Patents
Literature
41results about How to "Solution can not be reused" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
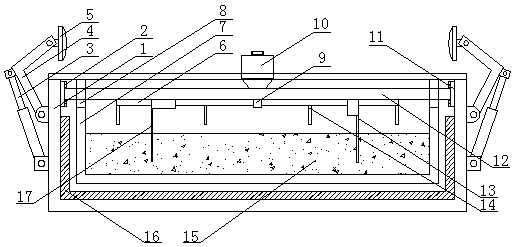
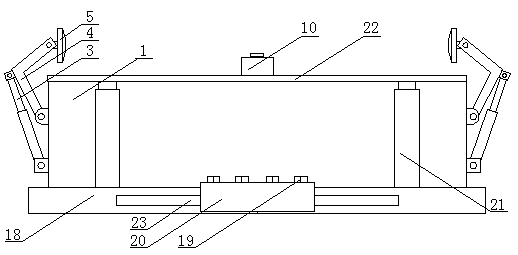
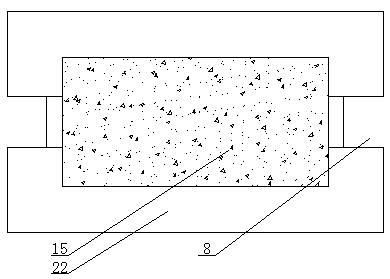
Polyvinyl formal sponge material with uniform abscesses and rapid imbibition and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102020816ASolution can not be reusedSolve the shortcomings of high closed cell rate and slow water absorption rate of the productPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAbsorbent padsCross-linkLiquid waste
The invention discloses a polyvinyl formal sponge material with uniform abscesses and rapid imbibition and a preparation method thereof. The material comprises polyvinyl alcohol, a cross-linking agent, a catalyst and a pore-forming agent, wherein the cross-linking agent is formaldehyde or paraformaldehyde or formaldehyde solution. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: stirring 2-9 parts of polyvinyl alcohol in 100-200 parts of water of which the temperature is 60-98 DEG C to obtain solution, and adding 0.05-8 parts of pore-forming agent to the solution; fully emulsifying the pore-forming agent to form evenly dispersed continuous solution phase; then adding 1-26 parts of catalyst and 1-15 parts of cross-linking agent or 5-50 parts of recovered liquid waste, 1-8 parts of catalyst and 1-15 parts of cross-linking agent, and mixing; pouring the mixture into a mould after 1-60 min for cross-linking reaction for 0.1-2 hours to form the abscesses under the action of the pore-forming agent; and continuing to heat and cure for 2-18 hours to prepare the polyvinyl formal sponge material. The invention has the advantages of good hydrophily, high compression strength, high dry wetting rate, high imbibition ratio and the like.
Owner:克林纳奇(荆州)高分子科技有限公司
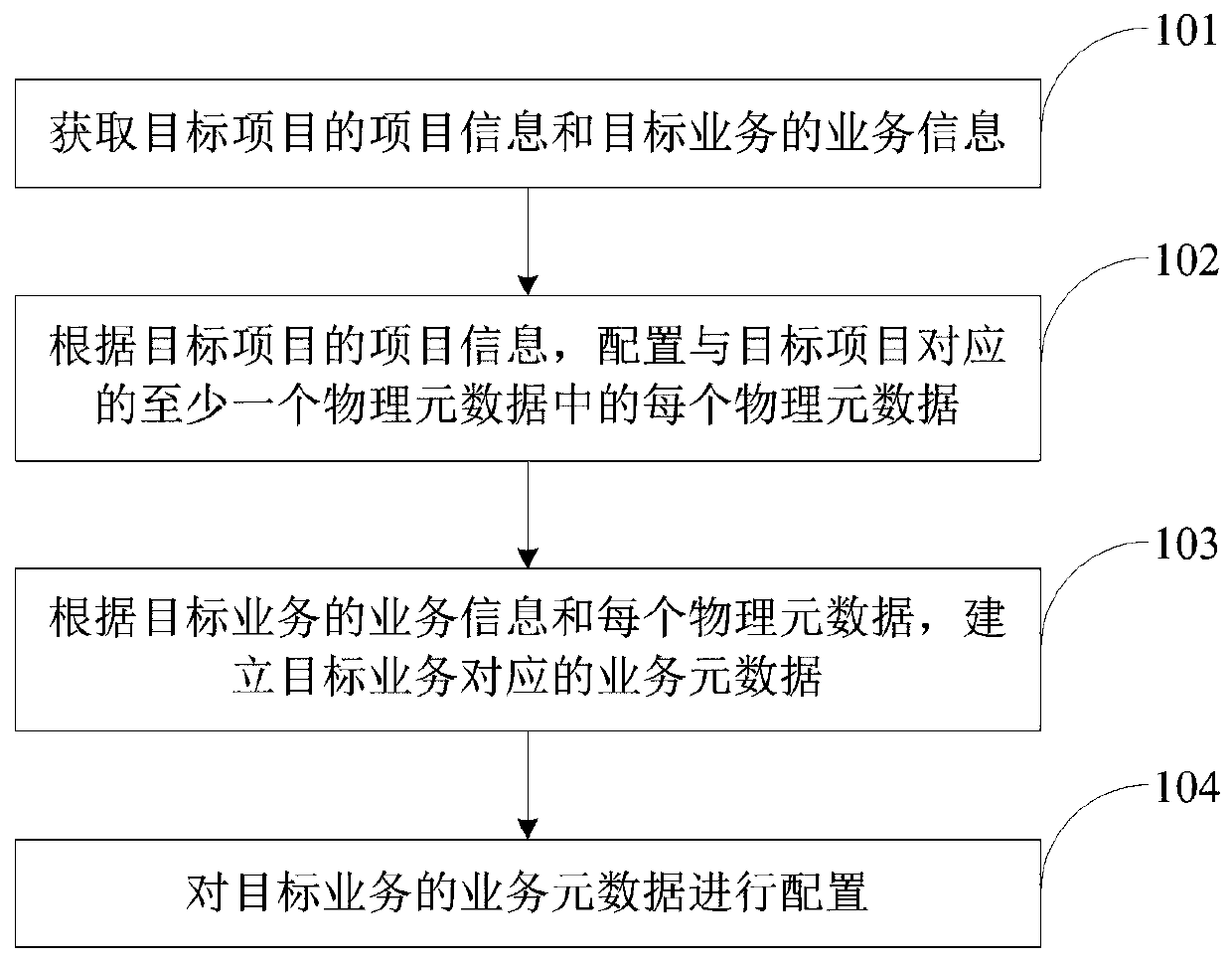
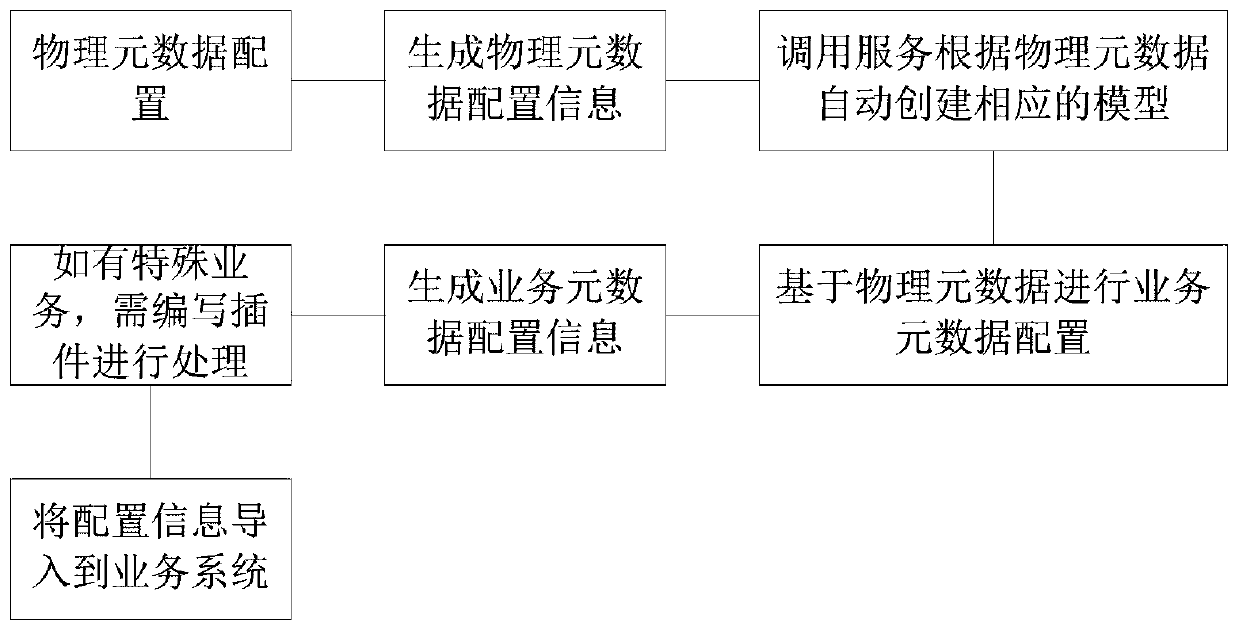
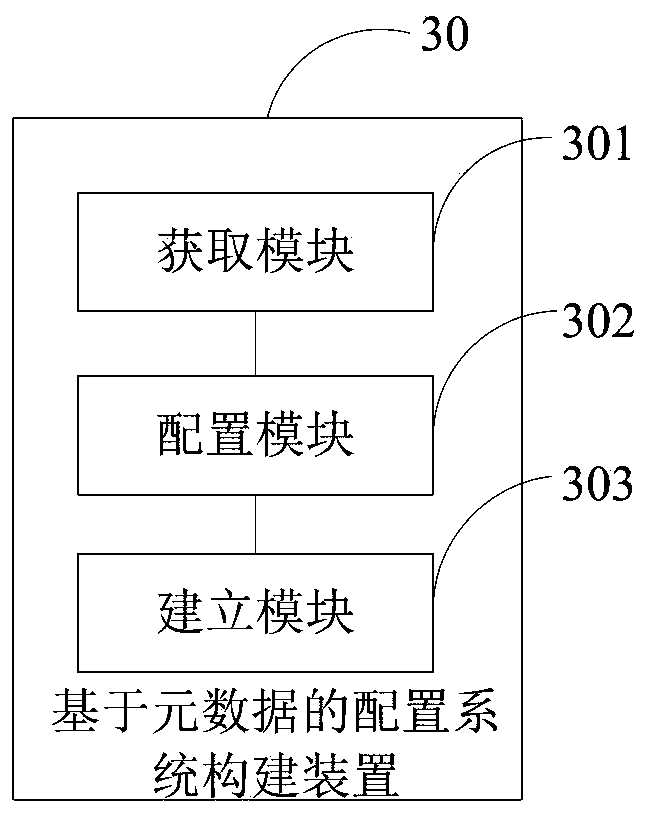
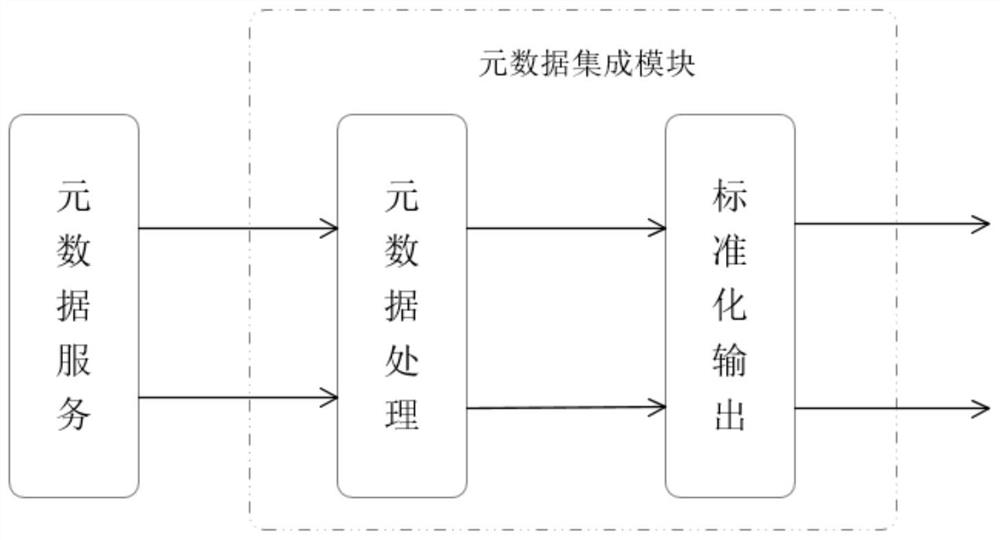
System construction method and device based on metadata configuration
InactiveCN109753492ARealize multiplexingSolve efficiency problemsSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase design/maintainanceHard codingMultiplexing
The invention provides a system construction method and device based on metadata configuration, relates to the technical field of data processing, can solve the problems of low hard coding developmentefficiency and incapability of multiplexing, reduces coding errors of a system, and improves the robustness of the system. The specific technical scheme comprises the steps of obtaining project information of a target project and service information of a target service, wherein the target service belongs to the target project; configuring each piece of physical metadata in at least one piece of physical metadata corresponding to the target project according to the project information of the target project; establishing service metadata corresponding to the target service according to the service information and the physical metadata of the target service, the service metadata being associated with at least one physical metadata; And configuring the service metadata corresponding to the target service.
