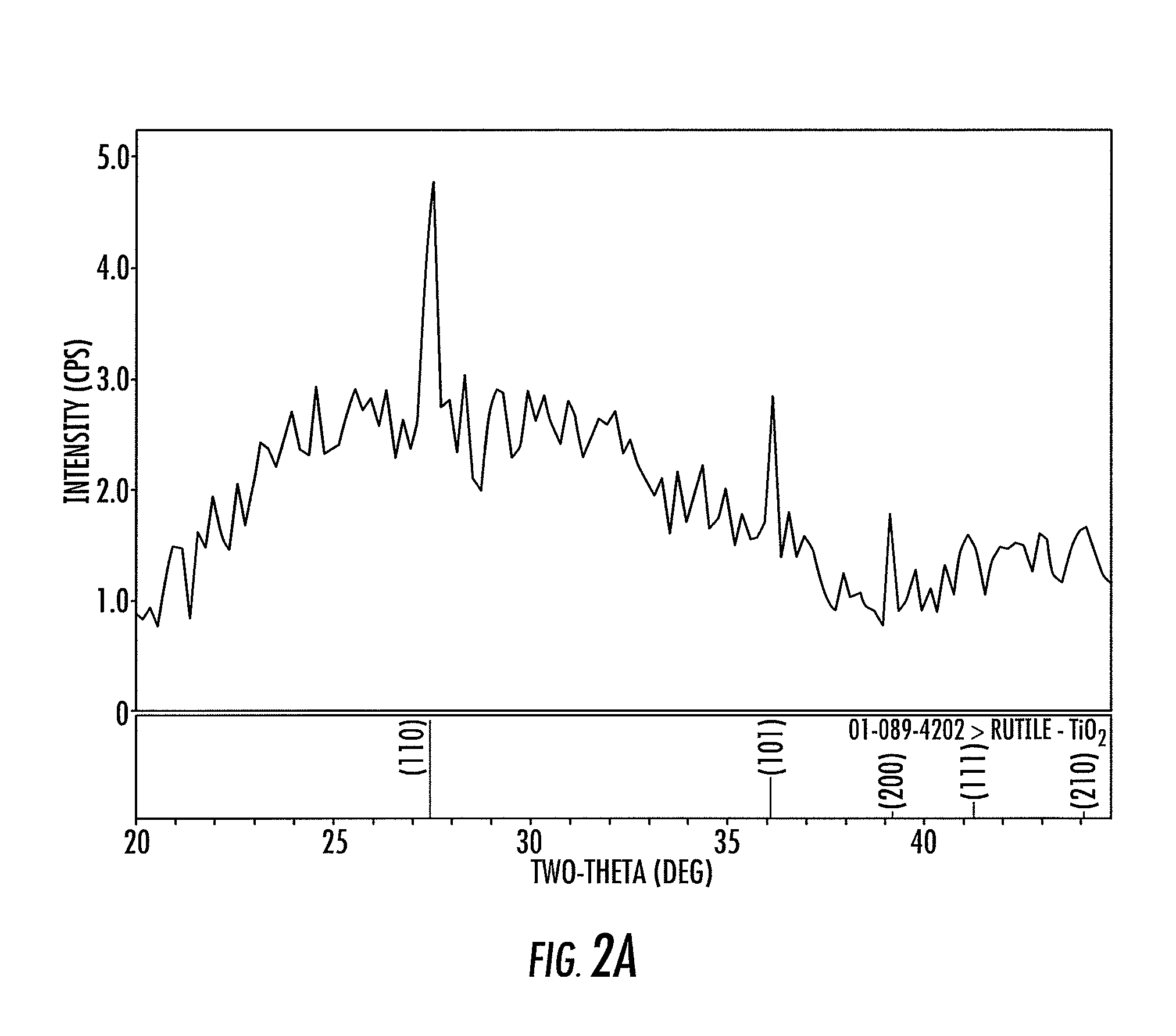
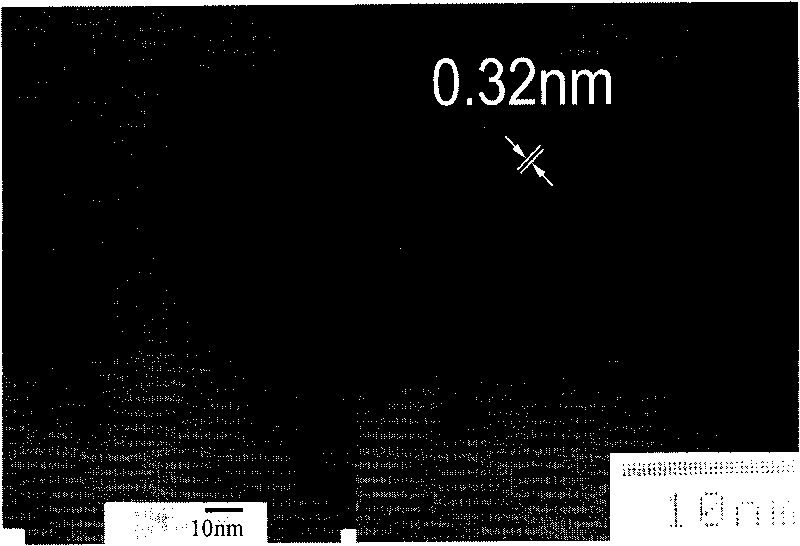
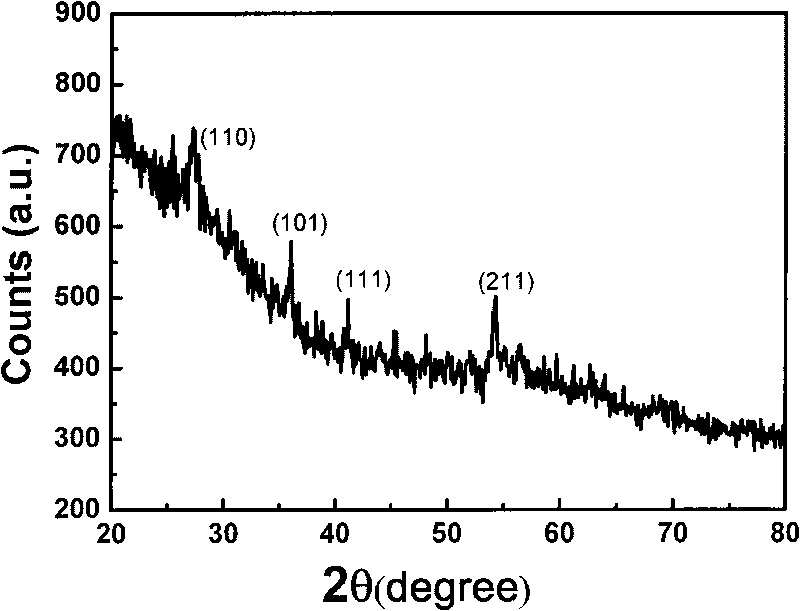
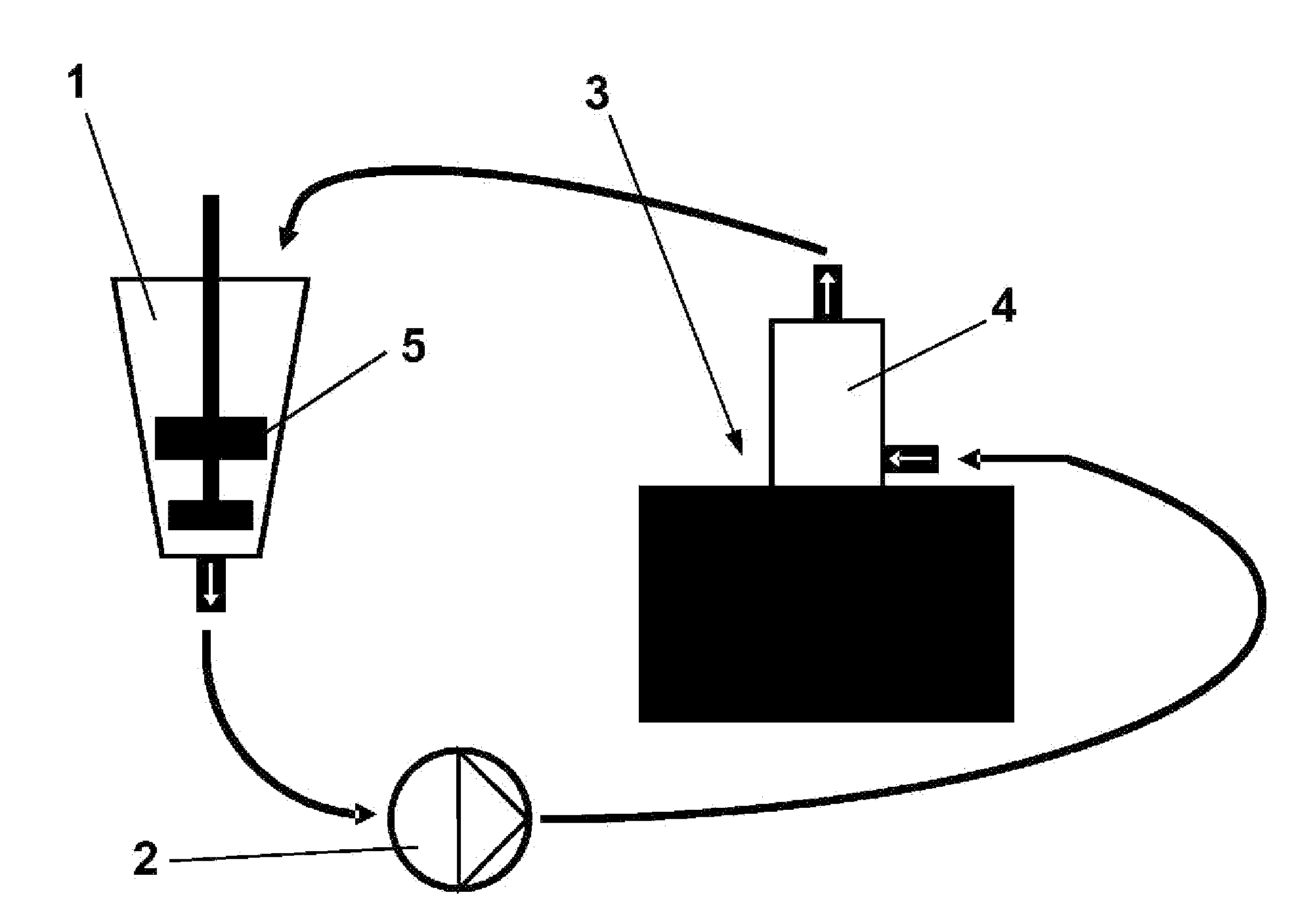
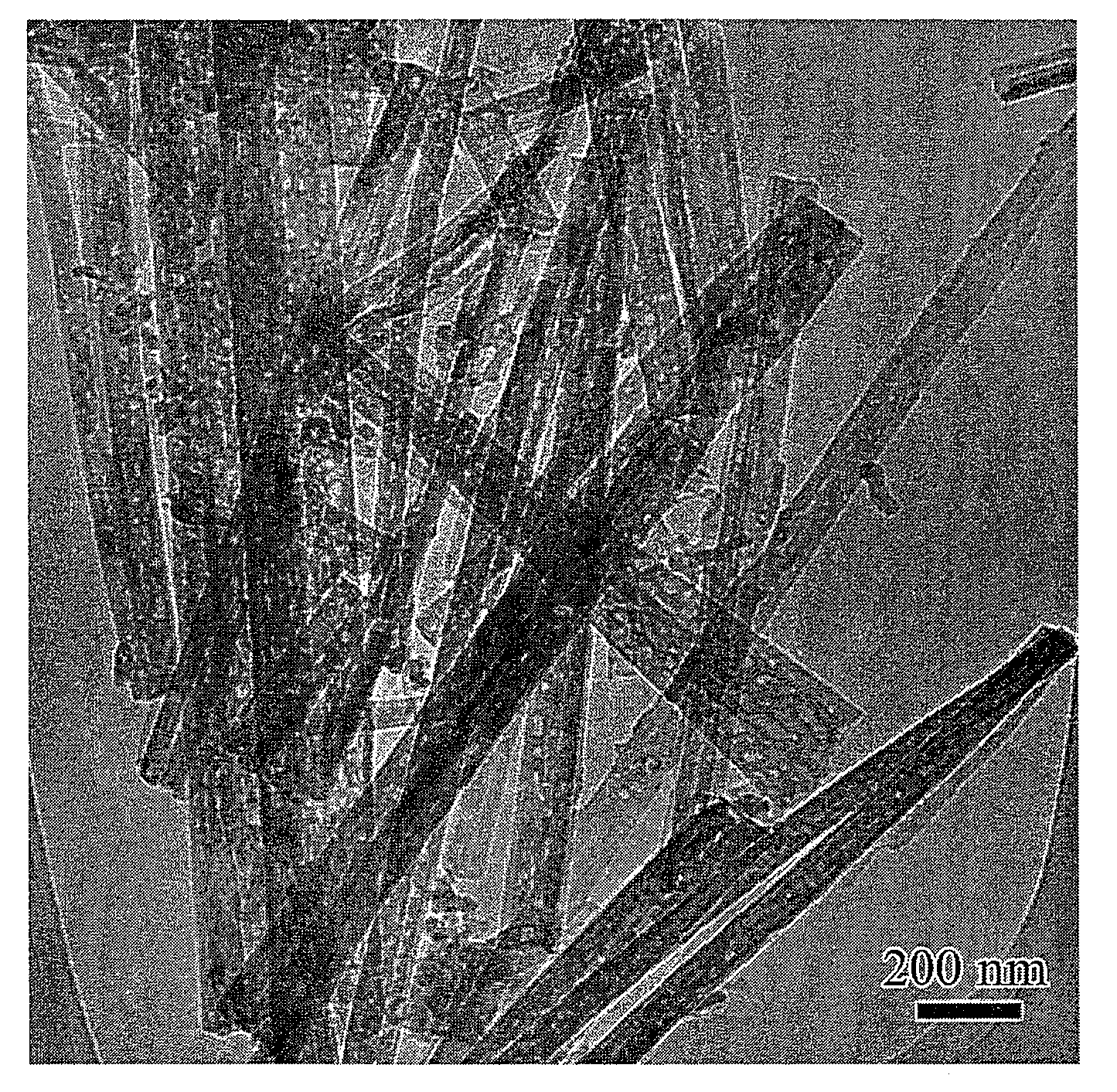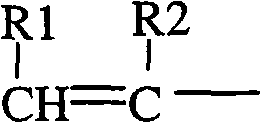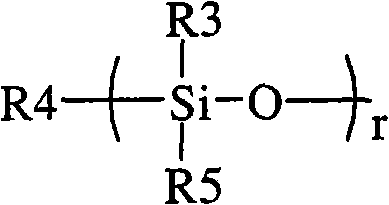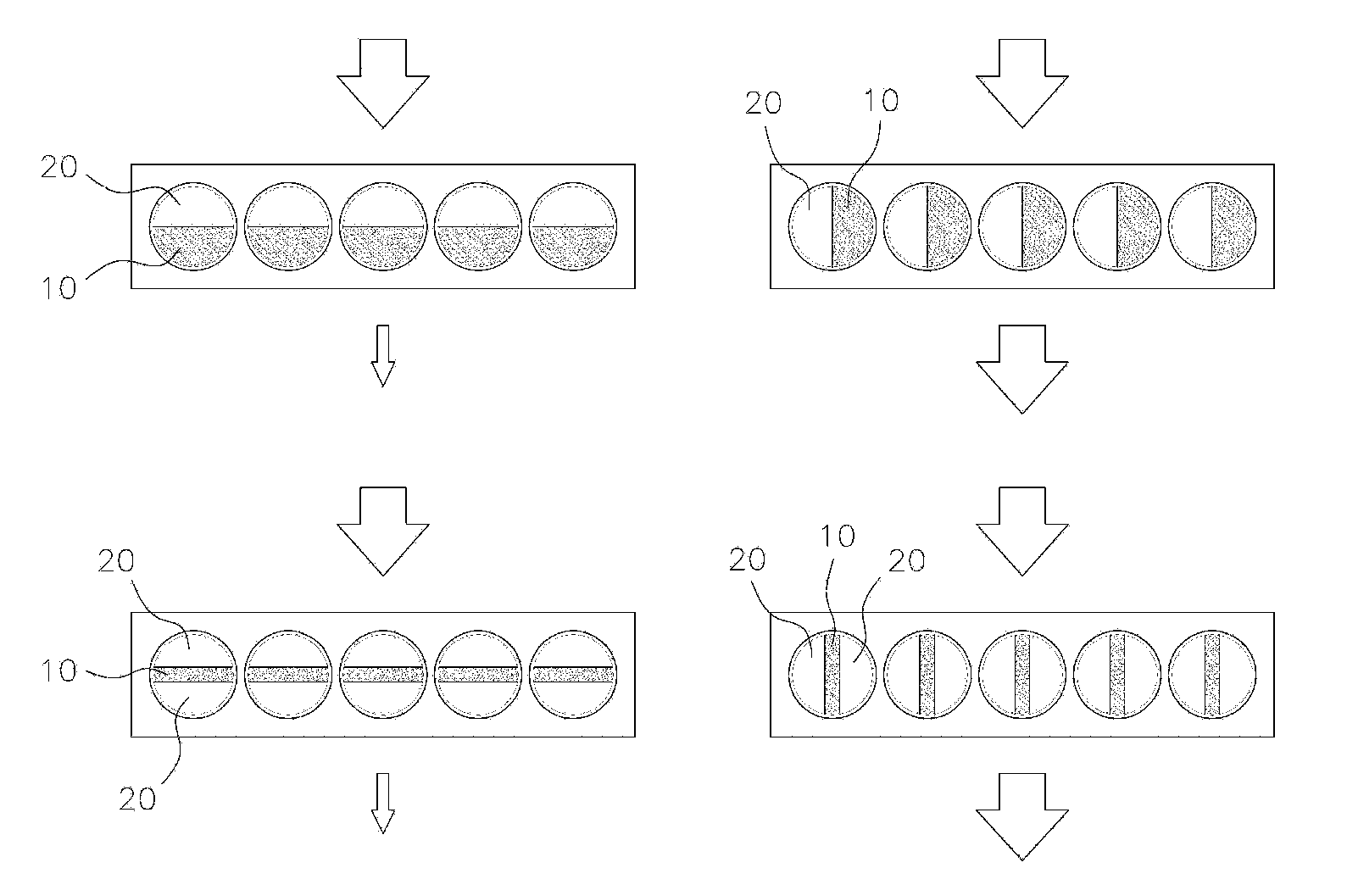Patents
Literature
47 results about "Titania nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cosmetic formulations comprising ZnO nanoparticles
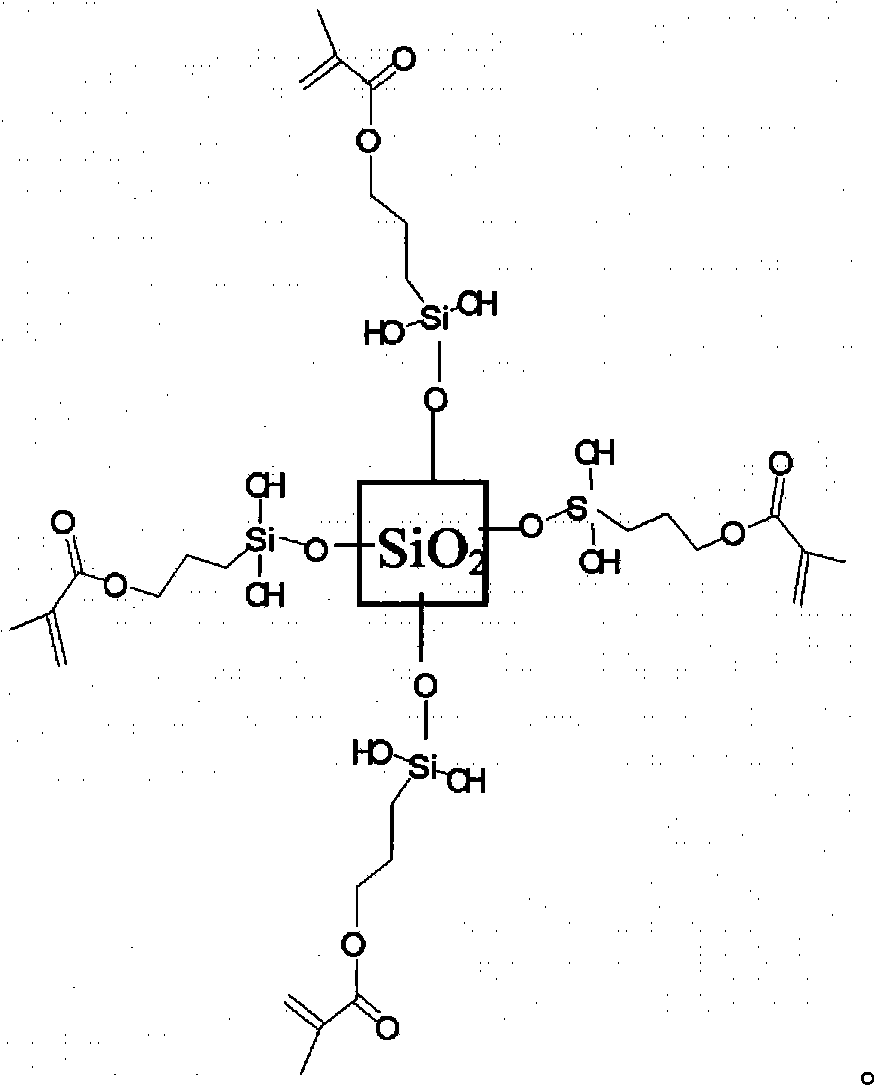
The present invention relates to the formation of surface treated zinc oxide and titania particles, and in particular zinc oxide and titania nanoparticles, with a siloxane star-graft copolymer coating, comprising a looped and / or linear polymeric structure on a star-graft copolymer coating, on a particle surface to control the interfacial surface interactions between the particle and the oil phase of the cosmetic skin formulation.
Owner:BASF AG
Cosmetic formulations comprising ZnO nanoparticles
The present invention relates to the formation of surface treated zinc oxide and titania particles, and in particular zinc oxide and titania nanoparticles, with a siloxane star-graft copolymer coating, comprising a looped and / or linear polymeric structure on a star-graft copolymer coating, on a particle surface to control the interfacial surface interactions between the particle and the oil phase of the cosmetic skin formulation.
Owner:BASF AG
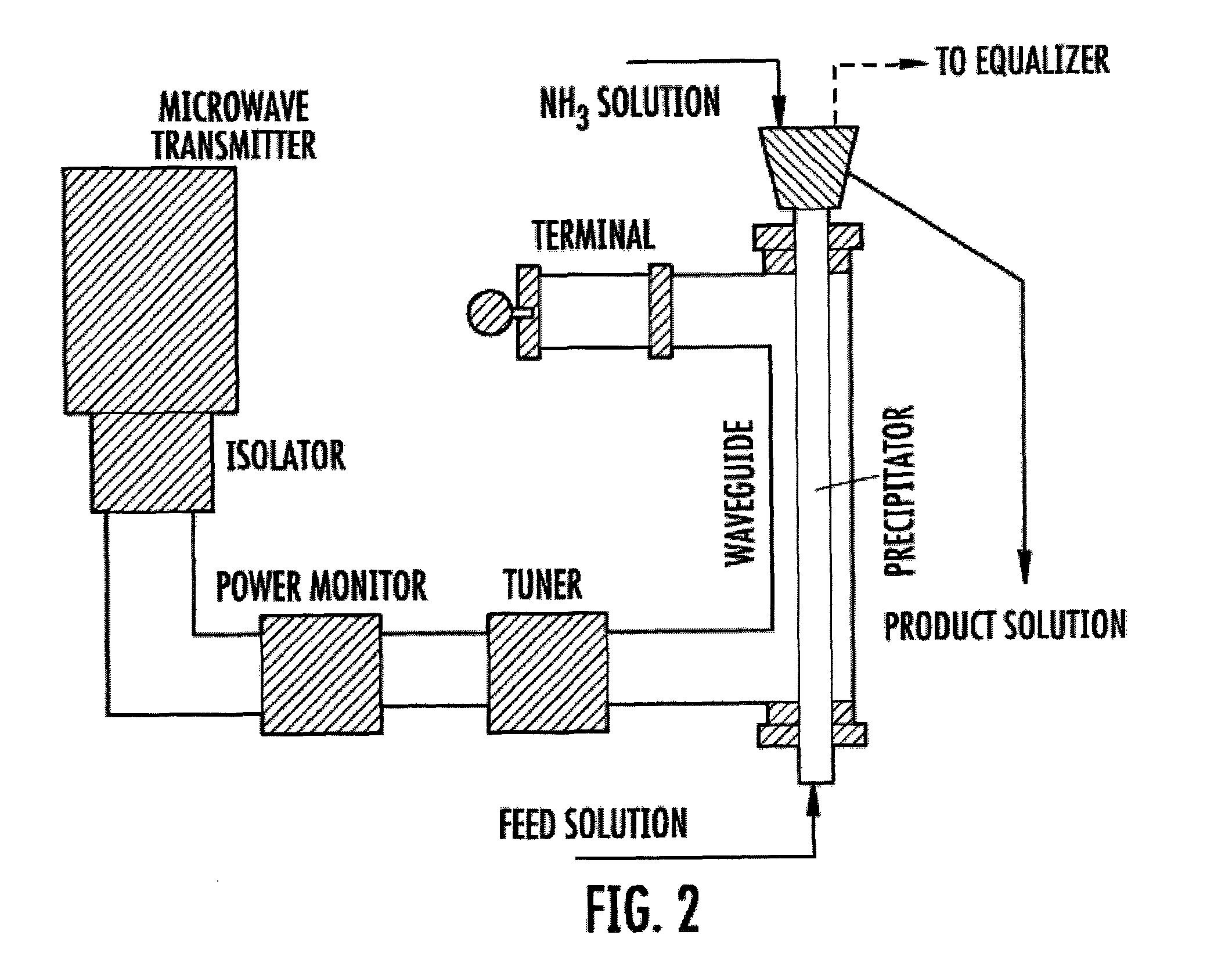
Method for depositing crystalline titania nanoparticles and films
InactiveUS20080187684A1Easily realizedImprove photocatalytic activityPolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge heatingVolumetric Mass DensityPicosecond
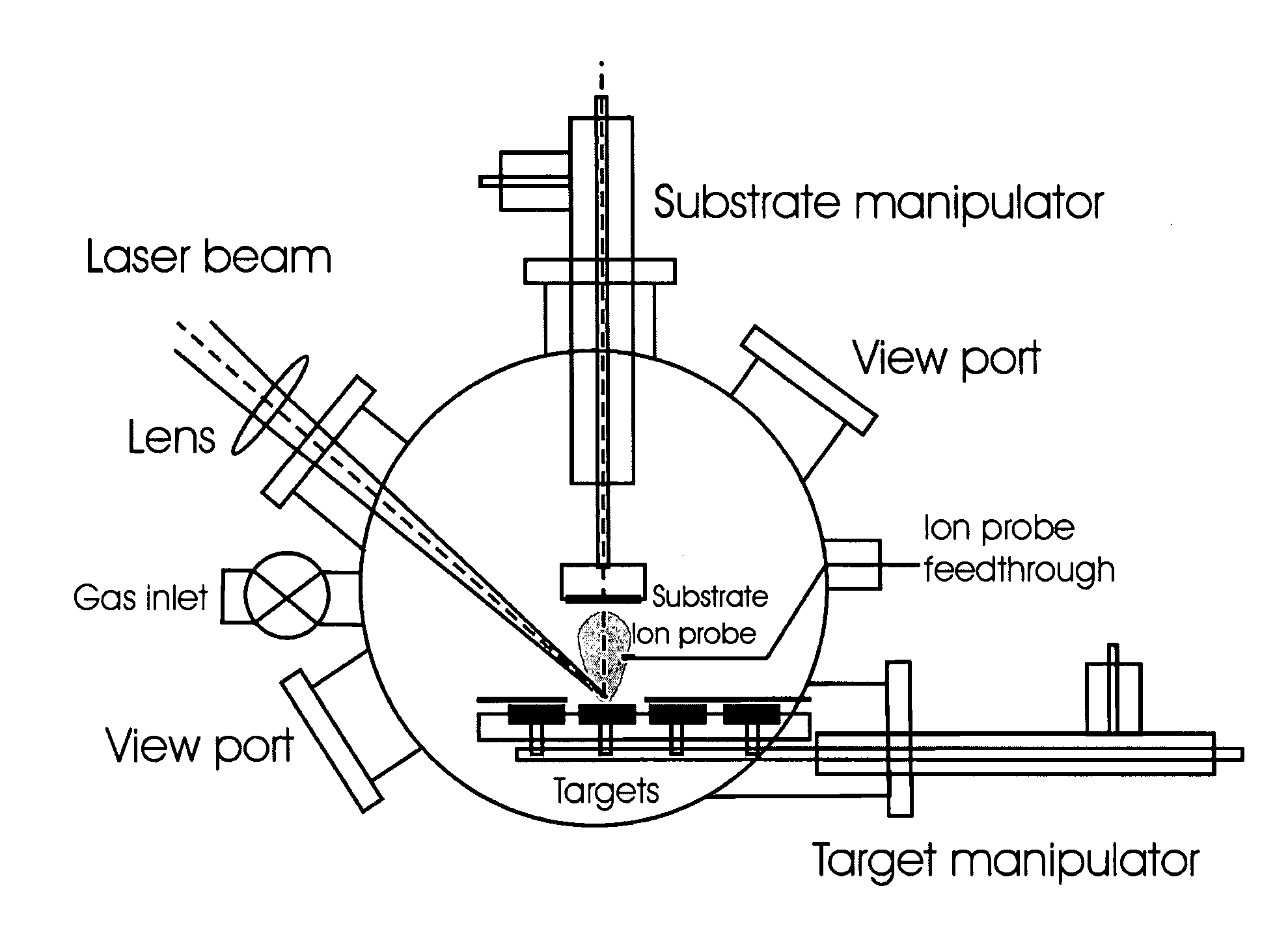
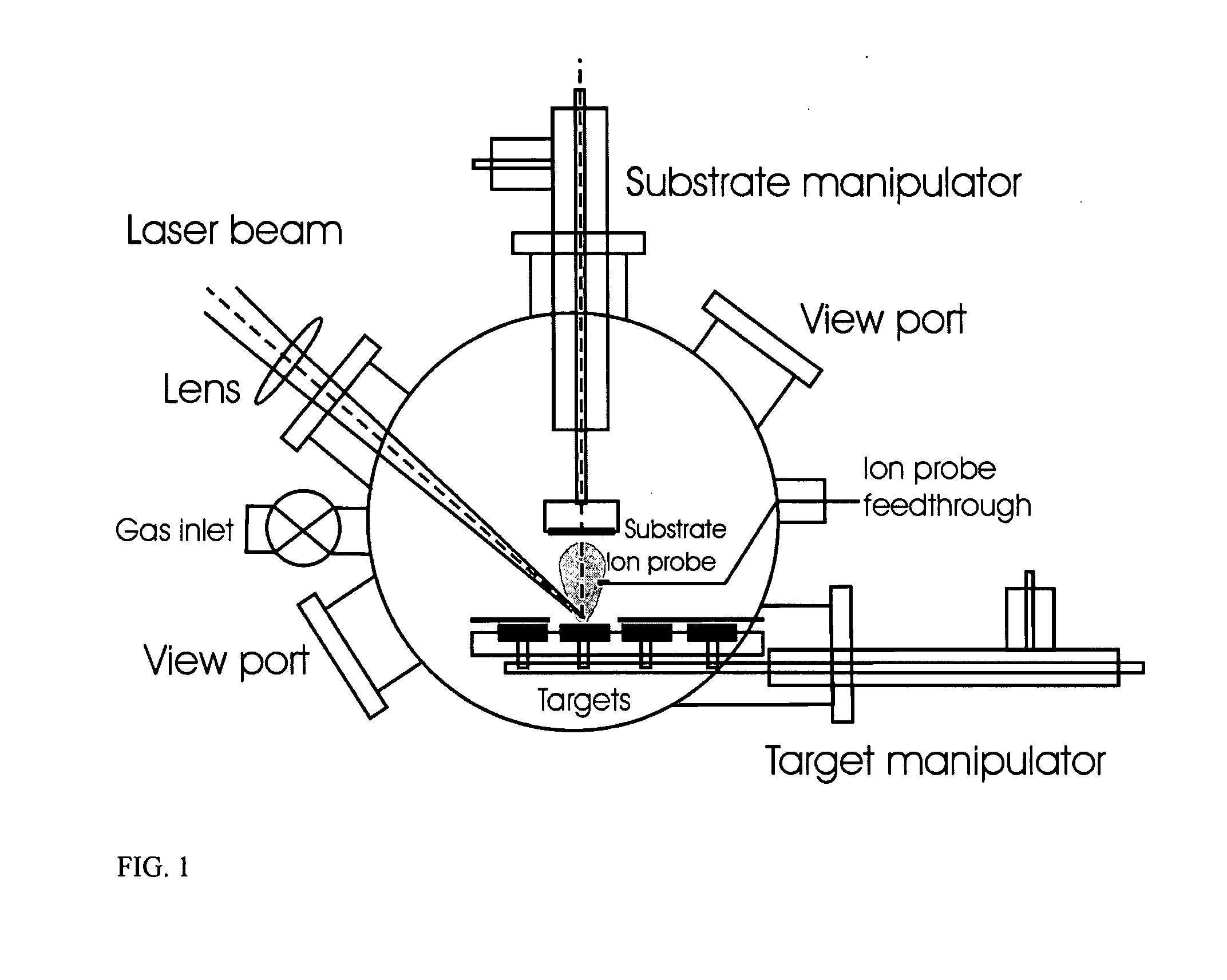
The present invention provides a one-step and room-temperature process for depositing nanoparticles or nanocomposite (nanoparticle-assembled) films of crystalline titanium dioxide (TiO2) onto a substrate surface using ultrafast pulsed laser ablation of Titania or metal titanium target. The system includes a pulsed laser with a pulse duration ranging from a few femtoseconds to a few tens of picoseconds, an optical setup for processing the laser beam such that the beam is focused onto the target surface with an appropriate average energy density and an appropriate energy density distribution, and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Self-cleaning filtration nanofiber membrane
Owner:CEO ESPINEX
Method for depositing crystalline titania nanoparticles and films
