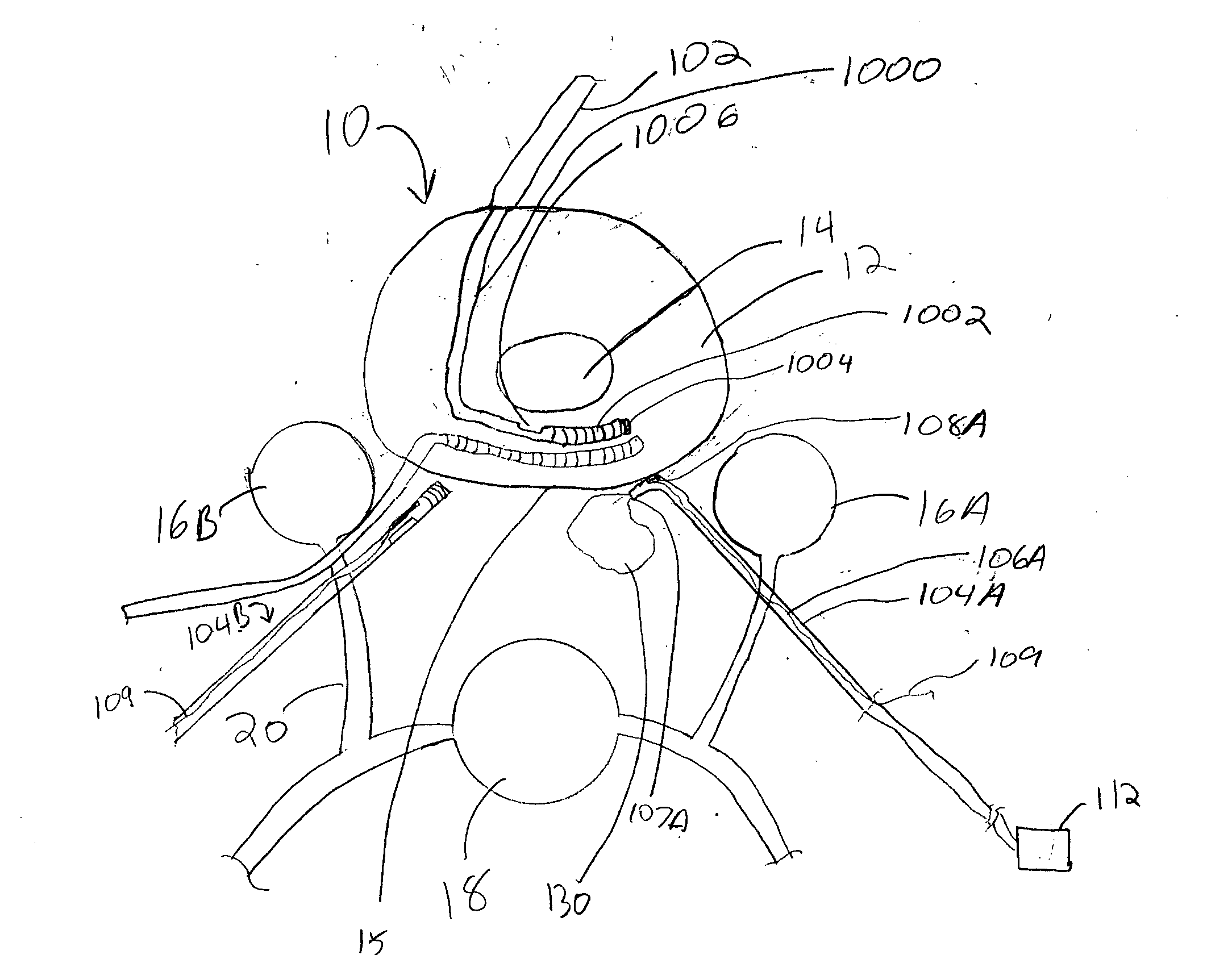
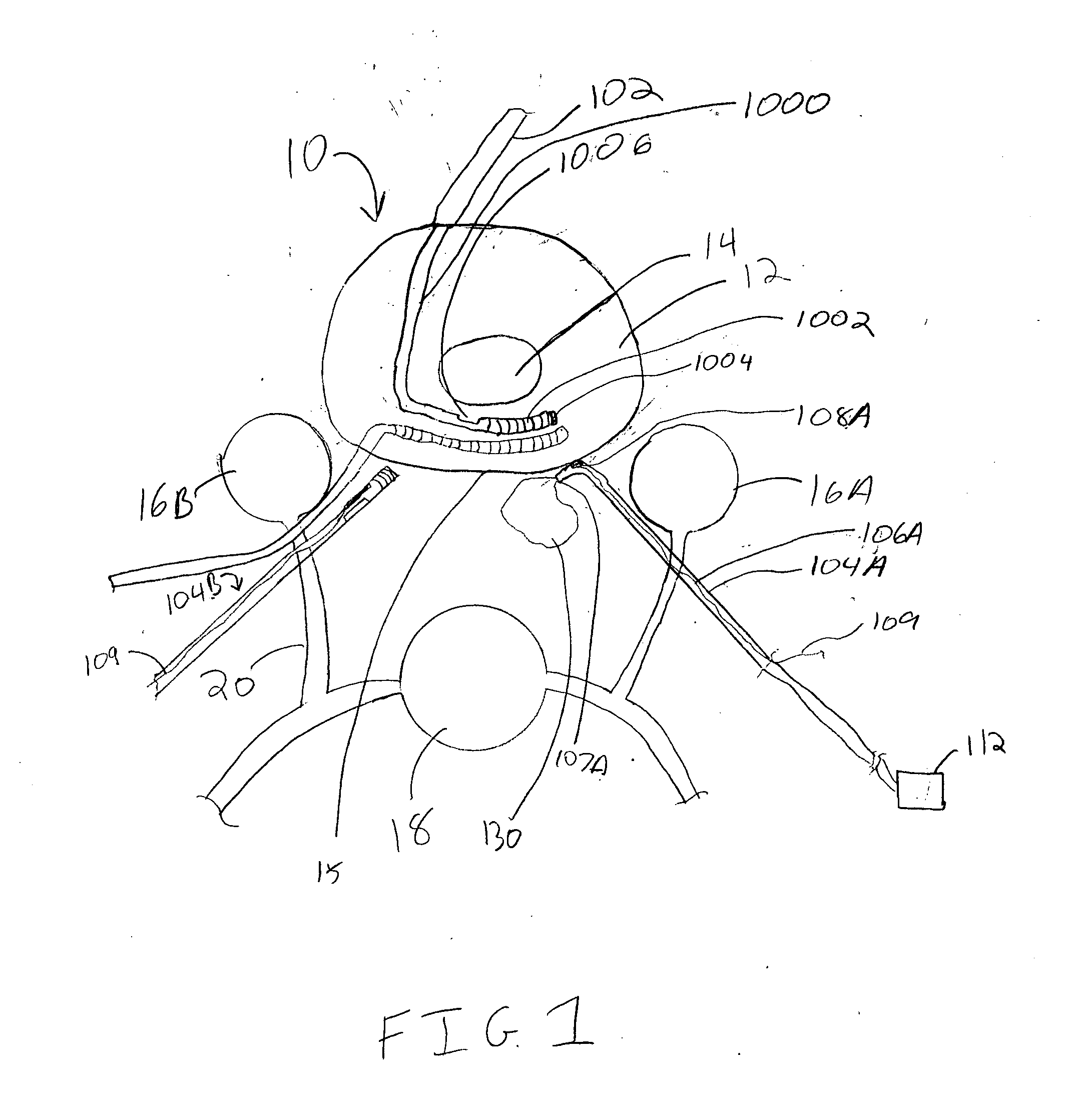
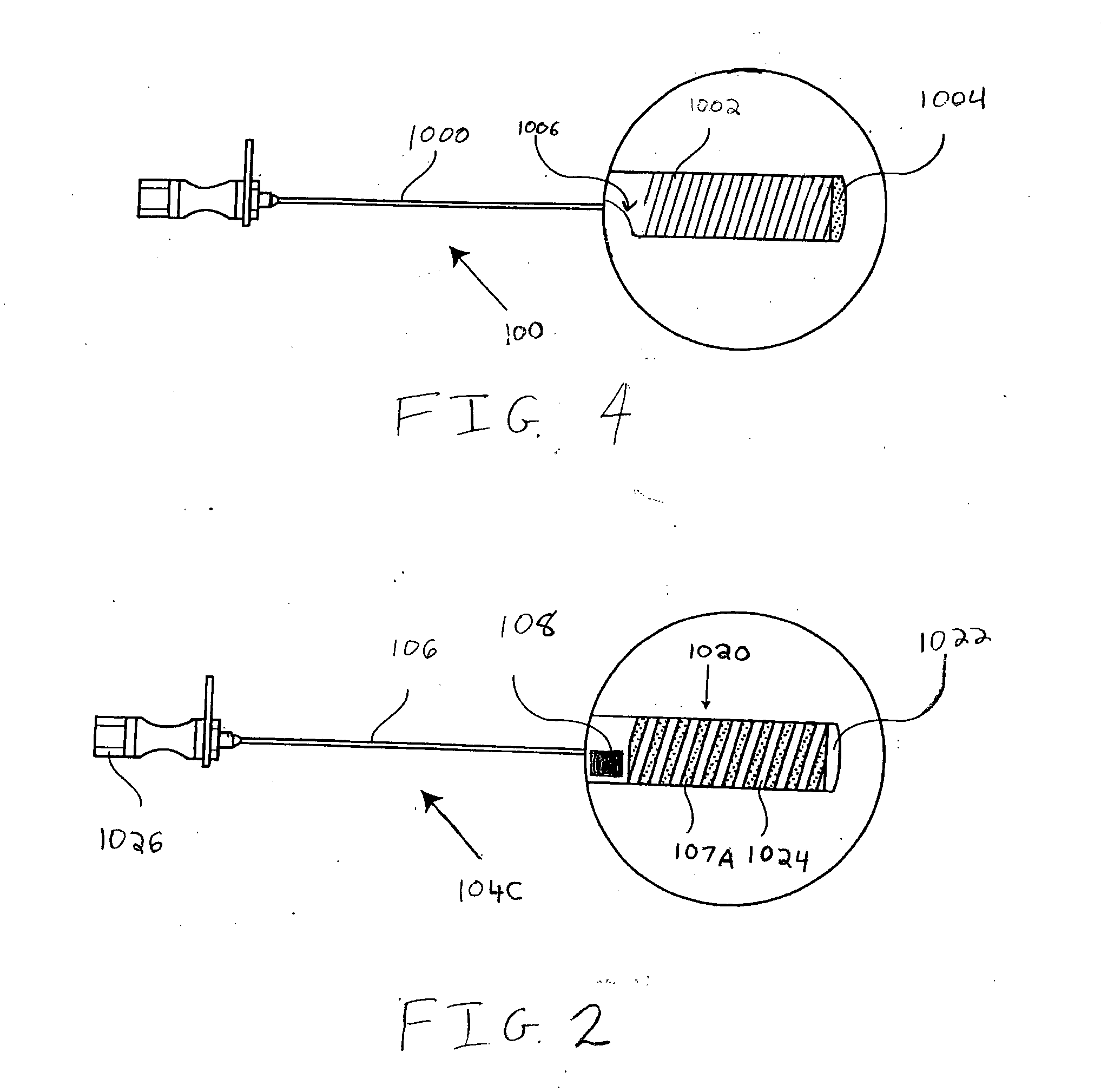
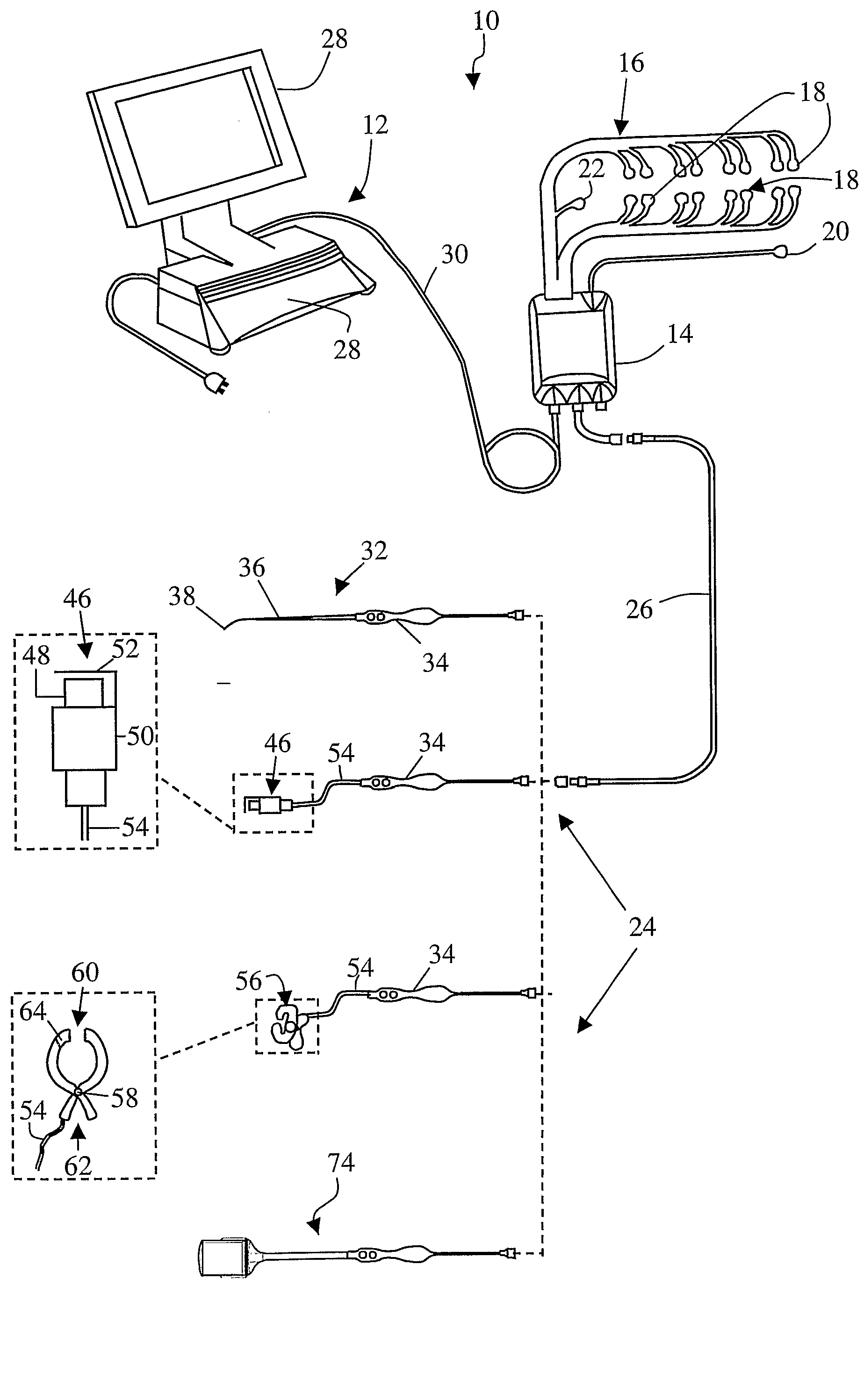
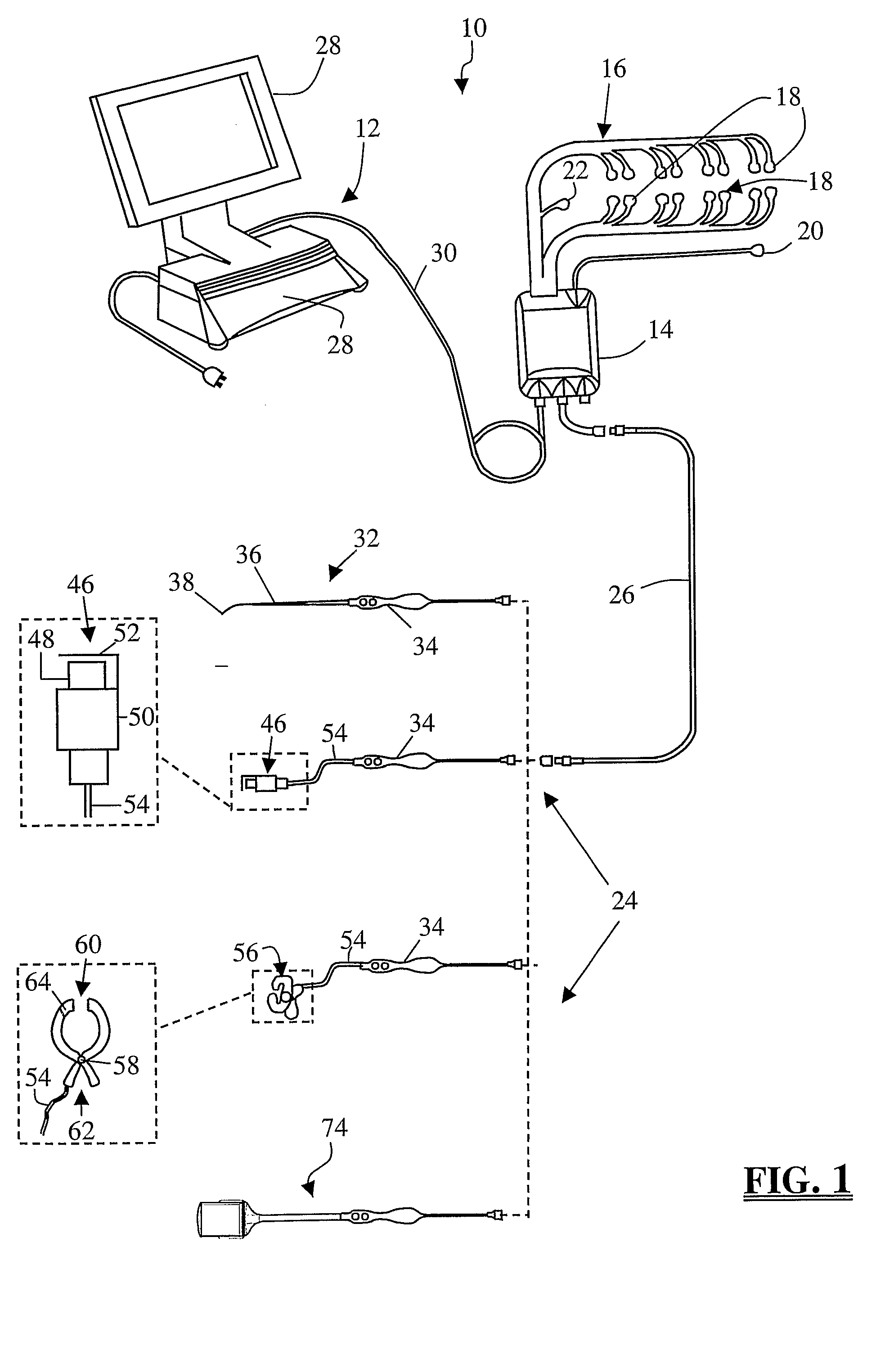
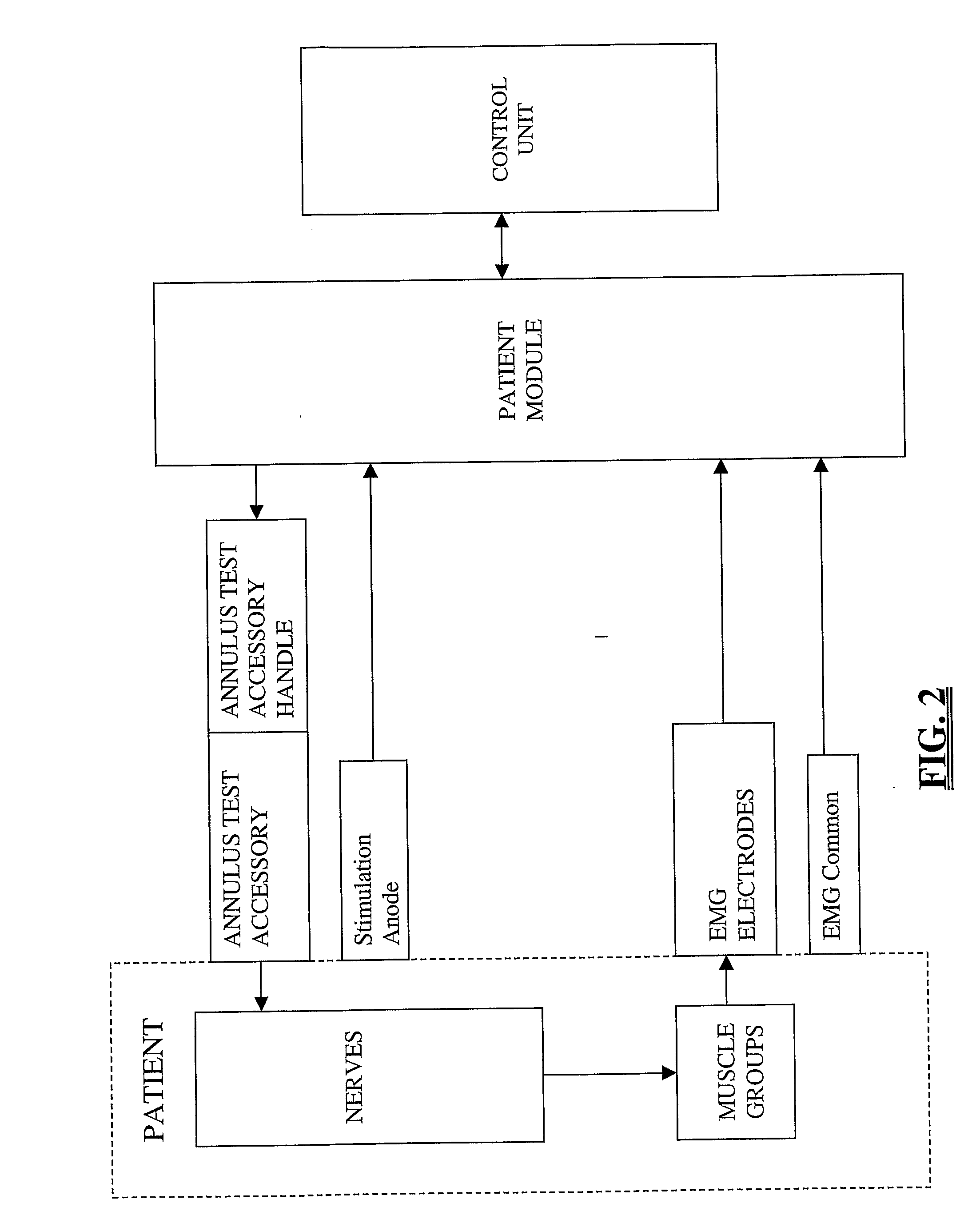
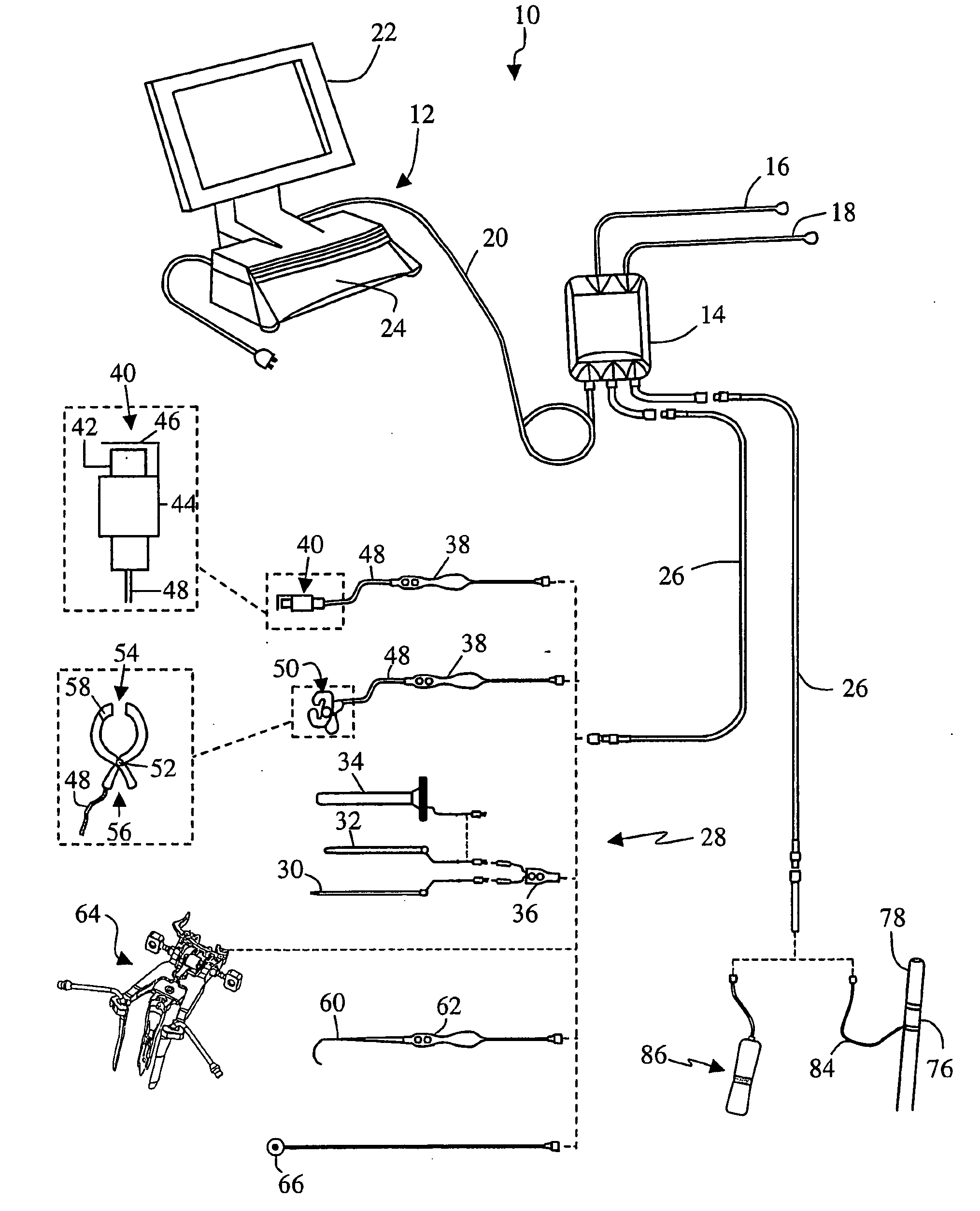
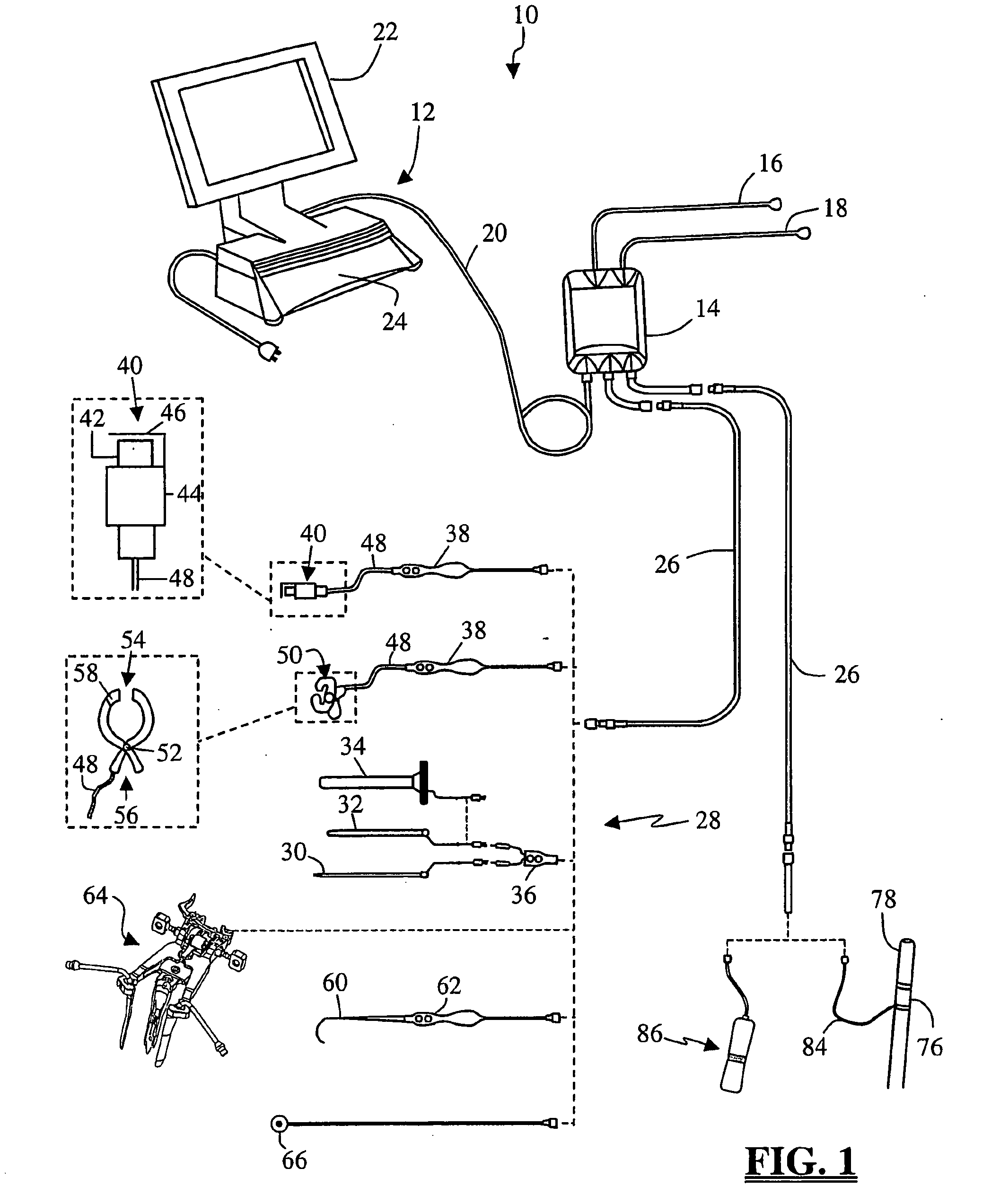
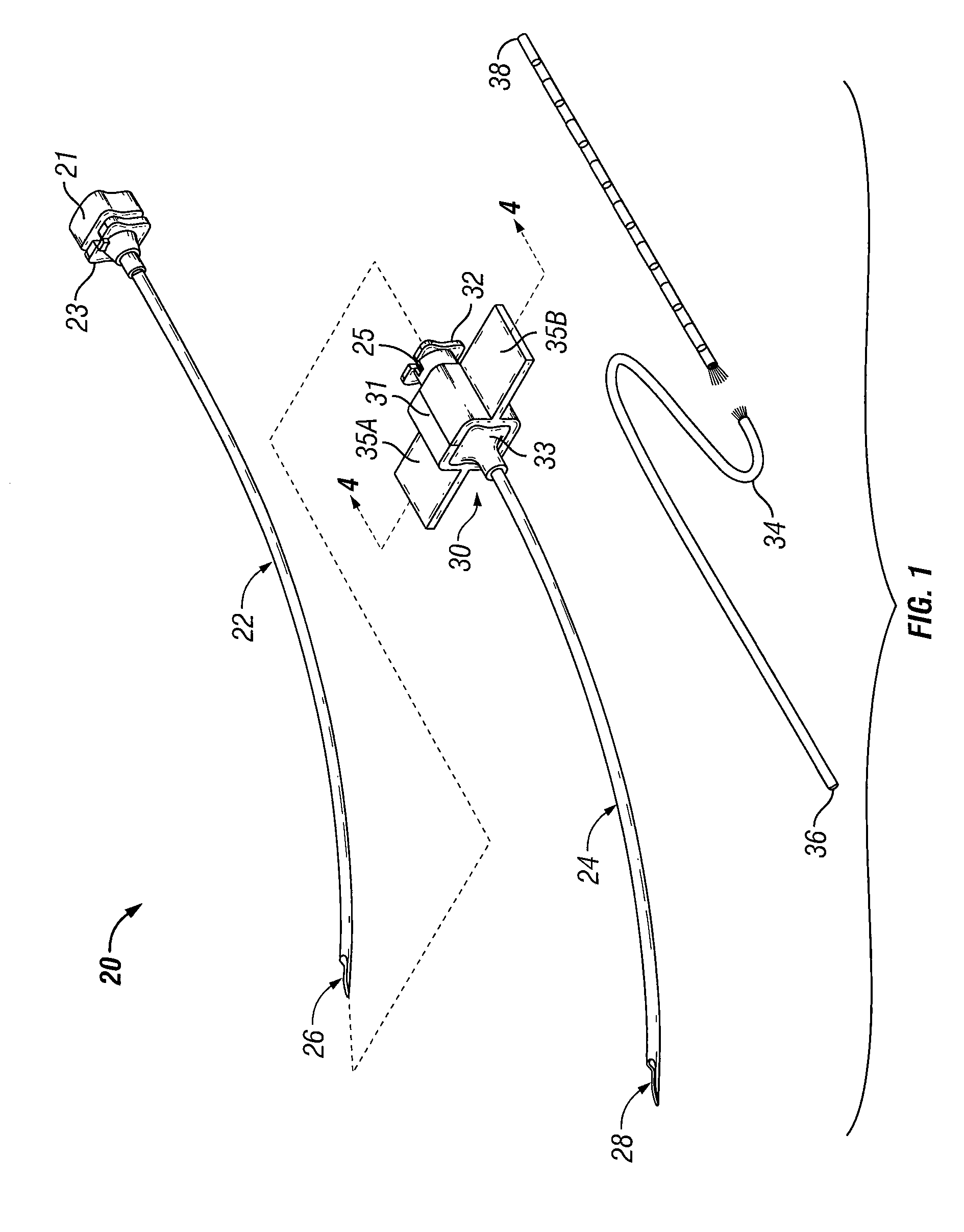
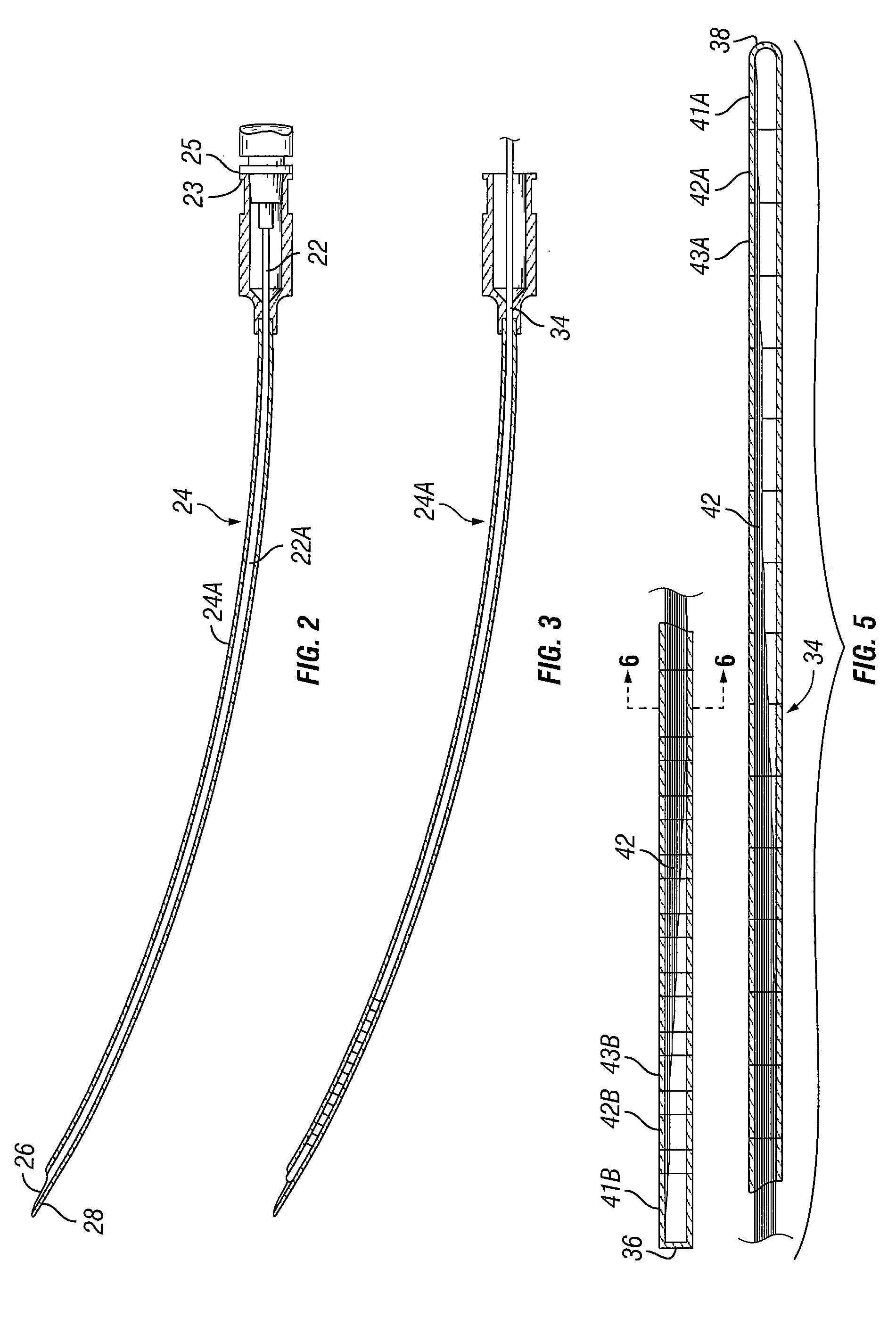
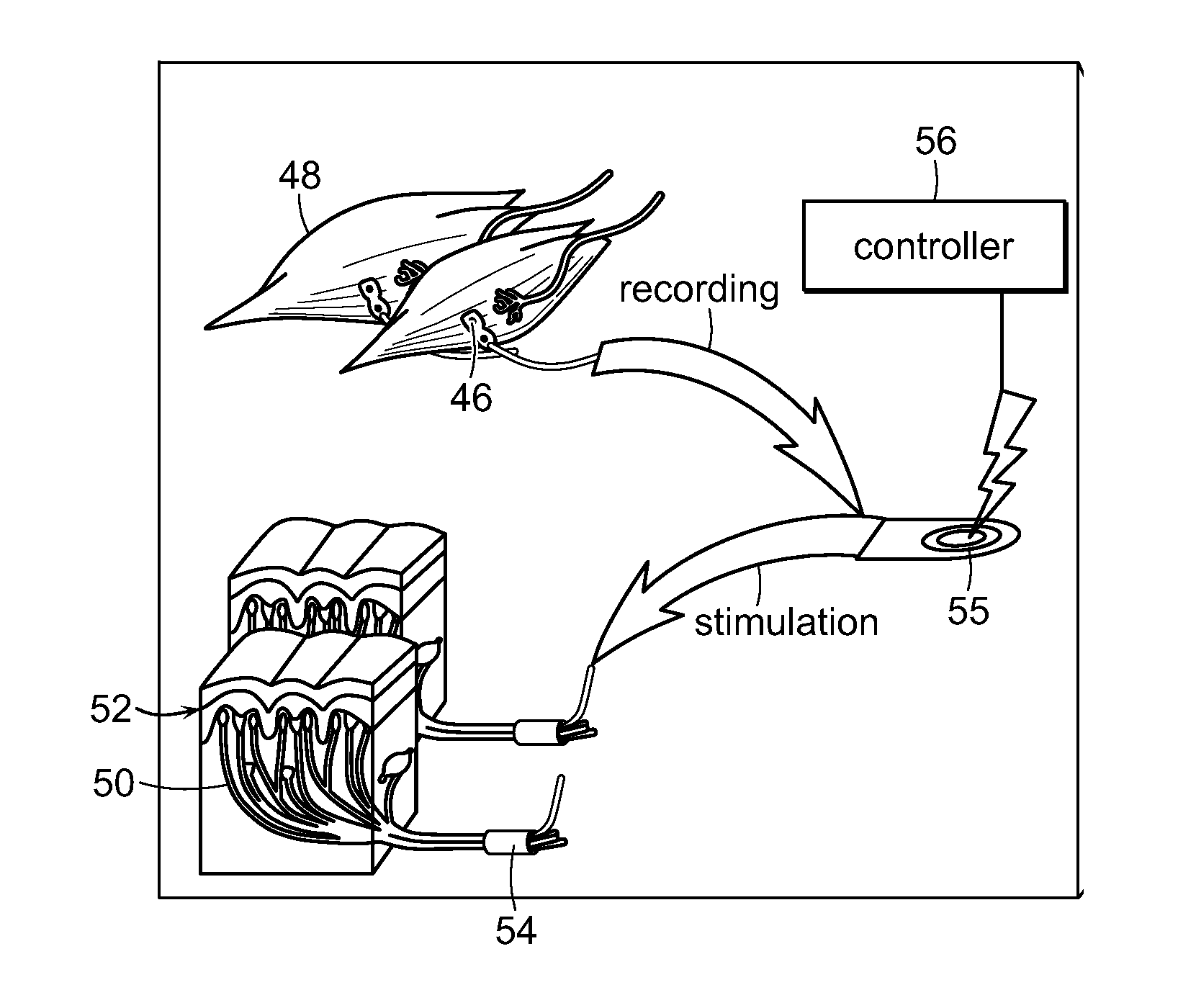
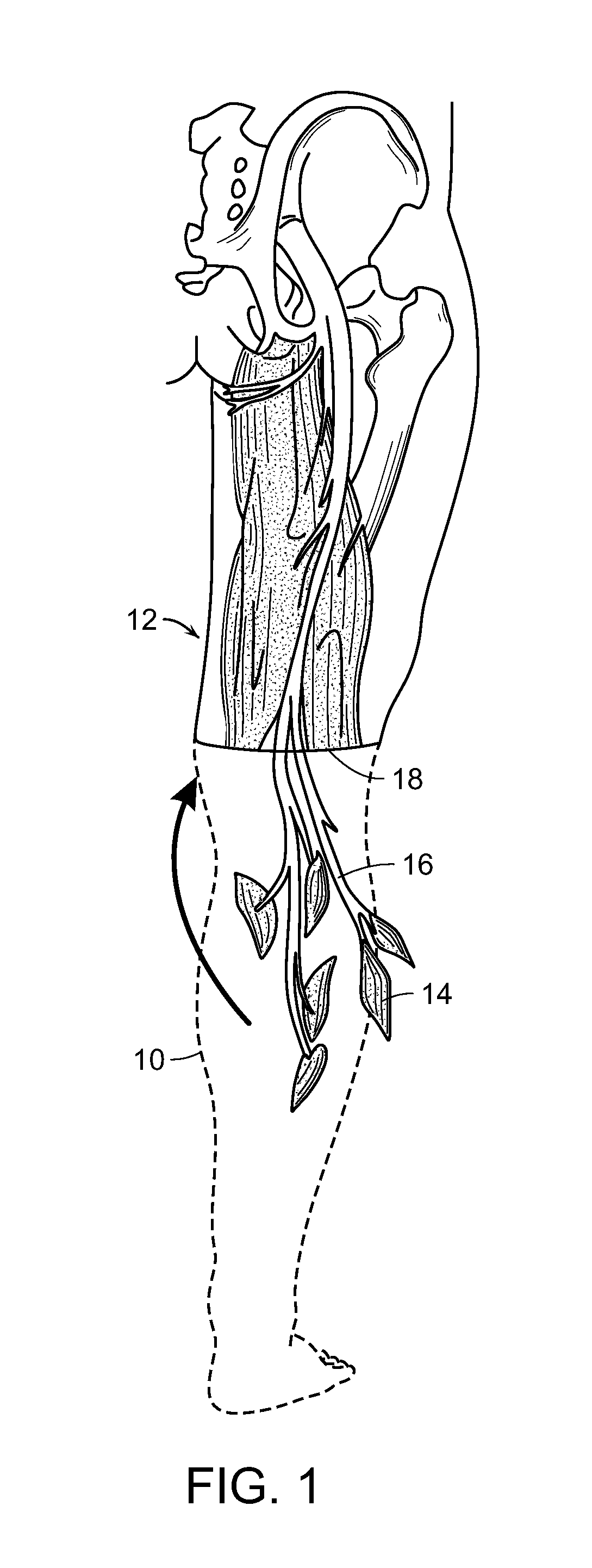
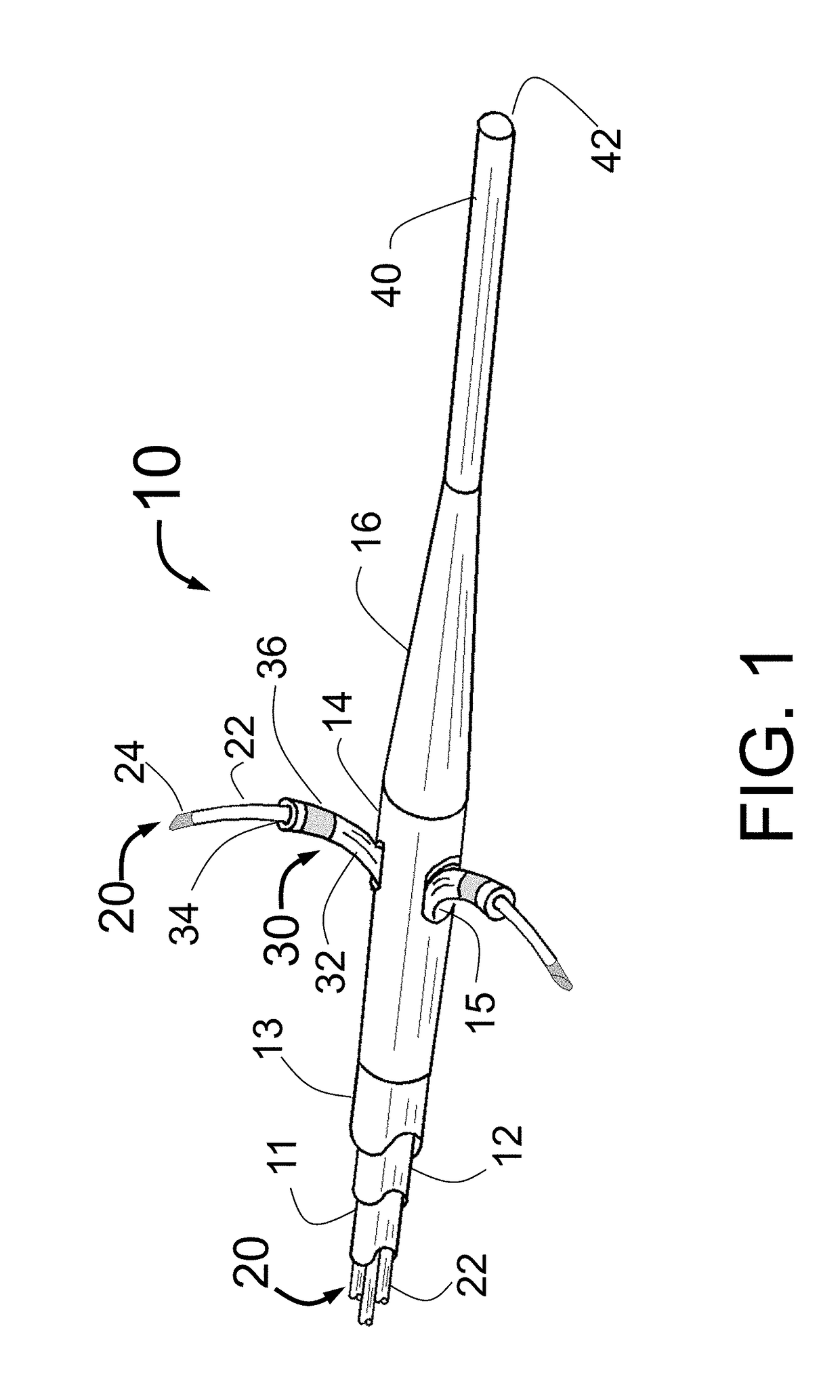
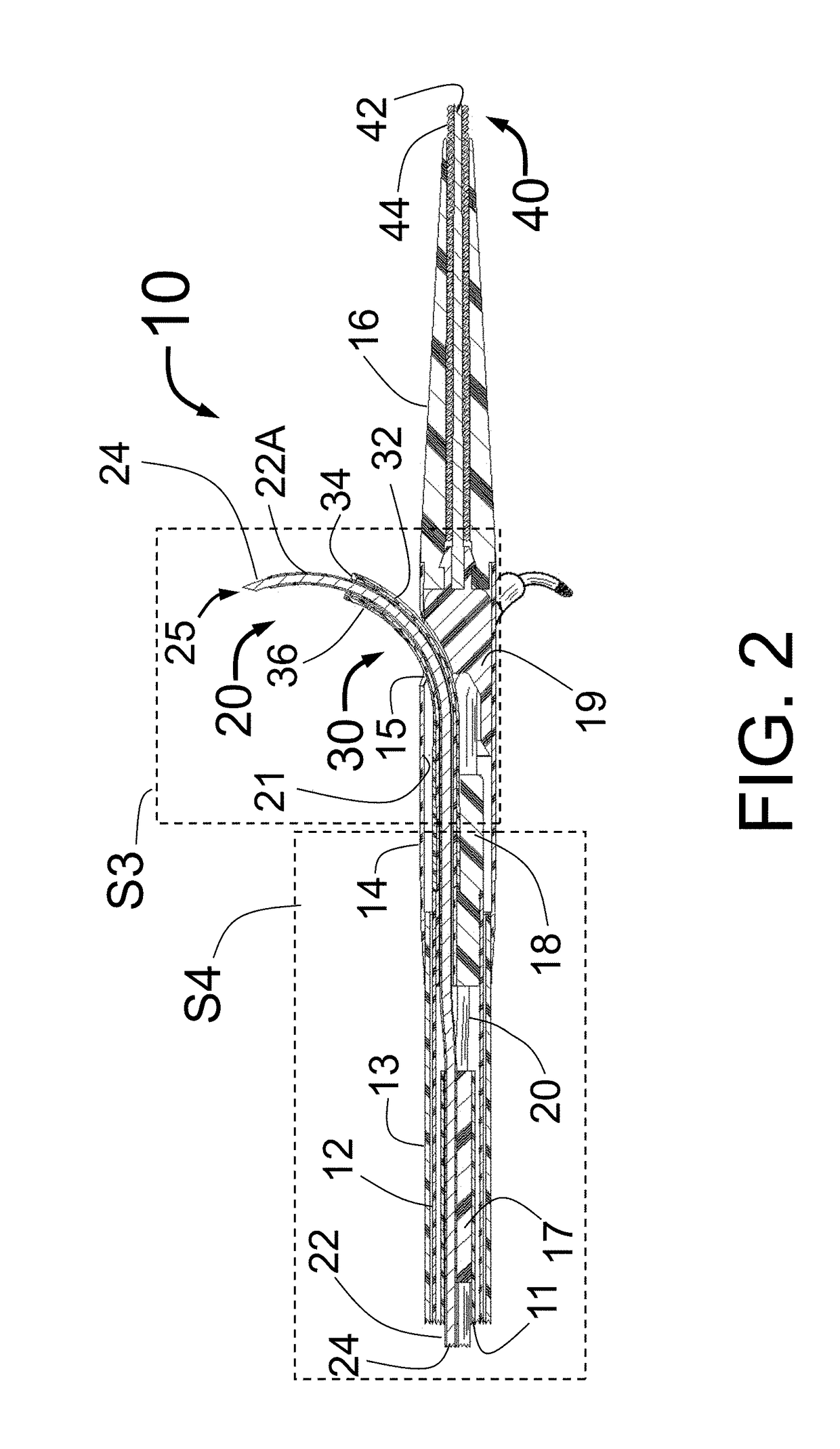
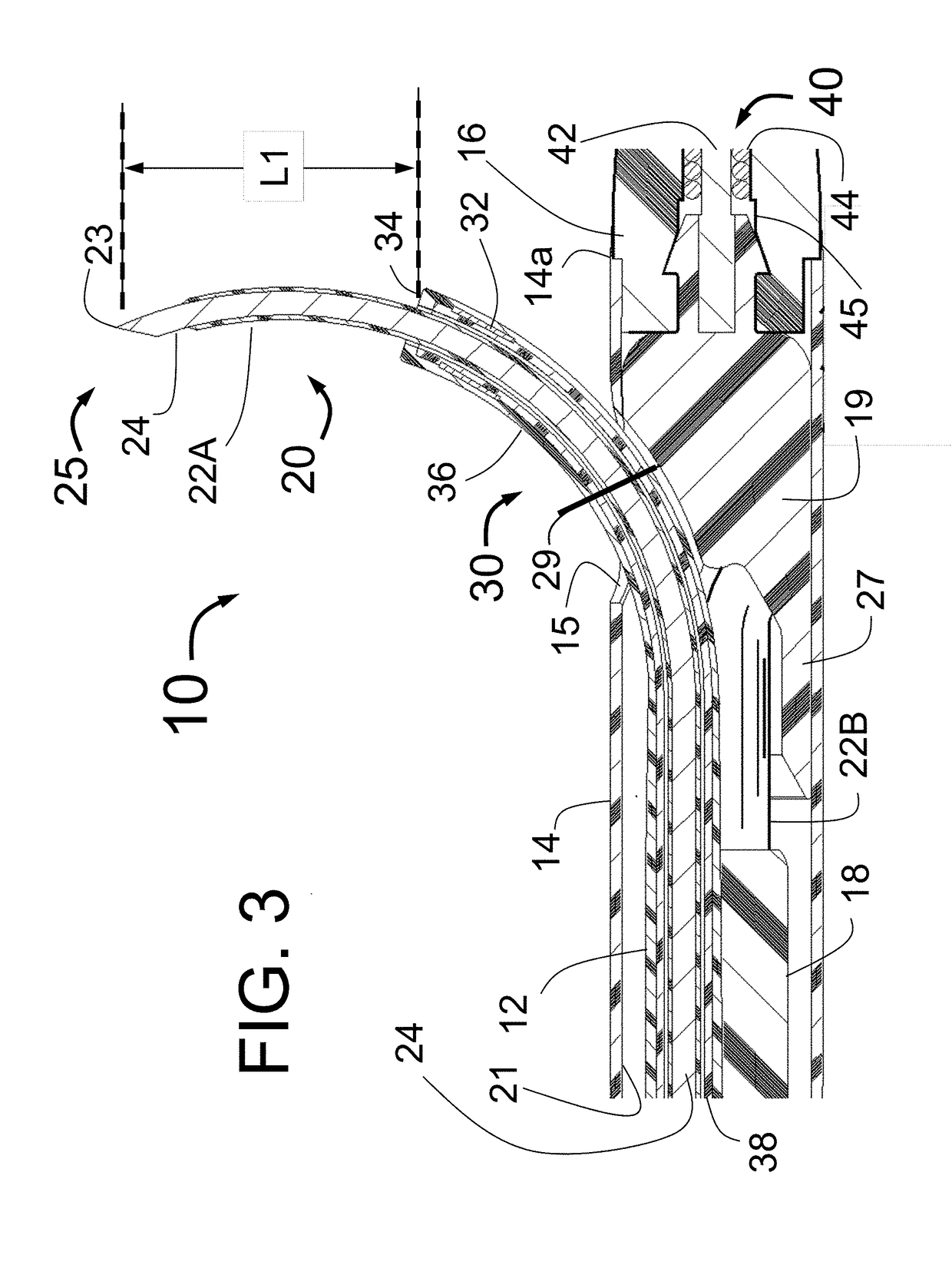
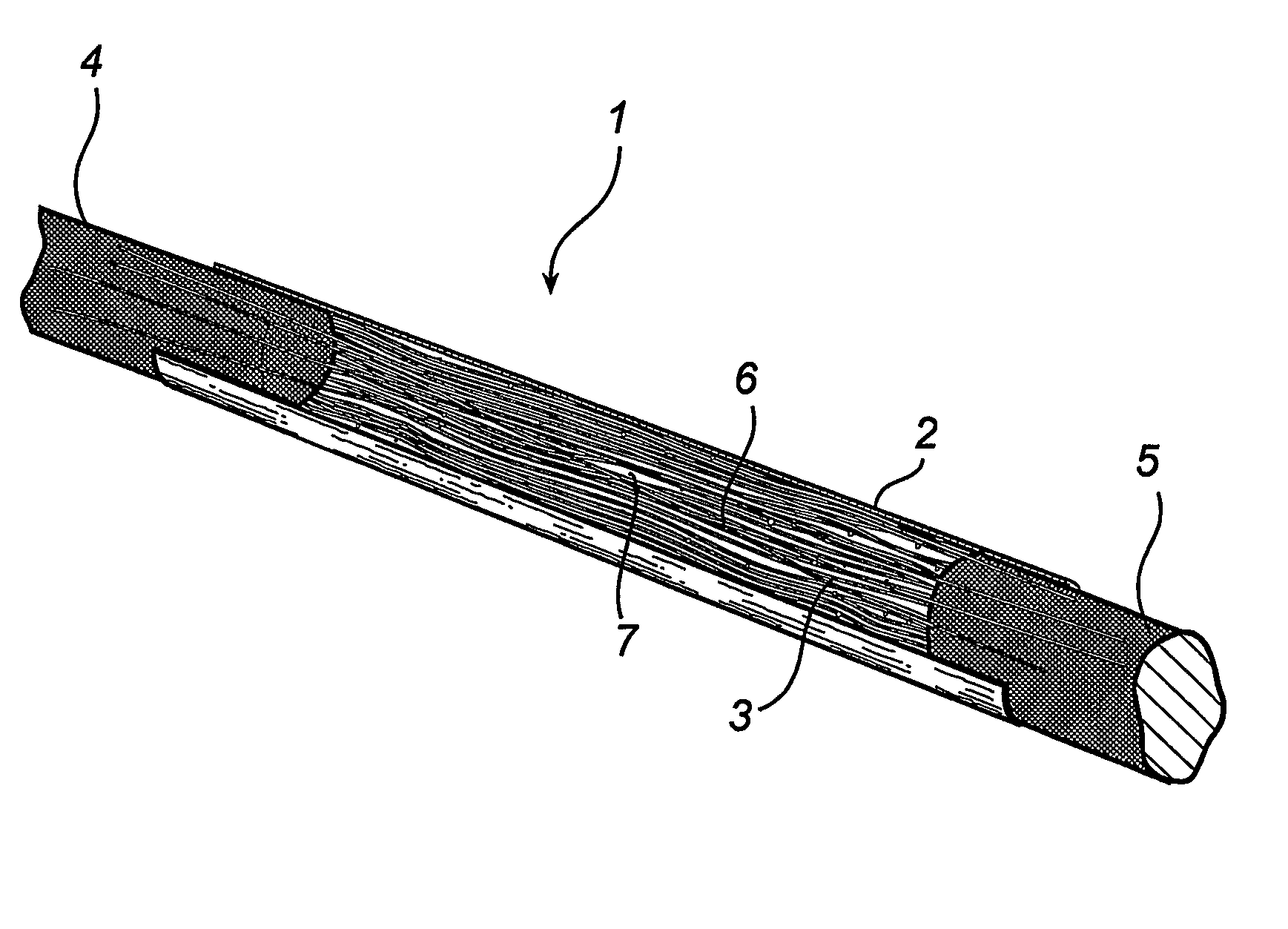
Patents
Literature
74 results about "Ulnar digital nerve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and methods for sensing and cooling during application of thermal energy for treating degenerative spinal discs
InactiveUS20050004563A1Reduce the temperatureAvoid motor nerve damageSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingThermal energySpinal nerve
Apparatus and methods for performing spinal disc lesioning procedures while monitoring the temperature near the spinal nerve roots. A needle containing a thermocouple and an injection bore may be placed between the disc and a nerve root. Temperature near the nerve root may be monitored during the lesioning procedure and if raised to a point where damage to the nerve could occur, the procedure may be stopped before damage is done. Coolant may be injected through the injection bore to lower the temperature near the nerve root. Additional dual purpose needles may be placed on the disc adjacent the opposite nerve root or in the spinal canal at the level of the disc for additional control. A hollow, flexible tip electrode needle may be used to repair and lesion the disc tissue. Prior to lesioning, the electrode may be stimulated to assess motor nerve response and avoid motor nerve damage.
