Patents
Literature
125results about How to "Prevent tire blowout" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
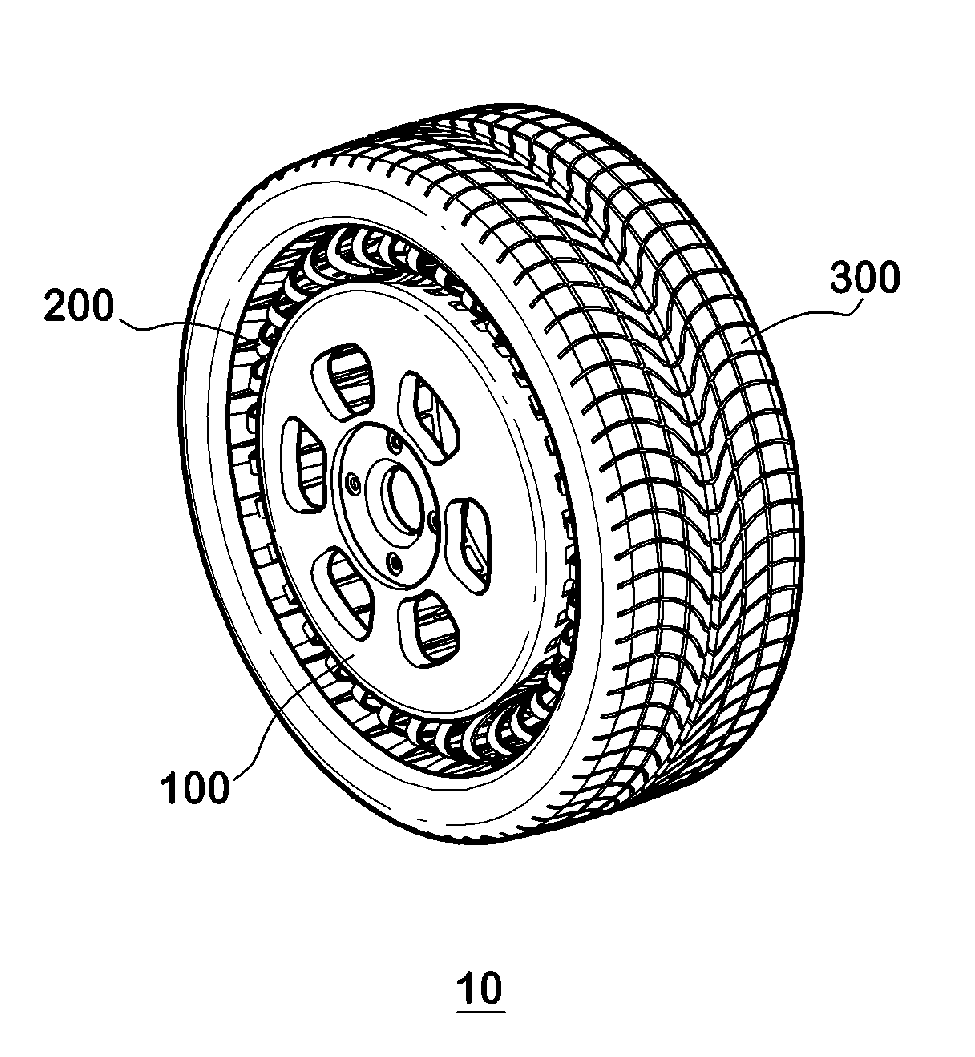
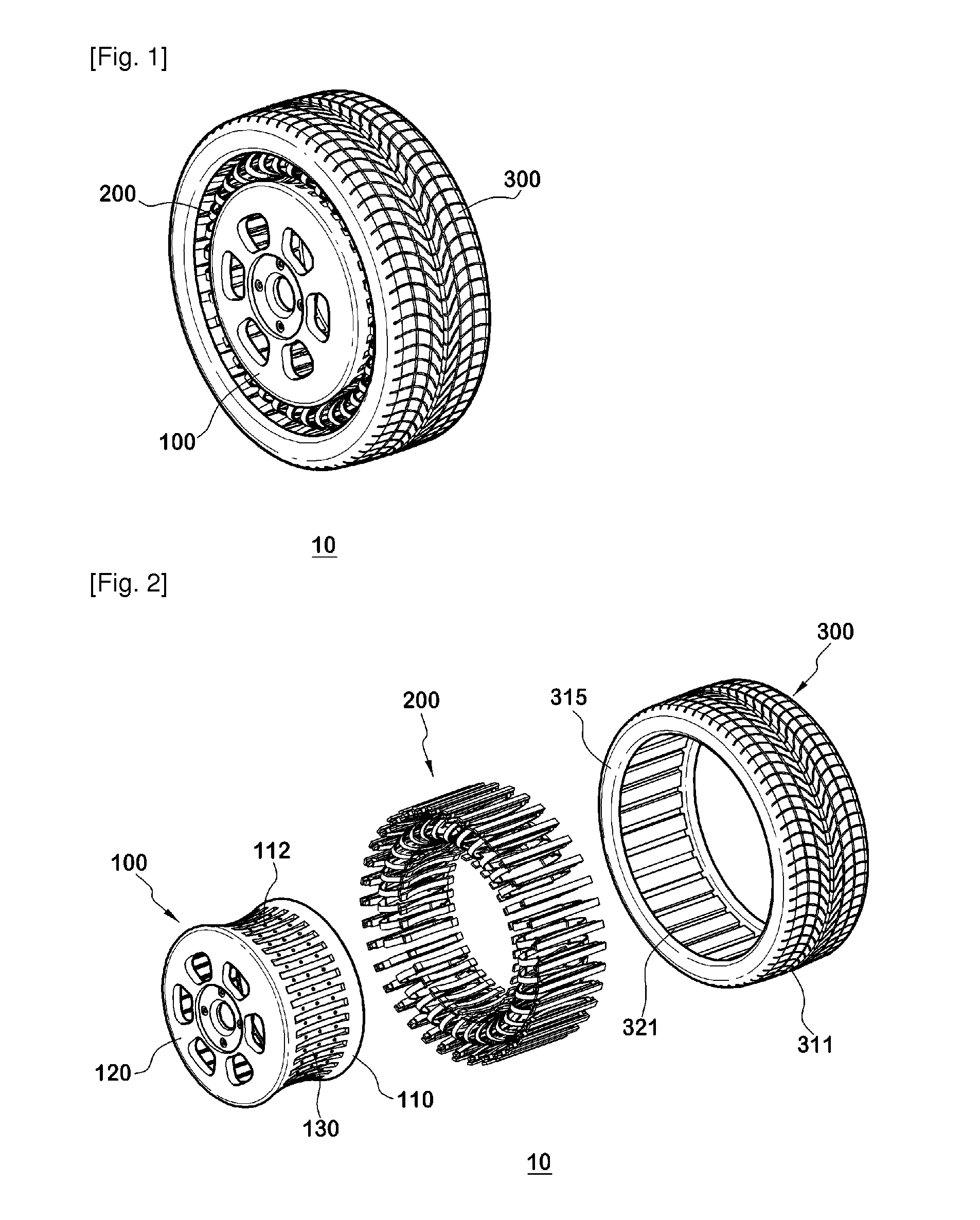
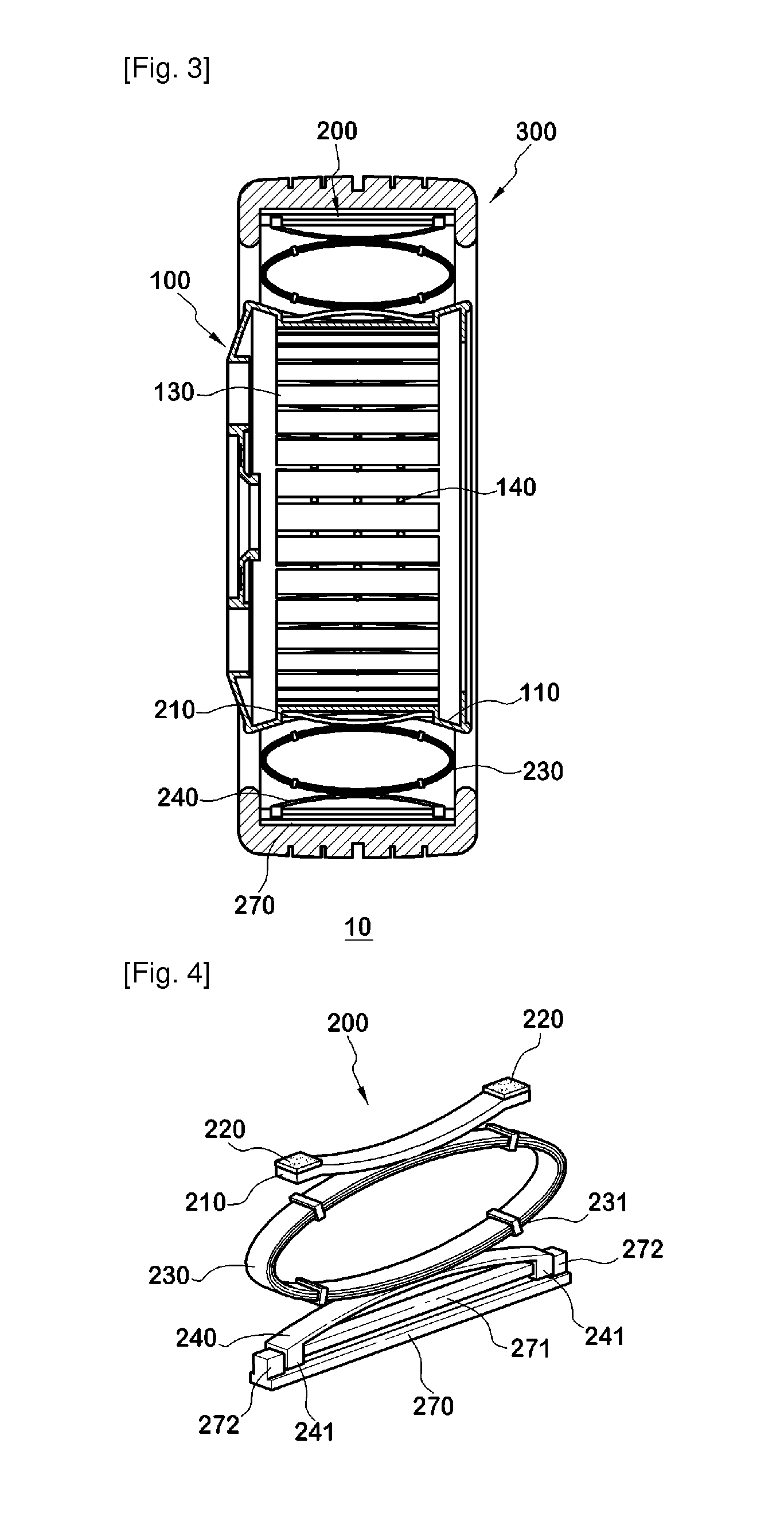
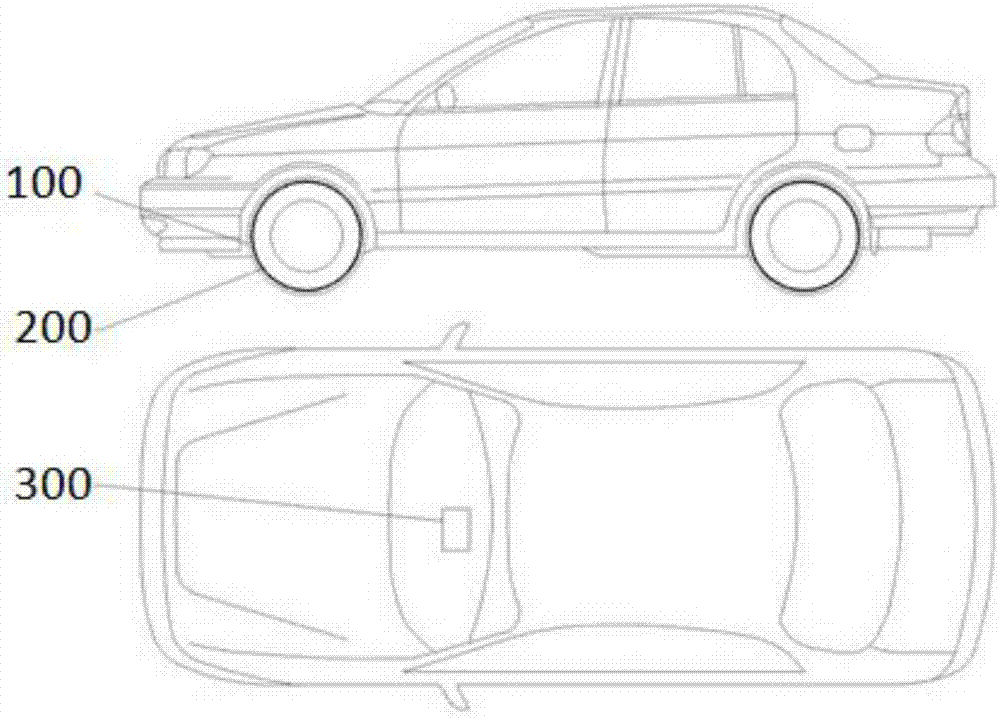
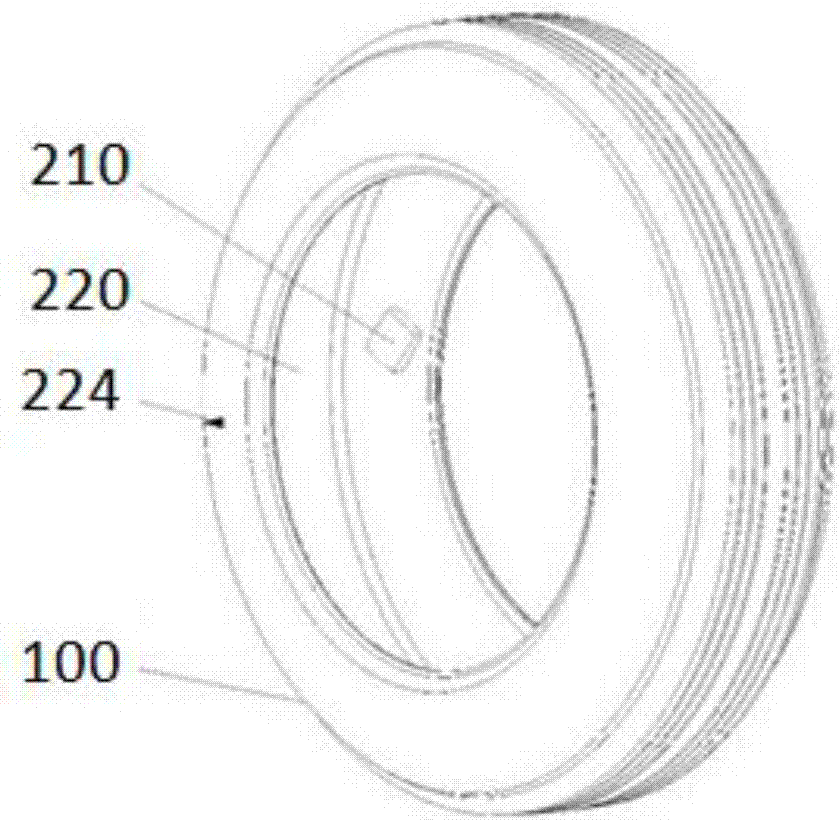
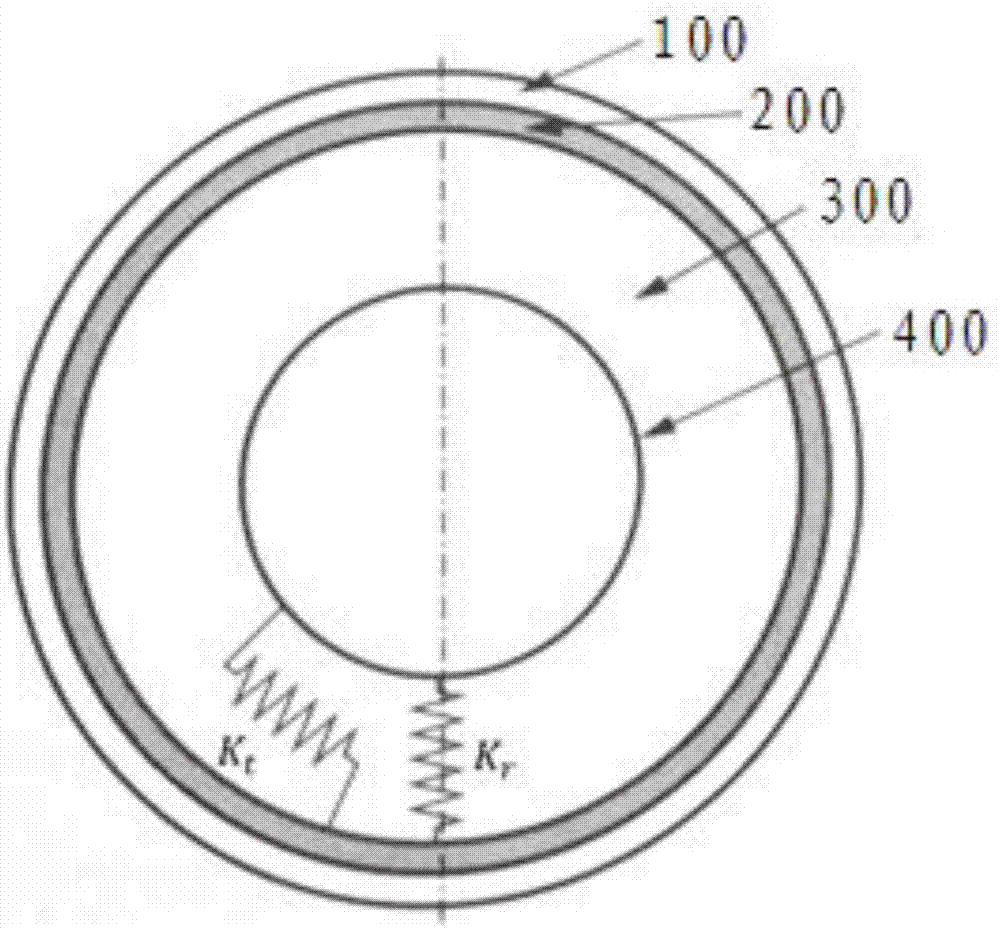
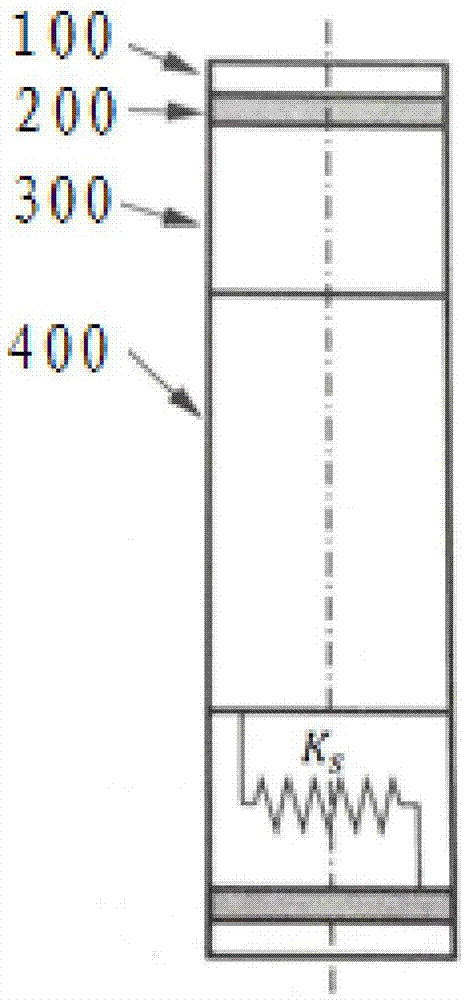
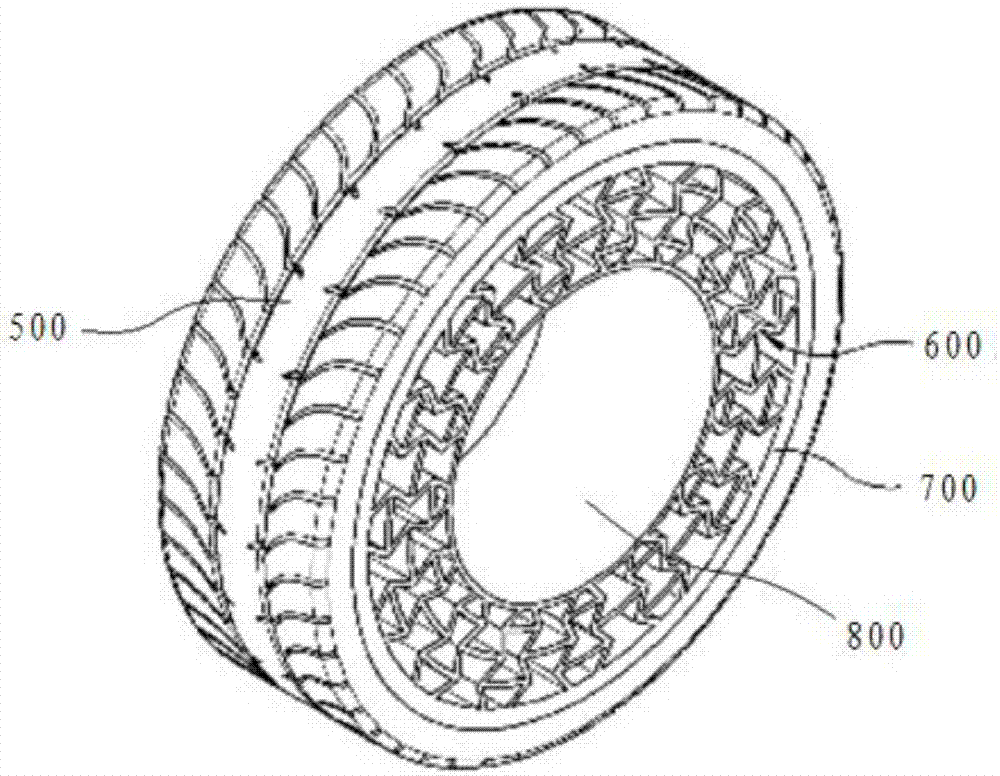
Non-pneumatic wheel and wheel, suspension and tire used therein
InactiveUS20110248554A1Prevent tire blowoutReduce vehicle accidentRimsLeaf springsCornering forceBrake fade
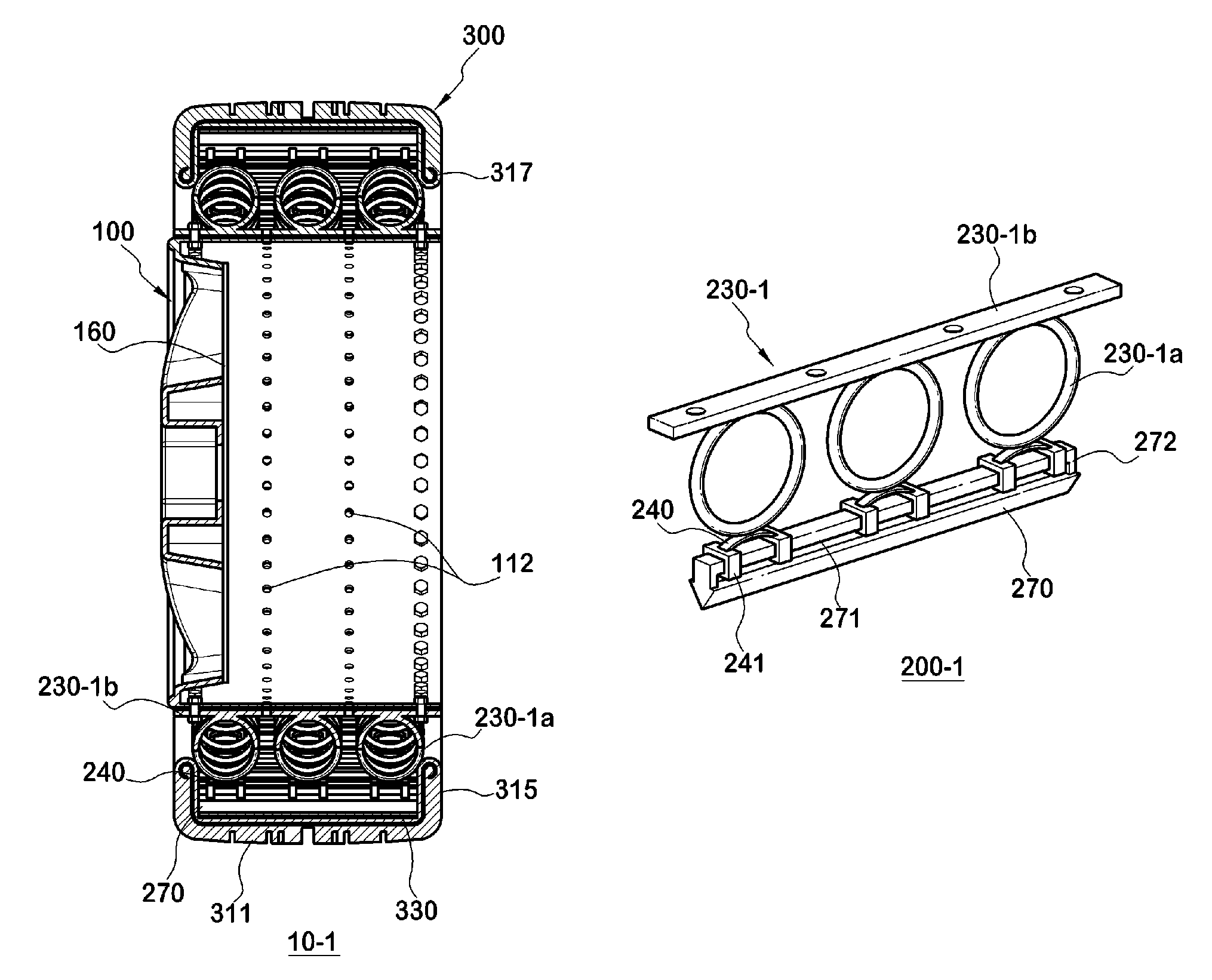
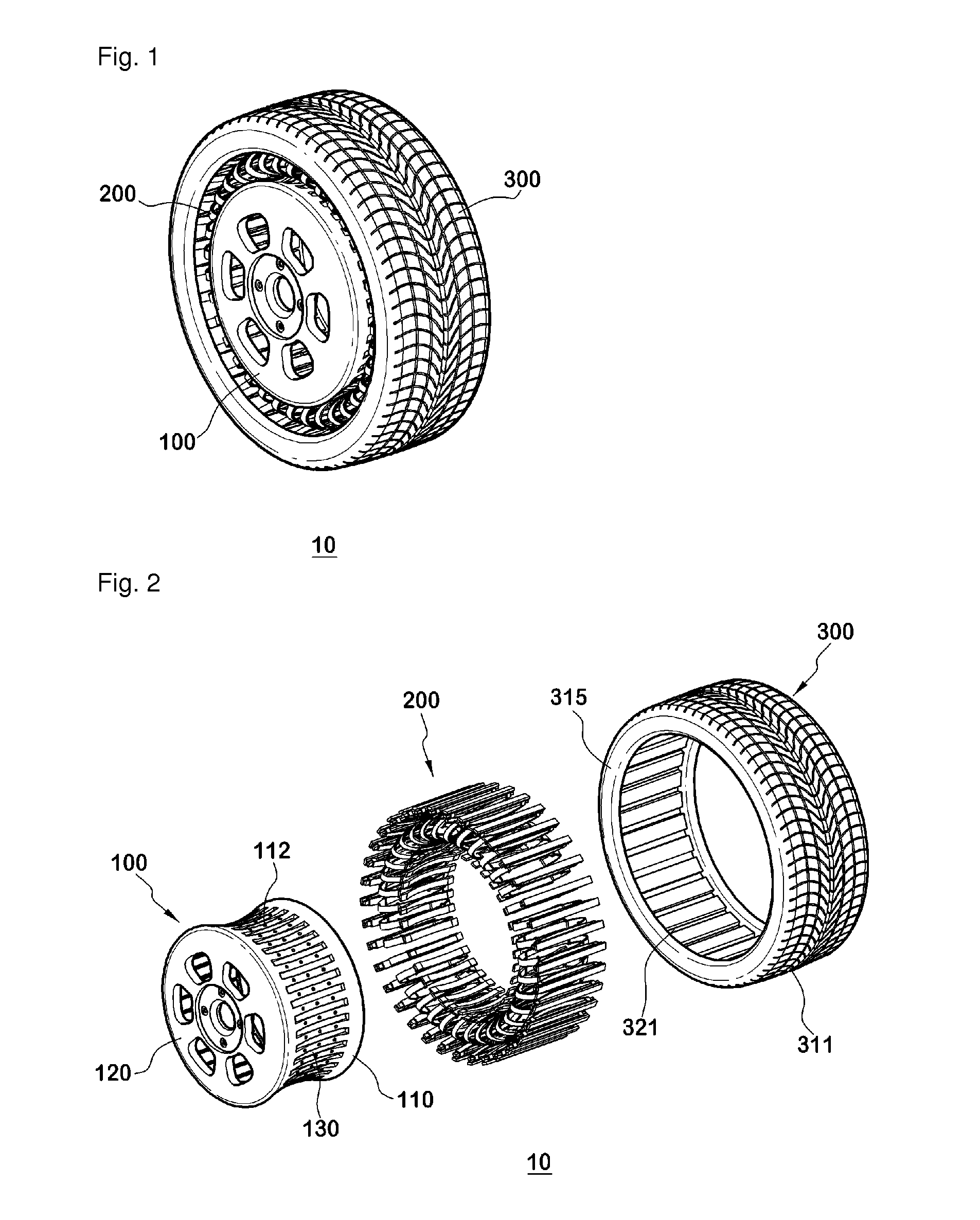
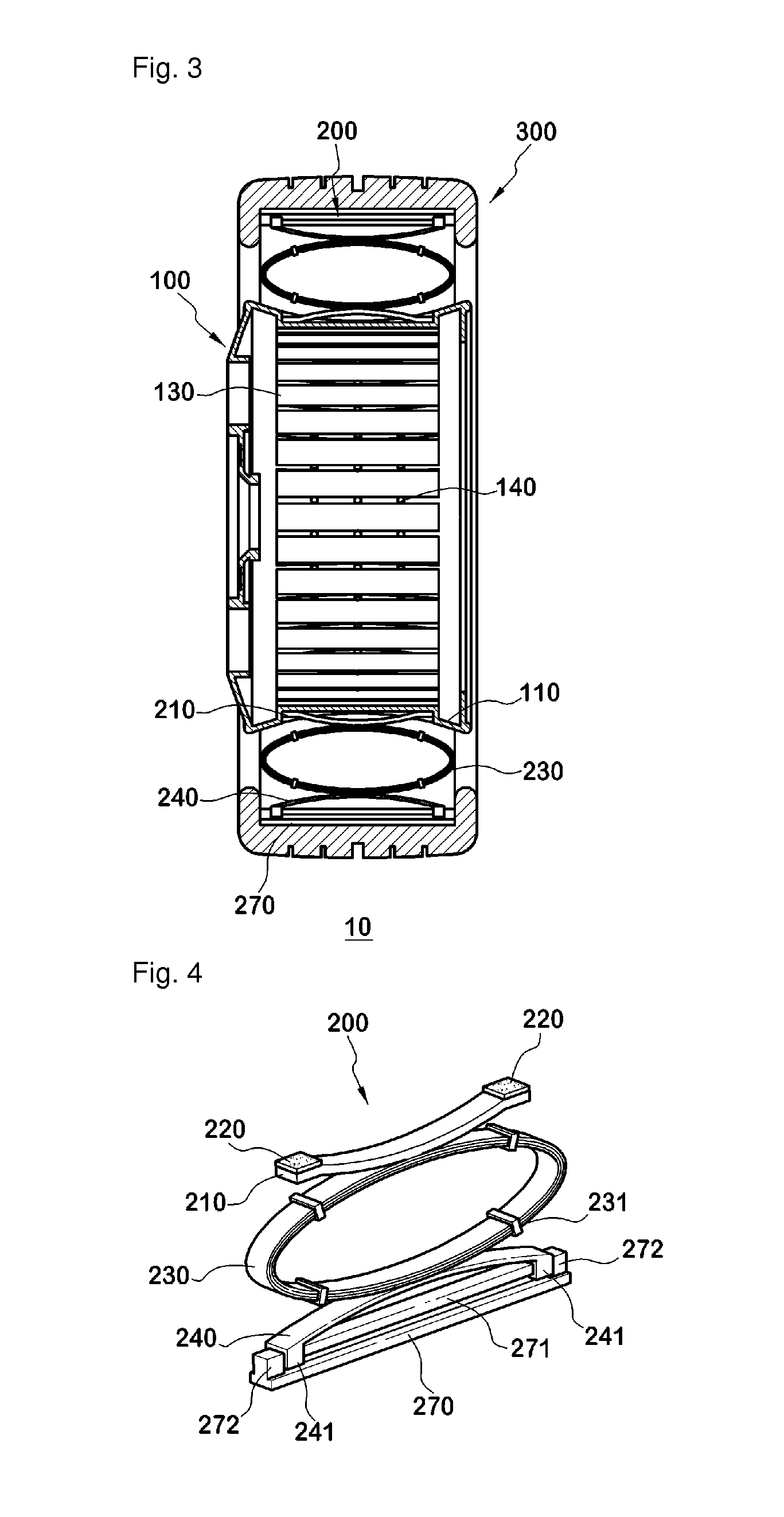
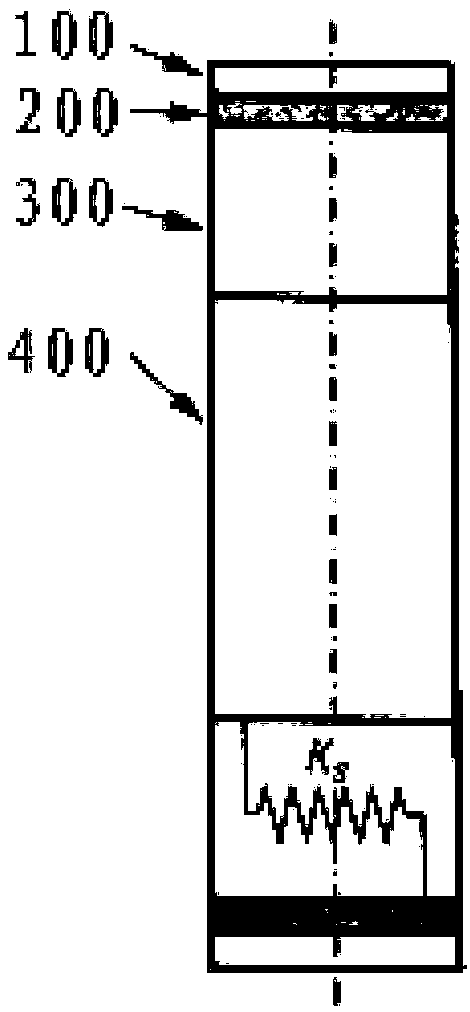
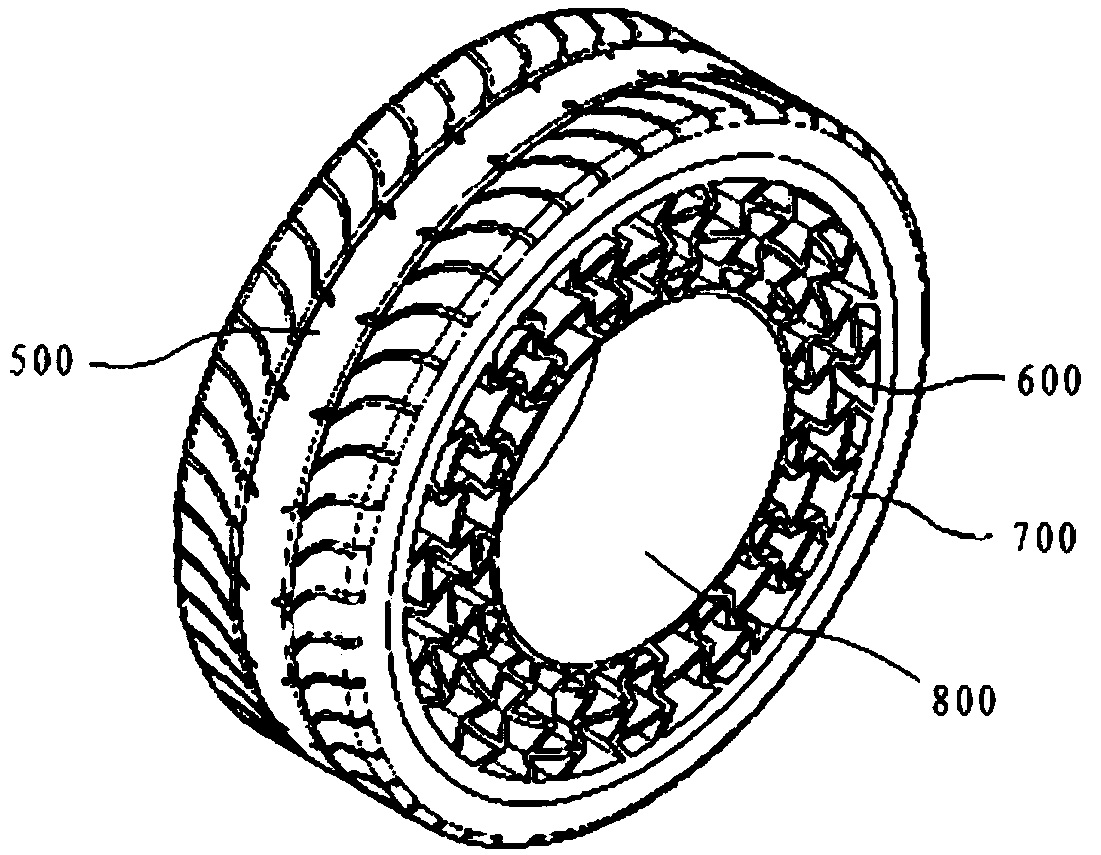
