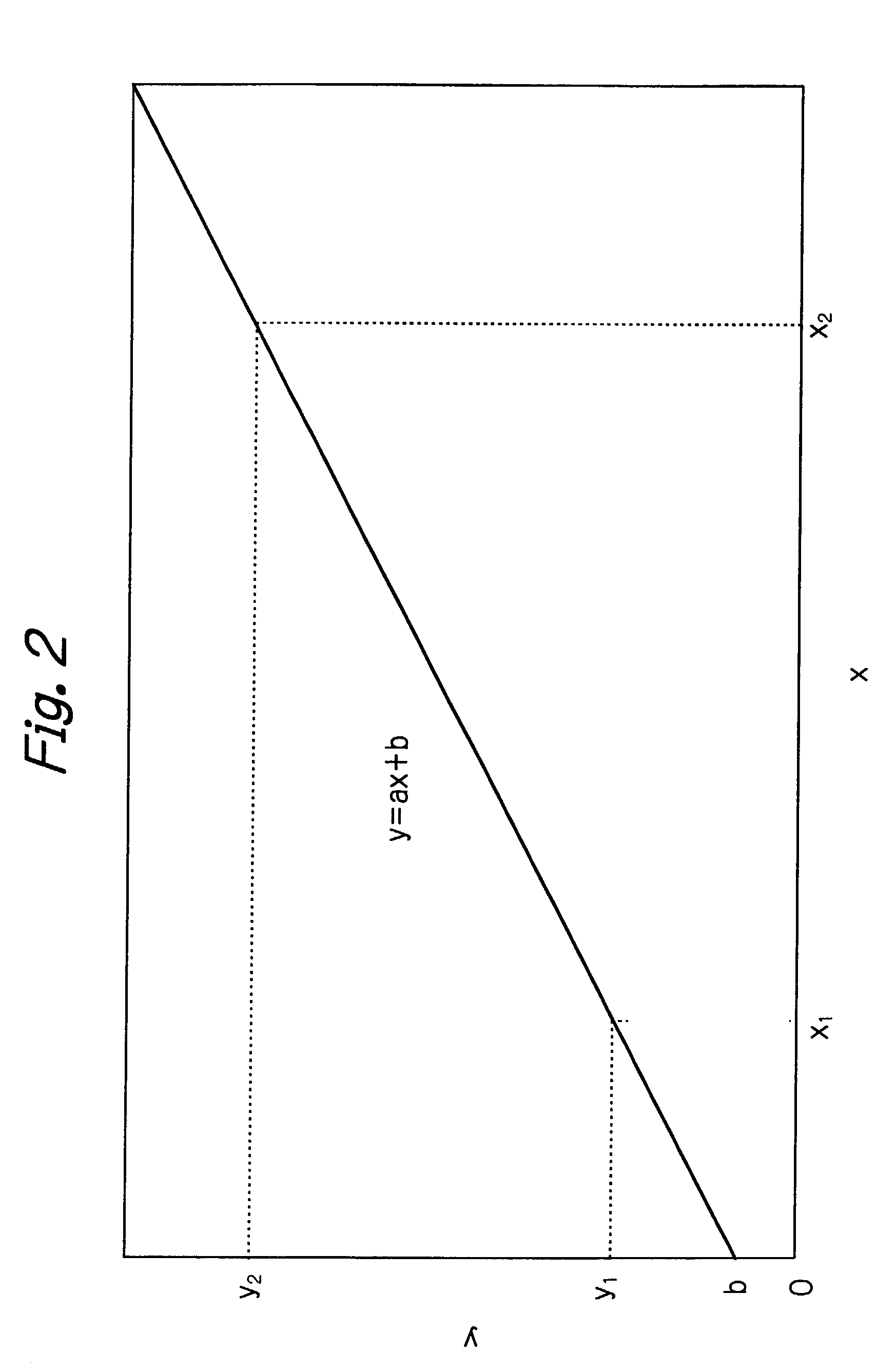
InactiveUS7025870B2Eliminate needConsistent measurementAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistancePhysical chemistryProduct gas
A method for analyzing the oxygen concentration of a gas with an oxygen concentration analyzer of such a type that a probe sensor, when supplied with a gas to be analyzed, produces an electrical output which is proportional to the concentration of oxygen in the gas, comprising the steps of preparing a first gas mixture in which an oxygen-free gas and a sample gas are mixed at a certain flow ratio and a second gas mixture in which the oxygen-free gas and the sample gas are mixed at a different flow ratio than in the first gas mixture, passing the first gas mixture and the second gas mixture asynchronously into the probe sensor, and comparing the electrical outputs from the sensor for the first gas mixture and the second gas mixture, as well as the proportions of the flow of the sample gas in the first gas mixture and the second gas mixture to thereby calculate the oxygen concentration in the sample gas. The method eliminates the need to perform frequent zero adjustment and enables the oxygen concentration in the sample gas to be measured with consistent results.
