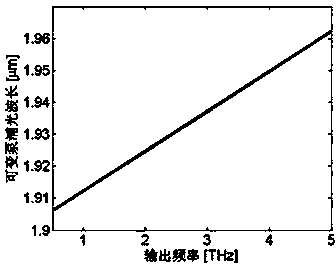
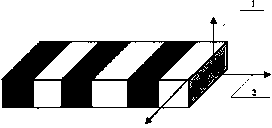
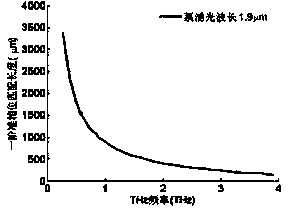
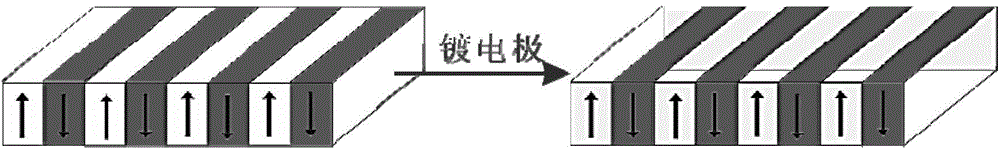
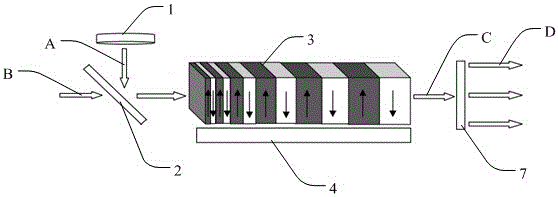
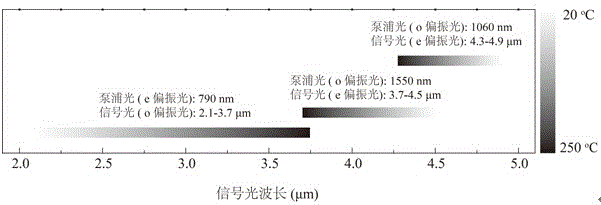
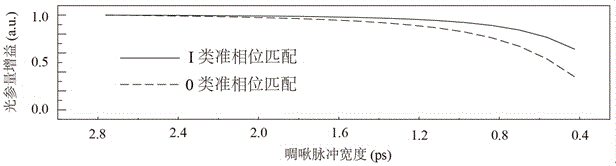
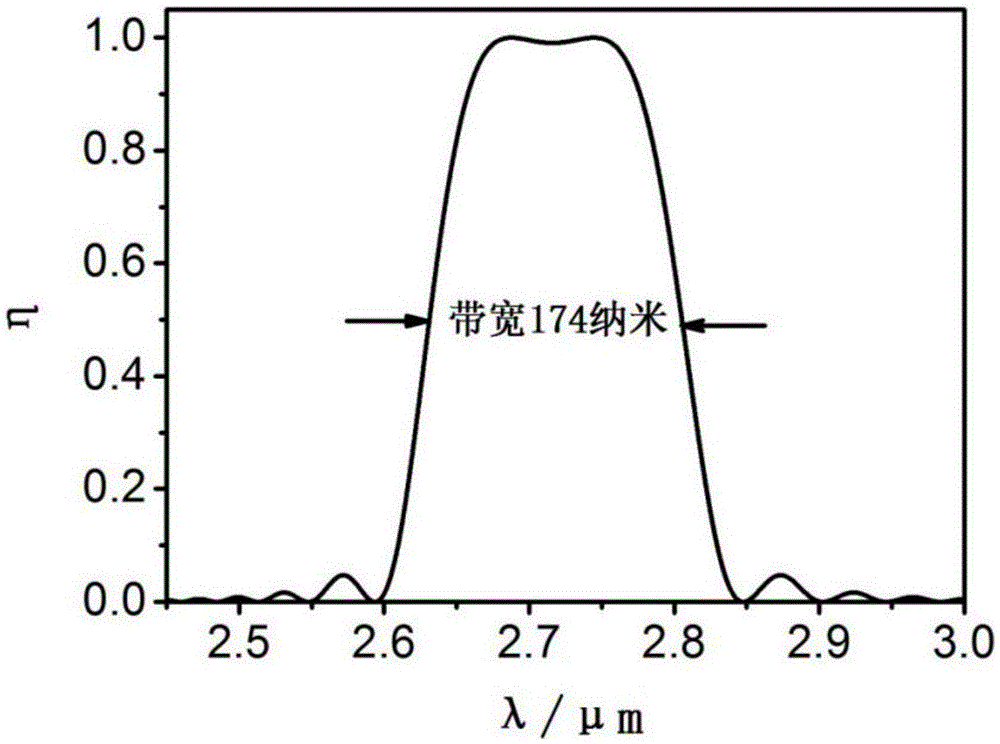
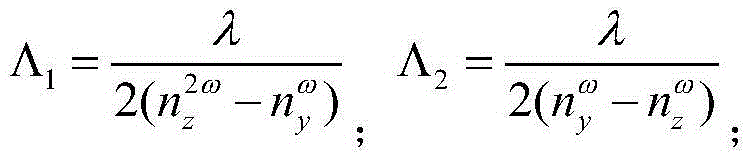Patents
Literature
203 results about "Quasi-phase-matching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
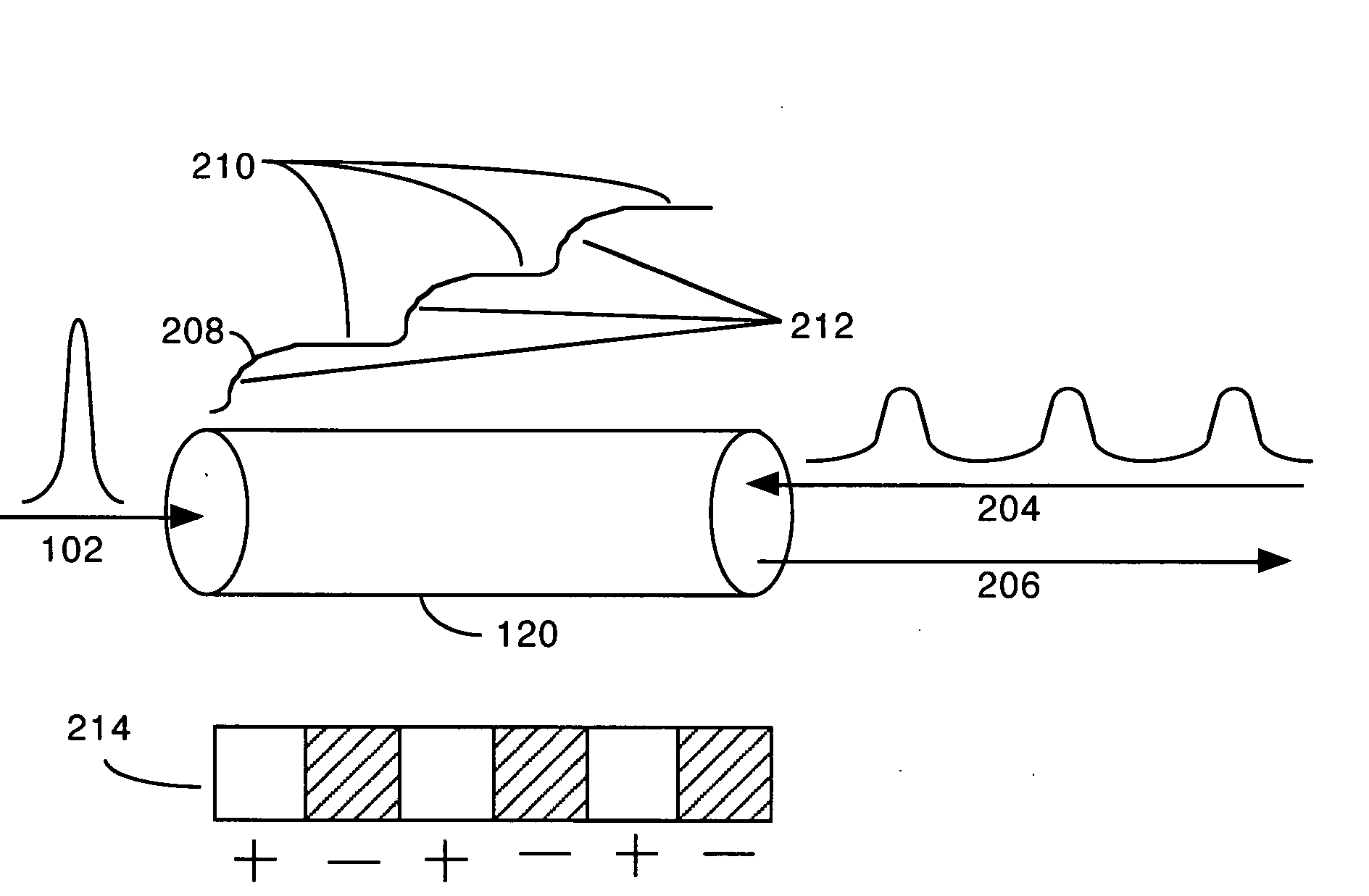
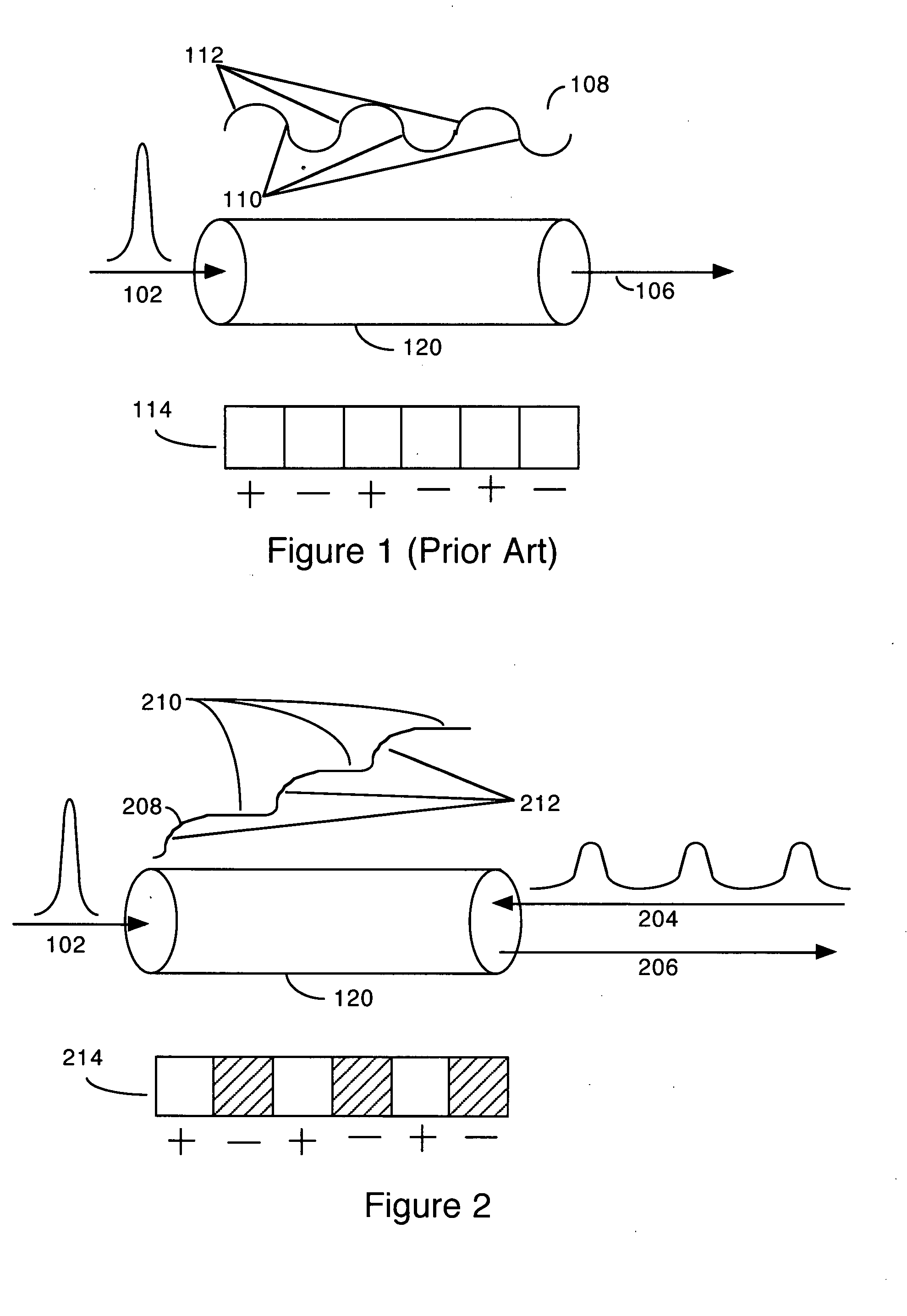
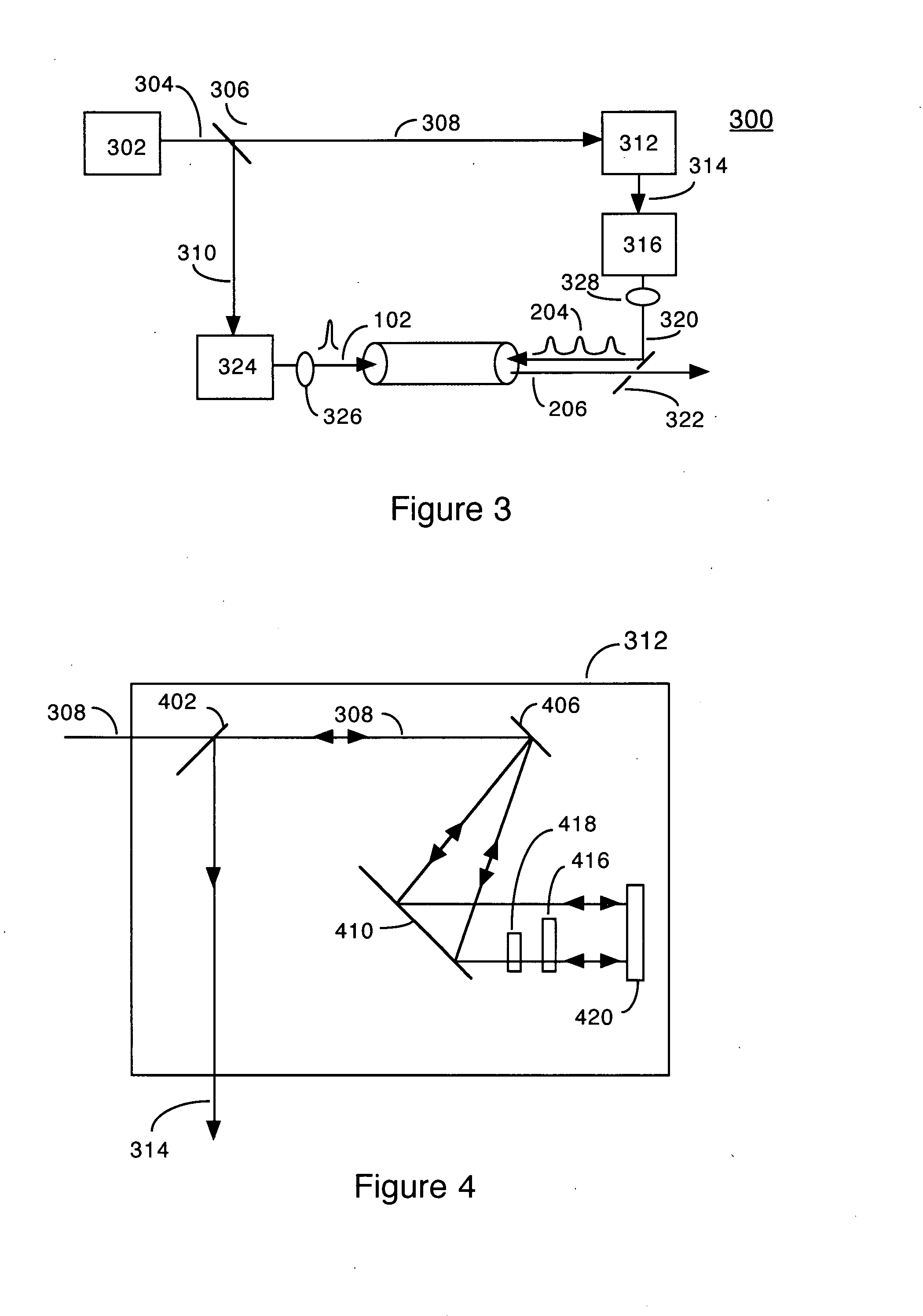
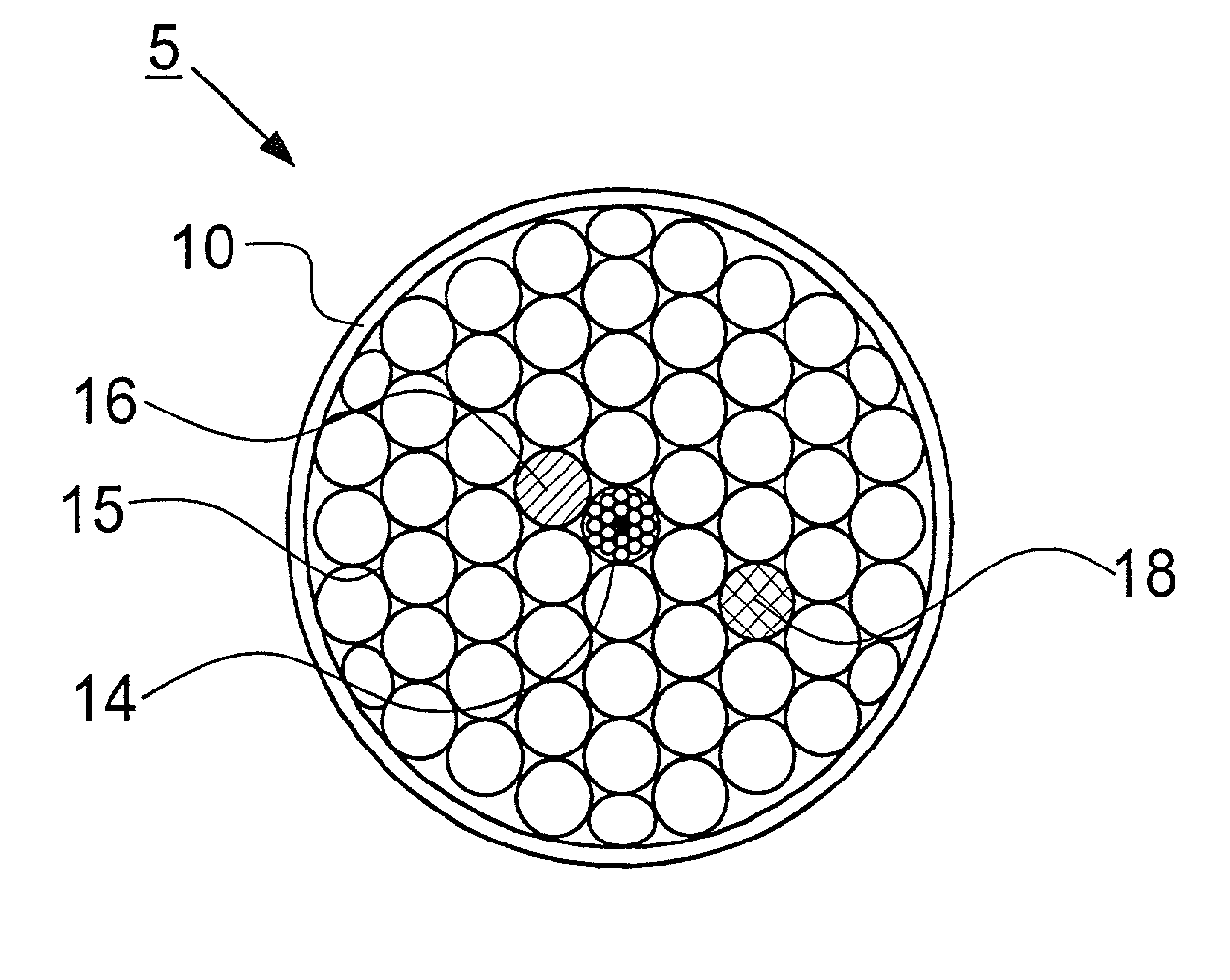
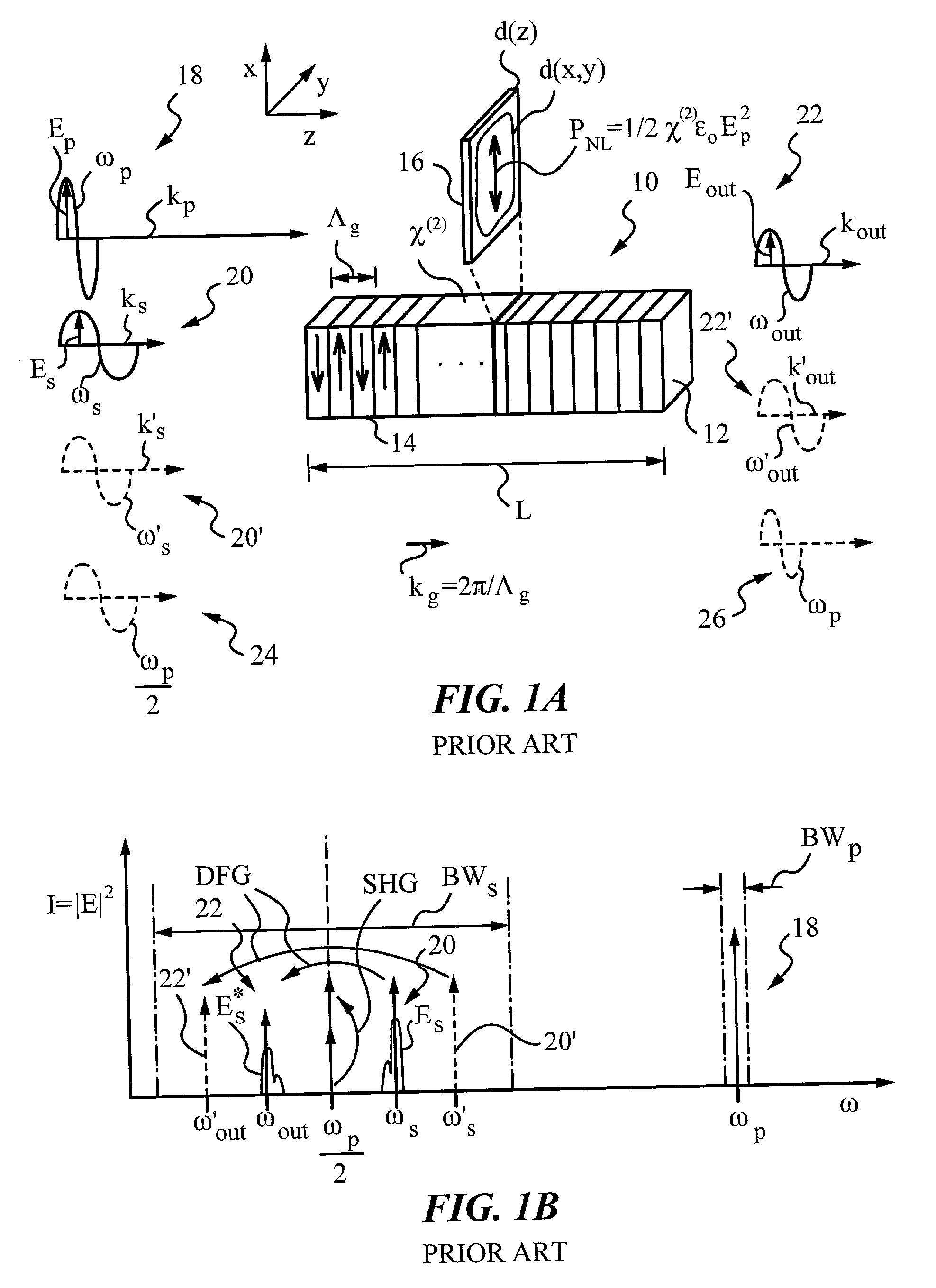
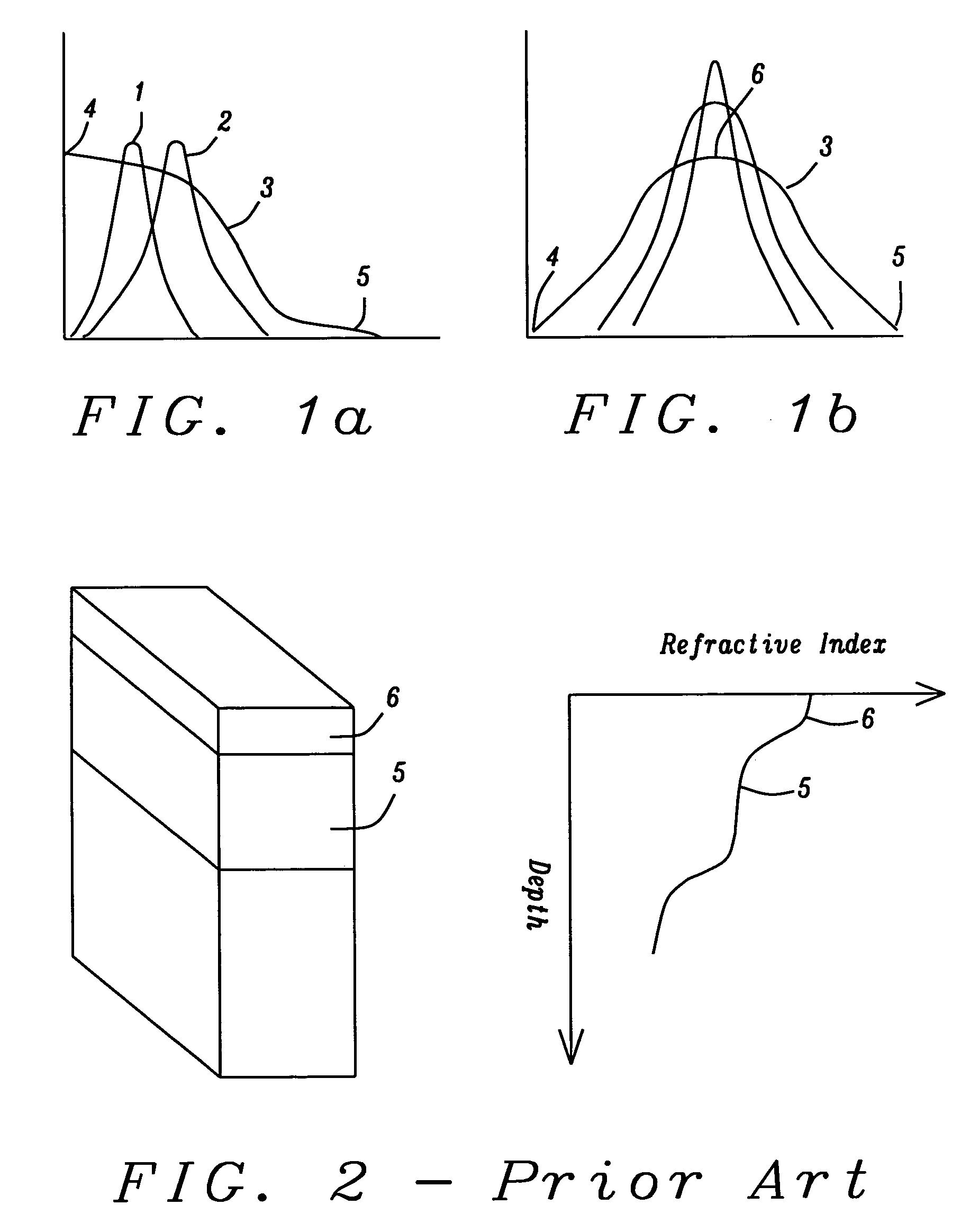
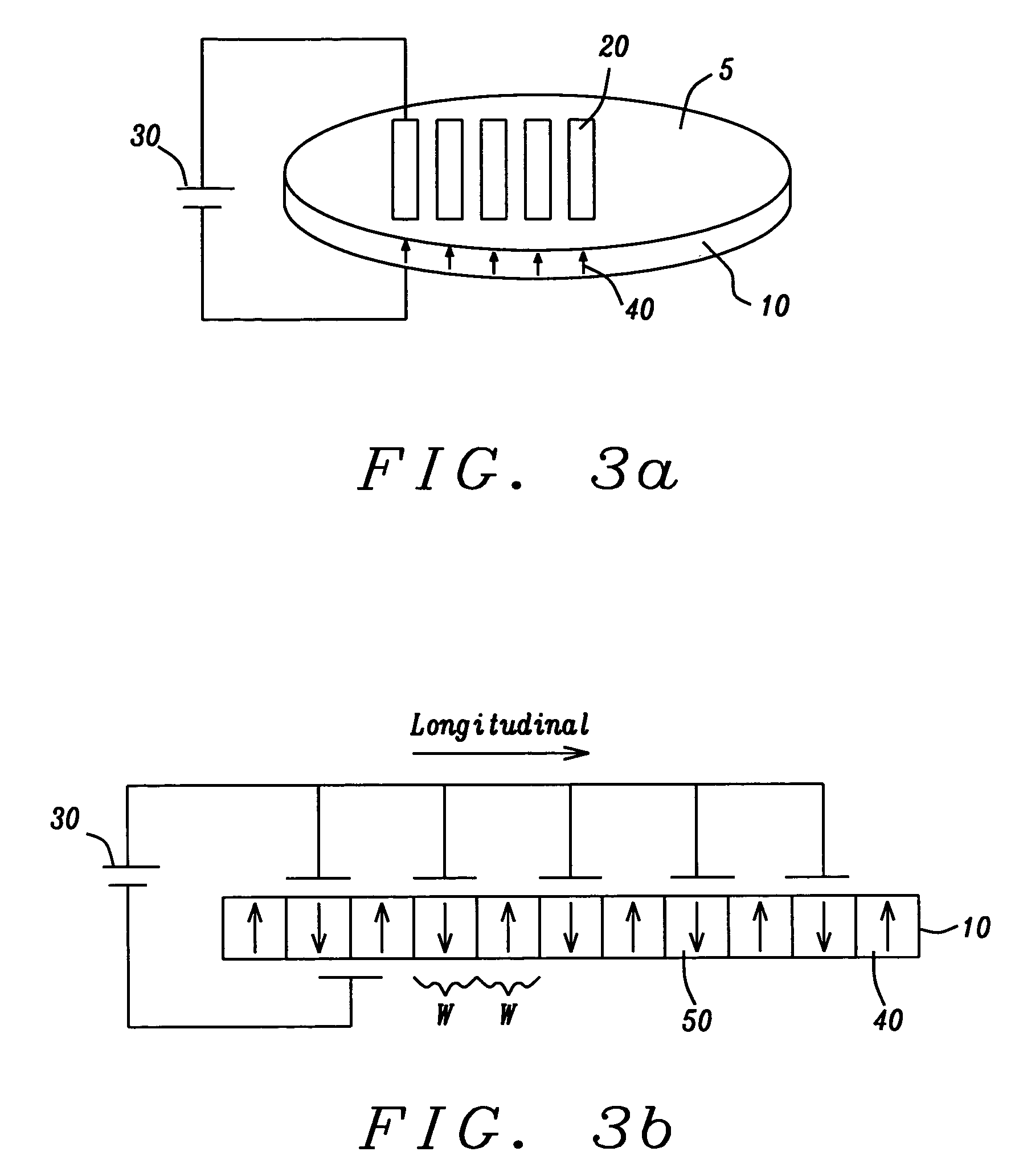
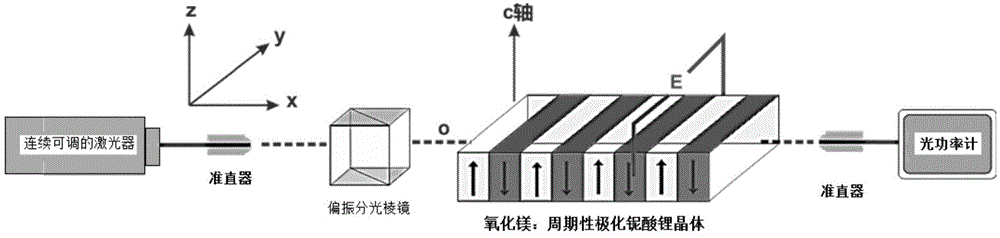
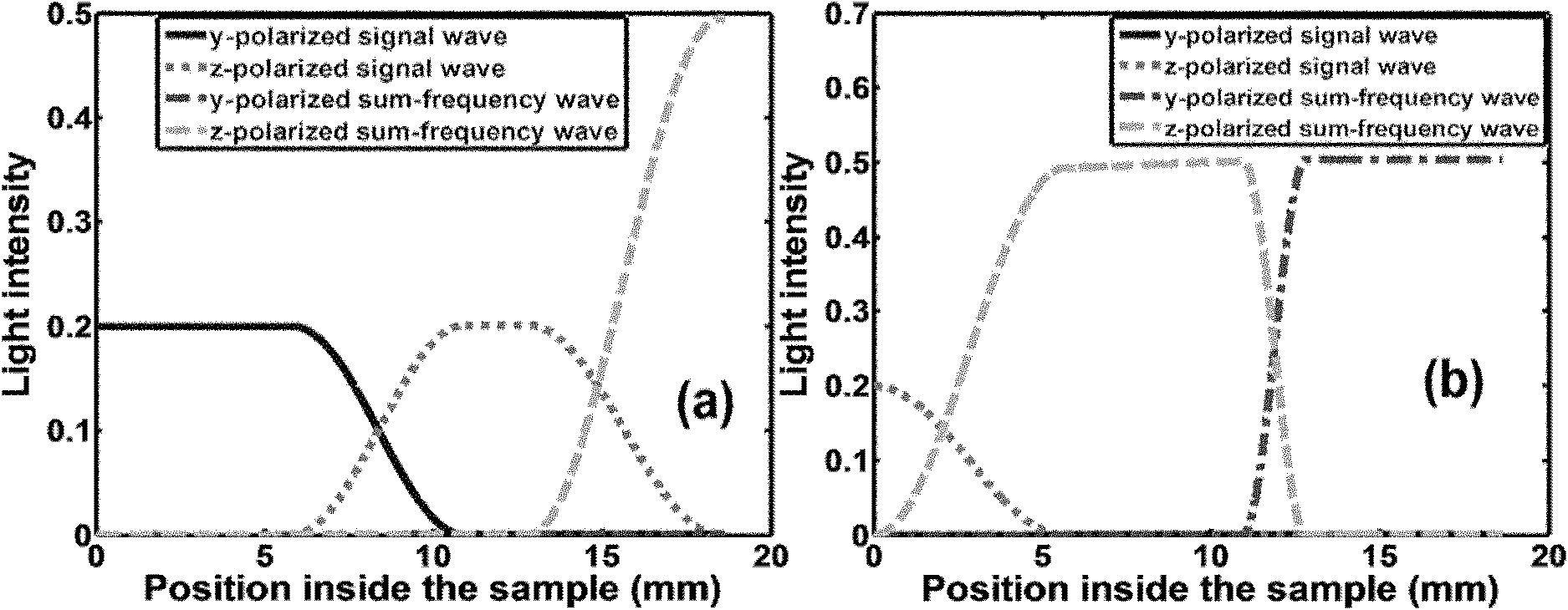
