Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Large amount of energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
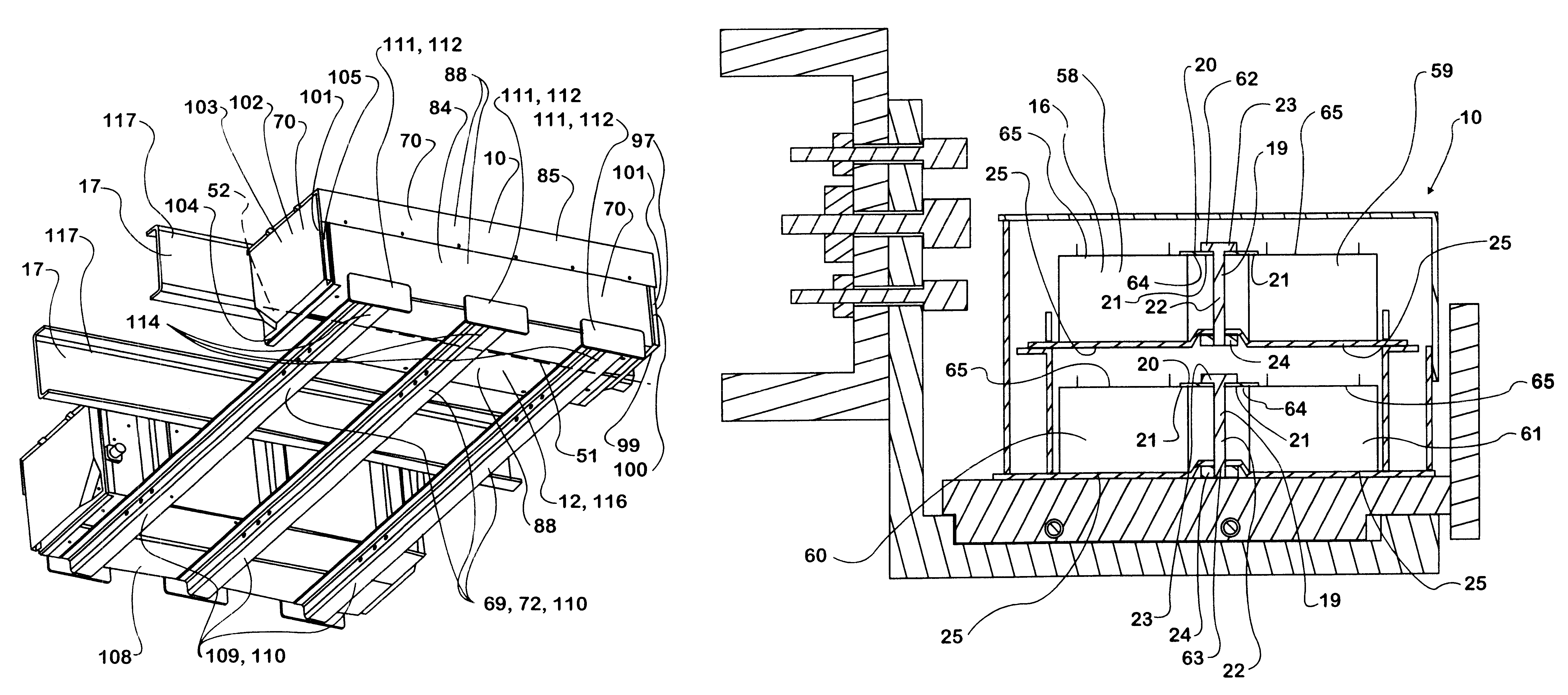
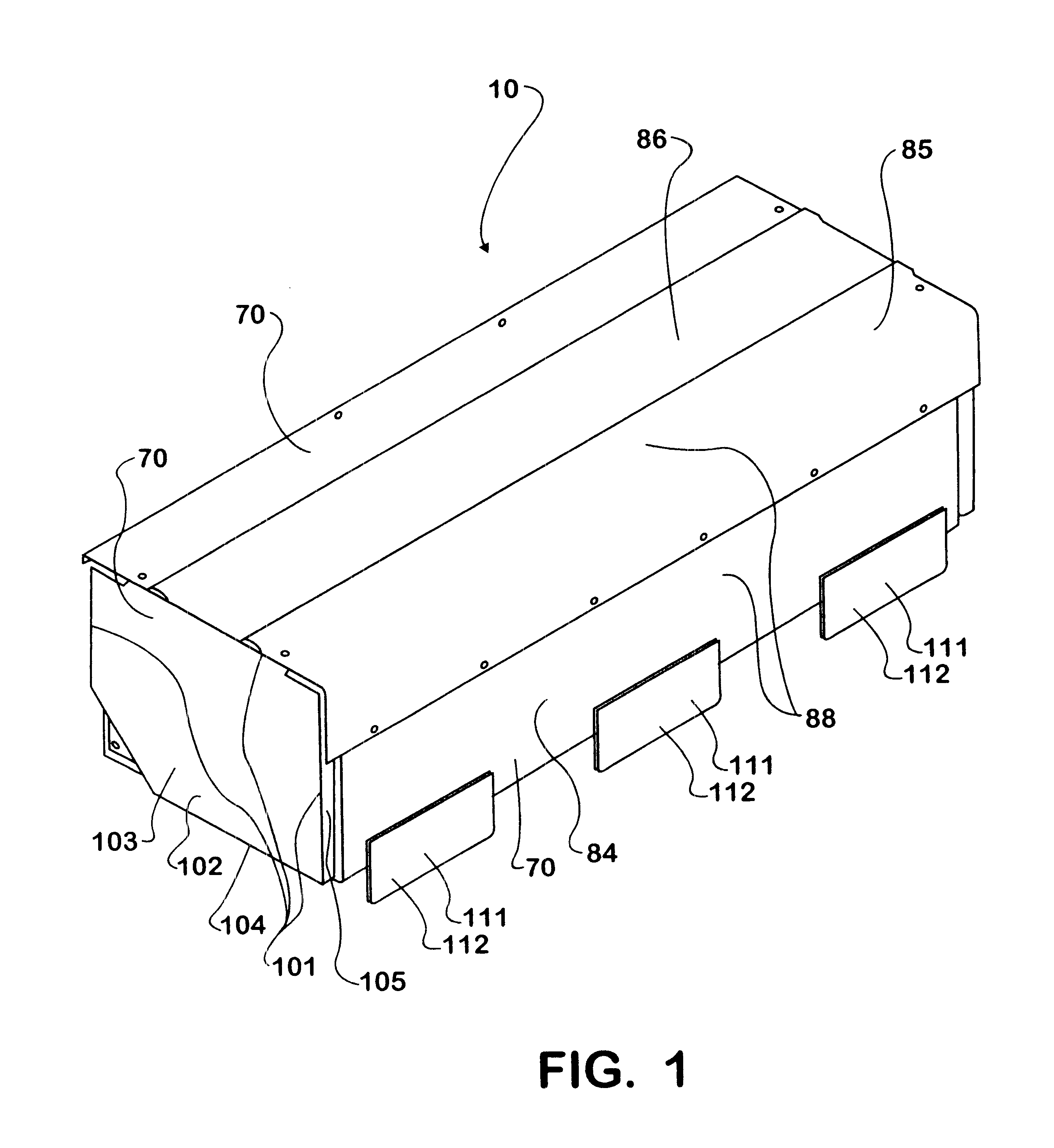
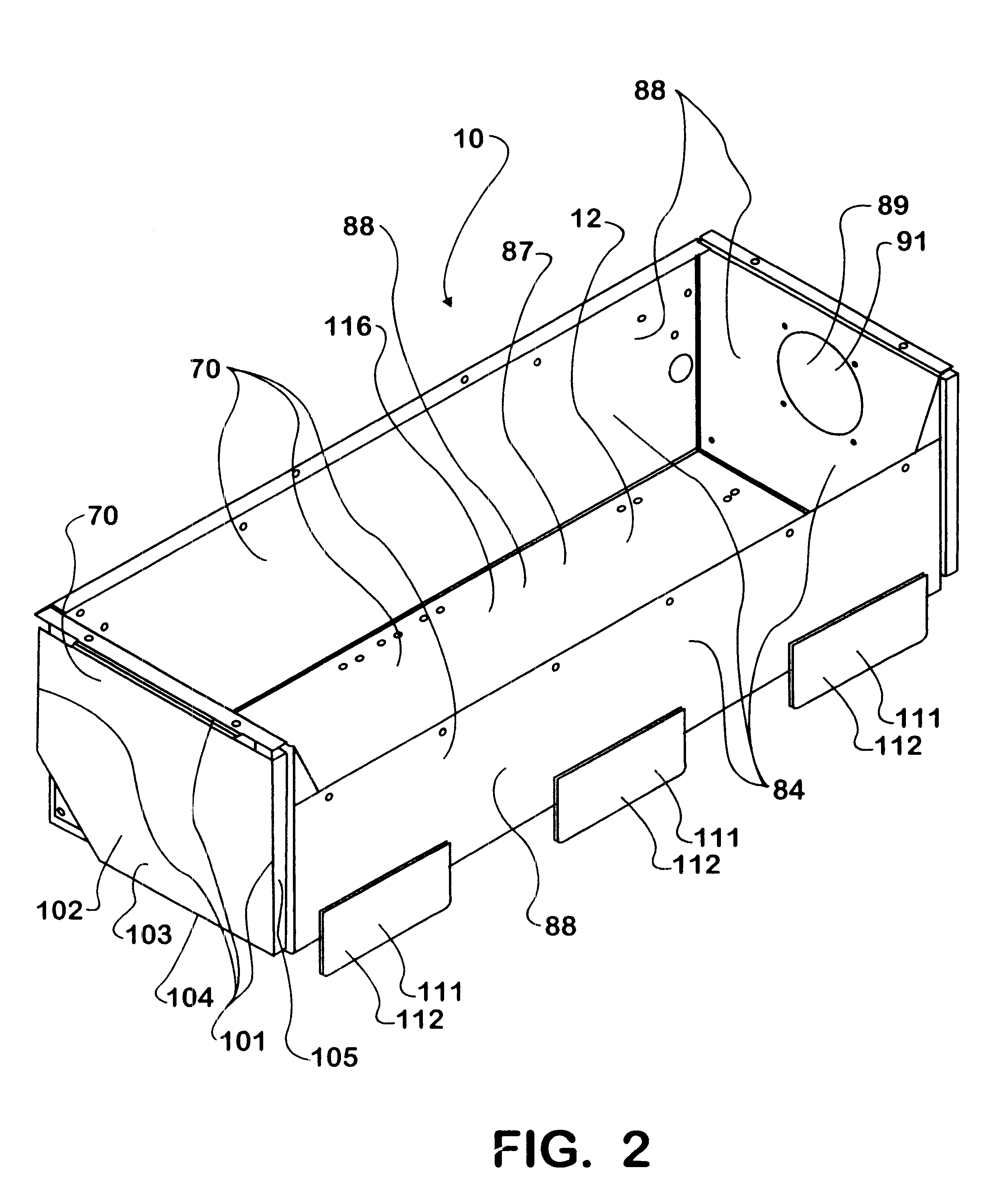
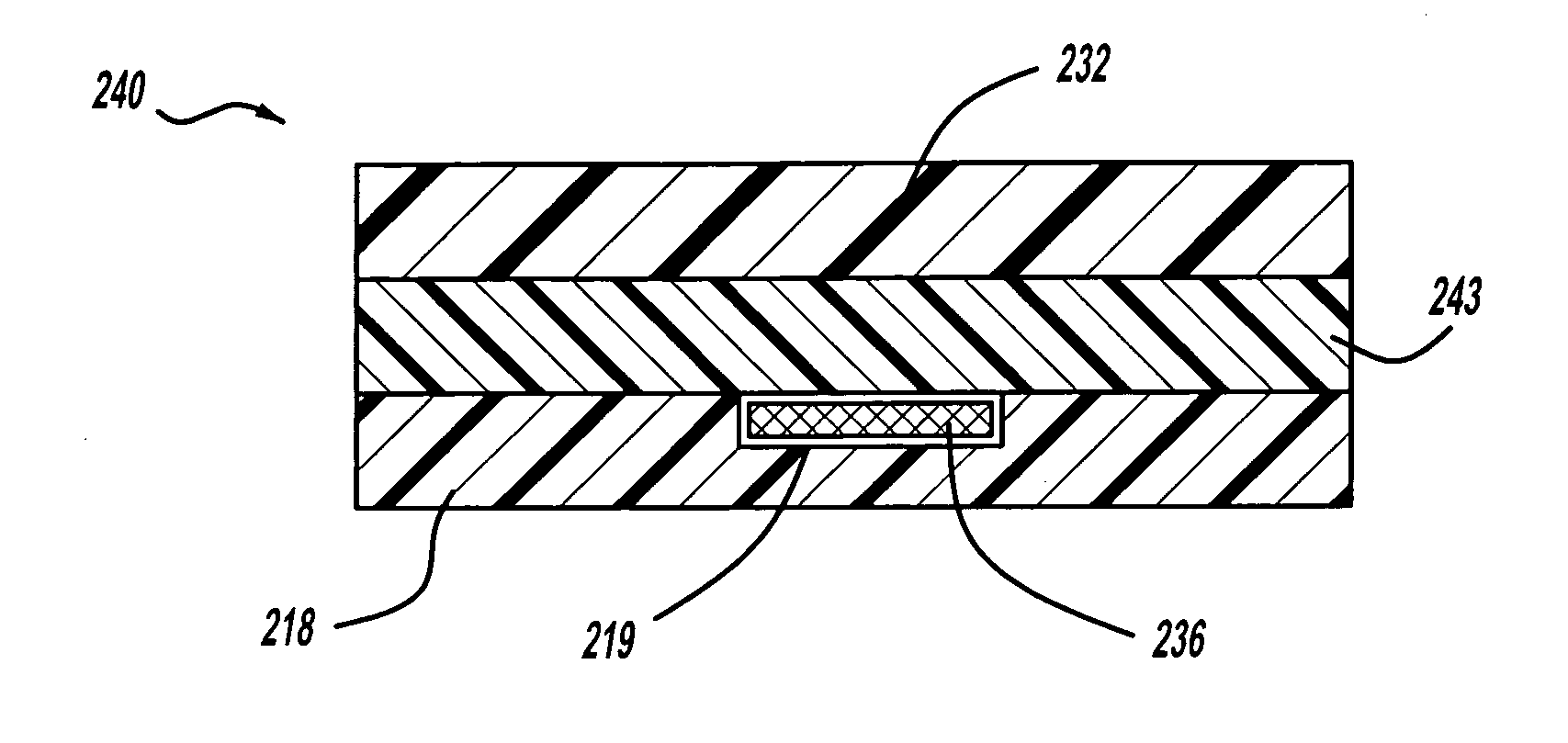
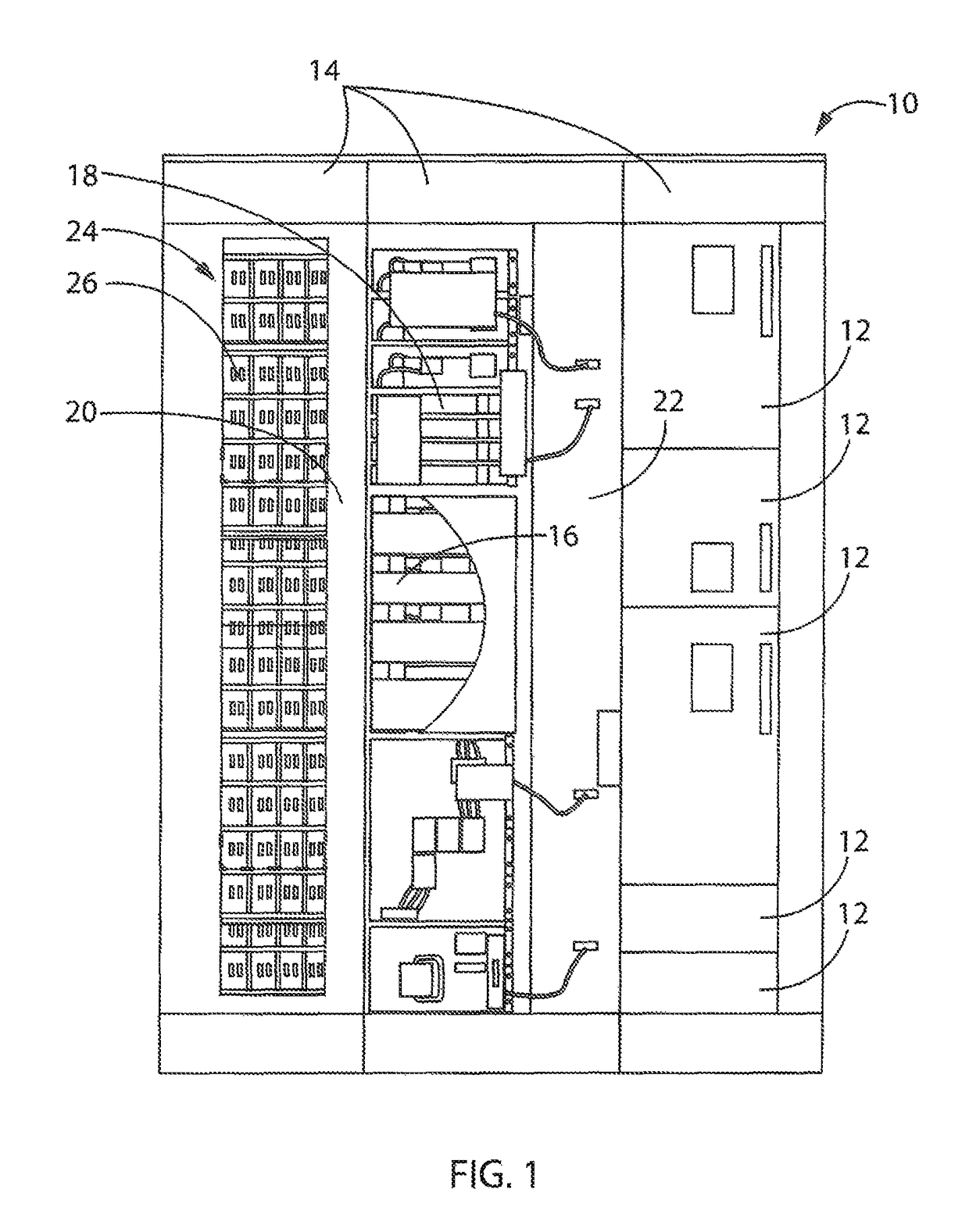
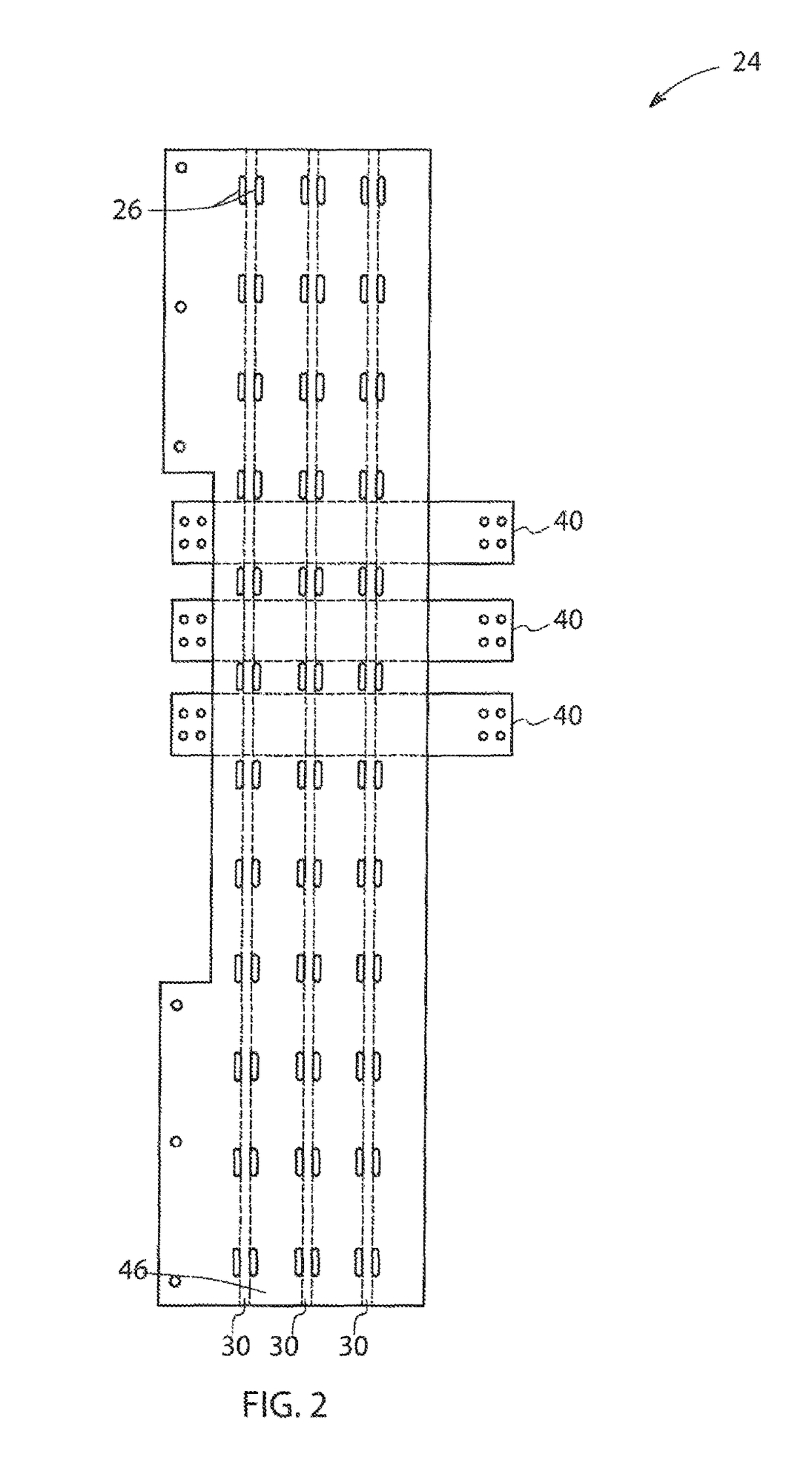
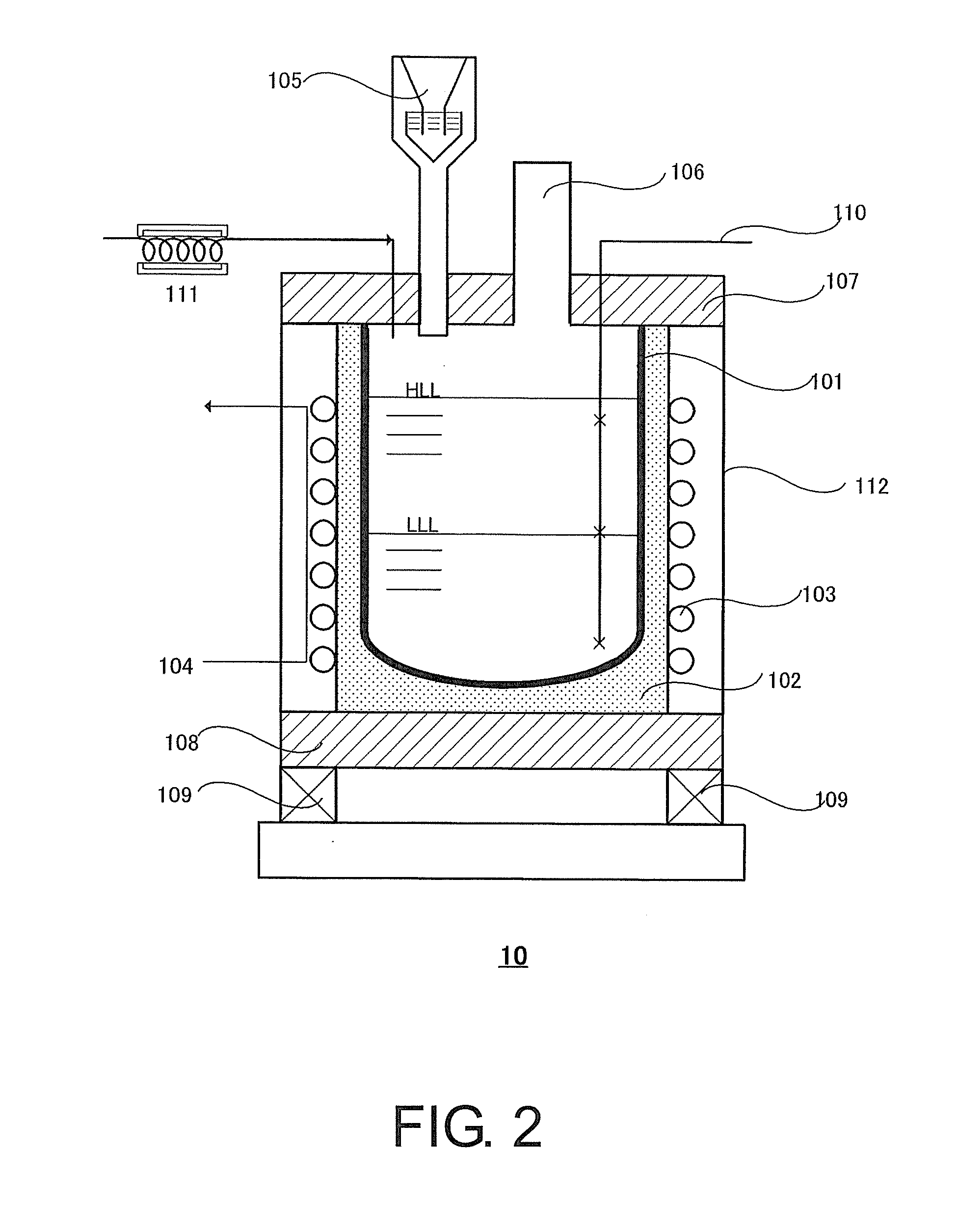
Battery mounting assembly
InactiveUS6547020B2Increase in sizeCompact spaceVehicle seatsSteering linkagesElectrical resistance and conductanceElastomer
A battery mounting assembly for mounting batteries to a vehicle. The battery mounting assembly has lower battery tray and an upper battery tray disposed below and above one another respectively. The battery mounting assembly is constructed to move and deform in predetermined ways when it is subjected to relatively large forces such as might occur when the vehicle is involved in a traffic accident. The battery mounting assembly has one or more bumper components intended to protect batteries mounted to the battery mounting assembly from being subjected to a direct impact. Steel components of the battery mounting assembly are coated with an elastomer that has a high electrical resistance.
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
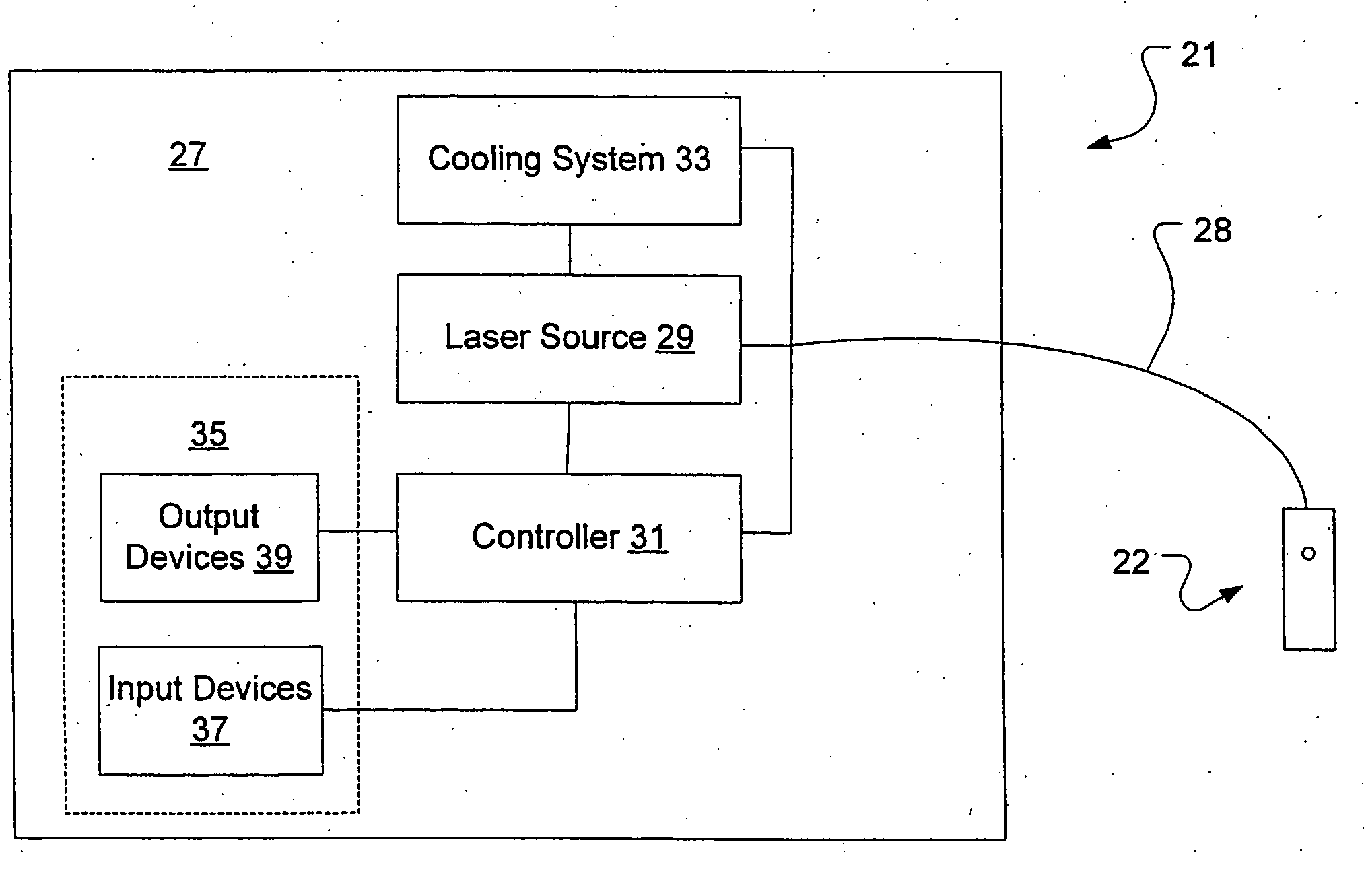
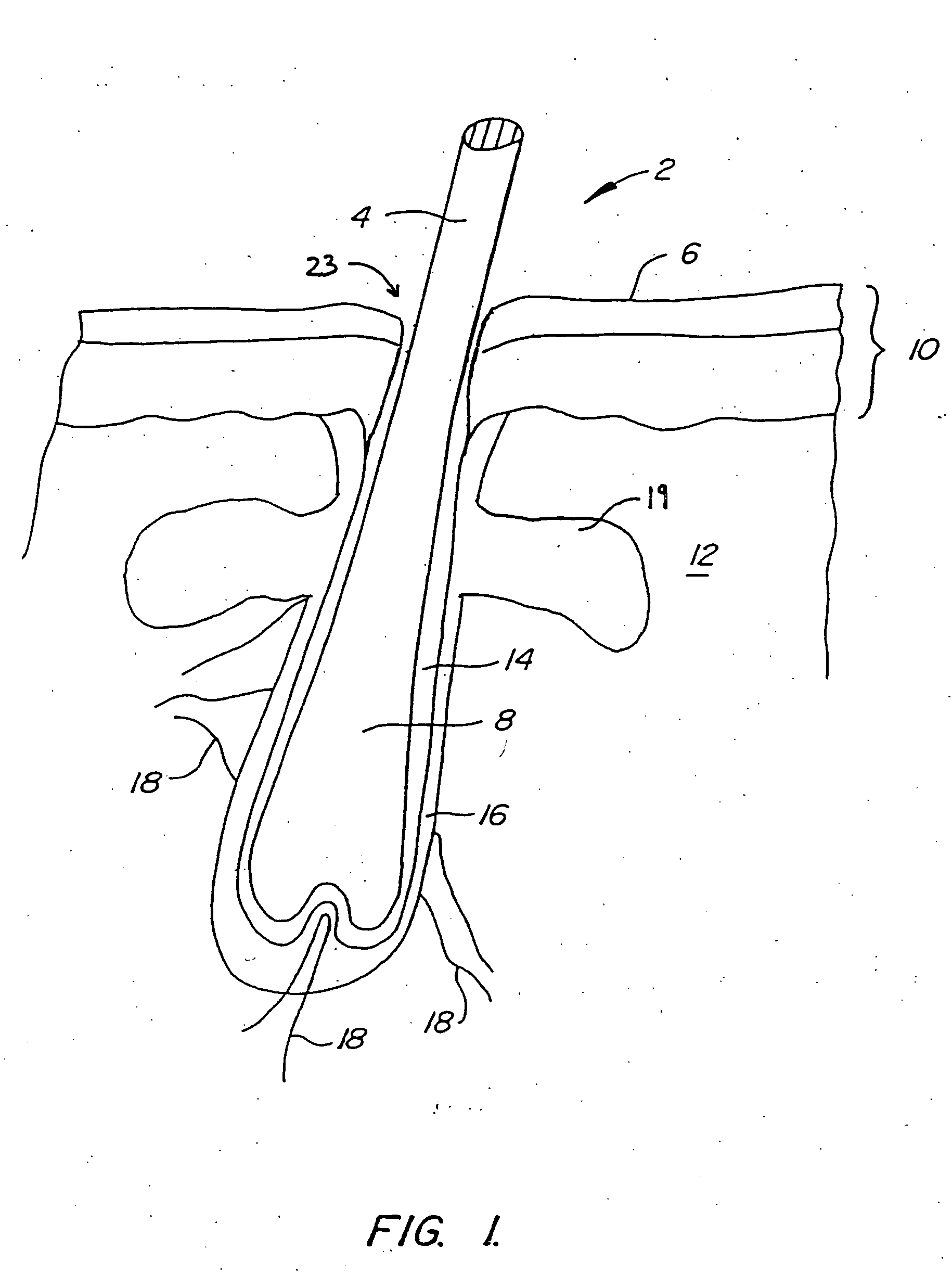
Methods and devices for non-ablative laser treatment of dermatologic conditions
ActiveUS20050107852A1Short pulse operationLarge amount of energyElectrotherapyDiagnosticsWrinkle skinCelsius Degree
The invention comprises a system and method for non-ablative laser treatment of dermatologic conditions. A laser energy is transmitted to an underlying target element in the skin. The target element is heated to a temperature of at least forty degrees Celsius. In some embodiments, a pulsed, near infrared, high peak power laser energy is used. The systems and methods of the present invention may be used to treat acne, smooth wrinkles, remove hair, treat leg veins, treat facial veins, improve skin texture, decrease pore sizes, reduce rosacea, reduce “blush / diffuse redness, reduce striae, reduce scarring, or the like.
