Patents
Literature
38 results about "N carboxyanhydride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
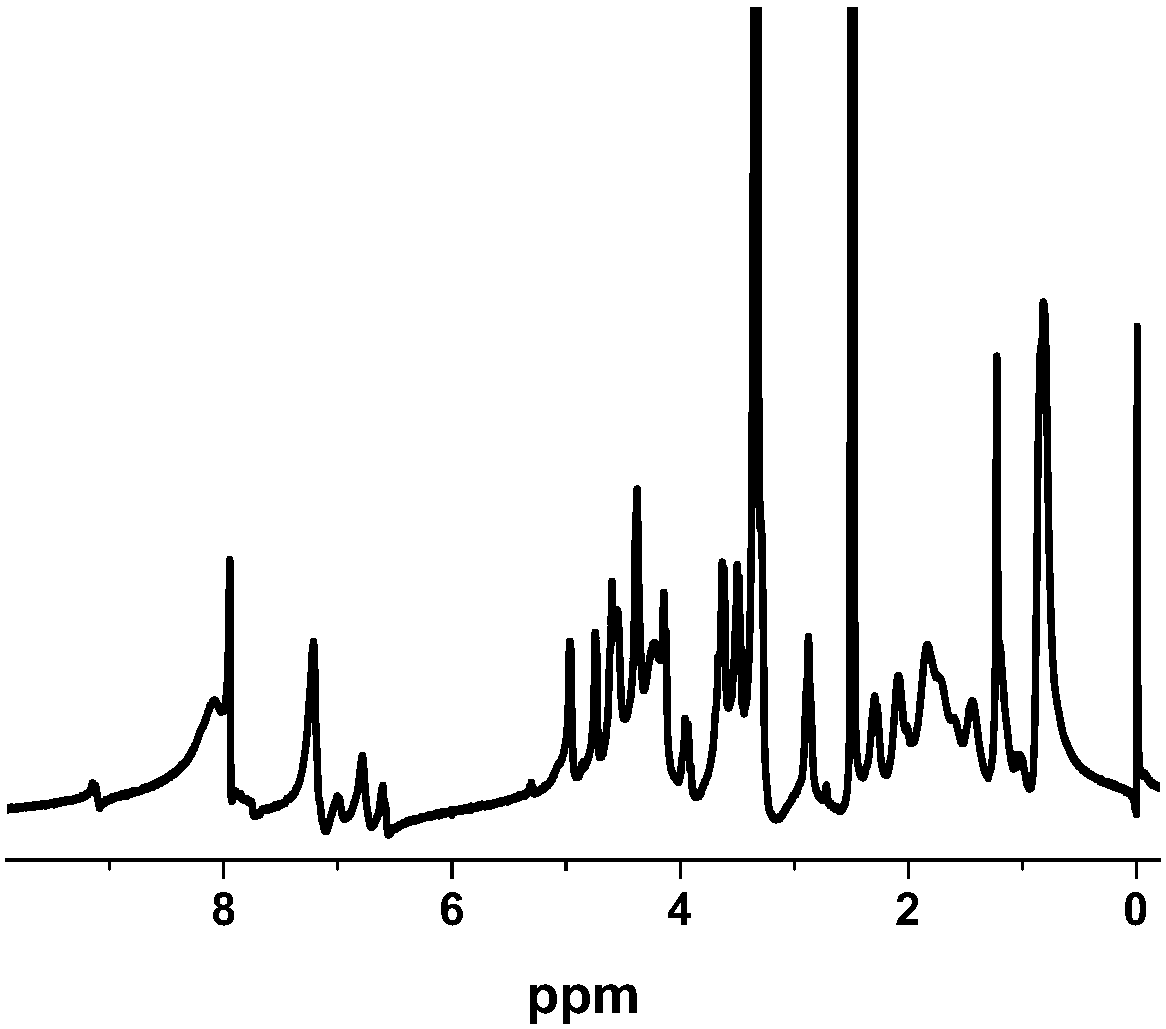
Urethane-protected amino acid N-carboxyanhydride (UNCA) is regarded as an activated urethane protected amino acid species. 149 The commercially available UNCA derivatives are generally stable crystalline compounds that can be stored for reasonably long periods of time. 150 The advantages of utilization of UNCA as an active species of amino acid ...
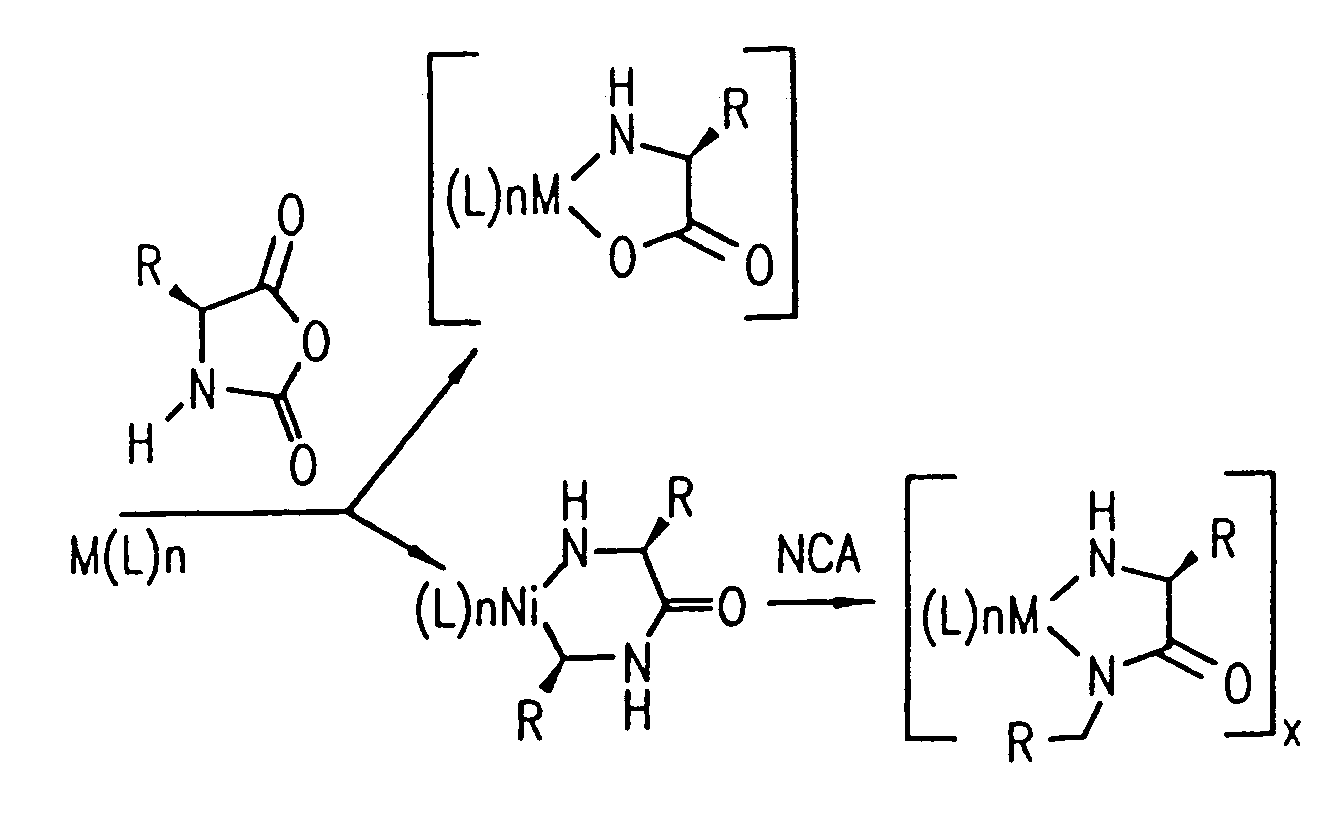
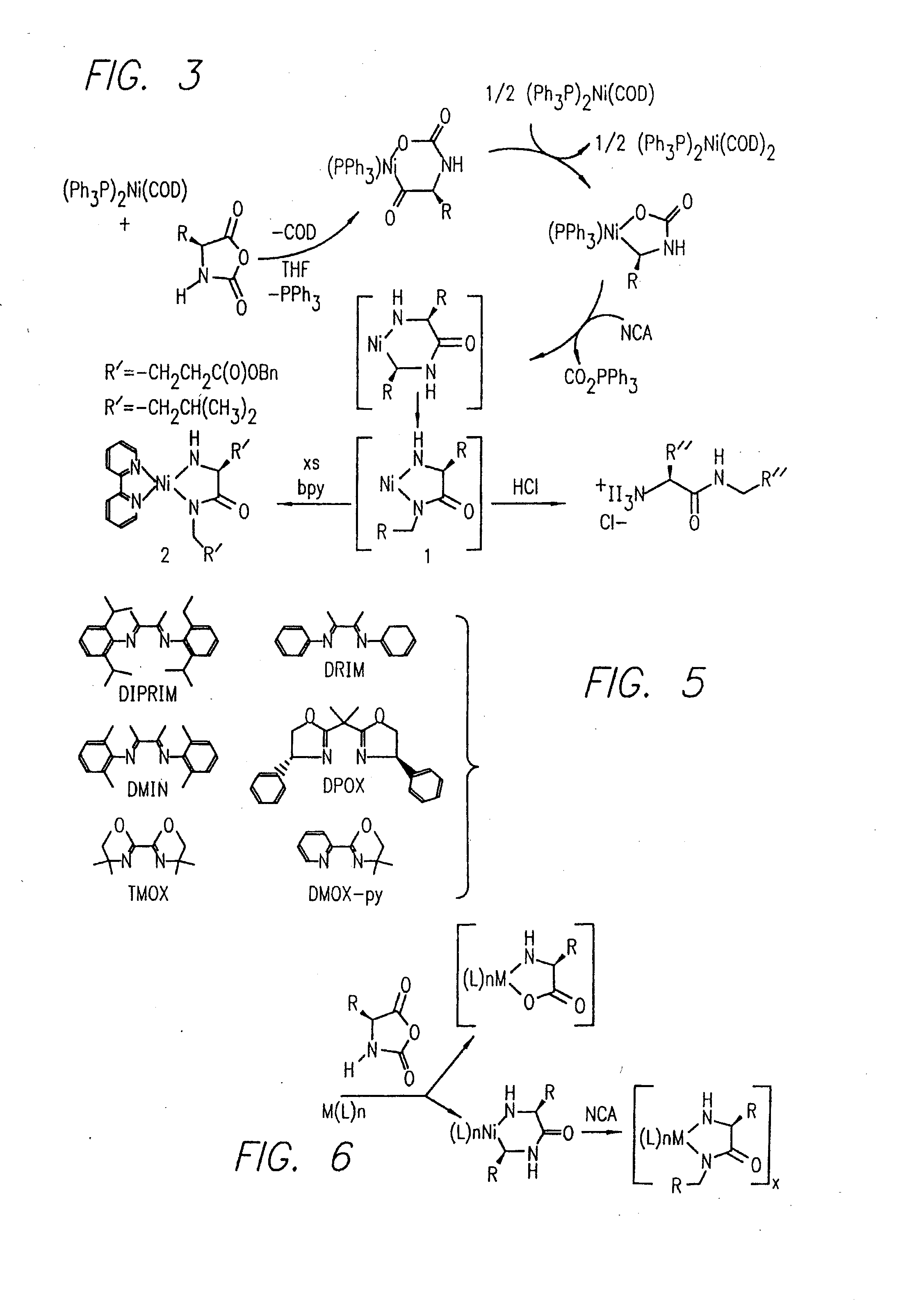
Methods and compositions for controlled polypeptide synthesis
InactiveUS20080125581A1Elimination reactionEasy to controlPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsSynthesis methodsEnd-group
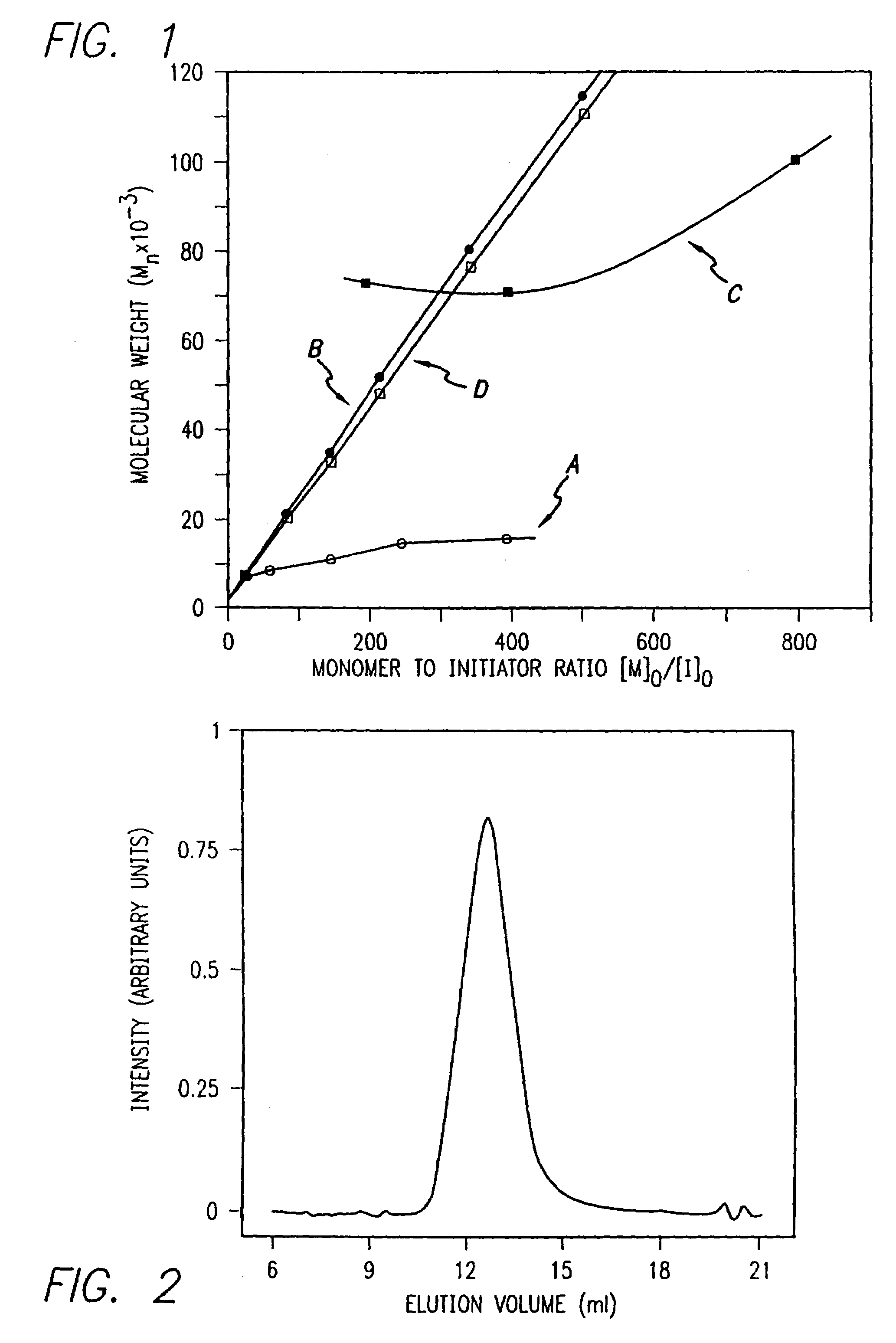
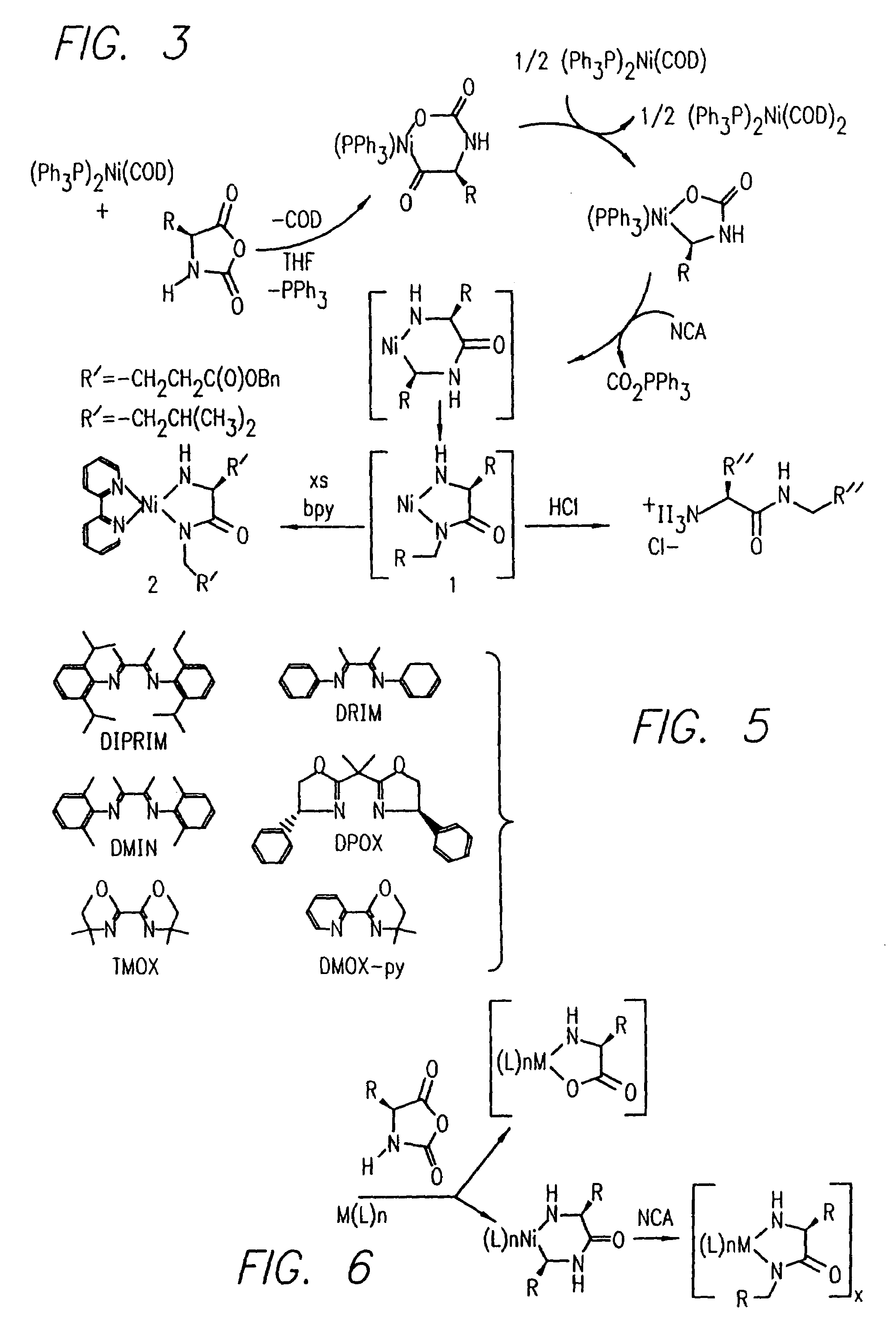
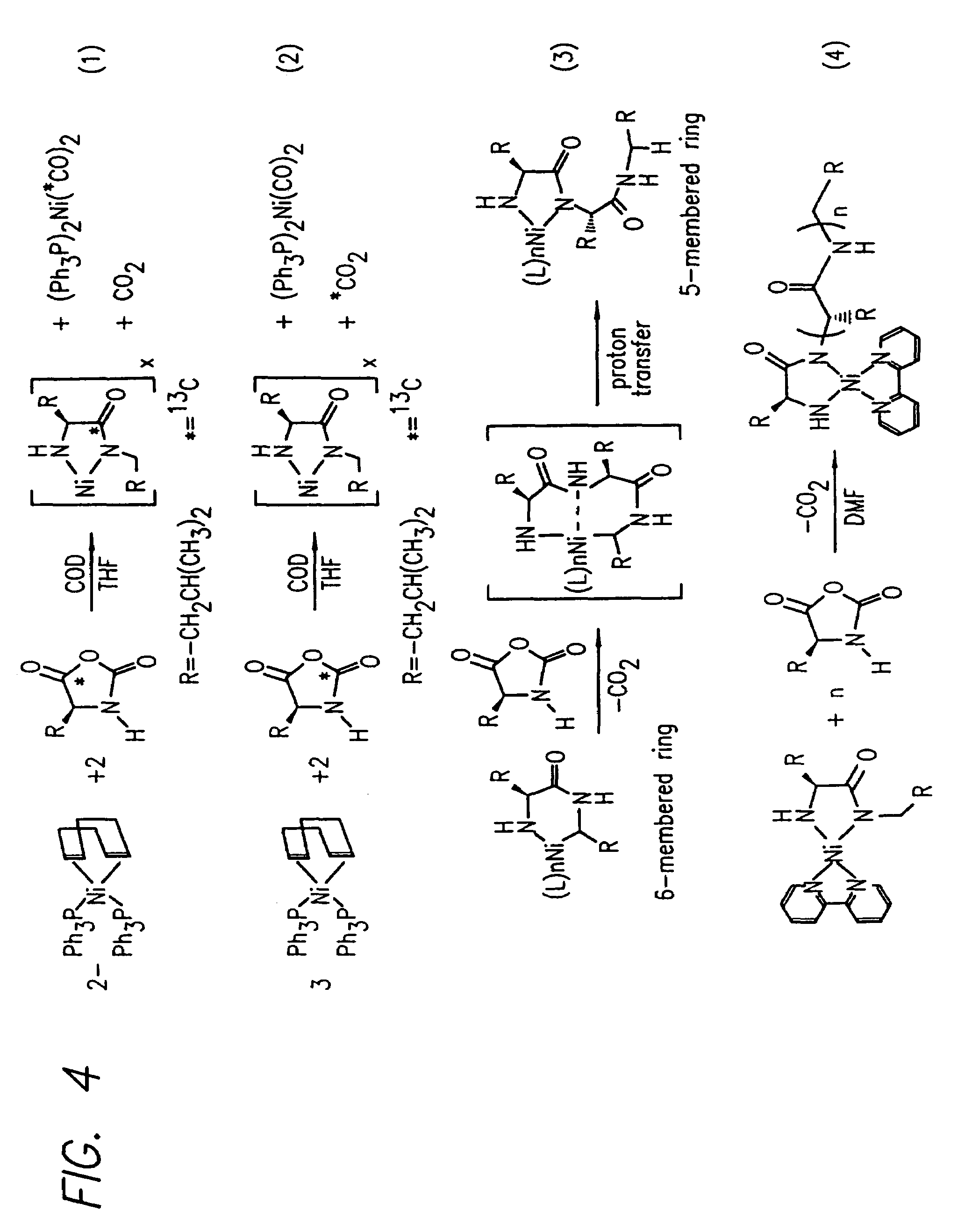
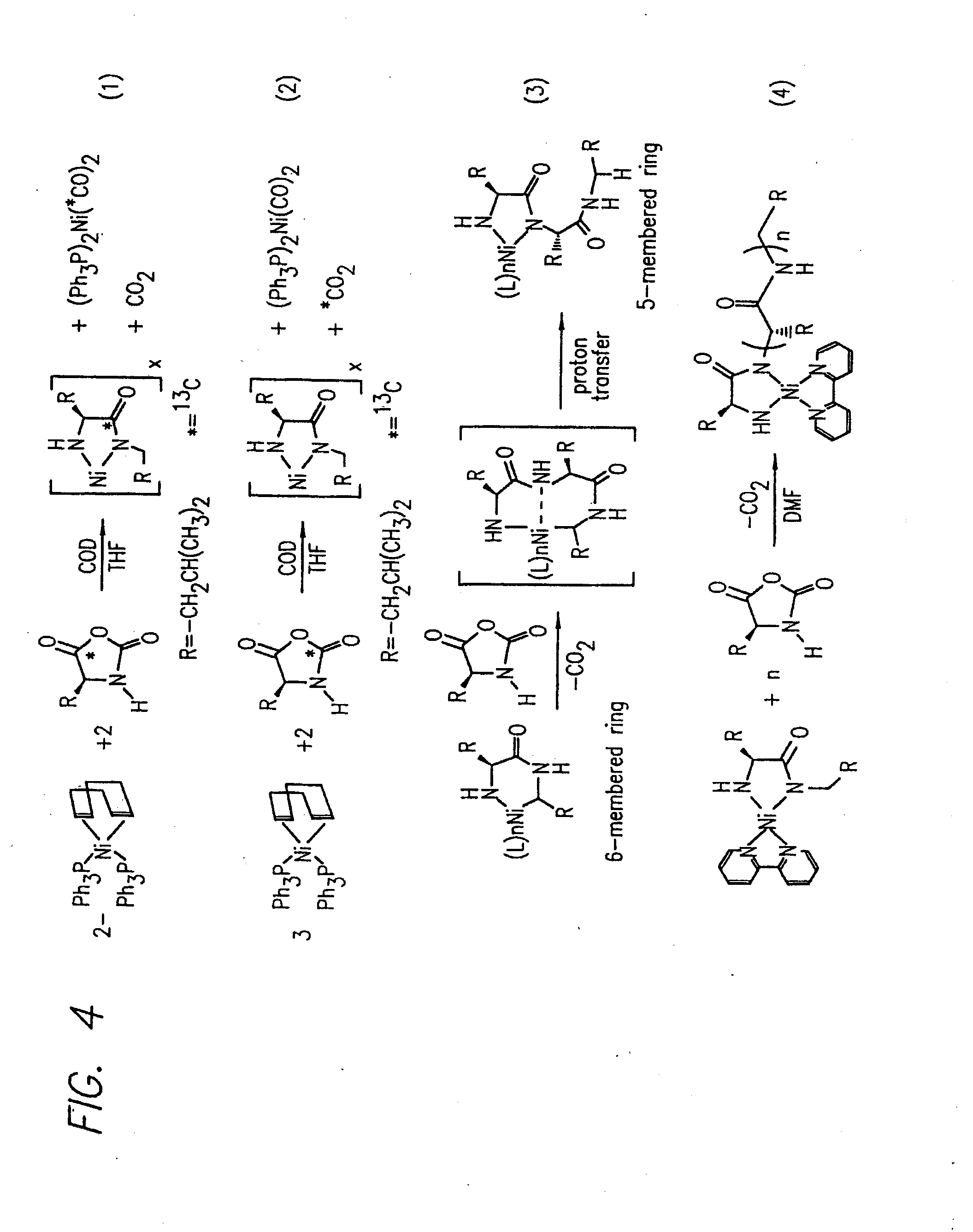
Methods and compositions for the generation of polypeptides having varied material properties are disclosed herein. Methods include means for initiating the polymerization of aminoacid-N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) monomer by combining the monomer with an amido-containing metallacycle, for making self assembling amphiphilic block copolypeptides and related protocols for adding oligo(ethyleneglycol) functionalized aminoacid-N-carboxyanhydrides (NCAs) to polyaminoacid chains. Additional methods include means of adding an end group to the carboxy terminus of a polyaminoacid chain by reacting an alloc-protected amino acid amide with a transition metal-donor ligand complex to forming an amido-amidate metallacycle for use in further polymerization reactions. Novel compositions for use in peptide synthesis and design including five and six membered amido-containing metallacycles and block copolypeptides are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Polymerization method for the synthesis of polypeptide imaging agents
InactiveUS20060104908A1Improve bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesPresent methodImaging agent
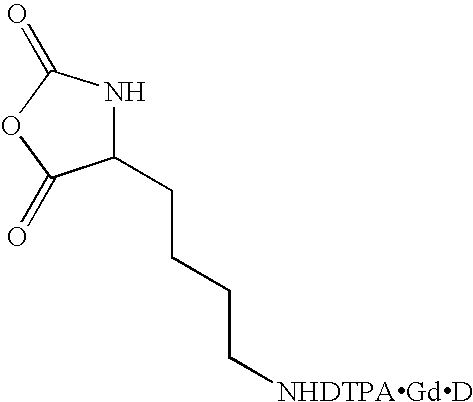
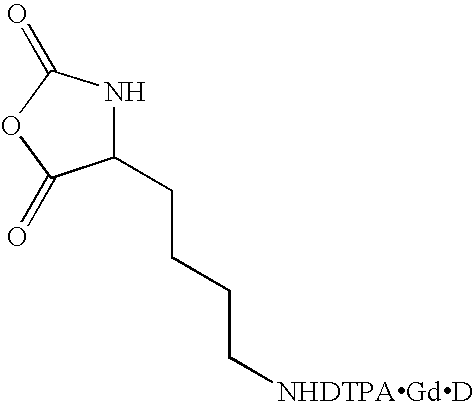
A method for synthesizing extended poly(amino acids) conjugated to imaging agents, such as DTPA, is disclosed. The amino acid is initially conjugated to the imaging agent at the monomer stage, followed by formation of the corresponding N-carboxyanhydride. The method utilizes catalyzed ring opening polymerization of the N-carboxyanhydride of the amino acid-imaging agent monomer allowing the formation of a poly(amino acid) backbone having 100% imaging agent conjugation if desired. However, the present method also permits the degree of conjugation to be controlled by copolymerizing the N-carboxyanhydride of the amino acid-imaging agent monomer with one or more unconjugated monomers, i.e. N-carboxyanhydrides of the same or of other amino acids. Various imaging agents may be employed, and new hybrid random, block, and mixed copolymers may be prepared.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Process for the preparation glatiramer acetate (copolymer-1)
InactiveUS20100324265A1Easy to optimizeShort reaction timePeptide-nucleic acidsNervous disorderBenzoyl bromideTyrosine
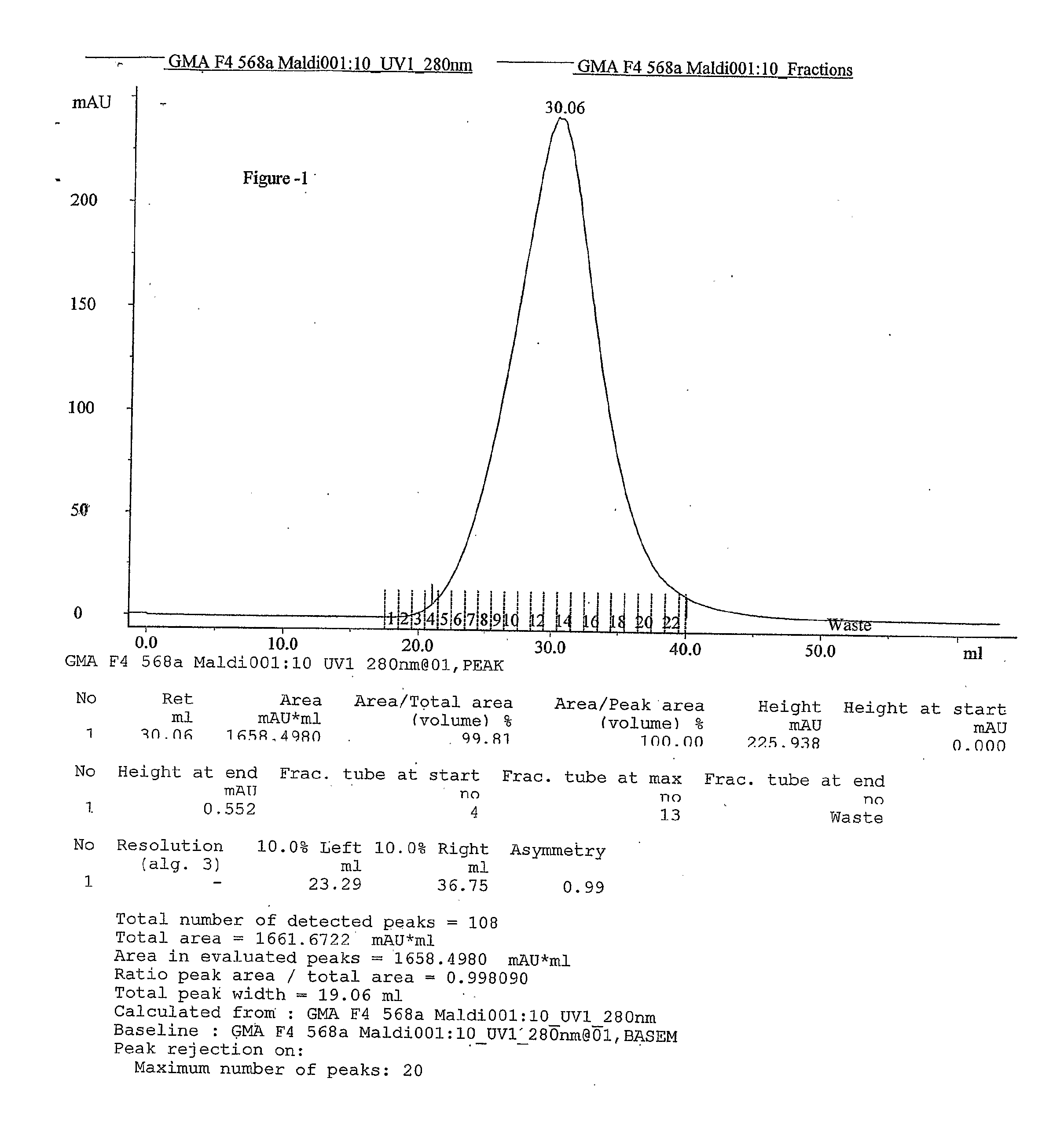
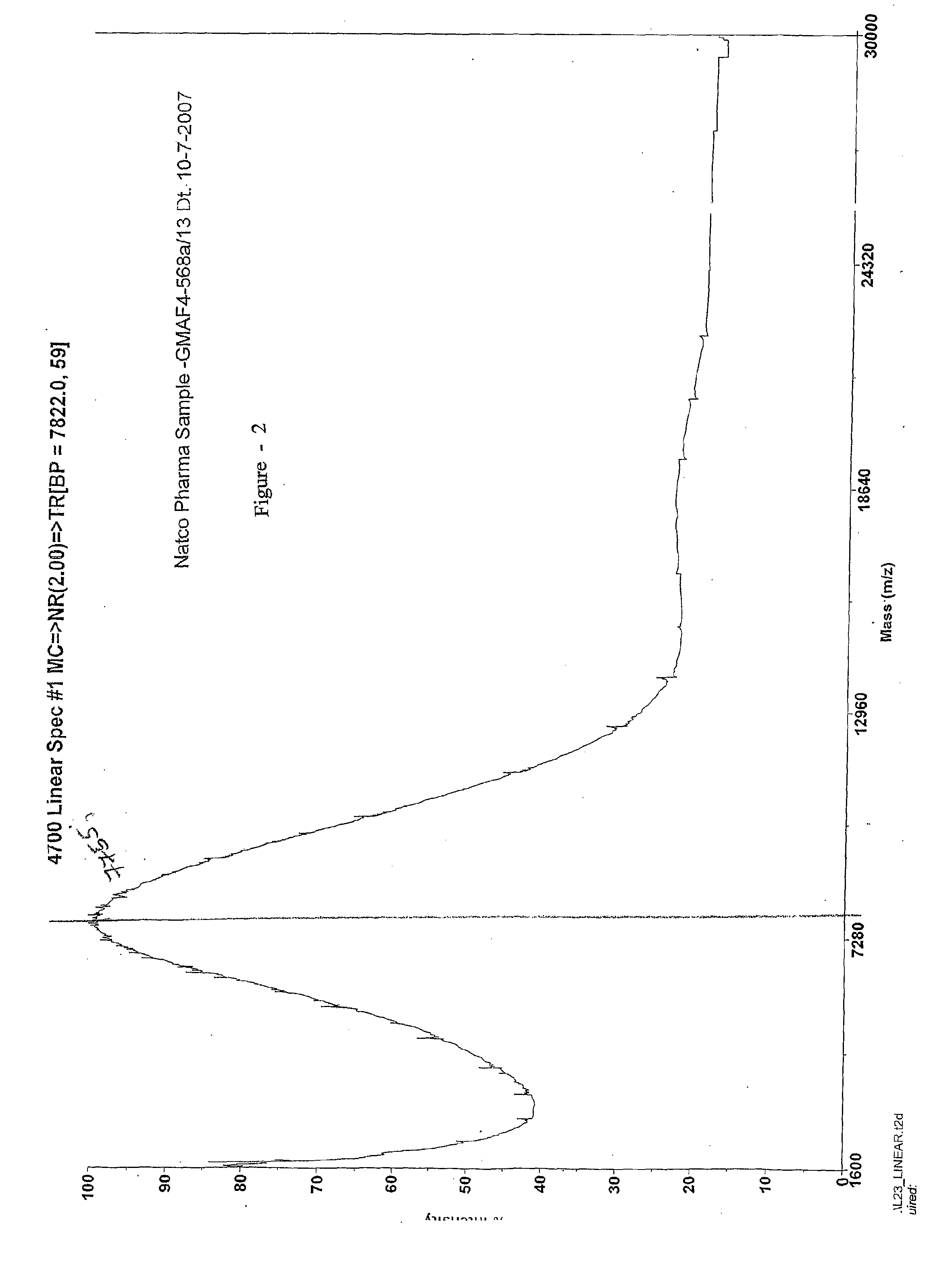
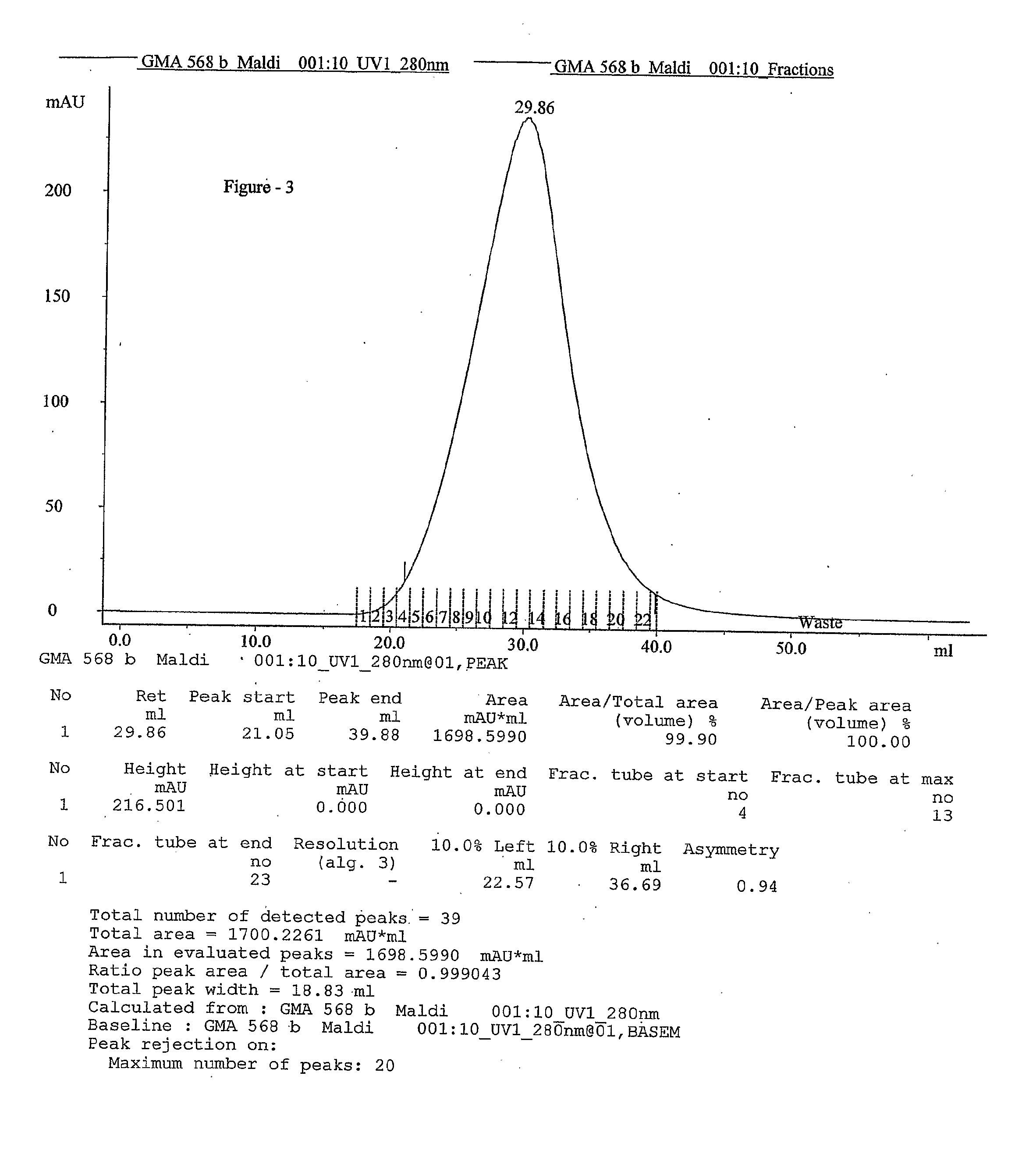
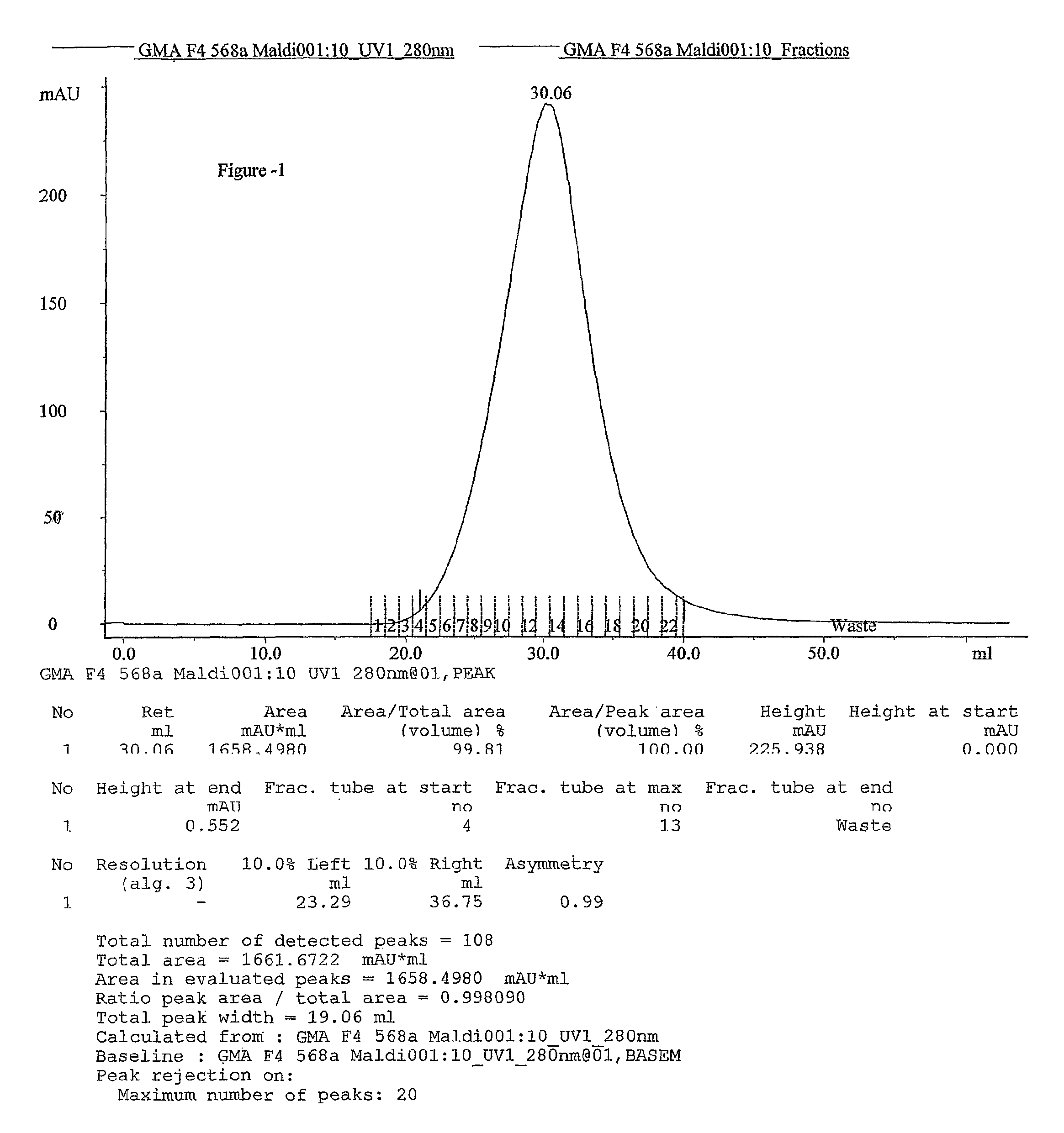
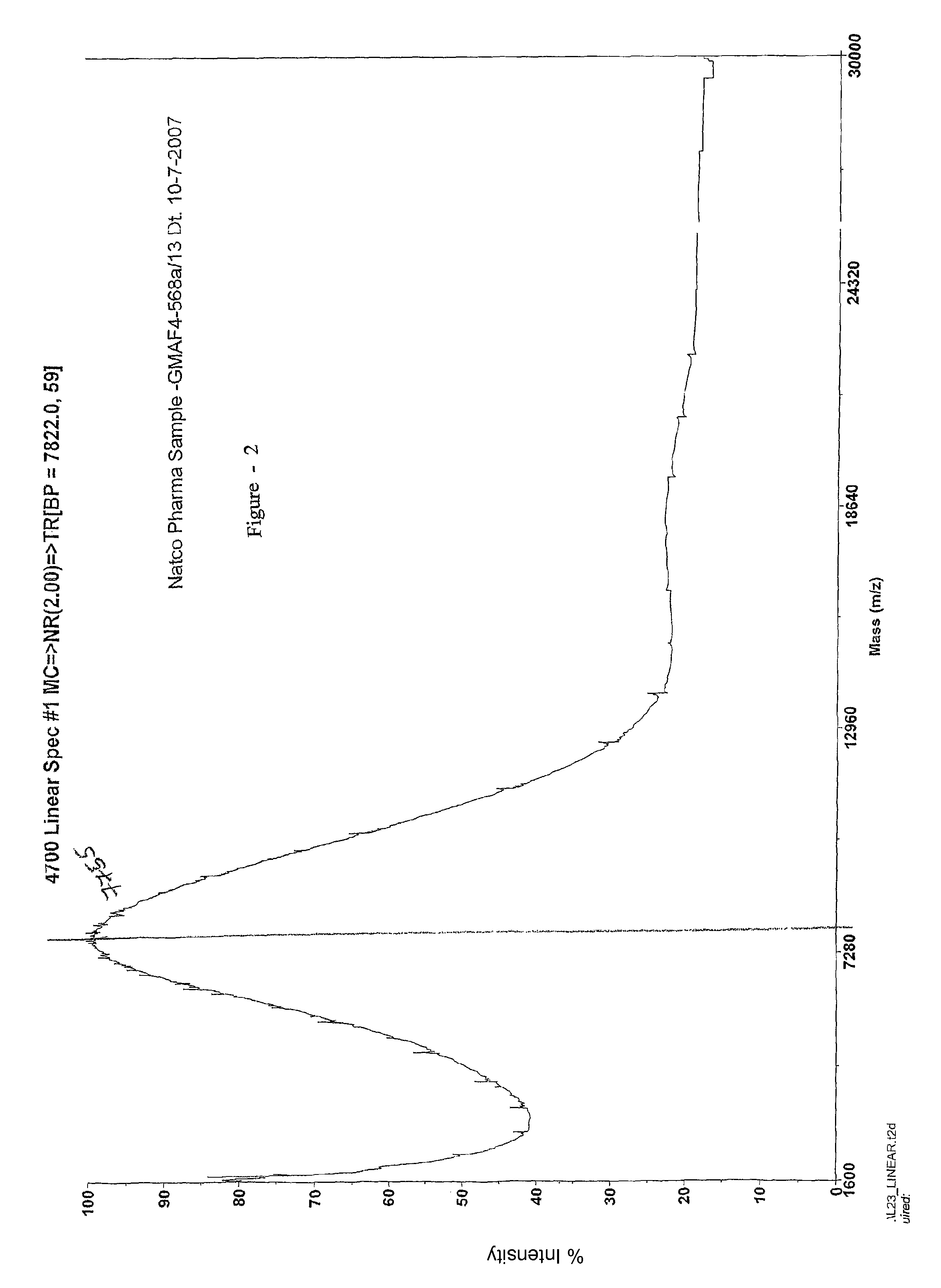
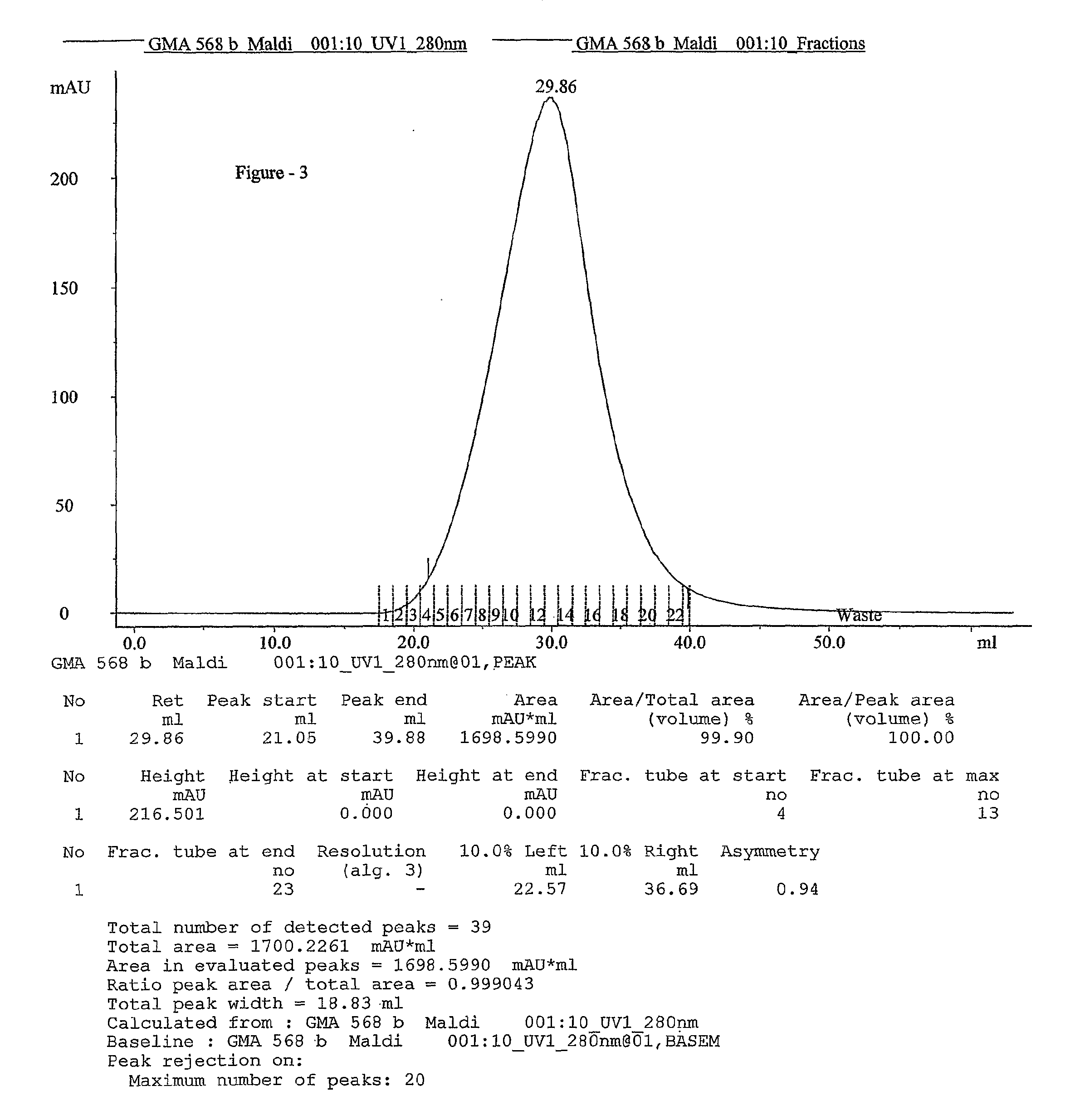
This invention relates to a convenient and improved process for preparation of glatiramer acetate (copolymer-1) of pharmaceutical grade. The process involves polymerizing N-carboxyanhydrides of tyrosine, alanine, y-benzyl glutamate and &egr;-N-trifluoroacetyllysine in dioxane with diethylamine as initiator to afford protected copolymer-1. Treatment with hydrogen bromide in acetic acid at 35° C. for 3-5 h cleaves benzyl group to produce trifluoroacetyl copolymer-1. The trifluoroacetyl copolymer-1 is washed with an organic solvent to remove reactive benzyl bromide generated during debenzylation. Deprotection with aqueous piperidine, followed by dialysis offers glatiramer acetate (copolymer-1) of Molecular weight 5000-9000 daltons.
Owner:NATCO PHARMA LTD
Methods and compositions for controlled polypeptide synthesis
InactiveUS7329727B2Elimination reactionEasy to controlPeptide/protein ingredientsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsEnd-groupSynthesis methods
Methods and compositions for the generation of polypeptides having varied material properties are disclosed herein. Methods include means for initiating the polymerization of aminoacid-N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) monomer by combining the monomer with an amido-containing metallacycle, for making self assembling amphiphilic block copolypeptides and related protocols for adding oligo(ethyleneglycol) functionalized aminoacid-N-carboxyanhydrides (NCAs) to polyaminoacid chains. Additional methods include means of adding an end group to the carboxy terminus of a polyaminoacid chain by reacting an alloc-protected amino acid amide with a transition metal-donor ligand complex to forming an amido-amidate metallacycle for use in further polymerization reactions. Novel compositions for use in peptide synthesis and design including five and six membered amido-containing metallacycles and block copolypeptides are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
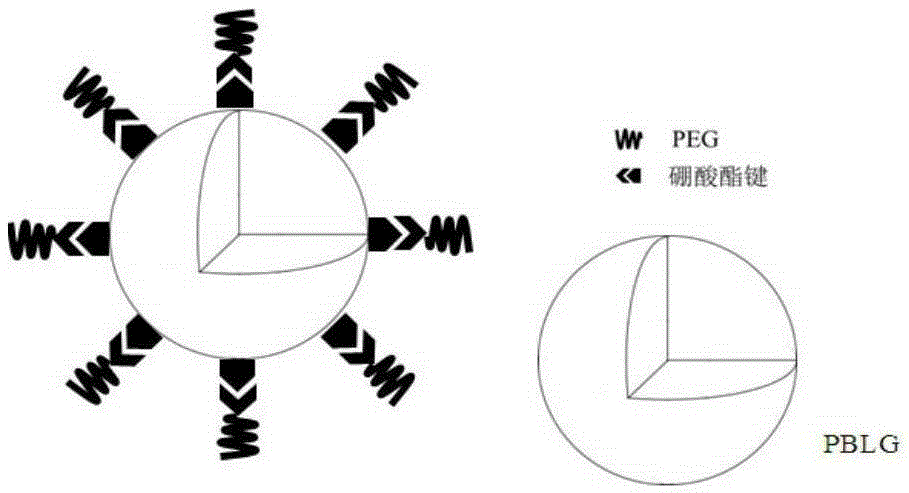
Block polymer with benzeneboronic acid ester as connecting unit, synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN105273205AGood drug releasePromote phagocytosisOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer scienceSynthesis methods
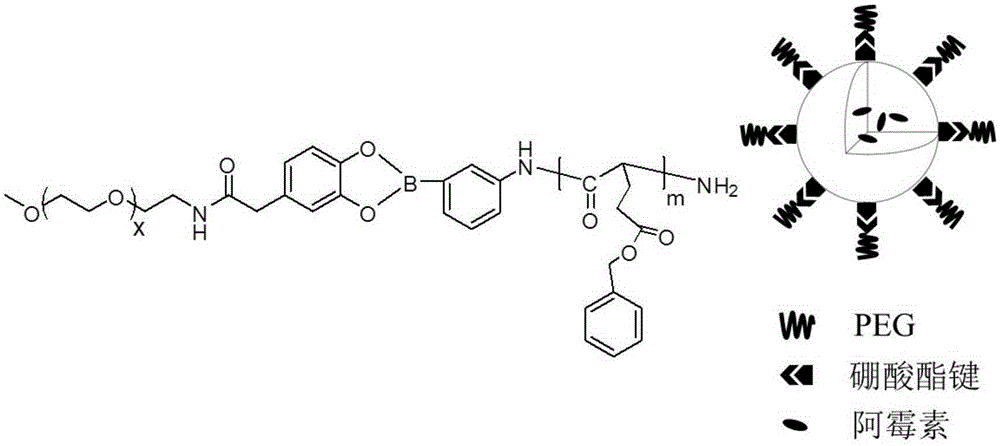
The invention discloses a diblock polymer with benzeneboronic acid ester as the connecting unit. Benzeneboronic acid catechol ester (BC) is adopted as the connecting unit to synthesize PEG-BC-PBLG diblock polymer so as to construct doxorubicin loaded micelle (PEG-BC@PBLG.Dox). The invention also discloses a preparation method of the diblock polymer, and the method includes: (1) preparing the dopa derivative PEG-3, 4-DA of PEG-NH2; (2) subjecting PEG-3, 4-DA and 3-aminophenylboronic acid to dehydration condensation so as to synthesize the benzeneboronic acid ester derivative PEG-BC of PEG; and (3) using PEG-BC to perform ring opening on 5-benzyl ester-L-glutamic acid-N-carboxyanhydride (BLG-NCA), thus obtaining the diblock polymer PEG-BC-PBLG with benzeneboronic acid ester as the connecting unit. The diblock polymer prepared by the method provided by the invention can be used for construction of a nano-micelle, and has the advantages of good drug release, low cytotoxicity and good cell phagocytosis.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for preparing nano hydroxylapatite hybridized material with surface grafting polypeptide
