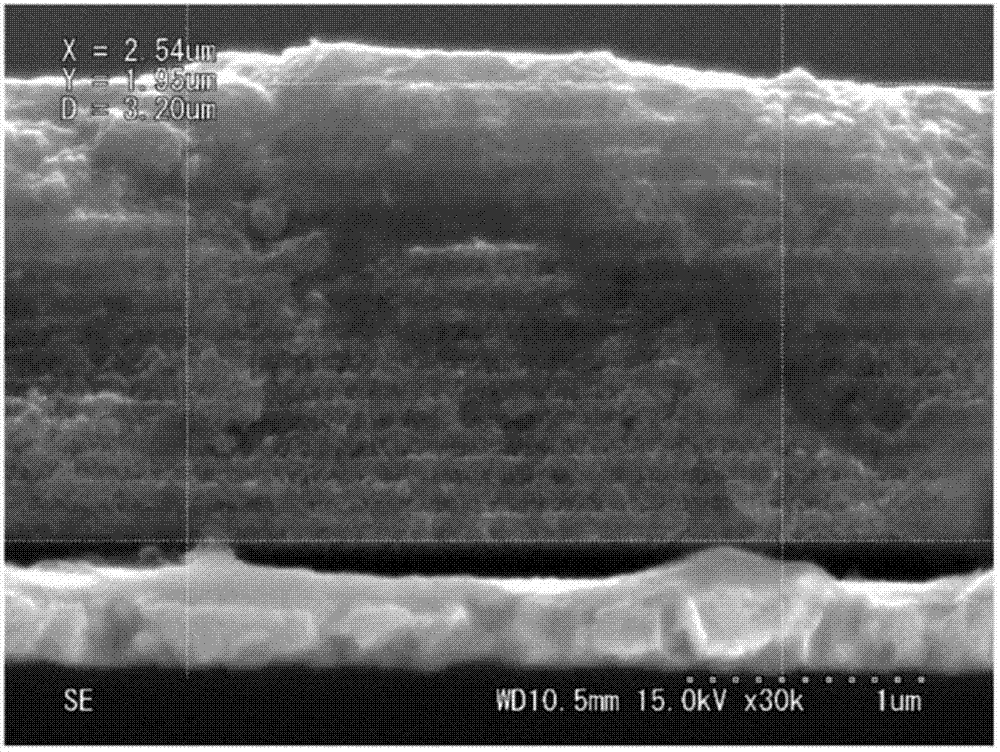
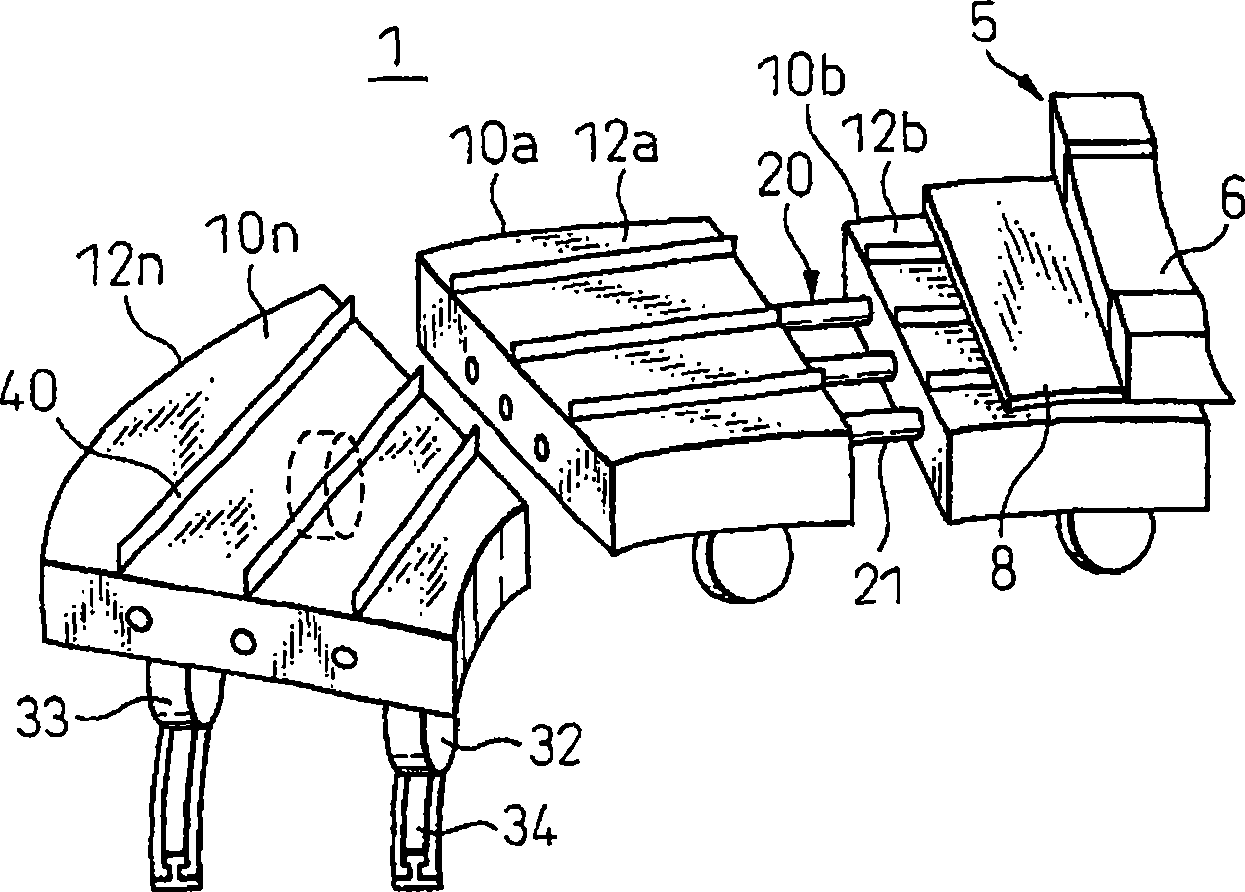
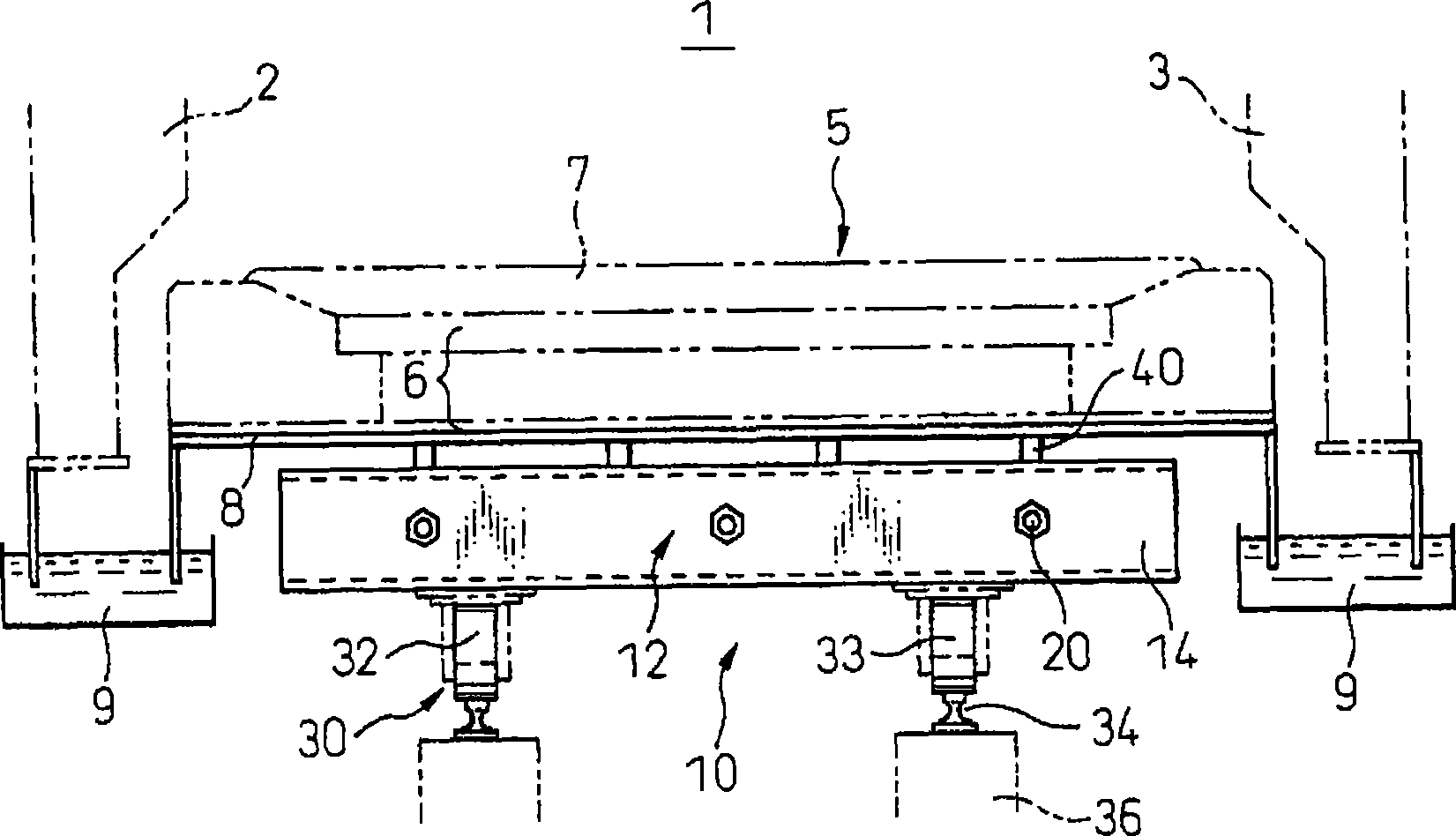
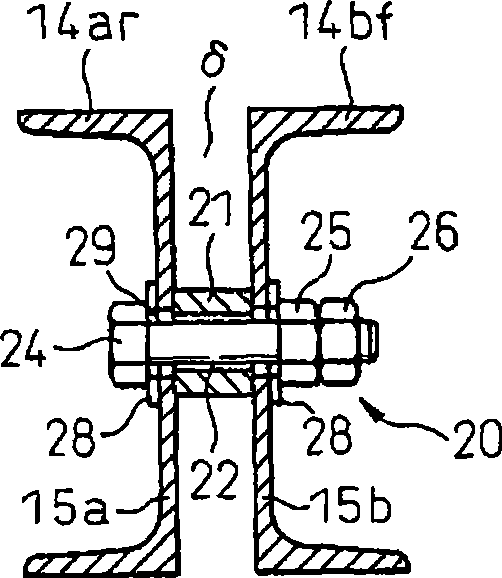
Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Avoid tensile stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Road surface interlayer cementing shearing strength test method
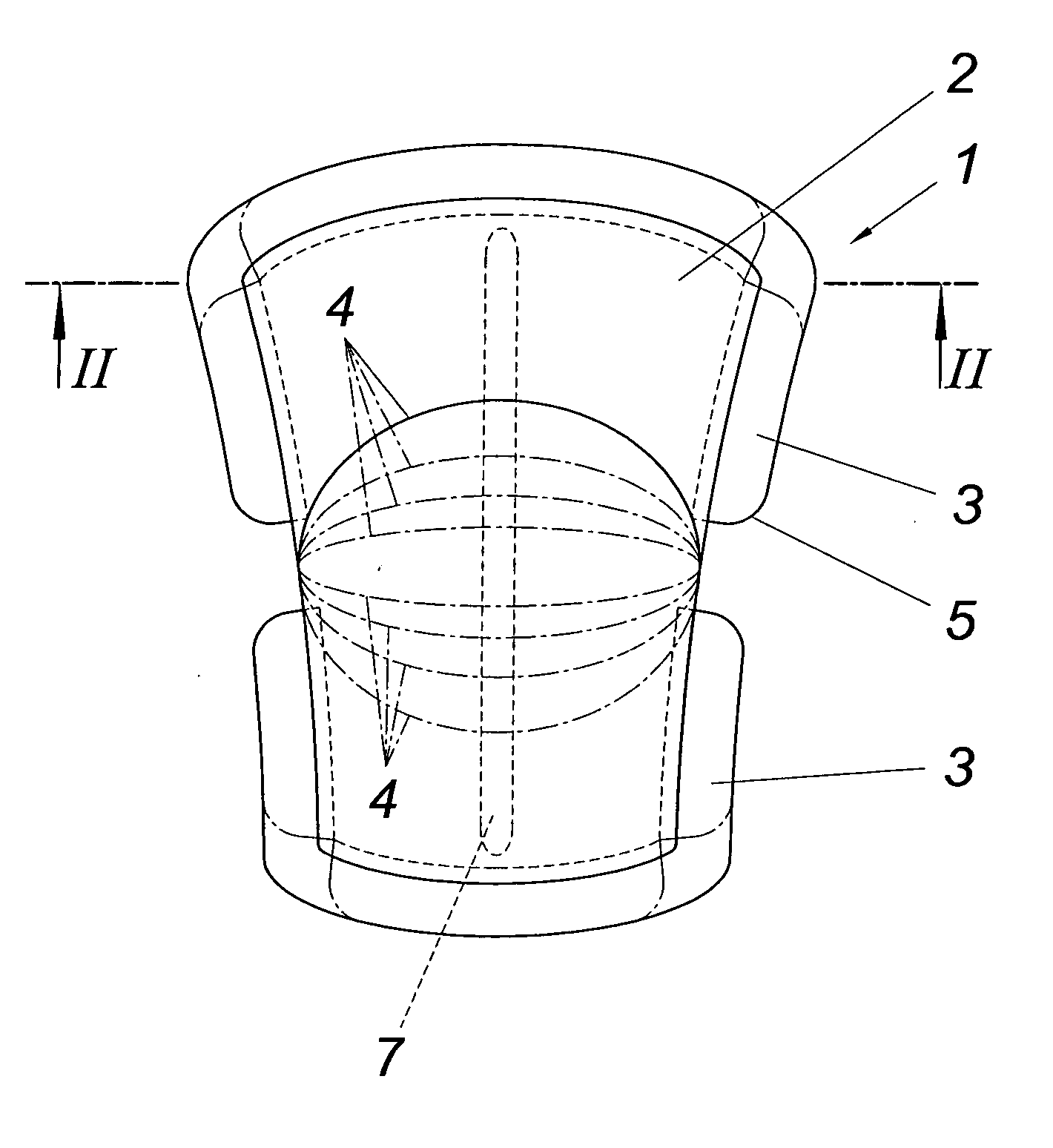
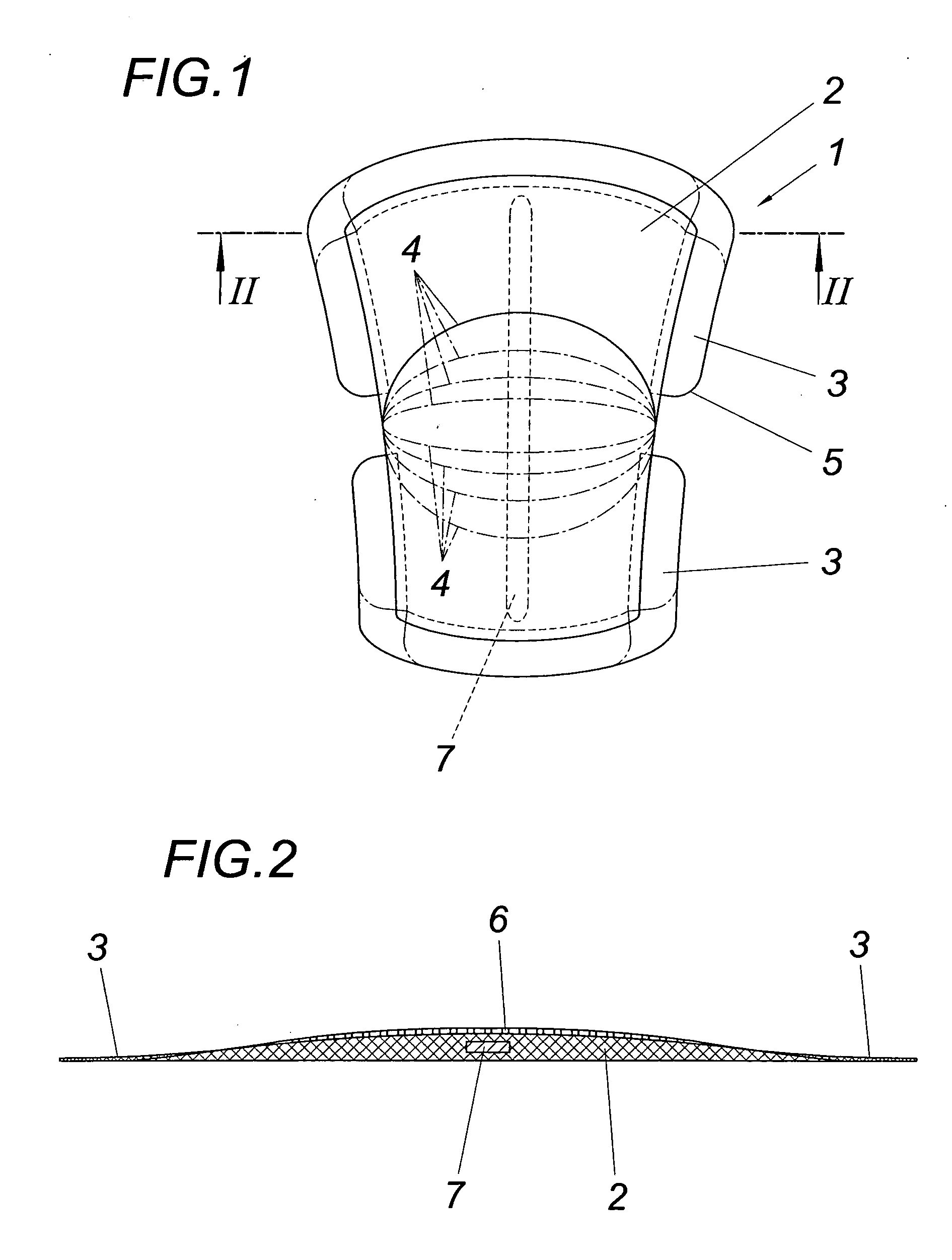
InactiveCN101275903AAvoid tensile stressThe test data is accurate and reliableUsing mechanical meansMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesSurface layerRoad surface
An adhesive shearing strength between surface layers test method is a method for effective evaluation of the shearing strength of adhesive materials between surface layers, especially an easier solution whose test mode is also easier of the current problem that the shearing strength of adhesive materials between surface layers is inaccurately tested because of a unreasonable loading method. This method has the following steps: 1. indoor test: step one, preparing a sample and fixing the sample; step two: starting a motor and do a twisting and shearing test; step three, collecting and analyzing data. 2. Field test: step one: drilling a core of the surface layer, but not taking it out, and then drying the upper surface of it with hot wind; step two, bonding a shearing test fixture head and a core sample together; step three, implementing a twisting and shearing test after 30 minutes; step four, collecting and analyzing the data.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
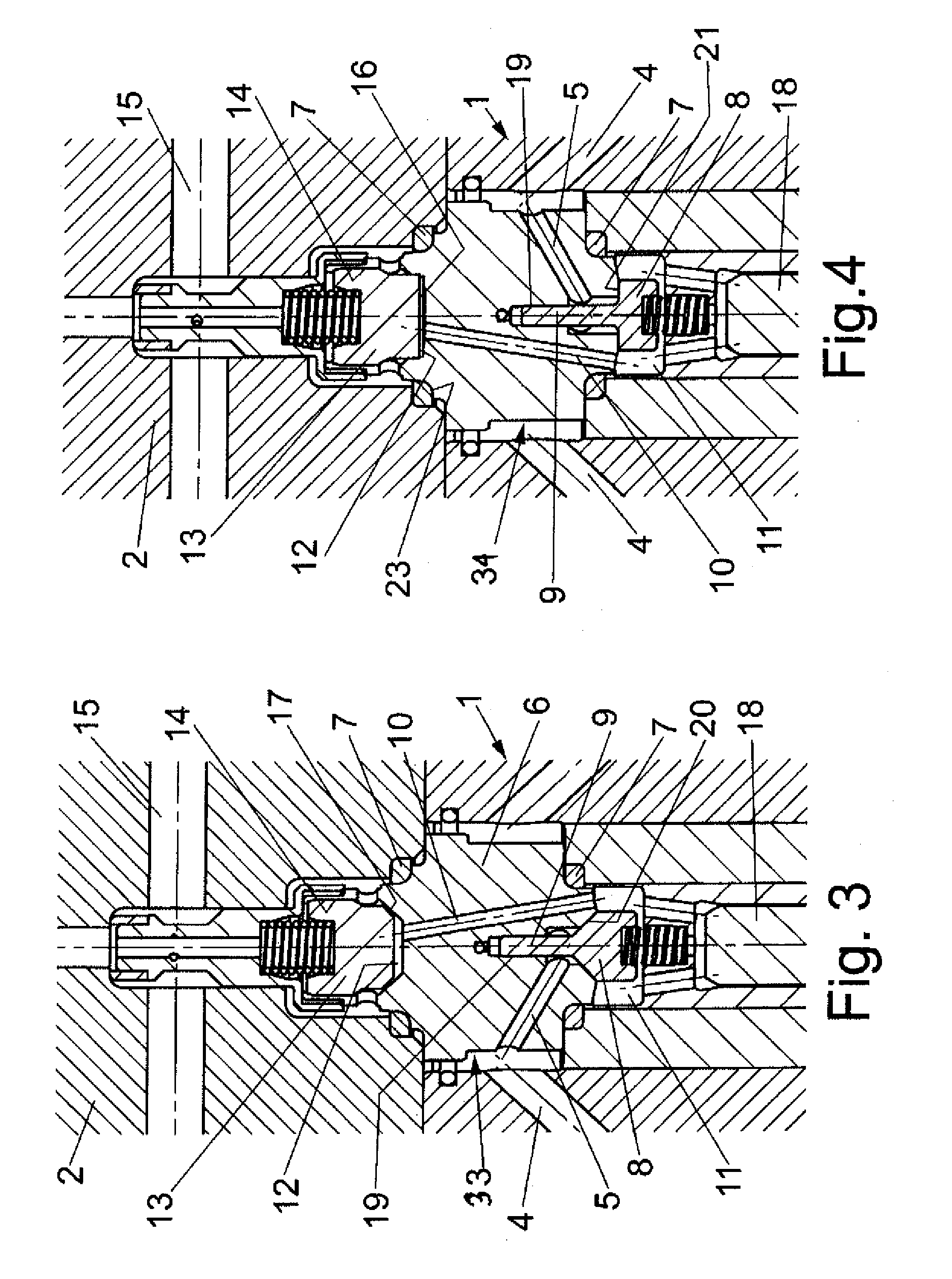
High-pressure valve assembly
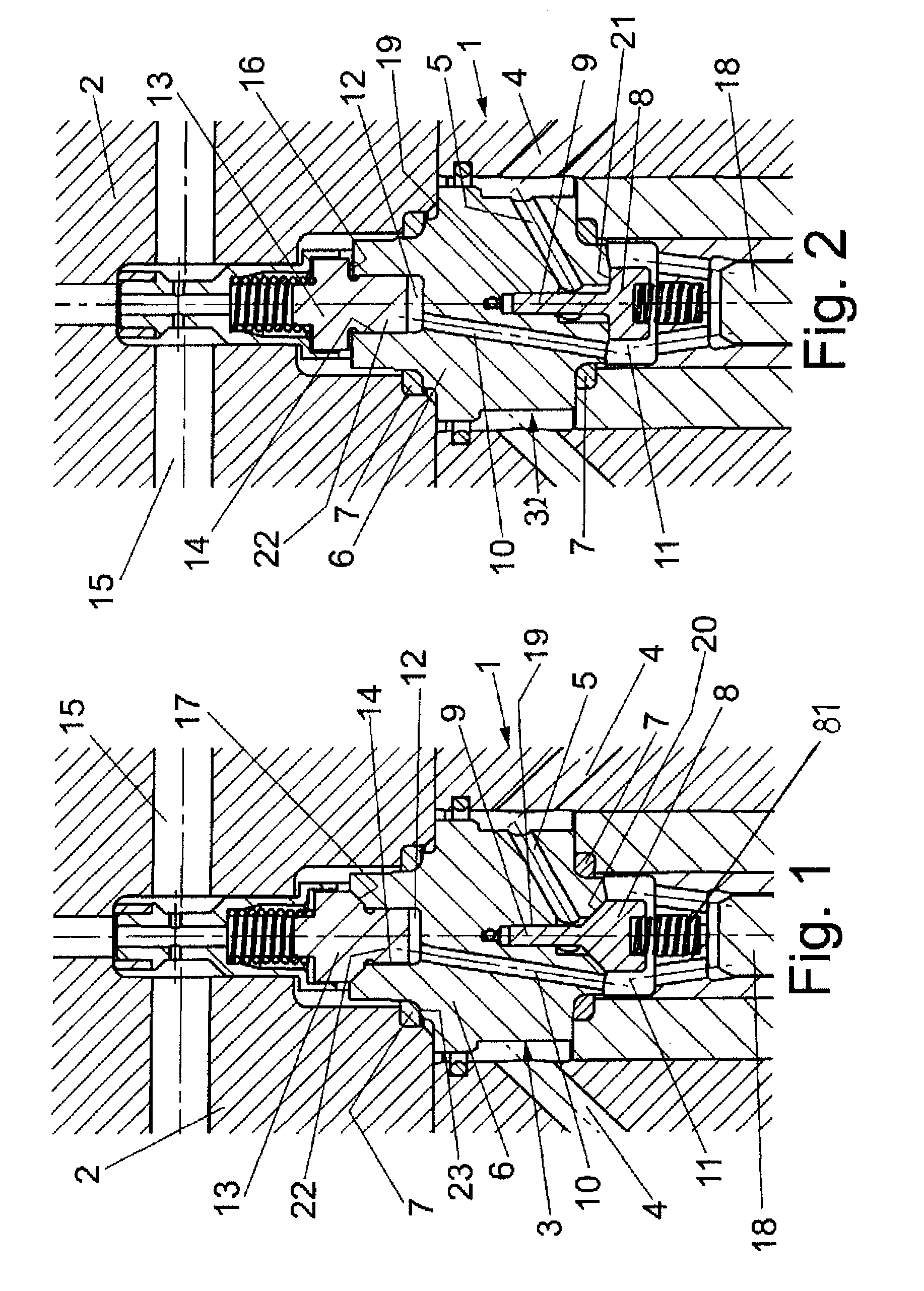
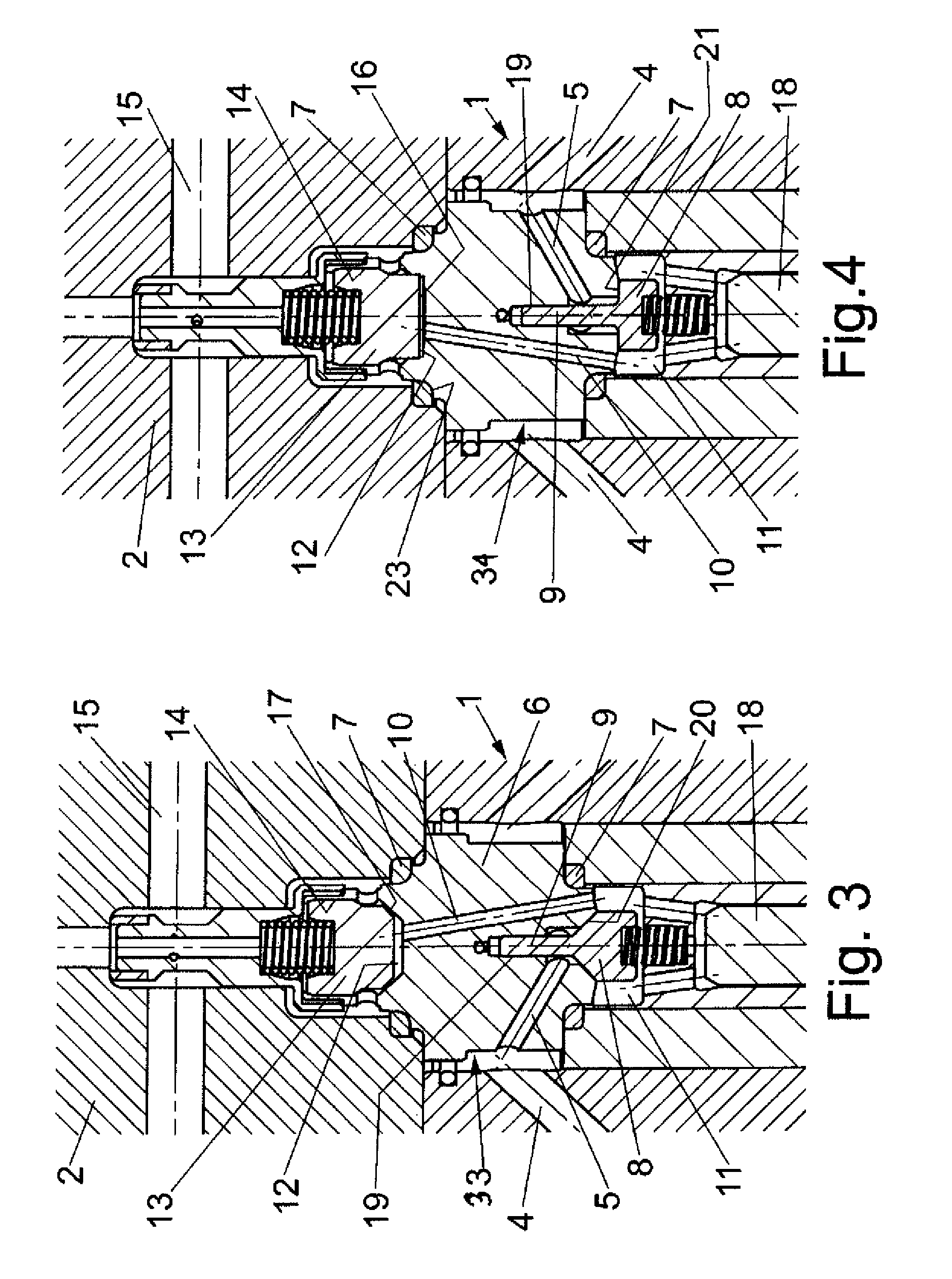
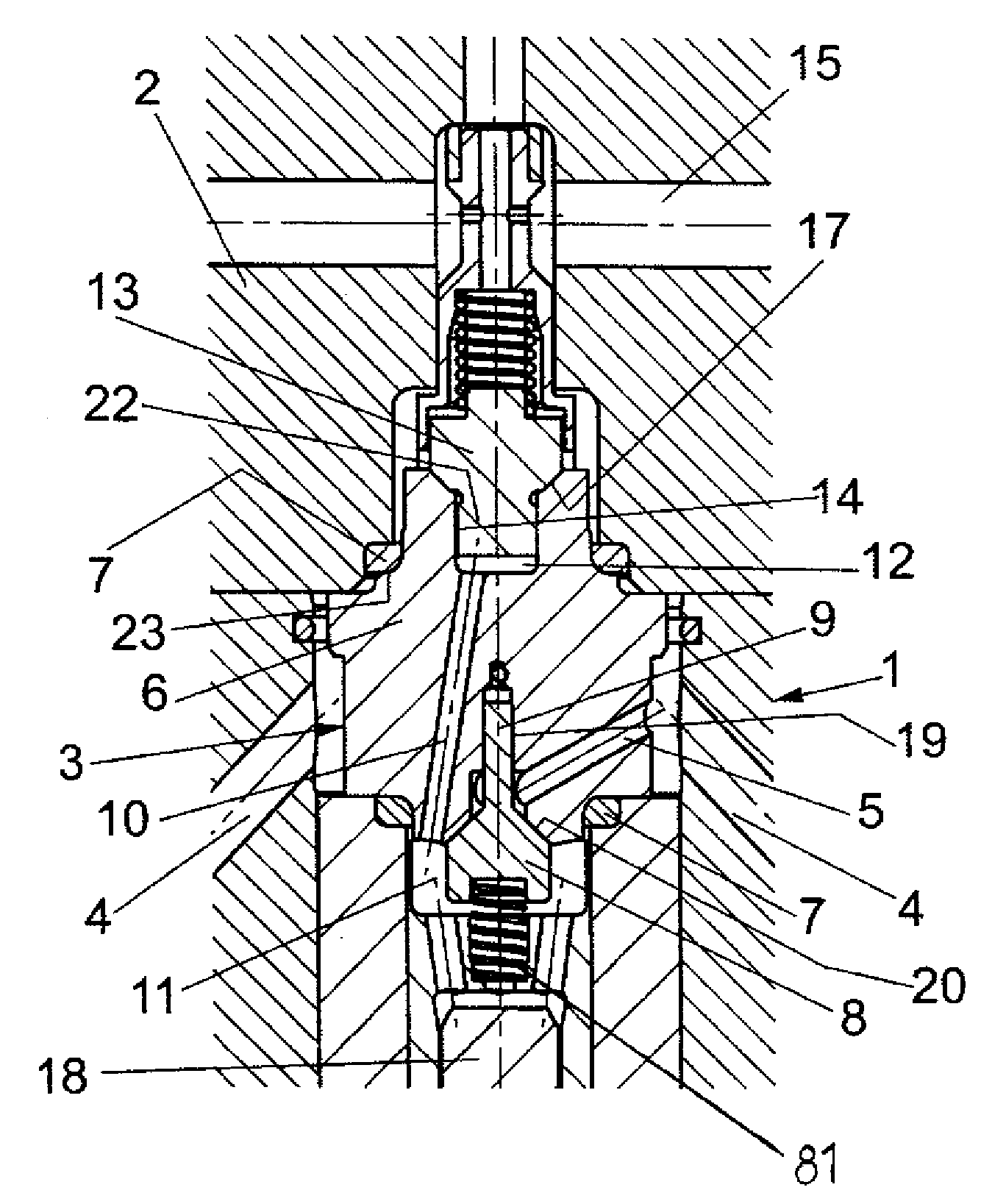
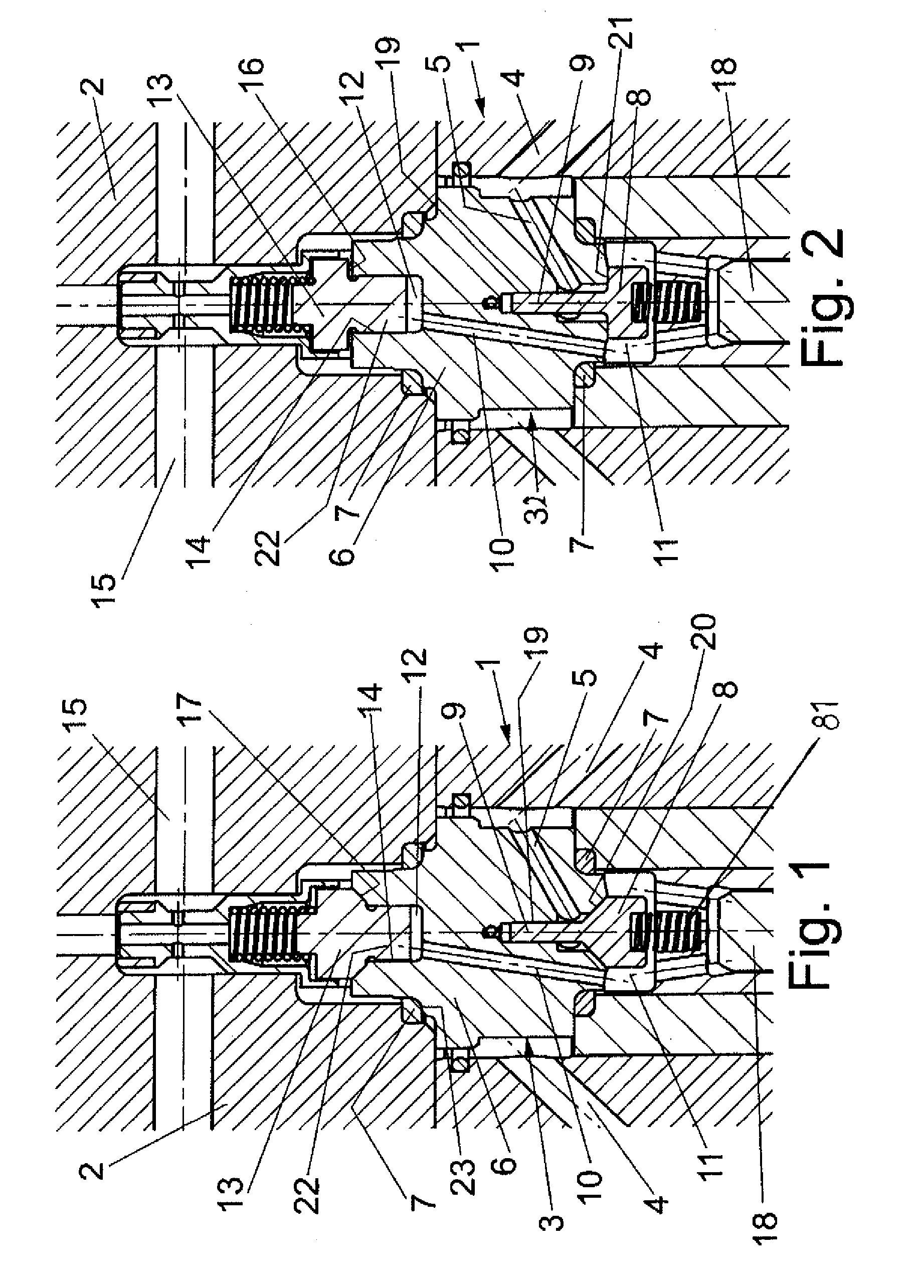
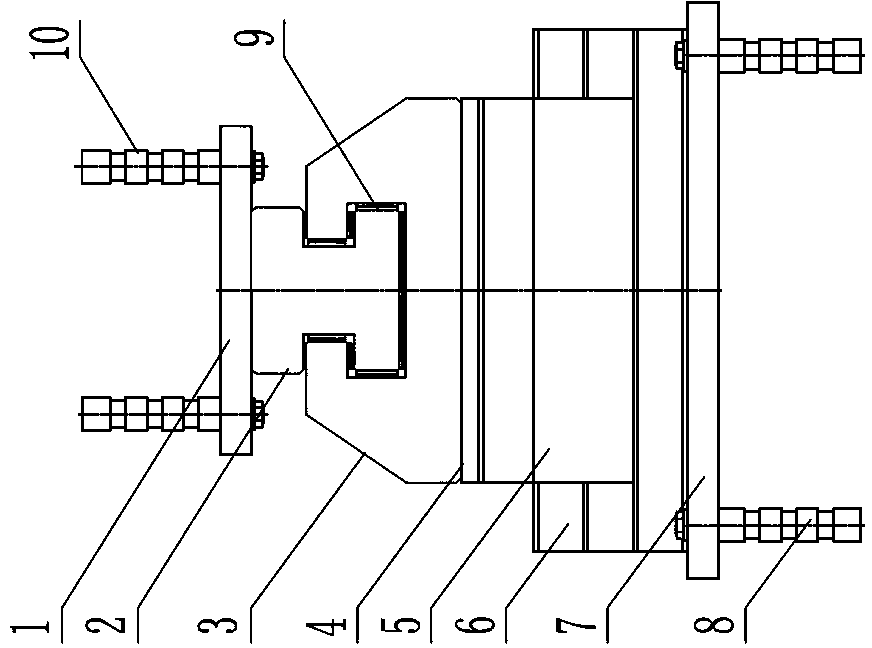
ActiveUS8240634B2Stress minimizationImprove versatilityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive displacement pump componentsEngineeringHigh pressure
A high-pressure valve assembly includes a flange defining an axis. Projecting into the flange is a valve body which is sealed against the flange by a static ring seal. Provided on one side of the valve body is a spring-loaded closure member which is supported for movement in a direction of the axis to form a suction valve, and on another side of the valve body in opposition to the one side is a spring-loaded tappet which is supported for movement in the direction of the axis to form a pressure valve. A channel connects the suction valve with the pressure valve and has one end porting into a pressure chamber of the valve body adjacent to the pressure valve. The pressure chamber extends in axial direction of the tappet and is sized to extend substantially above a bottom edge of the ring seal.
Owner:HAMMELMANN MASCHFAB
High-pressure valve assembly
ActiveUS20090194717A1Stress minimizationImprove versatilityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive displacement pump componentsHigh pressureTappet
A high-pressure valve assembly includes a flange defining an axis. Projecting into the flange is a valve body which is sealed against the flange by a static ring seal. Provided on one side of the valve body is a spring-loaded closure member which is supported for movement in a direction of the axis to form a suction valve, and on another side of the valve body in opposition to the one side is a spring-loaded tappet which is supported for movement in the direction of the axis to form a pressure valve. A channel connects the suction valve with the pressure valve and has one end porting into a pressure chamber of the valve body adjacent to the pressure valve. The pressure chamber extends in axial direction of the tappet and is sized to extend substantially above a bottom edge of the ring seal.
