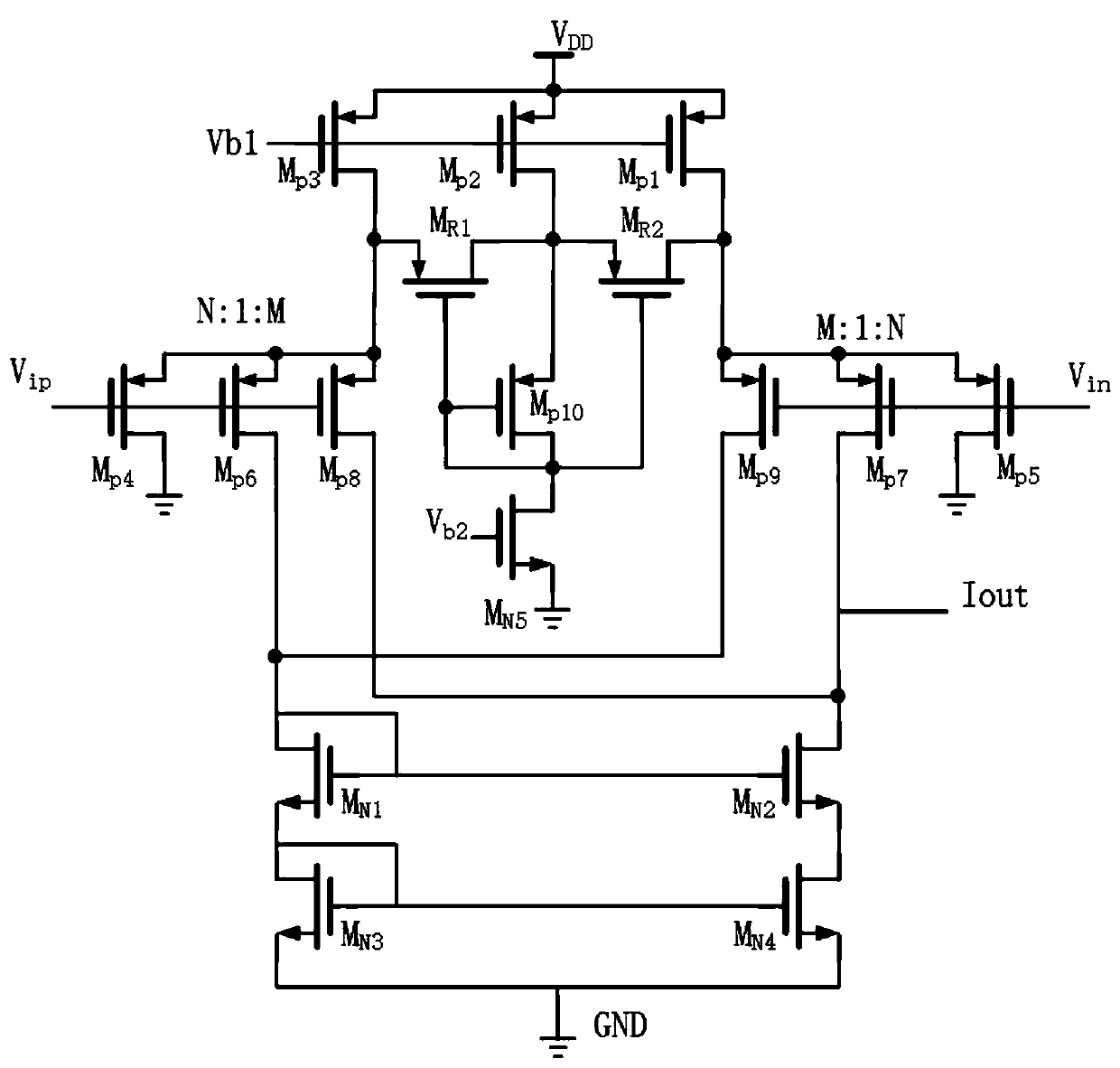
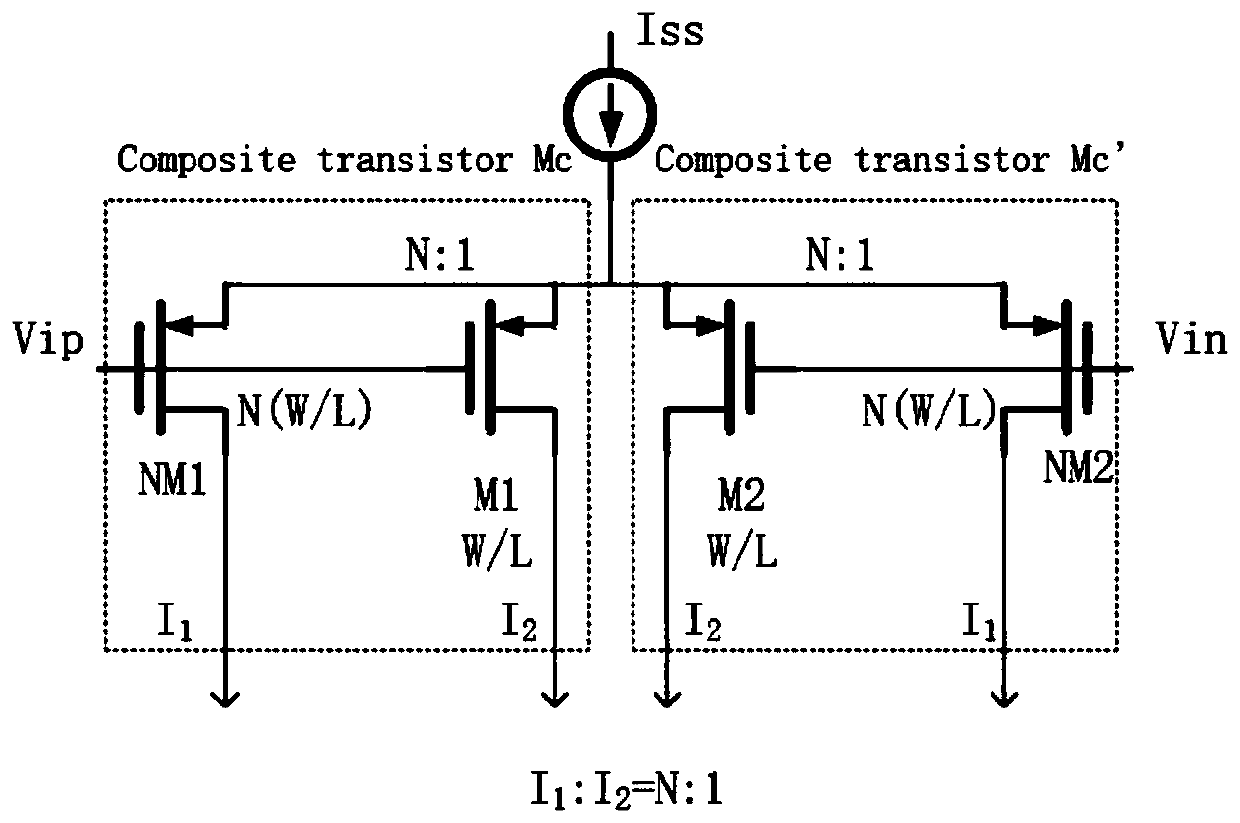
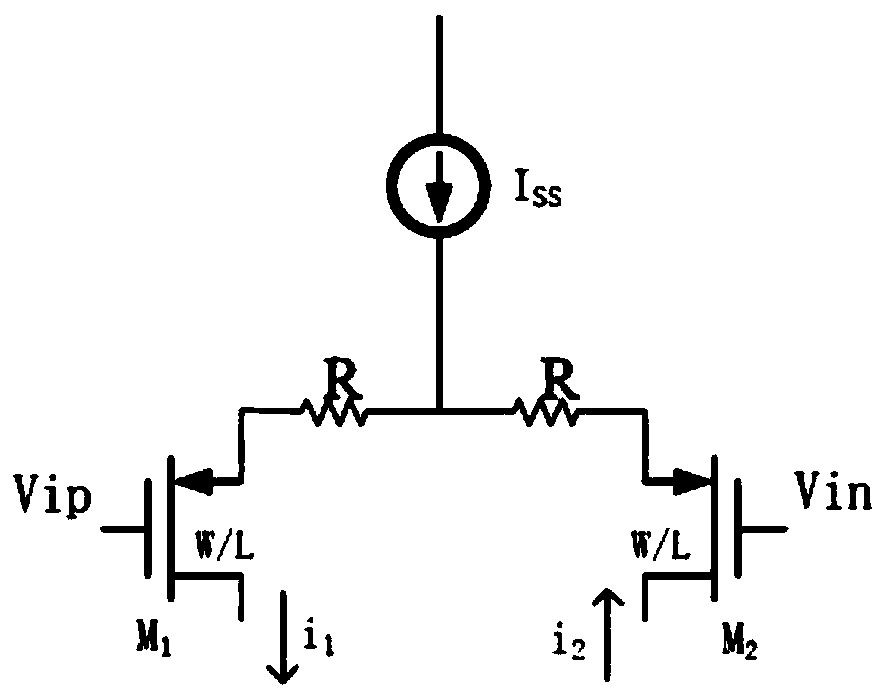
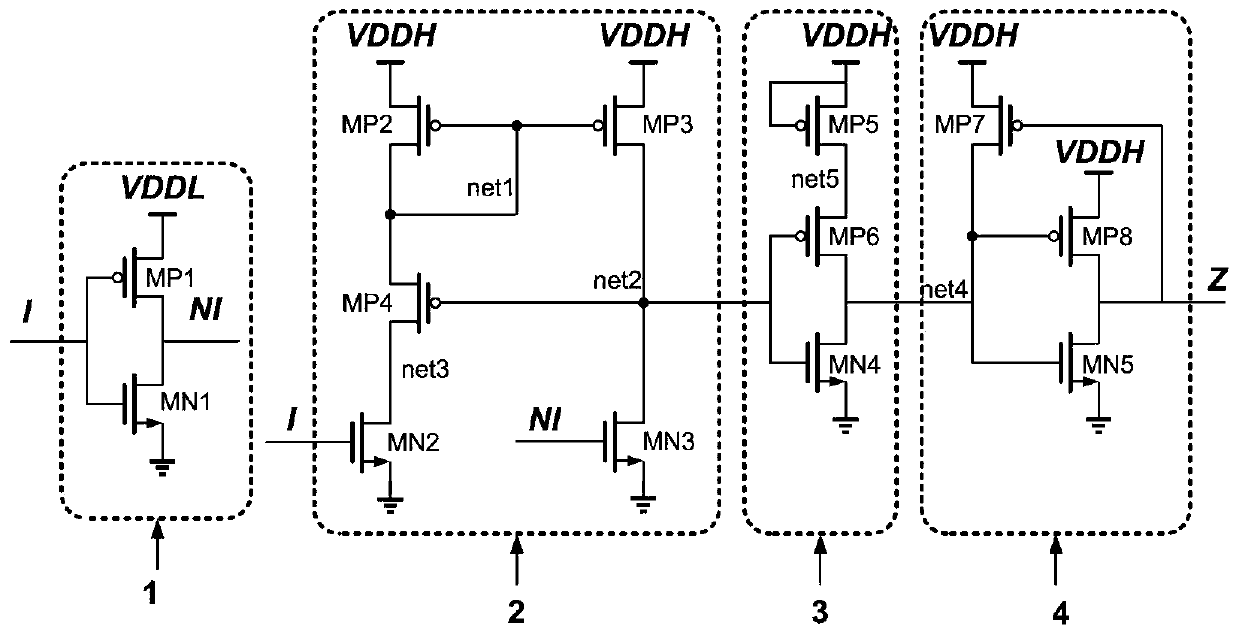
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Wilson current mirror" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
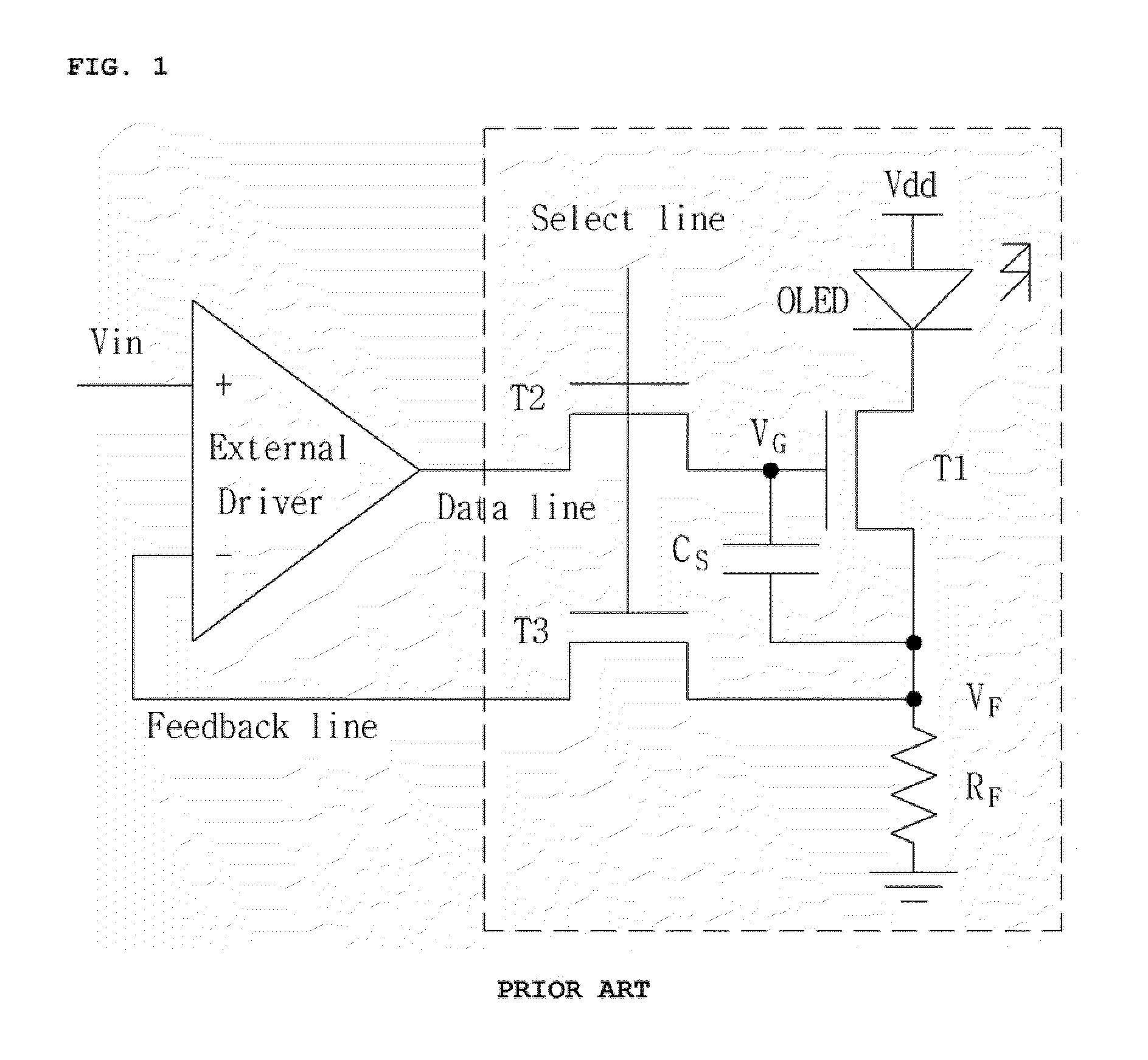
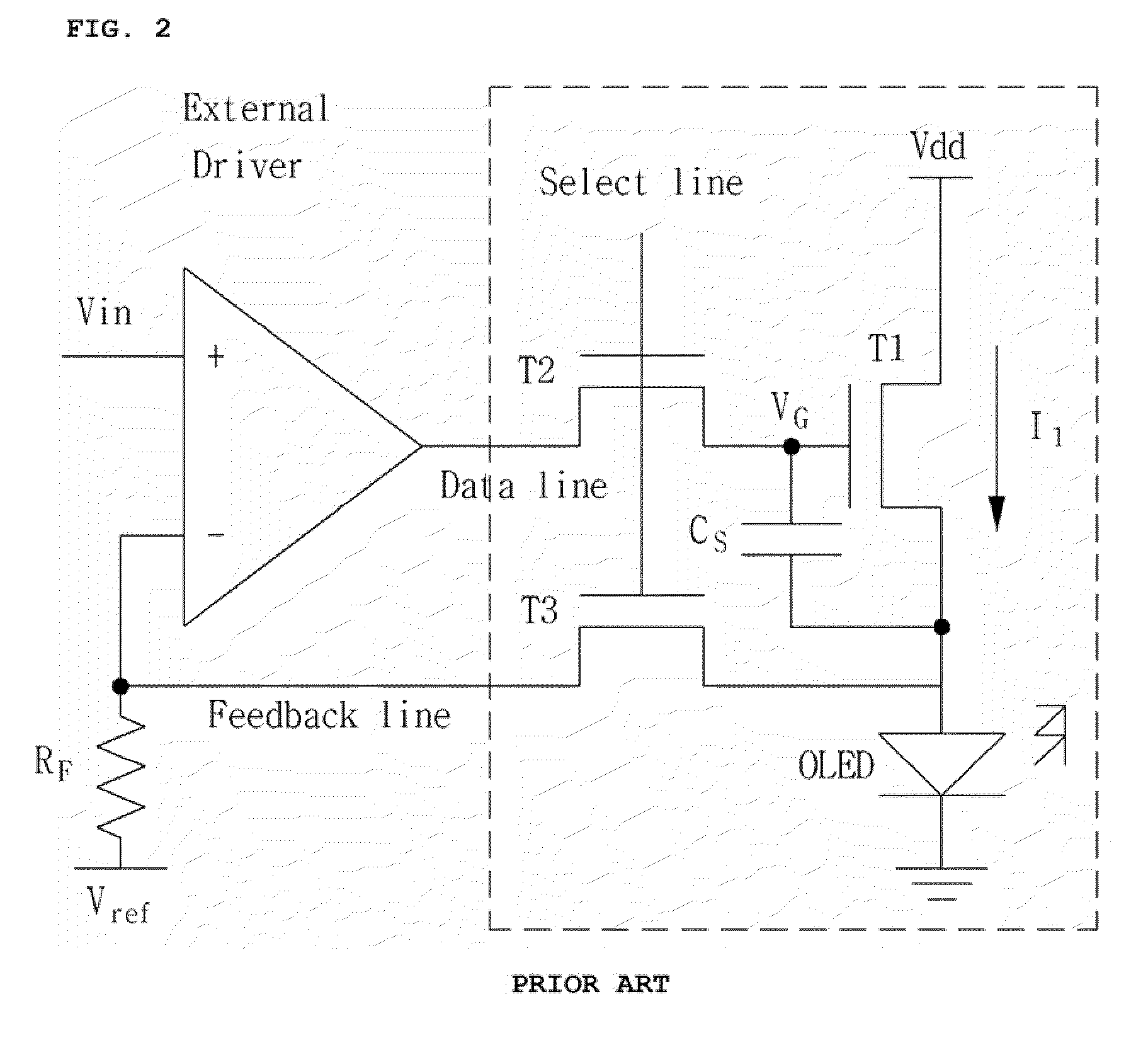
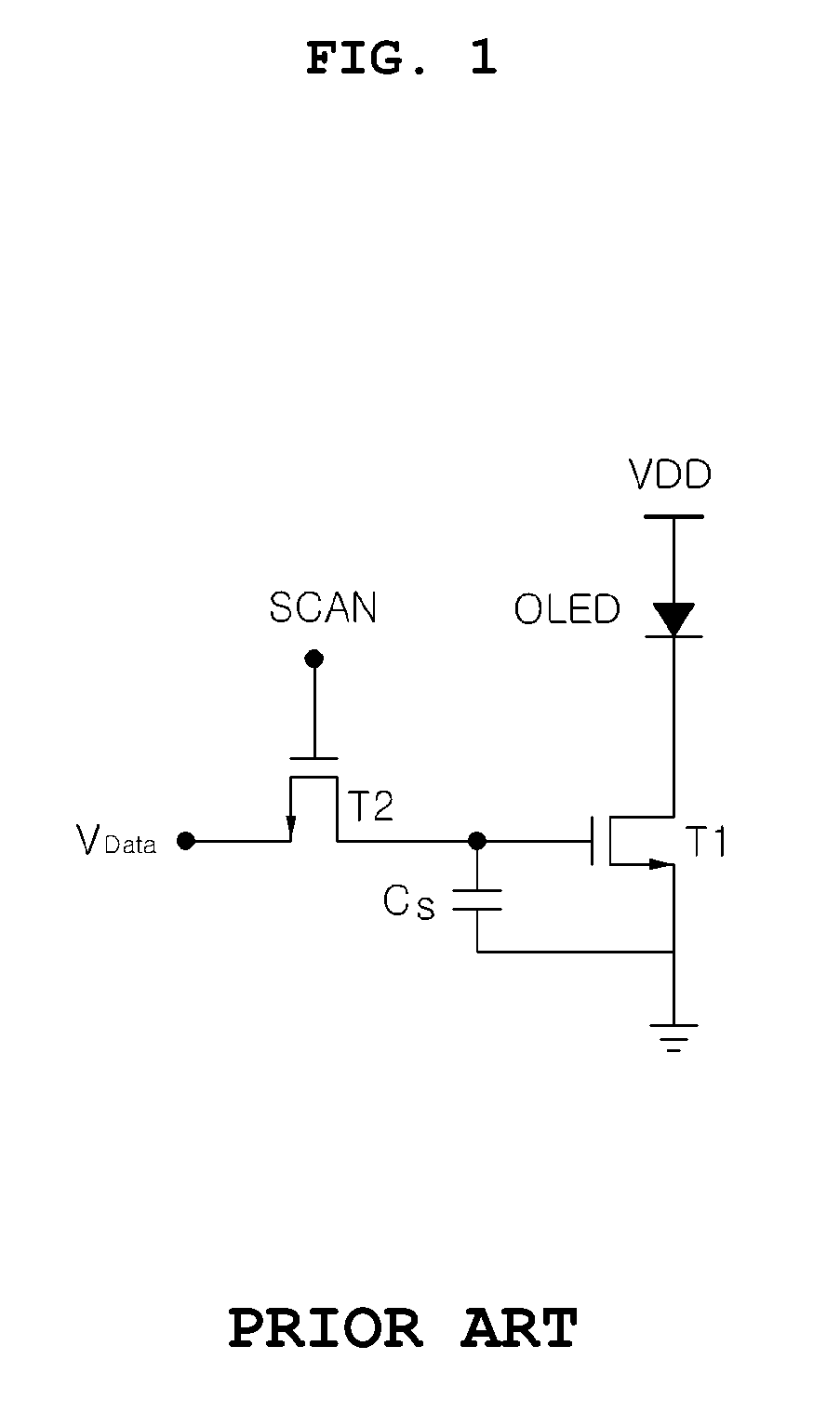
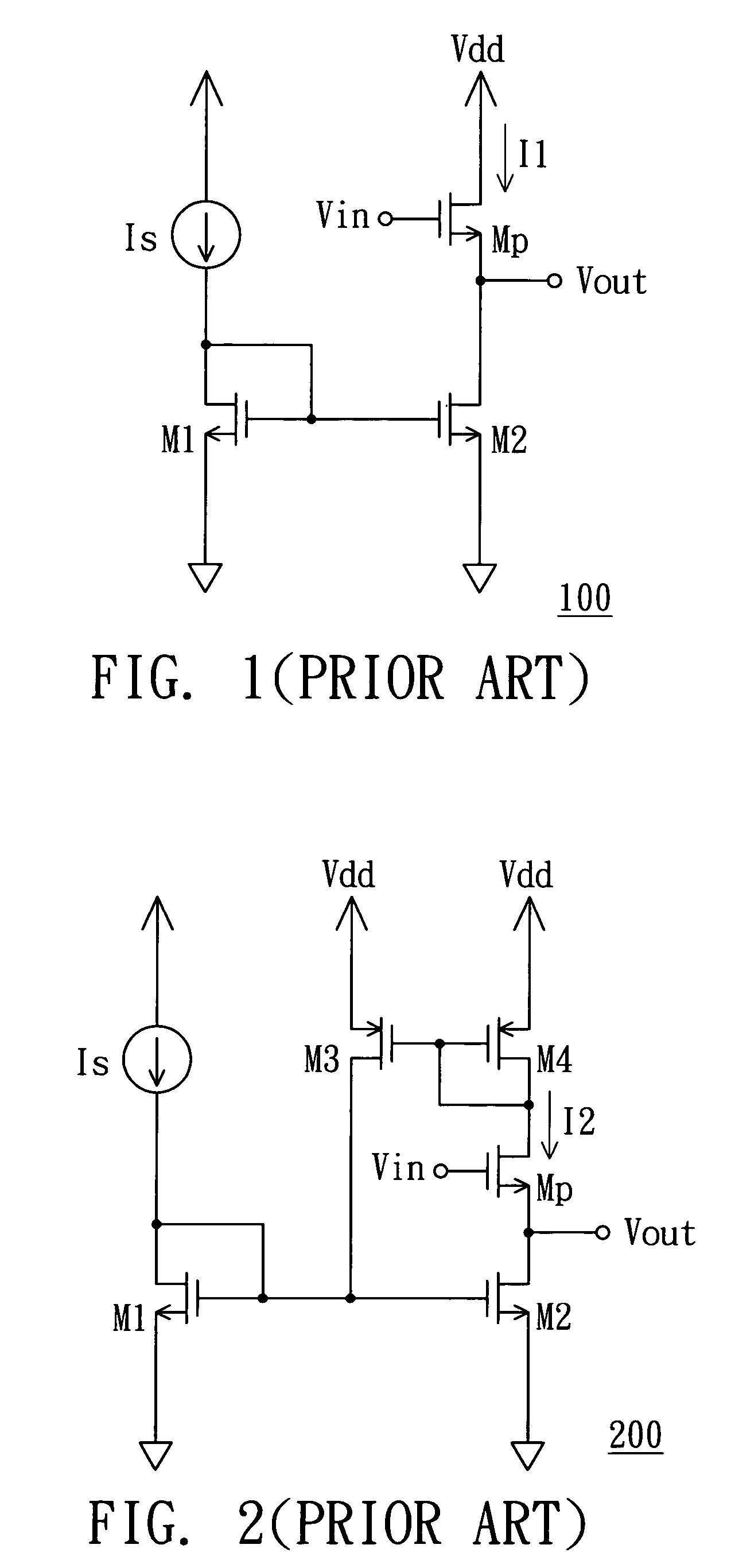
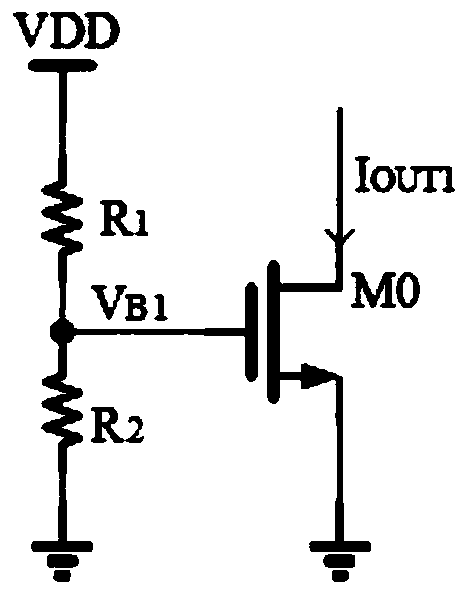
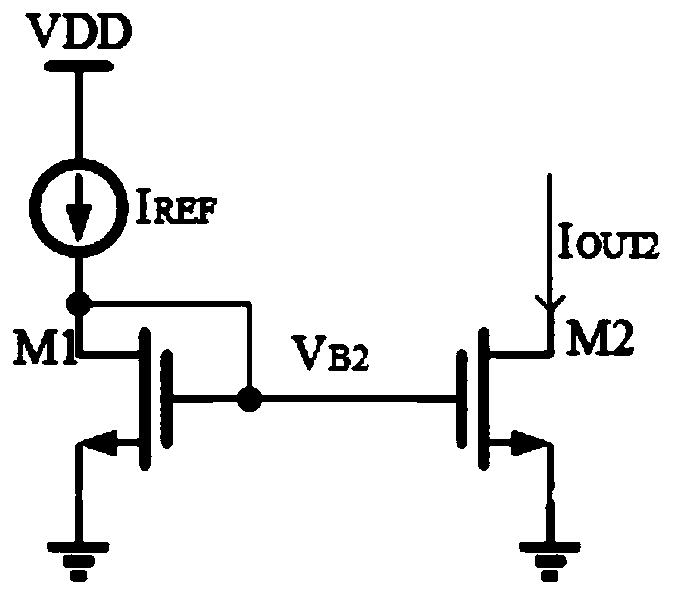
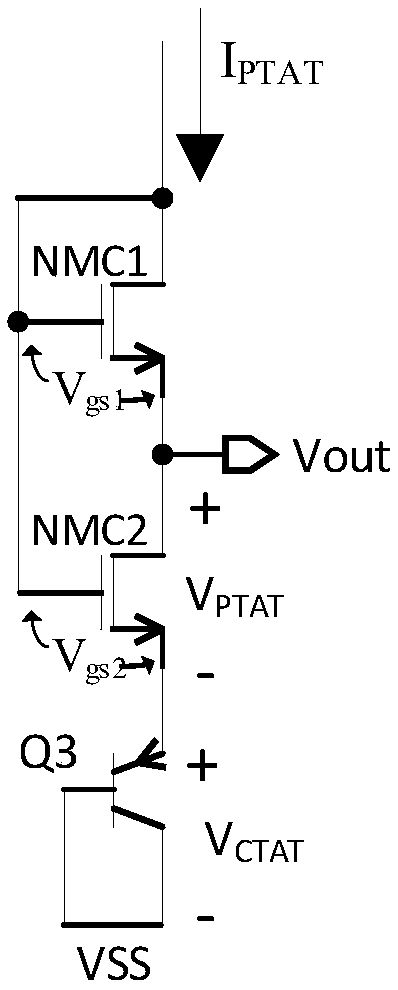
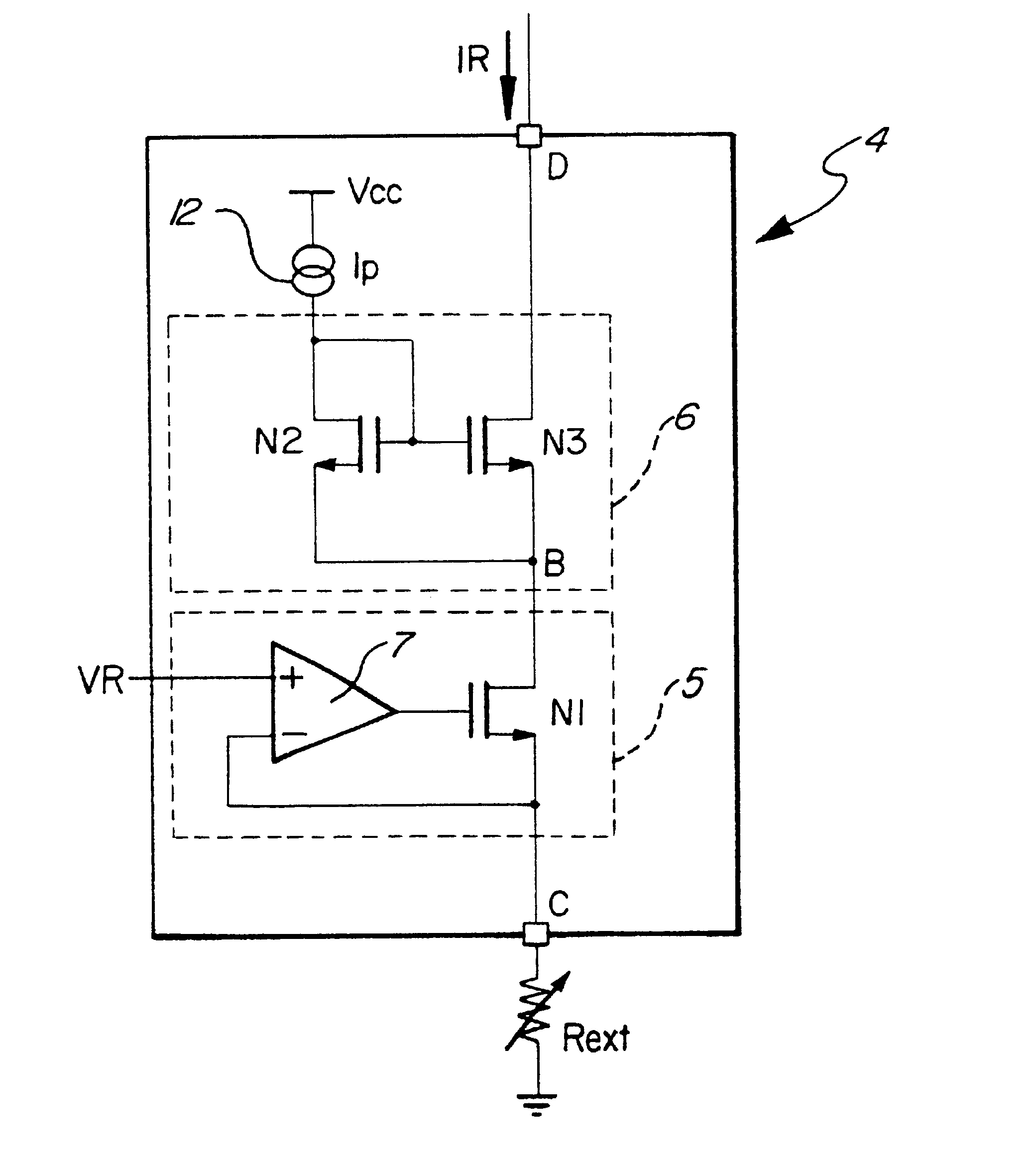
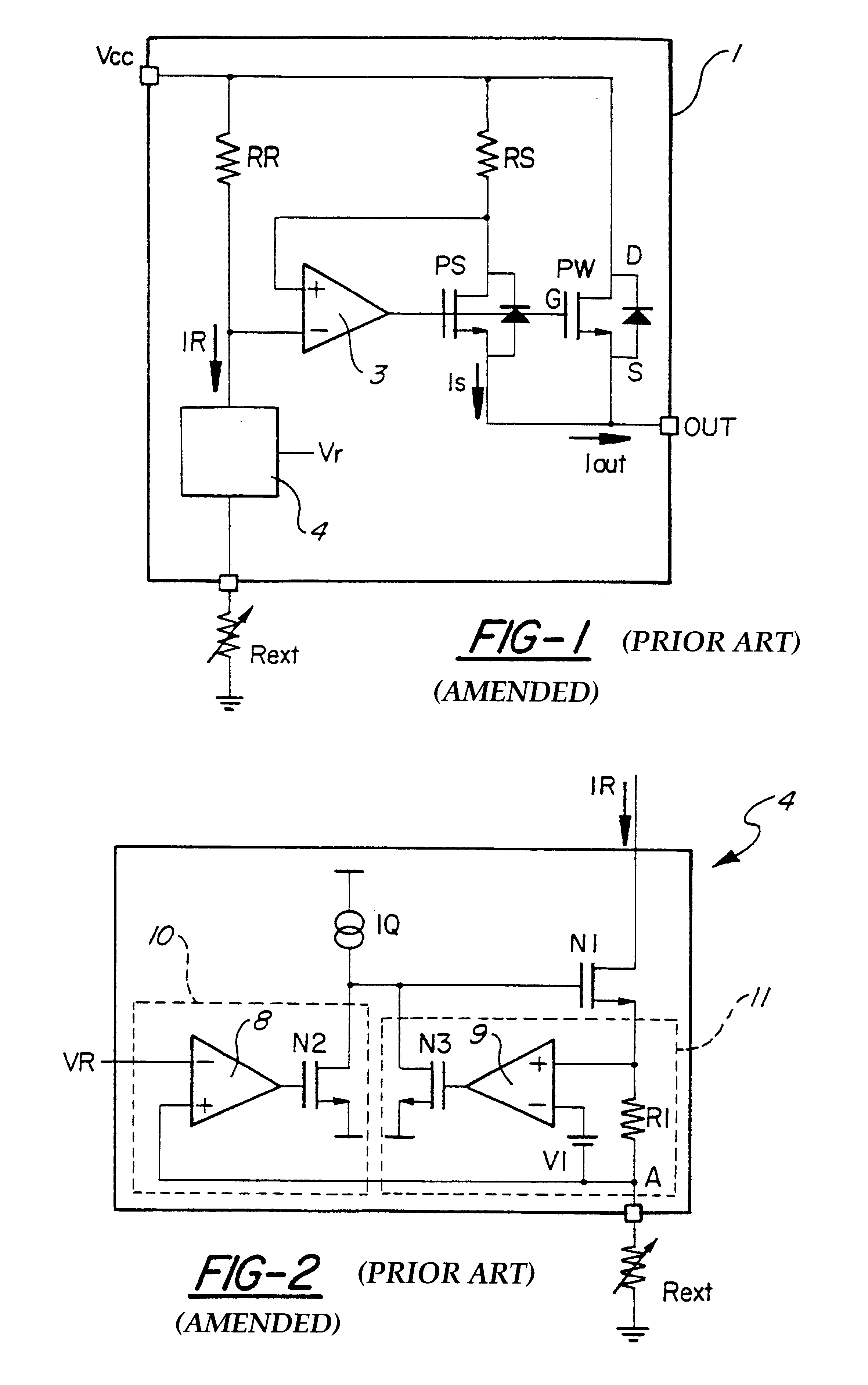
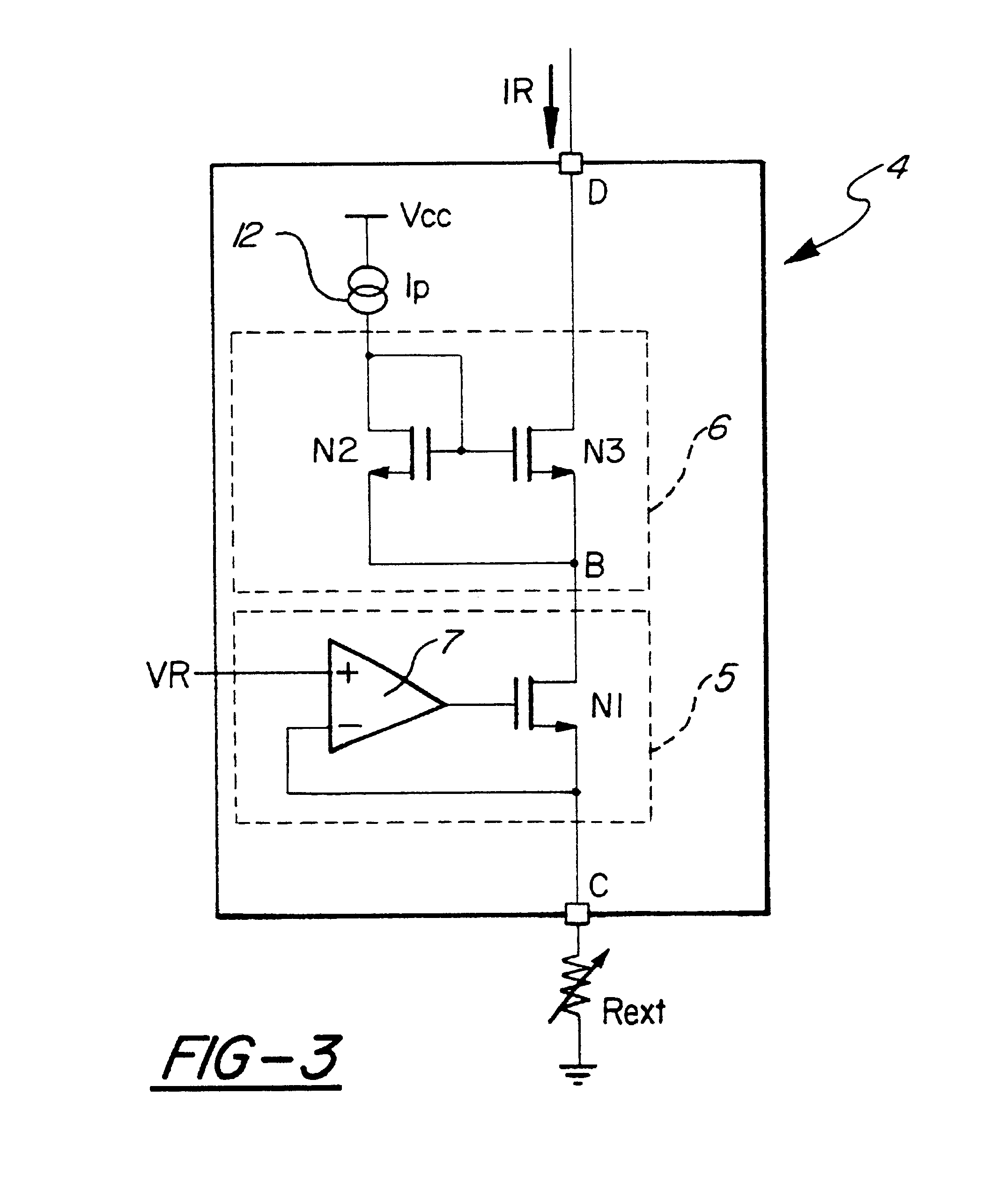
A Wilson current mirror is a three-terminal circuit (Fig. 1) that accepts an input current at the input terminal and provides a "mirrored" current source or sink output at the output terminal. The mirrored current is a precise copy of the input current. It may be used as a Wilson current source by applying a constant bias current to the input branch as in Fig. 2. The circuit is named after George R. Wilson, an integrated circuit design engineer who worked for Tektronix. Wilson devised this configuration in 1967 when he and Barrie Gilbert challenged each other to find an improved current mirror overnight that would use only three transistors. Wilson won the challenge.
