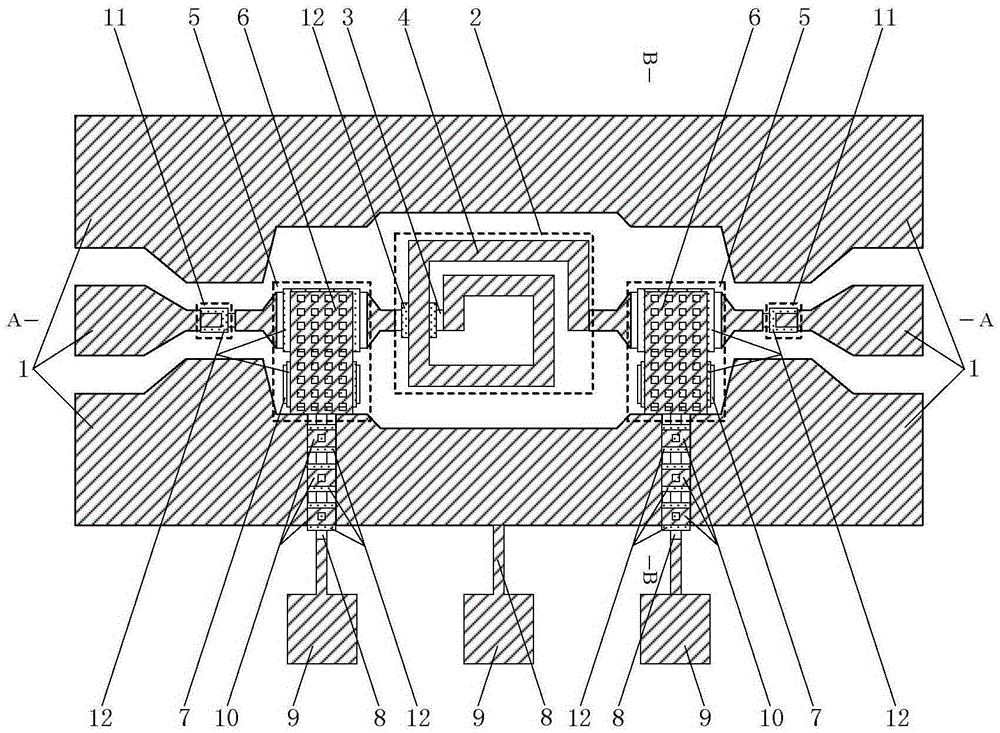
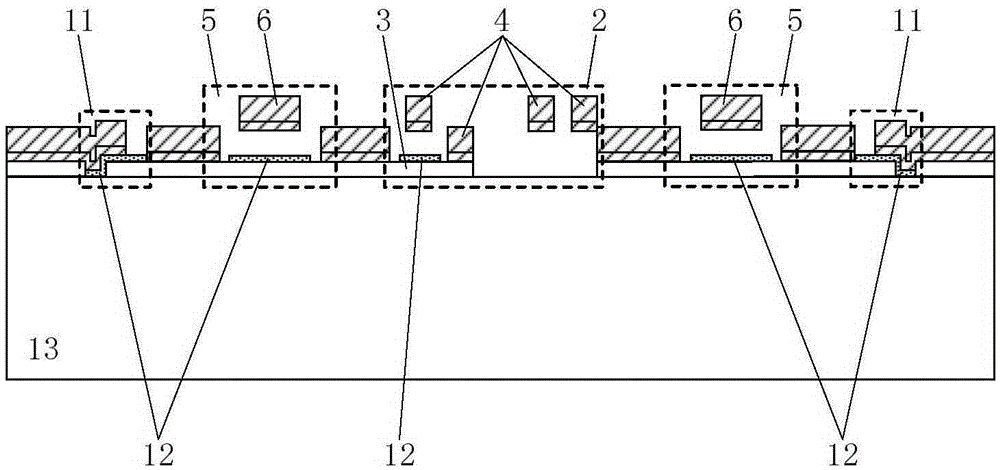
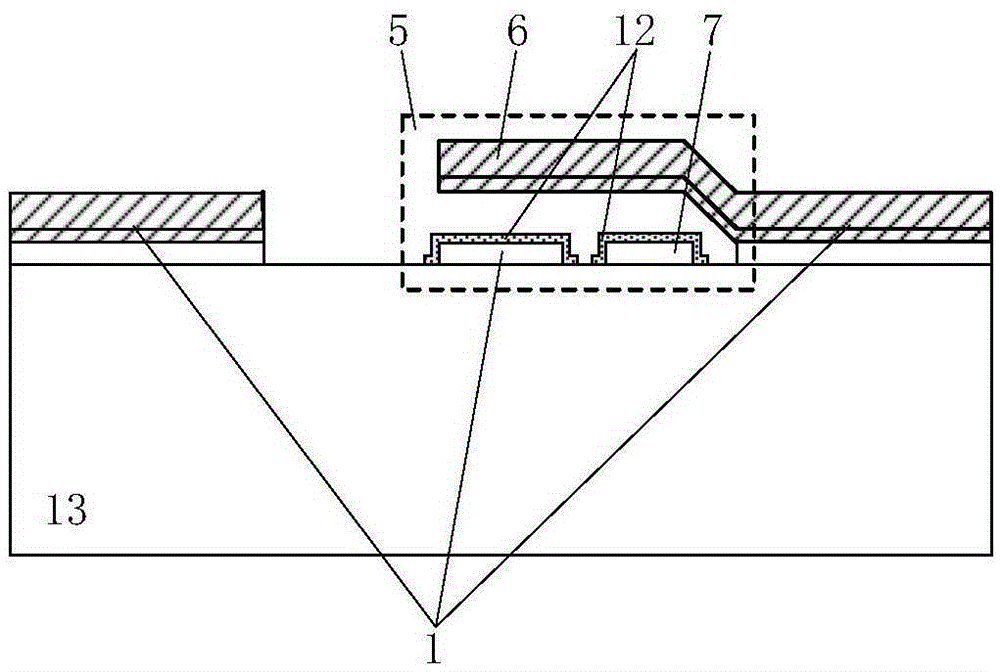
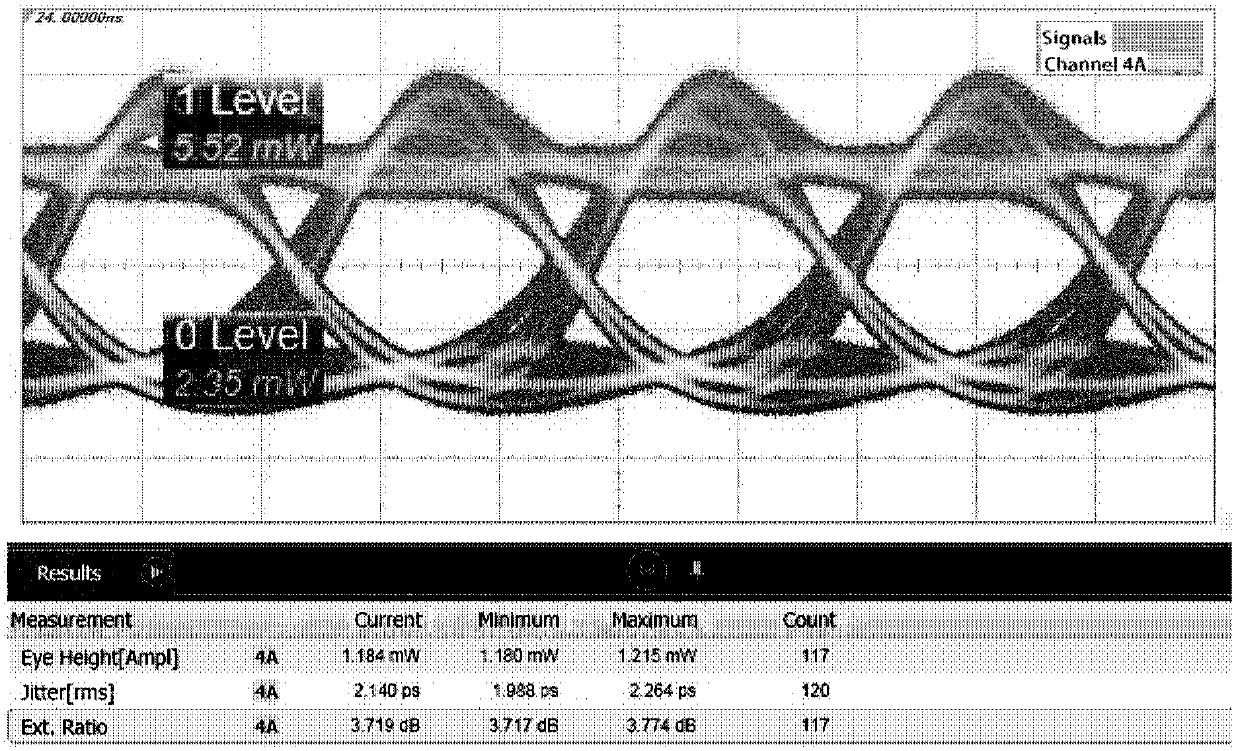
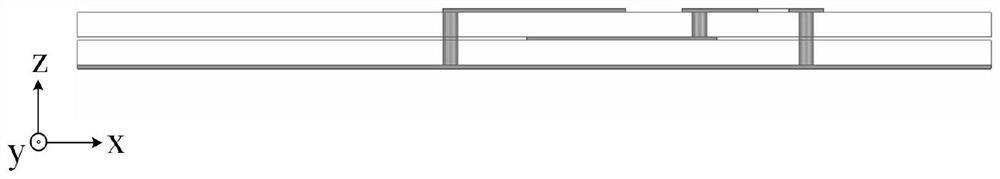
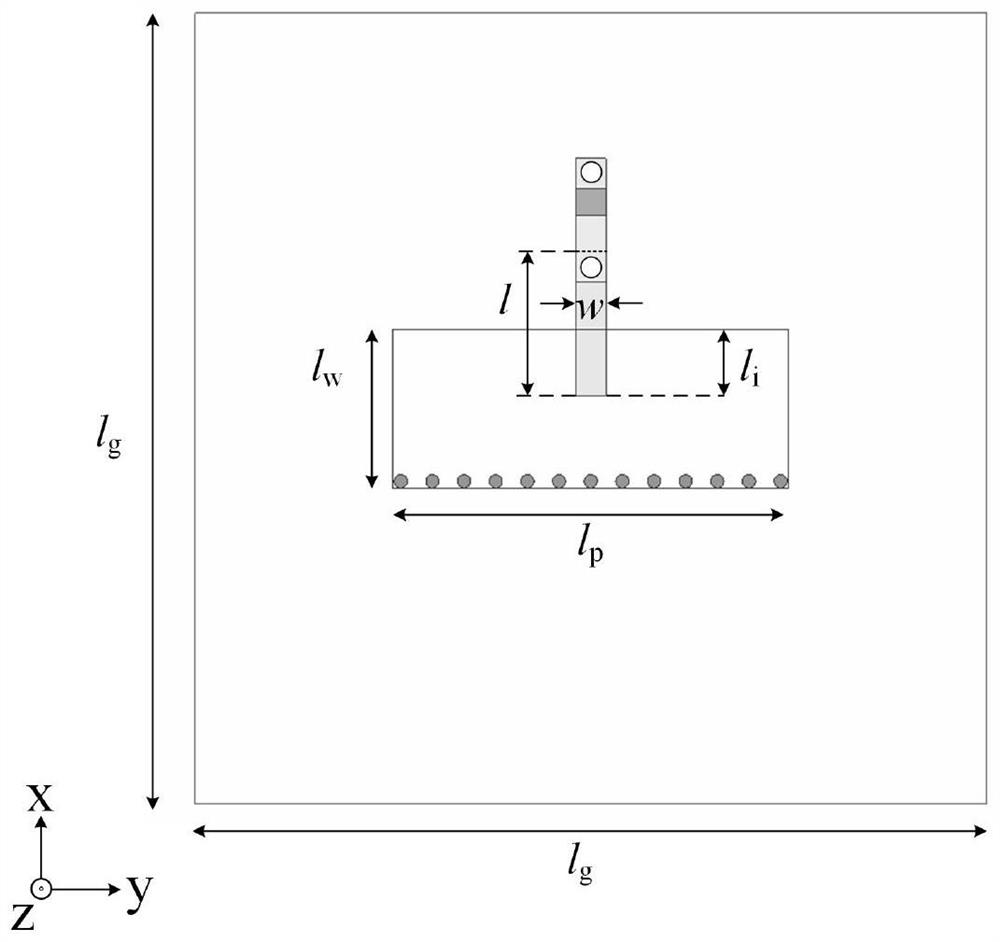
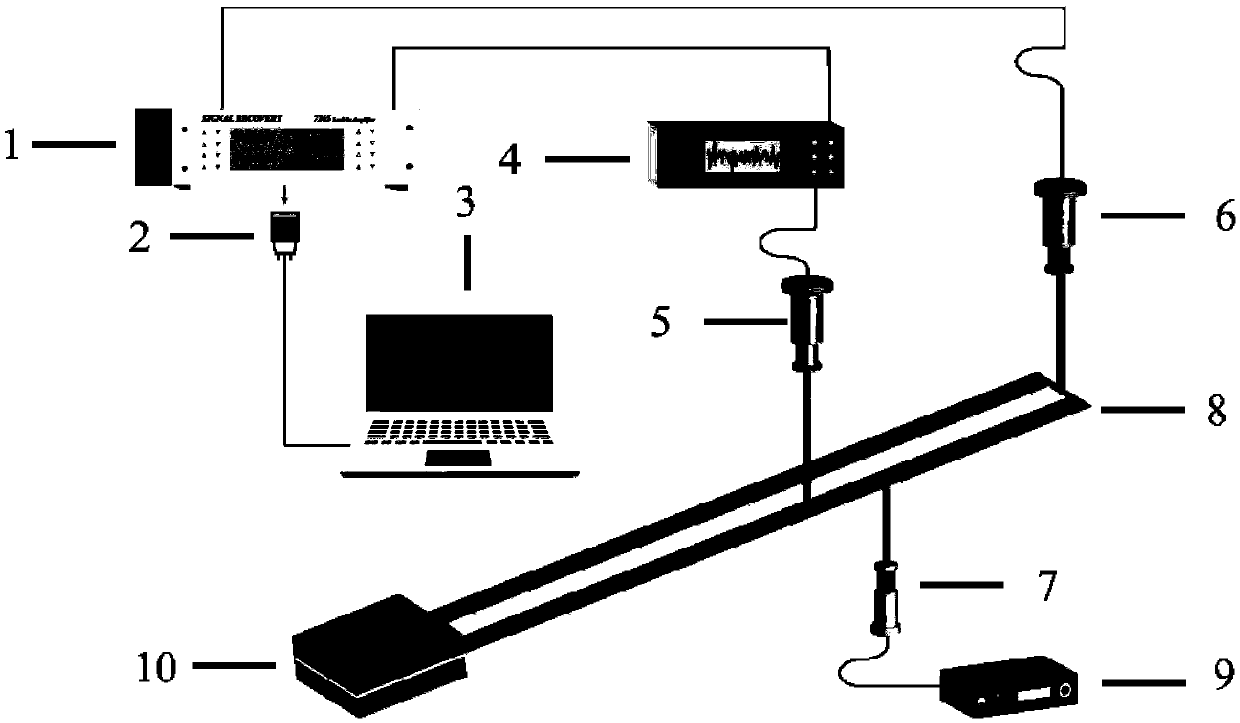
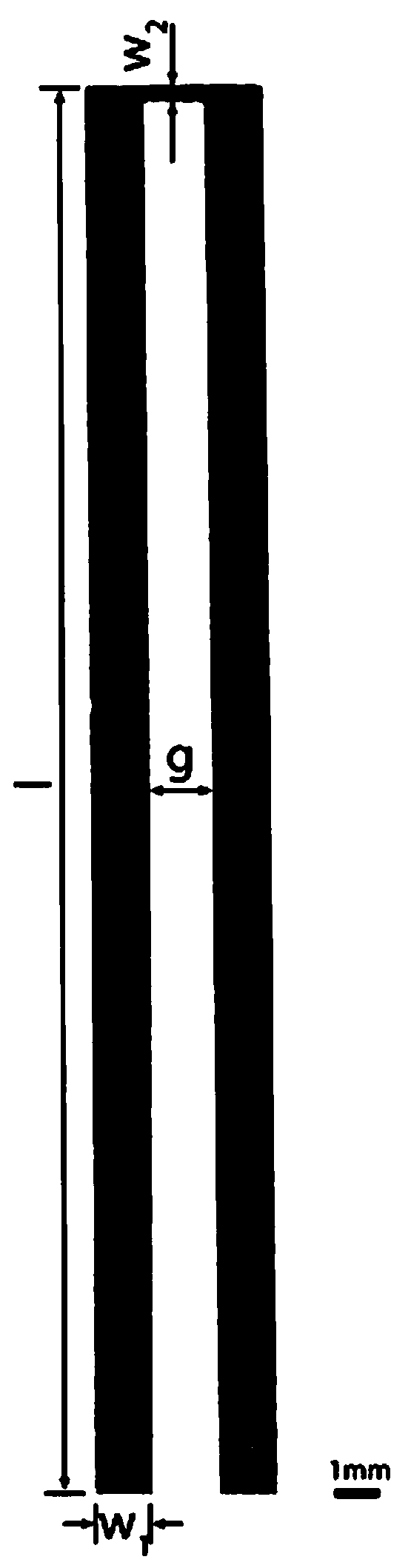
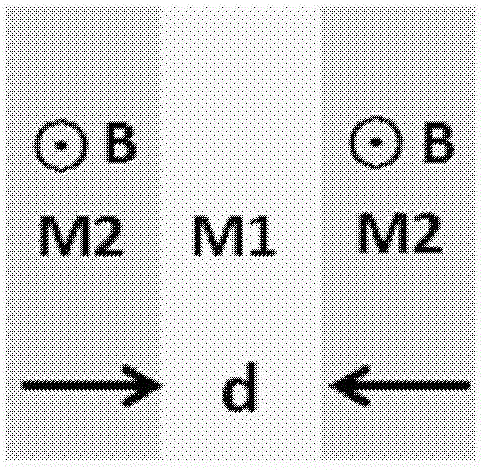Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Enables continuous tuning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
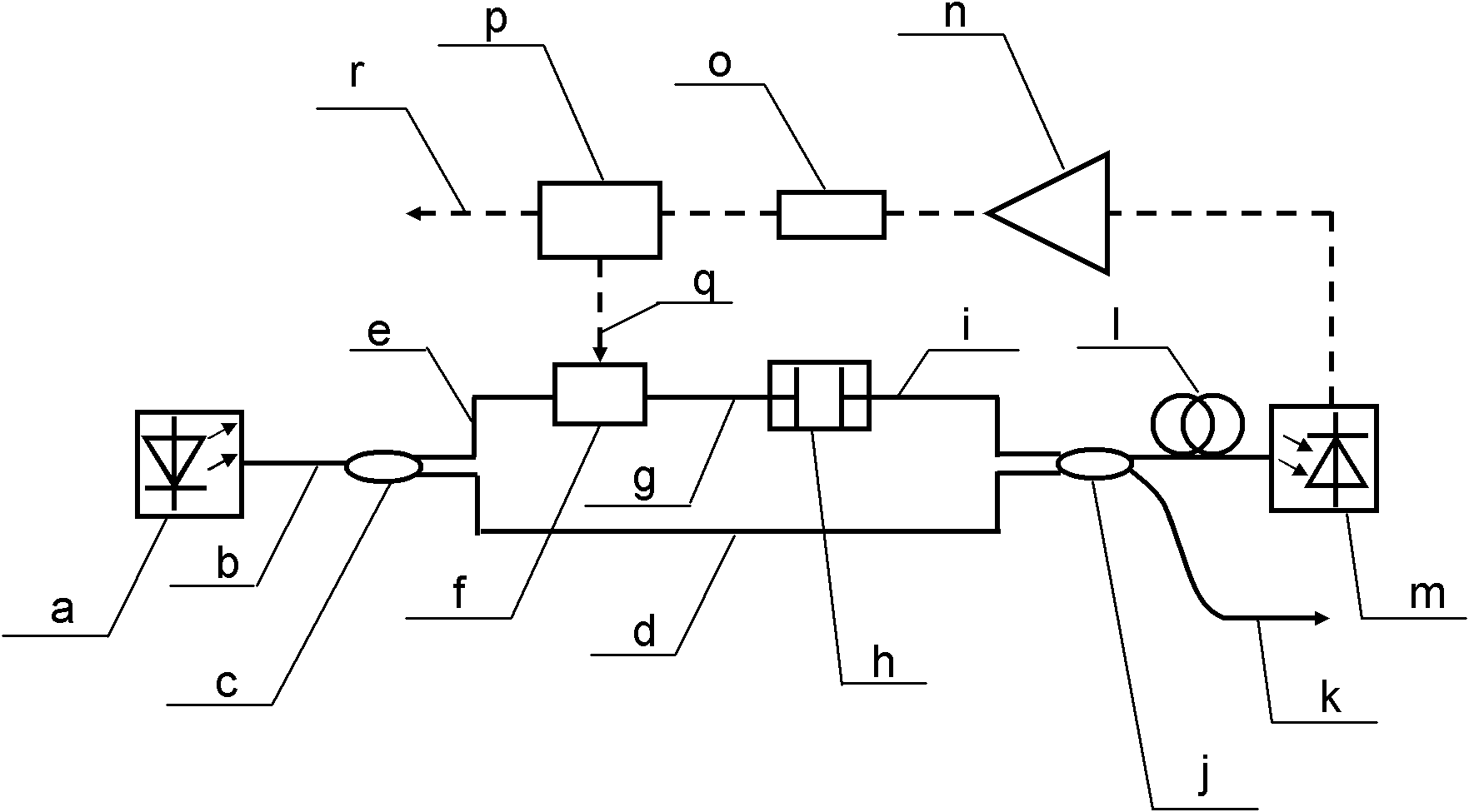
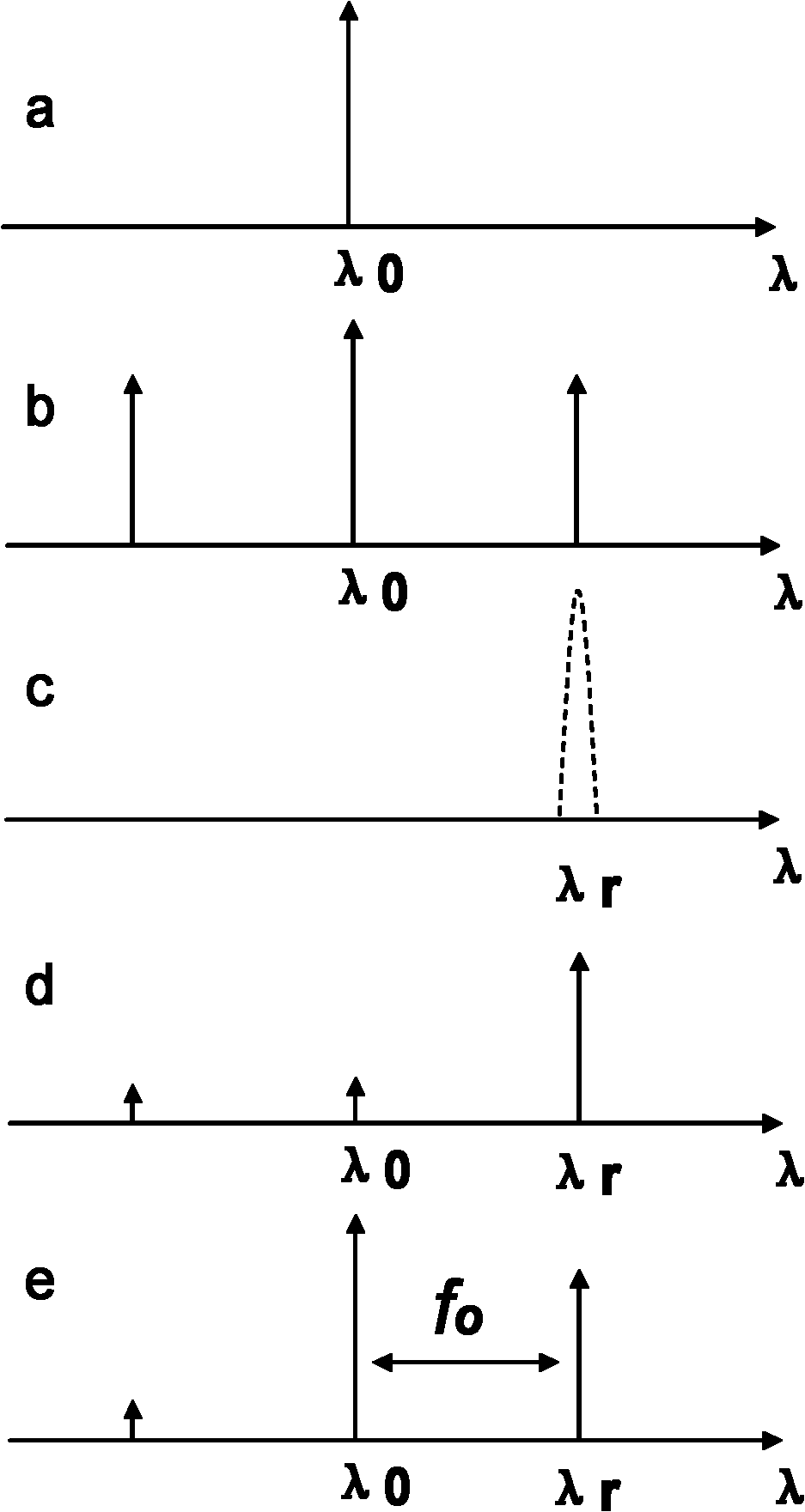
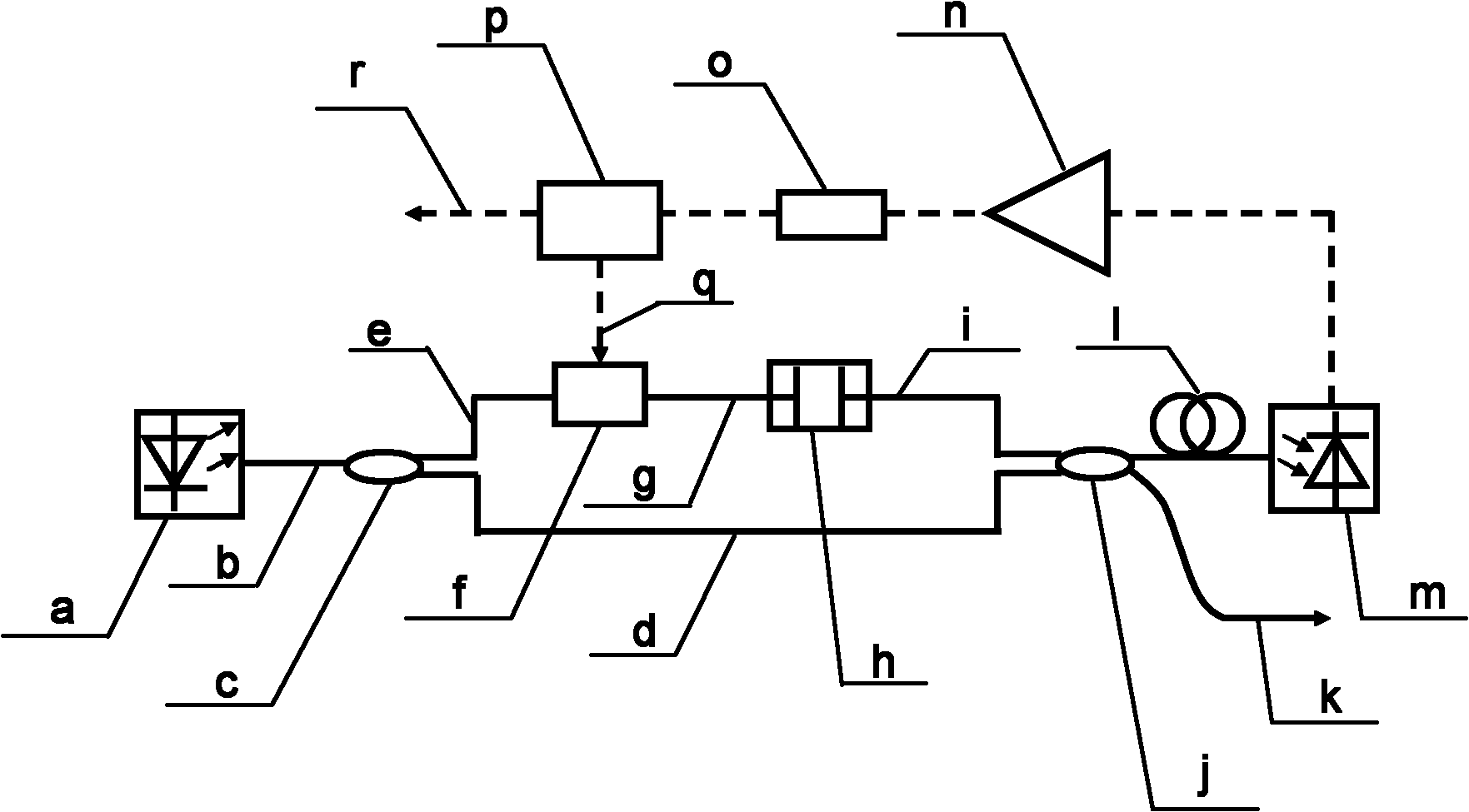
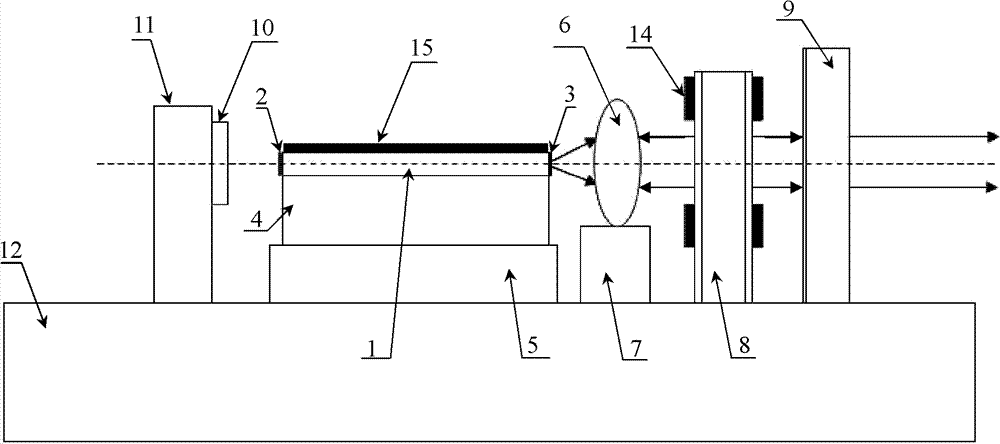
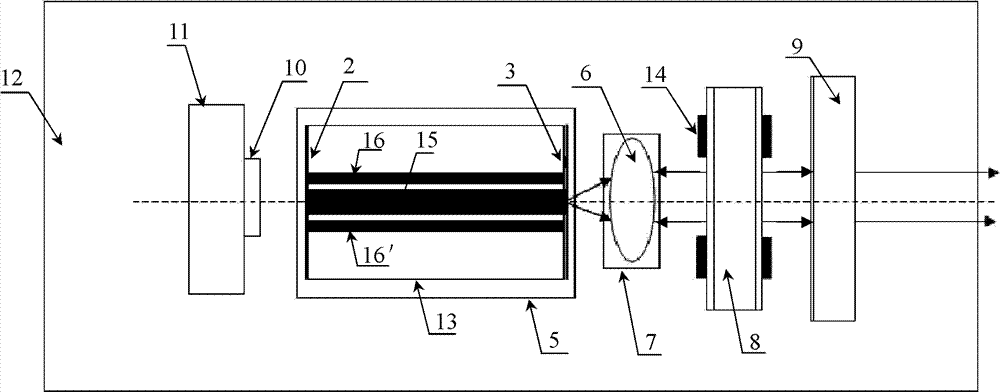
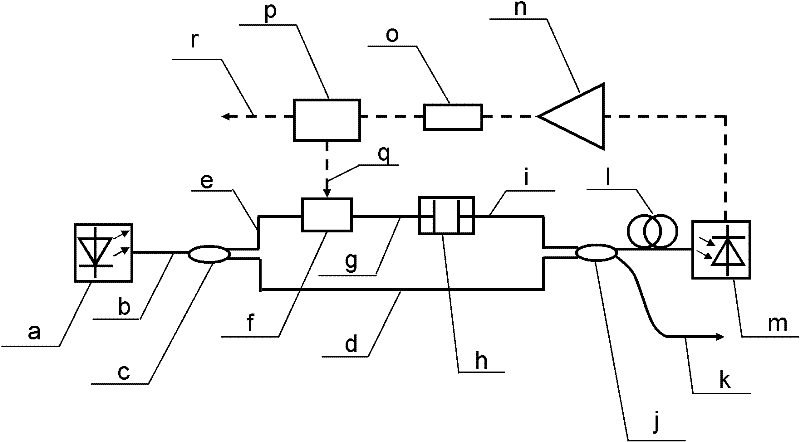
Optoelectronic oscillator with tunable broadband frequency
ActiveCN102163795AEnables continuous tuningGood phase noise characteristicsLaser detailsLaser lightMicrowave filter
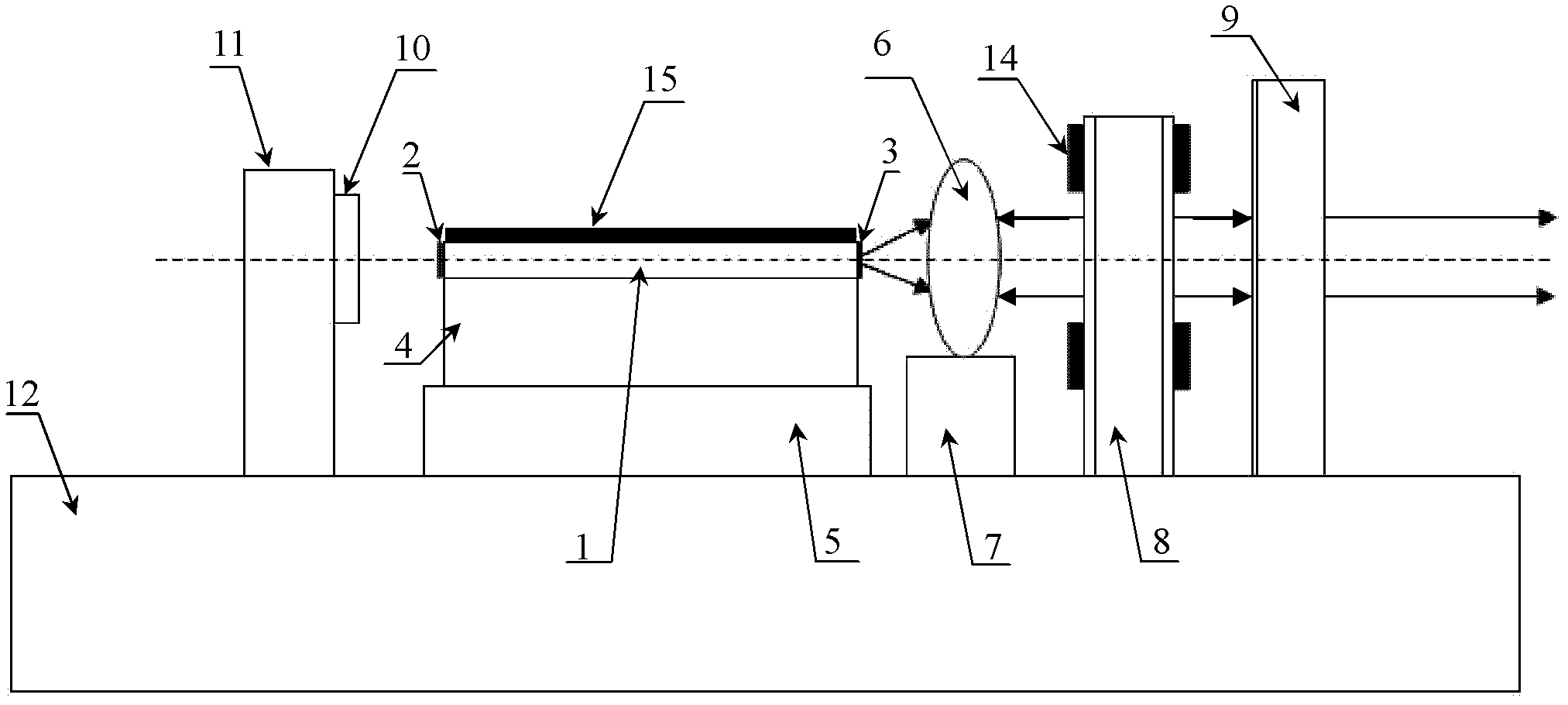
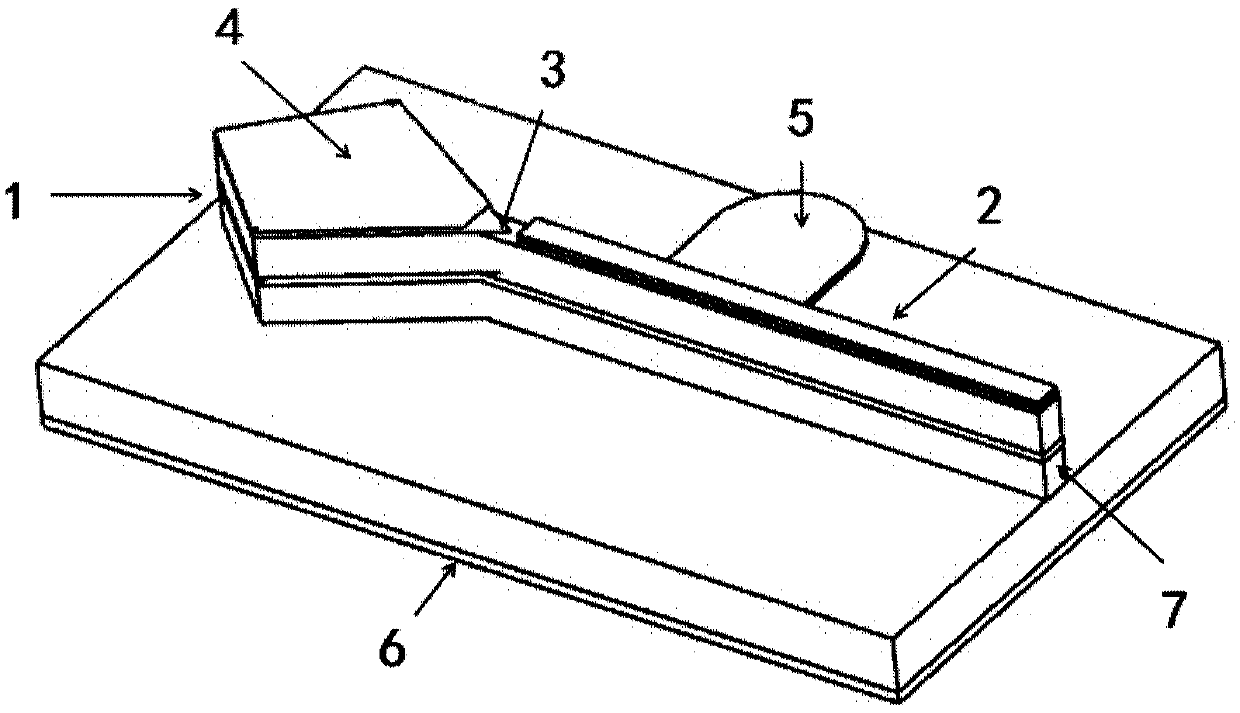
The invention discloses an optoelectronic oscillator with tunable broadband frequency, which is characterized in that a photon microwave filter is composed of an optical modulator, a high-fineness Fabry-Perot etalon and two fiber couplers and is applied to the optoelectronic oscillator. By tuning wavelength of laser light sources, the filtering peak of the photon microwave filter can be tuned; meanwhile, a microwave phase shifter is used cooperatively, thus continuous large-scale tuning of the optoelectronic oscillator can be realized finally.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
External cavity type single-wavelength tunable laser using FP (Fabry-Perot) laser as grain light source