InactiveUS20090311513A1Easily realizedImprove photocatalytic activityPolycrystalline material growthLiquid surface applicatorsVolumetric Mass DensityPicosecond
A one-step and room-temperature process for depositing nanoparticles or nanocomposite (nanoparticle-assembled) films of metal oxides such as crystalline titanium dioxide (TiO2) onto a substrate surface using ultrafast pulsed laser ablation of Titania or metal titanium target. The system includes a pulsed laser with a pulse duration ranging from a few femtoseconds to a few tens of picoseconds, an optical setup for processing the laser beam such that the beam is focused onto the target surface with an appropriate average energy density and an appropriate energy density distribution, and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
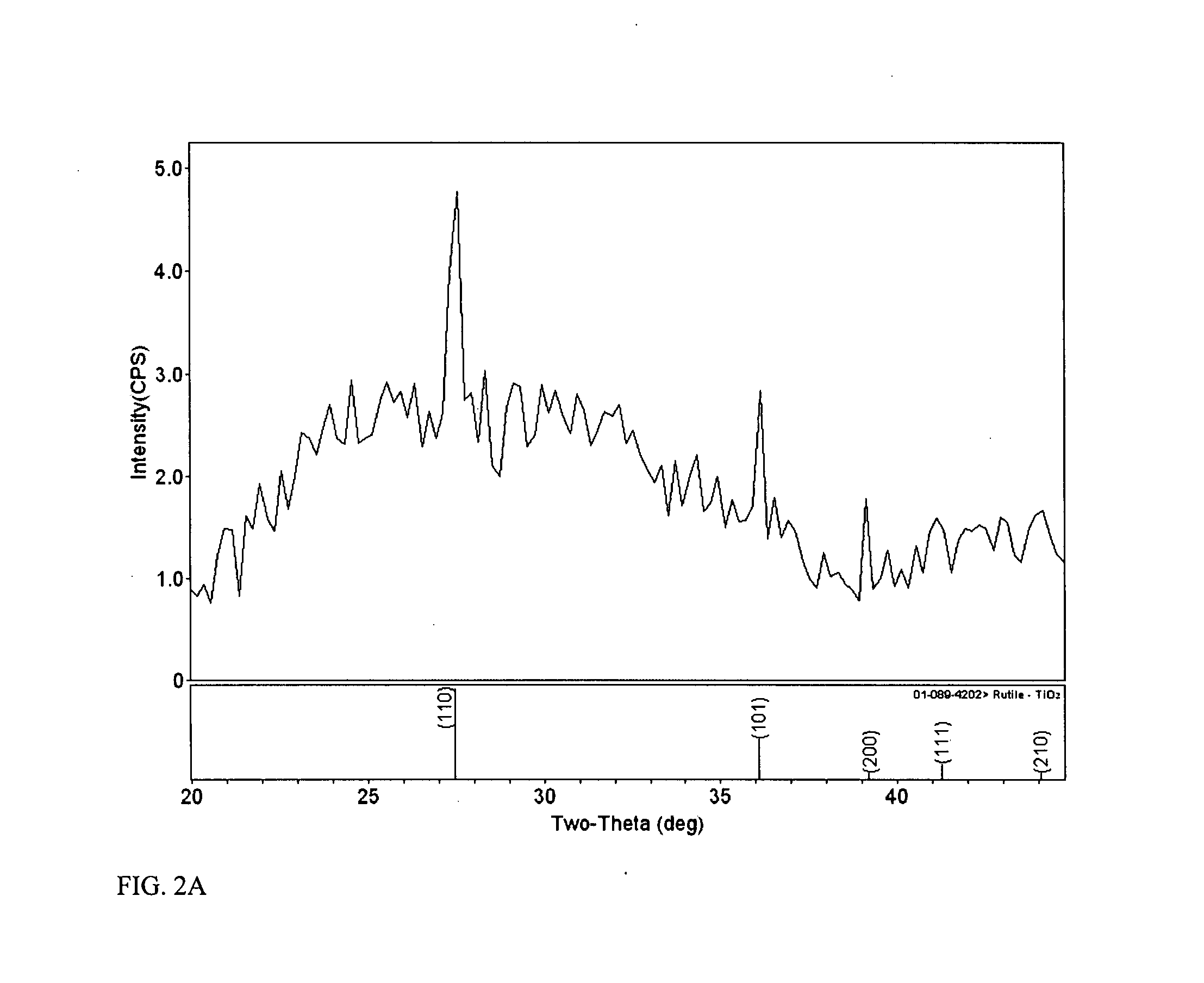
Method for preparing rutile titania nanoparticles
The invention discloses a method for preparing rutile titania nanoparticles, which comprises a liquid phase method and particularly comprises the following steps: 1, mixing polyvinylpyrrolidone and water to obtain polyvinylpyrrolidone solution with the concentration between 0.01 and 0.2M, and putting a titanium plate into the polyvinylpyrrolidone solution with stirring; 2, radiating the titanium plate for 20 to 40min with laser of which the wavelength is 1,064nm, the power is between 70 and 130mJ / pulse, the frequency is between 5 and 15Hz and the pulse width is between 5 and 15ns to obtain titania colloid; and 3, centrifuging, washing and drying the titania colloid to prepare the spherical rutile titania nanoparticles of which the particle size is between 5 and 80n, wherein the weight-average molecular weight of the polyvinylpyrrolidone is between 2,000 and 40,000; the purity of the titanium plate is more than or equal to 99.9 percent; a laser emitting the laser with the wavelength of 1,064nm is a Nd:YAG solid laser; and the spot diameter of the laser is between 1 and 2mm. The method can be widely used for industrially producing the rutile titania nanoparticles on a large scale.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
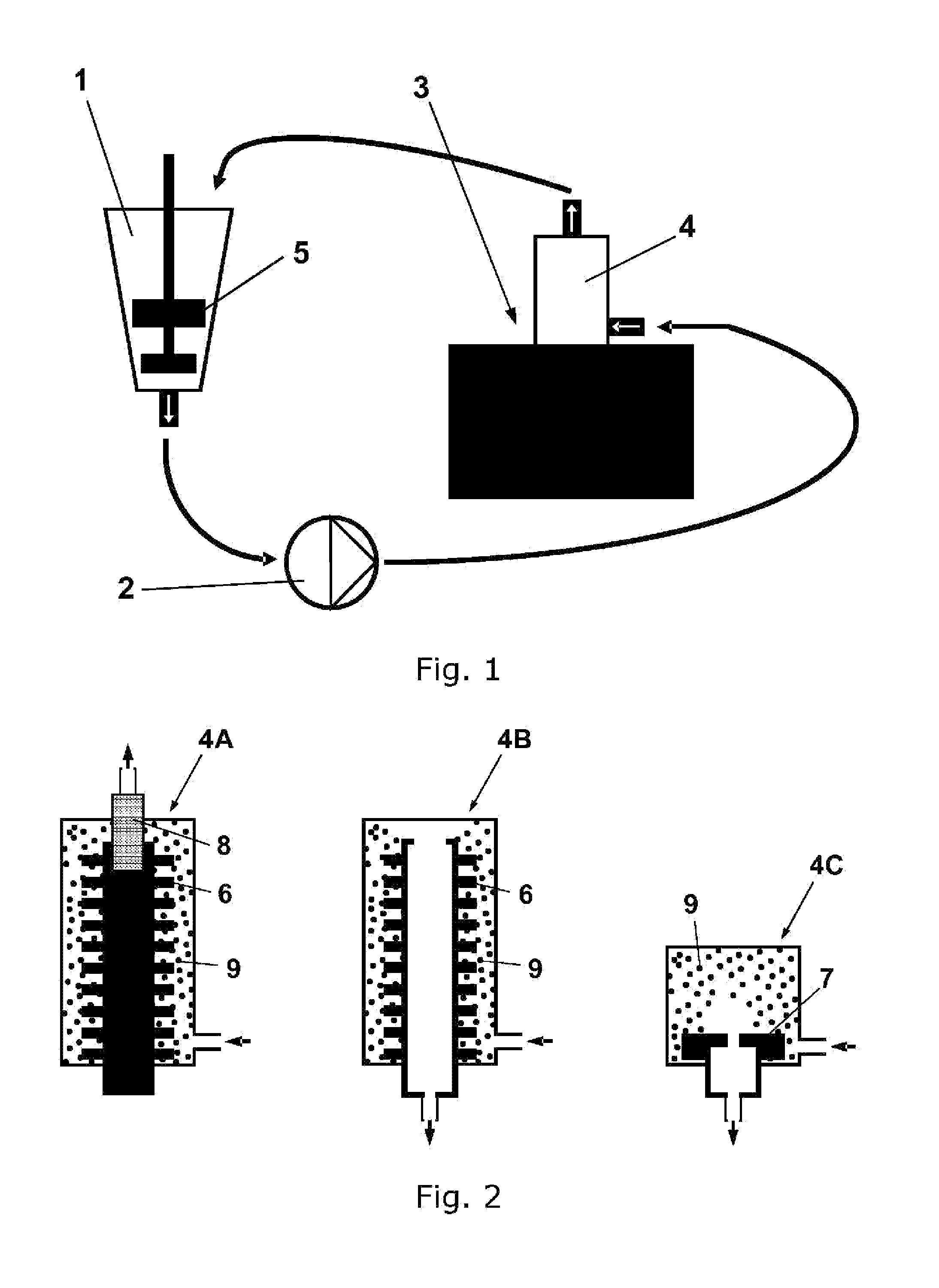
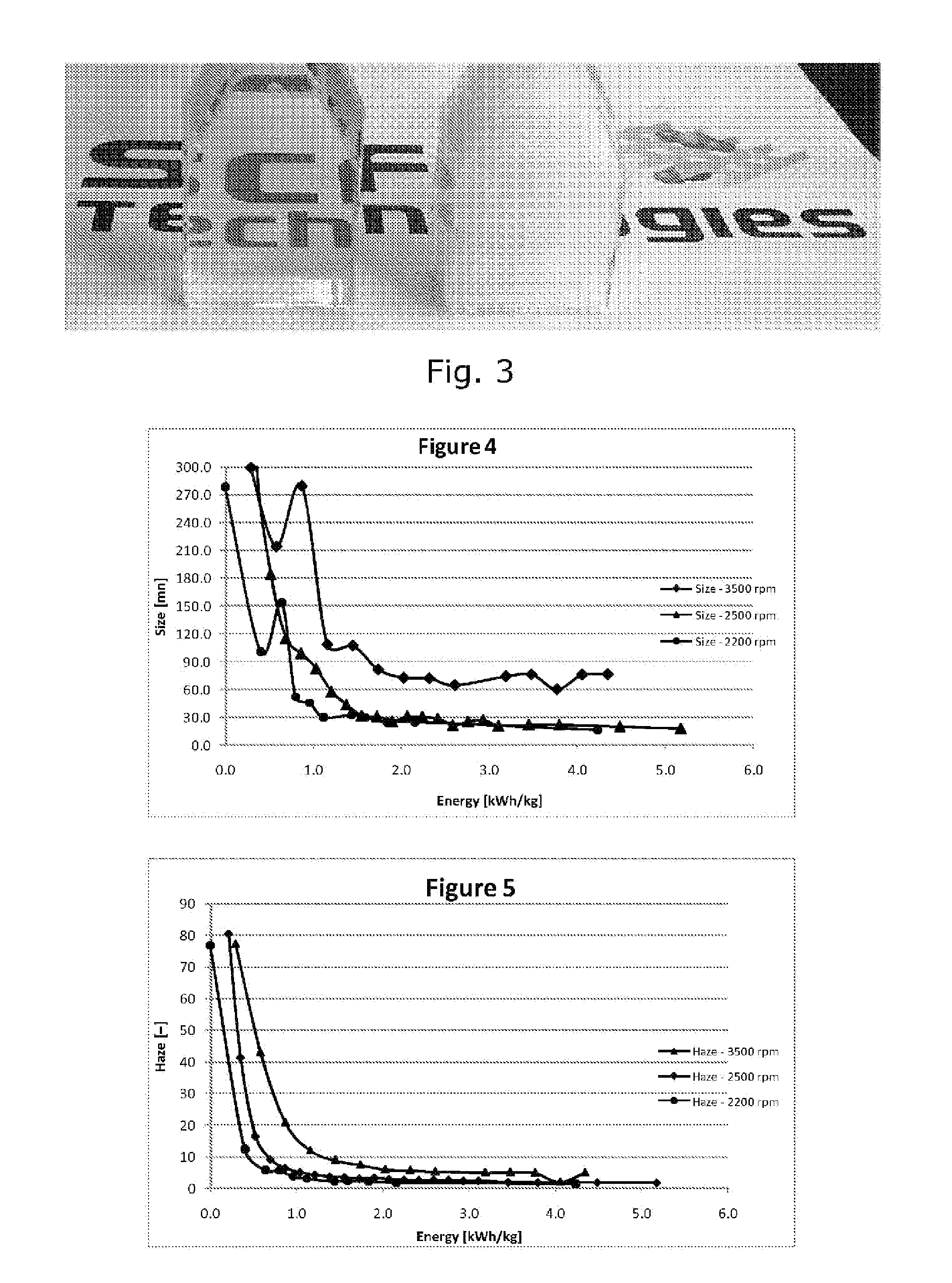
Production of titania nanoparticle colloidal suspensions with maintained crystallinity by using a bead mill with micrometer sized beads
ActiveUS20120064787A1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsPigmenting treatmentPrillMicrometer