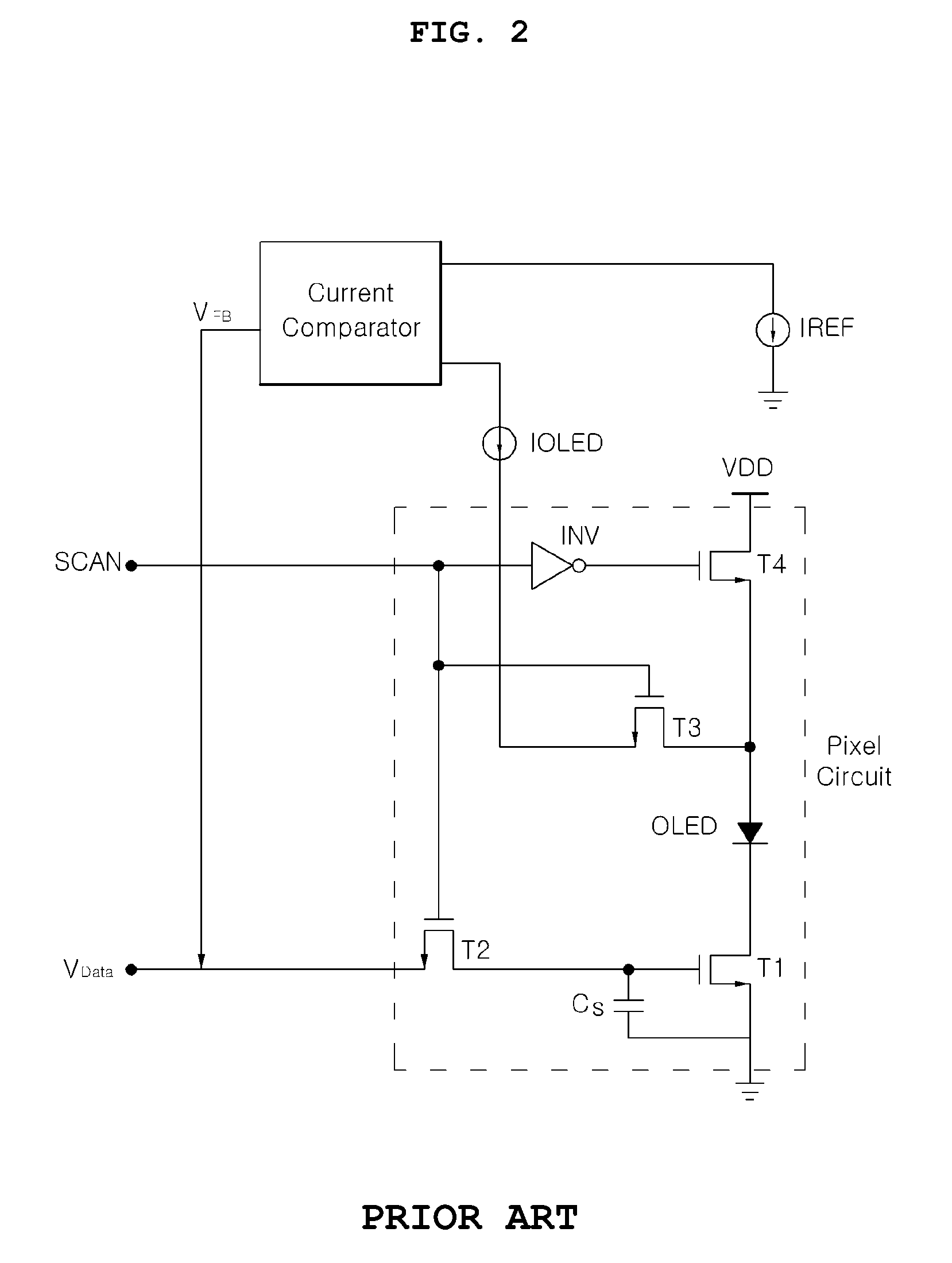
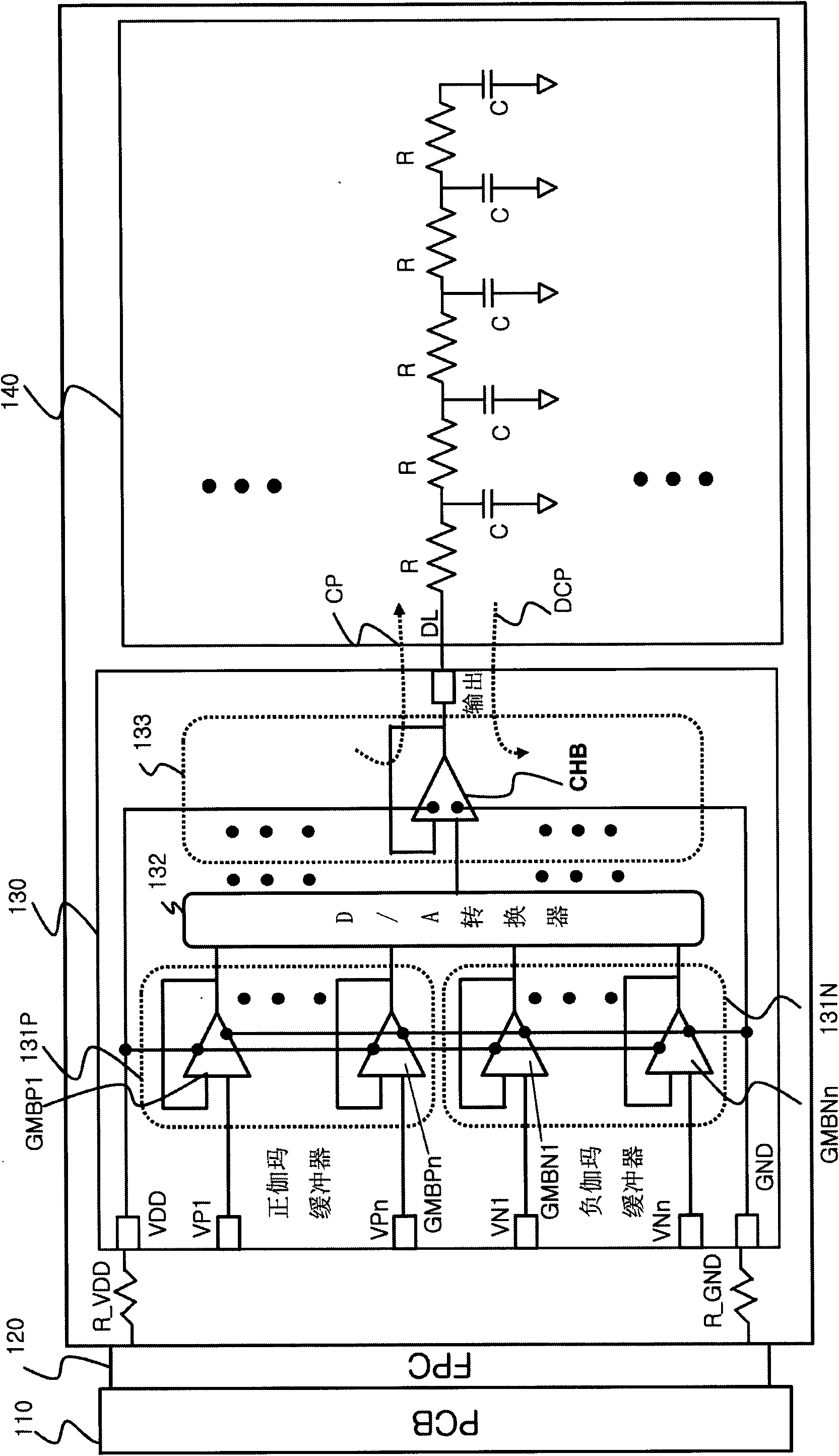
Display driving apparatus
InactiveUS20100097360A1Chip area be minimizedMinimize delaySolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsWilson current mirrorCharge current
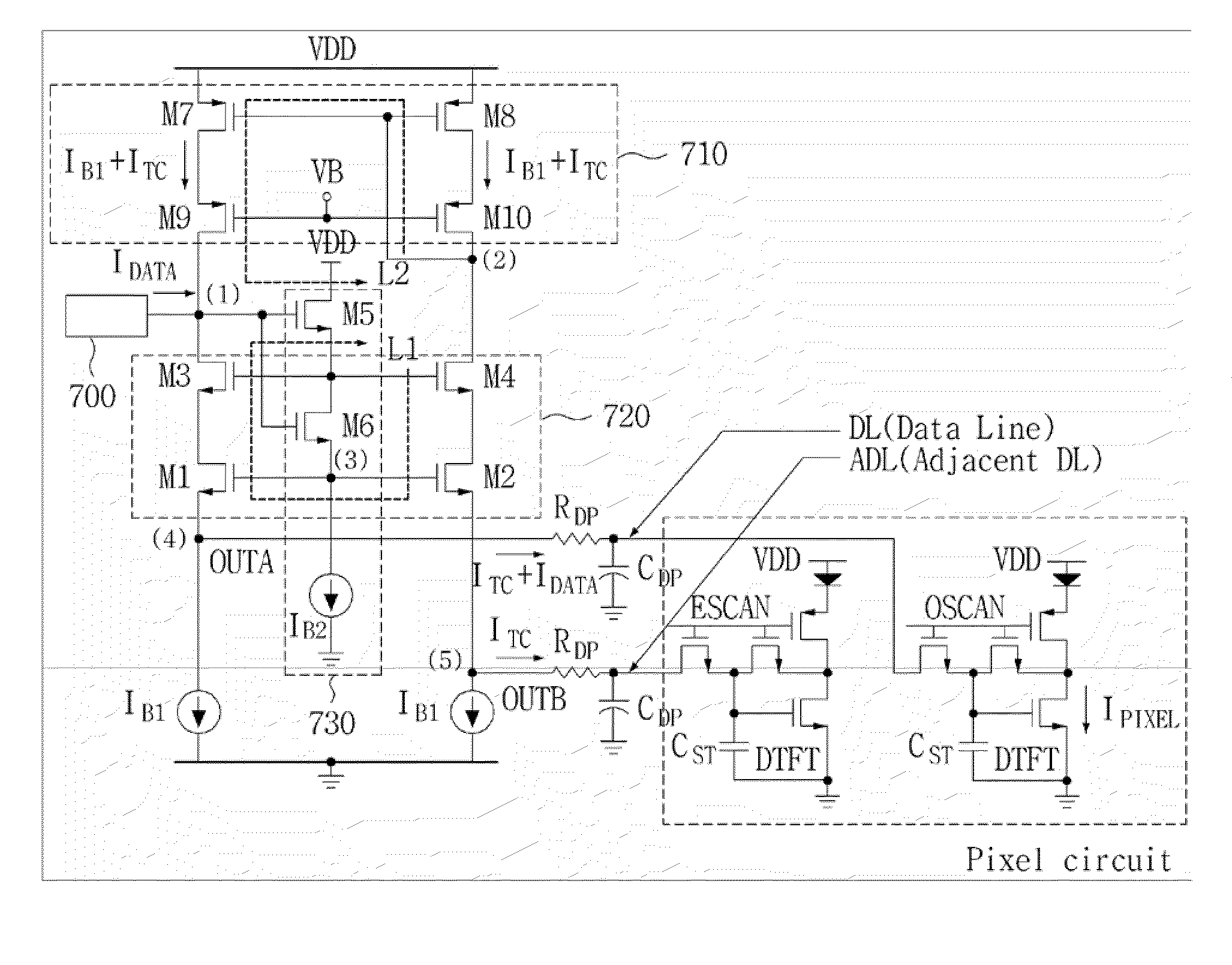
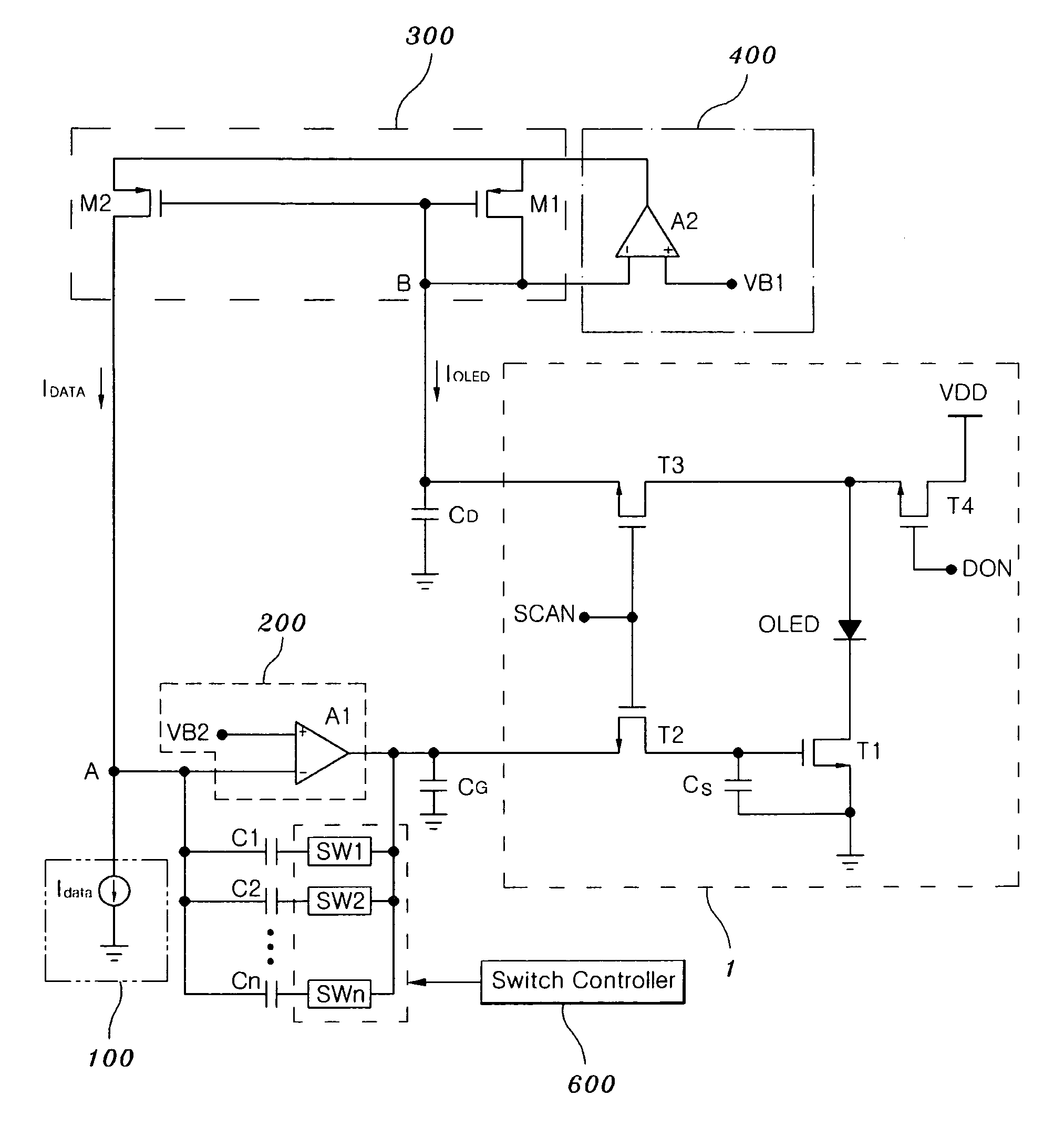
Disclosed is a display driving apparatus. The display driving apparatus comprises: a current DAC generating a data current; a data line connected to a pixel circuit requiring data writing on a matrix array of a display panel; an adjacent data line located adjacent to the data line; a current mirror feedbacking an excessive charging current generating due to parasitic capacitance of the adjacent data line as a charging current for charging parasitic capacitance of the data line; a current output unit connected to the current mirror and including a first driving transistor unit for driving the data line, and a second driving transistor unit for driving the adjacent data line; a source follower driving the current output unit according to an output node voltage of the current DAC; and a first constant current source discharging parasitic capacitance excessively charged in the data line and the adjacent data line.
Owner:SILICON WORKS CO LTD
Analog counting circuit used for single photon detector
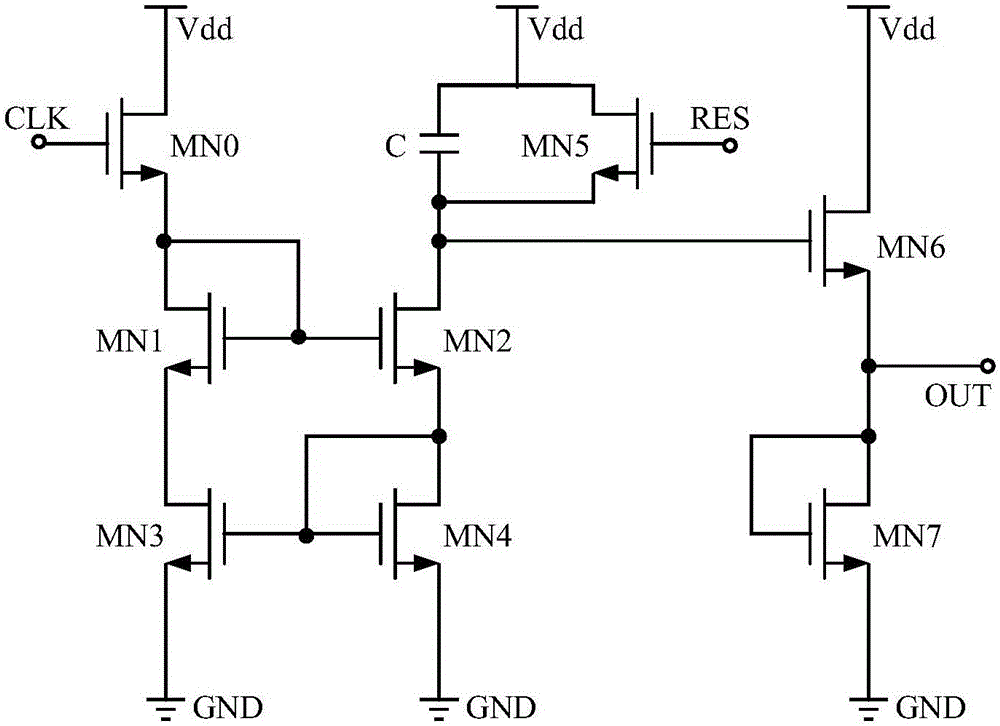
The invention discloses a linear analog counting circuit based on capacitor discharging. The circuit is constituted by a counting capacitor C and eight NMOS tubes. The eight NMOS tubes comprise an MN0, an MN1, an MN2, an MN3, an MN4, an MN5, an MN6, and an MN7. The MN0 is a signal input switch, and the MN1, the MN2, the MN3, and the MN4 are used to form an improved Wilson current mirror. The MN5 is a reset switch, and an MOS tube MN 6 and an MOS tube MN7 are used to form a voltage following circuit, which is used as the output stage of the circuit, and the output stage of the circuit is used to output the final counting results of the counting capacitor. The counting circuit has advantages of small circuit area, high filling coefficient, high linearity, large counting range, and applicability in counting of number of photons of high-density, full-integration, and low-cost SPAD array detector.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Active matrix OLED driving circuit using current feedback
InactiveUS7876292B2Ensure brightness uniformityDifferenceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDigital dataWilson current mirror
An active matrix organic light emitting diode AMOLED driving circuit using current feedback that ensures the uniformity of brightness in pixels of a flat panel display and shortens the time required to input accurate current to respective pixels in the driving circuit.The prevent invention provides an AMOLED driving circuit using current feedback, comprising: a current digital-to-analog converter outputting a current corresponding to input digital data; a first differential amplifier connected to the current digital-to-analog converter and controlling the input data current and a driving current of a driving transistor of a pixel circuit to be identical to each other; a current mirror mirroring driving current of an organic light emitting diode of the pixel circuit to an input side of the first differential amplifier; and a second differential amplifier coupled to the current mirror and controlling charge and discharge speeds of parasitic capacitance of the pixel circuit.