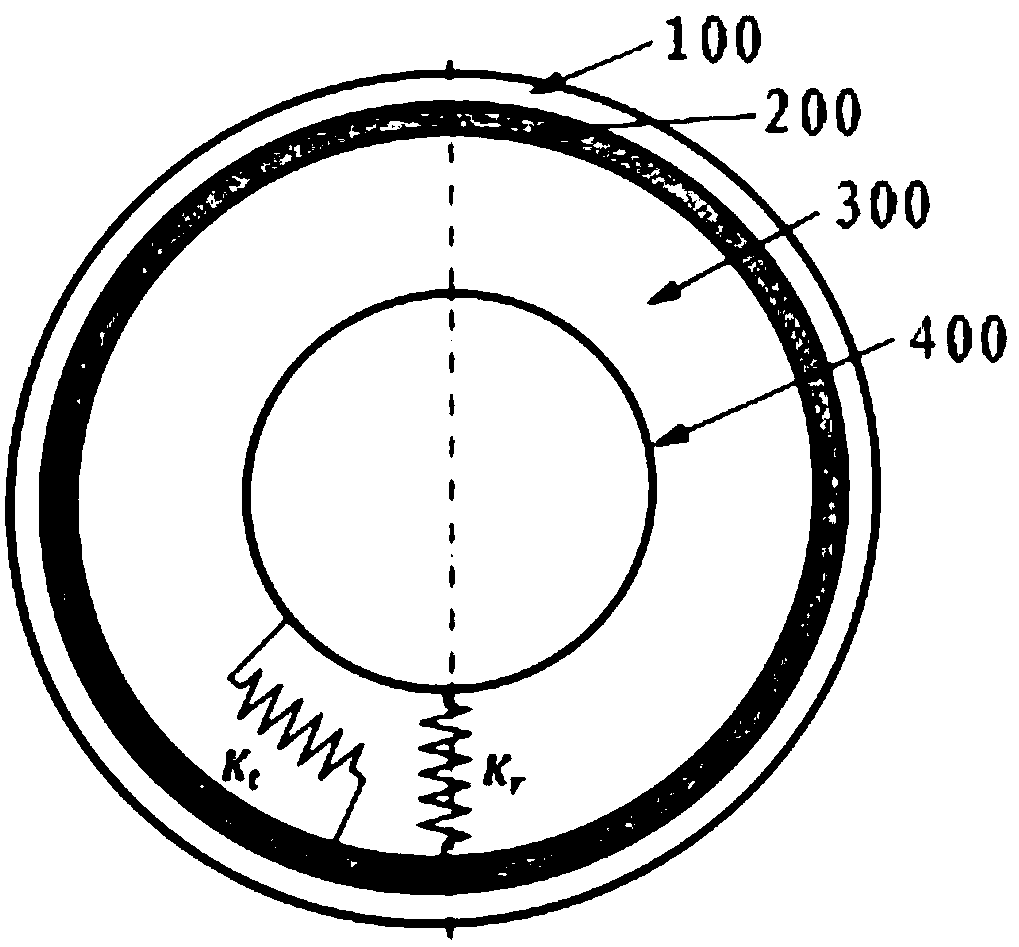
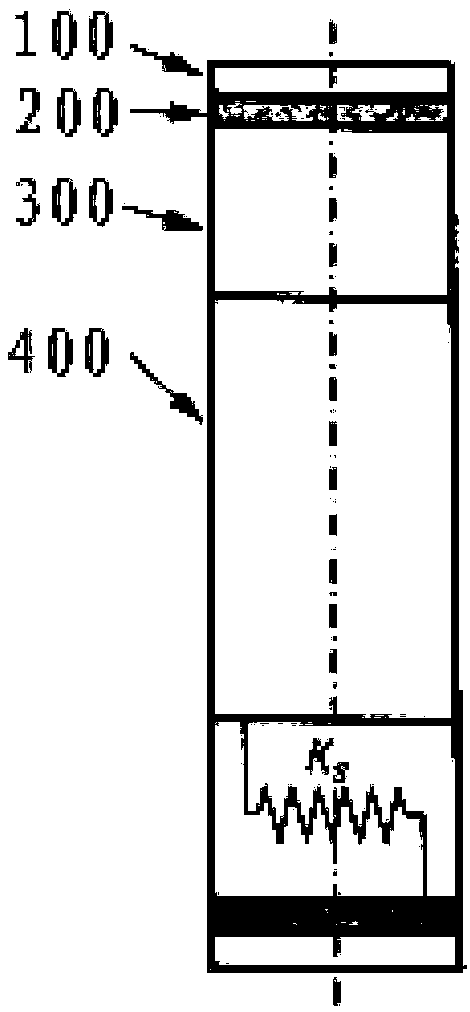
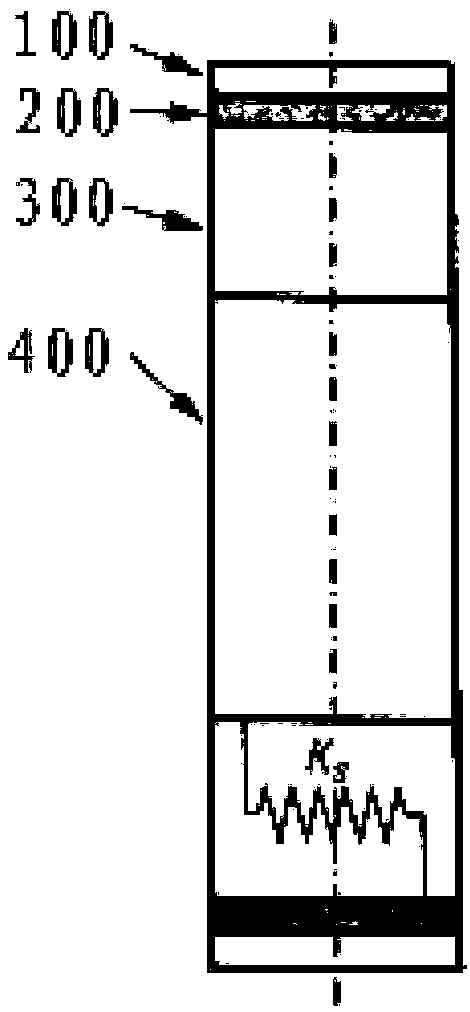
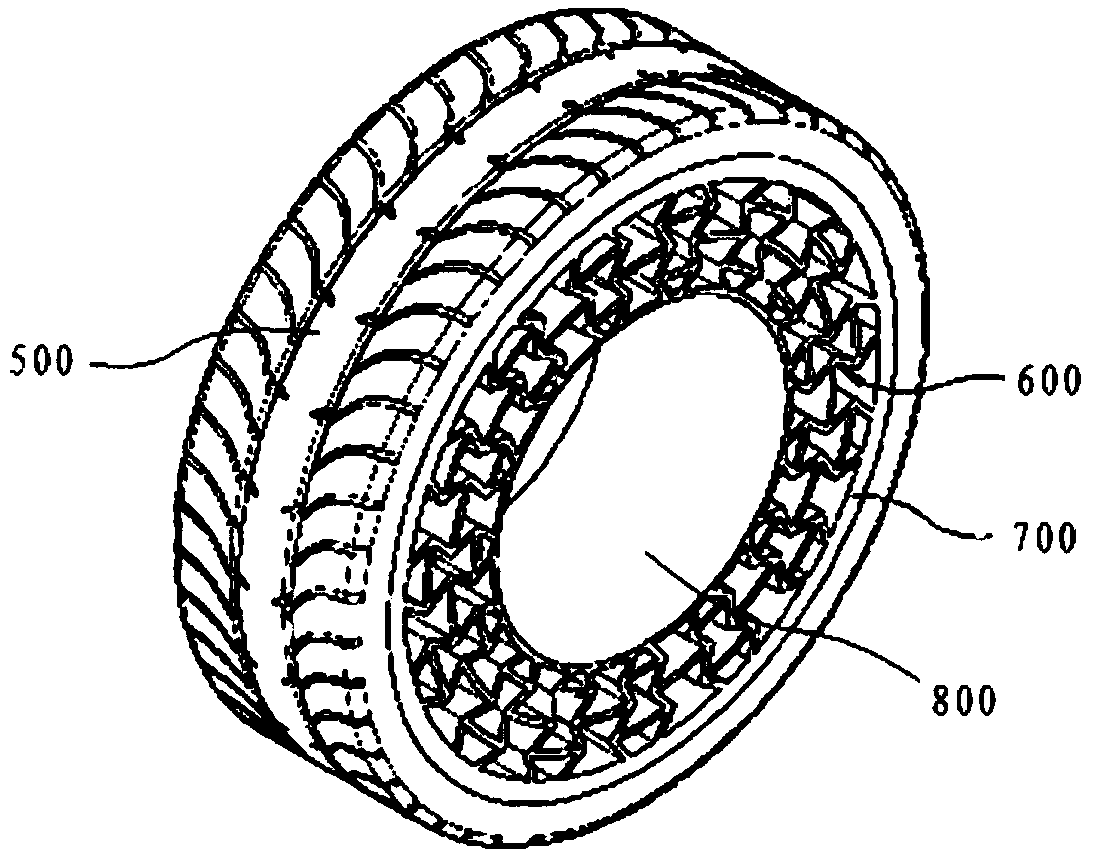
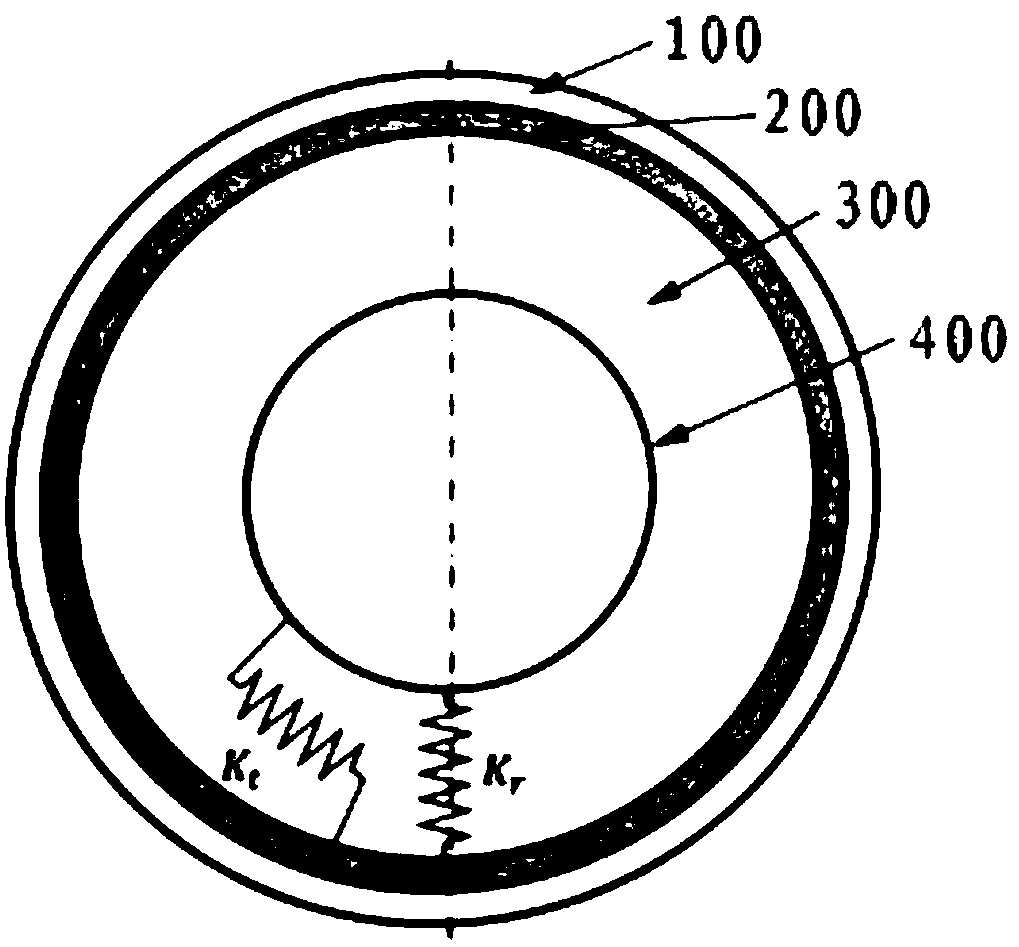
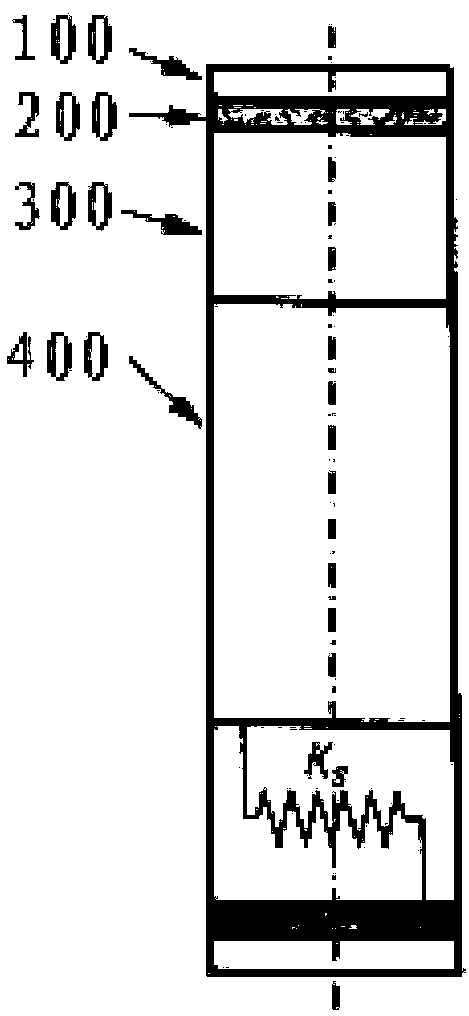
Provided is a non-pneumatic wheel (100) for a vehicle, and a wheel (100), suspension (200; 200-1), and tire (300) used therein that are capable of ensuring driving stability because there is no air chamber between a wheel (100) and a tire (300) to blowout. They are also capable of ensuring good road holding, preventing standing waves, reducing brake fade and cornering force, providing good handling and ride comfort, staying quiet when rolling, and are economical and environmentally friendly. The non-pneumatic wheel (100) includes a wheel (100), a shock absorbing member (220; 