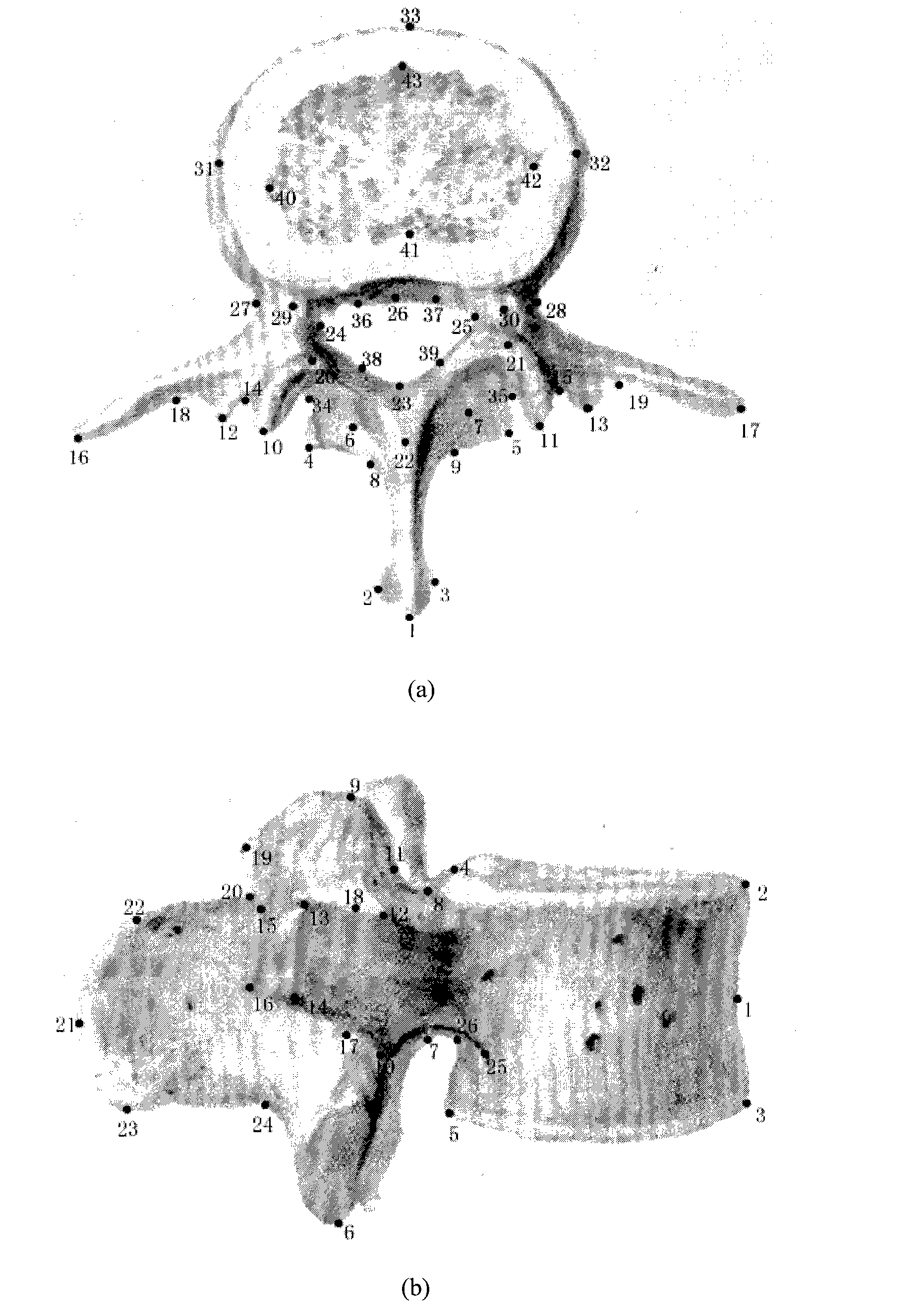Patents
Literature
280 results about "Three dimensional geometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The x, y and z axes: 3 -dimensional geometry is the geometry that deals with geometry in three dimensions namely x, y and z axis. It deals with the mathematics of 3d shapes like cubes, cuboids, tetrahedrons, parallelepiped etc.
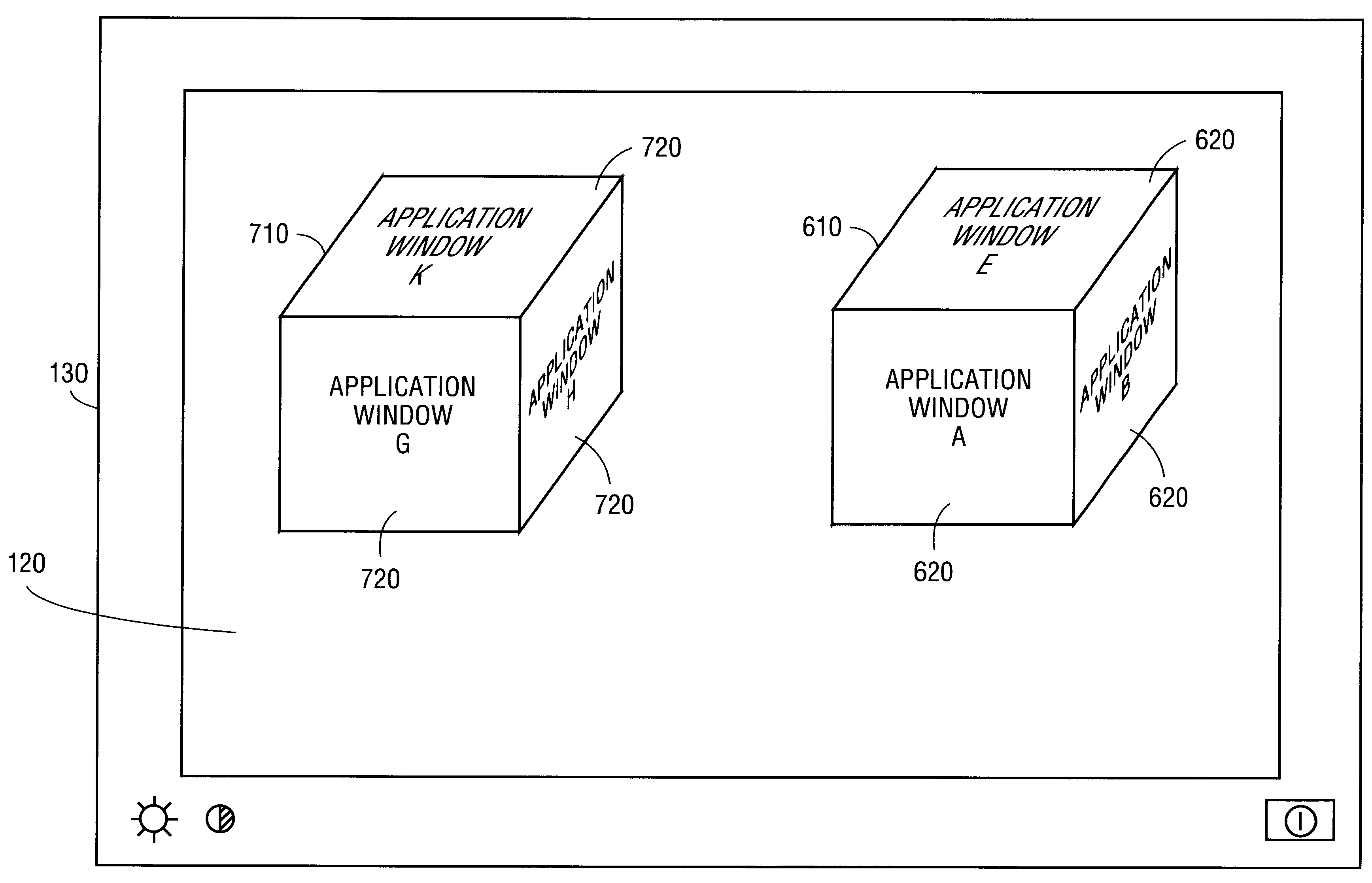
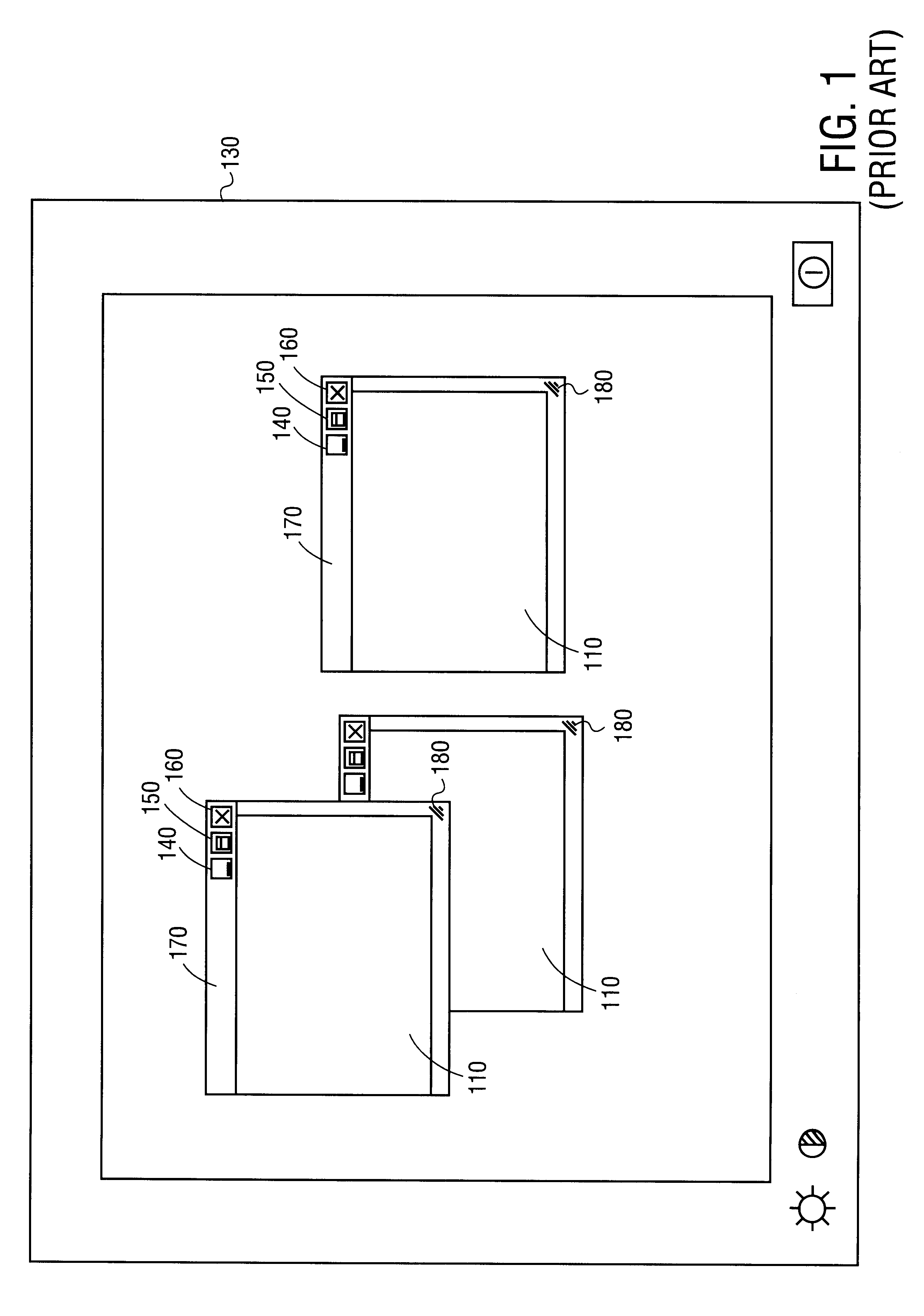
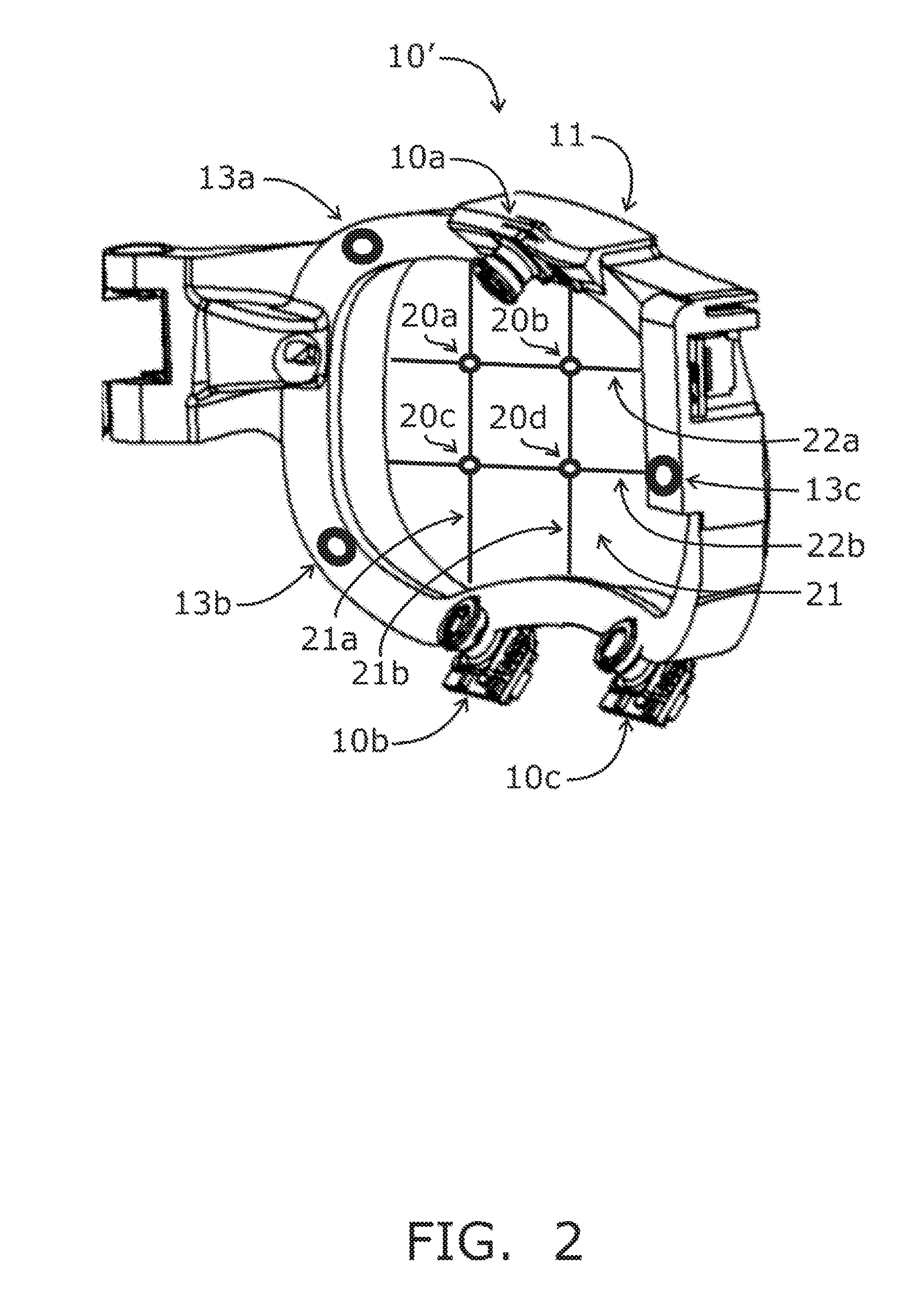
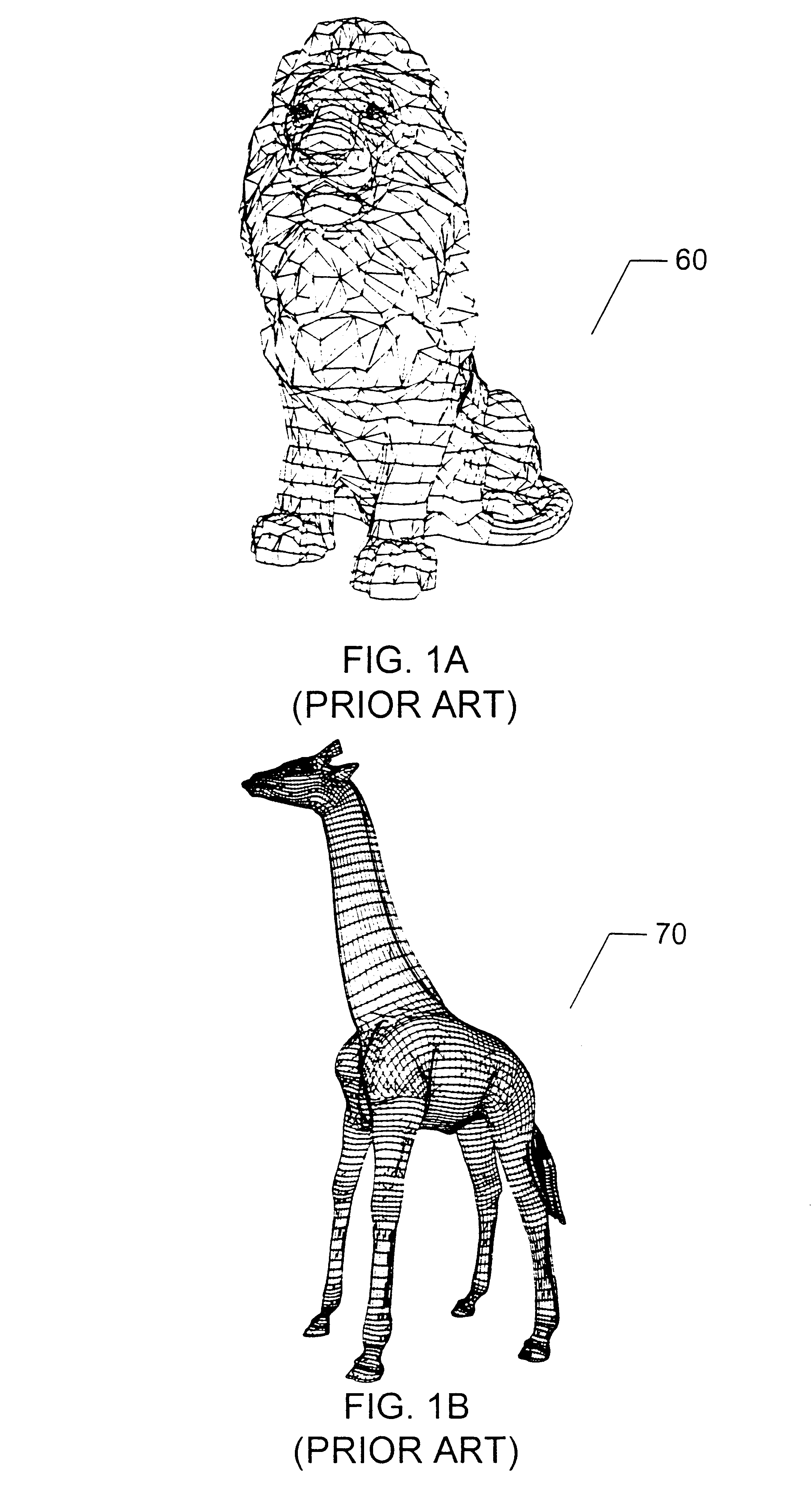
Method and apparatus for presenting two and three-dimensional computer applications within a 3D meta-visualization
InactiveUS6597358B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsData set
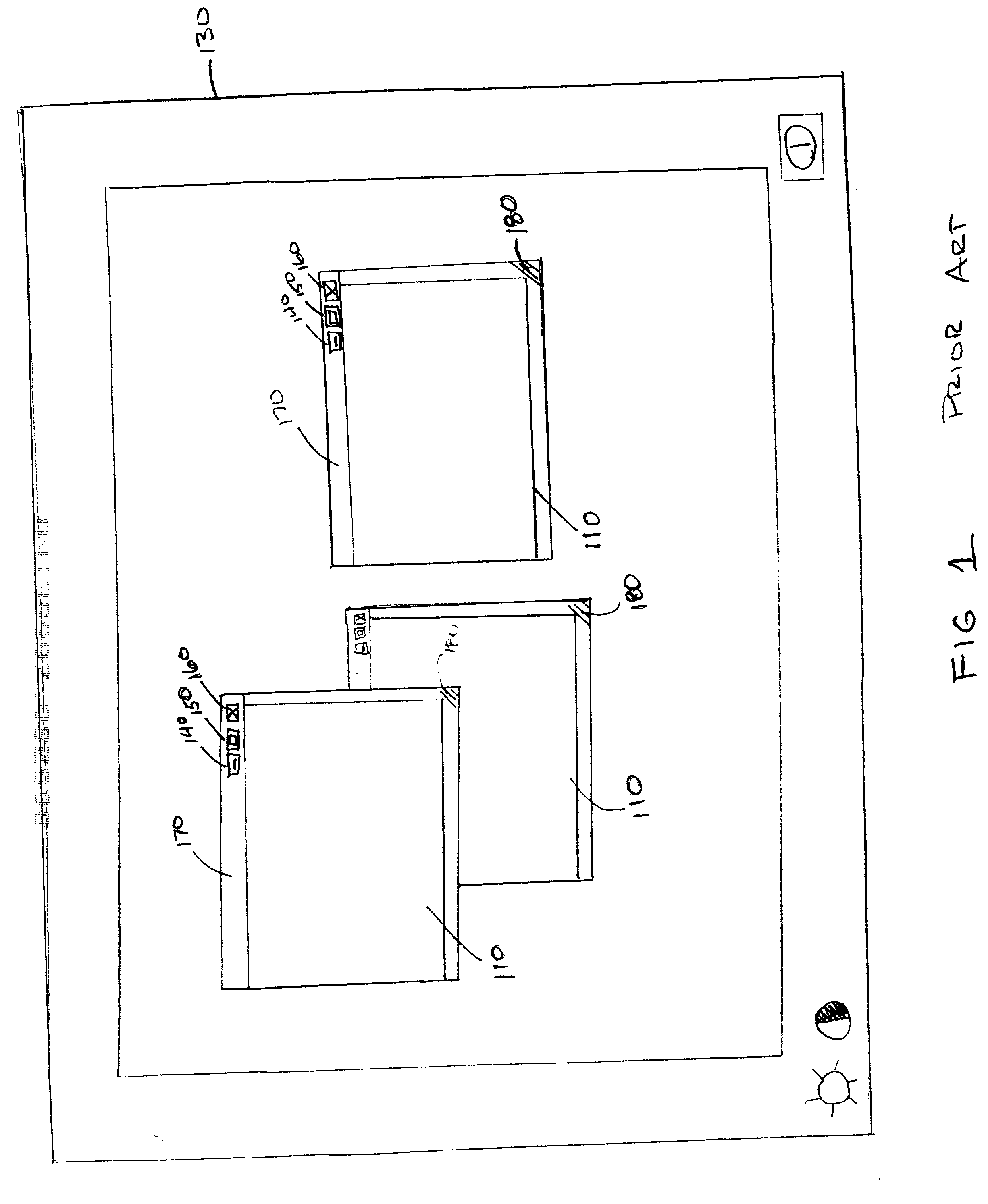
A method and apparatus for organizing two and / or three-dimensional computer applications on a display in a three-dimensional viewing perspective. A two-dimensional bitmap is created for each respective computer application and applied to a three-dimensional geometry (i.e., primitive). In one embodiment, the three-dimensional geometry is a cube and each respective computer application is mapped onto a respective surface of the cube. The computer user has the ability to manipulate the orientation of the cube, via a computer mouse, for example, to view the different surfaces, and, thus, different computer applications mapped thereon. The user is further given the capability to manipulate or interact with each computer application on each respective surface of the cube. In another embodiment, two or more cubes could be employed for displaying the various computer applications running on the computer's processor. The user could also allocate a particular group or category of applications to each respective cube to accomplish different tasks.
