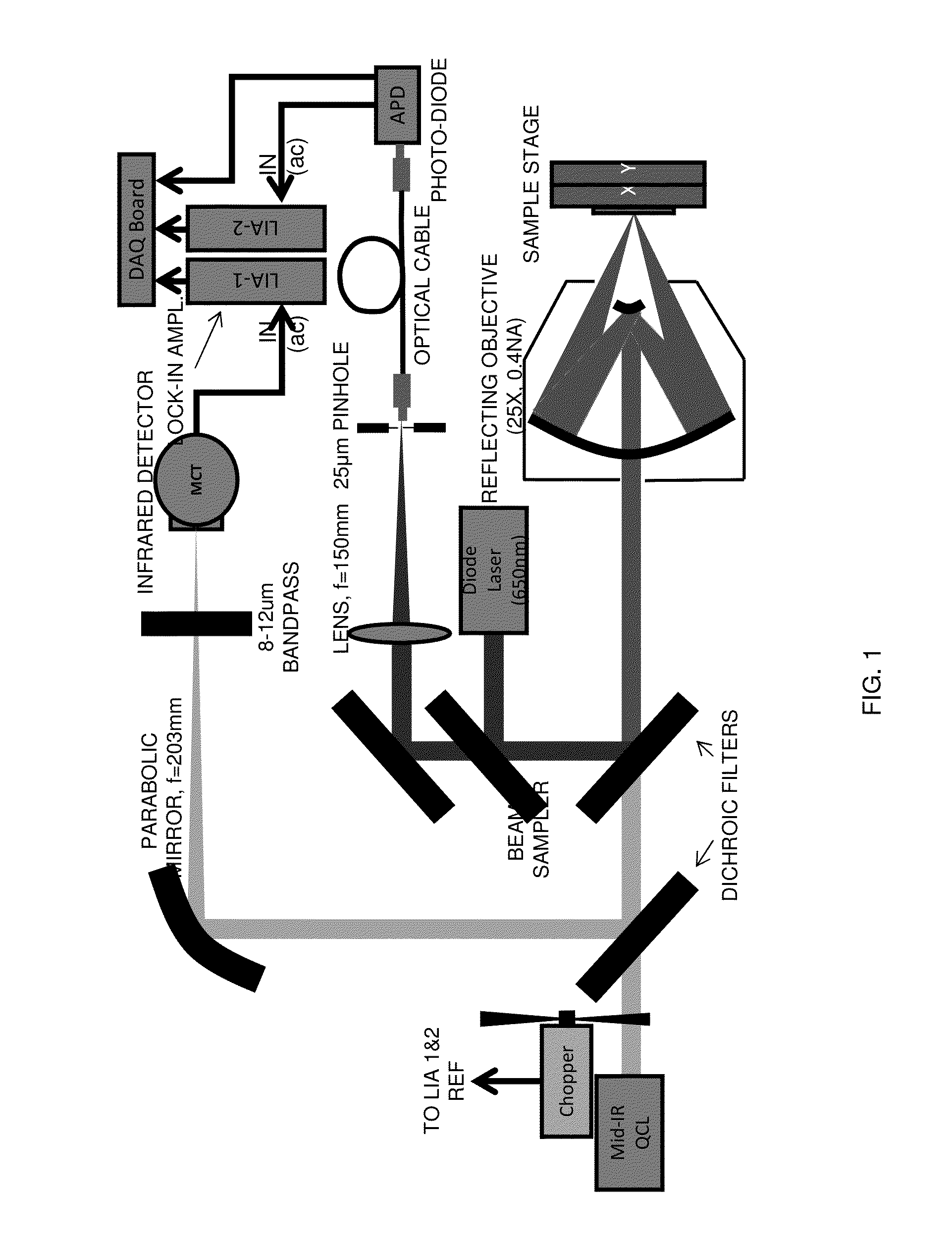
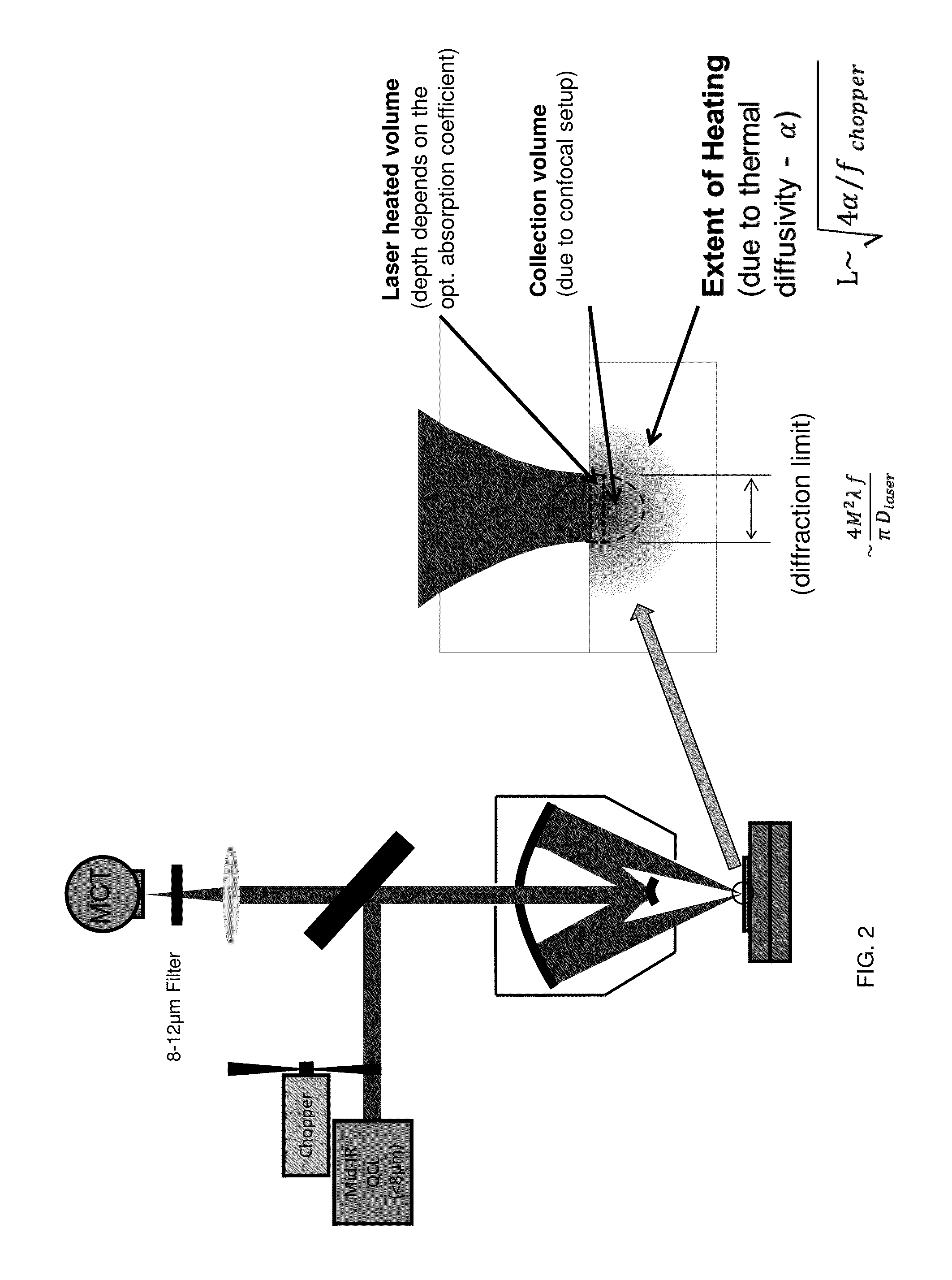
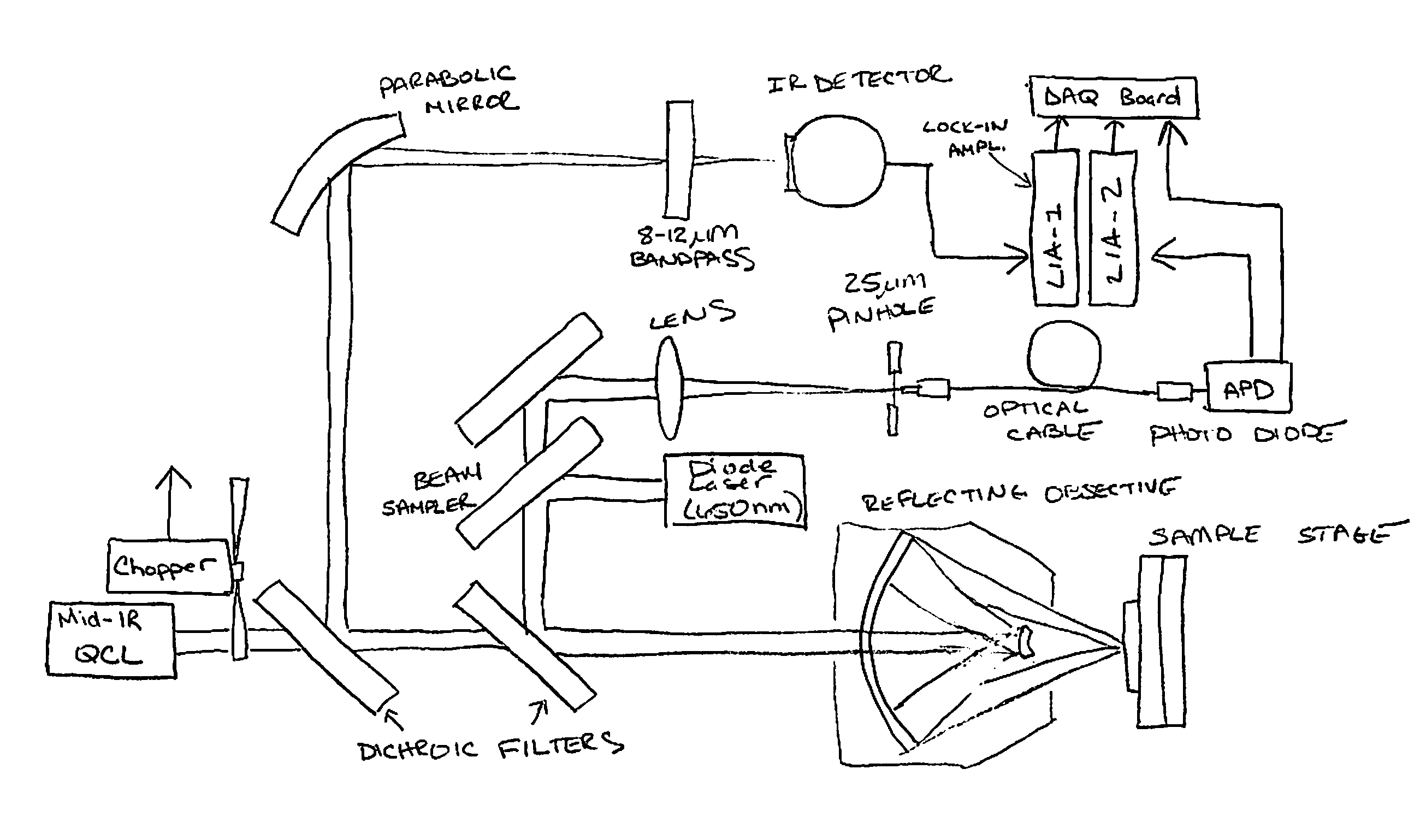
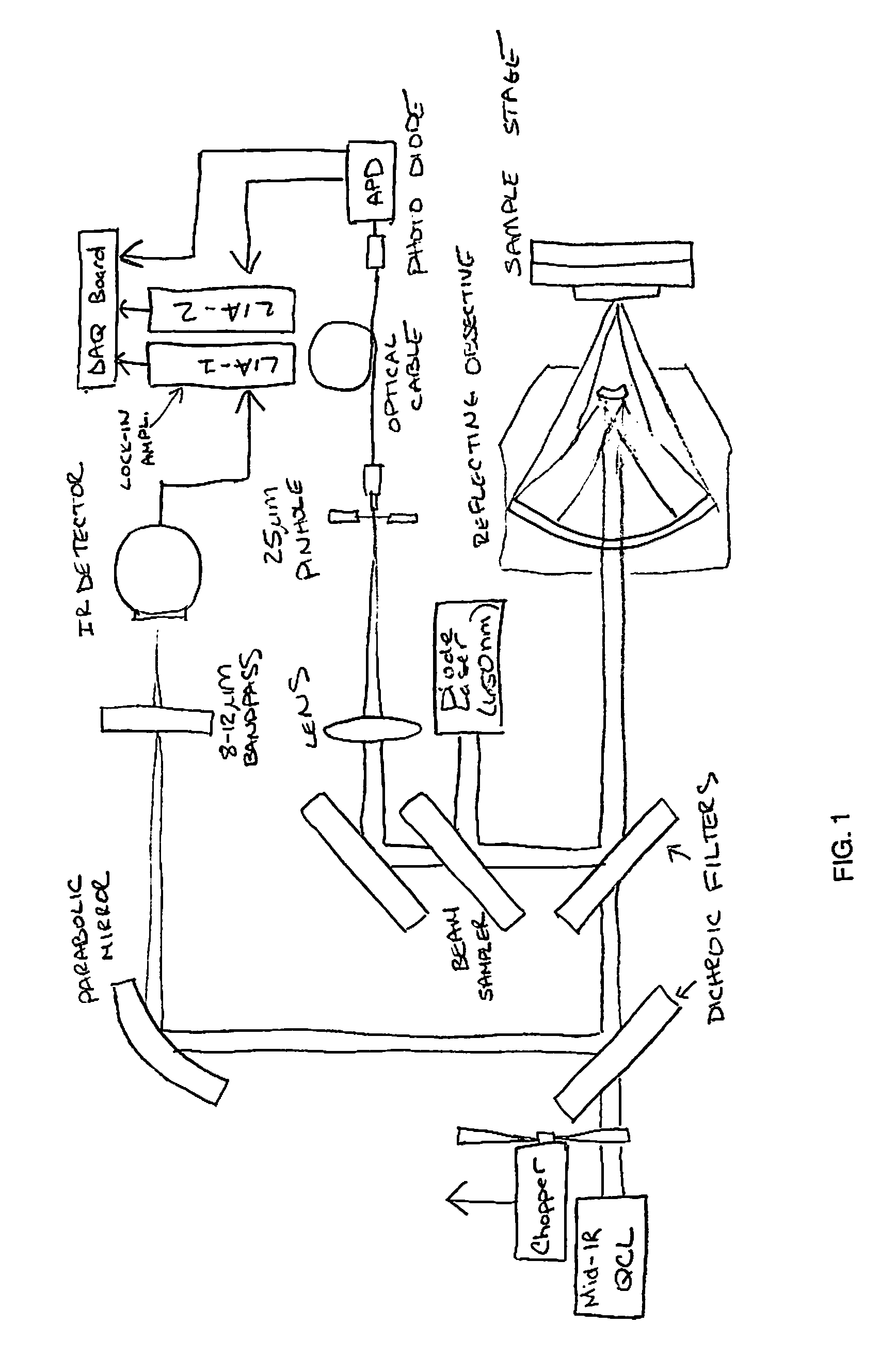
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Scanning thermal microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
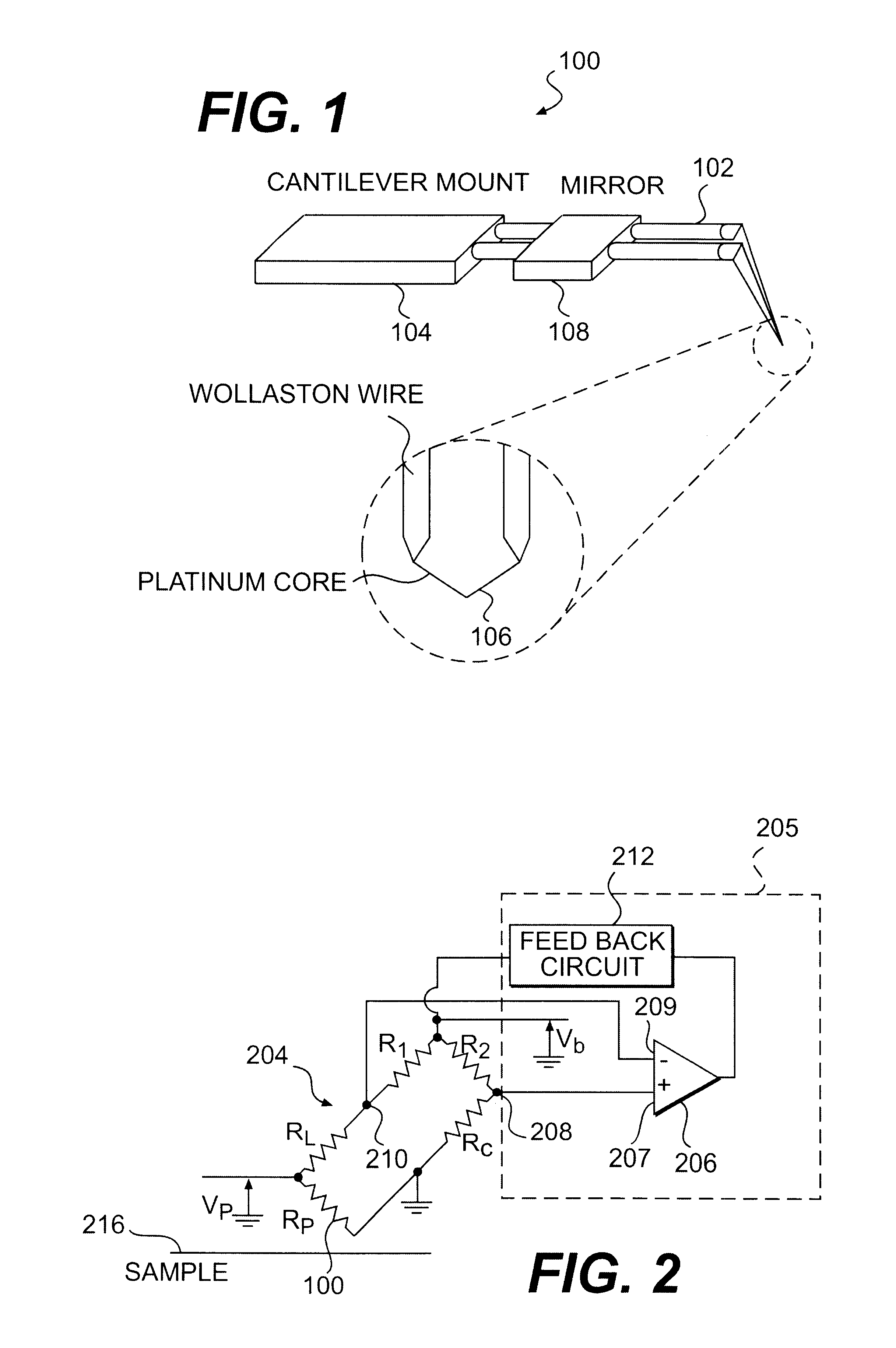
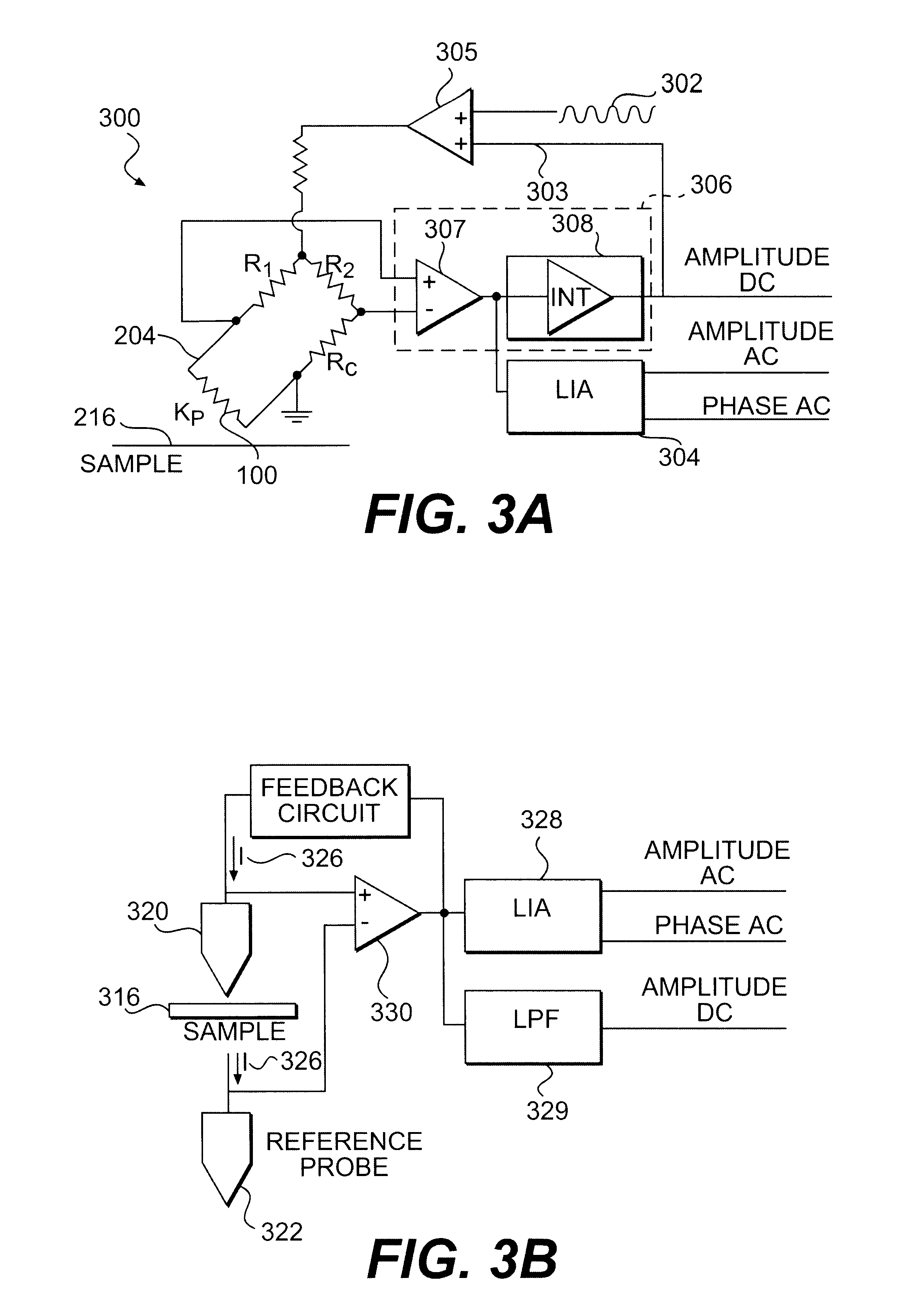
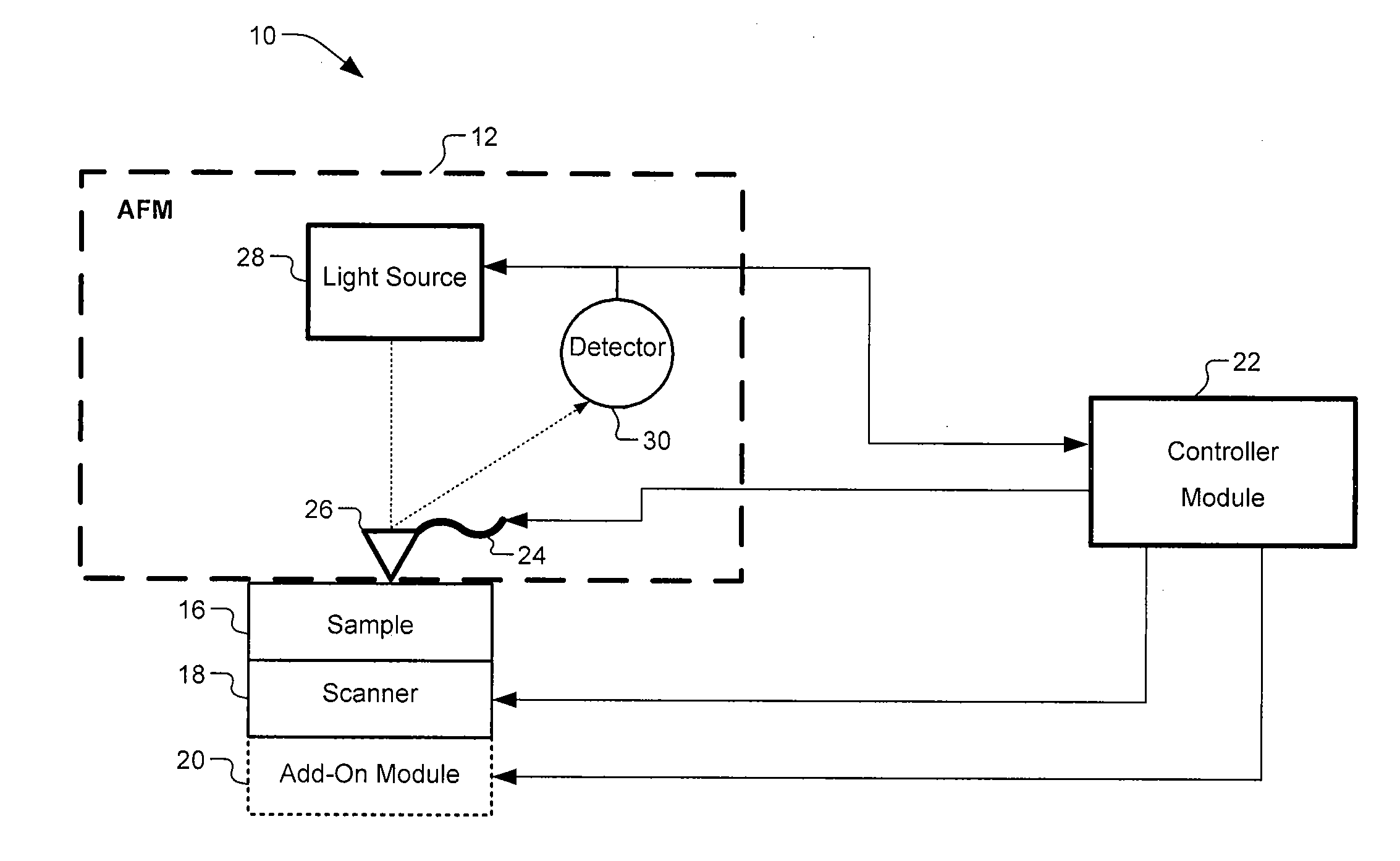
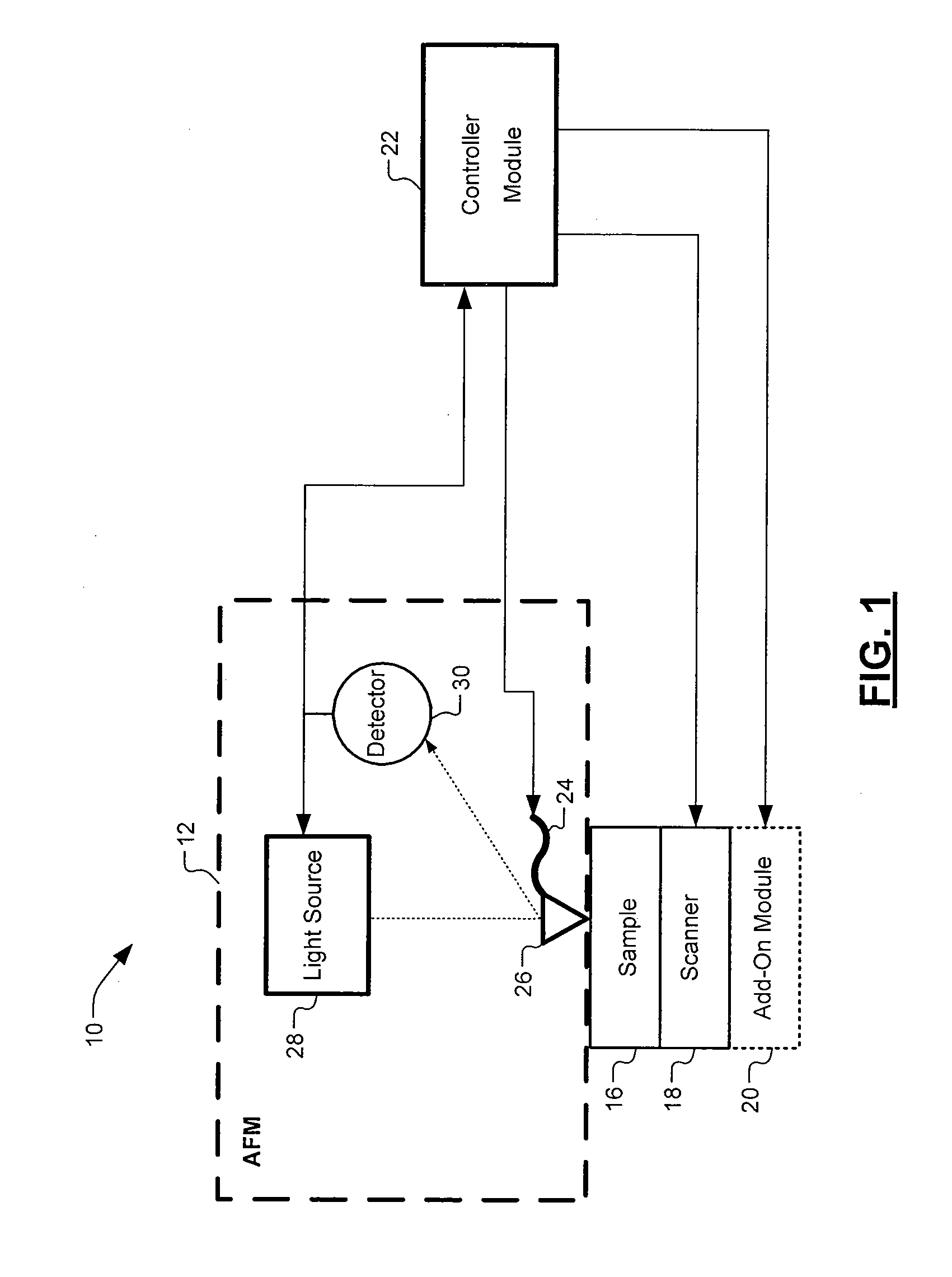
Scanning thermal microscopy (SThM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy that maps the local temperature and thermal conductivity of an interface. The probe in a scanning thermal microscope is sensitive to local temperatures – providing a nano-scale thermometer. Thermal measurements at the nanometer scale are of both scientific and industrial interest.
