Patents
Literature
31 results about "Cycle per second" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
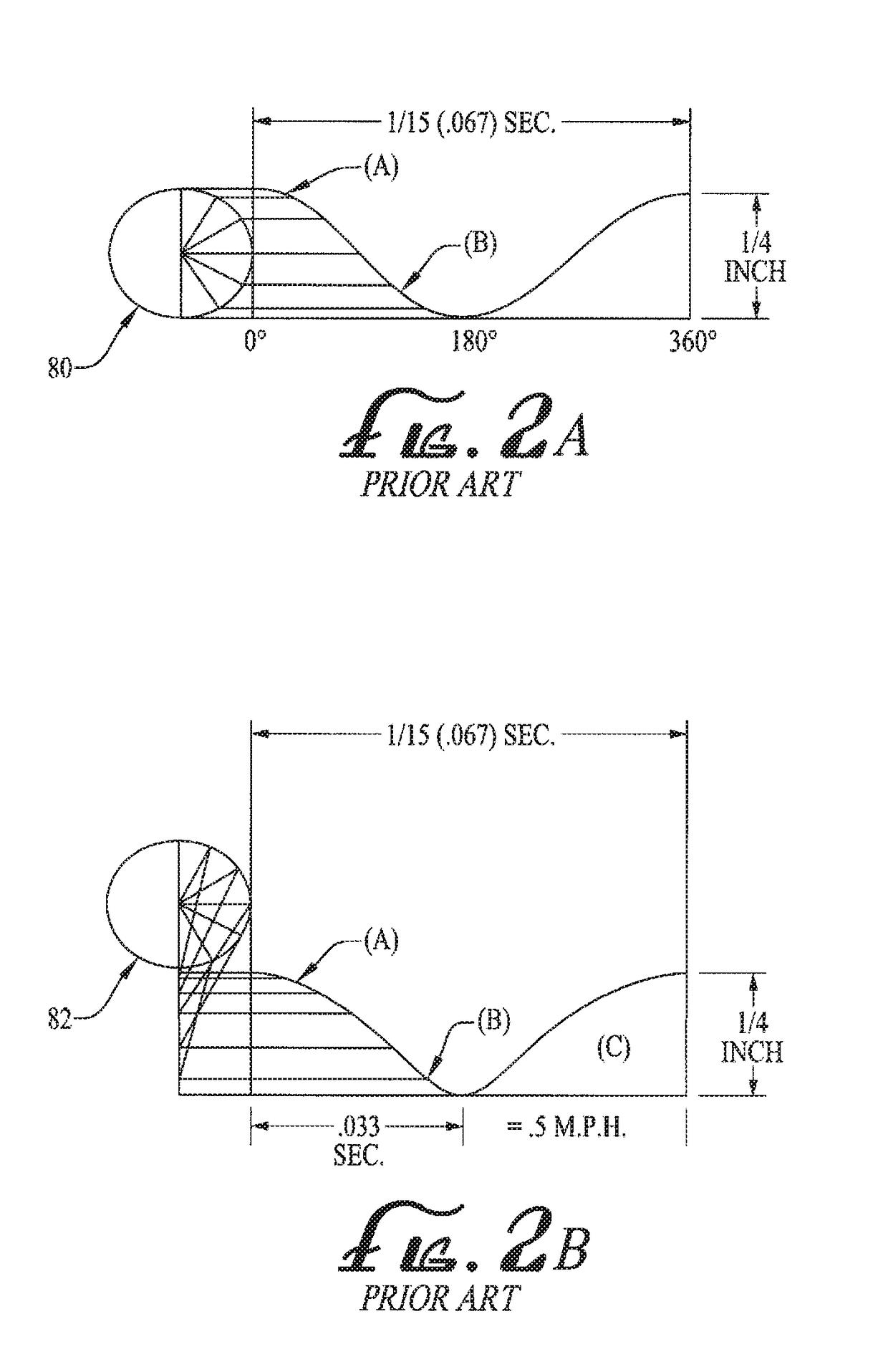
The cycle per second was a once-common English name for the unit of frequency now known as the hertz (Hz). The plural form was typically used, often written cycles per second, cycles/second, c.p.s., c/s, ~, or, ambiguously, just cycles. The term comes from the fact that sound waves have a frequency measurable in their number of oscillations, or cycles, per second.
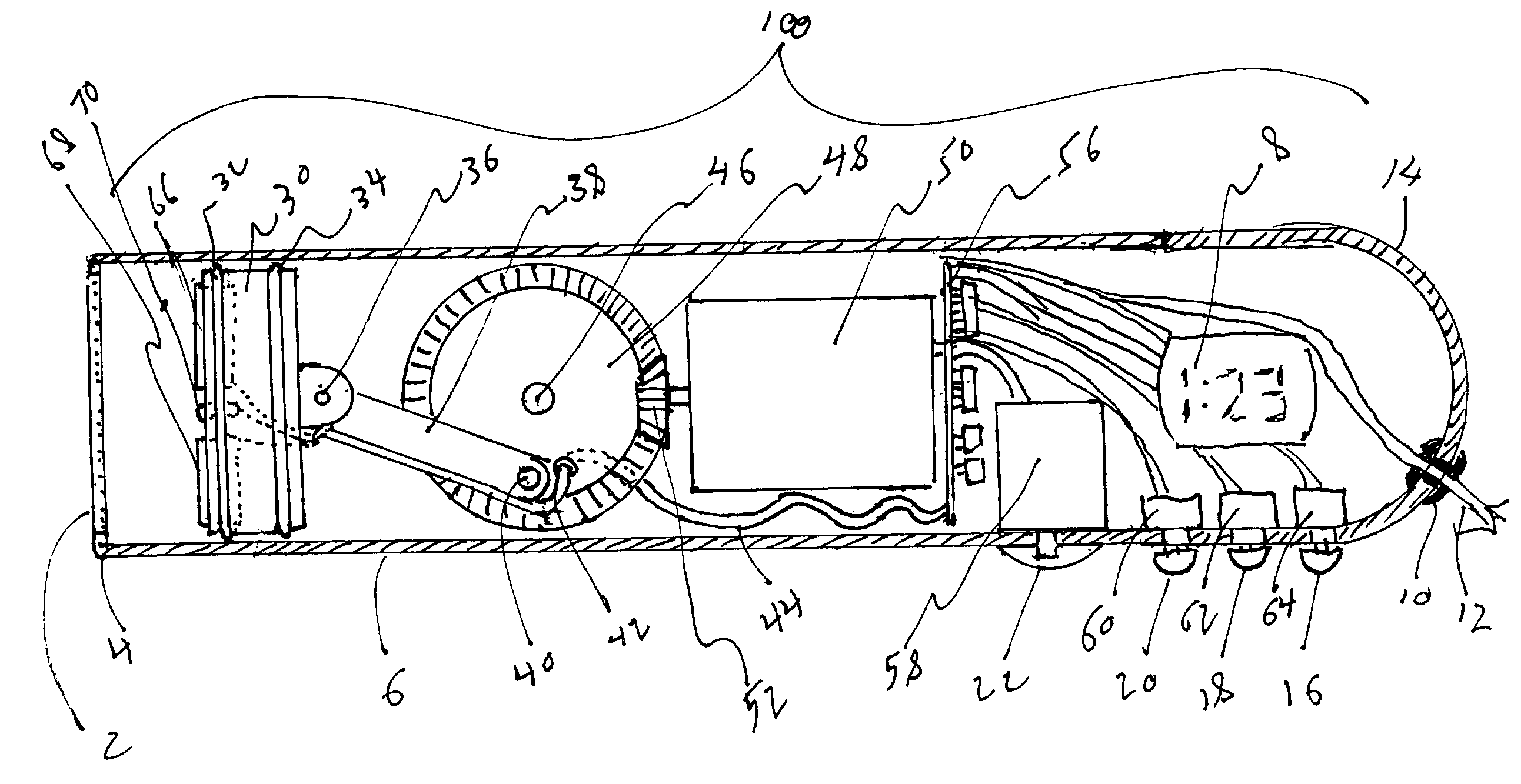
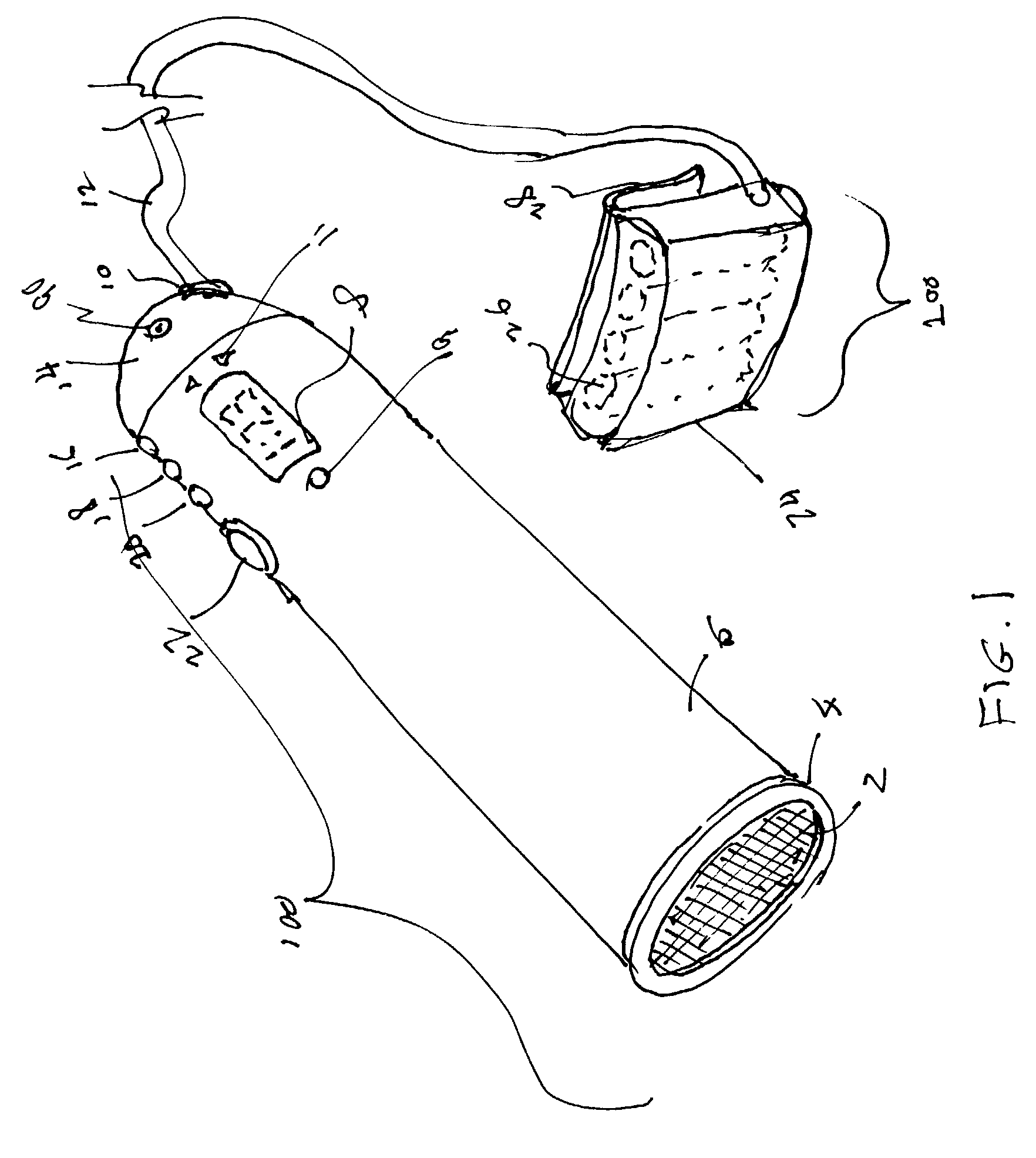
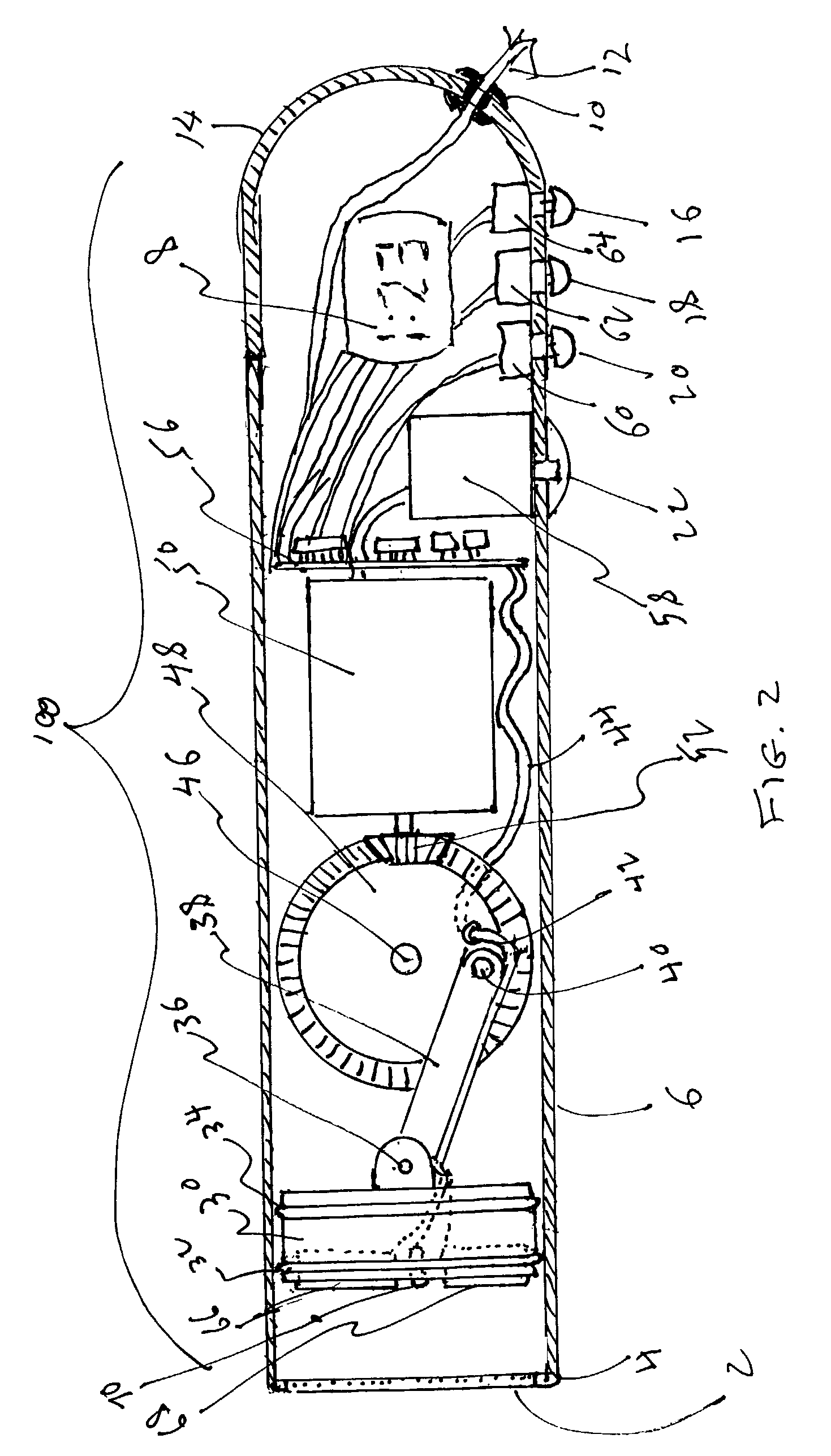
Methods of high rate, low profile tissue removal
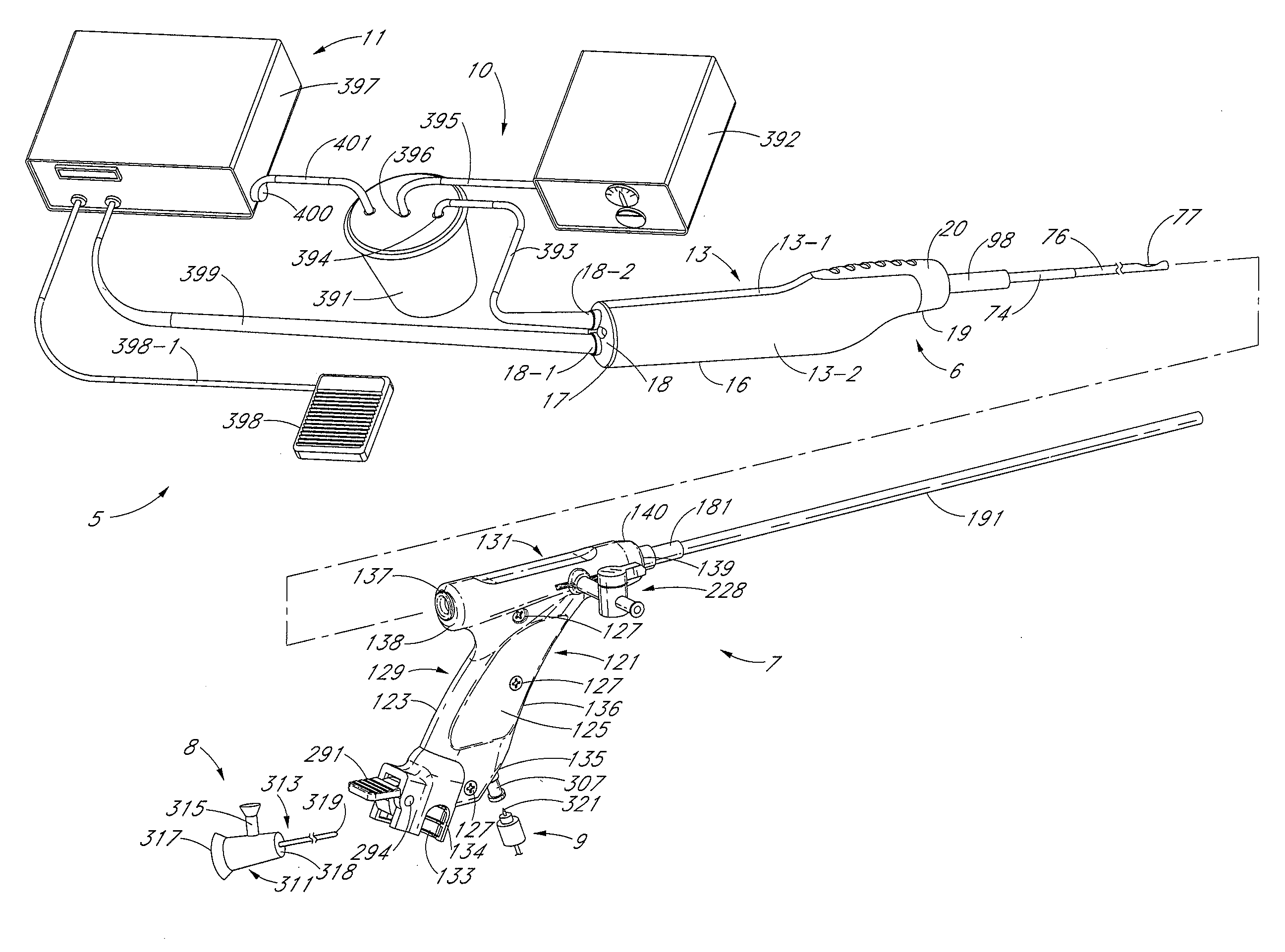
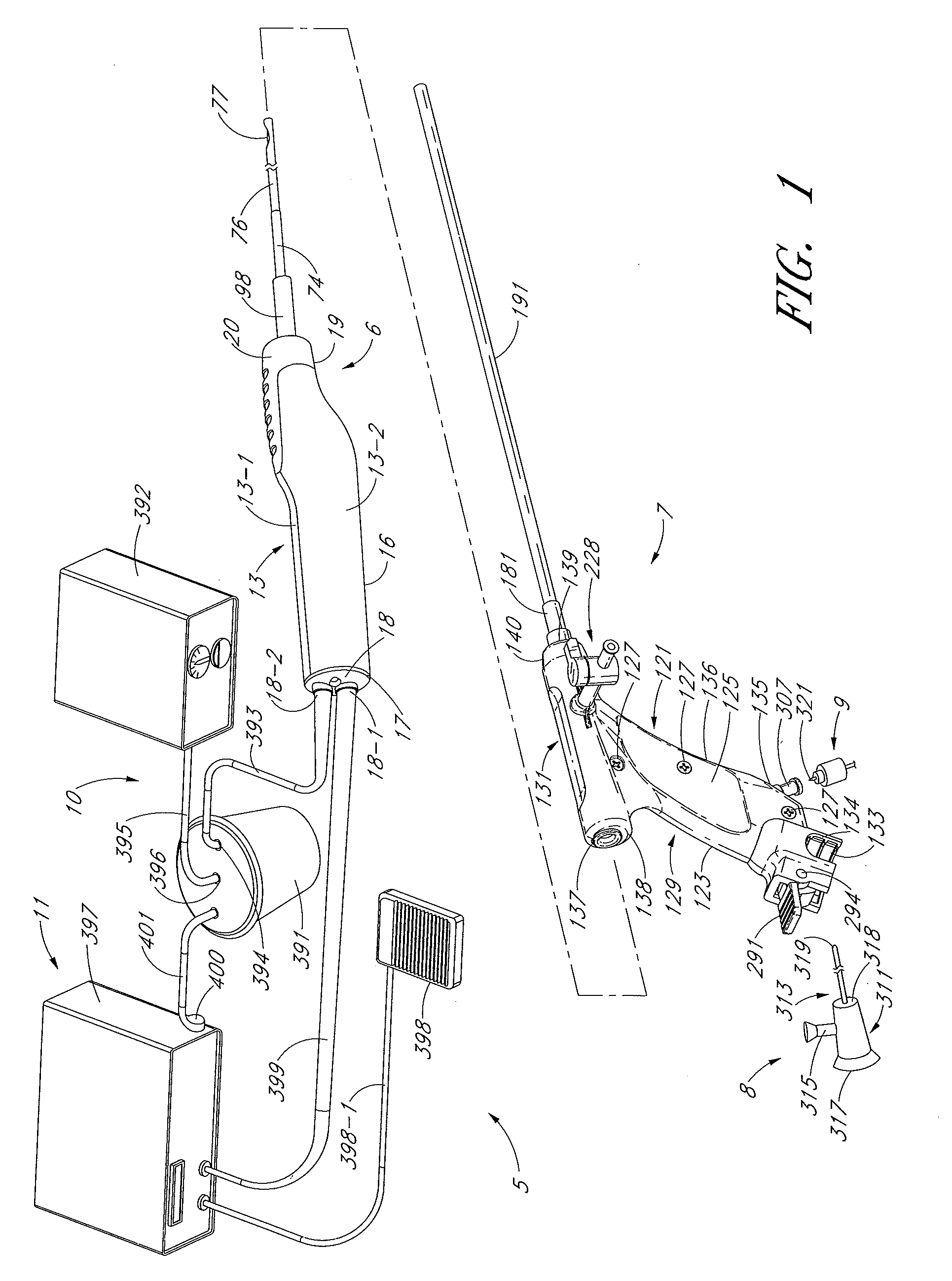
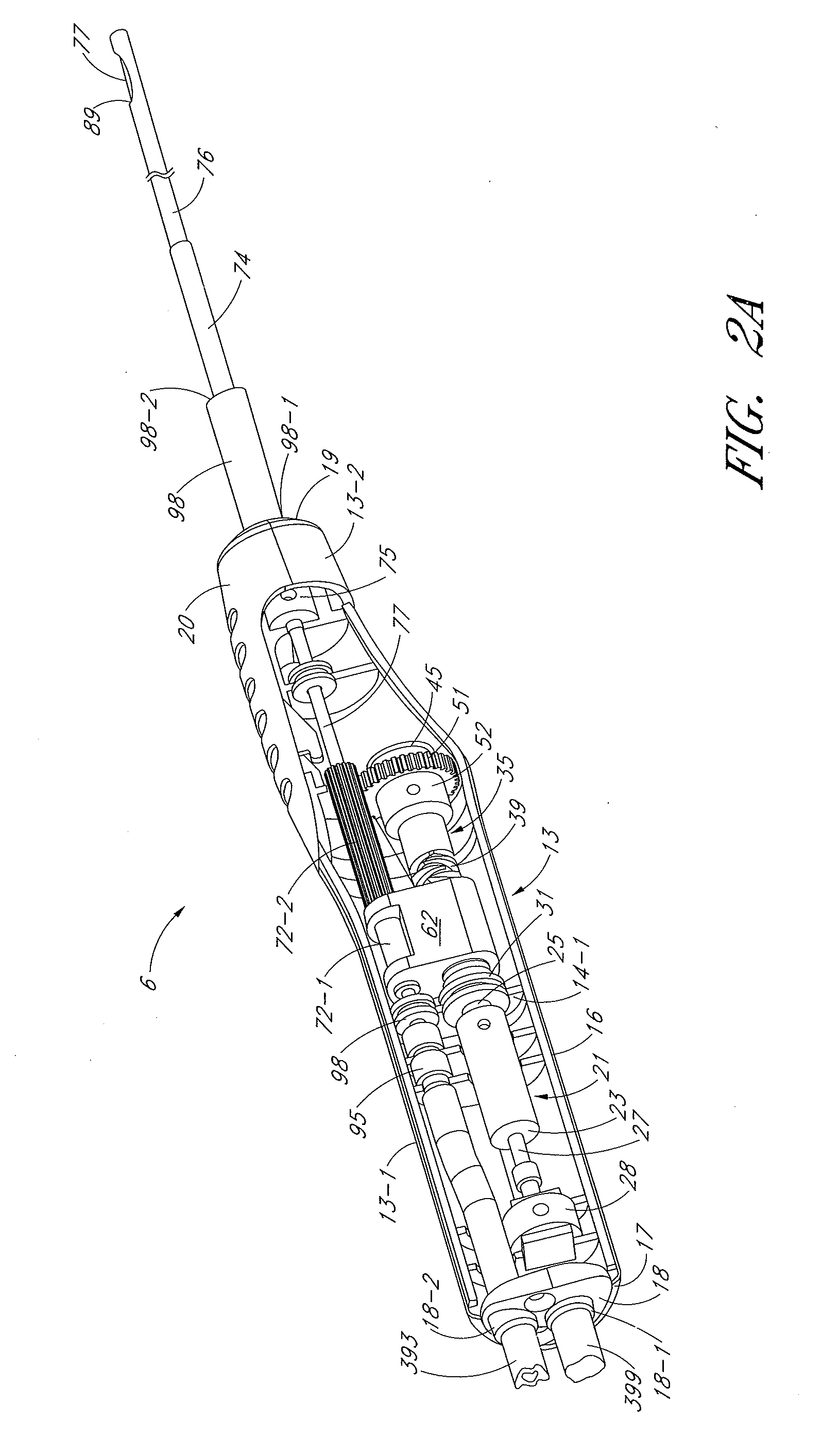
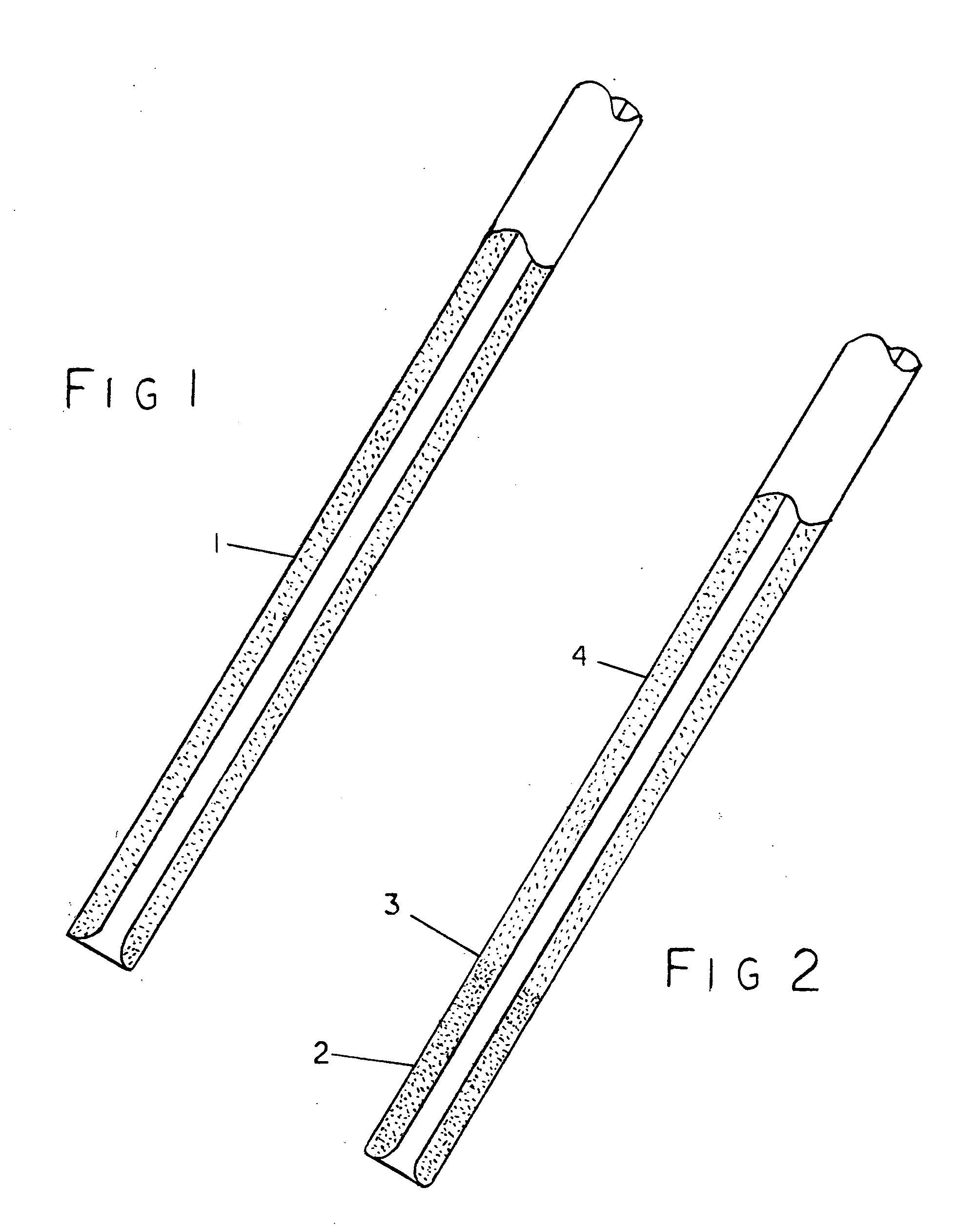
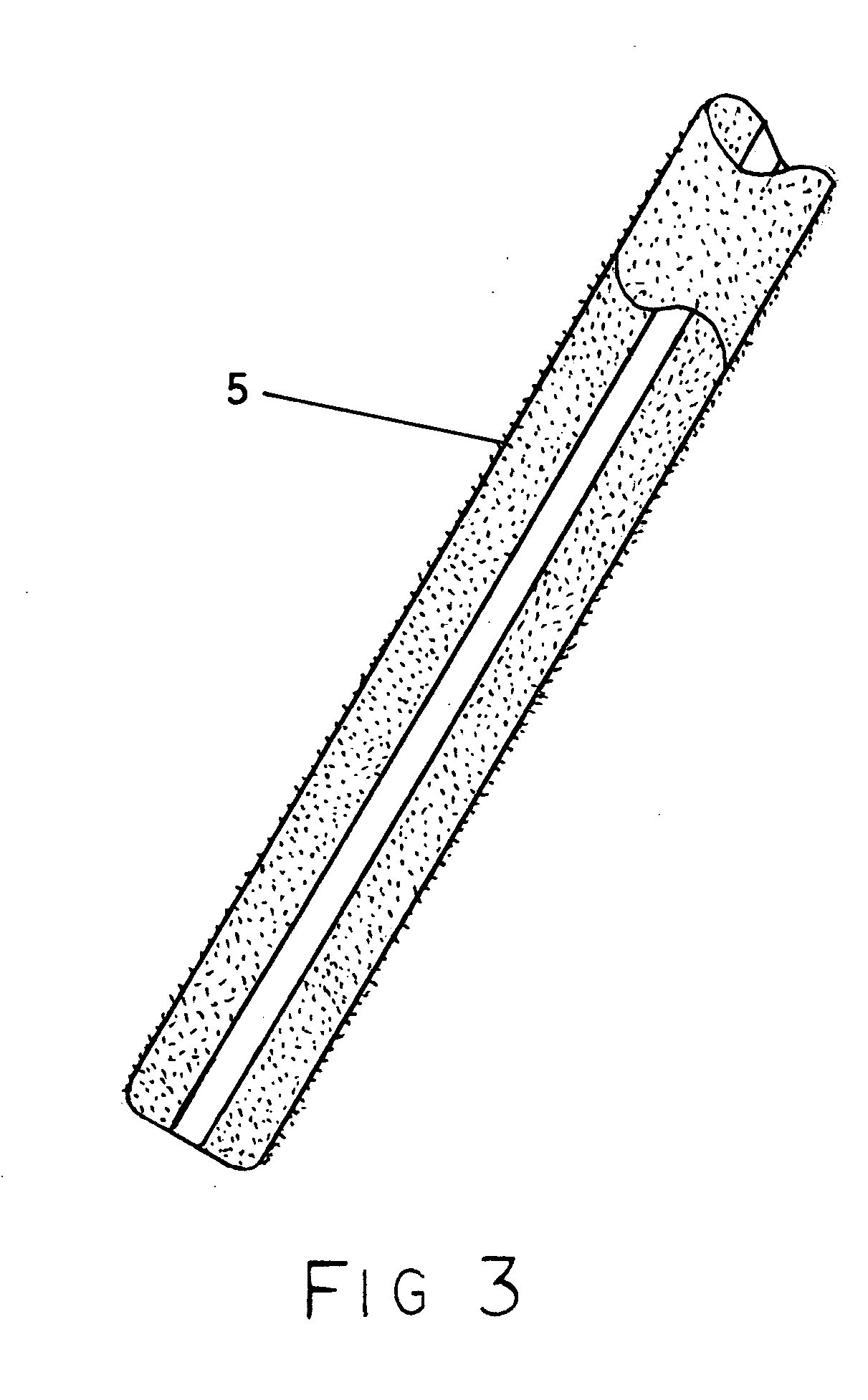
Disclosed are methods and devices for removing tissue from a site in a hollow organ, where the device has a low crossing profile and is capable of removing tissue at a high rate of speed. The device includes an elongate outer tube with a side opening and an inner tube moveably coaxially positioned within the outer tube. Tissue drawn into the side opening can be severed by moving the inner tube across the opening. Tissue may be removed through the device at a rate of at least about 1.4 cc per minute, through a lumen having a cross-sectional area of no greater than about 12.02 mm. Cutting may be accomplished by rotating the inner tube at a speed of at least about 4000 rpm, and axially reciprocating the inner tube at a rate of at least about 1.5 cycles per second. The window may have a rho value of no more than about 1, and the outside diameter of the device may be no more than about 3 mm.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Vibrating, magnetically guidable catheter with magnetic powder commingled with resin, extruded as an integral part the catheter
InactiveUS20050245846A1Preventing accumulative adhesionLongitudinal stiffness is smallCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineUltimate tensile strength
A catheter that is produced in which magnetic powder is commingled and becomes an integral part of the catheter, which makes it not only guidable within the body by an external device, but can be made to vibrate at various speeds (cycles per second) and at varying intensities (voltages) to not only prevent its adhesion to vascular walls, but to render plaque into a viscous state, for easy suctioning from the body.
Owner:CASEY DON EWARD
Nightlight for phototherapy
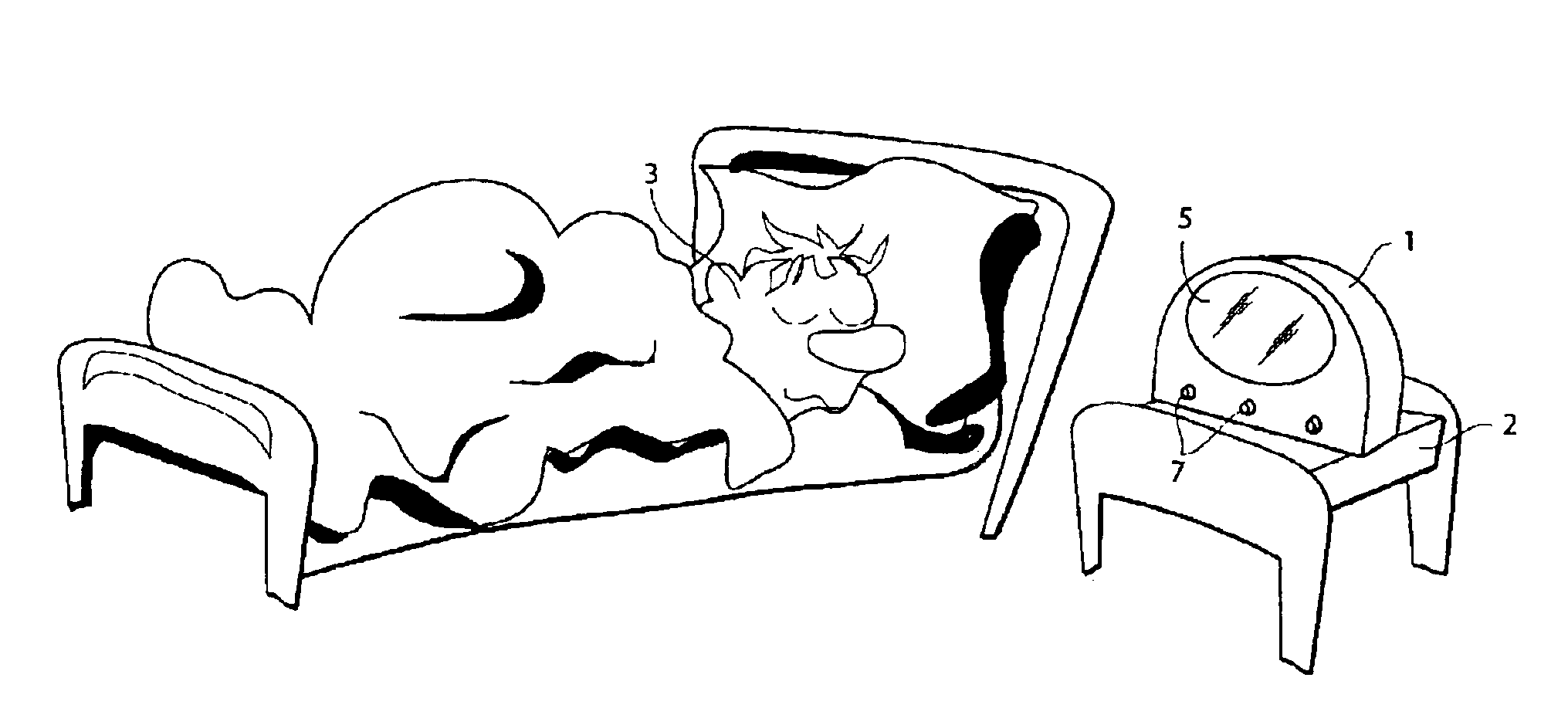
ActiveUS6902296B2Bright enoughEasy to relaxMechanical clocksLighting support devicesHuman bodyCycles per minute
A nightlight is provided for providing therapeutic effects on the human body and mind including promoting relaxation, sleep and wakefulness. The nightlight includes a housing, a light source, a central processor, one or more controls, and a power supply. The light source produces at least three modes having various light properties. The light modes include a sleep readiness mode, a sleep help mode and a wake-up mode. The sleep readiness mode produces light at about 40 lumens and preferably includes only light from the blue and yellow portions of the visible light spectrum. The sleep help mode produces monochromatic light in the blue or green spectrum. Preferably, the light undulates at a frequency of one cycle per second to one cycle per minute at a luminosity of between 5 lumens and 25 lumens. Meanwhile, the wake-up mode produces substantially full spectrum light at approximately 1,600 lumens. The processor and controls allow a person to select and control the various light modes. Moreover, the nightlight may include biological sensors for measuring physiological activity of the body.