InactiveCN102738702ASmall sizeRealize wavelength-tunable high-speed digital signal transmissionLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlTunable laserLight source
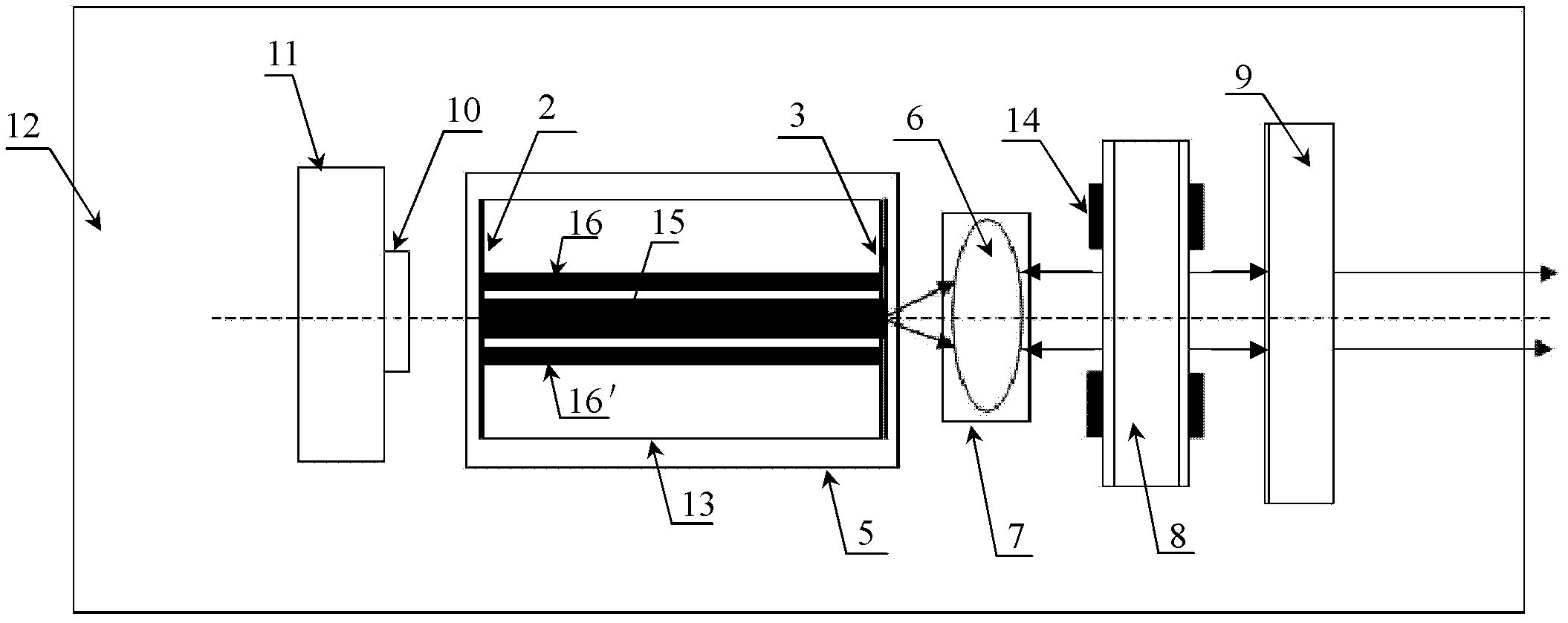
The invention discloses an external cavity type single-wavelength tunable laser using an FP (Fabry-Perot) laser as a grain light source. The external cavity type single-wavelength tunable laser comprises an FP laser chip; light waveguide is arranged in the FP laser chip; a partial transmission and reflection lens is arranged on the end face of a port for deriving an excitation light source in an optical waveguide port, and a high-reflection membrane is arranged on the end face of the other port; and an optical lens, an optical etalon for carrying out transmission filtering on a transmission light beam of the excitation light source, and a partial reflector for carrying out partial reflection and partial transmission on light beams transmitting the optical etalon are arranged at one side of the port for deriving the excitation light source in the optical waveguide port in sequence. One wavelength peak of the excitation light source is overlapped to one wavelength position of a transmission peak of the optical etalon by changing the distribution of a comb-shaped wavelength wave of the excitation light source, or changing the distribution of the comb-shaped wavelength peak of the excitation light source and the transmission peak of the optical etalon, so that maximum feedback is obtained by a wavelength of a photon at an overlapped position. With the adoption of the external cavity type single-wavelength tunable laser provided by the invention, single-wavelength laser can be output, and a wavelength of output laser can be continuously or selectively changed.
