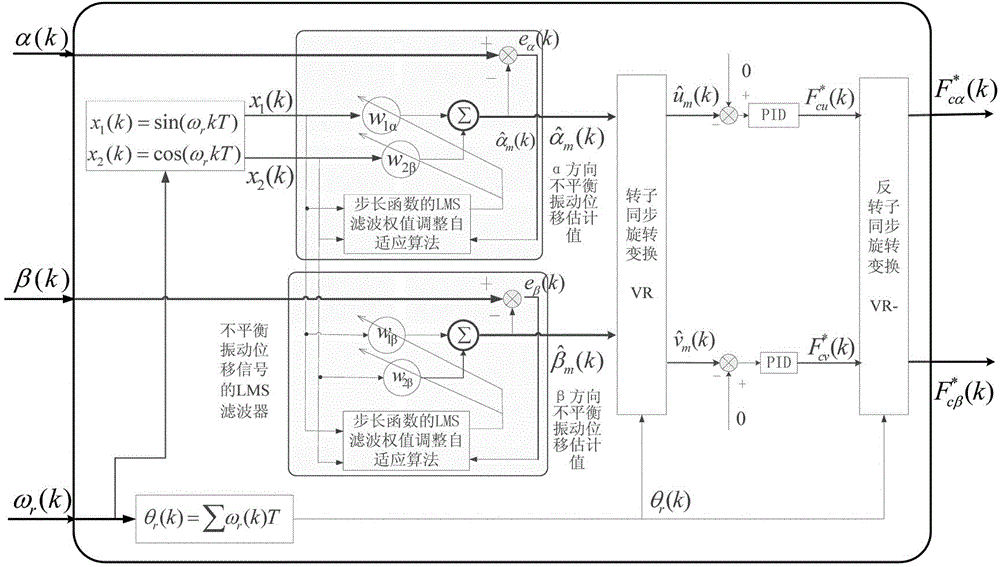
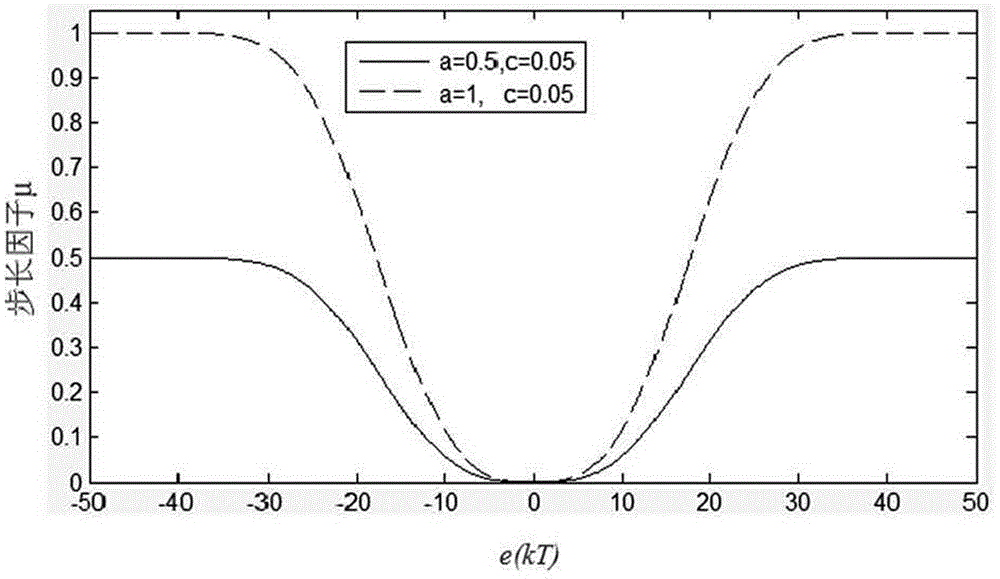
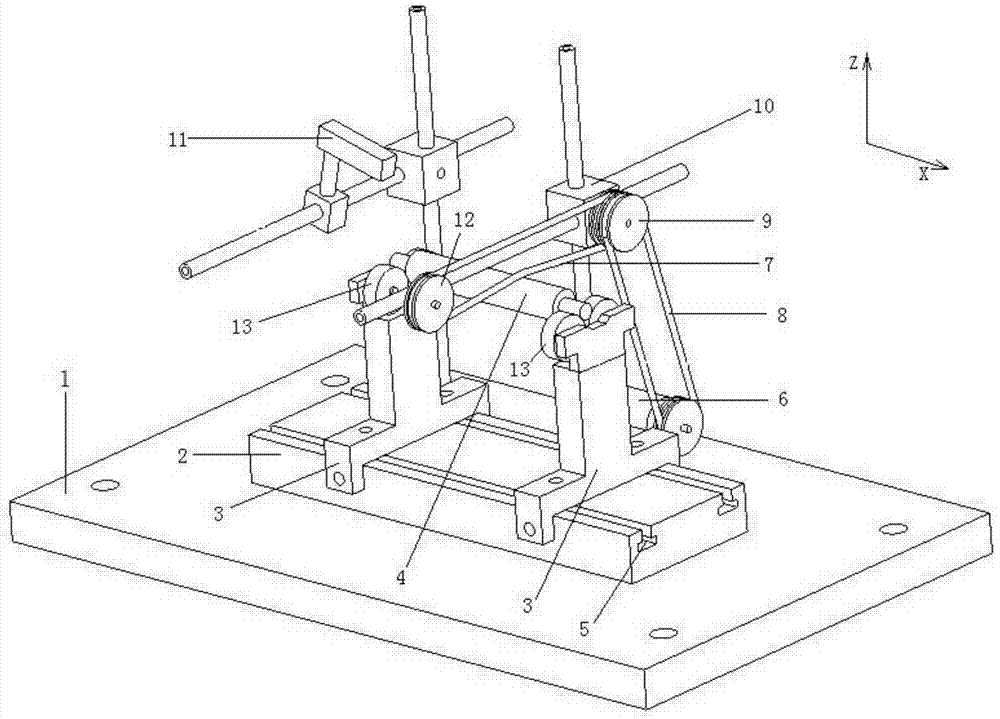
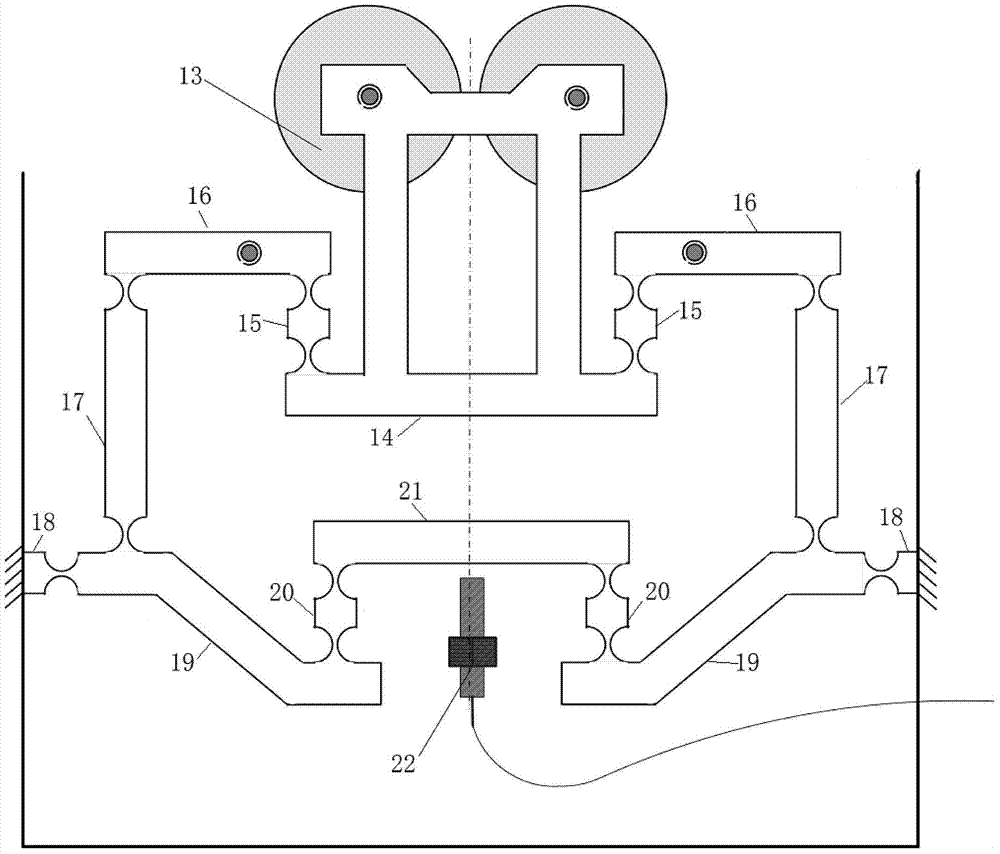
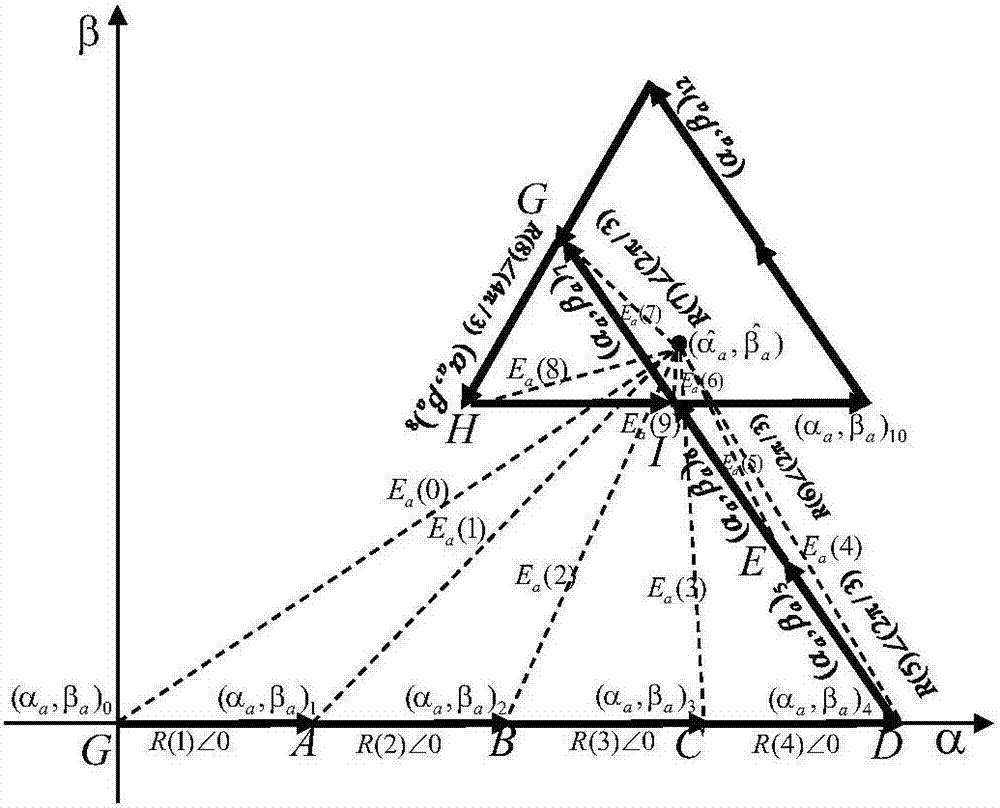
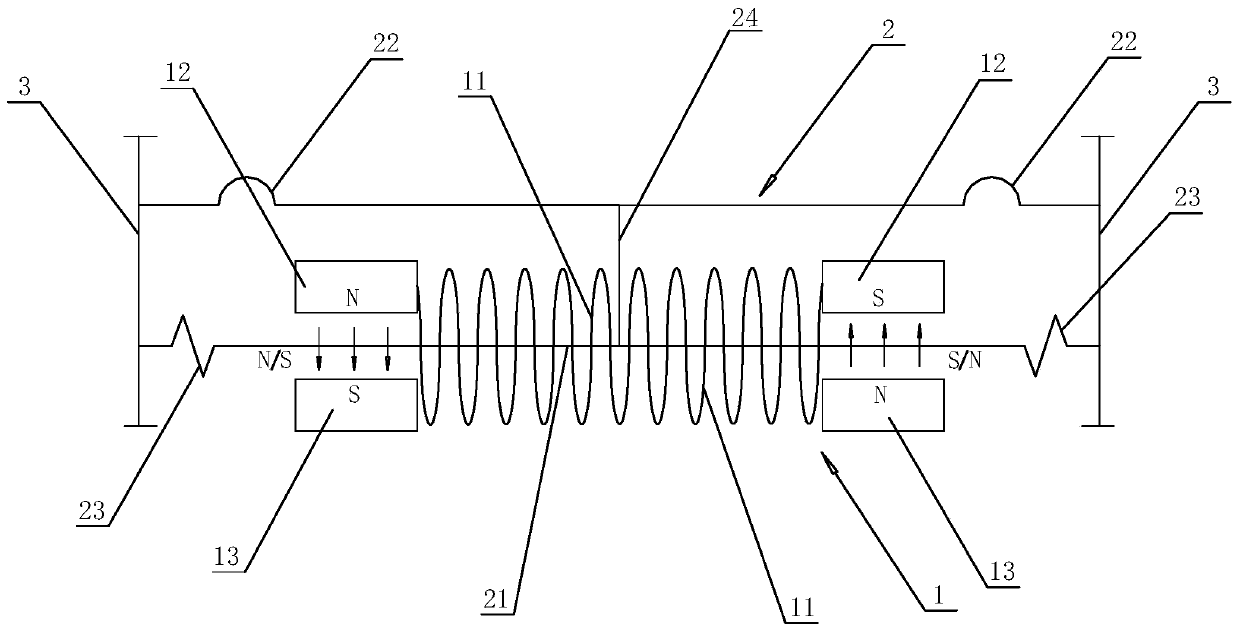
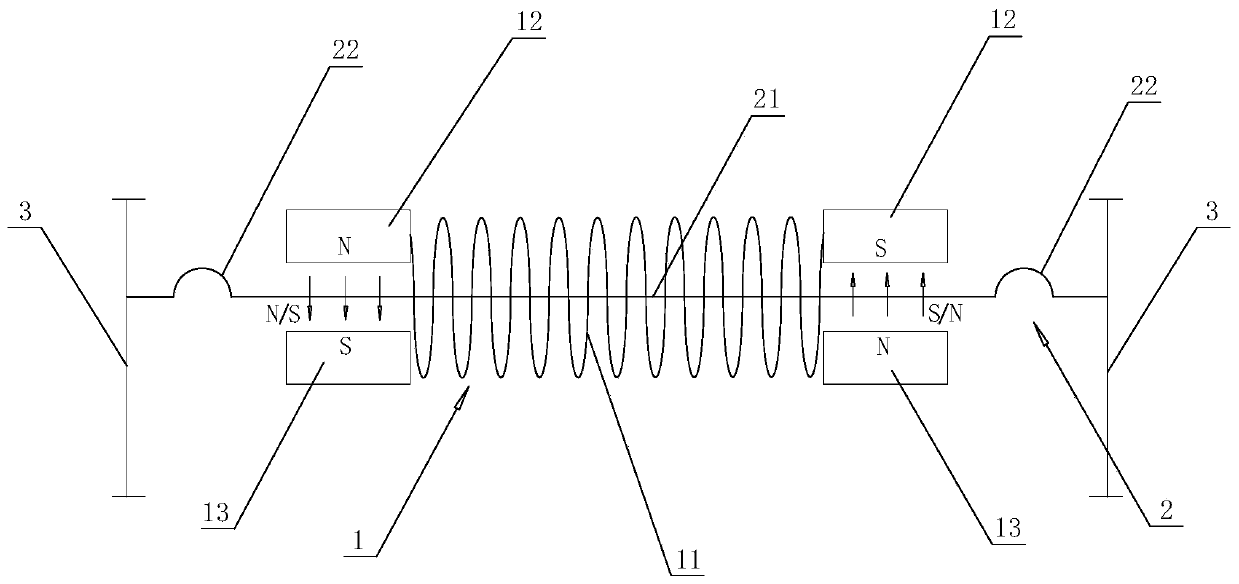
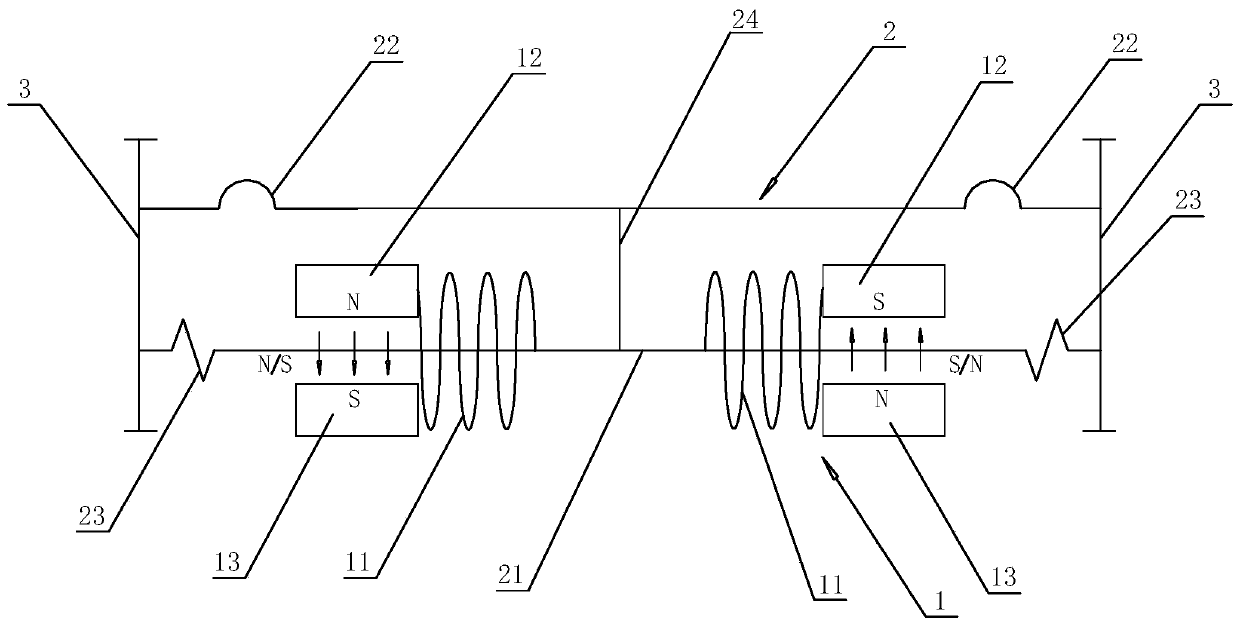
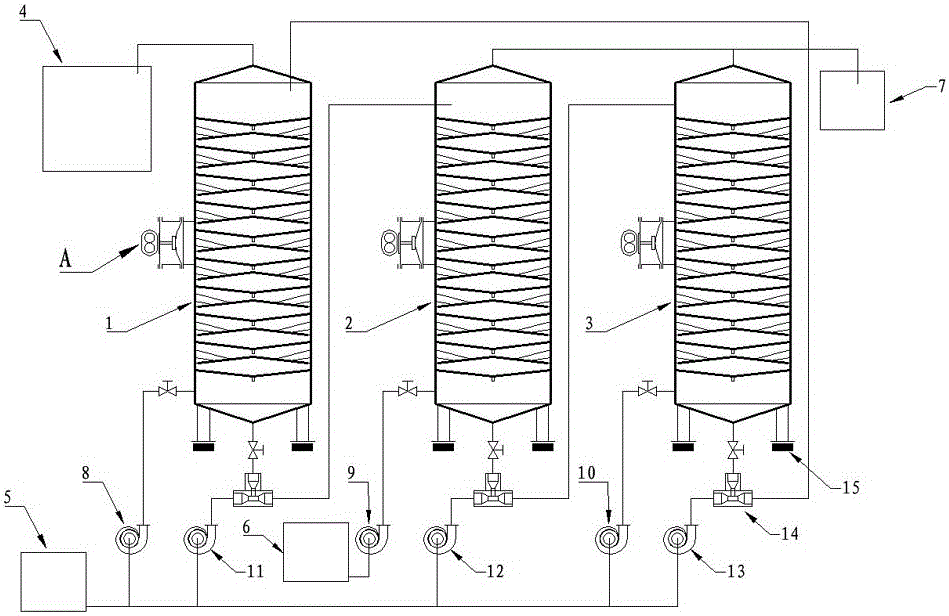
Patents
Literature
127 results about "Balancing vibrations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
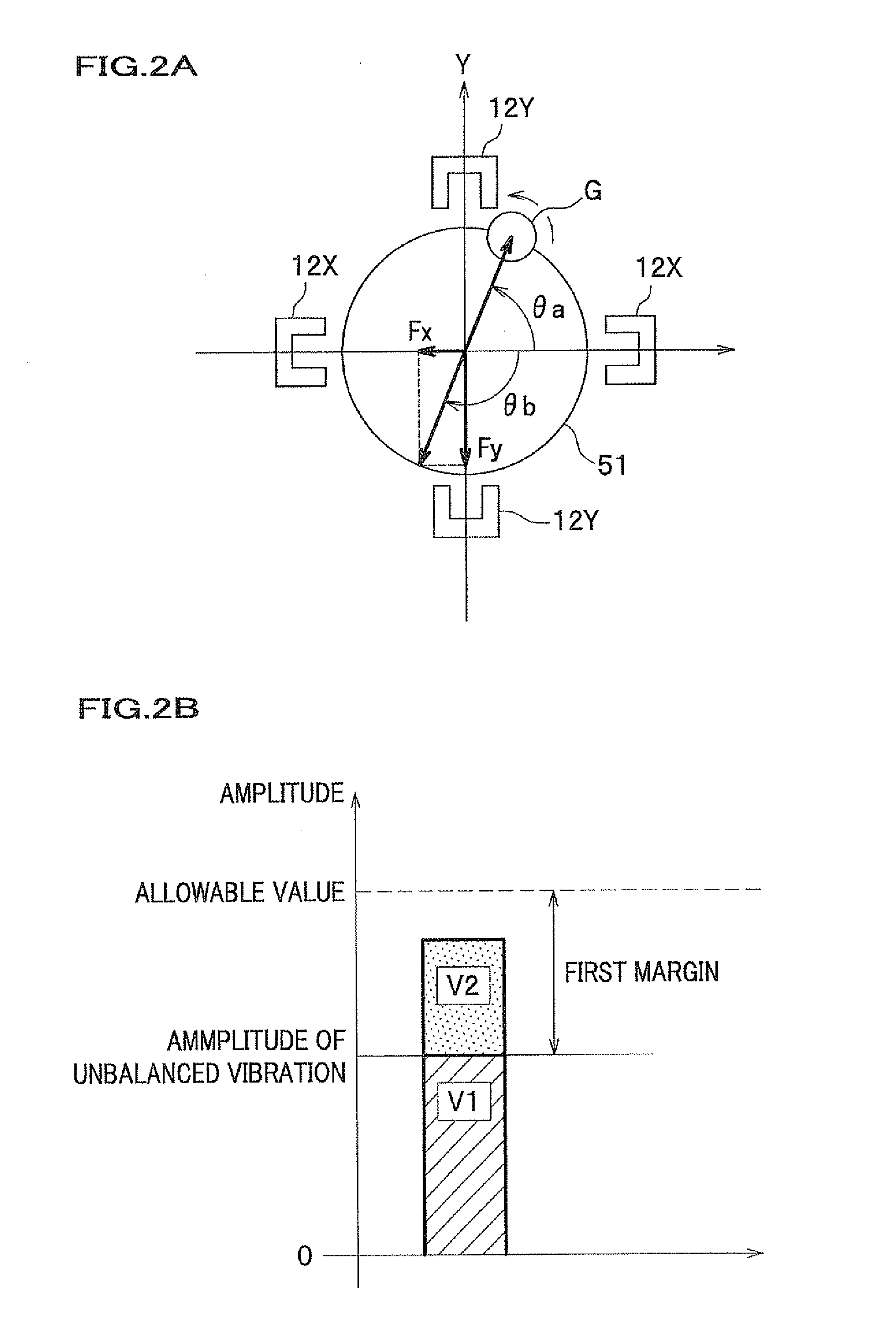
Balancing is a process of correcting or eliminating, either partially of completely, the effects due to inertia forces and couples acting on the machine parts or components. thus purpose of balancing is to avoid the vibration of the machine by balancing the resultant inertia forces and couples. Vibration can have huge effects on the balancing and efficiency of vehicles and machinery. Over time excessive vibrations can even lead to damage to your vehicle or machinery, resulting in expensive replacement or repair costs. A huge variety of machinery is at risk from long term vibration damage including high speed tooling machines, generators, compressors, fans and electric motors. All kinds of vehicles are also at risk, especially high speed vehicles, where mechanical failure can result in catastrophic injuries. The balancing is highly essential, especially in high speed applications such as electric motors, generators, turbines, pumps, air crafts etc.
