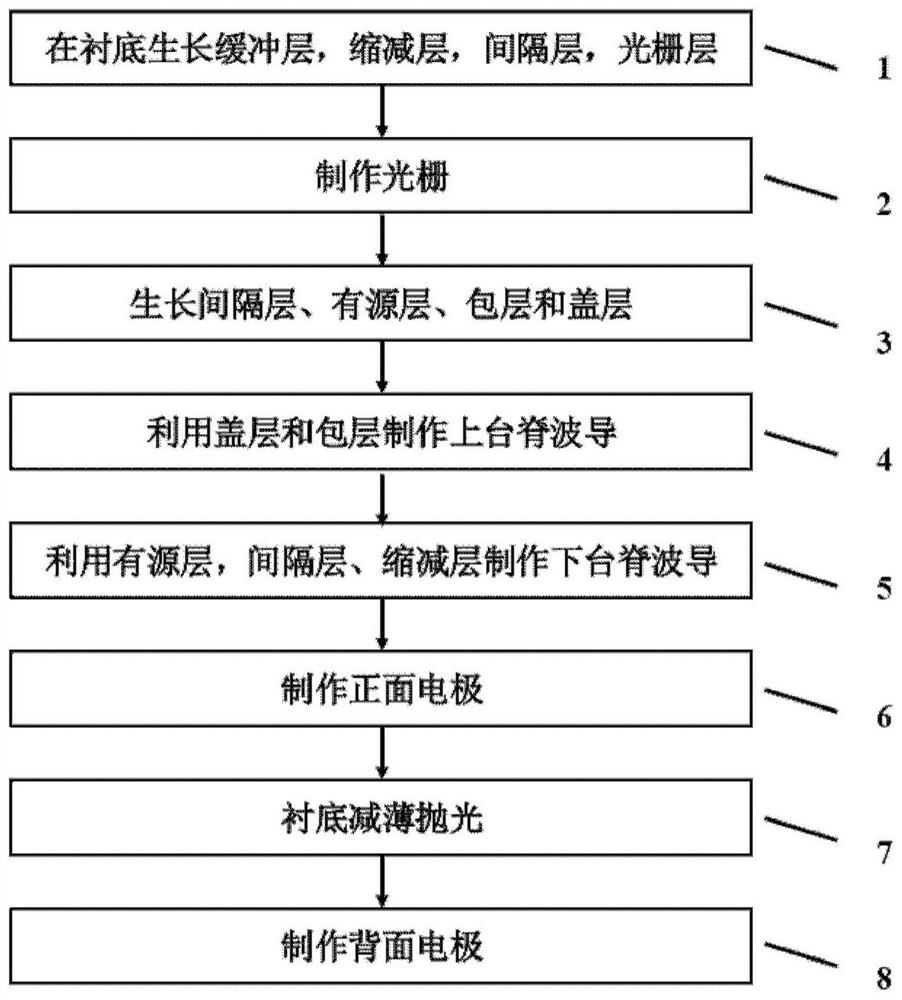
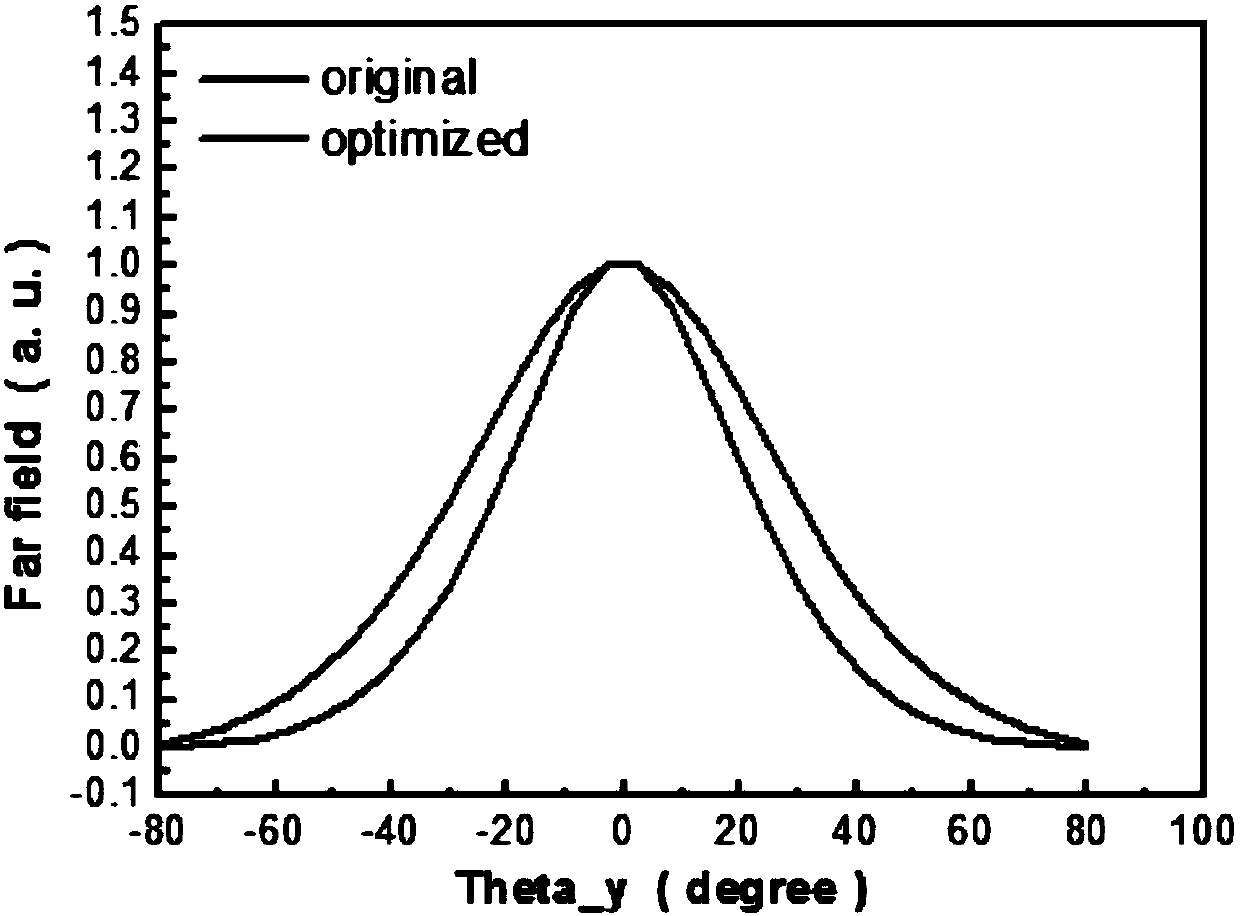
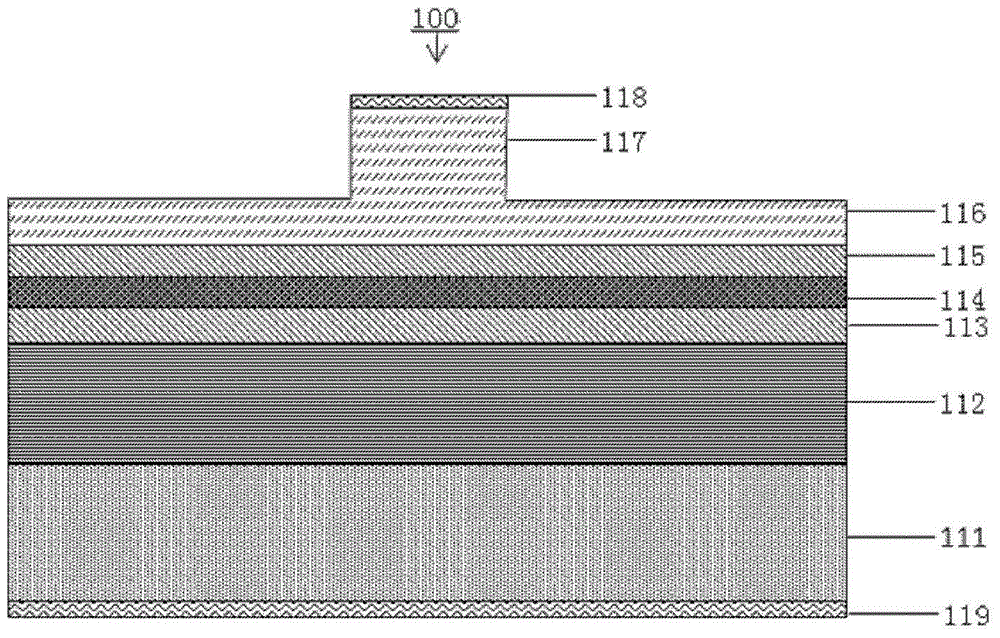
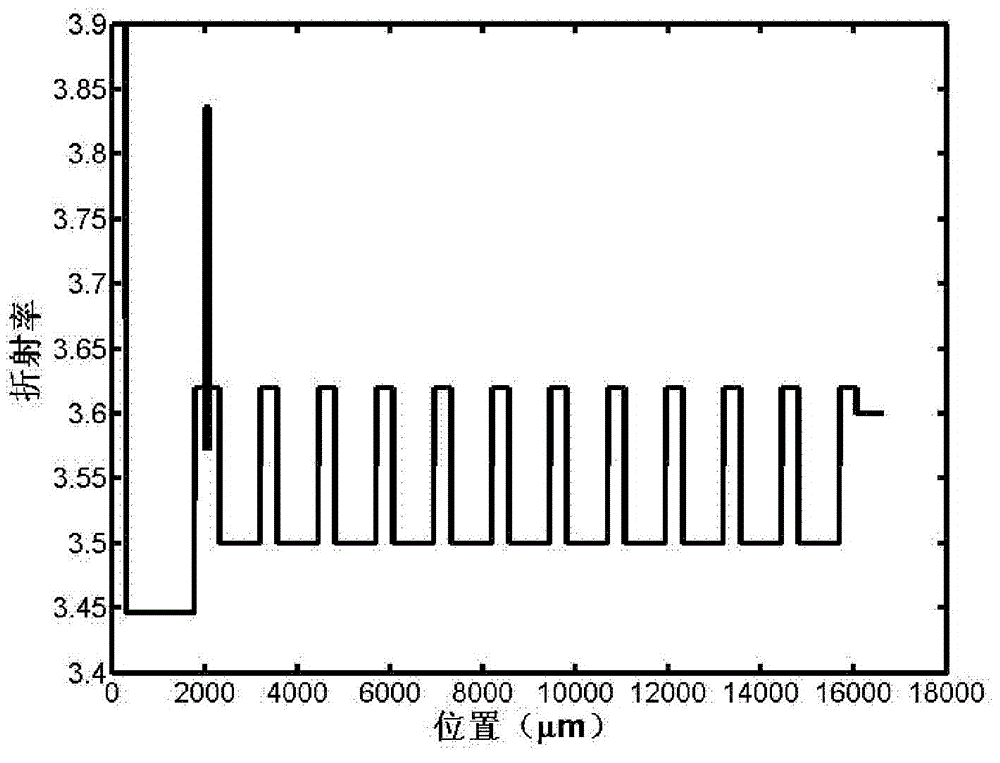
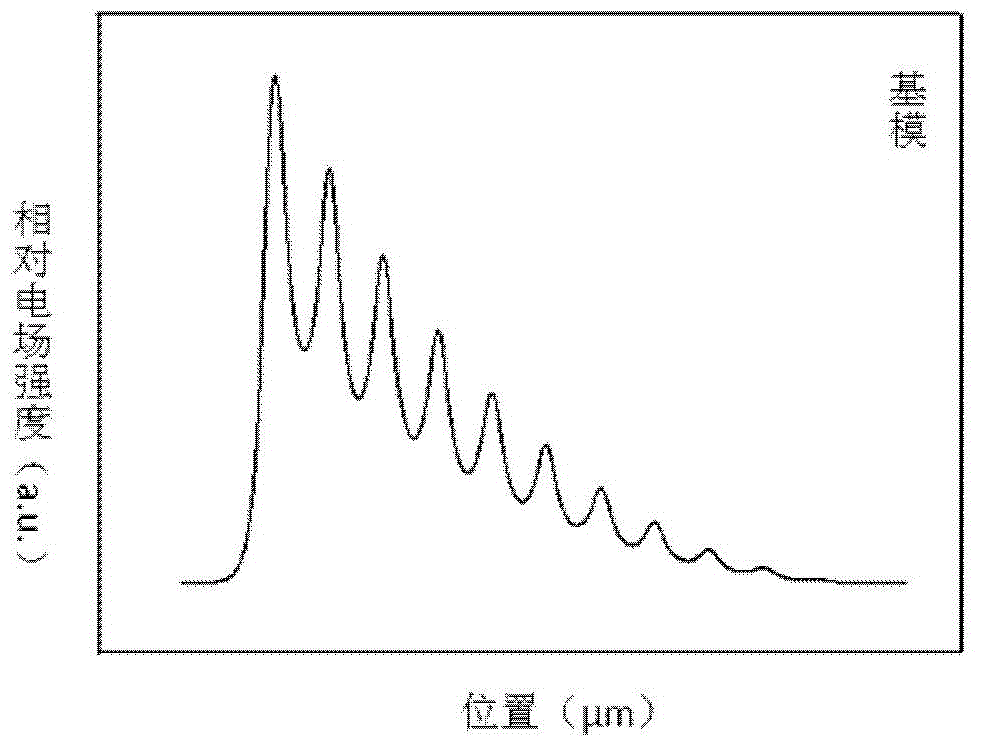
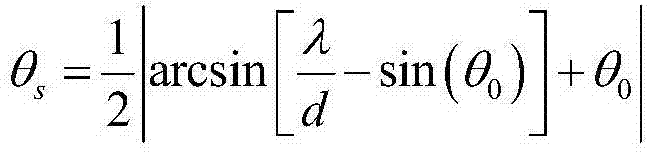Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Reduce far-field divergence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
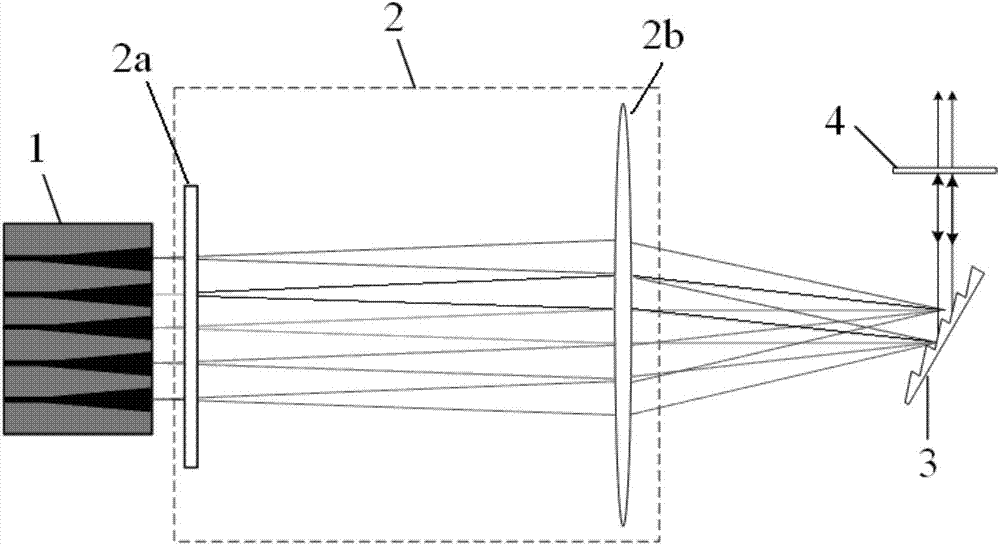
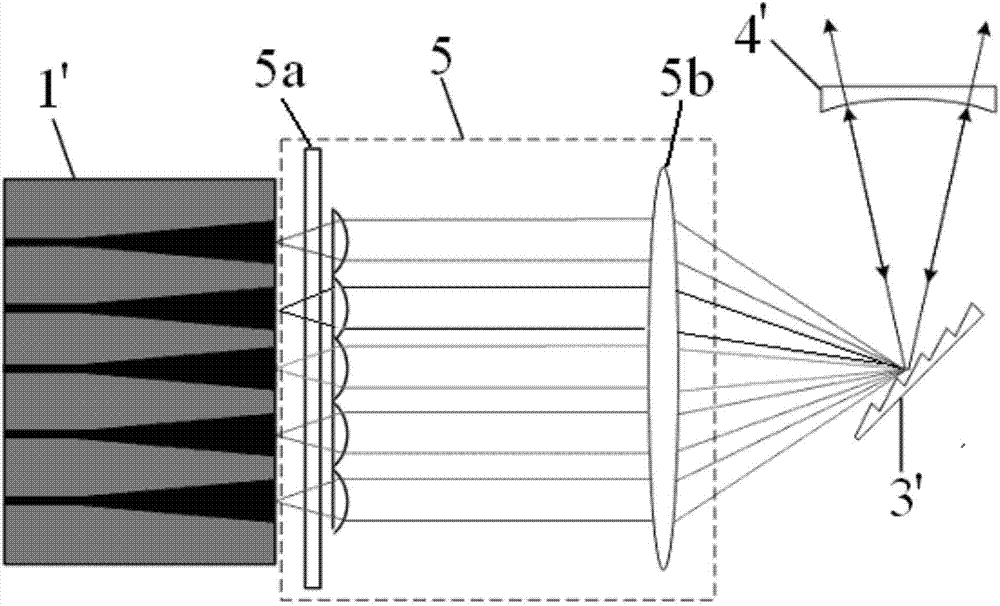
Red light semiconductor area array light source device for laser display
InactiveCN103412406ASimple structureImprove reliabilityLaser detailsProjectorsEffect lightLight beam
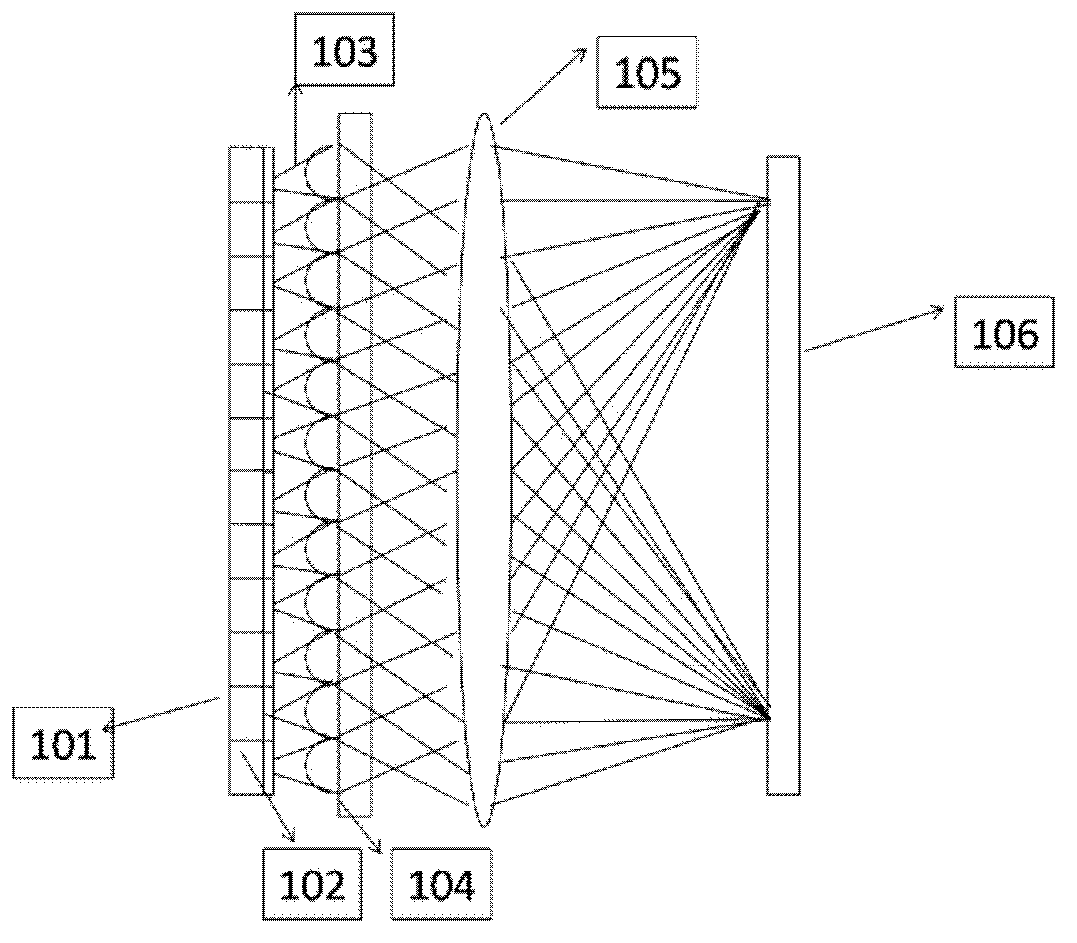
The invention discloses a red light semiconductor area array light source device for laser display. The red light semiconductor area array light source device for laser display comprises a VCSEL area array and a microlens array, wherein the VCSEL area array at least comprises a plurality of VCSEL units which are used for emitting circular laser beams, and the microlens array is formed by a plurality of microlens and used for performing collimation rounding on the laser beams output by the VCSEL area array and outputting the laser beams. The light source device can reduce optical elements in a projection display optical path, shorten the length of a lighting optical path, and improve the optical energy utilization rate. In addition, the VCSEL area array can reduce interference between VCSEL lasers and weaken laser speckles, and therefore projection display quality is improved. According to the red light semiconductor area array light source device, the area array light source packaging technology and VCSEL are adopted, a two-dimensional array is easy to integrate, and the defect that power transmitted by a single tube is poor can be overcome. The VCSEL is available in wafer test, reduces cost greatly and is easy in modularization and packaging.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gallium stibino mid-infrared circular spot output low divergence angle edge photon emission crystal laser
ActiveCN103346478AIncrease light field areaReduce far-field divergenceOptical wave guidancePhoton emissionPhotonic crystal
The invention provides a gallium stibino mid-infrared circular spot output low divergence angle edge photon emission crystal laser. The laser comprises an n type substrate, an n type electrode which is deposited on the reverse side of n type substrate, one-dimensional photonic crystals, a lower waveguide layer, an active layer, an upper waveguide layer, a p type cover layer, a ridge strip waveguide and a p type electrode, wherein the one-dimensional photonic crystals, the lower waveguide layer, the active layer, the upper waveguide layer, the p type cover layer, the ridge strip waveguide and the p type electrode are sequentially deposited on the front side of the n type substrate, and the ridge strip waveguide, the p type cover layer, the upper waveguide layer, the active layer, the lower waveguide layer, and the one-dimensional photonic crystals form a P-N knot. The alternating growth direction of the one-dimensional photonic crystals is perpendicular to the direction of the P-N knot, the direction of the ridge strip waveguide is parallel to the direction of the P-N knot, and the ridge strip waveguide and the one-dimensional photonic crystals form asymmetrical photonic crystal composite waveguides. The one-dimensional photonic crystals are imported to a ridge strip waveguide laser, and the mode perpendicular to the direction of the P-N knot can be regulated and controlled, so that the light field area of a ground mode is increased, and the far field divergence angle of the ground mode in the direction perpendicular to the P-N knot is reduced.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor laser spectrum beam combining device and method based on collimation-deflection element
ActiveCN110676691AHigh beam combining efficiencyReduce off-axis aberrationsSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsLaser arrayLight beam