Owner:SICHUAN MARS TECH
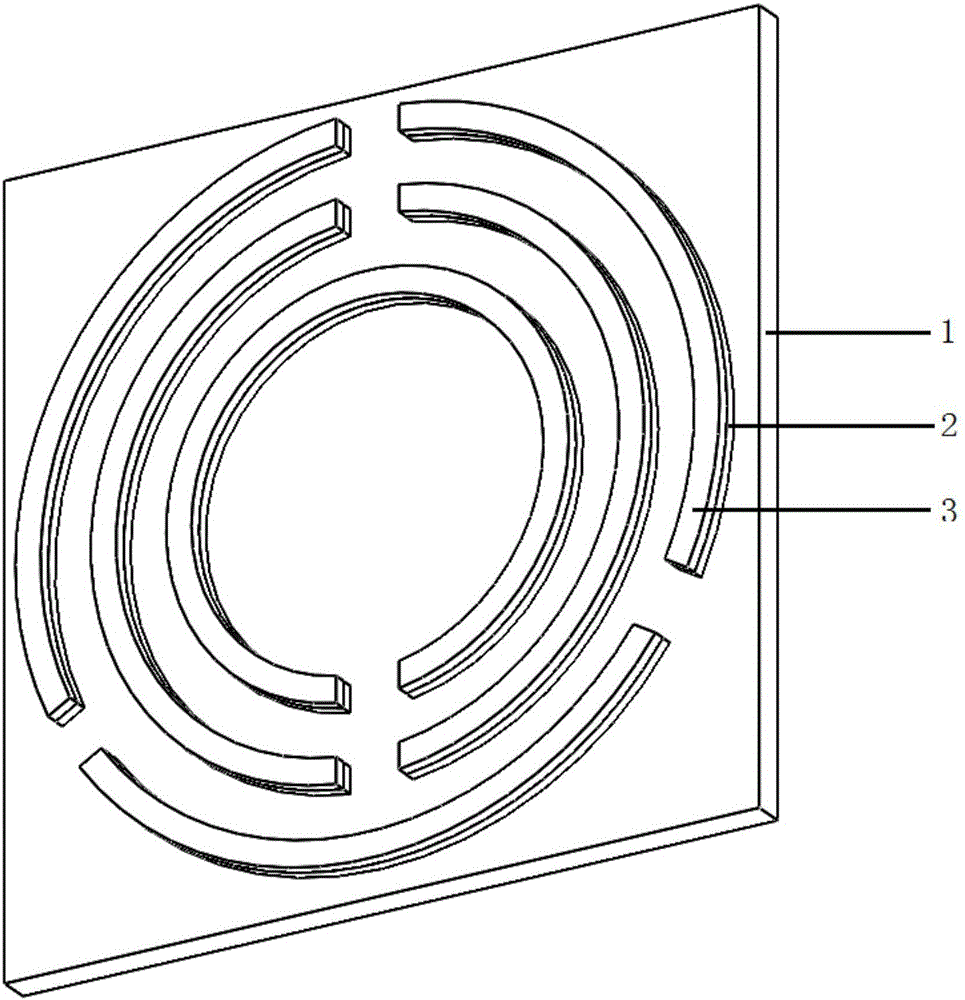
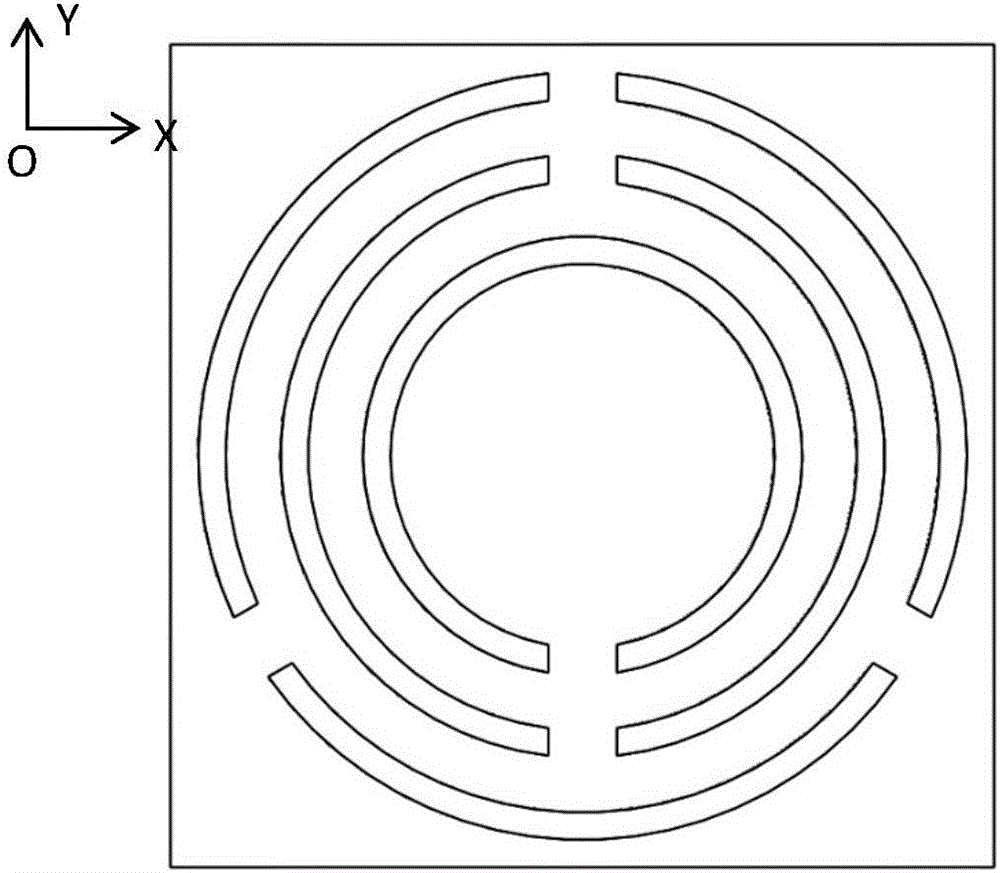
Continuously adjustable degradable terahertz meta-material based on optical driving and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105811120AGood biocompatibilityChange frequencyNon-linear opticsAntennasTerahertz metamaterialsCharge carrier
The invention provides a continuously adjustable degradable terahertz meta-material based on optical driving and preparation method thereof. The degradable terahertz meta-material comprises a sodium alginate substrate, a metal layer and a semiconductor film which are arranged on the sodium alginate substrate; the patterns of the metal layer and the semiconductor film are completely same: three equally spaced openings are formed on the outer ring, two equally spaced openings are formed on the middle ring, and one opening is formed on the inner ring; one of the three openings on the outer ring is aligned with one opening on the middle ring, and the other opening on the middle ring is aligned with the opening on the inner ring. Since the concentrations of carriers produced by the semiconductor film under different optical power excitations are different, the continuous tuning on the electromagnetically responded resonance strength from different conductivities is realized. The meta-material provided by the invention is simple in structure and processing technique, has degradable property and can be used for biomolecule detection, so that the incident electromagnetic wave of the terahertz meta-material has a plurality of frequency bands with continuously tuned strength in the terahertz waveband transmission.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Micro-mechanical cantilever beam type pi type continuous reconfigurable microwave band-pass filter
ActiveCN103811834AReduce the modulus of elasticityReduce the driving voltageWaveguide type devicesCapacitanceOut of band rejection
The invention discloses a micro-mechanical cantilever beam type pi type continuous reconfigurable microwave band-pass filter. The micro-mechanical cantilever beam type pi type continuous reconfigurable microwave band-pass filter comprises a planar spiral inductor, two identical MEMS variable planar plate capacitors and two identical MIM capacitors are symmetrically arranged at the left and right sides of the planar spiral inductor in sequence, wherein each MEMS variable planar plate capacitor is connected between a CPW signal wire and a ground wire in parallel while each MIM capacitor is connected with the CPW signal wire in series so as to make up a pi type topological structure with band-pass characteristics. The MEMS variable planar plate capacitors achieve different capacitances based on an electrostatic principle; the upper pole plate of each MEMS variable planar plate capacitor is an MEMS cantilever beam while the lower pole plate thereof is the CPW signal wire, wherein the MEMS cantilever beam stretches across the CPW signal wire, and a drive electrode is arranged near the CPW signal wire; an Si3N4 insulating medium layer covers each of the CPW signal wire under the MEMS cantilever beam and the drive electrode. The filter realizes the continuous tuning for the center frequency and the band width and has advantages of low loss, good out-of-band rejection, wide frequency band tuning and small chip area.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Ultrathin flexible electric-heating tunable meta-material based on three-dimensional Ohm structure and preparation of same
InactiveCN105896096AEnables continuous tuningImplementing non-planar applicationsAntennasElectromagnetic responseThermal expansion
The invention provides an ultrathin flexible electric-heating tunable meta-material based on a three-dimensional Ohm structure and preparation of the same. The meta-material comprises a flexible parylene-C substrate and the three-dimensional Ohm structure, wherein the three-dimensional Ohm structure is composed of a lower parylene-C dielectric layer and an upper metal layer; and the three-dimensional Ohm structure is an Ohm ring or an Ohm circle. According to the invention, a dielectric medium and metal with different residual stresses and thermal expansion coefficients constitute the three-dimensional Ohm structure; and current or temperature control is used to control a relative rotation angle between the three-dimensional Ohm structure and the parylene-C substrate, so that continuous tuning is implemented to resonant frequency of electromagnetic responses. The meta-material provided by the invention has the advantages that structural design is novel; processing technologies are simple; a sacrificial layer is not needed; non-planar applications of the meta-material can be realized; and the continuous tuning can be implemented to the resonant frequency of the electromagnetic responses of the meta-material and incident electromagnetic waves.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and system for achieving resonant frequency tuning of miniature cantilever beam through photothermal effect, and application
The invention relates to a method and system for achieving the resonant frequency tuning of a miniature cantilever beam through a photothermal effect, and an application. The method comprises the following steps: (1), illuminating the surface of the miniature cantilever beam by modulating the laser to excite the vibration of the miniature cantilever beam; (2), illuminating the surface of the miniature cantilever beam by continuous laser irradiation, generating a thermal effect on the surface of the miniature cantilever beam, and tuning the resonant frequency by controlling the power of the continuous laser; (3), collecting and processing a vibration signal of the miniature cantilever beam. The method can realize the continuous tuning of the resonant frequency of the miniature cantilever beam. Compared with a mode of increasing the frequency bandwidth, the method expands the application bandwidth of the miniature cantilever beam, and the higher the resonance order of the miniature cantilever beam is, the larger the frequency tuning range thereof is. The system can be used as a detector for detecting vibration frequencies. Since the miniature cantilever beam can convert the energy ofa physical quantity into the kinetic energy of the beam by interacting with the external physical quantity with a certain frequency, the detection of the physical quantity frequency is realized according to the vibration frequency of the beam.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
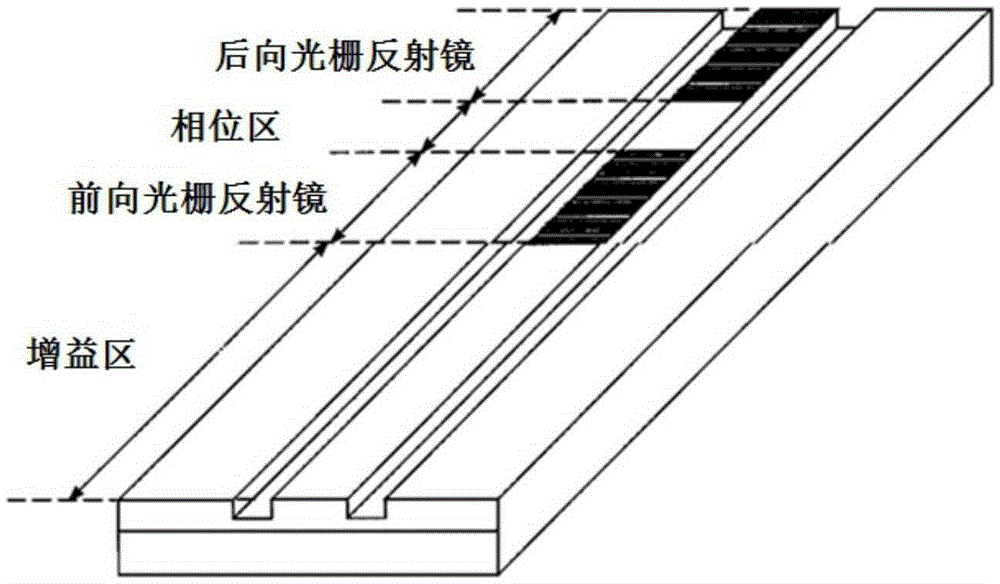
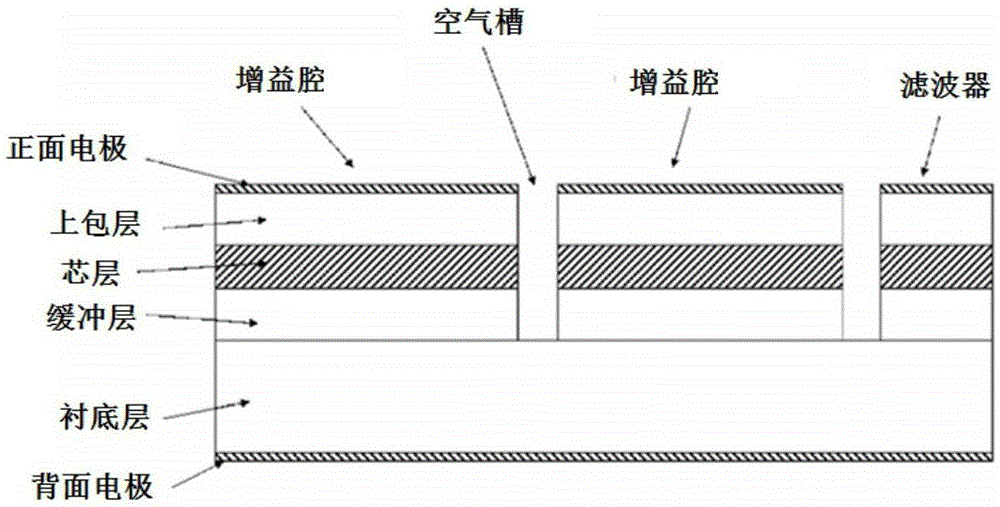
