Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Pressure fluctuation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
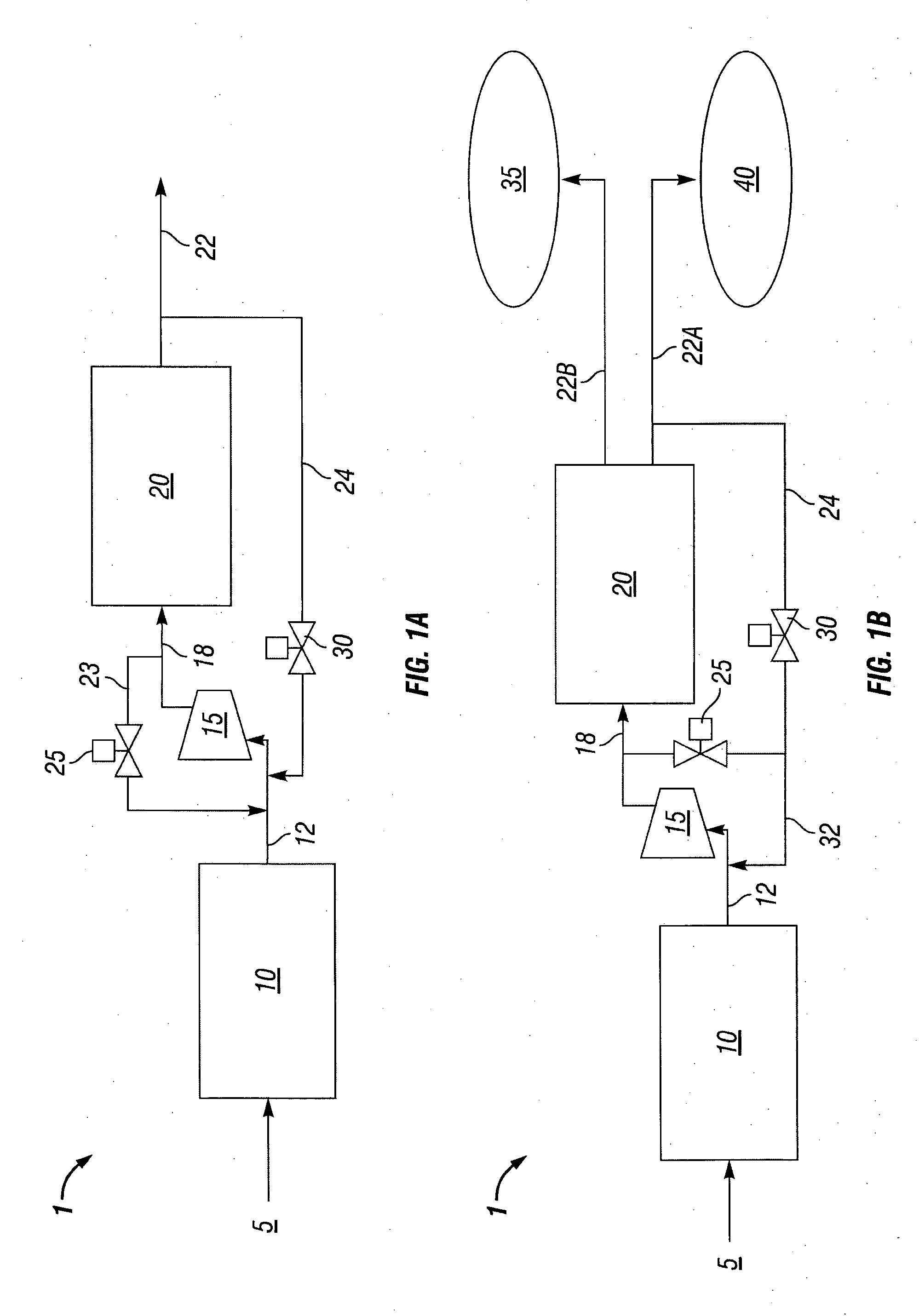
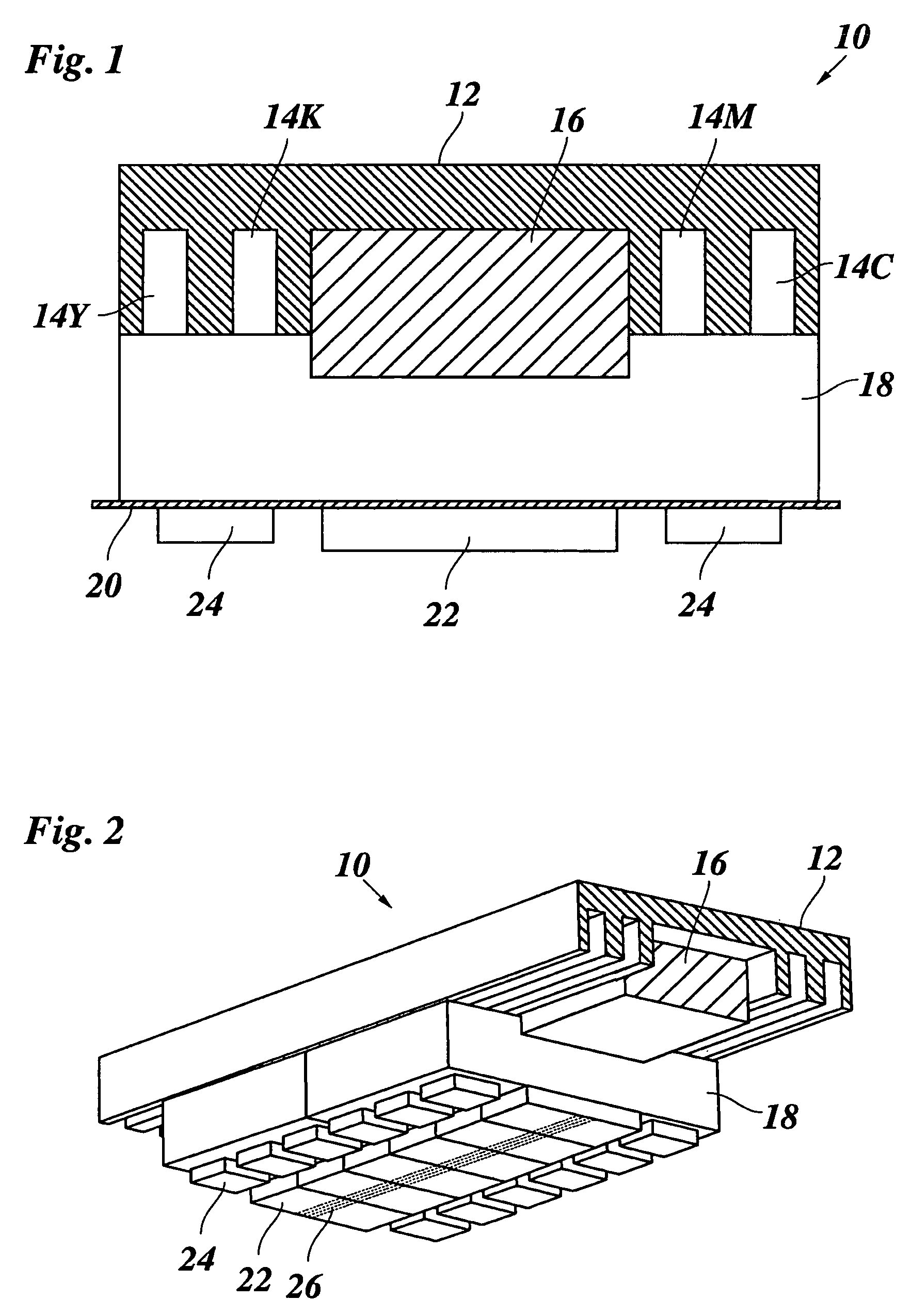
Purification and recovery of fluids in processing applications
InactiveUS20050006310A1Weaken energyReduce equipment costsSolid sorbent liquid separationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisLiquid stateEngineering
A fluid purification and recovery system includes a buffer section configured to receive a fluid delivered from a process station, where the fluid pressure is maintained within the buffer section within a predetermined range and the fluid is maintained within the buffer section in at least one of a gas state, a liquid state and a supercritical state. The system further includes a purification section disposed downstream from the buffer section to receive the fluid from the buffer section, where the purification section includes at least one purification unit that separates at least a portion of at least one component from the fluid. In one embodiment, the fluid is maintained in at least one of a liquid state and a supercritical state in both the buffer section and the purification section. In addition, the buffer section delivers the fluid to the purification with minimal or substantially no fluctuations in pressure.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE +1
Apparatus and method for producing hydrogen
InactiveUS20060137245A1Reduce fluctuationPressure fluctuationLevel controlHydrogen separation using solid contactProcess engineeringStorage cell
An apparatus and method for producing a hydrogen-enriched reformate. The apparatus includes a fuel processor for converting a fuel to a reformate having fluctuations in pressure and or flow rate, means for reducing the fluctuations, a compression unit for compressing the reformate and one or more of a purification unit and a storage unit downstream of a compression unit. Means for reducing the fluctuations in the reformate can include one or more of a buffer and a conduit for providing a controlled flow of a supplemental fluid to an inlet of the compression unit. The supplemental fluid can include the compressed reformate, a hydrogen-enriched reformate, and mixtures thereof. The apparatus can include means for regulating power to the compression unit that can incrementally increase power to the compression unit particularly during start up. The purification unit can include one or more of a hydrogen selective membrane and a pressure swing adsorption unit. Methods for producing hydrogen are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXACO INC
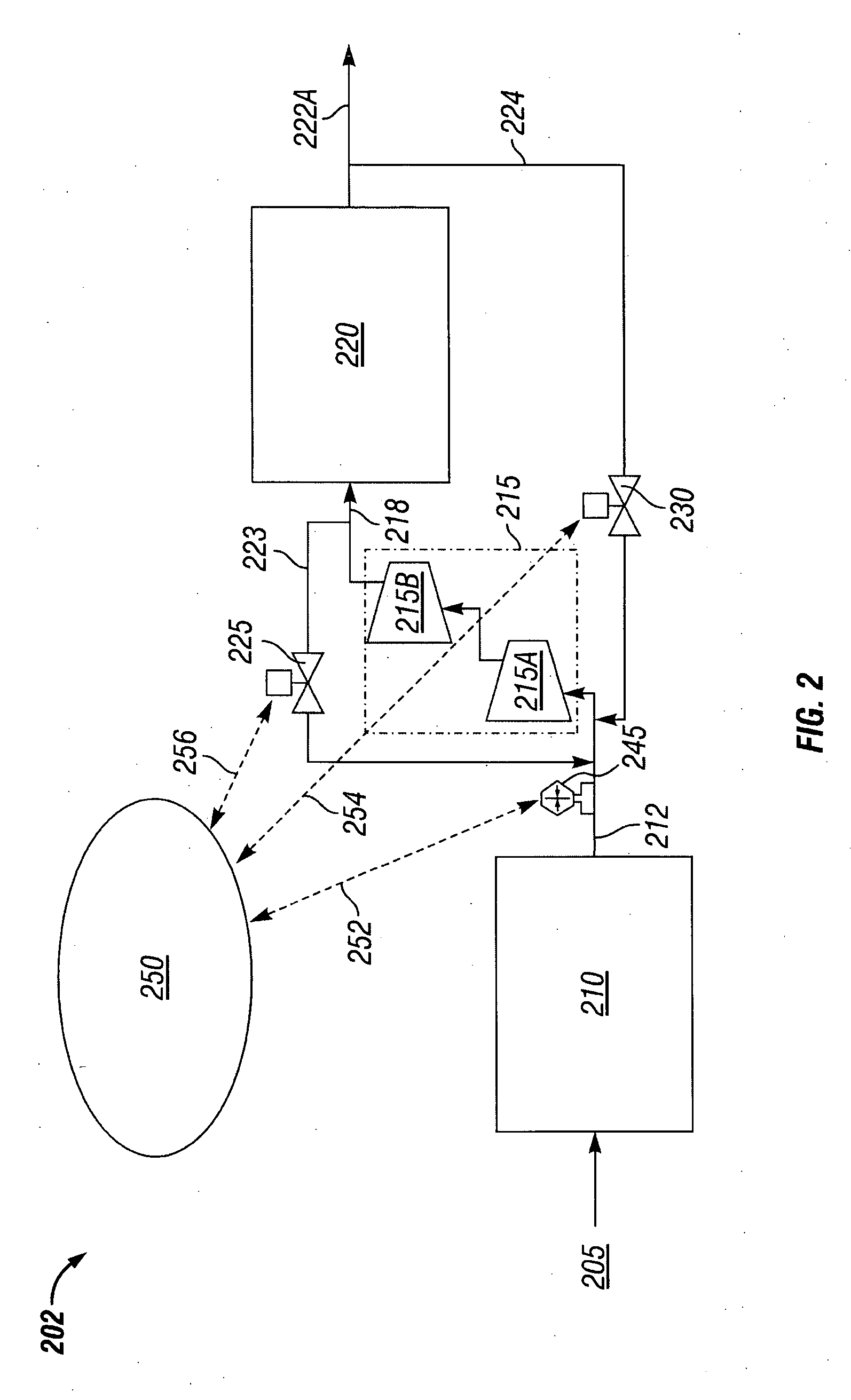
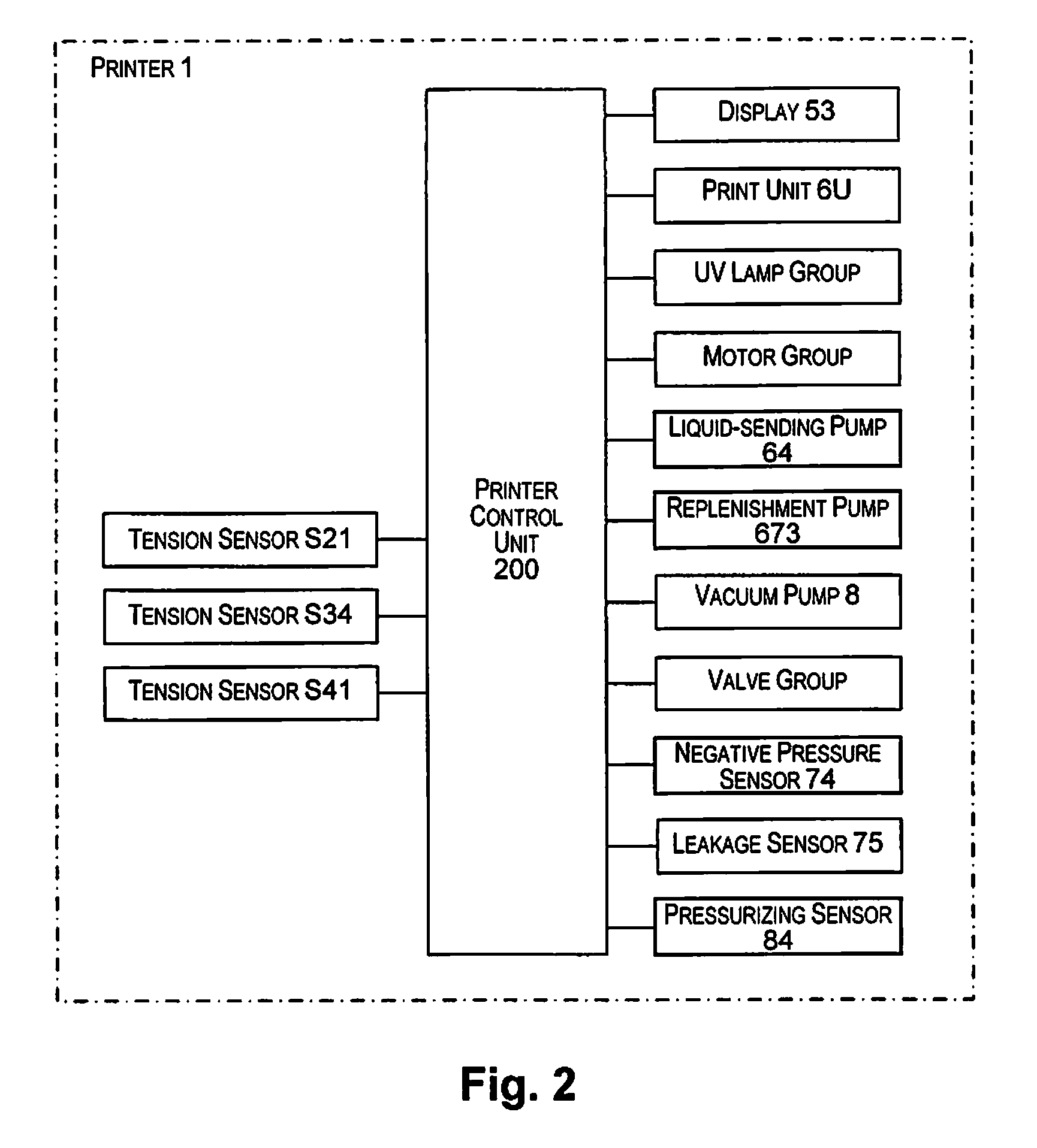
Liquid ejecting apparatus
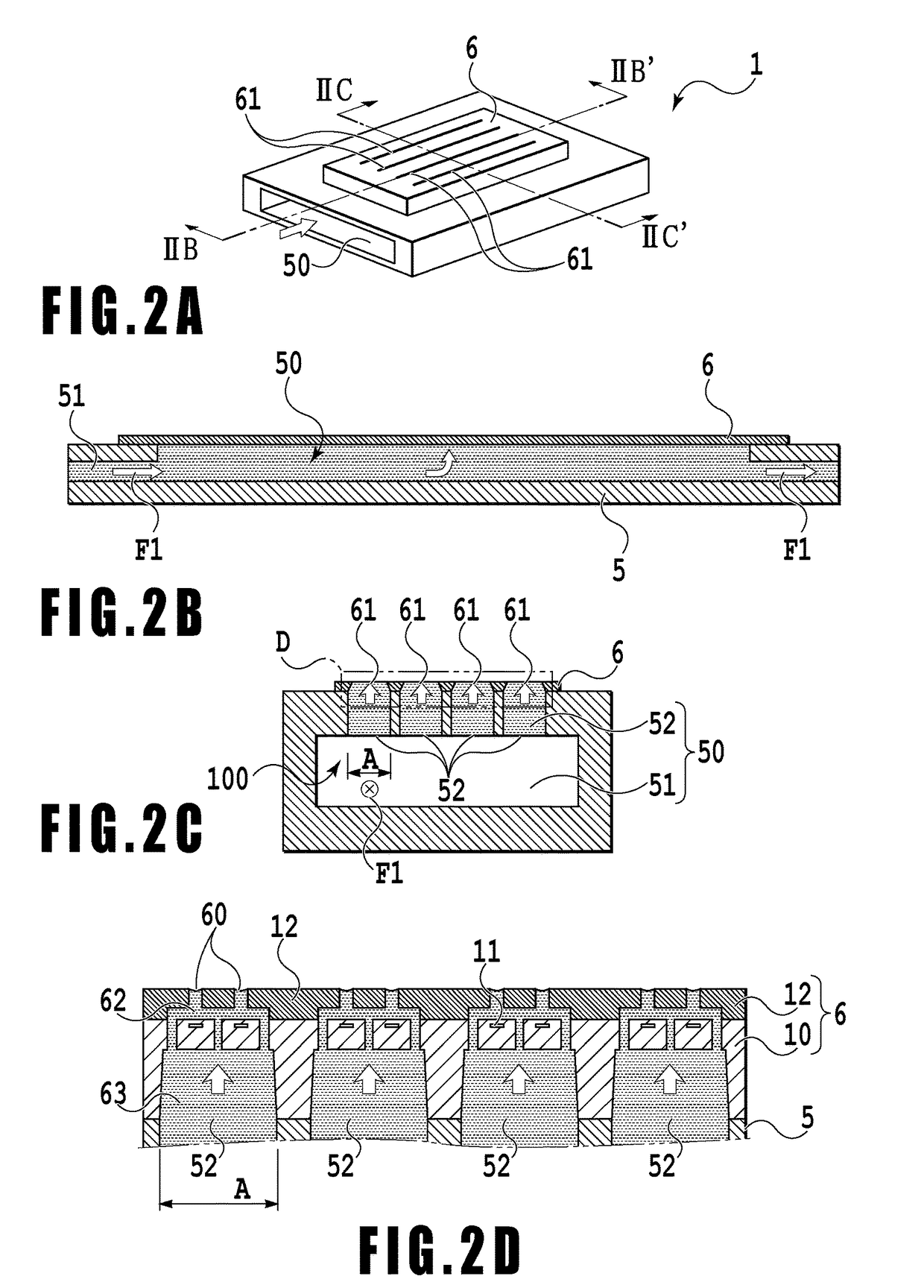
ActiveUS9216587B2Uniform pressureLarge fluctuationsInking apparatusTypewritersLiquid jetLiquid circulation
A liquid circulation part has a recovery path where a liquid flows into a retaining part from a first head and a second head. The recovery path has a first merging point where the liquid flowing from the first head and the liquid flowing from the second head are merged, a first recovery path part where the liquid flowing from the first head flows into the first merging point, and a second recovery path part where the liquid flows from the first merging point. The cross-sectional area of the second recovery path part, orthogonal to a direction of flow of the liquid in the second recovery path part, is greater than the cross-sectional area of the first recovery path part, orthogonal to the direction of flow of the liquid in the first recovery path part.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