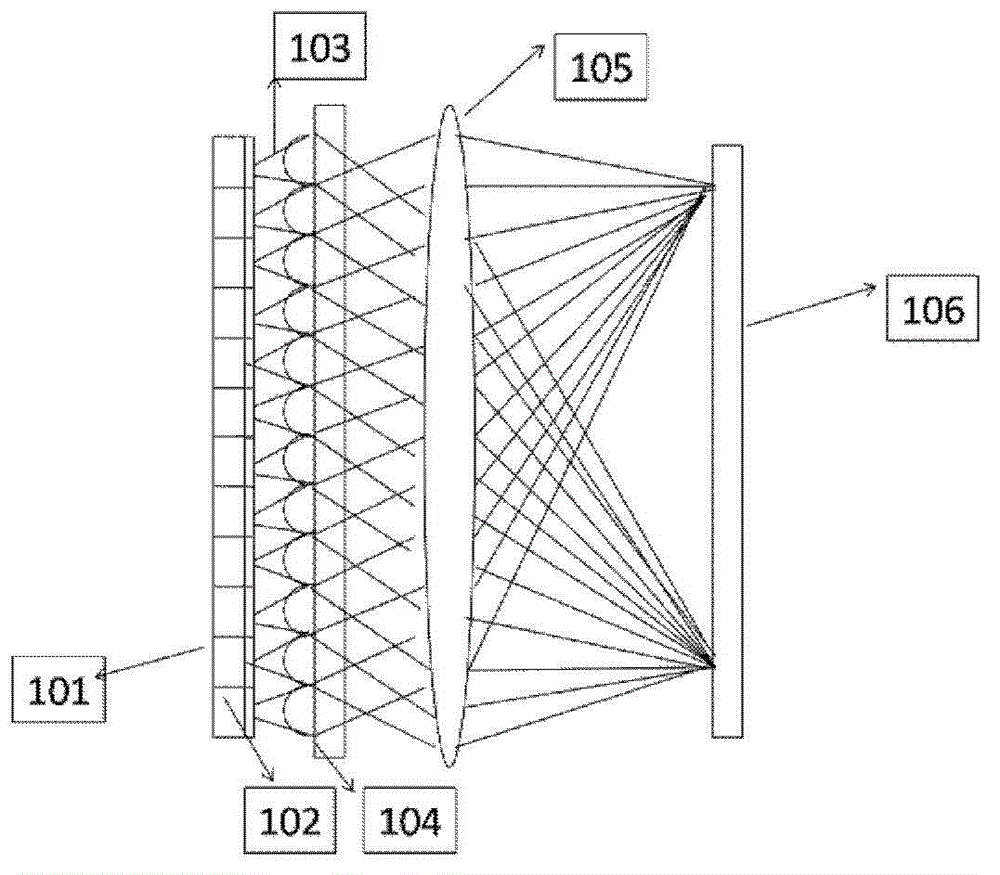
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor laser, and discloses a semiconductor laser spectrum beam combining device and method based on a collimation-deflection element. The devicecomprises a semiconductor laser array (1), and a fast axis collimating mirror (2), a light beam rotating element (3), a collimation-deflection element (4), a diffraction grating (5) and an output coupling mirror (6) which are sequentially arranged along a light path, wherein the collimation-deflection element (4) is used for refracting light beams emitted by different emission units and enablingthe light beams to enter the same area of the diffraction grating (5), and the diffraction grating (5) is used for diffracting a plurality of light beams overlapped in the same area at the same diffraction angle, so that the light beams become the same light beam and are outputted. Thus, by improving the composition of each component in the beam combining device, the arrangement mode and the internal structure of each component and the like, the problems of feedback of light beams emitted by an off-center emission unit, low beam combining efficiency and the like in the traditional semiconductor laser array spectrum beam combining mode can be effectively solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Long-distance sub-wavelength grating structure applied to optical phased array transmitting unit
PendingCN111679529AIncrease effective lengthReduce the intensity of the disturbanceWave based measurement systemsOptical light guidesGratingDivergence angle
The invention provides a long-distance sub-wavelength grating structure applied to an optical phased array transmitting unit. The structure comprises an upper-layer structure and a lower-layer structure which are arranged in an up-down stacked mode; the lower-layer structure is made of a material of which the refractive index is lower than that of the upper layer, such as various oxides; the upper-layer structure is a sub-wavelength grating structure made of materials such as silicon, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, aluminum oxide and the like, and the refractive index of the materials is higher than that of the lower layer; the middle part of the upper-layer structure is a straight waveguide; sub-wavelength square blocks are arranged on two sides of the straight waveguide; and the sub-wavelength square blocks are arranged along the waveguide direction to form a grating. The long-distance sub-wavelength grating structure has the beneficial effects that the sub-wavelength grating waveguide is used for reducing the disturbance intensity of the grating to transmission light and increasing the effective length of the grating, so that the effective length of the grating is increased,and the far-field divergence angle of a light beam is reduced; the uniform emission of a near field can be controlled by controlling the position of the sub-wavelength square blocks; the structure issimple, the manufacturing difficulty is low, and the cost is low.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Resonant optical gyroscope based on high-K fluoride resonant cavity
InactiveCN104075703AWide transmission bandHigh transparencySagnac effect gyrometersBeam splitterHigh voltage
The invention discloses a resonant optical gyroscope based on a high-K fluoride resonant cavity. The resonant optical gyroscope comprises a laser, a beam splitter, phase modulators, ring-shaped resonators, a triangular prism, a fluoride wedge-shaped cavity, detectors, lock-in amplifiers, a PI circuit, an adder, a high-voltage amplifier, signal generators and an isolator; the PI circuit is used for modulating optical signals to enable physical quantities extracted from signals output from the detector A and B to be capable of reacting the rotation angle of a carrier, and the frequency of the emergent light of a light source and a modulating voltage of the phase modulators can be respectively changed according to the physical quantities, the feedback of an optical path can be realized, and the purpose that the optical paths propagating in the fluoride wedge-shaped cavity clockwise and anti-clockwise are resonant can be realized.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