Owner:CUTERA
Microwave heating apparatus and method for whole-body or regional heating
ActiveUS20070244530A1Rapid of regionLarge amount of energyElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyWhole bodyEngineering
The invention provides a microwave heating method and apparatus for evenly heating an object, such as a person's body. The methods and apparatus involve use of microwave source (or sources) that outputs multiple microwaves that are non-correlated with each other in phase; an array of antennas that radiate substantially plane microwaves to form a pseudo uniform microwave electromagnetic field, where the microwaves are not phase-correlated, in order to eliminate non-uniform heating caused by interference. Each of the antenna array consists of multiple antenna units, each antenna unit consists of at least one microwave radiator and at least one converter that converts the spherical microwave to plane microwave. A computer based control system and a temperature monitoring subsystem can be used to adjust the output of each antenna, in order to enhance the uniform heating effect. The apparatus and method can be used to perform whole-body hyperthermia or regional hyperthermia.
Owner:HUNAN YOULI MEDICAL TECH
Battery mounting assembly
InactiveUS20020162696A1Increase in sizeCompact spaceBattery isolationElectric propulsion mountingElectrical resistance and conductanceElastomer
A battery mounting assembly for mounting batteries to a vehicle. The battery mounting assembly has lower battery tray and an upper battery tray disposed below and above one another respectively. The battery mounting assembly is constructed to move and deform in predetermined ways when it is subjected to relatively large forces such as might occur when the vehicle is involved in a traffic accident. The battery mounting assembly has one or more bumper components intended to protect batteries mounted to the battery mounting assembly from being subjected to a direct impact. Steel components of the battery mounting assembly are coated with an elastomer that has a high electrical resistance.