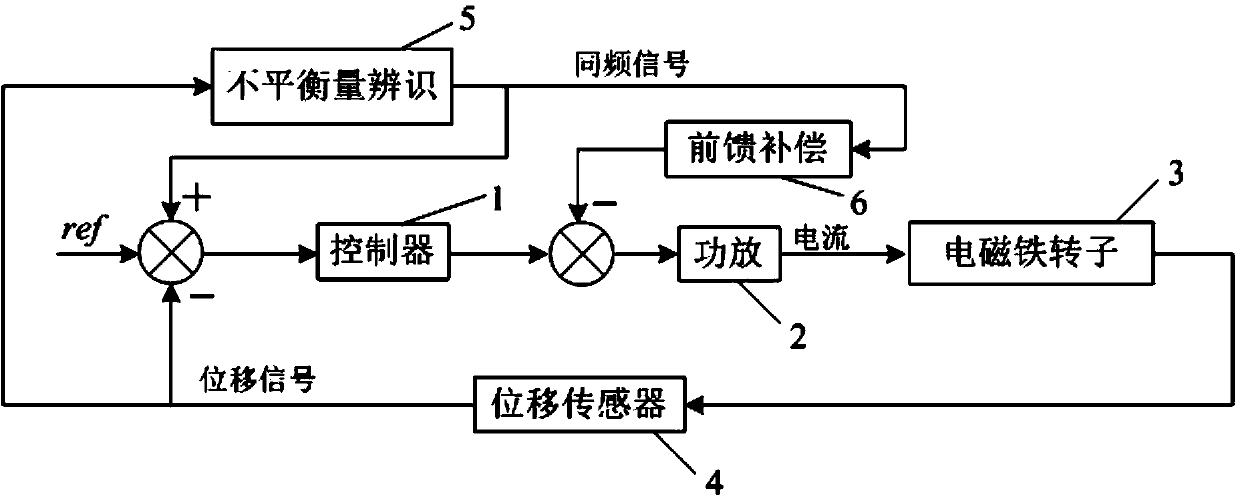
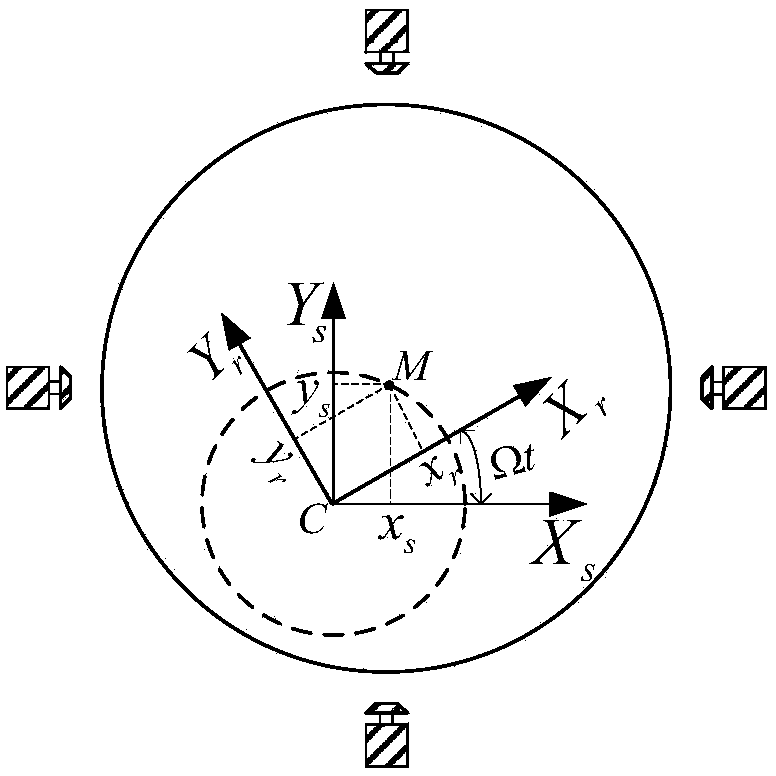
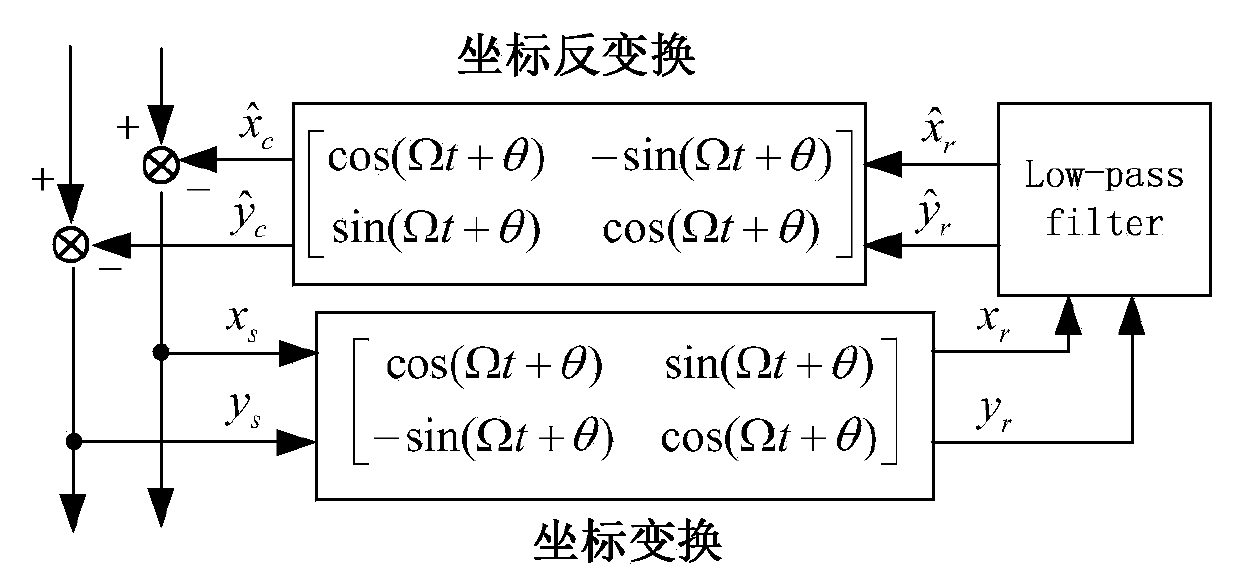
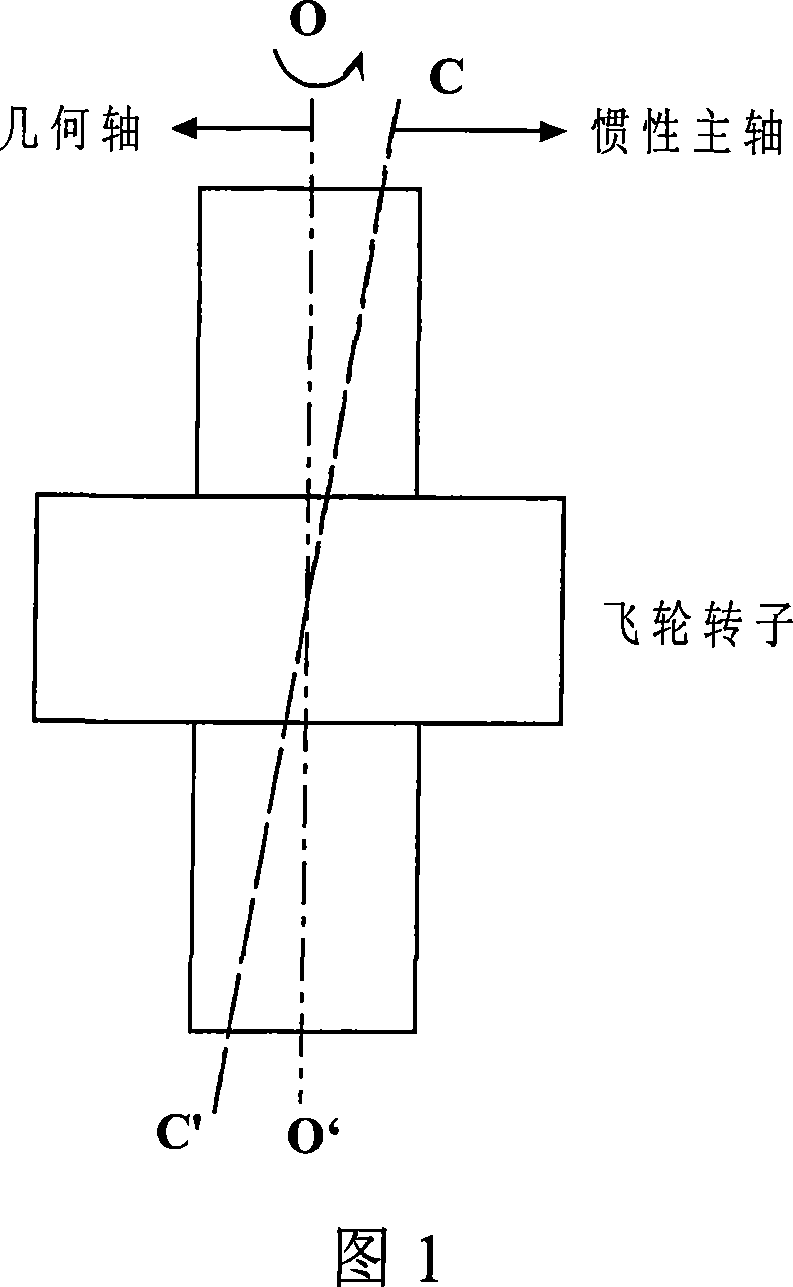
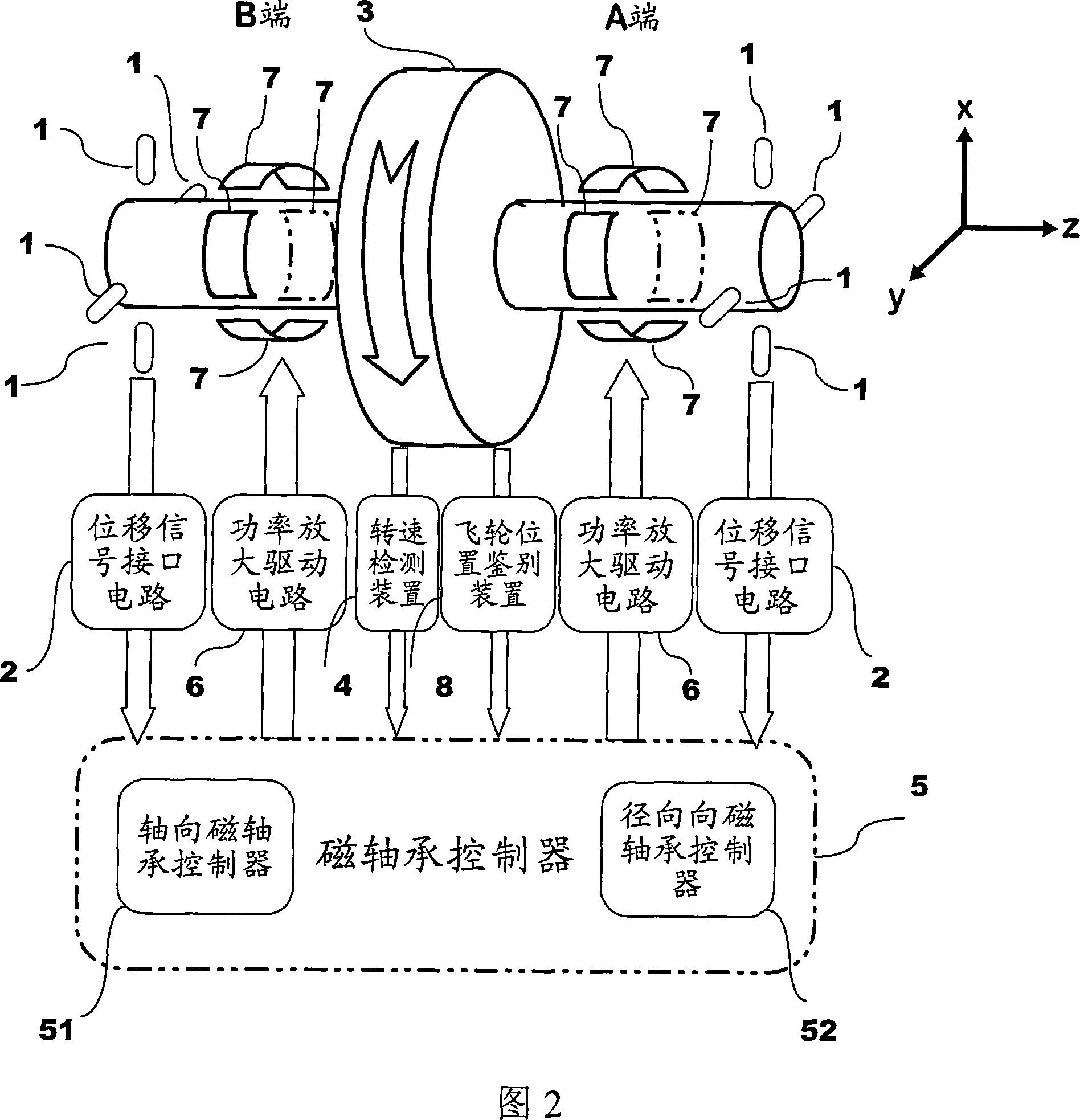
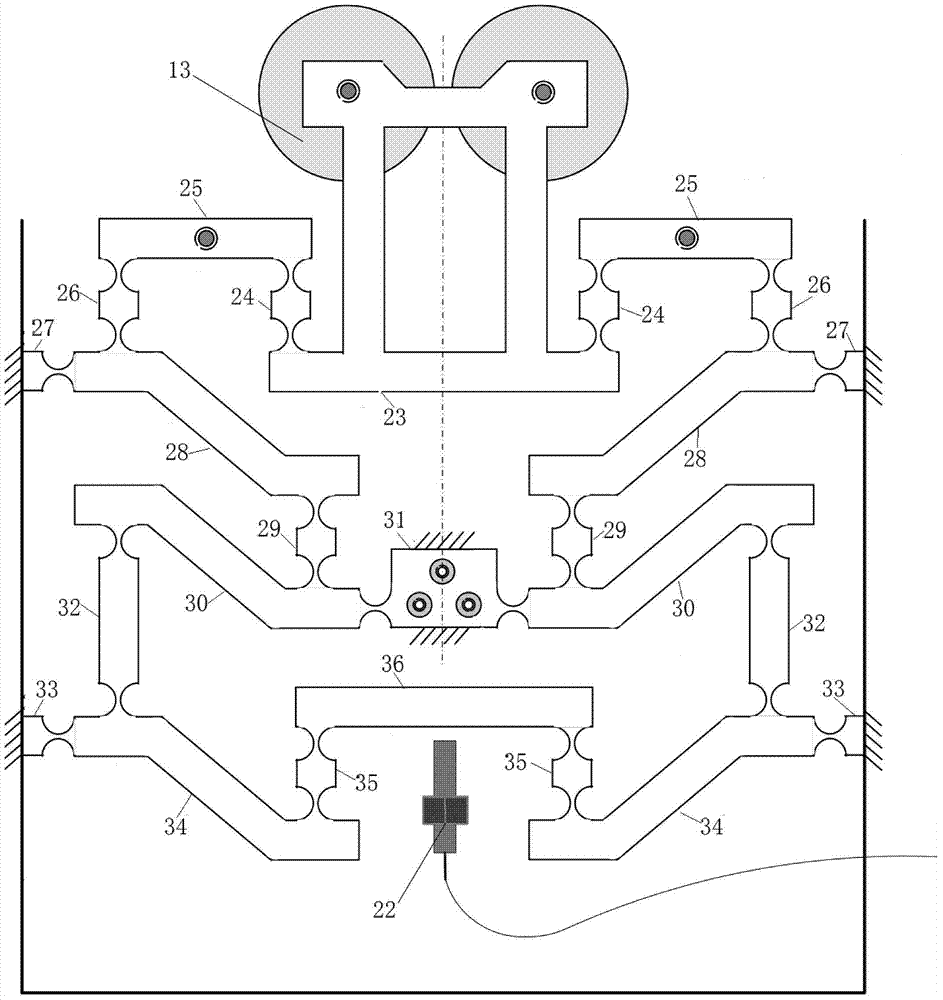
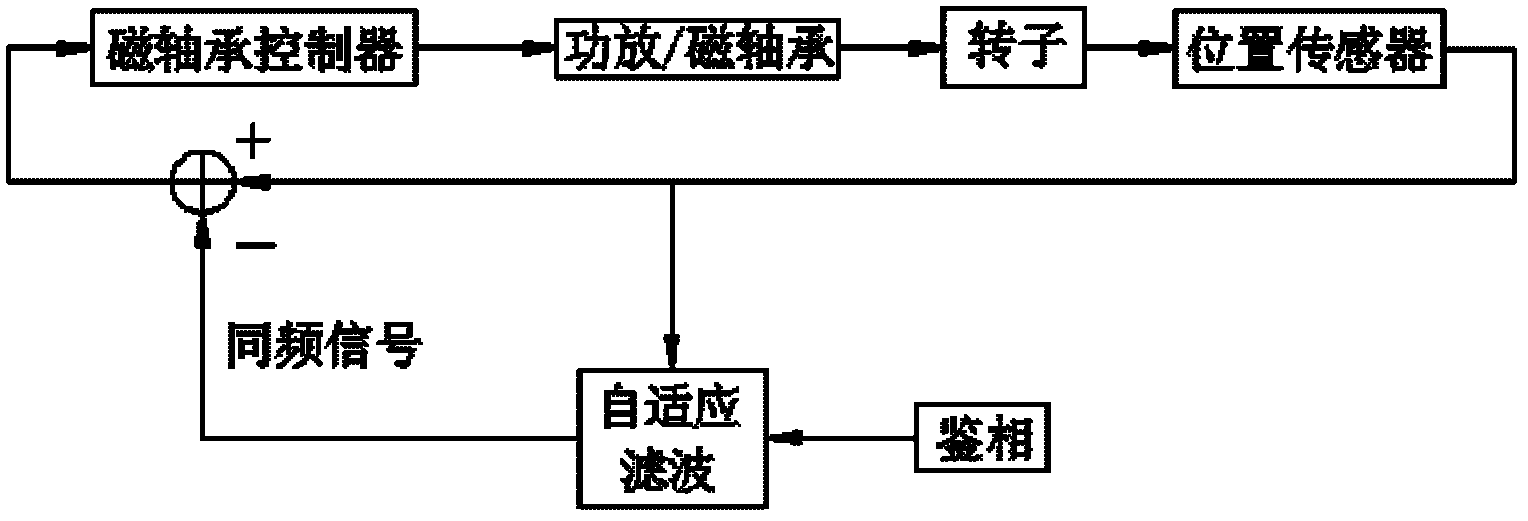
Unbalance identification and vibration suppression control system for magnetic suspension rotating machinery
ActiveCN103425051AHigh compensation accuracyOvercoming Compensation Attenuation ProblemsMechanical oscillations controlAdaptive controlMagnetic bearingStabilization control
An unbalance identification and vibration suppression control system for a magnetic suspension rotating machinery comprises an unbalance identification module, an unbalanced force compensation module, a magnetic bearing power amplifier, an electromagnet rotor and a displacement sensor. Based on stable control of a magnetic suspension rotor, the unbalance of a magnetic bearing is identified in an online manner by a novel wave trap based on coordinate transformation, on one hand, the identification amount is used for compensating common-frequency current stiffness force, on the other hand, proper common-frequency current stiffness force is generated according to the identification amount to compensate common-frequency displacement stiffness force, and the influence of the low-pass characteristic of the power amplifier on compensation precision of the common-frequency displacement stiffness force is eliminated by leading a simplified inverse model of the magnetic bearing power amplifier into a feed-forward channel. When the magnetic suspension rotor rotates at a high speed, common-frequency bearing force is greatly reduced, and unbalanced vibration of the magnetic suspension rotor is remarkably suppressed. The unbalance identification and vibration suppression control system is simple, convenient, easy and particularly suitable for an actual high-speed magnetic suspension rotor system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Split-ring high precision unbalance vibration control system of magnetic suspension reaction flywheel
InactiveCN101046692AFix stability issuesRealization of high-precision unbalanced vibration controlIgnition automatic controlAttitude controlVibration controlMagnetic bearing
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Magnetic levitation flywheel high precision initiative vibration control system
InactiveCN101261496AAchieve high-precision active vibration controlElectric controllersMagnetic tension forceMagnetic bearing
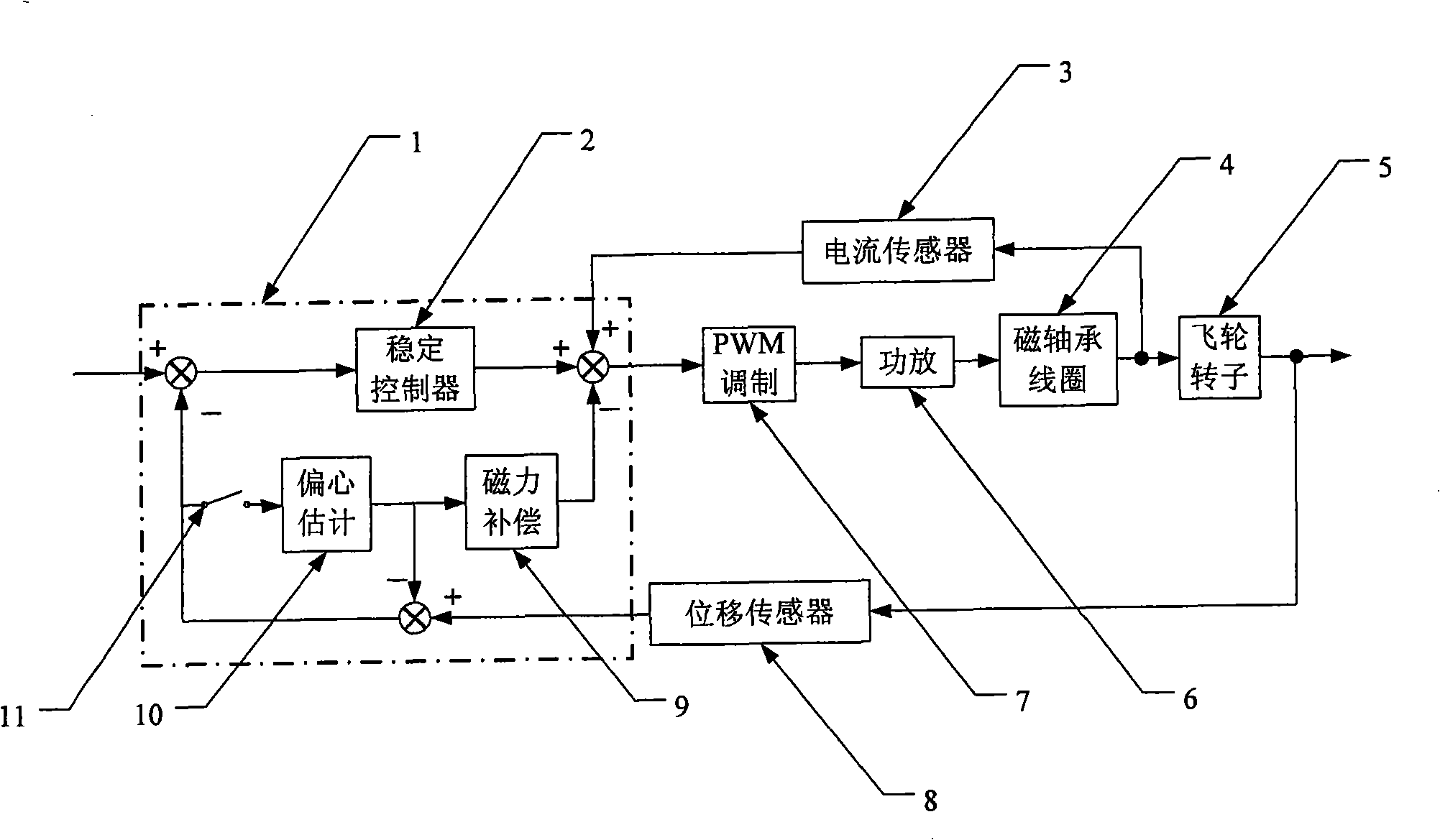
A magnetic levitation flywheel high-precision active vibration control system comprises a displacement sensor, a current sensor, a magnetic bearing controller and a PWM modulation and a power amplifier, wherein, the magnetic bearing controller comprises stabilization of the controller, eccentric estimation, magnetic force compensation and action of a switch. The magnetic levitation flywheel high-precision active vibration control system introduces the eccentric estimation and the magnetic force compensation on the basis of the stable control and utilizes the unbalance vibration parameters of a flywheel to carry out the compensation of the unbalance amount and the displacement negative stiffness of the flywheel within the entire rotation speed range, thus realizing the control of the unbalance vibration of the flywheel within the entire rotation speed range and allowing the flywheel to be operated around a principal axis of inertia with high precision during the whole process of speed increasing and speed reducing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Online elastic mode testing system for magnetically suspended electromechanical equipment