Owner:IKAIST CO LTD
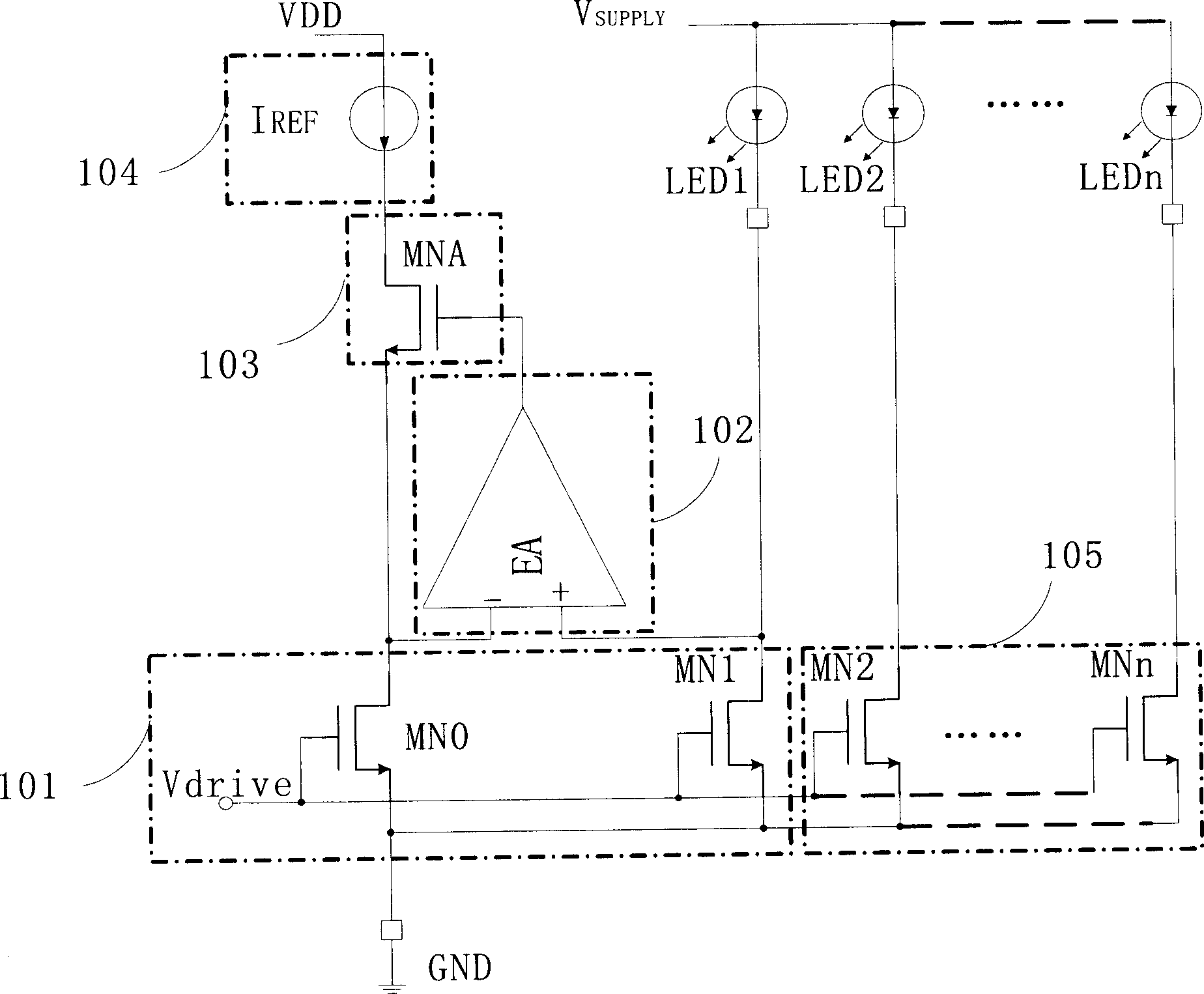
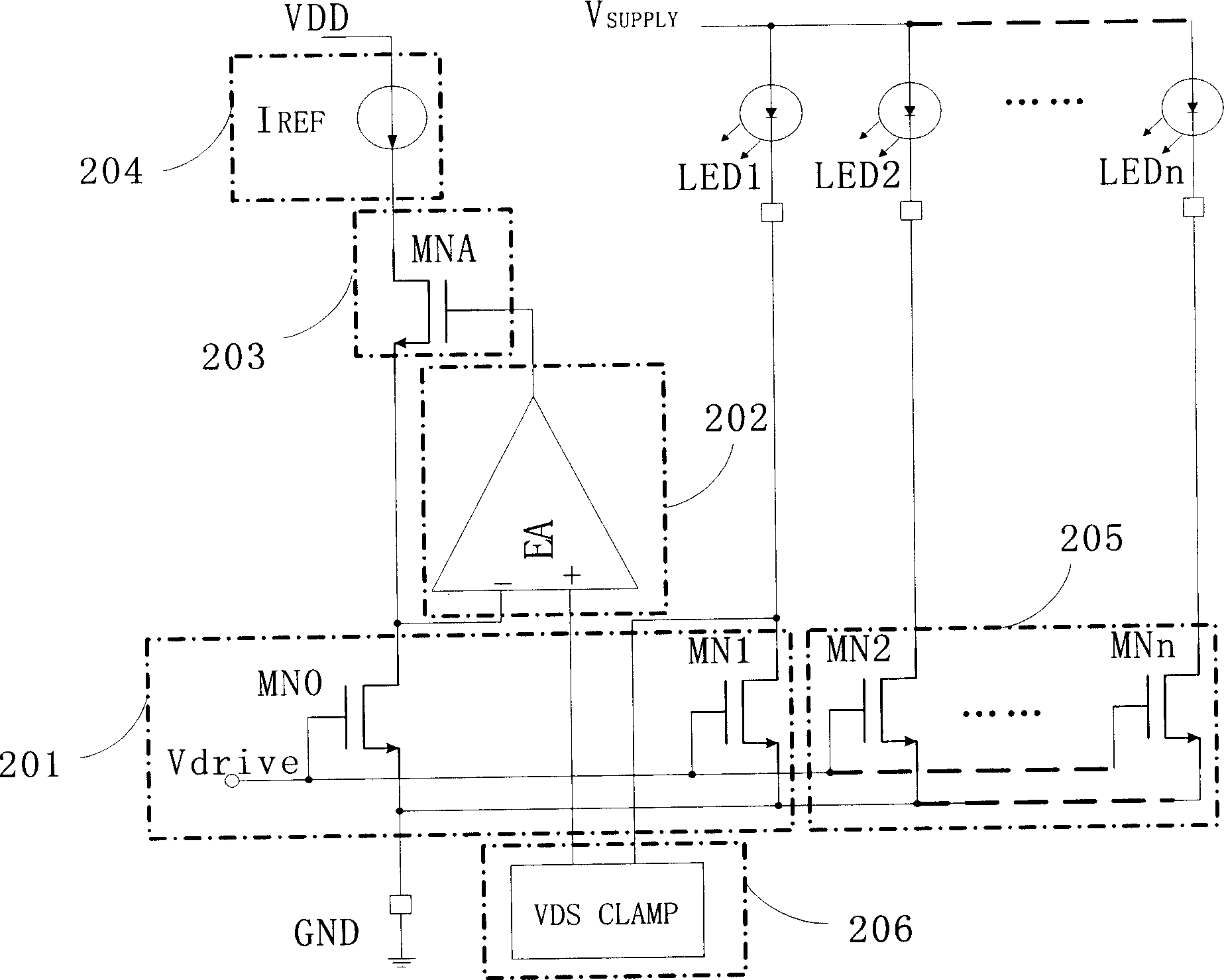
Current source circuit of multiplex parallel LED driven by one reference current
InactiveCN1913736AGood current matchingImprove work efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectric lighting sourcesWilson current mirrorReference current
A current source circuit for the multi-parallel circuited LED driven by a single reference current including: a current mirror, a error amplifier, a regulator tube, a reference current, other multi-driving tubes and VDS clamp circuit. The characteristic is that: the VDS clamp circuit respectively connects with the drain-leakage end of the MN1 and the input of the error amplifier. The current mirror and the grid terminals of other multi-driving tubes are driven by a common Vdrive signal. During the normal working hours, the MN0 and MN1 drain-leakage end voltages of the MOS tube keep consistent under the effects of the error amplifier and the regulator tubes, the other driving tubes and MN1 can obtain a good current-matching even there is a small difference between the drain-leakage end voltages. During the abnormal working hours, the VDS clamp circuit can provide an appropriate bias voltage to make sure that the other driving tubes do not guide a high current and keep the LED in a normal state regardless of the leakage of MN1.
Owner:CHIPHOMER TECH SHANGHAI
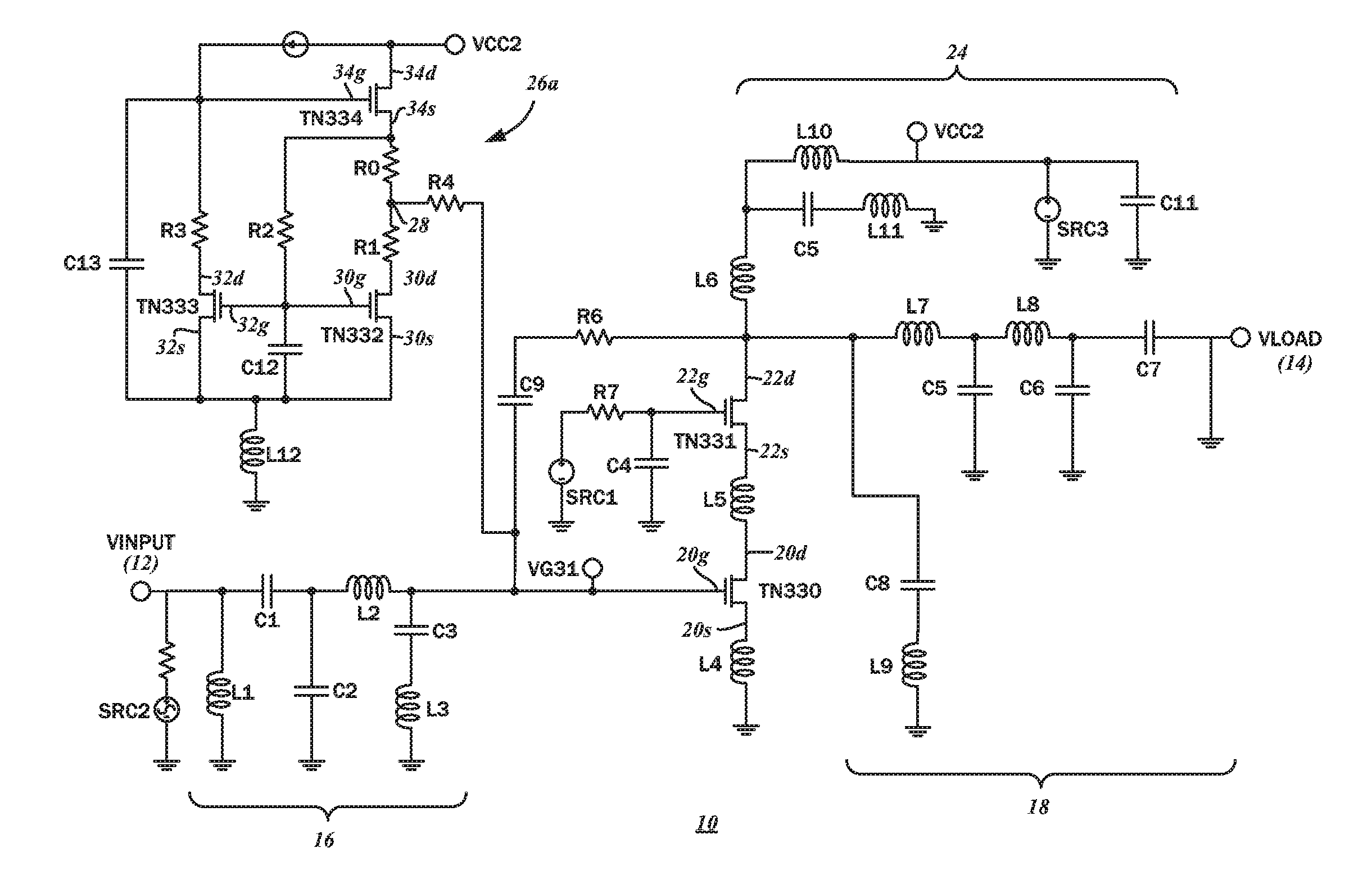
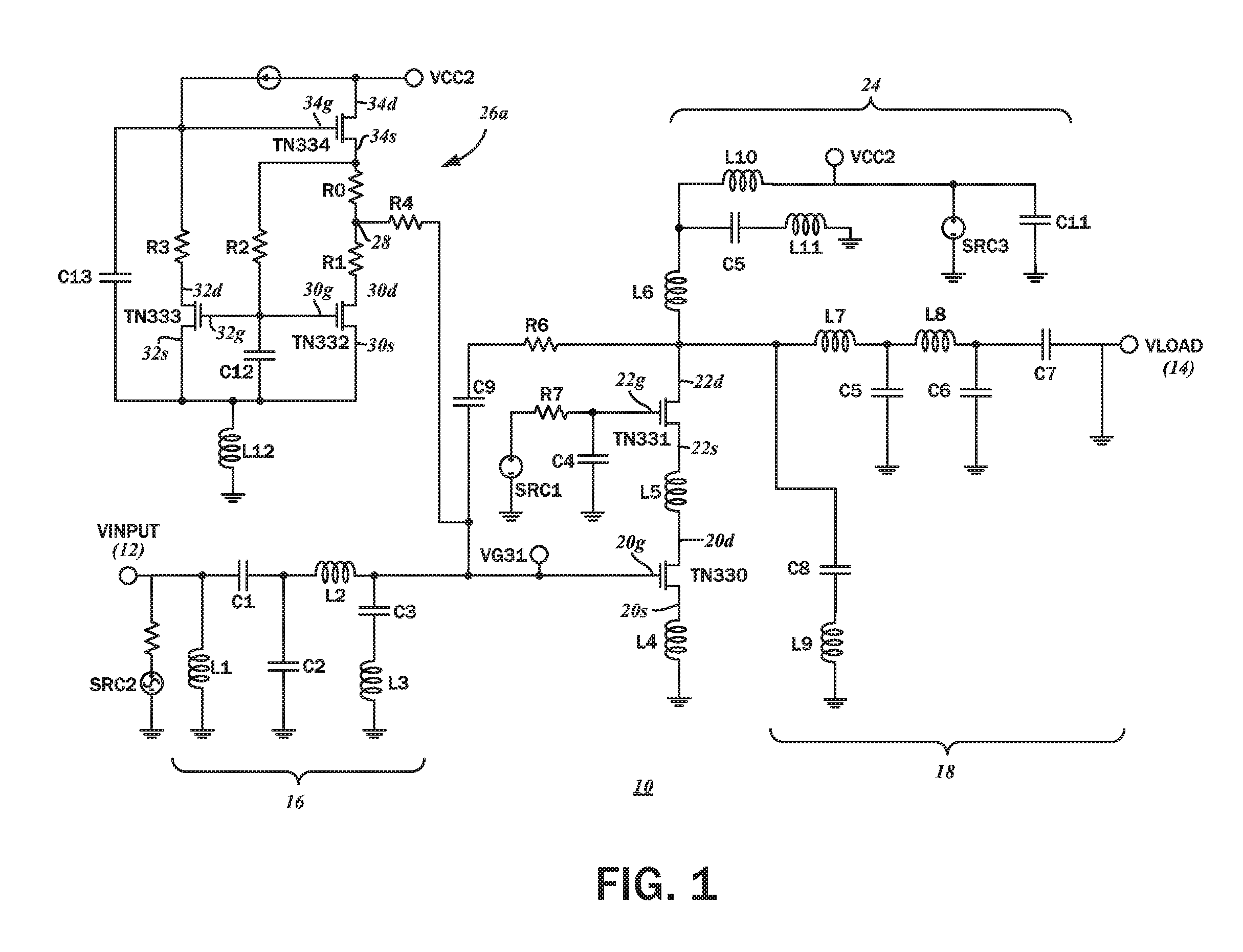
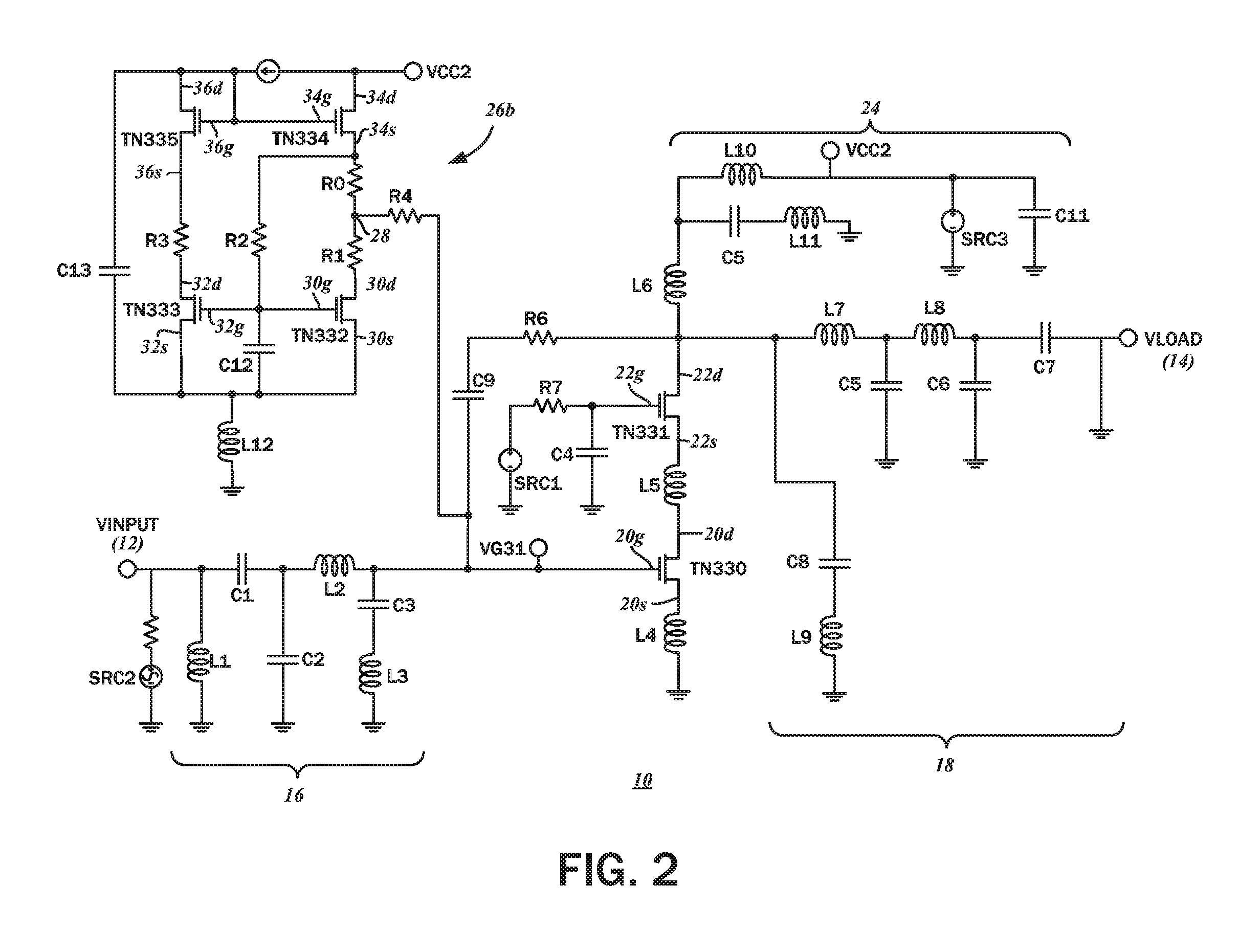
Bias-boosting circuit with a modified wilson current mirror circuit for radio frequency power amplifiers
InactiveUS20160308500A1Increase pointsReduced semiconductor die footprintAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierWilson current mirror
A current mirror circuit for biasing a power amplifier includes a modified Wilson current mirror with a pair of first and second mirror transistors connected to a third transistor. The first mirror transistor is configured for operating in a saturation mode, with a gate voltage of the first mirror transistor being lower than a gate voltage of the power amplifier. The third transistor charges the power amplifier circuit during a positive half cycle of an input signal and the first mirror transistor discharges the power amplifier circuit during a negative half cycle of the input signal at different rates.
