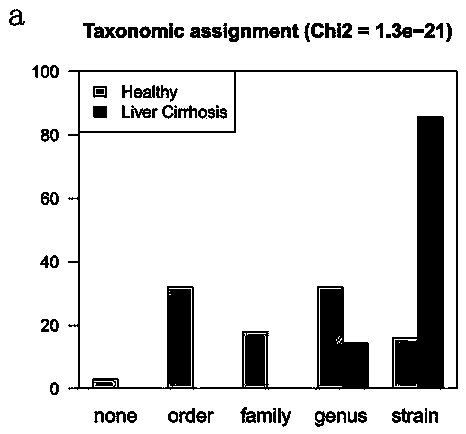
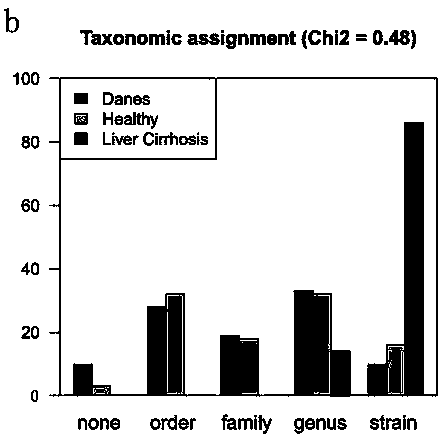
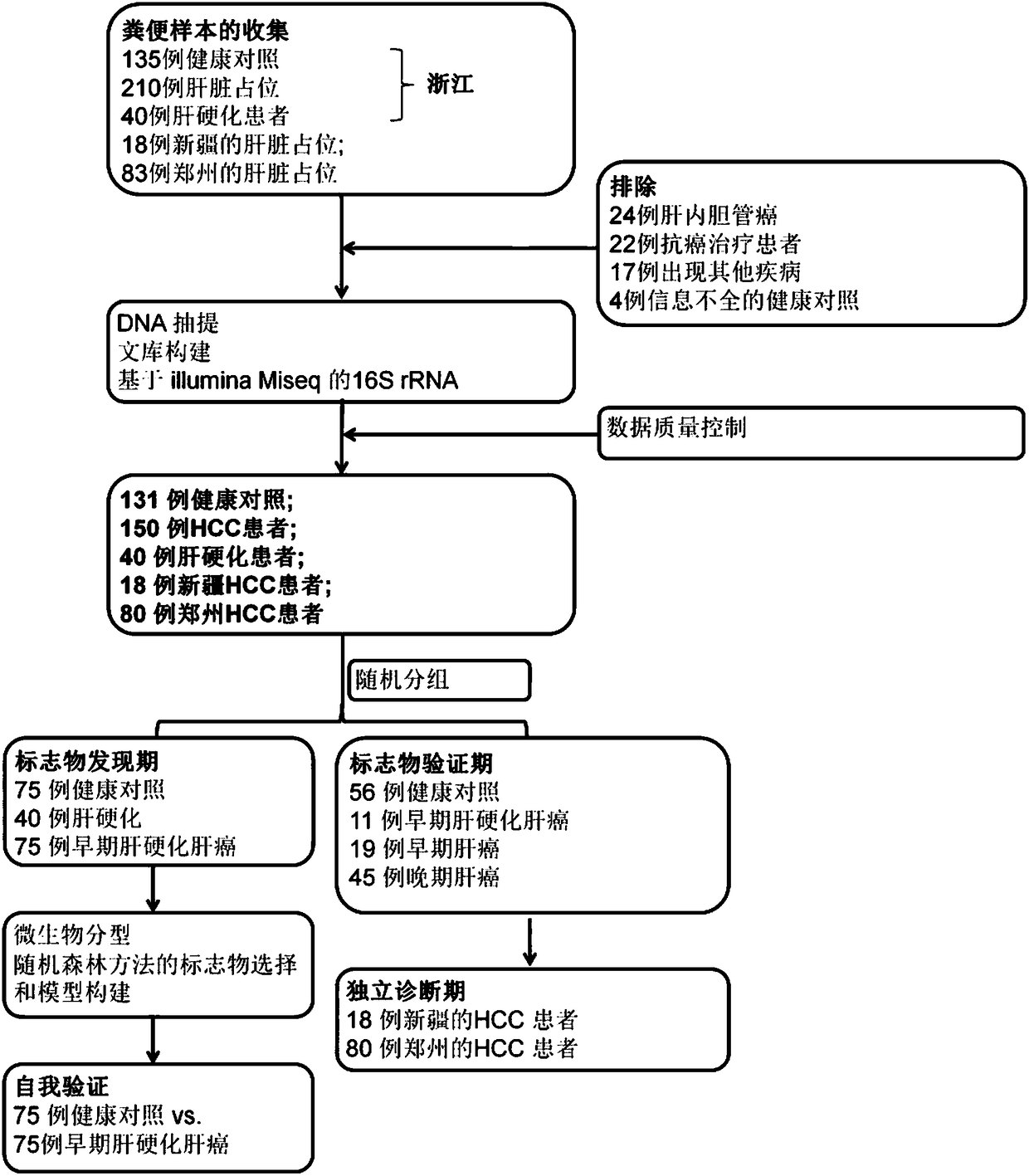
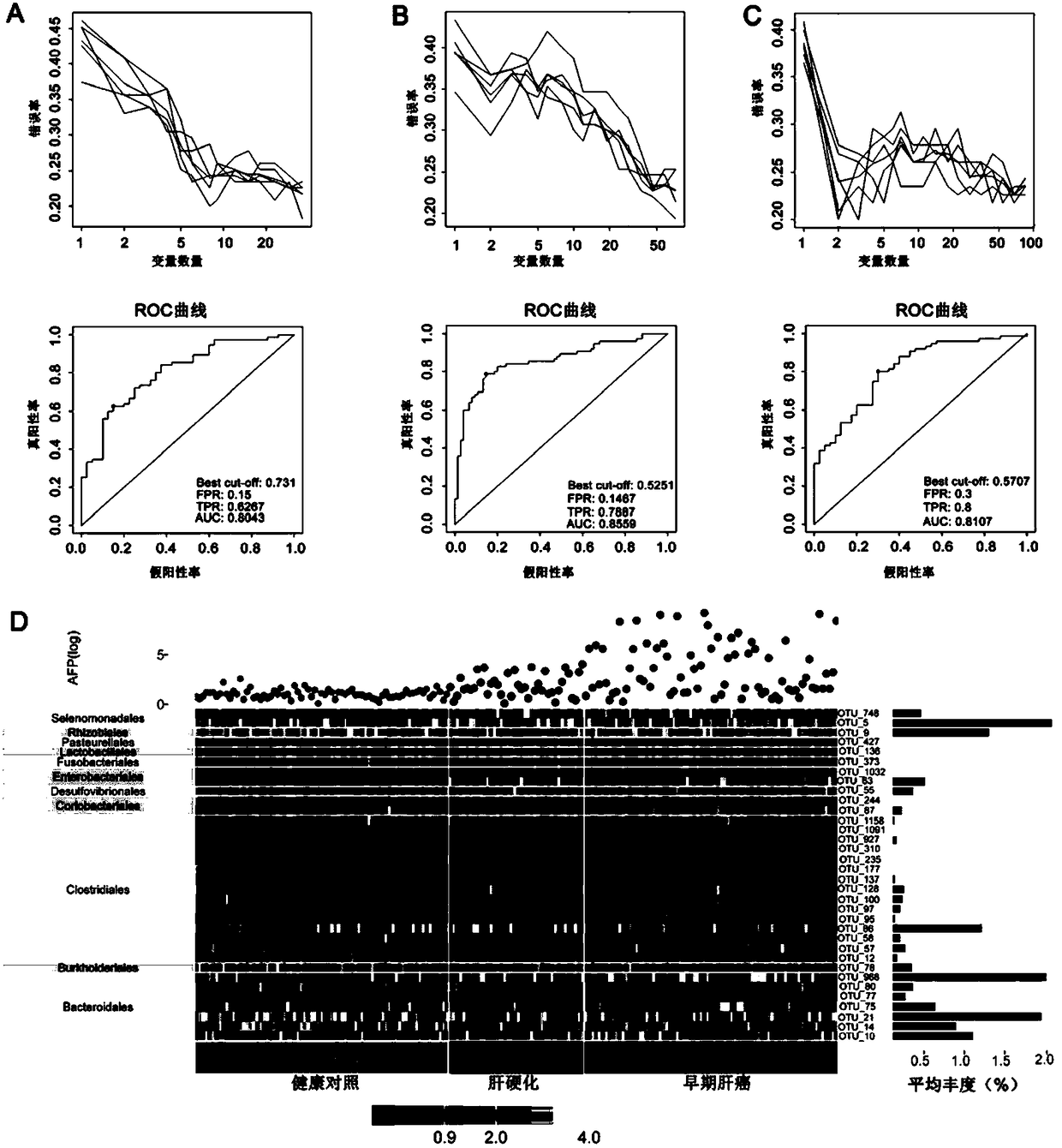
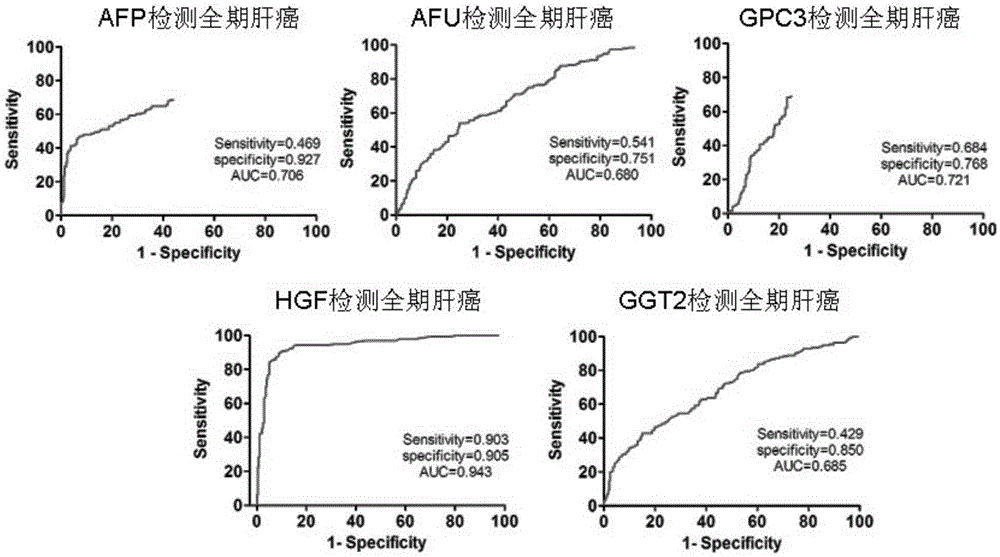
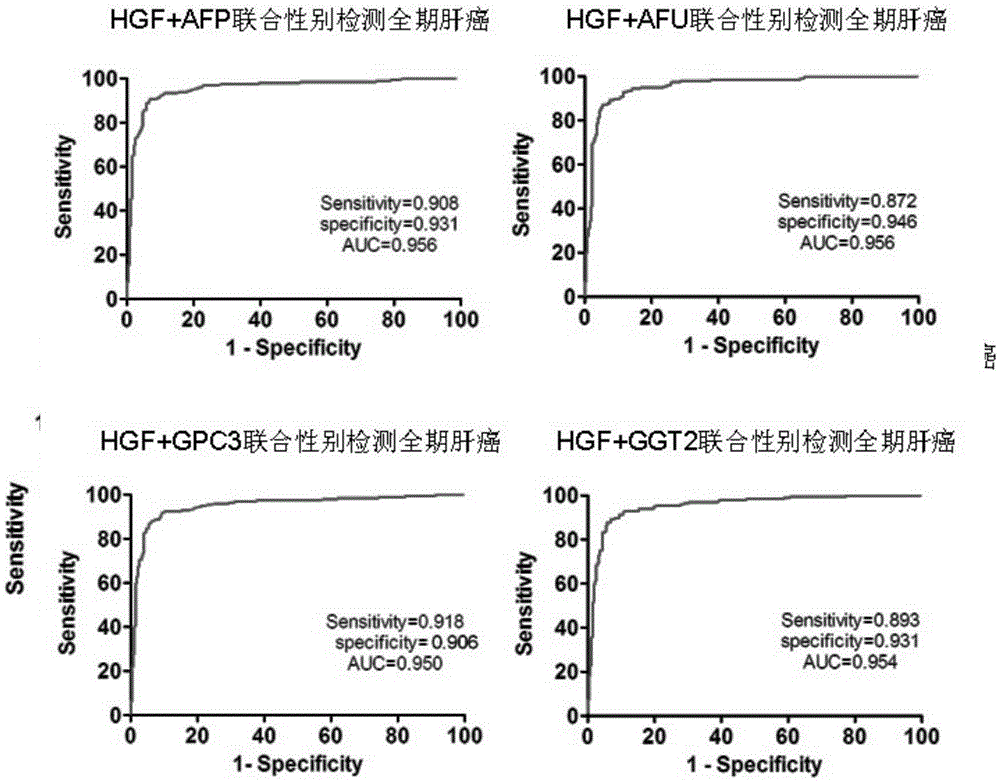
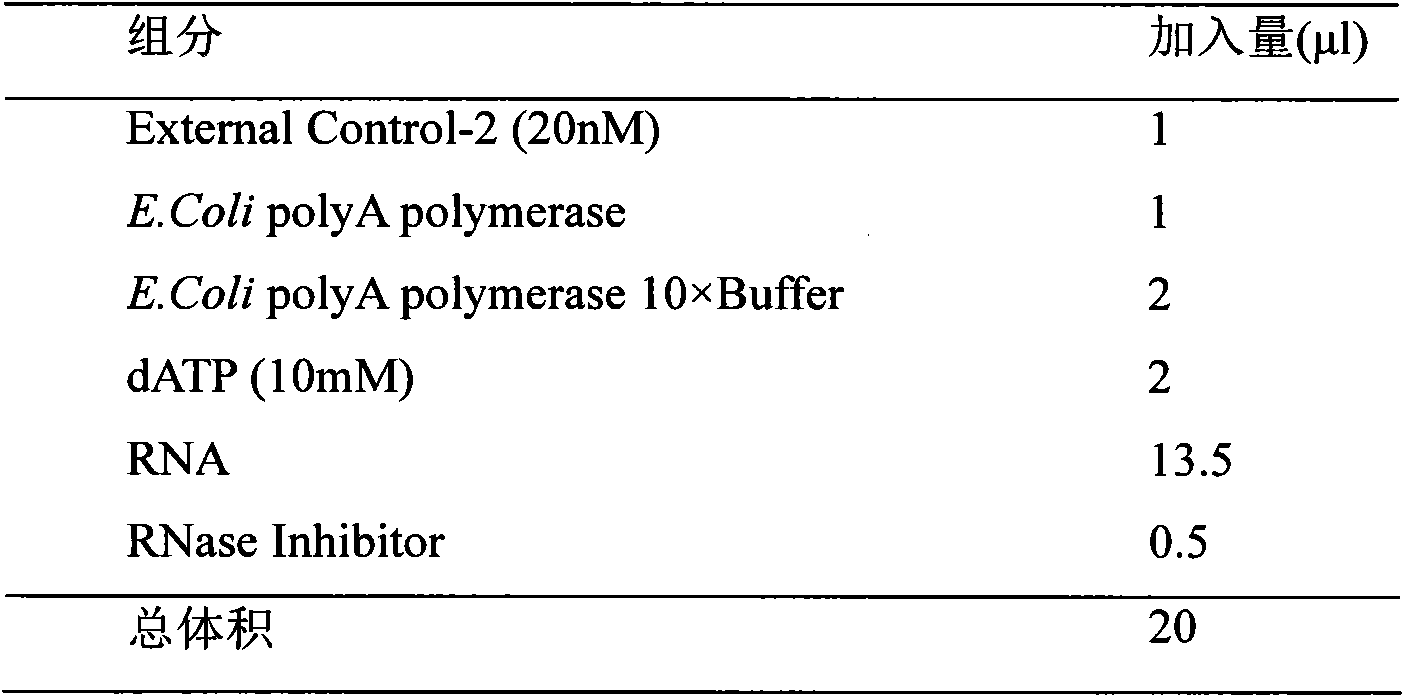
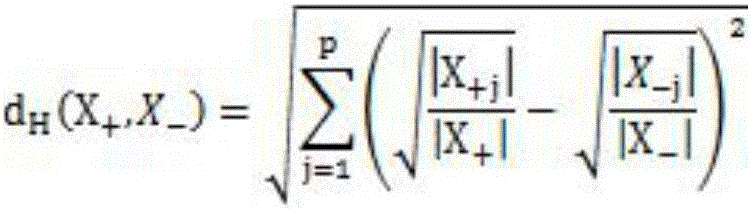Patents
Literature
109 results about "Cirrhotic patient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
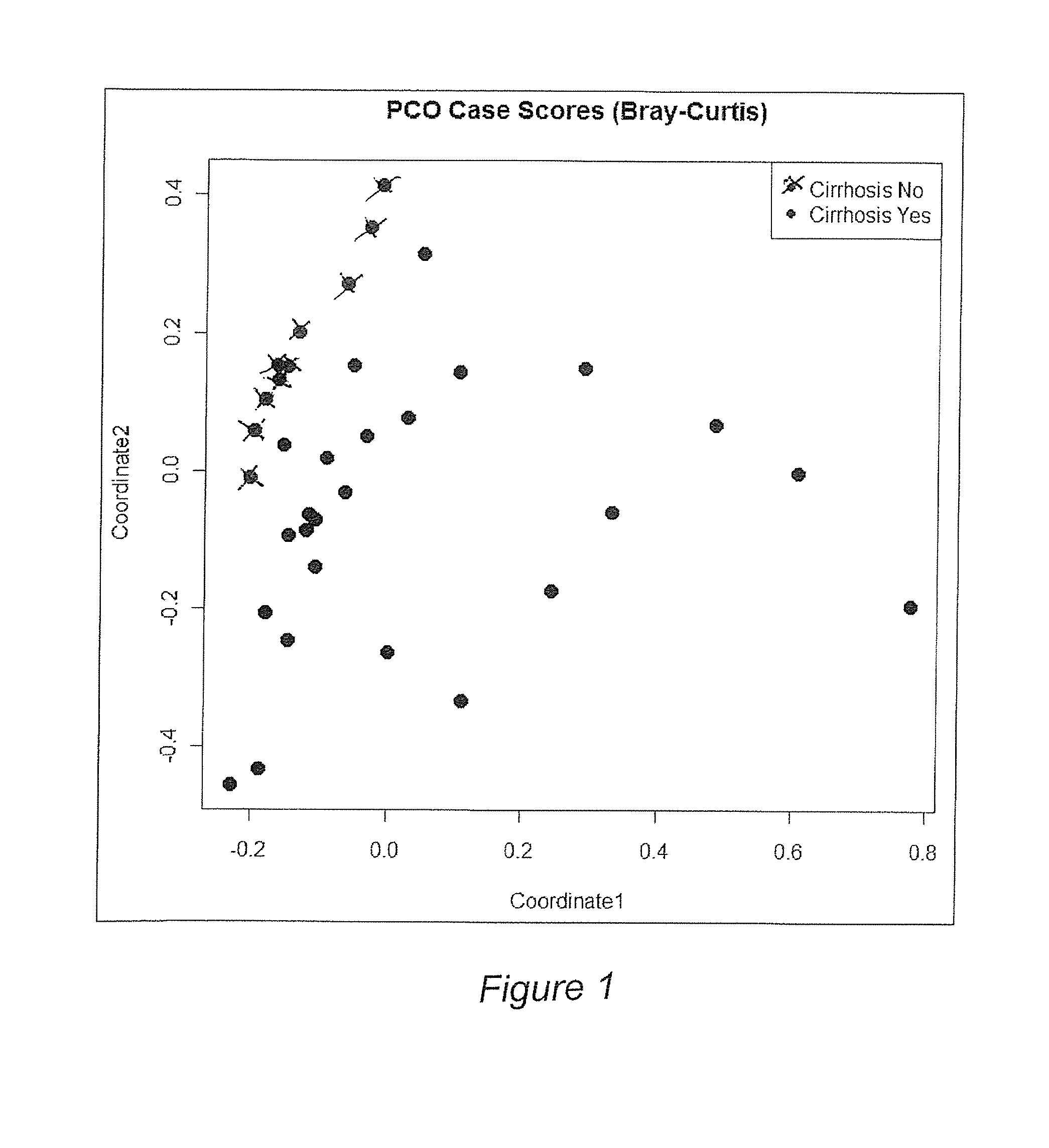
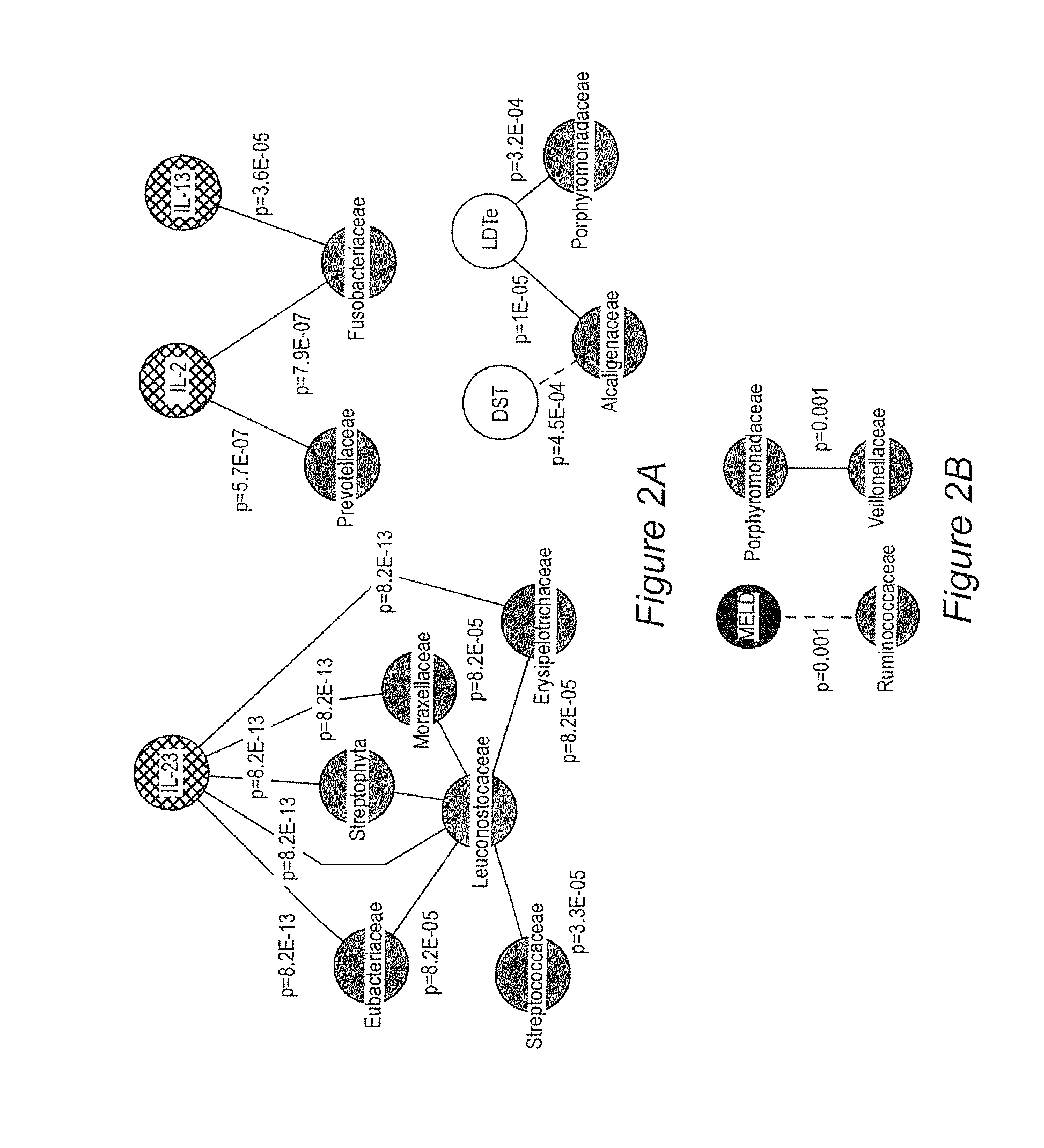
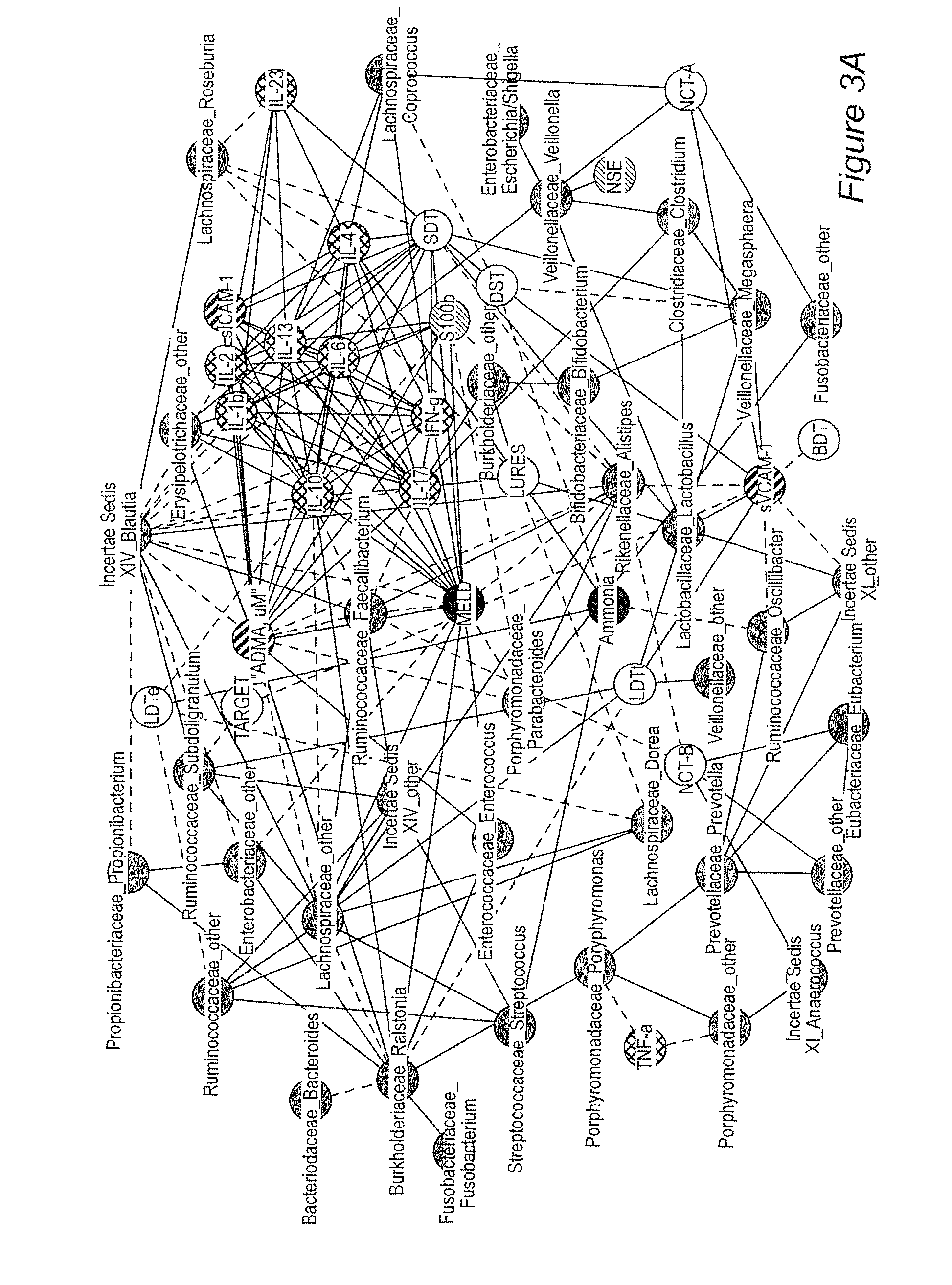
Gut microflora as biomarkers for the prognosis of cirrhosis and brain dysfunction
InactiveUS20140179726A1Efficacy of treatmentReduce the amount requiredBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseTreatment targets
A systems biology approach is used to characterize and relate the intestinal (gut) microbiome of a host organism (e.g. a human) to physiological processes within the host. Information regarding the types and relative amounts of gut microflora is correlated with physiological processes indicative of e.g., a patient's risk of developing a disease or condition, likelihood of responding to a particular treatment, for adjusting treatment protocols, etc. The information is also used to identify novel suitable therapeutic targets and / or to develop and monitor the outcome of therapeutic treatments. An exemplary disease / condition is the development of hepatic encephalopathy (HE), particularly in patients with liver cirrhosis.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV +1
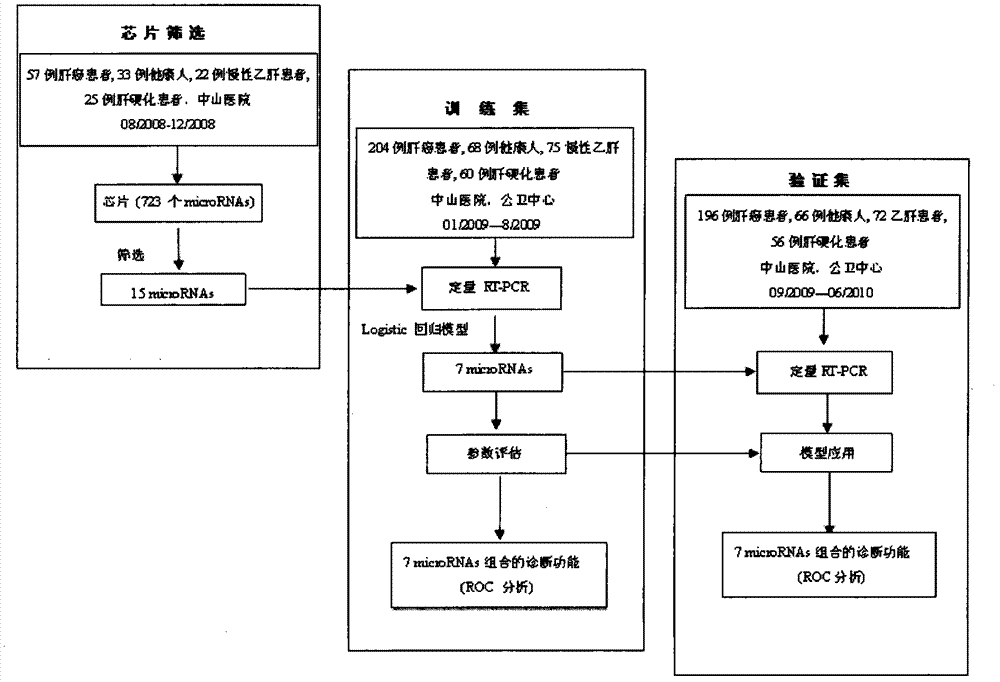
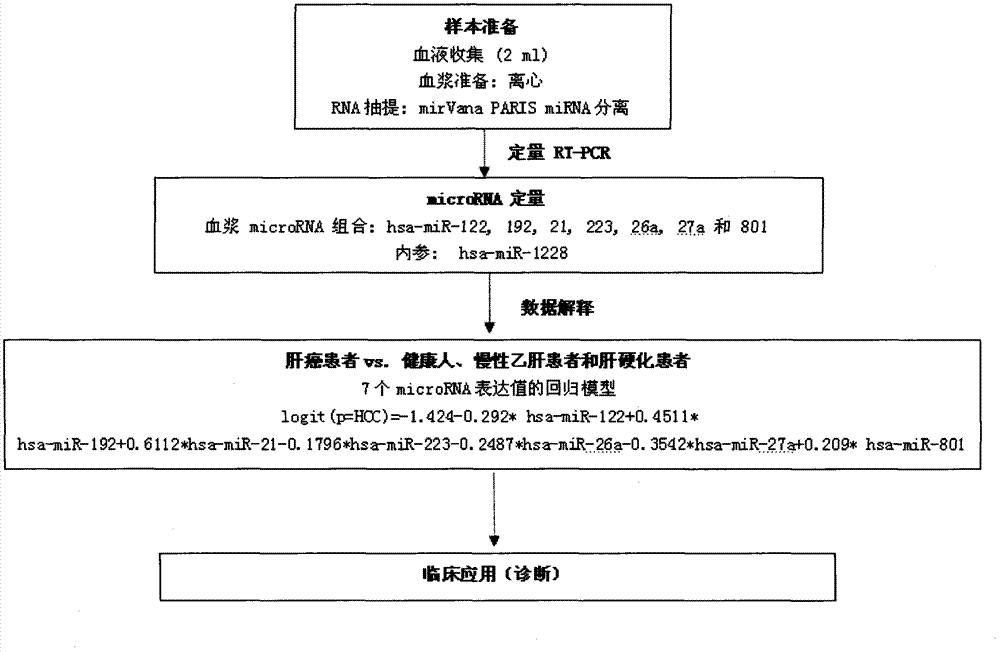
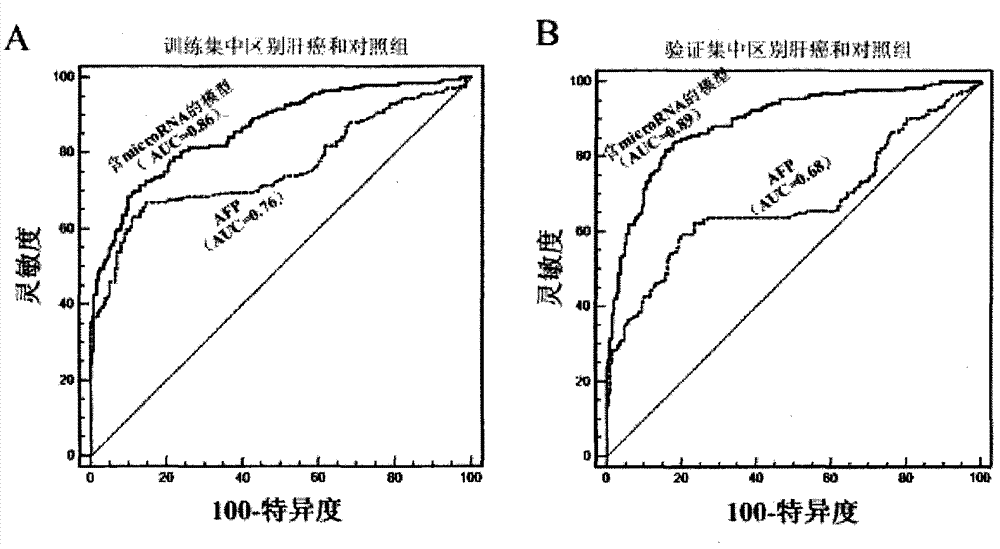
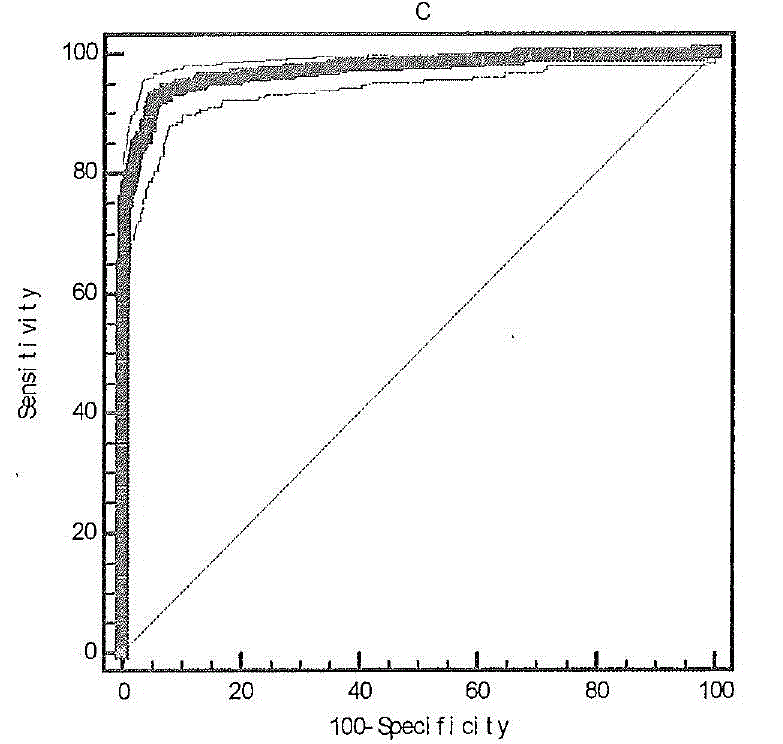
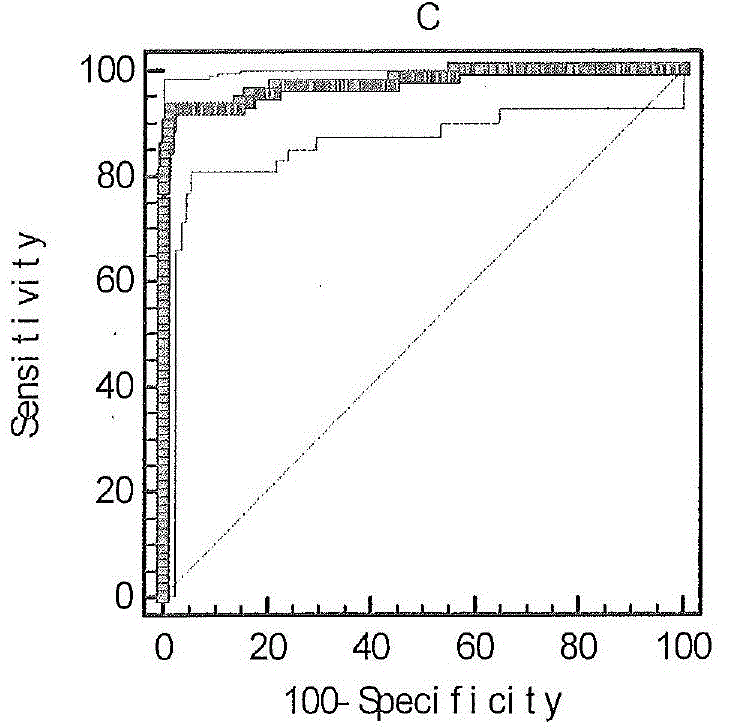