Owner:HAMMELMANN MASCHFAB
Method for preparing TiAl+Ti2AlNb composite materials by laser melting deposition
ActiveCN110449581ATurn up the plasticityControl the preheating temperatureAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingStress concentrationLaser additive manufacturing
The invention belongs to the technical field of laser added material manufacturing, and relates to a method for preparing TiAl+Ti2AlNb composite materials by laser melting deposition. The laser melting deposition method is adopted to form the TiAl+Ti2AlNb composite materials; and the feeding quantity of Ti2AlNb is adjusted to achieve a pinning effect in composite material structures to improve overall plasticity of the materials. Meanwhile, circular samples are formed, and scanning paths are changed to concentric arcs to prevent the tensile stress of linear scanning paths of rectangular samples; and concentric circle openings on each layer are converted by 60-90 degrees, that is, the positions of scanning initial points on each layer are changed, so that the thermal stress concentration isreduced to prevent cracks. The heat input quantity in the forming process is controlled, and the substrate preheating temperature in the forming process is adjusted to slow down the formed metal solidification speed and cooling speed, so that the stress is released for a longer time.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
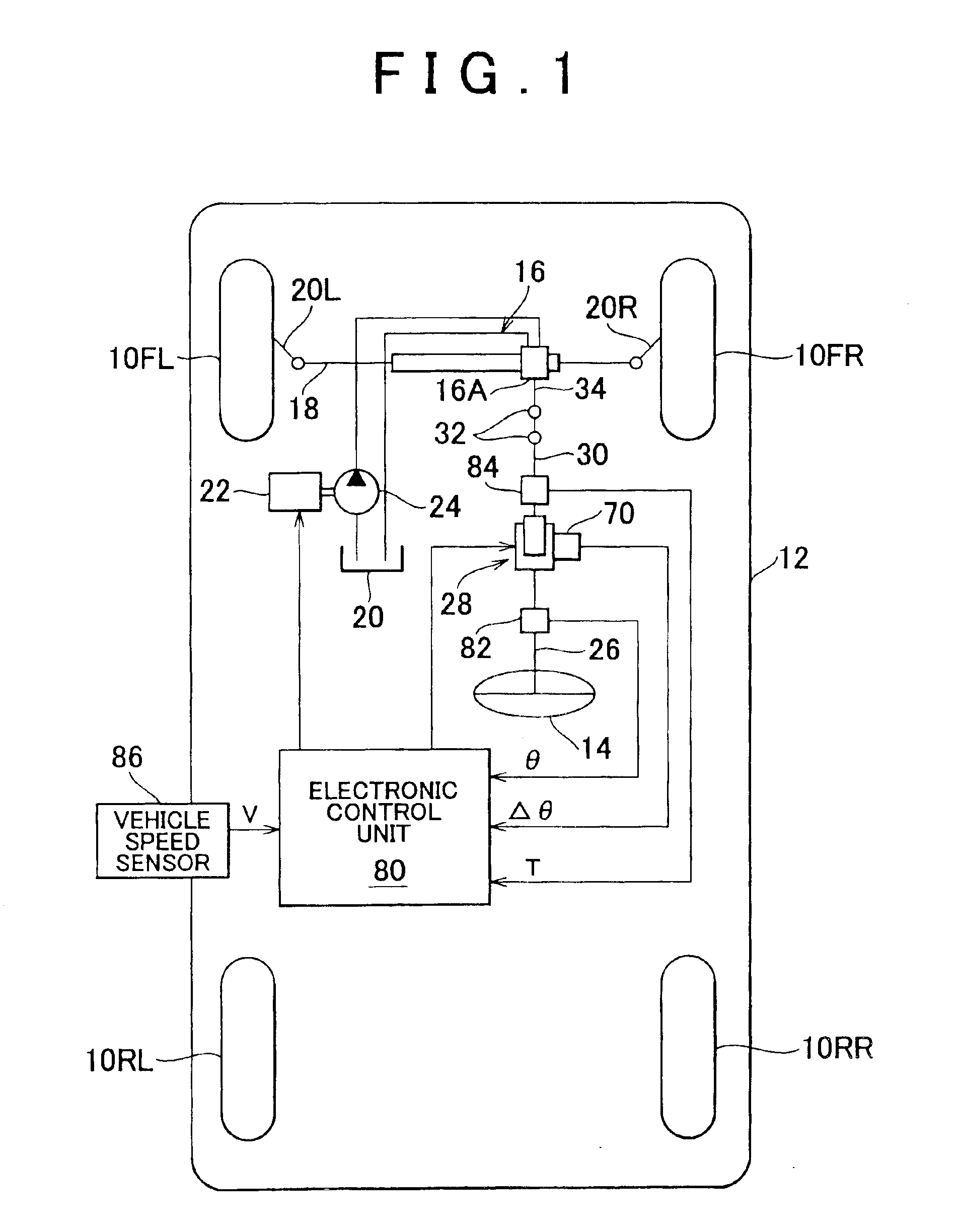
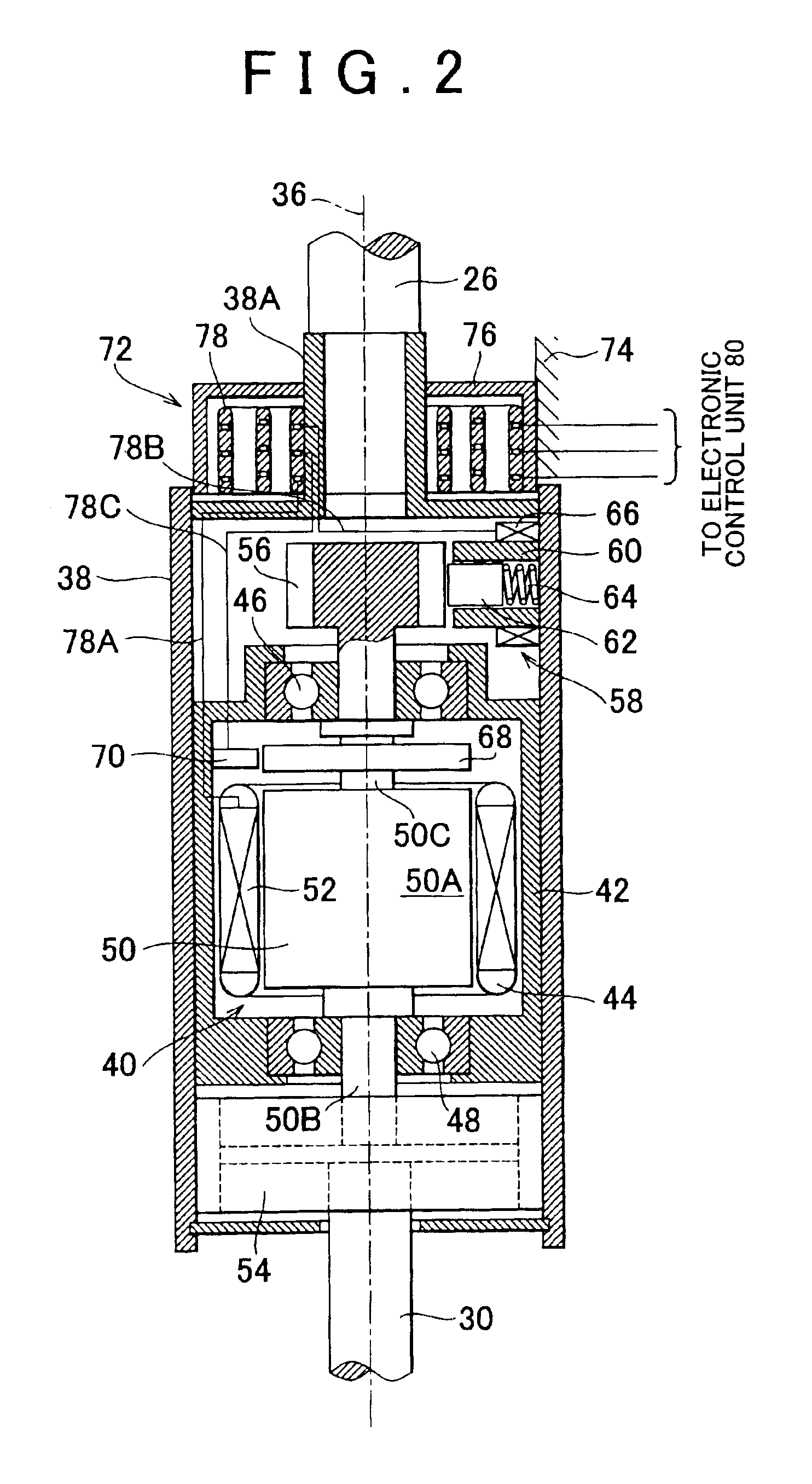
Vehicular steering control device and vehicular steering control method
A target relative rotational angle Δθt which is created by a steering gear ratio change unit and which is formed by a lower steering shaft relative to an upper steering shaft is calculated on the basis of a steering angle θ, and a post-correction target relative rotational angle Δθta to be created by the steering gear ratio change unit is calculated on the basis of the target relative rotational angle Δθt and a vehicle speed range that has been determined on the basis of a vehicle speed V. Thus, a target relative rotational angle in one lateral direction is so corrected as to be equal to or smaller than a difference between a permissible rotational angle to be defined by a spiral cable in the other lateral direction and a maximum possible rotational angle of the lower steering shaft in the other lateral direction. An electric motor is controlled on the basis of the post-correction target relative rotational angle Δθta.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
System and method for electromagnetic pulse surface treatment
ActiveUS7378622B2Convenience to workReduce stress concentrationSoldering apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyElectromagnetic pulseEngineering
A system and method for electromagnetic surface treatment of a work piece has an electromagnetic pulse generator and an electromagnetic pulse tool. The work piece has a working surface. A current pulse generated by the electromagnetic pulse generator travels through the tool producing an electromagnetic pulse. The electromagnetic pulse interacts with the working surface causing an indentation to form. A residual compressive stress layer is also formed. The indentation has a smooth and continuous topography that is described by an indentation perimeter, an indentation transition region, an indentation sidewall, an impact transition region, and an impact region. The method may also simultaneously, or subsequently, form a second indentation which overlaps with the indentation. An inter-indentation overlap region is formed when the indentations overlap. The inter-indentation overlap region is smooth and continuous. Multiple treated surfaces may easily be formed on the working surface of the work piece.