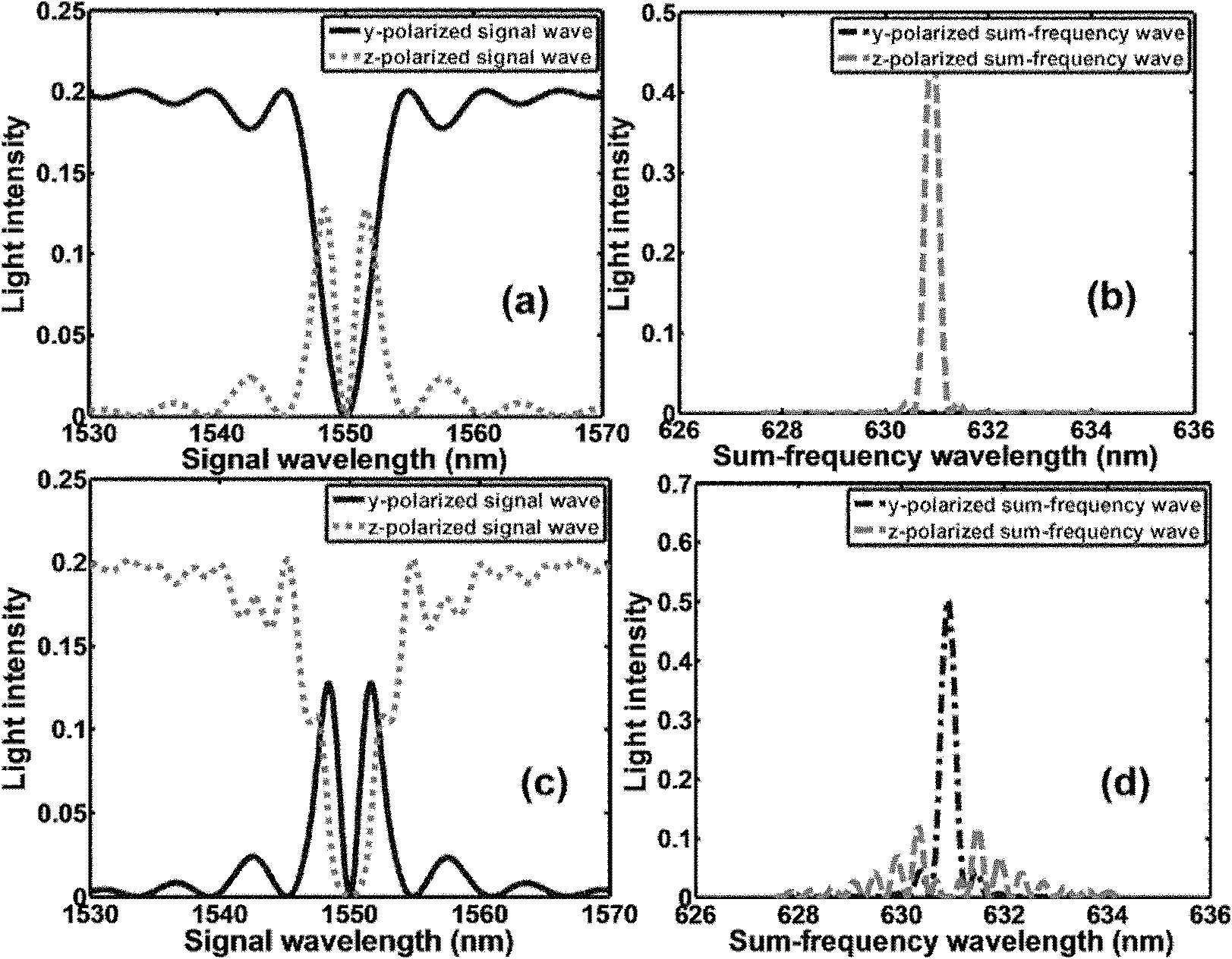
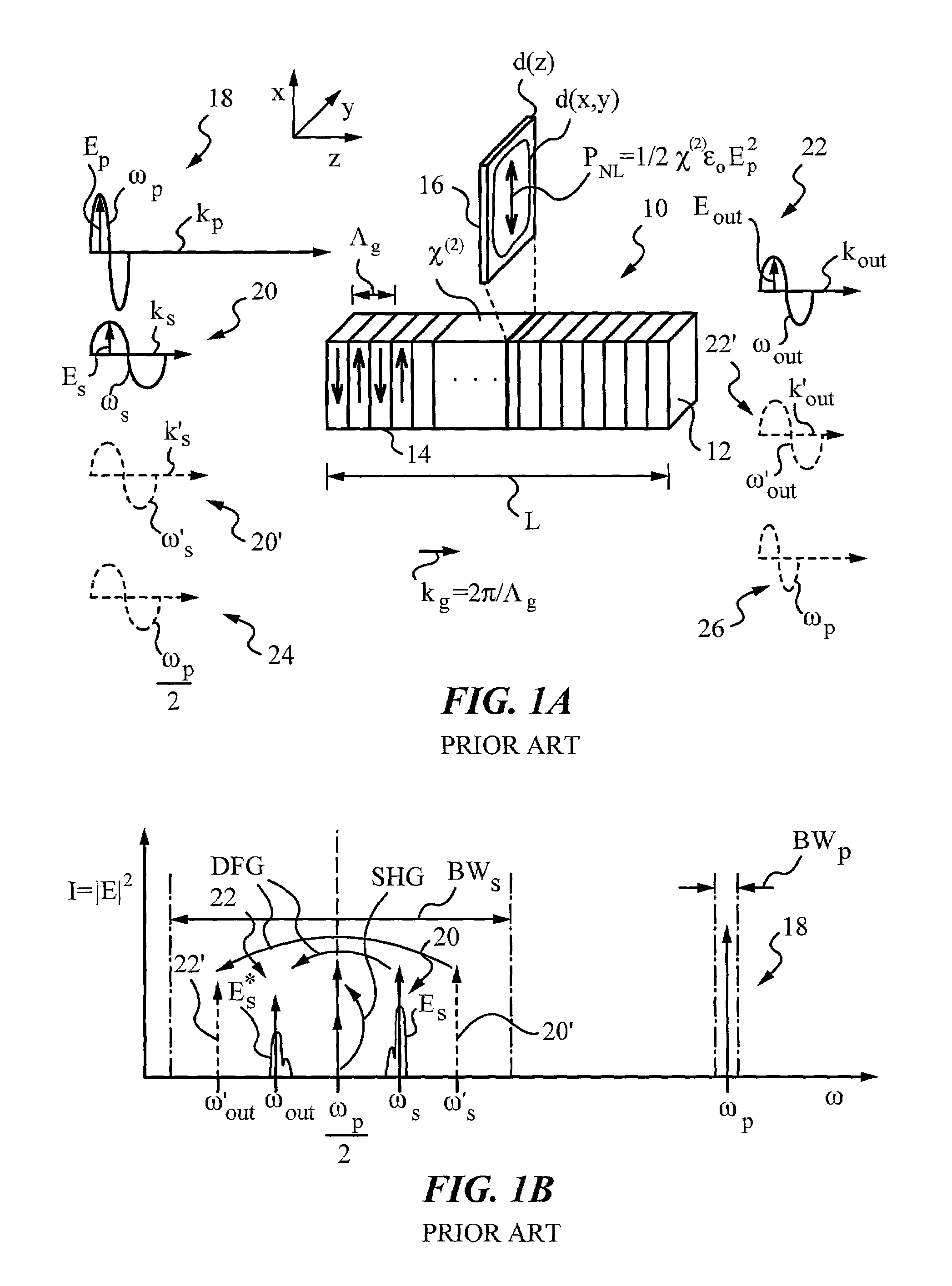
Quasi-phase-matching is a technique in nonlinear optics which allows a positive net flow of energy from the pump frequency to the signal and idler frequencies by creating a periodic structure in the nonlinear medium. Momentum is conserved, as is necessary for phase-matching, through an additional momentum contribution corresponding to the wavevector of the periodic structure. Consequently, in principle any three-wave mixing process that satisfies energy conservation can be phase-matched. For example, all the optical frequencies involved can be collinear, can have the same polarization, and travel through the medium in arbitrary directions. This allows one to use the largest nonlinear coefficient of the material in the nonlinear interaction.