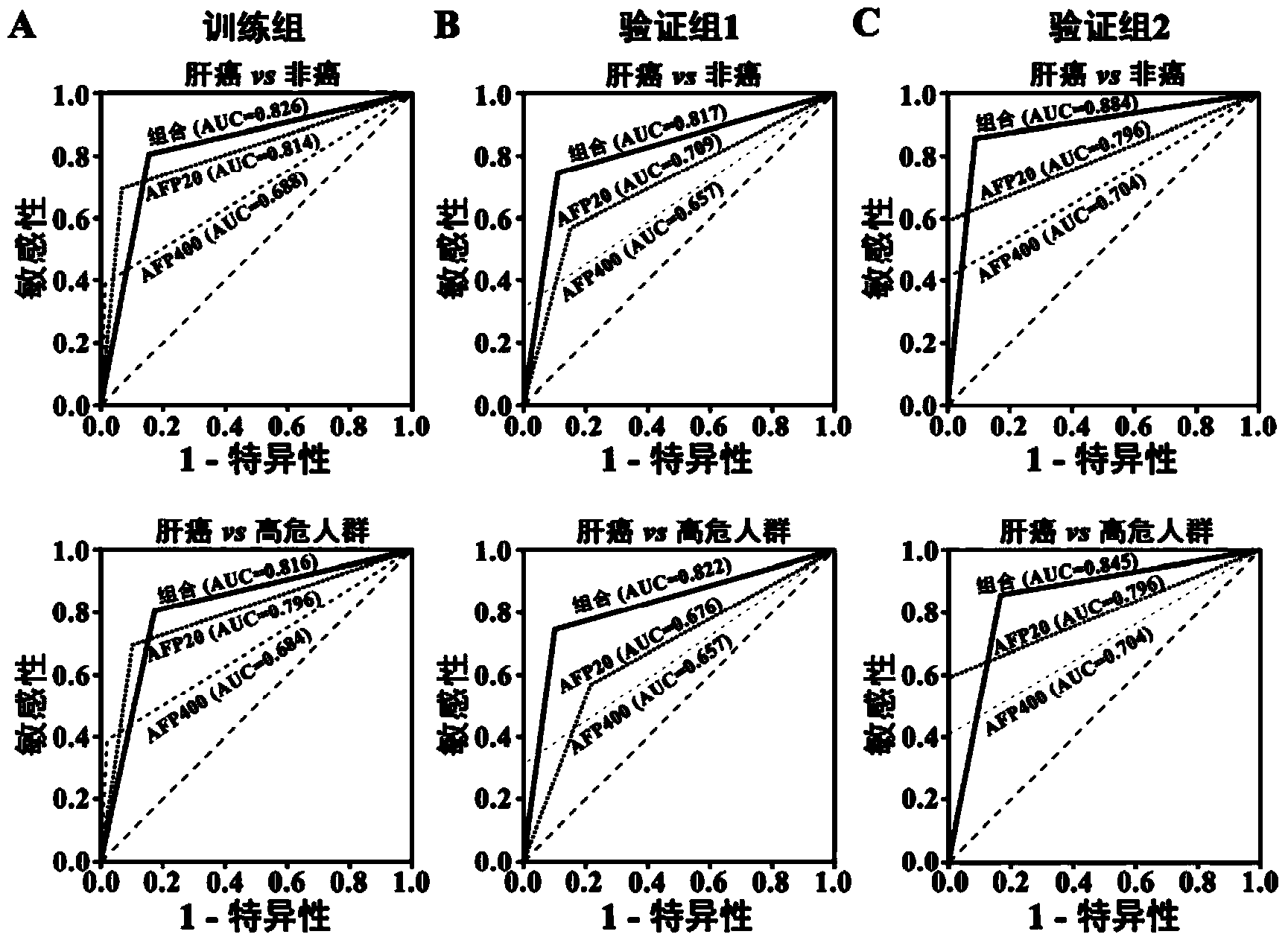
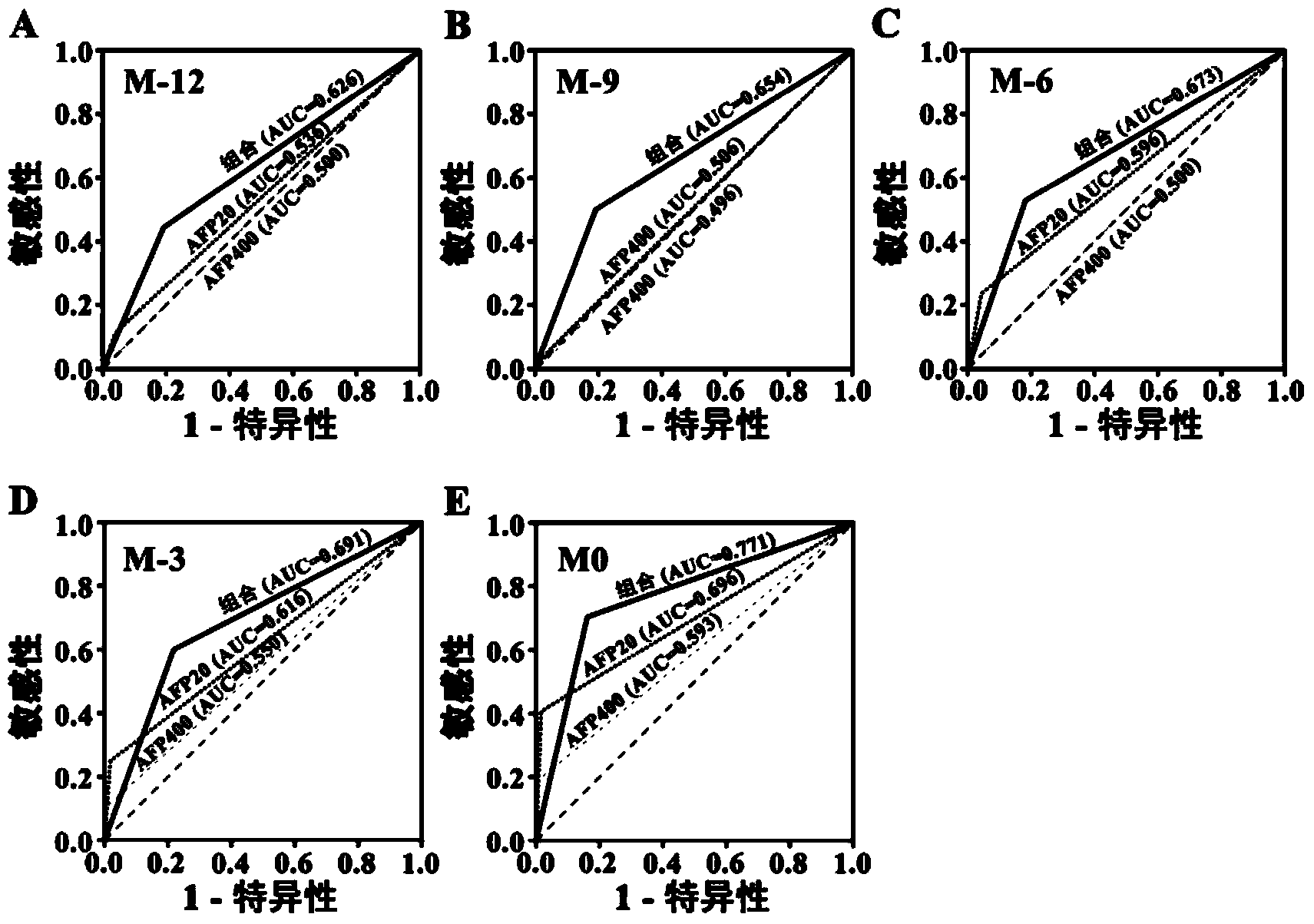
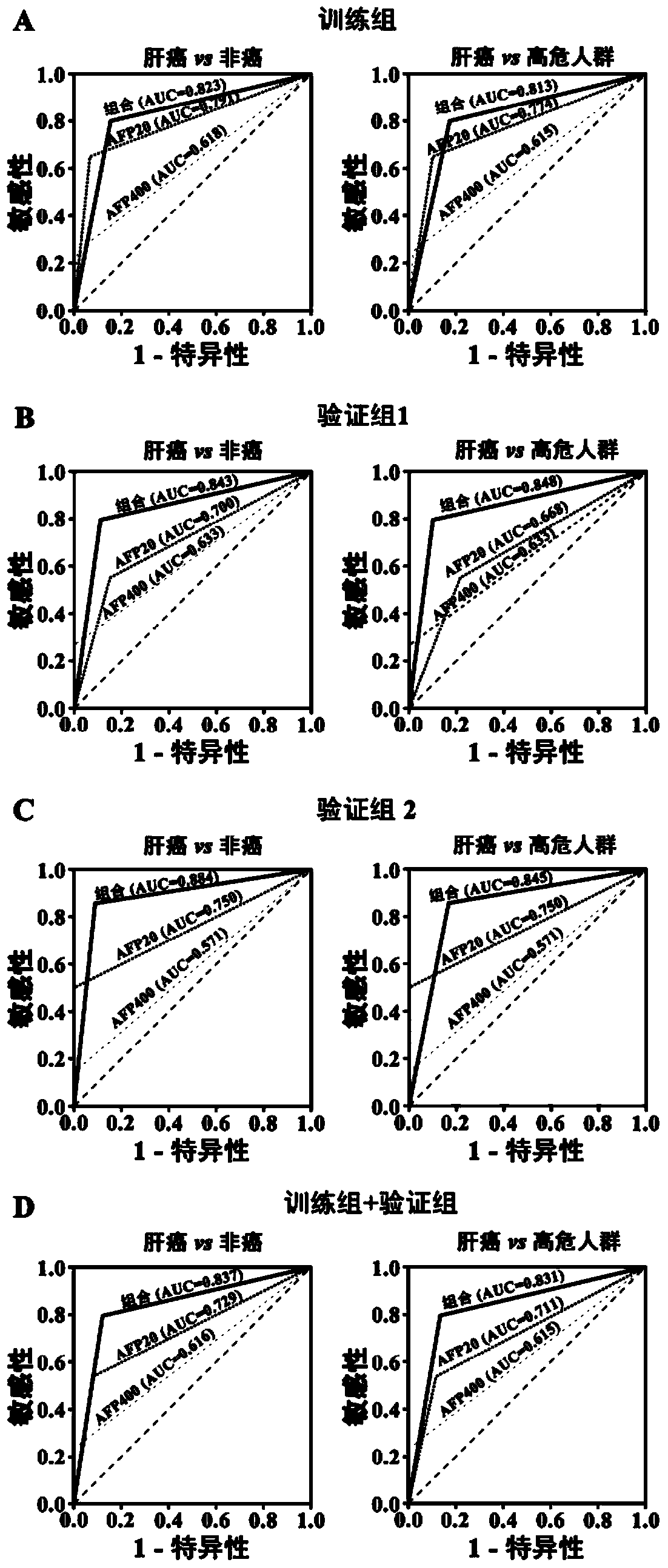
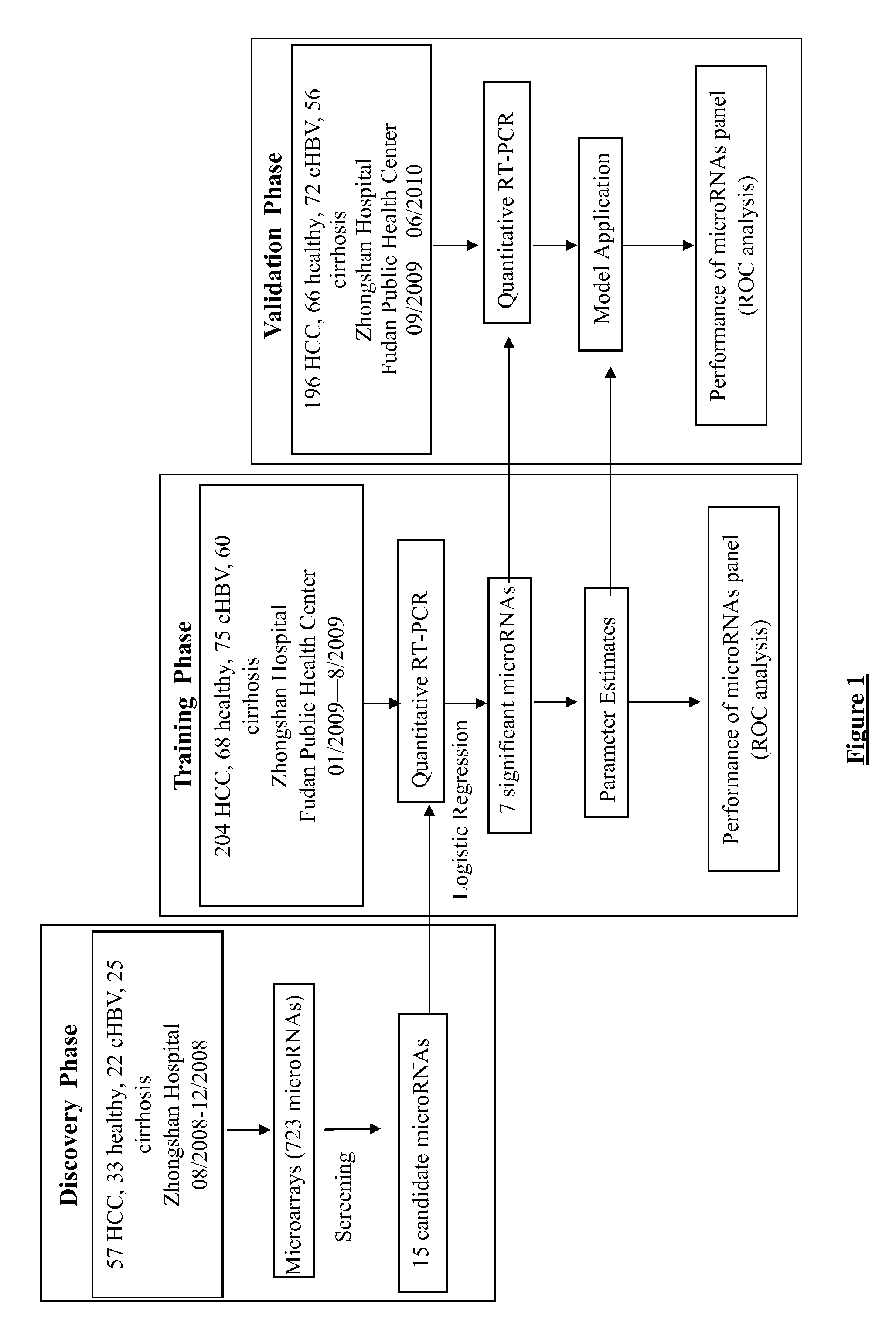
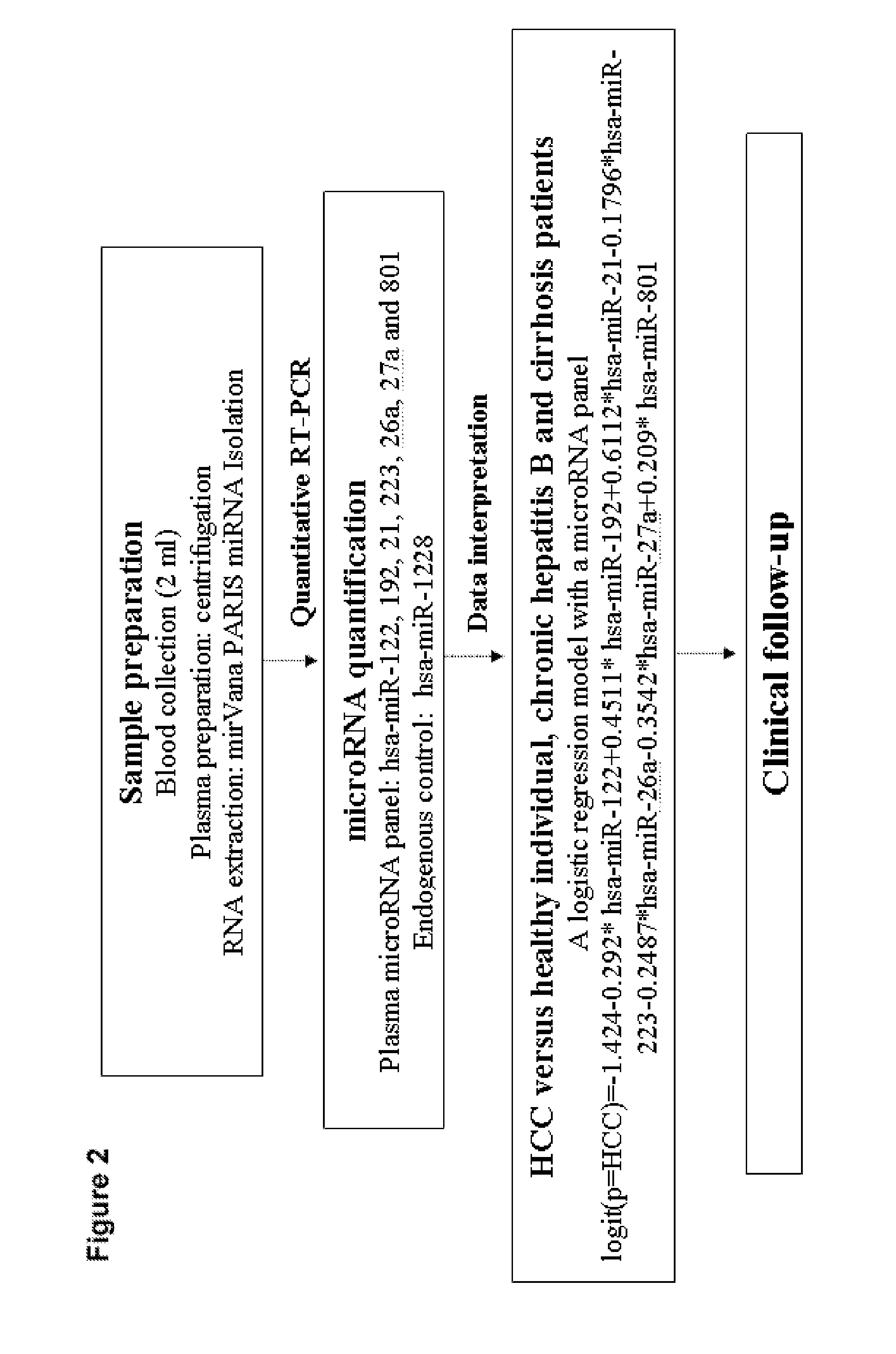
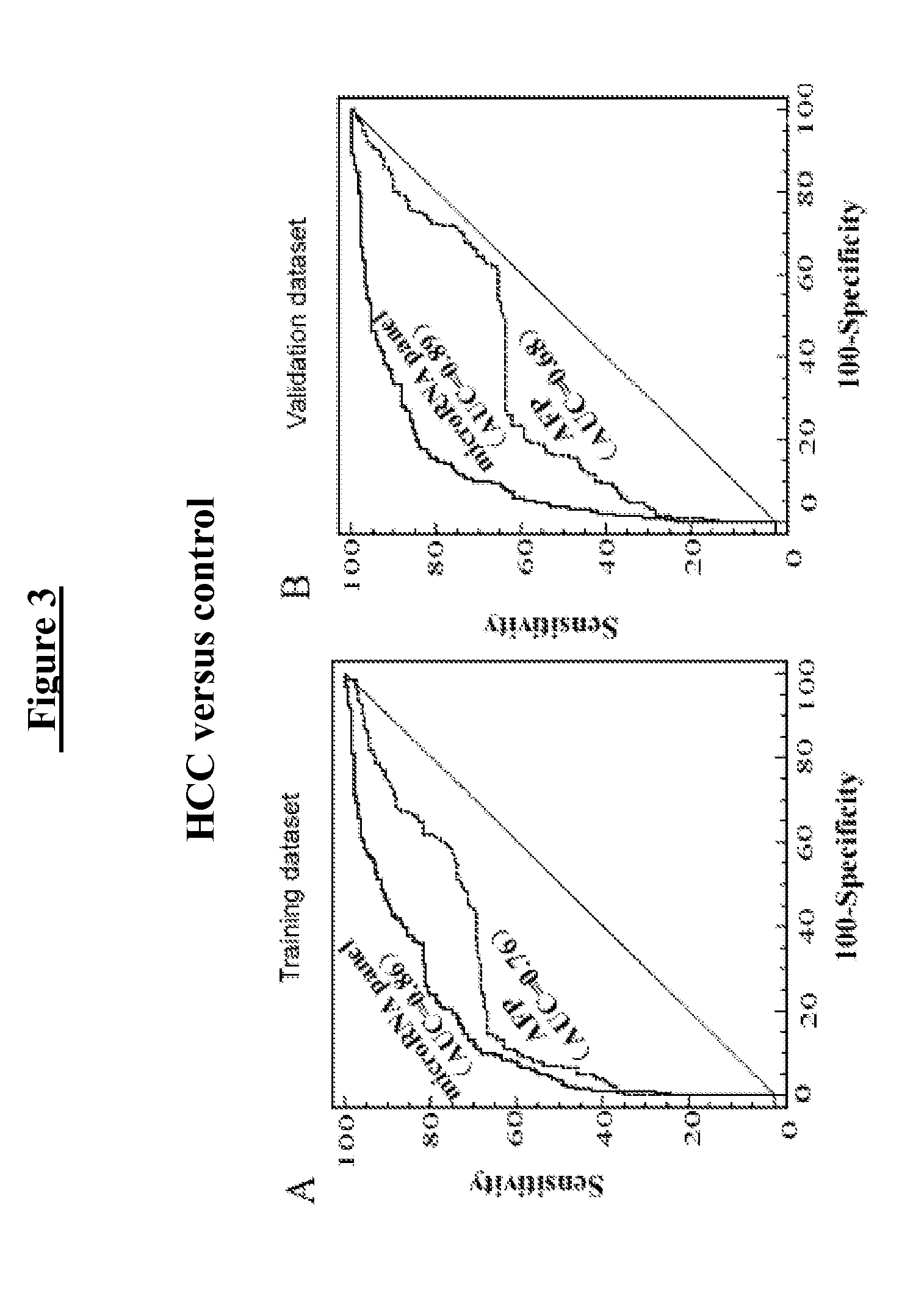
Liver cancer diagnostic marker composed of blood plasma microRNA (micro ribonucleic acid) and new method for diagnosing liver cancer
ActiveCN102776185AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationChronic hepatitisEarly Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The invention relates to a liver cancer diagnostic marker composed of blood plasma microRNA (micro ribonucleic acid), a kit containing the marker and a new method for diagnosing liver cancer (in particular early liver cancer). The liver cancer diagnostic marker is composed of a plurality of nucleic acid molecules, wherein each nucleic acid molecule is used for coding at least one microRNA sequence; and preferably, the liver cancer diagnostic marker is composed of nucleic acid molecules for coding hsa-miR-122, hsa-miR-192, hsa-miR-21, hsa-miR-223, hsa-miR-26a, hsa-miR-27a, hsa-miR-801 and hsa-miR-1228. The kit can be applied to diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma, in particular early hepatocellular carcinoma, or to differentiating the blood plasma of at least one hepatocellular carcinoma sufferer from the blood plasma of at least one healthy individual, and the blood plasma of at least one chronic hepatitis b sufferer or the blood plasma of at least one cirrhosis sufferer.
Owner:JUSBIO SCI SHANGHAI CO LTD
Kit for detecting liver fibration and liver cirrhosis
