Patents
Literature
52results about How to "Optimizing light path" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
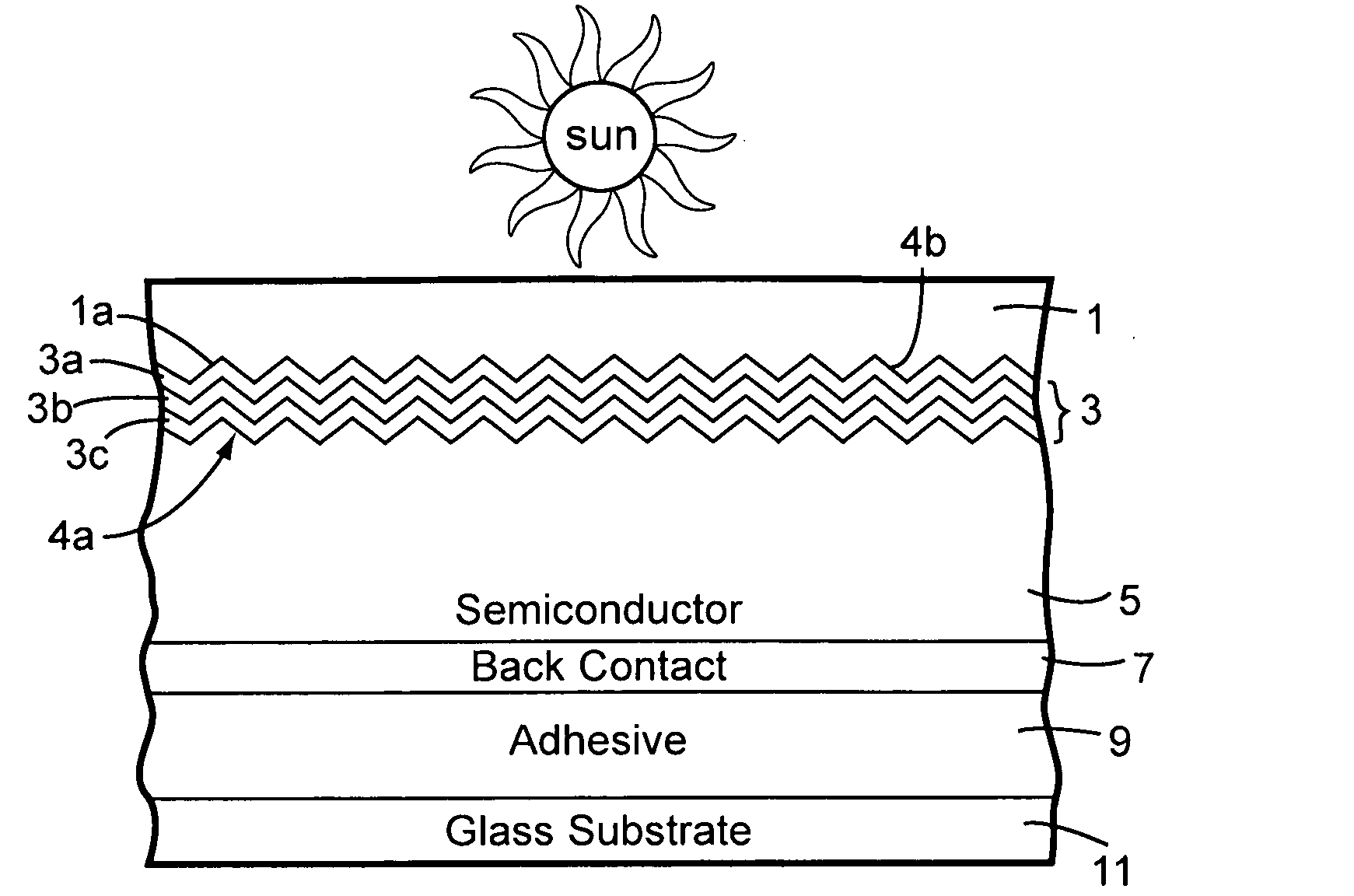
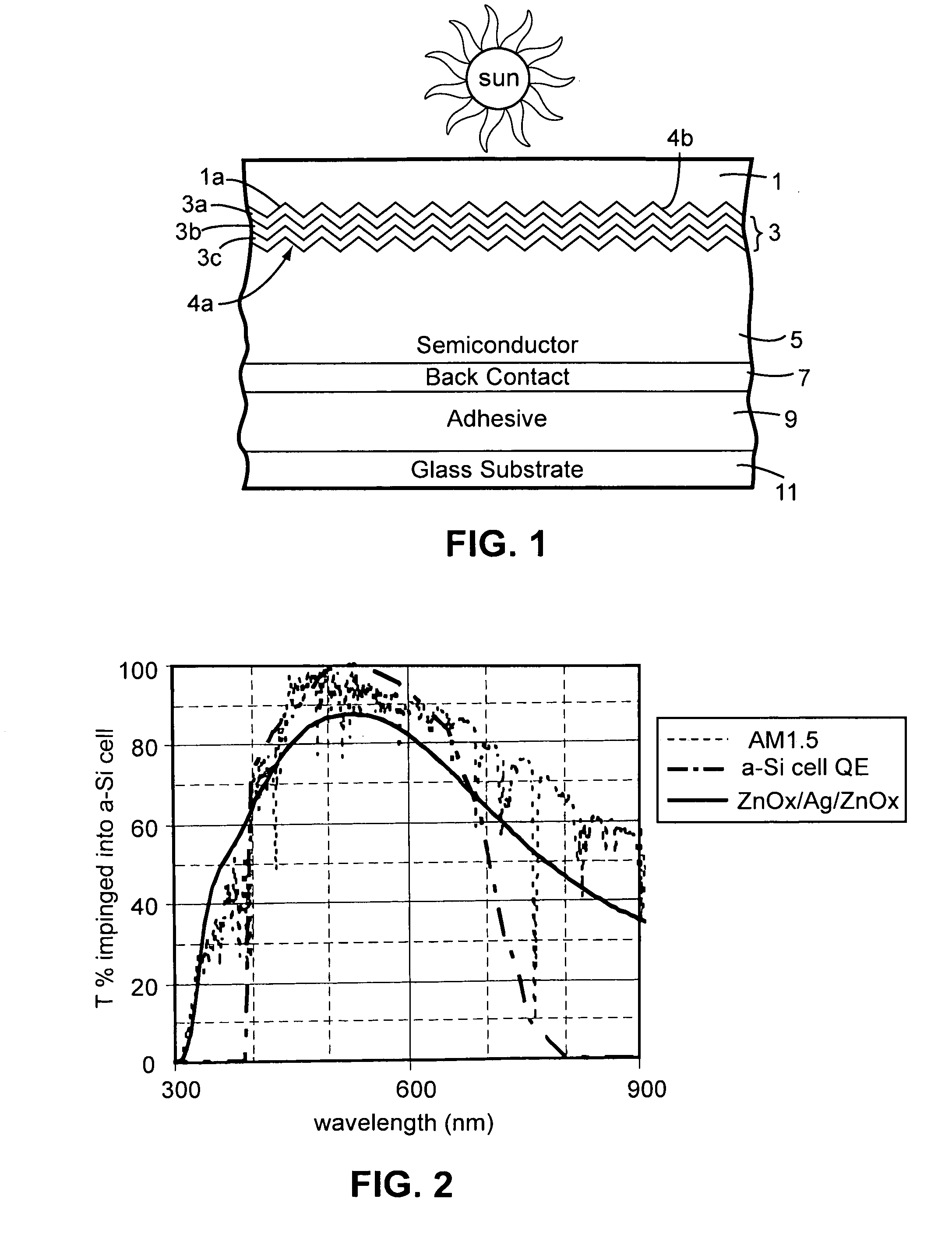
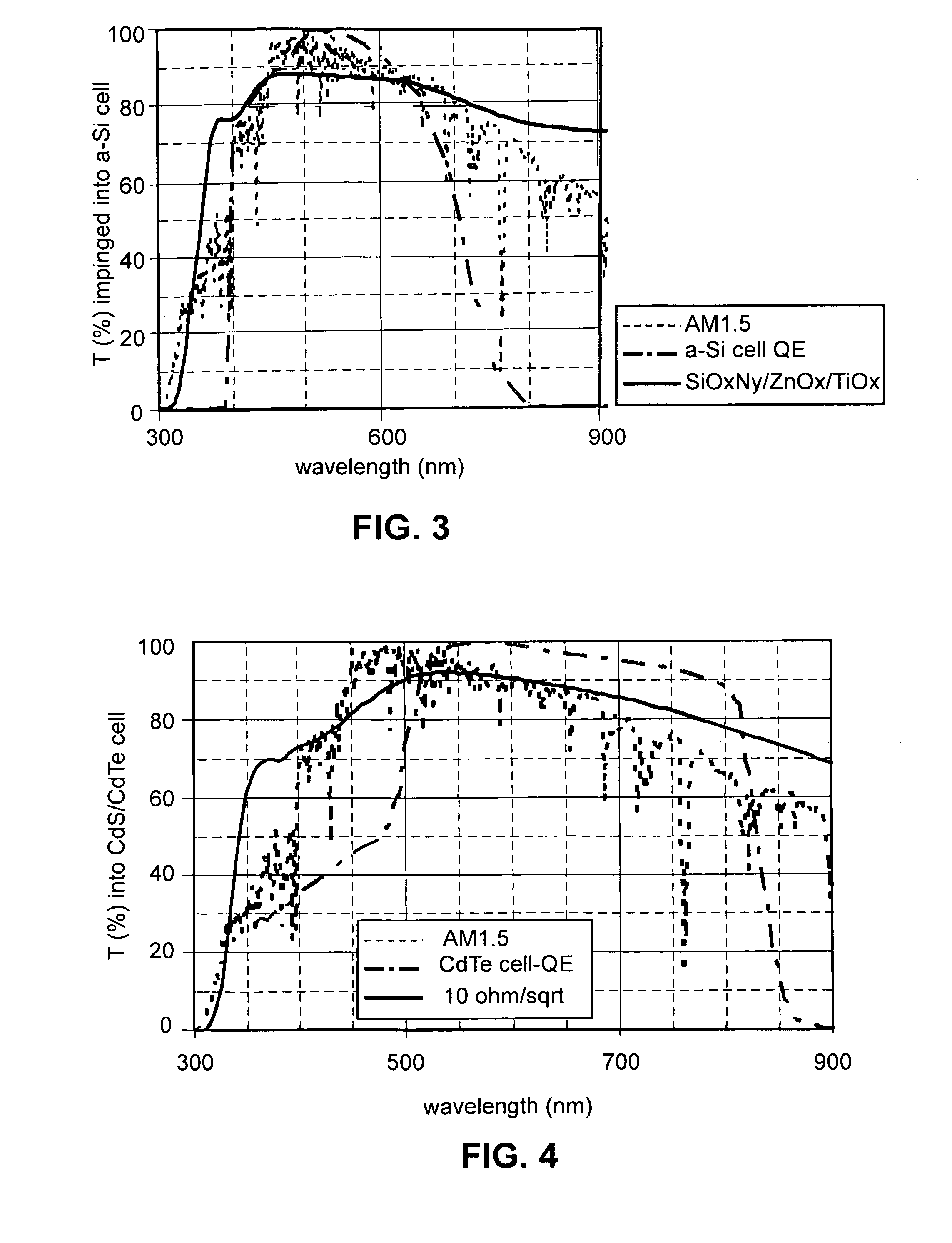
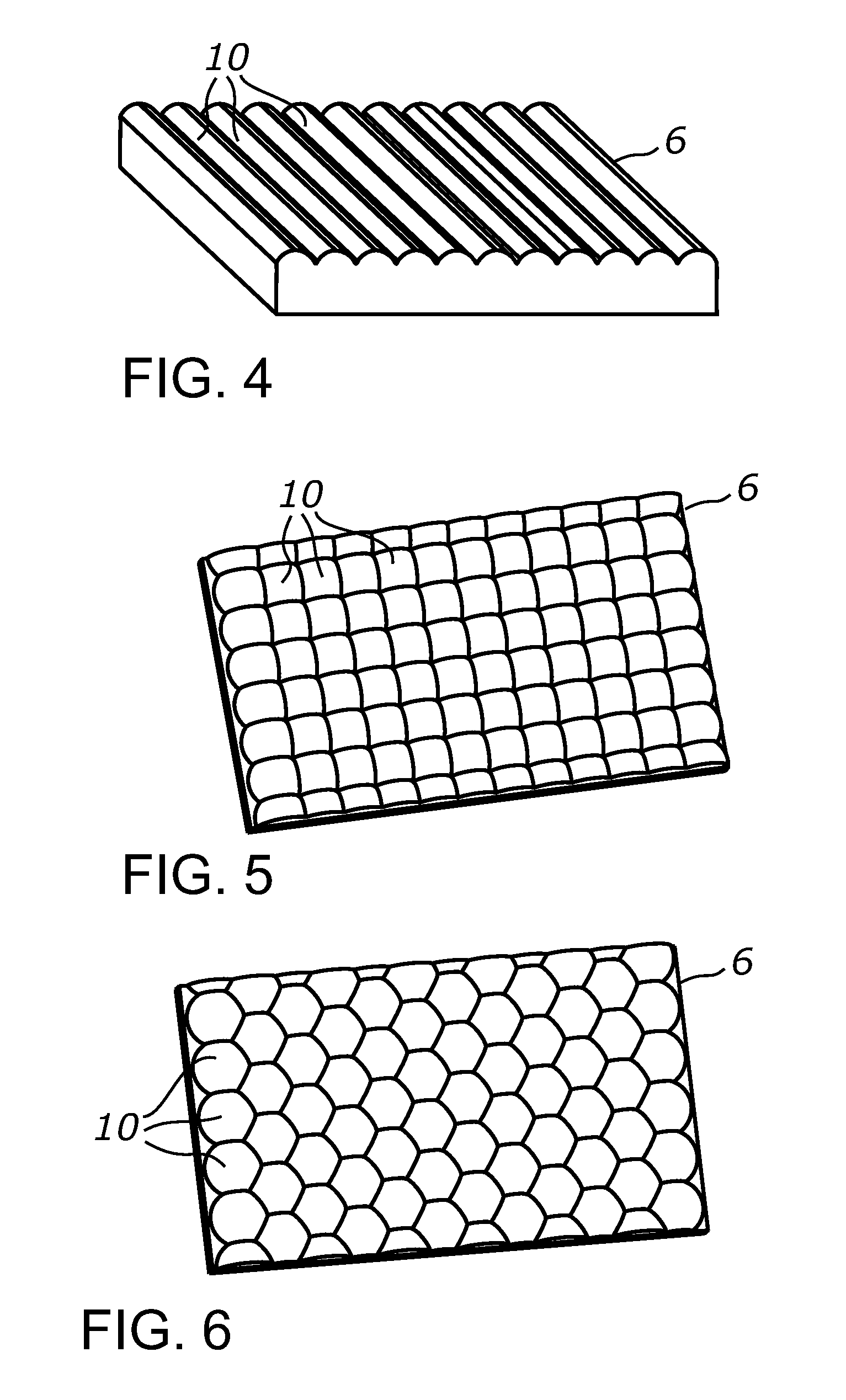
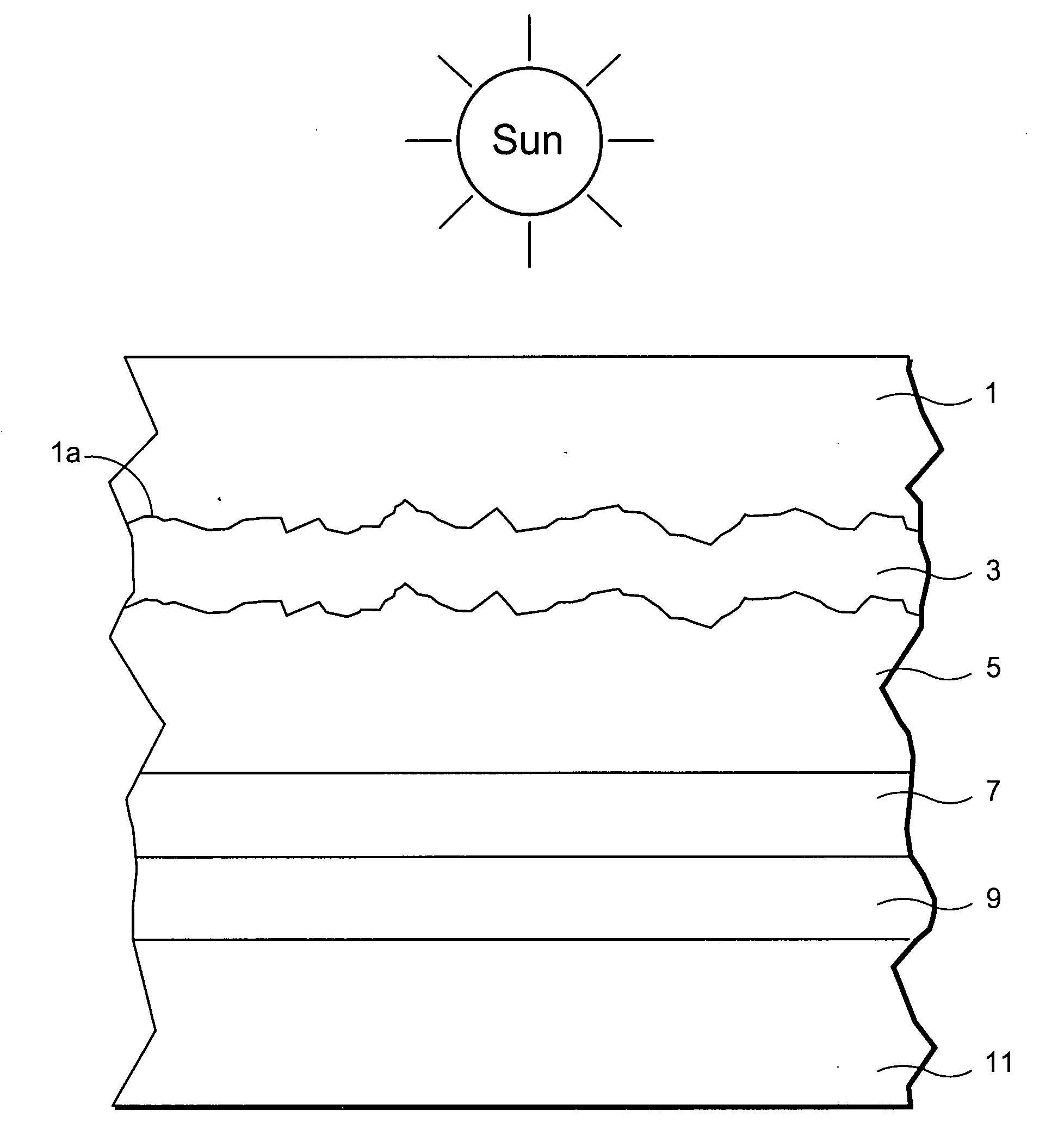
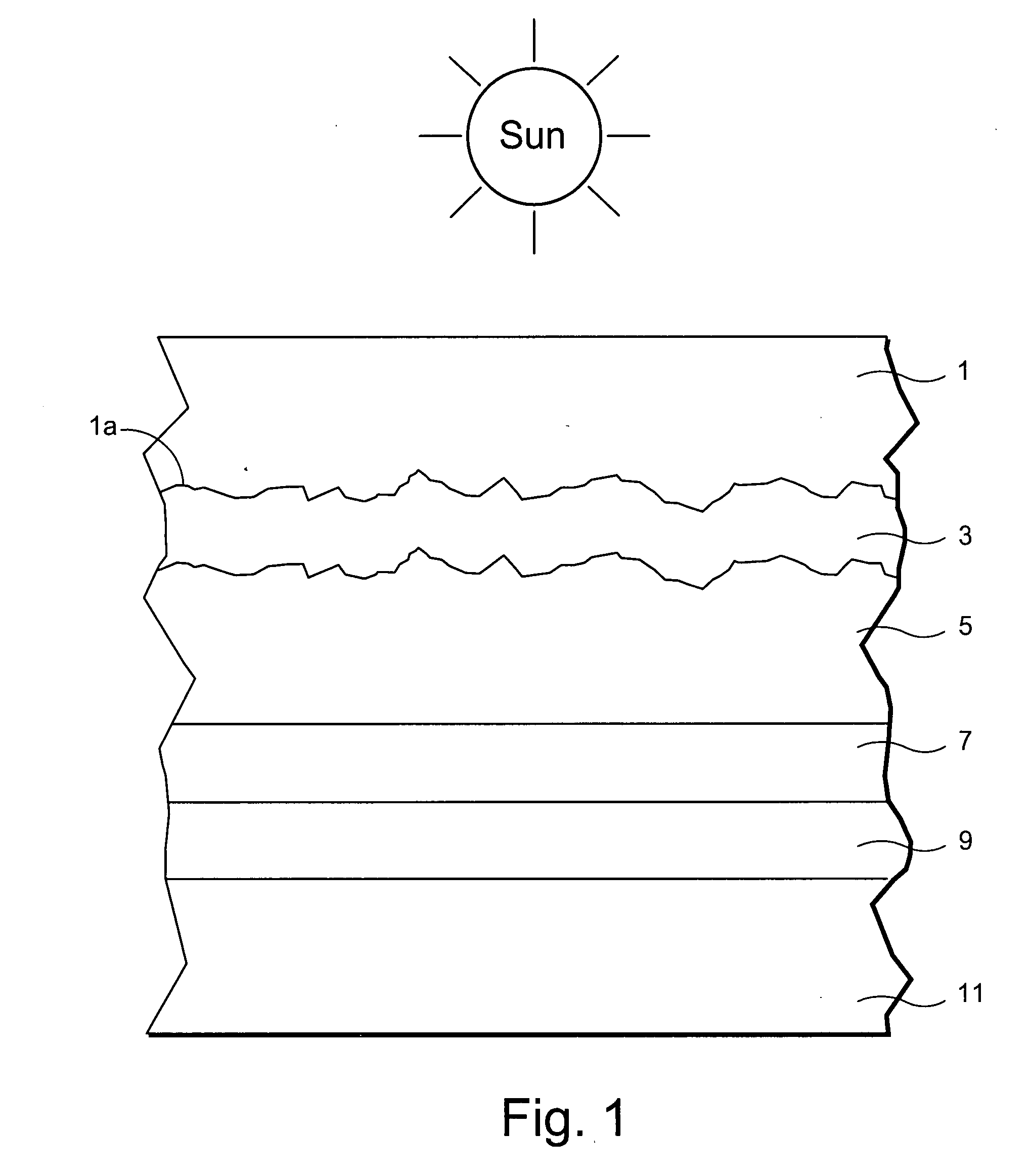
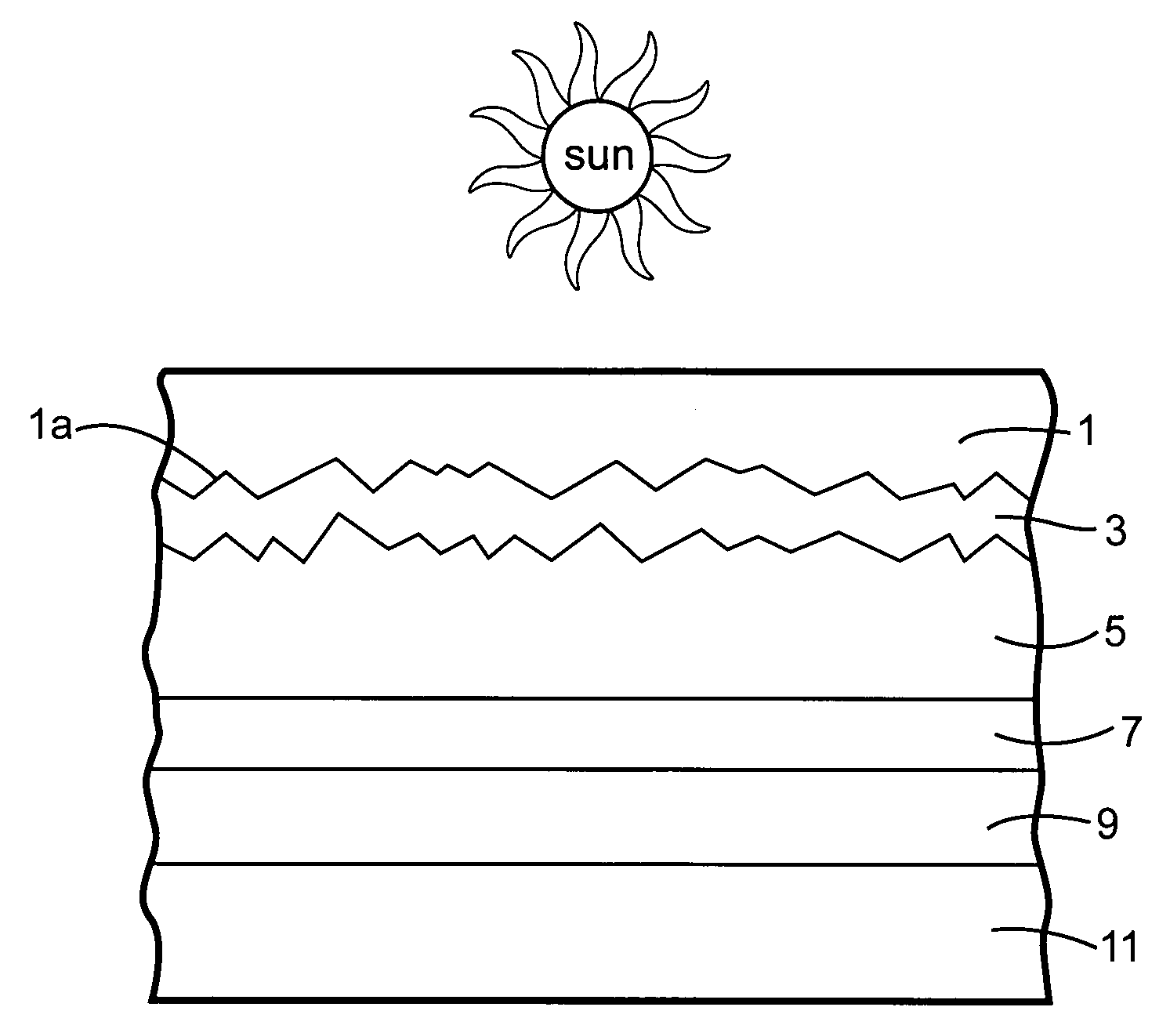
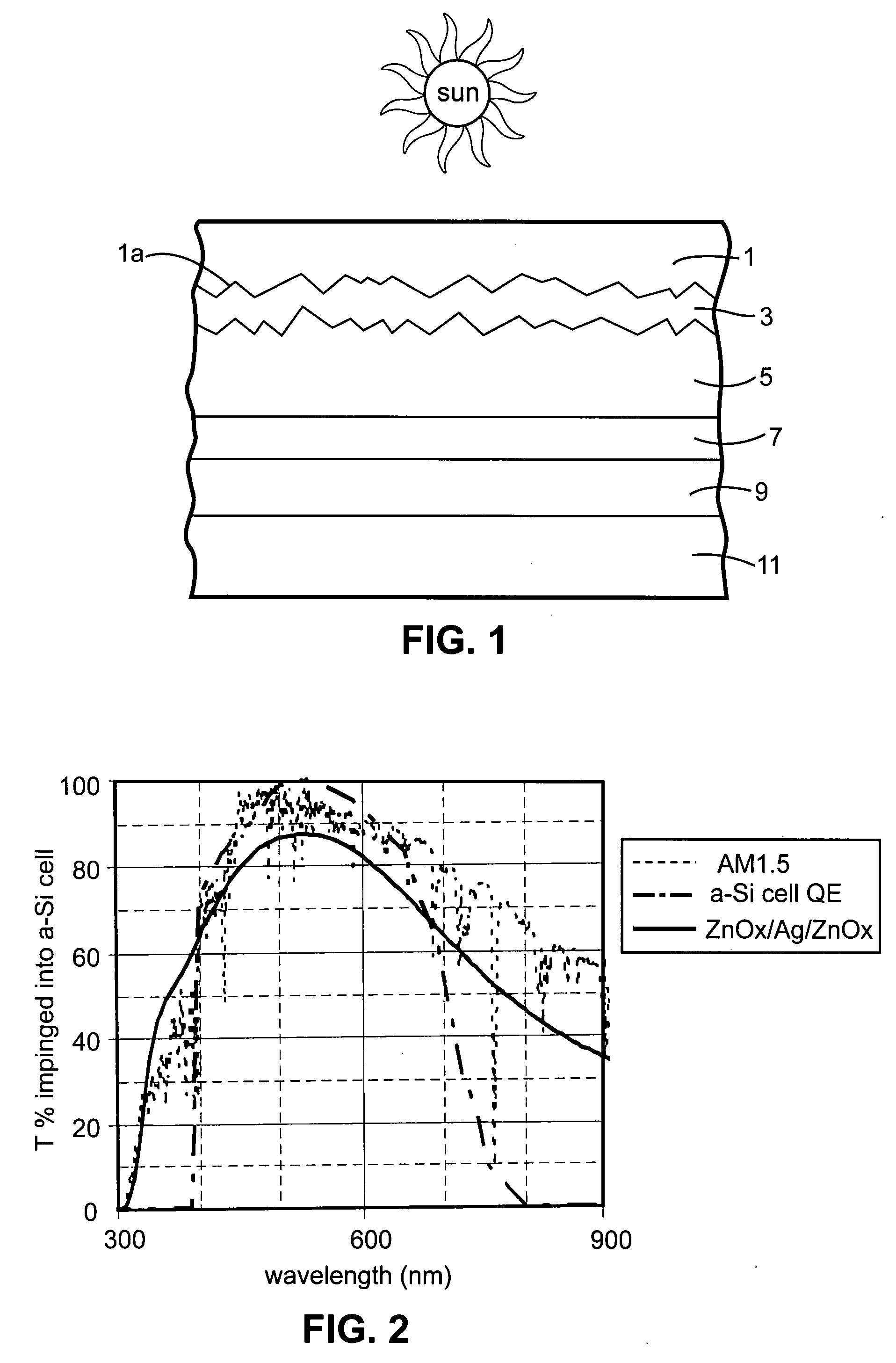
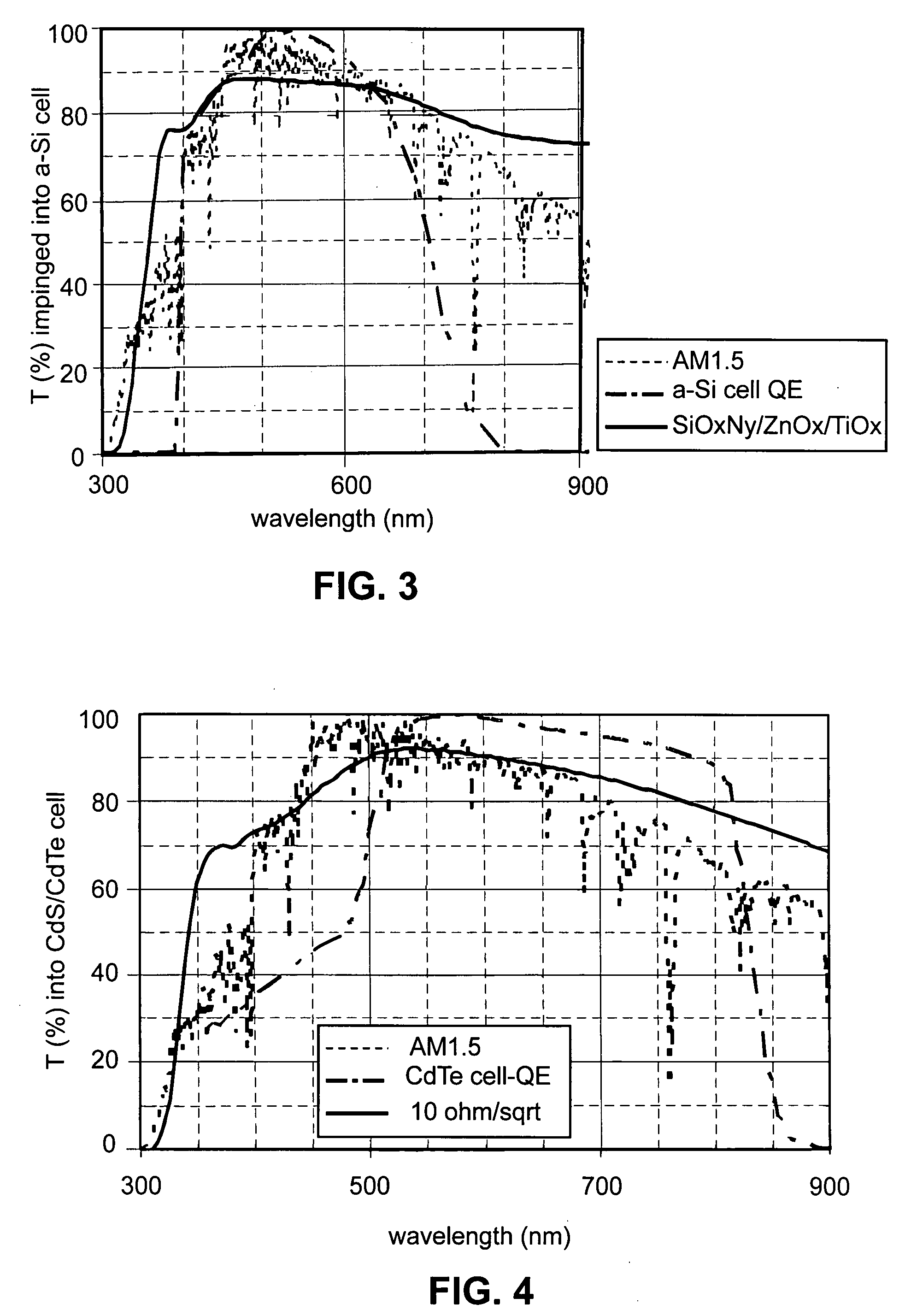
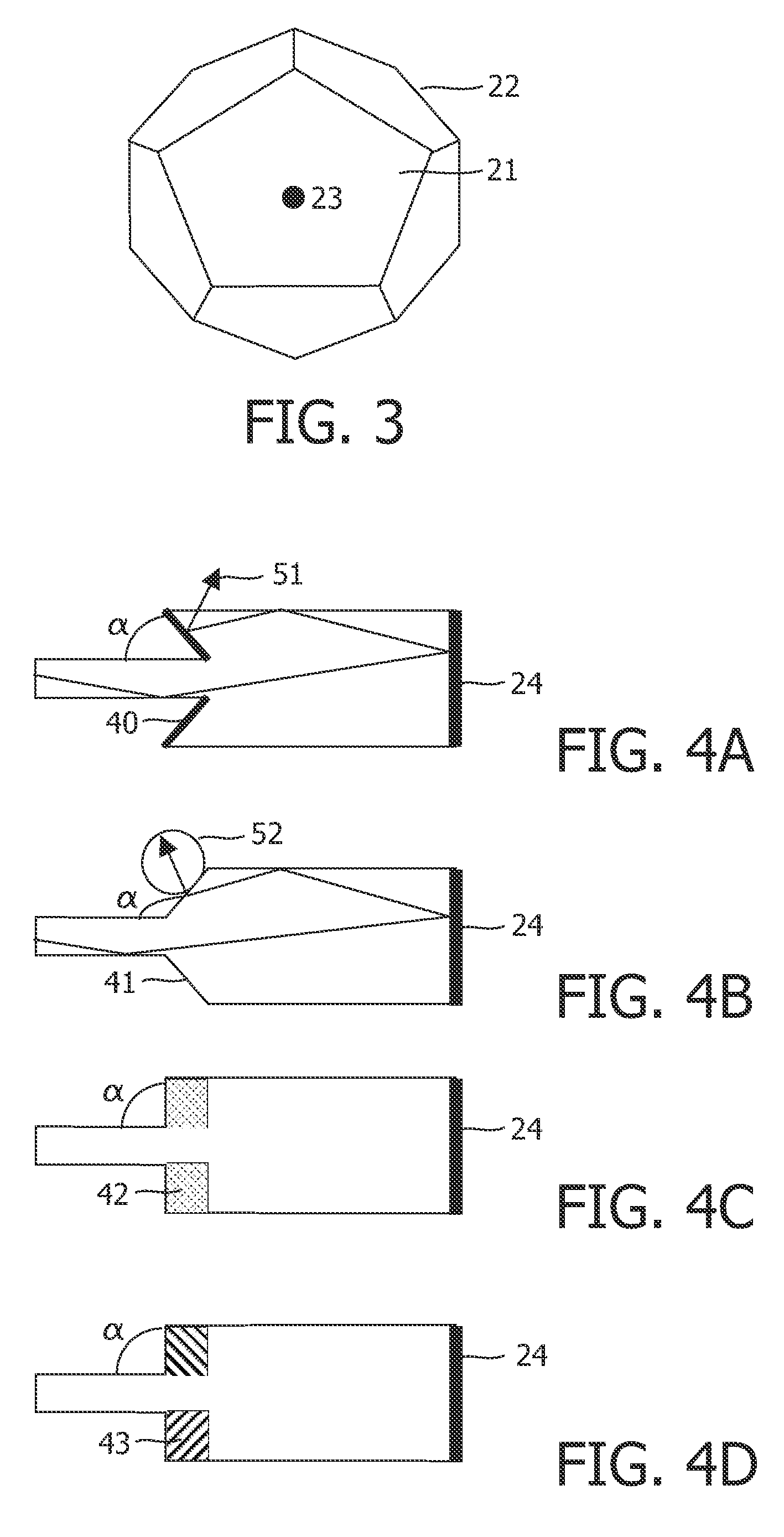
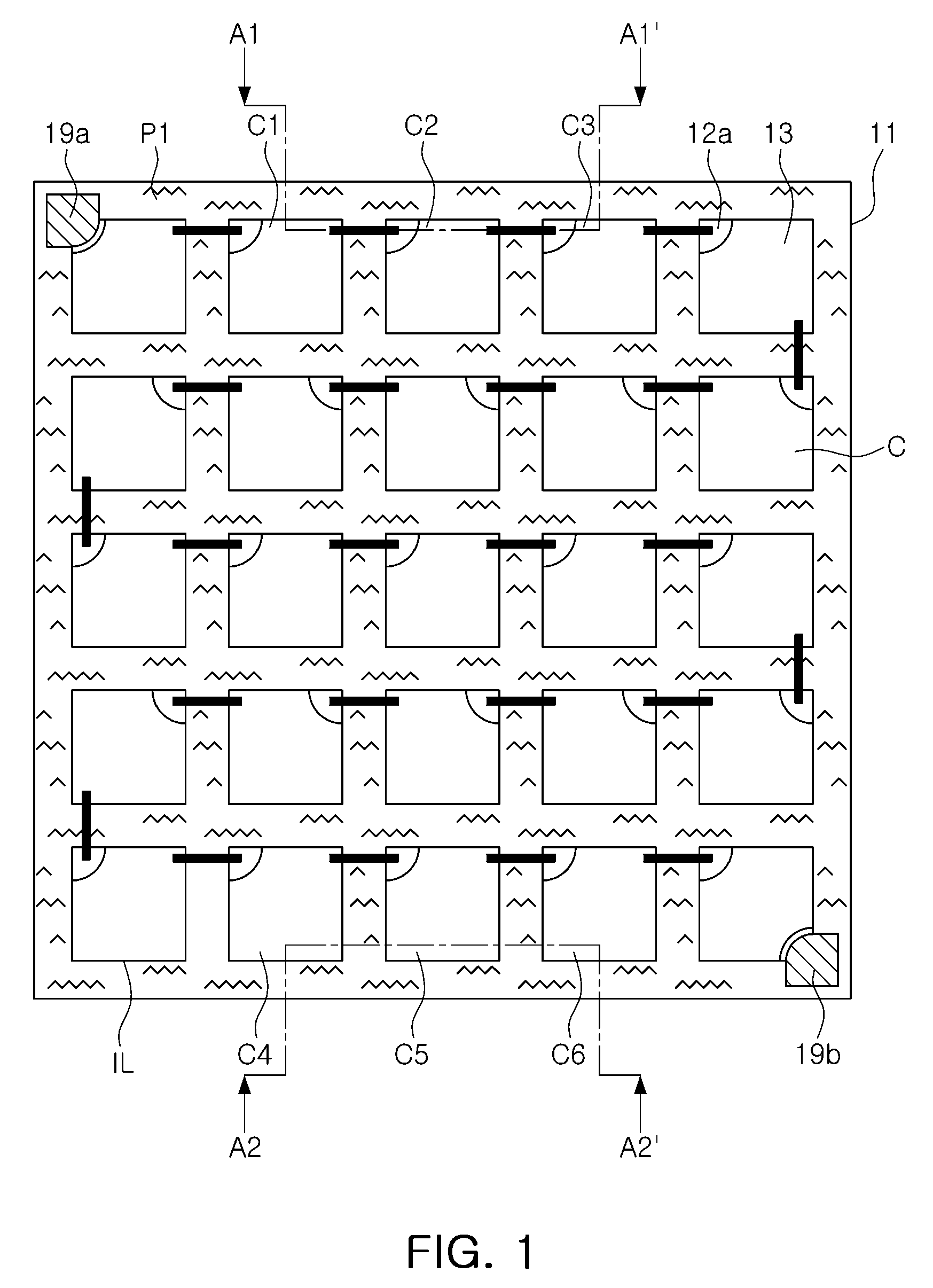
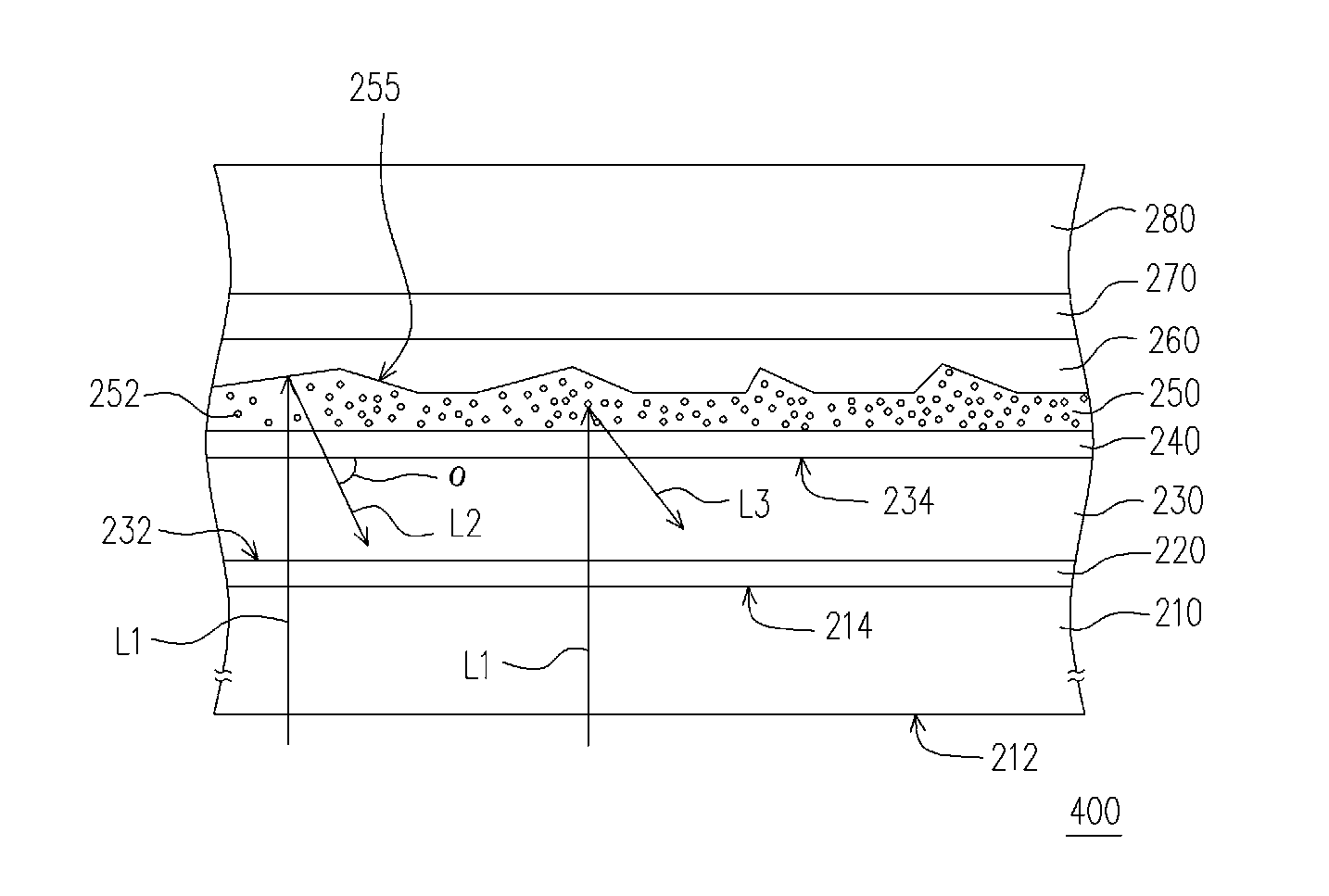
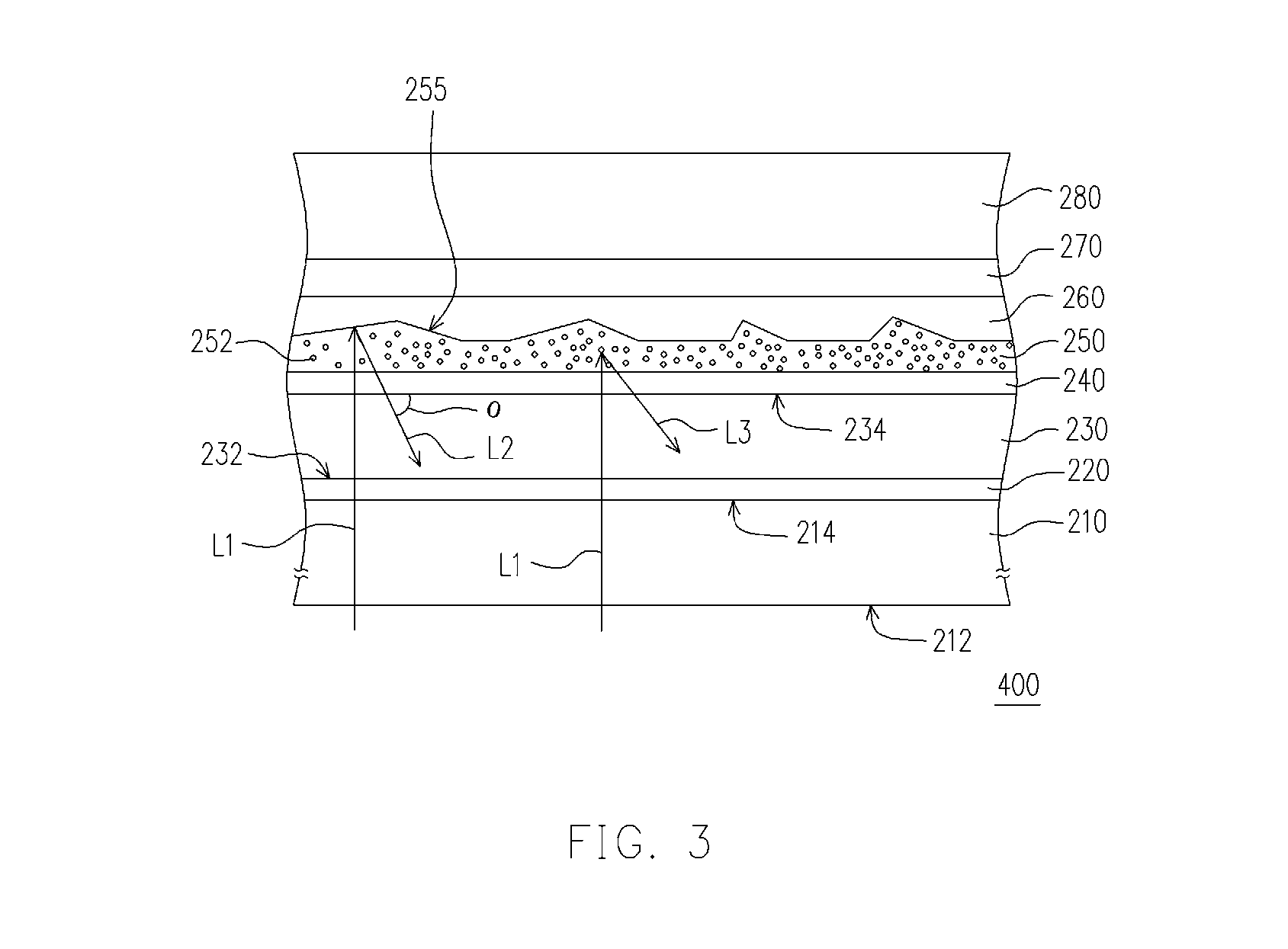
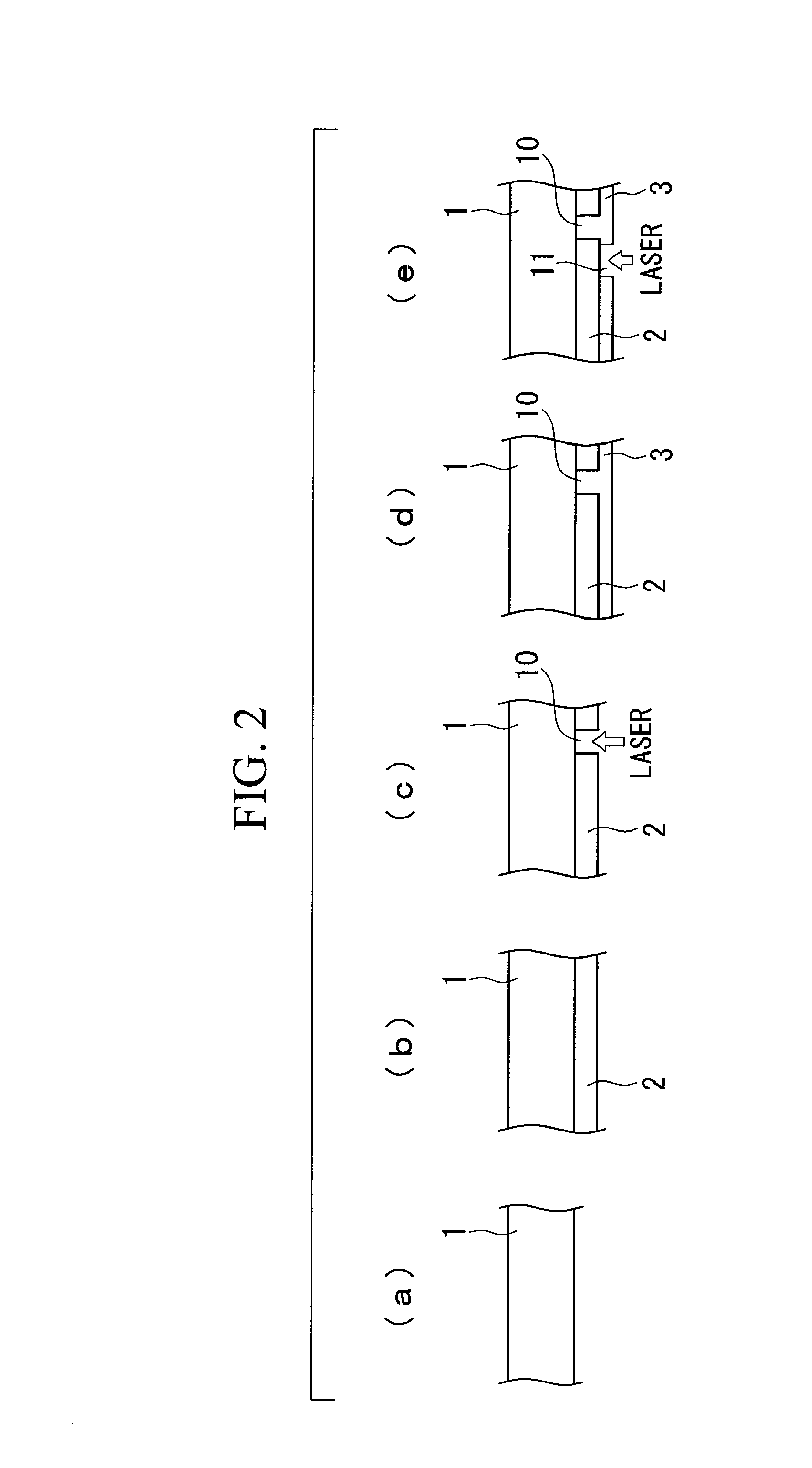
Front electrode including transparent conductive coating on patterned glass substrate for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20080178932A1Reduced visible light reflectionImprove conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationPeak valuePeak area
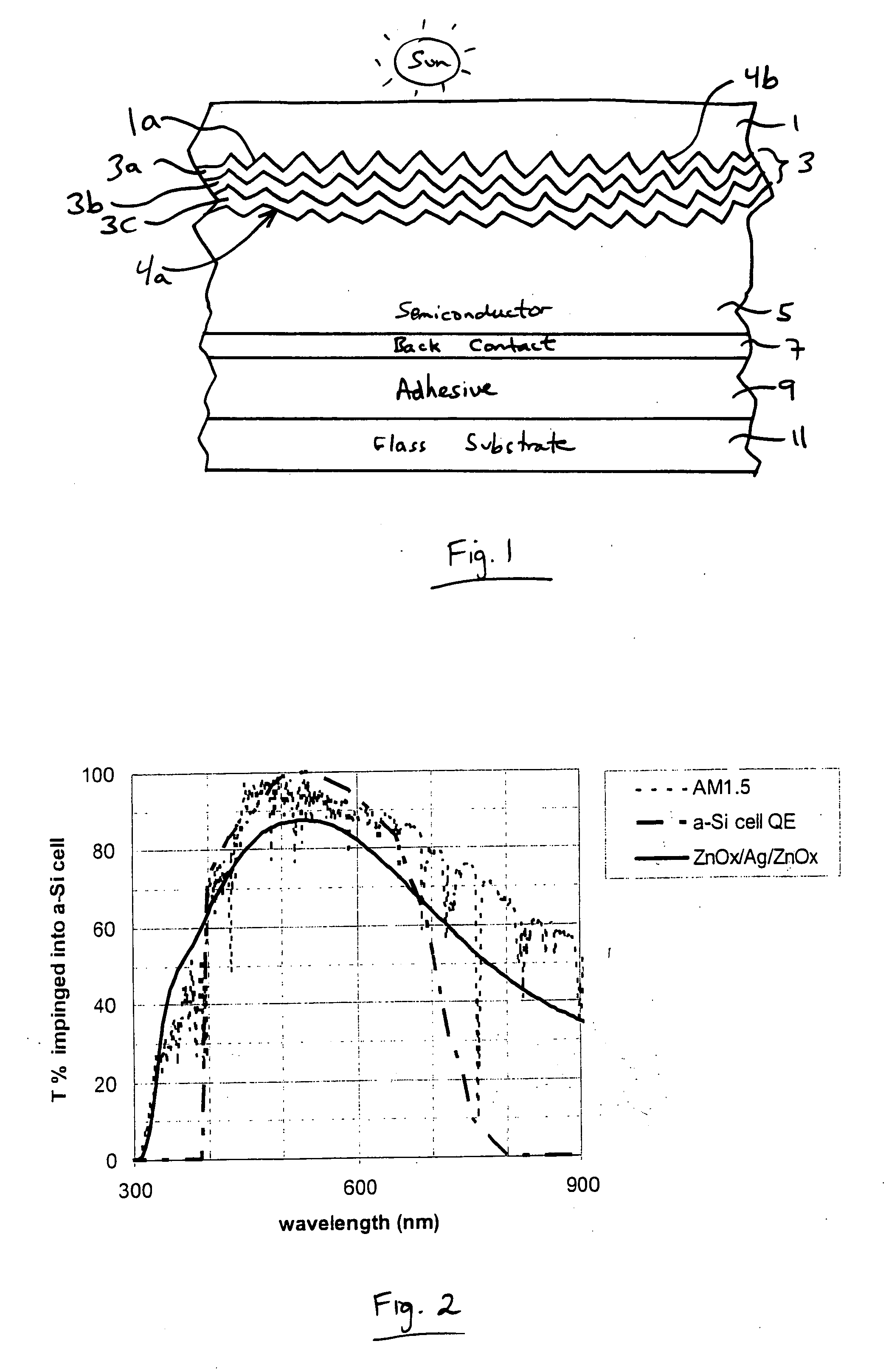
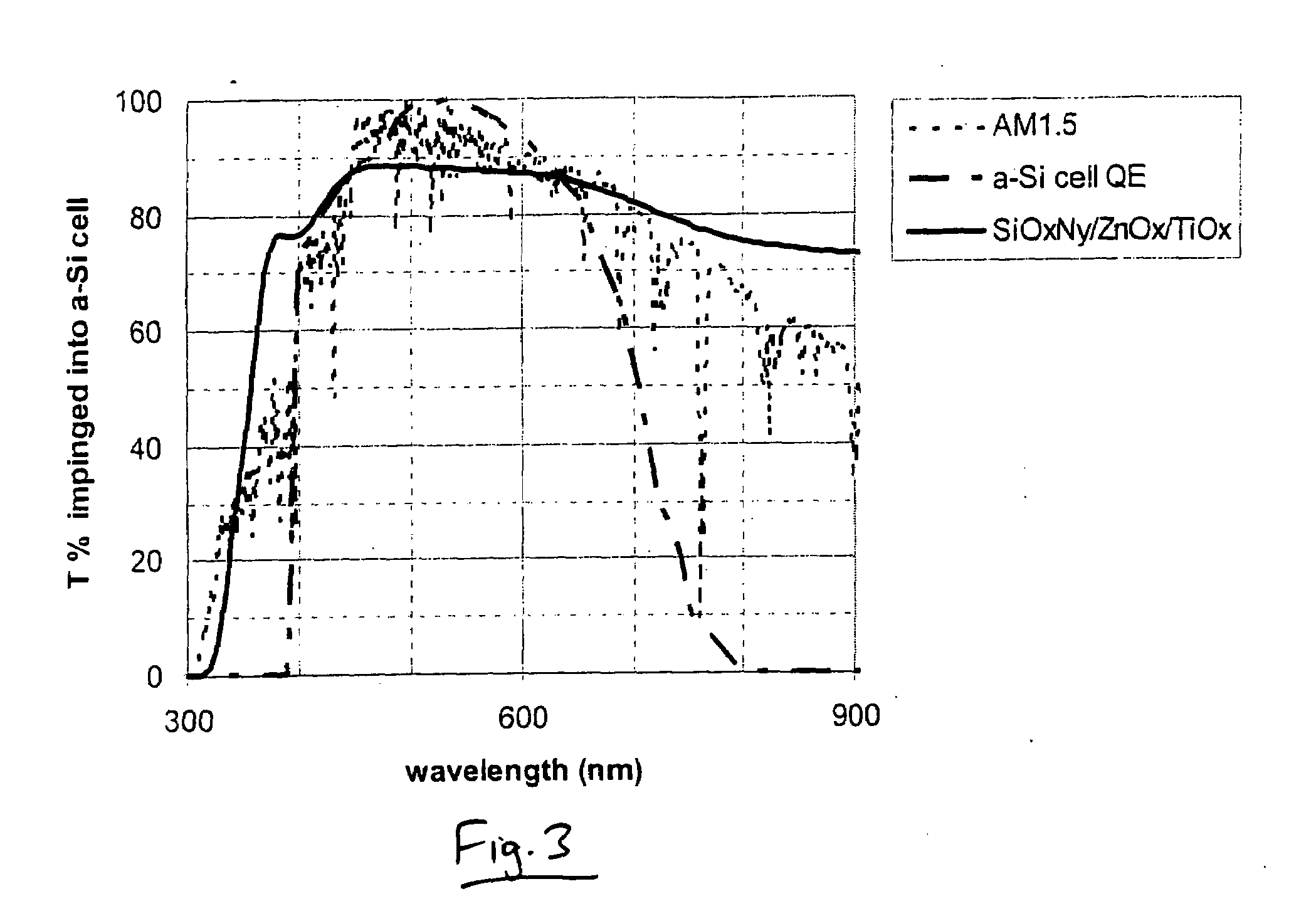
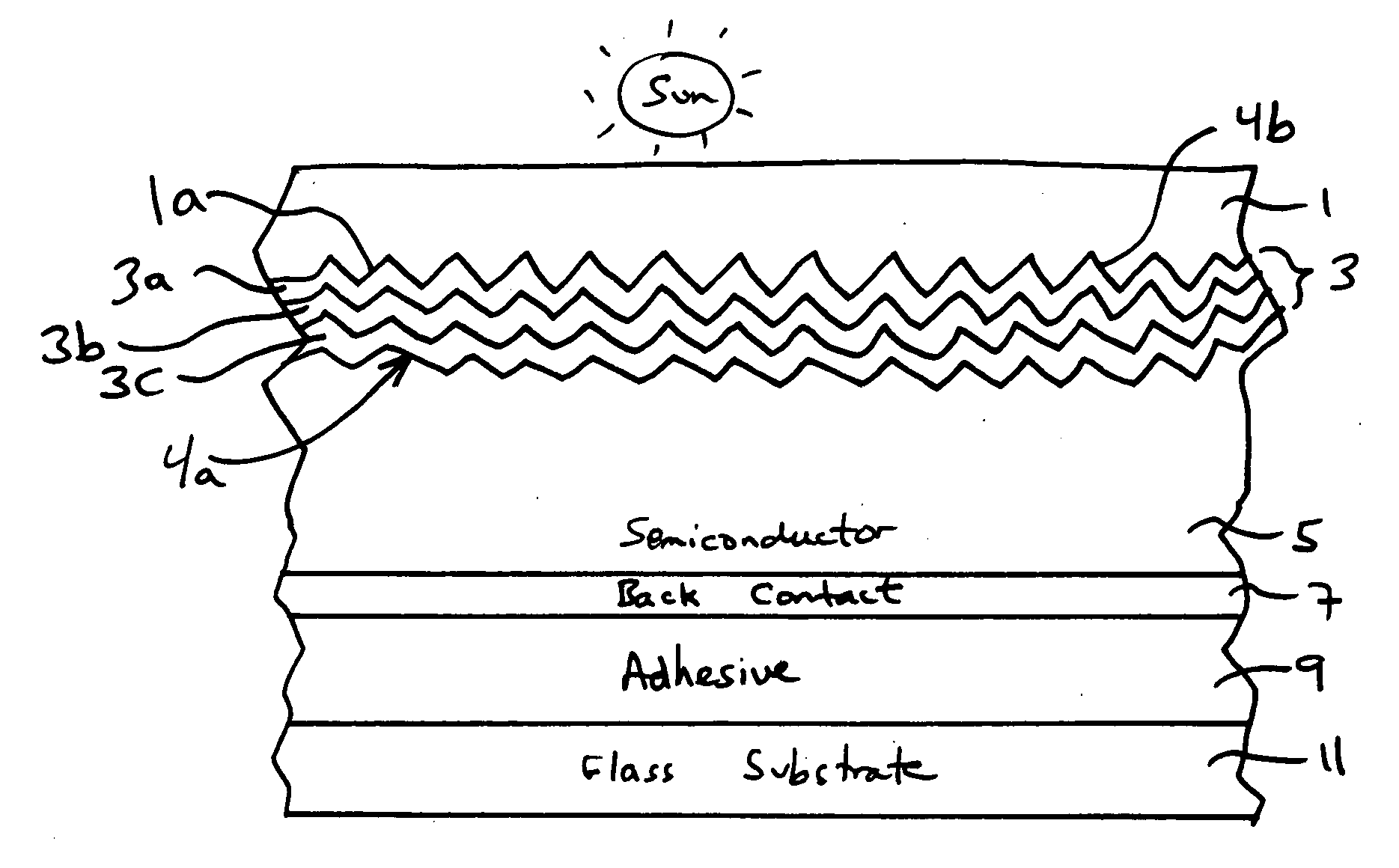
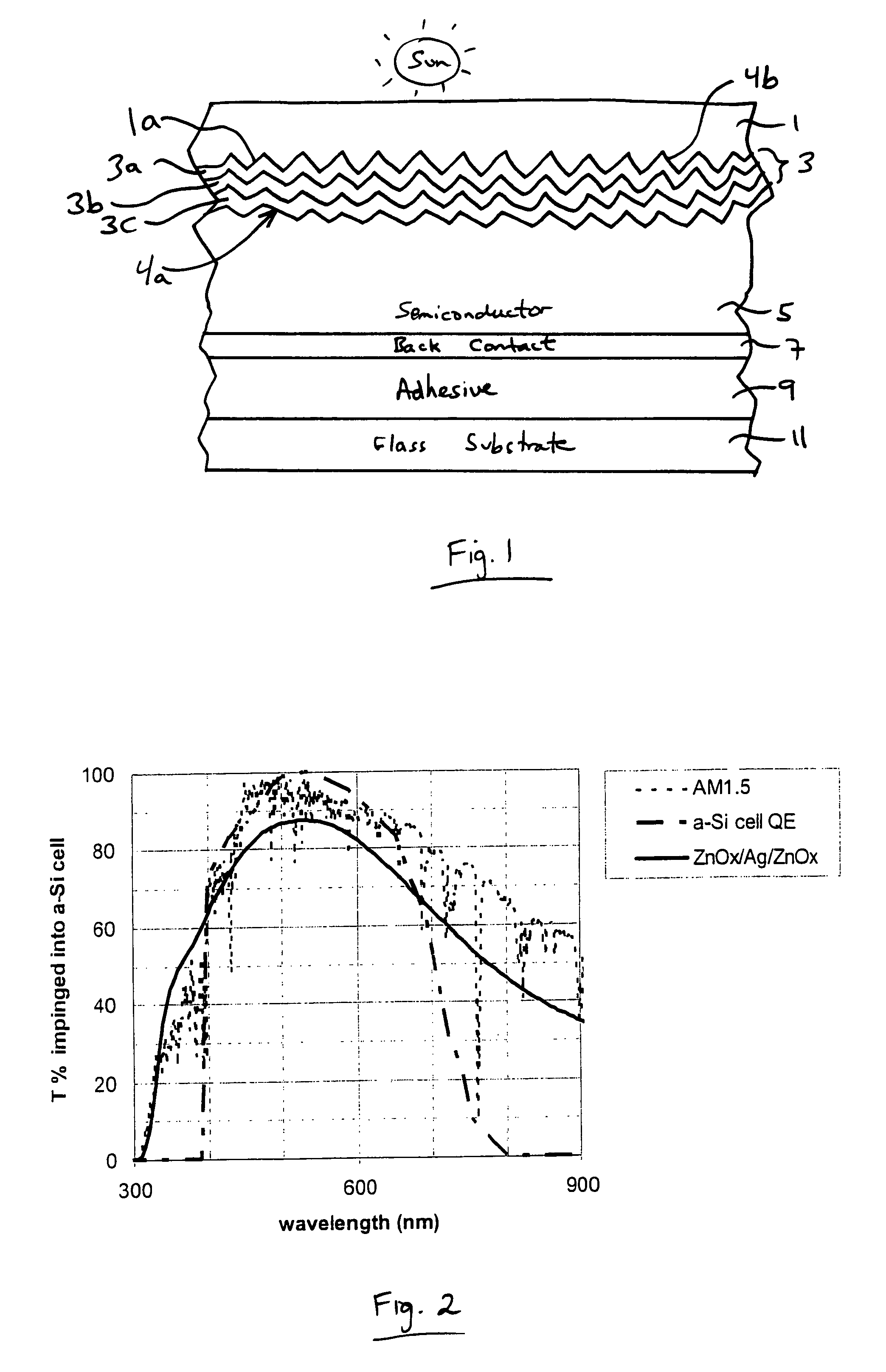
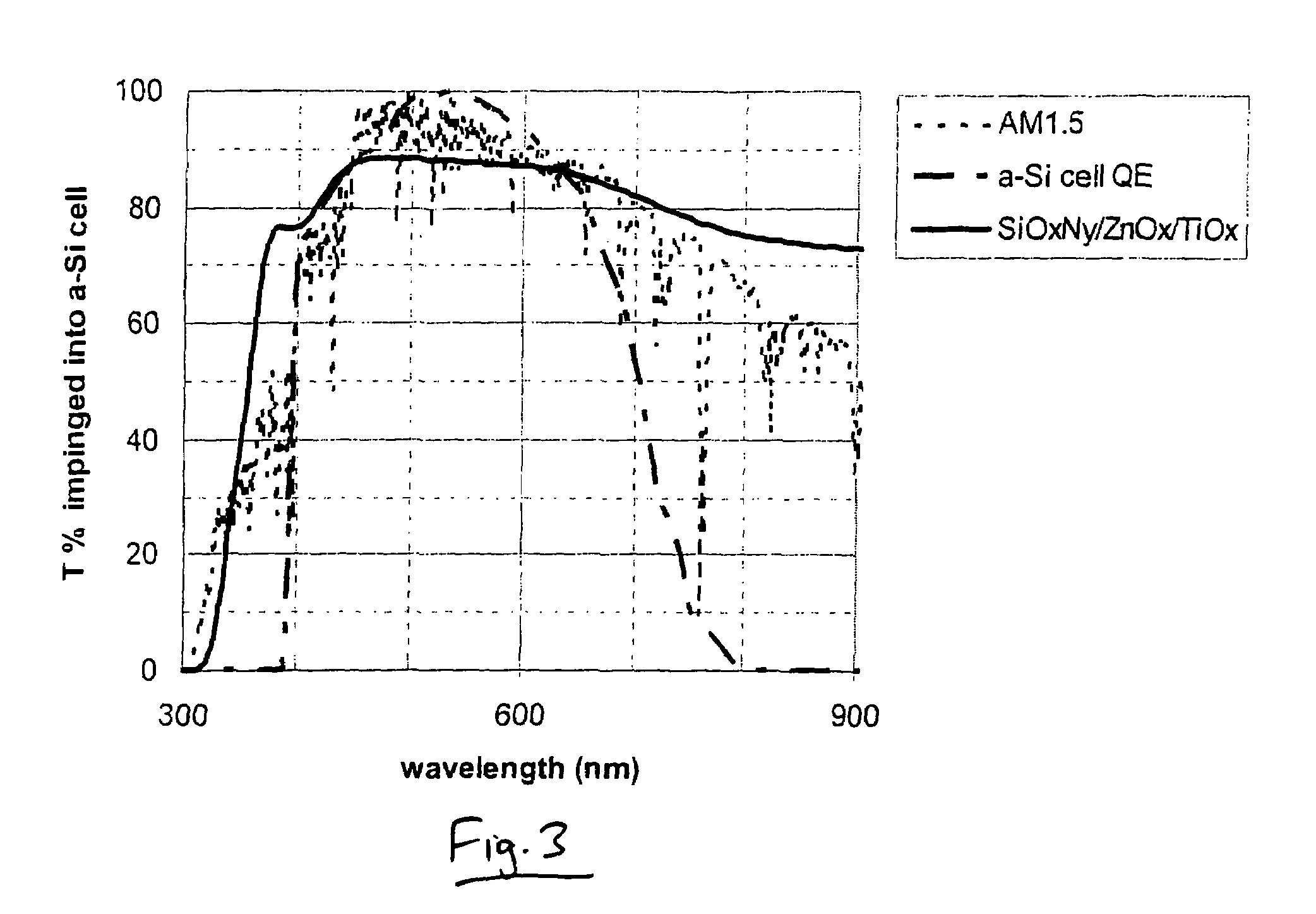
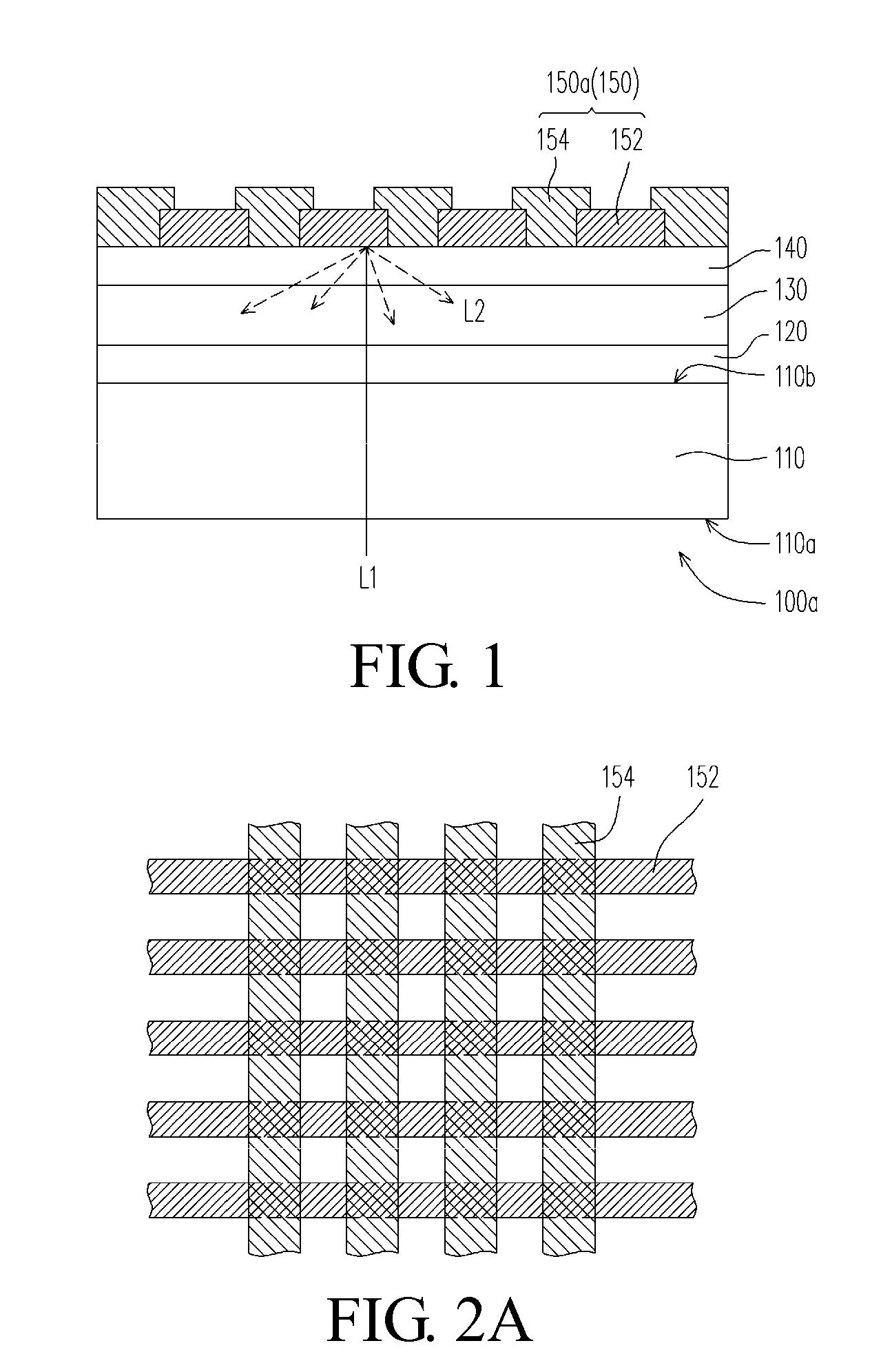
This invention relates to a photovoltaic device including an electrode such as a front electrode / contact. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of the photovoltaic device includes a multi-layered transparent conductive coating which is sputter-deposited on a textured surface of a patterned glass substrate. In certain example embodiments, a maximum transmission area of the substantially transparent conductive front electrode is located under a peak area of a quantum efficiency (QE) and / or QEx (photon flux of solar radiation) curve of the photovoltaic device and a light source spectrum used to power the photovoltaic device. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode includes a transparent conductive layer of or including one or more of (i) titanium zinc oxide doped with aluminum and / or niobium, and / or (ii) titanium niobium oxide.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Front electrode including transparent conductive coating on patterned glass substrate for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20080107799A1Reduced visible light reflectionImprove conductivityPV power plantsVacuum evaporation coatingQuantum efficiencyConductive coating