Owner:GATEKEY ENG
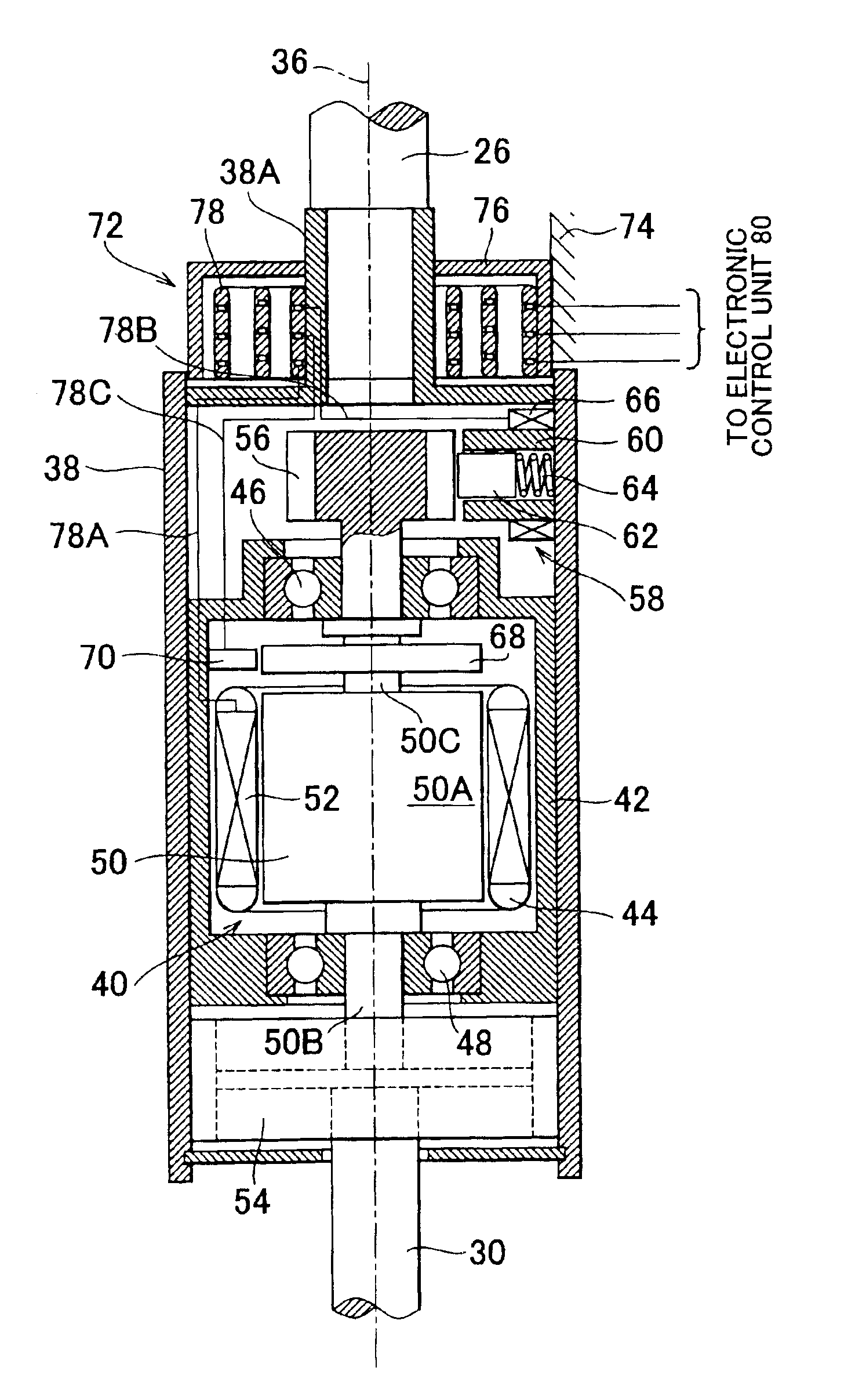
Piezoelectric Power Generator
ActiveUS20110148256A1Improve power generation efficiencyImprove vibration efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesElectricityEngineering
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Catheter
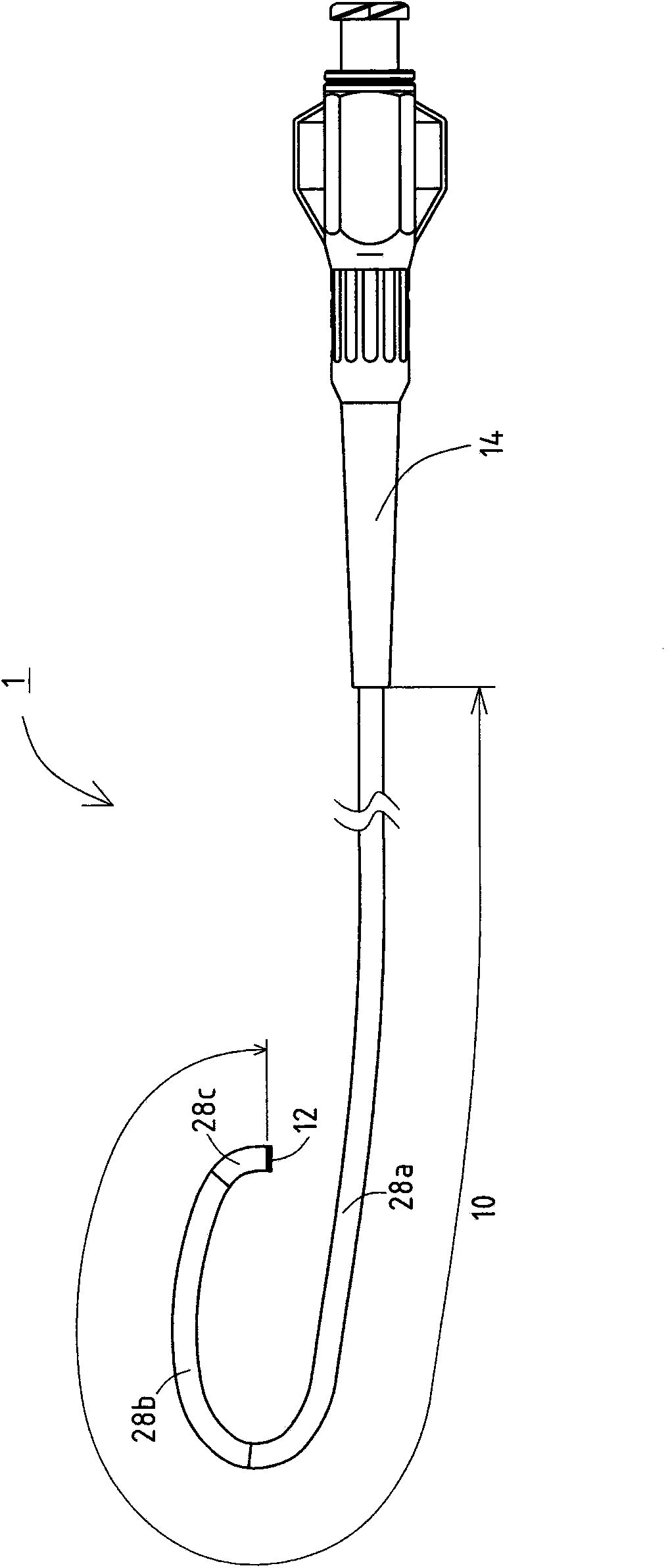
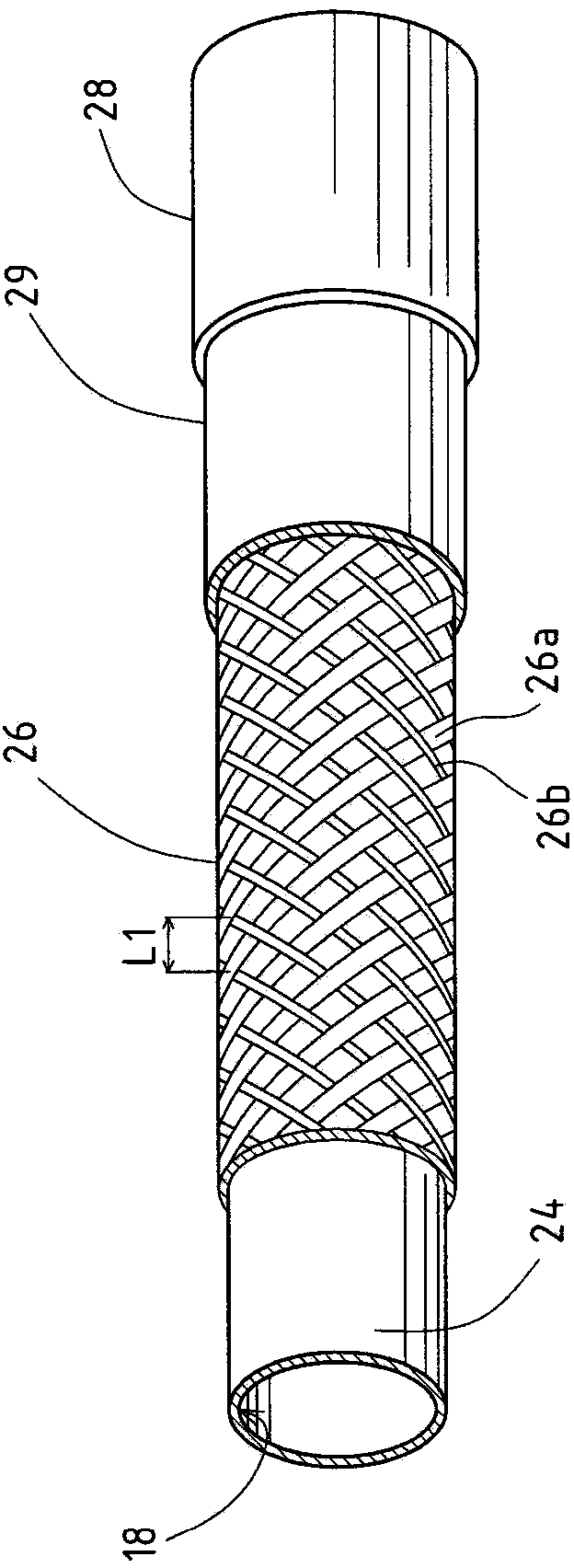
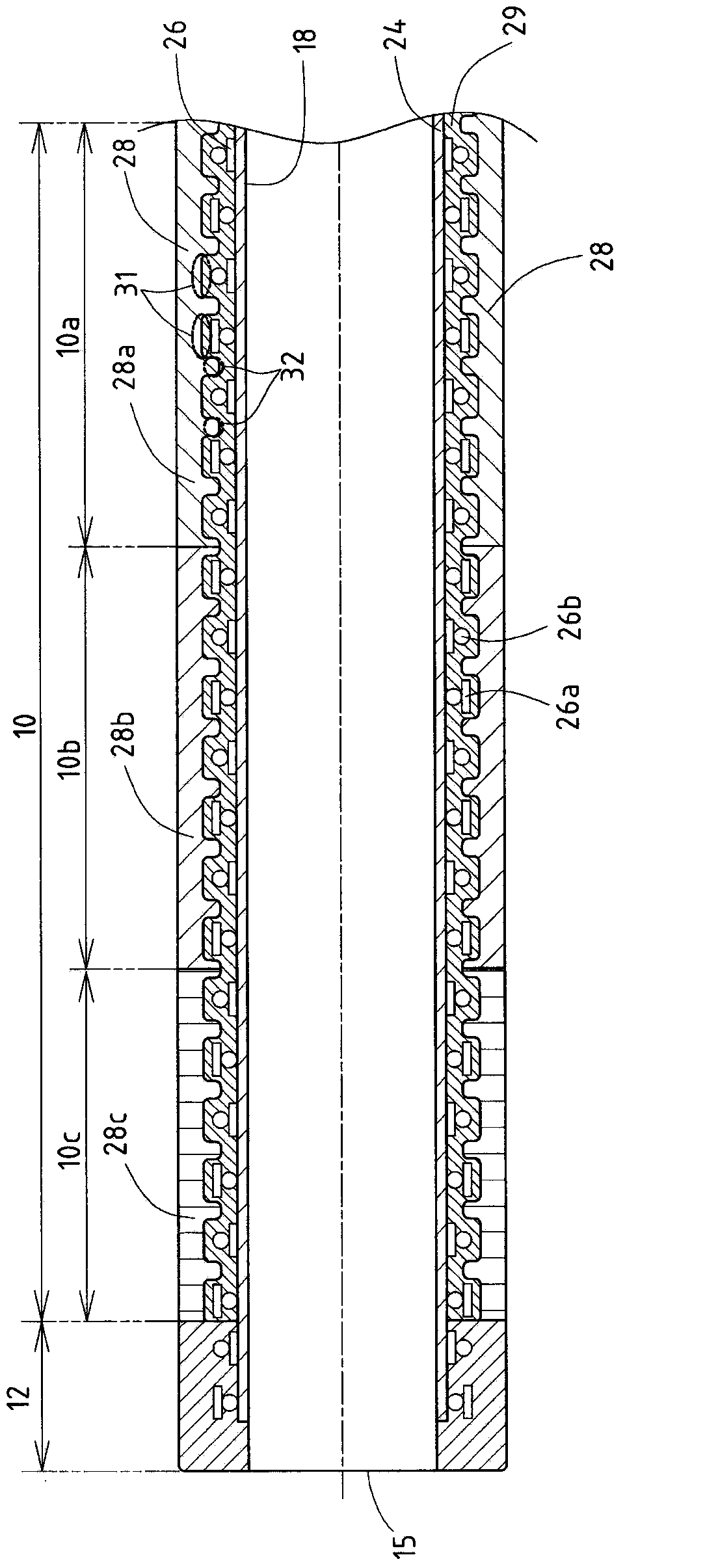
InactiveCN103990218APrevent peelingInhibitionLayered productsCatheterBlood vesselBiomedical engineering
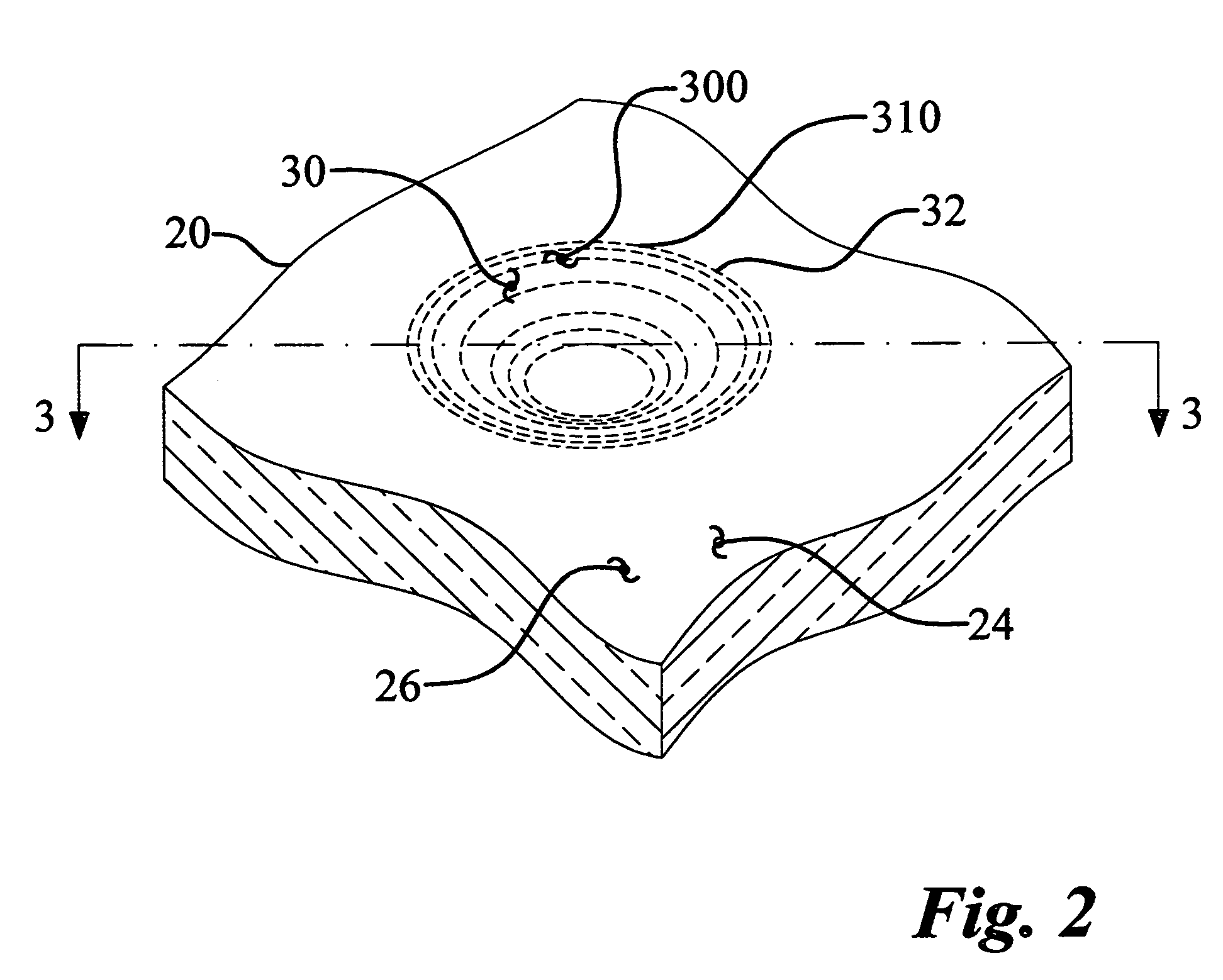
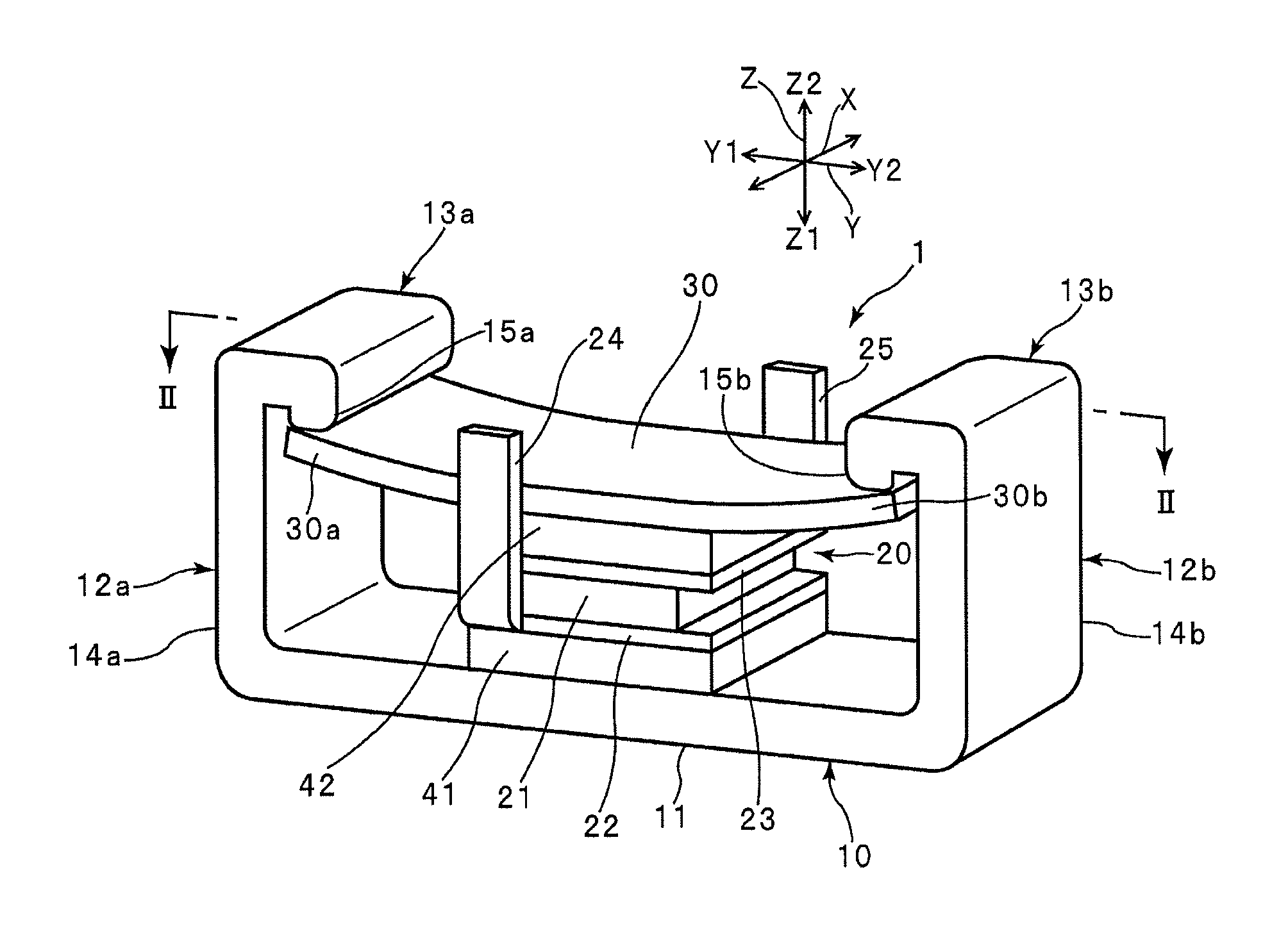
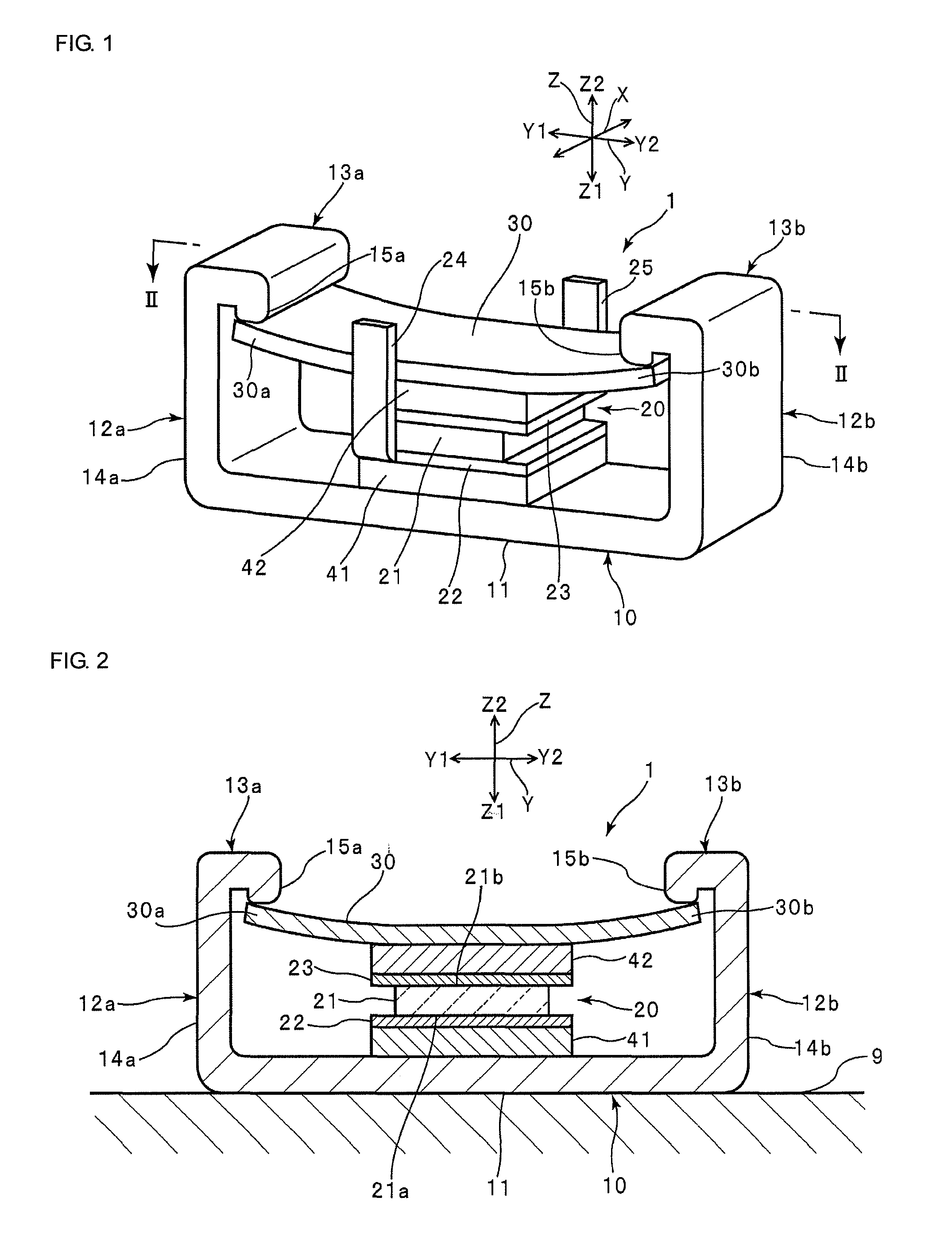
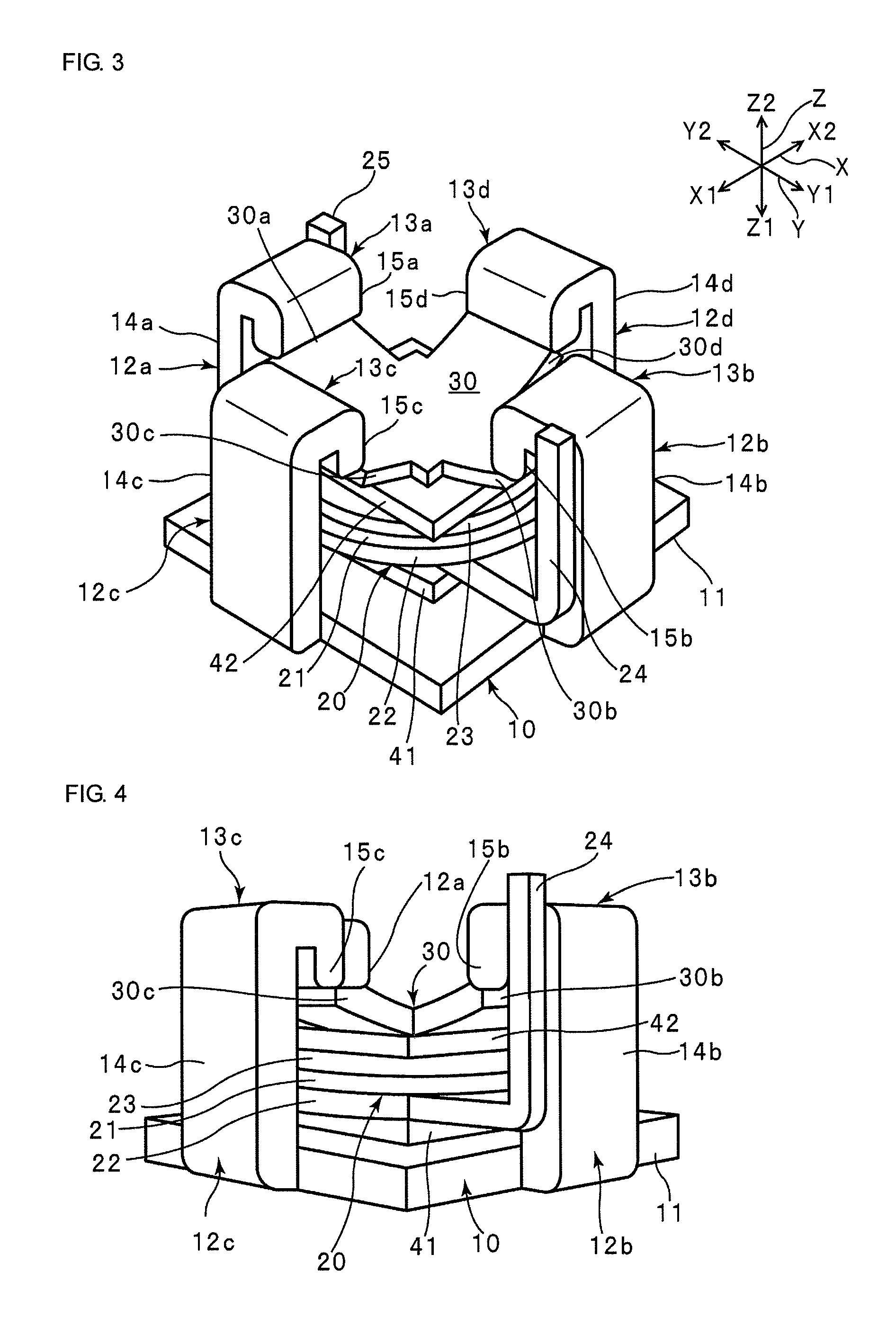
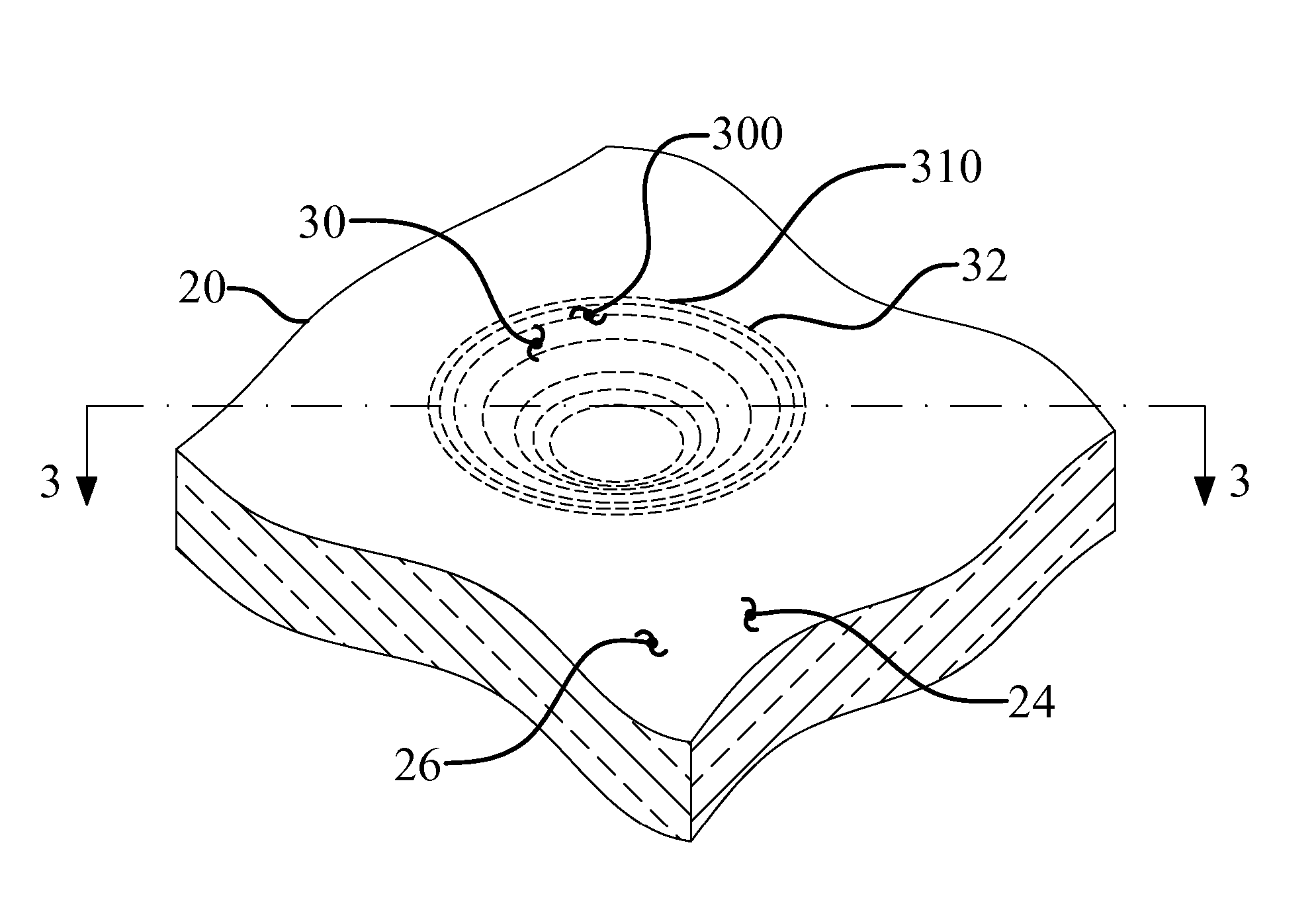
In a catheter (1), since the thickness of an intermediate layer (29) is constant from a body (10a) to a distal end portion (10b), the adhesive strength (adhesiveness) between the intermediate layer (29) and an inner layer (24) is uniform from the body (10a) to the distal end portion (10b) of a catheter shaft (10). Therefore, when the catheter (1) is curved, the movement of a braid (26) caused by the curving of the catheter (1) can be uniformly suppressed from the body (10a) to the distal end portion (10b) that is adjacent thereto. Even if, when the catheter (1) is curved, a tensile stress (30a) towards a proximal end acts upon a first outer layer (28a) at the body (10a) and a tensile stress (30b) towards a distal end acts upon a second outer layer (28b) at the distal end portion (10b) adjacent to the body (10a), the first and second outer layers (28a, 28b) are caught by an uneven contour of the intermediate layer (29) by an anchor effect, so that it is possible to prevent peeling of the first and second outer layers (28a, 28b) from an intermediate layer (29).