The invention discloses a kit for detecting liver fibration or liver cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B virus infection. Whether an individual has liver fibration or liver cirrhosis conditions or not is determined through detecting the level of CHI3L1 in an individual sample. The kit includes: (1) an antibody bound to the CHI3L1; (2) a labeled antibody bound to the CHI3L1 when the CHI3L1 is bound to the antibody limited in (1); and (3) a standard sample composed of a solution containing a known amount of the CHI3L1, wherein the CHI3L1 is from serum of a liver fibration or liver cirrhosis patient caused by the hepatitis B virus infection.
Owner:HANGZHOU PROPRIUM BIOTECH
Molecular markers of hepatocellular carcinoma and their applications
InactiveUS20090181379A1Precise definitionFacilitate prognosisCompound screeningApoptosis detectionEtiologyProteomics methods
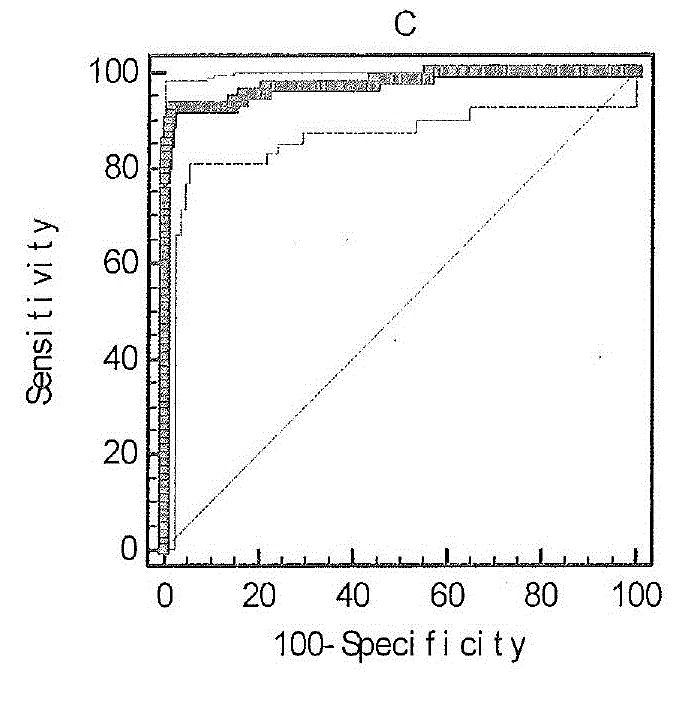
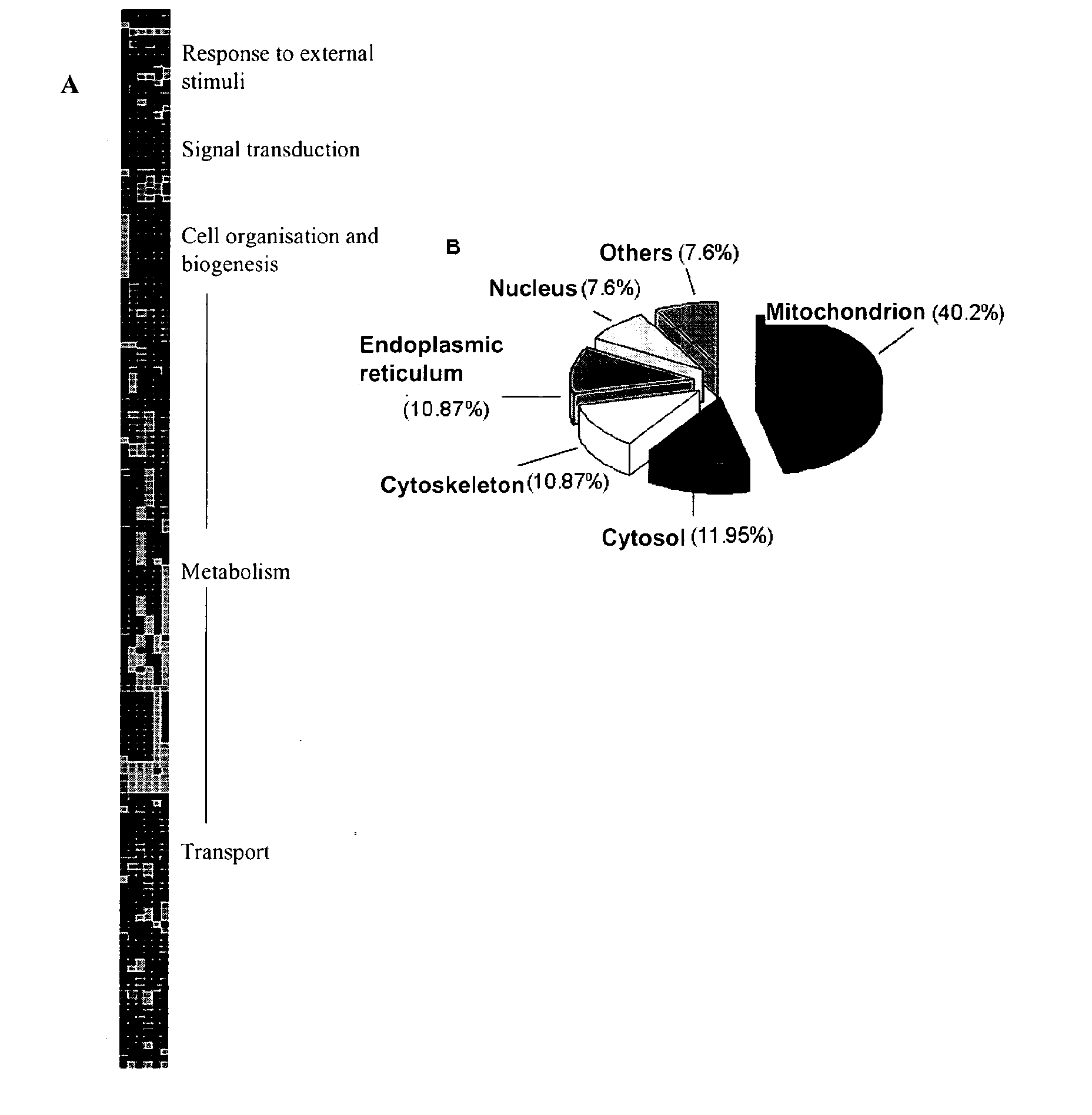
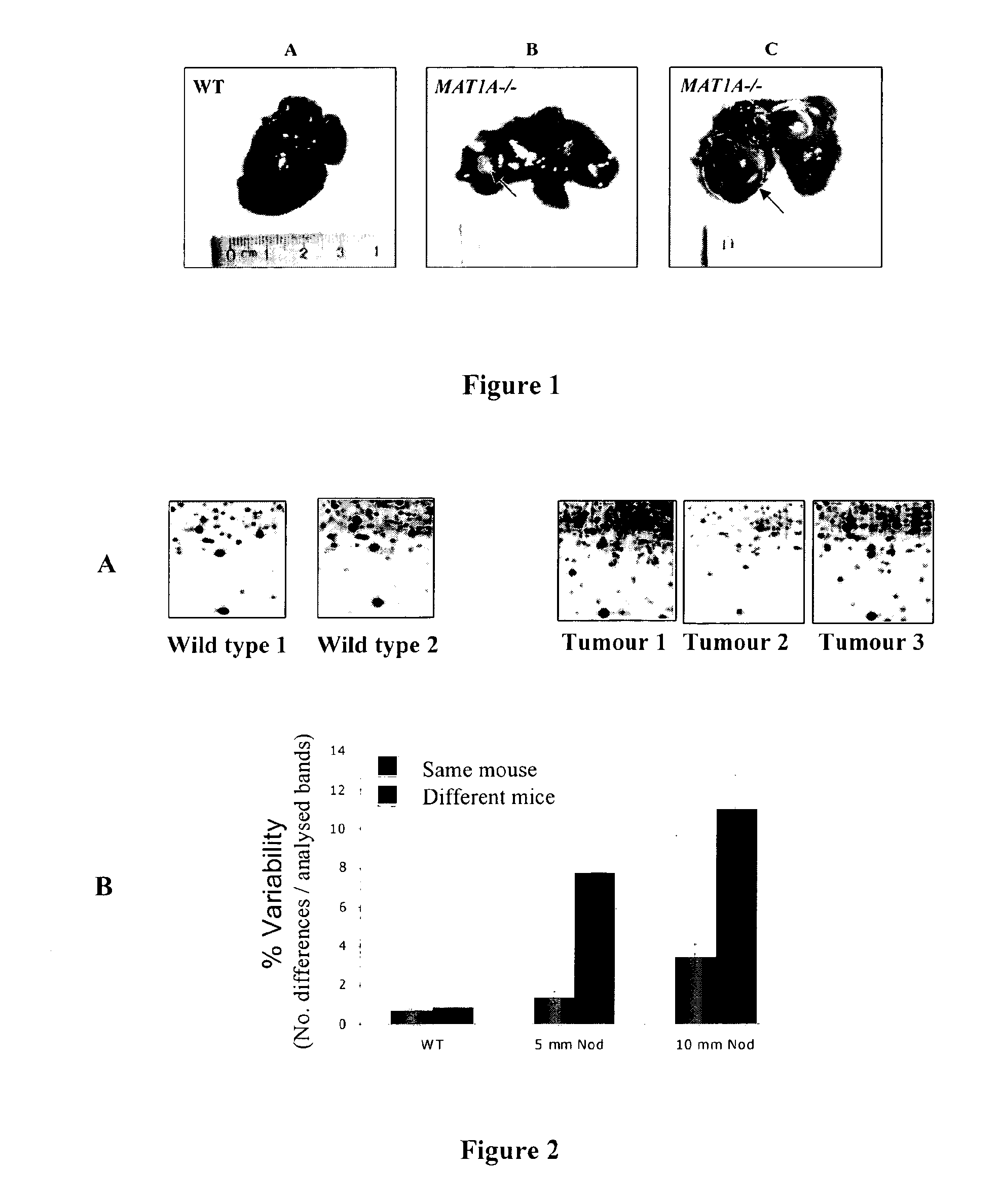
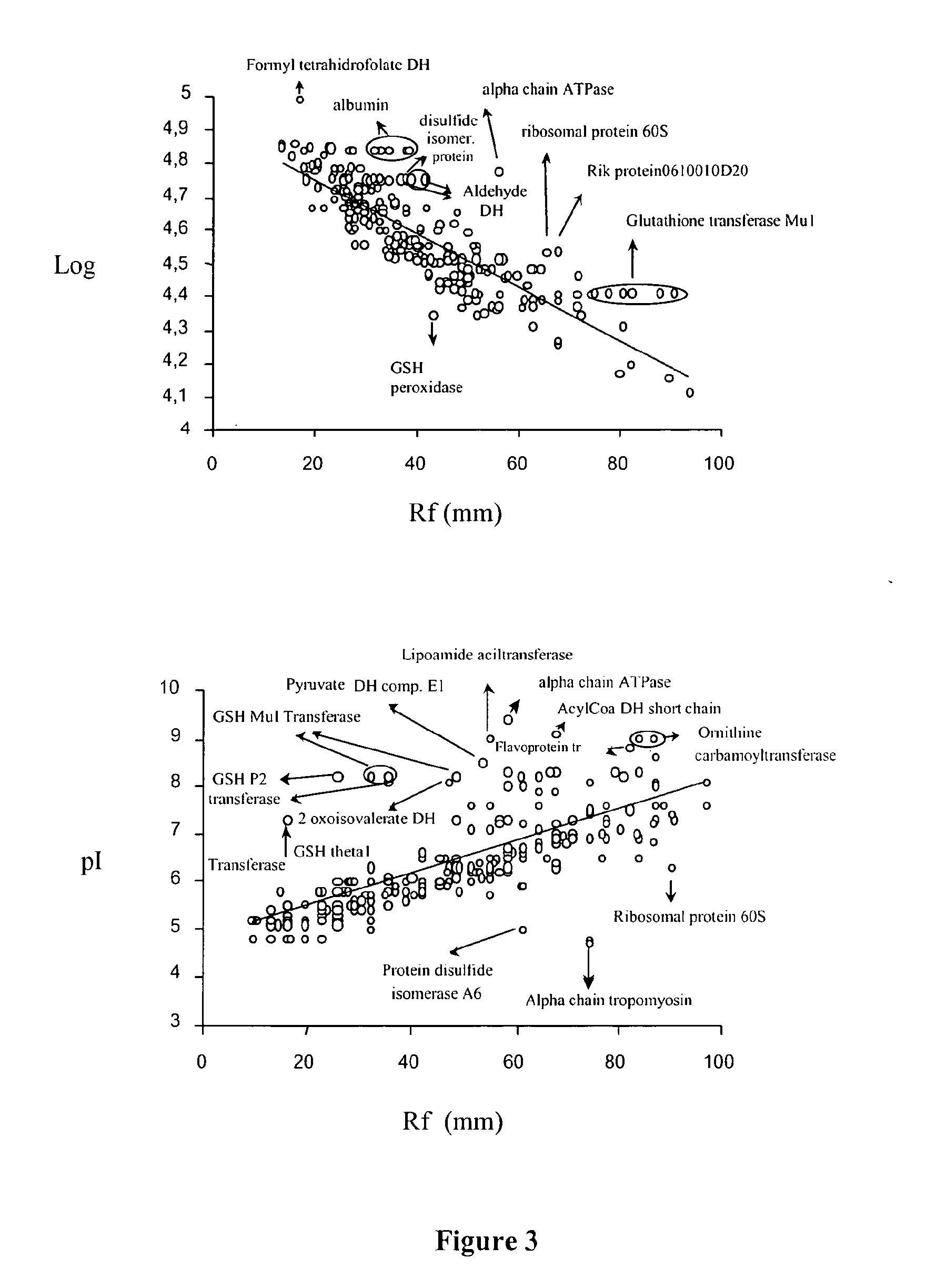
By means of a proteomic approach, the markers of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the liver of a knockout mouse (MAT1A− / −) have been identified for the MAT1A gene (deficient in the synthesis of S-adenosylmethionine). 27 proteins have been detected the expression thereof is altered in, at least, 50% of the analysed tumours. Amongst them, 13 proteins have been validated in biopsies of patients with HCC of different etiology, and 7 of them have been validated in biopsies of patients with liver cirrhosis, a stage prior to the development of HCC, which makes it possible to differentiate between prior stages of the disease and even between different etiologies (viral and alcoholic). Having a panel of markers available may contribute to more accurately defining the alterations associated with the development of HCC and thus facilitate prognosis and diagnosis of this disease.