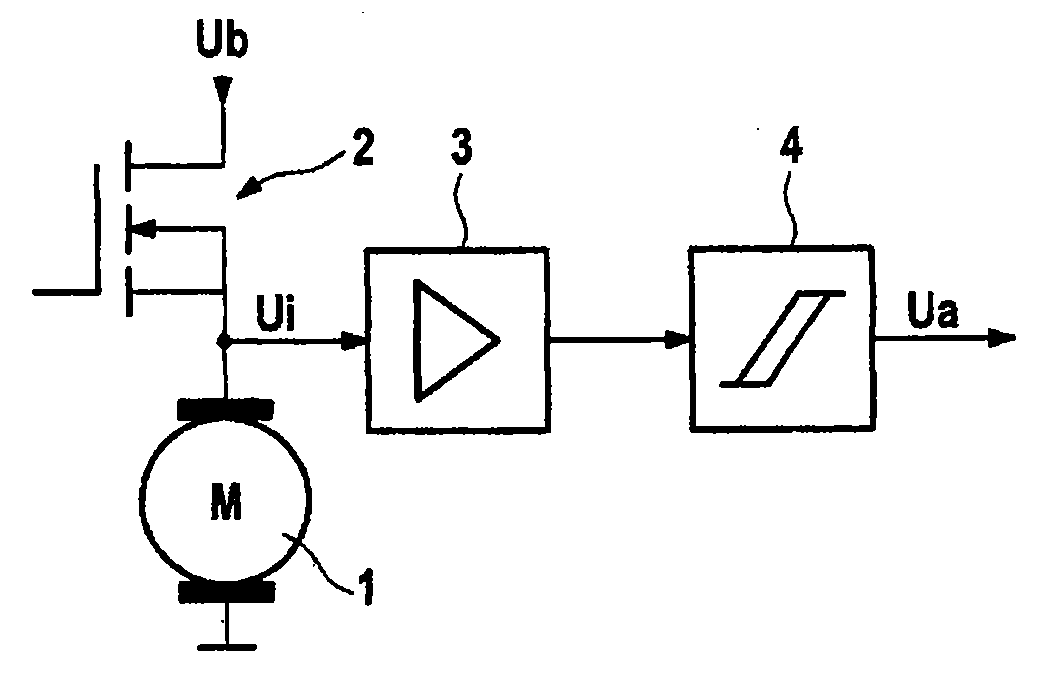
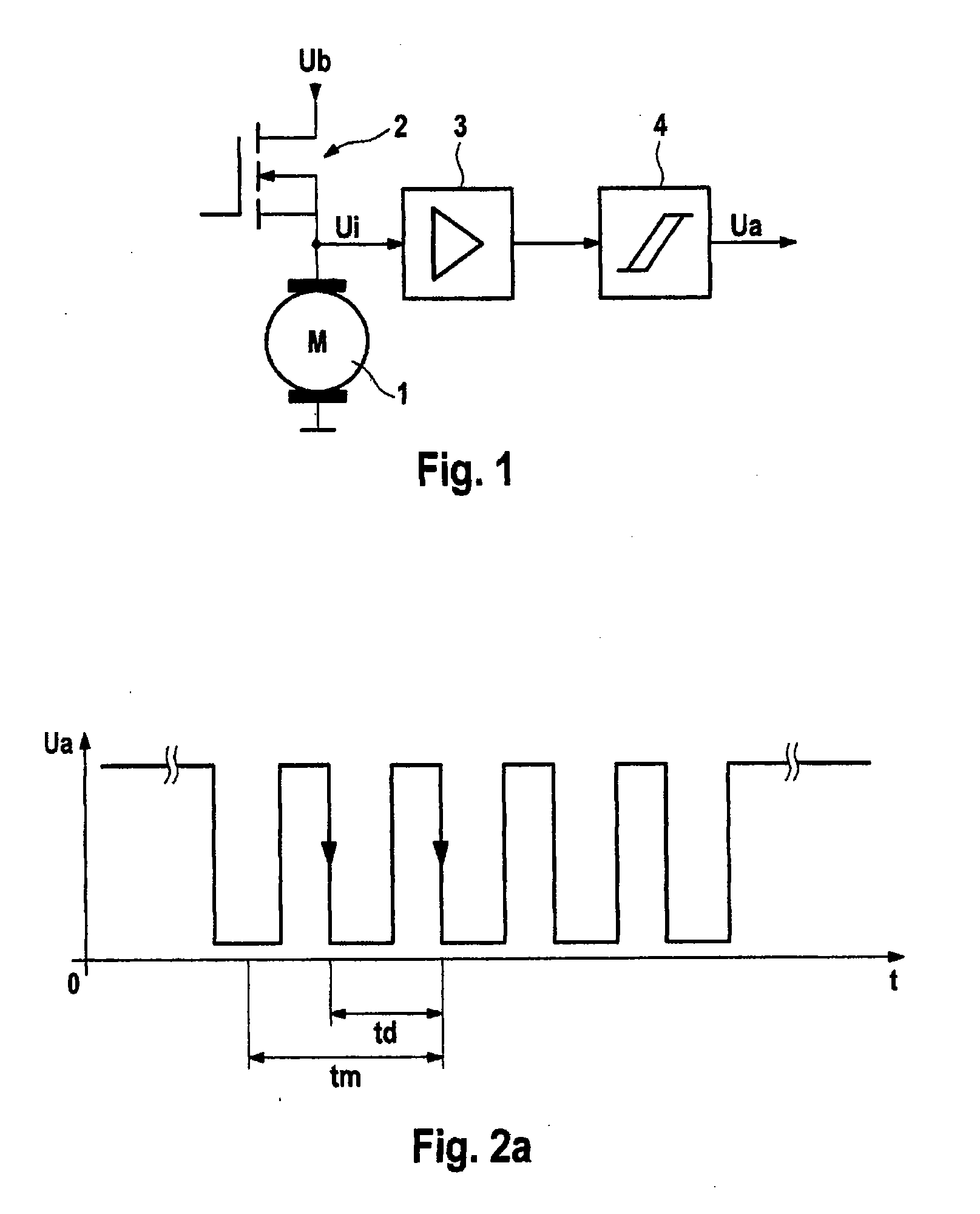
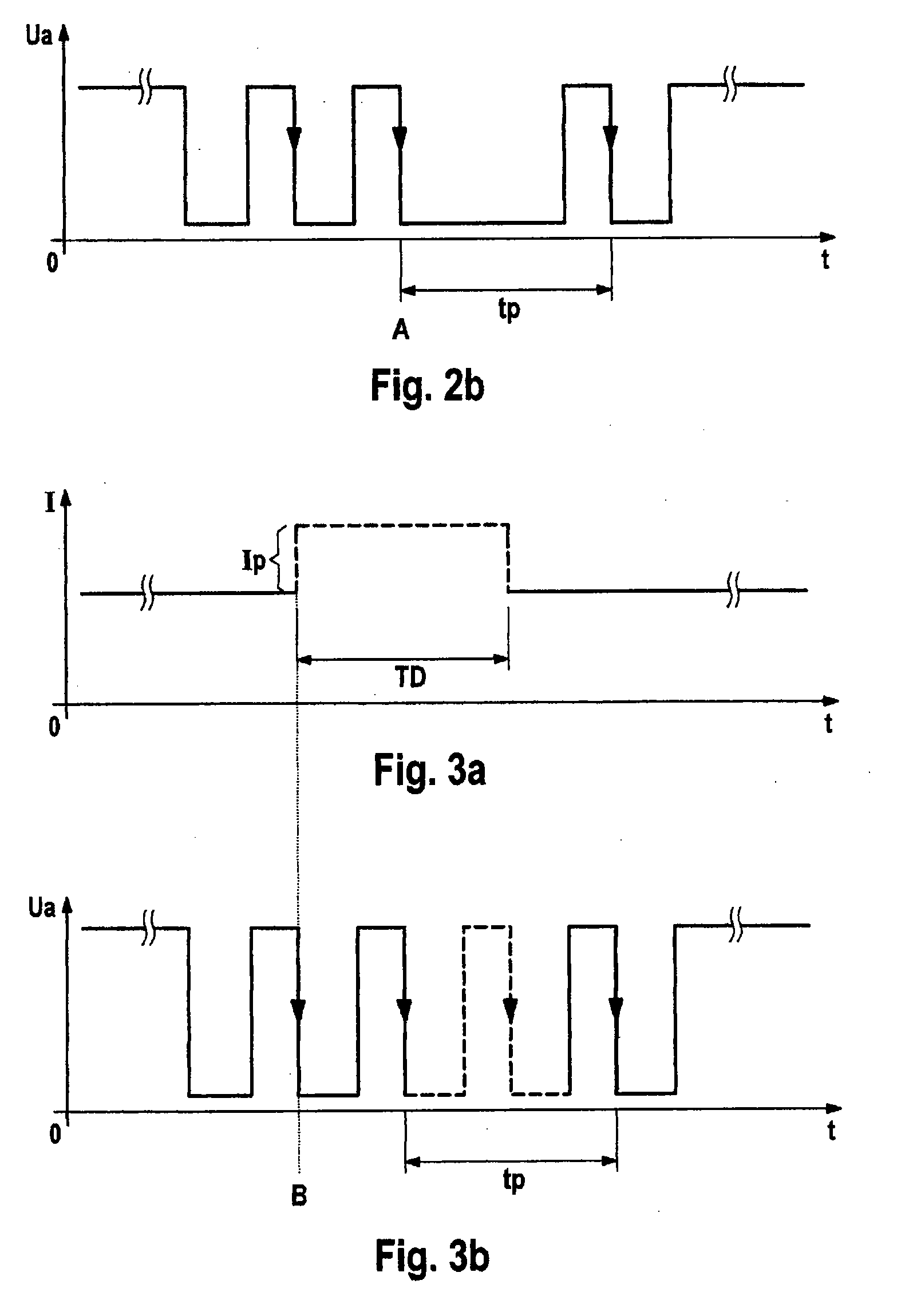
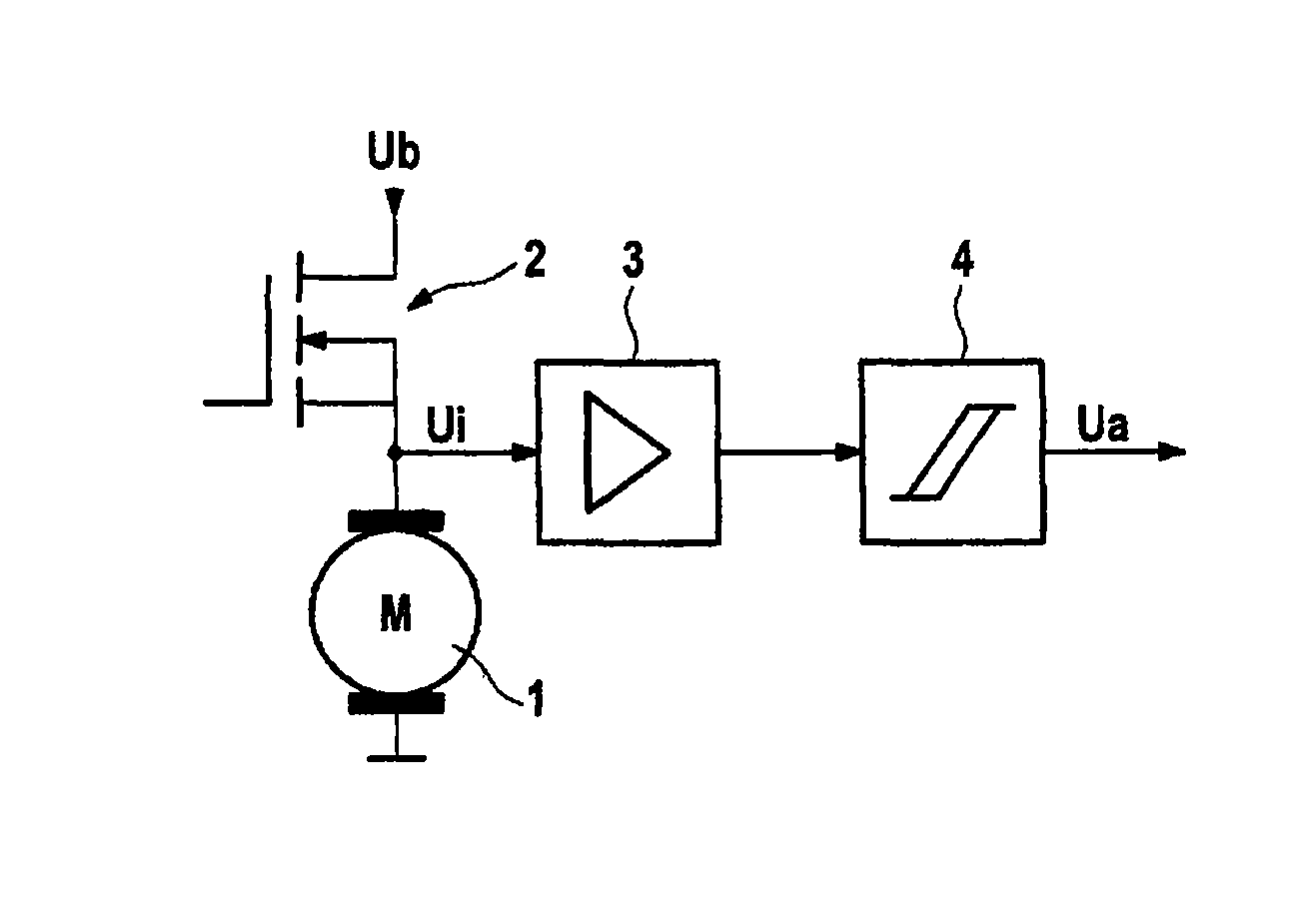
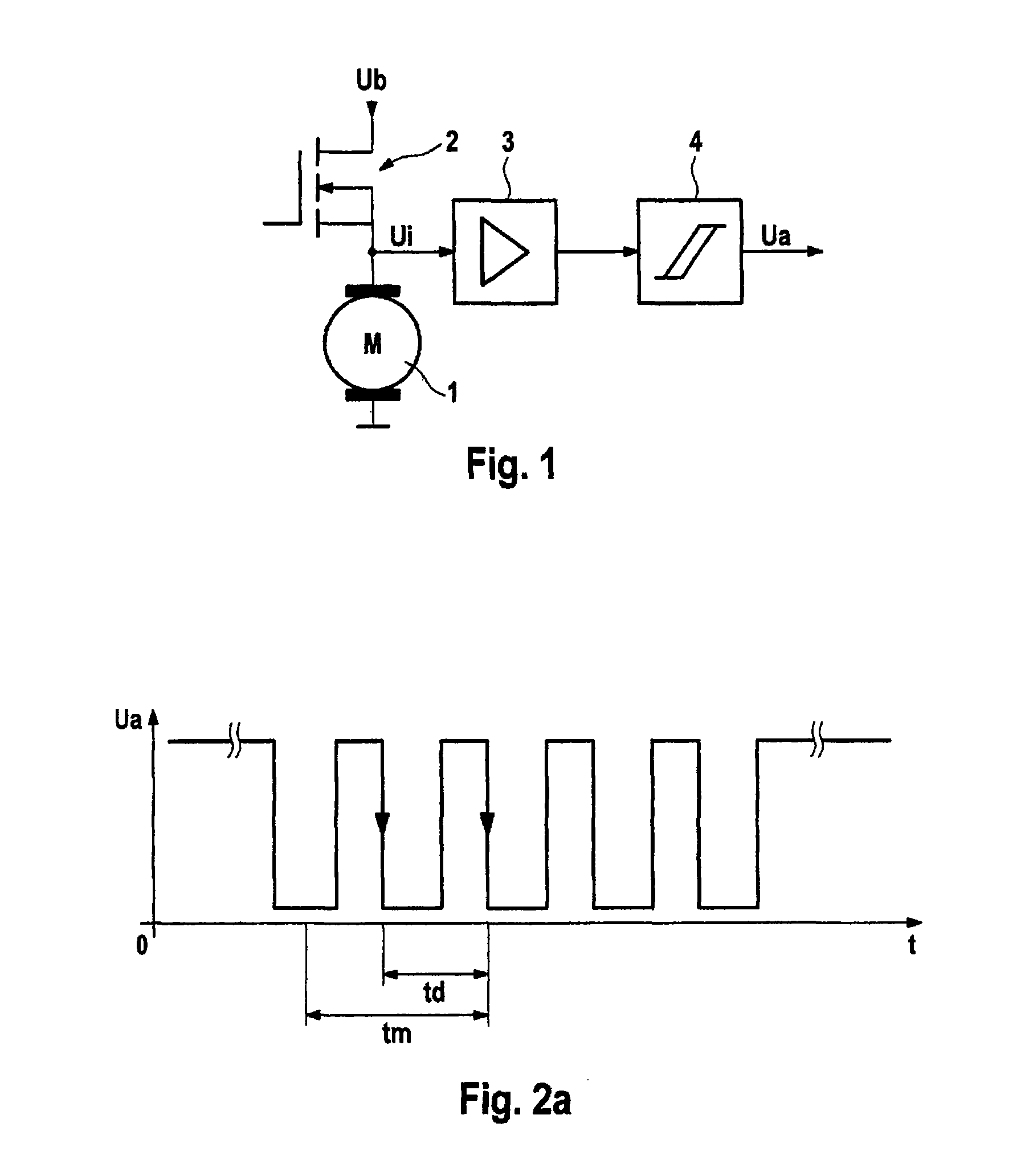
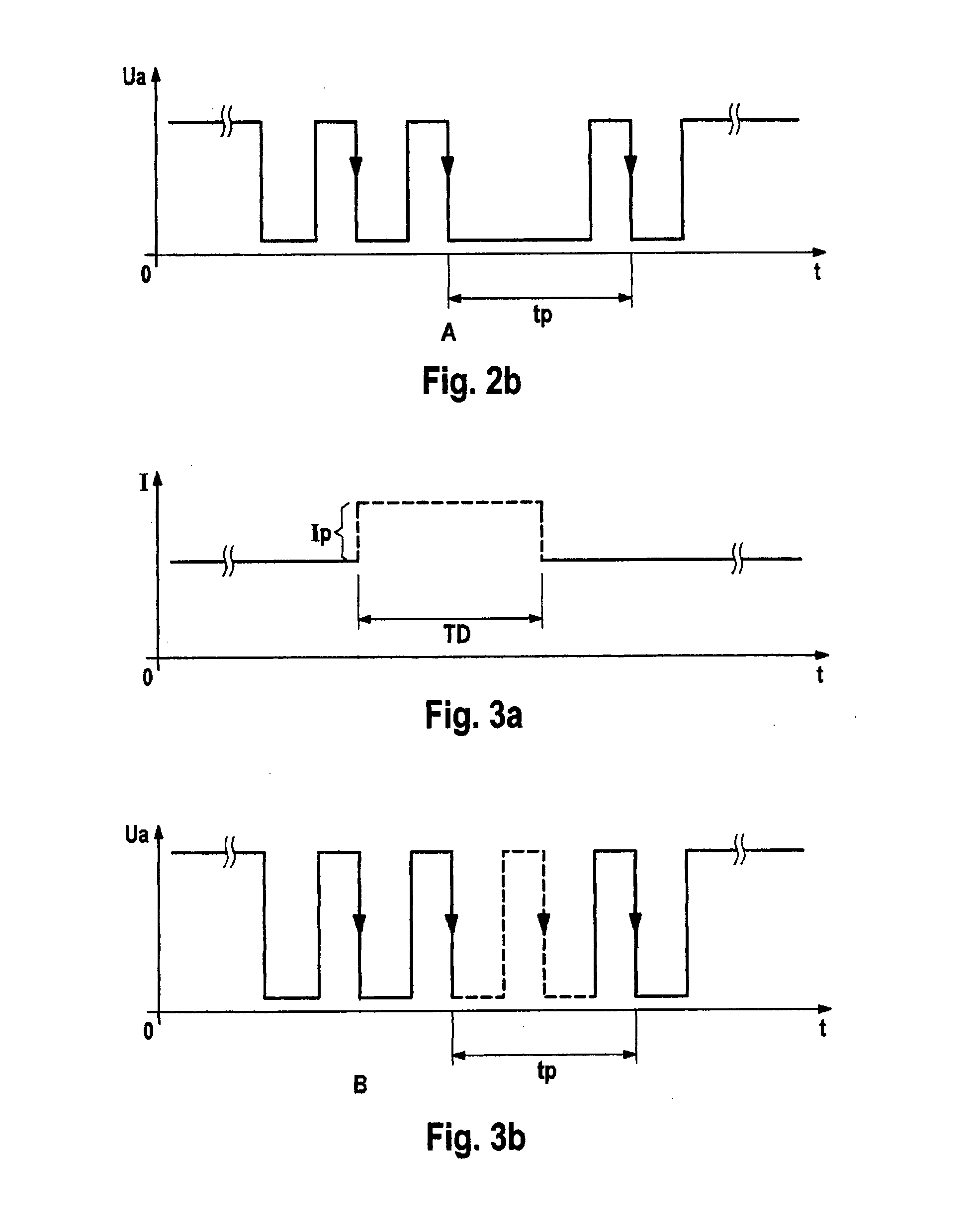
Electrical motor activation method having load torque adaptation
InactiveUS20110033322A1Reduce loadLoad fluctuationMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlLoad torqueControl theory
An electrical motor activation method for an electric motor including a rotor, connected to a motor shaft, and a stator having brushes. The stator comprises multiple commutator laminations for the commutation of windings disposed on the rotor and is activated by a pulsed or linearly controllable power source. The motor shaft is connected to a radially driven load, in particular a pump, which has a nonlinear torque curve via a motor revolution. A waviness signal is obtained from a voltage potential applied to the motor and / or from the motor current and rotor position information is obtained from the curve of said waviness signal.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
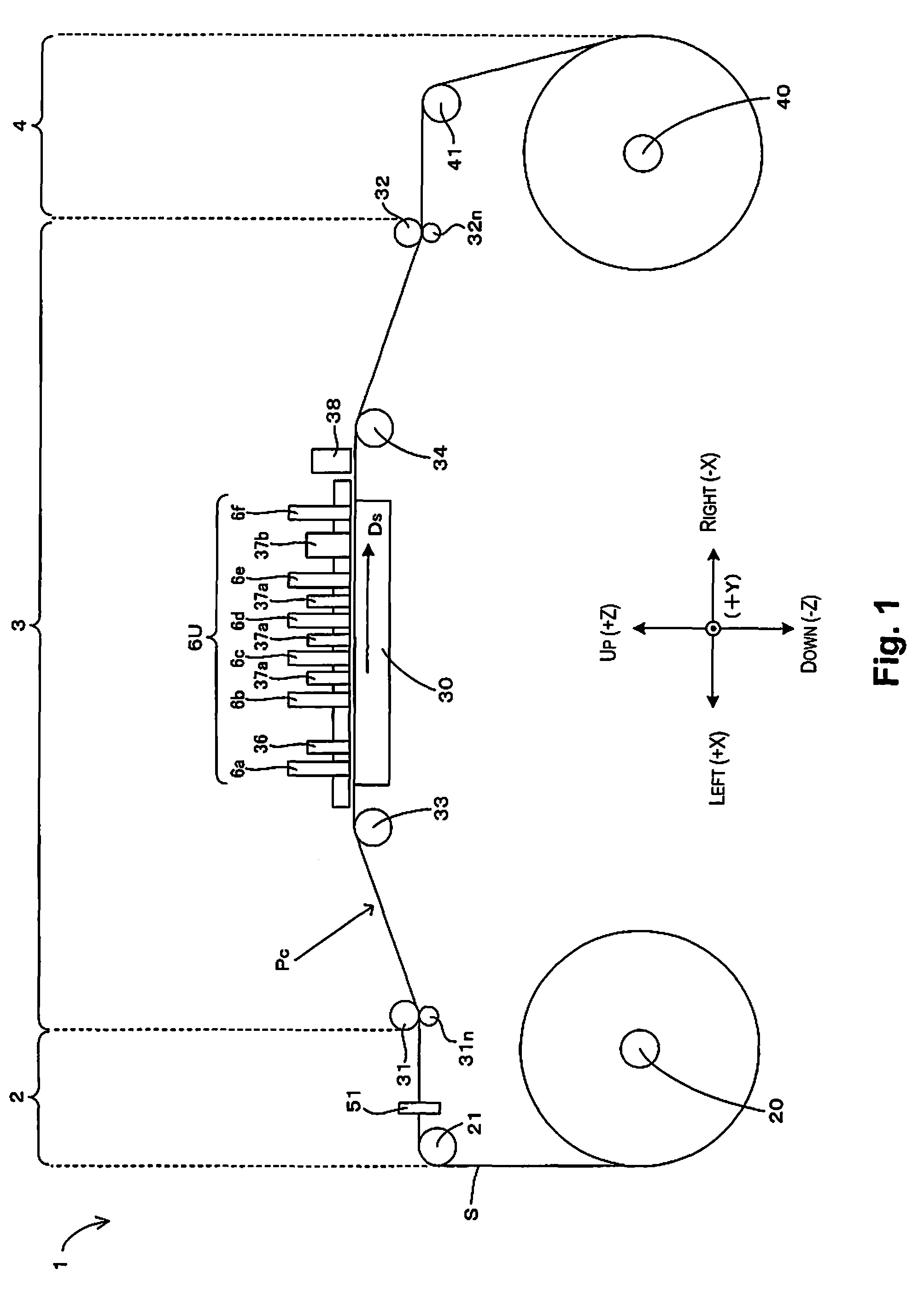
Ink supply assembly for an ink jet printing device
An ink supply assembly includes at least one inlet port. At least one outlet port is connected to the inlet port via an ink cavity and is adapted to be connected to an ink discharge unit of an ink jet device. The ink supply assembly has a sandwich structure formed by at least two plate members and a foil that is interposed therebetween and has a part forming a wall of said ink cavity. At least one of the plate members defines a pressure equalization chamber adjacent to the ink cavity and separated therefrom by the foil.
Owner:OCE TECH
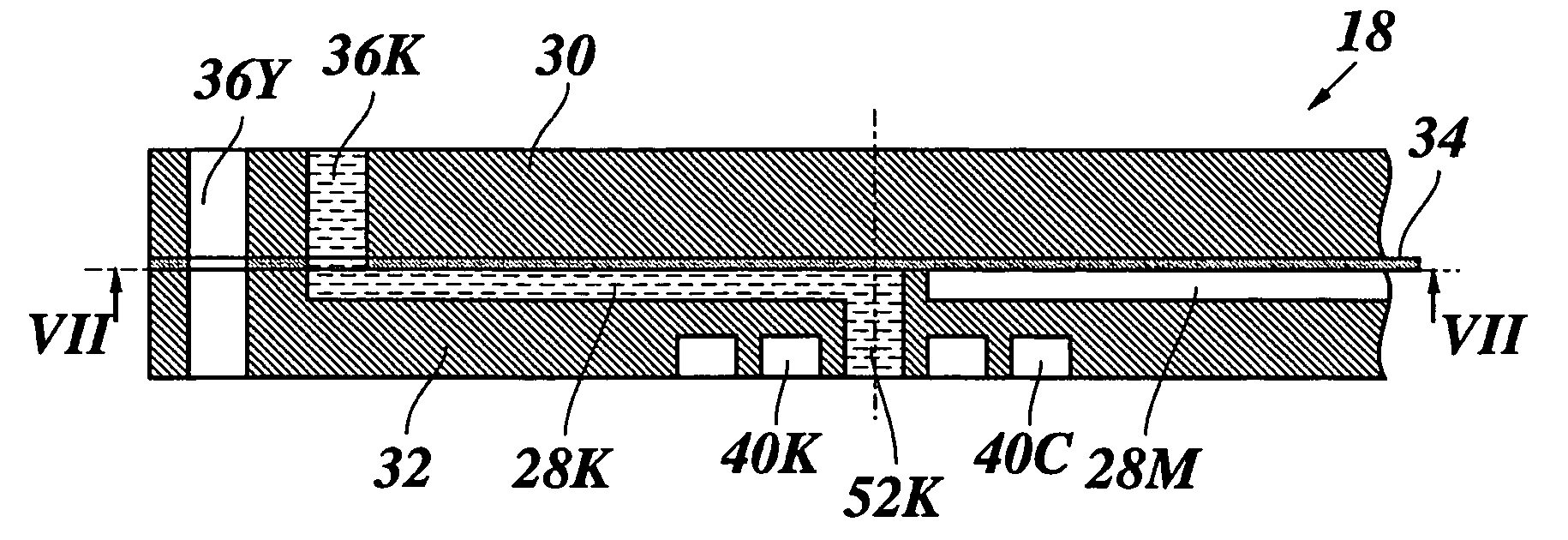
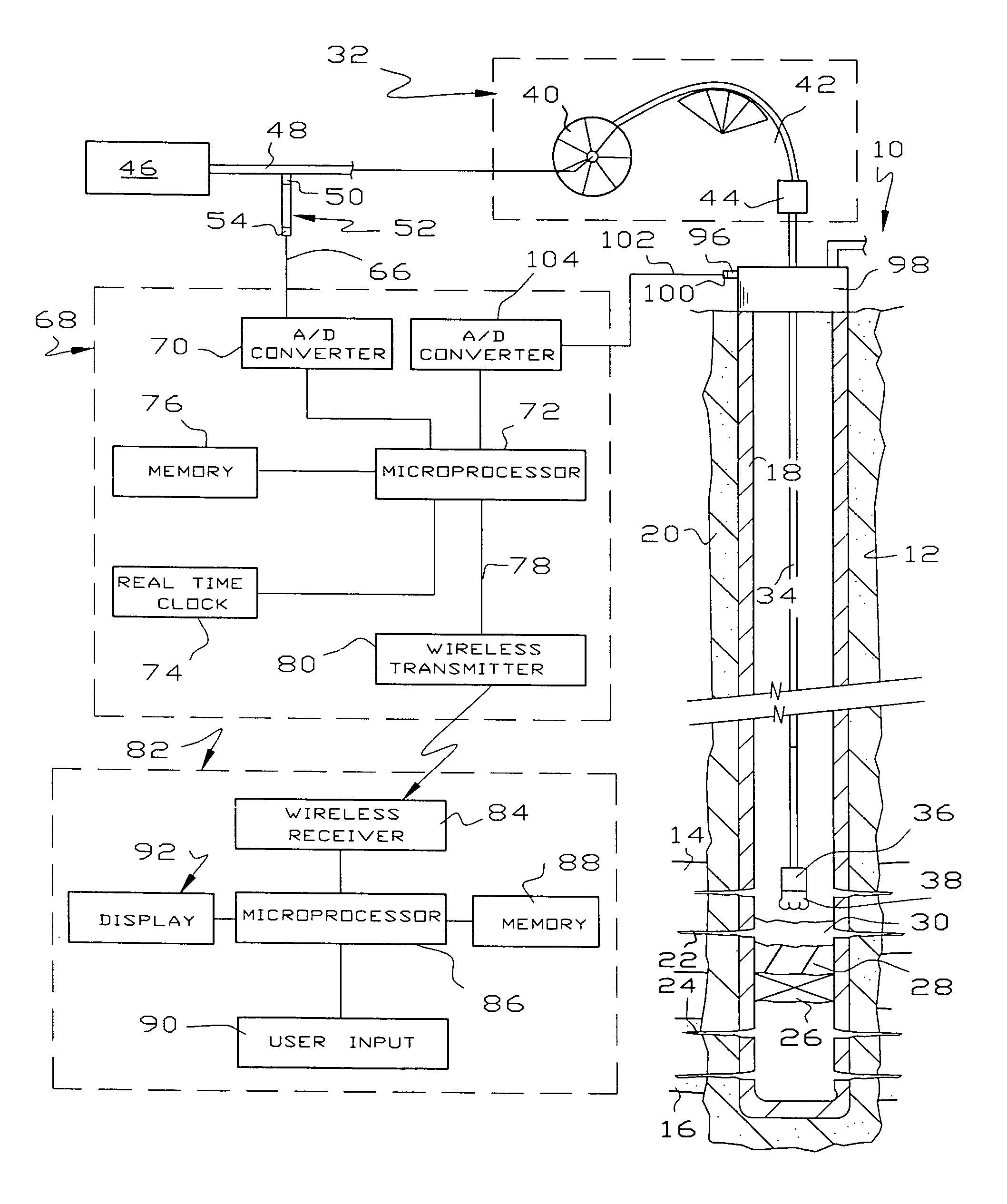
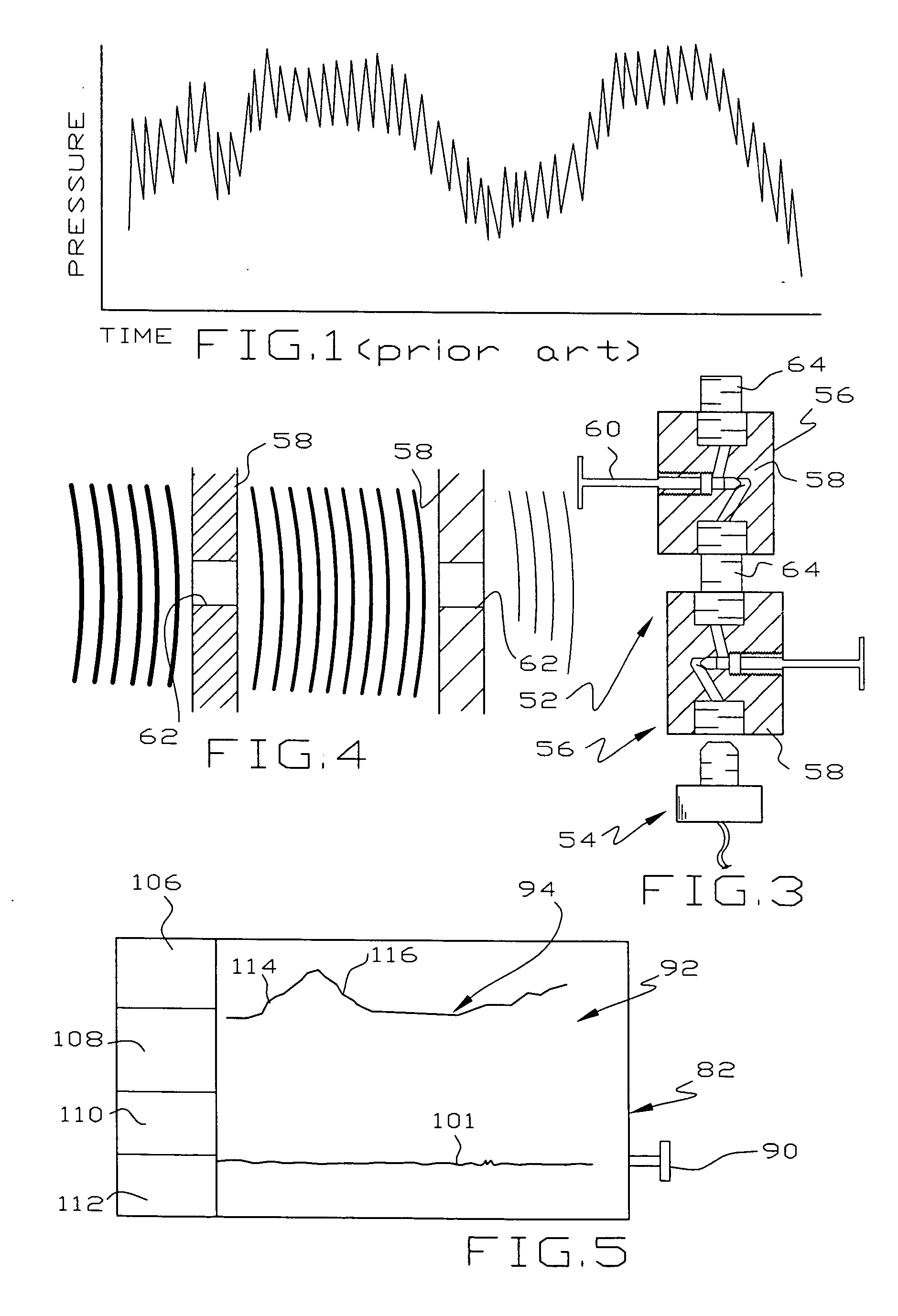
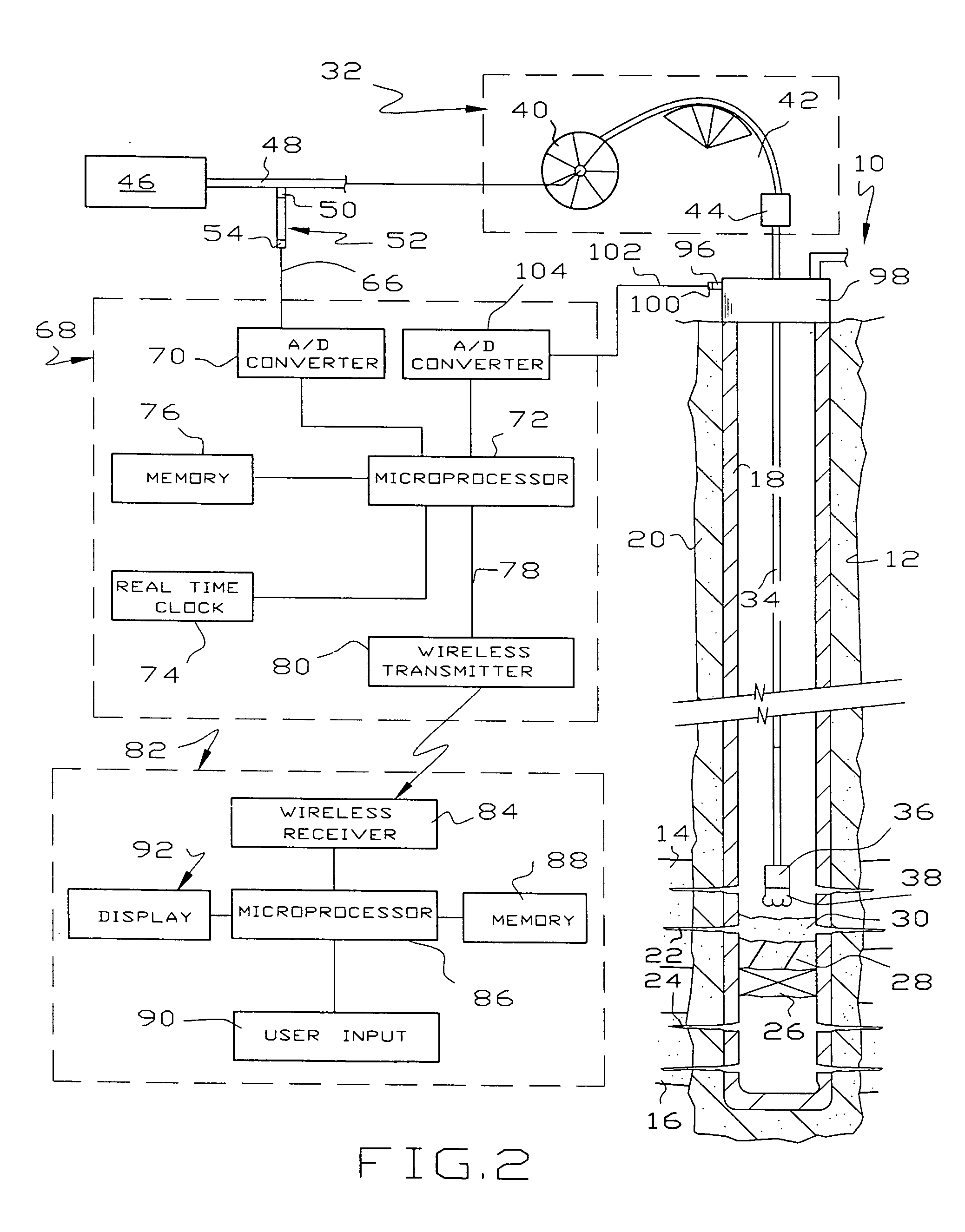
Pressure monitoring technique
InactiveUS20050199053A1Effective and inexpensive damperPressure fluctuationPump testingSurveyLine tubingMud motor
The outlet pressure of a pump that fluctuates rapidly, as is typical of high pressure multiplex pumps, is sensed in a pressure line leading from the main flow line to a damping mechanism. The damping mechanism comprises a pair of small spaced openings, which are preferably adjustable in size. The damping mechanism is ideally a pair of needle valves placed in series so the pressure downstream of the second needle valve fluctuates considerably less than upstream of the first needle valve. The damped pressure is sensed to provide an input to real time graphs showing various pertinent pressure measurements involving the application of pressure, e.g. to monitor downhole tools in hydrocarbon wells. The downhole tools may be fluid driven motors, whipstocks, packers, wiper plugs and the like. In the case of fluid driven or mud motors, a base line pressure taken when the motor is idling is compared to the pressure when the motor is drilling to detect the onset of motor stall.