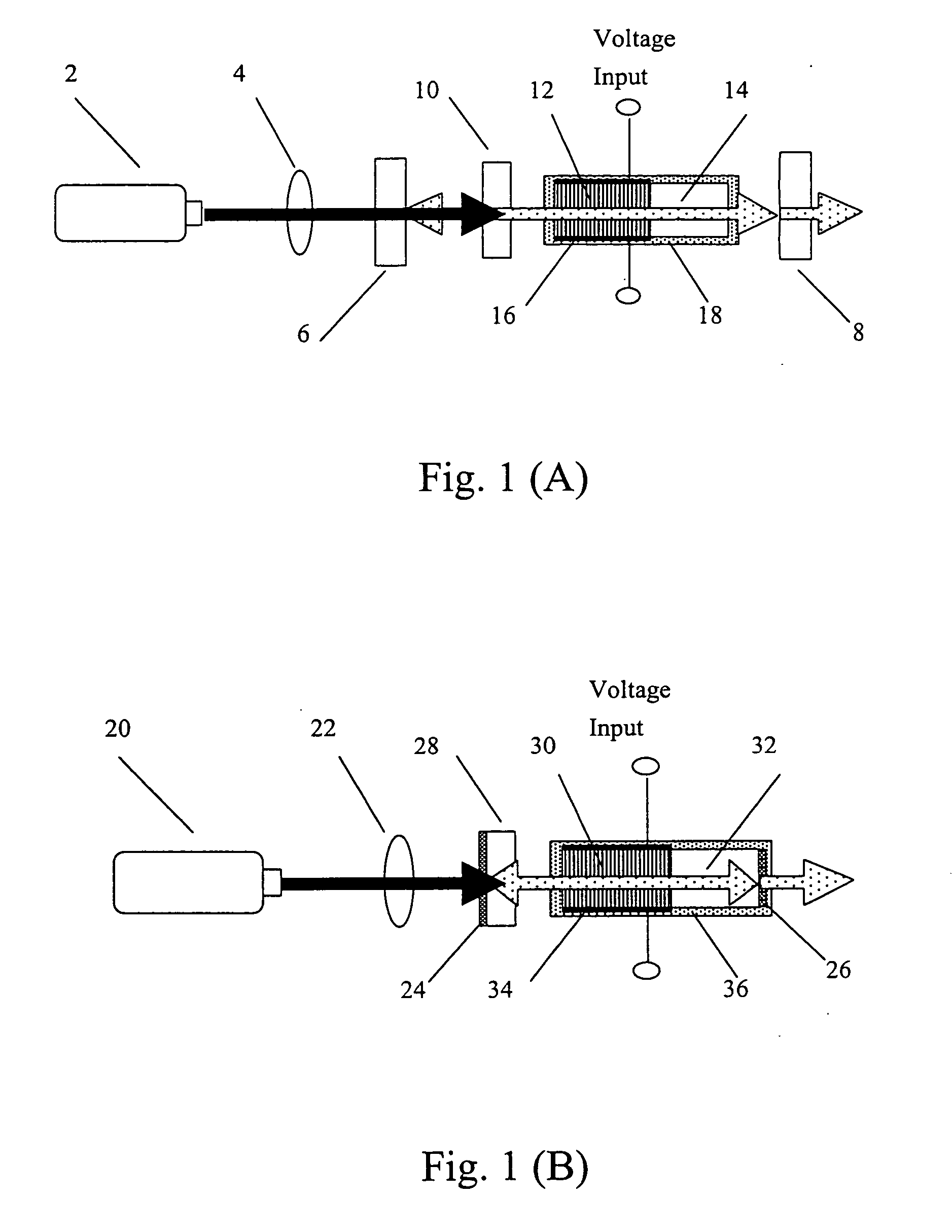
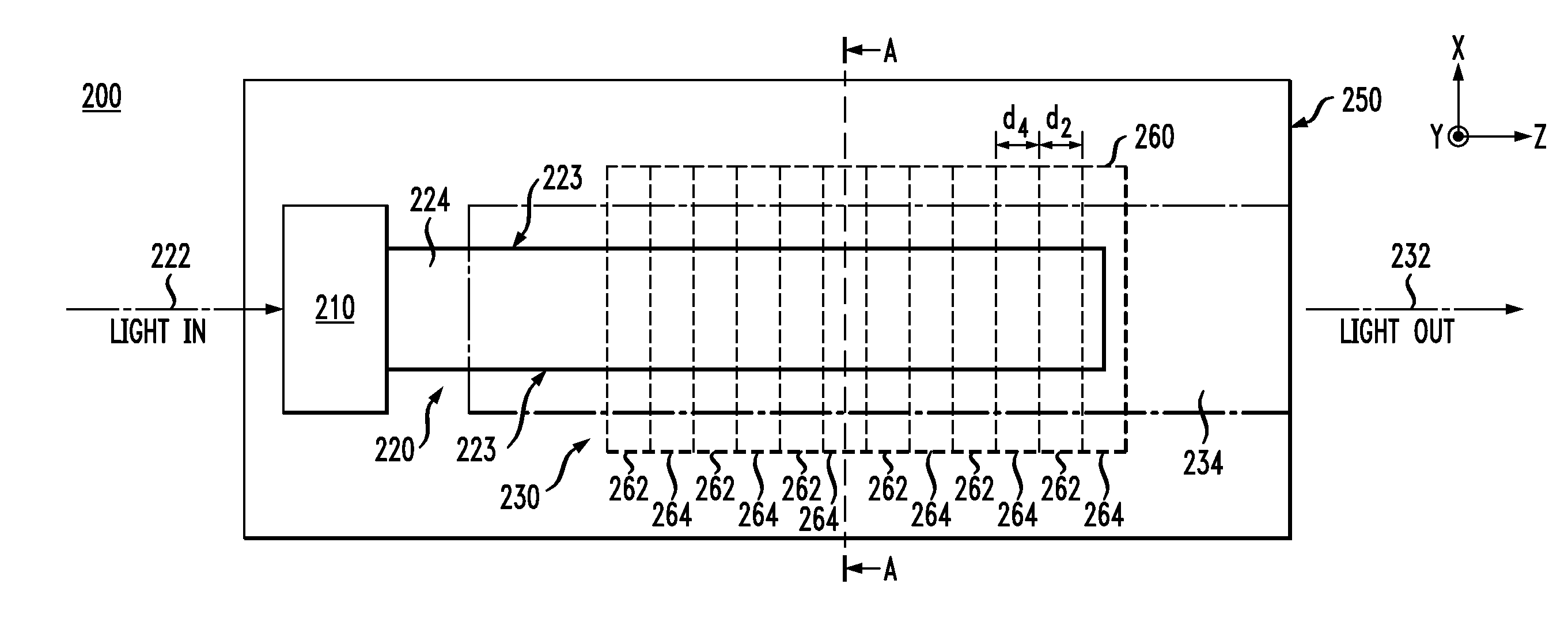
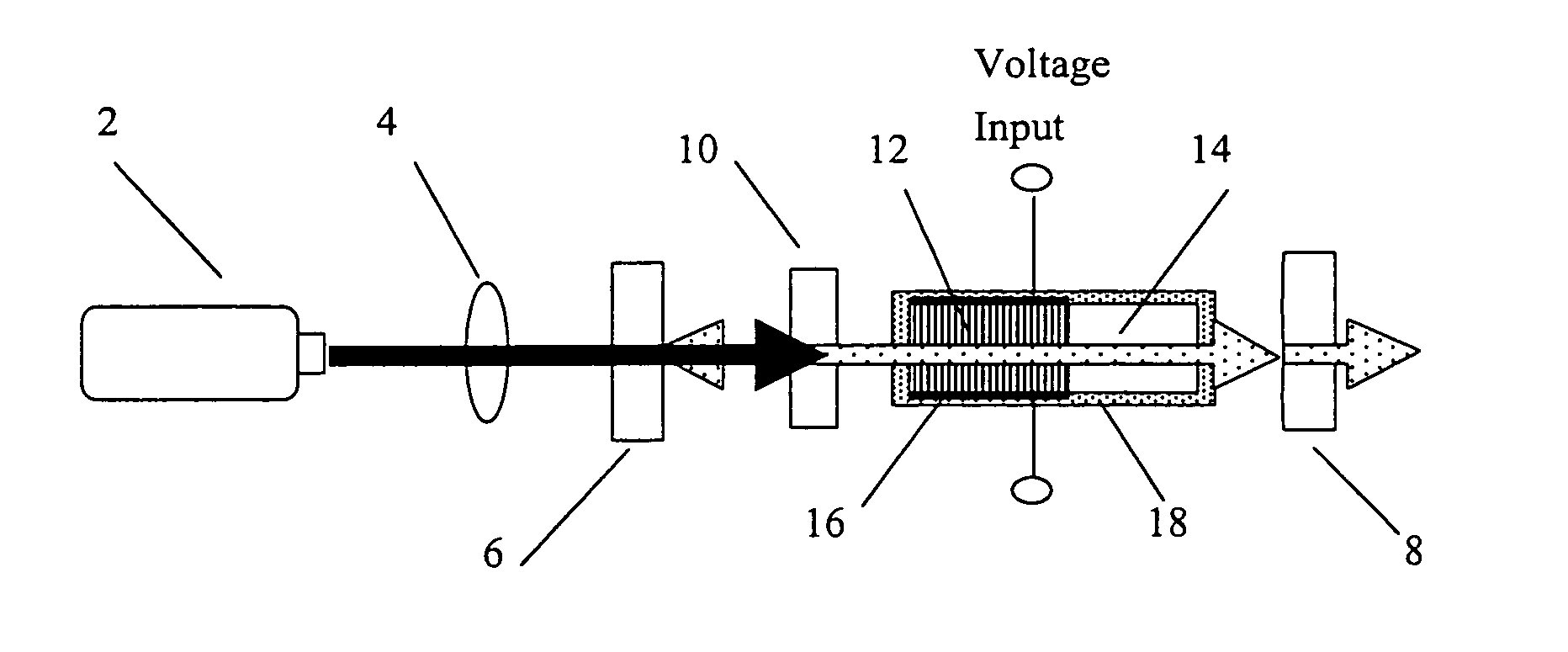
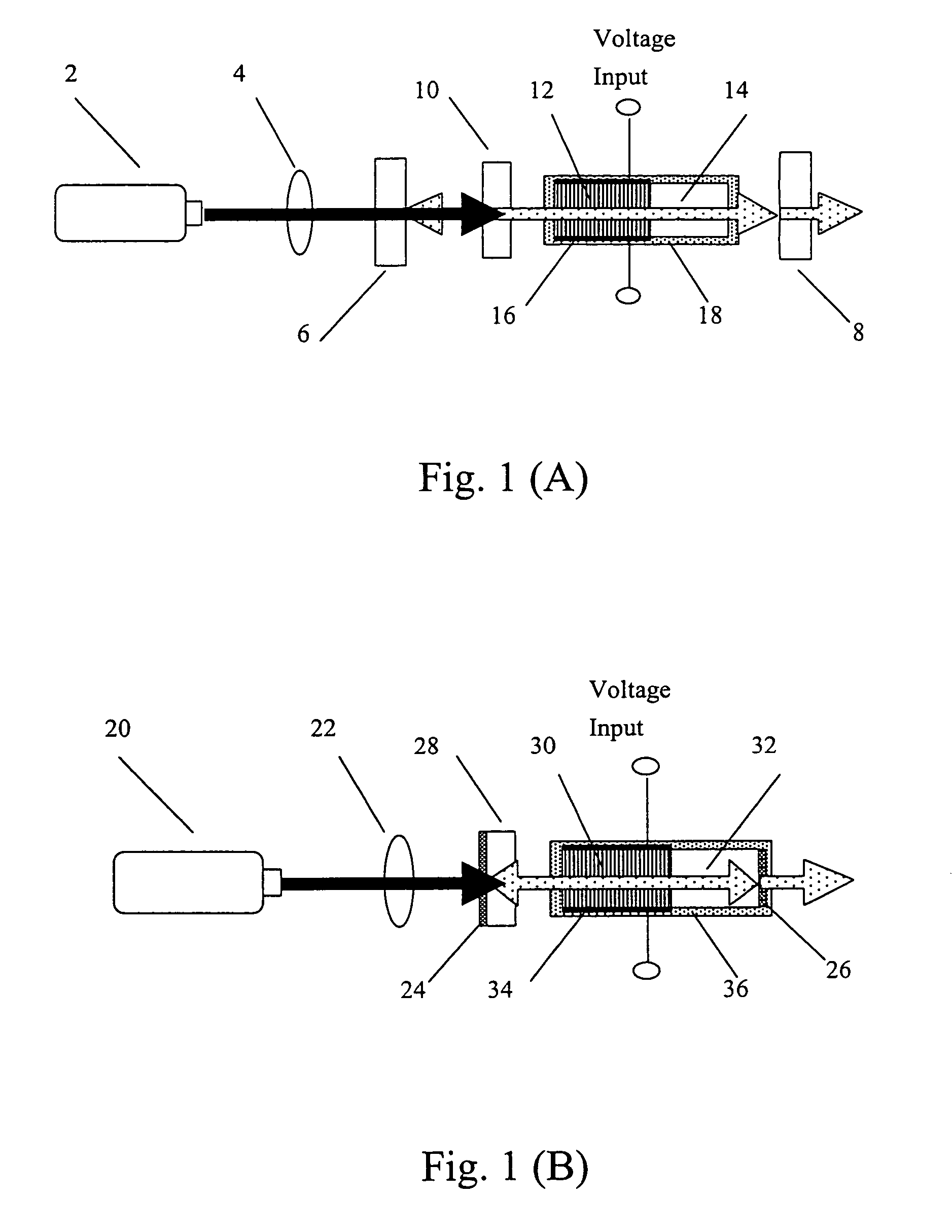
Polarization-insensitive integrated wavelength converter
InactiveUS6862130B2Lower Level RequirementsSolid-state devicesLight demodulationOptical circulatorProton
A polarization-insensitive integrated wavelength converter system includes polarization-separating, polarization-rotating and wavelength-converter structures integrated into a monolithic optical structure. In one embodiment, a lithium niobate waveguide structure includes an integrated polarization separator which comprises two coupled Zinc-diffused and annealed-proton-exchanged waveguides, an electro-optic quarter-wave retarder, a mirror structure and a quasi-phasematching structure. In another embodiment, an electro-optic half-wave retarder and bent waveguide are used in place of the electro-optic quarter-wave retarder and mirror structure. In a further embodiment, an optical circulator is used in conjunction with the waveguide structure in order to discriminate between input and output optical signals.