Owner:PROYECTO DE BIOMEDICINA CIMA
Liver cancer diagnosis markers composed of serum microRNA (microribonucleic acid) and diagnosis kit
ActiveCN104372087AEasy to getTimely responseMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSerum igeSerum microrna
The invention discloses a liver cell liver cancer diagnosis combination composed of serum microRNA (microribonucleic acid) and a kit the combination. The liver cancer diagnosis combination comprises microRNAs:hsa-miR-29a, hsa-miR-29c, hsa-miR-133a, hsa-miR-143, has-miR-145, hsa-miR-192 and hsa-miR-505. The diagnosis combination and kit can be used for distinguishing a liver cancer patient from a healthy person, hepatitis virus carrier, chronic hepatitis patient or hepatocirrhosis patient.
Owner:江苏阔然生物医药科技有限公司
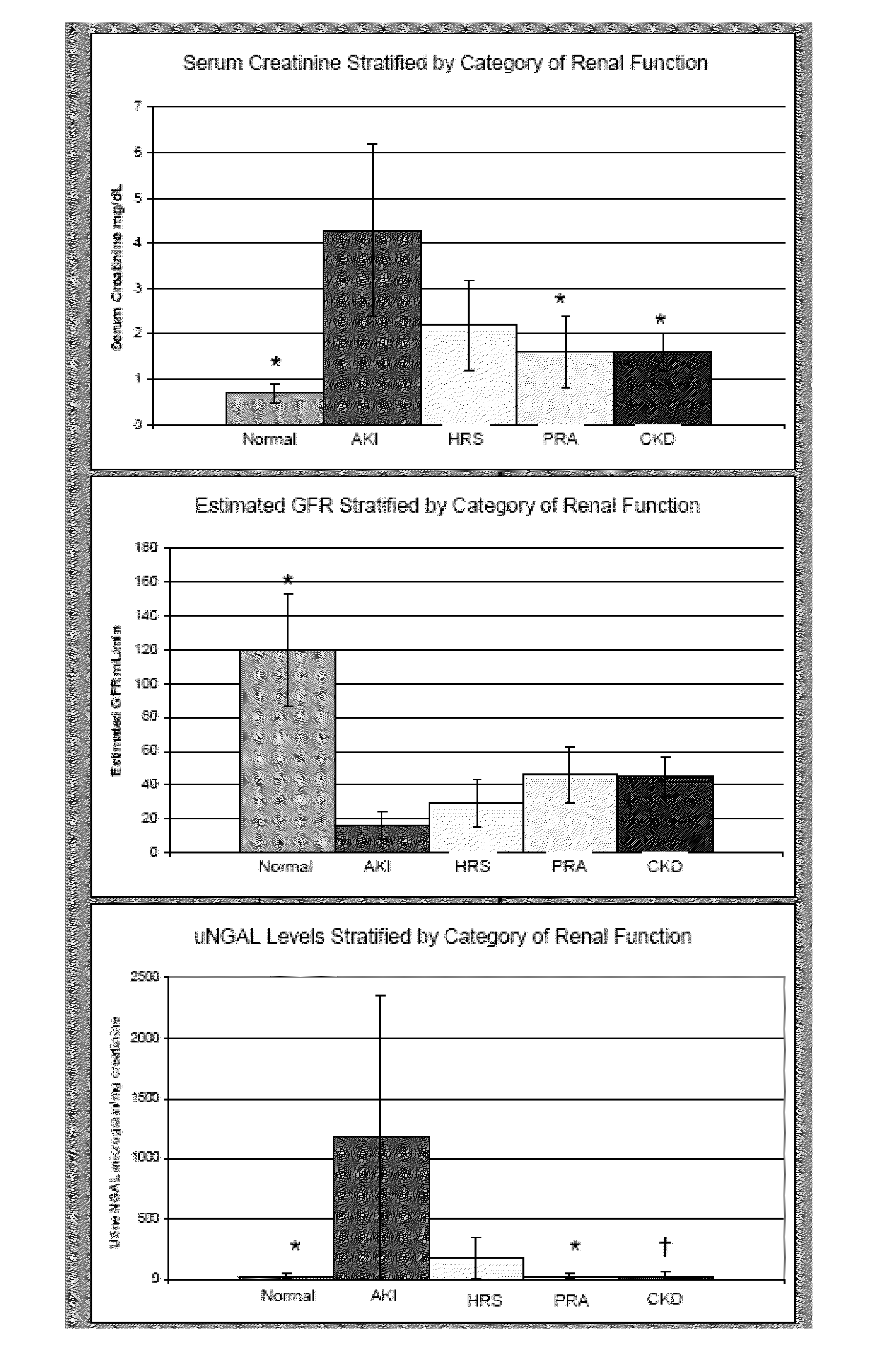
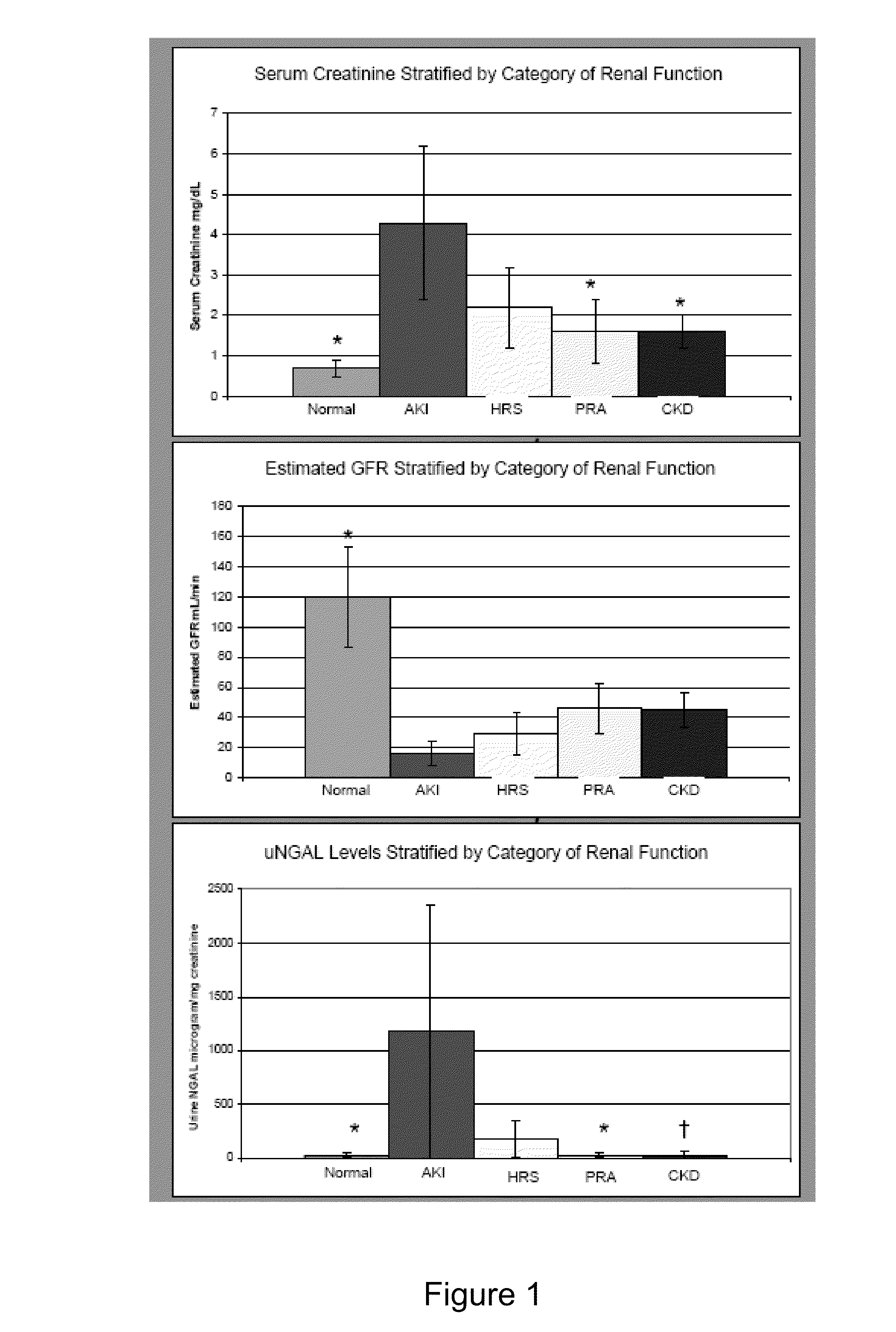
Use of urinary ngal to distinguish kidney disease and predict mortality in subjects with cirrhosis
InactiveUS20100233740A1Increase opportunitiesLow chanceDisease diagnosisBiological testingMortality rateNGAL Protein
In one embodiment, the present invention is directed to methods for diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI) and hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) in cirrhosis patients, and to methods for distinguishing between AKI and / or HRS and / or other kidney diseases in cirrhosis subjects. In another embodiment, the present invention is directed to prognostic methods for predicting disease-specific mortality in cirrhosis patients. In some aspects, the diagnostic and prognostic methods of the invention are based on determining whether a bodily fluid sample, such as a urine sample, contains an amount of NGAL protein that exceeds or is less than a certain threshold level, or that falls within a certain range.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Inhibitor for the onset and progress of liver cancer to be used in hepatitis c virus-positive human liver cirrhosis patients
InactiveUS20070197647A1Avoid developmentInhibit progressBiocideOrganic active ingredientsIsoleucine+LeucineTert-leucine
The present invention provides, as a pharmaceutical agent having an effect to inhibit the development and / or progression of liver cancer in hepatitis C virus-positive human cirrhosis patients, an agent for inhibiting the development and / or progression of liver cancer in hepatitis C virus-positive human cirrhosis patients, which contains three kinds of amino acids of isoleucine, leucine and valine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
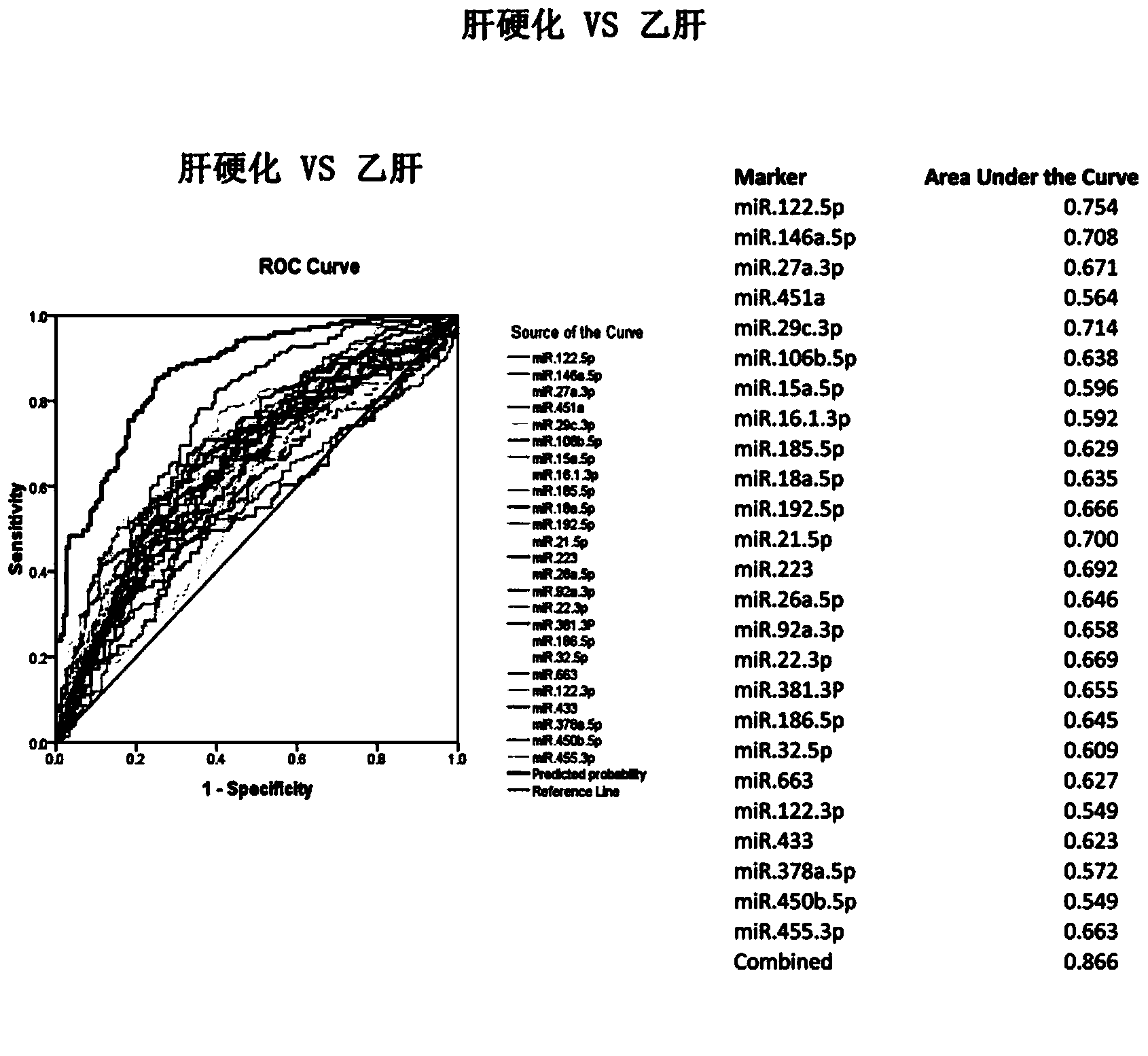
microRNA molecular marker of liver cirrhosis and use thereof
InactiveCN104232637AEasy to operateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicroRNABlood plasma
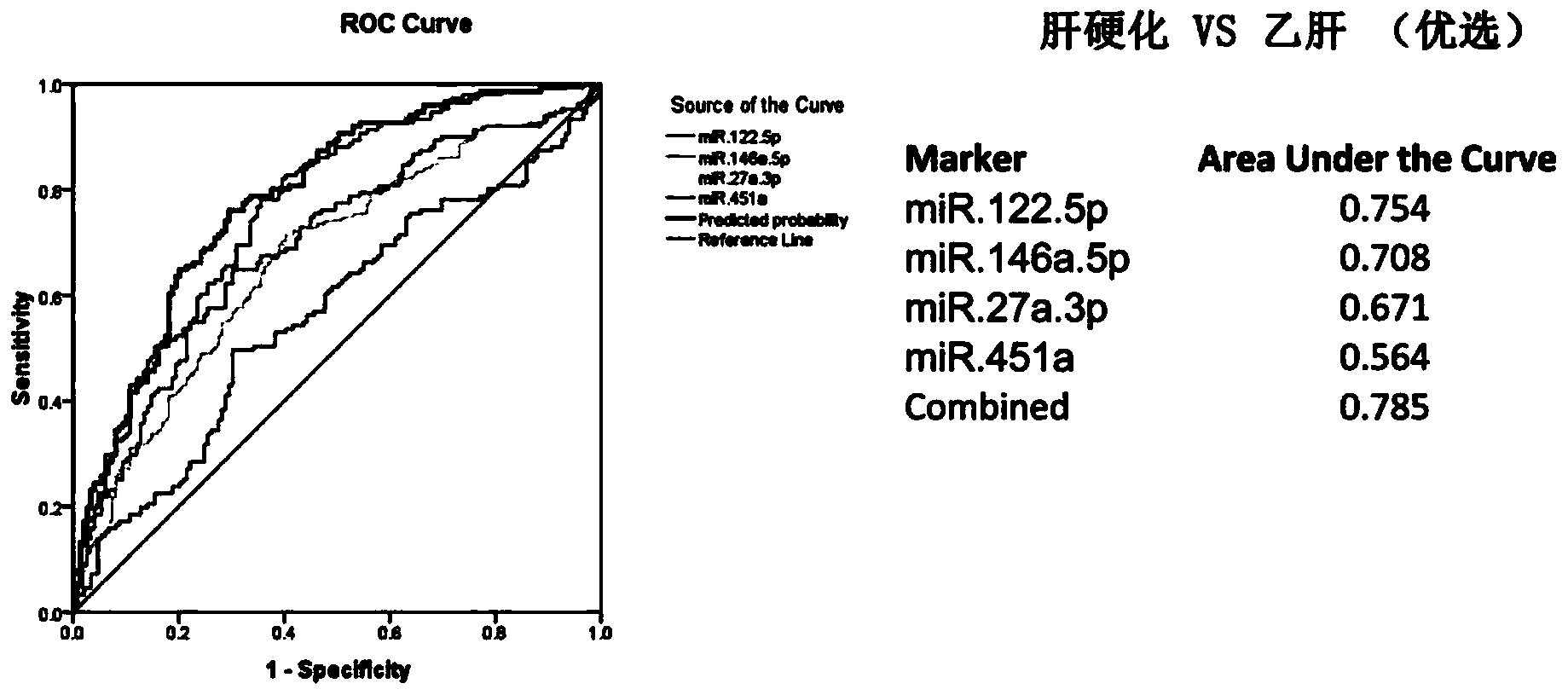
The invention provides microRNA molecular marker combination of liver cirrhosis. The combination comprises more than one microRNA molecules of nucleic acid with sequence numbers of 1-24 and 54. The invention further provides use of preparing a liver cirrhosis diagnostic reagent. Compared with the content of the microRNA molecular marker of a hepatitis B patient in plasma / serum, the content of the microRNA molecular marker of a liver cirrhosis patient in plasma / serum is remarkably different, so that the liver cirrhosis patient and the hepatitis B patient can be effectively differentiated. When the expression level of the microRNA molecular marker reaches the level of liver cirrhosis, liver cirrhosis can be diagnosed. The invention further provides a diagnostic reagent kit for liver cirrhosis. The microRNA molecular marker of liver cirrhosis provided by the invention is used for guiding diagnosis of liver cirrhosis and has the characteristics of being simple in operation, safe, free from damage, high in specificity, high in sensitivity and easy to screen massively.