Owner:BUTLER THOMAS L +1
Ultrasonic device unit, probe, electronic device and ultrasonic imaging device
ActiveUS20150266058A1Length minimizationAvoid lengthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonic imagingElectron
An ultrasonic device unit includes a substrate having a planar part and a recess part recessed from the planar part, an ultrasonic device which has an element array including a plurality of thin film ultrasonic transducer elements disposed in an array and is disposed in the recess part, a first flexible printed board, one end of which is superimposed on a portion of an array surface of the ultrasonic device and connected to the same, the other end of which is superimposed on a portion of the planar part and connected to the same, wherein the array surface of the ultrasonic device which the one end of the first flexible printed board is superimposed on is positioned within a plane including the planar part or a plane outside of the recess part.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Breather structure for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7743758B2Sufficient breathing effectSmall sizeCombustion enginesGearing detailsBreatherEngineering
A breather structure for internal combustion engine, the structure making a breather chamber smaller and thus making an internal combustion engine as a whole smaller. A breather chamber and a small chamber are formed. The breather chamber includes a first side face cover. The first side face cover is joined to a case to cover a first one of the right and left side faces of the case. Inside the first side face cover, an auxiliary apparatus chamber is formed. The auxiliary apparatus chamber houses a clutch mechanism connecting or disconnecting the power transmission route. Additionally, formed inside a housing are an external communication port communicating to the outside of the housing, and the small chamber communicating to a crank chamber and to the auxiliary apparatus chamber. Moreover, the auxiliary apparatus chamber communicates to the breather chamber.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Liquid ejection apparatus and liquid ejection head
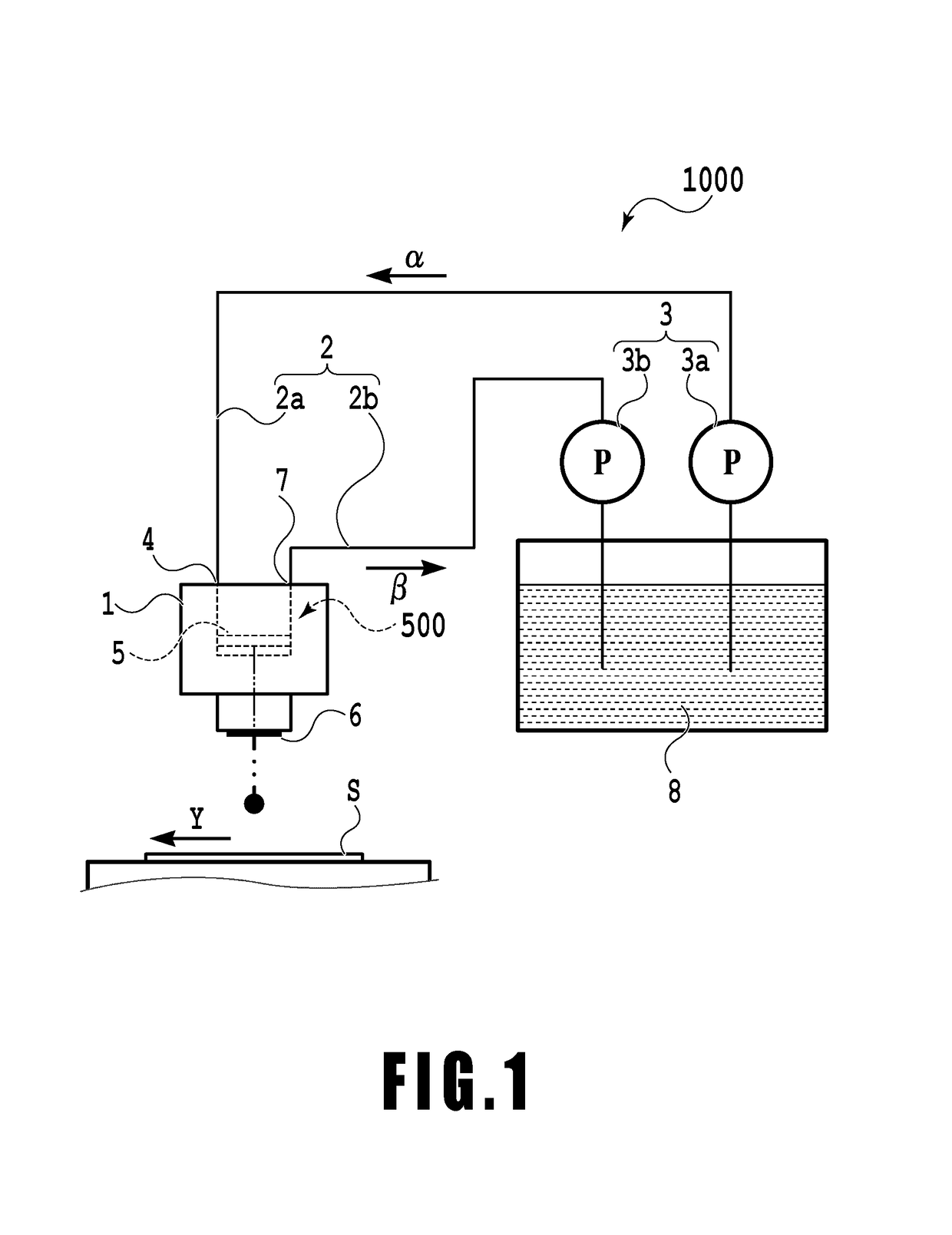
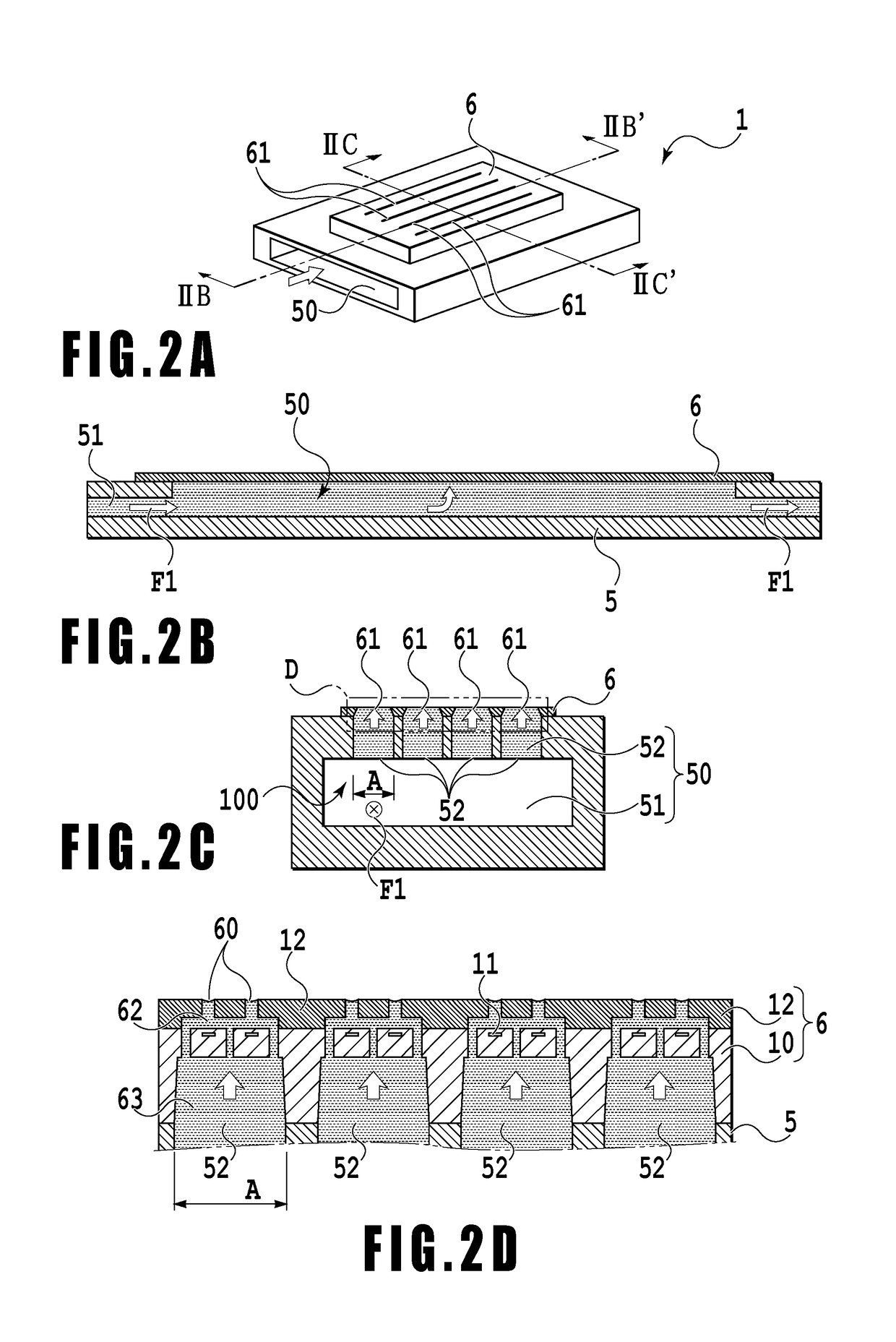
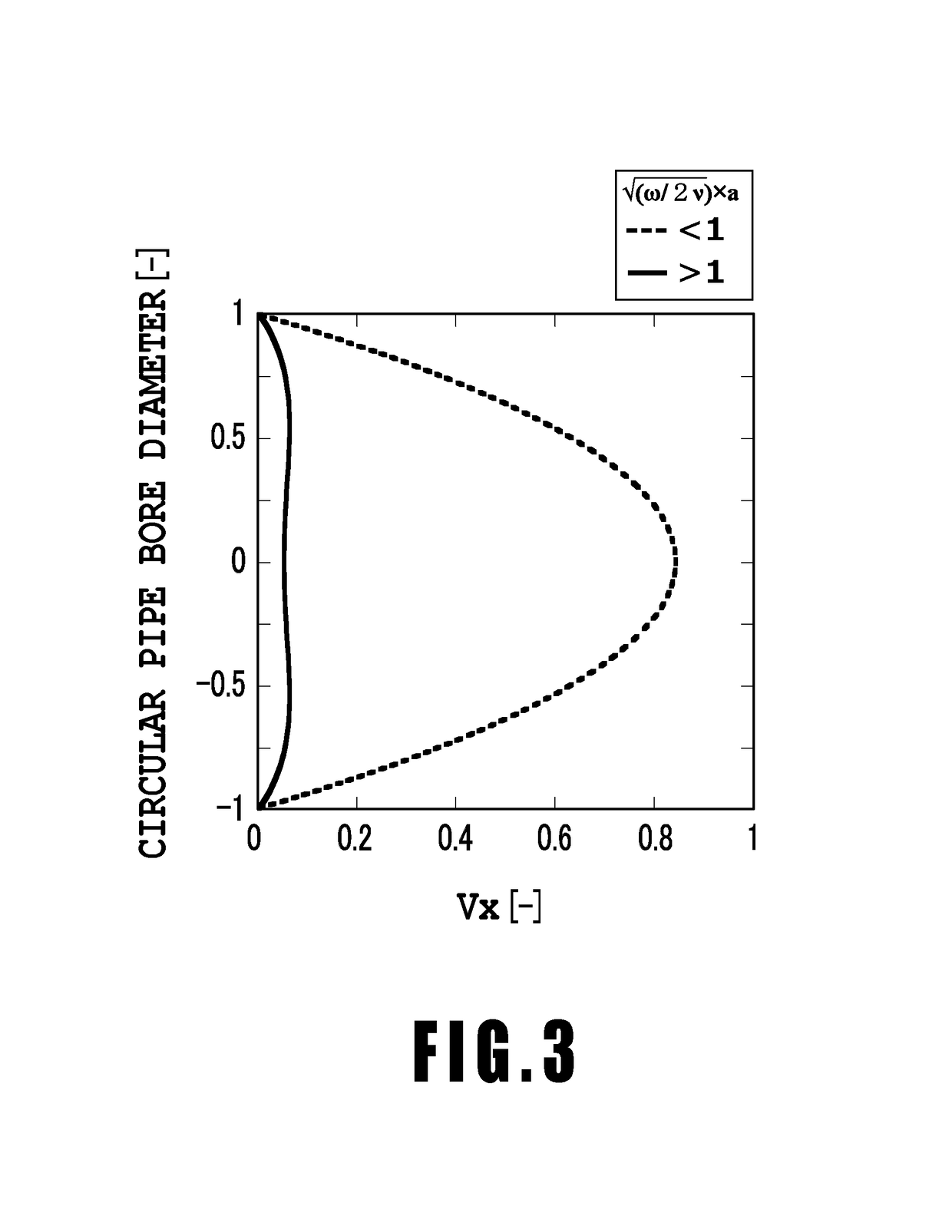
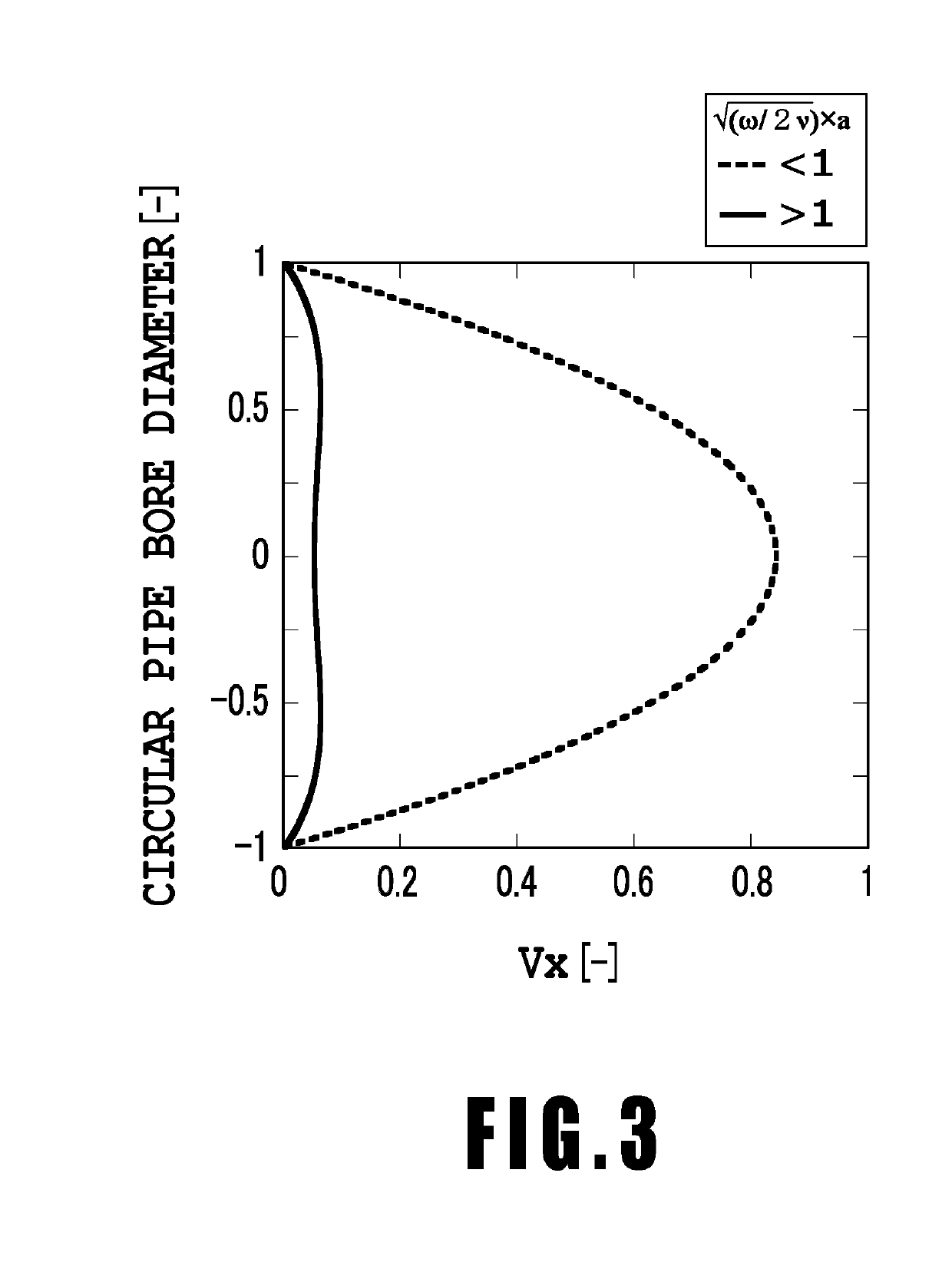
An object is to provide a liquid ejection apparatus that allows suppression of a fluctuation in a pressure of a liquid in a flow path caused by a liquid delivery unit, enabling the liquid to be stably ejected through an ejection port. The liquid ejection apparatus including a liquid ejection head having an ejection port through which a liquid is ejected, a flow path configured to communicate with the ejection port, and a liquid delivery unit configured to feed the liquid to the flow path. A relation between an angular frequency ω of the liquid delivered from the liquid delivery unit, a coefficient of kinematic viscosity ν of the liquid, and an equal diameter a of at least a part of a section of an extra-head flow path in a direction normal to a direction in which ink flows satisfies √(ω / 2ν)×a>1.
Owner:CANON KK
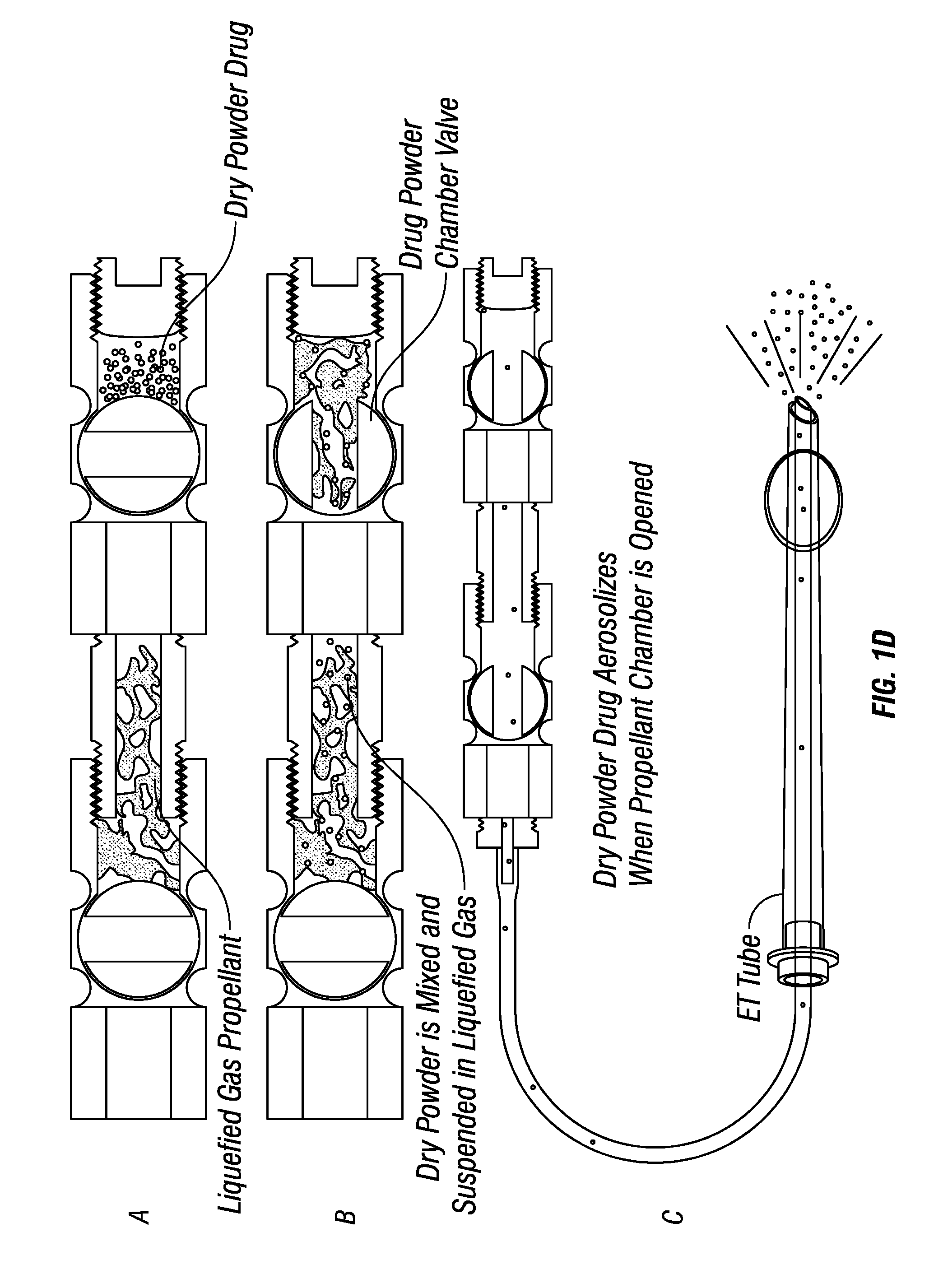
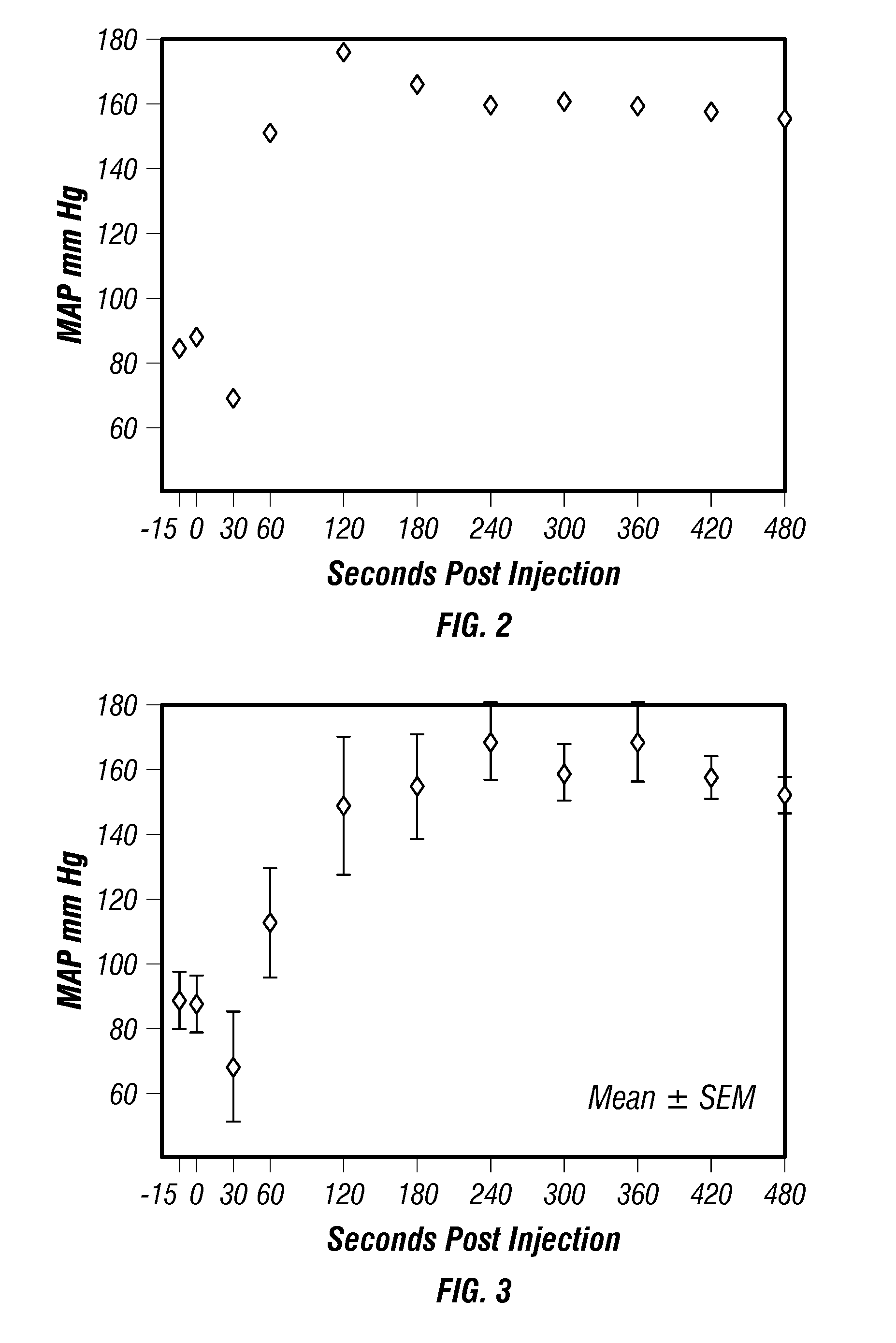
Dry powder drug delivery formulations, methods of use, and devices therefore
The present disclosure relates to systems, methods, and formulations for the pulmonary administration of one or more therapeutic agents, in dry powder form, in a single, large dose quantity. These formulations, methods, and systems are useful in the treatment of patients suffering from toxic or harmful gas exposure, such as nerve gas exposure, as well as in the treatment of patients suffering from diseases of the pulmonary system, including tuberculosis, cystic fibrosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