Owner:INTEL CORP
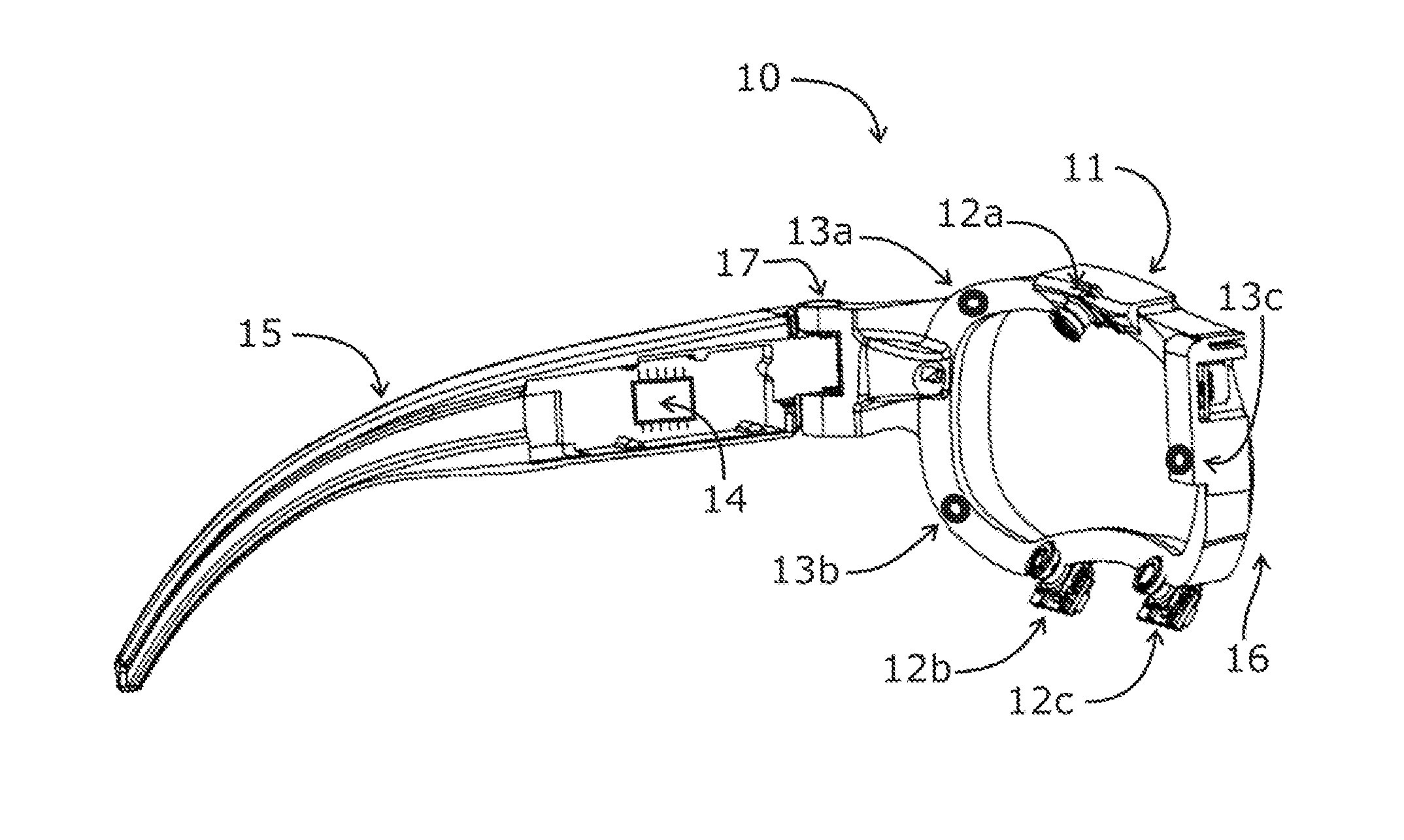
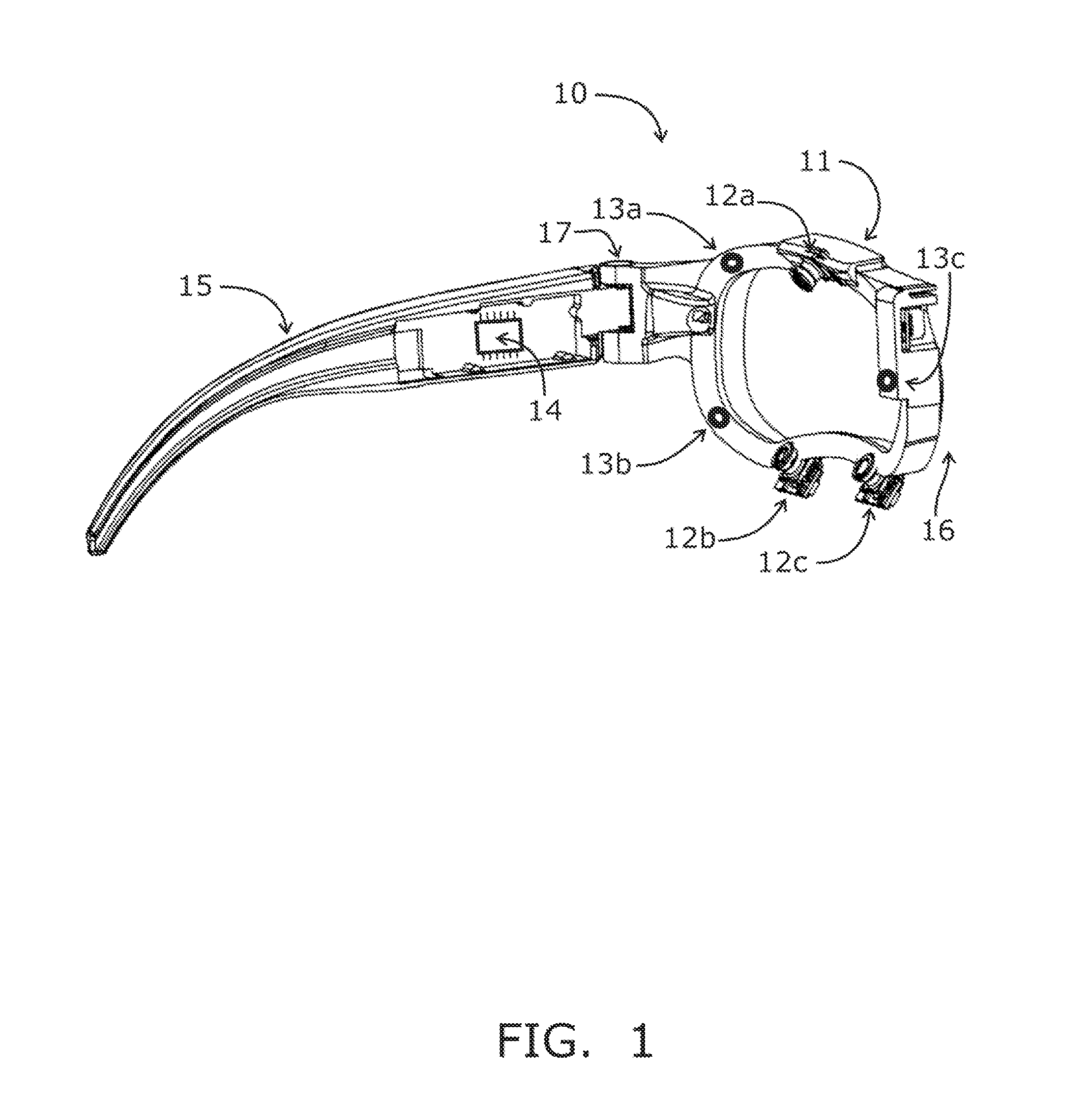
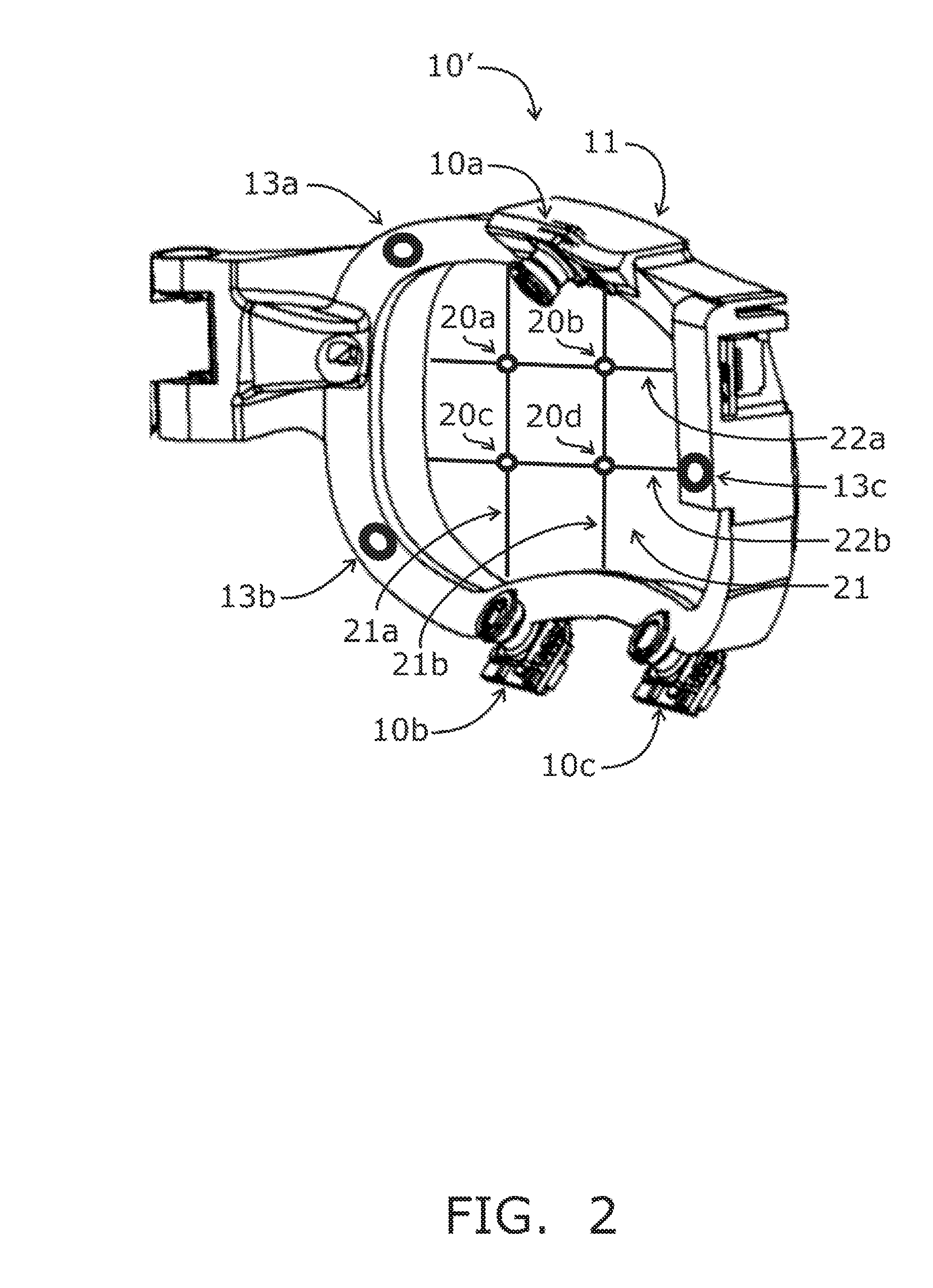
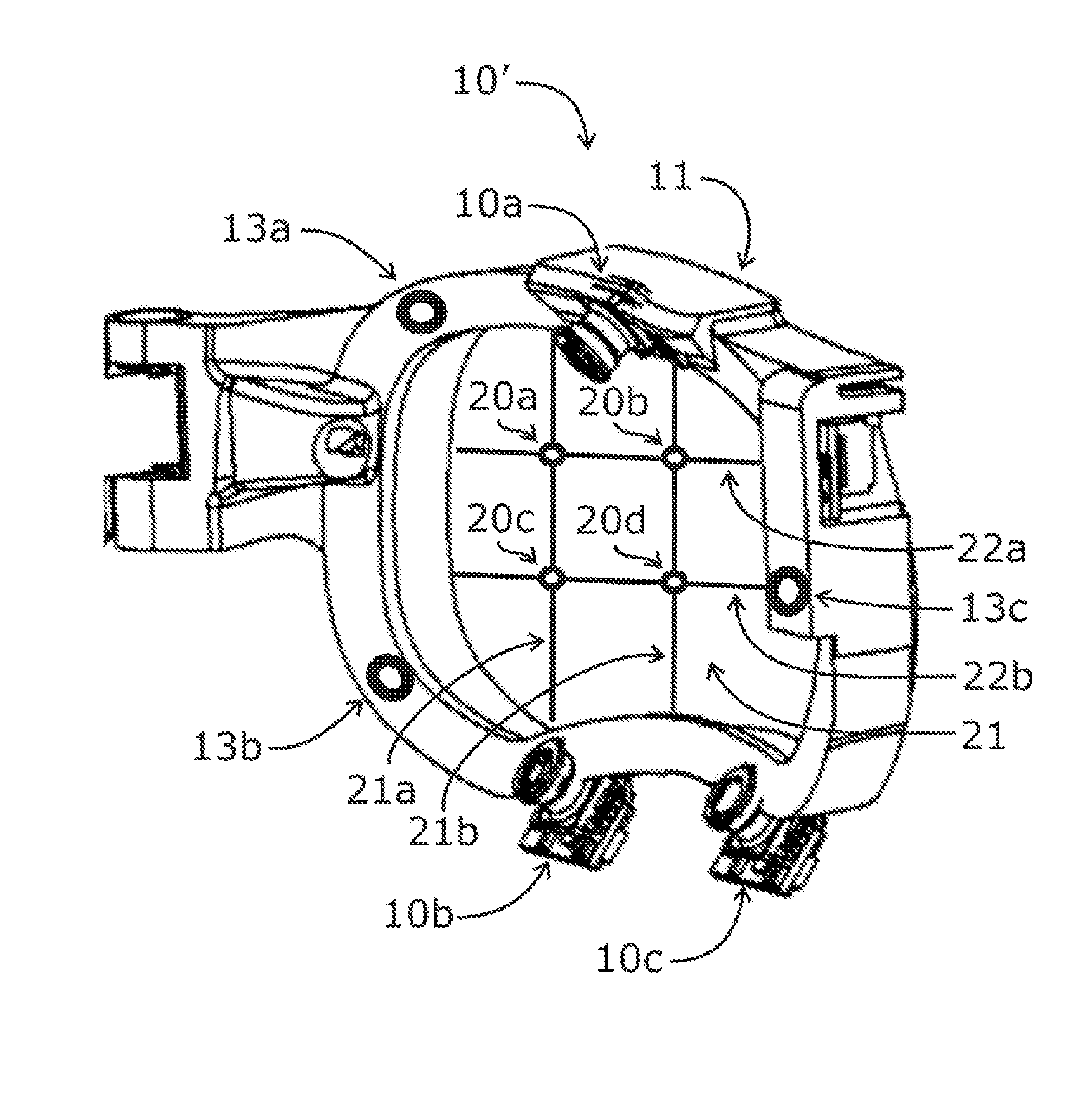
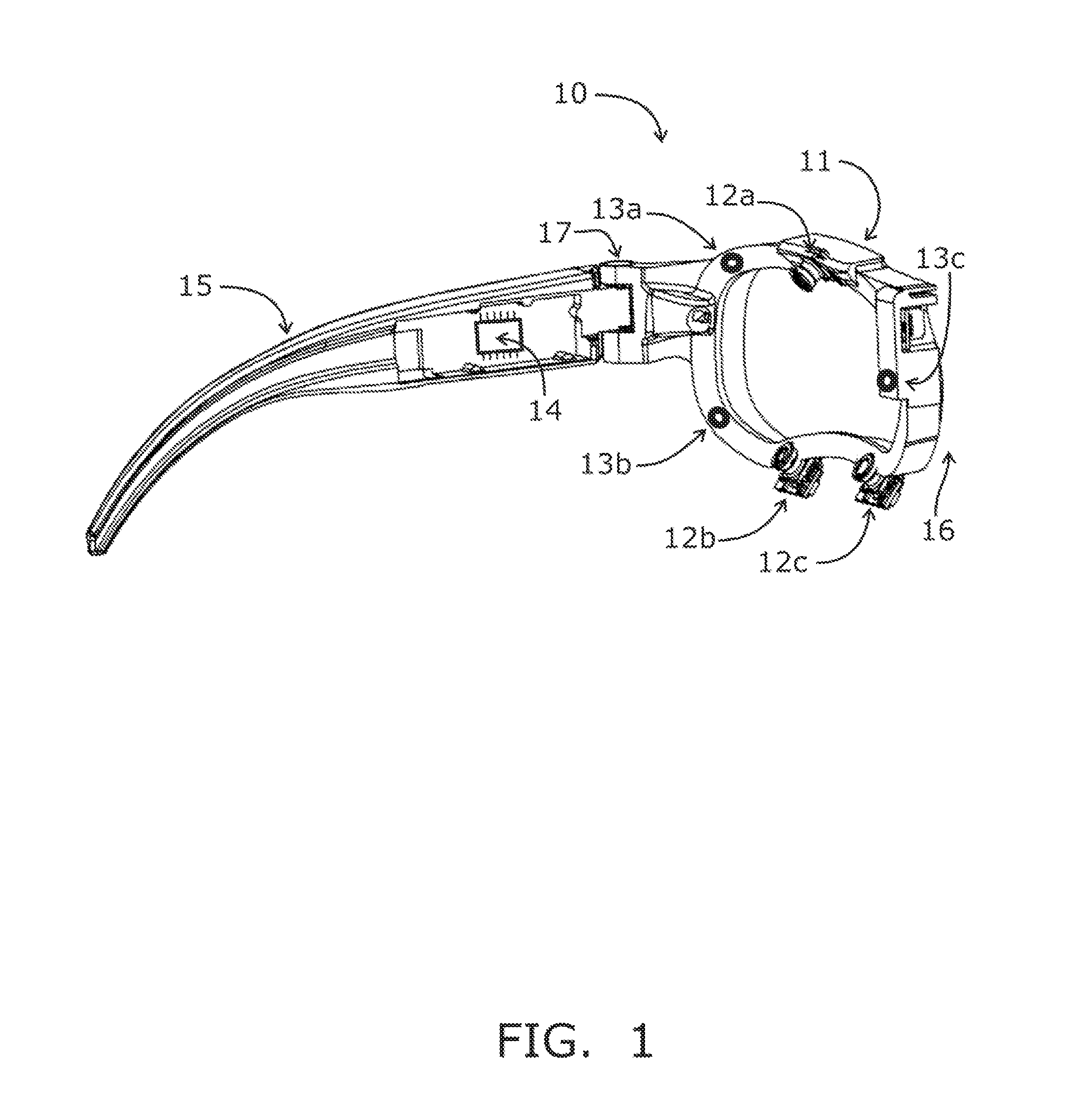
Systems and methods for high-resolution gaze tracking
ActiveUS20130114850A1Accurate trackingSure easyImage enhancementImage analysisReference vectorEyewear
A system is mounted within eyewear or headwear to unobtrusively produce and track reference locations on the surface of one or both eyes of an observer. The system utilizes multiple illumination sources and / or multiple cameras to generate and observe glints from multiple directions. The use of multiple illumination sources and cameras can compensate for the complex, three-dimensional geometry of the head and anatomical variations of the head and eye region that occurs among individuals. The system continuously tracks the initial placement and any slippage of eyewear or headwear. In addition, the use of multiple illumination sources and cameras can maintain high-precision, dynamic eye tracking as an eye moves through its full physiological range. Furthermore, illumination sources placed in the normal line-of-sight of the device wearer increase the accuracy of gaze tracking by producing reference vectors that are close to the visual axis of the device wearer.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Systems and methods for high-resolution gaze tracking
A system is mounted within eyewear or headwear to unobtrusively produce and track reference locations on the surface of one or both eyes of an observer. The system utilizes multiple illumination sources and / or multiple cameras to generate and observe glints from multiple directions. The use of multiple illumination sources and cameras can compensate for the complex, three-dimensional geometry of the head and anatomical variations of the head and eye region that occurs among individuals. The system continuously tracks the initial placement and any slippage of eyewear or headwear. In addition, the use of multiple illumination sources and cameras can maintain high-precision, dynamic eye tracking as an eye moves through its full physiological range. Furthermore, illumination sources placed in the normal line-of-sight of the device wearer increase the accuracy of gaze tracking by producing reference vectors that are close to the visual axis of the device wearer.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Rendering and Navigating Photographic Panoramas with Depth Information in a Geographic Information System
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Geometry of heat exchanger with high efficiency
ActiveUS20130206374A1Additive manufacturing apparatusRecuperative heat exchangersHigh energyEngineering
The present disclosure includes geometry of a two-fluid heat exchanger to provide higher energy efficiency than conventional heat exchangers. The geometry is based upon sequential branching of nearly circular passages in sets, followed by some deformation and twisting of the sequential branches that intermingle flow passages of one fluid with flow passages of another fluid. The flow passages gradually vary in dimension from larger branching at fluid entrance and exit to smaller branching in the middle section of the heat exchanger. The heat exchanger is substantially symmetric, with the sequential branching in the first half being mirrored as serial regrouping in the second half. The present disclosure also provides stacking methods and layered manufacturing methods for fabricating the three-dimensional geometry of the heat exchanger.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
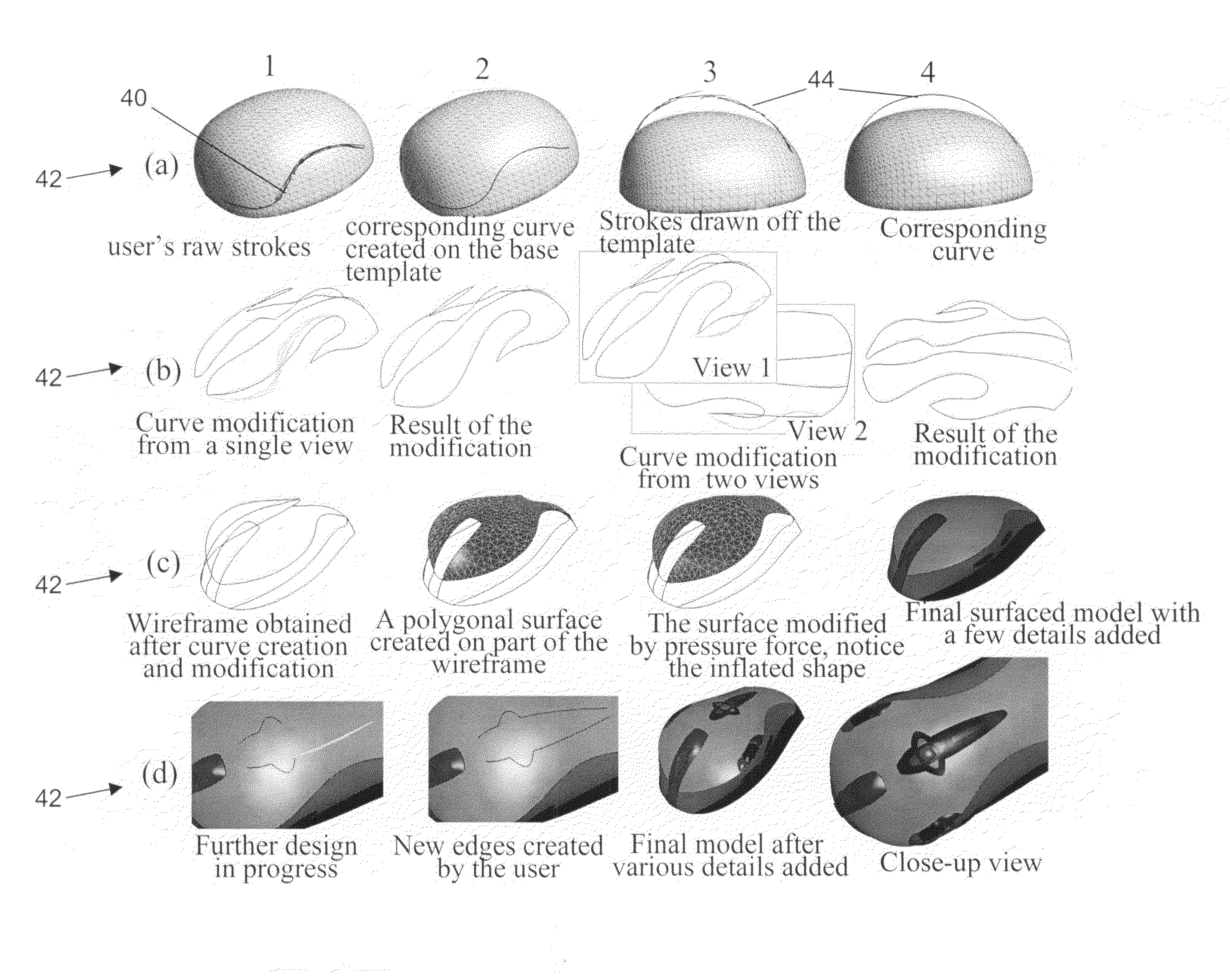
Sketch-Based Design System, Apparatus, and Method for the Construction and Modification of Three-Dimensional Geometry
InactiveUS20090284550A1Geometric CADDrawing from basic elementsComputer graphics (images)Display device
