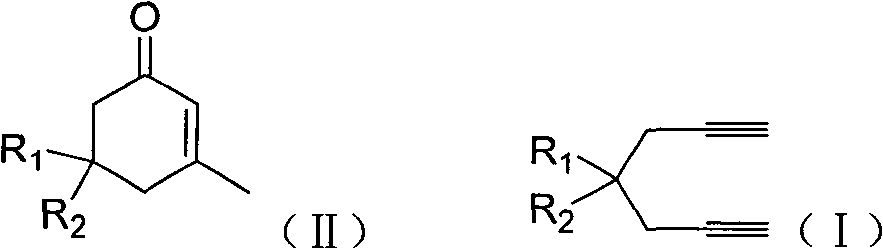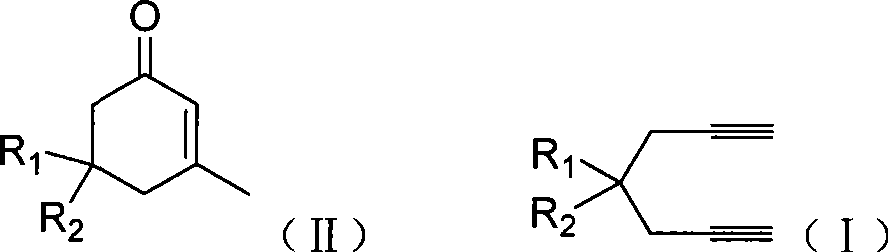Patents
Literature
45 results about "2-cyclohexenone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cyclohexenone is an organic compound which is a versatile intermediate used in the synthesis of a variety of chemical products such as pharmaceuticals and ... which fail to decarboxylate using 2-cyclohexenone and another route must be found instead. References ...
Organisms for the production of cyclohexanone
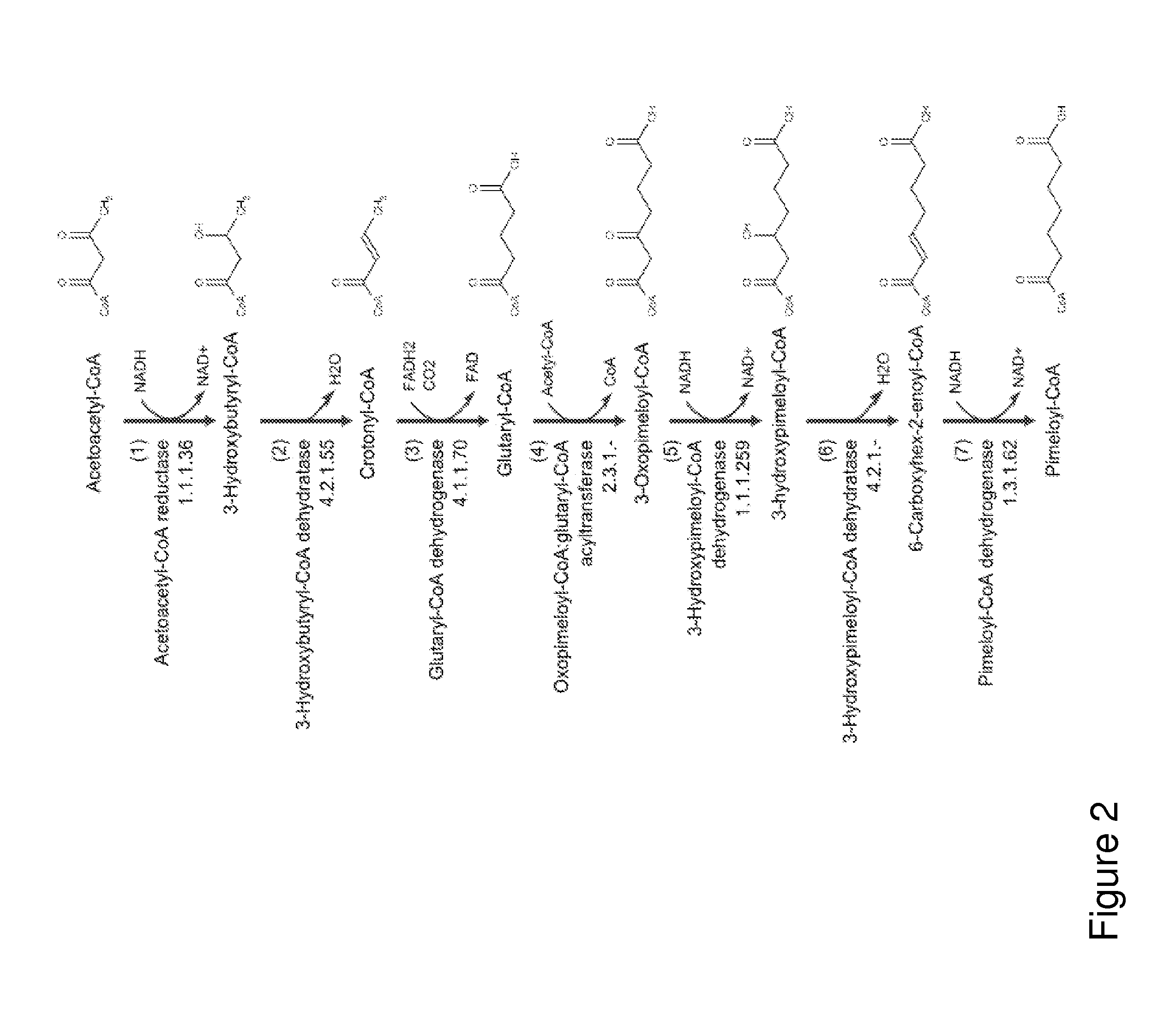
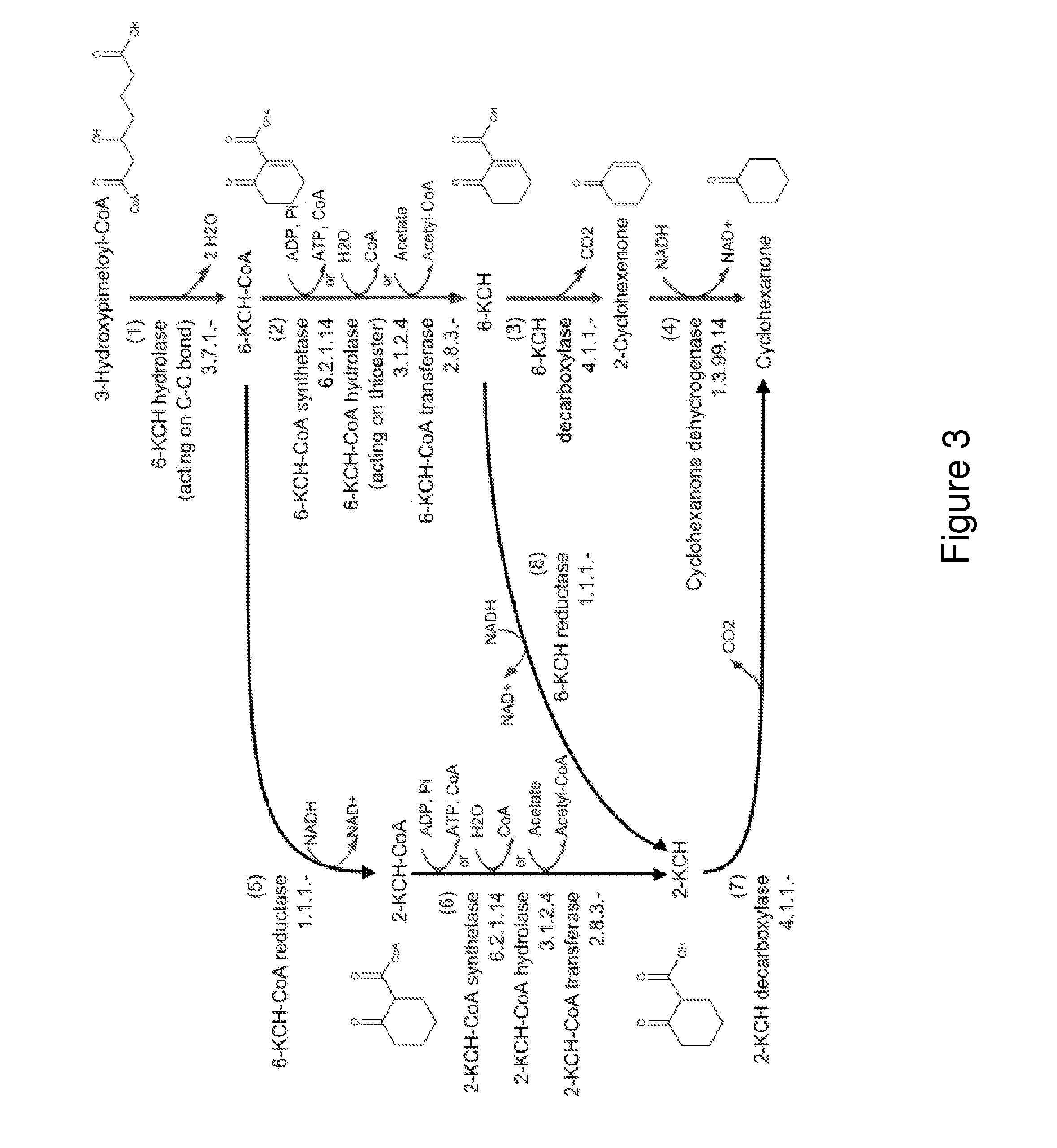
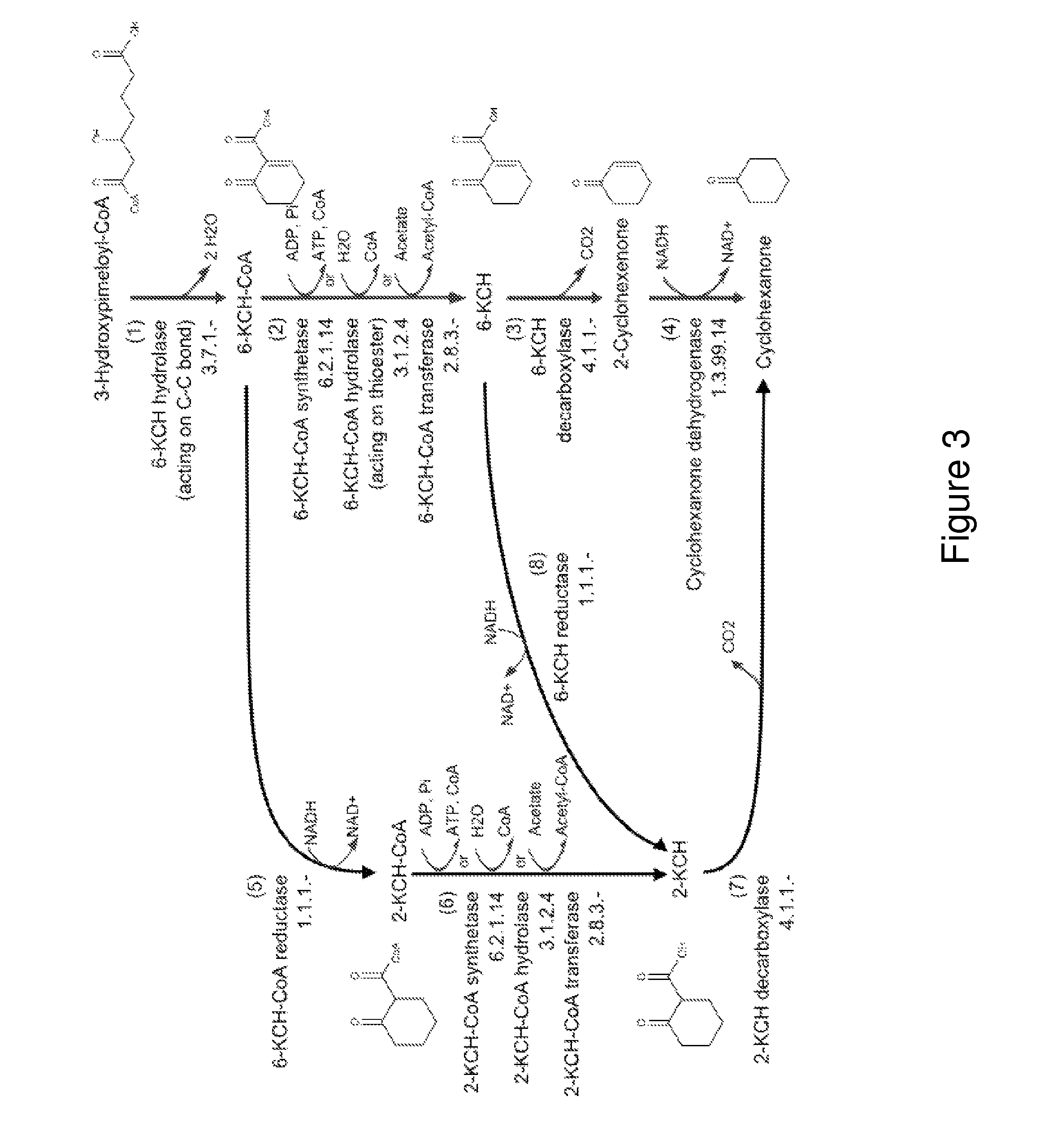
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has cyclohexanone pathways that include at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a cyclohexanone pathway enzyme. A pathway includes a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase and an enzyme selected from a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, and a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase. A pathway includes an enzyme selected from a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA reductase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate reductase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, and a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase. A pathway includes an adipate semialdehyde dehydratase, a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydrogenase, and a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydratase. A pathway includes a 3-oxopimelate decarboxylase, a 4-acetylbutyrate dehydratase, a 3-hydroxycyclohexanone dehydrogenase, a 2-cyclohexenone hydratase, a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase and an enzyme selected from a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA synthetase, a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), and a 3-oxopimeloyl-coA transferase. Each these pathways can include a PEP carboxykinase. A method for producing cyclohexanone includes culturing these non-naturally occurring microbial organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Preparation method of fluororesin-containing modified polyimide film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a fluororesin-containing modified polyimide film. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps of firstly, adding ultrafine fluororesin powder into a precursor polyamide acid solution of polyamide; then, adding and stirring a mixed solvent of N-methyl pyrrolidone and 3,5,5-trimethyl-2-cyclohexenone to form a sizing agent; mixing the sizing agent with the polyamide acid solution in an appropriate amount, and simultaneously adding a chemical imidization additive to form a polyamide acid blended solution after high-speed stirring; coating, drying and imidizing the blended solution to obtain a modified polyimide film material. The modified polyimide film prepared by the invention has excellent corona resistance while the characteristics of high strength, high heat resistance and the like of polyimide are maintained, the stability and the durability of the polyimide film in an electric field can be increased, and the polyimide film can be well applied to the fields of a high-speed motor and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanone by selectively hydrogenating isophorone
InactiveCN102718641AOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationCyclohexanoneIsophorone
The invention provides a method for preparing 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanone by selectively hydrogenating isophorone (namely 3,3,5-trimethyl-2- cyclohexenone). The method comprises the step of selectively hydrogenating to reduce isophorone into 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanone through combined use of supported Pd or Pt catalyst and co-catalyst under the condition that the reaction temperature is 20-100 DEG C. The method is remarkably characterized in that the byproduct 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanol is inhibited by adding the preferred cocatalyst, so that the product 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanone has relatively high selectivity and yield on the premise of realizing the high conversion rate of the isophorone under a relatively mild condition.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
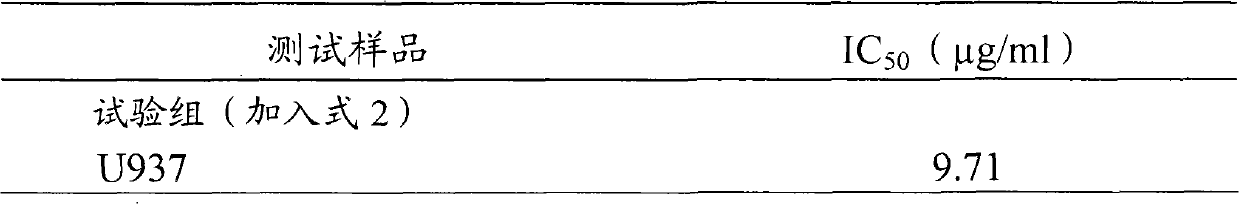
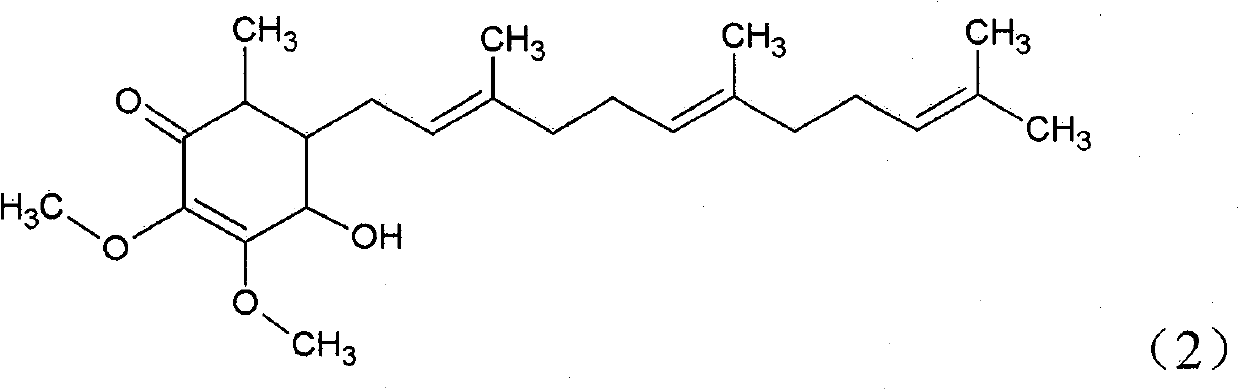
Antrodia camphorata cyclonene compound for restraining growth of bone cancer cells
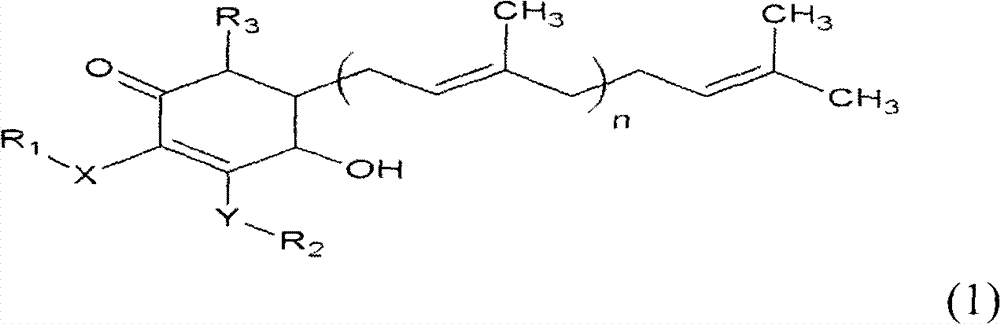
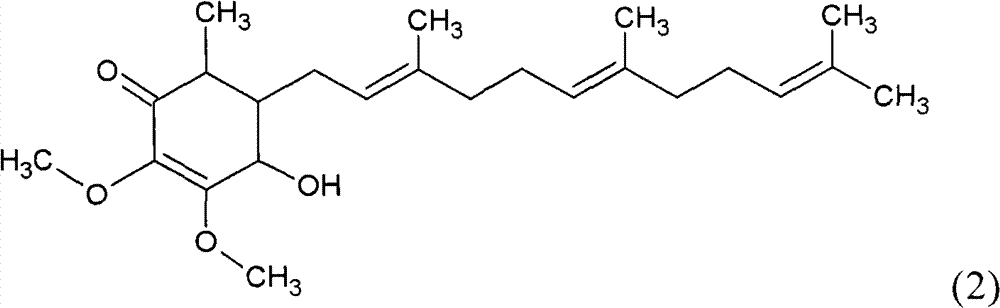
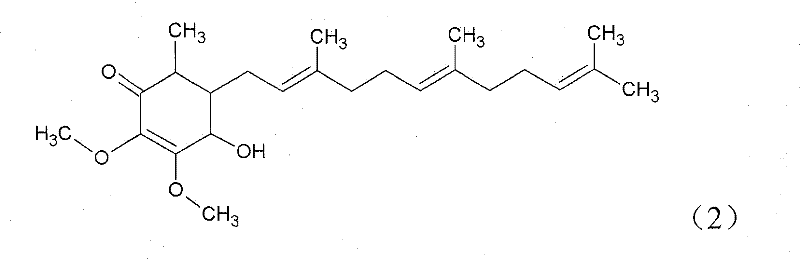
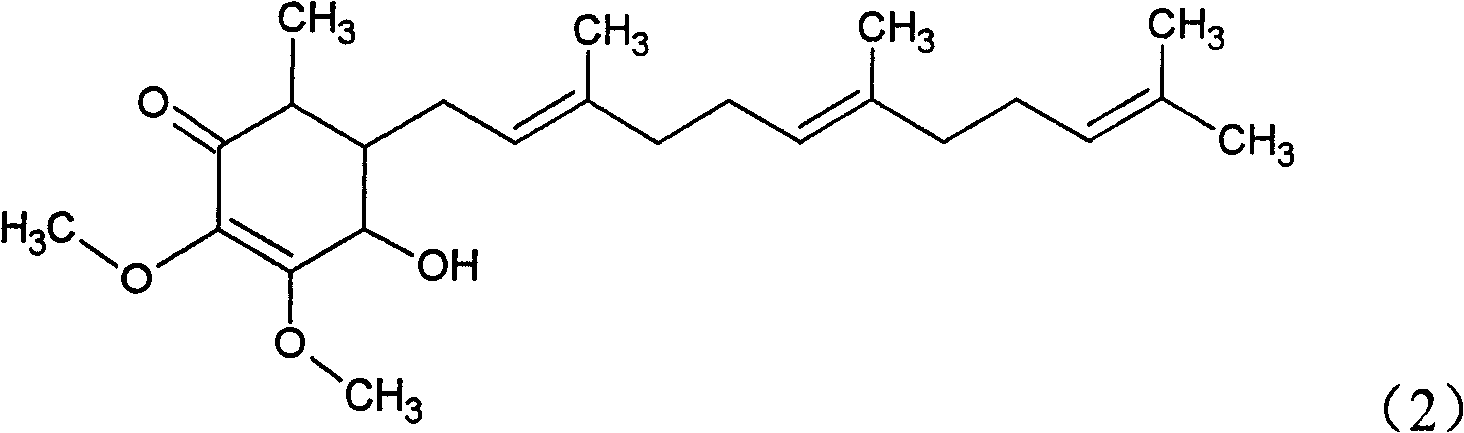
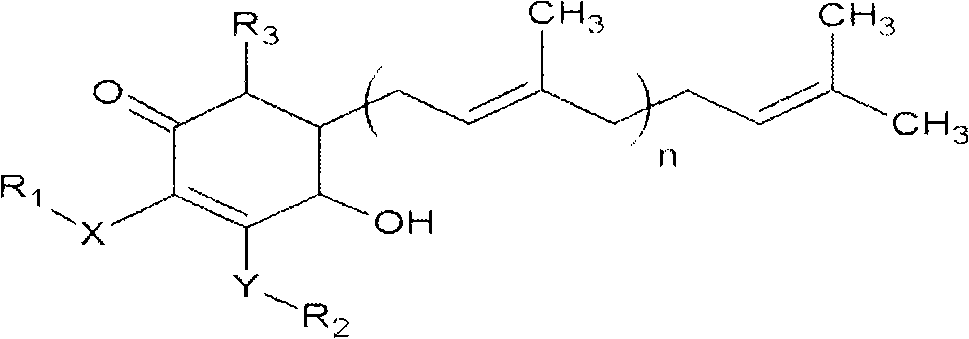
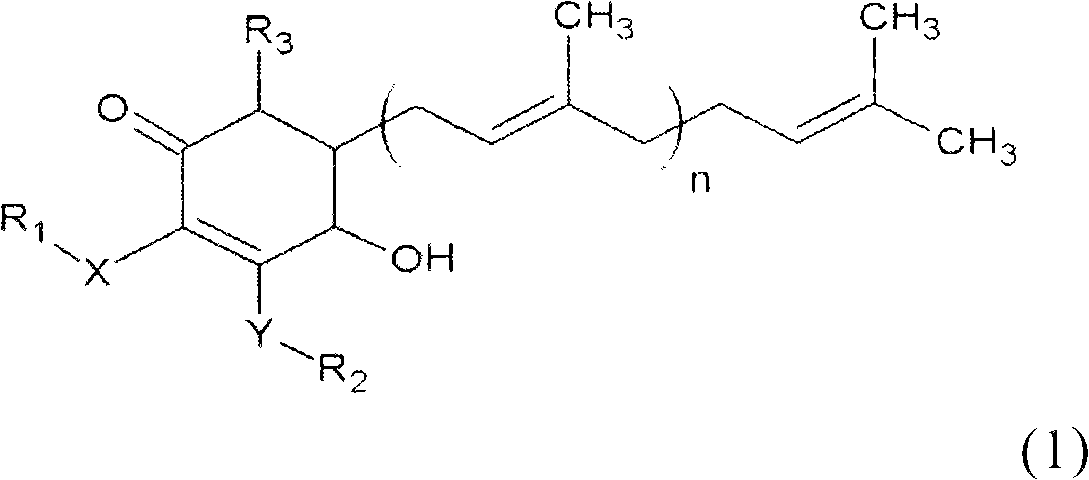
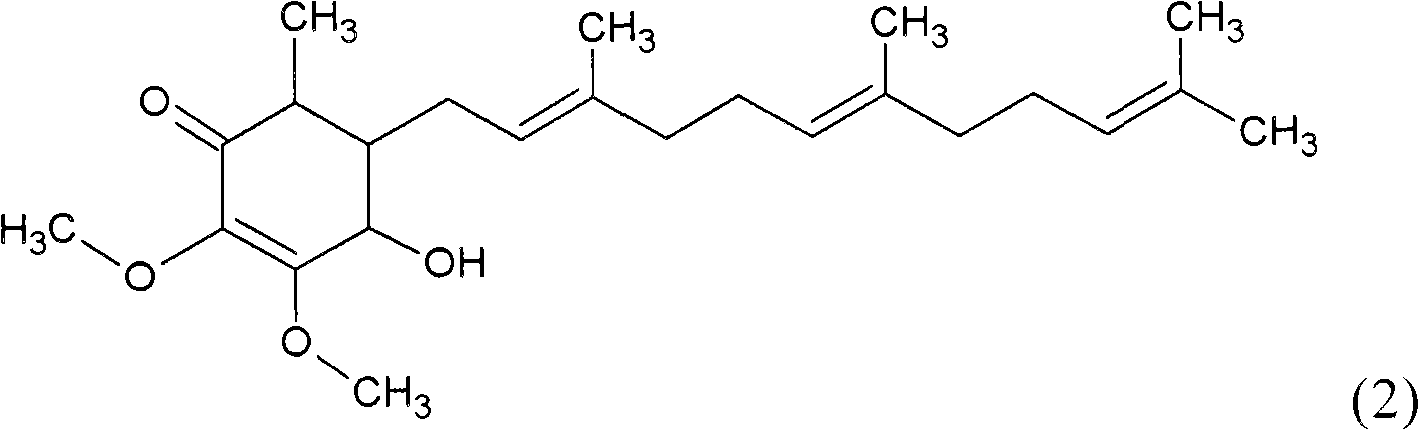
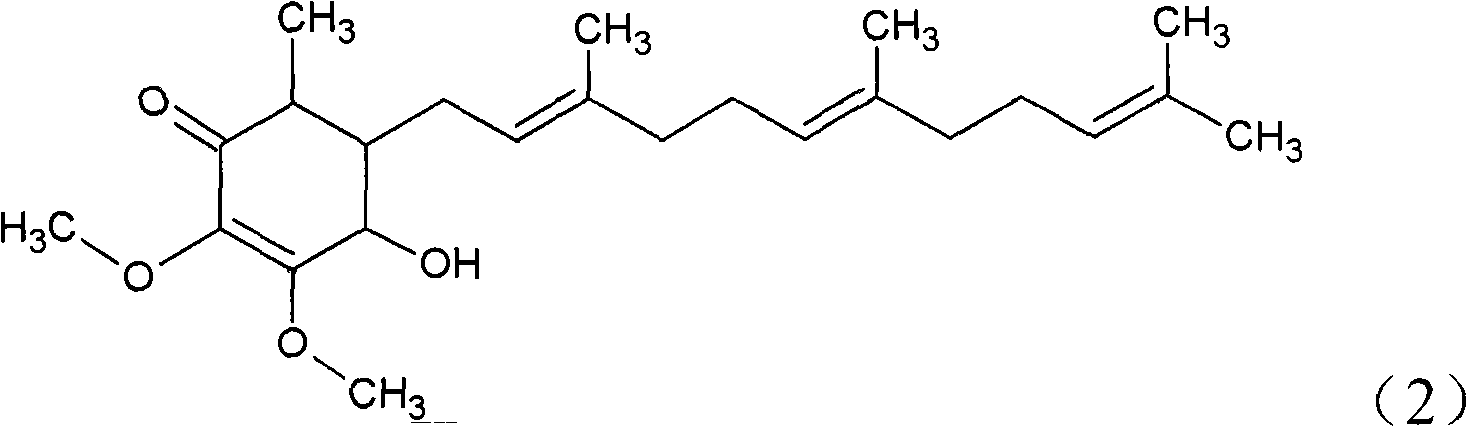
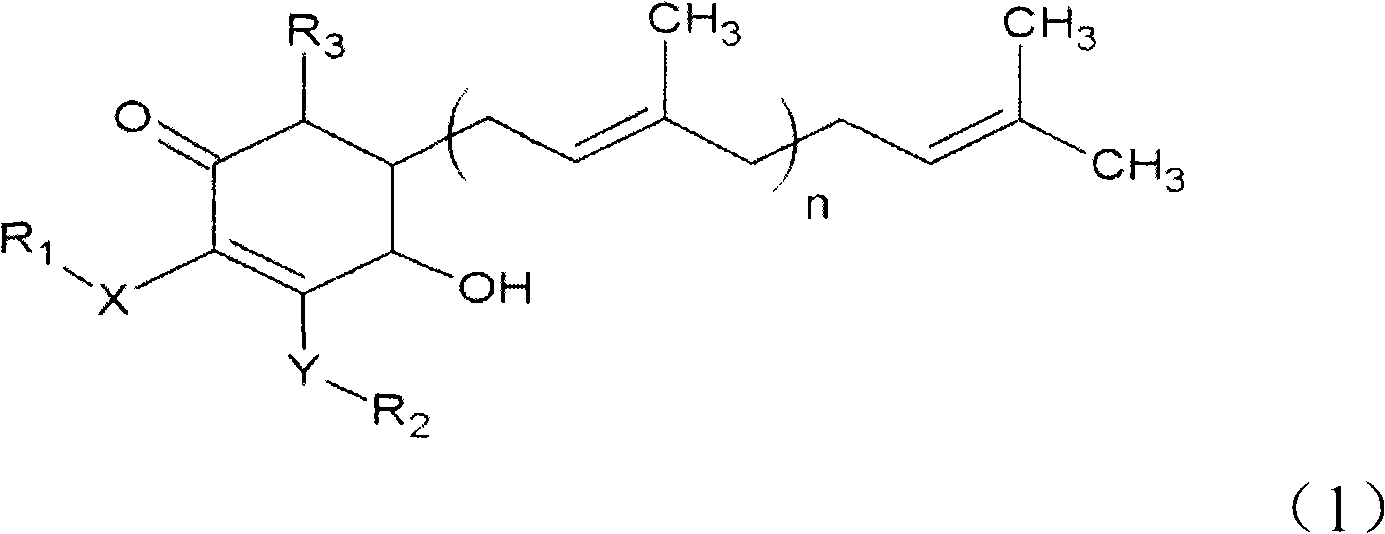
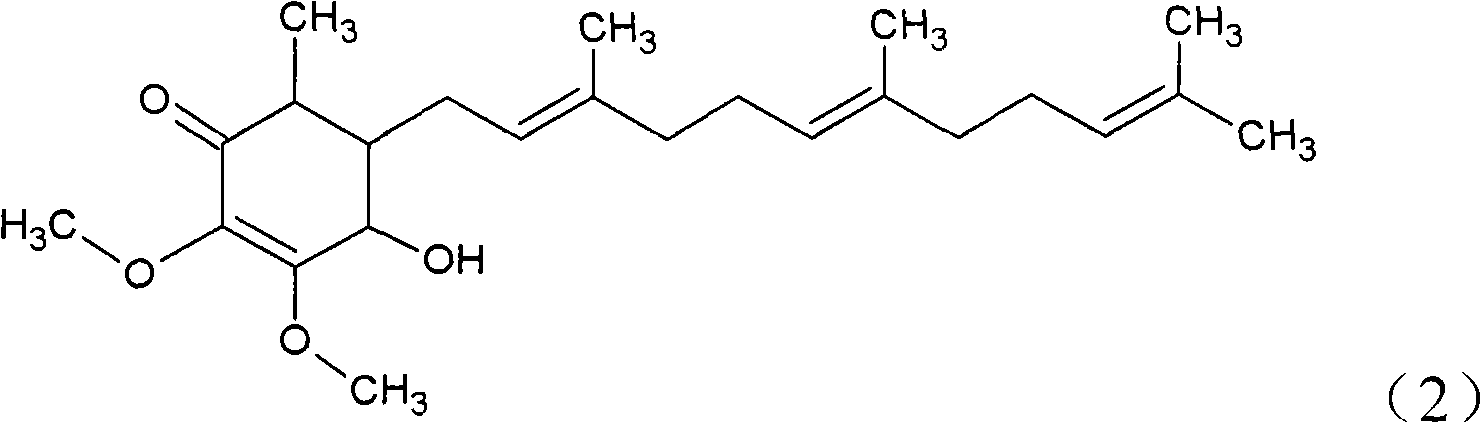
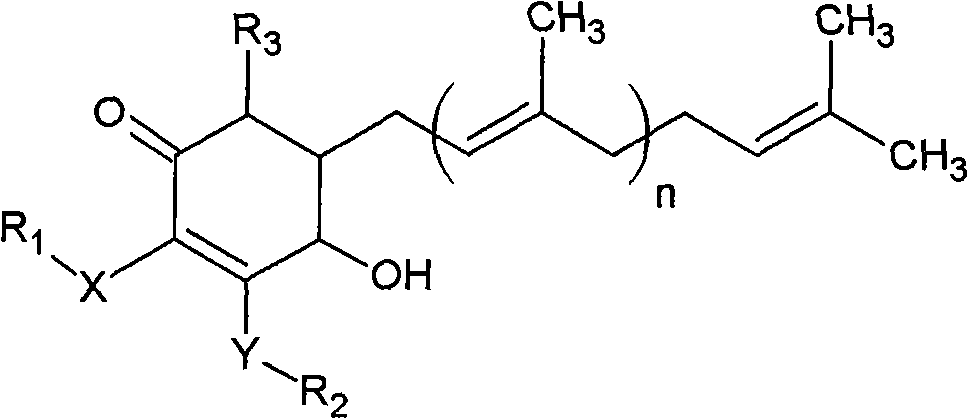
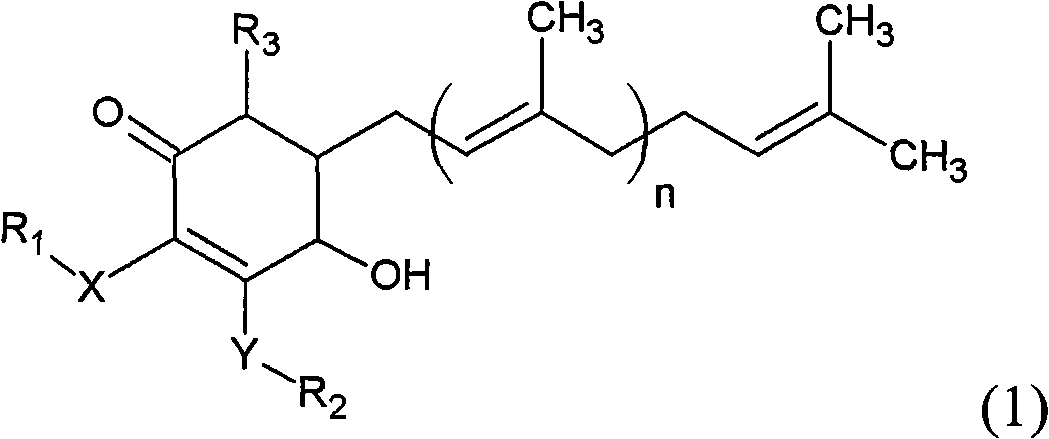
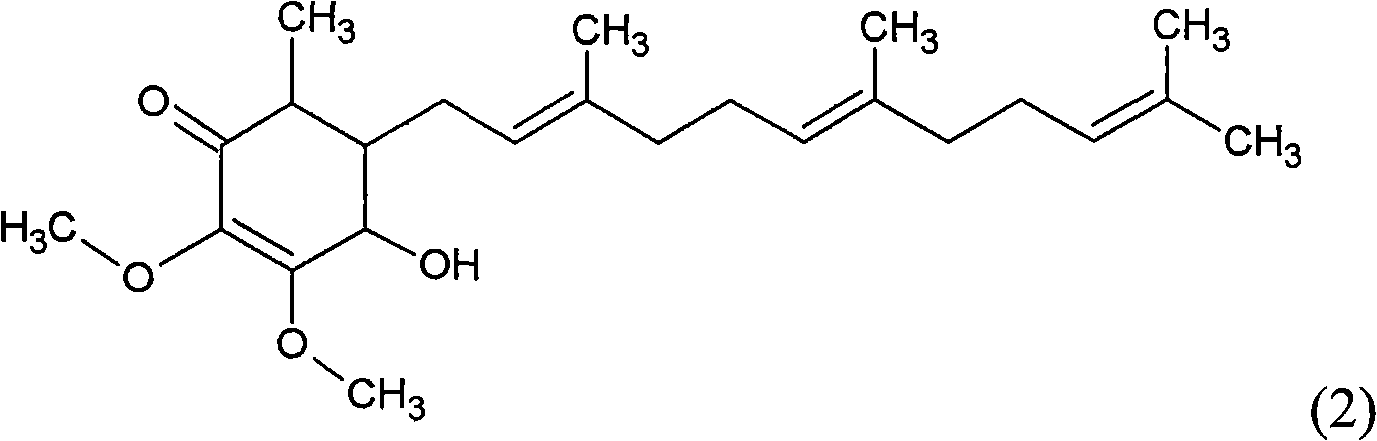