Owner:OSAKA OXYGEN IND LTD
Exhaust gas sensor
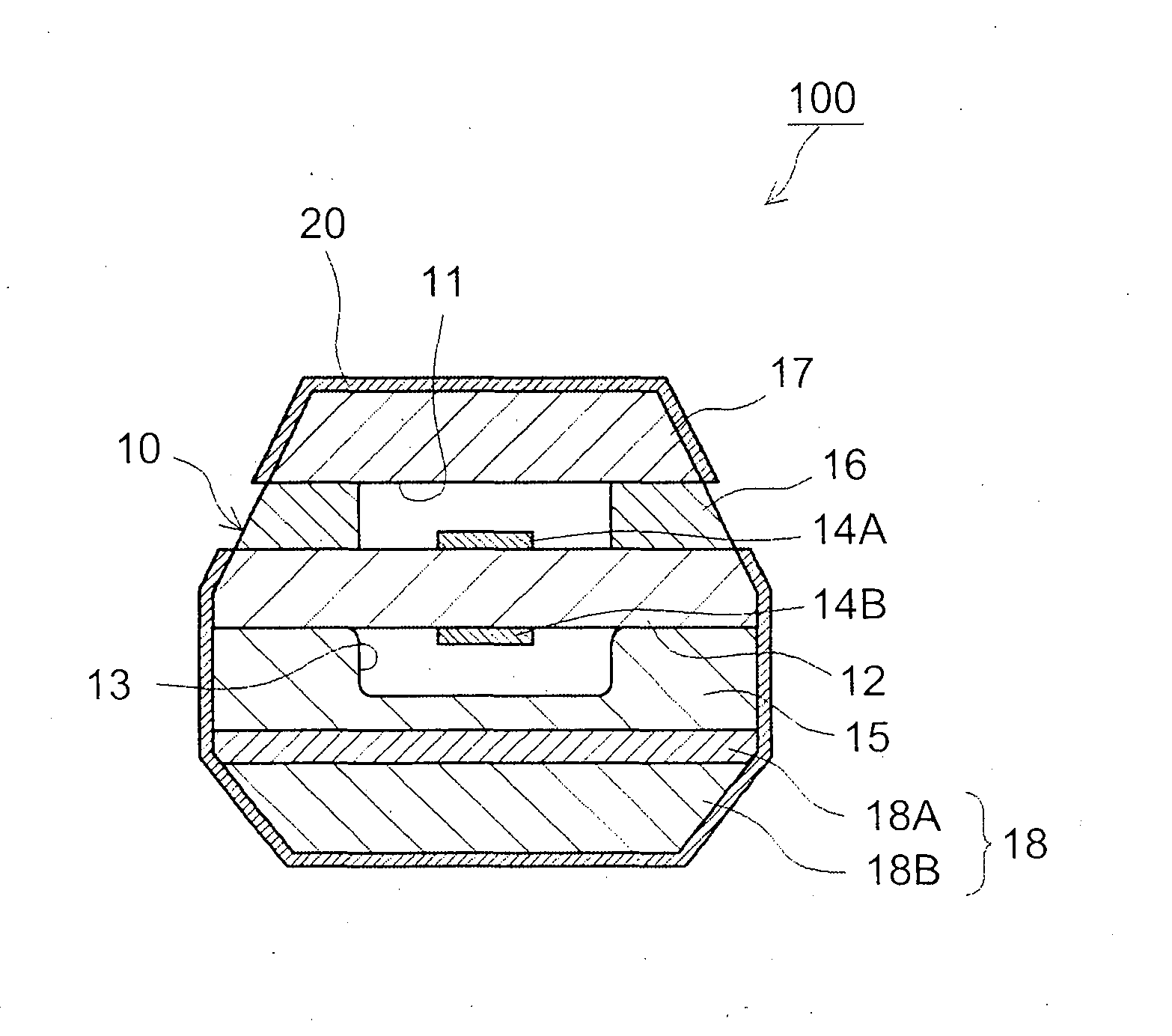
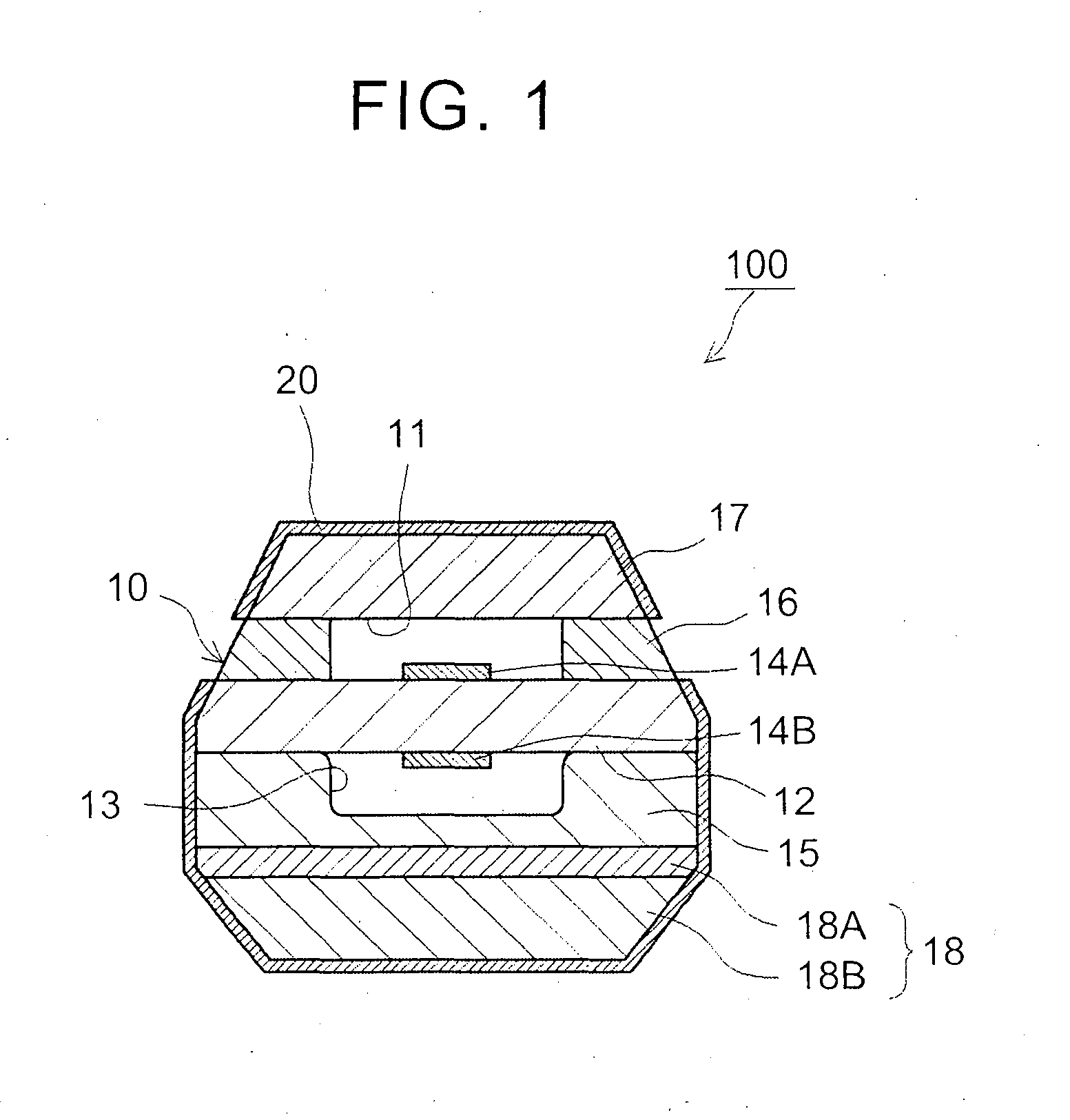
ActiveUS20150144487A1Improve thermal efficiencyBoost octaneMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansReaction layerExhaust fumes
An exhaust gas sensor (100; 200) is configured so as to detect an oxygen concentration or air-fuel ratio in exhaust gas. The exhaust gas sensor includes a sensor element (10) and a manganese reaction layer (20). The sensor element detects an oxygen concentration or