Patents
Literature
80 results about "Gain margin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gain margin is defined as the margin in gain allowable by which gain can be increased till system reaches on the verge of instability.
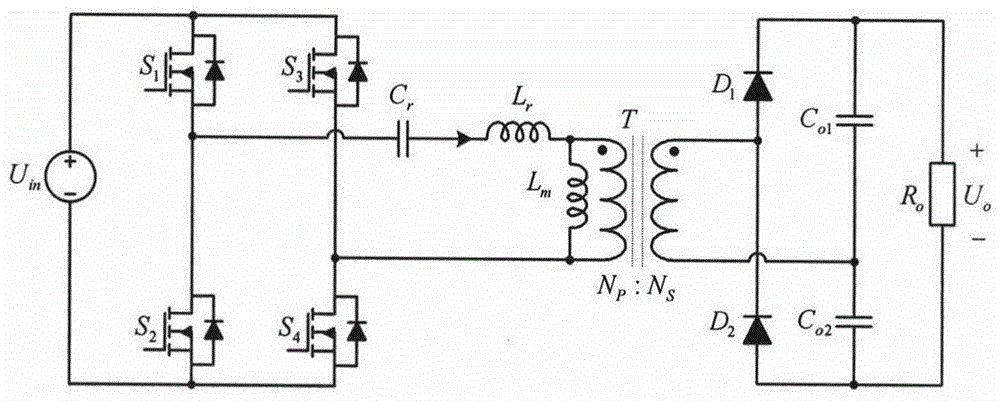
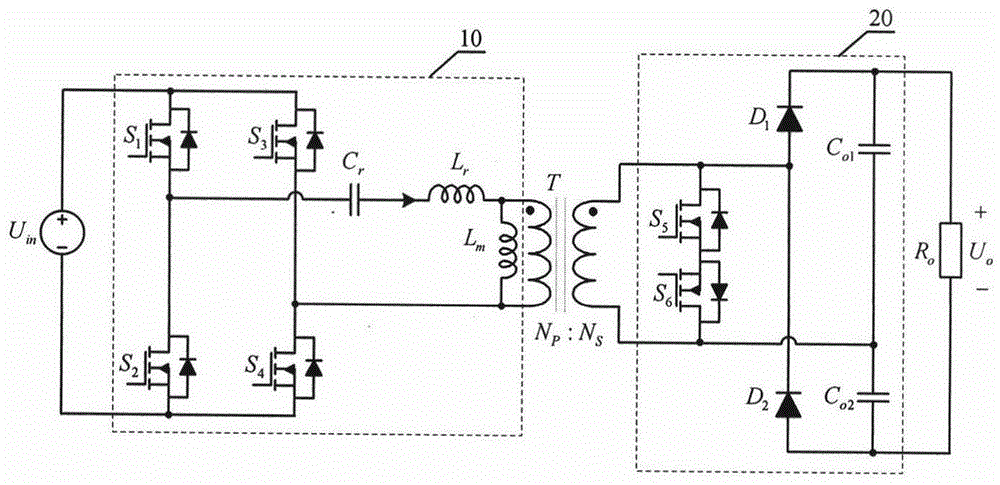
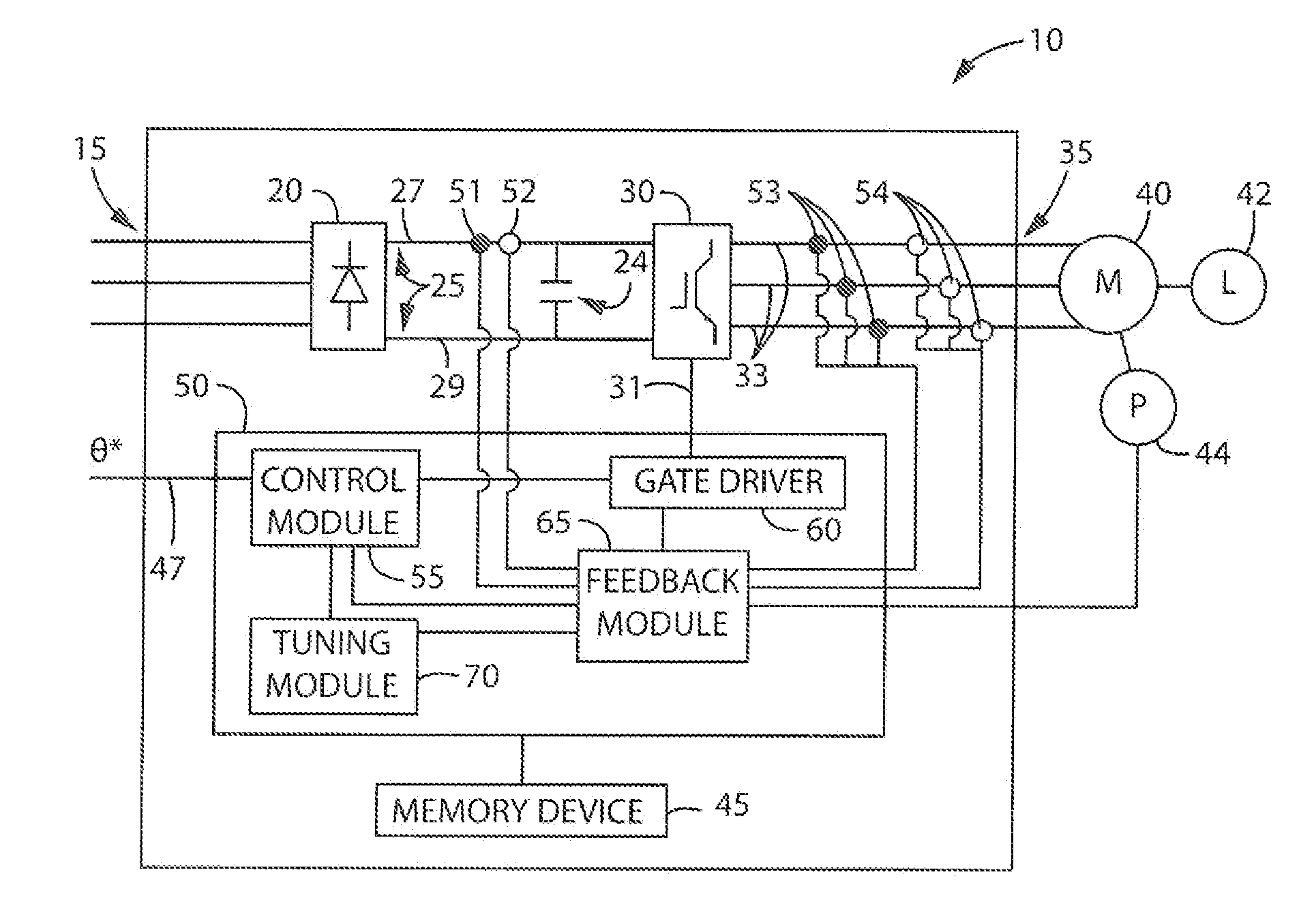
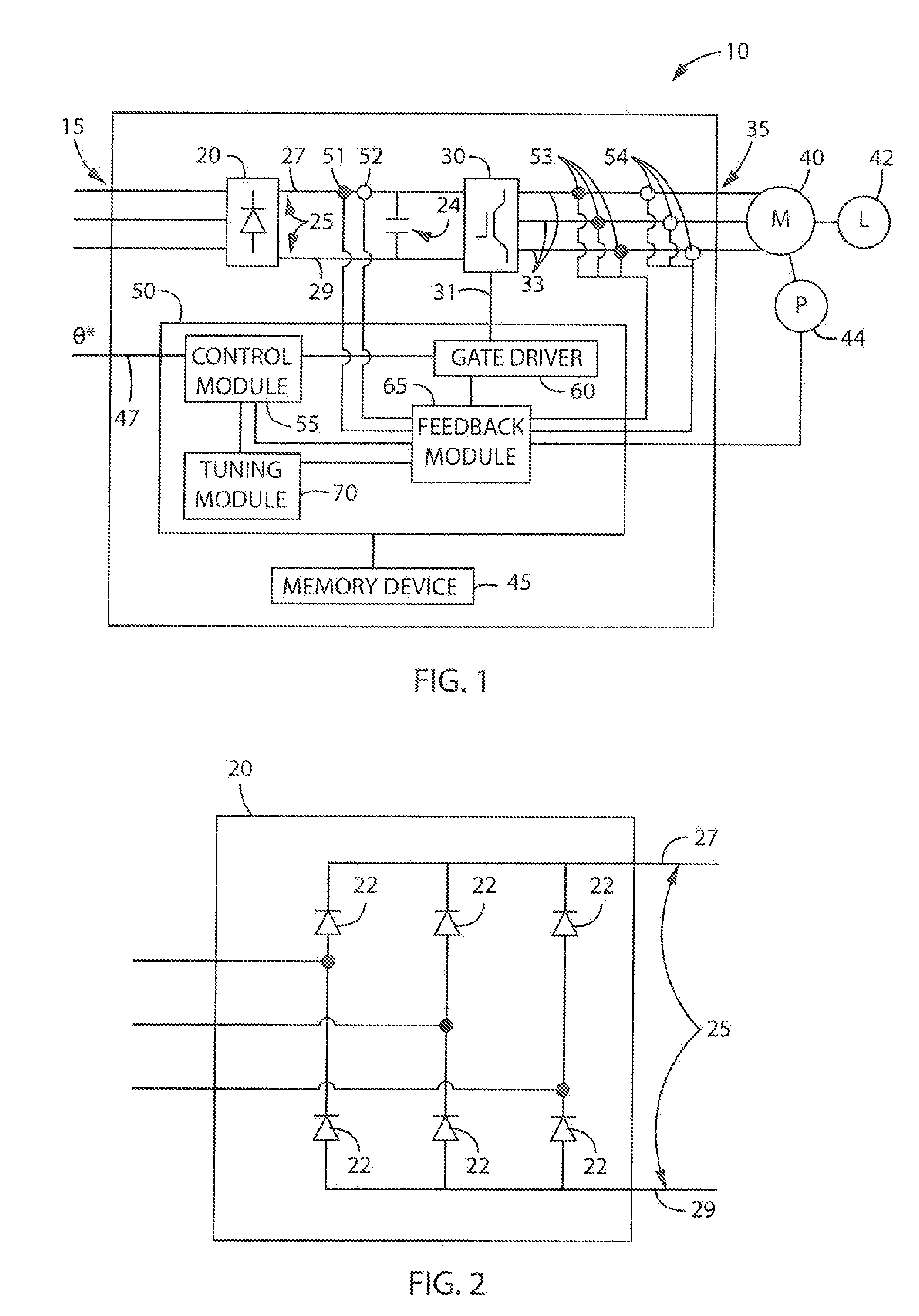
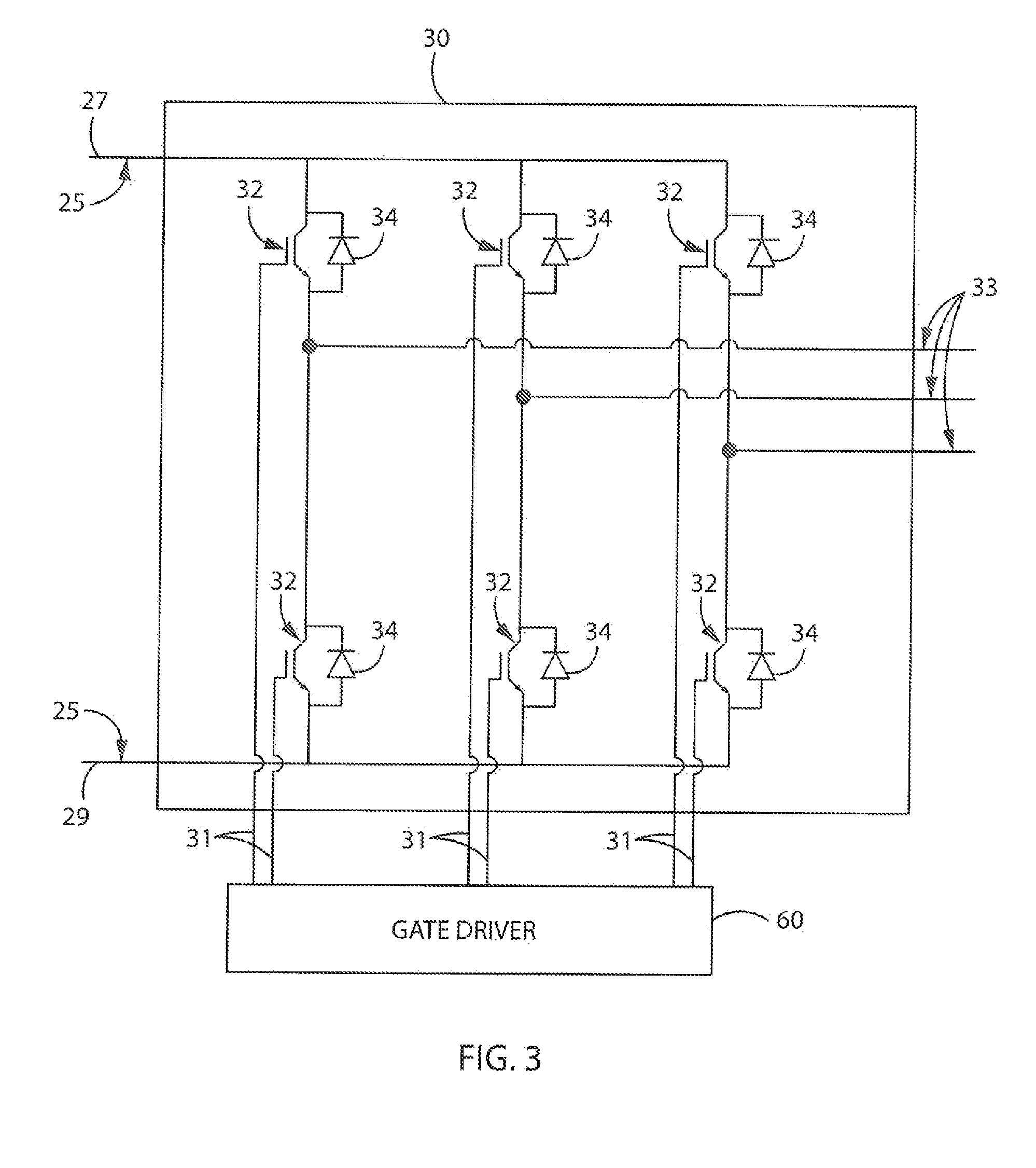
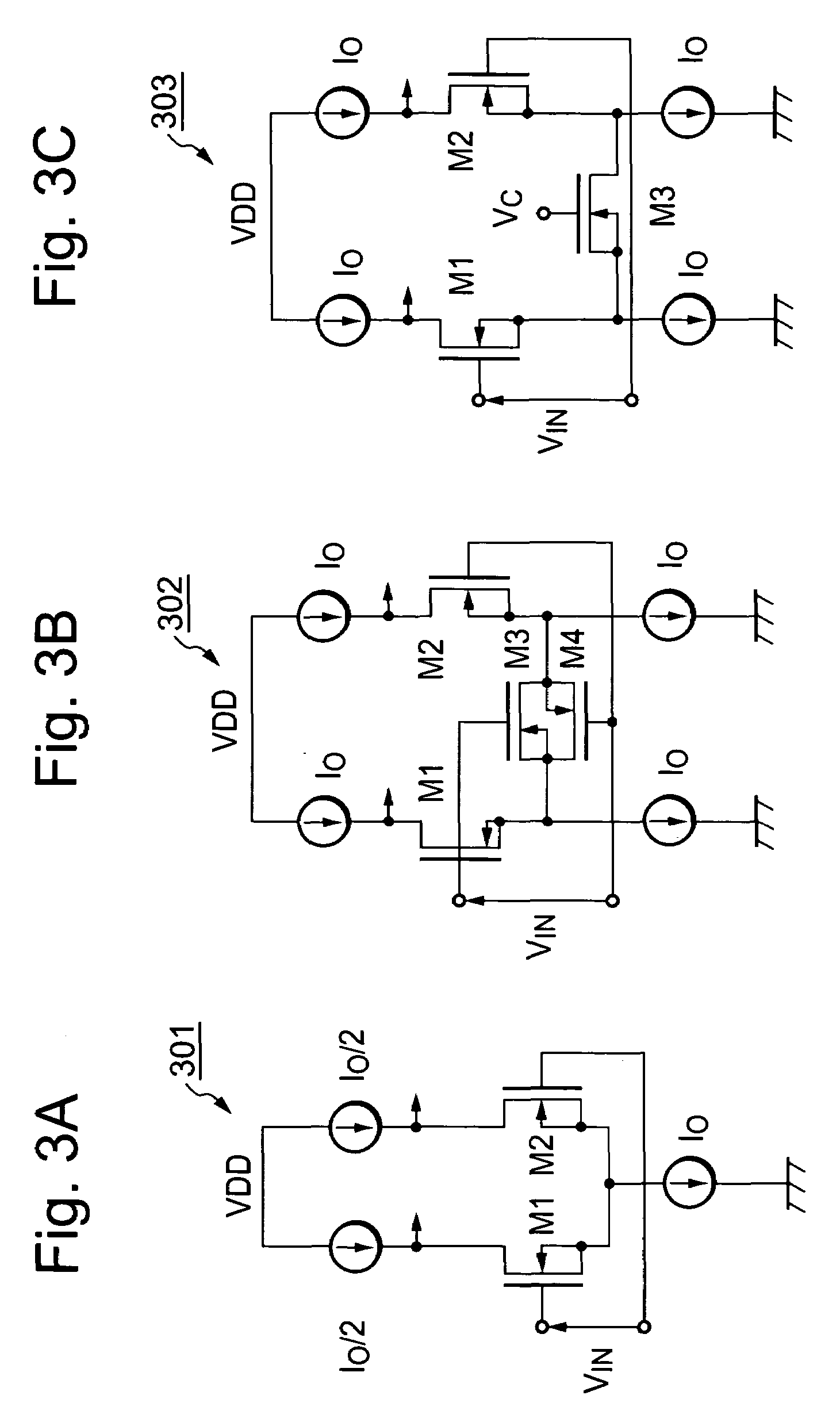
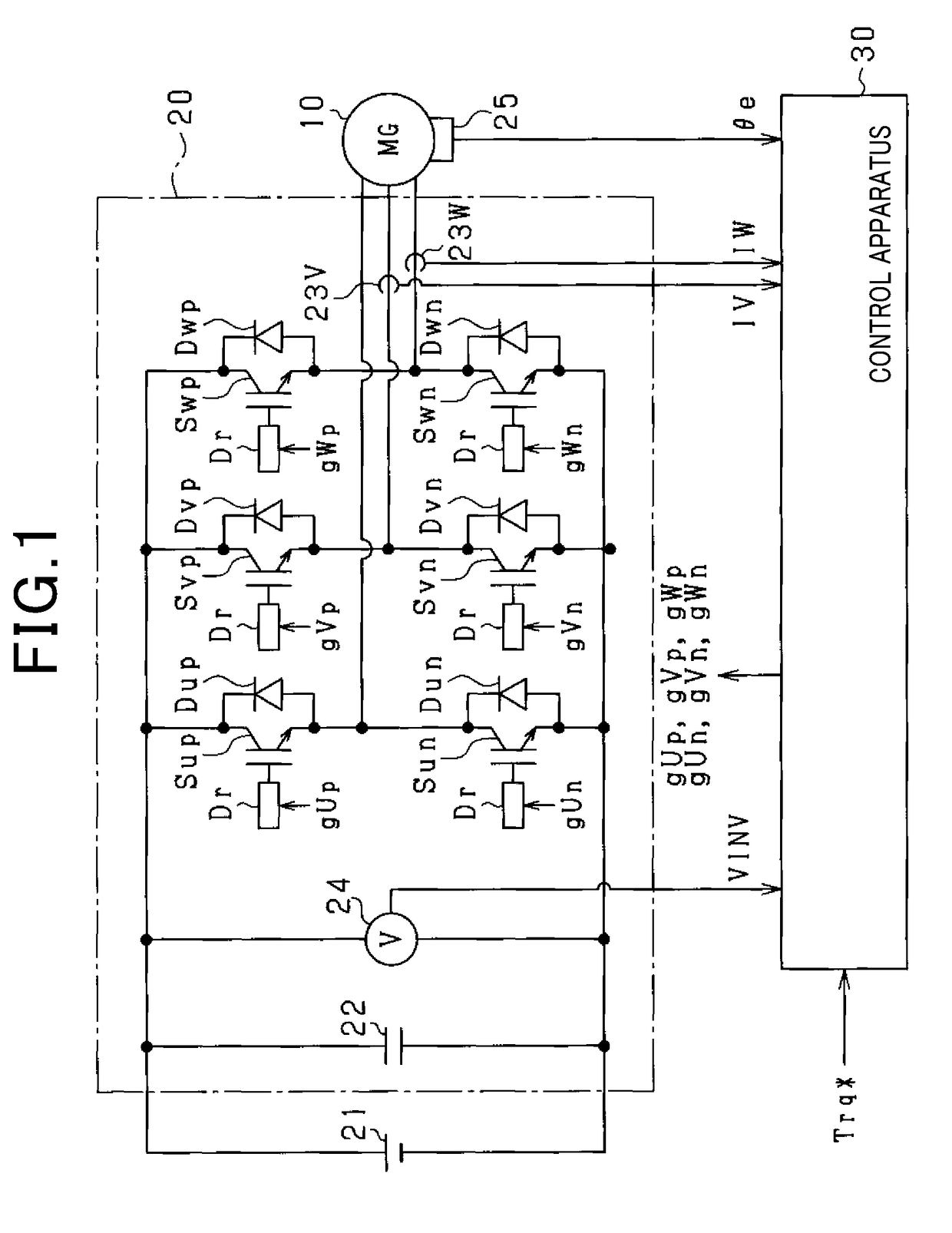
Power supply apparatus
InactiveUS6963190B2High speed responseHighly practicalDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSignal transfer functionEngineering
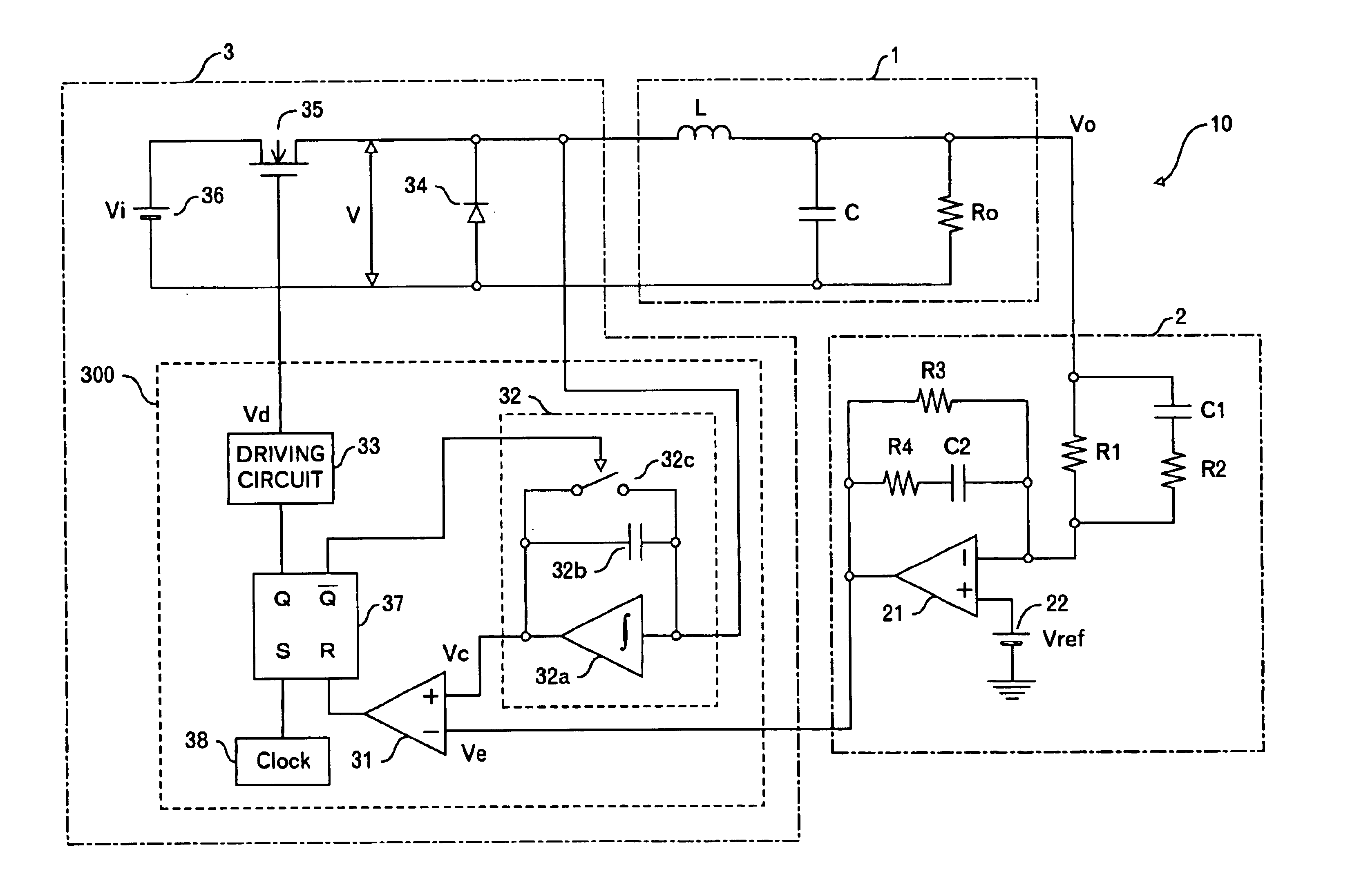
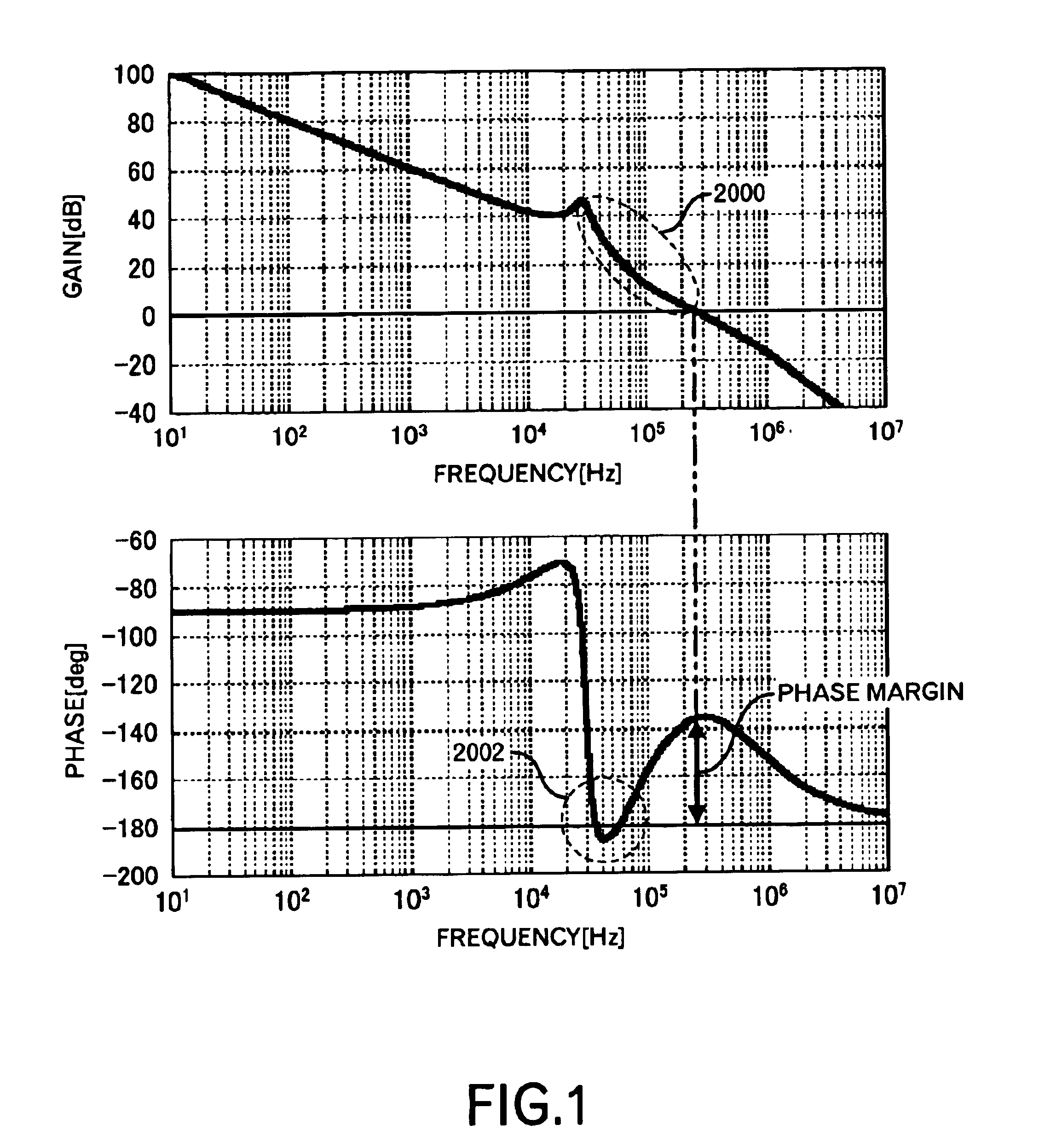
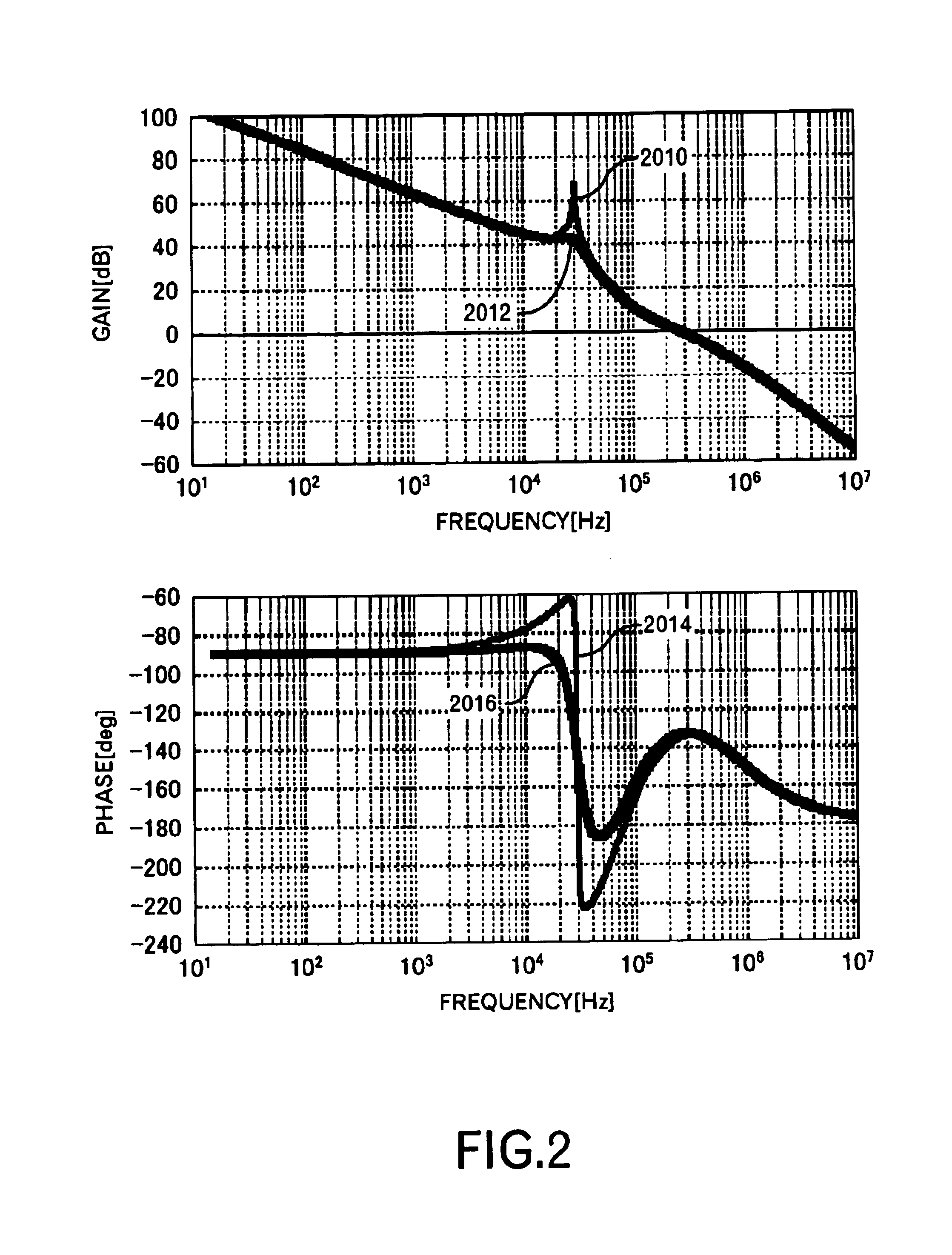
An object of this invention is to provide a power supply apparatus, which realizes a frequency characteristic of an open-loop transfer function having a trap point, and can deal with input fluctuation. A controller of the power supply apparatus of the invention is a circuit in which although the form of its transfer function is the same as a conventional one, values of respective coefficients are different, only a phase margin is ensured without ensuring a gain margin, and the transfer function is realized which provides a frequency