Owner:LIGHTBIT CORP
Compact continuous wave tunable infrared lasers and method therefor
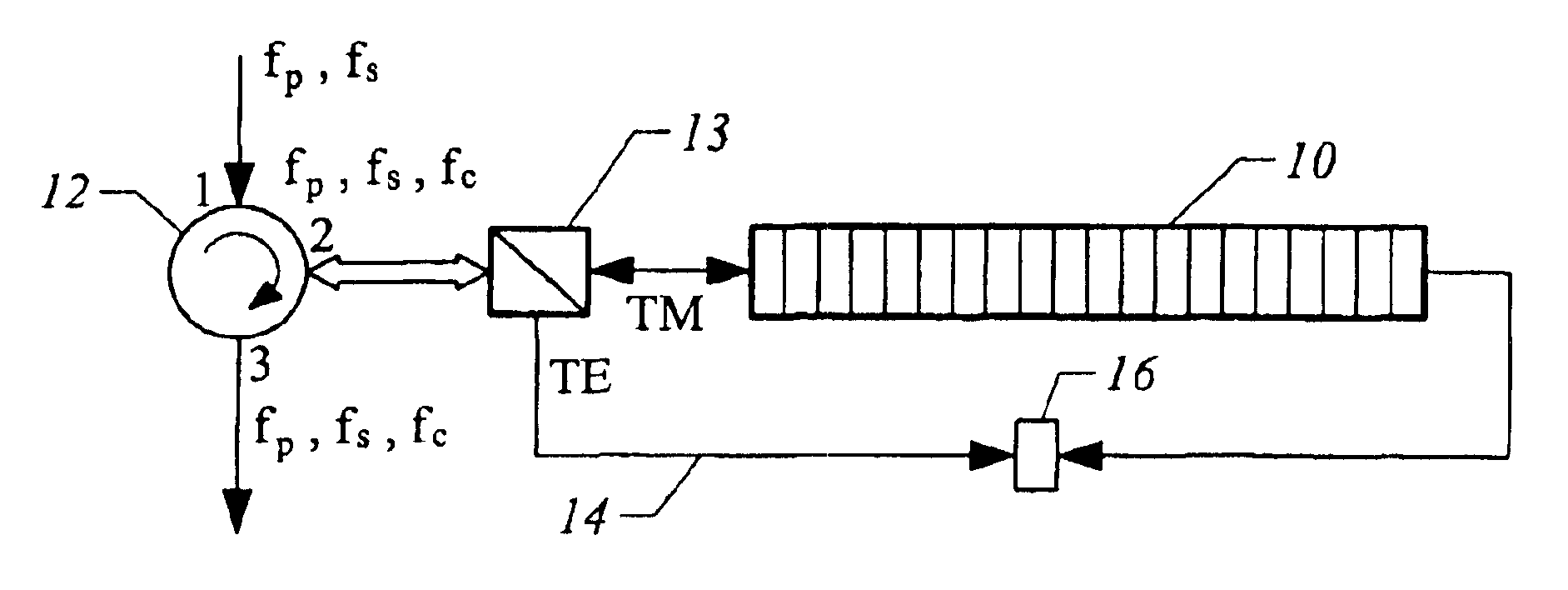
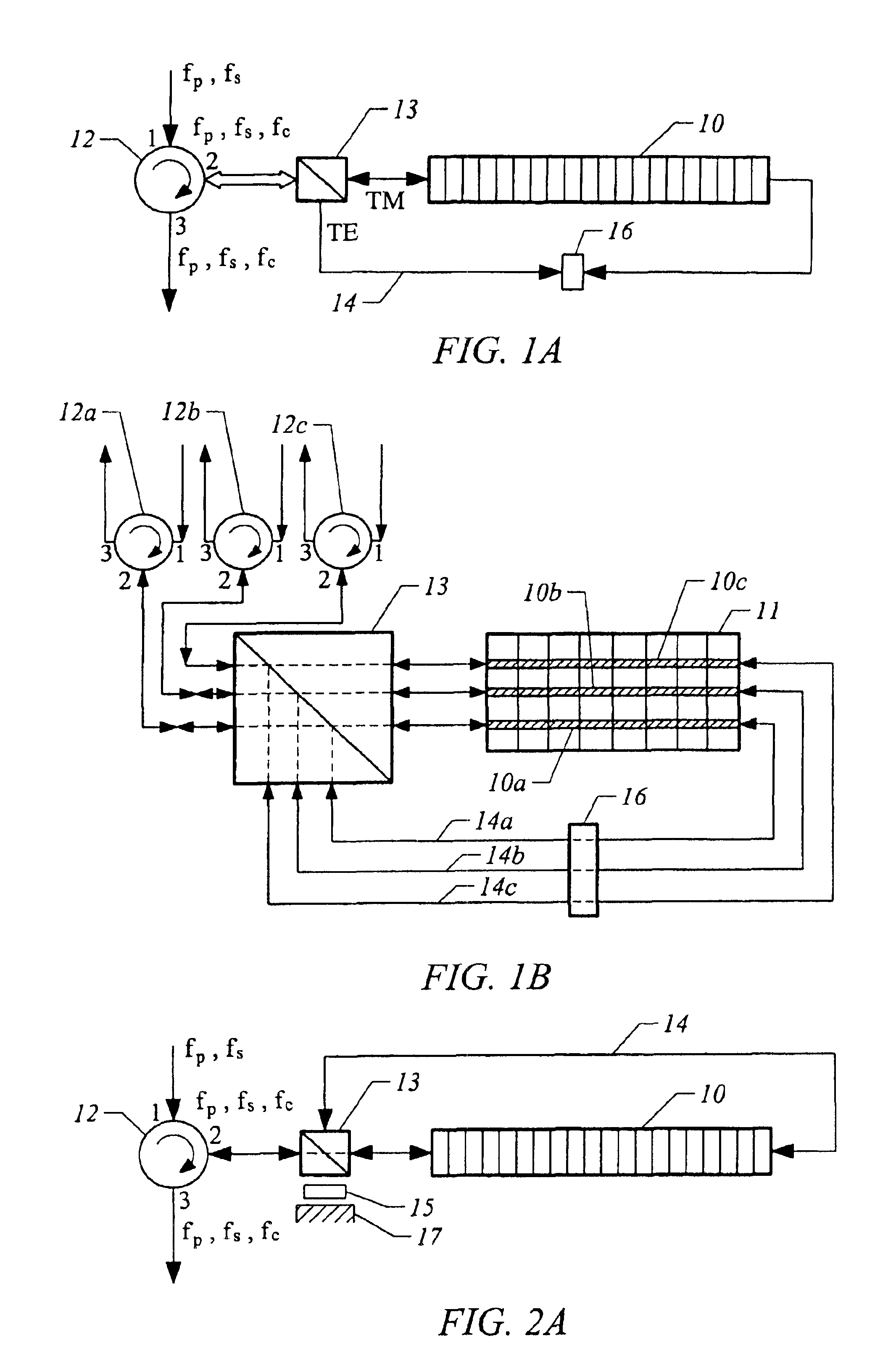
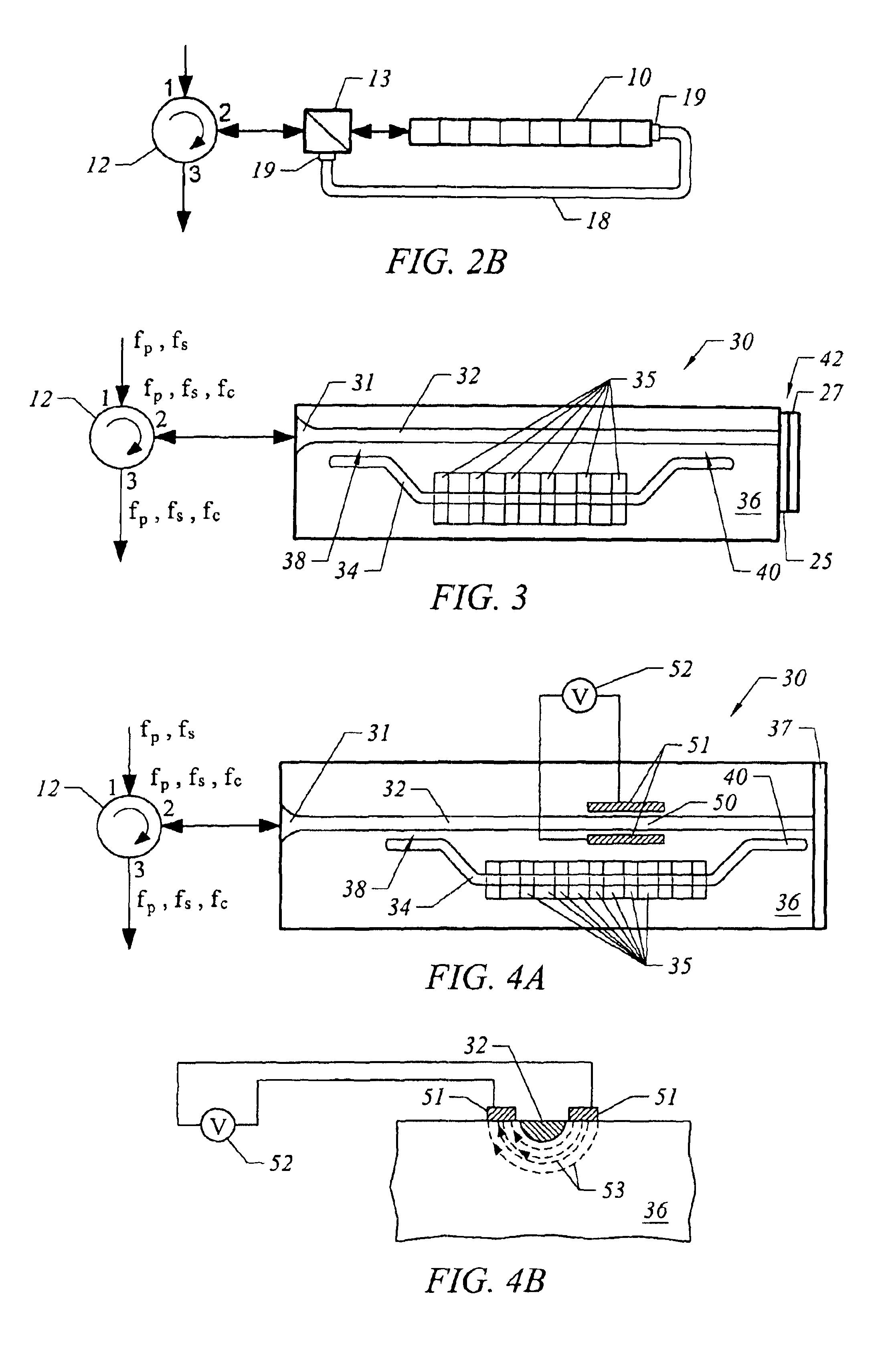
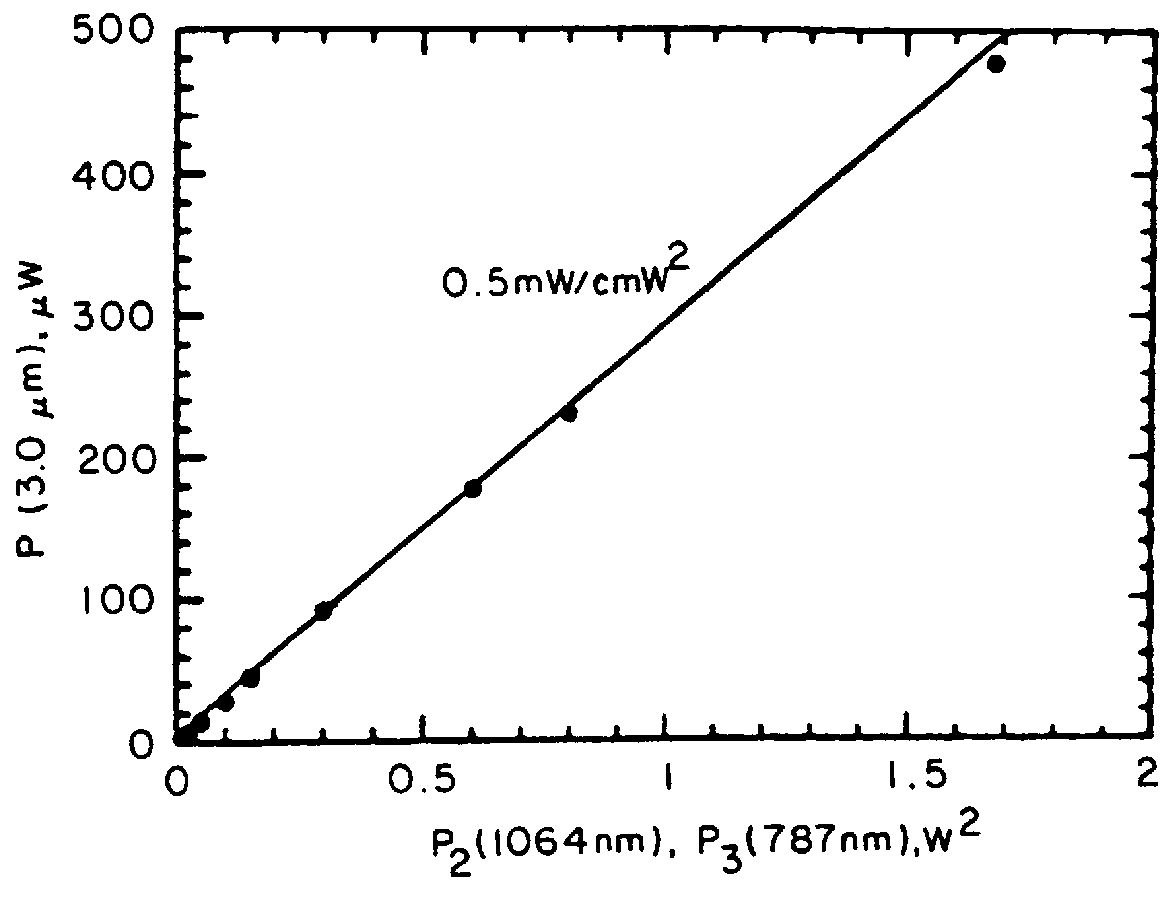
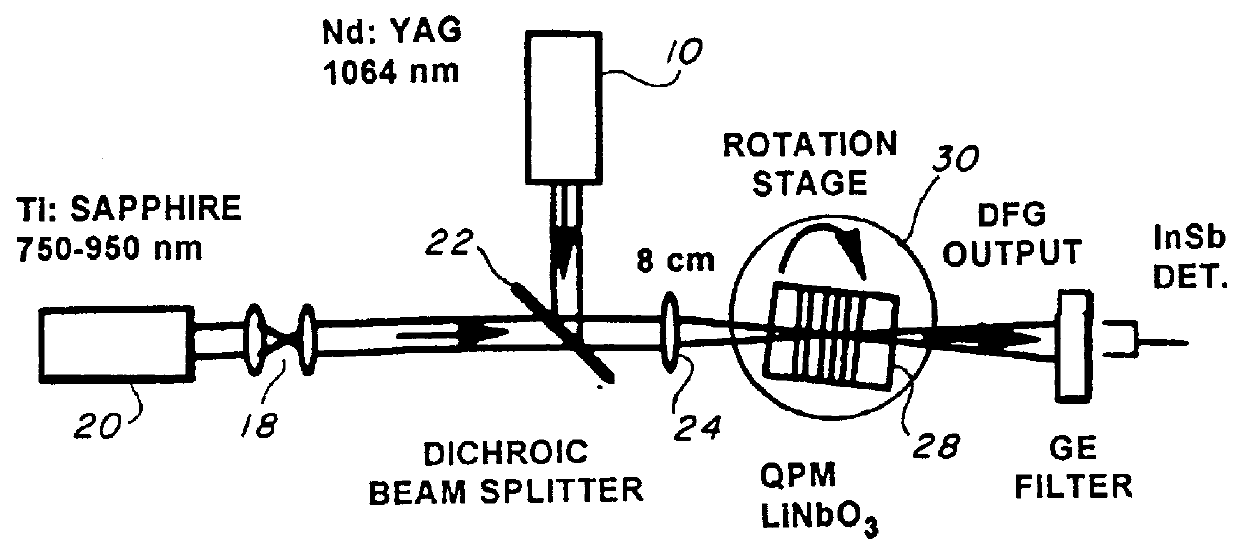
A bulk, quasi-periodic phase-matched difference-frequency (DFG) process in field-poled LiNbO.sub.3 bulk crystal permits continuous tunability of the output radiation in the 3.0-4.1 .mu.m wavelength range through grating rotation. DFG in QPM-LiNbO.sub.3 crystal, carried out using a Nd:YAG laser and a high power semiconductor laser at the quasi-phased matching (QPM) degeneracy point, results in an ultra wide 0.5 .mu.m acceptance bandwidth, permitting crystal rotation-free wavelength tuning of 4.0-4.5 .mu.m, with 0.2 mW output power at 4.5 .mu.m.
Owner:BURNS WILLIAM K +2
Quasi-phase-matching higher harmonic device based on ultrasonic modulation
InactiveCN101515105AExpand the adjustment rangeLarge adjustment rangeNon-linear opticsUltrasonic sensorFemto second laser
The invention relates to a quasi-phase-matching higher harmonic device based on ultrasonic modulation in the laser technical field, which comprises a femto-second laser, a focusing lens, an ultrasonic transducer, a bar type nozzle, a metallic film, an X ray spectrometer, a computer, a vacuum chamber, a decompression gas valve and a control panel. The output light path of the femto-second laser is sequentially provided with the focusing lens, the ultrasonic transducer, inert gases, the metallic film and the X ray spectrometer. Lasers emitted by the femto-second laser is focused below the bar type nozzle by the lens and interact with the inert gases with density periodic variation which is spouted by the nozzle and modulated by an ultrasonic field to radiate higher harmonics which are reflected into the X ray spectrometer after being filtered by the metallic film and then are sent into the computer. The device meets the quasi-phase-matching condition of the higher harmonics by using ultrasonic modulation gas density, is convenient to be operated and simple and easy, can propel the coherent light source of the higher harmonics soft X ray to shorter waver.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Actively Q-switched laser system using quasi-phase-matched electro-optic Q-switch
A Q-switched laser system is disclosed. The laser system employs a quasi-phase-matched electro-optic (QPM EO) crystal as the laser Q-switch. When applied with a certain modulating electric field, the QPM EO crystal can function as a polarization rotator to rotate the polarization direction of the resonant laser beam in a polarization-dependent laser resonator, thereby switching the laser resonator between high-loss and low-loss cavity states to achieve laser Q-switching. Compared with traditional electro-optic Q-switched laser system, the disclosed laser system is characterized by a low switching-voltage, reduced cost, and compactness. A quasi-phase-matched electro-optically Q-switched wavelength-conversion and wavelength-tunable laser system is also disclosed. The disclosed laser system integrates a QPM electro-optic Q-switch and a QPM nonlinear wavelength converter in a single crystal substrate to perform a high-efficiency intracavity wavelength conversion. The disclosed laser system is therefore simple and compact and has lower system requirements on wall-plug power and higher overall conversion efficiency.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Wide-tuning and narrow-linewidth nanosecond pulse double-resonance medium-infrared parameter oscillator
ActiveCN106711745AEasy to tuneWide coverageOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionLine widthSpectroscopy