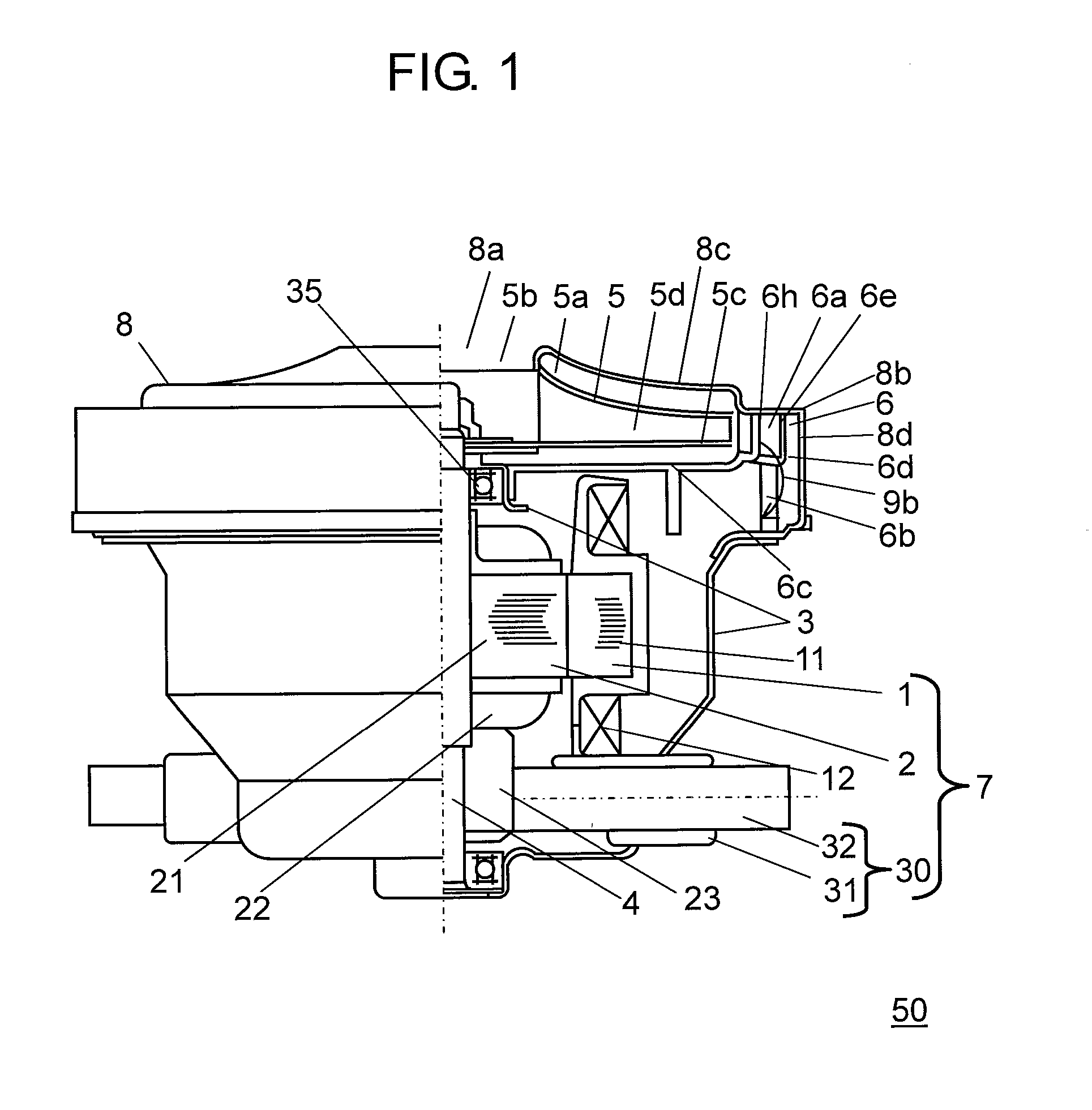
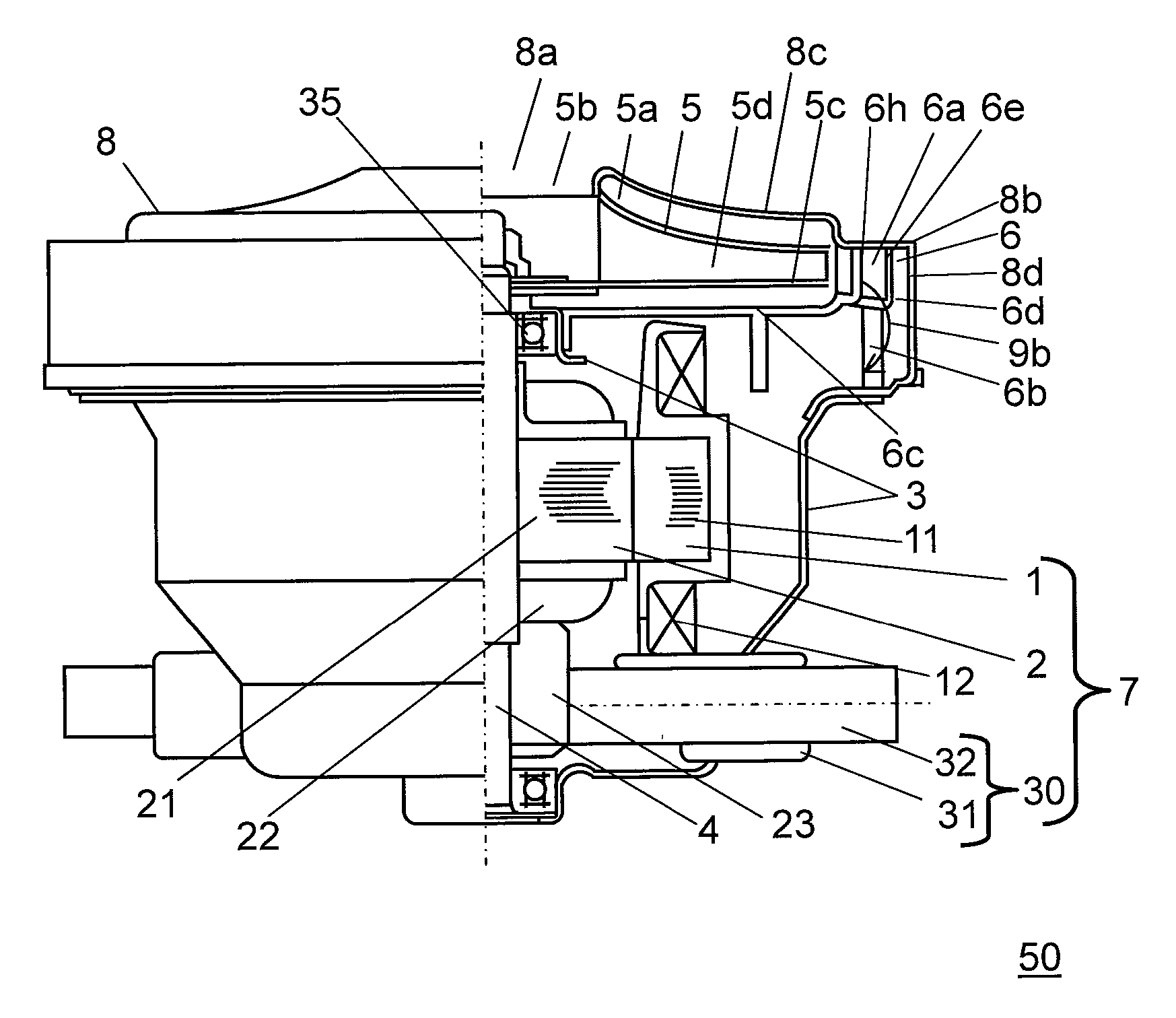
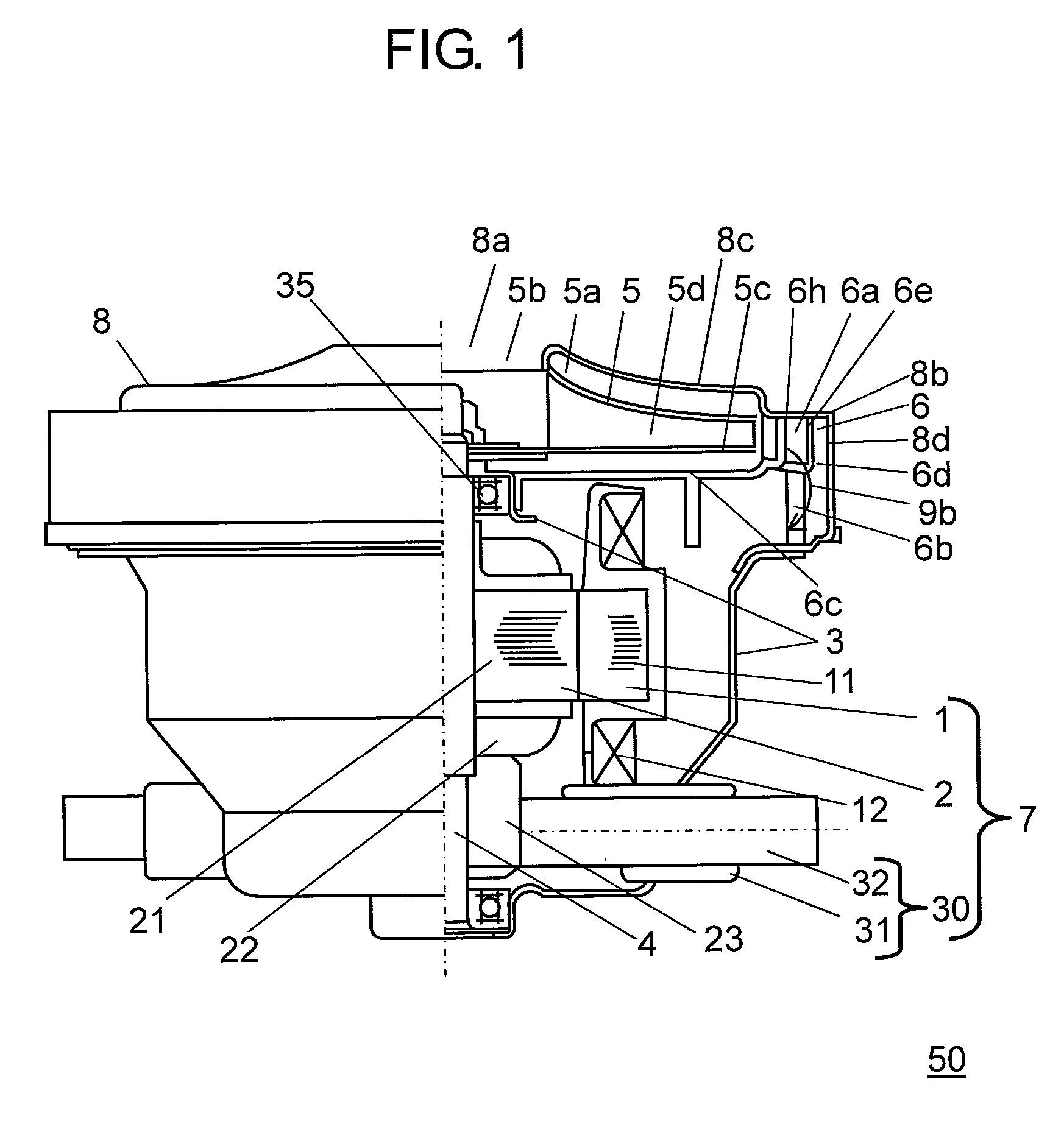
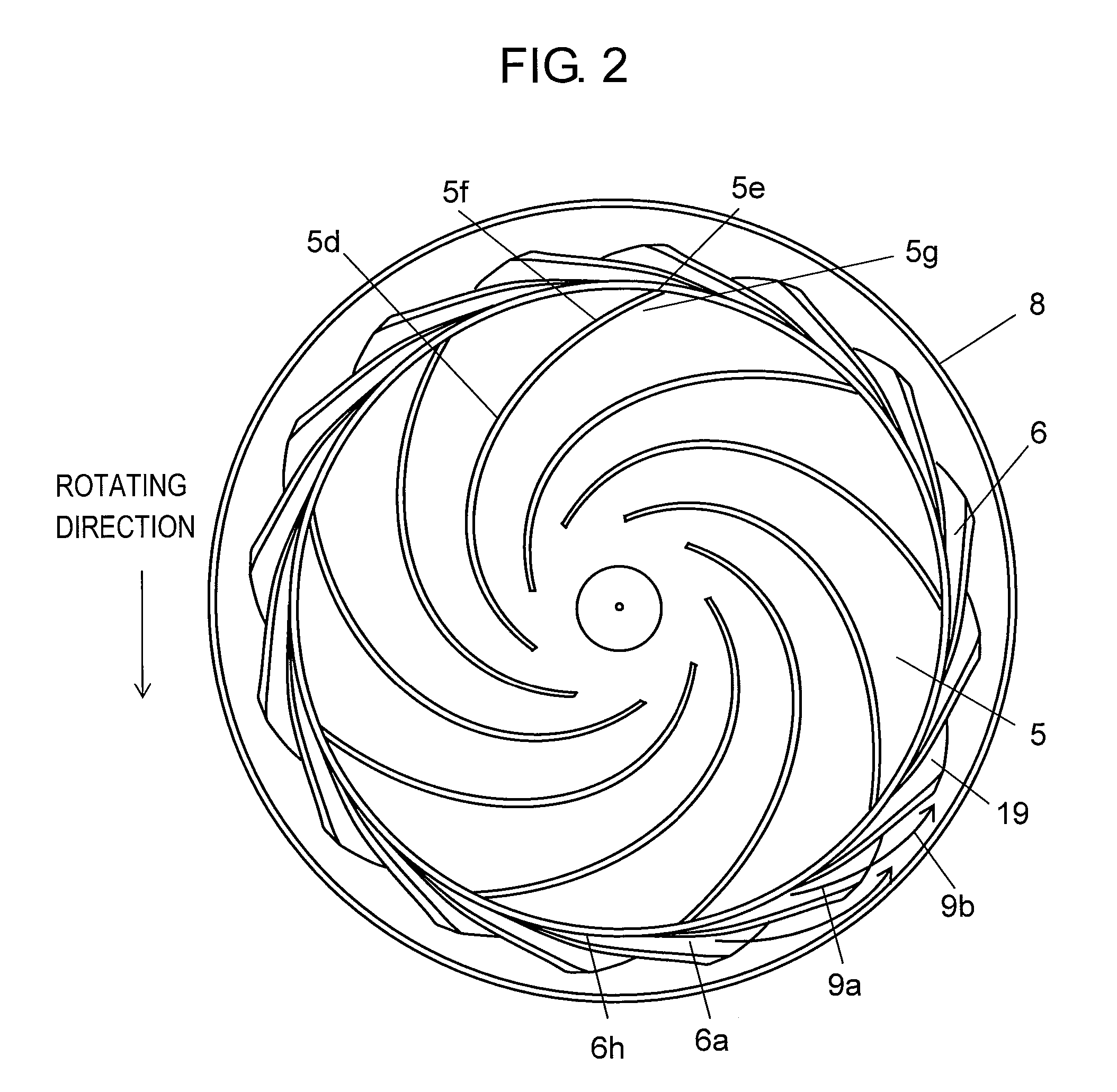
Electric blower and vacuum cleaner comprising same
InactiveUS20130125339A1Reduce running noiseStrong suctionEngine manufacturePump componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Disclosed is an electric blower having a stator, a rotor, a bracket, a rotary fan, an air guide and a fan case. The air guide comprises a partition plate, a diffuser disposed around outer periphery of the rotary fan in the air guide, a partition-plate sloped portion and a guide vane. The fan case has a fan-facing portion, a fan case shoulder bent at the outermost part of the fan-facing portion, and a cylindrical portion extending cylindrically in an axial direction from the fan case shoulder. The fan case shoulder is so bent that it forms substantially a right angle.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
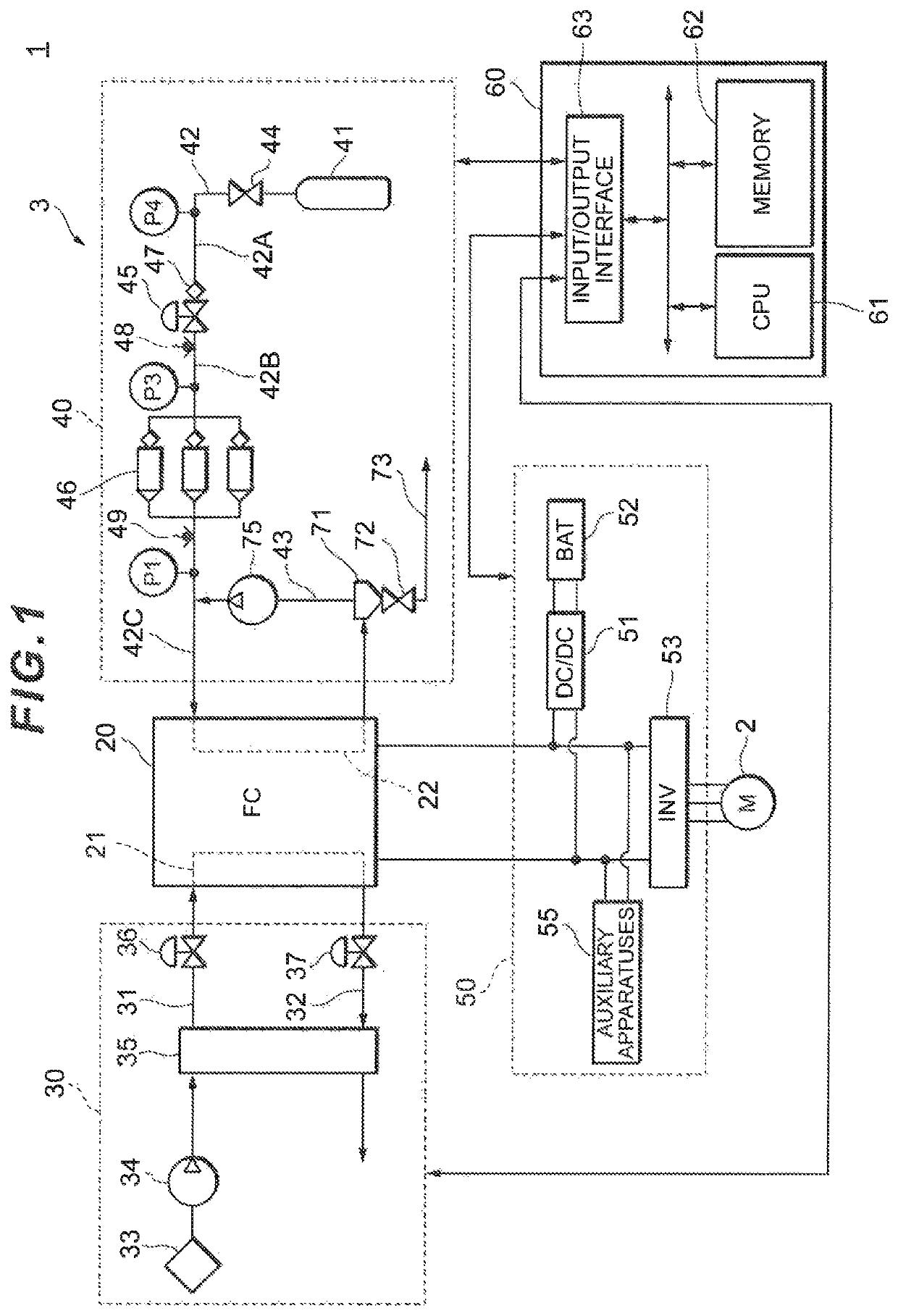
Fuel cell system and control method therefor
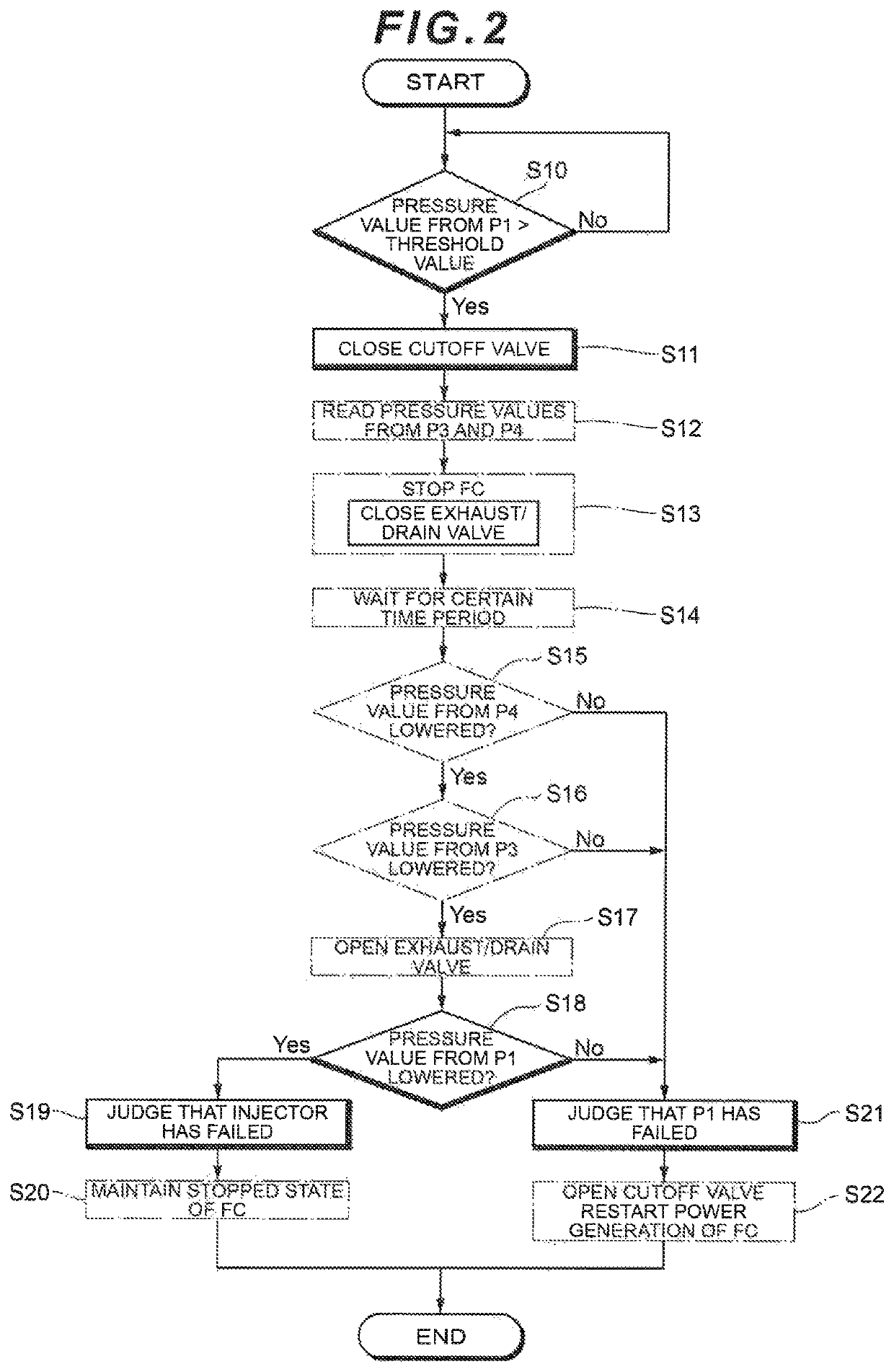
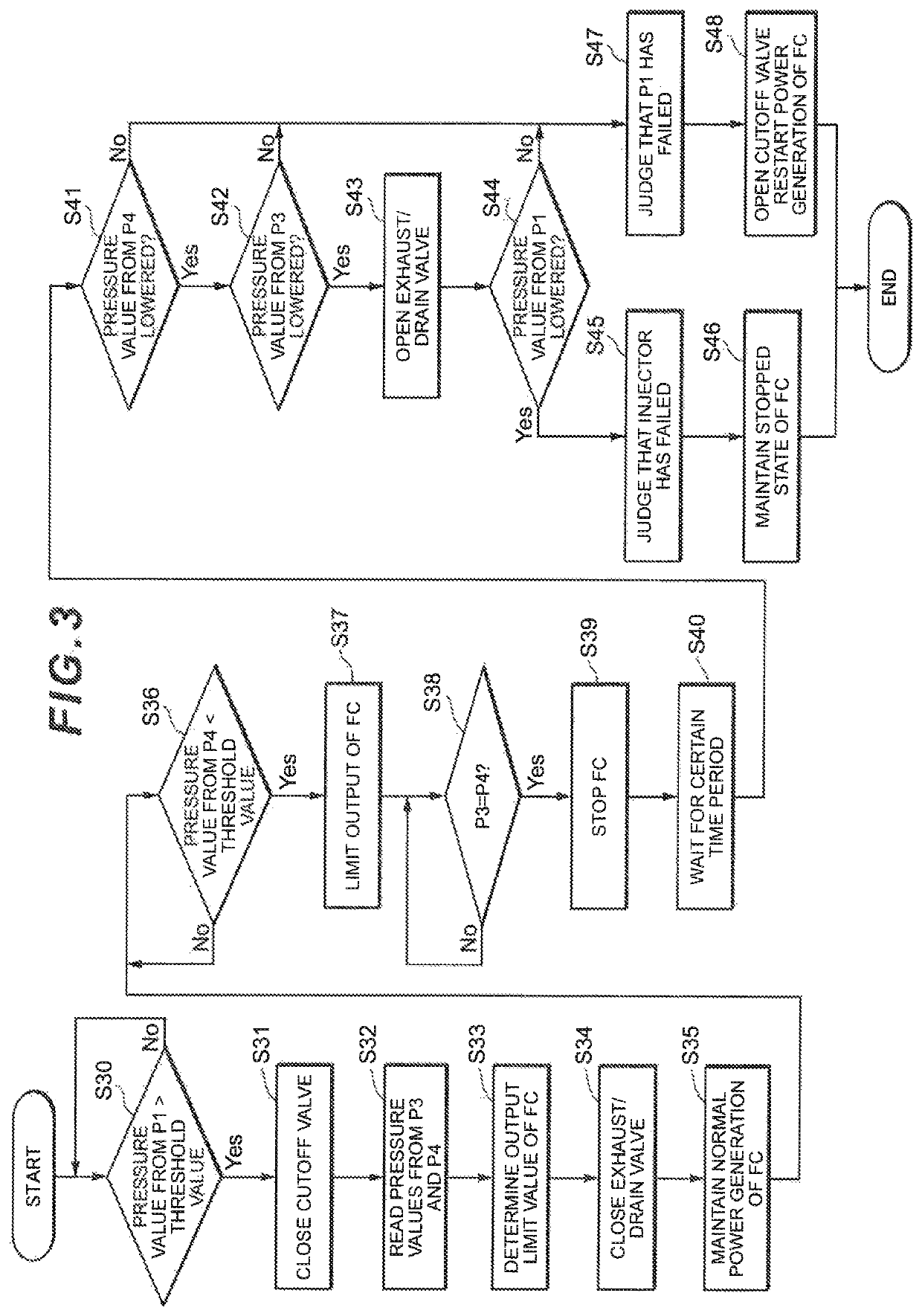
ActiveUS20180269499A1Easily judgeImprove accuracyReactant parameters controlMotive system fuel cellsFuel cellsControl theory
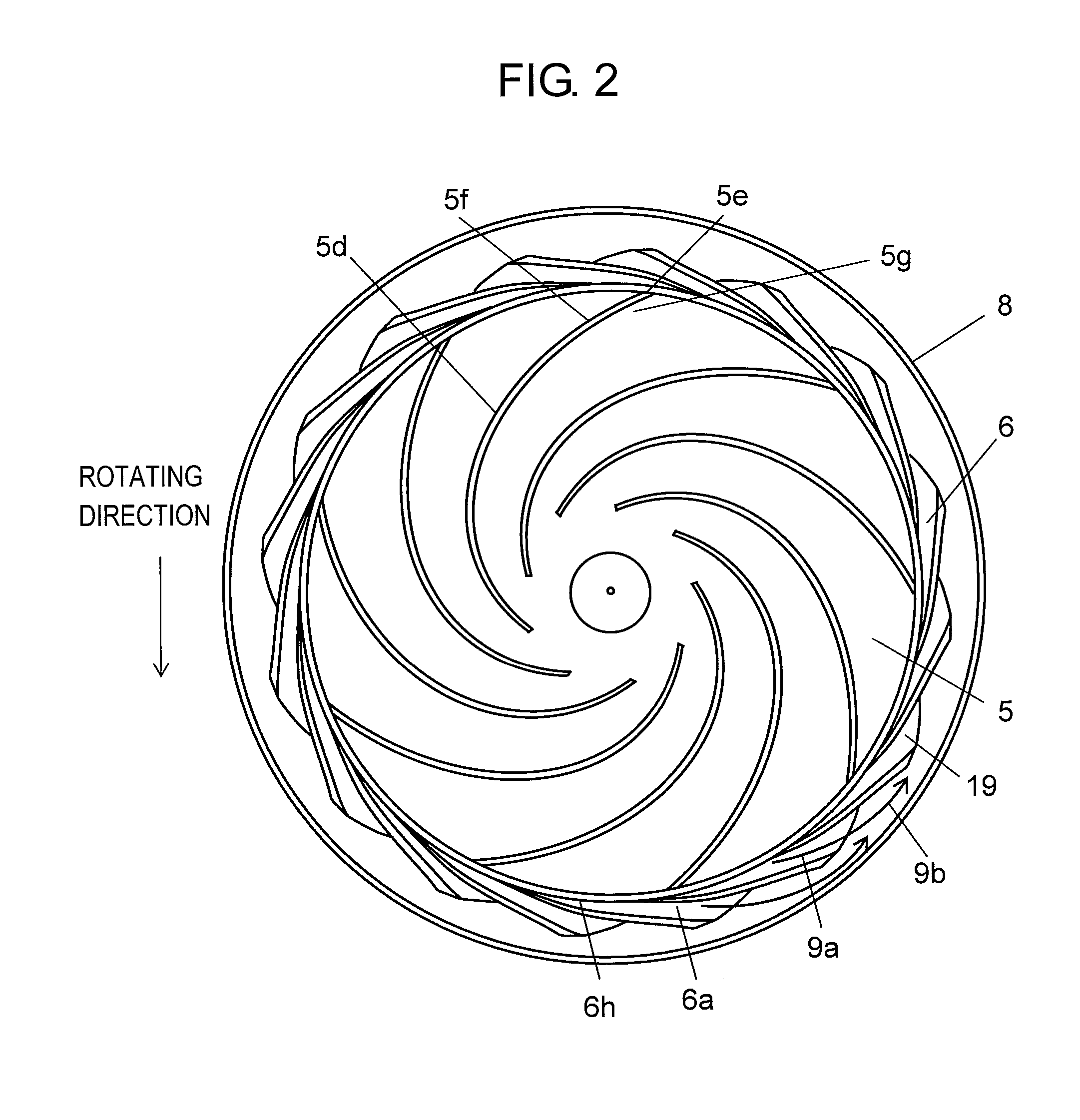
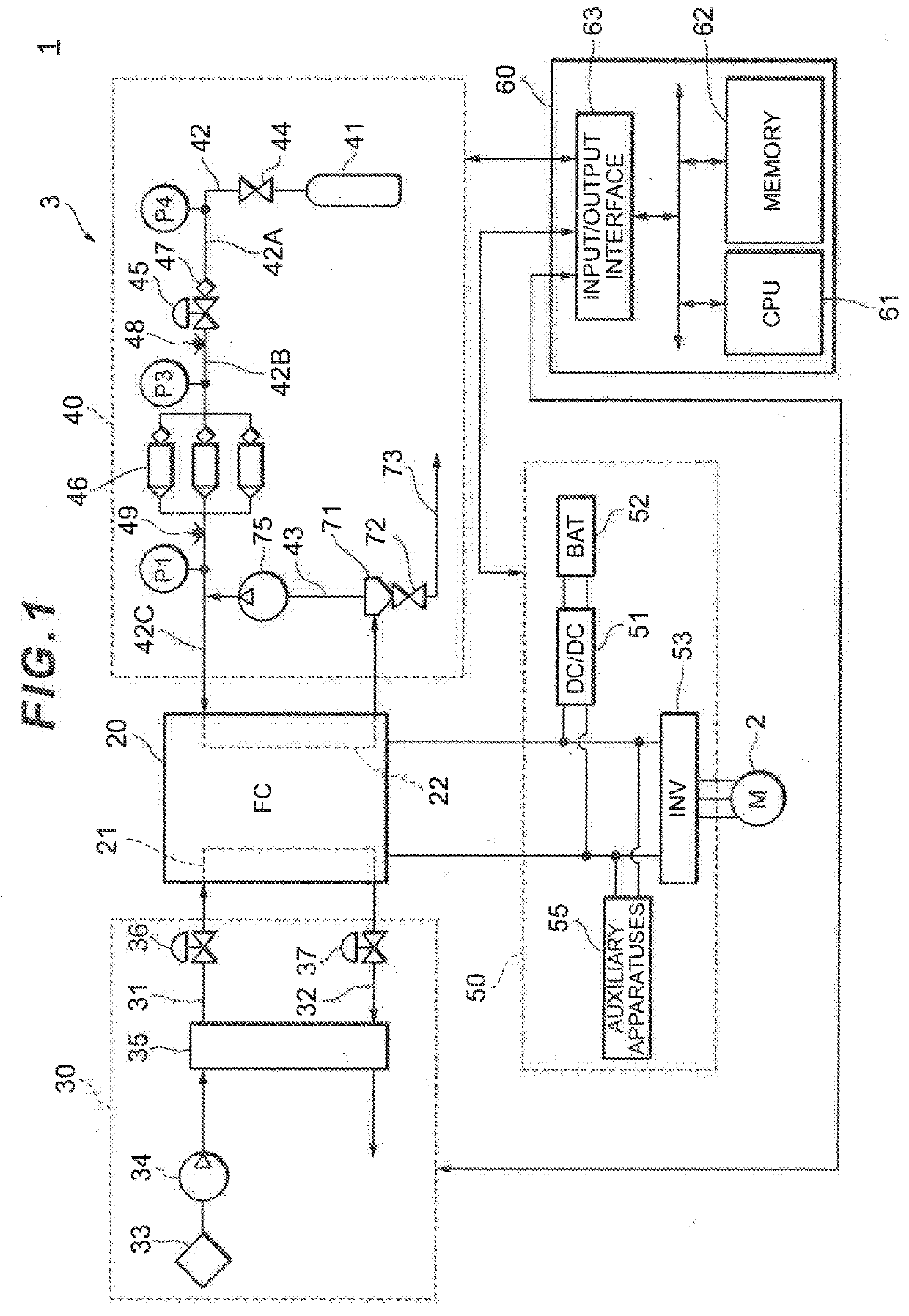
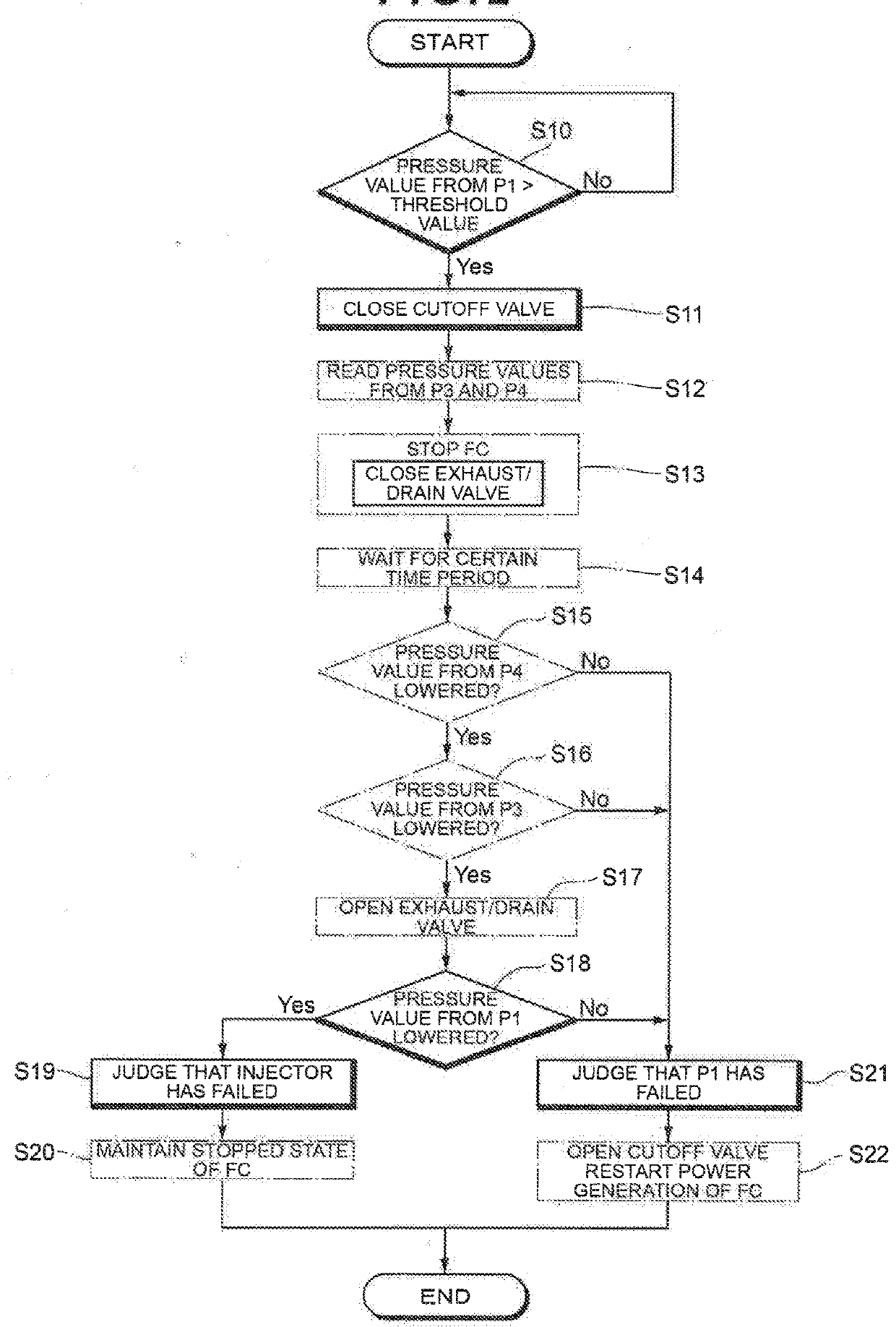
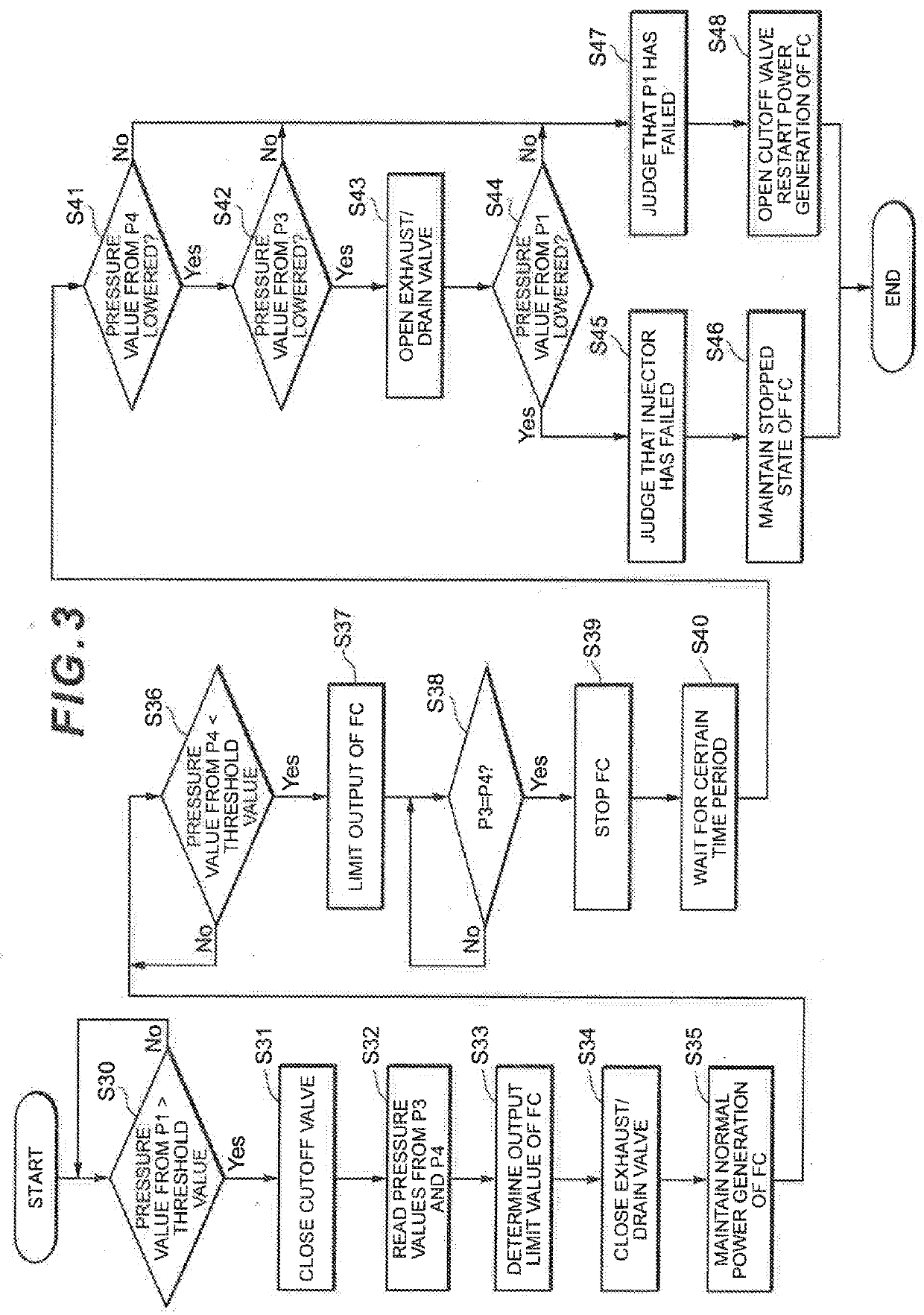
A controller closes a cutoff valve and a purge valve when a pressure value detected by a pressure sensor is an abnormal value. The controller then judges that an on-off valve has failed when the pressure value detected by the pressure sensor P1 has lowered, whereas the controller judges that the pressure sensor has failed when the pressure value detected by the pressure sensor has not lowered.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Plant with Piping Mounted on Branch Pipe and Boiling Water Reactor Plant
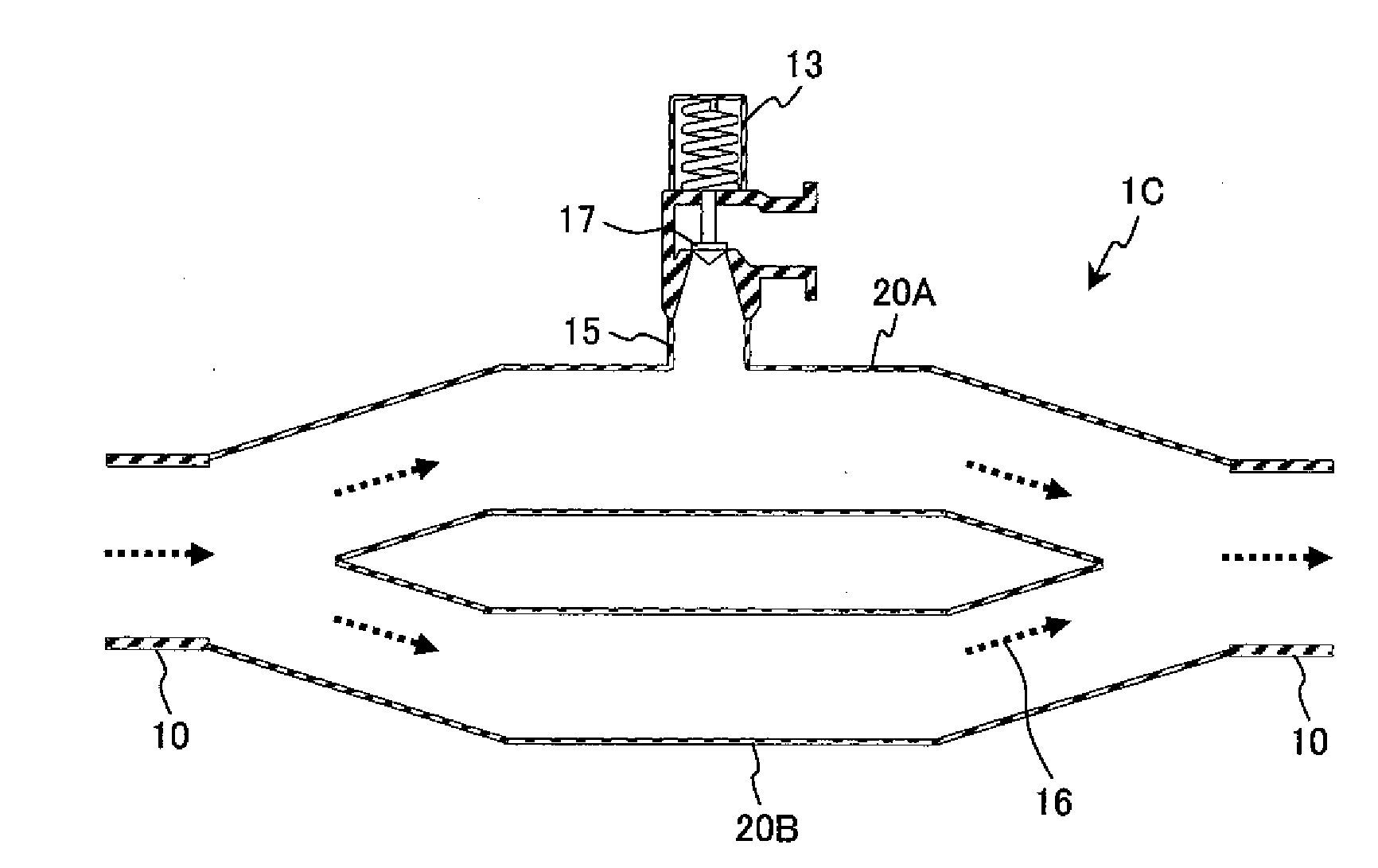
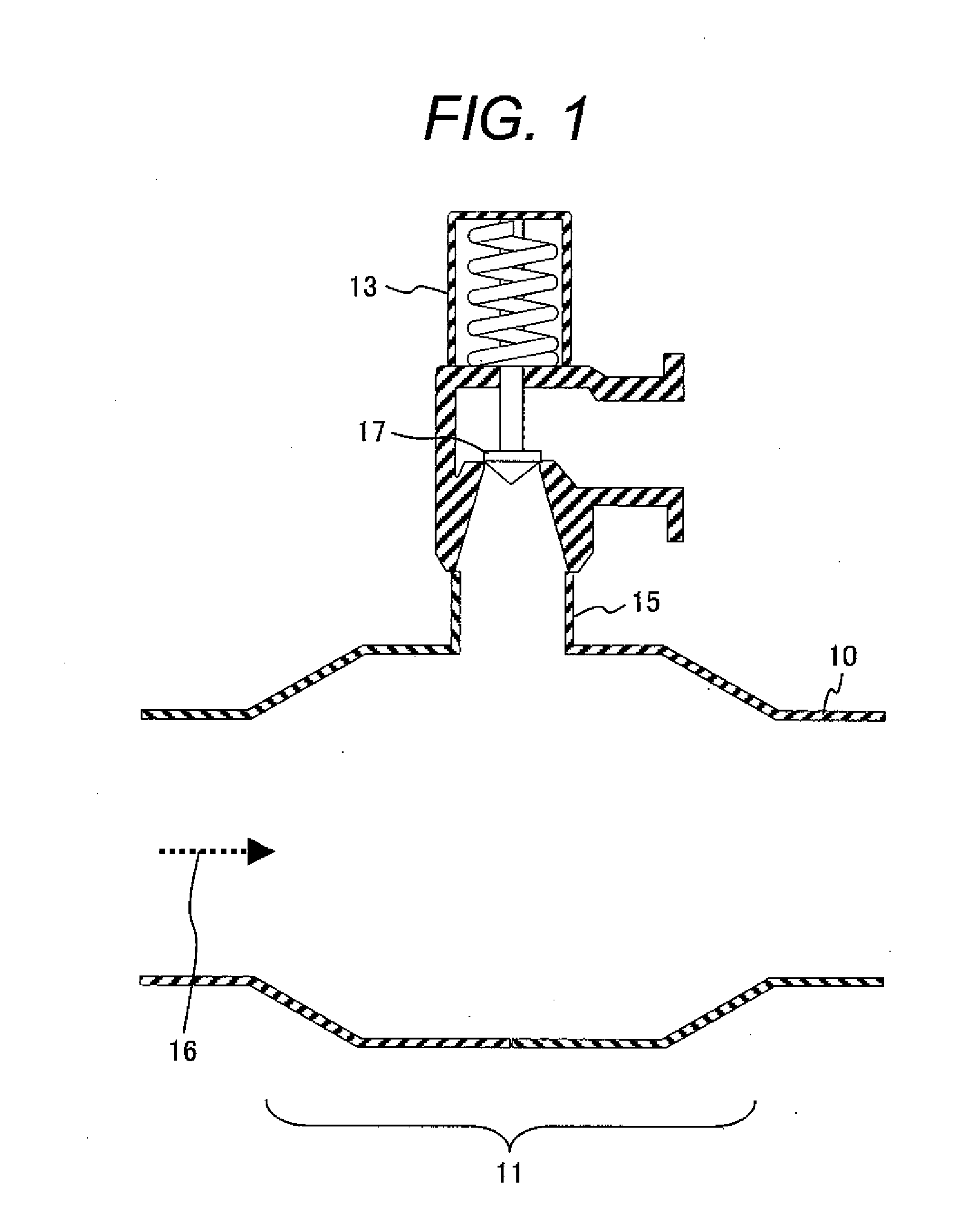
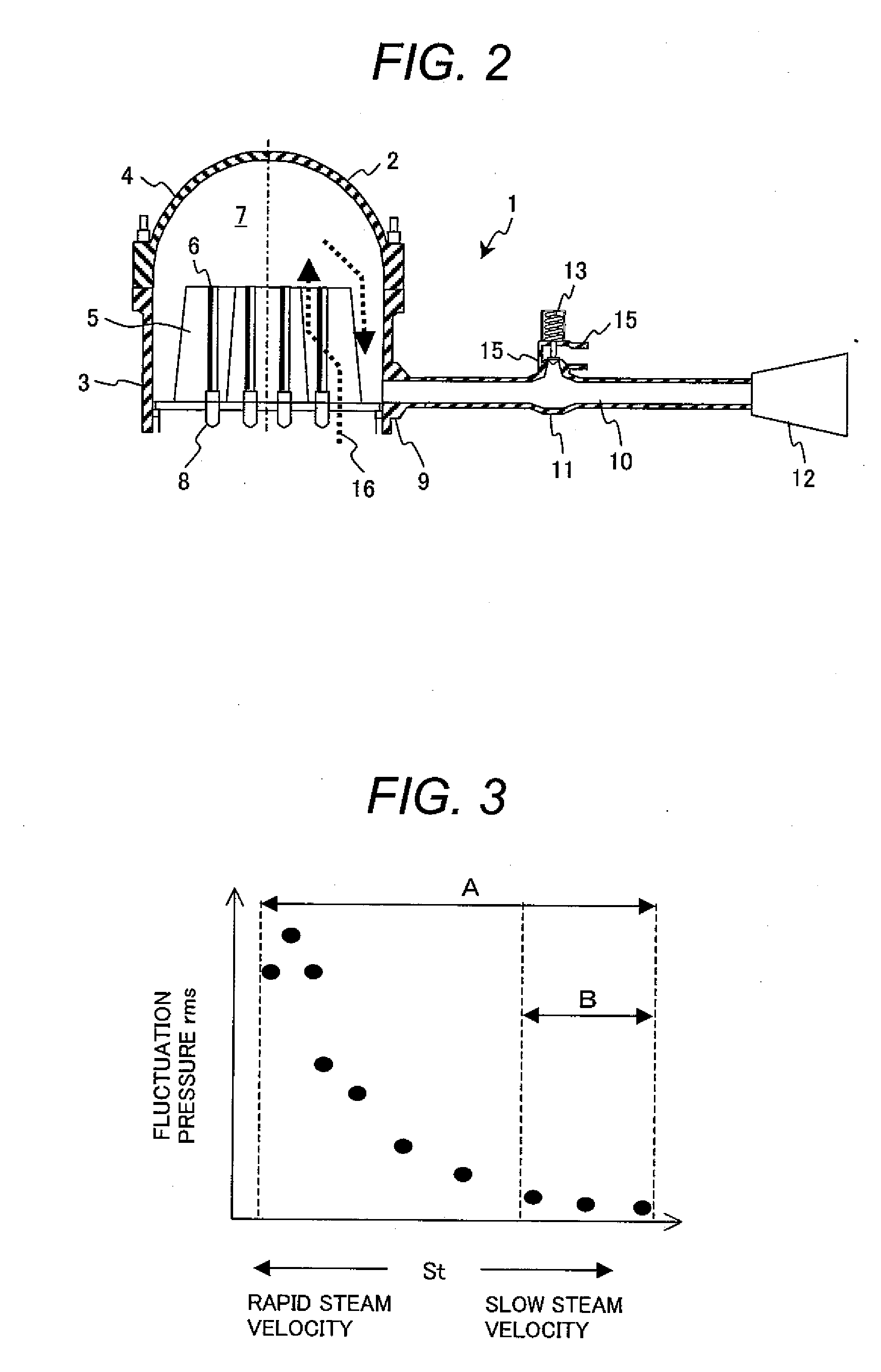
ActiveUS20090296874A1Fluctuation pressure of the gas flowing in the piping can be reducedPressure fluctuationNuclear energy generationEqualizing valvesEngineeringBoiling water reactor
A plant with piping mounted on branch pipe,wherein said piping which introduces gas has a nozzle portion as a joint portion to a vessel and a branch portion connected with a branch pipe; and wherein an enlarged passage portion is formed at least at one of said branch portion and said nozzle portion, and a passage sectional area of said enlarged passage portion is larger than that of said piping other than said enlarged passage portion. Since the flow velocity of the gas flowing inside slows down at the enlarged passage portion, the occurrence of acoustic resonance at the branch portion or the nozzle portion can be suppressed. Accordingly, the fluctuation pressure of the gas flowing in the piping can be reduced even more.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Electrical motor activation method having load torque adaptation
InactiveUS8562304B2Reduce loadLoad fluctuationMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlLoad torqueEngineering