This invention relates to a photovoltaic device including an electrode such as a front electrode / contact. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of the photovoltaic device includes a multi-layered transparent conductive coating which is sputter-deposited on a textured surface of a patterned glass substrate. In certain example embodiments, a maximum transmission area of the substantially transparent conductive front electrode is located under a peak area of a quantum efficiency (QE) curve of the photovoltaic device and a light source spectrum used to power the photovoltaic device.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
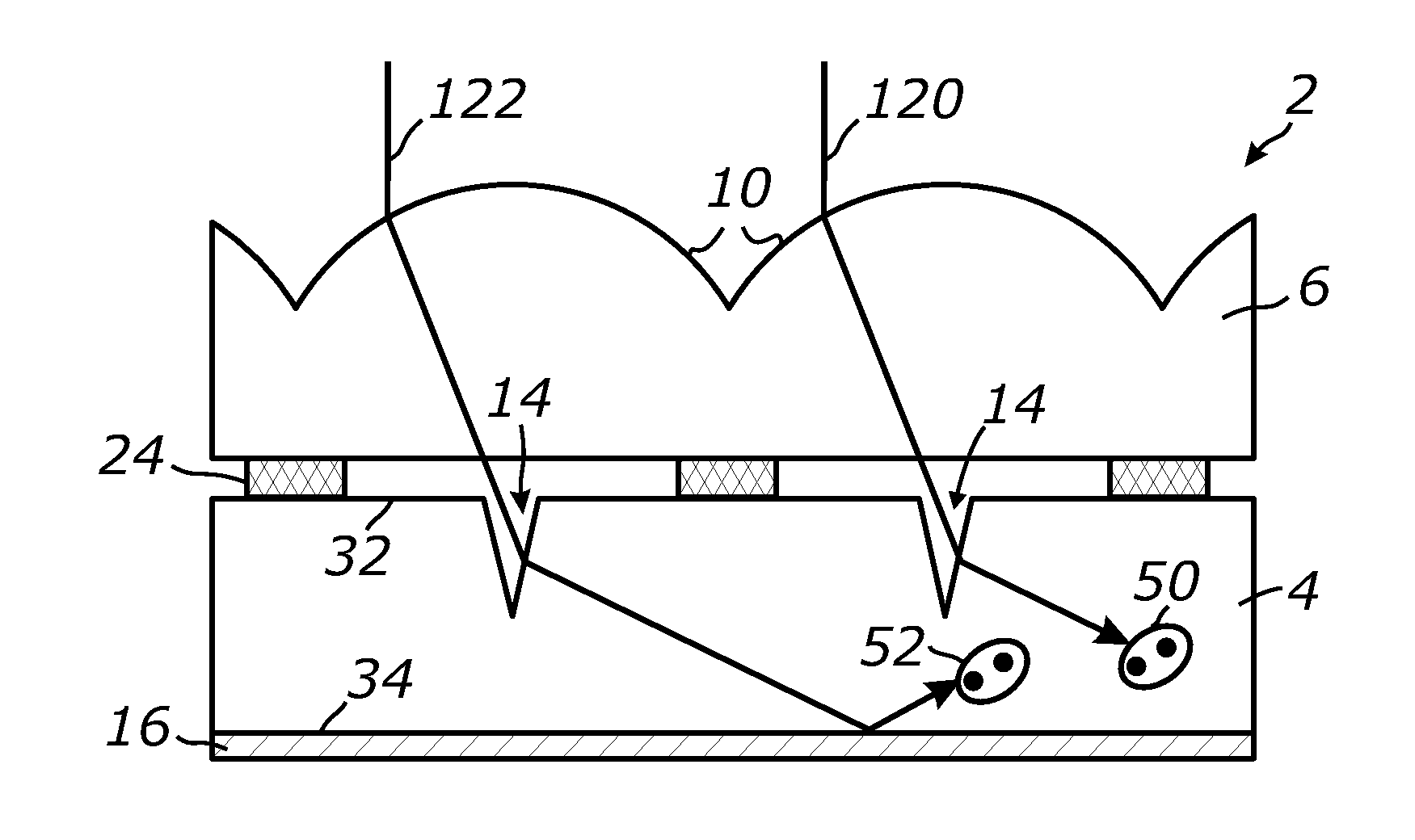
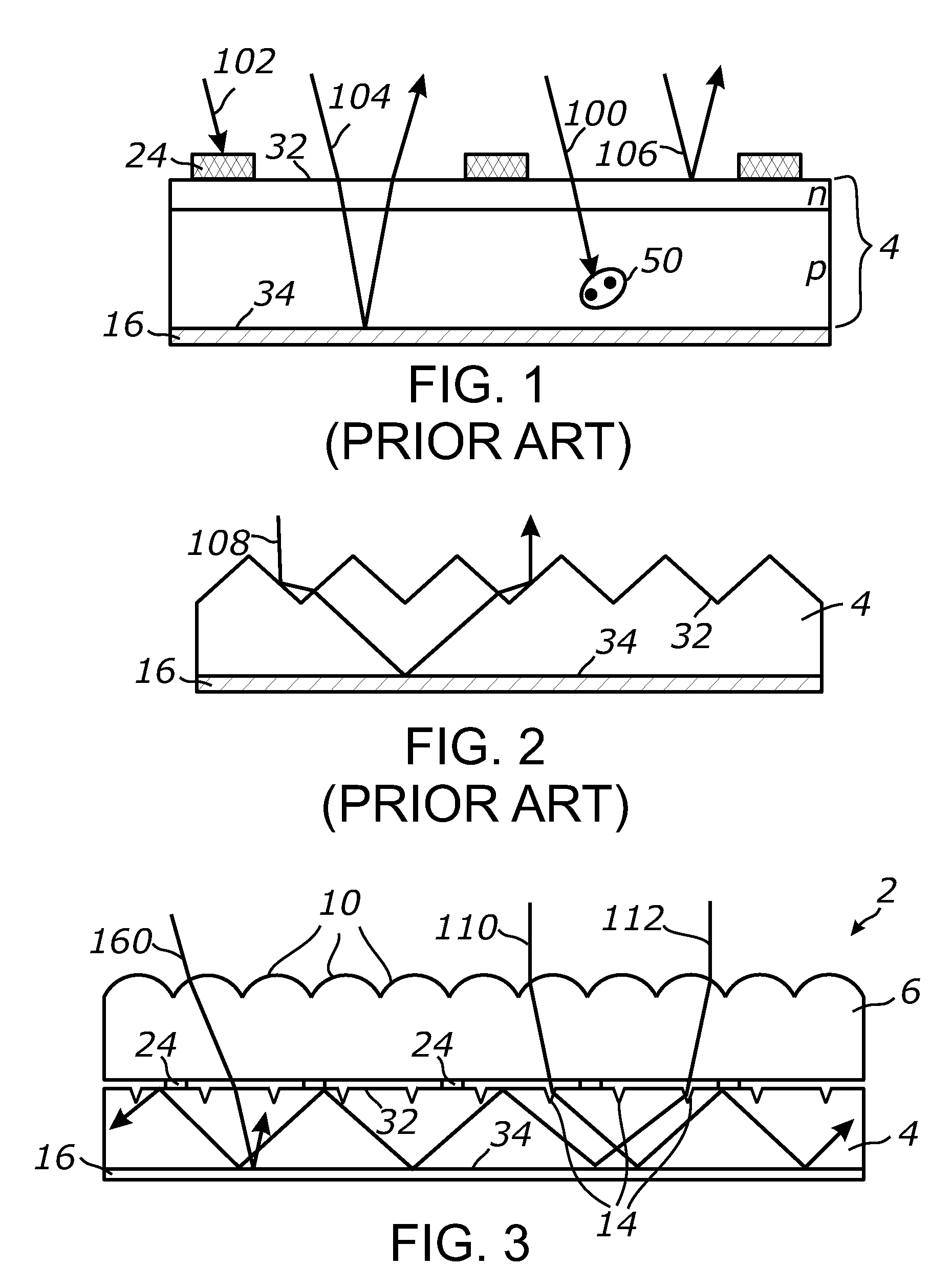
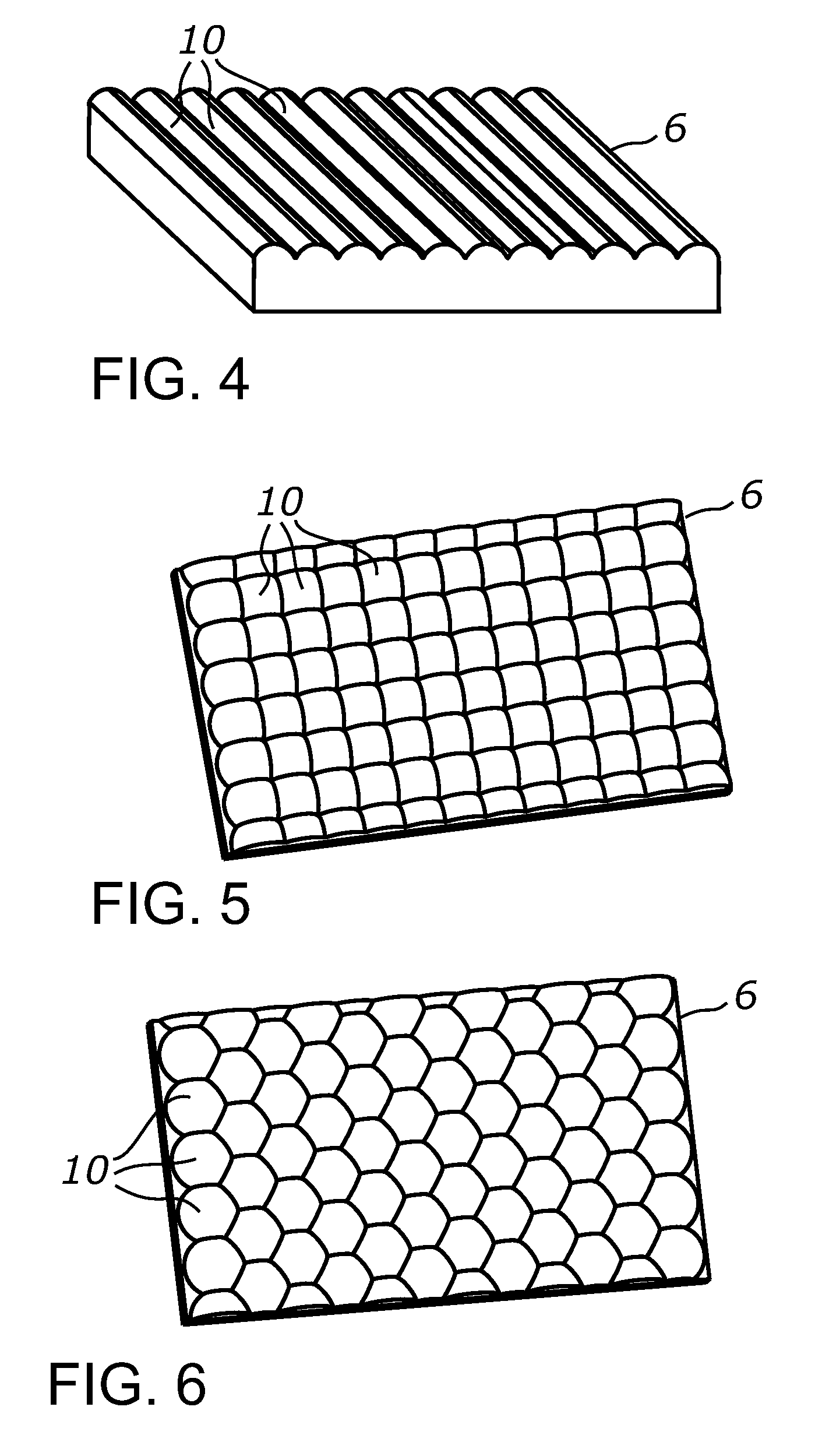
Light harvesting system employing microstructures for efficient light trapping
ActiveUS20120012741A1Enhanced light absorptionOptimizing light pathRadiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTotal internal reflectionTrapping
A light harvesting system employing a focusing array and a photoresponsive layer in which a plurality of microstructured areas is formed. Light received by the focusing array is injected transmissively into the photoresponsive layer through the microstructured areas. The injected light is retained in the photoresponsive layer by at least a total internal reflection and is propagated within the layer until it is substantially absorbed.
Owner:S V V TECH INNOVATIONS
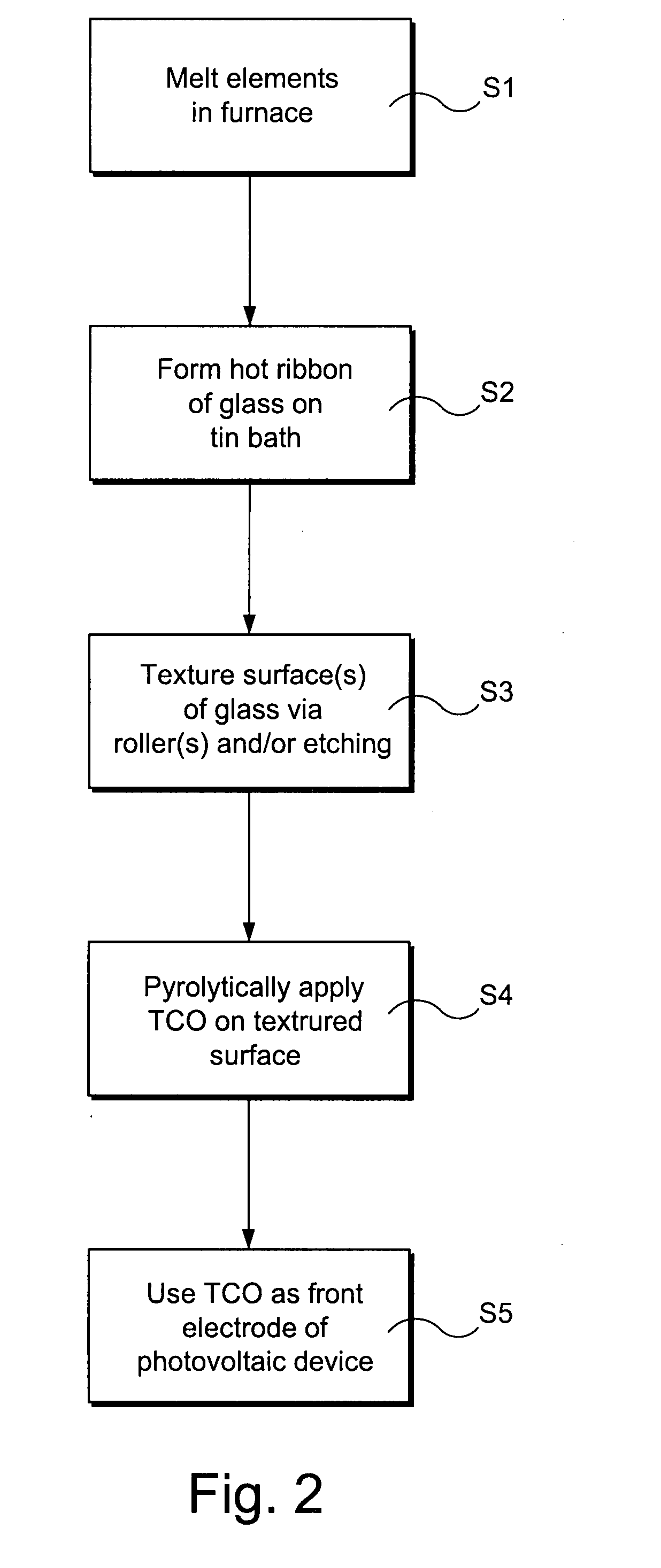
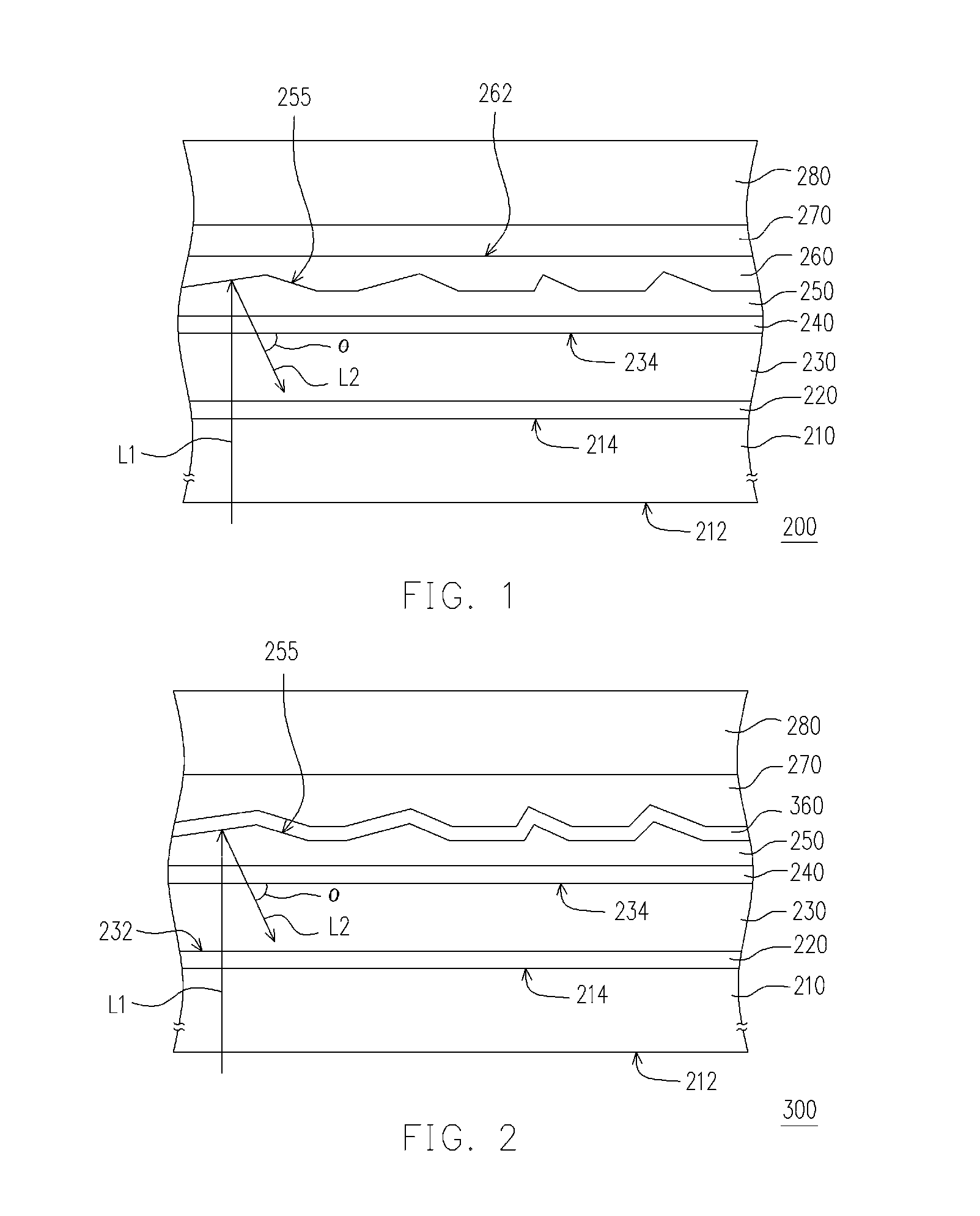
Front electrode including pyrolytic transparent conductive coating on textured glass substrate for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20080308146A1Low efficiencyImprove efficiencyOptical articlesPhotovoltaic energy generationConductive coatingSemiconductor
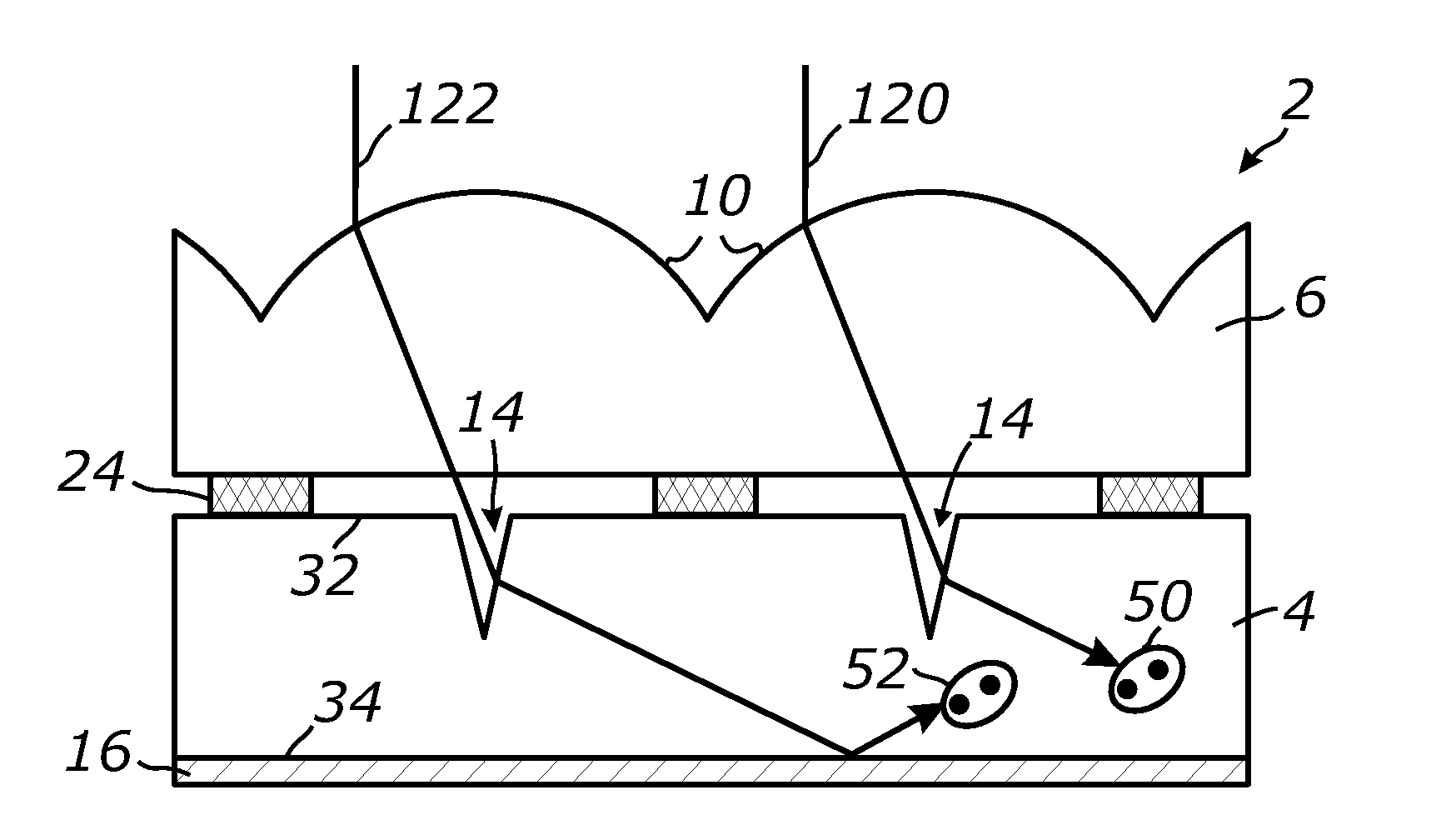
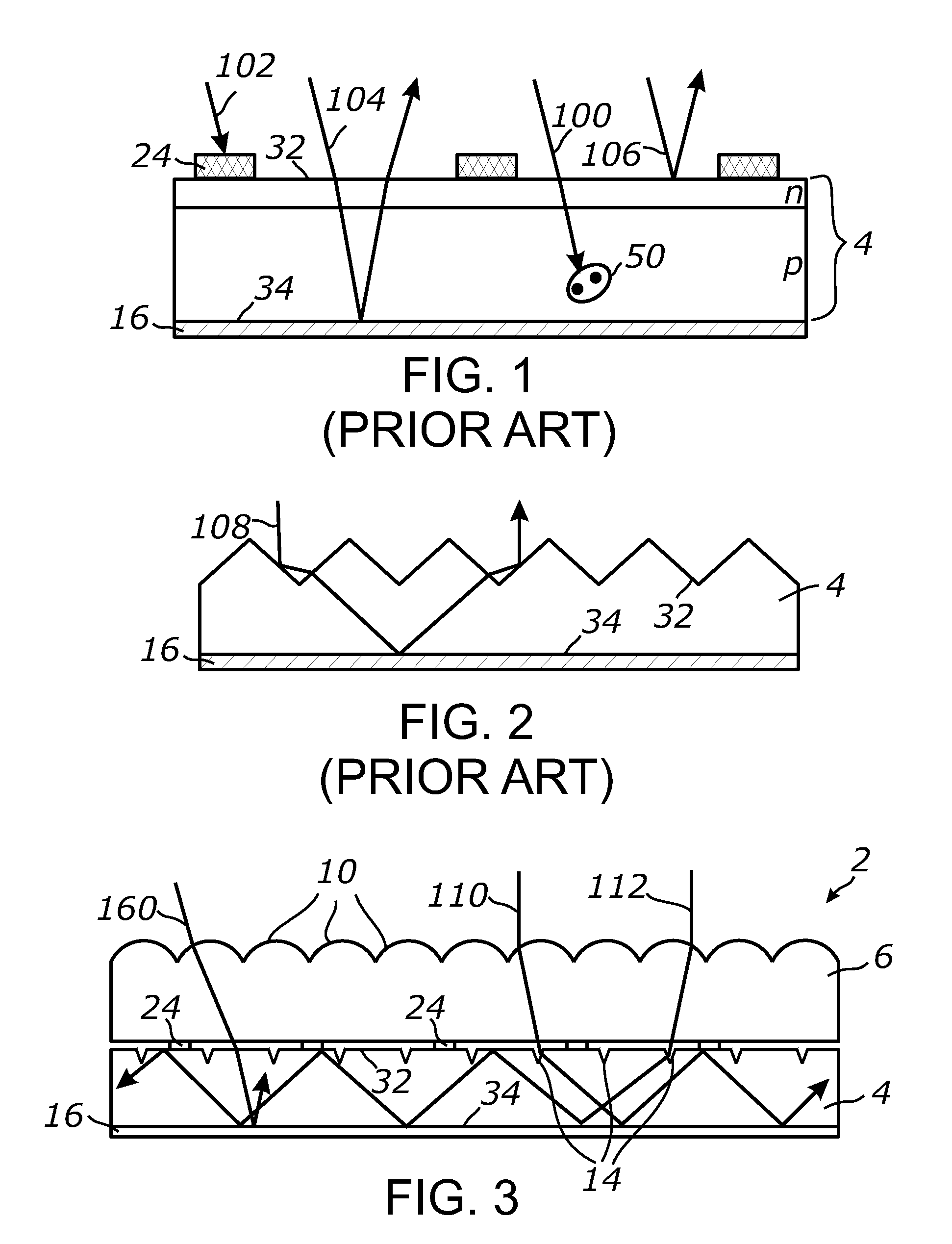