220-1) coupled to an outer periphery of the wheel (100) and absorbing or attenuating noise and vibration due to external shock, a plurality of resilient members (230; 230-1; 230-2) arranged around and coupled to an outer periphery of the shock absorbing member (220; 220-1) in a radial direction and having a plurality of resilient rings (230-1a) that are resiliently deformed in response to an external force, resilient links (240) respectively coupled to the resilient rings (230-1a) to evenly transmit external shock to the resilient rings (230-1a), rail plates (270) to which sliders (261) formed at both ends of the resilient links (240) are slidably coupled, and a tire (300) having a plurality of coupling grooves (321) formed along an inner periphery such that the rail plates (270) are inserted into the coupling grooves (321).
Owner:CHON YOUNG ILL +4
Pressure balancing device, hydro-pneumatic suspension automatic leveling system and engineering vehicle
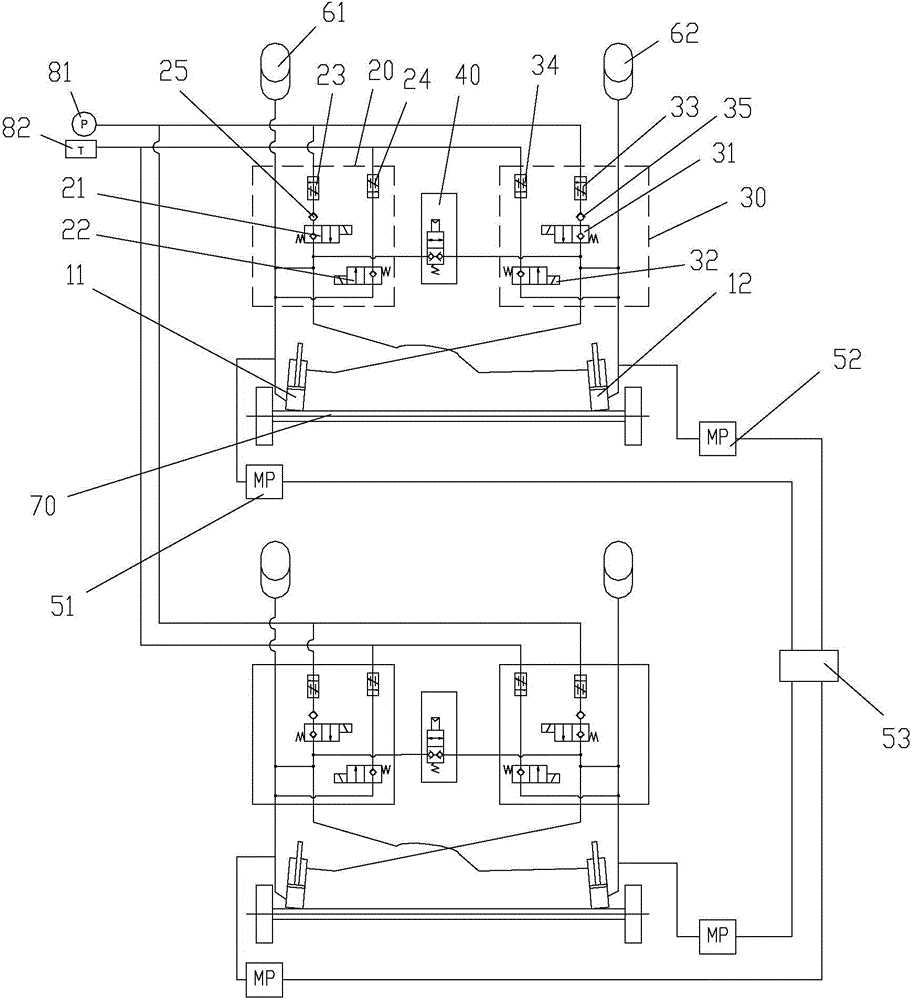
ActiveCN103204042AReduce distortionReduce excessive wearServomotorsResilient suspensionsEngineeringPressure balance
The invention provides a pressure balancing device, a hydro-pneumatic suspension automatic leveling system and an engineering vehicle. The pressure balancing device comprises a switch valve and a pressure stabilizing circuit which is in series connection with the switch valve to control pressure differences of two terminals of the pressure stabilizing circuit within a preset range. The pressure balancing device has the advantages of being capable of effectively keeping balance of a vehicle and prolonging the service life of axles.