Continuously adjustable frequency interval V-shaped coupled cavity double-wavelength semiconductor laser
ActiveCN105281199AReduce manufacturing costShorten the lengthLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsEtchingExternal reference
The invention discloses a continuously adjustable frequency interval V-shaped coupled cavity double-wavelength semiconductor laser. One end of a first active resonator cavity and one end of a second active resonator cavity are coupled in the shape of V to form a multi-mode coupled region. A cavity surface reflecting surface is arranged on the end face of the multi-mode coupled region. The other end of the first active resonator cavity and a first passive filter are connected in series through a deep etching groove to form an arm of the laser. The other end of the second active resonator cavity and a second passive filter are connected in series through a deep etching groove to form the other arm of the laser. Shallow etching grooves are arranged on the first active resonator cavity and the second active resonator cavity. The laser provided by the invention has the advantages of compact structure, simple production process, low cost and the like, and does not need an external reference light source.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
U-waveband high-power picosecond pulse laser generating method
InactiveCN103928839AFlexible accessOvercoming the limitation of output power boostLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialWave bandOptical communication
The invention discloses a work U-waveband high-power picosecond pulse laser generating method. According to the method, a model locking picosecond pulse seed laser on the communication waveband is amplified through an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier (EDFA) to obtain a high-power picosecond pulse laser, the output picosecond pulse laser is coupled to a regular multimode fiber or a double-clad fiber, and then picosecond pulse laser output is obtained through intra-resonant cavity feedback; the U-waveband Raman laser with a picosecond-magnitude pulse width is obtained by means of stimulated Raman frequency shift. There is no report currently about high-power picosecond or even shorter ultrafast pulses for lasers working on the wavelength. The high-power picosecond pulse laser output with the method is needed greatly in the aspects such as high-speed optical communication, Doppler anemometry laser radar, differential absorption laser radar and intermediate infrared lasers.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
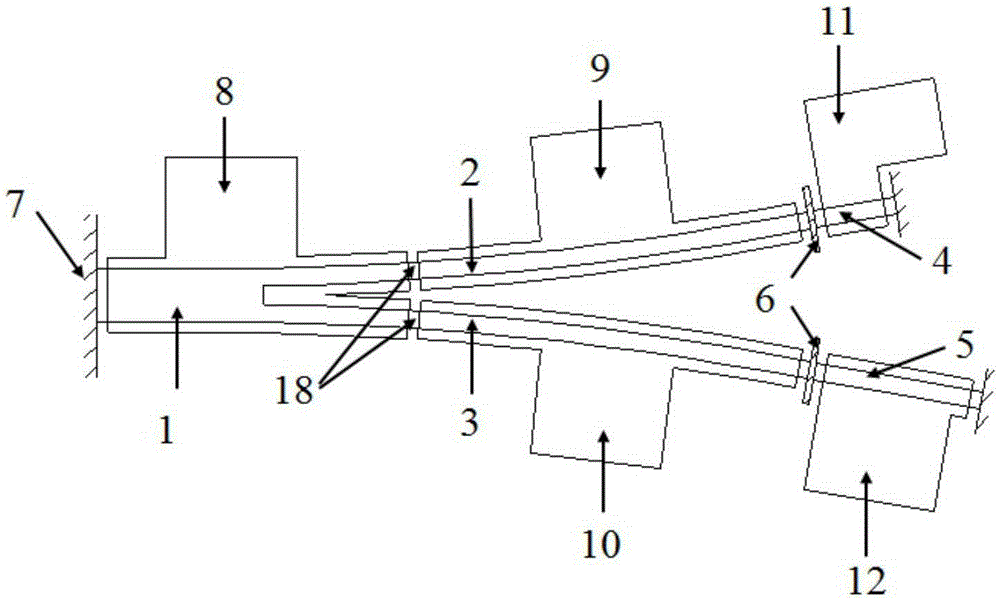
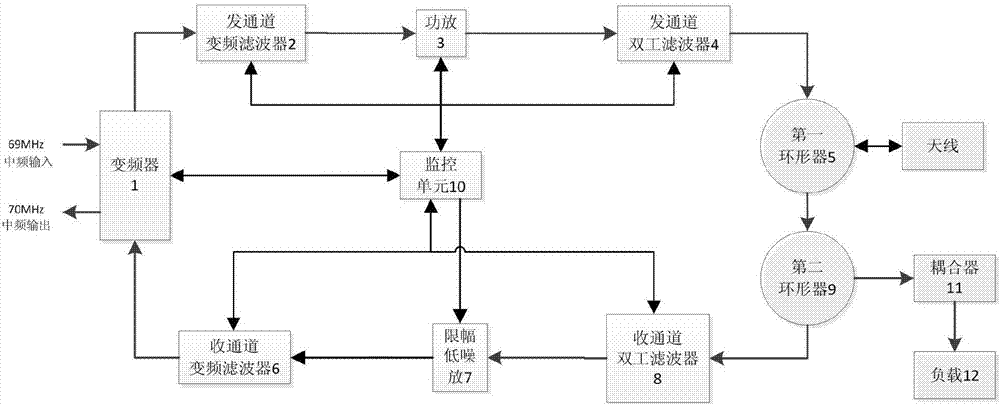
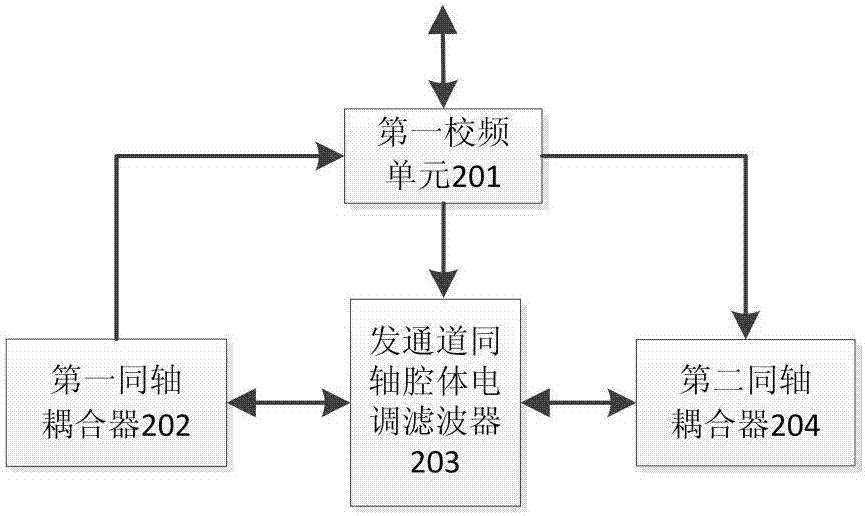
Scatter communication high frequency equipment for full-band operation
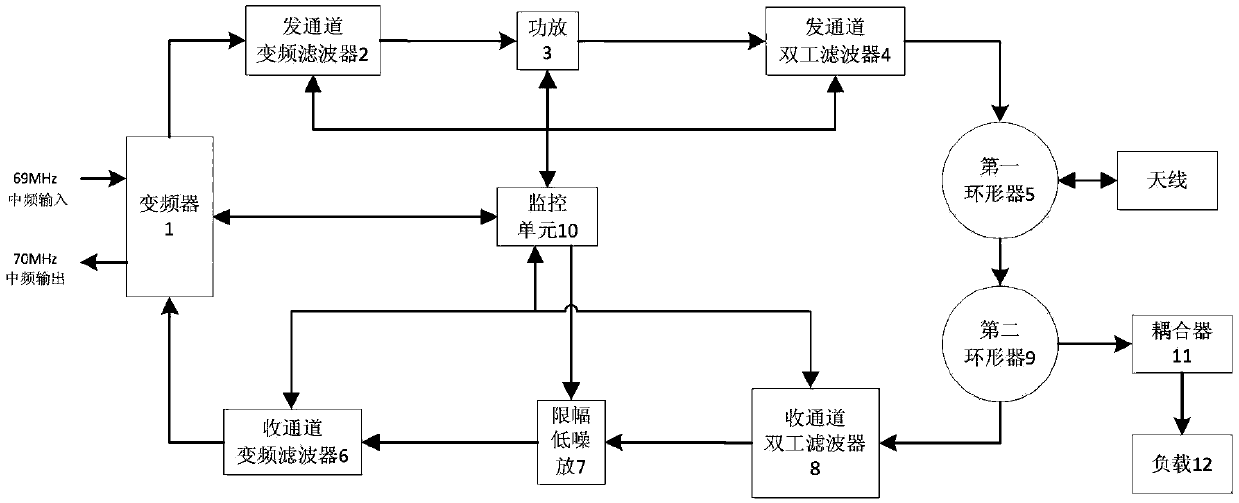
The invention discloses scatter communication high frequency equipment for full-band operations. The scatter communication high frequency equipment comprises a frequency converter, a power amplifier, a limiting low noise amplifier, a first circulator, a second circulator, a coupler and a loader, a transmitting channel frequency conversion filter, a receiving channel frequency conversion filter, a transmitting channel duplexing filter, a receiving channel duplexing filter and a monitoring unit. An intermediate frequency input signal is firstly up-converted to a radio frequency signal through the frequency converter, the radio frequency signal is subjected to frequency selection through the transmitting channel frequency conversion filter and then is sent to the power amplifier, the power amplifier carries out power amplification for the radio frequency signal that is subjected to frequency selection, and a high-power signal output by the power amplifier is fed to an antenna through the transmitting channel duplexing filter and then is emitted through the antenna; and a radio frequency small signal received from the antenna is firstly subjected to frequency selection through the receiving channel duplexing filter, then enters the limiting low noise amplifier to perform low-noise limiting amplification, is filtered by the receiving channel frequency conversion filter, then enters a down-conversion area of the frequency converter to be converted to an intermediate frequency signal, and then is transmitted to a low-frequency unit after being amplified to an appropriate level.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
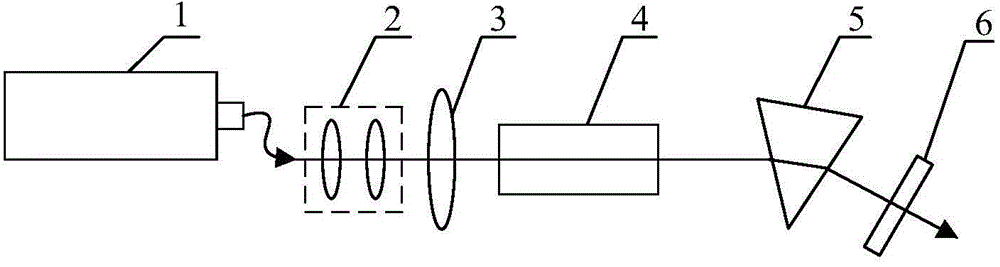
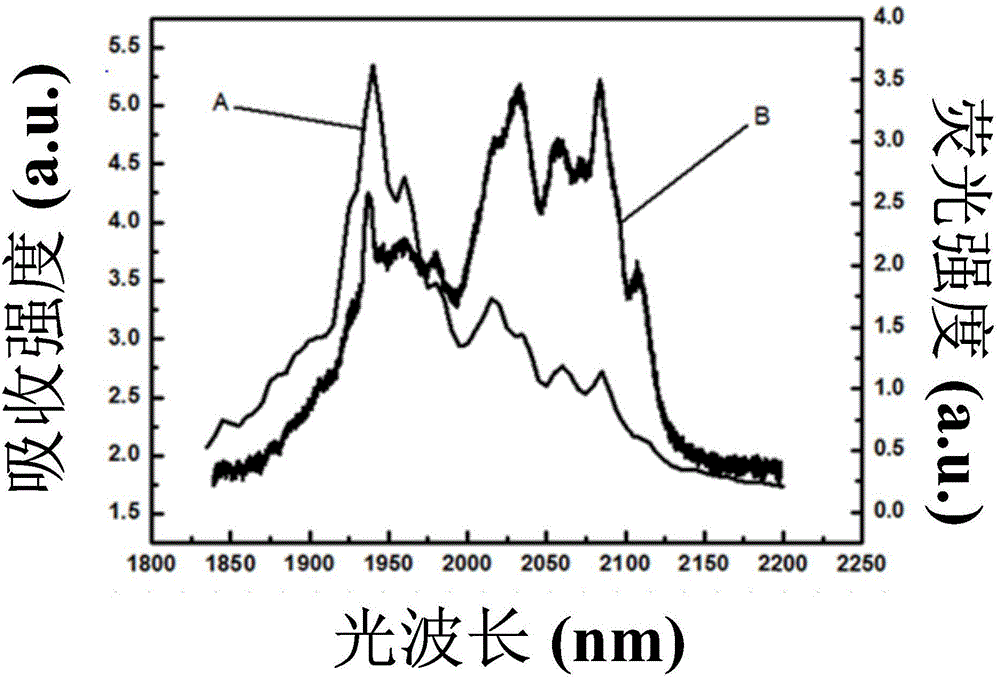
Laser for realizing 2-micron waveband tuning narrow linewidth laser output
InactiveCN104682186ALarge energy level splittingWidely tuned continuous laser outputActive medium materialWave bandWavelength modulation
The invention provides a laser for realizing 2-micron waveband tuning narrow linewidth laser output. The laser comprises a laser pumping source, a coupled focusing system, an input mirror, a laser crystal and an output mirror, wherein a wavelength modulation prism is arranged between the laser crystal and the output mirror; the laser crystal is an Ho: SSO crystal. According to the laser provided by the invention, the problem that the conventional 2-micron waveband lasers are narrow in tuning range is solved; Ho: SSO is adopted as the laser crystal; the wavelength modulation prism is adopted to realize the continuous tuning of laser wavelength; a volume grating is adopted as the output mirror; a Tm: YAP laser is adopted as the pumping source; a resonant cavity is an L-shaped plane concave cavity. The laser has the advantages of realizing high-power narrow-tuning continuous laser output of 2-micron waveband and satisfying the requirements for high-energy wide-spectrum laser light sources in spectral measurement.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
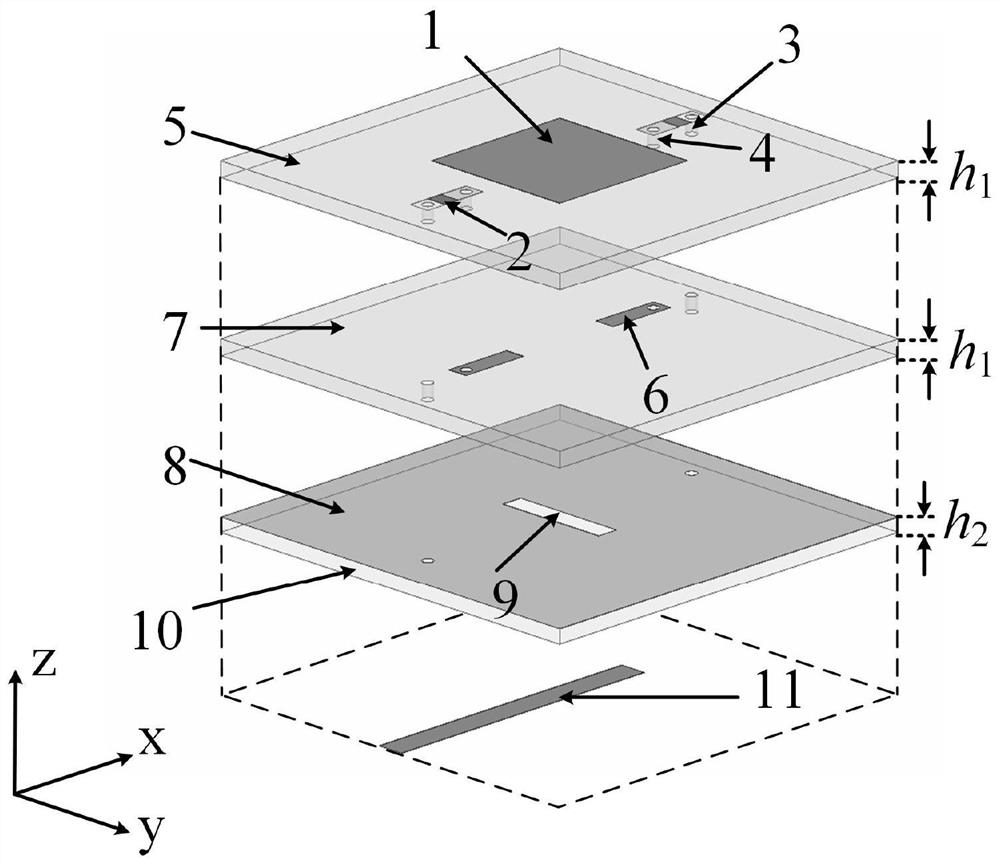
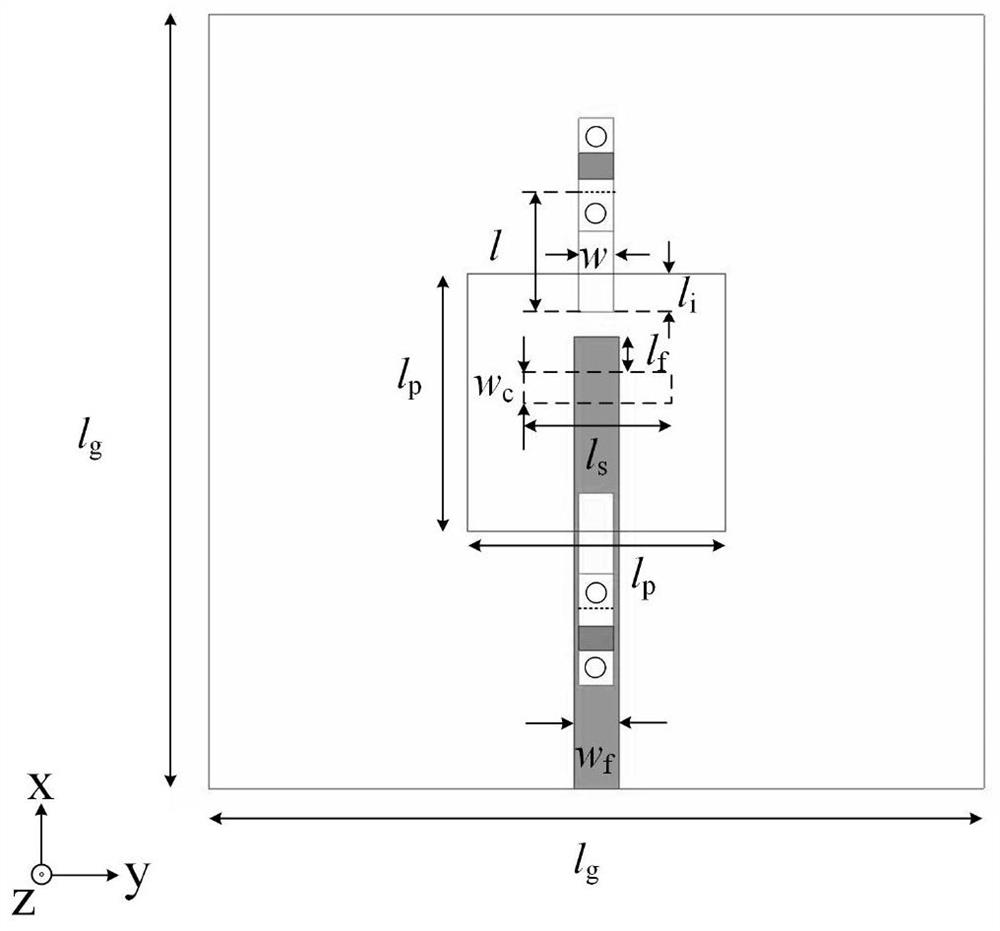
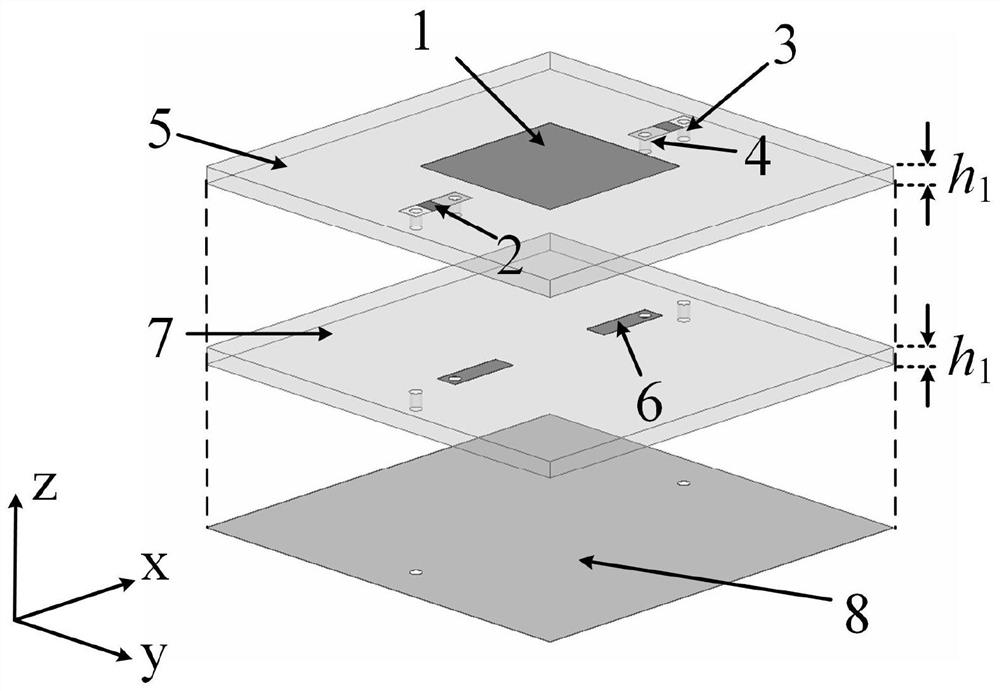
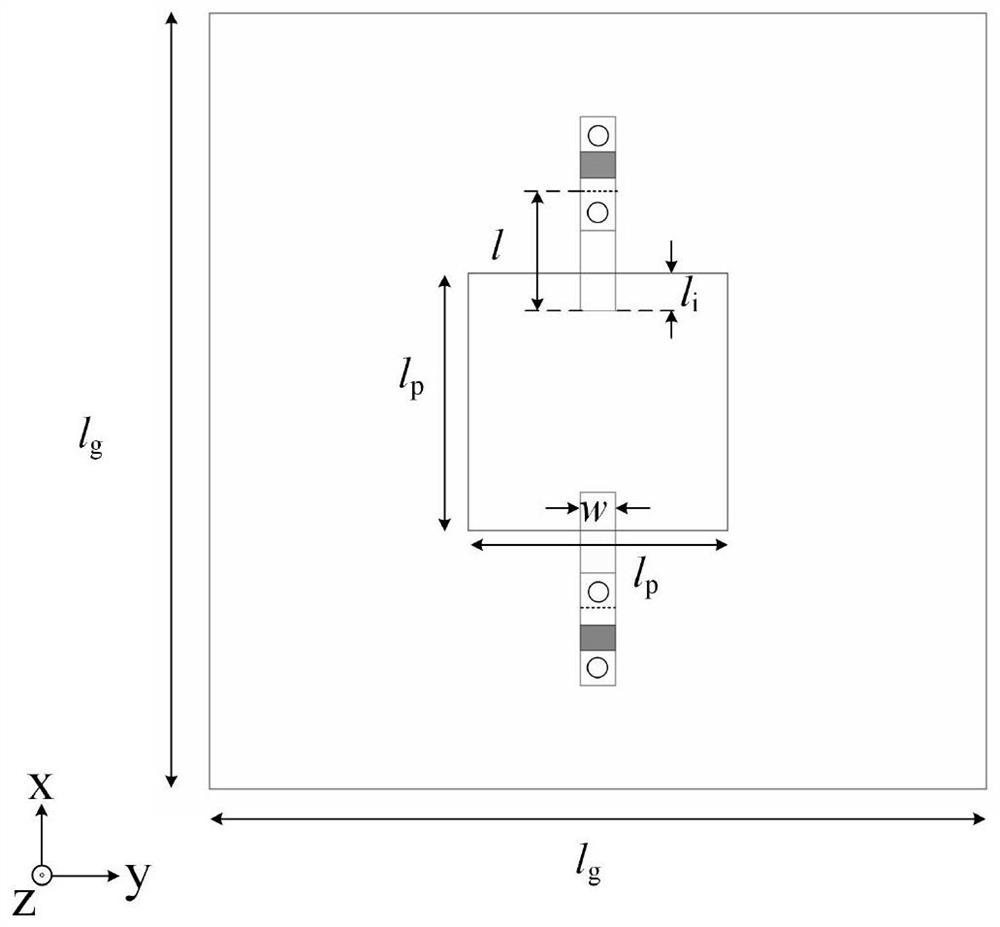
Non-contact variable capacitor-loaded frequency-tunable microstrip patch antenna
ActiveCN112599973AReduce the impact of radiation performanceEnables continuous tuningRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationMicrostrip patch antennaFeed line
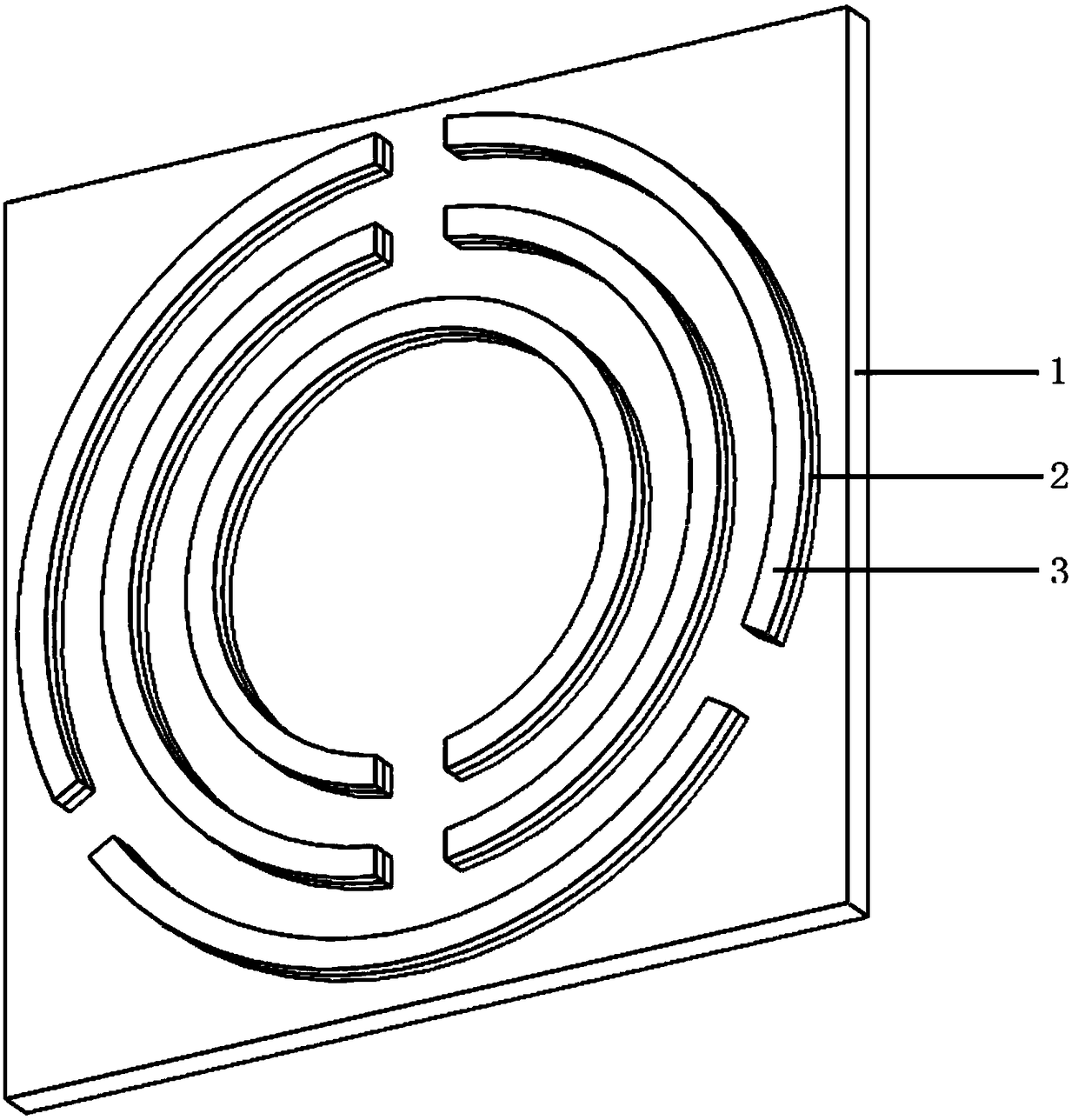
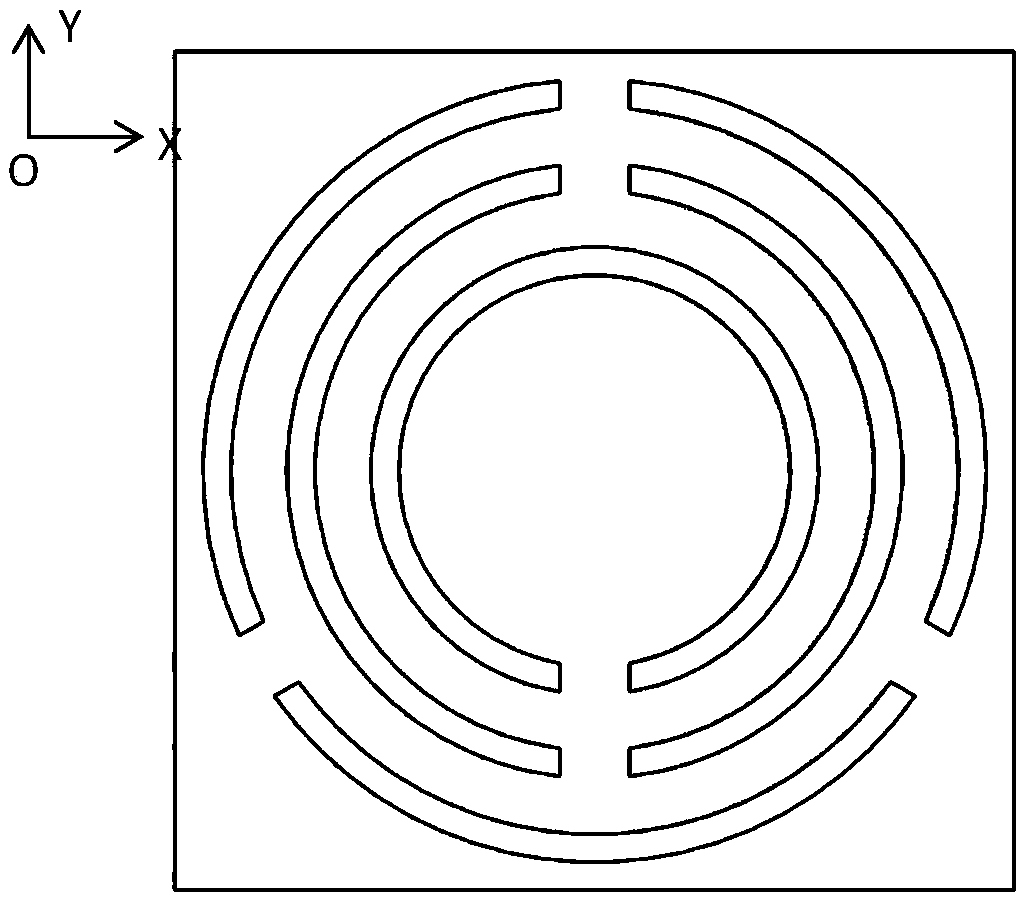
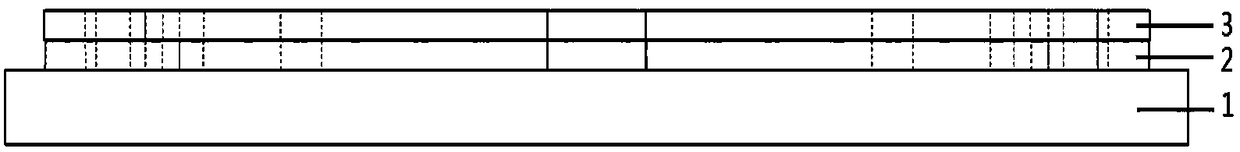