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
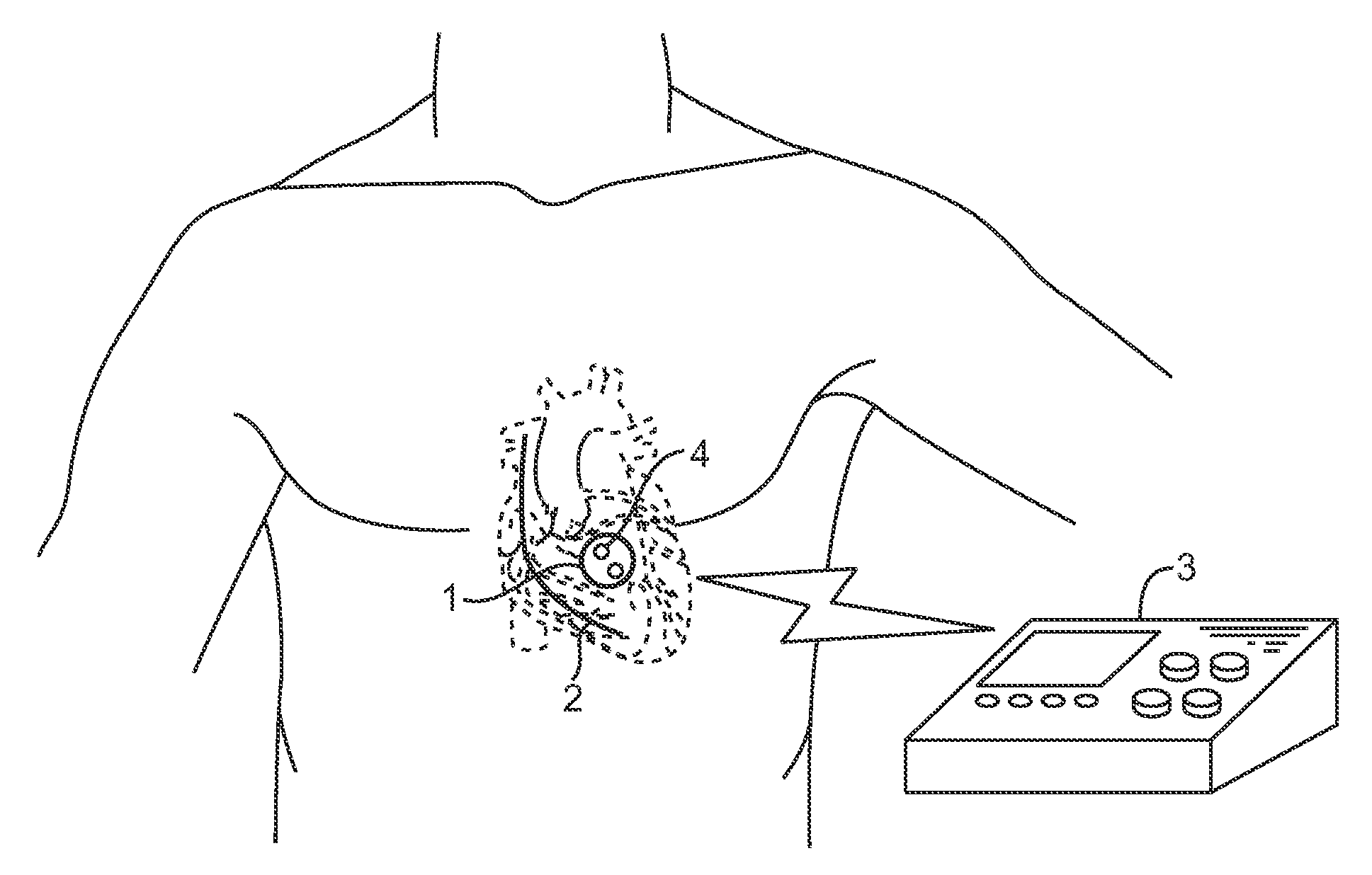
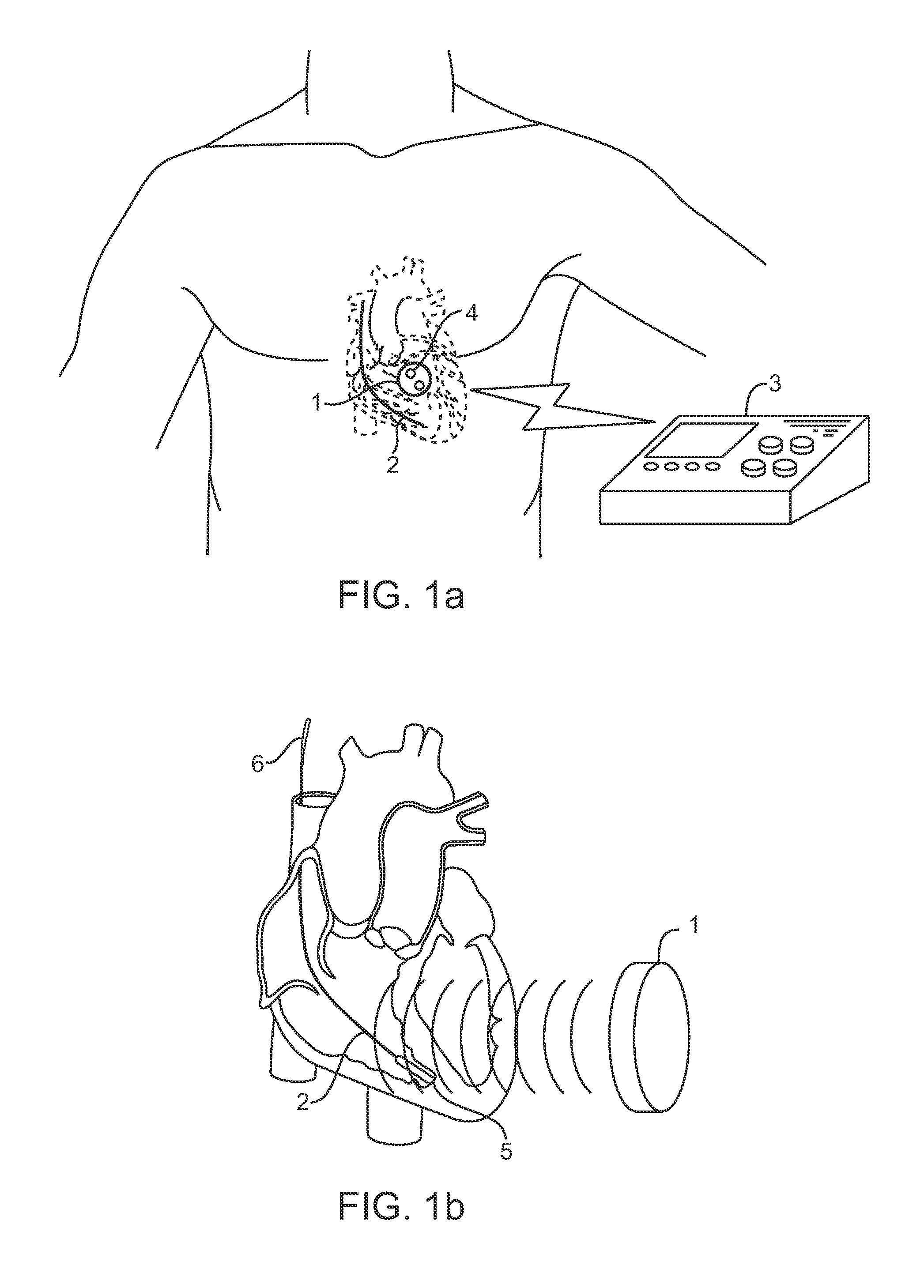
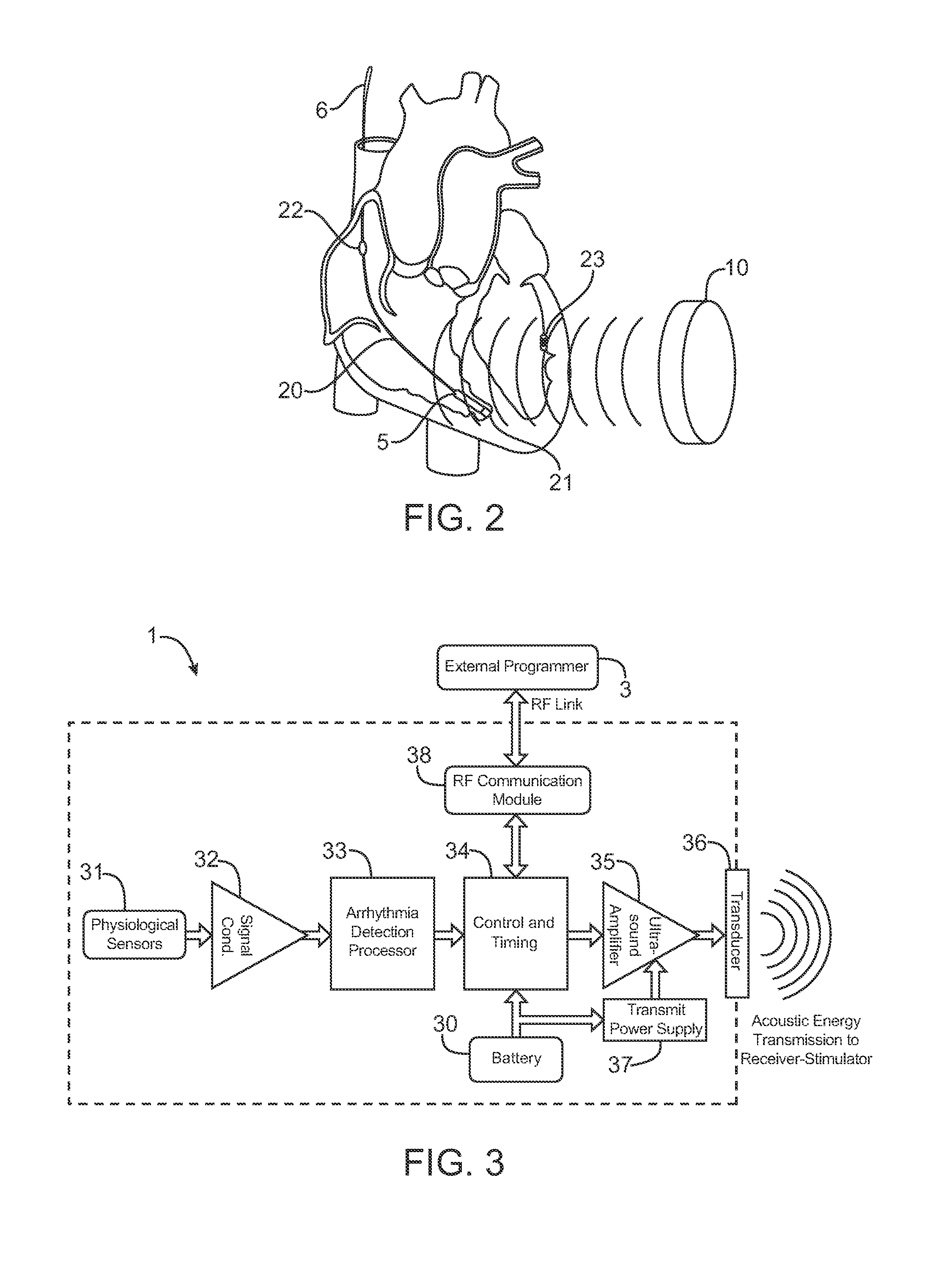
Acoustically-powered wireless defibrillator
ActiveUS20070293895A1Large amount of energyIncrease amplitudeHeart defibrillatorsElectricitySonification
An acoustic transmitter produces a pulsed ultrasound waveform which is transmitted through body tissues to an implanted receiver-stimulator device. The waveform has an acoustic amplitude, pulse width, and pulse repetition period, which corresponds to a pacing pulse electrical amplitude, pacing pulse width, and pacing cycle length, respectively. The receiver-stimulator device intercepts at least a portion of the transmitted acoustic energy and coverts that acoustic energy into electrical energy using piezoelectric or other devices. This electrical energy is applied to circuitry, which produces a desired stimulating pulse waveform, which is then applied to tissue-contacting electrodes.
Owner:EBR SYST
Jounce bumper
InactiveUS20050230891A1More travelOvercome effectMultiple spring combinationsResilient suspensionsEnergy absorptionEngineering
An energy absorption device for providing a softer stop arrangement between a pair of components. A compressible bumper is placed into a flexible cup. A ring is place around the flexible cup. Upon application of force between the components, the compressible bumper collapses into the flexible cup and the cup begins to expand radially. The ring prevents the cup from expanding to the point of flattening and provides the device with a definite rigid stop. The device is usable between any two components to prevent collisions between the components up to a certain force between them and is also usable between a strut assembly and a vehicle suspension frame.
Owner:EDWARDS INDS
Apparatus for creating therapeutic charge transfer in tissue
InactiveUS20050065394A1Avoid high pressureConsume energyElectrotherapySurgeryGrowth phaseTherapeutic effect
An apparatus for creating therapeutic charge transfer in tissue includes a coil. The coil generates a changing magnetic field to induct an electric field in the tissue exceeding 10 mV / cm when the coil is 5 cm from the tissue. Preferably, the magnetic field has a growth phase and a decay phase and a duration of the growth phase is at least ten times a duration of the decay phase. The apparatus can include a control circuit to control a current fed to the coil. The control circuit includes two subcircuits and a switch for switching between a first of the subcircuits and a second of the subcircuits; preferably, a λ of the second subcircuit is at least ten times a λ of the first subcircuit. To generate the therapeutic effect, the coil should have a duty cycle of at least ten percent.
Owner:ADVATECH CORP
Device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20050075760A1The device operates reliablyImprove applicabilityDigital data processing detailsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsVisibilityDisplay device
The invention relates to a device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle, having a radiation source for infrared radiation for irradiating the surroundings of the vehicle, having an infrared-sensitive camera for taking images of at least part of the irradiated surroundings, having a display unit for displaying collected image data, and having a control unit for controlling the device. Furthermore, a sensing unit for a recommended maximum velocity vmax is provided and is connected to the control unit. A velocity sensor which is connected to the control unit is provided in such a way that the control unit causes the display to be switched off when the vehicle velocity v exceeds the maximum velocity vmax. The display is preferably switched on when the vehicle velocity v drops below the maximum velocity vmax. The sensing unit for a recommended maximum velocity vmax is preferably designed in such a way that the recommended maximum velocity vmax is determined from the road profile or from the driving behavior of the vehicle or from received radio signals. This device ensures that the vehicle with the device operates in a safe way for the user.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
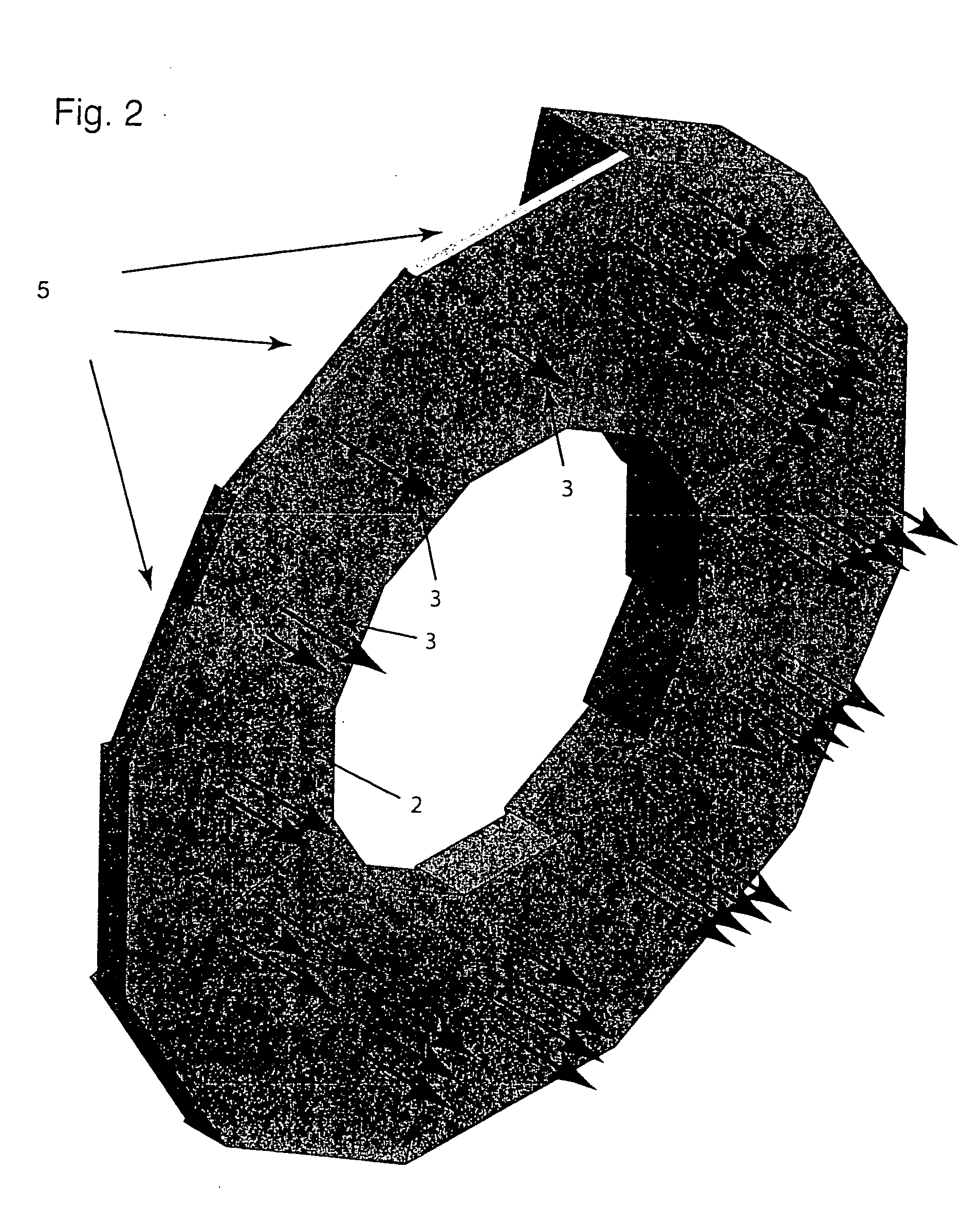
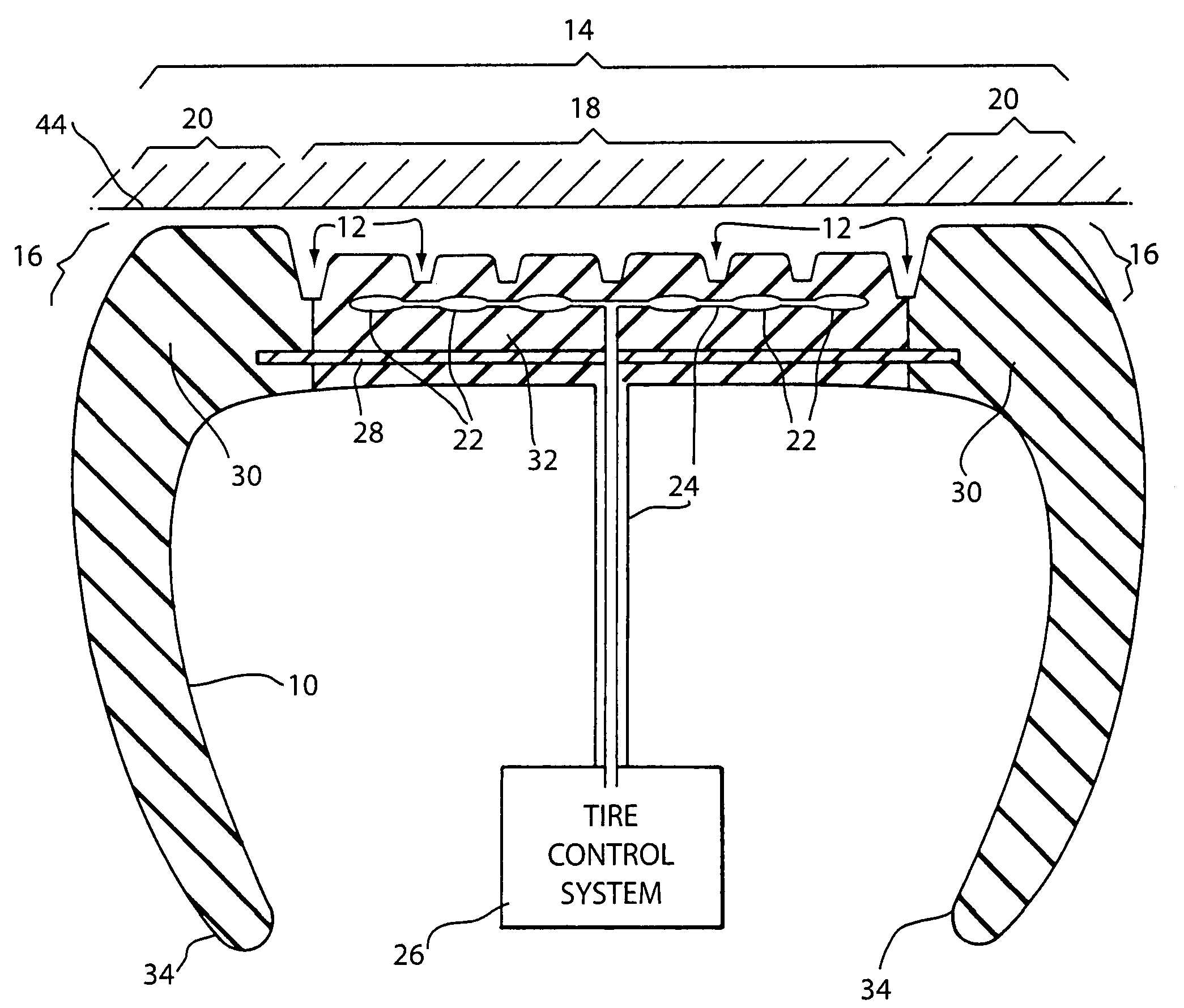