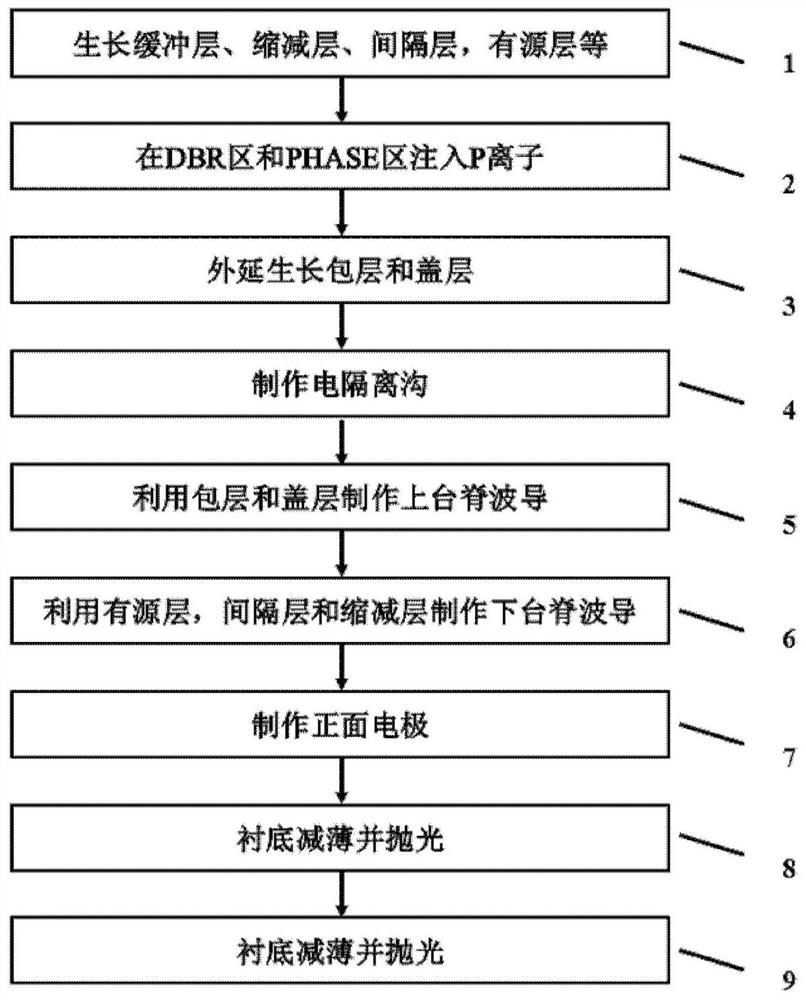
Single-mode tunable terahertz quantum cascade laser device structure and manufacturing method
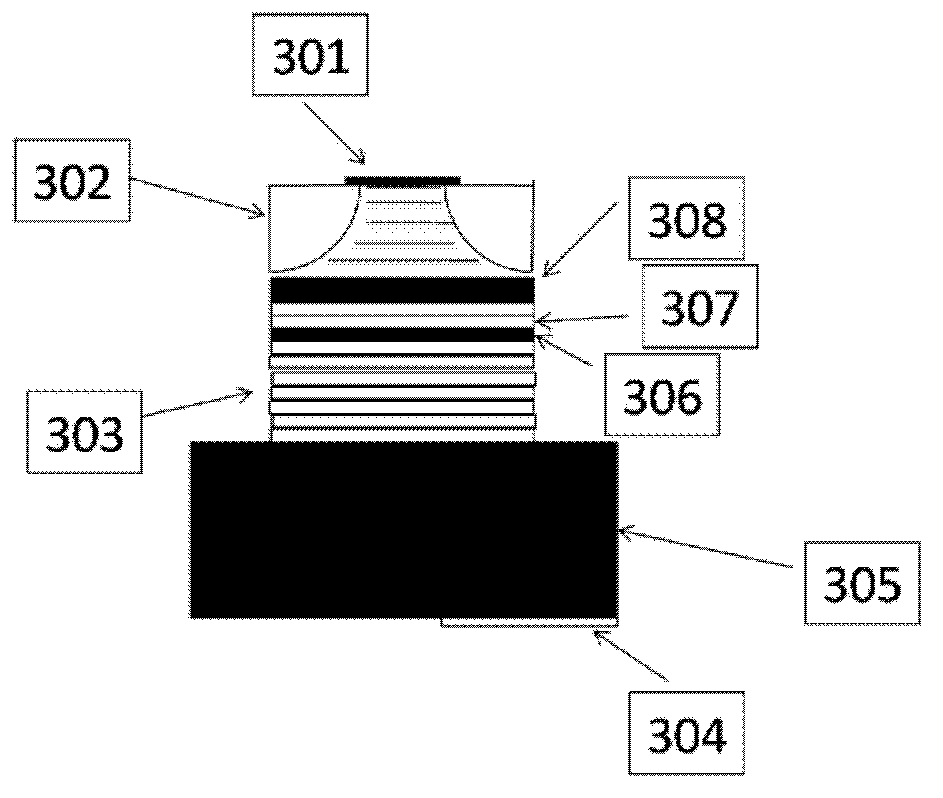
ActiveCN104767122AHigh selectivityReduce far-field divergenceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsPower flowRefractive index
The invention provides a single-mode tunable terahertz quantum cascade laser device structure and a manufacturing method. The single-mode tunable terahertz quantum cascade laser device structure at least comprises a semi-insulating GaAs substrate, a GaAs buffer layer, a first contact layer, an active area, a second contact layer, a first metal layer and a second metal layer. The active layer, the second contact layer and the first metal layer form a ridge structure on the first contact layer. The side face of the ridge structure is inclined relative to the end face. The ridge structure is cut into a first sub-ridge structure and a second sub-ridge structure through an interstitial structure in the length direction. By the adoption of the oblique waveguide structure, the transverse mode selection capacity can be improved; on the premise that device single transverse mode output is ensured, the device width is larger, the outgoing beam far-field divergence angle is decreased, the refractive index is changed by injecting current of different magnitudes into two waveguides of a coupled cavity structure THz QCL, the Vernier effect is utilized for achieving the tunable wavelength, and the wavelength tunable range of the single-mode tunable terahertz quantum cascade laser device structure is larger than that of an existing device structure changing the refractive index only through current injection.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A laser light source device for laser display
InactiveCN101192738ASimple structureLow costTelevision system scanning detailsSemiconductor laser arrangementsOptical pathLaser light
The invention provides a laser source device used for laser display, which comprises laser generating devices of red light, green light and blue light and a first, a second and a third nonlinear frequency doubling crystals, which are respectively arranged on the outputting light paths of the laser generating devices of red light, green light and blue light. The invention is characterized in that: the laser generating devices of red light, green light and blue light respectively comprise at least one launching semiconductor laser with a vertical plane, wherein, the outputting wavelength of a launching semiconductor laser with a vertical plane of red light is 1,200nm-1,400nm; the outputting wavelength of a launching semiconductor laser with a vertical plane of green light is 1,000nm-1,100nm; the outputting wavelength of a launching semiconductor laser with a vertical plane of blue light is 880nm-980nm. Compared with the present laser display source, the invention requires no laser crystal and other complicated optical systems, thus having the advantages of simple structure, low cost and high reliability.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
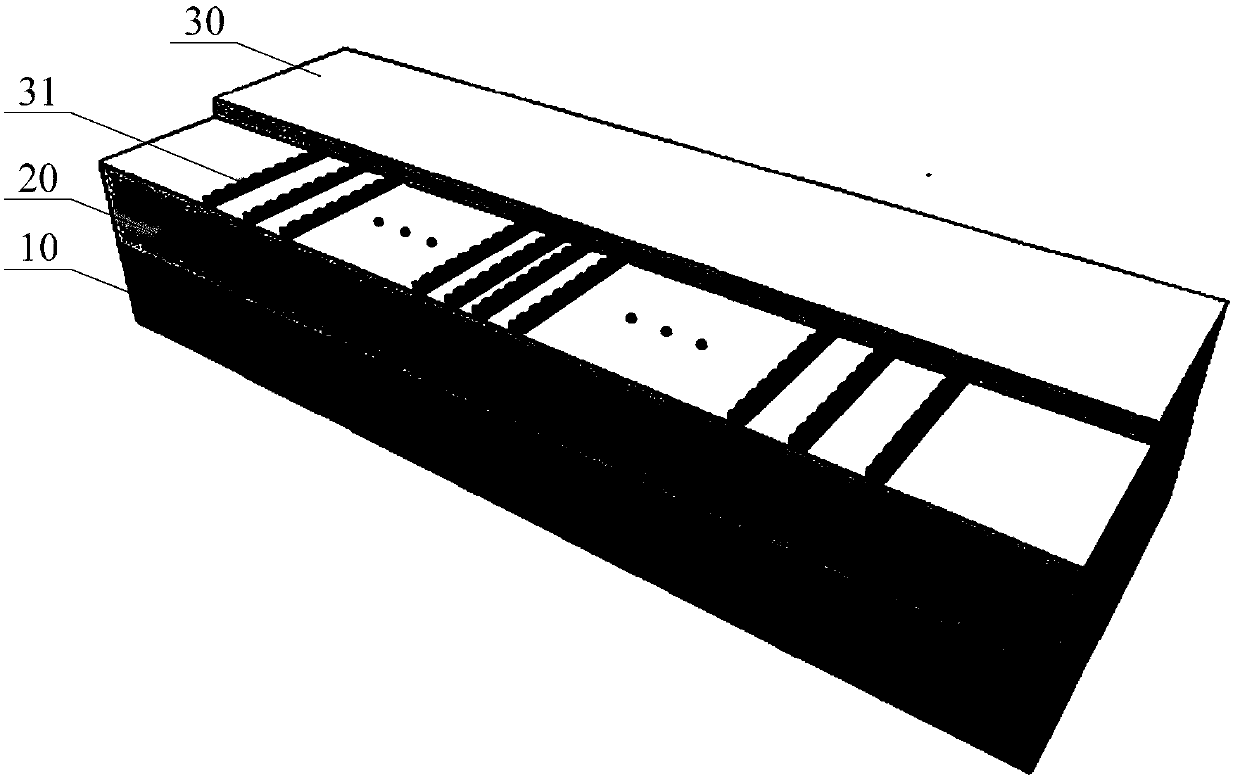
Laser and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111711074ALower effective refractive indexGuaranteed single-mode operationLaser detailsLaser active region structureHigh power lasersGrating