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for sketch-based design, construction, and modification of three-dimensional geometry, including a computer drawing system, comprising a two dimensional input device, a display device, and a processor connected to the input device and the display device. The processor includes memory containing computer readable instructions which, when executed, cause the processors to define a three dimensional shape model, receive from the two dimensional input device an input indicative of a two dimensional hand drawn element, map the two dimensional hand drawn element to a corresponding portion of the three dimensional shape model, and modify the corresponding portion of the three dimensional shape model to resemble the two dimensional hand drawn element.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
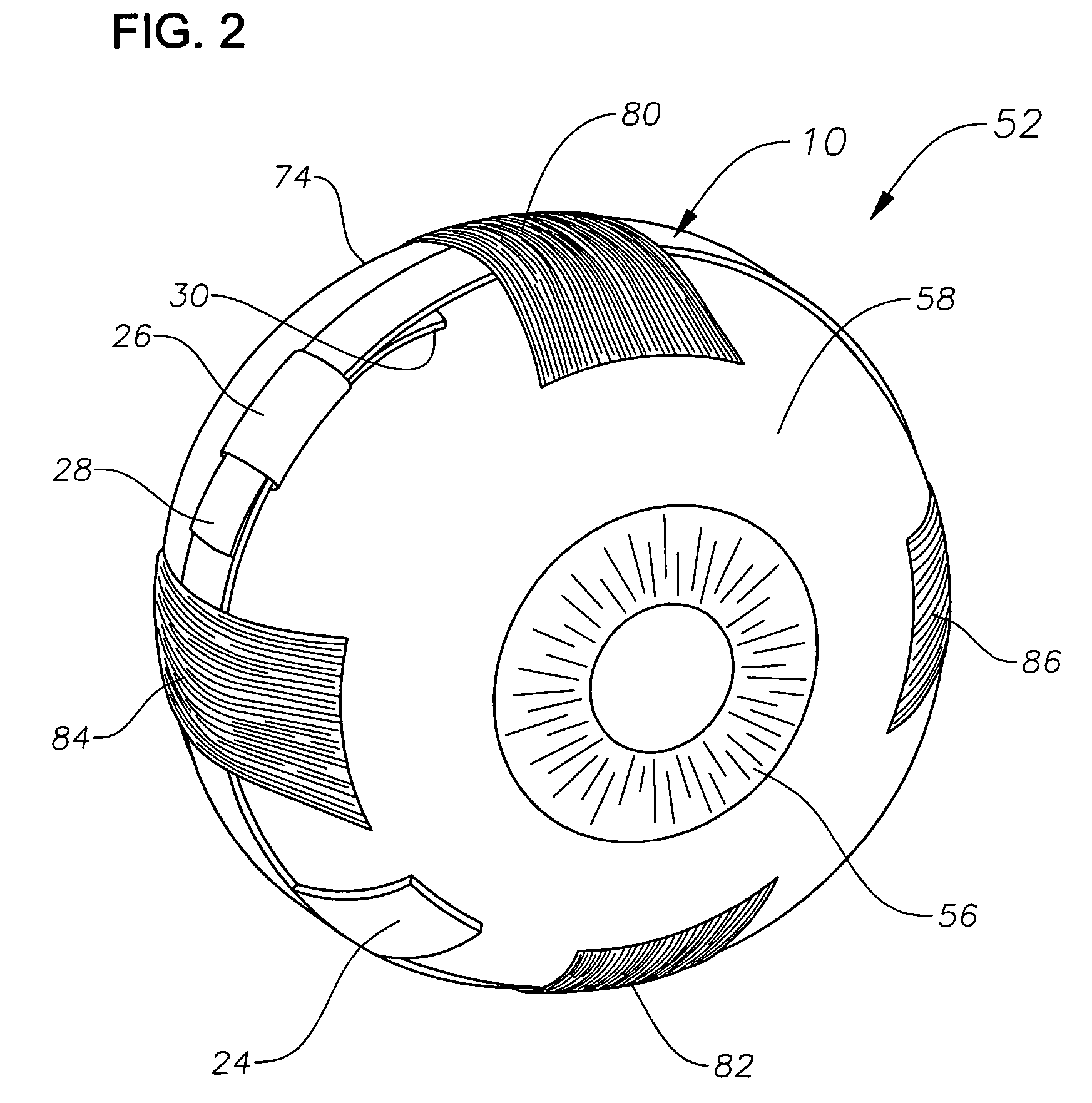
Ophthalmic drug delivery device
An ophthalmic drug delivery device having a first end and a second end, an injection port, a reservoir, and a sleeve is disclosed. The injection port is for sealingly engaging a needle of a syringe, which is for providing a fluid comprising a pharmaceutically active agent. The reservoir is disposed within the device, is fluidly coupled to the injection port, and has an opening for communicating the fluid to an outer surface of a sclera of an eye. The sleeve is for engaging the device proximate overlapping portions of the first end and the second end for forming a generally ring-shaped three-dimensional geometry upon implantation of the device on the outer surface of the sclera. The device is useful for the treatment of a disease of the posterior segment of the eye.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
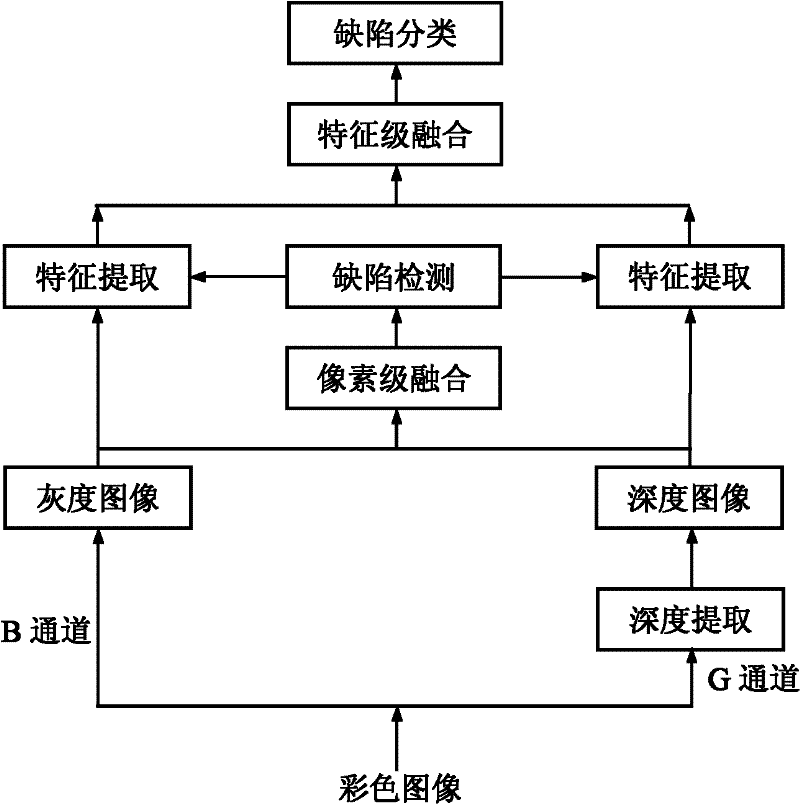
A Surface Defect Detection Method Based on Fusion of Gray Level and Depth Information
ActiveCN102288613AImprove accuracyAccurate detectionImage enhancementOptically investigating flaws/contaminationEdge extractionSurface structure
The invention relates to an on-line detecting method for surface defects of an object and a device for realizing the method. The accuracy for the detection and the distinguishing of the defects is improved through the fusion of grey and depth information, and the method and the device can be applied to the detection of the object with a complicated shape and a complicated surface. A grey image and a depth image of the surface of the object are collected by utilizing the combination of a single colored area array CCD (charge-coupled device) camera and a plurality of light sources with different colors, wherein obtaining of the depth information is achieved through a surface structured light way. The division and the defect edge extraction of the images are carried out through the pixel level fusion of the depth image and the grey image, so that the area where the defects are positioned can be detected more accurately. According to the detected area with the defects, the grey characteristics, the texture characteristics and the two-dimensional geometrical characteristics of the defects are extracted from the grey image; the three-dimensional geometrical characteristics of the defects are extracted from the depth image; further, the fusion of characteristic levels is carried out; and a fused characteristic quantity is used as the input of a classifier to classify the defects, thereby achieving the distinguishing of the defects.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
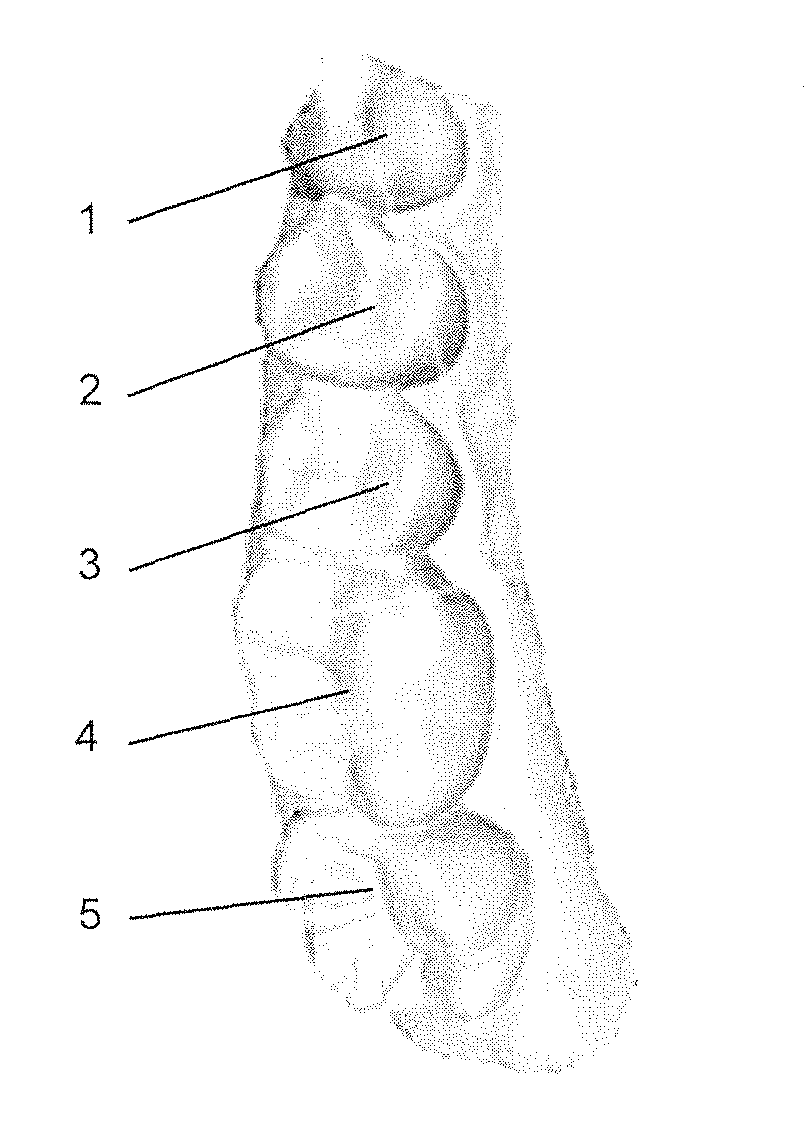
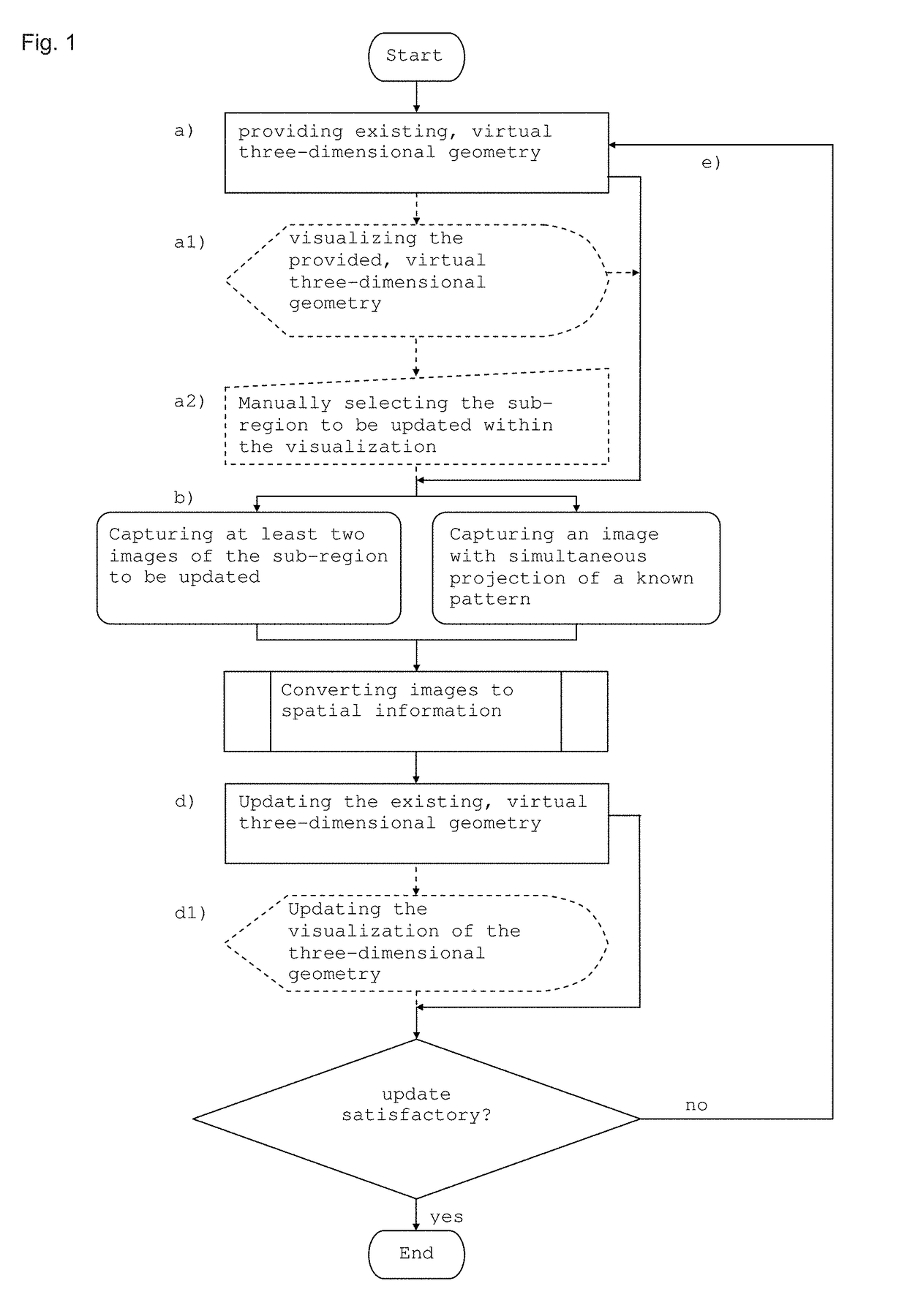
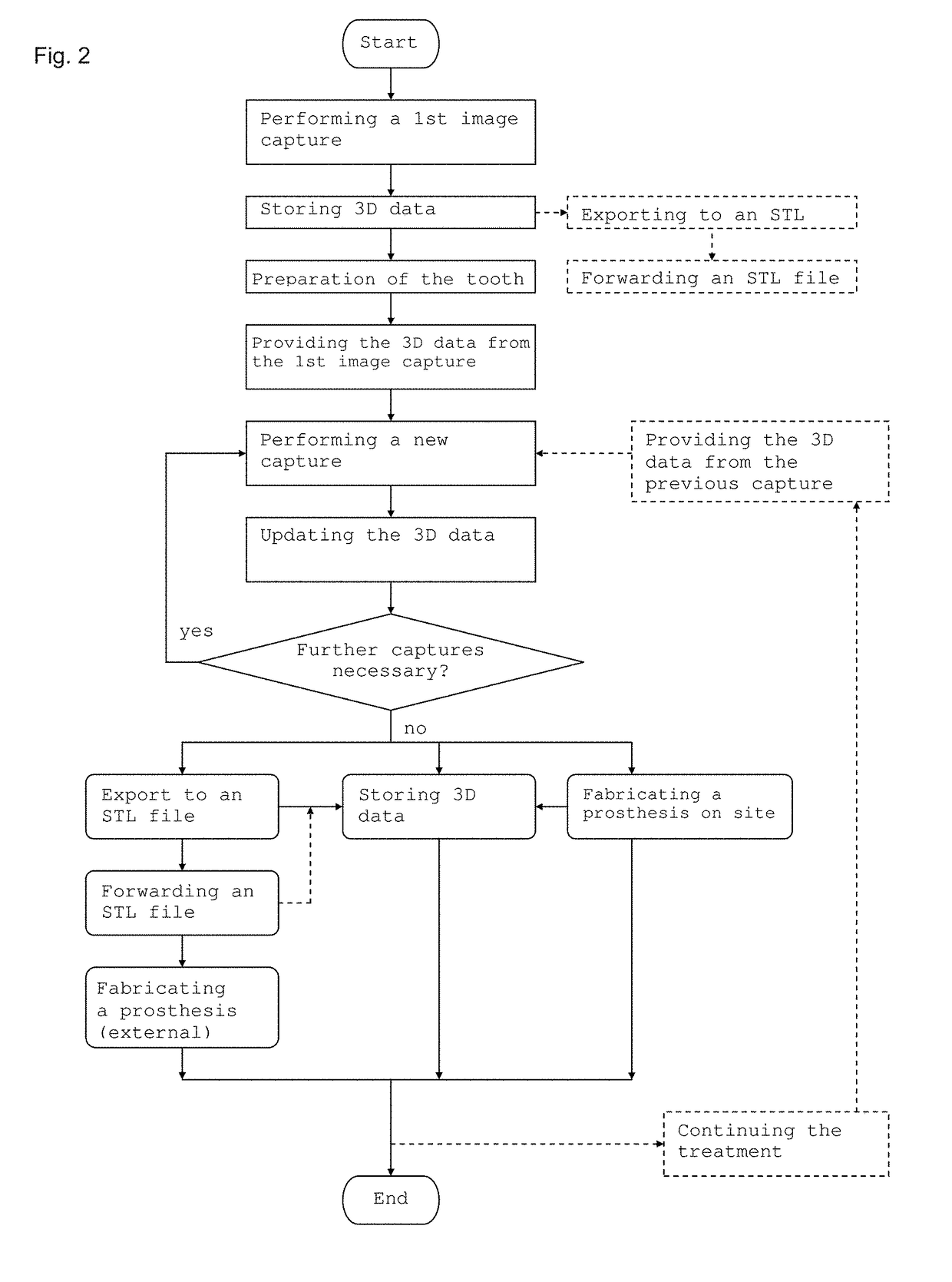
Method for continuation of image capture for acquiring three-dimensional geometries of objects
ActiveUS9936186B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce pointsImpression capsImage data processingContinuationObject based
A method for capturing at least one sub-region of a three-dimensional geometry of at least one object, for the purpose of updating an existing virtual three-dimensional geometry of the sub-region, optionally after elements of the object present in the sub-region have been modified, removed and / or added, wherein the method includes the following steps: a) providing the existing virtual three-dimensional geometry of the object, for example, from an earlier image capture, b) capturing of two-dimensional images from which spatial information of the three-dimensional geometry of the objects is obtained, c) automatic addition of spatial information obtained to existing spatial information, if applicable d) updating the existing virtual three-dimensional geometry of the sub-region of the object based on added information, e) optionally repeating the process from step b).