Owner:SEARFOSS III ROBERT LEE
Nightlight for phototherapy
A nightlight provides therapeutic effects on the human body and mind including promoting relaxation, sleep and wakefulness. The nightlight includes a housing, a light source, a central processor, one or more controls, and a power supply. The light source produces at least three illumination modes having various light properties. The light modes include a sleep readiness mode, a sleep help mode and a wake-up mode. The sleep readiness mode produces light at about 40 lumens and preferably includes only light from the blue and yellow portions of the visible light spectrum. The sleep help mode produces substantially monochromatic light in the blue or green spectrum. Preferably, the light undulates at a frequency of one cycle per second to one cycle per minute at a luminosity of between 5 lumens and 25 lumens, which can be selected to automatically decrease by the user. Meanwhile, the wake-up mode produces substantially full spectrum light at approximately 1,600 lumens. The controls allow a person to control the various light modes. Moreover, the nightlight may include biological sensors for measuring physiological activity of the body. The nightlight may be incorporated into a bedside alarm clock which includes numerous features found in a traditional alarm clock such as a display for displaying the time or alarm time. The alarm function may be provided by illumination of one of the three nightlight's illumination modes, which is preferably the wake up mode which may illuminate slowly or substantially immediately to full brightness.
Owner:SEARFOSS III ROBERT LEE
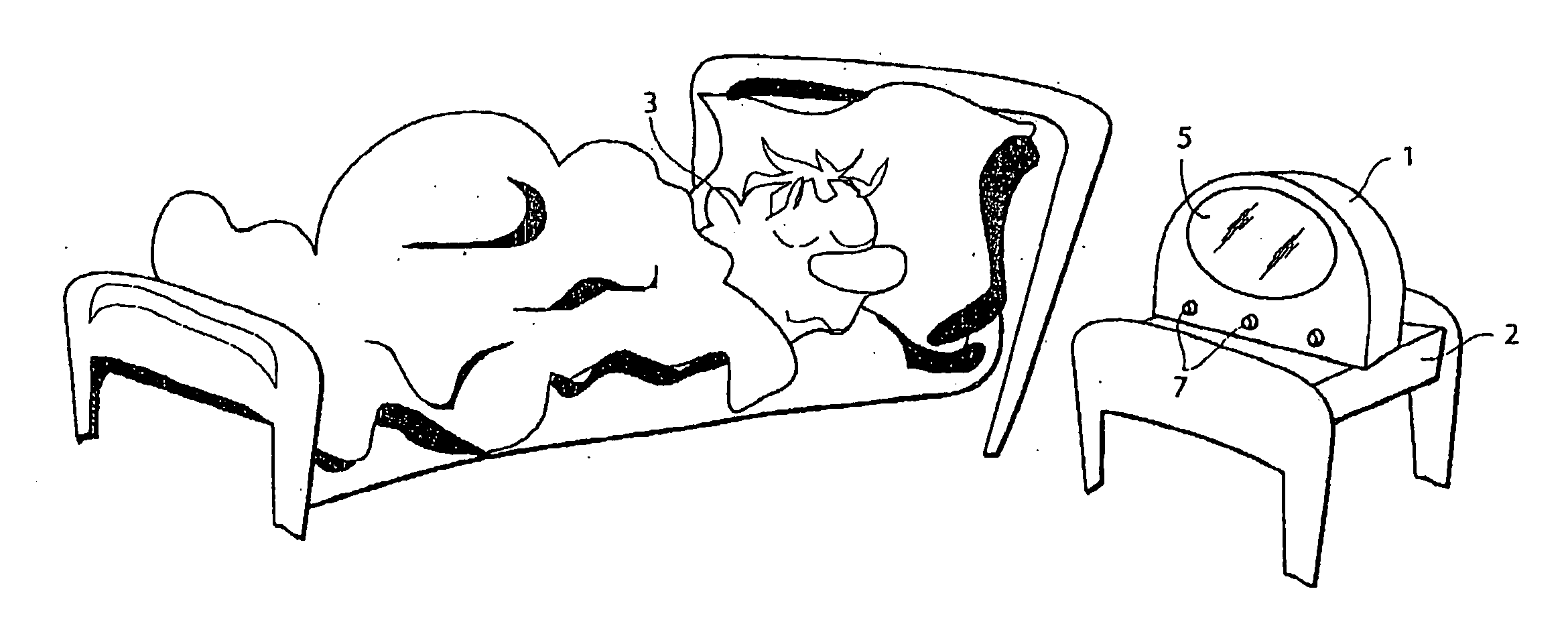
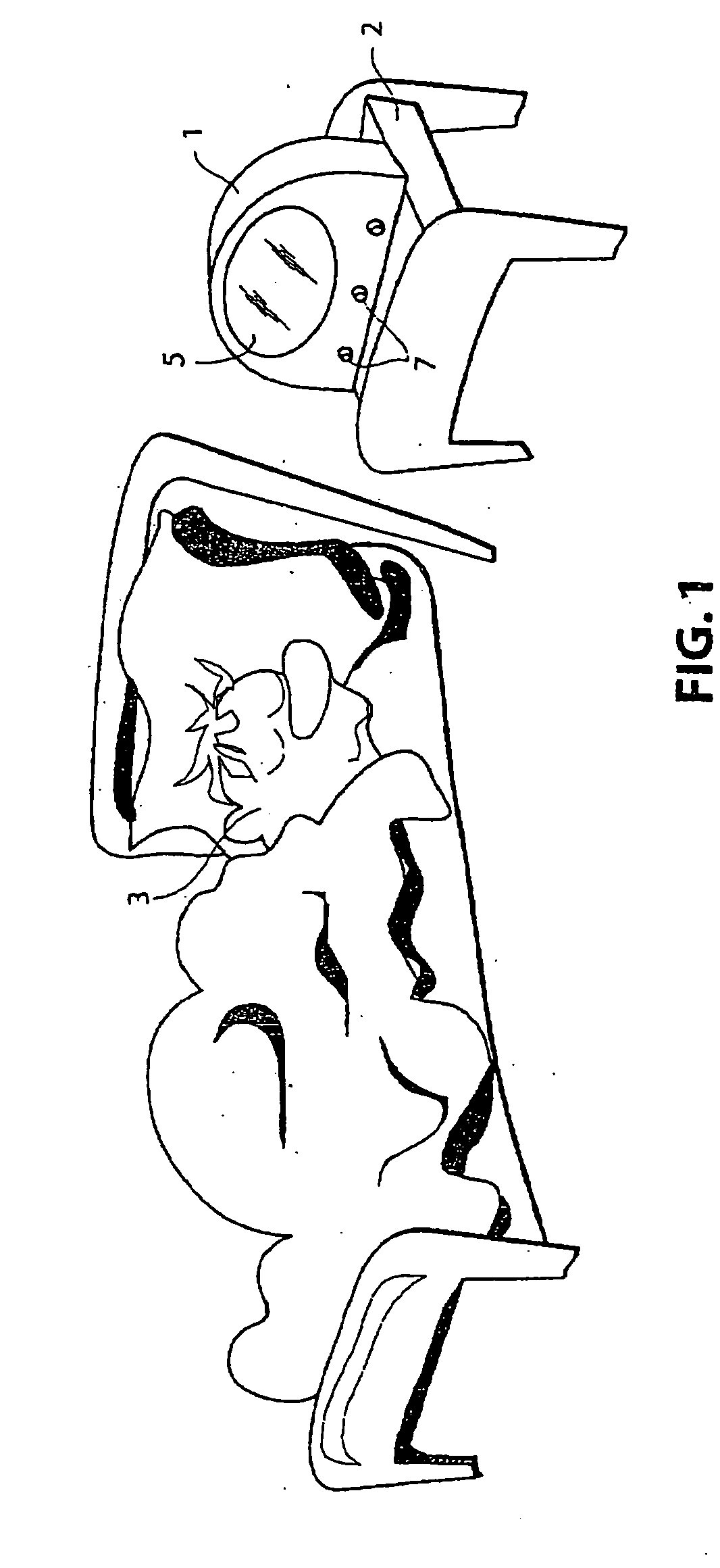
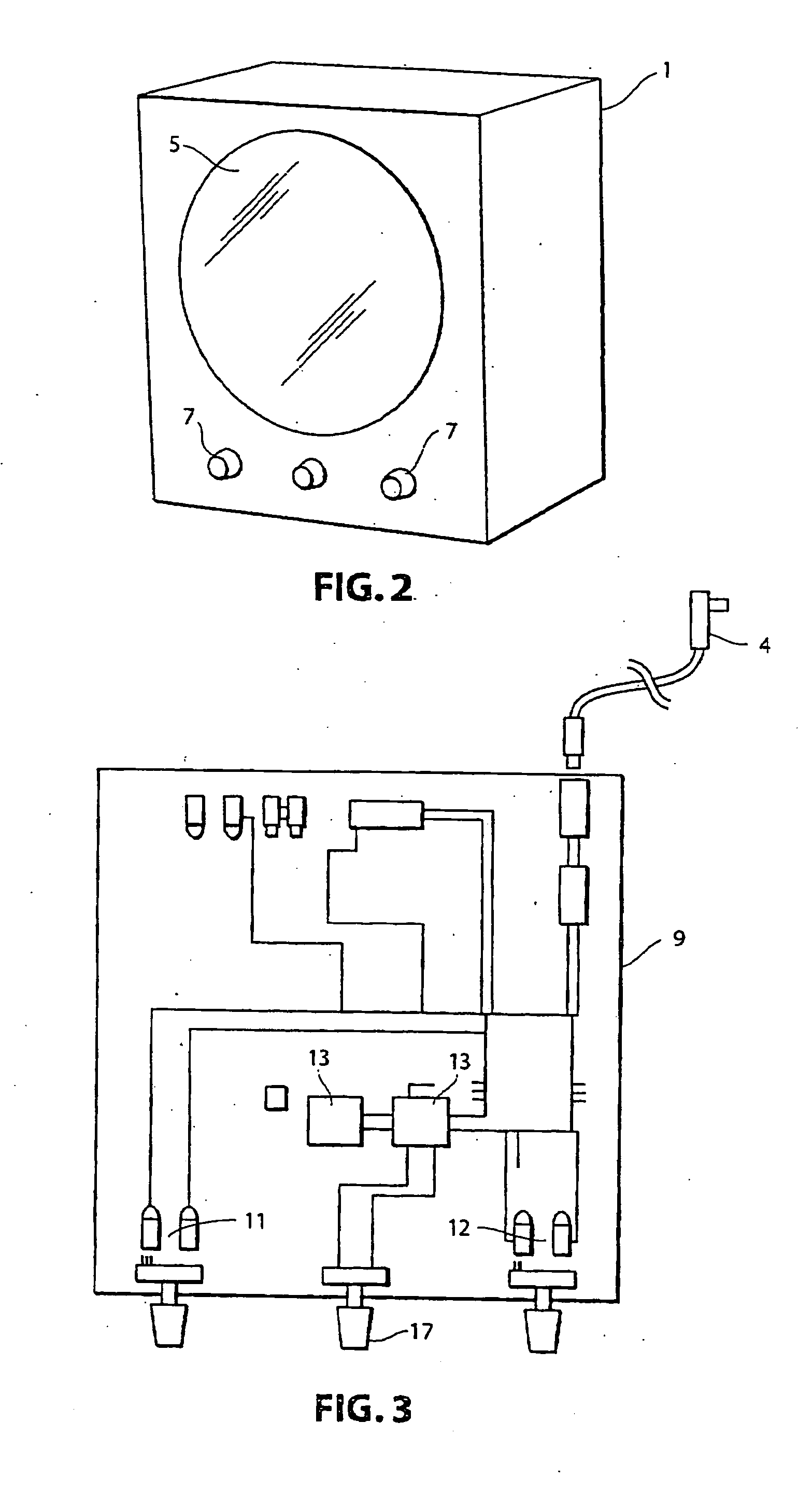
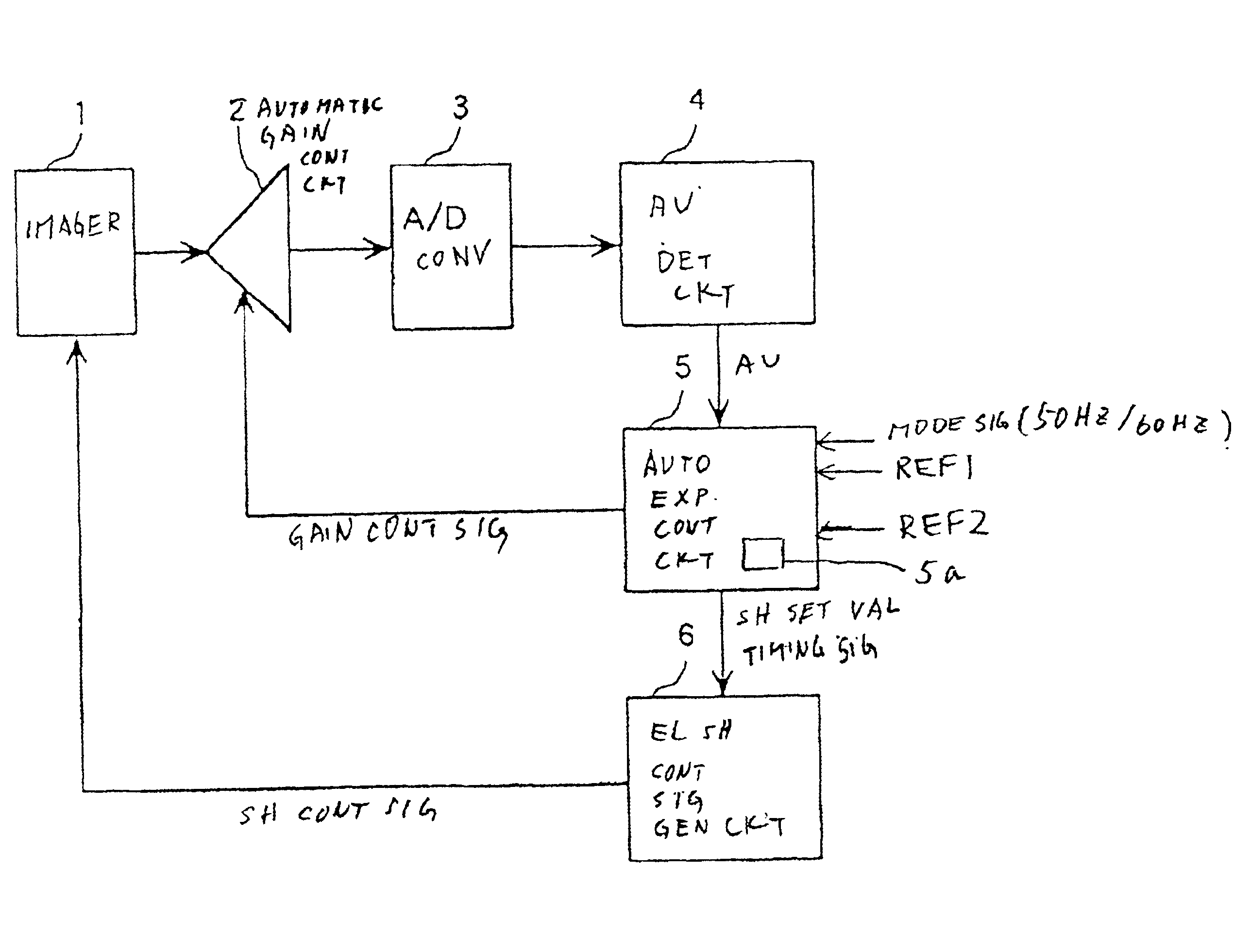
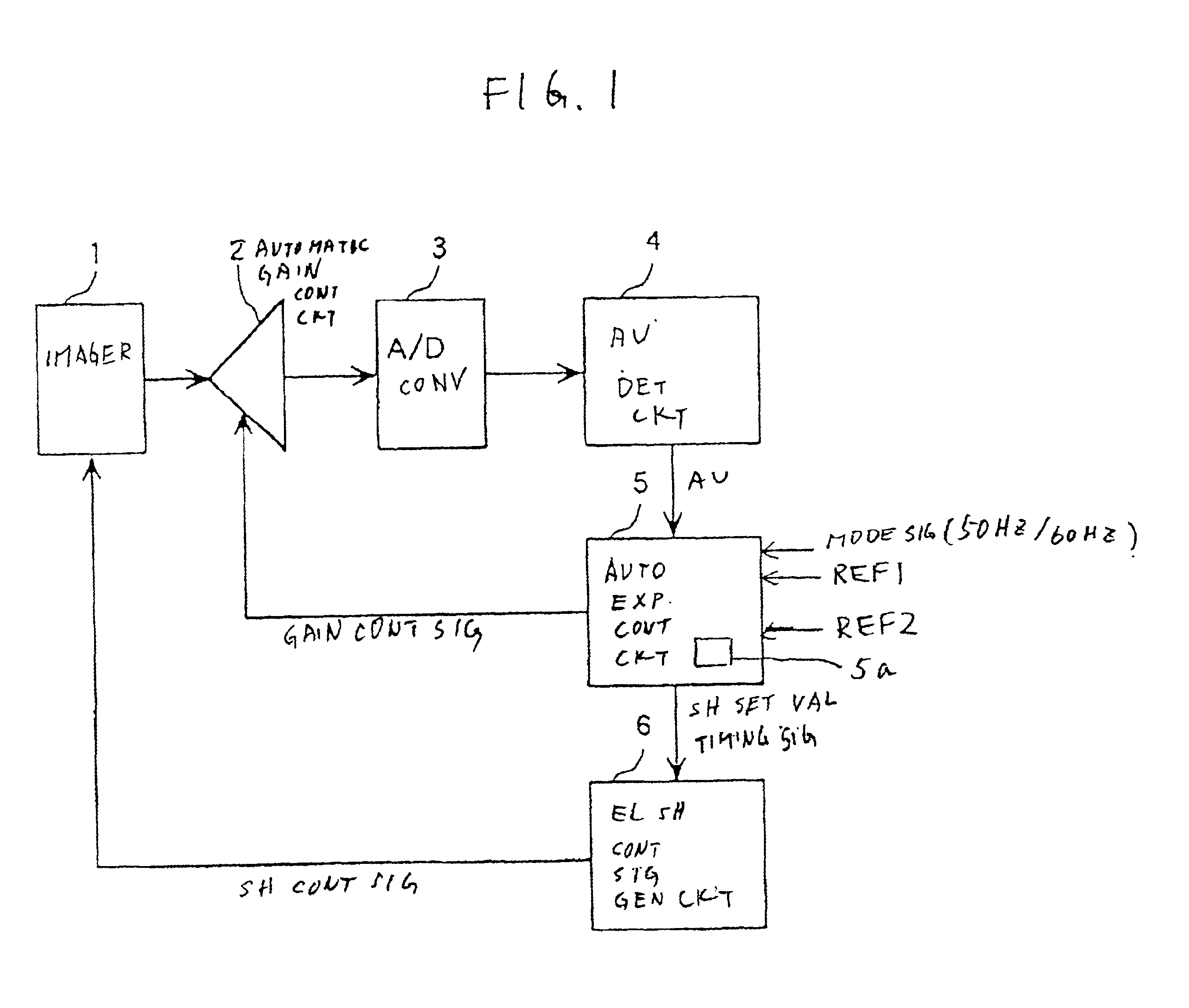
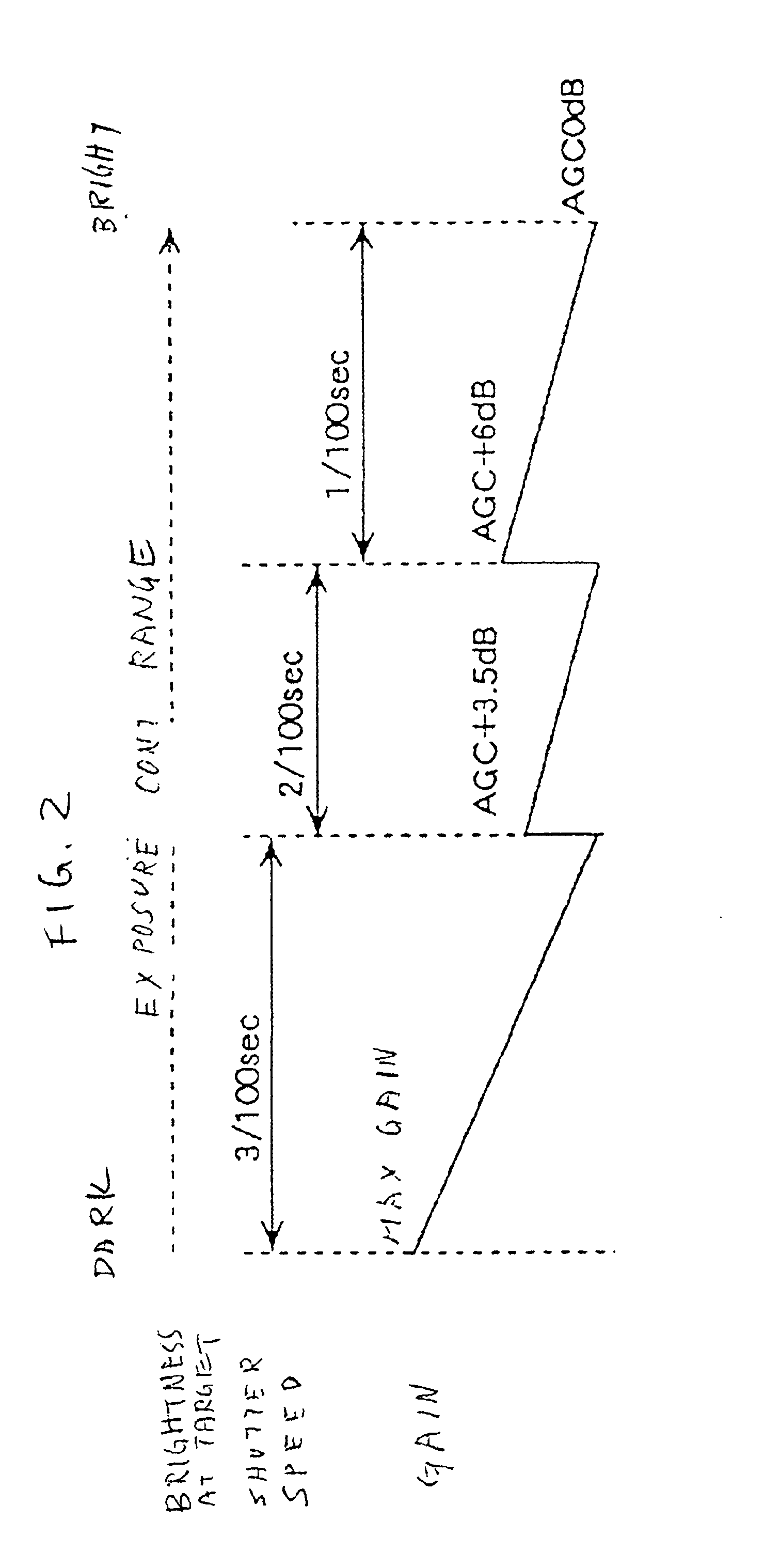
Video signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS6882363B1Easy to optimizeEasy to processTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsElectronic shutterControl signal
An automatic gain controlling circuit controls a gain of a video signal from an imager having an electronic shutter function according to a gain control signal. An average detecting circuit detects an average level of a luminance signal of the video signal. An automatic exposure controlling circuit generates the gain control signal according to the luminance average level in response to a mode signal indicative of the cycles per second of the ac line and generates a timing signal corresponding to the ac line and a shutter speed control signal together with electronic shutter control signal generation circuit at a unit of the voltage variation cycle of the ac line according to the luminance average level such that a shutter interval of the imager is changed stepwise and each of the shutter intervals is an integer times the voltage variation cycle of the ac line. The automatic exposure controlling range is expanded by changing the shutter speed stepwise from {fraction (1 / 100)} sec, {fraction (2 / 100)} sec {fraction (3 / 100)} sec at 50-Hz-ac area, for example, to provide coarse exposure controlling and fine automatic gain controlling is provided every shutter interval to suppress flicker.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