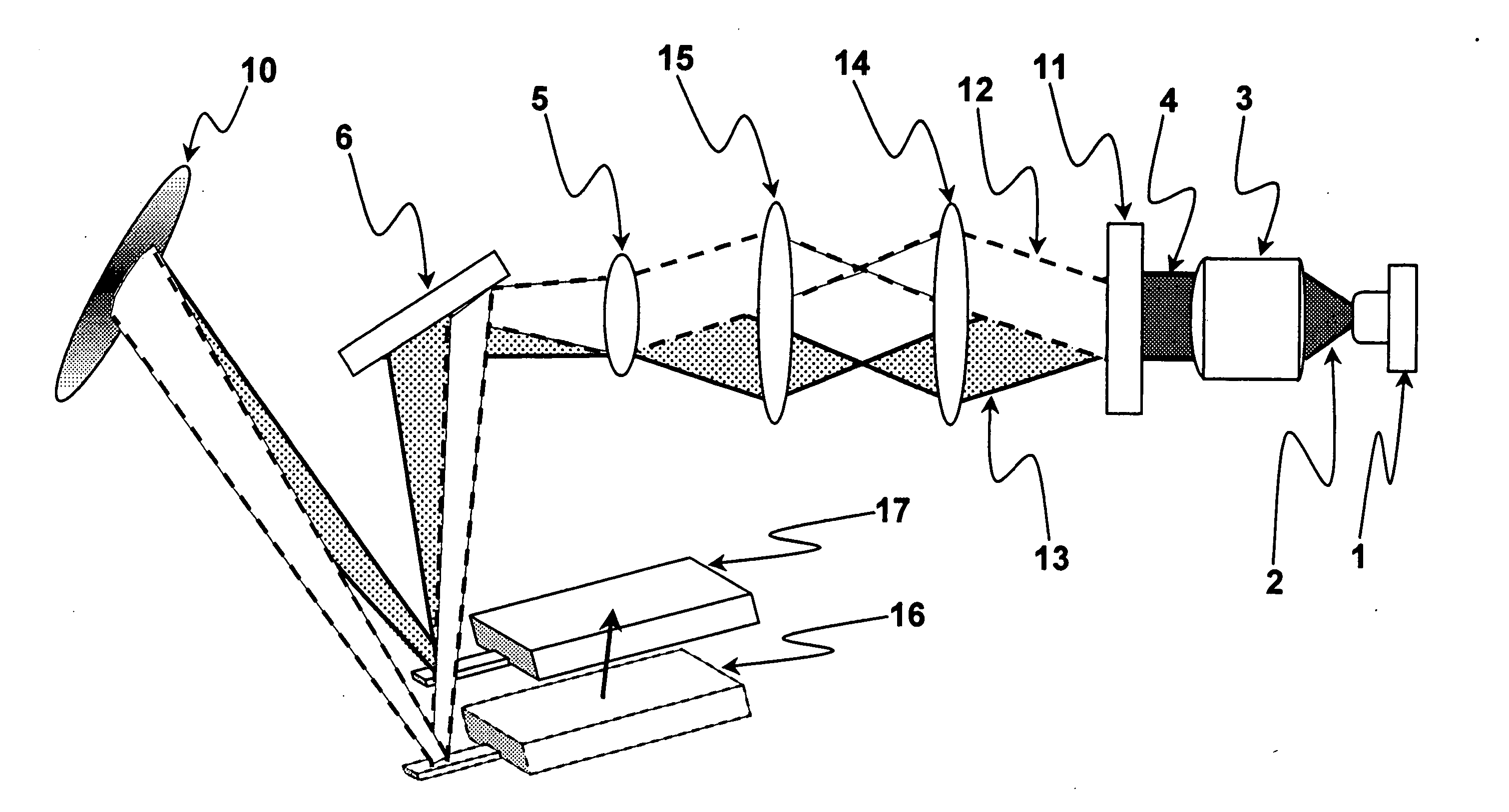
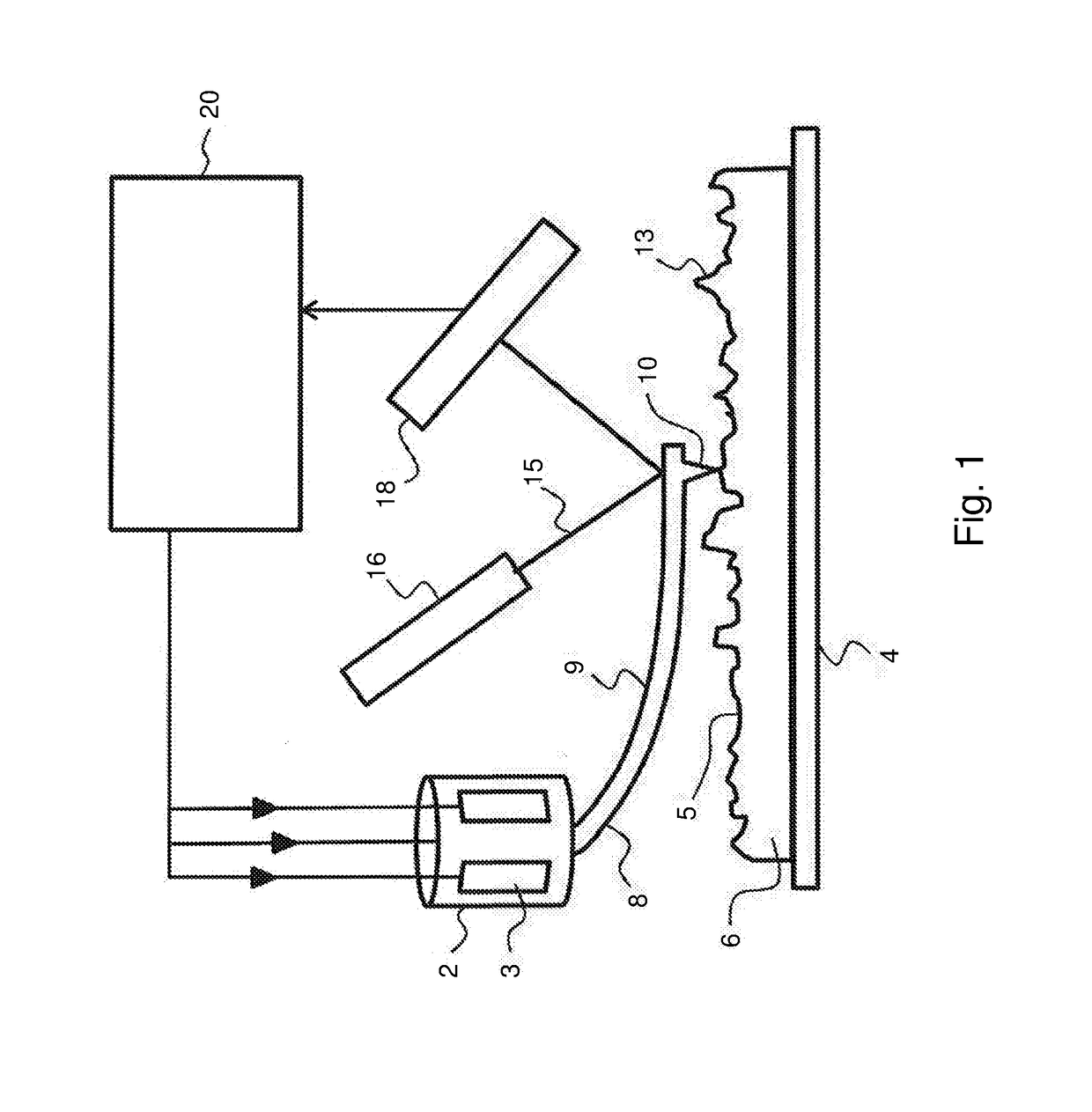
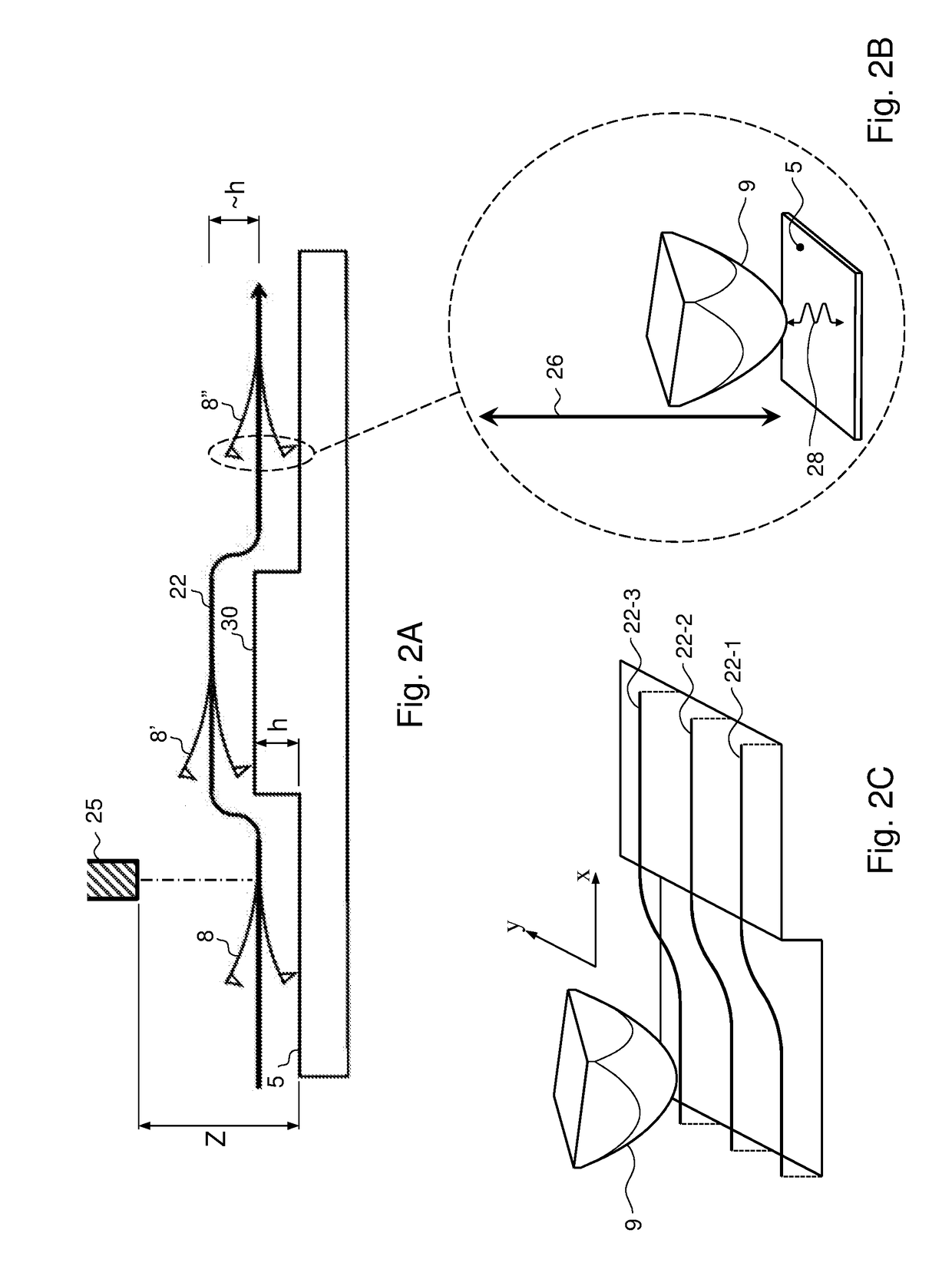
Method and apparatus for performing localized thermal analysis and sub-surface imaging by scanning thermal microscopy
InactiveUS6491425B1Reduce areaSuitable shapeNanotechMaterial heat developmentMaximum depthTemperature wave
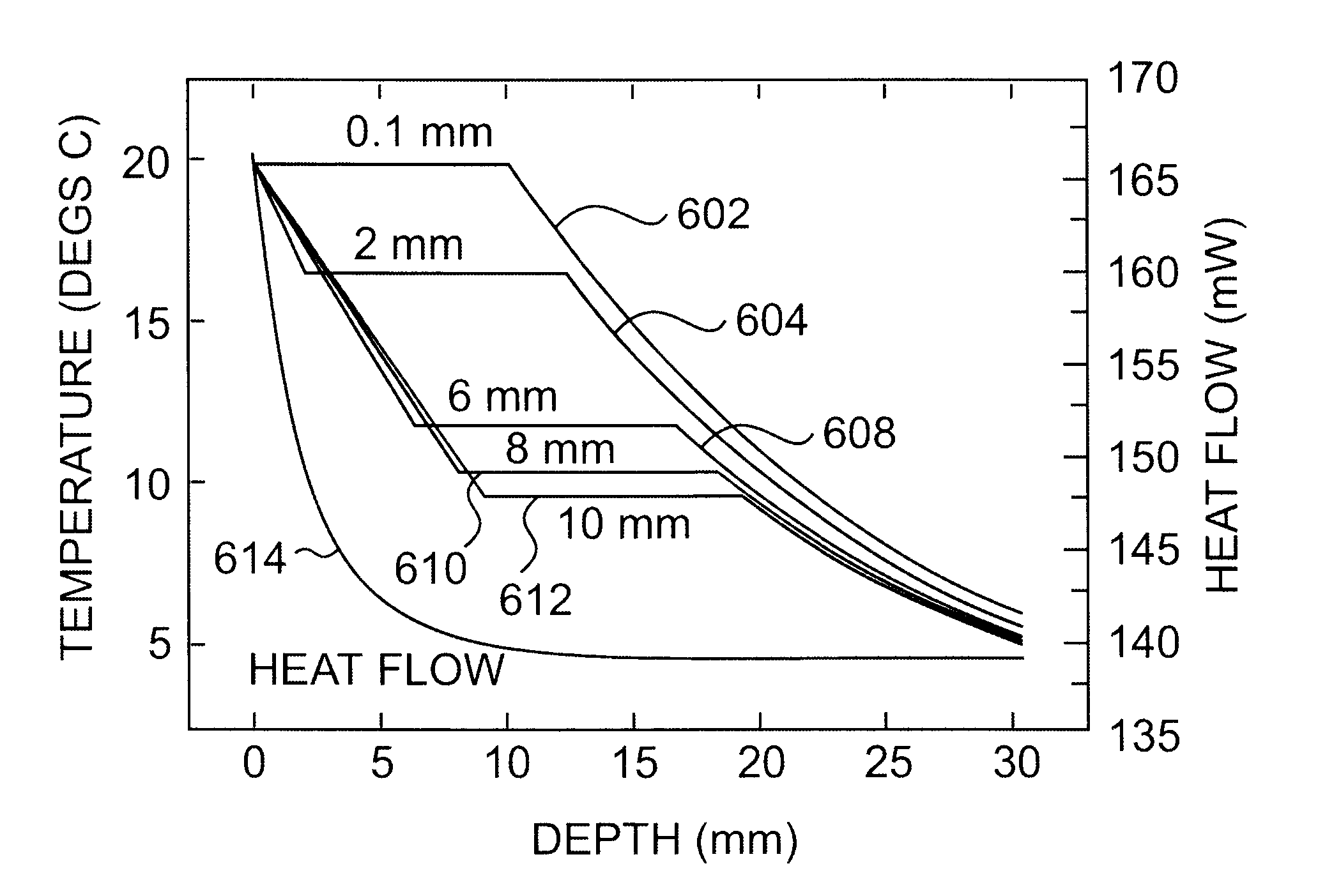
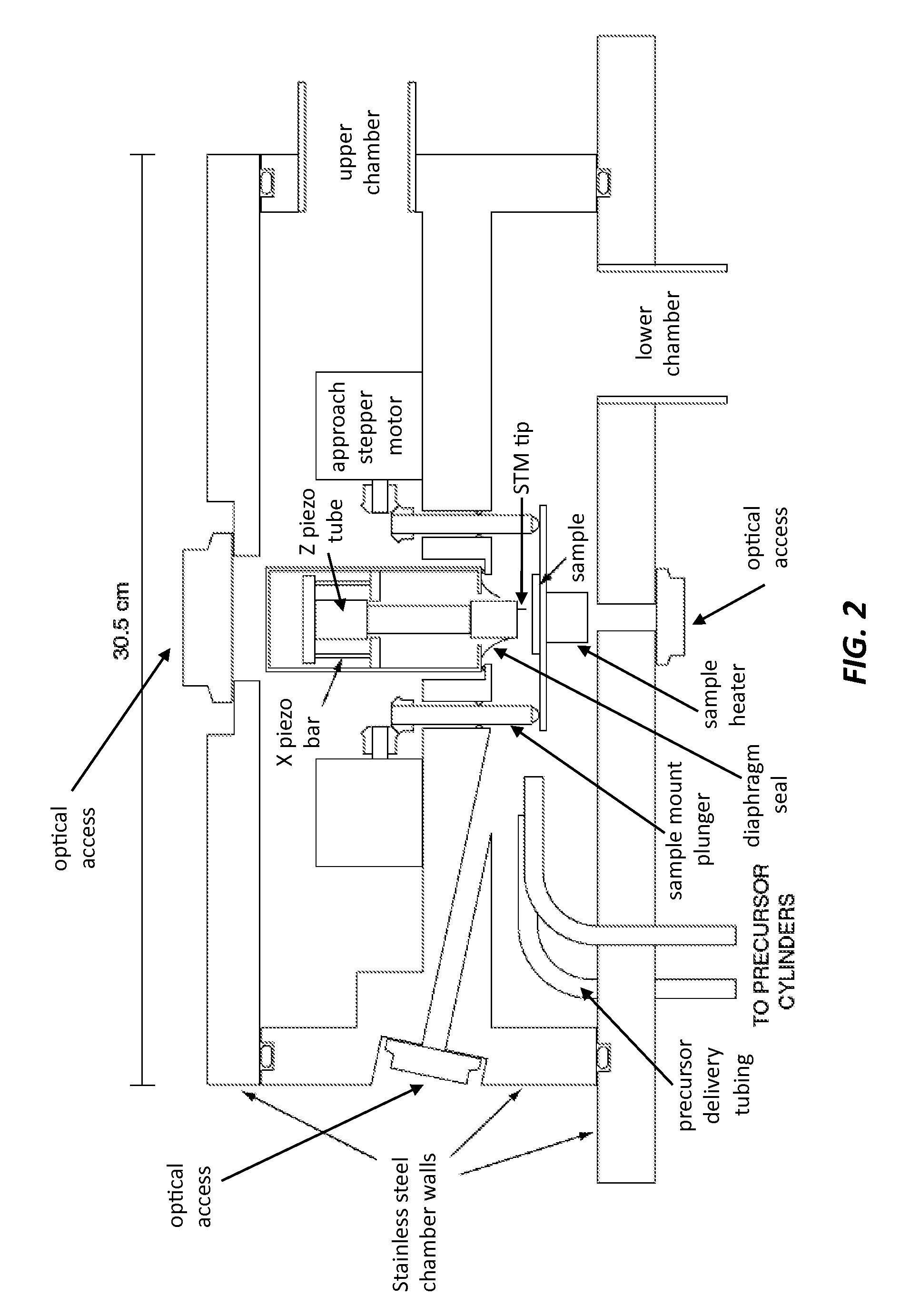
A platinum / Rhodium resistance thermal probe is used as an active device which acts both as a highly localized heat source and as a detector to perform localized differential calorimetry, by thermally inducing and detecting events such as glass transitions, meltings, recystallizations and thermal decomposition within volumes of material estimated at a few mum3. Furthermore, the probe is used to image variations in thermal conductivity and diffusivity, to perform depth profiling and sub-surface imaging. The maximum depth of the sample that is imaged is controlled by generating and detecting evanescent temperature waves in the sample.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for performing localized thermal analysis and sub-surface imaging by scanning thermal microscopy
InactiveUS6095679AReduce areaSuitable shapeNanotechMaterial thermal conductivityMaximum depthTemperature wave
A platinum / Rhodium resistance thermal probe is used as an active device which acts both as a highly localized heat source and as a detector to perform localized differential calorimetry, by thermally inducing and detecting events such as glass transitions, meltings, recystallizations and thermal decomposition within volumes of material estimated at a few mu m3. Furthermore, the probe is used to image variations in thermal conductivity and diffusivity, to perform depth profiling and sub-surface imaging. The maximum depth of the sample that is imaged is controlled by generating and detecting evanescent temperature waves in the sample.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Chemical mapping using thermal microscopy at the micro and NANO scales
ActiveUS20130134310A1Small sizeReduce impactEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryThermionic emissionLaser probe
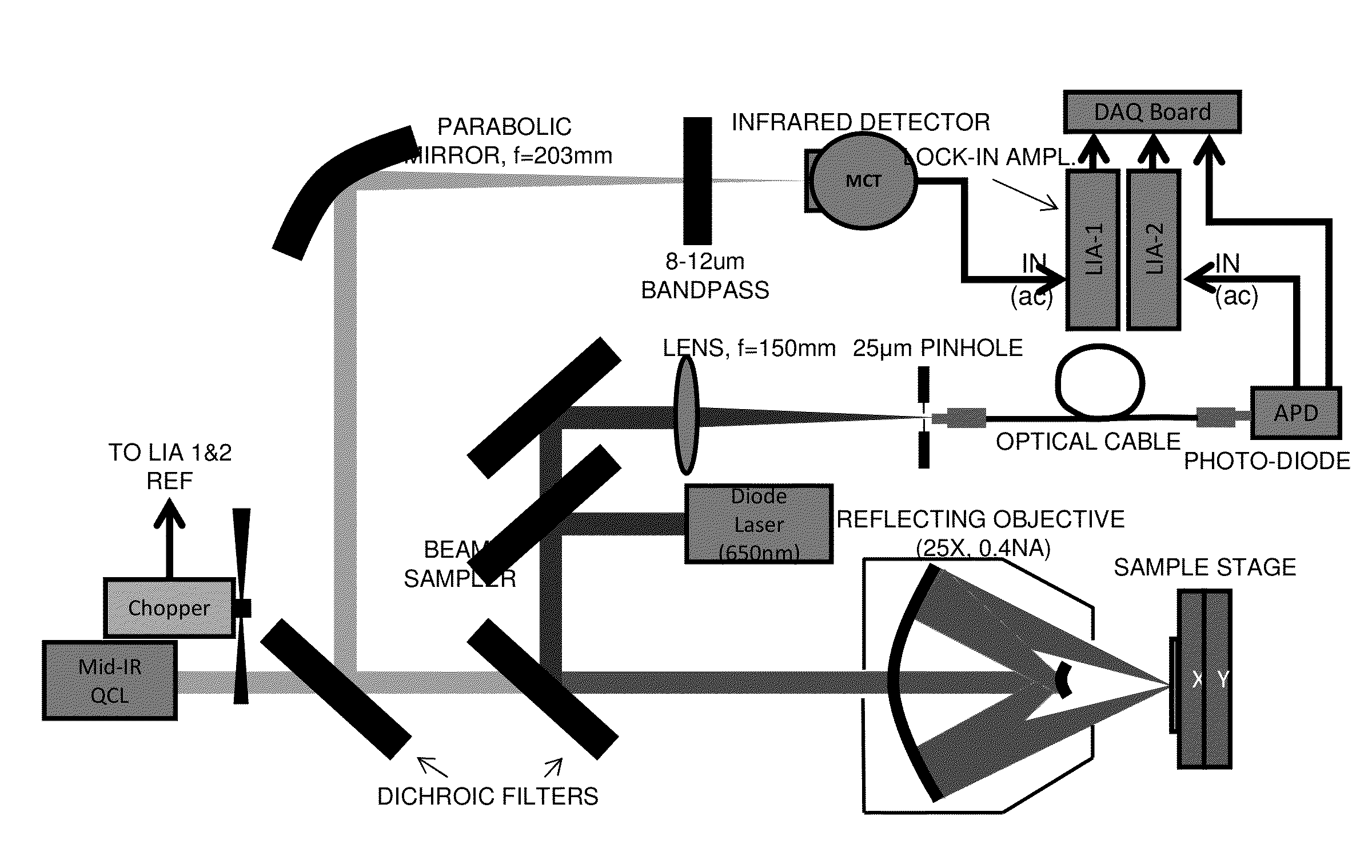
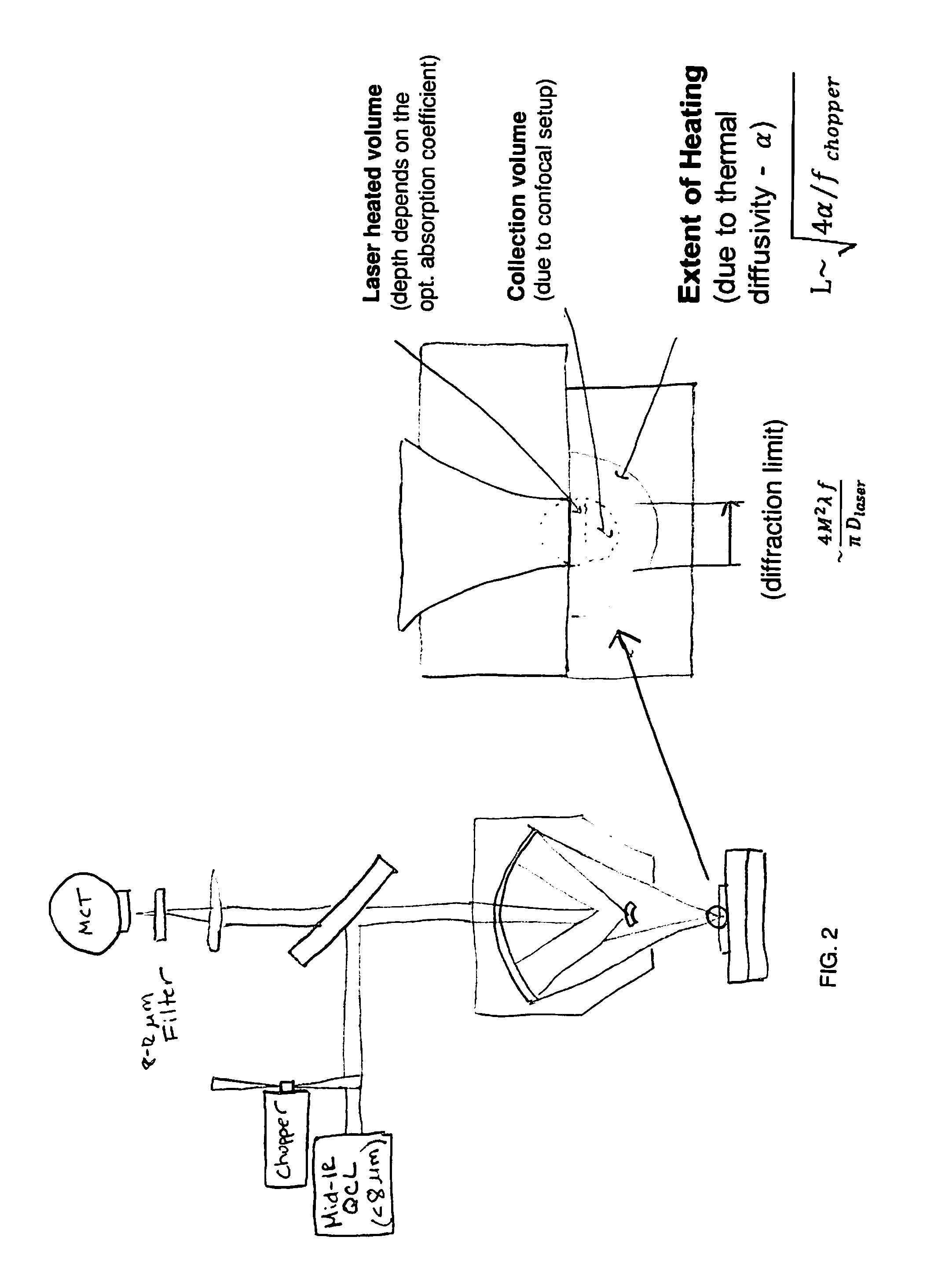
A non-destructive method for chemical imaging with ˜1 nm to 10 μm spatial resolution (depending on the type of heat source) without sample preparation and in a non-contact manner. In one embodiment, a sample undergoes photo-thermal heating using an IR laser and the resulting increase in thermal emissions is measured with either an IR detector or a laser probe having a visible laser reflected from the sample. In another embodiment, the infrared laser is replaced with a focused electron or ion source while the thermal emission is collected in the same manner as with the infrared heating. The achievable spatial resolution of this embodiment is in the 1-50 nm range.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Chemical mapping using thermal microscopy at the micro and nano scales
ActiveUS9091594B2Small sizeReduce impactEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryThermionic emissionLaser probe
A non-destructive method for chemical imaging with ˜1 nm to 10 μm spatial resolution (depending on the type of heat source) without sample preparation and in a non-contact manner. In one embodiment, a sample undergoes photo-thermal heating using an IR laser and the resulting increase in thermal emissions is measured with either an IR detector or a laser probe having a visible laser reflected from the sample. In another embodiment, the infrared laser is replaced with a focused electron or ion source while the thermal emission is collected in the same manner as with the infrared heating. The achievable spatial resolution of this embodiment is in the 1-50 nm range.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Spatially resolved quantitative mapping of thermomechanical properties and phase transition temperatures using scanning probe microscopy