range (i.e. trap point) in which a decrease in gain is remarkable and a phase is considerably delayed. Besides, in order to ensure the stability against input fluctuation, a power conversion circuit is used which converts an input voltage from an input DC power supply so as to be constant in multiplying voltage by time.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
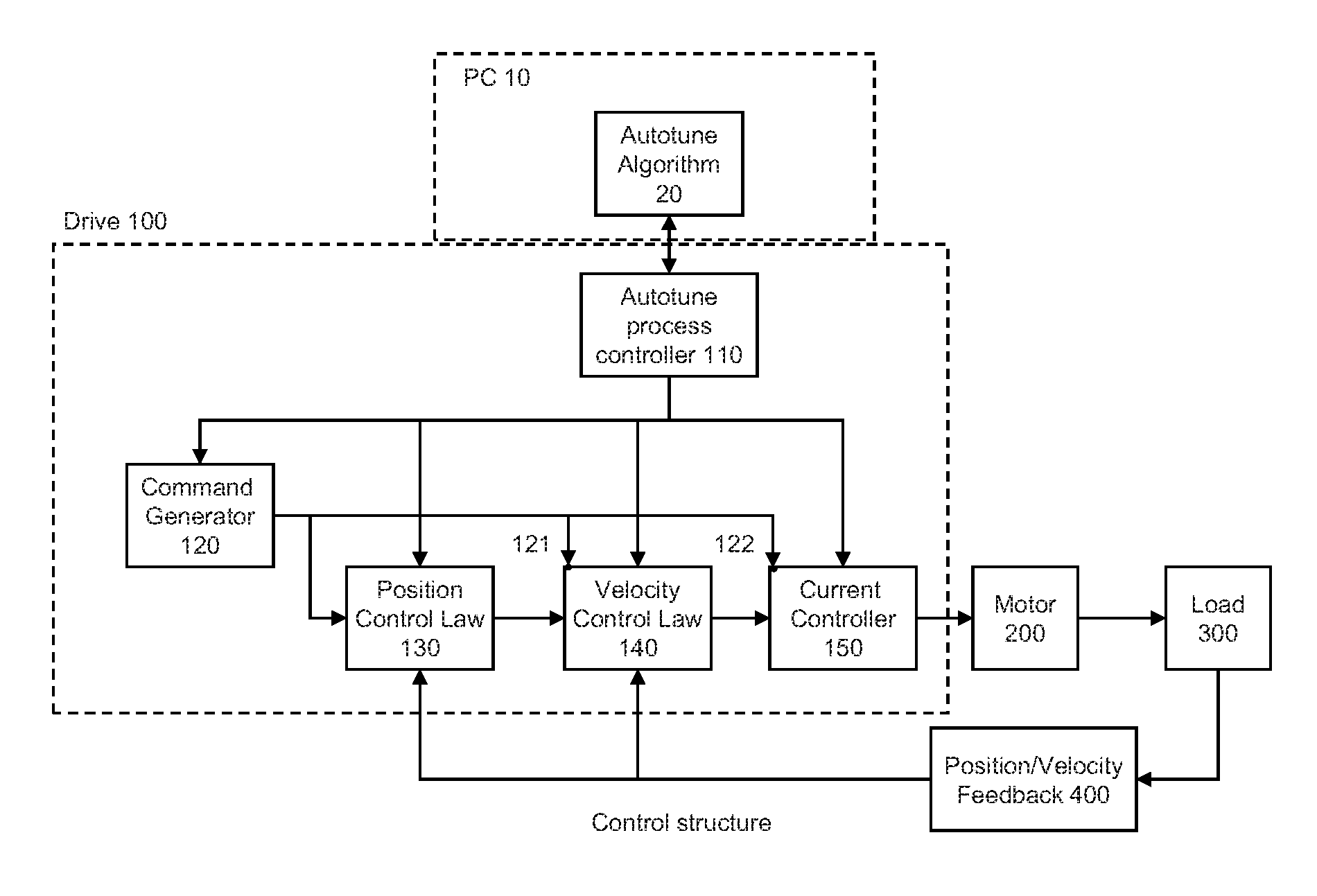
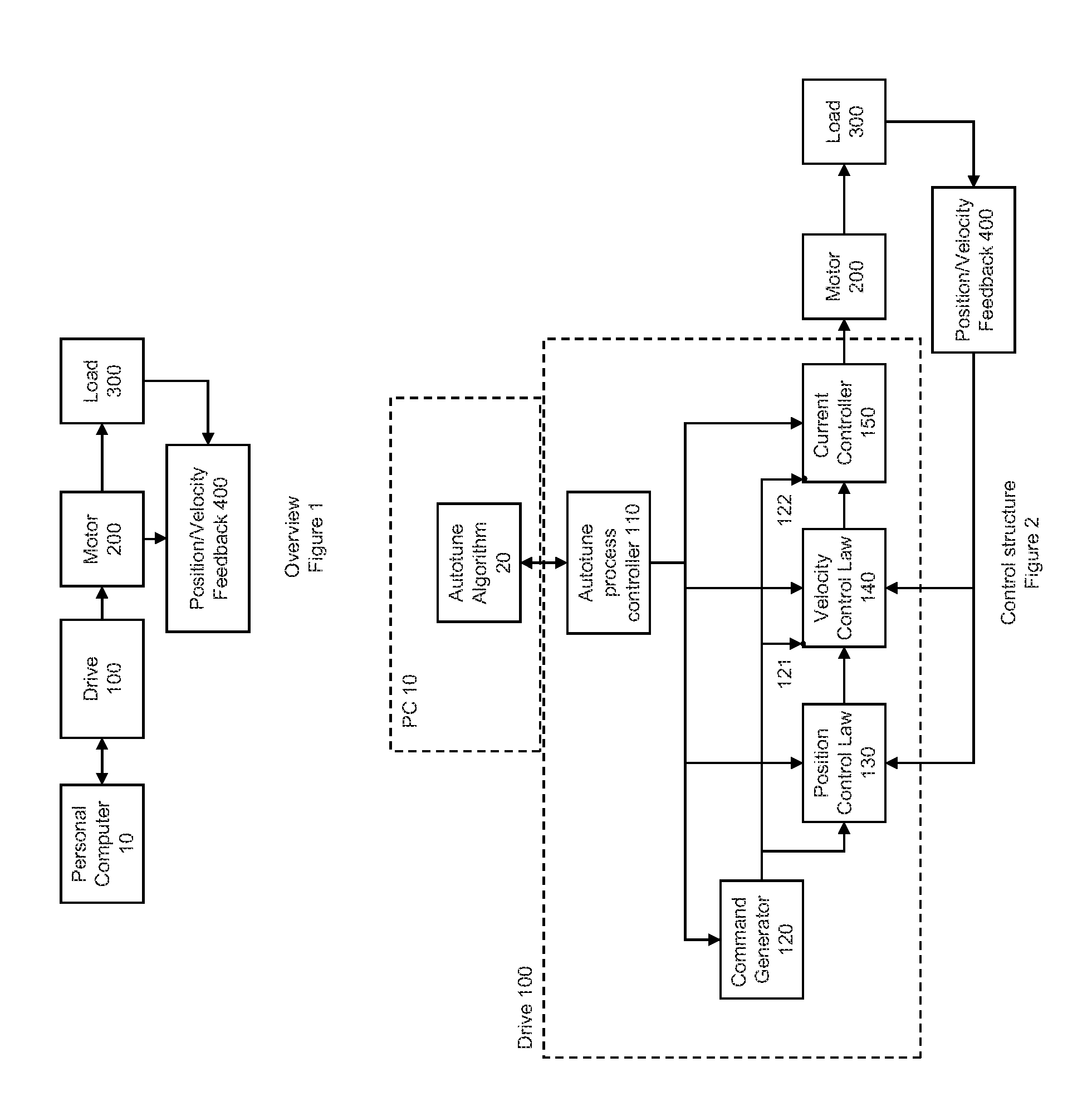
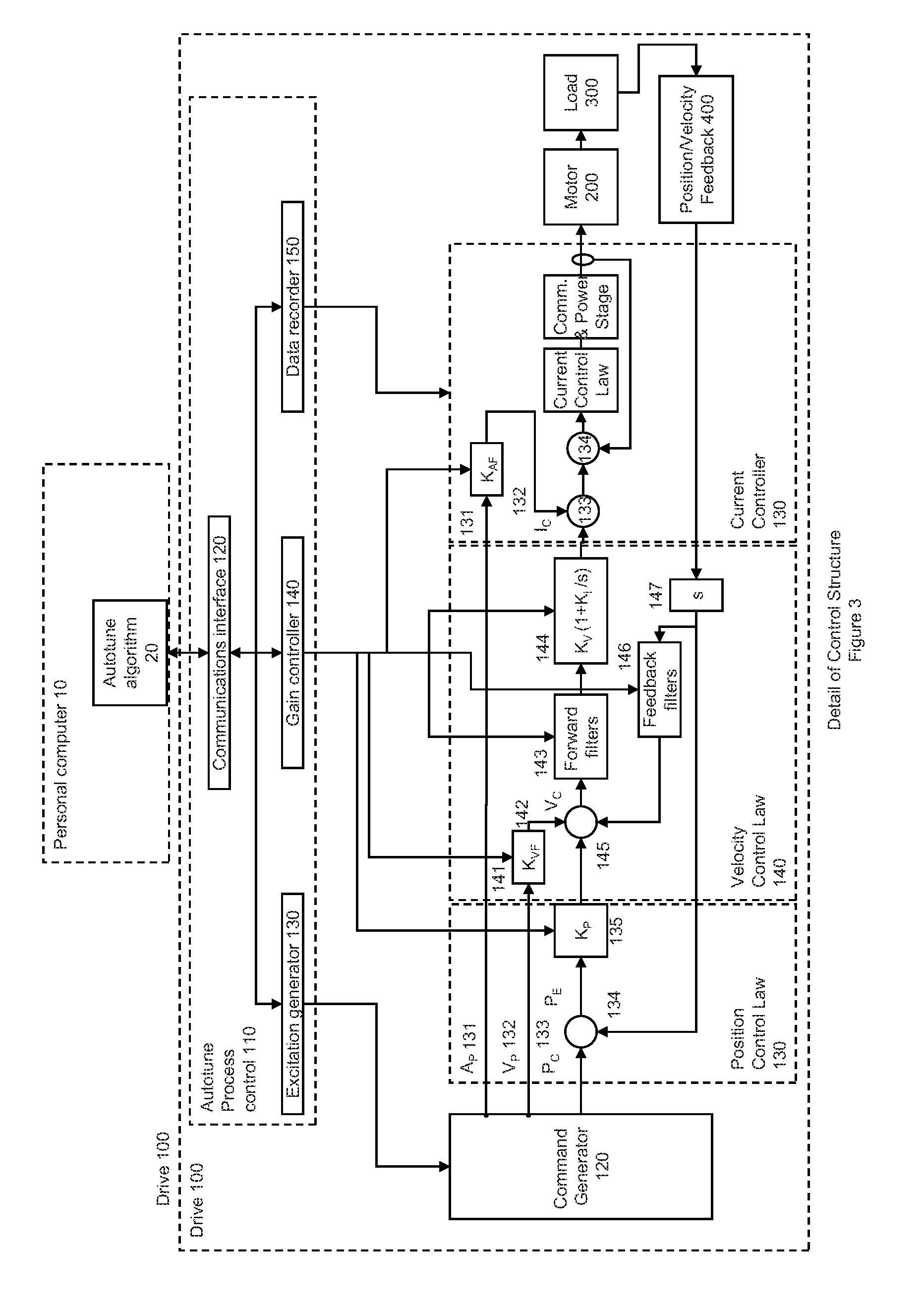
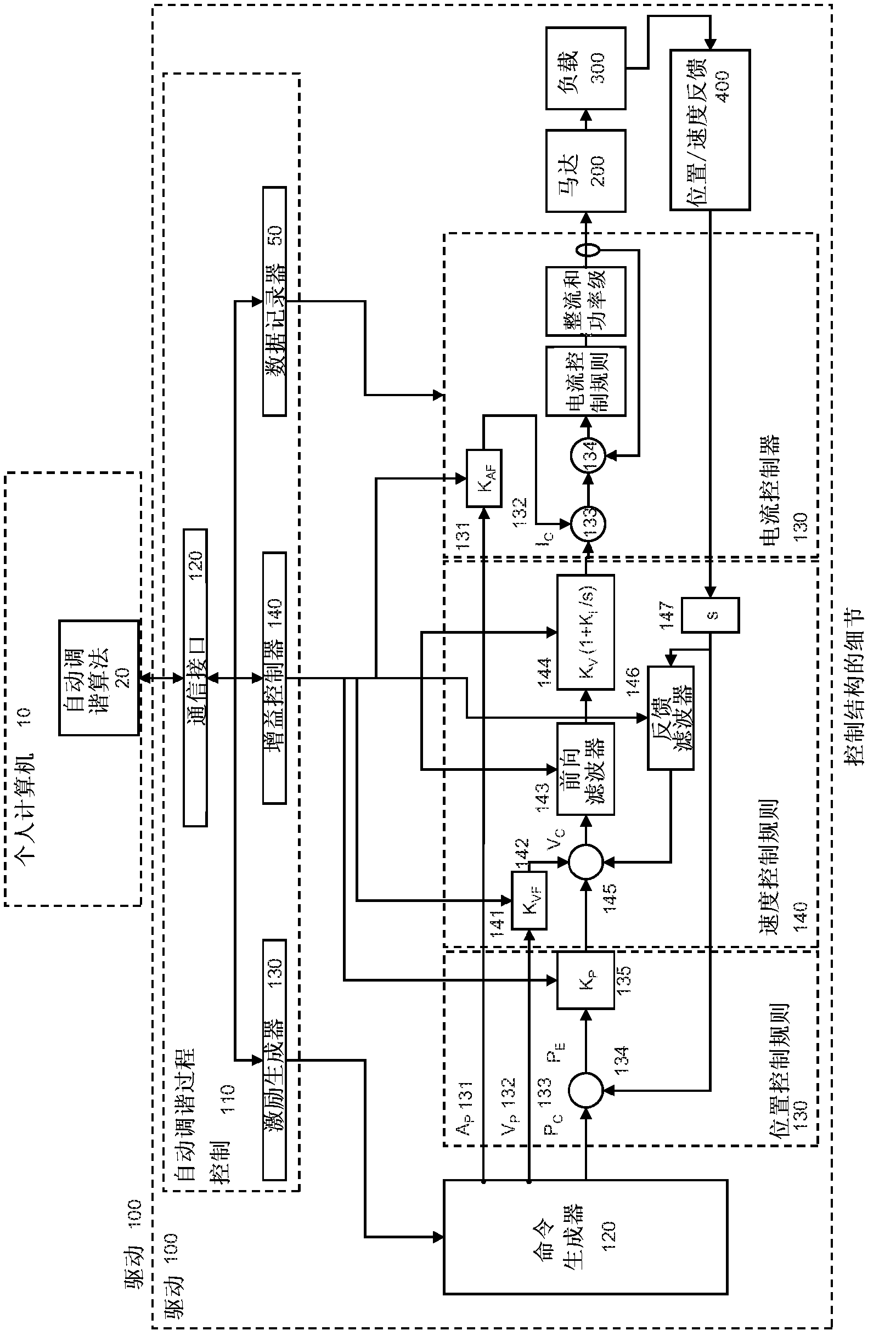
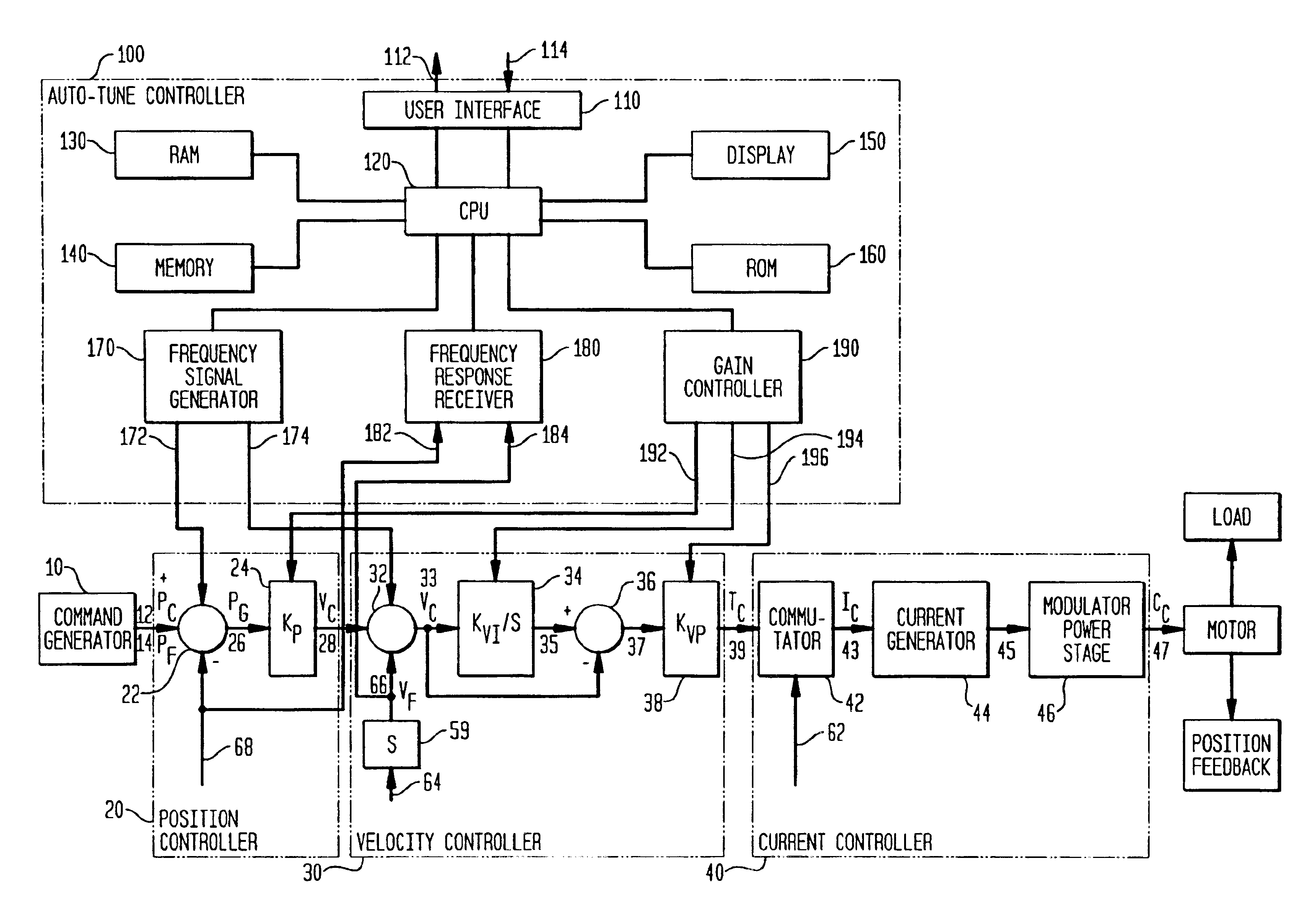
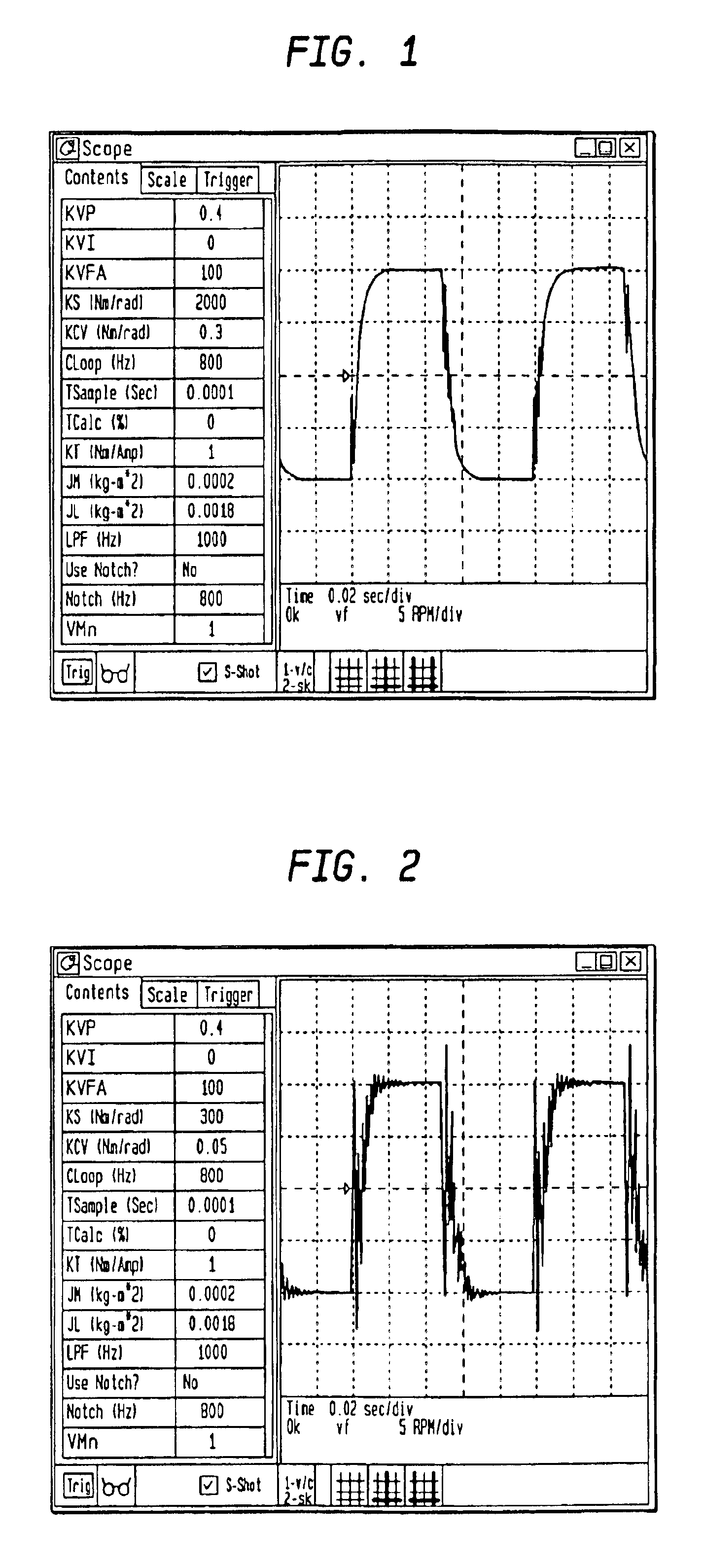
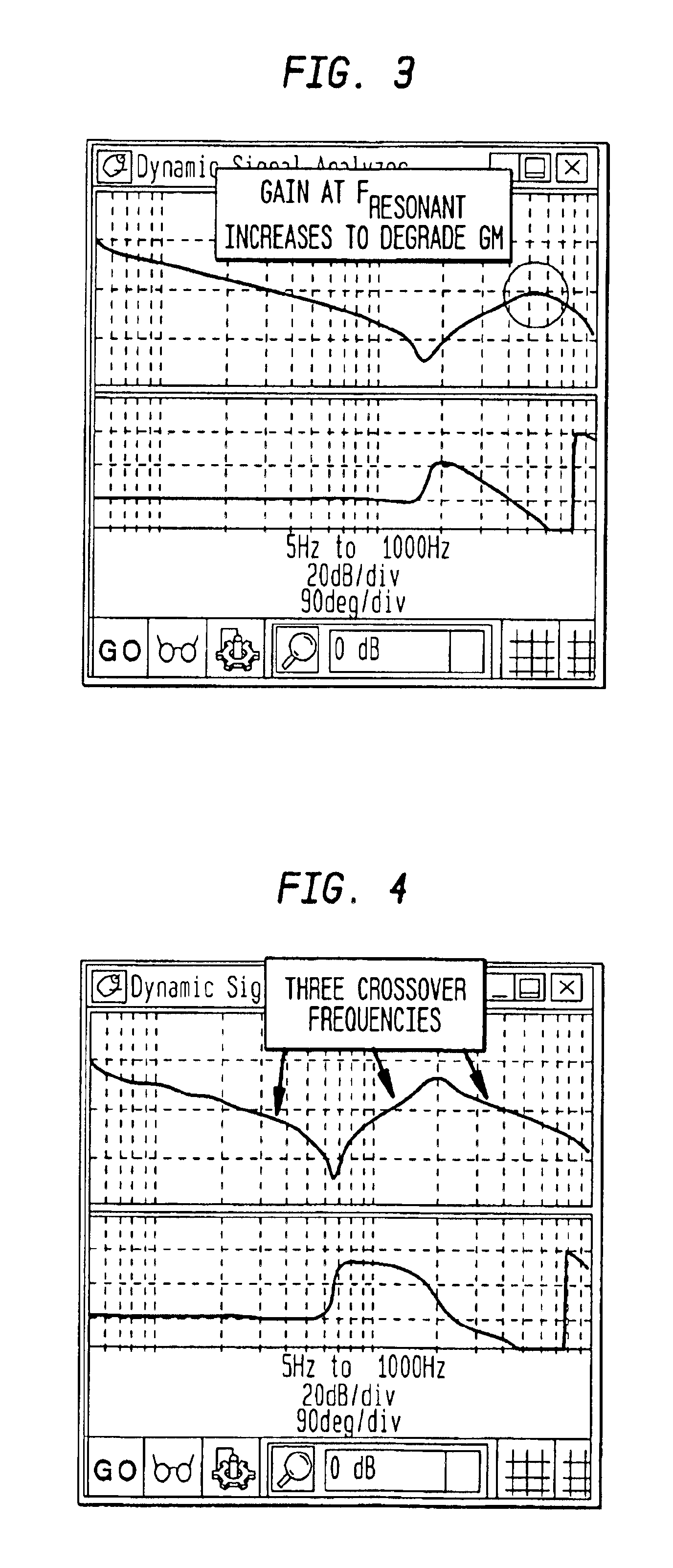
Auto-tune of a control system based on frequency response
ActiveUS20110074330A1Reduce the amount requiredShorten the timeAdaptive controlControl systemControl engineering
A method and system of determining tuning parameters for use in tuning a controller used in a process control loop for a motor and associated load. The method includes providing tuning parameters, applying an excitation test signal, receiving frequency response data to determine phase and gain margins, creating an instability region defined by a bounded area that connects the phase and gain margins with a boundary on a gain vs. phase plot, assigning and applying cost functions, and computing stability determinations.