Owner:EPIMED INT
System and Methods for Monitoring During Anterior Surgery
The present invention involves a system and methods for nerve testing during anterior surgery, including but not limited to anterior total disc replacement surgery, nucleus replacement, and interbody fusion.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Methods and systems for spinal radio frequency neurotomy
InactiveUS20110213356A1Increase the effective areaIncrease surface areaSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingAnatomical structuresProximate
Methods and systems for spinal radio frequency neurotomy. Systems include needles capable of applying RF energy to target volumes within a patient. Such target volumes may contain target medial branch nerves along vertebrae or rami proximate the sacrum. Such procedures may be used to ablate or cauterize a portion of the targeted nerve, thus blocking the ability of the nerve to transmit signals to the central nervous system. Disclosed needles may be operable to asymmetrically, relative to a central longitudinal axis of the needle, apply RF energy. Such asymmetry facilitates procedures where a tip of the needle is placed proximate to anatomical structures for location verification. Then RF energy may be applied in a selectable direction relative to the needle tip to ablate volumes that include the targeted medial branch nerves or rami, thus denervating facet joints or the sacroiliac joint, respectively, to relieve pain in a patient.
Owner:NIMBUS CONCEPTS
Low-profile, radial nerve splint with interchangeable resilient digit extensor elements and supination adjustment means
Owner:PHELAN CAROLYN HOYNE +2
Peripheral nerve field stimulator curved subcutaneous introducer needle with wing attachment specification
An apparatus for use in peripheral nerve field stimulation (PNFS) whereby a plurality of curved introducer needles, of varying curvatures, are provided to permit the physician to best locate the region of oligodendrocytes that contain the A Beta fibers by matching the lumbar lordosis. A wing device is also provided that is attachable to the hub of the curved needle introducer which gives the physician better ability to maneuver the needle during insertion as well as permitting tenting of the skin. The invention benefits a large number of painful disorders arising from pathology in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. In addition, this invention can also help a large number of other conditions including but not limited to failed back surgery syndrome / post-laminectomy pain, occipital / suboccipital headaches, scar pain, post herpetic neuralgia pain, mononeuritis multiplex, and pain following joint surgery (e.g., knee, hip, shoulder).
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Peripheral Neural Interface Via Nerve Regeneration to Distal Tissues
ActiveUS20150173918A1Easy to controlRaise the potentialSpinal electrodesMusculoskeletal system evaluationSensory FeedbacksNeurulation
At least partial function of a human limb is restored by surgically removing at least a portion of an injured or diseased human limb from a surgical site of an individual and transplanting a selected muscle into the remaining biological body of the individual, followed by contacting the transplanted selected muscle, or an associated nerve, with an electrode, to thereby control a device, such as a prosthetic limb, linked to the electrode. Simulating proprioceptive sensory feedback from a device includes mechanically linking at least one pair of agonist and antagonist muscles, wherein a nerve innervates each muscle, and supporting each pair with a support, whereby contraction of the agonist muscle of each pair will cause extension of the paired antagonist muscle. An electrode is implanted in a muscle of each pair and electrically connected to a motor controller of the device, thereby simulating proprioceptive sensory feedback from the device.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
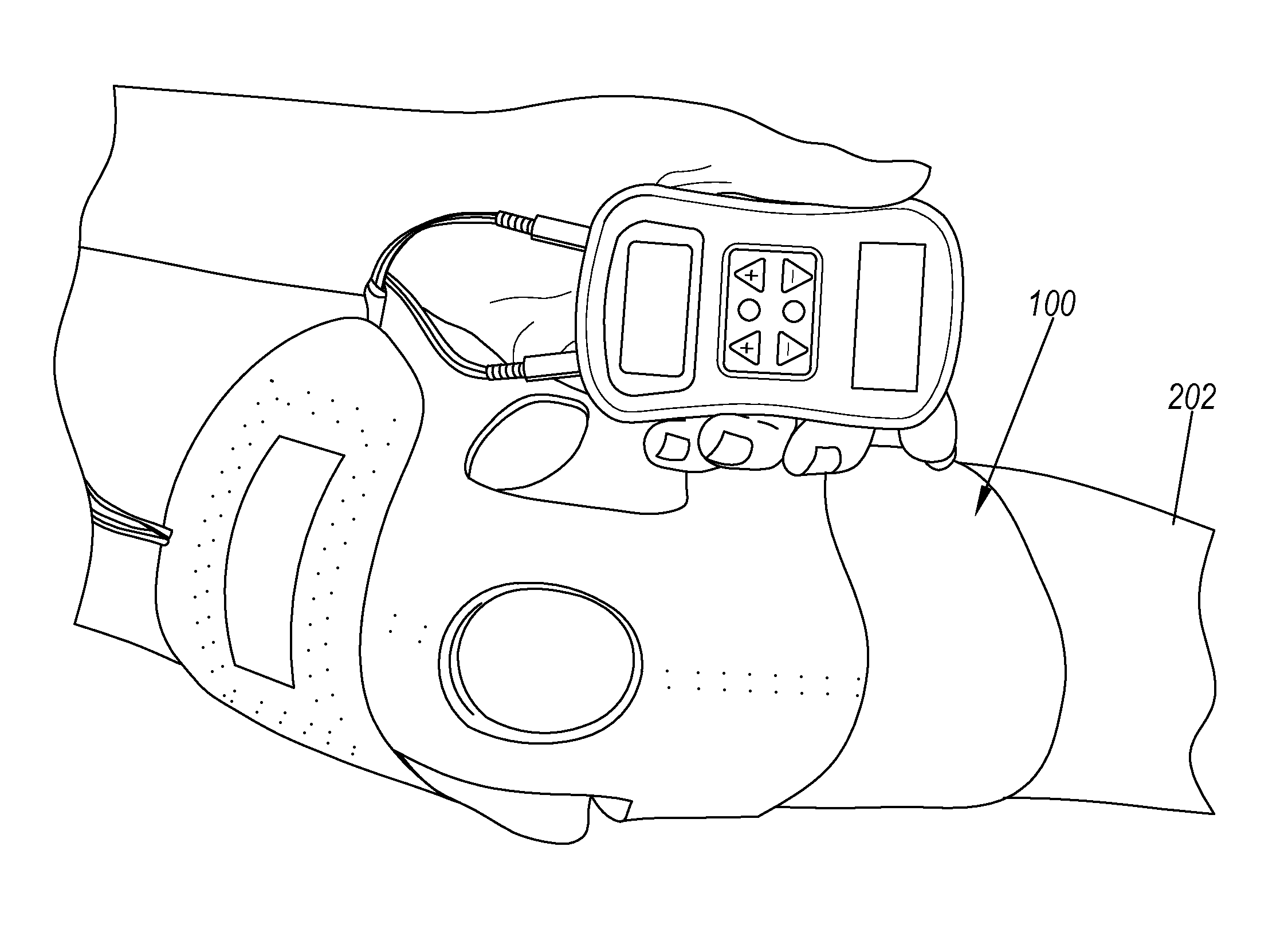
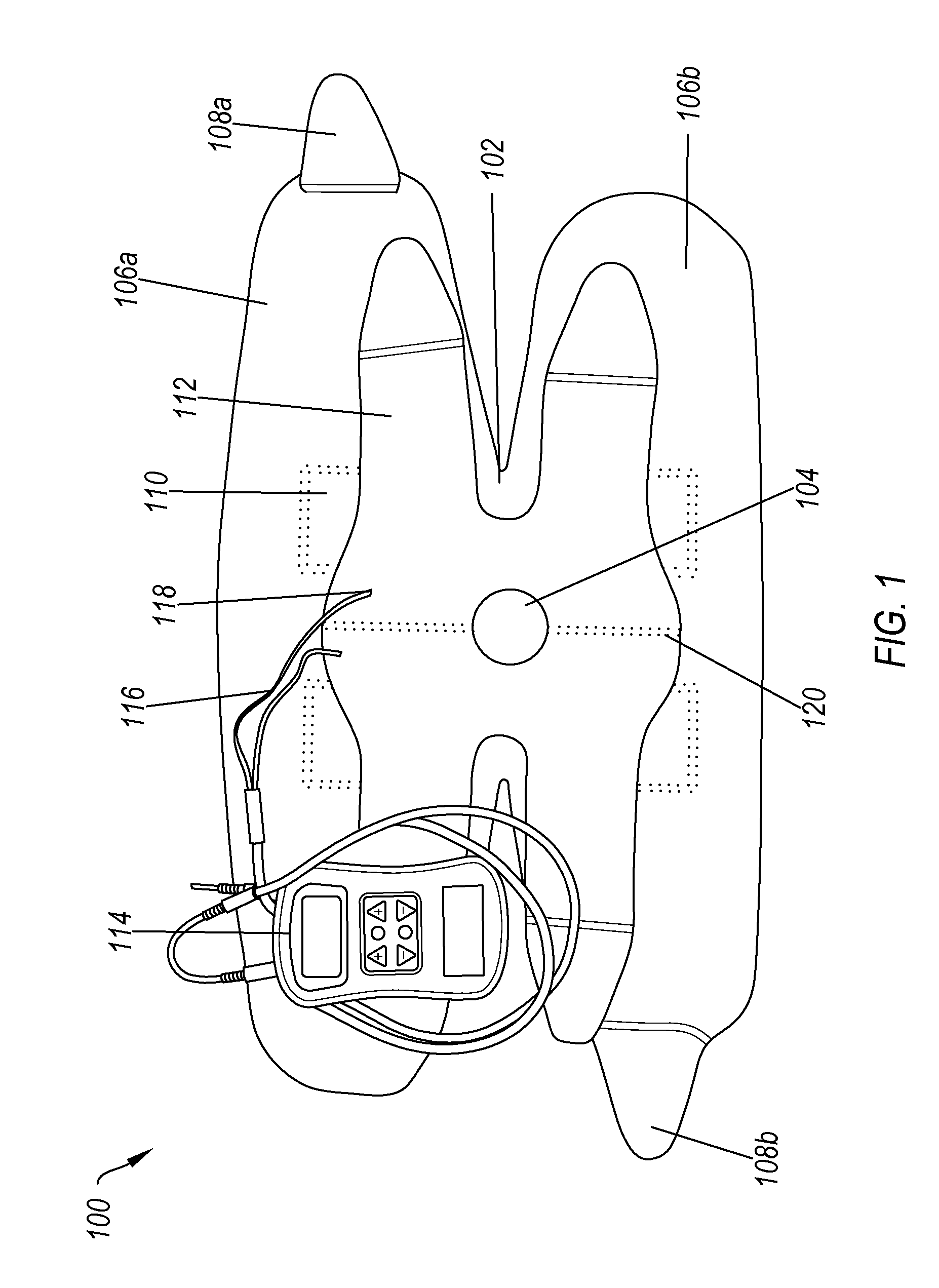
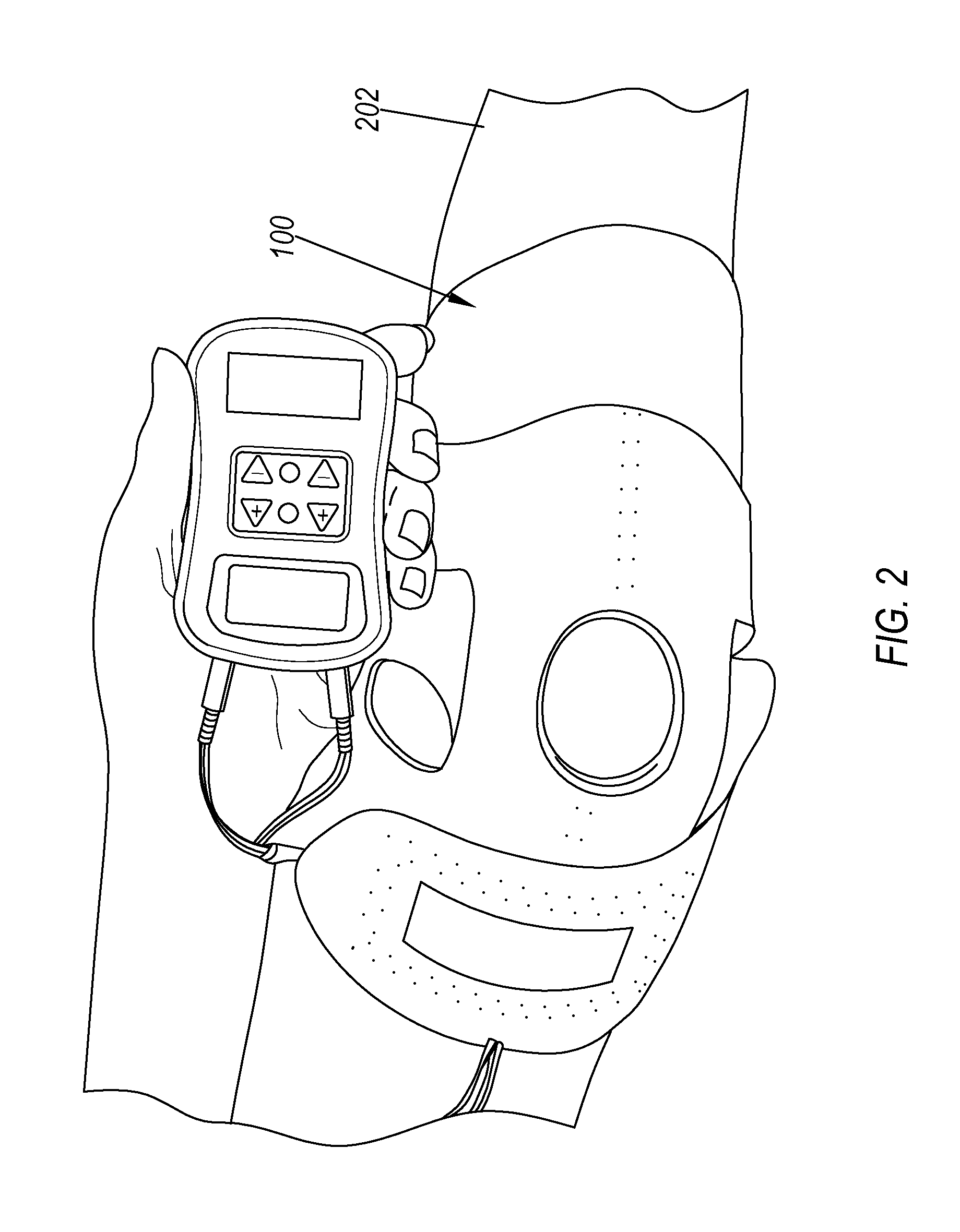
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation of the knee
A system for providing electrical stimulation of a joint. The system includes a wrap. The wrap includes a body, wherein the body is configured to be placed over the joint. The wrap also includes a first arm configured to be placed on a first side of the joint and attached to the body. The wrap further includes a second arm configured to be placed on a second side of the joint and attached to the body opposite the first arm. The wrap also includes a set of electrode locators. The set of electrode locators includes a first electrode locator, configured to receive a first electrode, a second electrode locator, configured to receive a second electrode, a third electrode locator, configured to receive a third electrode and a fourth electrode locator, configured to receive a fourth electrode.
Owner:BROWN MARTIN
Apparatus for effective ablation and nerve sensing associated with denervation
ActiveUS20190008580A1Minimize damageAvoid damageUltrasound therapySurgical needlesHuman bodyGuide tube
An intravascular catheter for nerve activity ablation and / or sensing includes one or more needles advanced through supported guide tubes (needle guiding elements) which expand to contact the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the needles to be advanced though the vessel wall into the extra-luminal tissue including the media, adventitia and periadvential space. The catheter also includes structures which provide radial and lateral support to the guide tubes so that the guide tubes open uniformly and maintain their position against the interior surface of the vessel wall as the sharpened needles are advanced to penetrate into the vessel wall. Electrodes at the distal ends of the guide tubes allow sensing of nerve activity before and after attempted renal denervation. In a combination embodiment ablative energy or fluid is delivered to ablate nerves outside of the media.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Device for promoting regeneration of an injured nerve, a kit and a biodegrade sheet for preparing such a device
The invention relates to promotion of a process for regeneration of an injured nerve using a plurality of guiding means, preferably a plurality of guiding fibres, presenting an in vivo biodegradability being such that at least a majority of said guiding means becomes essentially disintegrated by degradation (and / or dissolution) during a pre-contact period extending from application of the device at the injured nerve up to a first occurrence of a re-established (regenerated) contact between the ends of the injured nerve. During a post-contact period extending from the end of the pre-contact period and up to the end of the regeneration process, the disintegrated guiding means will provide no substantial axon growth guiding function and no substantial axon growth blocking effect.
Owner:AXONGEN
Apparatus for effective ablation and nerve sensing associated with denervation
ActiveUS10517666B2Saving time at the cost of adding complexityLarge potential marketSurgical needlesMedical devicesIntravascular catheterGuide tube
An intravascular catheter for nerve activity ablation and / or sensing includes one or more needles advanced through supported guide tubes (needle guiding elements) which expand to contact the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the needles to be advanced though the vessel wall into the extra-luminal tissue including the media, adventitia and periadvential space. The catheter also includes structures which provide radial and lateral support to the guide tubes so that the guide tubes open uniformly and maintain their position against the interior surface of the vessel wall as the sharpened needles are advanced to penetrate into the vessel wall. Electrodes at the distal ends of the guide tubes allow sensing of nerve activity before and after attempted renal denervation. In a combination embodiment ablative energy or fluid is delivered to ablate nerves outside of the media.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Tissue structure perforation system and method
ActiveUS20120029543A1Relieve stressReduce lossesIncision instrumentsCTS - Carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal ligament
A surgical treatment can involve creating a pattern of perforations in a tissue structure to allow lengthening of that tissue structure. For example, a pattern of perforations can be created in the transverse carpal ligament of a patient suffering from carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) that allows the carpal ligament to lengthen slightly. This lengthening can relieve pressure on the median nerve, thereby reducing the symptoms of CTS while maintaining the structural integrity of the wrist. A surgical instrument for use in perforating a tissue structure (such as the transverse ligament) can be an elongate structure with one or more retractable blades. Such a tool can be used in either an open or minimally invasive procedure to create a desired pattern of perforations in the tissue structure.