The invention provides a double-resonance, wide-tuning and narrow-linewidth all-solid-state nanosecond pulse medium-infrared optical parameter oscillator comprising four parts including single-frequency pump light, a double-resonance resonant cavity, an electrical control part and seed light. A 1.064 <mu>m single-frequency pulse laser pump quasi-phase matching multi-cycle polarized crystal double-resonance parameter oscillator is adopted to acquire dual-band laser output of wide-tuning range near-infrared signal light and medium-infrared idle light. The output central wavelength is tunable within the wide spectral range, and the cavity length is dynamically adjusted through electro-optical crystal by combining a single-frequency continuous semiconductor laser seed injection technology so as to realize narrow-linewidth laser output of the optical parameter oscillator. The oscillator can be widely applied to the field of high-resolution laser spectroscopy, laser radar, laser remote sensing, environmental detection, optical-electro countermeasure and laser medicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quasi-phase matching and quantum control of high harmonic generation in waveguides using counterpropagating beams
InactiveUS20080137696A1Enhance high-harmonic emissionSuppress emissionLaser using scattering effectsX-ray apparatusHigher order harmonicsLight beam
All-optical quasi-phase matching (QPM) uses a train of counterpropagating pulses to enhance high-order harmonic generation (HHG) in a hollow waveguide. A pump pulse enters one end of the waveguide, and causes HHG in the waveguide. The counterpropagation pulses enter the other end of the waveguide and interact with the pump pulses to cause QPM within the waveguide, enhancing the HHG.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
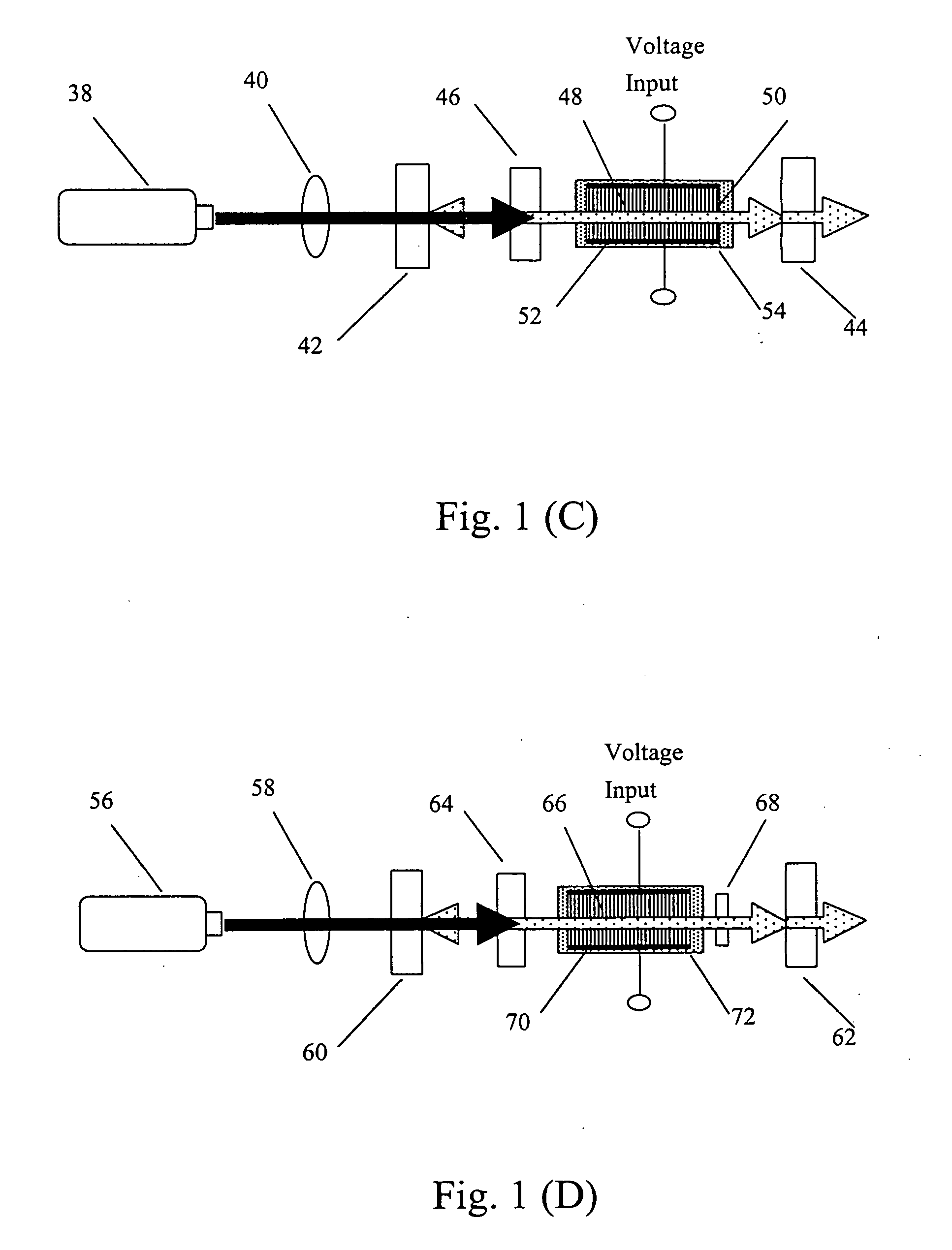
Optical parametric devices and methods for making same
InactiveUS20020126370A1Improve efficiencyBandwidth-length productLight demodulationOptical waveguide light guideOmegaWide band
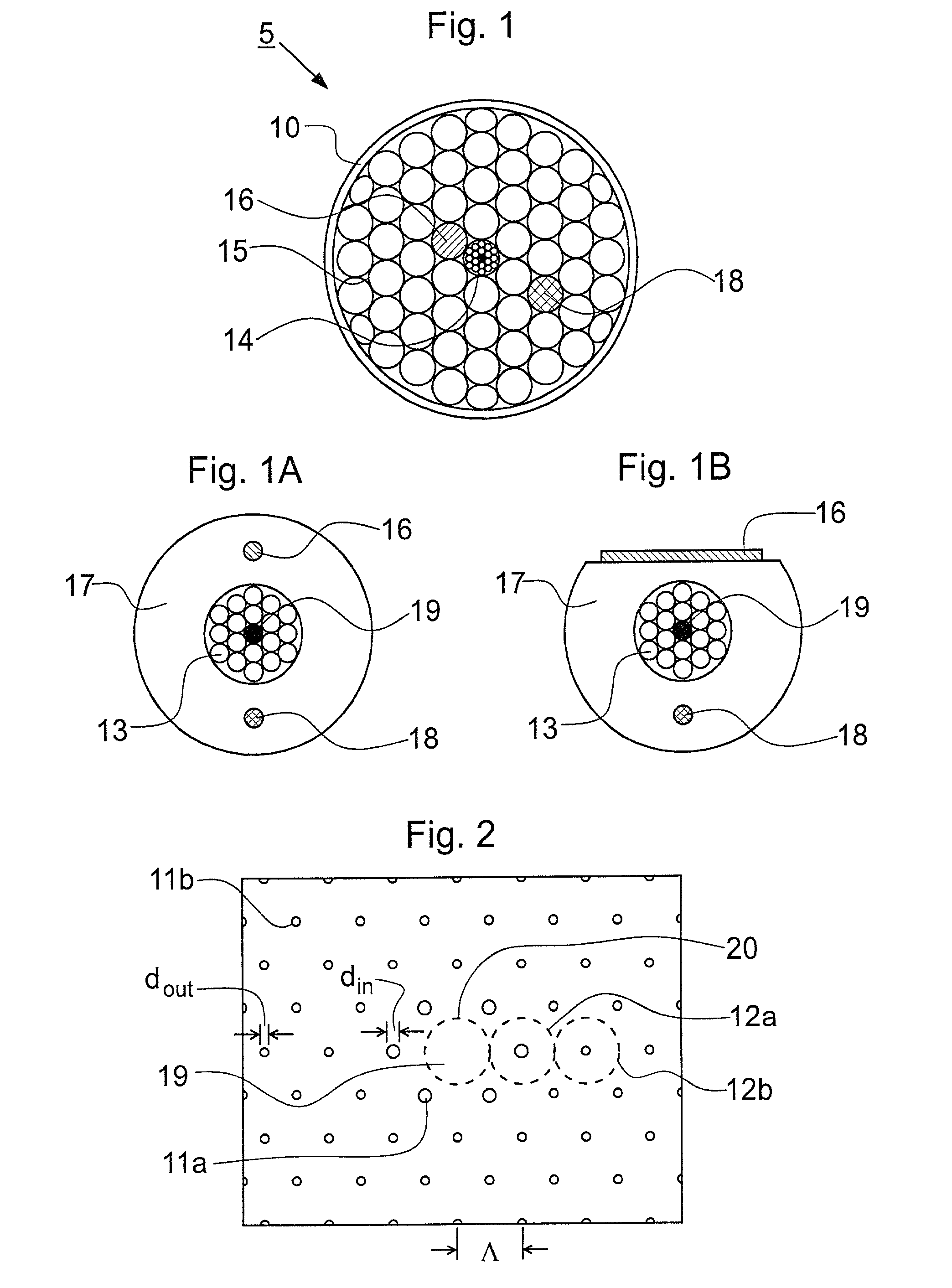
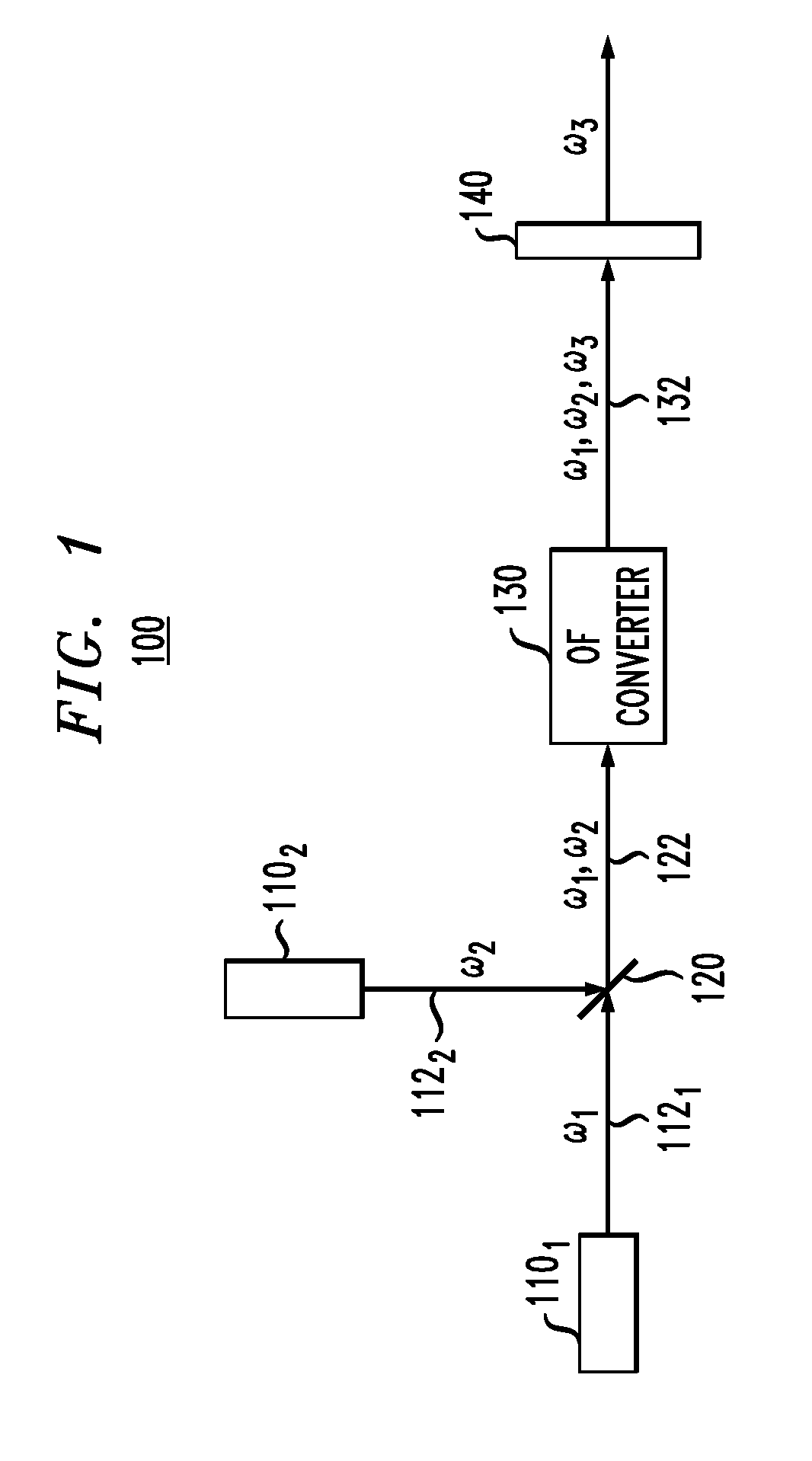
An optical parametric device for broadband parametric processes involving first and second frequencies .omega..sub.1 and .omega..sub.2. The device comprises an optical fiber comprising a core and a cladding, the cladding being microstructured with holes for providing waveguiding confinement of at least one optical mode in the core. The optical fiber is poled lengthwise with a non-linearity profile having a period that satisfies a quasi phase matching (QPM) condition including the first and second frequencies. Through the use of a poled holey fiber of suitable hole structure, it is possible to increase the second harmonic (SH) efficiency in comparison with poled conventional (non-holey) fiber. This is achieved by a combination of a low mode overlap area between the fundamental and SH waves, a low absolute value of the mode area, and a large SH bandwidth per unit length of the fiber, all of which can be provided together in a poled holey fiber.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Quasi-phase-matching higher harmonic device based on ultrasonic modulation
InactiveCN101515105BExpand the adjustment rangeLarge adjustment rangeNon-linear opticsUltrasonic sensorFemto second laser
The invention relates to a quasi-phase-matching higher harmonic device based on ultrasonic modulation in the laser technical field, which comprises a femto-second laser, a focusing lens, an ultrasonic transducer, a bar type nozzle, a metallic film, an X ray spectrometer, a computer, a vacuum chamber, a decompression gas valve and a control panel. The output light path of the femto-second laser issequentially provided with the focusing lens, the ultrasonic transducer, inert gases, the metallic film and the X ray spectrometer. Lasers emitted by the femto-second laser is focused below the bar type nozzle by the lens and interact with the inert gases with density periodic variation which is spouted by the nozzle and modulated by an ultrasonic field to radiate higher harmonics which are reflected into the X ray spectrometer after being filtered by the metallic film and then are sent into the computer. The device meets the quasi-phase-matching condition of the higher harmonics by using ultrasonic modulation gas density, is convenient to be operated and simple and easy, can propel the coherent light source of the higher harmonics soft X ray to shorter waver.