ActiveUS20110041223A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using physical/chemical changesContact forceScanning probe microscopy
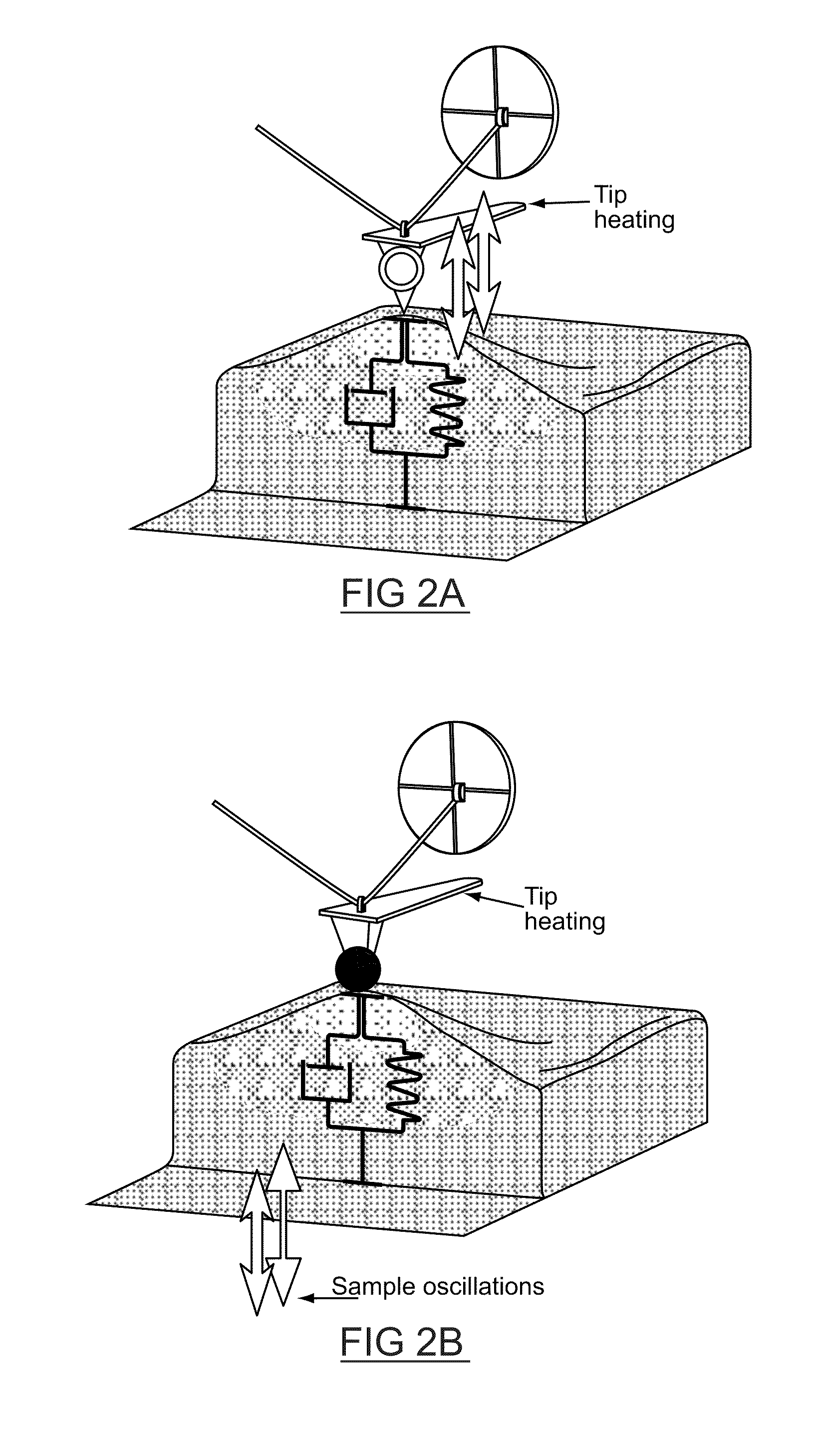
An approach for the thermomechanical characterization of phase transitions in polymeric materials (polyethyleneterephthalate) by band excitation acoustic force microscopy is developed. This methodology allows the independent measurement of resonance frequency, Q factor, and oscillation amplitude of a tip-surface contact area as a function of tip temperature, from which the thermal evolution of tip-surface spring constant and mechanical dissipation can be extracted. A heating protocol maintained a constant tip-surface contact area and constant contact force, thereby allowing for reproducible measurements and quantitative extraction of material properties including temperature dependence of indentation-based elastic and loss moduli.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Fine-adjustment mechanism for scanning probe microscopy
InactiveUS7288762B2Improve rigidityHigh measurement accuracyNanotechMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectricityEngineering
The invention provides a fine-adjustment mechanism for a scanning probe microscopy with high rigidity and high degree of measurement accuracy wherein a strain gauge displacement sensor which can be installed in a small space is arranged so that temperature compensation is achieved. The fine-adjustment mechanism composed of a piezoelectric device is provided with at least two-piece electrode. One of the electrodes is configured as a dummy electrode, to which no voltage is applied, and the other electrode is configured as an active electrode which generates strain when voltage is applied. One or two resistors are provided on each of the active electrode and dummy electrode, and a bridge circuit is configured by the resistors.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
Method for preparing miniature thermocouple probe of scanning thermal microscopy
InactiveCN102175894AEase of manufacture and simplicitySimplify processing stepsScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyNano machining
The invention discloses a method for preparing a miniature thermocouple probe of a scanning thermal microscopy, which belongs to the technical fields of nano machining, nanoscale performance measurement and electronic science. The method for preparing the miniature thermocouple probe of the scanning thermal microscopy comprises the following steps of: a) manufacturing a first metal layer on the front of a cantilever pinpoint of an atomic force microscopy; b) manufacturing an insulating layer on the first metal layer; c) removing the insulating layer in a set area on the tip of the pinpoint; and d) manufacturing a second metal layer on the insulating layer, wherein the second metal layer is in contact with the first metal layer in the set area, and is made from a material different from that of the first metal layer. The method can be used for the technical fields of nano machining, nanoscale performance measurement and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Deposition method for heteroepitaxial diamond
InactiveUS6063187AHigh densityIncrease chancePolycrystalline material growthMolten spray coatingPolycrystalline diamondScanning probe microscopy
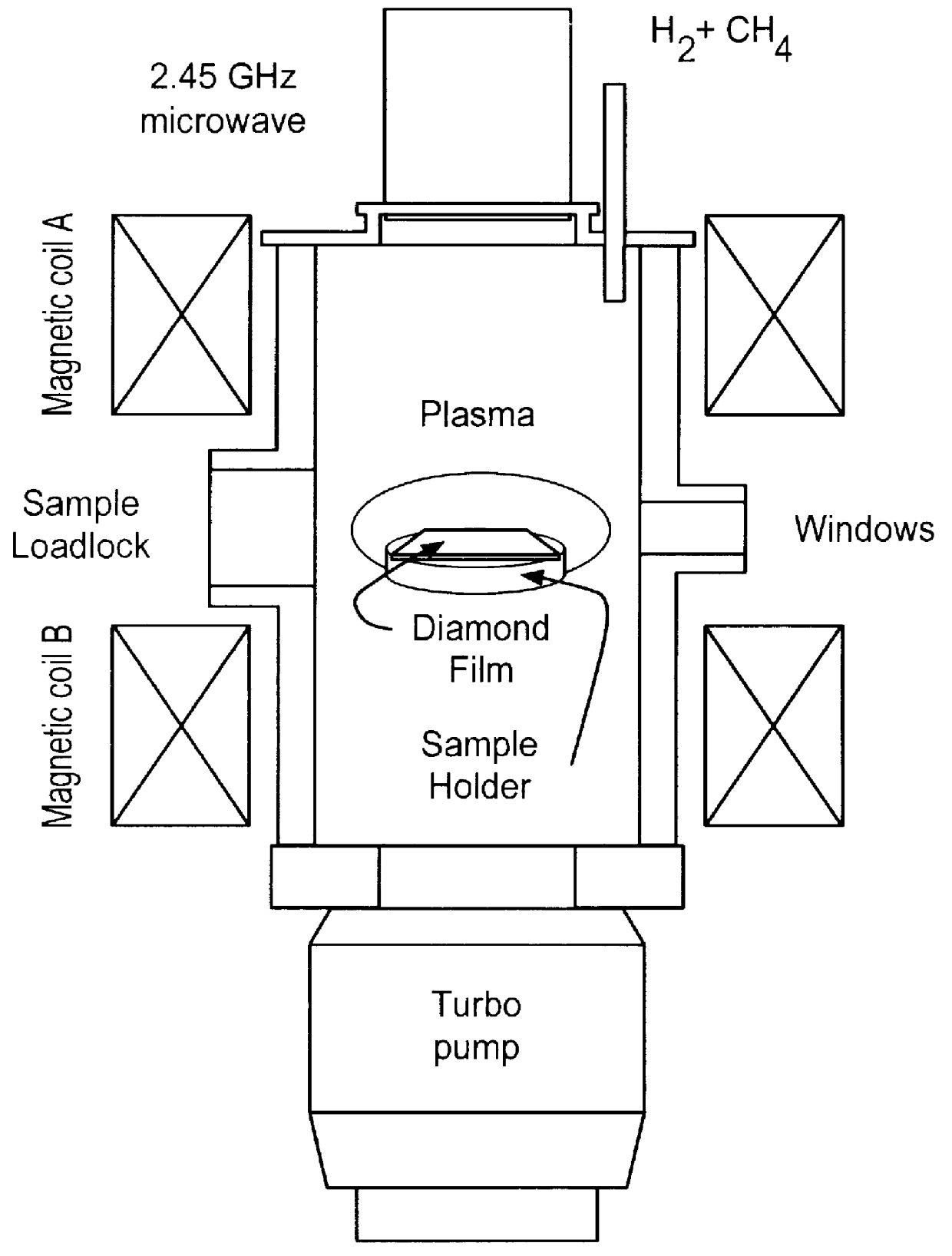
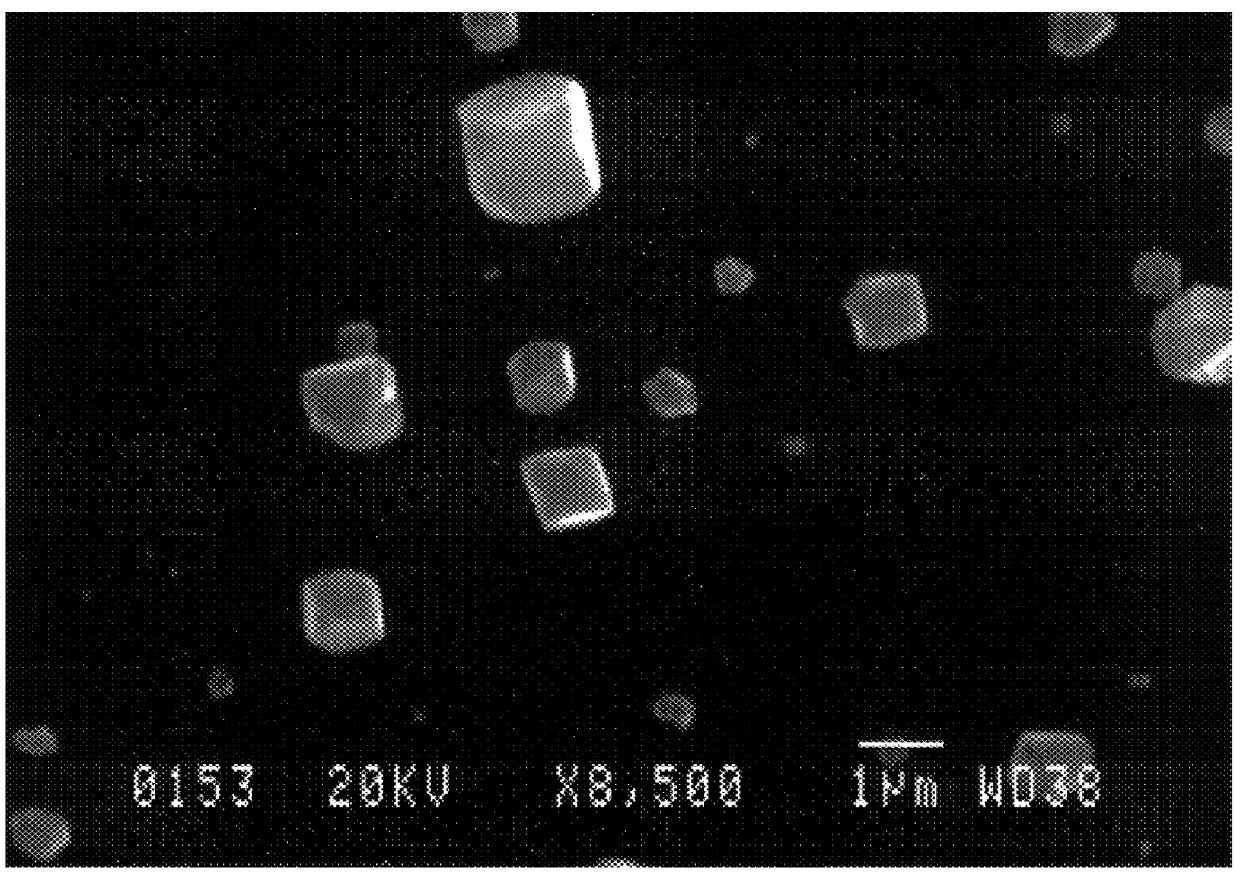
A method for the growth of diamond on a substrate combines an ECR (Electron cyclotron resonance) MPCVD (Microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition) method with a MPCVD method in one system. A two-step diamond growing method comprises firstly etching and nucleation performed by the ECR method and then diamond grown by the microwave plasma CVD method. Not only are high quality continuous polycrystalline diamond films on silicon wafer obtained but also heteroepitaxial growth has been achieved in the present invention. Auger electron spectroscopy (AES), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Raman spectroscopy have been used to characterize the structure and morphology of the synthesized diamond films.