Owner:ASAHI INTECC CO LTD
Pin for insertion into a receiving opening in a printed circuit board and method for inserting a pin into a receiving opening in a printed circuit board
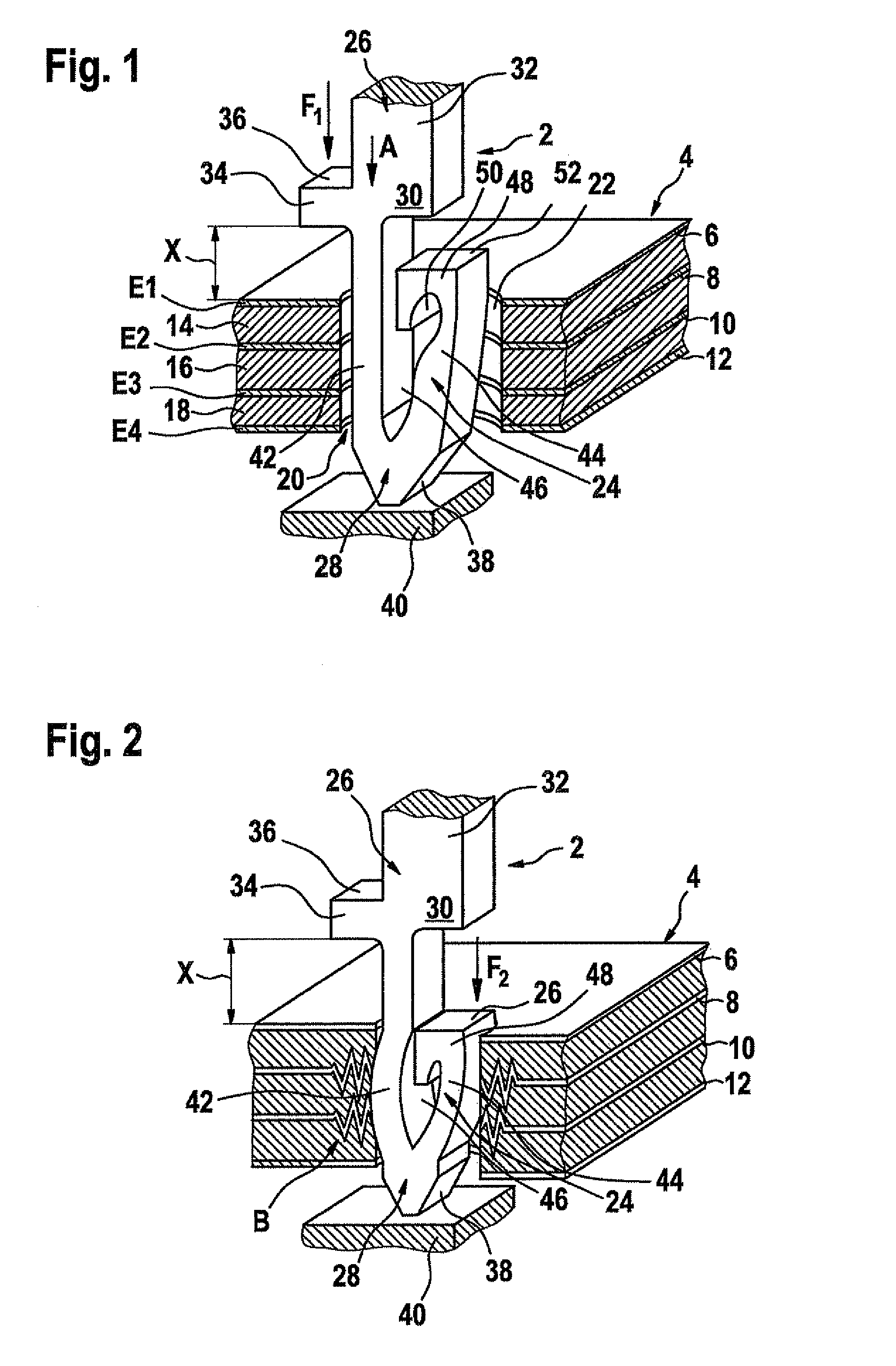
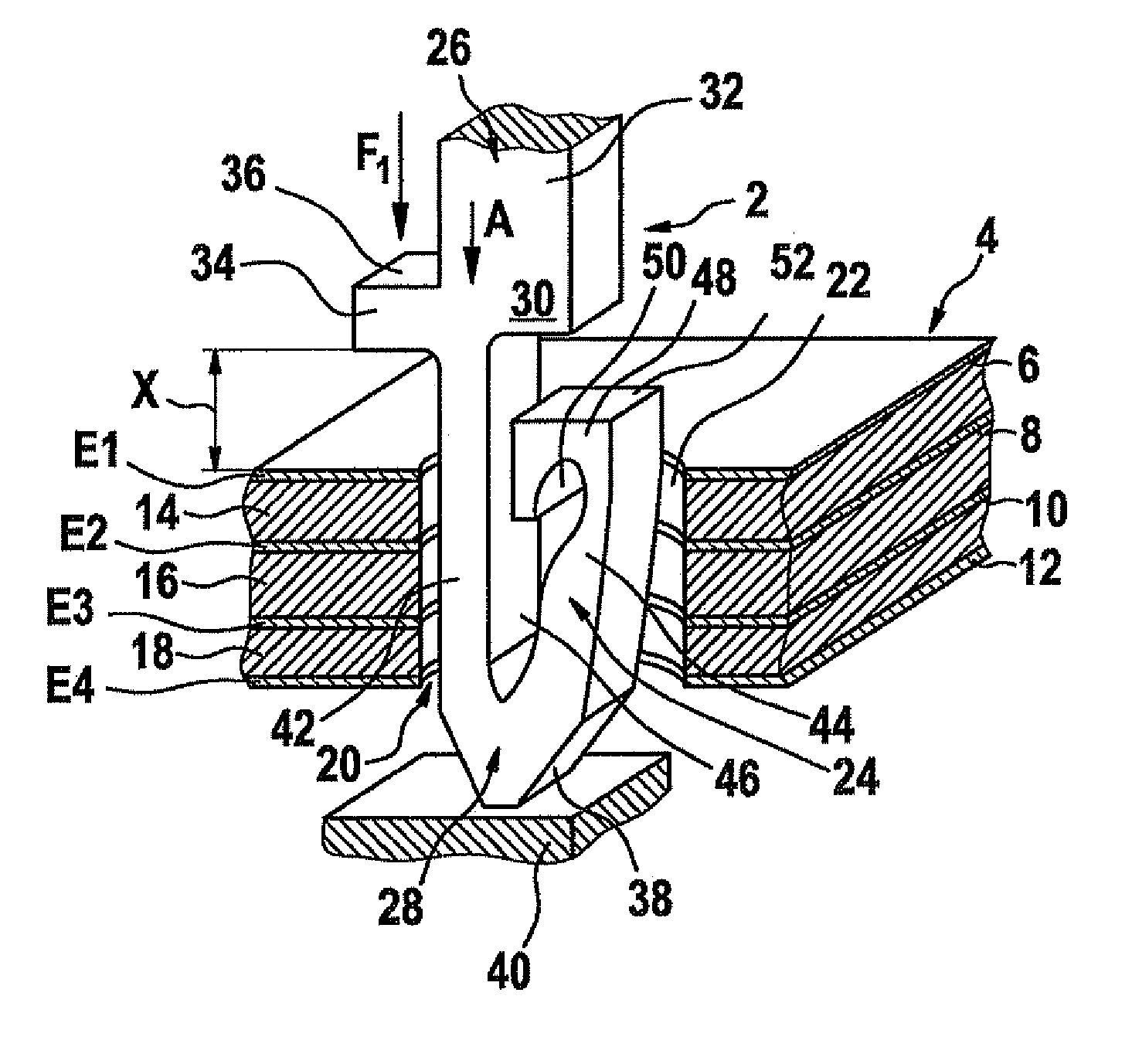
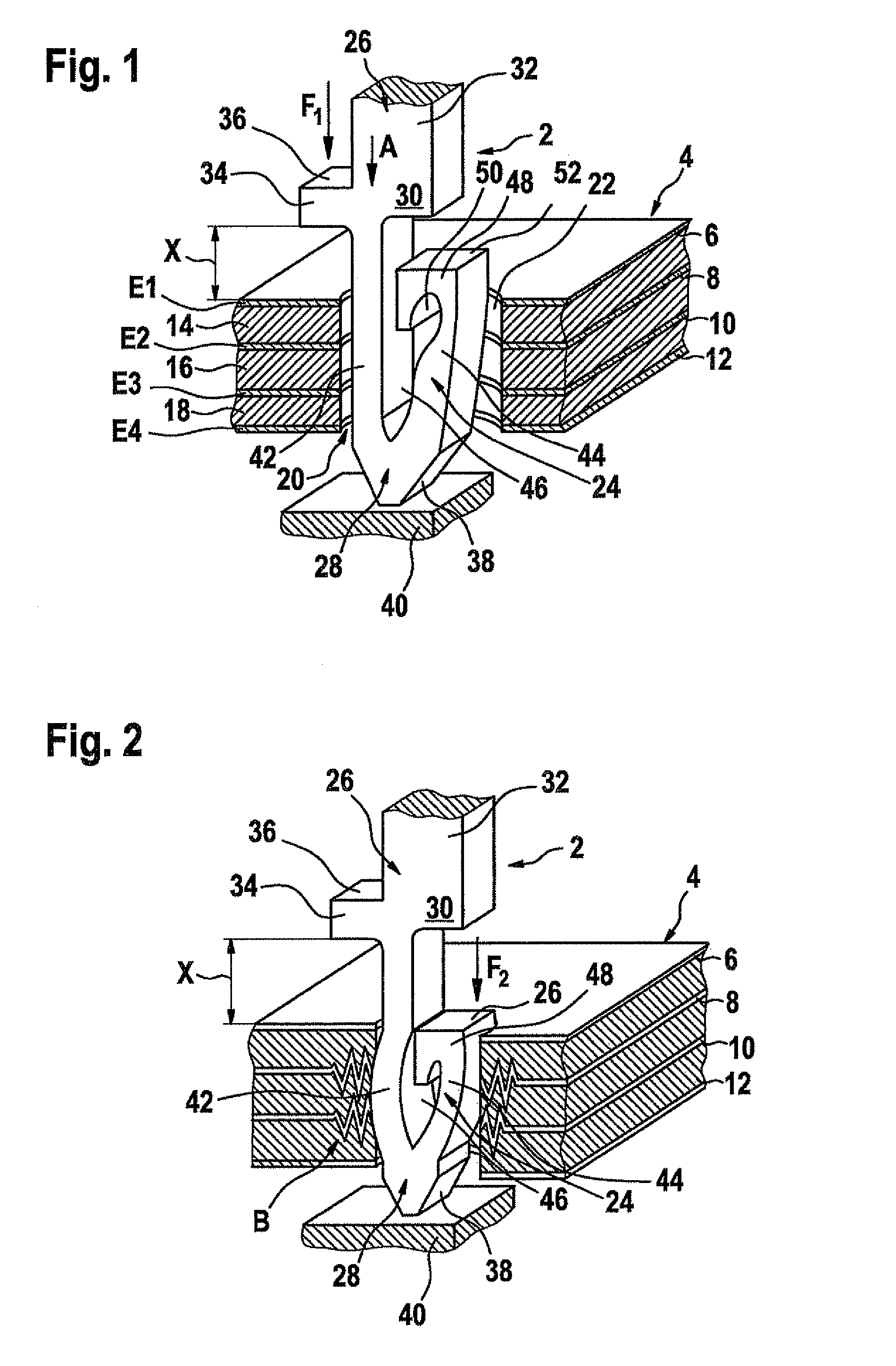
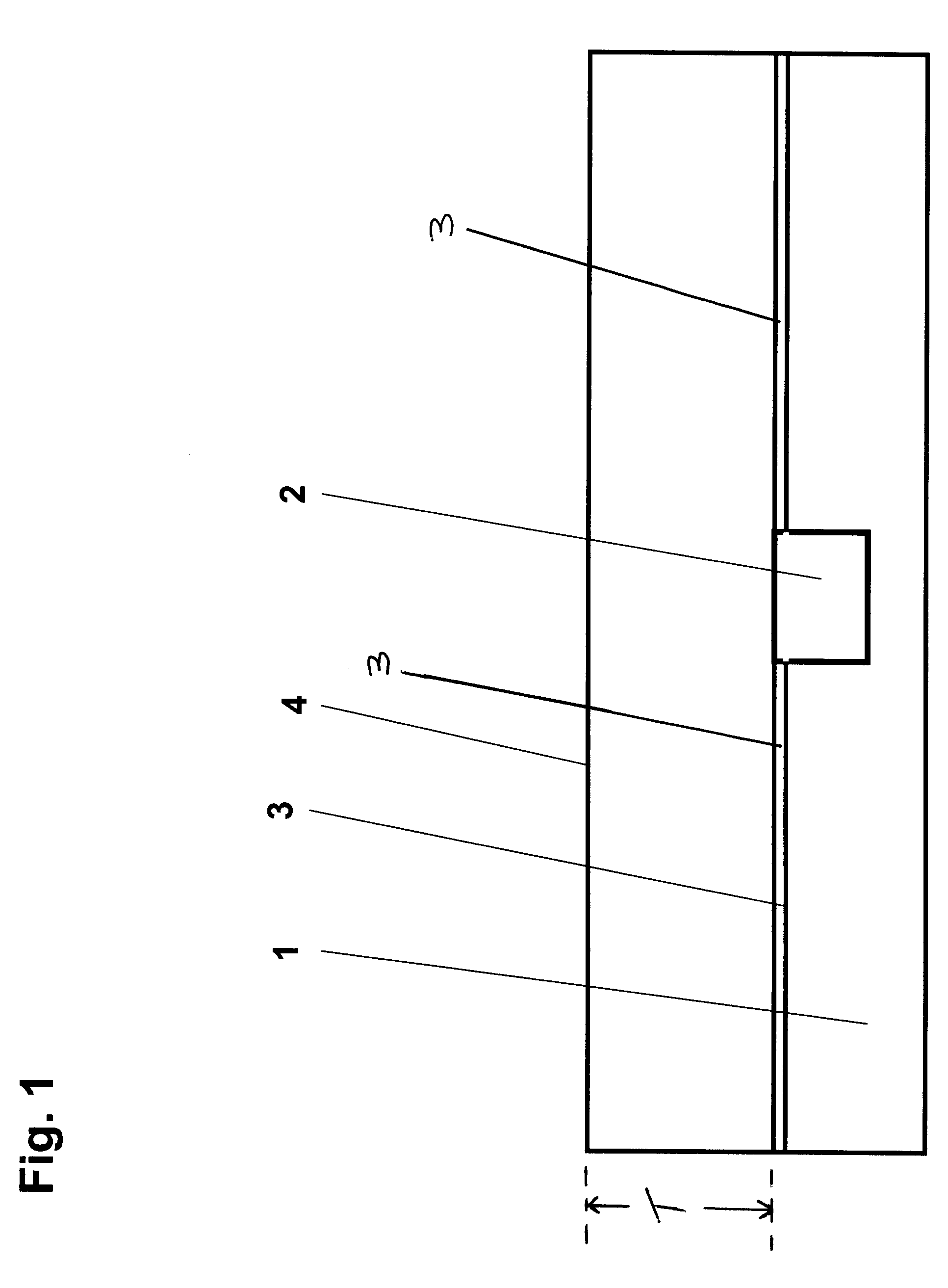
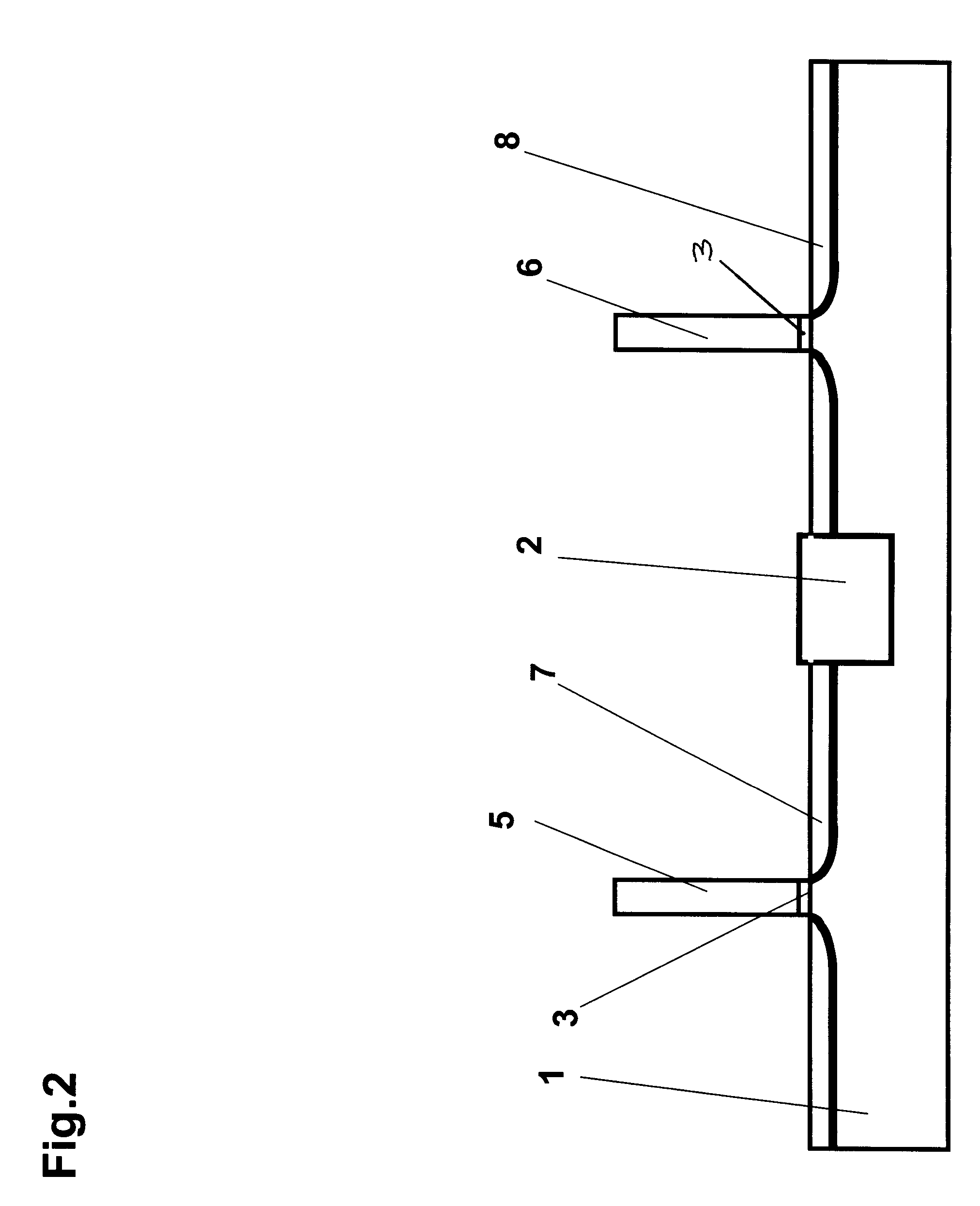
InactiveUS7828561B2Savings for the electroplating of the pinsAvoid tensile stressVehicle connectorsSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersEngineeringPrinted circuit board
A pin having a contact part may be inserted into a receiving opening in a printed circuit board and anchored in the receiving opening with a press fit. Also, a method provides for inserting a pin into a receiving opening in a printed circuit board, in which the pin is inserted into the receiving opening from one side of the printed circuit board, and a contact part of the pin is anchored in the receiving opening with a press fit. The contact part is inserted into the receiving opening in a contactless manner or with a sliding fit and is subsequently deformed within the receiving opening by expansion transversally to the insertion direction in order to anchor the contact part in the receiving opening with a press fit.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Pin for insertion into a receiving opening in a printed circuit board and method for inserting a pin into a receiving opening in a printed circuit board
InactiveUS20090298312A1Easy to insertEasy to manufactureVehicle connectorsSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersPrinted circuit boardEngineering
A pin having a contact part may be inserted into a receiving opening in a printed circuit board and anchored in the receiving opening with a press fit. Also, a method provides for inserting a pin into a receiving opening in a printed circuit board, in which the pin is inserted into the receiving opening from one side of the printed circuit board, and a contact part of the pin is anchored in the receiving opening with a press fit. The contact part is inserted into the receiving opening in a contactless manner or with a sliding fit and is subsequently deformed within the receiving opening by expansion transversally to the insertion direction in order to anchor the contact part in the receiving opening with a press fit.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
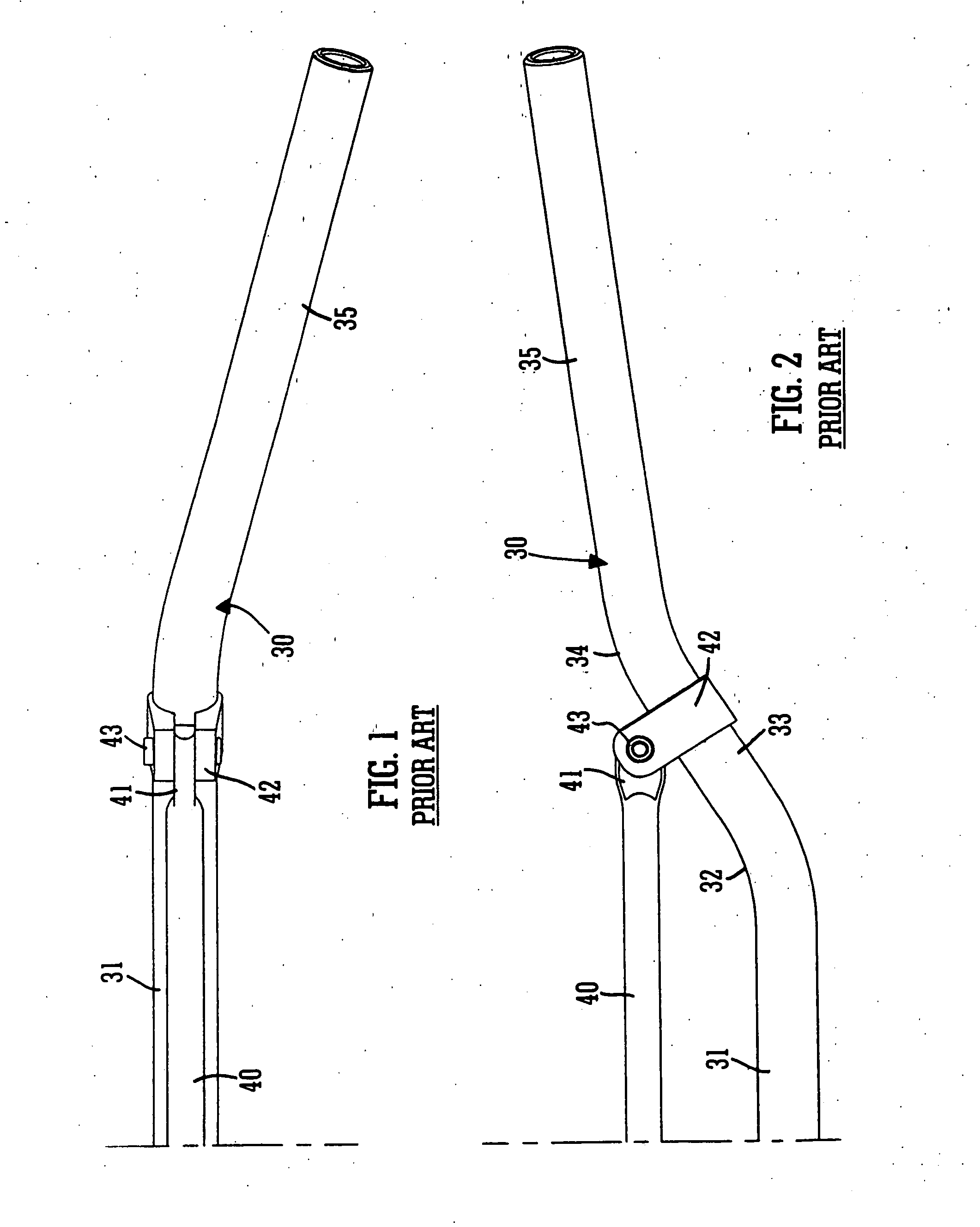
Handlebar clamp
InactiveUS20050199090A1Avoid damageReduce compressive stressMechanical apparatusSteering deviceEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:RENTHAL
Anti-pulling system
An anti-pulling system comprises an upper connecting plate, a lower connecting plate, an upper layer of sliding mechanism, a lower layer of sliding mechanism and intermediate layers, the upper layer of sliding mechanism and the lower layer of sliding mechanism are respectively connected with the upper connecting plate and the lower connecting plate, the intermediate layer is connected between the upper layer of sliding mechanism and the lower layer of sliding mechanism, and the upper layer of sliding mechanism and the lower layer of sliding mechanism have the same structure, are mounted opposite from each other, and can slide in directions perpendicular to each other. The upper (lower) layer of sliding mechanism comprises n sets of upper (lower) guide rails and upper (lower) sliders, the upper (lower) guide rails are mounted in parallel, the upper (lower) sliders are slidably fitted on the upper (lower) guide rails, the top surfaces of the upper guide rails are connected with the upper connecting plate, the top surfaces of the lower guide rails are connected with the lower connecting plate, and the intermediate layers are respectively connected with the bottoms of the upper sliders and the lower sliders. Under the load action of an earthquake or wind, the anti-pulling system can resist the high upward pulling force of a building structure, meanwhile, the anti-pulling system can allow a seismic isolation structure to slide, resist upsetting moment and enhance the anti-leaning or anti-shaking capability of the building structure, and the anti-pulling system can be used along with intermediate seismic isolation rubber bearings and dampers to form a foundation seismic isolation system which can provide the capability of resisting and balancing the horizontal leaning moment of the structure.