Owner:KOLLMORGEN CORP
Resonant converter and control method thereof
InactiveCN105896986ASimple designWide voltage gain rangeDc-dc conversionEnergy industryResonant converterPower electronics converters
The present invention discloses a resonant converter and a control method thereof, belonging to the field of the power electronic converter technology. The resonant converter and control method thereof are composed of an input source, an original edge LLC resonance circuit, a transformer, a secondary active Boost rectification circuit and an output load. Based on the traditional LLC resonance converter, the secondary active Boost rectification circuit is substituted for the active Boost rectification circuit so as to realize the fixed frequency phase-shifting control of a converter, the frequency conversion control of the converter and the frequency conversion and fixed frequency phase-shifting combined control to facilitate the design of magnetic elements, reduce the voltage stress of the original edge switch tube and the secondary rectifier tube so as to realize the soft switch of each power semiconductor device, improve the voltage gain range, the efficiency and the power density of the converter and satisfy the requirement of a wide voltage gain margin conversion occasion.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
D-axis and A-axis current vector composite controller of permanent-magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN105680754AAvoid phase shiftWide speed rangeElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlPhase currentsLoop control
The invention relates to a D-axis and A-axis current vector composite controller of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. The D-axis and A-axis current vector composite controller is characterized by comprising a position sensor, a speed measurement feedback link, a counter potential feed-forward compensator, a rotational speed closed-loop controller, an A-axis current composite controller, a D-axis current composite controller and a vector converter. By the D-axis and A-axis current vector composite controller, decoupling composite control is separately carried out on i<d> and i<q> under a dq coordinate, the speed regulation range is wide, phase shift of a phase current closed-loop control structure caused by limited bandwidth of the controller is prevented, and the D-axis and A-axis current vector composite controller has favorable performance in all ranges of speed regulation; through the adoption of a composite controls structure with combination of feed-forward and feedback, the dynamic characteristic is improved, the feedback control gain is reduced, and the gain margin of the system is improved; feed-forward is designed on the basis of the dynamic characteristic of an object, and D-axis and A-axis current vector composite controller is clear in physical concept, simple in structure and stable in working, and is easy to be implemented; and meanwhile, feedback control is introduced, the control precision is improved, and an error caused by model inaccuracy and disturbance is overcome.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
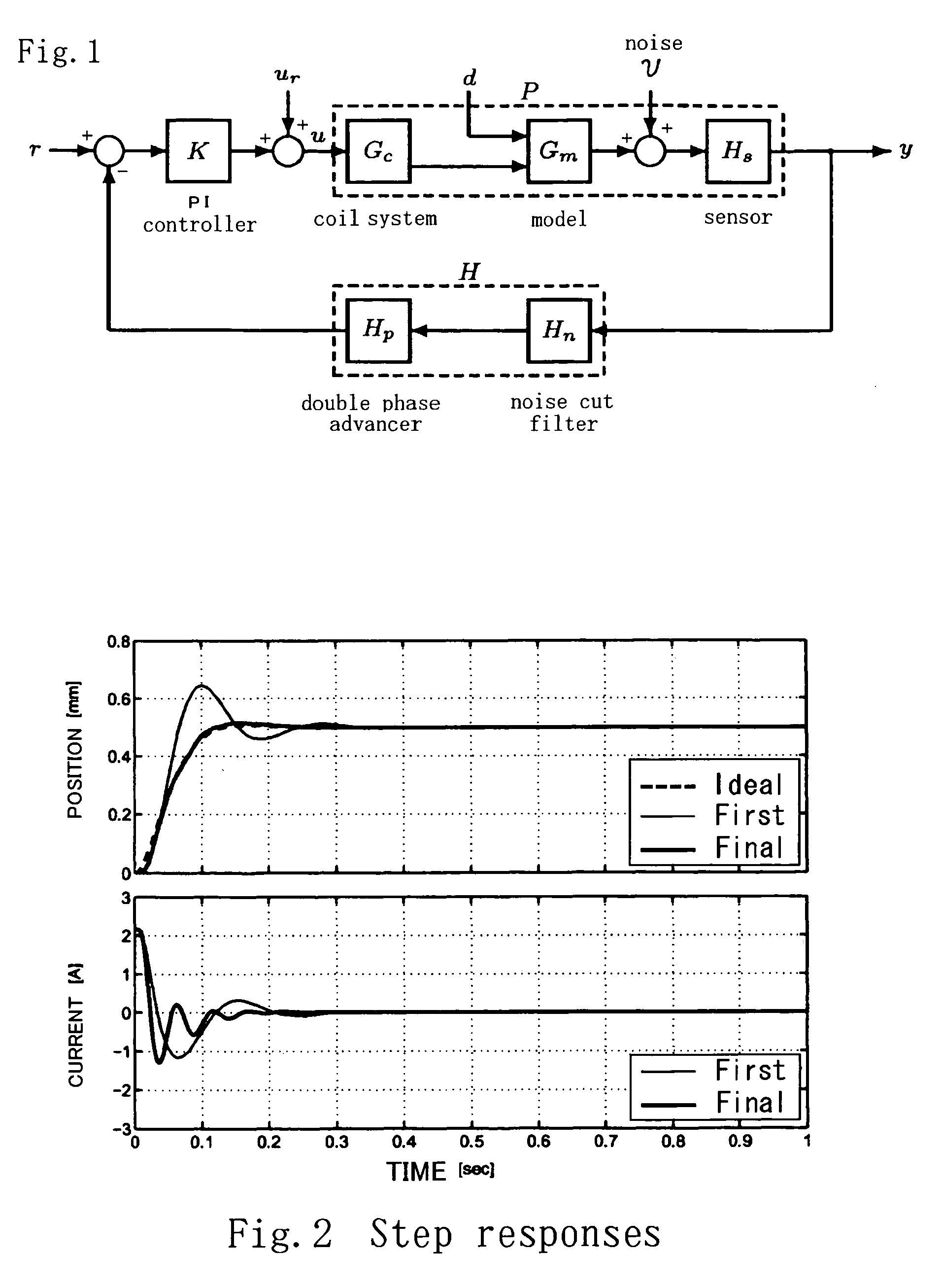
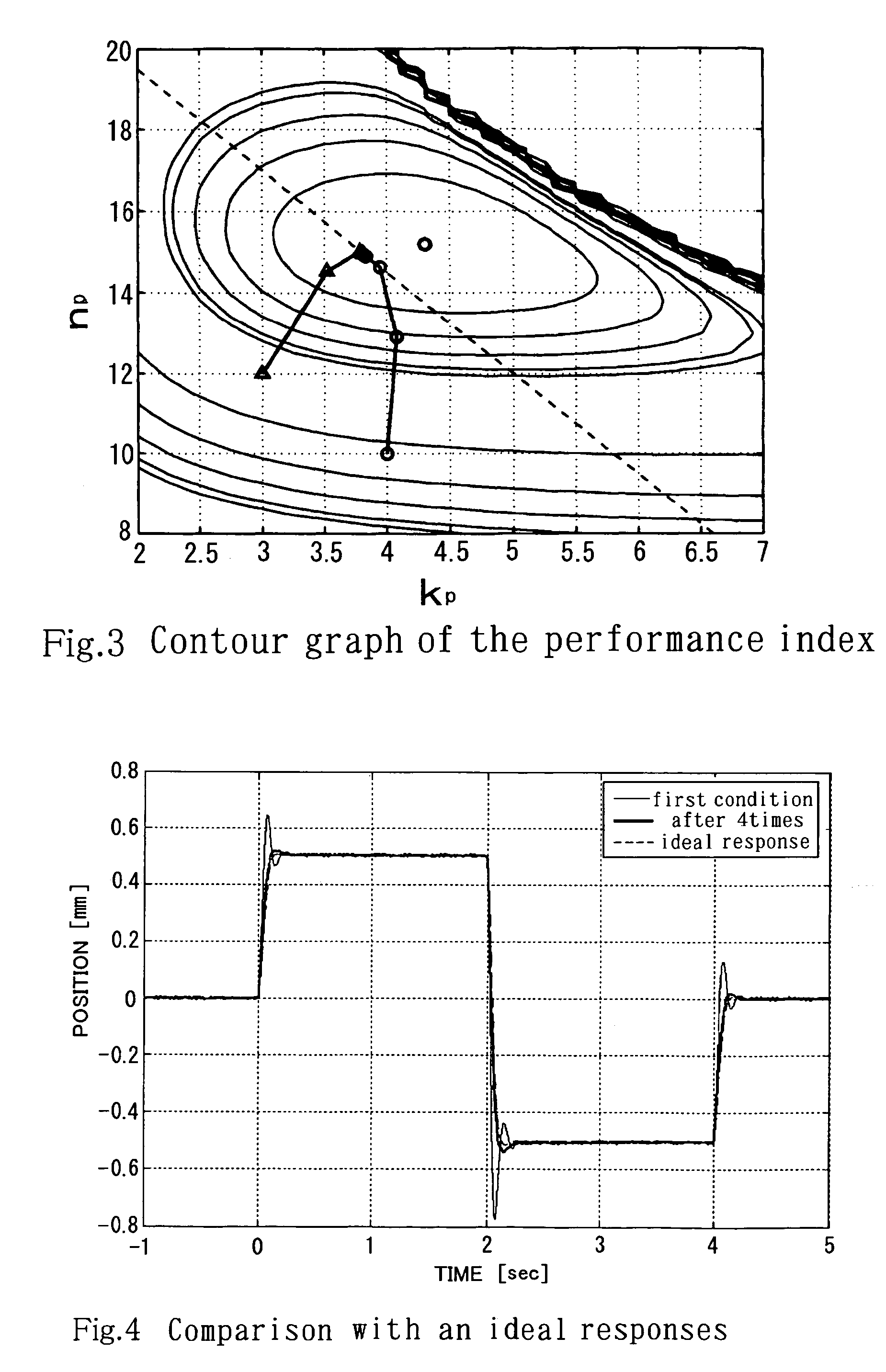
Method of automatic adjustment of the control parameters of a magnetic suspension system
InactiveUS20060111863A1Process safety and stabilityIncreased complexityResistance/reactance/impedenceAerodynamic testingAuto regulationControl subjects
In adjustment of the control parameters of a magnetic suspension system, an object of the present invention is to provide a technique for adjusting the control parameters to optimum values automatically by employing the iterative feedback tuning method, without increasing the complexity of the program, the amount of calculation and the overall size of the system, and still reducing the amount of calculation required for calculation of the safety margin (gain margin and phase margin). In a method of automatic adjustment of control parameters according to the invention, when applying the iterative feedback tuning method to a feedback control system for a magnetic suspension system, only those control parameters that have a significant effect on the control performance of the system are selectively adopted / discarded from among control parameters so that the control parameters are guided to optimum values to obtain a response waveform desired by a designer directly from input / output data of a control subject.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
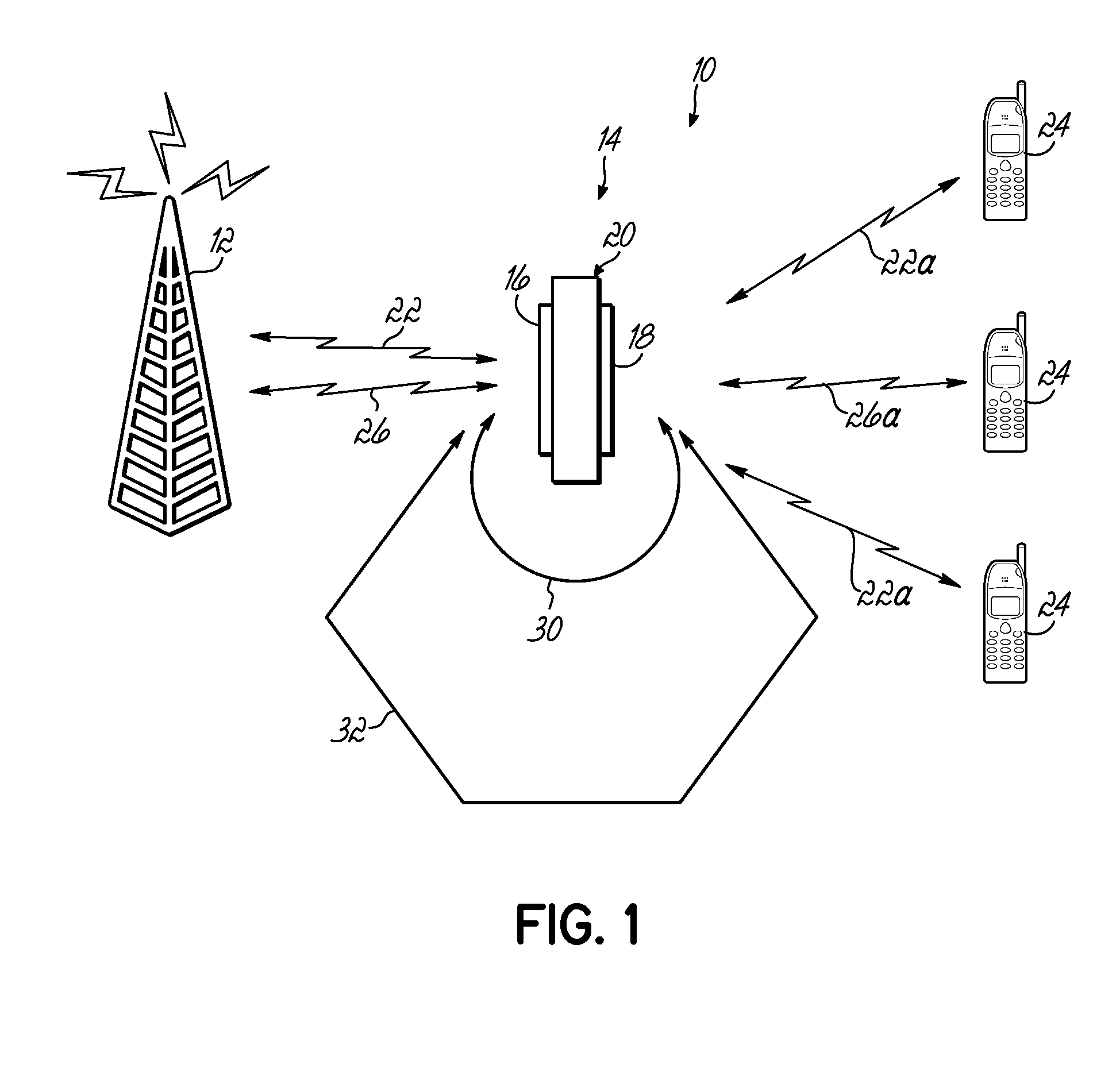
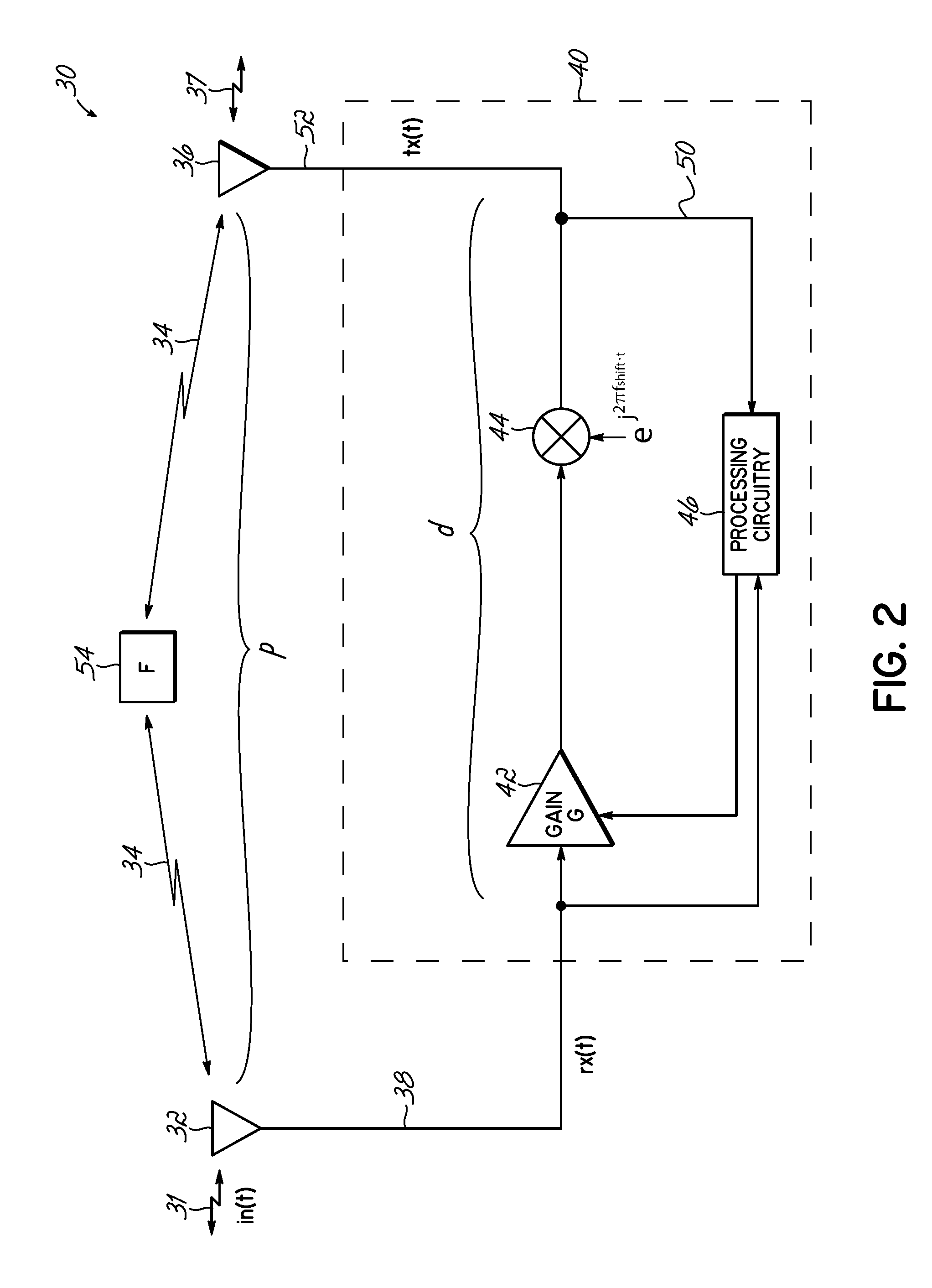
System and method for determining and controlling gain margin in an RF repeater
An apparatus for repeating signals includes a receive antenna for capturing a receive signal, processing circuitry for processing the receive signal to form a repeated signal, and a transmit antenna for transmitting the repeated signal. The processing circuitry includes gain circuitry for gain in the repeated signal and decorrelation circuitry configured for modifying the repeated signal with respect to the receive signal to thereby decorrelate the repeated signal from the receive signal. The processing circuitry further comprises circuitry configured for calculating a gain margin for the apparatus utilizing the decorrelated receive and repeated signals.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Auto-tune of a control system based on frequency response
A method and system of determining tuning parameters for use in tuning a controller used in a process control loop for a motor and associated load. The method includes providing tuning parameters, applying an excitation test signal, receiving frequency response data to determine phase and gain margins, creating an instability region defined by a bounded area that connects the phase and gain margins with a boundary on a gain vs. phase plot, assigning and applying cost functions, and computing stability determinations.
Owner:KOLLMORGEN CORP
Autotuning method and system based on the bilinear-quadratic filter
A built-in autotuning system of a motor control system provides an autotuning of the motor control system based on BQF. The system measures the effective inertia and determines whether there exists a high-frequency resonance. If there is a high-frequency resonance, the system sets the BQF as a low pass filter, otherwise the system sets the BQF as a high pass filter. The system then adjusts the gains of the controller to set the phase and gain margins within a specified values.