The invention relates to a novel application of a compound. In the invention, 4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methyl-5(3,7,11-trimethyl-2,6,10- cyclododecatriene)-2- cyclonene(4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-mehty-5(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone) is separated and purified from an antrodia camphorate extract. The cyclonene compound can be applied to restricting the growth of a bone cancer cell and the medical composition for restricting the growth of bone cancer cells.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
Method for preparing 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanone by selectively hydrogenating isophorone
InactiveCN102718641BHigh yieldHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationCyclohexanoneIsophorone
The invention provides a method for preparing 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanone by selectively hydrogenating isophorone (namely 3,3,5-trimethyl-2- cyclohexenone). The method comprises the step of selectively hydrogenating to reduce isophorone into 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanone through combined use of supported Pd or Pt catalyst and co-catalyst under the condition that the reaction temperature is 20-100 DEG C. The method is remarkably characterized in that the byproduct 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanol is inhibited by adding the preferred cocatalyst, so that the product 3,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexanone has relatively high selectivity and yield on the premise of realizing the high conversion rate of the isophorone under a relatively mild condition.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
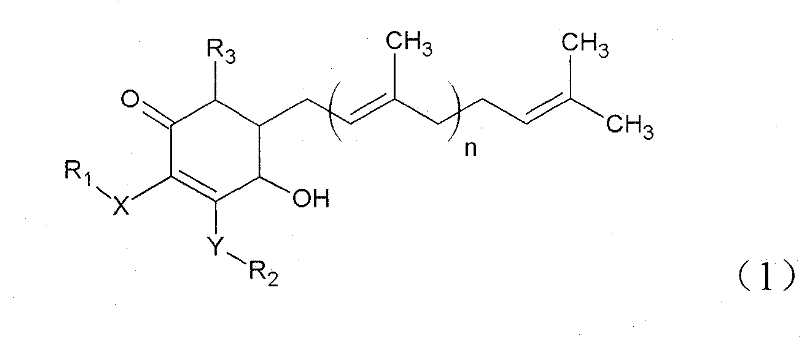
2-cyclohexenones and process for preparing same
InactiveCN1827577AReasonable designSimple and fast operationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationDistillationAlkyne
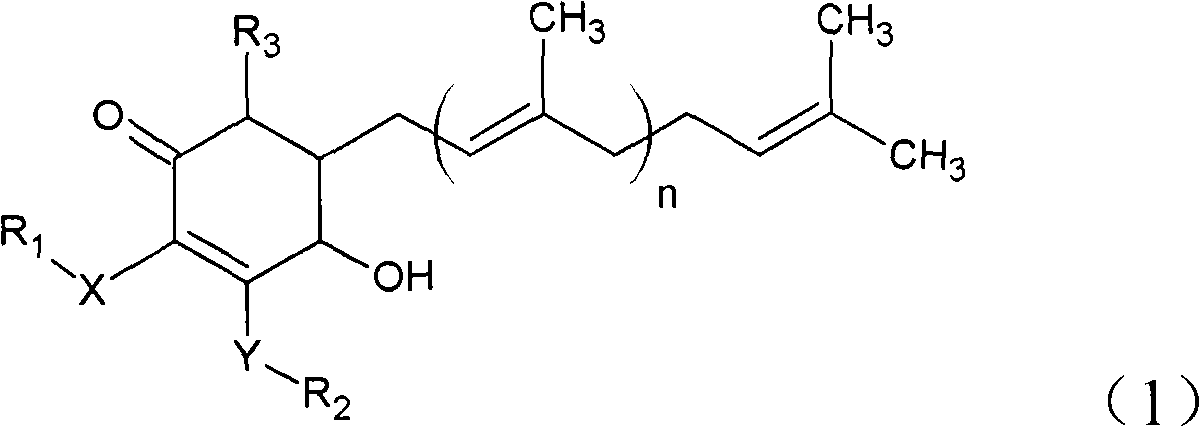
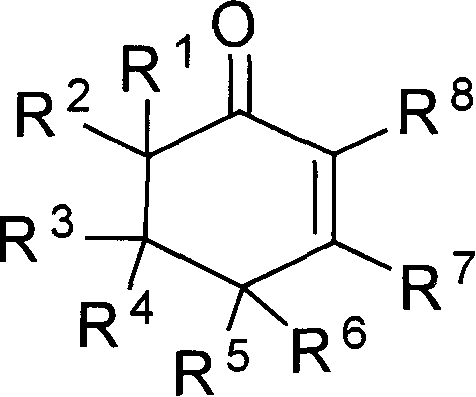
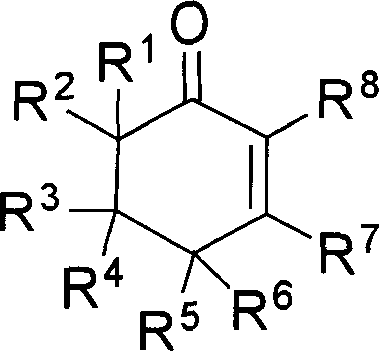
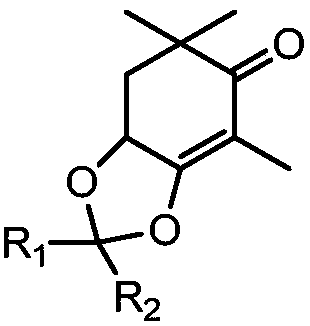
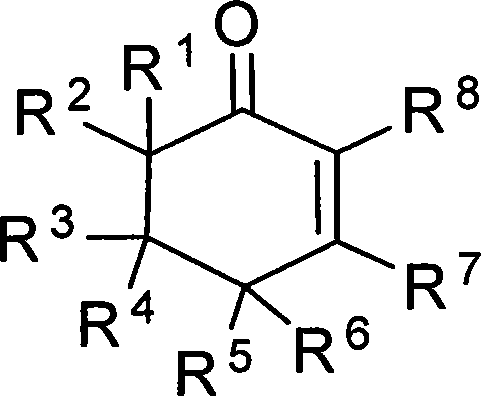
The invention provides compounds of 2-cyclohexenone with its constitutional general formula on the right, in which R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, and R8 may be the same or be different and their species are function groups of alkyl, carbonyl, phosphoryl, cyano and so on. The method for preparing them consists of hydrating and cyclizing 1, 6-heptadiynes and water catalyzed by transient metal-aurum complen compound to prepare 2-cyclohexenones. The subtractive process of the compound reaction of this invention can