A method is disclosed of producing stable nanosized colloidal suspensions of particles with limited crystallinity loss, products thereof, use of the products and an apparatus for the method. In particular the present invention relates to a wet milling method with small beads wherein the size of the final particles in suspension are stabilized in the nanorange (D50<75 nm) and at the same time the particles substantially maintain the crystallinity.
Owner:VAELINGE PHOTOCATALYTIC AB
Preparation of molybdenum-doped nano-TiO2 by sol-gel method
InactiveCN102258996AImprove photocatalytic activitySave energyCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPhotocatalytic reactionPack material
The invention relates to the environment-friendly technical field of semiconductor nanomaterials, in particular to a sol-gel preparation method of molybdenum-doped nano-titanium dioxide with relatively high photocatalytic activity. The present invention is based on current research, and aims to better overcome the defect of high recombination rate of photogenerated electron-hole pairs in photocatalytic reaction, and prepare molybdenum-doped nano-titanium dioxide photocatalyst by sol-gel method. The production method of the invention is simple and the cost is low; the molybdenum-doped nano titanium dioxide prepared by the invention has the characteristic of high photocatalytic activity. It is widely used in automotive topcoats, photosensitive materials, photocatalysts, cosmetics, food packaging materials, ceramic additives, gas sensors and electronic materials.
Owner:张旭星
Titania Nanocavities and Method of Making
InactiveUS20090117384A1Simple and safe and inexpensive to produceEnhanced UV absorbanceMaterial nanotechnologyCosmetic preparationsMetal oxide nanoparticlesUltraviolet
Disclosed herein are compositions of metal oxide nanoparticles having regular polyhedral nanocavities, where the metal oxide can be titania, and where the nanoparticles be nanorods. Also disclosed are titania nanoparticles with nanocavities that are doped with dopants. Methods of making metal oxide nanoparticles with nanocavities are also disclosed. Also disclosed are ultraviolet-blocking compositions including metal oxide nanoparticles with nanocavities, as well as methods of enhancing ultraviolet absorbance efficiency of an ultraviolet blocking composition. Additional uses of metal oxide nanoparticles with nanocavities include solar energy conversion systems and lithium-ion batteries.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Method for preparing broadband spectrum response photo-catalytic film
InactiveCN107457002ARegulatory formStructural regulationGas treatmentOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPorosityMatrix solution