Owner:CITY UNIV OF HK
Nano thermoelectrical Seebeck coefficient in-situ characterization device based on scanning thermal microscope
ActiveCN103344790AExpand the evaluation function of nanothermoelectric propertiesScanning probe microscopyMacroscopic scaleScanning tunneling microscope
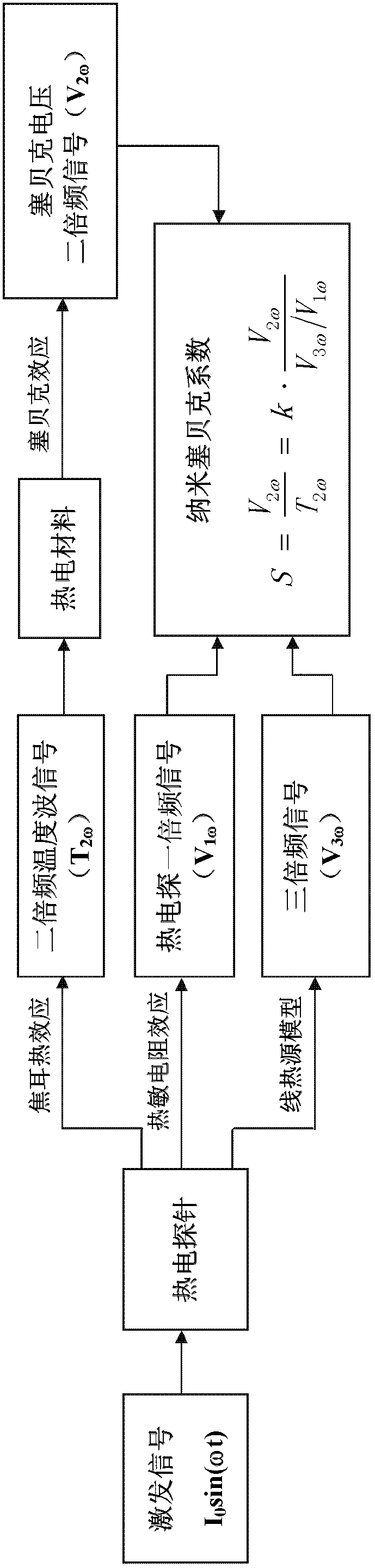
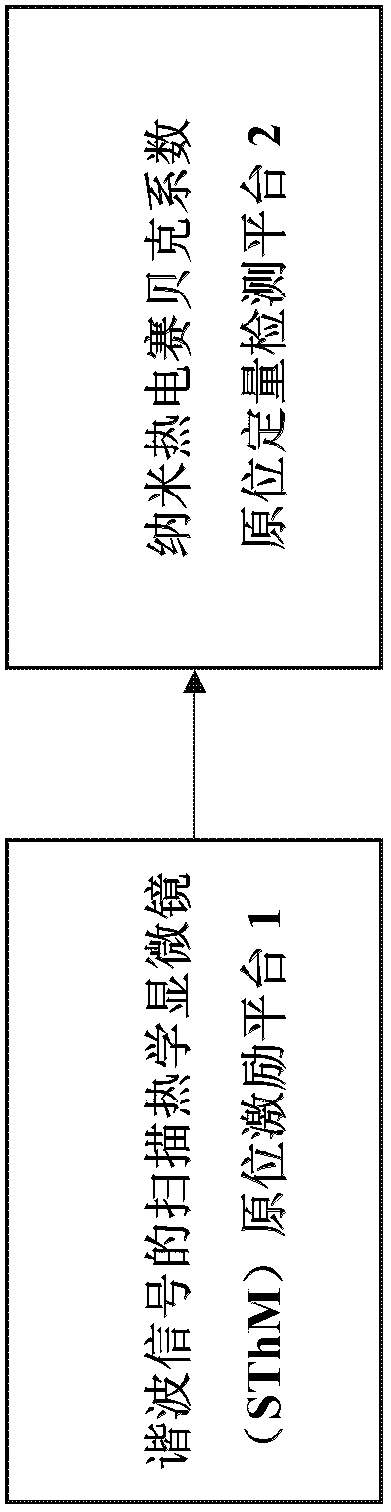
The invention discloses a nano thermoelectrical Seebeck coefficient in-situ characterization device based on a scanning thermal microscope. The device is used for detecting the microcell Seebeck coefficient of thermal nano-materials. The device further comprises a scanning thermal microscope in-situ excitation platform of harmonic signals and a nano thermoelectrical Seebeck coefficient in-situ detection platform, wherein the microcell thermoelectrical Seebeck coefficient is as follows, wherein S is the microcell Seebeck coefficient, V<1omega>, V<2omega> and V<3omega> are a first harmonic generation harmonic signal, a second harmonic generation harmonic signal of a microcell of the thermal nano-materials and a third harmonic generation harmonic signal of the microcell of the thermal nano-materials respectively, and k is a coefficient. The nano-detection function of the scanning thermal microscope, a one-dimensional linear heat source model, the Joule heat effect principle and the macroscopic Seebeck coefficient testing principle are combined to build the new nano thermoelectrical Seebeck coefficient in-situ characterization device based on the scanning thermal microscope.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
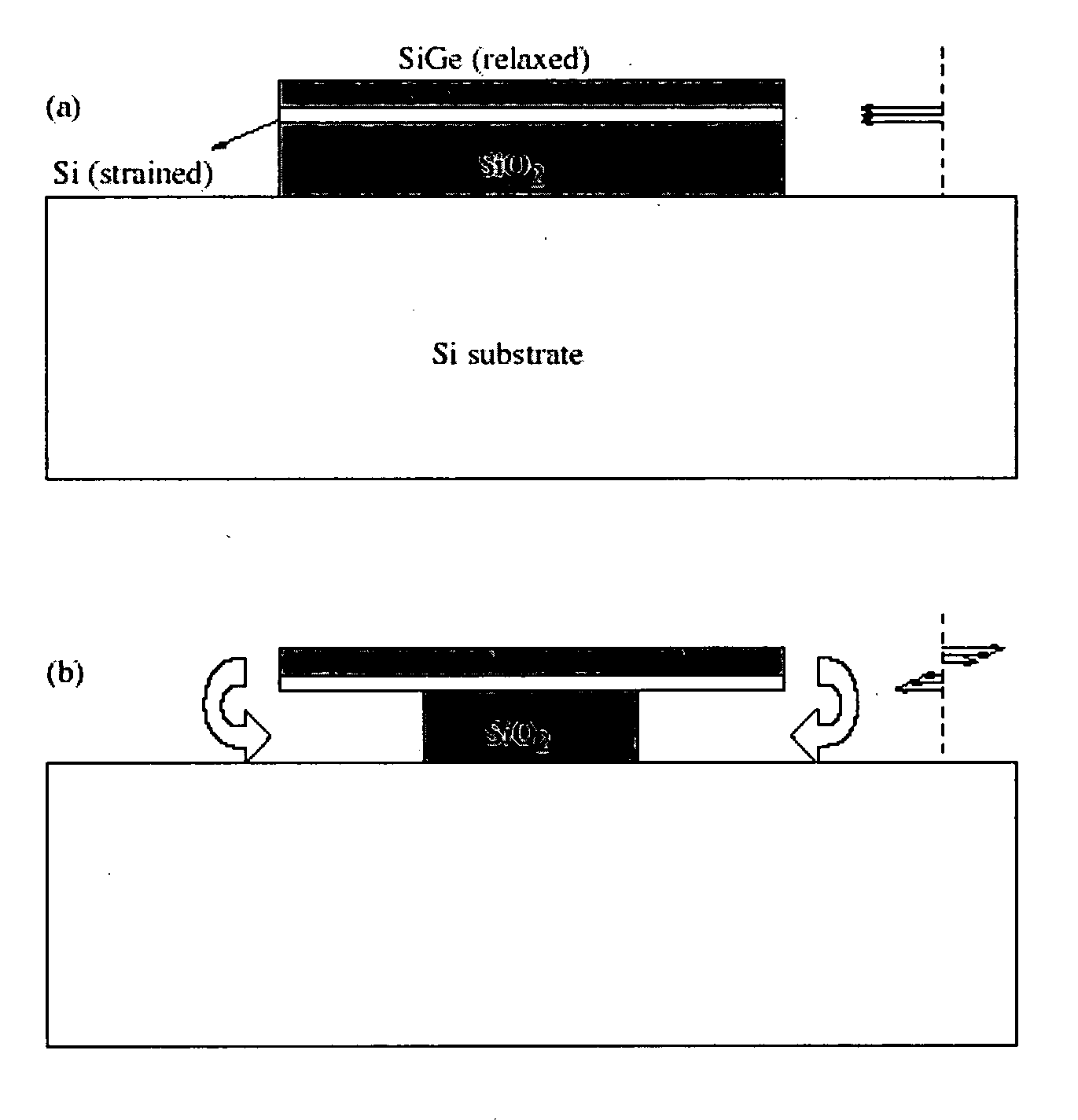
Microcoaxial probes made from strained semiconductor bilayers
ActiveUS20080061798A1NanotechMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAtomic force microscopyMicrowave
The present invention provides microcoaxial probes fabricated from semiconductor heterostructures that include strained semiconductor bilayers. The microcoaxial probes are well suited for use as scanning probes in scanning probe microscopy, including scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning microwave microscopy, or a combination thereof.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
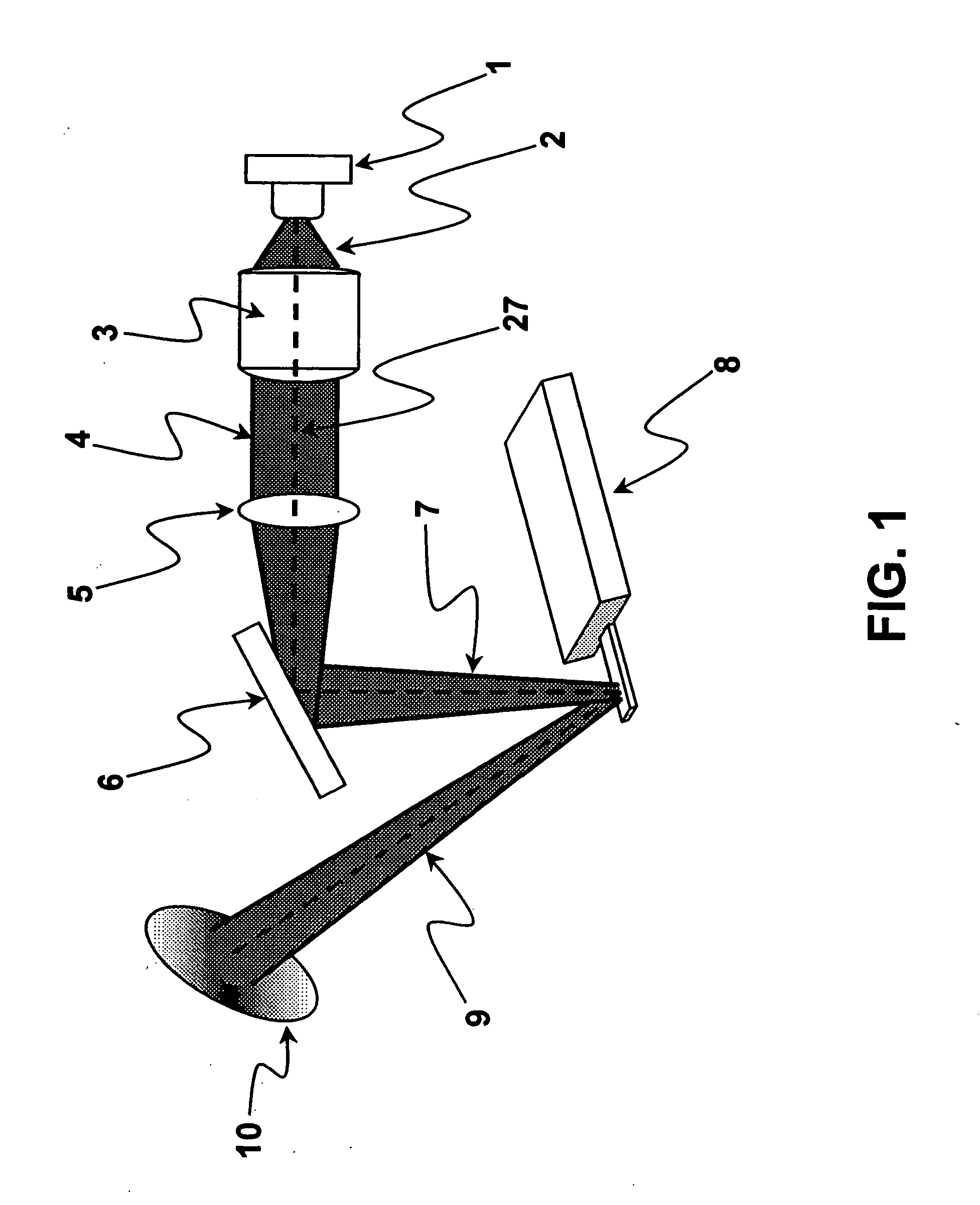
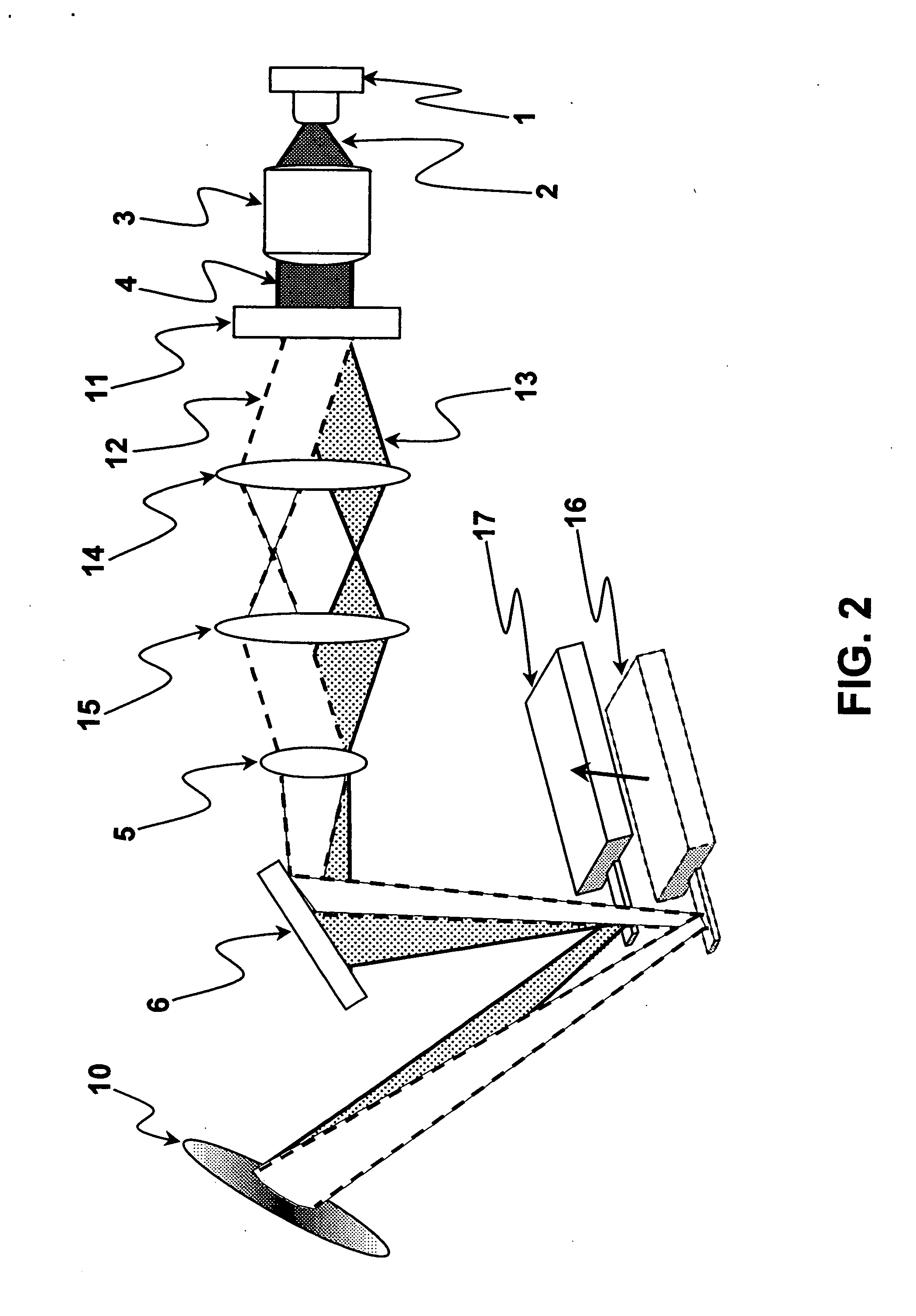
Photothermal actuation of a probe for scanning probe microscopy
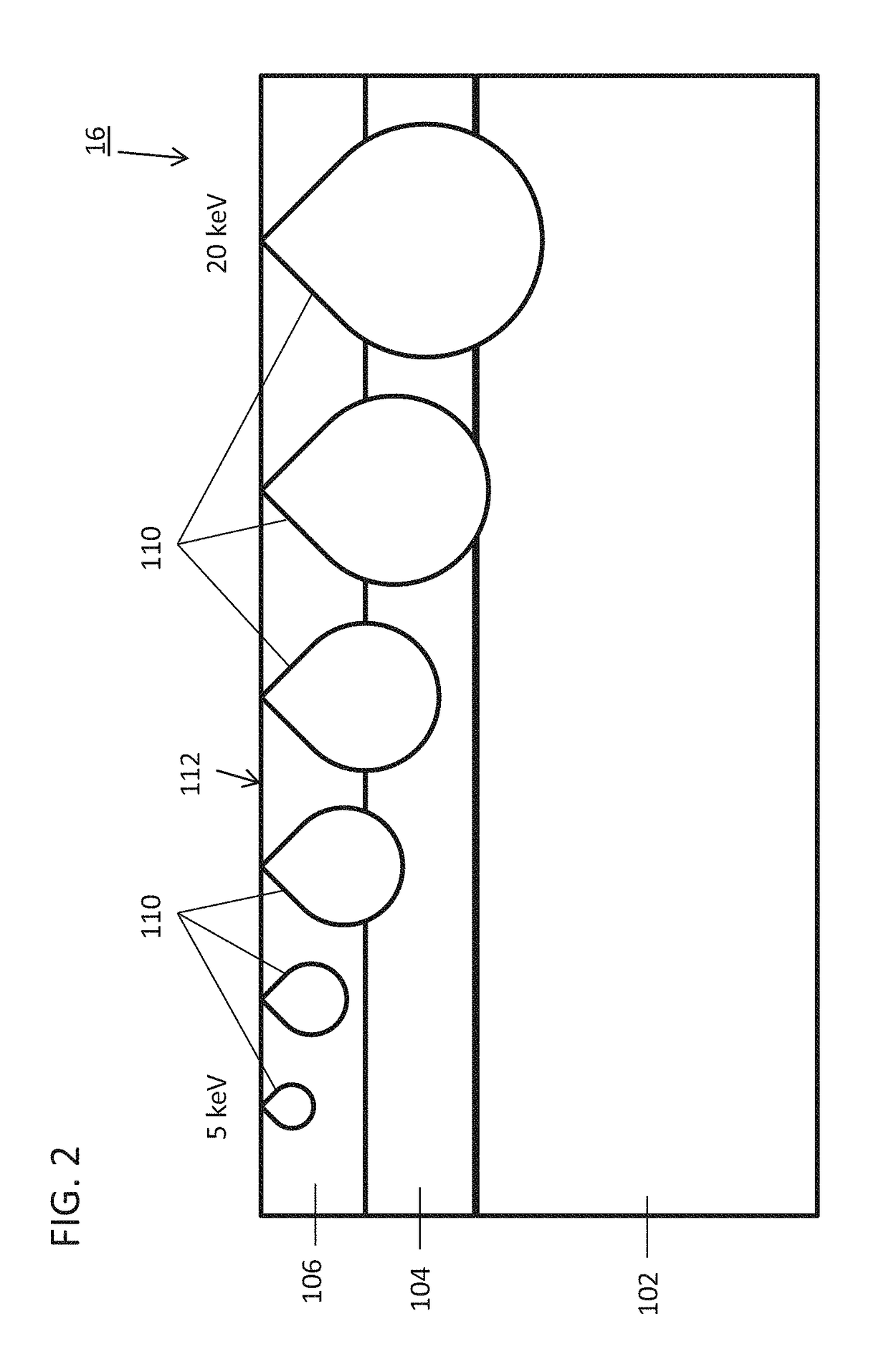
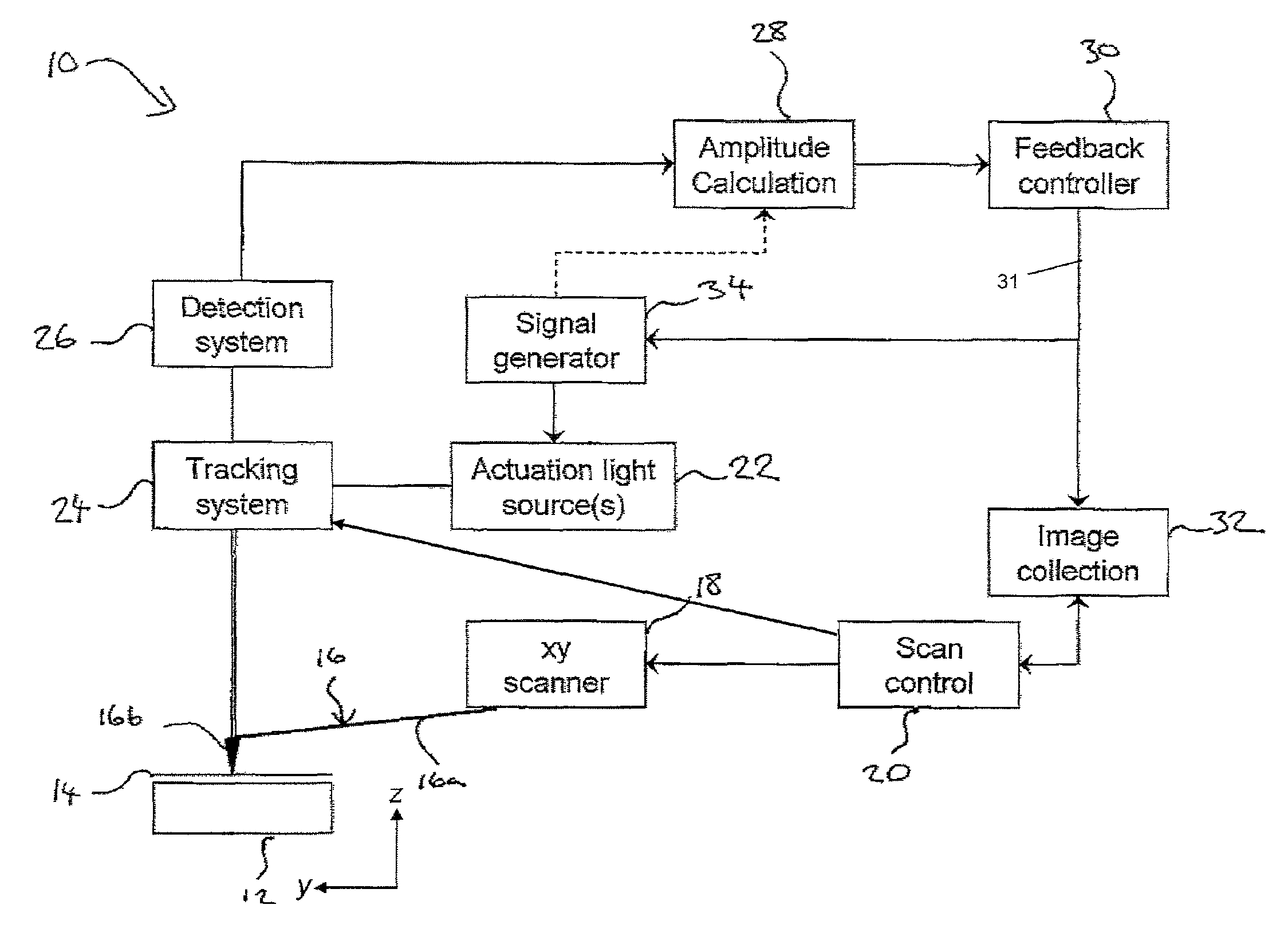
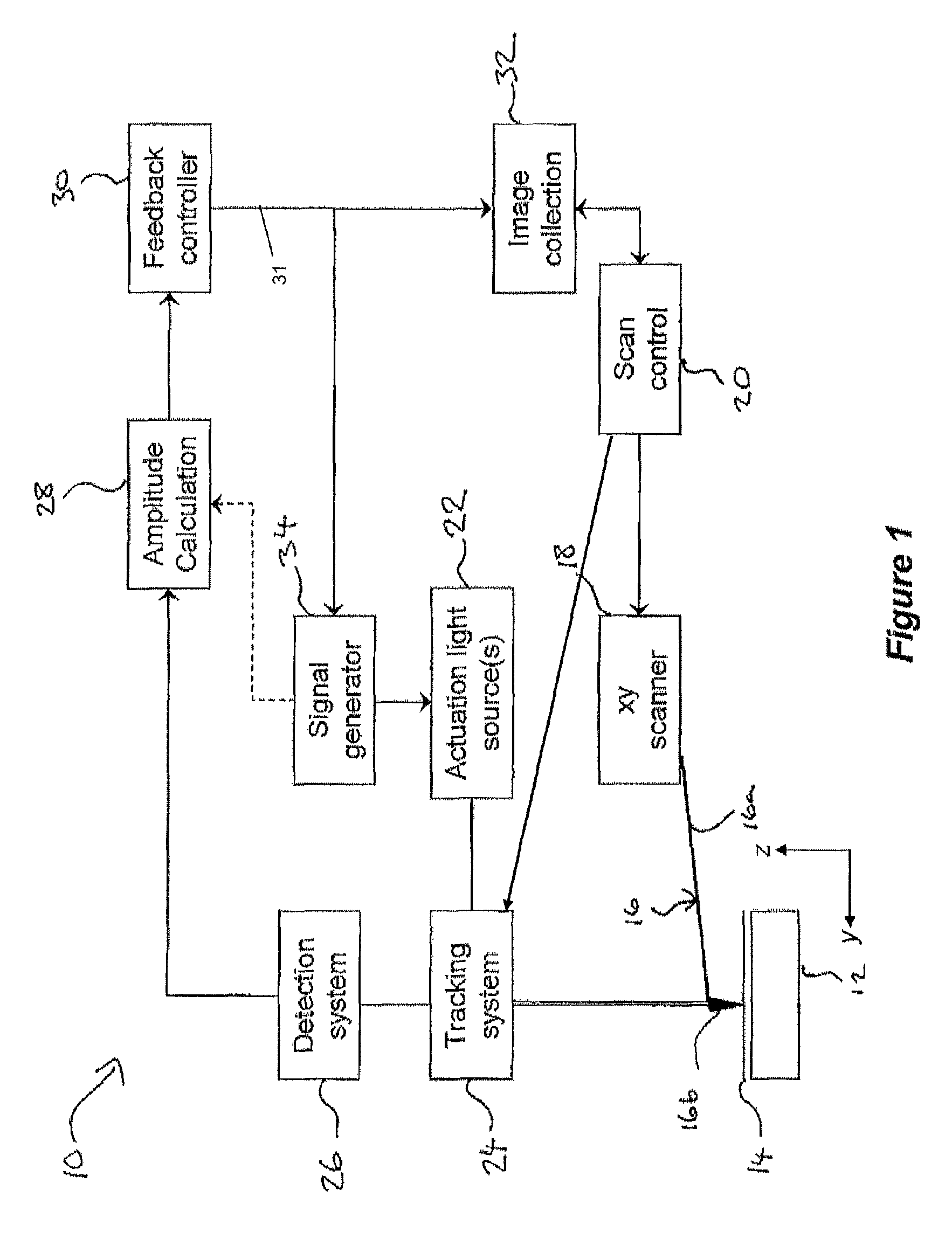
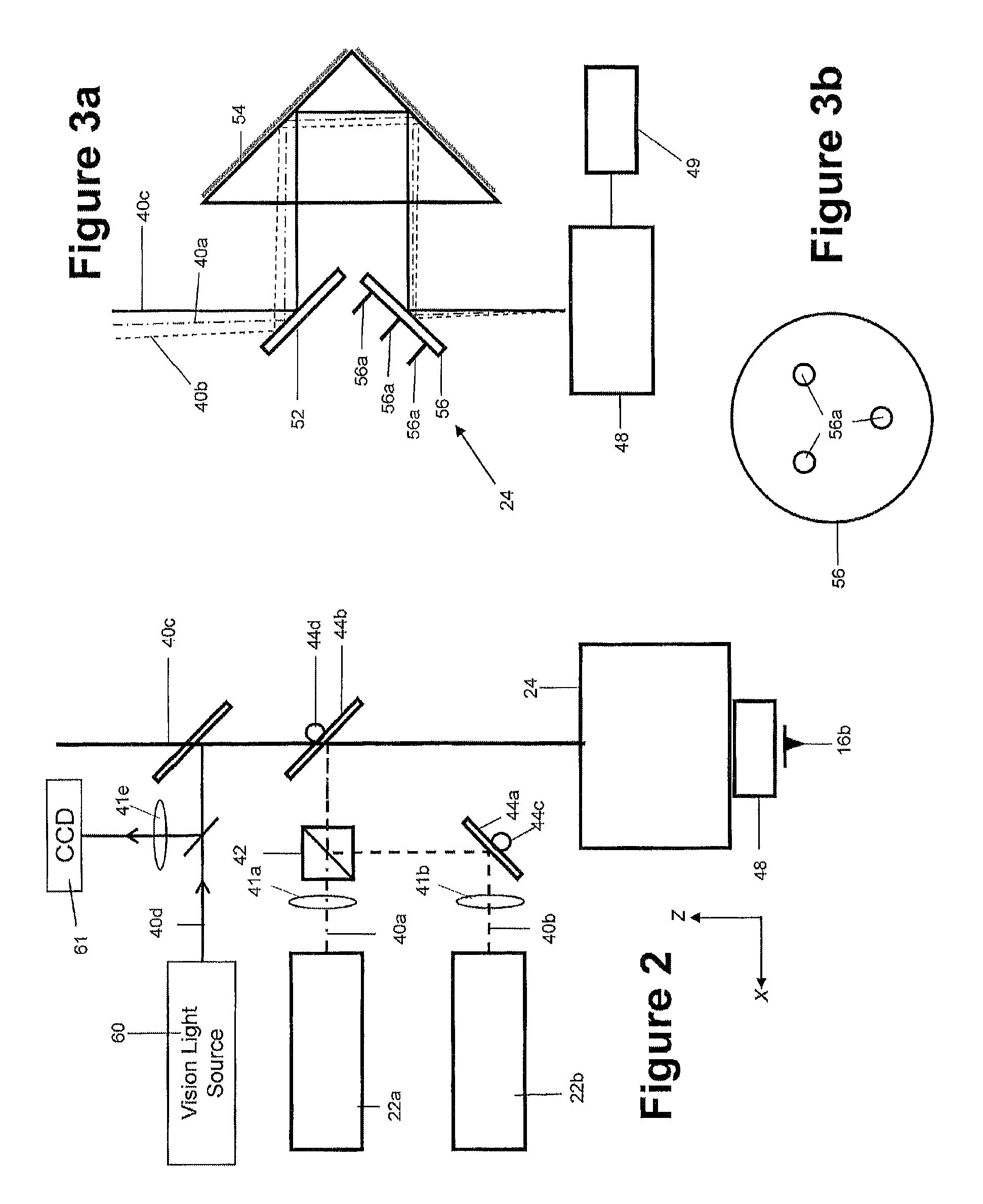
ActiveUS20150219684A1Improve performanceOvercome the heatNanotechnologyScanning probe techniquesLight beamScanning probe microscopy
Various methods of driving a probe of a scanning probe microscope are disclosed. One set of methods distribute the energy of a radiation beam over a wide area of the probe by either scanning the beam or increasing its illumination area. Another method changes the intensity profile of the radiation beam with a diffractive optical element, enabling a more uniform intensity profile across the width of the illumination. Another method uses a diffractive optical element to change the circumferential shape of the radiation beam, and hence the shape of the area illuminated on the probe, in order to match the shape of the probe and hence distribute the energy over a wider area.
Owner:INFINITESIMA