Owner:陕西西部资信股份有限公司
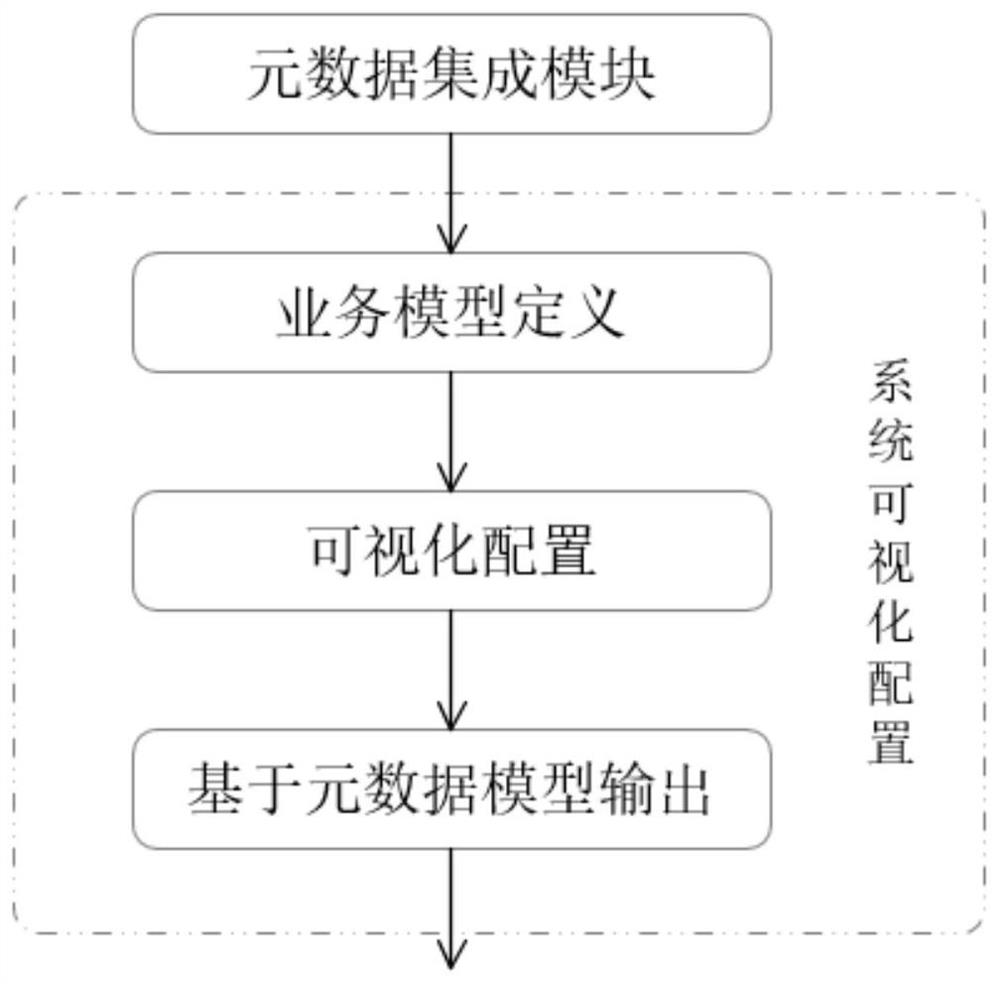
Method and device for quickly establishing system based on metadata
PendingCN113986223AAchieve standardized outputSolve efficiency problemsSoftware reuseFault toleranceHard coding
The invention particularly relates to a method and a device for quickly establishing a system based on metadata. According to the method and the device for quickly establishing the system based on the metadata, the metadata in a data warehouse system is subjected to conversion adaptation and standardized output, system establishing is performed according to a standardized structure and a business related model in the system, and business logic operation and analysis are performed on a business logic model configured based on the metadata; technical conversion between the system and the business model is realized; a business model generated by the system is explained, a standard business database language is generated, interaction with an actual business center library management system is carried out, and the requirements of related business systems are met. According to the method and the device for quickly establishing the system based on the metadata, the problems that hard coding is low in development efficiency and cannot be reused are solved, the coding quantity is reduced, the development cost is reduced, and the development efficiency is improved; and meanwhile, the coupling degree is reduced, rapid fault tolerance can be realized, and the robustness and rapid adaptability of the system are enhanced.
Owner:SHANDONG LANGCHAO YUNTOU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Process for recycling products from mother liquid containing ammonium chloride, sodium chloride, ammonium hydrogen carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate through thermal method
ActiveCN109879297AHigh puritySolution can not be reusedProductsReagentsSodium bicarbonateEvaporation
The invention provides a process for recycling products from mother liquid containing ammonium chloride, sodium chloride, ammonium hydrogen carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate through a thermal method. The process comprises a method for recycling gas generated after deaminizing the mother liquid. The method for recycling the gas generated after deaminizing the mother liquid comnprises the following steps: preheating the mother liquid, then feeding the mother liquid into an ammonia still for deaminizing, feeding carbon dioxide and ammonia gas generated after deaminizing into an ammonia absorption tower for generating carbon-containing ammonia water, adding carbon dioxide into the carbon-containing ammonia water, enabling carbon dioxide in the carbon-containing ammonia water to be excessive and generate ammonium hydrogen carbonate. The process also comprises a method for recycling the deaminized mother liquid and obtaining ammonium chloride and sodium chloride. The method for recycling the deaminized mother liquid and obtaining ammonium chloride and sodium chloride comprises the following steps: carrying out five-effect cross-flow evaporation to obtain sodium chloride, carrying out four-effect flash evaporation and crystallization to obtain ammonium chloride, feeding salt thickener overflowing liquid and salt centrifugal machine post-throwing liquid into a V-effect evaporation tank and enabling the salt thickener overflowing liquid and the salt centrifugal machine post-throwing liquid to participate in circulation again; feeding ammonium thickener overflowing liquid and ammonium centrifugal machine post-throwing liquid into an IV-effect flash evaporation and crystallization tank by using a pump, and enabling the ammonium thickener overflowing liquid and the ammonium centrifugal machine post-throwing liquid to participate in production circulation again. The process is capable of simultaneously recycling to obtain ammonium chloride and sodium chloride; meanwhile, the recycling rate is extremely high; the process is also capable of effectively increasing the heat utilization rate.
Owner:衡阳爱洁科技股份有限公司
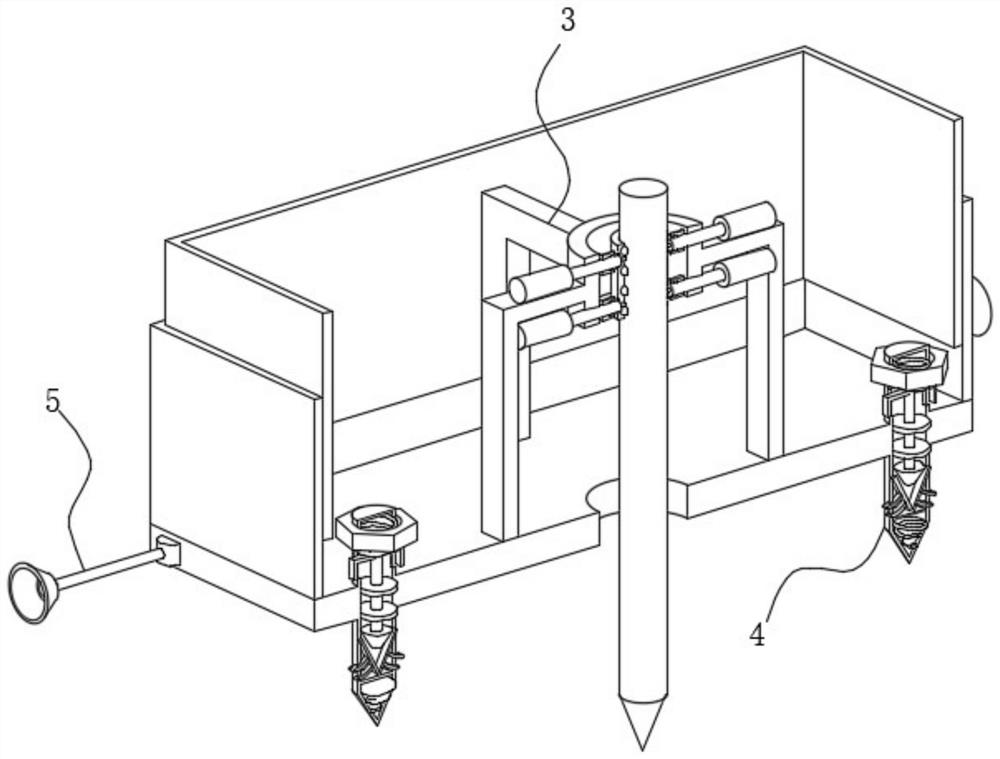
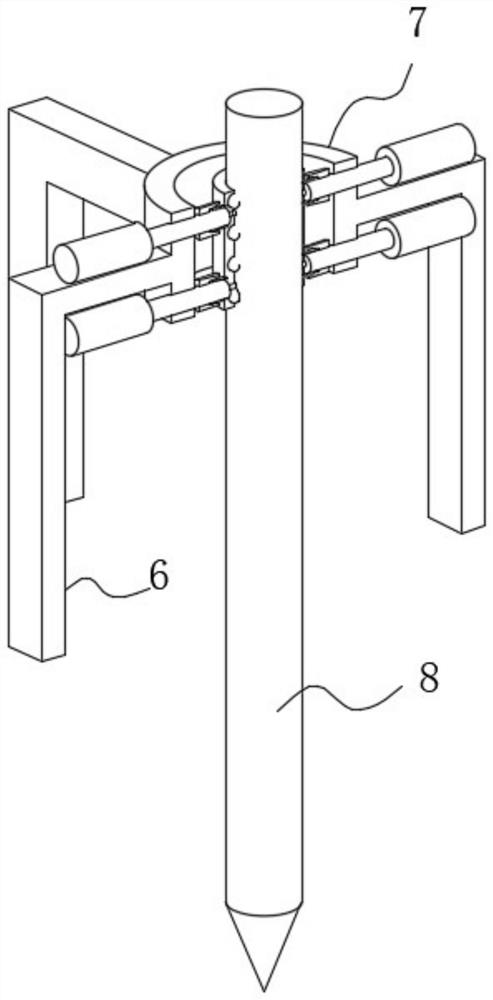
External fixator for skeleton reduction and Kirschner wire mounting position determining method
InactiveCN111388073AAchieve precise positioningSolution can not be reusedExternal osteosynthesisExternal fixatorStructural engineering
The invention provides an external fixator for skeleton reduction and a Kirschner wire mounting position determining method to solve the problems of low position accuracy of positioning skeleton reduction ends and failure of reuse of an external fixator during skeleton reduction in the prior art. The external fixator comprises support rods, three supports and Kirschner wire fastening mechanisms, wherein the multiple support rods are arranged in parallel and in series, at least three supports are perpendicularly mounted on the support rods, the relative positions of all supports are relativelyadjustable by adjusting the positions of the supports on the support rods, and the Kirschner wire fastening mechanisms are used for mounting Kirschner wires, mounted on the brackets and can be adjusted and locked in the circumferential direction of the supports. The Kirschner wire fastening mechanisms are adjusted to be matched with the Kirshner wires for fixing skeleton reduction to realize accurate positioning of the reduction end during skeleton reduction, 3D printing of the Kirschner wire fastening mechanisms corresponding to positions of the Kirschner wires after skeleton reduction is only required for different patients, and the support rods and the supports can be reused.
