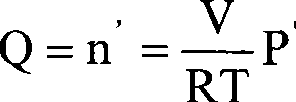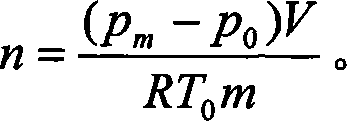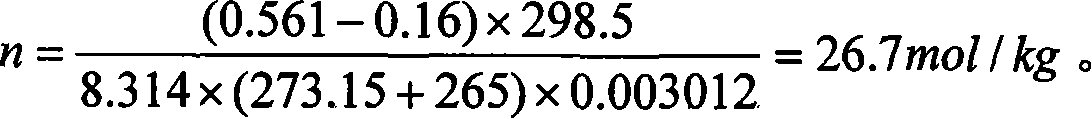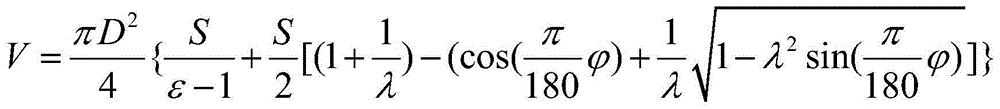Patents
Literature
79 results about "Ideal gas law" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written as PV=nRT, where P, V and T are the pressure, volume and absolute temperature; n is the number of moles of gas; and R is the ideal gas constant.
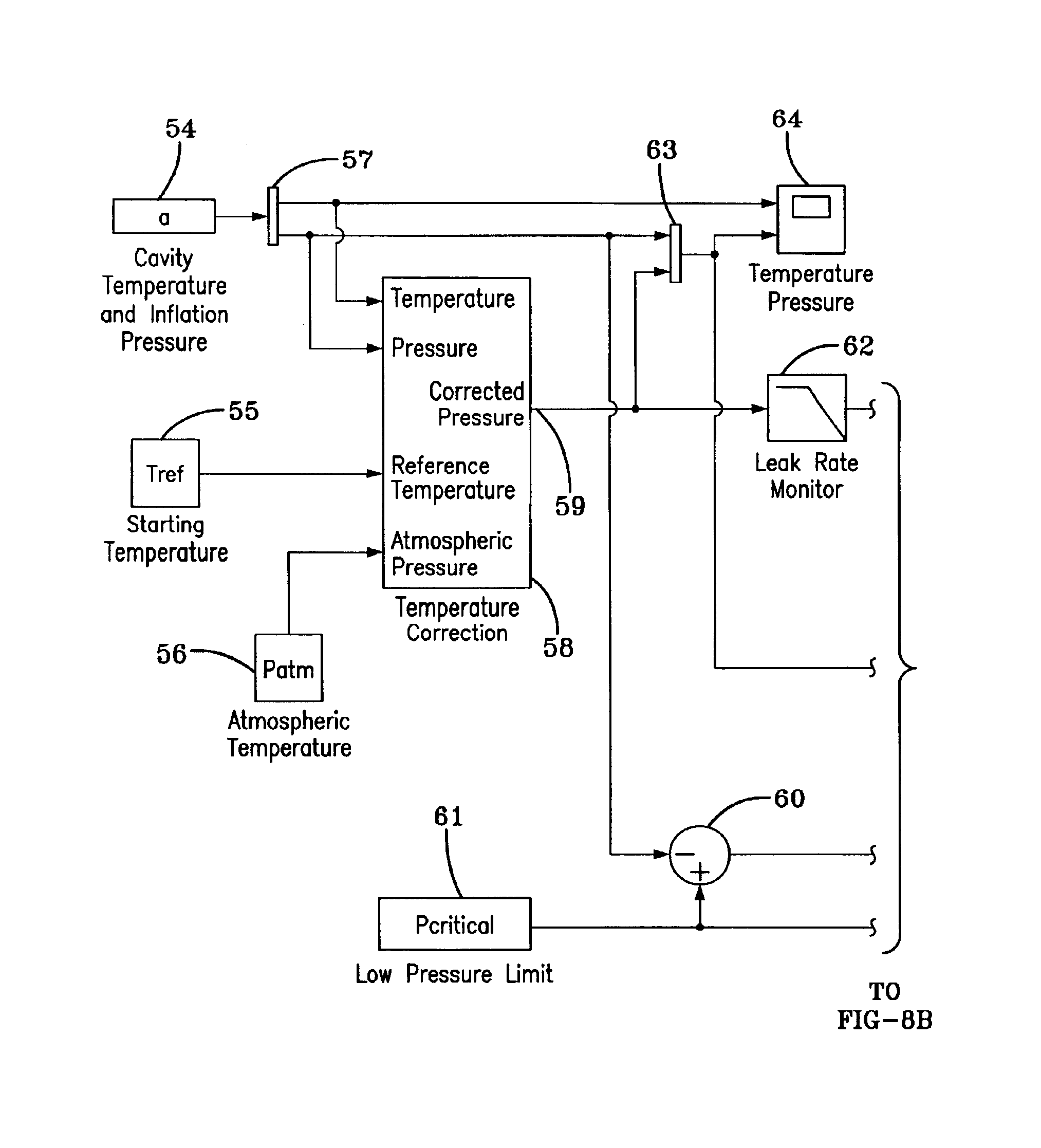
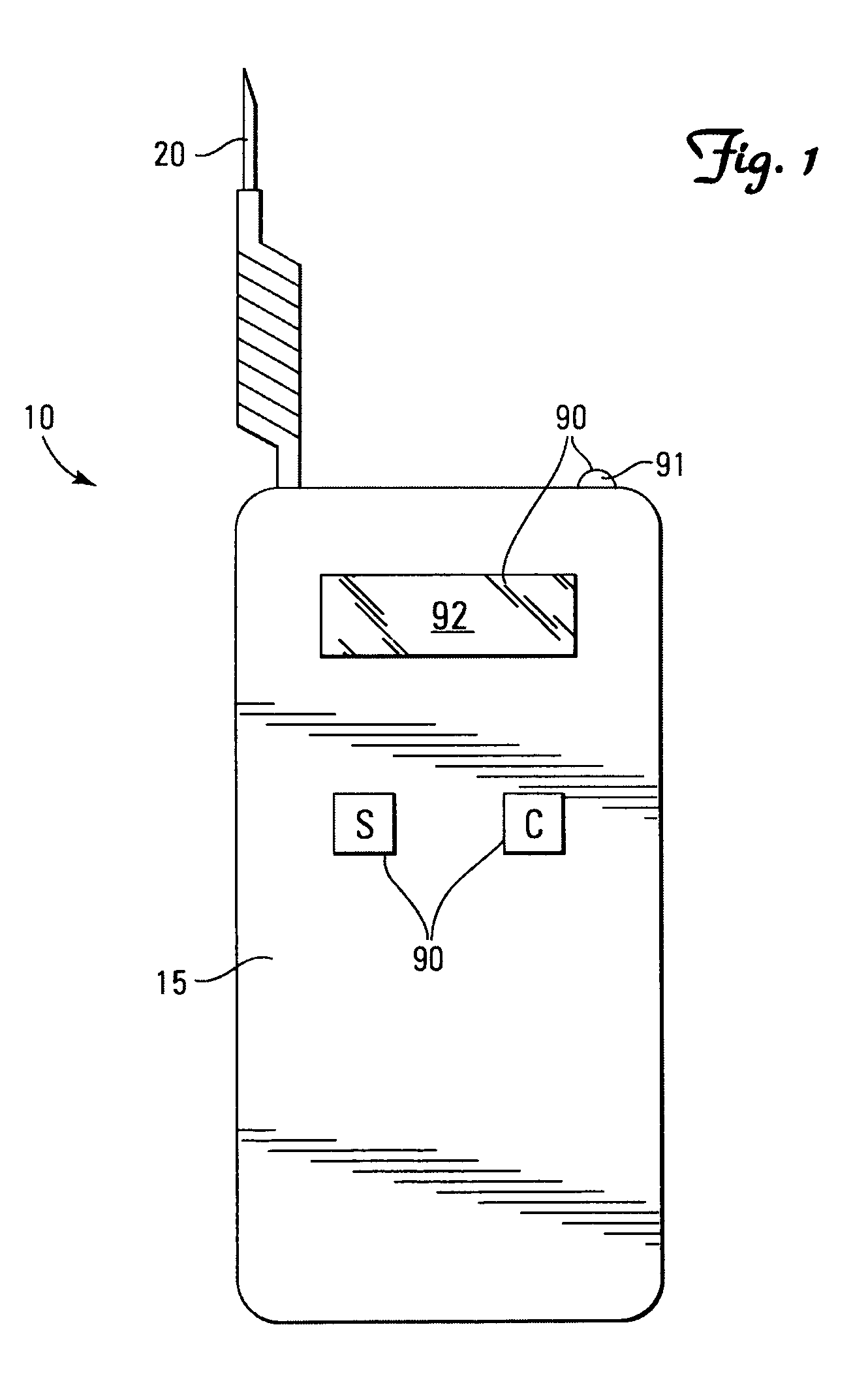
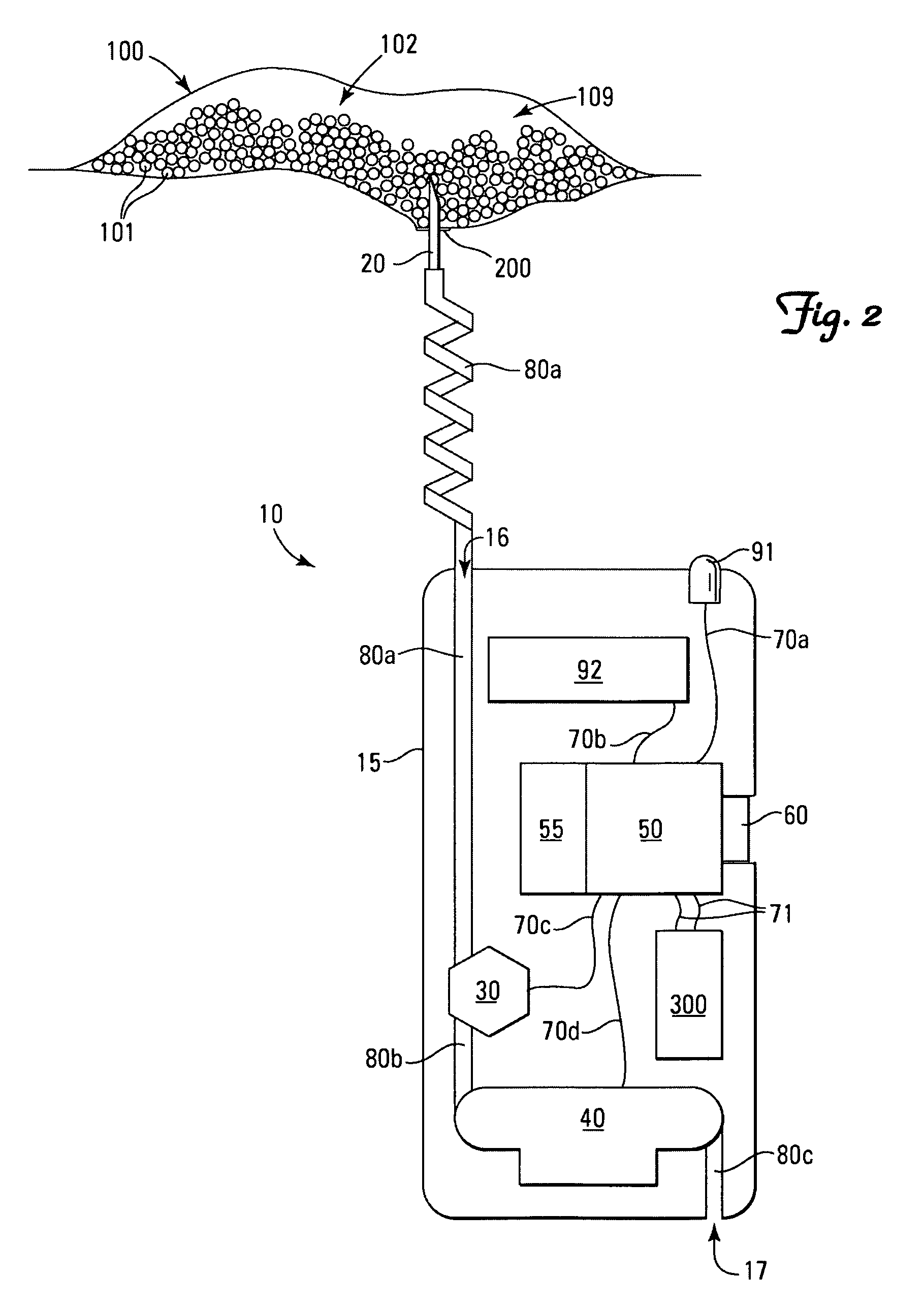
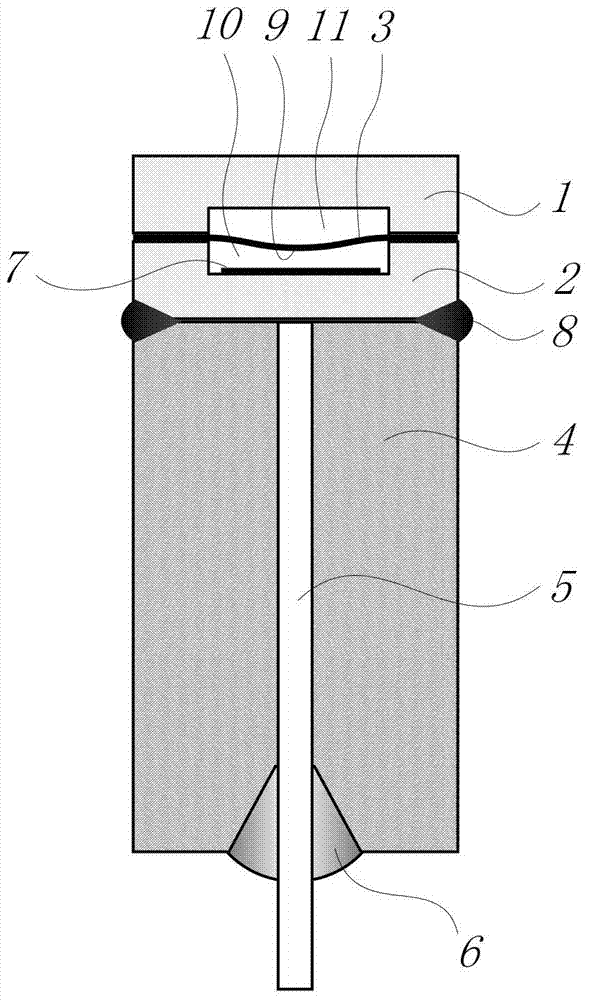
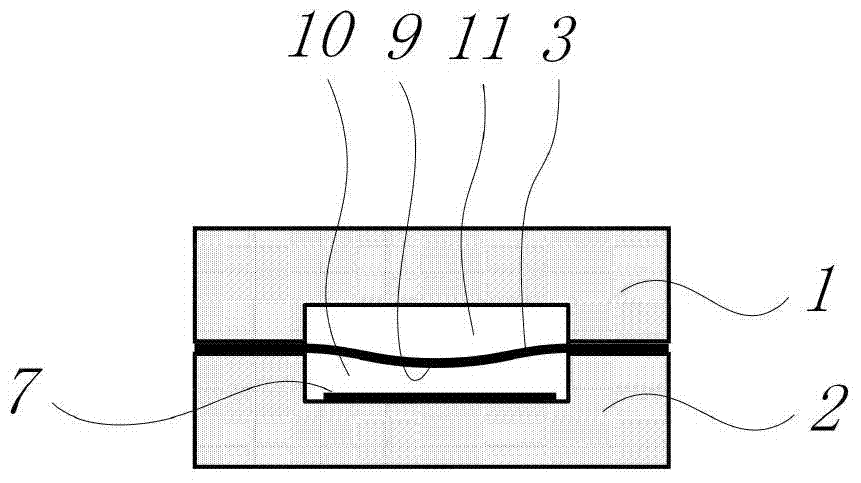
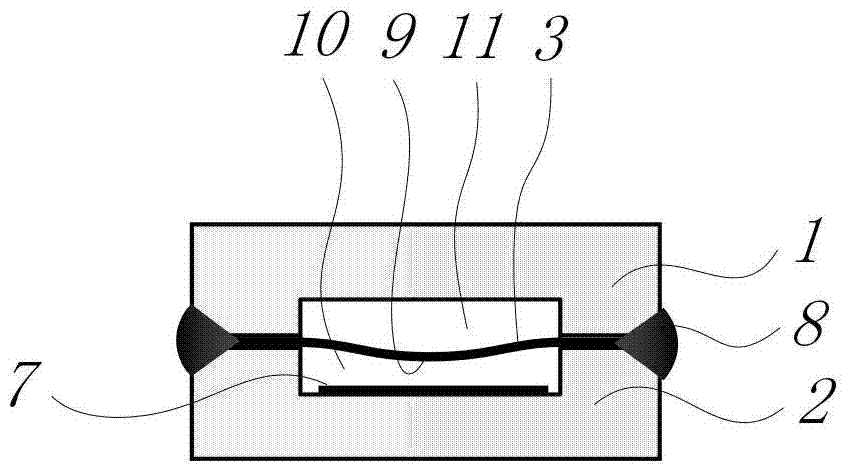
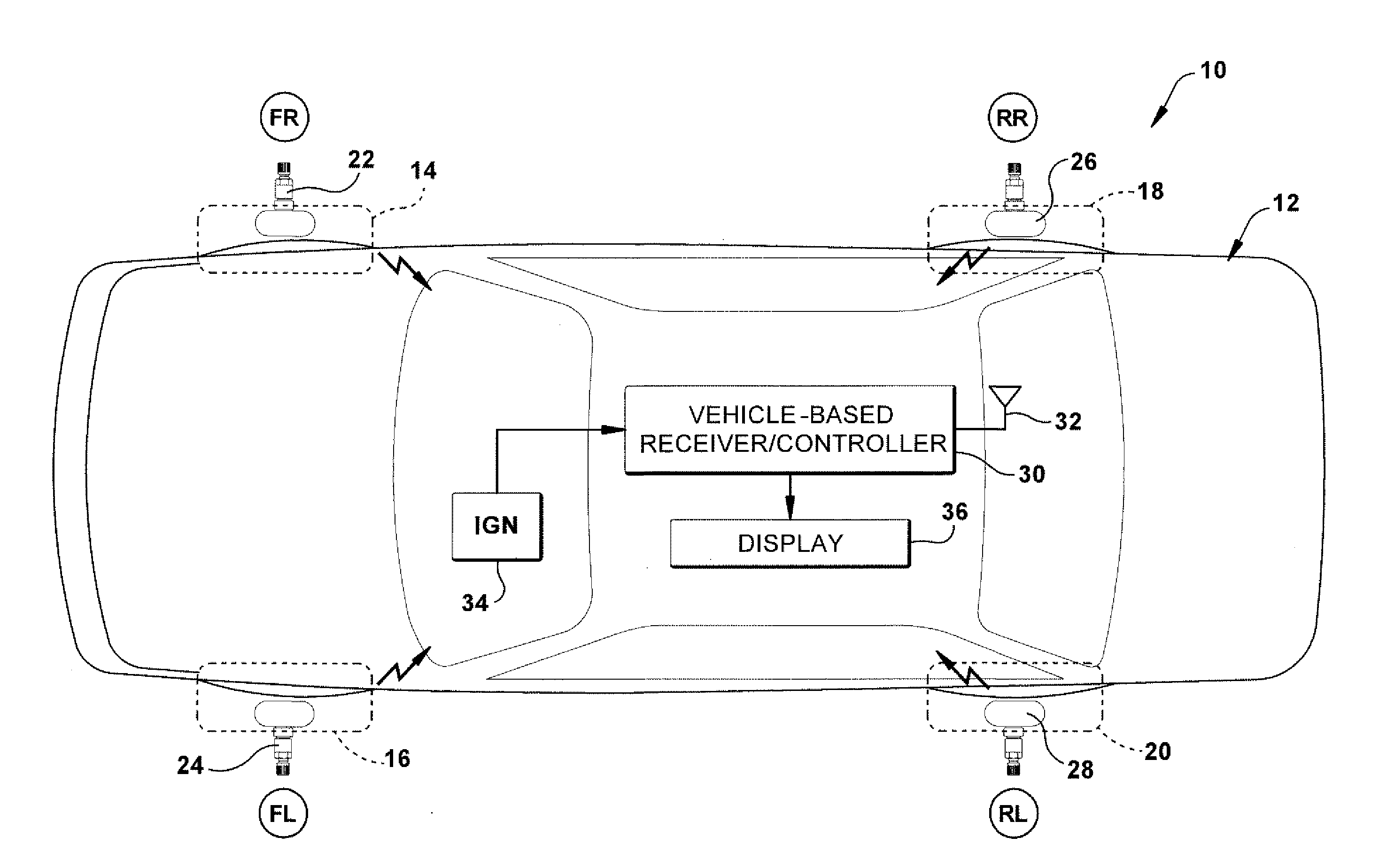
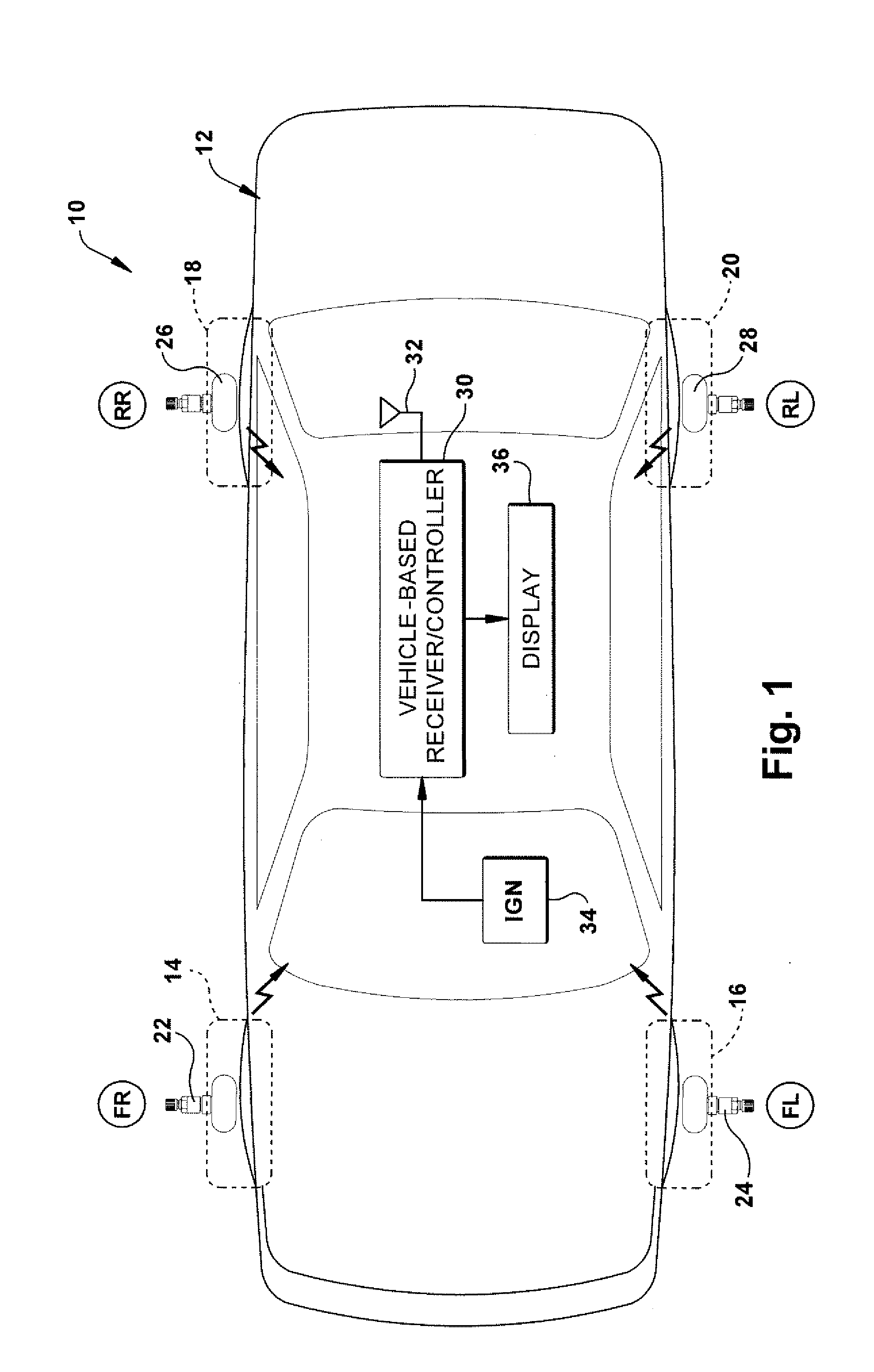
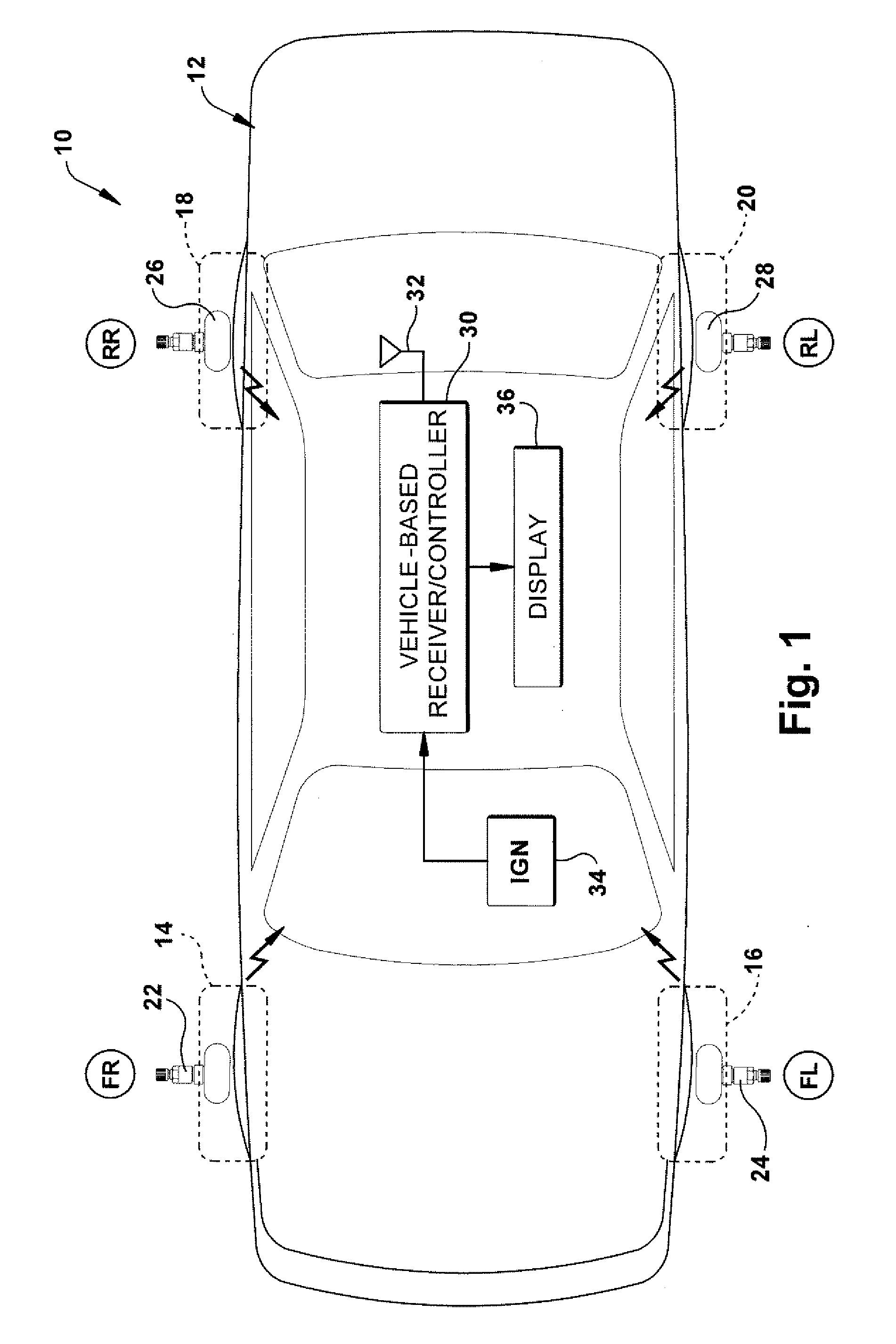
Method for processing information in a tire pressure monitoring system
InactiveUS6868358B2Improve utilizationAccurate detectionInflated body pressure measurementRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringTire-pressure monitoring system
A method of processing information in a tire pressure monitoring system includes the steps of: establishing a reference temperature; determining a pressure warning threshold at the reference temperature; measuring gauge pressure and gauge temperature within a tire cavity; correcting the gauge pressure to a filtered pressure value at the reference temperature using the Ideal Gas Law; and comparing the filtered pressure value against the pressure warning threshold to determine the necessity for a warning signal. In an advanced form of the invention, the method includes determining a pressure leak rate; predicting the time interval that the filtered pressure value will cross the pressure warning threshold at the leak rate and generating progressive warnings to the driver over the time interval. Fuzzy logic is used to quantify the probability of a warning state for each data point, allow for measurement error; and report the state of maximum probability to minimize the occurrence of false warning. A warning utility function is derived based upon a combination of the filtered pressure and leak rate.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
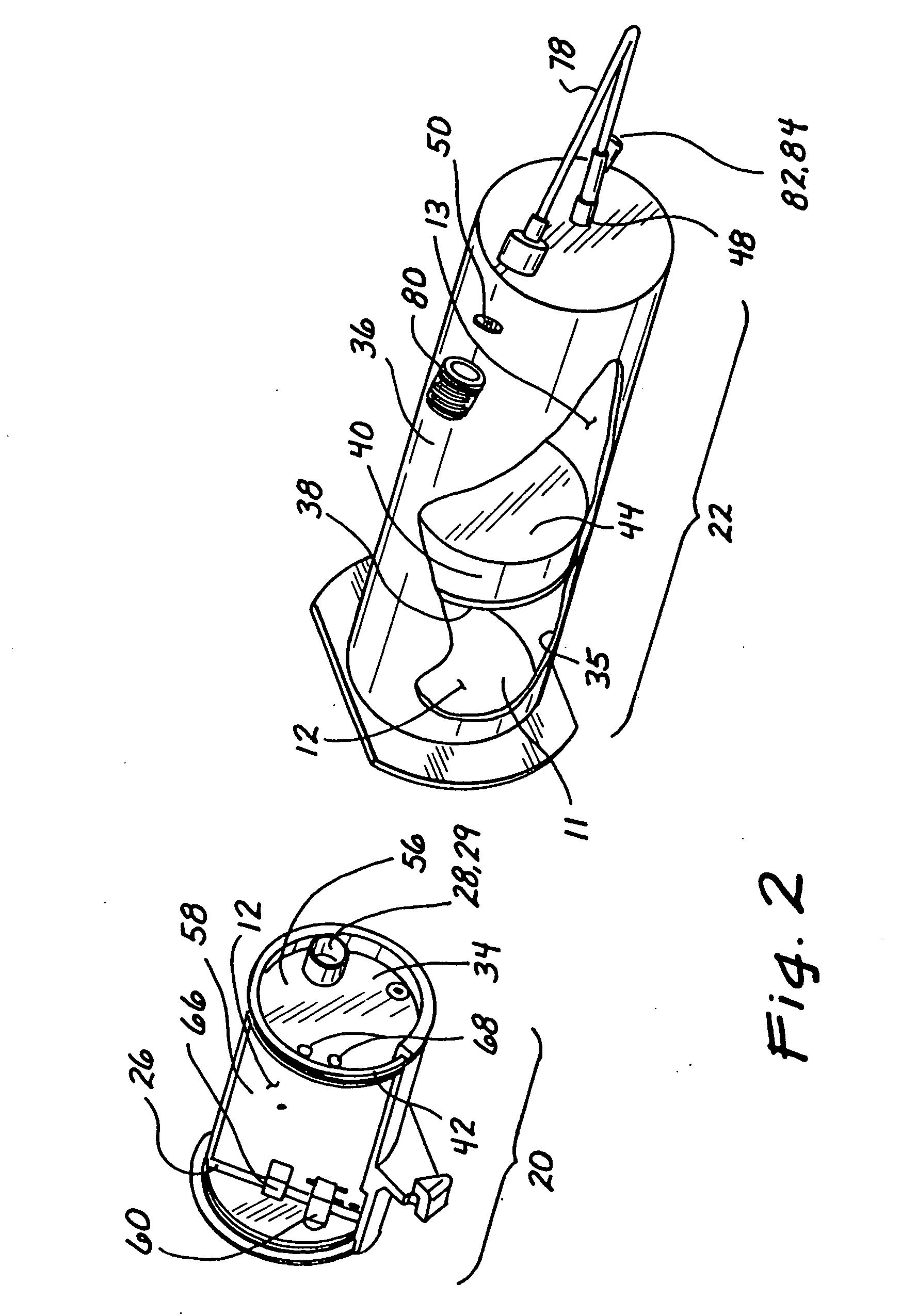
Infusion pump and method for use
InactiveUS7008403B1Small and lightLess componentsContracting/expanding measuring chambersVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusSolenoid valveContact method