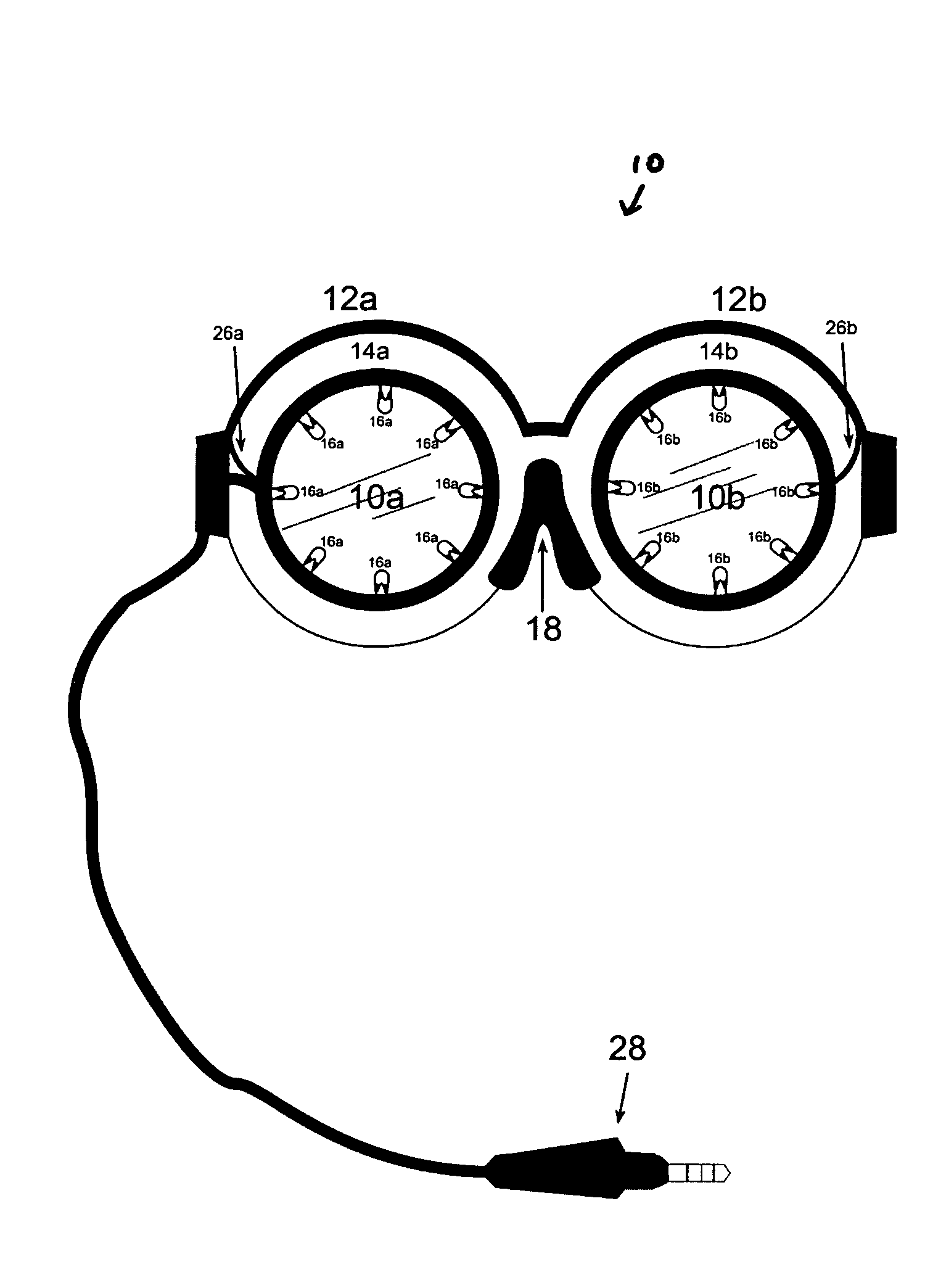
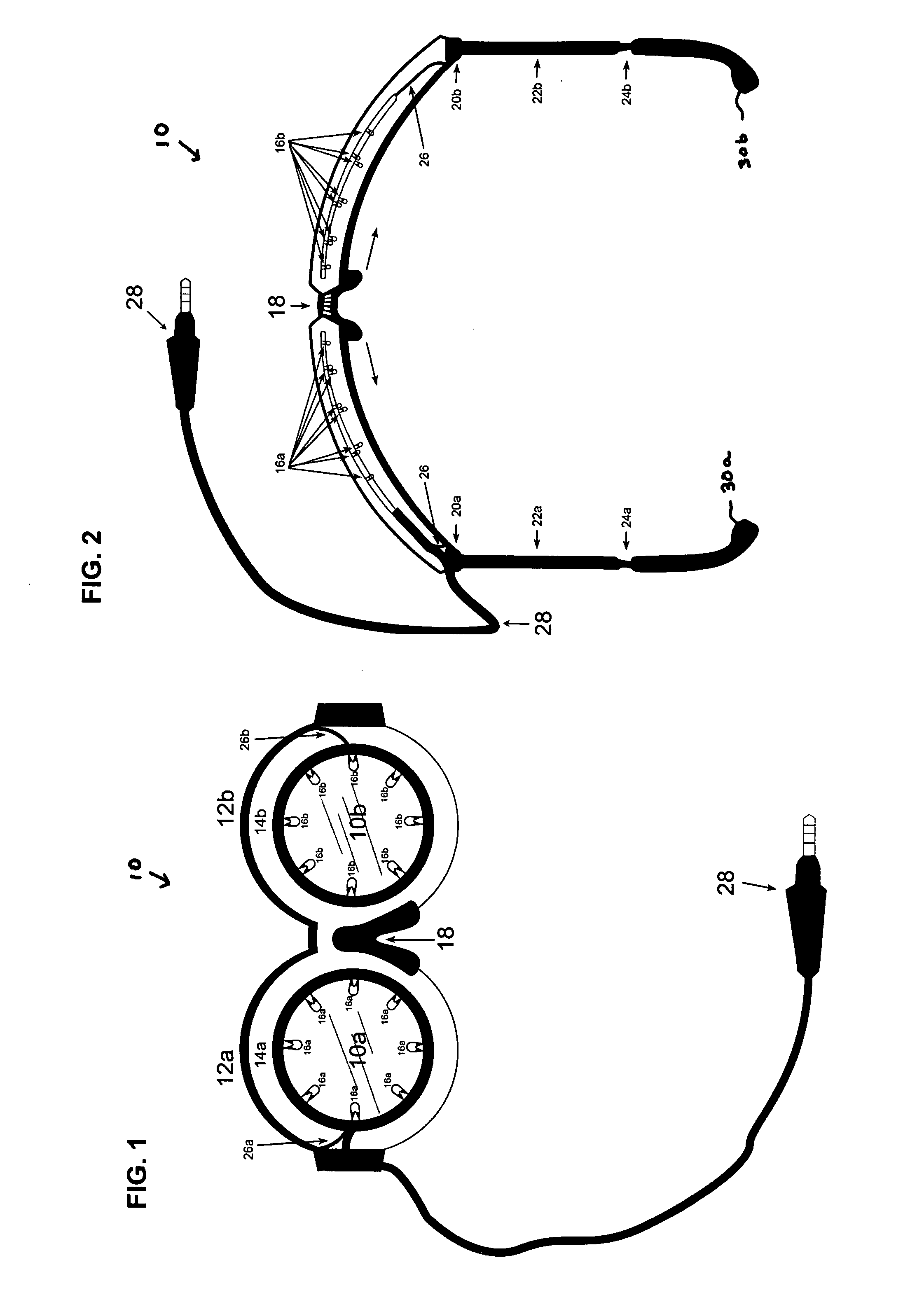
Method and apparatus for stimulating the neurochemistry of the brain resulting in increased overall brain function, cognitive performance, and intelligence quota
An apparatus and method for stimulating the neurochemistry of the brain including enzymes, nucleosides, nucleotides, neuropeptides, neurotransmitters, amino acids, brain glucose, steroids, and hormones, and more specifically, an apparatus and method for enhancing overall brain function, including cognitive abilities and intelligence quota (IQ). Other treatment interventions the apparatus and method can positively affect include neurological, physiological, and psychological disorders and diseases. The inventive method utilizes a specially designed goggle which contains two round eye pieces to which are attached the light assemblies. These light assemblies are comprised of 1-20 white full spectrum lights which are directed toward both eyes, within a two inch radius of the retina to avoid overstimulation. The goggle has an expandable nose piece with a mechanism to allow the eye pieces to swing outward and adjust over the eye of any individual, in accordance with the specified retinal placement. The inset lights flash or flicker utilizing intermittent “fuzzy” light, and encompass frequencies ranging from 1-1200 Hz (cycles per second), specifically excluding the range between 55-65 Hz to prevent any form of seizure. The light stimulus is accompanied by unmatched, intermittent sound stimulation, called “fuzzy” sound. The sound is audible through the use of any type headphone. The method is in the form of computerized programs, and includes a variety of formulas translated as “sessions” to be downloaded into any existing light / sound device or apparatus. These formulas are in the form of a variety of sessions, lasting no more than 40 minutes each, to address and or treat a variety of symptoms, disorders, and diseases. The sessions control the light goggle apparatus and sound. Neither the “fuzzy” light nor the “fuzzy” sound are synchronized.
Owner:OLMSTEAD RUTH
Pain relieving and healing device
InactiveUS7079898B2Relief the painPromote healingHeart defibrillatorsChiropractic devicesMotor speedGear wheel
Pain Relieving and Healing Device with a rigid tubular member being relatively open at the forward use end and closed by an end plate at the rear end. The inside of the tube contains a rigid piston slidably fitting within the inside diameter of the tube and an attached motor and gear assembly for driving the piston between two and five cycles per second. The piston has embedded within it a heat source and a heat radiating plate. The piston capable of traveling at various speeds by use of a solid state motor speed circuit. A preferred embodiment includes a timer circuit and associated LCD display for tracking the time for each healing session.