Owner:岳肖华
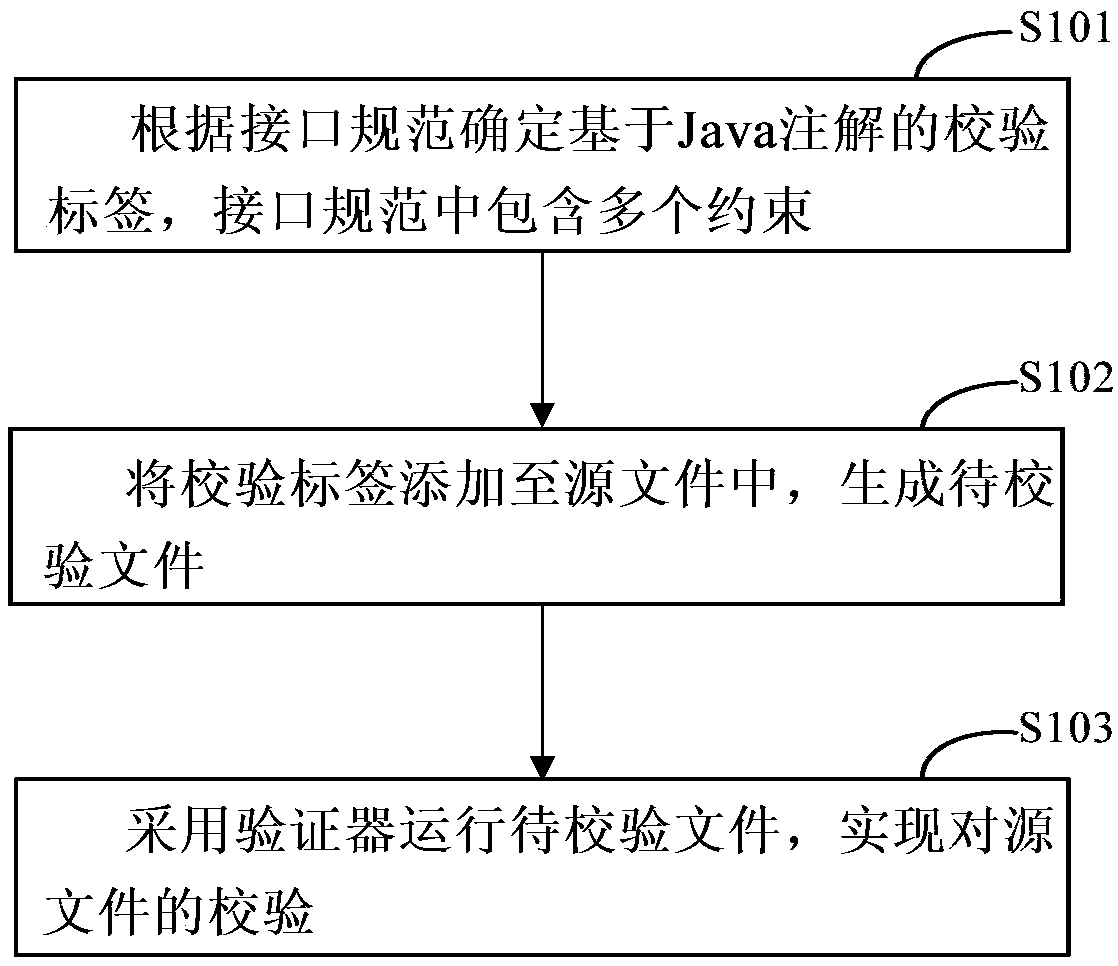
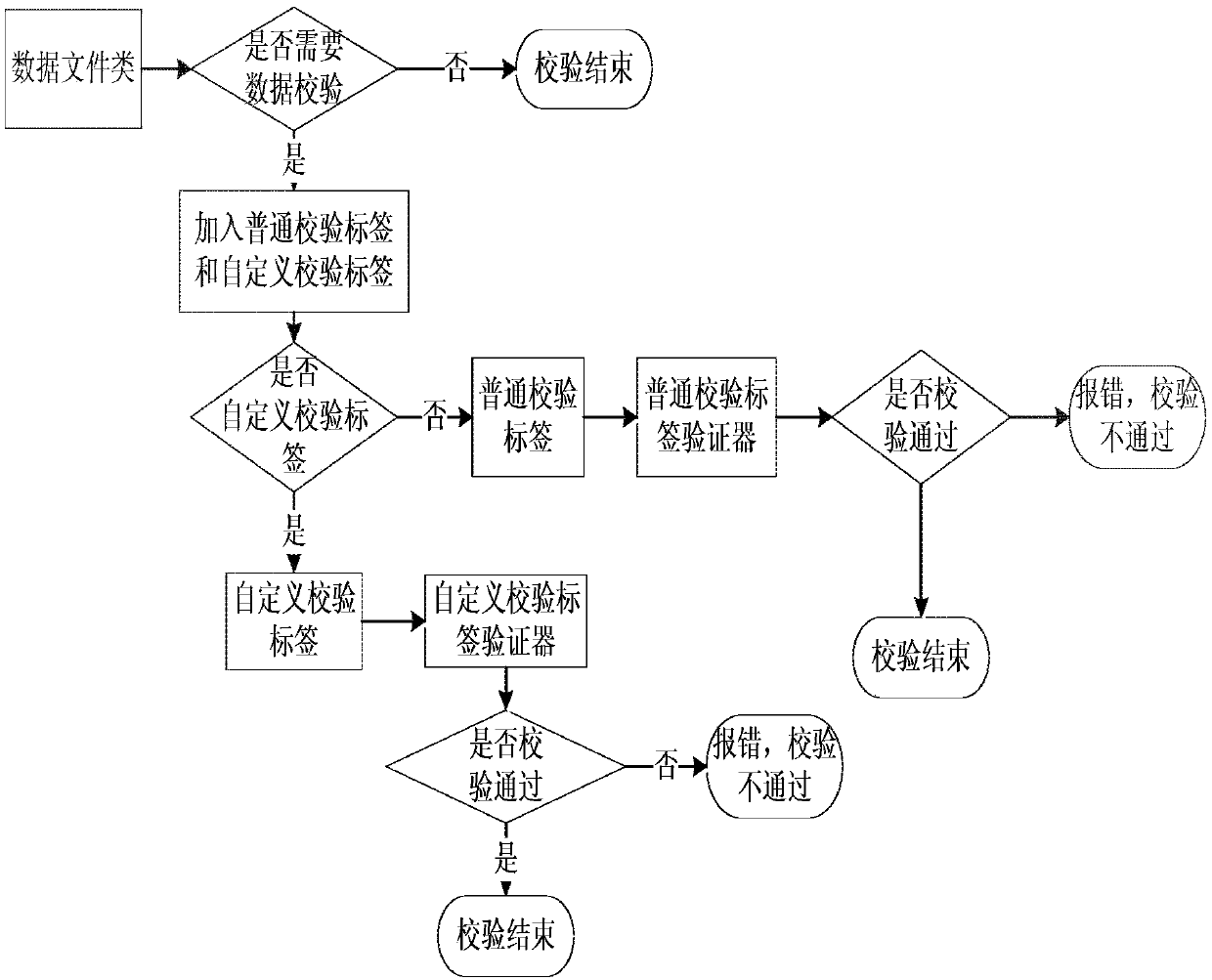
A method and a device for realizing data verification and injection based on Java annotations
InactiveCN109656744ASolve technical problems without universalitySolution can not be reusedRedundant data error correctionSource Data VerificationReusability
The invention discloses a method and a device for realizing data verification and injection based on Java annotations, and relates to the technical field of computers. A specific embodiment of the method comprises the steps that the method for achieving data verification based on the Java annotation comprises the steps: determining a verification label based on the Java annotation according to aninterface standard, wherein the interface standard comprises a plurality of constraints; Adding the verification label into a source file to generate a to-be-verified file; And adopting the verifier to operate the to-be-verified file to realize verification of the source file. According to the embodiment, the data verification step can be greatly simplified, the configurability of data verification is realized, the reusability is high, and the universality is good.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG SHANGKE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
Polyvinyl formal sponge material with uniform abscesses and rapid imbibition and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102020816BSolution can not be reusedReduce utilizationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAbsorbent padsCross-linkLiquid waste
The invention discloses a polyvinyl formal sponge material with uniform abscesses and rapid imbibition and a preparation method thereof. The material comprises polyvinyl alcohol, a cross-linking agent, a catalyst and a pore-forming agent, wherein the cross-linking agent is formaldehyde or paraformaldehyde or formaldehyde solution. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: stirring 2-9 parts of polyvinyl alcohol in 100-200 parts of water of which the temperature is 60-98 DEG C to obtain solution, and adding 0.05-8 parts of pore-forming agent to the solution; fully emulsifying the pore-forming agent to form evenly dispersed continuous solution phase; then adding 1-26 parts of catalyst and 1-15 parts of cross-linking agent or 5-50 parts of recovered liquid waste, 1-8 parts of catalyst and 1-15 parts of cross-linking agent, and mixing; pouring the mixture into a mould after 1-60 min for cross-linking reaction for 0.1-2 hours to form the abscesses under the action of the pore-forming agent; and continuing to heat and cure for 2-18 hours to prepare the polyvinyl formal sponge material. The invention has the advantages of good hydrophily, high compression strength, high dry wetting rate, high imbibition ratio and the like.
Owner:克林纳奇(荆州)高分子科技有限公司
Novel turnover tool type beam side wall connecting piece fixing device and method
InactiveCN110863644AReduced quality hazardsLess steel pipe consumablesScaffold accessoriesSteel tubeFastener
The invention discloses a novel turnover tool type beam side wall connecting piece fixing device and method, and relates to the technical field of building construction. The device comprises a beam side embedded bolt shaping wall connecting piece and a double-row scaffold, wherein the beam side embedded bolt shaping wall connecting piece comprises an embedded bolt sleeve, a screw rod and a shapingwall connecting piece, the screw rod is arranged on the side, close to the double-row scaffold, of the embedded bolt sleeve, and the screw rod is fixedly connected with the double-row scaffold through the shaping wall connecting piece. According to the novel turnover tool type beam side wall connecting piece fixing device and method, the beam side embedded bolt shaped wall connecting piece is matched with the double-row scaffold, so that the problem that a steel pipe embedded by a steel pipe wall connecting piece and part of fasteners cannot be reused is solved, the steel pipe and part of fasteners are only connected with the outer side of a main structure of a building without penetrating through a wall, procedures such as masonry, plastering, external wall brick sticking and the like ofthe external wall can be achieved by one step, and the quality hidden danger such as water seepage and water leakage can be greatly reduced.
Owner:CHINA MCC17 GRP
Iodine removing filter device with replaceable carbon
ActiveCN104637560AReduce friction ratioReduce wind resistanceRadioactive decontaminationChemistryActivated carbon
The invention relates to purification equipment for iodine, in particular to an iodine removing filter device with replaceable carbon. The iodine removing filter device structurally comprises a metal shell and activated carbon adsorbent placed in the metal shell. A plurality of V-shaped through hole metal folding plates are arranged in the metal shell, a parallel space is formed between every two adjacent V-shaped hole penetrating metal folding plates, and the activated carbon adsorbent is placed in the parallel spaces. A side wall baffle is arranged between the two ends of every two adjacent V-shaped hole penetrating metal folding plates, the side wall baffles and the metal shell are welded at the angle of 90 degrees in a sealing mode, and the edges of the two ends of the V-shaped hole penetrating metal folding plate which corresponds to an intake air face are surrounded. The iodine removing filter device effectively reduces the friction-resistance ratio, effectively lowers wind resistance, and meanwhile solves the problem that the improvement of purification coefficients is influenced by a side wall effect.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Dismantling system of glass curtain wall and using method thereof
PendingCN108824843AAvoid destructionAchieve reuseWallsBuilding repairsStructural engineeringSafety monitoring
The invention provides a dismantling system of a glass curtain wall and a using method thereof in order to improve safety monitoring and controlling of a dismantling spot of the glass curtain wall, realize recycling and reusing of the glass curtain wall and reduce the garbage collection working of the glass curtain wall after dismantling. The dismantling system of the glass curtain wall is used for the dismantling of a hidden type glass curtain wall. The dismantling system of the glass curtain wall is characterized by comprising a truss framework, a hoisting original production and suction cupdevices. The truss framework comprises a frame body and connecting rods, wherein the connecting rods are arranged perpendicularly on the frame body. A plurality of bolt holes are formed in the framebody at intervals, the suction cup devices are arranged on the end portions of the connecting rods, and the hoisting original production is arranged on the top of the dismantling system of the glass curtain wall and connected with the truss framework through penetrating through connecting bolt assemblies of the bolt holes.
Owner:SHANGHAI NO 4 CONSTR
Method and device for managing 5G radio access network RAN scene
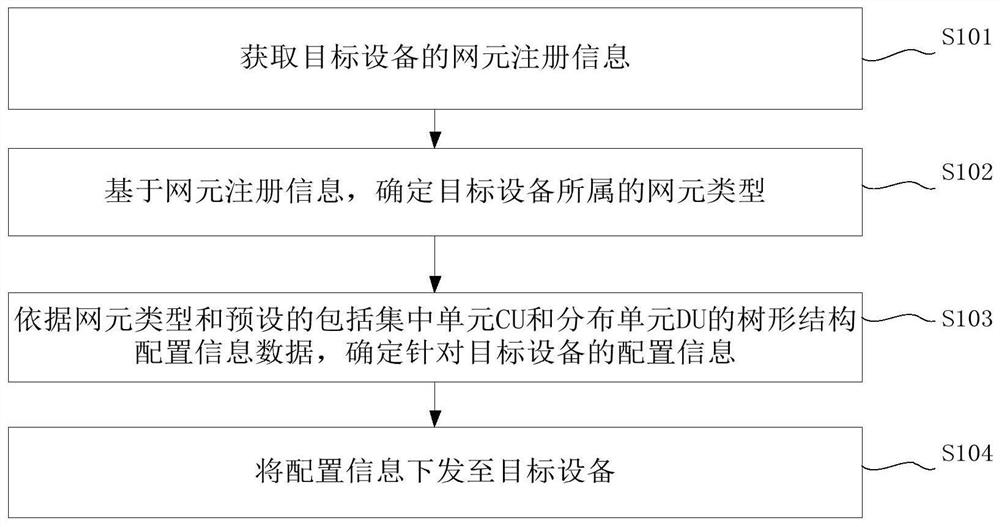
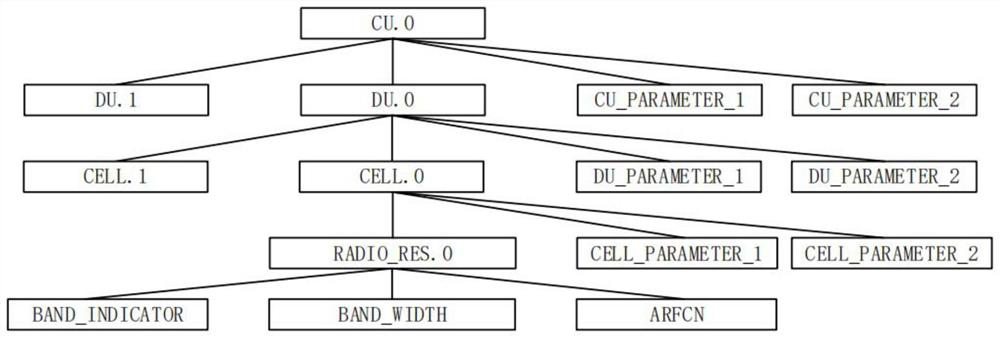
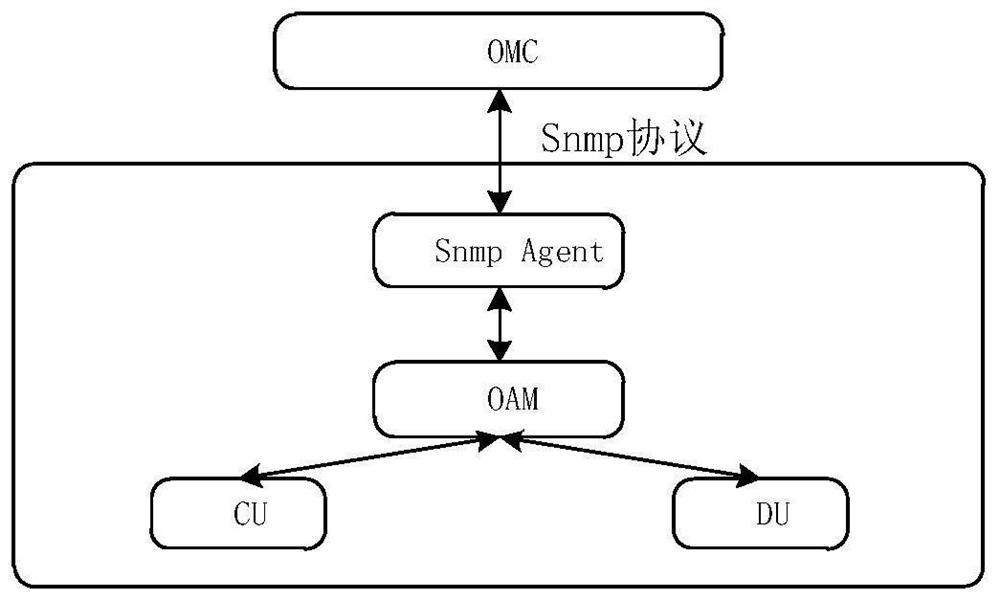
ActiveCN113133030AReduce development costsSolution can not be reusedWireless communicationAccess networkRadio access network
The invention discloses a management method and device in a 5G radio access network RAN scene. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring network element registration information of target equipment; determining a network element type to which the target equipment belongs based on the network element registration information; determining configuration information for the target equipment according to the network element type and preset tree structure configuration information data comprising a centralized unit (CU) and a distributed unit (DU); and issuing the configuration information to the target device. According to the method and the device, the effect of maintaining and managing the network elements in the 5G RAN scene is achieved in a manner of uniformly maintaining the configuration information of the centralized unit CU and the distributed unit DU through the tree structure, so that the management and control program can be suitable for different 5G RAN scenes, different programs do not need to be developed for different 5G RAN scenes, the development cost of the management and control program is reduced. The problem that the management and control program cannot be reused in the related technology is solved, the flexibility of the management and control software is improved, and a user can conveniently deploy equipment and carry out management and maintenance.