Owner:KOLLMORGEN CORP (US)
Method and device for power management
ActiveCN101588208ASimple designReduce construction costsElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsTransfer procedureEngineering
The invention discloses a device for power management, which is used for regulating the output power in the transmission process. The device comprises a monitoring module, a control module and a processing module, wherein the monitoring module is used for counting the distribution condition of the output power of signals with various wavelengths in the transmission process so as to obtain a counting result which comprises the output power of the signals with various wavelengths and sending the counting result to the control module; the control module is used for confirming a power control parameter according to the counting result from the monitoring module and sending the power control parameter to the processing module; and the processing module is used for regulating the gain slope of the output power according to the power control parameter from the control module. The invention also discloses a method for power management. The invention simplifies the design method of a system, lowers the construction cost of the system and increases the gain margin.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for tuning a PID controller
Owner:IMB CONTROLS
LCL-LC based active damping parameter design method for grid-connected system
InactiveCN105743123AImprove performanceImprove robustnessSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationCapacitanceDamping factor
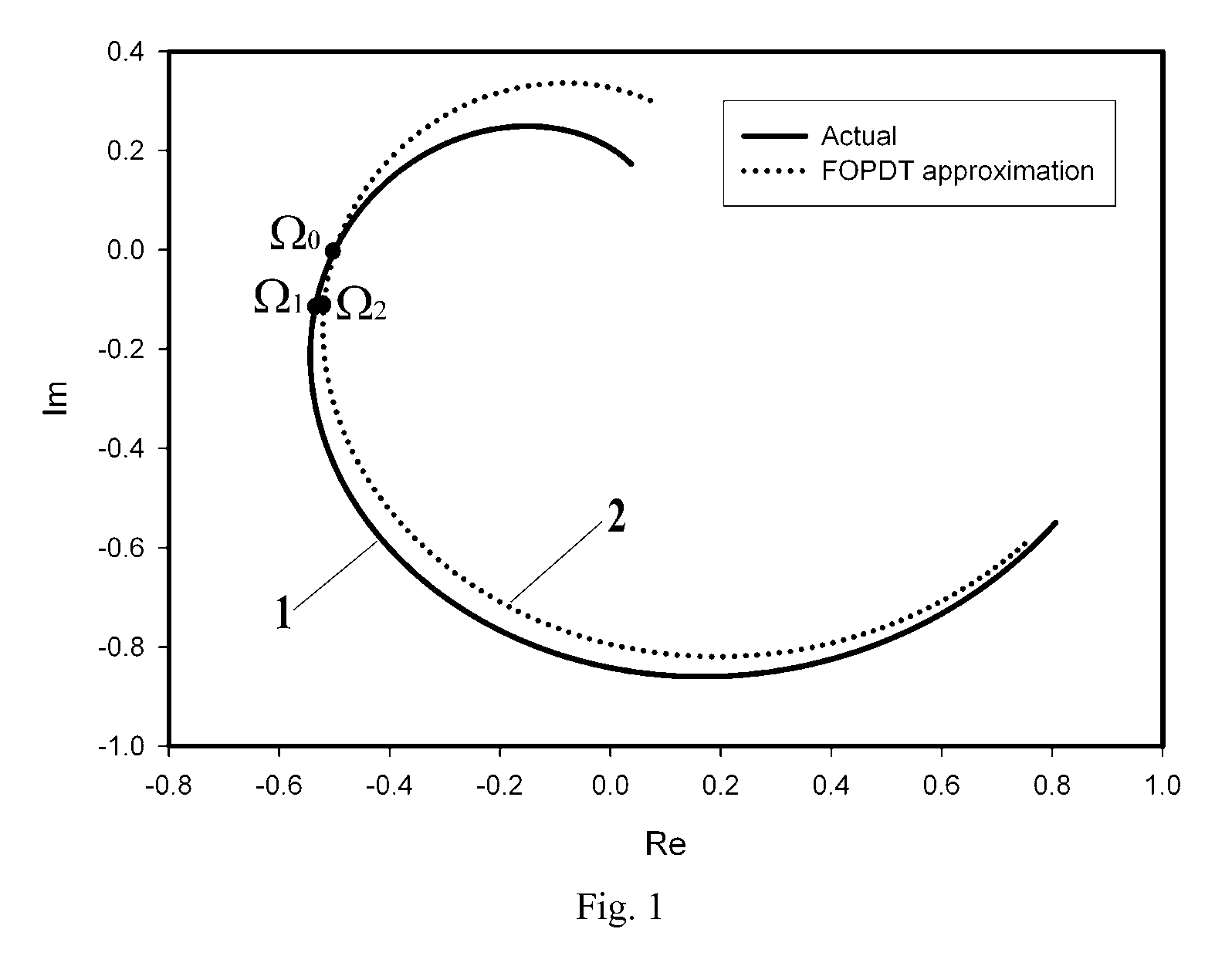
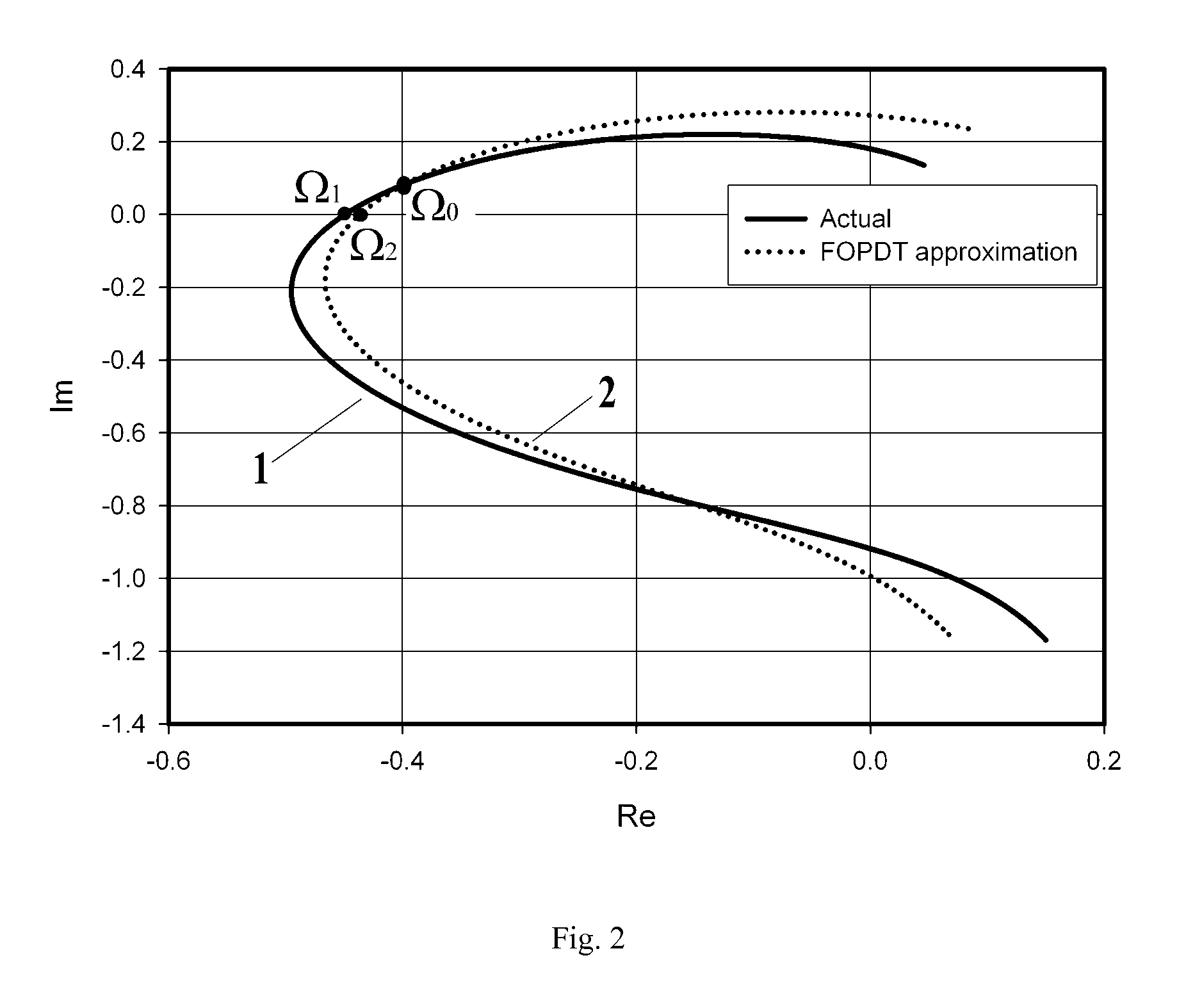
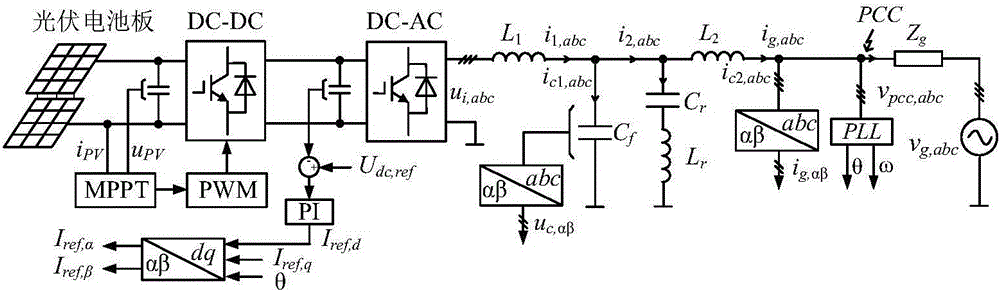
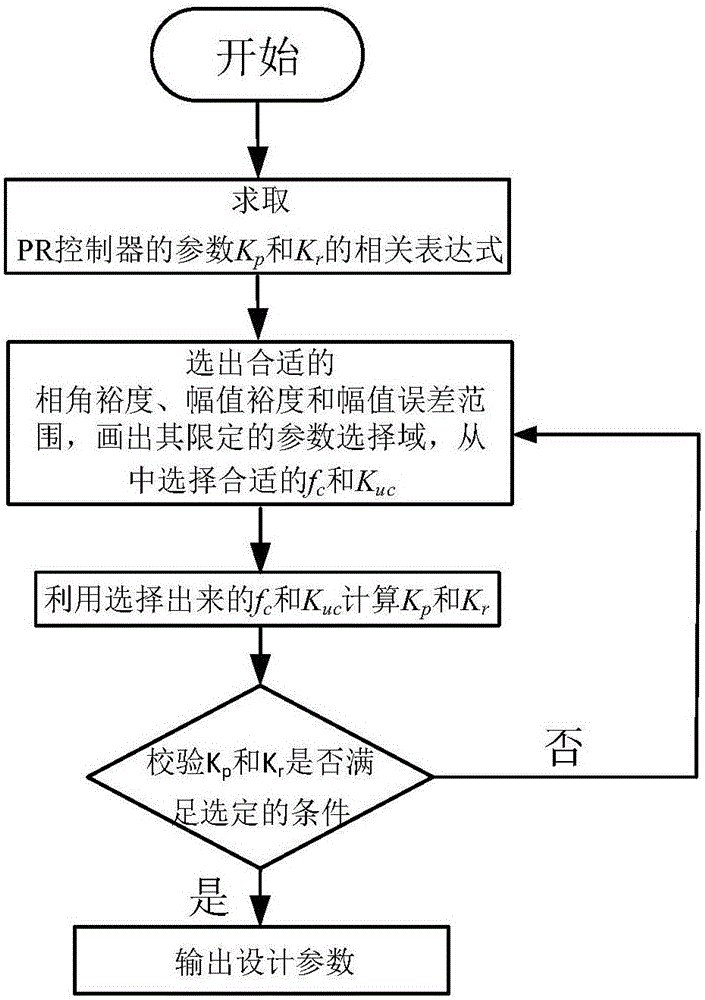
The invention discloses a capacitor voltage feedback LCL-LC based controller parameter and active damping parameter design method for a grid-connected system. The design method is on the basis of taking control delay into consideration, and ensures stable phase margin (PM), gain margin (GM) and error of amplitude (EA) of the system, configures a reasonable parameter selection domain, and chooses reasonable controller parameters and active damping coefficients from the parameter selection domain. By adoption of the method, the LCL-LC filter resonance can be effectively restrained, and the stability and the dynamic response performance of the photovoltaic grid-connected system are both effectively improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Actuator-link assembly manufacturing method, actuator-link assembly designing method, and actuator-link assembly
ActiveUS20110220761A1StrengthReduce weightAircraft stabilisationWithout power ampliicationActuatorGain margin
In a material determining step, the material constituting an actuator and the material constituting a link are determined such that at least one of the materials contains fiber reinforced plastic. In a computing step, a computation model that defines the relationship between a control surface, the actuator, and the link is used to compute the change in gain margin with the change in a rigidity ratio, which is the ratio of the rigidity of the link to the rigidity of the actuator. The rigidities of the actuator and the link are determined in a rigidity determining step based on a result of the above-described computation, the shapes of the actuator and the link are determined in a shape determining step, and the actuator and the link are formed in a formation step, and are assembled in an assembly step.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
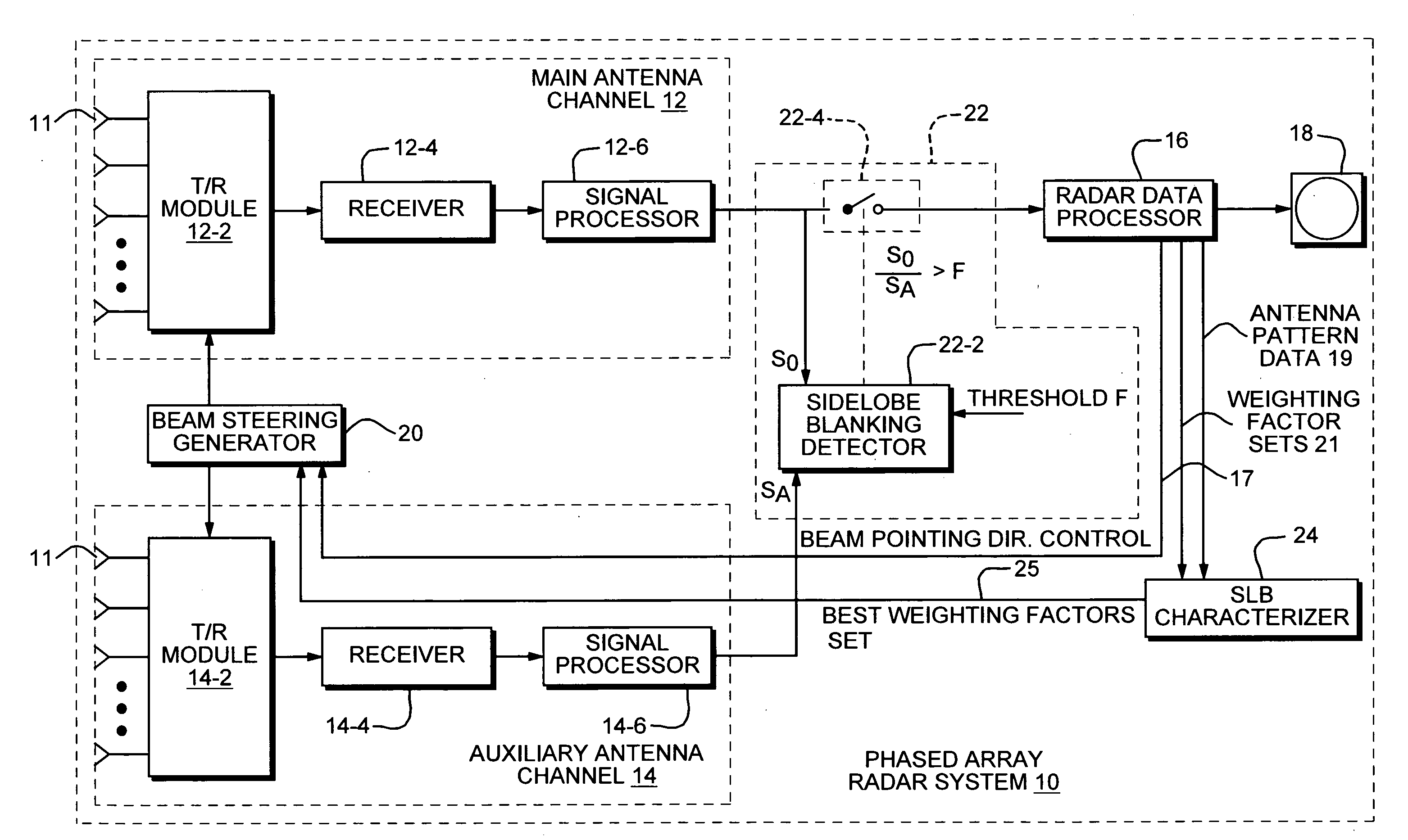
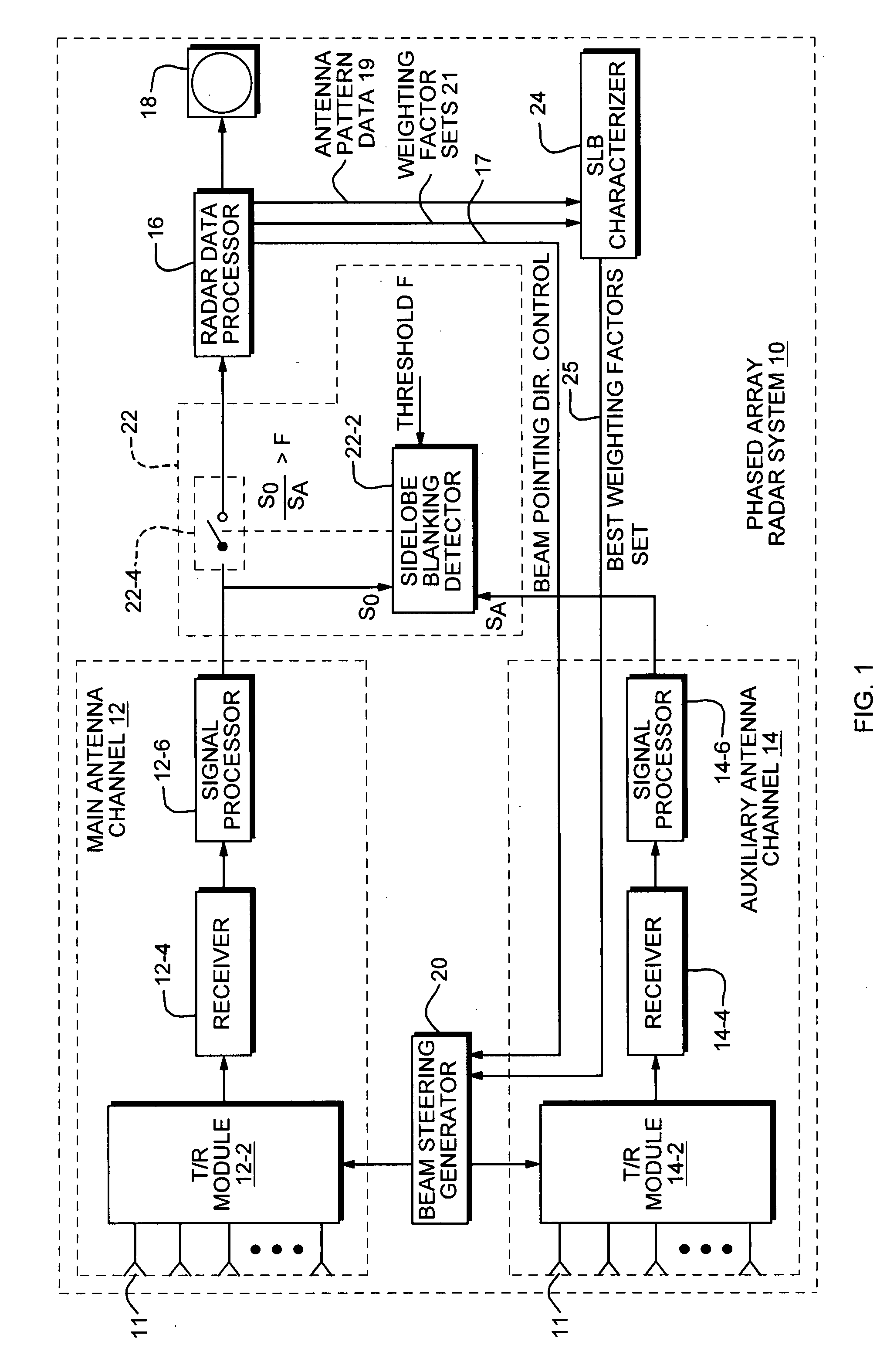
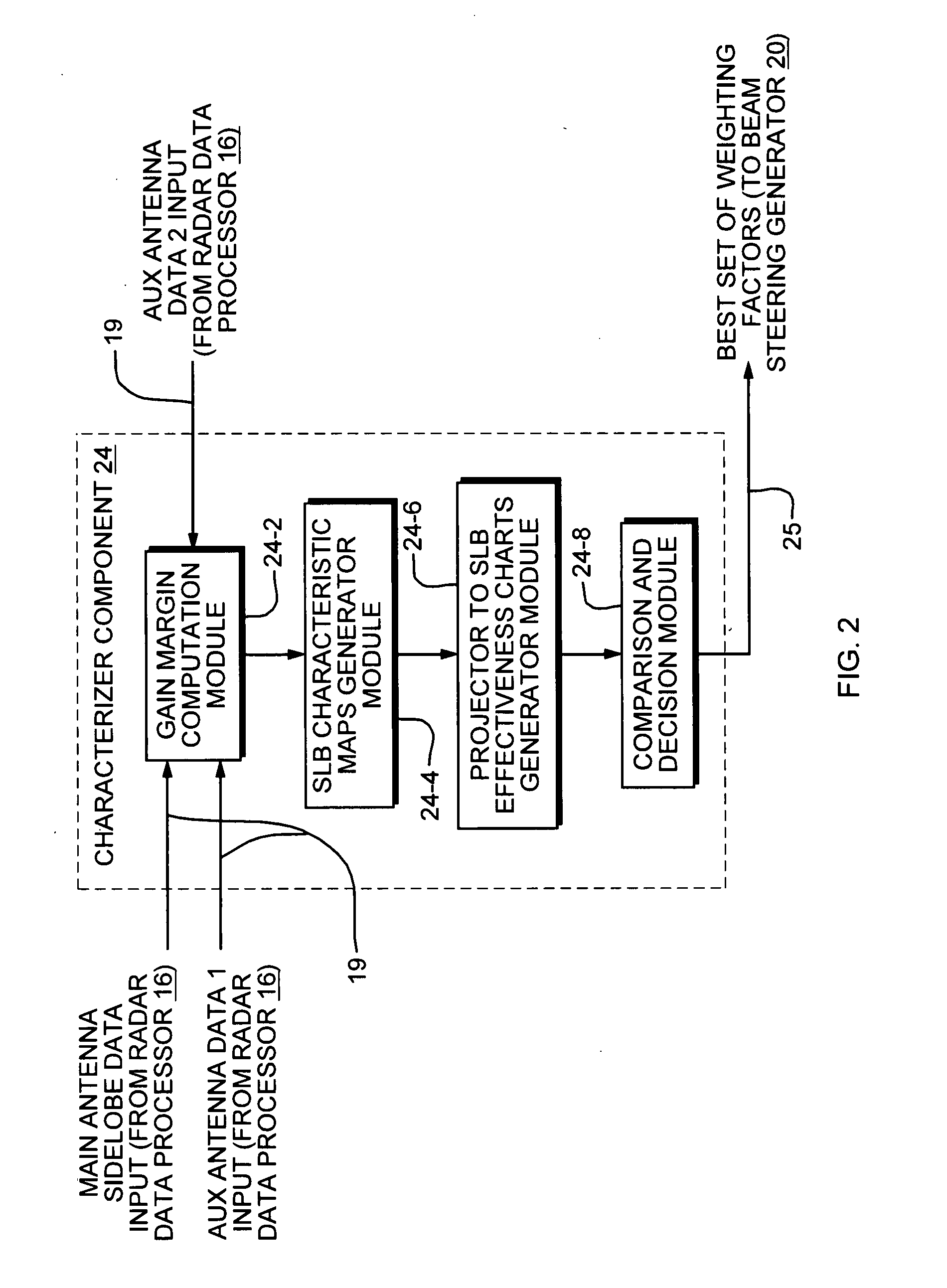
Sidelobe blanking characterizer system and method
ActiveUS20090102717A1Improve efficiencyRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna designRadar systems
The method and system of the present invention includes a SLB characterizer component for achieving optimum sidelobe blanking through the combining of multiple dimension data into a single figure of merit comparison. The SLB characterizer component is positioned between a radar data processor and beam steering generator of a radar system. The radar data processor provides several sets of antenna patterns which are used by the characterizer component to compute gain margins according to the teachings of the present invention. From the computed gain margins, the component generates SLB characteristic maps which provide a much less complex method for evaluating antenna design independent of other system parameters. Based on such SLB characteristic maps, the characterizer component generates SLB effectiveness charts which it uses to compare SLB performance and determine which auxiliary antenna pattern has the best performance. This method is also applicable as a stand alone software tool for auxiliary antenna evaluation and comparison.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
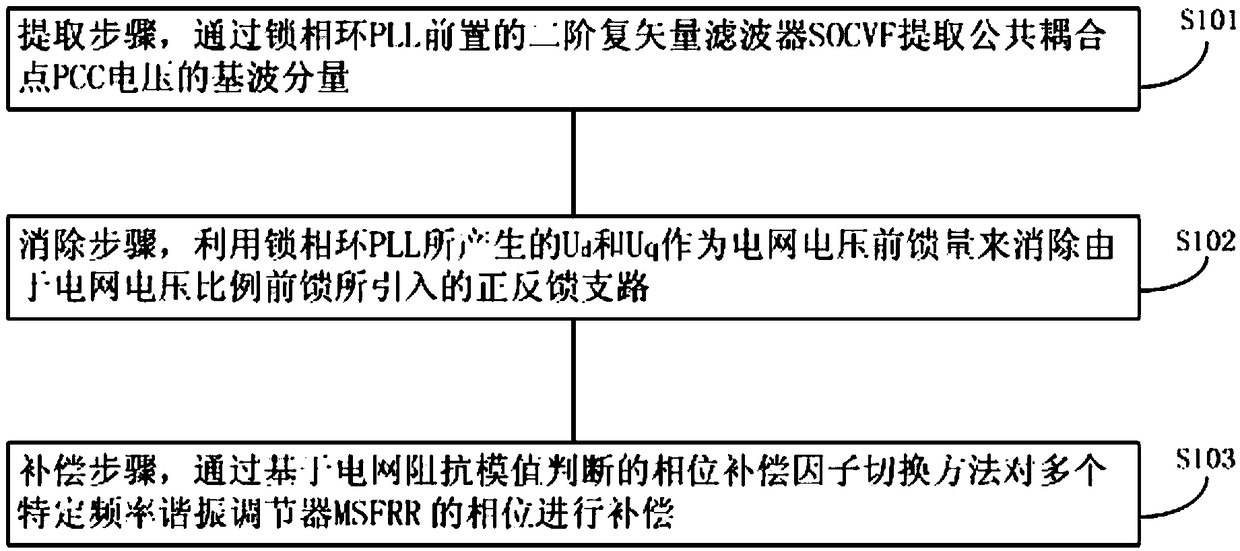
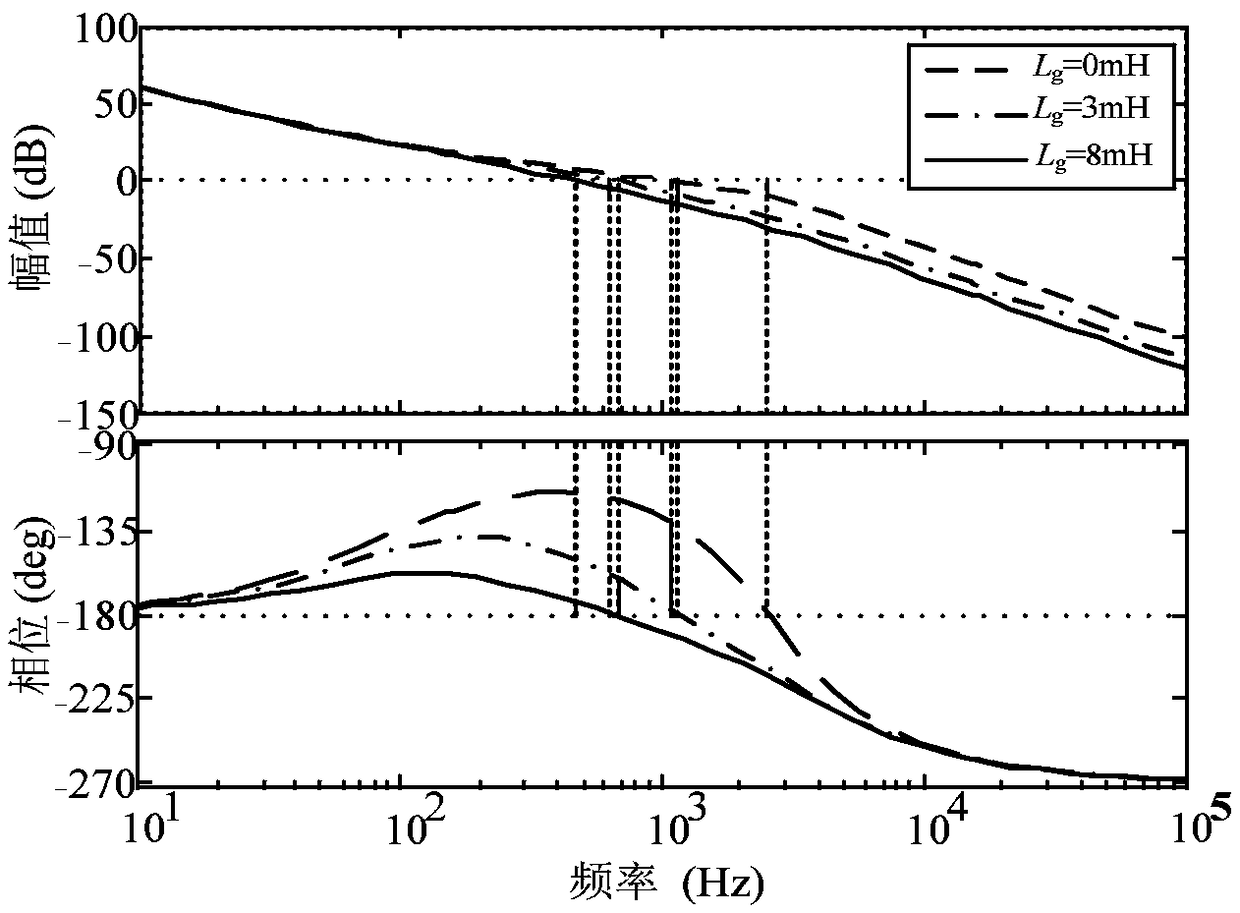
SOCVF feedforward and phase compensation factor switching control method for grid-connected inverter in weak power network
ActiveCN109193792AEliminate the effects ofEnhanced inhibitory effectSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionGrid impedancePower factor
The invention provides a SOCVF feedforward and phase compensation factor switching control method of grid-connected inverter under weak power network. The method comprises: The fundamental component of the PCC voltage at the common coupling point is extracted by SOCVF in front of the PLL, Ud and uq generated by PLL are used as voltage feedforward quantities to eliminate the positive feedback branch introduced by voltage proportional feedforward. The phase compensation factor switching method based on impedance modulus judgment is used to compensate the phase of MSFRR. The invention provides acontrol method for grid-connected inverter under weak power network, so as to eliminate the influence of grid impedance on the grid-connected control system of the inverter. The stability of the system is greatly improved, and the adaptability of the system is strong, and the power factor is high, and the ability to suppress the background harmonics of the power network is improved, so that the inverter control system can maintain a high shear frequency, phase margin and gain margin, and the system 's rapidity and stability is enhanced.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
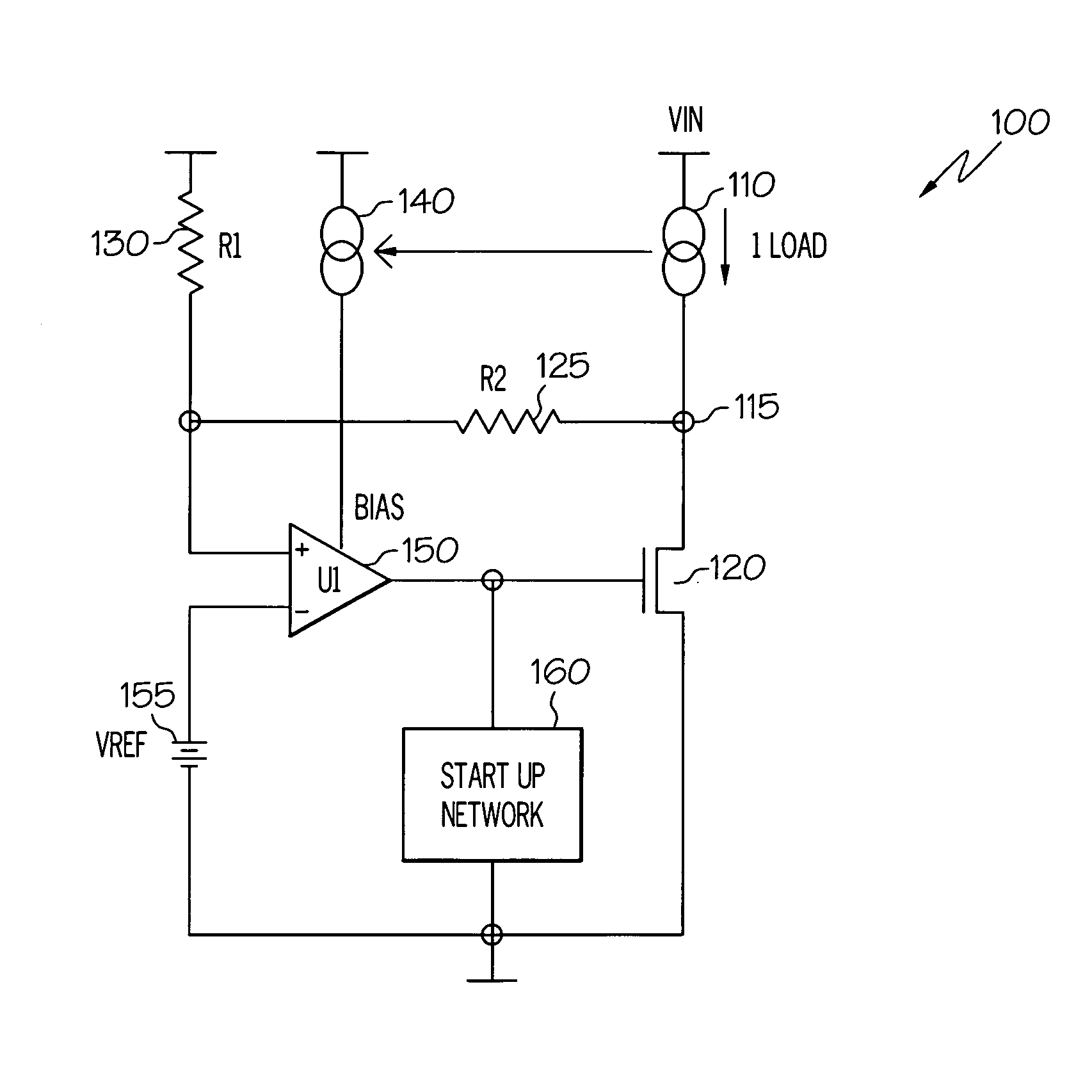
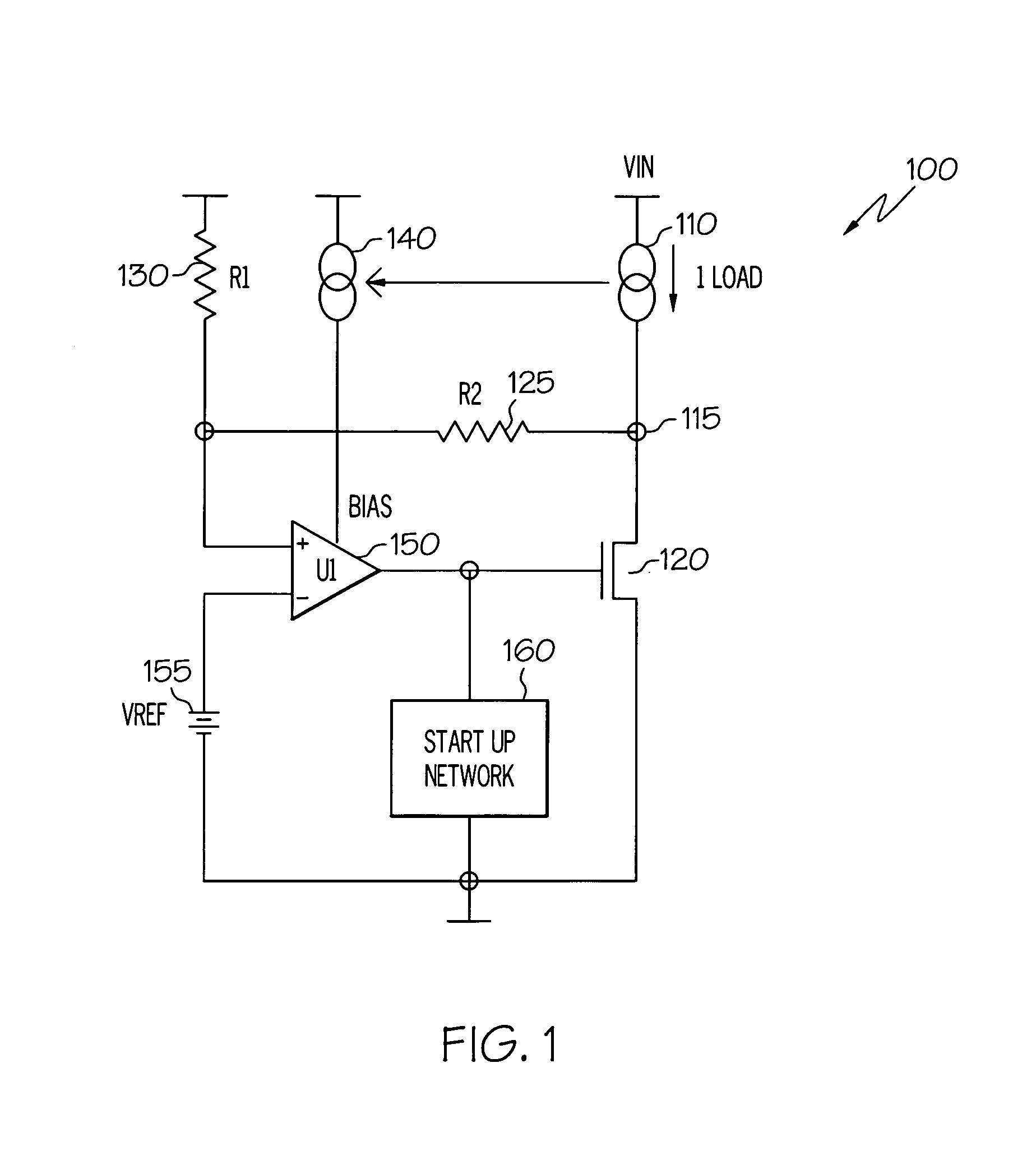
Regulator with load tracking bias
InactiveUS20070096702A1Improve power supply rejection ratioThe output voltage is accuratePower supply linesElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierVoltage regulation
An electrical circuit that provides accurate, regulated output voltage over a wide range of input voltages, while exhibiting each of three desired characteristics: accuracy across different supply / process / temperature; stability and linearity yielding phase / gain margins; and high (good) power supply rejection ratio (PSRR). The circuit comprises an output node having a load current and an amplifier having a first input coupled to a reference voltage and receiving a bias input current that is a pre-established proportionate size of the load current across the output node, such that a change in the load current results in a proportionate change in the bias input current. The electrical circuit represents a voltage regulator that provides accurate, linear output voltage that is a predictable portion of the reference voltage.