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Solid-state laser apparatus, display apparatus and wavelength converting element
InactiveUS20100103088A1Improve conversion efficiencyAllowable temperature range can be increasedLaser detailsStatic indicating devicesSolid-state laser deviceOptical axis
A solid-state laser apparatus includes: a semiconductor laser light source for emitting laser light; an optical resonator having a solid-state laser medium to be excited by incidence of the laser light to oscillate fundamental laser light, and a mirror; and a quasi phase matching wavelength converting element, disposed in the optical resonator, for converting a wavelength of the fundamental laser light, wherein the quasi phase matching wavelength converting element is formed with a polarization inversion region having a predetermined cycle, and the length of the polarization inversion region in an optical axis direction is 1.0 mm or less.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
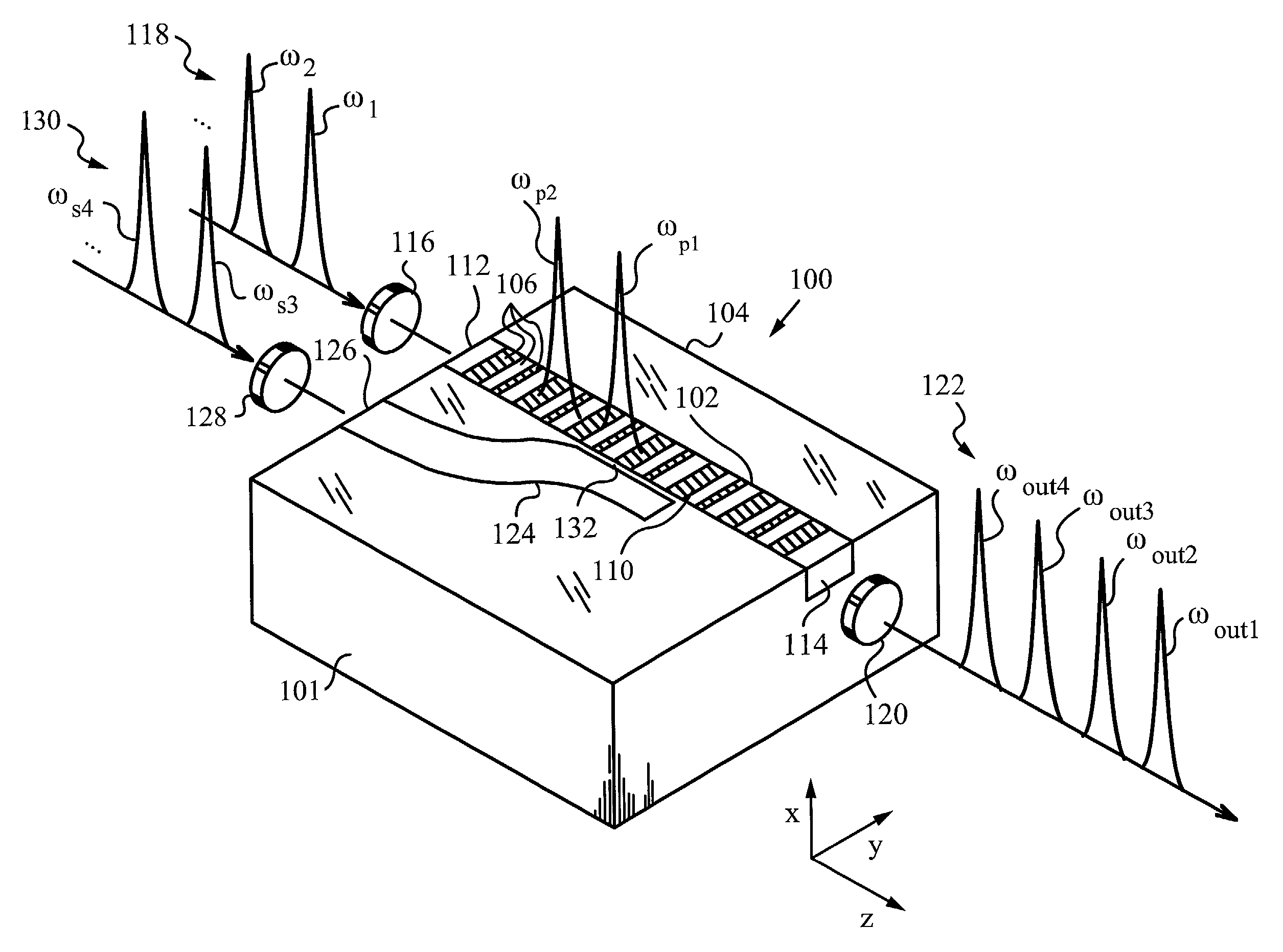
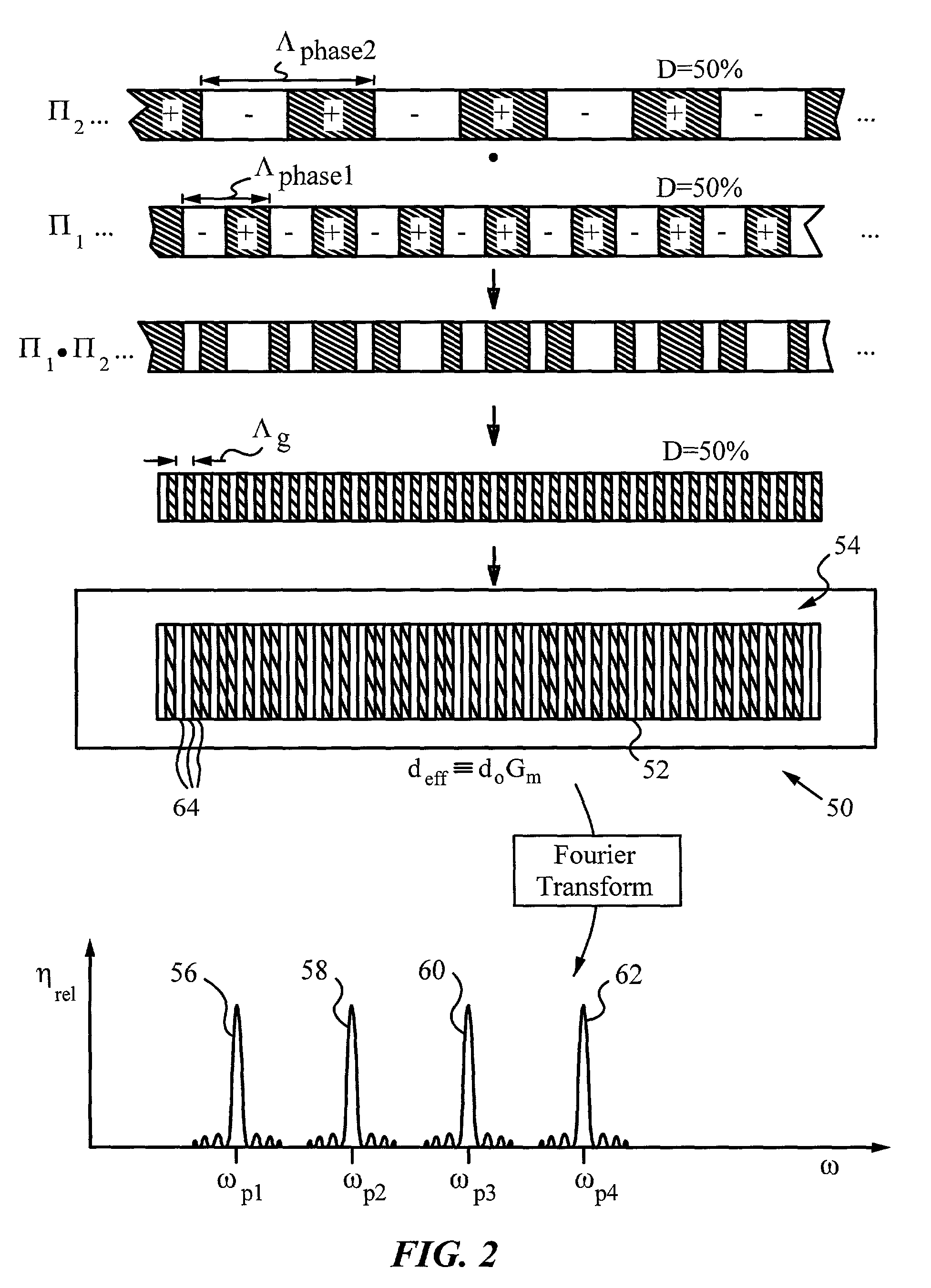
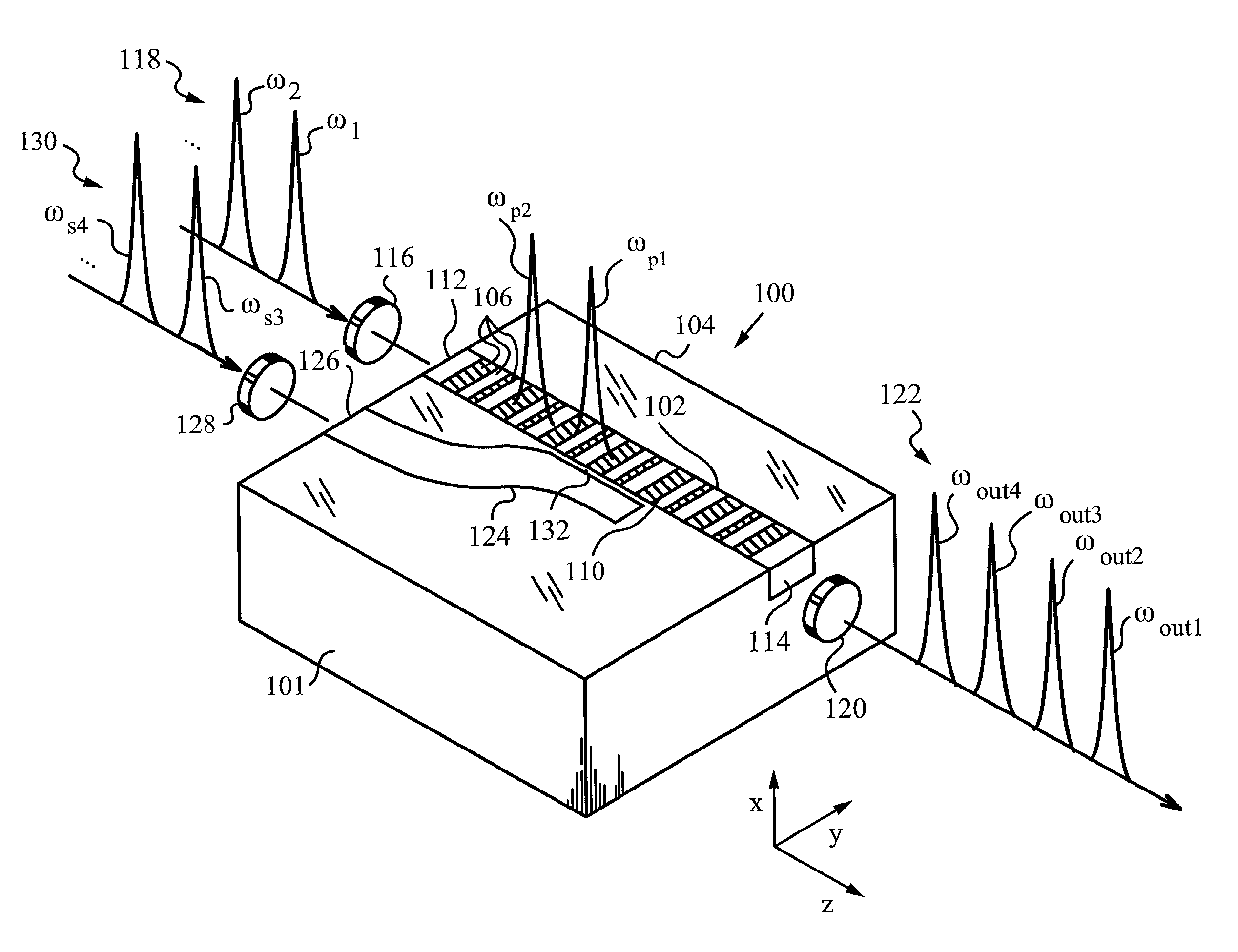
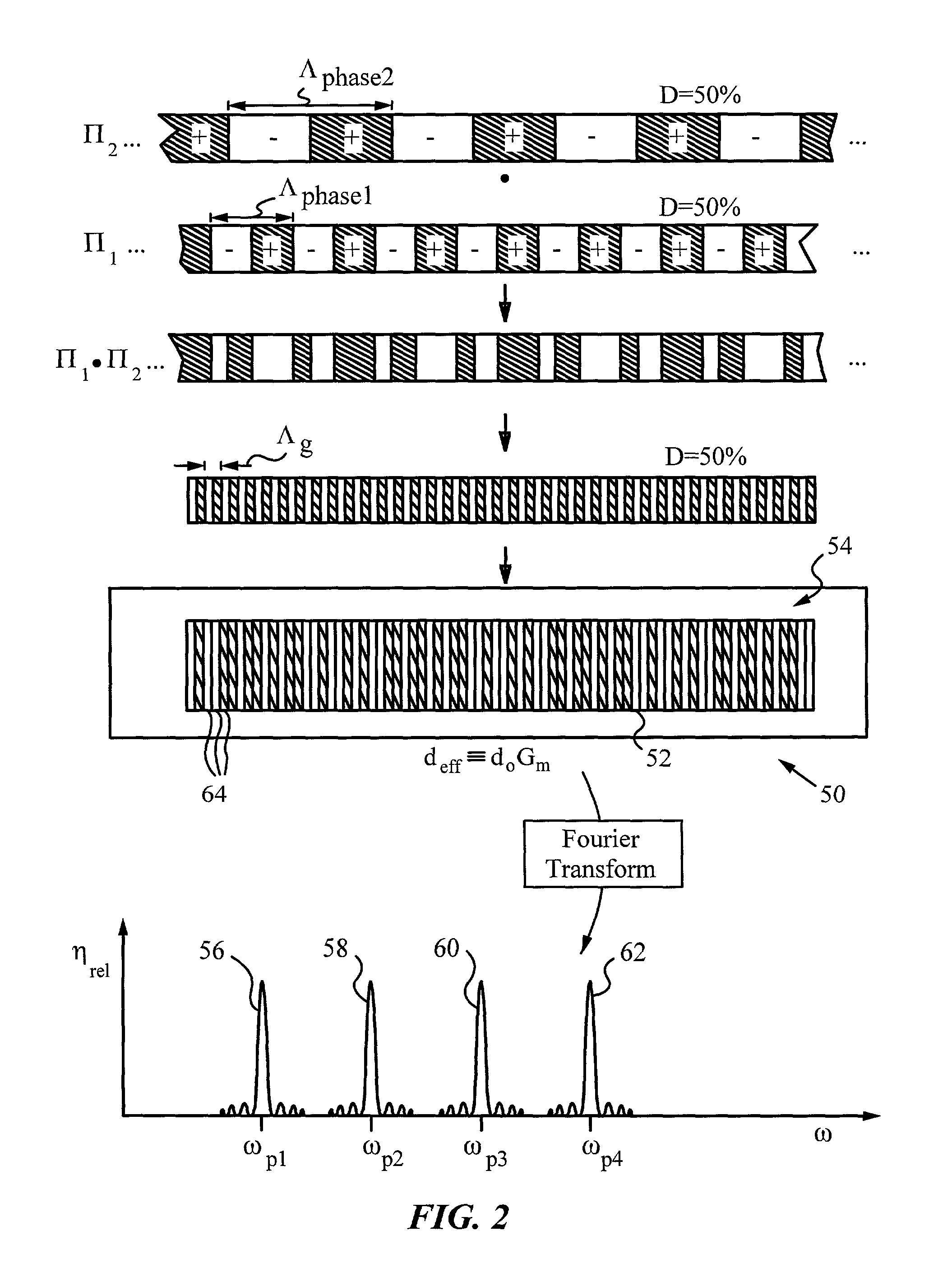
Multiple channel optical frequency mixers for all-optical signal processing
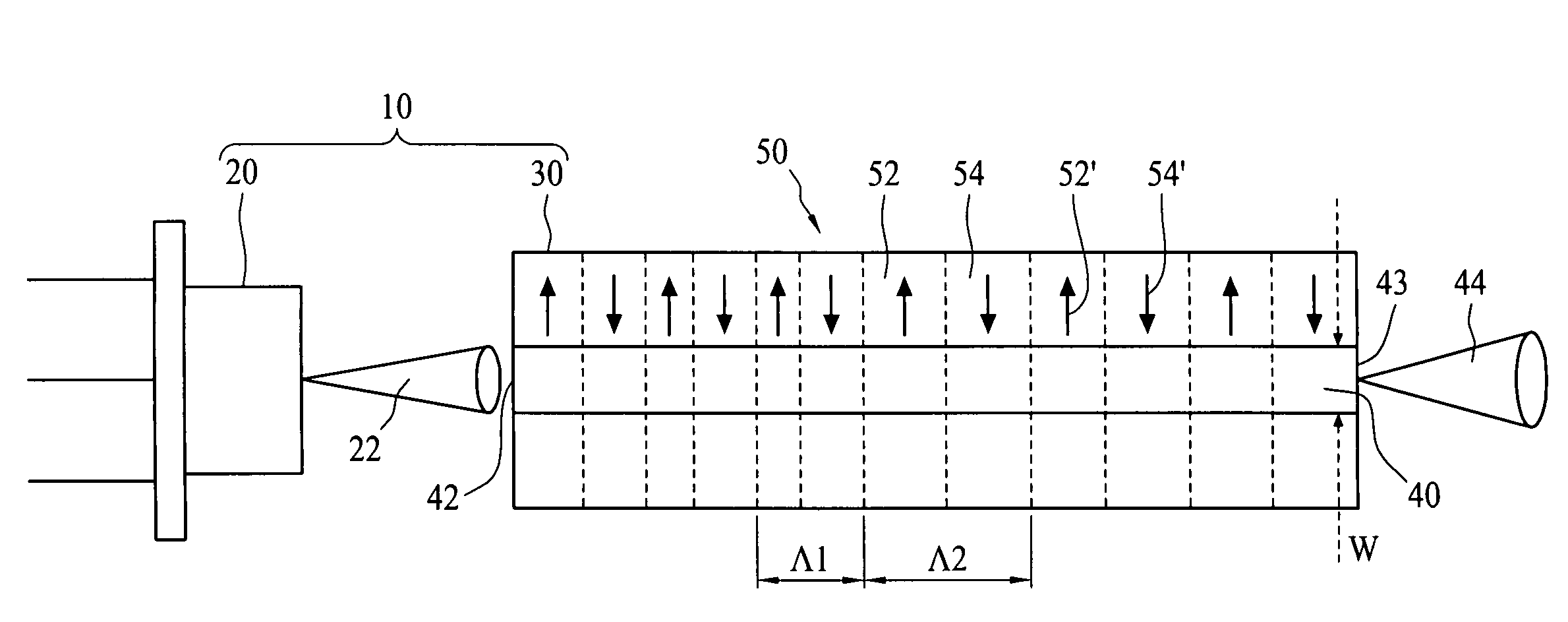
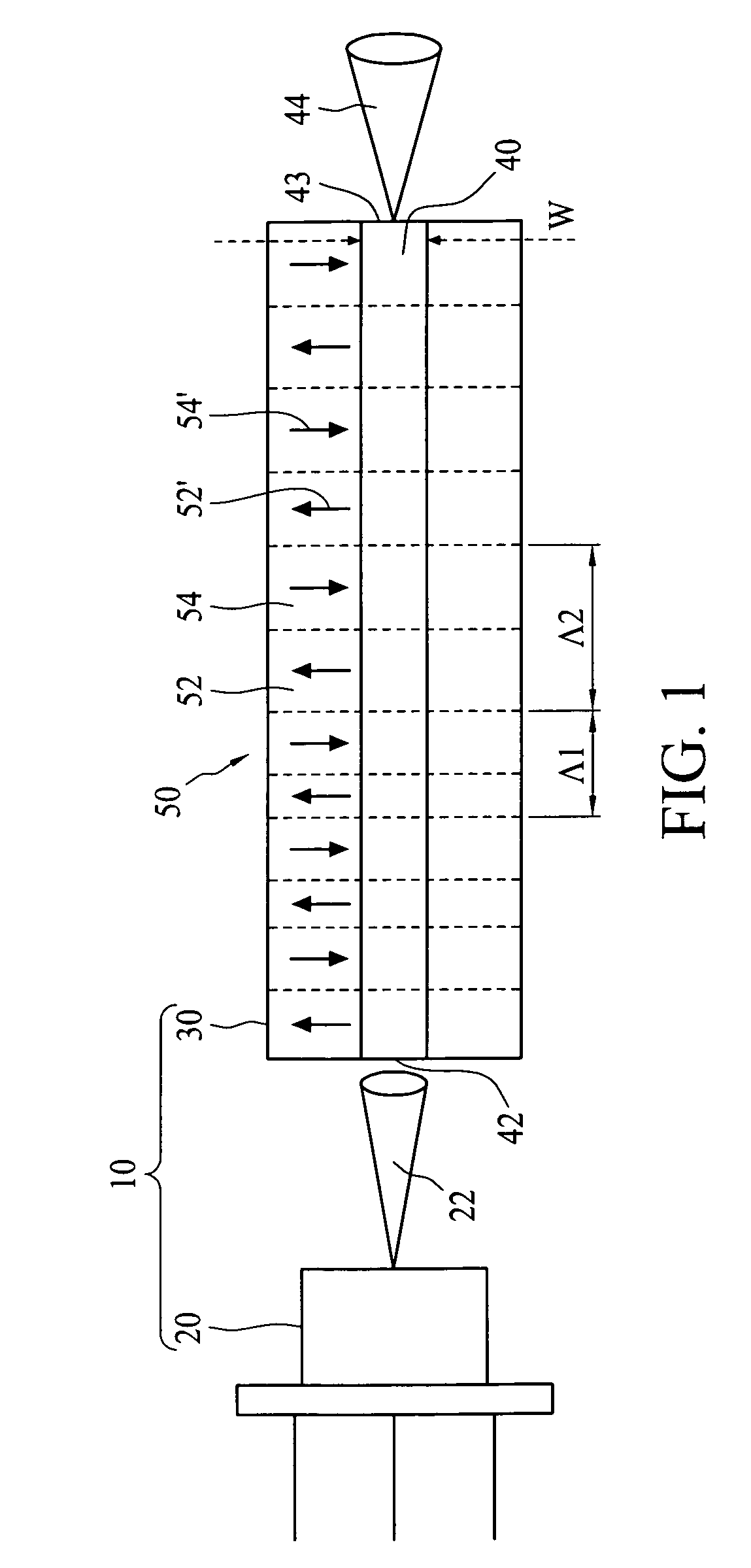
A multi-channel optical frequency mixer for all-optical signal processing and a method for engineering the same. The multi-channel mixer uses a nonlinear optical material exhibiting an effective nonlinearity deff whose spatial distribution is defined by a quasi-phase-matching grating, e.g., a QPM grating. The spatial distribution is defined such that its Fourier transform to the spatial frequency domain defines at least two wavelength channels which are quasi-phase-matched for performing optical frequency mixing. The wavelength channels correspond to dominant Fourier components and the Fourier transform is appropriately adjusted using grating parameters such as grating periods, phase reversal sequences and duty cycles to include an odd or even number of dominant Fourier components. The multi-channel mixer can perform frequency mixing operations such as second harmonic generation (SHG), difference frequency generation (DFG), sum frequency generation (SFG), and parametric amplification.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
High efficiency wavelength converters
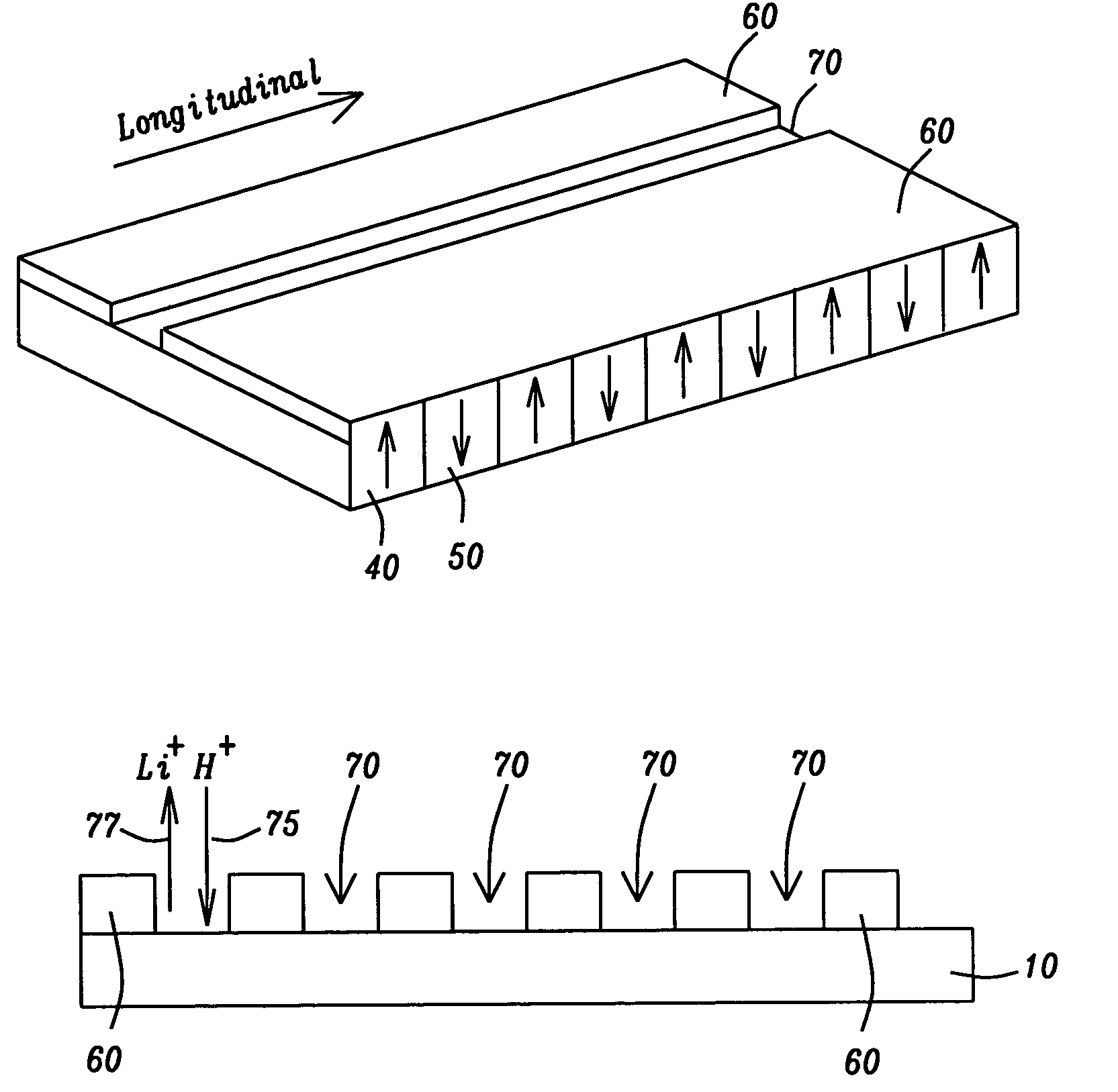
InactiveUS7170671B2Efficiently obtainedAvoid surface damageAfter-treatment detailsBy pulling from meltEnergy transferHigh rate
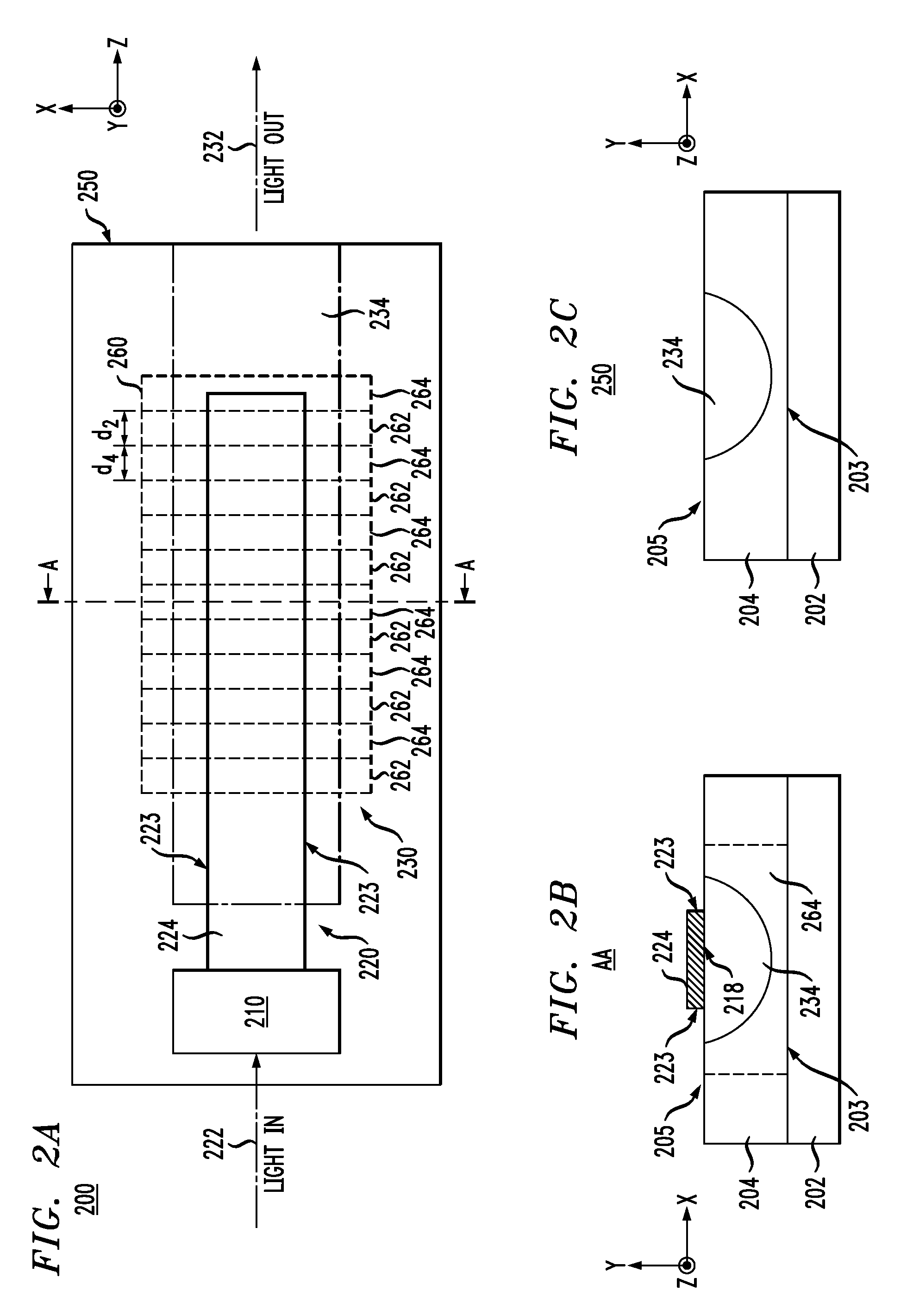
A method is provided for forming a waveguide region within a periodically domain reversed ferroelectric crystal wherein the waveguide region has a refractive index profile that is vertically and horizontally symmetric. The symmetric profile produces effective overlapping between quasi-phasematched waves, a corresponding high rate of energy transfer between the waves and a symmetric cross-section of the radiated wave. The symmetric refractive index profile is produced by a method that combines the use of a diluted proton exchange medium at a high temperature which produces a region of high index relatively deeply beneath the crystal surface, followed by a reversed proton exchange which restores the original crystal index of refraction immediately beneath the crystal surface.