A fluid dispensing system provides a non-contact method of monitoring the change in the fluid volume over time. This approach avoids the use of probes or sensors that come into direct contact with the fluid to be dispensed. The system comprises an apparatus comprising three chambers. The first chamber has a fixed volume and contains a pressurized gas. A solenoid valve is used to control the flow of gas from the first chamber into the second. The second chamber is sealed so that the combined mass of air in the first and second chambers remains fixed. The third chamber is adjacent to the second and contains medication in the form of incompressible fluid that is to be administered to a human or animal subject via a suitable delivery port. A piston is disposed between the second and third chambers and is movable responsive to the flow of gas into the second chamber to dispense fluid from the third chamber as desired. By sensing the pressure in the first and second chambers at any point in time, a processor is programmed to calculate the flow rate or dispensed volume of the fluid being delivered using principles derived from the Ideal Gas Law.
Owner:TANDEM DIABETES CARE INC
Infusion pump and method for use
InactiveUS20060150747A1Increased riskMeasurement is limitedContracting/expanding measuring chambersVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusSolenoid valveContact method
A fluid dispensing system provides a non-contact method of monitoring the change in the fluid volume over time. This approach avoids the use of probes or sensors that come into direct contact with the fluid to be dispensed. The system comprises an apparatus comprising three chambers. The first chamber has a fixed volume and contains a pressurized gas. A solenoid valve is used to control the flow of gas from the first chamber into the second. The second chamber is sealed so that the combined mass of air in the first and second chambers remains fixed. The third chamber is adjacent to the second and contains medication in the form of incompressible fluid that is to be administered to a human or animal subject via a suitable delivery port. A piston is disposed between the second and third chambers and is movable responsive to the flow of gas into the second chamber to dispense fluid from the third chamber as desired. By sensing the pressure in the first and second chambers at any point in time, a processor is programmed to calculate the flow rate or dispensed volume of the fluid being delivered using principles derived from the Ideal Gas Law.
Owner:TANDEM DIABETES CARE INC