be accomplished by the usual refining partition method such as the solvent extraction, the recrystallization, the distillation and the column chromatography. The invention can obtain many kinds of compounds of 2-cyclohexenone by hydration and intermolecular cyclisation of various types of 1, 6-bis-alkynes with the accelerating effect of the given metal complen compound and groups of protonic acid. Preparing 2-cyclohexenones in this method is of simple and dependable operation and is suitable for industrial administration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Stable carteolol hydrochloride, preparation method thereof and eye medicine combination
ActiveCN107337639AOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCarteolol HydrochlorideOcular hypertension
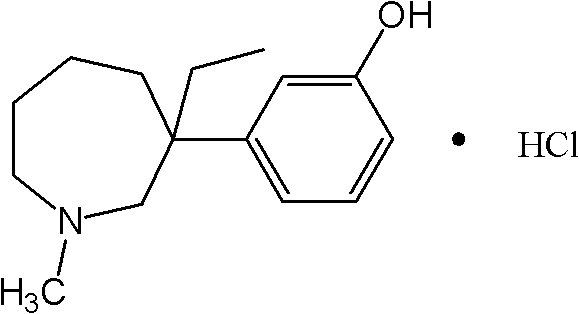
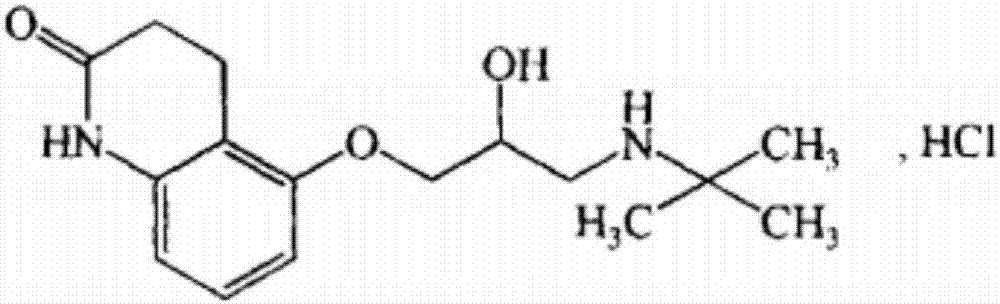
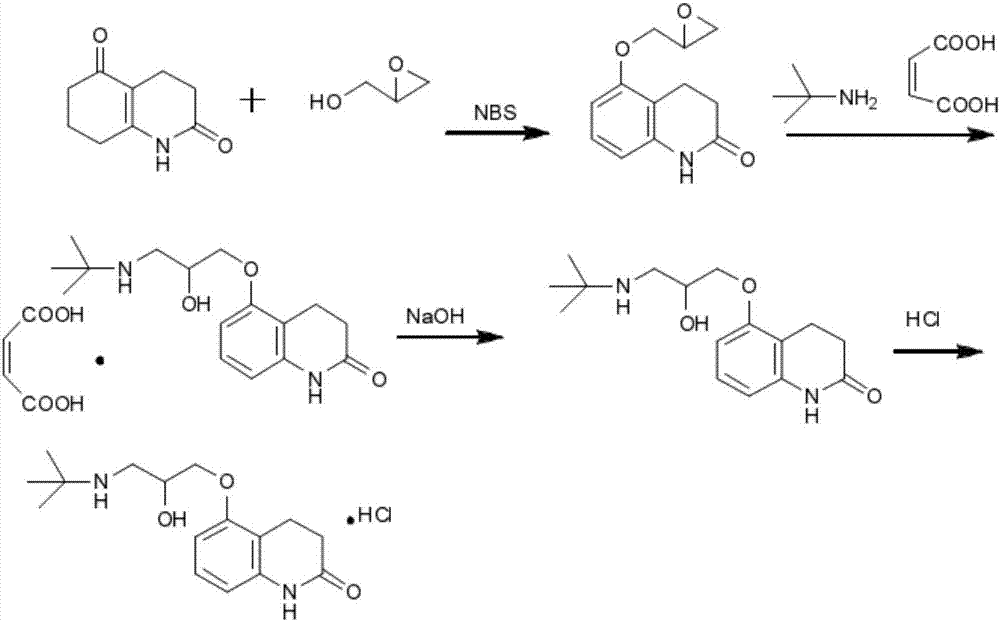
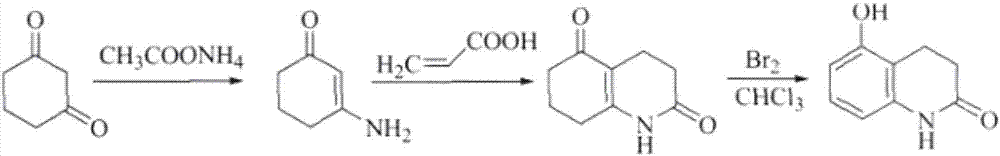
The invention relates to stable carteolol hydrochloride, a preparation method thereof and an eye medicine combination, in particular to a method for preparing carteolol hydrochloride. The method comprises the following steps of preparing 3-amino-2-cyclohexenone, tetrahydro-2,5(1H, 6H)-quinolinone, 5-hydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-carbostyril and 5-(2,3-epoxypropoxy)-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-carbostyril, and then the carteolol hydrochloride is obtained. Furthermore, the invention provides the carteolol hydrochloride crude medicine obtained according to the method, the eye medicine combination prepared by using the obtained carteolol hydrochloride as the crude medicine, and applications of the obtained carteolol hydrochloride to preparation of drugs for treating or preventing glaucoma or ocular hypertension. The method has excellent pharmaceutical characteristics, for example, the obtained crude medicine and a preparation has excellent stability.
Owner:深圳市瑞霖医药有限公司
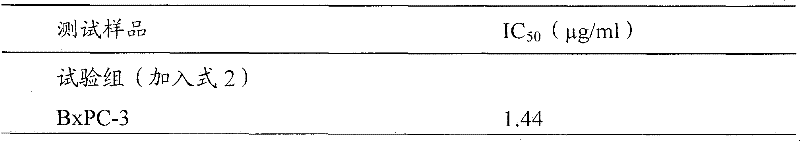
Antrodia camphorata cyclohexenone compound for inhibiting growth of pancreatic cancer tumor cells
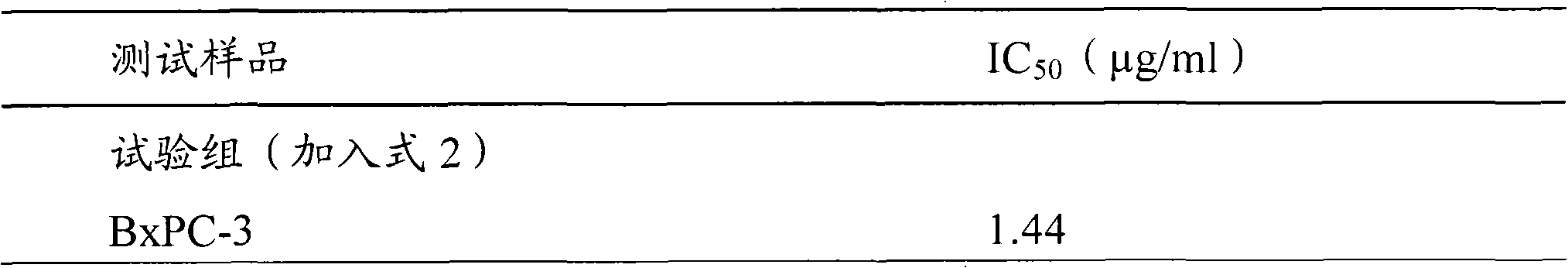
The invention relates to a new purpose of a compound. In the invention, antrodia camphorata extract is separated and purified to obtain 4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methy-5(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone. The cyclohexenone compound can be used for inhibiting growth of pancreatic cancer tumor cells and simultaneously can be used for pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting growth of pancreatic cancer tumor cells.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