Micromachined electron or ion-beam source and secondary pickup for scanning probe microscopy or object modification
InactiveUS7960695B1Reliable and low methodEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPositive pressureSecondary electrons
An e-beam or ion beam imaging and exposure system is built into the end of an AFM cantilever which images using the scanning capabilities built into the AFM. In one embodiment, a boron doped diamond cold cathode is formed into the cantilever with an associated accelerating electrode and secondary electron collection electrode. The assembly is brought within a few nanometers of the object to be imaged or exposed using the AFM. One or more gas channels built into the cantilever assembly provide a positive pressure of inert gas to prevent oxidative erosion of the cold cathode and can bleed any surface charge build up on the sample surface. After secondaries are collected the cantilever is moved to the next area to be exposed.
Owner:KLEY VICTOR B
Ultrahigh vacuum fast scanning microscopy method based on carbon nanotube probe
InactiveCN102768292AImprove reliabilityReliable scanningScanning probe microscopyIn planeScanning electron microscope
The invention belongs to the field of scanning probe microscopy and relates to an ultrahigh vacuum fast scanning microscopy method based on a carbon nanotube probe, comprising the following steps of: fixing a nanotube probe at the end of a probe of a scanning tunneling microscope; calibrating the field emission current sensitivity curve family of the carbon nanotube probe in the Z direction; fixing the carbon nanotube probe in a probe clamp and adjusting the carbon nanotube probe in a vacuum state required by scanning; enabling the carbon nanotube probe to enter a tunneling state under a constant current mode; keeping a piezoelectric ceramic scanner stationary in the Z direction; setting a scanning range, scanning velocity and sampling point parameters, recording the field emission current i of the carbon nanotube probe one point after another, and carrying out quick imaging scanning of a sample to be detected under a constant height mode. The ultrahigh vacuum fast scanning microscopy method based on the carbon nanotube probe is high in reliability and speed and capable of improving the in-plane resolution of scanning imaging.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Expanded graphite paper
ActiveCN106219525APromote expansionImprove stripping efficiencyElectrochemistryScanning probe microscopy
The invention belongs to the technical field of the preparation of graphene, and relates to a preparation method of expanded graphite paper. The method is as below: 1) immersing the graphite paper into a low-temperature liquid, maintaining for 30 seconds to 5 minutes, and taking out; 2) and then quickly immersing the graphite paper into a high temperature liquid, and using rapid gas precipitation and liquid solidification for rapid expansion of the sheet layer in the graphite paper; and 3) after expansion, taking out the expanded graphite paper, and then washing and drying to obtain the expanded graphite paper used for electrochemical stripping. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation shows that the treated expanded graphite paper has obviously changed morphology, surface wrinkles and destroyed edge structure, so as to provide favorable conditions for infiltration of electrolyte into the graphite paper in a subsequent electrochemical stripping process. The yield of graphene is more than 80%, which provides the possibility for the mass production of grapheme.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Scanning probe microscopy-based metrology tool with a vacuum partition