Owner:A TRON3D
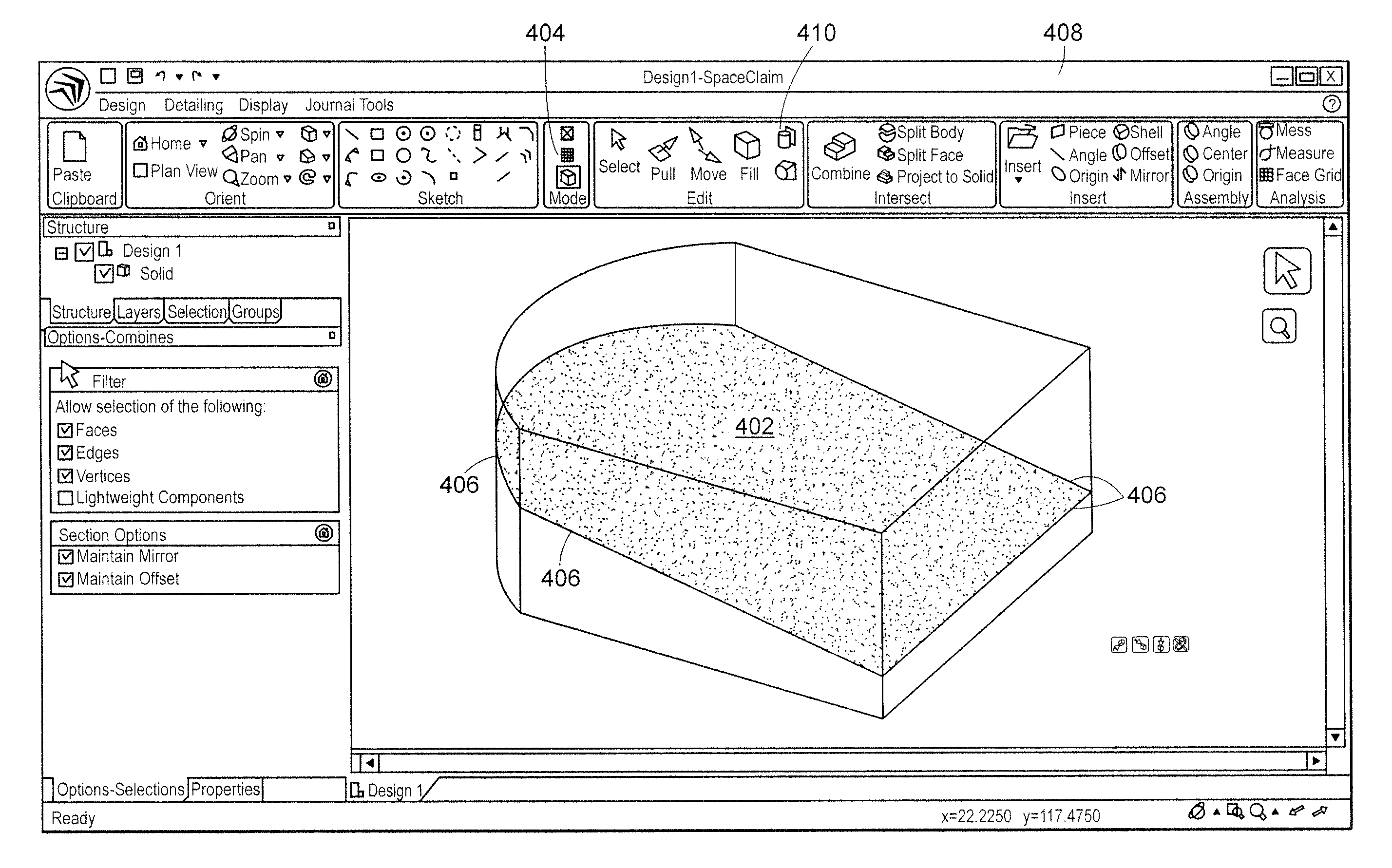
Systems and methods for modifying three dimensional geometry using an arbitrary cross-section plane
Embodiments of the invention comprise methods and systems for modifying the geometry data of a CAD object through modification of an arbitrary cross section, the CAD object being stored within a computer aided design modeling system. The method includes receiving, from a user the position and orientation of a cross section plane, the cross section plane being arbitrarily positioned relative to the orientation of a CAD object, and wherein the arbitrarily positioned and oriented plane is intersecting the CAD object. The CAD system generates a user modifiable two dimensional cross section from the intersection of the cross section plane and the CAD object, the cross section having a plurality user modifiable control elements. Changes to the control elements are correspondingly made to the cross section plane and the CAD object.
Owner:ANSYS
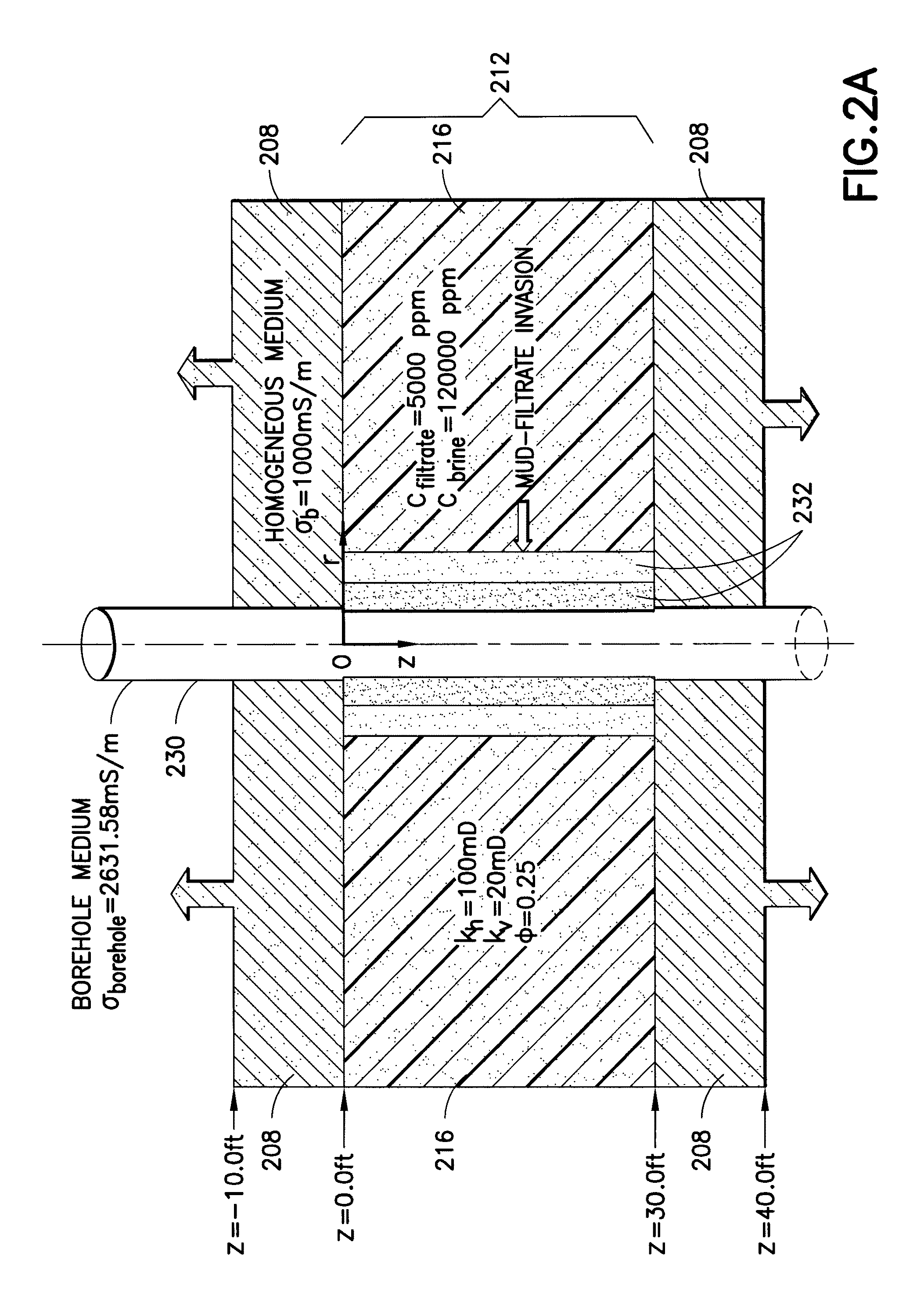
Estimating petrophysical parameters and invasion profile using joint induction and pressure data inversion approach
ActiveUS20100185393A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyRate of penetrationSegregation effect
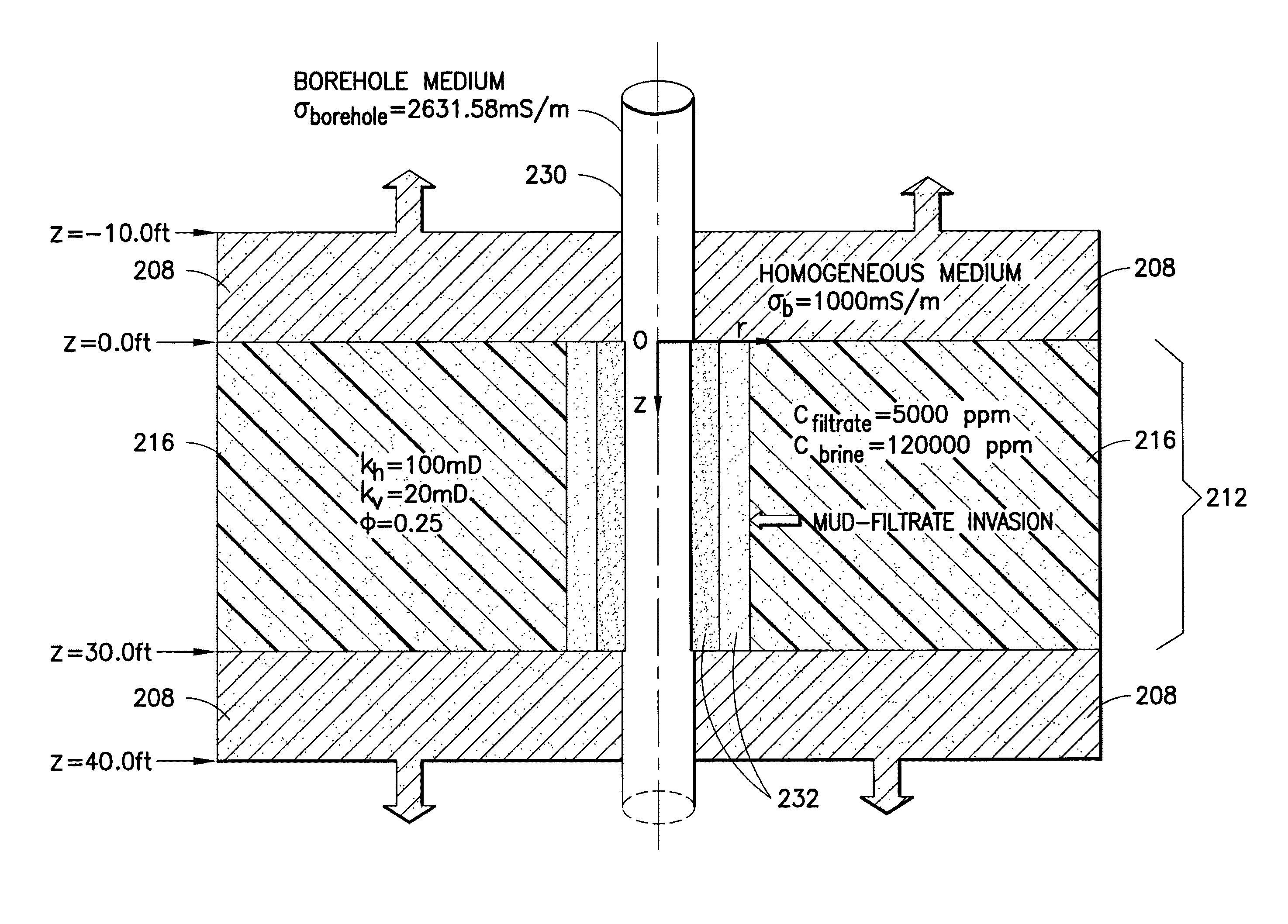
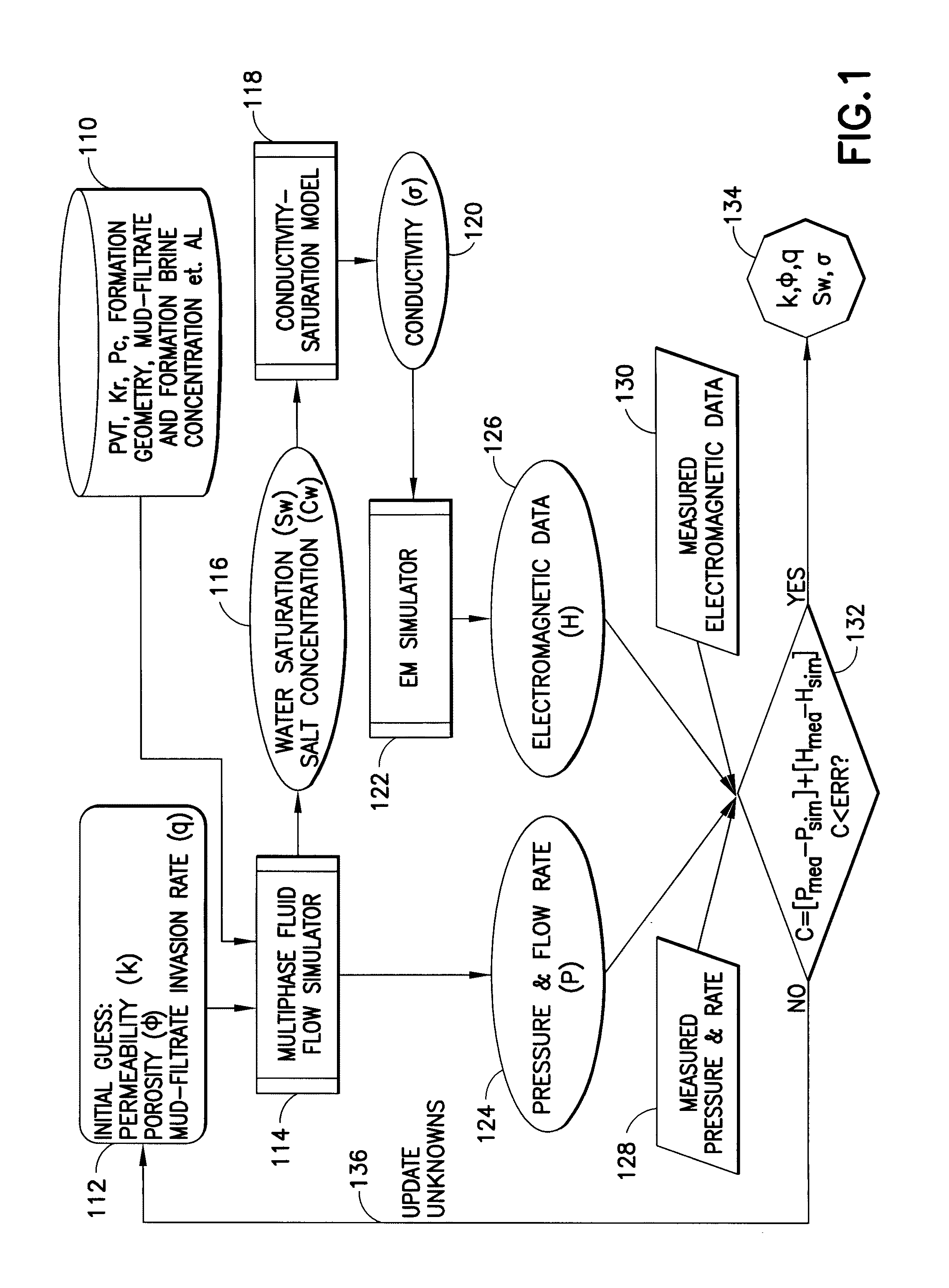
Methods and related systems are described relating to an inversion approach for interpreting the geophysical electromagnetic data. The inversion can be constrained by using a multiphase fluid flow simulator (incorporating pressure data if available) which simulates the fluid flow process and calculates the spatial distribution of the water saturation and the salt concentration, which are in turn transformed into the formation conductivity using a resistivity-saturation formula. In this way, the inverted invasion profile is consistent with the fluid flow physics and moreover accounts for gravity segregation effects. Jointly with the pressure data, the inversion estimates a parametric one-dimensional distribution of permeability and porosity. The fluid flow volume is directly inverted from the fluid-flow-constrained inversion of the electromagnetic data. The approach is not limited by the traditional interpretation of the formation test, which is based on a single-phase model without taking into account invasion or assuming that the fluid, for example mud-filtrate, has been cleaned up from the formation testing zone. The joint inversion of the electromagnetic and pressure data provides for a more reliable interpretation of formation permeability. One advantage of the approaches described herein, is its possible generalization to three-dimensional geometries, for example dipping beds and highly deviated wells.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