An electrical motor activation method for an electric motor including a rotor, connected to a motor shaft, and a stator having brushes. The stator comprises multiple commutator laminations for the commutation of windings disposed on the rotor and is activated by a pulsed or linearly controllable power source. The motor shaft is connected to a radially driven load, in particular a pump, which has a nonlinear torque curve via a motor revolution. A waviness signal is obtained from a voltage potential applied to the motor and / or from the motor current and rotor position information is obtained from the curve of said waviness signal.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Ultrasonic device unit, probe, electronic device and ultrasonic imaging device
ActiveUS9623443B2Curb bendingAvoid bendingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical vibrations separationUltrasonic imagingElectron
An ultrasonic device unit includes a substrate having a planar part and a recess part recessed from the planar part, an ultrasonic device which has an element array including a plurality of thin film ultrasonic transducer elements disposed in an array and is disposed in the recess part, a first flexible printed board, one end of which is superimposed on a portion of an array surface of the ultrasonic device and connected to the same, the other end of which is superimposed on a portion of the planar part and connected to the same, wherein the array surface of the ultrasonic device which the one end of the first flexible printed board is superimposed on is positioned within a plane including the planar part or a plane outside of the recess part.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
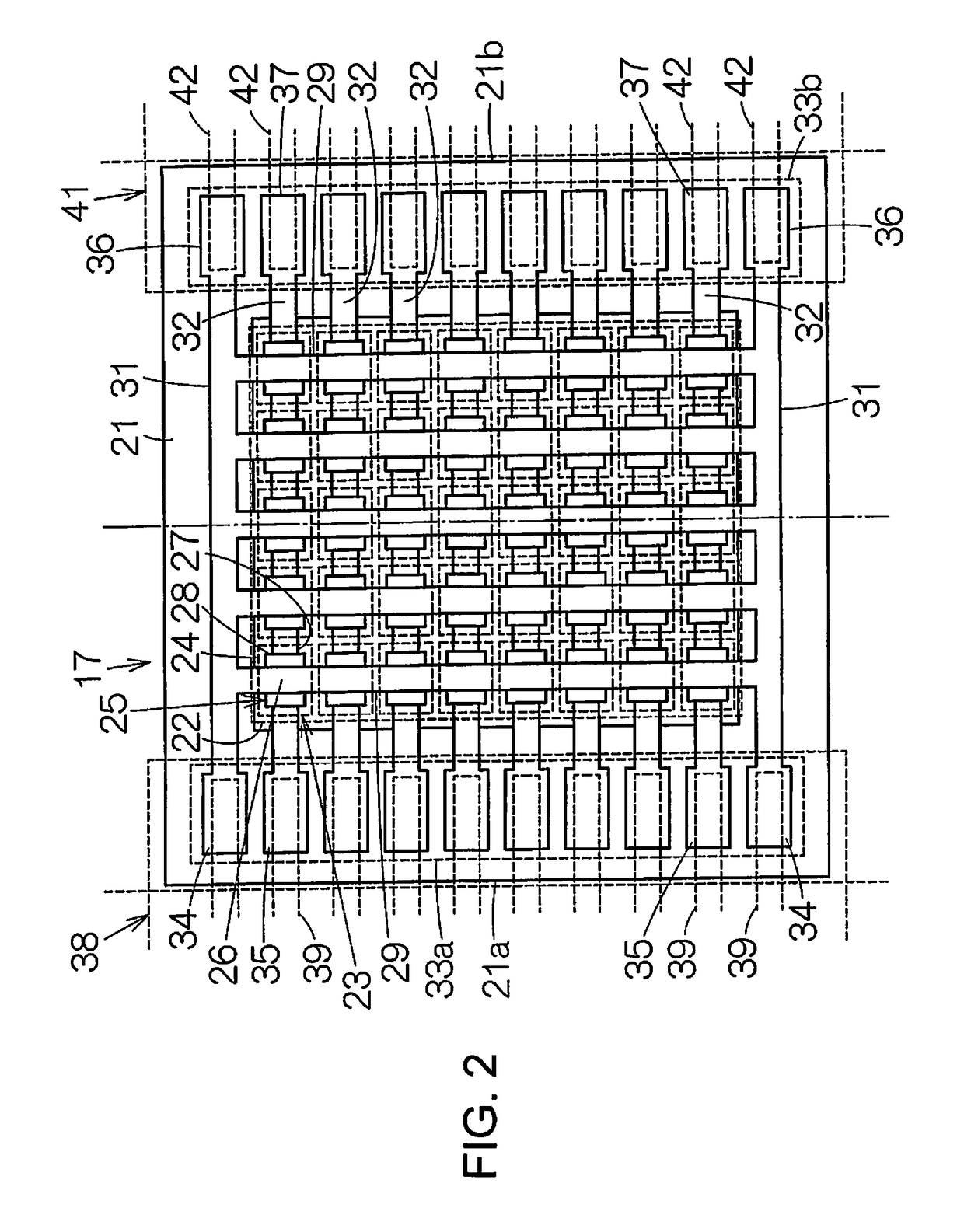
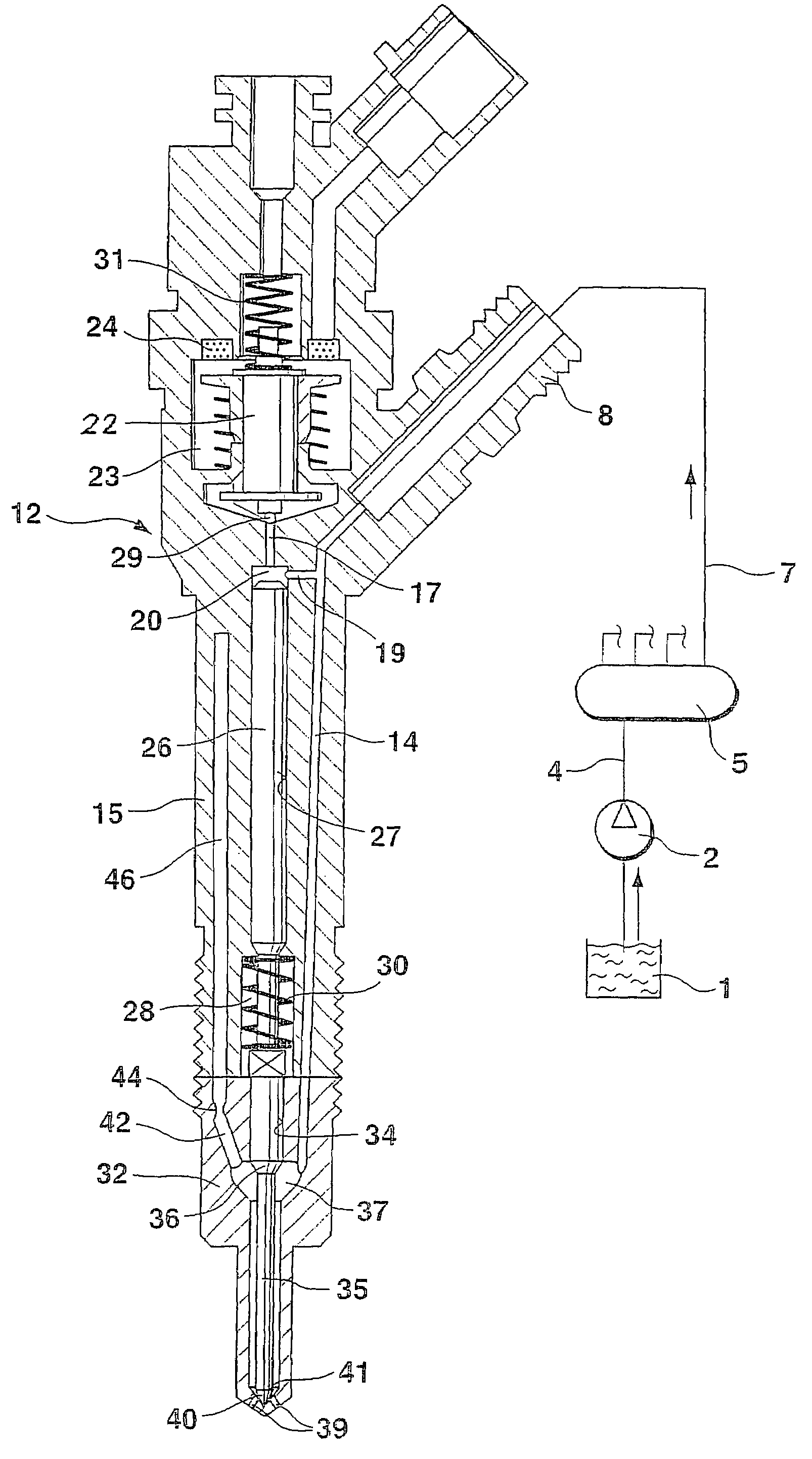
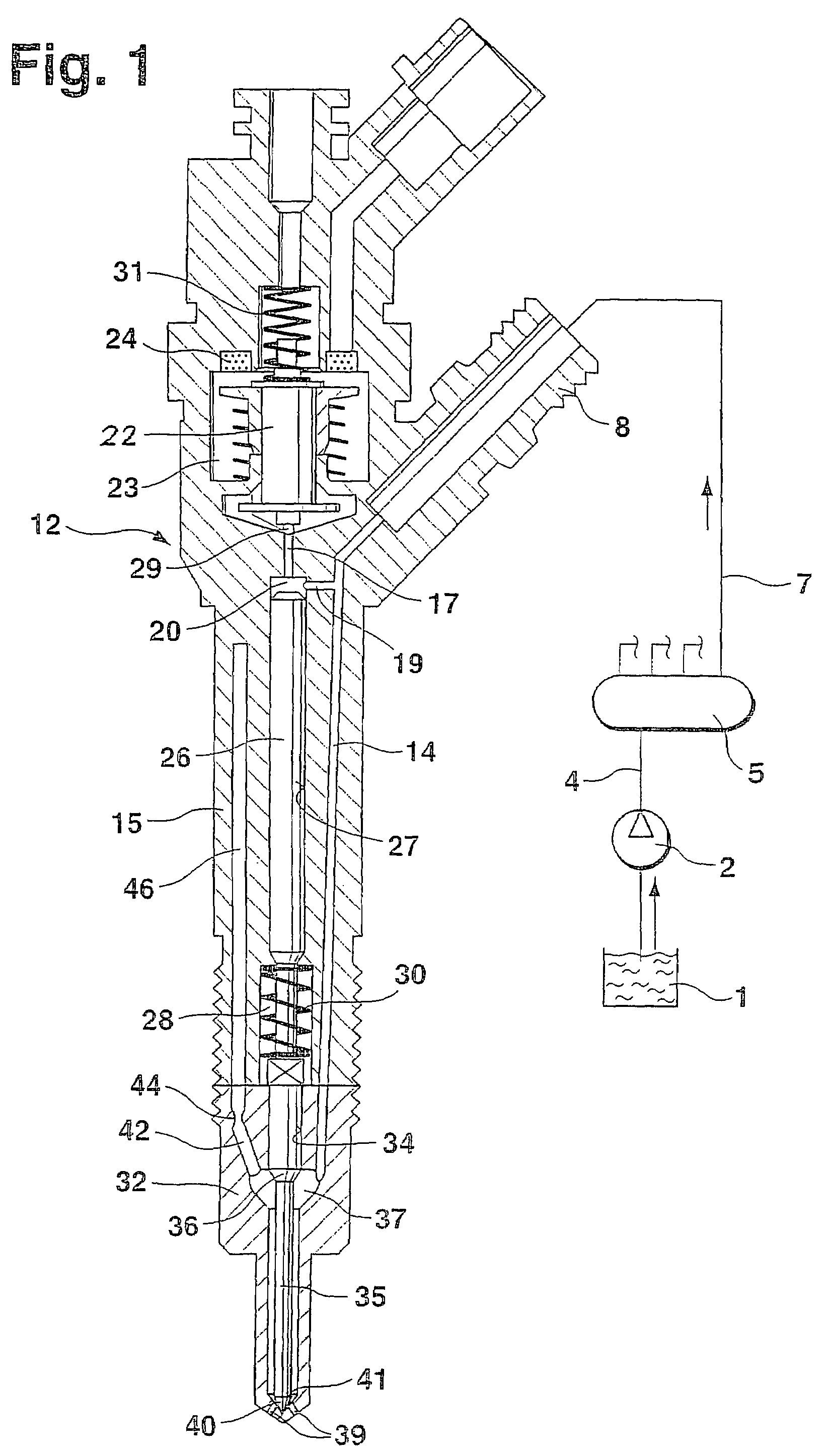
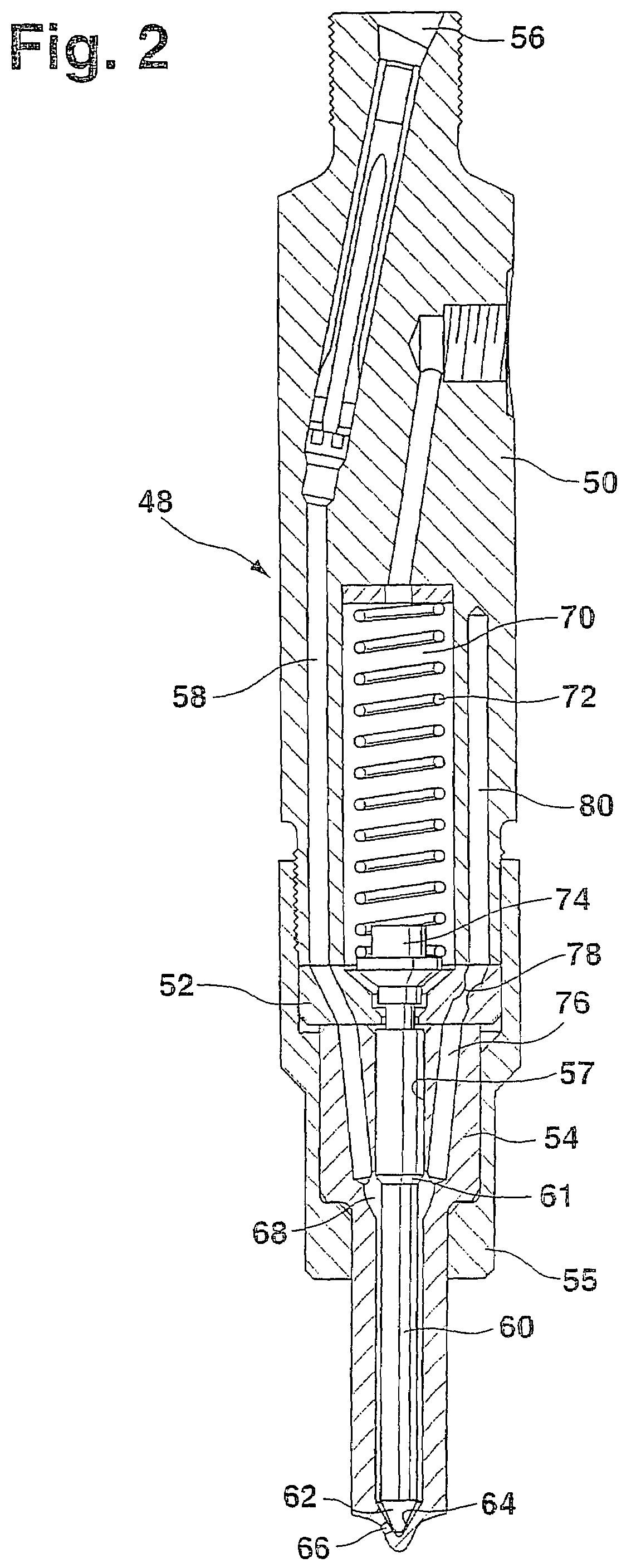
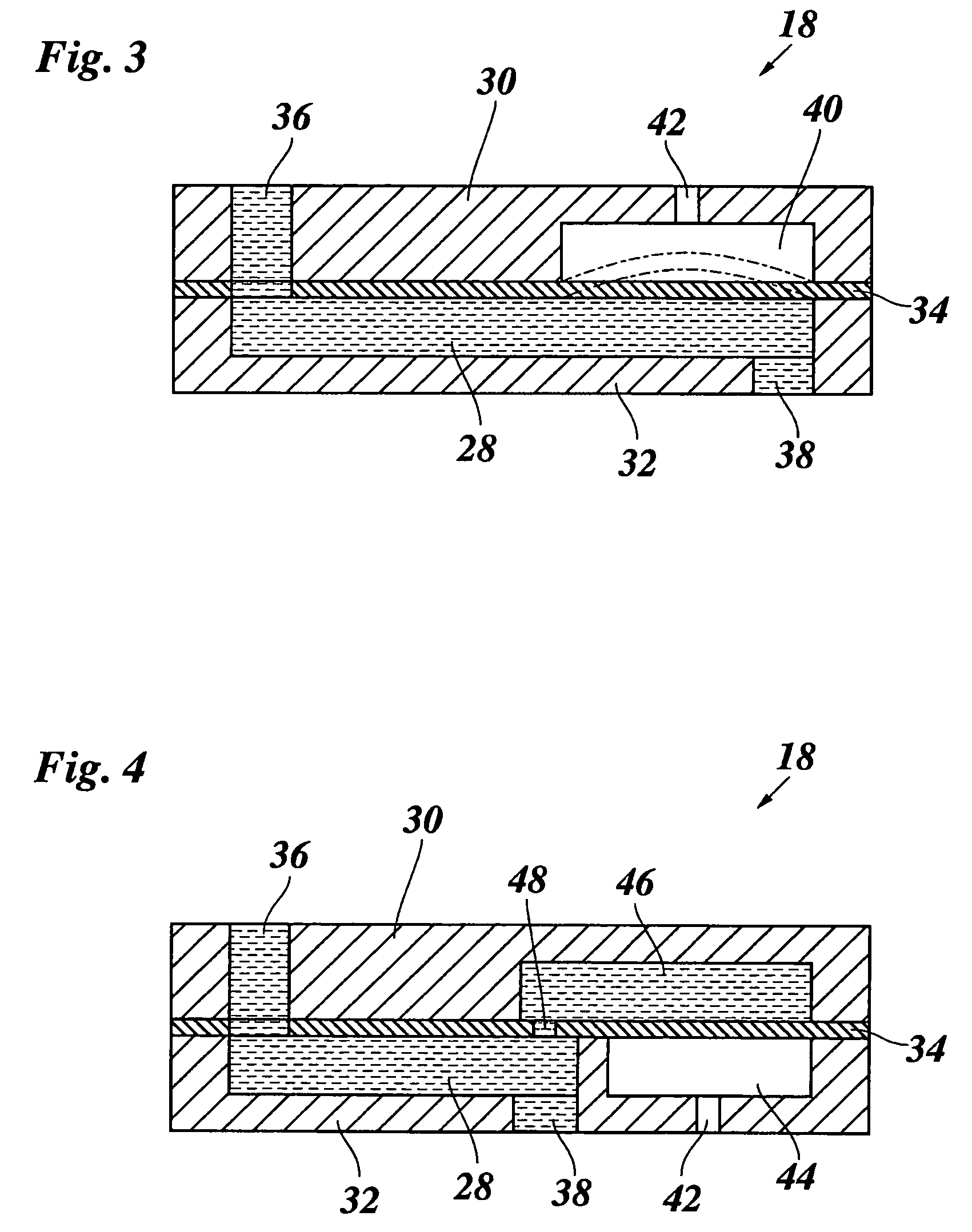
Fuel injection valve for internal combustion engines with damping chamber reducing pressure oscillations
InactiveUS7172140B2Pressure fluctuationStatic pressure levelSpray nozzlesMachines/enginesCombustionEngineering
A fuel injection valve for internal combustion engines, having a housing (12; 48) in which a pistonlike valve member (35; 60) is disposed longitudinally displaceably in a bore (34; 57). The valve member (35; 60) is surrounded, over at least part of its length, by a pressure chamber (37; 68), embodied in the housing (12; 48), that can be filled with fuel at high pressure; the valve member (35; 60) controls the communication of the pressure chamber (37; 68) with at least one injection opening (39; 66). The pressure chamber (37; 68) communicates with a damping chamber (46; 80), embodied in the housing (12; 48), via at least one throttle (44; 78) disposed in the housing (12; 48), so that pressure fluctuations that occur in the damping chamber (46; 60) rapidly fade (FIG. 1).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Liquid ejection apparatus and liquid ejection head
An object is to provide a liquid ejection apparatus that allows suppression of a fluctuation in a pressure of a liquid in a flow path caused by a liquid delivery unit, enabling the liquid to be stably ejected through an ejection port. The liquid ejection apparatus including a liquid ejection head having an ejection port through which a liquid is ejected, a flow path configured to communicate with the ejection port, and a liquid delivery unit configured to feed the liquid to the flow path. A relation between an angular frequency ω of the liquid delivered from the liquid delivery unit, a coefficient of kinematic viscosity ν of the liquid, and an equal diameter a of at least a part of a section of an extra-head flow path in a direction normal to a direction in which ink flows satisfies √(ω / 2ν)×a>1.