Owner:柳州东方工程橡胶制品有限公司
Stressed semiconductor device structures having granular semiconductor material
InactiveUS7122849B2Improve mobilityAvoid compressive stressTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsMaterials science
A method of fabricating a semiconductor device structure, includes: providing a substrate, providing an electrode on the substrate, forming a recess in the electrode, the recess having an opening, disposing a small grain semiconductor material within the recess, covering the opening to contain the small grain semiconductor material, within the recess, and then annealing the resultant structure.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Piezoelectric power generator
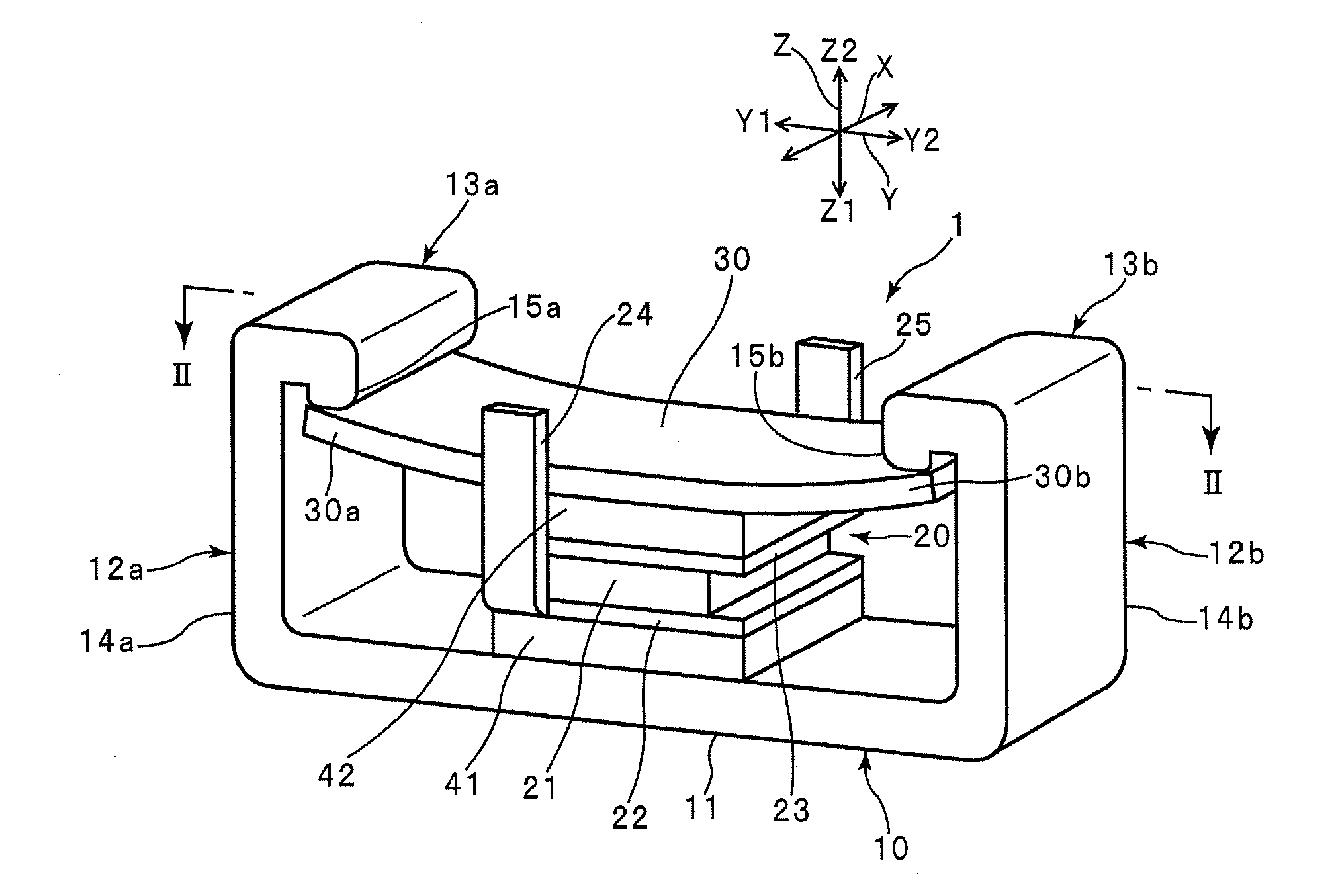
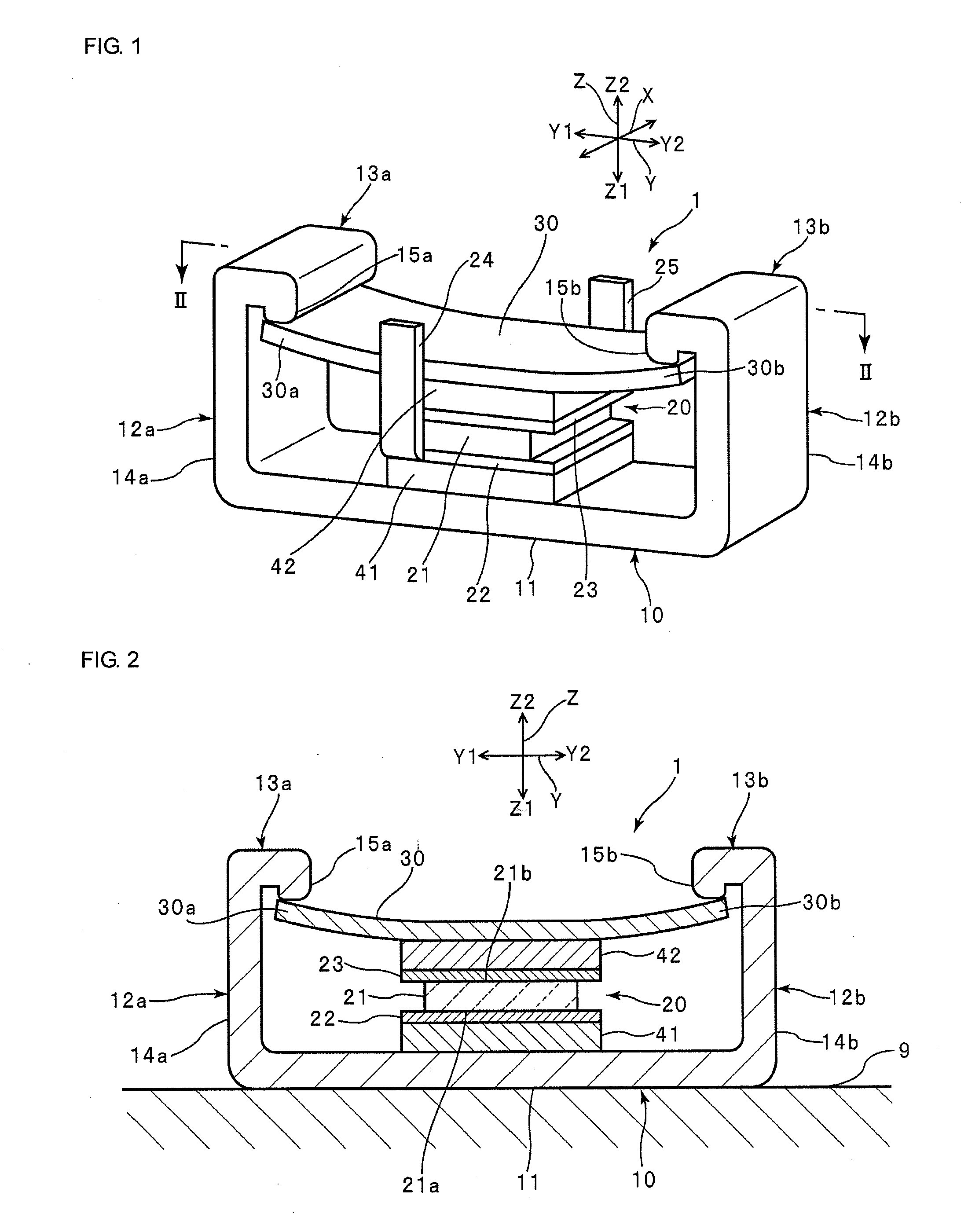
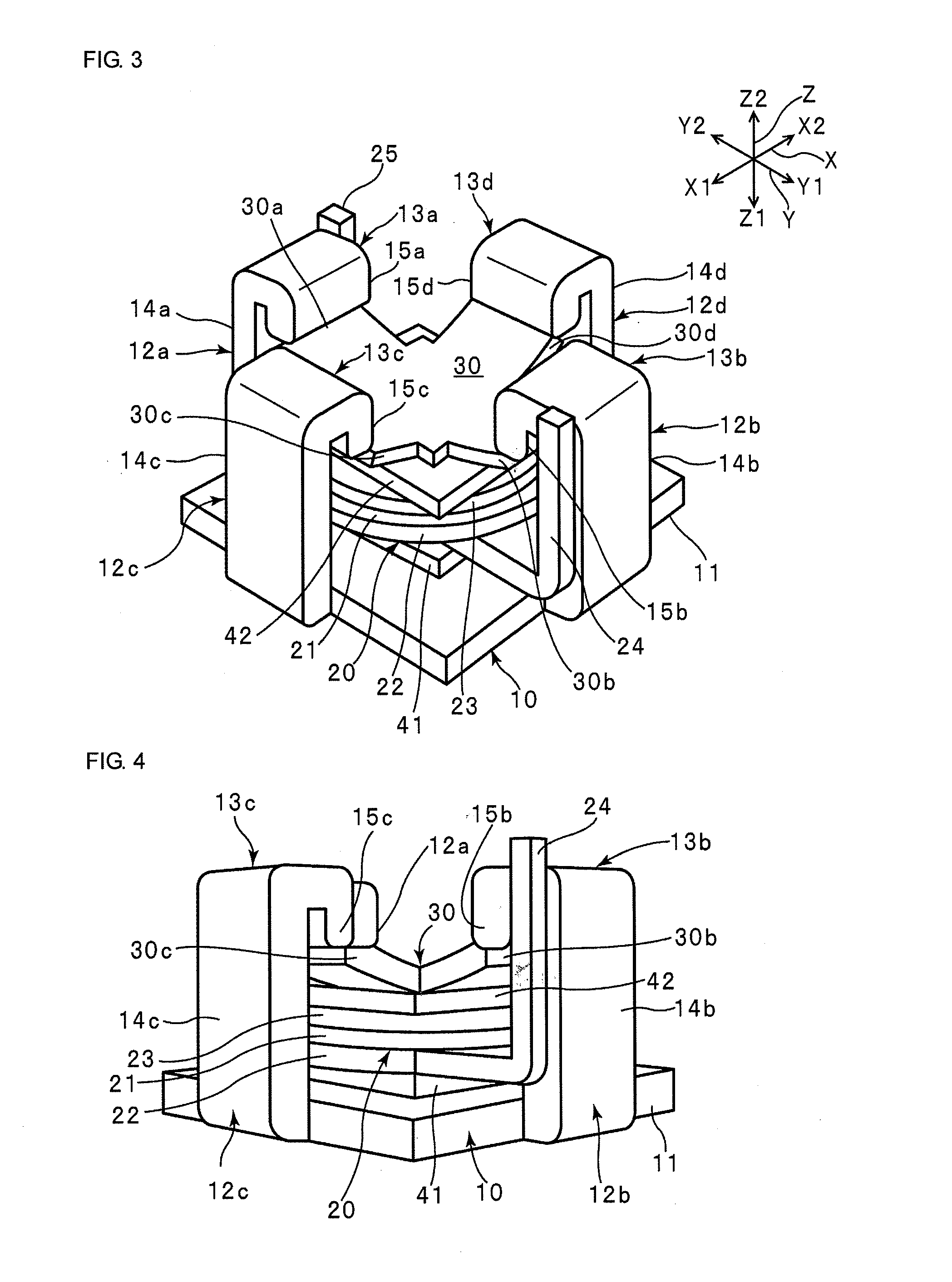
ActiveUS8013497B2Increased durabilityAvoid tensile stressPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesElectricityEngineering
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Strain wave gearing with full separation of two stresses
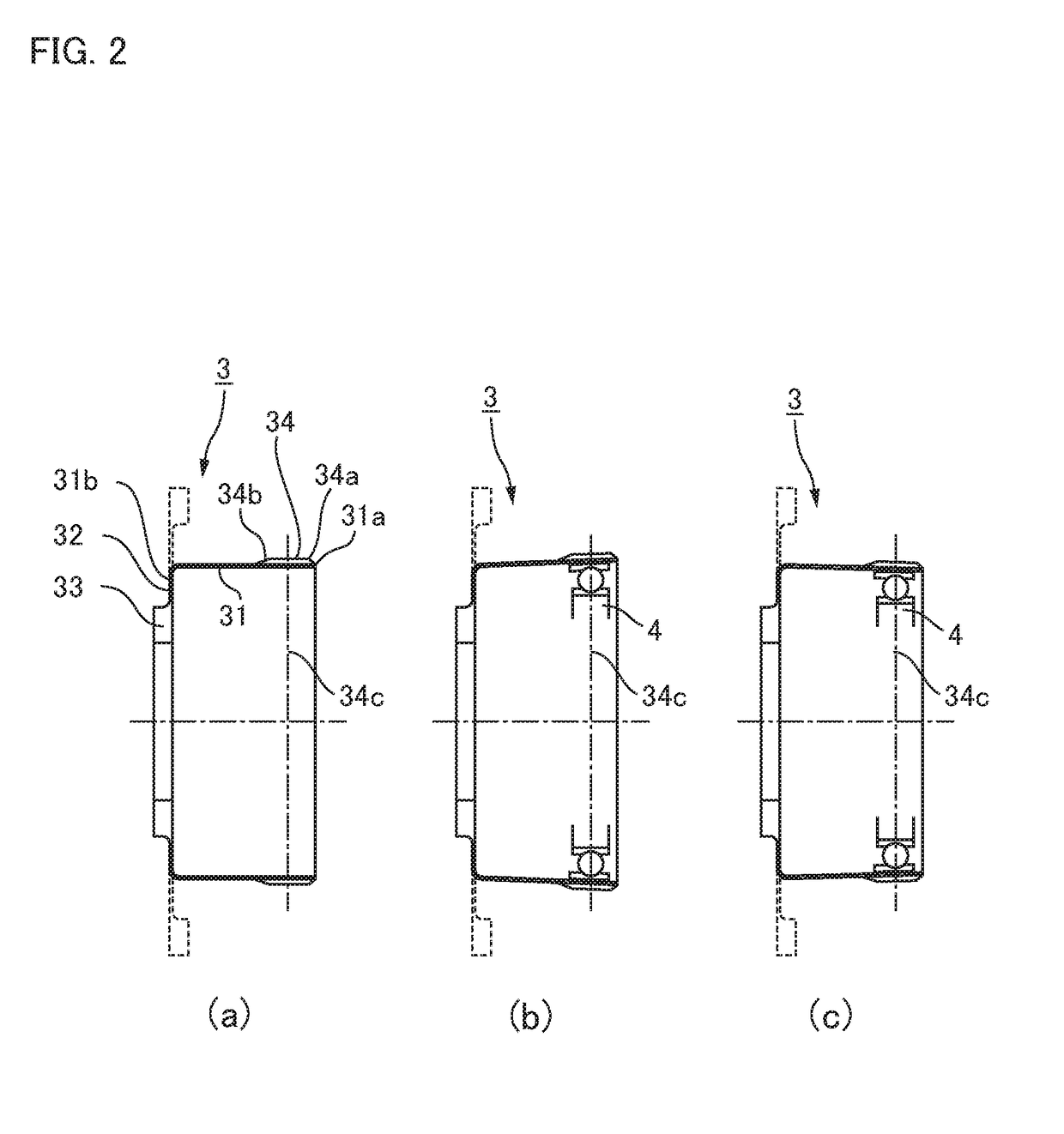
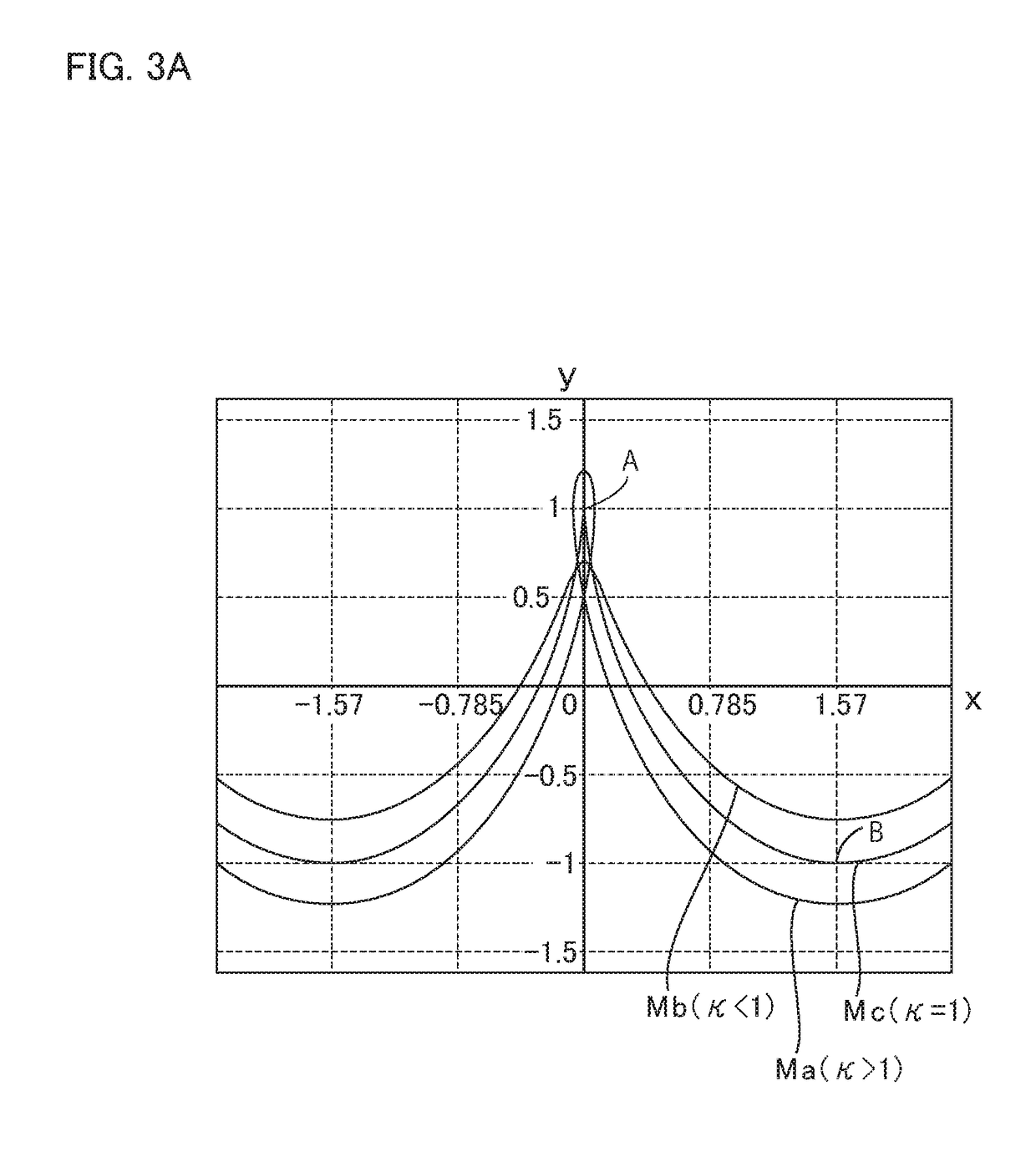
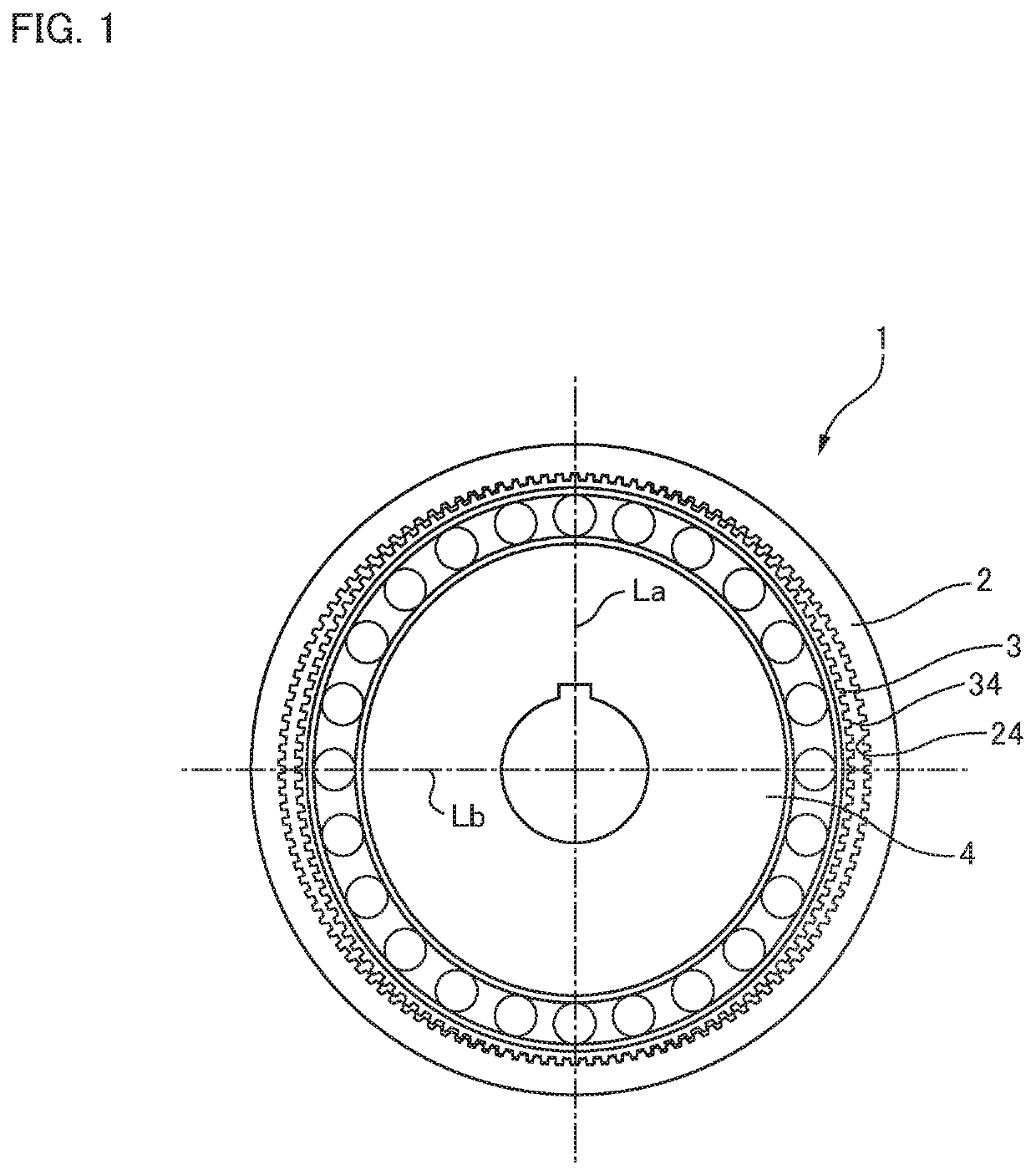
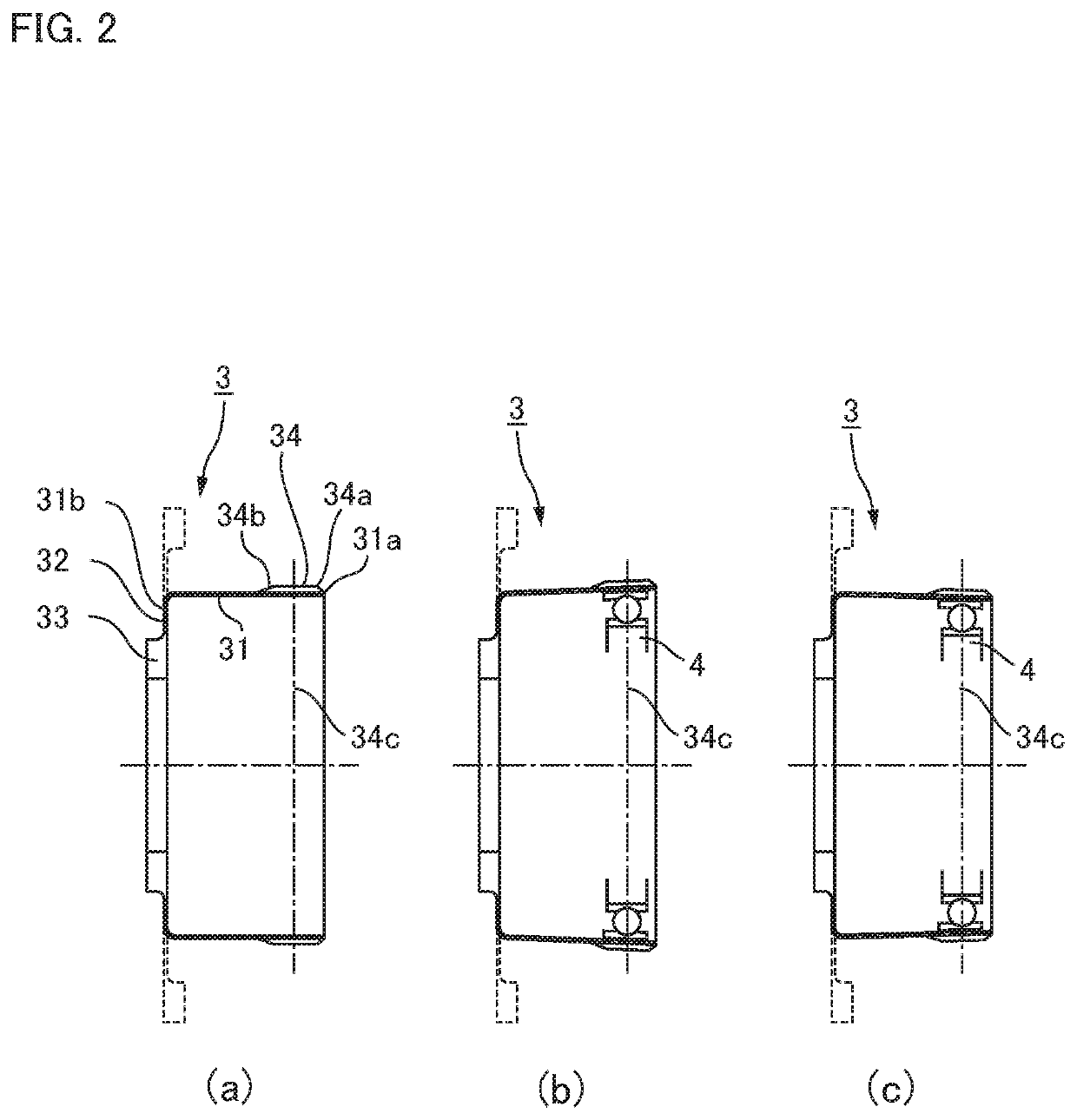
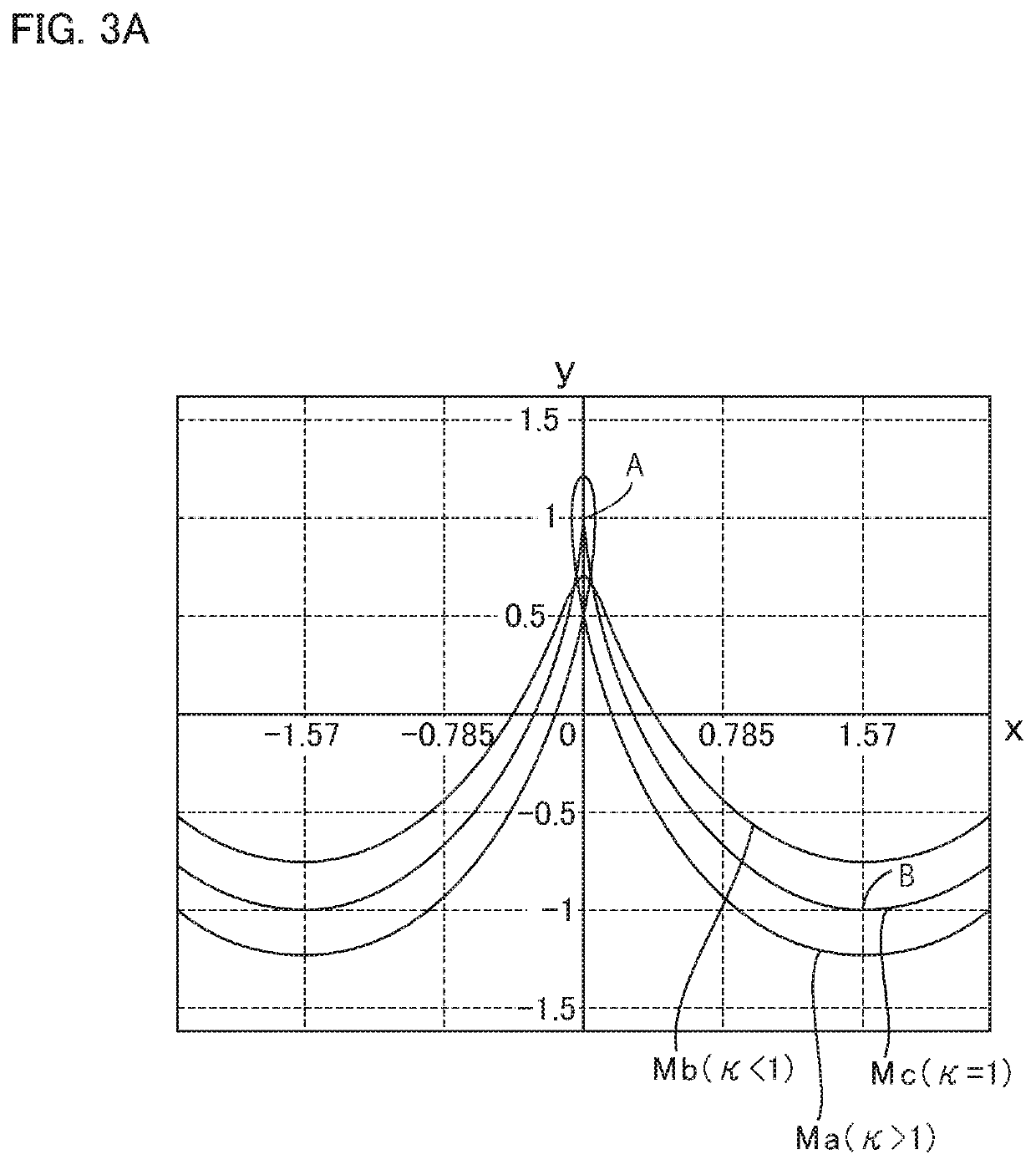
ActiveUS20180347679A1Avoid superimposed flexion-induced bending stressAvoid tensile stressToothed gearingsPortable liftingGear driveGear wheel
In a strain wave gearing, the addendum tooth profile of an internal gear is defined by the formula a and that of an external gear is by the formula b at a principal cross-section located at a tooth-trace-direction center of the external gear, on the basis of a movement locus (Mc) of κ=1 by the teeth of the external gear with respect to those of the internal gear. It is possible to avoid superimposition of flexion-induced bending stresses and tensile stresses caused by load torque at the major-axis locations of the external gear, and the transmission torque capacity of a strain wave gearing can be improved.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Rolling roll, rolling ring, rolling mill, and rolling roll assembling method
InactiveUS20090280972A1Avoid crackingAvoid tensile stressMetal rolling stand detailsShaft and bearingsRolling millEngineering
The present invention provides a rolling roll that has a shaft, which rotates around an axis and has one end that is connected to an output shaft of a rolling mill, and is configured such that a tubular sleeve member is mounted to a portion of the shaft on the side of another end, and a rolling ring, which is formed from a hard material, is fixed to an outer circumference of the sleeve member, wherein an inner circumferential support part is disposed on an outer circumferential side of the sleeve member; the rolling ring is supported by the sleeve member via the inner circumferential support part; a pressing member and a pressing mechanism are disposed on the other end side of the rolling ring; and the pressing member and the pressing mechanism press the rolling ring toward the one end side, thereby fixing it.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
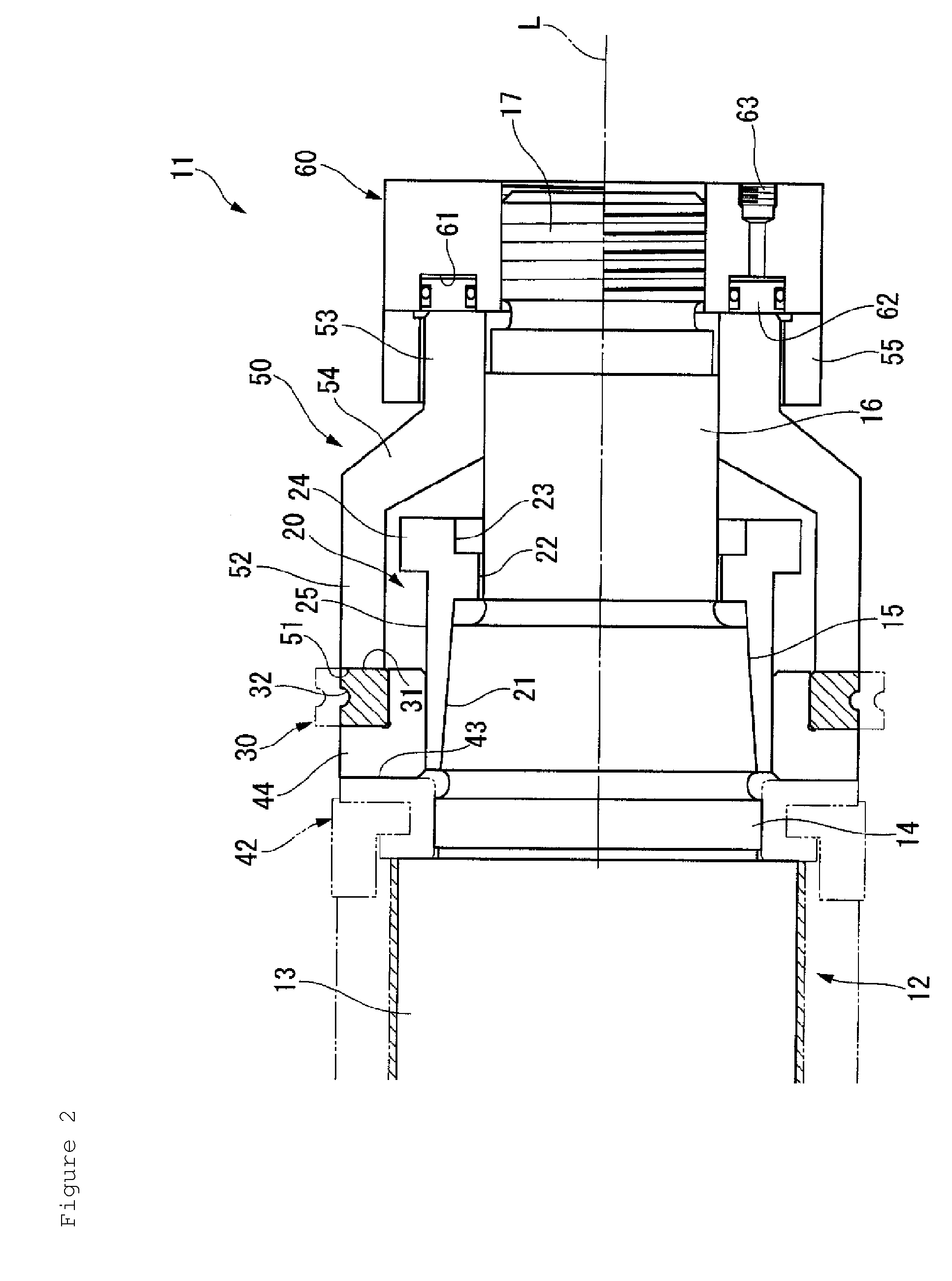
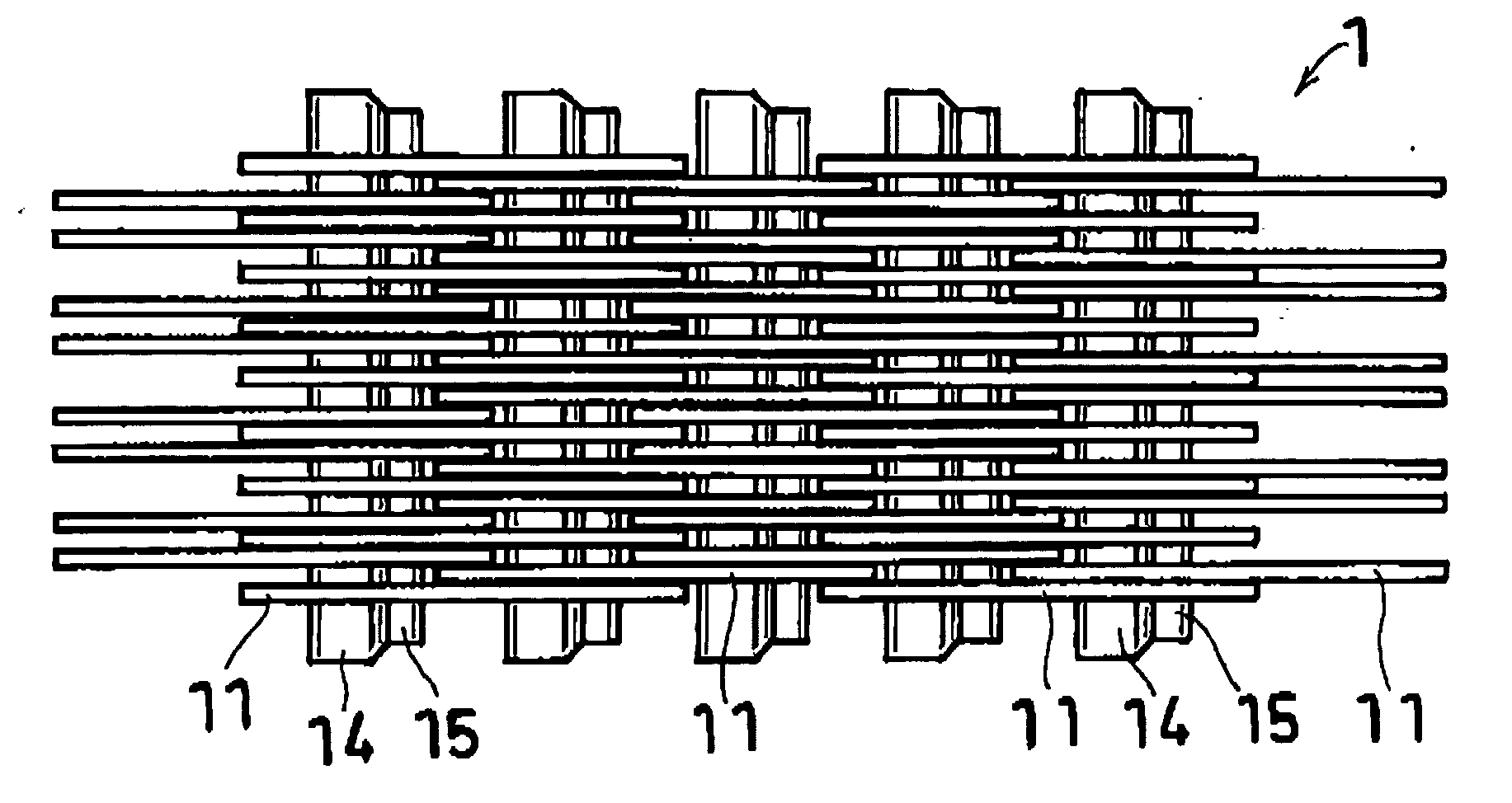
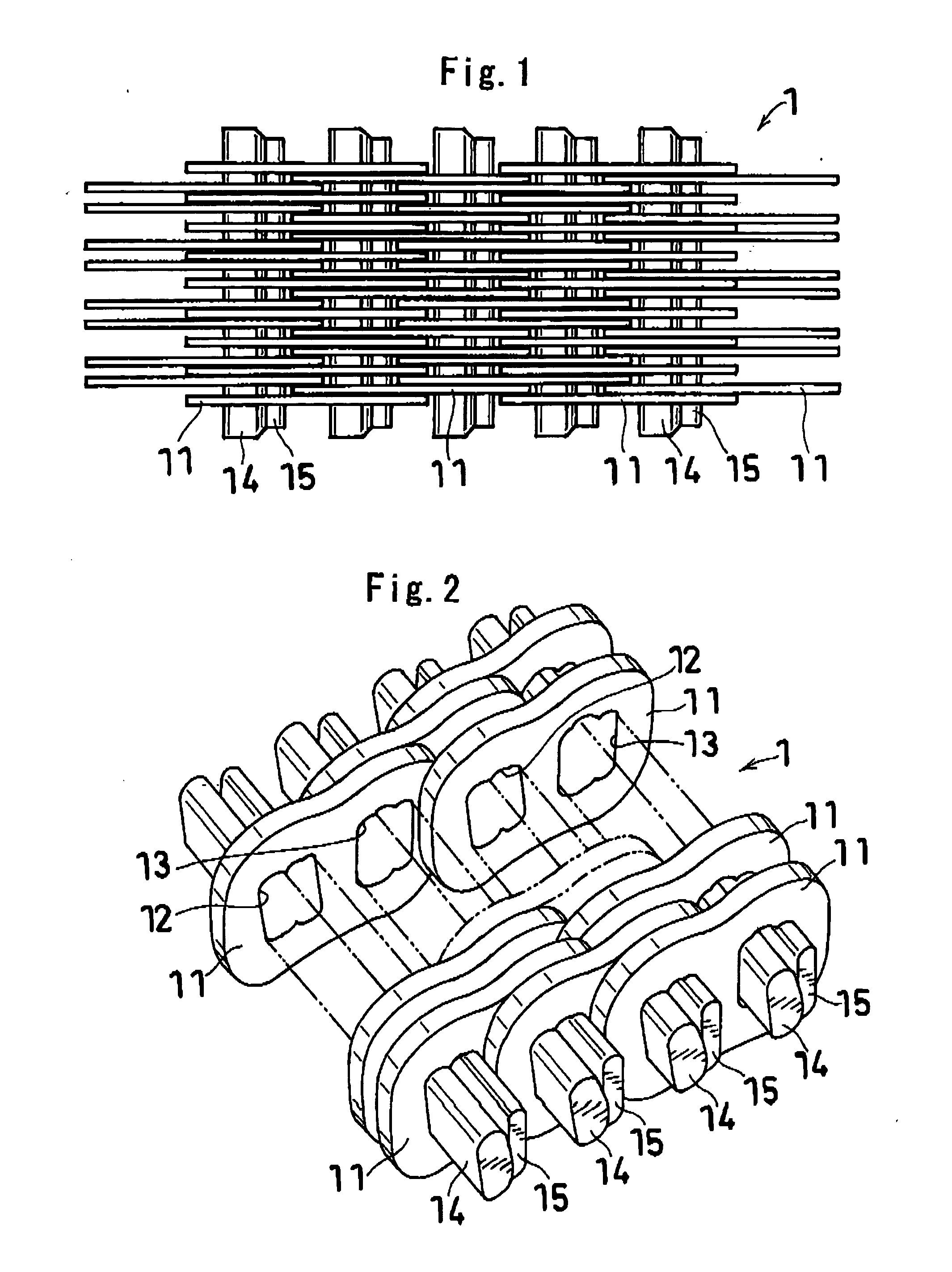
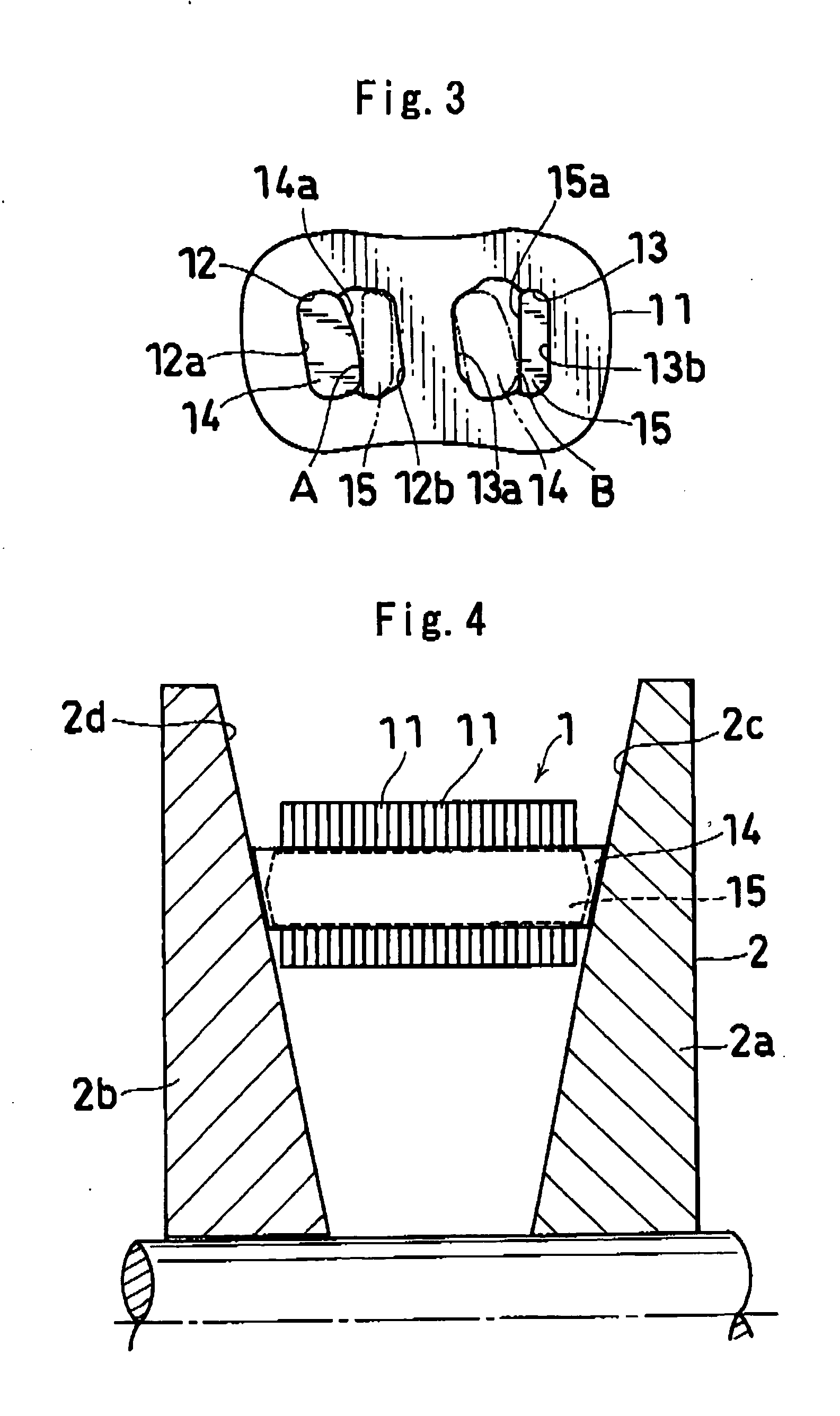
Power transmission chain, power transmission device, and method of producing the chain
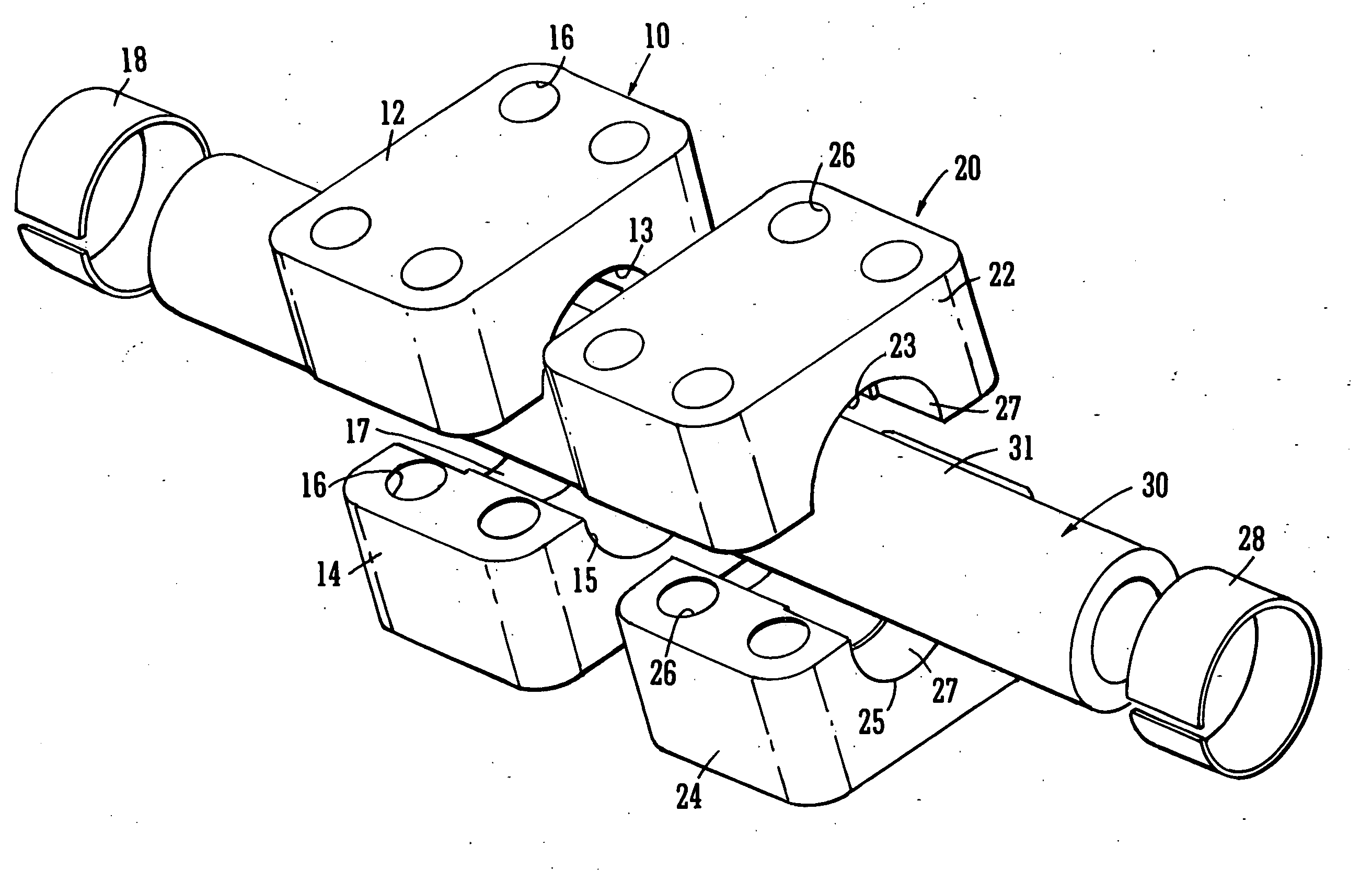
InactiveUS20070178738A1Increased Strength ReliabilityReduced strengthEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsV-beltsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A power transmission chain 1 includes a plurality of links 11 having front and back insertion parts 12, 13 into which pins are inserted, and a plurality of pins 14 and a plurality of interpieces 15 for connecting the links 11 aligned in a chain width direction so as to be bendable in a longitudinal direction such that a front insertion part 12 of one link 11 and a back insertion part 13 of another link 11 correspond to each other. Each pin 14 and each interpiece 15 are fitted and fixed to the peripheral faces of the insertion parts 12, 13 by fitting, and a difference in dimension before the fitting is 0.005 mm to 0.1 mm.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
X-Ray Emitter, Liquid-Metal Anode For An X-Ray Source and Method For Operating A Magnetohydrodynamic Pump For The Same
InactiveUS20070274451A1High heat conductivityAvoid tensile stressX-ray tube electrodesDynamo-electric machinesX-rayMagneto hydrodynamic