InactiveCN102169046AIncrease stimulus outputImprove discriminationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansSimulation noiseControl system
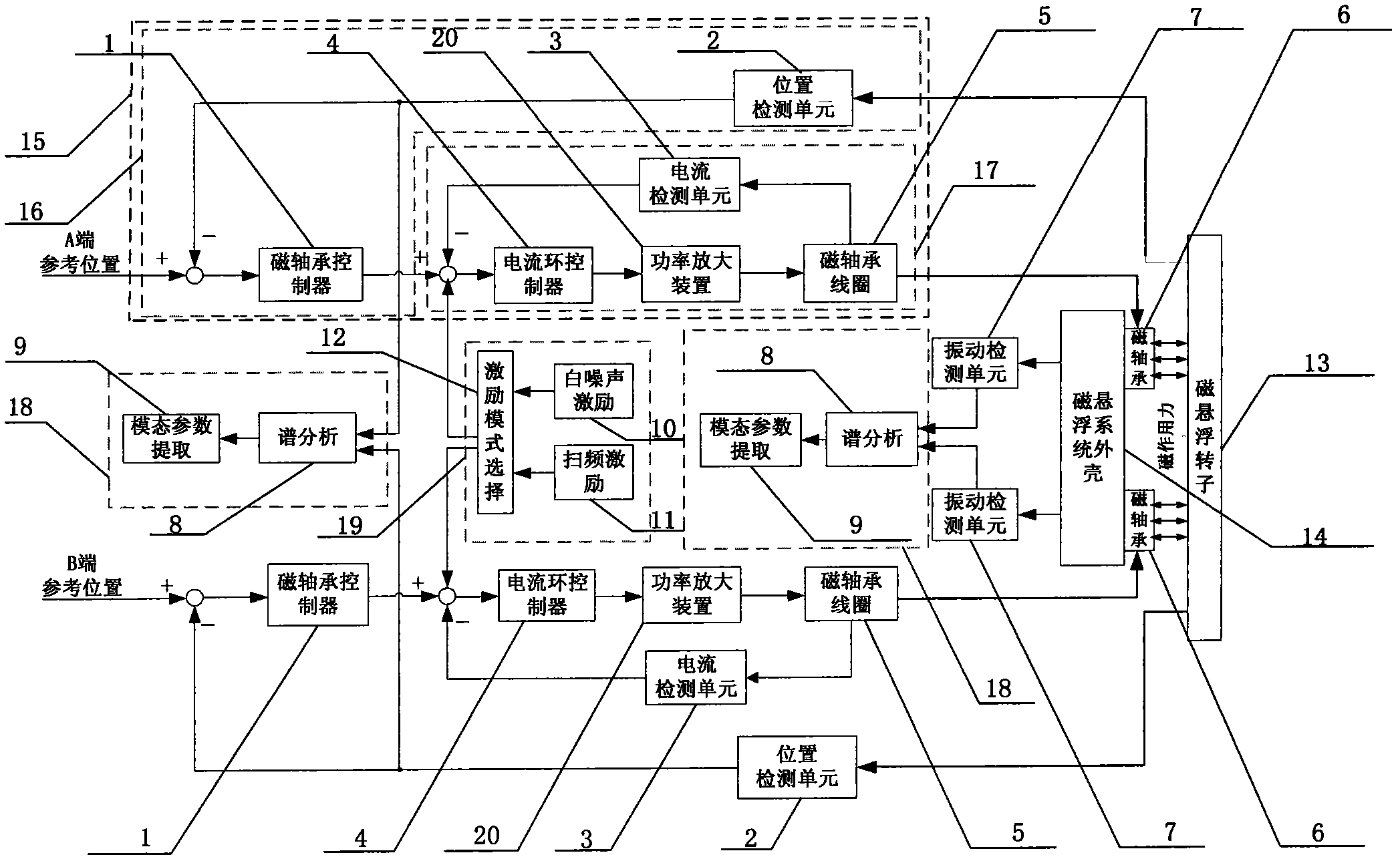
The invention discloses an online elastic mode testing system for magnetically suspended electromechanical equipment. The online elastic mode testing system mainly comprises a magnetically suspended system shell, a magnetically suspended rotor, a magnetically suspended control system, a signal excitation module, a vibration detection unit and an elastic mode recognizing module. The signal excitation module is integrated in the magnetically suspended control system, excitation force is applied to the rotor, unbalanced disturbance of translation and rotation and random environmental disturbance of the rotor are simulated, frequency sweeping excitation is increased under the gyroscopic action of a high-speed rotating rigid body, and output signals of a displacement sensor and the vibration detection unit are transmitted to the elastic mode recognizing module to obtain the translation and rotation elastic mode parameters of the rotor and the shell. By adopting the online elastic mode testing system, the influences of noise and unbalanced vibration on an elastic mode can be simulated close to the practical running state of a magnetically suspended, the frequency sweeping excitation output is increased, the near frequency discrimination of elastic modes is enhanced, a rotation elastic mode and a translation elastic mode can be distinguished, and the elastic modes of the rotor and the shell can be tested simultaneously.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
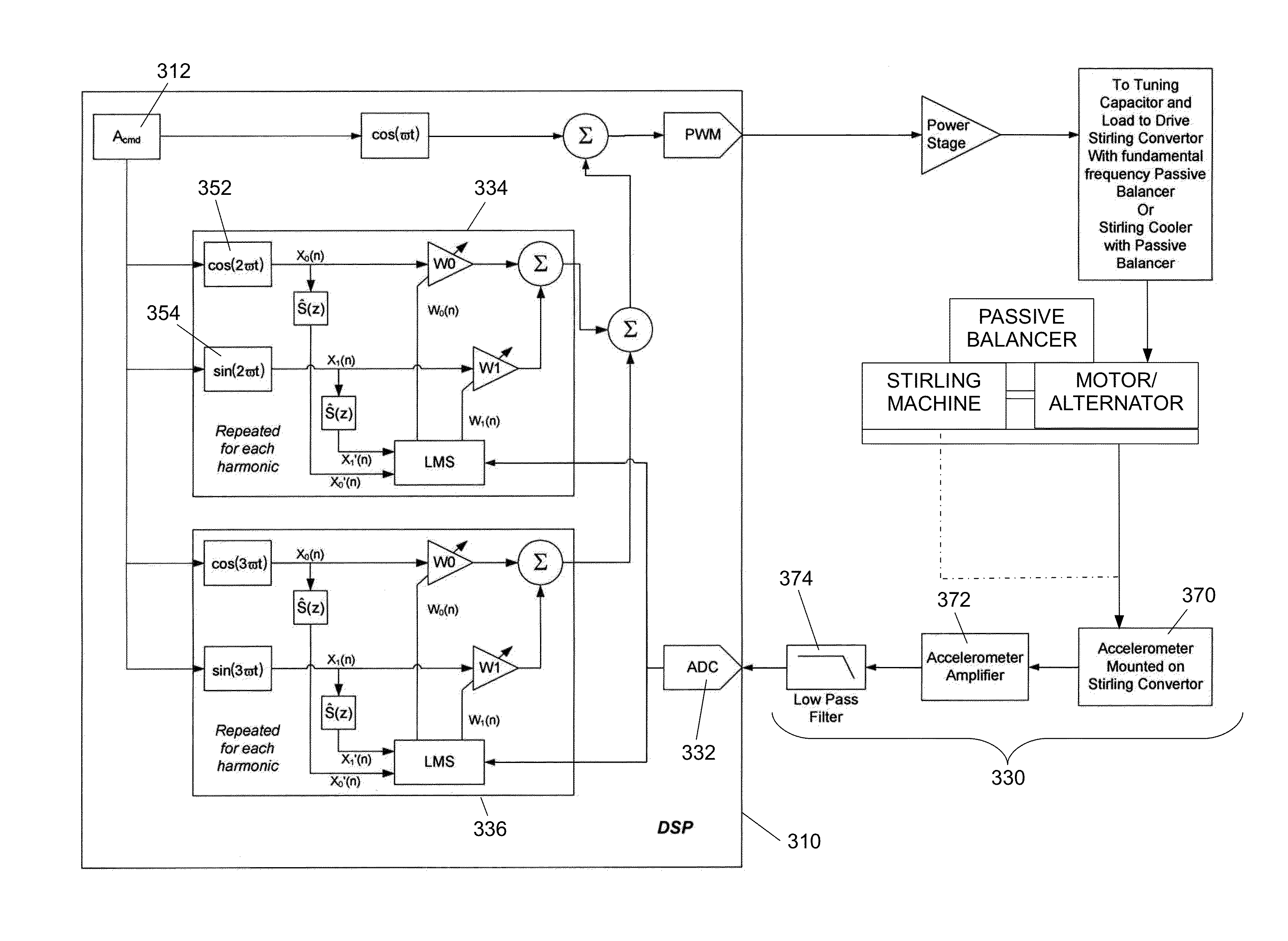
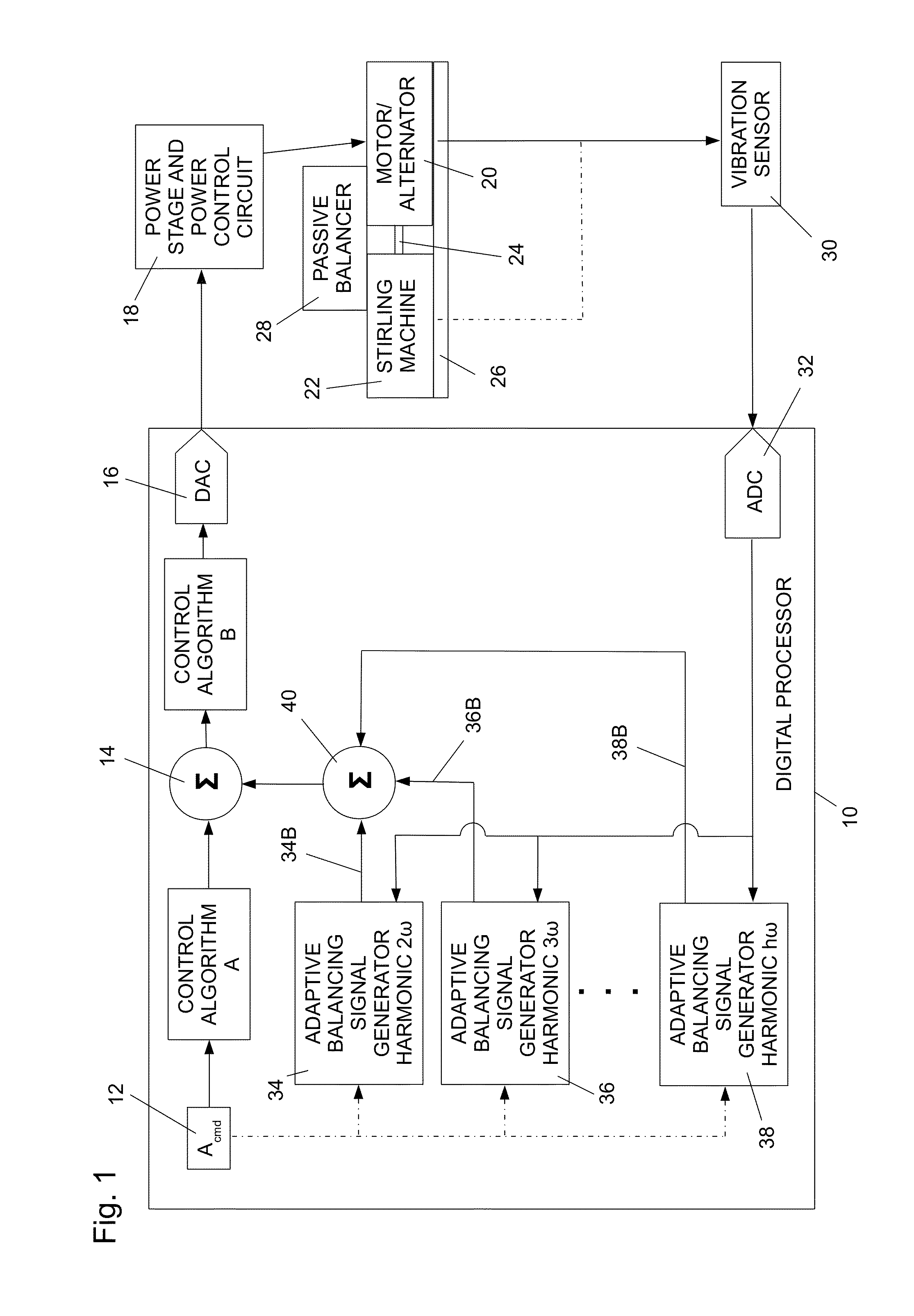
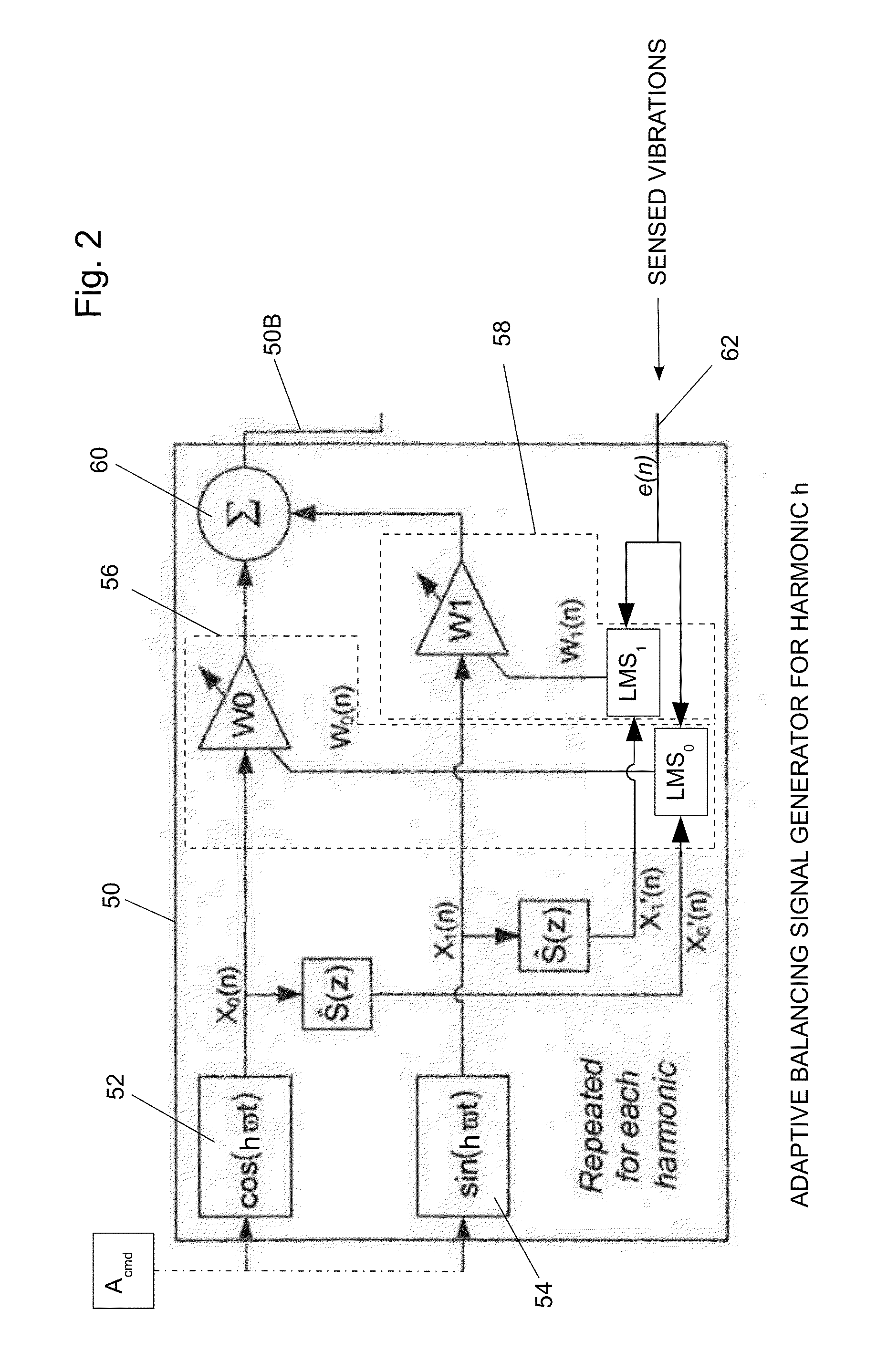
Balancing Vibrations At Harmonic Frequencies By Injecting Harmonic Balancing Signals Into The Armature Of A Linear Motor/Alternator Coupled To A Stirling Machine
ActiveUS20140015497A1Vibration minimizationMechanical oscillations controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAdaptive filtering algorithmMachining vibrations
Vibrations at harmonic frequencies are reduced by injecting harmonic balancing signals into the armature of a linear motor / alternator coupled to a Stirling machine. The vibrations are sensed to provide a signal representing the mechanical vibrations. A harmonic balancing signal is generated for selected harmonics of the operating frequency by processing the sensed vibration signal with adaptive filter algorithms of adaptive filters for each harmonic. Reference inputs for each harmonic are applied to the adaptive filter algorithms at the frequency of the selected harmonic. The harmonic balancing signals for all of the harmonics are summed with a principal control signal. The harmonic balancing signals modify the principal electrical drive voltage and drive the motor / alternator with a drive voltage component in opposition to the vibration at each harmonic.