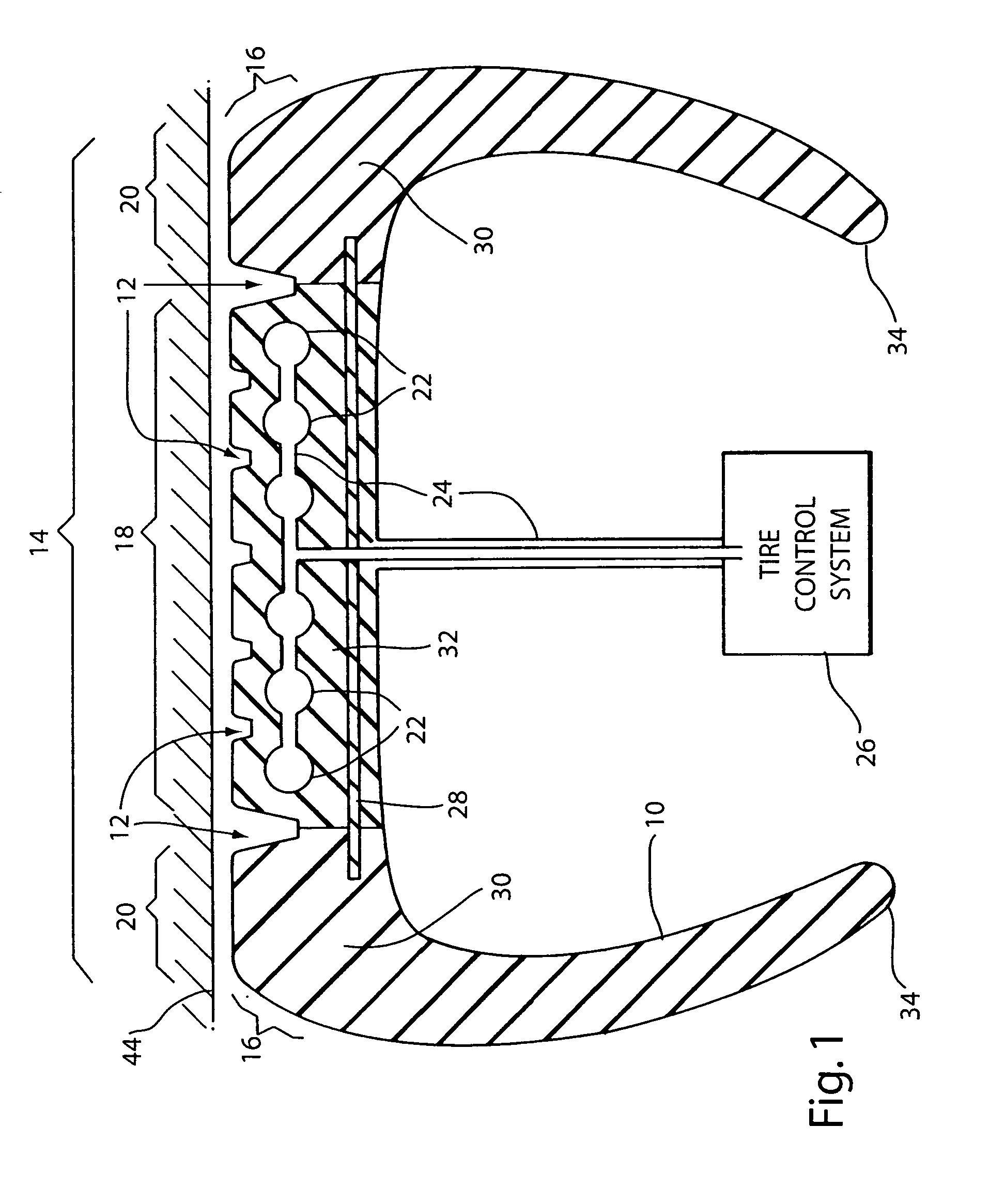
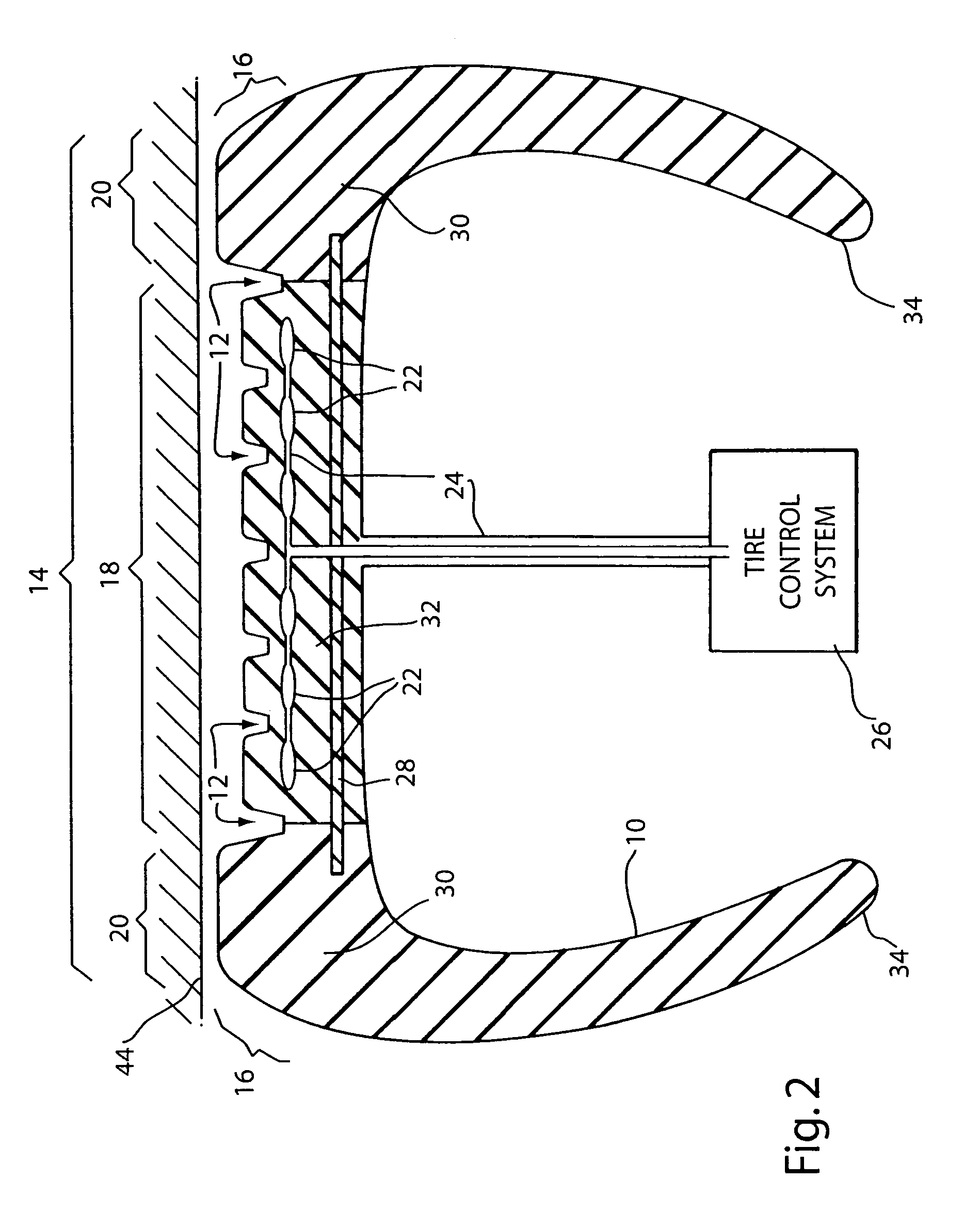
Fuel efficient vehicle tire having a variable footprint and low rolling resistance
InactiveUS7066226B1Low gas consumptionEffective dry tractionSpecial tyresTyre tread bands/patternsGround contactMicrocomputer
A tire for vehicles offering low rolling resistance wherein the ground-contact surface area is variable as a portion of the tread part can be retracted and / or extended using pneumatic, mechanical or hydraulic force to withdraw from, or come into contact with the road surface before, during or after operation permitting more efficient operation wherein the material used within the tread part that retains contact with the road may generally have a smaller internal friction loss than the material used in conventional tires and the rolling resistance is thereby reduced when the retractable portion of the tread is selectively withdrawn from contact with the road surface furthermore achieving a smaller ground-contact patch footprint. The achieved object of a tire with a lower rolling resistance yields improved fuel consumption efficiency. Improvements in exterior and interior noise levels and a reduced tendency to exhibit hydroplaning action are also attained with a variable groove volume to tread surface-contact ratio. Within one embodiment of the present invention, an automated microcomputer-based tire control system is disclosed useable to command the motion of the moveable tread portion of the said tire in response to various operational scenarios.
Owner:FIORE ROBERT ANGELO
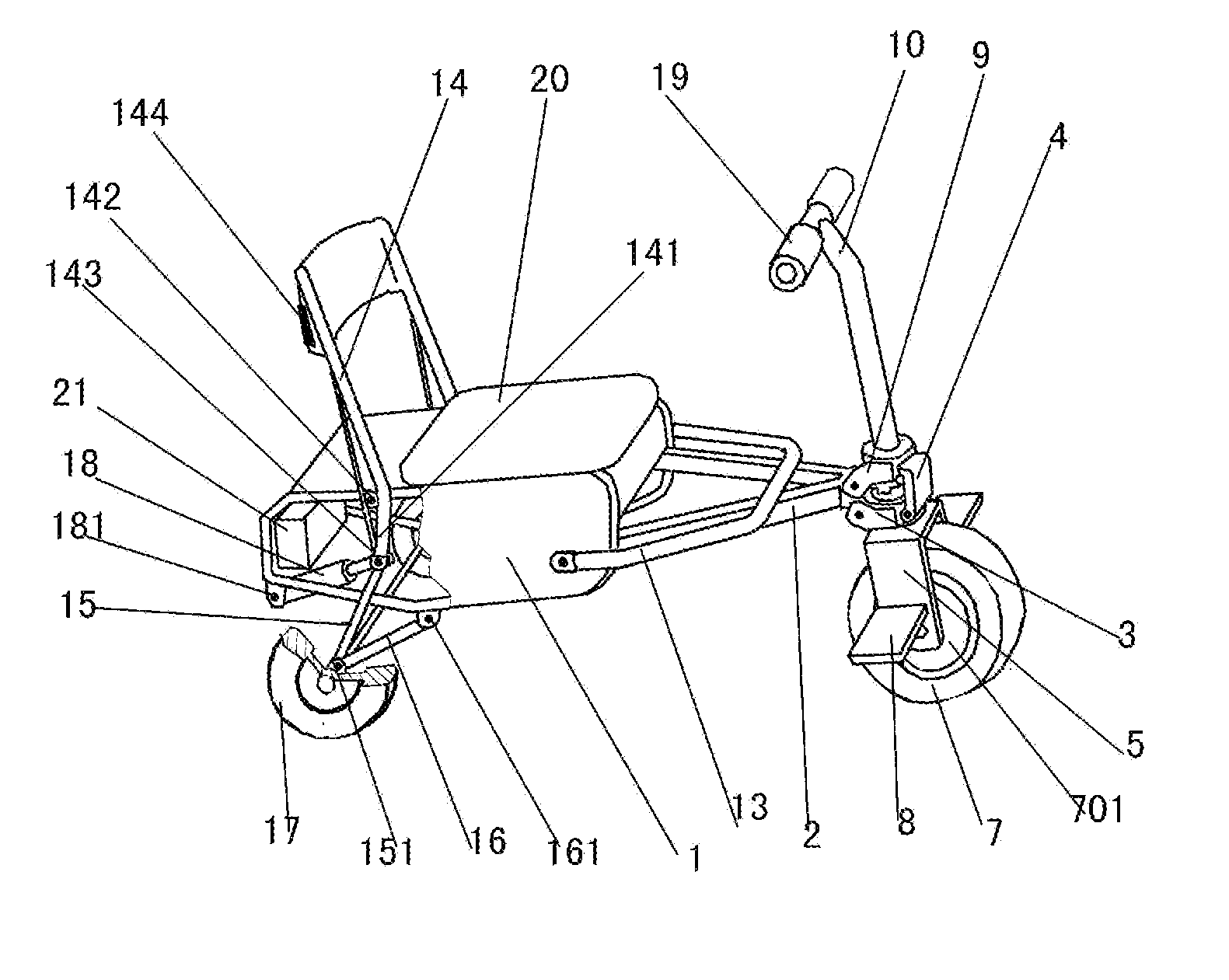
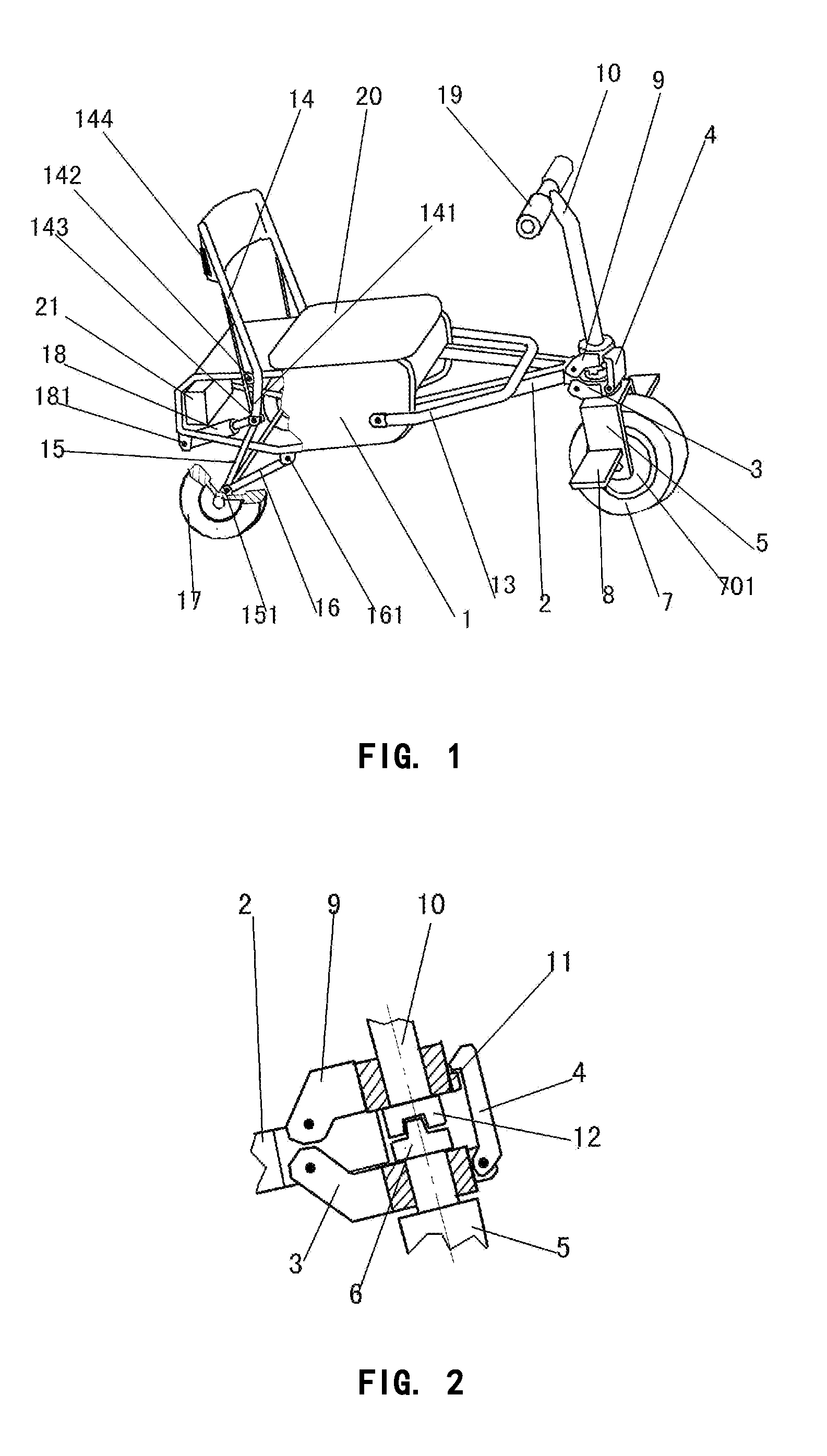
Draw-bar box type portable folding electro-tricycle with folding chair function
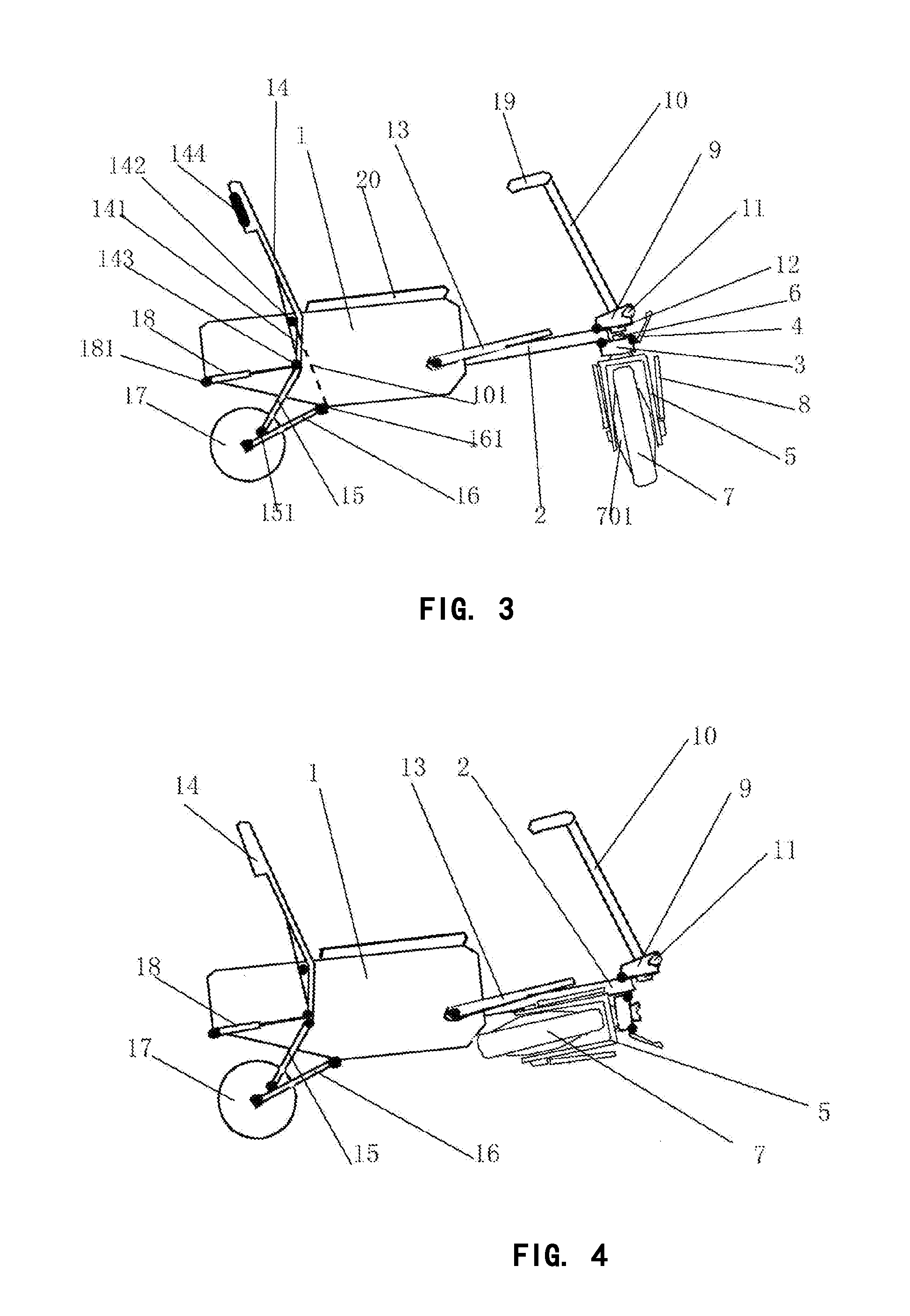
ActiveUS20160016629A1Easy to foldEasy to trainConvertible cyclesFoldable cyclesEngineeringUtility trolley
A portable foldable electric tricycle that can be folded to form a trolley suitcase shape and a chair includes a folding frame connecting a front wheel assembly and handlebar assembly to a seat. The front wheel assembly includes an electric motor to drive the front wheel. A backrest and rear wheel assembly are hinge connected with the seat by oppositely disposed four bar linkages. A stand is hinge connected to the seat. The folding frame, front wheel assembly and handlebar assembly can be folded to a position within the seat and the stand folded to a position in which it supports the seat to define the chair configuration of the electric tricycle. The backrest and rear wheel assembly can be folded to non-extended positions in which they are disposed adjacent the seat to define the trolley suitcase configuration of the case.
Owner:SUNTECH UK LTD
Rotating multi-monolith bed movement system for removing co2 from the atmosphere
ActiveUS20150273385A1Improve efficiencyLow costGas treatmentIsotope separationPorous substrateSorbent
A system for removing carbon dioxide from a carbon dioxide laden gas mixture, the system comprising two groups of carbon dioxide removal structures, each removal structure within each group comprising a porous solid mass substrate supported on the structure and a sorbent that is capable of adsorbing or binding to carbon dioxide, to remove carbon dioxide from a gas mixture, the sorbent being supported upon the surfaces of the porous mass substrate solid; an endless loop support for each of the groups of the removal structures, the endless loop support being so arranged as to move the support structures of each group along a closed curve while being exposed to a stream of the gas mixture; and a sealable regeneration box at one location along each of the endless loop supports, in which, when a porous solid mass substrate is sealed in place therein, carbon dioxide adsorbed upon the sorbent is stripped from the sorbent and the sorbent regenerated; each removal structural supporting a porous substrate in a position to be exposed to a flow of carbon dioxide laden gas mixture so as to allow for the removal of CO2 from the gas mixture; the number of removal structures to the number of regeneration boxes being directly determined by the ratio of the time to adsorb CO2, from a base level to desired level on the sorbent, to the time to strip the CO2 from the desired level back to the base level.