Owner:北京旷博生物技术股份有限公司
Biomarker of liver cirrhosis, and application thereof
InactiveCN104195145AEffective monitoring of susceptible populationsSurveillance of susceptible populationsMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemMicroorganismFeces
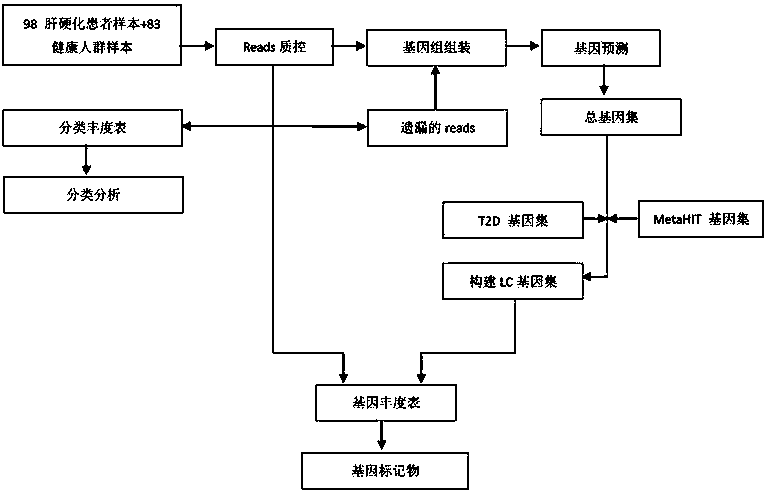
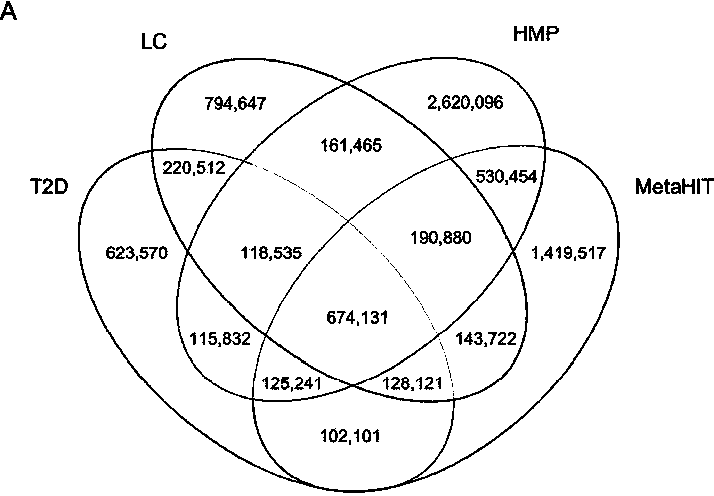
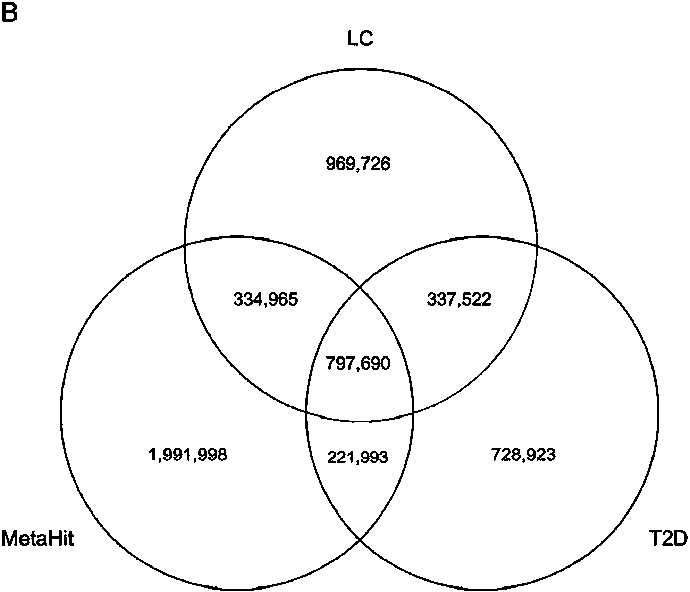
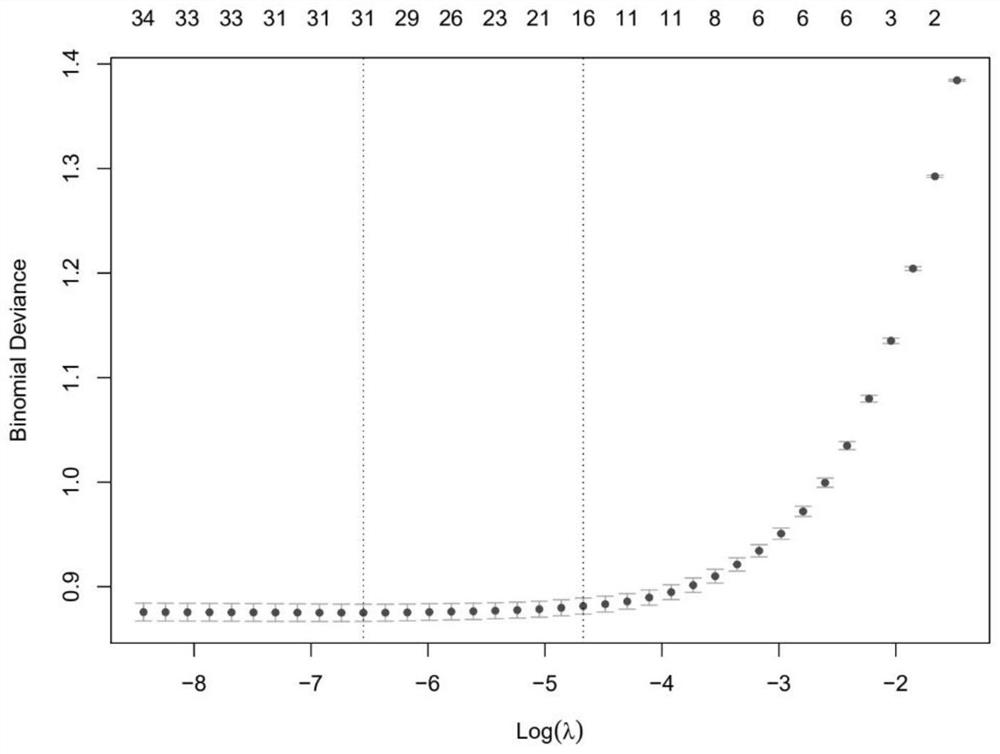
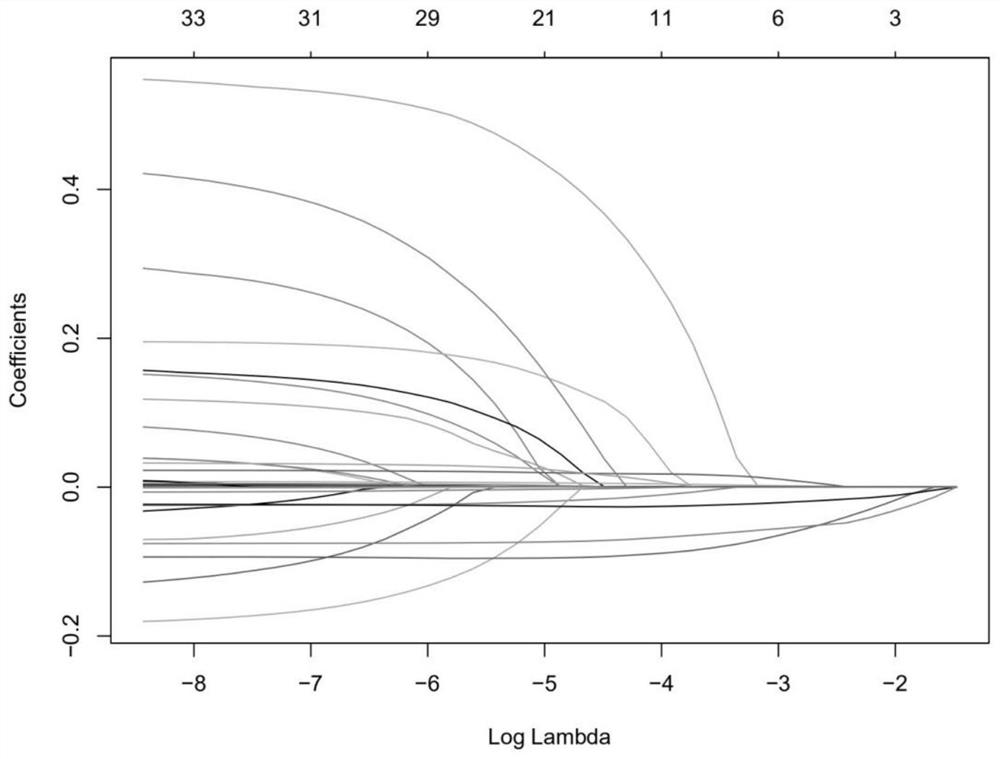
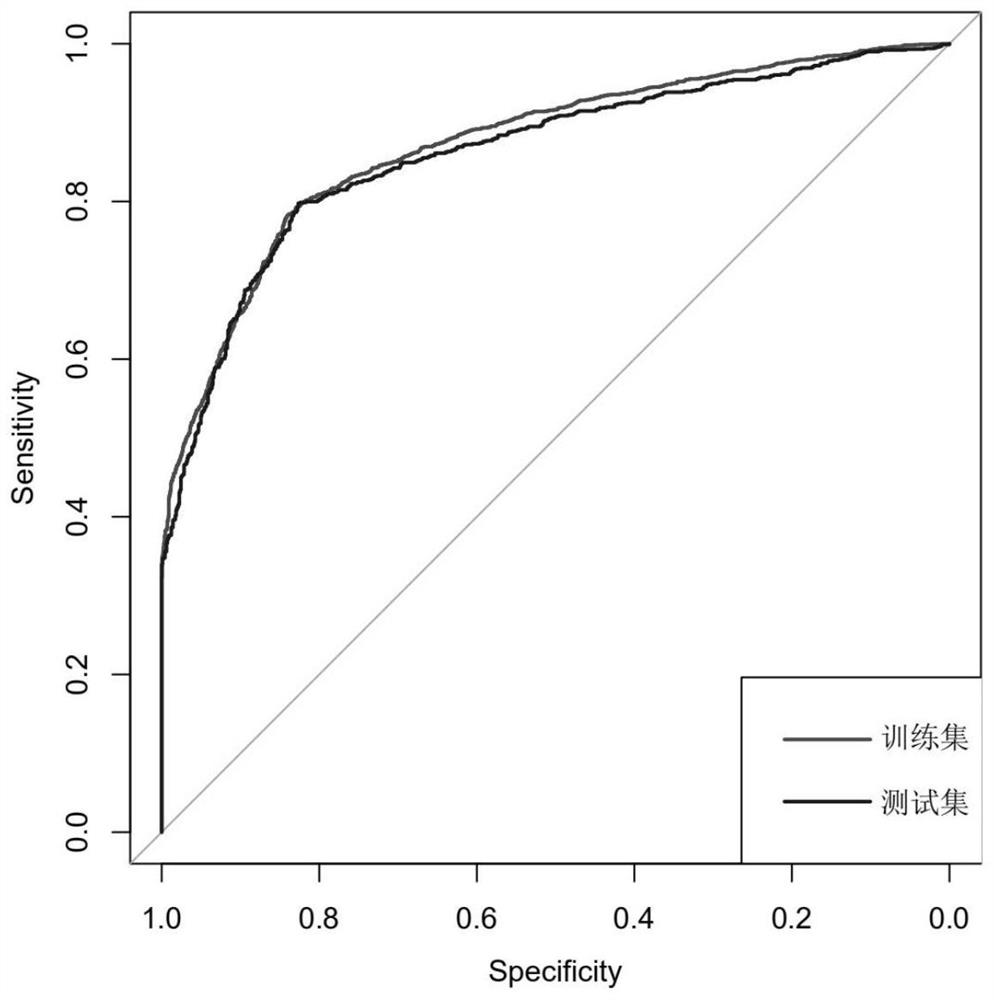
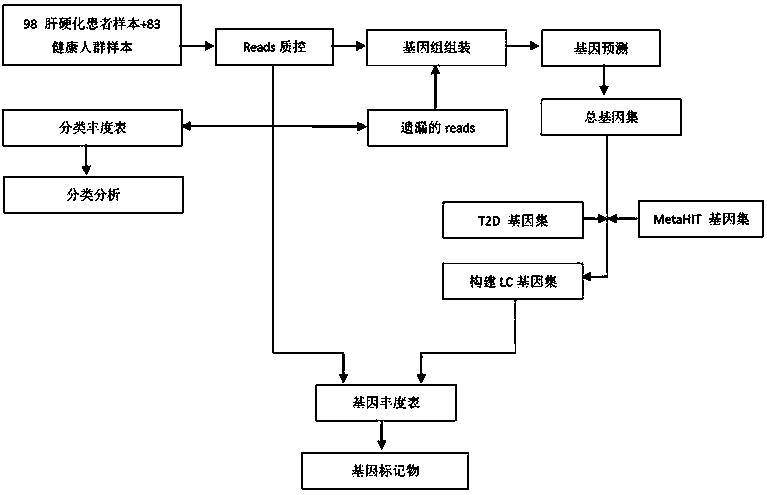
The invention discloses a biomarker of liver cirrhosis, and an application thereof. Association analysis of the whole intestinal flora microorganisms is developed from stool samples of 98 patients suffering from liver cirrhosis and 83 healthy references to study and describe stool microflora and functional component characteristics. 15 genes form the biomarker as a highly accurate index for distinguishing the patients. The discovery is examined in other independent population to confirm the accuracy of the biomarker; and associated robustness between the detection flora and the liver cirrhosis are confirmed. The biomarker is at least 10 genes selected from the following group of 15 genes. 15 genes are enriched in the intestinal flora of the patients suffering from the liver cirrhosis. The invention also relates to a drug for treating the liver cirrhosis. The drug can promote or increase the number or expression of the genes. The invention also relates to a method for producing or screening the drug. The drug can promote or increase the number or expression of the biomarker. The invention also relates to a kit for detecting the liver cirrhosis, monitoring a treatment process, or producing and screening the drug. The kit is used for detecting the biomarker.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Differential expression profile model of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infectivity and alcoholic cirrhosis, and construction method thereof
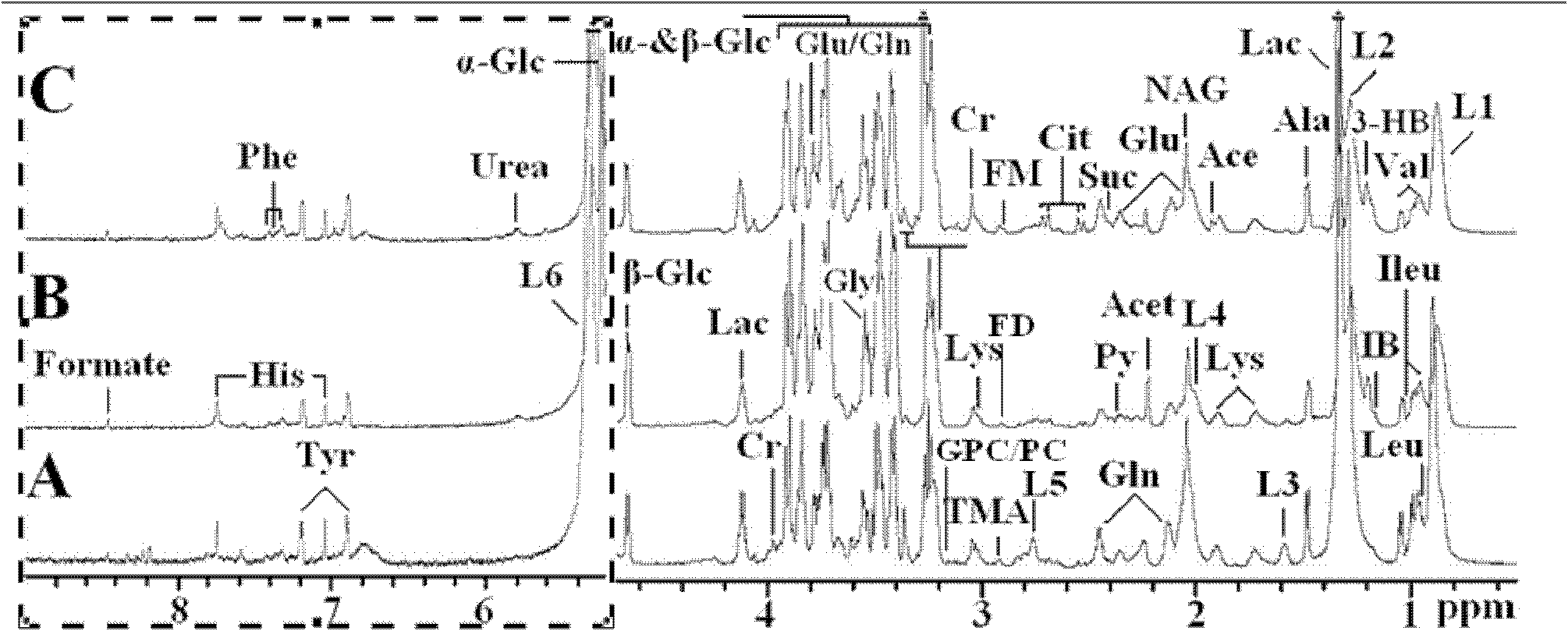
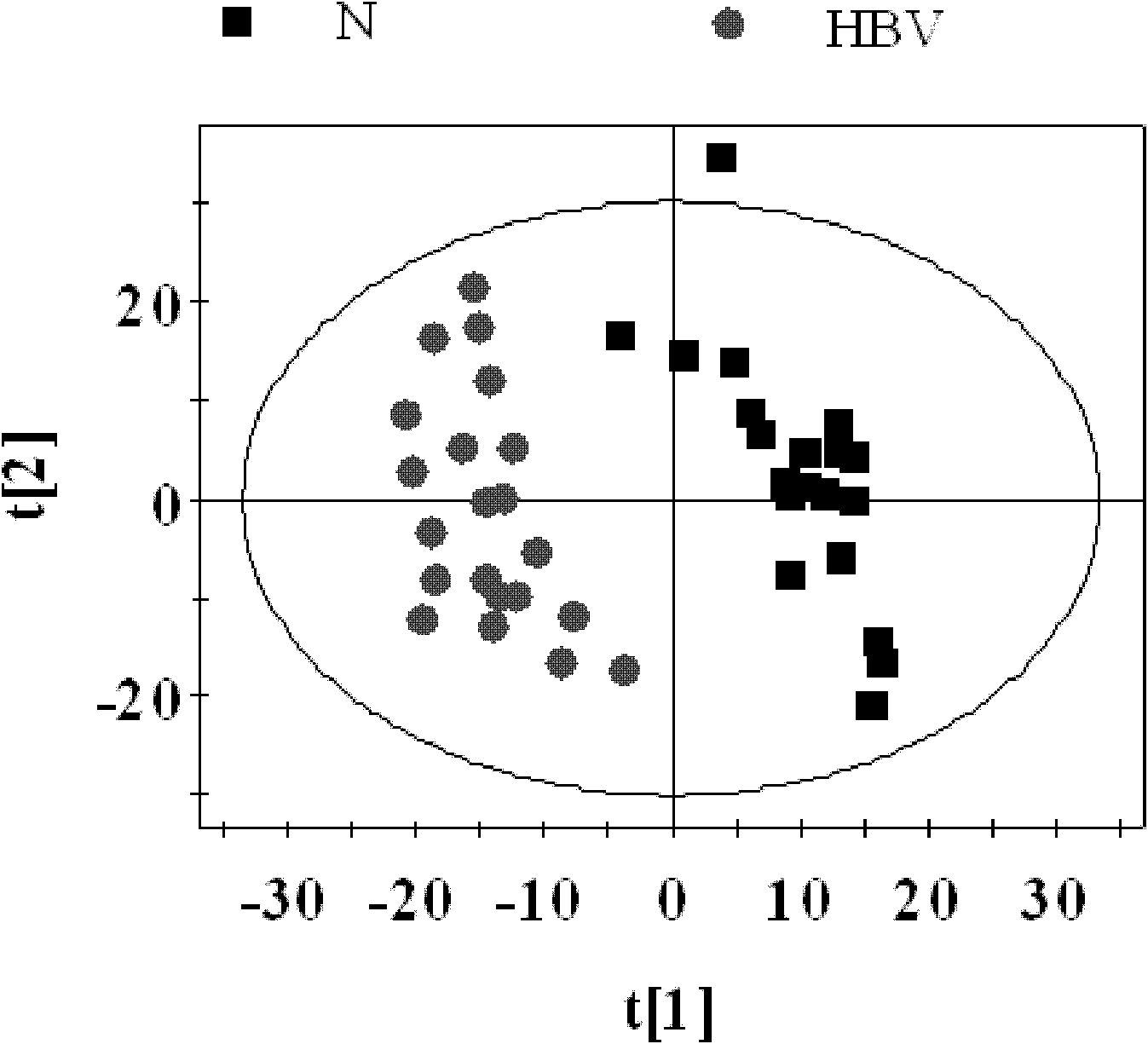
The invention relates to a construction method for a differential expression profile model of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infectivity and alcoholic cirrhosis. According to the method, peripheral blood samples of liver cirrhosis patients with HBV infections, alcoholic cirrhosis patients and healthy people are sampled to carry out nulcear magnetic resonance analysis, then a multi-variable statistical analysis is adopted for the resulting spectrograms from the nulcear magnetic resonance analysis to obtain the differential expression profile model of the HBV infectivity and the alcoholic cirrhosis. According to the present invention, the metabonomics analysis method is adopted for analyzing the metabolic products of the liver cirrhosis patients with HBV infections, the alcoholic cirrhosis patients and the healthy people, such that the specific metabolic products related to the pathologic mechanisms of the liver cirrhosis with the HBV infection and the alcoholic cirrhosis are found, the differential expression profile model of the HBV infectivity and the alcoholic cirrhosis is constructed; such that a support is provided for specific diagnosis and treatment of the liver cirrhosis with the HBV infection and the alcoholic cirrhosis. In addition, the invention further relates to a differential expression profile model of the HBV infectivity and the alcoholic cirrhosis.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Construction method of decompensated liver cirrhosis combined infection risk prediction model
InactiveCN112002427ANo invasive examination involvedNo operationalMedical data miningHealth-index calculationOriginal dataInfection risks
The invention discloses a construction method of a decompensated liver cirrhosis combined infection risk prediction model. The method comprises the following steps: S1, data acquisition: collecting decompensated liver cirrhosis patient information; S2, data preprocessing: cleaning and sorting the original data; S3, index screening by adopting LASSO regression: dividing the patients into an infection group and a non-infection group according to whether the patients have combined infection or not, and performing single-factor analysis on the grouped index data of the patients to obtain single-factor meaningful indexes; bringing the single-factor meaningful indexes into Lasso regression for index re-screening to obtain indexes for constructing a prediction model; and S4, prediction model construction: constructing the prediction model by using the indexes screened by Lasso regression through multi-factor Logistic regression. The method is based on application of a clinical big data methodand is high in reliability; the constructed model is simple and easy to use, and the used indexes can be obtained through conventional inspection and are easy to obtain.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Microbial marker of liver cirrhosis, and application
InactiveCN104195146AMonitor Treatment EffectsMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemMicroorganismVeillonella atypica
The invention discloses a microbial marker of liver cirrhosis, and an application. The microbial marker is one or more selected from one microorganism of Veillonella atypica ACS-134-V-Col7a enriched in a patient group suffering the liver cirrhosis or two microorganisms of Bacteroides uniformis ATCC8492 and Clostridiales enriched in a healthy group. The invention also relates to a drug for treating the liver cirrhosis. A drug for treating the liver cirrhosis can promote or increase one or two selected from the two microorganisms of Bacteroides uniformis ATCC8492 and Clostridiales enriched in the healthy group, and / or suppress or clear the microorganism of Veillonella atypica ACS-134-V-Col7a enriched in the patient group suffering the liver cirrhosis. The method detects relative abundance of the microbial marker in intestinal flora and compares the obtained relative abundance value and a predetermined cutoff value. The invention also relates to a beneficial microorganism combination or functional food. The beneficial microorganism combination or functional food comprises one or two of the two microorganisms of Bacteroides uniformis ATCC8492 and Clostridiales enriched in the healthy group. The invention also relates to a kit for detecting the liver cirrhosis, monitoring a treatment process, or producing and screening the drug. The kit is used for detecting the microbial marker.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Biomarker used for early diagnoses of liver cancer and application thereof