The invention provides a nano-hydroxyl apatite hybrid material which is grafted with peptide on the surface and a method for making the same. First of all, the nano- hydroxyl apatite is treated with a silane coupling agent gamma-amino propyl triethoxy which contains amido, the amido is introduced in the surface of the nano-hydroxy apatite; then, gamma-benzyl-L-glutamate N- carboxyanhydride ring-opening polymerization are caused by using the nano- hydroxyl apatite hybrid material which containing the amido on the surface, so as to get the nano- hydroxyl apatite hybrid material which is grafted with polypeptide on the surface. This method is universally used, by adopting the nano-hydroxy apatite with amido to evoke N-carboxyanhydride of other amino acid, the peptides with different functions are easily to be connected to the surface of hydroxyl apatite through chemical bond to give the hydroxyl apatite new biological properties, therefore having a very good application value.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and compositions for controlled polypeptide synthesis
InactiveUS20120088848A1Eliminate chain-breaking side reactionEasy to controlSugar derivativesIron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesEnd-groupSynthesis methods
Methods and compositions for the generation of polypeptides having varied material properties are disclosed herein. Methods include means for initiating the polymerization of aminoacid-N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) monomer by combining the monomer with an amido-containing metallacycle, for making self assembling amphiphilic block copolypeptides and related protocols for adding oligo(ethyleneglycol) functionalized aminoacid-N-carboxyanhydrides (NCAs) to polyaminoacid chains. Additional methods include means of adding an end group to the carboxy terminus of a polyaminoacid chain by reacting an alloc-protected amino acid amide with a transition metal-donor ligand complex to forming an amido-amidate metallacycle for use in further polymerization reactions. Novel compositions for use in peptide synthesis and design including five and six membered amido-containing metallacycles and block copolypeptides are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Process for the preparation glatiramer acetate (copolymer-1)
InactiveUS8993722B2Easy to optimizeShort reaction timePeptide-nucleic acidsNervous disorderAcetic acidBenzoyl bromide
This invention relates to a convenient and improved process for preparation of glatiramer acetate (copolymer-1) of pharmaceutical grade. The process involves polymerizing N-carboxyanhydrides of tyrosine, alanine, y-benzyl glutamate and ε-N-trifluoroacetyllysine in dioxane with diethylamine as initiator to afford protected copolymer-1. Treatment with hydrogen bromide in acetic acid at 35° C. for 3-5 h cleaves benzyl group to produce trifluoroacetyl copolymer-1. The trifluoroacetyl copolymer-1 is washed with an organic solvent to remove reactive benzyl bromide generated during debenzylation. Deprotection with aqueous piperidine, followed by dialysis offers glatiramer acetate (copolymer-1) of Molecular weight 5000-9000 daltons.
Owner:NATCO PHARMA LTD
Method for preparing amino acid N-carboxyanhydride
InactiveCN103204821AImprove decomposition rateHigh yieldOrganic chemistryDecompositionN carboxyanhydride
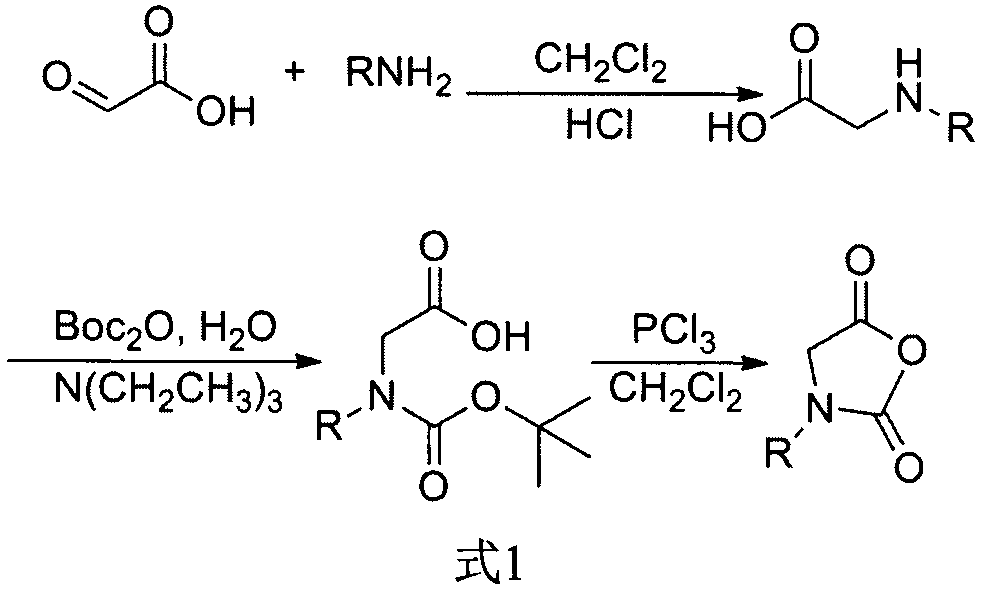
The invention provides a method for preparing amino acid N-carboxyanhydride. The method includes enabling amino acid to react with triphosgene to generate the corresponding amino acid N-carboxyanhydride in the presence of triphosgene decomposition catalysts under the condition that anhydrous tetrahydrofuran is used as a solvent. The method has the advantages that the triphosgene decomposition catalysts are utilized and are beneficial to increasing the decomposition rate of the triphosgene, accordingly, the reaction time is shortened, the yield of the amino acid-NCA (N-carboxyanhydride) is increased, and the reaction yield is particularly greatly increased when R-groups of the amino acid are short.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
Synthesis of amino acid, N-carboxyanhydrides
ActiveUS20060106229A1Easy to handleFaster rateOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationN carboxyanhydrideCarbonylation
A process for producing N-carboxyanhydrides is disclosed. The process produces N-carboxyanhydrides as a product and HCl as a by-product. The HCl by-product is purged from the reaction mixture by passing a purge gas through the reaction mixture as a carbonylation reagent is reacting with an amino acid or a salt thereof. The N-carboxyanhydrides produced by this process have a relatively lower chloride impurity content, relatively higher yields can be achieved, and the N-carboxyanhydrides can be produced on a larger scale.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
MPEG-poly(L-glutamic acid-gamma-hydrazide)-PDMAPMA triblock copolymer, and synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN104086721AAvoid enzymatic actionAchieve removalOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsN carboxyanhydrideHydrazide