Antrodia camphorata cyclohexenone compound for suppressing growth of lymphoma tumor cells
The invention relates to a new use of a compound. In the invention, (4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methy-5(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone is obtained from extract of Antrodia camphorata by separation and purification, and the cyclohexenone compound can be used for suppressing the growth of lymphoma tumor cells and can also be used in medical composition for suppressing the growth of the lymphoma tumor cells.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
Cyclohexenone extract of Antrodia camphorata
ActiveCN101343247AHas antioxidant activityAvoid mutationOrganic chemistryKetone active ingredientsCyclohexenoneAdditive ingredient
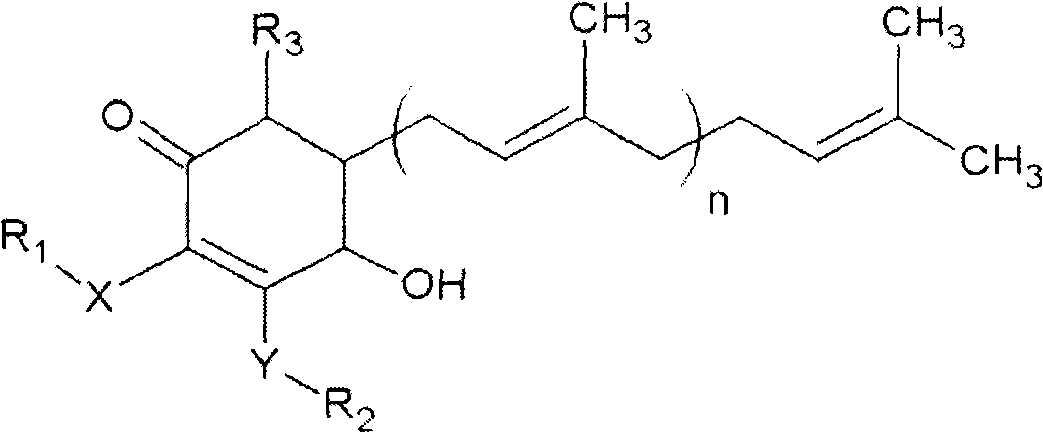
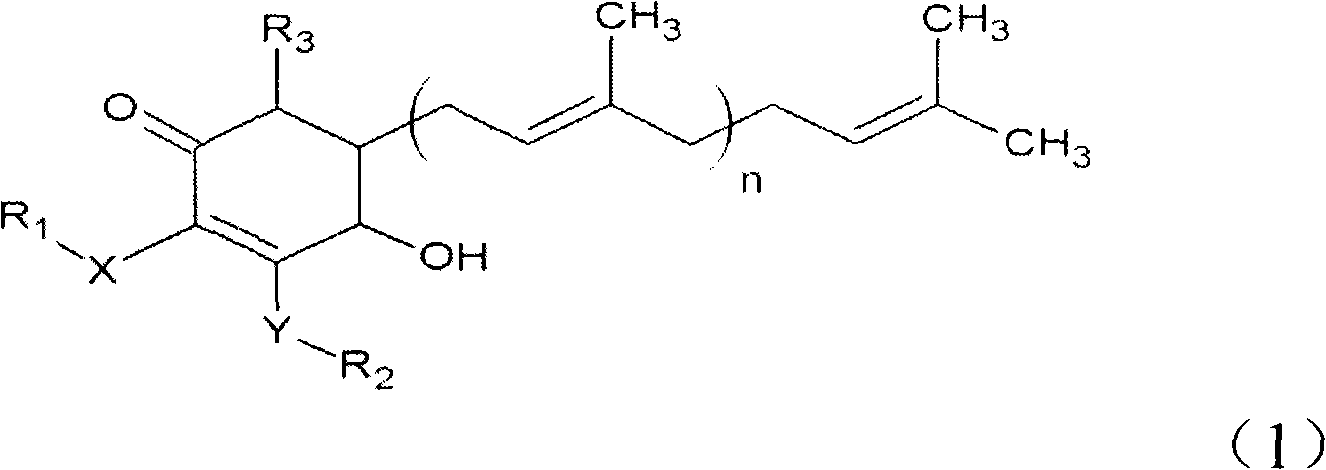
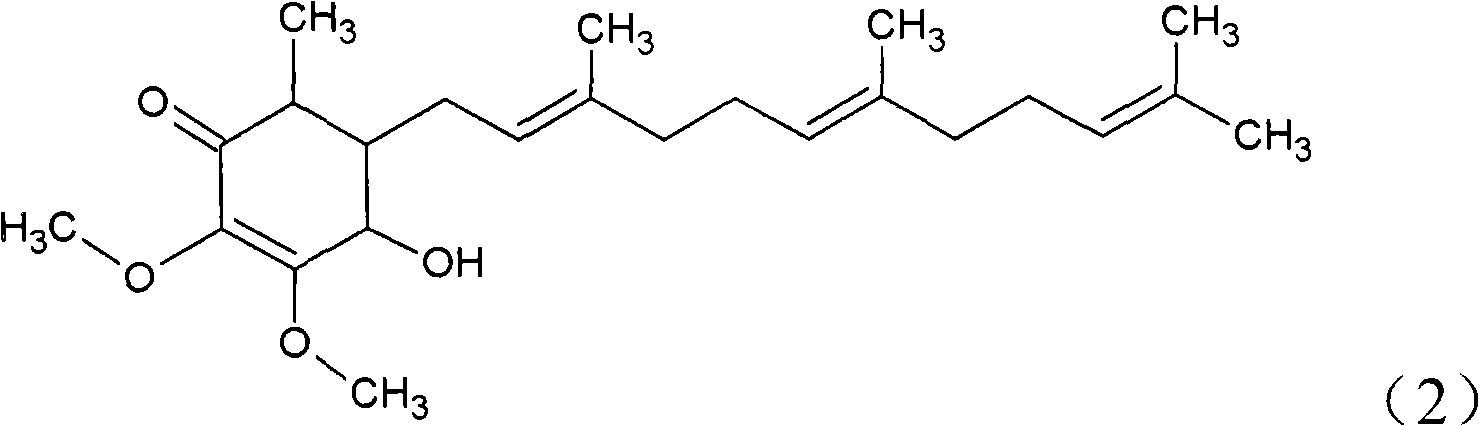
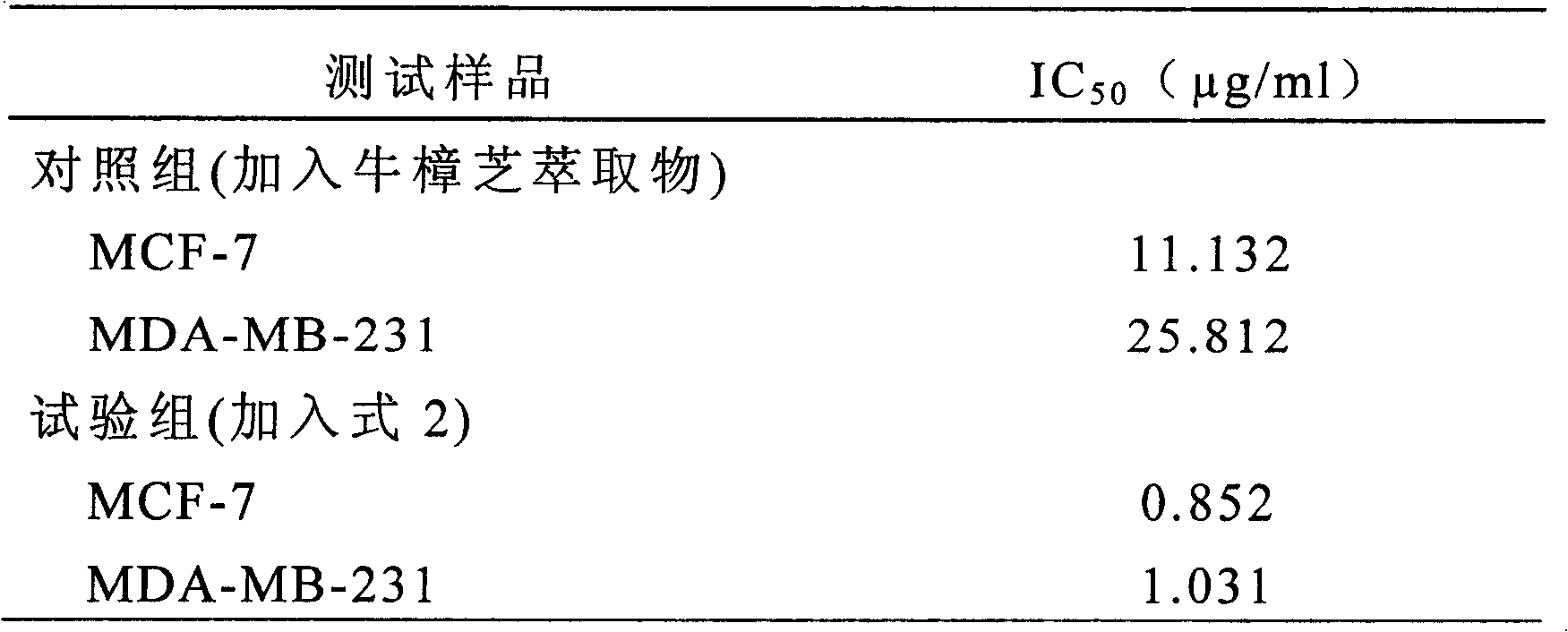
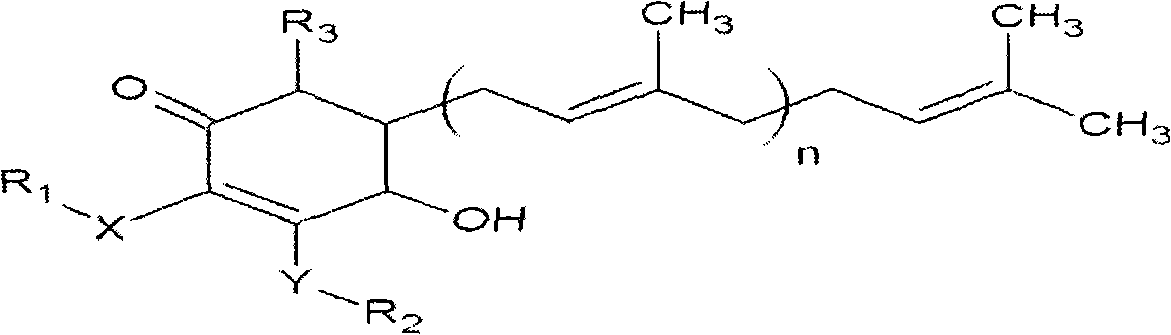
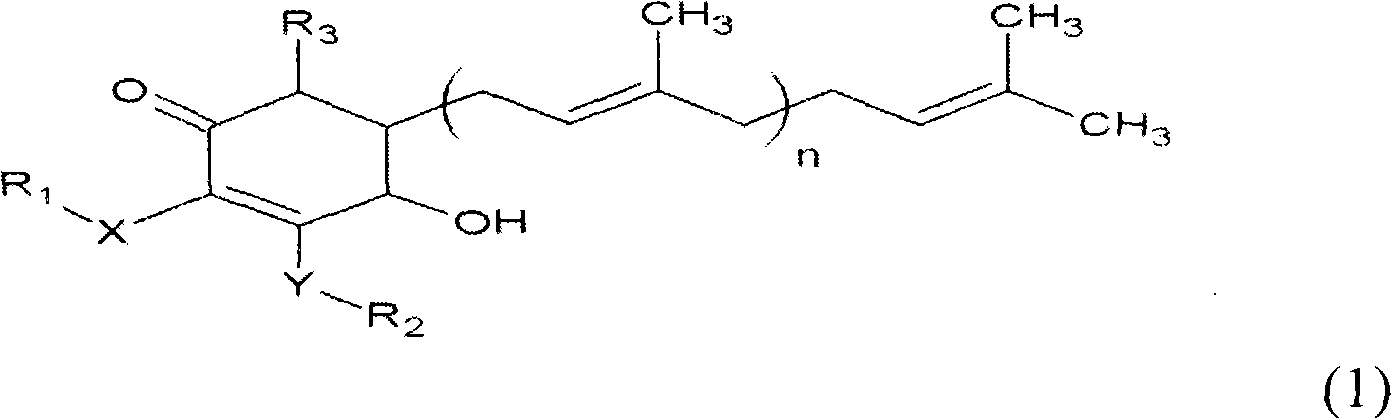
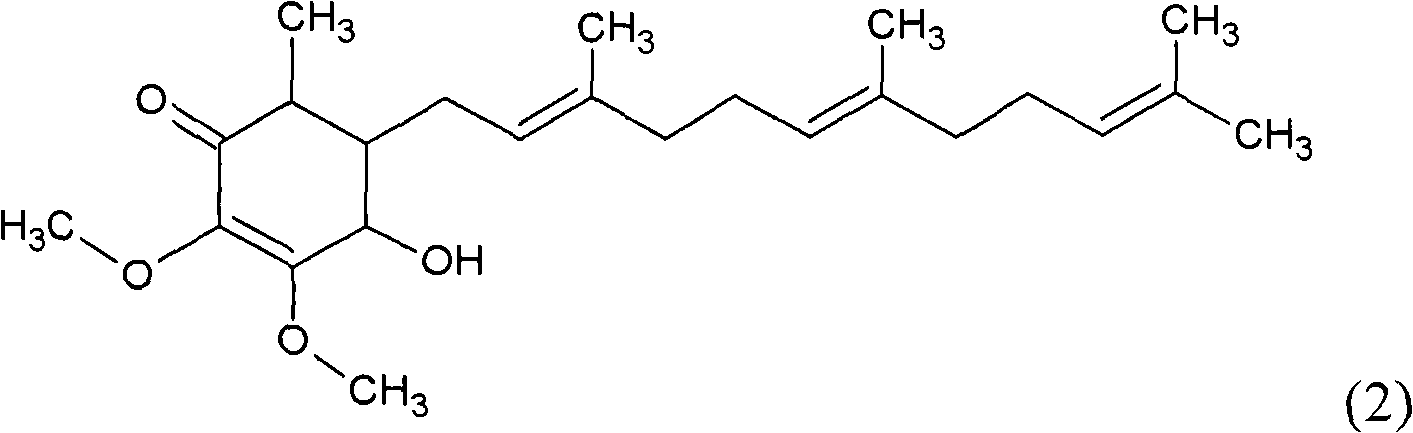
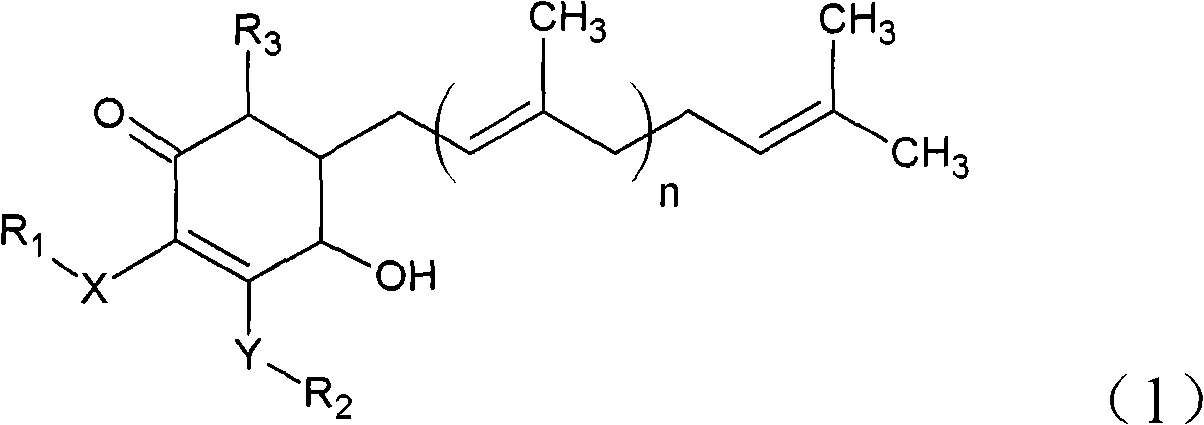
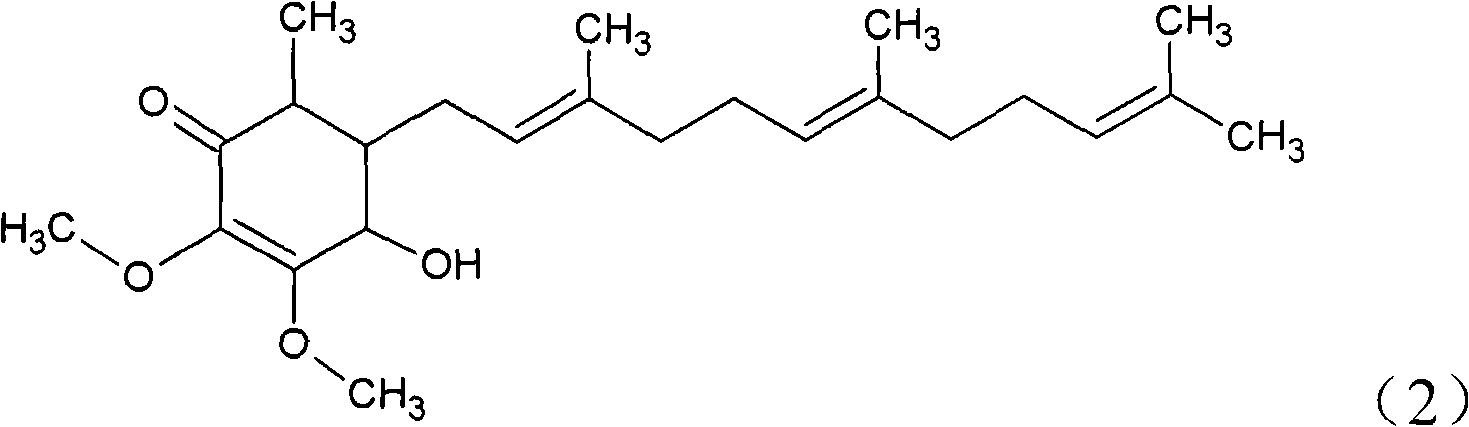
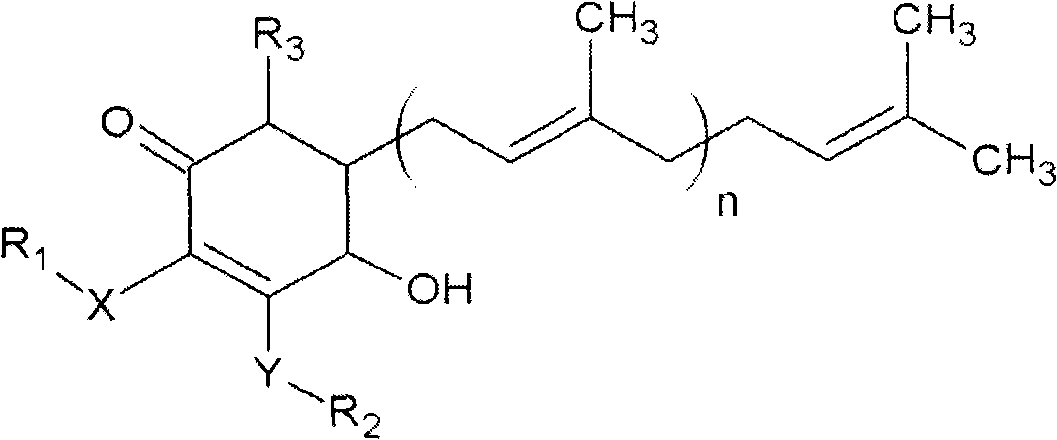
The invention relates to a novel compound as well as purposes thereof, particularly relating to 4-oxhydryl-2, 3-dimethoxy-6-methyl-5(3, 7, 11-trimethyl-2, 6, 10-dodecatriene)-2-cyclohexenone (4-hydroxy-2, 3-dimethoxy-6-methy-5(3, 7, 11-trimethyl-dodeca-2, 6, 10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone) separated from an Antrodia camphorata extract as well as the applications thereof in inhibiting the growth of tumor cells. The compound in the invention is firstly found in Antrodia camphorata, and can be applied to the inhibition of growth of tumor cells of breast cancers, liver cancers and prostate cancers, meanwhile serving as an ingredient of pharmaceutical compositions for restricting the growth of the tumor cells, or being applied to the prevention of cardiovascular diseases or added to healthy beverage and food by further leveraging the oxidation resistance activity thereof.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
Preparation of 2-pimelie kelone compound
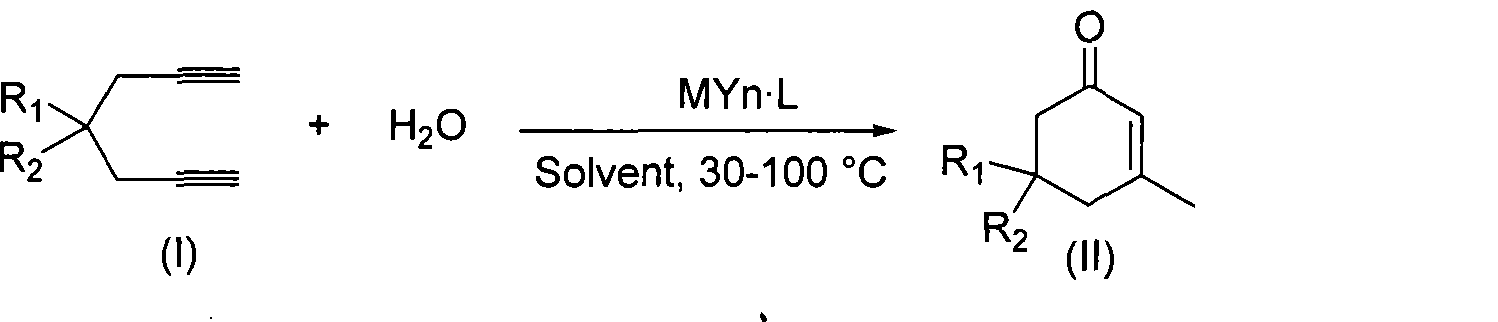
ActiveCN101412667AEasy to operatePromote reaction efficiencyOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCyclohexenoneChemical products
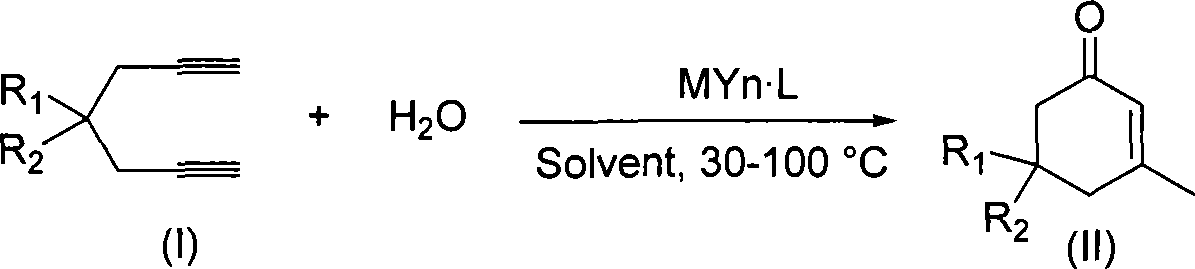