Owner:CANON KK
Flexible spacer for double-glazing
InactiveUS20160265265A1Low heat lossReduce thermal stressCorner/edge jointsUnits with parallel planesElastomerSulfur
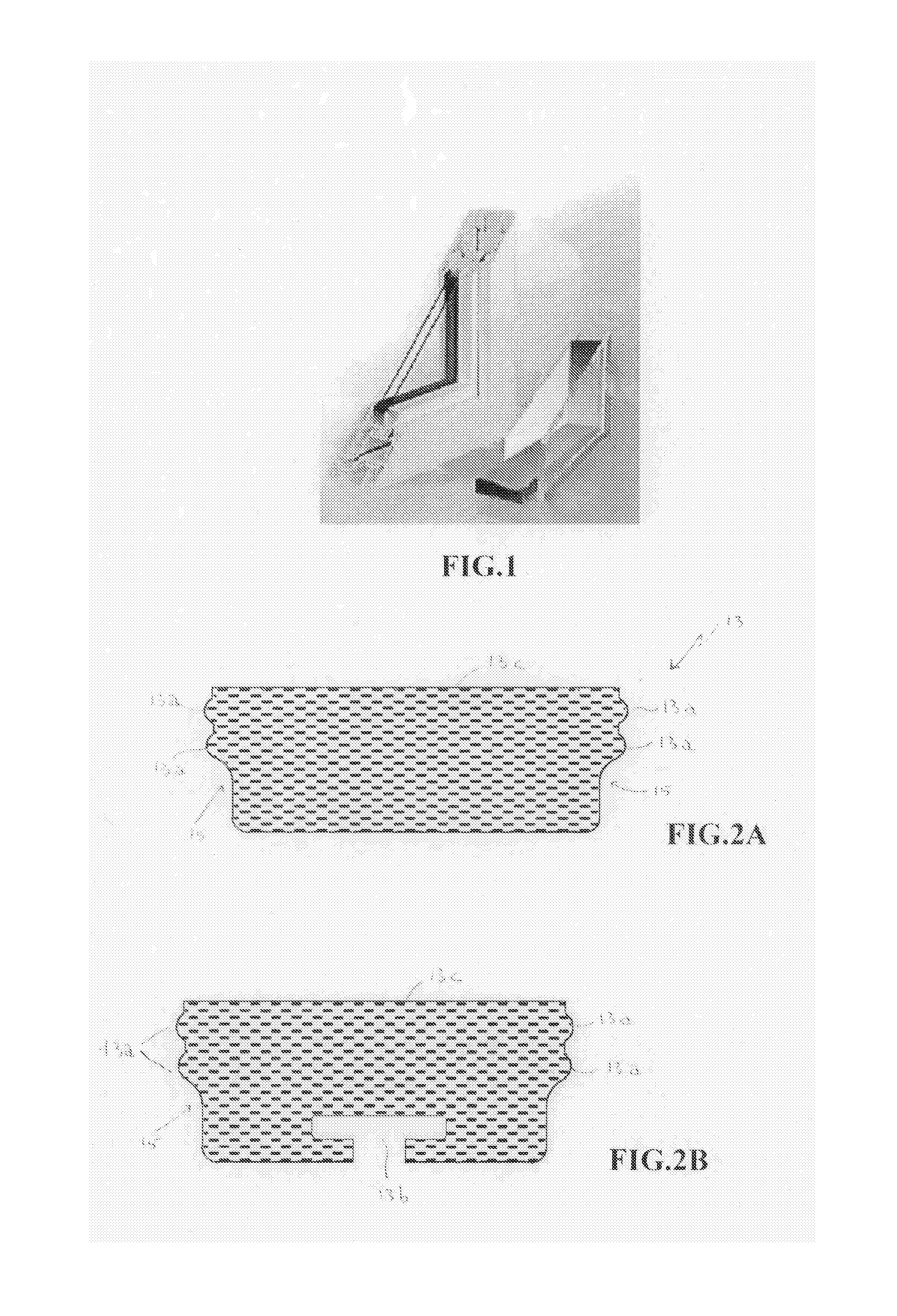
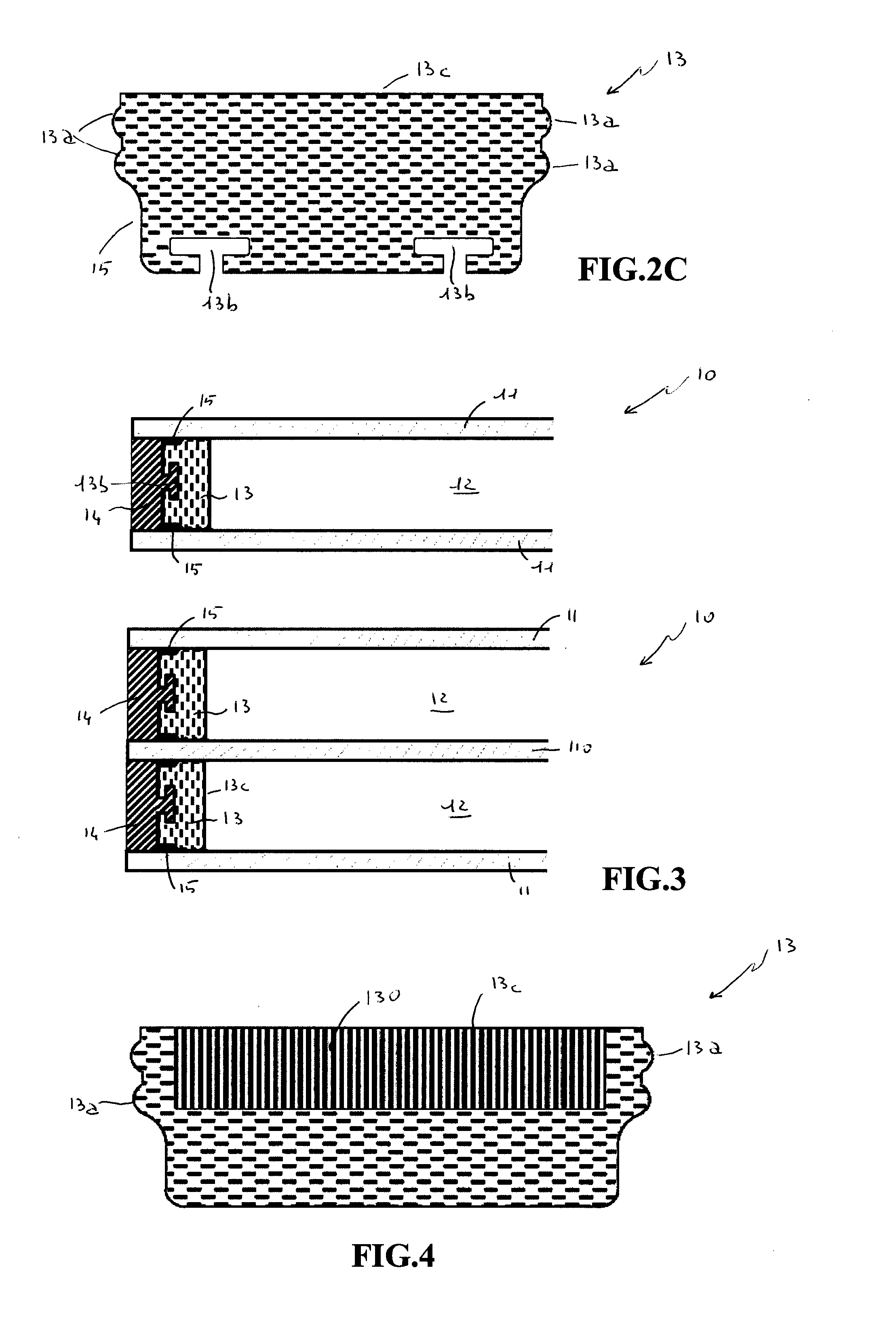
A description is made of a flexible spacer for double glazing made of Polyisobutylene elastomer or butyl rubber IIR (simple or halogenated), suitably loaded with both reinforcing and inert fillers. The spacer can be cross-linked with sulphur or peroxides. The spacer is impermeable to moisture and has high low thermal conductivity gas sealing capacity, and incorporates moisture absorbing material. In particular, the spacer features—on each side wall—at least a small wave (13a) positioned immediately above the accumulation area of the internal or primary sealant (15) so as to ensure an optimal adhesion to the glass of the double / triple glazing unit within which the spacer is fitted and features at least one recess (13b), with a configuration such as to allow the external sealant to penetrate and create a strong mechanical bond between the two materials.
Owner:MERLO LUCA
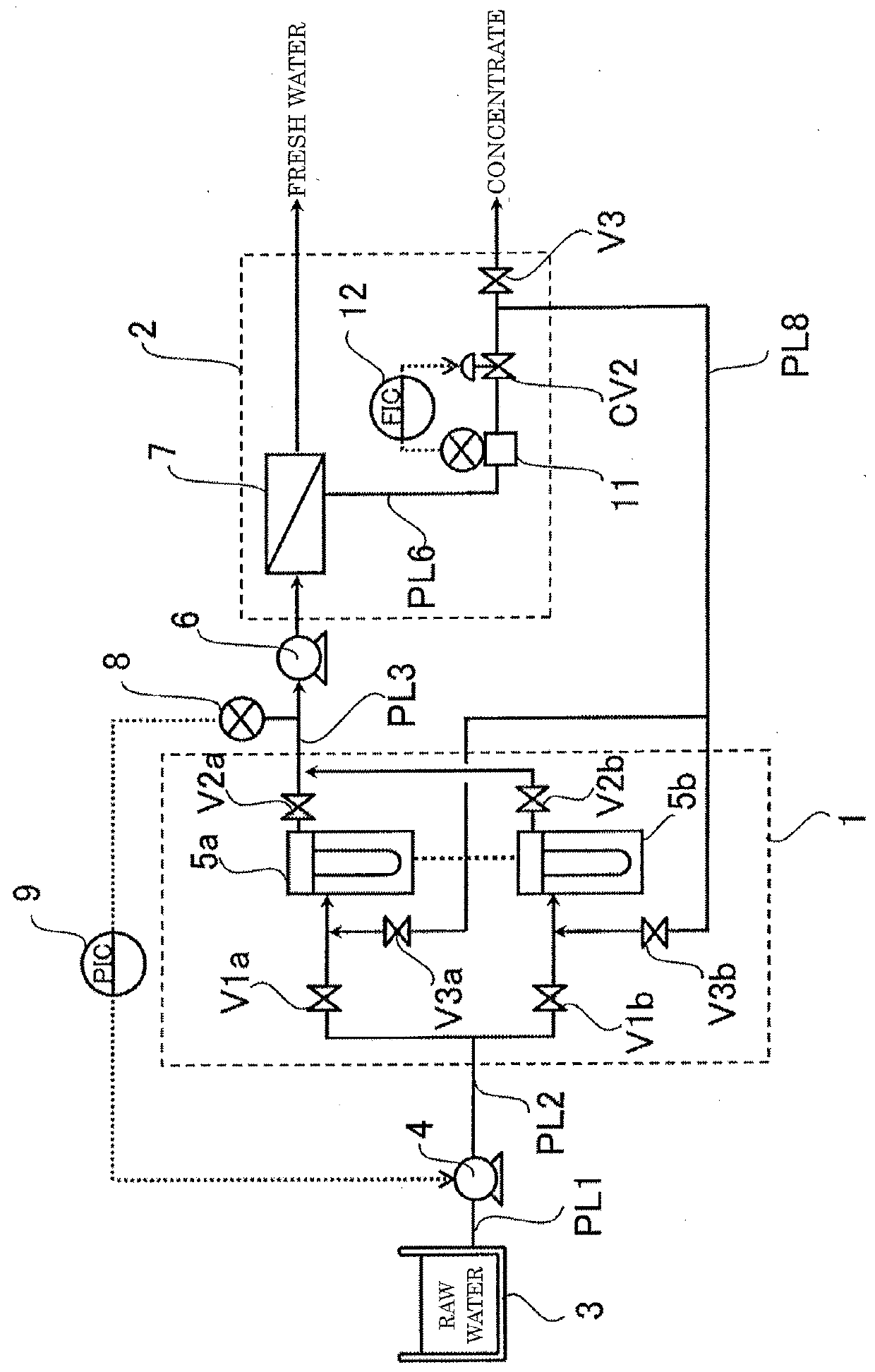
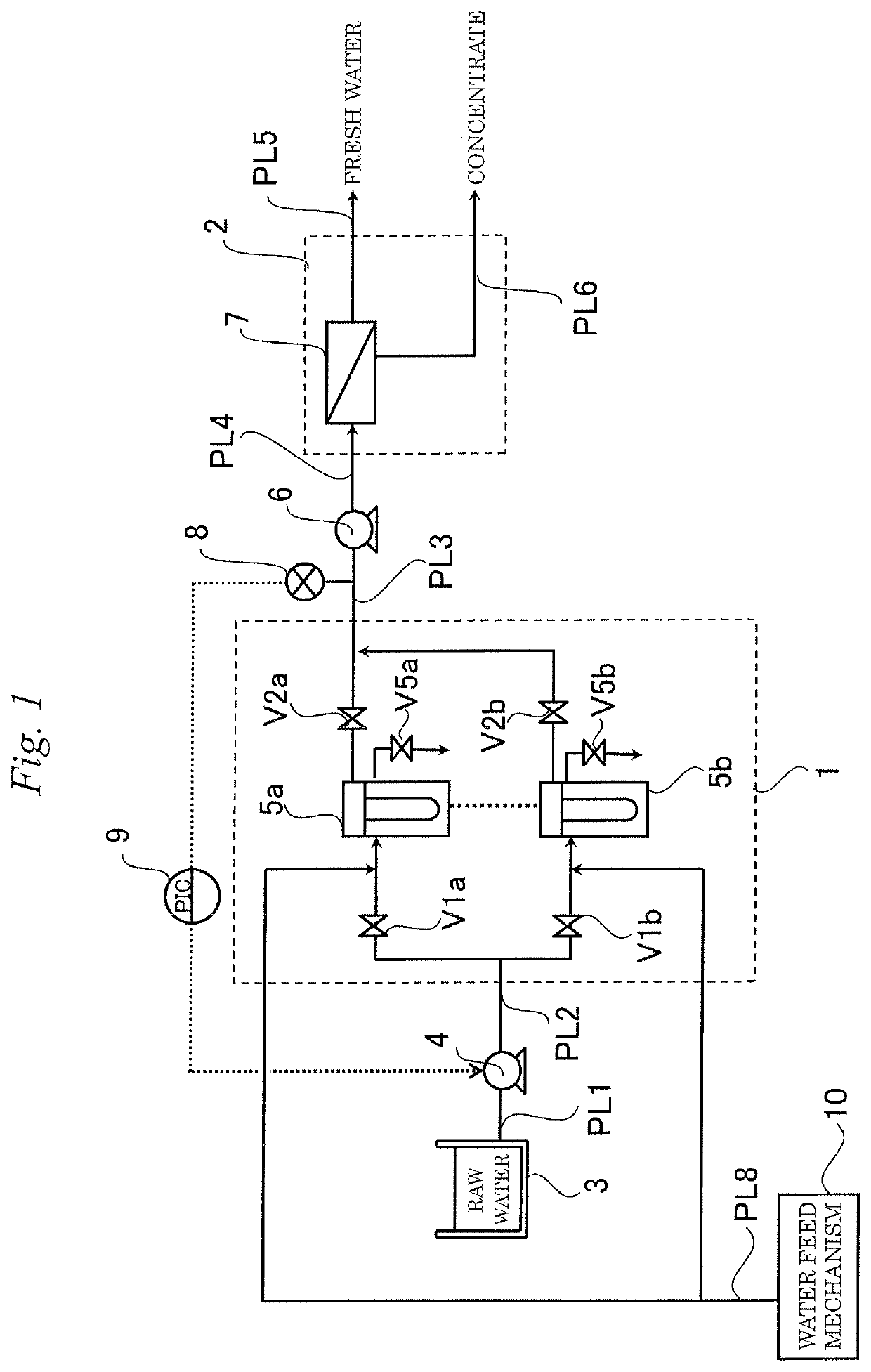
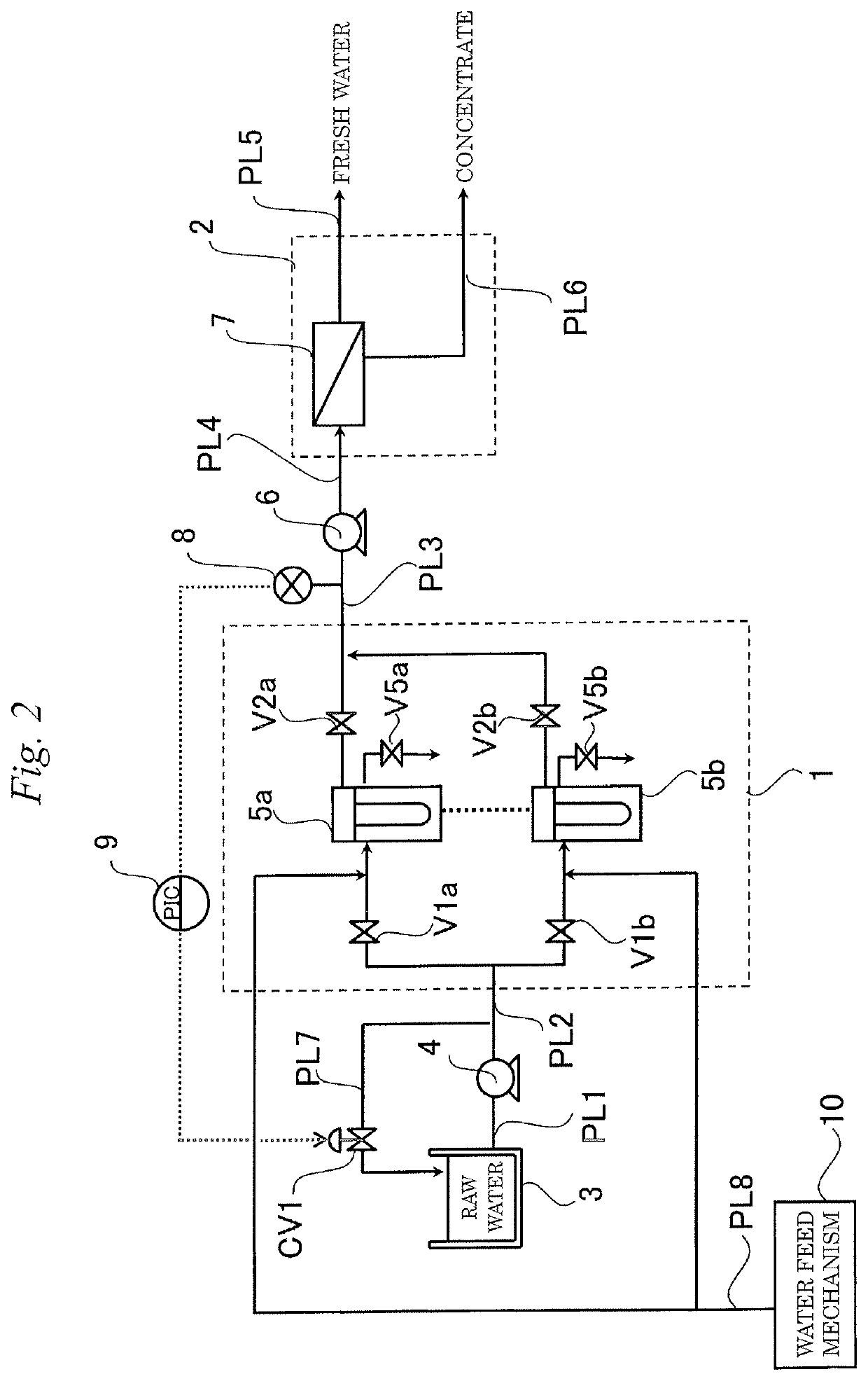
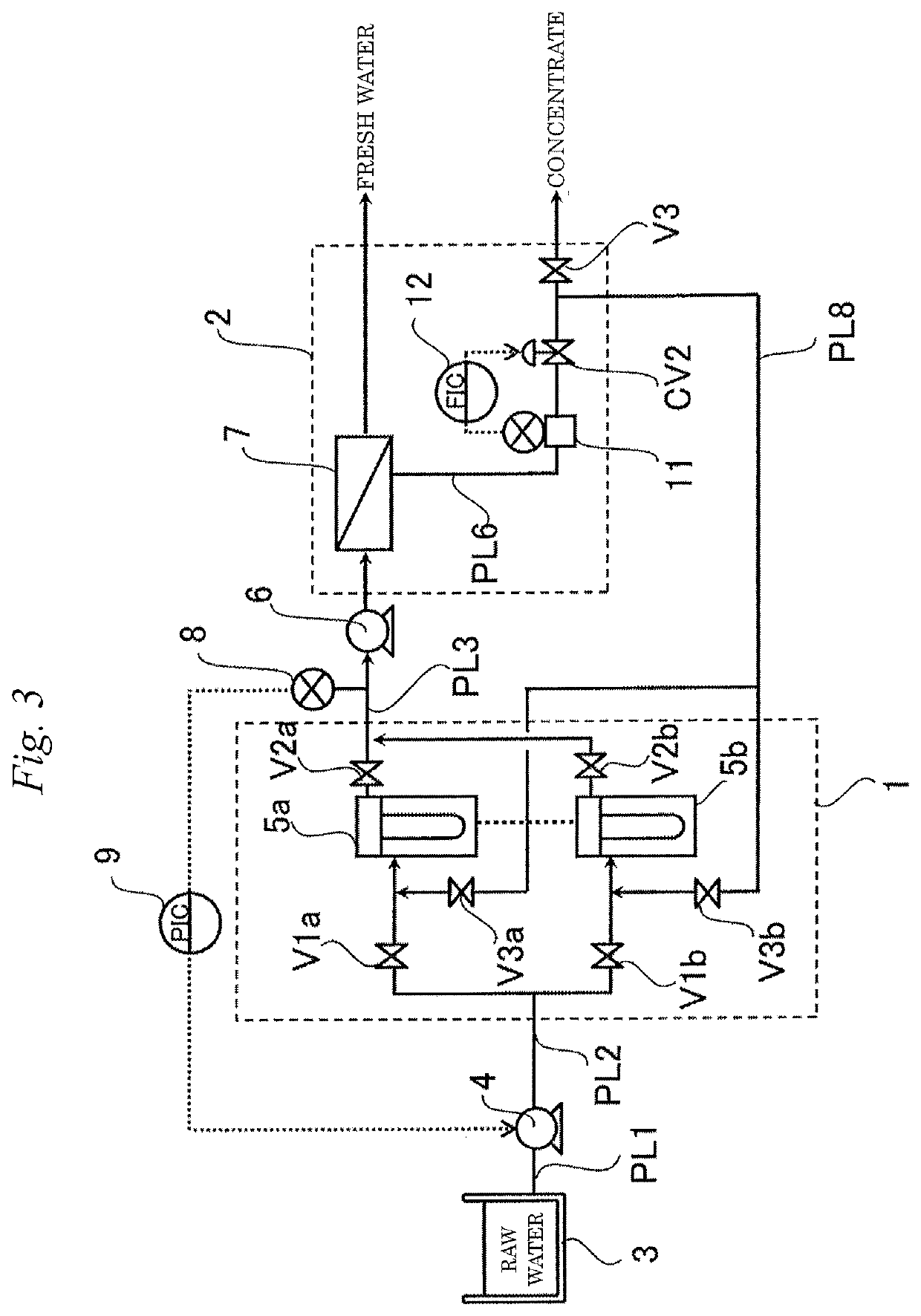
Fresh water production device and method for operating fresh water production device
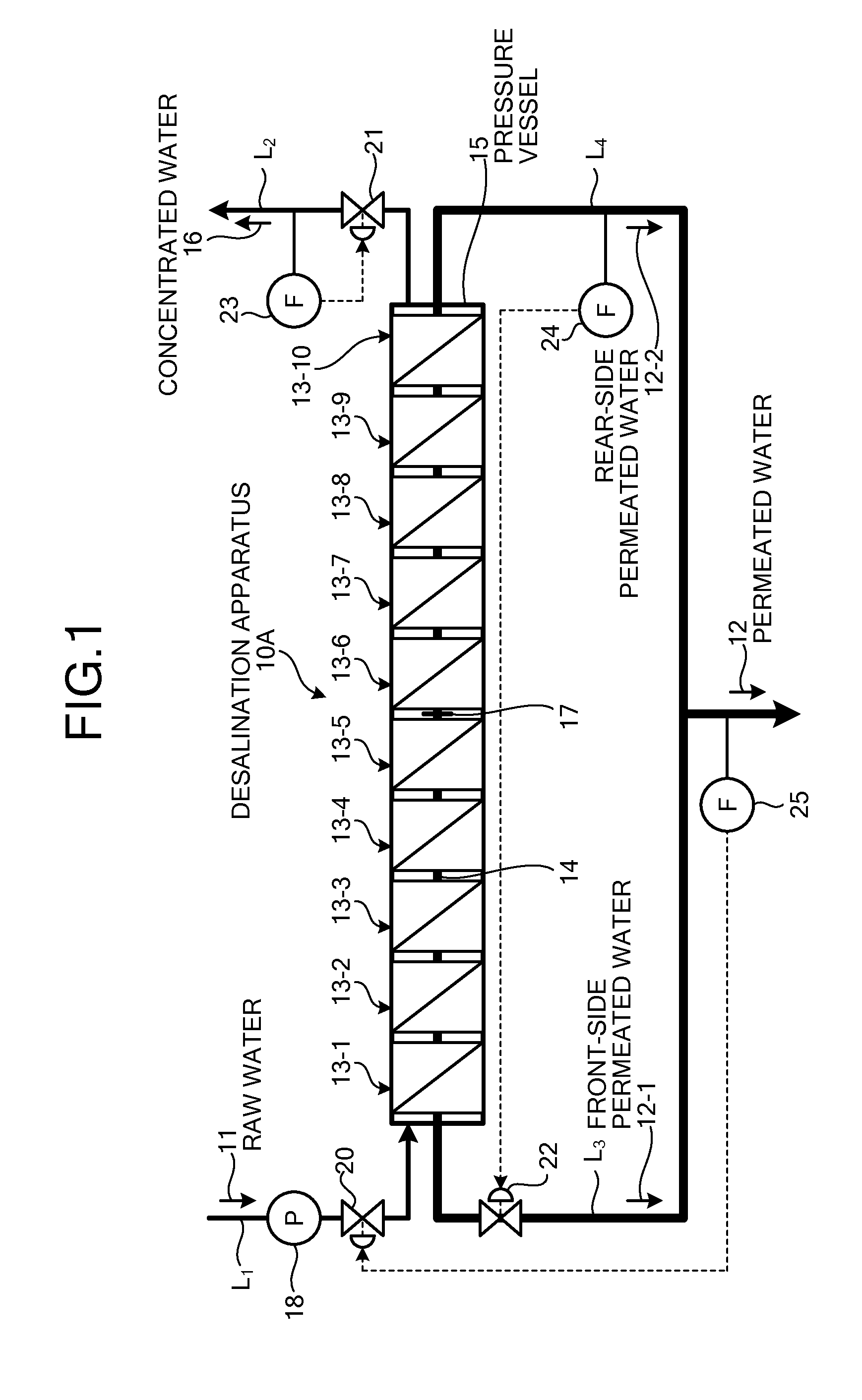
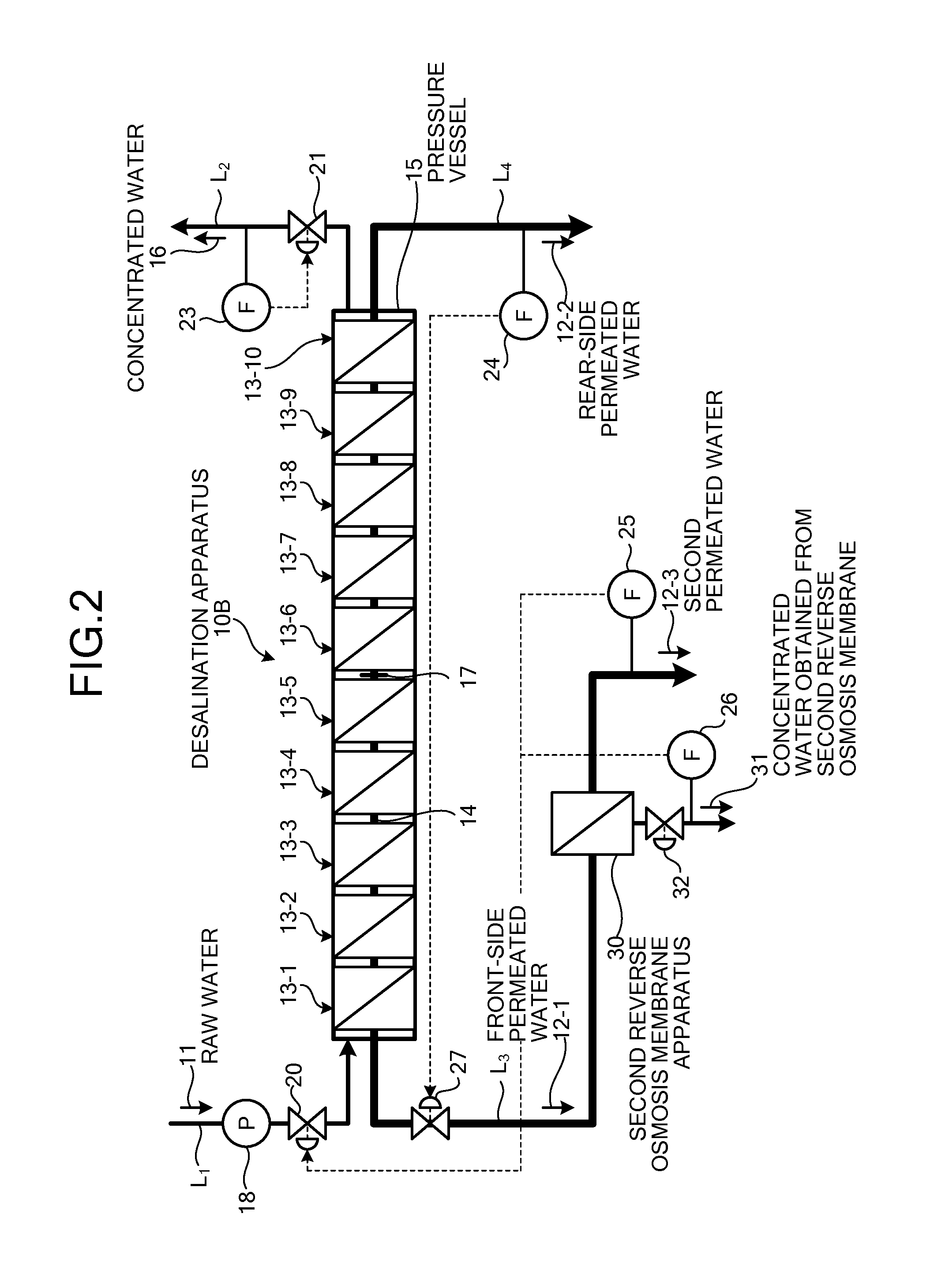
ActiveUS20180161728A1Guaranteed uptimeShorten the overall cycleMembranesWater treatment parameter controlDesalinationWater production
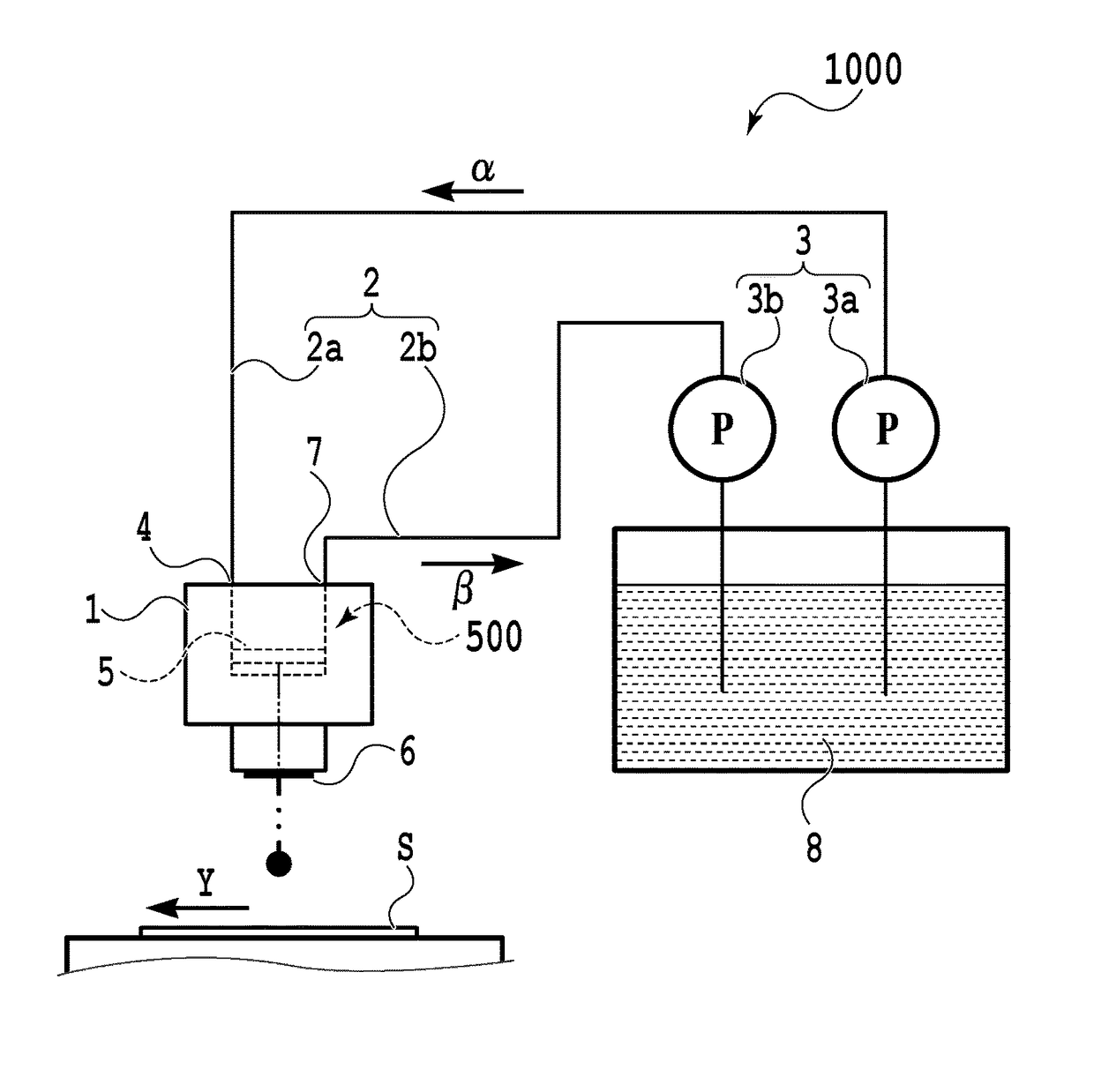
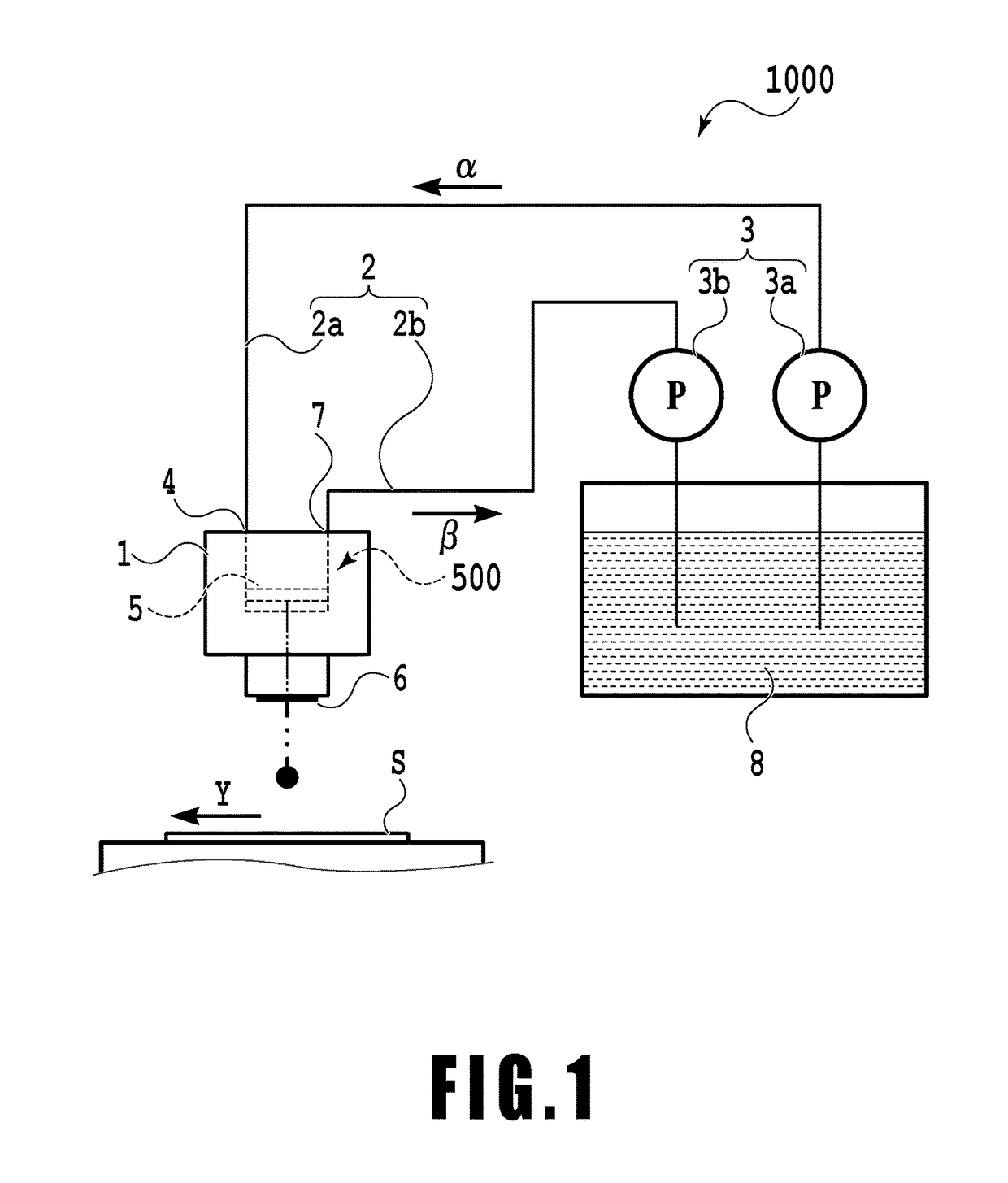
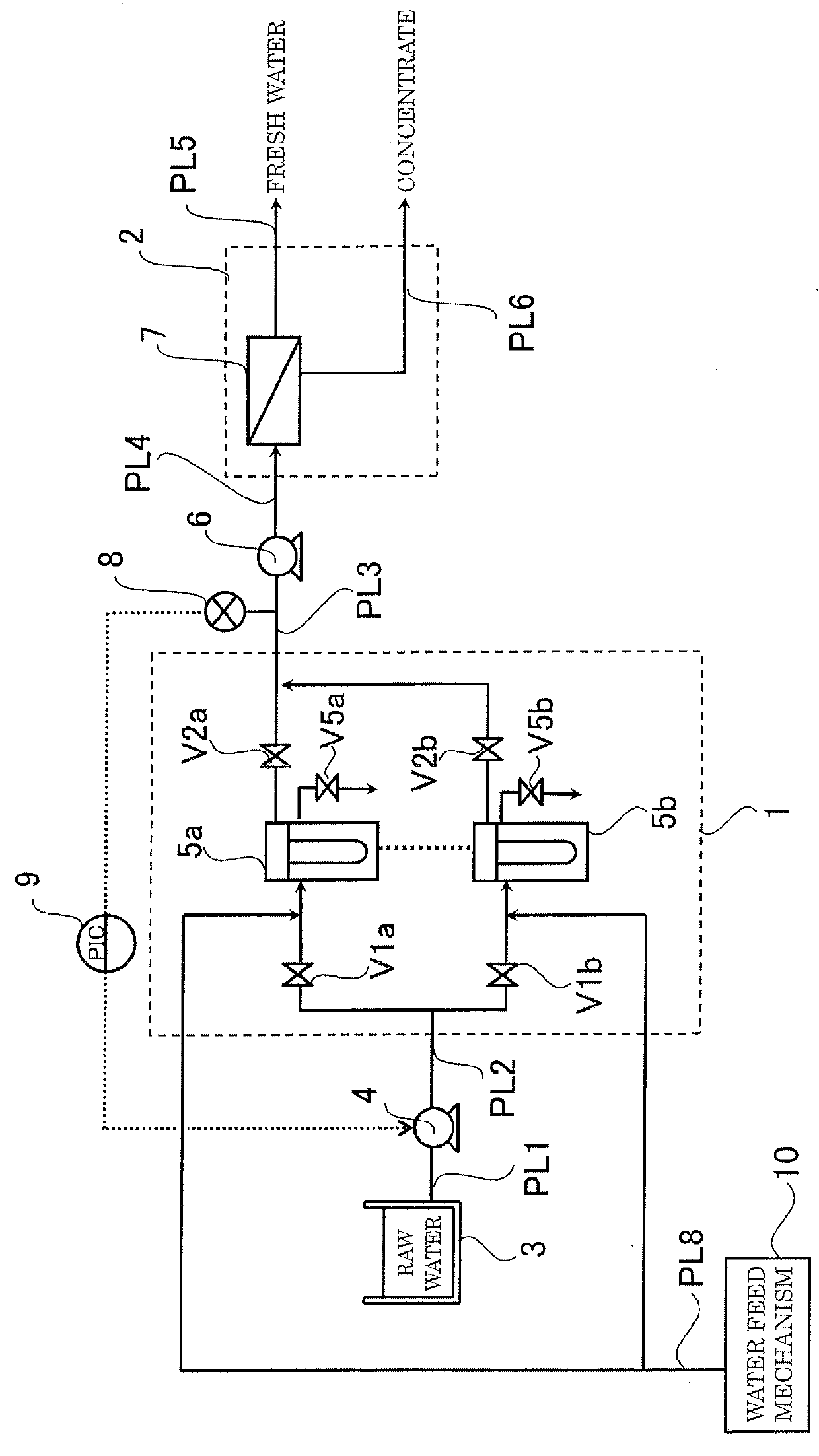
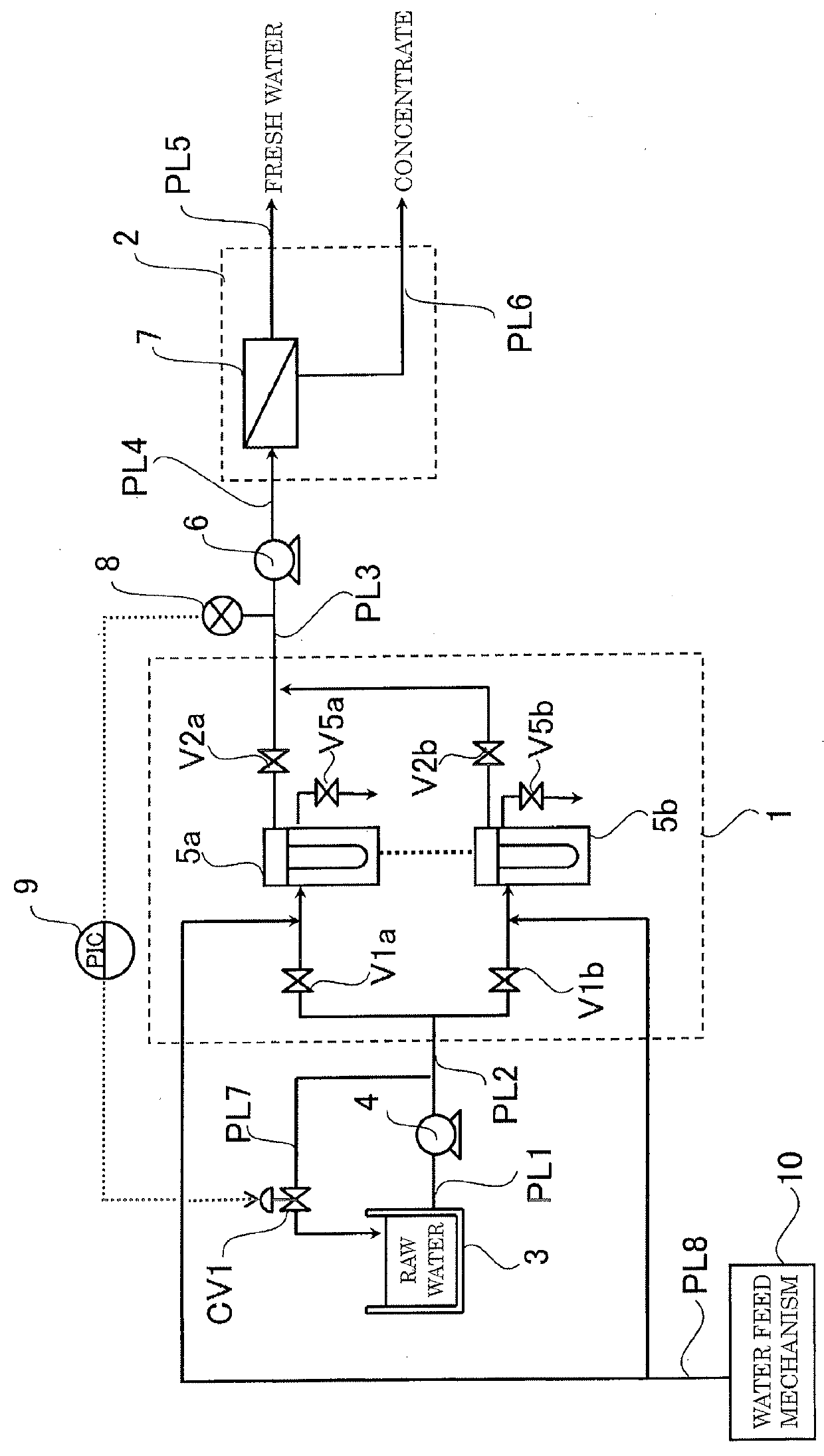
According to the present invention, since a pretreatment mechanism can be operated while inhibiting the pretreated water from fluctuating in pressure, a fresh-water production apparatus is obtained in which the desalting mechanism can be stably operated. Furthermore, the period of water supply or flushing in the step of washing the pretreatment mechanism can be shortened, and the load on the lines where washing is not being performed is hence reduced. Consequently, a fresh-water production apparatus is obtained in which the pretreatment mechanism can be operated while inhibiting the pretreatment membranes from being fouled.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Electric blower and vacuum cleaner comprising same
InactiveUS8695162B2Reduce output powerReduce noiseEngine manufacturePump componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Disclosed is an electric blower having a stator, a rotor, a bracket, a rotary fan, an air guide and a fan case. The air guide comprises a partition plate, a diffuser disposed around outer periphery of the rotary fan in the air guide, a partition-plate sloped portion and a guide vane. The fan case has a fan-facing portion, a fan case shoulder bent at the outermost part of the fan-facing portion, and a cylindrical portion extending cylindrically in an axial direction from the fan case shoulder. The fan case shoulder is so bent that it forms substantially a right angle.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Machine for the production/processing of a material web and damping device