A photovoltaic device includes a front electrode on a textured front glass substrate. In certain example embodiments, the glass substrate is textured via roller(s) and / or etching to form a textured surface. Thereafter, a front electrode is formed on the textured surface of the glass substrate via pyrolysis. The front electrode may be of or include a transparent conductive oxide (TCO) such as tin oxide and / or fluorinated tin oxide in certain example embodiments. In certain example instances, this is advantageous in that efficiency of the photovoltaic device can be improved by increasing light absorption by the active semiconductor via both increasing light intensity passing through the front glass substrate and front electrode, and increasing the light path in the semiconductor photovoltaic conversion layer.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Front electrode including transparent conductive coating on etched glass substrate for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20080308145A1Low efficiencyImprove efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingConductive coatingSputter deposition
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to a front electrode provided on an etched / patterned front glass substrate for use in a photovoltaic device or the like. The glass is a low-iron soda-lime-silica based glass. Etching of the glass may include immersing the soda-lime-silica based glass in an acid inclusive solution such as hydrofluoric acid (e.g., HF in aqueous solution) and / or hydrofluoric acid with a buffer, in order to selectively dissolve some of the glass thereby producing at least one textured / patterned substantially transparent surface of the glass substrate. A front electrode (single or multi-layered) is then formed (e.g., via sputter-deposition) on the textured surface of the front glass substrate, and may be used in a photovoltaic device or the like.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
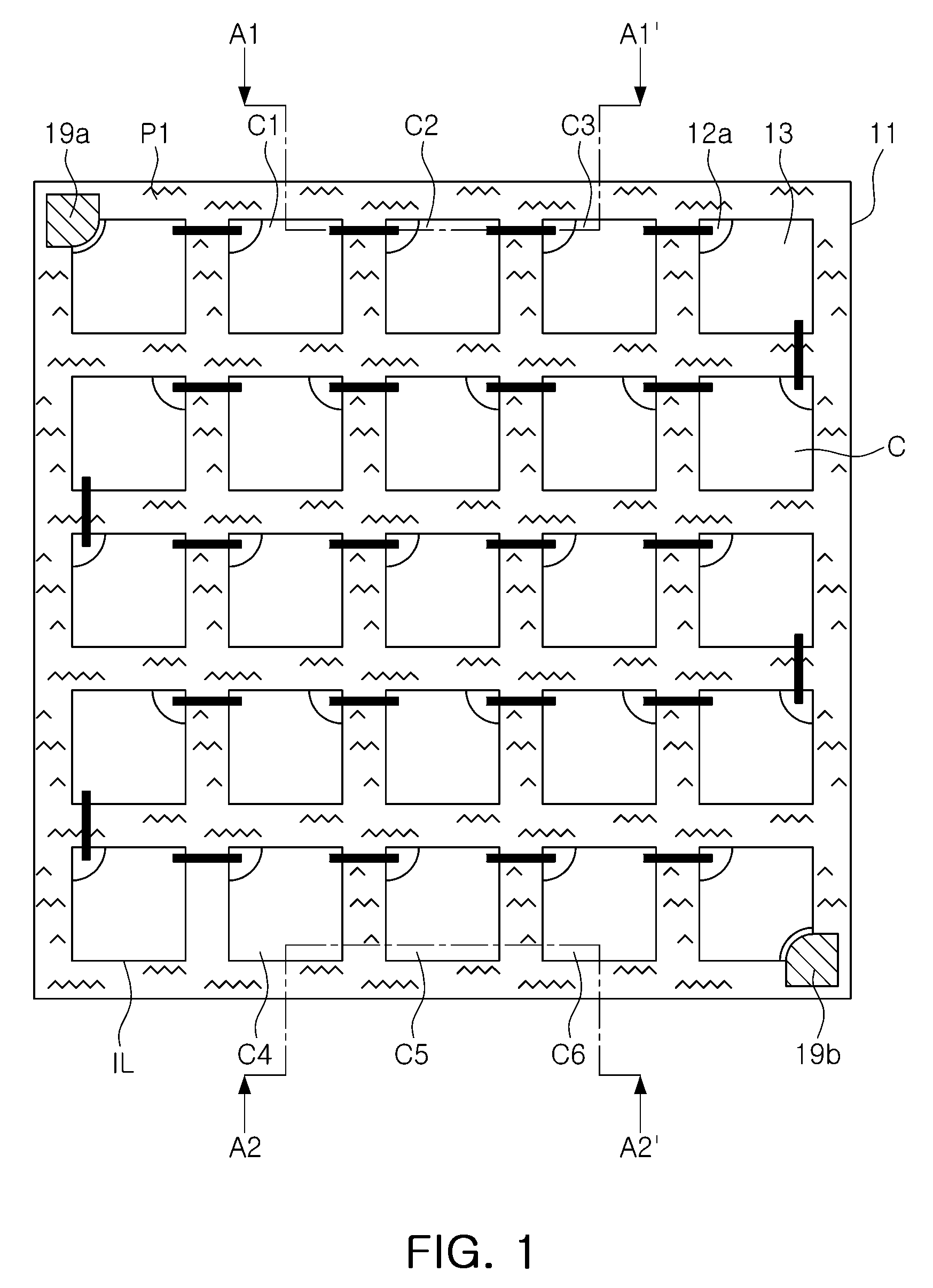
Semiconductor light emitting device having multi-cell array, light emitting module, and illumination apparatus
ActiveUS20110204387A1Increase the areaImprove lighting efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesActive layerLight emitting device
A semiconductor light emitting device includes a substrate, a plurality of light emitting cells, a connection part, and a concavo-convex part. The light emitting cells are arrayed on the top surface of the substrate. Each of the light emitting cells has a first-conductivity-type semiconductor layer, an active layer, and a second-conductivity-type semiconductor layer that are sequentially