The invention relates to a non-contact variable capacitor-loaded frequency-tunable microstrip patch antenna. The microstrip patch antenna comprises a bottom substrate, a microstrip patch resonator anda microstrip feeder line, wherein the microstrip patch resonator and the microstrip feeder line are arranged on the upper surface and the lower surface of the bottom substrate respectively; the microstrip patch resonator comprises a metal reflection floor, a middle substrate, a top substrate and microstrip patches which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top; a pair of microstrip lines for frequency tuning is arranged between the middle substrate and the top substrate; the microstrip lines for frequency tuning are overlapped with the microstrip patches in a non-contact mode across the top substrate; and the outer ends of the microstrip lines for frequency tuning are electrically connected with the inner ends of variable capacitors loaded on the upper surface of the top substrate, andthe outer ends of the variable capacitors are grounded. The microstrip lines for frequency tuning and the corresponding variable capacitors form a non-contact frequency tuning structure which is usedfor continuously tuning the frequency of the antenna. The invention provides a novel non-contact variable capacitor loading scheme for the first time to design the frequency-reconfigurable microstrippatch antenna working under the main mode TM10.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
External cavity type single-wavelength tunable laser using FP (Fabry-Perot) laser as grain light source
InactiveCN102738702BEnables continuous tuningNo mechanical changes requiredLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlLight beamLength wave
Owner:SICHUAN MARS TECH
Frequency tunable microstrip patch resonator loaded by non-contact variable capacitor
ActiveCN112582771AReduce the impact of radiation performanceEnables continuous tuningAntennas earthing switches associationResonatorsElectrical connectionEngineering
The invention relates to a frequency tunable microstrip patch resonator loaded by a non-contact variable capacitor non-contact variable capacitor. The resonator comprises a metal ground, a bottom substrate, a top substrate and a microstrip patch which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top, and a pair of symmetrical microstrip lines for frequency tuning arranged along the central line of themicrostrip patch is arranged between the bottom substrate and the top substrate. The microstrip lines for frequency tuning are overlapped with the microstrip patch in a non-contact manner across the top substrate, the outer end of the microstrip line for frequency tuning is electrically connected with the first end of a variable capacitor loaded on the upper surface of the top substrate, and the second end of the variable capacitor is electrically connected with the metal ground. The microstrip line for frequency tuning and the variable capacitor form a non-contact frequency tuning structure,and the non-contact frequency tuning structure is used for continuously tuning the frequency of the resonator. The invention provides a novel non-contact variable capacitor loading scheme for the first time to design a frequency-reconfigurable microstrip patch resonator working under a main mode TM10.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Continuously tunable degradable terahertz metamaterial based on light drive and its preparation method
The invention provides a continuously adjustable degradable terahertz meta-material based on optical driving and preparation method thereof. The degradable terahertz meta-material comprises a sodium alginate substrate, a metal layer and a semiconductor film which are arranged on the sodium alginate substrate; the patterns of the metal layer and the semiconductor film are completely same: three equally spaced openings are formed on the outer ring, two equally spaced openings are formed on the middle ring, and one opening is formed on the inner ring; one of the three openings on the outer ring is aligned with one opening on the middle ring, and the other opening on the middle ring is aligned with the opening on the inner ring. Since the concentrations of carriers produced by the semiconductor film under different optical power excitations are different, the continuous tuning on the electromagnetically responded resonance strength from different conductivities is realized. The meta-material provided by the invention is simple in structure and processing technique, has degradable property and can be used for biomolecule detection, so that the incident electromagnetic wave of the terahertz meta-material has a plurality of frequency bands with continuously tuned strength in the terahertz waveband transmission.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
V-coupled cavity dual-wavelength semiconductor laser with continuously adjustable frequency interval
ActiveCN105281199BReduce manufacturing costShorten the lengthLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsLaser etchingResonant cavity
The invention discloses a V-shaped coupled cavity double-wavelength semiconductor laser with continuously adjustable frequency interval. The first active resonant cavity and the second active resonant cavity are coupled in a V-shape at one end to form a multimode coupling region, the end face of the multimode coupling region has a cavity surface reflection surface, the other end of the first active resonant cavity and the first passive The source filters are connected in series through deep etched grooves to form one arm of the laser; the other end of the second active resonator and the second passive filter are connected in series through deep etched grooves to form the other arm of the laser; the first active Shallow etching grooves are arranged on the resonant cavity and the second active resonant cavity. The laser of the invention has the advantages of compact structure, simple manufacturing process, low cost, no external reference light source and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
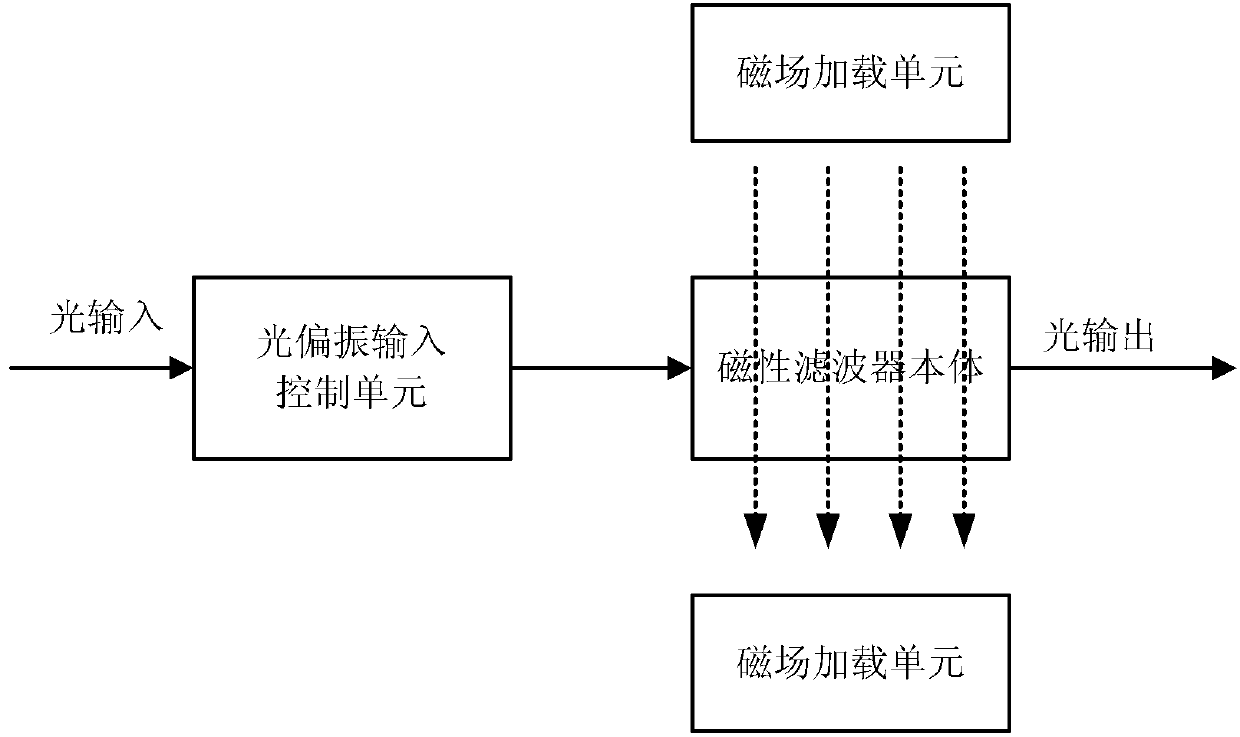
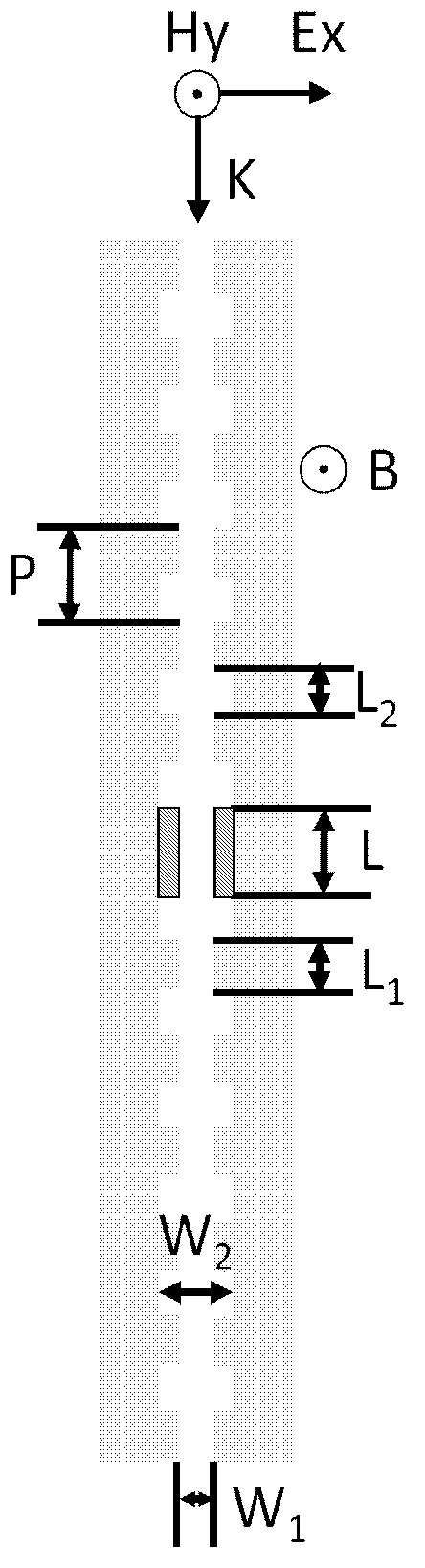
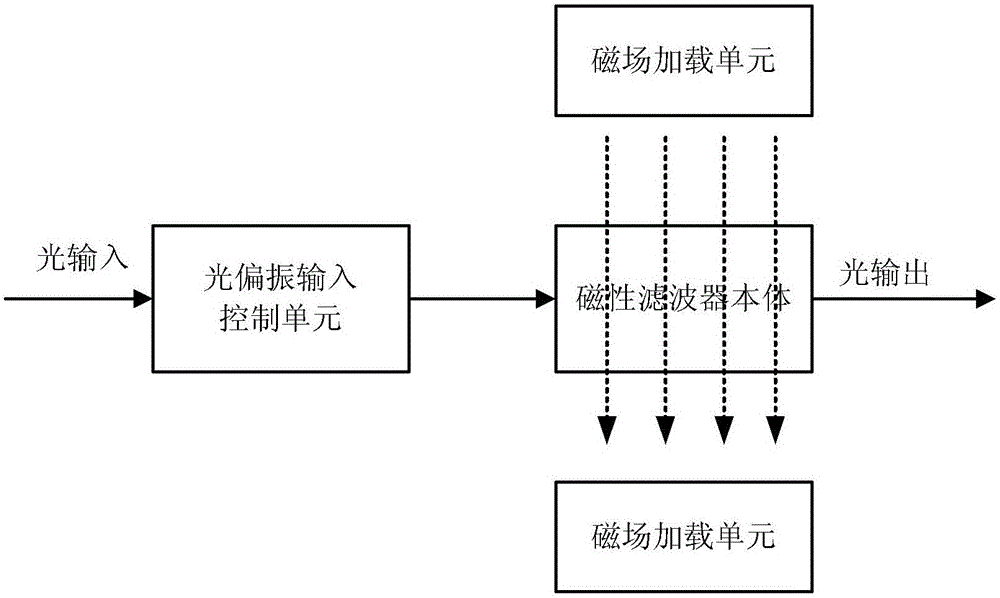
Tunable active filter
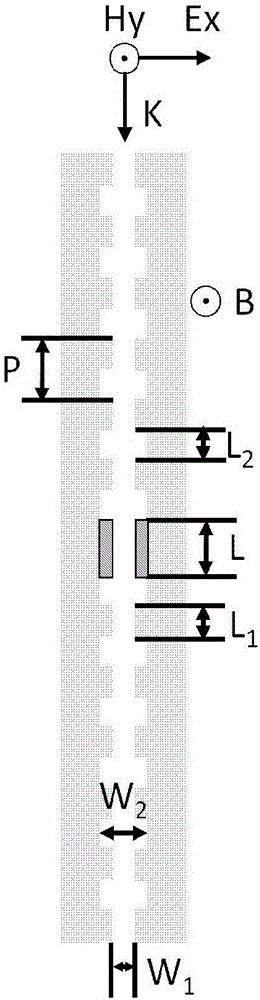
ActiveCN103278942AHigh quality factorEnables continuous tuningNon-linear opticsInput controlOptoelectronics
The invention provides a tunable active filter which comprises a light polarization input control unit, a magnetic filter body and a magnetic field loading unit, wherein the light polarization input control unit is used for converting input light into TM-mode polarized light which incomes in the K direction, the magnetic filter body is arranged at the rear end of an optical path of the light polarization input control unit and prepared through magnetic materials and dielectric substances, the magnetic filter body is of a periodic Bragg structure which has defects, extends in the K direction and is used for filtering the polarized light which incomes from the light polarized input control unit by means of a transmission peak generated by the defects of the periodic Bragg structure, and the magnetic loading unit is used for generating a magnetic field which is perpendicular to the K direction and the incident polarized light electric field direction and modulating the position of the transmission peak generated by the defects of the Bragg structure. The tunable active filter is easy to manufacture, quick in response, flexible in tuning process and high in tuning precision.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