The invention discloses a method for preparing 2-cyclohexenone compound, which comprises the following steps: under the action of a metallic catalyst MYn.L, 1, 6-heptadiyne compound showed in formula (I) taken as a raw material is reacted in an ionic liquid at a temperature of between 0 and 150 DEG C; after the reaction liquid is treated, the 2-cyclohexenone compound showed in formula (II) is prepared; and at the same time, the ionic liquid fixed with the metallic catalyst can be recycled. The method has the advantages of simple and reliable operation, high yield and selectivity, repeated recycling and use of the noble metal catalyst, environmental protection, and the like. Because the cyclohexenone compound is a good raw material for synthesizing medicines, pesticides and chemical products, the method has wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
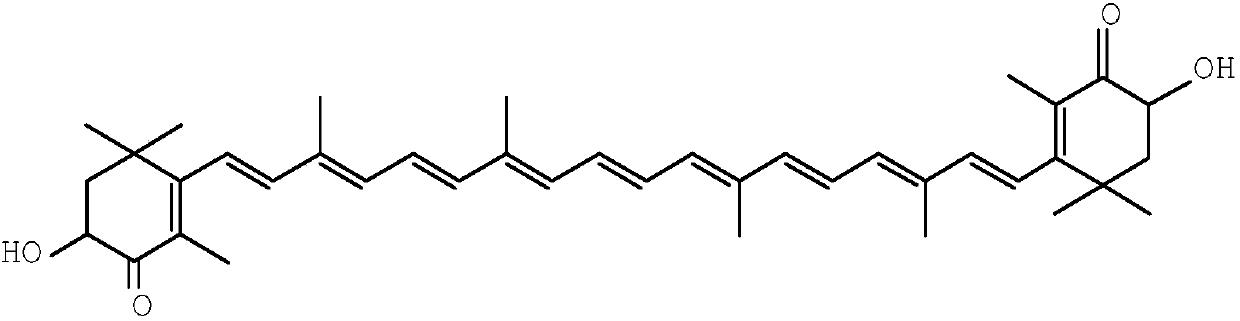
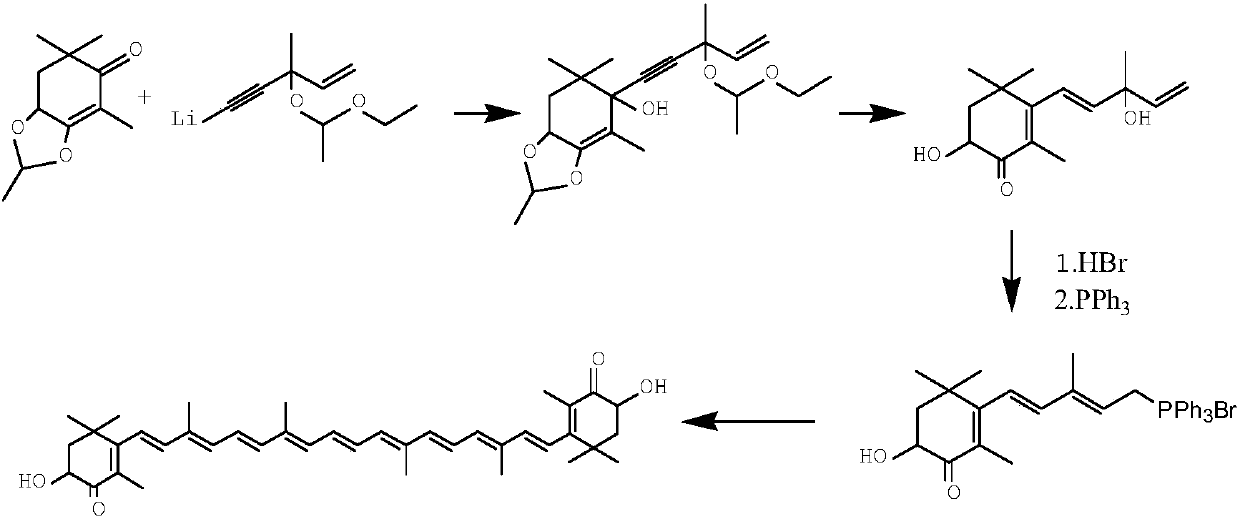
Method for synthesizing astaxanthin intermediate
ActiveCN107739390AAvoid multiple importsAvoid repeated hydrolysisGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsBetaxanthinsAstaxanthin
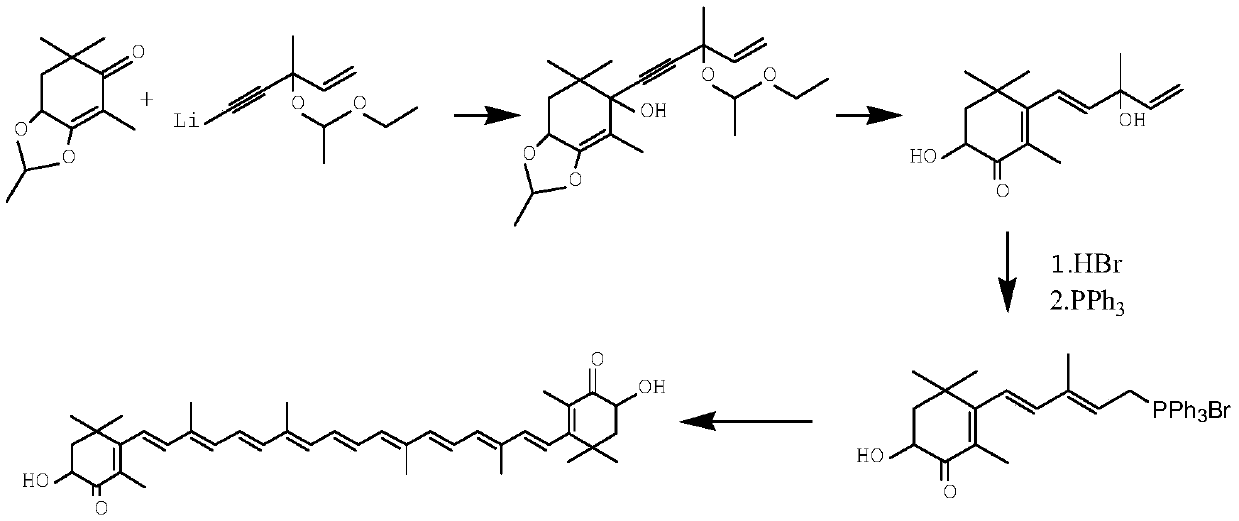
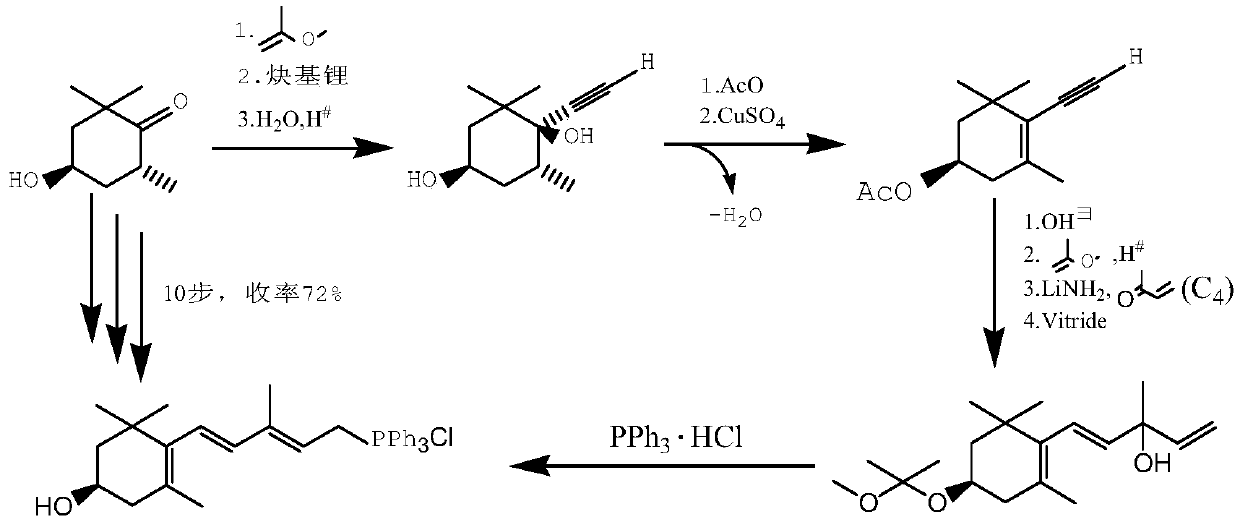
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing an astaxanthin intermediate. The method specifically comprises the following steps: 1) adding lithium into liquid ammonia to implement a reaction, introducing acetylene to synthesize acetylene-based lithium, replacing the liquid ammonia with an organic solvent, and adding 1-butene-3-ketone to implement a reaction continuously, so as to generate 3-methyl-1-amylene-4-alkyne-3-lithium alkoxide; 2) adding lithium into the liquid ammonia to implement a reaction, and further adding the product obtained in the step 1) to generate 3-methyl-1-amylene-4-alkynyl based lithium-3-lithium alkoxide; 3) performing a condensation reaction on the product obtained in the step 2) with heterogeneous diketone so as to generate a condensation compound; 4) performing acid hydrolysis on the condensation compound obtained in the step 3), and treating with a reduction triple bond so as to obtain 2,4,4-trimethyl-6-hydroxy-3-(3-methyl-1,4-dipentene-3-hydroxy)-2-cyclohexenone; 5) enabling 2,4,4-trimethyl-6-hydroxy-3-(3-methyl-1,4-dipentene-3-hydroxy)-2-cyclohexenone to react with hydrobromic acid and triphenylphosphine in sequence, thereby finally generating the astaxanthin intermediate. By adopting the method, multiple times of introduction and repeated hydrolysis of extra protection groups are avoided, so that the raw materials are saved, and the preparation route is simplified.