Owner:GLOBAL THERMOSTAT OPERATIONS LLC
Resistive implant welding for adhesive curing for thermoplastic and thermoset applications
ActiveUS20110212331A1Reduce amountLarge amount of energyLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticElectrical conductor
A welded joint for structural component having two or more portions fused together at a weld line. An adhesive layer is placed between the two or more portions at the location of the weld line and a conductor is placed between the two or more portions in operable contact with the adhesive. Energy is transmitted through the conductor and into the adhesive layer to activate the adhesive layer and create the weld line that defines the welded joints between the two or more portions. The welded joint of the structural component allows energy to be injected into the adhesive layer via the conductor in order to cause the adhesive layer to activate from the inside of the adhesive outward. The conductor can be placed adjacent the adhesive layer or within the adhesive layer in order to cause the adhesive to be activated from the inside outward.
Owner:MAGNA INTERNATIONAL INC
Hand-held hot air device with a digital operating device with a universal operating element
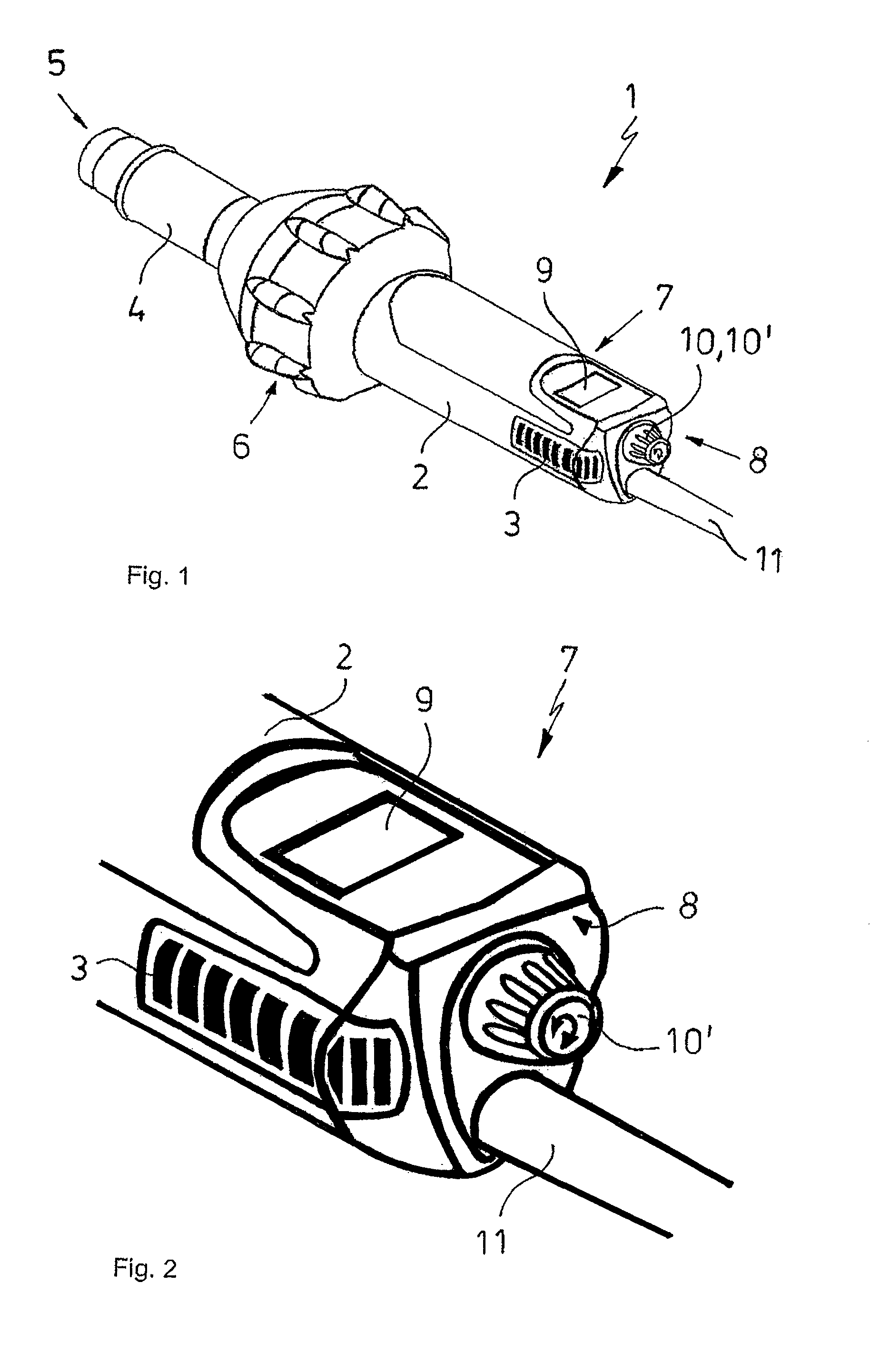
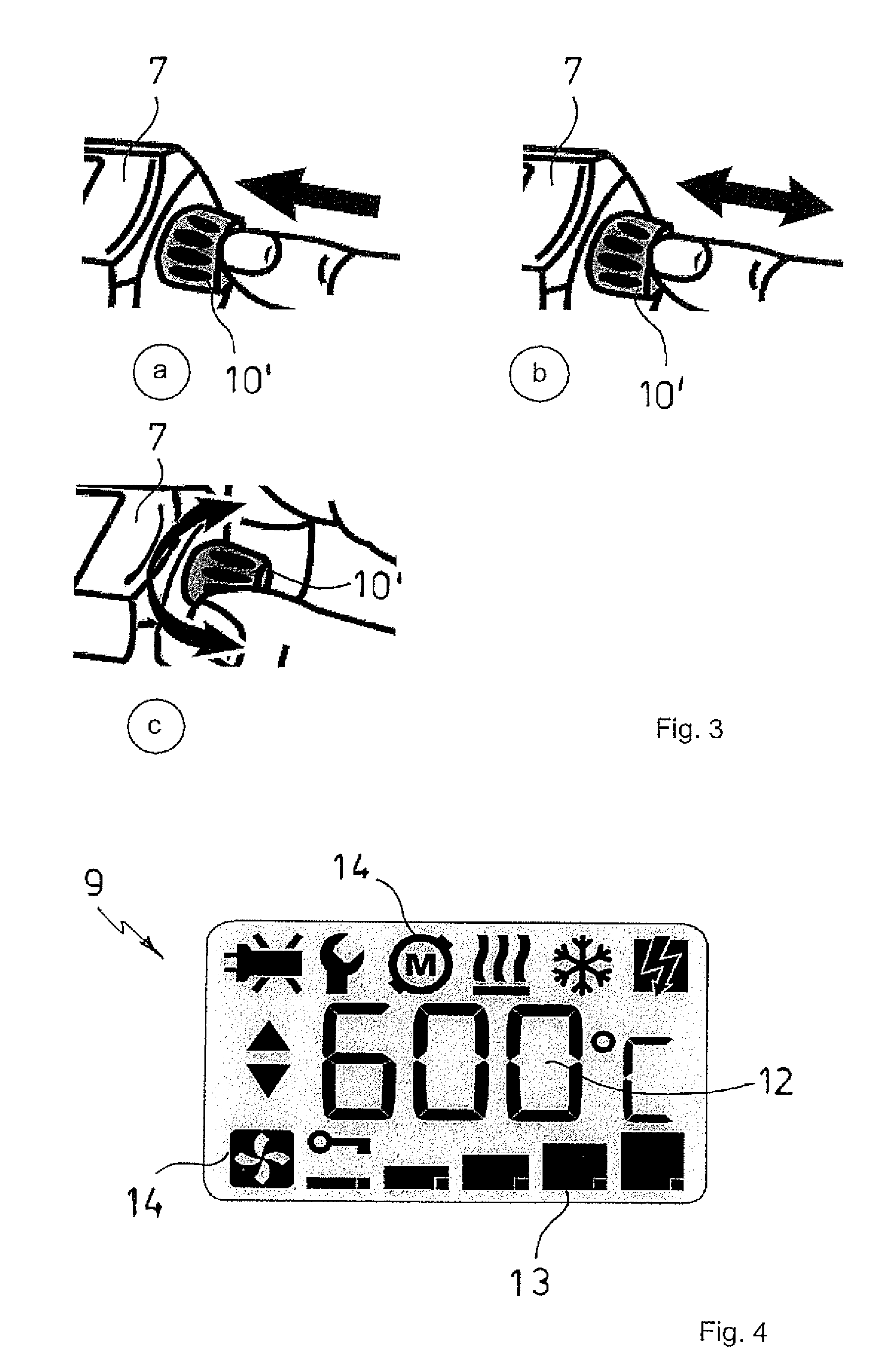
ActiveUS8948577B2Easy to operateThe process is simple and easy to understandAir heatersBathing devicesElectronic control systemControl system
The hand-held hot air device, preferably for the local heating of thermoplastic materials, with a housing that forms a wand-shaped handle part with air inlet openings, and with an air guidance tube that protrudes from the handle part and radially delimits an air canal, with an electric heating element contained in the air guidance tube and an electric motor with a fan wheel contained in the handle part, and with an electronic control system arranged inside the handle part with one semiconductor power switch each arranged upstream of both the heating element and the electric motor, and with a display screen and an operating device for the hand-held hot air device arranged on the outside of the handle part. The electronic control system is implemented as microprocessor control system, the display screen as an electronic digital display, and the operating device as a digital operating device, with the digital operating device comprising a single universal operating element that is movable in at least two directions relative to the handle part for the purpose of switching the hand-held hot air device on and / or off and for determining control data of the microprocessor control system.
Owner:LEISTER TECHNOLOGIES
Device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS20050073431A1Increase awarenessImprove securityAnti-collision systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsVisibilityDisplay device
The invention relates to a device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle, having a radiation source for infrared radiation for irradiating the surroundings of the vehicle, having an infrared-sensitive camera for taking images of at least part of the irradiated surroundings, having a display unit for displaying collected image data, and having a control unit for controlling the device. In this context, the control unit is embodied in such a way that, while the device is operating, the display represents image data in a chronologically limited fashion by means of controlled switching on and switching off, and in the process the switching off of the representation of images on the display is made gradual. The gradual switching off is carried out in particular by changing the brightness limiting values, the contrast limiting values and / or by increasing or reducing the noise of the image data to be represented. Furthermore, the gradual switching off preferably has a time-dependent or velocity-dependent profile. This device ensures that the vehicle with the device operates in a very safe way for the user.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Fuel cell system having a fuel cell, a hydrogen storage tank, and an anode circuit
InactiveUS20070190389A1Large amount of energyHigh trafficReactant parameters controlFuel cells groupingProcess engineeringHydrogen supply
A fuel cell system has at least one fuel cell, a hydrogen storage tank in which hydrogen is stored at a pressure above atmospheric and which communicates via a hydrogen supply line with an anode chamber of the fuel cell. An anode circuit, via which unreacted hydrogen is able to be recirculated from a region downstream of the anode chamber into the hydrogen supply line, is provided. At least one pumping device is provided between the outlet of the anode chamber and its inlet in the anode circuit and / or the hydrogen supply line. Between the hydrogen storage tank and the anode chamber, a turbine is provided, which supplies at least a portion of the power required for driving the pumping device.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
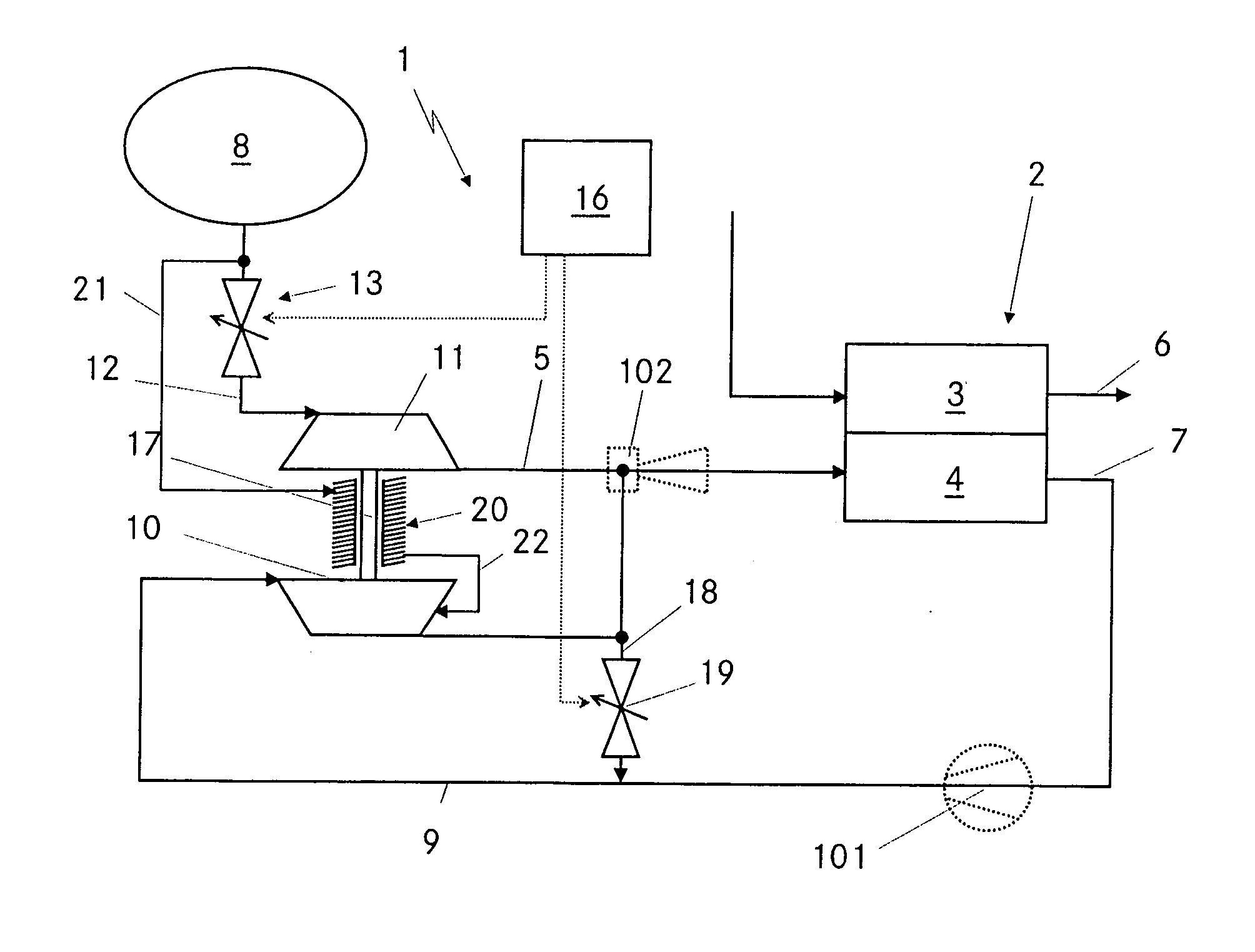
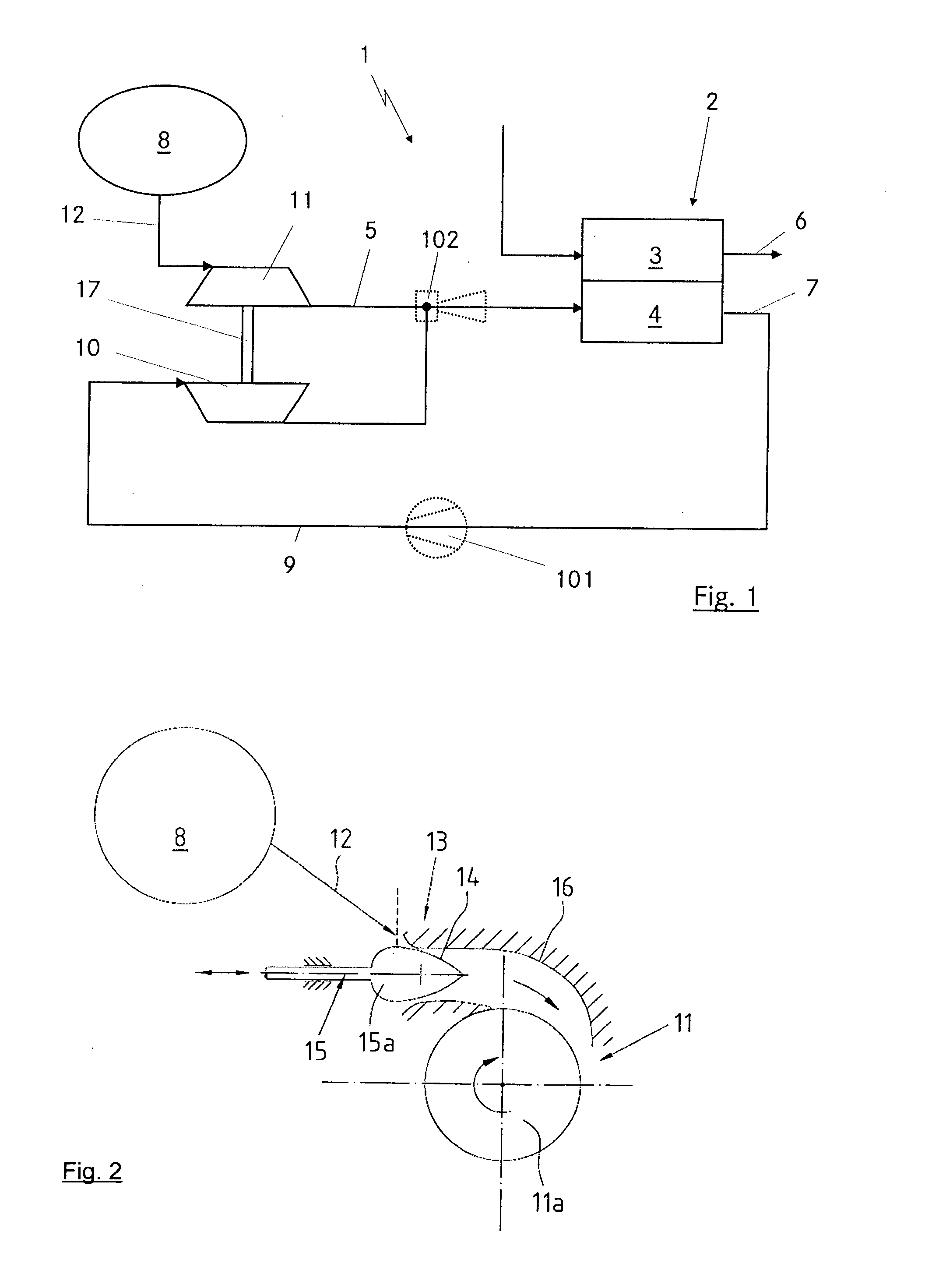
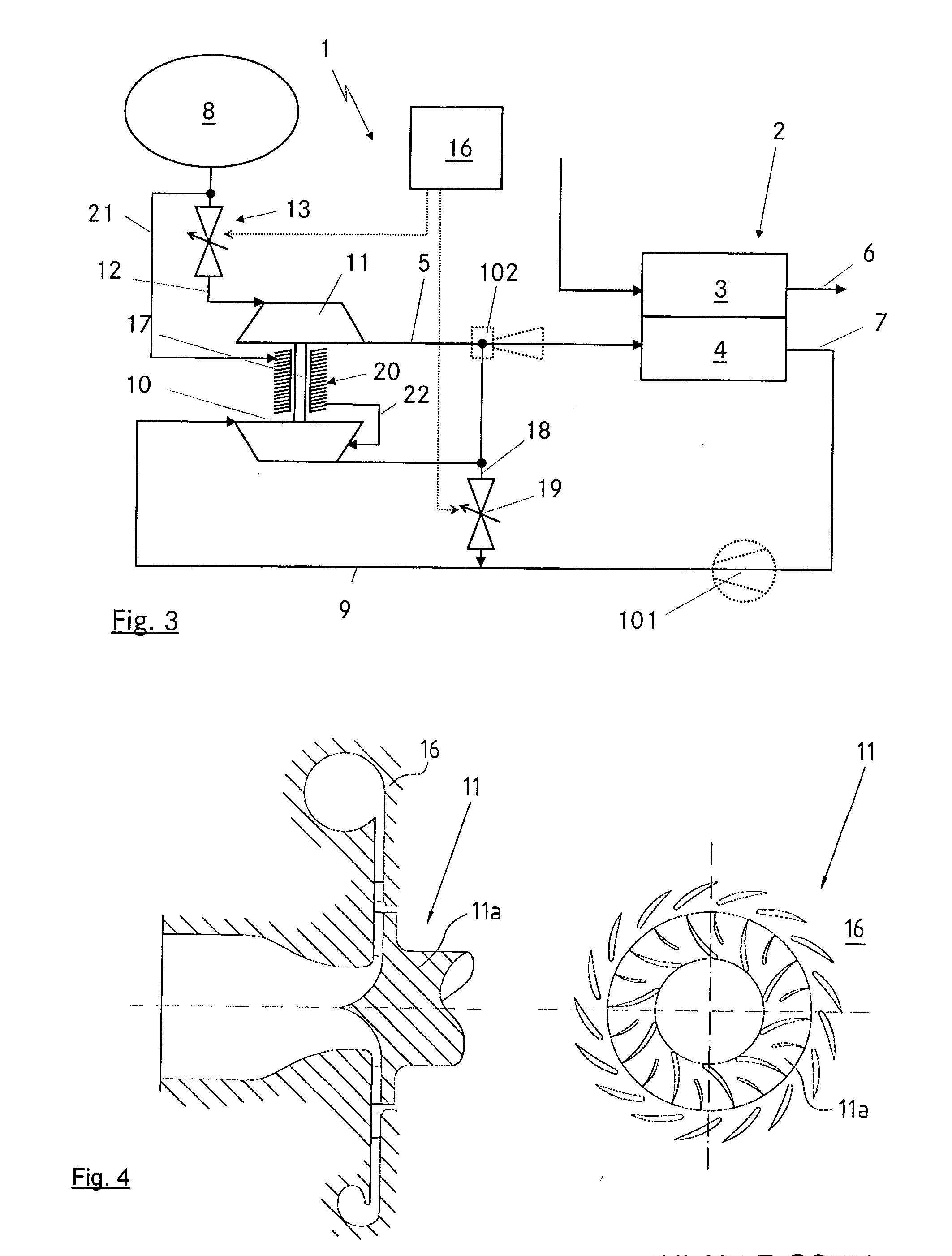
Joint source channel coding based on channel capacity using neural networks
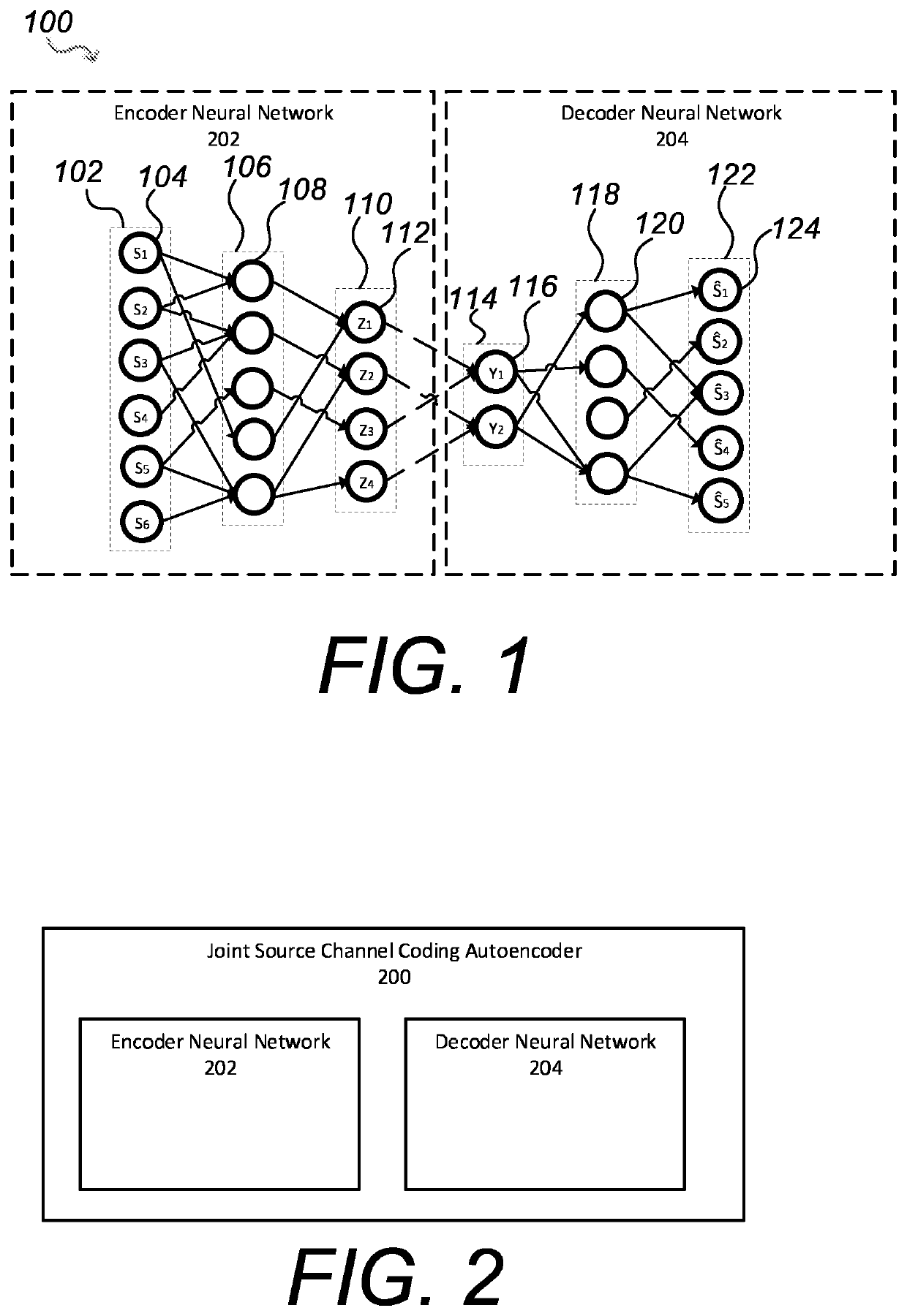
PendingUS20210351863A1Reduce data redundancyLarge amount of energyCode conversionCoding detailsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
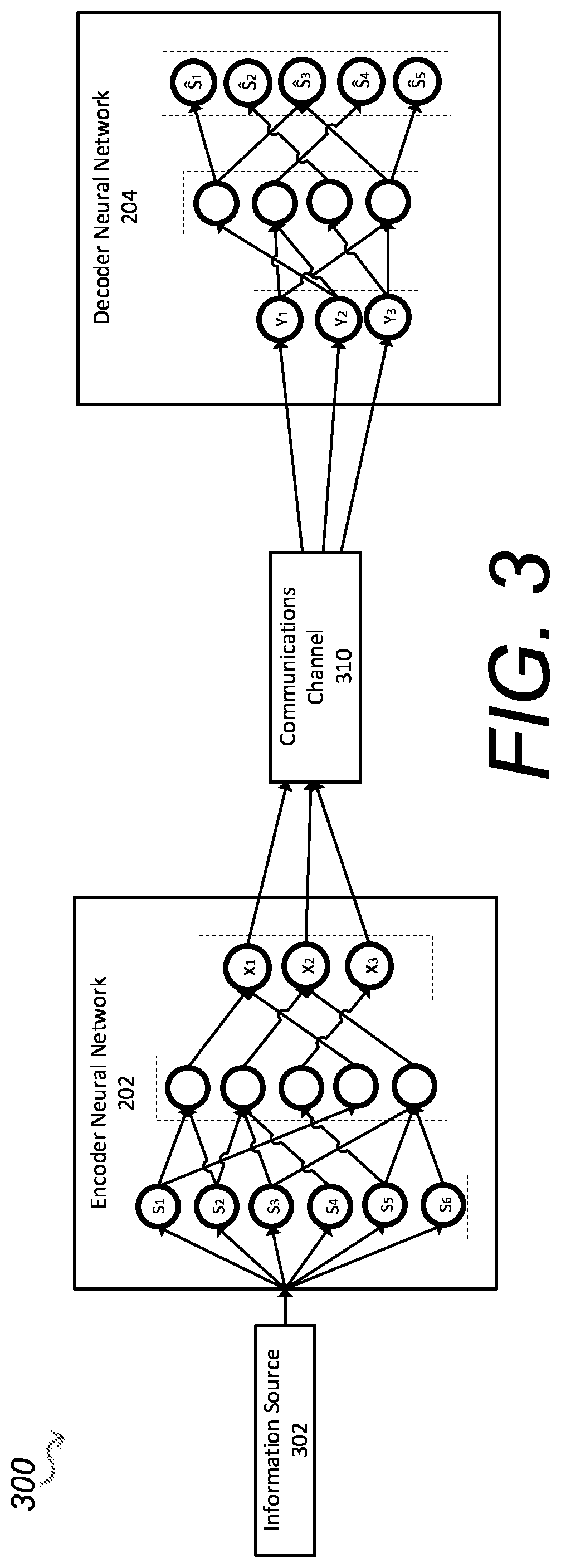
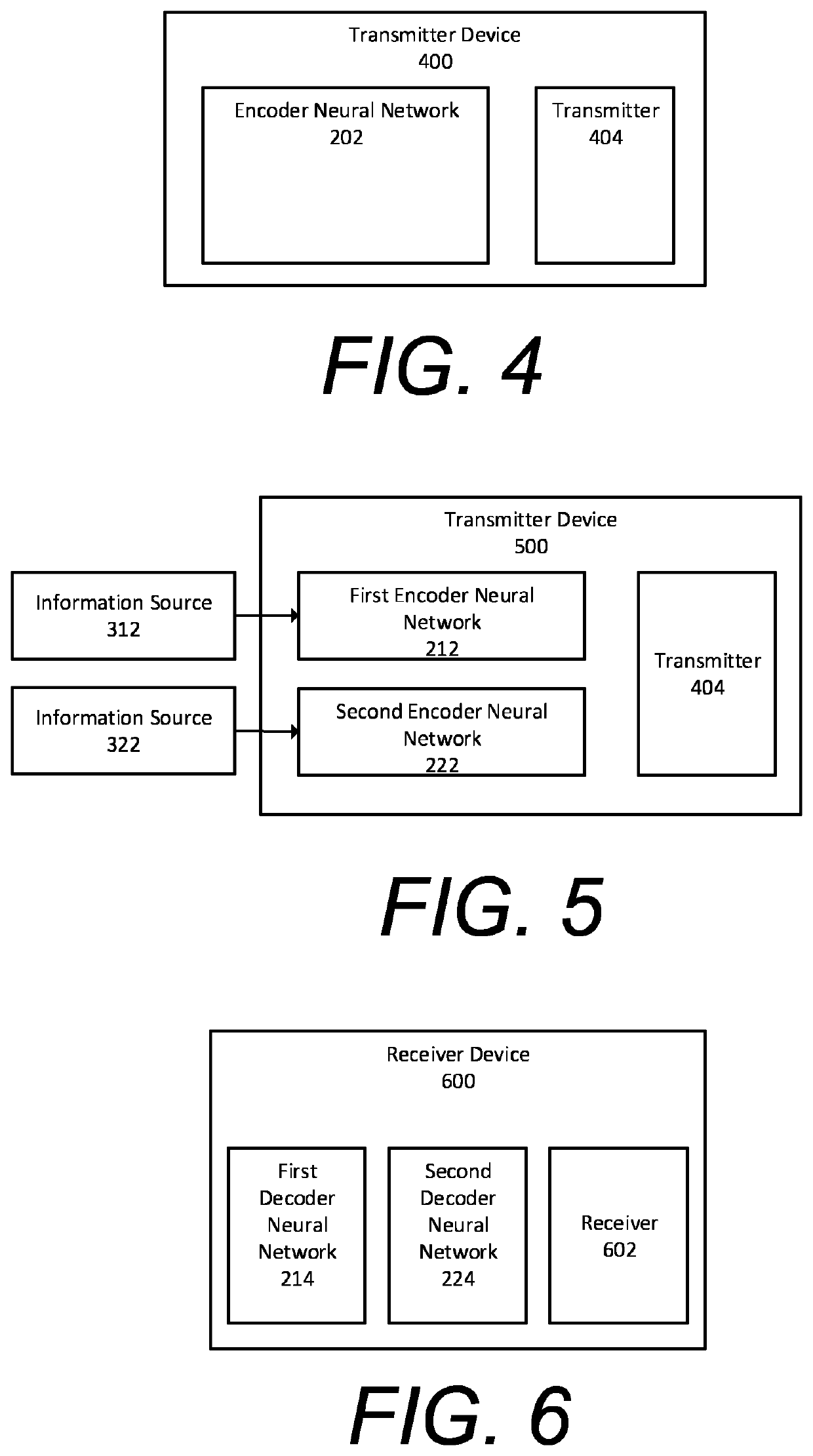