Owner:IBM CORP
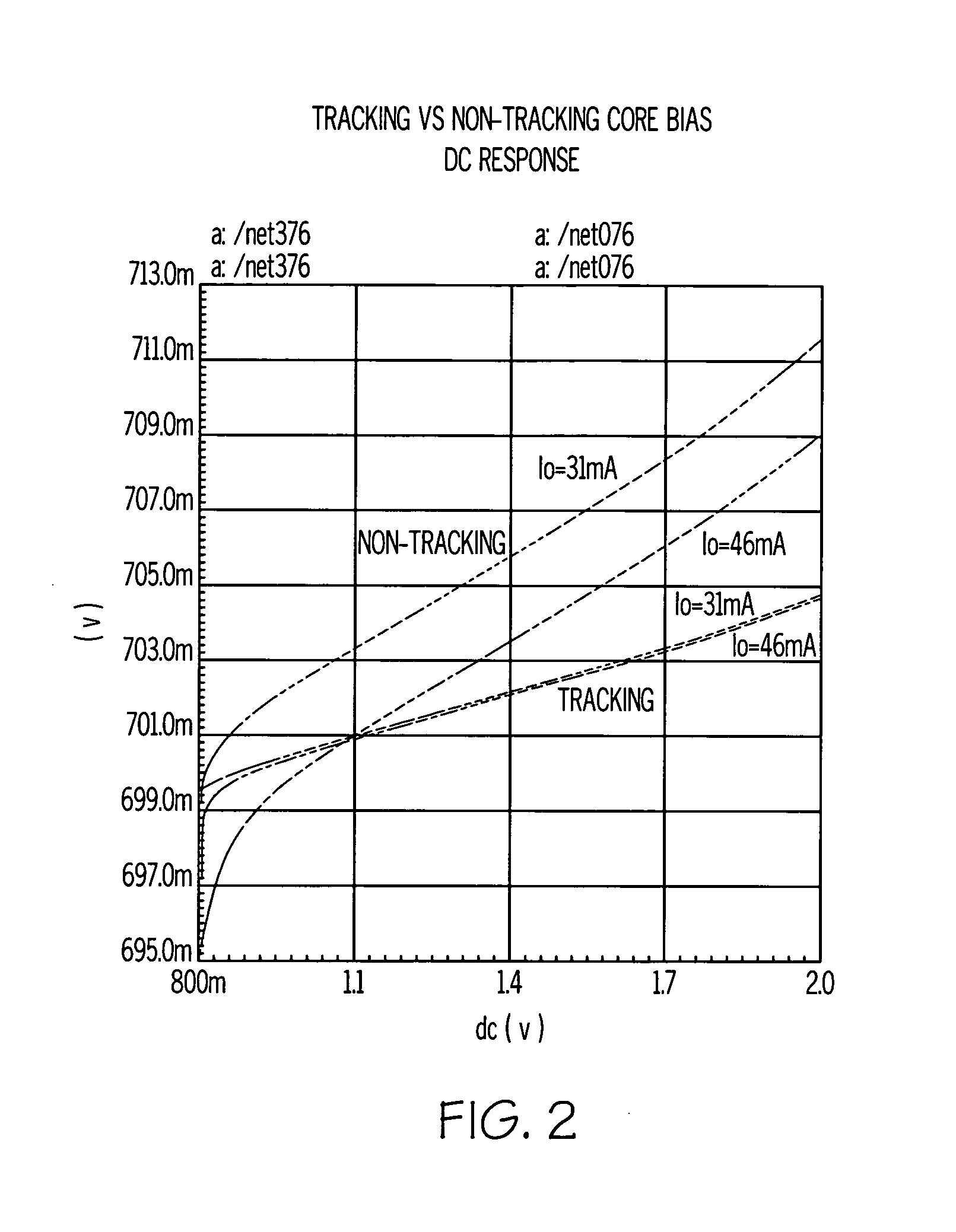
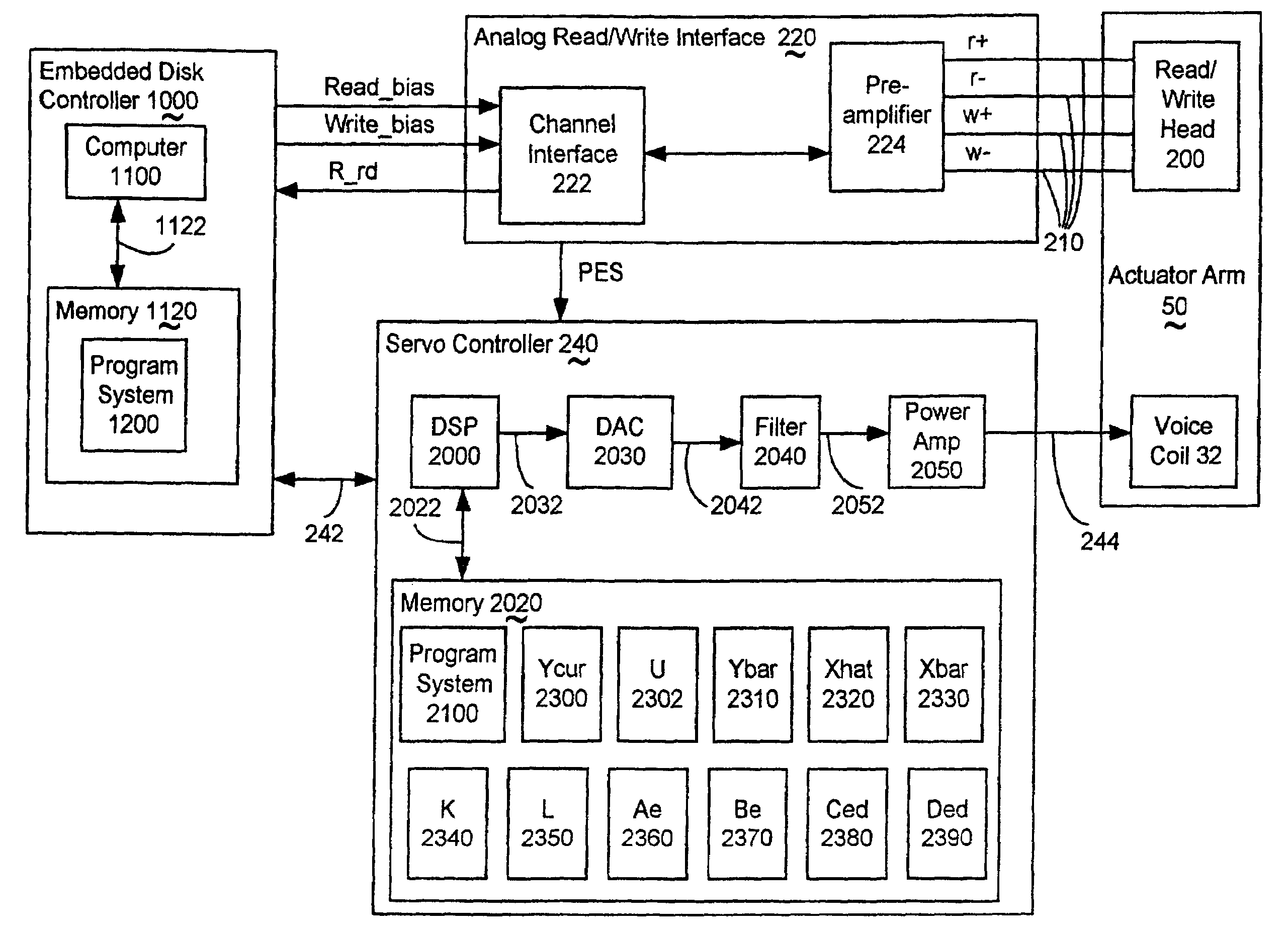
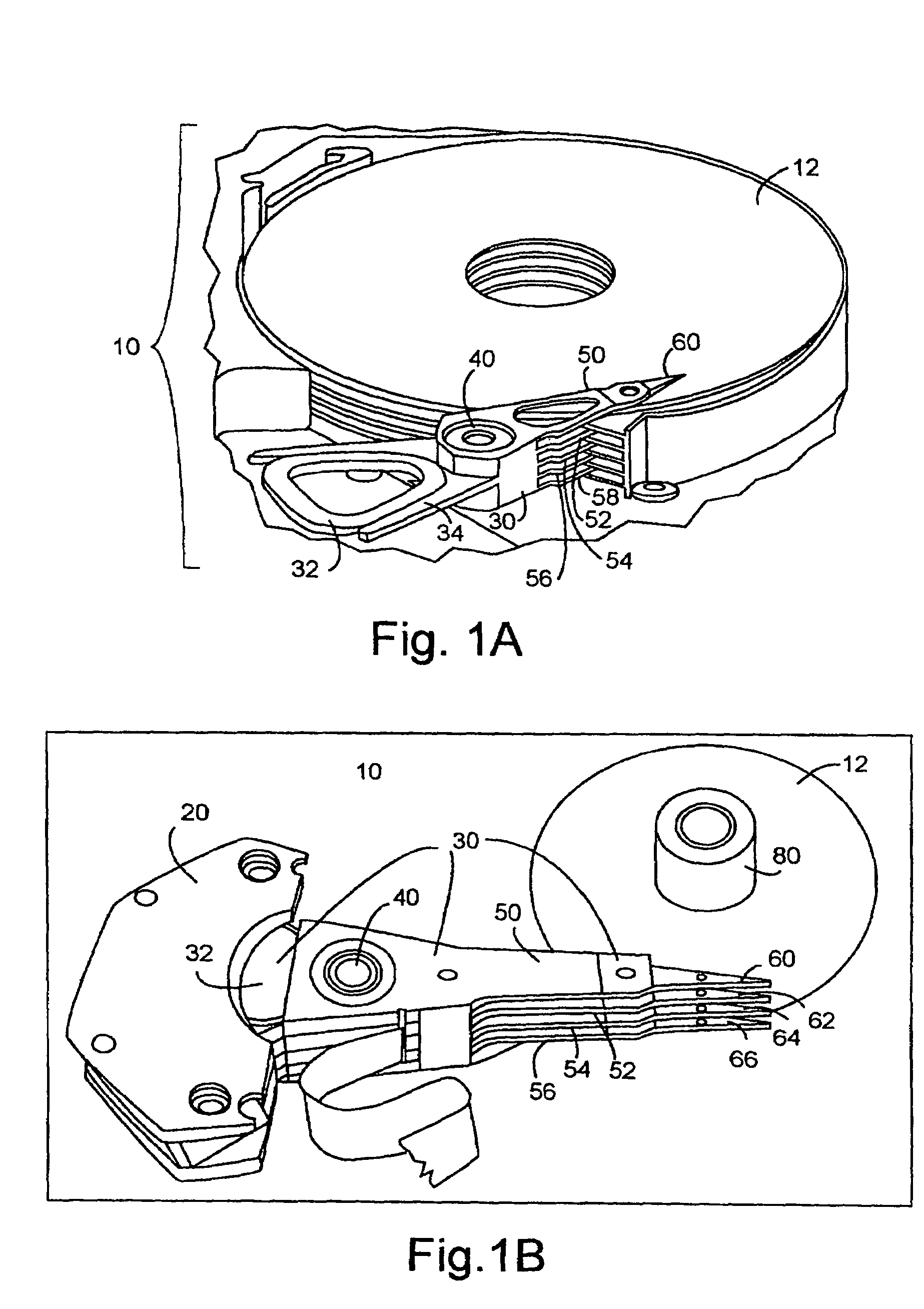
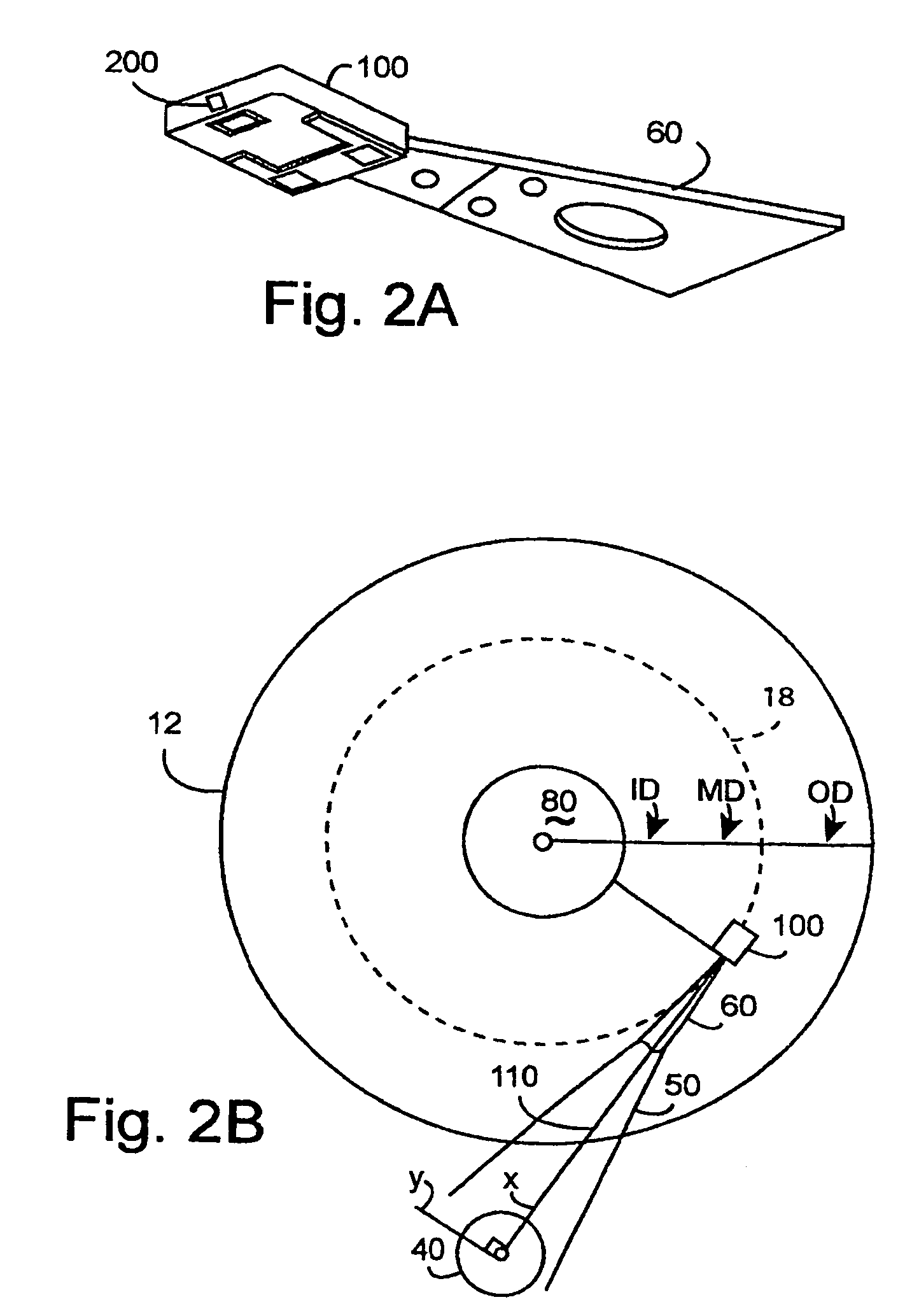
Servo controller method and apparatus for high tracks per inch hard disk drives using a delay accomodating state estimator
InactiveUS20060023340A1Reduced stabilityIncreasing the phase margin and the gain marginTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveControl system
The invention applies to servo controllers for at least the voice coil motor of a hard disk drive. Today, many control algorithms require 80 to 90 percent of the sampling period to complete their calculation of the next control, making computation time delay no longer negligible. The invention accommodates the transport delay, such as computation time delay, into the state estimator and into the whole control system. Experimental results using a commercial hard drive, as well as simulation results, show that the invention's method effectively improves the hard disk drive control system stability by increasing the phase margin and gain margin. The invention includes the method of operating the servo-controller, as well as the apparatus implementing that method. The invention also includes hard disk drives containing servo-controllers implementing the method, and program systems residing in accessibly coupled memory to a computer within the servo controller implementing the method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
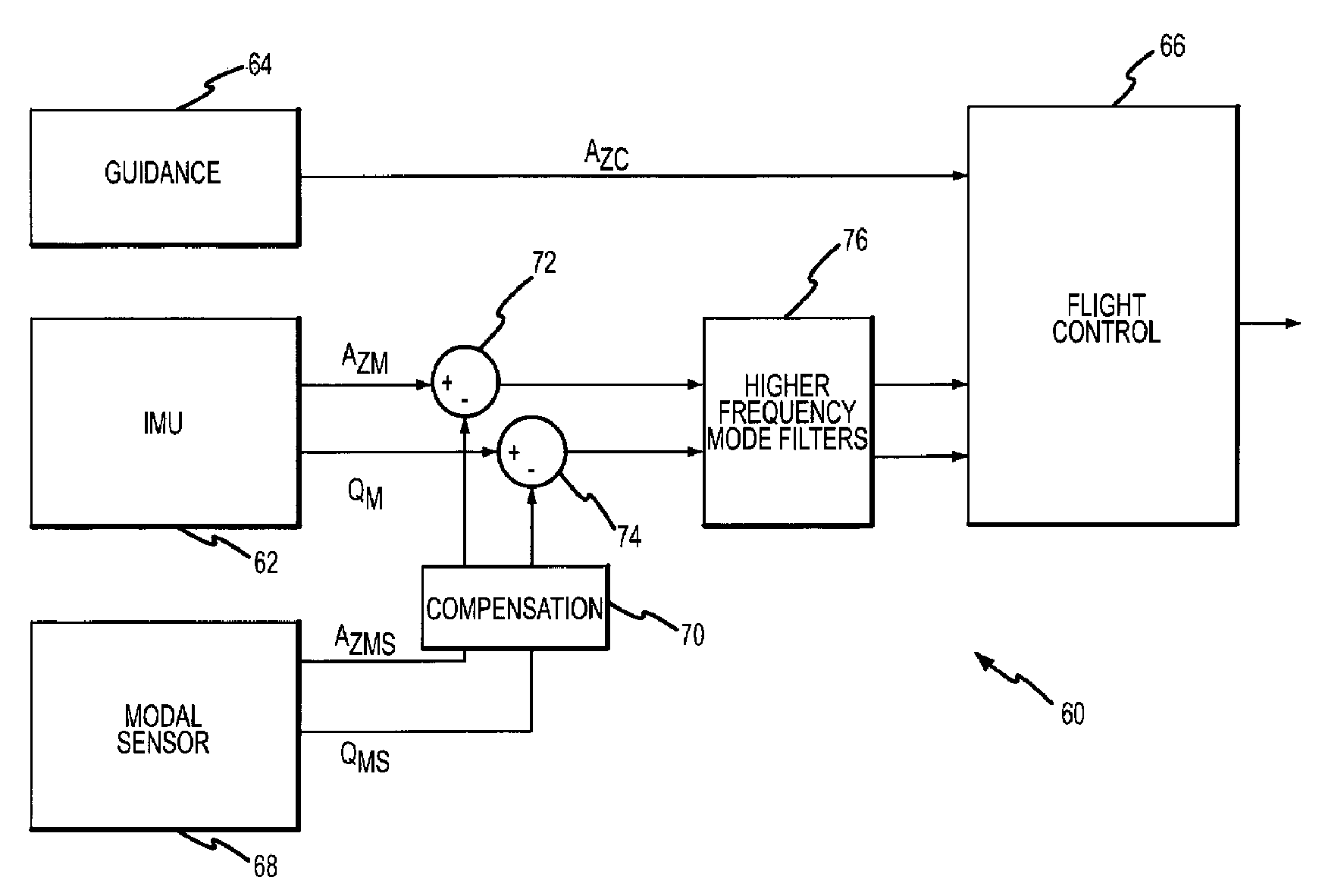
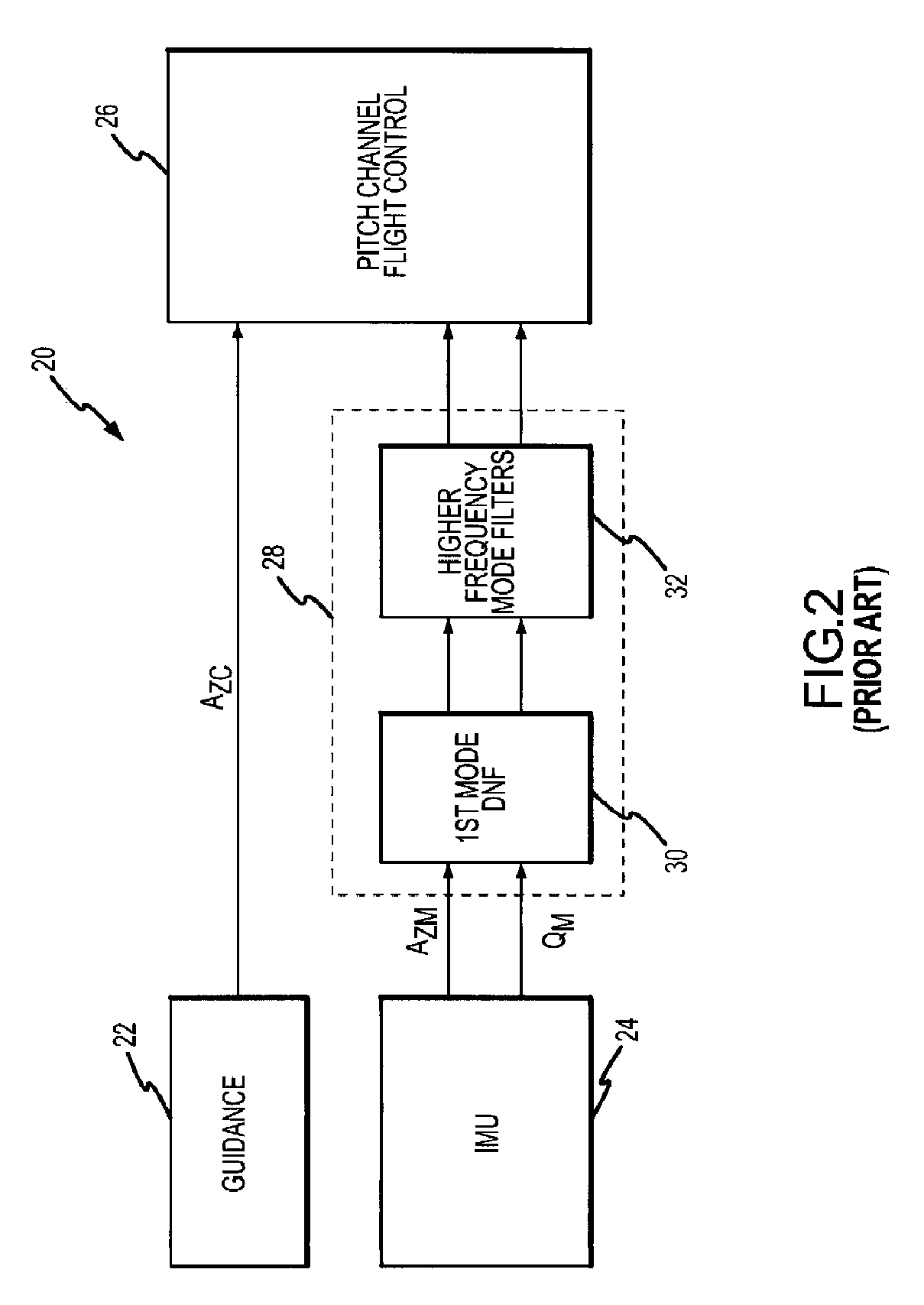
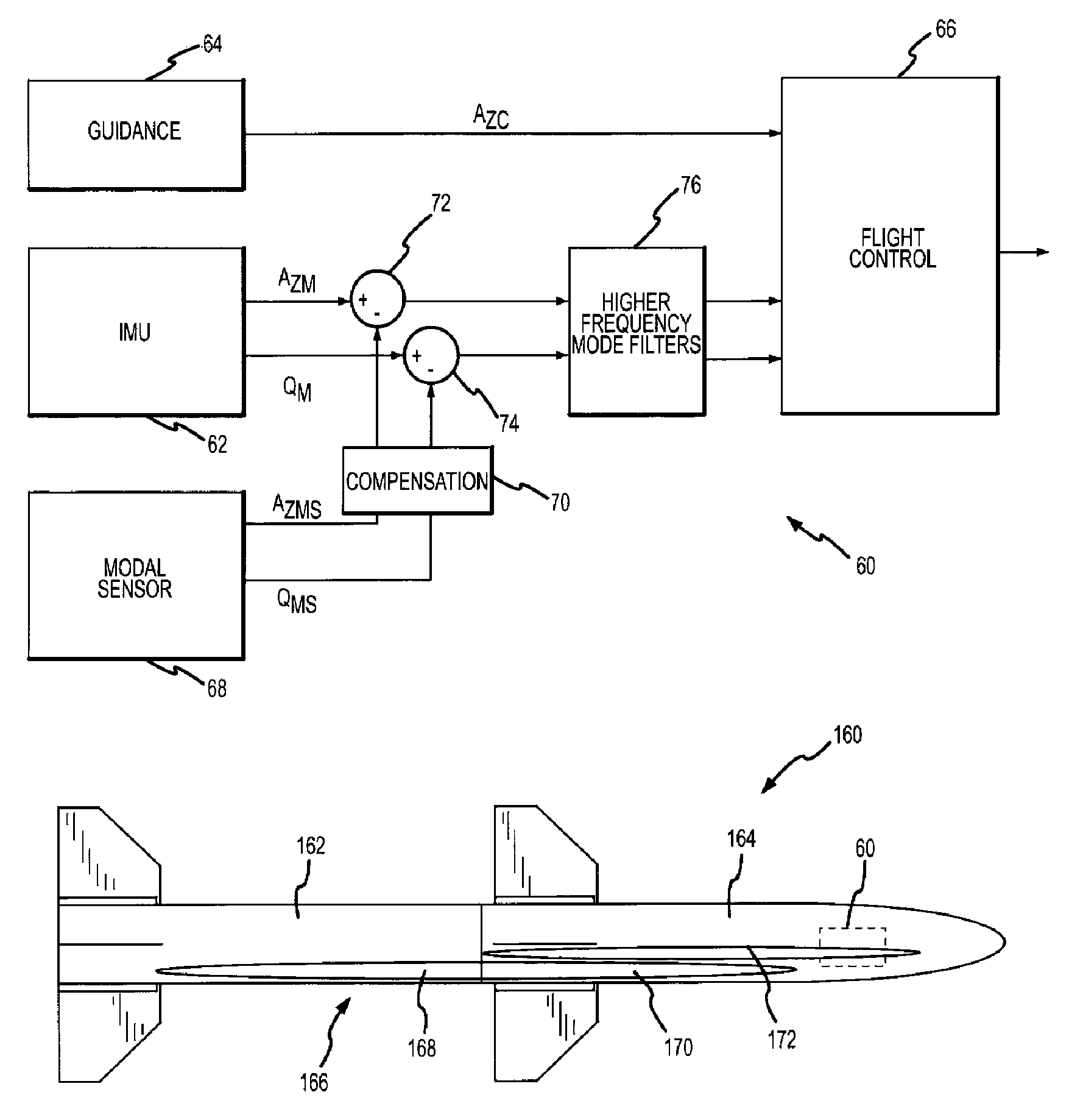
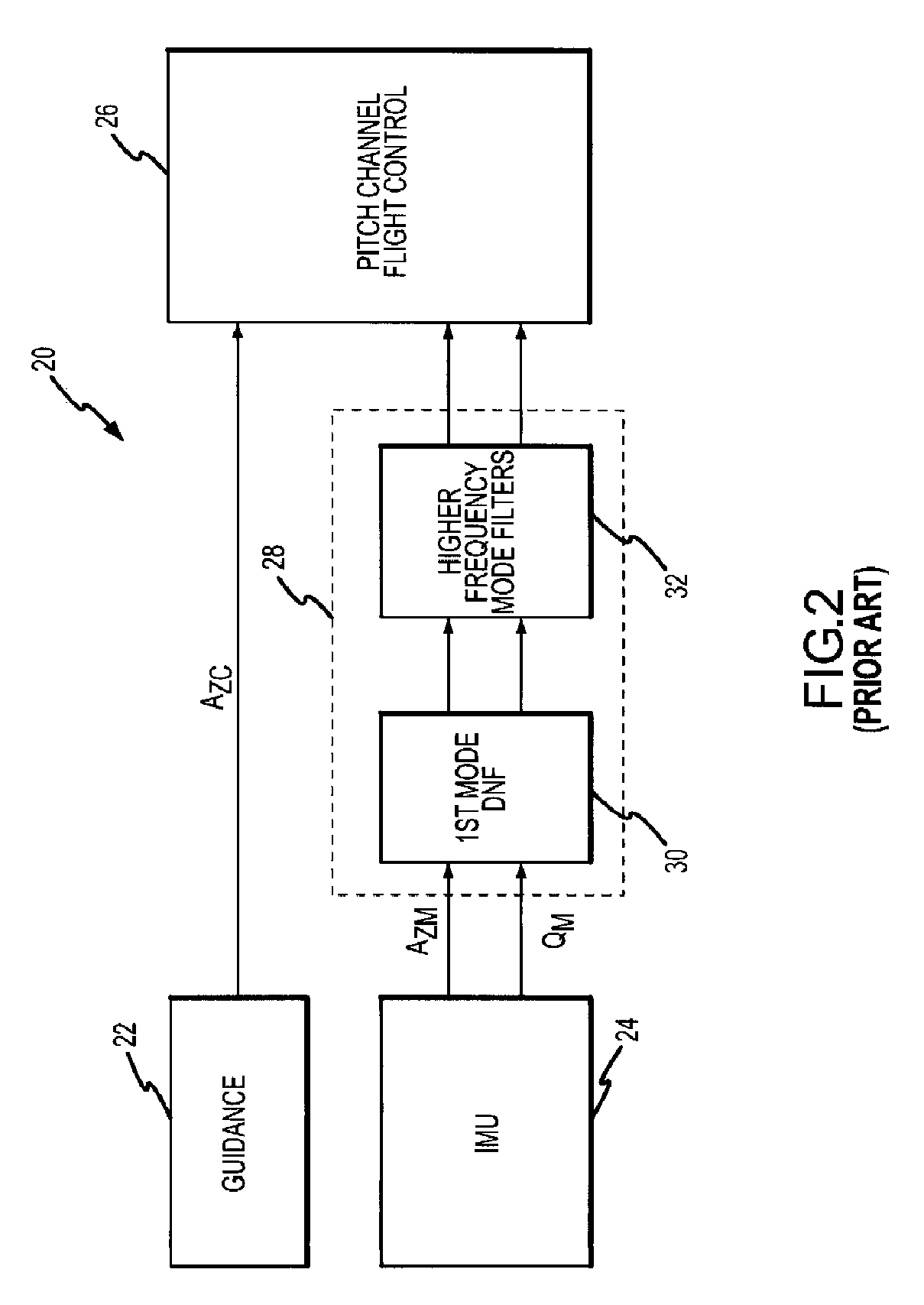
Flight control system and method of using piezoelectric modal sensors to mitigate flexible body dynamics
ActiveUS20080169384A1Simple and inexpensiveReduce the impactAircraft stabilisationDigital data processing detailsElectricityFlight vehicle
A flight control system is provided with one or more modal sensors that are each configured to measure the rate and possibly acceleration for a flexible body mode of the flight vehicle. The modal sensor's rate and suitably acceleration are subtracted from the rate and acceleration measured by the IMU such that the values provided to the flight controller more closely represent only the rate and acceleration of the flight vehicle's rigid airframe component. A piezoelectric modal sensor is capable of sensing a particular flexible body mode over variations in the modal frequency without inducing additional phase loss in the control loop in order to maintain suitable phase and gain margins. Sensors are suitably provided for at least and possibly only the 1st lateral bending modes in the pitch and yaw channels.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method of automatic adjustment of the control parameters of a magnetic suspension system
InactiveUS7328075B2Increased complexityReduce the amount of solutionResistance/reactance/impedenceAerodynamic testingAuto regulationControl subjects
In adjustment of the control parameters of a magnetic suspension system, an object of the present invention is to provide a technique for adjusting the control parameters to optimum values automatically by employing the iterative feedback tuning method, without increasing the complexity of the program, the amount of calculation and the overall size of the system, and still reducing the amount of calculation required for calculation of the safety margin (gain margin and phase margin). In a method of automatic adjustment of control parameters according to the invention, when applying the iterative feedback tuning method to a feedback control system for a magnetic suspension system, only those control parameters that have a significant effect on the control performance of the system are selectively adopted / discarded from among control parameters so that the control parameters are guided to optimum values to obtain a response waveform desired by a designer directly from input / output data of a control subject.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
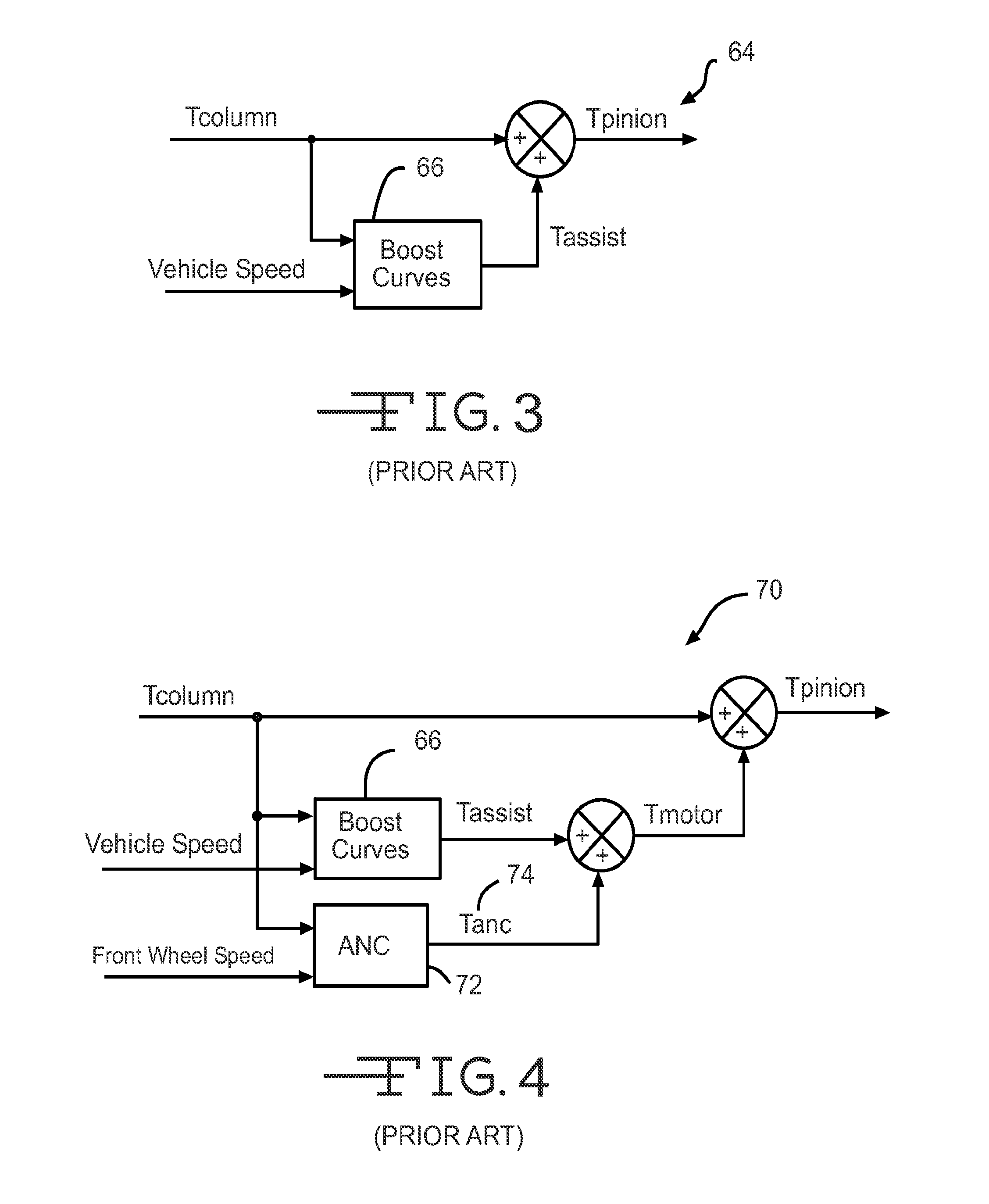
System and Method for Wheel Disturbance Order Detection and Correction
InactiveUS20150094912A1Eliminate nibbleImprove performanceSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsResonator filterFilter gain