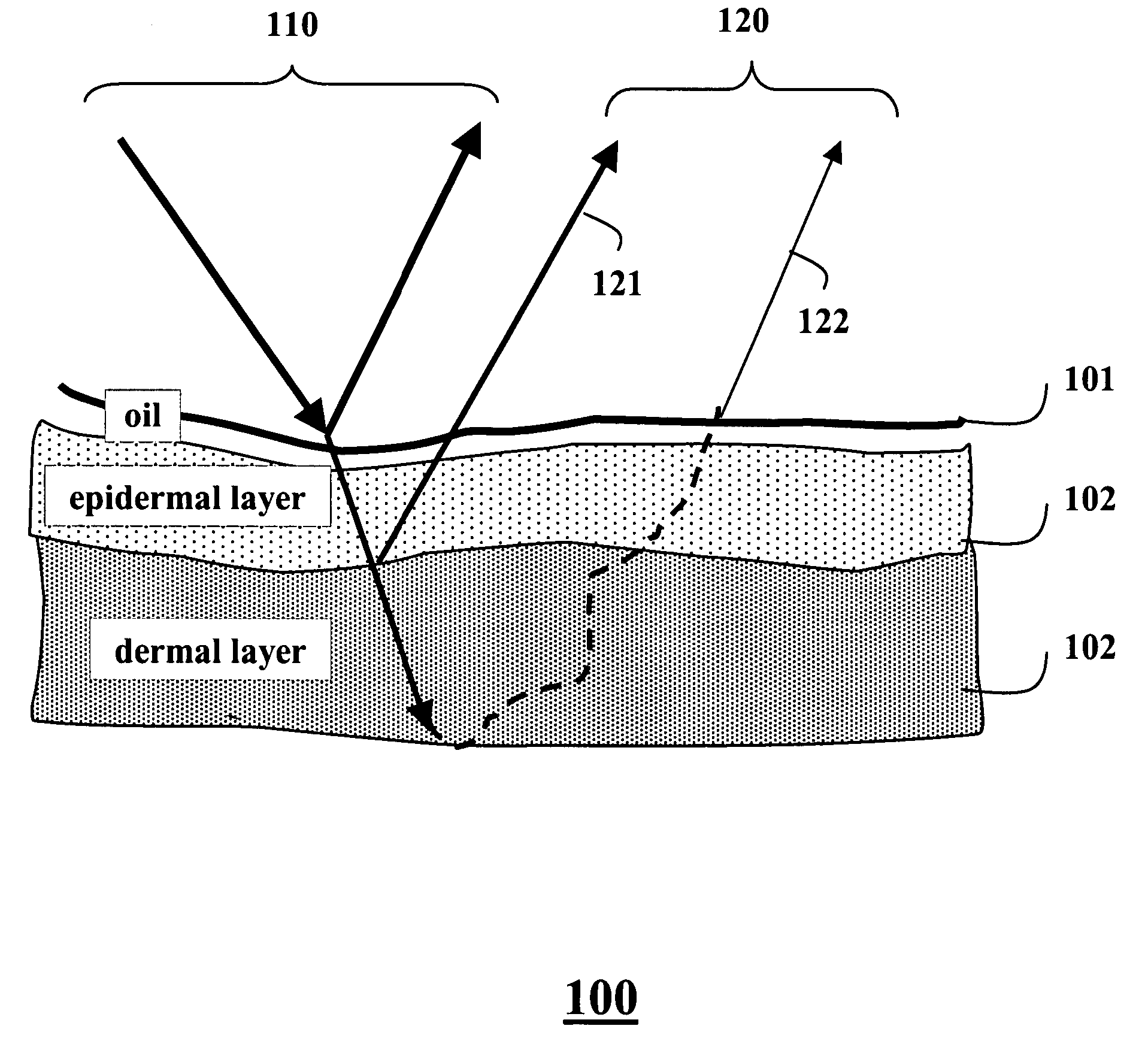
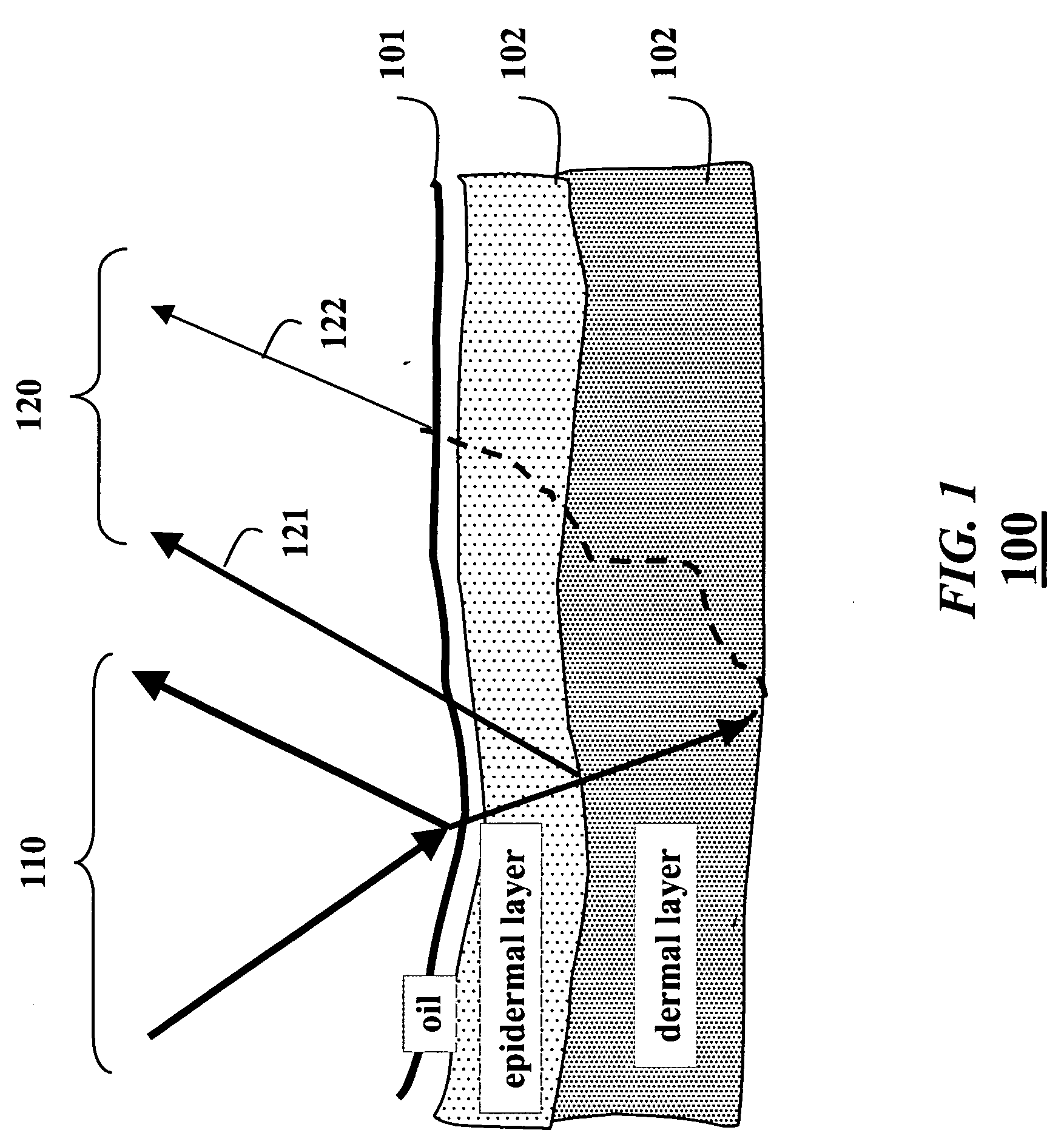
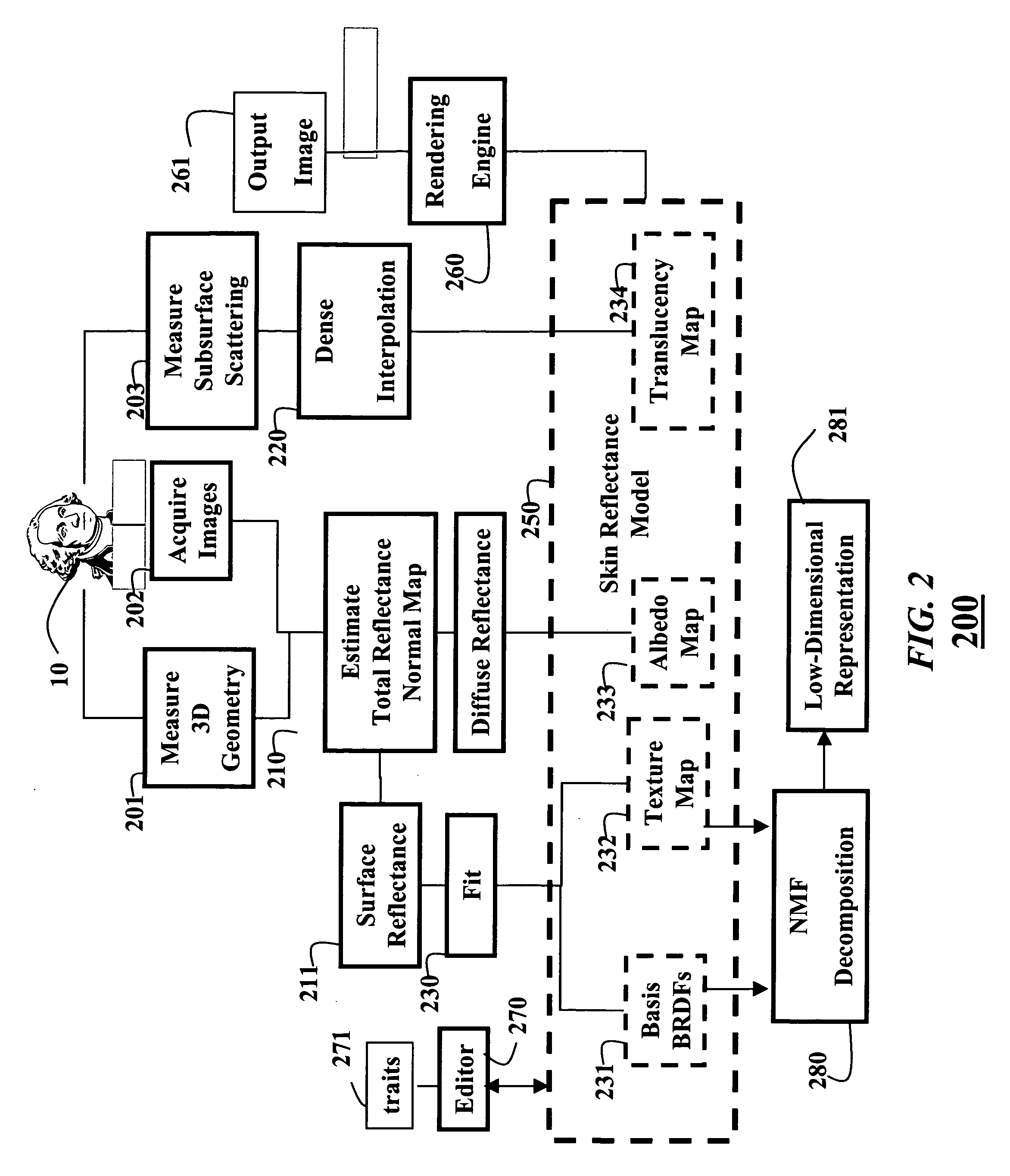
Skin reflectance model for representing and rendering faces
InactiveUS20060227137A1Scattering properties measurements3D-image renderingAlbedoSubsurface scattering
A face is scanned to obtain a three-dimensional geometry of the face, images are also acquired of the face, and subsurface scattering of the face is measured. A translucency map is determined from the subsurface reflectance. A total surface reflectance and a normal map are estimated from the three-dimensional geometry and the images, and diffuse reflectance is estimated using the total reflectance. An albedo map is determined from the diffuse reflectance. The diffuse reflectance is subtracted from the total reflectance to obtain a surface reflectance. A set of bi-directional reflectance functions is fitted to the surface reflectance. Then, the set of bi-directional reflectance distribution functions, the albedo map, and the translucency map are combined to form a skin reflectance model of the face.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC +1
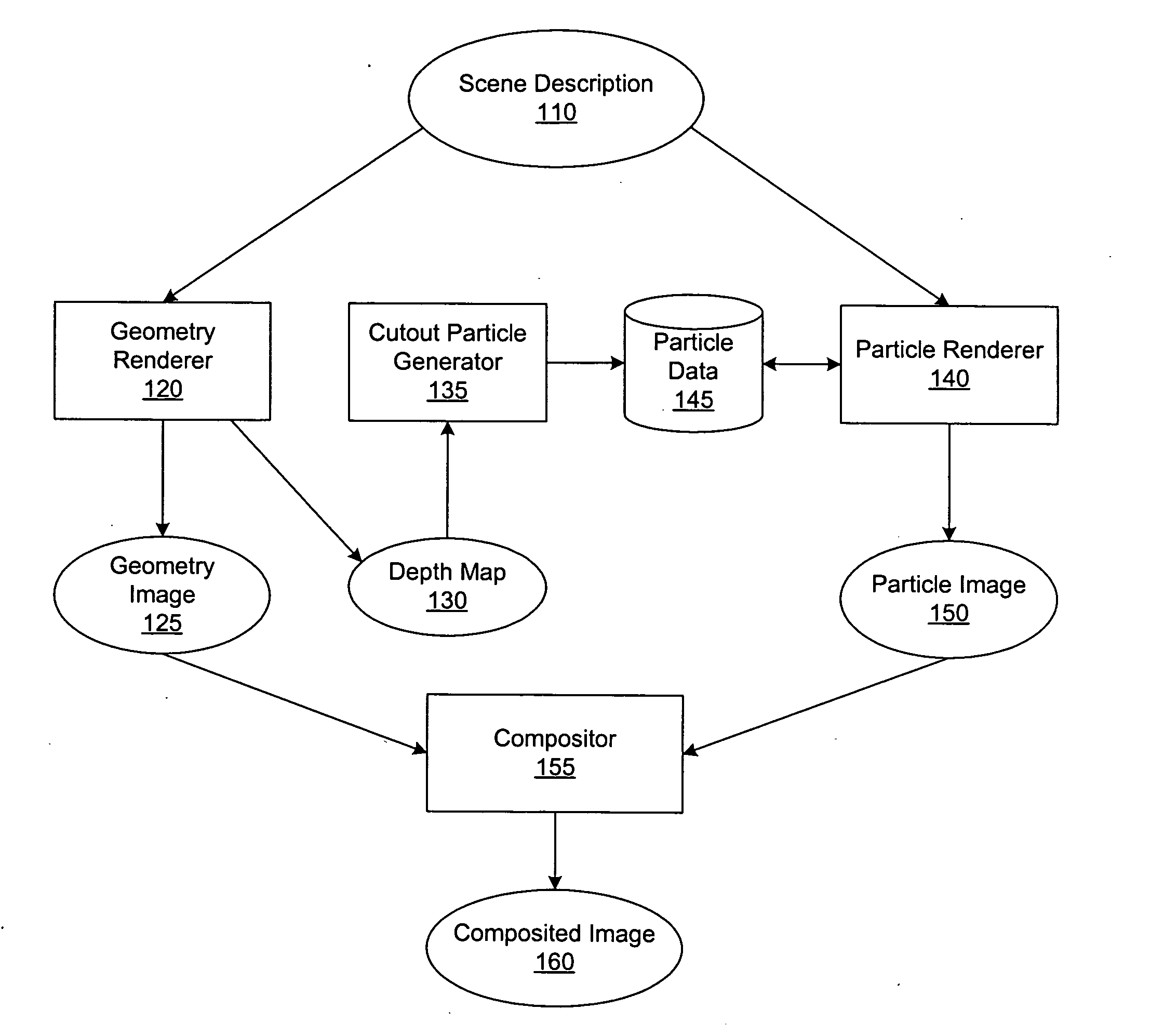
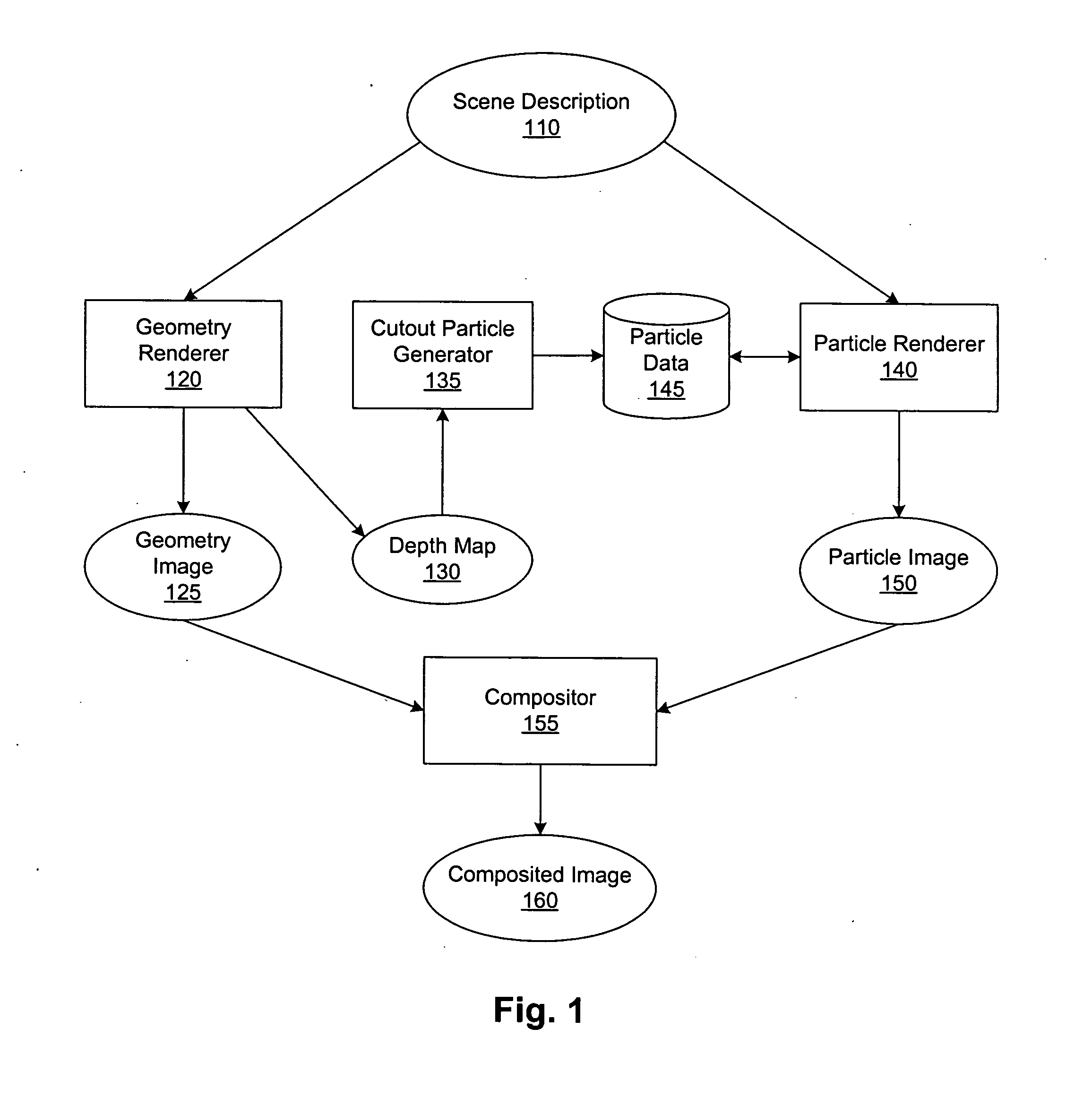
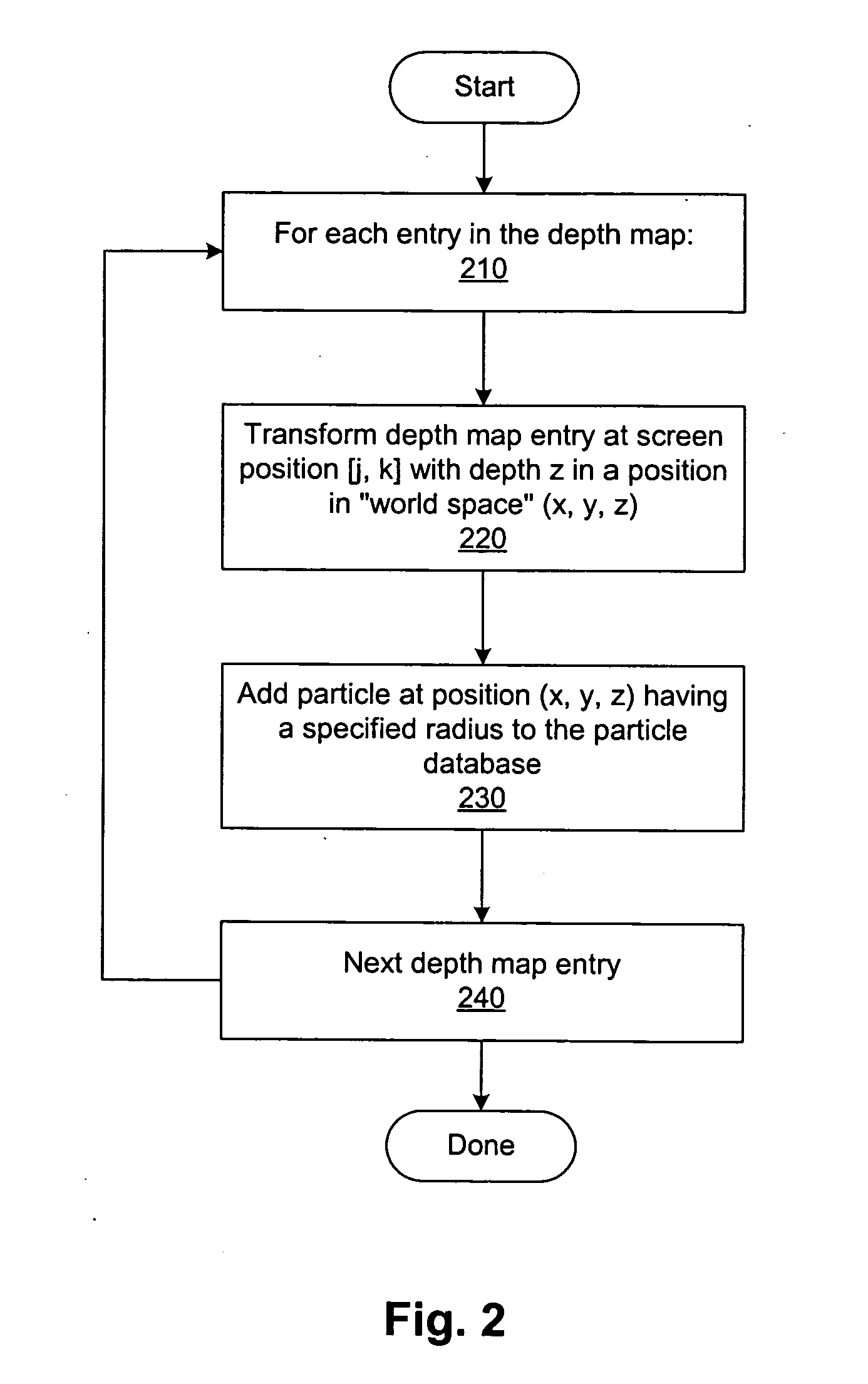
Integrating particle rendering and three-dimensional geometry rendering
InactiveUS20050219249A1Facilitates depthFacilitates motionAnimationImage generationGraphicsImage resolution
Images from geometry renderers and particle renderers are composited by incorporating geometry information from the geometry image as a number of special cutout particles in the particle renderer. Instead of contributing to the color and opacity of pixels in the particle-rendered image, these cutout particles occlude or subtract from the accumulated color and opacity of those pixels. In this way, depth resolution is performed as part of the particle rendering process, and the geometry and particle images may be combined using a simple process such as alpha blending. In one embodiment, the cutout particles are obtained from a depth map associated with the geometry image.