A communication system for conveying information from an information source across a communications channel using a joint source channel coding autoencoder, comprising: an encoder neural network of the joint source channel coding autoencoder, the encoder neural network having: an input layer having input nodes corresponding to a sequence of source symbols Sm={S1, S2, . . . , Sm}, the Si, taking values in an alphabet S, received at the input layer from the information source as samples thereof, and a channel input layer coupled to the input layer through one or more neural network layers, the channel input layer having nodes usable to provide values for the Xi, of a channel input vector Xn={X1, X2, . . . , Xn}, the Xi, taking values from the available input signal alphabet X of the communications channel, the channel input vector Xn comprising a plurality of signal values Xp usable to reconstruct an information source, wherein the number p of the plurality of signal values Xp is smaller than the total number n of signal values of the channel input vector Xn, and wherein at least one of the remaining signal values of the channel input vector Xn is usable to increase the quality of the reconstructed information source, and wherein the encoder neural network is configured through training to be usable to map sequences of source symbols Sm received from the information source directly to a representation as a channel input vector Xn, usable to drive a transmitter to transmit a corresponding signal over the communications channel; a first decoder neural network and a second decoder neural network of the joint source channel coding autoencoder, each decoder neural network having: a channel output layer having nodes corresponding to a channel output vector Y received from a receiver receiving a signal corresponding to at least the plurality of signal values Xp of the channel input vector Xn transmitted by the transmitter and transformed by the communications channel, and an output layer coupled to the channel output layer through one or more neural network layers, having nodes matching those of the input layer of the encoder neural network, wherein the first decoder neural network is configured through training to map the representation of the source symbols as the channel output vector Y transformed by the communications channel to a reconstruction of the source symbols Ŝm output from the output layer of the joint source channel coding autoencoder, the reconstruction of the source symbols Ŝm being usable to reconstitute the information source; and wherein the number of signal values of the channel output vector Y received by the first decoder network is more than the number of signal values of the channel output vector Y received by the second decoder neural network.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Battery system for micro-hybrid vehicles comprising high-efficiency consumers
ActiveUS20130026823A1Easy to useEasy feedingHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsMobile vehicleLow voltage
A battery system for a motor vehicle having an internal combustion engine includes at least one starting circuit, a low-voltage on-board supply system, and an on-board supply system with an increased voltage. The starting circuit has a first battery and a starter that is configured to be connected to the first battery. The low-voltage supply system has at least one electrical consumer and a second battery configured to produce a first voltage. The supply system with increased voltage has an electrical generator and a third battery configured to produce a second voltage that is higher than the first voltage. The electric generator is configured to produce a third voltage that is higher than the second voltage. A first coupling connects the supply system with increased voltage to the low-voltage supply system and transfers energy therebetween. A second coupling connects the low-voltage on-board supply system to the starter circuit.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
Device for Drying Bulk Material in at least one Storage Container
InactiveUS20110283554A1Increase temperature differenceSave energyDrying solid materials with heatGranular material dryingCold sidePulp and paper industry
Before being processed, bulk material is dried in a storage container. A drying medium such as air is passed through the bulk material for drying. The drying medium heats the bulk material and removes moisture at the same time. For dehumidifying the drying medium, a dehumidifying unit with a Peltier device is provided whose cold side and whose hot side are positioned within the flow path of the drying medium. The drying medium loaded with moisture is passed across the cold side and dehumidified. The hot side of the Peltier device is used to preheat the dehumidified drying medium.
Owner:MOTAN HLDG
Organic electroluminescent element and display device using the same
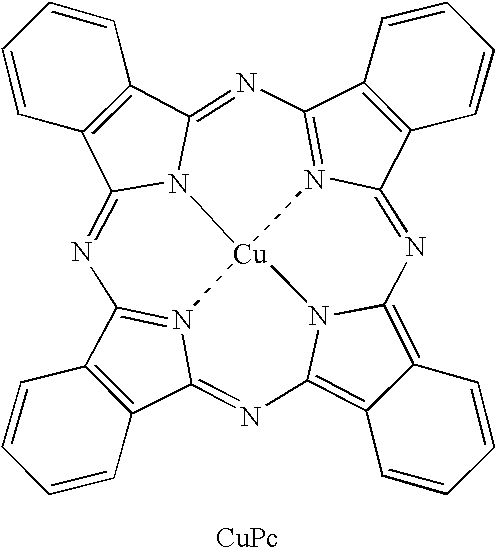
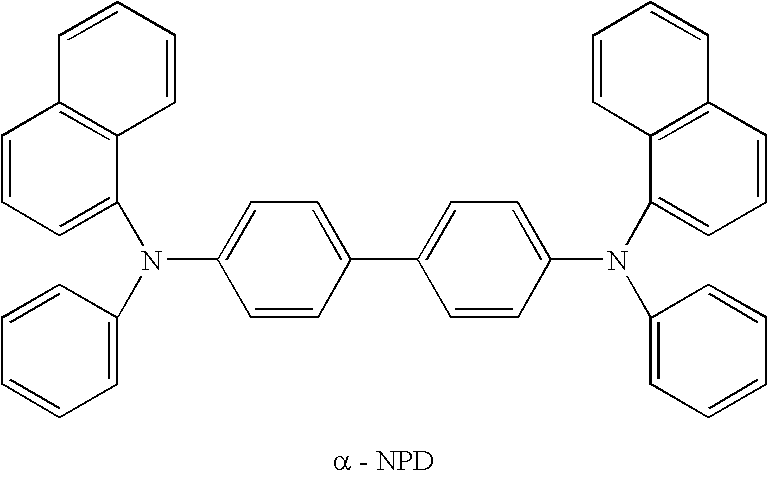
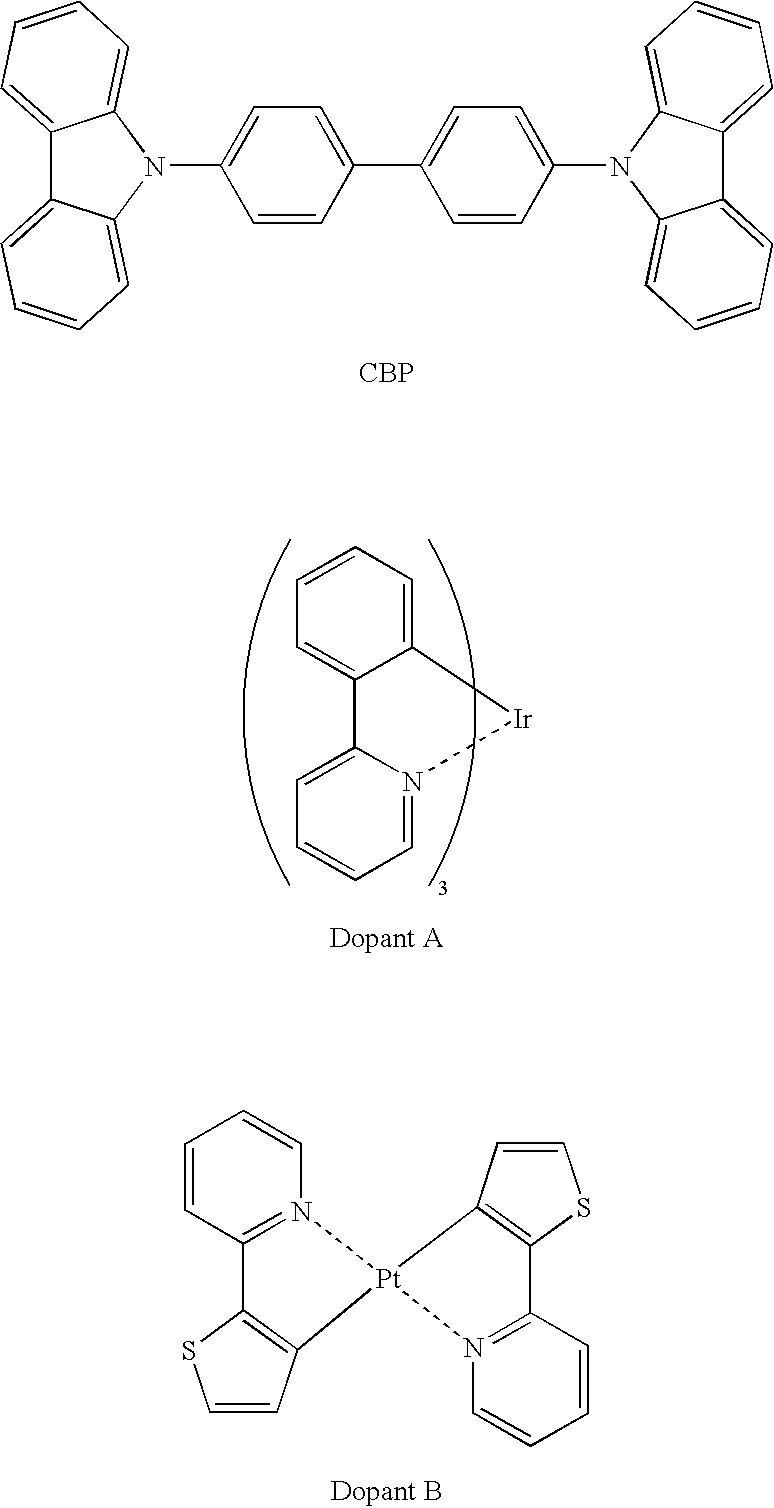
ActiveUS20060012292A1Large amount of energyIncreased durabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceHost material
The present invention provides an organic electroluminescent element including an anode, a cathode, and a plurality of organic compound layers including at least one organic luminescent layer between the anode and the cathode, in which the organic luminescent layer contains a host material and two or more phosphorescent materials; the organic luminescent layer is adjacent to the organic compound layers at both an anode side and a cathode side thereof; the organic compound layer disposed adjacent to the organic luminescent layer at the anode side thereby has a thickness of 50 nm or less in thickness; and the organic compound layer disposed adjacent to organic luminescent layer at the cathode side thereby contains a compound having an ionization potential of 6.0 eV or less. The present invention also provides a display device using the organic electroluminescent element.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
High-damping absorbing coating
ActiveUS7553533B2Easy to manufactureImprove scalabilityNon-rotating vibration suppressionLayered productsEngineeringCoating
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Method for preparing fatty acid esters with alcohol recycling
ActiveUS20100048930A1Large amount of energyFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationChemistryFatty acid ester
A method produces fatty acid esters by transesterification of fats and oils with the aid of an alcohol, at a high pressure and temperature. Unreacted alcohol is separated inline from the reaction mixture and continuously recycled into the transesterification process. The separation is performed by obtaining a vapour phase and higher density phases of the reaction mixture and concentrating the alcohol in the vapour phase.