Owner:ZOOMLION HEAVY IND CO LTD
Haze treating and lighting integrated device
ActiveCN104075200AFully automatedRealize irrigation automationUsing liquid separation agentElectric circuit arrangementsEffect lightEngineering
A haze treating and lighting integrated device is characterized by mainly comprising a haze monitoring device (1), a city water supply pipeline (2), a branch water pipe (3), a maintenance control window (4), a pressurization pump (5), a valve (6), a spherical spray head (7), a lightning rod (8), a street lamp (9) and a street rod (10). The haze monitoring device is used for monitoring the PM2.5 concentration value, the pressurization pump (5) is started when the concentration value is larger than a set value, pumped high-pressure water enters the spherical spray head (7) through the valve (6), spherical water mist is sprayed, and then haze treatment is realized. The device has both the haze prevention and control function and the road lighting function, and automation of haze prevention and control and automation of sprinkling irrigation of greening trees on the two sides of the road are facilitated.
Owner:孙文婧
Non-pneumatic wheel assembly and wheel, suspension and tire used therein
A non-pneumatic wheel assembly includes a wheel, a shock absorbing member coupled to an outer periphery of the wheel and absorbing or attenuating noise and vibration due to external shock, a plurality of resilient members arranged around and coupled to an outer periphery of the shock absorbing member in a radial direction and having a plurality of resilient rings that are resiliently deformed in response to an external force, resilient links respectively coupled to the resilient rings to evenly transmit external shock to the resilient rings, rail plates to which sliders formed at both ends of the resilient links are slidably coupled, and a tire having a plurality of coupling grooves formed along an inner periphery such that the rail plates are inserted into the coupling grooves.
Owner:CHON YOUNG ILL +4
Vehicle, vehicle leveling system, vehicle leveling method and oil-gas suspension leveling device
InactiveCN104129250AReduce distortionReduce excessive wearResilient suspensionsVehicle framePressure balance
The invention provides a vehicle, a vehicle leveling system, a vehicle leveling method and an oil-gas suspension leveling device. In the oil-gas suspension leveling device, a first oil cylinder and a second oil cylinder which are correspondingly arranged are symmetrically mounted between a vehicle shaft and a vehicle frame of the vehicle, a first working oil opening of a control valve group of the first oil cylinder is respectively communicated with a rodless cavity of the first oil cylinder and a rod cavity of the second oil cylinder, and a first working oil opening of a control valve group of the second oil cylinder is respectively communicated with a rodless cavity of the second oil cylinder and a rod cavity of the first oil cylinder; and the oil-gas suspension leveling device also comprises a pressure balancing valve, wherein one end of the pressure balancing valve is communicated with the first working oil opening of the control valve group of the first oil cylinder, and the other end of the pressure balancing valve is communicated with the first working oil opening of the control valve group of the second oil cylinder. The pressure difference between the first oil cylinder and the second oil cylinder is over the set value, the first working oil opening of the control valve group of the first oil cylinder is communicated with the first working oil opening of the control valve group of the second oil cylinder through the pressure balancing valve.
Owner:ZOOMLION HEAVY IND CO LTD
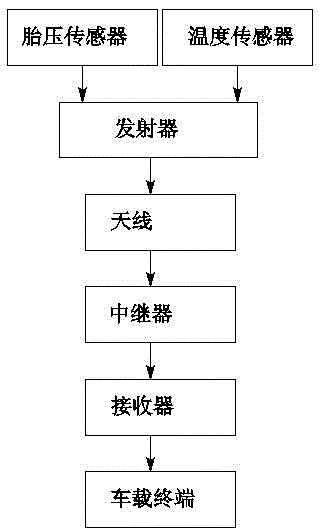
Method and system for monitoring tire pressure of dangerous chemical carrier vehicle
InactiveCN102910041AAvoid vehicle blowoutsPrevent tire blowoutTyre measurementsLower limitComparator
The invention discloses a system for monitoring a tire pressure of a dangerous chemical carrier vehicle. The system comprises a vehicle-mounted terminal, a tire pressure sensor, a temperature sensor, a receiver and an emitting device, wherein the tire pressure sensor is used for detecting tire pressure data and transmitting the data to the emitting device; the emitting device is used for receiving the data detected by the tire pressure sensor and emitting the data in a wireless manner; the receiver is connected with the vehicle-mounted terminal for receiving the data transmitted by the emitting device and transmitting the data to the vehicle-mounted terminal; the vehicle-mounted terminal is provided with a memory and a comparator; an upper limit value and a lower limit valve of the tire pressure are stored in the memory; and the comparator is used for comparing the received data with the upper limit value and the lower limit value.
Owner:NINGBO KINYOUNG CHEM LOGISTICS
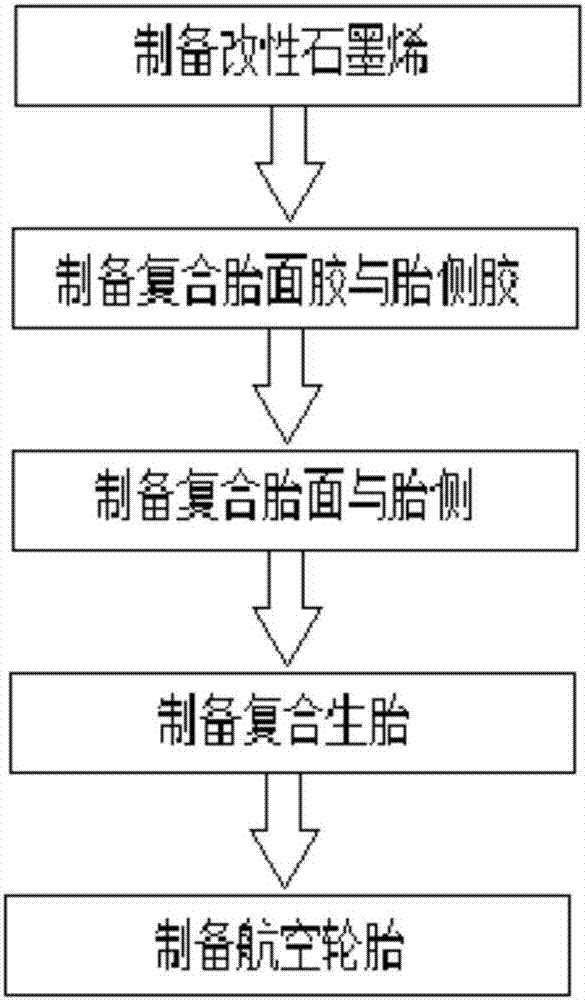
Preparation method of graphene functional aviation tire
InactiveCN107459676AEasy to addGood dispersionSpecial tyresRolling resistance optimizationAviationVulcanization
The invention belongs to the technical field of new material tire preparation, and relates to a preparation method of a graphene functional aviation tire. The technological process comprises the following five steps: preparing modified graphene, preparing compound tread rubber and sidewall rubber, preparing compound tread and sidewall, preparing a compound green tire and preparing an aviation tire. Based on specific functional characteristics of graphene material, on the basis of the modified graphene and a basic recipe of an aircraft tire in the prior art, 0.1 to 15 weight parts of modified graphene is added into the tread rubber and sidewall rubber separately, a plastic mixing and calendaring process is adopted, mould pressing bonding forming is carried out under high-temperature conditions with functional layers such as an air impervious liner, a buffer layer and a cord fabric according to a tire manufacturing basic technology, and finally the aviation tire is compositely prepared and obtained through subsequent fabrication processing of vulcanization; the technology is simple and practicable, the conventional production equipment is fundamentally utilized, large-scale technical transformation is not needed, the preparation method is applicable for the preparation of various types of aviation tires, and the preparation method is convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:QINGDAO HUAGAO GRAPHENE CORP LTD
Automobile tire anti-blasting early warning device based on conductive film and control method thereof
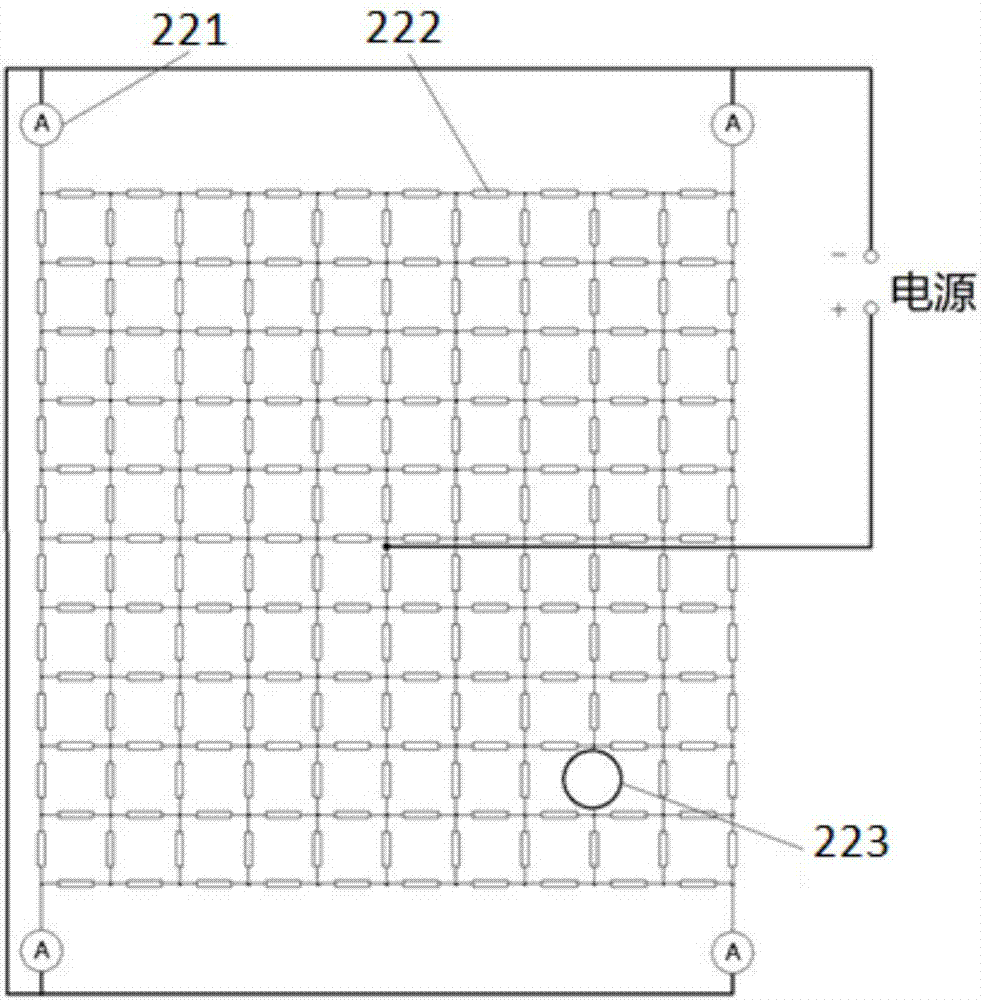
ActiveCN106864181AEnsure safetyPrevent tire blowoutTyre measurementsSignalling/lighting devicesDisplay deviceElectrical current
The invention discloses an automobile tire anti-blasting early warning device based on a conductive film. The automobile tire anti-blasting early warning device comprises a conductive film group, current detection devices and a controller, wherein the conductive film group uniformly covers the surface of the inner wall of a tire, and is connected with a power source; the current detection devices are respectively arranged at four edge corners of the conductive film; the controller is electrically connected with the current detection devices, and is used for detecting tire damage information and outputting according to current information. The invention discloses a control method of the automobile tire anti-blasting early warning device based on the conductive film. The control method comprises the following steps of 1, detecting the current of the conductive film, and judging whether the conductive film is damaged or not; 2, after the damage is verified, comparing current changes, determining rough tire damage information and / or specific damaged tire information, and sending out the damaged tire information; 3, after an early warning device receives the damaged tire information, enabling a buzzer to sound, and / or enabling a display device to display the damaged tire and a damaged position.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Automatic positioning glue spraying method and equipment for tires
InactiveCN103506257APrevent air leakagePrevent tire blowoutLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsAutomotive engineeringSpray method
The invention provides an automatic positioning glue spraying method for tires of the same category. The method includes the steps that a tire is placed on double rollers to be driven by the double rollers to rotate; the tire is dynamically fixed through rotation of the tire and the effect of a fixed tire stopping bar and an adjustable fixed tire stopping bar; a glue material is sprayed on the inner side of the tire through a spray gun according to a preset glue spraying quantity. The invention further provides automatic positioning glue spraying equipment for the tires of the same category. The equipment comprises a machine body, a control device, a glue spraying device, an automatic locating device, a power device and a transmission device.