Owner:SUNPOWER
Engine balancing system and method
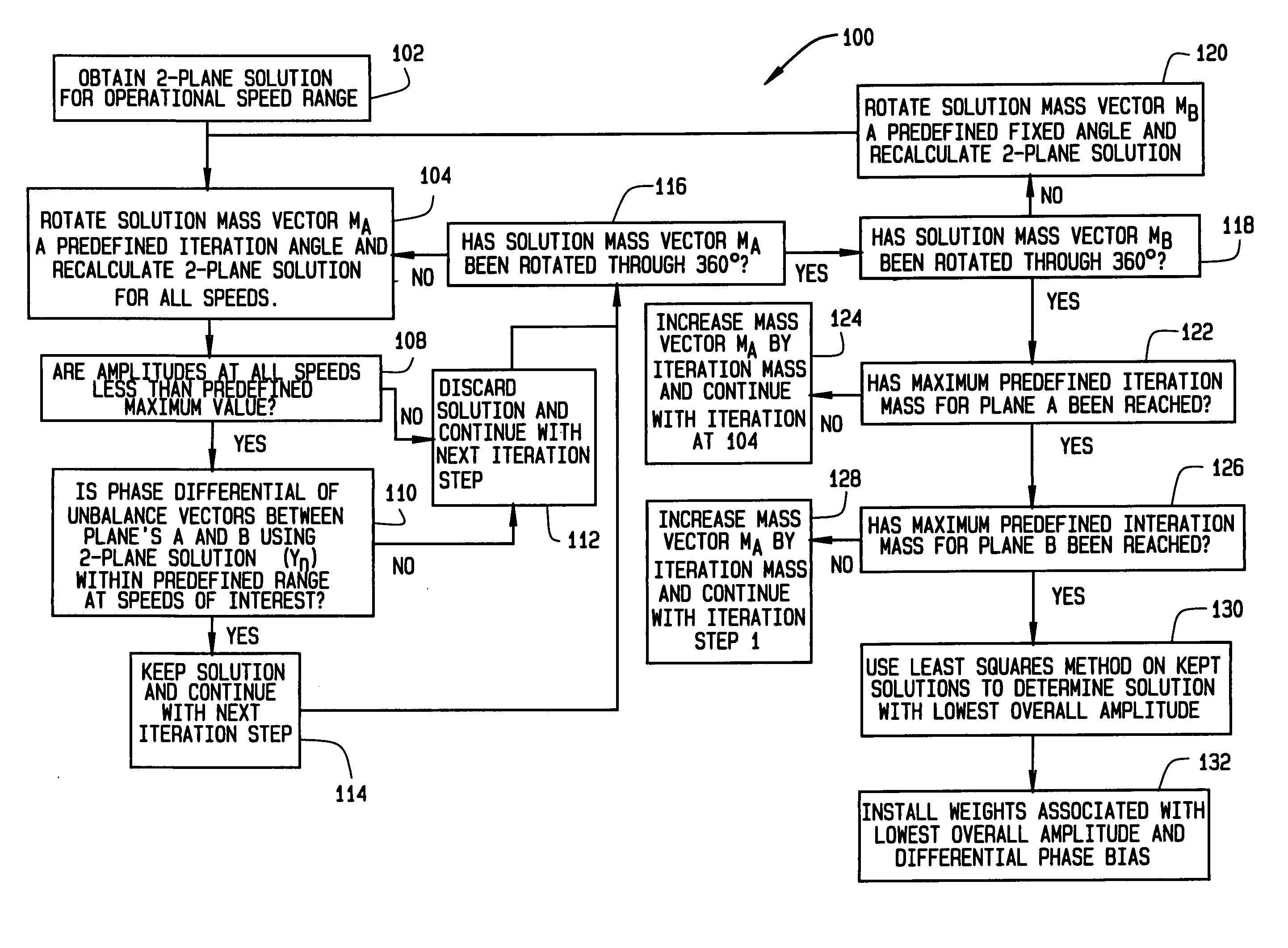
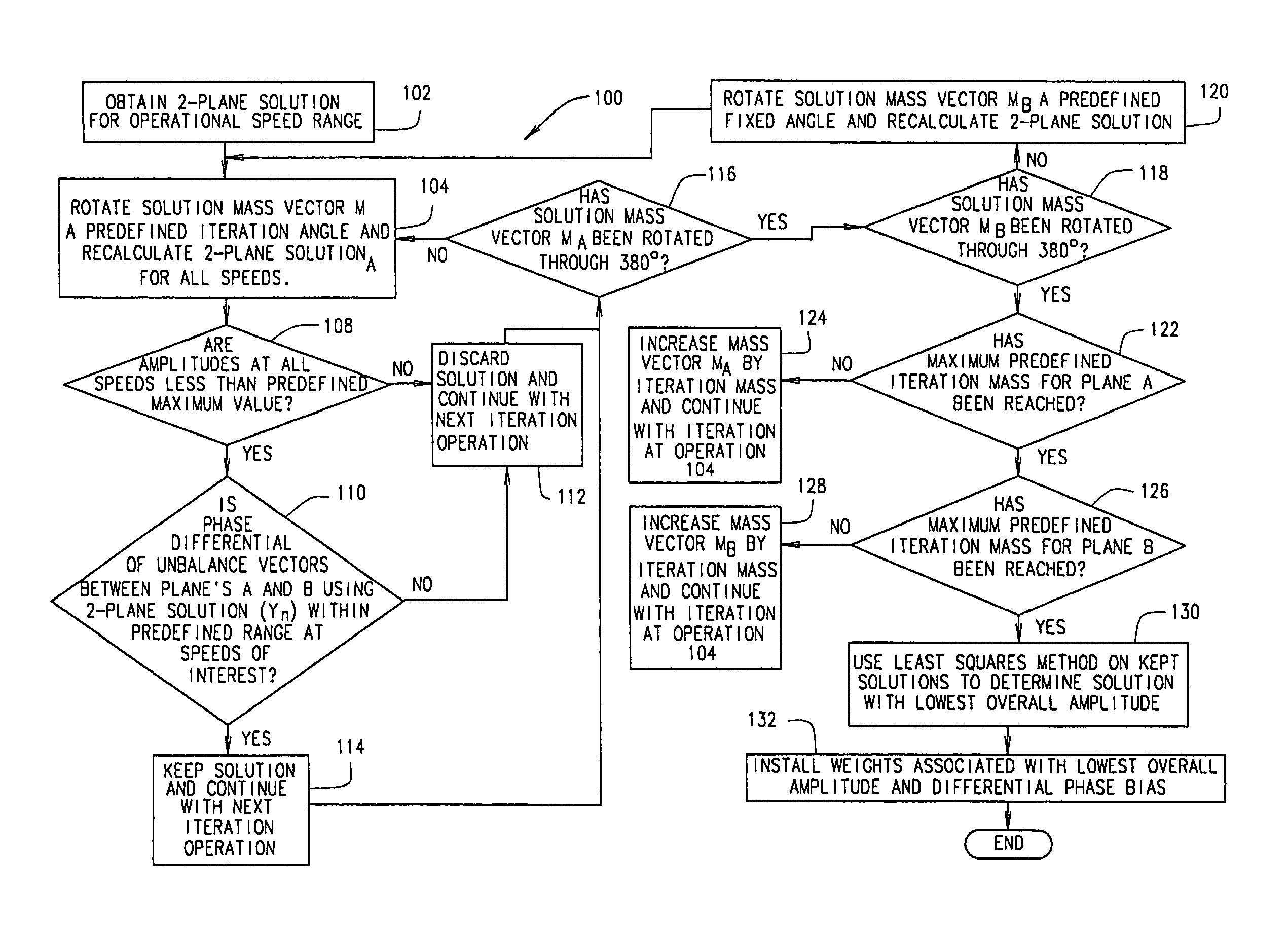
ActiveUS20050065712A1Reduce vibrationAchieve relative motionDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlPhase differenceComputational physics
A method for balancing vibrations in a rotating machine is provided. The rotating machine has a first and a second plane of imbalance. The method includes determining a first set of solution mass vectors that includes a first solution mass vector for the first plane and a first solution mass vector for the second plane. Each first solution mass vector includes a mass and a phase angle. A first phase difference between a phase angle of the first solution mass vector for the first plane and a phase angle for the first solution mass vector for the second plane is calculated. The first phase difference is compared to a pre-selected value. If the first phase difference is less than the pre-selected value, the first set of solution mass vectors is retained. The first set of solution mass vectors is then incremented to create a second set of solution mass vectors that includes a second solution mass vector for the first plane and a second solution mass vector for the second plane. A second phase difference between a phase angle of the second solution mass vector for the first plane and a phase angle for the second solution mass vector for the second plane is then compared to the pre-selected value. If the second phase difference is less than the pre-selected value, the second set of solution mass vectors is retained. Finally, selected retained solution mass vectors are determined that balance the rotating machine such that vibration of the rotating machine is reduced.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Current compensation-based unbalance vibration control system for bearingless asynchronous motor
InactiveCN105048913ANovel structureGuaranteed real-timeElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlMotor speedVibration control
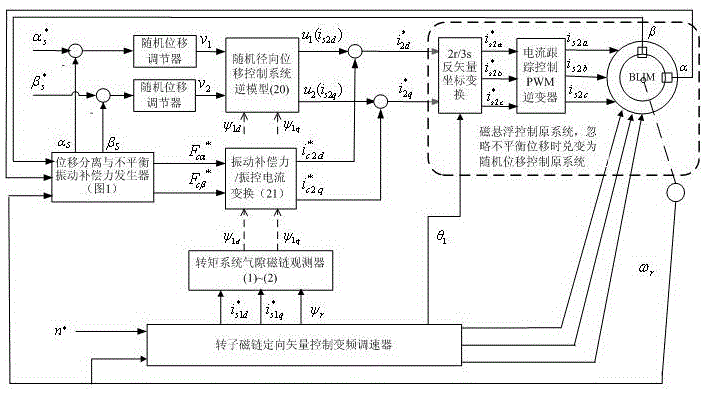
The invention discloses a current compensation-based unbalance vibration control system for a bearingless asynchronous motor. A rotor flux linkage-oriented vector control variable-frequency governor provides current to a torque winding to control the rotating speed of the motor and the rotor flux linkage; torque winding stator current components and rotor flux linkage signals are output to an air gap flux linkage observer; two linear integration sub-systems are formed before a random displacement control inverse system is connected to the original system in series; rotor radial displacement is fed into a displacement separation and unbalance vibration compensation force generator to obtain random displacement and unbalance vibration compensation force; the random displacement is fed into the inverse system through a random displacement adjustor to form closed loop control; the inverse system outputs random displacement control current; the unbalance vibration compensation force is subjected to force / flow transformation to obtain unbalance vibration compensation control current; the unbalance vibration compensation control current is correspondingly compared with the random displacement control current to obtain synthetic magnetic levitation control current; and the synthetic magnetic levitation control current is fed into the original system to generate three-phase magnetic levitation control current, so that the unbalance vibration current compensation control on the bearingless asynchronous motor is realized.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Low rotating speed high precision control method of control moment gyro gimbal servo system
ActiveCN108319148AImprove anti-interference abilityReduce conservatismAdaptive controlLow speedControl vector
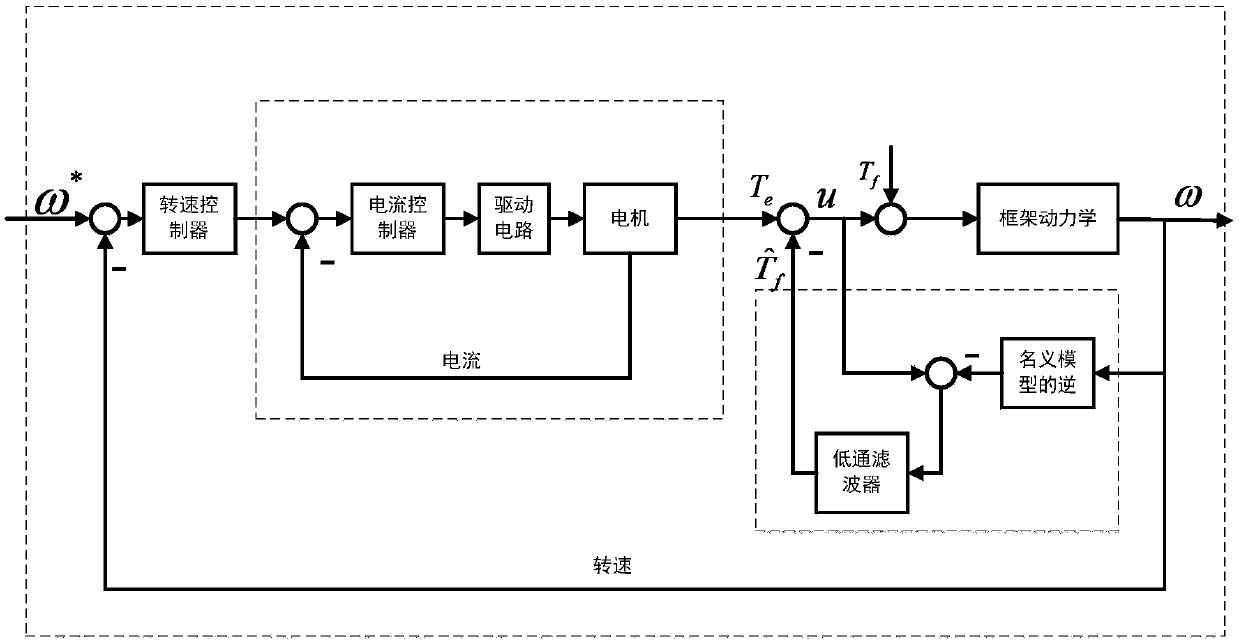
The invention relates to a low rotating speed high precision control method of a control moment gyro gimbal servo system. The method solves the problems of friction interference and a disturbing moment caused by unbalanced rotor vibration of the control moment gyro gimbal servo system in a low speed operation process. The method comprises the steps of establishing a control moment gyro gimbal servo system kinetic model containing the friction interference and an unbalanced rotor vibration interference moment, performing control design on a frame servo system current loop via vector control andPI (proportional-integral) control methods, designing an interference observer to estimate equivalent interference formed by the friction interference and the disturbing moment caused by the unbalanced rotor vibration at a frame servo system speed loop, allowing the interference observer to offset an equivalent interference estimated value via a feedforward channel and designing a composite controller. The method has the advantages of high engineering practicability, high interference immunity and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Engine balancing system and method
ActiveUS7243023B2Temperatue controlDigital data processing detailsPhase differenceComputational physics
A method for balancing vibrations in a rotating machine is provided. The rotating machine has a first and a second plane of imbalance. The method includes determining a first set of solution mass vectors that includes a first solution mass vector for the first plane and a first solution mass vector for the second plane. Each first solution mass vector includes a mass and a phase angle. A first phase difference between a phase angle of the first solution mass vector for the first plane and a phase angle for the first solution mass vector for the second plane is calculated. The first phase difference is compared to a pre-selected value. If the first phase difference is less than the pre-selected value, the first set of solution mass vectors is retained. The first set of solution mass vectors is then incremented to create a second set of solution mass vectors that includes a second solution mass vector for the first plane and a second solution mass vector for the second plane. A second phase difference between a phase angle of the second solution mass vector for the first plane and a phase angle for the second solution mass vector for the second plane is then compared to the pre-selected value. If the second phase difference is less than the pre-selected value, the second set of solution mass vectors is retained. Finally, selected retained solution mass vectors are determined that balance the rotating machine such that vibration of the rotating machine is reduced.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Unbalance vibration control system of bearingless asynchronous motor
InactiveCN104660136ARealize dynamic decouplingSimple structureElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVibration controlLoad torque
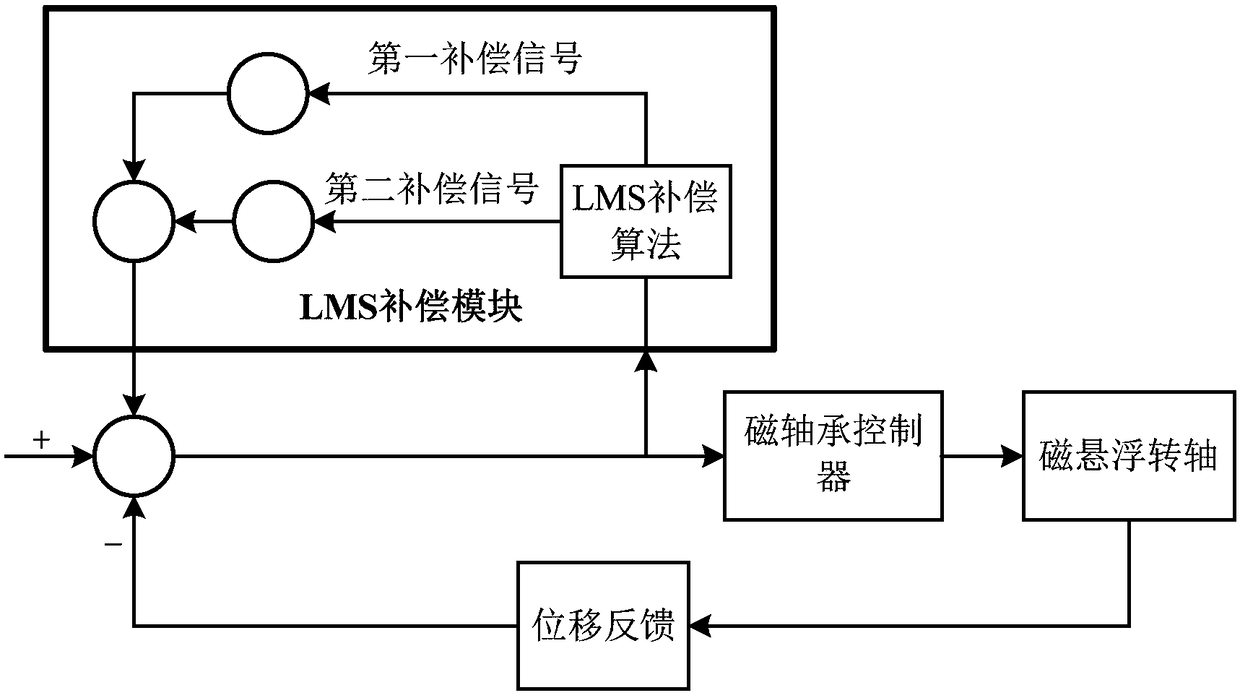
The invention provides an unbalance vibration control system of a bearingless asynchronous motor. The system consists of a directional inverse decoupling control system of a rotor flux linkage of the bearingless asynchronous motor and an unbalance exciting force feedforward compensation system, wherein the directional inverse decoupling control system of the rotor flux linkage of the bearingless asynchronous motor comprises an original system, an inverse system and four adjustors and realizes dynamic decoupling control of an electromagnetic torque, the rotor flux linkage and a random displacement component; the unbalance exciting force feedforward compensation system comprises an LMS self-adapted filter unbalance exciting force compensator and a force / flow conversion module and dynamically adjusts the unbalance displacement extraction speed and precision by using a simple step-length factor adjusting function; output of the feedforward compensation system and a steady random displacement current output by the inverse system are overlaid to form a magnetic suspension dynamic decoupling control system. The system provided by the invention cancels the links of online identification of a predictable load torque in the inverse system and a closed loop of a stator current of the original system, so that the influence of the unbalance exciting force can be effectively inhibited and the control precision and performance are improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ultra-precision dynamic balancing device applicable to micro rotor
ActiveCN104848990AMeet the needs of enlarged measurementMeet needsStatic/dynamic balance measurementVibration amplitudeDynamic balance