InactiveCN108504739AAchieve early screeningAchieve early diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseFeces
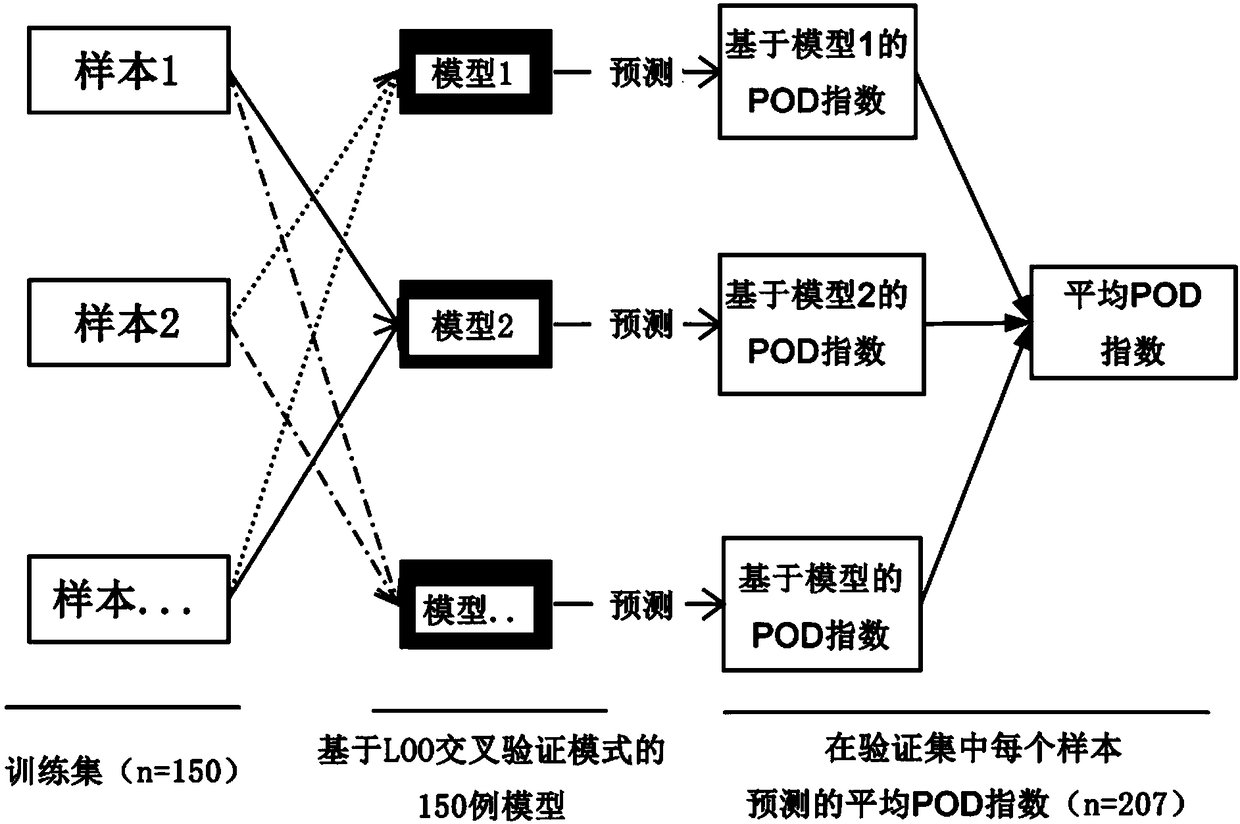
The invention relates to a marker for intestinal microecology and application thereof, in particular to a biomarker used for early diagnoses of liver cancer. The biomarker used for early diagnoses ofliver cancer is composed of 34 kinds of genes shown as SEQ ID NO:1-34, and the genes are enriched in intestinal tracts. The invention also provides a detection reagent, and the reagent includes a primer used for detecting the 34 kinds of genes shown as SEQ ID NO:1-34. Feces of patients in groups are collected through a noninvasive method, and 16S rRNA Miseq sequencing of intestinal florae is conducted. During a discovery period of the biomarker, through a random forest law, microorganism gene markers with specificity of early liver cancer are identified among patients suffering from early cirrhosis and liver cancer, patients suffering from cirrhosis and healthy comparisons, an index of a probability of disease (POD) of liver cancer is created, and verification of the markers during the discovery period is achieved. During the verification period of the markers, the POD index of the patients during the verification period is calculated, and verification of the diagnosis value of the patients suffering from liver cancer during the verification period according to the POD index is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Detection method of IgG (immunoglobulin G) core fucosylation level and use thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of proteins, and relates to the detection of glycoprotein, specifically to a detection method of the IgG core fucosylation level and a use thereof, wherein the method comprises the step of calculating the IgG amount of the core fucosylation / the glycoprotein total amount of the core fucosylation. The method can not distinguish healthy persons from hepatitis B patients, but can distinguish whether the diagnosed hepatitis B patient is a chronic hepatitis patient or a cirrhosis patient.
Owner:HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
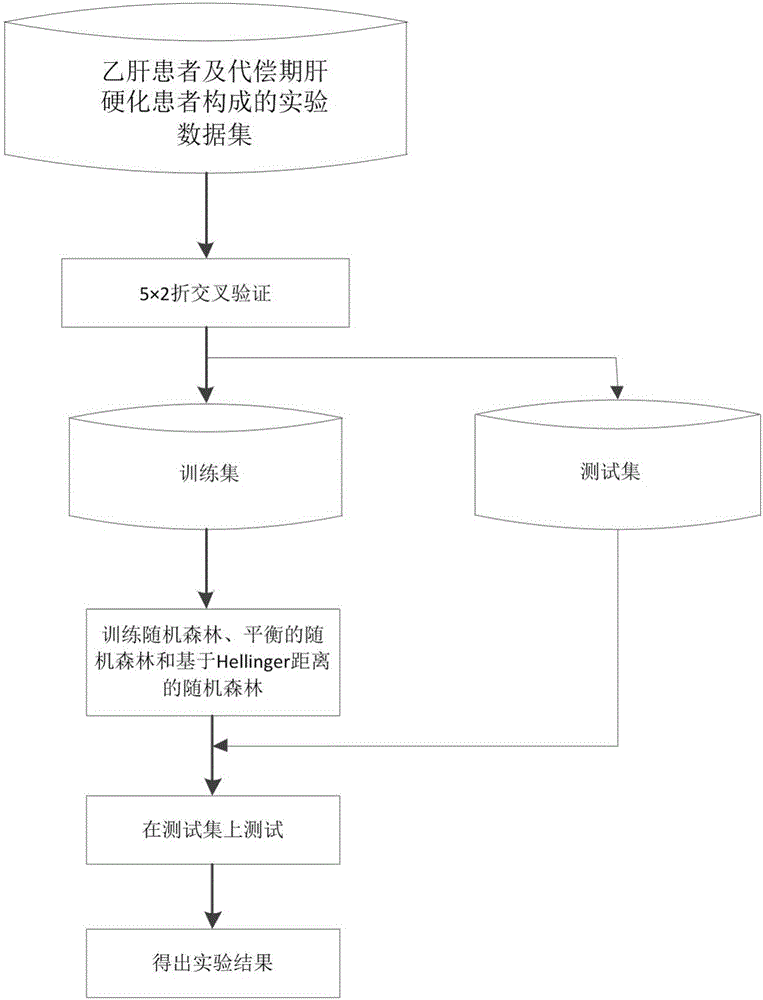
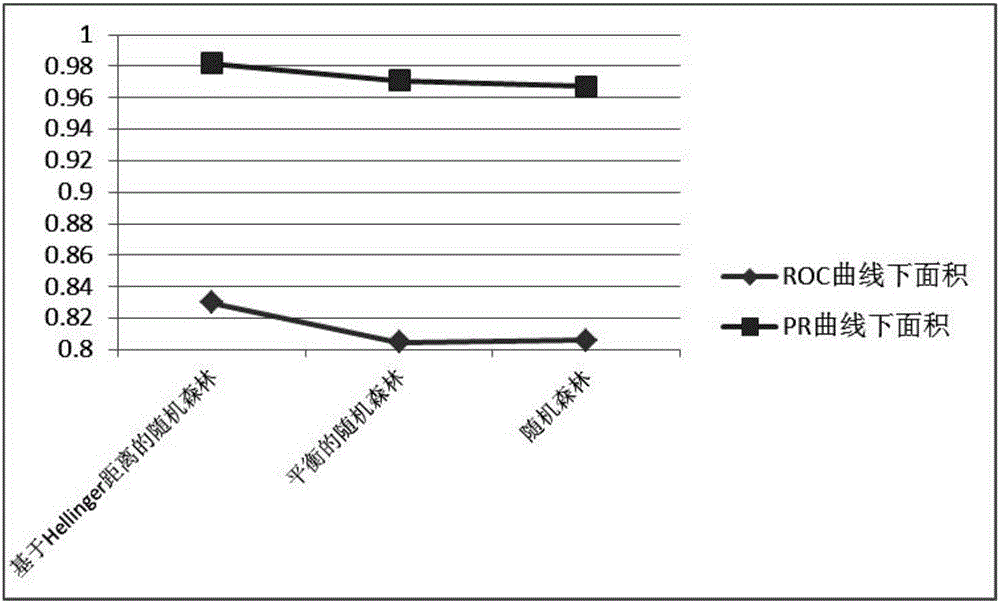
Hepatitis B compensated stage liver cirrhosis screening model building method based on random forest algorithm
PendingCN106295148AGood effectAssess disease progressionMedical simulationMedical automated diagnosisLiver tissueTest sample
The invention relates to a hepatitis B compensated stage liver cirrhosis screening model building method based on a random forest algorithm. The method comprises the steps of collecting data; preprocessing data; building a hepatitis B compensated stage liver cirrhosis screening classification model based on the random forest algorithm; testing and evaluating the classification model. According to the technical scheme, serum indexes, type-B ultrasonic imaging features and other sample data, collected in recent three years, of hepatitis B patients and compensated stage liver cirrhosis patients are used for building a noninvasive hepatitis B compensated stage liver cirrhosis forewarning model. On the basis of the model, whether a hepatitis B patient (to-be-tested sample) is in the period of compensated stage liver cirrhosis or not can be effectively predicted, and the disease progression and prognosis conditions of the hepatitis B patient can be evaluated. On the basis of evaluation of the model, unnecessary liver tissue biopsy pathological examinations can be reduced.
Owner:苏翀
Marker composition and detection kit for liver cancer detection
ActiveCN106814192AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresBiological material analysisBiological testingLiver cancerHepatitis B
The invention relates to a marker or a composite thereof for liver cancer detection, a reagent and a detection kit for detecting liver cancer, and application of the marker or the composite thereof, the reagent and the detection kit in detecting liver cancer and distinguishing patients with liver cancer, patients with liver cirrhosis and / or healthy people.
Owner:合众赛博(北京)科技发展有限责任公司
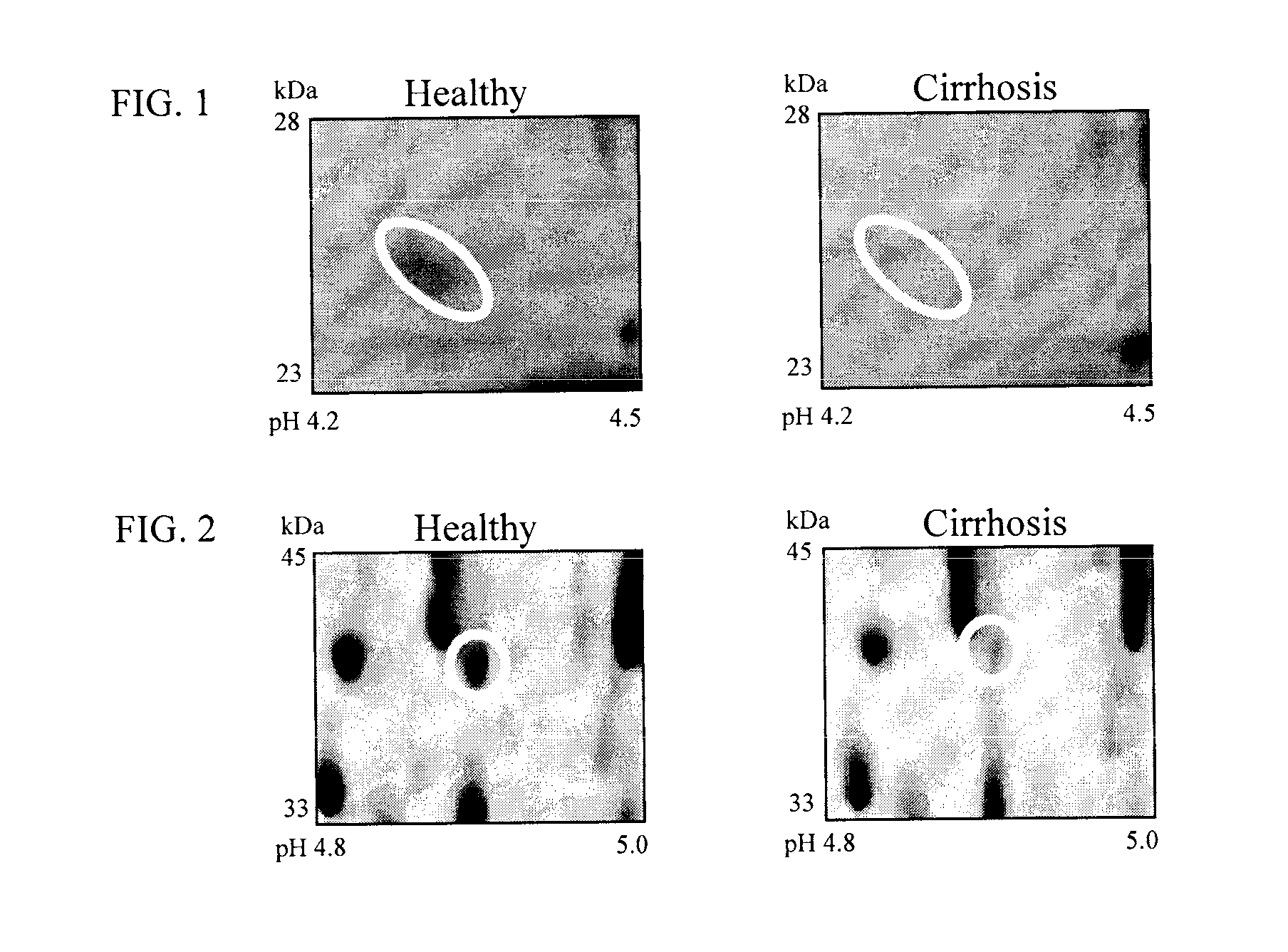
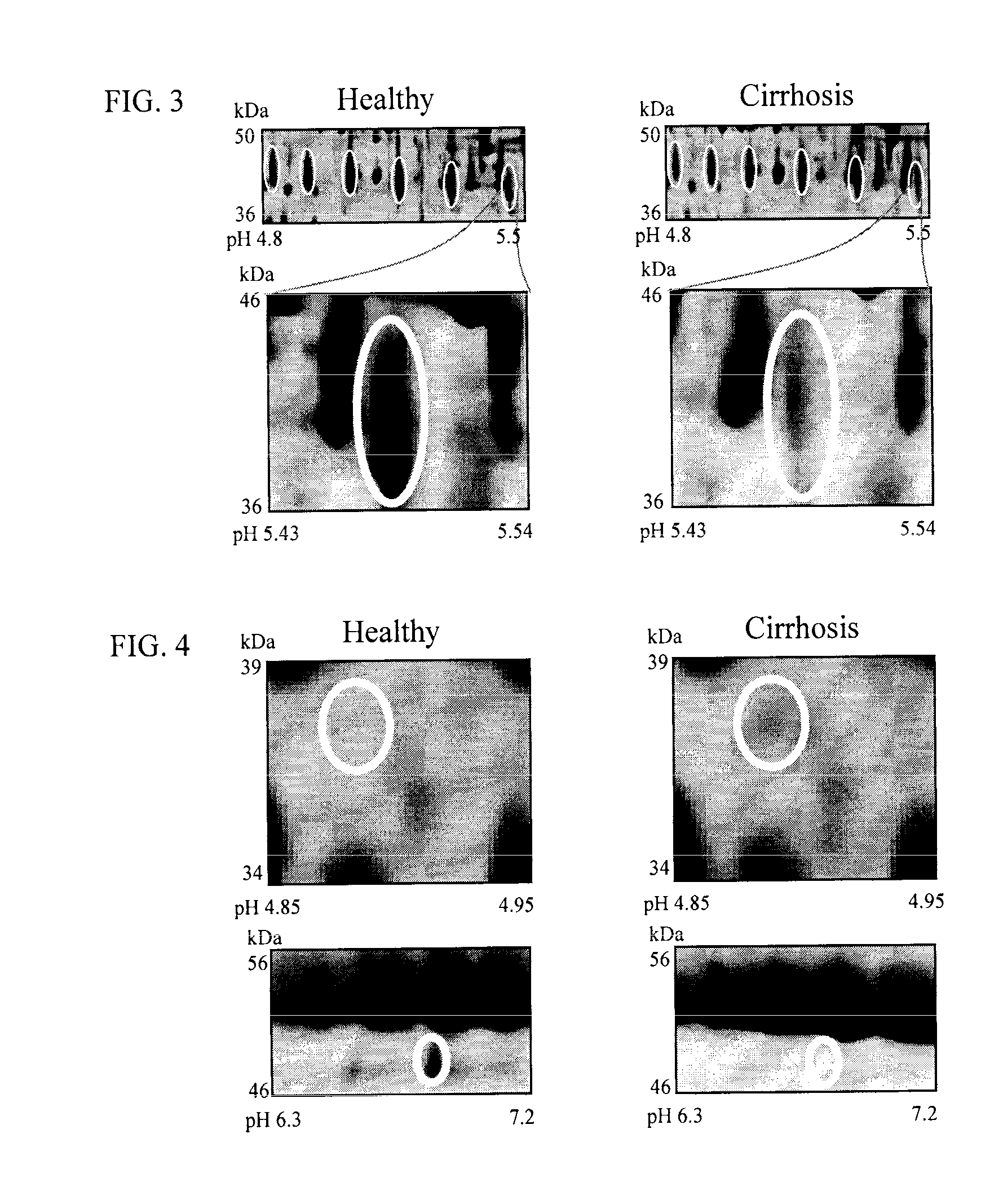
Clinical diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis using a novel panel of low abundant human plasma protein biomarkers
The inventors have proposed a novel panel of human plasma protein biomarkers for diagnosing hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Presently there is no reliable non-invasive way of assessing liver fibrosis. A 2D-PAGE based proteomics study was used to identify potential fibrosis biomarkers. Plasma from patients with hepatic cirrhosis induced by infection with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) were analysed. Several proteins associated with liver scarring and potentially also related to viral infection were identified. These proteins include 14-3-3 protein zeta / delta, adiponectin, afamin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein, apolipoprotein C-III, apolipoprotein E, C4b-binding protein beta chain, intact / cleaved complement C3dg, corticosteroid-binding globulin, fibrinogen gamma chain, beta haptoglobin at pH 5.46-5.49, haptoglobin-related protein, hemopexin, immunoglobulin J chain, leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein, lipid transfer inhibitor protein, retinol-binding protein 4, serum paraoxonase / arylesterase 1, sex hormone-binding globulin and zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein. These biomarkers can be used in conjunction with polypeptides in WO / 2008 / 031051. The concentrations of these novel biomarkers can be determined using an immunoassay where the concentrations would reflect the extent of fibrosis. A fibrosis scoring scale for each of the novel biomarkers is proposed. The additive result from the scores of all the novel biomarkers would give a more reliable indication of the degree of fibrosis rather than examining individual biomarkers.