stacked on the top surface of the substrate. The connection part is formed to connect the light emitting cells in series, parallel or series-parallel. The concavo-convex part is formed in at least one of the bottom surface of the substrate and the top surface of an isolation region between the light emitting cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Illumination device comprising a light source and a light-guide
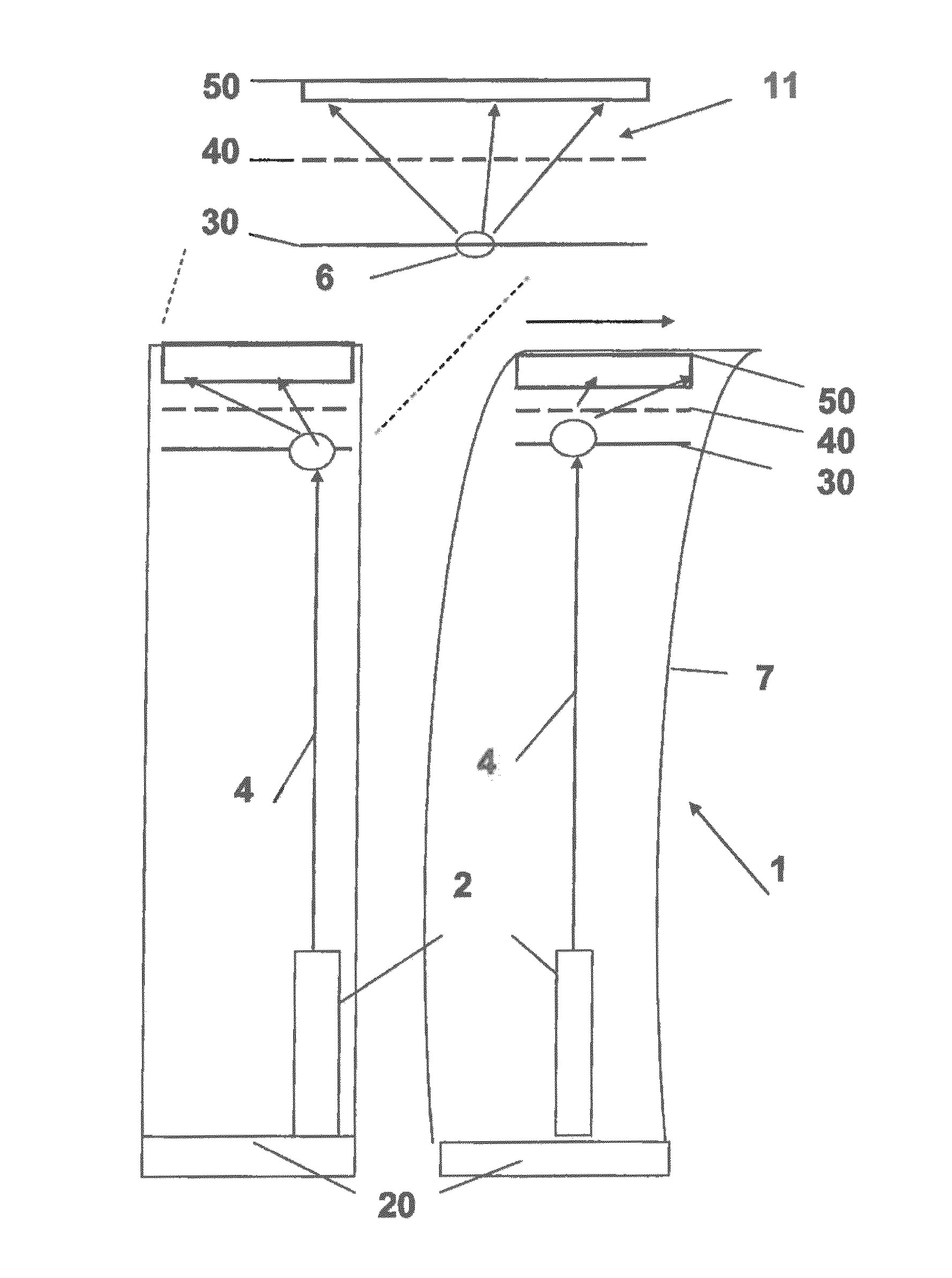
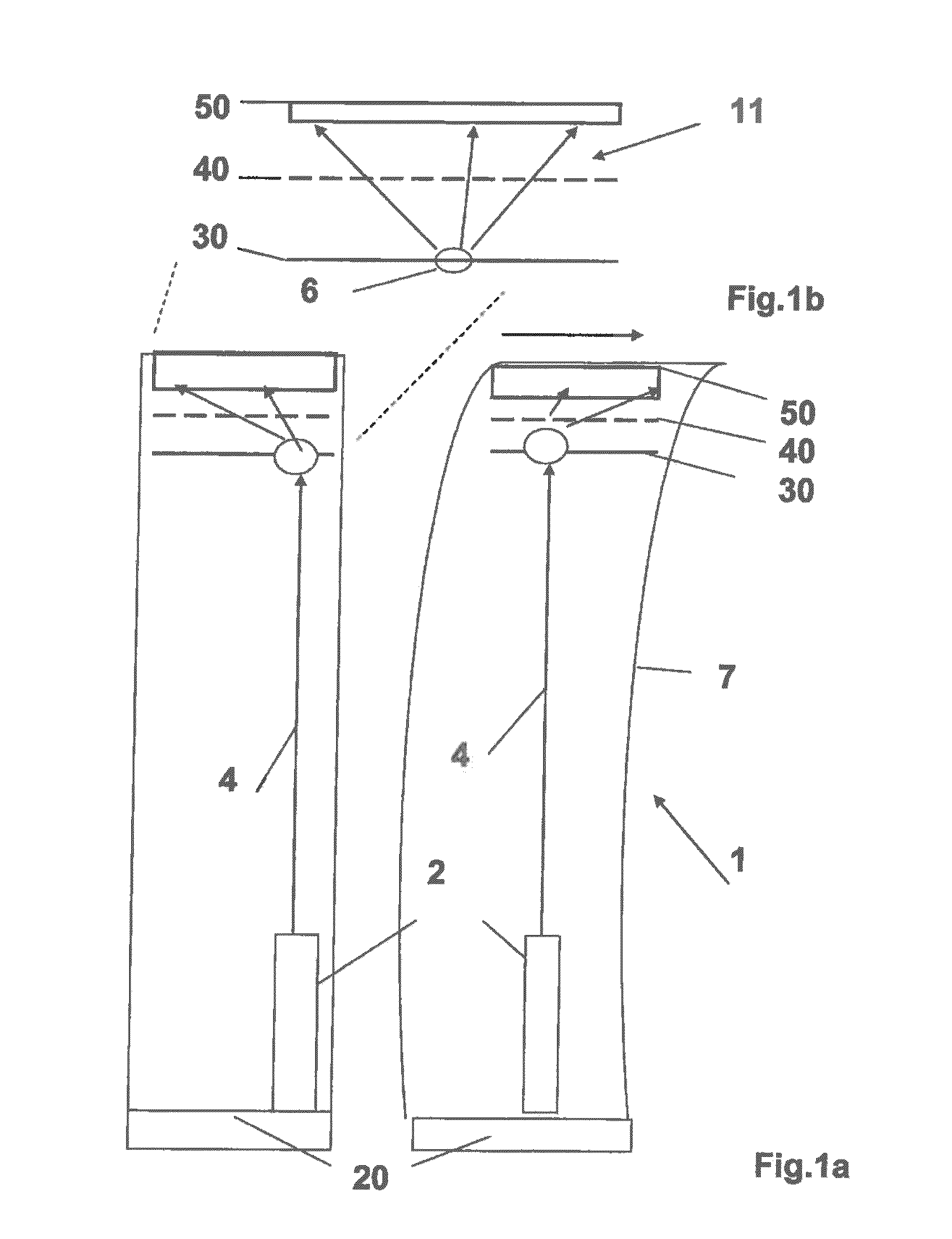
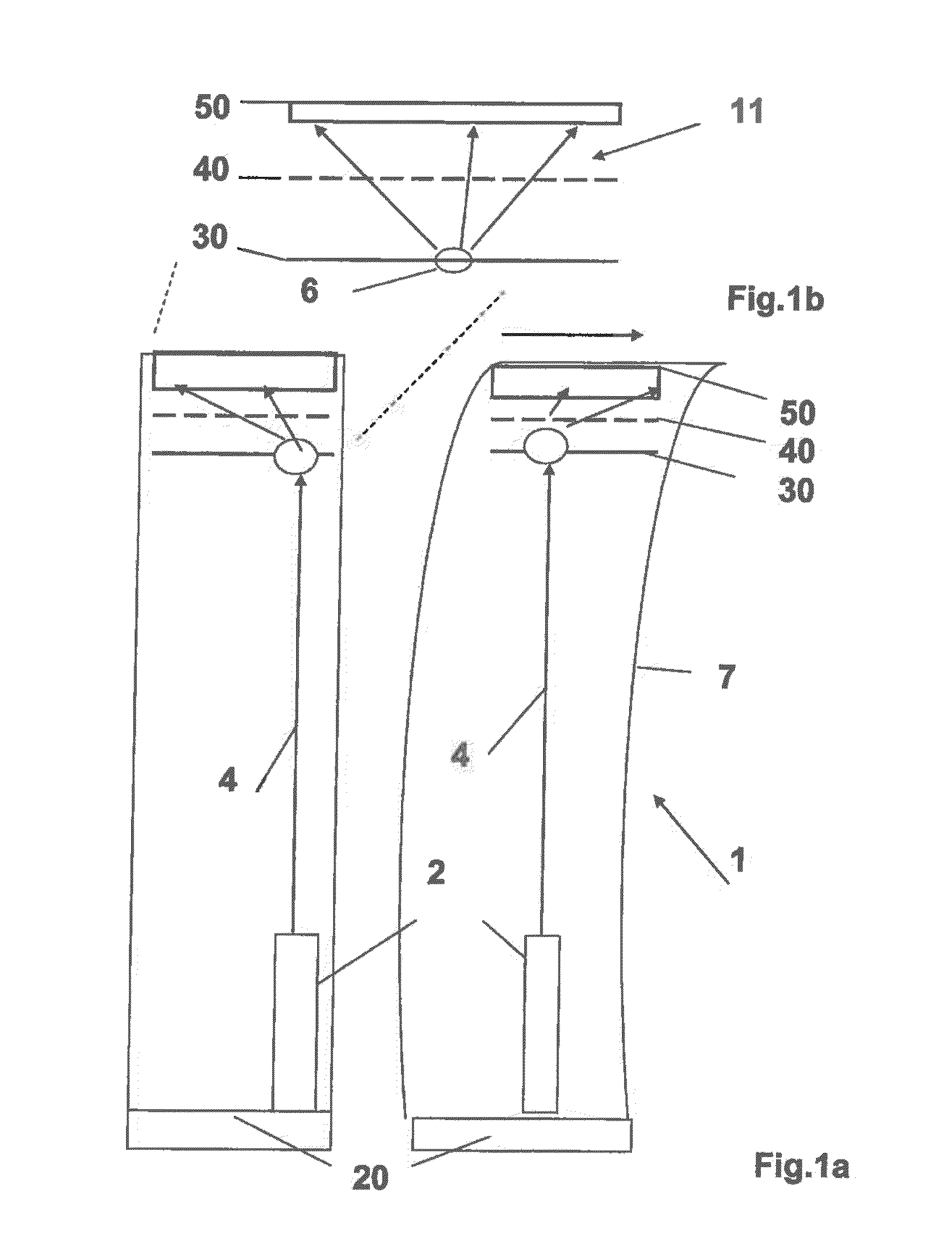
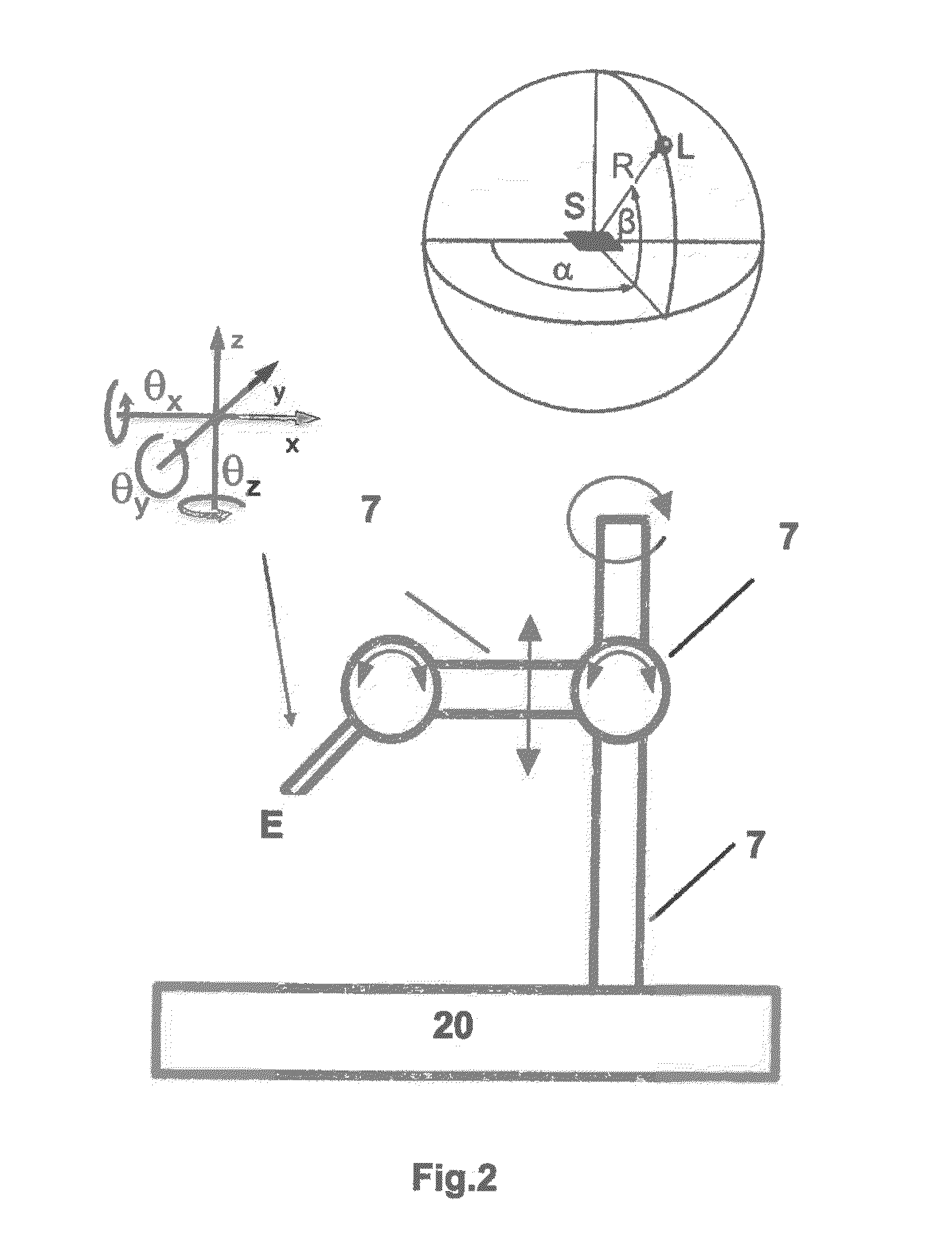
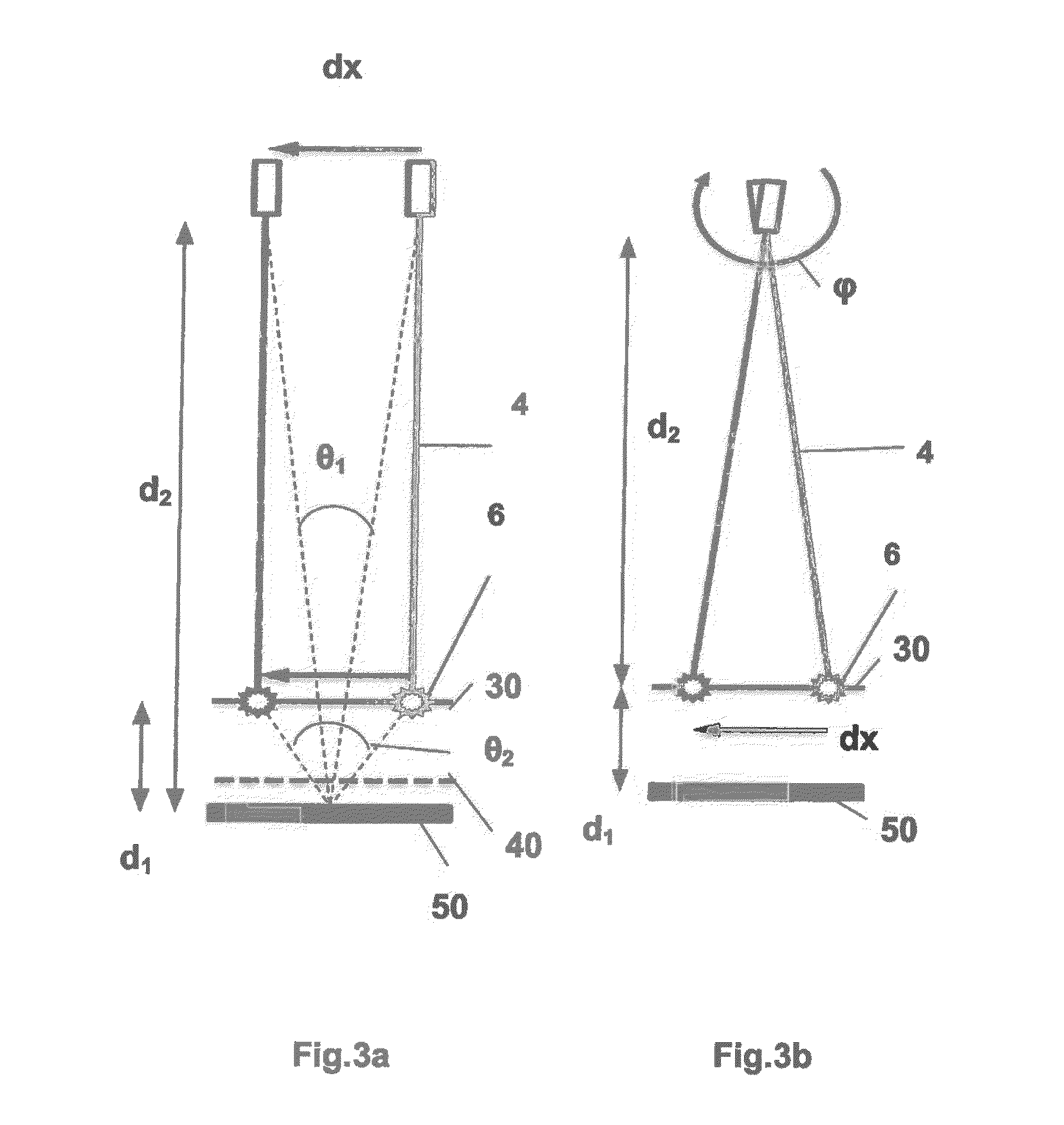
ActiveUS7854539B2Optimizing light pathEconomical to usePoint-like light sourceOptical light guidesLight guideRadiation mode
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
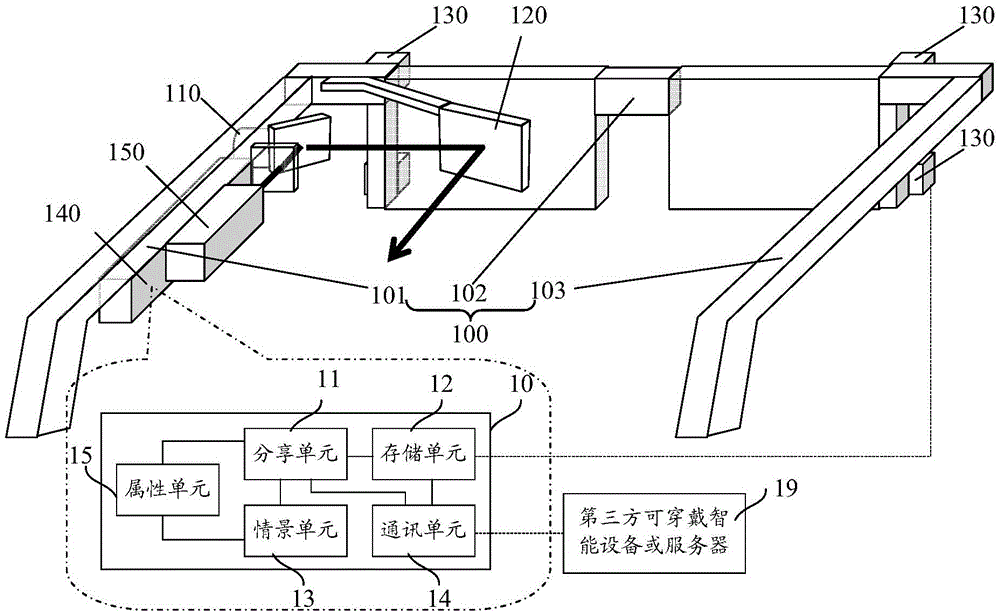
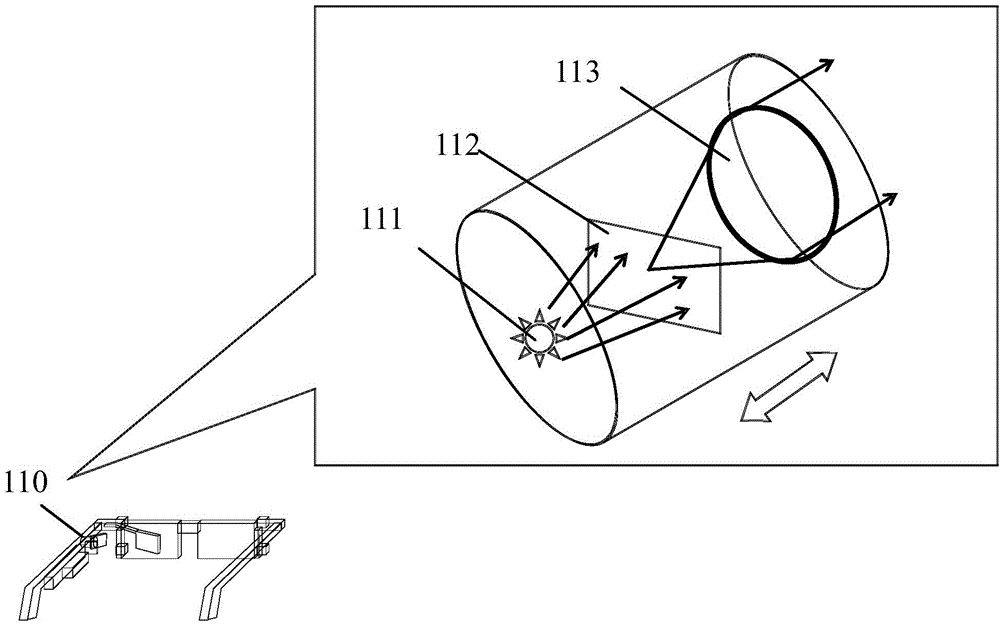
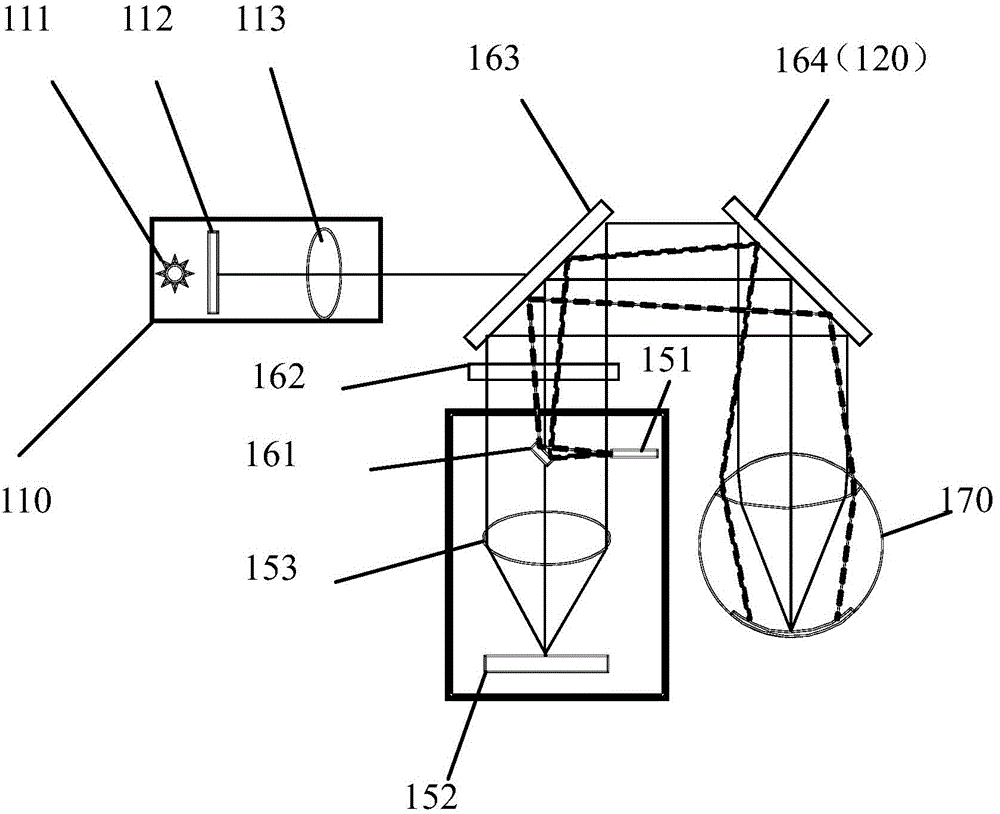
Wearable intelligent device, interaction method of wearable intelligent device and wearable intelligent device system
ActiveCN105446474AOptimizing light pathGood product performanceInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingHuman eyeThird party
The invention relates to a wearable intelligent device, an interaction method of the wearable intelligent device and a wearable intelligent device system. The wearable intelligent device comprises a device frame, a micro projector, a spectroscope, an image sensing unit, a retina position sensing unit, and a central data center, wherein the micro projector is suitable for projecting a graphic interface to the spectroscope; the spectroscope is suitable for receiving the projected graphic interface and forming a real image of the graphic interface in human eyes; the image sensing unit is suitable for sensing external scene information, and converting the external scene information into scene image data; the retina position sensing unit is suitable for sensing positions of the eyes and a changing mode of the positions along with time, and converting the positions into position data; the central data center is at least suitable for converting the changing mode of the positions along with time and the position data into corresponding operation instructions; the central data center further comprises a sharing module; and the sharing module