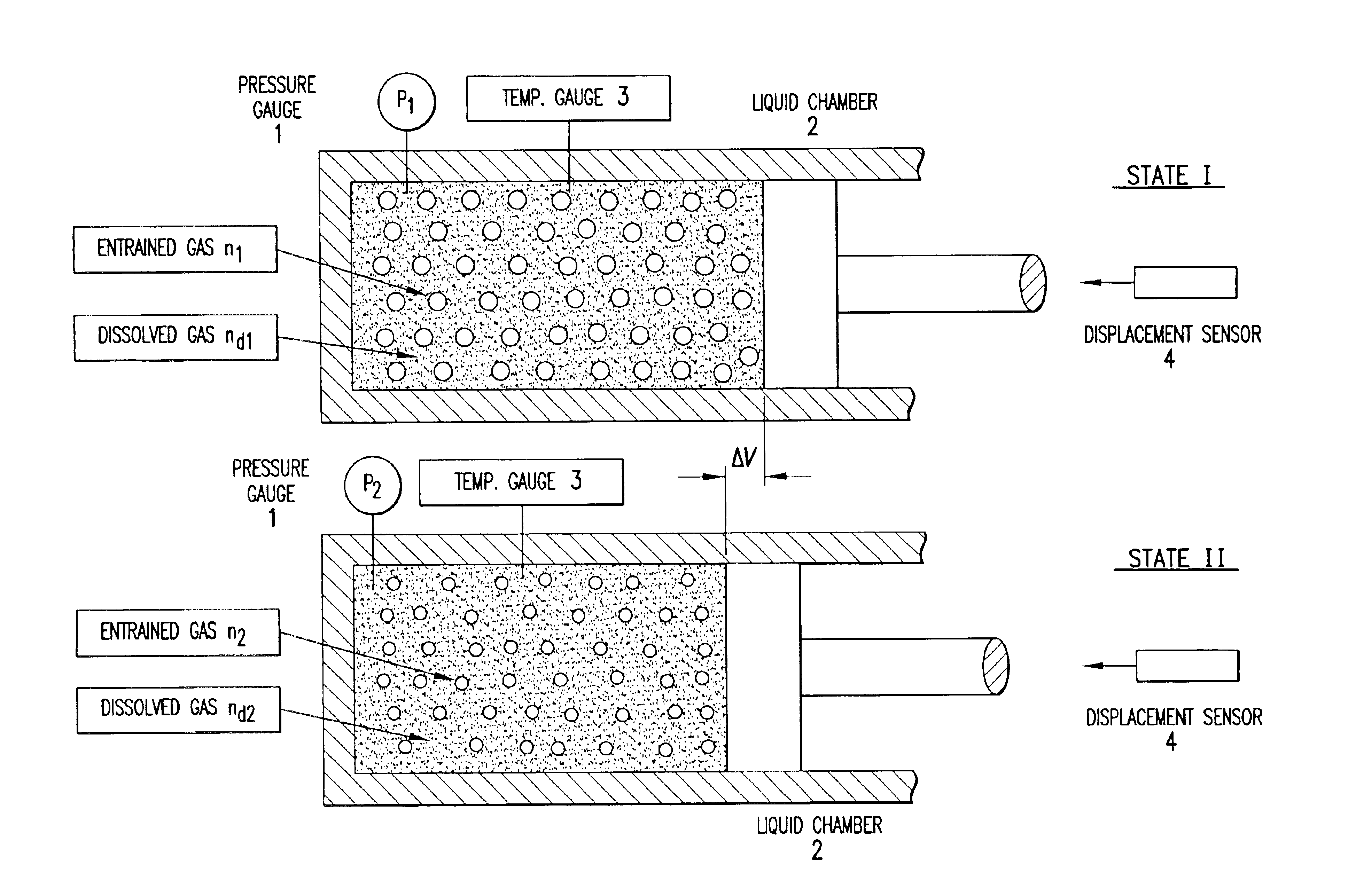
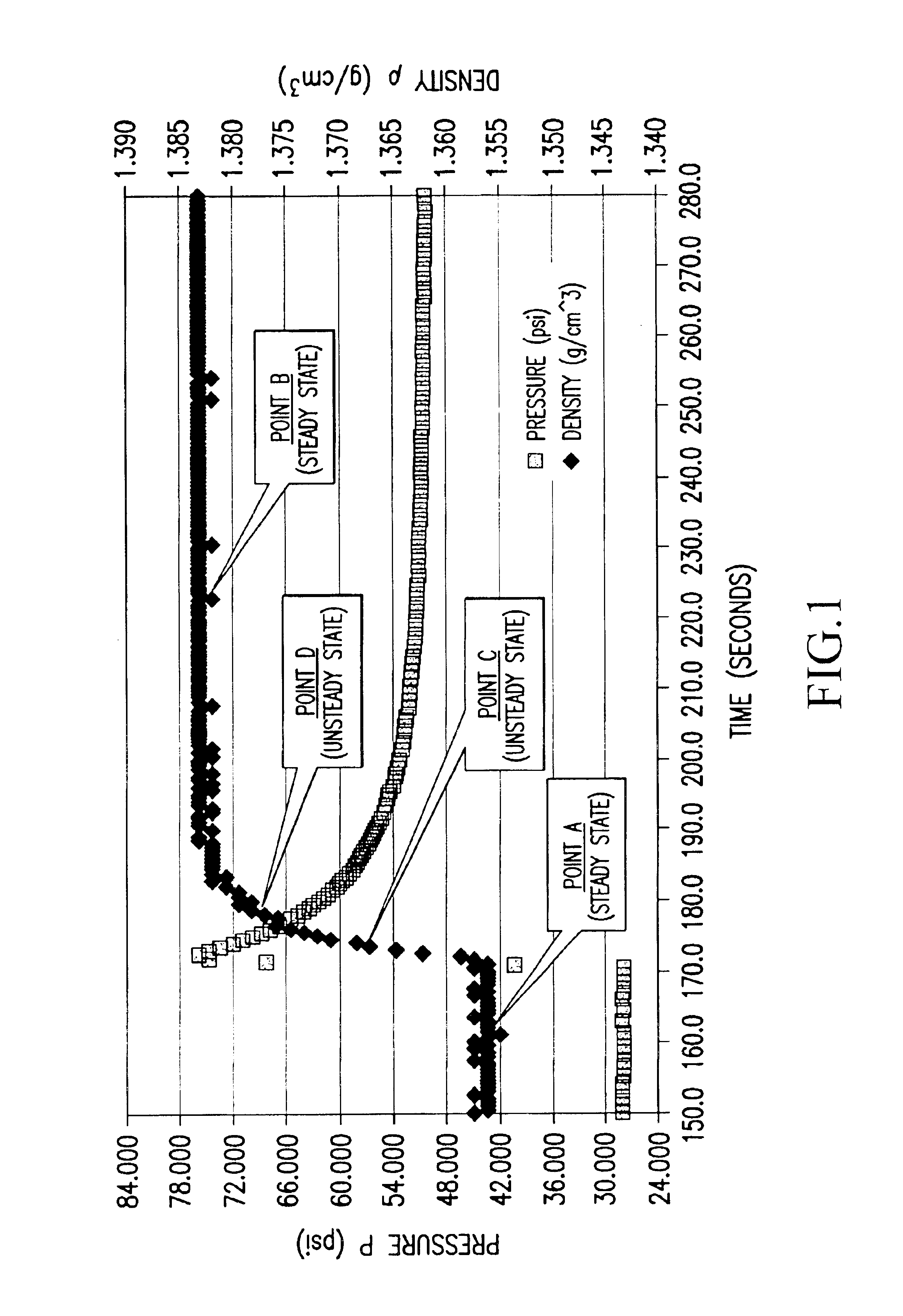
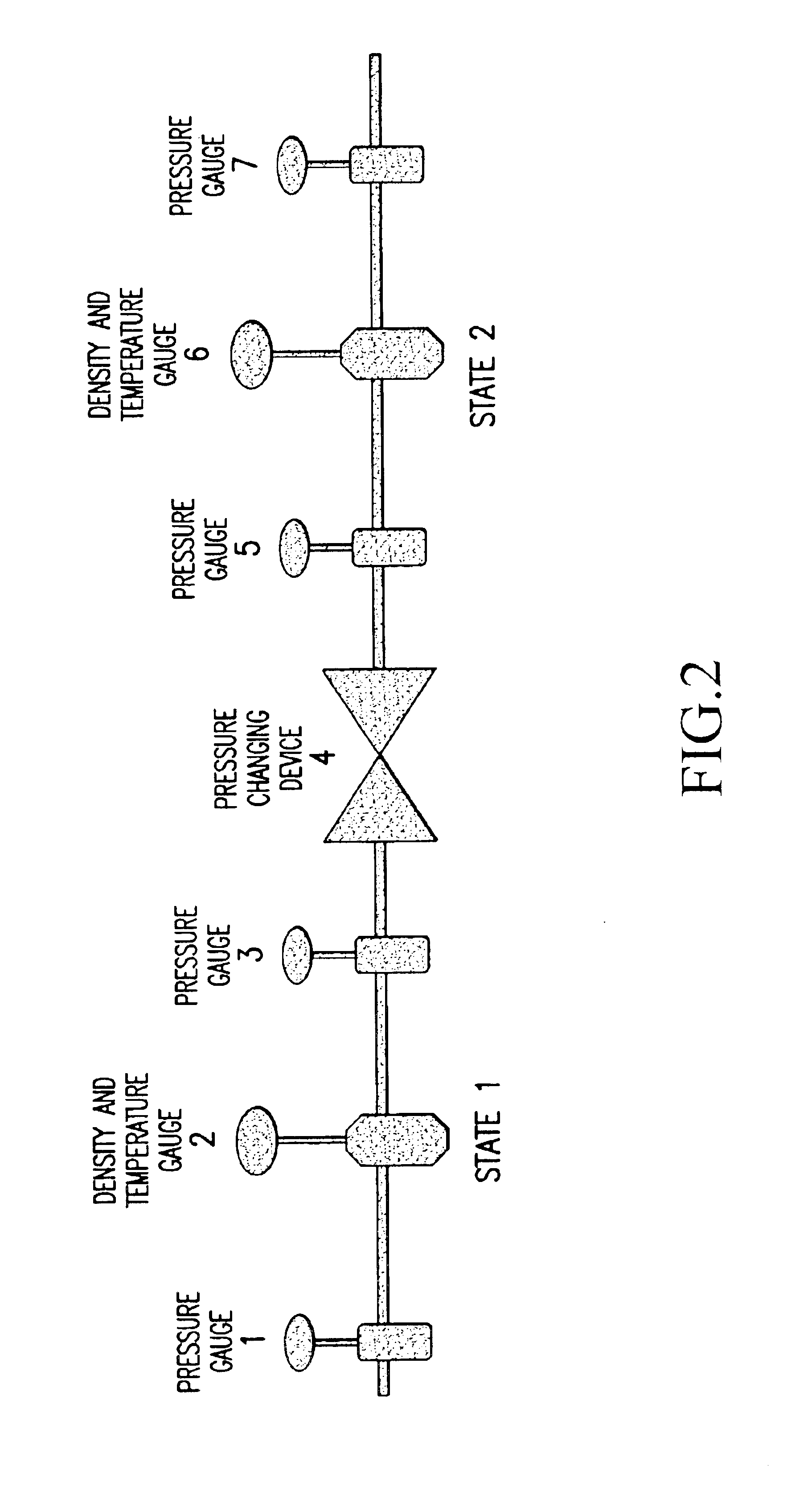
Real time determination of gas solubility and related parameters in manufacturing processes
InactiveUS6847898B1Easy to controlEasy to handleTesting beveragesSpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesSolubilityApparent density
Methods and apparatuses for determining entrained and / or dissolved gas content of gas-liquid mixtures. Data generated is used to control the True (air-free) or Apparent (air-containing) Density or Entrained Air content of liquids within optimum ranges, e.g. in paper coating processes and in the manufacture of food products, personal care products, pharmaceutical products, paints, petroleum blends, etc. For example, an indirect method of continuously determining the amount of gas entrained in a liquid, by: continuously measuring the temperature, flow rate, and apparent density of the mixture at two different pressure states, and calculating the volume percentage of the gas in the liquid by using equation (28) x%=VsVs+V(28)wherein V is the volume of the gas-free liquid calculated by equation (23) V=1ρ1-[P2P2-P1(1ρ1-1ρ2)-RTP2-P1g(Δ PQa)](23)in which P1 and P2 are two different ambient pressures and ΔP=P2−P1, ρ1 and ρ2 are apparent densities of the liquid sample measured at P1 and P2, respectively, R is the constant of the Ideal Gas Law, T is the liquid temperature, Q is the flow rate, g(ΔP / Qa) is a function for determining the amount of gas being dissolved between P2 and P1, and Vs is determined by equation (27) Vs=TsTP1P2Ps(P2-P1)(1ρ1-1ρ2)-RTsPs(P1P2-P1g(Δ PQa)-g(P1-PsQa)).(27)
Owner:APPVION INC
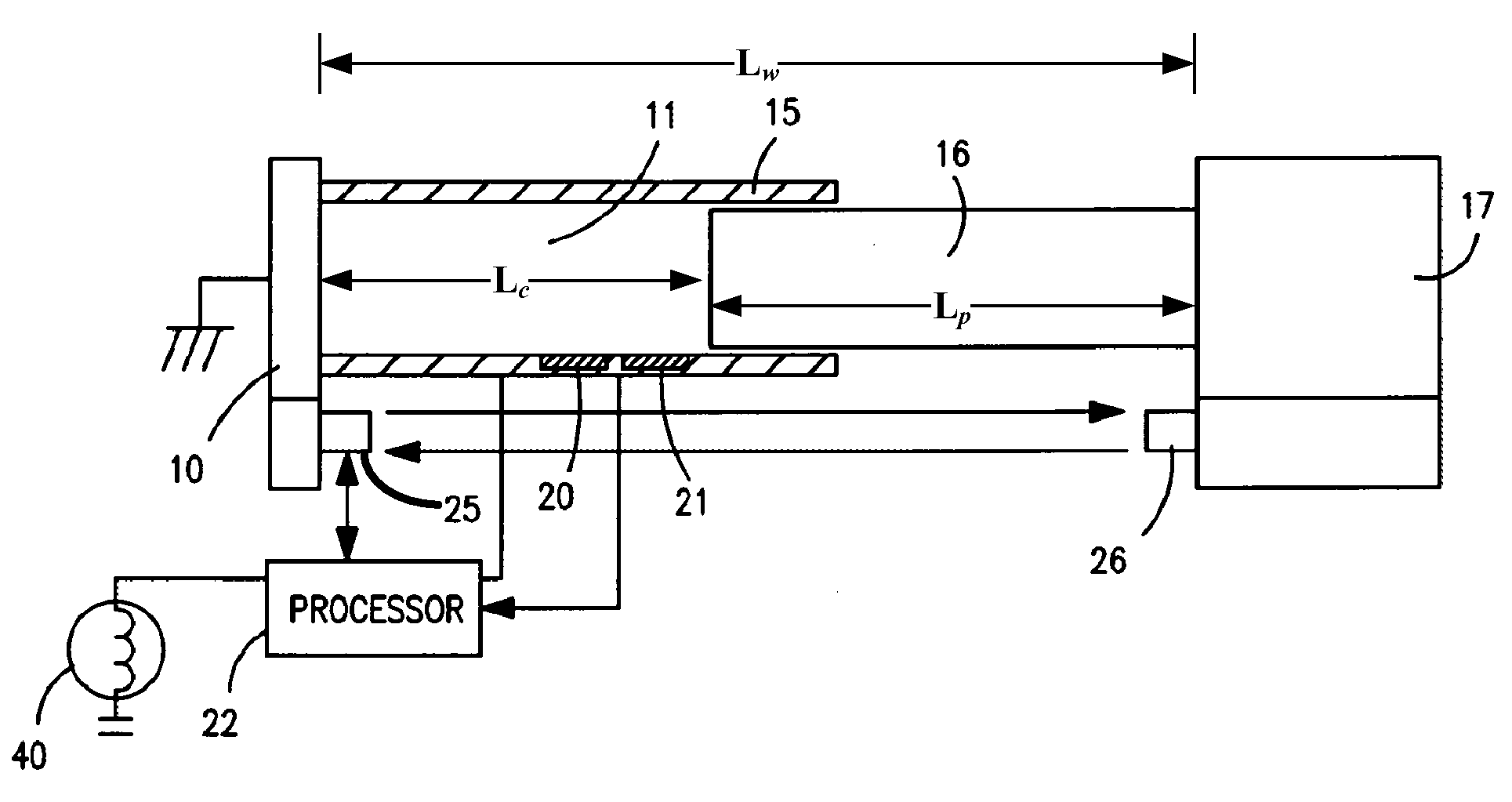
Leak detector for a pressurized cylinder
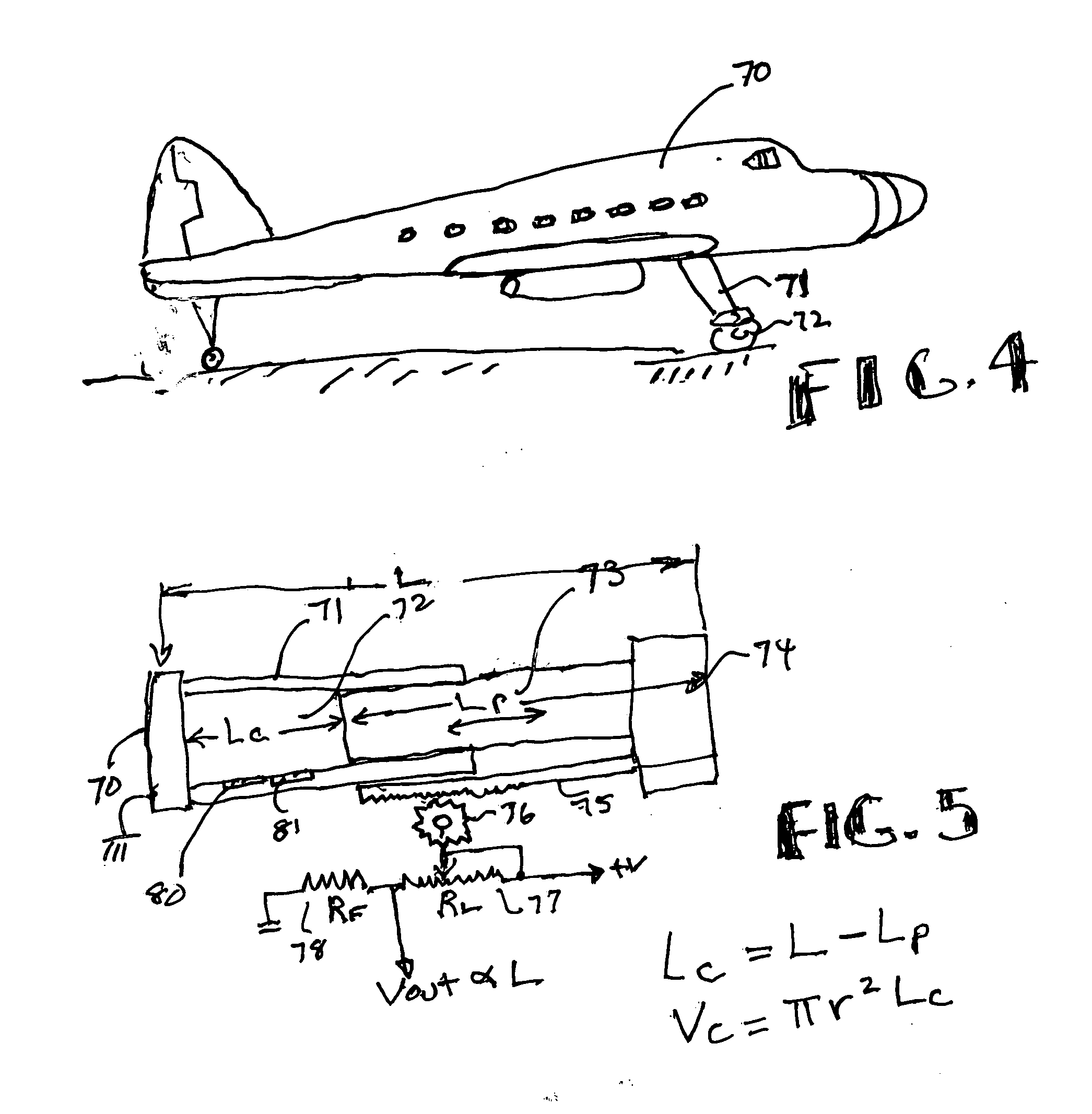
A leak detector apparatus for a pressurized cylinder having a cylinder of a radius (r) with a slidable piston in the cylinder with a gas filled chamber positioned between a cylinder end and the piston face. The length (L) of the chamber is calculated according to load changes on the piston where the volume (Vc) of the chamber changes. The pressure and temperature of the chamber are measured as well as the length. These values are inputted to a processor to solve the ideal gas law equation PV=nRT where a change in n for a change in length indicates a leak.
Owner:KULITE SEMICON PRODS
Instrument and method for measuring the volume of a hermetically sealed variable volume and pressure conforming container