The invention provides a method for preparing a broadband spectrum response photo-catalytic film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a polymer matrix solution; preparing a broadband spectrum response titania photocatalyst through a supercritical hydrothermal method, and preparing the broadband spectrum response photo-catalytic film through electrostatic spinning. The photo-catalytic film prepared by the invention has the advantages of high porosity and high specific area, has a specific surface area reaching 300m<2> / g or higher, and has a special structure with micro-pore and mesoporous coexistence, so that the titania nanoparticles are uniformly dispersed and loaded on a polymer matrix non-woven fabric. The photo-catalytic film prepared by the invention has filtering and purifying functions, is capable of filtering the nano-scale particles, greatly adsorbing formaldehyde, VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) and other pollutants and efficiently performing catalytic degradation on the formaldehyde, VOCs and the other pollutants to produce CO2 and water under sunshine conditions, and achieves dual effects of catalytic degradation and filtration.
Owner:江苏科来材料科技有限公司
Self-cleaning corrosion-resistant aluminum profile
InactiveCN108250903AImprove corrosion resistanceStrong adhesionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesPolyethylene glycolResin coating
The invention discloses a self-cleaning corrosion-resistant aluminum profile and relates to the technical field of aluminum profiles. The self-cleaning corrosion-resistant aluminum profile comprises an aluminum profile matrix and an epoxy resin coating coating the surface of the aluminum profile matrix, wherein the epoxy resin coating is prepared by mixing a component A and a component B accordingto a weight ratio of 3-5 to 1; the component A comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-50 parts of a bisphenol A epoxy resin emulsion, 5-10 parts of modified titania nanoparticles, 0.5-2 parts of fumed silica, 5-10 parts of diatomite, 2-5 parts of graphene oxide, 3-7 parts of texanol, 2-5 parts of polyethyleneglycol diglycidyl ether, 0.5-2 parts of a dispersing agent, 0.5-2 parts of a flatting agent, 12-15 parts of water, 2-5 parts of a coupling agent and 0.2-1 part of nonylphenol polyoxyethylene ether; the component B is a waterborne epoxy amine curing agent. The coatingprepared by the invention is excellent in pollution resistance, bactericidal activity, corrosion resistance and wear resistance and is excellent in bonding strength with an aluminum alloy base material, a long-term protection effect is achieved, the service life of the aluminum alloy is prolonged, and the application range is widened.