is at least suitable for receiving the operation instructions, and executing an operation of sharing the scene image data to a third-party wearable intelligent device. According to the wearable intelligent device disclosed by the invention, rapid sharing of data is achieved, and user experience is improved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Imaging lens system, image capturing unit and electronic device
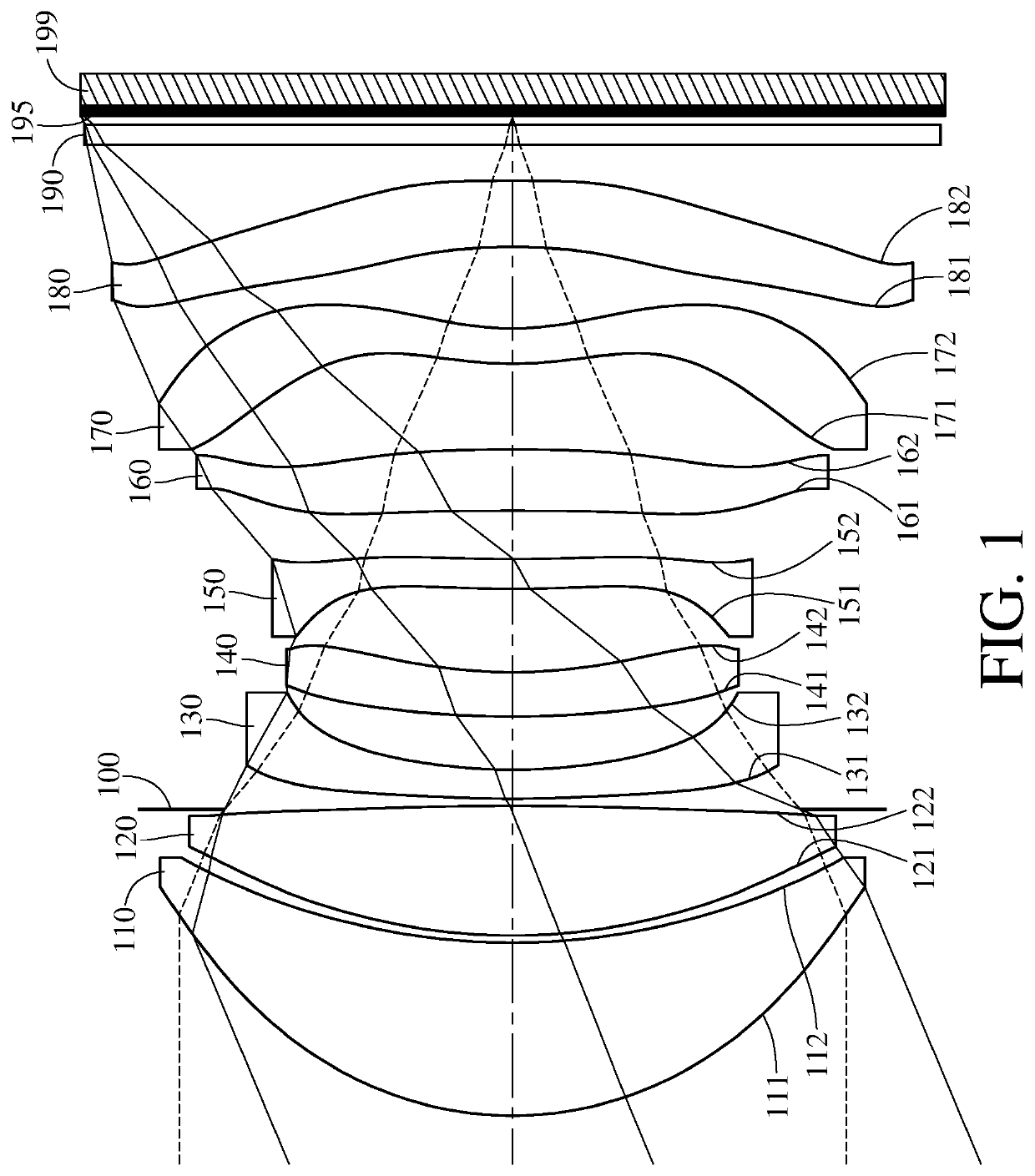
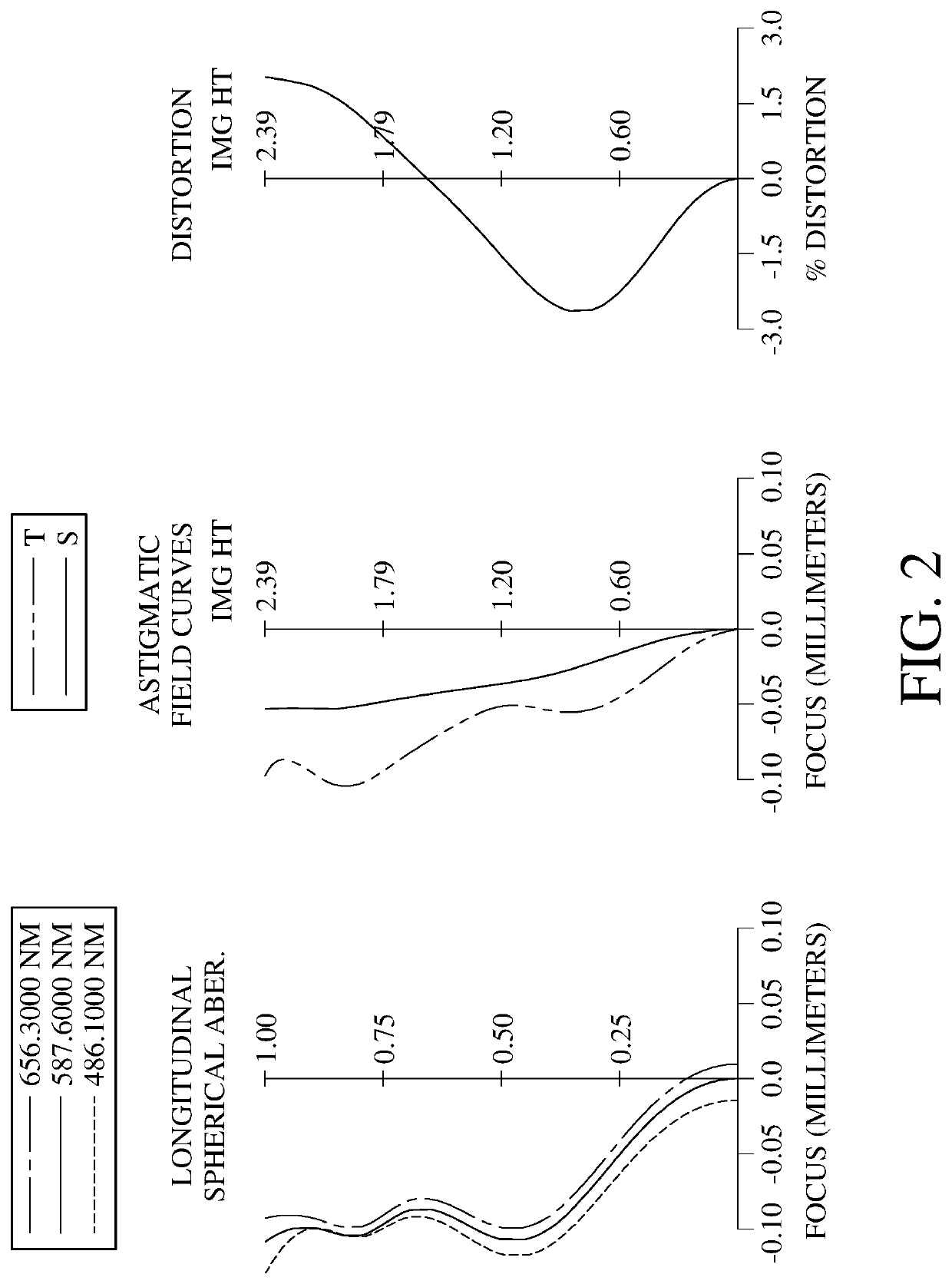
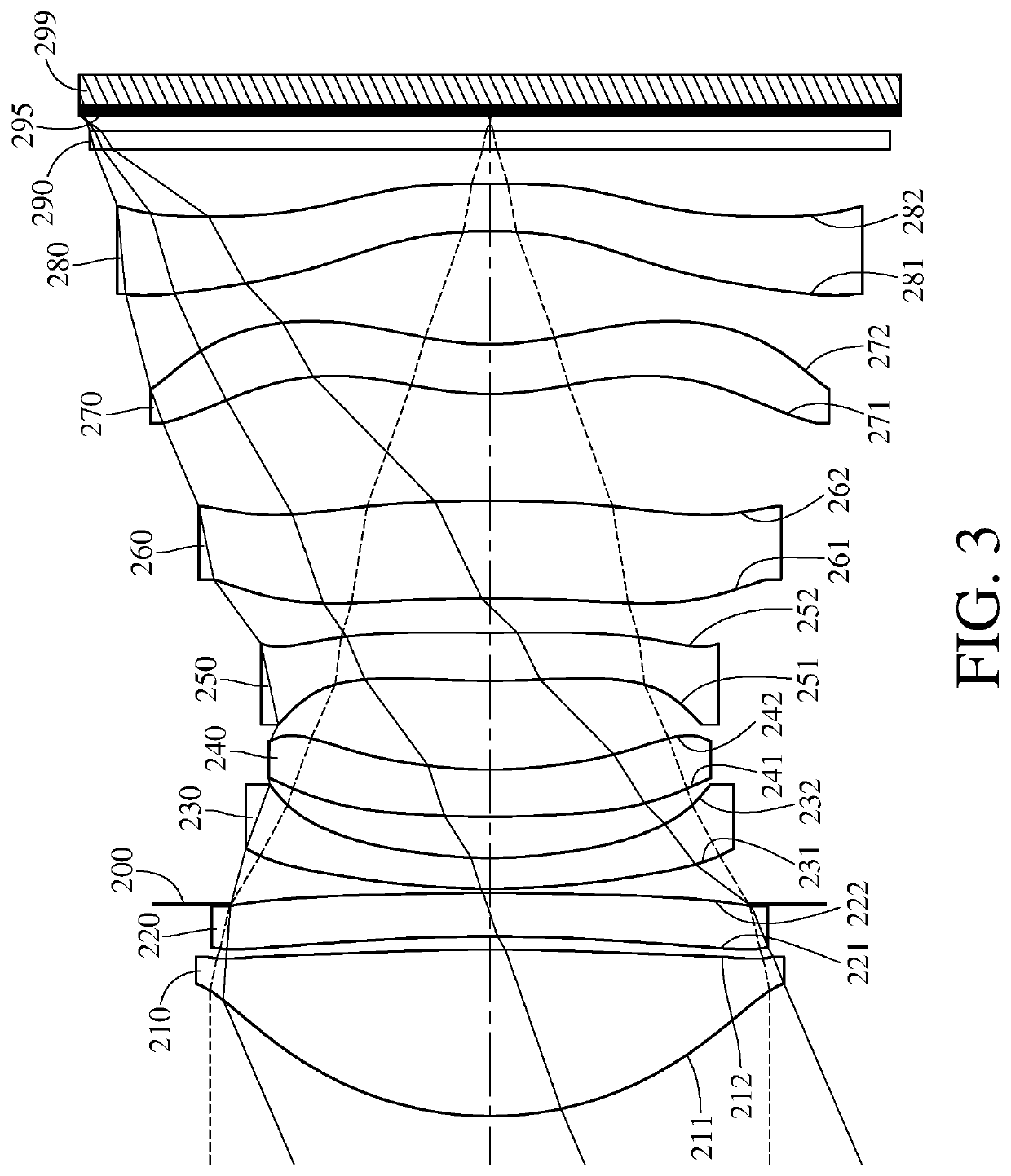
ActiveUS20200132969A1Optimizing light pathCorrect chromatic aberrationSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesOphthalmologyImaging lens
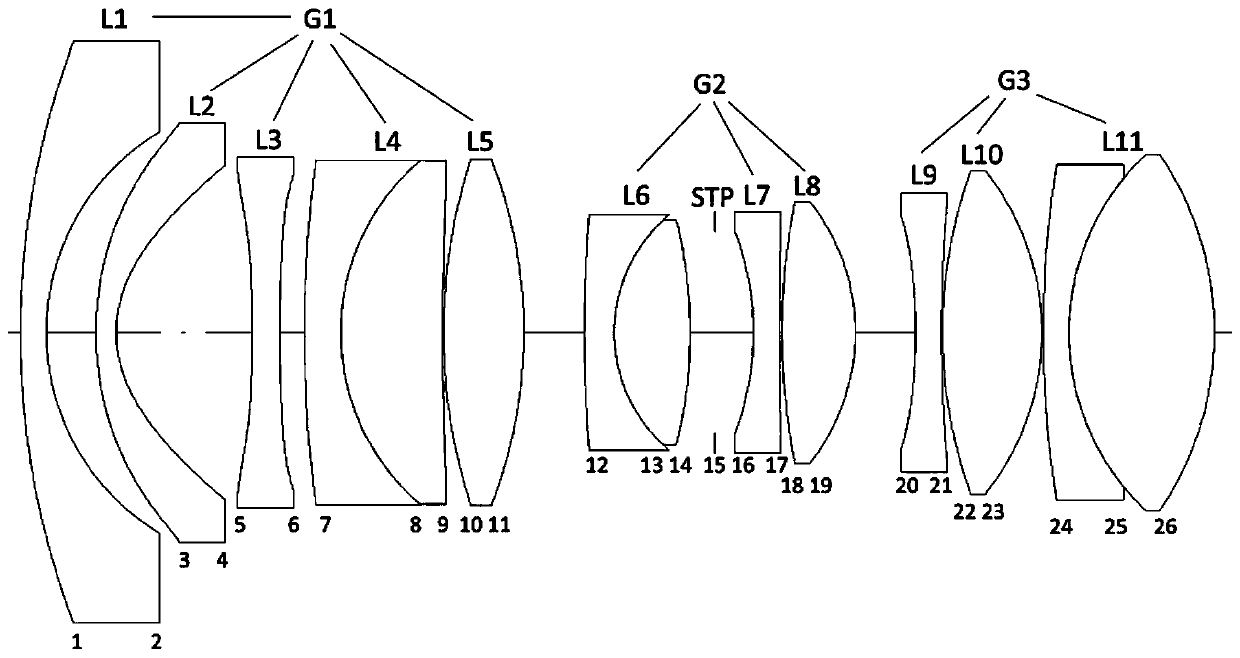
An imaging lens system includes eight lens elements which are, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element, a second lens element, a third lens element, a fourth lens element, a fifth lens element, a sixth lens element, a seventh lens element and an eighth lens element. Each of the eight lens elements has an object-side surface facing toward the object side and an image-side surface facing toward the image side. At least one lens element of the imaging lens system has at least one lens surface having at least one inflection point. The imaging lens system has a total of eight lens elements.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Semiconductor light emitting device having multi-cell array, light emitting module, and illumination apparatus
ActiveUS8829540B2Increase the areaImprove lighting efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesActive layerLight emitting device
A semiconductor light emitting device includes a substrate, a plurality of light emitting cells, a connection part, and a concavo-convex part. The light emitting cells are arrayed on the top surface of the substrate. Each of the light emitting cells has a first-conductivity-type semiconductor layer, an active layer, and a second-conductivity-type semiconductor layer that are sequentially stacked on the top surface of the substrate. The connection part is formed to connect the light emitting cells in series, parallel or series-parallel. The concavo-convex part is formed in at least one of the bottom surface of the substrate and the top surface of an isolation region between the light emitting cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Integrated Lens With Multiple Optical Structures and/or Surfaces, Optical Module and Transceiver Including the Same, and Methods of Making and Using the Same