The invention discloses an ultra-precision dynamic balancing device applicable to a micro rotor, which comprises a device fixing portion, a rotor supporting bracket portion, a rotor driving mechanism portion and an unbalanced vibration monitoring portion, and is characterized in that a supporting bracket fixing frame of the device fixing portion can slide on a guide rail, and a base for installing the guide rail is fixed on a bottom plate; the rotor supporting bracket portion can realize amplification for weak unbalanced vibration, and can be divided into two types of supporting structure forms according to different vibration amplifying scales; a motor of the rotor driving mechanism portion can drive an unbalanced rotor to rotate in a belt driving mode; and the unbalanced vibration monitoring portion acquires the unbalanced vibration amplitude and the unbalanced vibration phase of the rotor through a displacement sensor and a phase. Compared with a traditional dynamic balancing device, the device disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, small in size, high in measurement precision for the weak unbalanced vibration, and more applicable to ultra-precision dynamic balance of the micro rotor.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
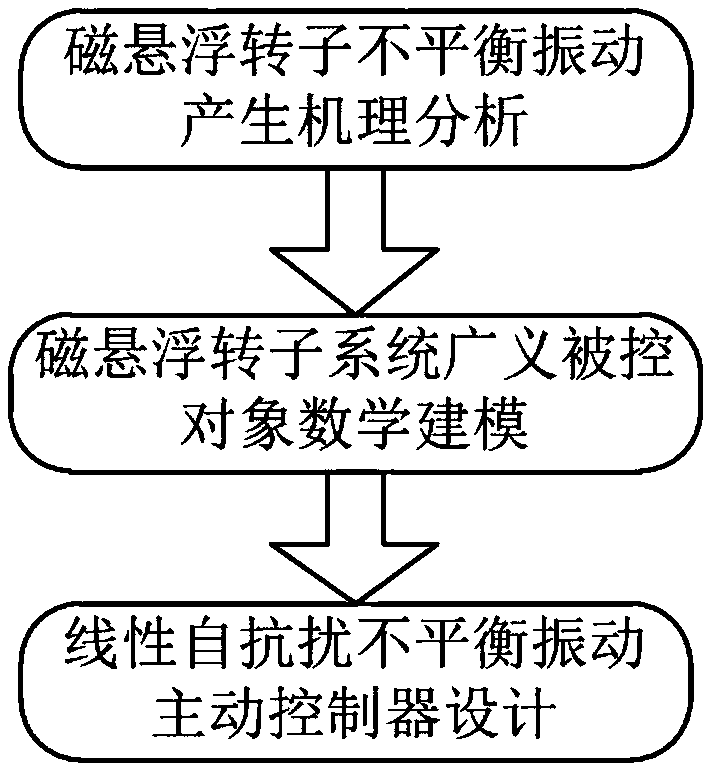
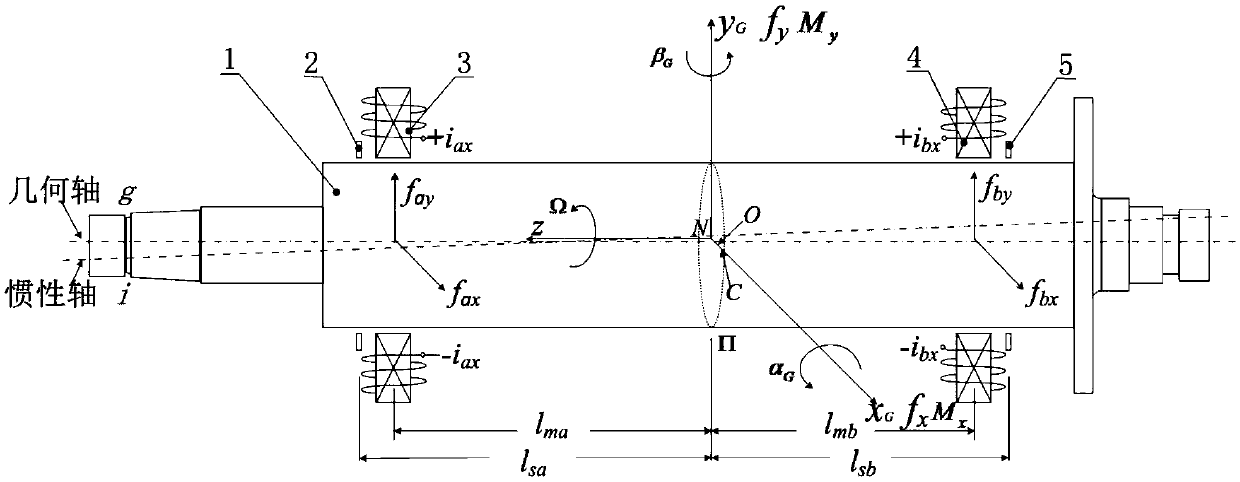
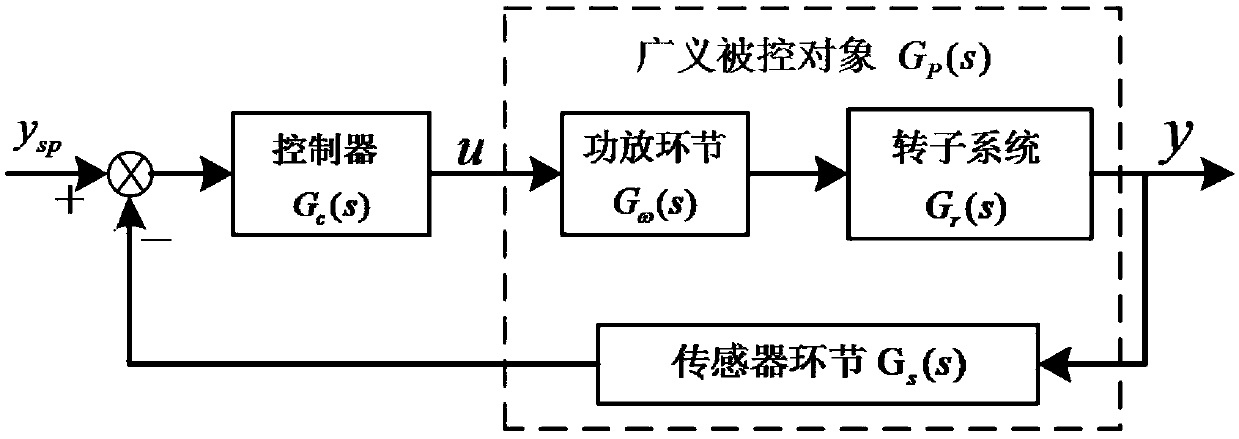
Active control method for minimal displacement of magnetic suspension molecular pump rotor
ActiveCN108716471AEasy to prepareSimple structurePump componentsPump controlFrequency compensationControl signal
The invention relates to an active control method for minimal displacement of a magnetic suspension molecular pump rotor. A mathematical model of a generalized controlled object of a magnetic suspension rotor system is established by analyzing a formation mechanism of unbalanced vibration of the magnetic suspension rotor system. Channel controllers are designed based on the principle of linear auto disturbance rejection control. The unbalanced vibration of the system is regarded as an external disturbance, the disturbance is estimated and compensated in real time by using a linear extended state observer, and so same frequency compensation signals with appropriate amplitude and phase are superimposed on a control signal to offset rotor unbalanced exciting force to realize high speed and high precision rotation of the rotor around a geometric axis, thereby realizing the active control of the minimal displacement of the magnetic suspension rotor system. Compared with a conventional control method, the active control method has advantages of simple parameter adjustment, easy implement, small rotor whirl radius and high rotation precision, can greatly reduce rotation speed same frequency components in a displacement signal, and is of great significance for improving the performance and reliability of the magnetic suspension rotor system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Unbalance magnitude online monitoring and de-weighting method in disc type workpiece processing
ActiveCN105222959APrevent large imbalancesUnbalance reduction or eliminationStatic/dynamic balance measurementMeasurement/indication equipmentsBalancing machineDynamic balance
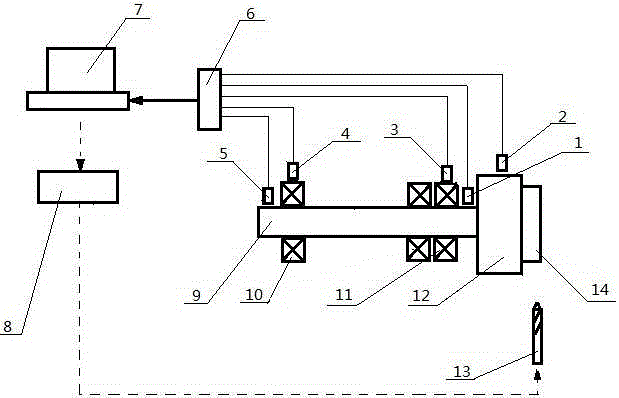
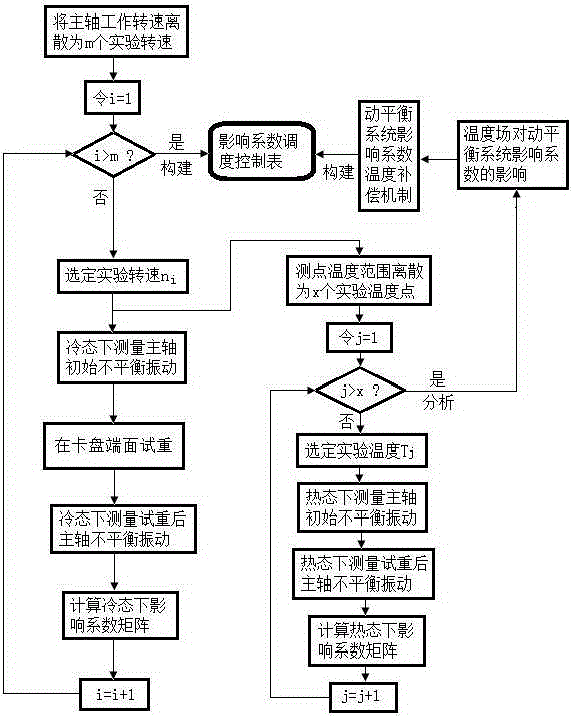
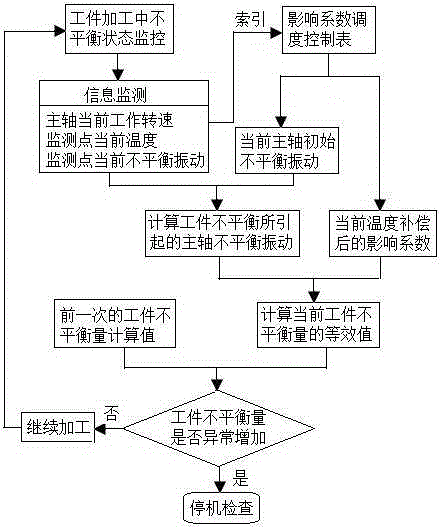
The invention relates to an unbalance magnitude online monitoring and de-weighting method in disc type workpiece processing, and brings forward a method for indirectly measuring unbalance magnitude of a disc type workpiece in processing through monitoring change of unbalance vibration signals of a main shaft, for overcoming the disadvantages in the prior art that dynamic balancing of a conventional disc type workpiece requires a special-purpose dynamic balancing machine, the balancing efficiency and the precision are low and the like. Based on the method brought forward by the invention, through monitoring of the unbalance state of the disc type workpiece in a processing process, formation and deterioration of too large unbalance magnitude of the disc type workpiece are prevented; and after the disc type workpice is processed, the clamping position of the disc type workpiece on a main shaft of a machine tool maintains unchanged, the unbalance magnitude of the disc type workpiece is measured in an online mode during rotation of the main shaft, and the unbalance magnitude of the disc type workpiece is reduced or eliminated through a method of controlling de-weighing of the machine tool. The method provided by the invention has great significance in improving the balance efficiency and precision of the disc type workpiece and reducing the balance cost.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TECH & EDUCATION TEACHER DEV CENT OF CHINA VOCATIONAL TRAINING & GUIDANCE
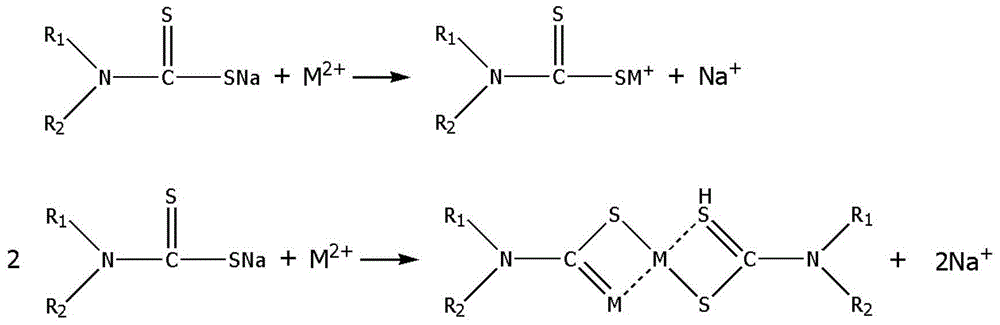
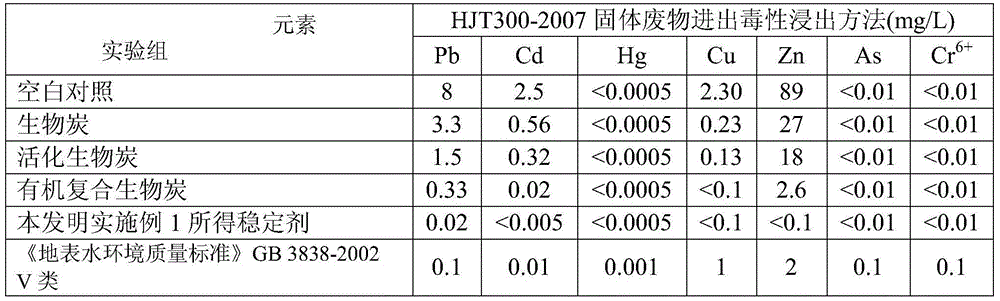
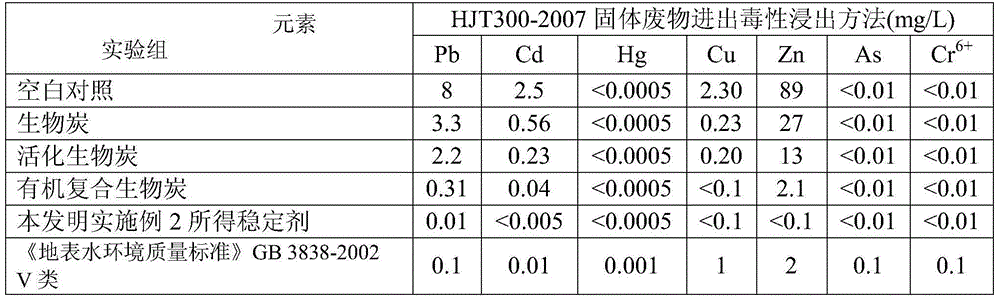
Preparation method of soil heavy-metal stabilizer
ActiveCN104549152AReduce absorptionReduce the risk of ingesting heavy metalsOther chemical processesContaminated soil reclamationSoil heavy metalsSodium carbamate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a soil heavy-metal stabilizer, and belongs to the technical field of soil remediation and treatment. The preparation method comprises the following steps of a, preparing active charcoal, namely, drying organic matter, crushing, immersing by an alkali salt solution, and then firing under the protection of N2 so as to obtain the active charcoal; and b, preparing active organic composite charcoal, namely, mixing a sodium dithiocarbamate derivative solution with the active charcoal, carrying out balance vibration under a dark condition, then centrifuging, collecting a precipitate mixture, and drying so as to obtain the soil heavy-metal stabilizer. The preparation method of the soil heavy-metal stabilizer has the advantages that adsorption and fixing effects for heavy metal in soil are obvious; the absorption of heavy metal in soil cy plants or crops can be relieved effectively; the hazard of taking in heavy metal from crops by human beings is reduced.
Owner:银发环保股份有限公司
Apparatus and method for measuring vibration characteristics
InactiveUS20120272740A1Eliminate unbalance vibrationEliminate vibrationVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingVibration amplitudeMagnetic tension force
A vibration characteristic measuring apparatus includes a magnetic bearing that generates magnetic force on the rotating body of a multi-stage centrifugal compressor, a displacement sensor that measures the vibration amplitude of the rotating body, a current amplifier that supplies a current to the magnetic bearing, and an excitation controller which outputs an excitation control signal for applying vibration to the rotating body and which measures the response characteristics of the vibration of the rotating body to the excitation control signal. The excitation controller outputs a rotating body control signal obtained by adding a vibration eliminating signal for eliminating unbalance vibration of the rotating body to the excitation control signal when measuring the response characteristics, and the current amplifier supplies a current that generates magnetic force in accordance with the rotating body control signal to the magnetic bearing.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic suspension bearing control device, magnetic suspension bearing and control method thereof
ActiveCN108087423AEffective controlReduce noiseStatic/dynamic balance measurementBearingsEngineeringControl theory
The invention discloses a magnetic suspension bearing control device, a magnetic suspension bearing and a control method thereof. The device comprises a displacement feedback module (5) and a trappedwave unbalance vibration controller (4), wherein the displacement feedback module (5) is used for acquiring displacement information of a magnetic suspension rotating shaft (3) of the magnetic suspension bearing; the displacement information comprises rotary displacement information of rotation around a geometric center of a magnetic suspension rotating shaft (3) and unbalance displacement information of rotation around the centroid of the magnetic suspension rotating shaft (3); and the trapped wave unbalance vibration controller (4) is used for compensating the unbalance displacement information in the displacement information to obtain effective displacement information. By the scheme, the shortcomings of large unbalance disturbance, high control difficulty, poor running stability and the like in the prior art can be overcome, and beneficial effects of low unbalance disturbance, low control difficulty and good running stability are achieved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC +1
Measurement mechanism and measurement method for crankshaft assembly dynamic poise
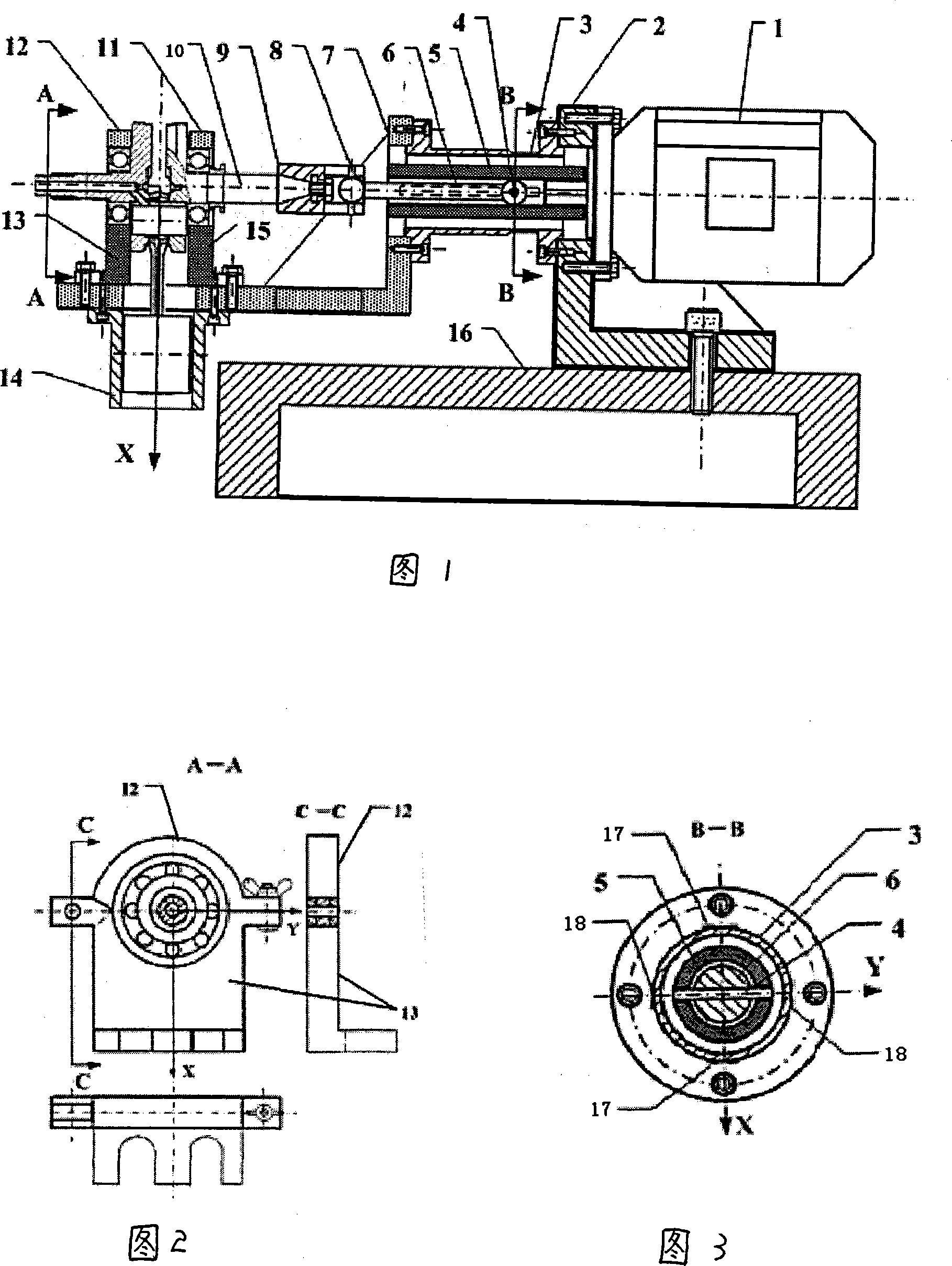
InactiveCN101135597AAccurate measurementImprove detection efficiencyStatic/dynamic balance measurementMeasurement deviceDynamic balance
The invention comprises a motor, a right angle support base, a cylinder elastic support whose both ends are flanges, a hollow shaft, a drive shaft, a L-shaped bracket, a dynamic balancing machine, and a train gauge coated on the cylinder elastic support. In the rotation plane of the crank shaft assembly, along with the orthogonal X,Y directions, simultaneously measuring the unbalance vibration or force signal of the crank shaft assembly running in high speed; after processed by computer, synthesizing the unbalance value along with different directions to form a closed curve graph. The invention also reveals a method thereof.