Owner:COHN SALOMON
Method and apparatus for measurement of processor-utilization
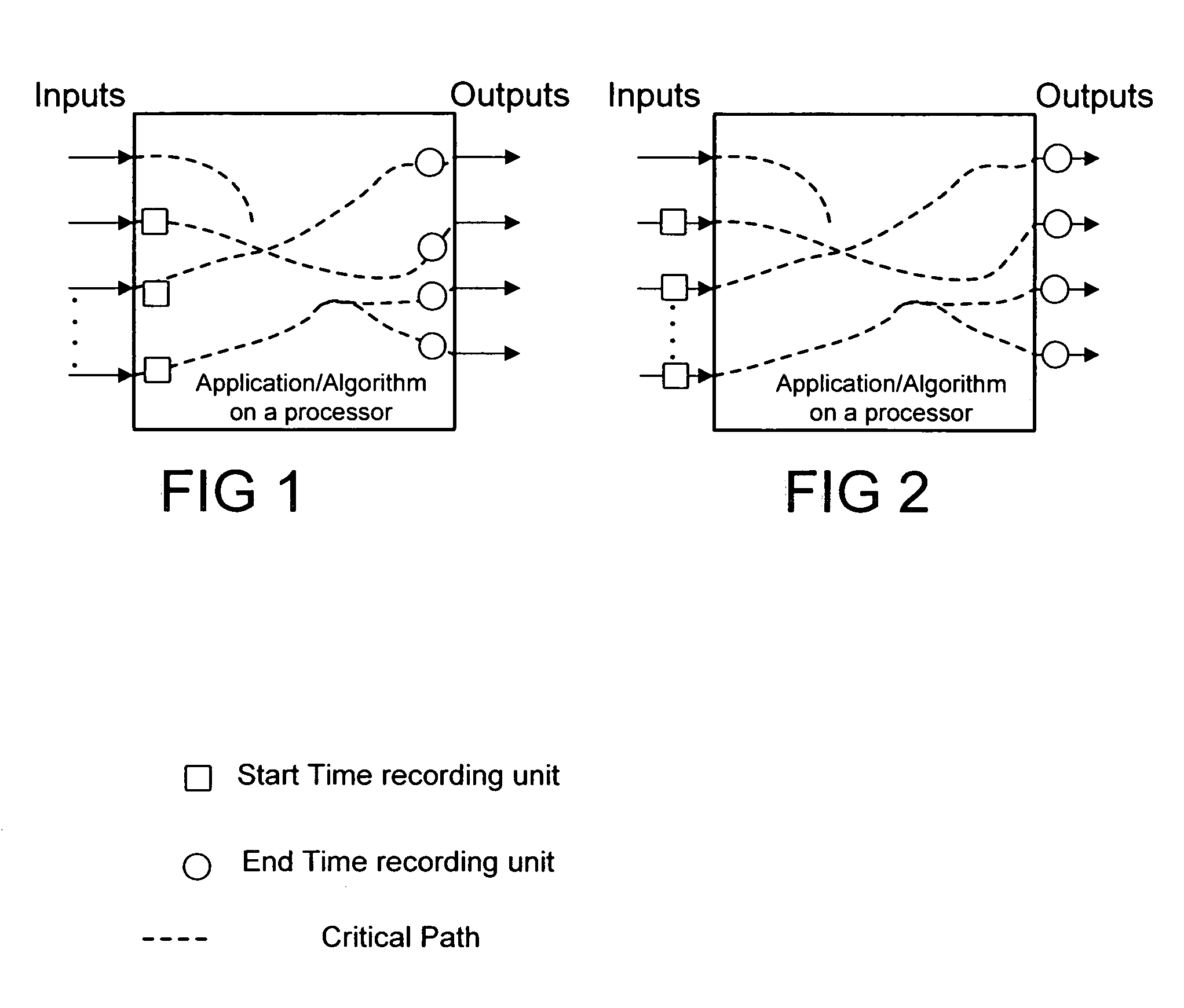
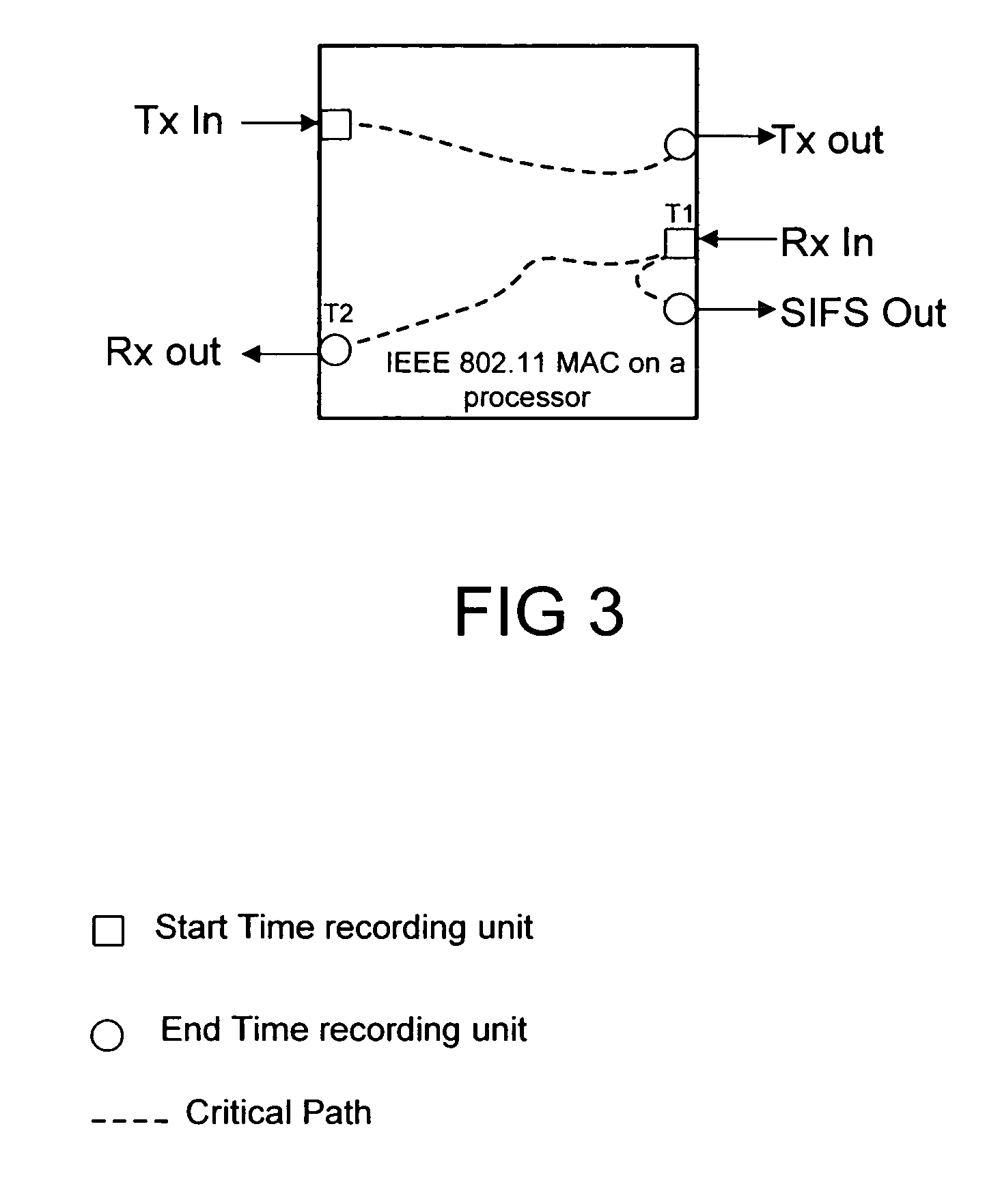
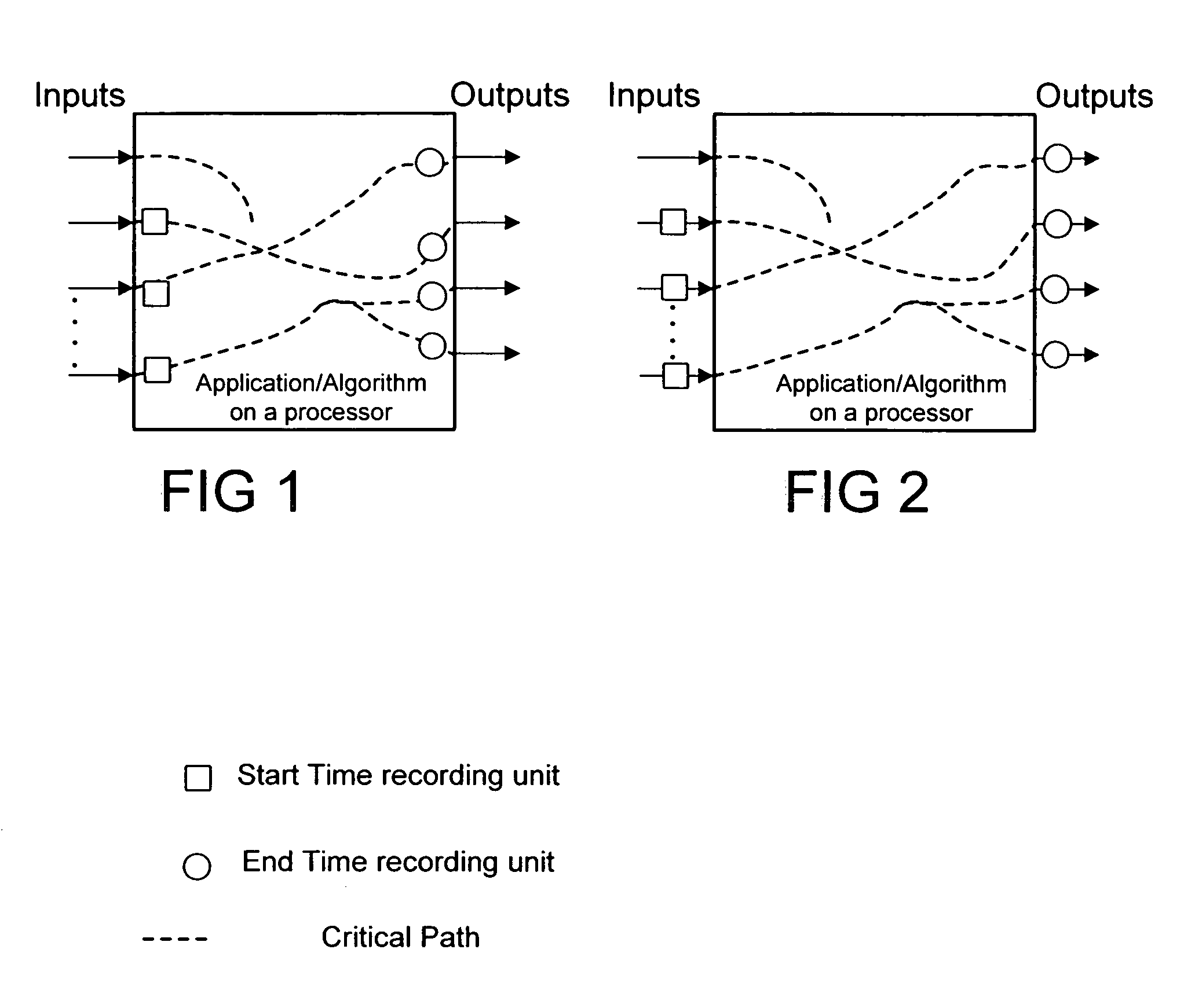
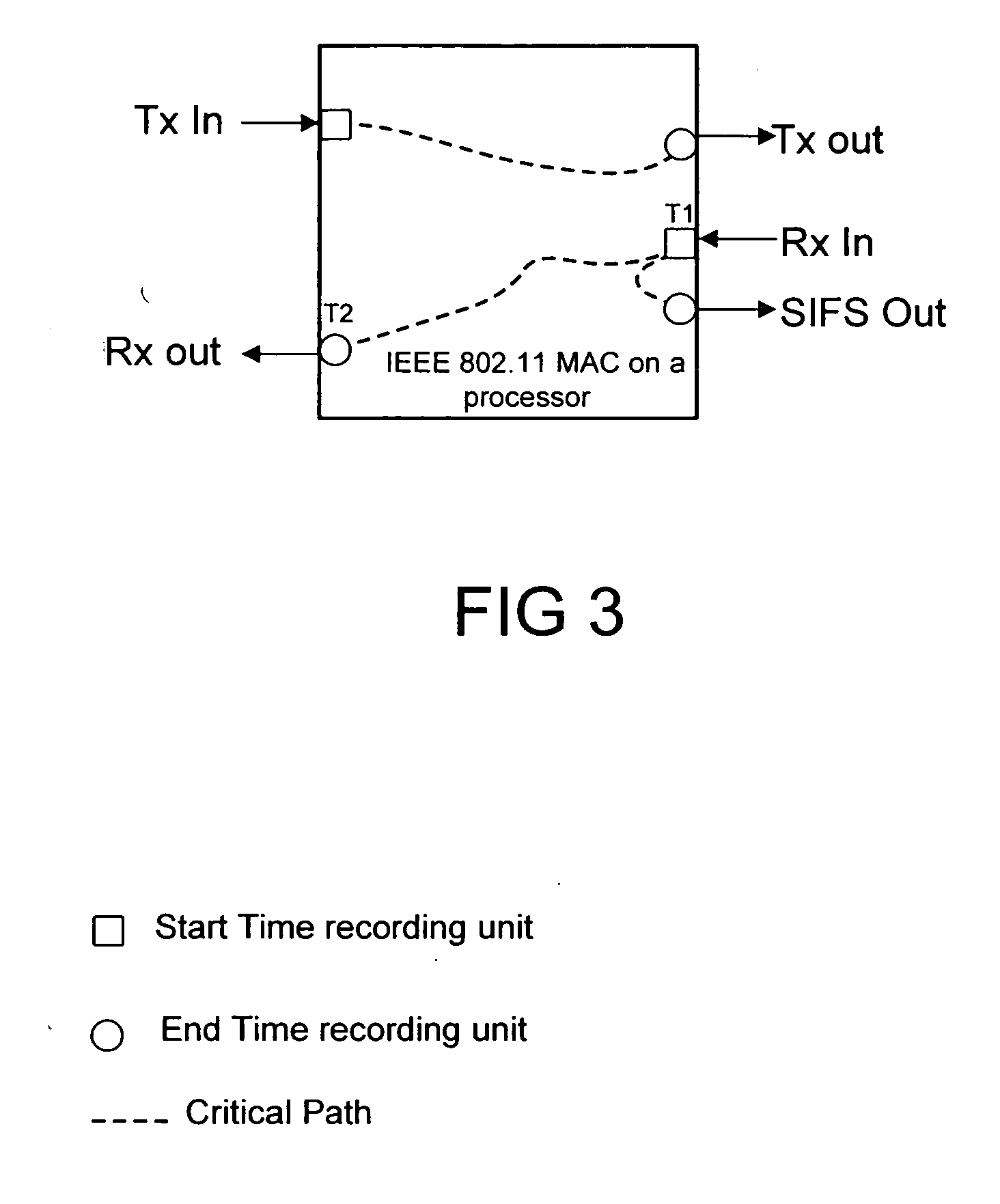
InactiveUS7133806B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCritical path methodHandling system
A method of managing a processing system that has at least one processor, uses the steps of: measuring MCPS (million cycles per second) utilization in the at least one processor; estimating a cycle count requirement for an algorithm on least one processor based on measured MCPS utilization; and, estimating an ability to run multiple applications on the at least one processor by assessing MCPS requirements and estimated cycle count requirement. Measurement of the MCPS utilization is preferably done by using the steps of: choosing a critical path in the processor, e.g., by taking hard real time requirements into consideration; measuring time taken for processing along said critical path; and, calculating MCPS requirements along said critical path using the measured time taken and a current processor clock speed. The inventive method has application in 802.11 MAC. Also described is a programmed storage medium to execute the described method.
Owner:ITTIAM SYST P +1
Device for delivery of resonant frequencies to treated muscles
A drumming device for delivering a repetitive percussive strike to muscles below a skin surface comprises a main housing enclosing an electric motor with a shaft having a fixed rotational speed, a drive pulley, a toothed belt encircling the drive pulley and a driven pulley with an integral cam mounted on said pulley such that the rotating shaft causes the driven pulley to rotate at a predetermined number of cycles per second, the assembly causing a repetitive, reciprocal movement of a plunger body a fixed distance and at 16.6 cycles / sec, said plunger movable in a downward direction following contact with the cam, such that the plunger reciprocates within said housing when said cam member contacts the plunger causing the plunger shaft to move laterally outward. When the massaging device is properly position in contact with the skin the moving plunger causes muscle spindles to vibrate at their resonant frequency.
Owner:HEALTHY MUSCLES
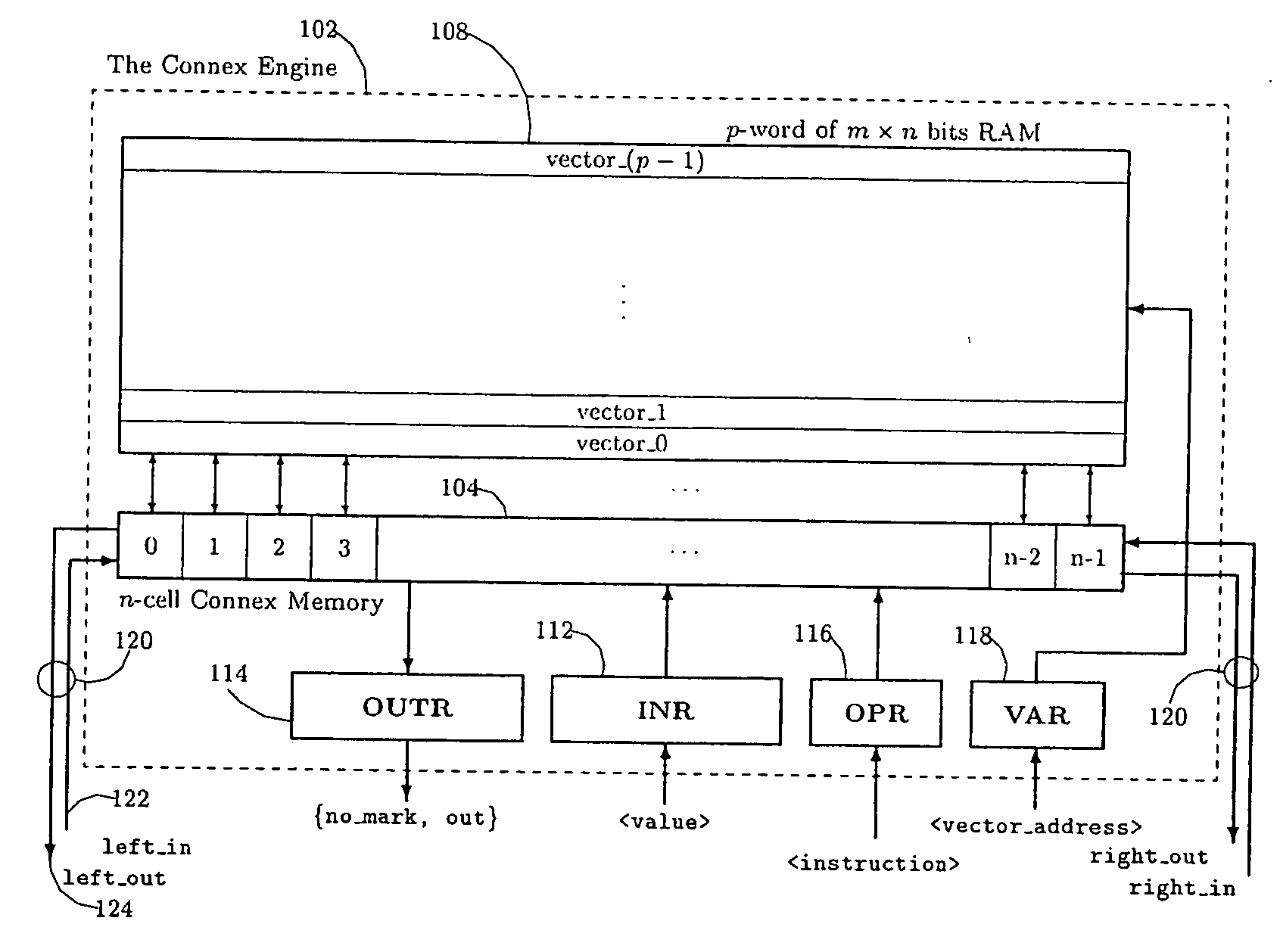
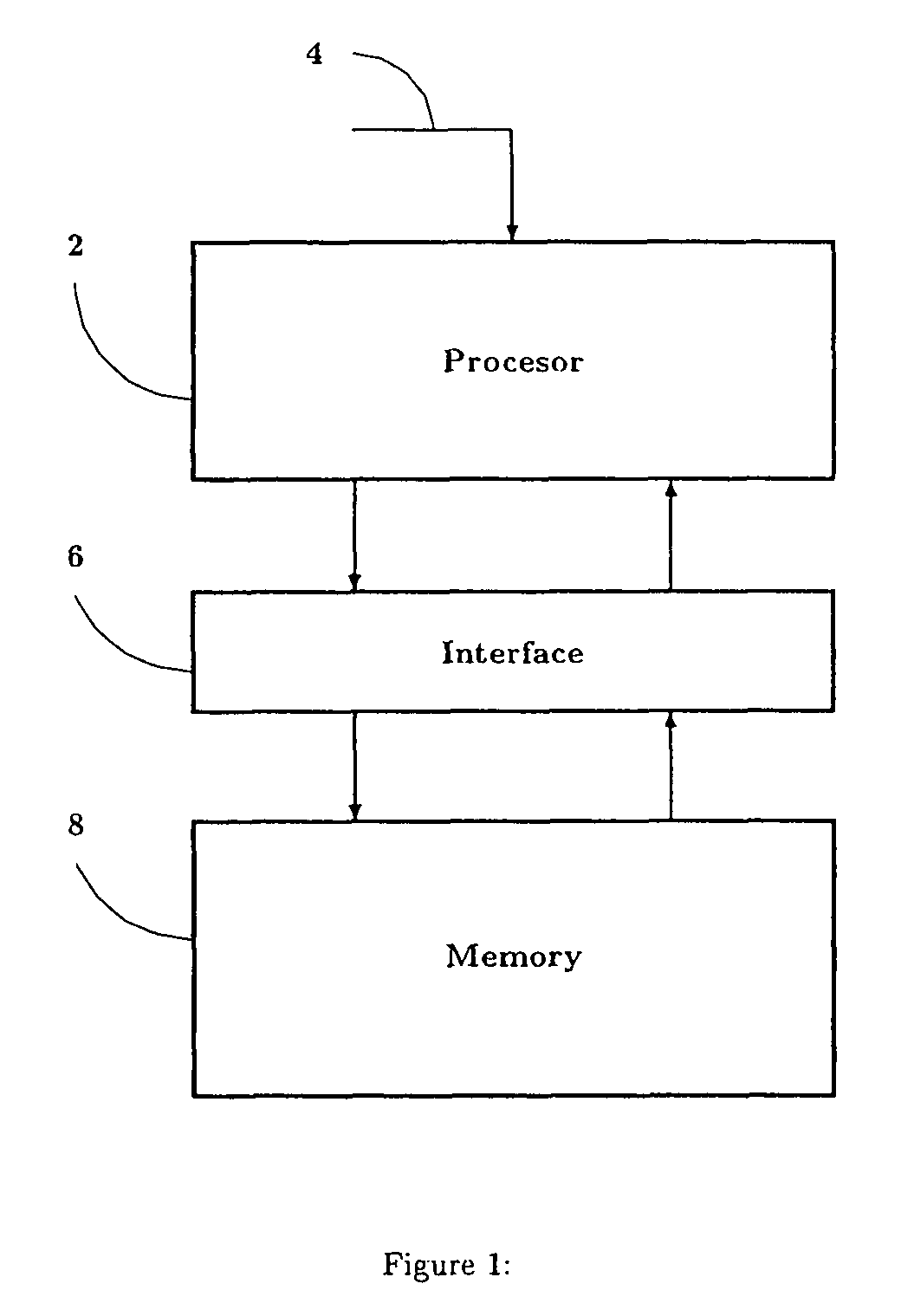
Associative memory device
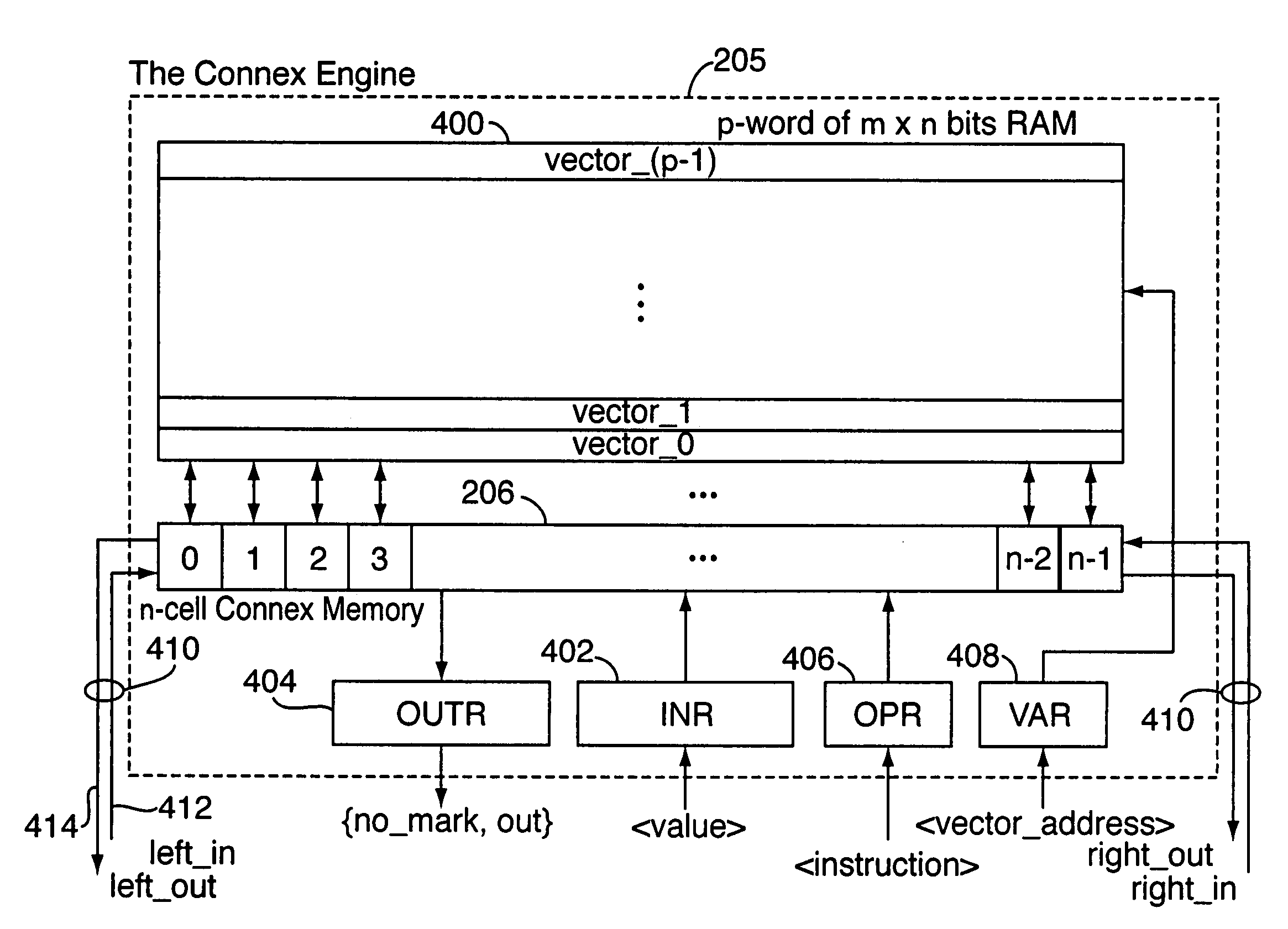
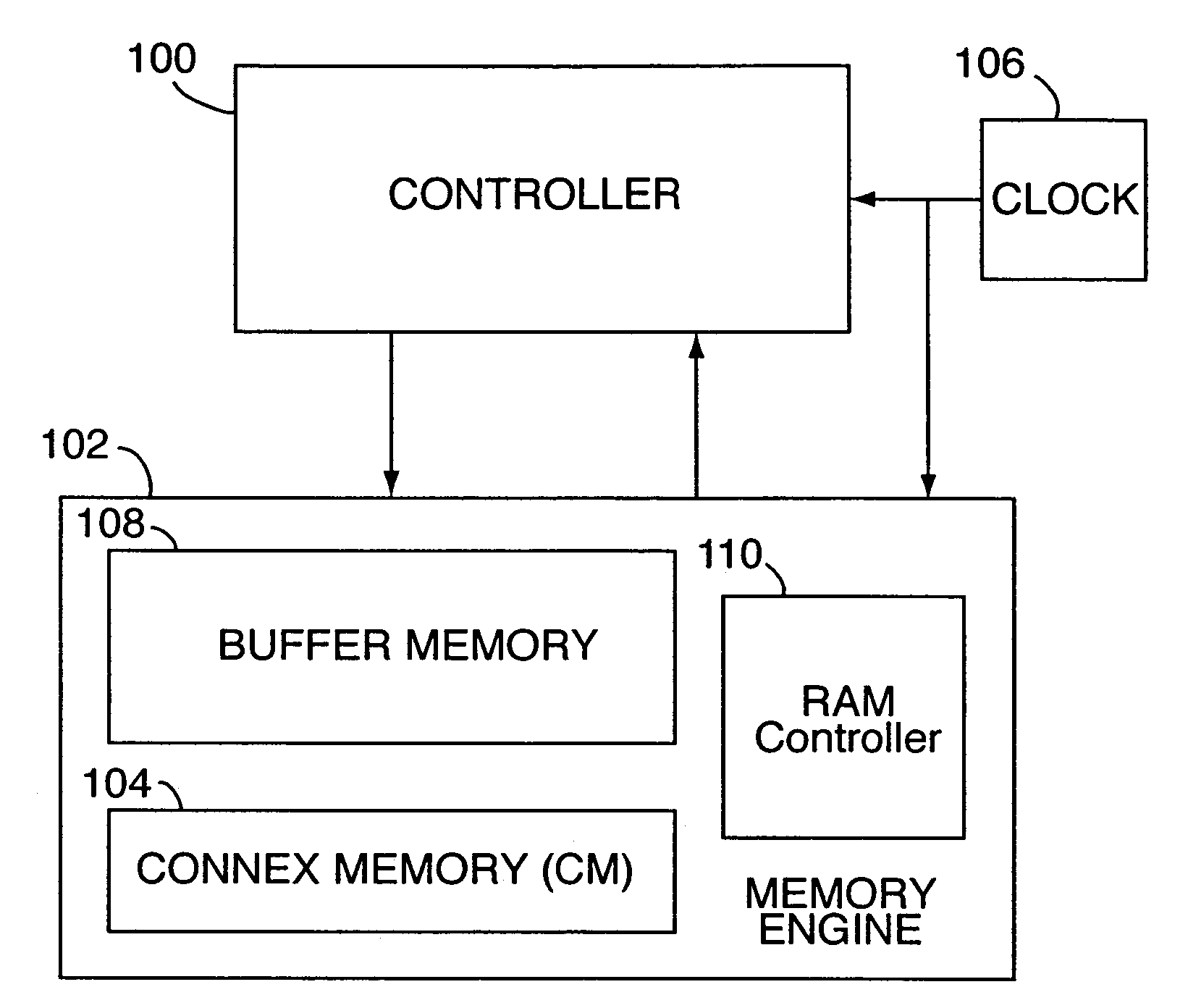
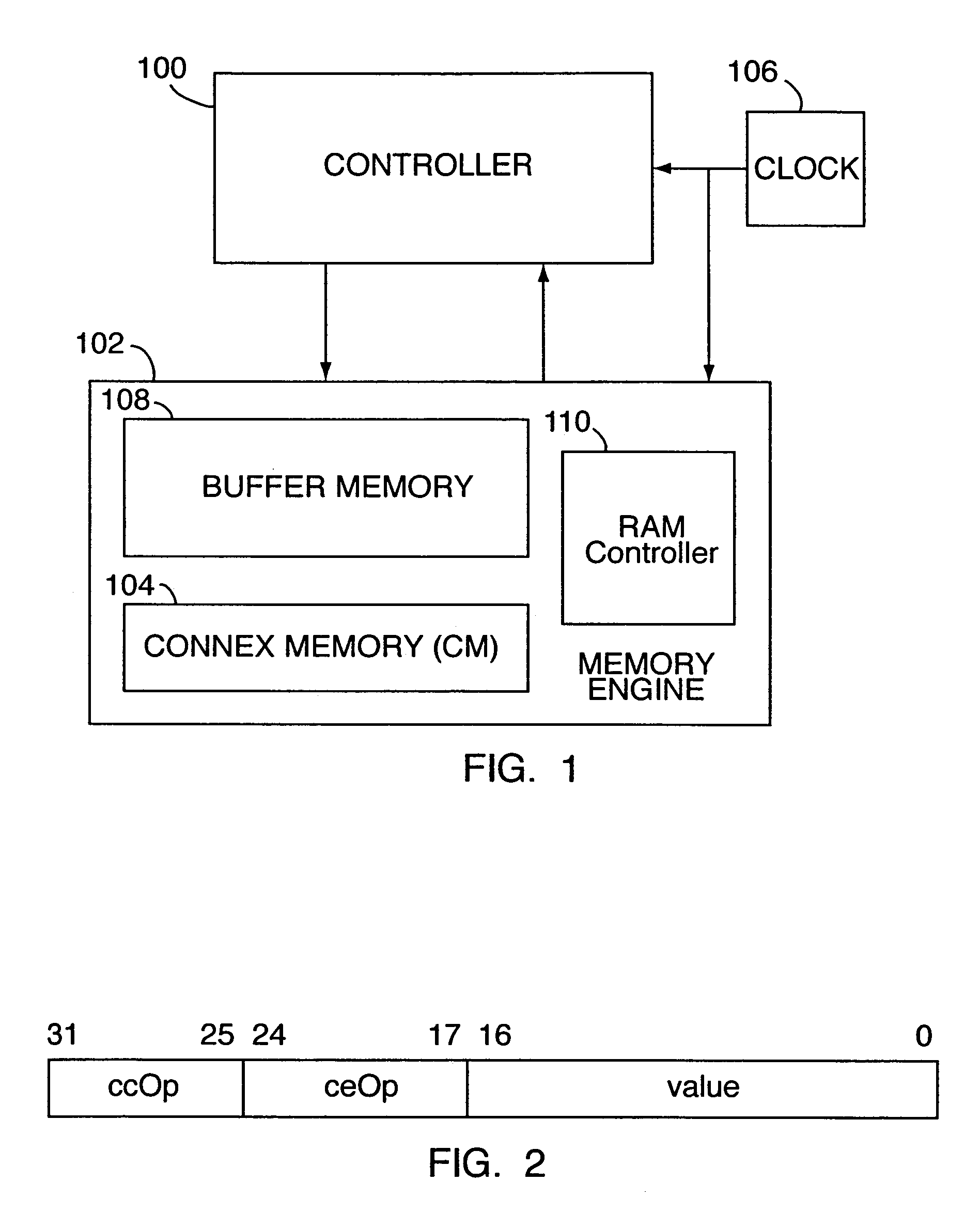
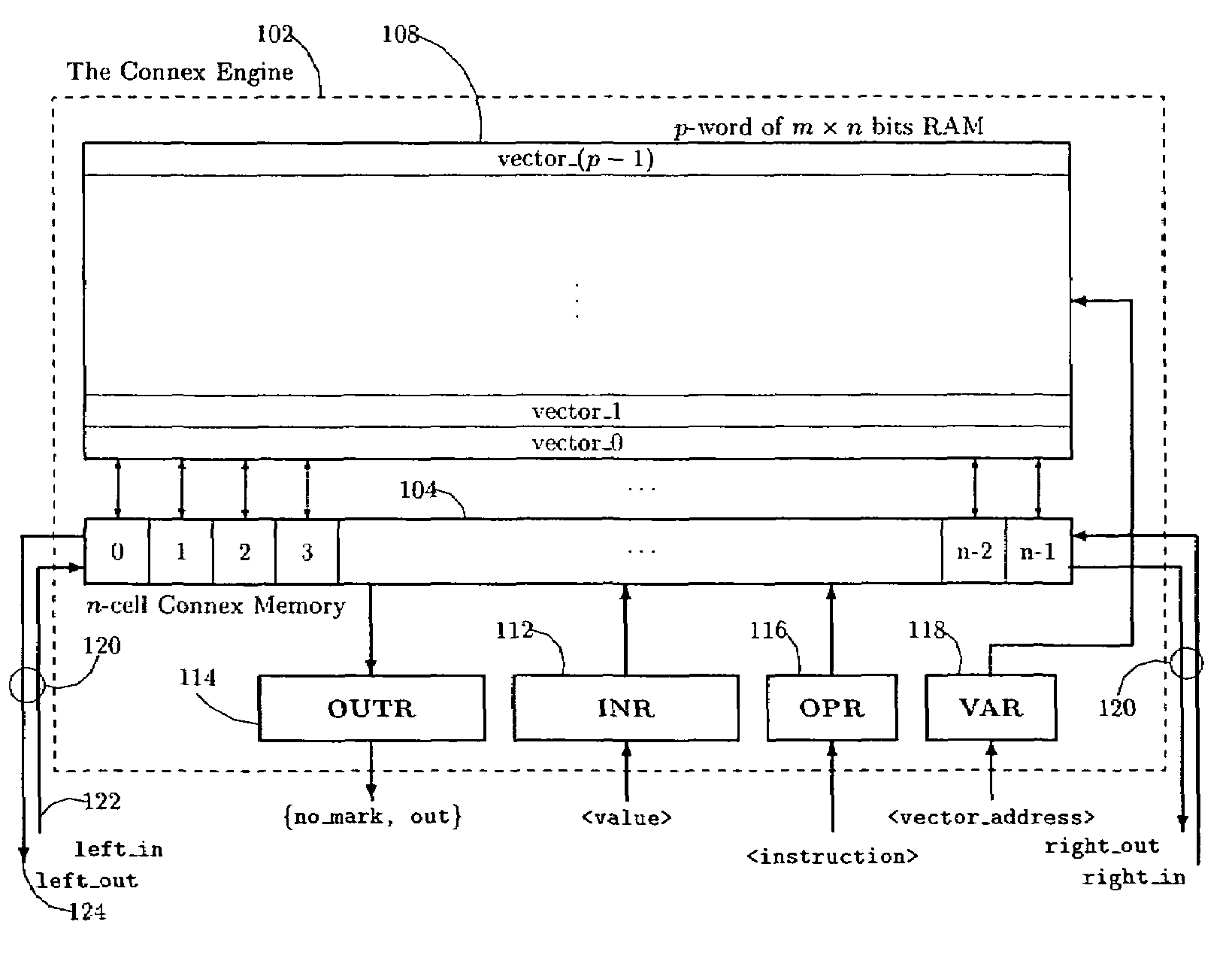
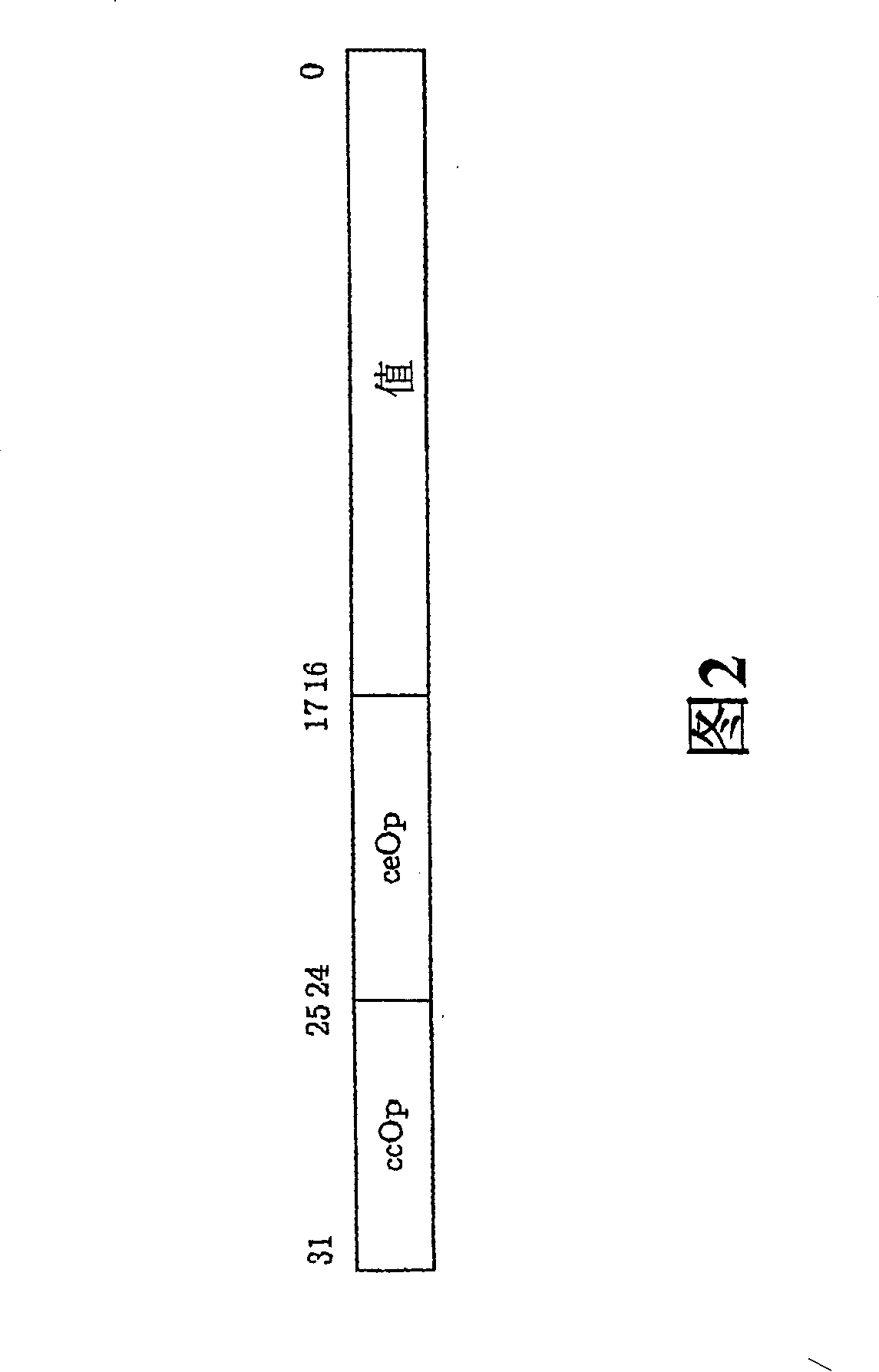
InactiveUS7069386B2Efficient data processing systemImprove efficiencyDigital storageMemory systemsData processing systemCycle per second
An associative memory support for a data processing system includes an associative memory device containing n-cells. A controller is provided for issuing an instruction to the associative memory device. A clock device outputs a synchronizing clock signal that includes a predetermined number of clock cycles per second, the clock device outputting the synchronizing clock signal to the associative memory device and the controller. The controller globally communicates the instruction to all of the n-cells simultaneously, within one of the clock cycles and the instruction is applied equally to each of the n-cells.
Owner:ALLSEARCH SEMI
Stimulating galvanic or slow AC current for therapeutic physiological effects
InactiveUS20070203534A1Efficient deliveryReduce stimulationElectrotherapyPreventing injuryCarbon particle
Basically, the present invention is directed to a new and improved system for the therapeutic use of currents which includes conducting direct electrical current through the skin of a body being treated, and periodically reversing the electrical current and conducting the current through the skin in the opposite direction, to effectively deliver very low frequency AC current, substantially in the critical range of approximately 0.0027 Hz to 20 Hz. It has been discovered that, within this substantially critical frequency window between approximately six minutes per full cycle and approximately ten cycles per second, a dramatic cancellation of skin damaging ions takes place. At frequencies higher than approximately 20 Hz, the effect is to diminish its DC-like blood stimulation. At frequencies lower than approximately 0.0027 Hz, the risk of skin injury increases substantially. It is well known that the positive electrode unfortunately produces skin damaging hydrochloric acid. Likewise, the negative electrode unfortunately also produces skin damaging sodium hydroxide. However, within the aforementioned frequency range of the present invention, either polarity stimulates blood circulation, but also cancels the undesired skin damaging ions with the reverse portion of the electrical cycle. The reason for neutralization of the harsh injury producing