Owner:KYPHON
NIR/red light for lateral neuroprotection
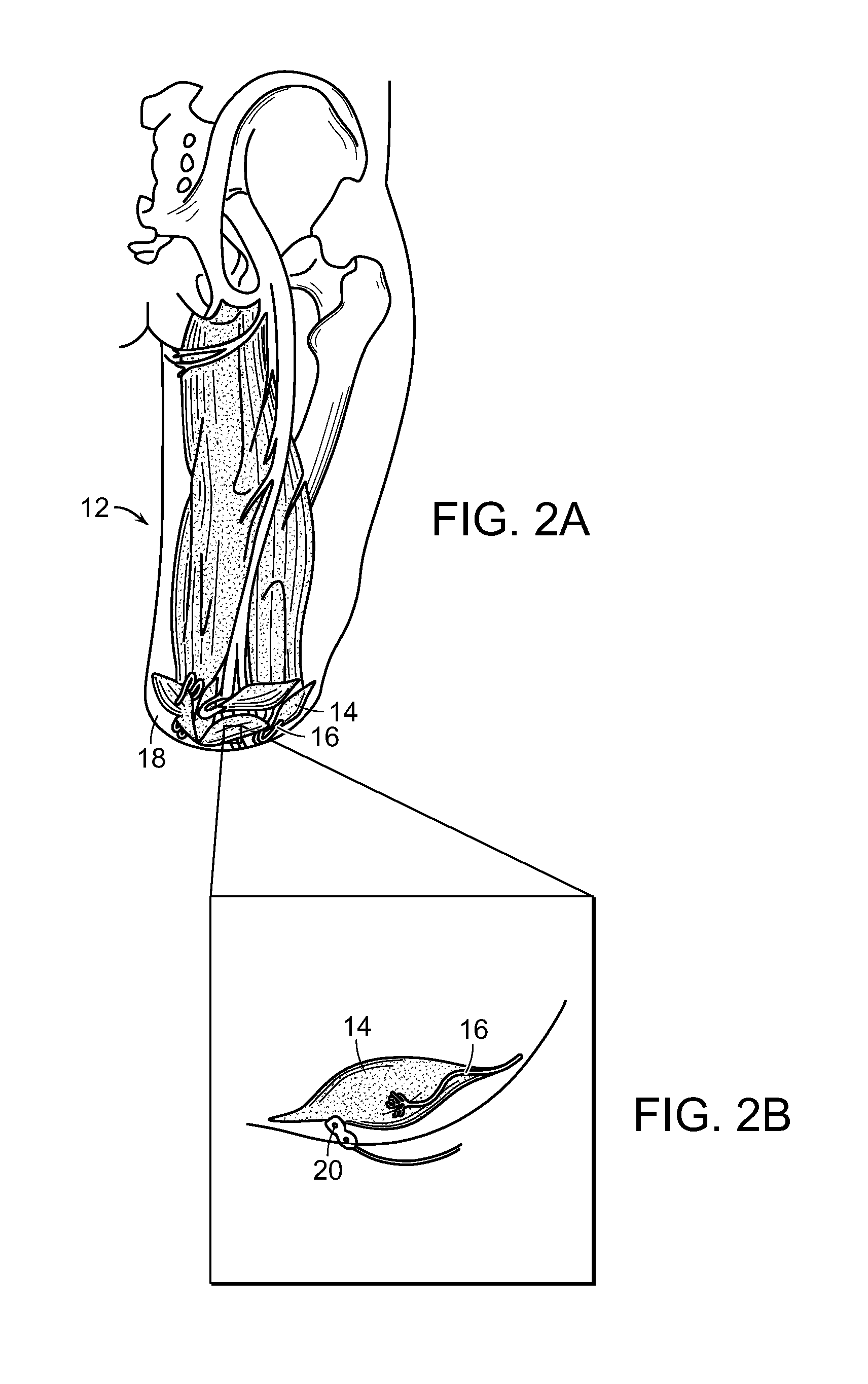
ActiveUS9480855B2Reduce incidenceReduce severitySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringSpinal columnUlnar digital nerve
The use of red or near infrared light upon neurons of the lumbar plexus that are in distress due to retraction-induced ischemia. The surgeon may protect nerves made ischemic in the surgery by:a) making an incision in a patient,b) inserting an access device into the patient through the incision to at least partially create a path to a spine of the patient, andc) irradiating nervous tissue adjacent the path with an amount of NIR or red light effective to provide neuroprotection.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Spinal implants and methods
InactiveUS20090138084A1Reduce relative motionSmooth motionBone implantDiagnosticsPosterior regionIntervertebral disk
Spinal implants are disclosed that can be used for annular repair, facet unloading, disc height preservation, disc decompression, or for sealing a portal through which an intervertebral implant was placed. In some embodiments, an implant is placed within the intervertebral disc space, primarily within the region of the annulus fibrosus. In some embodiments, the implant is expandable. In some embodiments, the implant has a sealing tail structure comprising a tail flange and a linkage. In some embodiments, the sealing tail structure limits the extrusion or expulsion of disc material, either annulus fibrosus or nucleus, into the posterior region of the spine where it could impinge on nerves. In some embodiments, the tail structure is retained in place within the annulus fibrosus by means of an anchor. In some embodiments, the anchor is constructed from multiple components.
Owner:MAGELLAN SPINE TECH
Co-axial actuated scissors
InactiveUS7909841B1Increase binding forceMinimize complicationSurgical scissorsMetal working apparatusEngineeringDetent
Co-axial actuated scissors for slidable positioning along a nerve for cutting the nerve or other anatomical surgical structure in a plane normal to the longitudinal axis of the scissors and away from the surgery site without harming adjacent tissues includes a first scissor portion having an offset handle attached to a slotted cylinder and a second scissor portion having an offset handle attached to an inner cylindrical member with the inner member telescoped within the slotted cylinder for concentric rotation therewith and the slotted cylinder and rotating member defining the longitudinal axis such that the cylinder and the rotating member include a loop end comprising a pair of cutting jaws whose cutting action is normal to the longitudinal axis and which are movable from an open position to a gripping position to a fully closed position for cutting the nerve through rotatable concentric actuation of the rotating member relative to the slotted cylinder and with detents positioned on an arcuate arm of the first scissor portion successively engaging a receiving notch located on the handle of the second scissor portion for holding the cutting jaws in each position as needed in order to effectuate the surgical operation.
Owner:NELSON CHRIS L
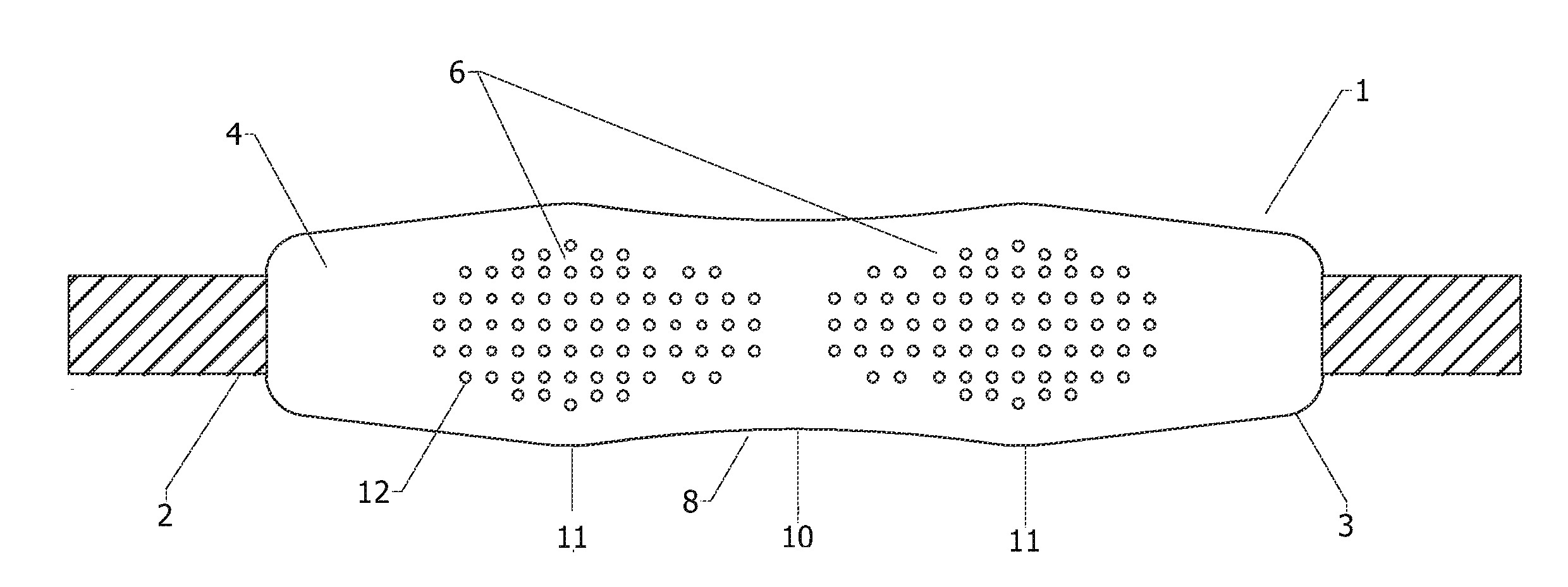
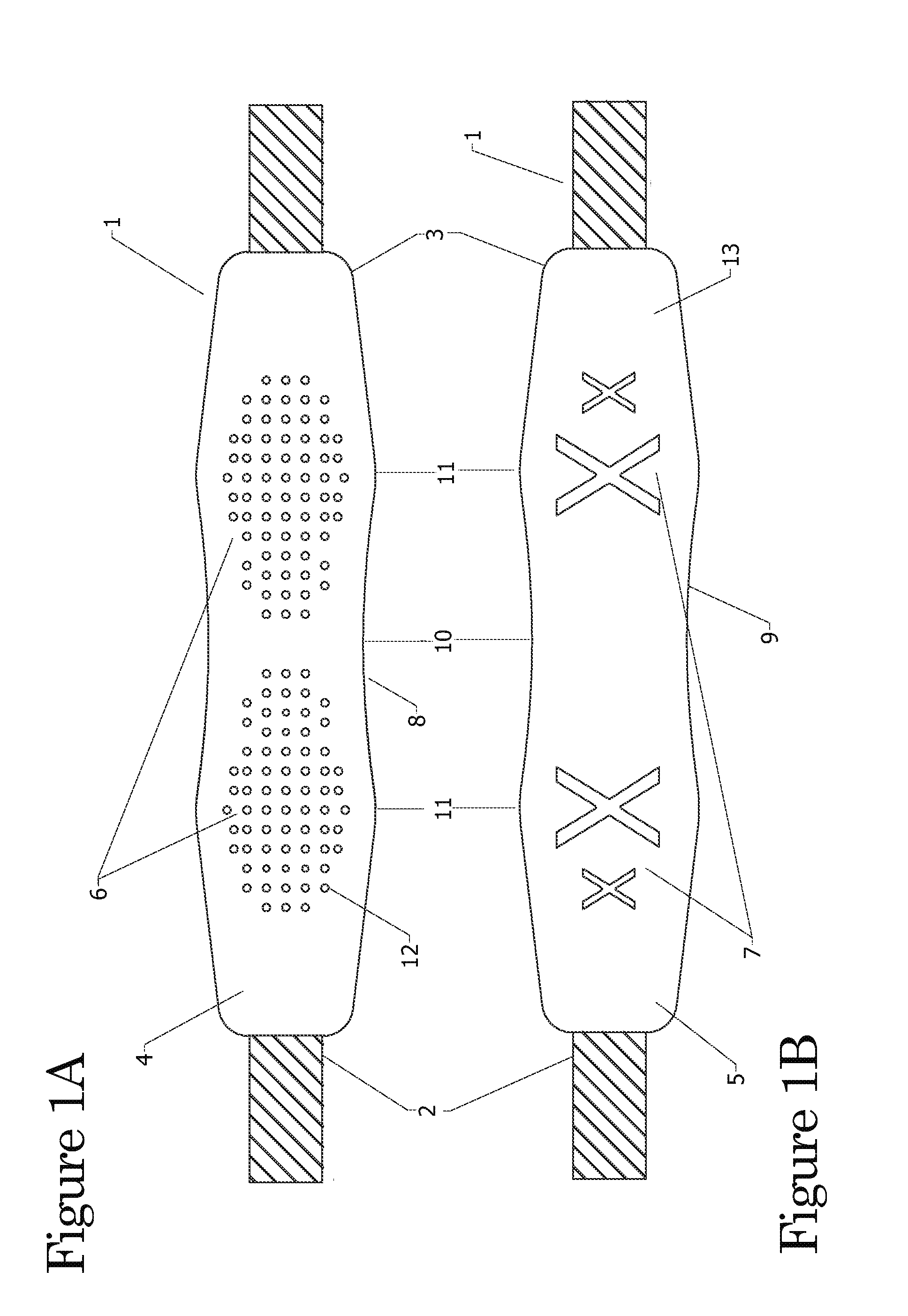
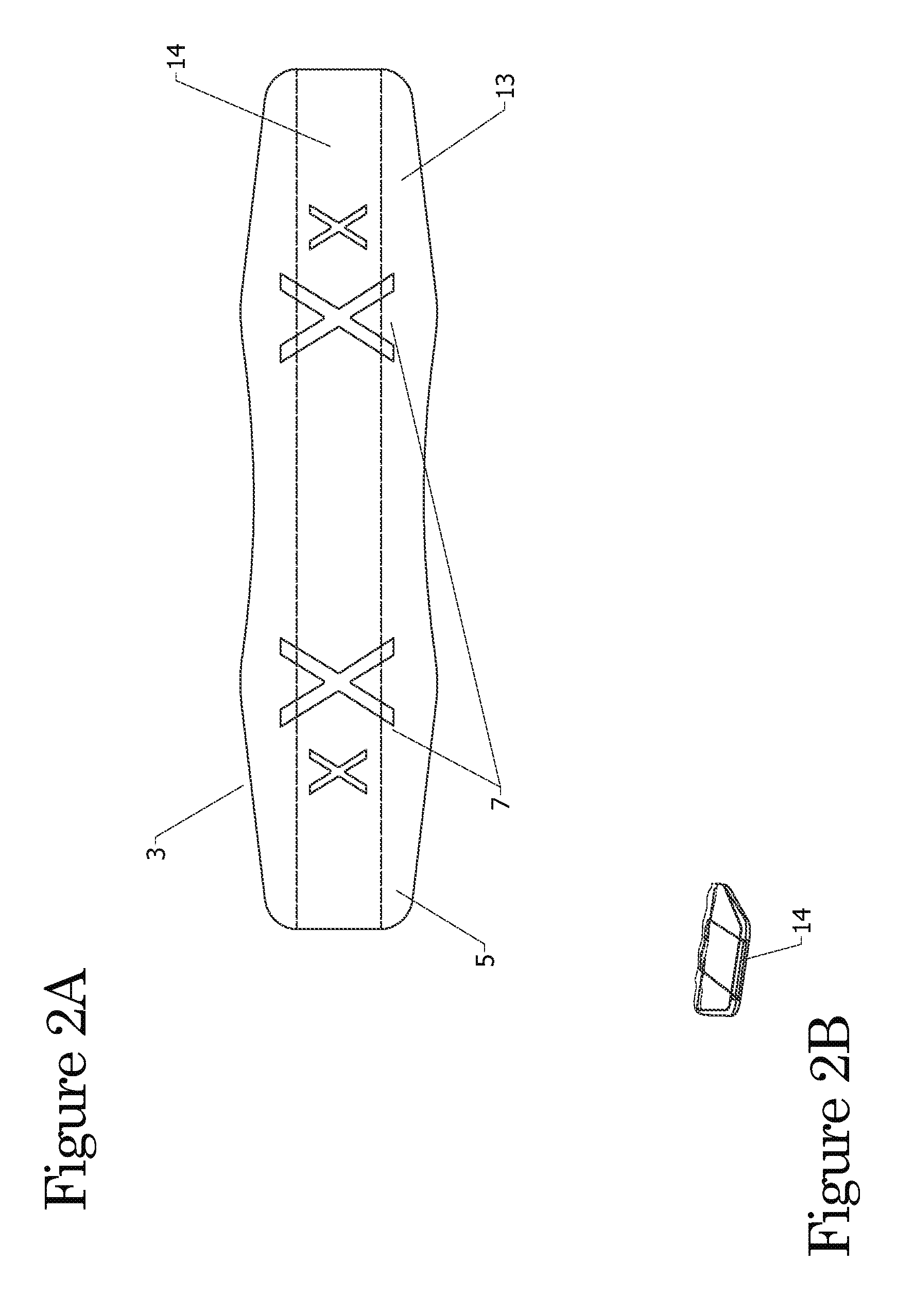
Shoulder strap and neck strap comprised of an oblong shaped pad and a strap
InactiveUS20120261446A1Reduce loadImprove comfortTravelling sacksShoulder strapPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPerspiration
A shoulder strap that has a strap member and a pad member and the pad member has a front side and a back side. The oblong shoulder pad shape allows for contour at the shoulder and neck putting the load to the left and right of the shoulder and reducing the pressure on the vertebra and cervical thoracic spinal nerves of the wearer's neck. The front side of the pad member has Non-Slip Traction Nibs (NSTNs) molded in a pattern so the traction nibs are facing outward from the surface at the outer shoulder. The back side of the pad member has a smooth or non-skid abrasive surface with inward X perspiration grooves (2-IPG) at a section by the side of the neck.
Owner:STEGMEYER ALFRED W
Apparatus that improves discovery of cancer mass, and reduces inflammation - onset of symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome or arthritis - tactile deficit of fingers, and increases discovery of foreign mass in breast and other self examinations
ActiveUS20050197539A1Work lessReduce incidence of injuryData processing applicationsSurgeryFinger flexionInterossei
An apparatus to increase identification of cancer mass in subcutaneous tissue, by palpation by self examination, to accommodate disability, to increase therapy of medical and physical recovery and treatment, and method of using devices or compounds which reduce onset of symptoms of median nerve entrapment or carpal tunnel syndrome or repetitive stress syndrome, reduce tactile deficit of fingers, and as well as many other applications. This includes improving the efficiency of the movement of the fingers, reducing the inflammation in the carpal canal, reducing the tendon excursion in the carpal canal, reducing finger flexion, reducing loss of nerve sensation, reducing loss of tactile sensation, increasing tactile sensitivity of the fingers, increasing movement of the dorsal interossei muscles of the hand, increasing movement of the volar interossei palmar muscles of the hand, and increasing movement of the lumbrical muscles of fingers.