An active nibble control (ANC) includes an anti-notch filter that increases the gain margin of the control and, therefore, greater disturbance rejection. The closed loop frequency response of the ANC is further enhanced by the addition of a lag-lead phase compensator filter. The addition of the lag-lead compensation filter allows use of the higher ANC gains at higher wheel frequencies to increase disturbance rejection, thereby compensating for anti-notch filter gain reduction with increasing wheel frequency. Similar results are obtained by adding a lag-lead phase compensator filter to a resonator filter in an active ANC.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE US LLC
Method For Tuning A Motor Drive Using Frequency Response
ActiveUS20170063268A1Quick fixDesired level of performanceGeneral control strategiesMotor parameters estimation/adaptationMotor driveControl system
An improved system for tuning a motor controller is disclosed. The controller gains are initially set based on the measured frequency response for the controlled system. A desired level of performance is defined by setting a desired phase margin and a desired gain margin to be observed in the frequency response. An improved method of determining the frequency response provides for a reduced computational intensity. The initial tuning routine uses the frequency response to set not only controller gains, but also settings for filters in the control module. Having obtained the desired level of performance from the initial tuning, the motor drive executes an adaptive tuning routine while controlling the motor. The adaptive tuning routine tracks changes in the operating performance and adjusts the filter settings or the controller gains to return operation to within the desired level of performance while the motor continues to operate.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Flight control system and method of using piezoelectric modal sensors to mitigate flexible body dynamics
ActiveUS7645970B2Simple and inexpensiveReduce impactDirection controllersActuated automaticallyElectricityFlight vehicle
A flight control system is provided with one or more modal sensors that are each configured to measure the rate and possibly acceleration for a flexible body mode of the flight vehicle. The modal sensor's rate and suitably acceleration are subtracted from the rate and acceleration measured by the IMU such that the values provided to the flight controller more closely represent only the rate and acceleration of the flight vehicle's rigid airframe component. A piezoelectric modal sensor is capable of sensing a particular flexible body mode over variations in the modal frequency without inducing additional phase loss in the control loop in order to maintain suitable phase and gain margins. Sensors are suitably provided for at least and possibly only the 1st lateral bending modes in the pitch and yaw channels.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Servo controller method and apparatus for high tracks per inch hard disk drives using a delay accomodating state estimator
InactiveUS7031095B2Reduced stabilityIncreasing the phase margin and the gain marginTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveElectric machine
The invention applies to servo controllers for at least the voice coil motor of a hard disk drive. Today, many control algorithms require 80 to 90 percent of the sampling period to complete their calculation of the next control, making computation time delay no longer negligible. The invention accommodates the transport delay, such as computation time delay, into the state estimator and into the whole control system. Experimental results using a commercial hard drive, as well as simulation results, show that the invention's method effectively improves the hard disk drive control system stability by increasing the phase margin and gain margin. The invention includes the method of operating the servo-controller, as well as the apparatus implementing that method. The invention also includes hard disk drives containing servo-controllers implementing the method, and program systems residing in accessibly coupled memory to a computer within the servo controller implementing the method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
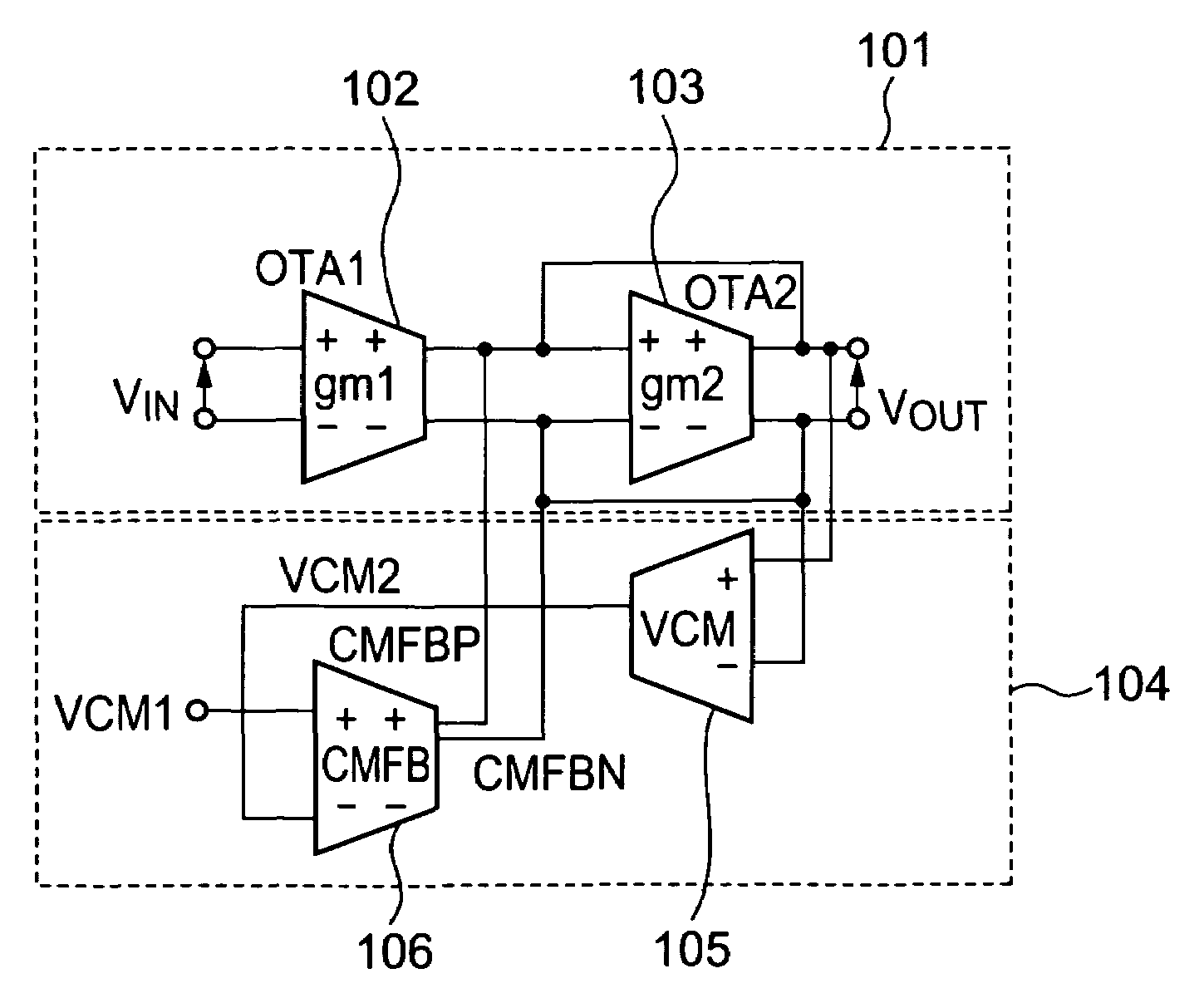
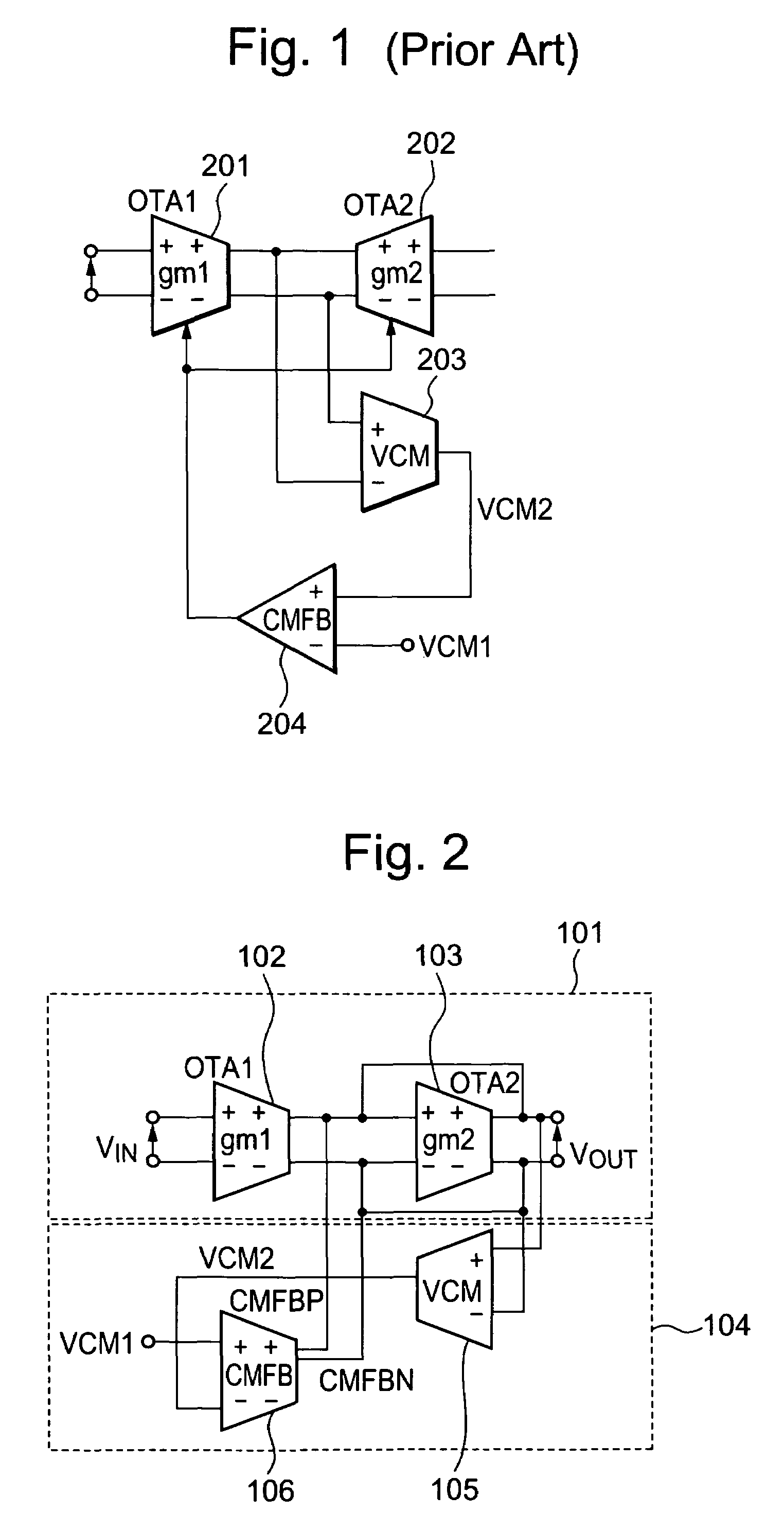
Voltage control circuit for common mode voltage and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS7126425B2Effective controlAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersControl signalEngineering