chemicals, i.e., hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, is that both of these chemicals require a finite period of time on the skin to cause damage. Hence, these damaging chemicals are made to cancel each other before damage takes place, by critical frequency selection, in accordance with the invention, of the AC driving signal. Therefore, optimization of a long sought electrotherapeutic device with reduced side effects has been achieved. Another use of the safe AC currents cited above and / or a DC signal with charged membranes preventing injury is its application to wound healing. The conductive electrodes for these devices may take either of two forms, i.e., one may be non-metallic carbon-filled silicone or, preferably of powdered carbon particles. A second form may be a metallic electrode preferably of aluminum, copper, zinc and / or magnesium as examples of metallic electrodes but not necessarily limited to these metals. These metals are preferably in powdered form and contained within a porous membrane with a small opening to attach a conductive lead to a battery source. Still other applications of the innovative use in electrotherapy of charged membranes and / or powdered metal electrodes is its use for drug delivery and diagnostic purposes. For instance, a membrane enclosed stainless steel powdered negative electrode may be used in the pickup probe for glucose detection. Charged membranes would surround the probe as an intervenor between skin and the electrode.
Owner:TAPPER ROBERT
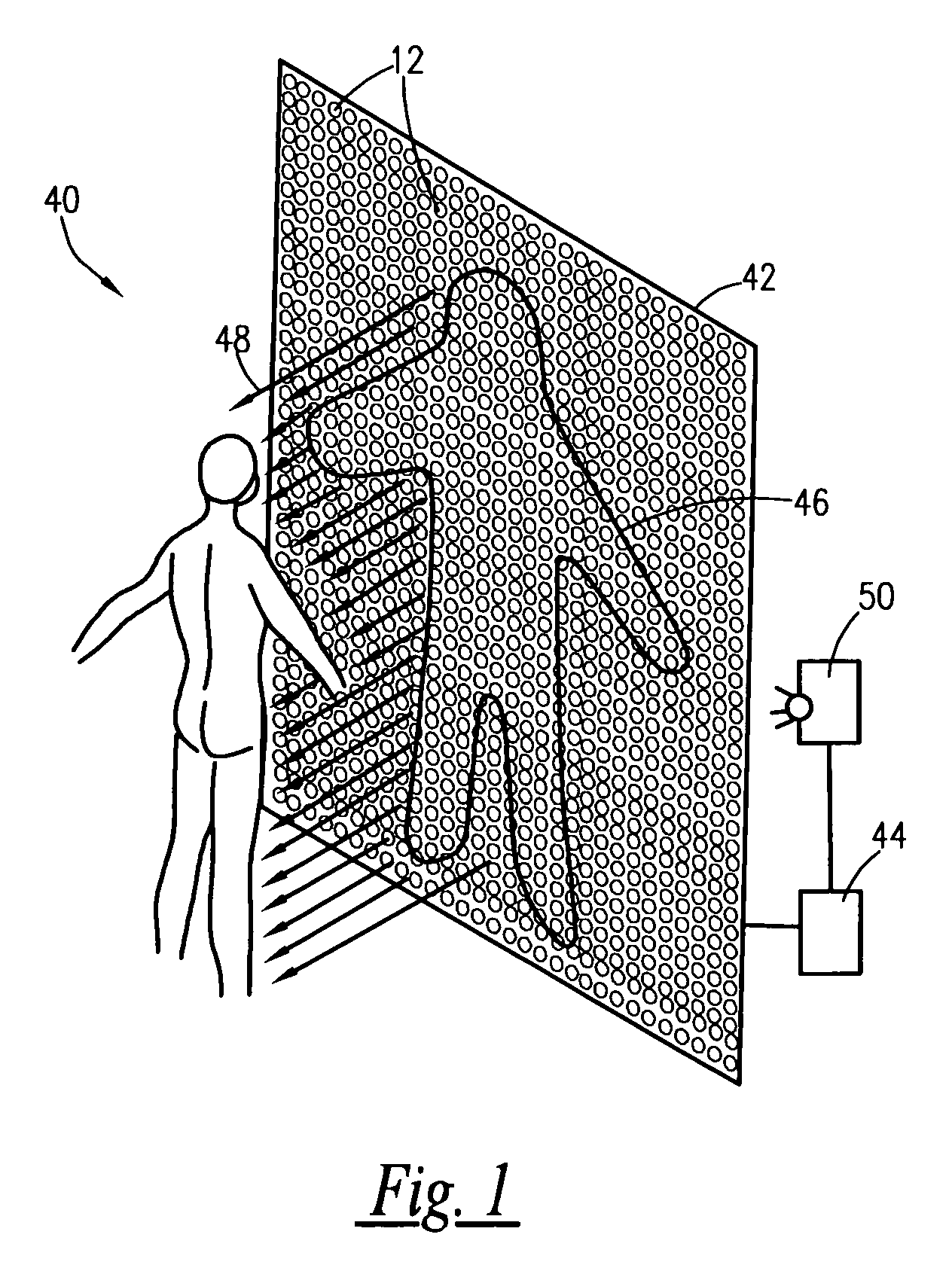
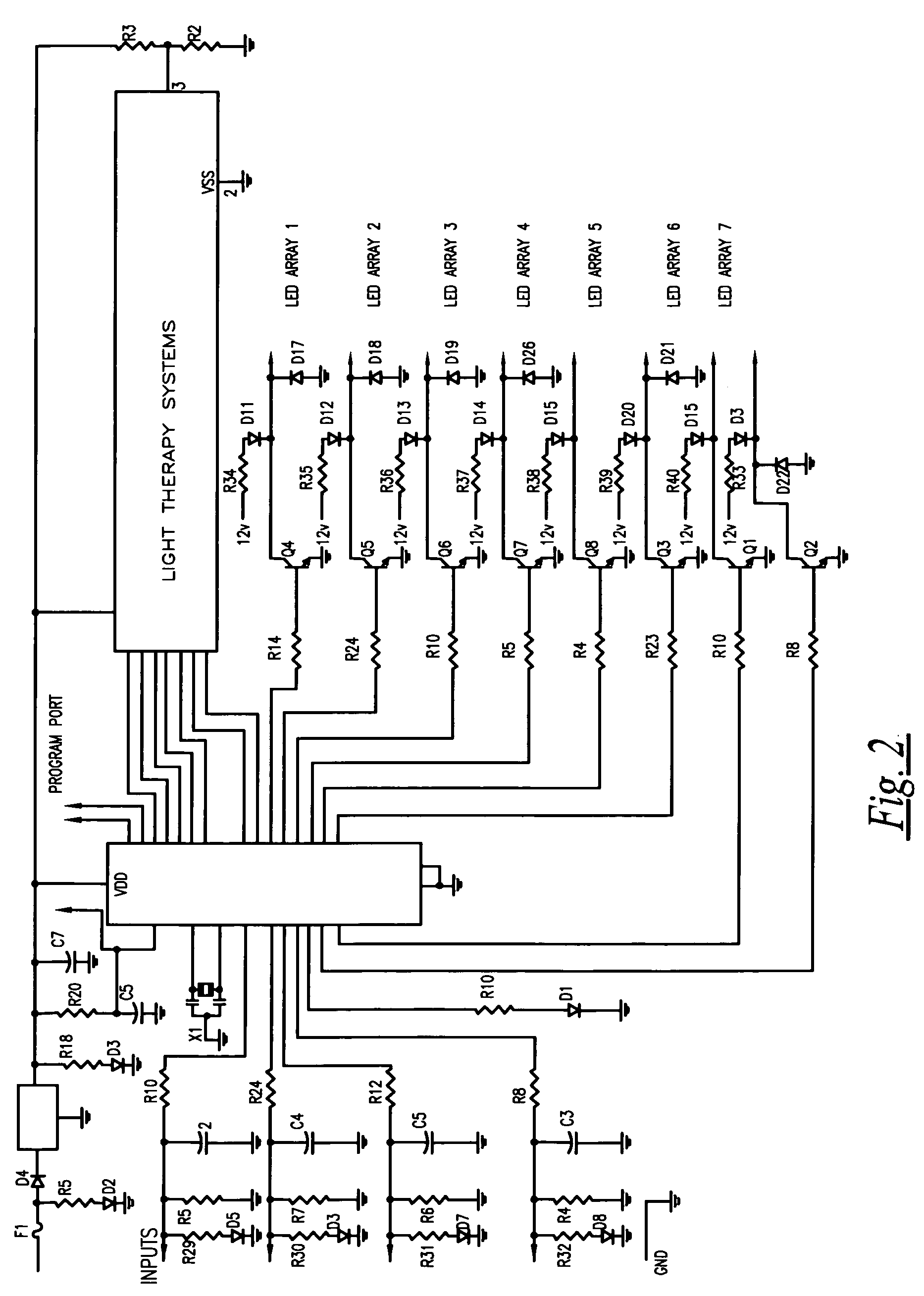
Therapeutic Light System
A non-thermal low dose light emitting diode (LED) array provides for the application of therapeutically specific radiation is provided. The array delivers radiation to the intended target surface at a controlled intensity. The intensity is controlled with a specific sequence of pulsing by pulse driving a matrix-arrayed LED. The modulation of the therapeutically specific radiation is at a frequency outside the user's visually perceptive range, but with a visually perceptible cycle. The cycle is initiated by a strobe rate very slow and perceptible to the user and then ramp up rapidly to over 30 cycles per second for the dosage period. The cycle is terminated by ramping down the strobe rate from above 30 cycles per second to a slower, visually perceptible level at the end of the dosage period. The instant abstract is neither intended to define the invention disclosed in this specification nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:SPIVAK PAUL
Purr pillow
Purr pillow with a microprocessor chip, a flat speaker, a power supply, an on off switch, a frequency selector switch, a random selection switch, a volume control, a standard amplifier circuit, a PC board and a housing. The microprocessor is programmed to produce purring sounds at frequencies ranging from 20 to 140 cycles per second, and the microprocessor, the speaker and additional the components are housed within the housing. A preferred embodiment includes the housing having a relatively low profile of approximately one quarter of an inch.
Owner:HAYES DANA L
Device for delivery of resonant frequencies to treated muscles
A drumming device for delivering a repetitive percussive strike to muscles below a skin surface comprises a main housing enclosing an electric motor with a shaft having a fixed rotational speed, a drive pulley, a toothed belt encircling the drive pulley and a driven pulley with an integral cam mounted on the pulley such that the rotating shaft causes the driven pulley to rotate at a predetermined number of cycles per second, the assembly causing a repetitive, reciprocal movement of a plunger body a fixed distance and at 16.6 cycles / sec, the plunger movable in a downward direction following contact with the cam, such that the plunger reciprocates within the housing when the cam member contacts the plunger causing the plunger shaft to move laterally outward. When the massaging device is properly position in contact with the skin the moving plunger causes muscle spindles to vibrate at their resonant frequency.
Owner:HEALTHY MUSCLES
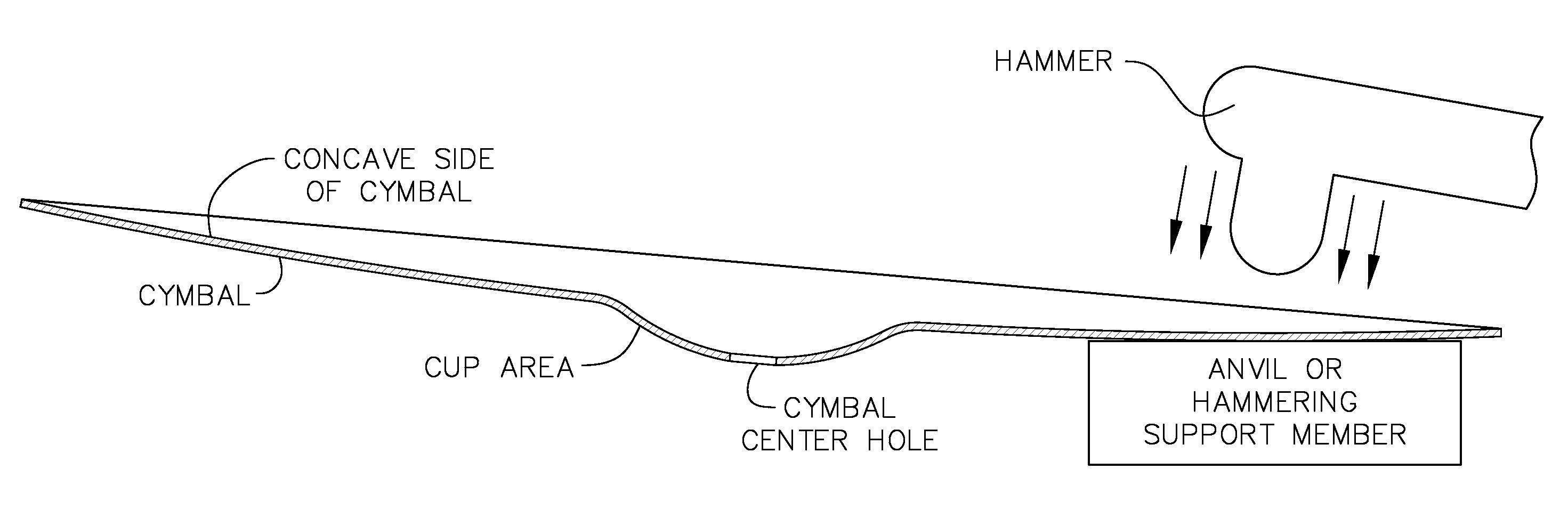
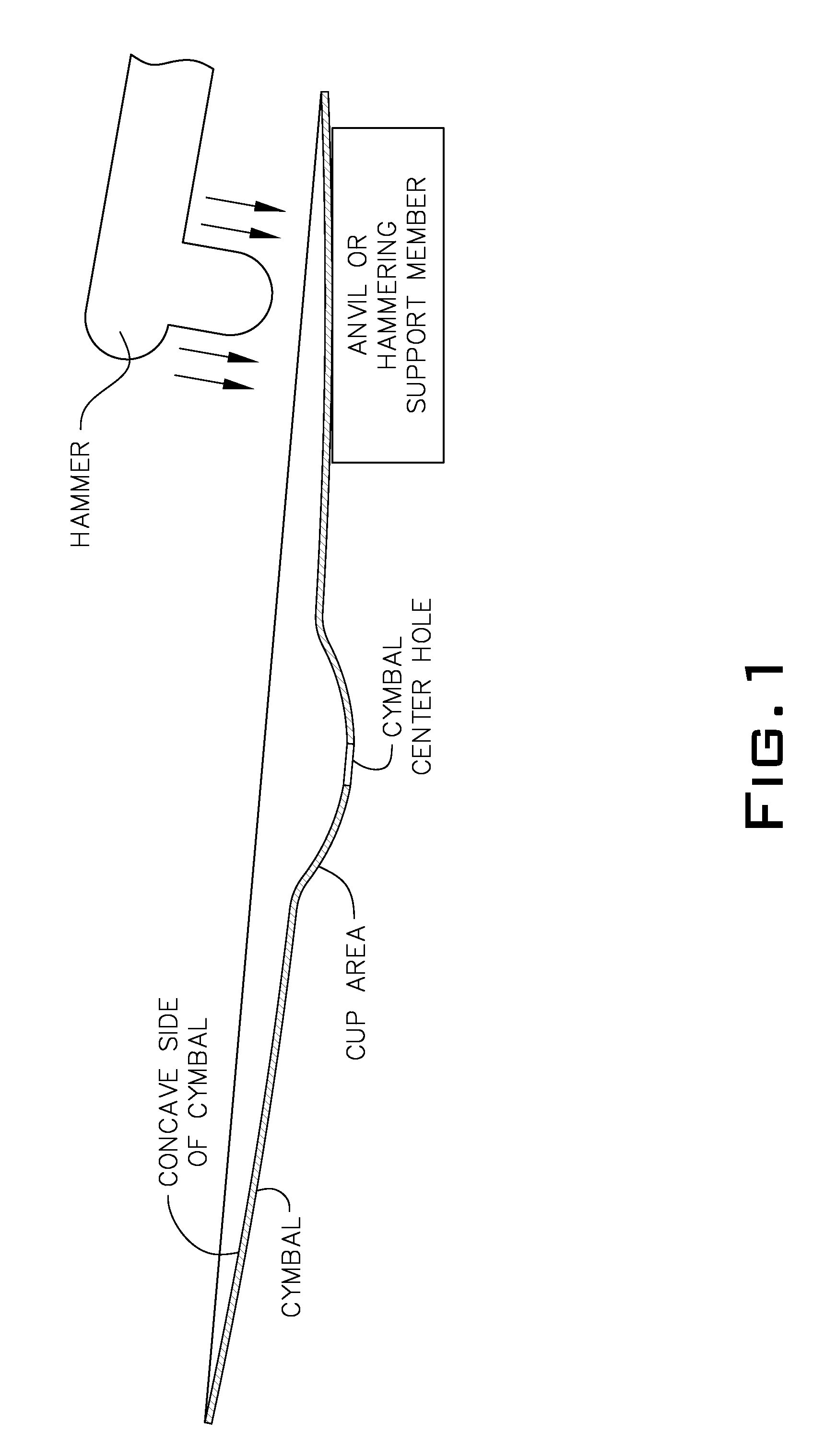
Cymbal with low fundamental frequency
Owner:STANNARD JOHN
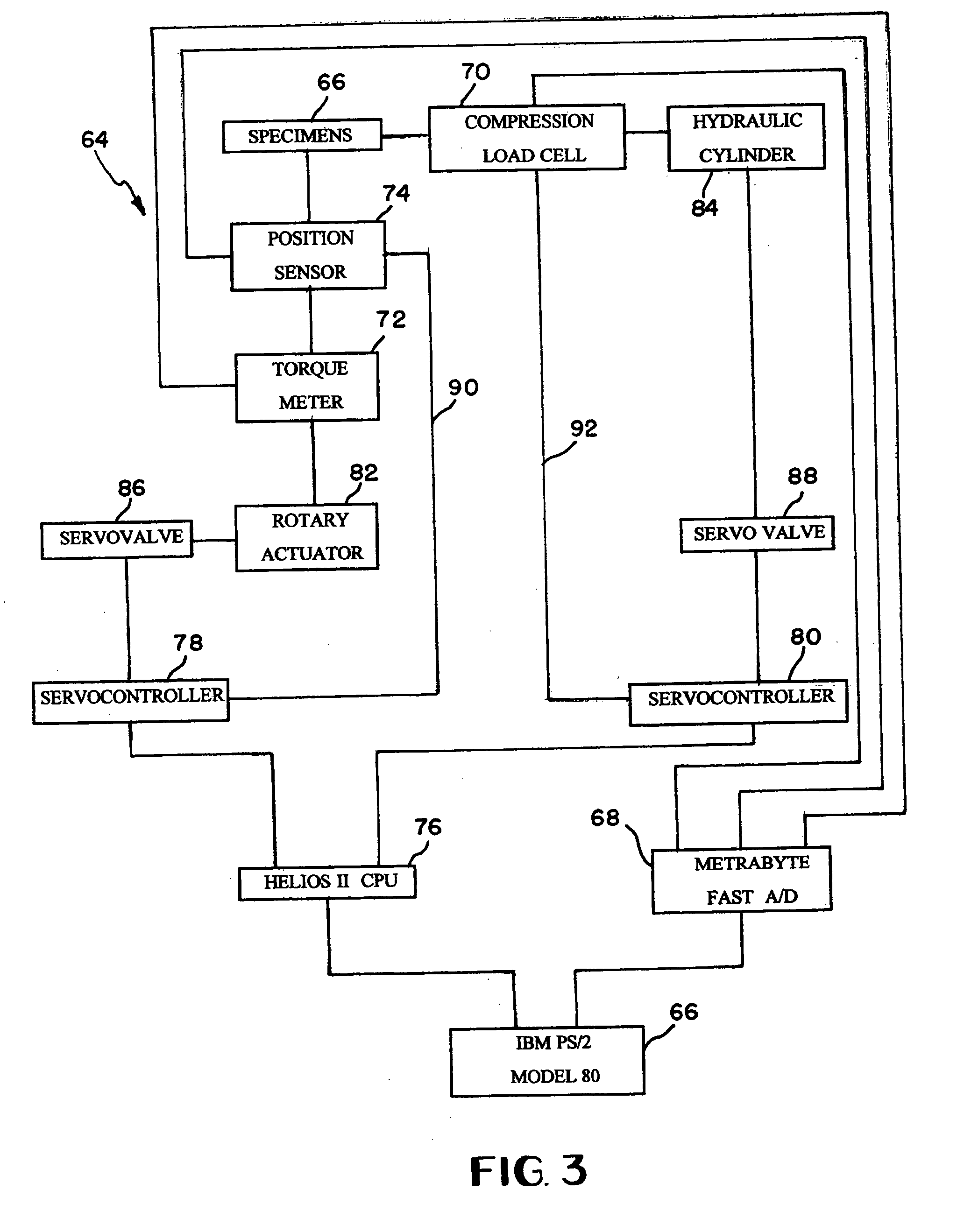
Single ball bearing lubricant and material evaluator
A test apparatus provides an applied load to a monoball through a trolley which moves along a loading axis. While applying the load to the monoball, the torque meter is in communication with the spherical monoball, and a load cell senses the application of applied force to the monoball. Meanwhile, a rotary actuary imports rotary oscillating motion to the monoball which is sensed by a position sensor and a torque meter. Accordingly, a processor can determine the coefficient of friction in substantially real time along with a cycles per second rate.