Owner:中科南京移动通信与计算创新研究院
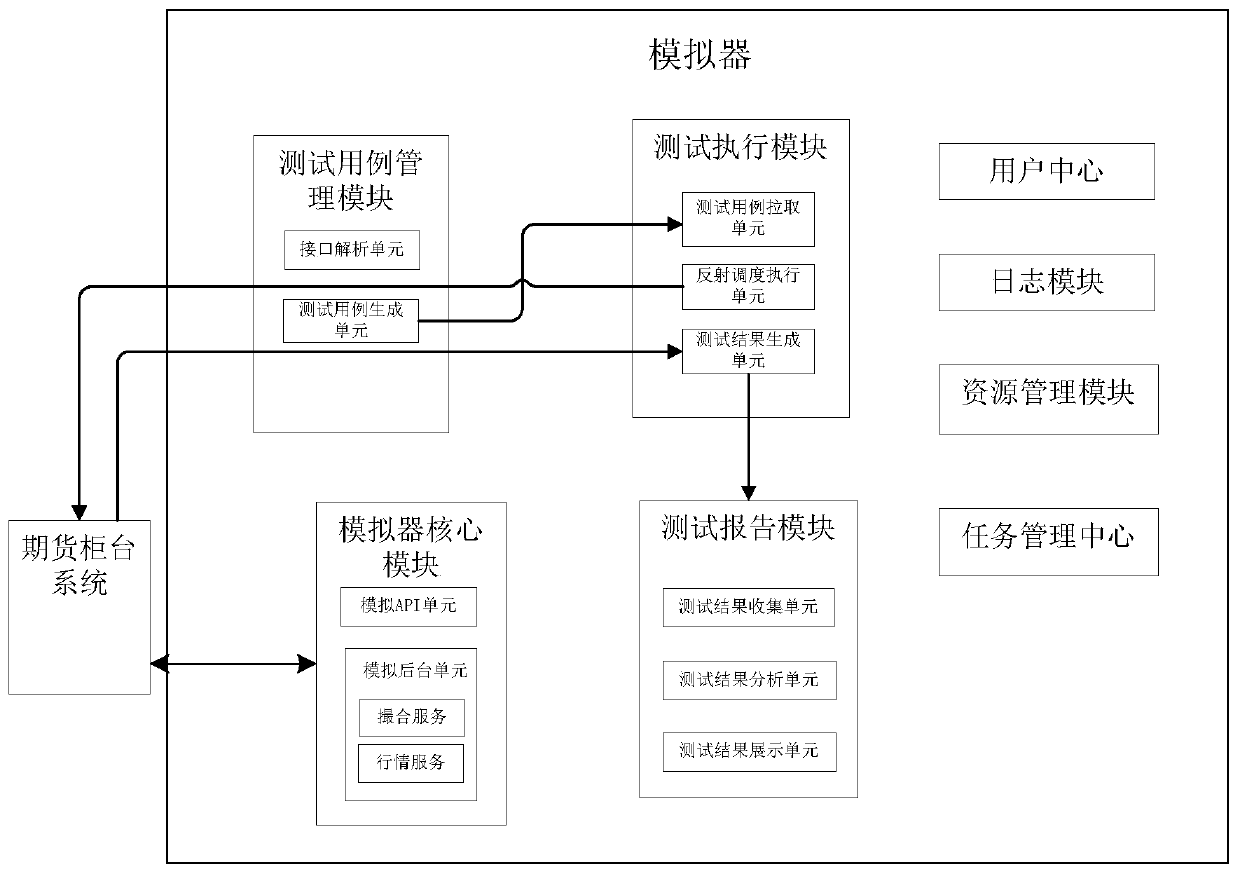
Automatic test method and simulator for financial transaction platform
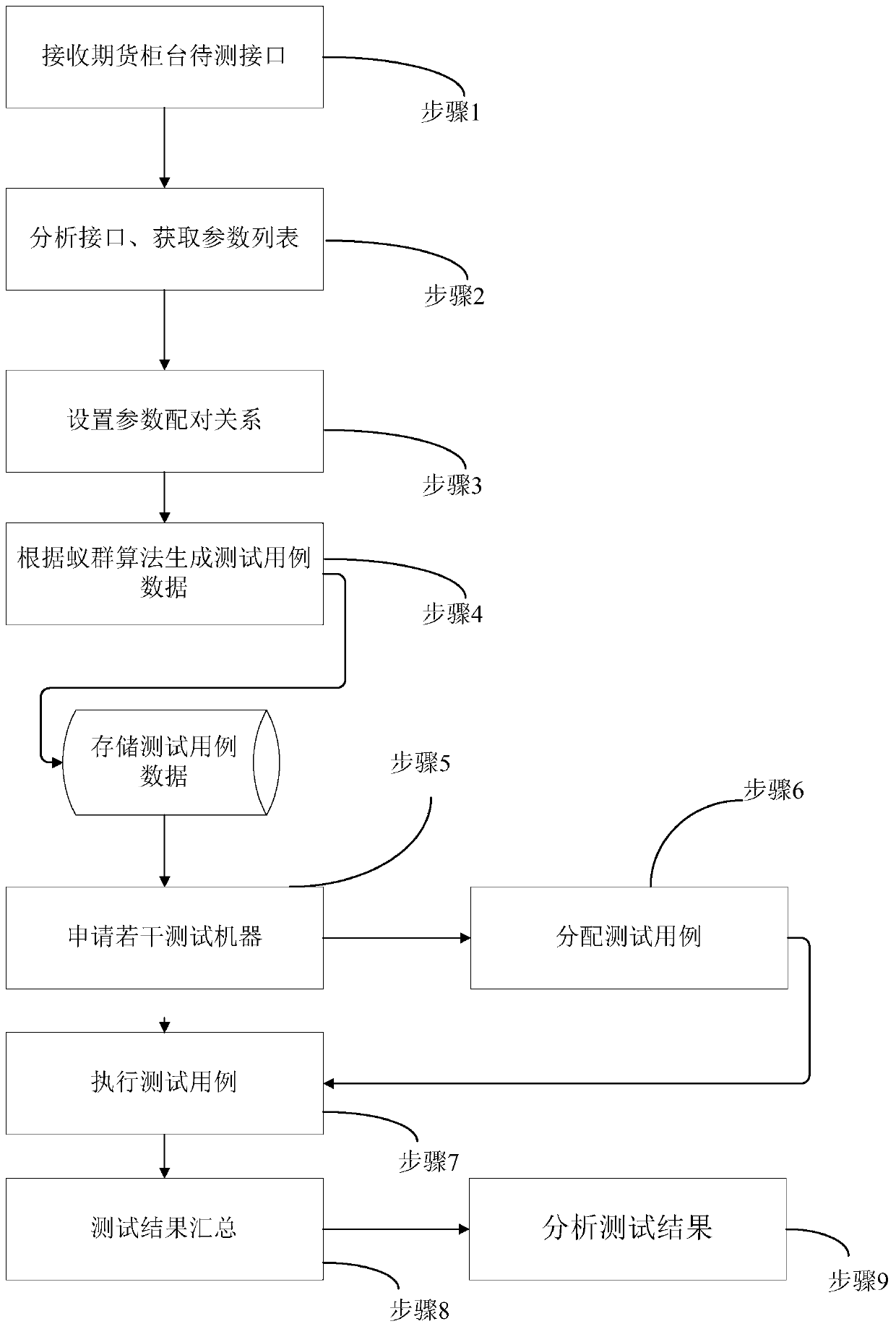
ActiveCN111309590AReliable Test ExpectationsReliable Test Expected ResultsArtificial lifeSoftware testing/debuggingTest efficiencyAnt colony optimization algorithms
The invention discloses an automatic test method and simulator for a financial transaction platform, which can provide a reliable test expected result, and a system test case can be reused, so that the correctness, reliability and research and development test efficiency of a system are improved. According to the technical scheme, a to-be-tested interface of a financial transaction platform is received; automatically analyzing the received to-be-tested interface and obtaining a parameter list from the to-be-tested interface; setting a parameter pairing relationship according to the obtained parameter list; generating test case data through an ant colony algorithm according to the obtained parameter list and the set parameter pairing relationship; automatically applying for a test machine according to the number of cases of the generated test case data and a historical case execution baseline; allocating a test case according to the applied test machine; automatically executing the correspondingly distributed test cases through the applied test machine; automatically summarizing test results after the test cases are executed; and analyzing the summarized test results.
Owner:上海金融期货信息技术有限公司
Limestone-gypsum desulfurization wastewater chloride ion extraction system
PendingCN112299607ASolve corrosiveSolution can not be reusedWaste water treatment from gaseous effluentsMultistage water/sewage treatmentWastewaterClean water
The invention discloses a limestone-gypsum desulfurization wastewater chloride ion extraction system. A desulfurization wastewater inlet pipeline is communicated with an inlet of a pretreatment system, an outlet of the pretreatment system is communicated with an inlet of an extraction phase splitter through an extraction reactor, an extract outlet of the extraction phase splitter is communicated with an inlet of the back extraction phase splitter sequentially through a back extraction reactor, an organic phase NR3 outlet of a back extraction phase splitter is communicated with an inlet of a centrifuge, a waste liquid outlet of the back extraction phase splitter is communicated with an inlet of a waste liquid recoverer, a waste liquid outlet of the centrifuge is communicated with an inlet of the waste liquid recoverer, and an outlet of a diluent storage tank and an outlet of an extractant storage tank are communicated with an inlet of a dilution tank; and a water phase outlet of the extraction phase splitter is communicated with the inlet of a clean water tank, and the outlet of the clean water tank is communicated with the inlet of the extraction reactor. According to the present invention, with the system, the treatment and the reuse of the desulfurization wastewater are achieved, the treatment cost is low, and the zero emission is achieved.
Owner:XIAN TPRI WATER & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Seismic isolation seam covering apparatus for seismic isolation building wall joints and construction method thereof
ActiveCN106759967ASimple constructionEnsuring integrity and consistencyBuilding insulationsEngineeringSealant
The invention relates to a seismic isolation seam covering apparatus for seismic isolation building wall joints and a construction method thereof; the seismic isolation seam covering apparatus for seismic isolation building wall joints is arranged at a seismic isolation seam of a seismic isolation tier wall joint and comprises a silicate cover plate and sealant, the silicate cover plate is square and has four corners chambered at 45 DEG C, four edges of the silicate cover plate are hermetically bonded to L-shaped walls on two sides of one diagonal of the silicate cover plate respectively through the sealant, the chamfered portions of the four corners of the silicate cover plate fill the wall joint seismic isolation seam through the sealant, the sealant fills between a horizontal long part of one L-shaped wall and a vertical short part of the other L-shaped wall, the sealant also fills between a vertical short part of one L-shaped wall and a horizontal long part of the other L-shaped wall, and the sealant has maximum tension strength elongation of > / =300%. The integrity and uniformity of a wall are guaranteed, seismic destruction degree of a joint is decreased, building maintenance cost is saved, and good attractive appearance and construction simplicity are achieved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIVERSITY
Filtering device and filtering method for reducing nuclear power filtering solid waste quantity
InactiveCN113599882AReduce solid waste generationReduce processing costsStationary filtering element filtersNuclear powerFiltration
The invention discloses a filtering device and a filtering method for reducing nuclear power filtering solid waste quantity. The filtering device comprises a filter shell, a filter element assembly, a water inlet pipe, a water outlet pipe, a water inlet valve, a water outlet valve and a filter element cleaning structure, wherein the filter element assembly is arranged inside the filter shell, a water inlet and a water outlet are formed in the filter shell, a water inlet pipe is arranged at the water inlet, and a water inlet valve is arranged on the water inlet pipe; the water outlet pipe is arranged at the water outlet and is provided with a water outlet valve; and the water inlet is positioned below the water outlet. According to the filtering device, the filter element cleaning structure is arranged, the filter element assembly can be cleaned and regenerated, the problem that an original filter element cannot be recycled is solved, the filtering device is adopted for filtering, long-term operation can be achieved, the filter element does not need to be frequently replaced, and the filtering device has the advantages of reducing the maintenance frequency, reducing the solid waste output of the filter element and reducing filter element solid waste quantity. And the device is suitable for radioactive water filtration of the nuclear power station.