air-fuel ratio. The manganese reaction layer is formed on at least part of a surface of the sensor element and is formed of a substance containing an element capable of generating a complex oxide having manganese through reaction with a manganese oxide in the exhaust gas. The exhaust gas sensor is configured to detect an oxygen concentration or air-fuel ratio in exhaust gas of an internal combustion engine that utilizes a fuel having a Mn concentration in excess of 20 ppm.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
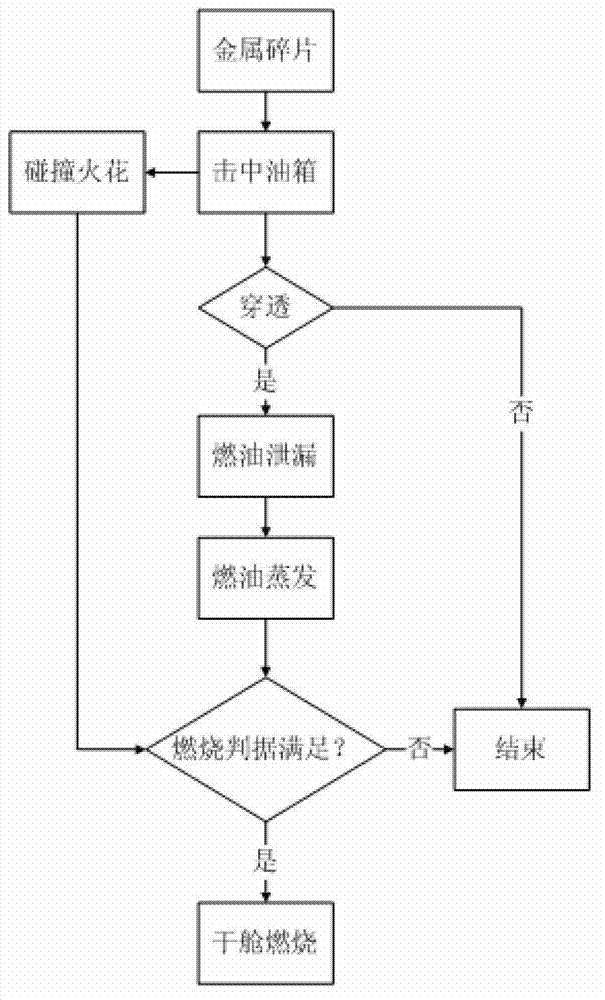
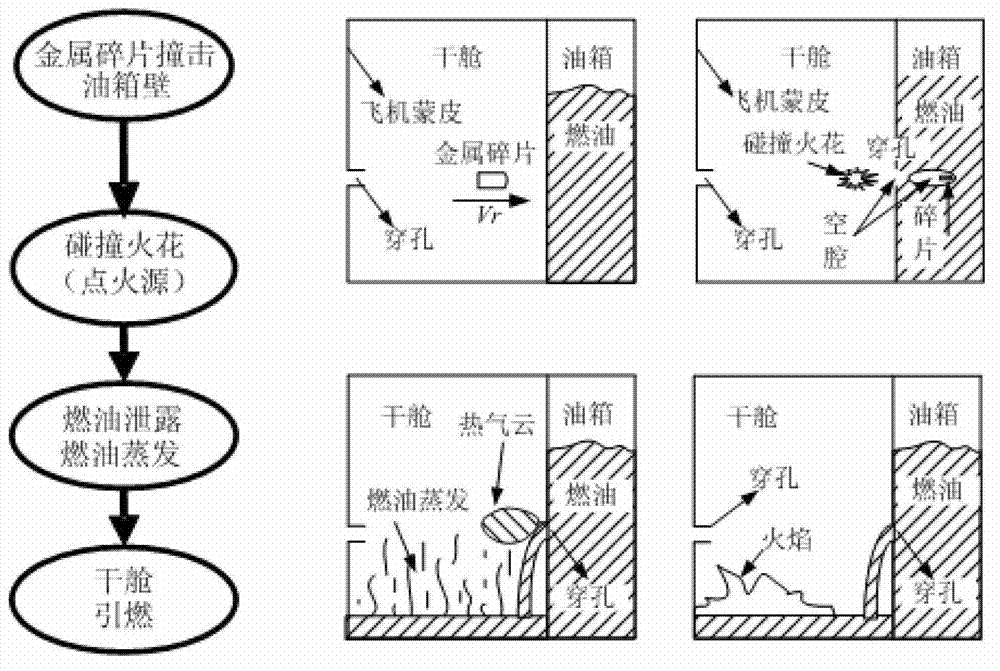
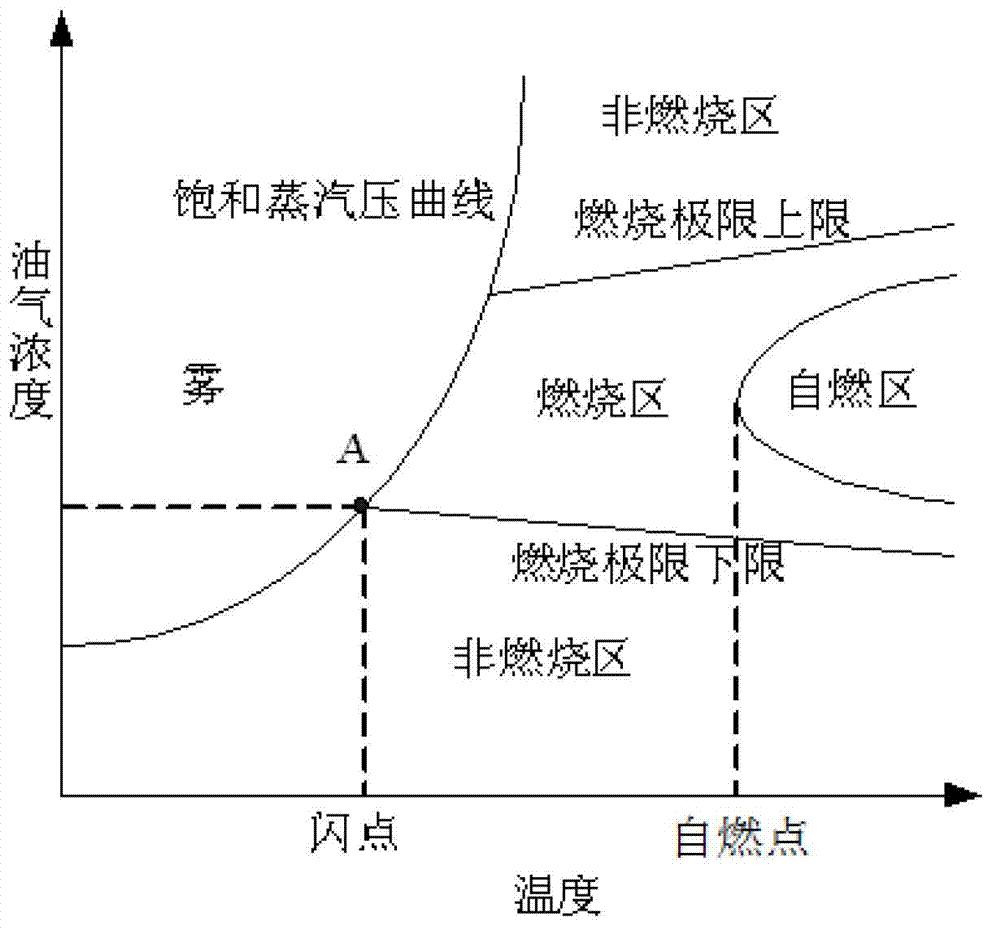
Combustion criterion analyzing method of dry chamber near oil tank under impact of metal chips
ActiveCN103164620AConcise and intuitive form of expressionReduce combustion explosionSpecial data processing applicationsTriangular diagramFuel oil
The invention provides a combustion criterion analyzing method of a dry chamber near an oil tank under impact of metal chips. A relation diagram of changes of an airplane