Owner:CHOATE JOHN I M
Operation supporting sleeve and puncture guiding needle capable of being used by combination
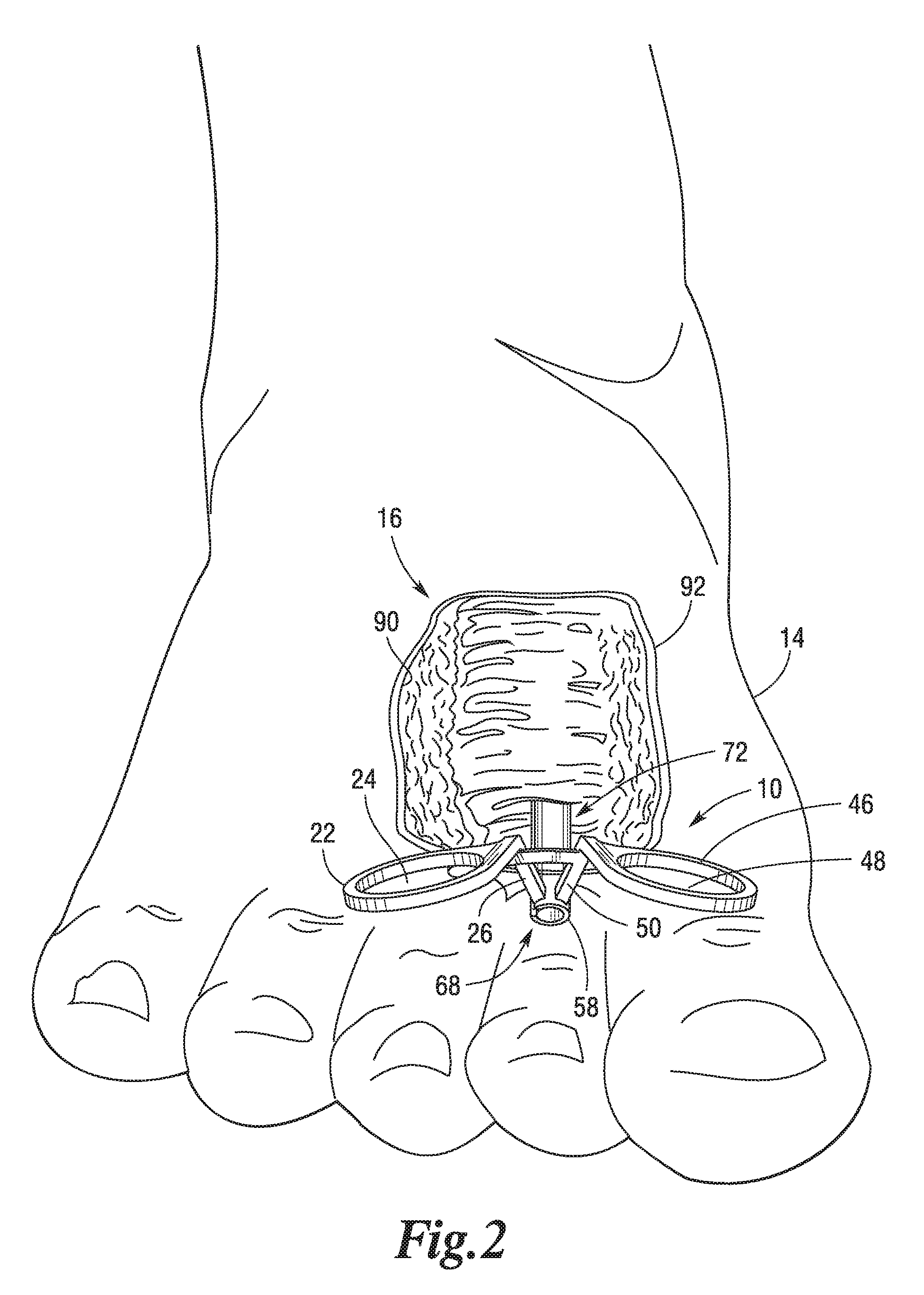
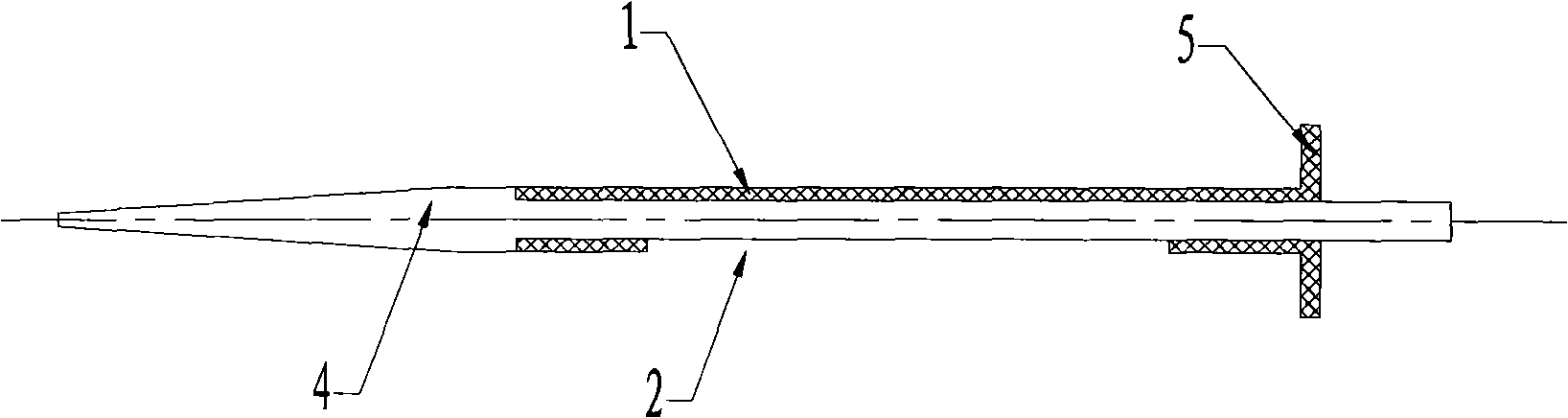
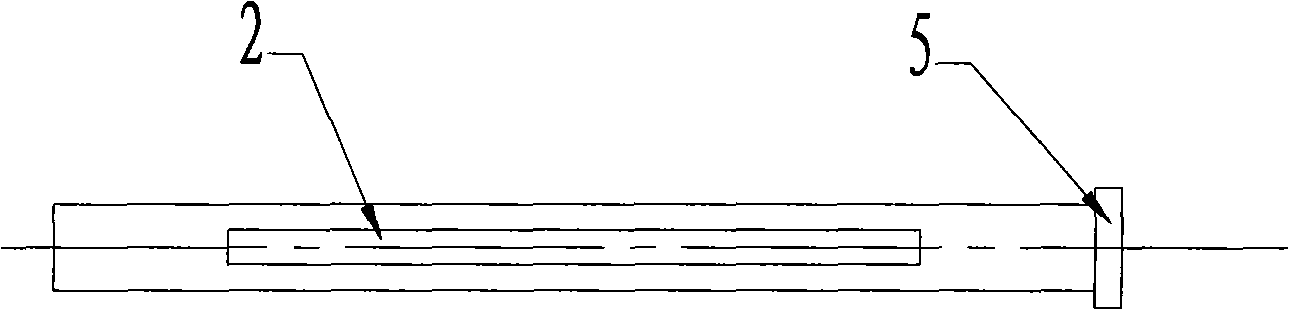
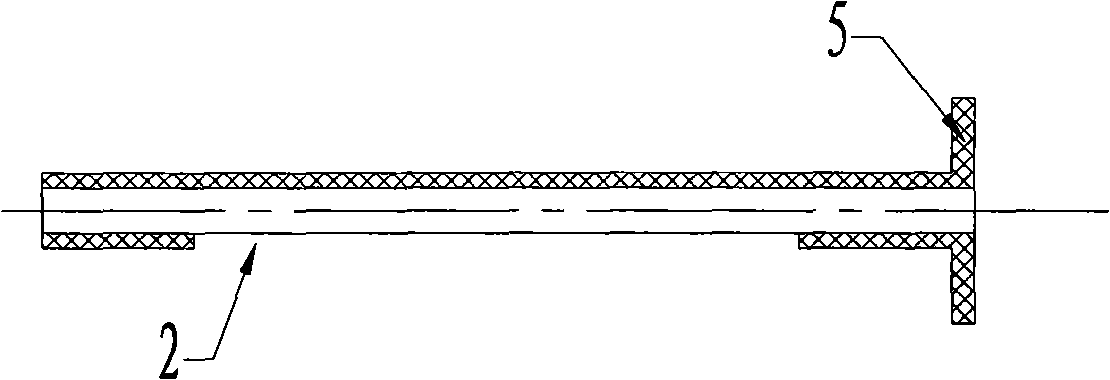
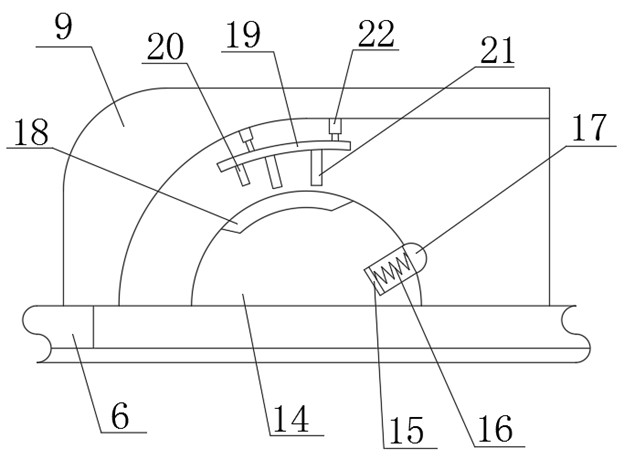
InactiveCN101543423BReduce manufacturing costImprove securitySurgical needlesTrocarUlnar digital nerveDeep tissue
The invention discloses an operation supporting sleeve and a puncture guiding needle capable of being used by combination, which are characterized in that the main body of a sleeve (1) is a round tube provided with an opening (2) on the tube wall, the head of the puncture guiding needle (4) is spiny, and when used by combination, the sleeve (1) is sleeved on the tail of the puncture guiding needle (4). The operation supporting sleeve and the puncture guiding needle are convenient to use and have high security. The operation supporting sleeve and the puncture guiding needle are mainly used forcutting off ligamenta or cutting part of the ligamenta in operative treatment of nerve compression wounds on a wrist or other parts and incising deep tissues in a minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF DEYANG CITY
Elbow brace
InactiveUS20140031733A1Preventing and reducing muscularPreventing and reducing and nerve disorderNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPhysical therapyElbow brace
The invention is for an elbow brace for preventing or reducing muscular and nerve disorders in the region of the elbow, such as tennis elbow. The brace comprises a tubular sleeve adapted for fitting over a wearer's arm with one end terminating above the wearer's elbow and the other end terminating below the wearer's elbow. The sleeve includes a protective opening configured to surround and avoid contact with the medial aspect of the wearer's elbow to protect the medial aspect from contact, pressure and friction.
Owner:MARTINO STEPHEN J
Implant devices with a pre-set pulley system
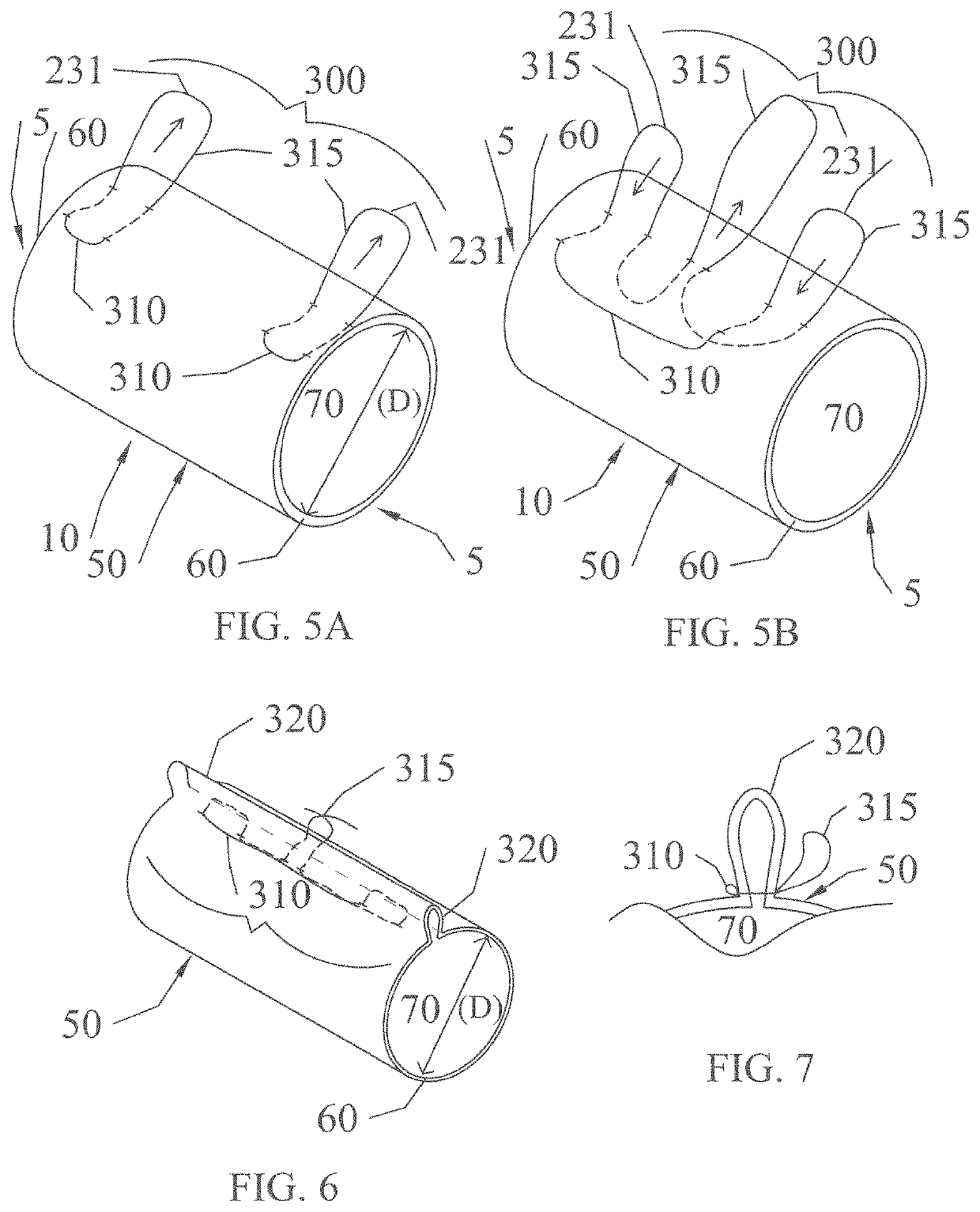
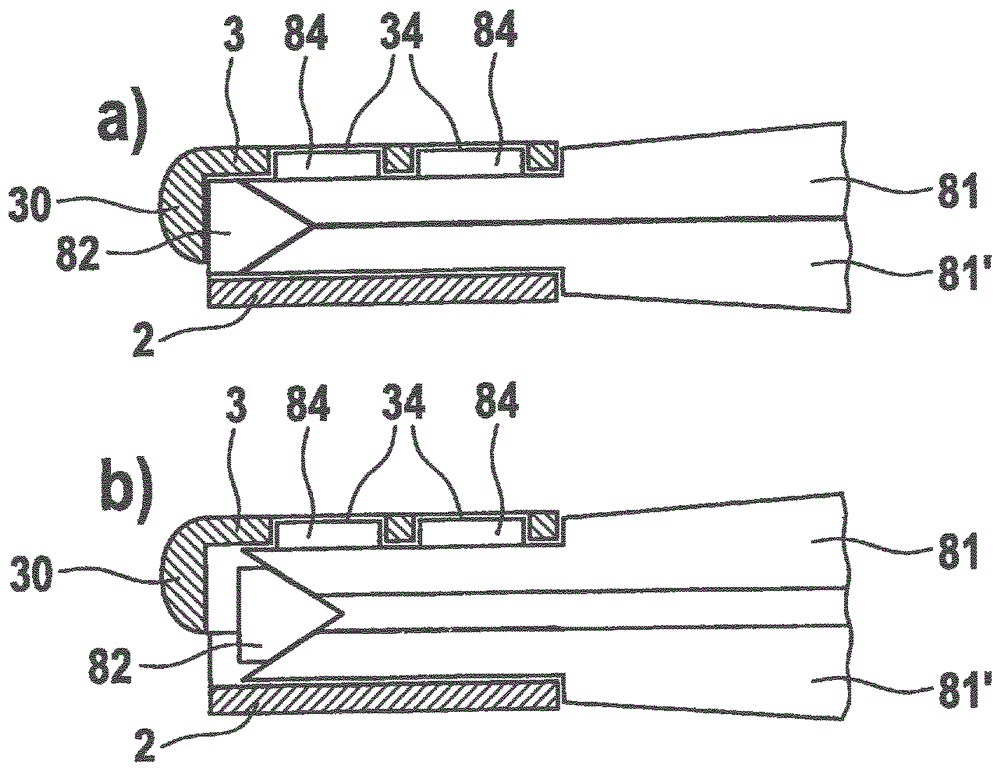
ActiveUS10945737B2Novel and inexpensive and highly effective improvementMinimal bending and crimping and distortionSuture equipmentsUlnar digital nerveAnatomy
The problem of positioning one or more nerve ends inside a sheathing implant is solved by the use of a pulley and cinching systems that pull a nerve end into an implant and that can adjust the diameter of an implant to conform the implant to the diameter of the nerve, respectively. The pulley system utilizes a suture that traverses the wall of an implant leaving one end outside the implant wall and another end that can be attached to a nerve. Pulling the suture end outside the wall pulls the nerve attached to the other end of the suture into the bore of the implant. A cinching system utilizes specially arranged sutures within the wall of an implant to tighten or cinch up the wall after a nerve is placed therein, so as to conform at least part of the implant to the diameter of the nerve. Methods are also disclosed by which such pulley systems can be formed during an intraoperative procedure.
Owner:AXOGEN CORP
Non-invasive nerve stimulation devices, electrode assemblies, and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS11071855B2Minimize occurrenceExternal electrodesArtificial respirationGreater auricular nerveUlnar digital nerve
Nerve stimulation devices and methods for performing non-invasive nerve stimulation are provided that are particularly well suited for performing non-invasive stimulation of one or both of the great auricular nerve and auricular branch of the vagus nerve through a target nerve junction in the neck of the subject. The nerve stimulation devices use dry electrolyte electrodes that (1) are comfortable to use, (2) suitable for long-term use, (3) avoid delivering painful shocks to the subject, (4) do not require soaking of the electrodes in saline solutions or covering them in sticky or wet gels, (5) do not require skin preparation, and (6) avoid causing muscle contraction in areas outside of the target nerve junction containing the great auricular nerve and the auricular branch of the vagus nerve during use.