An instrument and method for measuring the volume of a hermetically sealed, variable volume, pressure conforming container. The instrument includes a needle, a vacuum pump, a mass flow rate sensor and an integrator. The needle has a lumen operable for sealingly perforating a container and thereby placing the lumen of the needle in fluid communication with a retention chamber defined by the container. The vacuum pump evacuates the gaseous content from the retention chamber through the lumen defined by the needle and past a mass flow rate sensor for sensing mass flow rates pulled through the lumen and transmitting corresponding mass flow rate signals over time to the integrator. The integrator is programmed to integrate the received mass flow rate signals over time through achievement of an evacuated retention chamber to generate a total mass value, and calculate a volume from the total mass value employing the Ideal Gas Law.
Owner:MODERN CONTROLS
Leak detector for a pressurized cylinder
InactiveUS20080163668A1Machine part testingDetection of fluid at leakage pointIdeal gas lawMechanical engineering
A leak detector apparatus for a pressurized cylinder having a cylinder of a radius (r) with a slidable piston in the cylinder with a gas filled chamber positioned between a cylinder end and the piston face. The length (L) of the chamber is calculated according to load changes on the piston where the volume (Vc) of the chamber changes. The pressure and temperature of the chamber are measured as well as the length. These values are inputted to a processor to solve the ideal gas law equation PV=nRT where a change in n for a change in length indicates a leak.
Owner:KULITE SEMICON PRODS
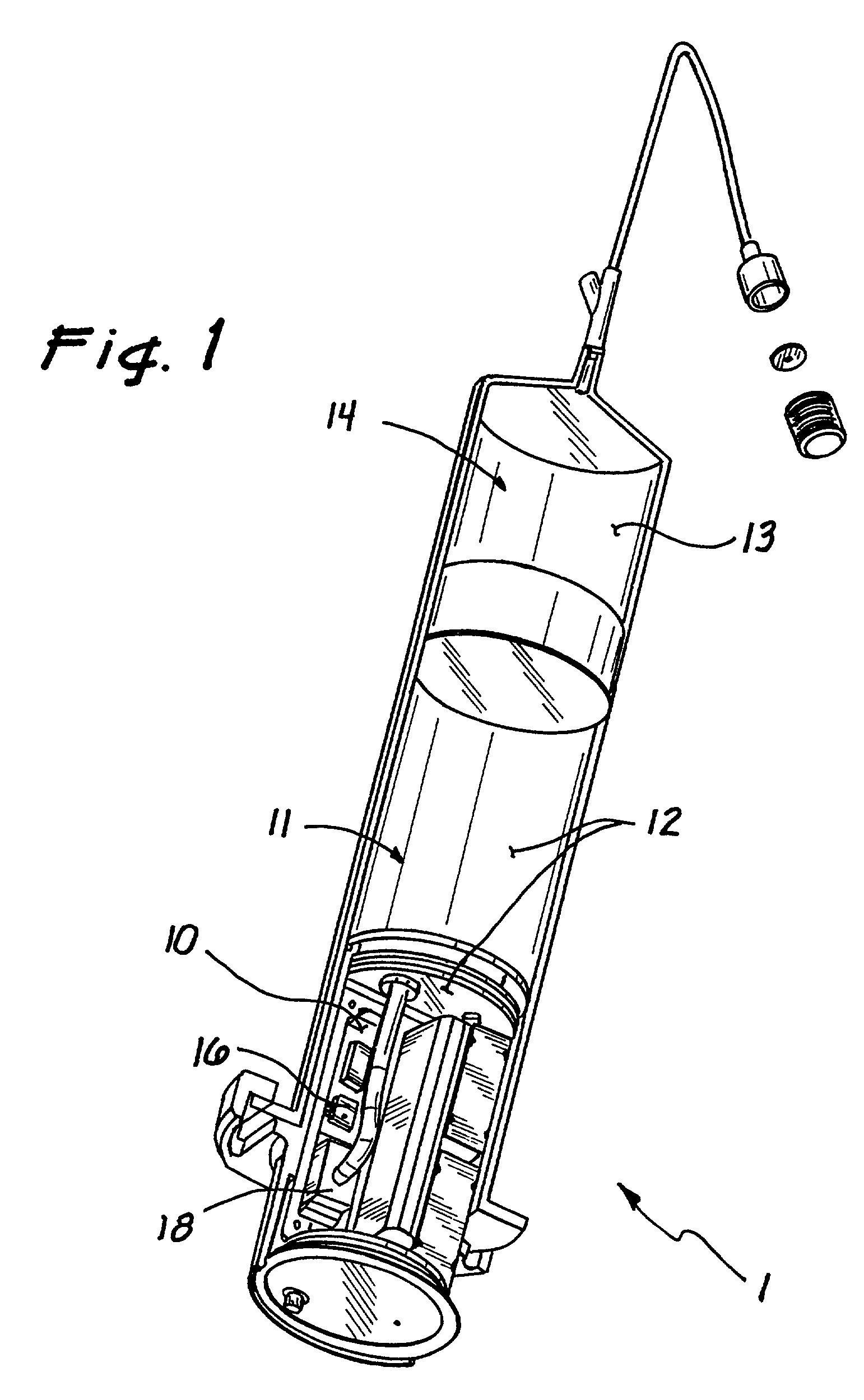
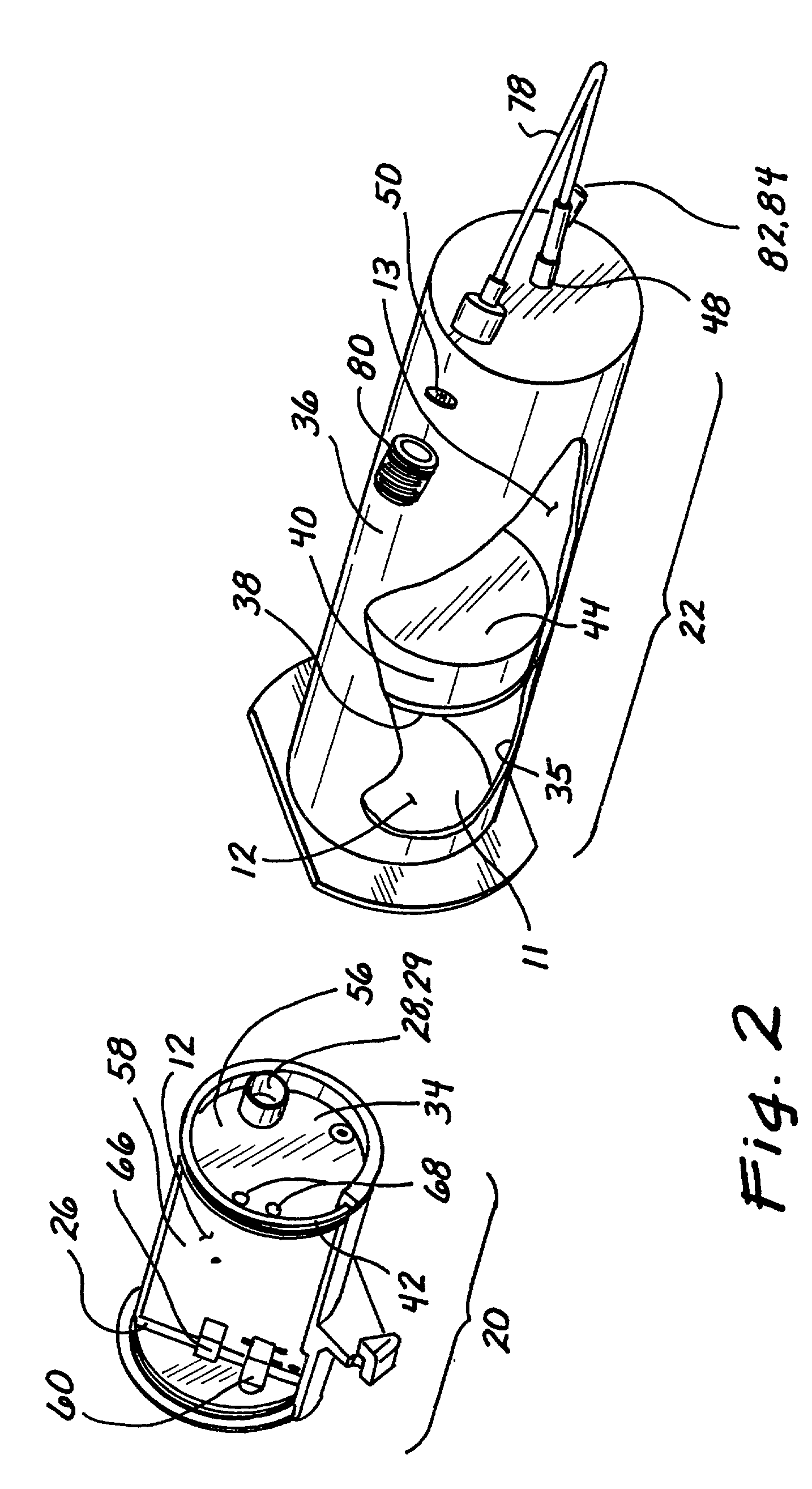
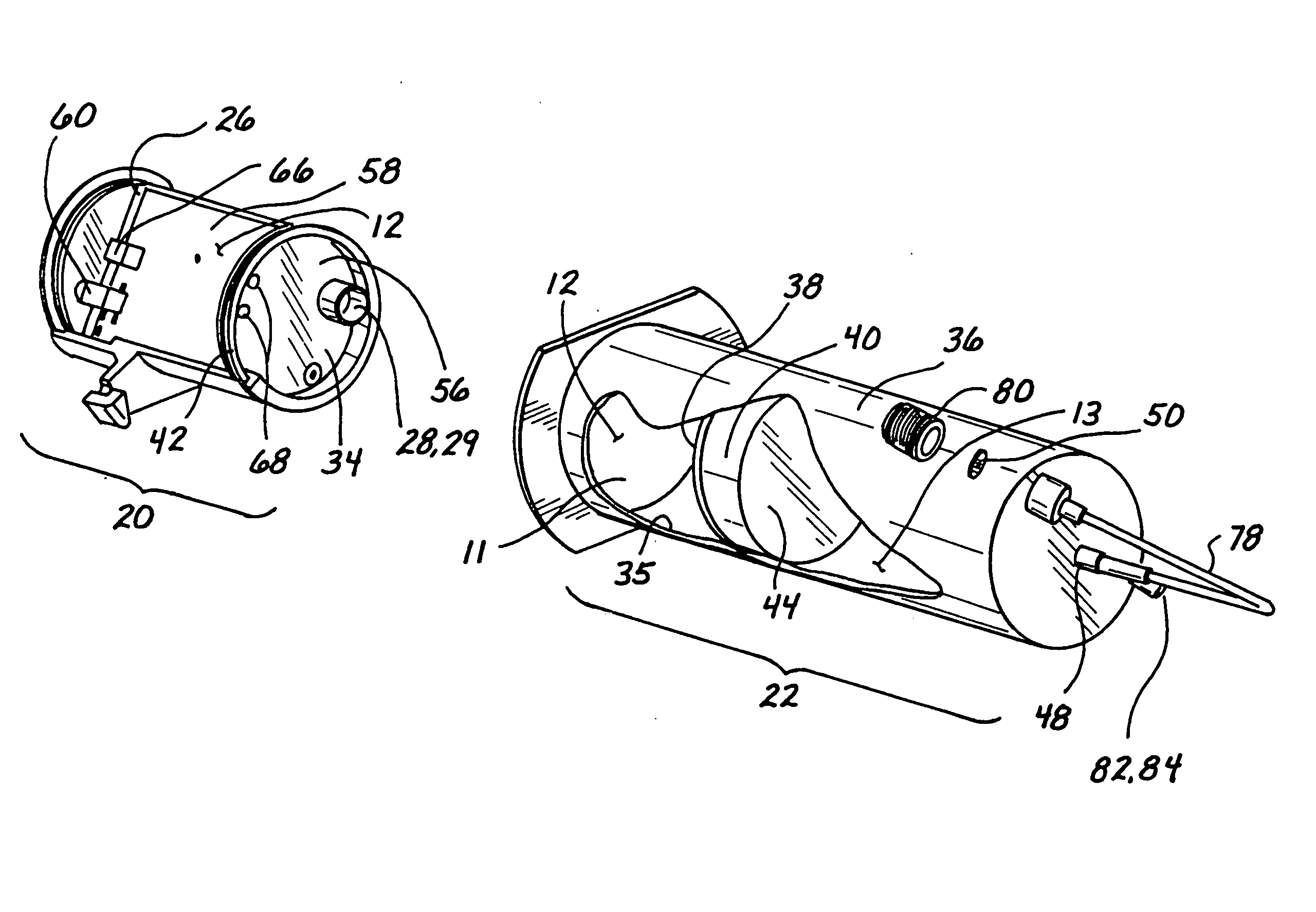
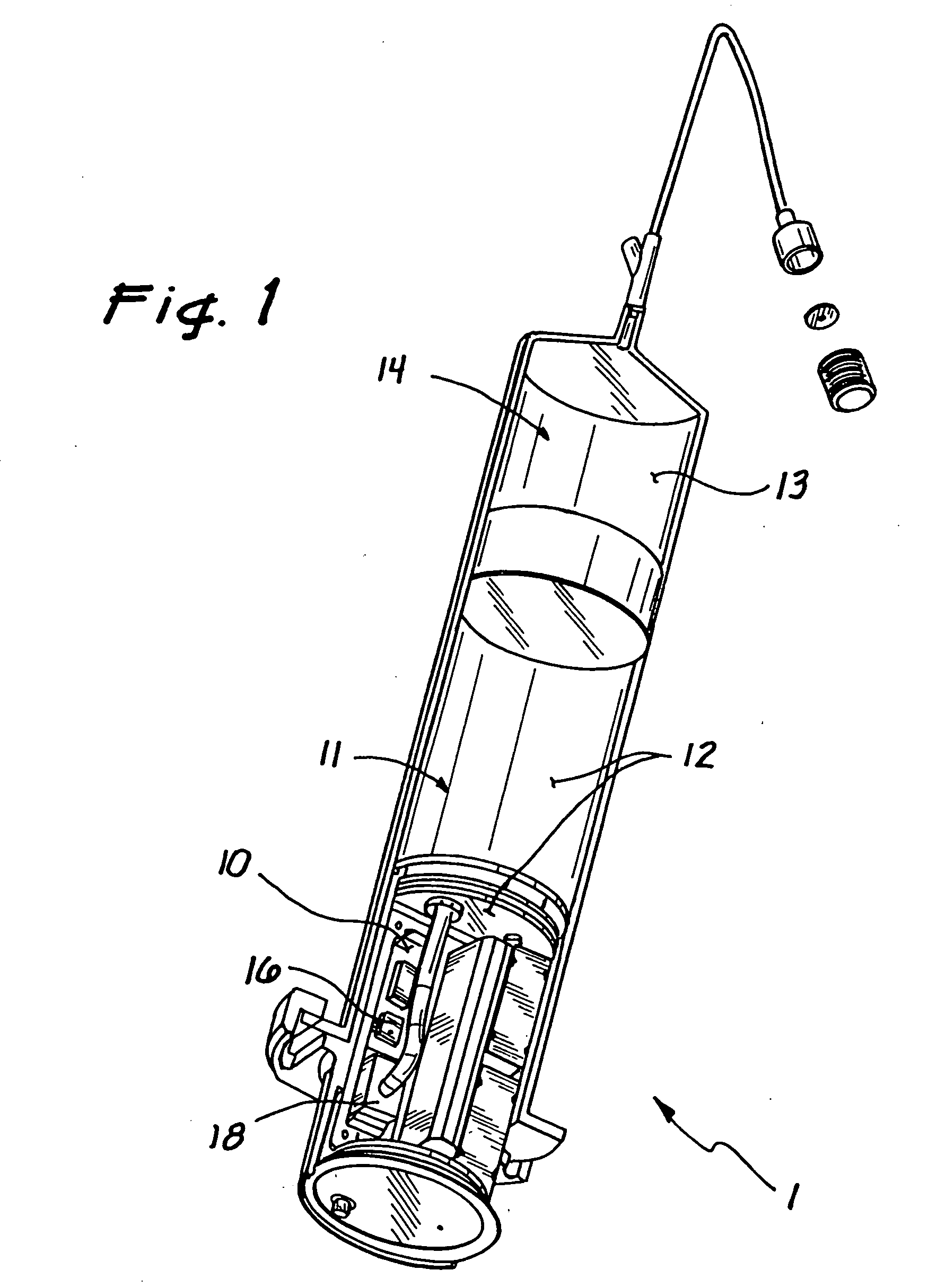
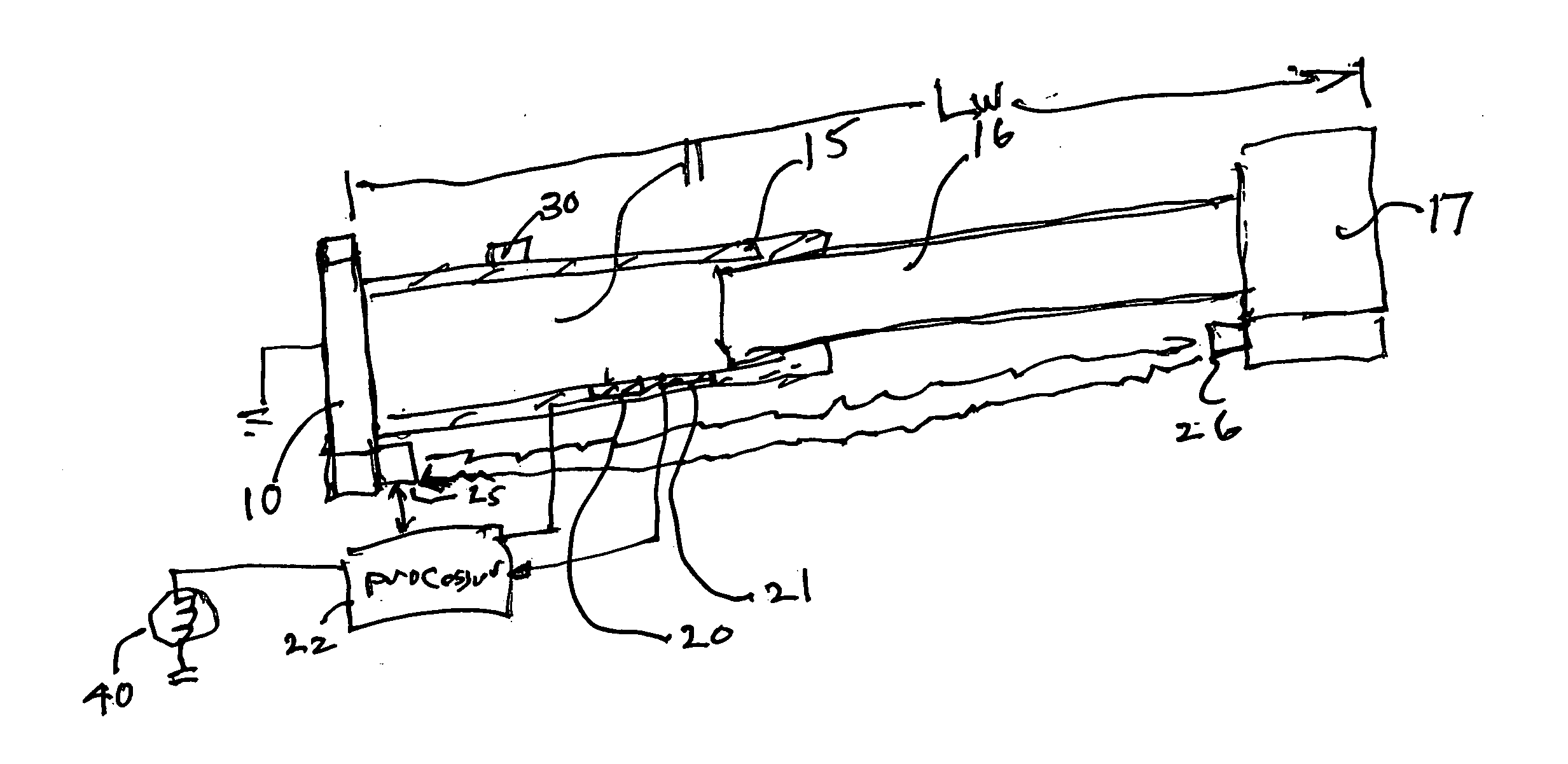
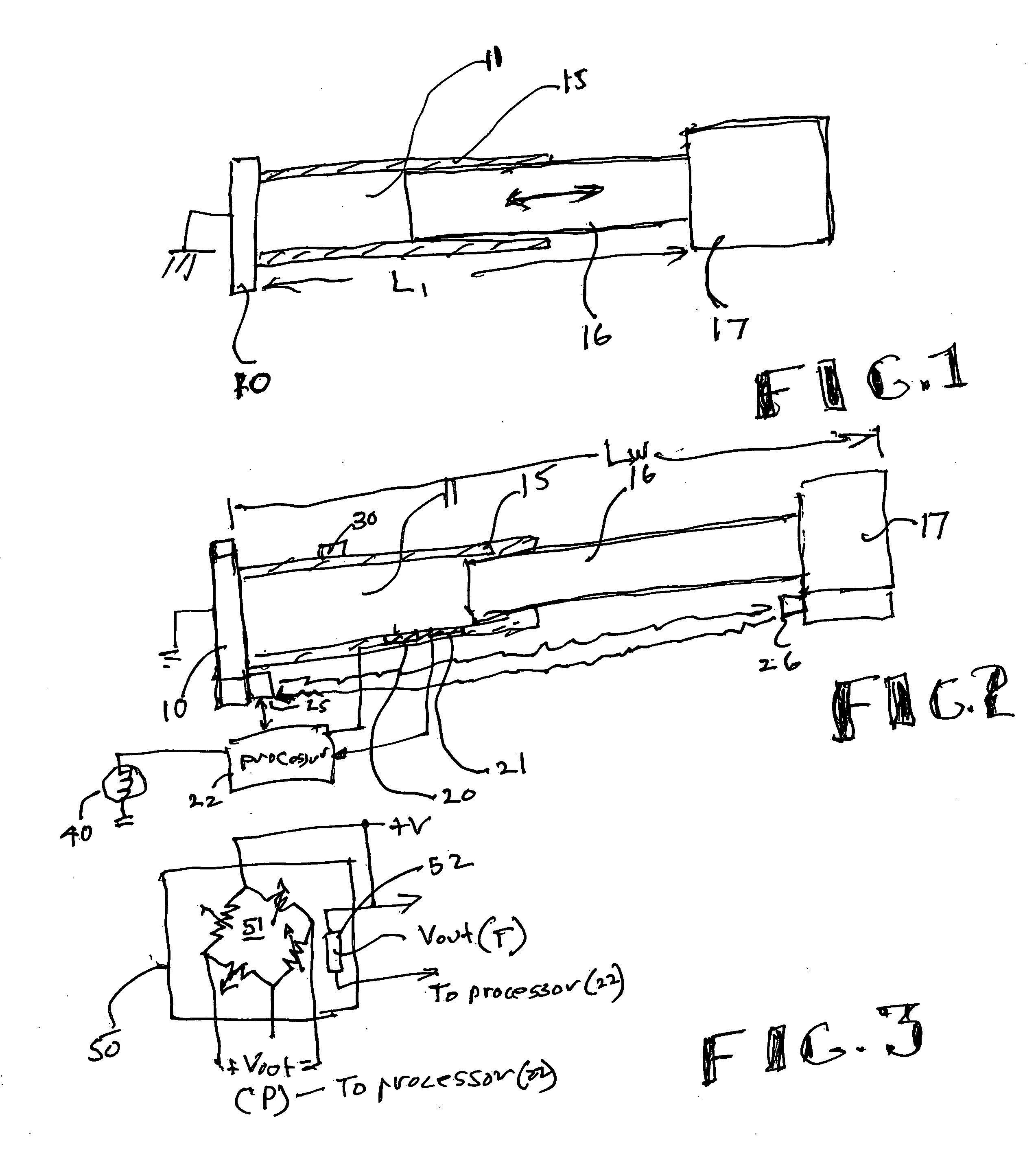
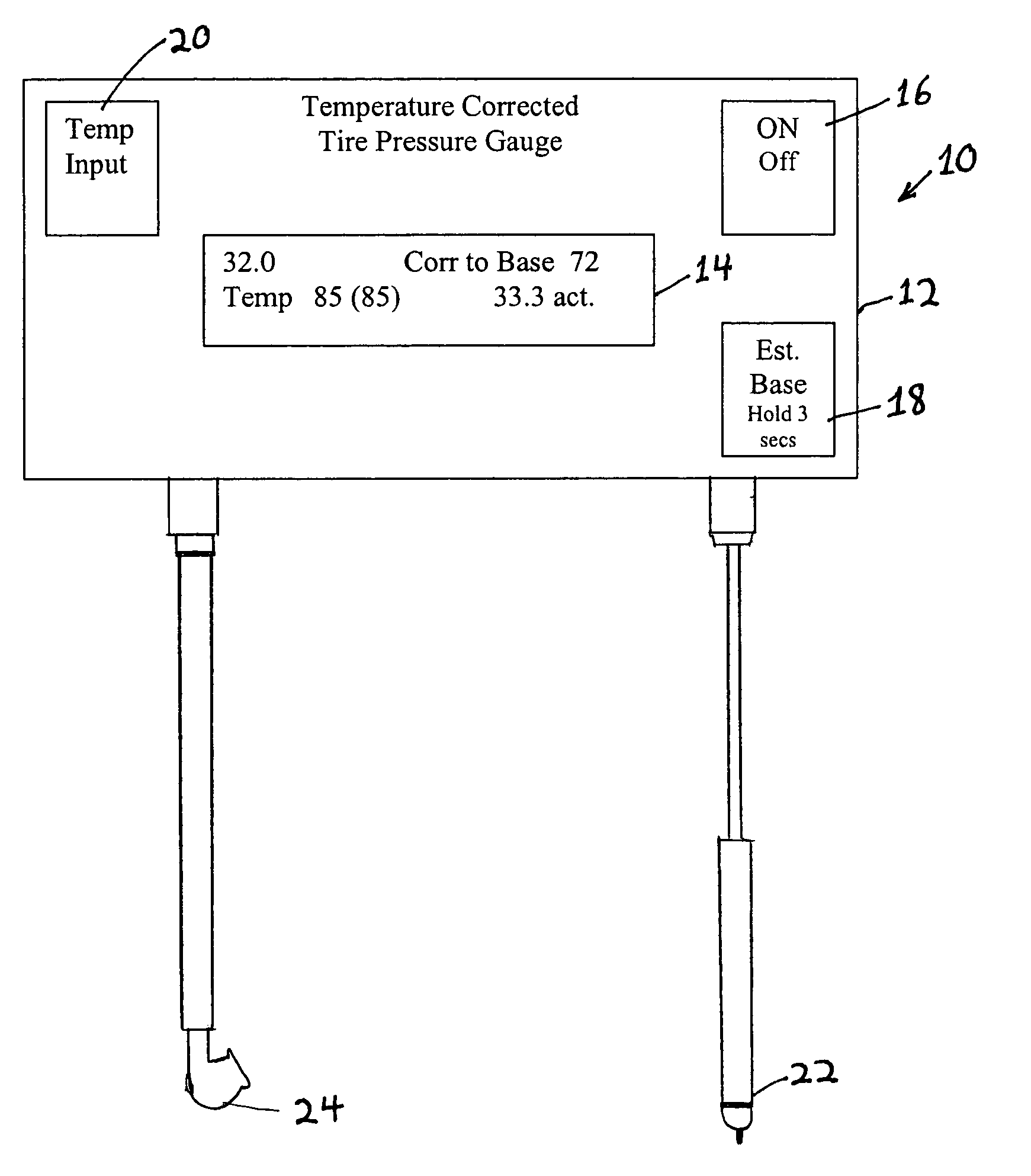
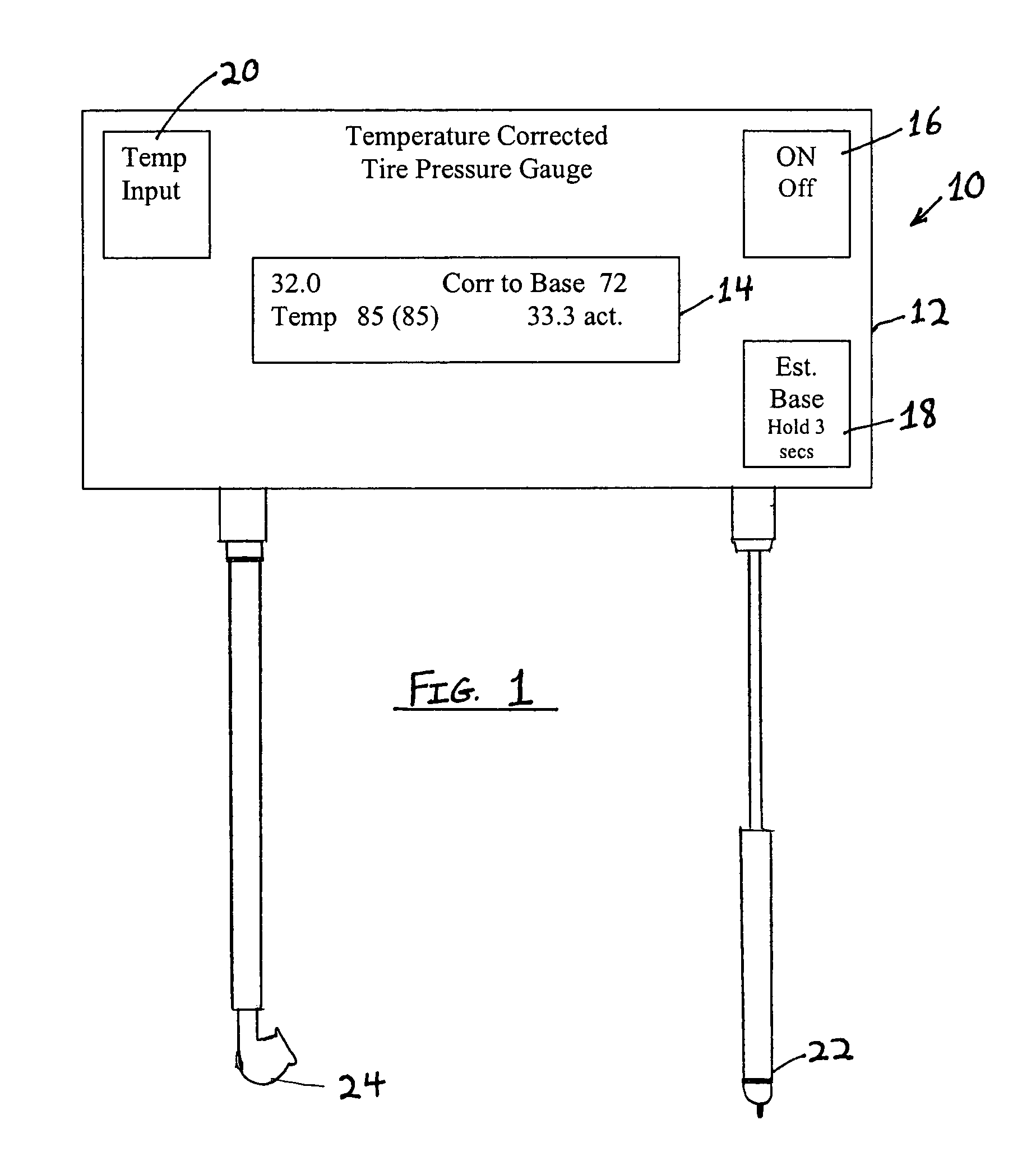
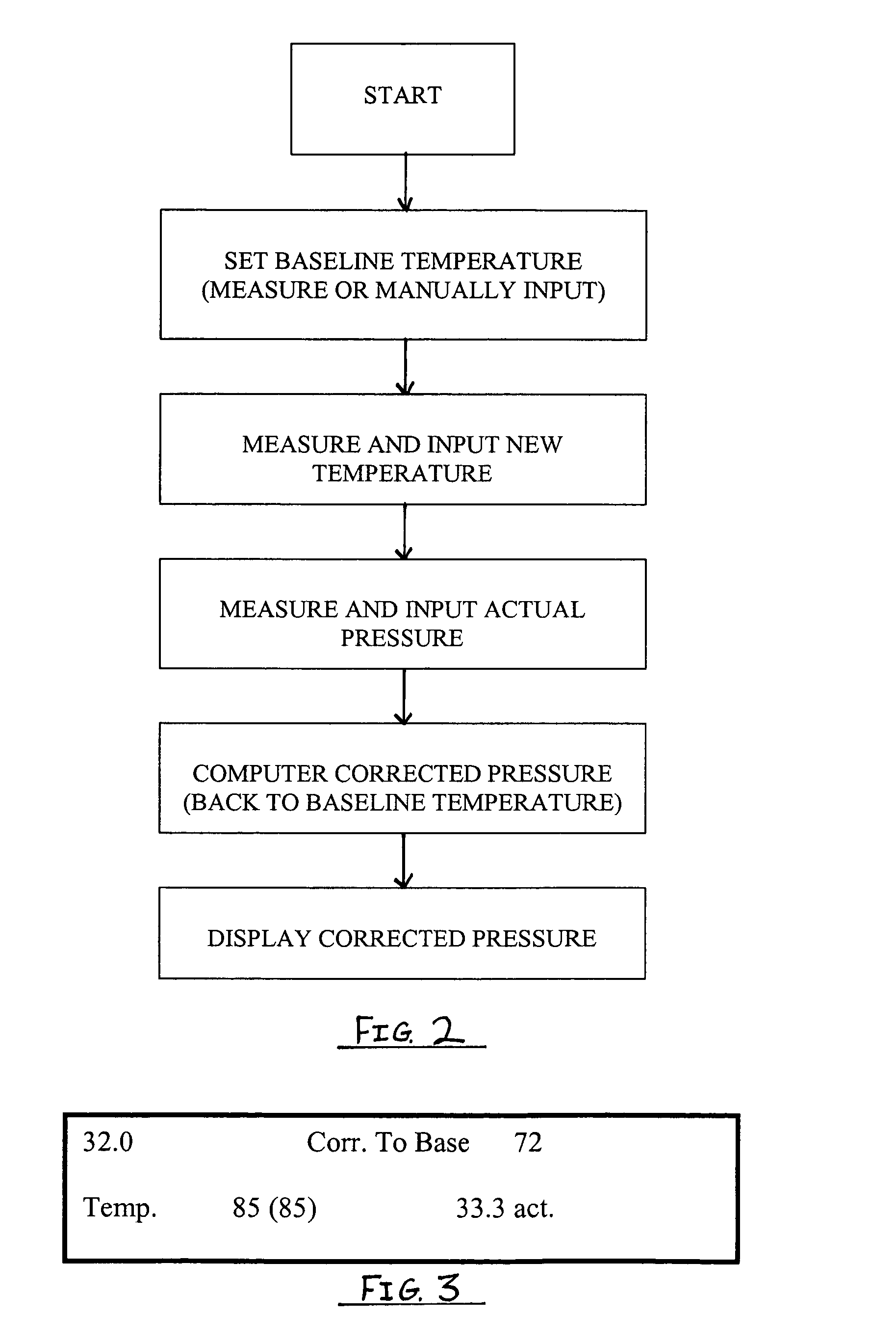
Temperature corrected tire pressure gauge and method
Disclosed is a device (10) and method for determining a temperature-corrected tire pressure. A preselected baseline temperature (26) is measured or selected. A second temperature (28) is measured using a temperature probe (22). An actual tire pressure (30) is measured (24). A programmed processor calculates and displays (14) a corrected tire pressure (32) corresponding to the baseline temperature (26) according the ideal gas law.