Owner:HC PHOTONICS
Continuous-wave ultraviolet laser
ActiveUS20080240177A1Increase stability of laserEfficient frequency conversionOptical resonator shape and constructionNon-linear opticsResonant cavityUltraviolet
A laser is disclosed, which is suitable for efficient generation of continuous-wave laser light having a wavelength of about 400 nm or less. The short-wavelength light is generated by first frequency-doubling a fundamental wave, and then sum-frequency mixing the frequency-doubled wave and the fundamental wave. The non-linear interactions are effected by means of quasi-phasematching structures inside a resonant cavity where the fundamental wave is circulating. The sum-frequency mixing is effected using second or higher order quasi-phasematching, which allows for wider domains to be inverted for the quasi-phasematching structure compared to first order quasi-phasematching. Preferably, the sum-frequency mixing is effected using periodically poled stoichiometric lithium tantalate (PPSLT) for second or third order quasi-phasematching.
Owner:COBOLT
Nonlinear frequency mixer using quasi-phase-matching gratings having beam-modifying patterns
A method and a nonlinear frequency mixer employing the method to generate at least one output light from at least one input light with the aid of a quasi-phase-matching (QPM) grating for quasi-phase-matching the input and output light involved in a nonlinear frequency mixing operation such as three-wave mixing, four-wave mixing or other nonlinear operation mediated by a susceptibility of the nonlinear optical material. The QPM grating has a beam-modifying pattern with features for wave front shaping. More specifically, the features shape the wave fronts of the output light by diffraction or phase front shaping to thereby modify its propagation. This modification of propagation can be used to steer, focus, defocusing, split and / or collimate the output light. The features themselves can have various geometric shapes and sizes, even on the order of the wavelength of the output light, and they can include domains exhibiting a nonlinear optical susceptibility χ, such as the second-order susceptibility χ(2), domain edges, and / or spacings between such domains.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Doped stoichiometric lithium niobate and lithium tantalate for self-frequency conversion lasers
In accordance with the present invention, a crystal laser material that is suitable for self doubling is presented. A crystal according to the present invention includes a stoichiometric lithium niobate crystal isomorph host material doped with at least one laser ion. In some embodiments, the stoichiometric lithium niobate crystal isomorph host material is lithium niobate. In some embodiments, the stoichiometric lithium niobate crystal isomorph host material is lithium tantalate. In some embodiments, the at least one laser ion includes Ytterbium. In some embodiments, the at least one laser ion includes a rare-earth ion. In some embodiments, the stoichiometric lithium niobate crystal isomorph host material is periodically poled to provide quasi-phase matching. Additionally, further dopant ions, for example Magnesium, can be included.
Owner:NOVA PHASE
Single-shot pulse contrast measuring device based on non-harmonic long-wavelength sampling pulse
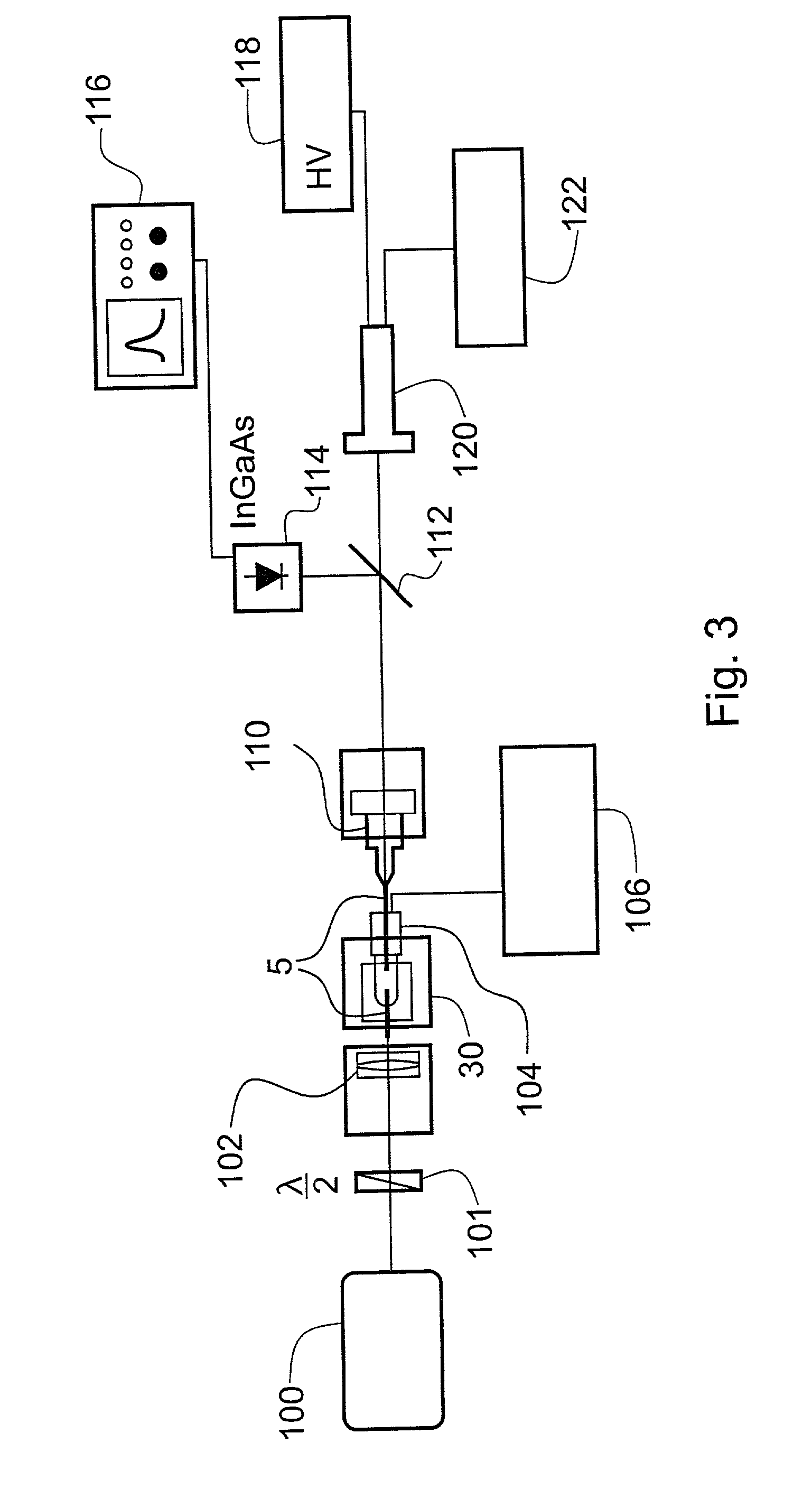
ActiveUS20120228501A1Increase attainable maximum NPM angleMaximum effectiveRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansExtensibilityHigh power lasers
A single-shot pulse contrast measuring device based on non-harmonic long-wavelength sampling pulse includes a long-wavelength sampling light generation unit, a large-angle non-collinear sum-frequency cross-correlation unit and a high sensitivity signal receiving unit. The long-wavelength sampling light sum-frequency cross-correlator can allow that the beams are interacted with each other at the large non-collinear angle in the quasi-phase matching crystal, match the measuring window of the high sensitivity signal receiving system, and is in favor of eliminating the scattered light noise, thereby achieving the single measurement of the pulse contrast with large temporal window and high dynamic range. The single-shot pulse contrast measuring device of the present invention has good extensibility at the temporal window and dynamic range, and is adapted for measuring the contrast of the high-power laser with various wavelengths.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Doped stoichiometric lithium niobate and lithium tantalate for self-frequency conversion lasers
In accordance with the present invention, a crystal laser material that is suitable for self doubling is presented. A crystal according to the present invention includes a stoichiometric lithium niobate crystal isomorph host material doped with at least one laser ion. In some embodiments, the stoichiometric lithium niobate crystal isomorph host material is lithium niobate. In some embodiments, the stoichiometric lithium niobate crystal isomorph host material is lithium tantalate. In some embodiments, the at least one laser ion includes Ytterbium. In some embodiments, the at least one laser ion includes a rare-earth ion. In some embodiments, the stoichiometric lithium niobate crystal isomorph host material is periodically poled to provide quasi-phase matching. Additionally, further dopant ions, for example Magnesium, can be included.
Owner:NOVA PHASE
Light-generating apparatus with broadband pumping laser and quasi-phase matching waveguide
InactiveUS20090154508A1Avoid low lightAvoid problemsLaser detailsNon-linear opticsSum-frequency generationBroadband
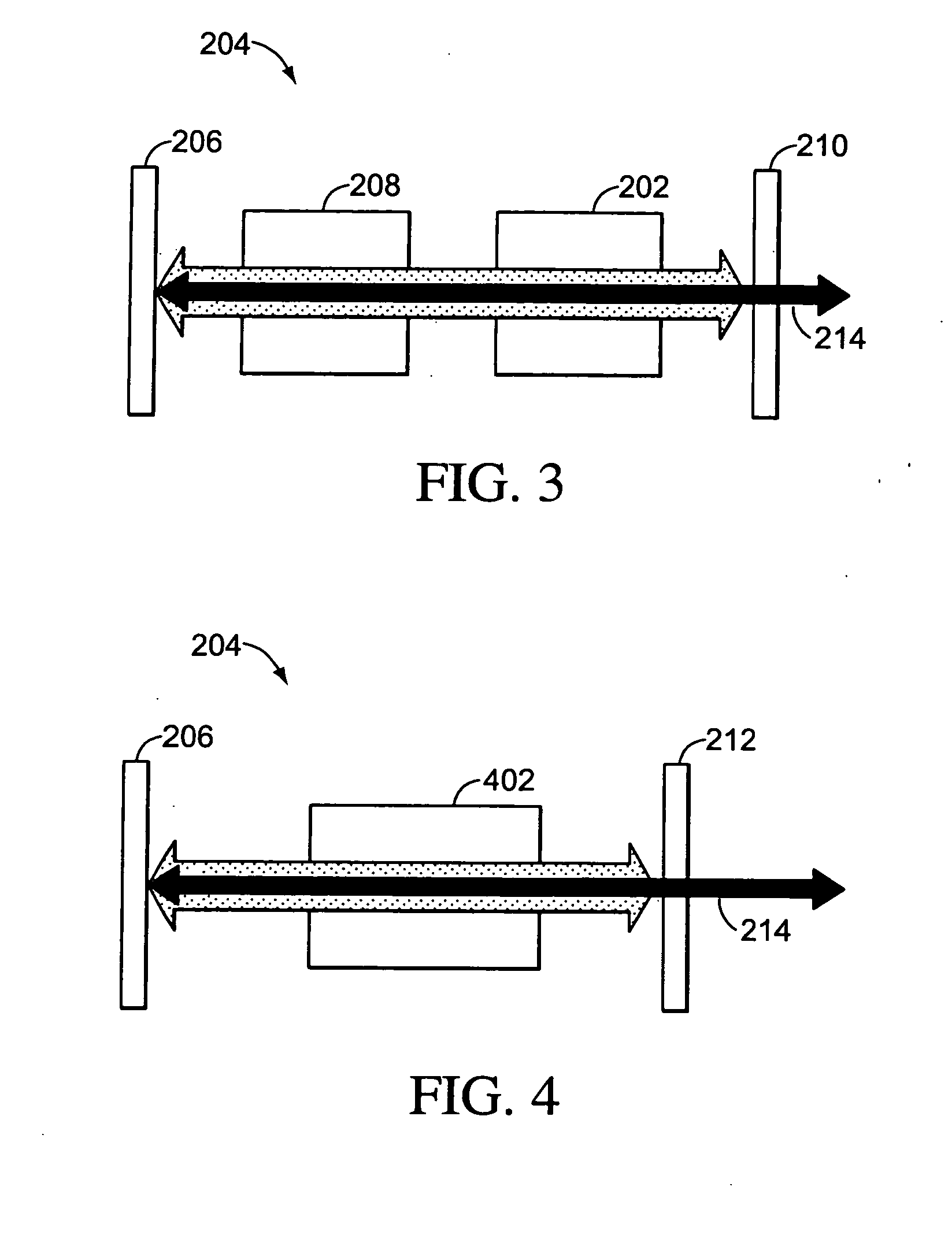
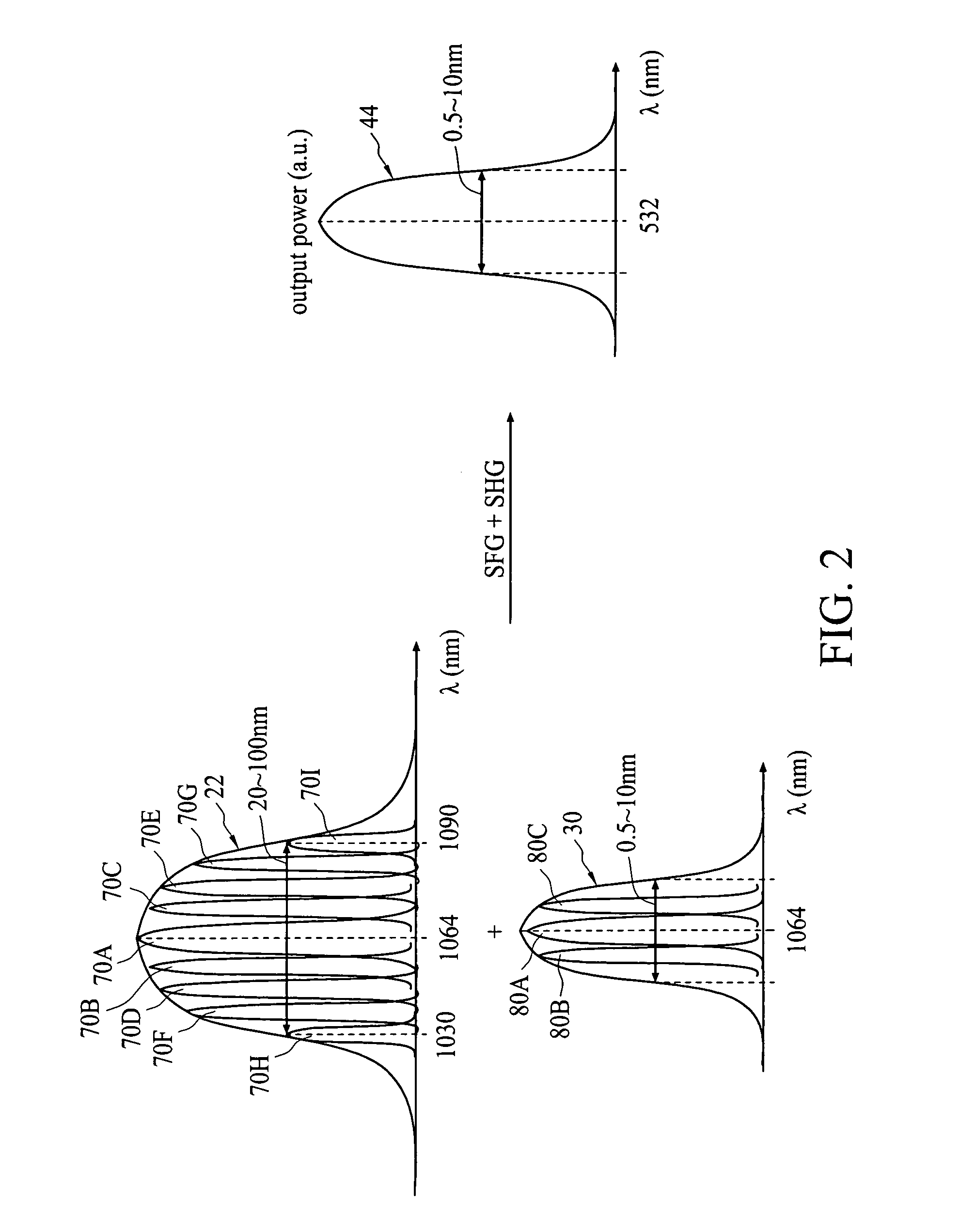
A light-generating apparatus comprises a broadband pumping laser configured to emit a broadband pumping light having a bandwidth larger than 10 nanometers and a broadband wavelength-converting device. The broadband wavelength-converting device includes a domain-inverted structure configured to convert the broadband pumping light into at least one conversion light by using at least a sum frequency generation mechanism and at least one waveguide positioned in the domain-inverted structure, and the waveguide has an input end configured to receive the broadband pumping light and an output end configured to output the conversion light. Since the light-generating apparatus uses the broadband pumping laser and the broadband wavelength-converting device, it is temperature-insensitive and speckle-free.
Owner:HC PHOTONICS
Difference-frequency tunable single-frequency terahertz source with external cavity strengthened
InactiveCN103633545AImprove utilization efficiencyOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialResonant cavityOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a difference-frequency tunable single-frequency terahertz source, with an external cavity strengthened, on the basis of pumping of two single-frequency fiber lasers. As the two tunable single-frequency fiber lasers are taken as pumping sources, a periodical reversal crystal in quasi-phase-matching is utilized as a difference-frequency crystal, and a four-mirror ring resonant cavity is utilized to form an external cavity strengthened structure, the single-frequency terahertz radiated output is realized. Single-frequency fiber laser is output and coupled into the quasi-phase matching crystal by means of a pumping coupling system, pumping light passes through the crystal repeatedly by the aid of the four-mirror ring cavity structure to increase photon utilization efficiency to strength the external cavity, and finally terahertz wave is output through a terahertz radiated output mirror set on the right side of the quasi-phase-matching crystal. The difference-frequency tunable single-frequency terahertz source with the external cavity strengthened has the advantages of compact structure, high efficiency, high reliability and the like.