Owner:HOOLEST PERFORMANCE TECH INC
Alternative wrist-elbow joint prosomatosensory reconstruction method based on nerve electrical stimulation system
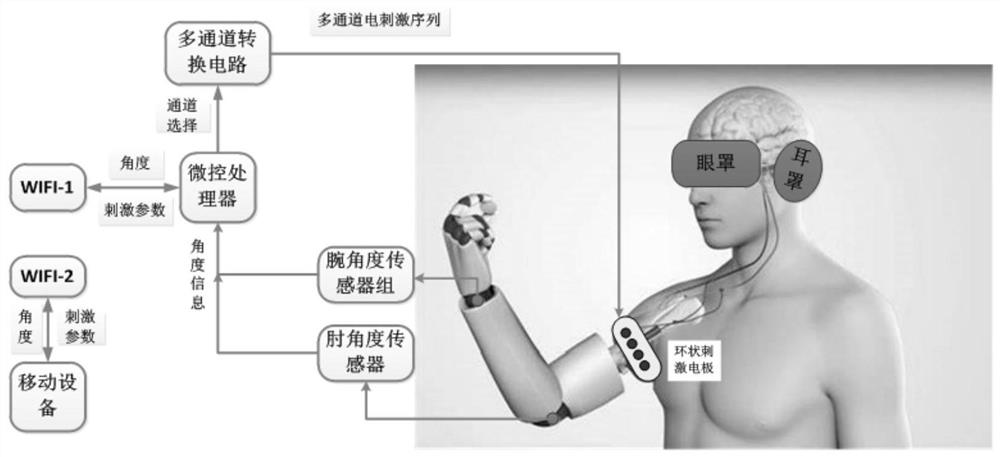
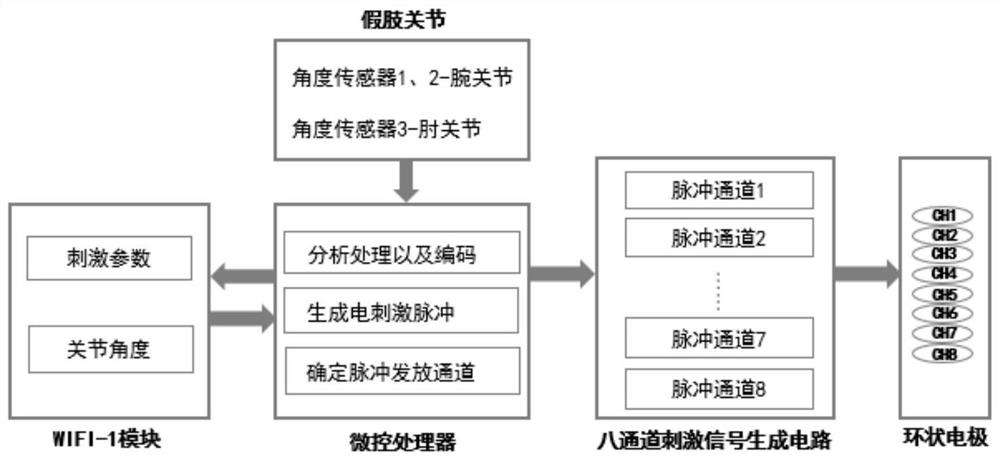
PendingCN114652958AAvoid damageElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerUlnar digital nerve
The invention discloses an alternative wrist elbow joint prosomatosensory reconstruction method based on a nerve electrical stimulation system, and the method comprises the following steps: 1) pasting a discharge stimulation module on the upper arm of a user, and wearing an artificial limb; an angle sensor is arranged in the artificial limb; (2) the angle sensor monitors limb movement posture information of a user and transmits the limb movement posture information to the microcontroller; 3) the microcontroller generates an electrical stimulation mode according to the motion posture information or the electrical stimulation parameter information; and 4) the microcontroller controls the electrical stimulation module to generate electrical stimulation acting on the user according to the electrical stimulation mode, and transmits the electrical stimulation mode to the mobile terminal for display through the data transmission module. According to the invention, the proprioceptive feeling of the user is combined with the motion state of the artificial limb by utilizing the skin superficial feeling mode of the residual limb of the amputee, so that the induced alternative feeling is closer to the natural feeling.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Massage rehabilitation equipment for neurology department
InactiveCN114305959AAvoid misjudgmentEasy to adjust the massage intensity in timeOperating chairsChiropractic devicesUlnar digital nerveNeurology department
The invention discloses massage rehabilitation equipment for the neurology department, which comprises a rehabilitation chair, a fixing plate, an upper limb training module, a hand positioning module and an upper limb nerve relaxation module, and is characterized in that the upper limb training module is used for performing massage rehabilitation training on upper limb parts; the hand positioning module is used for judging the state of the rehabilitation patient in the working process of the upper limb training module and ensuring that the patients with different arm lengths can take proper exercises; and the upper limb nerve relaxation module is used for relieving the region with pain during training so as to avoid erroneous judgment caused by troubleshooting the region with excessive training friction. By means of the upper limb training module, branch nerves on fingers, median nerves at wrist joints, ulnar nerves at elbow joints, axillary nerves at shoulder joints and muscular skin nerves at front arms and upper arms can be sufficiently massaged.
Owner:滑县人民医院
Mechanical wound cleansing device
PendingUS20210007764A1Efficient propertyEasy to controlNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersUlnar digital nerveArterial ulcer
The present invention relates to a mechanical wound cleansing device comprising a carrier layer and an abrasive loop system arranged above the carrier layer, whereby the loop system is an intermeshed fiber system which is intermeshed above the carrier layer and / or a loop system comprising highly and softly abrasive loops. The present invention further relates to a method of producing said mechanical wound cleansing device. The present invention finally relates to the use of said wound cleansing device for the abrasive removal of and cleansing of wounds, especially for venous leg ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers (neuropathic and neuro-ischemic), arterial ulcers, mixed etiology ulcers, pressure ulcers or traumatic wounds.
Owner:BSN MEDICAL GMBH & CO KG
Method for a neuromodulation treatment
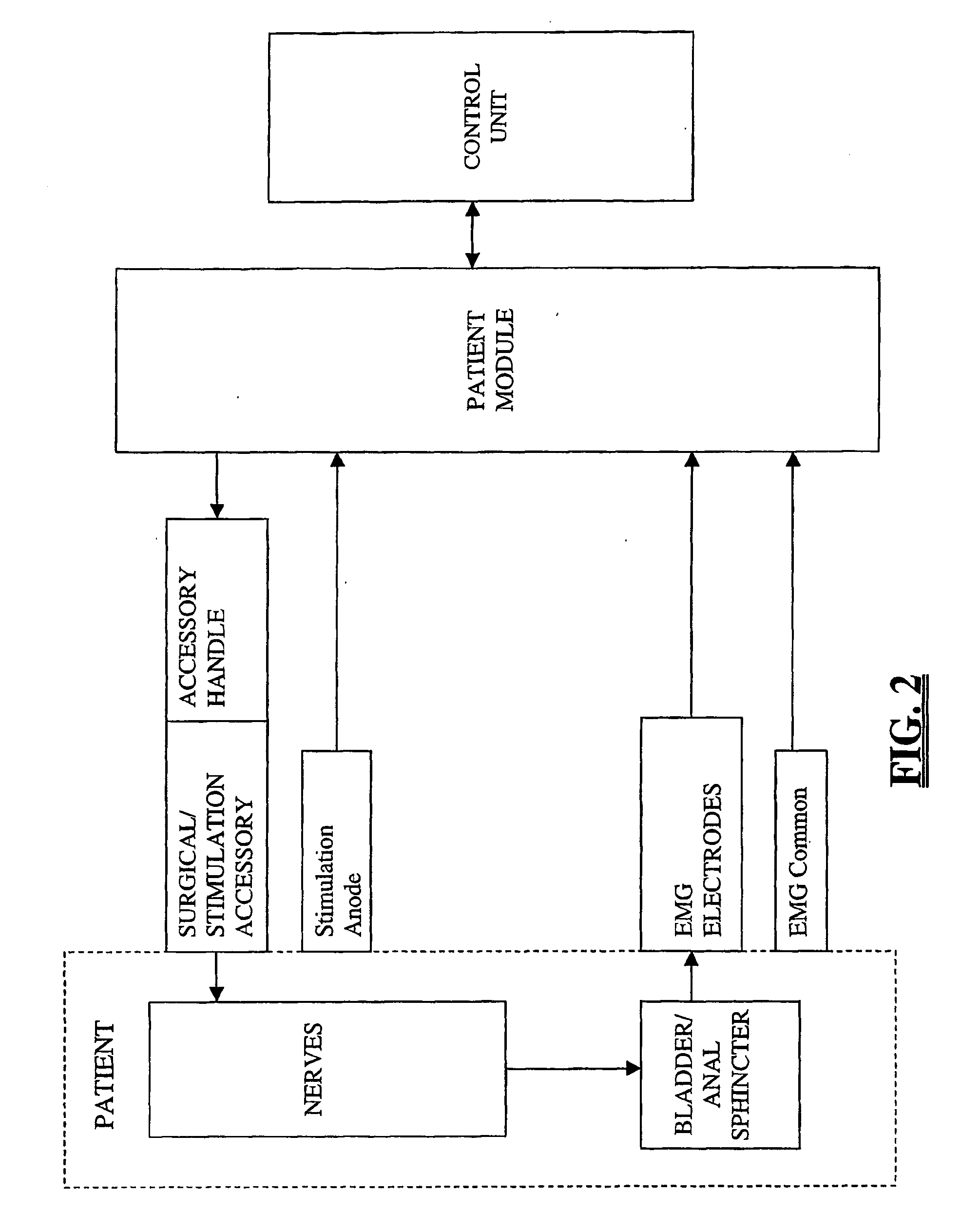
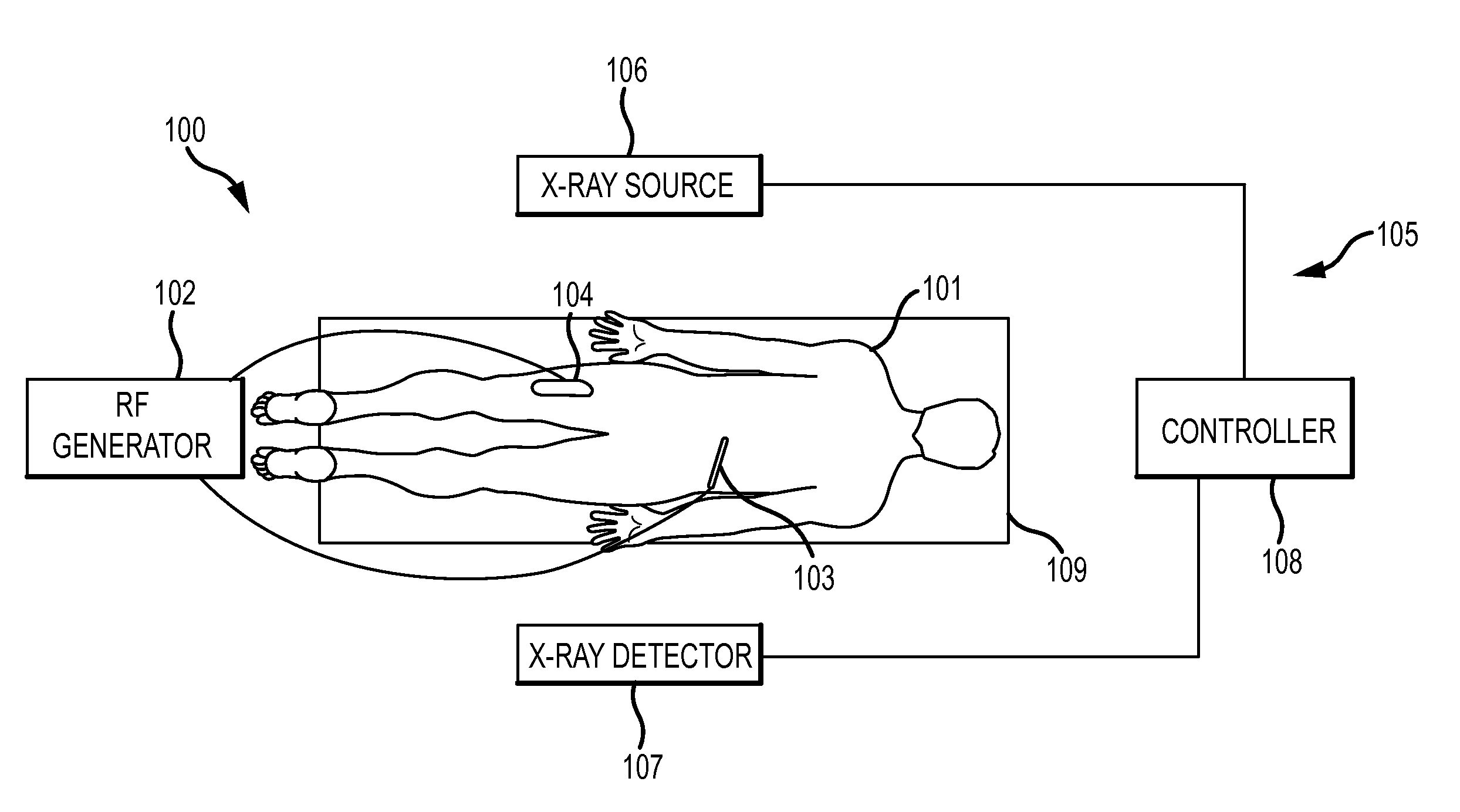
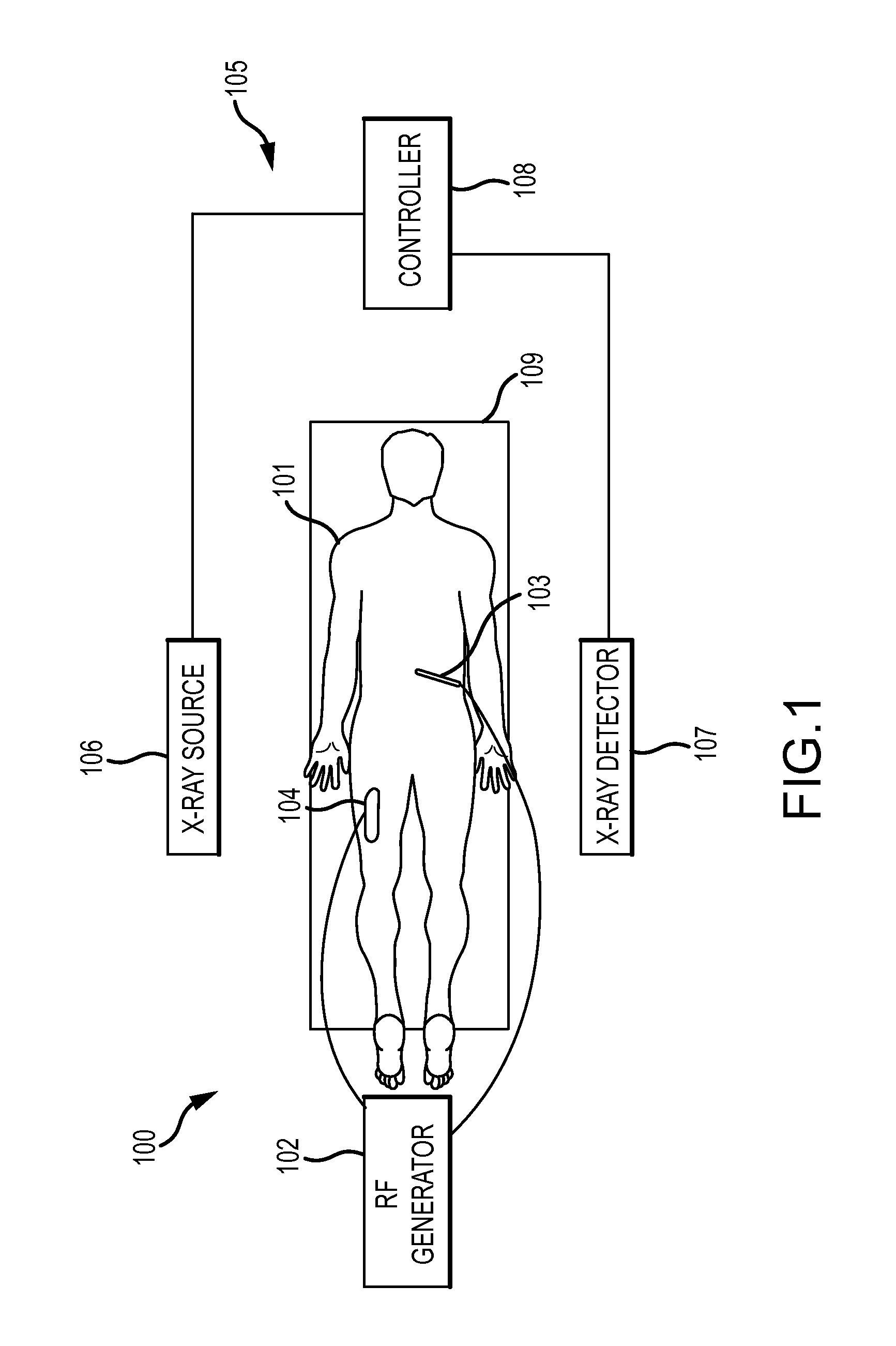
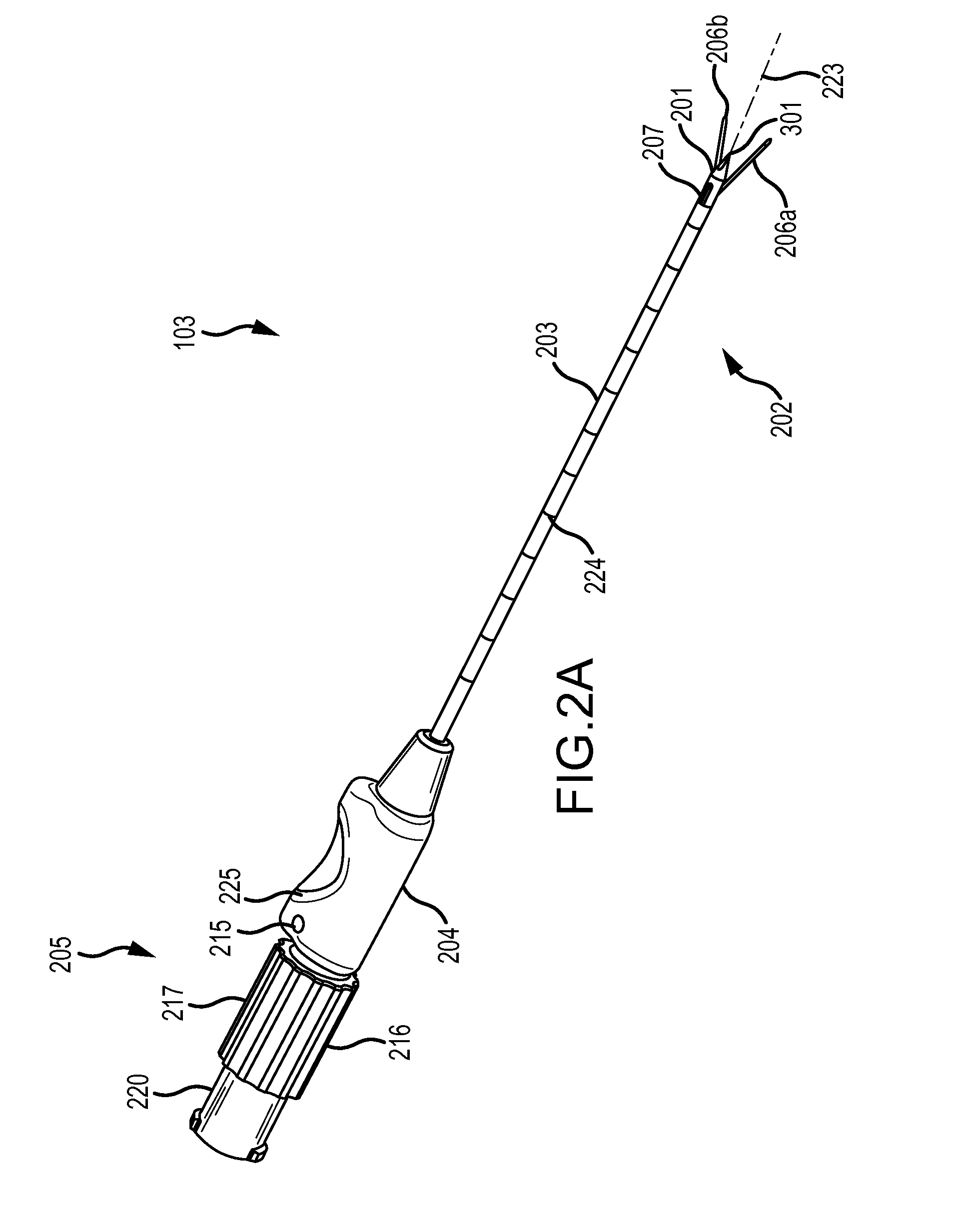
The present disclosure provides a neuromodulation method for treating the syndromes of a low urinary tract dysfunction. The neuromodulation method comprises attaching a first active electrode to a first patient's leg in the back of the knee area in proximity of a peroneal nerve of the first leg. Attaching a second active electrode to a second patient's leg in the back of the knee area in proximity of a peroneal nerve of the second leg. Attaching a grounding electrode to the patient's body. Generating electrical pulses by a pulse generator connected to the first, the second active electrode and a grounding electrode. Stimulating by the first and the second active electrodes the peroneal nerve of the first and the second leg and controlling via control unit a flow of the generated pulses to each of the first and second active electrode.