Owner:重庆迪佳科技股份有限公司
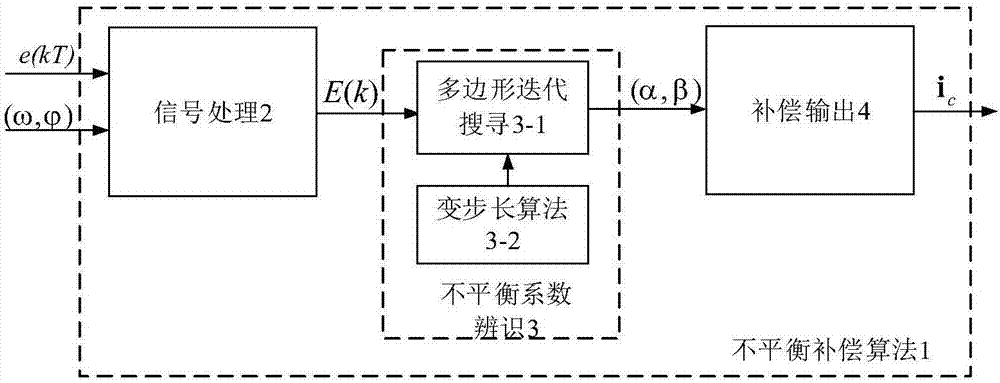
Unbalanced compensation algorithm of polygonal iterative search with variable step size for rotor imbalance coefficient
ActiveCN107133387AFix stability issuesGuaranteed identification accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsIterative searchFundamental frequency
The invention discloses an unbalanced compensation algorithm of polygonal iterative search with variable step size for rotor imbalance coefficients. The algorithm comprises the steps that in the step of signal processing, identification and compensation output of unbalanced coefficients, the signal processing is based on the rotor vibration signal and the rotor speed obtained by a displacement sensor and the rotor speed and phase signals obtained by a phase detection device, the amplitude values of the fundamental frequency of rotor vibration signals are obtained by calculation; the amplitude values of the fundamental frequency of rotor vibration signals are used as the judgment criterion for the identification of unbalanced coefficients, unbalance coefficients are obtained through the identifications by the polygon iterative search method with variable step size; unbalanced compensation electric currents are generated by the compensation output based on the unbalanced coefficients, and inputted in electromagnetic coils, then suppression is conducted on the rotor imbalance vibrations. The unbalanced compensation algorithm of polygonal iterative search with variable step size for rotor imbalance coefficients can be applied to active rotor systems with active control units, online compensation of the imbalance of the active rotor system is achieved, so that suppression is conducted on unbalanced vibration of the rotor system of the entire rotor speed range in the acceleration and deceleration operation process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Balanced vibration system
PendingCN110012398AHigh signal conversion efficiencyReduce power consumptionLoudspeakersDiaphragm mounting/tensioningEngineeringDistortion
The invention discloses a balanced vibration system which comprises a magnetic circuit unit, a vibration unit and a shell, and the magnetic circuit unit and the vibration unit are located in the shell. Wherein the vibration unit comprises a balance iron core and a vibration diaphragm, the balance iron core is movably connected with the shell, the vibration diaphragm is fixed on the shell, and thebalance iron core can drive the vibration diaphragm to move. The magnetic circuit unit comprises a magnetic circuit coil and two magnet sets, the balance iron core is sleeved in the magnetic circuit coil, and the two magnet sets are located at the two ends of the axis direction of the balance iron core respectively. Each magnet set comprises two magnets, and the two magnets of the same magnet setare oppositely arranged on the two sides of the balance iron core. And when the magnetic coil is in a power-on state, the directions of the two magnet groups applied to the balance iron core are the same. Overall vibration of the iron core is balanced through the magnetic circuit unit and the vibration unit, so that the signal conversion efficiency is higher, power consumption is reduced, and distortion caused by unilateral vibration is eliminated.
Owner:潘国昌
Magnetic suspension spherical flywheel imbalance vibration inhibition method
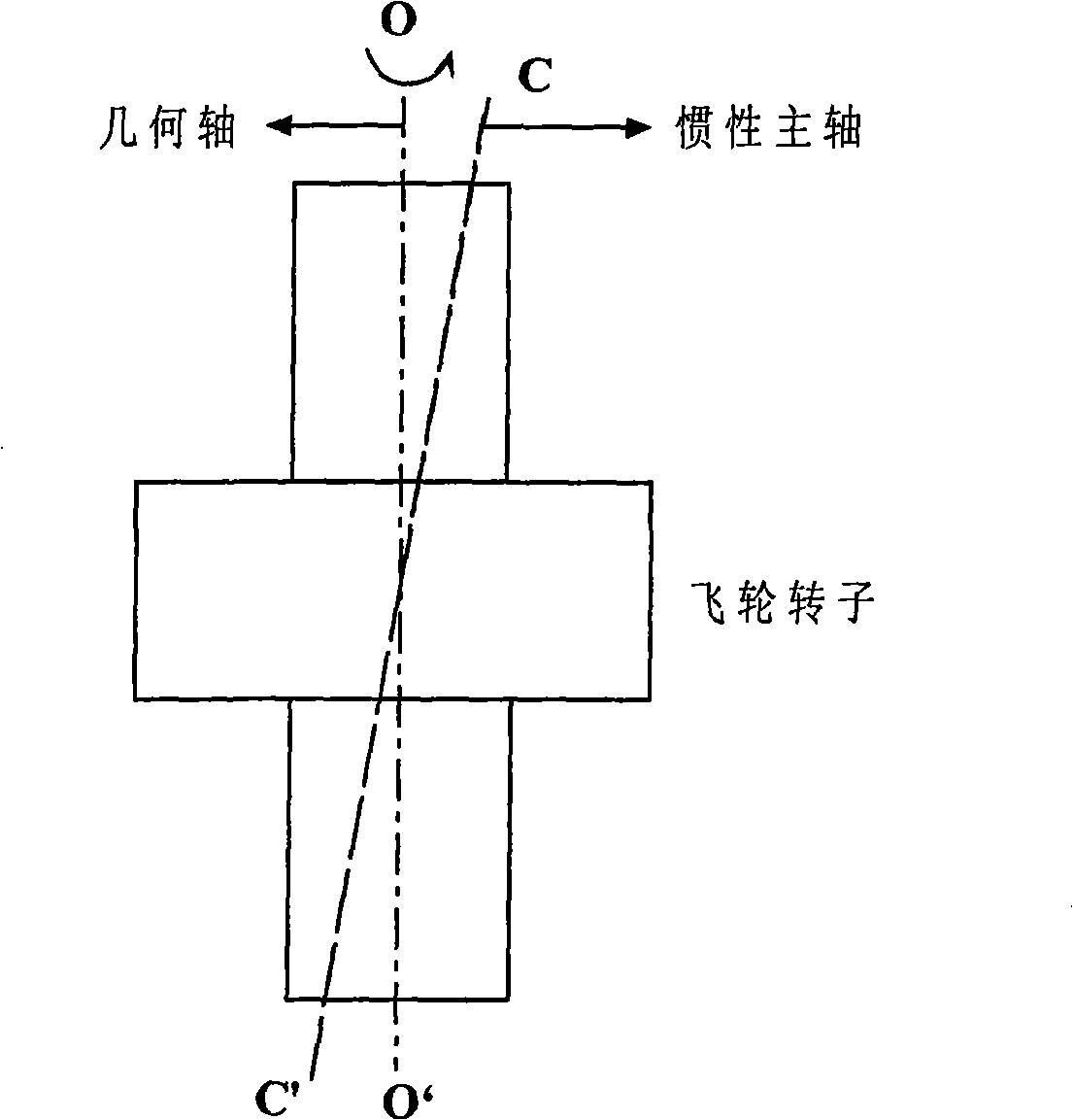
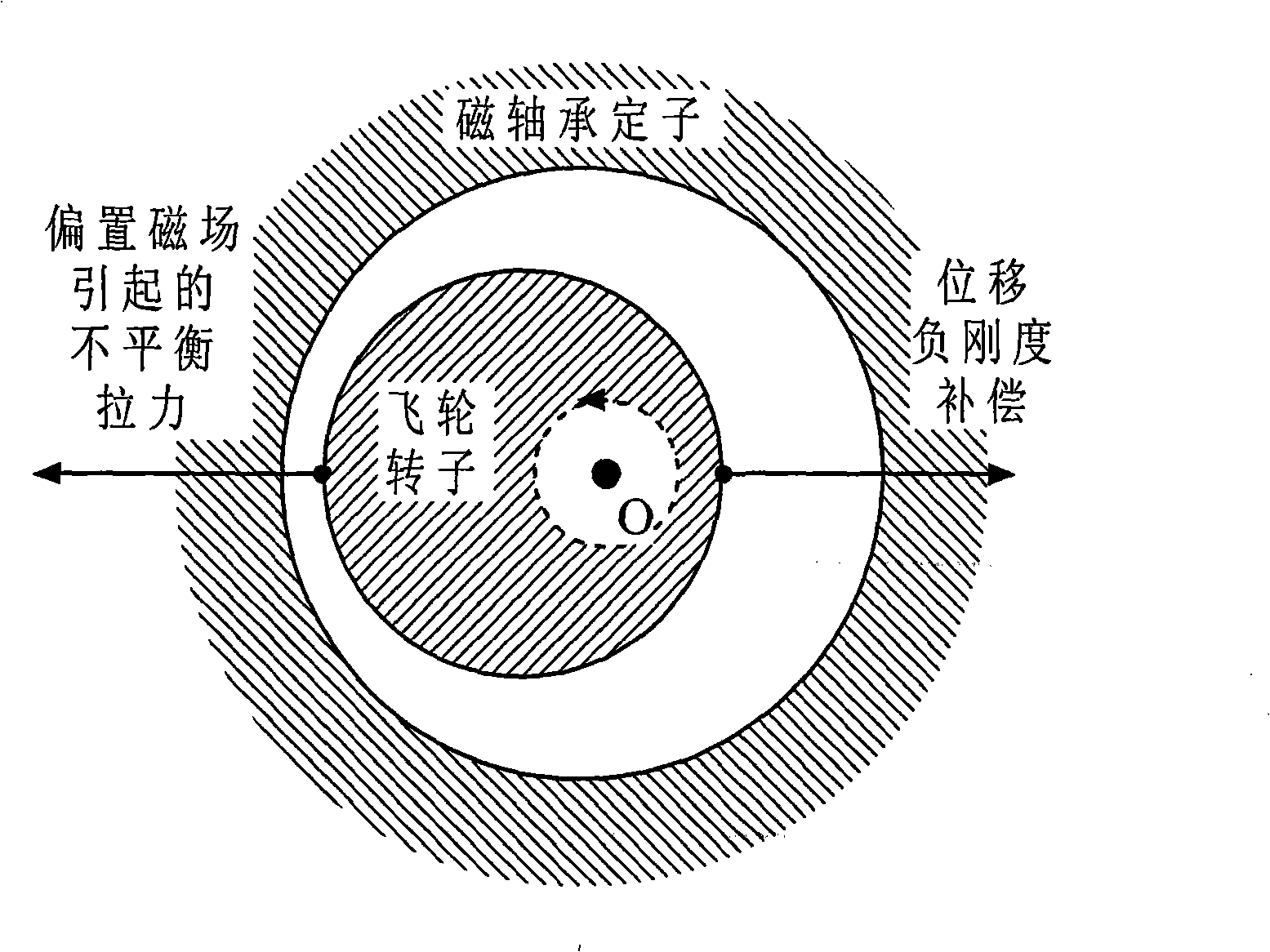
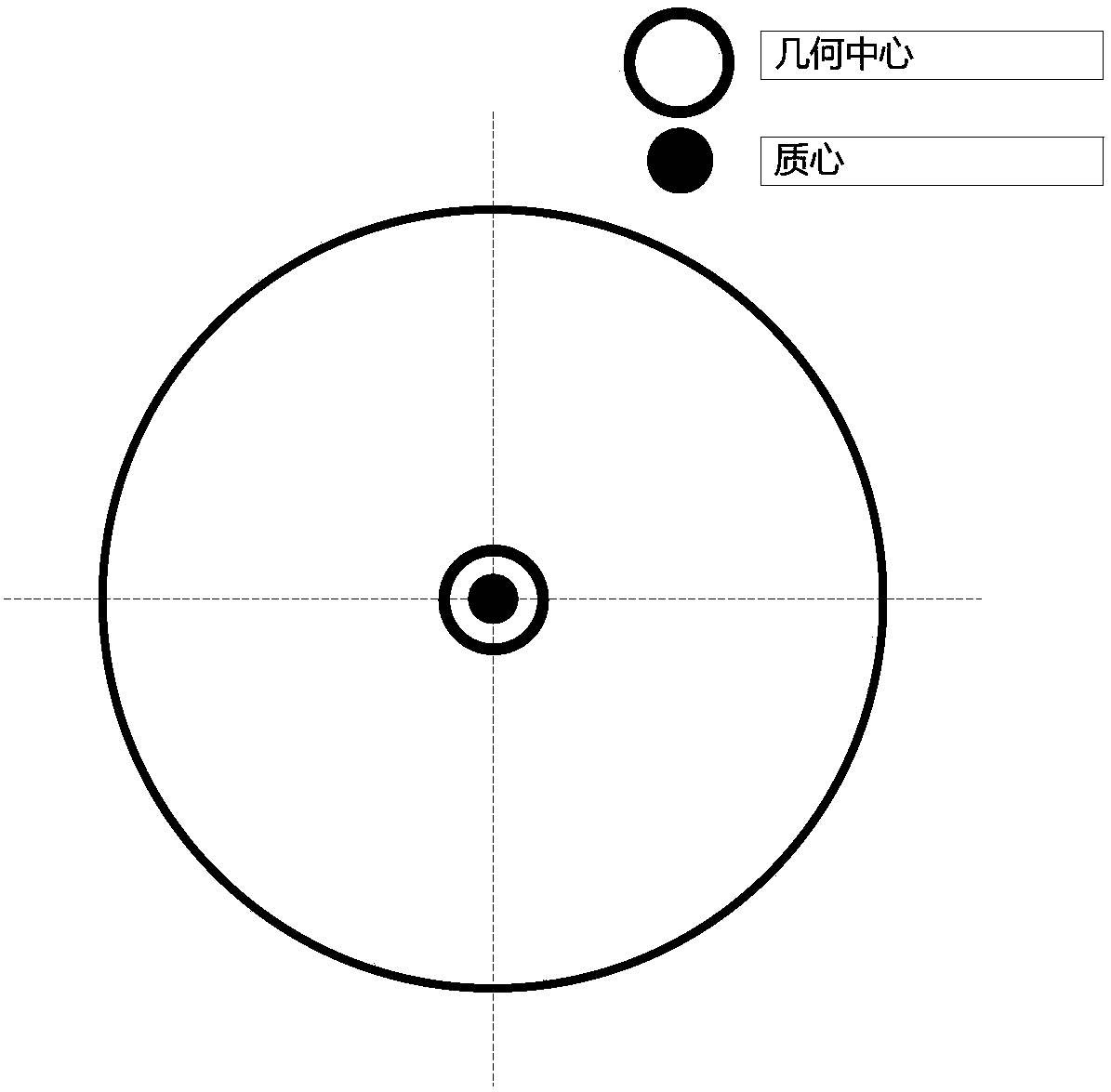
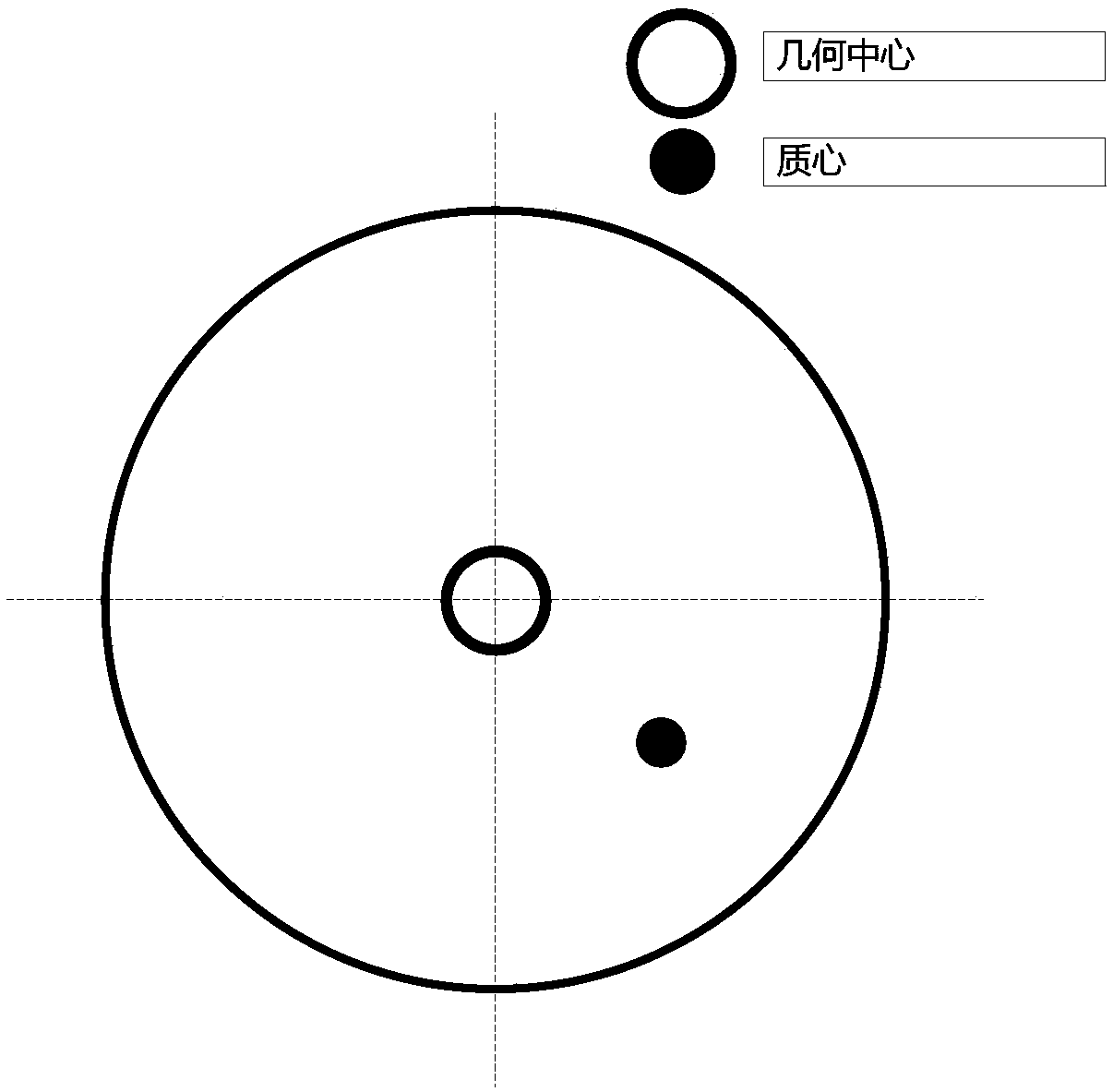
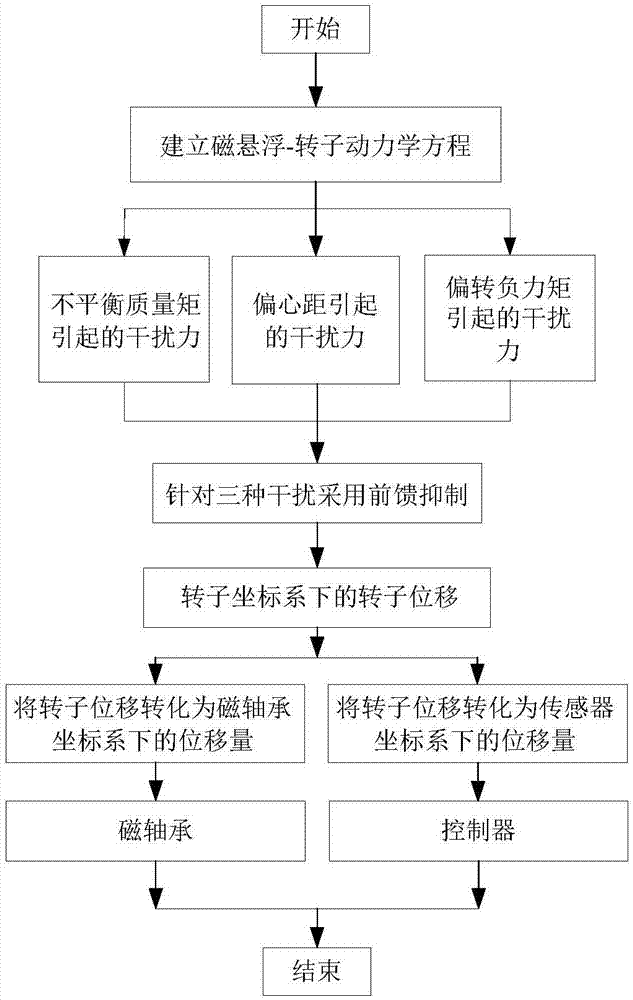
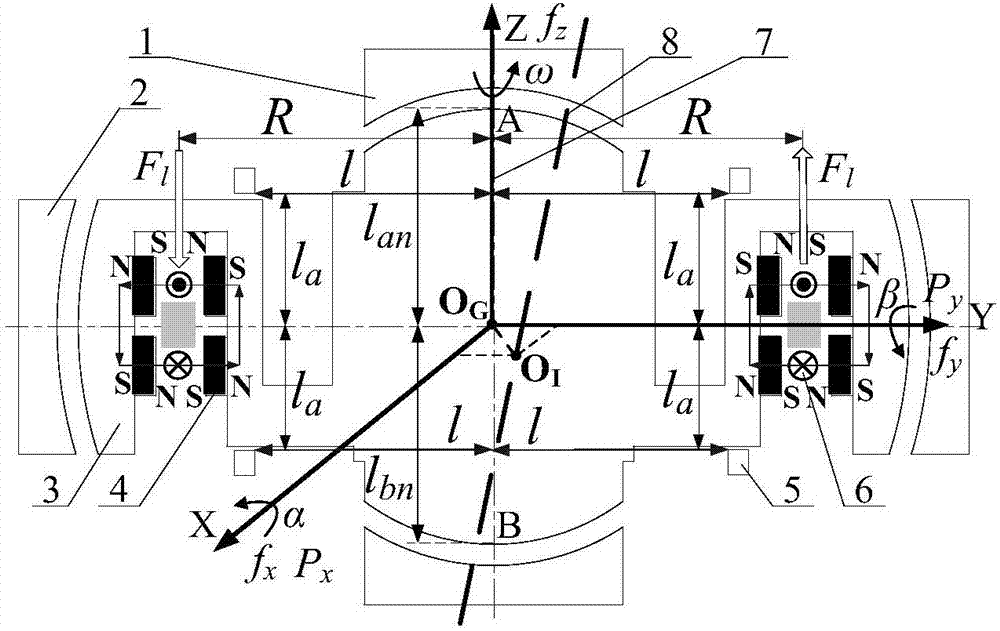
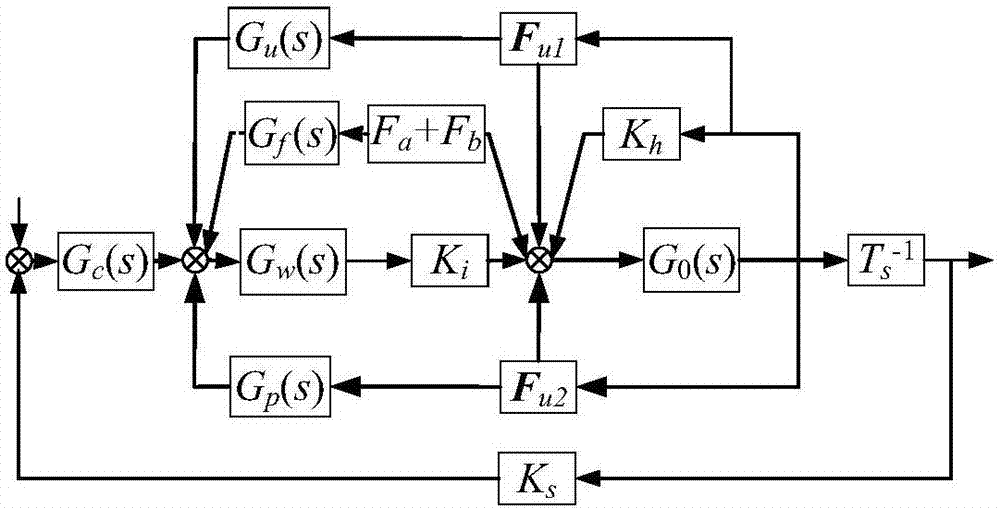
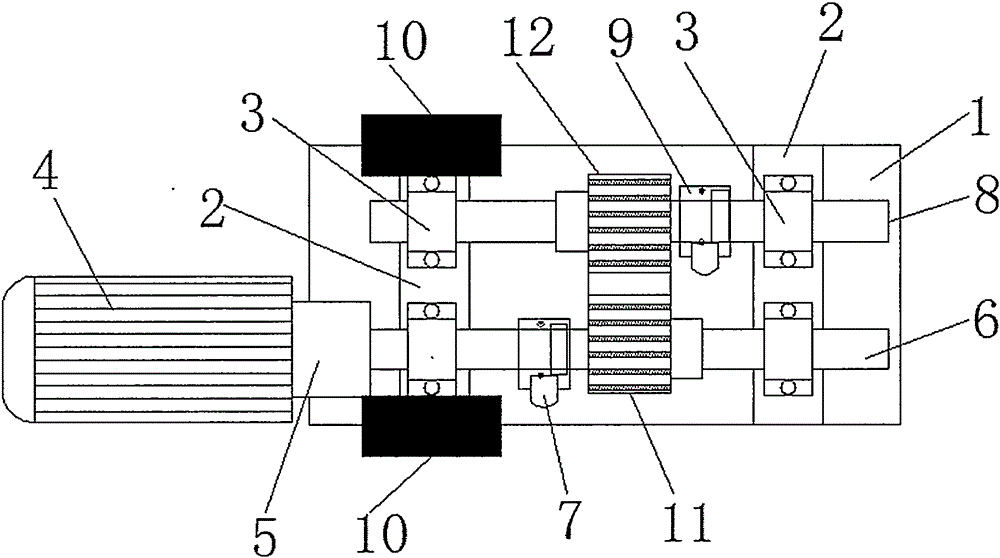
The present invention relates to a magnetic suspension spherical flywheel imbalance vibration inhibition method. The Newton's second law and the gyro technique equation are employed to establish a magnetic bearing-rotor dynamics equation, based on the D'Alembert's principle, the disturbing force of imbalance mass moment on a rotor caused by deviation of rotor inertial axis from a geometrical axis, the disturbing force of the eccentricity on the rotor caused by the deviation of the rotor mass center from the geometrical axis and the disturbing force of the deflection negative moment on the rotor caused by suspension force passing through the rotor centroid and not passing through the rotor mass center are obtained. Rotor displacement amounts under the three disturbing forces are converted to the displacement amount under a sensor coordinate system and the displacement amount under a magnetic bearing coordinate system through a conversion matrix, the two displacement amounts are respectively acted in the controller and the magnetic bearing, and the feedforward inhibition method is employed to perform inhibition of the three disturbing forces. The magnetic suspension spherical flywheel imbalance vibration inhibition method can effectively improve the control precision of the imbalance vibration of the magnetic bearing-rotor system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Vibration transmission test bench for magnetorheological damper controlled gear box shaft system
InactiveCN106546425AReduce vibrationImprove vibration suppression performanceMachine gearing/transmission testingMachine bearings testingGear wheelDrive shaft