Owner:安徽鑫铂铝业股份有限公司
Olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same
ActiveCN102850159AEfficient deoxidationExtended service lifeChemical modification purification/separationAlkali metal oxideRoom temperature
The invention discloses an olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same. The preparation method includes (by weight parts) (1) mixing manganese source (as Mn3O4) 100 and titania nanoparticle (modified by alkali metal oxide) 58-100 to obtain a mixture; (2) kneading the mixture and a silver compound (as Ag2O) aqueous solution 8-35, and forming; (3) aging and drying; and (4) calcining. The inventive olefin deoxygenation agent has high room-temperature deoxygenation capacity up to 29.3 mL / g, deoxygenation depth smaller than 0.01 ppm, low reduction temperature, and wide applicability in industrial production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
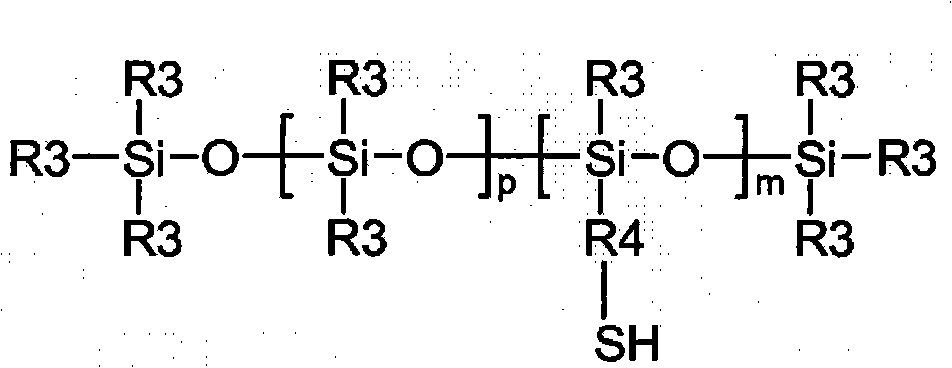
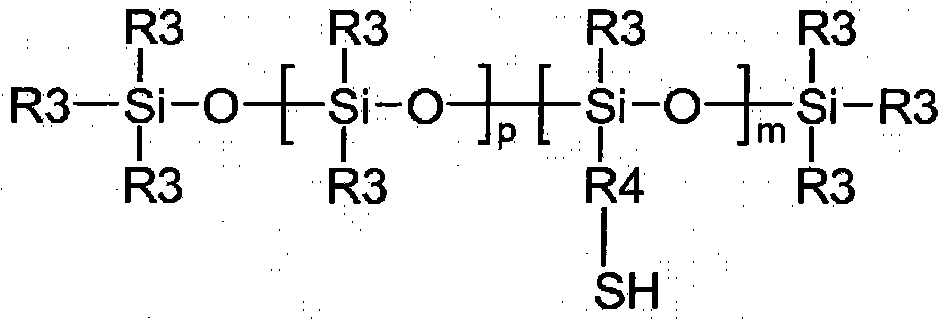
Copolymers of nanoparticles, vinyl monomers and silicone
InactiveCN101910228AStable peel forceMaterial nanotechnologyFilm/foil adhesivesSilica nanoparticlesMeth-
A copolymer comprises the reaction product of (a) (meth)acrylate functionalized nanoparticles, (b) vinyl monomer, and (c) mercapto-functional silicone. The (meth)acrylate functionalize nanoparticles are selected from the group consisting of silica nanoparticles, zirconia nanoparticles, titania nanoparticles, and combinations thereof.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Making Method for Titania Nanoparticle
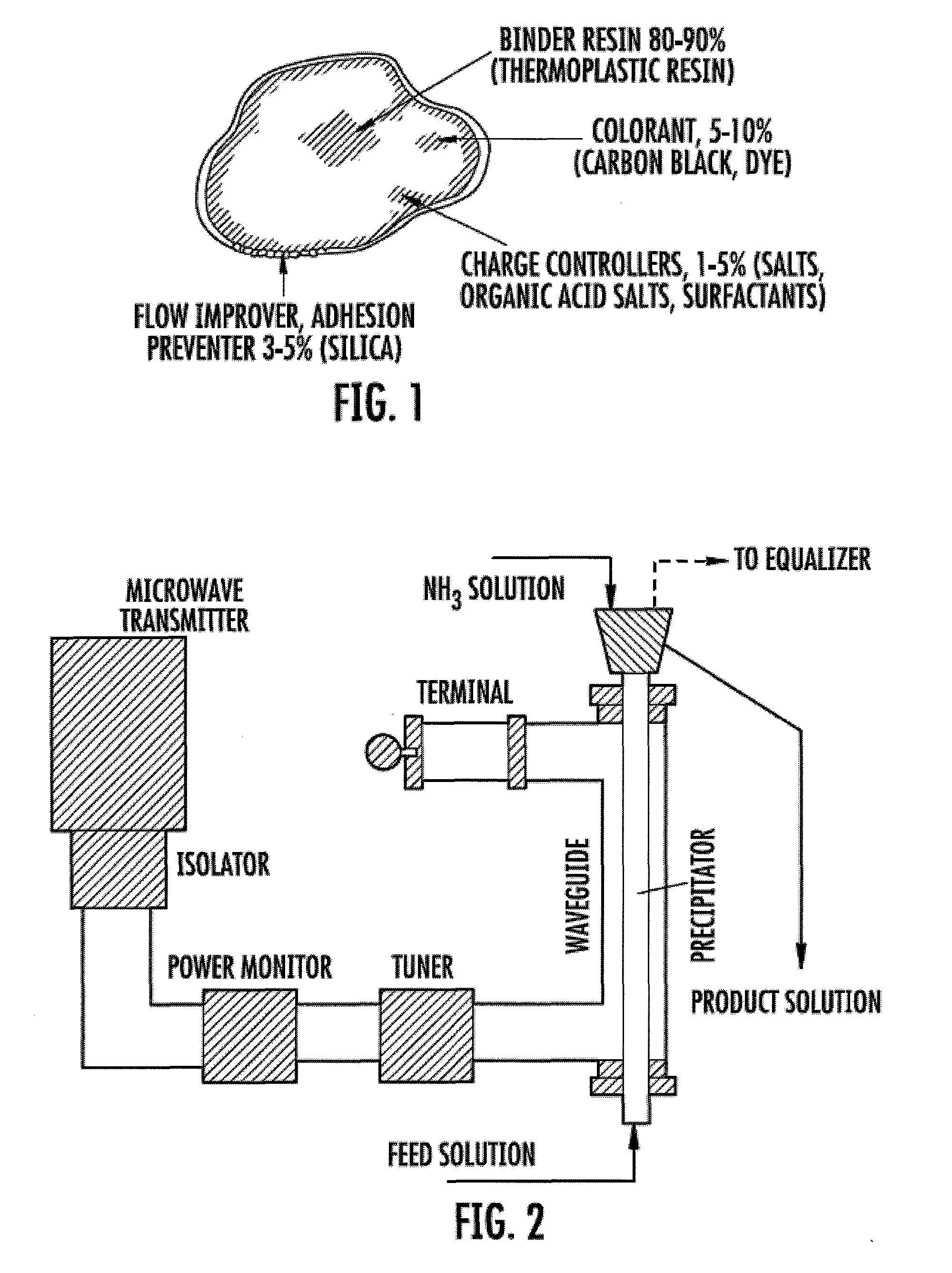
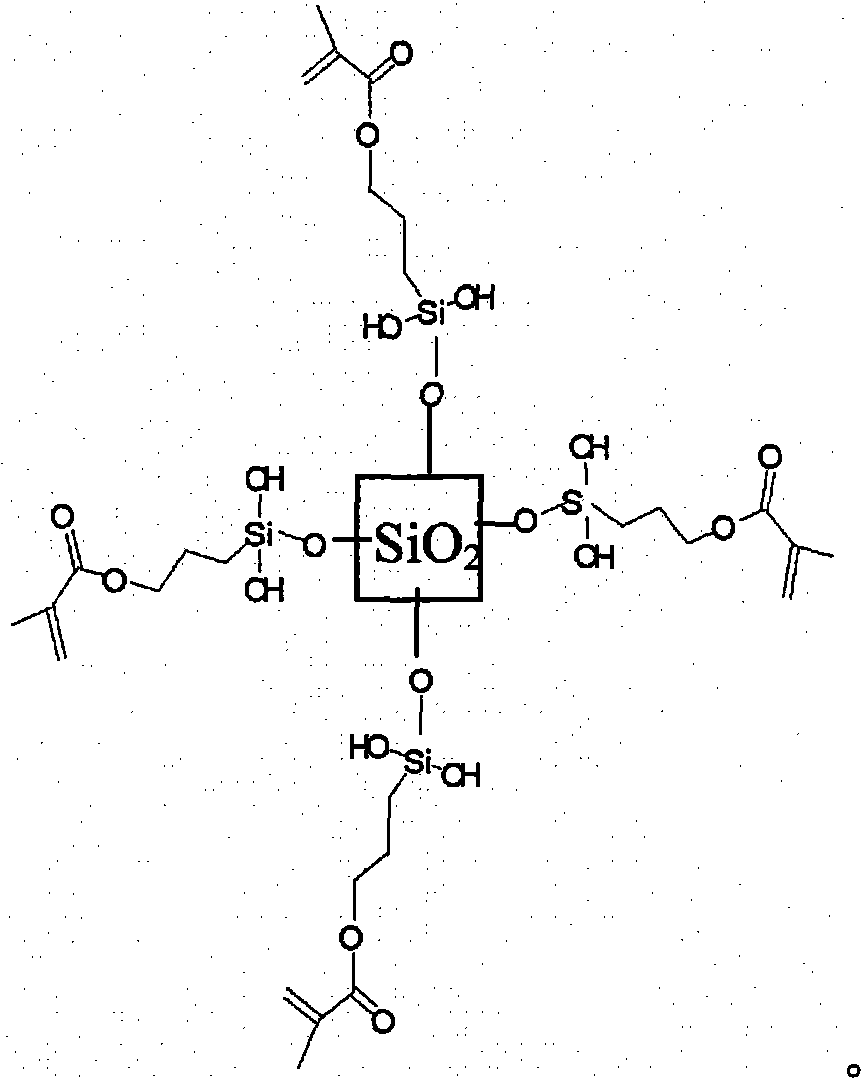
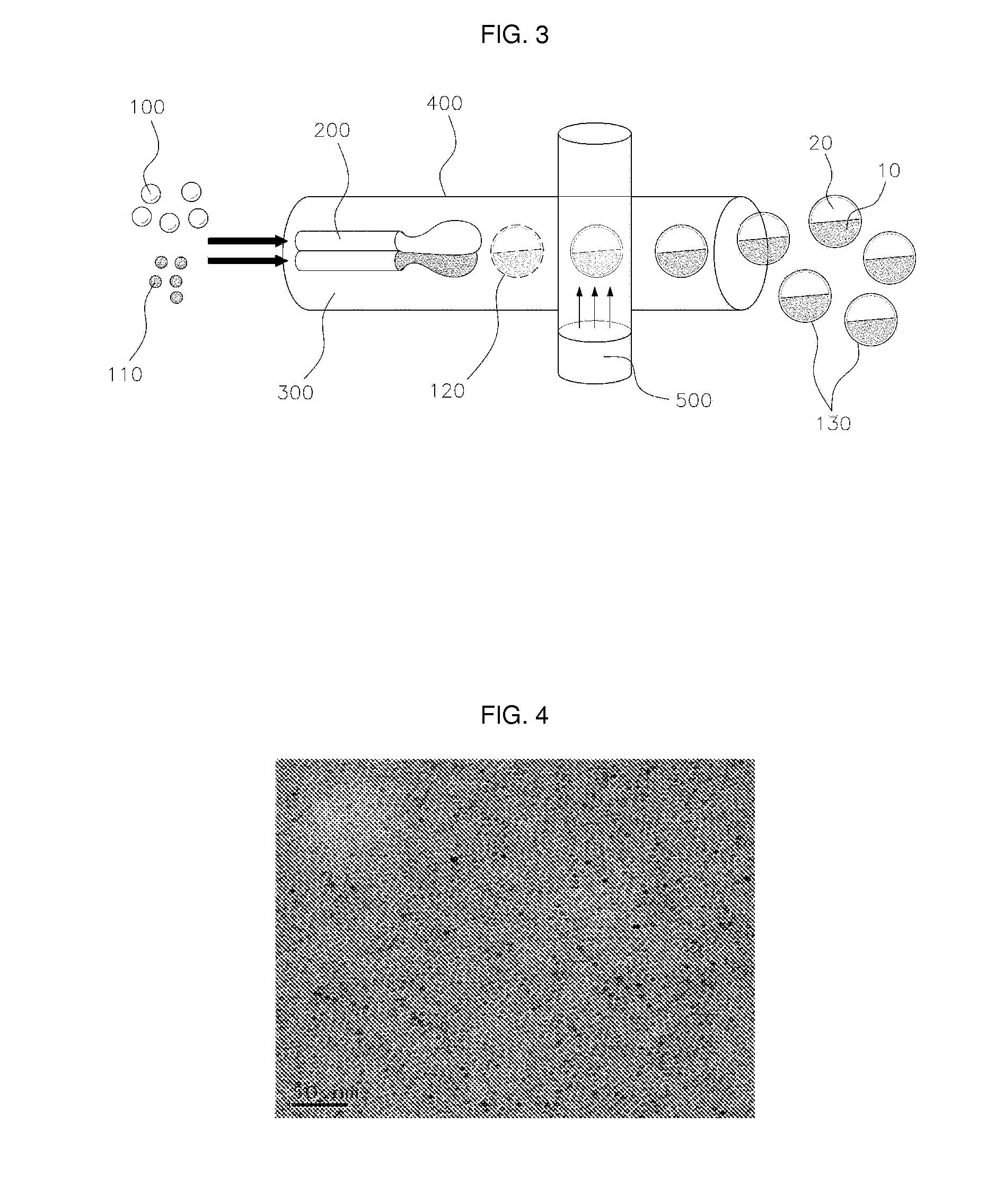
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing titania nanoparticles, and specifically to a method of manufacturing titania nanoparticles wherein the particle size is uniform, it is possible to manufacture monodisperse particles without aggregation among particles, a uniform coating can be applied, that is suitable to large-scale production, and that can obtain high-resolution images by maintaining the toner electric charge and electric charge distribution; and the developer included in said titania nanoparticles.
Owner:SUKGYUNG AT
Copolymers of nanoparticles, vinyl monomers and silicone
InactiveCN101910224AStable peel forceMaterial nanotechnologyFilm/foil adhesivesSilica nanoparticlesFunctionalized nanoparticles
A copolymer comprises the reaction product of (a) (meth)acrylate functionalized nanoparticles, (b) vinyl monomer, and (c) silicone macromer. The (meth)acrylate functionalize nanoparticles are selected from the group consisting of silica nanoparticles, zirconia nanoparticles, titania nanoparticles, and combinations thereof.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Cosmetic formulations comprising zno nanoparticles
The present invention relates to the formation of surface treated zinc oxide and titania particles, and in particular zinc oxide and titania nanoparticle s, with a siloxane star-graft copolymer coating, comprising a looped and / or linear polymeric structure on a star-graft copolymer coating, on a particle surface to control the interfacial surface interactions between the particle and the oil phase of the cosmetic skin formulation.