Owner:NAT AEROAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION
Cellular engine for a data processing system
InactiveUS20080126757A1Efficient data processing systemImprove efficiencyArchitecture with single central processing unitSpecific program execution arrangementsData processing systemData treatment
A data processing system includes an associative memory device containing n-cells, each of the n-cells includes a processing circuit. A controller is utilized for issuing one of a plurality of instructions to the associative memory device, while a clock device is utilized for outputting a synchronizing clock signal comprised of a predetermined number of clock cycles per second. The clock device outputs the synchronizing clock signal to the associative memory device and the controller which globally communicates one of the plurality of instructions to all of the n-cells simultaneously, within one of the clock cycles.
Owner:ALLSEARCH SEMI
Hypocycloidal drive unit for conversion of rotary to linear motion particularly for use in fiberglass insulation production machinery
InactiveUS20060264294A1Extended and continuous operationReduce destructive stressGearingMachines/enginesLinear motionGlass fiber
A hypocycloidal drive unit converts rotary to linear motion for use in high speed, high volume repetitive operations such as folding and lifting operations in the fiberglass insulation production industry. The drive unit is of low cost and low maintenance construction using a ring assembly with an inner planet wheel. An eccentric arm extends from the planet wheel and connects to crank arms joined to a lift arm which linearly and reciprocatingly slides in guides. The drive unit is characterized by the absence of gear teeth on the inner surface of the ring and on the planet wheel outer diameter. Various embodiments are disclosed including a circumferential chain around the ring and an inner planet wheel sprocket engaging the chain, a smooth inner ring circumferential surface and rubber faced planet wheel or tire traveling around the inner ring and an elastomeric cog belt and toothed planet wheel. The drive unit is able to withstand high cycle rates of up and down lift cycles per second during continuous operation.
Owner:KCI
Method and apparatus for measurement of processor-utilization
InactiveUS20050259592A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCritical path methodMultiple applications
A method of managing a processing system that has at least one processor, uses the steps of: measuring MCPS (million cycles per second) utilization in said at least one processor; estimating a cycle count requirement for an algorithm on least one processor based on measured MCPS utilization; and, estimating an ability to run multiple applications on the at least one processor by assessing MCPS requirements and estimated cycle count requirement. Measurement of the MCPS utilization is preferably done by using the steps of: choosing a critical path in the processor, e.g., by taking hard real time requirements into consideration; measuring time taken for processing along said critical path; and, calculating MCPS requirements along said critical path using the measured time taken and a current processor clock speed. The inventive method has application in 802.11 MAC. Also described is an article having a storage medium to execute the described method.
Owner:ITTIAM SYST P +1
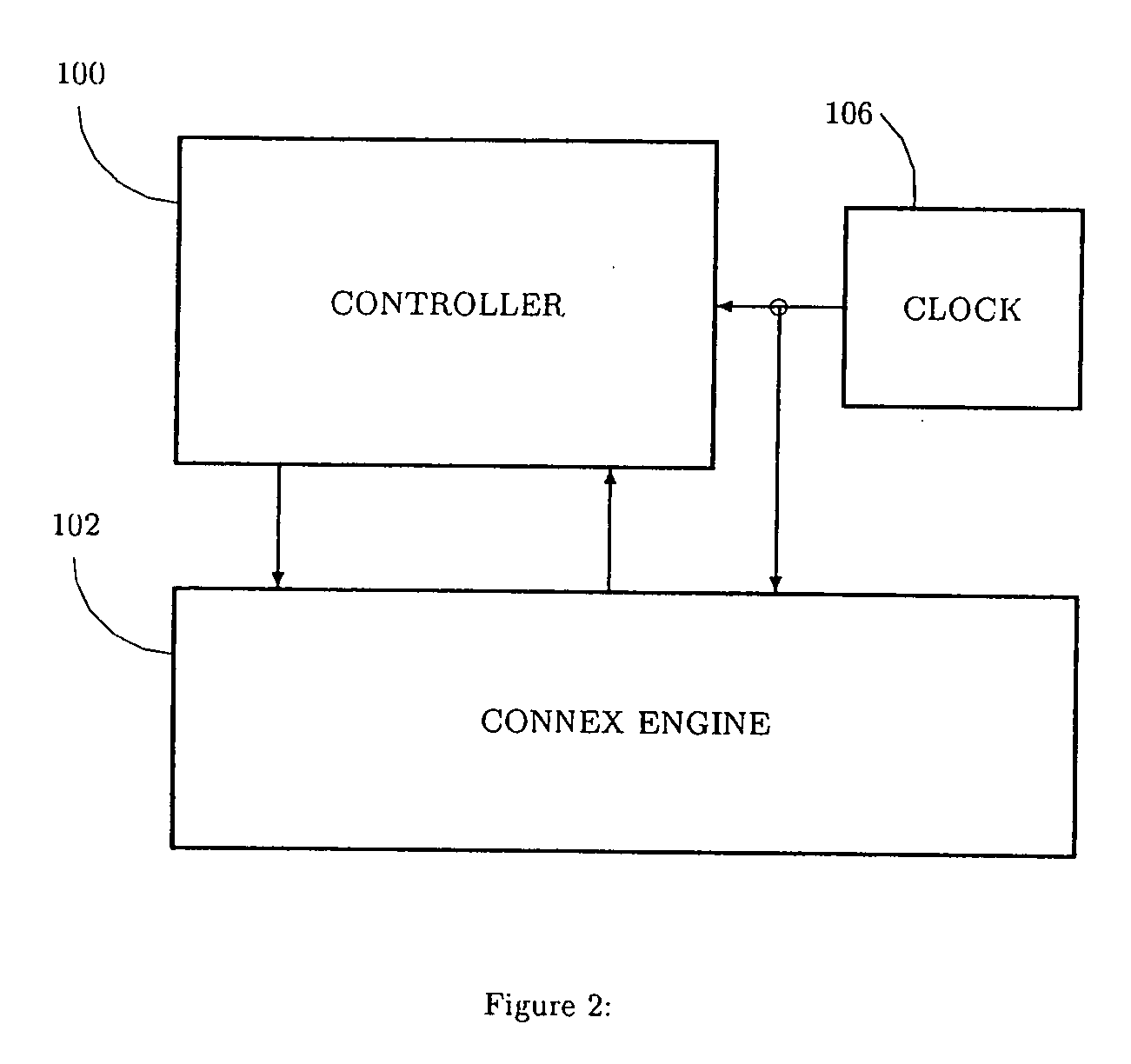
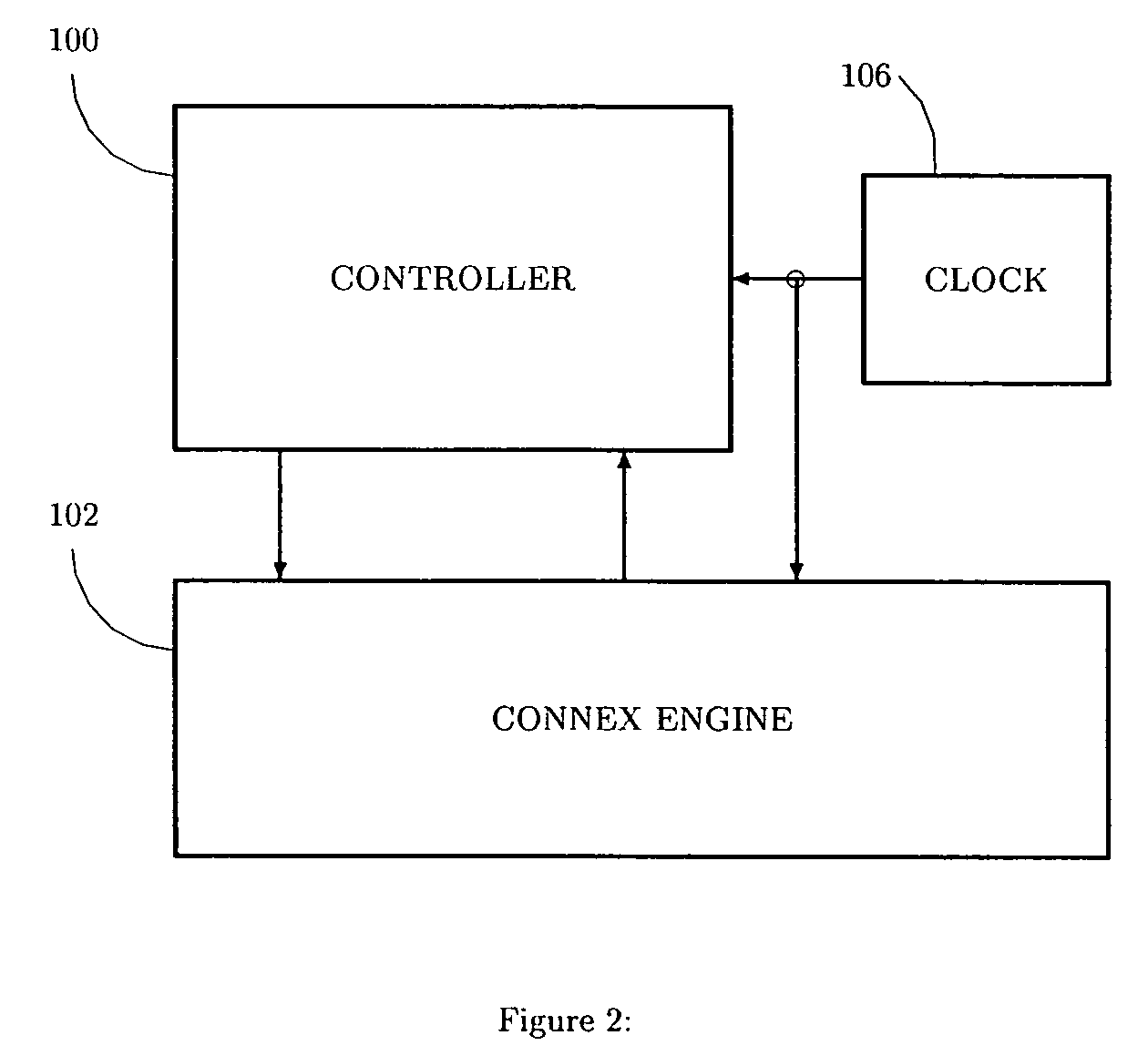
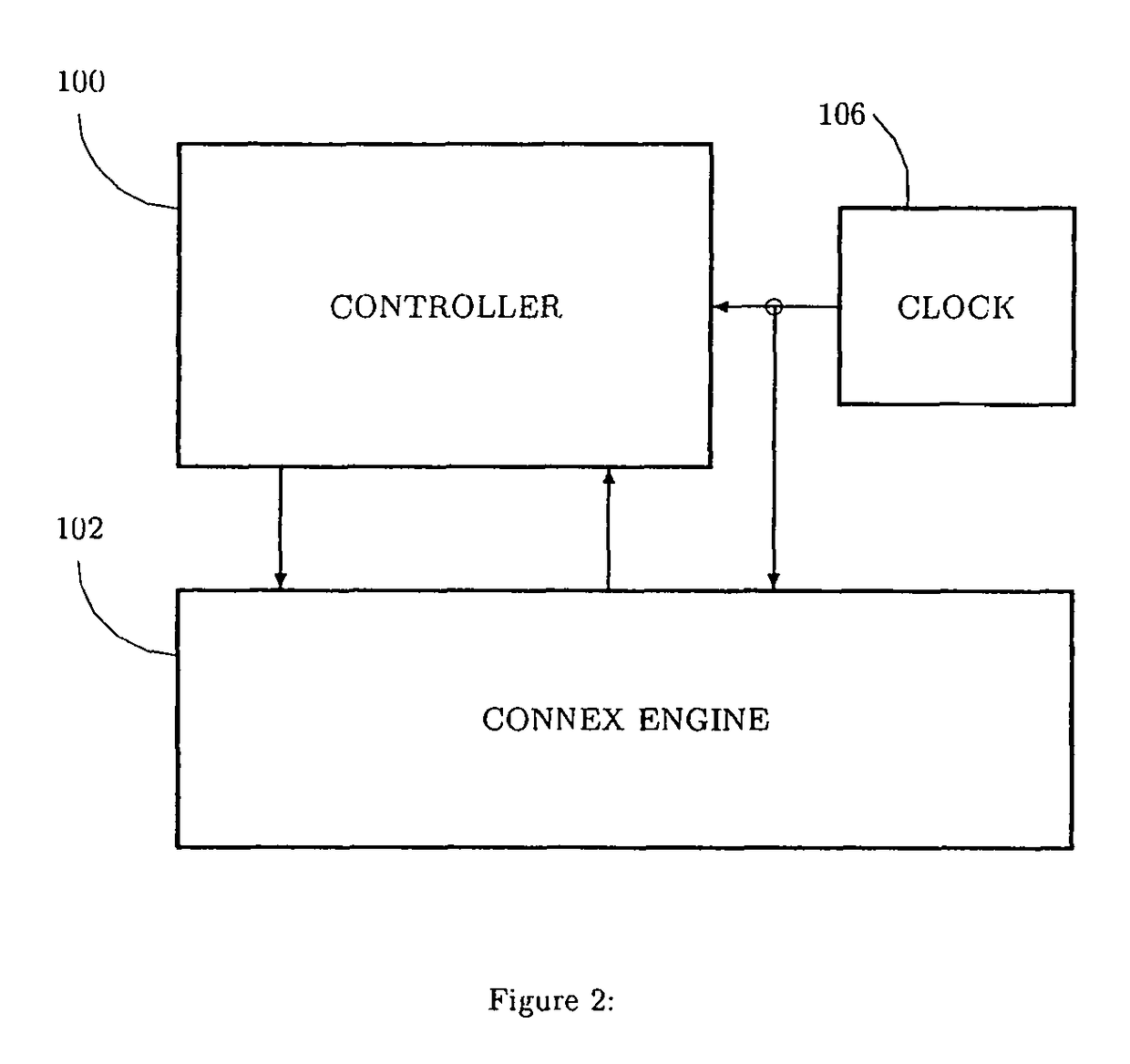
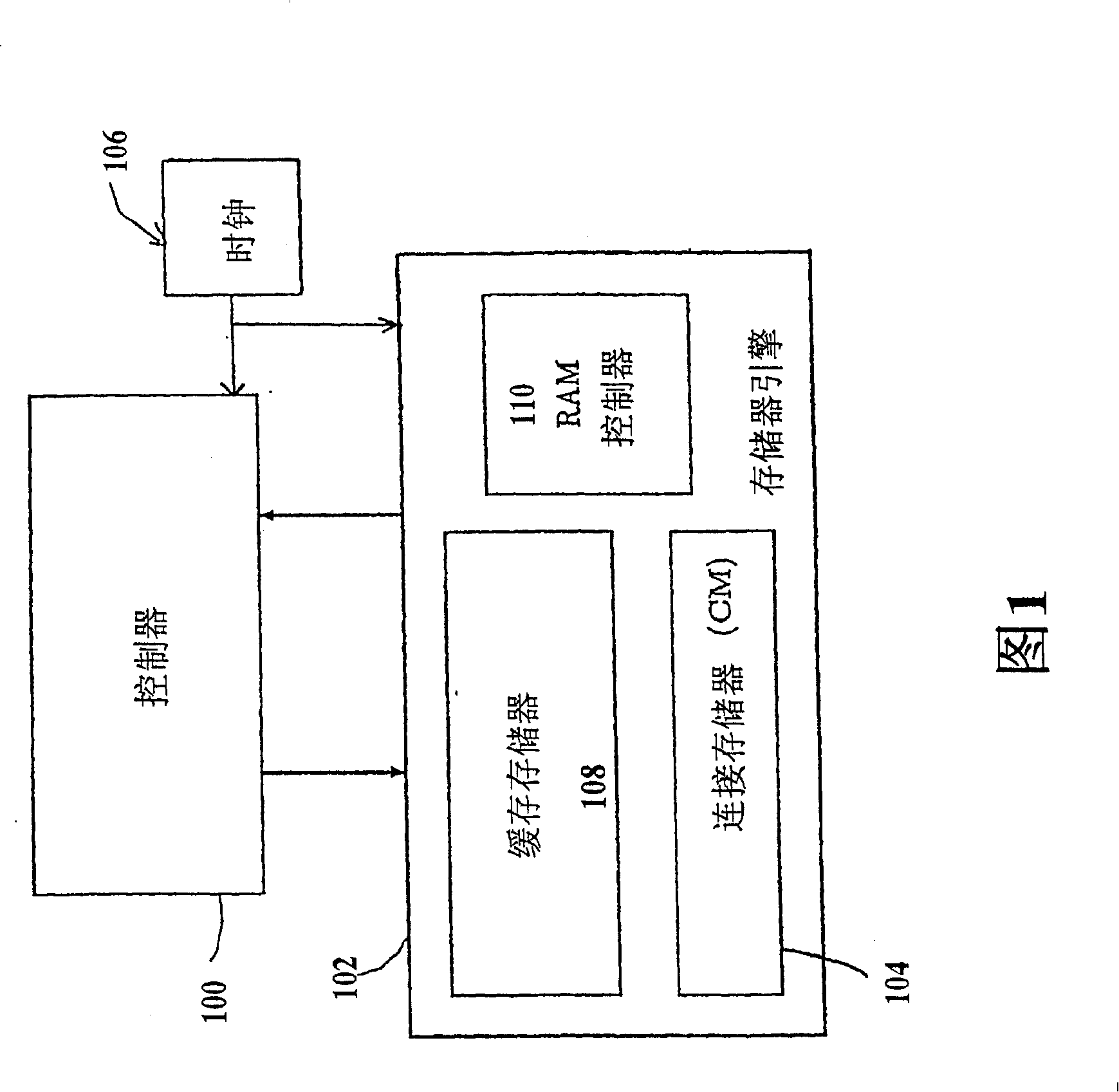
Data processing system having a Cartesian Controller
InactiveUS7107478B2Efficient data processing systemConcurrent instruction executionGenerating/distributing signalsData processing systemCycle per second
A data-processing system includes a data device for selectively storing data and an engine having access to the memory device, the engine supporting a plurality of machine executable programs. A controller is utilized which selectively outputs one of a plurality of instructions to the engine for driving the execution of the programs enabled by the engine, while a clock device is utilized for outputting a synchronizing clock signal comprised of a predetermined number of clock cycles per second. The clock device outputs the synchronizing clock signal to the data device, the engine and the controller. The controller outputs one of the instructions to the engine for execution of one of the programs, while also executing an operation within itself, all within a single clock cycle.