Owner:浙江奇林实业有限公司
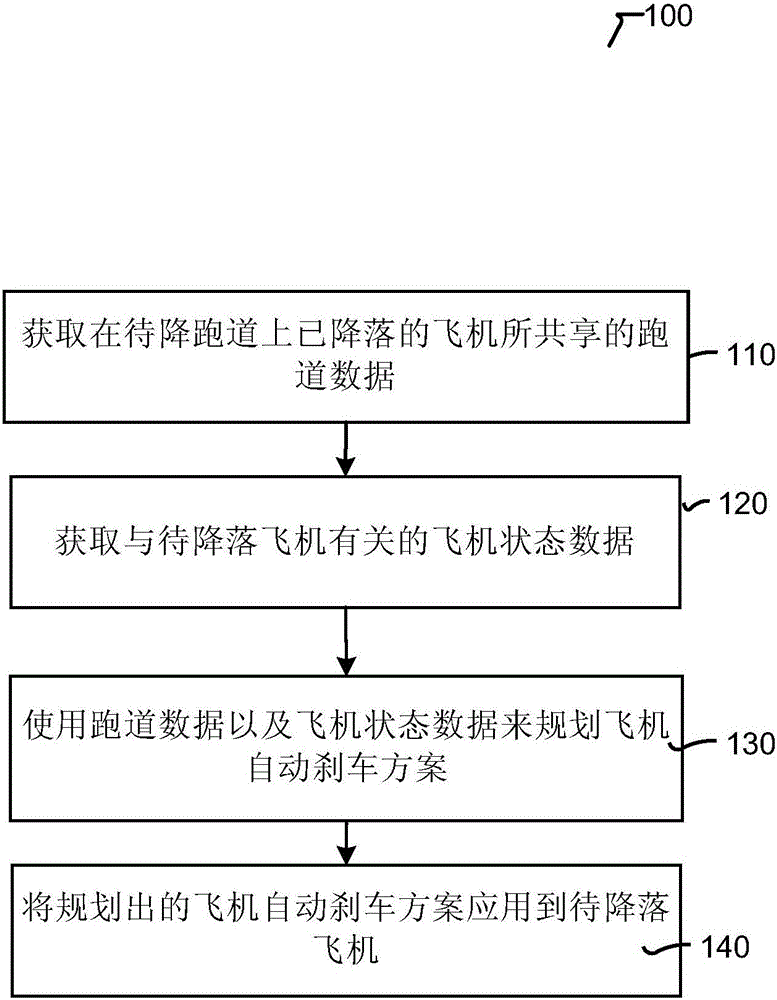
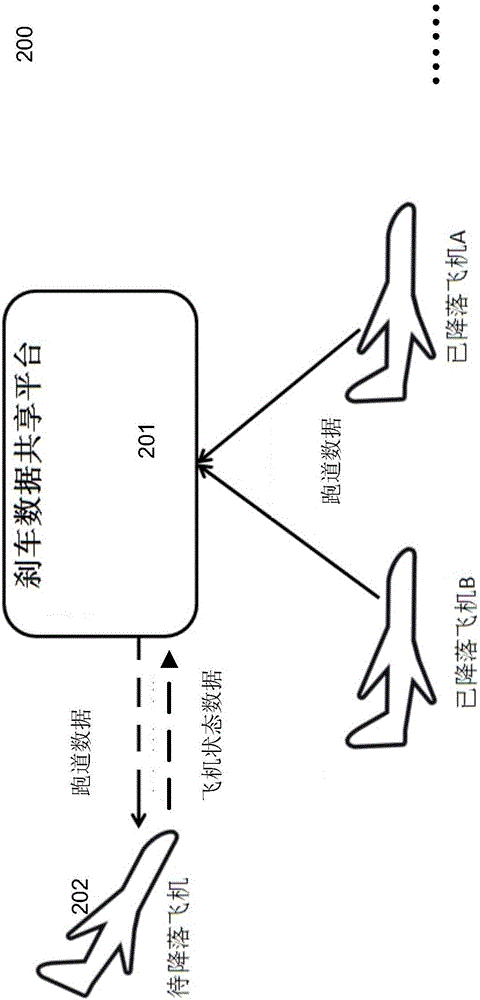
Method and system for intelligently and automatically braking airplane based on data sharing
InactiveCN106228500AImprove comfortPrevent tire blowoutData processing applicationsBraking systemsJet aeroplaneAutomatic braking
The invention relates to a method and a system for intelligently and automatically braking an airplane based on data sharing. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring track data shared by the airplane landed on a landing track; acquiring airplane state data related to the to-be-landed airplane; planning an airplane automatic braking scheme on the basis of the track data and the airplane state data; applying the planned airplane automatic braking scheme to the to-be-landed airplane.
Owner:COMAC +1
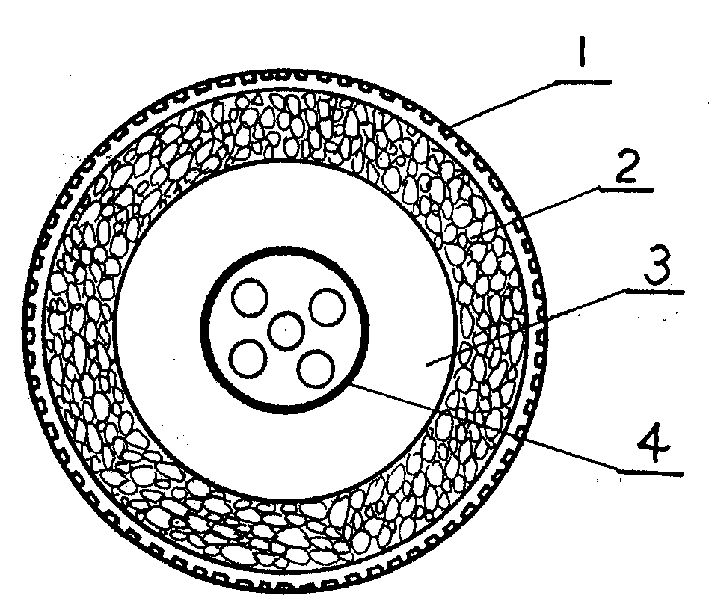
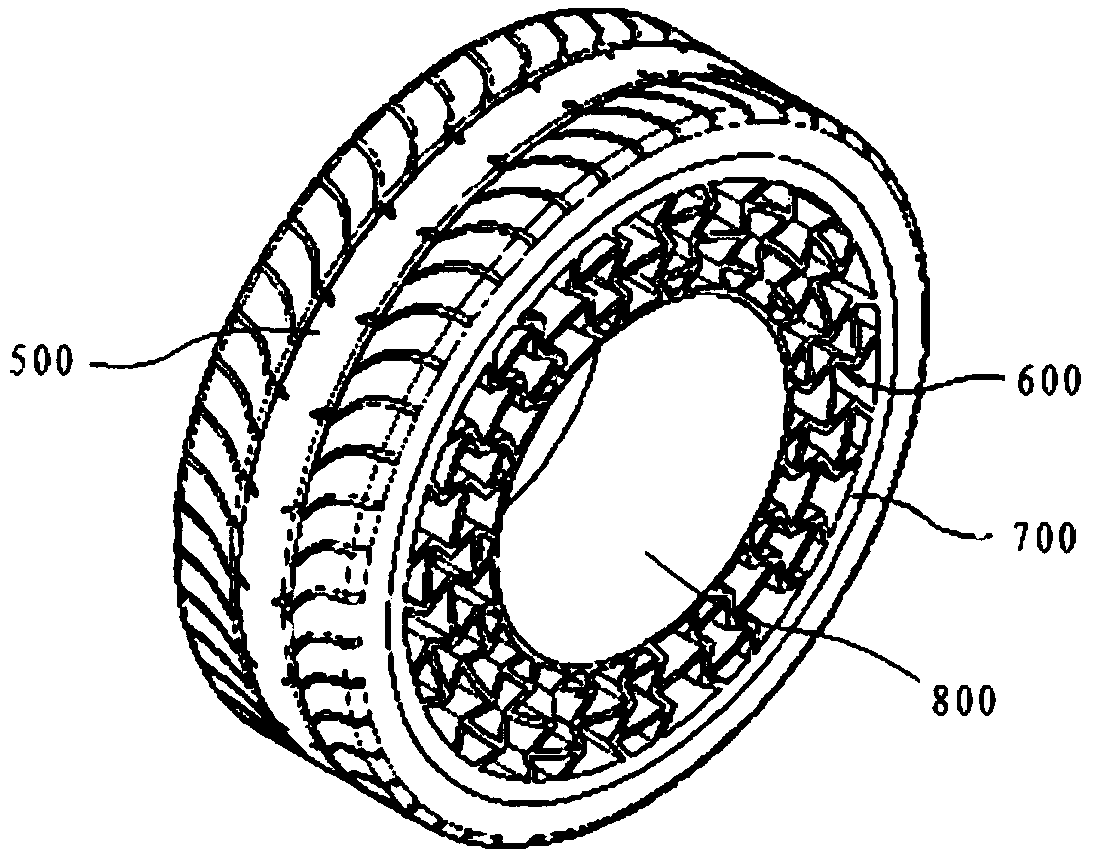
Honeycomb type prick and burst resisting tire and its producing method
InactiveCN1458002ADoes not affect normal operationIncrease elasticityNon-inflatable tyresRubber materialFoaming agent
The tire features the inner tube of relatively small diameter, and the honeycomb lining between the outer casing and the inner tube. The lining is adhered to the outer casing and forms together the inner tube one sealed cavity to maintain the inflated pressure. The honeycomb lining is formed with rubber material and through foaming process, in which raw rubber is formed into foamed material inside a container with foaming agent and the foamed material is molded, heated and cured. The tire of the present invention is suitable for all vehicles, and has the advantages of resisting heat, resisting prick and burst, long service life, etc.
Owner:马进显
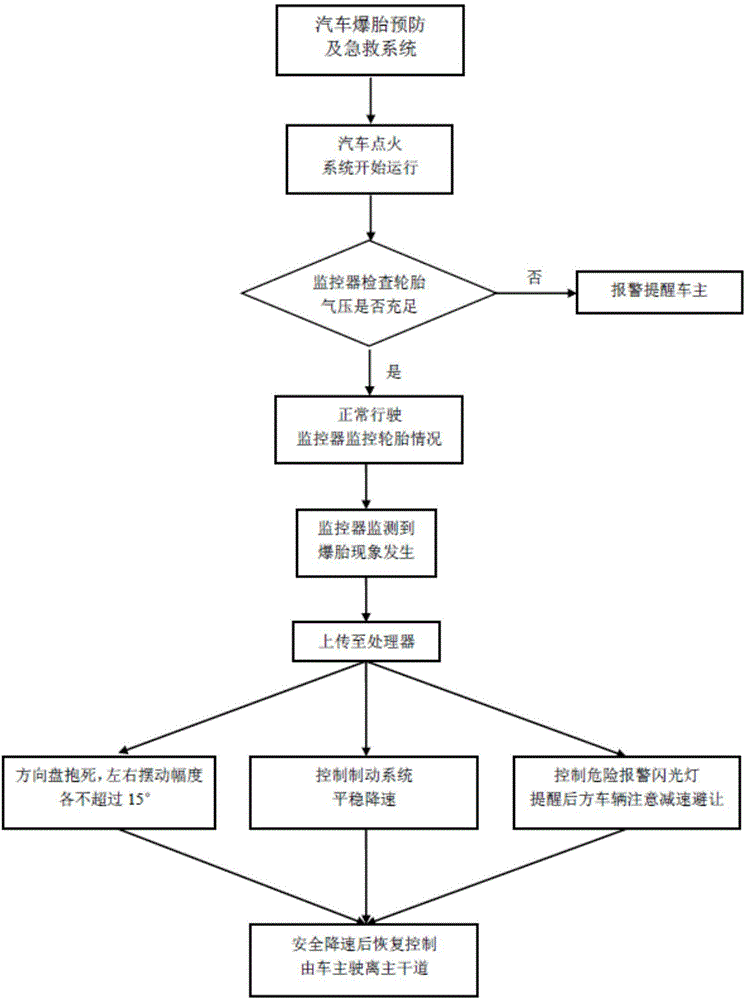
Automobile tire burst prevention and first-aiding system
InactiveCN105172487APrevent tire blowoutAvoid accidentsVehicle fittingsAutomatic initiationsAtmospheric pressureIntelligent control
The invention relates to an automobile tire burst prevention and first-aiding system. The system is mainly composed of a monitor, a processor, a controller and an alarm. The monitor mainly monitors the automobile speed and the load of a tire, preliminarily inspects the tire before the automobile moves, uploads information of whether an air pressure is too high or too low or not and whether the tire is severely worn or not to the processor, and uploads information to the processor if a tire burst phenomenon occurs in the driving process. The processor receives data provided by the monitor, analyzes the data, and issues an order to the controller and the alarm; and the controller and the alarm receive and enforce the order issued by the processor. The above intelligent control analysis system can effectively prevent tire burst, adopts corresponding measures when tire burst occurs to safely reduce the speed of the automobile and void accidents, and provides great safety guarantee for the driver and others.
Owner:NANJING DAWU EDUCATION TECH
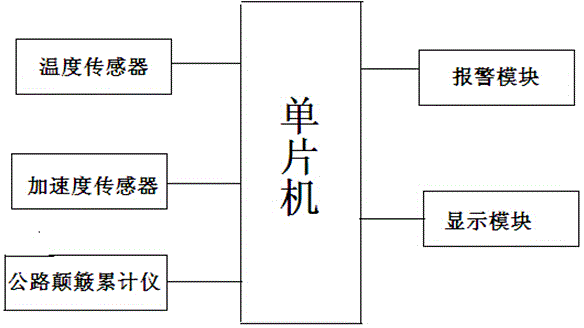
Vehicle-mounted vehicle safety detection device
InactiveCN104057899ASimple structureLow costTyre measurementsElectric/fluid circuitIntegratorRoad surface
The invention discloses a vehicle-mounted vehicle safety detection device, which comprises a control module, an alarm module, a display module, a temperature sensor, an accelerated speed sensor and a road bump integrator, wherein the temperature sensor is used for measuring tire temperature; the accelerated speed sensor is used for measuring vehicle driving speed; the road bump integrator is used for measuring the bump degree of a driving road surface. The device has the advantages of simple structure and low cost, the vehicle driving speed and the bump degree of the driving road surface can be automatically detected, and the tire temperature can be detected so as to effectively avoid tire burst caused by overhigh temperature; most importantly, the vehicle driving state can be visually displayed on a screen to bring brand-new experience for drivers.