Owner:PACIFIC DATA IMAGES
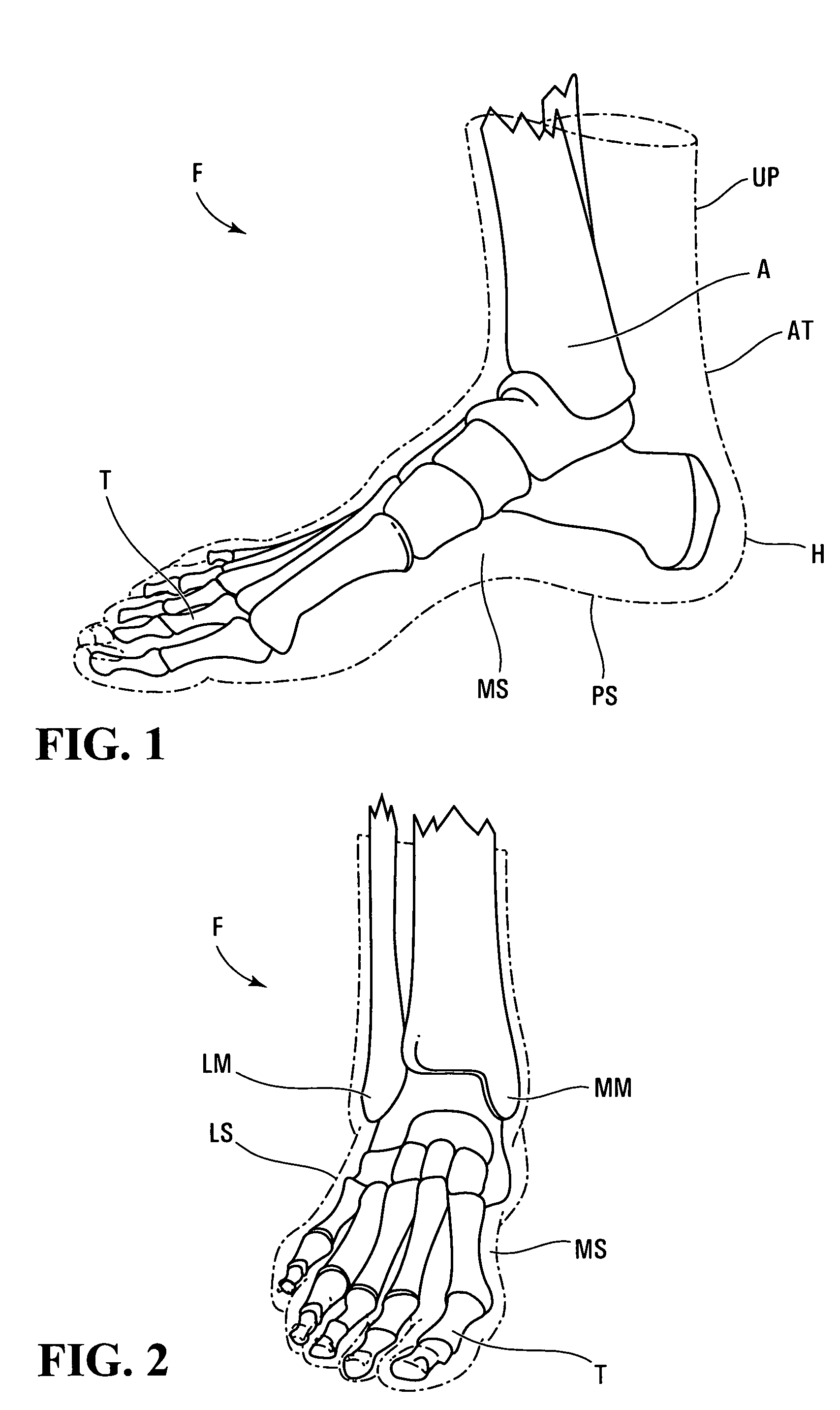
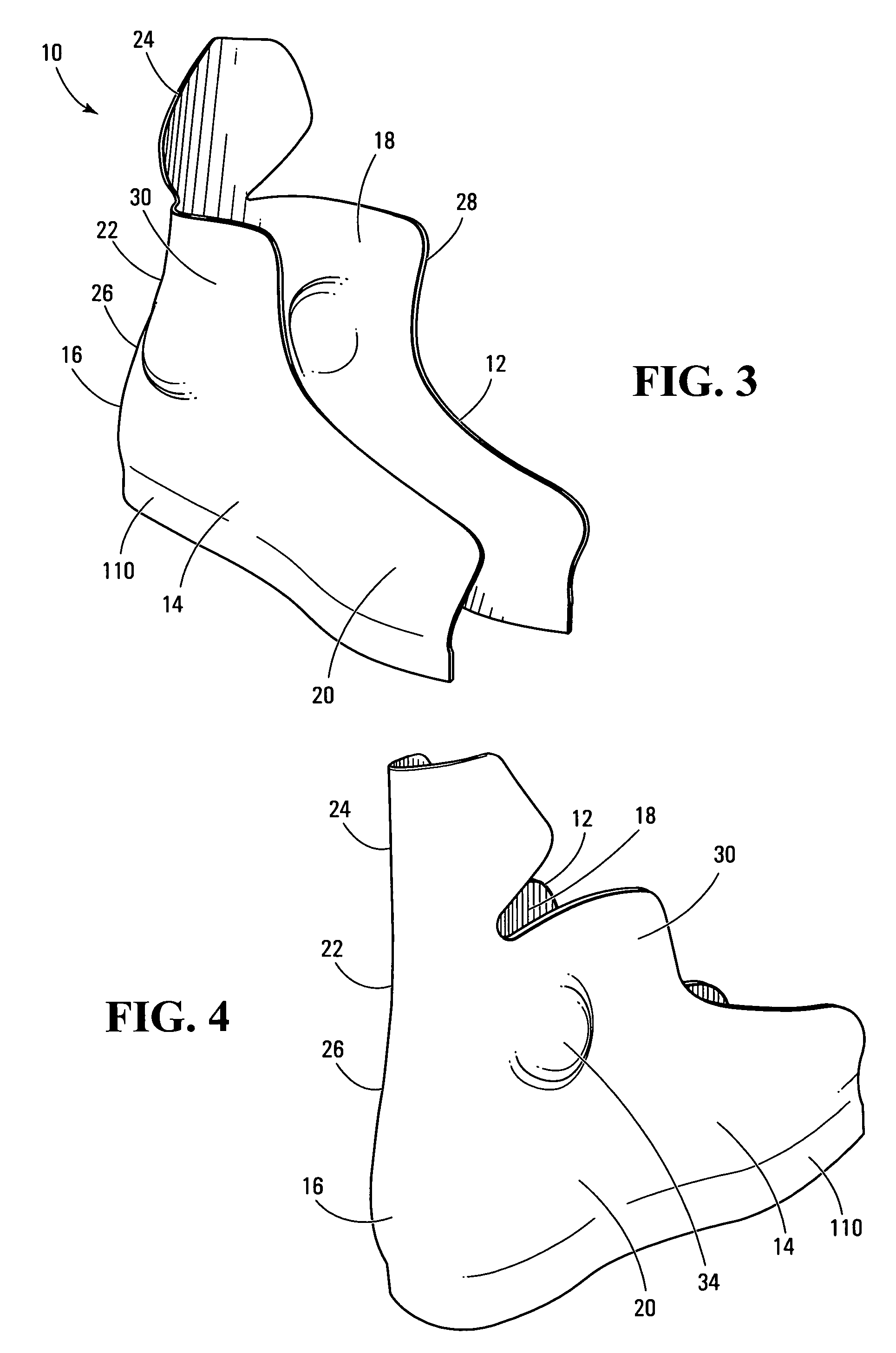
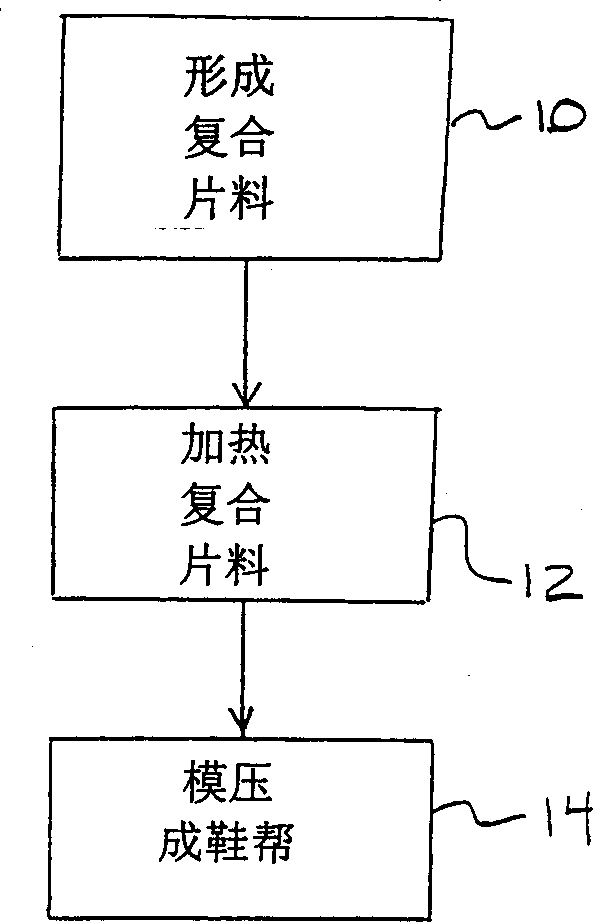
Footwear having an outer shell of foam
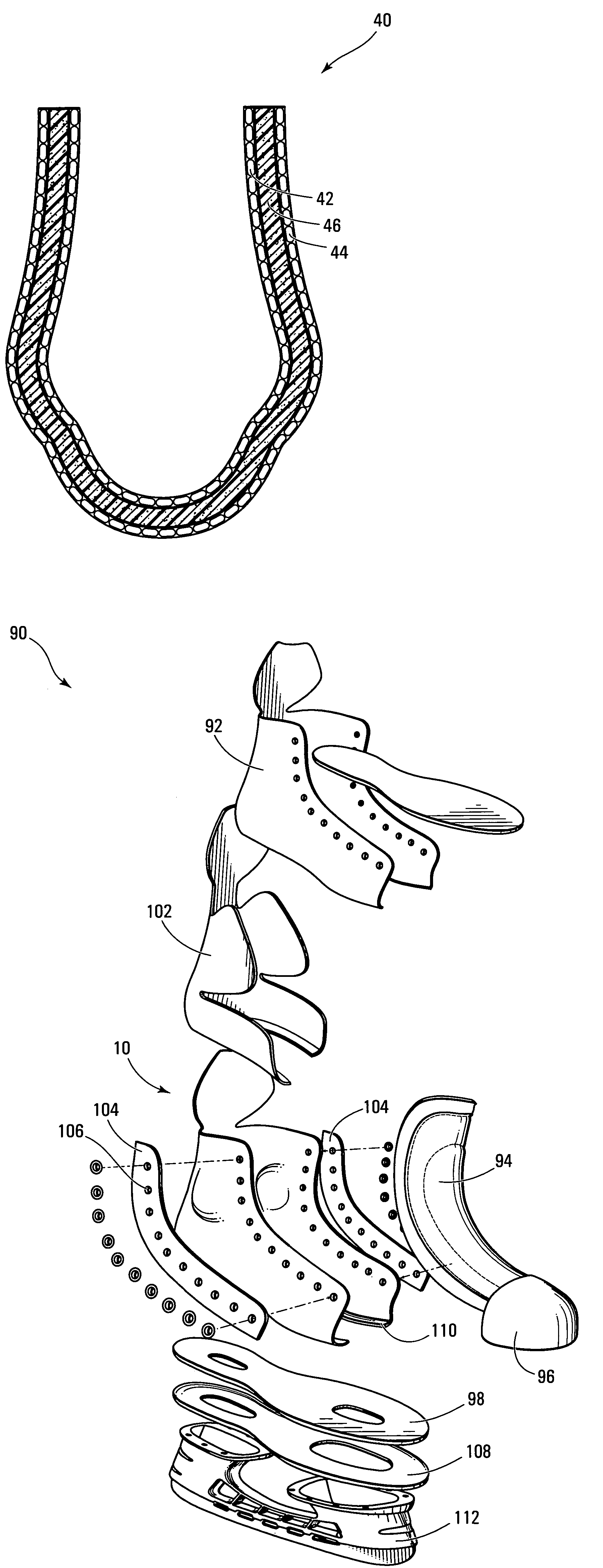
The invention relates to a lasted footwear for enclosing a human foot having a heel, an ankle and medial and lateral sides. The footwear comprises an outer shell for receiving the foot and an inner lining mounted in the outer shell. The inner lining is less rigid than the outer shell and has an inner surface adapted to contact the foot in use and an outer surface being affixed to the outer shell. The outer shell is made of a multi-layer composite sheet that is thermoformed for defining a foot-receiving cavity having a three-dimensional geometry that conforms to the foot. The multi-layer composite sheet has a first layer of thermoformable foam having a core and first and second opposite surfaces and a second layer of fibers. One of the first and second opposite surfaces of the layer of thermoformable foam has a skin formed by exposing the surface to temperatures between 200° F. and 300° F. The invention also relates to a method of making a lasted skate boot comprising such an outer shell.