Owner:ALLSEARCH SEMI
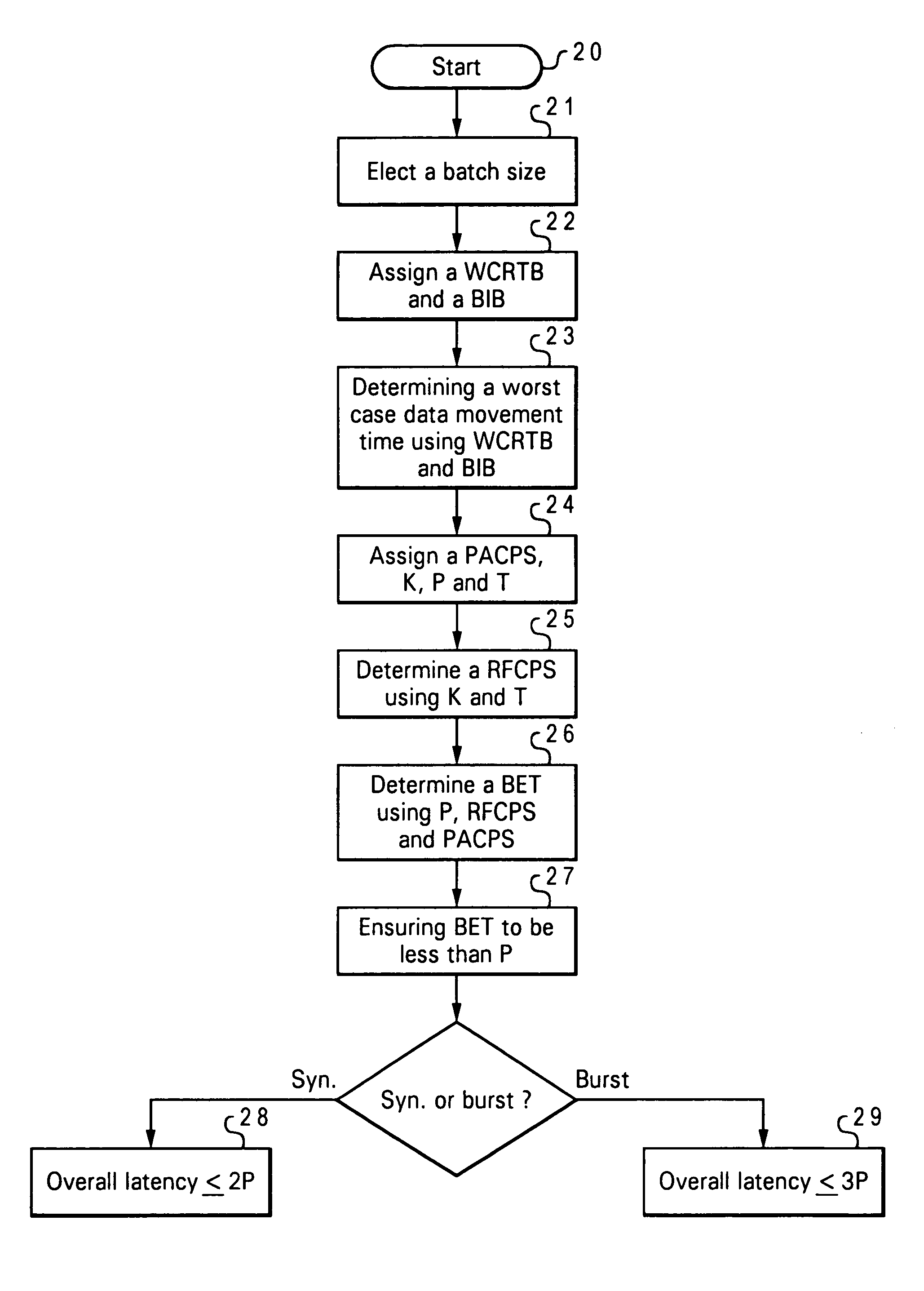
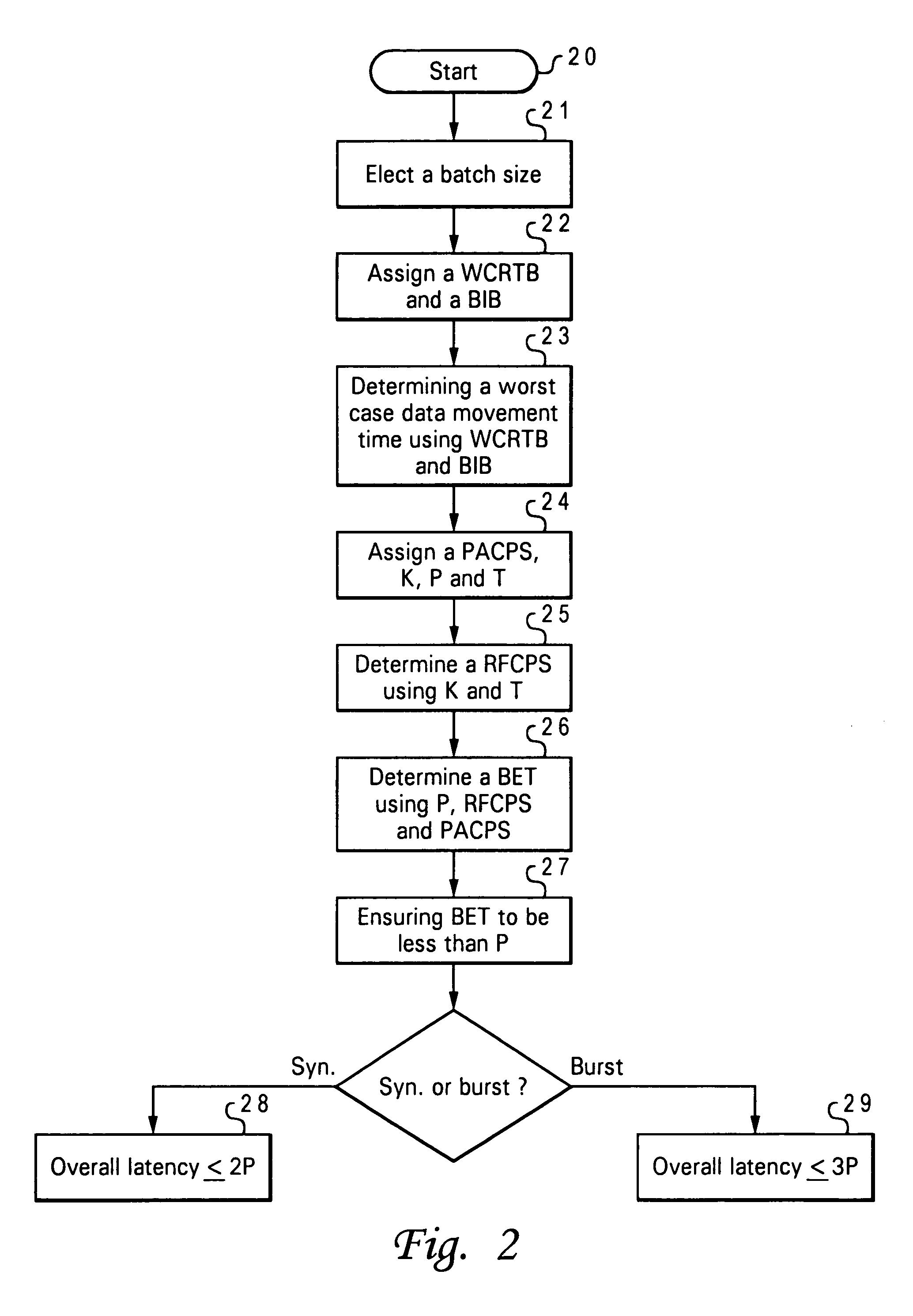
Method for providing bounded latency in a real-time data processing system
A method for providing bounded latency in a real-time data processing system is disclosed. Initially, a batch size is selected. Then, a worst case real time bandwidth (WCRTB) and a bytes-in-batch (BIB) are assigned. Next, a worst case data movement time (WCDMT) is calculated by using the WCRTB and BIB. A processor available cycles per second (PACPS), a processor cycle per sample to execute a function (K), a batch period (P) and a sample period (T) are then assigned. A required function cycles per second (RFCPS) is calculated by using the K and T. Subsequently, a BET is calculated by using the P, RFCPS and PACPS. Finally, BET is maintained to be less than P for ensuring the real-time data processing system to function properly.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method for detecting dispersion ratio of soy protein isolate product
InactiveCN110398436AEasy to operateShort detection timeWeighing by removing componentProtein isolateSlurry
The invention discloses a method for detecting the dispersion ratio of a soy protein isolate product and relates to the field of detection of dispersion ratios of protein isolate. The method includesthe following steps: weighing 200g of water, pouring the water into a 500ml beaker, adding 10g of soy protein isolate into the beaker in a pouring manner, stirring with a glass rod at a rate of one cycle per second for 30 seconds, and stirring for 5 seconds with an electric milk foam machine, filtering a stirred slurry with a 60-mesh screen, weighing a slurry that can passes through the screen, and obtaining the dispersion ratio of the product by calculating the ratio between the weight of the screened slurry and the original slurry. The detection method provided by the invention is simple inoperation, short in detection time, and accurate in results, and a detection process and a detection result are referential in practice.
Owner:山东嘉华生物科技股份有限公司
Storage and retrieval method for GPS satellite broadcast ephemeris data
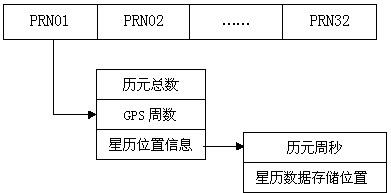
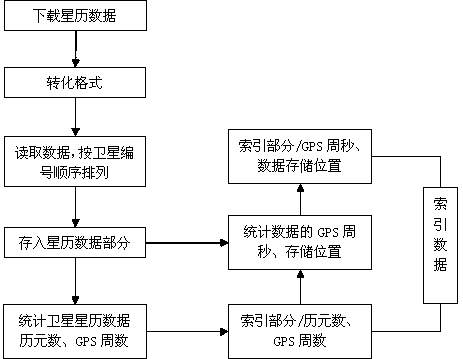
ActiveCN104035976ATargetedImprove retrieval efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsDatabase indexingObservation dataEphemeris
The invention discloses a storage and retrieval method for GPS satellite broadcast ephemeris data. The method comprises the steps that a data storage area is divided into an ephemeris data part and an indexing data part, and the GPS satellite broadcast ephemeris data are stored according to satellite serial numbers, wherein the indexing data part comprises the total number of epoches, the number of CPS and ephemeris position information, and the ephemeris position information comprises cycles per second of a GPS and the stored position of the ephemeris data. According to the storage and retrieval method for the GPS satellite broadcast ephemeris data, when observation station observation data and the satellite ephemeris data are utilized for calculating the coordinates of a satellite, the target performance is high, retrieval efficiency is high, and calculating efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Methods and apparatus for constructing a power supply capable drawing power from fluorescent lamps
InactiveUS20050184680A1Improve efficiencyImprove operationElectric lighting sourcesTransmissionFluorescenceEffect light
Methods and Apparatus are provided for a power supply capable of being operated directly from fluorescent lighting fixture and capable to functioning properly when supplied by conventional 60 cycles per second (cps) “Core and Coil’ fluorescent lamp power supply (ballasts) as well as ‘Electronic’ or ‘Solid State’ ballasts functioning at frequencies from 20,000 cps to as much as 40,000 cps, without adversely affecting normal lighting fixture operation.
Owner:THOMAS J MAYER
Cellular engine for a data processing system
InactiveUS7383421B2Efficient data processing systemImprove efficiencyArchitecture with single central processing unitMemory systemsData processing systemData treatment
A data processing system includes an associative memory device containing n-cells, each of the n-cells includes a processing circuit. A controller is utilized for issuing one of a plurality of instructions to the associative memory device, while a clock device is utilized for outputting a synchronizing clock signal comprised of a predetermined number of clock cycles per second. The clock device outputs the synchronizing clock signal to the associative memory device and the controller which globally communicates one of the plurality of instructions to all of the n-cells simultaneously, within one of the clock cycles.
Owner:ALLSEARCH SEMI
Cellular engine for a data processing system
InactiveUS7908461B2Efficient data processing systemImprove efficiencyArchitecture with single central processing unitSpecific program execution arrangementsData processing systemData treatment