Owner:VLAAMSE INSTELLING VOOR TECHNOLOGISCH ONDERZOEK NV VITO
Rotating multi-monolith bed movement system for removing CO2 from the atmosphere
ActiveUS9925488B2Improve efficiencyLow costGas treatmentDispersed particle separationPorous substrateSorbent
Owner:GLOBAL THERMOSTAT OPERATIONS LLC
System for isolating power conductors using molded assemblies
ActiveUS9917432B2Significant challengeLarge amount of energyBus-bar/wiring layoutsOpen bus-bar installationsElectricityElectrical conductor
An improved electrical system may be provided by electrically isolating horizontal power distribution bus bars of differing phases, disposed along a preconfigured isolated bus support molding, from one another by covering each bus bar with an electrically insulating molded assembly. The electrically insulating molded assembly has contours configured to cover a particular bus bar (with respect to another bus bar or live fastener), arranged within the constraints of the preconfigured isolated bus support molding in the electrical system (such as along the back of the isolated bus support, between the isolated bus support and a wall of the electrical system).
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
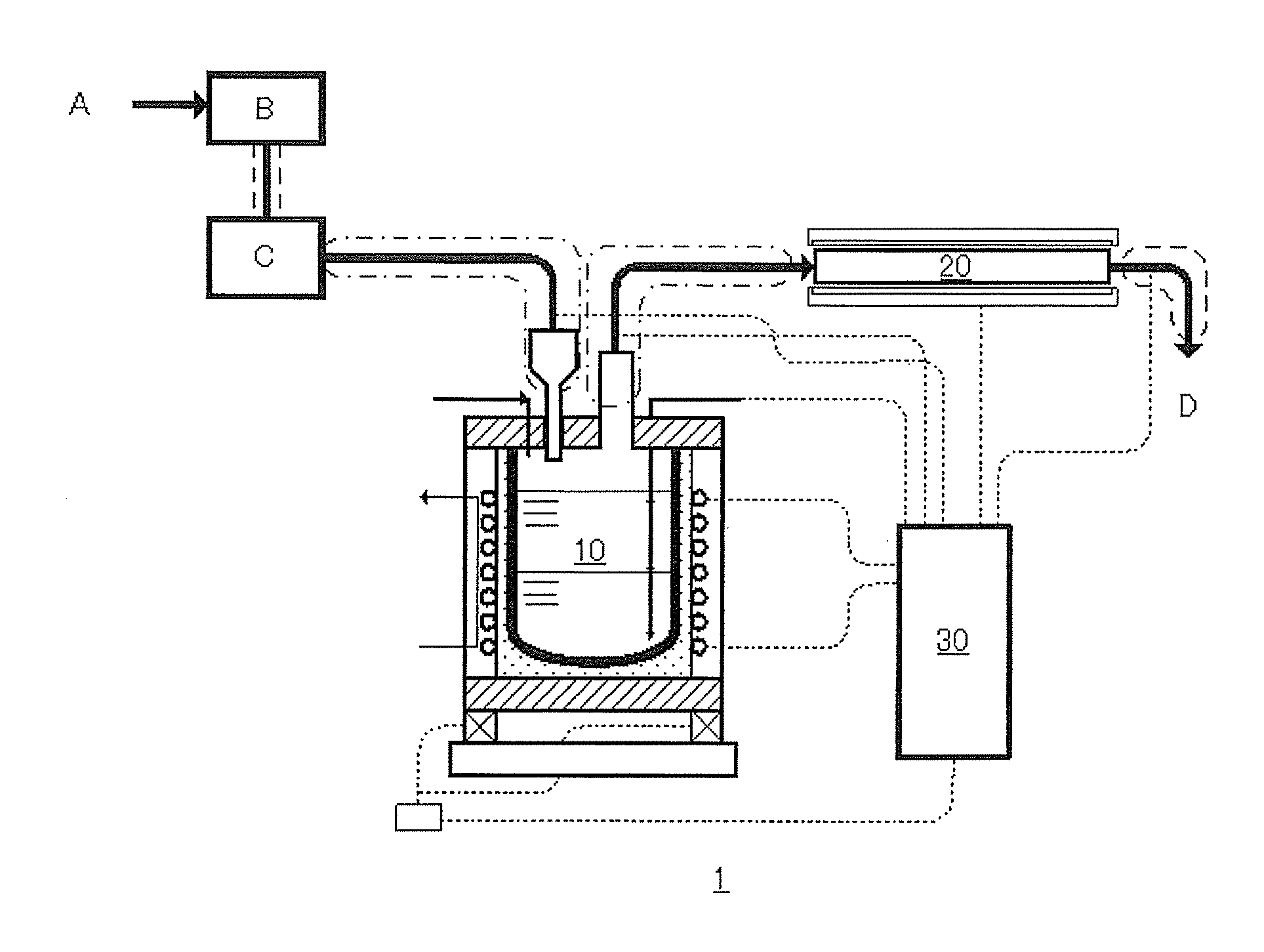
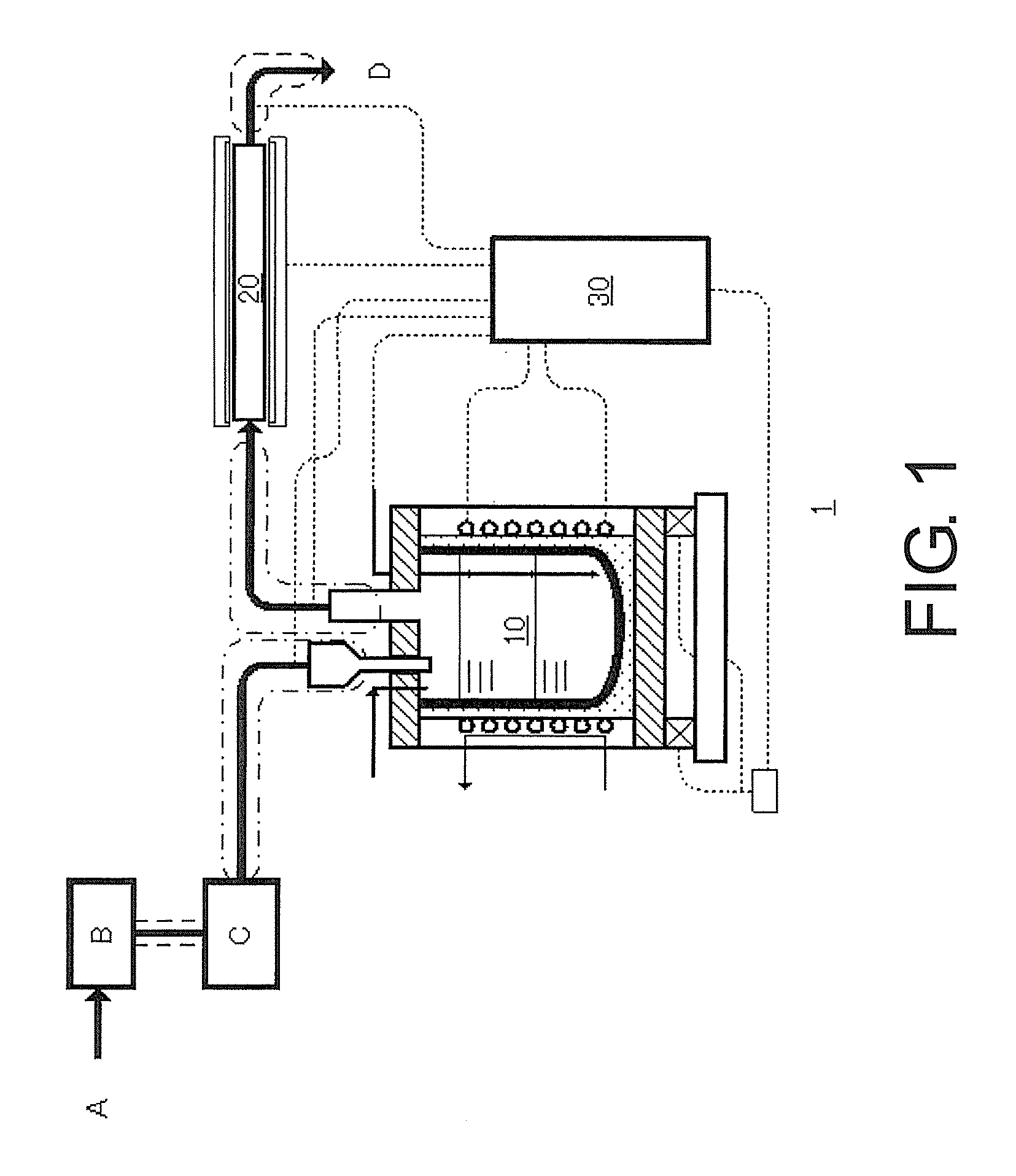
Method for feeding zinc gas and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20130247998A1Easy to controlLarge amount of energyValve members for heating/coolingPipe heating/coolingElectrical resistance and conductanceBoiling point
To provide a method and an apparatus for feeding a zinc gas superheated to a boiling point of zinc or higher at a controlled rate of feed. The method for feeding the zinc gas according to the invention includes a step for introducing melt zinc into a zinc gas evaporation apparatus, a step for generating the zinc gas from the melt zinc by inputting electric power corresponding to a rate of feed of the zinc gas to allow zinc to cause self-heating by high-frequency induction heating, a step for introducing the generated zinc gas into a gas heating apparatus, and a step for heating the zinc gas by resistance heating to form a superheated zinc gas. An apparatus for feeding the zinc gas according to the invention is applied to the method, and includes a zinc gas evaporation apparatus, a gas heating apparatus and a control apparatus.
Owner:JNC CORP +2
Device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS20050073583A1The device operates reliablyImprove applicabilityTelevision system detailsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementVisibilityImage evaluation
The invention relates to a device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle, having a radiation source for infrared radiation for irradiating the surroundings of the vehicle, having an infrared-sensitive camera for taking images of at least part of the irradiated surroundings, having a display unit for displaying collected image data, and having a control unit for controlling the device. Furthermore, an image evaluation unit is provided which is connected to the camera and the control unit and which evaluates the sensed image data with respect to the recommended maximum velocity Vmax. A velocity sensor which is connected to the control unit is provided in such a way that the control unit causes the display to be switched off when the vehicle velocity v exceeds the maximum velocity vmax. The display is preferably switched on when the vehicle velocity v drops below the maximum velocity vmax. This device ensures that the vehicle with the device operates in a safe way for the user.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
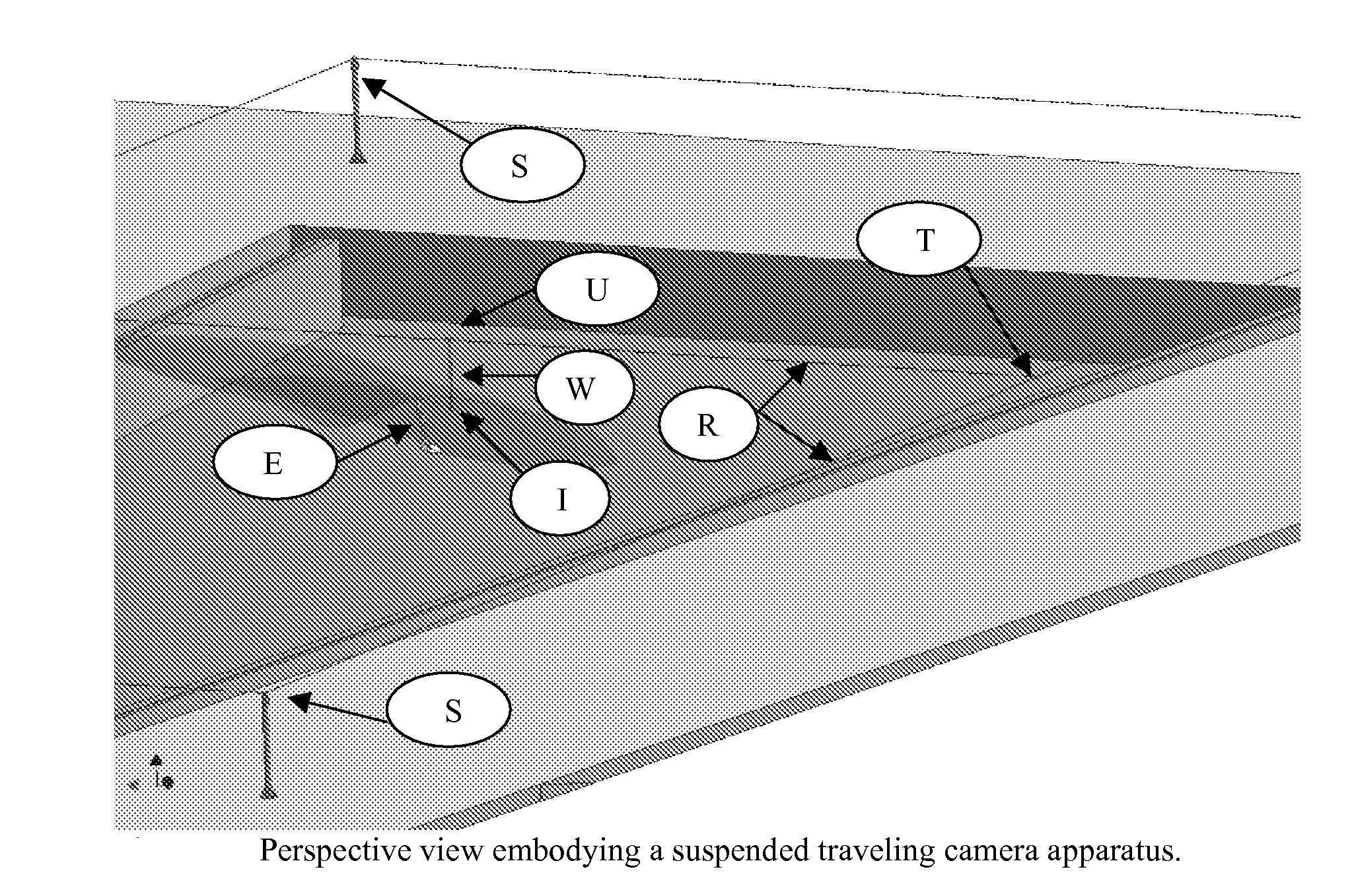
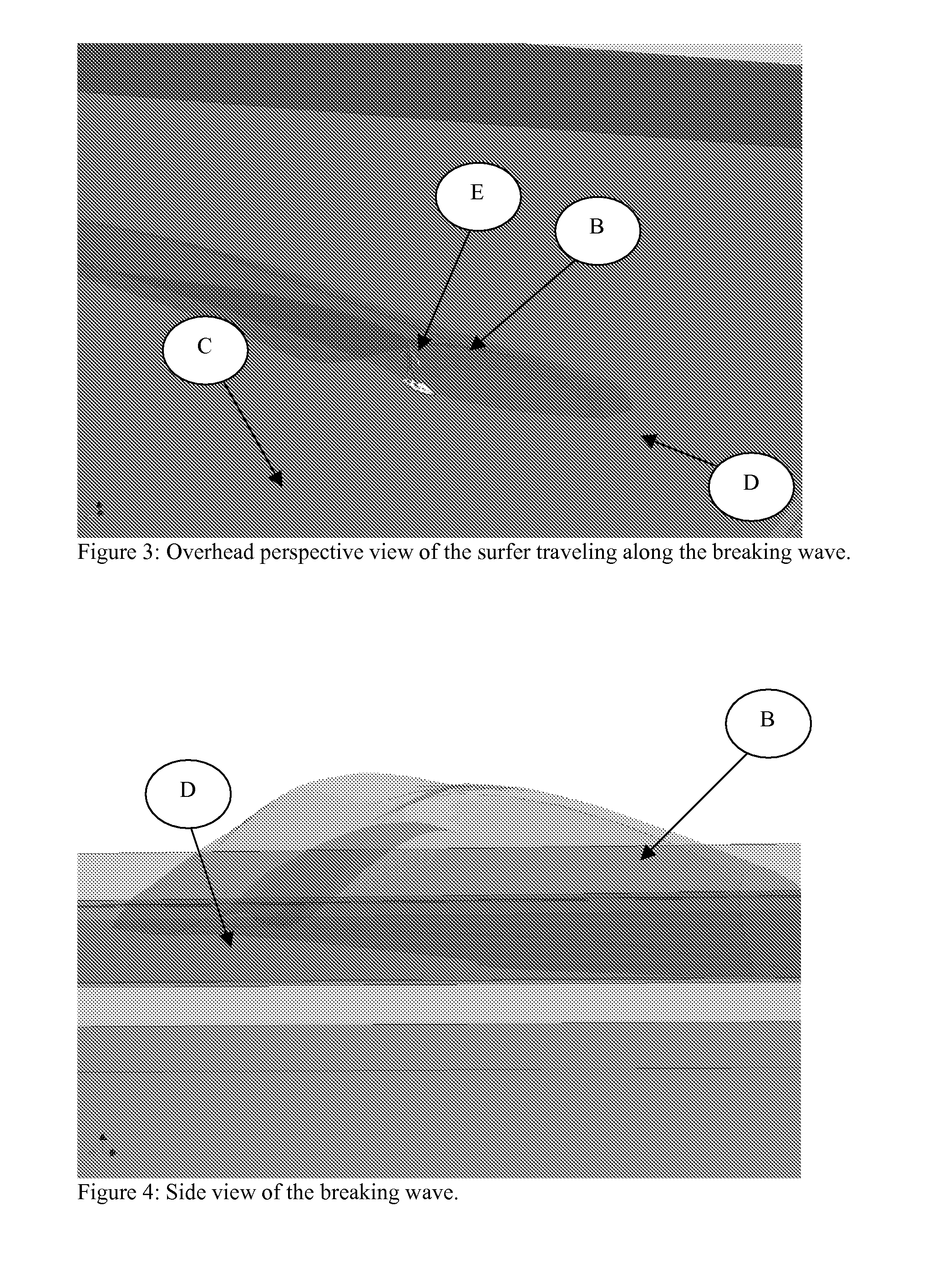
A Traveling Camera Apparatus for Surfing
InactiveUS20080317451A1Large amount of energyGenerate dragStands/trestlesCamera body detailsRange of motionDegrees of freedom
The Traveling Camera Apparatus for Surfing is embodied to film and photograph a surfer in motion on a breaking wave. The Traveling Camera Apparatus for Surfing is intended to have a full range of motion with functionality in 6 degrees of freedom and with the ability to operate in and out of the water. The advent for such an apparatus is motivated by the advance of the surfing photography / videography industry. The economic feasibility of the invention is spawned by the advent of wavepools equipped with breaking wave making devices that impart to creating breaking waves for surfing in a controlled environment. In such a wavepool a surfer may travel an entire length of the wavepool as permitted by the propagation of the breaking wave. The Traveling Camera Apparatus for Surfing shall be designed to follow along side the subject and create a multitude of images not possible if the camera were stationary in the wavepool. Some popular and sought after vantage points in the surfing photography industry are obtained when the camera is located directly behind the surfer submerged in the breaking wave and directly adjacent to the surfer where the camera is actually submerged in the water body of the breaking wave. In order to film the motion the surfer over the entire duration of the breaking wave, these camera angles require that the camera actually travel a path across the pool similar to that of the surfer on the breaking wave.