The invention discloses a synthesis method and an application of an mPEG-poly(L-glutamic acid-gamma-hydrazide)-PDMAPMA triblock copolymer. According to the invention, end methoxy polyethylene glycol is subjected to cystamine modification; a gamma-benzyl ester-L-glutamic acid-N-carboxyanhydride ring-opening polymerization reaction is initiated; with a carbodiimide method, a small-molecular RAFT polymerization chain-transfer agent is bonded to an obtained diblock copolymer; RAFT polymerization is carried out with N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)methacrylamide as a monomer; and benzyl group is removed through hydrazinolysis, such that polyethylene glycol-poly(L-glutamic acid-gamma-hydrazide)-poly(N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)methacrylamide) triblock copolymer is obtained. With the synthesis method provided by the invention, molecular weights and chain lengths of all blocks of polymers can be flexibly controlled. Reaction conditions are mild, and raw materials are easy to obtain. The copolymer has a characteristic that the copolymer is amphiphilic when loading adriamycin, such that the block copolymer can be self-assembled into nano-particles. The copolymer can load chemotherapeutic drugs and genetic drugs at a same time. Drug potency is high, and toxic and side effects are greatly reduced.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Convertible surface charge nano-gel, preparation method thereof and convertible surface charge nano-gel drug-loaded particle
ActiveCN104817688AGood biocompatibilityRealize smart releasePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a preparation method of convertible surface charge nano-gel. The preparation method includes the steps: A) dissolving an initiating agent with a morpholinyl group and L-glutamic acid polyethylene glycol single methyl ether-N-carboxyanhydride into an organic solvent for reaction to obtain mixed solution; B) mixing a compound with a formula (I) structure, a compound with a formula (II) structure and the mixed solution obtained in the step A) for reaction to obtain reaction solution; C) mixing and filtering the reaction solution obtained in the step B) and the organic solvent to obtain the convertible surface charge nano-gel. A convertible surface charge nano-gel drug-loaded particle has no toxic and side effects on human bodies and has excellent water solubility, stability and biocompatibility.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Amphiphilic molecule hydrogel based on polyamino acid
The invention discloses an amphiphilic molecule hydrogel based on polyamino acid. The structural formula of the amphiphilic molecule hydrogel based on the polyamino acid is as shown in a formula I, wherein x in the formula is a natural number in the range from 4-16, and n is a natural number in the range of 10-50. A preparation method of the amphiphilic molecule hydrogel based on the polyamino acid provided by the invention and shown in the formula I comprises the following steps: (1) reacting glutamic acid with 2-(2-Methoxyethoxy)ethanol under the action of an acid catalyst so as to obtain an amino acid compound, the lateral chain of which has the 2-(2-Methoxyethoxy)ethanol; (2) reacting the amino acid compound, the lateral chain of which has the 2-(2-Methoxyethoxy)ethanol, with triphosgene so as to obtain an N-carboxyanhydride compound; and (3) carrying out ring-opening polymerization reaction on the N-carboxyanhydride compound under the triggering action of alkyl chain primary amine, thus obtaining the amphiphilic molecule hydrogel based on polyamino acid. The amphiphilic molecule hydrogel based on the polyamino acid has biocompatibility, biodegradability and other properties. Compared with other polyamino acid-based hydrogel, the amphiphilic molecule hydrogel has the advantages of low cost and easiness in realization of large-scale production and a very wide application prospect in the field of biological materials.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Genetic vector system and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103497961ALow toxicityImprove binding efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting groupCytotoxicity
The invention provides a genetic vector system. The genetic vector system comprises a pH sensitive masking system, a cation carrier and a genetic material, wherein the pH sensitive masking system is a polymer obtained by reaction of polyglutamate, 2-(Boc-amino)ethanethiol and mercaptoacetic acid and with removal of t-butyloxycarboryl protection, the polyglutamate is obtained by gamma-propinyl-L-glutamic acid-N-carboxyanhydride initiated by polyethyleneimine or micromolecule alkyl amine through ring opening polymerization, the mass ratio of the pH sensitive masking system and the cation carrier is (2-100):1, the mass ratio of the pH sensitive masking system and the genetic material is (5-80):1, and the genetic material is plasmid DNAs or siRNAs. The invention also provides a preparation method of the genetic vector system and an amino acid polymer. The genetic vector can introduce relatively multiple electrified groups, the using amount of the masking system is reduced, and the cytotoxicity generated by the masking system can be reduced when the genetic vector system is used.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Synthesis of amino acid, N-carboxyanhydrides
ActiveUS7294719B2Faster rateReduce concentrationOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationN carboxyanhydrideCarbonylation
A process for producing N-carboxyanhydrides is disclosed. The process produces N-carboxyanhydrides as a product and HCl as a by-product. The HCl by-product is purged from the reaction mixture by passing a purge gas through the reaction mixture as a carbonylation reagent is reacting with an amino acid or a salt thereof. The N-carboxyanhydrides produced by this process have a relatively lower chloride impurity content, relatively higher yields can be achieved, and the N-carboxyanhydrides can be produced on a larger scale.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Process for the synthesis of an ace inhibitor
InactiveUS20090069574A1Organic chemistryHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsOrganic solventN carboxyanhydride
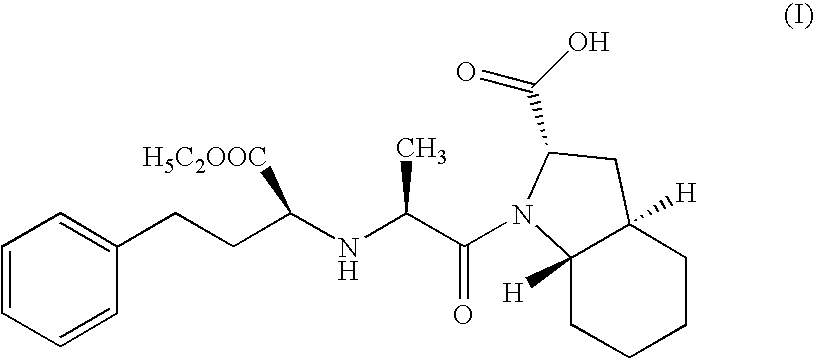
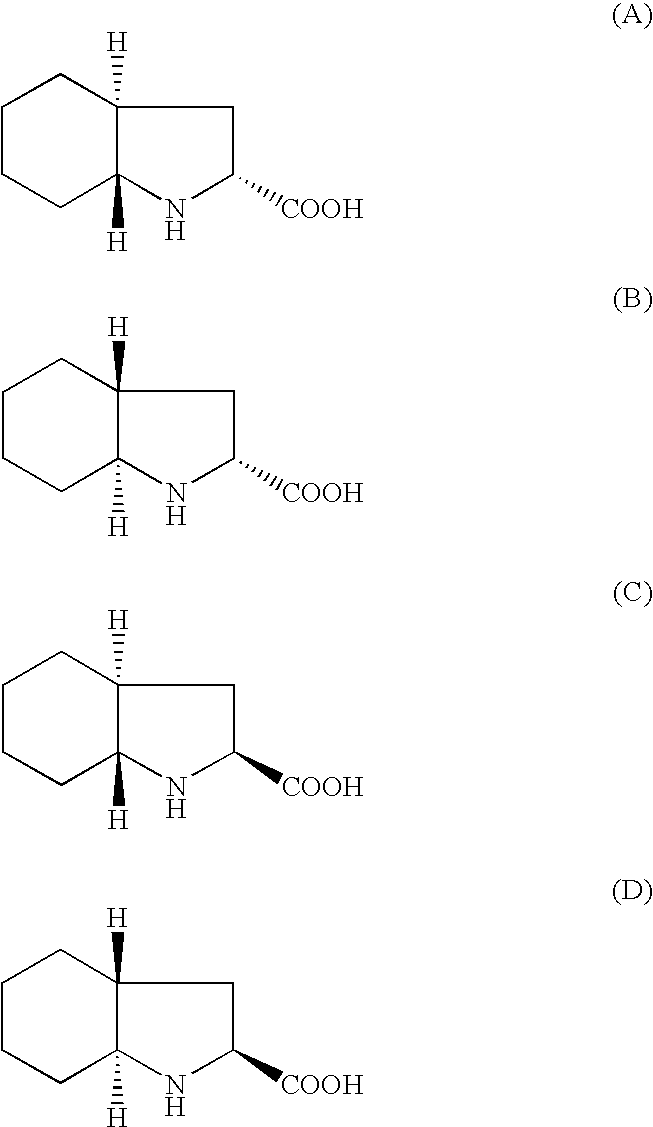
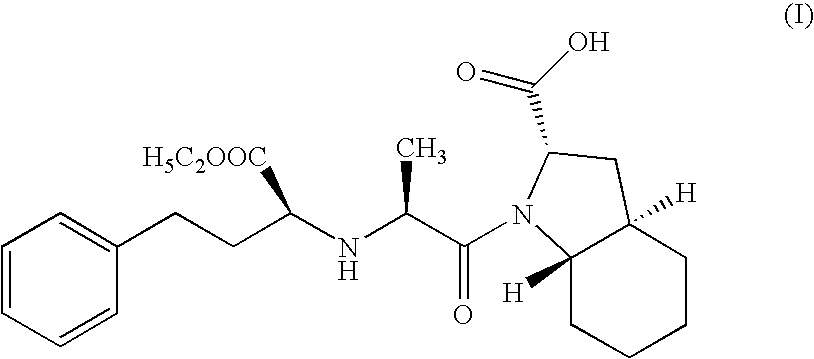
A process for the synthesis of trandolapril which comprises condensing N-[I-(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl]-L-alanine N-carboxyanhydride with trans octahydro-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid in a first organic solvent comprising a water immiscible inert organic solvent and in the presence of a base, and isolating trandolapril from a second organic solvent. N-[1-(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl]-L-alanine N-carboxyanhydride may also be condensed with (2S,3aR,7aS) octahydro-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid in a first organic solvent and in the presence of a base, and trandolapril isolated. There is also provided a process for the resolution of racemic trans octahydro-1H-indole-2-carboxylc acid.