A data processing system includes an associative memory device containing n-cells, each of the n-cells includes a processing circuit. A controller is utilized for issuing one of a plurality of instructions to the associative memory device, while a clock device is utilized for outputting a synchronizing clock signal comprised of a predetermined number of clock cycles per second. The clock device outputs the synchronizing clock signal to the associative memory device and the controller which globally communicates one of the plurality of instructions to all of the n-cells simultaneously, within one of the clock cycles.
Owner:ALLSEARCH SEMI
Data processing system having a Cartesian controller, and method for processing data
InactiveCN100409221CImprove efficiencyGeneral purpose stored program computerData processing systemCycle per second
A data-processing system includes a data device (104) for selectively storing data and an engine (element 102) having access to the memory device, the engine (element 102) supporting a plurality of machine executable programs. A controller (element 100) is utilized which selectively outputs one of a plurality of instructions to the engine (element 102) for driving the execution of the programs enabled by the engine, while a clock device (element 106) is utilized for outputting a synchronizing clock signal comprised of a predetermined number of clock cycles per second. The clock device outputs the synchronizing clock signal to the data device (104), the engine (element 102) and the controller (element 100). The controller outputs one of the instructions to the engine for execution of one of the programs, while also executing an operation within itself, all within a single clock cycle.
Owner:ALLSEARCH SEMI
Associative memory device
InactiveCN101076787ALimit the search spaceDigital storageMemory systemsData processing systemCycle per second
An associative memory support for a data processing system includes an associative memory device containing n-cells. A controller is provided for issuing an instruction to the associative memory device. A clock device outputs a synchronizing clock signal that includes a predetermined number of clock cycles per second, the clock device outputting the synchronizing clock signal to the associative memory device and the controller. The controller globally communicates the instruction to all of the n-cells simultaneously, within one of the clock cycles and the instruction is applied equally to each of the n-cells.
Owner:ALLSEARCH SEMI
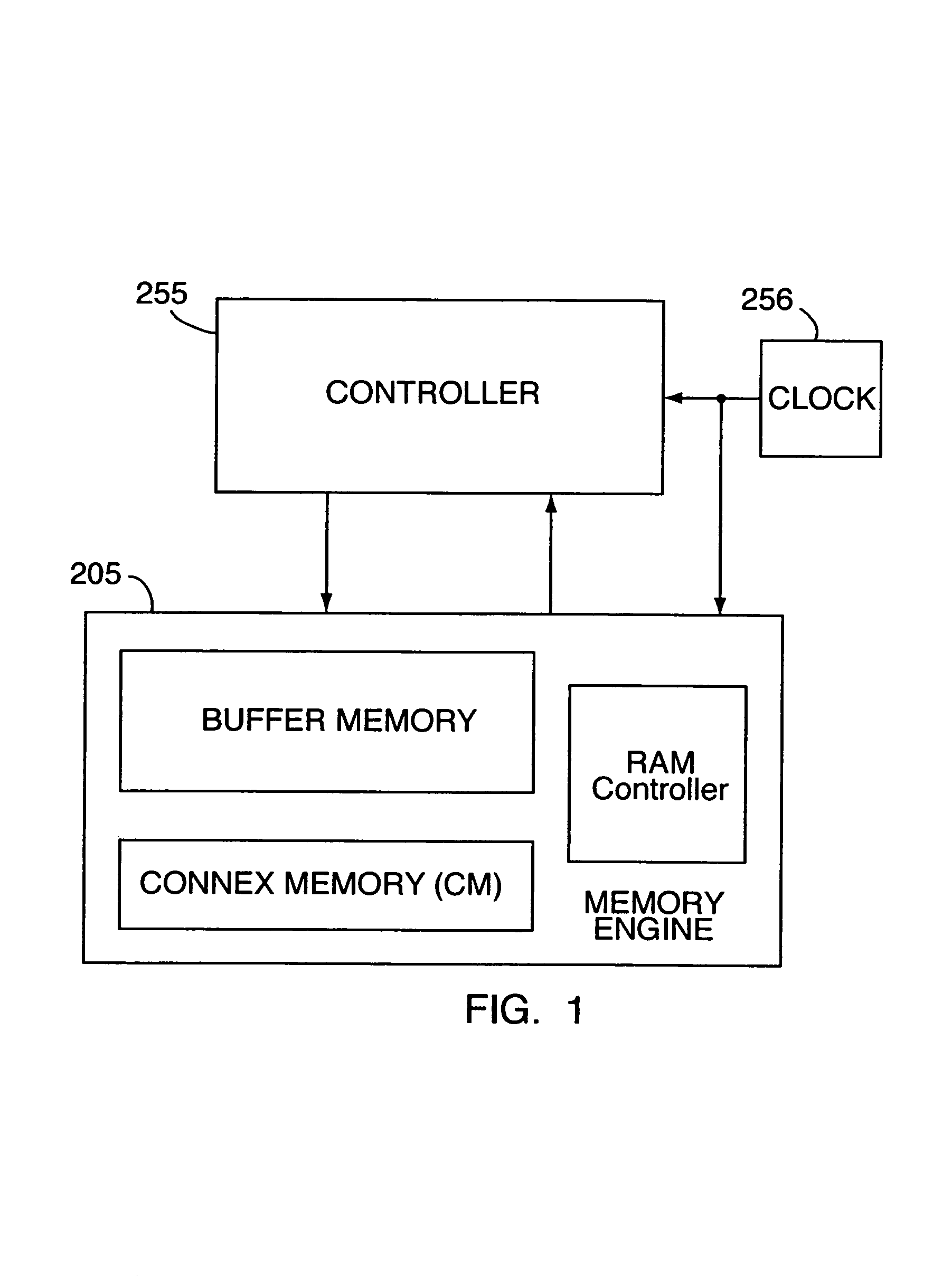
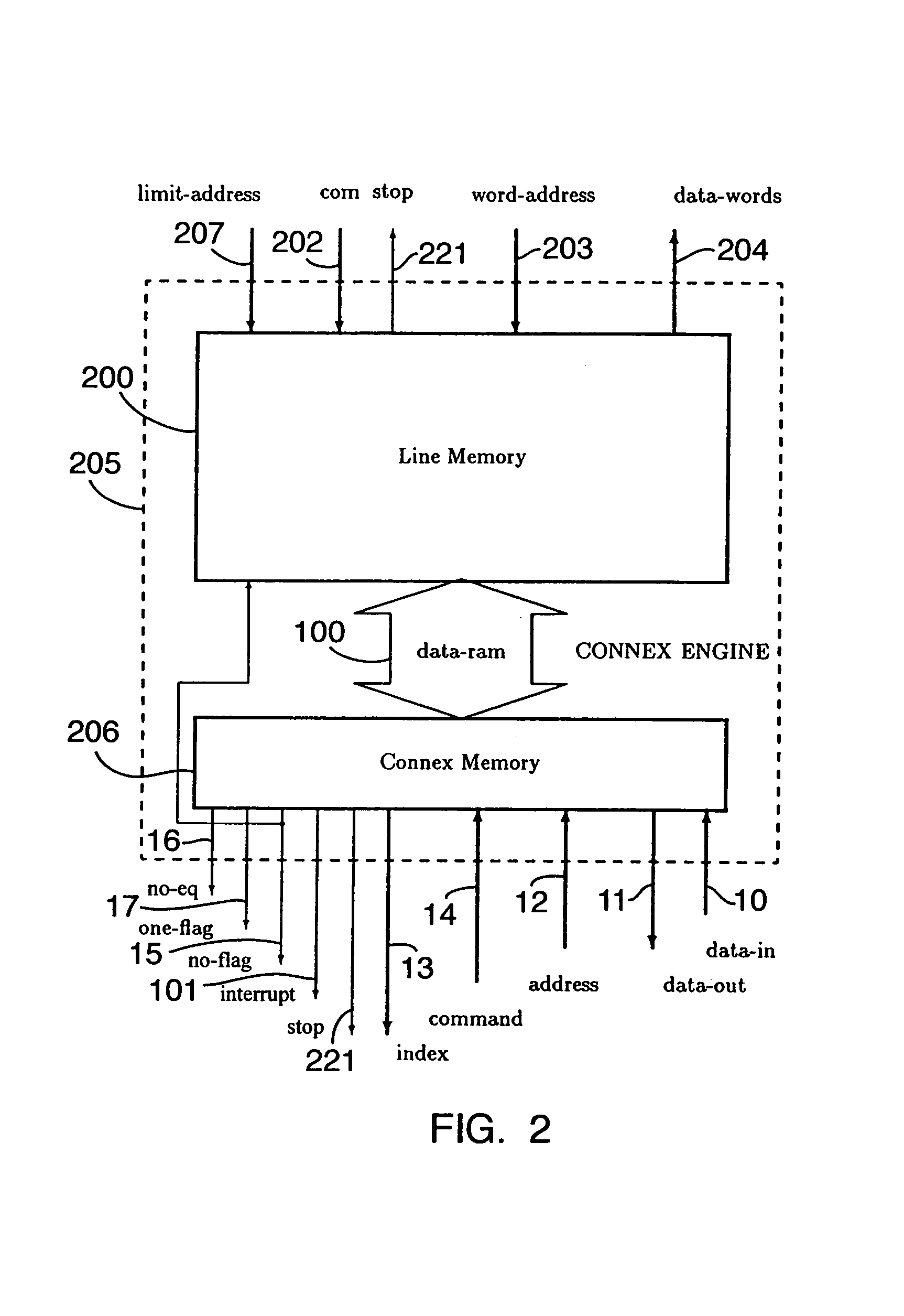
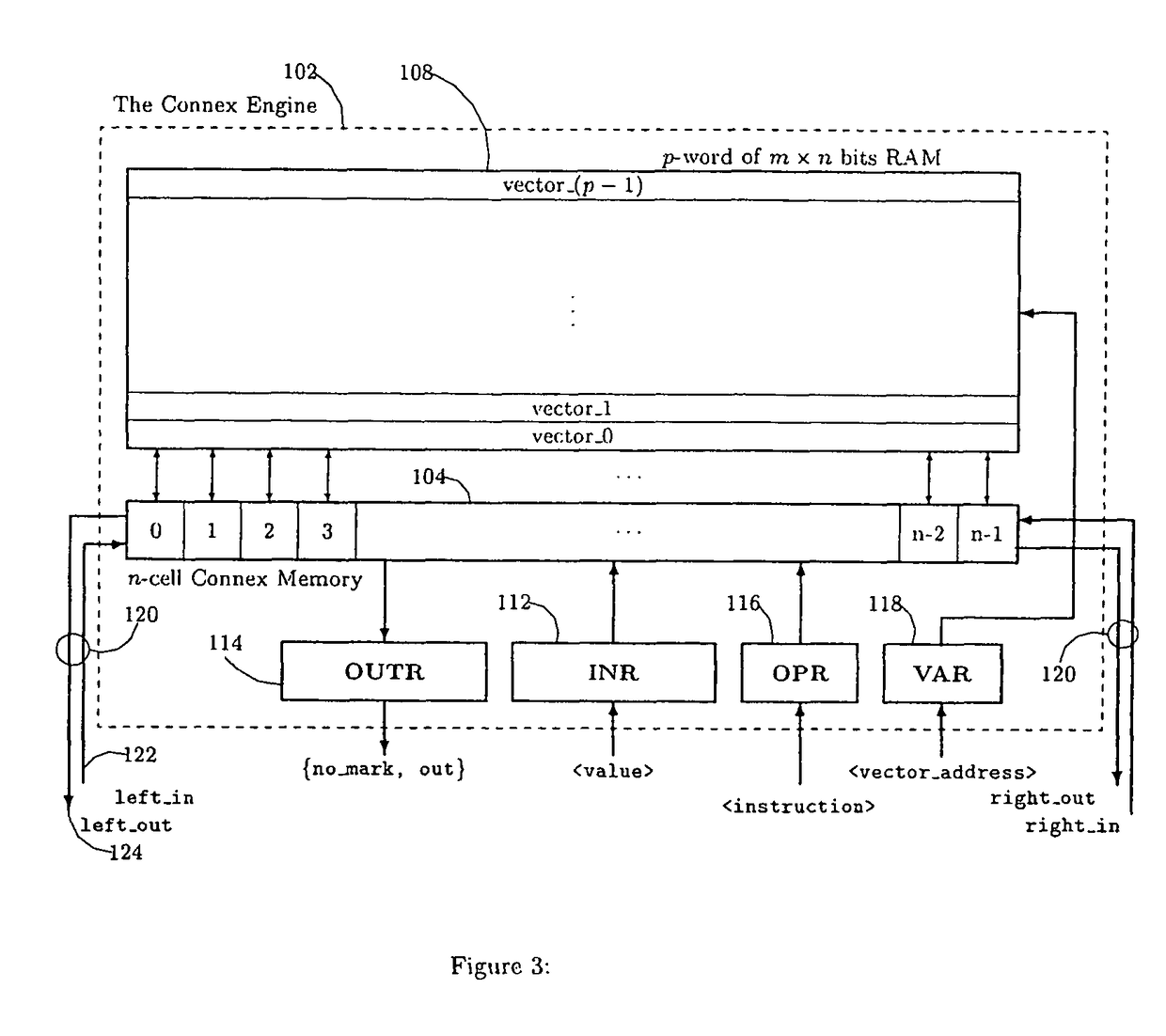
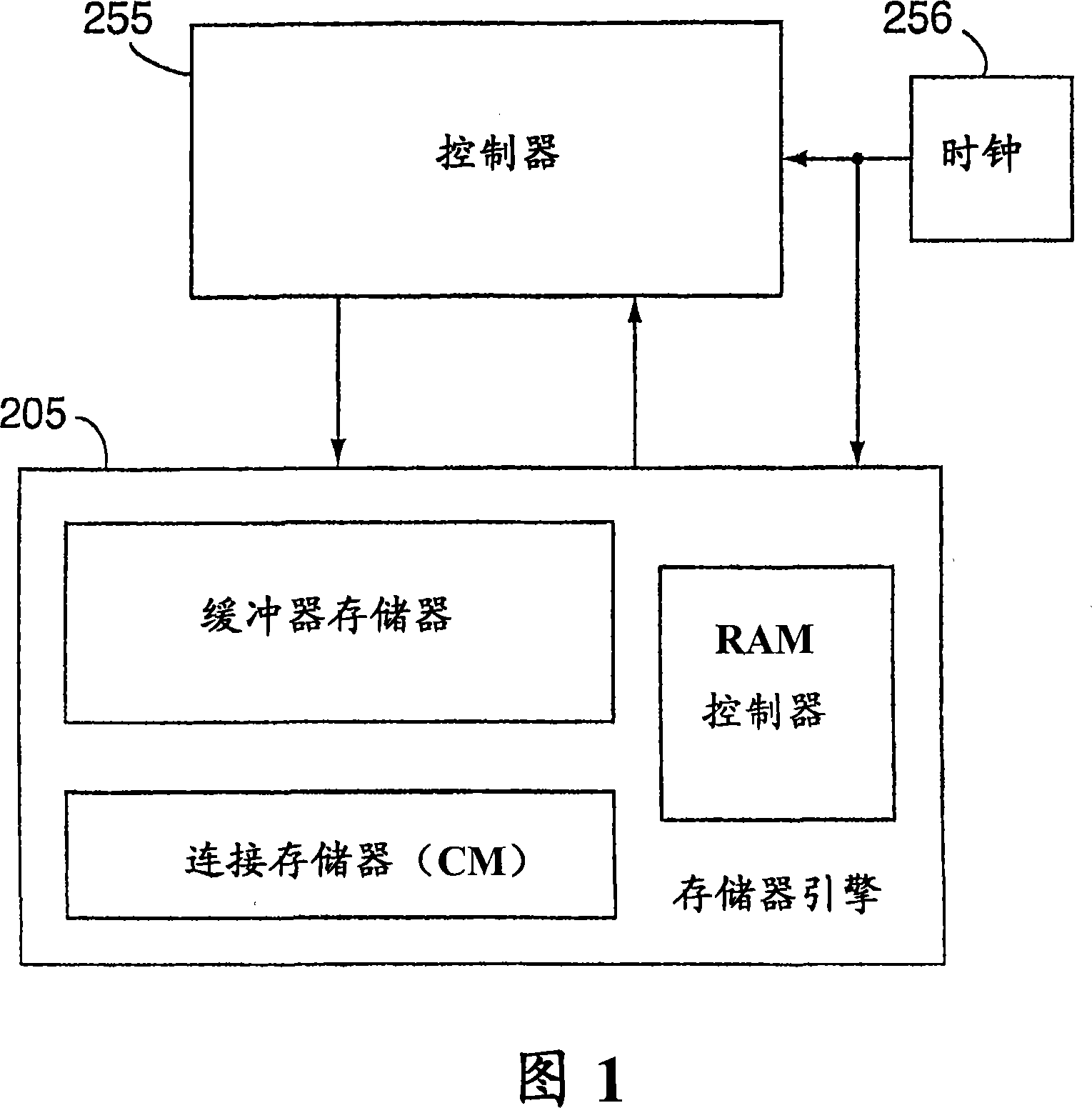
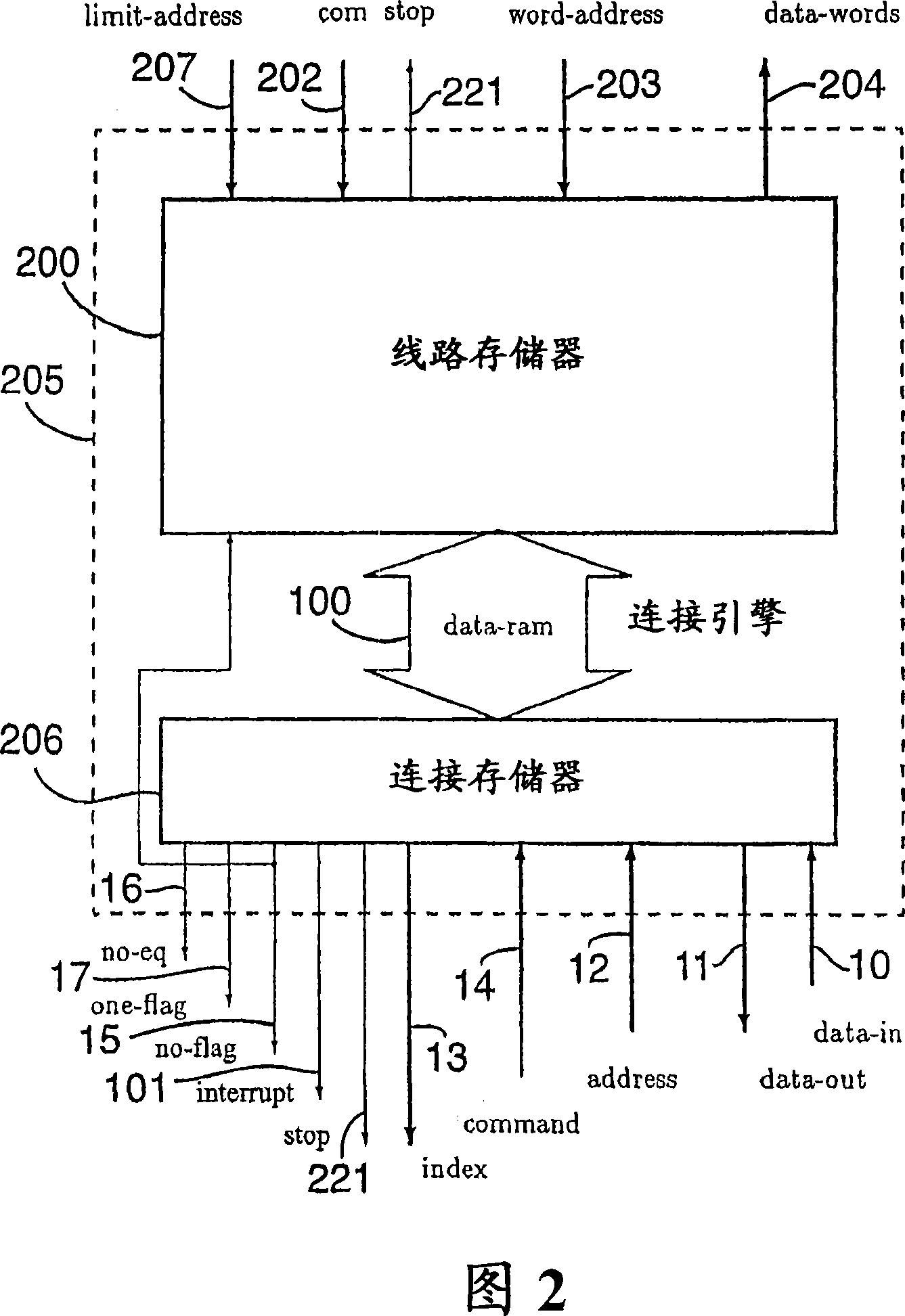
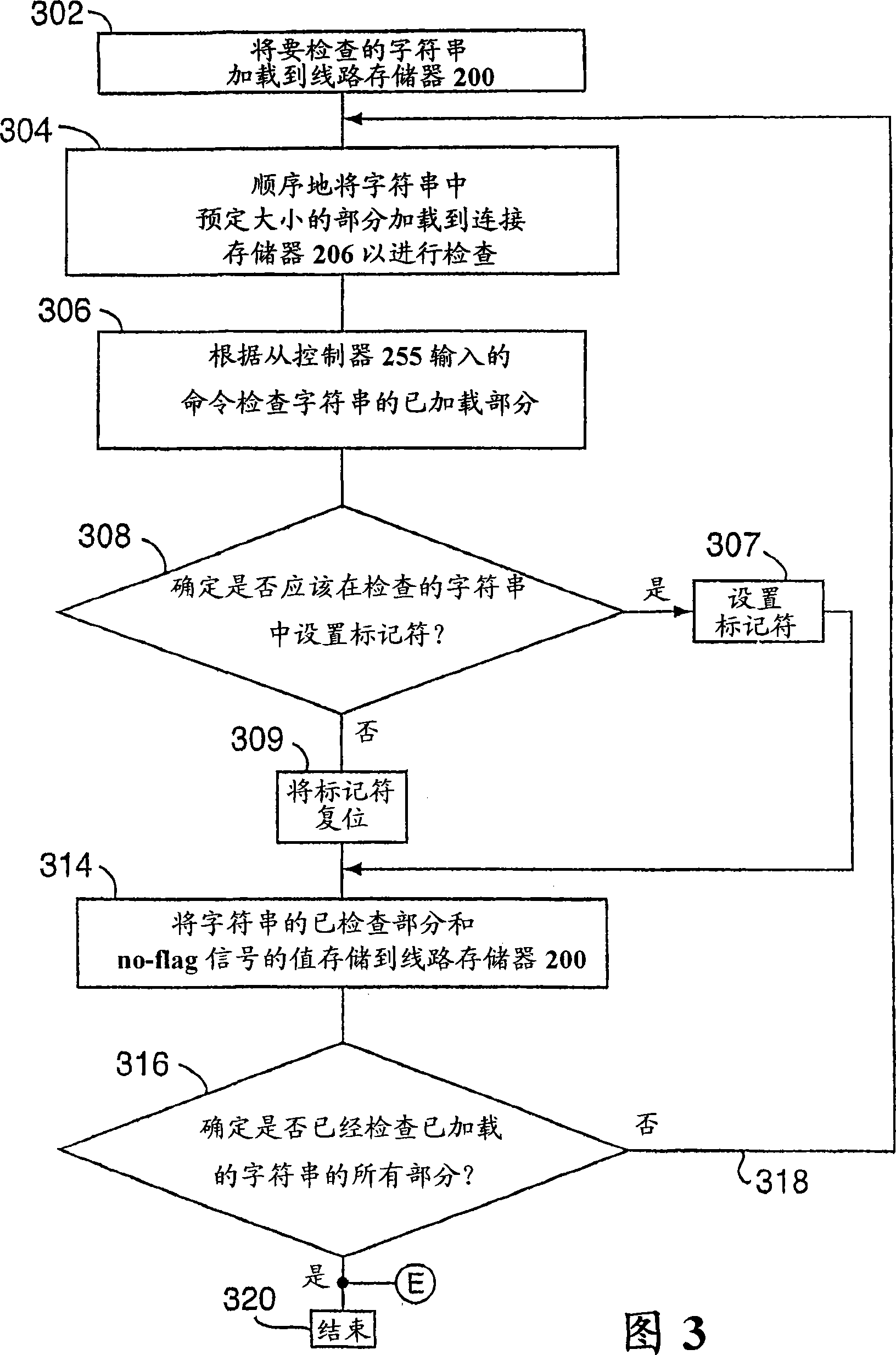
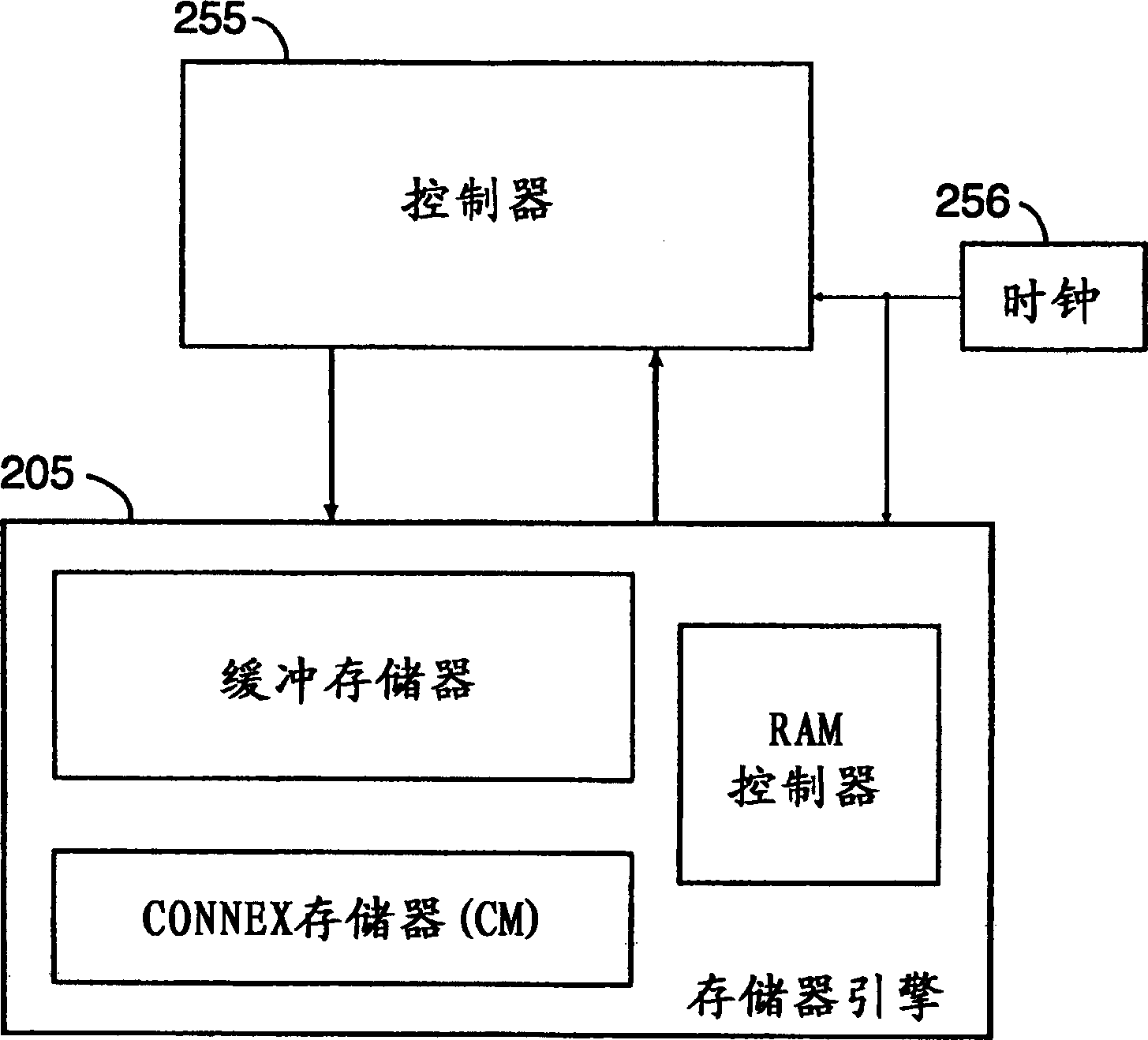
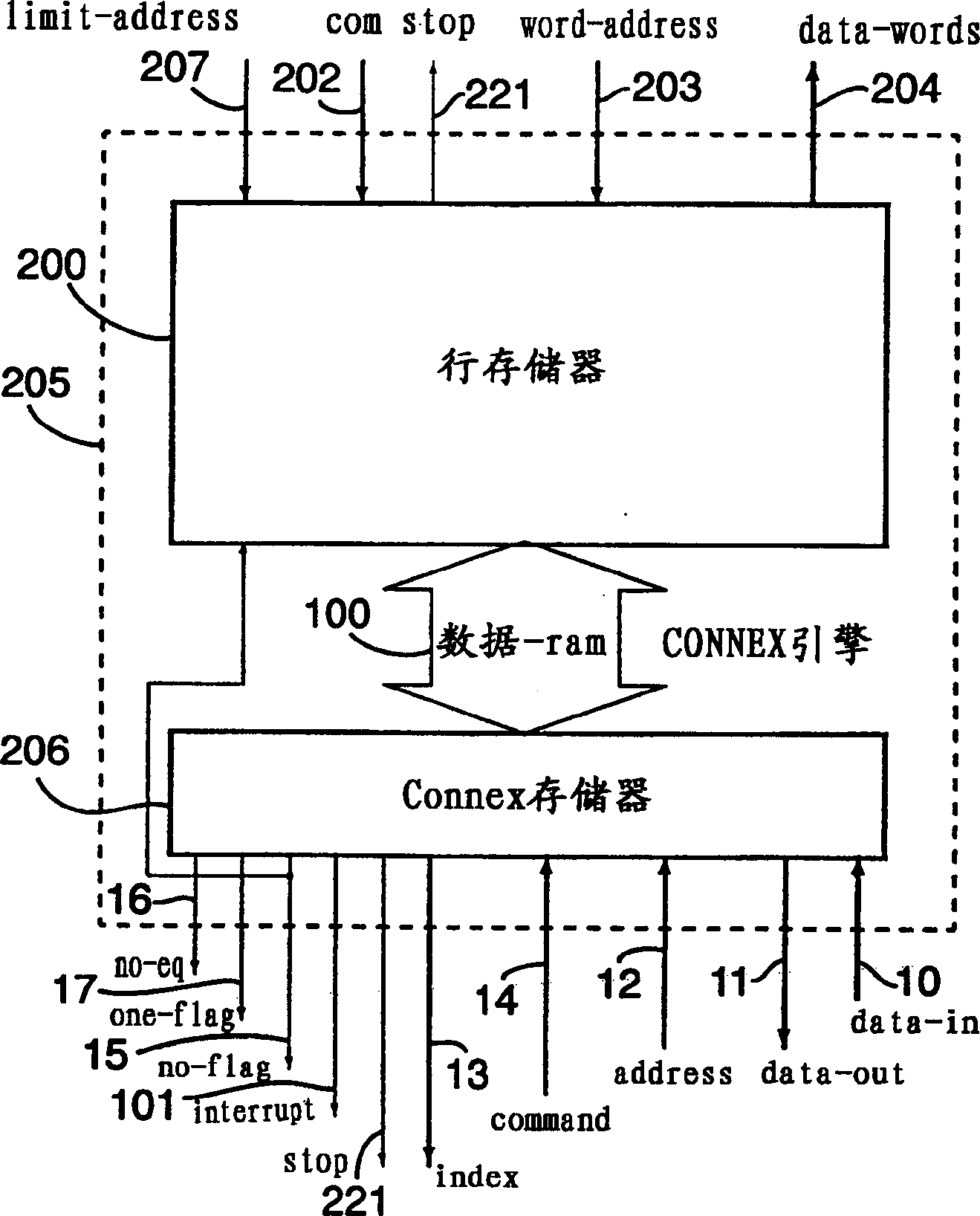
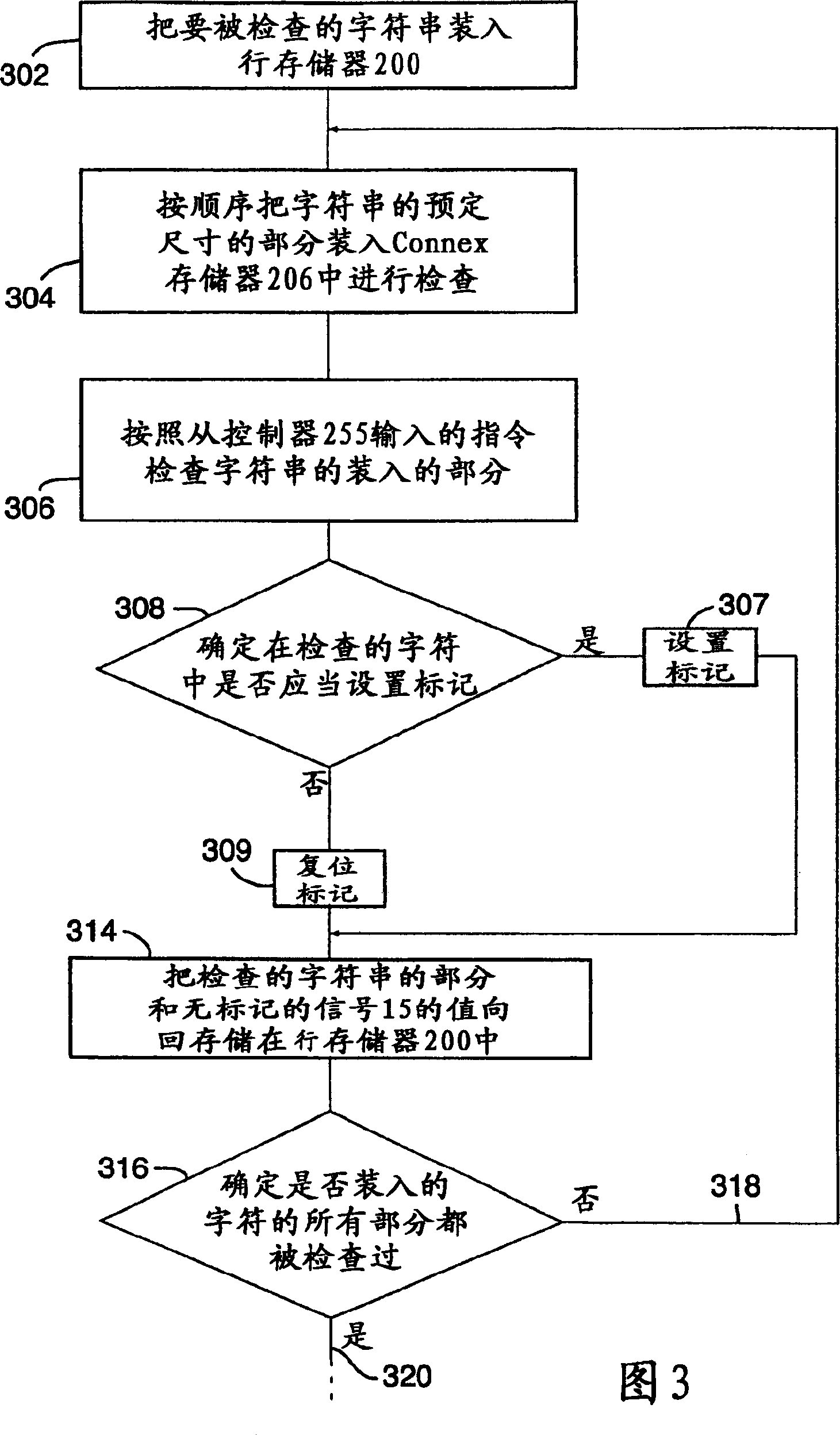
A memory engine for the inspection and manipulation of data
InactiveCN1554048ADigital data information retrievalDigital storageRandom access memoryCycle per second
A memory engine combines associative memory and random-acces memory for enabling fast string search, insertion, and deletion operations to be performed on data and includes a memory device for temporarily storing the data as a string of data characters. A controller is utilized for selectively outputting one of a plurality of commands to the memory device and receives data feedback therefrom, the memory device inspects data characters in the string in accordance with the commands outputted by the controller. A clock device is also utilized for outputting a clock signal comprised of a predetermined number of clock cycles per second to the memory device and the controller, the memory device inspecting and selectively manipulating one of the data characters within one of the clock cycles.
Owner:傲搜SEMI有限责任公司
High speed probing apparatus for semiconductor devices and probe stage for the same
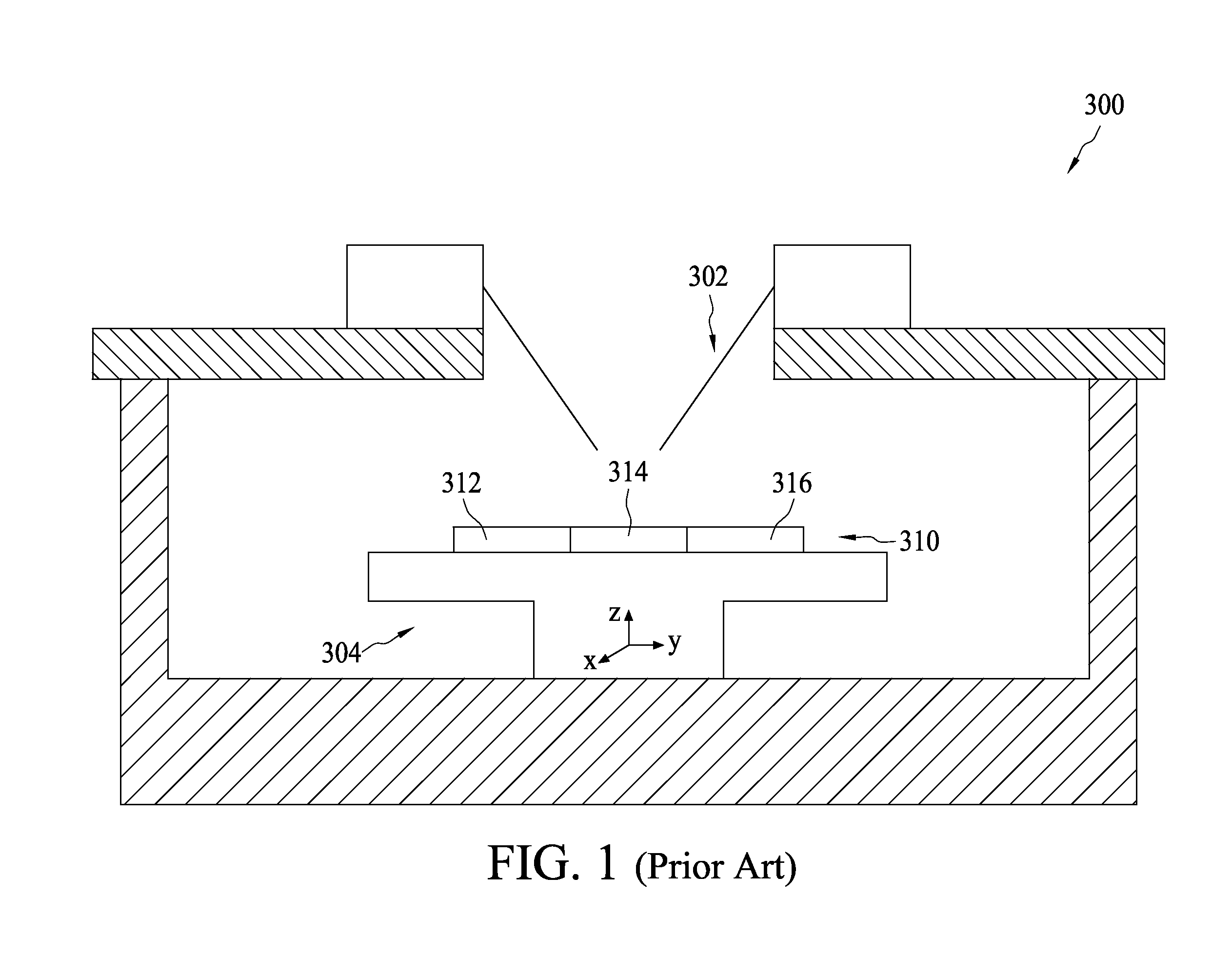
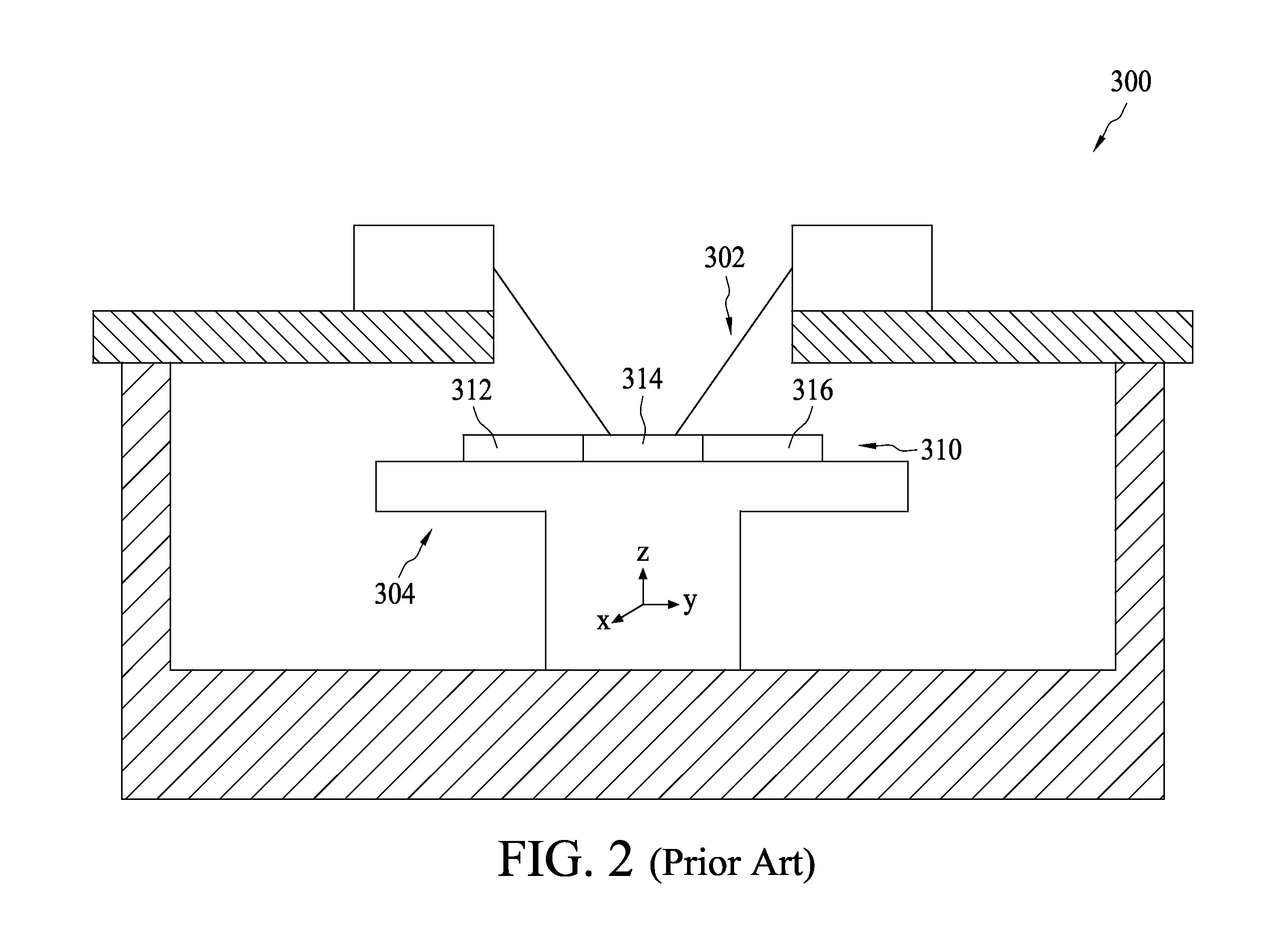
ActiveUS7986157B1High frequencyElectrical measurement instrument detailsIndividual semiconductor device testingEngineeringCycle per second
A probing apparatus for semiconductor devices includes a housing configured to define a testing chamber, a device holder positioned in the housing and configured to receive at least one device under test, and at least one probe stage positioned in the housing. In one embodiment of the present disclosure, the probe stage includes a base, a retaining arm pivotally coupled with the base and having a retaining portion configured to retain at least one probe, and a stepper positioned on the base. In one embodiment of the present disclosure, the stepper is configured in response to an electric signal to move the probe downward through the retaining arm to contact a device under test and to move the probe upward through the retaining arm to separate from the device under test such that the up-and-down movement of the probe can be performed at relatively high frequency of typically greater than six cycles per second. In one embodiment of the present disclosure, the stepper further equipped with a contact sensor configured to sense the contact of the probe to the device under test.
Owner:STAR TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com