Owner:MORFIS SEMICON
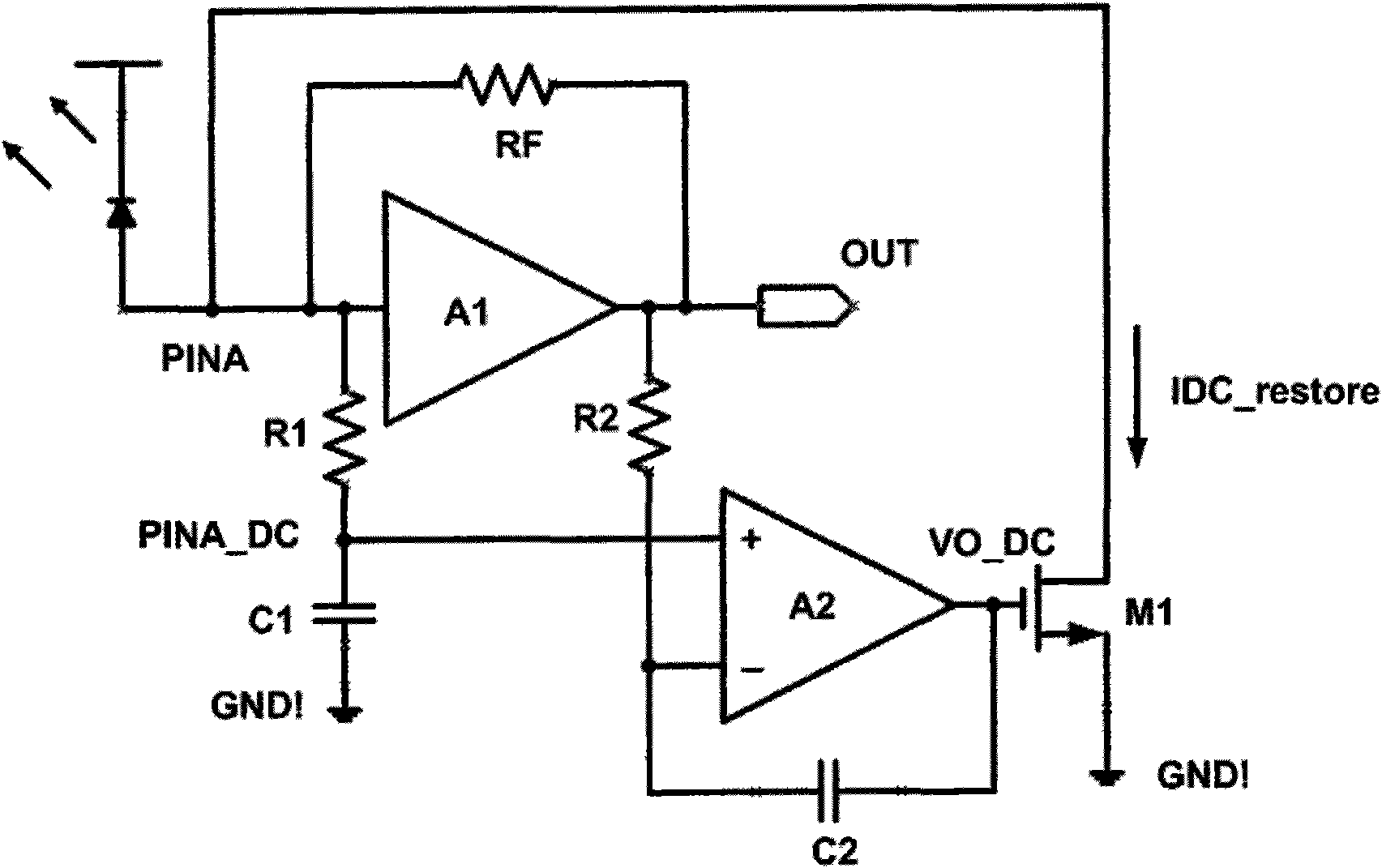
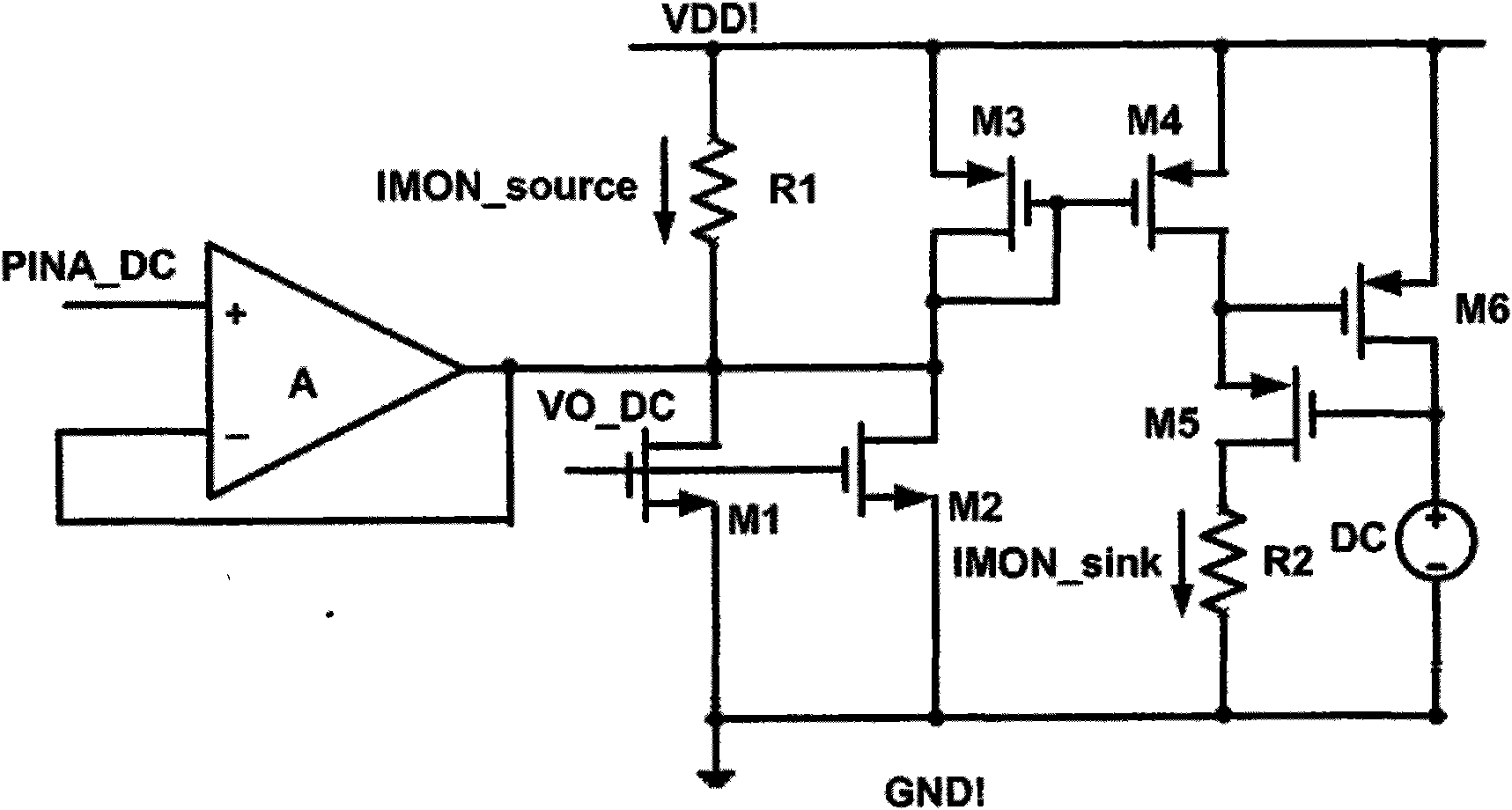
Direct-current (DC) restoration and DC monitoring circuit
InactiveCN101621252AReduce gainAmplify the impactDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationIntegratorWilson current mirror
The invention relates to a direct-current (DC) restoration and DC monitoring circuit comprising a transimpedance amplifier, a DC restoration circuit and a DC monitoring circuit. The transimpedance amplifier is connected with the DC restoration circuit and the DC monitoring circuit, and the integrator theory is applied to the DC restoration circuit and the DC monitoring circuit. The gain of an integrator at a low-frequency stage can achieve the open loop gain of an operational amplifier and ensures an input DC current to completely flow through the DC restoration circuit but not flow through the transimpedance amplifier; the gain of the integrator is extremely low at a high-frequency stage and can not generate great influence on signal amplification. A Wilson current mirror is applied to copy a monitoring current and ensures that the error of the copied current is smaller than 2 per thousand, in addition, the output of the monitoring current can be a current sink or a power supply.
Owner:TIANJIN VAST TECH
Source driver circuit of liquid crystal display device
InactiveCN102110425AShorten recovery timeStatic indicating devicesAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceDriver circuitWilson current mirror
A source driver circuit of a liquid crystal display device including a gamma buffer. The gamma buffer includes a differential amplification section configured to differentially amplify an input signal; a current mirror section configured to operate as a current mirror; an enable section configured to convert the differential amplification section from a standby mode to an enable mode by a bias voltage; a power drop speed improvement section configured to respectively connect drains of the two PMOS transistors of the current mirror section and drains of the two NMOS transistors of the differential amplification section through two diode coupling type MOS transistors, and shorten a recovery time after a power drop; and an output section configured to be determined in a bias level thereof by the bias voltage and generate an output voltage according to a voltage of a downstream node on one side of the current mirror section.
Owner:SILICON WORKS CO LTD
Subthreshold level shifter having wide input voltage range
ActiveCN105958994AReduce generationSmall power leakageLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsWilson current mirrorCoupling
The invention discloses a subthreshold level shifter having a wide input voltage range. The subthreshold level shifter comprises a Wilson current mirror and an inverter. The Wilson current mirror comprises three PMOS and two NMOS. The source electrode of the first PMOS and the source electrode of the second PMOS are connected with a high power supply voltage. The drain electrode of the first PMOS is connected with the source electrode of the third PMOS, and the drain electrode of the third PMOS is connected with the drain electrode of the first NMOS, and the source electrode of the first NMOS is grounded. The drain electrode of the second PMOS is connected with the drain electrode of the second NMOS, and the source electrode of the second NMOS is grounded. The grid of the first PMOS and the grid of the second PMOS are connected with the drain electrode of the first PMOS, and the grid of the third PMOS is connected with the drain electrode of the second PMOS. The grid of the first NMOS is used as the first input end of the Wilson current mirror, and is connected with one end of the inverter, and the grid of the second NMOS is used as the second input end of the Wilson current mirror, and is connected with the other end of the inverter. The drain electrode of the second PMOS is the output end of the Wilson current mirror, and the inverter is connected with an input level. The subthreshold level shifter is used to solve the voltage drop problem of the Wilson current mirror structure and a power consumption problem of a cross coupling structure under a subthreshold voltage.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
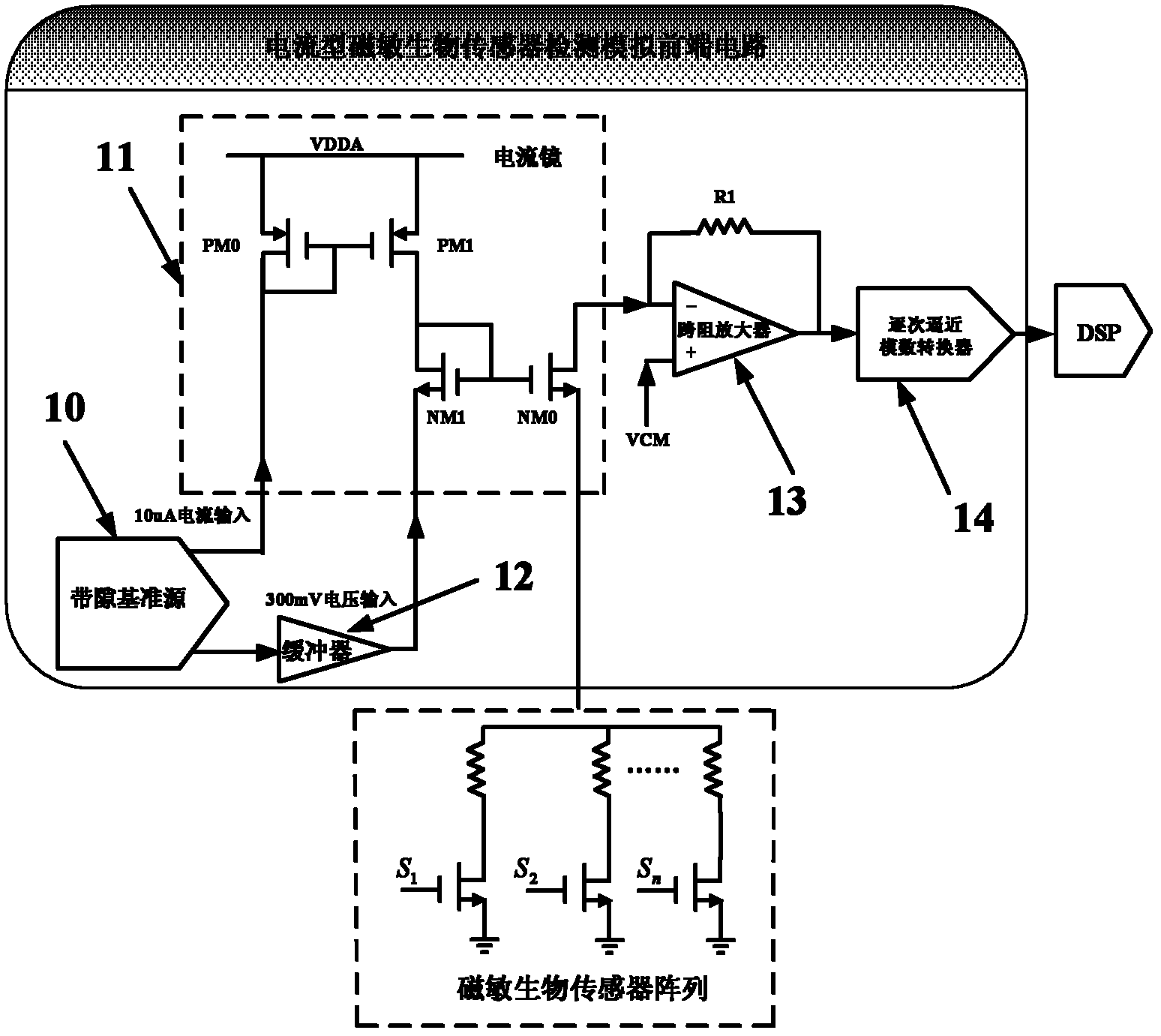
Current type signal detection analog front end circuit
ActiveCN102645451AImprove reliabilityReduce power consumptionMaterial resistanceWilson current mirrorTransimpedance amplifier
The invention discloses a current type signal detection analog front end circuit which comprises a band-gap reference source, a current mirror, a buffer, a transimpedance amplifier and a successive approximation analog-to-digital converter, wherein the band-gap reference source is used for generating 10 microamperes current required by the current mirror and providing 300 mV bias voltage, the current mirror loads the mirror image of the 300 mV bias voltage to a magnetic sensitive biosensor array and provides an output path for detection current, the buffer is used for reducing the influence of circuit vibration on the 300 mV bias voltage, the transimpedance amplifier converts the detection current into detection voltage and amplifies the detection voltage, the successive approximation analog-to-digital converter converts the detection voltage into a digital code and outputs the digital code to DSP (Digital Signal Processor), and thus the detection is finished. According to the invention, the mode of single-chip full integration and current detection is adopted, weak variation signals in magnetic sensitive biosensors are extracted effectively, the transimpedance amplifier is used for converting the detection current into the detection voltage and amplifying the detection voltage reasonably, and finally the analog-to-digital converter outputs the digital code.
Owner:SOI MICRO CO LTD
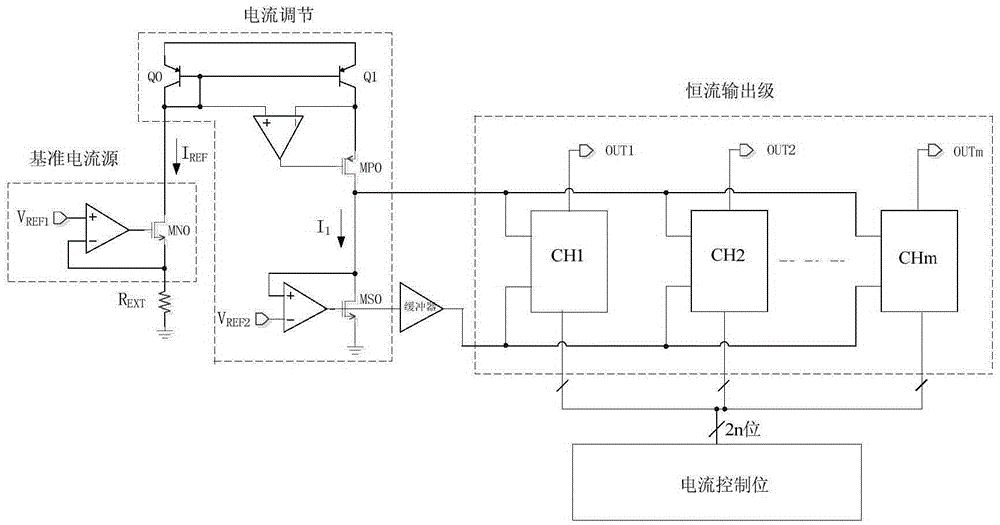
Digital adjustable constant-current driving circuit
ActiveCN105261327AEnables wide range adjustmentStatic indicating devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceWilson current mirror
The invention relates to a digital adjustable constant-current driving circuit comprising a reference current source module, a constant-current adjusting module, a buffer, a constant-current output stage module, a current control bit module, first reference voltage, second reference voltage, and an external resistor. The reference current source module is connected with the first reference voltage, the constant-current adjusting module, and the external resistor. The constant-current adjusting module is connected with the buffer and the second reference voltage. The buffer is connected with the constant-current output stage module. The constant-current output stage module is connected with the current control bit module and comprises a plurality of same constant-current output channels. The second power tubes in the constant-current output channels are divided into a plurality of groups. The connection and disconnection of each group is controlled by a current bit. The number of connected power tubes is changed by an external write current control bit and thus the mirror image proportion of a current mirror formed by a first power tube and a second power tube is adjusted. As a result, a purpose of adjusting a constant-current output value is achieved.
Owner:江阴元灵芯旷微电子技术有限公司
Current mirror with improved output impedance at low power supplies
InactiveUS20070194838A1Increases available headroomIncrease output impedanceElectric variable regulationWilson current mirrorLow voltage
A current mirror circuit arrangement is formed to maintain a high output impedance when utilized with a relatively low voltage power supply. A common mode voltage regulator circuit is utilized in conjunction with the output branch of the current mirror to eliminate the need for an additional active device in series with the output transistor of a current mirror to control its drain voltage. The elimination of the second active device thus increases the available headroom for the output branch (i.e., adds one VDS). The increased headroom in the inventive current mirror is particularly advantageous for low voltage applications, since it is capable of maintaining the high output impedance required for accurate mirroring of the input current.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