Owner:UNIV OF OXFORD
Recombinant adenoviral vectors and their utility in the treatment of various types of fibrosis: hepatic, renal, pulmonary, as well as hypertrophic scars
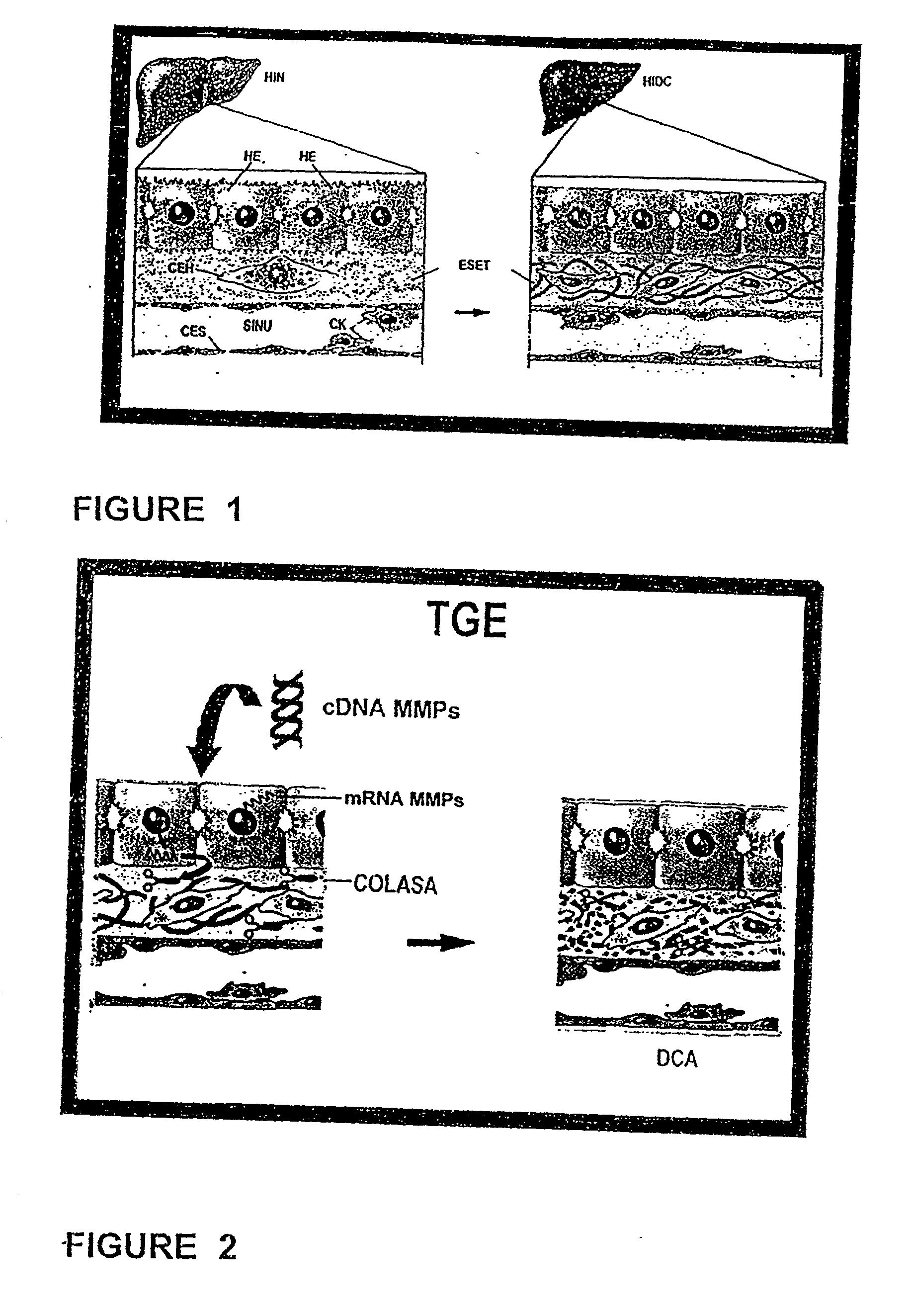
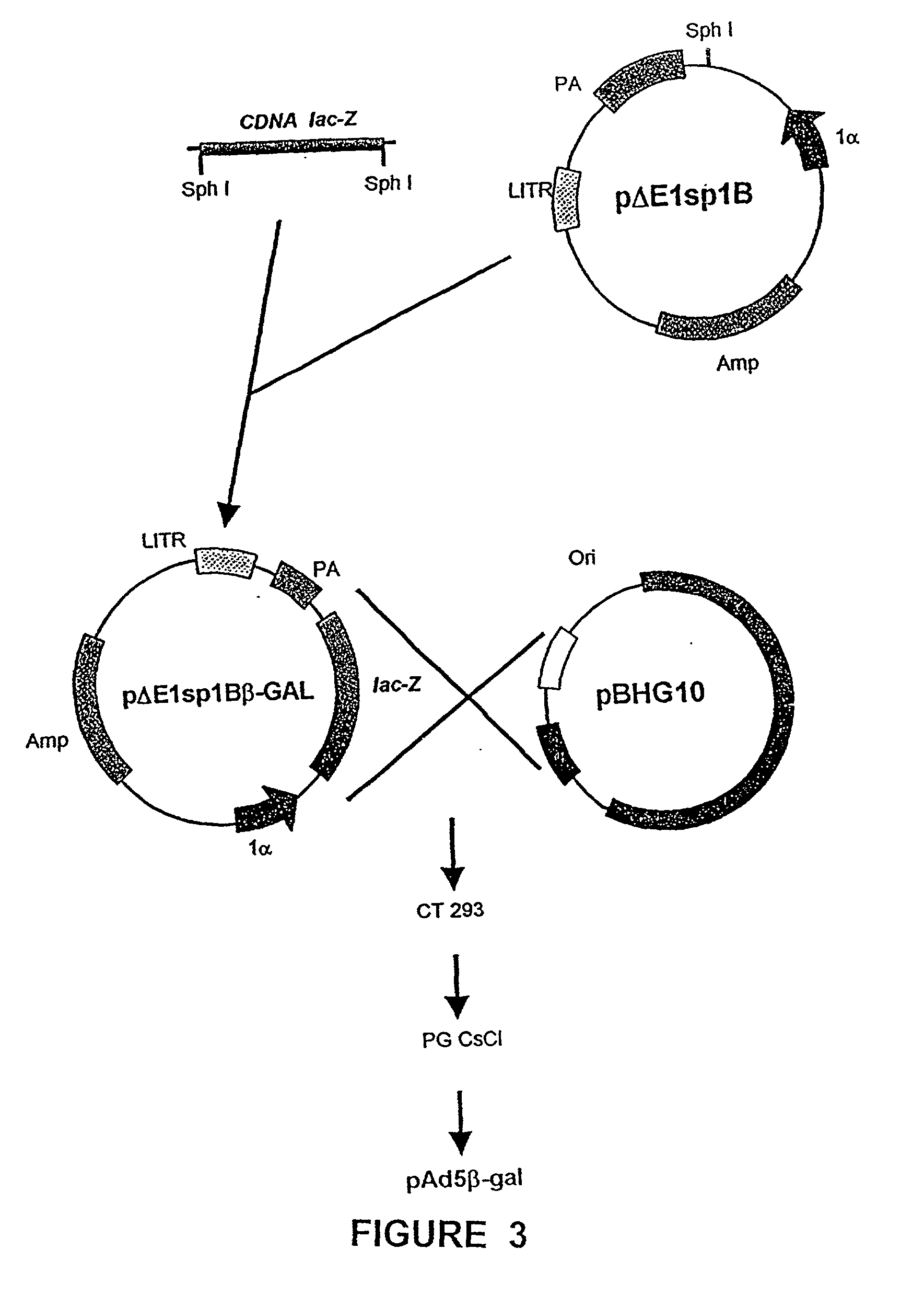
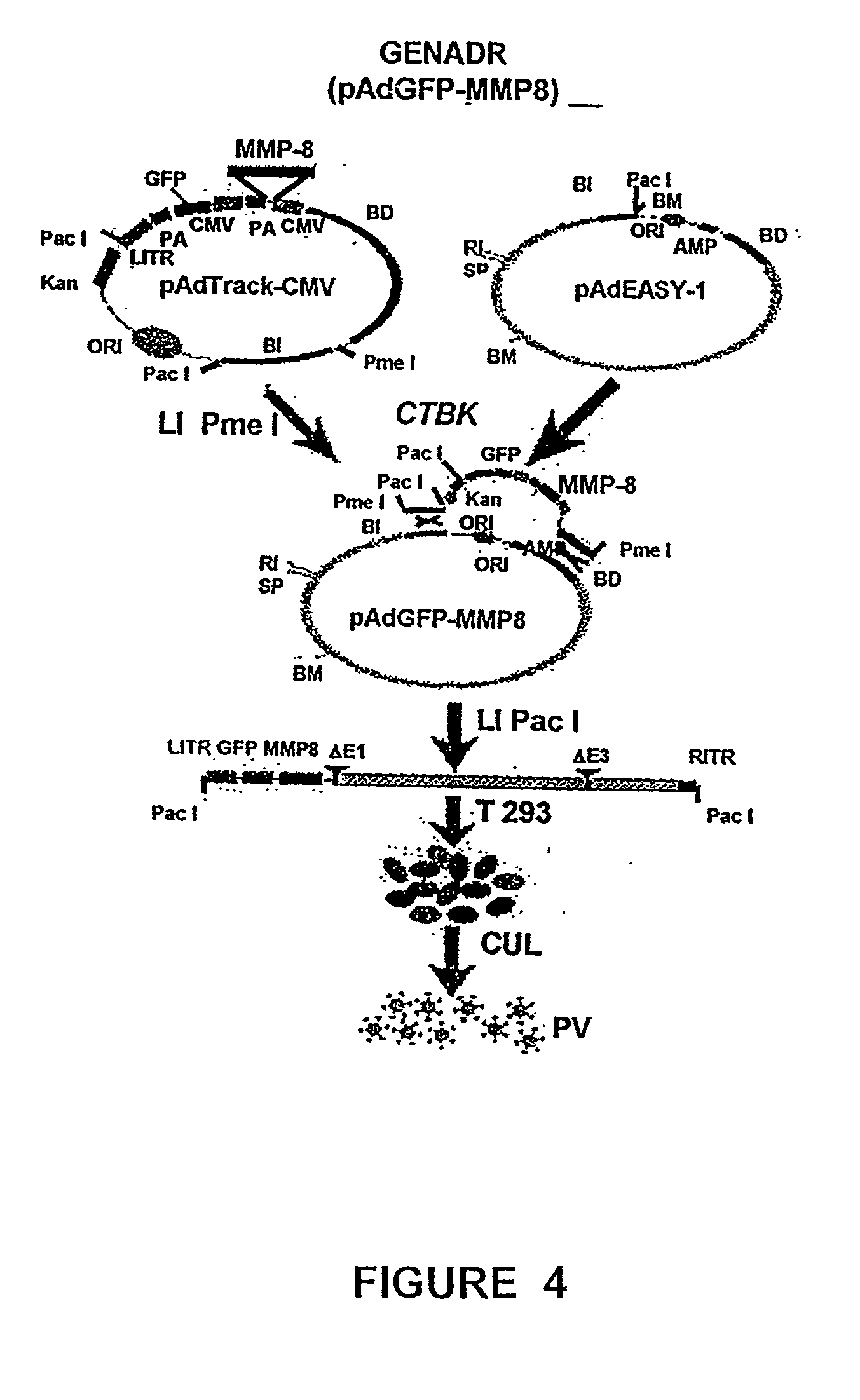
<heading lvl="1">SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION < / heading> The use of gene therapy for the treatment of different kinds of fibrosis in human beings is disclosed. The purpose is the use of "therapeutic2 genes specifically directed to target organs to revert and / or prevent the development of the fibrosis process. The potential application of gene therapy to patients with fibrosis and / or cirrhosis will depend to a large extent on the successful delivery of genes which encode for therapeutic proteins to livers with severe fibrosis and that these genes which encode for proteins human MMP-8 active and latent, MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-9 and MMP-13; human uPA wild type and / or modified (or its truncated version), the truncated receptor for TGF-beta type II and Smad-7 can be directed by adenovirus and / or other recombinant vectors that cannot transduce (infect) others organs. The recombinant adenoviruses (AdR) are vectors highly efficient for the transduction of therapeutic genes to diverse target cells. We have proved that they can carry genes to cirrhotic livers. The delivery of therapeutic genes through such adenoviral vectors and other recombinant vectors could also be performed using cationic and anionic liposomes (DOTMA). Therefore, we propose the use of this patent to be applied in the same manner to: Renal fibrosis Pulmonary fibrosis Hypertrophic and keloid scars (skin fibrosis), and Other kinds of fibrosis.
Owner:TGT LAB DE C V
Test kit for detecting content of 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine and application thereof
PendingCN111961729AWide range of sourcesStrong acceptabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue biopsyCytosine
The invention provides a test kit for detecting the content of 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine and application thereof. The content of a gene marker 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine is detected through the test kit,and the canceration condition of a patient with liver cirrhosis is judged by using the detection result of the content of 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine in the gene marker. The test kit provided by the invention has high accuracy and can quickly react when being applied to liver cancer detection, and has high sensitivity and specificity for liver cirrhosis detection and dynamic monitoring of liver cirrhosis to liver cancer; the operability is high, and detection can be carried out only by collecting venous peripheral blood; compared with a conventional tissue biopsy technology, the detection methodusing the test kit is non-invasive, and can be frequently carried out for many times; the test kit disclosed by the invention is relatively low in detection cost and relatively high in acceptabilityof subjects.
Owner:深圳泰莱生物科技有限公司
Cirrhosis microRNA molecular marker composition and application thereof
InactiveCN104232638AEasy to operateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationUse medicationMedicine
The invention discloses a cirrhosis microRNA molecular marker composition, with sequence No. ranging from 1 to 13, as well as application of the molecular marker composition in preparing a cirrhosis personalized medicine diagnostic reagent. Due to a significant difference between content of a microRNA molecular marker of a cirrhosis patient in plasma / serum and content in plasma / serum in health control, cirrhosis patient can be effectively distinguished from people of the health control; in a process of applying medicines to the cirrhosis patient, administration can be stopped by guiding and assistance, when cirrhosis outcome microRNA molecular marker is adjusted to a normal level. Furthermore, the invention discloses a diagnostic kit for guiding personalized administration of the cirrhosis. The liver cirrhosis outcome microRNA molecular marker disclosed by the invention, when being used for guiding personalized administration of cirrhosis patients, has characteristics of being simple to operate, safe and noninvasive, high in specificity, high in sensitivity and easy in massive screening.
Owner:北京旷博生物技术股份有限公司
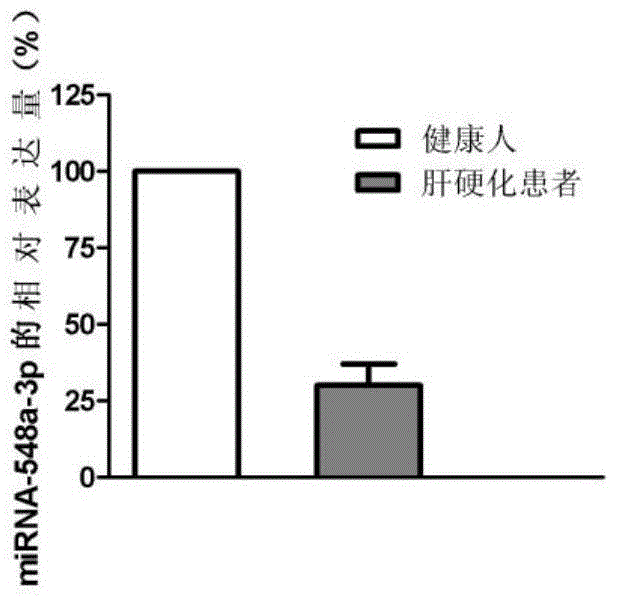
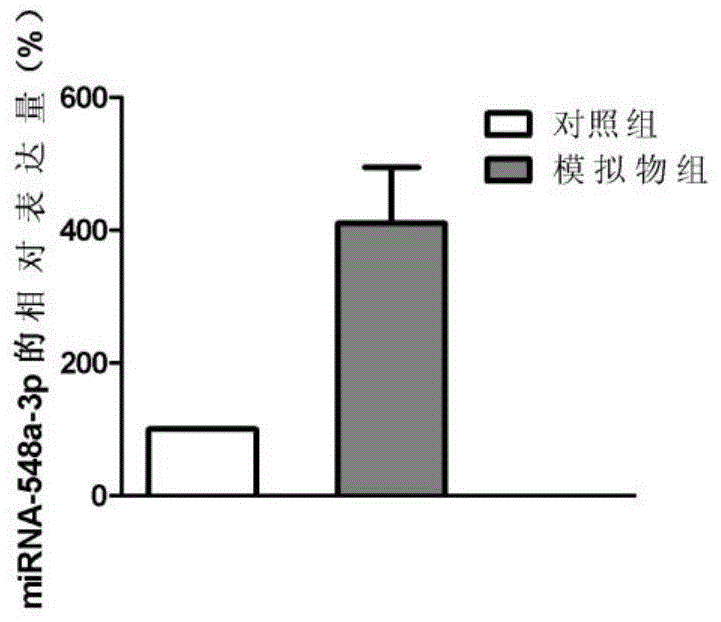
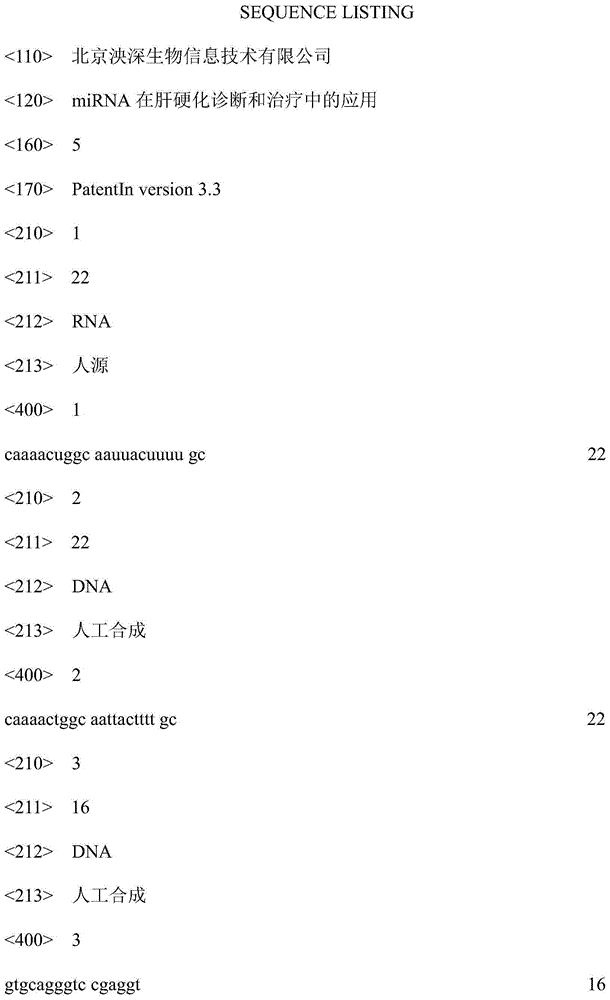
Application of miRNA in liver cirrhosis diagnosis and treatment
The invention discloses application of miRNA in liver cirrhosis diagnosis and treatment. miRNA is miRNA-548a-3p. By detecting the expression level of miRNA-548a-3p, miRNA-548a-3p can be used for diagnosing whether a patient has liver cirrhosis or is in the liver cirrhosis risk. As is shown in tests, the expression level of miRNA-548a-3p in a patient with liver cirrhosis is obviously lower than that of miRNA-548a-3p in a healthy person. On this basis, miRNA-548a-3p can also be used for preparing liver cirrhosis treatment medicine. Through miRNA-548a-3p, the sensitivity and specificity of liver cirrhosis diagnosis are greatly improved, and meanwhile a new target spot is provided for gene treatment of liver cirrhosis.
Owner:BEIJING MEDINTELL BIOMED CO LTD
Marker consisting of plasma microrna and a new method for diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
InactiveUS20130237456A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementChronic hepatitisEarly Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The present invention relates to a kit for diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma consisting of plasma microRNA, a kit containing the same, and a new method therefor. The marker for diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma consists of a plurality of nucleic acid molecules, each nucleic acid molecule encoding at least one microRNA sequence, preferably consists of nucleic acid molecules encoding hsa-miR-122, hsa-miR-192, hsa-miR-21, hsa-miR-223, hsa-miR-26a, hsa-miR-27a, hsa-miR-801 and hsa-miR-1228. The kit can be used for diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma, especially early hepatocellular carcinoma, and also for discriminating plasma of at least one hepatocellular carcinoma patient from that of at east one healthy individual, at east one chronic hepatitis B patient, or at east one cirrhosis patient.
Owner:FAN JIA +5
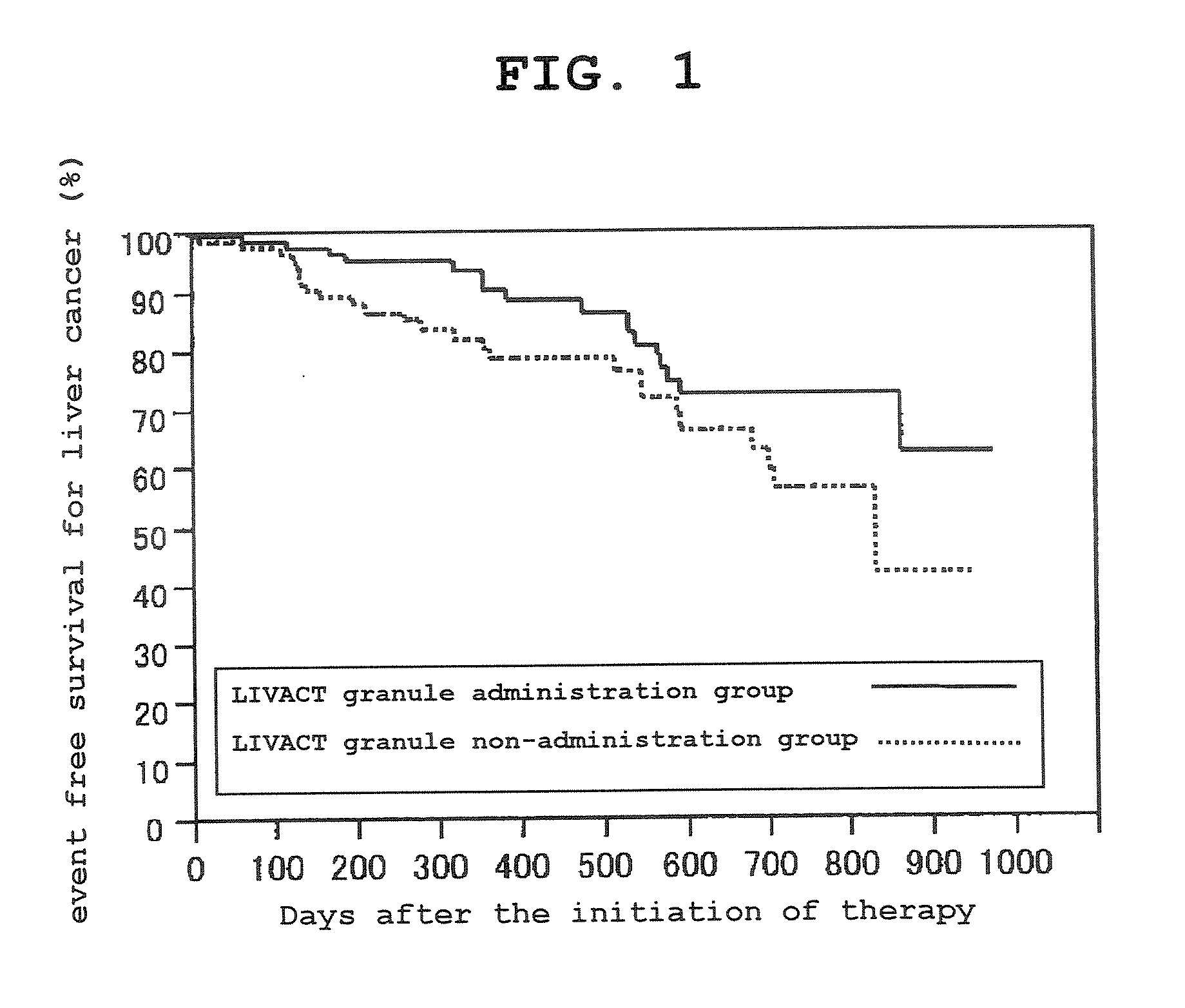
Medicament containing pemafibrate
ActiveUS11419854B2Therapeutic treatmentOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderRegimenLiver function
To provide an appropriate method of treatment with pemafibrate for a liver cirrhosis patient.The present invention relates to the use of pemafibrate in a liver cirrhosis patient.More particularly, the present invention relates to a regimen for administering a reduced dose of pemafibrate to a liver cirrhosis patient in need of treatment with pemafibrate than to persons with normal liver function.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Hepatitis b/hepatic cirrhosis microRNA molecular marker combination and purpose thereof
PendingCN106337051AEasy to operateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseChronic hepatitis
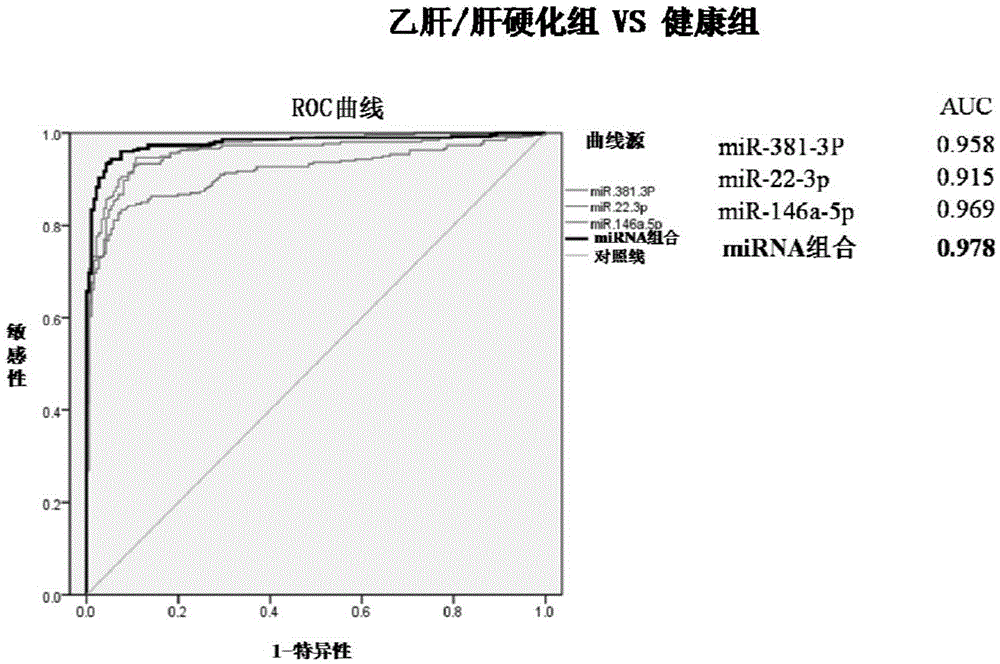
The invention provides a hepatitis b / hepatic cirrhosis microRNA molecular marker combination, which comprises more than one micro RNA nucleic acid molecules selected from mir.146a-5p, miR-22-3P and miR-381.3P, and a purpose of the marker combination for preparing hepatitis b / hepatic cirrhosis infection diagnosis and / or prognosis assessment kit. Due to a significant difference between content of a microRNA molecular marker of a hepatitis b / hepatic cirrhosis patient in plasma / serum and content in plasma / serum in health control, the hepatitis b / hepatic cirrhosis patient can be effectively distinguished from people of the health control; a chronic hepatitis b / hepatic cirrhosis disease state can be comprehensively analyzed, which can be used for guiding the patient treatment and usage of medication. The invention also provides a diagnostic kit for guiding the hepatitis b / hepatic cirrhosis infection diagnosis and / or prognosis assessment. By using the hepatitis b / hepatic cirrhosis microRNA molecular marker and the diagnostic kit, infection diagnosis and / or prognosis assessment of the hepatitis b / hepatic cirrhosis patient can be guided, and the combination has the characteristics of simple operation, safety and no wound, high specificity, high sensitivity and easy massive screening.