The invention discloses a laser and a manufacturing method thereof. The laser comprises a substrate and a double-ridge waveguide; the double-ridge waveguide comprises a lower ridge waveguide and an upper ridge waveguide; the lower ridge waveguide is formed on the substrate and comprises a light spot amplification layer, a first spacer layer, a grating layer, a second spacer layer and an active layer sequentially from bottom to top; the upper ridge waveguide is formed on the lower ridge waveguide and comprises a cladding layer and a cover layer from bottom to top; and the upper ridge waveguidecomprises two sections of wedge-shaped waveguides and a section of straight waveguide, wherein the two sections of wedge-shaped waveguides are respectively distributed at two ends of the straight waveguide. The high-power laser is realized, and at the same time, the coupling efficiency of the laser and an optical fiber is improved, and the power consumption and cost are effectively reduced.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
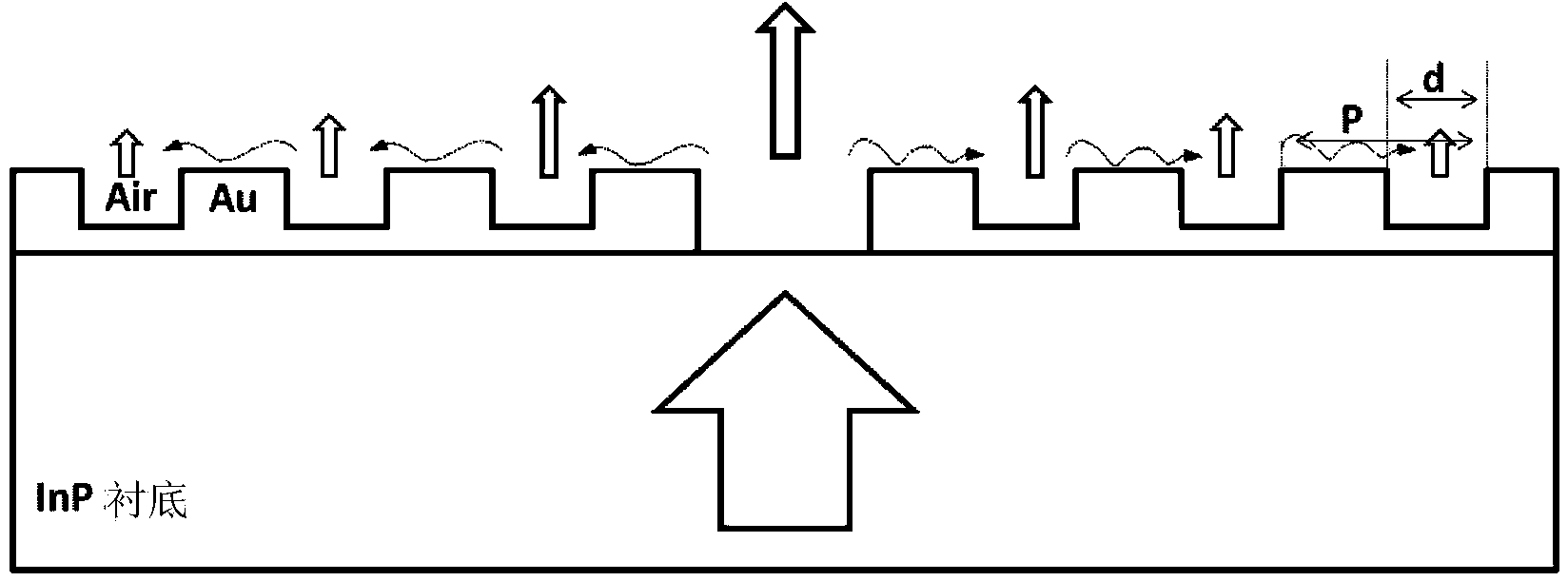
Metal antenna structure for improving slow axis far field of surface emission semiconductor laser unit
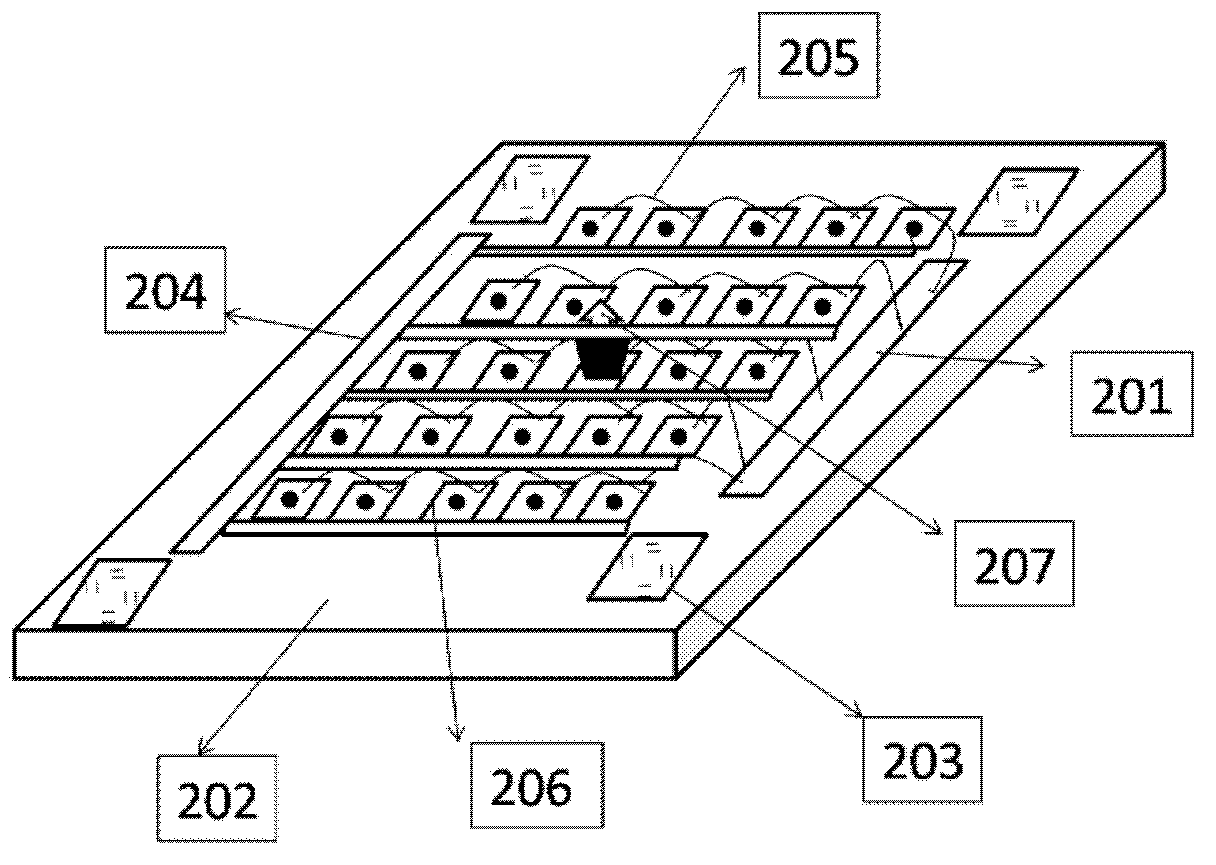
The invention discloses a metal antenna structure for improving the slow axis far field of a surface emission semiconductor laser unit. The metal antenna structure comprises a substrate, a grating layer, an electrical isolation layer, double-channel filler, a lower ohmic contact layer and a sub-wavelength metal plasma antenna, wherein the substrate is provided with a double-channel ridge-shaped waveguide structure, and a laser unit active region is arranged inside a ridge-shaped region; the grating layer is arranged on the upper surface of the substrate; the electrical isolation layer is arranged on the upper surface of the grating layer, and an electric injection window is formed by breaking the position, corresponding to the ridge-shaped region, on the upper surface of the grating layer; double channels are filled with the double-channel filler; the lower ohmic contact layer is arranged on the lower surface of the substrate; the sub-wavelength metal plasma antenna is arranged on the upper surface of the electrical isolation layer and the upper surface of the double-channel filler, and an electric injection ohmic contact region and a light output window are formed at the same time in the mode that the position, corresponding to the ridge-shaped region, of the sub-wavelength metal plasma antenna is broken. The metal antenna structure effectively reduces the far field divergence angle in the slow axis direction of the surface emission laser unit, and realizes manufacturing of a small-divergence-angle quasi-circular spot or even circular spot surface emission device.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Silicon-based optical antenna and preparation method
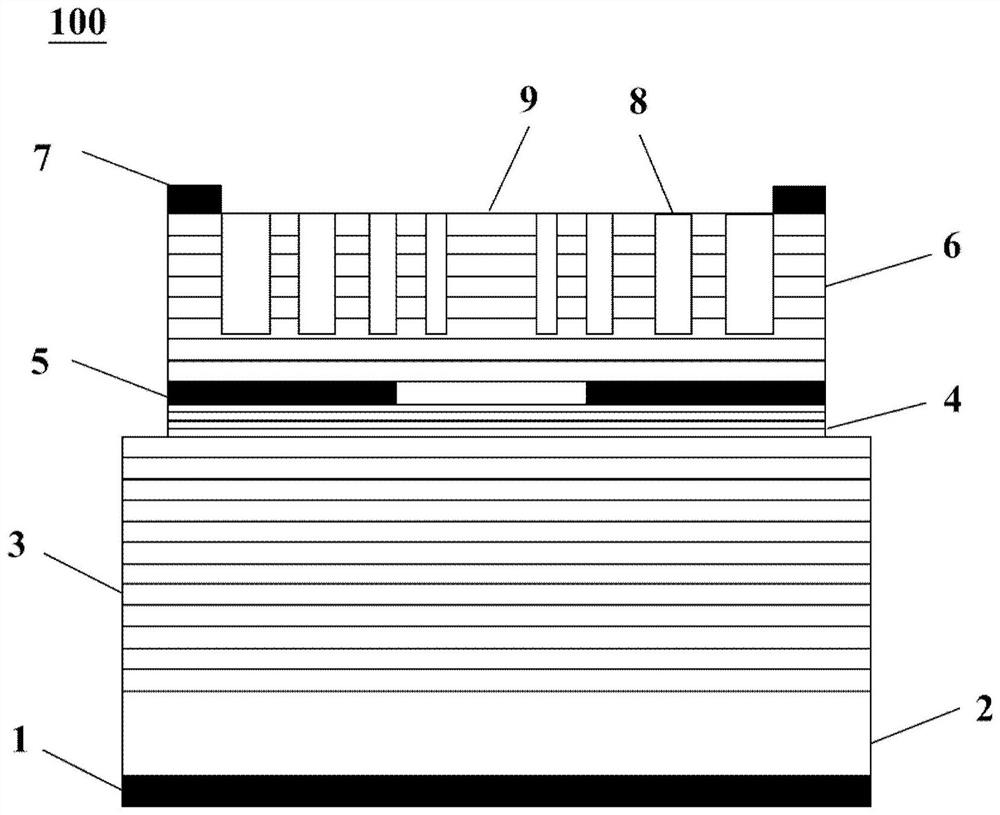
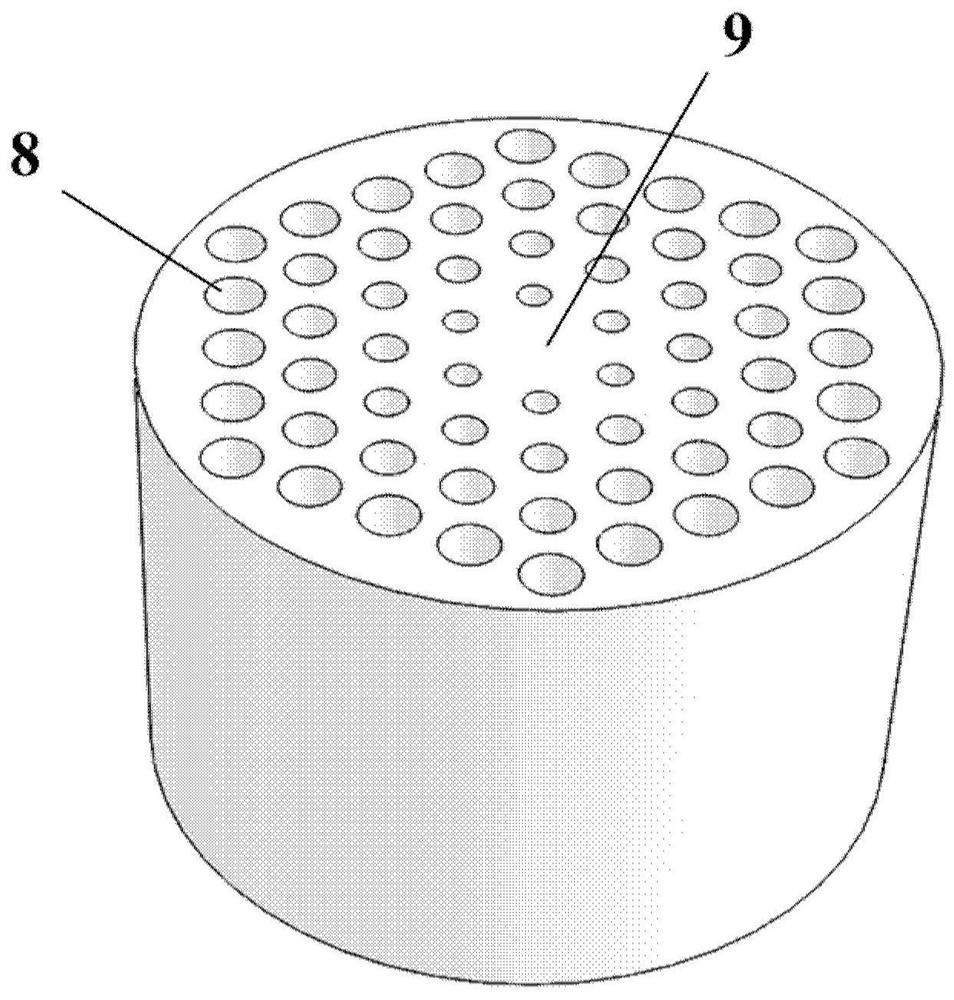
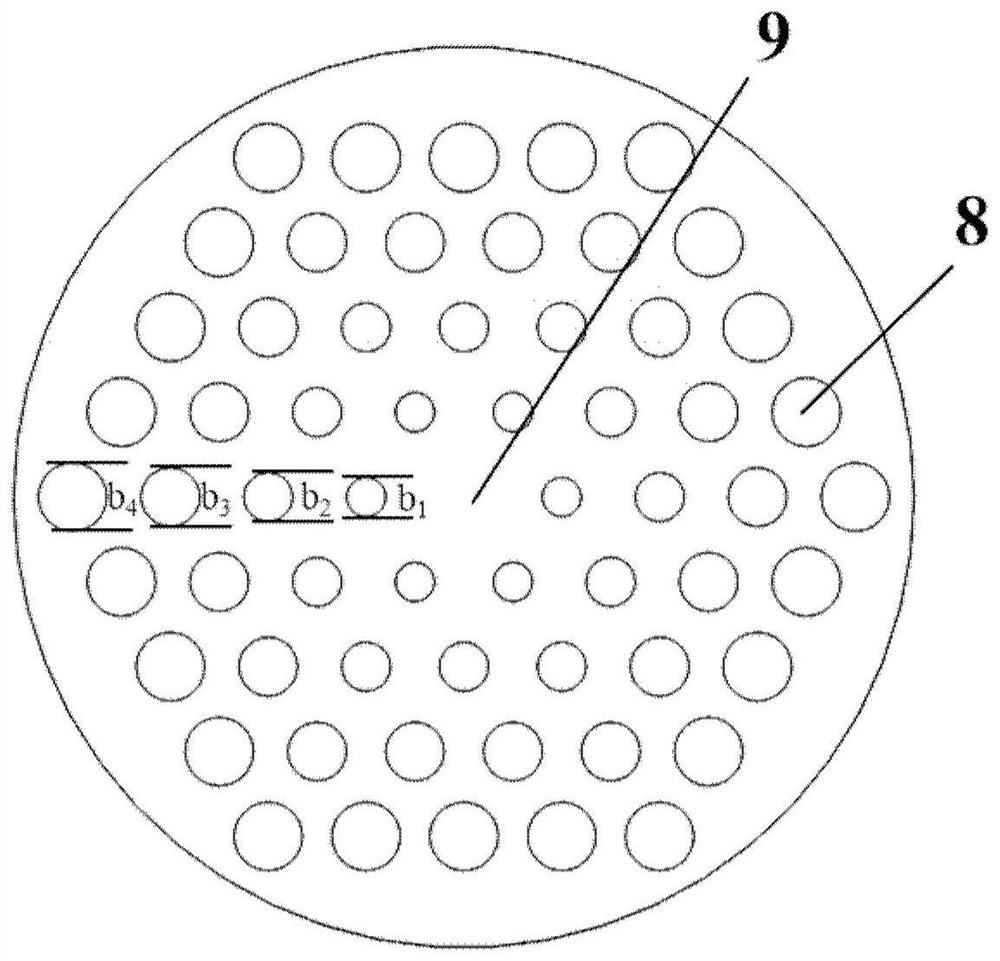
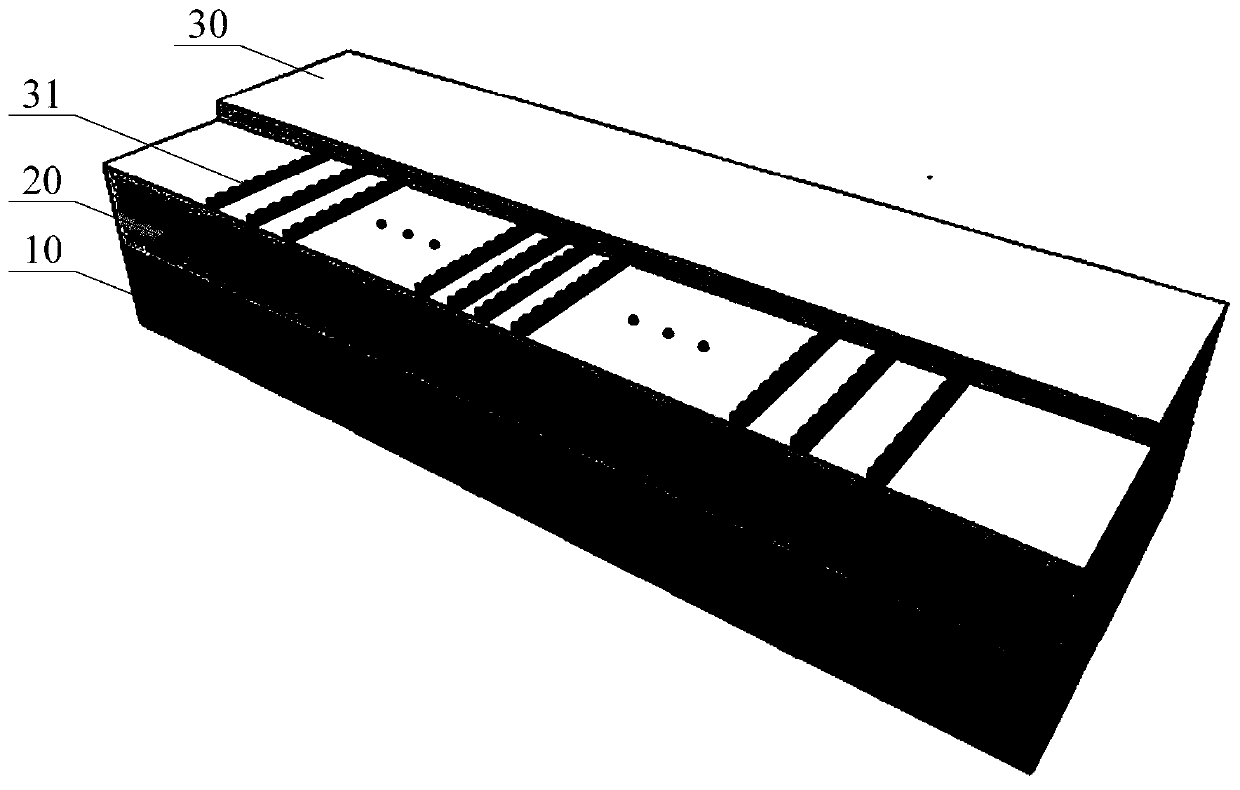
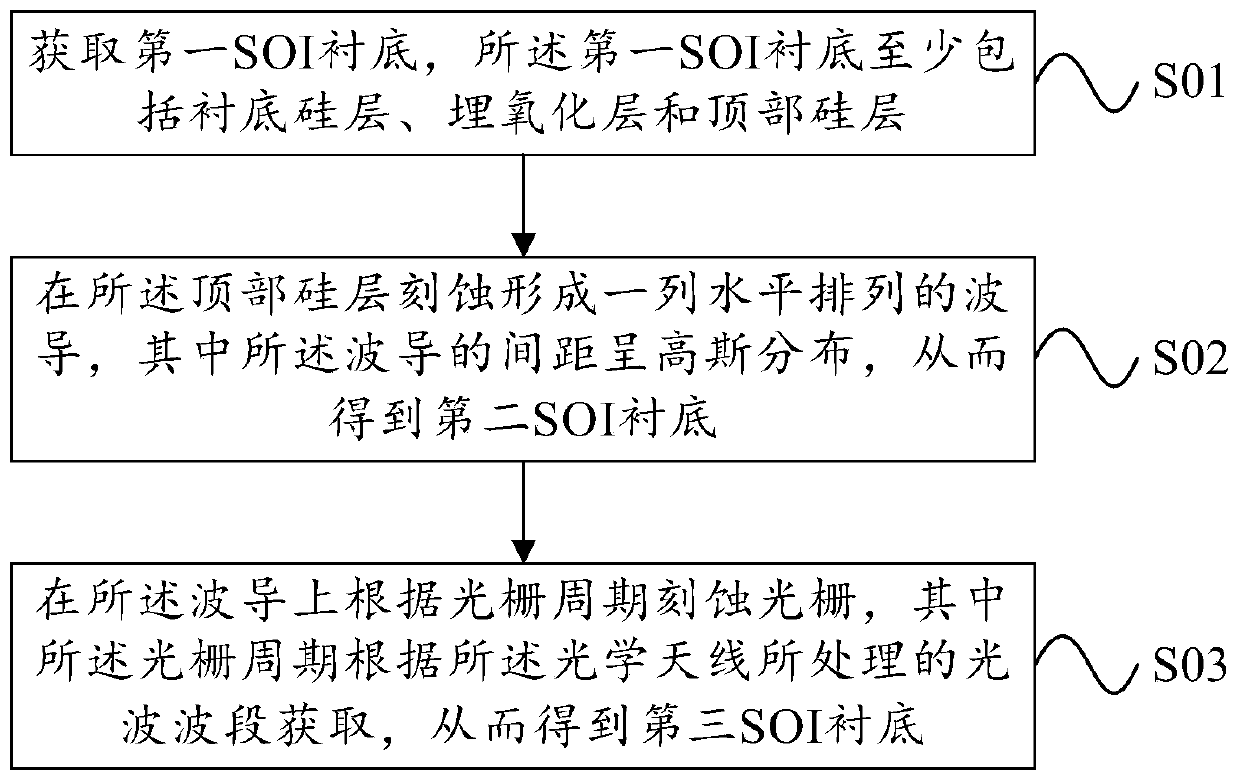
ActiveCN109541743AEnhanced inhibitory effectIncrease scan resolutionWave based measurement systemsOptical waveguide light guideRadarDivergence angle
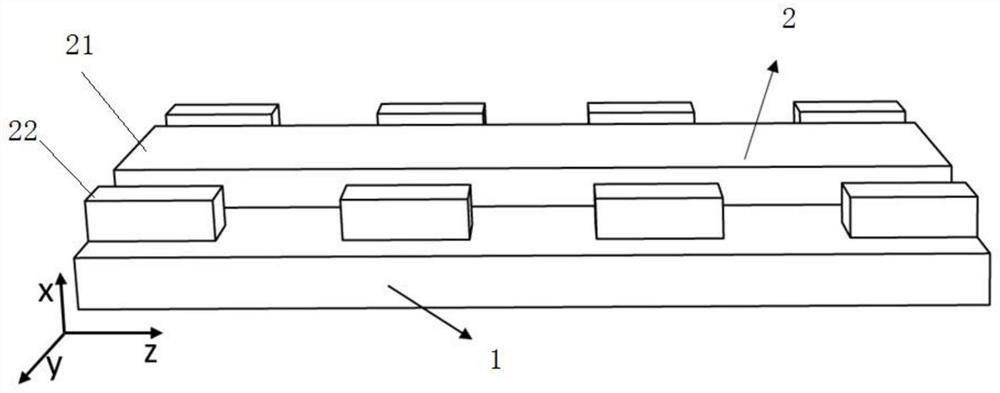
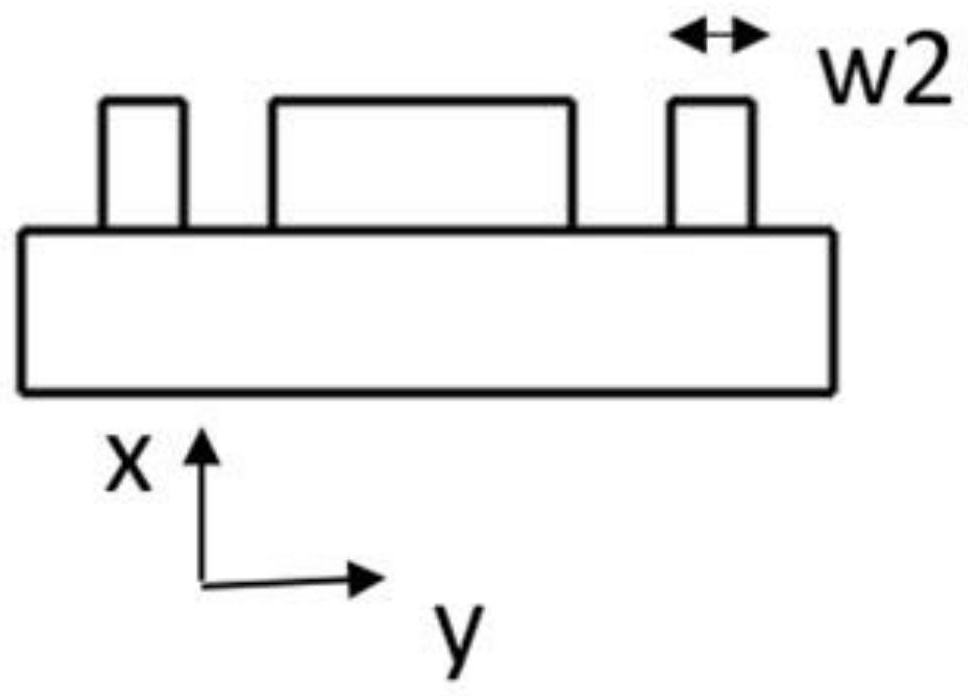
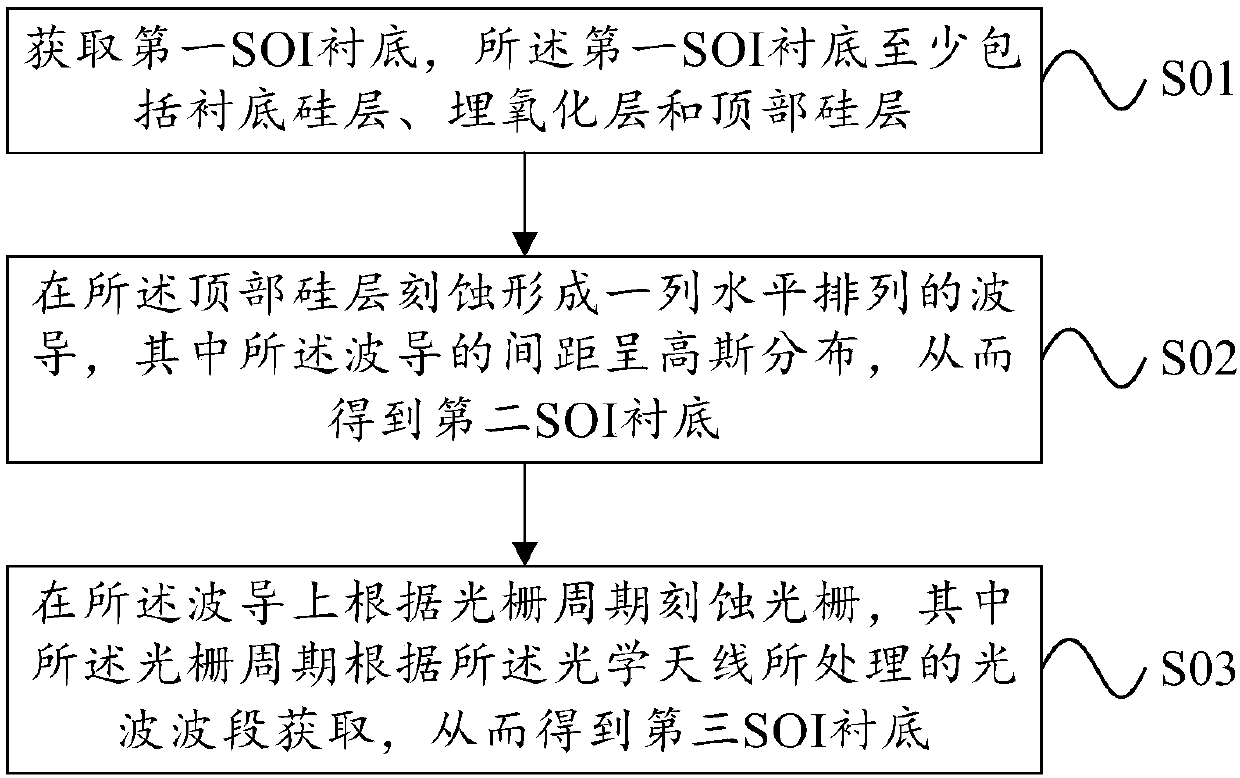
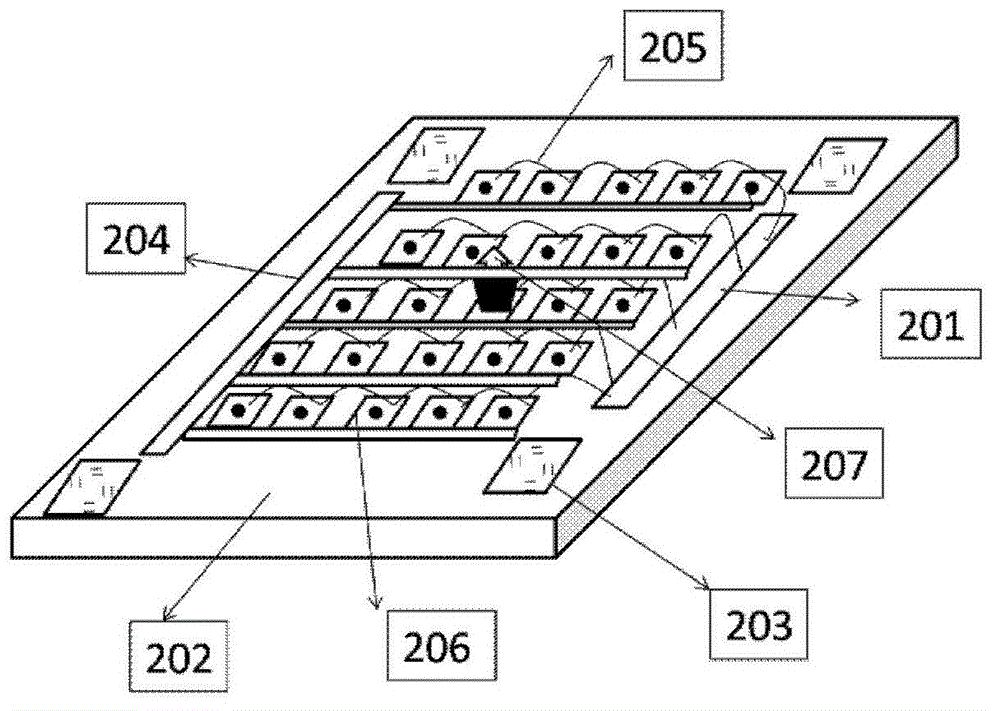
The invention provides a silicon-based optical antenna and a preparation method. The silicon-based optical antenna comprises an SOI substrate, the SOI substrate at least comprises a substrate siliconlayer, a buried oxidation layer and a top silicon layer, the buried oxidation layer is positioned between the substrate silicon layer and the top silicon layer, the top silicon layer of the SOI substrate is etched to form a row of waveguides arranged horizontally, the spacing of the waveguides is in Gaussian distribution, and each waveguide is engraved with a grating. A waveguide array in the optical antenna is arranged in Gaussian distribution, so that light waves can realize a low far-field divergence angle, a good grating lobe inhibition effect, and high horizontal and vertical radar scanning resolution when passing a 2D diffraction grating.