Owner:CIPLA LTD
Polymerization method for the synthesis of polypeptide imaging agents
A method for synthesizing extended poly(amino acids) conjugated to imaging agents, such as DTPA, is disclosed. The amino acid is initially conjugated to the imaging agent at the monomer stage, followed by formation of the corresponding N-carboxyanhydride. The method utilizes catalyzed ring opening polymerization of the N-carboxyanhydride of the amino acid-imaging agent monomer allowing the formation of a poly(amino acid) backbone having 100% imaging agent conjugation if desired. However, the present method also permits the degree of conjugation to be controlled by copolymerizing the N-carboxyanhydride of the amino acid-imaging agent monomer with one or more unconjugated monomers, i.e. N-carboxyanhydrides of the same or of other amino acids. Various imaging agents may be employed, and new hybrid random, block, and mixed copolymers may be prepared.
Owner:GENRERAL ELECTRIC CO
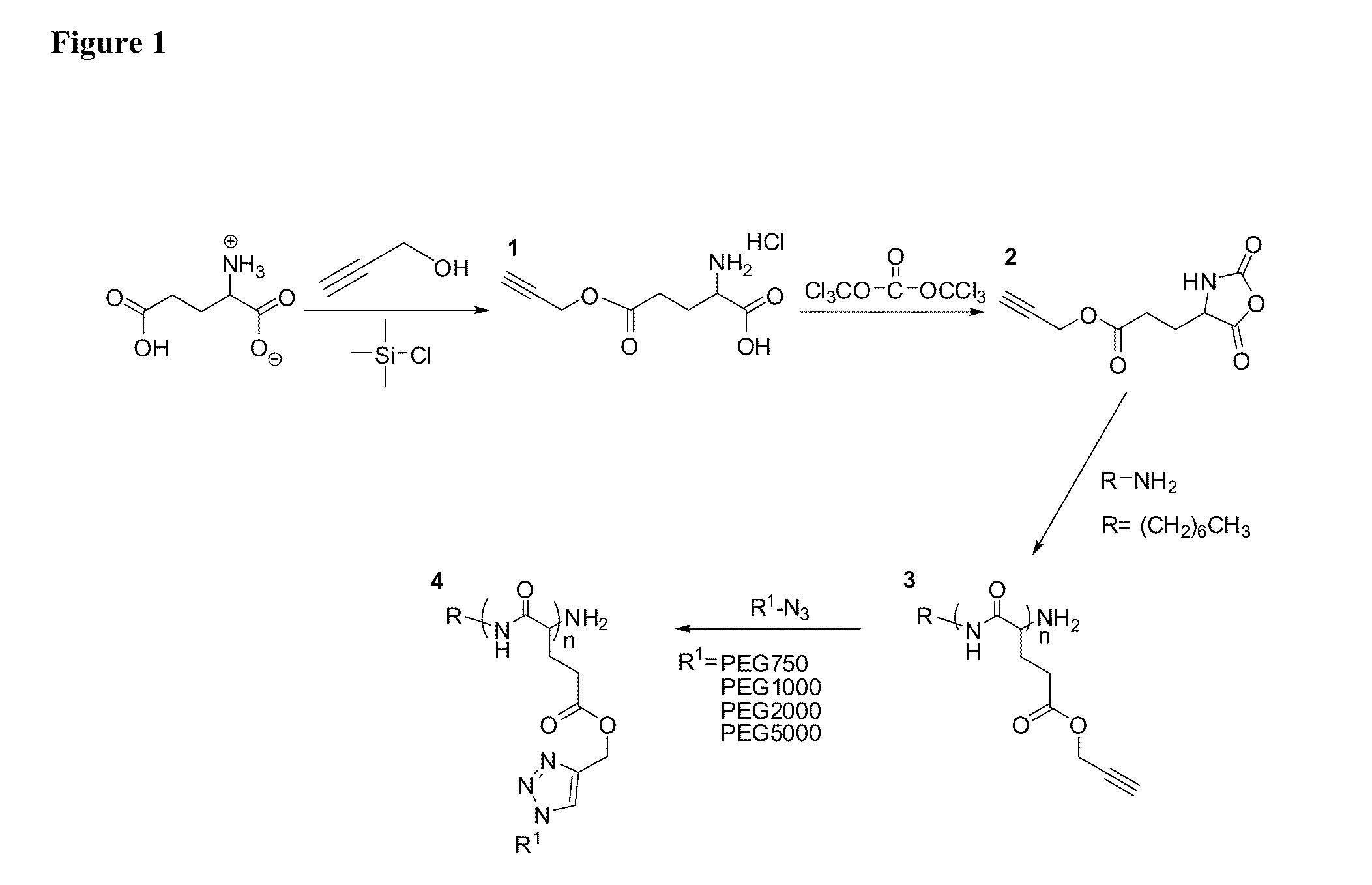
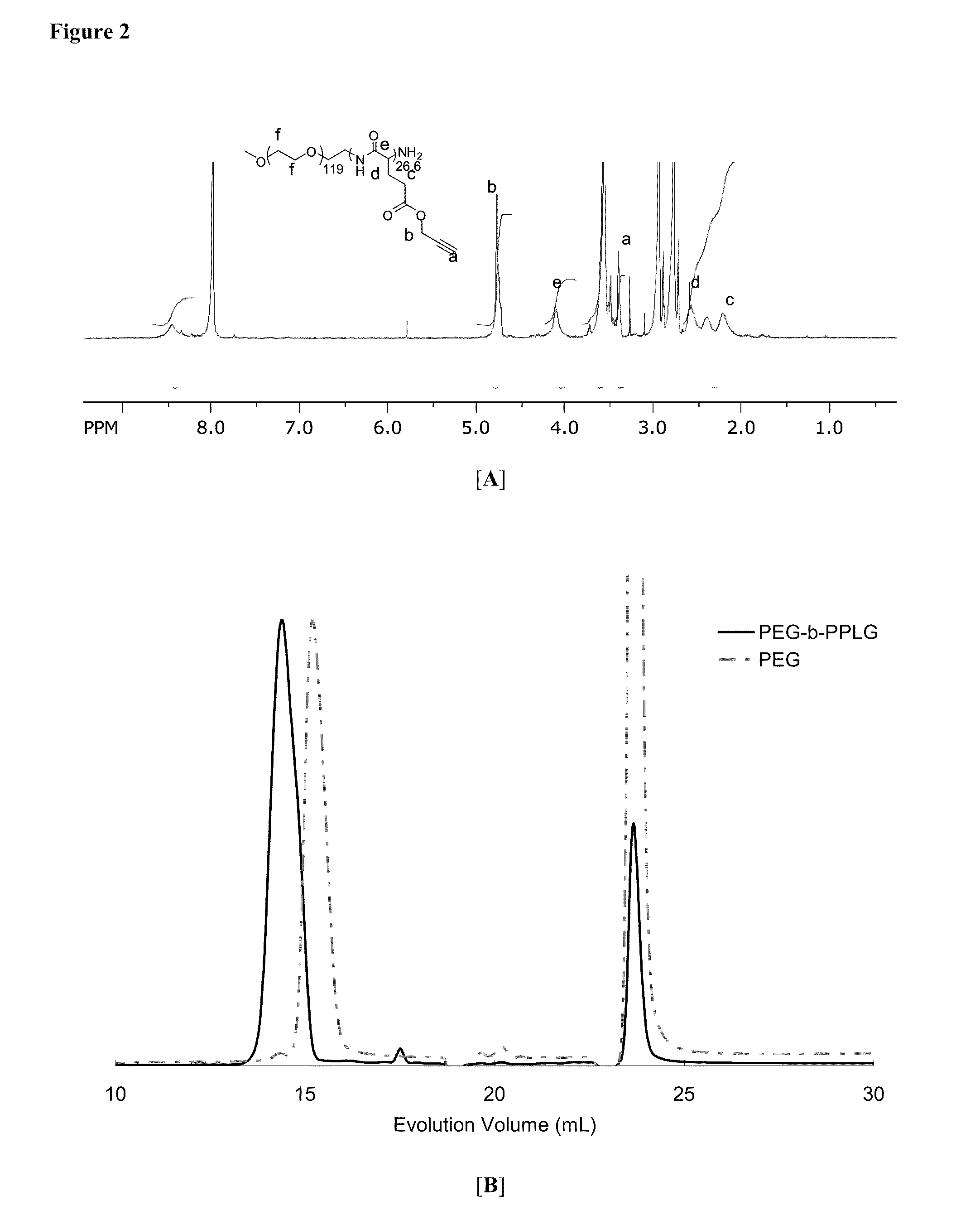
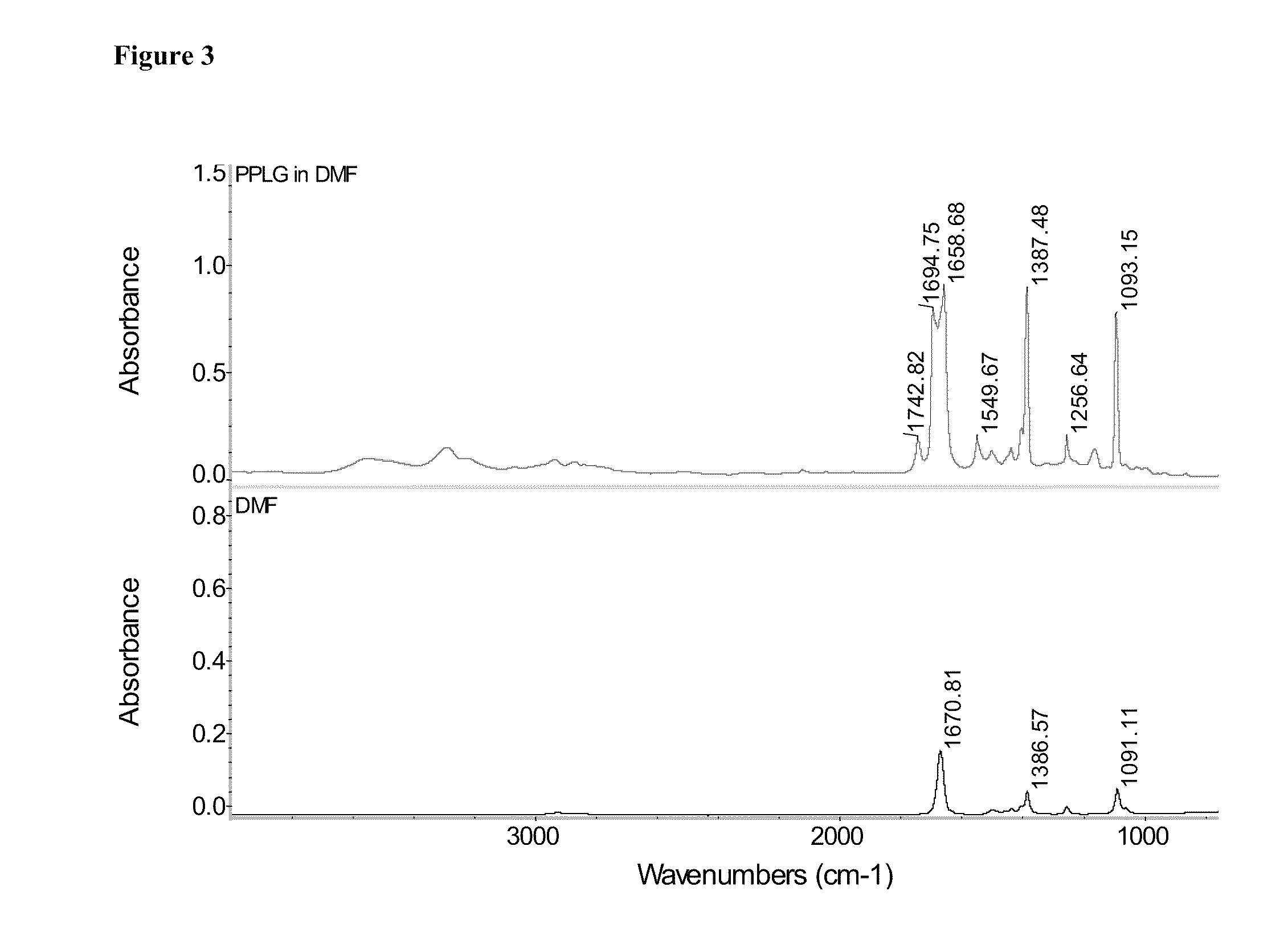
Poly(Propargyl-L-Glutamate) and Derivatives Thereof
A process of the present invention is directed toward conducting highly selective, high yield post-polymerization reactions on polypeptides to prepare functionalized polypeptides. In certain embodiments, the polypeptides can be prepared by ring opening polymerization of N-carboxyanhydrides. In certain embodiments, the post-polymerization reaction is a “click chemistry” reaction. In certain embodiment, the “click chemistry” reaction is a triazole-forming reaction involving an alkyne on the polypeptide and an azide.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
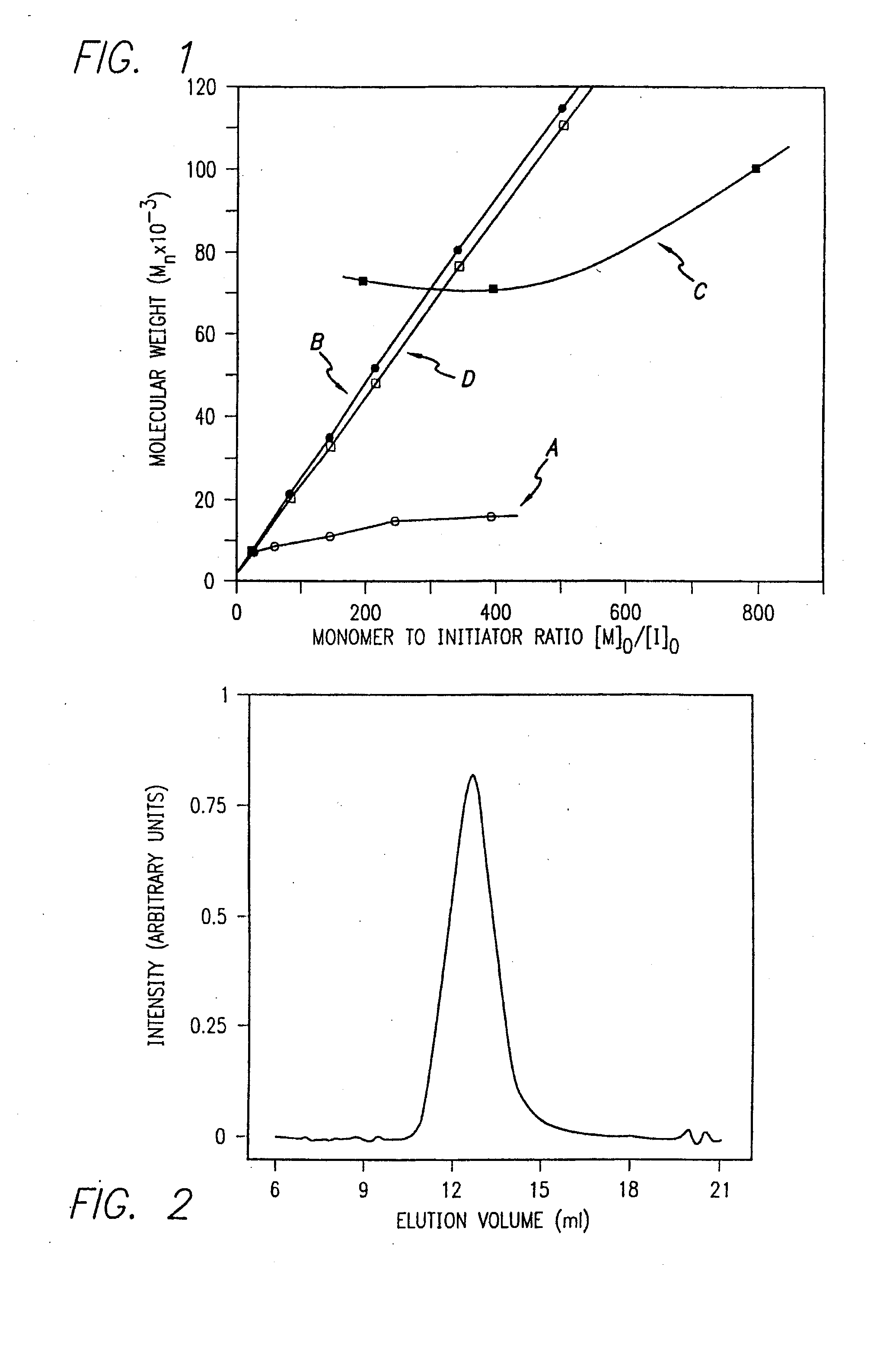
Controlled Synthesis of Polyglutamates with Low Polydispersity and Versatile Architectures
ActiveUS20150087788A1Lowering indexDegree of improvementRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsDispersityImaging agent
Polyglutamates are well known to be highly biocompatible, biodegradable and multifunctional polymers, which have been already used as building blocks in polymer drug conjugates and polymeric micelles. Those systems have been applied to various medical applications ranging from therapy to molecular imaging. Furthermore a polyglutamic acid (PGA) paclitaxel conjugate has already entered clinical studies (Opaxio™ PGA-PTX conjugate currently in phase III of Clinical trials).In this context, a synthetic pathway to a plethora functional polyglutamates (homopolymers, block-co-polymers, triblocks) with well-defined structure, adjustable molecular weight (Mw) and low dispersity (D=Mw / Mn<1.2) applying the ring opening polymerization (ROP) of N-carboxyanhydrides (NCA) has been developed. Additionally, the acid moieties of the polyglutamates can be activated with 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium (DMTMM) and various functionalities can be easily introduced by “post-polymerization modification” yielding a set orthogonal reactive attachment sides. The reactive moieties, such as azides, maleimides, thiols, alkynes (linear or cyclic) offer the opportunity of specific conjugation of the drugs, targeting moieties or markers. Besides introducing reactive groups the functionalization strategy was also used for PEGylation of PGA reducing charge induced interactions and therefore pharmacological properties, such as blood circulation time may be adjusted.In summary, a tool kit of various polyglutamates has been developed enabling the synthesis of a variety of polymer drug conjugates or polymer based imaging agents. The functional polymeric precursors developed will allow us to functionalize and therefore adjust the polymer properties to a desired application.