Owner:BEIJING YOUAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV +1
Diuresis inducing plaster for relieving ascites due to cirrhosis
ActiveCN105079201AEasy to acceptSmall toxicityDigestive systemUnknown materialsOral medicineSide effect
The invention provides a diuresis inducing plaster for relieving ascites due to cirrhosis. The plaster is prepared by the following steps: selecting and drying the following raw materials by weight: euphorbia kansui, semen pharbitidis, astragalus membranaceus, bighead atractylodes rhizome, cortex cinnamomi and pericarpium citri reticulatae viride, grinding the raw materials and filtering by virtue of a sieve of 200 meshes; blending the ground materials with honey and a transdermal penetration enhancer to obtain a paste, and uniformly stirring; spreading 80-100 of the paste on patch according to the ascites area of a patient; and sticking and applying to Shenque acupuncture point, Guanyuan acupuncture point, Shuifen acupuncture point, Shuidao acupuncture point and Zhongwan acupuncture point, wherein the diuresis inducing plaster is mainly used for treating intractable ascites caused by decompensated liver cirrhosis. The diuresis inducing plaster has functions of warming kidney and invigorating spleen, regulating qi circulation and inducing diuresis; the diuresis inducing plaster is capable of overcoming the shortcoming of an oral medicine which is always poor in effect on cirrhosis patients who have poor metabolism and detoxification capacities, and the plaster has the advantages of being low in toxic and side effects and capable of attacking pathogen without causing hurt to healthy qi; the plaster can make up the deficiency of internal therapy by Western medicine and traditional Chinese medicine; the plaster is convenient and easy in administration, easily acceptable to patients, significant in diuresis effect and durable in curative effect; and upon clinical observation, total effective rate of treatment is 93.3%.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF TCM
A medicine for treating hepatitis
InactiveCN1876061AWith promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasisSignificant effectDigestive systemReptile material medical ingredientsMedicinal herbsScrophularia
The invention discloses a medicament for treating hepatic diseases, which is prepared from the following medicinal herbs (by weight ratio): honeysuckle flower 6-16 parts, dandehon herb 3-12 parts, Chinese angelica root 4-14 parts, scrophularia root 1-11 parts.
Owner:张永顺
Ultra-early liver cancer screening and evaluating product based on saliva specific glycoprotein sugar chain structure and application
PendingCN111239396ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMedical automated diagnosisMaterial analysisSaliva samplePharmaceutical drug
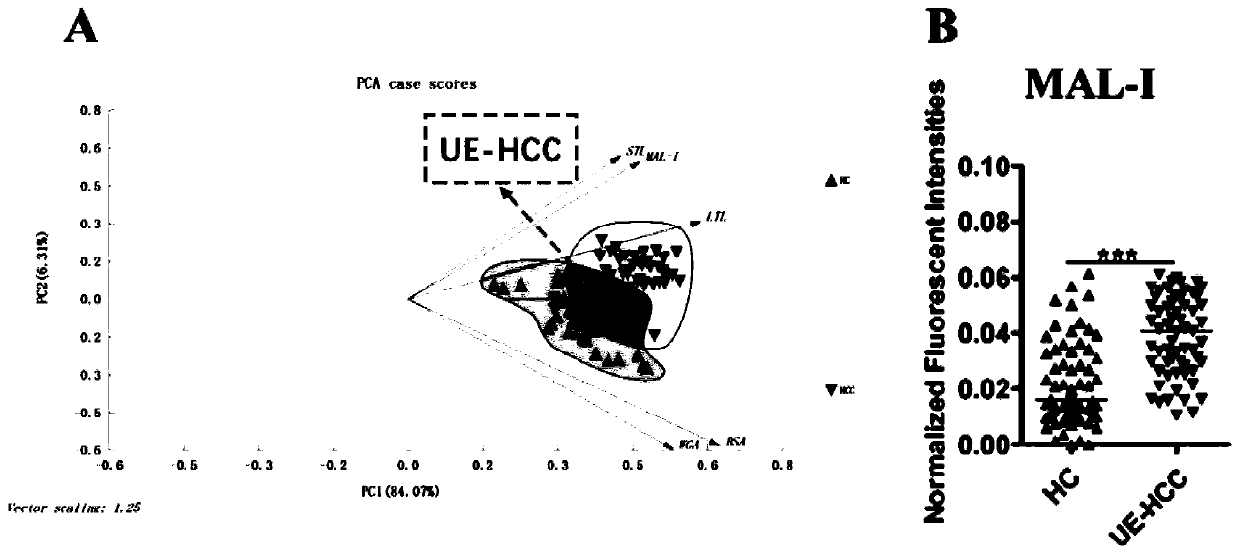
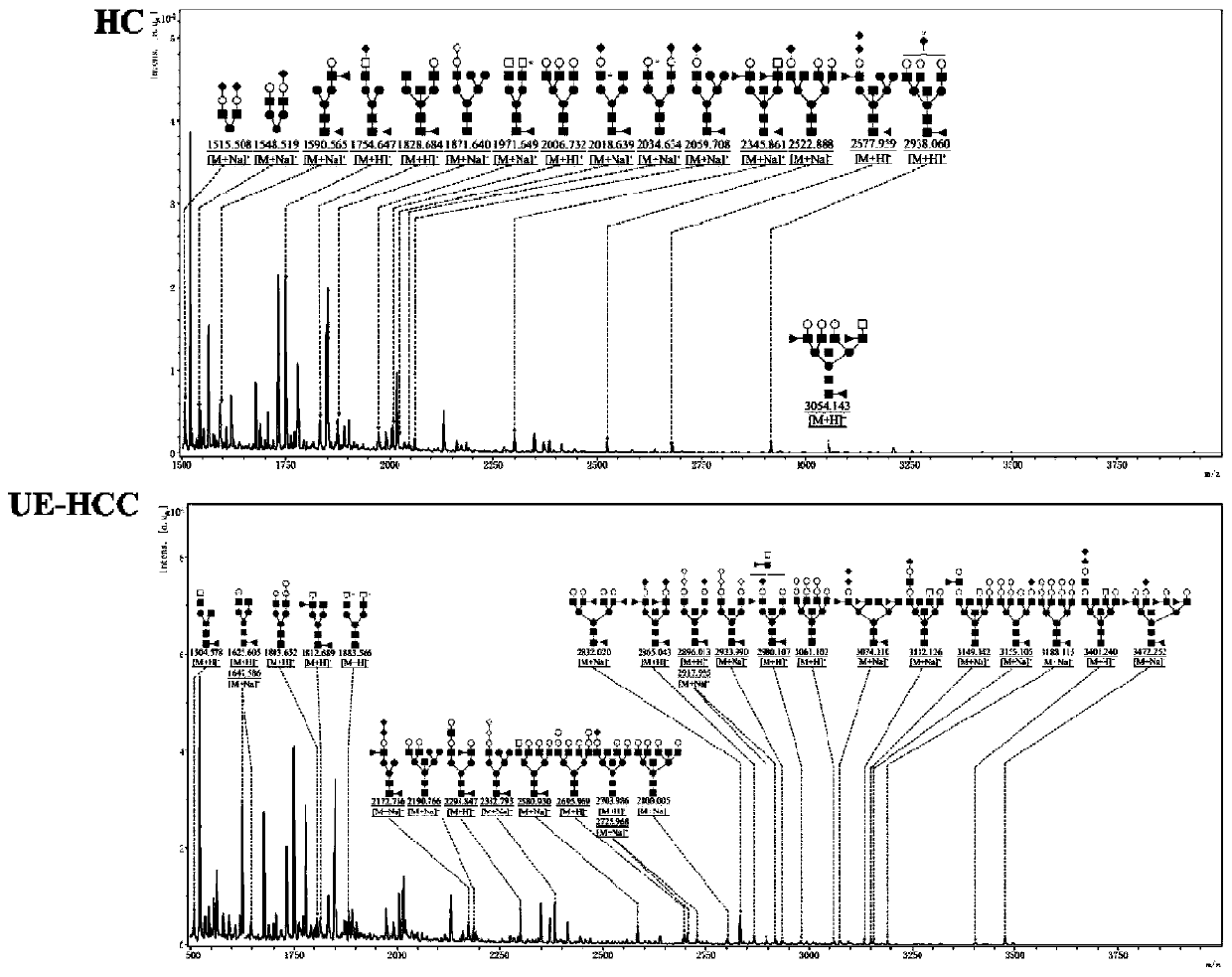
The invention discloses an ultra-early liver cancer related screening and evaluating product based on a saliva specific glycoprotein sugar chain structure and application. Aiming at a saliva sample, aproduct for screening, early diagnosis, risk assessment, drug screening and / or curative effect assessment of the ultra-early liver cancer is provided, whether the saliva sample contains any one or any combination of specific 26 N-sugar chains or not is detected, and whether a saliva sample main body is an ultra-early liver cancer patient (not a liver cirrhosis patient) or not can be judged. Correspondingly, lectin playing a role in specific binding recognition is MAL-I and can be independently used as a reagent for recognizing a saliva specific glycoprotein sugar chain structure to be used for preparing related medical products.
Owner:深圳格道糖生物技术有限公司
Method for identifying liver cirrhosis based on serum N-carbohydrate fingerprint spectrum
InactiveCN111141807AExcellent identification efficiencyIncreased sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLiver tissueSerology
The invention belongs to the field of clinical medical diagnostics, relates to seroglycoid N-carbohydrate glycome detection, and particularly relates to a method for identifying liver cirrhosis basedon a serum N-carbohydrate fingerprint spectrum. A log (P2 / P8) value is calculated. Liver cirrhosis is the final stage of various liver diseases and is the fourteenth major lethal cause of the world. At present, the gold standard of liver cirrhosis diagnosis is liver tissue biopsy, and the risk and trauma of the liver tissue biopsy are large, so that the clinical application of the liver tissue biopsy is limited. The serological marker, as a non-invasive detection means for liver cirrhosis patients, is clinically paid attention to. On the basis, the invention provides a method for identifying liver cirrhosis by N-carbohydrate spectra and a corresponding detection system. The detection method and the detection system are used for early screening and diagnosis of LC; the sensitivity and specificity of the detection method and the detection system are improved compared with those of liver fiber indexes, namely, hyaluronic acid and IV type collagen; and it can be considered that the log (P2 / P8) is a characteristic serological marker for LC diagnosis.
Owner:高春芳
Method for predicting prognosis and risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in liver cirrhosis patient
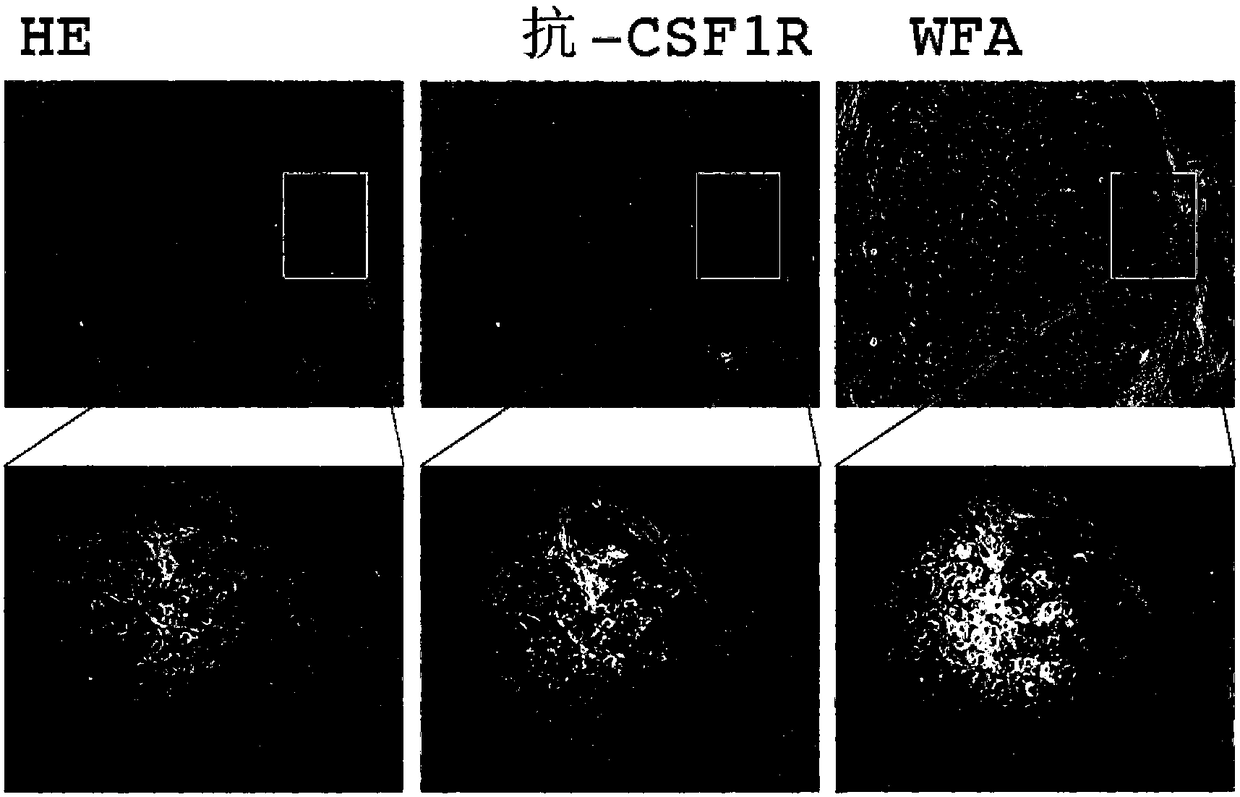
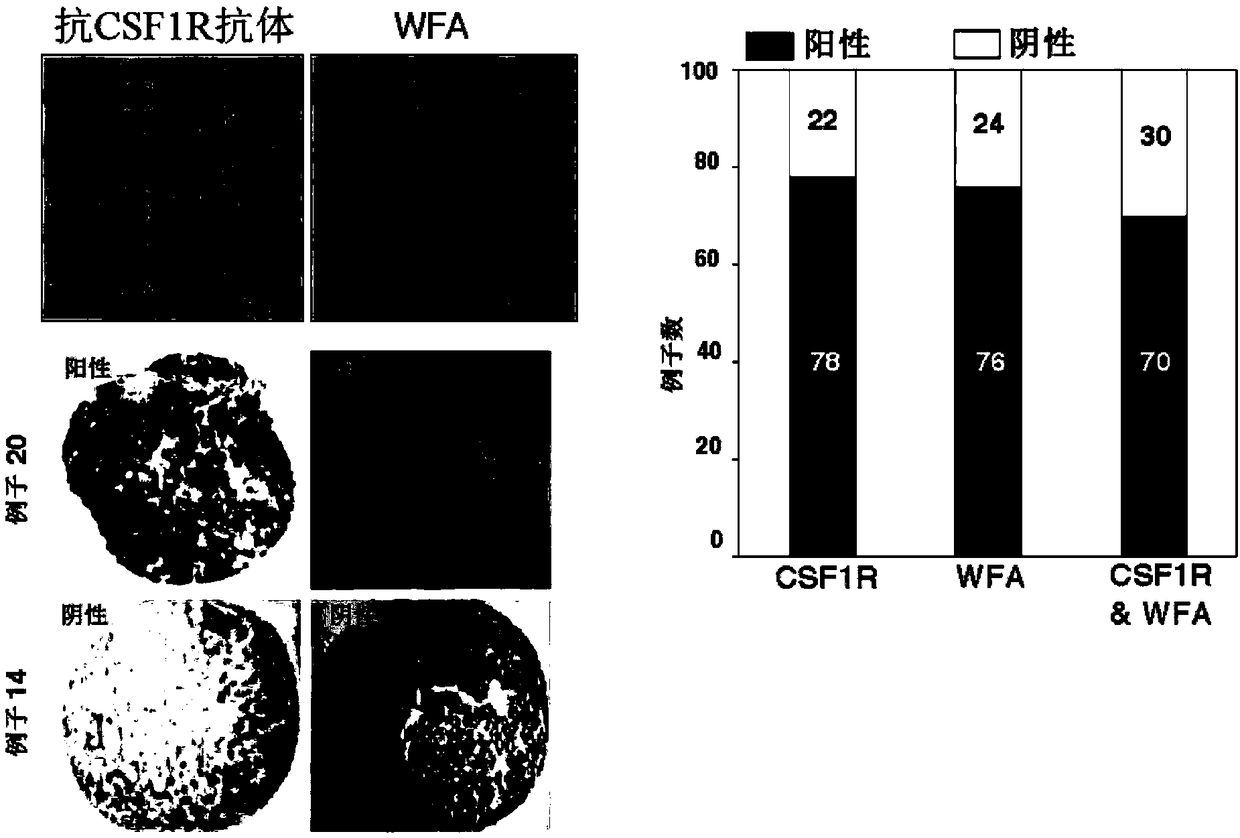
The present invention provides a method and a kit for accurately predicting the prognosis (mortality rate) and risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in liver cirrhosis patients. The present invention provides: a method by which an 'index for evaluating the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma, 'which is used for predicting the prognosis and risk of developing hepatocellular carcinomain liver cirrhosis patients, is calculated as the ratio of CSF1R that contains WFA / VVA-binding sugars relative to the total CSF1R content of bodily fluid (blood serum) (WFA+-CSF1R%); and a method by which a 'prognosis evaluation index ' is calculated as the amount of CSF1R that contains WFA / VVA-binding sugars (WFA+-CSF1R ng / mL). Furthermore, an optimal cutoff value was determined for each of the indices, and it was proven that: the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma was significantly high when the 'index for evaluating the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma ' in a subject wasequal to or greater than the optimal cutoff value; and the prognosis was significantly poor when the 'prognosis evaluation index ' was equal to or greater than the optimal cutoff value. In addition,anti-CSF1R antibodies (CSR-1-30), which are exceptional for detecting CSF1Rs such as CSF1Rs that contain WFA / VVA-binding sugars in a bodily fluid sample, were provided. It was discovered that srWFA and VVA lectins other than WFA lectins can be used, and it was additionally proven that measuring the amount of CSF1R that binds to a CSF1R-specific lectin is preferable to measuring the total amount ofCSF1R. It was also possible to provide, inter alia, a kit for measuring the 'prognosis evaluation index ' and / or 'index for evaluating the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma ' in a liver cirrhosis patient, the kit including these anti-CSF1R antibodies and lectins as constituent elements.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Spleen-invigorating and diuresis-promoting preparation for patients with earlier period cirrhosis and a preparation method
InactiveCN104587417ANot easy to relapseReduce financial burdenDigestive systemPlant ingredientsPatriniaSide effect
The invention discloses a spleen-invigorating and diuresis-promoting preparation for patients with earlier period cirrhosis and a preparation method for the preparation. The spleen-invigorating and diuresis-promoting preparation is prepared from the following main raw materials in parts by weight: 10-15 parts of curcuma aromatica, 8-16 parts of rhizoma anemarrhenae, 12-18 parts of poria cocos, 5-10 parts of cortex acanthopanacis, 7-15 parts of kummerowia striata, 16-20 parts of angelica sinensis, 11-17 parts of dahurian patrinia herb, 6-13 parts of rosa davurica pall, 11-16 parts of dried radix rehmanniae, 15-20 parts of codonopsis pilosula, 9-13 parts of fingered citron, 4-9 parts of fried malts and 8-15 parts of sargentodoxa cuneata. The preparation can be used for treating both symptoms and root causes; low possibility of relapse is achieved, and the treating cost is low; the economic burden of the patient can be relieved; no side effect, and no adverse effect are achieved; the paint of the patient can be obviously relieved.
Owner:聂玮
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com