Owner:WUXI CITY CHONGAN DISTRICT TECH ENTREPRENEURSHIP SERVICE CENT
Airless tires and cars
ActiveCN106739817BImprove maneuverabilityReduce wearRoad vehicle tyresNon-inflatable tyresHardnessEngineering
The invention discloses an air-free tire and an automobile. The air-free tire comprises a rubber tread and a wheel arm. The wheel arm is sleeved with the rubber tread and comprises an outer wheel arm ring, a middle wheel arm ring and an inner wheel arm ring. The outer wheel arm ring is fixedly connected with the middle wheel arm ring through outer spokes. The middle wheel arm ring is fixedly connected with the inner wheel arm ring through inner spokes. Recessed portions are formed in the two sides of the wheel arm and formed in the outer spokes, the middle wheel arm ring and the inner spokes. The automobile comprises the above air-free tire. The tire can be prevented from bursting in the high-speed traveling process of the automobile, and the automobile traveling safety and reliability are improved; the radial elastic performance and buffering capacity of the air-free tire are improved, and the steadiness of the automobile in the traveling process is improved; and the hardness of a tire shoulder can be effectively reduced, and the problem of abnormal wear is solved.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Airless tires and cars
The invention discloses an airless tire and a car. The airless tire comprises a rubber tread and a spoke, the spoke is sleeved with the rubber tread and is divided into a left-side spoke part and a right-side spoke part along the center face of the airless tire, the left-side spoke part and the right-side spoke part each comprise a spoke outer ring, a spoke middle ring and a spoke inner ring, the spoke outer ring is fixedly connected with the spoke middle ring through outer wire spokes, and the spoke middle ring is fixedly connected with the spoke inner ring through inner wire spokes; and the walking directions of the outer wire spokes and the inner wire spokes of the left-side spoke part are opposite to the walking directions of the outer wire spokes and the inner wire spokes of the right-side spoke part. The car comprises the airless tire. By means of the airless tire and the car, tire bursting of the car during high-speed running can be prevented, and the car travelling safety and reliability are improved; and meanwhile, it is guaranteed that braking and acceleration are not lagged.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Tire self-inflating system
The invention discloses a tire self-inflating system which comprises a sensor, a controller, a gas compressed bottle, an inflation air valve, a bleed valve, a gas generation chamber, an air flow channel and a vacuum tire, wherein the sensor monitors the state of the tire pressure and transmits monitoring signals to the controller; the controller judges according to the signals and controls the inflation valve of the gas compressed bottle to open and inflate the vacuum tire or controls the bleed valve of the gas generation chamber to open and deflate the vacuum tire. The tire self-inflating system maintains the tire pressure at a reasonable level though the closed-loop feedback regulation, solves the problem of automobile overpressure or underpressure, prolongs the service life of the tire and prevents the tire burst.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Airless tires and cars
ActiveCN106515313BReduce radial stiffnessImprove reliabilityNon-inflatable tyresHigh resiliency wheelsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an air-free tire and an automobile. The air-free tire comprises a rubber tread and a wheel spoke, and the rubber tire face is arranged on the wheel spoke in a sleeving mode; the wheel spoke comprises a wheel spoke outer ring, a wheel spoke middle ring, a wheel spoke inner ring, inner spokes and outer spokes. The two ends of the outer spokes are fixedly connected with the wheel spoke outer ring and the wheel spoke middle ring correspondingly, the two ends of the inner spokes are fixedly connected with the wheel spoke middle ring and the wheel spoke inner ring correspondingly, and the outer spokes, the wheel spoke middle ring and the inner spokes form a fishbone-shaped structure. The automobile comprises the air-free tire. According to the air-free tire and the automobile, the phenomenon that tire burst occurs when the automobile travels at high speed is prevented, and safety and reliability of automobile driving are improved.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Airless tires and cars
InactiveCN106541785BPlay a stretching effectGuaranteed rotational stiffnessNon-inflatable tyresAirless tireAutomotive engineering
The invention discloses an airless tire and a car. The airless tire comprises a rubber tread and a spoke, the spoke is sleeved with the rubber tread and comprises a spoke outer ring, a spoke middle ring and a spoke inner ring, the spoke outer ring is fixedly connected with the spoke middle ring through outer wire spokes, and the spoke middle ring is fixedly connected with the spoke inner ring through inner wire spokes; any two adjacent outer wire spokes are symmetrically distributed with respect to the center line of the two outer wire spokes and any two adjacent inner wire spokes are symmetrically distributed with respect to the center line of the two outer wire spokes. The car comprises the above airless tire. By means of the airless tire and the car, tire bursting of the car during high-speed running can be prevented, and the car travelling safety and reliability are improved; the radial elastic performance and the buffer capacity of the airless tire are improved, and the car travelling smoothness is improved; and meanwhile, it is guaranteed that braking and acceleration are not lagged.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
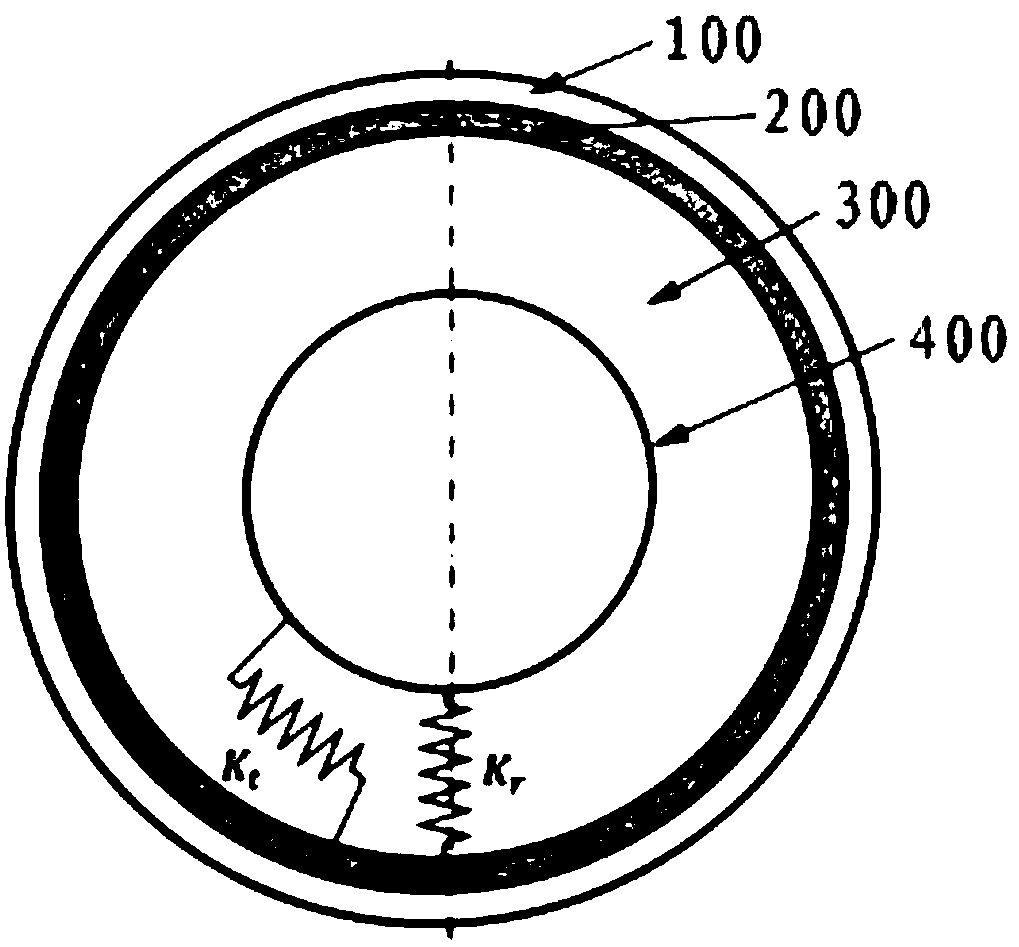
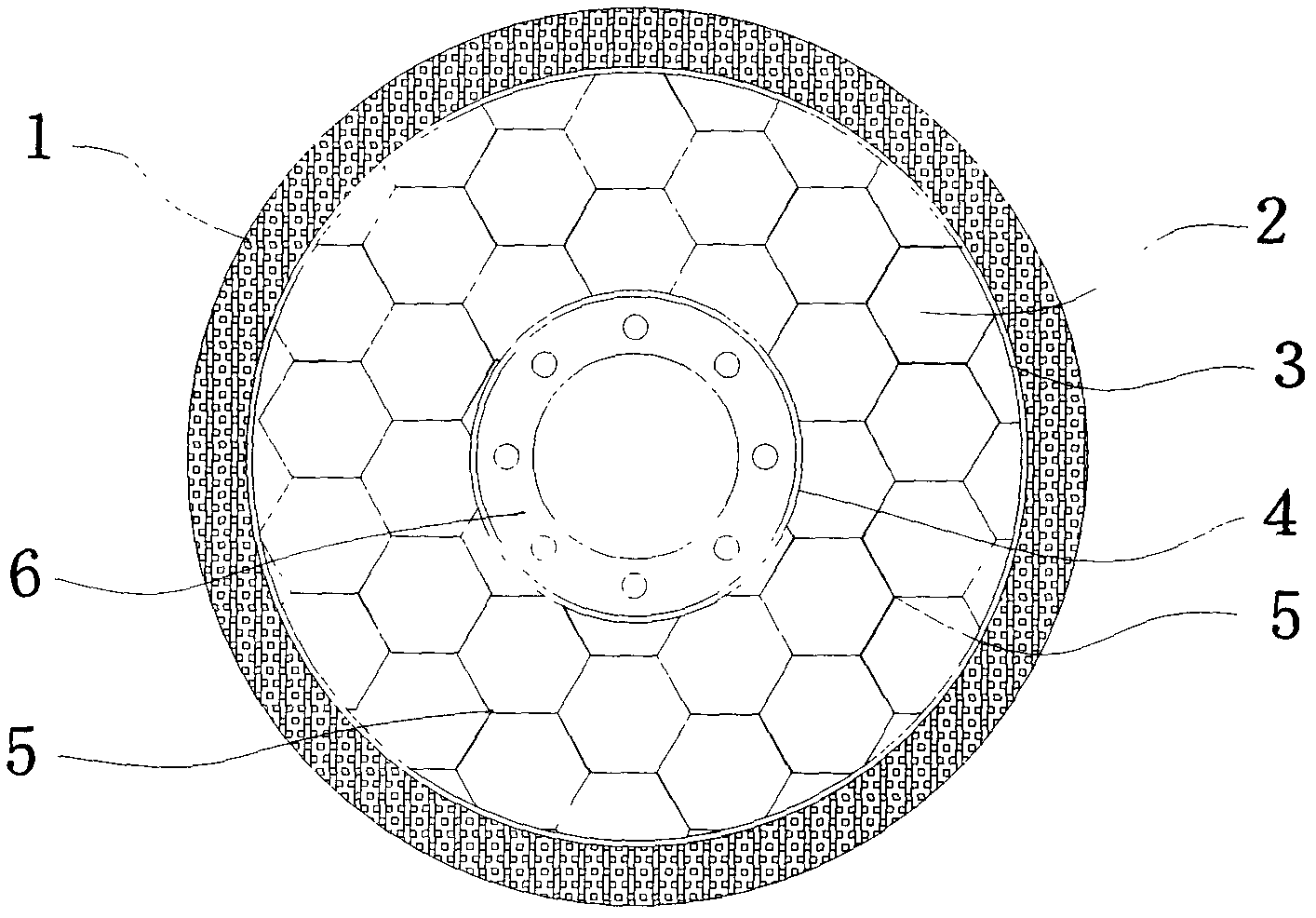
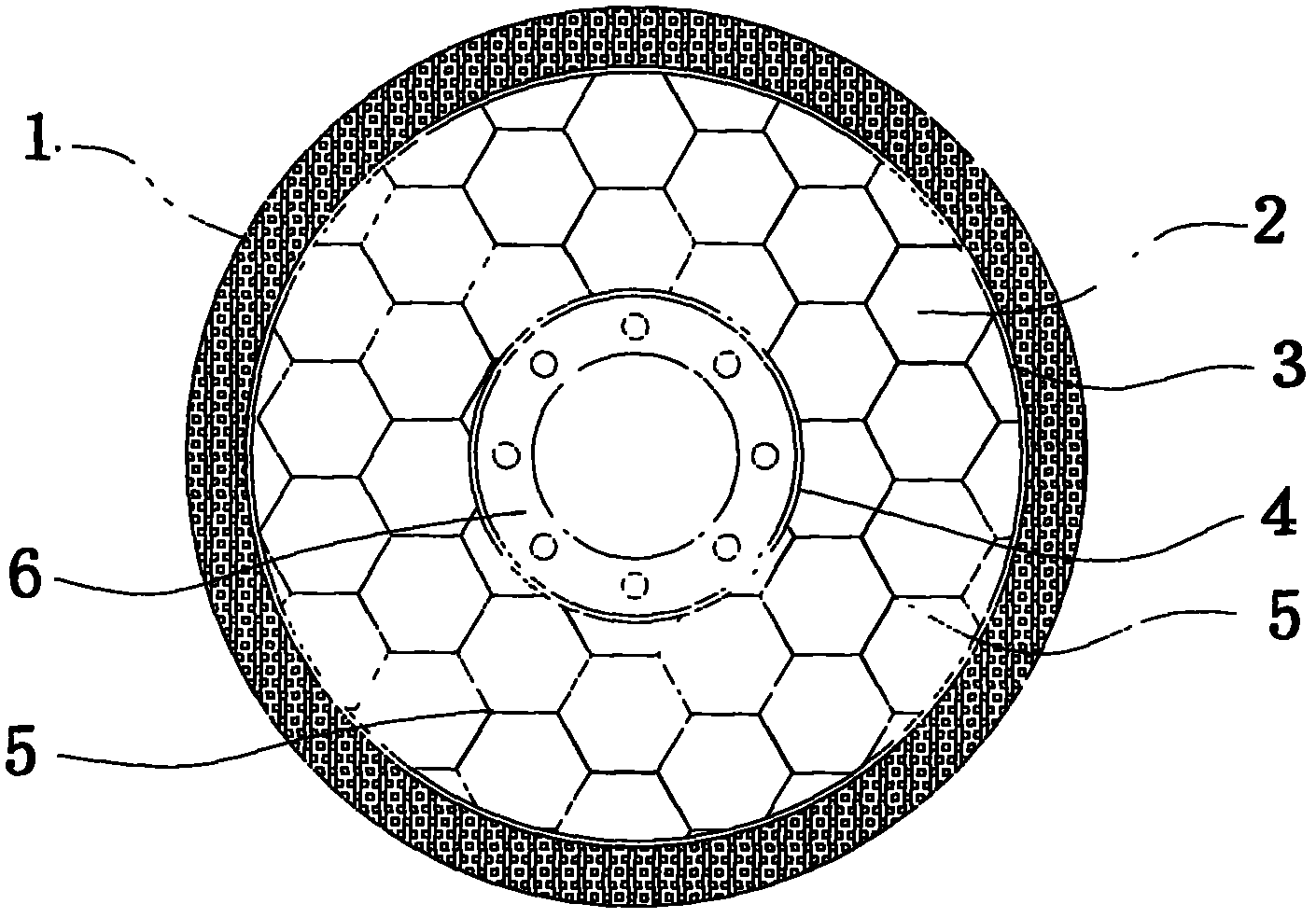
Bionic cellular tire
InactiveCN102501728AHigh strengthImprove structural strengthNon-inflatable tyresInterference fitBionics
The invention relates to the technical field of tires, in particular to an air inflation-free bionic cellular tire. The bionic cellular tire comprises a solid cover tire and a cellular tire body, wherein the solid cover tire is made of rubber and clamped at the periphery of the cellular tire body through interference fit; the cellular tire body comprises an outer ring, an inner ring and a cellular cylinder structure between the outer ring and the inner ring; and the section of the cellular cylinder structure has a hexagonal shape. According to the bionic cellular tire, by using the advantages of a structural design, the strength of the tire is improved maximally while certain damping performance is maintained, and the bionic cellular tire has the advantages that: the bionic cellular tire is free of air inflation and easy to maintain, has high environment adaptability and light self-weight, cannot be burst, and the like.