Owner:FUNDACION DE LA COMUNIDAD VALENCIANA CENT DE INVESTIGACION PRINCIPE FELIPE
Controlled synthesis of polyglutamates with low polydispersity and versatile architectures
ActiveUS9623125B2Degree of improvementImprove versatilityRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsDispersityImaging agent
Polyglutamates are well known to be highly biocompatible, biodegradable and multifunctional polymers, which have been already used as building blocks in polymer drug conjugates and polymeric micelles. Those systems have been applied to various medical applications ranging from therapy to molecular imaging. Furthermore a polyglutamic acid (PGA) paclitaxel conjugate has already entered clinical studies (Opaxio™ PGA-PTX conjugate currently in phase III of Clinical trials).In this context, a synthetic pathway to a plethora functional polyglutamates (homopolymers, block-co-polymers, tribocks) with well-defined structure, adjustable molecular weight (Mw) and low dispersity (D=Mw / Mn<1.2) applying the ring opening polymerization (ROP) of N-carboxyanhydrides (NCA) has been developed. Additionally, the acid moieties of the polyglutamates can be activated with 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium (DMTMM) and various functionalities can be easily introduced by “post-polymerization modification” yielding a set orthogonal reactive attachment sides. The reactive moieties, such as azides, maleimides, thiols, akynes (linear or cyclic) offer the opportunity of specific conjugation of the drugs, targeting moieties or markers. Besides introducing reactive groups the functionalization strategy was also used for PEGylation of PGA reducing charge induced interactions and therefore pharmacological properties, such as blood circulation time may be adjusted.In summary, a tool kit of various polyglutamates has been developed enabling the synthesis of a variety of polymer drug conjugates or polymer based imaging agents. The functional polymeric precursors developed will allow us to functionalize and therefore adjust the polymer properties to a desired application.
Owner:FUNDACION DE LA COMUNIDAD VALENCIANA CENT DE INVESTIGACION PRINCIPE FELIPE
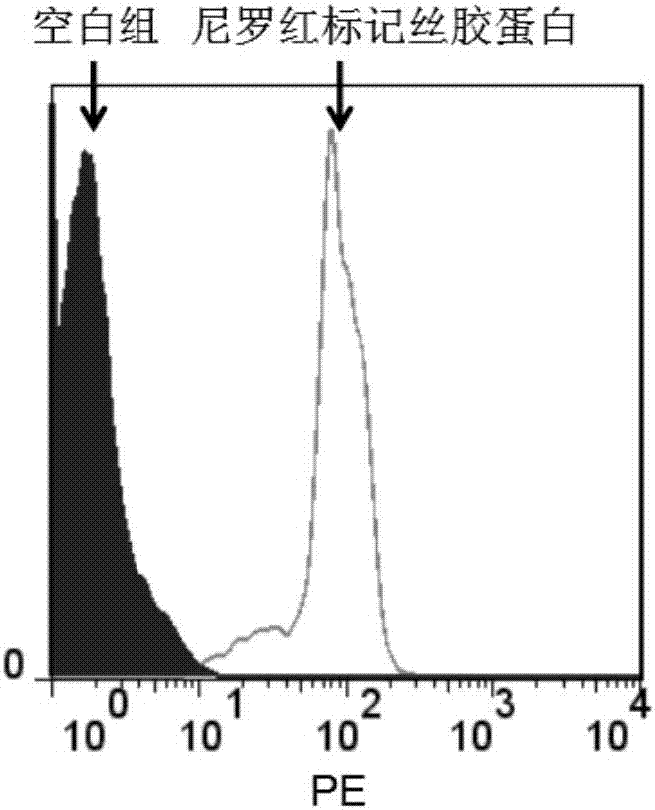
Preparation of sericine bound paclitaxel nano-drug sericin-PBLG-PTX-Nile-red and application thereof in tumor tracing and treatment
InactiveCN106963732AEfficient and fast accessSafe entryOrganic active ingredientsEmulsion deliverySericinWilms' tumor
The invention discloses preparation of a sericine bound paclitaxel nano-drug sericin-PBLG-PTX-Nile-red and application thereof in tumor tracing and treatment. According to the invention, sericine is adopted as the hydrophilic segment, hydrophobic polypeptide is taken as the hydrophobic segment, and alpha-amino acid-N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) ring-opening reaction is carried out to prepare an amphiphilic sericine polymer. At the same time, amphiphilic sericine is taken as the carrier to load a non-water soluble antitumor drug paclitaxel and a Nile red fluorescent agent by means of hydrophobic interaction, thus obtaining the sericin-PBLG-PTX-Nile-red. The sericin-PBLG-PTX-Nile-red is expected to be applied in the tumor field as a novel controlled release drug with excellent performance and efficient antitumor activity.
Owner:胡彦锋 +2
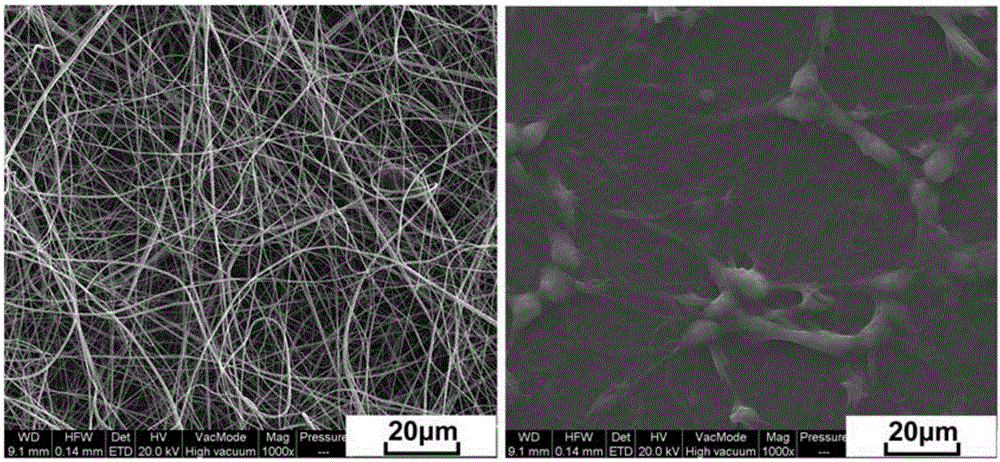
Zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105713205AMechanical controlRegulation of biodegradabilityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsChemical structureClick chemistry
The invention discloses a zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that firstly, inherent amidogens of zein macromolecules are utilized to trigger an N-carboxyanhydride monomer containing azide functional groups for ring opening polymerization, azide-containing side-group polypeptide modified zein is obtained, and galactose is grafted to a polypeptide chain segment side group so as to obtain the zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer. The zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer prepared by means of the preparation method can be used for preparing a corresponding electrospun fibrous membrane serving as a liver cell scaffold material by adopting an electrospinning technique. The main raw material used for the zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer belongs to a natural vegetable protein, a grafted glycopolypeptide chain segment is of a chemical structure similar to a glycoprotein in a living body, and therefore the prepared zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer and the electrospun membrane scaffold material thereof have very good biocompatibility and bionic characteristics.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
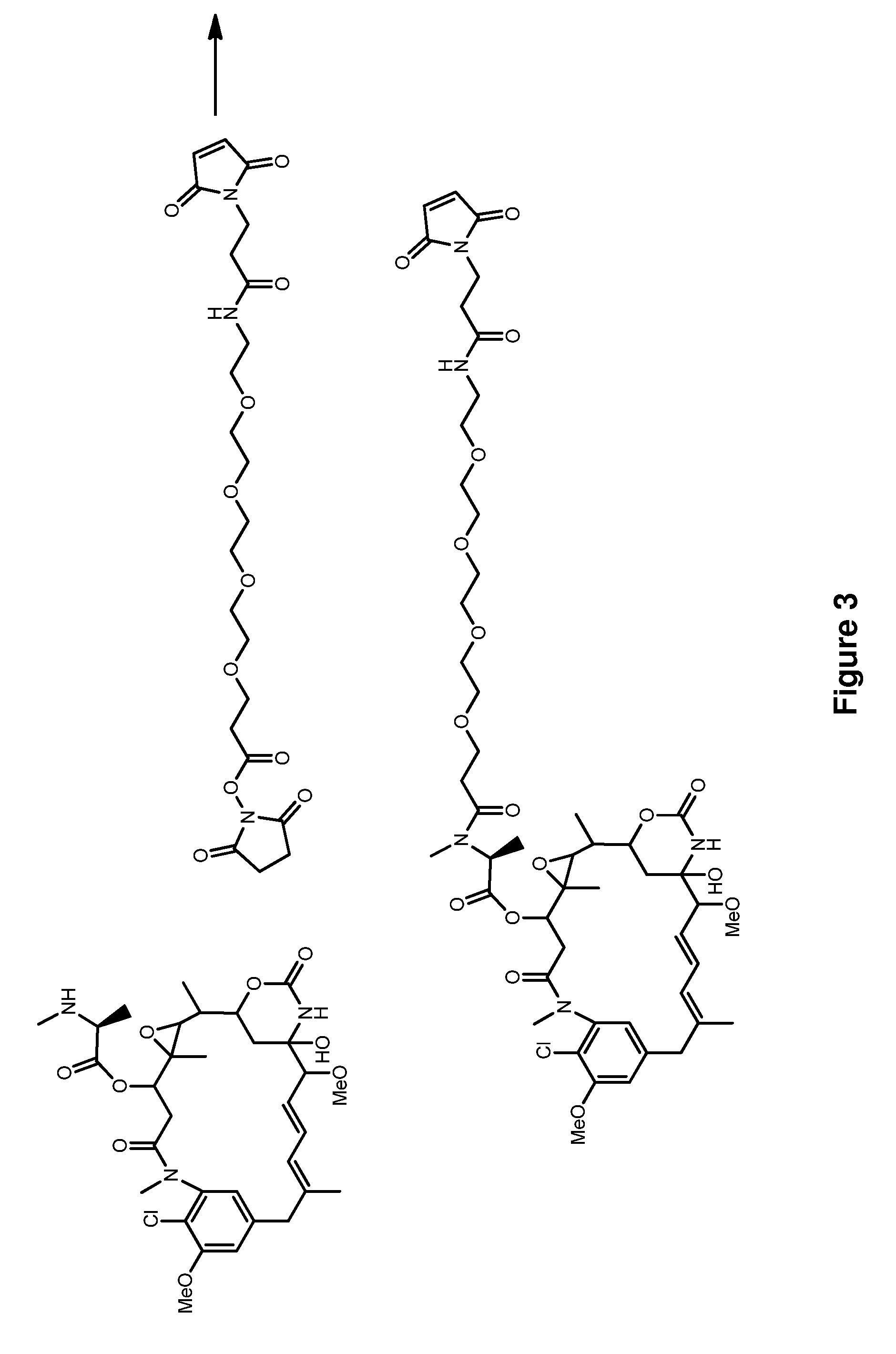
Methods for the acylation of maytansinol
ActiveUS9012629B2Increase productionReduce formationOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsN carboxyanhydrideImproved method
Disclosed is a method of preparing an amino acid ester of maytansinol by reacting maytansinol with an N-carboxyanhydride of an amino acid (NCA) in the presence of a drying agent. Also disclosed is an improved method of preparing an amino acid ester of maytansinol in which a nucleophile is added to the reaction mixture after completion of the reaction between maytansinol and an N-carboxyanhydride of an amino acid.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Process for the synthesis of an ACE inhibitor
A process for the synthesis of trandolapril which comprises condensing N—[I—(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl]-L-alanine N-carboxyanhydride with trans octahydro-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid in a first organic solvent comprising a water immiscible inert organic solvent and in the presence of a base, and isolating trandolapril from a second organic solvent. N-[1-(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl]-L-alanine N-carboxyanhydride may also be condensed with (2S,3aR,7aS) octahydro-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid in a first organic solvent and in the presence of a base, and trandolapril isolated. There is also provided a process for the resolution of racemic trans octahydro-1H-indole-2-carboxylc acid.
Owner:CIPLA LTD
Method for synthesizing quantum dot-polypeptide compound with peptoid connecting arm
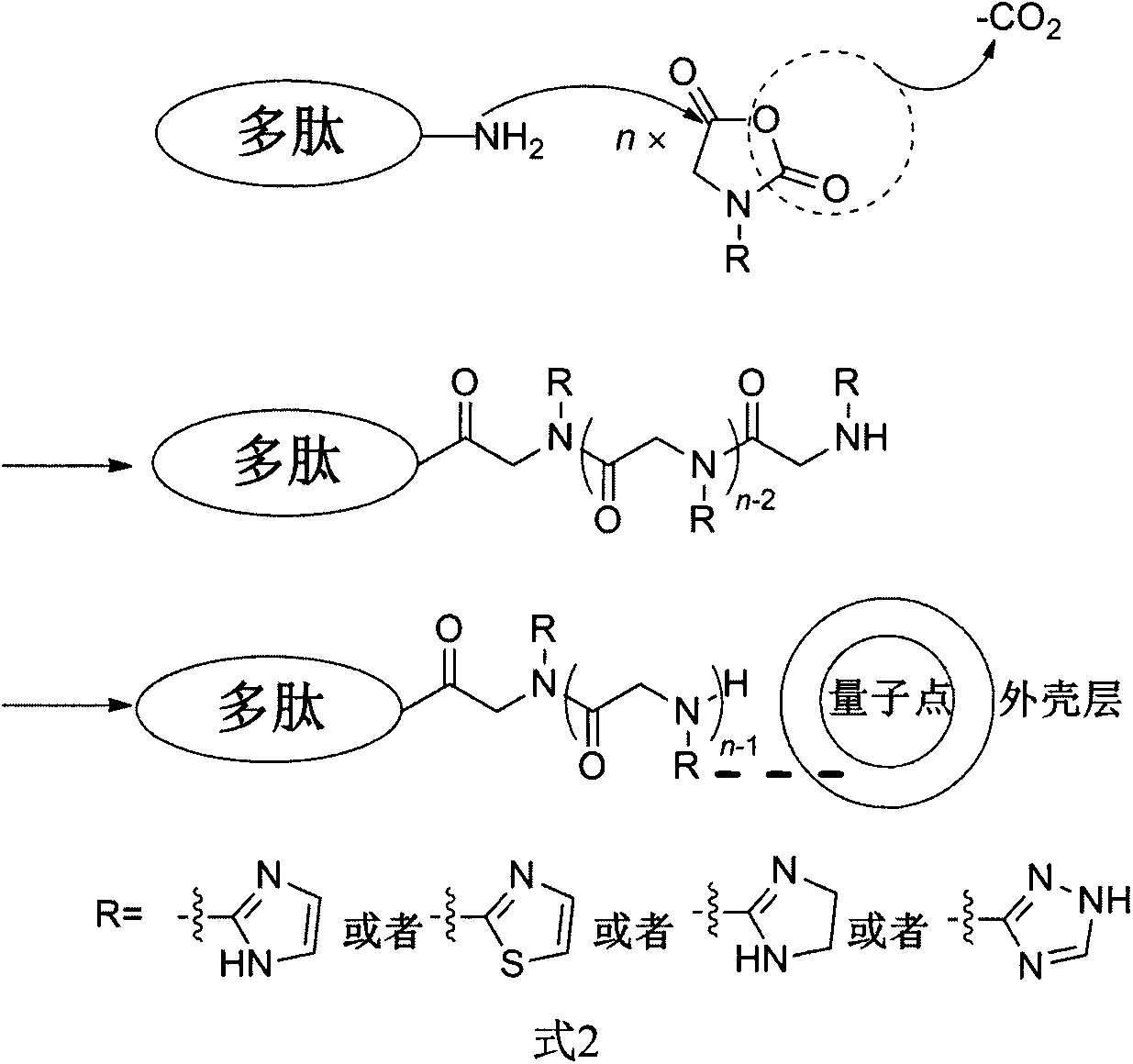
ActiveCN104231036AImprove luminescence stabilityAchieve connectionPeptide preparation methodsLuminescent compositionsMetalloleSide chain
The invention provides a method for synthesizing a quantum dot-polypeptide compound with a peptoid connecting arm. The method comprises the following steps: initiating ring opening polymerization of N-substituted-N-carboxyanhydride by the terminal amino group of polypeptide to form a peptoid connecting arm with a designated polymerization degree; and chelating the base substituent group of a peptoid side chain and metal ions on the outer shell layer of the quantum dot to synthesize the quantum dot-polypeptide compound.