InactiveUS7531064B2Cost-effectivePressure fluctuationNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCardboardBiomedical engineering
Machine for the production / processing of a material web, in particular a fibrous web, for example of paper or board, which comprises at least one treatment section in which the material web can have a treatment fluid applied to it, the treatment section being connected or able to be connected to a treatment fluid source via at least one line connection, an elastically deformable compensating material arranged in a fluid holding chamber of the treatment fluid source or of the treatment section. Alternatively, a damping device may be connected to the line connection or arranged in the latter and / or delimits such a fluid holding chamber, and / or elastically deformable compensating material which, in at least one section of the line connection, defines or co-defines an effective line cross section.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Ink supply assembly for an ink jet printing device
An ink supply assembly includes at least one inlet port. At least one outlet port is connected to the inlet port via an ink cavity and is adapted to be connected to an ink discharge unit of an ink jet device. The ink supply assembly has a sandwich structure formed by at least two plate members and a foil that is interposed therebetween and has a part forming a wall of said ink cavity. At least one of the plate members defines a pressure equalization chamber adjacent to the ink cavity and separated therefrom by the foil.
Owner:OCE TECH
Liquid ejection apparatus and liquid ejection head
An object is to provide a liquid ejection apparatus that allows suppression of a fluctuation in a pressure of a liquid in a flow path caused by a liquid delivery unit, enabling the liquid to be stably ejected through an ejection port. The liquid ejection apparatus including a liquid ejection head having an ejection port through which a liquid is ejected, a flow path configured to communicate with the ejection port, and a liquid delivery unit configured to feed the liquid to the flow path. A relation between an angular frequency ω of the liquid delivered from the liquid delivery unit, a coefficient of kinematic viscosity ν of the liquid, and an equal diameter a of at least a part of a section of an extra-head flow path in a direction normal to a direction in which ink flows satisfies √ / (ω / 2ν)×a>1.
Owner:CANON KK
Governor
InactiveUS20160047479A1Suppress pressure fluctuationsAvoid damageOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCheck valvesEngineeringCheck valve
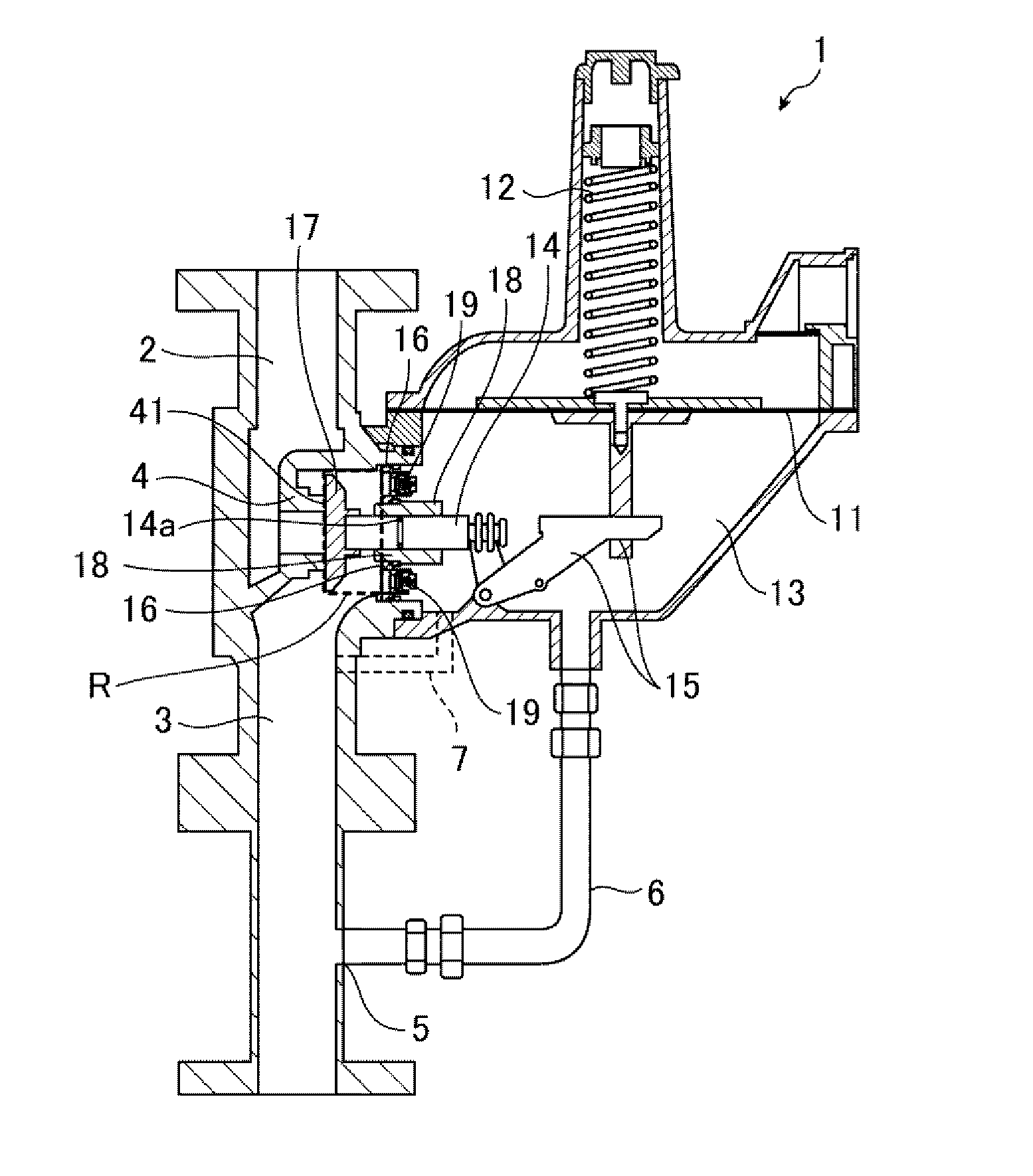
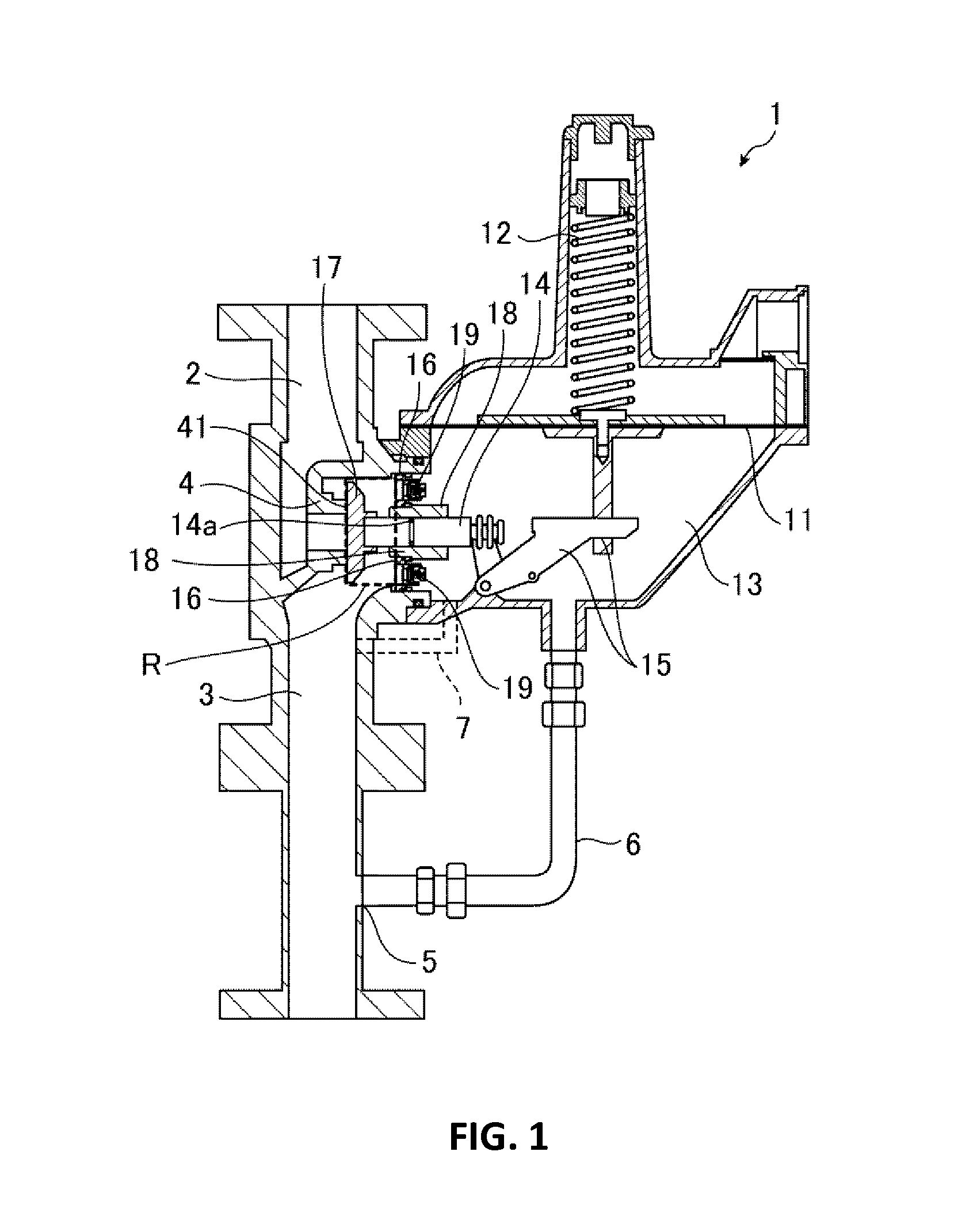
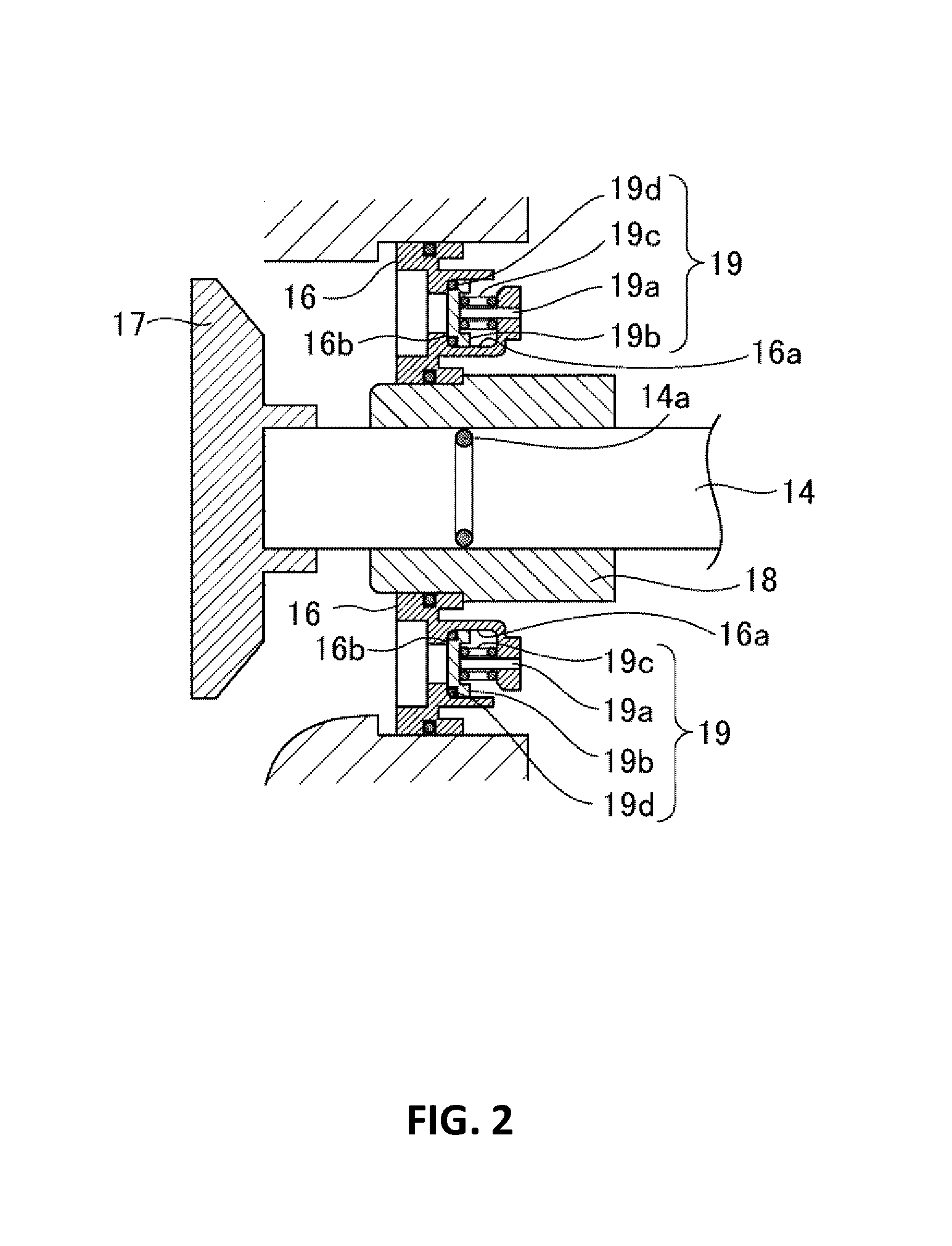
[Problem(s)] To provide a governor capable of preventing damage to parts when the pressure in the primary side channel rapidly rises, and of alleviating pressure fluctuation in the secondary side channel.[Solution] A governor 1 is provided with a non-return valve 19 at a shield plate 16 such that when the pressure in the primary side channel 2 rapidly rises, the fluid from the primary side channel 2, which has passed through the port 4, can immediately flow into the pressure detection chamber 13 through the non-return valve 19. As a result, when the pressure in the primary side channel 2 rapidly rises, the governor 1 is capable of entering a closed valve state within a short amount of time.