The invention relates to a method for operating a magnetohydrodynamic pump 5 for a liquid-metal anode 1 of an X-ray source. It is provided according to the invention that it can be operated in at least two modes, wherein the first mode is a thawing mode in which the liquid metal 2 is melted in a line 3 of the liquid-metal anode 1, the second mode is an operating mode in which the liquid metal 2 is pumped through the line 3 and X-ray beams are produced. In addition, the invention relates to a liquid-metal anode 1 for an X-ray source with a liquid metal 2 which is located in a line 3, wherein an anode module 15 is inserted into the line 3 in the region of focus 4, with a pump 5 for circulating the liquid metal 2 in the line 3 and with a cooling system 6 for the liquid metal 2. According to the invention, such a liquid-metal anode 1 has a magnetohydrodynamic pump 5 as described above.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Method of forming ferrite thin film and ferrite thin film obtained using the same
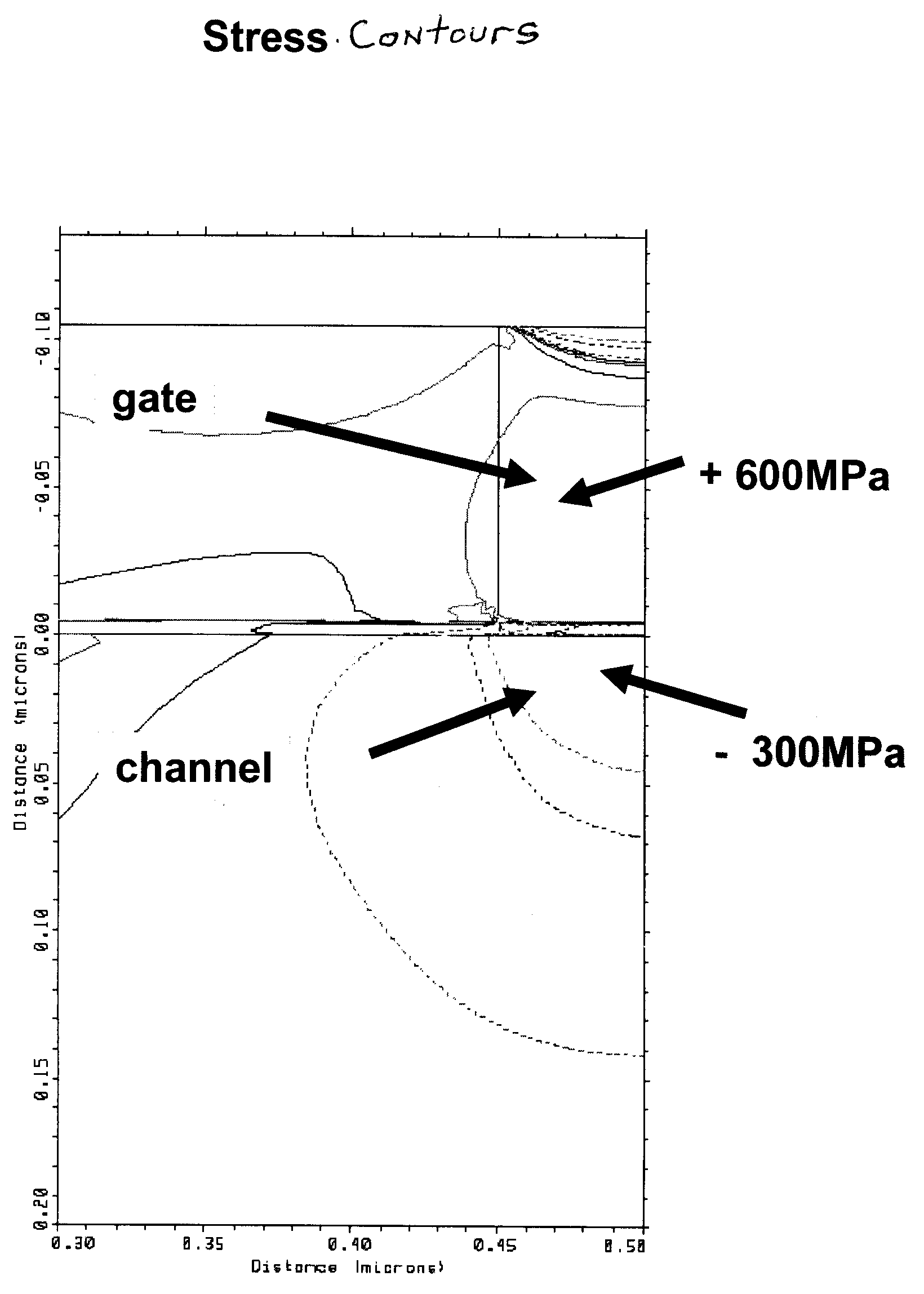
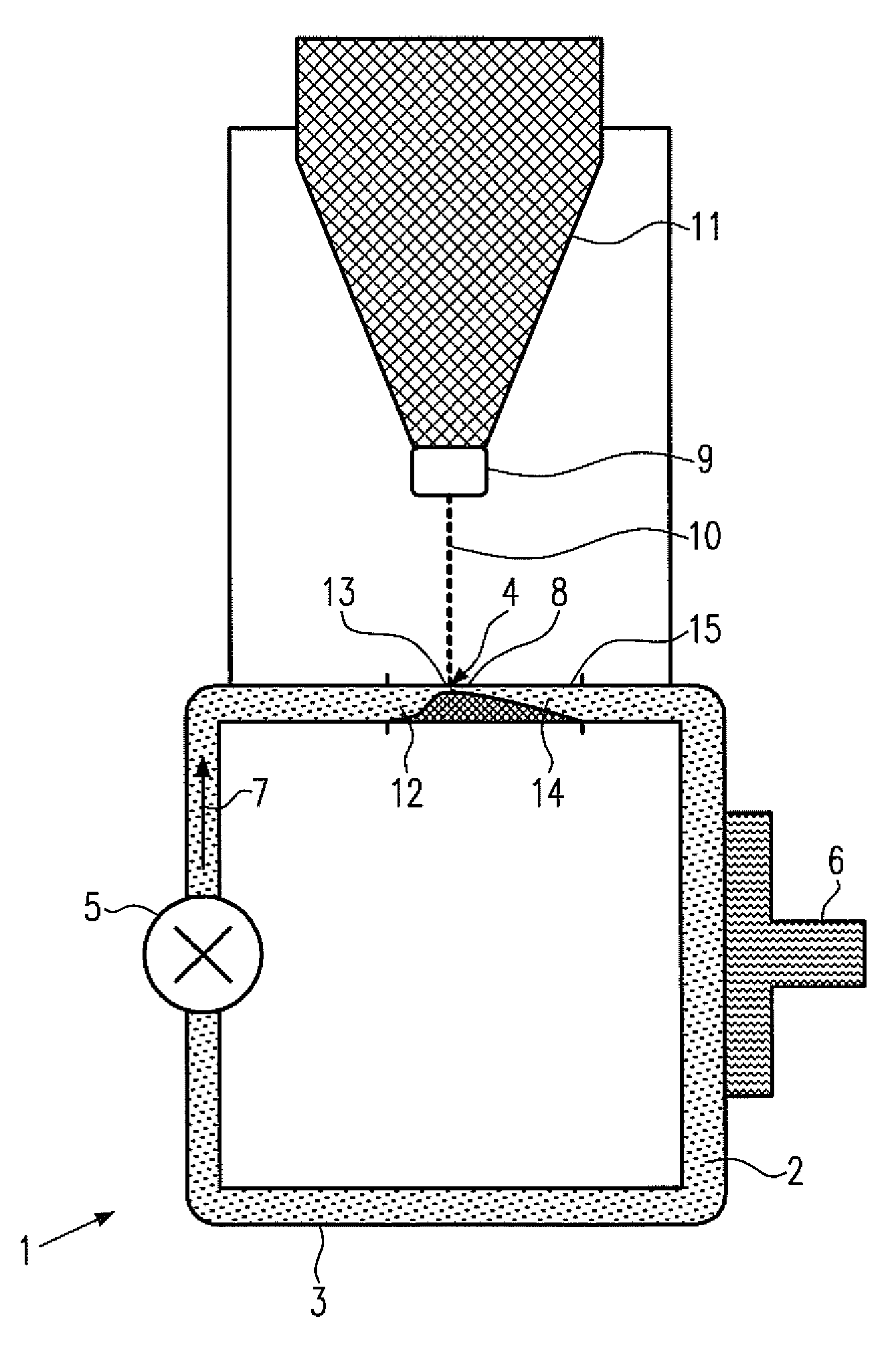
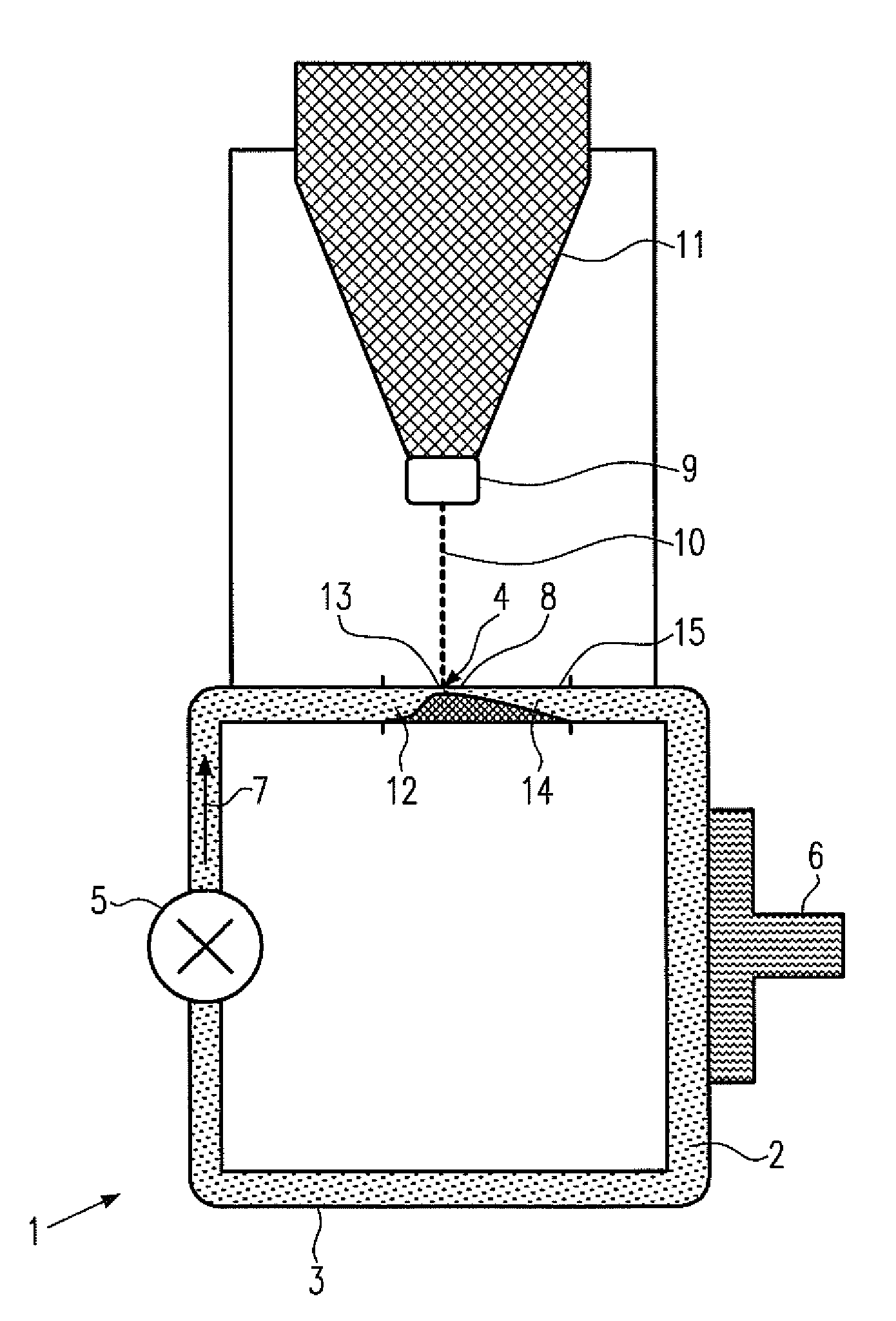
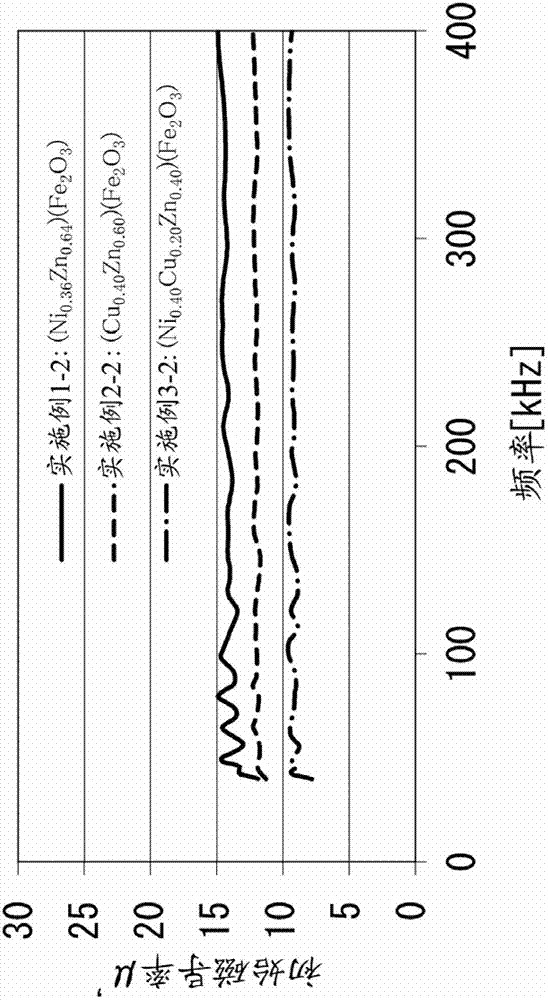
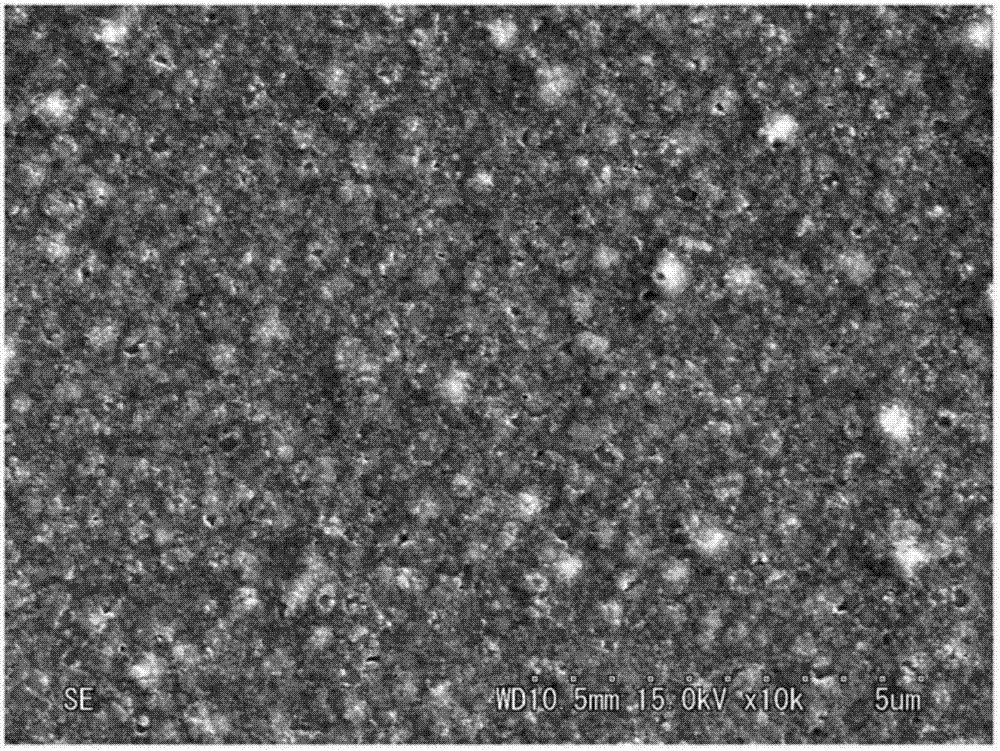
InactiveCN103360043AAvoid tensile stressExcellent magnetic propertiesChemical vapor deposition applicationLiquid applicationHeat resistanceOptoelectronics
[Task] To provide a method of forming a ferrite thin film in which it is possible to manufacture a thick film having a film thickness of 1 µm or more using a sol-gel method without causing cracking. [Means for Resolution] A method of forming a ferrite thin film by carrying out a process for forming a coated film by coating a ferrite thin film-forming composition on a heat-resistant substrate and a process for calcining the coated film once or a plurality of times so that the thickness of the calcined film on the substrate becomes a desired thickness, and firing the calcined film formed on the substrate, in which the conditions for firing the calcined film formed on the substrate are under the atmosphere or an oxygen gas or inert gas atmosphere, a temperature-rise rate of 1°C / minute to 50°C / minute, a holding temperature of 500°C to 800°C, and a holding time of 30 minutes to 120 minutes.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Hearth carriage connection structure of rotary hearth furnace
ActiveCN101438117AReduce distance variationSuppression of bending stressCharge manipulationFurnace typesStable stateEngineering
A rotary furnace hearth wherein a hearth carriage carrying a hearth comprises a plurality of hearth carriages respectively having propulsion systems, wherein adjoining hearth carriages are coupled by coupling bolts and nuts via spacers interspaced in a single row in a horizontal plane, whereby even if the hearth carriages deform due to heat at the time of operation, they are structured to be able to freely deform without mutual constraint in the event of curved deformation, so the hearth carriages are maintained in individually stable states at all times.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
Perspiration insert
The invention relates to a perspiration pad for insertion into the armpit with an absorbent pad (2) consisting of two mutually bendable sections and a self-adhesive film (3) projecting beyond the edge of the pad. In order to provide advantageous constructional conditions it is proposed that the self-adhesive film (3) is interrupted at least in the bending region of the two sections of the pad (2).
Owner:AMMER BARBARA +1
Non-load crack prevention method for layered pouring of zero block web plate
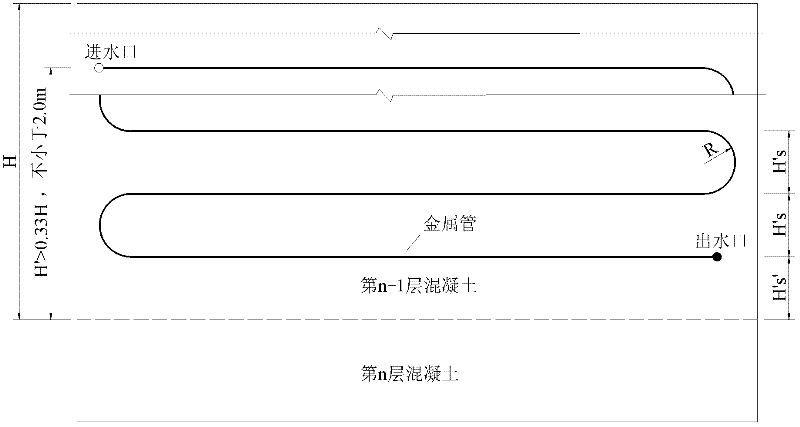
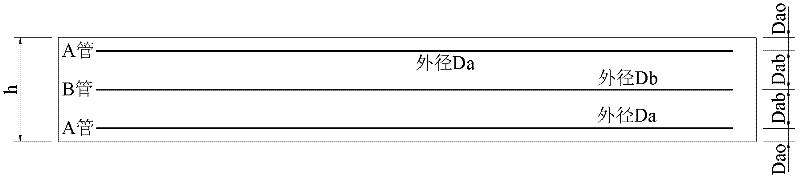
ActiveCN102518048AReduce temperature riseInhibit temperature riseBridge erection/assemblyThick wallCement mortar
The invention relates to a non-load crack prevention method for layered pouring of a zero block web plate. In the method, a thick-wall metal pipe is pre-buried into upper layer concrete which is poured on the zero block web plate in a layered way. The method comprises the following steps of: I, preparing cooling pipes of corresponding specifications including a cooling pipe A and a cooling pipe B according to the thickness of the web plate; II, arranging the cooling pipes; III, performing leak detection on the cooling pipes; IV, opening the water inlets and the water outlets of the cooling pipes after a square of concrete is put into a mold for 5-10 hours, filling cooling water into the water inlets of the cooling pipes, and adjusting the flow speed of the cooling water according to specific conditions; and V, after cooling is complete, pouring cement mortar into the cooling pipes and enclosing the cooling pipes. Due to the adoption of the prevention method, the internal heat dissipating time of the concrete is shortened, the temperature rise of the concrete is reduced, pulling stress is avoided, and cracks are prevented effectively; and moreover, the method is easy to operate, and does not influence a construction process.
Owner:GUANGXI TRANSPORTATION SCI & TECH GRP CO LTD