Owner:JAYNES HARRY M
Fiber optic temperature sensor based on sealed micro cavity gas thermal effect and manufacturing method of fiber optic temperature sensor
ActiveCN104515621AImprove consistencyWith mass productionThermometers using physical/chemical changesIdeal gas lawMaterials science
The invention discloses a fiber optic temperature sensor based on a sealed micro cavity gas thermal effect and a manufacturing method of the fiber optic temperature sensor. A sensor structure comprises a Fabry-Perot micro cavity and an air micro cavity, and the two micro cavities are partitioned through a thin silicon membrane. The atmospheric pressure environments of the two micro cavities are respectively controlled in the sensor manufacturing process, so that the two micro cavities have pressure difference. When the temperature changes, according to an ideal gas state equation, the atmospheric pressure inside the two micro cavities is changed, so that a silicon wafer in the middle of the two micro cavities is deformed because of the change of the pressure difference. At the same time the inner surface of the silicon wafer and the reflection surface inside the Fabry-Perot micro cavity form a low-fineness Fabry-Perot interferometer, the deformation of the membrane is just the length change of the Fabry-Perot micro cavity, and temperature measurement is achieved by demodulating the length change of the cavity. Compared with the prior art, the temperature sensitivity of the sensor disclosed by the invention can be flexibly controlled by designing the diameter, the temperature and the pressure difference of the silicon wafer, and expected temperature sensitivity is achieved. In addition, the in-batch production of the senor is beneficial to cost reduction, and commercialization can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
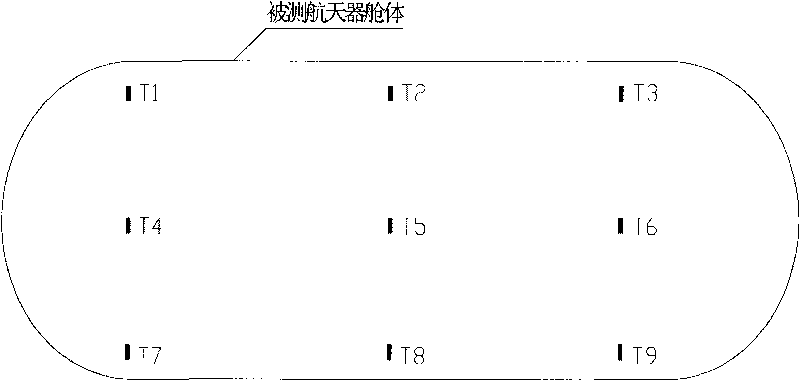
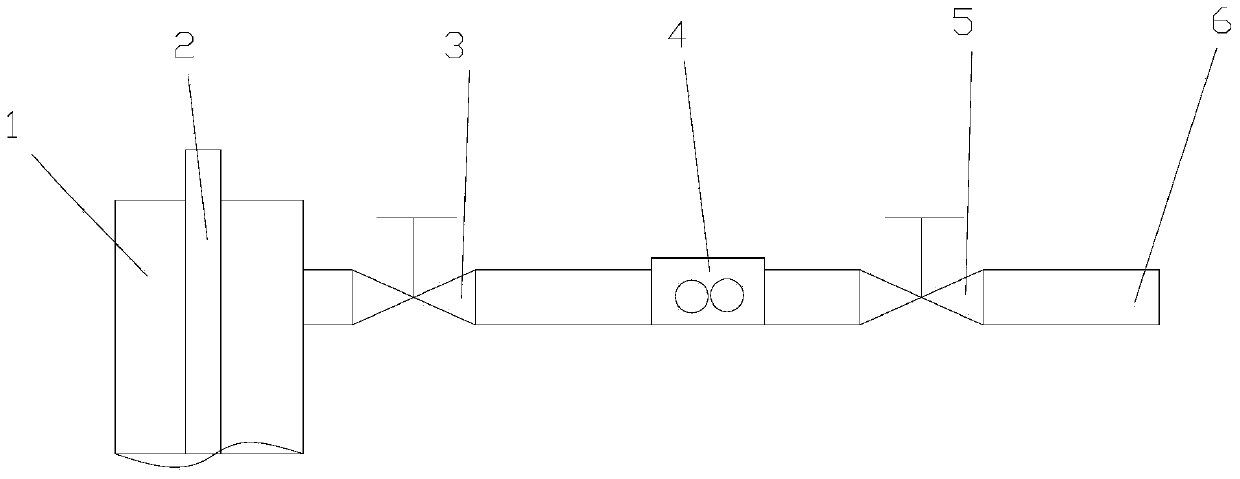
Method for detecting leakage of spacecraft cabin by differential pressure
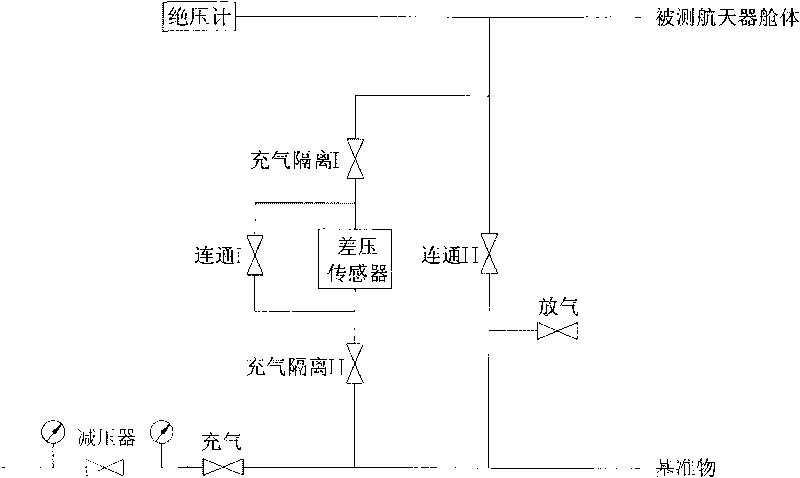
InactiveCN101738296AReduce differential pressureAccurate leak rateMeasurement of fluid loss/gain ratePrimary standardDifferential pressure
The invention provides a method for detecting leakage of a spacecraft cabin by differential pressure. The method comprises the following processes: aerating, balancing, testing and gas deflating. In the method, a small-volume primary standard substance is put in a large-volume spacecraft cabin; standards and a temperature inside the measured cabin are measured when the differential pressure is measured; actually measured differential pressure is compensated by a temperature lagging for some time according to an ideal gas state equation; and finally integral leakage of the measured spacecraft cabin is acquired. In a gas path of the method, an aerating isolating valve is arranged on both sides of a differential pressure sensor respectively and used for avoiding an overrange phenomenon of the differential pressure sensor in the process of aerating or deflating.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Real time determination of gas solubility and related parameters in manufacturing processes
InactiveUS20050109078A1Easy to controlEasy to handleAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting beveragesApparent densitySolubility
Owner:APPVION OPERATIONS INC
Method for the onboard determination of the volatility of a fuel
InactiveUS20090114288A1Less fuel excessElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMobile vehicleIn vehicle
Method for the determination of the volatility of a fuel stored in a fuel tank which is part of a fuel system controlled by a fuel system control unit (FSCU) and comprising pressure, temperature and fuel level sensors, according to which the FSCU uses the ideal gas law and measurements performed by the sensors in order to predict the distillation curve and / or the Driveability Index (DI) of the fuel; use of said method for adjusting the amount of fuel to be injected in a mixing chamber of an internal combustion engine of a motor vehicle.
Owner:INERGY AUTOMOTIVE SYST RES (SA)
Leak detection method for floating air bag
InactiveCN103674452ASuitable for leak detectionQuantitative measurement of leakageMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateEngineeringIdeal gas law
The invention discloses a leak detection method for a floating air bag. The leak detection method for the floating air bag is characterized in that the air bag is controlled to leak quantitatively at different leakage rates, an equation: deltaV=alpha0+alpha1(T / P)+alpha2(T / P)2+ ... + alphan(T / P)n, is built according to an ideal air state equation; the leak detection method for the floating air bag comprises: detecting air bag pressure P and air bag temperature T in any state, and then working out the volume deltaV of leak air according to the equation. According to the leak detection method for the floating air bag, leakage can be judged in a simple and rapid manner, and the leakage rate can be concretely detected.
Owner:滁州汽车与家电技术及装备研究院
Air supply system of semiconductor process equipment and its gas flow calibration method
ActiveCN101369514ALong calibration timeLow costFlow control using electric meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess equipmentIsolation valve
The invention discloses a gas supply system of a semiconductor processing device and a method for calibrating gas flow, the gas supply system comprises a gas path box for supplying gas to a reaction chamber, an mass flow controller (MFC) and a pipeline for cleaning the gas path box are provided on the gas path box, a calibrating isolation valve is provided on the pipeline for cleaning the gas path box and can insulate and close the pipeline for cleaning the gas path box, gas with a certain flow is supplied into the pipeline for cleaning the gas path box by the MFC, then actual flow of the gasentered into the pipeline for cleaning the gas path box can be calculated according to an ideal gas state equation, comparing with the actual flow of the gas and a setting flow of the MFC, the gas flow of the gas supply system can be calibrated based on the compared result. The costs of the system and the method are low, the calibrating times of the system and the method are short.
Owner:BEIJING NAURA MICROELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
Method and device for testing content of easily-volatile matters in explosive
The invention discloses a method for testing the content of easily-volatile matters in explosive, and provides a device improved based on a microcalorimeter correspondingly, wherein the device is formed by arranging a presser sensor used for measuring the real-time pressure in a sample cell on the sample cell of the microcalorimeter and arranging a reading device, a searching device and a comparing device on a control system of the microcalorimeter. In testing, the explosive is put into the sample cell firstly, and after vacuumization is carried out, the device provided by the invention is started, parameters including the start temperature, the temperature rise amplitude, the reaction judgment sensitivity, the constant temperature time, the waiting time, the reaction termination conditions and the like of the microcalorimeter are set, the pressure change and the temperature rise rate change in the sample cell are recorded, and then the content of the volatile matters is obtained by an ideal gas state equation. According to the invention, by analyzing the relationship between the gas discharge quantity and the heat flux change, the content of the easily-volatile matters in the explosive can be effectively tested.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Load detection method based on tyre pressure, and bus passenger flow volume computing method and device based on tyre pressure detection