Owner:BEIJING WANJI TECH
Photonic crystal vertical cavity surface emitting laser
ActiveCN113140961AIncrease the effective light emitting areaHigh power outputLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPhotonic crystal
The invention provides a photonic crystal vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser, and the laser comprises an oxidation limiting layer; a P-type DBR reflecting layer grown on the oxidation limiting layer, wherein the P-type DBR reflecting layer is etched with a light-emitting region and multiple layers of aperture gradient photonic crystal air hole structures which are periodically arranged along the radial direction of the light-emitting region; the multi-layer aperture gradient photonic crystal air hole structure is a two-dimensional photonic crystal air hole structure with a central point defect. According to the photonic crystal vertical cavity surface emitting laser, high-power single-mode lasing can be achieved, gradient distribution of refractive indexes is introduced in the radial direction of a light emitting area, the far-field divergence angle can be further reduced, and the light beam quality is improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
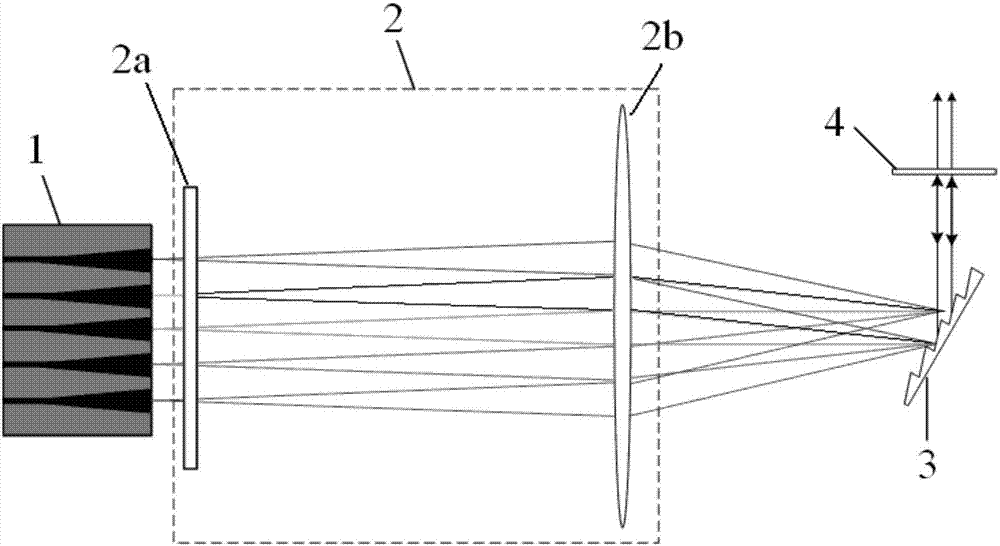
Semiconductor laser device with high-power and high-beam-quality lasers
ActiveCN103887707AImproved vibration modeIncrease output powerLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlLasing wavelengthHigh reflectivity
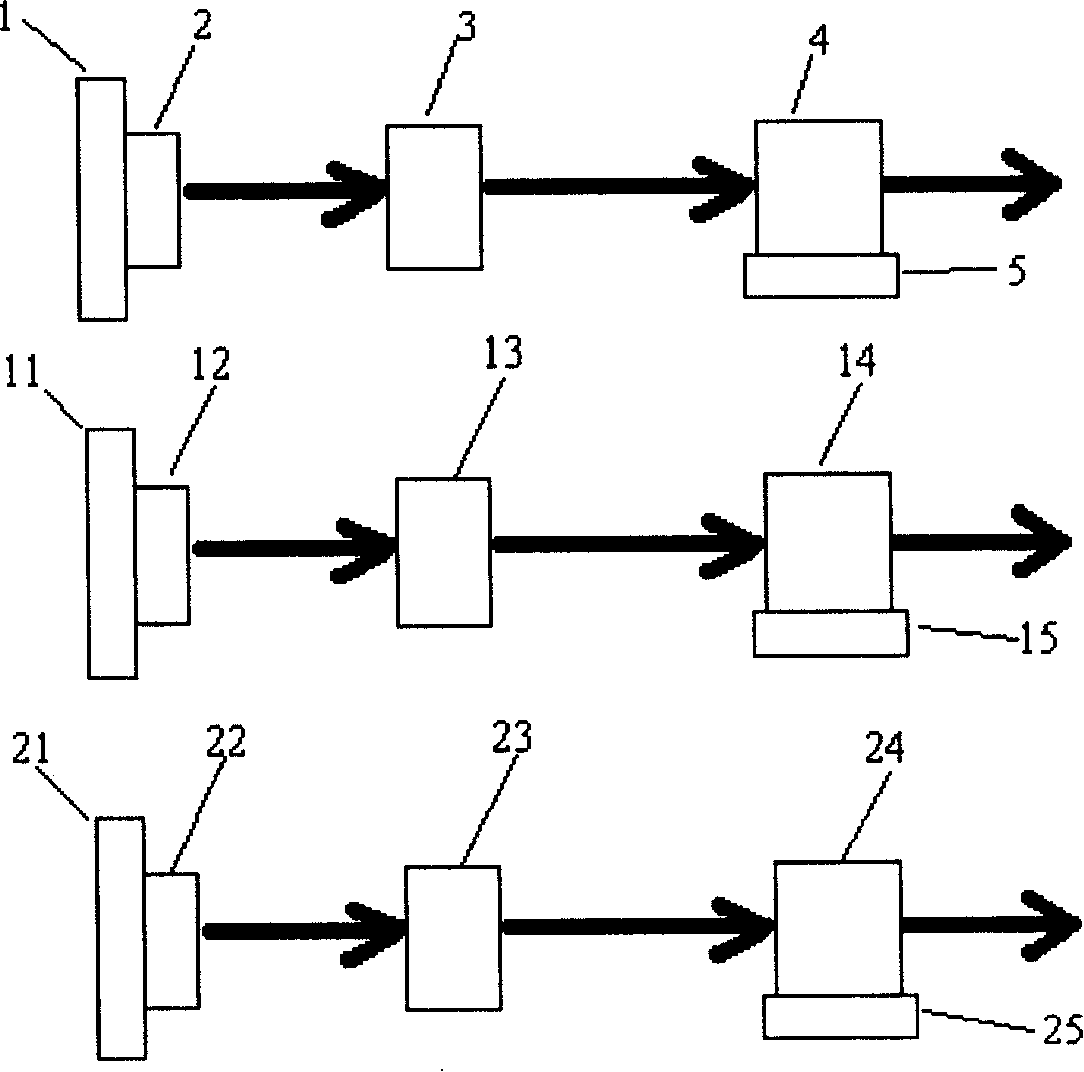
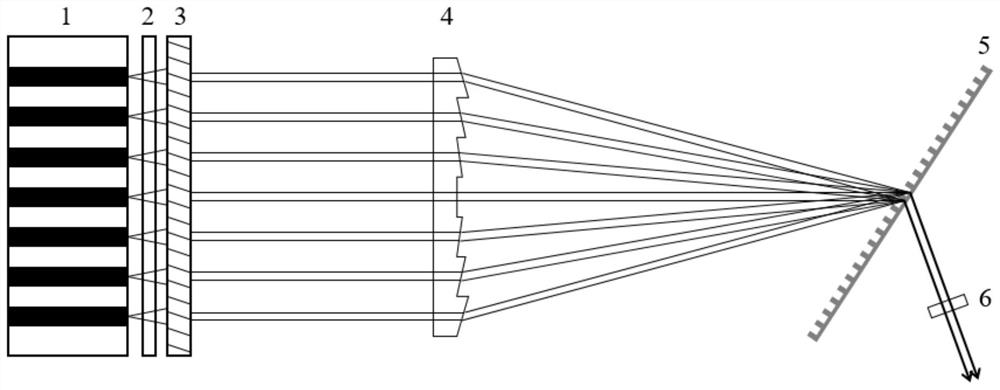
Disclosed is a semiconductor laser device with high-power and high-beam-quality lasers. An outer resonant cavity is constructed in the outer portion of a semiconductor booster element, and a collimation optical element, a spectral dispersion element and a coupling output mirror are sequentially arranged in the outer resonant cavity. The semiconductor booster element comprises a plurality of active gain areas which are linearly arranged in parallel, a coating with the high reflectivity on the laser wavelength is plated on one side of each active gain area, a coating with the high transmittance on the laser wavelength is plated on the other side of each active gain area, the collimation optical element is arranged behind the side, plated with high-transmittance coatings, of the semiconductor booster element, and the direction of a central optical axis coincides with the direction of the central optical axis of emitted light beams of the semiconductor optical booster element. The spectral dispersion element is placed behind the collimation optical element with a certain angle, and the coupling output mirror is arranged behind the spectral dispersion element in the beam propagation direction. According to the laser device, the mode of laser shock is improved, and the output power of the laser device is effectively improved on the premise of not affecting the laser beam quality.
Owner:华芯半导体科技有限公司
Semiconductor laser and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN112290382AThe vertical size of the spot increasesReduce far-field divergenceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOptical fiber couplingSemiconductor
The invention discloses a semiconductor laser and a manufacturing method thereof. The semiconductor laser integrates a first waveguide layer and a second waveguide layer of a passive area in a resonant cavity in a butt joint growth mode, and when current is injected into an active area to generate optical gain to achieve lasing for output, the current can pass through a double-layer waveguide of the passive area; when the light field is coupled to the lower waveguide to reach an output end face, the size of the light spot in the vertical direction is effectively increased, the near-field lightspot is expanded, and the far-field divergence angle is reduced, so that the light beam output quality is improved, the light beam adjustment is facilitated, the optical fiber coupling efficiency isimproved, and the packaging coupling cost is reduced. And meanwhile, when the light field is transmitted from the double-layer waveguide of the passive area to single-layer waveguide of the active area, the loss is increased compared with that of a single-layer waveguide, so that the loss of external feedback light is increased, and the anti-reflection capability of the laser is further improved.
Owner:武汉敏芯半导体股份有限公司
Tunable laser and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111711071AChange the output wavelengthReduce far-field divergenceLaser detailsLaser active region structureGratingLight spot
The invention discloses a tunable laser and a manufacturing method thereof. The tunable laser comprises a gain region and a distributed Bragg reflection region which are positioned on the same substrate, are equal in height and are attached to each other, wherein the gain region and the distributed Bragg reflection region are respectively of a double-ridge waveguide structure, and each of the gainregion and the distributed Bragg reflection region comprises a lower ridge waveguide and an upper ridge waveguide; the lower ridge waveguide of the gain region and the lower ridge waveguide of the distributed Bragg reflection region respectively and sequentially comprise a light spot amplification layer, a spacing layer and an active layer from bottom to top; the upper ridge waveguide of the gainregion and the upper ridge waveguide of the distributed Bragg reflection region respectively comprise a cladding layer and a cover layer from bottom to top; the upper ridge waveguide of the gain region is a wedge-shaped waveguide; and the upper ridge waveguide of the distributed Bragg reflection region is a side wall grating waveguide. According to the tunable laser, the light spot size of the end face of the laser can be amplified while the wavelength tuning function is achieved, and the coupling efficiency of the laser and the optical fiber is improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A semiconductor laser with high power and high beam quality laser
ActiveCN103887707BImproved vibration modeIncrease output powerLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlLaser beam qualitySpectral dispersion
A semiconductor laser with high-power and high-beam-quality lasers. An external resonant cavity is built outside the semiconductor gain element, and a collimating optical element, a spectral dispersion element, and a coupling output mirror are sequentially arranged in the external resonant cavity. The semiconductor gain element consists of several active gain regions arranged in parallel in a straight line. One side of each active gain region is coated with a film layer with high reflectivity to the laser wavelength, and the other side is coated with a film layer with high transmittance to the laser wavelength. film layer. The collimating optical element is located behind the side of the semiconductor gain element coated with a high-transmittance film layer, and its central optical axis coincides with the central optical axis of the light beam emitted by the semiconductor optical gain element. The spectral dispersing element is placed at an angle behind the collimating optics. The outcoupling mirror is located behind the spectral dispersion element along the beam propagation direction. The invention improves the mode of laser oscillation and effectively increases the output power of the laser without affecting the quality of the laser beam.