Owner:贾明宏
Methods for crystallization of n-(1(s)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl)-l-alanine n-carboxyanhydride
InactiveUS20020137944A1Promote crystallizationOrganic chemistryCardiovascular disorderAliphatic hydrocarbonN carboxyanhydride
A crystallization is carried out by adding a solution of N-(1(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl)-L-alanine N-carboxylic anhydride in a good solvent to an aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent while inhibiting the oil formation and scaling of said N-carboxylic anhydride. Further, a crystallization is carried out by adding an aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent sequentially to a solution of N-(1(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl)-L-alanine N-carboxylic anhydride in a good solvent over not less than ¼ of an hour and at a temperature of not higher than 60° C.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Methods for the acylation of maytansinol
ActiveUS20140142297A1Increase productionReduce formationOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsN carboxyanhydrideImproved method
Disclosed is a method of preparing an amino acid ester of maytansinol by reacting maytansinol with an N-carboxyanhydride of an amino acid (NCA) in the presence of a drying agent. Also disclosed is an improved method of preparing an amino acid ester of maytansinol in which a nucleophile is added to the reaction mixture after completion of the reaction between maytansinol and an N-carboxyanhydride of an amino acid.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Methods for crystallization of N-(1(s)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl)-L-alanine N-carboxyanhydride
A crystallization is carried out by adding a solution of N-(1(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl)-L-alanine N-carboxylic anhydride in a good solvent to an aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent while inhibiting the oil formation and scaling of said N-carboxylic anhydride.Further, a crystallization is carried out by adding an aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent sequentially to a solution of N-(1(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl)-L-alanine N-carboxylic anhydride in a good solvent over not less than ¼ of an hour and at a temperature of not higher than 60° C.