A common mode voltage detection circuit 105 detects a common mode voltage VCM from differential output terminals of a differential output circuit 101. The common mode voltage detection circuit outputs a detected voltage VCM2 in accordance with the common mode voltage VCM. An OTA 106 in the common mode feedback loop inputs or outputs multiple currents of the same phase in accordance with a voltage difference between a reference voltage VCM1 and the detected voltage VCM2. The respective multiple currents of the same phase are inputted / outputted to / from the two respective terminals of the differential output terminals. The common mode voltage can be reduced by flowing the currents into the differential output terminals, and can be increased by leading the currents from the differential output terminals. Thus, a phase margin or a gain margin of a control signal loop can be secured even with low current consumption, thereby realizing stable operation of the circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
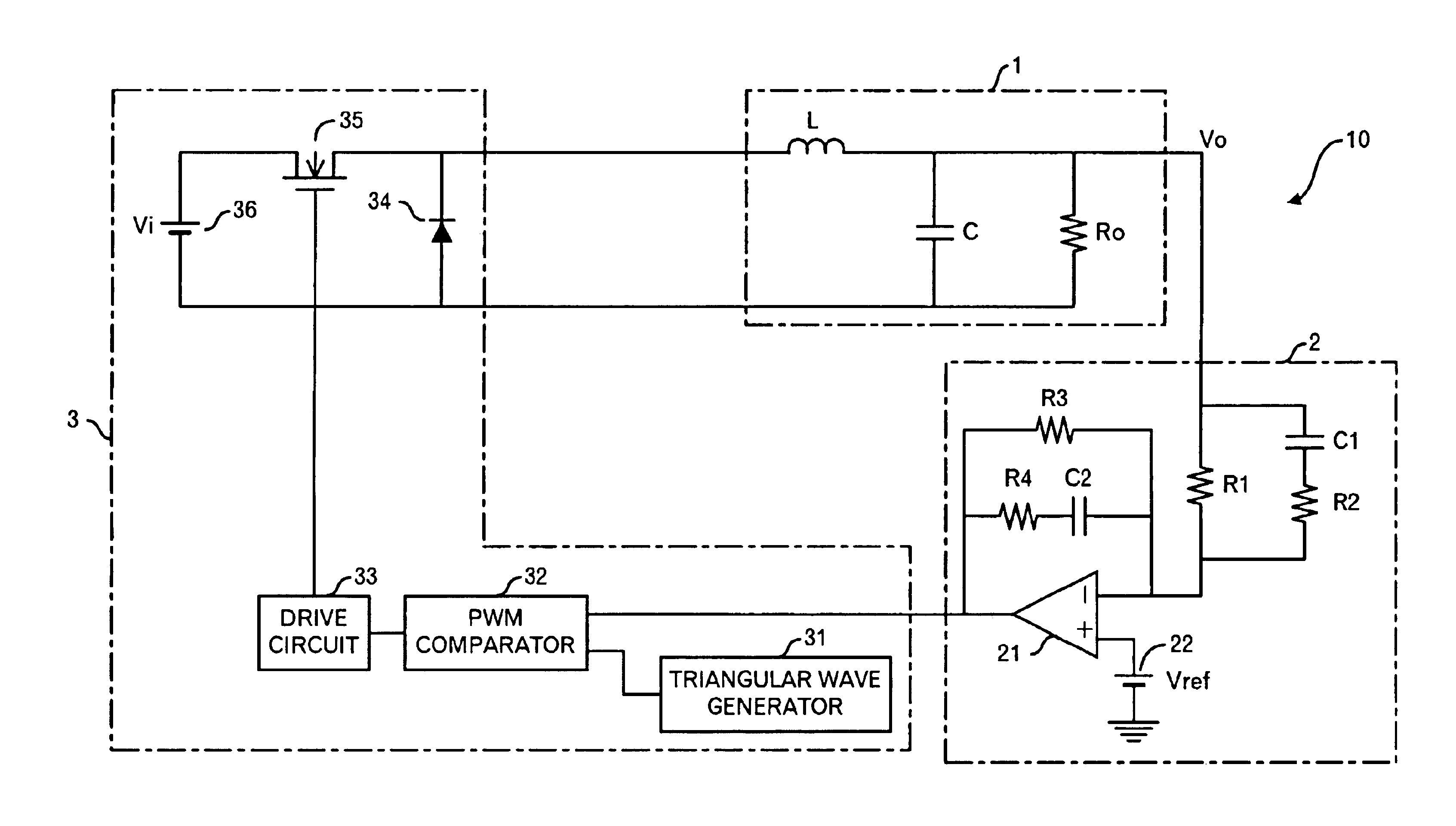
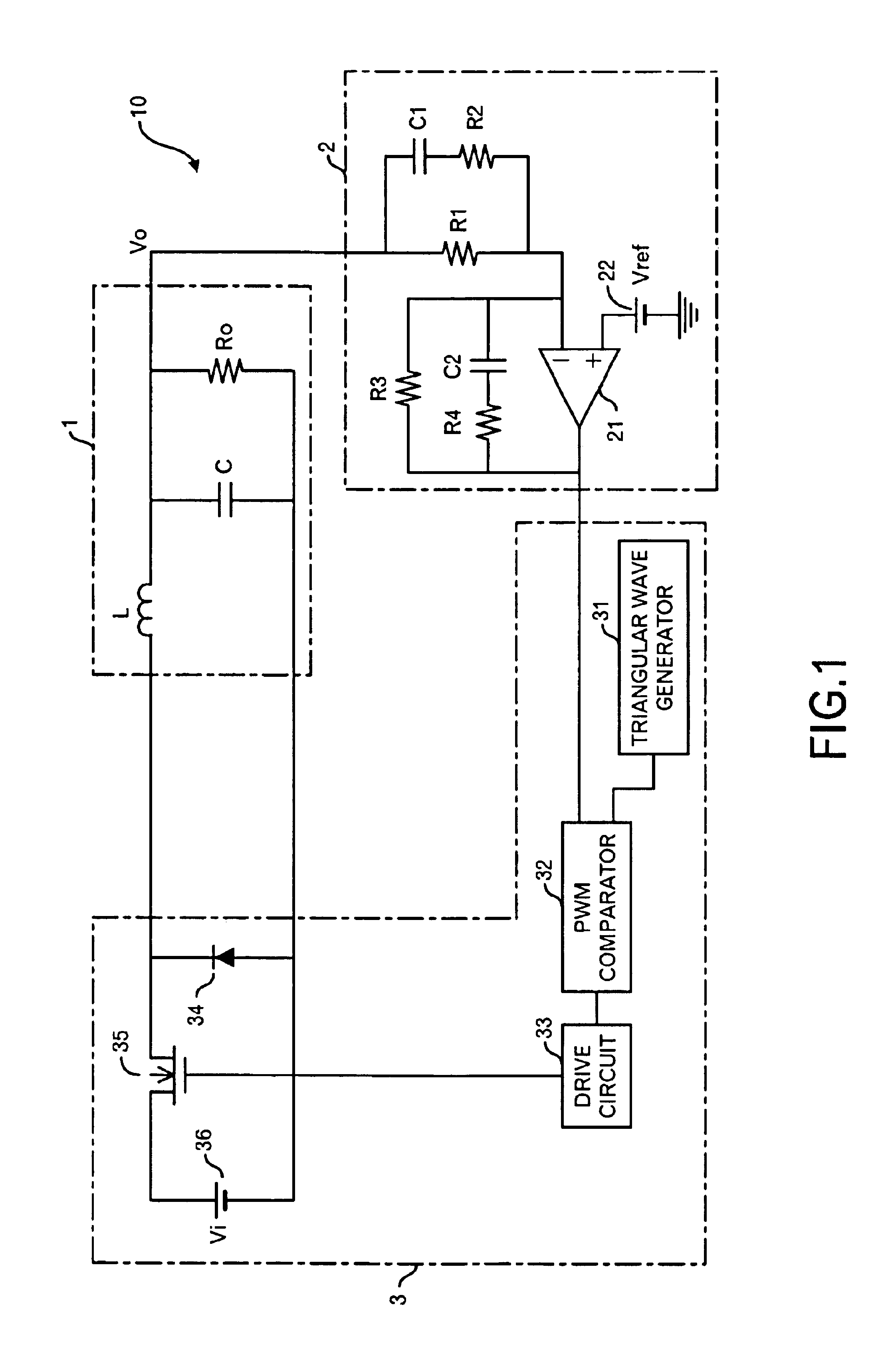
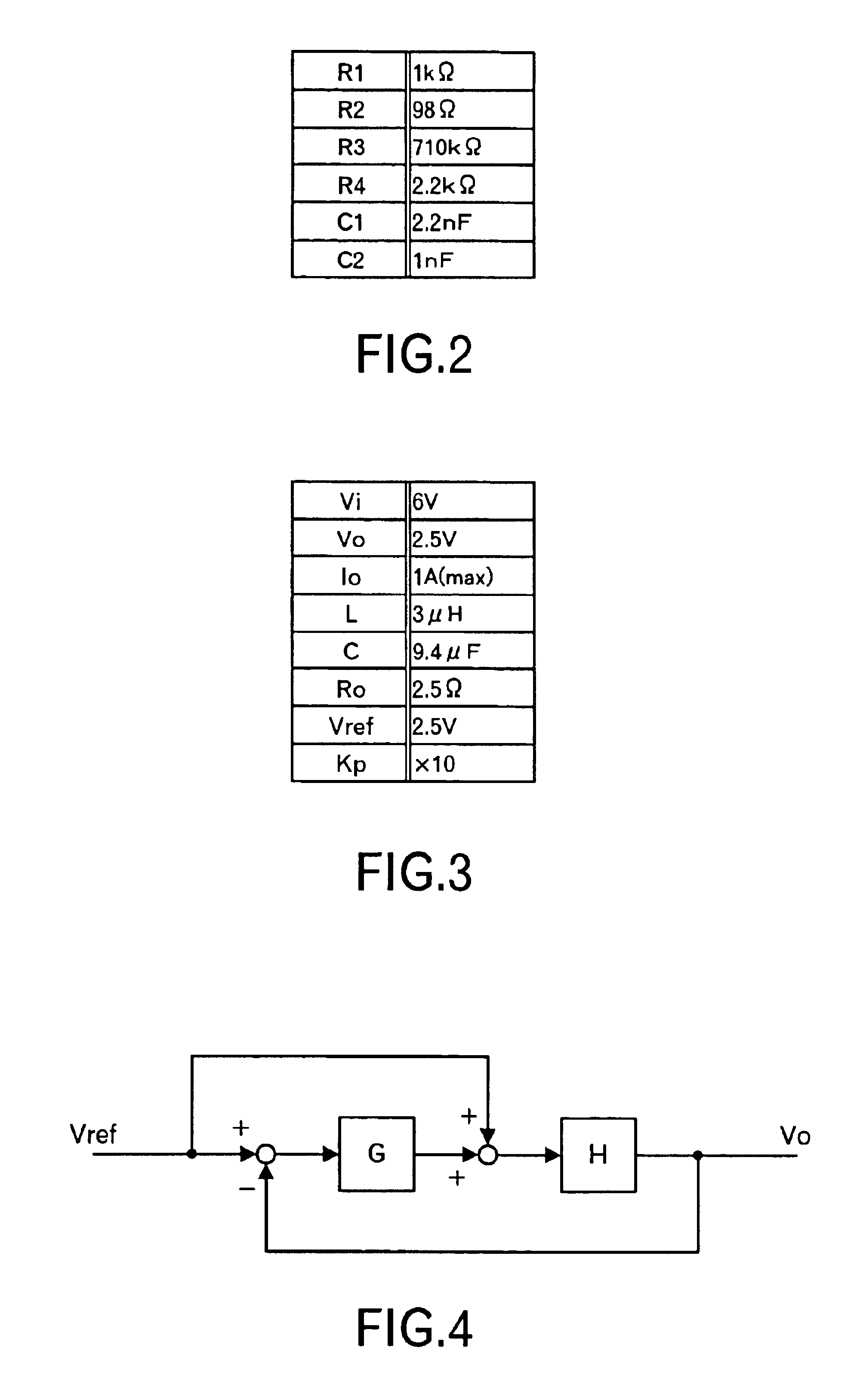
Power supply apparatus
InactiveUS6958593B2High speed responseSimple designDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationResonanceSignal transfer function
This invention provides a stable power supply apparatus enabling the high speed response. Hitherto, it was necessary to secure both of the gain margin and the phase margin on the Bode diagram of the loop transfer function when the PID feedback control was carried out in the power supply apparatus. The form of the transfer function of the controller in the power supply apparatus of this invention is the same, but a set of coefficient values in the transfer function is completely different, and the controller secures only the phase margin without securing the gain margin. Furthermore, the transfer function of the controller indicates a part with an extreme decrease in the gain and a trap point in which the phase is sharply delayed on the Bode diagram. This is achieved by applying the integral element of the PID to a frequency range that is higher than the resonance frequency of the LC filter. As a result, the high speed response becomes possible without losing the stability. Moreover, there is no case in which difficulty as to the setting of the circuit constants rises.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
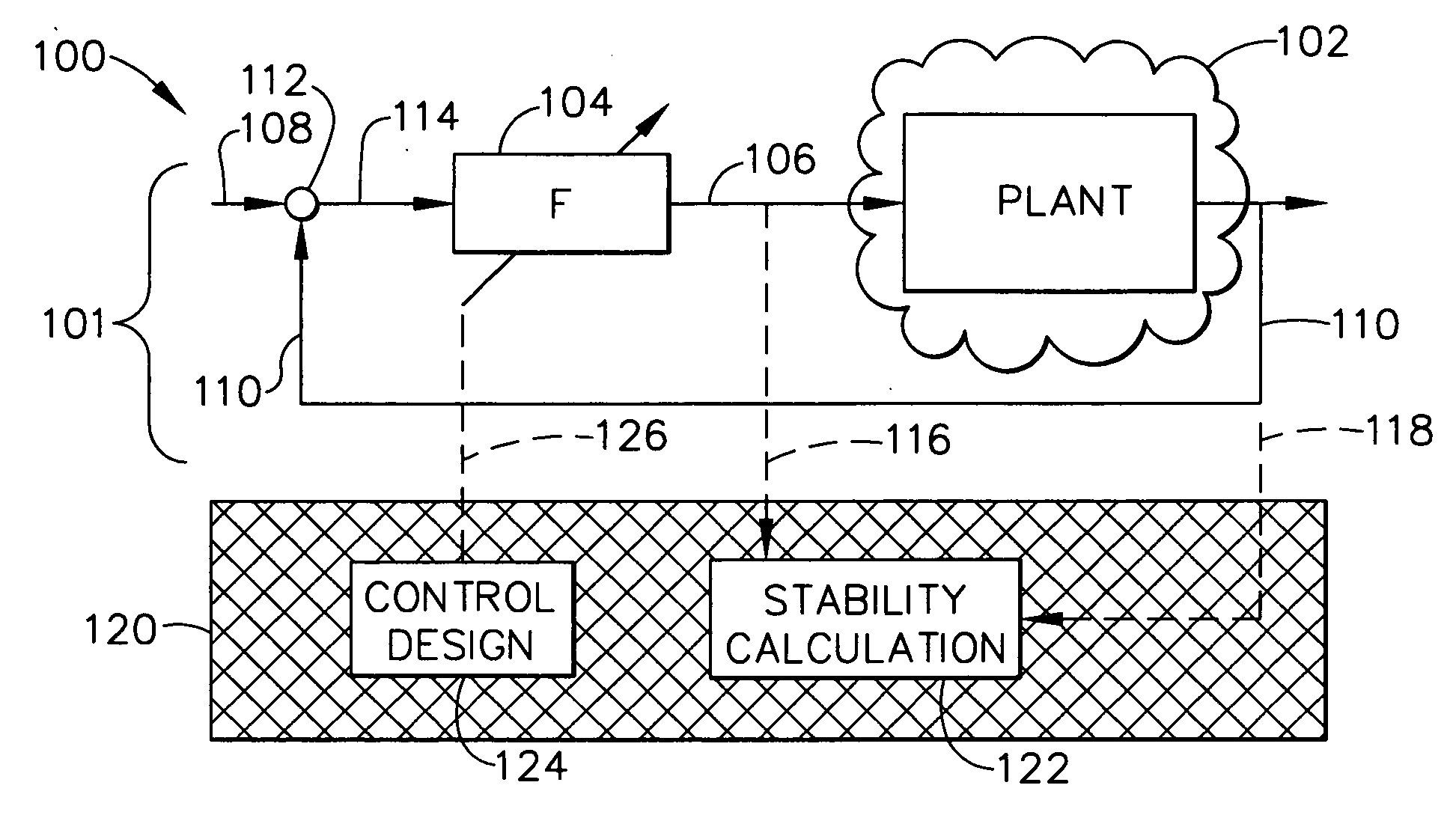
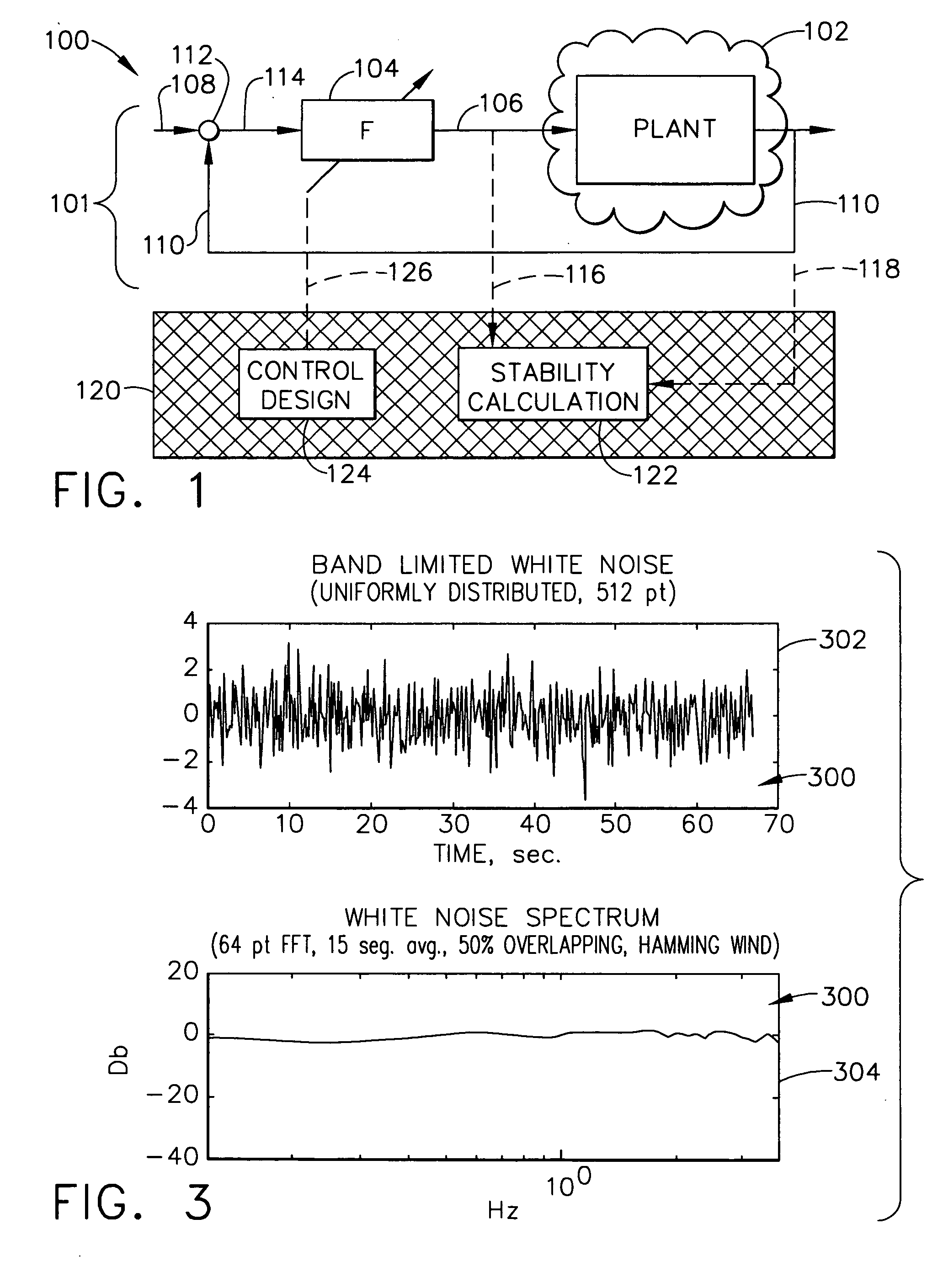
In-flight control system stability margin assessment
A method for in-flight stability margin assessment includes steps of: exciting a control system with a wide band spectrum excitation signal to produce in-flight data; storing the in-flight data in an on-board computer during operation of a spacecraft mission; downloading the in-flight data via telemetry during operation of the spacecraft mission; estimating a system sensitivity function by taking the ratio of an output power spectrum to an input power spectrum; and determining stability margins of the attitude control system from the system sensitivity function by determining a gain margin GM and a phase margin PM from the formulas: 11-amin<GM<11+aminPM>±sin-1(amin2)where “amin” is the reciprocal of the peak of the system sensitivity function. The method optionally includes redesigning and providing a new control law to the control system if deemed necessary.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
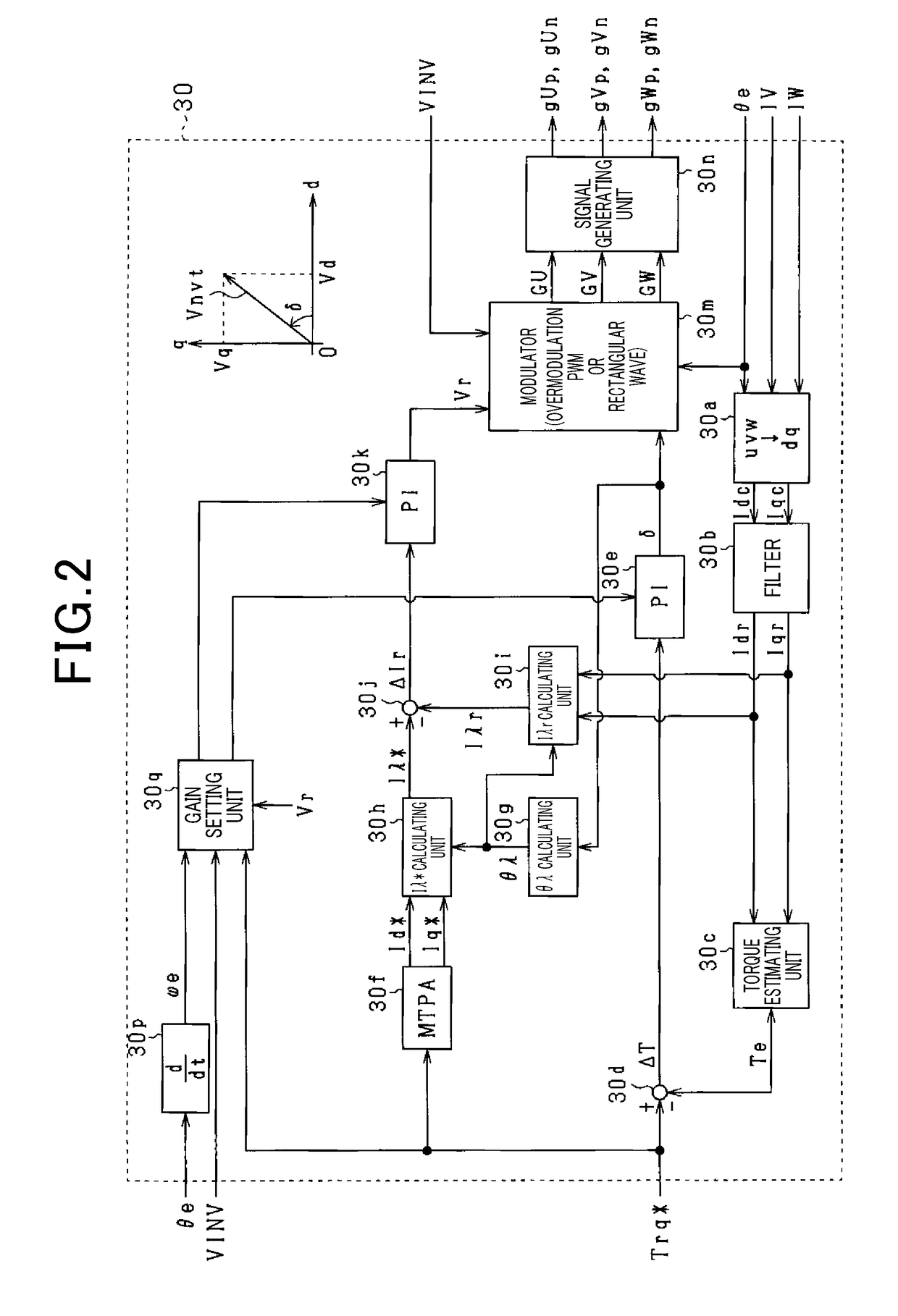
Control apparatus for rotating electric machine
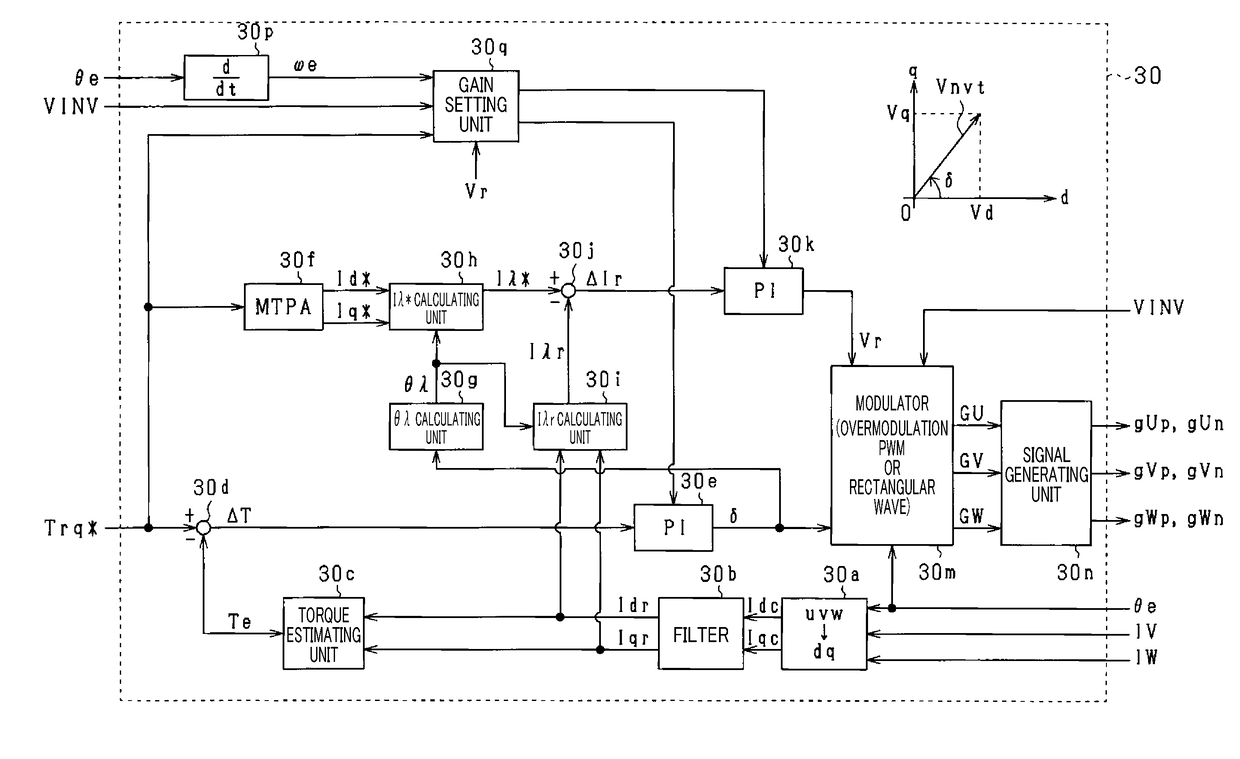
ActiveUS20170331403A1Reduced controllabilityAC motor controlVector control systemsElectric machineResonance
In a control apparatus for a rotating electric machine, a phase feedback gain is set such that first and second conditions are met. The first condition is that gain margin and phase margin in frequency characteristics of a first loop transfer function are ensured. The second condition is that a gain intersection angular frequency in frequency characteristics of the first loop transfer function is lower than respective resonance angular frequency in frequency characteristics of first and second transfer functions. An amplitude feedback gain is set such that third and fourth conditions are met. The third condition is that gain margin and phase margin in frequency characteristics of a second loop transfer function are ensured. The fourth condition is that a gain intersection angular frequency in frequency characteristics of a second loop transfer function is lower than respective resonance angular frequency in frequency characteristics of third and fourth transfer functions.