Owner:华芯半导体科技有限公司
Semiconductor laser integrated with slow optical waveguide on chip
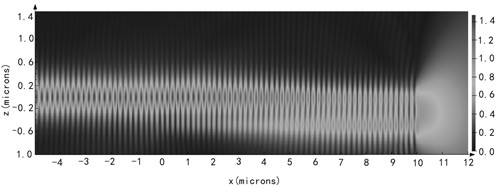
ActiveCN111478180AExpand the light apertureReduce far-field divergenceOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionPhysicsErbium lasers
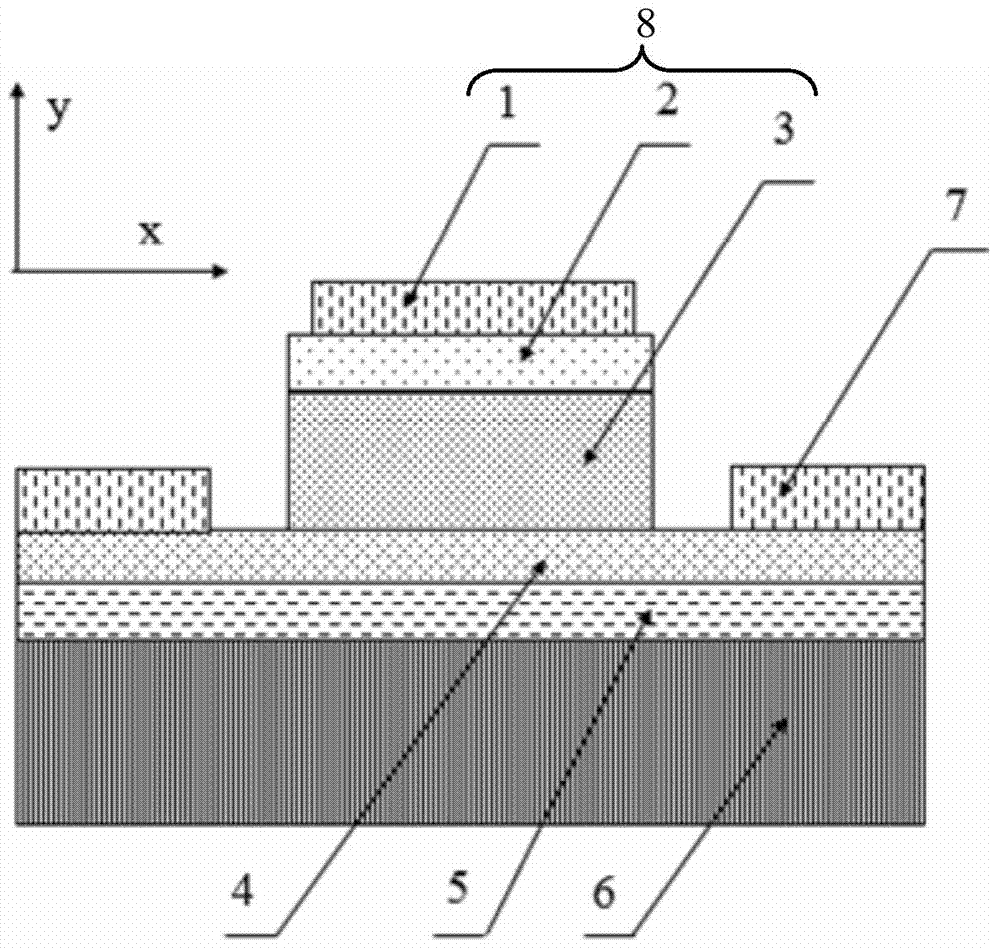
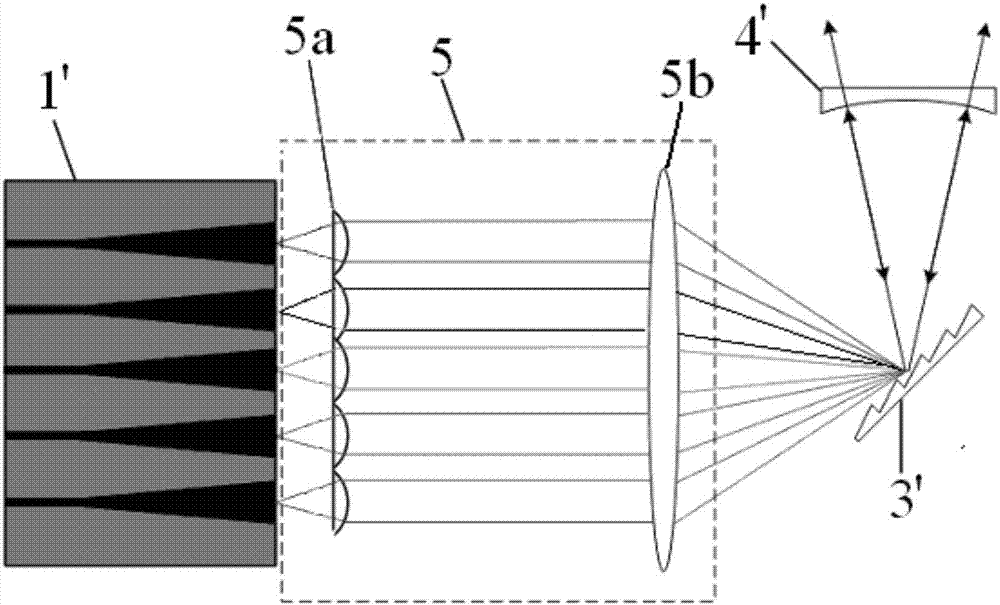
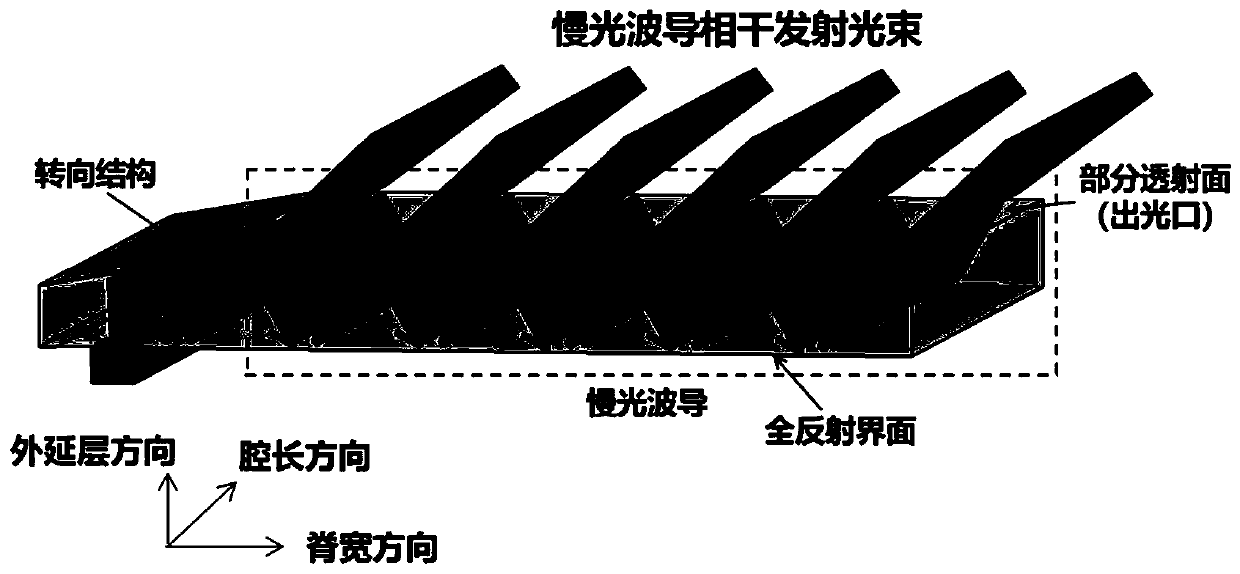
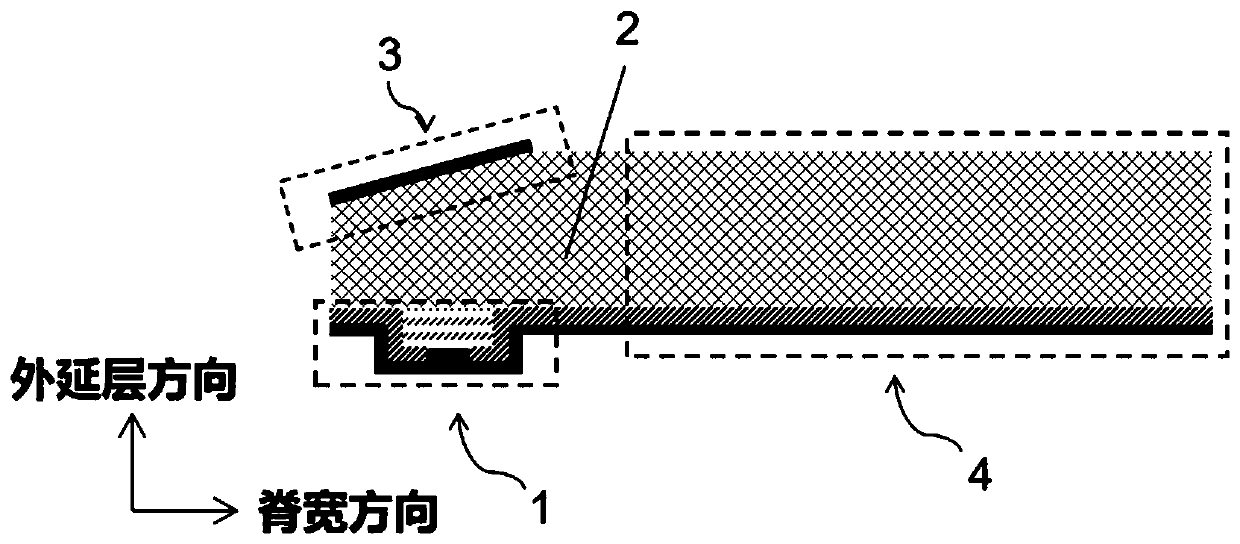
The invention discloses a semiconductor laser integrated with a slow optical waveguide on a chip. The semiconductor laser mainly solves the problem of far-field divergence of outgoing beams of an existing semiconductor laser. The laser comprises a laser active region (1), a substrate (2), a steering structure (3) and a slow optical waveguide structure (4), the laser active region (1) is located onone side of the substrate (2) in the epitaxial layer direction, and the steering structure (3) is located on the other side of the substrate (2) in the epitaxial layer direction and used for changingthe propagation direction of laser beams vertically emitted by the laser active region; and the slow optical waveguide structure (4) is positioned on one side of the substrate (2) along the ridge width direction and is used for realizing emission of a coherent light beam array and reducing a far-field divergence angle of a light beam. According to the semiconductor laser, the far-field divergenceangle of the semiconductor laser can be greatly reduced, so that the system integration level of the semiconductor light source is improved, and the semiconductor laser can be used for laser infraredinterference, on-chip optical interconnection and space optical communication.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-layer tunnel cascaded semiconductor laser
ActiveCN102651536BIncrease output optical powerMiniaturizationOptical wave guidanceLaser active region structureInternal resistanceEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a multi-overlaid layer tunnel cascaded semiconductor laser, which belongs to the field of semiconductor lasers. The multi-overlaid layer tunnel cascaded semiconductor laser comprises 2-4 single-layer laser units which are connected vertically, wherein two adjacent single-layer laser units are connected with each other by growing a tunnel junction unit layer with a special structure according to a semiconductor crystal growing rule; and a tunnel joint unit comprises a highly-doped PN junction and a super lattice layer which grows on the upper side or / and lower side of the PN junction regularly. The tunnel cascaded semiconductor laser is formed by a special tunnel junction with a super lattice, so that the output light power of the semiconductor laser is greatly increased, and the inner resistance and pressure drop at the tunnel junction in the semiconductor laser are lowered by using an optimized tunnel junction; an expansion waveguide is added into the semiconductor laser, so that a far-field divergence angle of light output is greatly reduced; and the multi-overlaid layer tunnel cascaded semiconductor laser has good economic benefit, and contributes to miniaturized application of a high-power semiconductor laser.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
High-power quasi-continuous semiconductor laser chip
PendingCN109616869ALower threshold currentReduce far-field divergenceLaser detailsLaser active region structureHigher PowerDivergence angle
The invention provides a high-power quasi-continuous semiconductor laser chip. A P-type limiting layer of the high-power quasi-continuous semiconductor laser chip is in a step shape, wherein the stepupper layer is limited to the middle region of the step foundation; a P type contact layer is limited to the surface of the step upper layer; an insulating layer correspondingly forms a bending shapeon the surface of a device, and sequentially covers 1) a region, not covered with a metal electrode, of the surface of the P type contact layer; 2) the side surface of the P type contact layer and theside surface o the stage upper layer; and 3) the surface of the step foundation. The high-power quasi-continuous semiconductor laser chip is simple in structure, and capable of effectively lowering the threshold current and the far-field divergence angle of the device, improving the performance of the device, and ensuring that the reliability is not affected, so that the chip meets the occasionswith higher requirements.