Owner:AT&M ENVIRONMENTAL ENG TECH CO LTD
Surface treatment method for iron wires used for civil engineering
InactiveCN106757079ALittle effortShorten pickling timeFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesPhosphoric acidWater resources
The invention provides a surface treatment method for iron wires used for civil engineering and belongs to the field of metal surface treatment processes. The surface treatment method for the iron wires used for the civil engineering is used for solving the problems that pickling in the prior art is performed through hydrochloric acid, lots of water resources can be wasted easily, and water after cooling water washing cannot be reused. The surface treatment method includes the steps that after the whole bundle of iron wires are subjected to first time of pickling dirt removing, first time of water washing, heat treatment and cooling water washing, the whole bundle of iron wires are unfolded and pulled into a line shape to be subjected to second time of pickling, second time of water washing, first time of neutralizing water washing and anti-rusting water washing; pickling liquid adopted during the second time of pickling is composed of phosphoric acid and a BW-500P phosphoric acid fast pickling agent, the temperature of the pickling liquid is kept between 35 DEG C to 50 DEG C, an ultrasonic device is placed on the middle rear portion of a pickling pond, and ultrasonic pickling is kept for more than 20 seconds; and cooling water after cooling treatment is discharged into a first water washing pond corresponding to the first time of water washing, a second water washing pond corresponding to the second time of water washing, a third water washing pond corresponding to the first time of neutralizing water washing and an anti-rusting water washing pond corresponding to the anti-rusting water washing.
Owner:赵玉
Device for solidifying fly ash and control system and control method
ActiveCN111604353ASolution can not be reusedWill not polluteSolid waste managementSolid waste disposalControl systemEngineering
The invention relates to a device for solidifying fly ash. The device comprises a power transmission system, an electric heating system, a mud sheet roll forming system used for forming a fly ash liquid mixture and an electromechanical control system, wherein the power transmission system is composed of a water-ash mixed pug placing barrel, a pug mixing conveying pump assembly and a pug conveyingspraying pipe which are connected through a pipeline, the electric heating system is composed of a transmission segment, a transmission power rotating wheel, a closed shell and a forming electric heating plate which are mechanically connected, the mud sheet roll forming system is composed of a slitting piece, a rolling forming roller control assembly, a screening channel, a mud sheet roll formingassembly, a conical end, a movable adjusting piece, ash solid block separation equipment and ash solid block output equipment which are mechanically connected, and the electromechanical control systemis composed of a driving unit, a transmission power system, a rotation sensing device, an output transmission piece, an input transmission piece, a power connecting rod, a feedback output power rod and a mud sheet roll forming movable assembly which are mechanically connected. The invention further discloses a control system and a control method of the device for solidifying the fly ash.
Owner:河南中釉环保科技有限公司
Small drilling device for hydraulic ring geological exploration
InactiveCN114151074ASolve the problem of fixed drilling diameterSolve the inconvenience of replacementEarth drilling toolsDrilling rodsElectric machineryEngineering
The invention discloses a small drilling device for hydraulic ring geological exploration, which comprises a bottom plate, the upper surface of the bottom plate is fixedly connected with a coaming, the interior of the coaming is movably connected with a drilling device, the two sides of the drilling device are provided with fixing devices, the exterior of each fixing device is provided with an adjusting device, and the adjusting devices are movably connected with the coaming. The invention relates to the technical field of drilling. According to the small drilling device for hydraulic ring geological exploration, by arranging the drilling device, when equipment is used, a locking device fixes a drill bit to the top of the support, the drill bit conducts drilling operation on the ground under driving of an external motor, when the drill bit is installed, the length of a telescopic rod is changed according to the actual diameter of the drill bit, and a clamping plate clamps the drill bit; the ball rotates along with rotation of the drill bit, the screw rod is screwed into the telescopic rod, the clamping plate is fixed under the action of the clamping device and the screw rod, and the problem that the drilling diameter of traditional drilling equipment is fixed is solved.