ActiveCN104132722AReduce estimation errorAccurate estimateSpecial purpose weighing apparatusRelational modelCarrying capacity
The invention relates to the technical field of traffic transportation, in particular to a load detection method based on tyre pressure, and a bus passenger flow volume computing method and device based on tyre pressure detection. The bus passenger flow volume computing method and device based on tyre pressure detection solve the complex problem that the volume of passengers getting on and getting off a bus can not be accurately detected in the prior art, changes of the passenger flow volume are estimated more accurately on the basis of the functional relation between tyre pressure and a load, optimized dispatching of the bus and reasonable programming of bus resources are facilitated, and the effects of energy conservation and emission reduction are achieved. The relation between the gas volume change and the pressure intensity change is obtained by analyzing stress on tyres of the bus and the ground, the relation between the load delta M and the current tyre pressure P1 is solved finally, then a model of the relation between the carrying capacity and the passenger capacity of the bus is built, and consequently the relation between the tyre pressure change and the passenger capacity change is obtained.
Owner:肖峰
Method and apparatus for determining tire condition using ideal gas law
InactiveUS20140039752A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDisplay deviceLaws of thermodynamics
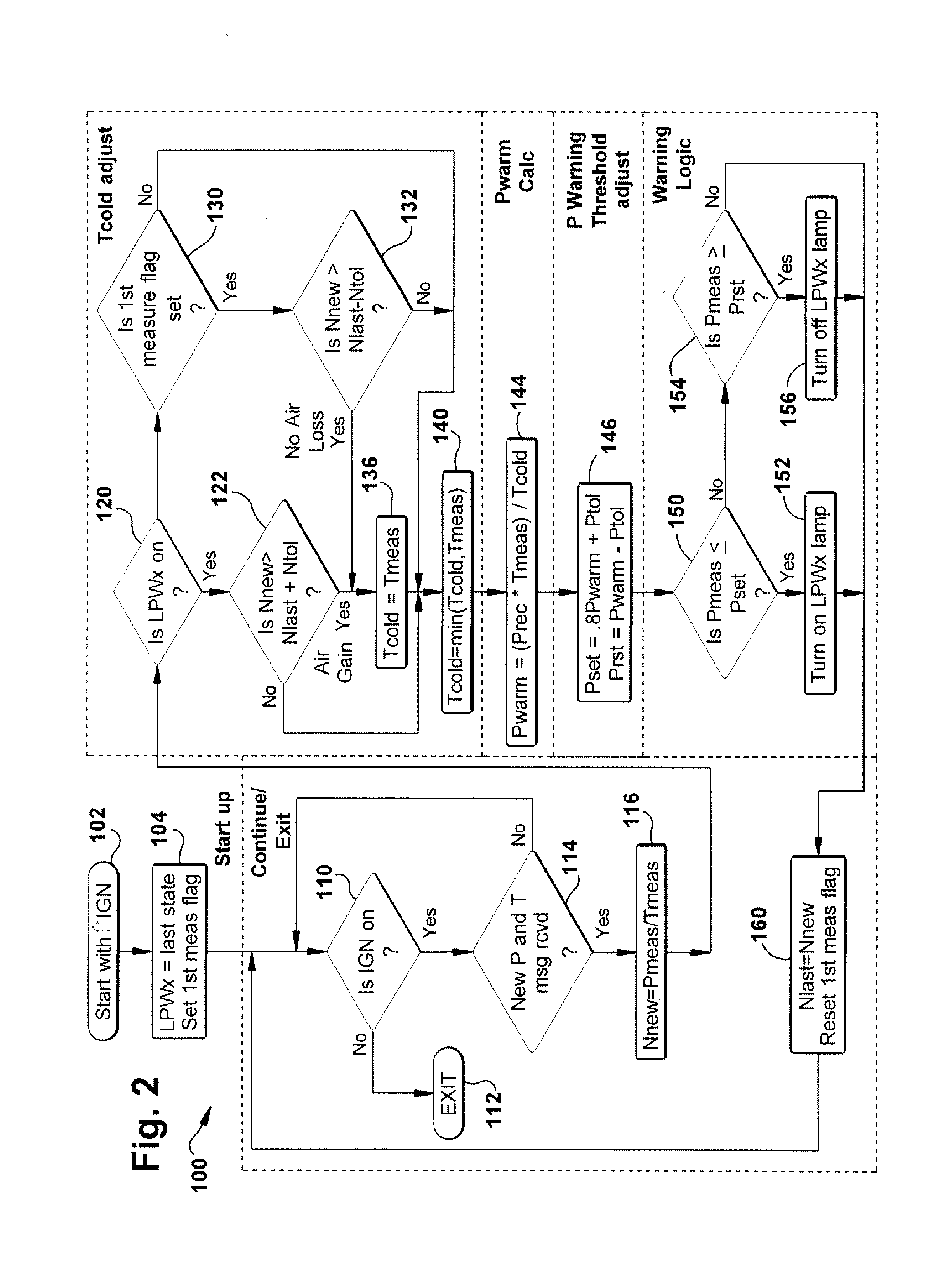
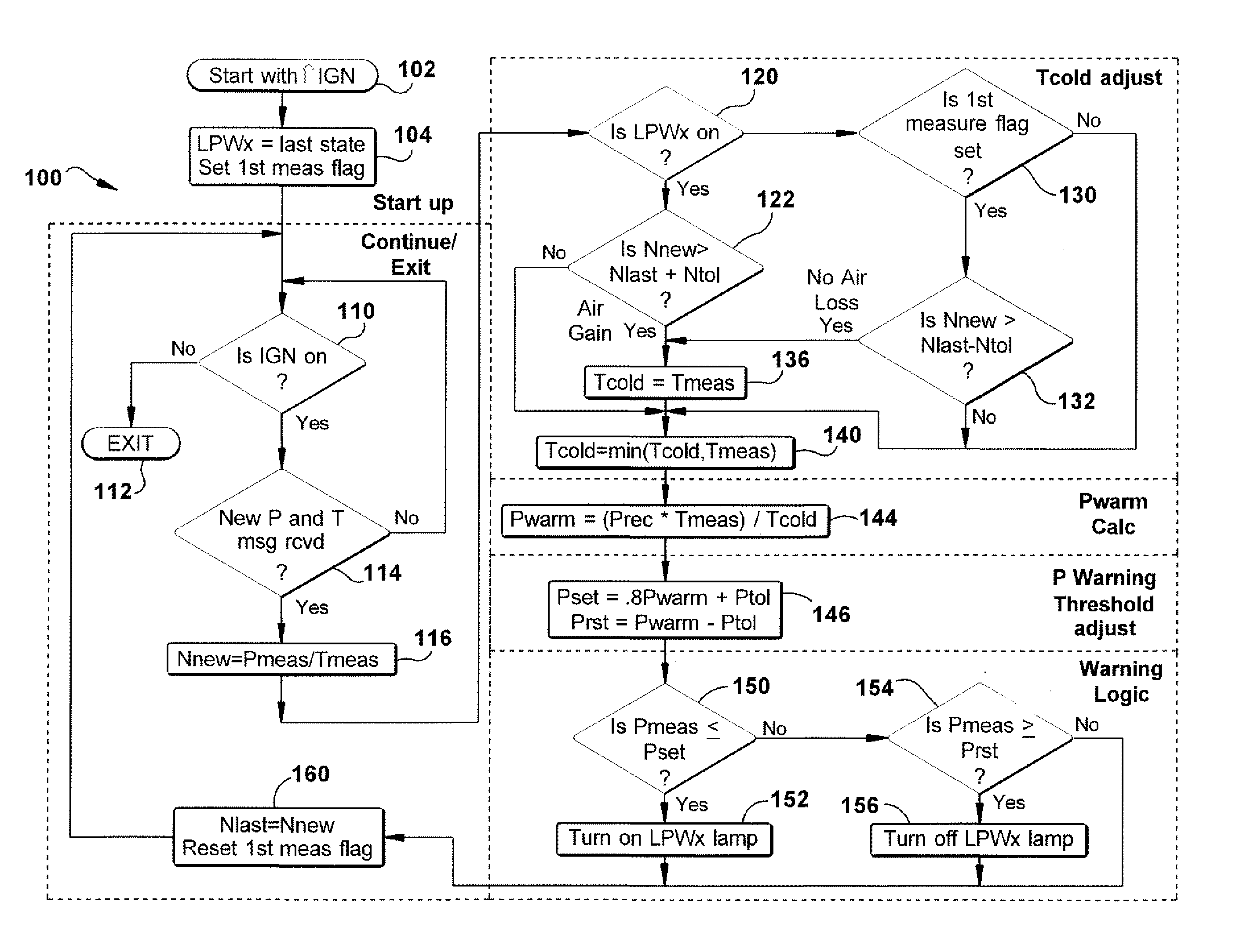
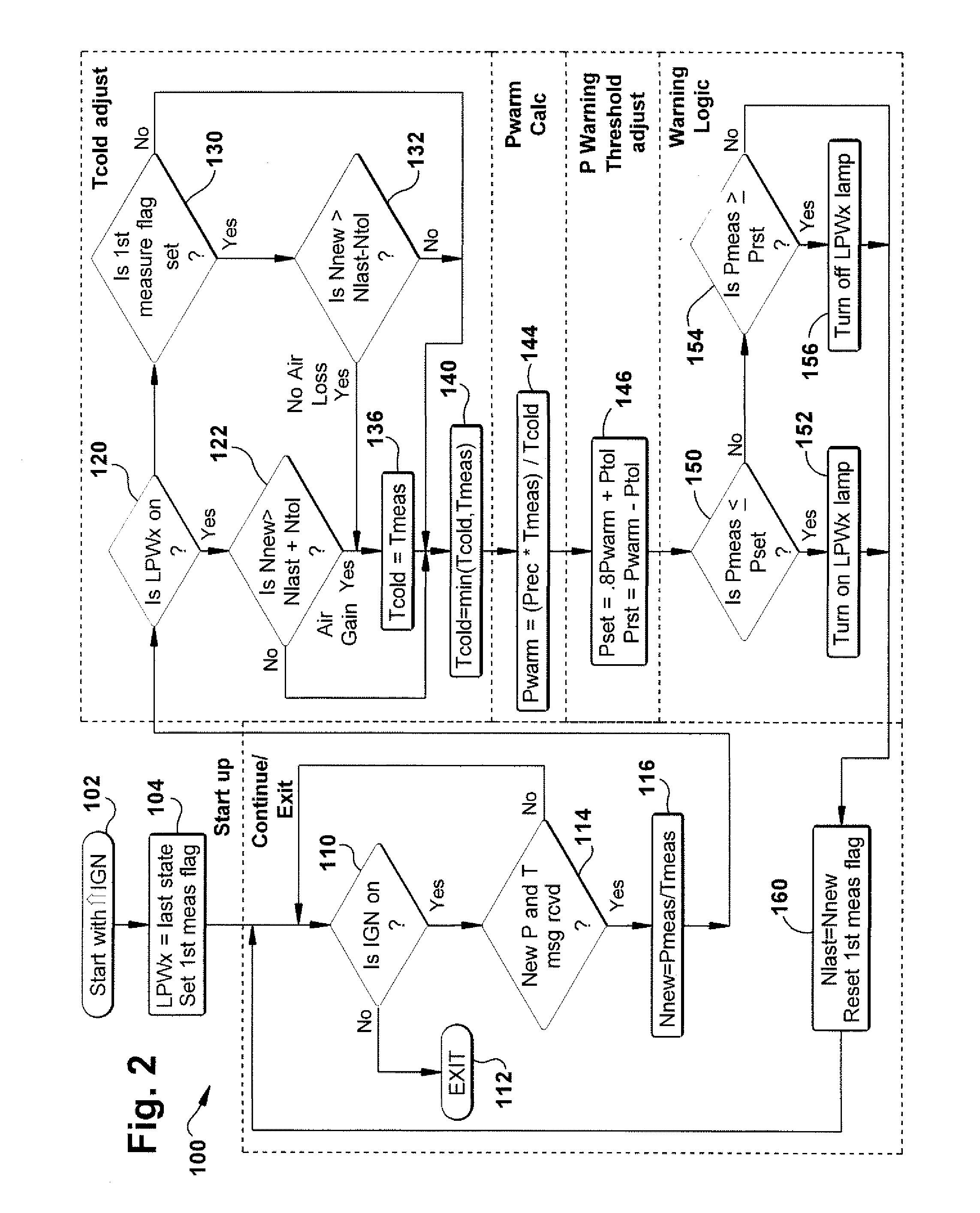
An apparatus is provided for determining a tire operating condition including a tire-based sensor for sensing tire pressure and temperature and transmitting a signal indicative thereof and a vehicle ignition system. A vehicle-based receiver / controller is provided for receiving the signal from the tire-based sensor and for detecting the state of the vehicle ignition system. The controller provides an error signal when the sensed tire pressure is less than a set threshold value Pset and resets the error signal when the sensed tire pressure is greater than a reset threshold value Prst. The receiver / controller determines the set threshold value Pset and the reset threshold value Prst as a function of a calculated warm tire pressure value Pwarm, determines a mole value N of the tire pressure, and adjusts the determined set threshold value Pset and the reset threshold value Prst in response to the vehicle ignition state and a change in the determined mole value N. A display is provided for displaying the error signal from the vehicle-based receiver / controller.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE US LLC
Numerical simulation of airflow within porous materials
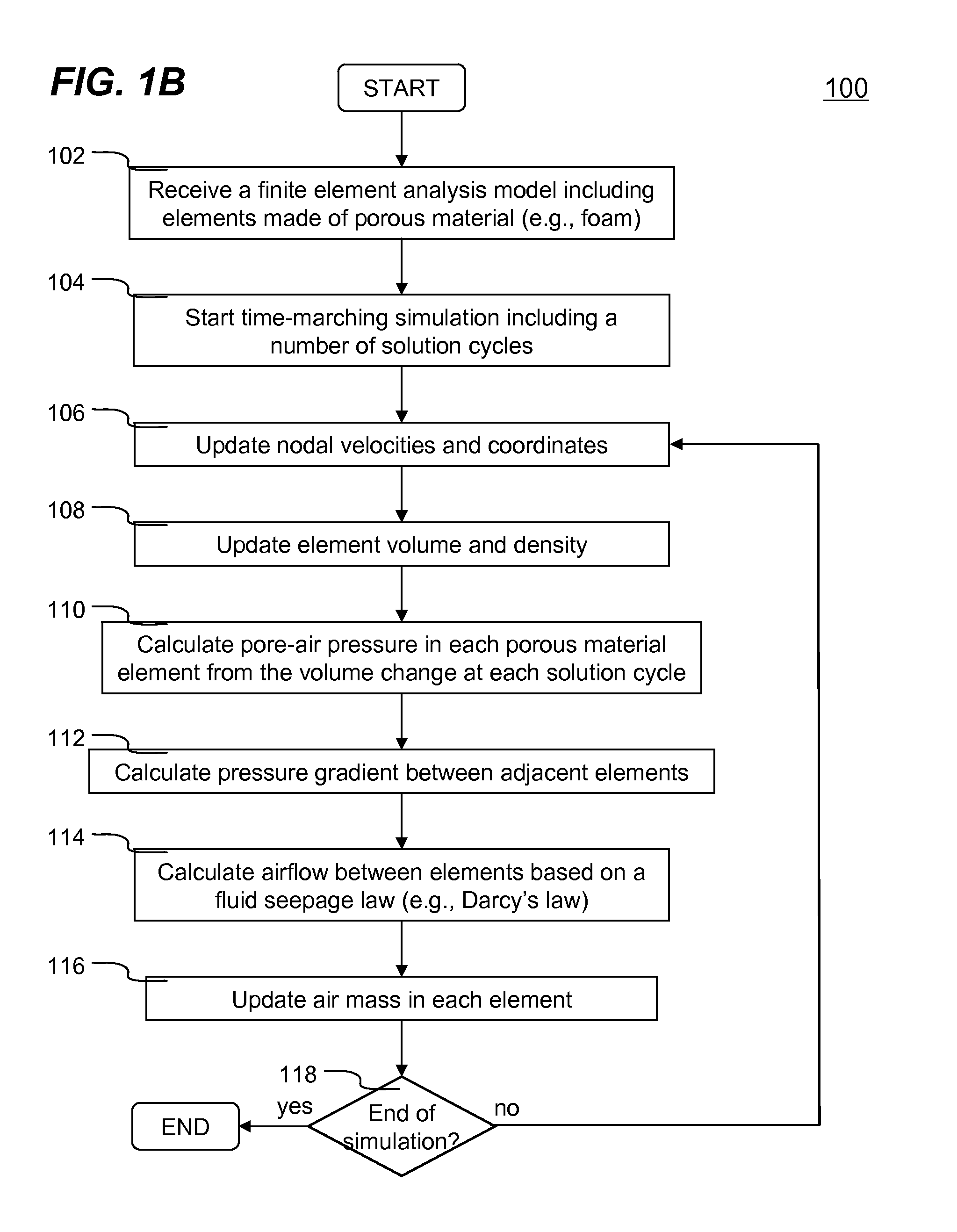
InactiveUS20110010137A1Realistic simulation of structural behavior of porous materialsComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationVolume variationElement analysis
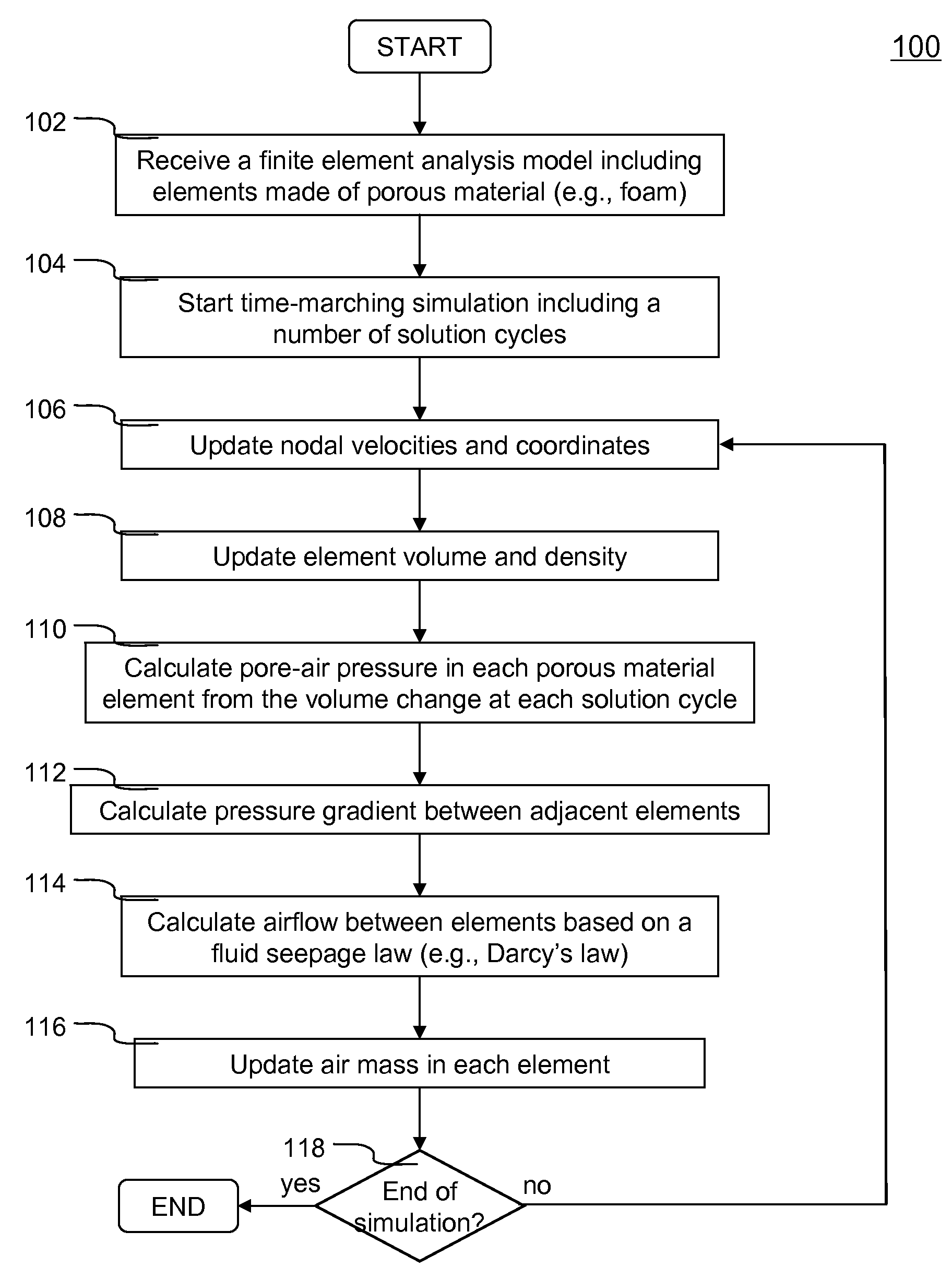
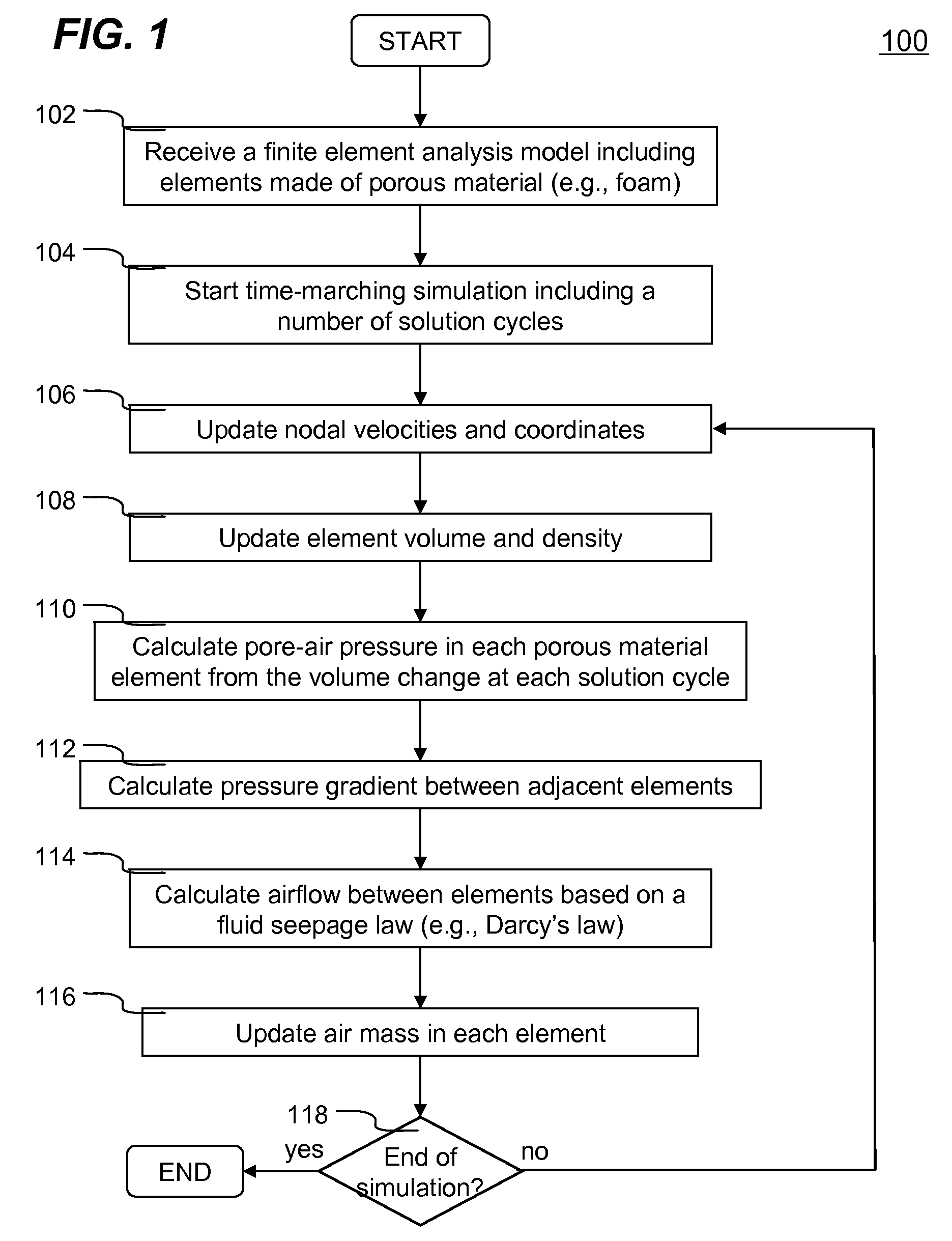
Systems and methods of numerically simulating airflow within porous materials are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, engineering product represented by a finite element analysis model containing in part porous material with permeability. In each solution cycle of a time-marching simulation, each of the elements of porous material is evaluated with airflow in conjunction with the traditional mechanical response. Each element's volume change results into different air-pore pressure hence a pressure gradient, which in turn is used for airflow calculated in accordance with a fluid seepage law that depends upon permeability of the porous material. Therefore, a more realistic simulation of structural behavior of porous materials can be achieved. The volume change and pressure of each element of porous material is evaluated using ideal gas law. A general form of Darcy's law includes user control parameters is used for evaluating airflow based on the pressure gradient and permeability.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
Propellant burning gas mole number test method and its device
InactiveCN101126694ASolve for moles of gasTests to Solve Specific VolumeVolume measurement apparatus/methodsMaterial analysisSteam pressureEngineering
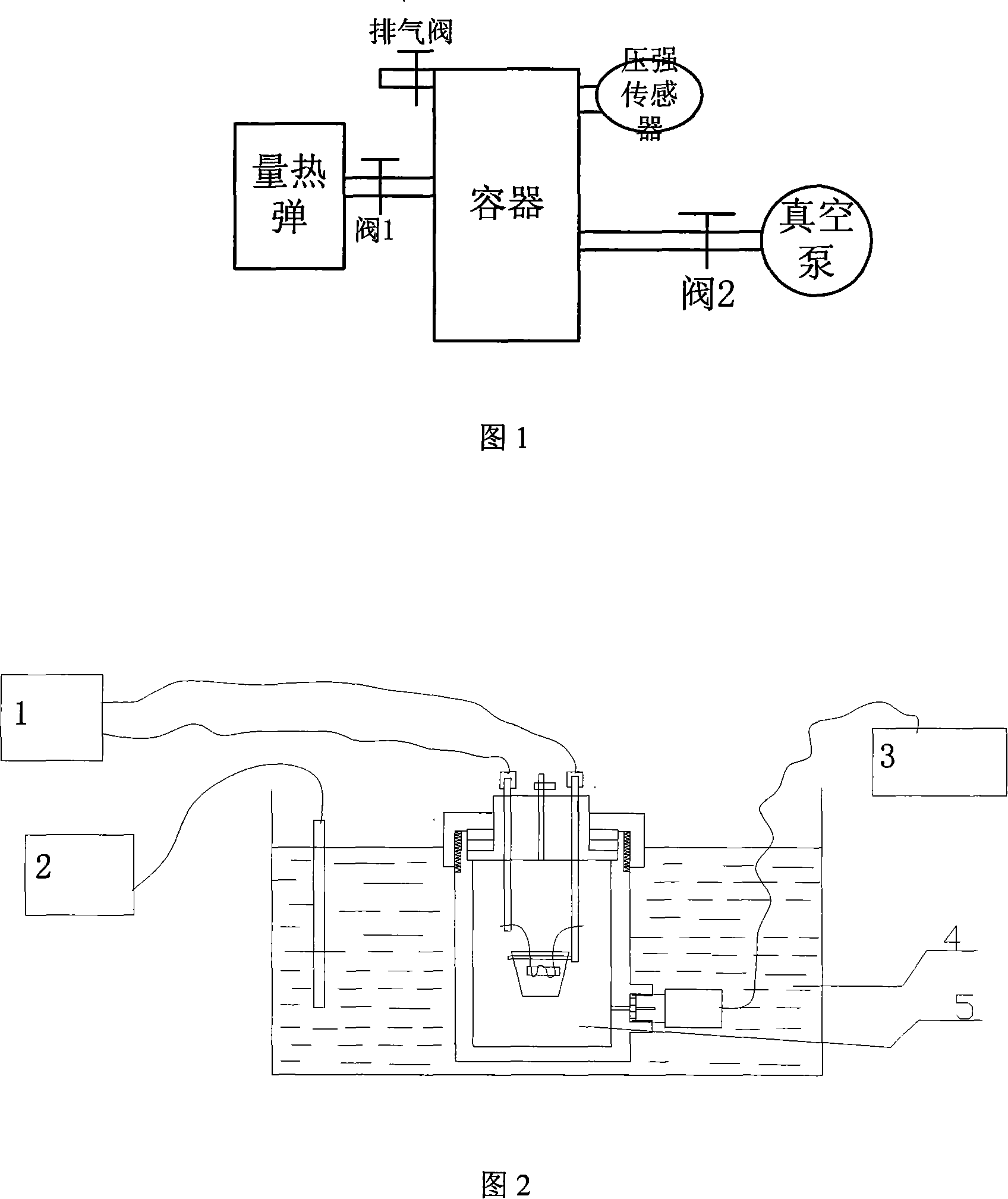
The utility model discloses a test method and the device for testing the mole number of combustion gas of propellant. A quantitative sample is arranged in a calorimetric bomb; the air in the calorimetric bomb is discharged through charging and discharging inert gas; finally the pressure of the inert gas remained in the calorimetric bomb is lower than 0.2 MPa; the calorimetric bomb is arranged in an oil bath thermostat; the temperature of the oil bath thermostat is higher than 100 DEG C; at the same time, the pressure in the calorimetric bomb is not bigger than the saturated steam pressure of the current temperature. The sample is energized and ignited to combust in the calorimetric bomb; the gas produced by sample combustion is isothermal in the oil bath constant temperature bath; a pressure sensor on the calorimetric bomb is used to detect the pressure change during the whole process from ignition to constant temperature; a temperature transmitter in the constant temperature bath is used for testing temperature. The gas mole number and gas volume under standard state is converted according to ideal gas state equation. The utility model is accurate in water measurement, and solves the problems of testing the specific volume and the mole number of combustion gas of propellant containing chlorine.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Numerical simulation of airflow within porous materials
InactiveUS20110282637A1Reduce needFeasible solutionGeometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationCar seatElement analysis
Systems and methods of numerically simulating airflow within porous materials are disclosed. Engineering product (e.g., car seat) represented by a finite element analysis model containing in part porous material with permeability. In each solution cycle of a time-marching simulation, each of the elements of porous material is evaluated with airflow in conjunction with the traditional mechanical response. Each element's volume change results into different pore air pressure hence a pressure gradient, which in turn is used for airflow calculated in accordance with a fluid seepage law that depends upon permeability of the porous material. Therefore, a more realistic simulation of structural behavior of porous materials can be achieved. The volume change and pressure of each element of porous material is evaluated using ideal gas law. A general form of Darcy's law includes user control parameters is used for evaluating airflow based on the pressure gradient and permeability.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
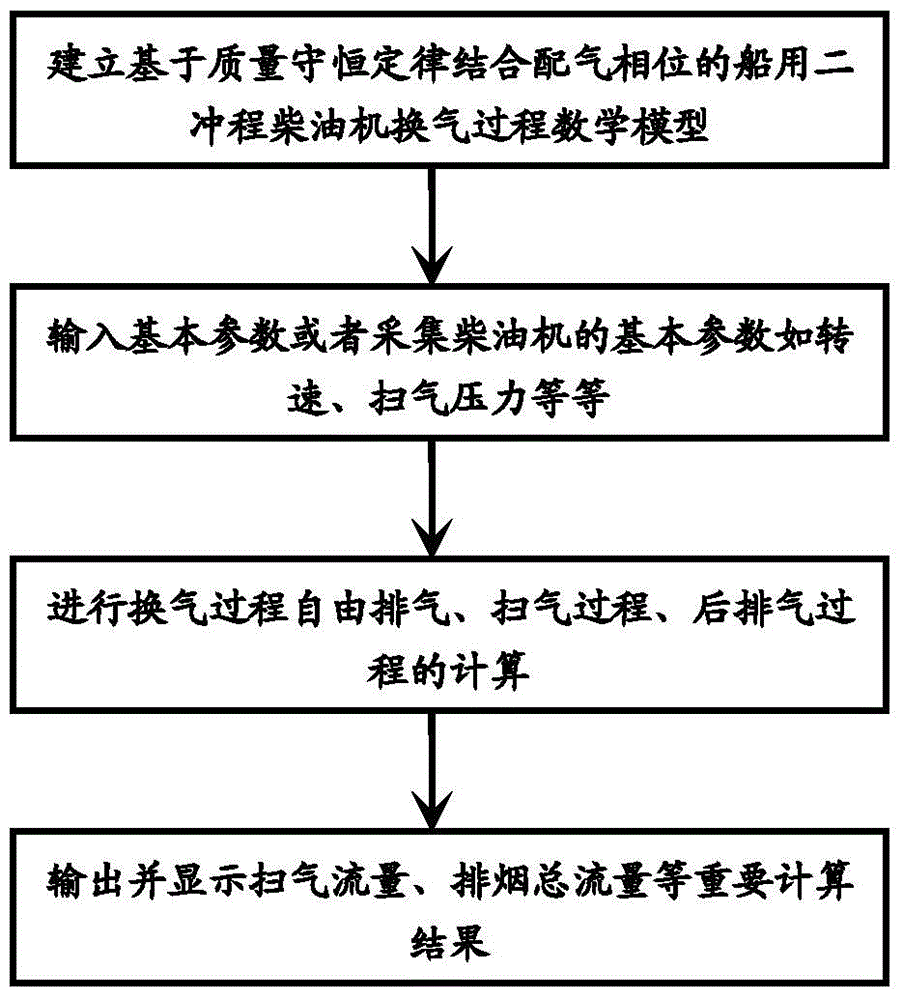
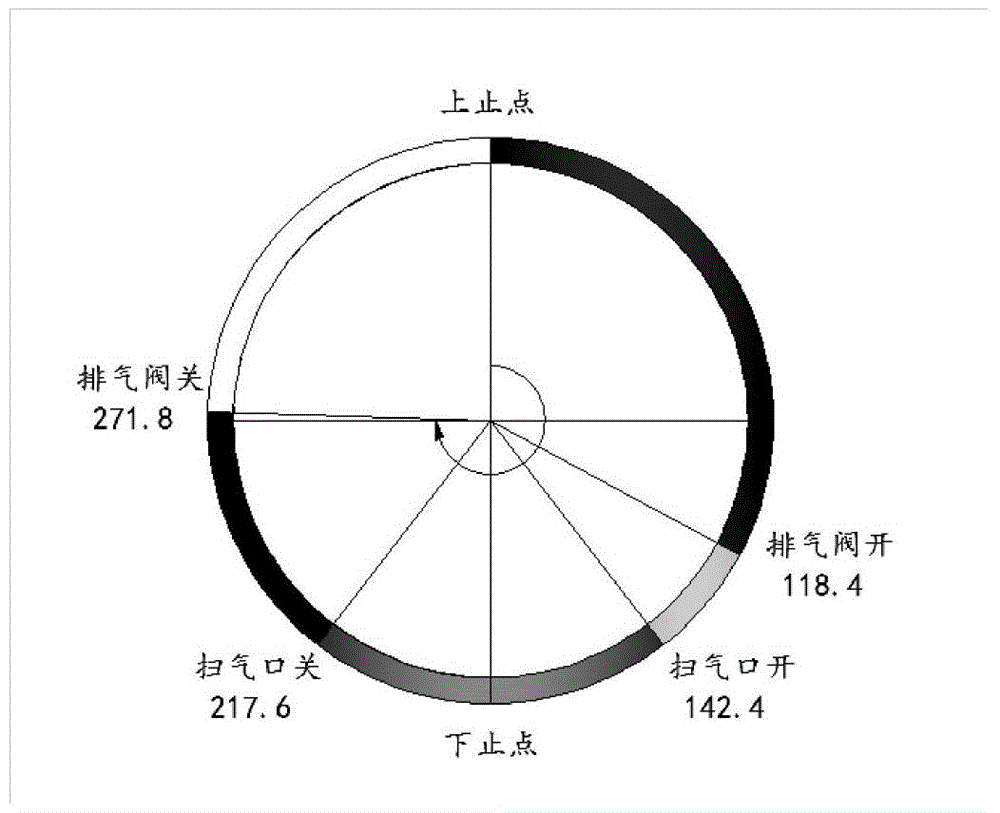