Owner:XIAN LIXIN PHOTOELECTRIC SCI & TECH
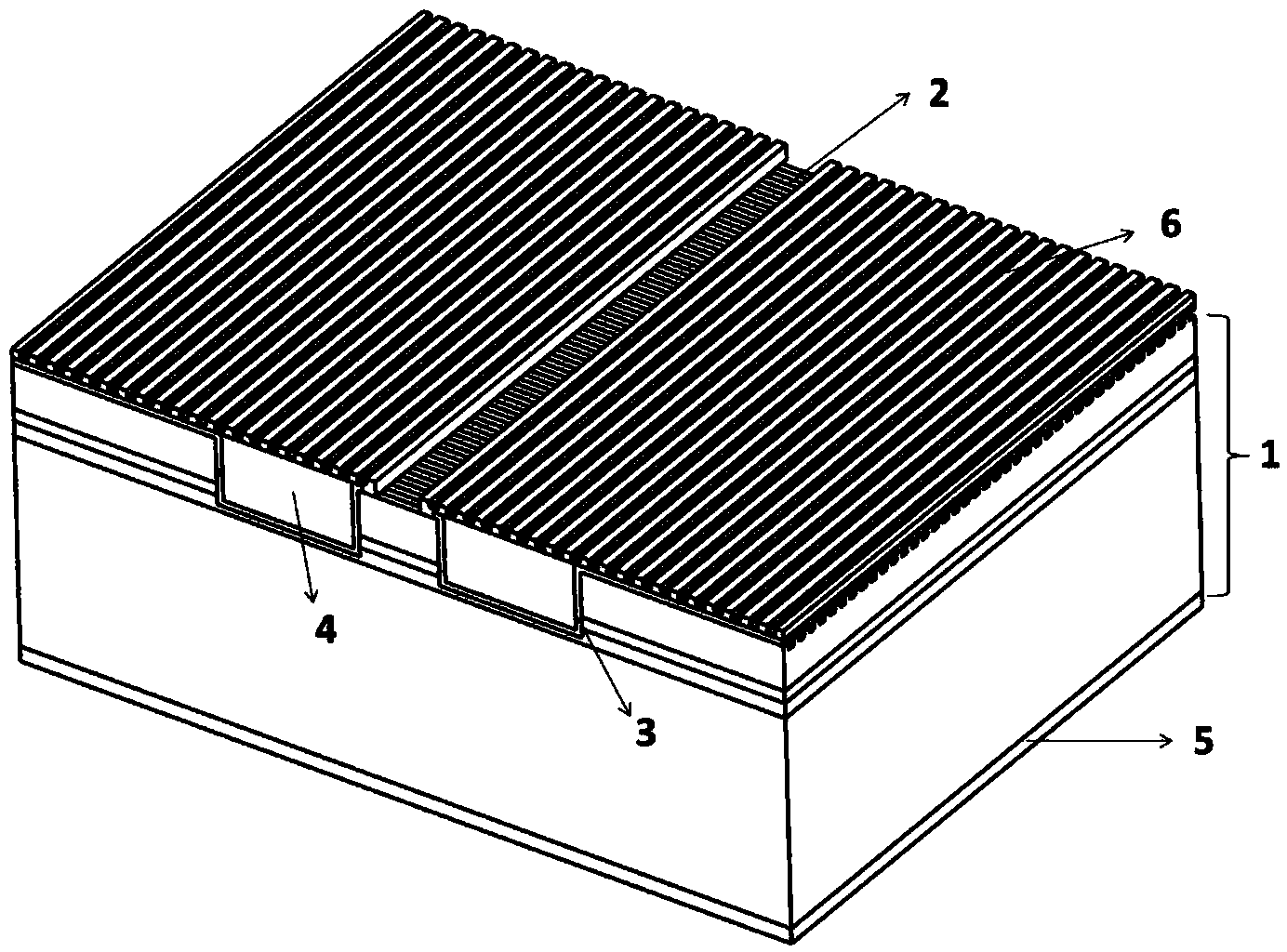
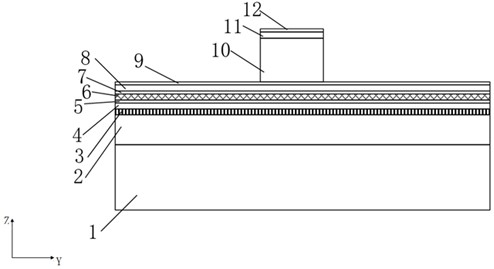
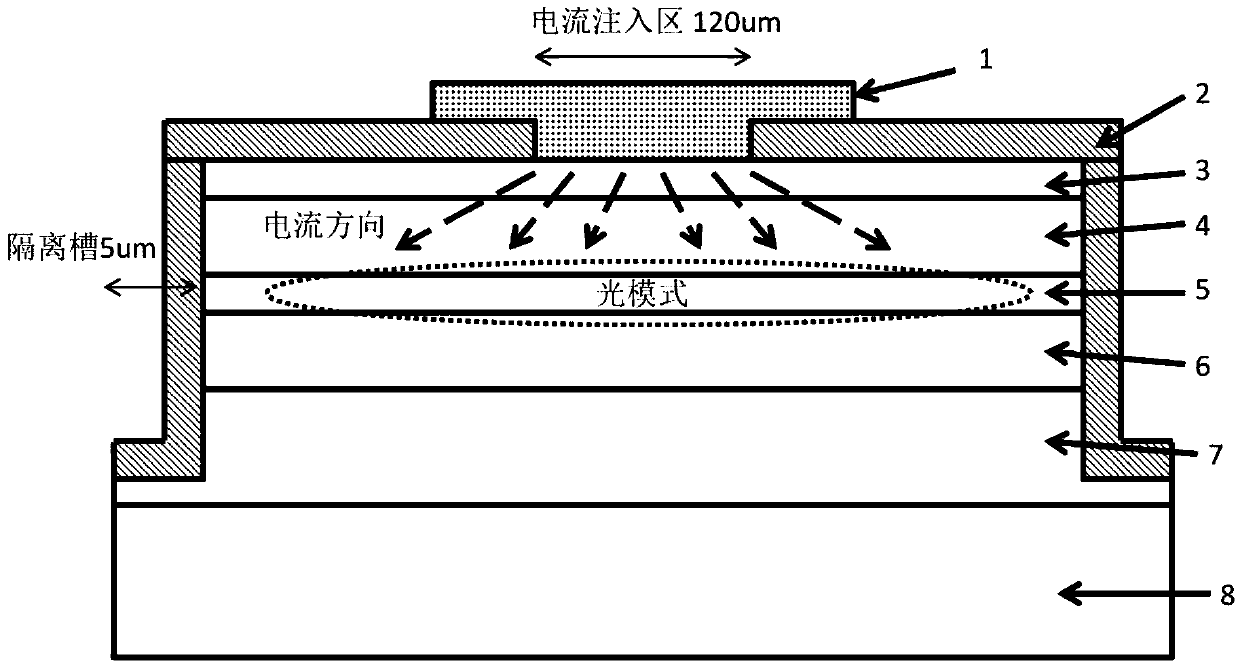
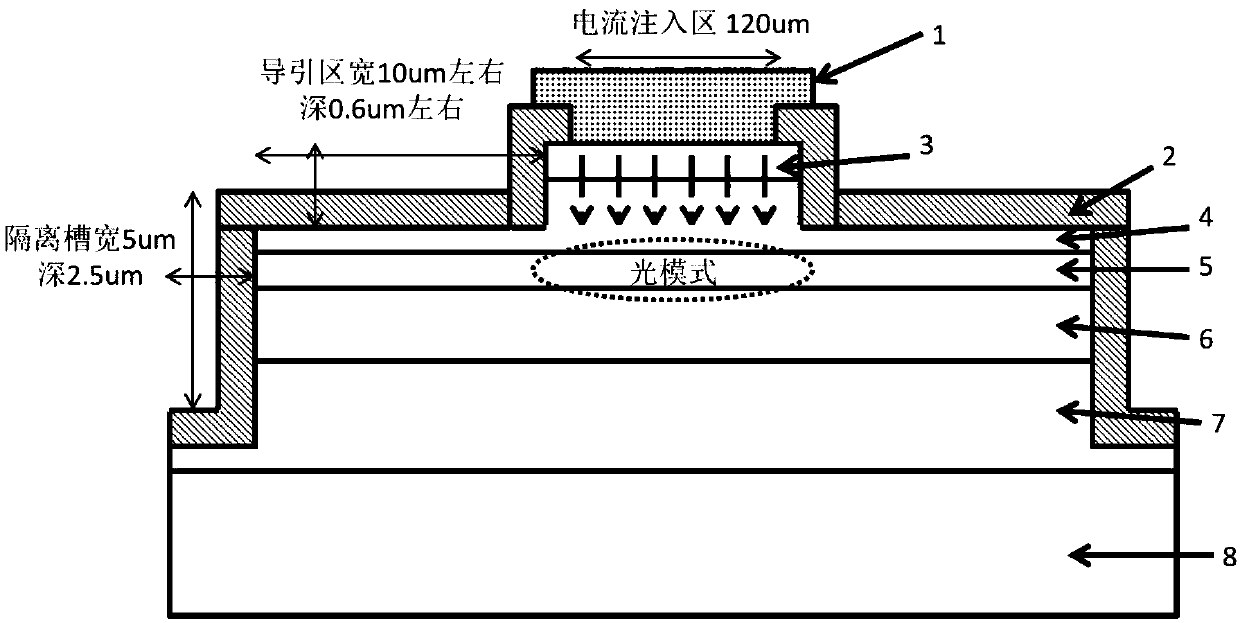
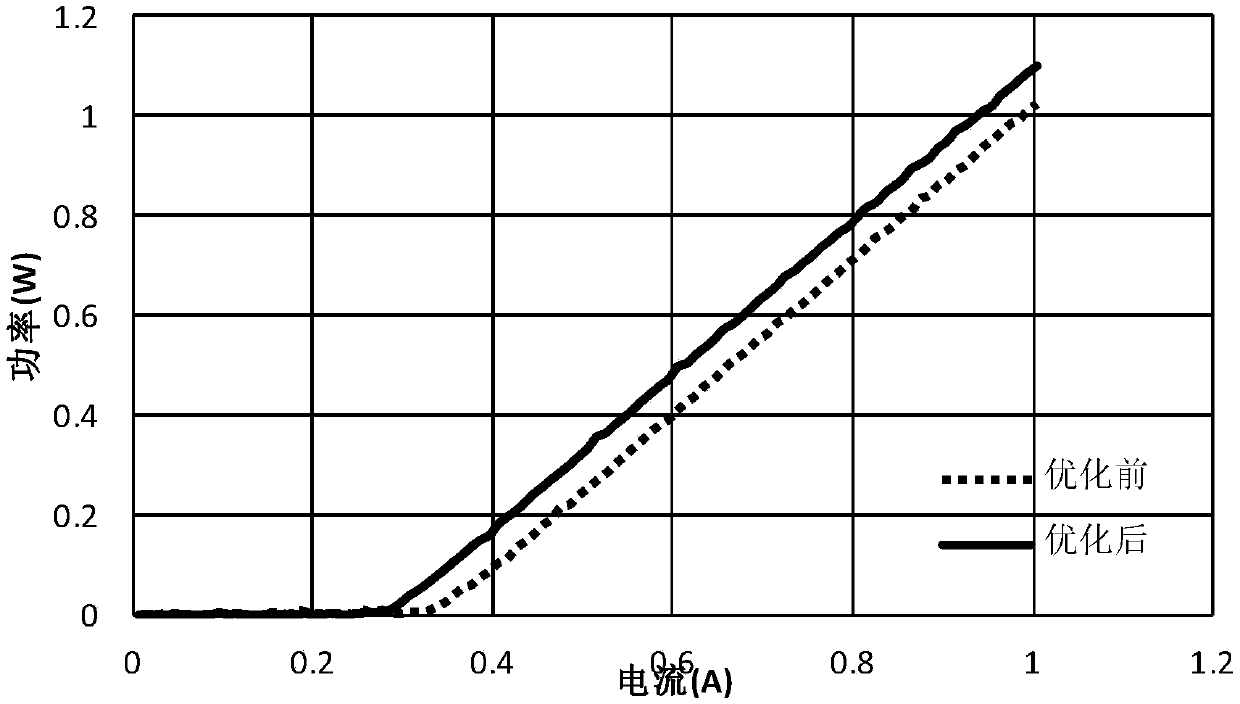
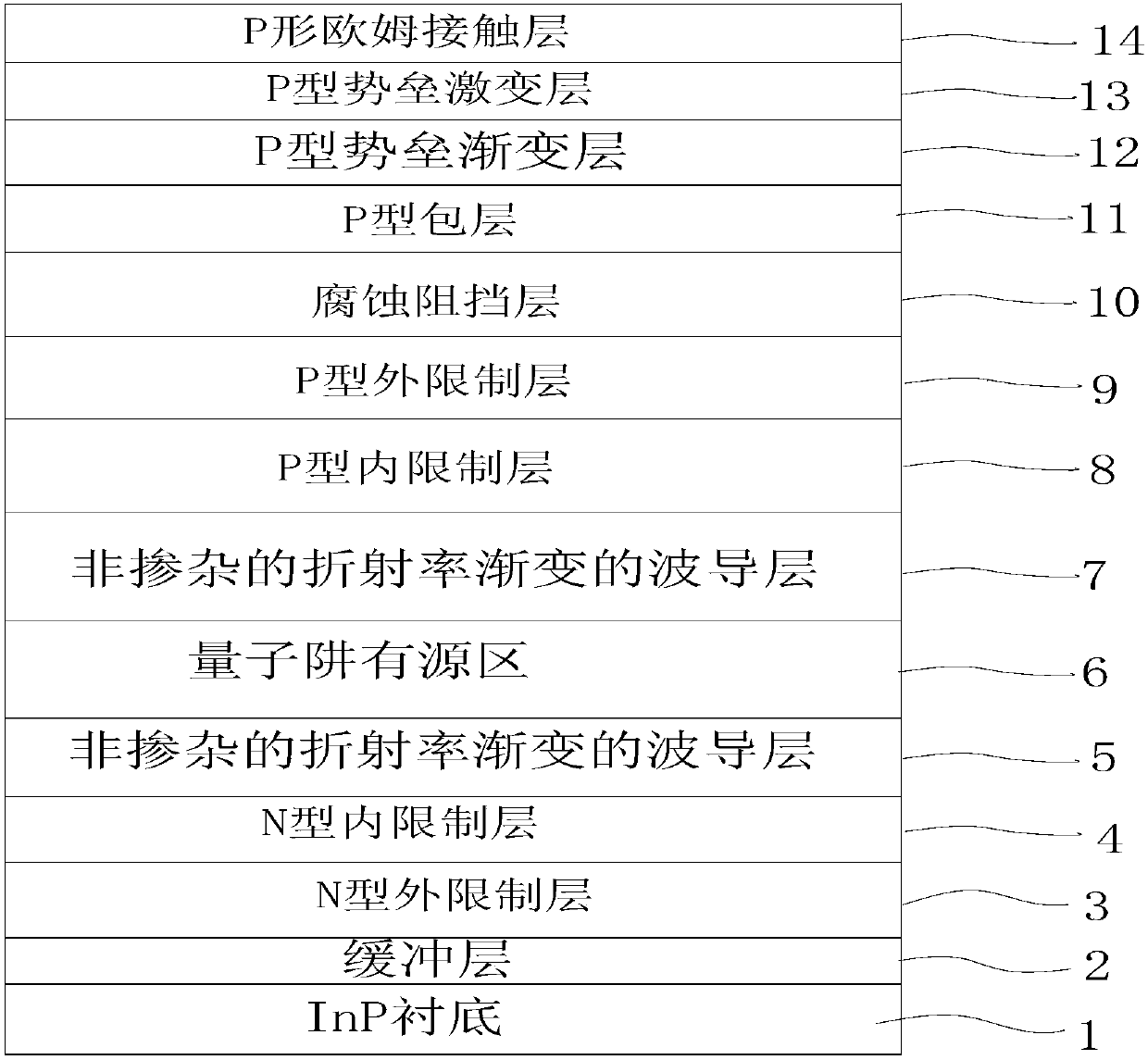
A laser with a narrow vertical far-field divergence angle and its preparation method
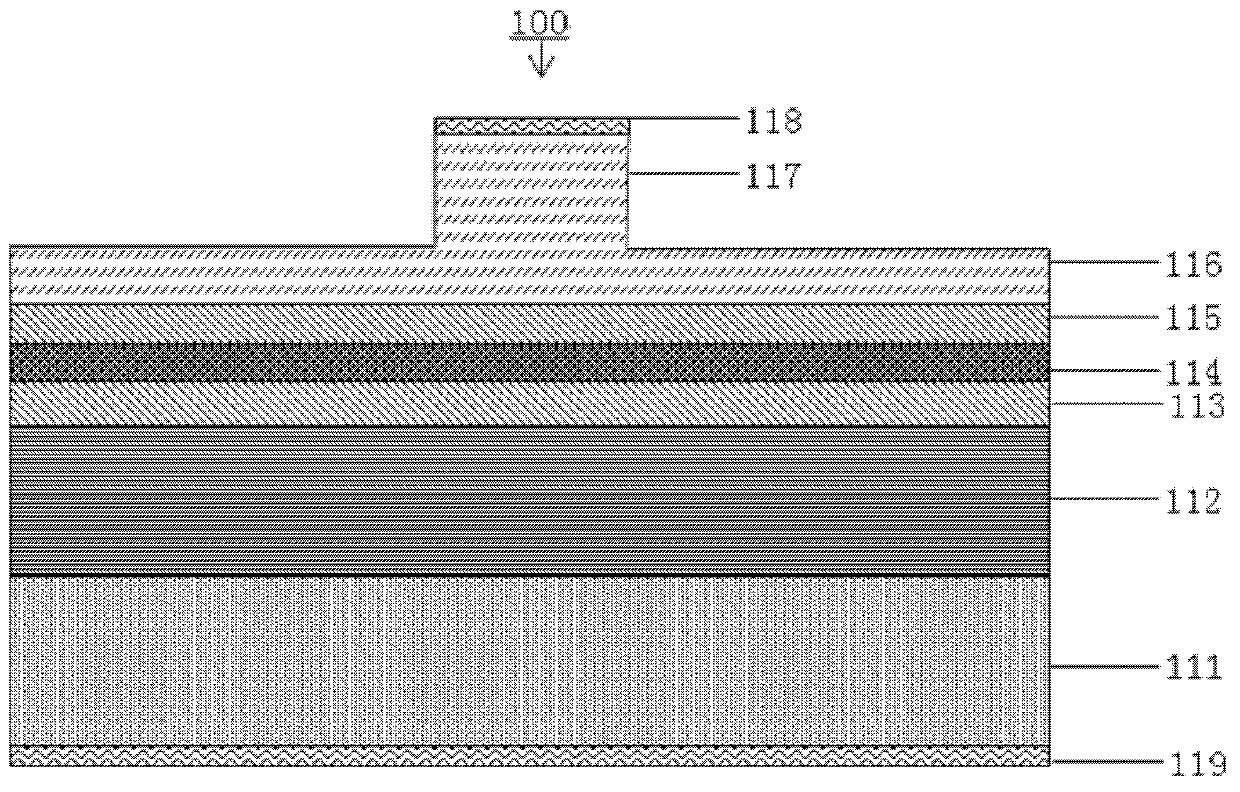
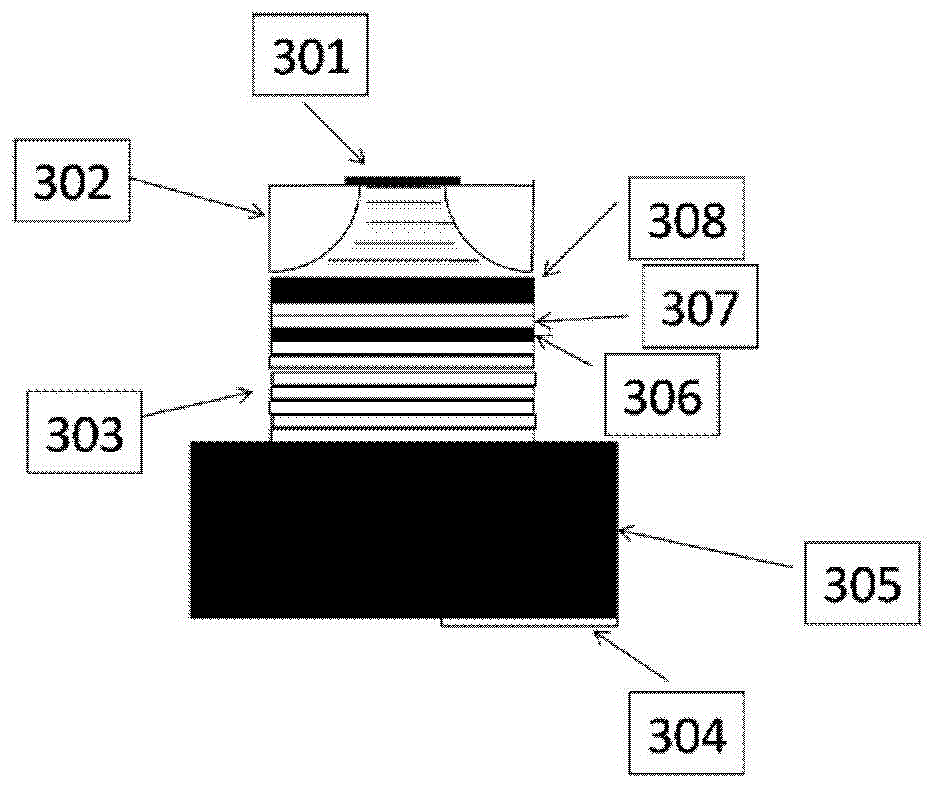
ActiveCN106532433BReduce far-field divergenceImprove coupling efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOhmic contactQuantum well
The invention provides an epitaxial structure of a laser. The epitaxial structure comprises a InP substrate, wherein a buffer layer, an N-type external limitation layer, an N-type internal limitation layer, a non-doping waveguide layer with graded refractive index, a quantum well active region, a non-doping waveguide layer with graded refractive index, a P-type internal limitation layer, a P-type external limitation layer, a corrosion blocking layer, a P-type wrapping layer, a P-type barrier gradually-changing layer, a P-type barrier abruptly-changing layer and a P-type ohmic contact layer are sequentially deposited on the InP substrate from bottom to top, wherein the pairs of quantum wells of the quantum well active region are not less than six, the quantum wells are of stress quantum well structures, wells are press stress, barriers are tension stress, the thickness of the barriers of the quantum well structures are not smaller than 10 nanometers, and the N-type internal limitation layer is a tension stress structural layer and employs a AlInAs material. By the laser, a far-field divergence angle of a semiconductor laser in a vertical direction can be reduced, and the coupling efficiency of the laser and an optical fiber is improved.