Owner:李占琪
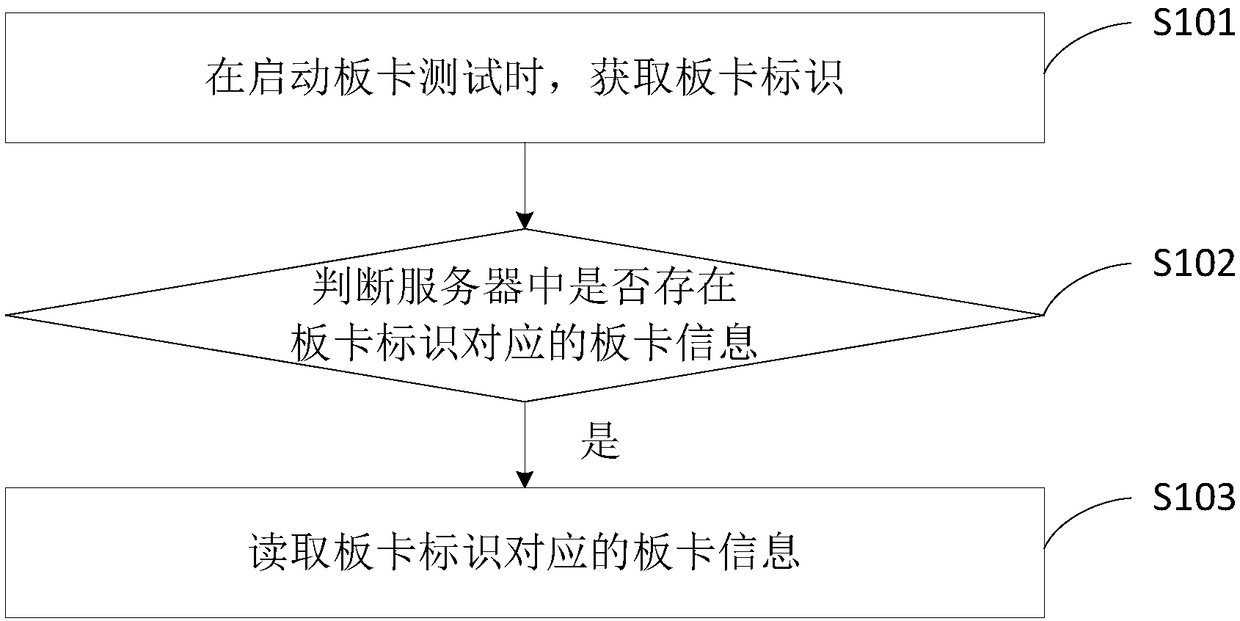
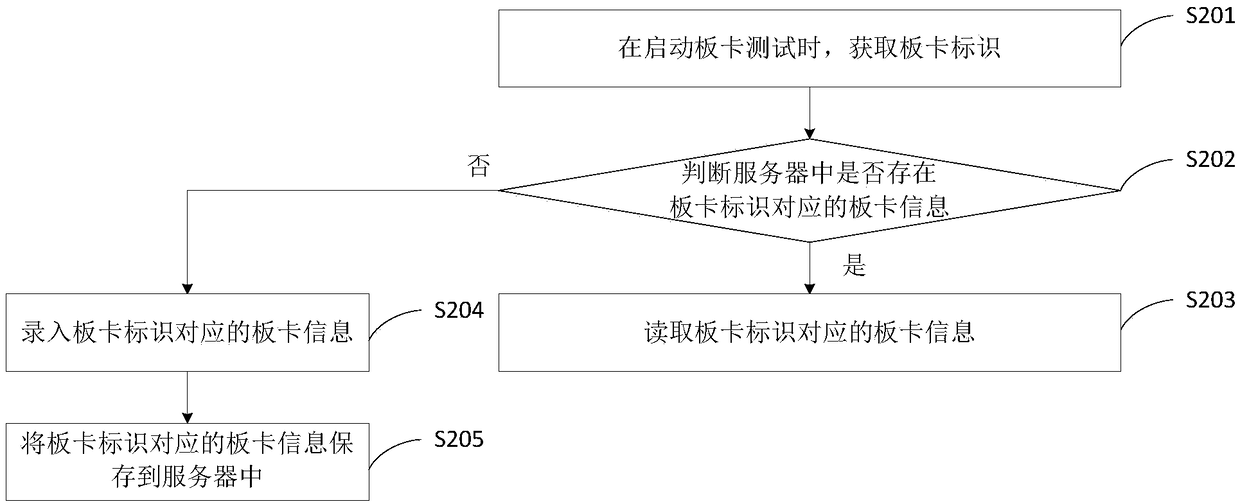
Method and apparatus for reading information
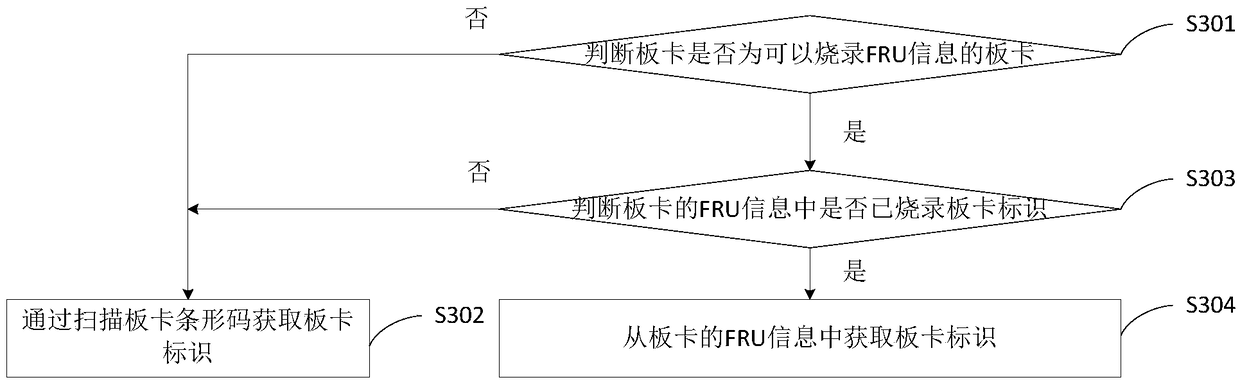
InactiveCN109117332AReduce complexityImprove board test efficiencyDetecting faulty computer hardwareSoftware deploymentComputer hardwareTest efficiency
The invention discloses an information reading method and a device. When a board test is started, a board identification is obtained. Whether the board information is judged corresponding to the boardidentification exists in the server; If so, the board information corresponding to the board identification is read. The invention solves the problem that the server board card test needs to re-inputthe board card information every time it is restarted and the input information cannot be reused, reduces the complexity of the board card test and improves the board card test efficiency.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Gas turbine starting structure
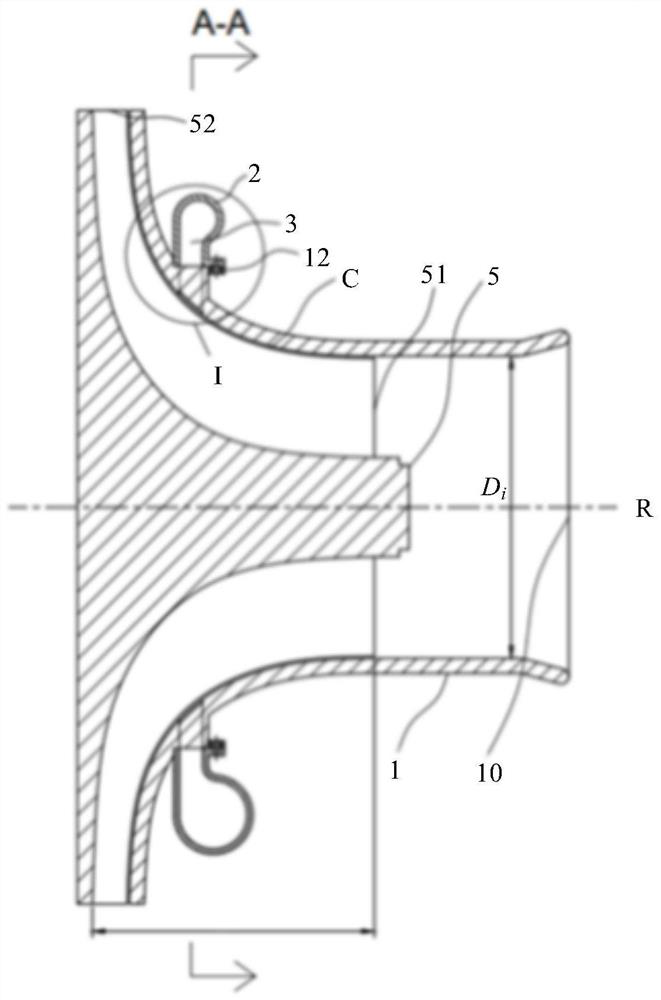
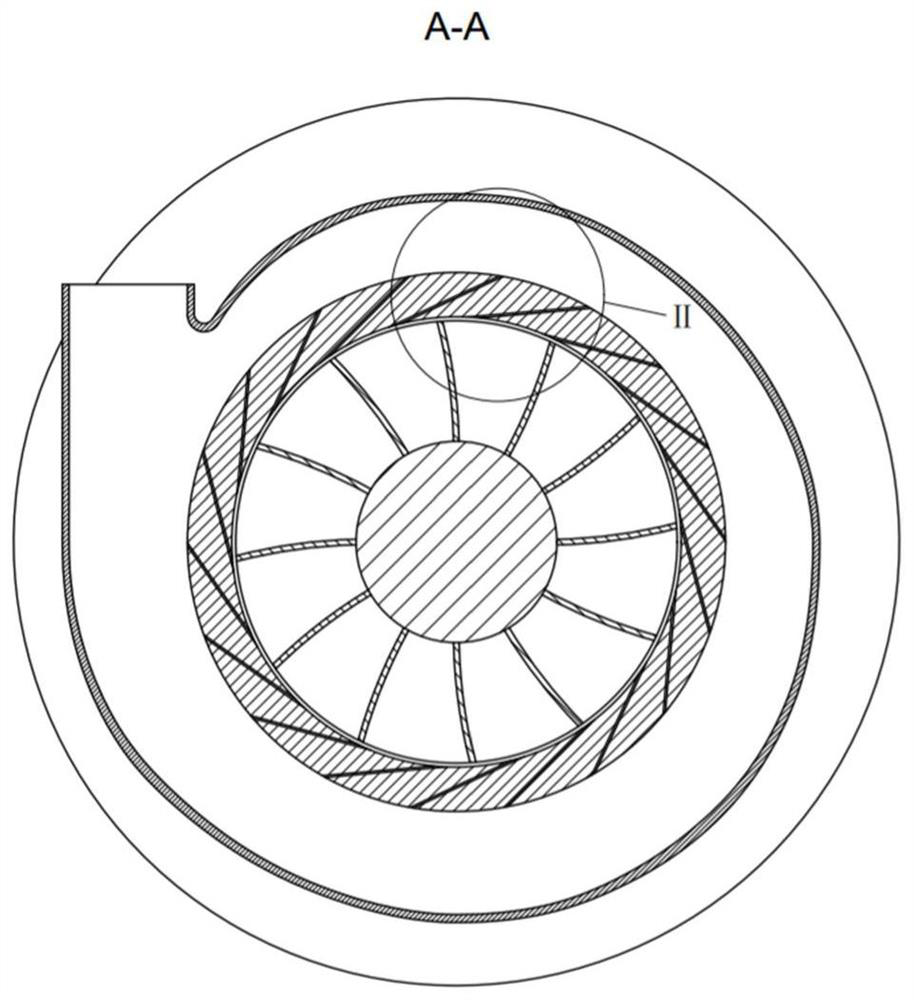
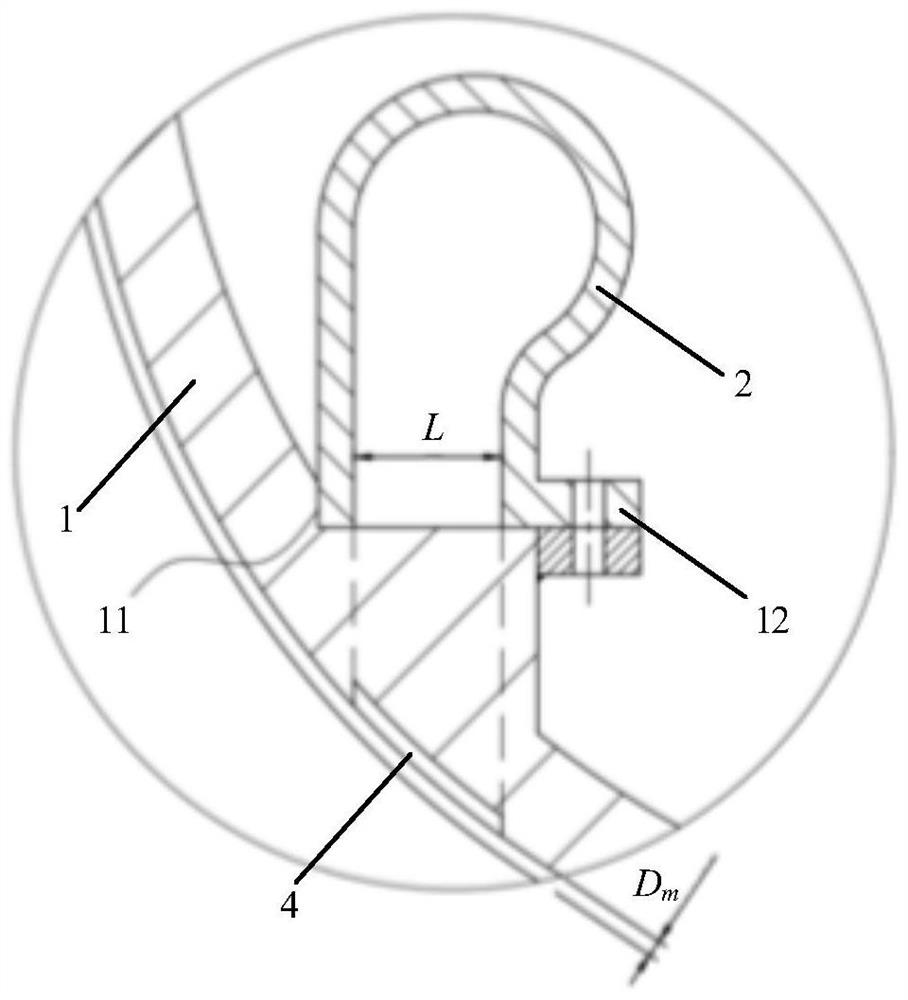
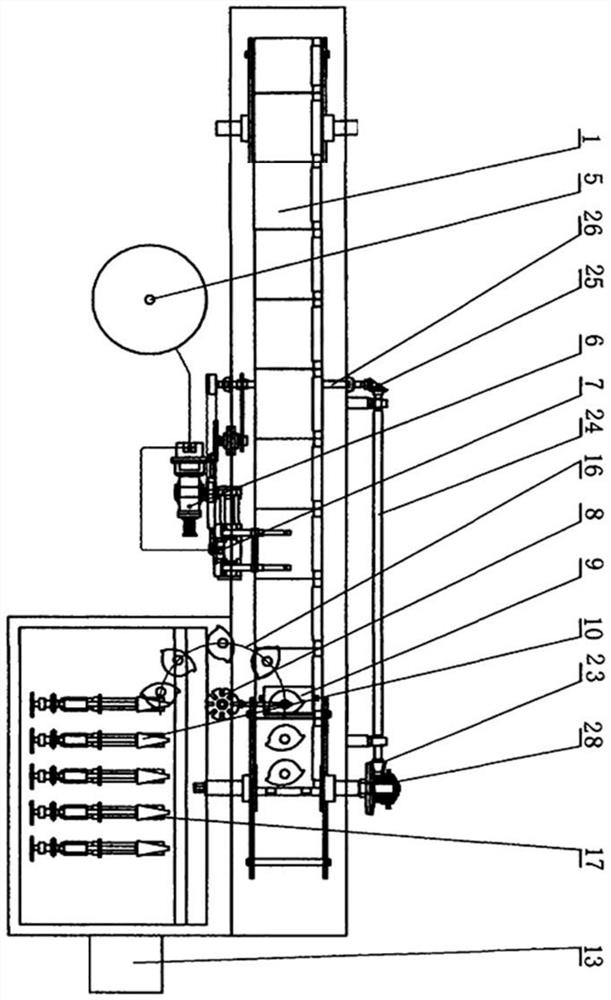
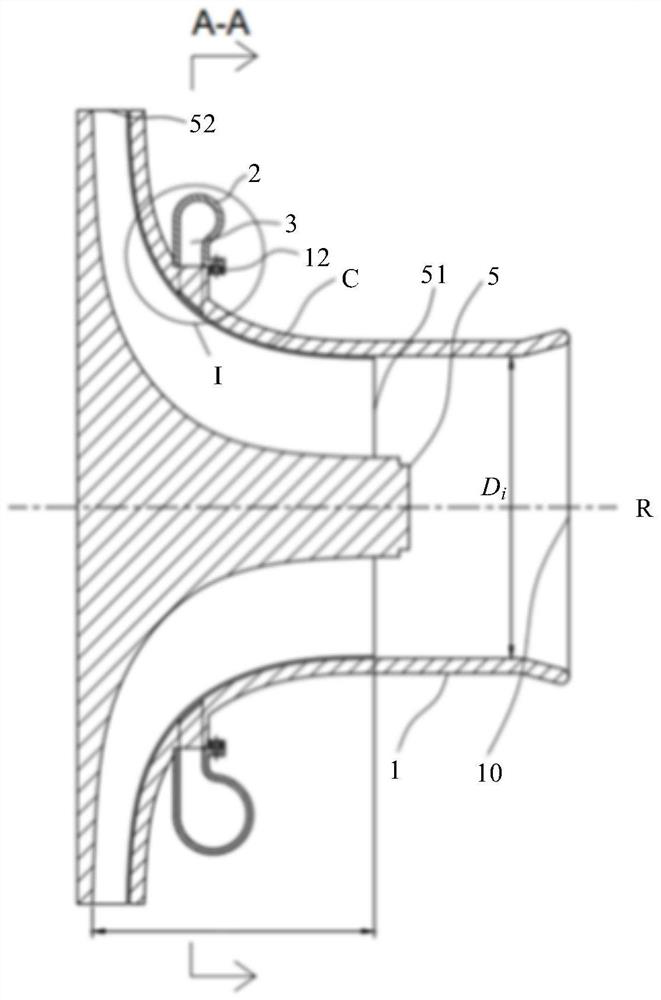
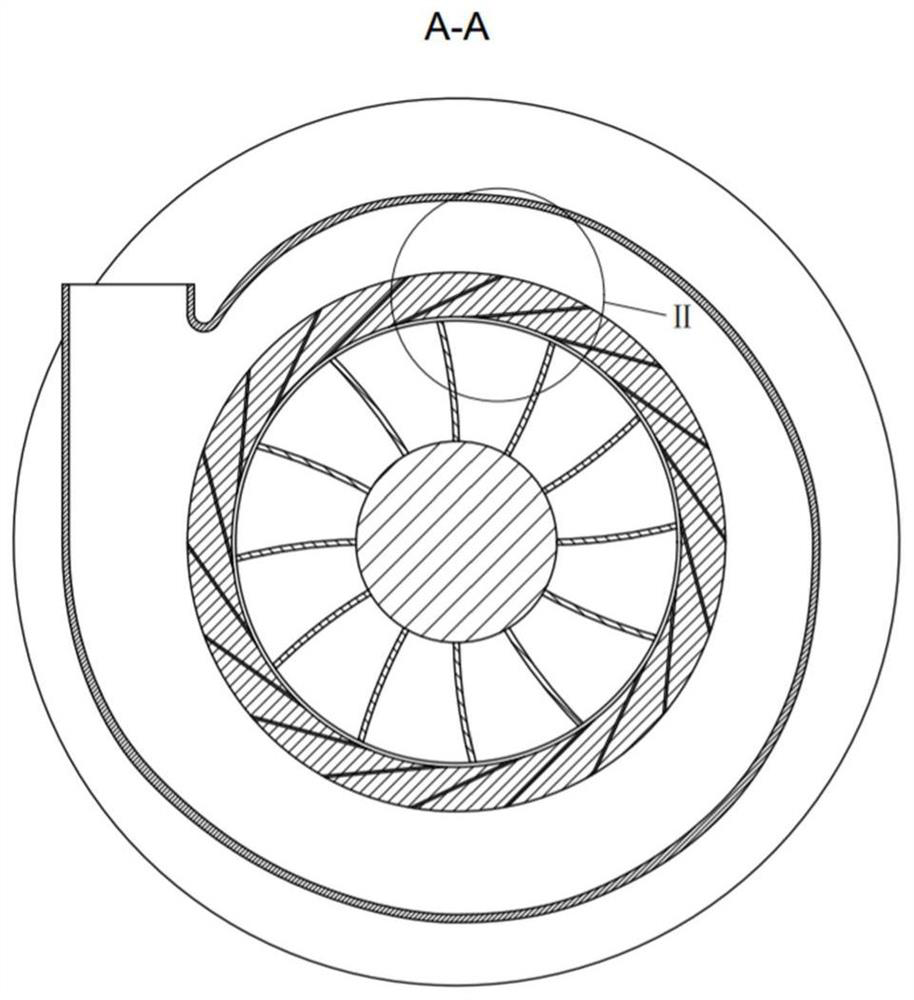
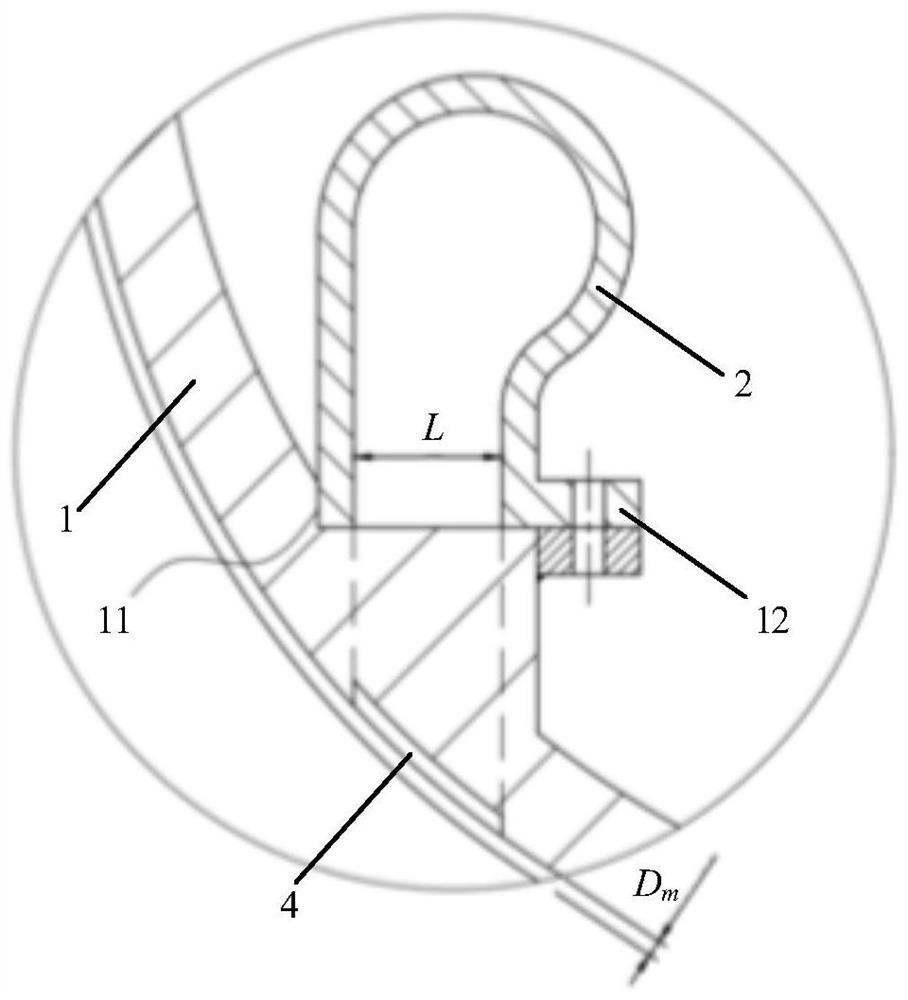
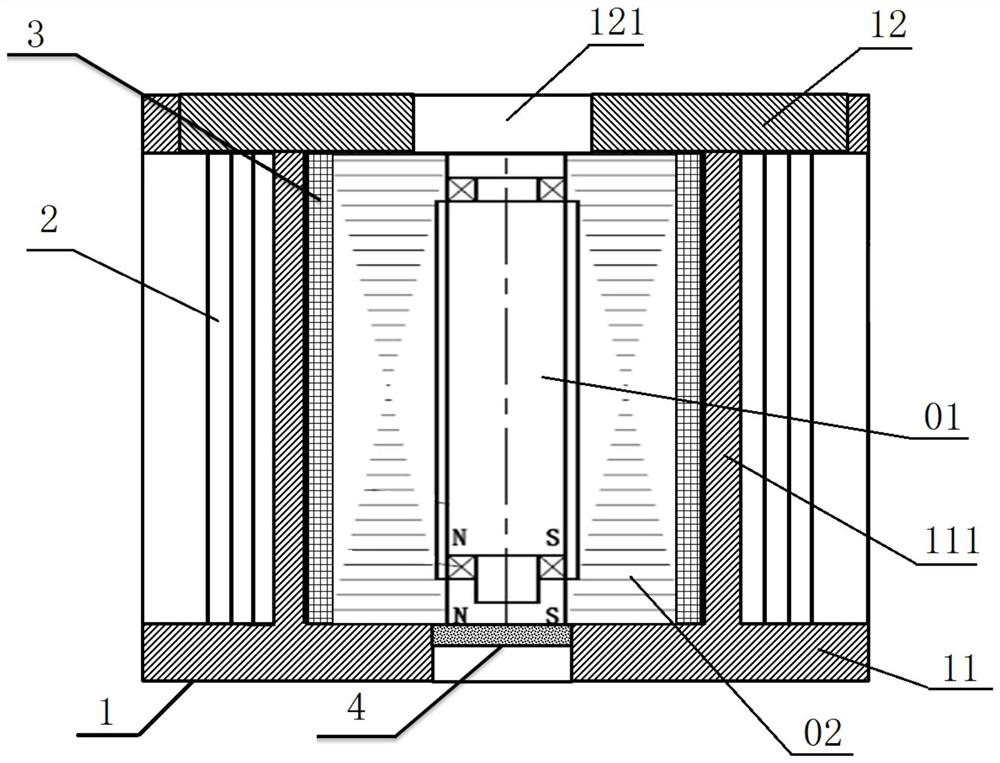
ActiveCN111911288AImprove stabilityWeight increaseGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsImpellerRotational axis
The embodiment of the invention provides a gas turbine starting structure. The gas turbine starting structure comprises a gas compressor casing (1), wherein a gas compressor impeller (5) is arranged on the inner side of the gas compressor casing (1) and rotates around a rotating axis (R) located in the center of the inner side of the gas compressor casing (1); and a gas entraining channel casing (2) which is located outside the gas compressor casing (1) and axially cooperates with the gas compressor casing (1) so as to form an annular gas flow channel (3) between the gas entraining channel casing (2) and the gas compressor casing (1). A gas entraining gap (4) is formed in the gas compressor casing (1) in the circumferential direction. On one hand, the structure has the beneficial effects of being simple and portable. On the other hand, the problem that in the prior art, a gas turbine starting device cannot be reused is solved through the structure.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A failure protection device and a failure protection method for medical equipment
ActiveCN106264582BSolution can not be reusedComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical equipmentMedicine
The invention relates to a fail-safe device and a fail-safe method for a medical device. The medical device includes a base for installing a device to be protected. a connection; and a sensor with a portion of the sensor located within the recess and a portion of the sensor located outside the recess.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Device, control system and control method for solidifying fly ash
ActiveCN111604353BSolution can not be reusedWill not polluteSolid waste managementSolid waste disposalControl systemEngineering
This application relates to a device for solidifying fly ash, including a power transmission system, an electric heating system, a mud roll forming system for forming a liquid fly ash mixture, and an electromechanical control system; wherein the power transmission system is a water-ash mixed mud connected by pipelines The material placement cylinder, the mud mixing conveying pump assembly and the conveying mud spray pipe; the electric heating system is composed of the transmission nodes mechanically connected with each other, the transmission power runner, the closed shell, and the forming electric heating plate; the mud roll forming system is composed of mechanical The connected cutting parts, rolling forming roller control assembly, screening channel, mud roll forming assembly, tapered end, movable adjustment part, ash solid block separation equipment, ash solid block output equipment; the electromechanical control system consists of mechanical It is composed of a connected driving unit, a transmission power system, a rotation sensing device, an output transmission member, an input transmission member, a power connecting rod, a feedback output power rod and a mud sheet roll forming movable assembly. The application also discloses a device control system and a control method for solidifying fly ash.
Owner:河南中釉环保科技有限公司
Gas Turbine Startup Structure
ActiveCN111911288BImprove stabilityWeight increaseGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsImpellerRotational axis