InactiveUS20130097740A1NanotechnologyChemical vapor deposition coatingMetrologyScanning probe microscopy
A method of monitoring of semiconductor processes is provided that includes monitoring the processes using a scanning probe microscope (SPM), where a first partition is located below a second partition, where the second partition is hermetically isolated from the first partition, where a SPM probe tip of the SPM is disposed in the first partition, where a remaining portion of the SPM is disposed in the second partition that is hermetically isolated from the first partition, and where the semiconductor processes may occur in either the first partition or a third partition.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
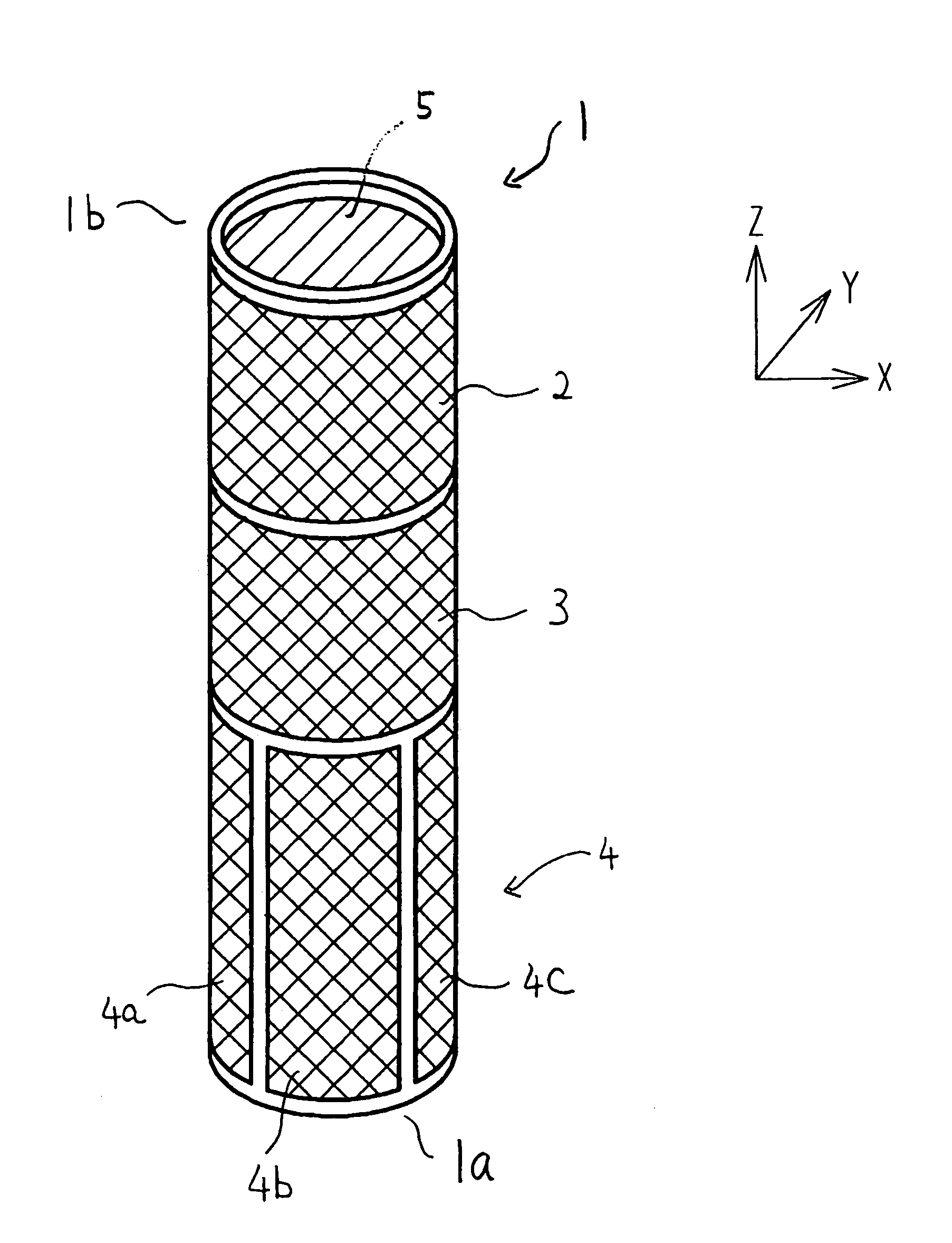
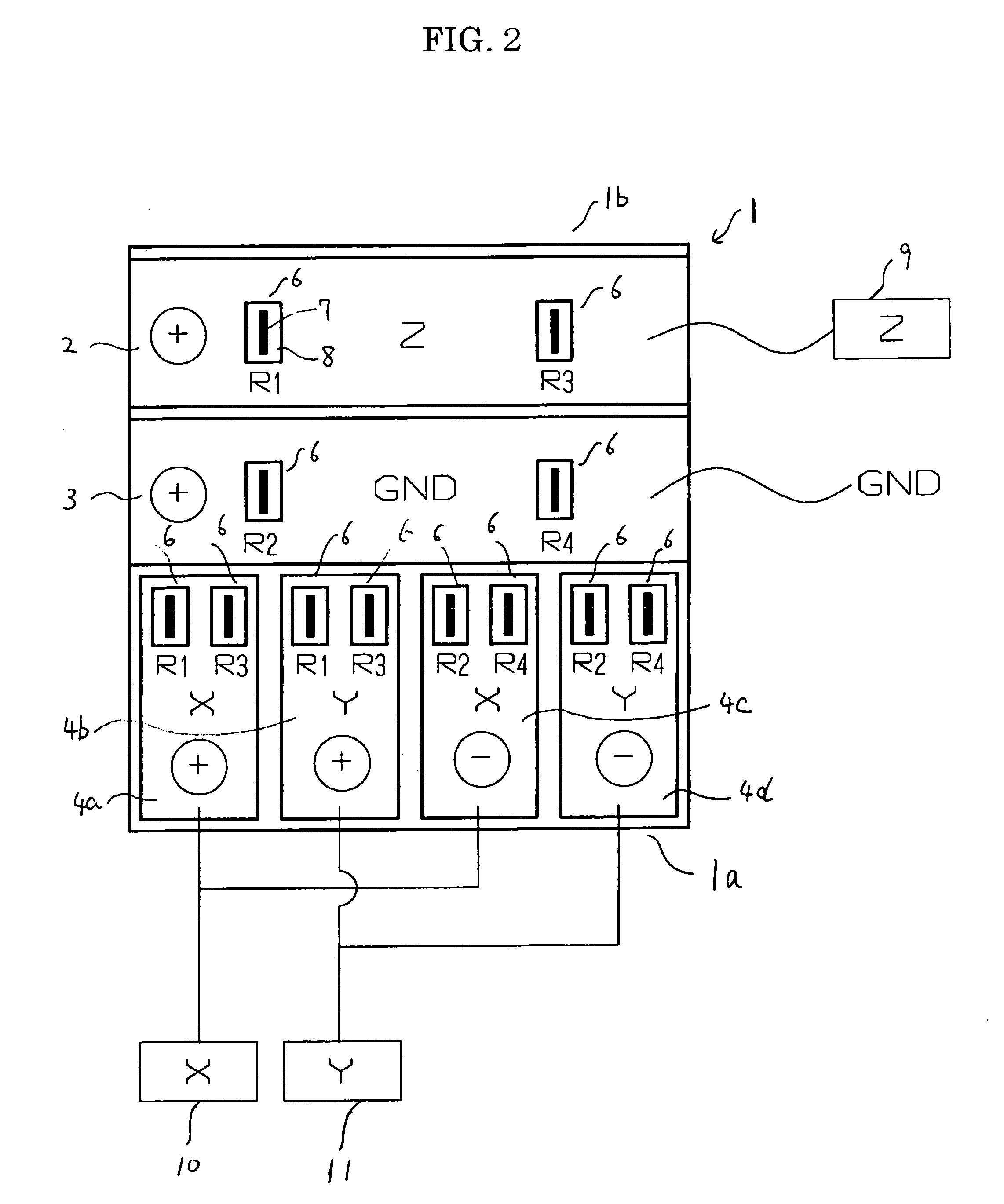
Scanning thermal microscope probe
InactiveCN1937094ANot easy to damageImprove spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesHeat conductingCarbon nanotube
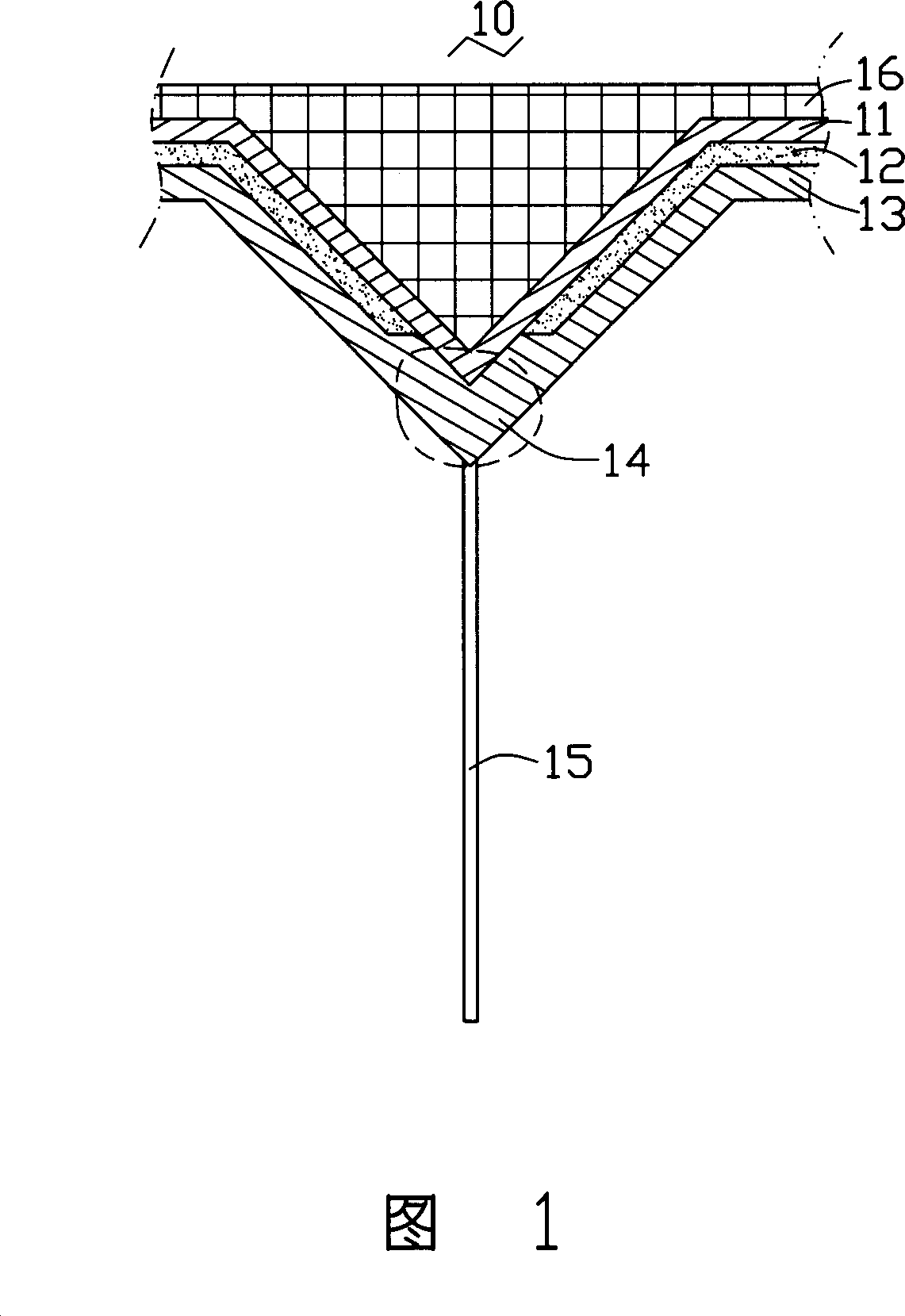
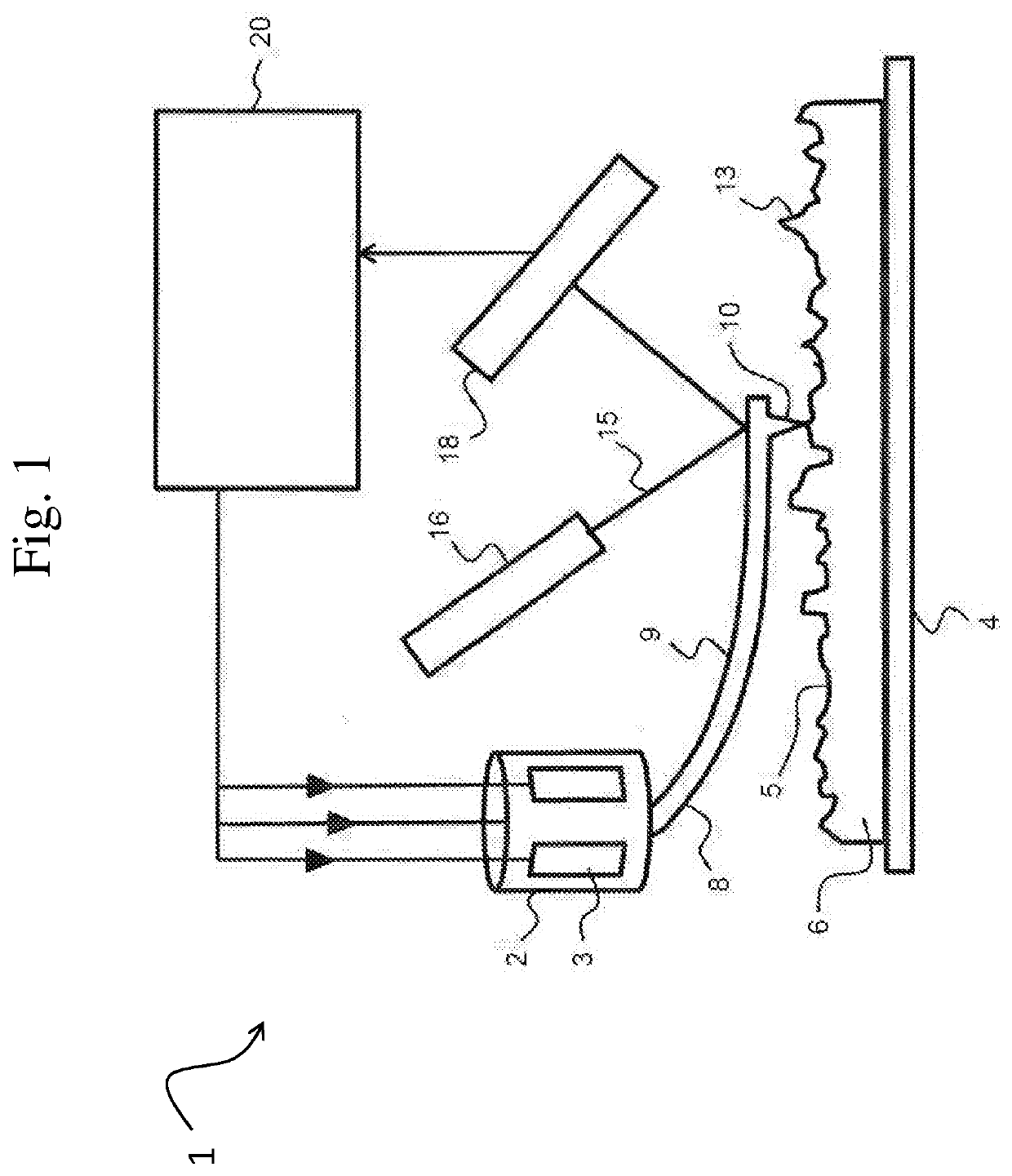
The probe includes following parts: a cantalever; a first conductive layer formed on surface of the cantalever; having a through hole, an insulating layer of covering on surface of the first conductive layer; a second conductive layer of covering on surface of the insulating layer; the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer are connected at the through hole so as to form a thermocouple area; a Nano carbon tube formed on the thermocouple area. One end of the Nano carbon tube is connected to the second conductive layer at the thermocouple area, and the other end is as a free end. The Nano carbon tube is placed at tip of probe. Using microsize and axial heat-conducting property raises space resolution of scanning heatable stage microscope remarkably.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
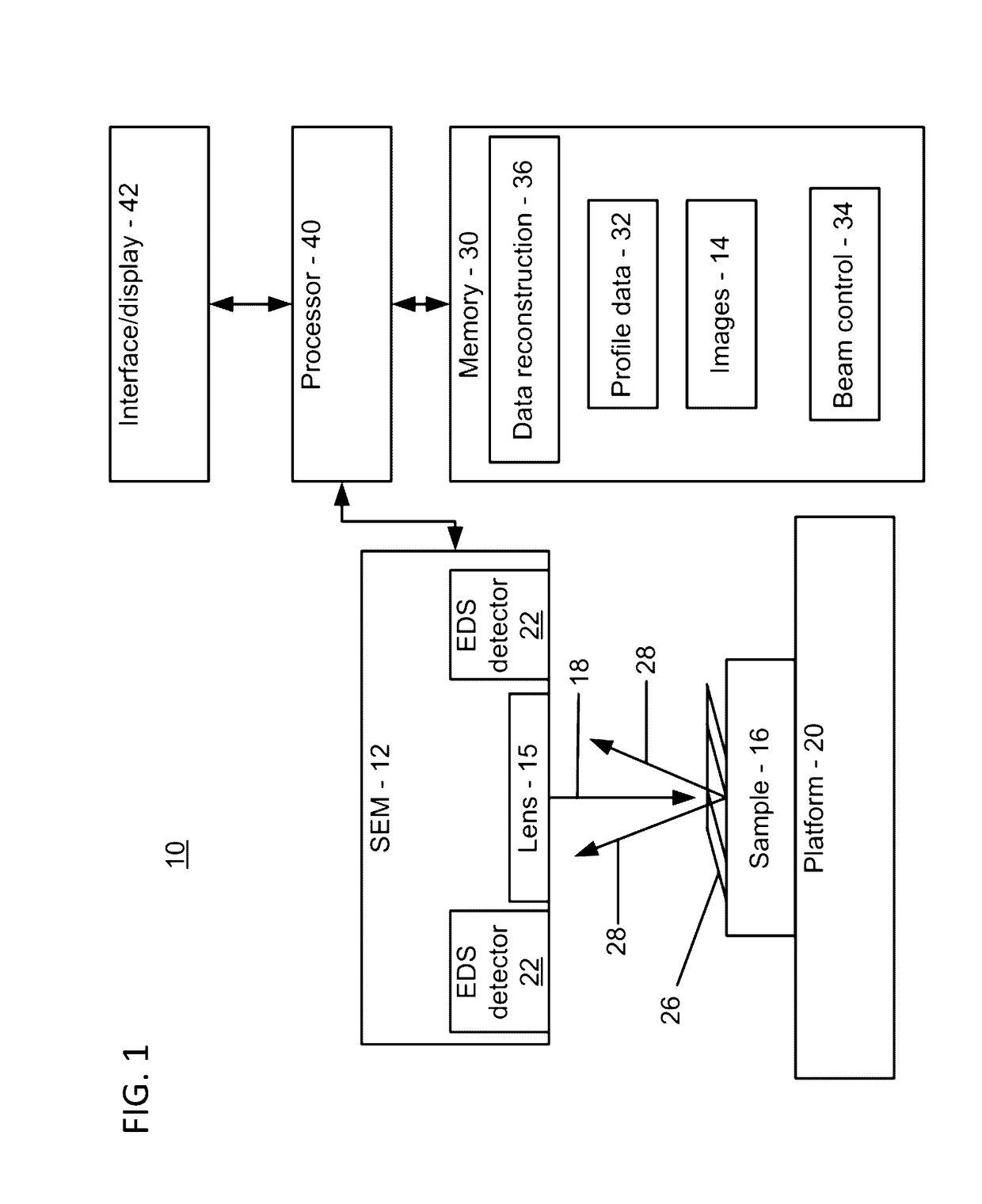
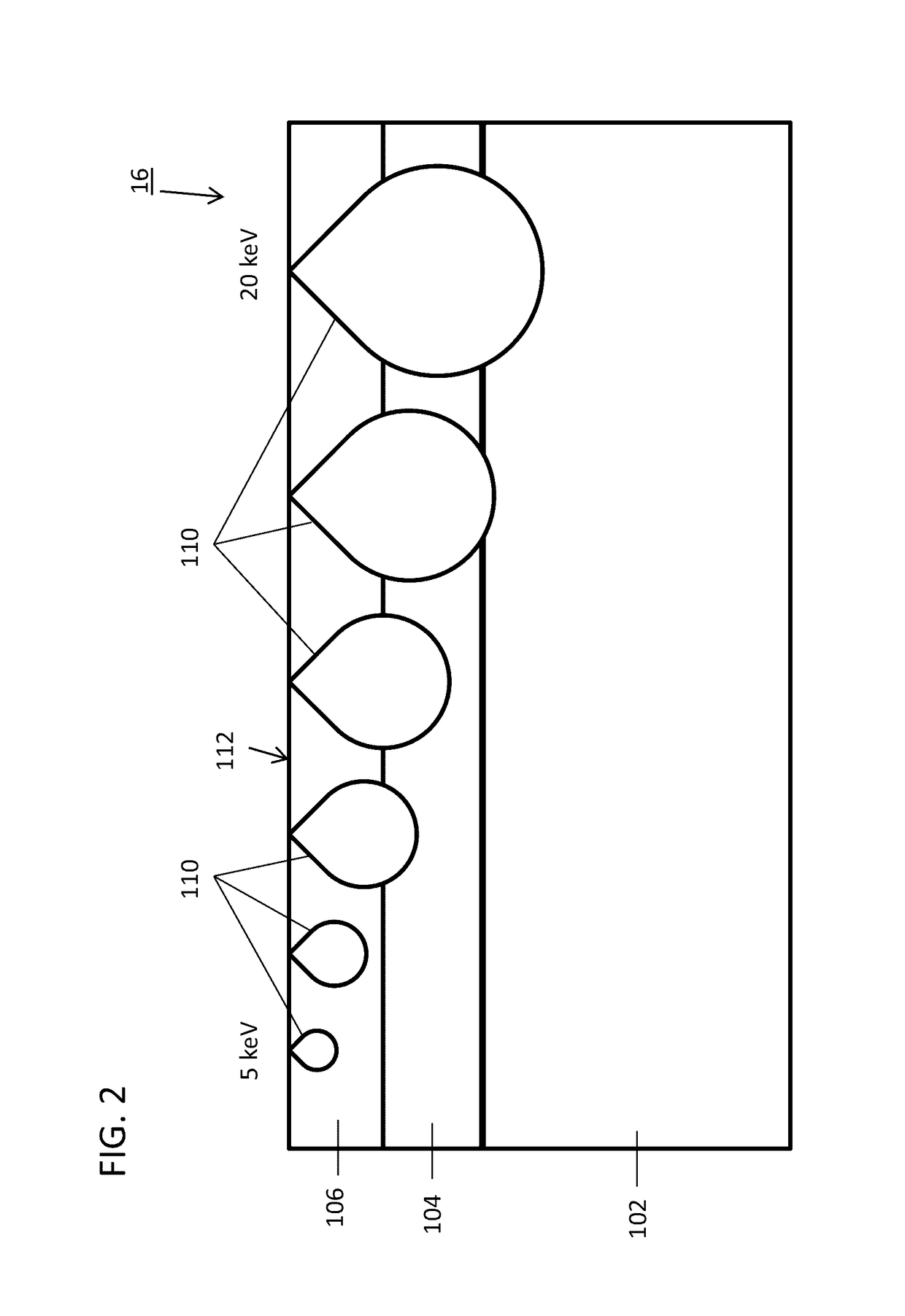
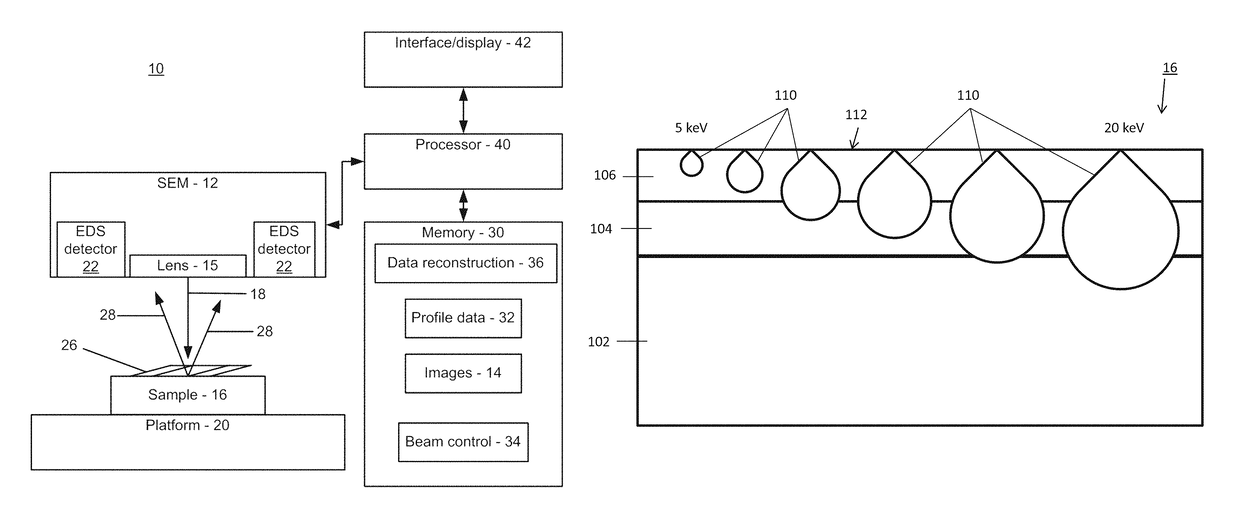
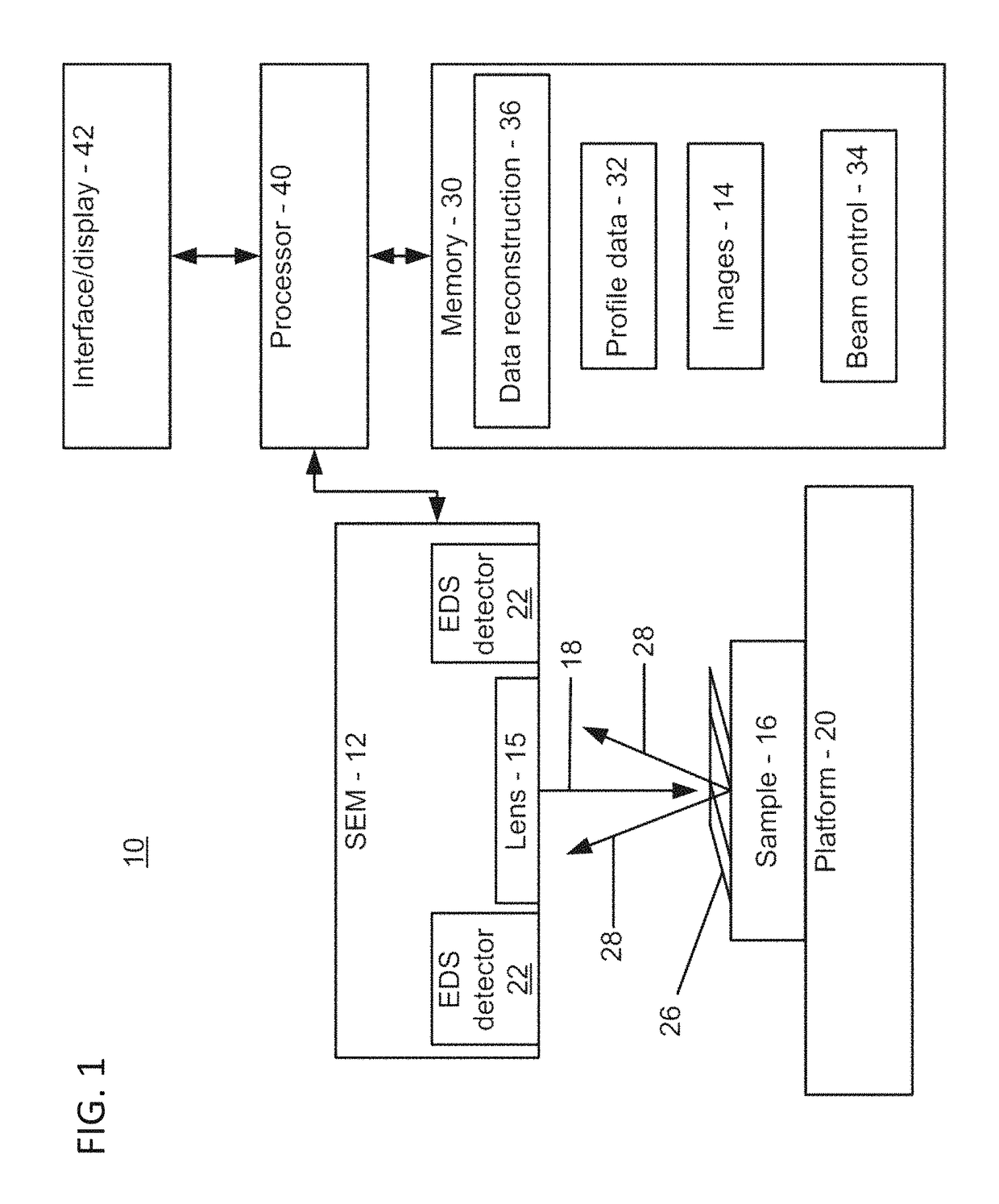
Cross sectional depth composition generation utilizing scanning electron microscopy
InactiveUS9625398B1Electric discharge tubesUsing wave/particle radiation meansBeam energyScanning probe microscopy
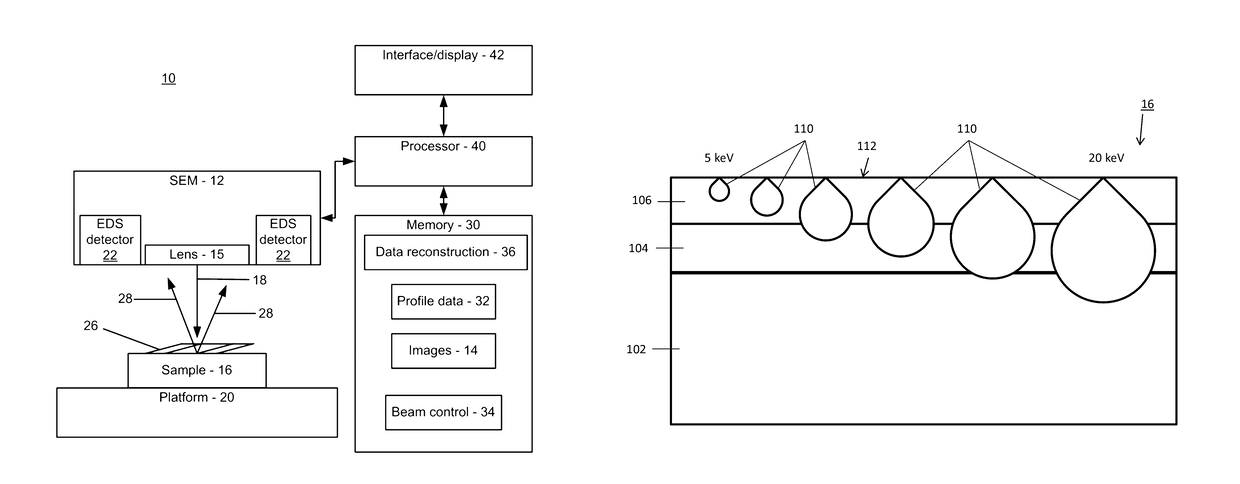
A method for generating cross-sectional profiles using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) includes scanning a sample with an electron beam to gather an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) spectrum for an energy level to determine element composition across an area of interest. A mesh is generated to locate positions where a depth profile will be taken. EDS spectra are gathered for energy levels at mesh locations. A number of layers of the sample are determined by distinguishing differences in chemical composition between depths as beam energies are stepped through. A depth profile is generated for the area of interest by compiling the number of layers and the element composition across the mesh.