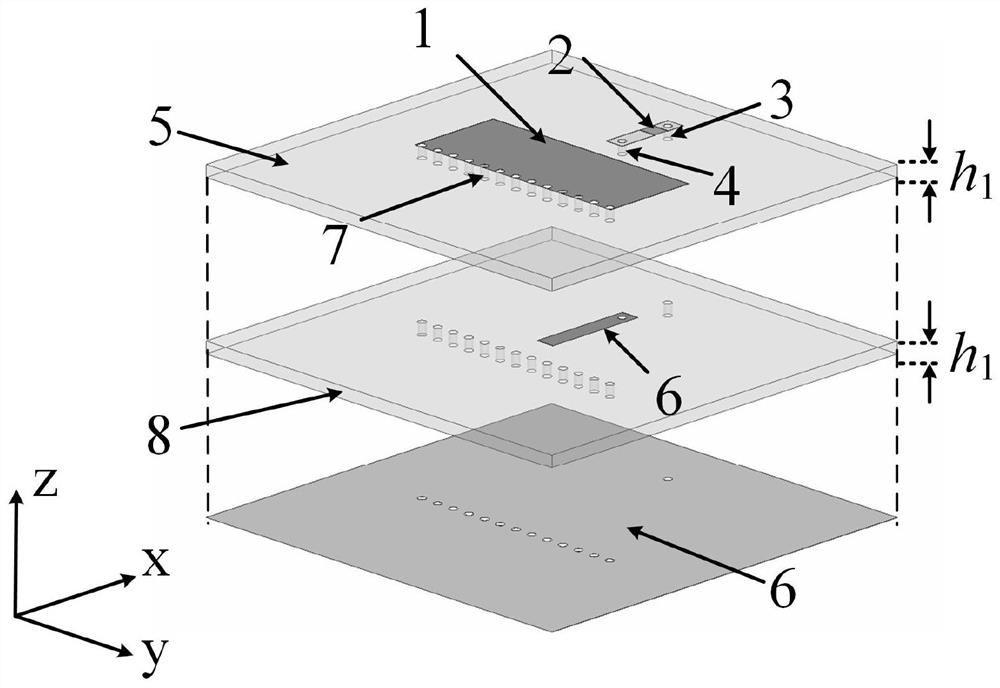
Frequency tunable microstrip patch antenna based on half-cut technology
ActiveCN112582792AHalf-cut implementationEnables continuous tuningRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsMicrostrip patch antennaFeed line
The invention relates to a frequency tunable microstrip patch antenna based on a half-cut technology. Thefrequency tunable microstrip patch antenna comprises a bottom layer substrate, and a microstrippatch resonator and a microstrip feeder which are respectively arranged on the upper surface and the lower surface of the bottom layer substrate, and is characterized in that the microstrip patch resonator comprises a metal reflecting floor, a middle layer substrate, a top layer substrate and a half-cut microstrip patch which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top; a microstrip line for frequency tuning is arranged between the middle-layer substrate and the top-layer substrate; the microstrip line for frequency tuning is overlapped with the microstrip patch in a non-contact manner acrossthe top-layer substrate; the outer end of the microstrip line for frequency tuning is connected with a variable capacitor loaded on the upper surface of the top-layer substrate; one side, far away from the variable capacitor, of the microstrip patch is grounded; and the microstrip line for frequency tuning and the variable capacitor form a non-contact frequency tuning structure used for continuously tuning the frequency of the antenna. The invention provides a novel non-contact variable capacitor loading scheme for the first time to design the frequency-reconfigurable microstrip patch antennaworking under a main mode TM10.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
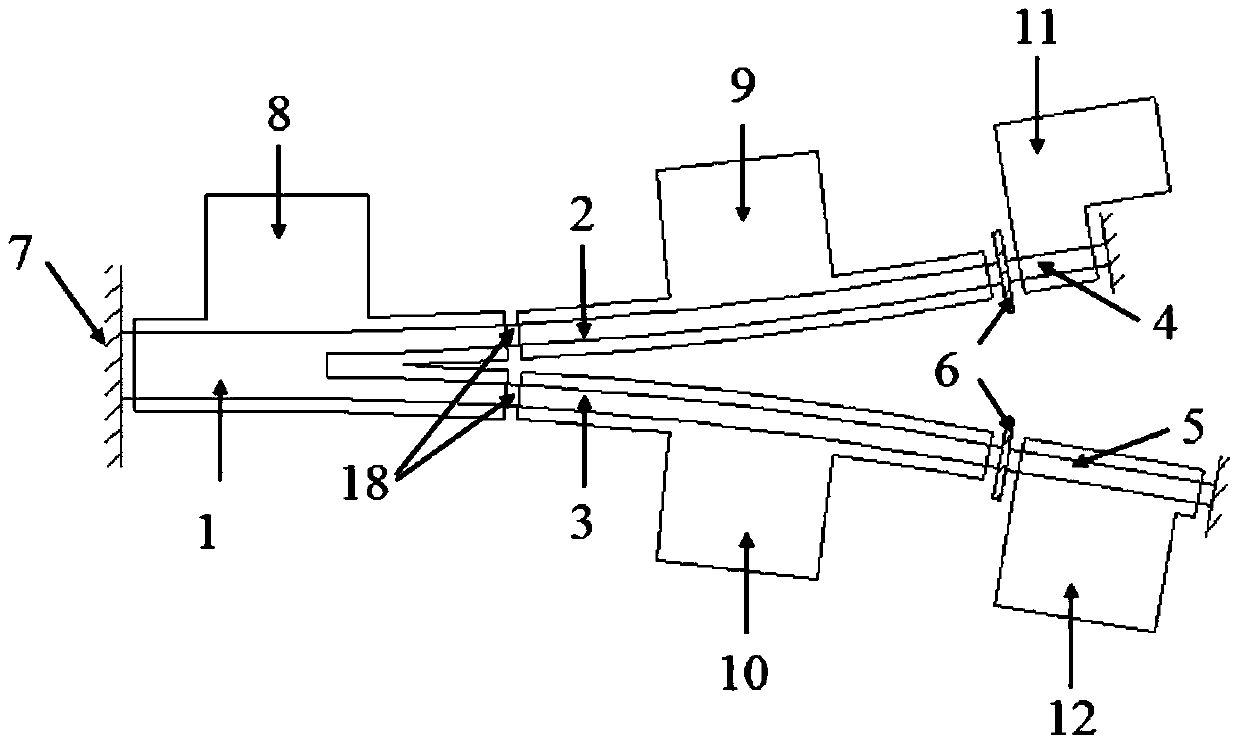
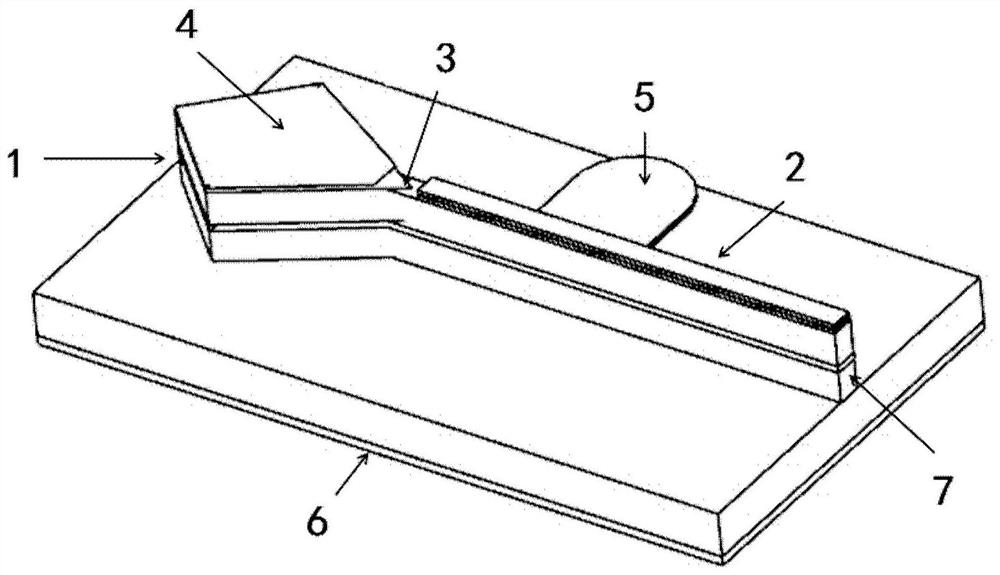
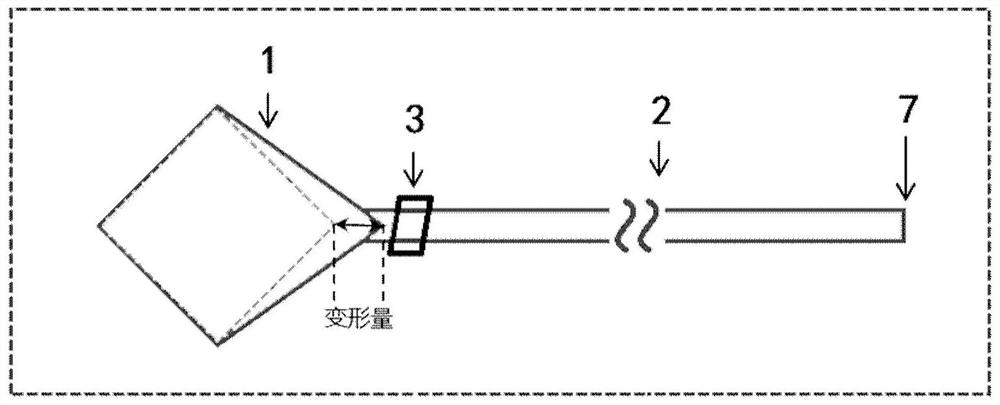
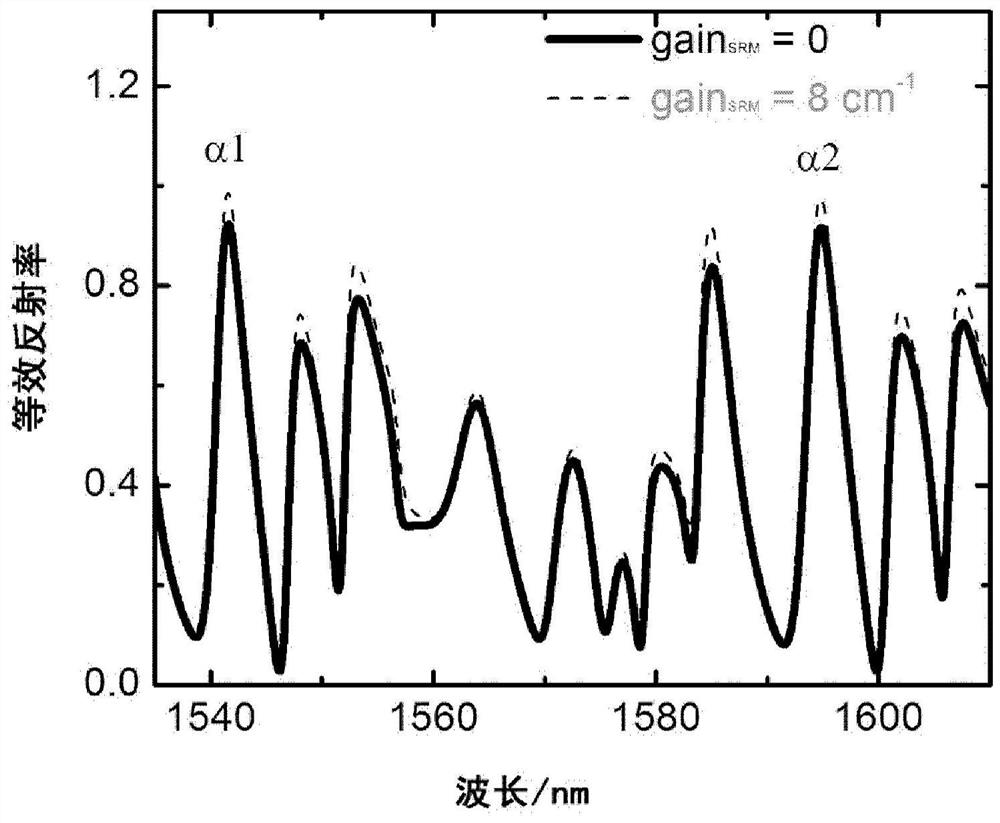
Tunable coupled cavity semiconductor laser
ActiveCN109638645BIncrease output powerLarge wavelength tuning rangeLaser optical resonator constructionLight reflectionEngineering
A tunable coupled cavity semiconductor laser, comprising: an FP cavity; a modified whispering gallery microcavity connected to the first end of the FP cavity as a reflective end face of the FP cavity, the modified whispering gallery microcavity is formed with the FP cavity A coupling cavity structure; and an electrical isolation groove, which is arranged between the FP cavity and the modified whispering gallery microcavity; wherein, light can enter the modified whispering gallery microcavity from the FP cavity, and pass through several times in the modified whispering gallery microcavity. After the secondary reflection, the light of a specific wavelength is reflected back into the FP cavity. The coupled mode of the tunable coupled cavity laser accounts for a high proportion of the fundamental mode of the FP intracavity mode, thereby reducing the loss of light in the FP cavity, and at the same time making the coupled cavity lasing mode more stable and the output power higher; at the same time , the equivalent reflectivity spectrum of the modified whispering gallery microcavity is insensitive to the gain change in the cavity, and the lasing mode is not easy to jump to the adjacent longitudinal mode, so that the tunable coupled cavity laser can obtain a large wavelength tuning range.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tunable Active Filter
ActiveCN103278942BHigh quality factorEnables continuous tuningNon-linear opticsInput controlOptoelectronics
The invention provides a tunable active filter which comprises a light polarization input control unit, a magnetic filter body and a magnetic field loading unit, wherein the light polarization input control unit is used for converting input light into TM-mode polarized light which incomes in the K direction, the magnetic filter body is arranged at the rear end of an optical path of the light polarization input control unit and prepared through magnetic materials and dielectric substances, the magnetic filter body is of a periodic Bragg structure which has defects, extends in the K direction and is used for filtering the polarized light which incomes from the light polarized input control unit by means of a transmission peak generated by the defects of the periodic Bragg structure, and the magnetic loading unit is used for generating a magnetic field which is perpendicular to the K direction and the incident polarized light electric field direction and modulating the position of the transmission peak generated by the defects of the Bragg structure. The tunable active filter is easy to manufacture, quick in response, flexible in tuning process and high in tuning precision.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
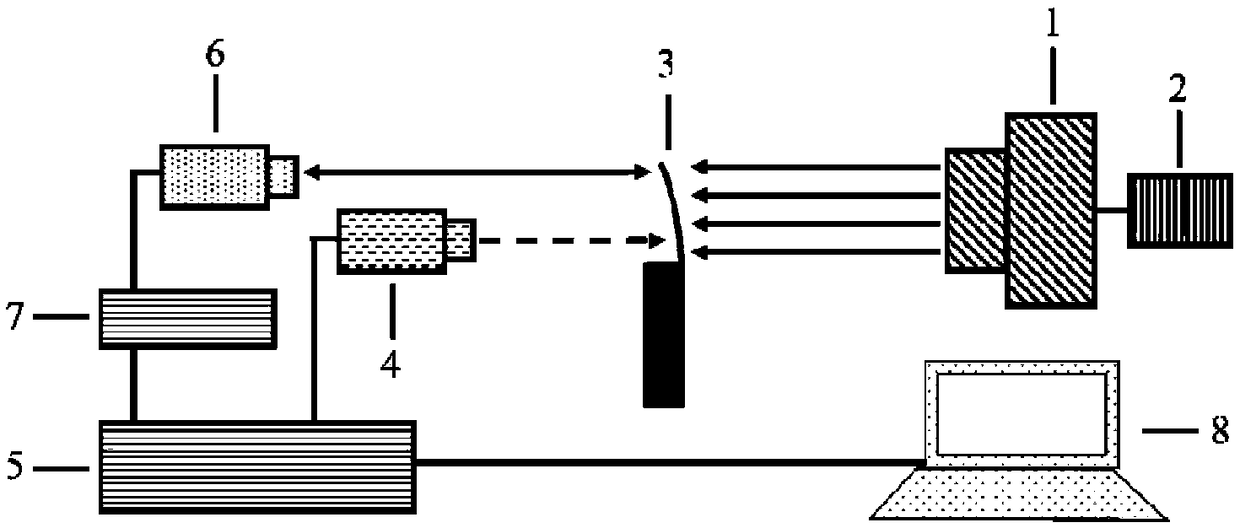
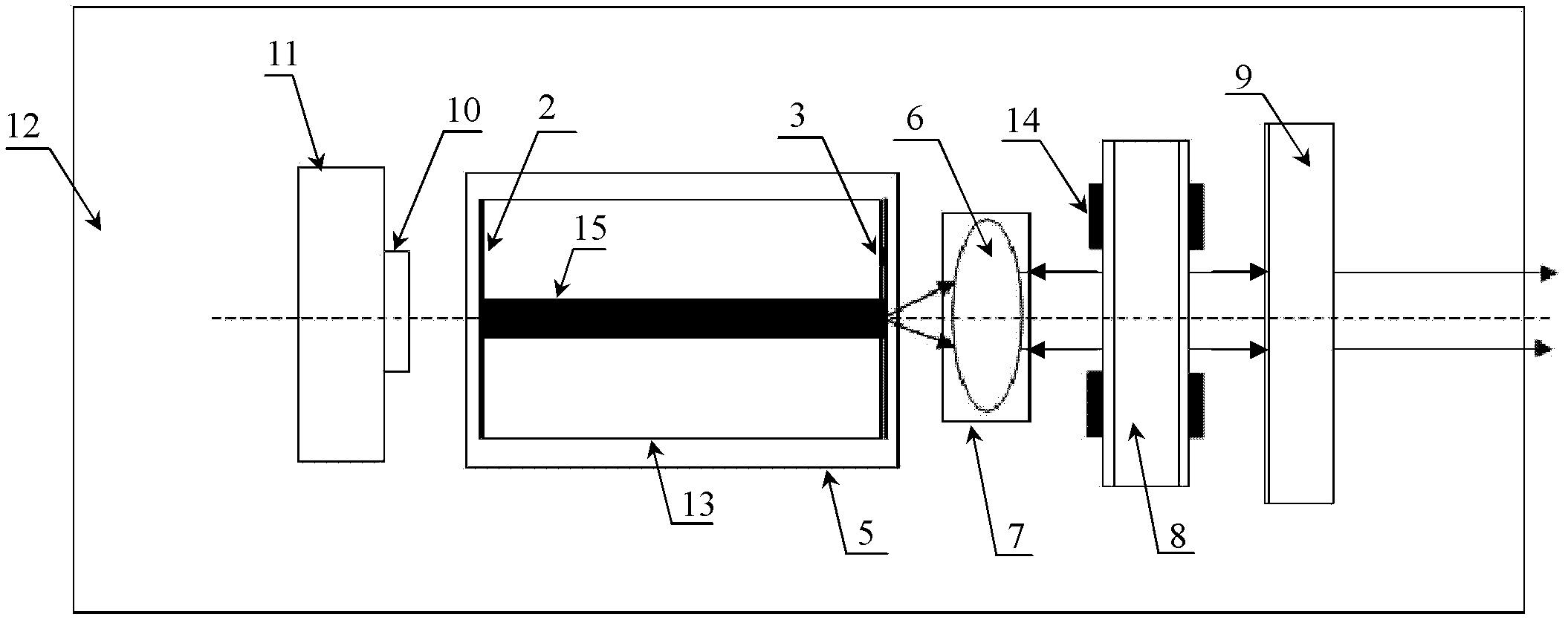
Frequency tunable optoelectronic oscillator based on broadband light source
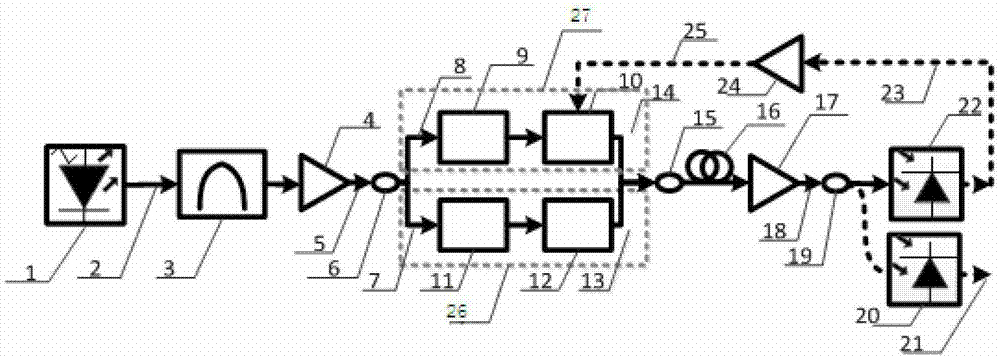
ActiveCN103166706BEnables continuous tuningRealize continuously adjustableFibre transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersPhase noiseOptical fiber coupler
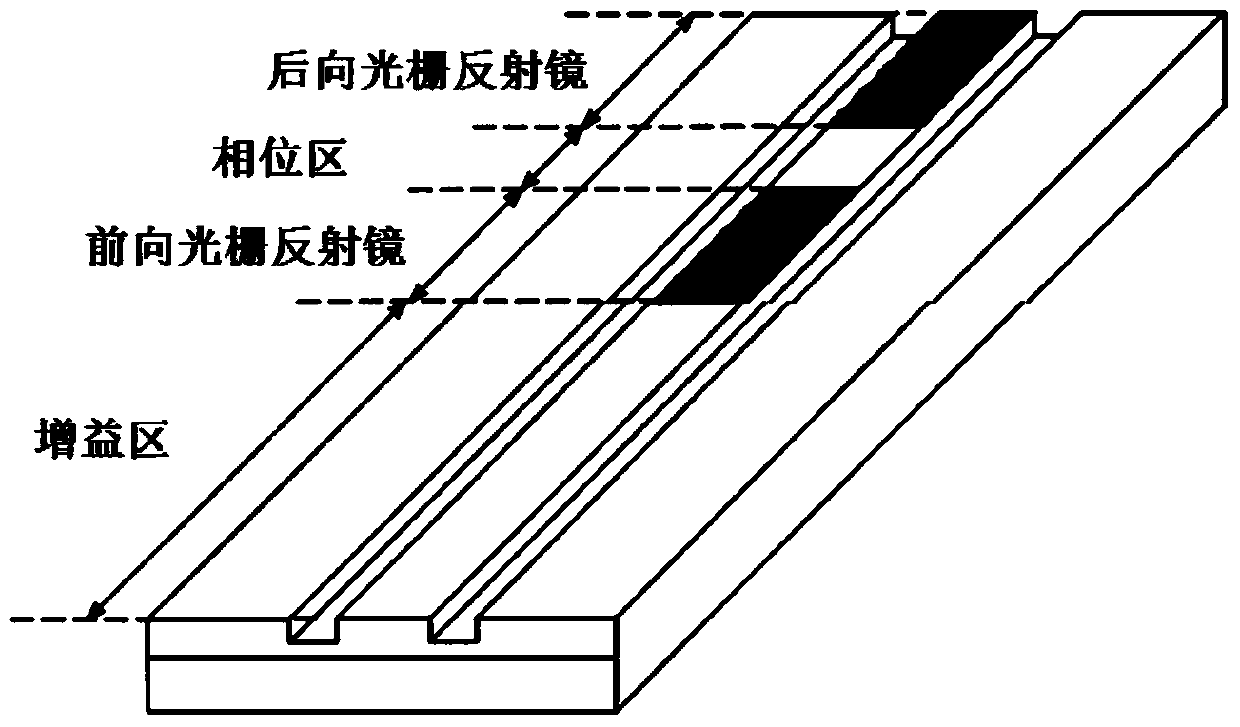
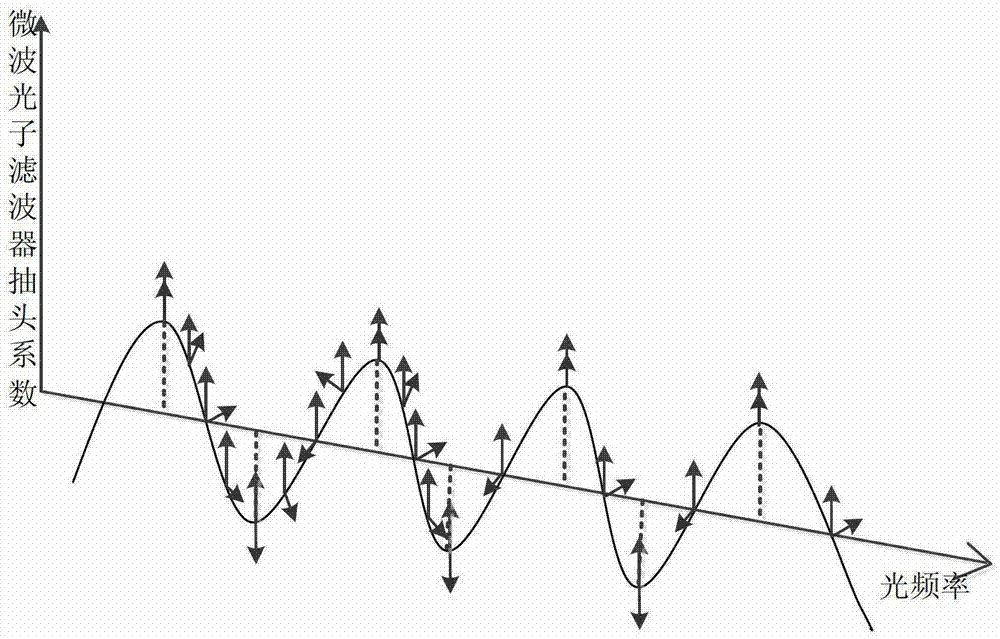
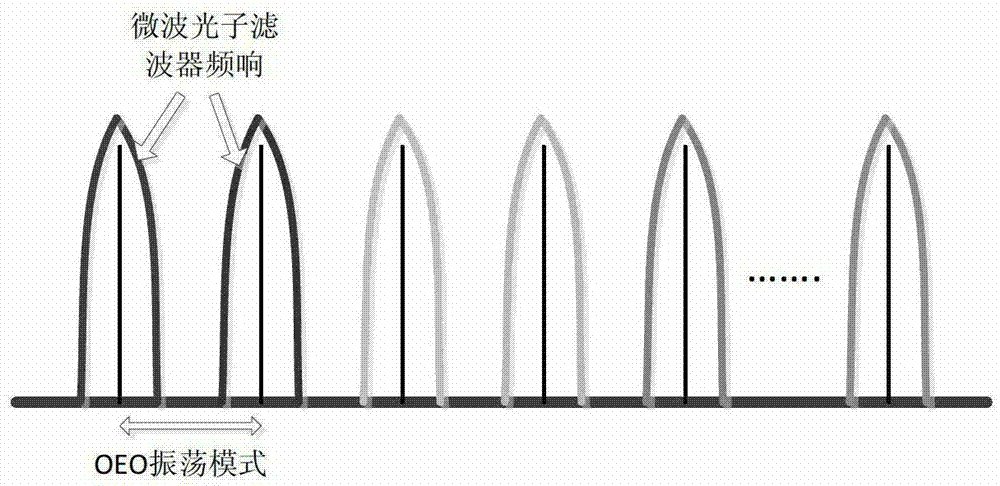
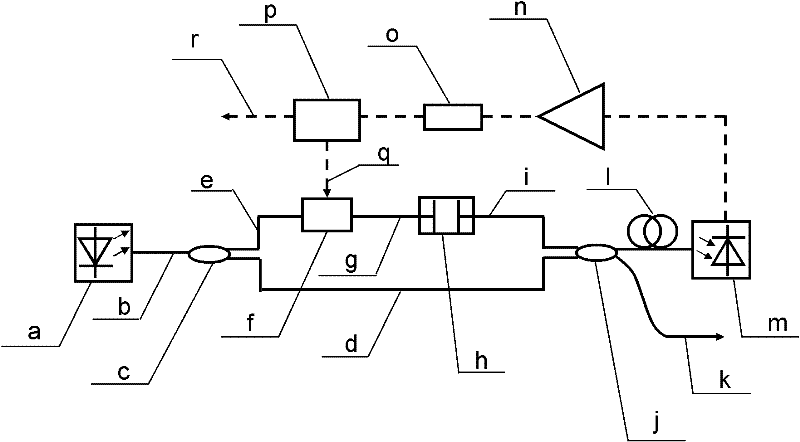
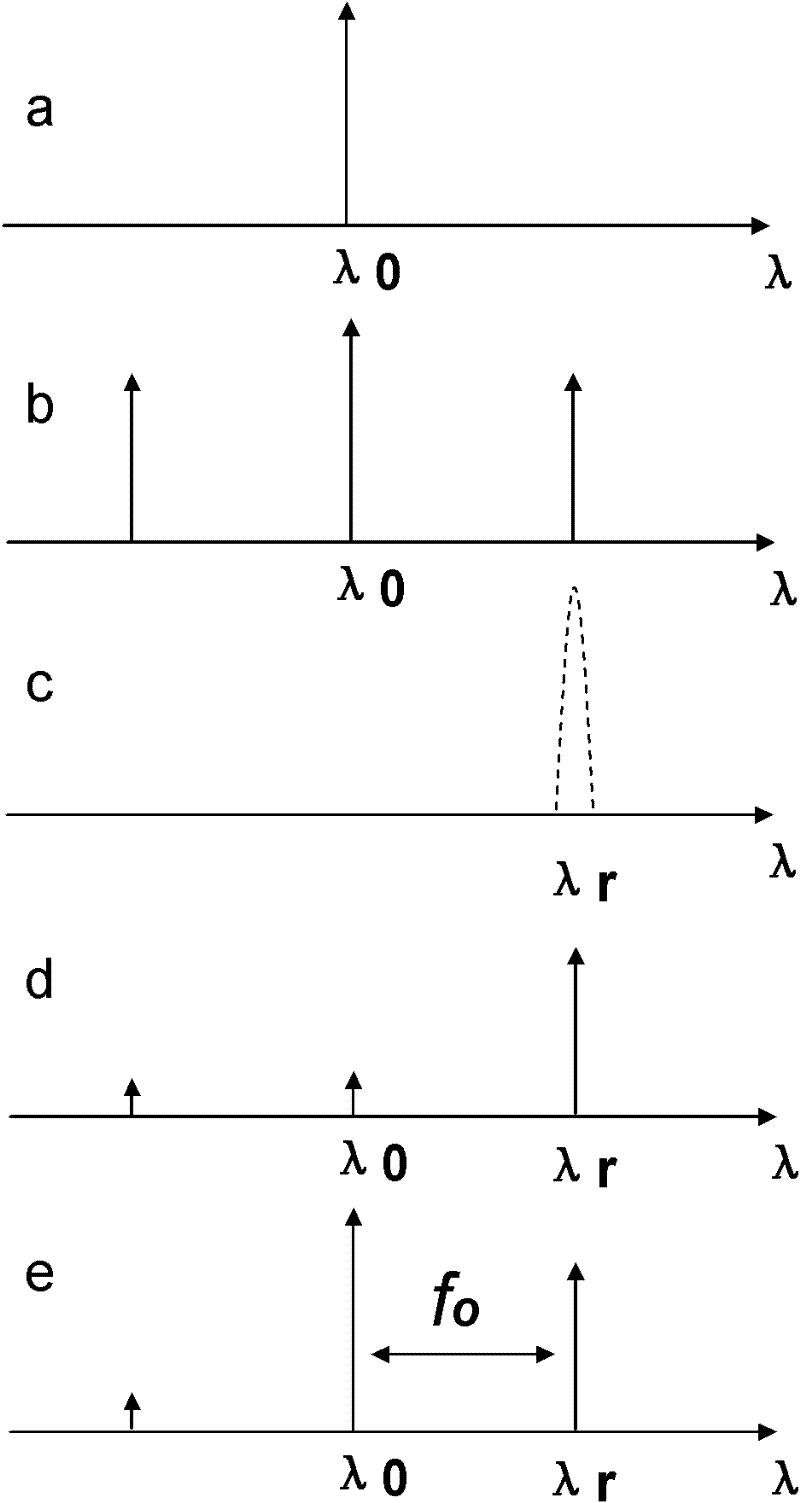
A tunable-frequency photoelectric oscillation device based on a wide spectrum light source comprises the wide spectrum light source, an optical filter, a first light amplifier, a second light amplifier, a first optical fiber coupler, a second optical fiber coupler, a third optical fiber coupler, a first polarization controller, a second polarization controller, a dimming-adjustable delay line, an photoelectric modulator, a color-dispersion optical fiber, a first photoelectric detector, a second photoelectric detector, a microwave amplifier, a first optical fiber patch cord, a second optical fiber patch cord, a third optical fiber patch cord, a fourth optical fiber patch cord, a fifth optical fiber patch cord, a sixth optical fiber patch cord, a seventh optical fiber patch cord, a first cable and a second cable. The tunable-frequency photoelectric oscillation device based on the wide spectrum light source can generate wideband-adjustable microwave signals, adopts a microwave photon filter to replace a traditional point filter, overcomes the defect that a traditional photoelectric oscillator based on wide spectrum source cutting can not generate signals at certain frequency points, and has the advantages of being low in cost, adjustable in wideband, and low in phase noise.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