ActiveUS20160341903A1Simple device structureOptimizing light pathCoupling light guidesFiberCamera lens
An integrated lens with integrated functional optical surfaces for use in optical communication is disclosed. The integrated lens includes first and second cavities and a fiber adapter. The device also includes integrated first and second lenses. The first cavity houses one or more optical transmitting and / or receiving devices. The second cavity has a first optical surface and an optional second optical surface. The fiber adapter has the second lens. The integrated lens enables a small size, a light weight, high coupling and a high transmission efficiency, and can be produced by injection molding using a single mold. The integrated lens is applicable to optical signal coupling, fiber connections, optical modules, and optical or optoelectronic communication.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS CHENGDU
Thin-film solar cell and manufacture method thereof
InactiveUS20110146794A1Increase profitImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationLight beamPhotoelectric conversion efficiency
A thin-film solar cell and a manufacture method thereof are provided. The thin-film solar cell comprises a transparent substrate, a first transparent conductive layer, a photovoltaic layer, a second transparent conductive layer and a light reflecting structure. The transparent substrate has a light incident surface and a back surface opposite to the light incident surface. The first transparent conductive layer is disposed on the back surface of the transparent substrate. The photovoltaic layer is disposed on the first transparent conductive layer. The second transparent conductive layer is disposed on the photovoltaic layer. The light reflecting structure is disposed on the second transparent conductive layer. The manufacture method forms the light reflecting structure having a texture structure on the thin film to enhance utilization of light beams in the thin-film solar cell so as to further improve photoelectric conversion efficiency of the thin-film solar cell.