Owner:SHANGYU NHU BIOCHEM IND
Organisms for the production of cyclohexanone
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
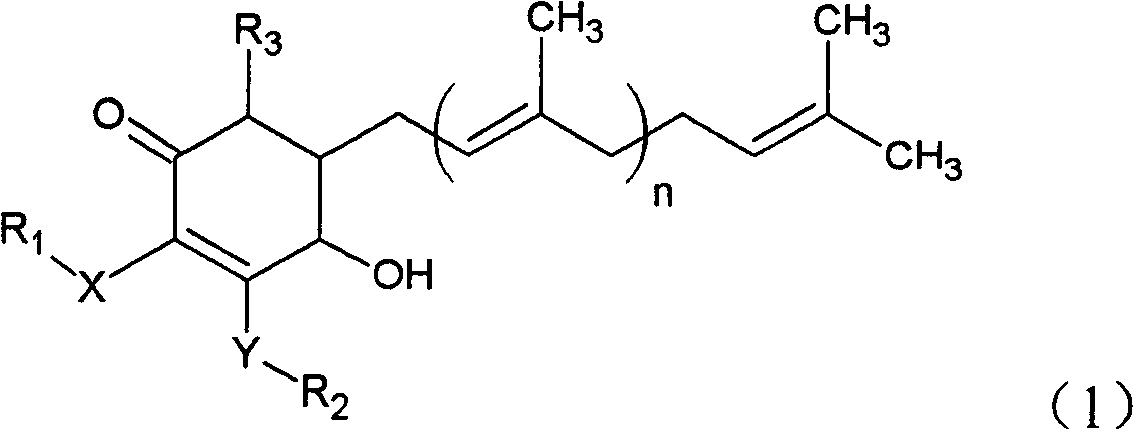
2-cyclohexenone compounds
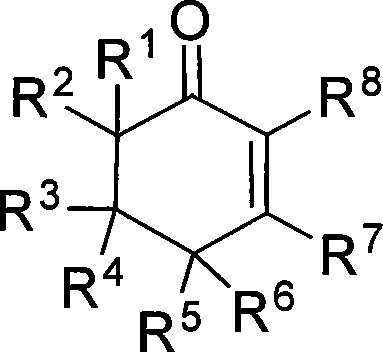
InactiveCN101104587AReasonable designSimple and fast operationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHydration reactionCyclohexenone
The invention provides 2-cyclohexyl ketene compounds with the following common molecular formula, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, and R8 are identical or different functional groups of alkyl group, carbonyl group, phosphoryl group or cyano-group. The preparation method is: use gold complex to catalyse the cyclized hydration reaction of 1,6-heptadiyne compounds and water. The refining process of the synthesizing reaction can be done with common separation and refining methods of solvent extraction, recrystallization, distillation and column chromatography. With simple and reliable operation, the method of the invention can be applied to the hydration of 1,6-dualalkyne compounds as well as to intramolecular cyclization reactions under the katalysis of special metal complex or different protonic acid to get different 2-cyclohexyl ketene compounds, thus the invention can be industrialized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Antrodia camphorata cyclohexenone compound for suppressing growth of lymphoma tumor cells
The invention relates to a new use of a compound. In the invention, (4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methy-5(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone is obtained from extract of Antrodia camphorata by separation and purification, and the cyclohexenone compound can be used for suppressing the growth of lymphoma tumor cells and can also be used in medical composition for suppressing the growth of the lymphoma tumor cells.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
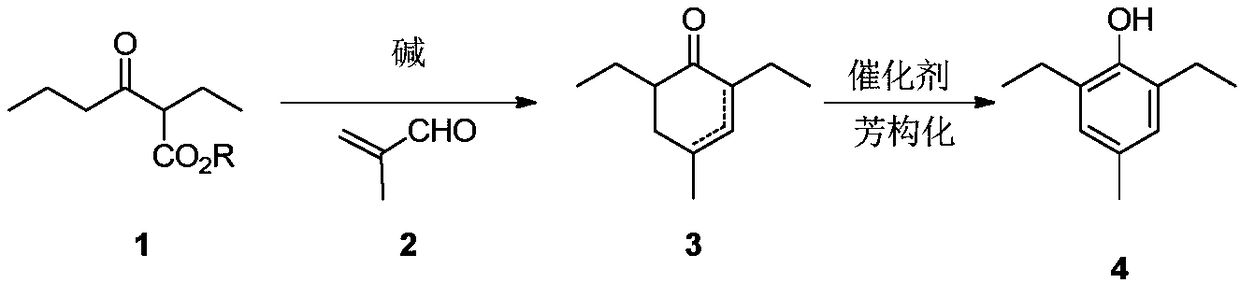
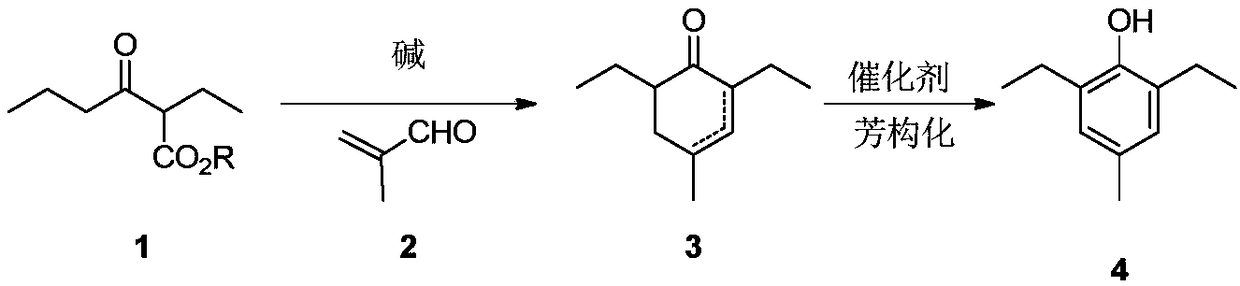
Preparation method of 2,6-diethyl-4-methylphenol
ActiveCN108264449ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getOperational securityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by condensationCyclohexenoneMetal catalyst
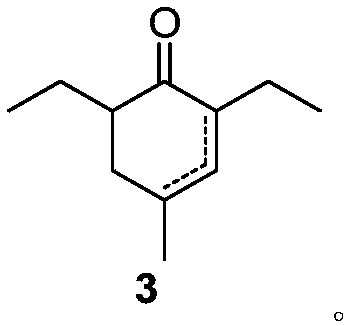
The invention provides a preparation method of 2,6-diethyl-4-methylphenol. The method uses a synthetic strategy which is completely different from the prior art, and comprises the following steps: taking 2-ethyl-3-oxohexanoate as a raw material; carrying out condensation reaction on the raw material and 2-methylacrolein under the effect of alkali to obtain an intermediate 2,6-diethyl-4-methyl-2-cyclohexenone and / or 2,6-diethyl-4-methyl-3-cyclohexenone; and carrying out aromatization on the 2,6-diethyl-4-methyl-3-cyclohexenone under the effect of a catalyst to obtain the target product 2,6-diethyl-4-methylphenol. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the raw materials are cheap and are easily obtained, an expensive metal catalyst and the corresponding ligand thereof are not required, the method is safe to operate, the three wastes are less and the like. Industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHUJI UNITED CHEM
Synthetic method of [60] fullerocyclopentanone and [60] fullero 2-cyclohexenone compounds
ActiveCN108863735AImprove compatibilityThe synthesis process is green and environmentally friendlyOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by condensationNitrogenCarbene
The invention discloses a synthetic method of [60] fullerocyclopentanone and [60] fullero 2-cyclohexenone compounds and belongs to the technical field of fullerene derivatives. The key points of the technical scheme of the invention are as follows: the synthetic method comprises the following step of by taking C60 and alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehyde compounds as reaction raw materials and organicmicromolecular N-heterocyclic carbine as a catalyst, realizing direct acylation of [60] fullerene through polarity inversion strategy of aldehyde to prepare the [60] fullerocyclopentanone and [60] fullero 2-cyclohexenone compounds as target products. In the synthetic method provided by the invention, the N-heterocyclic carbine as the organic micromolecular catalyst is used, and no metals participate to the reaction process, so that the synthetic process is environmentally friendly; a substrate is wide in application range and good in functional group compatibility; and the synthetic method has relatively high yield and is suitable for large-scale preparation.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Antrodia cinnamomea pimelie kelone compound for inhibiting growth of oral cancer tumor cells
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
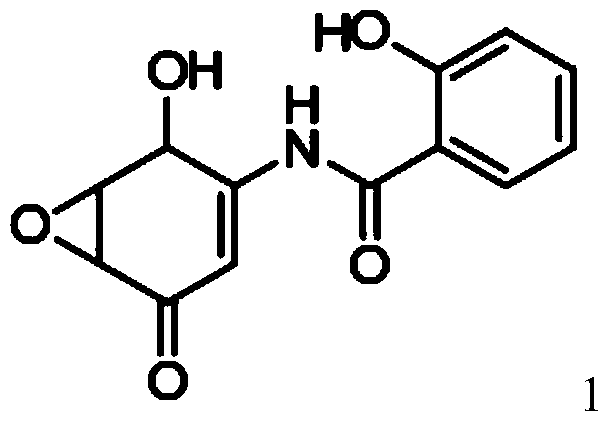
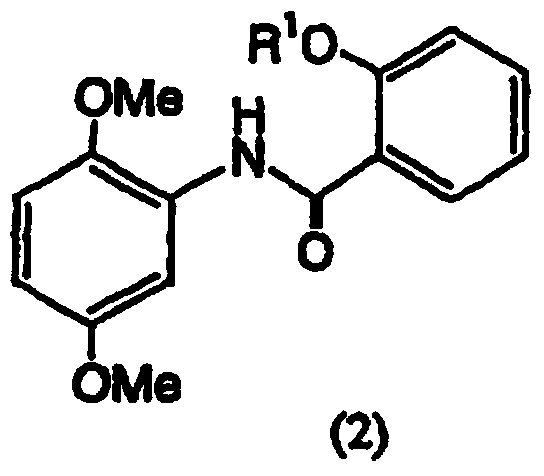
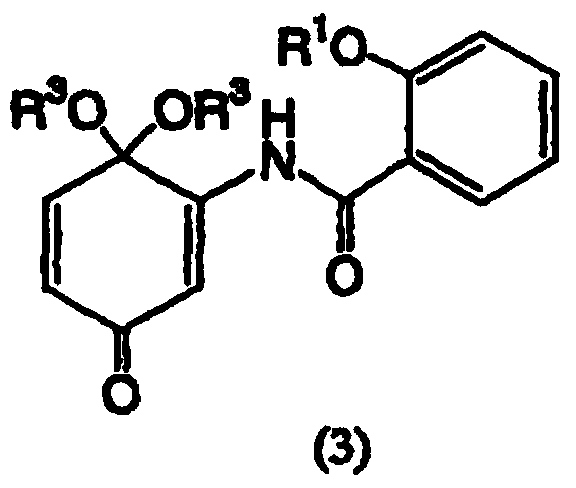
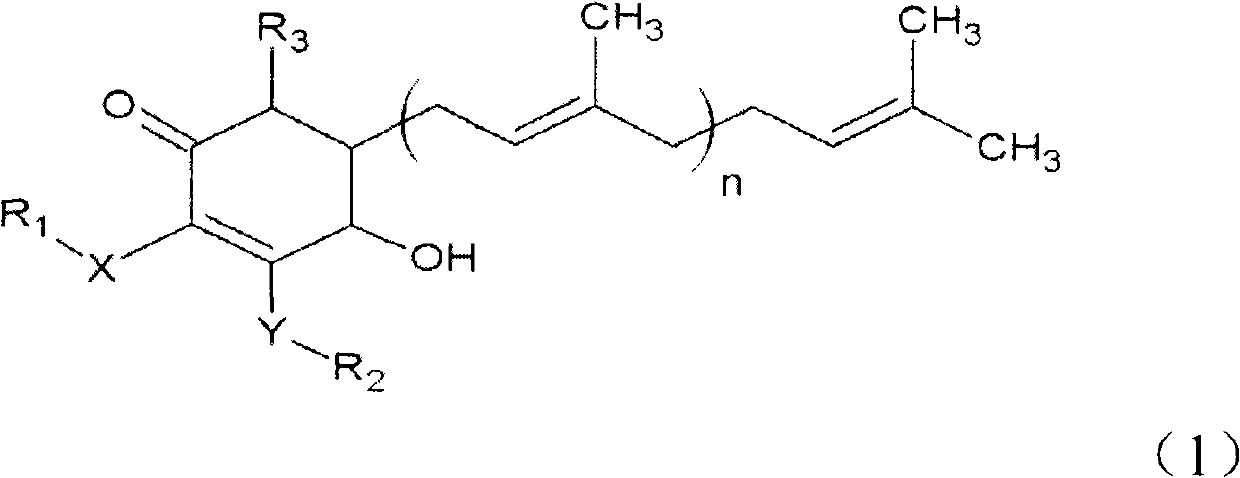
Salicylamide derivatives and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of salicylamide derivatives shown in the formula 1. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 2,5-dimethoxyaniline is dissolved in an organic solvent and reacts with ethyl acetate of O-alkylacylsalicyloyl chlorine to produce N-(2-alkylacyloxyformoxy)-2,5-dimethoxyaniline; the N-(2-alkylacyloxyformoxy)-2,5-dimethoxyaniline reacts with R3OH in the presence of iodobenzene diacetate to produce 3-(O-alkylacylsalicyloylamino)-4,4-dialkoxy-2,5-cyclohexadienone; in an organic solvent (such as tetrahydrofuran, methanol and dimethyl formamide and especially such as dimethyl formamide), the 3-(O-alkylacylsalicyloylamino)-4,4-dialkoxy-2,5-cyclohexadienone undergoes a reaction in the presence of a hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution and an inorganic base to produce 5,6-epoxy-4,4-dialkoxy-3-salicyloylamido-2-cyclohexenone; the 5,6-epoxy-4,4-dialkoxy-3-salicyloylamido-2-cyclohexenone undergoes a reaction in the presence of a boron trifluoride ether complex to produce 5,6-epoxy-2-salicyloylamido-2-cyclohexenyl-1,4-dione; and the 5,6-epoxy-2-salicyloylamido-2-cyclohexenyl-1,4-dione is reduced into 5,6-epoxy-4-hydroxy-3-salicyloylamido-2-cyclohexenone (DHM2EQ) shown in the formula (1). The invention also relates to a preparation method of the 5,6-epoxy-4-hydroxy-3-salicyloylamido-2-cyclohexenone.