Owner:全磊光电股份有限公司
GaSb-based mid-infrared circular spot output low divergence angle edge-emitting photonic crystal laser
ActiveCN103346478BIncrease light field areaReduce far-field divergenceOptical wave guidancePhoton emissionPhotonics
The invention provides a gallium stibino mid-infrared circular spot output low divergence angle edge photon emission crystal laser. The laser comprises an n type substrate, an n type electrode which is deposited on the reverse side of n type substrate, one-dimensional photonic crystals, a lower waveguide layer, an active layer, an upper waveguide layer, a p type cover layer, a ridge strip waveguide and a p type electrode, wherein the one-dimensional photonic crystals, the lower waveguide layer, the active layer, the upper waveguide layer, the p type cover layer, the ridge strip waveguide and the p type electrode are sequentially deposited on the front side of the n type substrate, and the ridge strip waveguide, the p type cover layer, the upper waveguide layer, the active layer, the lower waveguide layer, and the one-dimensional photonic crystals form a P-N knot. The alternating growth direction of the one-dimensional photonic crystals is perpendicular to the direction of the P-N knot, the direction of the ridge strip waveguide is parallel to the direction of the P-N knot, and the ridge strip waveguide and the one-dimensional photonic crystals form asymmetrical photonic crystal composite waveguides. The one-dimensional photonic crystals are imported to a ridge strip waveguide laser, and the mode perpendicular to the direction of the P-N knot can be regulated and controlled, so that the light field area of a ground mode is increased, and the far field divergence angle of the ground mode in the direction perpendicular to the P-N knot is reduced.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Resonant Optical Gyroscope Based on High-k Fluoride Resonant Cavity
InactiveCN104075703BWide transmission bandHigh transparencySagnac effect gyrometersBeam splitterHigh voltage
The invention discloses a resonant optical gyroscope based on a high-K fluoride resonant cavity. The resonant optical gyroscope comprises a laser, a beam splitter, phase modulators, ring-shaped resonators, a triangular prism, a fluoride wedge-shaped cavity, detectors, lock-in amplifiers, a PI circuit, an adder, a high-voltage amplifier, signal generators and an isolator; the PI circuit is used for modulating optical signals to enable physical quantities extracted from signals output from the detector A and B to be capable of reacting the rotation angle of a carrier, and the frequency of the emergent light of a light source and a modulating voltage of the phase modulators can be respectively changed according to the physical quantities, the feedback of an optical path can be realized, and the purpose that the optical paths propagating in the fluoride wedge-shaped cavity clockwise and anti-clockwise are resonant can be realized.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
a semiconductor laser
ActiveCN109768468BEasy to manufacturePromote growthOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsRefractive indexDivergence angle
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of semiconductor laser and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN112290382BImprove anti-reflection abilityIncrease in vertical sizeOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLight spotDivergence angle
Owner:武汉敏芯半导体股份有限公司
Structure and manufacturing method of third-order distributed feedback terahertz quantum cascade laser
ActiveCN106877174BOvercome the problem of large far-field divergence angleIncrease the number of cyclesLaser detailsLaser active region structureGratingDivergence angle
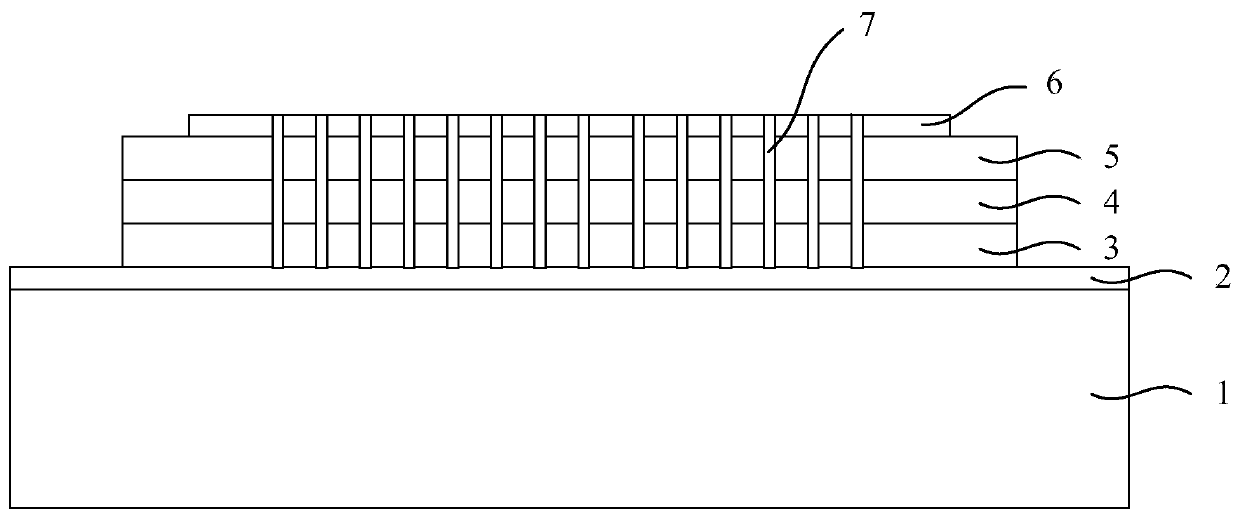
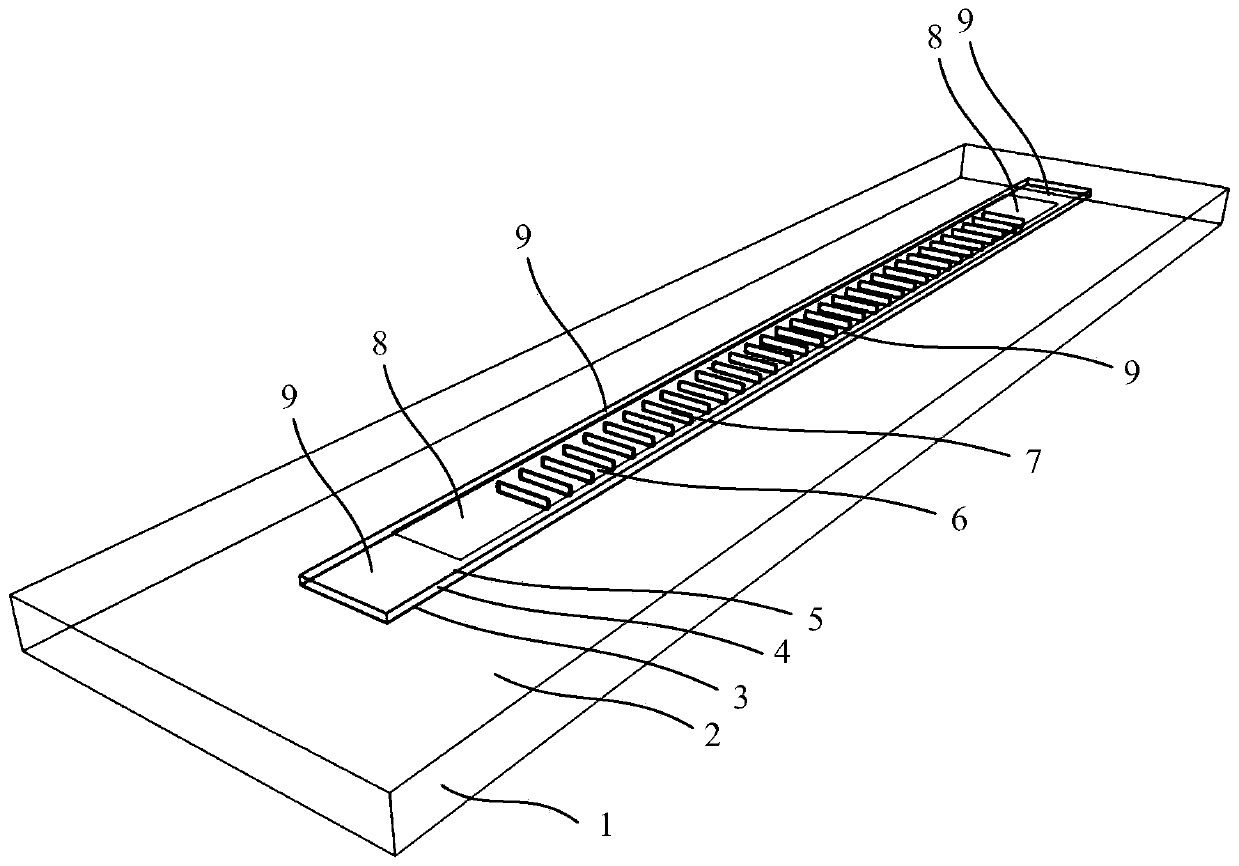
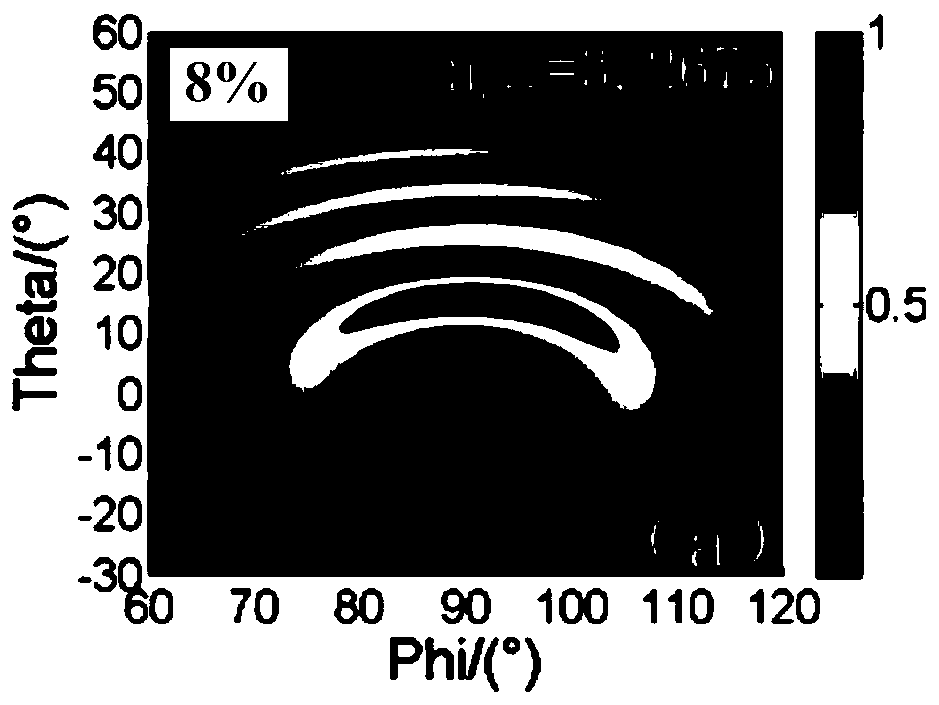
The invention provides a third-order distributed feedback terahertz quantum cascade laser structure and a making method thereof. The structure comprises a substrate, a ridge waveguide region and a third-order grating structure. The ridge waveguide region comprises a lower electrode, a sandwich region and an upper electrode in order from the bottom up. The sandwich region comprises a lower contact layer, an active region and an upper contact layer from the bottom up. The third-order grating structure comprises a plurality of parallel slits which are arranged in a periodic manner and pass through the upper electrode and the sandwich region in the vertical direction. The longitudinal duty ratio of the third-order grating structure is in the range from 8% to 15%. Terahertz wave is generated in the active region, is emitted from the slits by the mode selection effect of the third-order grating structure and is coupled in the space to the longitudinal ends of the ridge waveguide region. In the invention, the third-order grating is introduced in a waveguide structure of the terahertz quantum cascade laser and a relatively small far-field divergence angle is obtained by adjusting different grating duty ratios, thereby overcoming the problem that the third-order grating has a relatively big far-field divergence angle due to phase mismatch.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A red light semiconductor area array light source device for laser display
InactiveCN103412406BSimple structureImprove reliabilityLaser detailsProjectorsEffect lightLight beam
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN111711074BLower effective refractive indexGuaranteed single-mode operationLaser detailsLaser active region structureHigh power lasersGrating
A laser and a manufacturing method thereof, the laser comprising: a substrate and a double-ridge waveguide; wherein the double-ridge waveguide includes a lower-stage ridge waveguide and an upper-stage ridge waveguide; wherein the lower-stage ridge waveguide is formed on the substrate, It includes a spot enlargement layer, a first spacer layer, a grating layer, a second spacer layer, and an active layer from bottom to top; the upper mesa ridge waveguide is formed on the lower mesa ridge waveguide, and includes a cladding layer and a cover layer from bottom to top; The above-mentioned ridge waveguide includes two sections of wedge-shaped waveguides and one section of straight waveguides, and the two sections of wedge-shaped waveguides are respectively distributed at both ends of the straight waveguide. The invention realizes a high-power laser, improves the coupling efficiency between the laser and the optical fiber, and effectively reduces power consumption and cost.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor laser spectral beam combining device and method based on collimating-deflecting element
ActiveCN110676691BAvoid mutual interferencePrevent the adverse situation of chaosSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsLaser arrayLight beam
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor laser, and discloses a semiconductor laser spectrum beam combining device and method based on a collimation-deflection element. The devicecomprises a semiconductor laser array (1), and a fast axis collimating mirror (2), a light beam rotating element (3), a collimation-deflection element (4), a diffraction grating (5) and an output coupling mirror (6) which are sequentially arranged along a light path, wherein the collimation-deflection element (4) is used for refracting light beams emitted by different emission units and enablingthe light beams to enter the same area of the diffraction grating (5), and the diffraction grating (5) is used for diffracting a plurality of light beams overlapped in the same area at the same diffraction angle, so that the light beams become the same light beam and are outputted. Thus, by improving the composition of each component in the beam combining device, the arrangement mode and the internal structure of each component and the like, the problems of feedback of light beams emitted by an off-center emission unit, low beam combining efficiency and the like in the traditional semiconductor laser array spectrum beam combining mode can be effectively solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Semiconductor laser and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111244756BIncrease widthReduce manufacturing costLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionConvertersGrating
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Directional Output Ring Microcavity Laser
InactiveCN104979751BGood one-wayDirectional laser output with good unidirectionalityLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlResonant cavityGrating
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A silicon-based optical antenna and its preparation method
ActiveCN109541743BEnhanced inhibitory effectIncrease scan resolutionWave based measurement systemsOptical waveguide light guideImage resolutionDivergence angle
The invention provides a silicon-based optical antenna and a preparation method. The silicon-based optical antenna comprises an SOI substrate, the SOI substrate at least comprises a substrate siliconlayer, a buried oxidation layer and a top silicon layer, the buried oxidation layer is positioned between the substrate silicon layer and the top silicon layer, the top silicon layer of the SOI substrate is etched to form a row of waveguides arranged horizontally, the spacing of the waveguides is in Gaussian distribution, and each waveguide is engraved with a grating. A waveguide array in the optical antenna is arranged in Gaussian distribution, so that light waves can realize a low far-field divergence angle, a good grating lobe inhibition effect, and high horizontal and vertical radar scanning resolution when passing a 2D diffraction grating.
Owner:BEIJING WANJI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com