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
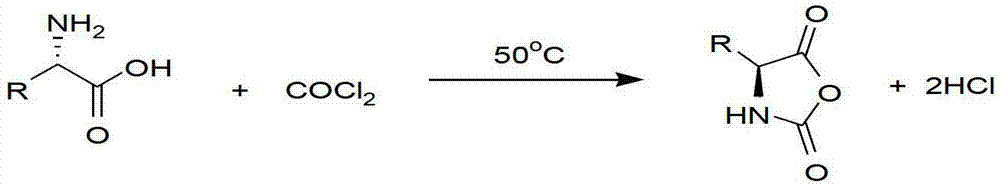
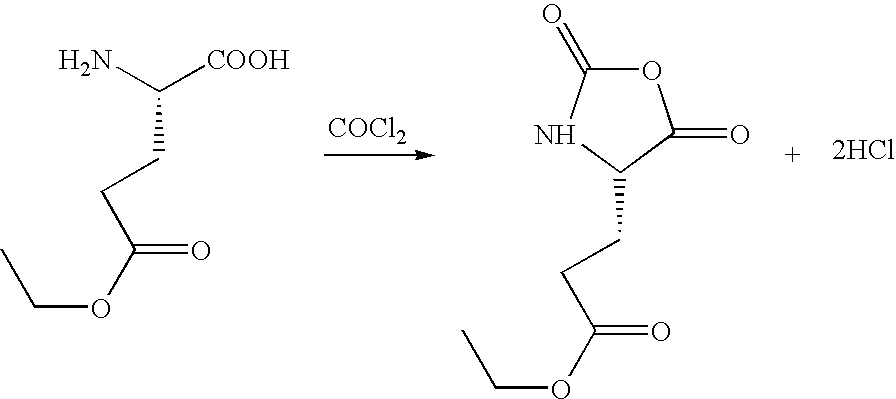
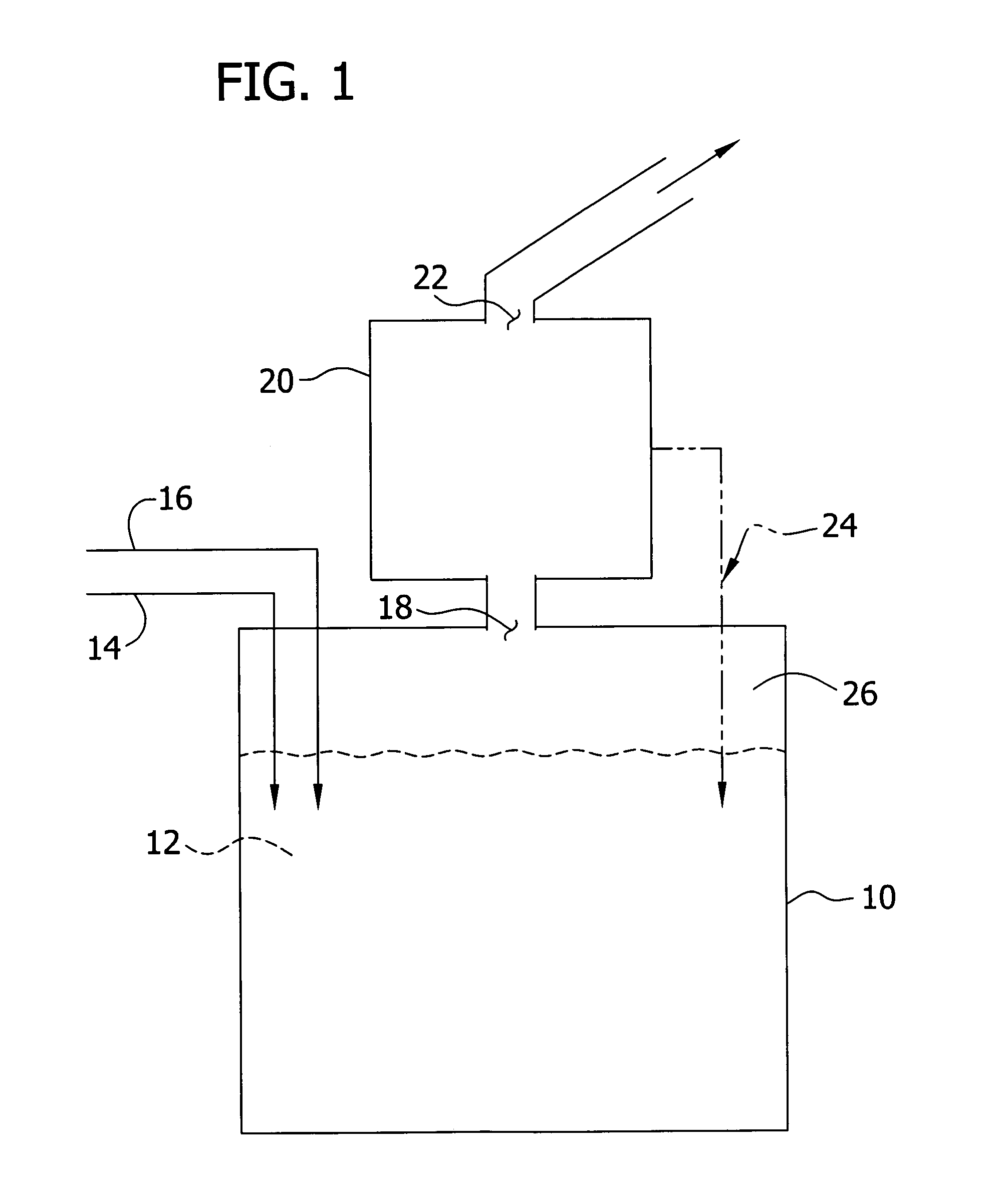
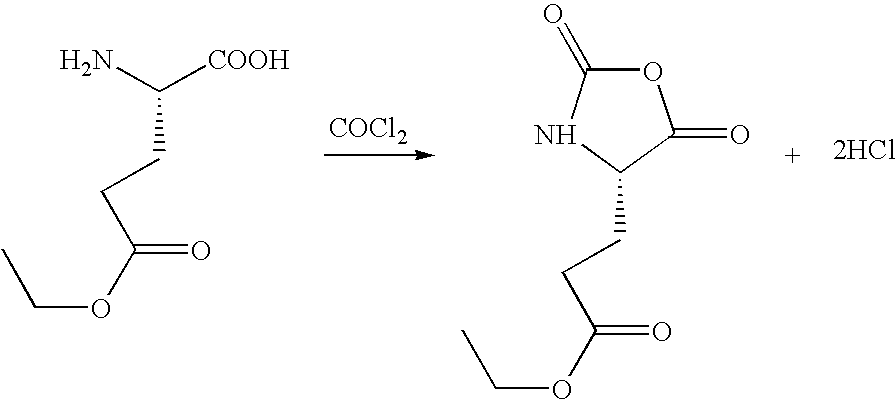
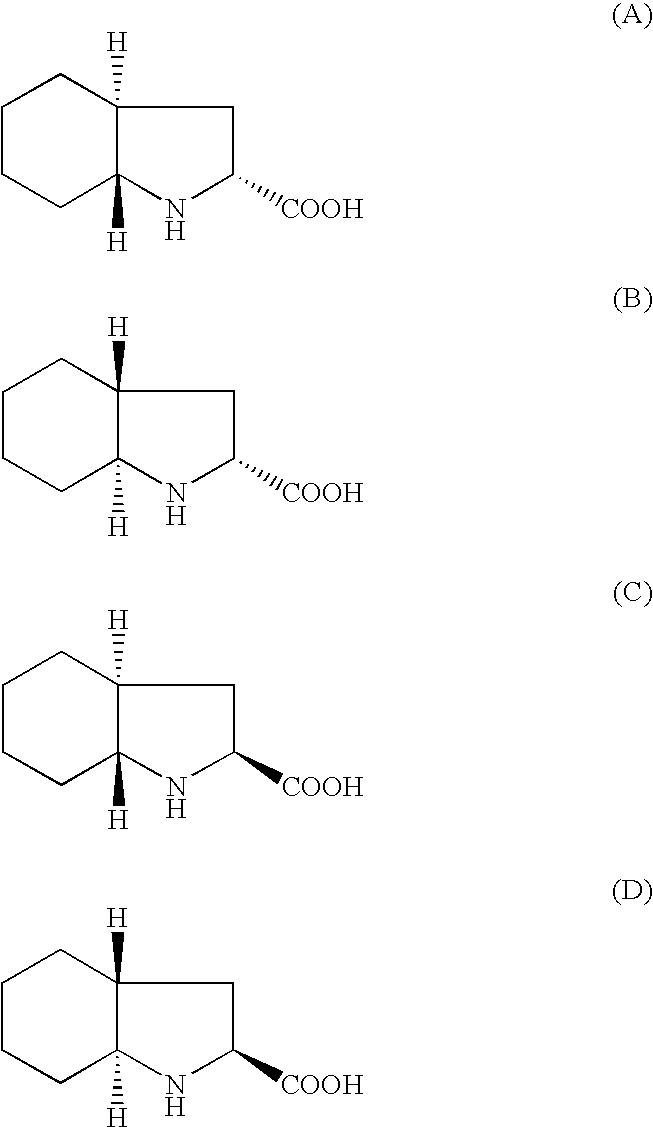
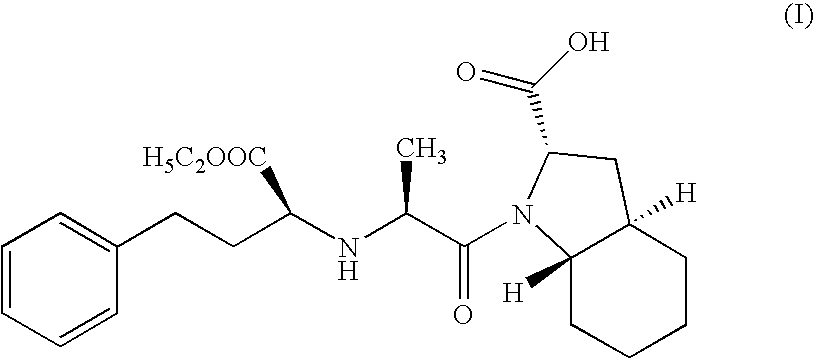
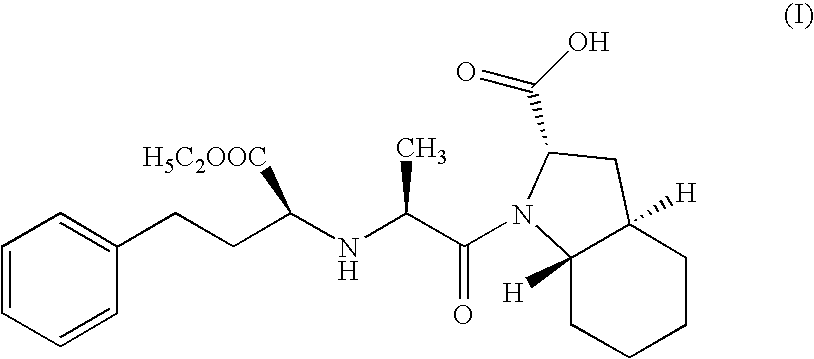
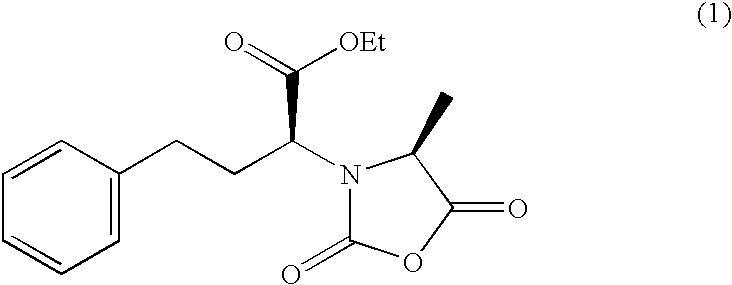
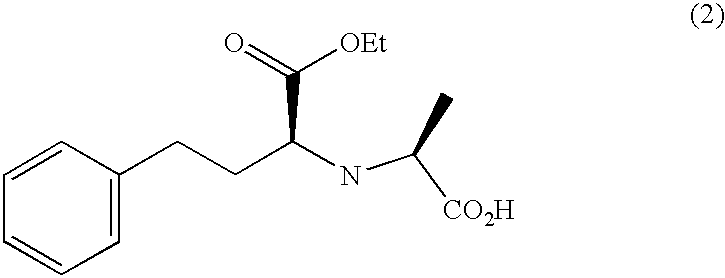
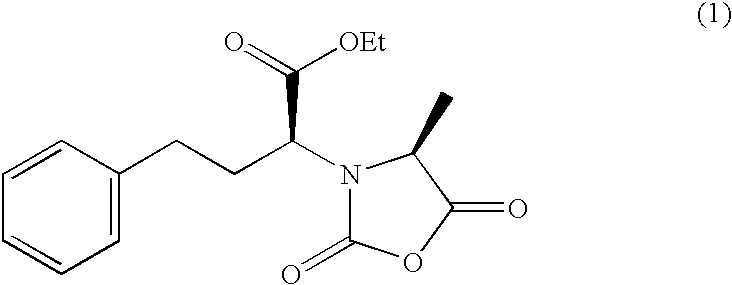
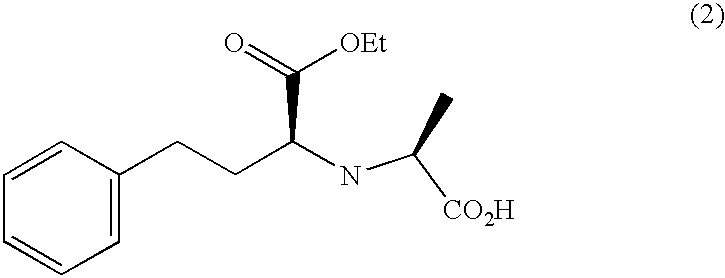
Method for preparing N-[1-(S)-carbethoxy-3-hydrocinnamyl] -L-alanine-N-carboxy acid anhydride
InactiveCN1187345CNoveltyCreativeCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationHalogenAcyl group
Owner:EVERLIGHT USA INC
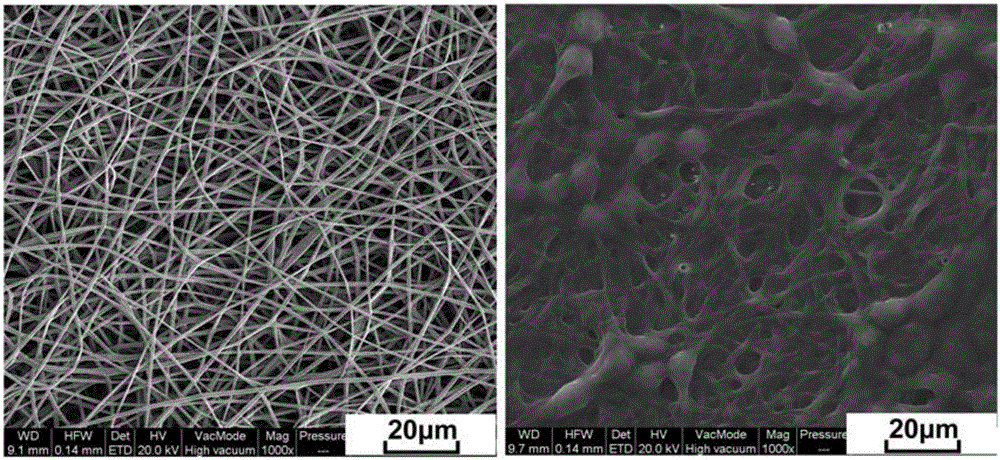
Zein and glycopolypeptide graft and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN105713205BGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsChemical structureBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that firstly, inherent amidogens of zein macromolecules are utilized to trigger an N-carboxyanhydride monomer containing azide functional groups for ring opening polymerization, azide-containing side-group polypeptide modified zein is obtained, and galactose is grafted to a polypeptide chain segment side group so as to obtain the zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer. The zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer prepared by means of the preparation method can be used for preparing a corresponding electrospun fibrous membrane serving as a liver cell scaffold material by adopting an electrospinning technique. The main raw material used for the zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer belongs to a natural vegetable protein, a grafted glycopolypeptide chain segment is of a chemical structure similar to a glycoprotein in a living body, and therefore the prepared zein and glycopolypeptide grafted copolymer and the electrospun membrane scaffold material thereof have very good biocompatibility and bionic characteristics.