Owner:IBM CORP
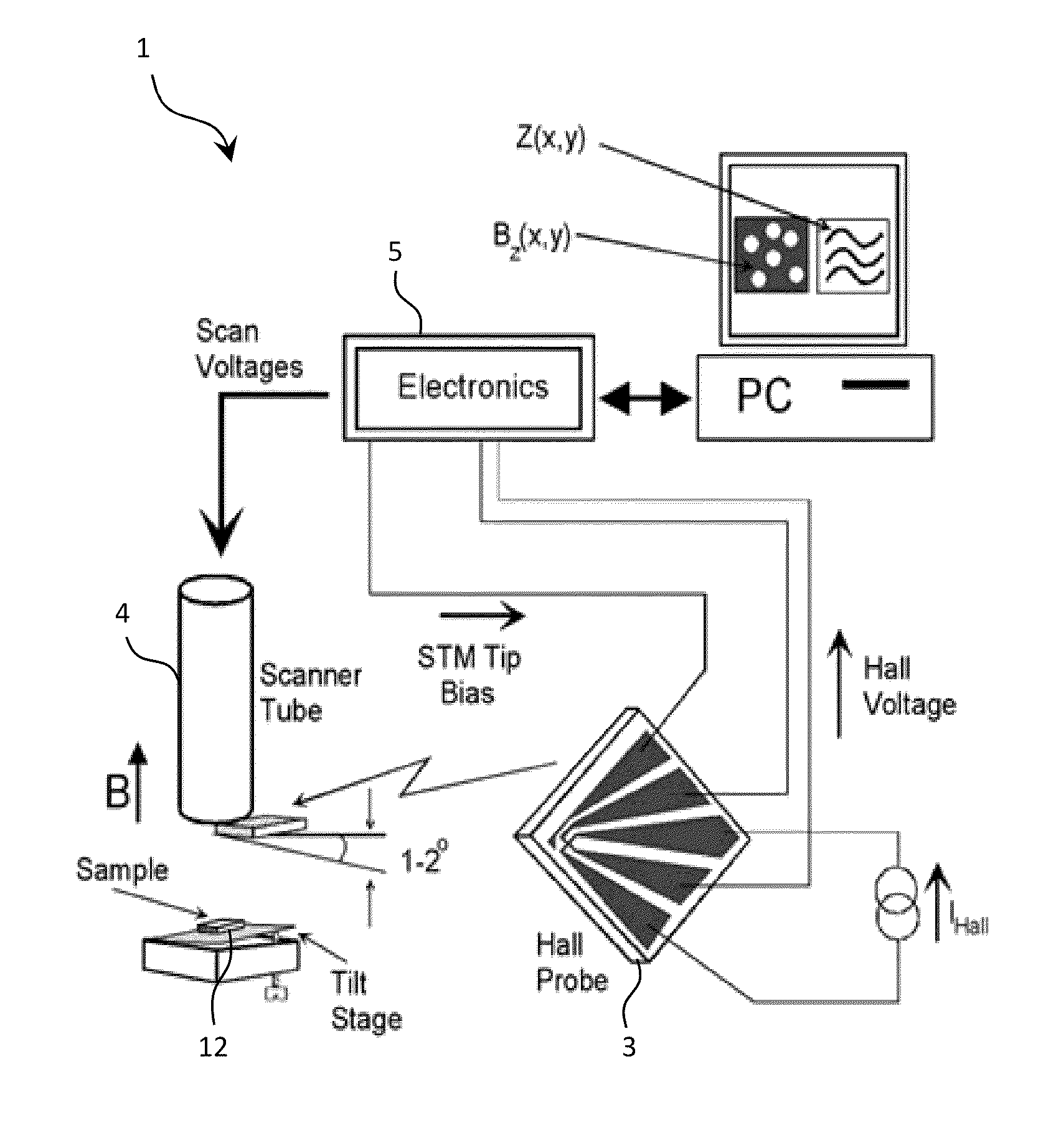
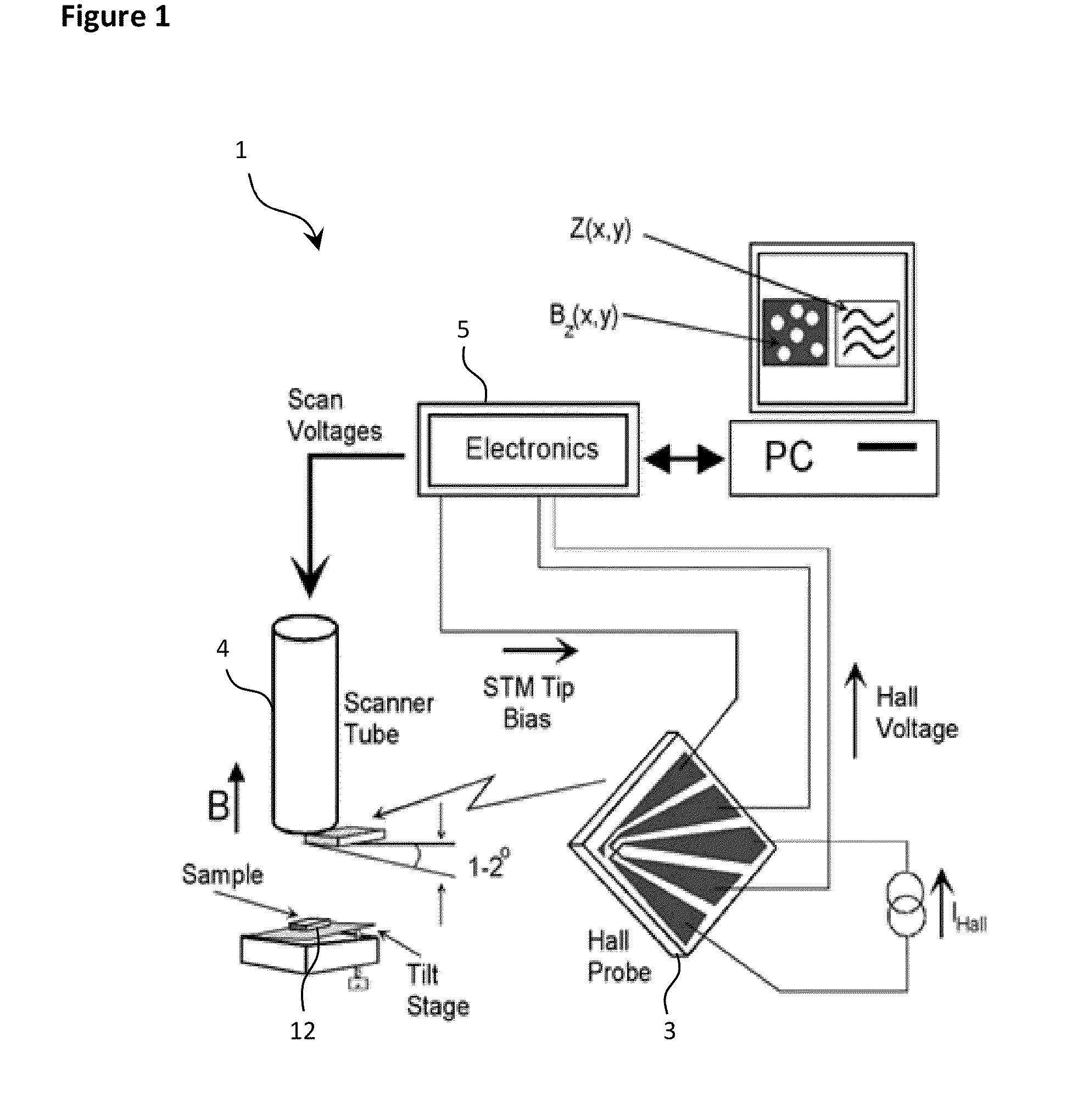
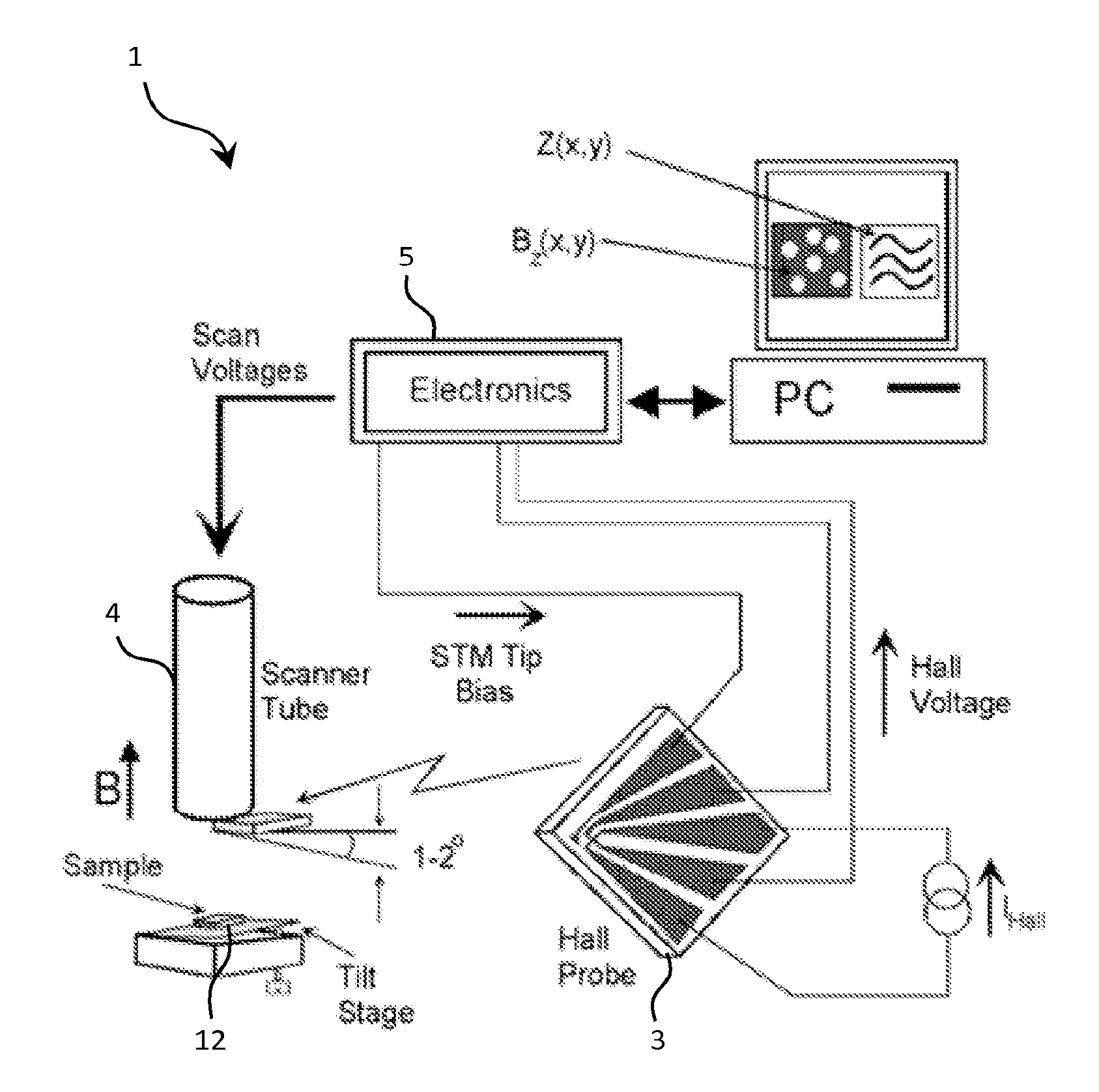
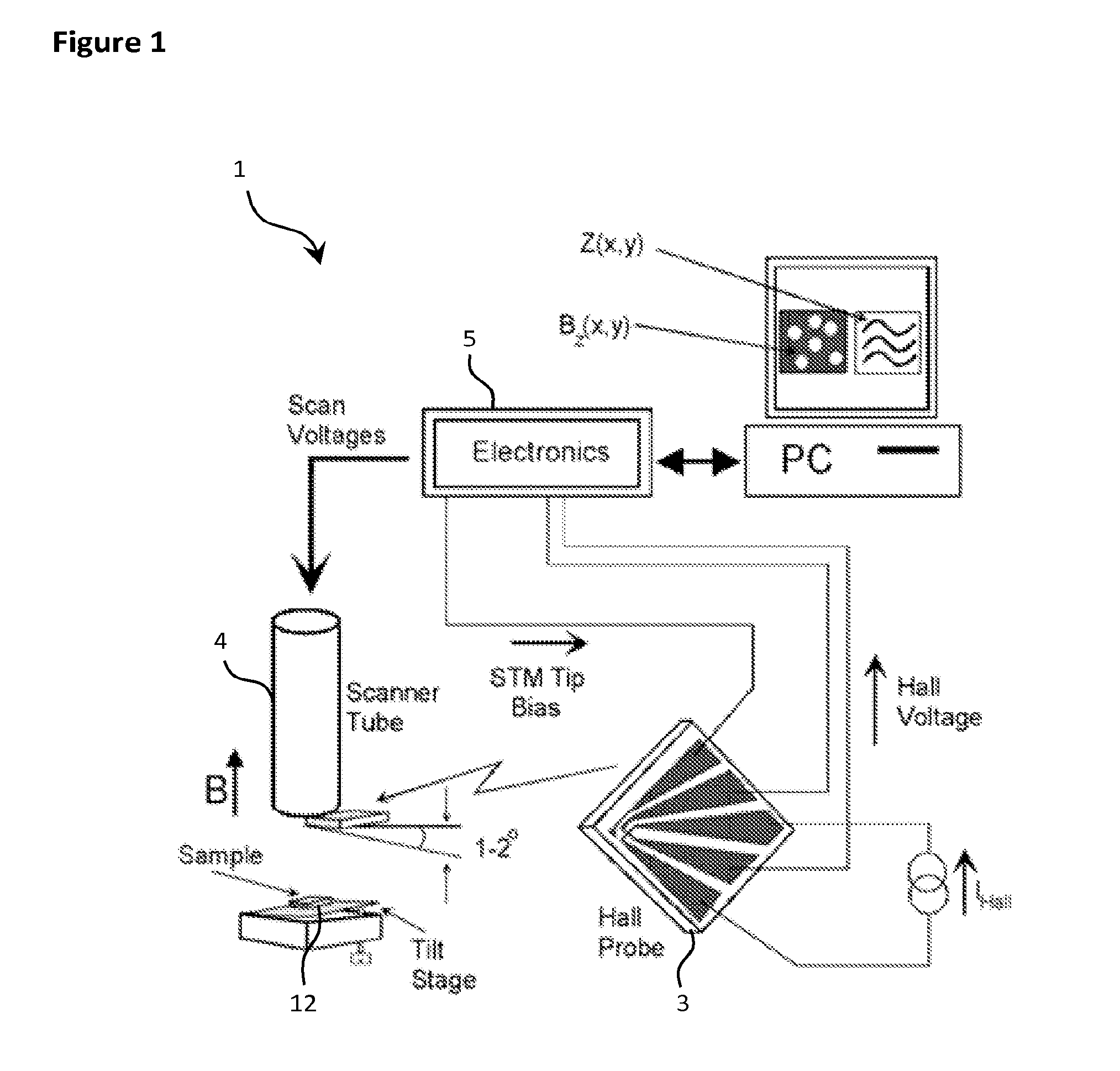
Method to measure 3 component of the magnetic field vector at nanometer resolution using scanning hall probe microscopy
InactiveUS20110061139A1Surface/boundary effectNanotechnologyElectricityScanning Hall probe microscope
Scanning hall probe microscopy is used to measure 3 components of the magnetic field vector at nanometer resolution by connecting of Hall probe to the end of the piezo scanner, then gluing of the sample to the sample holder, thereafter positioning of the SHPM head under the optical microscope with approximately ×40 magnification, then moving back of the slider puck around approximately 30 steps or moving the sensor or sample back by sufficient amount using motors, piezo or other positioner such that signal decays to negligible levels; thereafter setting the temperature of cryostat or to desired temperature, then offset nulling of the Hall sensor in gradiometer or normal conditions, and finally setting of the scan area, speed, resolution and the acquisition channels through SPM control program.
Owner:NANOMAGNETICS INSTR
Spatially resolved quantitative mapping of thermomechanical properties and phase transition temperatures using scanning probe microscopy
ActiveUS8484759B2Thermometer detailsThermometers using physical/chemical changesScanning voltage microscopyContact force
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
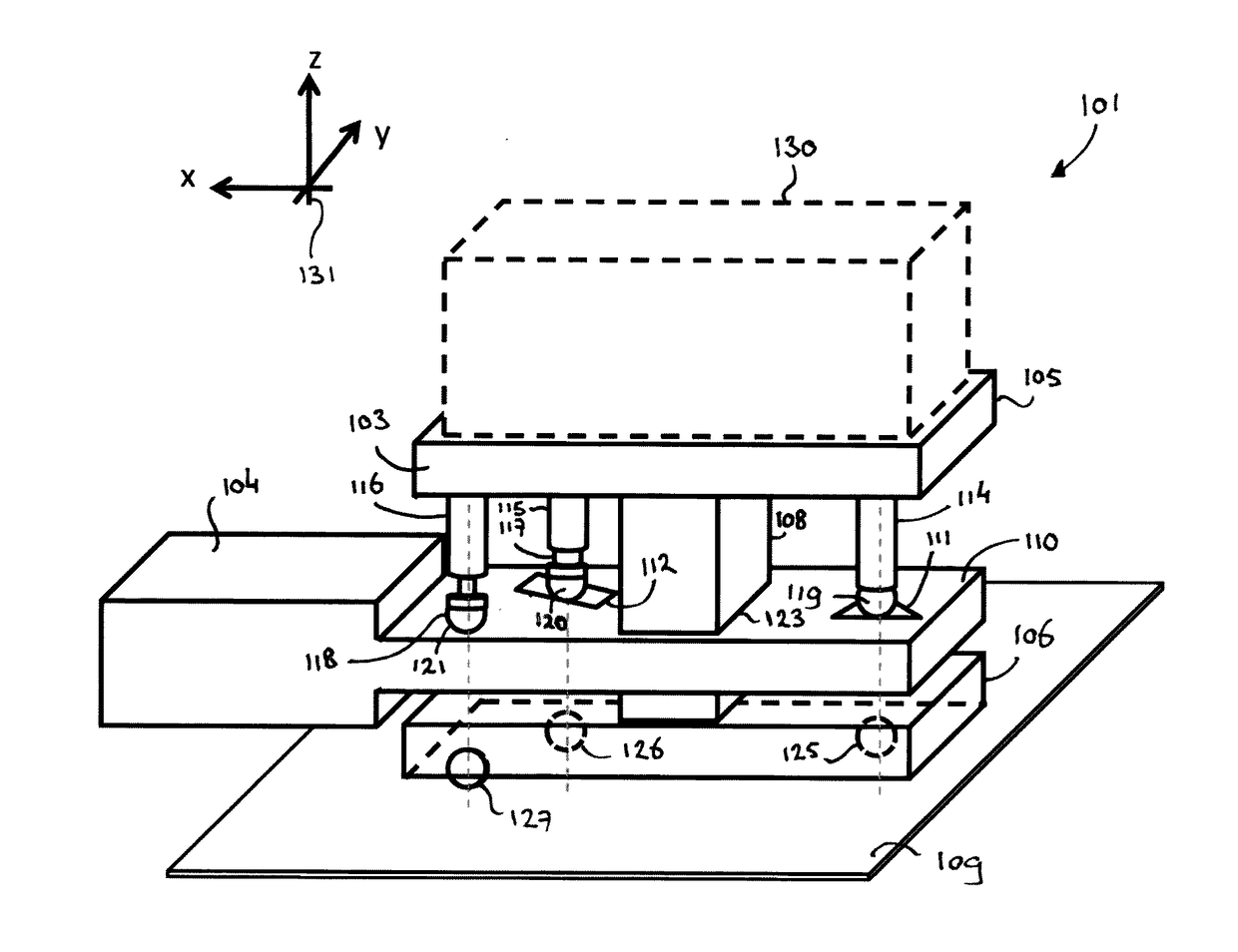
Diffractive optical position detector
InactiveUS20060072185A1Accurate measurementImprove throughputMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansAtomic force microscopyOptical measurements
An apparatus and method for measuring optically the position or angle of a variety of objects or arrays of objects, including cantilevers in scanning probe microscopy, micromechanical biological and chemical sensors and the sample or a probe in surface profilometry. The invention involves the use of one or more diffractive optical elements, including diffraction gratings and holograms, combined with conventional optical elements, to form a plurality of light beams, each with a selectable shape and intensity, from a single light source, reflect the beams off mechanical objects and process the reflected beams, all to the end of measuring the position of such objects with a high degree of precision. The invention may also be used to effect mechanical changes in such objects. Devices with these improvements have numerous applications, including molecular force measurements, atomic force microscopy and manipulation technology, lithographic manufacturing, nanometer scale surface profiling and other aspects of nanotechnology.
Owner:OXFORD INSTRUMENTS +1
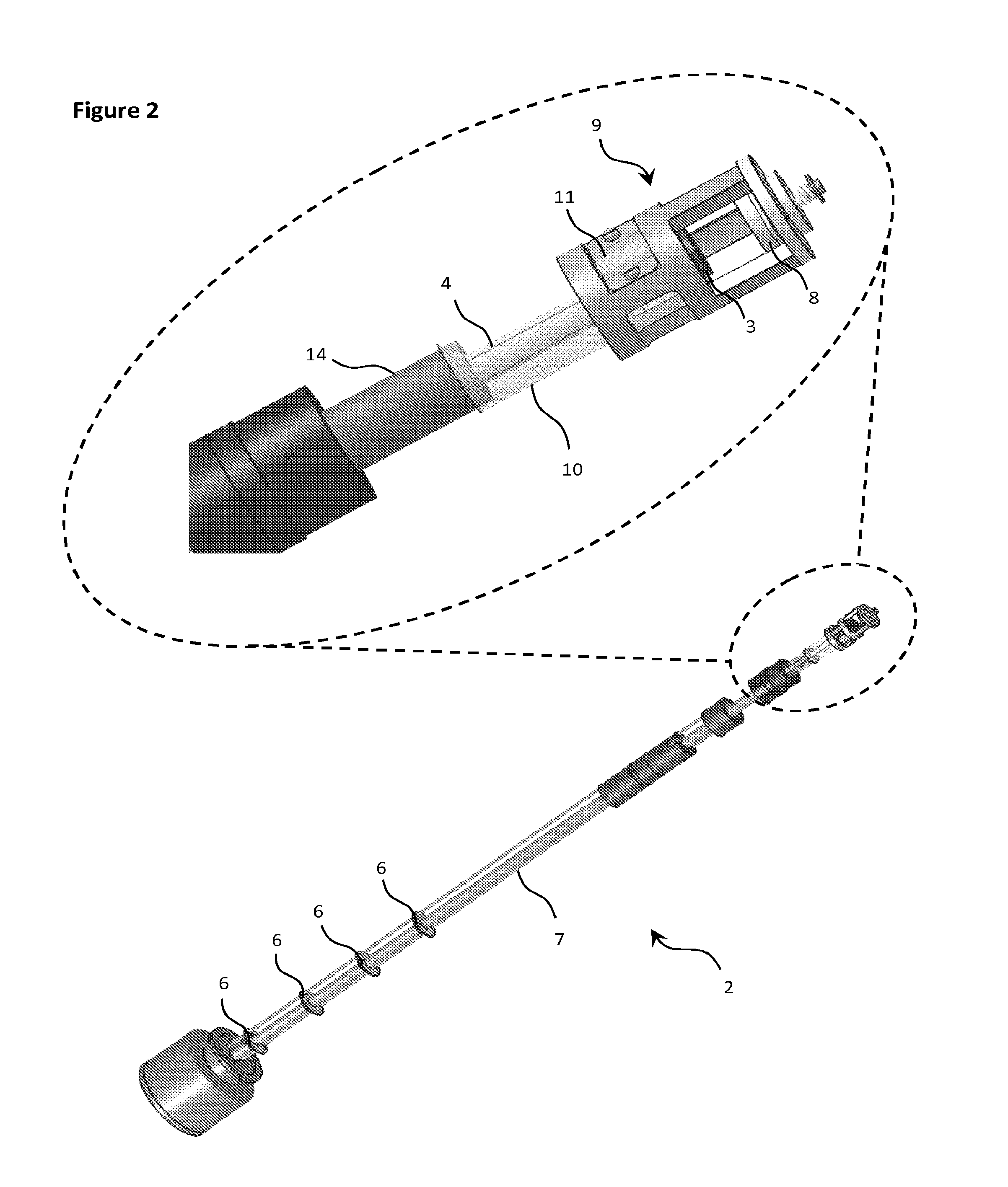
System and method of performing scanning probe microscopy on a substrate surface
ActiveUS20170131323A1Overcome disadvantagesNanotechnologyScanning probe microscopyTip positionScanning probe microscopy
The invention is directed at a method of performing scanning probe microscopy on a substrate surface using a scanning probe microscopy system, the system including at least one probe head, the probe head comprising a probe tip arranged on a cantilever and a tip position detector for determining a position of the probe tip along a z-direction transverse to an image plane, the method comprising: positioning the at least one probe head relative to the substrate surface; moving the probe tip and the substrate surface relative to each other in one or more directions parallel to the image plane for scanning of the substrate surface with the probe tip; and determining the position of the probe tip with the tip position detector during said scanning for mapping nanostructures on the substrate surface; wherein said step of positioning is performed by placing the at least one probe head on a static carrier surface.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
A method for preparing a micron ionic crystal powder sample for scanning electron microscopy
ActiveCN108169266AHigh resolutionAvoid cakingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning confocal electron microscopyIonic crystal
The invention relates to the technical field of preparation of samples for scanning electron microscopy, and particularly relates to a method for preparing a micron ionic crystal powder sample for scanning electron microscopy. The method includes steps of (1) dispersing, (2) sampling, (3) preparing resin glue, (4) performing cold mounting to prepare a sample and (5) spraying gold. The prepared powder scanning electron microscopy sample is uniform in powder dispersion so that particle caking and agglomeration can be avoided. The powder sample is tightly bound with the resin glue and adhesive force is high so that the powder can be firmly embedded. Compared with traditional methods, the method can effectively overcome a problem that samples fly away from sample tables during vacuumization and testing and pollute microscopy cavities due to low binding force between powder and conductive glue. After gold plating, electrical conductivity of the powder sample is improved, images are made clear and clear electron microscopy observation having high resolution can be achieved. The method has characteristics of a short sample preparing period, simple operation and good practicability.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cross sectional depth composition generation utilizing scanning electron microscopy
InactiveUS9702835B1Electric discharge tubesUsing wave/particle radiation meansBeam energyScanning voltage microscopy
A method for generating cross-sectional profiles using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) includes scanning a sample with an electron beam to gather an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) spectrum for an energy level to determine element composition across an area of interest. A mesh is generated to locate positions where a depth profile will be taken. EDS spectra are gathered for energy levels at mesh locations. A number of layers of the sample are determined by distinguishing differences in chemical composition between depths as beam energies are stepped through. A depth profile is generated for the area of interest by compiling the number of layers and the element composition across the mesh.
Owner:IBM CORP
Photothermal actuation of a probe for scanning probe microscopy
Various methods of driving a probe of a scanning probe microscope are disclosed. One set of methods distribute the energy of a radiation beam over a wide area of the probe by either scanning the beam or increasing its illumination area. Another method changes the intensity profile of the radiation beam with a diffractive optical element, enabling a more uniform intensity profile across the width of the illumination. Another method uses a diffractive optical element to change the circumferential shape of the radiation beam, and hence the shape of the area illuminated on the probe, in order to match the shape of the probe and hence distribute the energy over a wider area.