Source follower and current feedback circuit thereof
ActiveUS7304540B2Avoid distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlWilson current mirrorAudio power amplifier
A current feedback circuit is used in the source follower. The source follower includes a first MOS transistor and a current mirror. The first MOS transistor has a gate receiving an inputting signal and a source outputting an output signal. A drain current flows through the first MOS transistor. The current mirror generates the drain current according to an adding current. The current feedback circuit is used for stabilizing the drain current to a constant value substantially. The current feedback circuit includes a passive component and an operational amplifier. The passive component has a first end and a second end, which has an error voltage when a corresponding current flows through the passive component. The magnitude of the corresponding current changes with the magnitude of the drain current. The operational amplifier outputs a reference signal to adjust the adding current according to the error voltage and a reference voltage.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
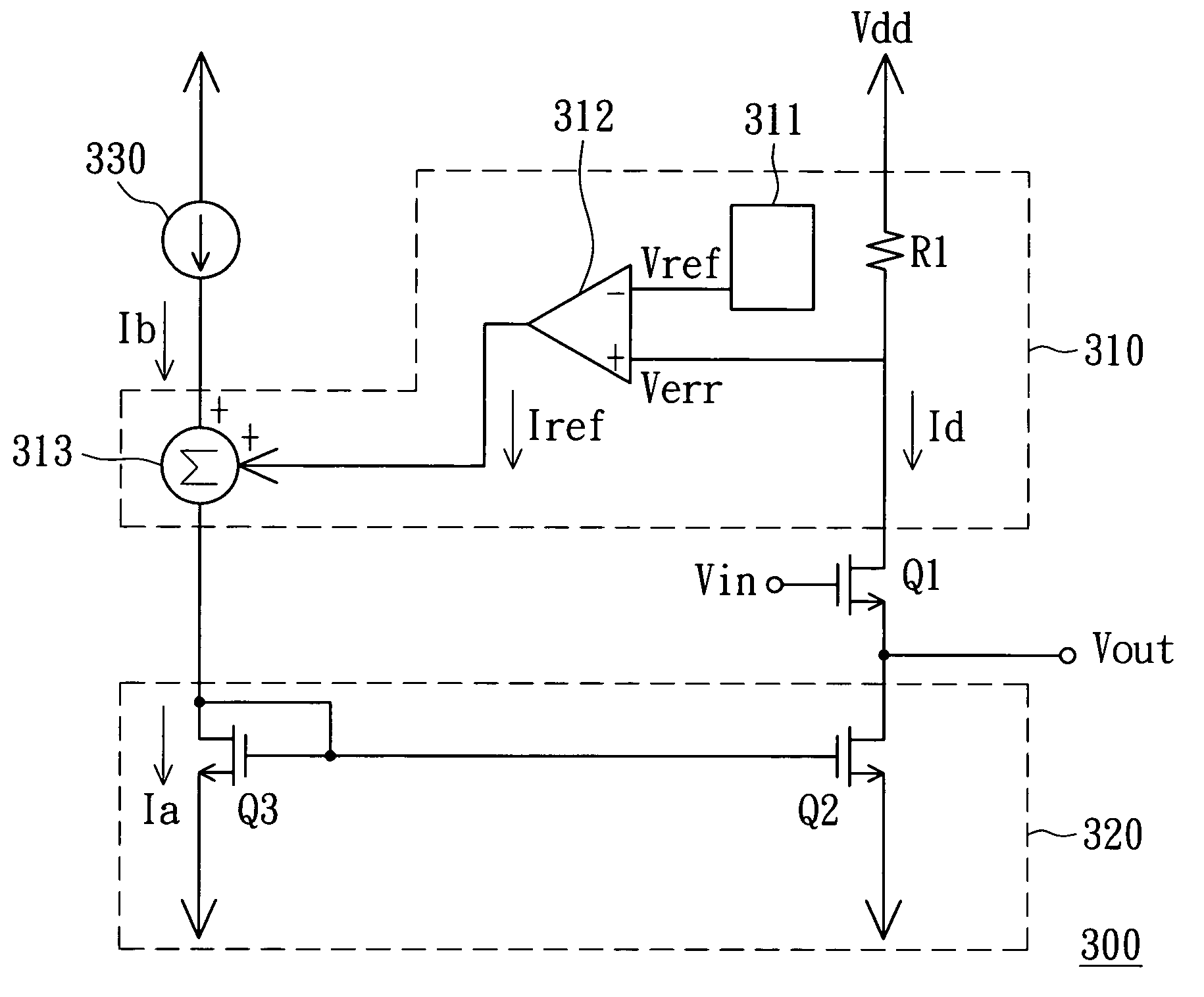
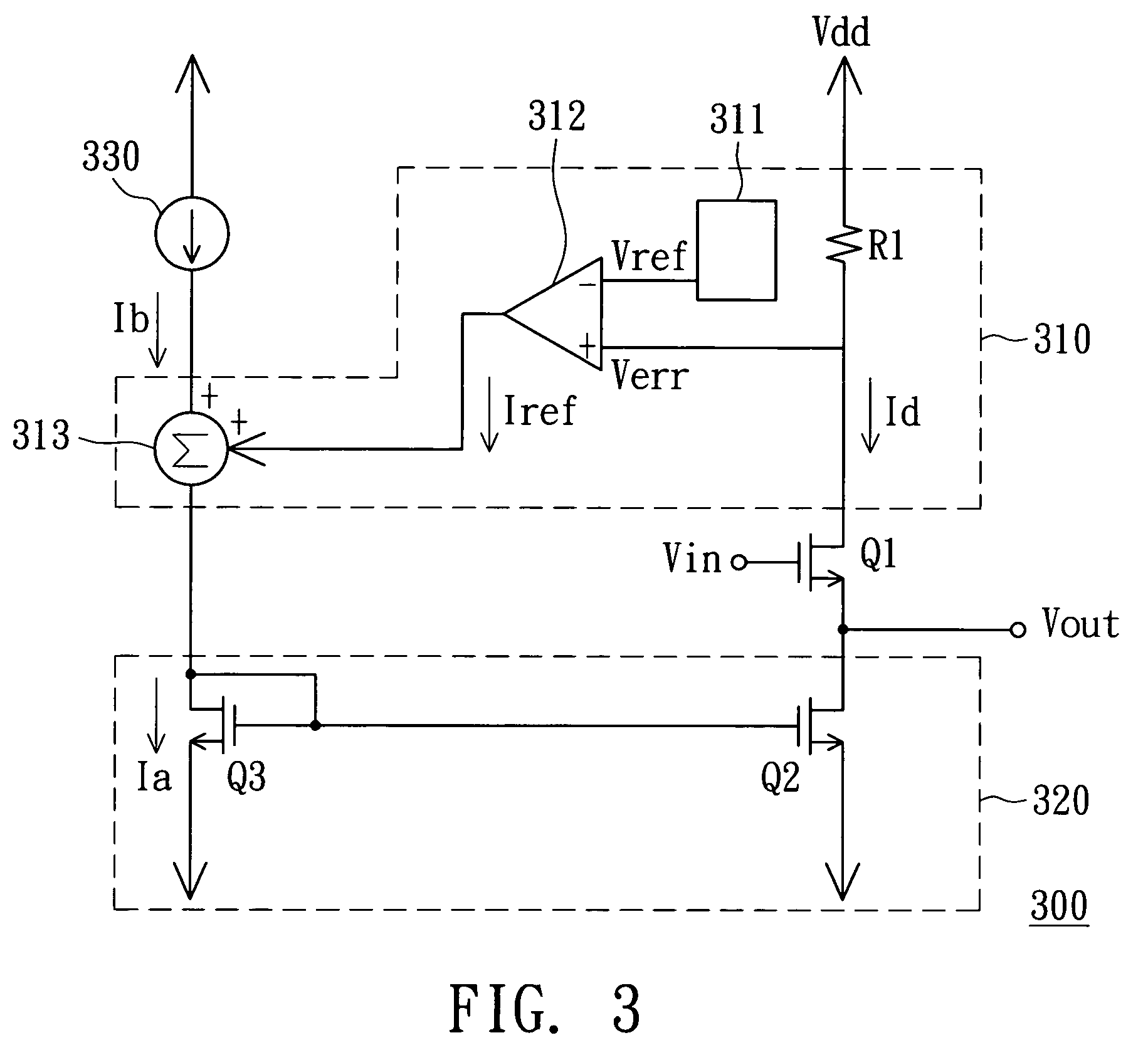
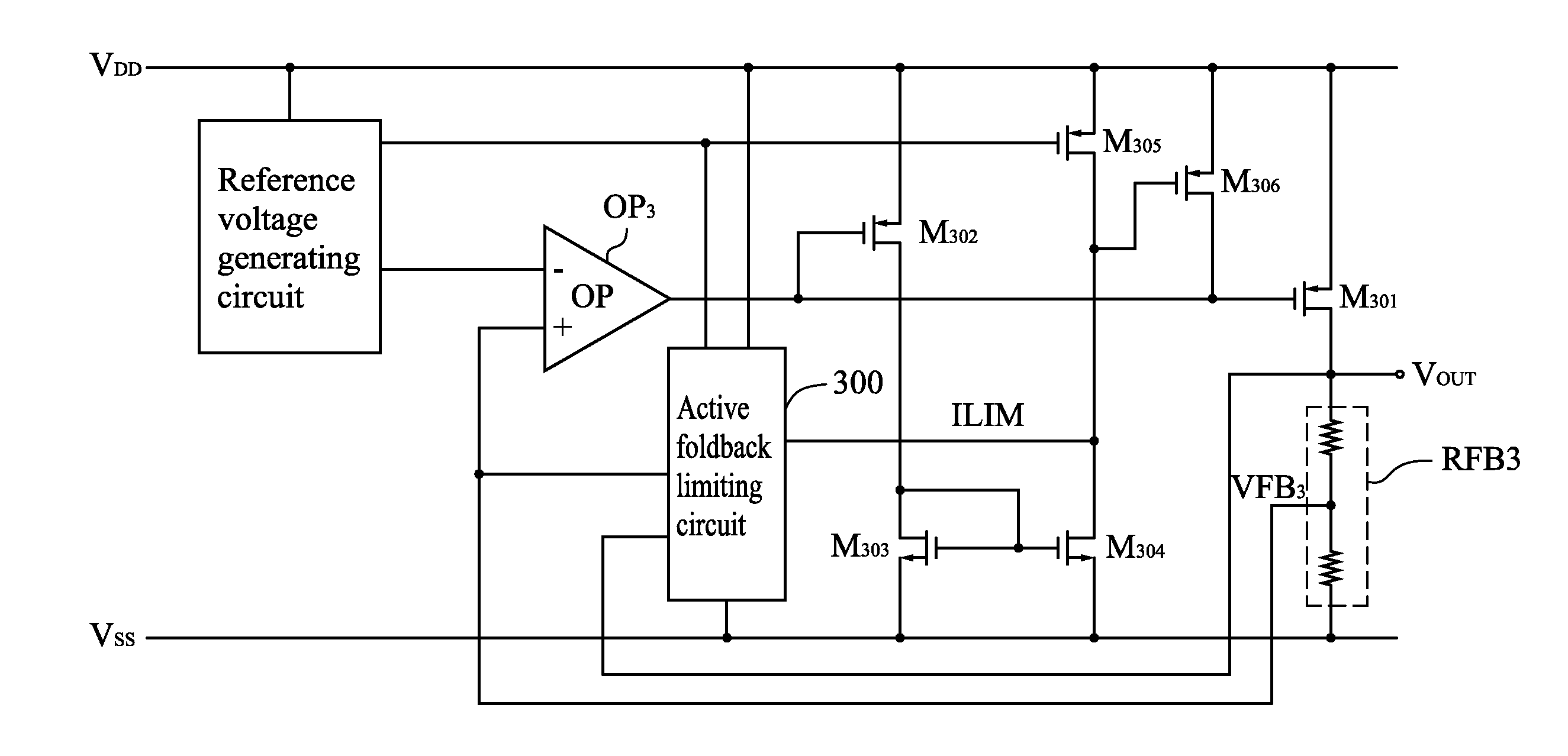
Voltage regulator having active foldback current limiting circuit
ActiveUS8089743B2Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectric variable regulationWilson current mirrorCurrent limiting
The present invention mainly relates to a voltage regulator, comprising: a P typed power MOS; a feedback circuit; a differential amplifier; a protecting circuit having a N-typed transistor current mirror; and an active foldback current limiting circuit rather than using a resistor. When the P typed power MOS is under short circuit current situation, the current at the output side of the current mirror is increased in order to limit the current flown through the power MOS. Meanwhile, the same purpose can also be served by increasing the current at the input side of the DC current mirror.
Owner:HOLTEK SEMICON
Photovoltaic detector read-out unit circuit applying inverted voltage follower
InactiveCN102722213AReduce power consumptionConstant bias voltageElectric variable regulationCapacitanceWilson current mirror
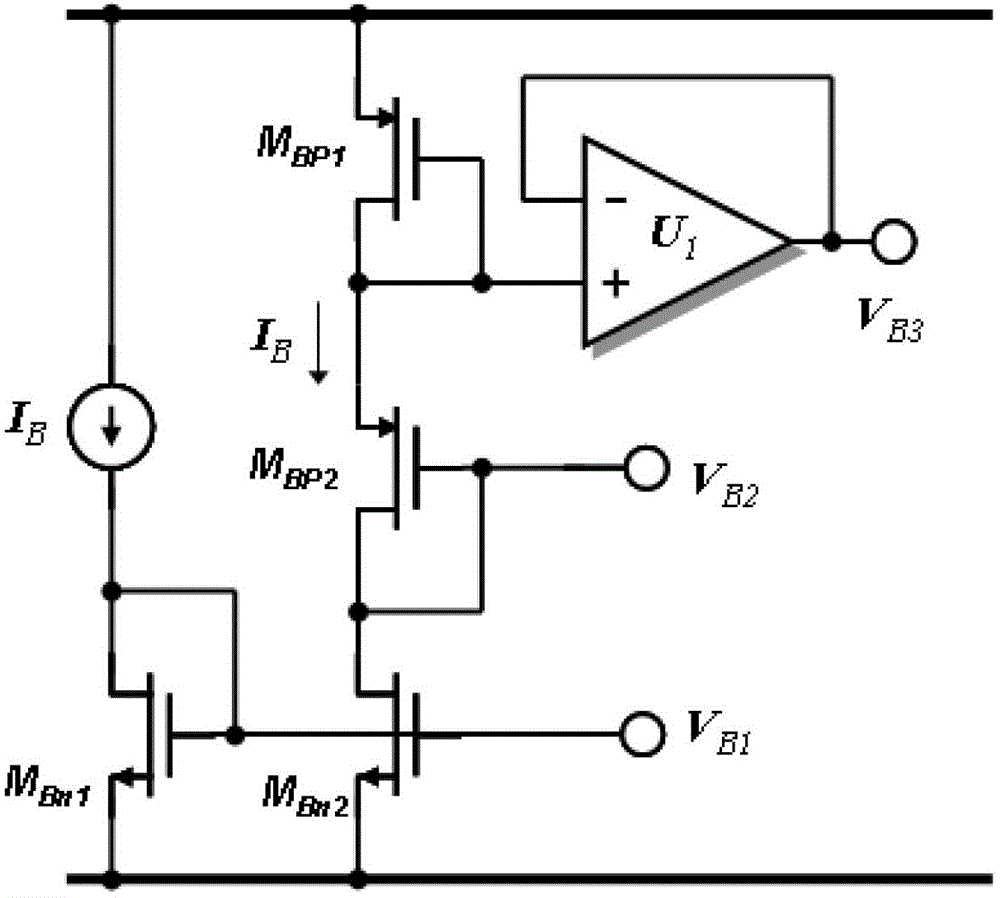
The invention relates to a photovoltaic detector read-out unit circuit applying an inverted voltage follower. The photovoltaic detector read-out unit circuit comprises a cascade current mirror circuit, a current integrating circuit and a bias voltage generating circuit, wherein transistors (Mp1 and Mp3) and transistors (Mp2 and Mp4) form the cascade current mirror circuit; transistors (Mp2, Mp4 and Mn2) and an integrating capacitor (Cint) form the current integrating circuit; and transistors (MBn1, MBn2, MBp1 and MBp2) form the bias voltage generating circuit. According to the circuit, an amplifier is not needed, the power loss is low, lower input resistance is realized and is unrelated to current of a detector, and the constant injection efficiency can be realized; bias voltage of the detector can be controlled accurately, and constant bias voltage of the detector can be provided; current gain of the read-out unit circuit can be changed through a dimension ratio of the transistors of a current mirror; a background current deduction circuit can be conveniently added, background suppression is realized, and the dynamic range of the circuit is enlarged; and the dynamic range is large, and input light current higher than bias current can be processed.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
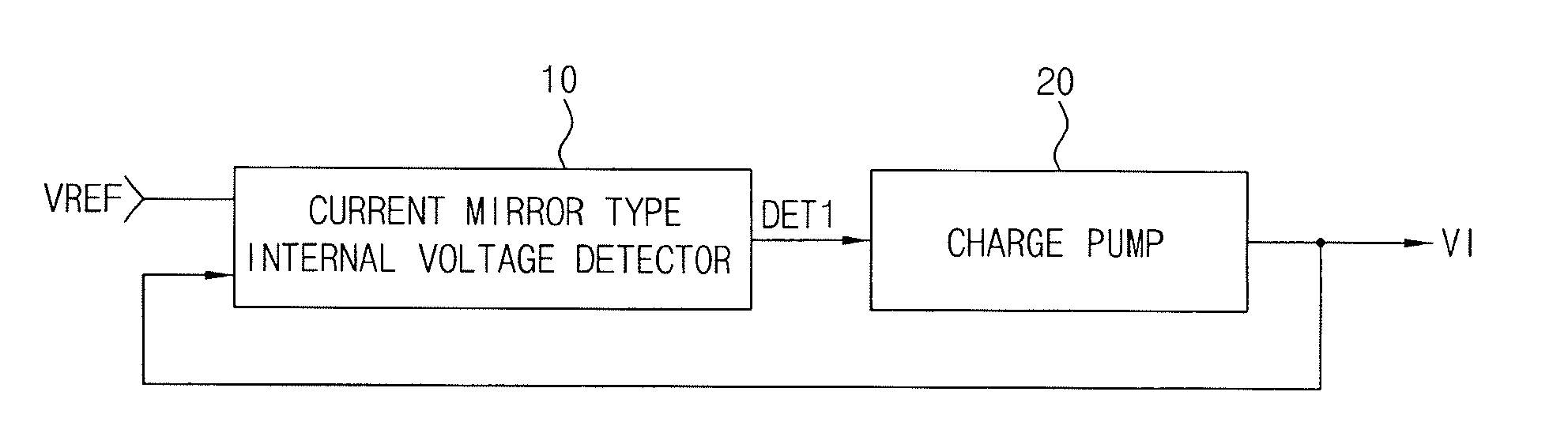
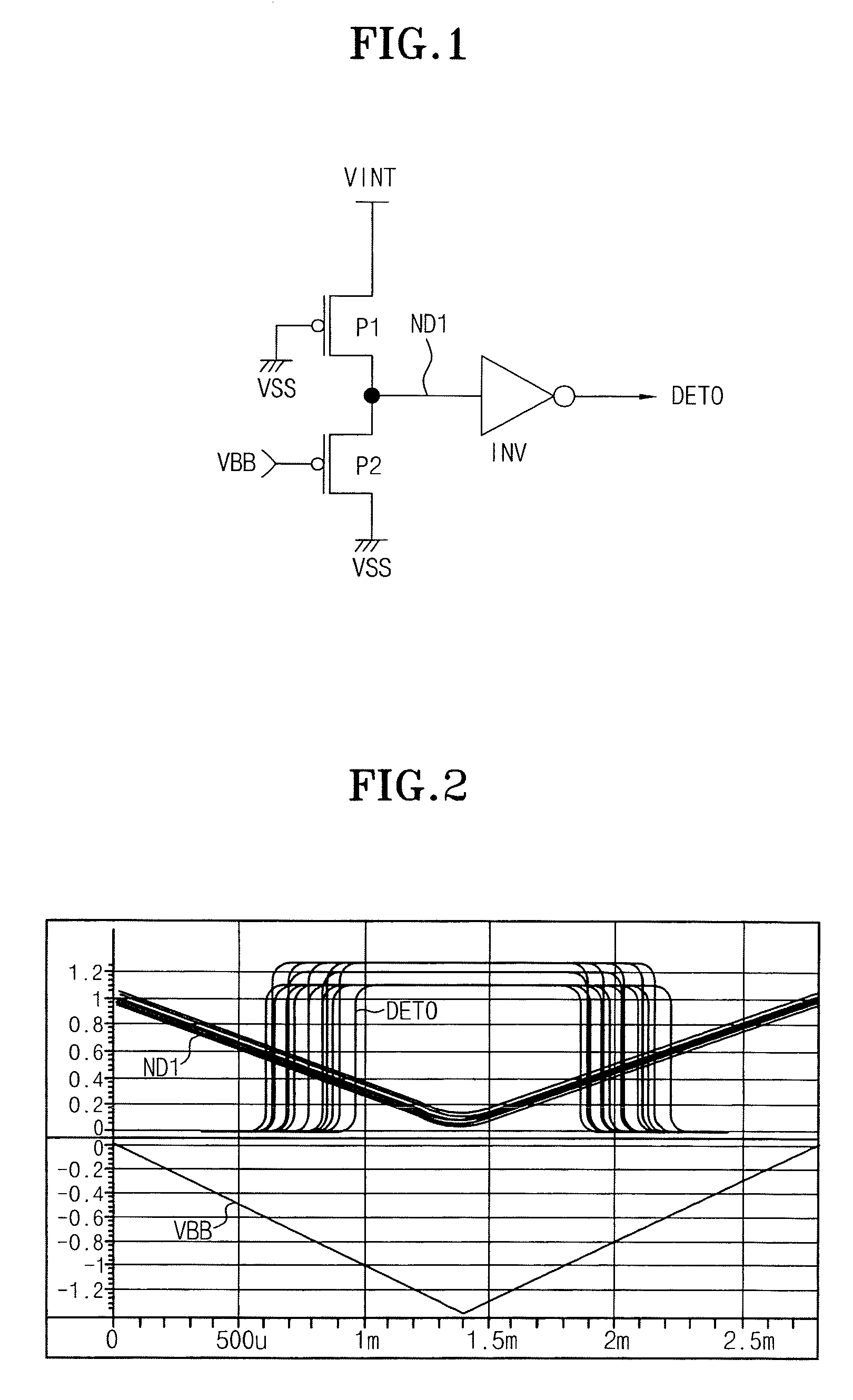
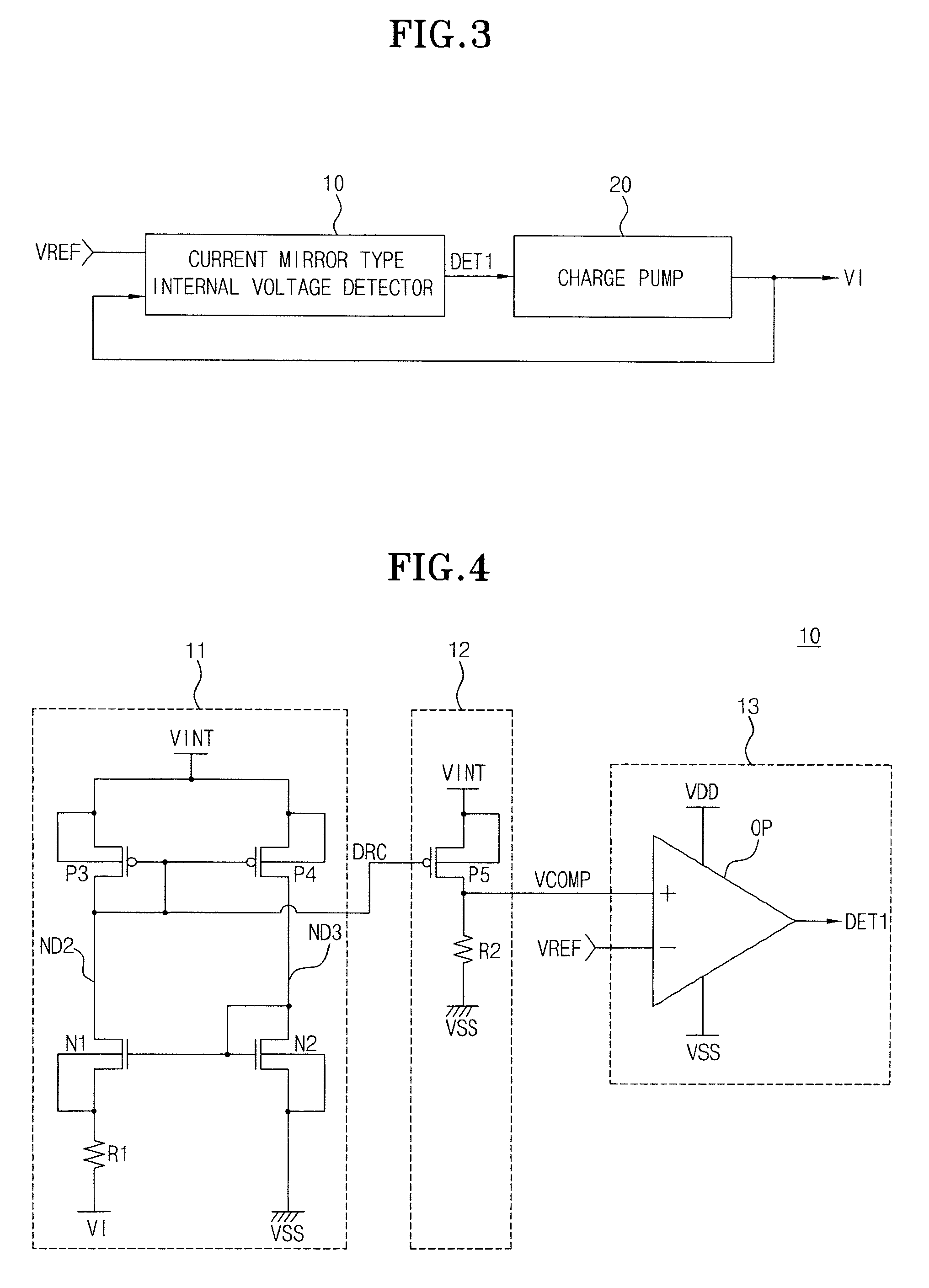
Internal voltage generation circuit for generating stable internal voltages withstanding varying external conditions
ActiveUS20080157860A1Slow changeStatic storageElectric variable regulationWilson current mirrorOutput compare
There is provided an internal voltage generation circuit generating an internal voltage used for a semiconductor memory device. The internal voltage generation circuit includes a current mirror type internal voltage detector generating a comparison voltage and comparing the comparison voltage with a reference voltage to output the comparison result as a detection signal, and a charge pump outputting the internal voltage and controlling the level of the internal voltage by the detection signal. The current mirror type internal voltage detector generates a comparison voltage whose level is determined in accordance with the output of the current mirror having a variable current source in which current varies in accordance the output internal voltage.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Digital regulation bias current source
ActiveCN109765963AWide range adjustableUnderstand the purposeElectric variable regulationWilson current mirrorEngineering
The invention discloses a digital regulation bias current source, and relates to the technical field of the bias current source design in the integrated circuit. The digital regulation bias current source comprises a first current mirror, an operational amplifier, a resistance regulation network, a second current mirror; an output end of the first current mirror is connected to a power supply through the resistance regulation network, a reverse-phase input end of the operational amplifier is connected with the output end of the first current mirror, an in-phase input end of the operational amplifier is connected with an input end of the second current mirror, the output end of the operational amplifier is connected with a control end of the second current mirror, and the input end of the second current mirror is connected to the power supply through a resistive element. By importing the operational amplifier and utilizing the short circuit principle thereof, the digital regulation biascurrent source provided by the invention can realize the current precise duplication in an assistant way, the control is realized by utilizing a digital logic level control bus, and the wide-range regulation of the mirror current is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI PANCHIP MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Current source with very high output impedance
InactiveCN1702589AIncrease output impedanceSmooth changeElectric variable regulationWilson current mirrorReference current
A current source provided with high output impedance comprises a current source-generating circuit and a equivalent negative resistance generating circuit, wherein, the said current source-generating circuit can comprise all the current source circuit such as Cascode, Wilson, or Widlar current mirror and so on to generate positive resistance and reference current; the said negative resistance generating circuit comprises a short-circuit grid-drip POMS pipe, a NMOS pipe and an amplifier to generate equivalent negative resistance whose absolute value is made larger than the former one through designing; then the said equivalent negative resistance is connected in parallel with the said positive resistance to get super high output resistance whose value is close to 109 ohm magnitude order.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Reference voltage source circuit structure suitable for image sensor
ActiveCN109491433AReduce usageEliminate the effect of temperature coefficientElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceWilson current mirror
The invention discloses a reference voltage source circuit structure suitable for an image sensor. Based on the structure of a conventional first-order band-gap reference source of a double-well CMOSprocess, a current mirror is adopted to clamp nodes X and Y, a resistor for producing PTAT voltage in a conventional circuit is omitted and is replaced by an NMOS pipe column structure, meanwhile BJTof an output branch is omitted, one BJT for producing , PTAT current is reused, and accordingly the purpose of negative temperature voltage is achieved. The noise and PSRR characteristics of internalreference voltage of a chip system can be further improved, and noise introduced by reference voltage and current in an imaging system is reduced as much as possible or eliminated.