Owner:DENSO CORP
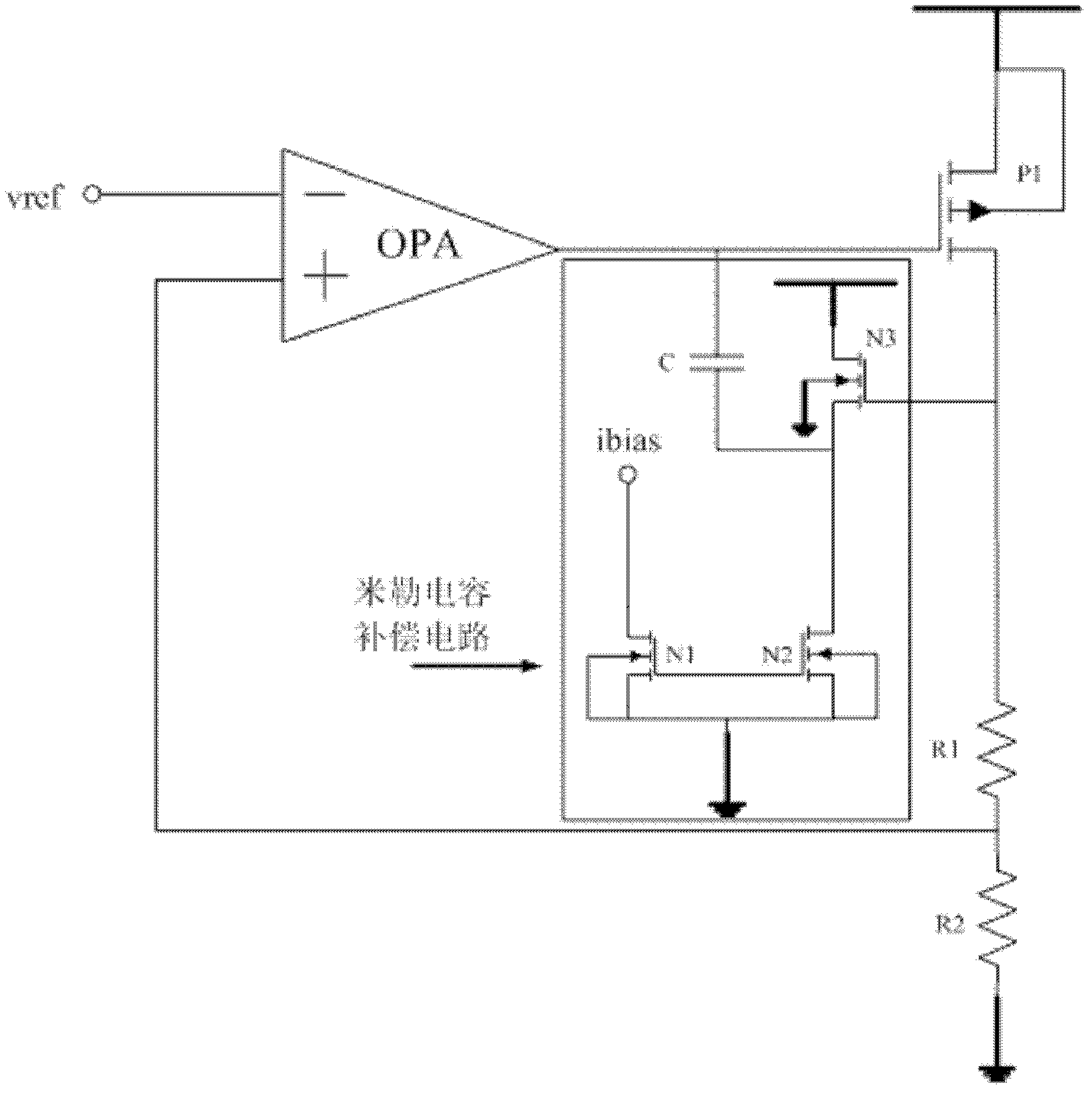
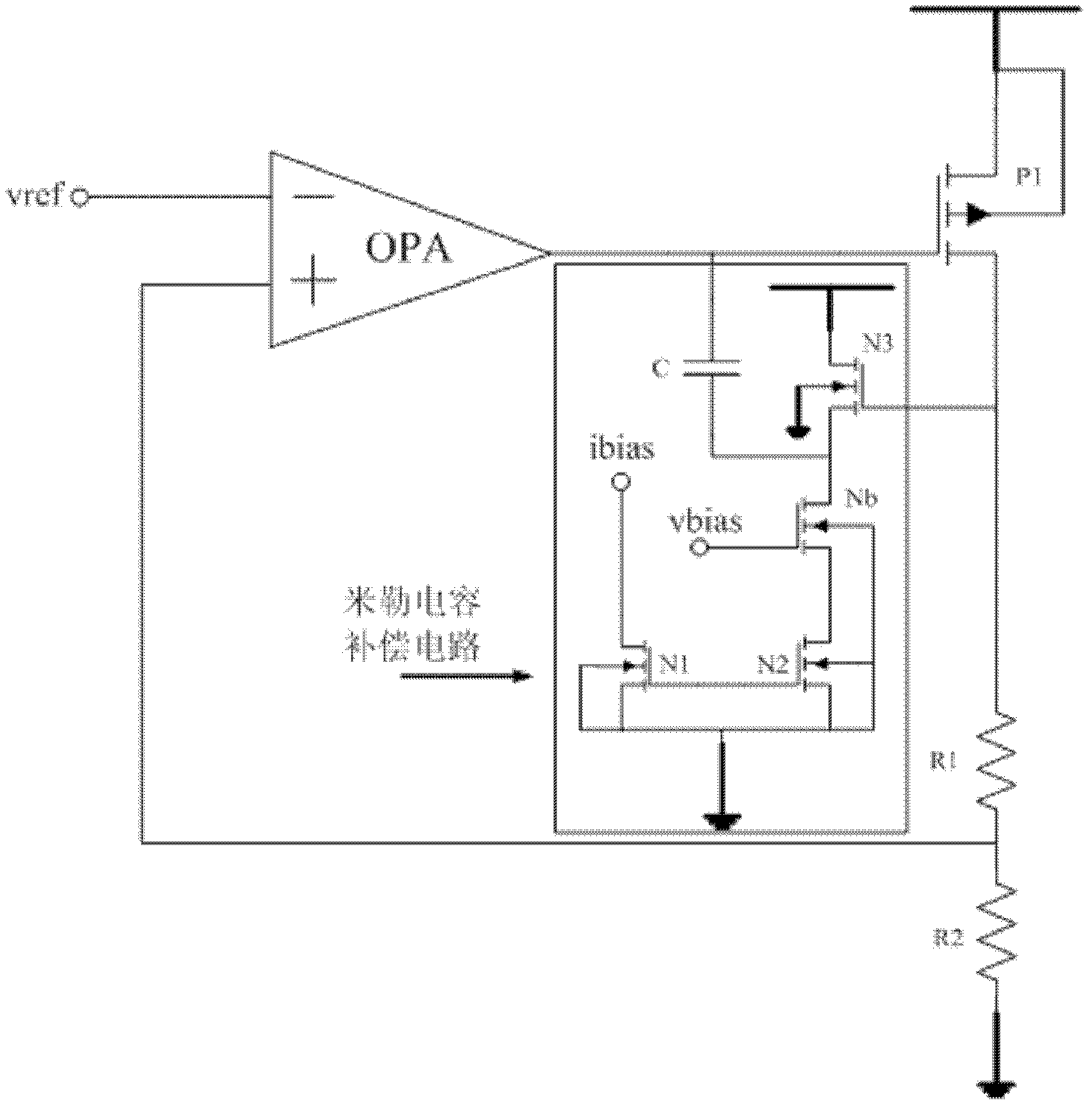
Loop circuit compensating circuit
ActiveCN103135642AGuaranteed performanceReduce the valueElectric variable regulationCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a loop circuit compensating circuit which comprises an operational amplifier (OPA), a p-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) pipe (P1), a capacitor (C), an n-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) pipe (N3), and an n-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) pipe (N1), wherein the negative input end of the OPA is connected with a reference voltage, the positive input end of the OPA is connected to the ground through a resistor R2, the output end of the OPA is connected with a grid electrode of the PMOS pipe (P1), a source electrode of the PMOS pipe (P1) is connected with a power source, a drain electrode of the PMOS pipe (P1) is connected to the ground through a resistor R1 and the resistor R2, the positive end of the C is connected with the grid electrode of the PMOS pipe (P1), the negative end of the C is connected with a source electrode of a NMOS pipe (N2), a source electrode of the NMOS pipe (N1) is connected with a source electrode of the NMOS pipe (N2) and then is connected to the ground, the source electrode of the NMOS pipe (N1) is connected with a grid electrode of the NMOS pipe (N2), a drain electrode of the NMOS pipe (N1) is connected with a configuration input bias current (IBIAS), substrates of the NMOS pipe (N1), the NMOS pipe (N2) and the NMOS pipe (N3) are connected with to the ground. The source electrode of the NMOS pipe (N3) is connected with the drain electrode of the NMOS pipe (N2) through a NMOS pipe (Nb), an drain electrode of the NMOS pipe (Nb) is connected with source electrode of the NMOS pipe (N3), a source electrode of the NMOS pipe (Nb) is connected with the drain electrode of the NMOS pipe (N2), and an grid electrode of the NMOS pipe (Nb) is connected with a bias voltage (VBIA), and a substrate of the NMOS pipe (Nb) is connected to the ground. The loop circuit compensating circuit can reduce a capacitance valve and a layout area on the premise that additional power consumption does not increased, and the fact that a phase margin and a gain margin are not changed is guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
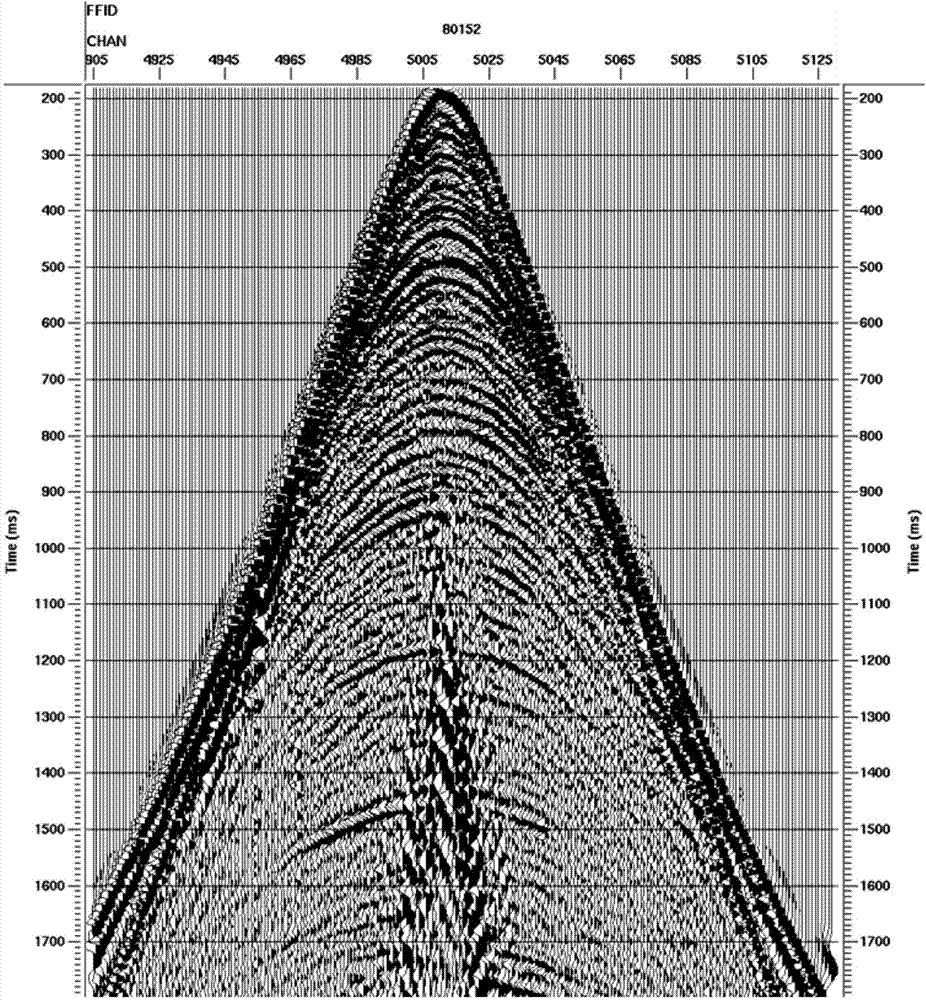
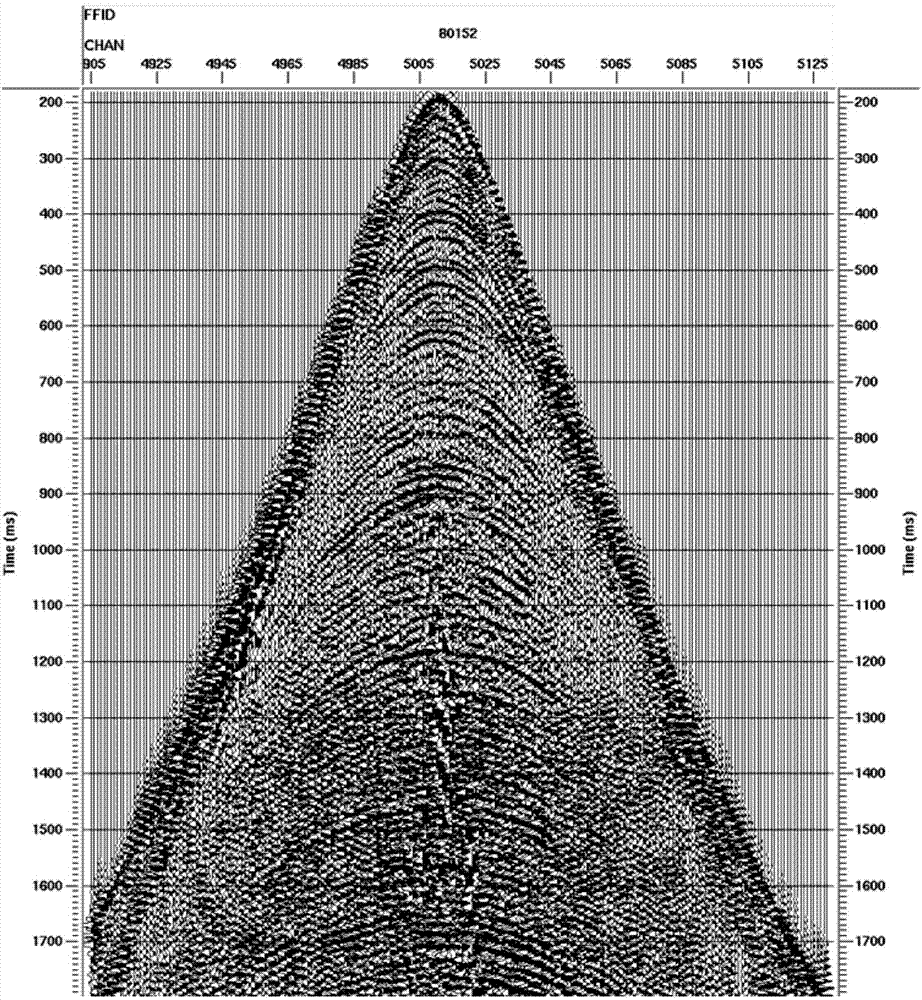
Well-control amplitude-preservation high-resolution seismic data processing method
ActiveCN104502977AHigh resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingVertical seismic profileWave field
The invention relates to a well-control amplitude-preservation high-resolution seismic data processing method, which comprises the following steps of selecting seismic data of a target area; obtaining an optimized amplitude compensation gain margin; performing inverse Q filtering amplitude compensation on the seismic data of the target area to obtain an optimized layer Q body by utilizing the optimized amplitude compensation gain margin; performing inverse Q filtering amplitude compensation on the seismic data of the target area by utilizing the optimized amplitude compensation gain margin and the optimized layer Q body; performing inverse Q filtering phase compensation on the seismic data of the target area by utilizing the layer Q body and a layer velocity body of the target area; performing inverse Q filtering amplitude compensation on zero- wellhead spacing vertical seismic profiling (VSP) data by utilizing the optimized amplitude compensation gain margin and the optimized layer Q body; performing wave field separation on the VSP data subjected to inverse Q filtering amplitude compensation, and obtaining the total energy of downgoing direct waves; performing inversion on the total energy of the downgoing direct waves to obtain an amplitude recovery factor; performing amplitude recovery on the target area subjected to inverse Q filtering amplitude and phase compensation by utilizing the amplitude recovery factor.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
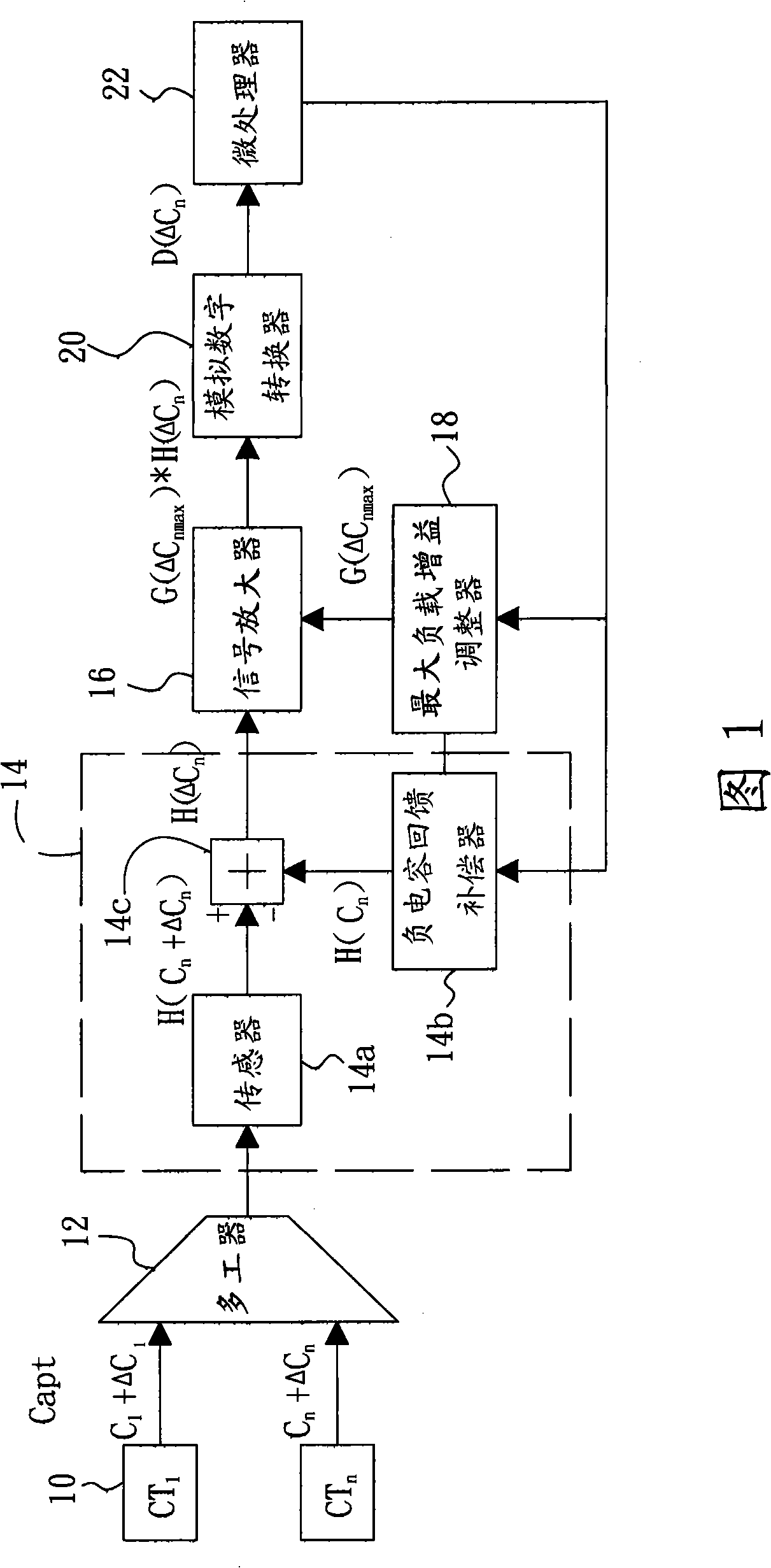
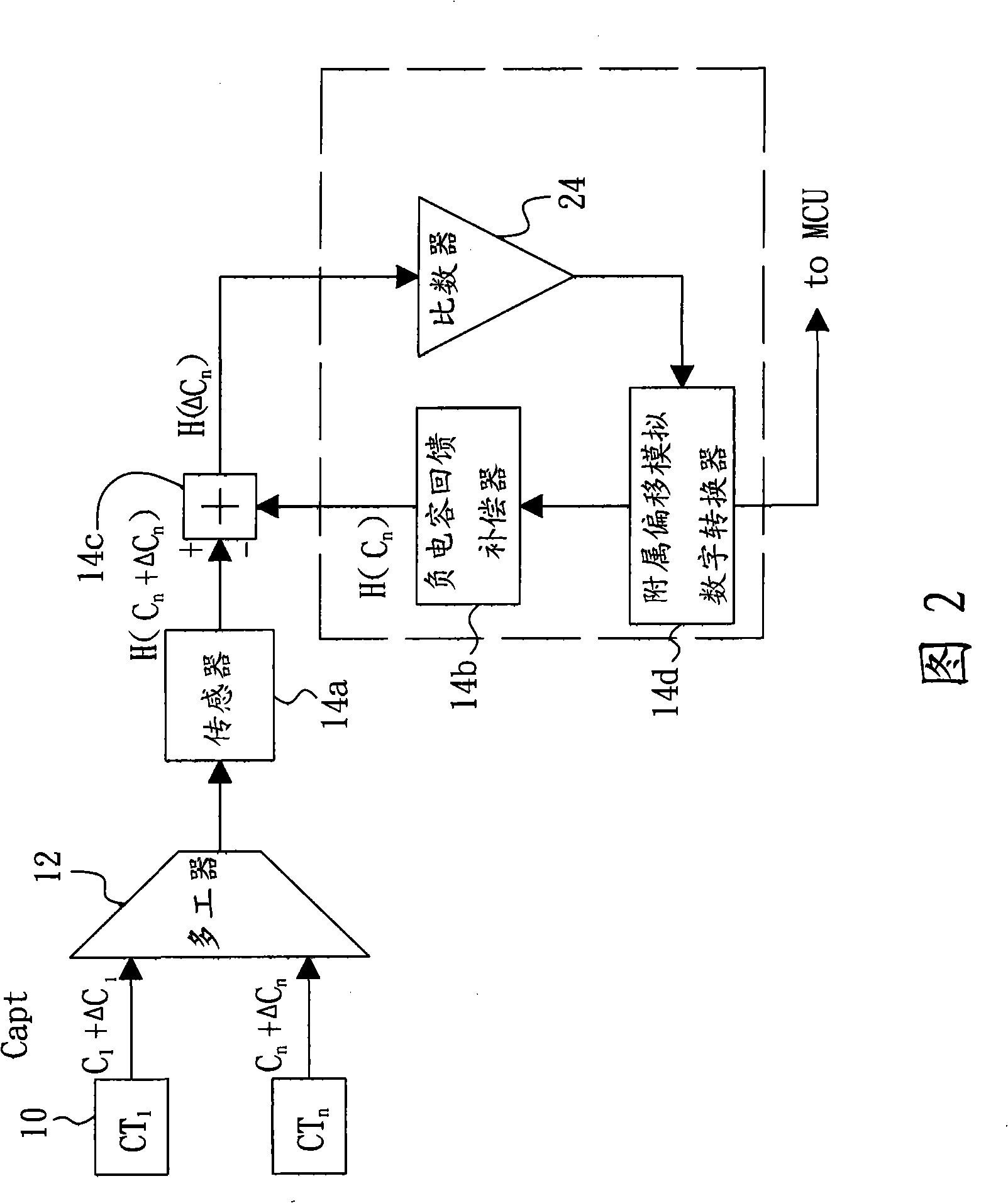
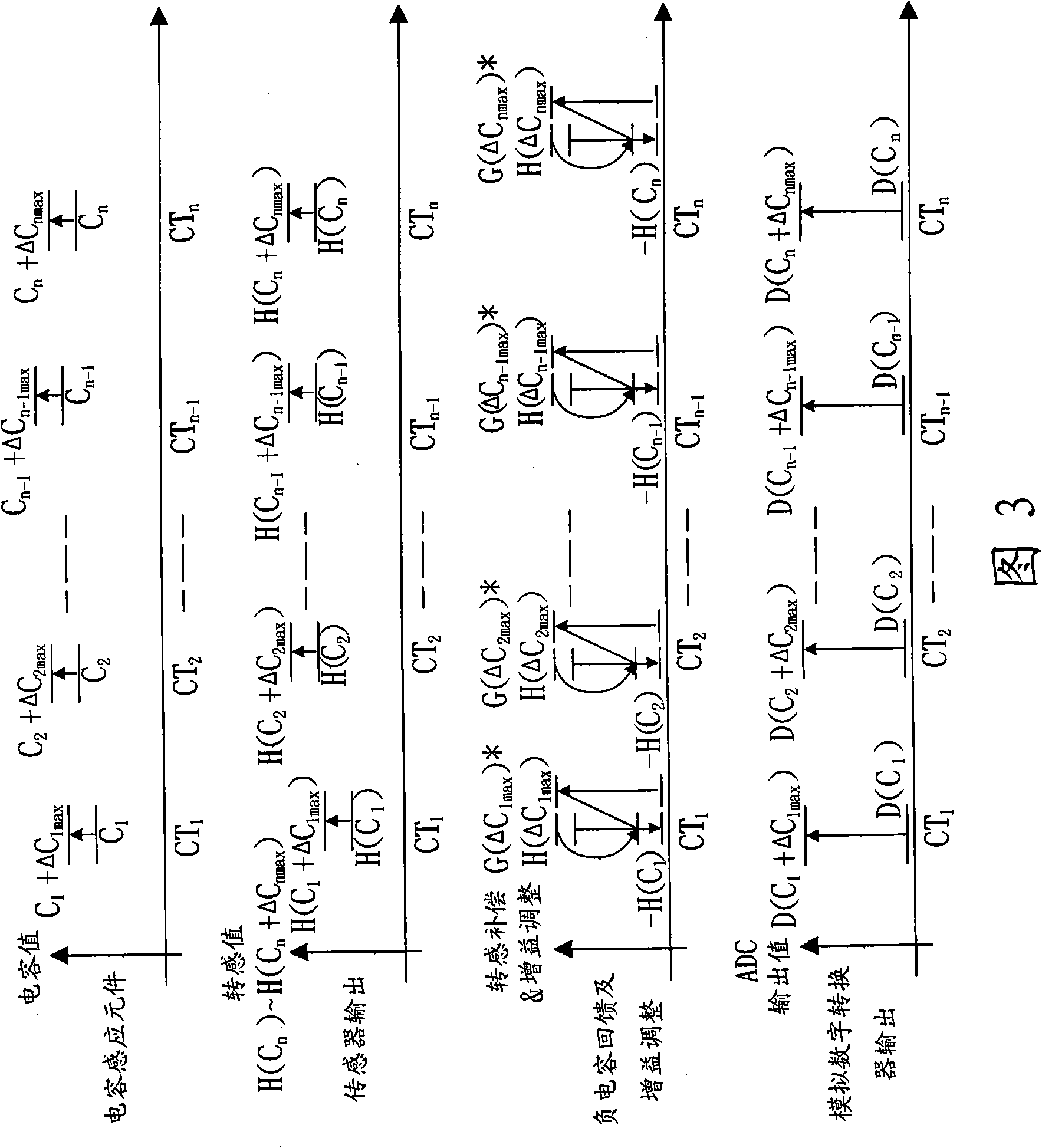
Article locating detector of capacitance touching control panel, and article locating method
ActiveCN101359906APrecise positioningReduce the impact of the operating dynamic rangeElectronic switchingCapacitanceGain margin
The invention relates to an object location detector of a capacitance type touch panel as well as an object location method. The object location detector of the capacitance type touch panel comprises a complex capacitance induction element, a basic negative capacitance compensation element, an analog-digital converter and a microprocessor; the basic negative capacitance compensation element is used to compensate the basic capacitance value of the capacitance induction element so as to obtain the variation of the capacitance value; and the microprocessor is used to calculate the position of the object under touch control according to the variation of capacitance value; and has the advantage of simple location. The object location method of the capacitance type touch panel comprises the following steps: stating an initial value of a sensor; inputting the negative capacitance compensation quantity of a channel; inputting the induction capacitance gain margin of the channel; measuring the capacitance value of the channel; and locating the object under touch control according to the capacitance value of the channel. The method for locating the object on the capacitance type touch panel needs no complex algorithm for locating the object on the touch panel, and makes the location of the object on the touch panel simpler.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Recording and/or reproducing apparatus with optical pickup actuator, and methods for same
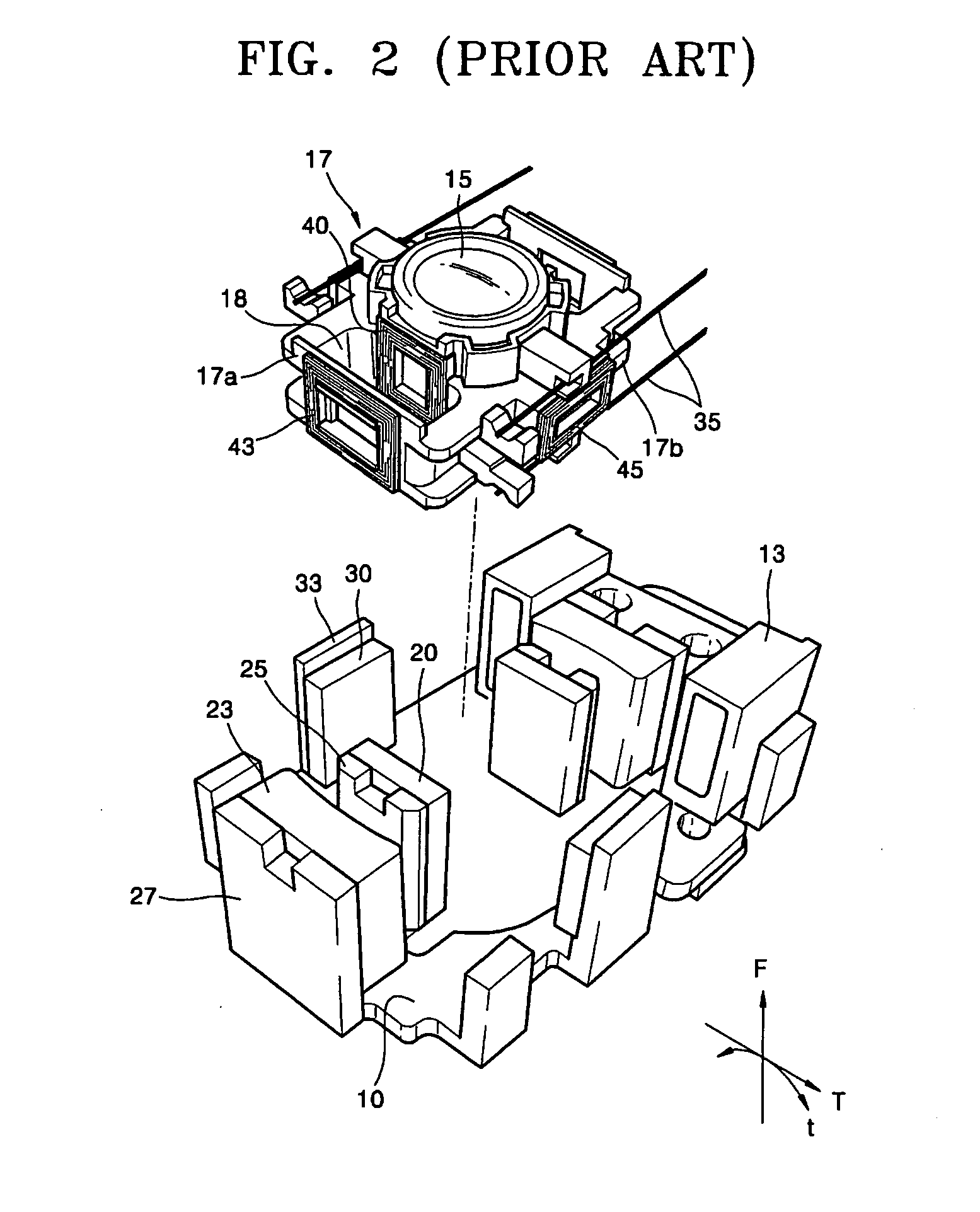
InactiveUS20050174901A1Reduce pliable vibration modeIncrease a gain marginRecord information storageOptical recording/reproducing/erasing methodsOptical pickupBobbin
A recording / reproducing apparatus and an optical pickup actuator, and corresponding methods, for driving a bobbin in a focusing direction, a tracking direction or a tilting direction by use of a magnetic driving unit movably supported by a support member, where an object lens is mounted on the bobbin and a plurality of slits are formed on side walls of the bobbin. According to embodiments of the present invention, a secondary resonant frequency and a value of a secondary resonant peak are increased, thereby improving a gain margin.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com