Owner:ENJO JUSTIN
High-damping absorbing coating
ActiveUS20060246257A1Easy to manufactureImprove scalabilityLayered productsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringCoating
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Image forming apparatus
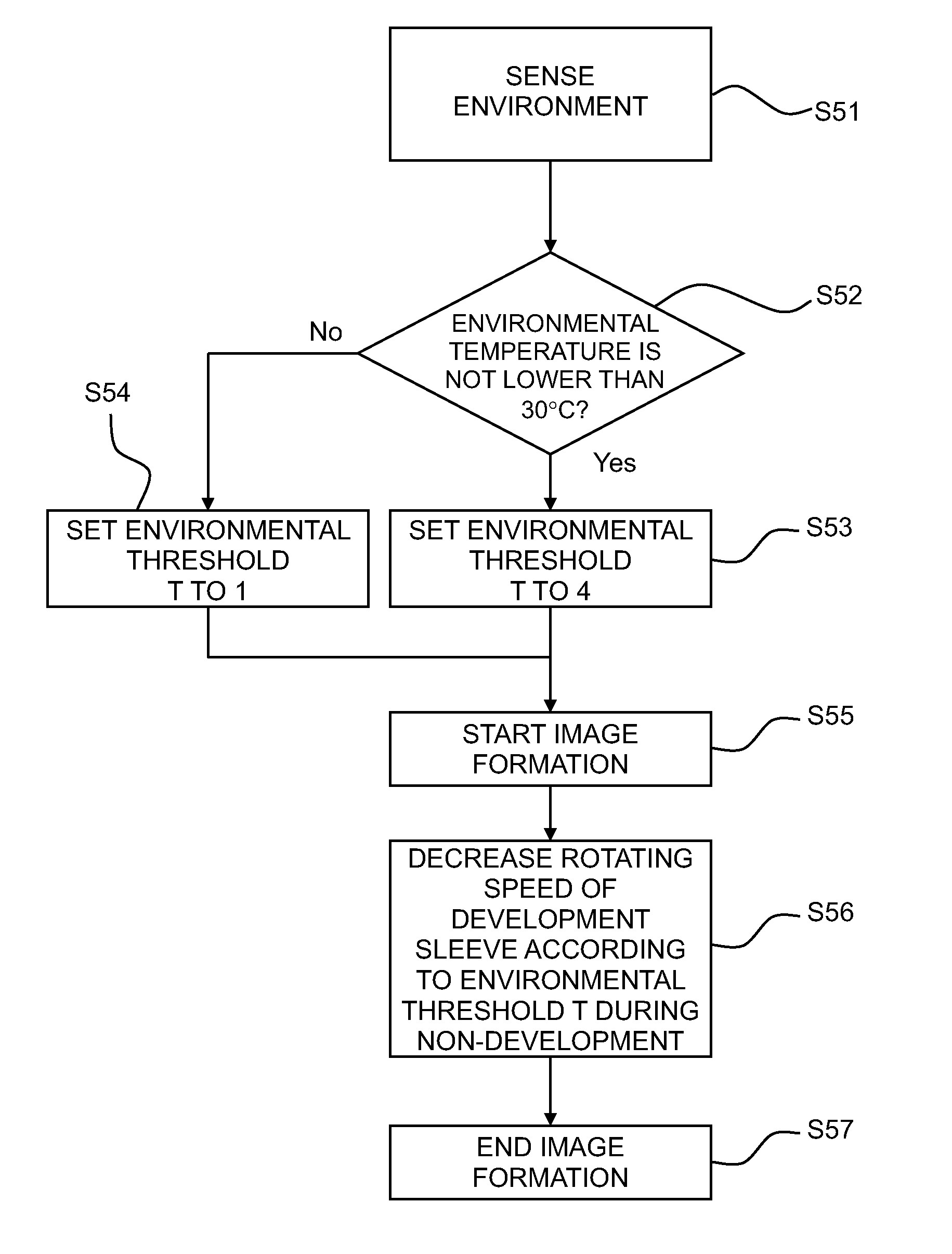
InactiveUS20110222880A1Large amount of energyReduce numberElectrographic process apparatusImage formationControl theory
An image forming apparatus includes: an image bearing member; a development device; a speed varying unit that can vary a speed of a developer bearing member; a sensing portion that senses an environmental temperature around the development device; and a controller that can perform a mode in which, compared with a period which an image forming region of the image bearing member passes through the developing region, the rotation speed of the developer bearing member slows down a period which a non-image forming region of the image bearing member passes through the developing region, wherein based on sensing result of the sensing portion, the controller performs the mode when the environmental temperature is higher than a predetermined value, and the controller does not perform the mode when the environmental temperature is lower than the predetermined value.
Owner:CANON KK
Device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS20050073582A1Efficient and safe operation of deviceWithout restricting operational capability of deviceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisibilityDriver/operator
The invention relates to a device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle, having a radiation source for infrared radiation for irradiating the surroundings of the vehicle, having an infrared-sensitive camera for taking images of at least part of the irradiated surroundings, having a display unit for displaying collected image data, and having a control unit for controlling the device. An image evaluation unit is also provided, which is connected to the camera and the control unit and which evaluates the collected image data with respect to the recommended velocity Vricht and makes it available to a vehicle driver as a velocity recommendation. In addition the recommended maximum velocity Vmax is optionally evaluated from the image data. A velocity sensor is provided, which is connected to the control unit in such a way that the control unit causes the display to be switched off when the vehicle velocity V exceeds the maximum velocity Vmax. This device ensures that the vehicle with the device operates in a very safe way for the user.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Mechanism for managing a communication session
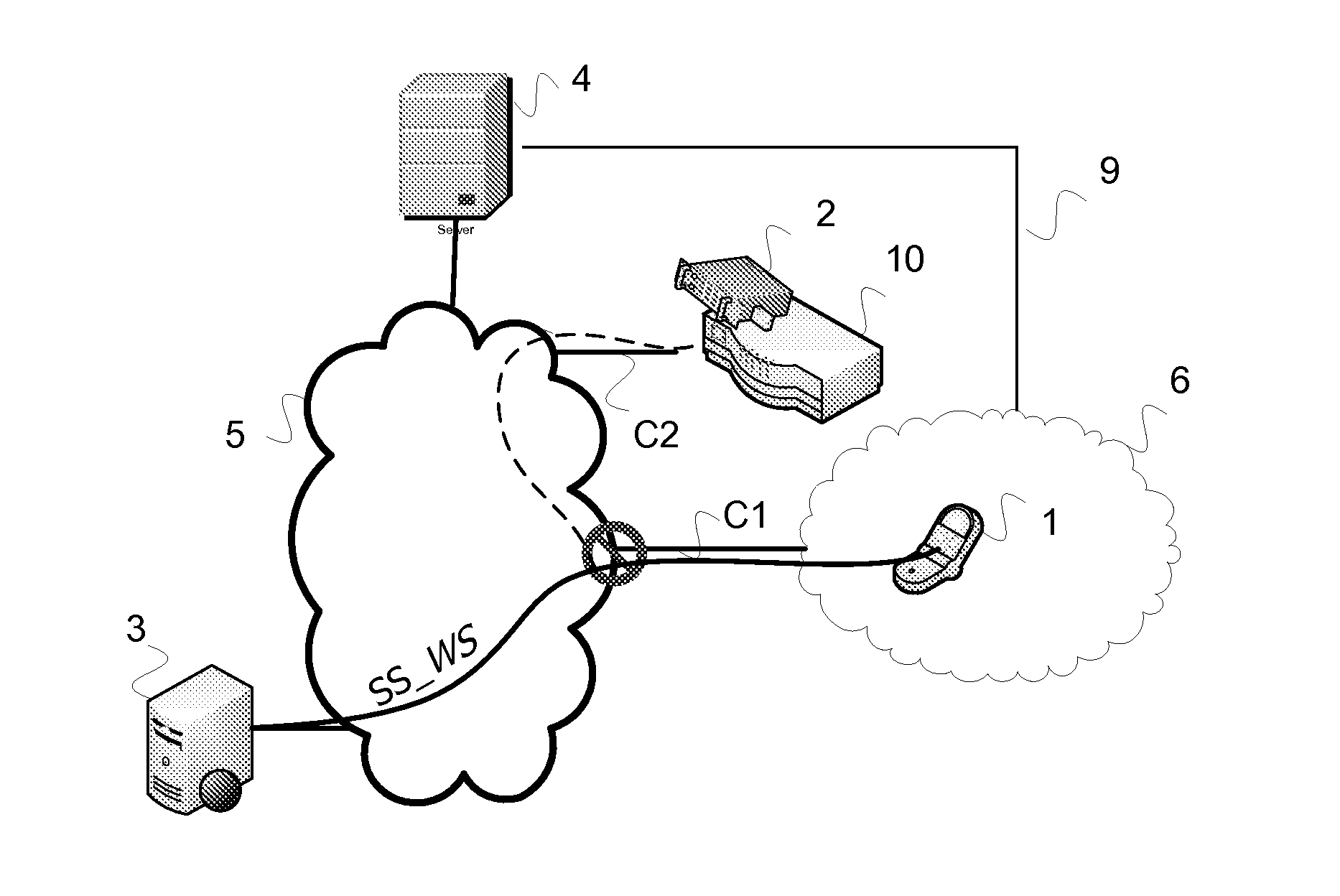
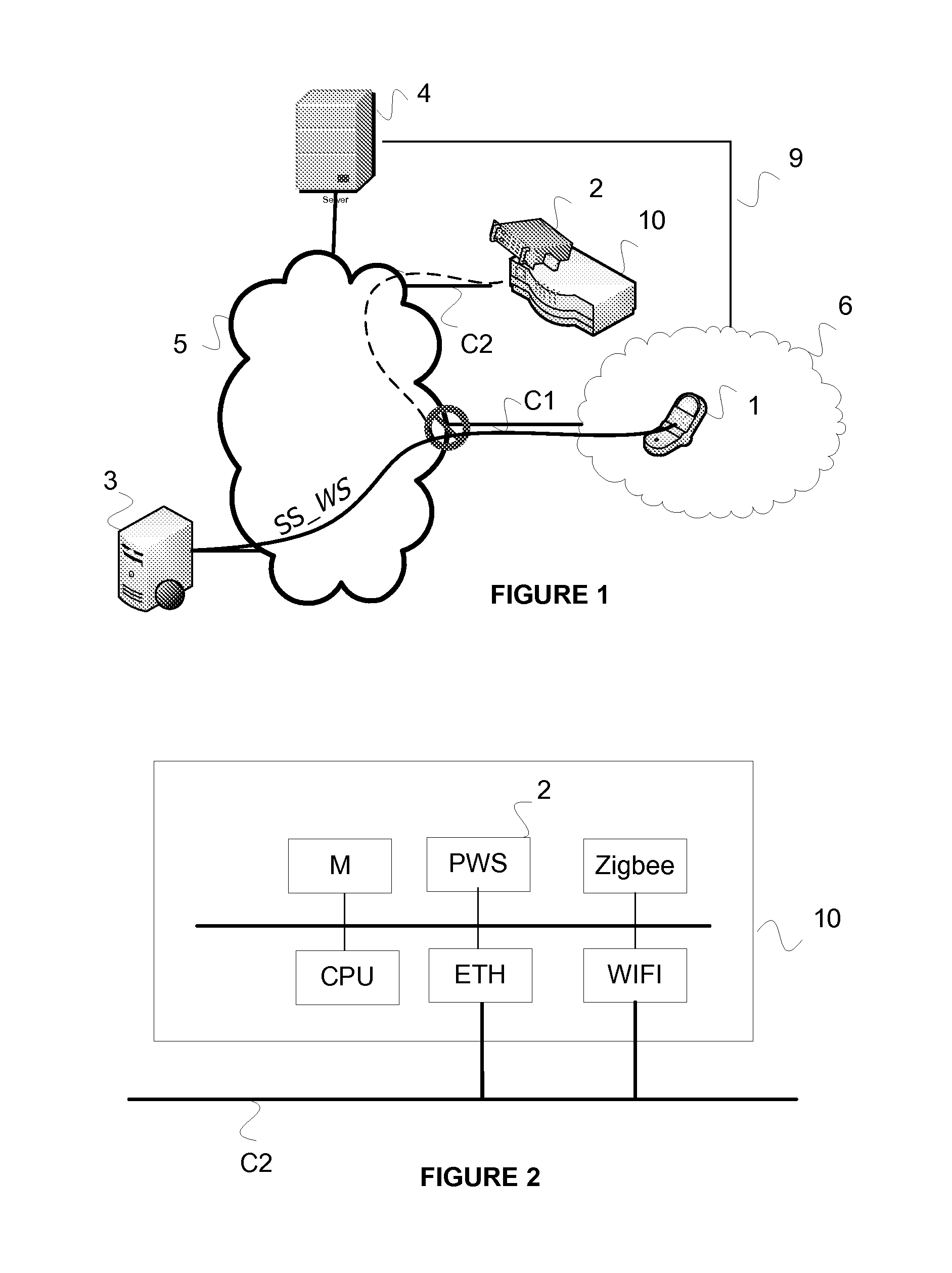
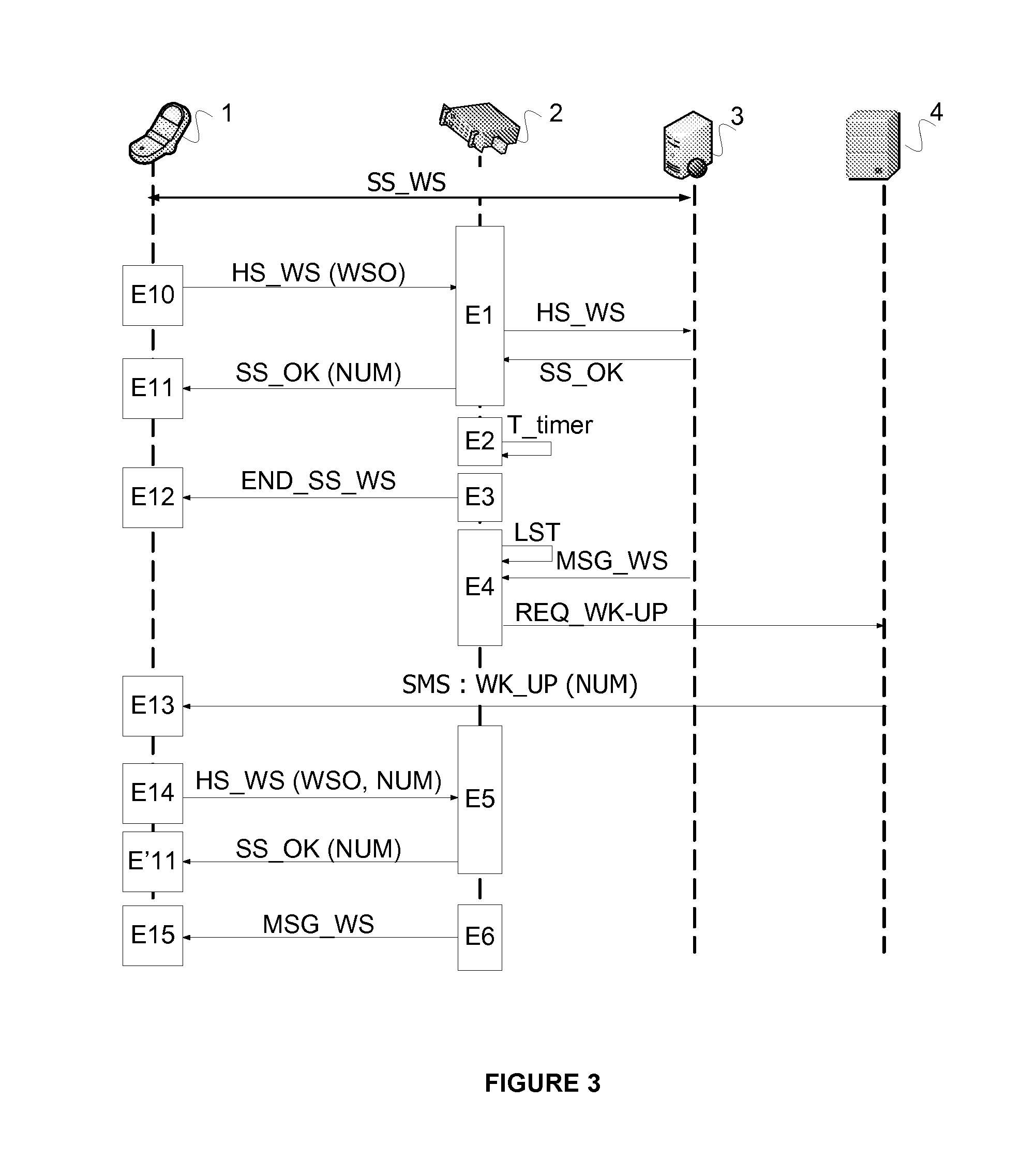
The invention relates to a management method for managing a communication session (SS_WS) between a terminal (1) suitable for exchanging application messages (MSG_WS) with at least one server (3) via the communication session (SS_WS). The method is characterized in that it comprises the following steps performed by a management device:setting up (E1) the communication session (SS_WS) for exchanging application messages between the terminal (1) and the server (3);initializing (E2) a time period (T_timer);partially closing (E3) the communication session (SS_WS) between the terminal and the management device at the end of the time period (T_timer) if no application message (MSG_WS) relating to the communication session has been received;detecting (E4) at least one application message (MSG_WS) relating to the communication session and coming from the server; andrequesting a notification server to restore (E4) the communication session (SS_WS), said notification server sending a restoration request in the form of a notification that is independent of the session.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com