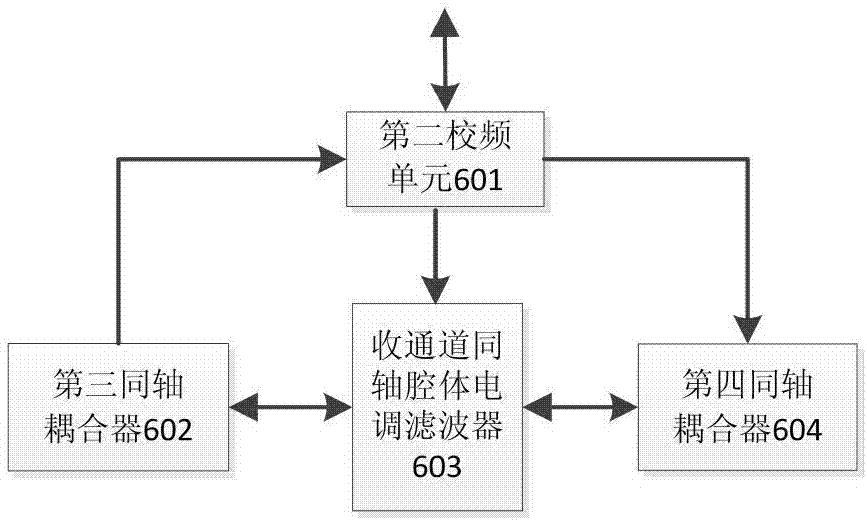
A high-frequency device for scattering communication with full-band operation
The present invention is a high-frequency device for scattering communication that works in the full frequency band, including a frequency converter, a power amplifier, a limiting low-noise amplifier, a first circulator, a second circulator, a coupler and a load, a frequency conversion filter for a transmitting channel, and a receiving channel Frequency conversion filter, transmit channel duplex filter, receive channel duplex filter and monitoring unit. The intermediate frequency input signal is firstly up-converted by the frequency converter to the RF signal, and the RF signal is sent to the power amplifier after being frequency-selected by the frequency conversion filter of the transmission channel. The duplex filter feeds the high-power signal into the antenna and is transmitted by the antenna; the small radio frequency signal received from the antenna first passes through the receiving channel duplex filter for frequency selection, and then enters the limiting low-noise amplifier for low-noise limiting amplification , and then filtered by the frequency conversion filter of the receiving channel, it enters the down conversion of the frequency converter, and the frequency is converted into an intermediate frequency signal, which is amplified to a suitable level and then sent to the low frequency unit.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Micromachined cantilever-type π-type continuous reconfigurable microwave bandpass filter
ActiveCN103811834BEnables continuous tuningContinuously changing bandwidthWaveguide type devicesBandpass filteringCapacitance
The invention discloses a micro-mechanical cantilever beam type pi type continuous reconfigurable microwave band-pass filter. The micro-mechanical cantilever beam type pi type continuous reconfigurable microwave band-pass filter comprises a planar spiral inductor, two identical MEMS variable planar plate capacitors and two identical MIM capacitors are symmetrically arranged at the left and right sides of the planar spiral inductor in sequence, wherein each MEMS variable planar plate capacitor is connected between a CPW signal wire and a ground wire in parallel while each MIM capacitor is connected with the CPW signal wire in series so as to make up a pi type topological structure with band-pass characteristics. The MEMS variable planar plate capacitors achieve different capacitances based on an electrostatic principle; the upper pole plate of each MEMS variable planar plate capacitor is an MEMS cantilever beam while the lower pole plate thereof is the CPW signal wire, wherein the MEMS cantilever beam stretches across the CPW signal wire, and a drive electrode is arranged near the CPW signal wire; an Si3N4 insulating medium layer covers each of the CPW signal wire under the MEMS cantilever beam and the drive electrode. The filter realizes the continuous tuning for the center frequency and the band width and has advantages of low loss, good out-of-band rejection, wide frequency band tuning and small chip area.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Tunable coupled cavity semiconductor laser
ActiveCN109638645AIncrease output powerLarge wavelength tuning rangeLaser optical resonator constructionLength waveSemiconductor
The invention discloses a tunable coupled cavity semiconductor laser, which comprises an FP cavity; a variable echo wall micro-cavity connected with the first end of the FP cavity and served as a reflection end face of the FP cavity, wherein the variable echo wall micro-cavity and the FP cavity form a coupled cavity structure; and an electric isolation groove formed between the FP cavity and the variable echo wall micro-cavity. The light enters the variable echo wall micro-cavity after being incident from the second end of the FP cavity. After that, the light with the specific wavelength is reflected back to the FP cavity after being reflected in the variable echo wall micro-cavity. According to the tunable coupled cavity laser, the fundamental mode proportion of a coupling mode of laser emission of the tunable coupled cavity laser in an FP cavity is very high, so that the loss of light in the FP cavity is reduced. Meanwhile, the laser emission mode of the coupled cavity is more stable, and the output power is higher. At the same time, the equivalent reflectivity spectrum of the deformable echo wall micro-cavity is insensitive to gain change in the cavity, and the laser emission mode is not liable to jump to an adjacent longitudinal mode. As a result, the tunable coupled cavity laser can obtain a large wavelength tuning range.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
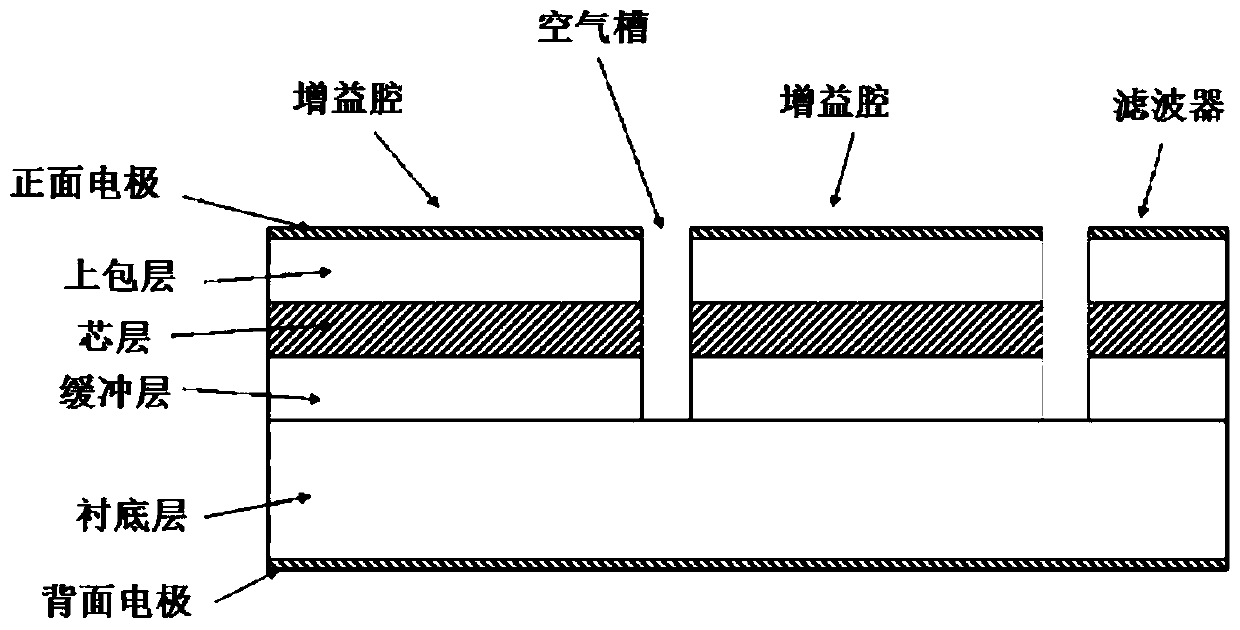
Optoelectronic oscillator with tunable broadband frequency
ActiveCN102163795BEnables continuous tuningGood phase noise characteristicsLaser detailsFiberFiber coupler
The invention discloses an optoelectronic oscillator with tunable broadband frequency, which is characterized in that a photon microwave filter is composed of an optical modulator, a high-fineness Fabry-Perot etalon and two fiber couplers and is applied to the optoelectronic oscillator. By tuning wavelength of laser light sources, the filtering peak of the photon microwave filter can be tuned; meanwhile, a microwave phase shifter is used cooperatively, thus continuous large-scale tuning of the optoelectronic oscillator can be realized finally.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Frequency-tunable microstrip chip resonators loaded with non-contact variable capacitance
ActiveCN112582771BReduce the impact of radiation performanceEnables continuous tuningResonatorsAntennas earthing switches associationCapacitanceElectrical connection