Owner:AZBIL KIMMON
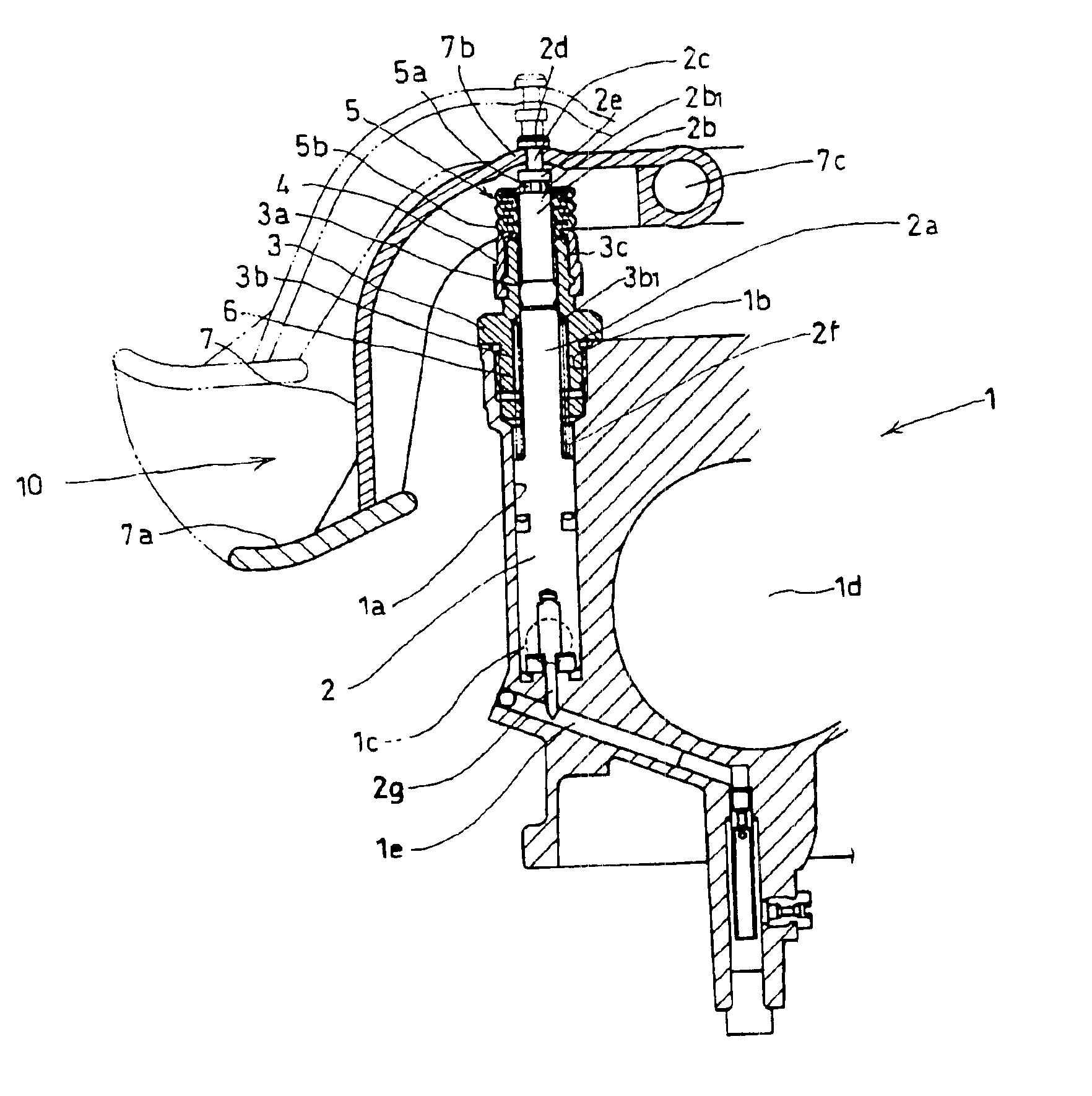
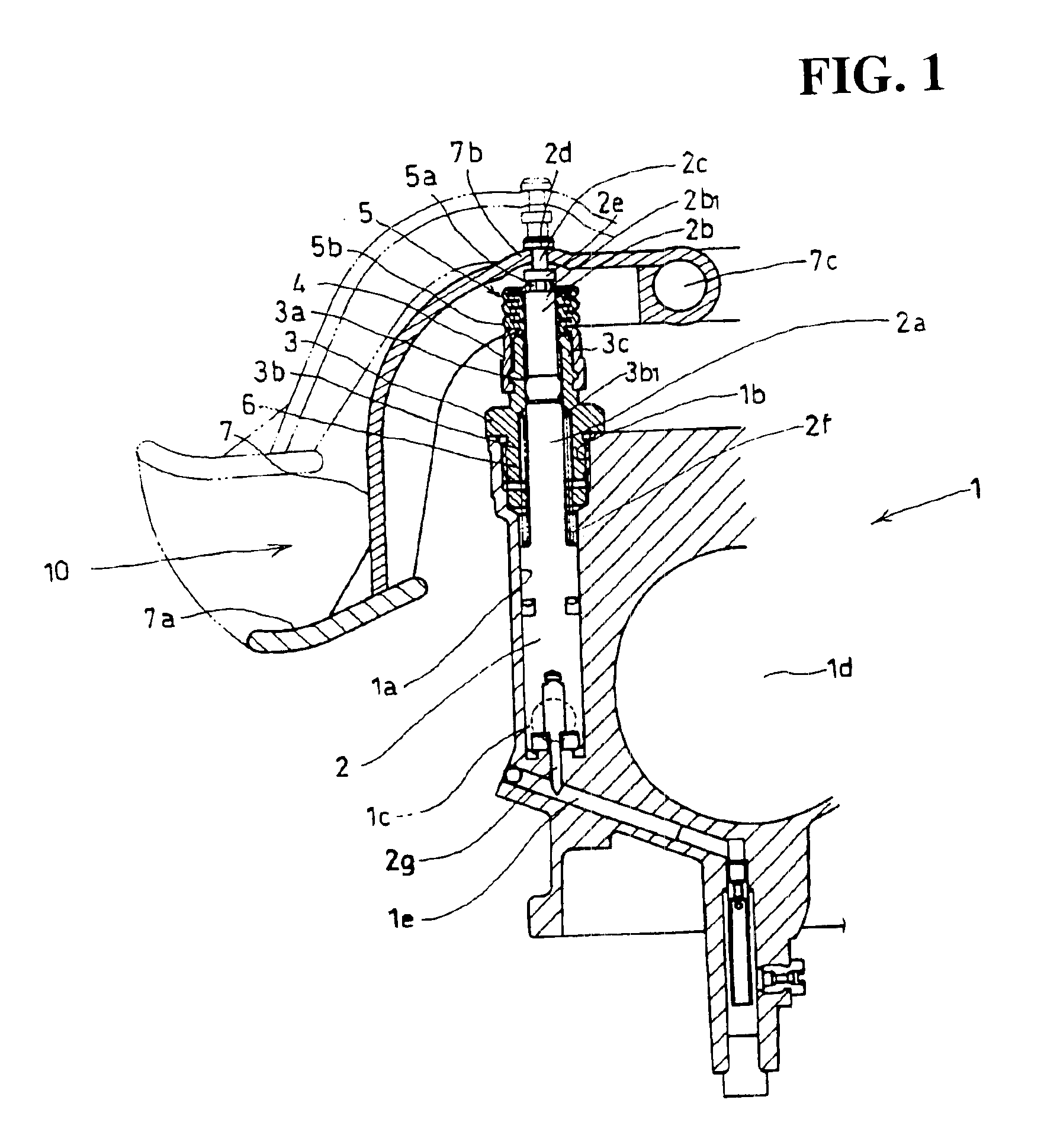
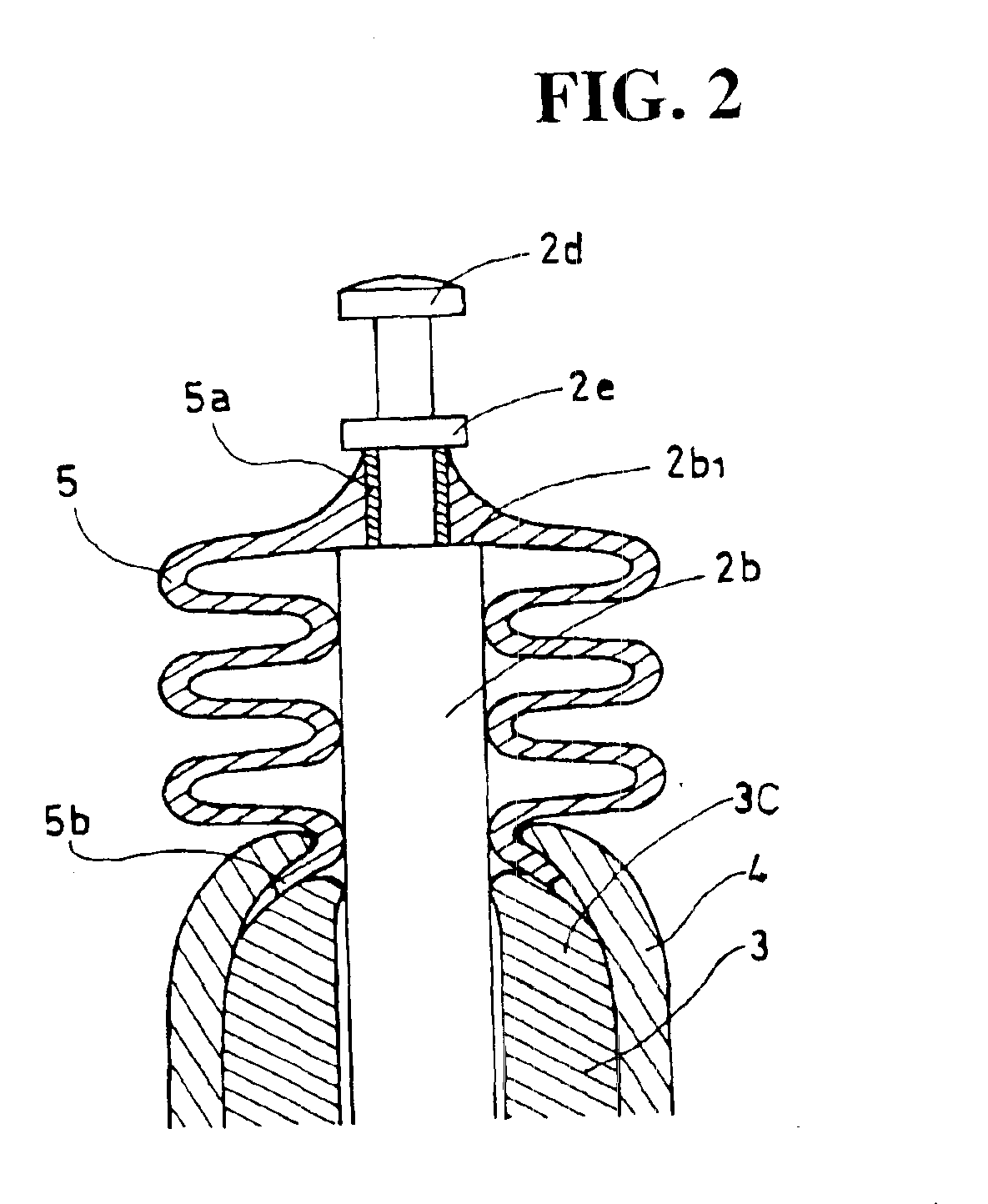
Sealing structure in direct acting type auto-by starter
InactiveUS6866015B2Prevent rustEliminating malfunctionEngine sealsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
To prevent the entry of ambient air and liquid such as rainwater into a direct acting type auto-by starter and thereby prevent the formation of rust in the auto-by starter, by adjusting pressure fluctuations in the auto-by starter caused by the operation of a starting valve for opening and closing a starting intake passage. A starting valve is lifted to open a starting intake passage to start an internal combustion engine. Pressure in a sliding space for the starting valve is increased, so that the gas in the sliding space flows out. The flow of the gas is absorbed by an increase in volume inside a bellows boot mounted on an upper portion of the starting valve. When the starting valve is lowered by the operation of a spring member, the pressure in the sliding space is reduced to allow the gas flow from the bellows boot into the sliding space.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
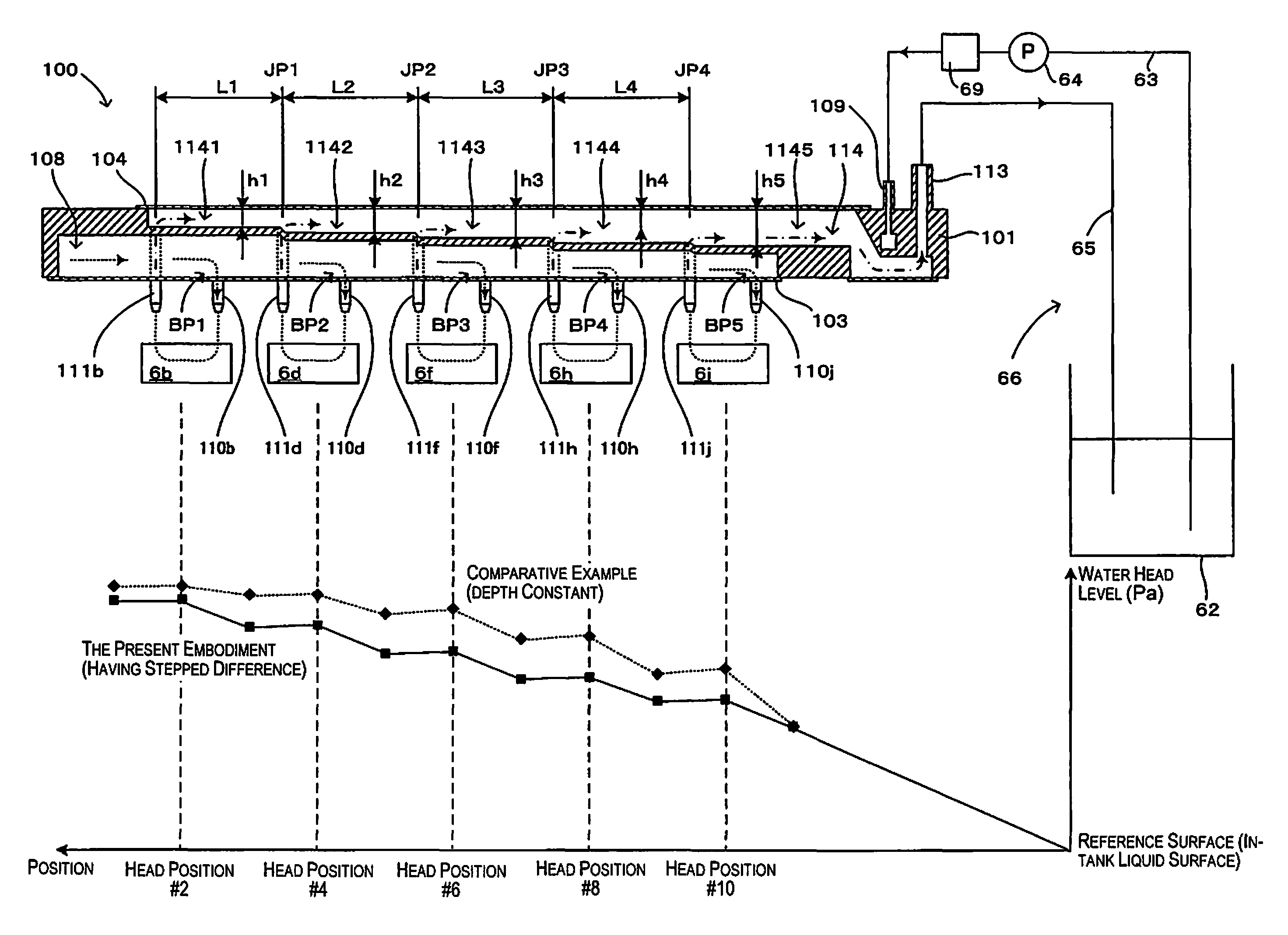
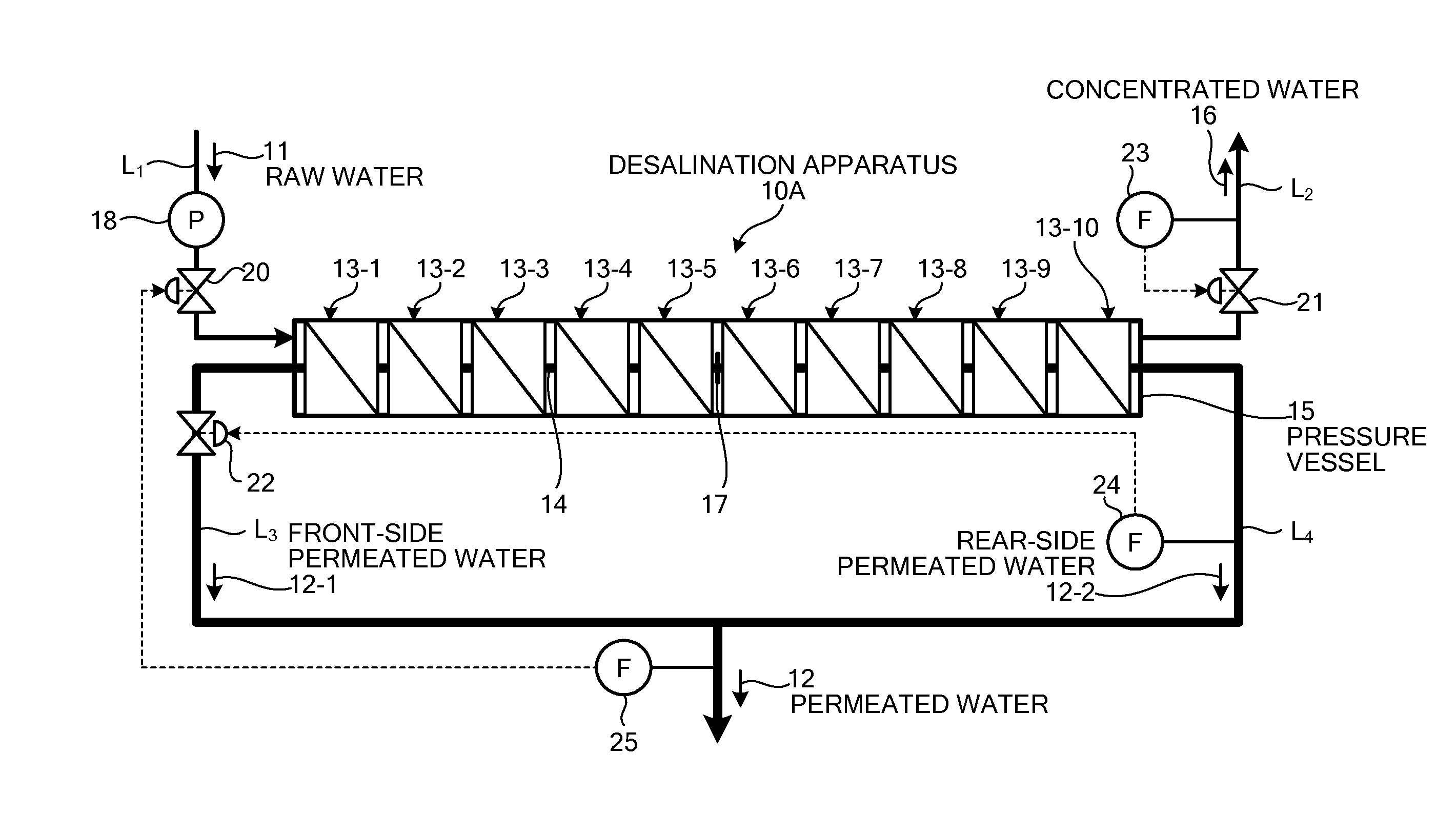
Spiral type seawater desalination apparatus
InactiveUS20160038882A1Reduce volatilityIncrease productionMembranesWater treatment parameter controlMembrane configurationSeawater
An embodiment of the present invention includes: a spiral type pressure vessel 15 in which a plurality of reverse osmosis membrane apparatuses 13-1 to 13-10 having spiral reverse osmosis membranes is connected through a permeated water pipe 14, and is housed in a connected state; a raw water supplying line that supplies raw water 11 into the pressure vessel 15; a concentrated water discharging line through which concentrated water 16 concentrated is discharged; a plug 17 that blocks the permeated water pipe 14 at the center of the reverse osmosis membrane apparatuses 13-1 to 13-10; a front-side permeated water line and a front-side permeated water line through which front-side permeated water 12-1 and rear-side permeated water 12-2 are discharged to the exterior, respectively, which are separated fore and aft, respectively, of the permeated water pipe 14 blocked by the plug 17; a pressure regulating valve 20 that is mounted in the raw water supplying line and regulates the supply pressure of the raw water 11; and a flow regulating valve 22 that is mounted in the front-side permeated water line and regulates the pressure of the front-side permeated water 12-1.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
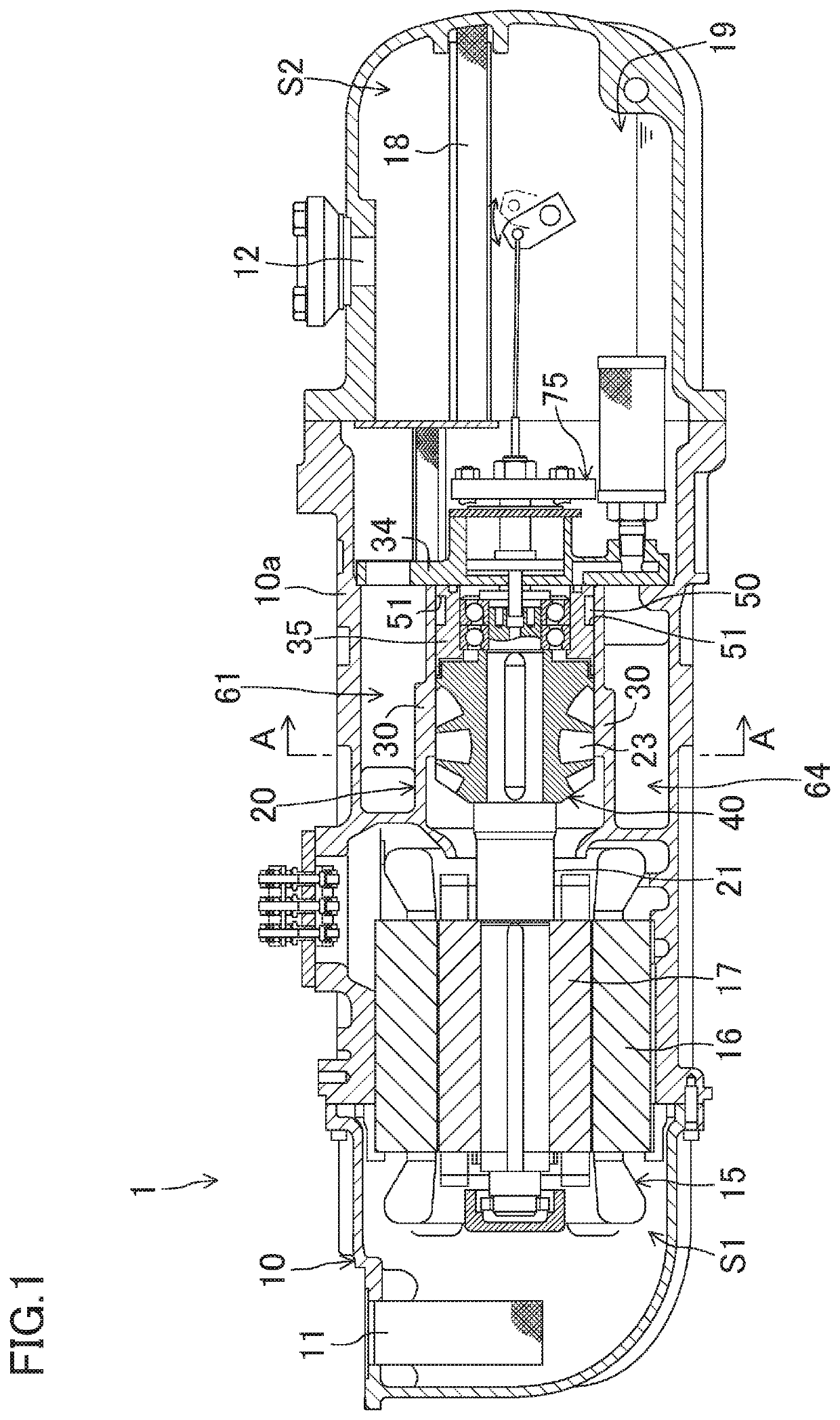
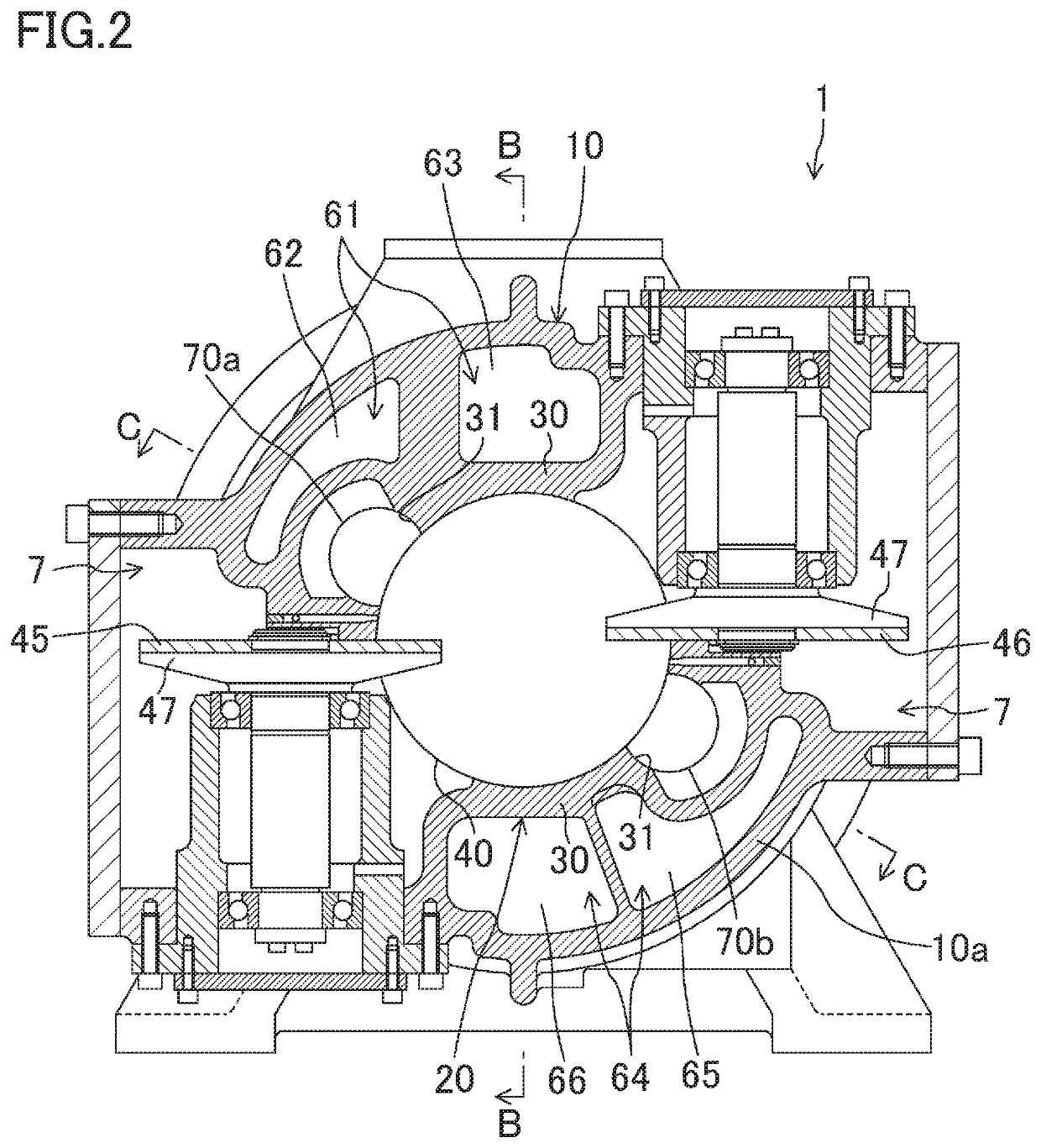
Screw compressor
ActiveUS11136982B2Suppress pressure fluctuationsReduce vibrationEngine fuctionsBall bearingsEngineeringMuffler
A screw compressor includes a casing, a screw rotor, a discharge passage, and at least one muffler space. The casing includes a cylindrically-shaped cylinder, a main body surrounding a vicinity of the cylinder, and a high-pressure fluid passage provided between the main body and the cylinder. The screw rotor includes a plurality of helical grooves. The screw rotor is inserted into the cylinder to define fluid chambers. A fluid is sucked into the fluid chambers to compress the fluid. The discharge passage is disposed in the casing. The discharge passage guides the fluid that has been discharged from the fluid chambers to the high-pressure fluid passage. The at least one muffler space is disposed in the casing. The at least one muffler space communicates with the discharge passage so as to reduce a pressure fluctuation of the fluid flowing from the discharge passage to the high-pressure fluid passage.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
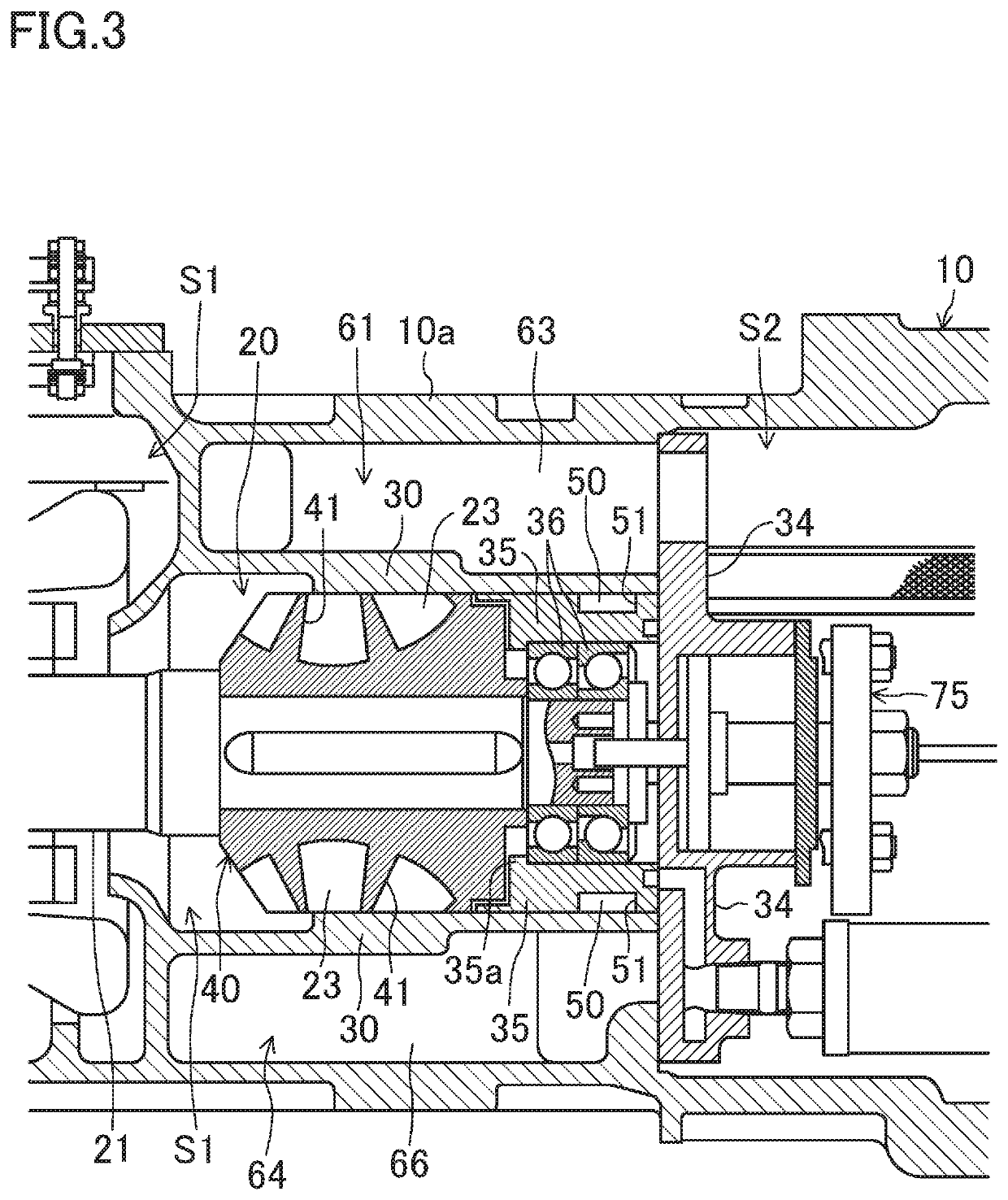
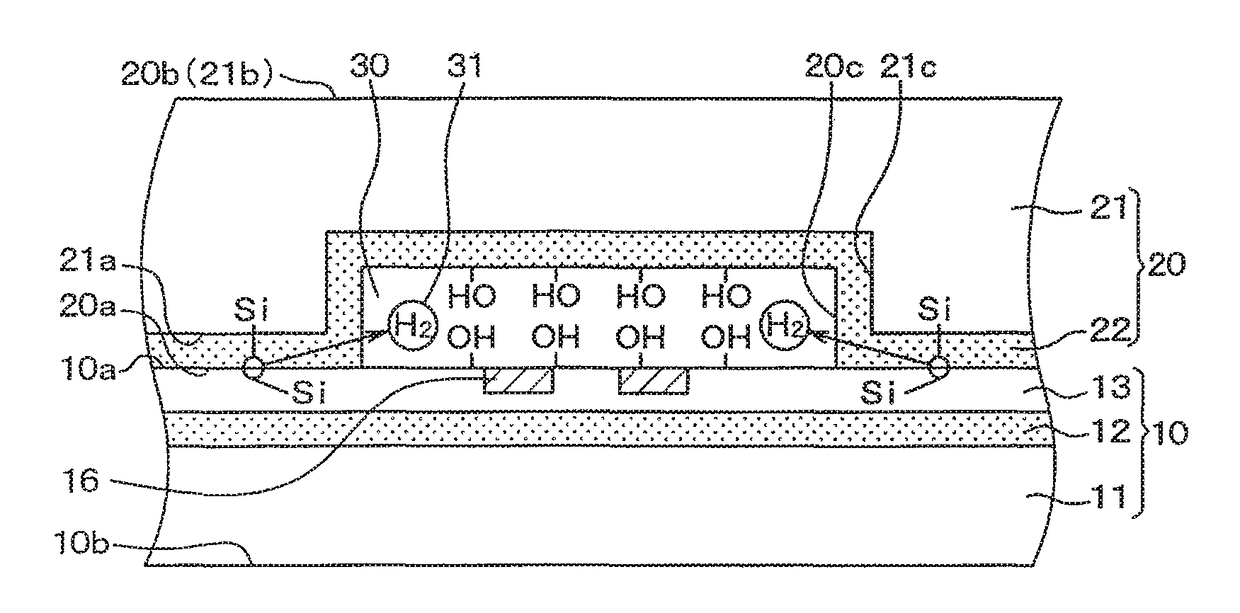
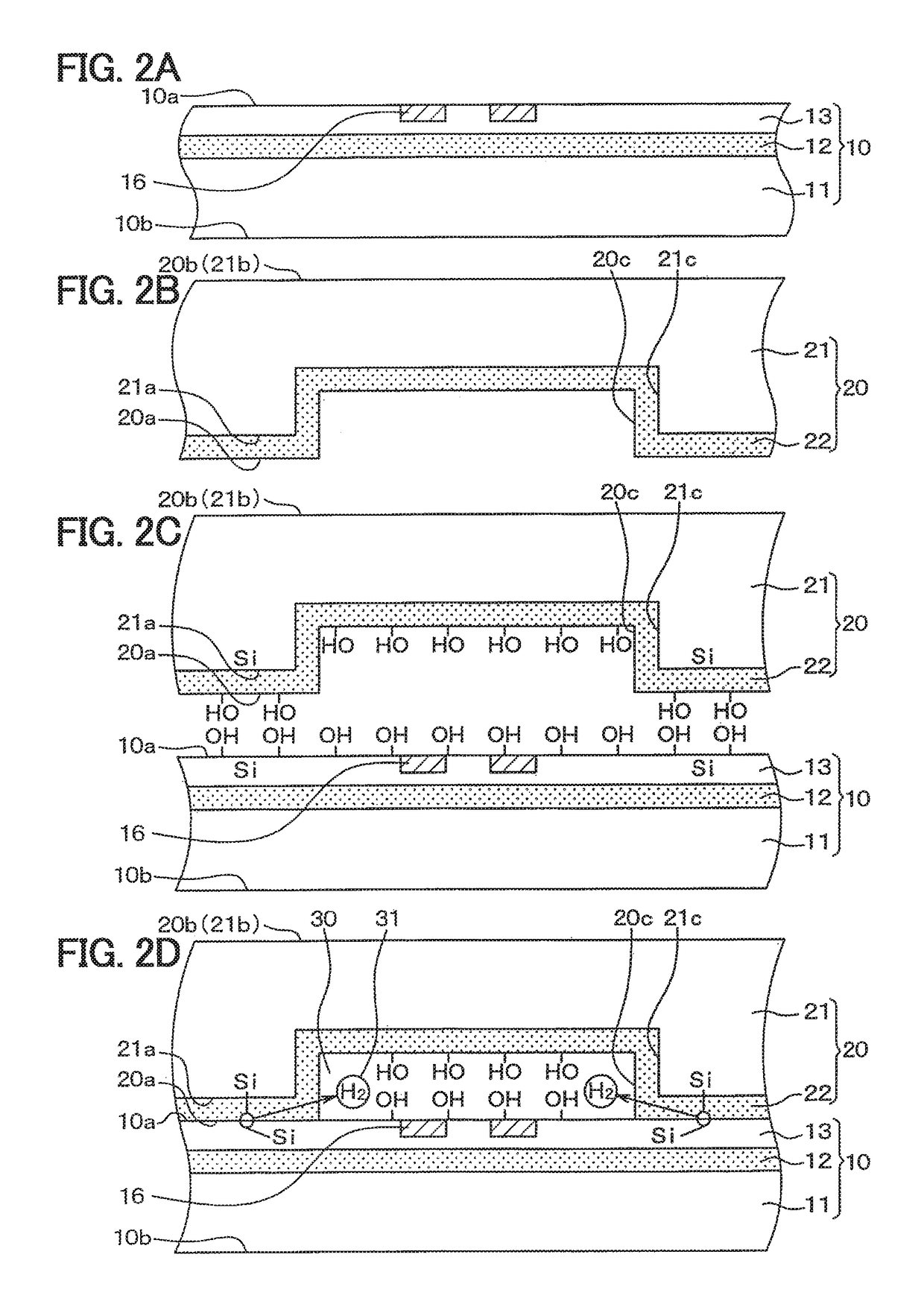
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
ActiveUS9944515B2Control generationPressure fluctuationDecorative surface effectsFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsHydrogenHeating time
A manufacturing method of a semiconductor device, in which a vacuum-pressure airtight chamber is defined by a space between a first substrate and a recessed portion of a second substrate, includes preparing the first substrate and the second substrate both of which contain silicon, joining the two substrates together, performing a heat treatment to emit hydrogen gas from the airtight chamber, and generating OH groups on the substrates before the joining. In the joining of the substrates together, the OH groups are bonded together to generate covalent bonds, and in the heat treatment, a part on which the OH groups are generated is heated at a temperature rise rate of 1° C. / sec or smaller until a temperature of the substrate increases to 700° C. or higher, and a heating temperature and heating time are adjusted to emit hydrogen gas from the airtight chamber.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Fresh water production device and method for operating fresh water production device
ActiveUS10583398B2Guaranteed uptimeShorten the overall cycleMembranesWater treatment parameter controlDesalinationWater production
According to the present invention, since a pretreatment mechanism can be operated while inhibiting the pretreated water from fluctuating in pressure, a fresh-water production apparatus is obtained in which the desalting mechanism can be stably operated. Furthermore, the period of water supply or flushing in the step of washing the pretreatment mechanism can be shortened, and the load on the lines where washing is not being performed is hence reduced. Consequently, a fresh-water production apparatus is obtained in which the pretreatment mechanism can be operated while inhibiting the pretreatment membranes from being fouled.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Fuel cell system and control method therefor
ActiveUS10629930B2Improve accuracyPressure fluctuationReactant parameters controlMotive system fuel cellsFuel cellsEngineering
A controller closes a cutoff valve and a purge valve when a pressure value detected by a pressure sensor is an abnormal value. The controller then judges that an on-off valve has failed when the pressure value detected by the pressure sensor P1 has lowered, whereas the controller judges that the pressure sensor has failed when the pressure value detected by the pressure sensor has not lowered.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com