Owner:HFB PHOTONICS CO LTD
Multiplier enhancing method based on periodically poled lithium niobate
InactiveCN103605248AImprove conversion efficiencyChange cycleNon-linear opticsInformation processingSlow light
The invention provides a multiplier enhancing method based on periodically poled lithium niobate, and belongs to the technical field of optical information processing. The method includes firstly, performing room temperature electric field polarization on lithium niobate crystals, changing the polarization direction of the electric domain in a negative domain region of the +Z face of the crystals, and performing vacuum coating sputter electrode on two Y-directional sides of the crystals; then irradiated the crystals with a normal light and applying voltage of the two Y-directional sides of the lithium niobate crystals through a high voltage source simultaneously, and realizing ordinary light multiplier enhancement through produced slow light effects. According to the method, the quasi-phase matching technique (QPM) is creatively combined with effective light power enhancement resulted from the slow light effects.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Single photon detector based on polarization unrelated frequency up-conversion
InactiveCN102147293AEasy to set upAchieving complete polarization independenceNon-linear opticsSemiconductor devicesSignal lightOptical coefficient
The invention relates to a signal photon detector based on polarization unrelated frequency up-conversion; the signal photon detector comprises a lithium niobate crystal which is formed by periodically superposing four parts and is periodically polarized, wherein for a first part and a fourth part, the periodic structures are same, the period length is lA and meets the quasi-phase matching condition of frequency up-conversion, and the period number is NA so that all signal lights can be converted into sum frequency lights; a second part is in a periodic structure used by reciprocal lattice vectors for compensating mismatching of wave vectors coupled and polarized by signal lights, and the period length is lB and meets the phase matching condition of signal light polarization rotation; and a third part is in a periodic structure used by reciprocal lattice vectors for compensating mismatching of wave vectors coupled and polarized by sum frequency lights, the period length is lC and meets the phase matching condition of signal light polarization rotation. An external direct-current power supply is applied to y-surfaces of the second part and the third part of a sample so as to realize the periodic modulation of optical coefficients, thereby leading the polarization direction of corresponding light waves to rotate. The signal photon detector is practicable in preparation and has wide application prospect in fields of quantum communication and photo-communication.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Bonding method for improving bonding force and optical properties of bonding crystal
InactiveCN102912449AGood optical performanceEliminate surface oxidesAfter-treatment detailsNonlinear optical crystalBond interface
The invention relates to a bonding method for improving the bonding force and the optical properties of a bonding crystal, which can be applied to preparing a quasi-phase-matched nonlinear crystal, belongs to the field of nonlinear optical crystals and mainly solves the problems that the quasi-phase-matched crystal obtained through conventional bonding is large in optical loss and small in bonding force. According to the bonding method, a gallium arsenide crystal is selected as a bonding material, ultrahigh vacuum ion source cleaning equipment is utilized, and the loss of a bonding interface is reduced and the bonding force of the bonding crystal is improved by solution cleaning, ion cleaning, ultrahigh vacuum low-temperature bonding, low-pressure heat treatment and other technologies. The bonding method for improving the bonding force and the optical properties of the bonding crystal is mainly used for preparing the quasi-phase-matched gallium arsenide crystal with nonlinear frequency conversion in an infrared band.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and Device for Multiplying Optical Frequencies by a Factor 1.5
InactiveUS20080055702A1Inexpensive to powerInexpensive to propertiesLaser detailsLight demodulationOptical radiationNonlinear optical crystal
An optical cavity is combined with non-linear optical crystals and a laser source to generate light radiation at a frequency about 1.5 times the frequency of the initial laser source having a wavelength ⅔ that of the initial laser source. The optical cavity comprises mirrors with relatively high reflectivity for optical radiation at a frequency of F / 2, superior transmission for radiation at a frequency of 3 / 2*F for extracting the final radiation and mirrors with relatively immediate or high reflectivity, or generally high transmission for radiation at frequency F. The effective optical length of the cavity is precisely tunable by acting on at least one of the mirrors that form the cavity. The optical cavity contains at least two non-linear optical crystals: at least one of which satisfies the phase-matching-quasi phase-matching-condition for non-linear conversion F 2*F / 2, and at least one of which satisfies the phase-matching—or quasi phase-matching-condition for non-linear conversion F+F / 2? 3 / 2*F. The length of the optical cavity, and its resonance modes, are actively stabilized such that the only process of frequency division is that by a factor of 2.
Owner:FERRARI GABRIELE
Polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102338966AConsistent strengthAvoid dependenceLaser detailsNon-linear opticsFrequency multiplierFundamental frequency
The invention discloses an implementing scheme of a polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier. The implementing scheme comprises the following steps of: according to quasi-phase-matching conditions at room temperature, calculating a period; according to the period, selecting two same crystals to carry out room temperature polarization; pumping a fundamental frequency light source to select an optical fiber laser of which emergent light is randomly polarized; in an optical path, ensuring a c-axis of a first crystal along a z-direction, ensuring a c-axis of a second crystal along a y-direction and placing a depolarizer in front of the first crystal; and after the light passes through the frequency multiplier, measuring the light intensity of the frequency multiplier by a power meter, so that the polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier can be implemented. The polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier is simple and practicable. The defect of dependence of the frequency multiplying process on the polarization direction of the fundamental frequency light can be overcome. Meanwhile, the polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier can be suitable for other nonlinear processes such as sum frequency, difference frequency, parametric oscillation, cascading and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Multiple channel optical frequency mixers for all-optical signal processing
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Surface-plasmon-assisted optical frequency conversion
InactiveUS20100202728A1Facilitates efficient energy transferImprove power conversion efficiencyLaser detailsNanoopticsEnergy transferMomentum
An optical frequency converter that uses a nonlinear optical process to transfer energy between a surface-plasmon (SP) wave that is guided along an electrically conducting strip and a light beam that is guided along an optical waveguide whose core is adjacent to the electrically conducting strip. The optical frequency converter has a periodic structure that spatially modulates the nonlinear susceptibility of the waveguide core with a spatial period that is related to a momentum mismatch in the nonlinear optical process. The spatial modulation provides quasi-phase matching for the SP wave and the light beam and enables efficient energy transfer between them.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Annular integrated laser frequency doubling device
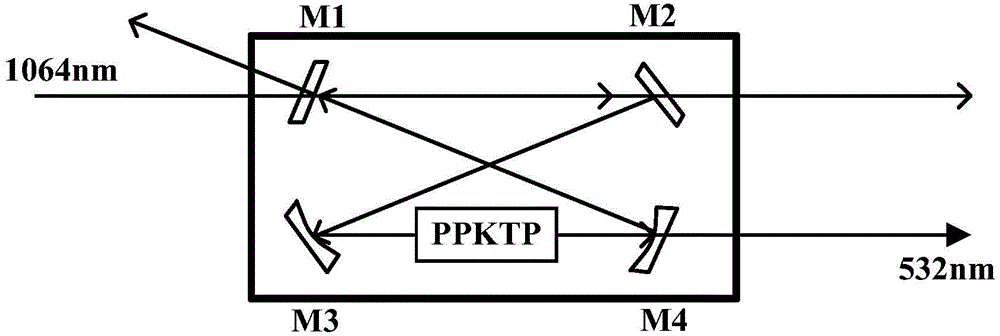
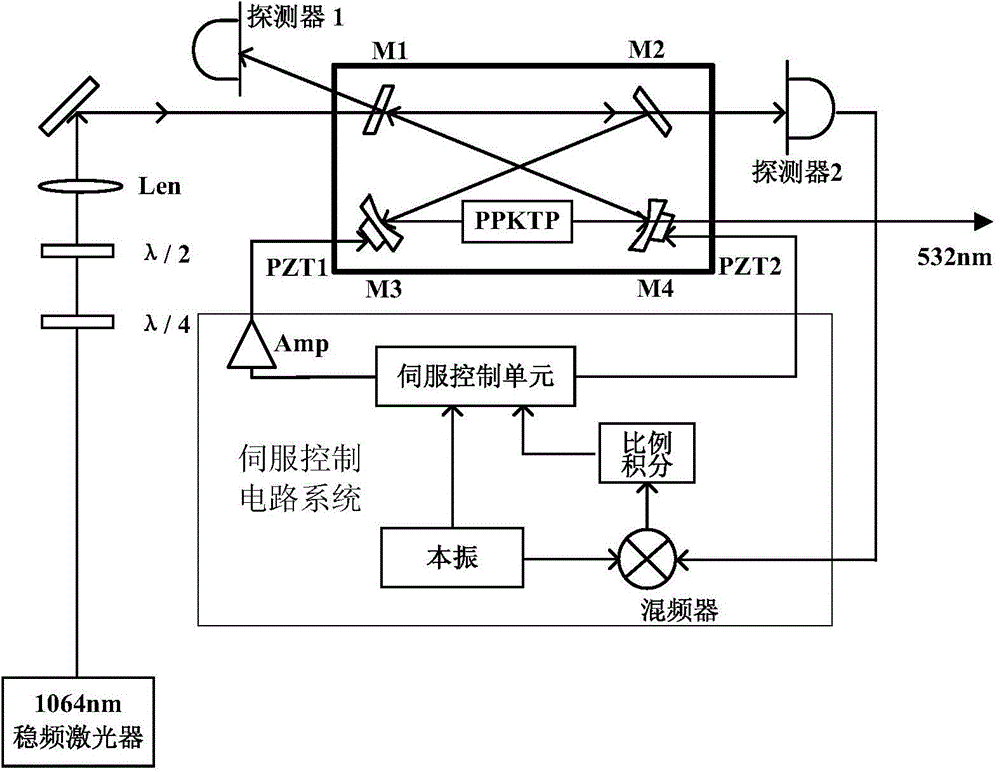
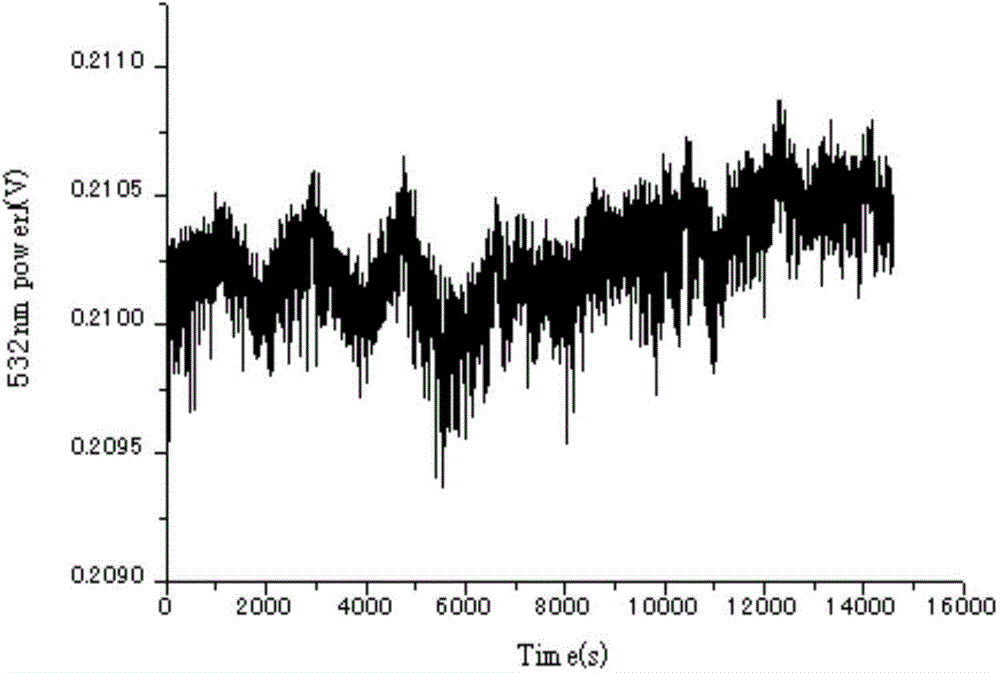
The invention provides an annular integrated laser frequency doubling device which comprises a periodic poling KTP (PPKTP) frequency doubling crystal and an annular frequency doubling cavity. The annular frequency doubling cavity comprises a plane reflecting mirror M1, a plane reflecting mirror M2, a concave surface reflecting mirror M3 and a concave surface reflecting mirror M4. The two end faces of the PPKTP frequency doubling crystal are each plated with an antireflection film special to fundamental frequency lasers and second harmonics. According to the annular integrated laser frequency doubling device, a frequency stabilized laser of 1064 nm and the PPKTP frequency doubling crystal are used for being combined with a quasi-phase matching and annular outer cavity frequency doubling technology, a stable laser of 1064 nm and a stable laser of 532 nm which have a strict diploid relation in wavelength can be output, the advantages of being good in wave length and power stability, small in line width and the like are achieved, and the wave length linearity of an optical grating spectrograph can be calibrated; a frequency stabilized laser wave length standard device of 1064 nm can be miniaturized, the performance is stable, the structure is compact and the anti-jamming capability is high.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP +1
Actively Q-switched laser system using quasi-phase-matched electro-optic Q-switch
A Q-switched laser system is disclosed. The laser system employs a quasi-phase-matched electro-optic (QPM EO) crystal as the laser Q-switch. When applied with a certain modulating electric field, the QPM EO crystal can function as a polarization rotator to rotate the polarization direction of the resonant laser beam in a polarization-dependent laser resonator, thereby switching the laser resonator between high-loss and low-loss cavity states to achieve laser Q-switching. Compared with traditional electro-optic Q-switched laser system, the disclosed laser system is characterized by a low switching-voltage, reduced cost, and compactness. A quasi-phase-matched electro-optically Q-switched wavelength-conversion and wavelength-tunable laser system is also disclosed. The disclosed laser system integrates a QPM electro-optic Q-switch and a QPM nonlinear wavelength converter in a single crystal substrate to perform a high-efficiency intracavity wavelength conversion. The disclosed laser system is therefore simple and compact and has lower system requirements on wall-plug power and higher overall conversion efficiency.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Spectrum regulating and controlling device for mid-infrared pulse lasers
ActiveCN106207718ARealize regulationSimplify complexityLaser detailsNon-linear opticsWorking temperatureSignal light
The invention discloses a spectrum regulating and controlling device for mid-infrared pulse lasers. In the spectrum regulating and controlling device, near-infrared pulse lasers emitted by a near-infrared pulse laser device and mid-infrared pulse lasers jointly enter an aperiodicity poled crystal through an optical coupling mirror, and are subjected to nonlinear frequency conversion, the near-infrared pulse lasers serve as pump light, different spectrum components of the mid-infrared pulse lasers are subjected to differentiation amplification so that spectrum regulating and controlling can be achieved. According to the spectrum regulating and controlling device for the mid-infrared pulse lasers, the I-type quasi-phase matching technology is adopted, the working temperature of the aperiodicity poled crystal is adjusted, and group velocity mismatching between the near-infrared pump light and mid-infrared signal light in the crystal is eliminated. In this way, the spectrum regulating and controlling device is suitable for femtosecond-magnitude-order mid-infrared ultra-short pulse lasers, and does not need to be chirped and broadened, spectrum shaping can be directly carried out through the near-infrared pulse lasers, and the complex degree of the spectrum regulating and controlling device based on nonlinear frequency conversion is greatly simplified.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Method for increasing bandwidth of quasi-phase matching frequency multiplication conversion
ActiveCN105573009ASecond Harmonic Conversion Bandwidth ImprovementNon-linear opticsGenetic algorithmContinuous signal
The invention provides a method for increasing the bandwidth of quasi-phase matching frequency multiplication conversion. A crystal used in the method is provided with a non-period structure, multi-wavelength frequency multiplication conversion can be achieved at the same time, and the crystal meets quasi-phase matching and group velocity matching conditions at the same time within a specific wavelength range. The optimal structure of the crystal is obtained through a genetic algorithm. The preference structure of the crystal is a non-period polarized lithium niobate crystal, the crystal is in a cuboid shape, the upper surface and the lower surface are parallel and are polished, the crystal is uniformly divided into unit domains with the equal length in the light wave propagation direction, the spontaneous polarization direction of each unit domain is selected to be upward or downward, and the unit domains with a few continuous signals being the same form one positive domain or one negative domain. According to the method, the quasi-phase matching and group velocity matching conditions are met at the same time, higher and smooth conversion efficiency is kept within a certain specific wavelength range, the bandwidth of the frequency multiplication conversion can be increased, and the method has great theoretical and practical significance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Angle tuning-free THz collinear difference frequency radiation system based on cadmium telluride
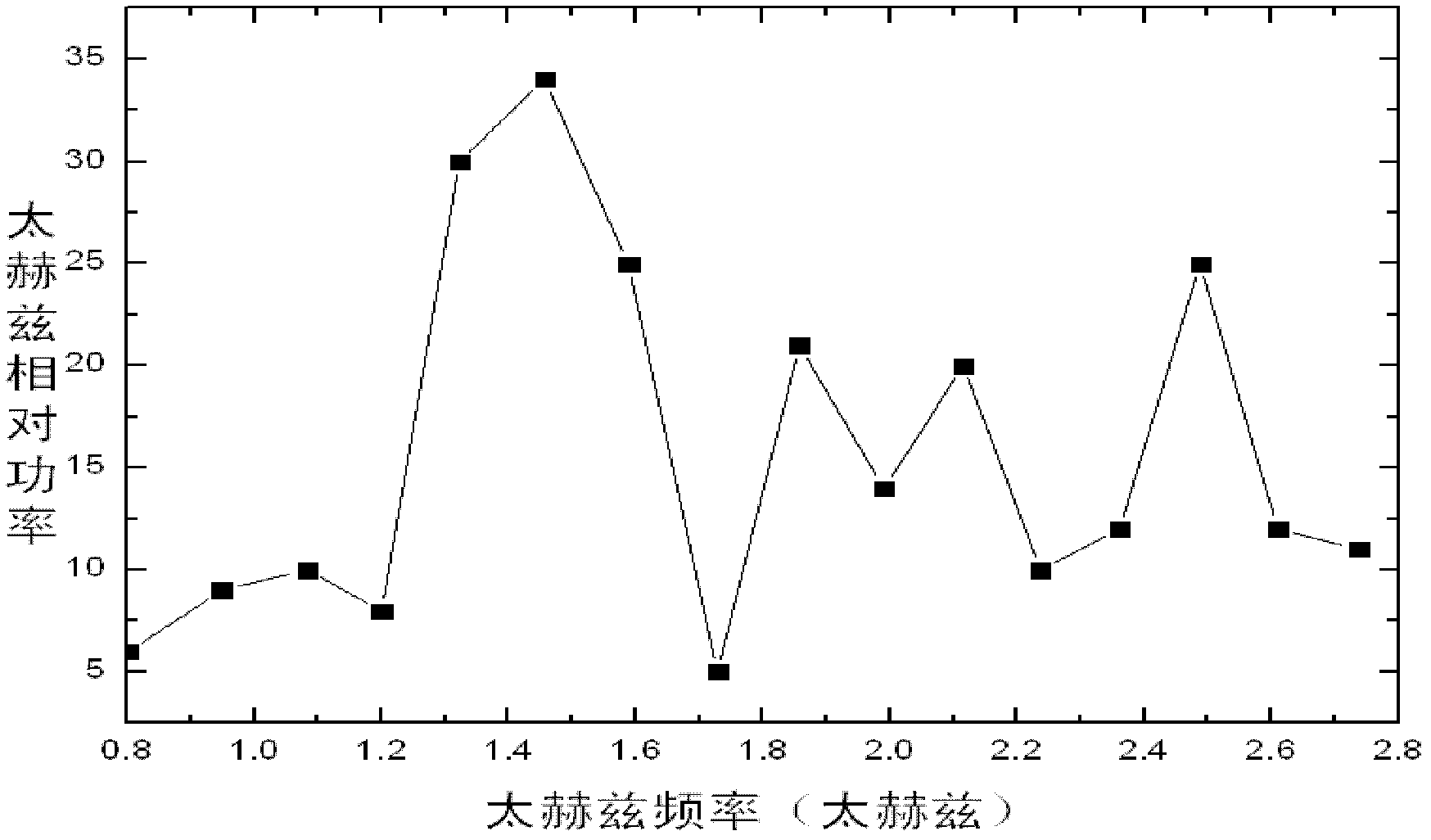
InactiveCN102570247AReduce the difficulty of operationImprove stabilitySolid masersNon-linear opticsBirefringent crystalLine width
The invention discloses an angle tuning-free nanosecond laser collinear difference frequency THz radiation system based on cadmium telluride crystals. The system can achieve THz light radiation without angle tuning by particularly using the principle of nonlinear optical collinear difference frequency and quasi-phase matching technology, and the wavelength tuning range of the system is 0.80THz to 2.74THz. The system not only has the characteristics of high power, quasi-continuity, narrow line width, room temperature operation and so on, but also has the advantages of convenient wavelength tuning by only tuning the output wavelength of a tunable laser, high easiness in adding an external infrared resonant cavity, compact structure, easy construction, high system stability, high convenience for actual large-scale application and so on in comparison with a radiation system using birefringent crystals as THz crystals and a parametric oscillation source based on lithium niobate crystals.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com