The invention relates to a frequency-tunable microstrip patch resonator loaded with a non-contact variable capacitance, which includes a metal ground, a bottom substrate, a top substrate and a microstrip patch stacked sequentially from bottom to top, the bottom substrate and the top layer There is a pair of symmetrical microstrip lines for frequency tuning arranged along the center line of the microstrip patch between the substrates. The first end of the variable capacitor on the upper surface of the top substrate is electrically connected, the second end of the variable capacitor is electrically connected to the metal ground, and the frequency tuning uses a microstrip line and the variable capacitor to form a non-contact frequency tuning structure for continuous tune the frequency of the resonator. The present invention proposes a new non-contact variable capacitance loading scheme for the first time to design a frequency reconfigurable microstrip patch resonator working under the main mode TM10.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
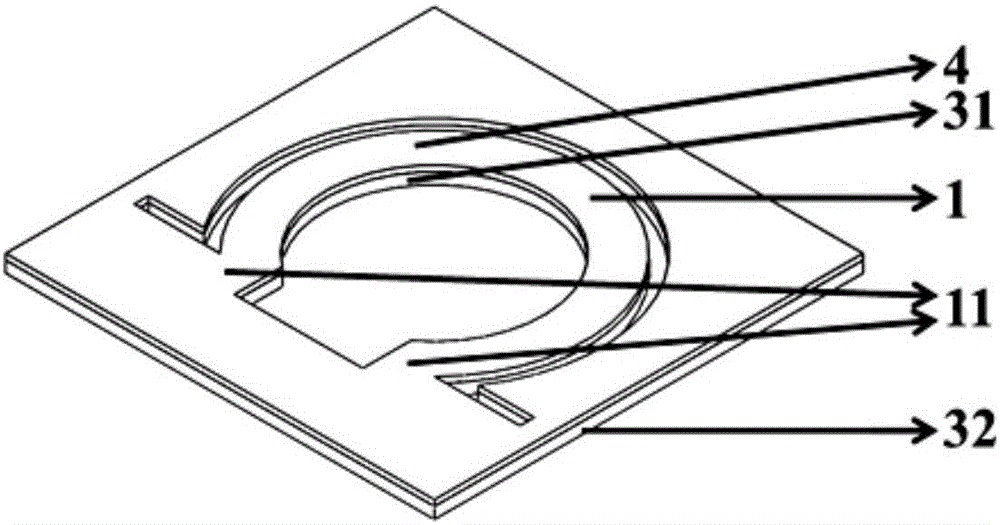
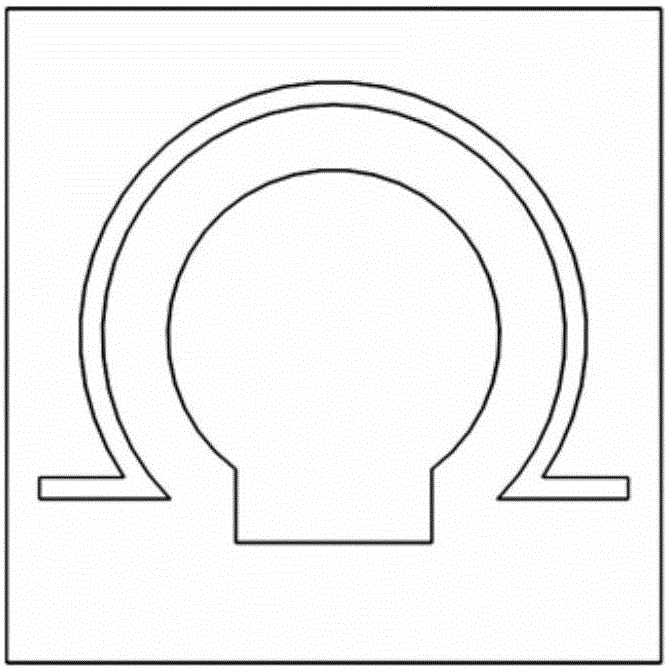
Frequency tunable microstrip patch resonator based on half-cut technology
ActiveCN112582772AAchieve half cutReduce the impact of radiation performanceAntennas earthing switches associationResonatorsElectrical connectionMaterials science
The invention relates to a frequency tunable microstrip patch resonator based on a half-cut technology. The frequency tunable microstrip patch resonator comprises a metal ground, a bottom layer substrate, a top layer substrate and a microstrip patch which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top, and a microstrip line for frequency tuning is arranged between the bottom layer substrate and the top layer substrate. The microstrip line for frequency tuning is overlapped with the microstrip patch in a non-contact manner across the top substrate, the outer end of the microstrip line for frequency tuning is electrically connected with the inner end of the variable capacitor loaded on the upper surface of the top substrate, and the outer end of the variable capacitor is electrically connectedwith the metal ground; one side, far away from the variable capacitor, of the microstrip patch is grounded, and the microstrip line for frequency tuning and the variable capacitor form a non-contact frequency tuning structure used for continuously tuning the frequency of the resonator. The invention provides a novel non-contact variable capacitor loading scheme for the first time to design the frequency-reconfigurable microstrip patch resonator working under a main mode TM10.
Owner:南通大学技术转移中心有限公司
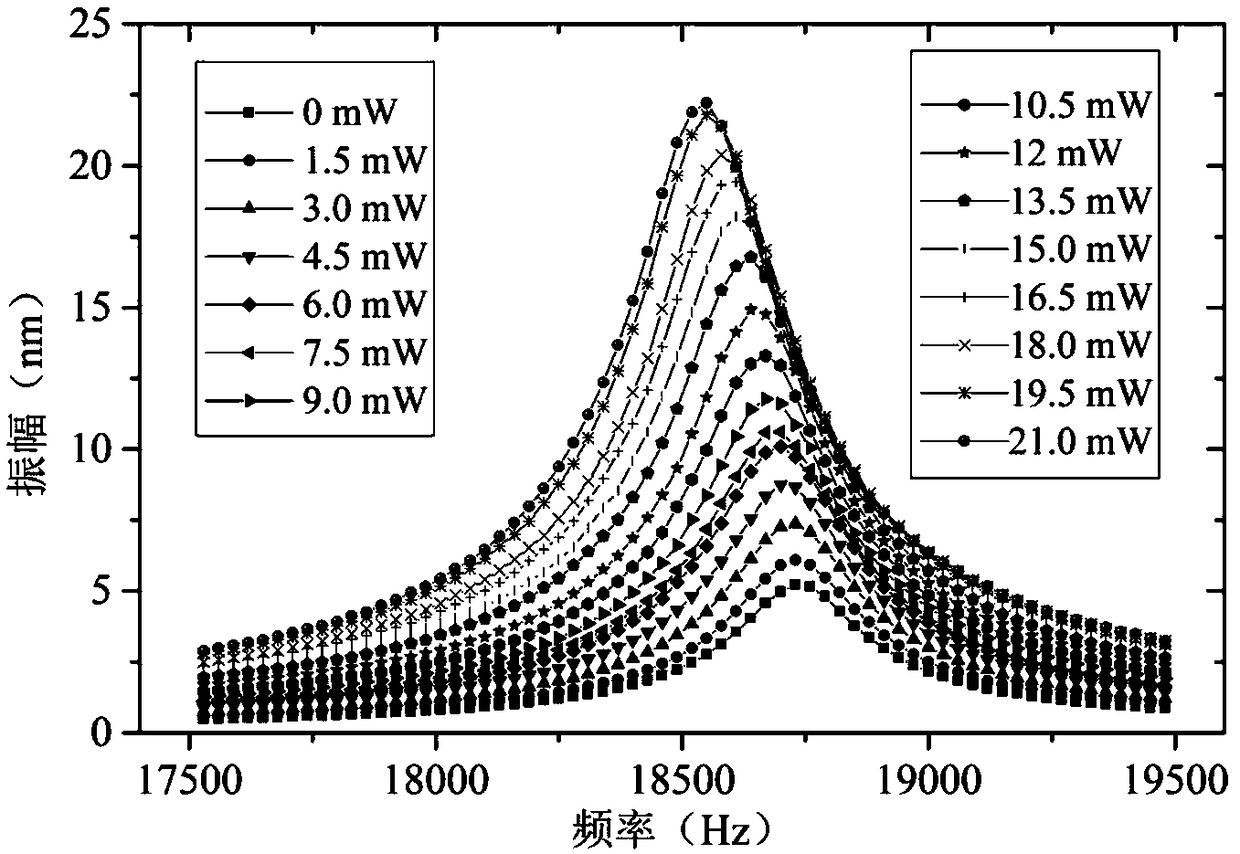
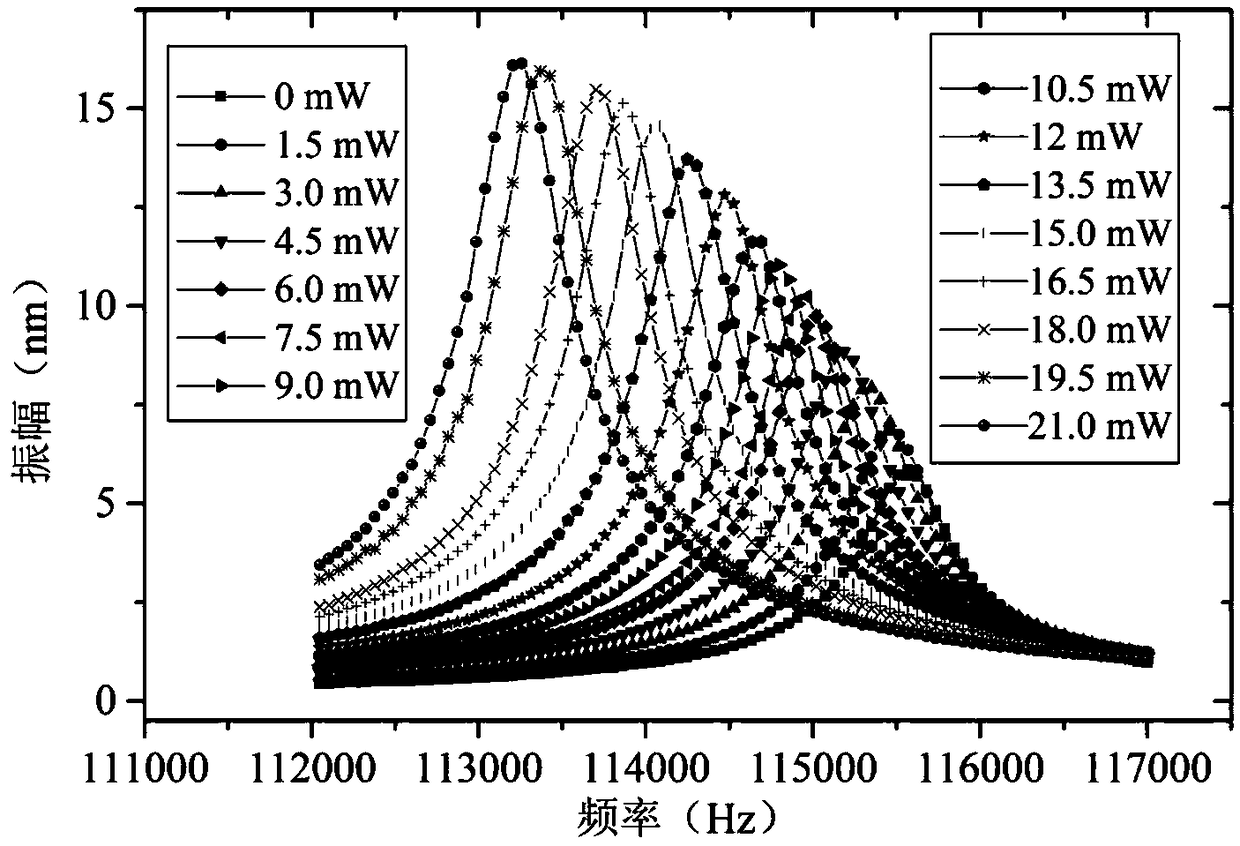
Method for improving quality factor of micro-resonator by using superposition of orthogonal mode, and realizing device thereof
ActiveCN109687833AReduce design requirementsWith remote contactlessImpedence networksIn planeExcitation signal
The invention relates to a method for improving quality factor of a micro-resonator by using superposition of orthogonal mode, and a realizing device thereof. The method comprises the steps of: (1) simultaneously stimulating and measuring the orthogonal mode: focusing a modulated pulse laser on a bridge connection part of the micro-resonator to vibrate the micro-resonator, so that two orthogonal modes of the resonator, which are vertical with each other, are stimulated; (2) adjusting the orthogonal modes to create superposition: radiating the micro-resonator by a continuous laser, so that theheat effect generated on a beam tunes a first-stage in-plane resonant mode of the micro-resonator to get close to the most close out-plane resonant mode of the micro-resonator until two resonant modesare superposed; and (3) measuring the vibration signal. Compared with the prior research, the method provided by the invention realizes the superposition of two orthogonal modes by using only one modulated sine excitation signal and one heating stationary laser, is simple, and is good in repeatability.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A laser with adjustable bandwidth and central wavelength
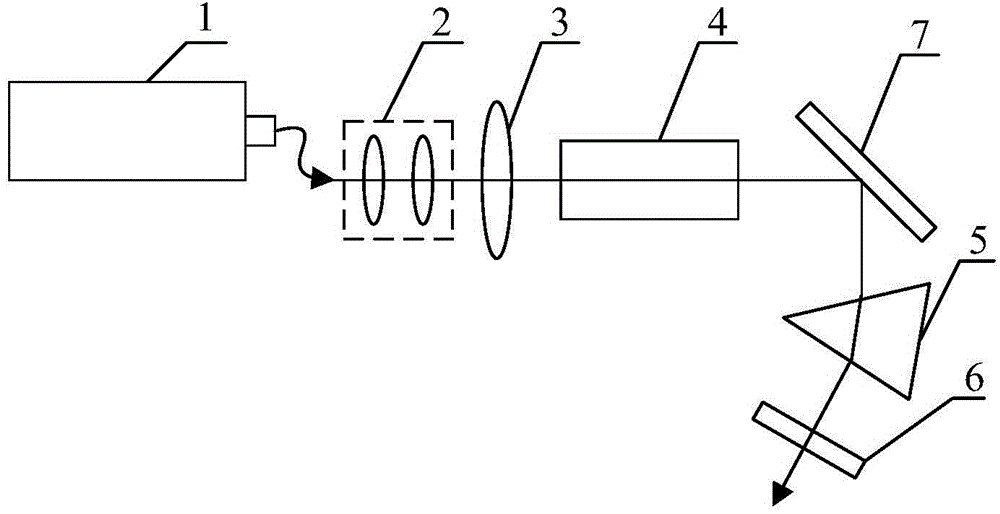
ActiveCN104319617BEnables continuous tuningSimple structureLaser detailsGratingPolarization beam splitter
The invention discloses a laser with adjustable bandwidth and center wavelength, including a pump source, a pump protector, a pump beam combiner, a gain fiber, a first collimator, a first quarter-wave plate, The first half wave plate, the first polarization beam splitting cube, the Faraday rotator, the second half wave plate, the second polarization beam splitting cube, a transmission grating, a pair of mirrors whose reflection surfaces are perpendicular to each other, a mirror, and Second collimator. This case adopts a combined structure of nonlinear rotational polarization mode-locking and intracavity filtering effect. The structure is simple and easy to implement. The pair of corner mirrors can be translated relative to the direction of its incident light, and the second collimator can be translated relative to the vertical direction of its incident light. In this way, without inserting or replacing any other redundant components in the optical path, continuous tuning of the mode-locking bandwidth and the central wavelength can be respectively realized, and its application range is wide.
Owner:广东华快光子科技有限公司 +1
Frequency-tunable microstrip patch resonator based on half-cut technology
ActiveCN112582772BAchieve half cutReduce the impact of radiation performanceResonatorsAntennas earthing switches associationCapacitanceElectrical connection
Owner:南通大学技术转移中心有限公司
A method for improving the quality factor of a microresonator by using the superposition of orthogonal modes and its realization device
ActiveCN109687833BReduce design requirementsWith remote contactlessImpedence networksEngineeringCw laser
The present invention relates to a method for improving the quality factor of a microresonator by superposition of orthogonal modes and its realization device, including: (1) Simultaneous excitation and measurement of the orthogonal mode: focusing the modulated pulse laser on the microresonator The bridge makes it vibrate, and excites two orthogonal modes of the resonator that are perpendicular to each other; (2) The adjustment of the orthogonal mode causes superposition: the thermal effect generated on the beam is tuned by using continuous laser irradiation on the microresonator Its first-order in-plane resonance mode and its nearest out-of-plane resonance mode are close to superposition; (3) measuring the vibration signal. Compared with the existing research, the invention only needs a modulated sinusoidal excitation signal and a heated steady-state laser to realize the superposition of two orthogonal modes, and the method is simple and repeatable.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com