Owner:AURIA SOLAR CO LTD
Thin film solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110174370A1Improve light utilizationImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamEngineering
A thin film solar cell includes a transparent substrate, a first transparent conductive layer, a photovoltaic layer, a second transparent conductive layer, a first adhesive layer and a reflective layer is provided. The first transparent conductive layer is disposed on a back surface of the transparent substrate. The photovoltaic layer is disposed on the first transparent conductive layer. The second transparent conductive layer is disposed on the photovoltaic layer. The first adhesive layer is disposed on the second transparent conductive layer. The reflective layer is disposed on the first adhesive layer. The surface of the first adhesive layer in contact with the reflective layer is a texture structure. The light beam passing the first adhesive layer is reflected by the texture structure or the reflective layer and transmitted back to the photovoltaic layer, and the wavelength range of the reflected light beam is substantially between 600 nm and 1,100 nm.
Owner:AURIA SOLAR CO LTD
Magnifying display screen device
InactiveUS20190369382A1Reduce the burden onEasy to getMirrorsBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsVideo playerDisplay device
The present invention relates to a magnifying display screen device, which includes a stand, a display module, a reflective module and a magnifying module, objects could be magnified several times and imaged far longer than several times of the object distance according to the principle of virtual imaging of concave mirrors, and a screen image of a mobile phone, a computer, a video player, a USB flash drive or a SD memory card can be magnified by a connection with the mobile phone, the computer the video player, the USB flash drive or the SD memory card, to thereby provide the optimized projection light path, so that users could watch an ideal magnified image to effectively reduce the burden on eyes.
Owner:E LEAD ELECTRONICS
Ultra-wide-angle interchangeable prime lens
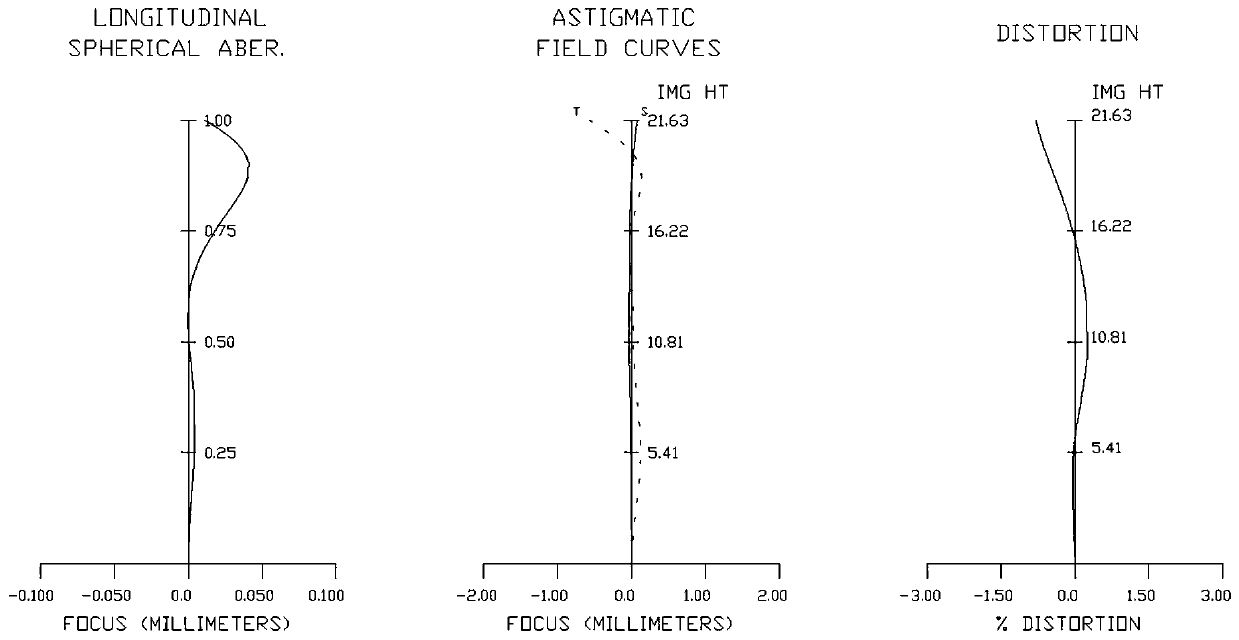
An ultra-wide-angle interchangeable prime lens comprises a first lens group, a second lens group and a third lens group in sequence from an object side to an image side, wherein the first lens group is fixedly disposed, and the second lens group and the third lens group move toward the object side from the image side for floating focusing. The ultra-wide-angle interchangeable prime lens comprisesa glass aspherical lens to improve resolution of the lens up to use requirement of a professional-grade camera with 8K resolution. The ultra-wide-angle interchangeable prime lens improves a peripheralbrightness ratio to more than 35% even at a maximal aperture, allowing light of the whole lens more uniform on a picture, thereby facilitating accurate exposure during film shooting. A lens structureand an optical path are optimized, in particular to enhance symmetry of the rear group of the lens, so that the TV distortion is below 1%, thereby ensuring that the picture is not deformed and distorted from the center to the periphery. Using floating focusing of the rear group of the lens and optimizing a distance between lenses in front and at back of the aperture at the same time make change of field of view within 1%, improving the problem of obvious breath effect of the camera lens.
Owner:JIAXING ZHONGRUN OPTICAL TECH
Device for analyzing a product to be analyzed located in a product space
ActiveUS20180306726A1Easy to cleanEasy to moveInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsPhysicsRadiation
A device for analysing a product to be analysed which is located in a product space having a probe body arranged in a probe housing and having a peripheral wall, and at least one radiation source and at least one optical receiver. At least one measurement window in the probe body has an entry region and an exit region for measurement radiation. An evaluation unit is also provided. The probe body can be brought into a measurement position, in which at least one part of the probe body in which the measurement window is located penetrates through an opening of the probe housing into the product space for the analysis. In addition, the probe body can be brought into a retracted position, in which the probe body is still located at least partially in the region of the opening of the probe housing and thus covers the opening.
Owner:ENDRESSHAUSER CONDUCTA GMBHCO
Integrated lens with multiple optical structures and/or surfaces, optical module and transceiver including the same, and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20160238794A1Simple device structureOptimizing light pathCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFiberCamera lens
An integrated lens with integrated functional optical surfaces for use in optical communication is disclosed. The integrated lens includes first and second cavities and a fiber adapter. The device also includes integrated first and second lenses. The first cavity houses one or more optical transmitting and / or receiving devices. The second cavity has a first optical surface and an optional second optical surface. The fiber adapter has the second lens. The integrated lens enables a small size, a light weight, high coupling and a high transmission efficiency, and can be produced by injection molding using a single mold. The integrated lens is applicable to optical signal coupling, fiber connections, optical modules, and optical or optoelectronic communication.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS CHENGDU
Light receiving and detection system for reading a radiographic image
InactiveUS20030136894A1Optimizing light pathExact reproductionPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansOphthalmologyLight spot
An apparatus and a method for receiving and detecting light from a plurality of light scanning operations on each scan line of a document, such as a radiographic image, which is being read. The light is detected by means of a photo-diode detector arrangement. Prior to detection, however, this light is received in an integrating arrangement. In effect, a progressive point of light from each optical fiber used for delivering of the light occurs from one end of a scan line to the other sequentially, from scan operation to scan operation. When the light emits from each of a plurality of optical fibers, the light then spreads somewhat into a cone. A reconcentrating and refocusing lens, such as a Selfoc lens, refocuses the spreading light into a point in the image plane of the radiographic film being scanned and essentially refocuses that light at that image plane. Detection of the light is made on a clock time basis so that the light content at each scan operation in a scan line so that recreation of the document is readily made.
Owner:ERADLINK
Photovoltaic device
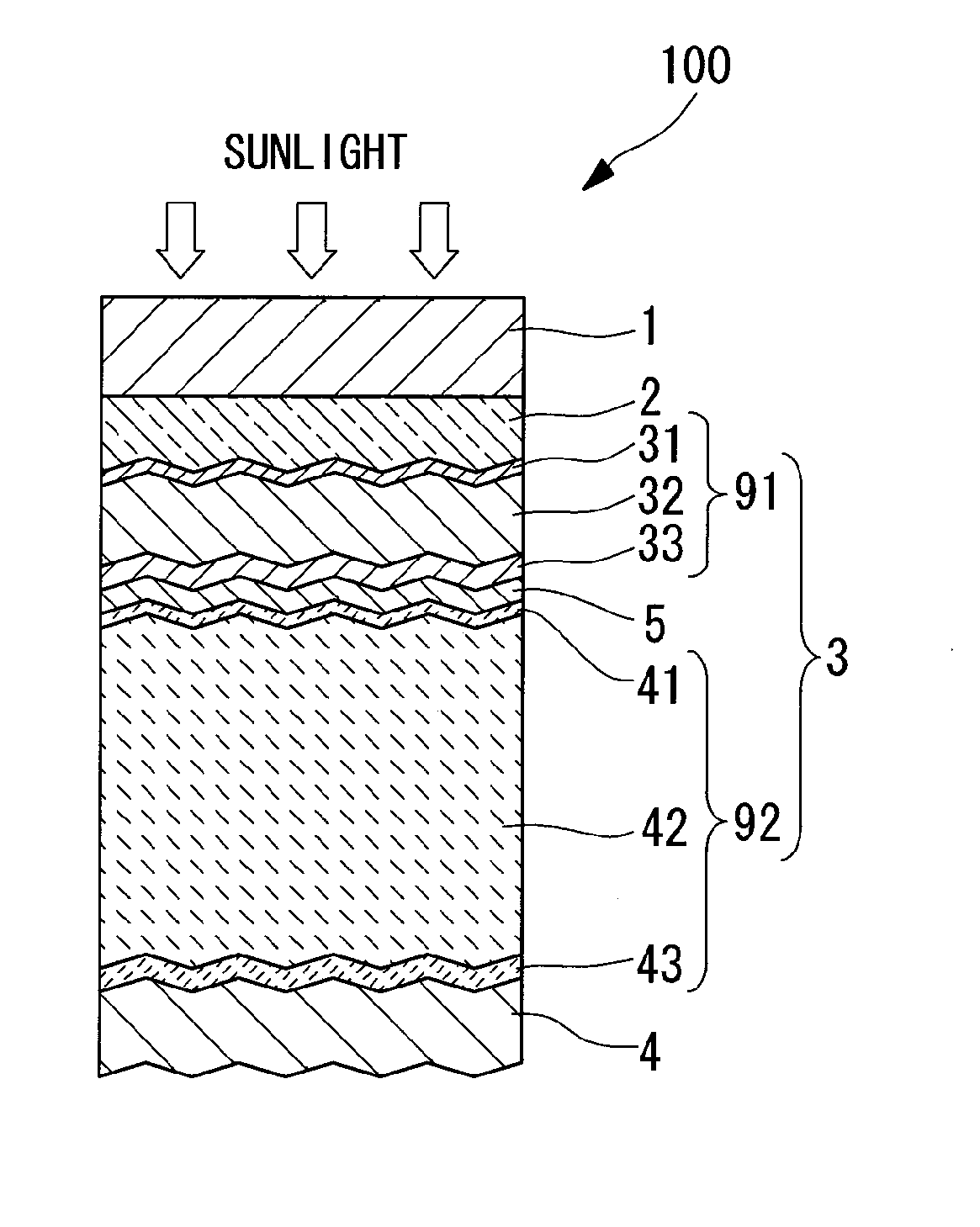
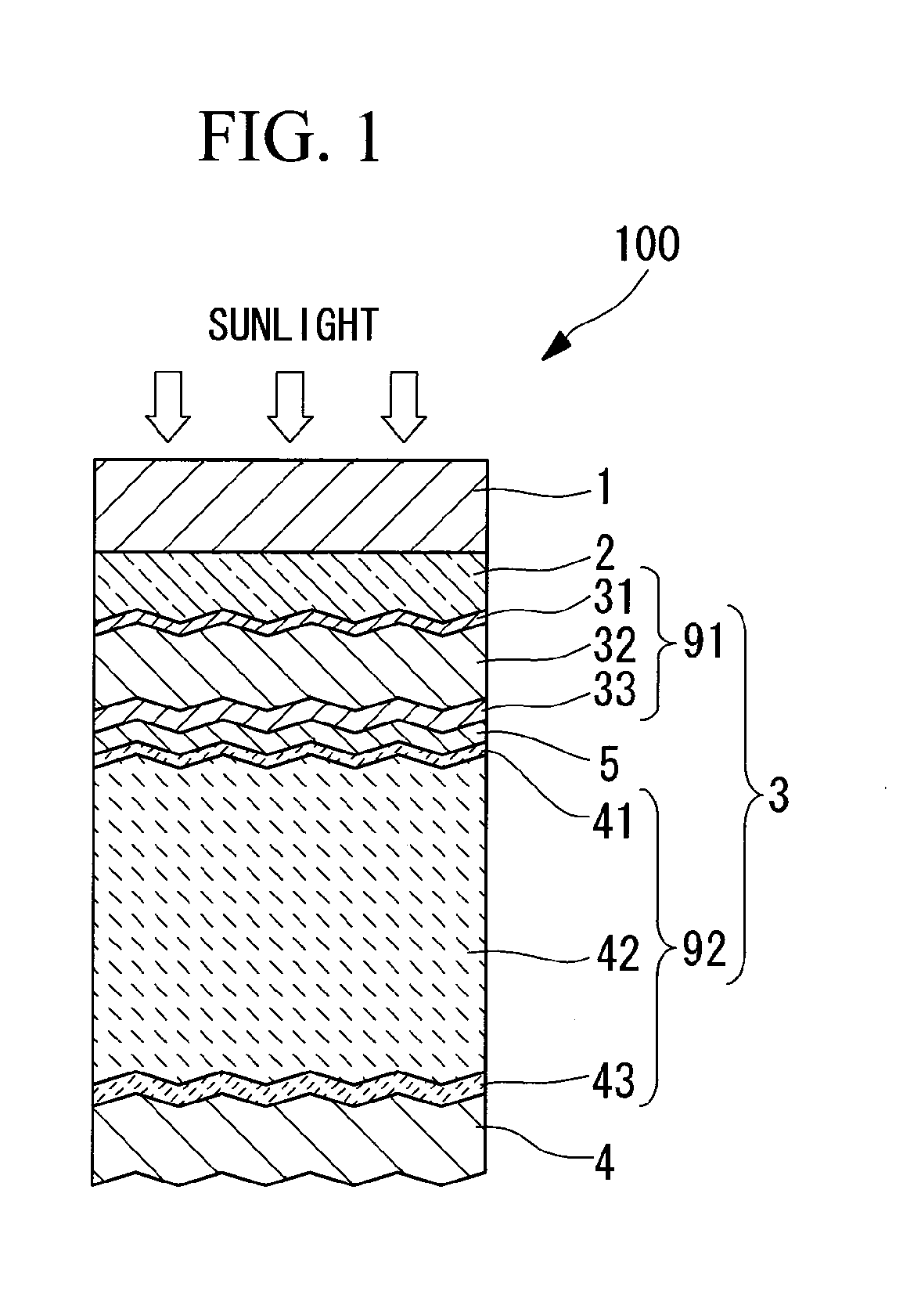
InactiveUS20100206373A1Improve conversion efficiencyImprove batch productivityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesProduction rateIn plane
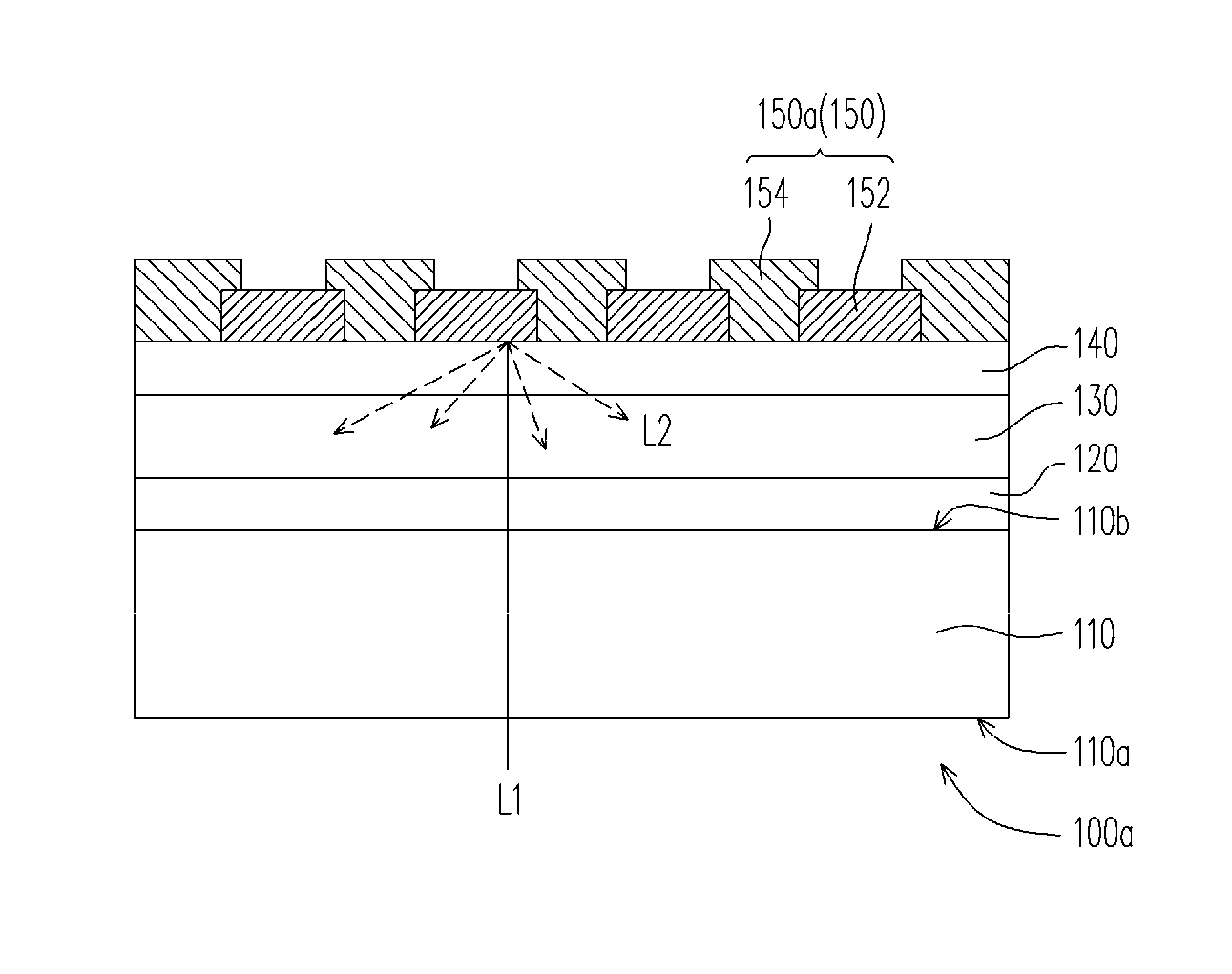
A large surface area photovoltaic device having high conversion efficiency and excellent mass productivity is provided. A photovoltaic device 100 having a photovoltaic layer 3 comprising a crystalline silicon layer formed on a substrate 1, wherein the crystalline silicon layer has a crystalline silicon i-layer 42, and the crystalline silicon i-layer 42 has a substrate in-plane distribution represented by an average value for the Raman peak ratio, which represents the ratio of the Raman peak intensity for the crystalline silicon phase relative to the Raman peak intensity for the amorphous silicon phase, that is not less than 4 and not more than 8, a standard deviation for the Raman peak ratio that is not less than 1 and not more than 3, and a proportion of regions in which the Raman peak ratio is not more than 4 of not less than 0% and not more than 15%. Also, a photovoltaic device 100 in which the size of the surface of the substrate 1 on which the photovoltaic layer 3 is formed is at least 1 m square, and in which the crystalline silicon i-layer 42 has a substrate in-plane distribution represented by an average value for the Raman peak ratio that is not less than 5 and not more than 8, a standard deviation for the Raman peak ratio that is not less than 1 and not more than 3, and a proportion of regions in which the Raman peak ratio is not more than 4 of not less than 0% and not more than 10%.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Light harvesting system employing microstructures for efficient light trapping
ActiveUS8735791B2Enhanced light absorptionOptimizing light pathPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryTotal internal reflectionTrapping
A light harvesting system employing a focusing array and a photoresponsive layer in which a plurality of microstructured areas is formed. Light received by the focusing array is injected transmissively into the photoresponsive layer through the microstructured areas. The injected light is retained in the photoresponsive layer by at least a total internal reflection and is propagated within the layer until it is substantially absorbed.
Owner:S V V TECH INNOVATIONS
Front electrode including transparent conductive coating on patterned glass substrate for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS8012317B2Improve photovoltaic efficiencyEnhanced light absorptionPV power plantsSolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyConductive coating
This invention relates to a photovoltaic device including an electrode such as a front electrode / contact. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of the photovoltaic device includes a multi-layered transparent conductive coating which is sputter-deposited on a textured surface of a patterned glass substrate. In certain example embodiments, a maximum transmission area of the substantially transparent conductive front electrode is located under a peak area of a quantum efficiency (QE) curve of the photovoltaic device and a light source spectrum used to power the photovoltaic device.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Thin-film solar cell and manufacture method thereof
InactiveUS20120042948A1Increase profitImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationLight beamThin film solar cell
A thin-film solar cell and a manufacture method thereof are provided. The thin-film solar cell comprises a transparent substrate, a first transparent conductive layer, a photovoltaic layer, a second transparent conductive layer and a light reflecting structure. The transparent substrate has a light incident surface and a back surface opposite to the light incident surface. The first transparent conductive layer is disposed on the back surface of the transparent substrate. The photovoltaic layer is disposed on the first transparent conductive layer. The second transparent conductive layer is disposed on the photovoltaic layer. The light reflecting structure is disposed on the second transparent conductive layer. The manufacture method forms the light reflecting structure having a texture structure on the thin film to enhance utilization of light beams in the thin-film solar cell so as to further improve photoelectric conversion efficiency of the thin-film solar cell.