Owner:INFINITESIMA
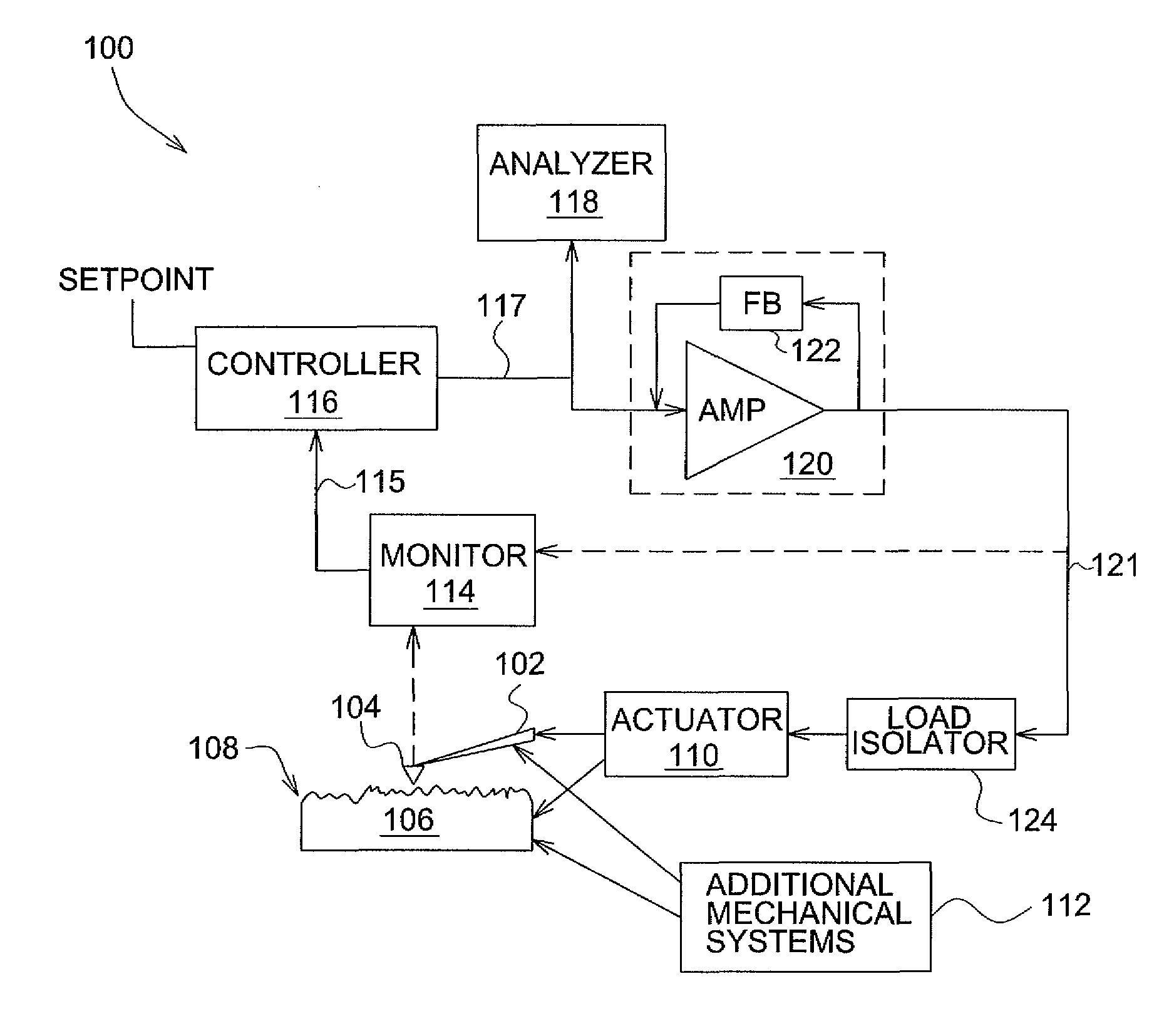
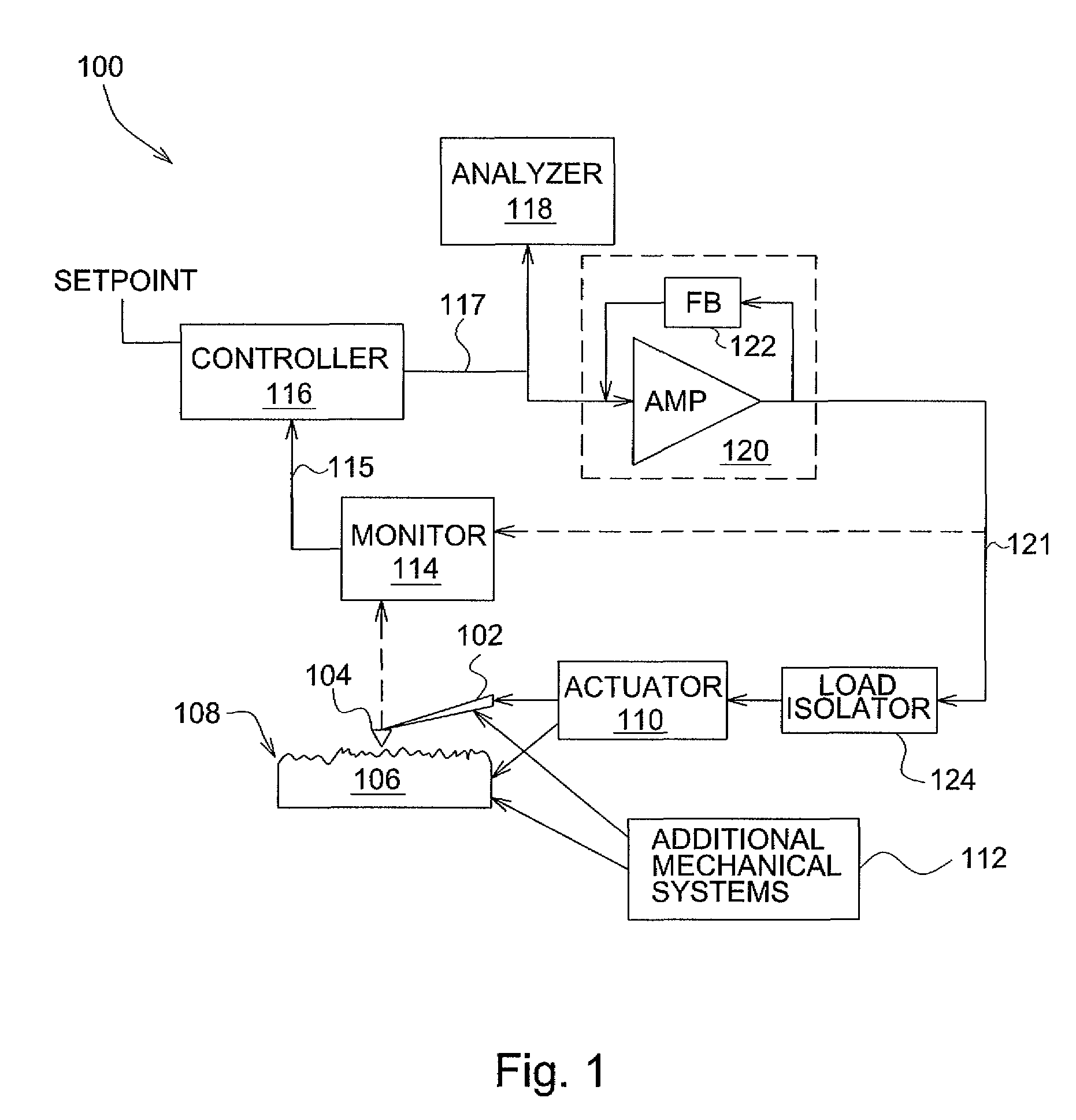
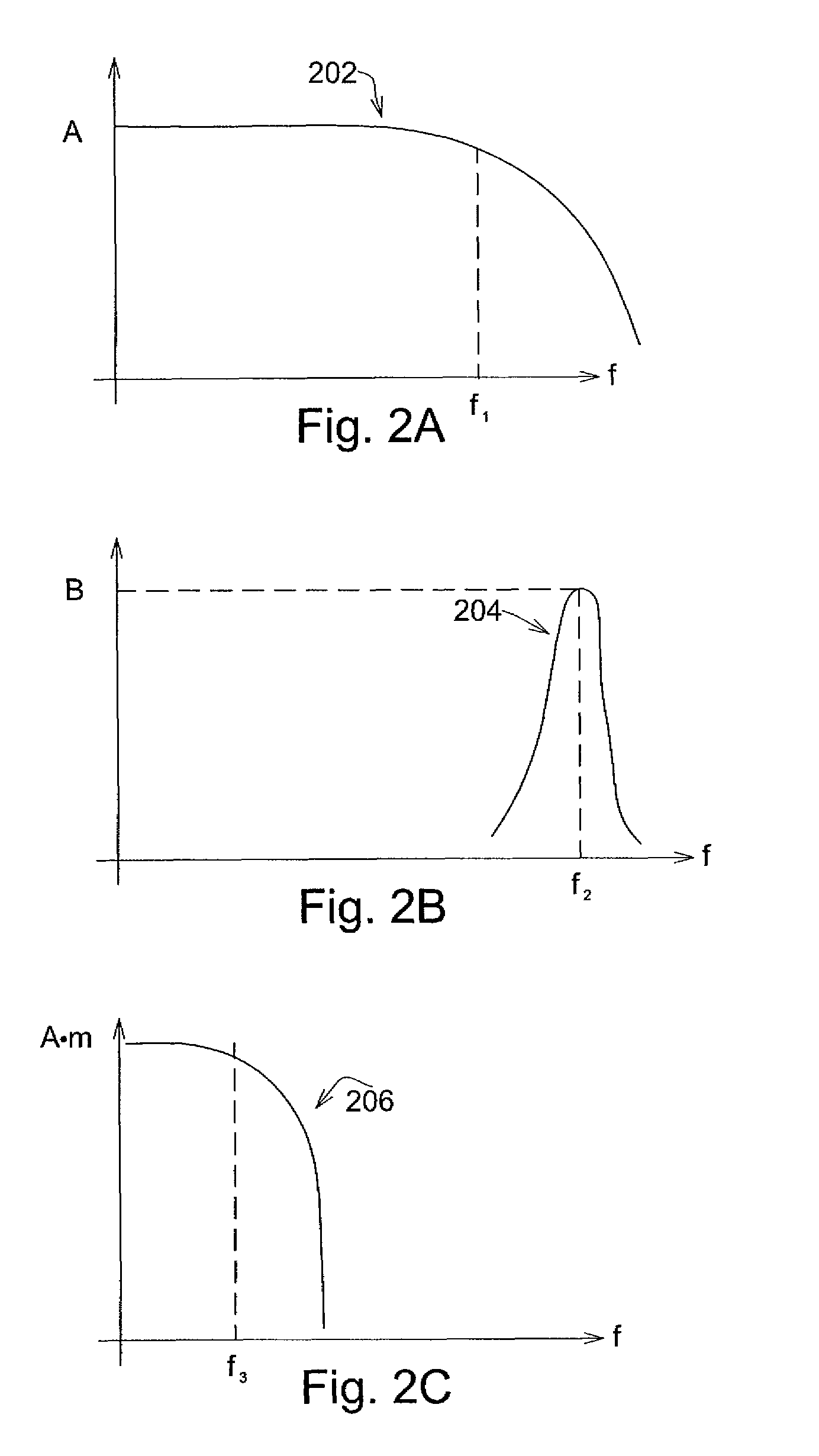
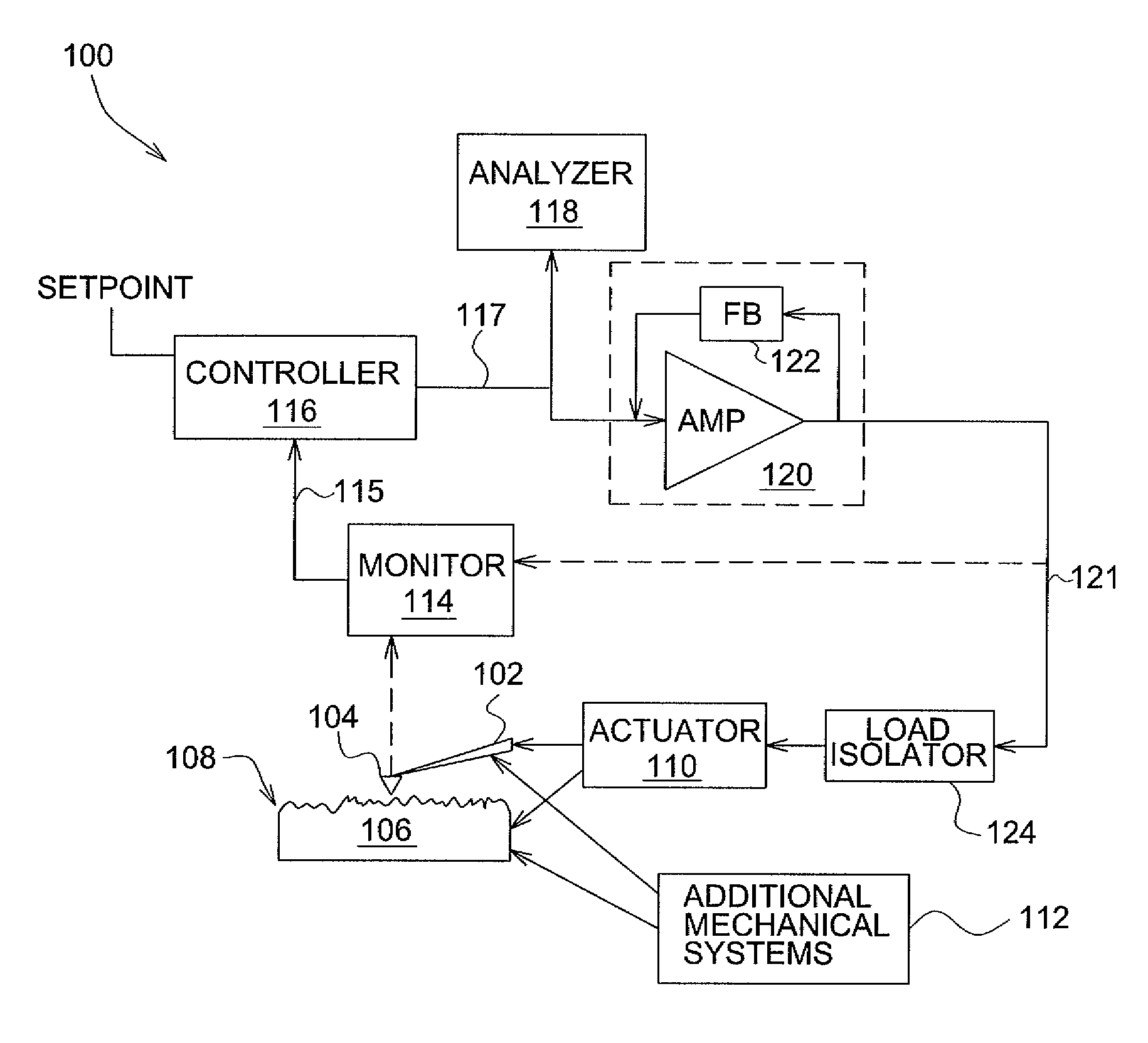
High-bandwidth actuator drive for scanning probe microscopy
InactiveUS7891015B2Improve throughputSignal bandwidth is smallMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNanotechnologyHigh bandwidthRange of motion
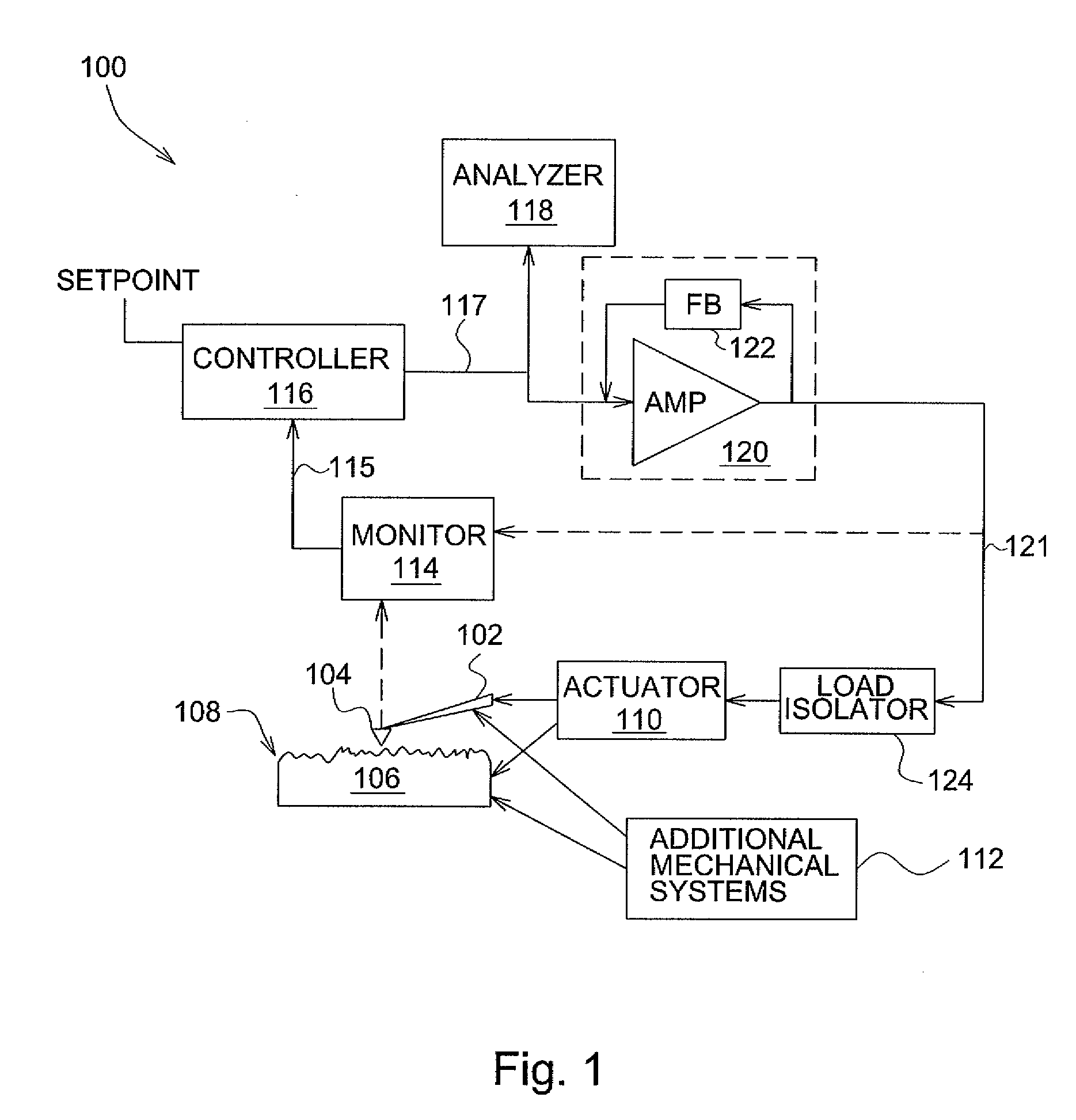
An actuator subsystem for use in a scanning probe microscope (SPM) system having a probe for measuring a sample comprises and actuator and an actuator driving circuit. The actuator operates in the SPM system to generate relative motion between the probe and the sample while the SPM system collects data indicative of a property of the sample. The relative motion includes a range of motion of at least 1 micron. The actuator driving circuit applies a drive signal to the actuator to cause the relative motion, and has a small signal bandwidth of at least 200 kHz with a phase lag of not more than 100 degrees within the small signal bandwidth.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
High-bandwidth actuator drive for scanning probe microscopy
InactiveUS20090032703A1Improve throughputSignal bandwidth is smallMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationInstrumental componentsHigh bandwidthRange of motion
An actuator subsystem for use in a scanning probe microscope (SPM) system having a probe for measuring a sample comprises and actuator and an actuator driving circuit. The actuator operates in the SPM system to generate relative motion between the probe and the sample while the SPM system collects data indicative of a property of the sample. The relative motion includes a range of motion of at least 1 micron. The actuator driving circuit applies a drive signal to the actuator to cause the relative motion, and has a small signal bandwidth of at least 200 kHz with a phase lag of not more than 100 degrees within the small signal bandwidth.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
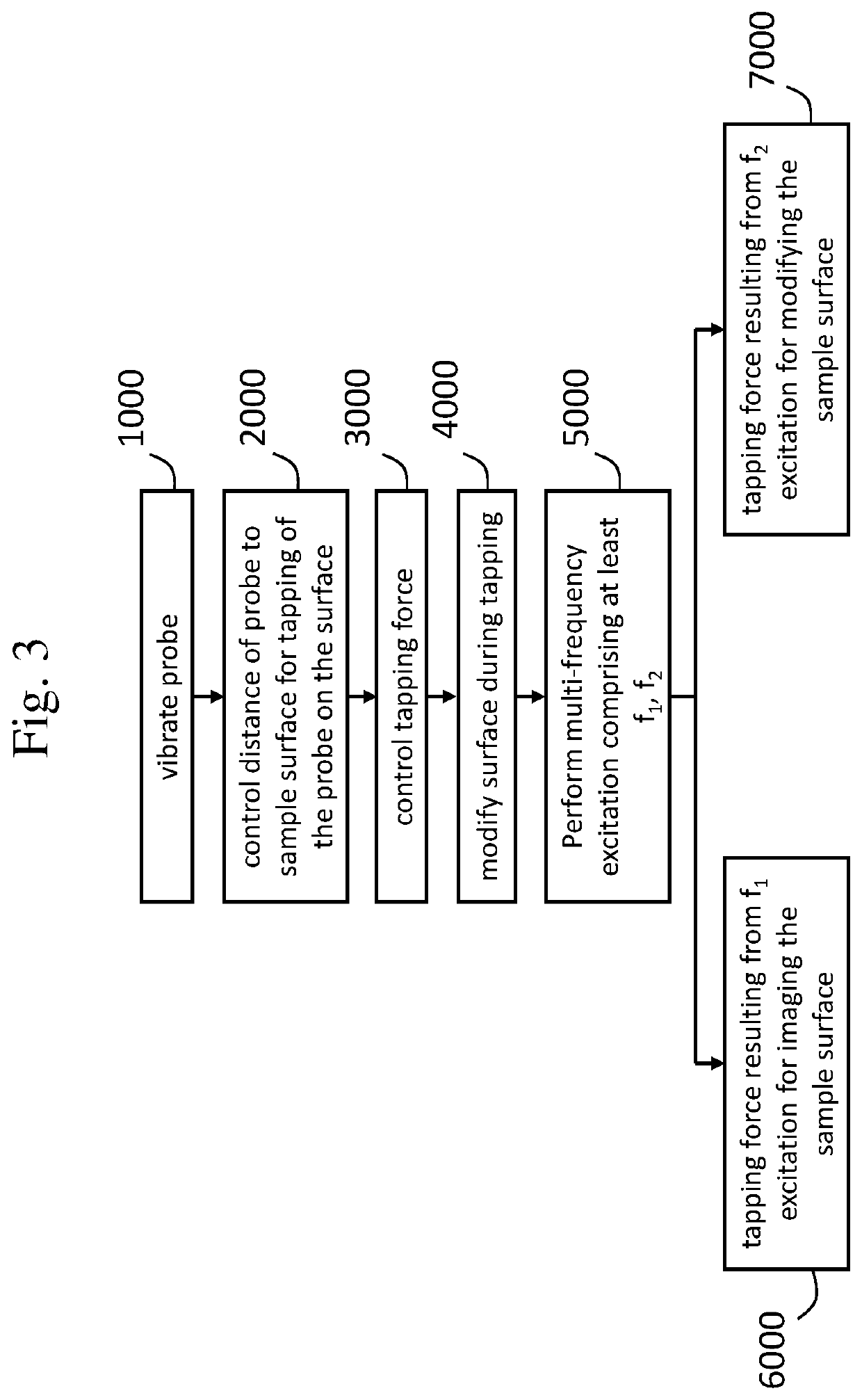
Method of modifying a surface of a sample, and a scanning probe microscopy system
InactiveUS20190353681A1Increase and decrease forceEasy to adjustScanning probe microscopyScanning probe microscopyCantilever
This document relates to a method and system for modifying a sample surface using a scanning probe microscopy system comprising a probe having a cantilever and a probe tip. The method comprises vibrating the probe; controlling a distance between the surface and the probe for tapping of the probe tip on the surface; and adjusting a tapping force of the probe tip on the surface during said tapping, so as to selectively modify the surface during the tapping. The probe is vibrated by employing a multi-frequency excitation comprising at least two frequencies for simultaneous imaging and modifying of the surface.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Method to measure 3 component of the magnetic field vector at nanometer resolution using scanning hall probe microscopy
InactiveUS20120079632A1NanotechnologyScanning probe microscopyElectricityScanning Hall probe microscope
Scanning hall probe microscopy is used to measure 3 components of the magnetic field vector at nanometer resolution by connecting of Hall probe to the end of the piezo scanner, then gluing of the sample to the sample holder, thereafter positioning of the SHPM head under the optical microscope with approximately X40 magnification, then moving back of the slider puck around approximately 30 steps or moving the sensor or sample back by suffient amount using motors, piezo or other positioner such that signal decays to negligible levels; thereafter setting the temperature of cryostat or to desired temperature, then offset nulling of the Hall sensor in gradiometer or normal conditions, and finally setting of the scan area, speed, resolution and the acquisition channels through SPM control program.
Owner:ORAL AHMET +2
Microcoaxial probes made from strained semiconductor bilayers
ActiveUS7485857B2NanotechMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAtomic force microscopyMicrowave
The present invention provides microcoaxial probes fabricated from semiconductor heterostructures that include strained semiconductor bilayers. The microcoaxial probes are well suited for use as scanning probes in scanning probe microscopy, including scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning microwave microscopy, or a combination thereof.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method of performing surface measurements on a surface of a sample, and scanning probe microscopy system therefore
ActiveUS20180306837A1Fast and accurate mannerStable minimal errorScanning probe microscopyFourier transform on finite groupsPaper document
This document relates to a method of performing surface measurements on a surface of a sample using a scanning probe microscopy system. The system comprises a sample support structure for supporting a sample, a sensor head including a probe comprising a cantilever and a probe tip arranged on the cantilever, and an actuator for scanning the probe tip relative to the substrate surface for mapping of the nanostructures. The method comprising the steps of: vibrating the cantilever using an actuator and moving the probe relative to the substrate surface for performing said scanning. The probe is held at a distance to the substrate surface such as to allow contact at a plurality of intermittent contact moments between the probe tip and the surface during said vibrating of the cantilever. The steps of vibrating of the cantilever and moving of the probe are performed concurrently. For performing the surface measurements, the method comprises obtaining a sensor signal indicative of a position of the probe tip during said scanning, and analyzing this signal by quantifying two or more frequency components in a Fourier transform for determining an estimate of a force value of a force between said substrate surface and said probe tip during said contact moments.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com