Owner:董玉芬
Airless tires and cars
InactiveCN106515312BReduce radial stiffnessImprove reliabilityNon-inflatable tyresHigh resiliency wheelsEngineeringAirless tire
The invention discloses an air-free tire and an automobile. The air-free tire comprises a rubber tread (1) and a wheel spoke (2), and the rubber tread (1) is arranged on the wheel spoke (2) in a sleeving mode; the wheel spoke (2) comprises a wheel spoke outer ring (21), a wheel spoke inner ring (22) and spokes (23), and the wheel spoke outer ring (21) is fixedly connected with the wheel spoke inner ring (22) through the spokes (23); and the spokes (23) are of a latticed structure. The automobile comprises the air-free tire. According to the air-free tire and the automobile, the phenomenon that tire burst occurs when the automobile travels at a high speed is prevented, and safety and reliability of automobile driving are improved.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Narrowing method of straddle-type monorail transit curved track beam
ActiveCN101851882ASmall compression deformationReduce wearRailway tracksTransit systemEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a narrowing method of a straddle-type monorail transit curved track beam, relating to the straddle-type monorail transit track beam. In the straddle-type monorail transit system, the breadth of the track beam of which the horizontal alignment is in a circular curve segment is narrowed according to the curve radius and the different vehicle types; and when the track beam is located at a straight line, a transition curve and a circular curve or a straight line and a circular curve, the track beam is adjusted in accordance with respective variation regularity of beam breadth. As the track beam is processed and produced, an outer template of the curved track beam is moved from the original place toward the curve central direction to reach the narrowed position by the distance of a corresponding narrowed value; and an inner template thereof remains the same. During setting up the track beam, the central line of the route remains unchanged, the measuring location and the setup of the track beam are performed based on that the inner side of the track beam is semi breadth of a standard beam away from the central line of the route. The invention overcomes the defects of excessive deformation, tire burst, excessive wear, short service life, large power consumption and the like for the vehicle tires resulted from excessive extrusion for the track beam, and simultaneously improves the economic benefit.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Airless tires and cars
ActiveCN106696605BGuaranteed radial stiffnessImprove reliabilityNon-inflatable tyresDisc wheelsRadial spokeEngineering
The invention discloses an airless tire and an automobile. The airless tire comprises a rubber tread (1) and a wheel arm (2), the rubber tread (1) is arranged on the wheel arm (2) in a sleeving mode, and the wheel arm (2) comprises a wheel arm outer ring (21), a wheel arm inner ring (22) and radial spokes (23). The wheel arm outer ring (21) is fixedly connected with the wheel arm inner ring (22) through the radial spokes (23). The automobile comprises the airless tires. According to the airless tire and the automobile, the automobile can be protected against tire burst during high-speed traveling, and safety and reliability of automobile traveling are improved.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Automatic tire pressure balancing device
PendingCN110549797AInflated to achieveRealize automatic adjustmentTyre measurementsWireless transmissionExhaust valve
An automatic tire pressure balancing device is composed of a three-position three-way solenoid valve, a tire valve opening, an exhaust valve opening, an inflation valve opening, a tire, an air cylinder inflation valve, an air cylinder cavity, a rim, a tire inflation valve, a movable iron core, a pressure sensor, a speed sensor, a control panel, an electric wire, a data output module, a wireless transmission module, a battery, an information collecting module and an ECU micro-processing module. The three-position three-way solenoid valve is connected with the rim with an air storage function through a thread, and the control panel carries out intelligent processing according to tire pressure information fed back by the pressure sensor and vehicle speed information fed back by the speed sensor, the communicating state of the three-position three-way solenoid valve is controlled, and then the tire pressure of the tire is adjusted. The automatic tire pressure balancing device has the advantages of being simple in structure and automatically adjusting the tire pressure, and has very high use value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Walking device with variable tire pressure
InactiveCN106739852ARaise the verticalGood adhesionWith separate inflatable insertsTyre measurementsWireless controlAttitude control
The invention discloses a walking device with variable tire pressure, and belongs to the technical field of active vehicle security. The walking device comprises a wireless signal transmission receiving device, a wireless control valve, a wireless control one-way valve, a tire pressure sensor, an air compressor and the like. The walking device is characterized in that a tire is internally partitioned into an inner cavity and an outer cavity through an inner / outer cavity partitioning plate; air of the inner cavity and the outer cavity is subjected to corresponding air exchange through the wireless control valve, the wireless control one-way valve and the air compressor, so that pressure increase and release of the outer cavity can be achieved, and pressure variation of a tire is achieved. The tire needs no air inflation, or even vehicle body posture control of a certain amplitude can be achieved, and the tire pressure can be increased or decreased according to the running situations of a vehicle and the brake and steering intention of a driver, so that the power performance, the brake performance and the security of the vehicle can be improved. The walking device has the advantages that vehicle tire pressure variability, no air inflation and vehicle body posture control of certain amplitude are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Fixing structure of front two-step bus air suspension
The invention relates to a fixing structure of a front two-step bus air suspension. The fixing structure of the front two-step bus air suspension comprises a wheel-guard assembly and a walkway assembly which are located above the air suspension. The wheel-guard assembly comprises a wheel-guard support, an upper wheel-guard seal plate and a wheel-guard vertical surface seal plate, wherein the wheel-guard support is fixedly arranged above a bus body frame, the upper wheel-guard seal plate is fixedly arranged above the wheel-guard support, and the wheel-guard vertical surface seal plate is fixedly arranged on the inner side of the wheel-guard support. The walkway assembly comprises a walkway support and a walkway seal plate, wherein the walkway support is fixedly arranged in the middle of the bus body frame, and the walkway seal plate is fixedly arranged above the walkway support. A support used for installing an air bag and a support used for installing a shock absorber are fixedly arranged below the wheel-guard support. A support used for installing a stabilization rod is fixedly arranged below the walkway support. The upper wheel-guard seal plate is provided with an assembly service port. The wheel-guard vertical surface seal plate is provided with a groove. The fixing structure of the front two-step bus air suspension is simple and reasonable in design, small in occupied space, and capable of not only enabling the heights of seats above a front wheel guard to meet the requirement for sitting comfort, but also enabling the width of a walkway to be suitable for increasing the speed of passengers getting on and off from the bus.
Owner:ANHUI ANKAI AUTOMOBILE
Automobile brake cooling control device and control method
ActiveCN114454853AThe effect of the run-flat tire is goodSimple structureBrake coolingTyre measurementsControl valvesControl theory
An automobile brake cooling control device comprises an automobile body controller, an air storage cylinder, a water storage barrel, a control valve assembly, a plurality of water spraying devices correspondingly arranged on tires and a plurality of tire pressure sensors correspondingly arranged on the tires, an air inlet of the water storage barrel is communicated with the air storage cylinder, and a water outlet of the water storage barrel is communicated with a water inlet of the control valve assembly. According to the control principle, when the vehicle runs, the vehicle body controller judges whether actual tire pressure values received from the tire pressure sensors are higher than corresponding tire pressure reference values or not and whether the difference value between the actual tire pressure values and the tire pressure reference values is larger than a set value or not, if yes, the vehicle body controller controls the control valve assembly to be opened, and if not, the vehicle body controller controls the control valve assembly to be closed; and the brake at the tire is cooled. When a high tire pressure value is detected, the control valve assembly is automatically opened to spray water to cool the brake, direct factors causing tire burst can be accurately detected, and the tire burst prevention effect is good.
Owner:DONGFENG AUTOMOBILE COMPANY
High-strength heat-resistant tread rubber composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104292521AImprove the protective effectGood dispersionSpecial tyresPolymer scienceMicrocrystalline wax
The invention discloses a high-strength heat-resistant tread rubber composition and a preparation method thereof. The tread rubber composition consists of the following components in parts by mass: 60-85 parts of natural rubber, 21-32 parts of butadiene rubber, 5-15 parts of microcrystalline wax, 7-17 parts of carbon black, 3-10 parts of sulfur, 2-18 parts of anti-aging agent, 3-11 parts of accelerant and 5-12 parts of zinc oxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding the natural rubber, butadiene rubber and microcrystalline wax into an internal mixer for mixing according to the mass parts, adding the carbon black, continuously mixing, extracting, and pressing, thereby obtaining a mixture; adding the mixture into an open mill, adding the sulfur, the anti-aging agent, accelerant and zinc oxide, mixing, thereby obtaining rubber cement; and heating and molding the rubber cement in a mold, thereby obtaining the high-strength heat-resistant tread rubber composition. The tread rubber composition prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high strength, high heat resistance and capacities of prolonging the service life of tires and preventing a flat tire.
Owner:青岛黄海轮胎有限公司
Centrally-mounted eddy current retarder
InactiveCN103078469AGood braking effectPrevent tire blowoutAsynchronous induction clutches/brakesCooling/ventillation arrangementWind forceMagnetic line
The invention discloses a centrally-mounted eddy current retarder. The centrally-mounted eddy current retarder comprises a stator assembly and a rotor assembly, wherein the stator assembly consists of a stator support, a bearing seat is arranged on the stator support which is connected with an iron core, a winding coil is arranged on the iron core, a front magnet yoke and a rear magnet yoke are arranged on the stator support, at two sides of the iron core, the rotor assembly comprises a bearing arranged in the bearing seat, and a shaft arranged in the bearing, and a front rotor disc adjacent to the front magnet yoke, and a rear rotor disc adjacent to the rear magnet yoke are arranged at two ends of the shaft. The centrally-mounted eddy current retarder cuts magnetic lines to produce eddy current through the rotor assembly, thereby forming brake moment, and being good in braking effect; and furthermore, heat produced in flowing of the eddy current inside the rotor assembly can be dissipated out through powerful wind generated by blades on the rotor disc, thereby effectively solving the problem that flat tires easily occur due to high temperature in summer, and being simple in structure and easy to realize.
Owner:KAILONG HIGH TECH
Solar power station applied to expressway and capable of realizing telescopic direction adjustment
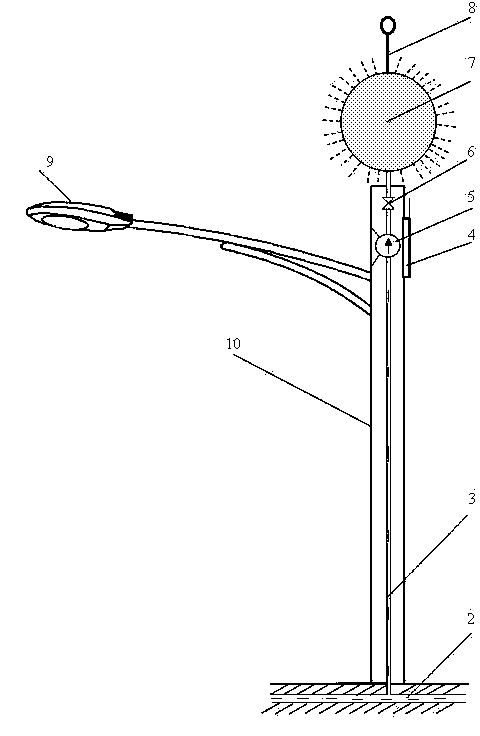
InactiveCN103490705AReduce heat radiationExtend your lifePhotovoltaic supportsPV power plantsDriving safetySteel columns
Discloses is a solar power station applied to an expressway and capable of realizing telescopic direction adjustment. The solar power station comprises solar cell panels, a first steel column, a second steel column, a third steel column, telescopic arms, a high-voltage cable support, an expressway roadbed and concrete piles. The first steel column and the second steel column are located on the two sides of the expressway roadbed respectively, the third steel column and the second steel column are located on the two sides of the expressway roadbed respectively, the first steel column, in this way, expressway guardrails are formed, each solar cell panel is installed above the two corresponding steel columns which form one expressway guardrail, one end portion of each solar cell panel is movably connected with one of the two corresponding steel columns, and the other end portion of each solar cell panel is connected with the other steel column of the two corresponding steel columns through one telescopic arm. Telescopic direction adjustment of the solar cell panels is realized by adjusting the telescopic arms so that the solar cell panels can be made to face the sun with the largest irradiation area at any time. The solar cell panels effectively reduce thermal radiation to the surface of the expressway from sunlight, prolong the service life of the expressway, and guarantee driving safety of vehicles. The solar cell panels are compact in structure, ingenious in concept and capable of guaranteeing that the solar power station can achieve the largest power generation amount, and meanwhile, effectively save land resources.
Owner:谢一龙
Novel inflation-free tire
PendingCN110422014AReasonable designCompact structureRimsNon-inflatable tyresAutomotive engineeringTweel
The invention relates to the technical field of equipment for inflation-free tires, and provides a novel inflation-free tire. The novel inflation-free tire comprises a tire and a wheel hub, wherein the tire sleeves the wheel hub; the tire comprises a tire body, a tire crown and a tire root, wherein one side, close to the wheel hub, of the tire body is connected with the tire root, the tire root sleeves the rim of the wheel hub, and the other end of the tire body is connected with the tire crown; and the tire body, the tire crown and the tire root are mutually connected to form a closed structure, and the closed structure is internally provided with a foaming tire core. According to the novel inflation-free tire, disadvantages of the prior art are overcome, the design is reasonable, the structure is compact, and the problems that a conventional inflatable tire is easy to burst, a solid tire is easy to slip and shift, and damping effect is poor can be solved. Rubber is used as a foamingmaterial in the novel inflation-free tire, so that damping effect can be improved through excellent elastic performance of the rubber, and meanwhile connection effect of the tire and the wheel hub isimproved, and the shifting is avoided; and in addition, the thickness of the tire body is reduced, thus preventing tire slip. Therefore, the novel inflation-free tire has very strong practicability.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHTD RUBBER SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com