An embodiment of the present invention provides a starting structure for a gas turbine, comprising: a compressor casing (1), a compressor impeller (5) is arranged inside, and the compressor impeller (5) is positioned around the compressor casing (1) The rotation shaft (R) at the inner center rotates; the bleed air channel casing (2) is located outside the compressor casing (1) and axially cooperates with the compressor casing (1) to cooperate with the compressor casing (1) An annular airflow channel (3) is formed between the machine casings (1); wherein, the compressor casing (1) is provided with an air-introduction slot (4) in the circumferential direction. On the one hand, the structure has the advantages of simple structure and light weight. On the other hand, it also solves the problem that the gas turbine starting device in the prior art cannot be reused.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A seismic isolation joint covering device and construction method for seismically isolated building wall nodes
ActiveCN106759967BSolution can not be reusedGuaranteed integrityBuilding insulationsUltimate tensile strengthSealant
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Screen-free double-rotor grinder
InactiveCN103736557ASolution can not be reusedReduce pollutionGrain treatmentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a screen-free double-rotor grinder. The grinder comprises a material inlet, a material distributing device, air supply outlets, a shell body, an upper liner plate, a lower liner plate, rotors, and a material outlet; the material distributing device is arranged on the material inlet, two sides of the upper part of the shell body are both provided with an air supply outlet, the arc outer shell of the mid-lower part of the shell body and the edges of the upper liner plate and the lower liner plate in the shell body cooperatively form two grinding chambers; rotors provided with hammering blades are arranged in the grinding chambers; the material outlet is arranged in the lower end of the grinding chambers, and a partition plate is arranged on a position on the inner wall of the shell body, wherein the position of the partition plate is in the same level as the top part of the upper liner plate. The screen-free double-rotor grinder can grind barks into flocculent substance, fluffy substance, granules, or bagasse-like stuffs, and has the advantages of simplicity and high efficiency.
Owner:广西奥士达环境工程有限公司
Farmland soil nitrogen and phosphorus loss biochar interception and reuse system and method
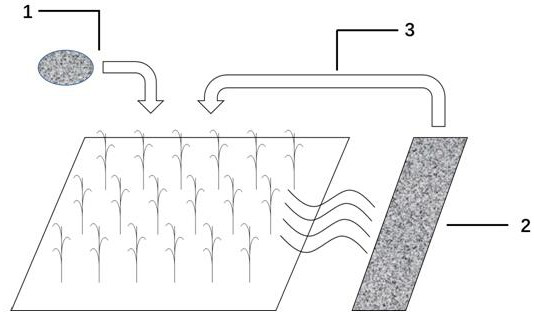
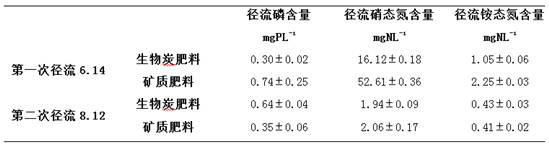
PendingCN111978115AImprove retentionReduce churnWater contaminantsAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSoil scienceSoil quality
The invention relates to a farmland soil nitrogen and phosphorus loss biochar interception and reuse system and method. The system comprises three links of application of nitrogen and phosphorus loaded biochar fertilizer to a farmland, a biochar interception zone of farmland runoff and reapplication of biochar in the interception zone to the farmland. Biochar is used for loading nitrogen and phosphorus and can serve as an improver to be applied to soil, so that control and recycling of farmland nitrogen and phosphorus non-point source loss are achieved. The system is simple in structure, easyand convenient to operate, high in practicability and low in cost, intercepted nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient elements are recycled while the soil nitrogen and phosphorus non-point source loss is controlled, and the soil quality is improved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Greening device for ecological environmental protection engineering
InactiveCN109392495AAchieve rapid growthSolve the problem of low breeding efficiencyClimate change adaptationGreenhouse cultivationNutrient solutionEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of ecological environmental protection engineering, and particularly relates to a greening device for ecological environmental protection engineering. Thegreening device comprises a protection box, wherein a cavity is formed in the protection box; a first opening is formed in the top of the cavity; the bottom and opposite side walls in the cavity are all provided with heating tubes; a cultivation box is arranged in the cavity; the cultivation box is located above the upper ends of the heating tubes; a second opening is formed in the upper end of the cultivation box; bearing plates are respectively fixed on two sides of the upper end of the cultivation box; openings are respectively formed in side walls of two ends of the cultivation box; and aplant growth layer is arranged at the bottom of the cultivation box. The device has the advantages that a collection box, a control valve, a temperature sensor, a humidity sensor and the heating tubesare matched with each other, a nutrient solution is added through the control valve, and the temperature is controlled by the heating tubes, so that a problem of low cultivation efficiency is solved,rapid growth of plants is realized, timeliness is improved, and the greening device is convenient to use.