Owner:BAUER HOCKEY LLC
Scanner with feedback control
InactiveUS20110292406A1Adjustable powerSpeckle reductionUsing optical meansLaser lightUltimate tensile strength
The present invention relates to non-contact optical scanning of an object for generation of a three-dimensional surface model of the scanned object. In particular the invention relates to a scanner for obtaining the three-dimensional geometry of at least a part of the surface of an object, said scanner comprising: —at least one light source, preferably a laser light source with adjustable power, —projection means for directing light from the at least one light source to a moving spot on the surface of the object, —at least one image sensor adapted to record at least one image of at least a part of the surface, —detection means, other than the at least one image sensor, for monitoring at least a part of the light reflected from the surface, —regulation means for adjusting the intensity of the at least one light source based on the amount of light reflected from the surface, and—means for transforming the at least one image to a three-dimensional model of the surface.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
Method and apparatus for fabricating shaped structures and shaped structures including one- , two- or three-dimensional patterns incorporated therein
InactiveUS20060228635A1NanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusThree dimensional shapeBiomedical engineering
The invention includes a template useful for the fabrication of devices having one, two, or three dimensional geometries. The template can include at least a first patterned surface and a mask integrated into the template for creating an interference pattern when radiation is passed through the mask. The template can be useful in the production of shaped structures including one-, two-, or three-dimensionally shaped patterns, and further including at least one shaped surface.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
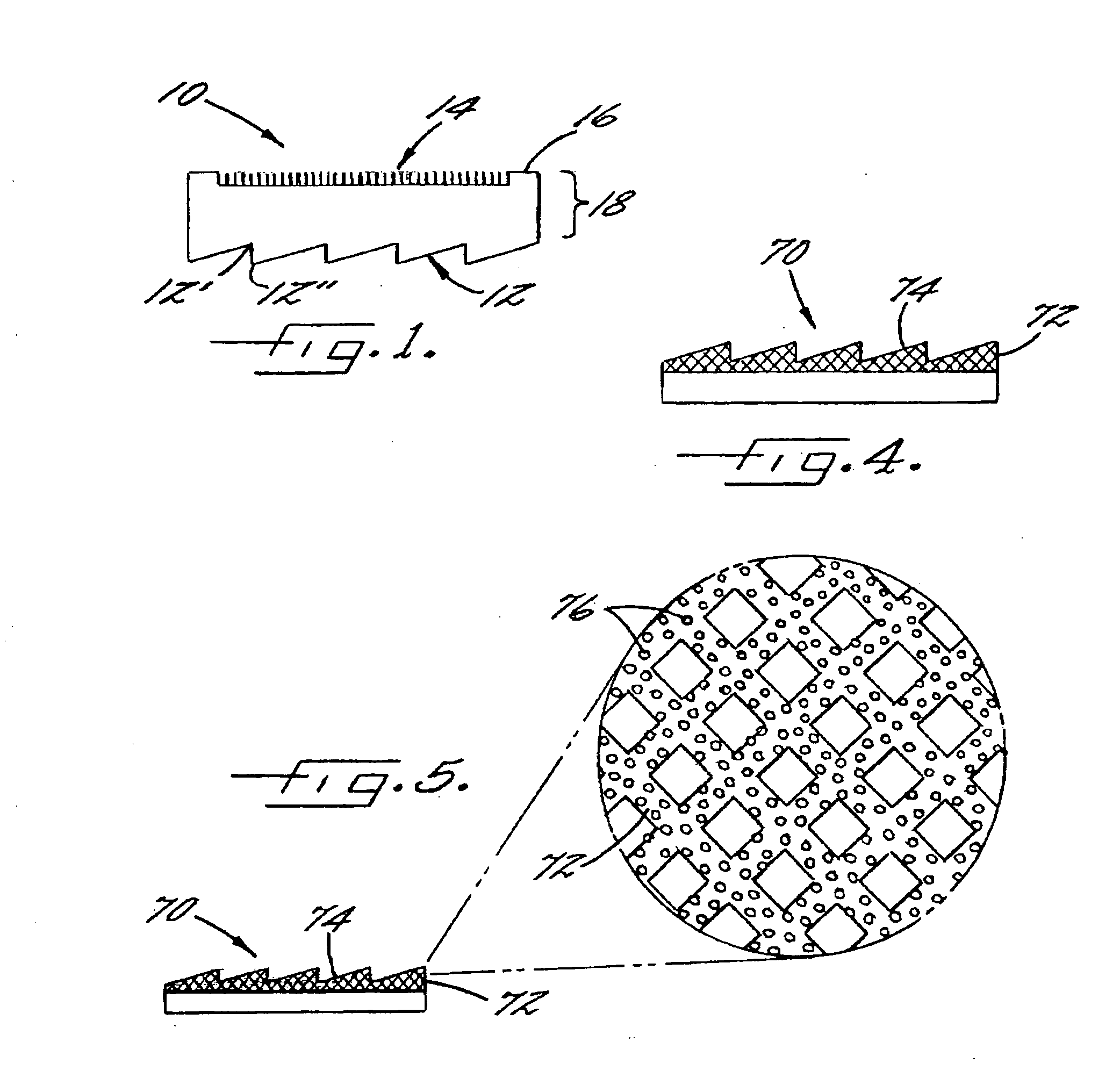
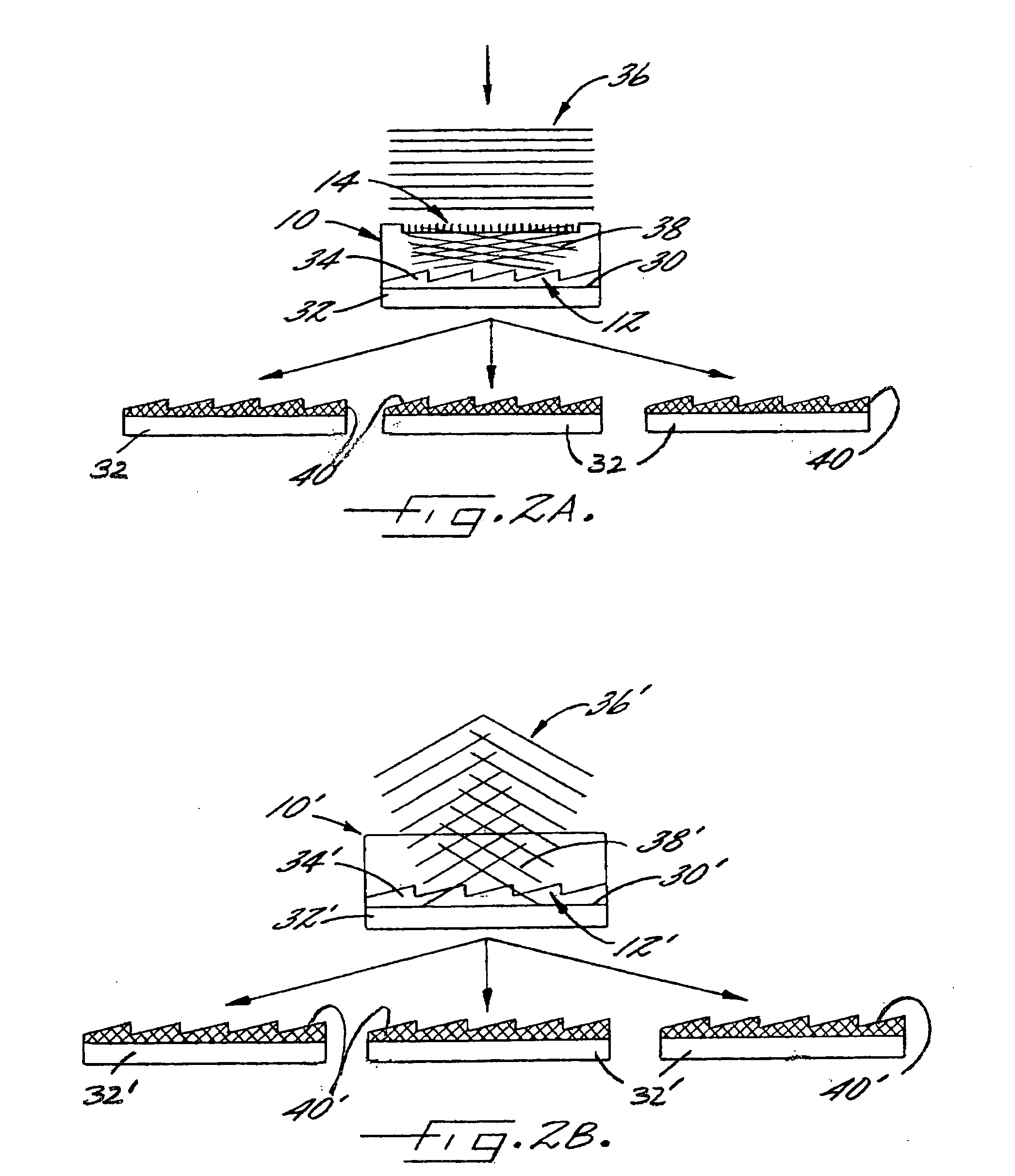
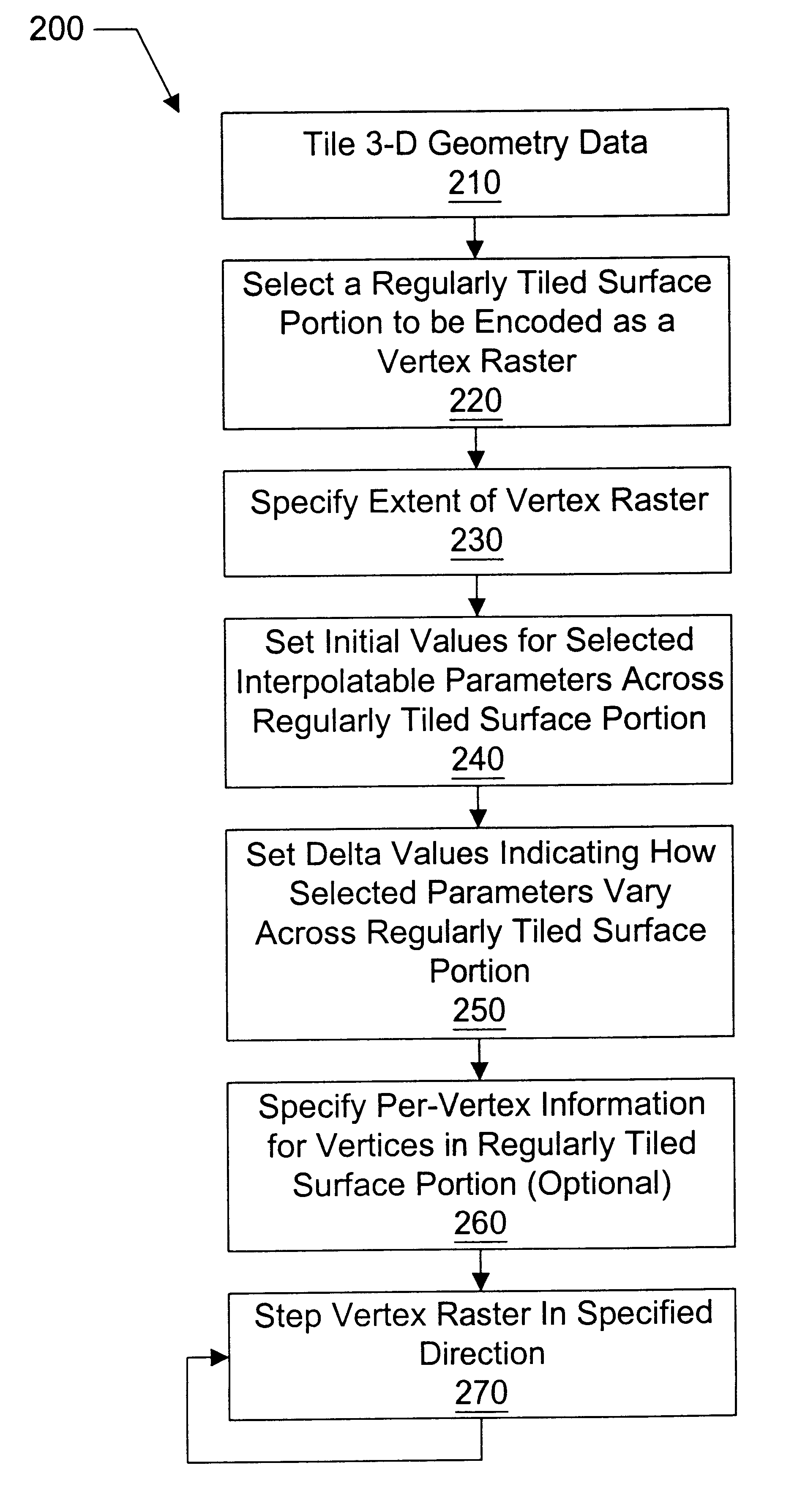
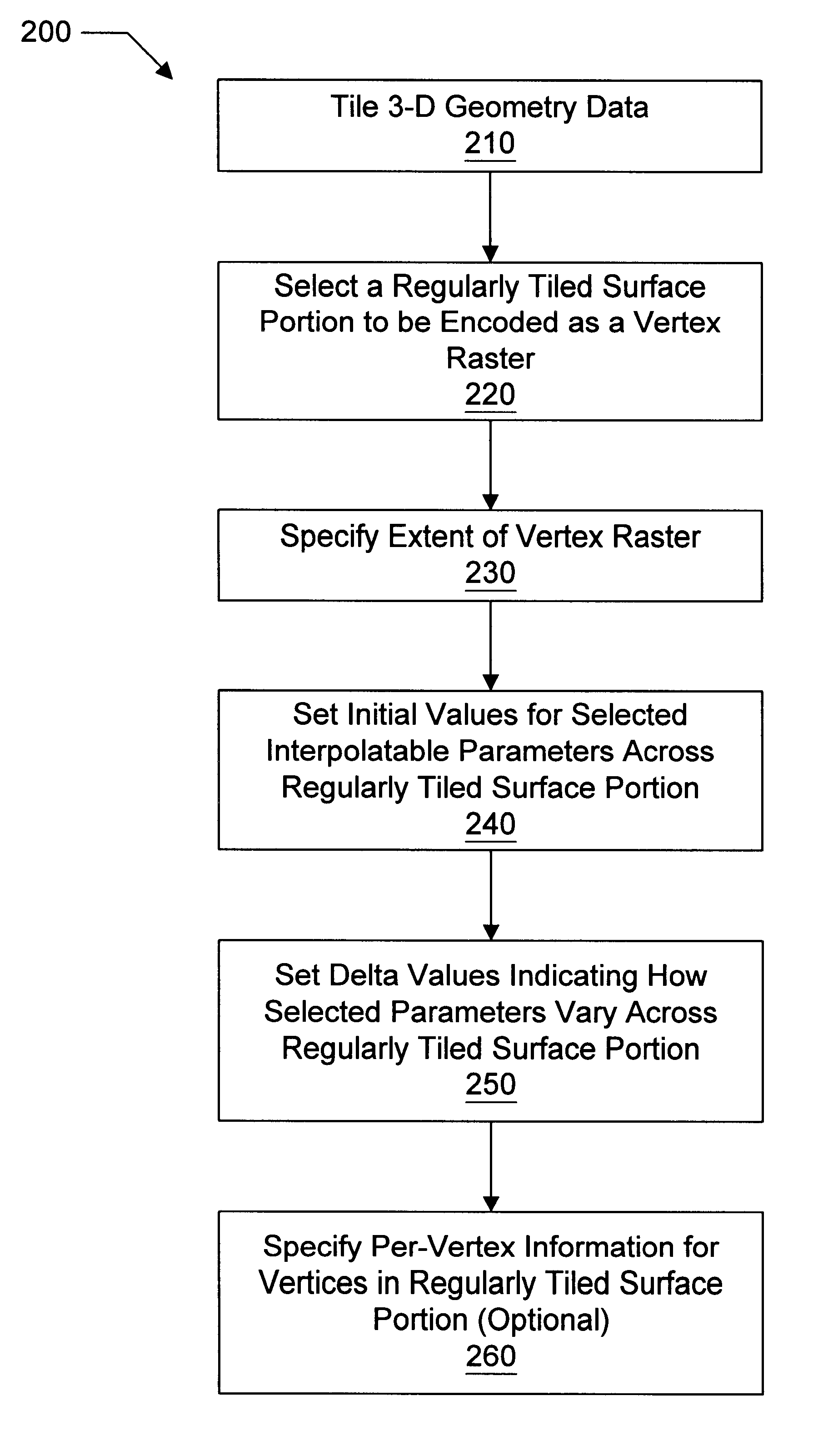
Compression of three-dimensional geometry data representing a regularly tiled surface portion of a graphical object
Methods and systems for compressing and decompressing 3-D geometry data which includes regularly tiled surface portions. One compression method includes representing a surface portion as a "vertex raster", which comprises specifying an extent value and encoding the vertex parameter values of vertices within the surface portion. The extent of the surface portion specifies the arrangement of vertices within the surface portion, and allows the vertices to be properly assembled into drawing primitives during decompression. The encoded vertex parameter values may be encoded globally (by setting initial values and corresponding delta values), locally (on a per-vertex basis), or using a combination of these techniques. Absolute, delta encoding, or delta-delta encoding may be utilized for these parameter values. Vertex parameters which may be encoded in this manner include position, color, normals, z-displacement values, texture map coordinates, and surface material properties. Additionally, connectivity information may also be encoded using this compression method by specifying quad split bits and half-resolution edges. Quad split bits are used to tessellate a quadrilateral formed by neighboring vertices of a surface portion according to the direction of the strongest color change. Half-resolution edges are utilized to gradually shift from an area of high resolution to an adjacent surface portion represented in lower resolution. For graphical objects which include a plurality of adjacent surface portions, a step command is disclosed which allows data from one surface portion to be advantageously reused. Decompression of a vertex raster representation may comprise decoding the extent value, global parameter values, and a per-vertex stream of local parameter values.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
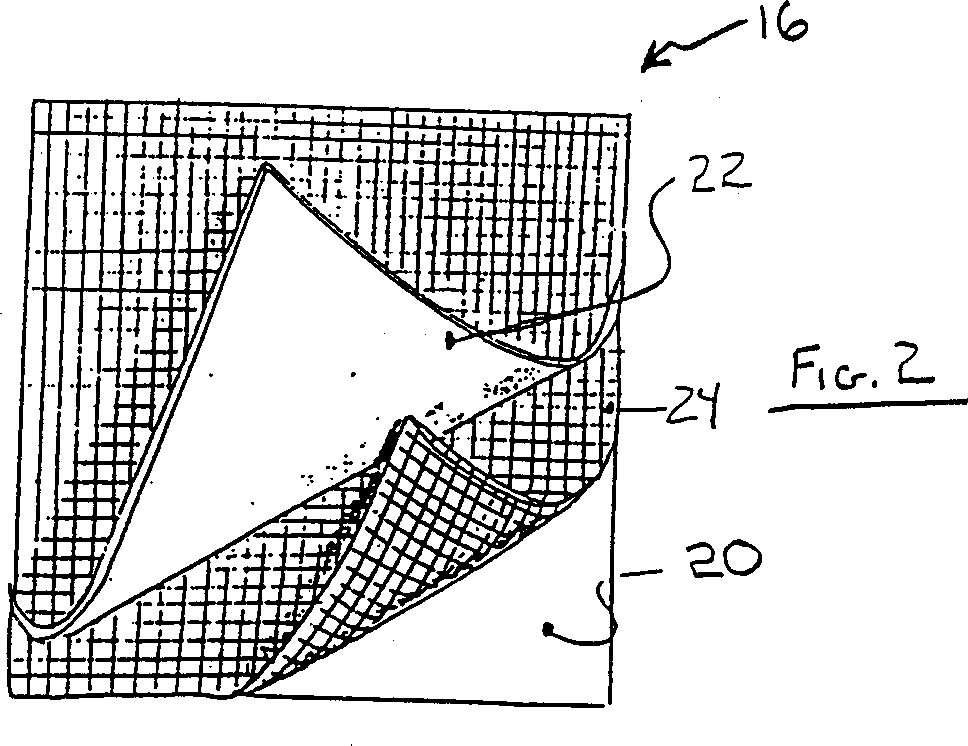
Composite footwear upper and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN1342046AEasy to processChange propertiesDomestic footwearUpperCompression moldingEngineering
A method of manufacturing a multi-layer, composite footwear upper having a three-dimensional geometry includes the steps of forming a substantially planar composite sheet from two or more layers, heating the composite sheet, and compression molding the composite sheet into the three-dimensional geometry of the footwear upper. The composite sheet is formed by laminating a first layer of thermoplastic foam to a second layer of thermoplastic urethane (TPU), preferably in the form of a TPU film. A third layer of mesh fabric can be interposed between the first and second layers. The composite sheet is compressed after heating in a mold cavity to achieve the desired three-dimensional geometry. The composite sheet can be compression molded into separate sections which are assembled after molding to form the footwear upper. Alternatively, the composite sheet can be compression molded into a seamless, unitary footwear upper that requires minimal, if any, assembly for completion. The multi-layer composite upper can be applied to a sole to form performance footwear suitable for use in a wide range of conditions.