Owner:STIMVIA SRO
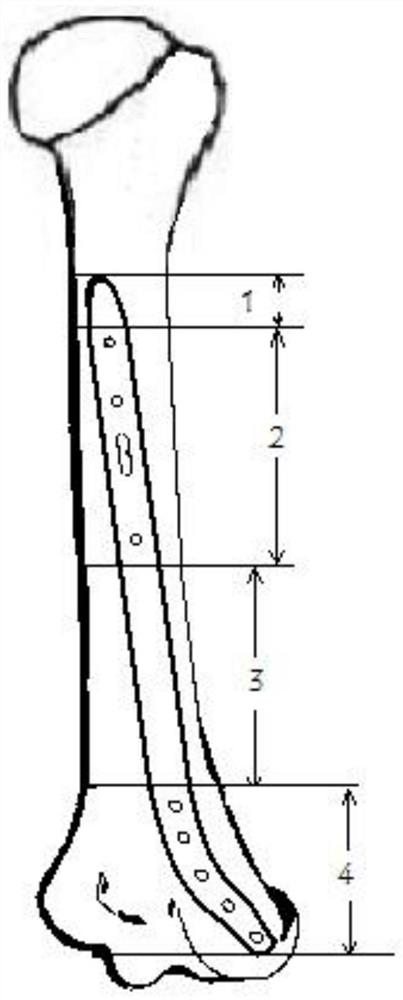
Bridging dissection locking bone plate for fixing comminuted fracture of humerus shaft on rear outer side
InactiveCN111658114AEffective protectionSelf-strength unchangedBone platesAnatomical structuresUlnar digital nerve
The invention provides a bridging dissection locking bone plate for fixing comminuted fracture of a humerus shaft on the rear outer side. The inner surface of a bone plate body is attached to the rearside surface of the humerus shaft and the external epicondyle of the humerus, and a dissection structure is matched with the bone fracture plate body; the bone plate body sequentially comprises a tapered periosteum stripping area, a first fixing area, a radial nerve decompression area and a second fixing area from the near end to the far end, the longitudinal section of the tapered periosteum stripping area is a right triangle, and one right-angle side of the right triangle is attached to the surface of the humerus shaft; the first fixing area is provided with a plurality of locking screw holes and locking and pressurizing combination screw holes which are perpendicular to the surface of the humerus shaft which is attached to the first fixing area; and a groove is formed in the outer surface of the radial nerve decompression area, and the edge of the groove is an arc-shaped transition area; the shape of the second fixing area is matched with that of a distal humeral epicondyle anatomical structure, and a plurality of locking screw holes are formed in the second fixing area in the length direction. In the process of fixing the comminuted fracture of the humerus shaft, blood supplyof the broken end of the fracture is not damaged, nerves are not damaged, and operation time is short.
Owner:JILIN UNIV FIRST HOSPITAL
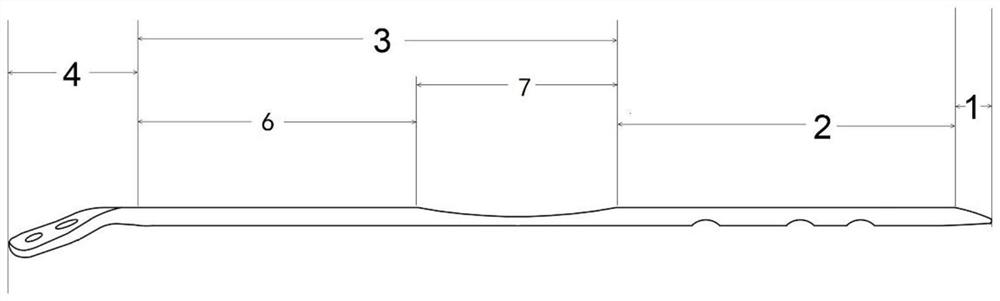
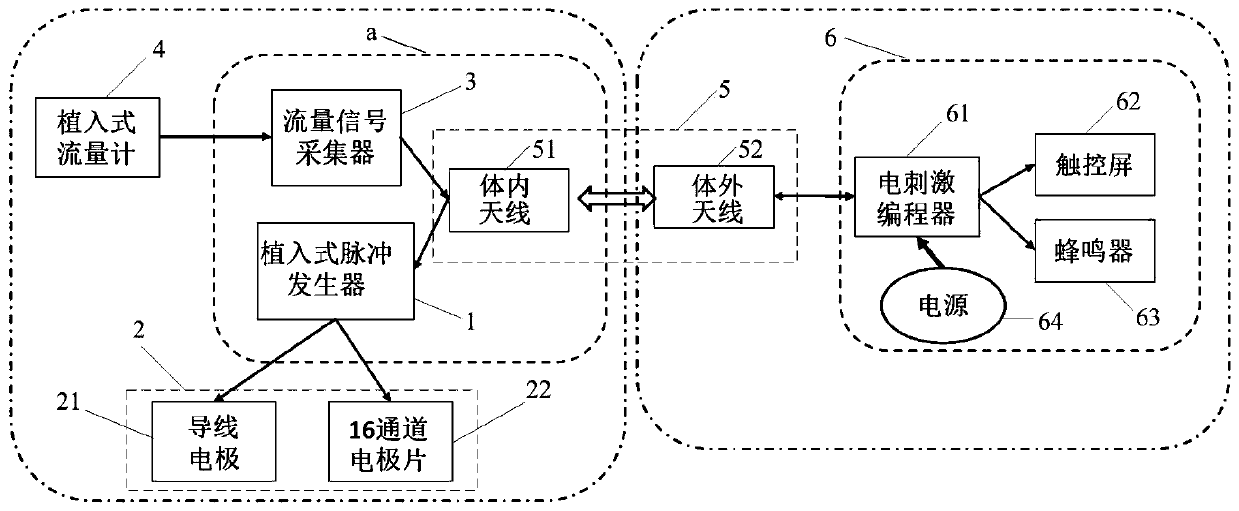
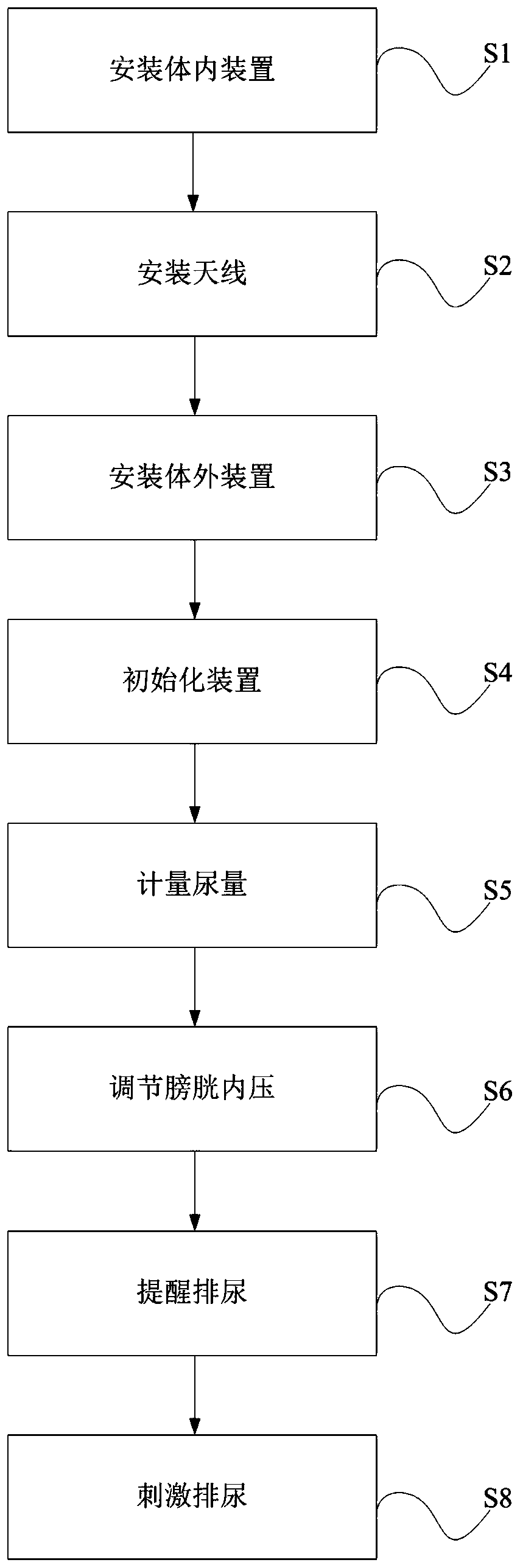
Independent urination assistant device and method
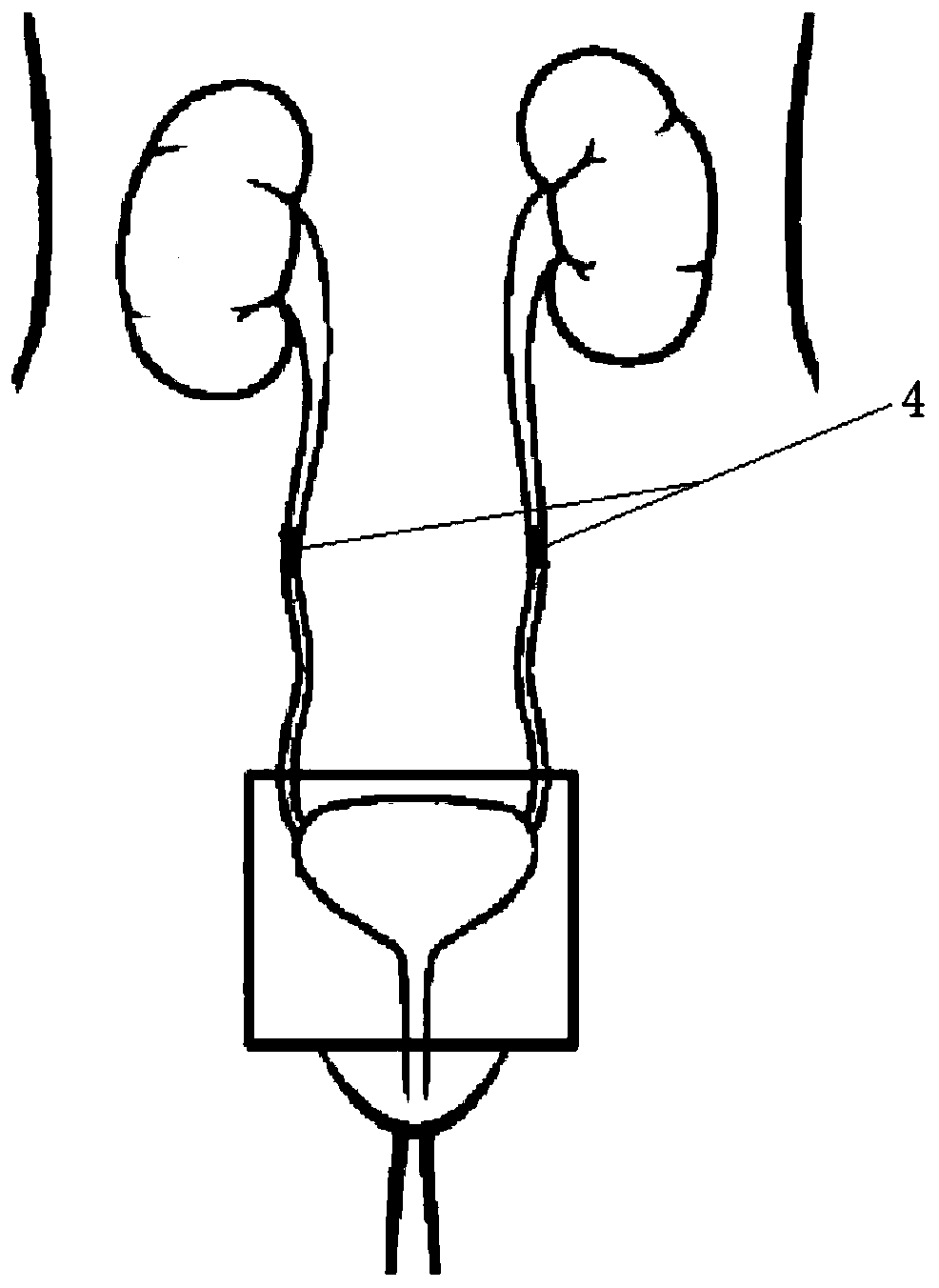
ActiveCN111298291AEnhance conduction functionIncrease bladder pressureElectrotherapySensorsUlnar digital nerveSphincter
The invention discloses an independent urination assistant device and method. By adopting a mode of combining 16-channel electrodes and a plurality of lead electrodes, the device is used for performing target stimulation on T12-L2 of the spinal cord and S2-S3 of spinal sacral nerves, working an electric stimulation signal on corresponding areas of the spinal cord and related sacral nerves to adjust synergistic effect of detrusor-sphincter, so that the intravesical pressure is increased to promote urination when the urine in the urinary bladder reaches a certain amount, and an assisted treatment function on frequent micturition and urinary incontinence can be achieved, and the uplink conduction function of the stimulation signal can be improved to a certain extent; and the device can be used for metering the urine amount in the urinary bladder through an implanted flowmeter and reminding patients to urinate at a proper time according to analysis on the urination amount and preset different thresholds, and discards a monitor mode of directly setting external parameters, thus being humanized and smart.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
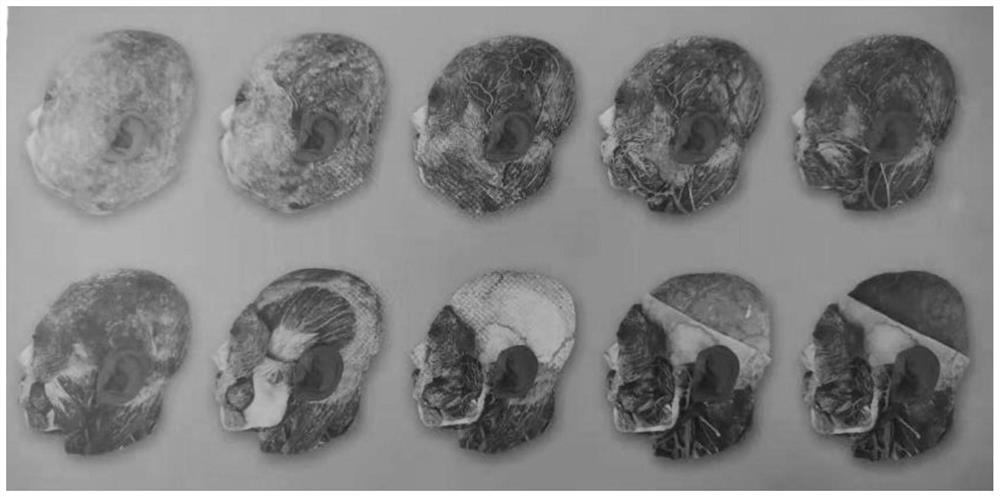
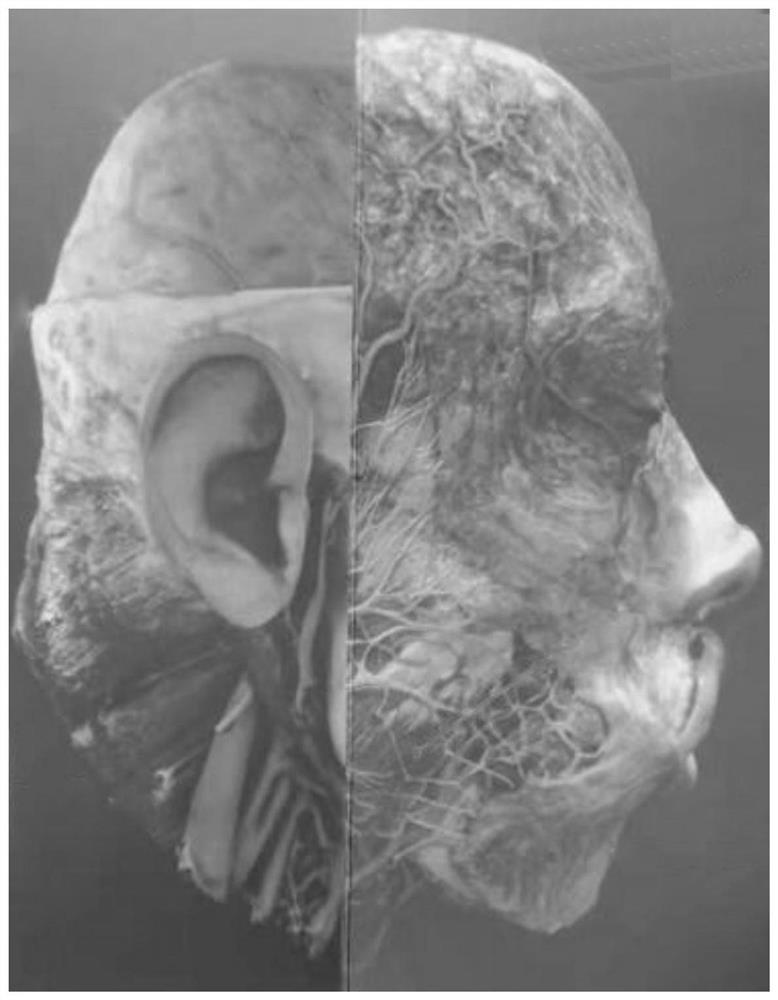
Head hierarchical dissection three-dimensional scanning specimen manufacturing method
PendingCN113628517AEasy to compare and learnConserve anatomical materialsEducational modelsDura mater encephaliRectus muscle
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a head hierarchical dissection three-dimensional scanning specimen. The method comprises the following steps: selecting materials; sequentially removing skin, superficial fascia, latissimus jugular muscle, parotid gland, superficial vascular nerve, cap aponeurosis, masseter, periosteum and temporal muscle, opening zygomatic arch and mandible, removing sternoclavicular mastoid muscle, parietal bone of cranial top, frontal bone, temporal bone and occipital bone, cutting to open superior sagittal sinus, removing dura mater, brain, mandible, zygomatic major muscle, zygomatic minor muscle, orbiculus oculi muscle, trapezius muscle, capsid muscle, diabdominal muscle, deorbital horn muscle cheekbone, endocranium, and veins, removing styloid process tongue bone muscles, external rectus, arteries, styloid process pharynx muscles and styloid process tongue muscles, removing auricles, opening temporal bones, and performing median sagittal incision; then, trimming and cleaning the dissected specimen, and pasting specimen muscles, blood vessels and nerves to the original corresponding positions; and finally, combining and processing the 3D scanned images into a complete digital 3D model, so that the scanned specimen is complete in shape and structure, free switching can be realized, and observation and learning are facilitated.
Owner:河南中博科技有限公司
Intervertebral cage which is expandable in steps and implantation instrument therefor
InactiveCN106714737AIncrease the cross sectionLow costSpinal implantsSpinal columnUlnar digital nerve
Owner:FACET LINK
Nerve retractor tool
PendingUS20210228196A1So as not to damageSafer procedureSurgical instrument supportAnatomical structuresUlnar digital nerve
Owner:SNJ PATENTS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com