Owner:BASF AG
Fine particles having a multiple structure, polymer film for smart glass and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20140183423A1Individual molecule manipulationTenebresent compositionsPolymer scienceIron oxide nanoparticles
Disclosed are fine particles having a multiple structure, a polymer film for smart glass, and a method of manufacturing the same. More particularly, disclosed are fine particles having a multiple structure, which include a reaction portion containing iron oxide nanoparticles, carbon black and / or carbon nanotubes, and at least one non-reaction portion containing silica and / or titania nanoparticles, and which rotate by means of an electric field or a magnetic field, a polymer film for smart glass including the fine particles to control light transmissivity, and a method of manufacturing the same.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
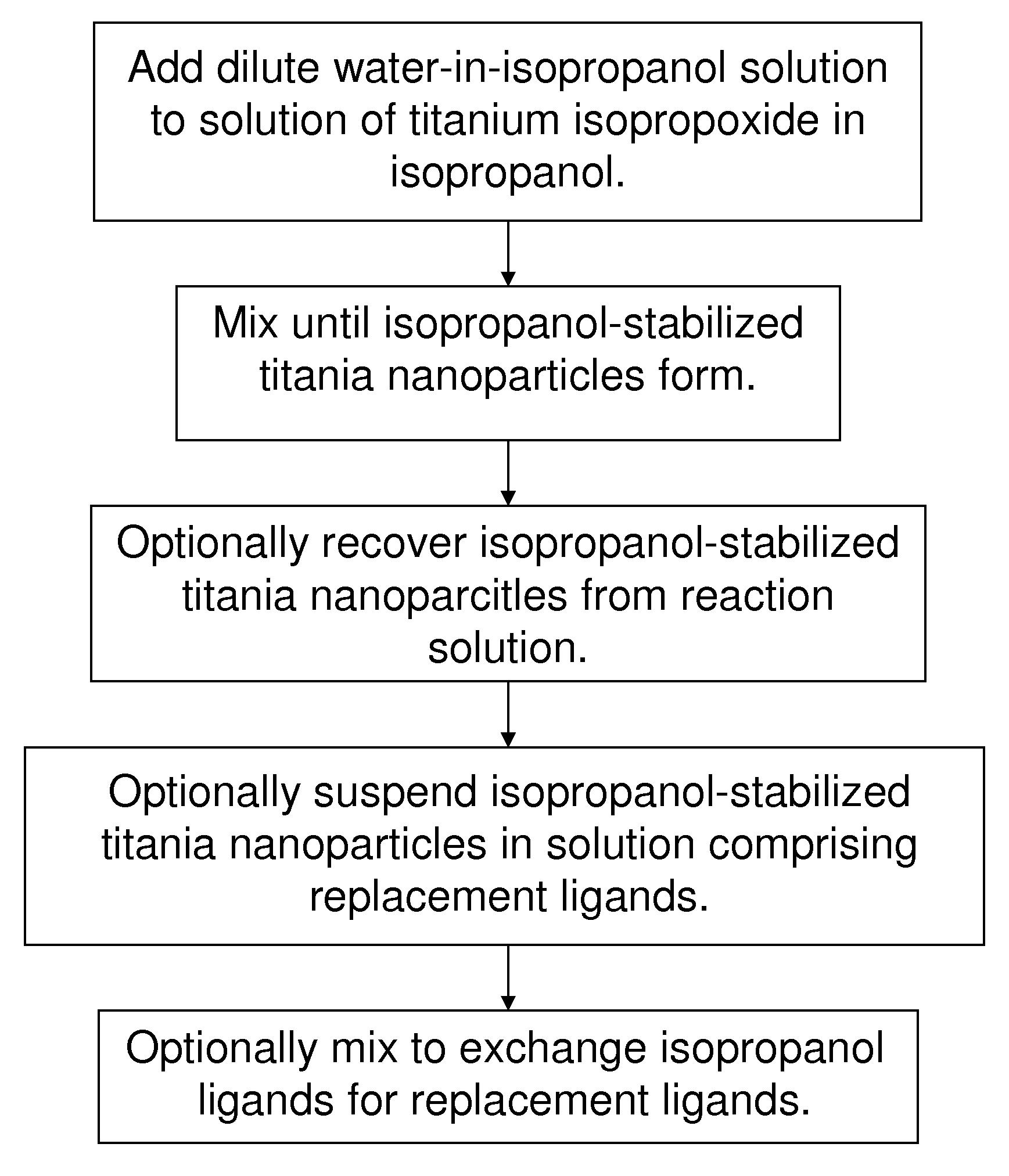
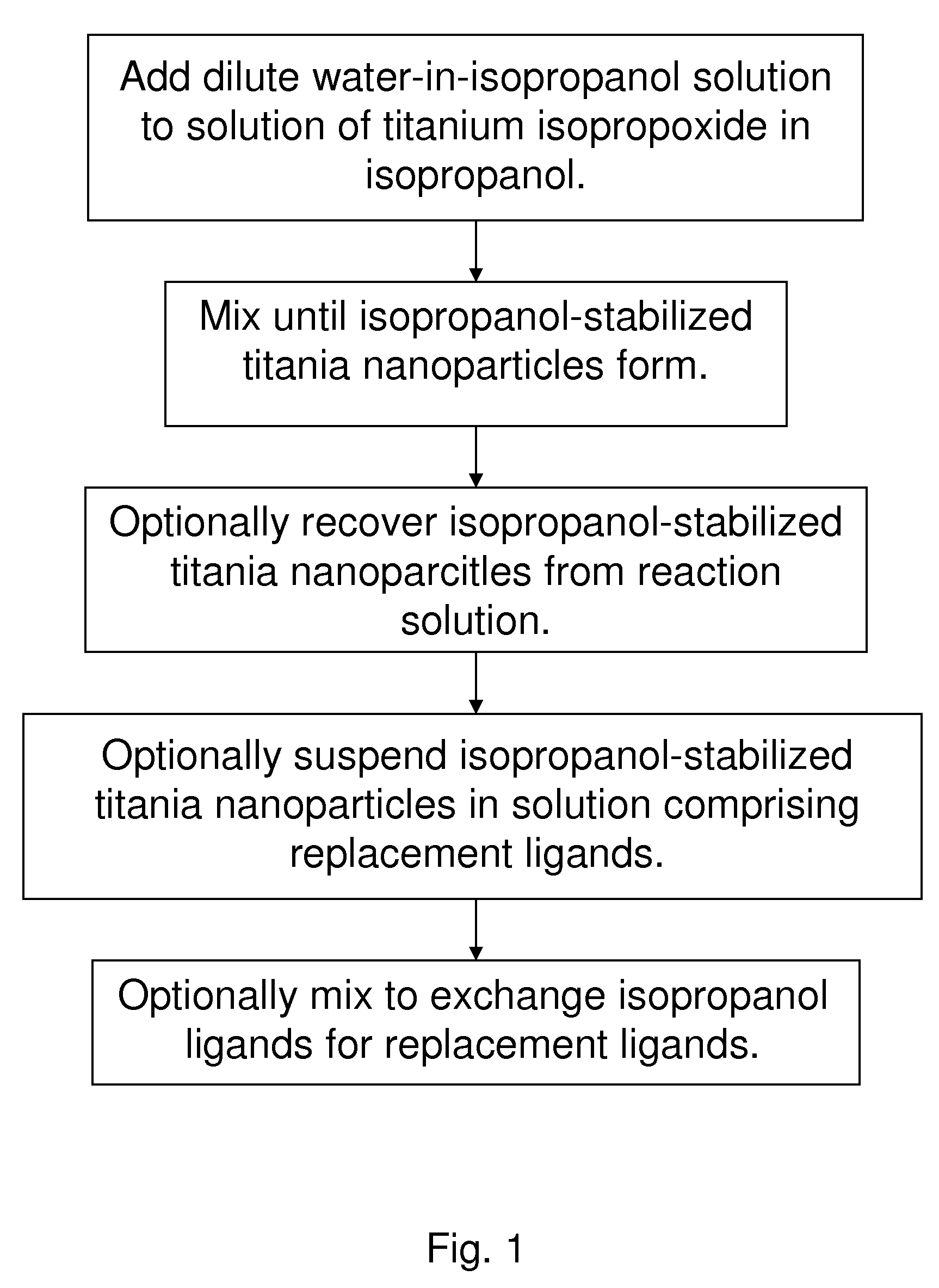
High-yield synthesis of brookite TiO2 nanoparticles
A method for forming non-agglomerated brookite TiO2 nanoparticles without the use of expensive organic surfactants or high temperature processing. Embodiments of this invention use titanium isopropoxide as the titanium precursor and isopropanol as both the solvent and ligand for ligand-stabilized brookite-phase titania. Isopropanol molecules serve as the ligands interacting with the titania surfaces that stabilize the titania nanoparticles. The isopropanol ligands can be exchanged with other alcohols and other ligands during or after the nanoparticle formation reaction.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
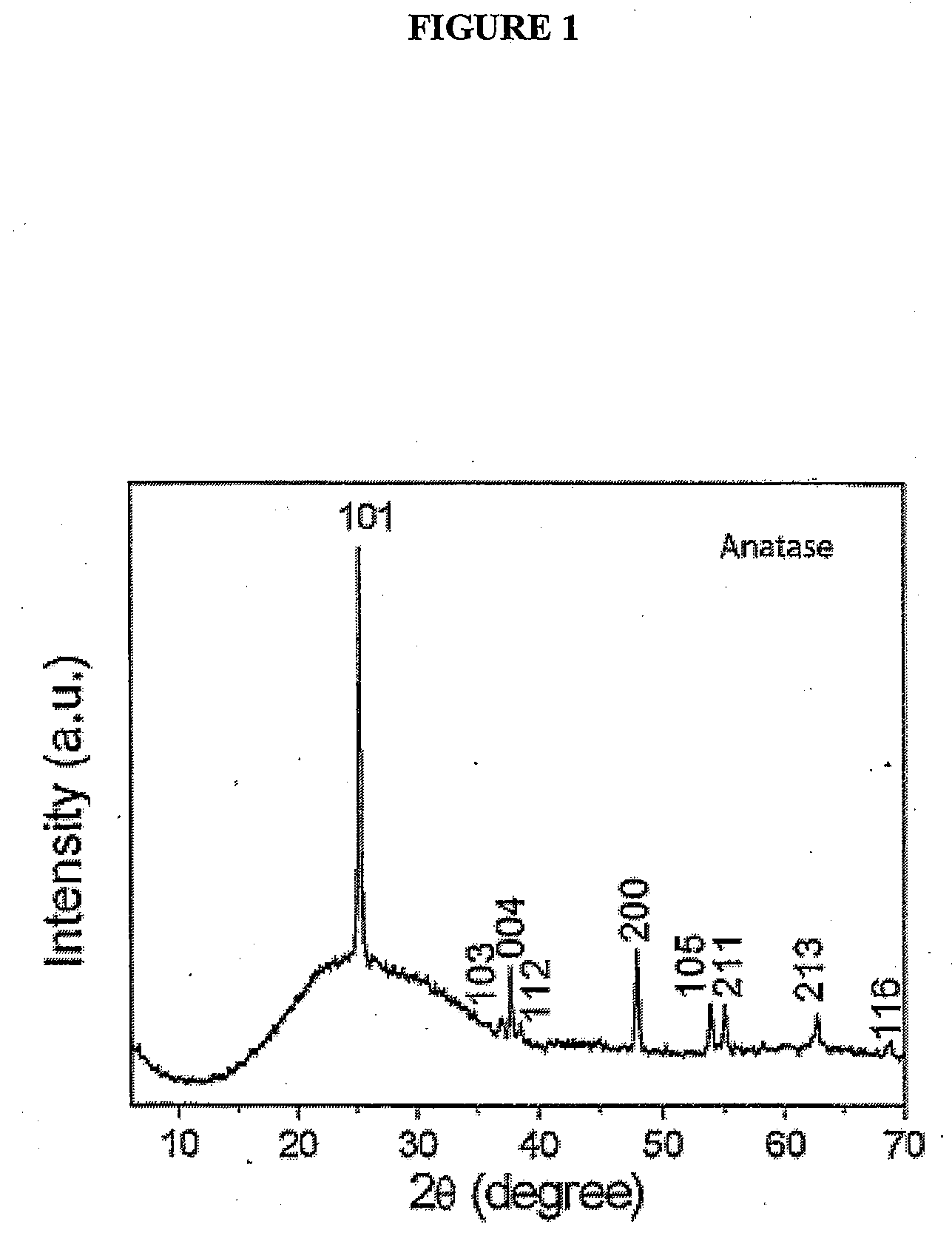
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles for fabricating photo-electrode for efficient, longlasting dye-sensitized solar cell and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20130247978A1Speed up the conversion processHigh electron mobilityMaterial nanotechnologyLight-sensitive devicesCrystallinityService condition
It is disclosed that a photo-electrode of a dye-sensitized solar cell comprising faceted anatase-type titania nanoparticles which adequate for fabricating a photo-electrode of a dye-sensitized solar cell which is efficient and longlasting and a fabrication method thereof. The titania nanoparticles can provide high photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell with help of fast electron mobility due to its high crystallinity and can reduce process time required for adsorbing the dye molecules on the surface of the titania nanoparticles.By modifying surface characteristics of the titania nanoparticles, it is allowed for dye molecules to be easily adsorbed on the surface of the titania nanoparticles and the life span of the dye molecules adsorbed on it is expanded with help of reduced photo-degradation rate of them at service conditions.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same
ActiveCN102850162AEfficient deoxidationHigh mechanical crush strengthChemical modification purification/separationMechanical crushingRoom temperature
The invention discloses an olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same. The preparation method includes (by weight parts) (1) mixing manganese source (as Mn3O4) 100, modified titania nanoparticle 58-100 and binder 1.5-25 to obtain a mixture; (2) kneading the mixture and a silver compound (as Ag2O) aqueous solution 8-35, and forming; (3) aging and drying; and (4) calcining. The inventive olefin deoxygenation agent has high room-temperature deoxygenation capacity up to 28.5 mL / g, high mechanical crushing strength up to 88 N / cm, deoxygenation depth smaller than 0.01 ppm, low reduction temperature, and wide applicability in industrial production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same
ActiveCN102850166AExtended service lifeEmission reductionChemical modification purification/separationRoom temperatureAqueous solution
The invention discloses an olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same. The preparation method includes (by weight parts) (1) mixing manganese source (as Mn3O4) 100 and titania nanoparticle 58-100 to obtain a mixture; (2) calcining; (3) kneading the calcined mixture and a silver compound (as Ag2O) aqueous solution 8-35, and forming; (4) aging and drying; and (5) calcining. The second calcining temperature is lower than the first calcining temperature. The inventive olefin deoxygenation agent has high room-temperature deoxygenation capacity up to 27.1 mL / g, deoxygenation depth lower than 0.01 ppm, low reduction temperature, and wide applicability in industrial production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same