The invention discloses a vibration transmission test bench for a magnetorheological damper controlled gear box shaft system, comprising a test bench, a motor, a first rotating shaft, a second rotating shaft, a first gear, and a second gear. A test device is arranged on one side of the first rotating shaft, and a test device is arranged on one side of the second rotating shaft. The first gear fixedly sleeves the first rotating shaft. A first magnetorheological damper is arranged at the bottom of the first rotating shaft. The second gear fixedly sleeves the second rotating shaft. A second magnetorheological damper is arranged at the bottom of the second rotating shaft. The first gear and the second gear are connected by means of meshing. According to the vibration transmission test bench for a magnetorheological damper controlled gear box shaft system, the vibration of a gear box body can be monitored, and the currents of the dampers can be changed in a timely manner to adapt to different working conditions of the gear box body, such as vibration change in the process of speed change or unbalanced vibration increase caused by wear. Thus, it is ensured that the vibration of the box body and the transmission shaft is kept at a low level.
Owner:上海真竞信息科技有限公司
Grinding wheel balance vibration-absorbing device based on EAP (electroactive polymer) driving and grinding wheel balance vibration-absorbing method based on EAP driving
ActiveCN109099112AAvoid processing powerPitfalls when avoidingCounterweightsMetal rubberVibration absorption
The invention discloses a grinding wheel balance vibration-absorbing device based on EAP (electroactive polymer) driving and a grinding wheel balance vibration-absorbing method based on EAP driving. The grinding wheel balance vibration-absorbing device based on EAP driving comprises an outer cover and a balance unit, an adjusting screw rod, a positioning slide rod, a driving rod and a counterweight unit. The driving rod controls and adjusts the screw rod to rotate through gear-rack engagement and then adjusts the position of the counterweight unit to achieve linear balance of a grinding wheel,and a first elastic support, a second elastic support, an elastic element, a main mass unit and a damping element are arranged in the counterweight unit to form dynamic vibration absorber effect withdamping. The grinding wheel balance vibration-absorbing device based on EAP driving has the advantages that vibration-absorbing balancing can be achieved timely and properly to avoid the defect thata traditional exterior balance head is untimely in treatment; a signal acquisition process is more precise to reduce exterior vibration interference; movable balance of a rotor is combined with dynamic vibration absorption on the basis of EAP driving, and metal rubber serves as the damping element, so that vibration is reduced and even eliminated, the grinding wheel is more stable to operate, andthe position and parameters of a counterweight are improved to subdue vibration conveniently.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
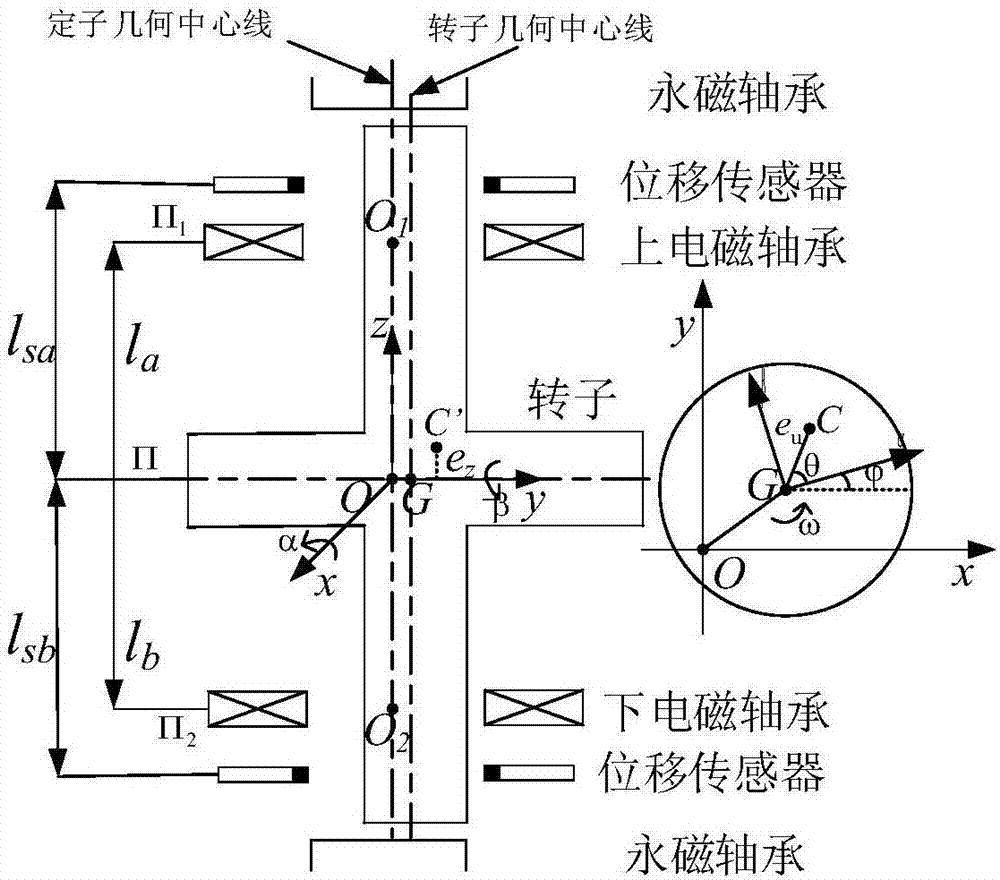
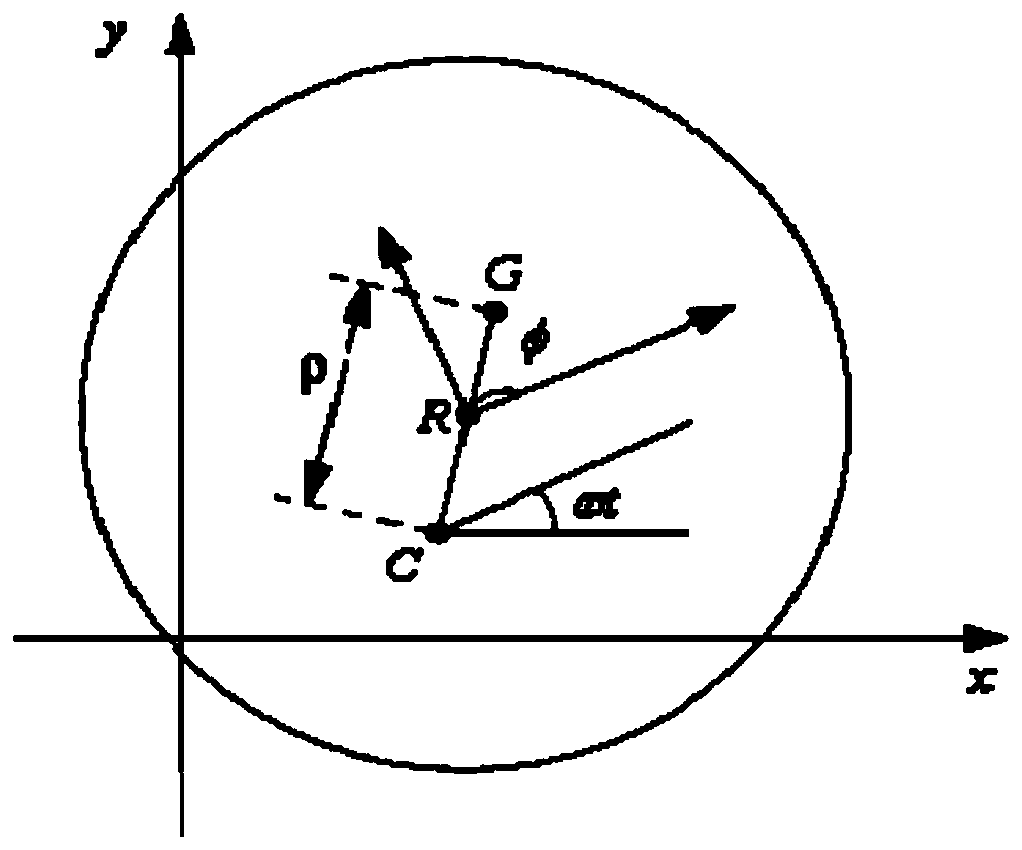
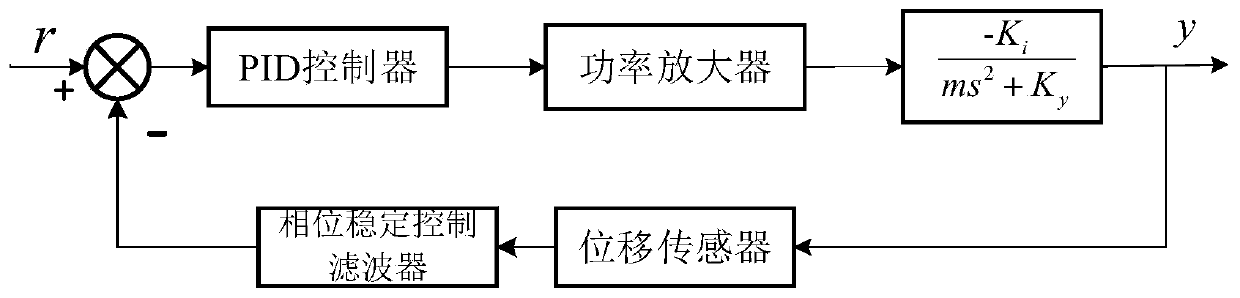
Control method of unbalanced motion of magnetic suspension bearing rotor based on phase stabilization
ActiveCN110145541AAddress the effects of switching back and forthShaftsRotary machine partsLow speedAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a control method of the unbalanced motion of a magnetic suspension bearing rotor based on phase stabilization. The control method comprises the steps of (S1) establishing a coordinate system of a magnetic suspension bearing rotor system, and establishing x and y axes in the radial direction of magnetic suspension and a z axis in the axial direction of magnetic suspension; (S2) establishing a four-degree-of-freedom kinematic model of the radial direction of the magnetic suspension bearing rotor; (S3) determining the number and position of position sensors according to theappearance and shape of a bearing, and establishing a displacement sensor model; (S4) establishing a power amplifier model; (S5) establishing a kinematic model of the magnetic suspension rotor; and (S6) restraining the unbalanced vibration of the rotor by utilizing a phase stabilization control method. According to the phase stabilization control method provided by the invention, the influence ofthe unbalanced vibration generated when the rotor rotates on a controller is effectively solved. According to the phase stabilization control method provided by the invention, the traditional influence of an automatic balance system and phase-change peak gain on the switching between high speed and low speed is effectively solved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Novel self-balanced vibration cleaning sieve
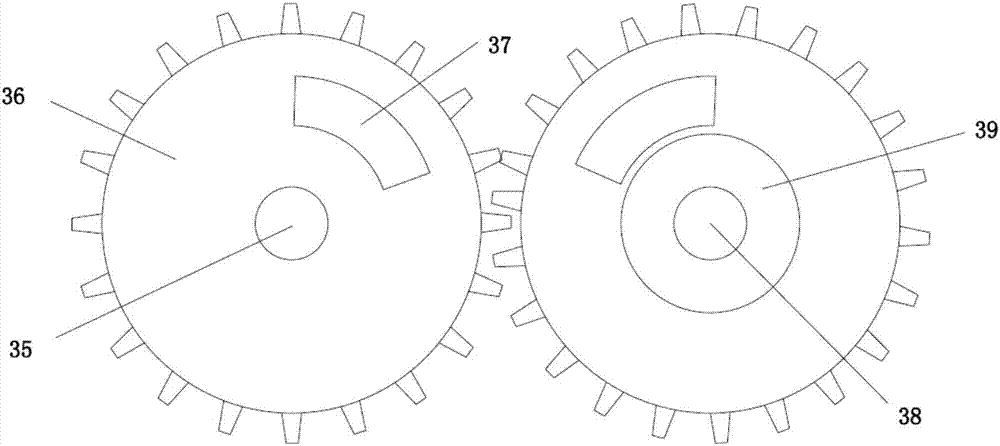
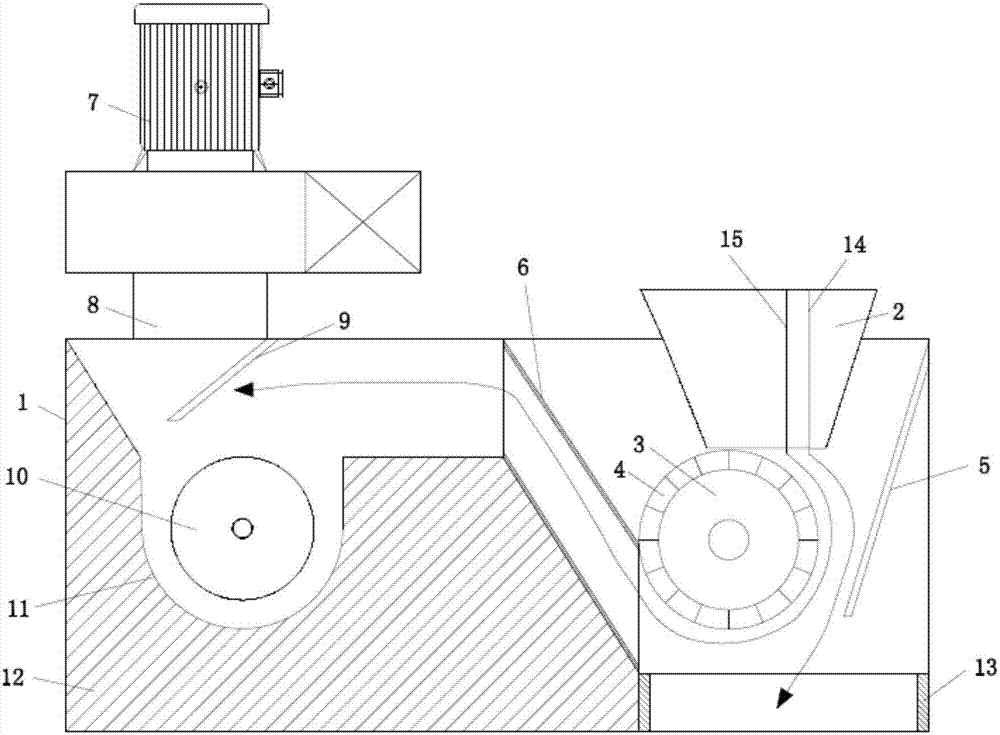
PendingCN107362976AIncrease productionAvoid cloggingSievingGas current separationCircular discButt joint
The invention discloses a novel self-balanced vibration cleaning sieve which comprises a feeding mechanism, a cleaning mechanism and a self-balancing mechanism, wherein the feeding mechanism and the self-balancing mechanism are connected onto the cleaning mechanism; the feeding mechanism comprises a box body, a shifting fork hub, an auger assembly and a fan; the cleaning mechanism comprises a sieve box, a chain, a scraper plate and a screen; a discharge pipe of the feeding mechanism is in butt joint with a feeding hole of the cleaning mechanism; the self-balancing mechanism comprises two gear discs meshed with each other; and eccentric blocks are fixedly arranged on the gear discs. According to the novel self-balanced vibration cleaning sieve disclosed by the invention, the phenomena that dust is adhered to the sieve surface and sieve pores are blocked are avoided, the oversize product is automatically cleaned, materials are effectively prevented from blocking the meshes by a sweeper, the tension of the screen can be adjusted without a frame, the screen can be rapidly replaced, and the gear discs made by a special design and a portable special material are balanced and do not produce strong vibration so as not to influence the overall structure. By monitoring the rotating speed of the chain wheel, the mechanism has an automatic fault detection function.