Method for calculating blown gas displacement of two-stroke low-speed diesel engine for boat
ActiveCN104484552AQuick forecastAccurate predictionSpecial data processing applicationsLow speedProcess engineering
The invention discloses a method for calculating blown gas displacement of a two-stroke low-speed diesel engine for a boat. The method comprises the following steps: calculating blown gas flow rate, exhausted smoke flow rate and amount of gas discharged to an exhausted smoke collection box in different stages of a ventilation process in real time by adopting a mathematic model; calculating the amount of waste gas freely exhausted in single circulation, gas input and output quantity during a gas blowing process and the amount of exhausted gas during a post-exhausting process by utilizing an ideal gas state equation in combination with a gas distribution phase position; obtaining the blown gas flow rate and the exhausted smoke flow rate according to the quantity and rotating speed of air cylinders of the two-stroke low-speed diesel engine for the boat. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately predicting the blown gas flow rate and the exhausted gas flow rate, is high in universality and provides reliable data support for analyzing the working state of the diesel engine and improving the performance of the diesel engine.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for computing air impermeability of gas storage cavity
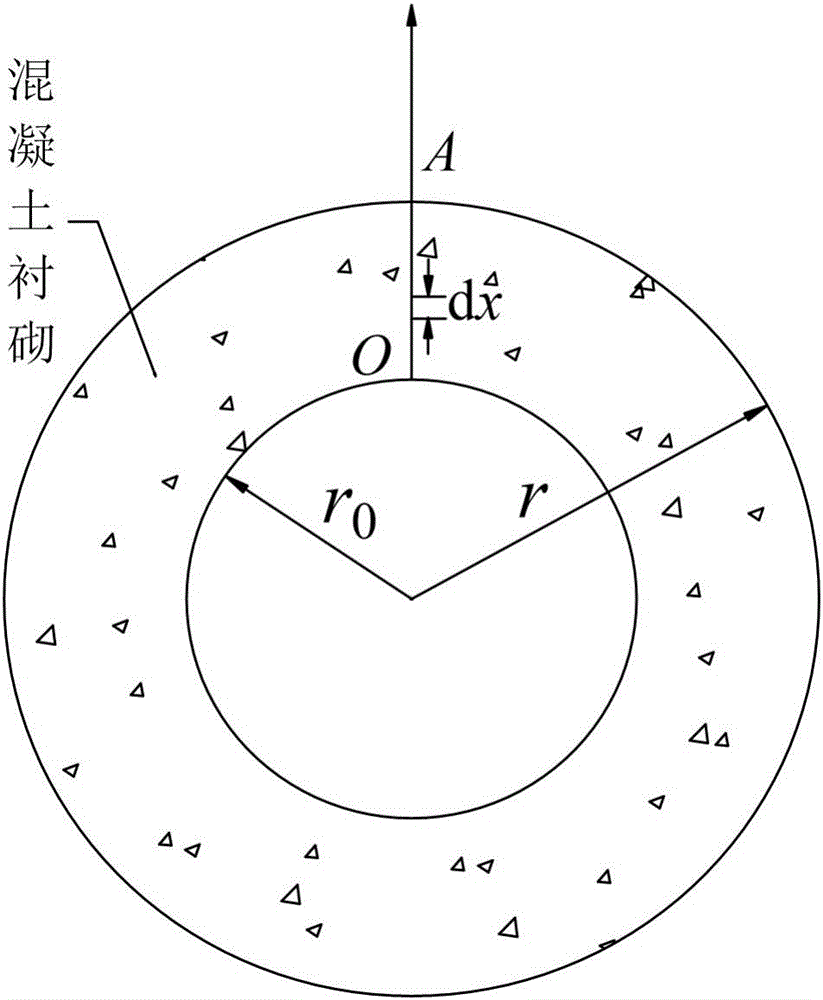
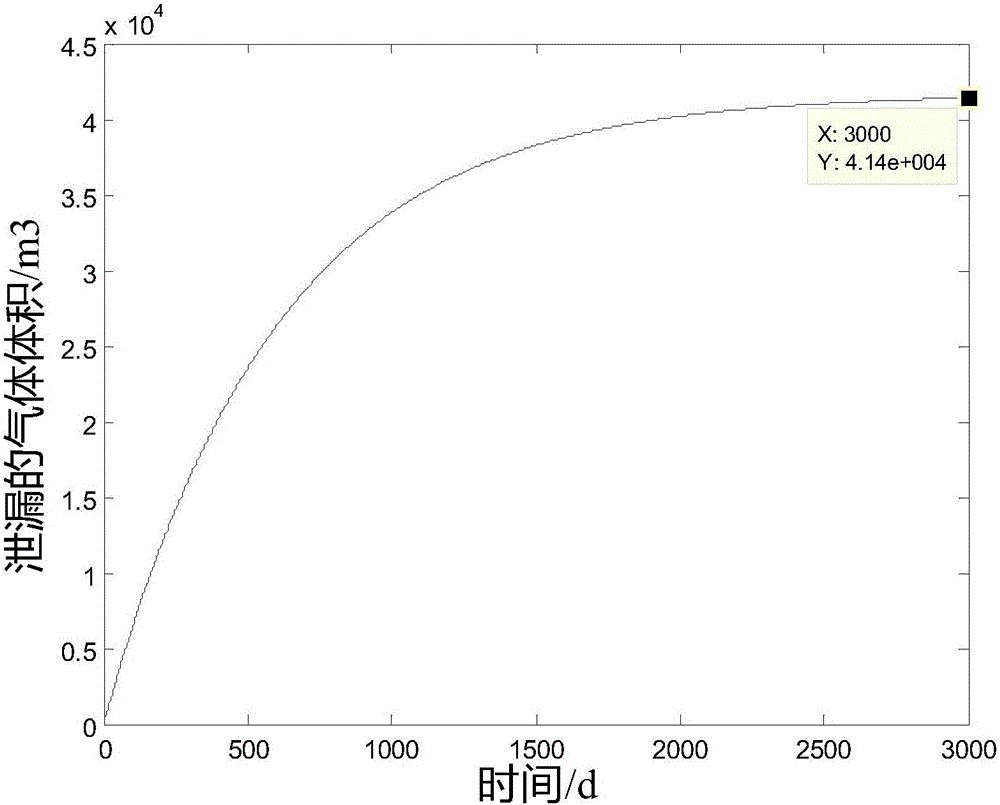
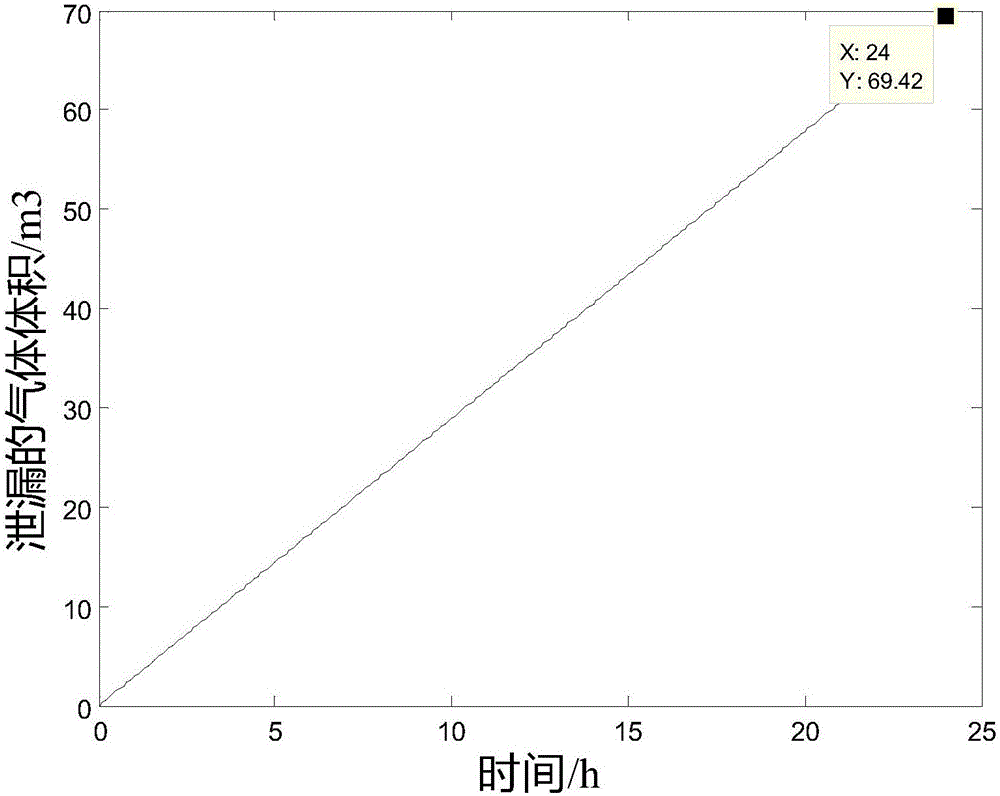
ActiveCN106092469AGuaranteed air tightnessUnderstand the purposeMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateProduct gasPressure difference
The invention discloses a method for computing the air impermeability of a gas storage cavity. The method comprises steps of: S1, setting seepage velocity computational formulas 1 for different seepage distances according to a Darcy law; S2, setting a computational formula 3 of the pressure difference [delta]px inside the cavity according to an ideal gas state equation computational formula 2; S3, supposing that the seepage velocity of a seeped gas is uA(t) when the gas reaches the outer surface of concrete, setting the leaked gas volume computational formula 4 within time dt; S4, setting the pore volume capable of containing air as V pore and obtaining a V pore computational formula 5; S5, setting the time when the gas just seep to a position A as a time start point and setting the volume of the seeped gas at the time t as [delta]V(t), setting a computational formula 6 of a pressure difference inside the cavity; and S6, integrating the computational formula 5 to obtain a differential equation, and solving the differential equation to obtain an expression of the volume of the leaked gas about time. The method may provide gas leakage cases with different lining permeability, and guarantees the air impermeability of the gas storage cavity by controlling the permeability of the lining.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST
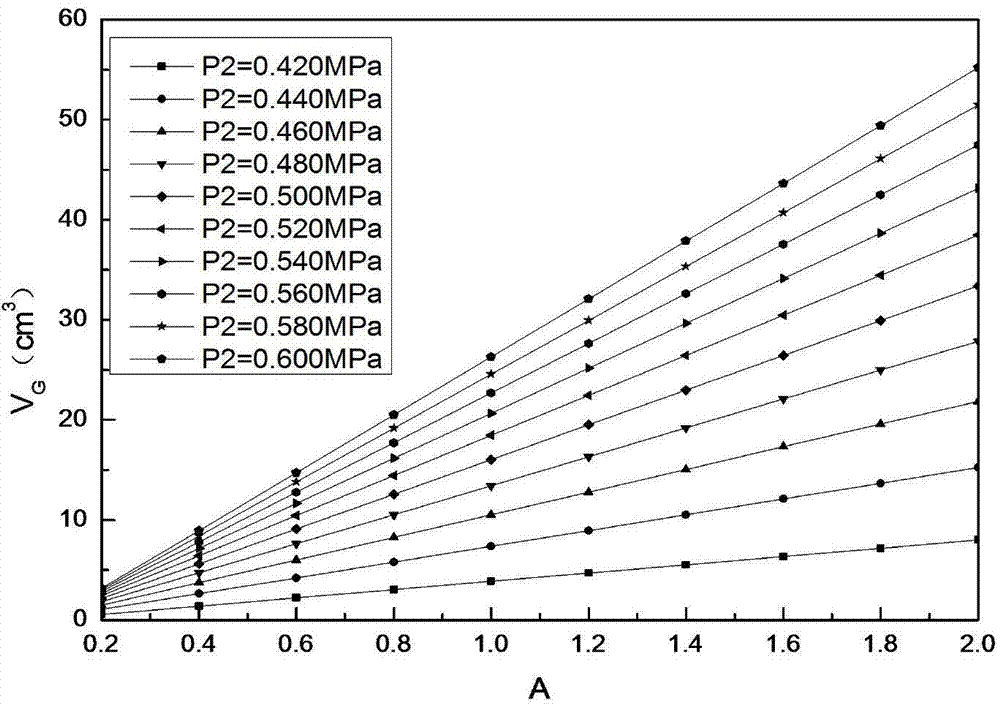
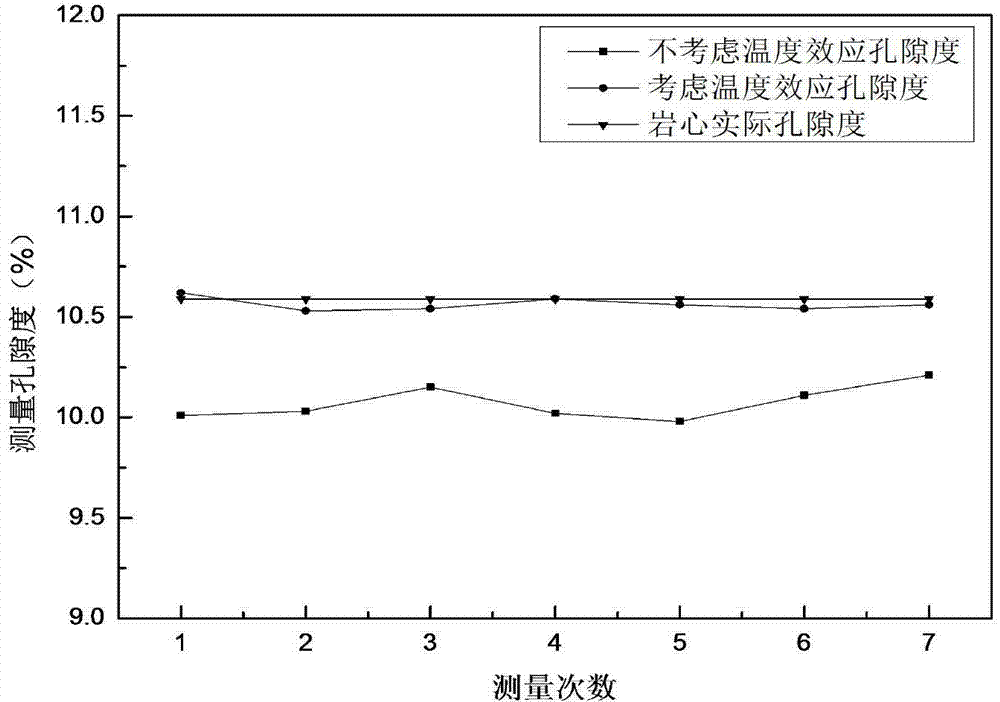
Gasometric porosity measuring method taking temperature effect into consideration
ActiveCN104729974AAvoid errorsAccurately reflectPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityTheoretical plate
The invention relates to a gasometric porosity measuring method taking temperature effect into consideration and belongs to the field of laboratory core porosity measurement. The method which is based on the equation of state of ideal gas includes the steps of 1, considering temperature changes during measurement, and acquiring unknown gas chamber volume V according to balance pressure P measured; 2, calibrating known gas chamber volume Vk and pressure change coefficient G of a measuring system; 3, determining core frame volume; 4, determining core porosity. The method has the advantages that the influence of temperature effect upon core gasometric porosity is considered, the porosity defect of the Boyle's law is made up theoretically, and a theoretical plate for volume relation of temperature effect factors and core frame is compiled, the measurement requirements of the method are fully implemented, and thus rock physics basis is more perfect and prediction precision is higher.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for processing concentration signal of infrared gas sensor
InactiveCN101949833AHigh precisionRealize secondary compensationColor/spectral properties measurementsLaws of thermodynamicsIdeal gas law
The invention relates to an infrared gas sensor, in particular to a method for processing a concentration signal of the infrared gas sensor for precisely determining the concentration of a target gas. The invention solves the problem of low detection precision of the existing method for determining the concentration of the gas used by the infrared gas sensor. The method for processing the concentration signal of the infrared gas sensor corrects the following factors: 1, influence of the zero-position output ratio of the infrared gas sensor on the detection result in the absence of the target gas; and 2, influence of the non-absorption wave band on the detection result within the wavelength range of infrared light of an incidence detection channel; twice temperature compensations are implemented as follows: 1, introducing a temperature compensation parameter to realize real-time temperature compensation; and 2, realizing secondary compensation for the temperature influence in the ideal gas law; and finally obtaining the concentration of the target gas with a high detection precision. The method is reasonable and effective and can maximize the detection precision of the infrared gas sensor and meet the practical application requirements of the occasions with high requirements on the detection precision.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Method and apparatus for determining tire condition using ideal gas law
InactiveUS8818619B2Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDisplay deviceLaws of thermodynamics
An apparatus is provided for determining a tire operating condition including a tire-based pressure and temperature sensor and transmitter and a vehicle ignition system. A vehicle-based receiver / controller receives sensor signals and state of the ignition system. The controller provides an error signal when the sensed tire pressure is less than a set threshold value Pset and resets the error signal when the sensed tire pressure is greater than a reset threshold value Prst. The receiver / controller determines the set threshold value Pset and the reset threshold value Prst as a function of a calculated warm tire pressure value Pwarm, determines a mole value N of the tire pressure, and adjusts the determined set threshold value Pset and the reset threshold value Prst in response to the vehicle ignition state and a change in the determined mole value N. A display is provided for displaying the error signal.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE US LLC
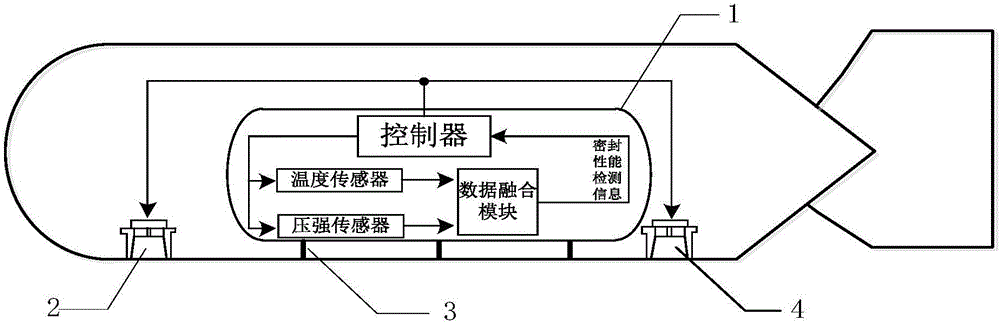
Active protection method of unmanned underwater vehicle based on sealing property detection of sealed cabin
ActiveCN106394839AEnsure safetyReal-time monitoring of tightnessMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateUnderwater vesselsLoad rejectionHysteresis