ActiveCN102850164AExtended service lifePrevent sinteringChemical modification purification/separationMechanical crushingRoom temperature
The invention discloses an olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same. The preparation method includes (by weight parts) (1) mixing manganese source (as Mn3O4) 100, modified titania nanoparticle 58-100 and binder 1.5-25 to obtain a mixture; (2) calcining; (3) kneading the calcined mixture and a silver compound (as Ag2O) aqueous solution 8-35, and forming; (4) aging and drying; and (5) calcining. The inventive olefin deoxygenation agent has high room-temperature deoxygenation capacity, high mechanical crushing strength, low deoxygenation depth, low reduction temperature, and wide applicability in industrial production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Omnidirectional polarization independent all-dielectric light trapping scheme
PendingUS20200144526A1Improve efficiencyExtend the lifespanSilicaSolid-state devicesNano structuringGain
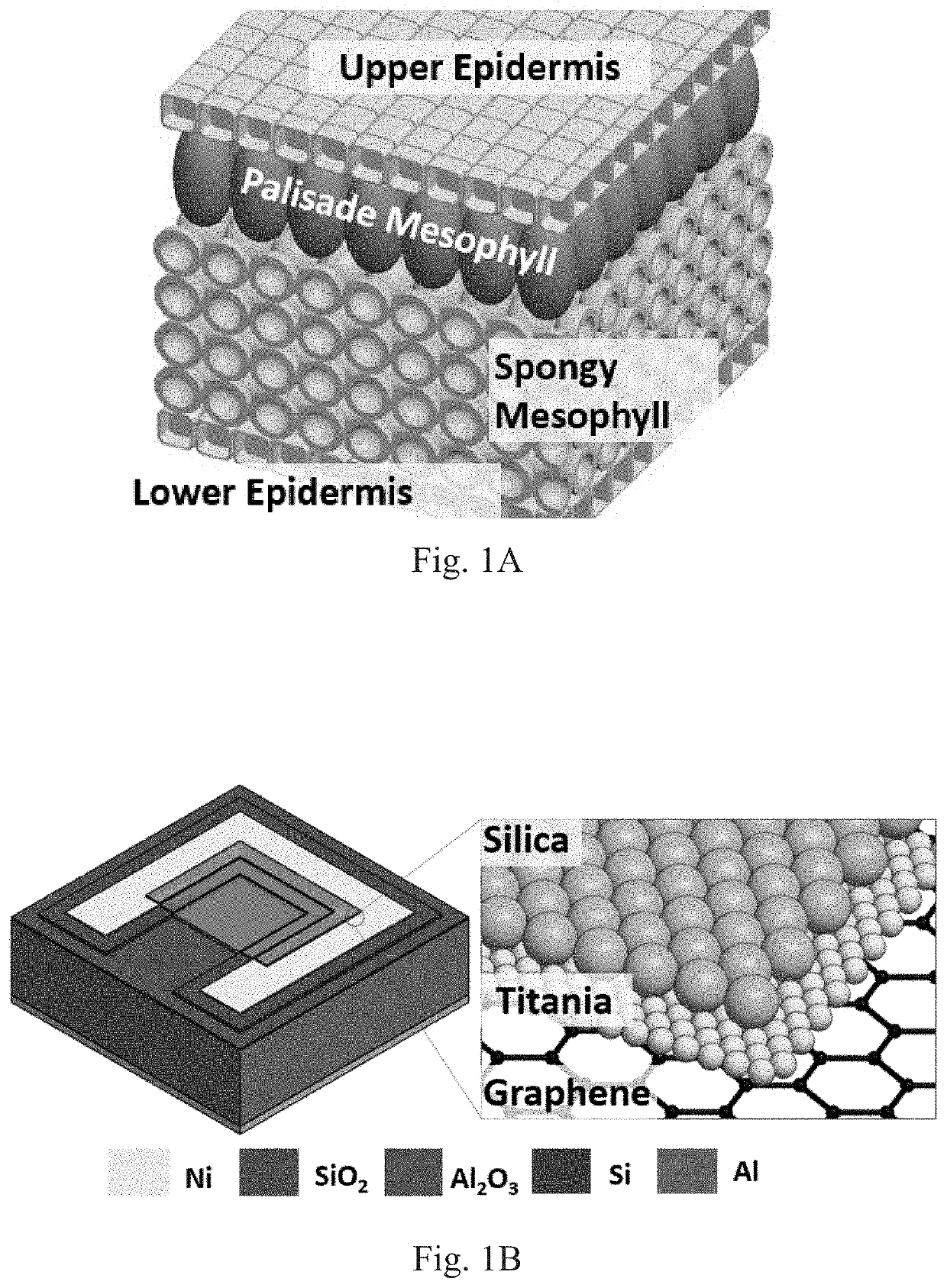
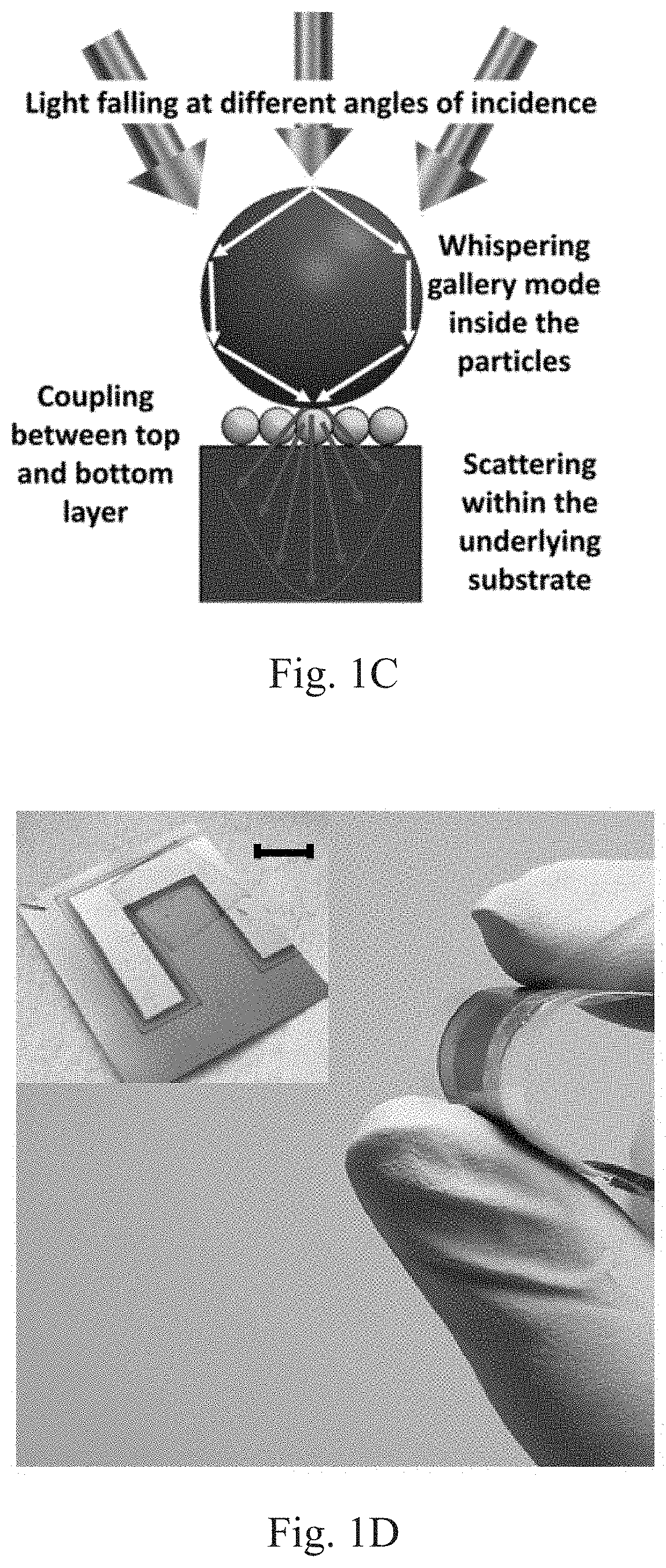
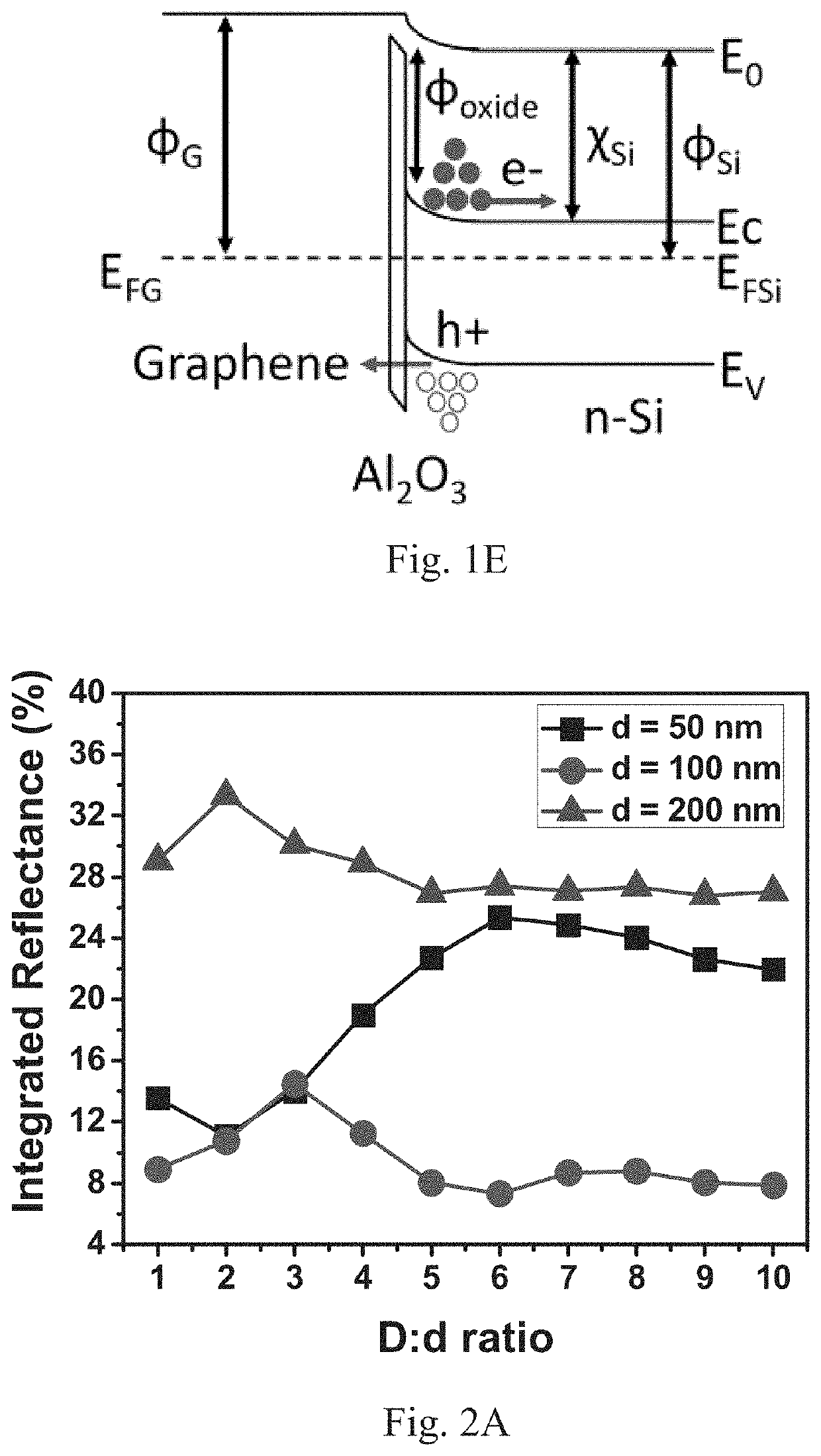
A leaf inspired biomimetic light trapping scheme for ultrathin flexible graphene silicon Schottky junction solar cell. An all-dielectric approach comprising of lossless silica and titania nanoparticles is used for mimicking the two essential light trapping mechanisms of a leaf: (1) focusing and waveguiding and (2) scattering. The light trapping scheme uses two optically tuned layers and does not require any nano-structuring of the active silicon substrate, thereby ensuring that the optical gain is not offset due to recombination losses.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same
ActiveCN102850161AEfficient deoxidationImprove deoxygenation capacityChemical modification purification/separationRoom temperatureAqueous solution
The invention discloses an olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same. The preparation method includes (by weight parts) (1) mixing manganese source (as Mn3O4) 100 and titania nanoparticle 58-100 to obtain a mixture; (2) kneading the mixture and a silver compound (as Ag2O) aqueous solution 8-35, and forming; (3) aging and drying; and (4) calcining. The inventive olefin deoxygenation agent has high room-temperature deoxygenation capacity up to 25.5 mL / g, deoxygenation depth smaller than 0.01 ppm, low reduction temperature, and wide applicability in industrial production. The agent realizes high-efficiency deoxygenation at room temperature.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Making method for titania nanoparticle
Owner:SUKGYUNG AT
Olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same
ActiveCN102850165AExtended service lifeEmission reductionChemical modification purification/separationRoom temperatureAlkene
The invention discloses an olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same. The preparation method includes (by weight parts) (1) mixing manganese source (as Mn3O4) 100 and modified titania nanoparticle 58-100 to obtain a mixture; (2) calcining; (3) kneading the calcined mixture and a silver compound (as Ag2O) aqueous solution 8-35, and forming; (4) aging and drying; and (5) calcining. The second calcining temperature is lower than the first calcining temperature. The inventive olefin deoxygenation agent has high room-temperature deoxygenation capacity up to 31 mL / g, deoxygenation depth lower than 0.01 ppm, low reduction temperature, and wide applicability in industrial production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Production of titania nanoparticle colloidal suspensions with maintained crystallinity by using a bead mill with micrometer sized beads
ActiveUS9963609B2Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsMaterial nanotechnologyPrillMicrometer
A method is disclosed of producing stable nanosized colloidal suspensions of particles with limited crystallinity loss, products thereof, use of the products and an apparatus for the method. In particular the present invention relates to a wet milling method with small beads wherein the size of the final particles in suspension are stabilized in the nanorange (D50<75 nm) and at the same time the particles substantially maintain the crystallinity.