Owner:ANHUI VISION OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Double vibration sensor-based rotor imbalance vibration response identification method
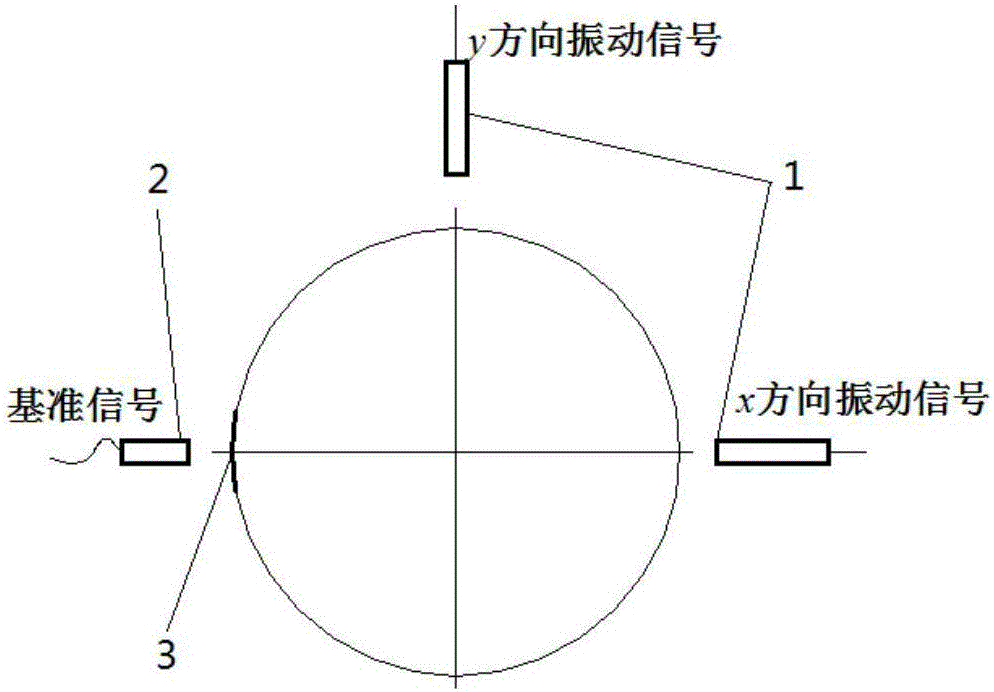
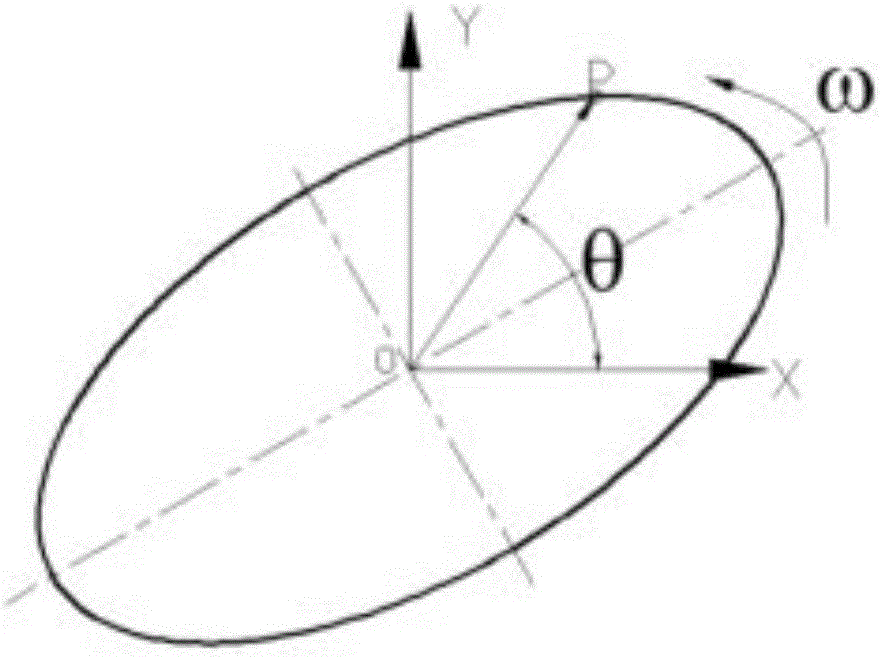
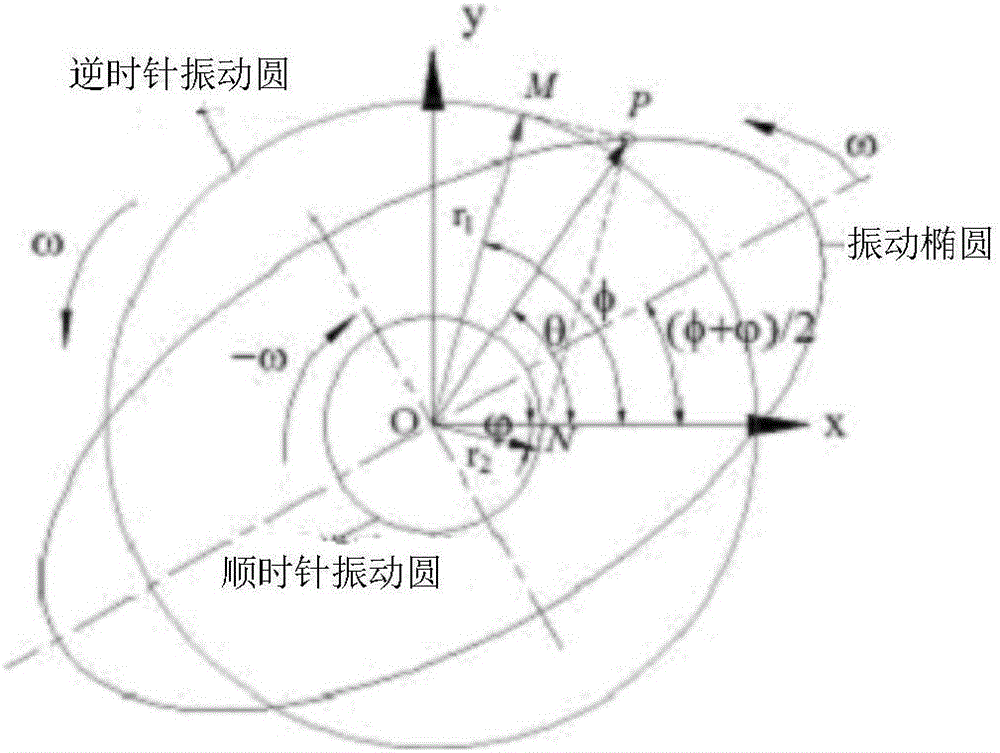
InactiveCN106323548AImprove dynamic balance accuracyUnbalanced Vibration Response SolutionStatic/dynamic balance measurementEllipseLight reflection
The invention discloses a double vibration sensor-based rotor imbalance vibration response identification method which comprises the following steps: a, vibration sensors of the same model are mounted on two random axial directions x and y that are perpendicular to each other on a measurement cross section of a rotor bearing seat, a piece of light reflection paper is pasted on a rotor shaft, a rotation speed sensor is positioned opposite to the light reflection paper, and the vibration sensors in the direction x and the direction y and the rotation speed sensor are subjected to vibration signal and reference signal sampling operation; b, cross correlation technologies are used for extracting amplitude and phase positions of rotation frequency vibration in the direction x and the direction y; c, rotation frequency vibration signals in the direction x and the direction y are fused into a vibration ellipse; d, the vibration ellipse is broken into a clockwise vibration circle and an anticlockwise vibration circle, and the anticlockwise vibration circle is used for representing imbalanced vibration response. The double vibration sensor-based rotor imbalance vibration response identification method can help solve a problem that imbalanced vibration response of an anisotropy rotor system in a circumferential direction of kinetics parameters such as rigidity, damping and the like cannot be effectively identified via a single vibration sensor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dynamic balancing method for high-speed rotors
ActiveCN104165729AGuaranteed Accurate AcquisitionImprove dynamic balance accuracyStatic/dynamic balance measurementLow speedDynamic balance
The invention belongs to the technical field of rotating equipment fault diagnosis and control, and particularly relates to a dynamic balancing method for high-speed rotors. According to the method, on the basis of acquiring vibration information of a rotor, vibration data at high speed and vibration data at low speed are cut down at the same scale through post processing, the interference of rotor measurement section profile error, phase discrimination mark, electromagnetic interference, bending and other non-imbalance factors is eliminated, and purification of unbalanced vibration is realized. Compared with a traditional dynamic balancing method, the method ensures precise acquisition of unbalanced vibration data and obviously improves the precision of dynamic balancing, and the method needs no phase discrimination sensors, reduces the dependence of a system to the installation space and reduces the complexity and the development cost of the system. Besides, the method has a wide range of applications, has a simple process, is conductive to the realization of computerized control, and has good practical application values.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Apparatus and method for measuring vibration characteristics
InactiveUS8960009B2Eliminate vibrationVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingVibration amplitudePower flow
A vibration characteristic measuring apparatus includes a magnetic bearing that generates magnetic force on the rotating body of a multi-stage centrifugal compressor, a displacement sensor that measures the vibration amplitude of the rotating body, a current amplifier that supplies a current to the magnetic bearing, and an excitation controller which outputs an excitation control signal for applying vibration to the rotating body and which measures the response characteristics of the vibration of the rotating body to the excitation control signal. The excitation controller outputs a rotating body control signal obtained by adding a vibration eliminating signal for eliminating unbalance vibration of the rotating body to the excitation control signal when measuring the response characteristics, and the current amplifier supplies a current that generates magnetic force in accordance with the rotating body control signal to the magnetic bearing.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Unbalance compensation method for rotor unbalance coefficient variable-angle iterative search
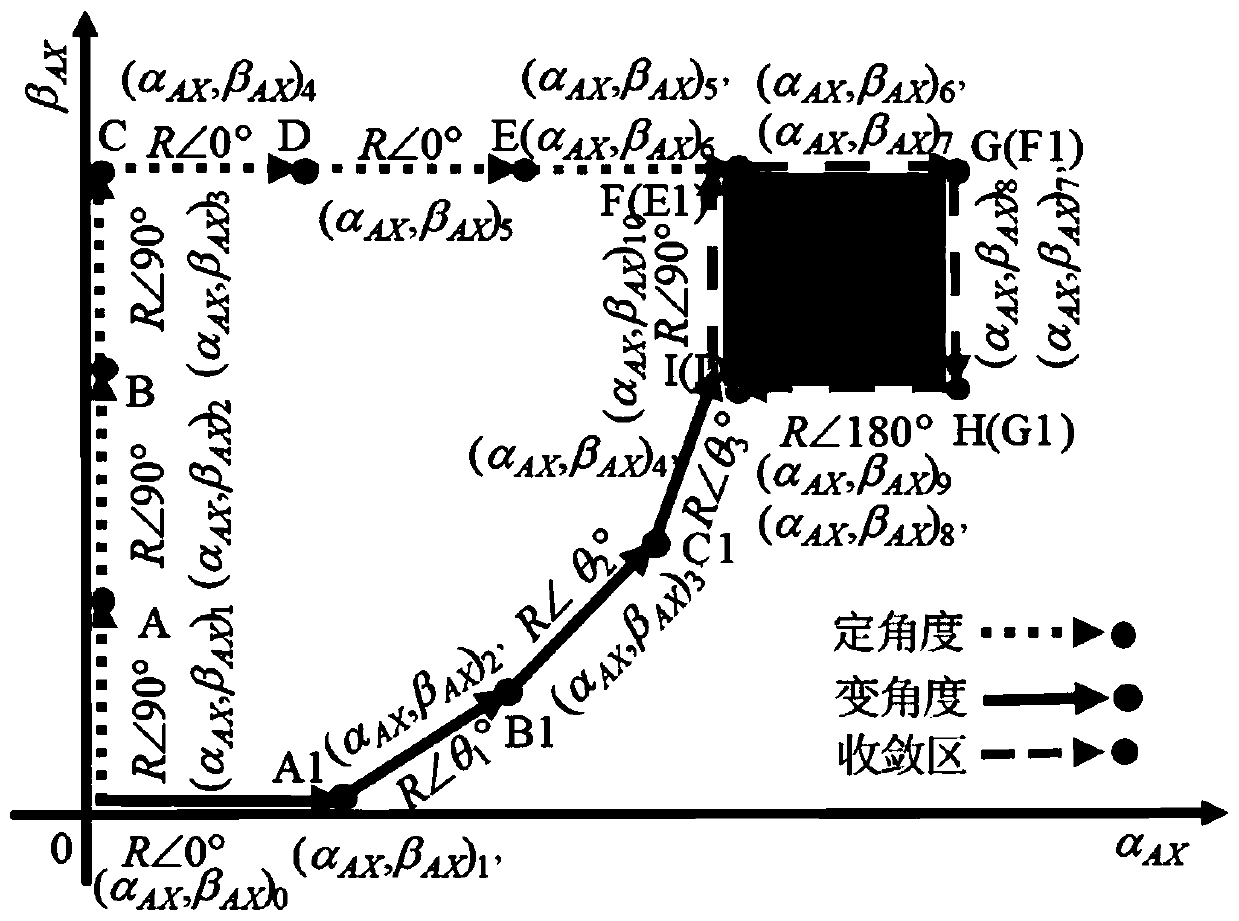
ActiveCN111177943ASimple structureStability impactGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationVibration amplitudeIterative search
The invention discloses an unbalance compensation method for rotor unbalance coefficient variable-angle iterative search. The method comprises the steps of vibration signal processing, variable anglecompensation algorithm recognition coefficient searching and compensation current calculation, wherein a vibration signal processing module calculates a rotor unbalance vibration signal amplitude according to rotor vibration information, rotor rotation angle information and rotation speed information; the variable-angle compensation algorithm is used for searching for recognition coefficients, the rotor unbalance vibration signal amplitude serves as the judgment basis, the unbalance coefficients are repeatedly identified and optimized through a variable-angle iterative search method, and a set of unbalance coefficients enabling the unbalance vibration amplitude to be reduced to the minimum are obtained through iteration. Corresponding compensation current is calculated according to the unbalance coefficient and input into the electromagnetic coil to restrain unbalance vibration of the rotor. The method can be used for an active rotor system with an active control unit, unbalance on-line compensation of the active rotor system is achieved, and unbalance vibration in the acceleration and deceleration operation process within the whole rotating speed range is restrained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dynamic balance method for magnetic suspension molecular pump
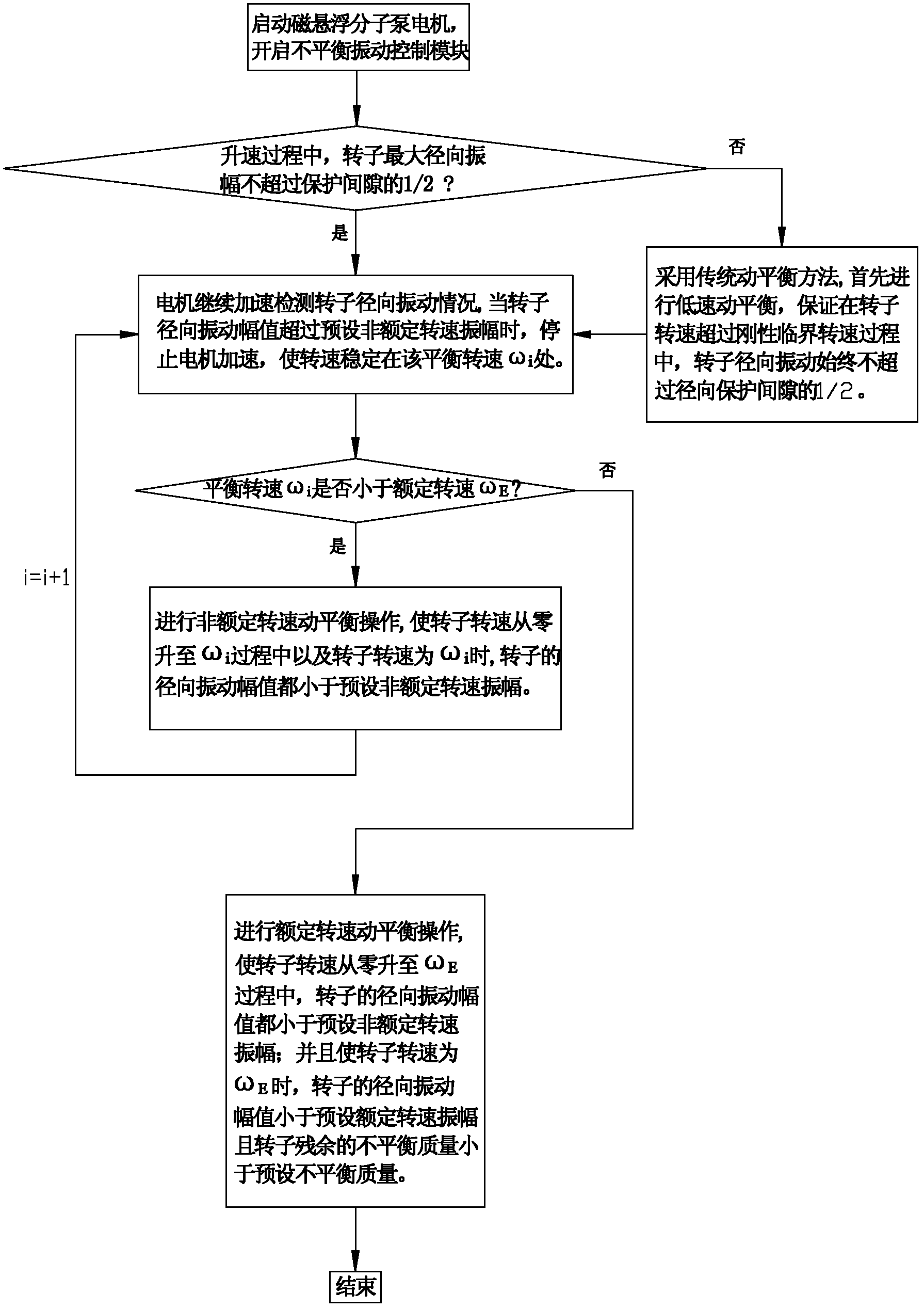
ActiveCN102425560AEasy to operateEfficient Balancing OperationPump controlAxial flow pumpsVibration controlDynamic balance
The invention discloses a dynamic balance method for a magnetic suspension molecular pump. After a motor of the magnetic suspension molecular pump is started, an unbalanced vibration control module is started; and if unbalanced mass of a rotor ensures that the maximum radial amplitude of the rotor is not greater than 1 / 2 a protection gap in a speed raising process under the control of the unbalanced vibration control module, the unbalanced vibration control module can inhibit the same frequency vibration of the rotor to ensure that the rotation speed of the rotor can exceed rigid critical rotation speed of the rotor quickly, so the rotor of the magnetic suspension molecular pump is subjected to dynamic balance in high speed. By the dynamic balance method, the rotor of the magnetic suspension molecular pump can be directly subjected to dynamic balance in high speed; and the steps are simple and the method is high in efficiency.
Owner:KYKY TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com