Owner:AURIA SOLAR CO LTD
Positioning device comprising a light beam
A position measurement system for determining 2D displacement or position of a mobile element with respect to a reference frame, including: a point light; an optical mask having transparent and opaque areas defining a repetitive pattern on at least one side of its surfaces; an imager, fixed to a mobile element, including integrated electronic circuits allowing detection, computing and analyzing of a shadow projected by the optical mask. The position measurement system includes an optical diffuser plate between the light source and the mask. The imager, mask and diffuser plate form an assembly so as to produce a light spot created by the scattering of the incident light beam emitted by the light source on the diffuser plate. The mask positioned between the diffuser plate and imager, produces a shadow on the imager, allowing to compute and provide 2D position of the mobile element relative to the fixed reference frame.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
System for Reading Data on a Holographic Storage Medium
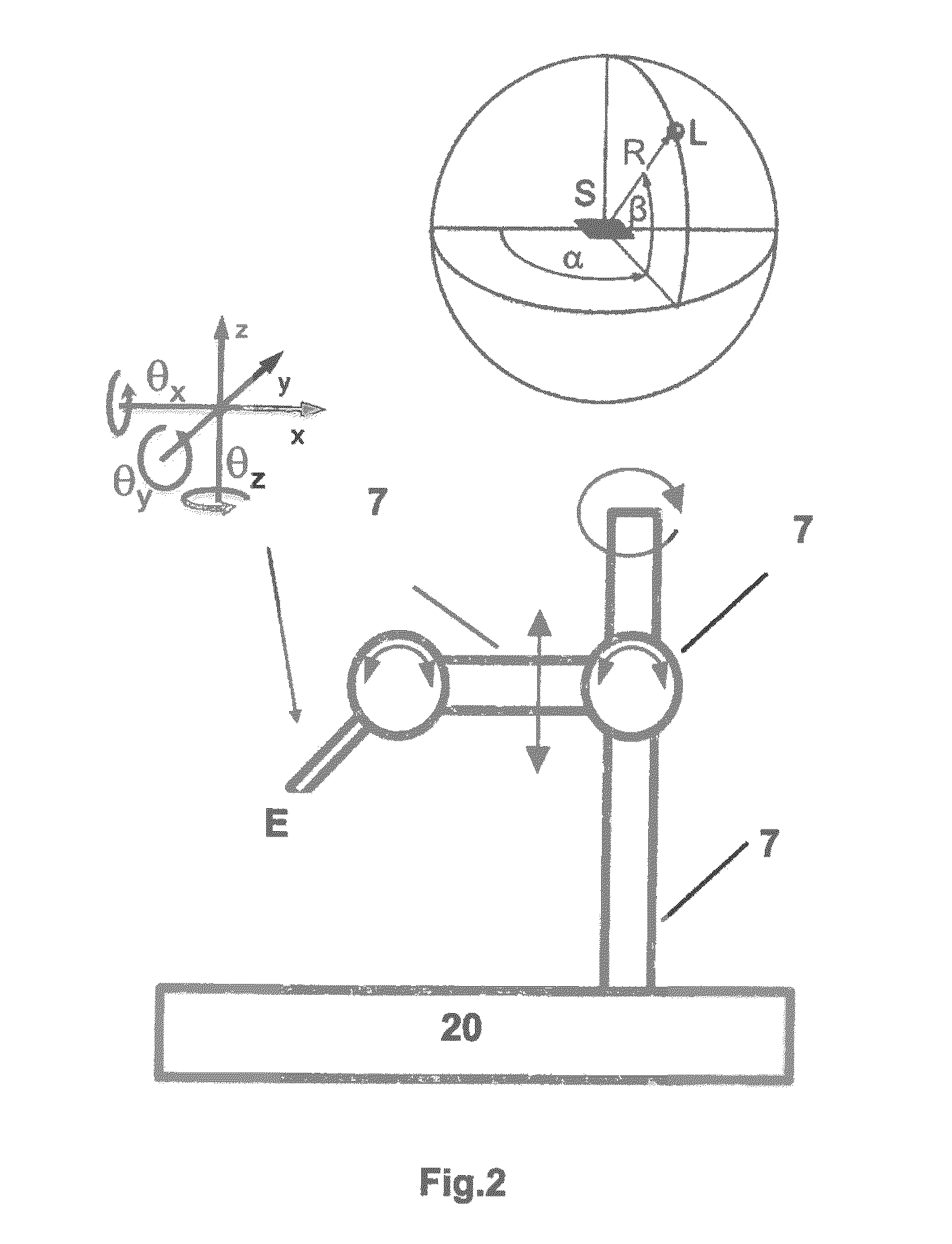
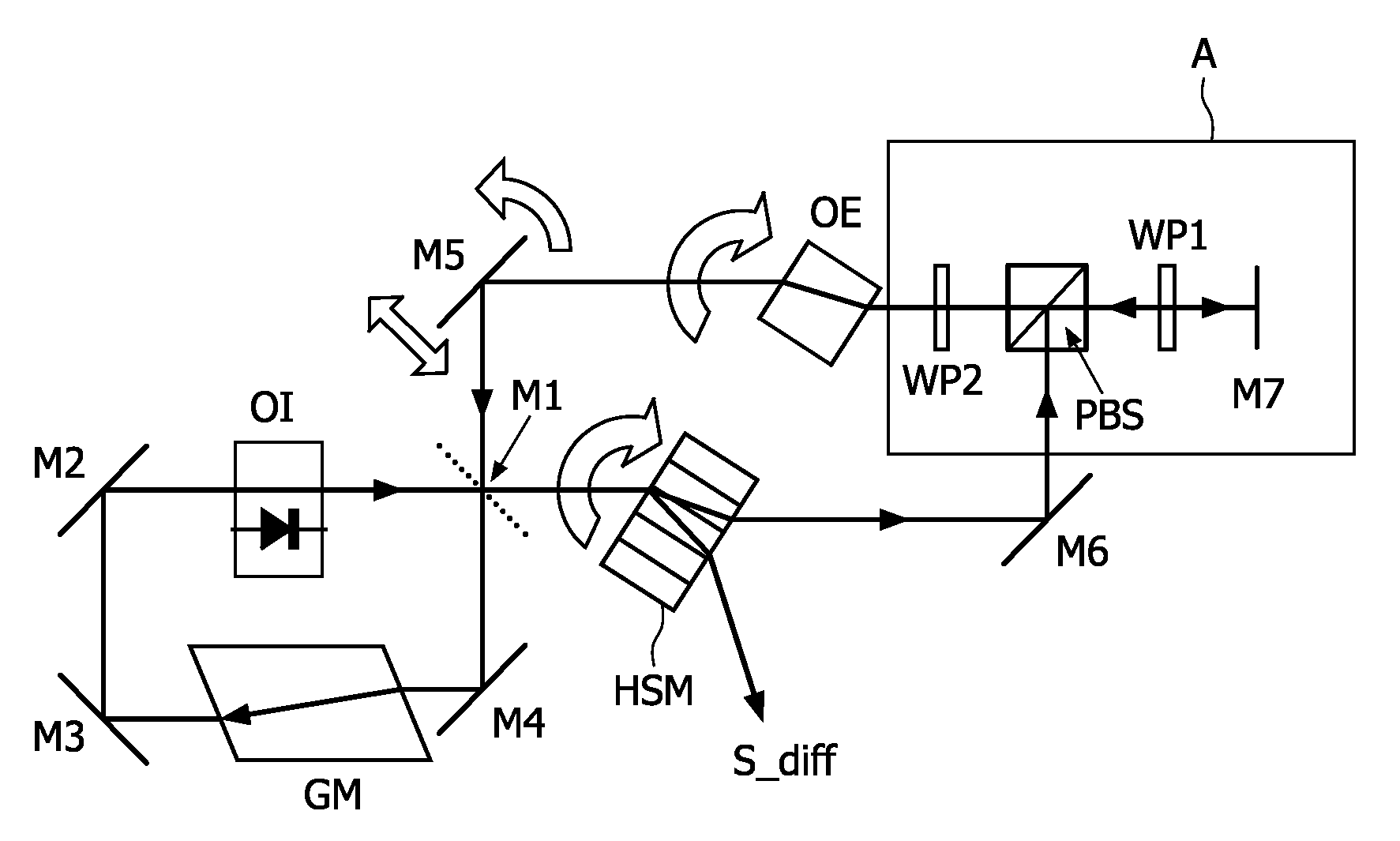
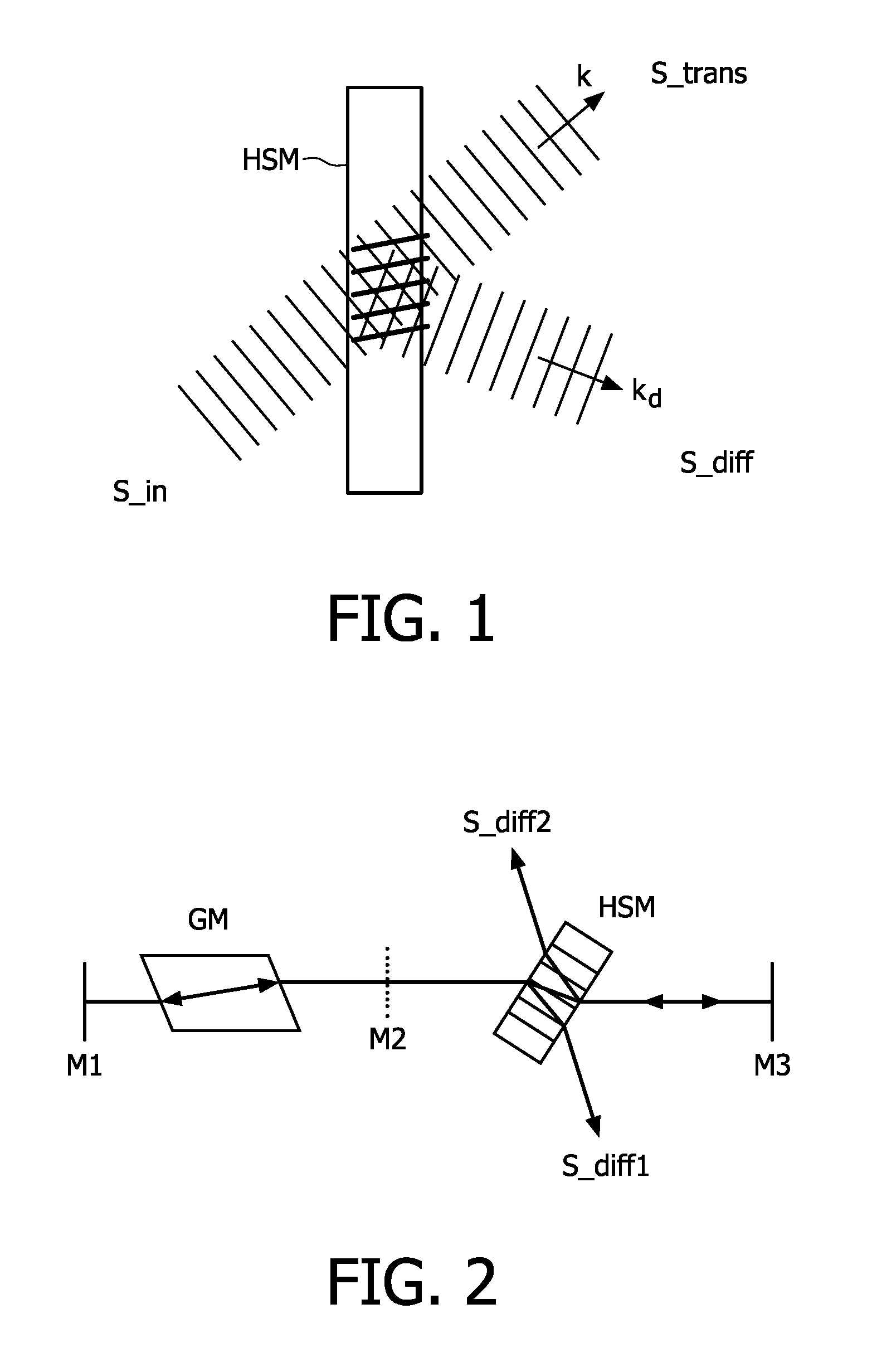
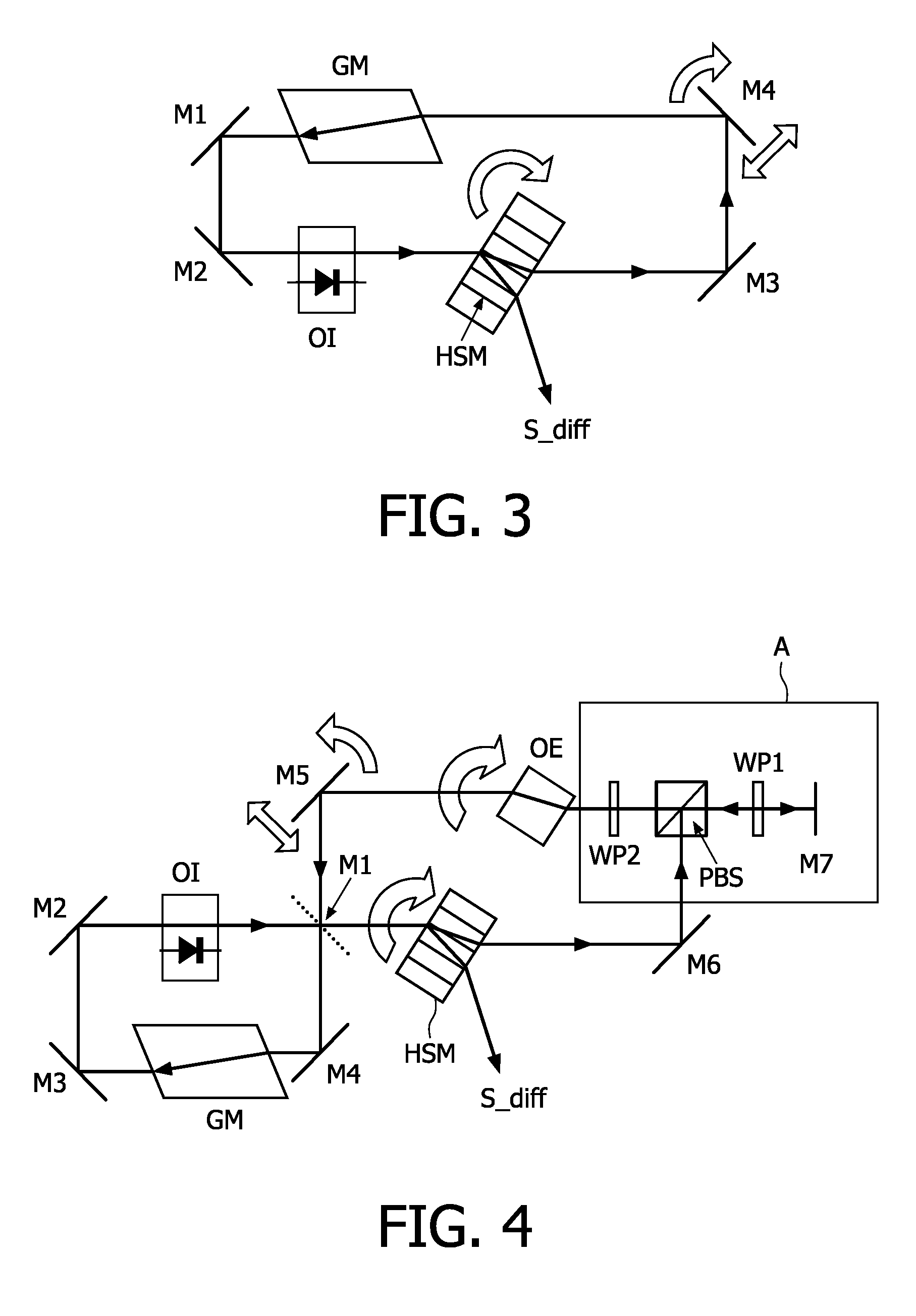
InactiveUS20080266625A1Increase light path efficiencyOptimizing light pathLaser detailsRecord information storageHolographic storageHolographic data storage
The invention relates to a system for reading data from a holographic storage medium (HSM), said system comprising an optical ring cavity defining a closed optical path so as to recycle the light of a reference beam that is used to read out the holographic storage medium, in view of increasing the light path efficiency by lengthening its path.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Apparatus and method for examining a specimen by means of probe microscopy
ActiveUS9063335B2Raise the possibilityDistanceNanotechnologyMicroscopesScanning probe microscopyMicroscope
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for examining a specimen by means of probe microscopy, in particular scanning probe microscopy. The apparatus comprises a probe microscope device which has a specimen holder for holding a specimen to be examined, a measurement probe and a displacement unit which is configured to displace the specimen holder and the measurement probe relative to one another for an examination of the specimen by means of probe microscopy, and comprises a condenser illumination and also an optical system which is arranged downstream of the condenser illumination and is configured to project condenser light, which is emitted by the condenser illumination in a condenser light path, into the region of the specimen holder for optical microscopy of the specimen to be examined, while at least partially maintaining condenser light parameters with which the condenser light is emitted by the condenser illumination.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC +1
Optimized integration dual-optical path laser ionization effect simulation system
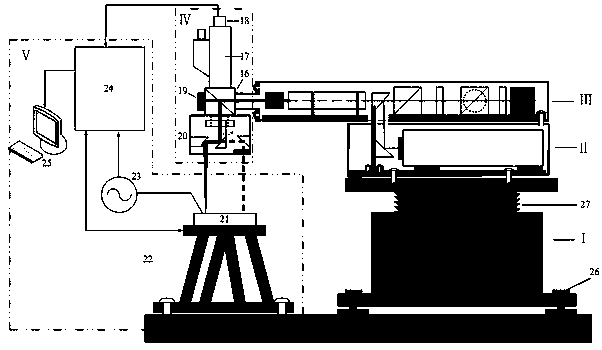
PendingCN107833511AOptimizing light pathReduce test costsEducational modelsOptical pathPhoto ionization
The present invention discloses an optimized integration dual-optical path laser ionization effect simulation system. The system mainly comprises four portions consisting of a dual-wavelength pulse laser, a dual-optical path attenuation module, a microscopic observation module and a test and control module. The system performs optical path and structure optimization of the whole simulation systemon the basis of achieving 532nm and 1064 dual-wavelength output to more flexibly and rapidly perform researching and verification of a semiconductor device radiation dose rate effect in a laboratory condition, especially to simulate sources of radiation such as a gamma ray and the like being acted on the semiconductor device radiation dose rate effect, and is convenient, rapid, convenient, accurate, high in safety, etc. The optimized integration dual-optical path laser ionization effect simulation system can effectively reduce the test cost, can improve the test efficiency and can shorten thedesign period of radiation hardening.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Light emitting diode structure
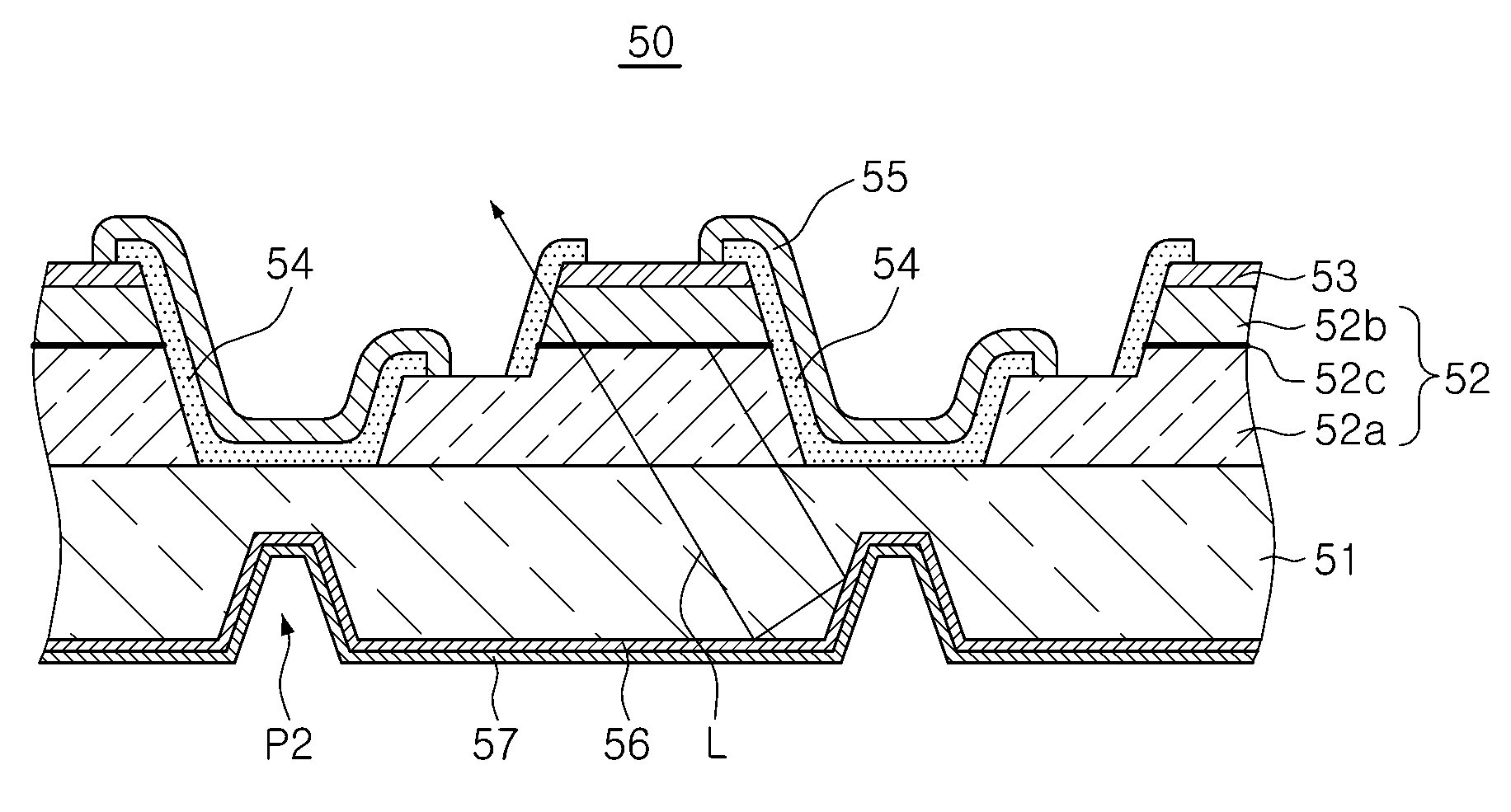
ActiveUS20140374767A1Reduce manufacturing costEfficient light emissionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorReverse current
A light emitting diode (LED) structure includes a substrate, an LED element, a reverse current protection element, a third conductor, and a fourth conductor. The LED element includes a first N-type semiconductor layer, a first lighting layer, a first P-type semiconductor layer, a first transparent conductive layer, a first electrode, and a second electrode. The reverse current protection element is located on the substrate and surrounds the LED element. The reverse current protection element includes a stack layer, a first conductor, and a second conductor. The stack layer is formed on the substrate by sequentially stacking a second N-type semiconductor layer, a second lighting layer, and a second P-type semiconductor layer. The third conductor is electrically connected to the first conductor and the second electrode. The fourth conductor is electrically connected to the second conductor and the first electrode.
Owner:LEXTAR ELECTRONICS CORP
Positioning device comprising a light beam
ActiveUS20140368836A1Reduce speckle effectOptimizing light pathPhotometryPosition fixationPoint lightLight spot
A position measurement system for determining 2D displacement or position of a mobile element with respect to a reference frame, including: a point light; an optical mask having transparent and opaque areas defining a repetitive pattern on at least one side of its surfaces; an imager, fixed to a mobile element, including integrated electronic circuits allowing detection, computing and analyzing of a shadow projected by the optical mask. The position measurement system includes an optical diffuser plate between the light source and the mask. The imager, mask and diffuser plate form an assembly so as to produce a light spot created by the scattering of the incident light beam emitted by the light source on the diffuser plate. The mask positioned between the diffuser plate and imager, produces a shadow on the imager, allowing to compute and provide 2D position of the mobile element relative to the fixed reference frame.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Reverse conductive nano array and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS8796749B2Optimizing light pathImprove absorption efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesPhotodiodeNanometre
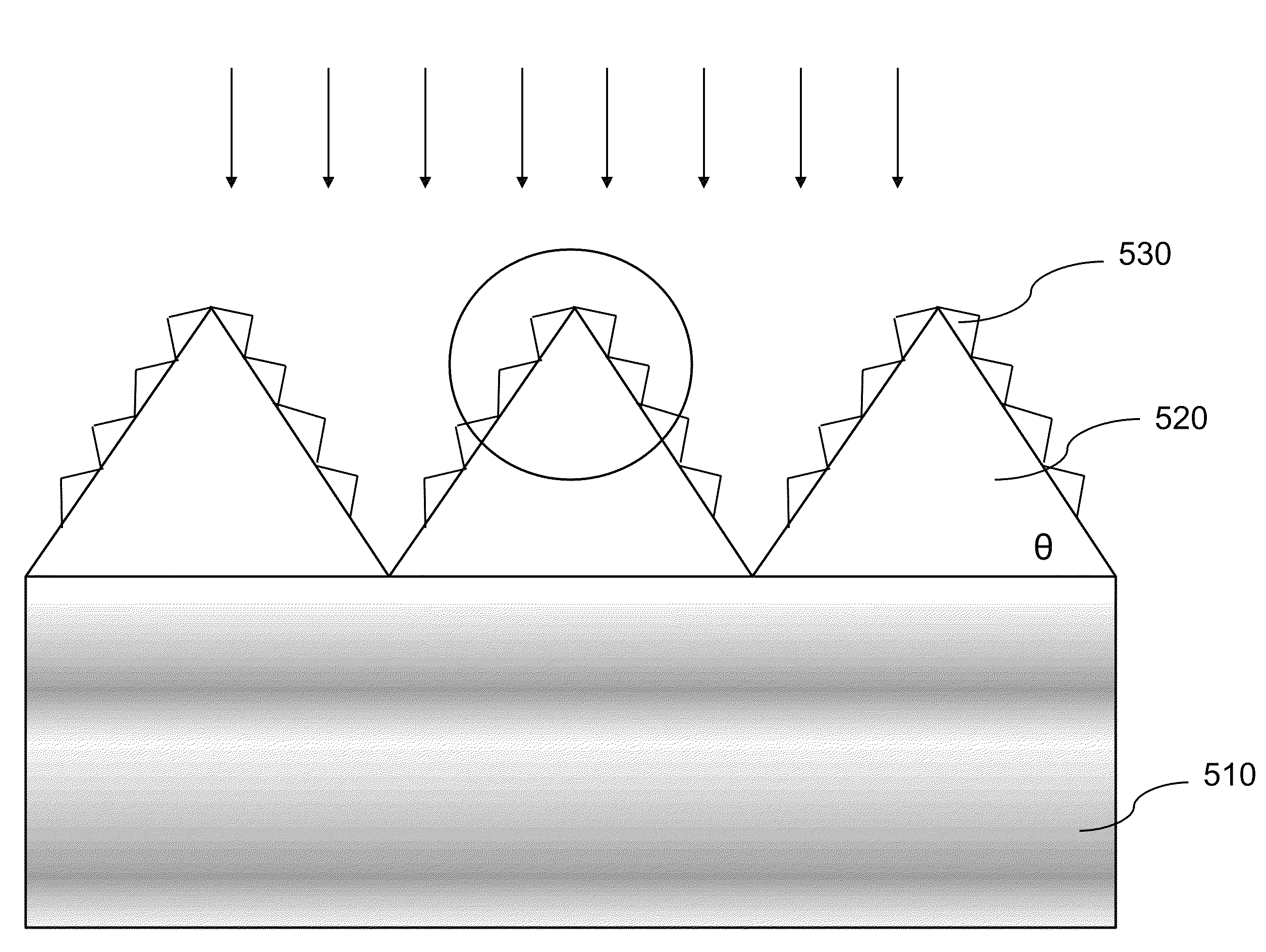
A high-speed photodiode may include a photodiode structure having a substrate, a light-absorbing layer and a light-directing layer that is deposited on a top surface of the photodiode structure and patterned to form a textured surface used to change the angle of incident light to increase a light path of the incident light when entering the photodiode structure. In one embodiment, the light-directing layer may include a plurality of polygon such as triangular projections to refract the incident light to increase the light path thereof when entering the photodiode structure. In another embodiment, a plurality of nanoscaled sub-triangular projections can patterned on both sides of each triangular projection to more effectively increase the light paths. In a further embodiment, porous materials can be used to form the light-directing layer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GUANGTE TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com