System and method for electromagnetic pulse surface treatment
ActiveUS20070158336A1Convenience to workReduce stress concentrationSoldering apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyEngineeringElectromagnetic pulse
A system and method for electromagnetic surface treatment of a work piece has an electromagnetic pulse generator and an electromagnetic pulse tool. The work piece has a working surface. A current pulse generated by the electromagnetic pulse generator travels through the tool producing an electromagnetic pulse. The electromagnetic pulse interacts with the working surface causing an indentation to form. A residual compressive stress layer is also formed. The indentation has a smooth and continuous topography that is described by an indentation perimeter, an indentation transition region, an indentation sidewall, an impact transition region, and an impact region. The method may also simultaneously, or subsequently, form a second indentation which overlaps with the indentation. An inter-indentation overlap region is formed when the indentations overlap. The inter-indentation overlap region is smooth and continuous. Multiple treated surfaces may easily be formed on the working surface of the work piece.
Owner:GATEKEY ENG
Strain wave gearing with full separation of two stresses
ActiveUS10788114B2Avoid stackingIncreased torque capacityToothed gearingsPortable liftingGear wheelLoad torque
In a strain wave gearing, the addendum tooth profile of an internal gear is defined by the formula a and that of an external gear is by the formula b at a principal cross-section located at a tooth-trace-direction center of the external gear, on the basis of a movement locus (Mc) of κ=1 by the teeth of the external gear with respect to those of the internal gear. It is possible to avoid superimposition of flexion-induced bending stresses and tensile stresses caused by load torque at the major-axis locations of the external gear, and the transmission torque capacity of a strain wave gearing can be improved.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Method for reinforcing connection of diaphragm plate and girder by aid of penetrating type prestress
InactiveCN106758873AFirmly connectedImprove crack resistanceBridge erection/assemblyBridge strengtheningCrack resistancePre stress
The invention discloses a method for reinforcing connection of a diaphragm plate and a girder by aid of penetrating type prestress. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) positions of additionally arranged prestress steel strands are determined on the diaphragm plate and a girder web, and then, holes are drilled in the girder web and the diaphragm plate to form mounting channels for prestress steel strands; (2) slots are formed in two ends of each mounting channel, and stress-dispersing steel cushion plates are mounted in the slotted positions; (3) the prestress steel strands penetrate through the channels in the girder and the diaphragm plate; steel strand anchoring devices are mounted; steel strands are tensioned. After external prestress is added between the girder and the diaphragm plate, connection between the girder and the diaphragm plate is effectively enhanced, so that the diaphragm plate prestores certain press stress when not bearing load of a vehicle, pulling stress produced under constant action of vehicle load is overcome, the cracking resistance of the diaphragm plate is effectively improved, the rigidity of the diaphragm plate is improved, the horizontal linkage is enhanced, and the overall stressing performance of a bridge is effectively improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
System and method for electromagnetic pulse surface treatment
ActiveUS20080061053A1Convenience to workReduce stress concentrationSoldering apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyEngineeringElectromagnetic pulse
A system and method for electromagnetic surface treatment of a work piece has an electromagnetic pulse generator and an electromagnetic pulse tool. The work piece has a working surface. A current pulse generated by the electromagnetic pulse generator travels through the tool producing an electromagnetic pulse. The electromagnetic pulse interacts with the working surface causing an indentation to form. A residual compressive stress layer is also formed. The indentation has a smooth and continuous topography that is described by an indentation perimeter, an indentation transition region, an indentation sidewall, an impact transition region, and an impact region. The method may also simultaneously, or subsequently, form a second indentation which overlaps with the indentation. An inter-indentation overlap region is formed when the indentations overlap. The inter-indentation overlap region is smooth and continuous. Multiple treated surfaces may easily be formed on the working surface of the work piece.