Owner:VAELINGE PHOTOCATALYTIC AB
Olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same
ActiveCN102850160BEfficient deoxidationImprove deoxygenation capacityChemical modification purification/separationPolymer scienceDeoxygenation
The invention discloses an olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same. The preparation method includes (by weight parts) (1) mixing manganese source (as Mn3O4) 100, titania nanoparticle 58-100 and binder 1.5-25 to obtain a mixture; (2) kneading the mixture and a silver compound (as Ag2O) aqueous solution 8-35, and forming; (3) aging and drying; and (4) calcining. The inventive olefin deoxygenation agent has high room-temperature deoxygenation capacity up to 24.8 mL / g, high mechanical crushing strength up to 89 N / cm, deoxygenation depth smaller than 0.01 ppm, low reduction temperature, and wide applicability in industrial production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same
ActiveCN102850163BExtended service lifePrevent sinteringChemical modification purification/separationMechanical crushingRoom temperature
The invention discloses an olefin deoxygenation agent, its preparation method, and olefin deoxygenation method using the same. The preparation method includes (by weight parts) (1) mixing manganese source (as Mn3O4) 100, titania nanoparticle 58-100 and binder 1.5-25 to obtain a mixture; (2) calcining; (3) kneading the calcined mixture and a silver compound (as Ag2O) aqueous solution 8-35, and forming; (4) aging and drying; and (5) calcining. The second calcining temperature is lower than the first calcining temperature. The inventive olefin deoxygenation agent has high room-temperature deoxygenation capacity, high mechanical crushing strength, low deoxygenation depth, low reduction temperature, and wide applicability in industrial production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
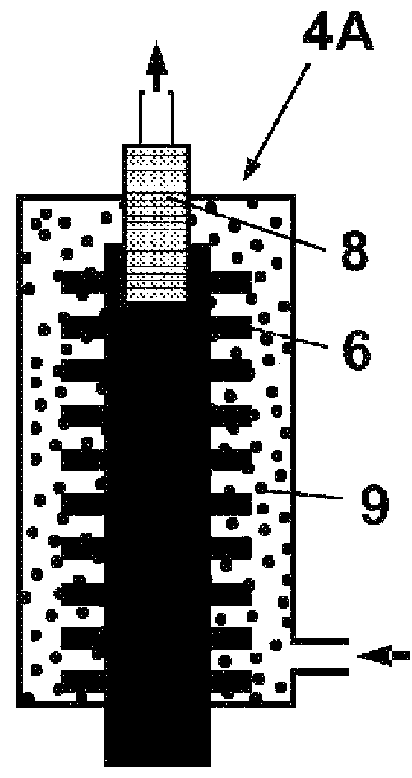
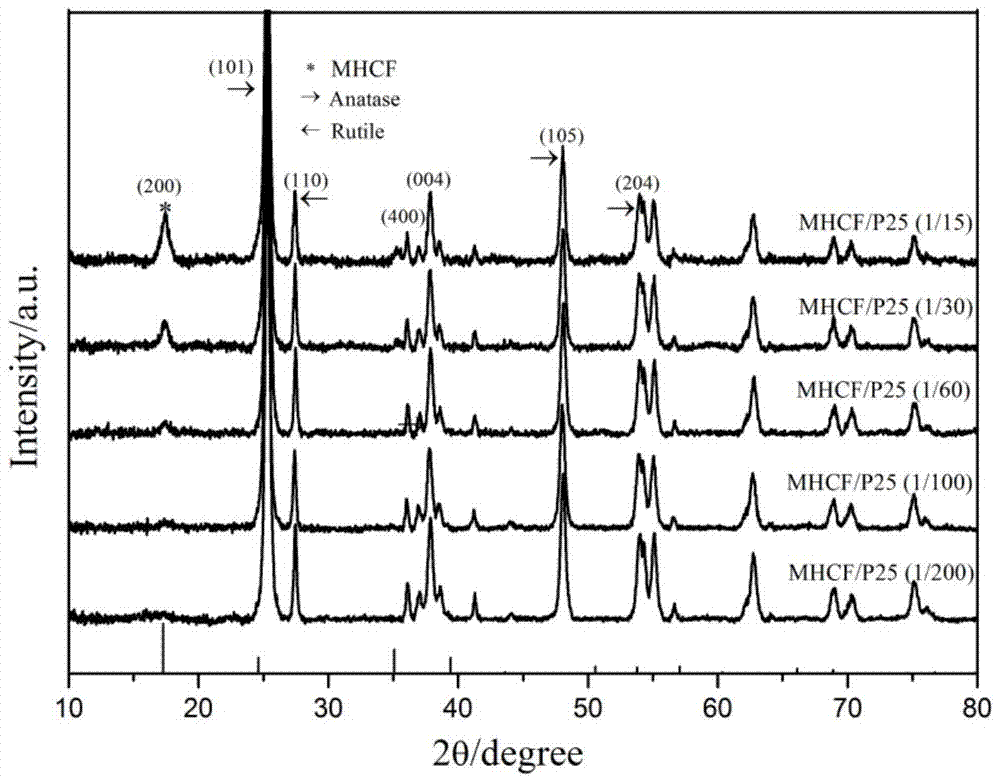
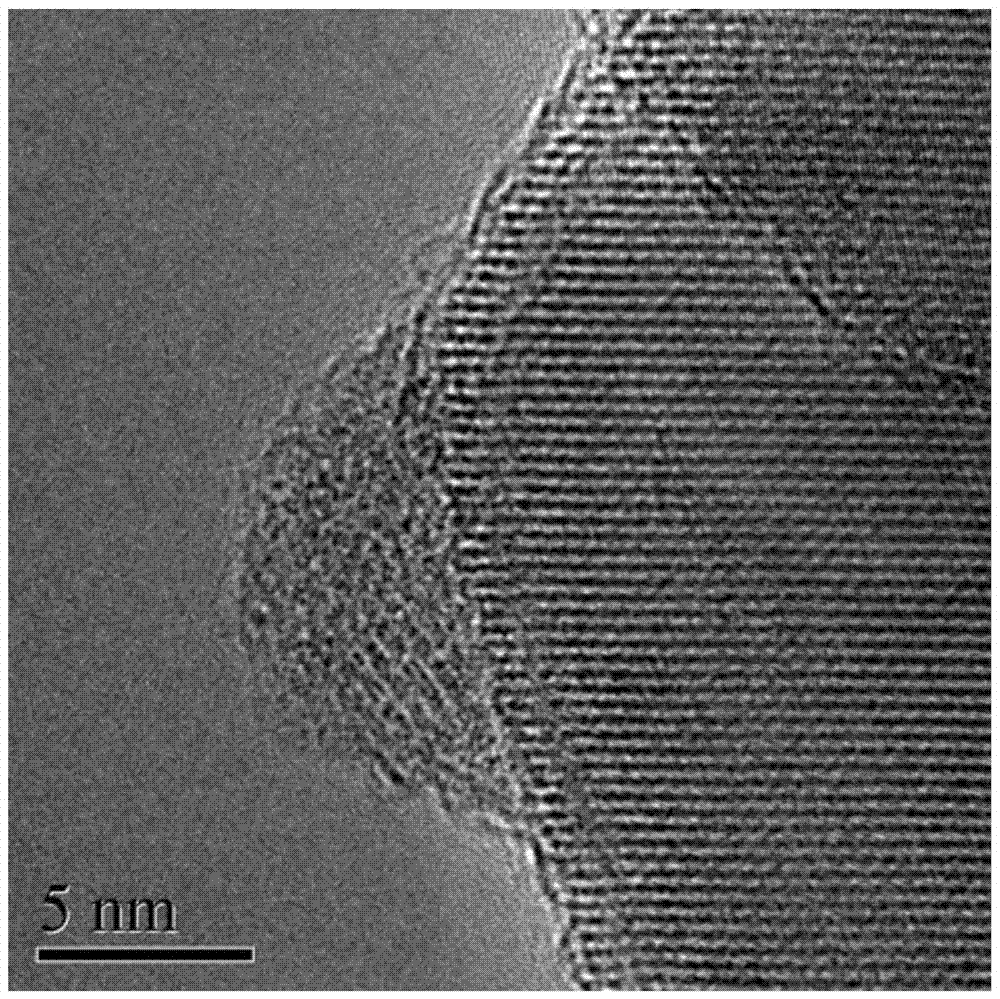
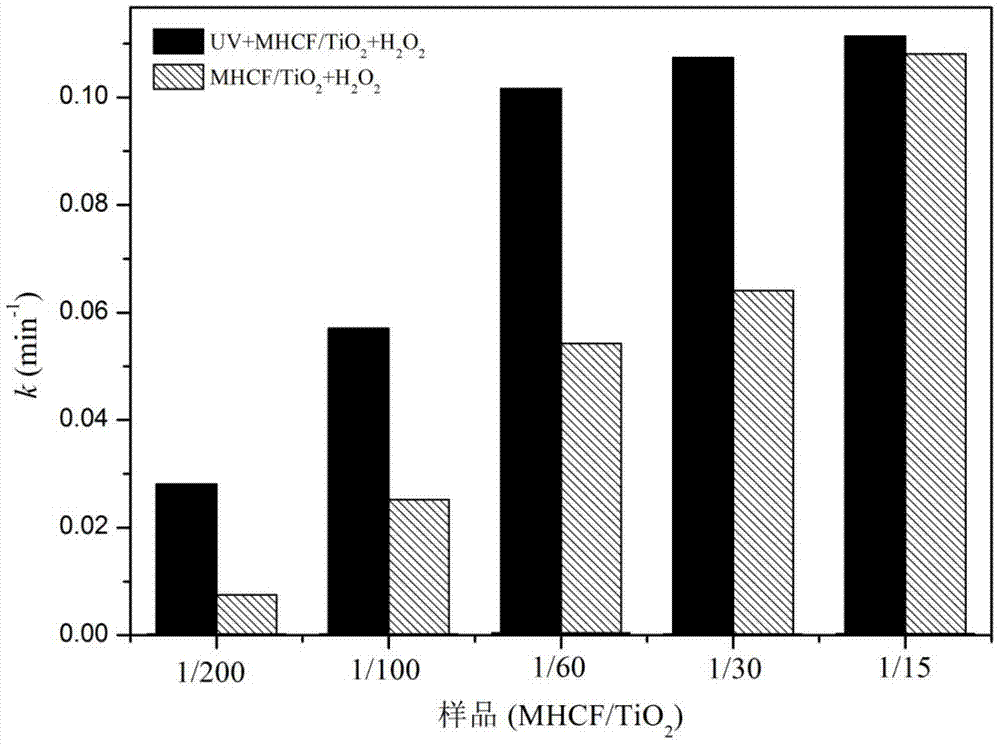
mhcf/tio 2 Nanocomposite Catalyst and Its Preparation and Application
InactiveCN105013520BImproved efficiency in degrading organic pollutantsImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsPtru catalystChemical solution
The invention provides a preparation of a transition metal hexacyanoferrate / titanium dioxide nanocomposite catalyst: using transition metal chloride or transition metal nitrate, potassium ferrocyanide, and titanium dioxide as raw materials, through an in-situ chemical solution method , in situ growth of transition metal hexacyanoferrate (MHCF) on the surface of titania nanoparticles yielded MHCF / TiO 2 nanocomposite catalysts. The present invention also provides a kind of MHCF / TiO 2 Nanocomposite catalyst light-Fenton synergistic reaction method for degrading organic pollutants: in the dark reaction without light, MHCF can degrade organic pollutants in the form of Fenton reaction, and under ultraviolet light irradiation, titanium dioxide (photocatalyst) can Electron-hole pairs are generated, and electrons can be accelerated by H in MHCF 2 o 2 The reduction of oxidized ferric iron, at the same time, MHCF can also inhibit the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes by accepting the electrons of titanium dioxide, thereby accelerating the Fenton reaction and the efficiency of hydroxyl radicals generated by the photocatalytic process. have very good degradation efficiencies.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com