The invention belongs to the field of safety protection of an unmanned underwater vehicle, and relates to an active protection method of the unmanned underwater vehicle based on sealing property detection of a sealed cabin. The active protection method comprises the following steps of: after the sealing work of the sealed cabin is completed, collecting the data of a temperature sensor and a pressure sensor in real time; performing compensation and correction so as to obtain the temperature and the pressure of gas; obtaining a variation quantity Delta V of an ideal gas volume by an ideal gas state equation; and if the Delta V is greater than a given threshold V<set>, sending an alarm signal, and energizing a ballast rejection device. The active protection method disclosed by the invention has high reliability, and a condition of false alarm due to dampness of a detection device in a conventional commonly used manner that a humidity sensitive resistor is used as the sensor is avoided; the adaptive compensation of the temperature sensor is performed, so that a loss caused by temperature hysteresis of the temperature sensor is avoided; and due to the arrangement of the load rejection device, a ballast can be rejected actively when the sealing property is abnormal, so that the unmanned underwater vehicle can float rapidly, the response speed is high, equipment in the sealed cabin can be furthest protected, and the safety of the unmanned underwater vehicle is guaranteed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Gas generator assembly suitable for automobile air bag
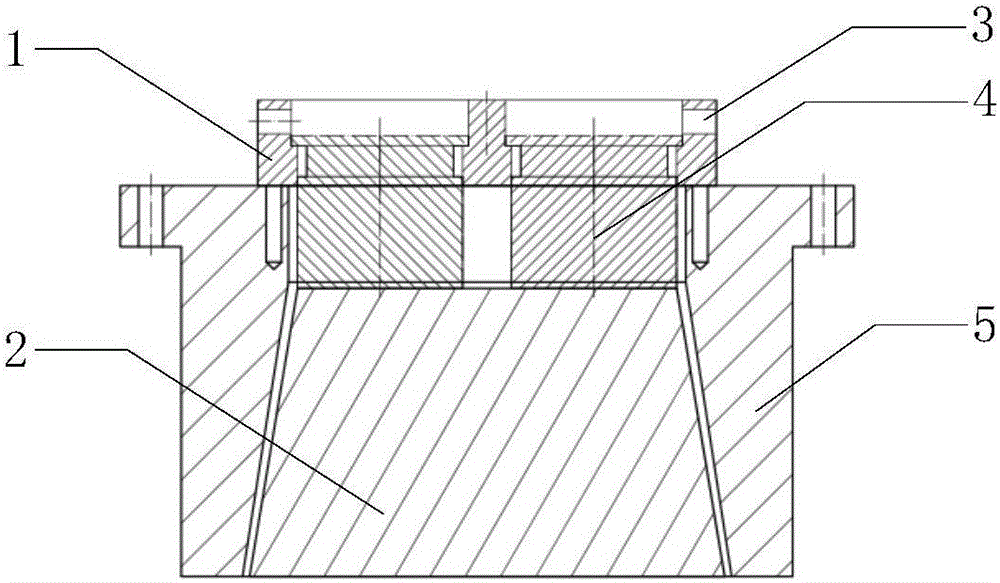
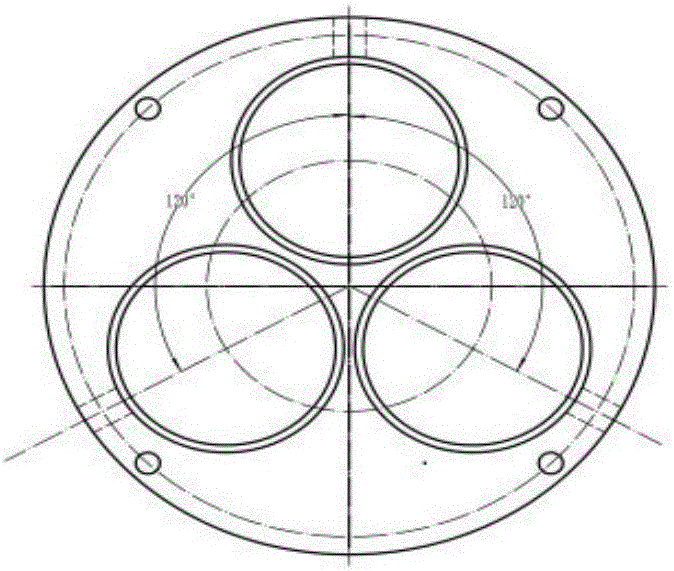
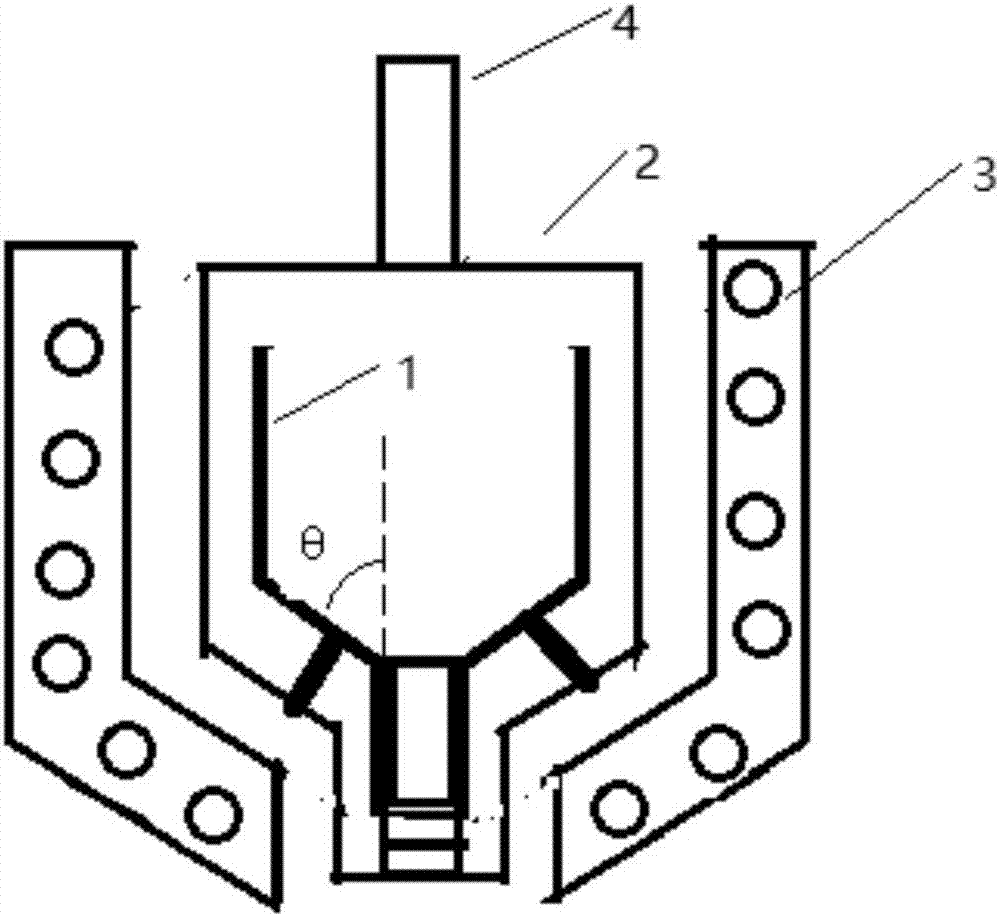
InactiveCN107600027AUniform expansionAvoid hurtingPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementProduct gasEngineering
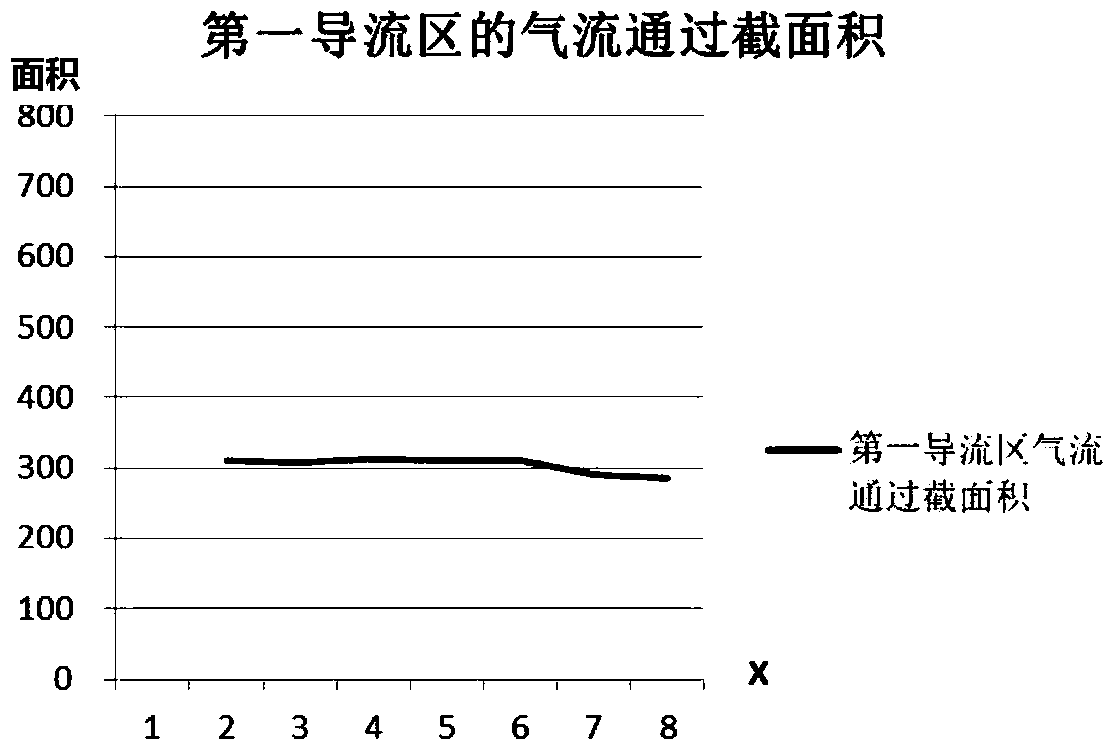
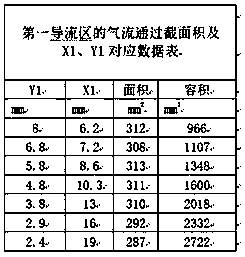
The invention discloses a gas generator assembly suitable for an automobile air bag. The gas generator assembly comprises an exhaust hood, an upper cover and a lower cover, wherein a closed gas generating cavity is formed by the upper cover and the lower cover; the exhaust hood is provided with a diversion cavity body which is covered on the top of the upper cover, and a diversion region is jointly formed by the diversion cavity and the upper cover; a gas inlet is formed in the upper cover; high-pressure gas enters from the gas generating cavity to the diversion region through the gas inlet; and the diversion region formed by the diversion cavity of the exhaust hood and the upper cover comprises a first diversion region and a decompression diversion region. According to the gas generator assembly disclosed by the invention, according to an ideal-gas equation: pV=nRT, finite element figure modeling is performed, after a large number of simulating test for repeatedly amending, so that the gas generator assembly suitable for the automobile air bag is provided; and the gas generator assembly is provided with a diversion region, so that stage decompressional expansion is performed on the generated high-pressure gas, the situation that damaging impact is generated on the gas generator is avoided, and the air bag injury accidents are avoided.
Owner:CHANGZHOU GONGLI SEIKI TECH
P-type indium phosphide single crystal preparation formula and preparation method
ActiveCN107313110AReasonable temperatureReduce residual stressPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsSingle crystalBoron trioxide
The invention discloses a P-type indium phosphide single crystal preparation formula and a preparation method. The formula comprises the following raw materials by 100g of P-type indium phosphide single crystal: 99.5g of an InP polycrystal material, 0.2-0.8g of metallic zinc, not less than 32g of diboron trioxide, and red phosphorus, wherein the amount of the red phosphorus is calculated according to ideal gas state equations; the pressure is controlled to 2.7-3.5MPa; the temperature is controlled to 1062-1100 DEG C. By strictly controlling chemical proportions and establishing a good thermal field, the radial temperature gradient and the longitudinal temperature gradient inside a melt are relatively reasonable, and P-type indium phosphide single crystal which is small in residual stress, low in displacement density, uniform in electric parameter and high in quality is generated.
Owner:TAISHAN HUAXING PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Method for measuring daily output of oil field gas
The invention discloses a method for measuring the daily output of oil field gas. The method is designed to solve the problems of low measurement efficiency, the high labor cost and the like in the prior art. According to the method, the oil field gas of a measured oil well sleeve pipe is emptied, and then pressure build-up is carried out for the time of delta t; the oil field gas in the oil well sleeve pipe is detected after pressure build-up is finished, and a first pressure value p1 and a first temperature value T1 of the gas are obtained; at least part of the oil field gas in the sleeve pipe is discharged, the oil field gas in the sleeve pipe is detected a second time after gas discharging is finished, a second pressure value p2 and a second temperature value T2 of the gas are obtained, and the gas discharging amount delta Vsta of the sleeve pipe between the first time of measurement and the second time of measurement is recorded and worked out; the daily output value Q of the oil field gas is calculated through a calculation formula derived from an ideal gas state equation according to parameters obtained from the above steps. The measurement time of the method is about one tenth that of a common method, the measurement efficiency is largely improved, the use efficiency of a flow metering device is improved, and the labor cost is reduced.
Owner:荆州市明德科技有限公司
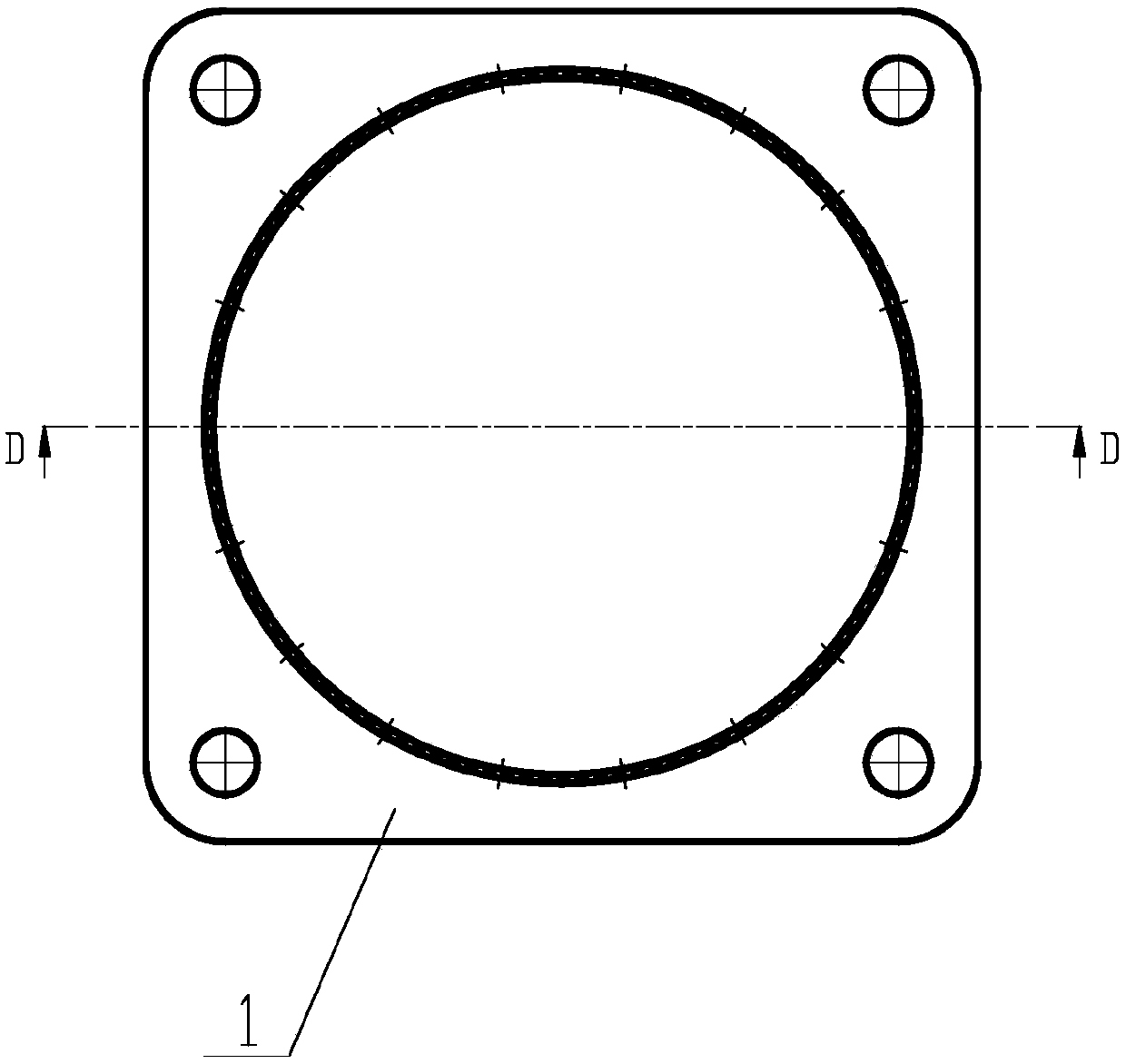
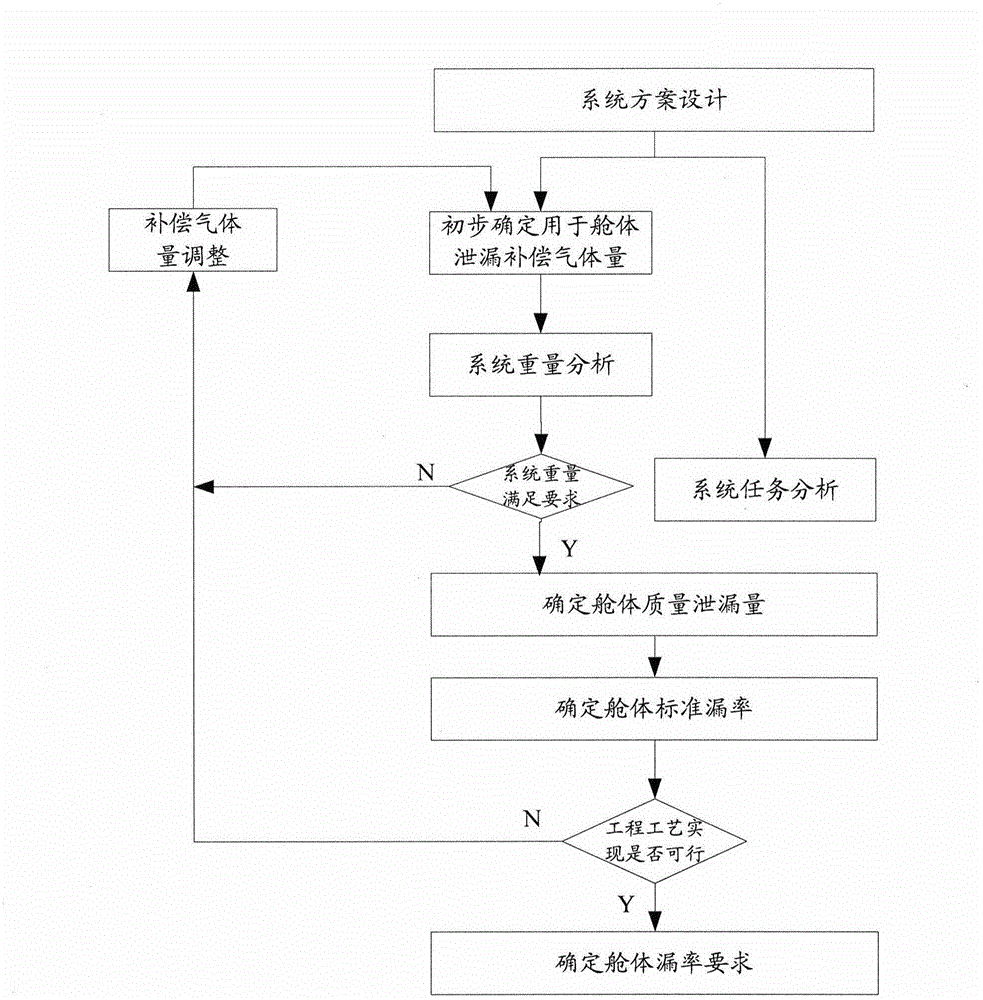
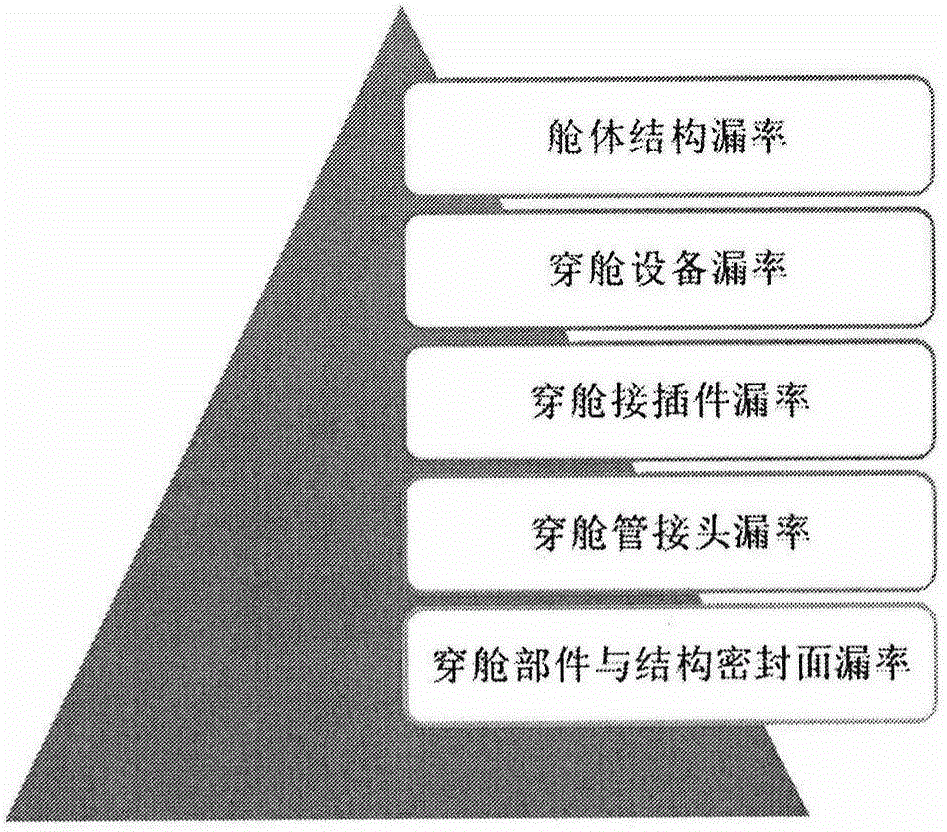
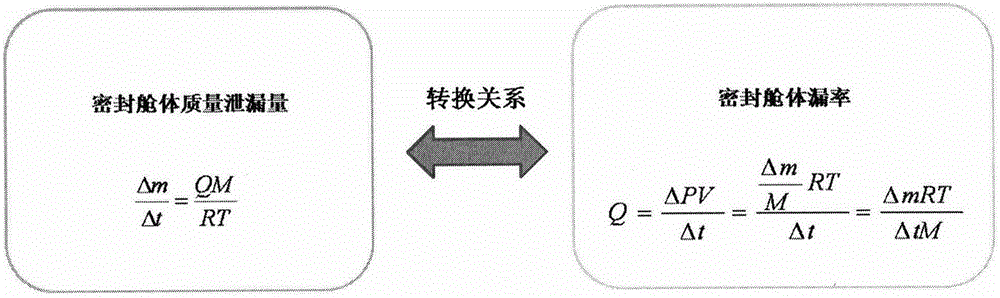
Leak rate design method for sealed cabin of manned spacecraft
InactiveCN105095638ASolve the difficult problem of realizing the leakage rate index of the sealed cabinSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringOrbit
The invention provides a leak rate design method for a sealed cabin of a manned spacecraft. The method is used for covering an overall process of an in-orbit flight. The method comprises the steps as follows: step 1, calculating mass leakage rate of the sealed cabin of the manned spacecraft according to a task time requirement of each flight phase in the overall process of the in-orbit flight and weight of leaked compensation gas; step 2, calculating a standard leak rate index of the sealed cabin according to the mass leakage rate, and step 3, executing engineering process check and iteration to the standard leak rate index so as to determine a sealed cabin leak rate index meeting a preset requirement. Therefore, the leak rate design method for the sealed cabin of the invention covers a gas leakage compensation requirement of all task stages of the manned spacecraft, and takes full advantage of a theoretical basis of an ideal gas state equation, and considers design constraints in a plurality of aspects such as flight mission planning, system weight control and product process so as to solve the problem of achieving a top flight task requirement to a specific sealed cabin leak rate index of the manned spacecraft.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com