combustion envelope along with an airplane flight profile is calculated through a formula according to an airplane flight profile diagram and a formula of the fuel oil flash point temperature. A combustion triangular diagram is drawn by analyzing the influence relation between the temperature and a fuel oil combustion limit, the pressure and the fuel oil combustion limit, the height and the fuel oil combustion limit and the fuel oil components and the fuel oil combustion limit respectively and calculating the limit oxygen concentration of the fuel oil. Combustion criteria can judge conditions of combustion of the dry chamber near the oil tank under different flight heights accurately, expression forms of a fuel combustion envelope and a combustion triangular form are simple and intuitionistic so that the method is beneficial for reduction of probability of occurrence of airplane combustion explosion, viability of an airplane is improved, and meanwhile the method can be applied to judgment of combustion when oil tanks of communication media such as motorbikes, automobiles and steamships are impacted by high-speed metal chips.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for determining interstitial oxygen concentration
InactiveCN103620394ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCharge carrier
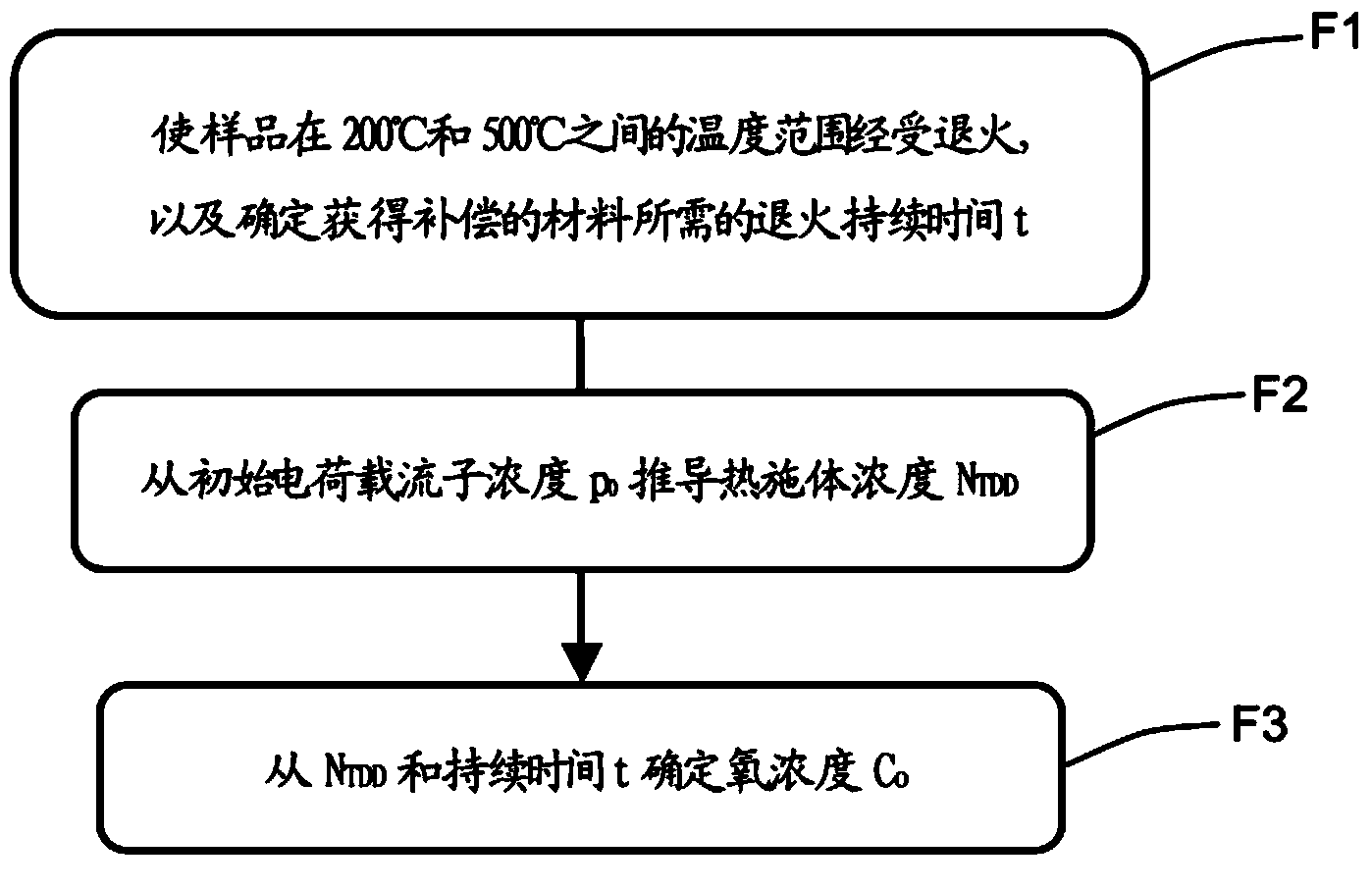
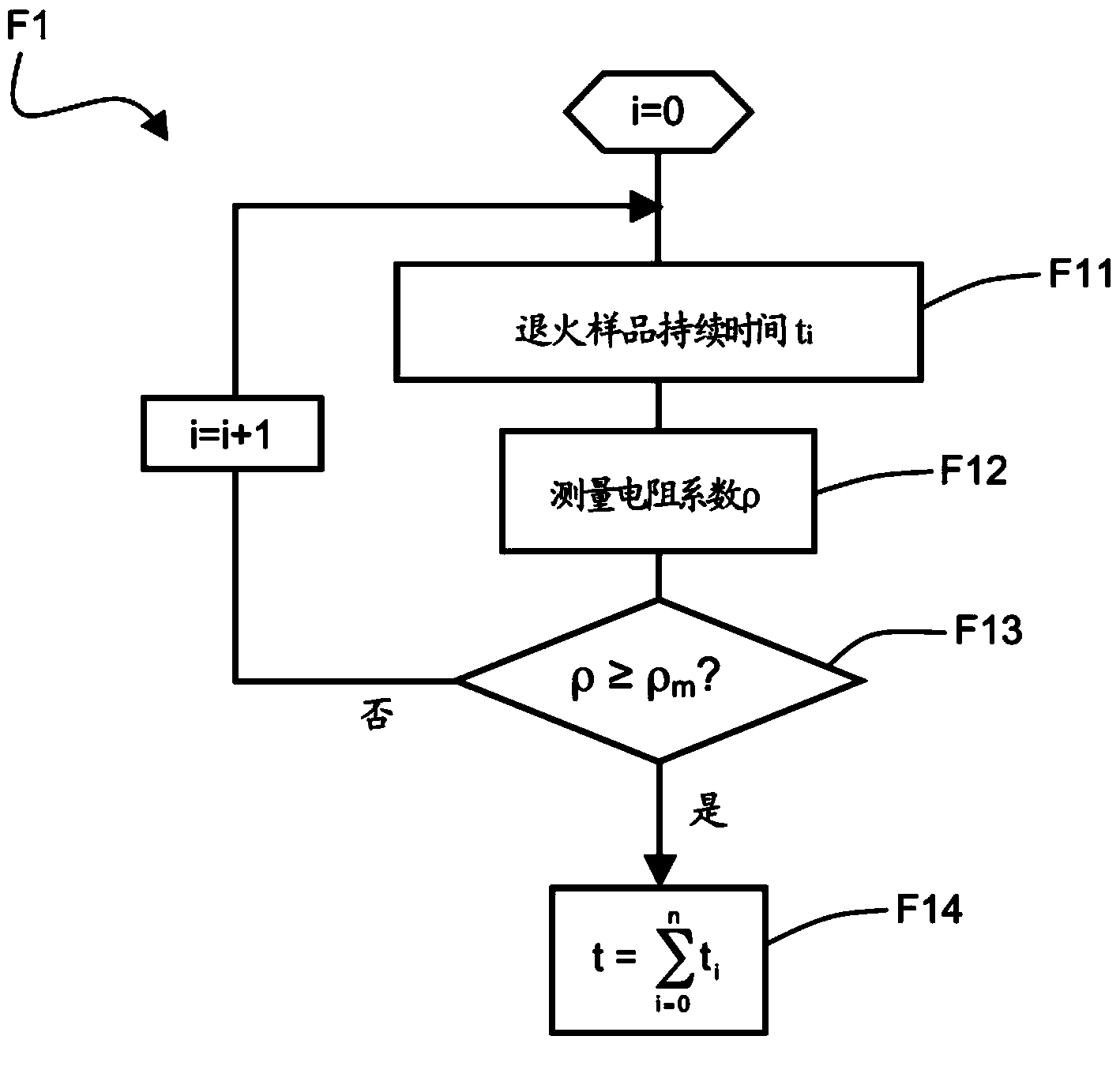
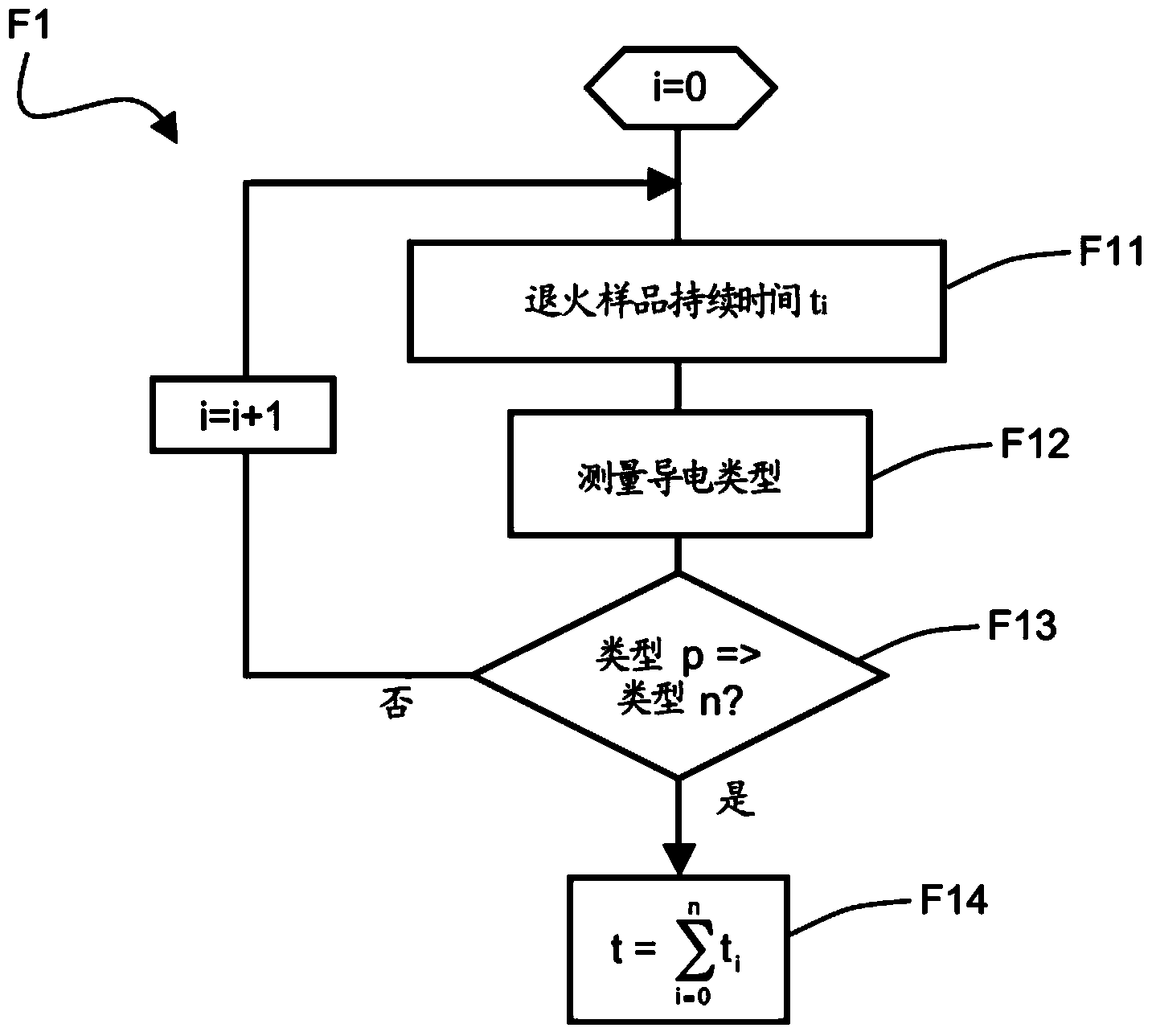
The invention relates to a method for determining the interstitial oxygen concentration of a sample made of a p-doped semiconductor material, which includes a step of thermal treatment (F1) of the sample in order to form thermal donors, determining (F1) the thermal treatment time (t) required to obtain a compensated semiconductor material, determining (F2) the concentration of thermal donors (NDDT) in the sample made of compensated semiconductor material, from the concentration of charge carriers (po), and determining (F3) the oxygen concentration (Co) from the concentration of thermal donors (NDDT) and the thermal treatment time (t).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com