Owner:SHENZHEN WANHE PHARMA
Preparation of 2-pimelie kelone compound
ActiveCN101412667BEasy to operatePromote reaction efficiencyOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCyclohexenoneChemical products
The invention discloses a method for preparing 2-cyclohexenone compound, which comprises the following steps: under the action of a metallic catalyst MYn.L, 1, 6-heptadiyne compound showed in formula (I) taken as a raw material is reacted in an ionic liquid at a temperature of between 0 and 150 DEG C; after the reaction liquid is treated, the 2-cyclohexenone compound showed in formula (II) is prepared; and at the same time, the ionic liquid fixed with the metallic catalyst can be recycled. The method has the advantages of simple and reliable operation, high yield and selectivity, repeated recycling and use of the noble metal catalyst, environmental protection, and the like. Because the cyclohexenone compound is a good raw material for synthesizing medicines, pesticides and chemical products, the method has wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Antrodia camphorata cyclohexenone compound for inhibiting skin cancer tumor cell growth
The invention relates to a new application of a compound. 4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methy-5(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone is separated and purified from antrodia camphorata extract. The cyclohexenone compound can be applied to inhibition of skin cancer tumor cell growth, and also can be applied to medicinal compositions for inhibiting skin cancer tumor cell growth.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
Application of antrodia camphorata cyclohexenone compound in preparing medicine for inhibiting growth of pancreatic cancer tumor cells
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
Cyclohexenone extract of antrodia camphorata
ActiveCN101225066BAvoid mutationAntioxidant capacity is quiteOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationCyclohexenoneProstate cancer
The invention discloses a new compound and the usage, in particular to a 4-hydroxy-2, 3- dimethoxy -6-methyl-5 (3, 7, 11- trimethyl-2, 6, 10-dodecatrien) -2- cyclohexenone (4-hydroxy- 2, 3-dimethoxy -6- methy-5 (3, 7, 11-trimethyl -dodeca-2, 6, 10- trienyl) -cyclohex-2-enone) separated from antrodia camphorate extract and the application in inhibiting the growth of tumor cell. The new compound isfirstly seen in antrodia camphorate. The 4-hydroxy-2, 3- dimethoxy -6-methyl-5 (3, 7, 11- trimethyl-2, 6, 10-dodecatrien) -2- cyclohexenone (4-hydroxy- 2, 3-dimethoxy -6- methy-5 (3, 7, 11-trimethyl -dodeca-2, 6, 10- trienyl) -cyclohex-2-enone) separated from antrodia camphorate extract and the application in inhibiting the growth of tumor cell has the advantages of inhibiting the growth of breast cancer, liver cancer and prostate cancer tumor cell, being a component of drug combination inhibiting the growth of the tumor cell at the same time or further being applied in preventing cardiovascular disease or being added into healthy food by right of antioxidant activity.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
Preparation method for intermediate II during meptazinol hydrochloride synthesis process
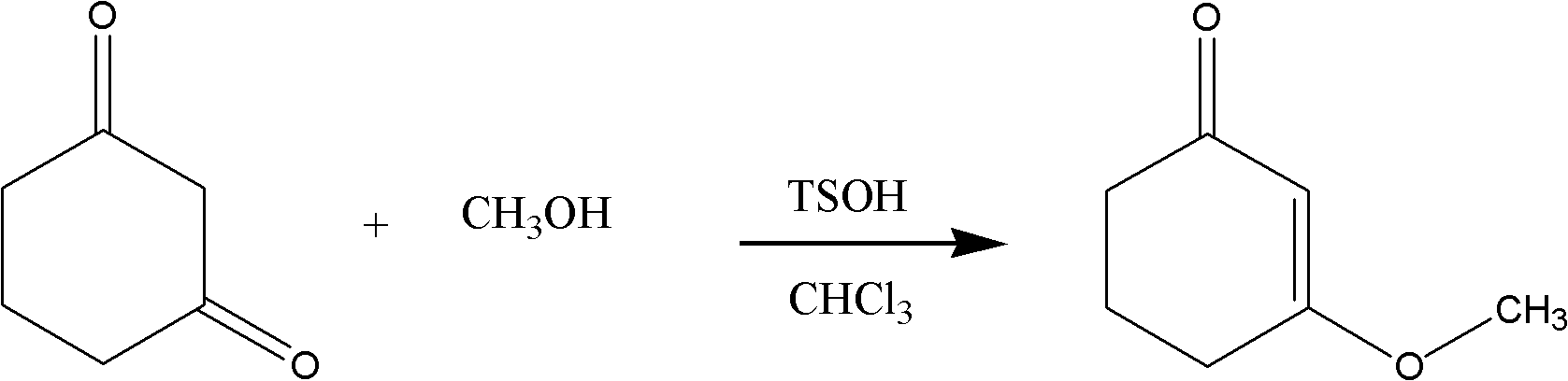
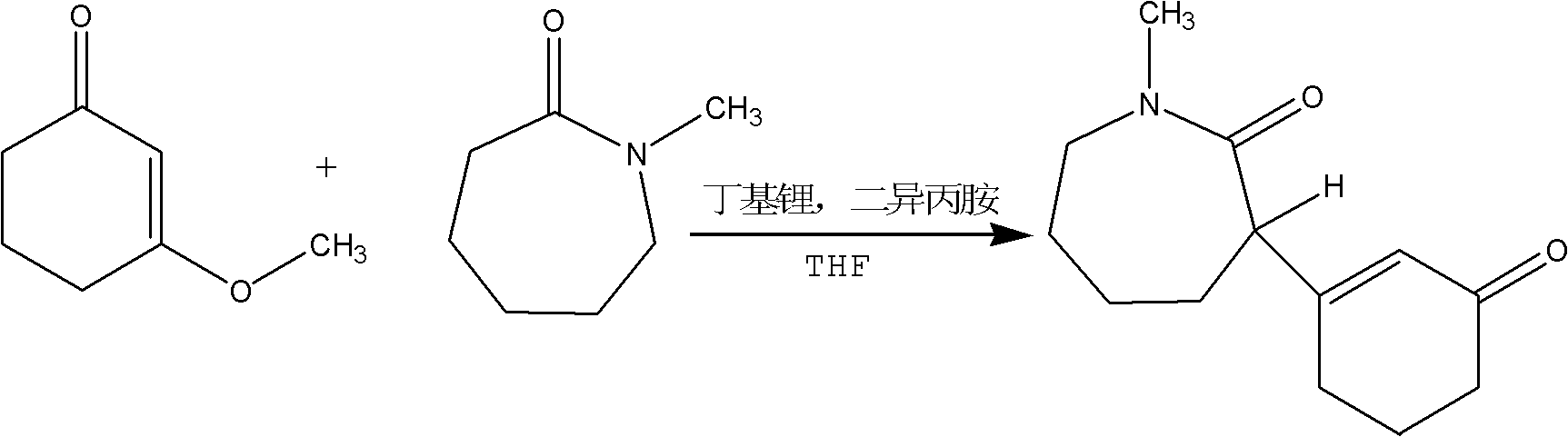
The present invention discloses a preparation method for a meptazinol hydrochloride intermediate II hexahydro-1-methyl-3-(3-oxo-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2H-azepin-2-one. According to the present invention, methanol is adopted to replace isopropanol to complete synthesis of an intermediate I 3-methoxy-2-cyclohexenone in the prior art, hydrochloric acid is slowly added to the material in a dropwise manner during the intermediate II synthesis process, and chloroform is adopted to extract the product (wherein the chloroform is more easily recovered than dichloromethane). The preparation process of the present invention has characteristics of mild production condition requirements, simple operation, high yield, and easily-recovered solvent.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER PHARM GRP SICHUAN HAIRONG PHARM CO LTD
Antrodia camphorata cyclohexenone compound for inhibiting colorectal cancer tumor cell growth
The invention relates to a new application of a compound and a medicinal composition for inhibiting colorectal cancer tumor cell growth. 4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methy-5(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone is separated and purified from antrodia camphorata extract. The cyclohexenone compound can be applied to inhibition of colorectal cancer tumor cell growth, and also can beapplied to medicinal compositions for inhibiting colorectal cancer tumor cell growth.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
Novel synthetic method for 4-(1,5-dimethyl-1-vinyl-4-hexenyl) phenol
InactiveCN1295204CFew reaction stepsEasy to operateOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationDehydrogenationKetone
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antrodia camphorata cyclohexenone compound for suppressing growth of bladder cancer tumor cells
The invention relates to a new use of a compound. In the invention, (4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methy-5(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone is obtained from the extract of Antrodia camphorate by separation and purification, and the cyclohexenone compound can be used for suppressing the growth of the bladder cancer tumor cells and can be used in medical compositions for suppressing the growth of bladder cancer tumor cells.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
A kind of synthetic method of astaxanthin intermediate
ActiveCN107739390BShort routeSave raw materialsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsBetaxanthinsAstaxanthin
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing an astaxanthin intermediate. The method specifically comprises the following steps: 1) adding lithium into liquid ammonia to implement a reaction, introducing acetylene to synthesize acetylene-based lithium, replacing the liquid ammonia with an organic solvent, and adding 1-butene-3-ketone to implement a reaction continuously, so as to generate 3-methyl-1-amylene-4-alkyne-3-lithium alkoxide; 2) adding lithium into the liquid ammonia to implement a reaction, and further adding the product obtained in the step 1) to generate 3-methyl-1-amylene-4-alkynyl based lithium-3-lithium alkoxide; 3) performing a condensation reaction on the product obtained in the step 2) with heterogeneous diketone so as to generate a condensation compound; 4) performing acid hydrolysis on the condensation compound obtained in the step 3), and treating with a reduction triple bond so as to obtain 2,4,4-trimethyl-6-hydroxy-3-(3-methyl-1,4-dipentene-3-hydroxy)-2-cyclohexenone; 5) enabling 2,4,4-trimethyl-6-hydroxy-3-(3-methyl-1,4-dipentene-3-hydroxy)-2-cyclohexenone to react with hydrobromic acid and triphenylphosphine in sequence, thereby finally generating the astaxanthin intermediate. By adopting the method, multiple times of introduction and repeated hydrolysis of extra protection groups are avoided, so that the raw materials are saved, and the preparation route is simplified.
Owner:SHANGYU NHU BIOCHEM IND
Synthetic method for 4-(1,5-dimethyl-1-vinyl-4-hexenyl) phenol
InactiveCN1254461CFew reaction stepsEasy to operateOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationHexahydropyridineEnamine
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing 4-(1,5-dimethyl-1-vinyl-4-hexenyl)phenol. 4-(1,5-Dimethyl-1-vinyl-4-hexenyl)phenol is also known as an antifeedant. The disadvantage of the current synthesis method of this substance is that there are many synthesis steps, most of which are between 5 and 15 steps , the reaction conditions are complicated, the reagents used are expensive, and the yield is also low. The method of the present invention uses geraniol as a raw material, reacts with vinyl ether to obtain 3-vinyl citronellal through Claisen rearrangement, and then reacts with hexahydropyridine for enamination and then conjugates with butenone Addition and cyclocondensation give 4-(1,5-dimethyl-1-vinyl-4-hexenyl)-2-cyclohexenone, and then dehydrogenate to get the product. The method uses natural products as raw materials, and the reaction process is simple to operate, easy to realize, high in selectivity and high in yield.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

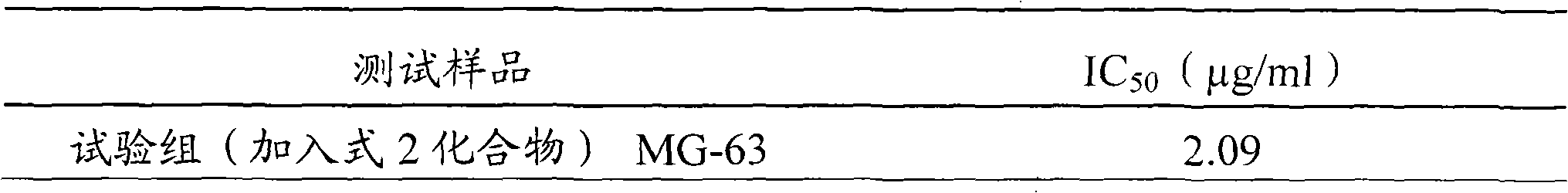
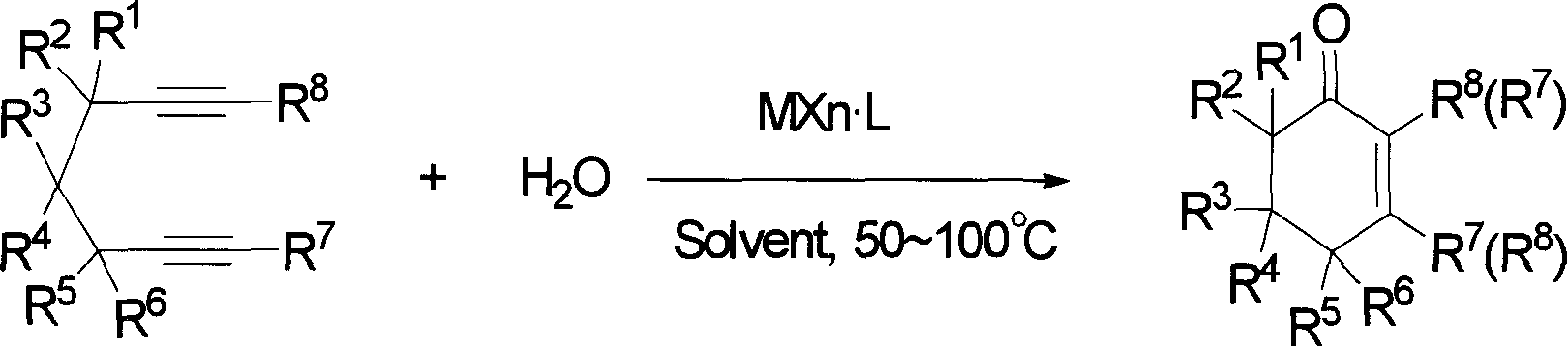
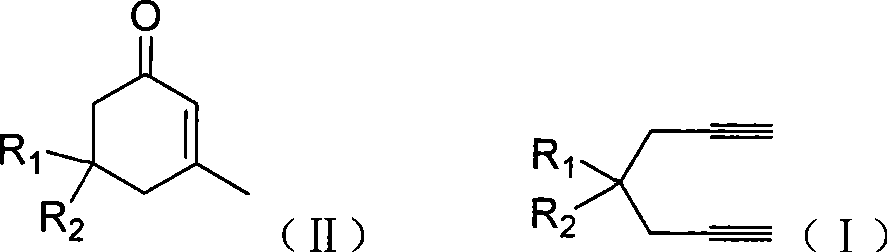
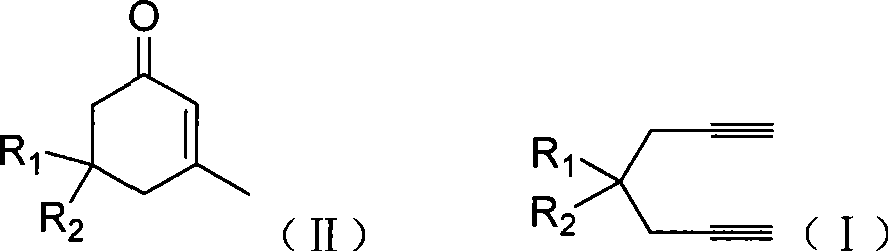


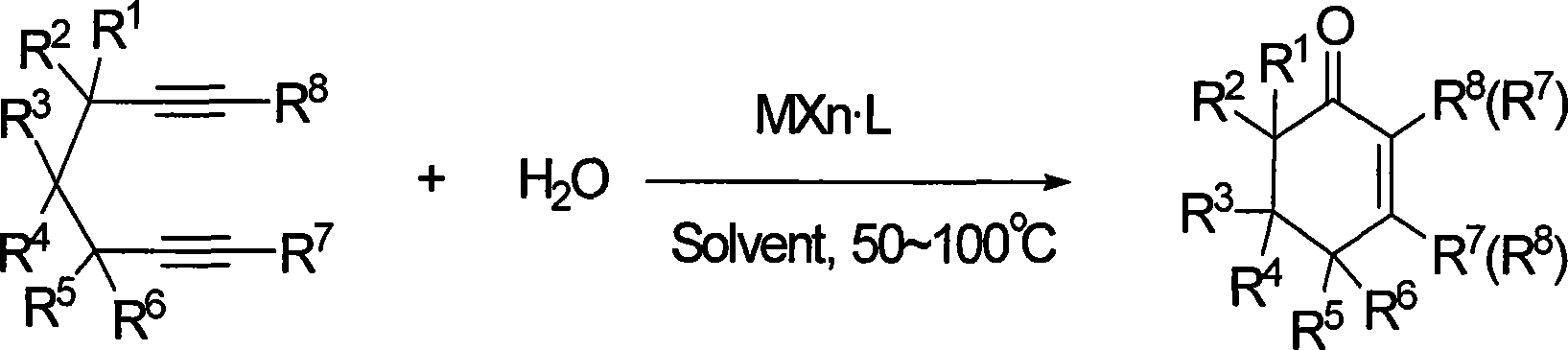
![Synthetic method of [60] fullerocyclopentanone and [60] fullero 2-cyclohexenone compounds Synthetic method of [60] fullerocyclopentanone and [60] fullero 2-cyclohexenone compounds](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a310dbf3-1f2b-44ae-98bb-8b39c9564e4c/BDA0001733490590000011.png)
![Synthetic method of [60] fullerocyclopentanone and [60] fullero 2-cyclohexenone compounds Synthetic method of [60] fullerocyclopentanone and [60] fullero 2-cyclohexenone compounds](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a310dbf3-1f2b-44ae-98bb-8b39c9564e4c/BDA0001733490590000031.png)
![Synthetic method of [60] fullerocyclopentanone and [60] fullero 2-cyclohexenone compounds Synthetic method of [60] fullerocyclopentanone and [60] fullero 2-cyclohexenone compounds](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a310dbf3-1f2b-44ae-98bb-8b39c9564e4c/BDA0001733490590000041.png)