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
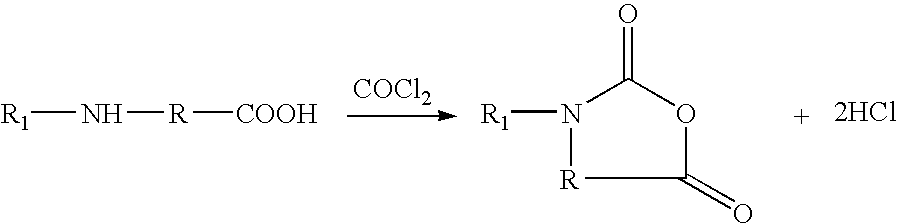
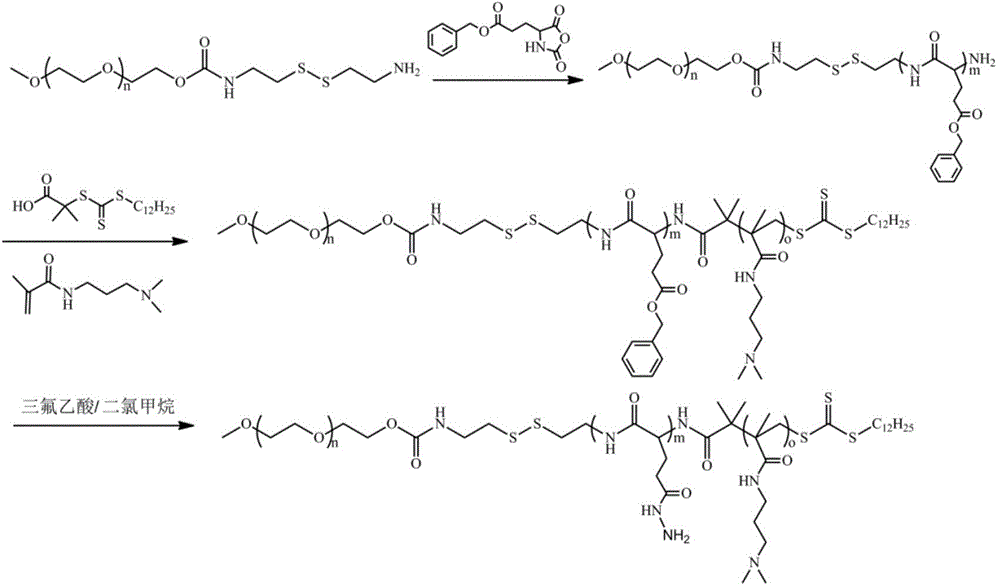
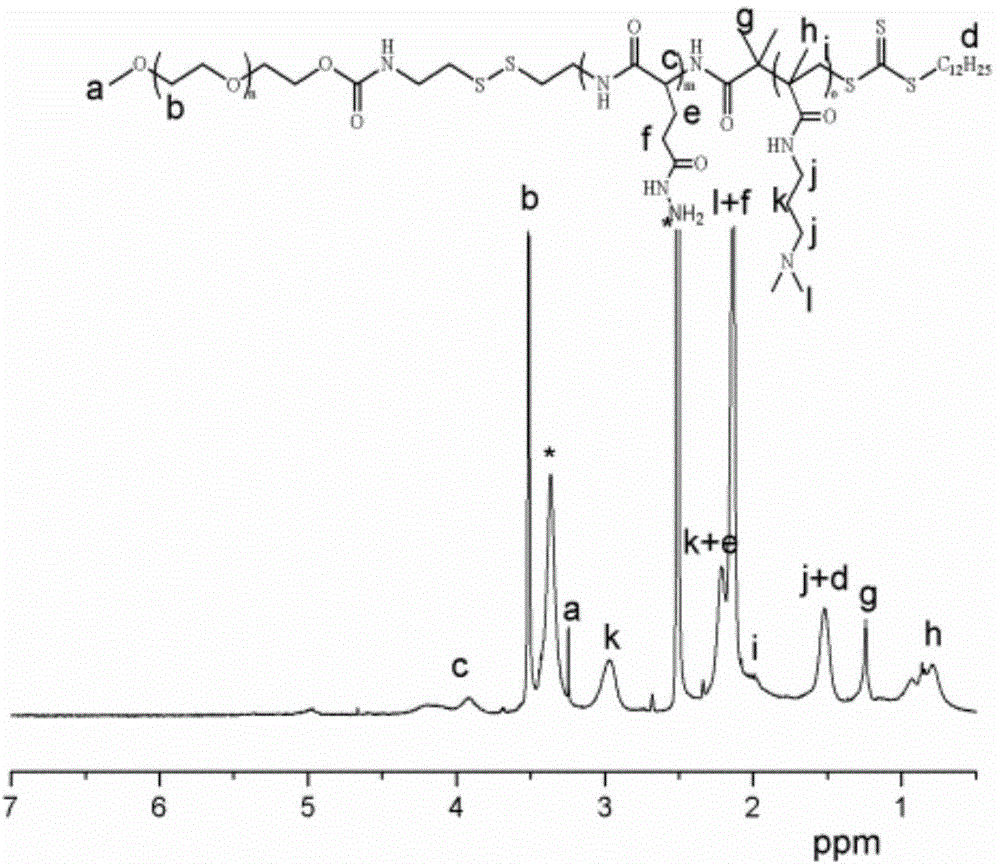
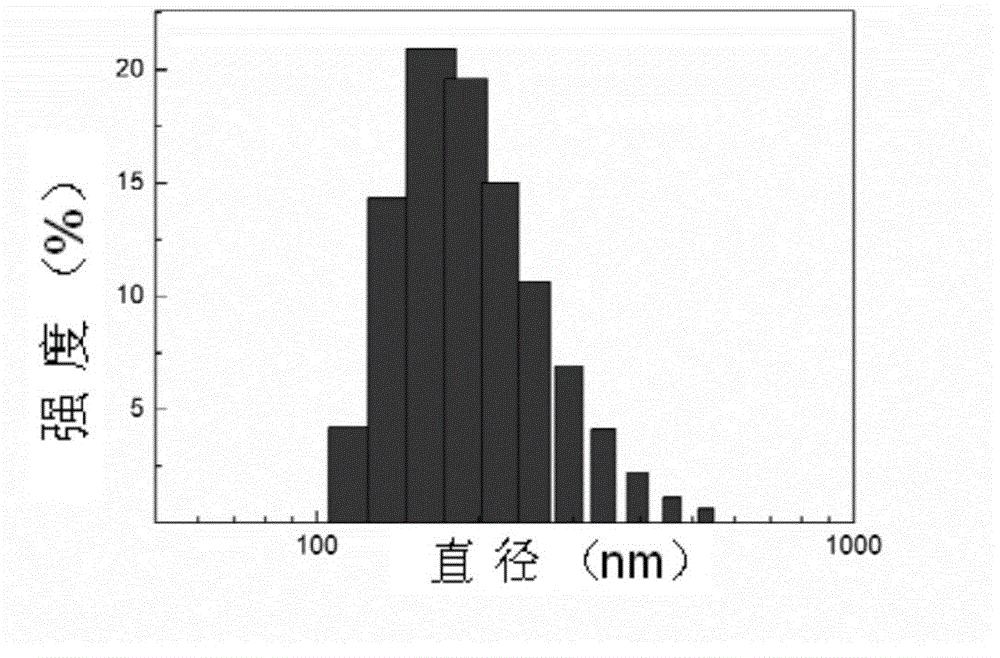
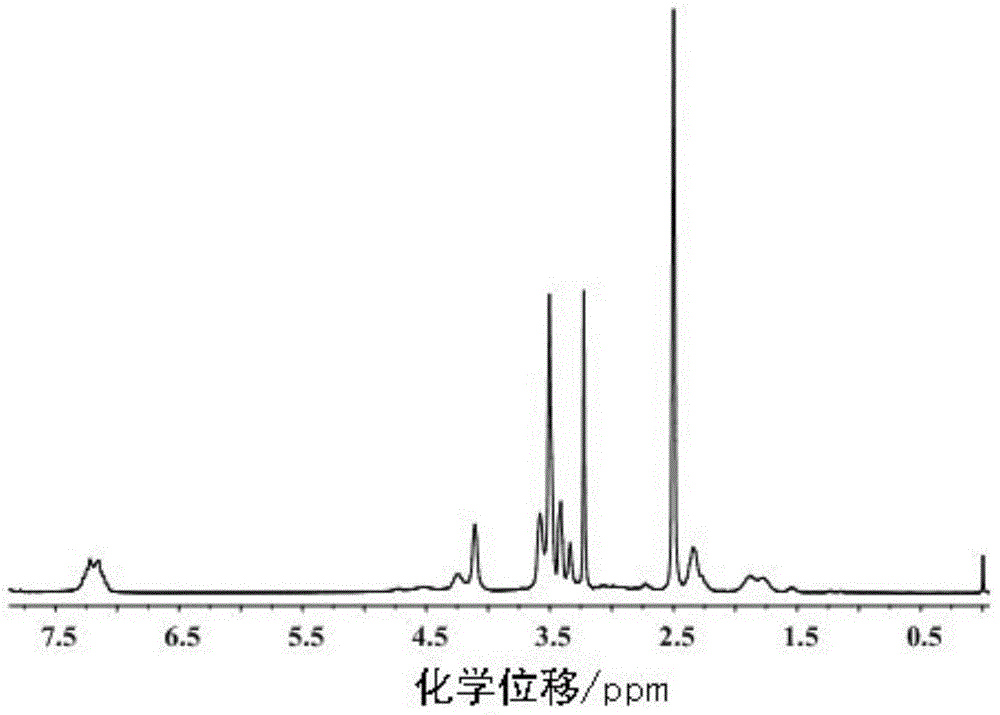
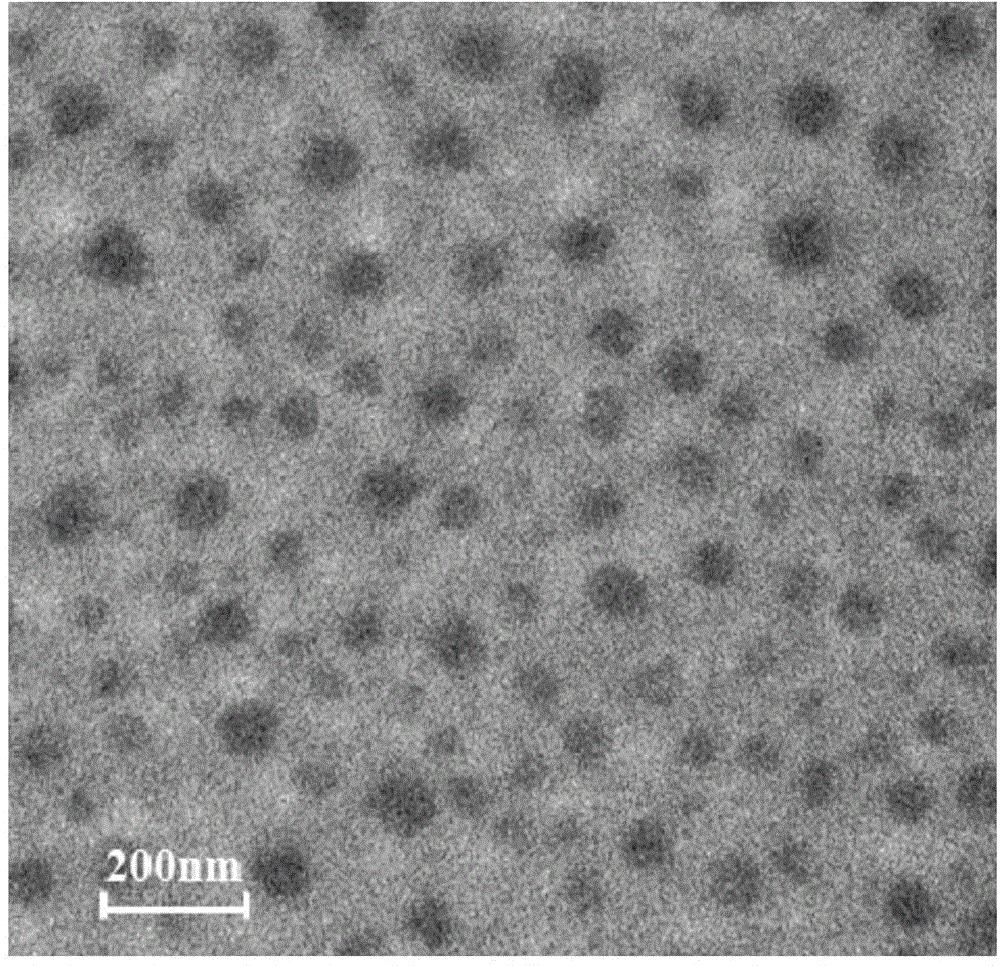
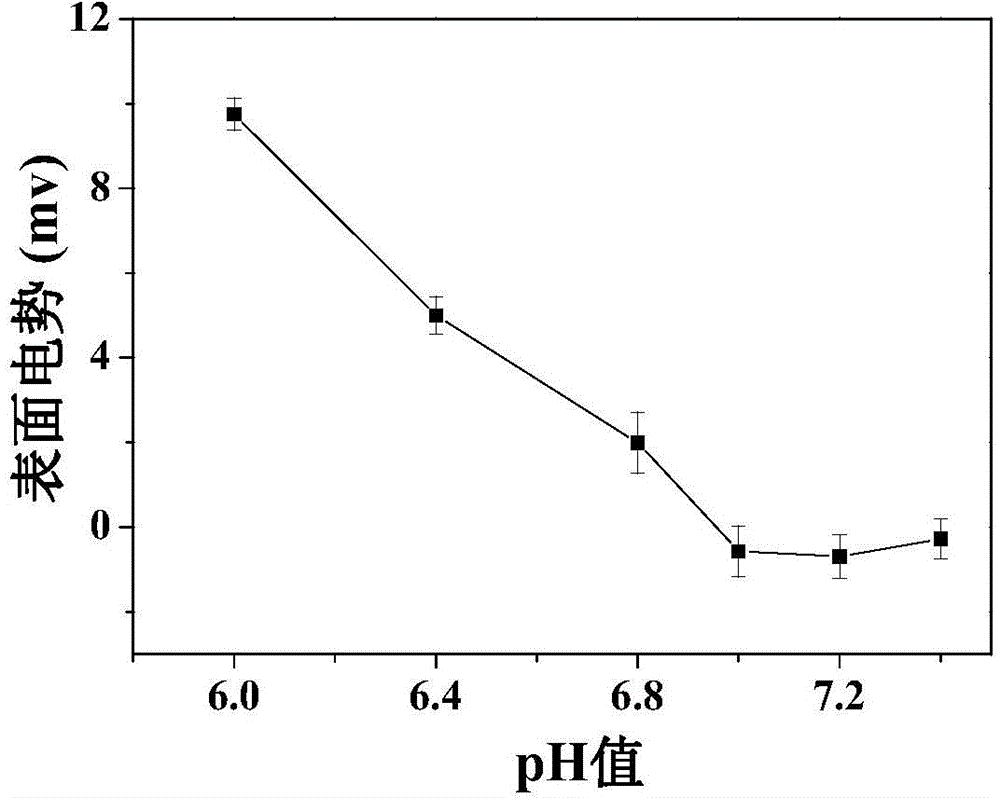
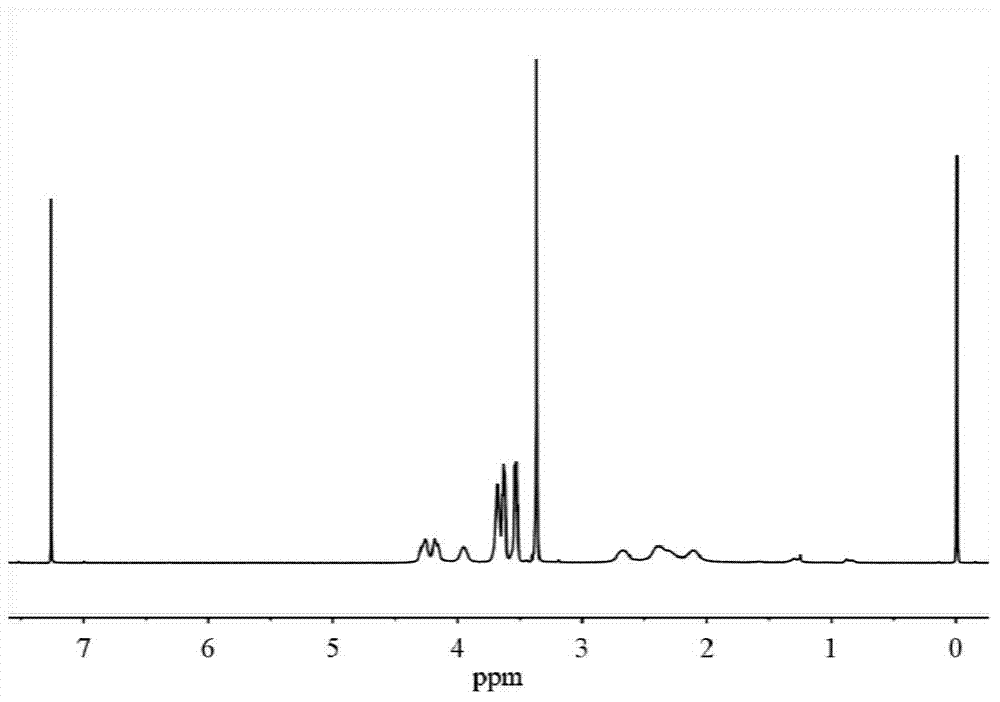
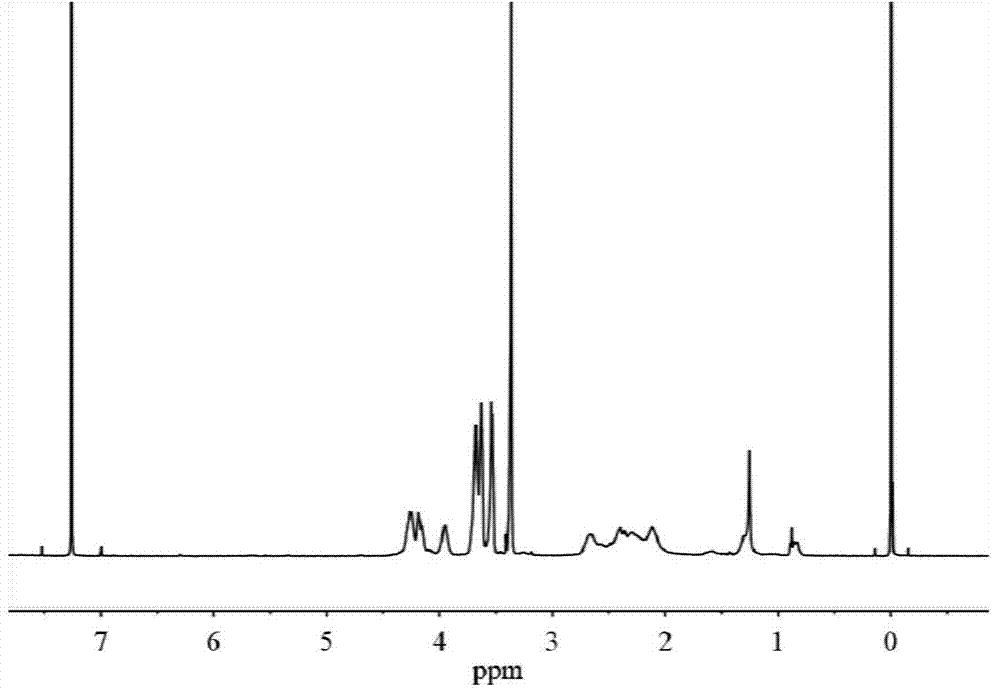
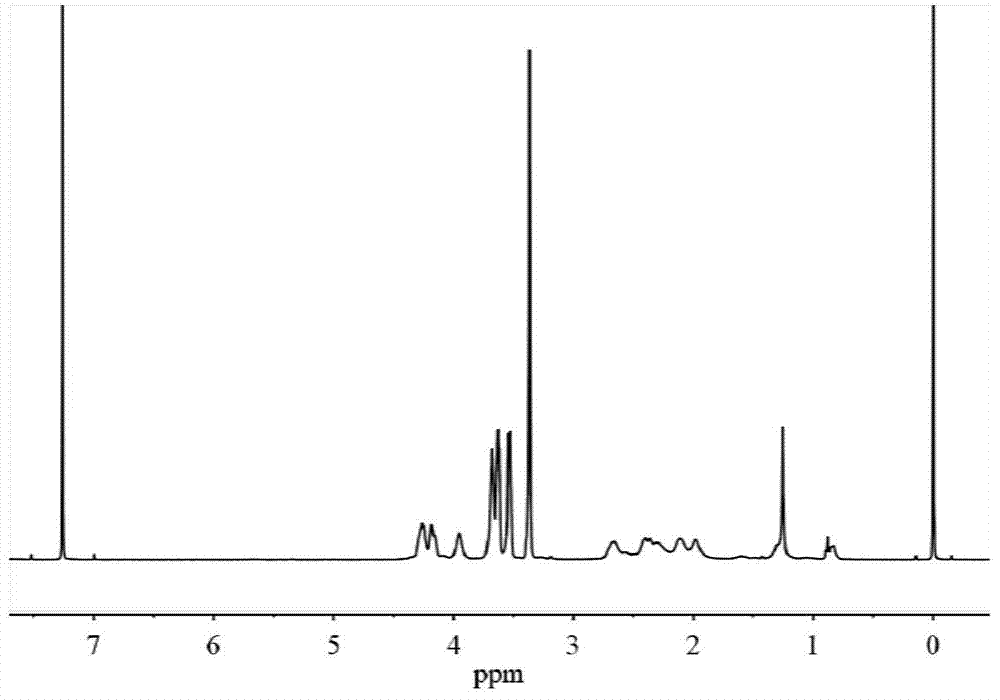
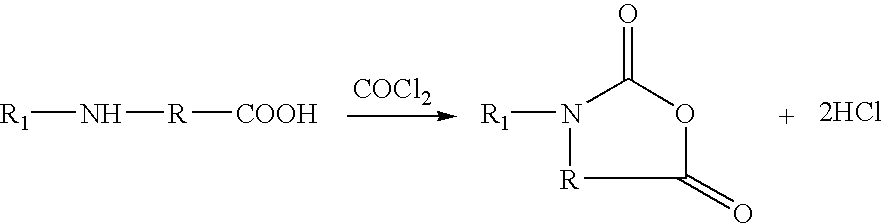
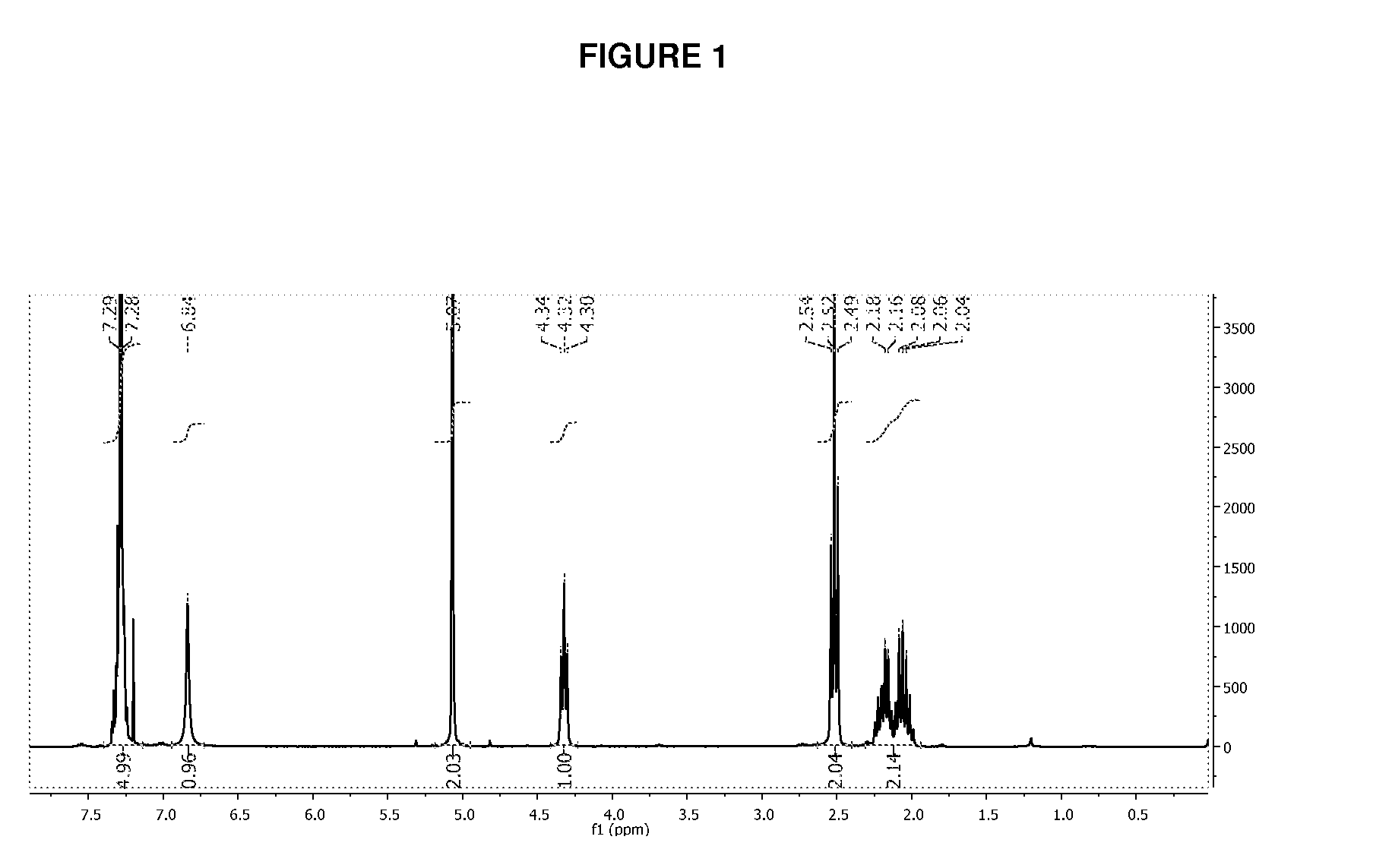
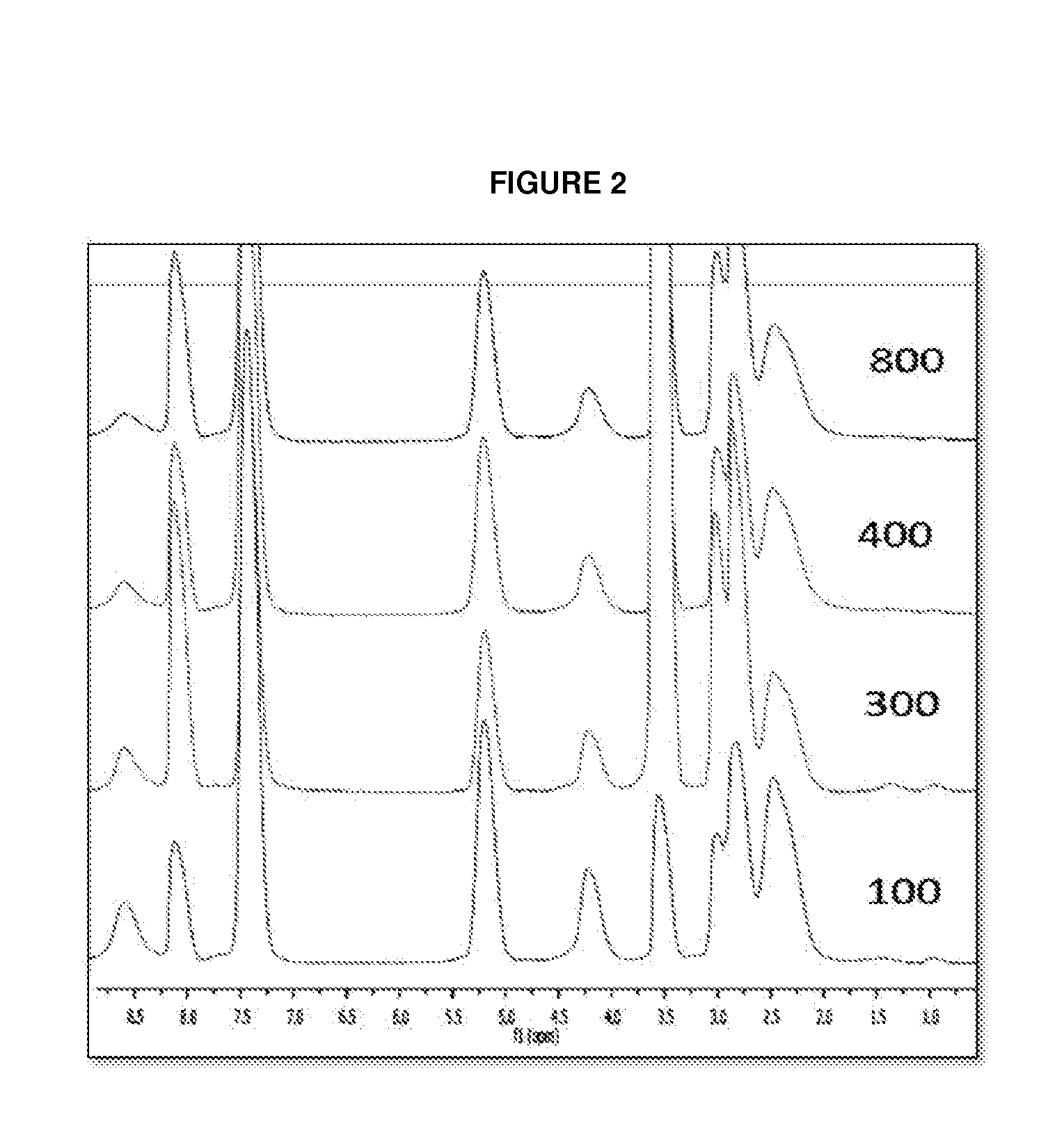
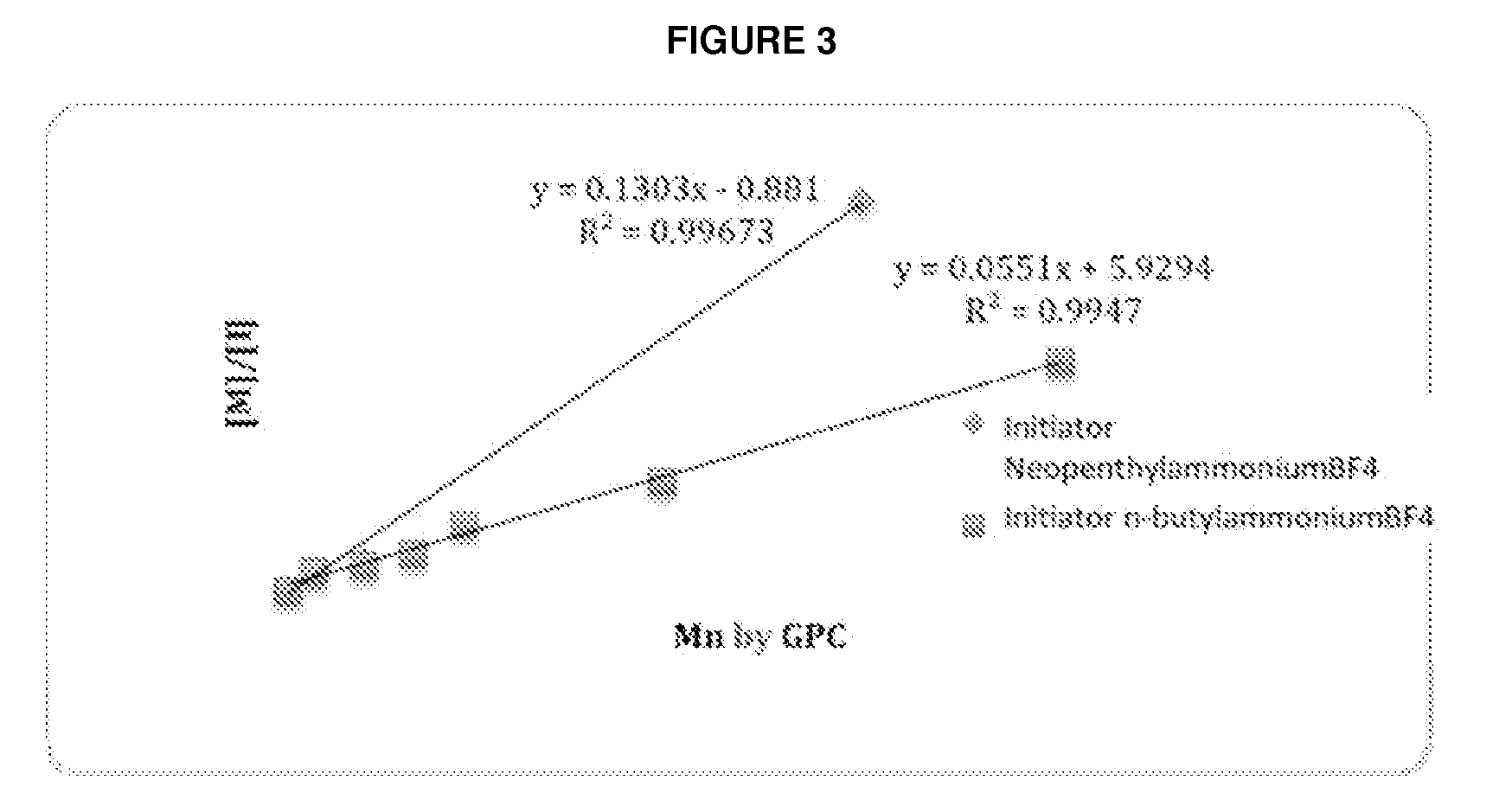
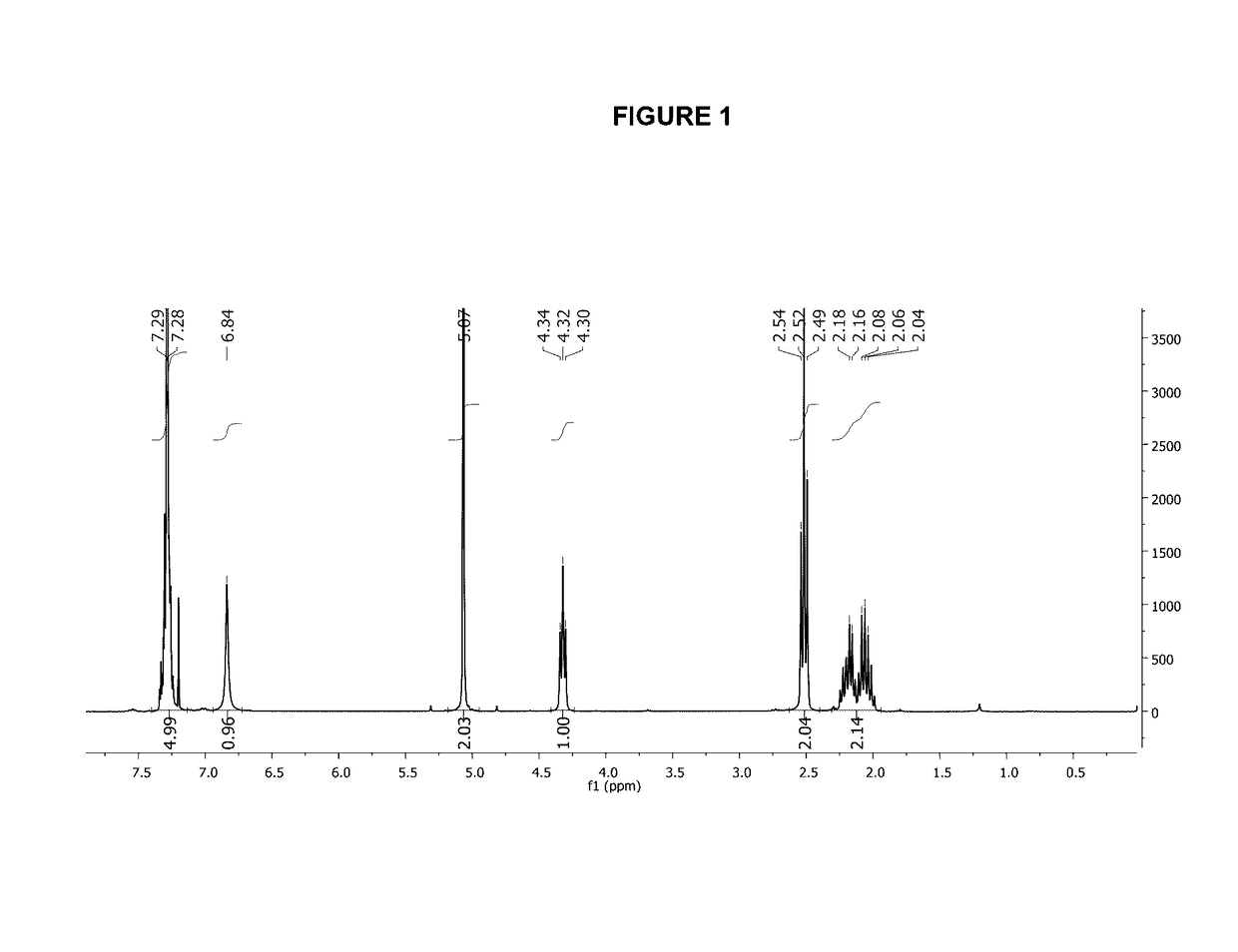
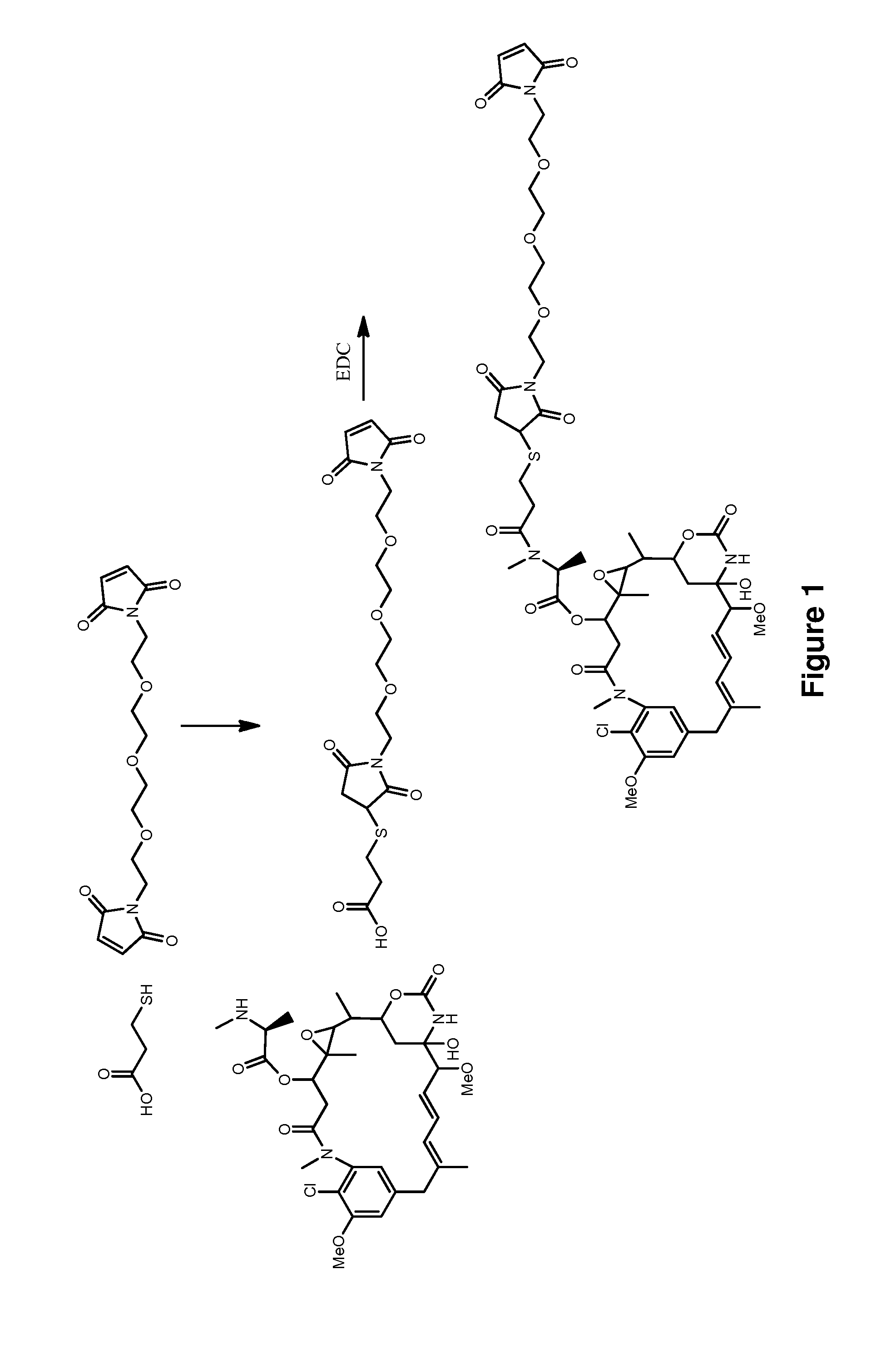
![Method for preparing N-[1-(S)-carbethoxy-3-hydrocinnamyl] -L-alanine-N-carboxy acid anhydride Method for preparing N-[1-(S)-carbethoxy-3-hydrocinnamyl] -L-alanine-N-carboxy acid anhydride](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/45733744-6da8-441b-8397-ea09a45c3071/01136054.PNG)
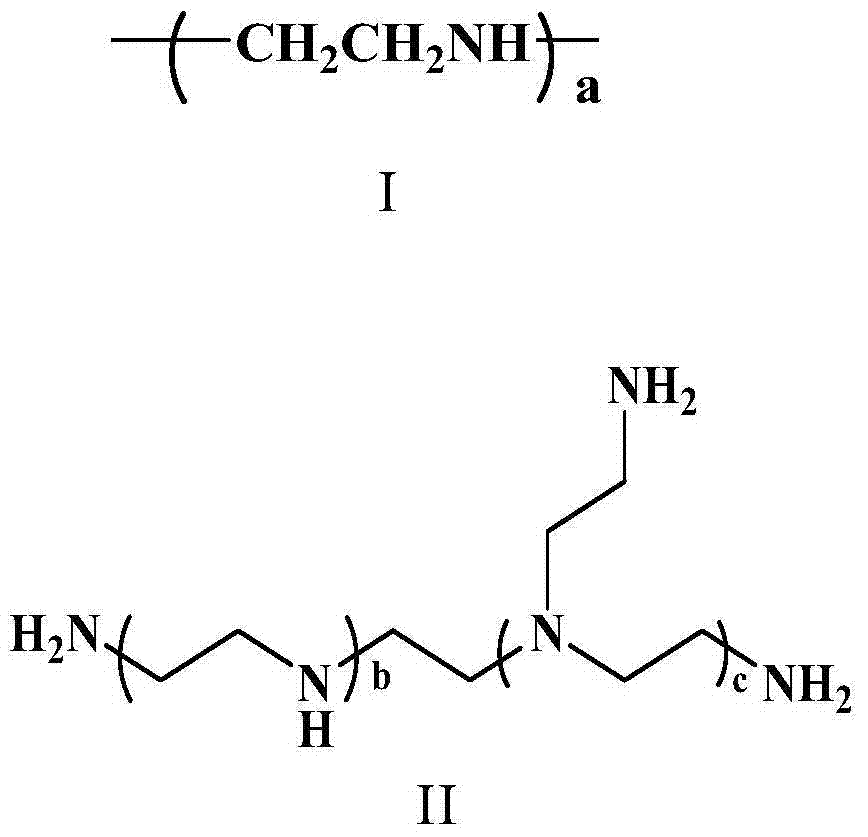
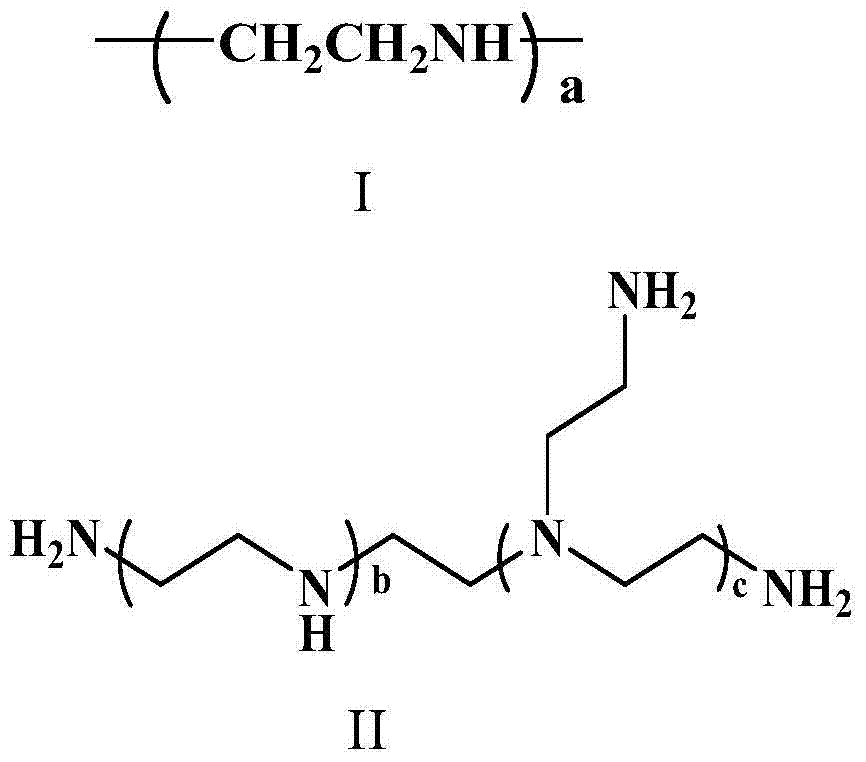
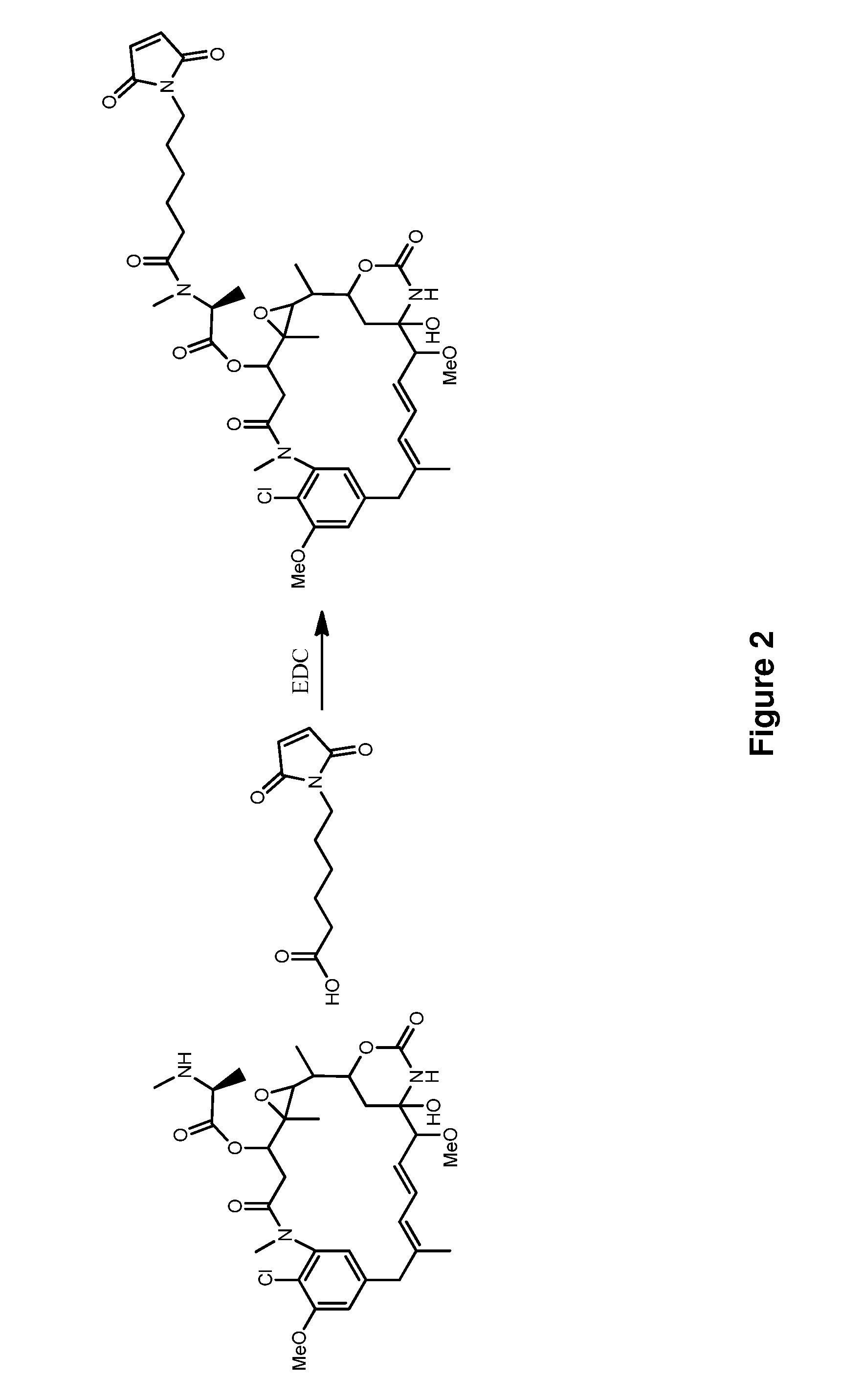
![Method for preparing N-[1-(S)-carbethoxy-3-hydrocinnamyl] -L-alanine-N-carboxy acid anhydride Method for preparing N-[1-(S)-carbethoxy-3-hydrocinnamyl] -L-alanine-N-carboxy acid anhydride](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/45733744-6da8-441b-8397-ea09a45c3071/C011360540002C1.PNG)
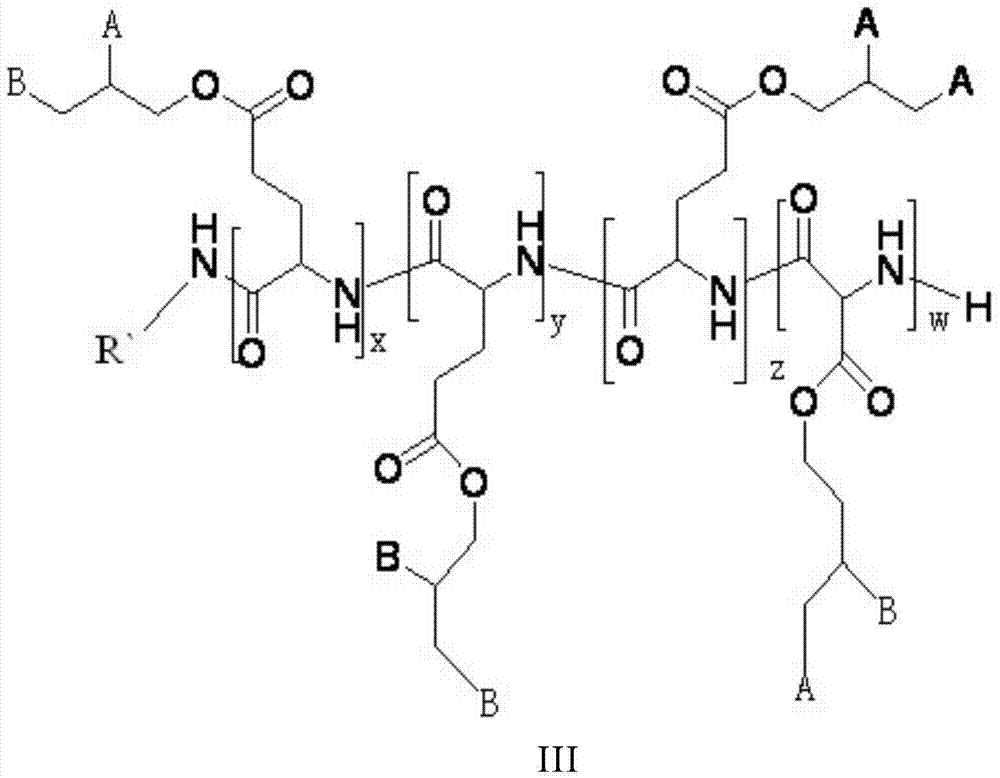
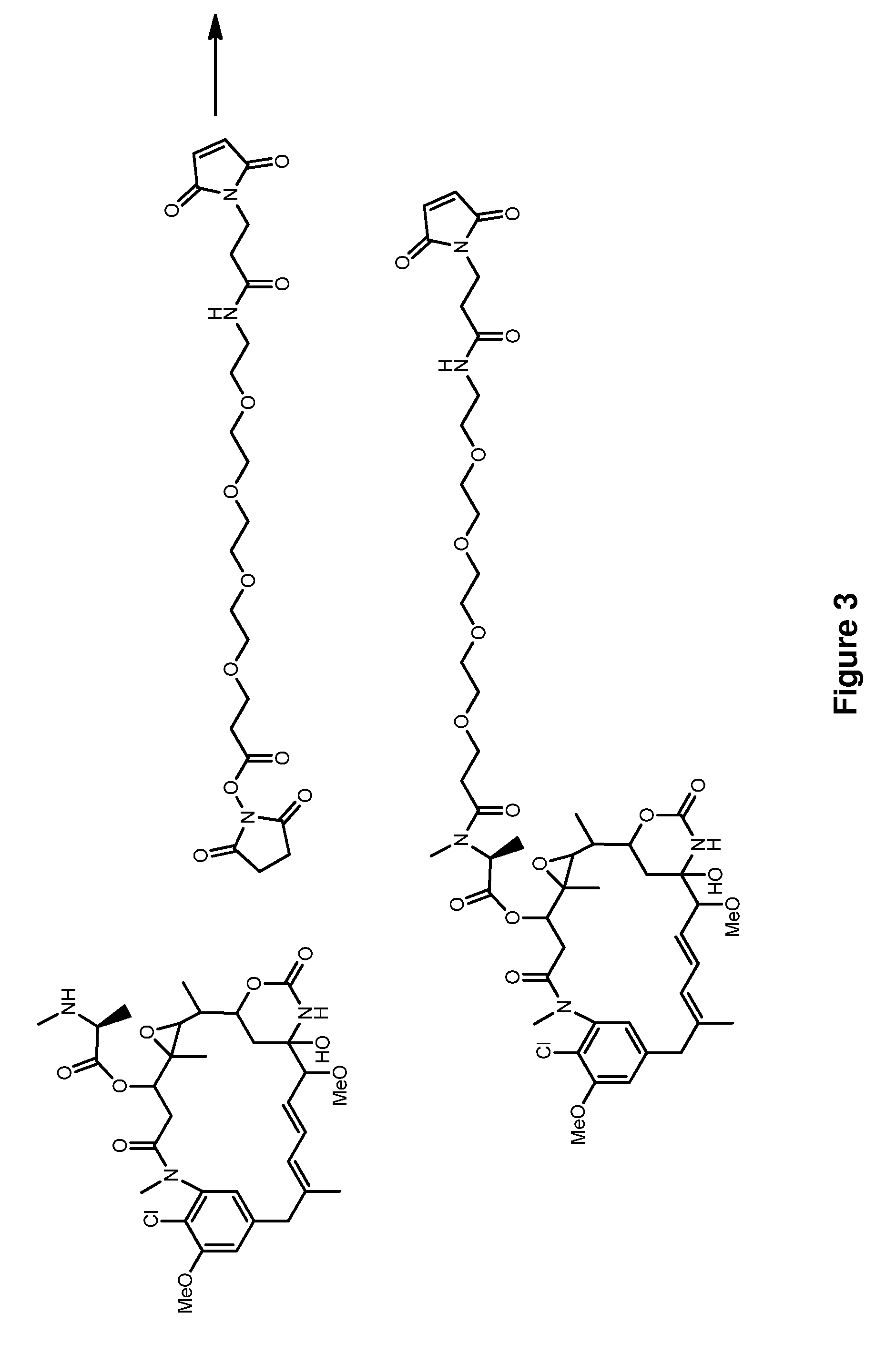
![Method for preparing N-[1-(S)-carbethoxy-3-hydrocinnamyl] -L-alanine-N-carboxy acid anhydride Method for preparing N-[1-(S)-carbethoxy-3-hydrocinnamyl] -L-alanine-N-carboxy acid anhydride](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/45733744-6da8-441b-8397-ea09a45c3071/C011360540002C2.PNG)