Owner:GATEKEY ENG
Method of attaching ring gear to differential case, jig, and differential case
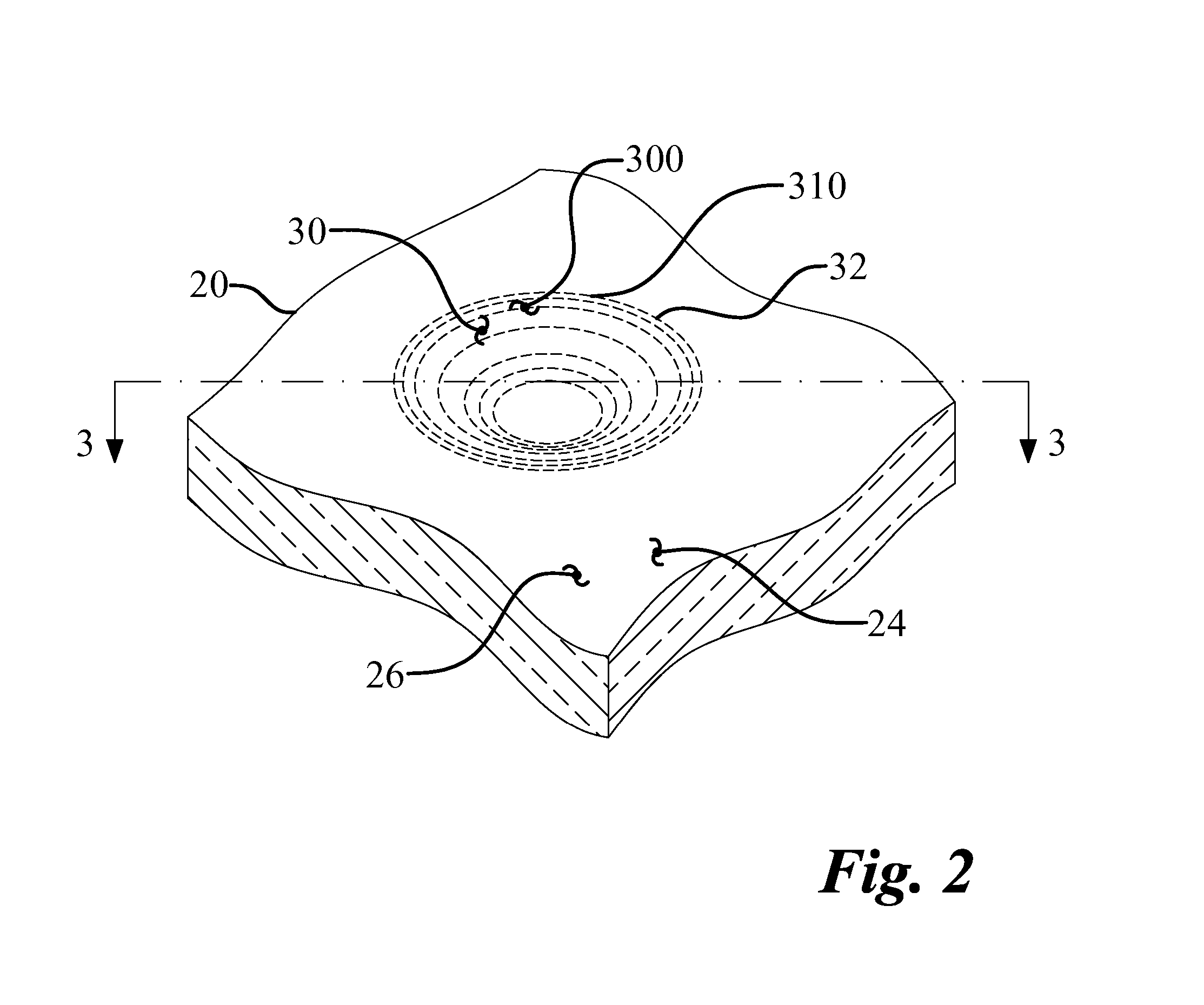
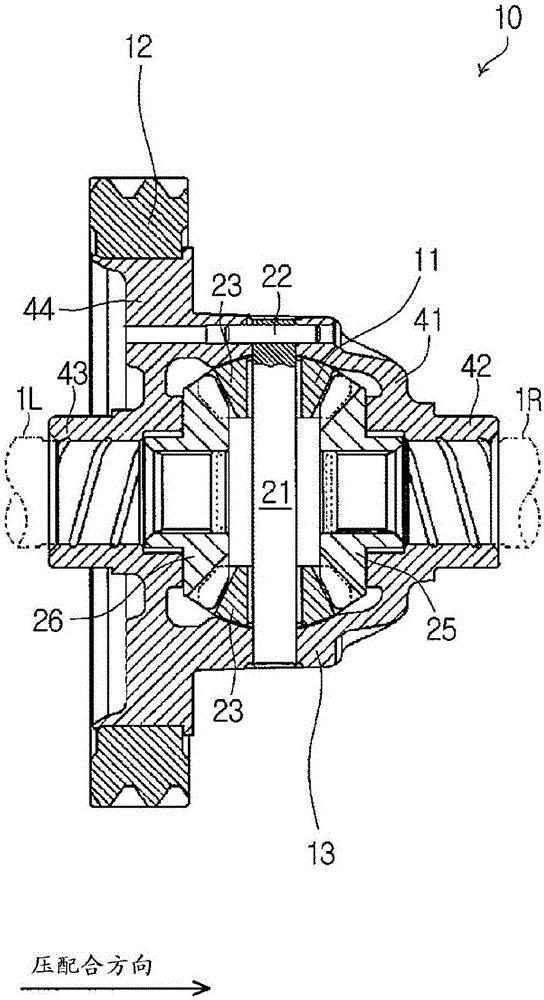
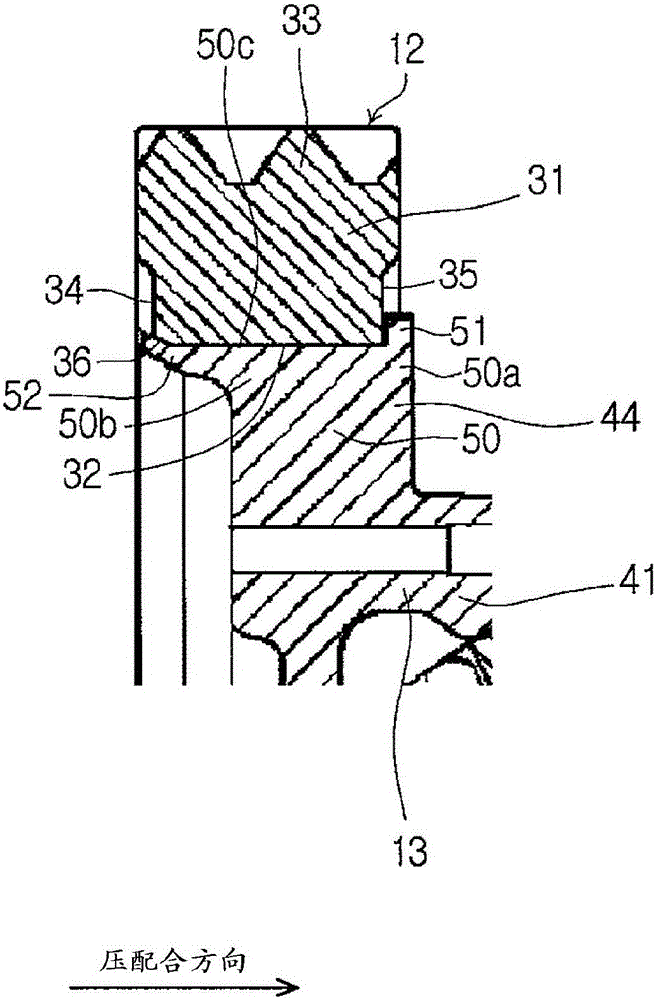
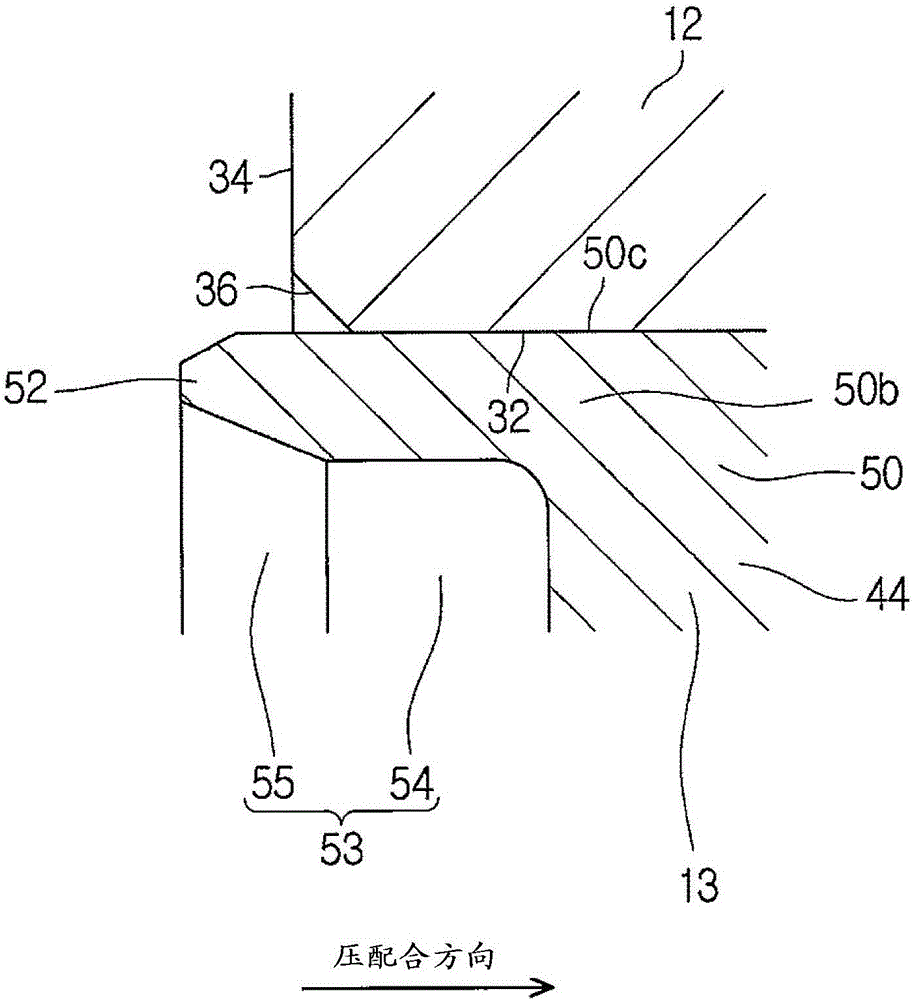
InactiveCN105983641AImprove surface roughnessAvoid tensile stressDifferential gearingsMetal working apparatusRotational axisEngineering
A method of attaching a ring gear to a differential case, a jig, and the differential case are provided. The method of attaching the ring gear (12) to the differential case (13) includes: a first step for fitting the ring gear (12) onto an outer peripheral side of the differential case (13); and a second step for outwardly deforming a caulk-fixed part (52) of the differential case (13) to prevent the ring gear (12) from being dropped out from the differential case (13). In the second step, the jig (60) having an inclined surface (61) that can contact an inner peripheral surface (53) of the caulk-fixed part (52) of the differential case (13) is pushed along a rotational axis direction of the differential case (13) to outwardly deform the caulk-fixed part (52). The inclined surface (61) of the jig (60) and the inner peripheral surface (53) of the caulk-fixed part (52) are subjected to a surface treatment to increase a friction between the inclined surface (61) of the jig (60) and the inner peripheral surface (53) of the caulk-fixed part (52).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Convertible
InactiveUS7429071B2Avoid tensile stressClosed and partitionedWindowsWindscreensHorizontal axisMechanical engineering
A convertible vehicle with at least one front roof area, having a flexible covering in the direction of travel, and a rigid roof area, including a rear window. The front roof area includes several lateral frame parts lying one behind the other, which can be folded opposite to each other, at least in the essentially horizontal axes, and can be covered by the rear roof area in the stored position.
Owner:WILHELM KARMANN GMBH
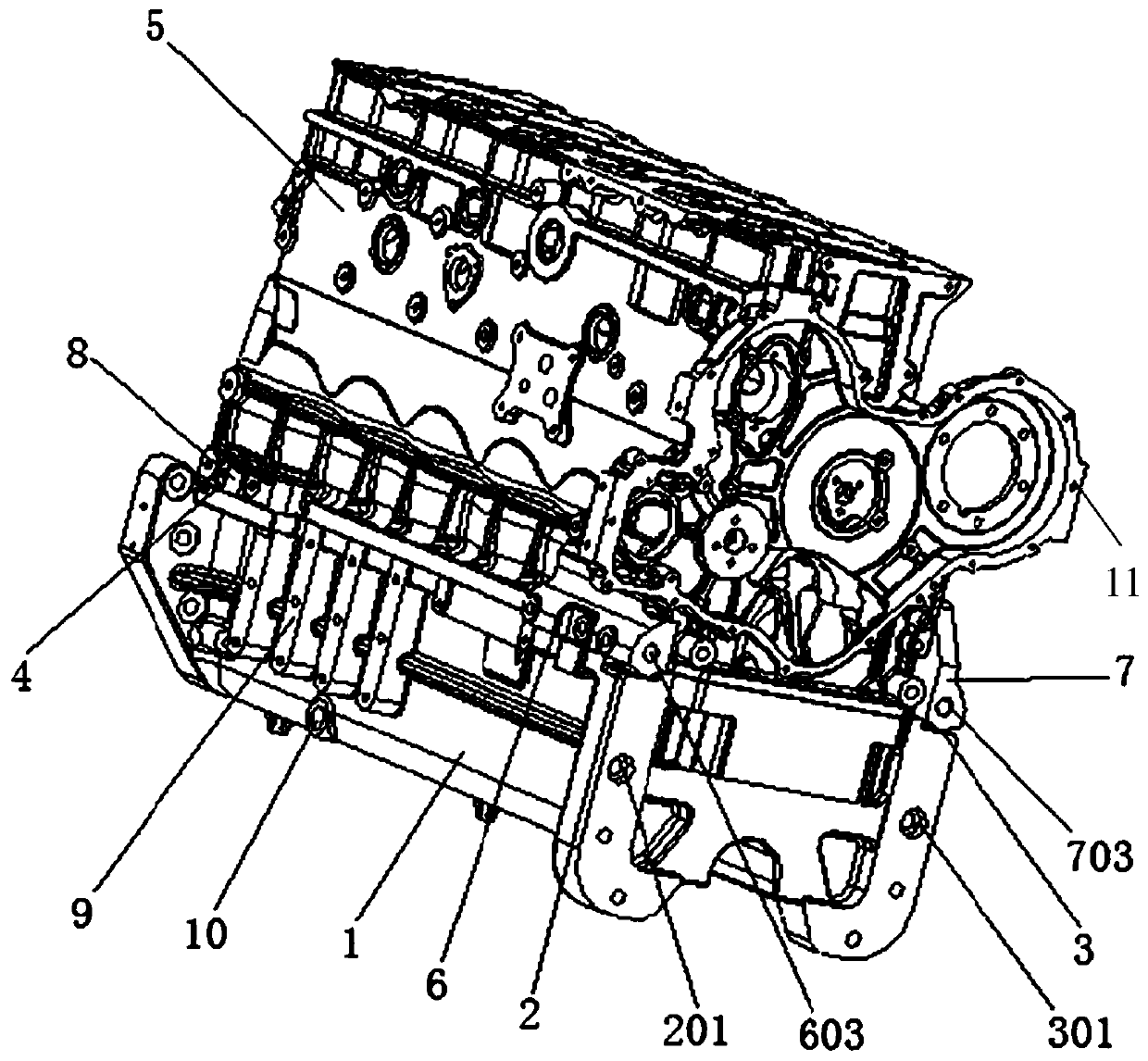
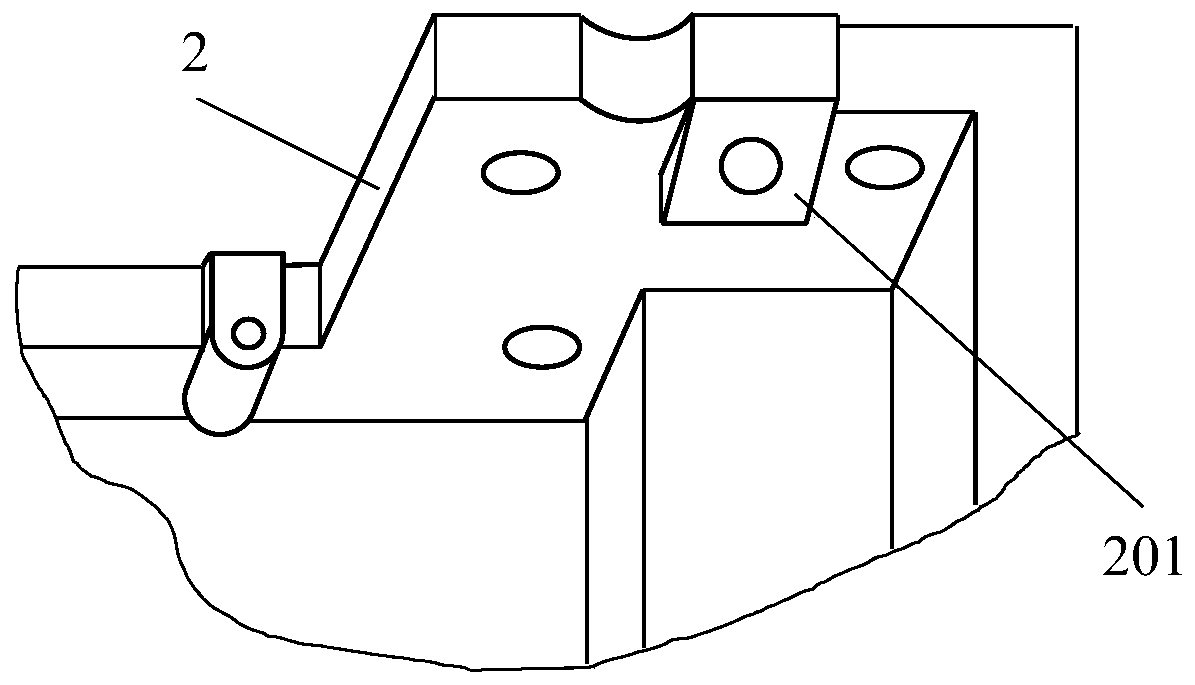
Tractor oil bottom shell connecting structure
InactiveCN110173322AImprove local strengthAvoid tensile stressOilsumpsMachines/enginesDiesel engineBack support
The invention discloses a tractor oil bottom shell connecting structure. The upper plane of an oil bottom shell is bonded and connected with the lower plane of a cylinder body; the connecting structure comprises a left support platform, a front left bracket, a right support platform, a front right bracket, back support platforms and back brackets. The left support platform is arranged on the leftside of the front end of the oil bottom shell; the front left bracket is arranged on the left support platform; the right support platform is arranged on the right side of the front end of the oil bottom shell; the front right bracket is arranged on the right support platform; the back support platforms are arranged on two sides of the back end of the oil bottom shell; and the back brackets are arranged on the back support platforms. The tractor oil bottom shell connecting structure reinforces the connection between the oil bottom shell and the cylinder body through three cylinders, so that the local strength of the oil bottom shell is improved, the oil bottom shell is effectively protected, and the service life of a diesel engine is prolonged.
Owner:GUANGXI YUCHAI MASCH CO LTD
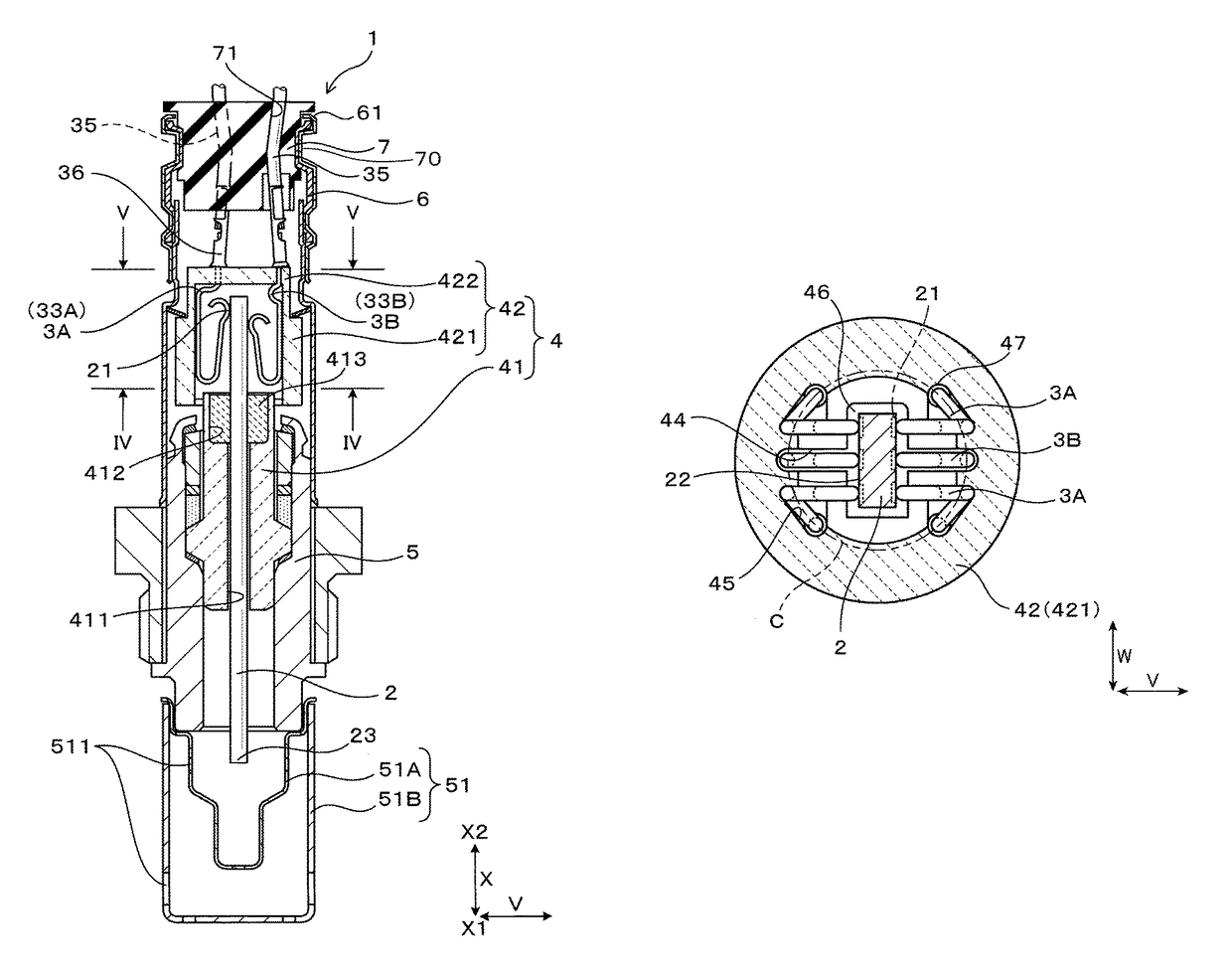
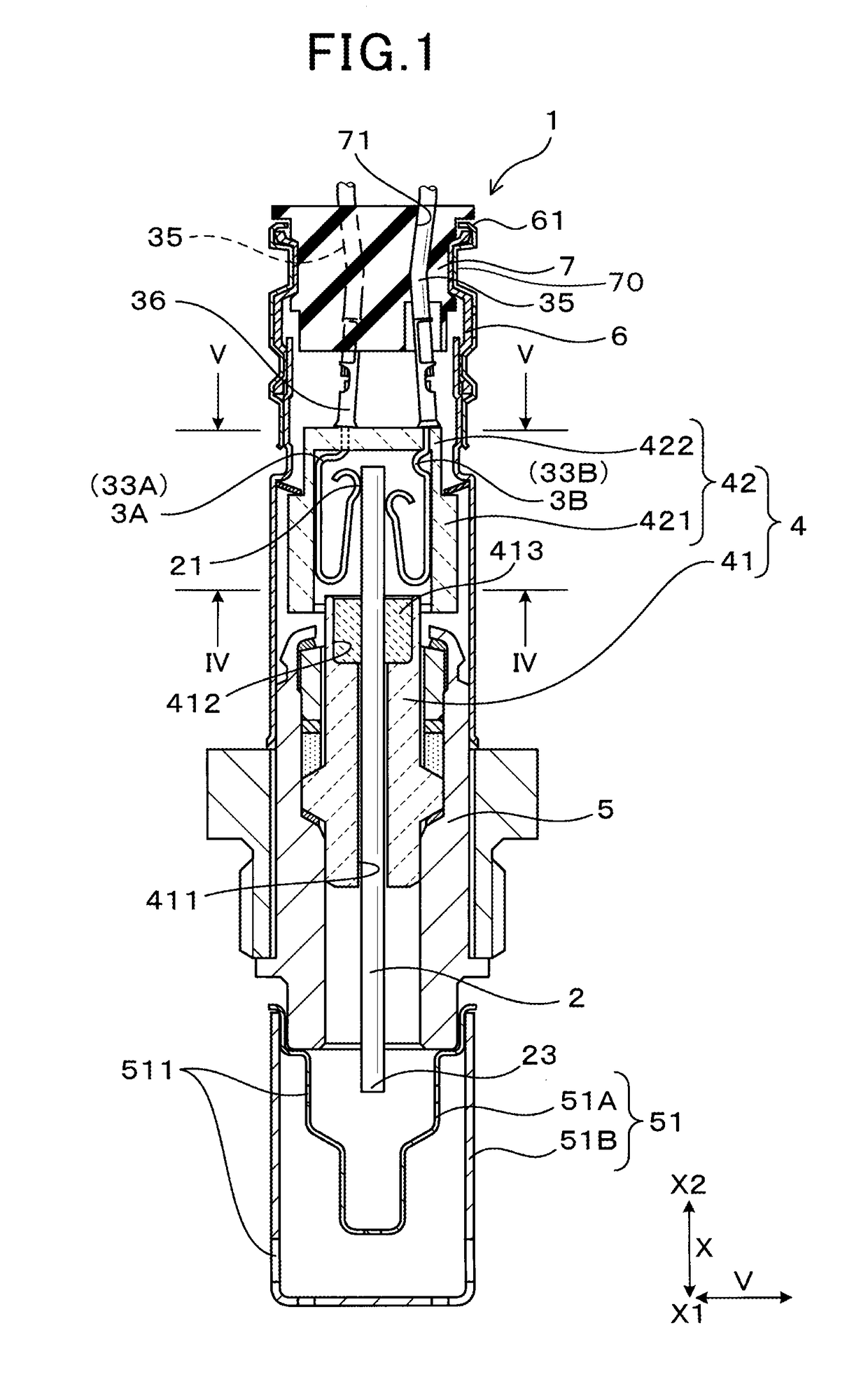
Sensor
ActiveUS9847592B2Reduce size and thicknessAvoid tensile stressInternal-combustion engine testingCoupling contact membersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A sensor includes contact springs placed in contact with electrode terminals on major surfaces of a sensor device. At least one of the contact springs includes a spring contact portion, a spring holding portion, a spring bent portion, and a spring connecting portion. The spring contact portion contacts an outer surface of one of the electrode terminals. The spring holding portion is turned from the spring contact portion and extends outside the spring contact portion so as to overlap the spring contact portion in the contacting direction. The spring bent portion is bent inwardly from the spring holding portion and extends at a given angle to the contacting direction. The spring connecting portion is bent from the spring bent portion and extends in the axial direction of the sensor. Such a structure enables the contact spring to be reduced in size and thickness without sacrificing a required mechanical strength thereof.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com