Owner:吉林天珈医疗管理有限公司
Industrial data processing method and device, storage medium and electronic device
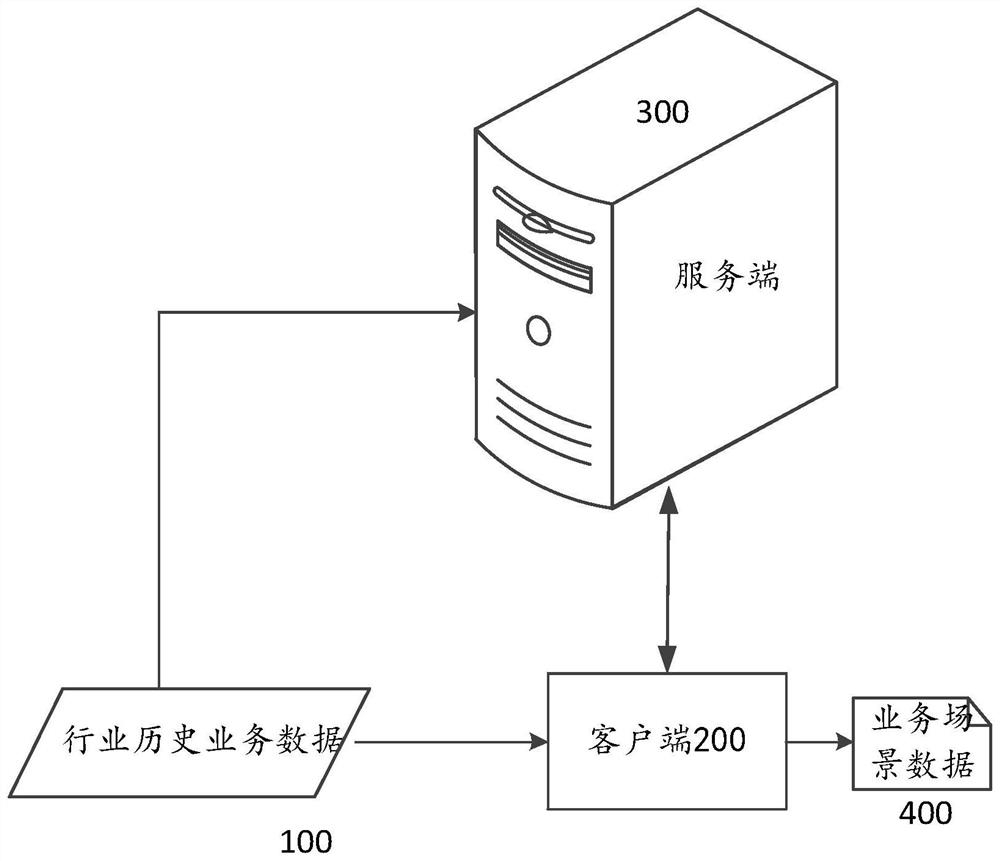
PendingCN114780560AAchieve sharingSolution can not be reusedDatabase updatingSpecial data processing applicationsBusiness dataData mining
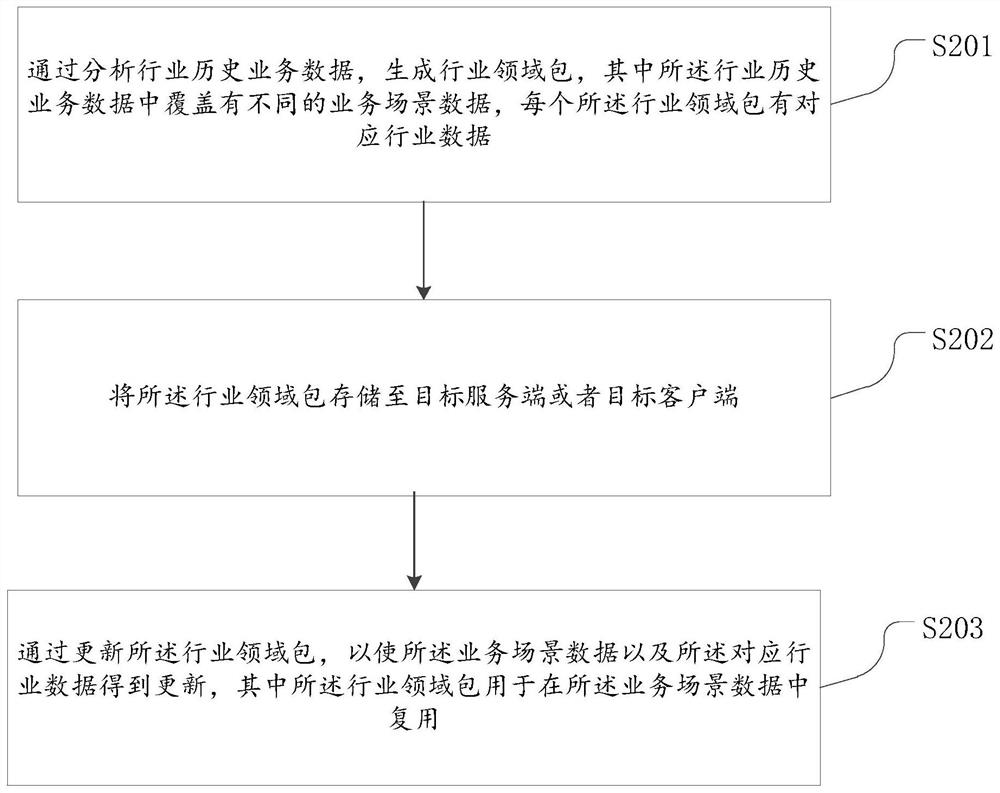
The invention discloses an industry data processing method and device, a storage medium and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps that industry field packets are generated by analyzing industry historical business data, the industry historical business data are covered with different business scene data, and each industry field packet is provided with corresponding industry data; storing the industry field package to a target server or a target client; the business scene data and the corresponding industry data are updated by updating the industry field packet, and the industry field packet is used for being reused in the business scene data. The technical problem that industry experience data cannot be reused or shared is solved.
Owner:普强时代(珠海横琴)信息技术有限公司
Composition of environmental glass used for TFT-LCDs
InactiveCN104071979AImprove heat resistanceHigh resistance to devitrificationDevitrificationExpansion factor
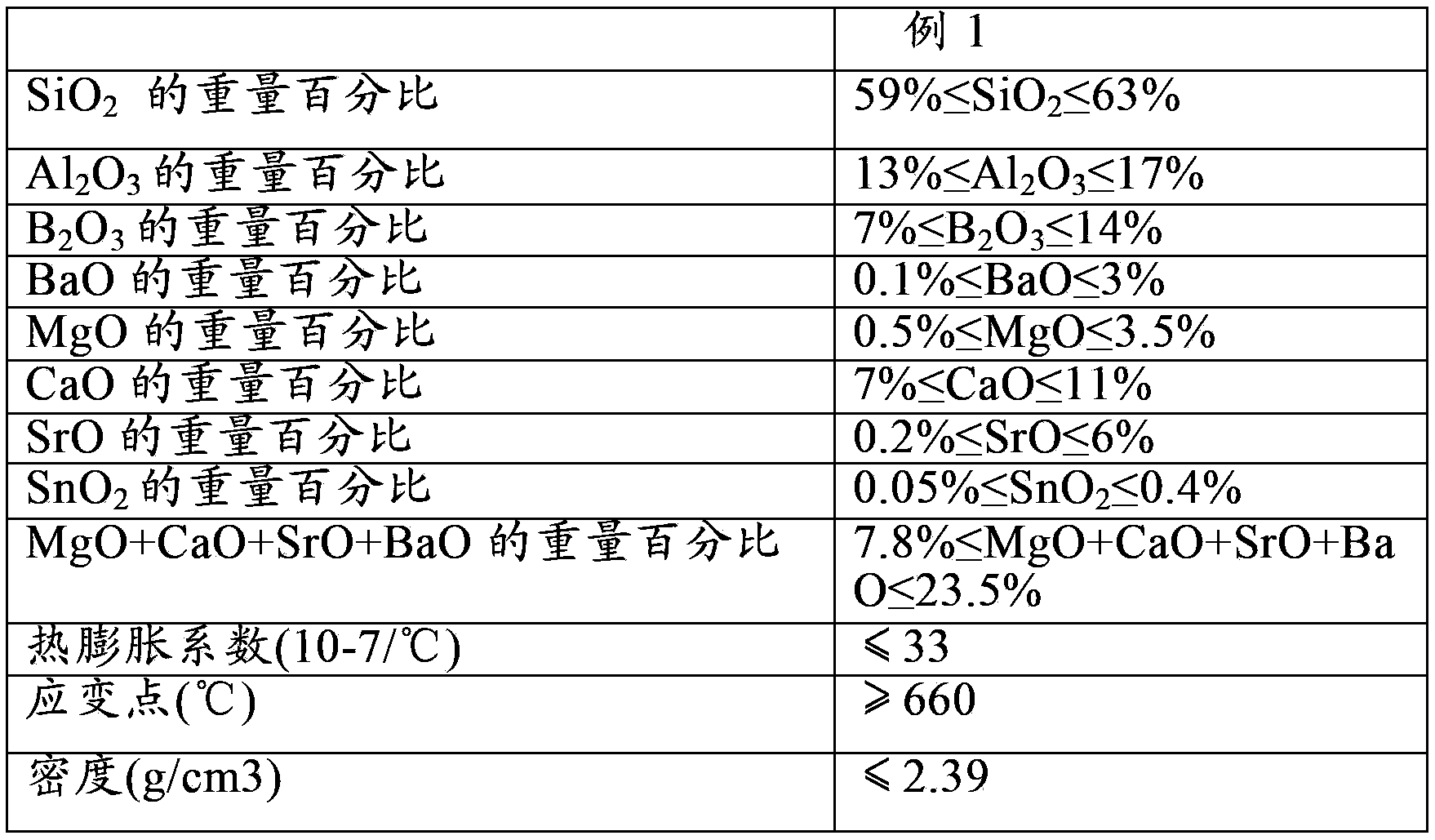
A composition of environmental glass used for TFT-LCDs is disclosed. The environmental glass is used in thin film transistor liquid crystal displays (also known as TFT-LCDs). The environmental glass comprises following components by weight: not more than 63% and not less than 59% of SiO2, not more than 17% and not less than 13% of Al2O3, not more than 14% and not less than 7% of B2O3, not more than 3% and not less than 0.1% of BaO, not more than 3.5% and not less than 0.5% of MgO, not more than 11% and not less than 7% of CaO, not more than 6% and not less than 0.2% of SrO, and not more than 0.4% and not less than 0.05% of SnO2, with the total content of the CaO, the BaO, the MgO, the SrO, and the like being 7.8%-23.5% to the best. Accordingly, the components are melt to form the hard and tough environmental glass used for the TFT-LCDs. Chemical resistance and devitrification resistance of the glass are enhanced and the viscosity and the expansion factor decrease, thus overcoming a problem of insufficient strength and hardness of glass at present and a problem that the glass at present comprises PbO, As2O3 or Sb2O3, and other components harmful to the environment.
Owner:FORTUNE TECH
Rotor dismounting method and device
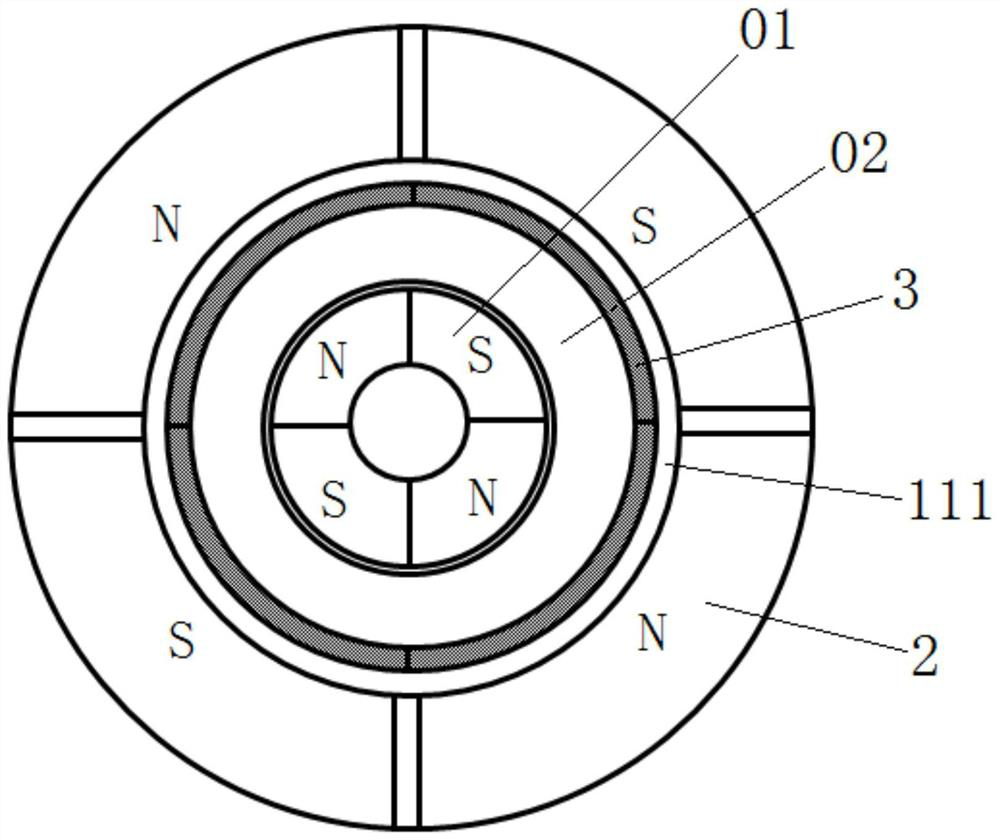
ActiveCN112202294ASolution can not be reusedAvoid bumpingManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesCentering/balancing rotorsMagnetic tension forceElectric machine
The invention relates to a rotor dismounting method and device, and aims to solve the problem that when a stator and a rotor of an inner rotor type permanent magnet synchronous motor are separated byadopting a traditional method, the stator and the rotor collide with each other, so that a permanent magnet of the rotor is damaged and cannot be reused. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) disassembling an end cover at one end of a to-be-disassembled motor, circumferentially arranging radial magnetic force counteracting units on the outer side of the to-be-disassembled motor, whereinmagnetic poles of the radial magnetic force counteracting units and magnetic poles of a rotor are consistent in number and are in one-to-one correspondence, and meanwhile the corresponding magnetic poles are identical in polarity; 2) adjusting the magnetic force of each magnetic pole of the radial magnetic force counteracting unit to counteract the radial attraction force of each magnetic pole ofthe rotor to the stator, thereby balancing the position of the rotor in the stator; and 3) taking the rotor out of the stator. The device comprises a fixing tool used for placing a to-be-disassembledmotor, a radial magnetic force counteracting unit used for applying magnetic force to the circumference of a rotor on the outer side of the to-be-disassembled motor, and a sensor unit used for sensing the magnetic force action condition.
Owner:XIAN AEROSPACE PRECISION ELECTROMECHANICAL INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com