Owner:CHENGDU LIGHT COLLECTOR TECH
Wide-range voltage stabilizing circuit for band-gap reference
The invention provides a wide-range voltage stabilizing circuit for band-gap reference. The circuit comprises a band-gap reference module, a bias voltage generating module and a current negative feedback module; the bias voltage generating module is connected with the band-gap reference module for outputting bias voltage to the band-gap reference module; the bias voltage generating module comprises a first Wilson current mirror circuit and a second Wilson current mirror circuit, and the second Wilson current mirror circuit is embedded into the first Wilson current mirror circuit; the current negative feedback module is connected with the bias voltage generating module and the band-gap reference module separately and used for configuring the bias voltage generating module and supplying power to the band-gap reference module. The bias voltage with the high power supply rejection ratio and power supply can be supplied to band-gap reference, and the band-gap reference can work normally under the wide-range chip power condition.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Failsafe for differential circuit based on current sense scheme
InactiveUS6927599B2Current/voltage measurementError detection/correctionWilson current mirrorEngineering
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Electric charge pump with wide output voltage area
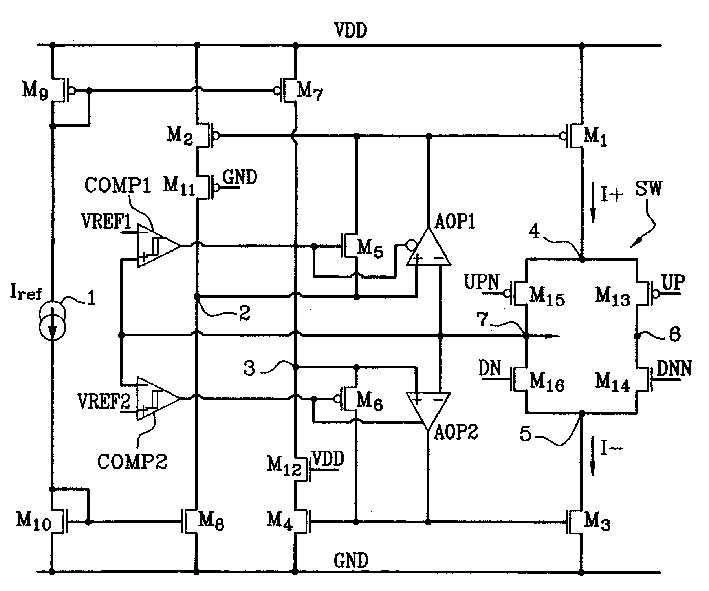
InactiveCN1430120AControl output currentPulse automatic controlElectric variable regulationWilson current mirrorAudio power amplifier
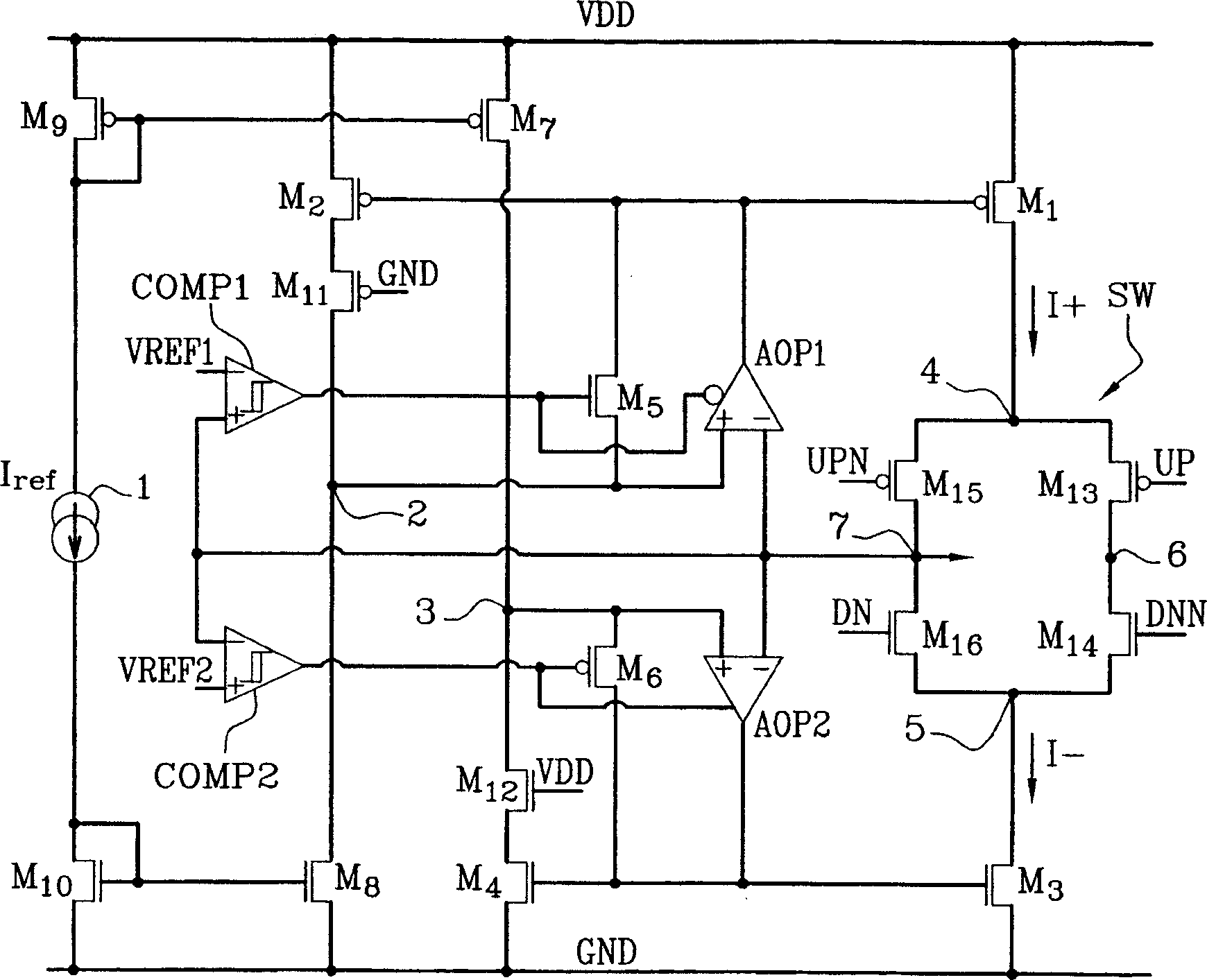
The invention concerns a load pump device able to provide a constant current, respectively positive or negative, over an extremely wide output voltage range. A symmetrical switching system activates a first operational amplifier (AOP1) associated with the positive current source or a second amplifier (AOP2) associated with the negative current source according to predetermined threshold values (Vref), the first amplifier being provided so as to restore the behavior of the current mirror (M2, M1) generating a positive current when the output voltage of the device approaches the feed voltage (VDD) and the second amplifier being provided so as to restore the behavior of the current mirror (M4, M3) generating a negative current when the output voltage of the device approaches the earth (GND), thus allowing the output current of the device to be always constant and equal to a reference value (Iref).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Input control diode-based level-shift circuit
InactiveCN107911110AImprove stabilityReduce power consumptionLogic circuit interface arrangementsWilson current mirrorLow voltage
The invention relates to an analog integrated circuit design and provides a novel topological structure based on an input control diode, in particular, an input control diode-based level-shift circuit. According to the structure, since the diode is adopted, the normal operation of the level shift circuit in the case of turning off source current can be ensured, and the standby power of a WCMLS (Wilson current mirror based level shifter) can be effectively reduced. The input control diode-based level-shift circuit of the invention is composed of N-type MOS devices from MN1 to MN4, P-type MOS devices from MP1 and MP2, a diode Di, a low-voltage inverter, and two high-voltage inverters; the source ends of MP1 and MP2 are connected with VDDH, and the gate ends of the MP1 and MP2 are connected together with the drain end of MN1, and therefore, a current source structure is formed; the source end of MN1 is connected with the drain end of MN3, and the source end of MN3 is grounded; and the drain end of MN1 is also connected with the upper end of the diode Di, the lower end of the diode is connected with the drain end of MN4, and the source end of MN4 is grounded. The input control diode-based level-shift circuit of the invention is mainly applied to the analog integrated circuit design and manufacturing field.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Transconductance operational amplifier circuit and filter circuit
ActiveCN111541433AReduce power consumptionReduce noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCapacitanceLow noise
The invention discloses a transconductance operational amplifier circuit and a filter circuit, the transconductance operational amplifier circuit comprises an input stage, an upper bias circuit, a lower bias circuit, a source electrode degradation structure and an improved Wilson current mirror structure, and a low-pass filter circuit comprises five identical transconductance operational amplifiers and five identical capacitors. The low-pass filter circuit structure based on the transconductance operational amplifier structure provided by the invention has the characteristics of low power consumption, low noise and low harmonic distortion, and has a very wide application prospect. Due to the fact that the OTA structure with the small transconductance value is used for achieving the function of the resistor, the capacitance value of the filter circuit under the cut-off frequency of 250 Hz is compatible with the CMOS technology. The OTA structure provided by the invention combines the technologies of current segmentation, current cancellation and source degradation, reduces the transconductance of OTA, and improves the linearity of OTA. The OTA provided by the invention works in a weak inversion working area, so that the power consumption of the circuit is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Near-threshold level shifter
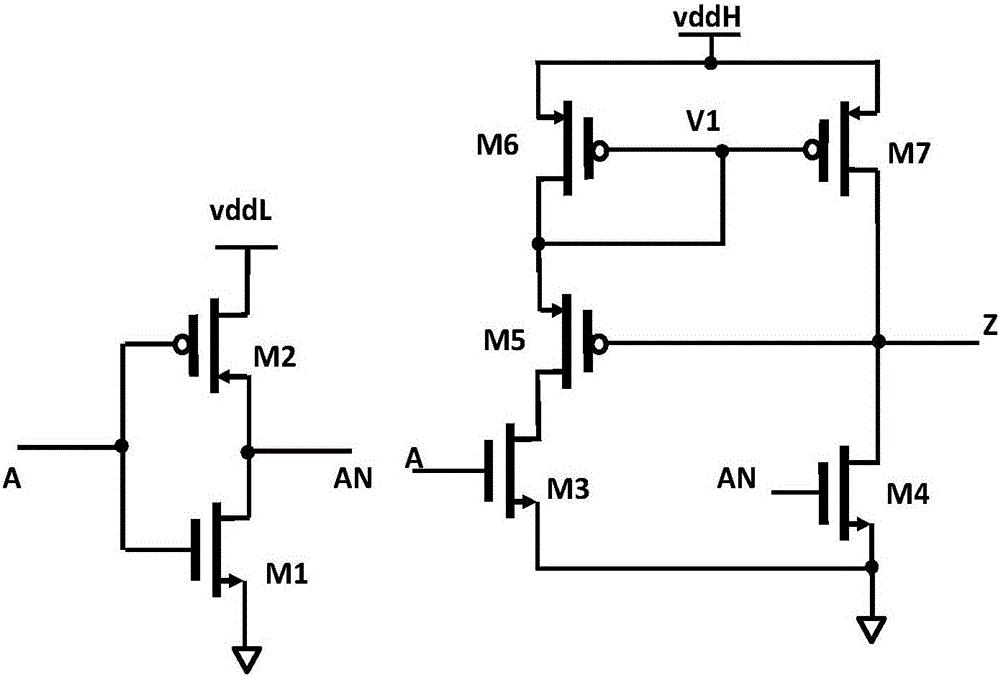
PendingCN111478693AEliminate leaksEliminate pressure dropLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsConvertersWilson current mirror
The invention relates to a near-threshold level shifter. The near-threshold level shifter comprises a low-voltage inverter, a Wilson current mirror, a first inverter circuit, a fifth PMOS transistor,a second inverter circuit and a seventh PMOS transistor. The first input end of the Wilson current mirror is connected with an input level; the output end of the low-voltage inverter is connected withthe second input end of the Wilson current mirror; the drain electrode of the fifth PMOS transistor is connected with the first end of the first inverter circuit; the second end of the first invertercircuit is connected with the output end of the Wilson current mirror; the third end of the first inverter circuit is connected with the input end of a second-stage output phase inverter; the drain electrode of the seventh PMOS transistor and the first end of the second inverter circuit are connected with the third end of the first inverter circuit; and the grid electrode of the seventh PMOS transistor is connected with the second end of the second inverter circuit. According to the invention, the problem of an electric leakage path caused by high-level voltage drop of a traditional Wilson current mirror is eliminated.
Owner:北京中科芯蕊科技有限公司
Current limitation programmable circuit for smart power actuators
A circuit for limitation of maximum current delivered by a power transistor comprises: a network for detection of the current delivered by the power transistor which generates a first electrical signal; a reference network for generating a reference current proportional to a resistor and self-limited, provided by means of a current generator circuit and a limiting circuit with current mirror; and an operational amplifier which compares the first electrical signal with the reference current and which tends to inhibit the power transistor if the current delivered exceeds a certain threshold value.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Level shifter
PendingCN111355481AReduce complexityFully consider the driving abilityLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsConvertersWilson current mirror
The invention discloses a level shifter. The level shifter comprises a Wilson current mirror circuit and a phase inverter circuit. The Wilson current mirror circuit is connected with the inverter circuit, the inverter circuit comprises an inverter circuit PMOS tube and an inverter circuit NMOS tube, an output end of the Wilson current mirror circuit is connected with a grid electrode of the PMOS tube of the inverter circuit and a grid electrode of the NMOS tube of the inverter circuit, a source electrode of the PMOS tube of the inverter circuit is connected with a inverter circuit power supply, a drain electrode of the PMOS tube of the inverter circuit is connected with the drain electrode of the NMOS tube of the inverter circuit, and a source electrode of the NMOS transistor of the inverter circuit is grounded. The level shifter has the advantages that the circuit structure is simple, and the delay time and the power consumption of the circuit can be effectively reduced.
Owner:北京中科芯蕊科技有限公司
Amplifier circuit having an extended Wilson current-mirror self-bias boosting circuit
ActiveCN100521511CIncrease the maximum output powerHigh gainHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationCapacitanceCommon base
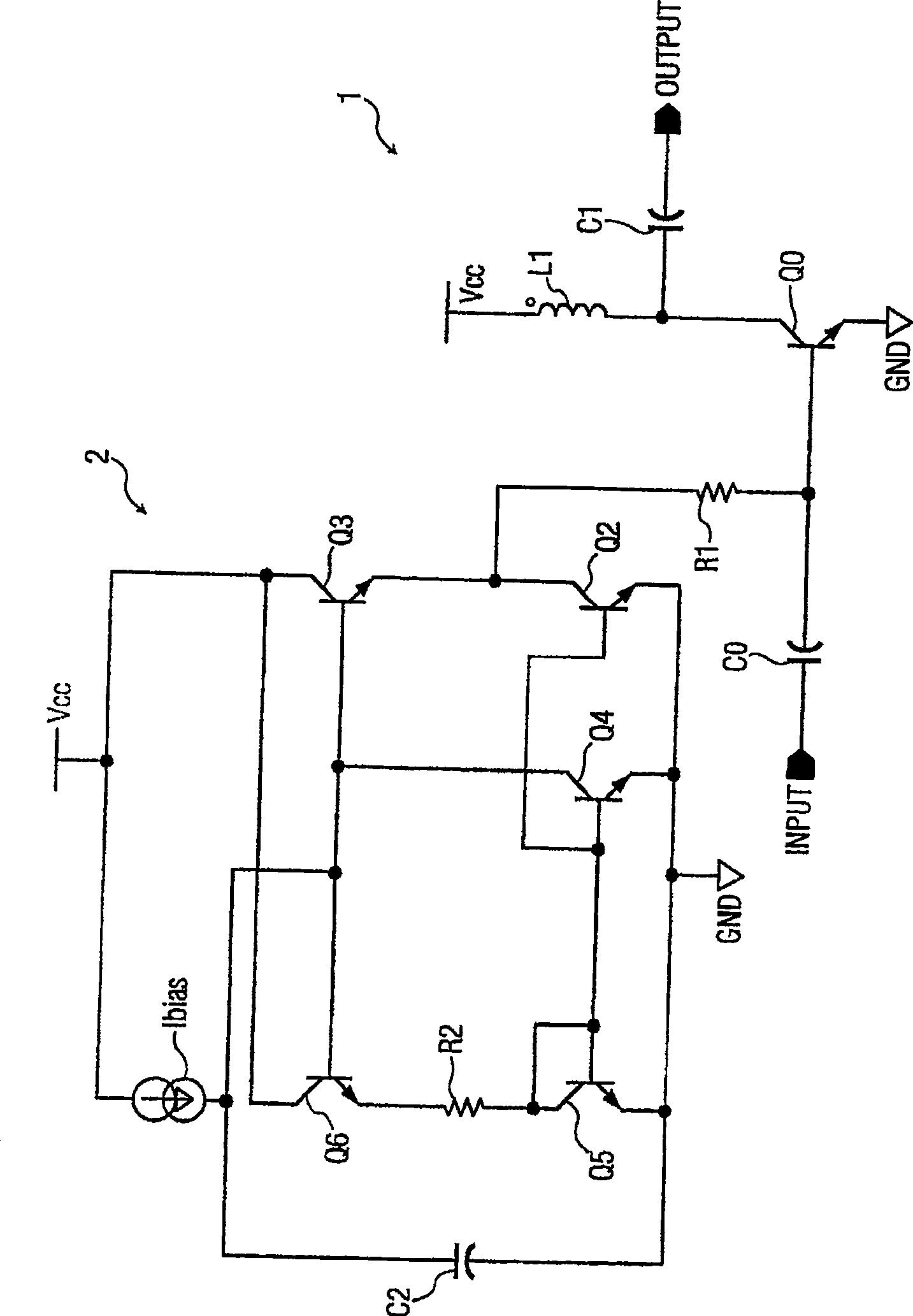
An amplifier circuit ( 1 ) includes an amplifying transistor (QØ) and a dc bias circuit ( 2 ) for biasing the amplifier transistor (QØ) to obtain a conduction angle of at least about 180°. The dc bias circuit ( 2 ) includes a self-bias boosting circuit which has a Wilson current-mirror (Q 4 , Q 5 , Q 6 ) integrated with a cascode current-mirror circuit (Q 2 , Q 3 ) to form an extended Wilson current-mirror circuit (Q 2 -Q 6 ) having an output coupled to a control terminal of the amplifying transistor (QØ) by a resistor (R 1 ), and a capacitor (C 2 ) coupled from the extended Wilson current-mirror circuit (Q 2 -Q 6 ) to a common terminal (Gnd).
Owner:NXP BV
Controlling bias current for optical source
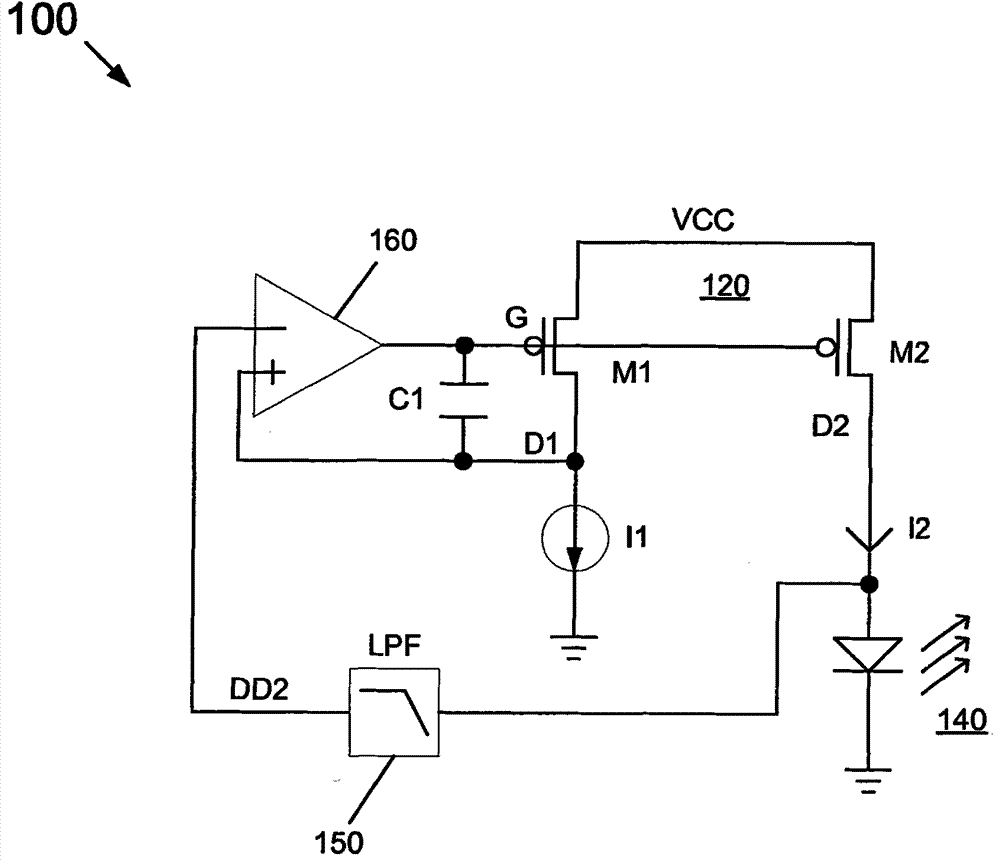
In one embodiment, the present invention includes an apparatus having a current mirror with a current source coupled to a first terminal and an output current to flow from an output terminal, a laser coupled to the output terminal to be biased by the output current, and a comparator to compare a voltage of the first terminal to the voltage of the output terminal and gate the current mirror based on the comparison. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
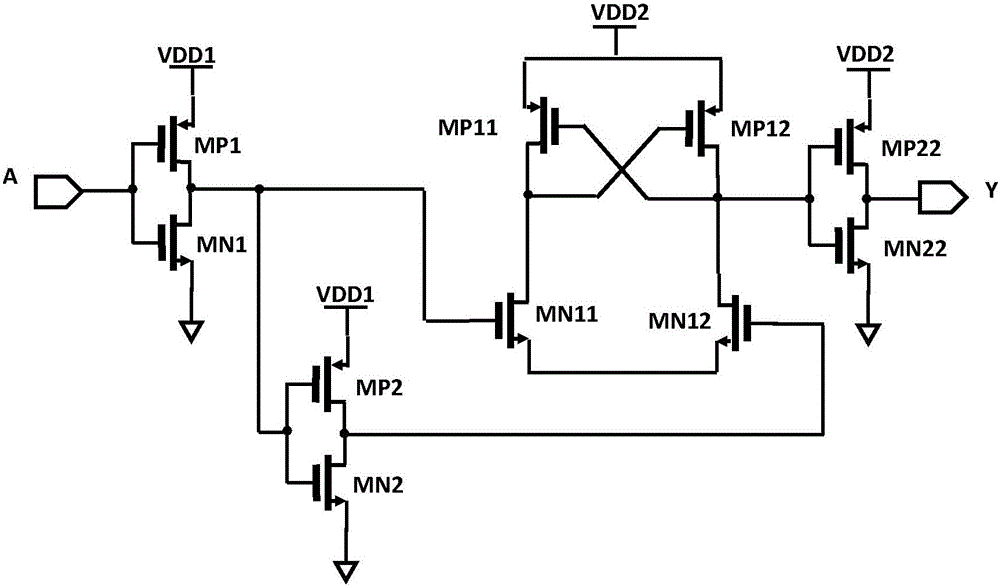
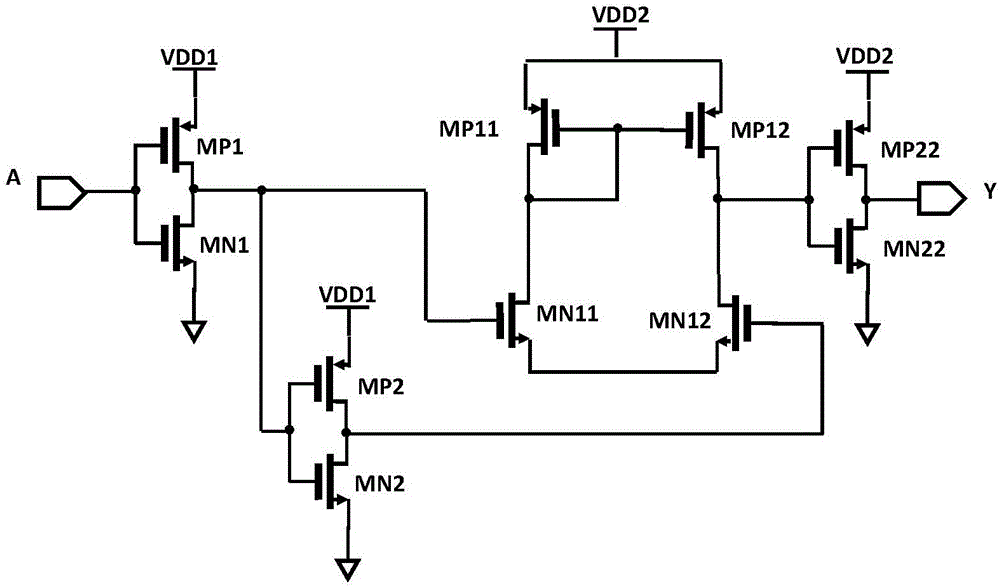
A new low voltage DCVSL circuit based on Wilson current mirror
PendingCN109299535AReduce power consumptionFast switching speedDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designSub thresholdWilson current mirror
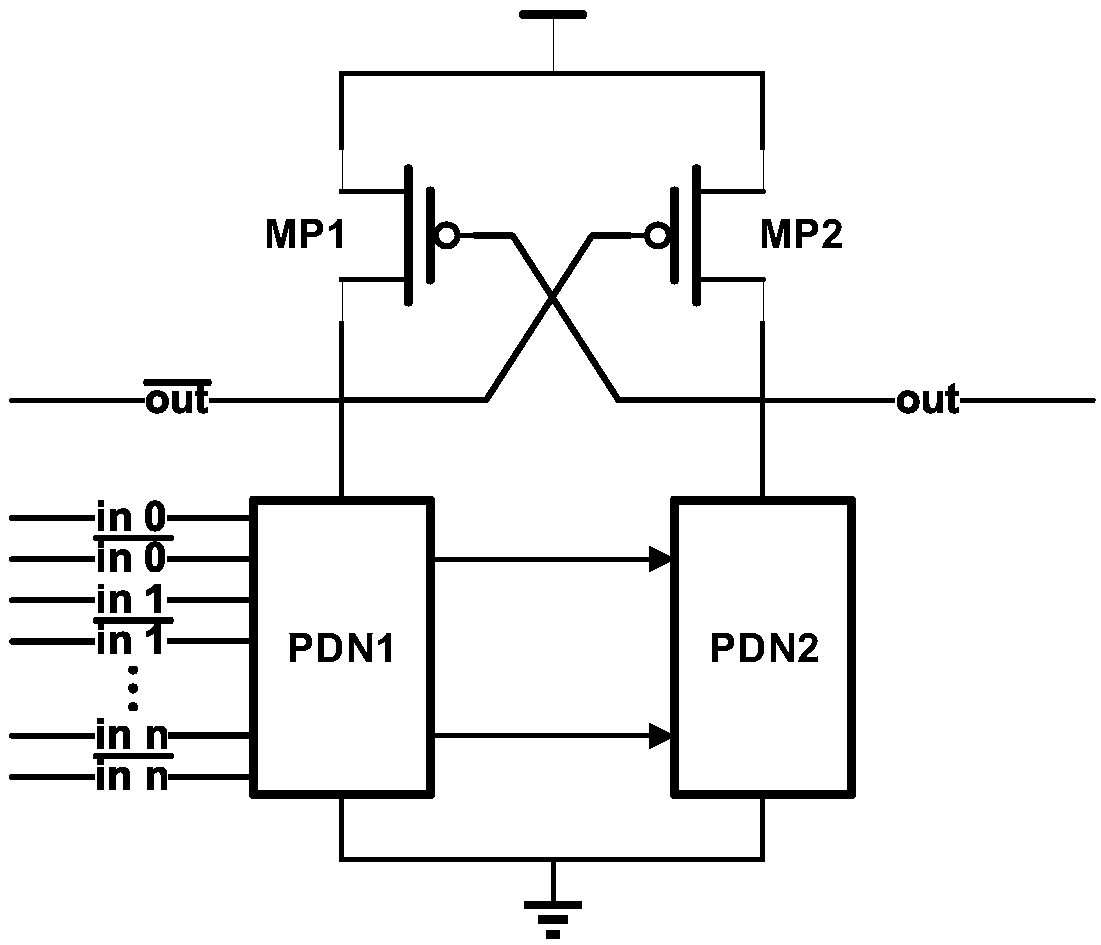
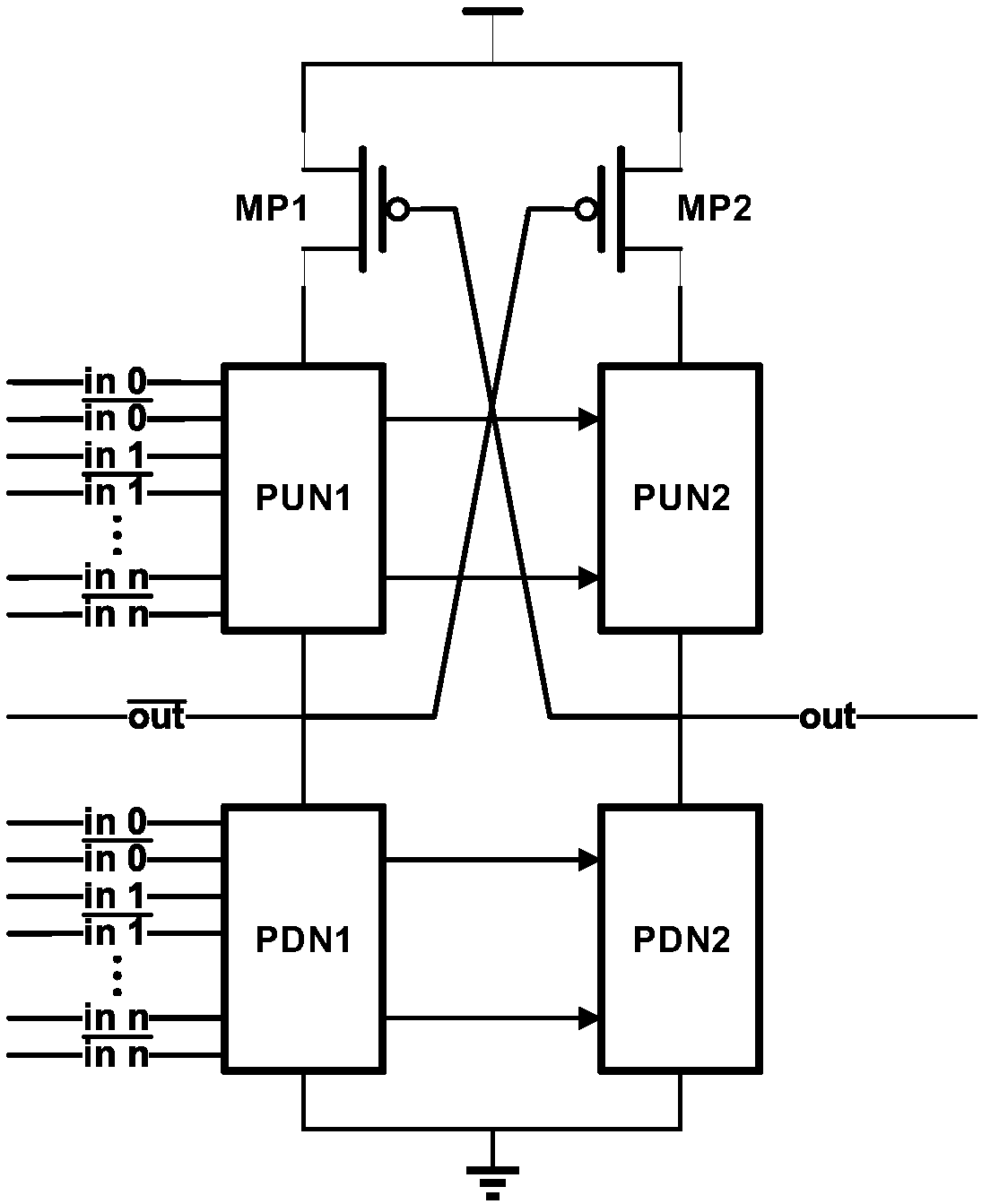
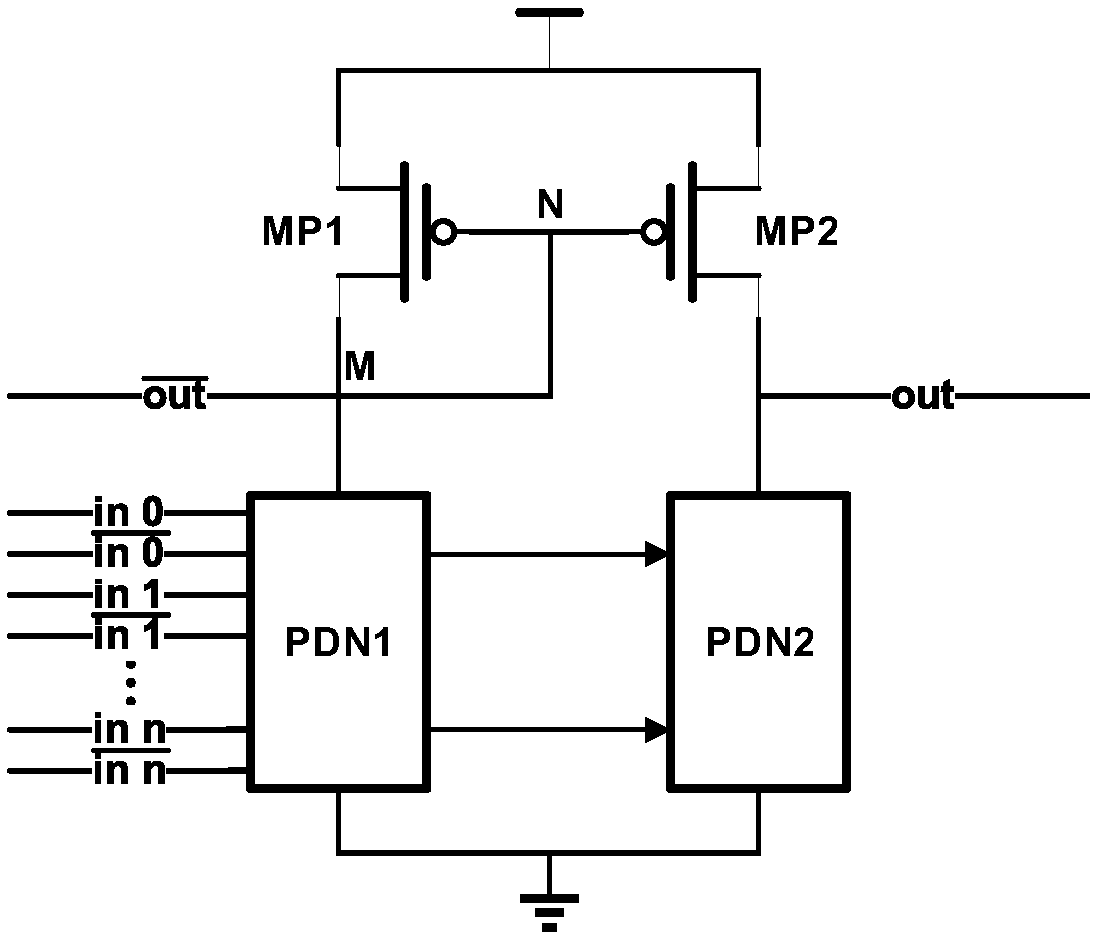
The invention discloses a novel low-voltage DCVSL circuit based on Wilson current mirror, comprises a pull-up network and a pull-down network, wherein the pull-up network comprises three PMOS devicesMP1 to MP3, and the pull-down network comprises a pull-down network PDN1 and a pull-down network PDN2, wherein the PDN1 and the PDN2 are composed of NMOS devices; The source of MP1 and MP2 is connected with high supply voltage. The drain of MP1 is connected to the source stage of MP3, the drain of MP3 is connected to the pull-down network PDN1, and the other end of PDN1 is grounded. The drain of MP2 is connected to the pull-down network PDN2, and the other end of PDN2 is grounded. The gates of MP1 and MP2 are connected to the drain of MP3 and the pull-down network PDN1, and the gates of MP3 are connected to the drain of MP2 and the pull-down network PDN2. The invention solves the stability problems of the conventional DCVSL circuit under the switching speed, the power consumption and the sub-threshold region.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Semiconductor laser current source based on complementary Wilson current mirror
InactiveCN112650352AImprove stabilityReduce volumeLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersWilson current mirrorHemt circuits
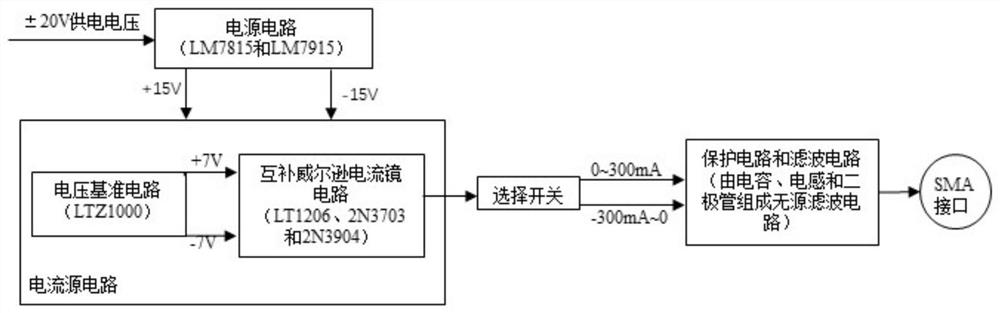
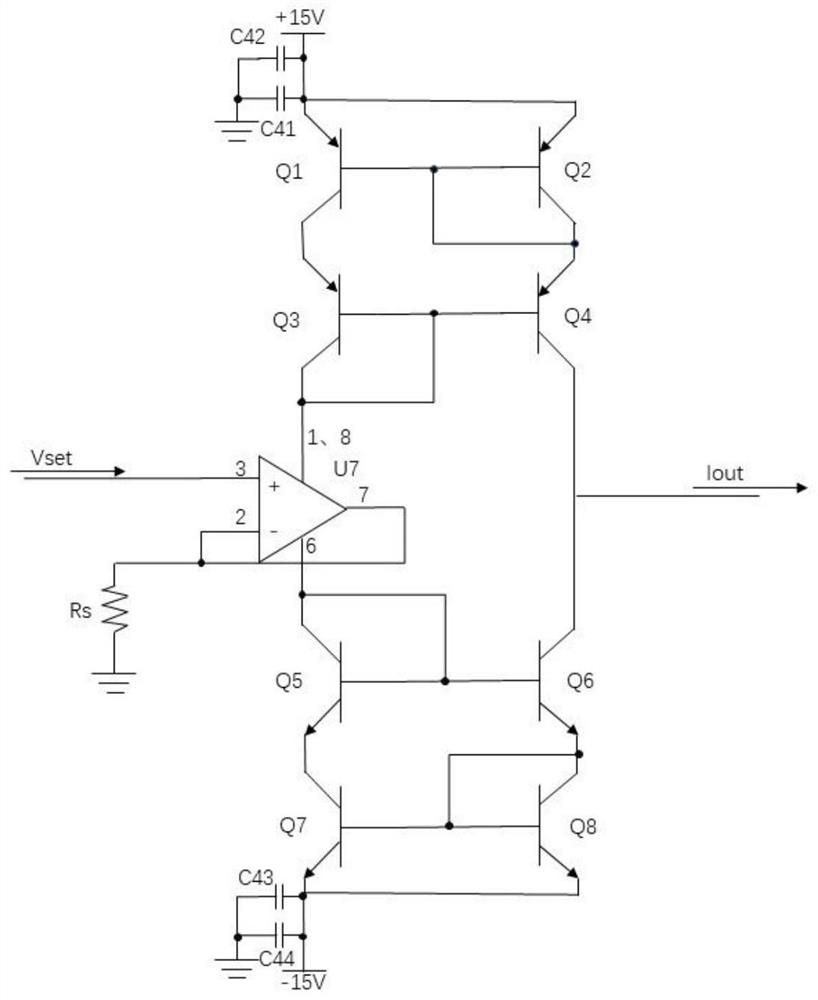
Provided is a semiconductor laser current source based on a complementary Wilson current mirror. Through the combination of a positive and negative bidirectional power supply circuit, a positive and negative bidirectional voltage reference circuit and a complementary Wilson current mirror circuit, positive and negative current bidirectional output of the current source can be realized, and the current source has high stability, so that two working modes of cathode grounding and anode grounding of a semiconductor laser can be satisfied.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com