Owner:爱德华·J·诺顿 +1
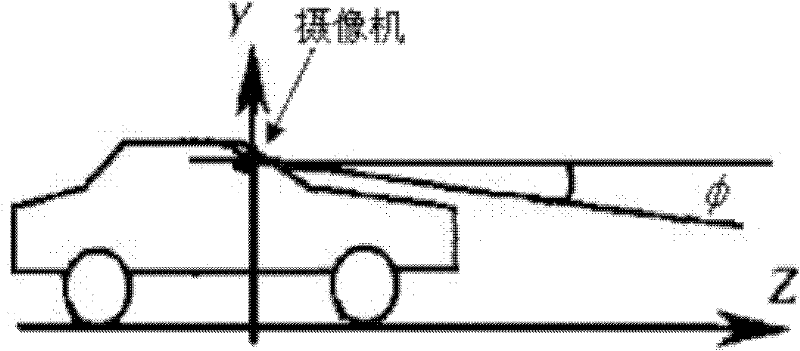
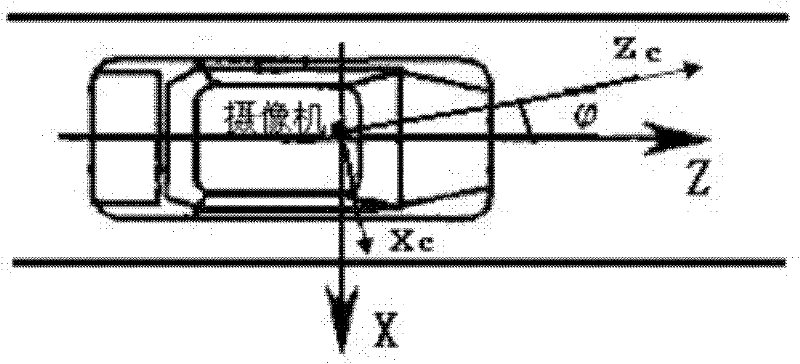
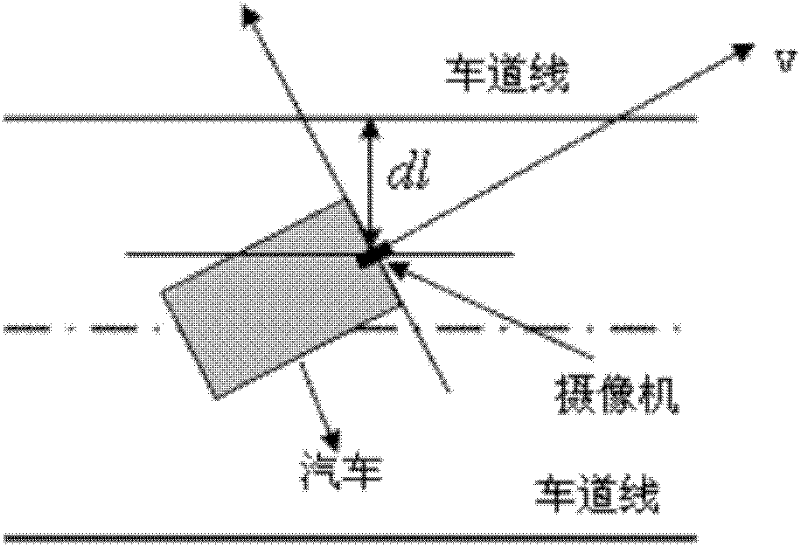
A Lane Departure Distance Measurement and Early Warning Method Based on Monocular Vision
ActiveCN102288121AImprove accuracyReduce measurement impactUsing optical meansVideo imageVisual perception
The invention discloses a method for measuring and pre-warning a lane departure distance based on monocular vision, belonging to the technical field of computer imaging processing. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting a video image through a monocular video camera installed in the front of an automobile at first, completing the detection of a lane line after processing through an image processing technology, and extracting geometrical information of the lane line; obtaining vertical distances between the automobile and the lane lines at left and right sides by utilizing thethree-dimensional geometry transformation relation of a pinhole imaging principle; and establishing a departure pre-warning decision method according to the vertical distances measured in real time, and providing effective information for an intelligent assistant driving technology. According to the method disclosed by the invention, when the lane line is detected by utilizing Hough transform, a constraint condition is added, a part of virtual lane line is excluded, and the operation speed and the lane line detection accuracy are increased; simultaneously, the lane departure pre-warning can be realized only by utilizing image information; the measurement influence of a vehicle departure angle on the lane departure distance is low; furthermore, the solving operation speed is high owing to the use of the three-dimensional geometry transform method; and the requirements of the intelligent assistant driving technology can be satisfied.
Owner:厚普清洁能源(集团)股份有限公司
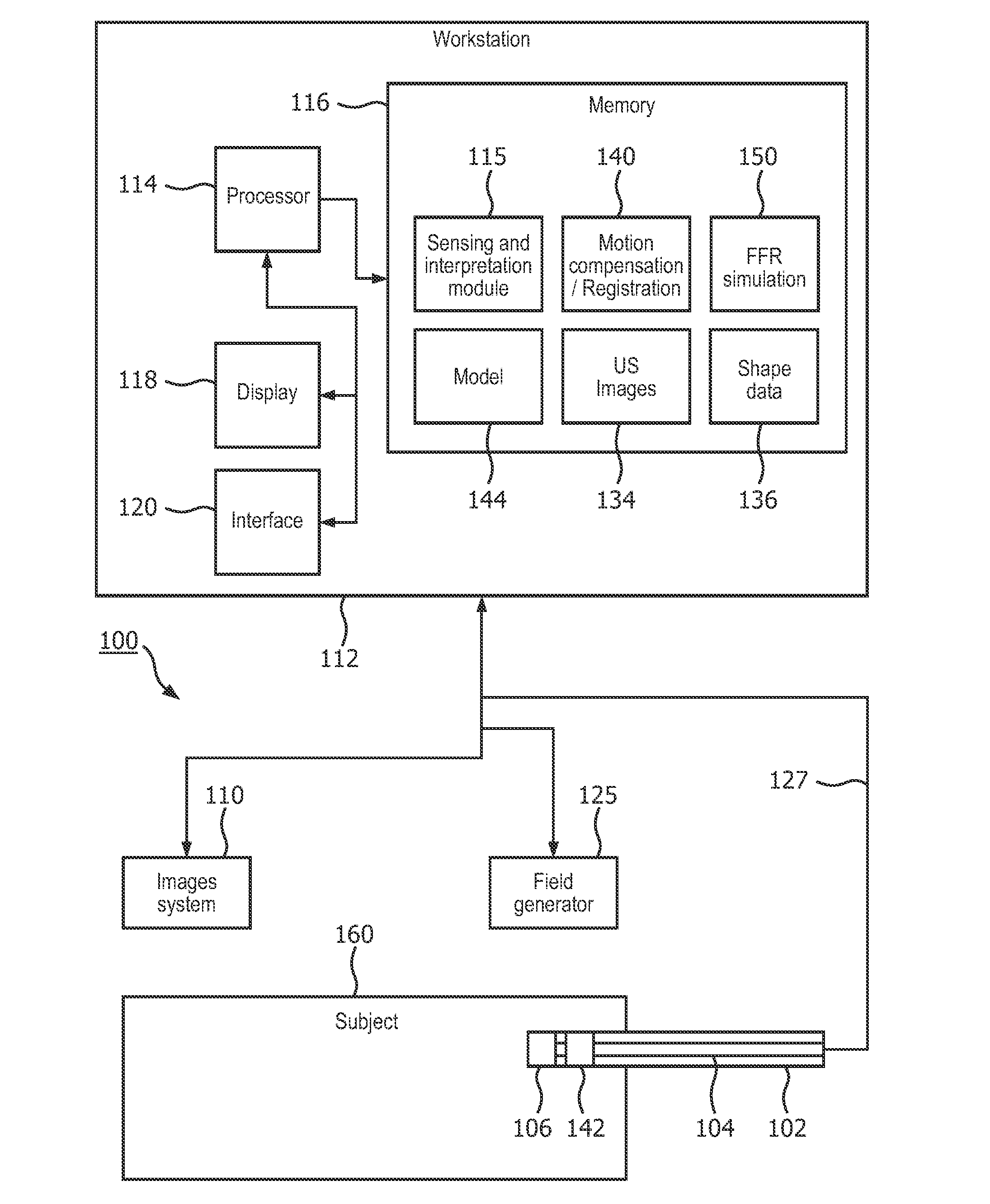
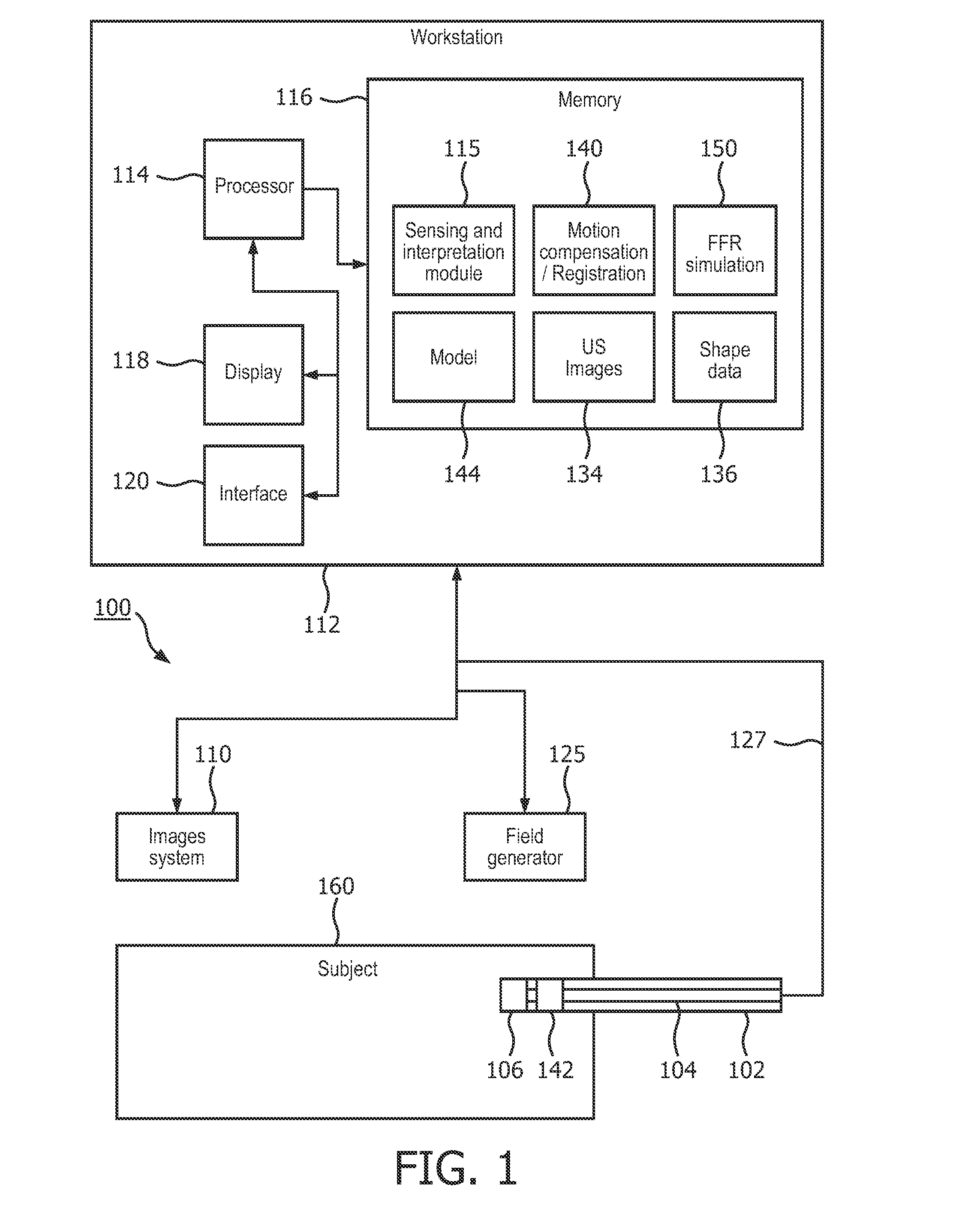
Shape sensed ultrasound probe for fractional flow reserve simulation
A medical system includes a medical instrument (102) configured for interventional deployment and a shape sensing system (104) mounted on or in the medical instrument and configured to measure a shape of the medical instrument during the interventional deployment. An imaging device (106) is mounted on or in the medical instrument and configured to image a lumen in which the imaging device is deployed. A registration module (140) is configured to register the shape of the medical instrument to an image of the lumen at a particular time to reconstruct a three-dimensional geometry of the lumen, accounting for motion.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
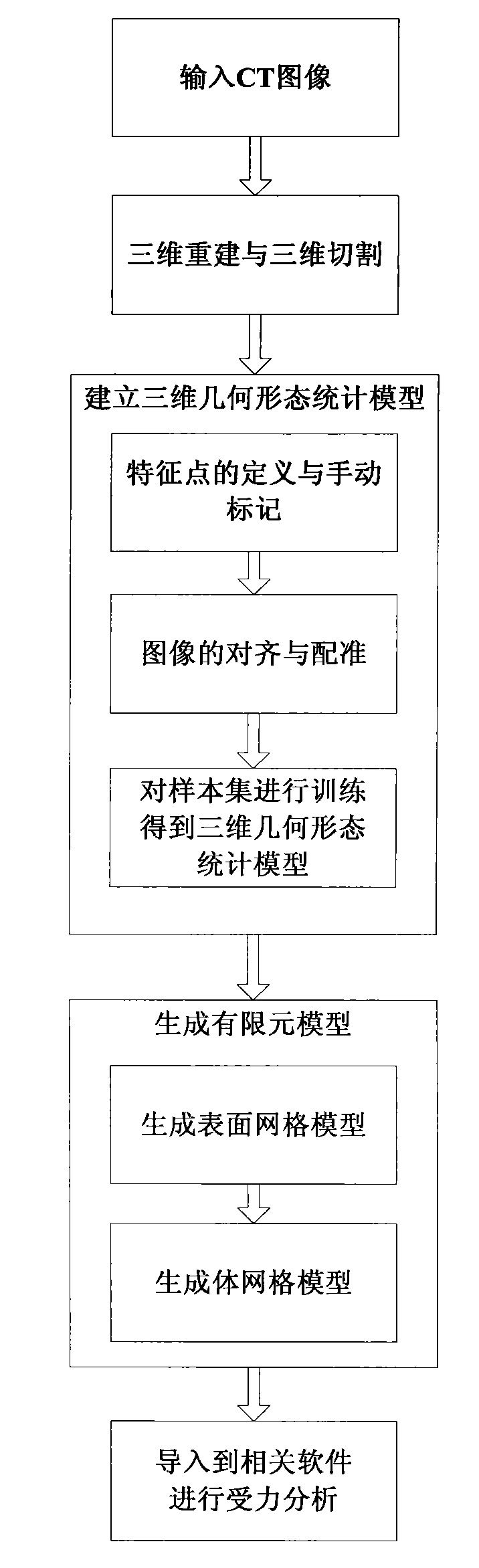
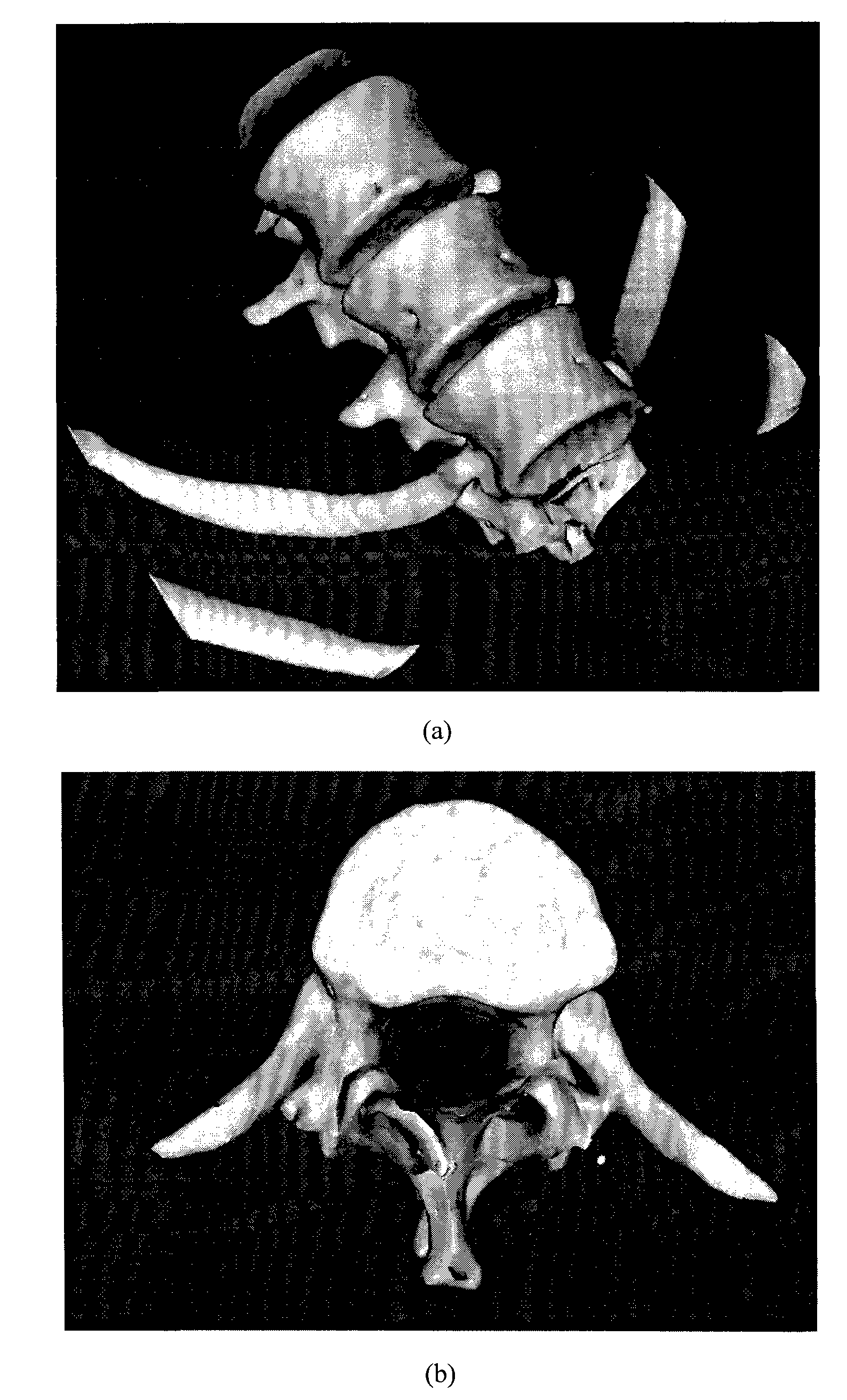
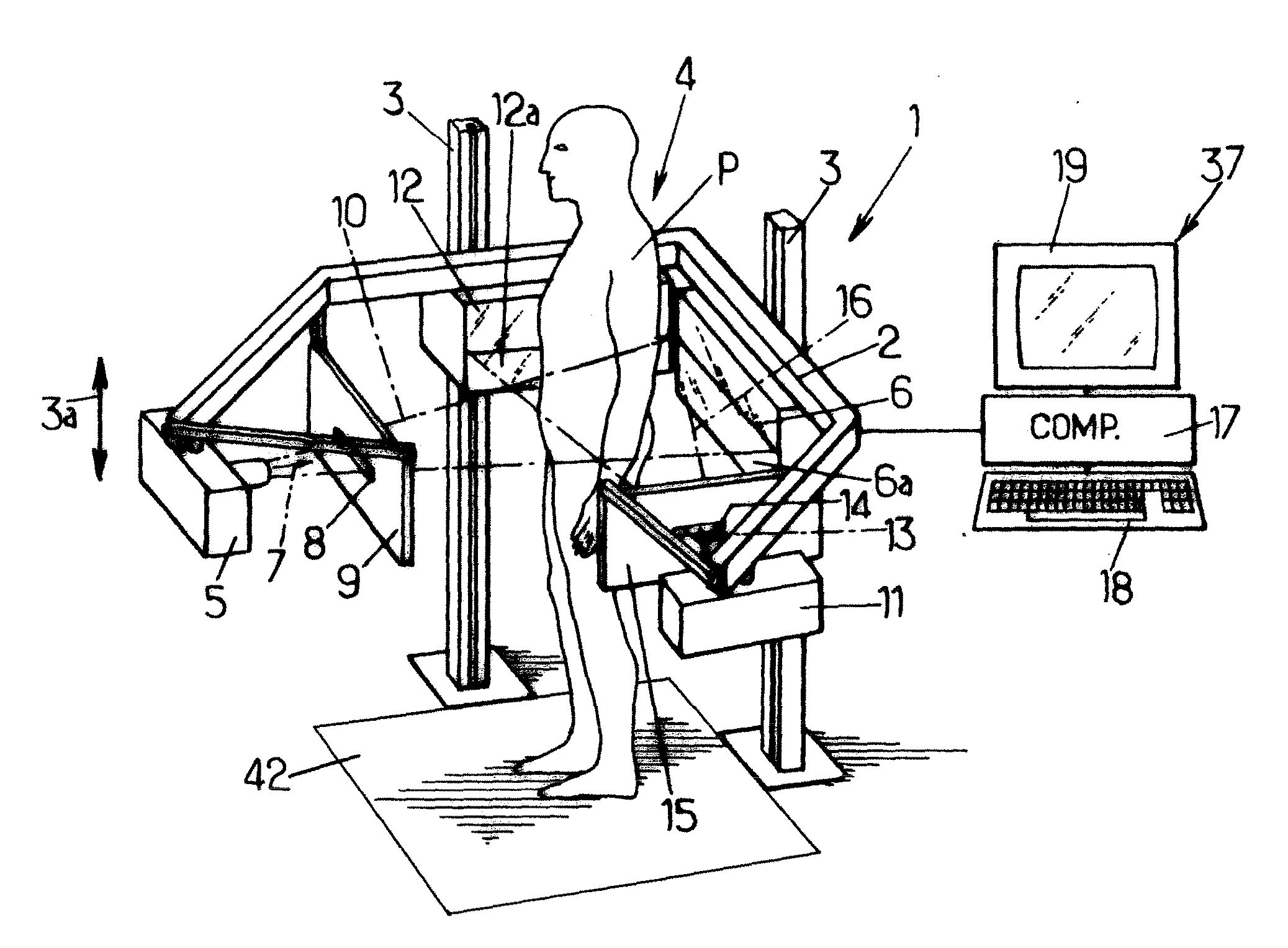
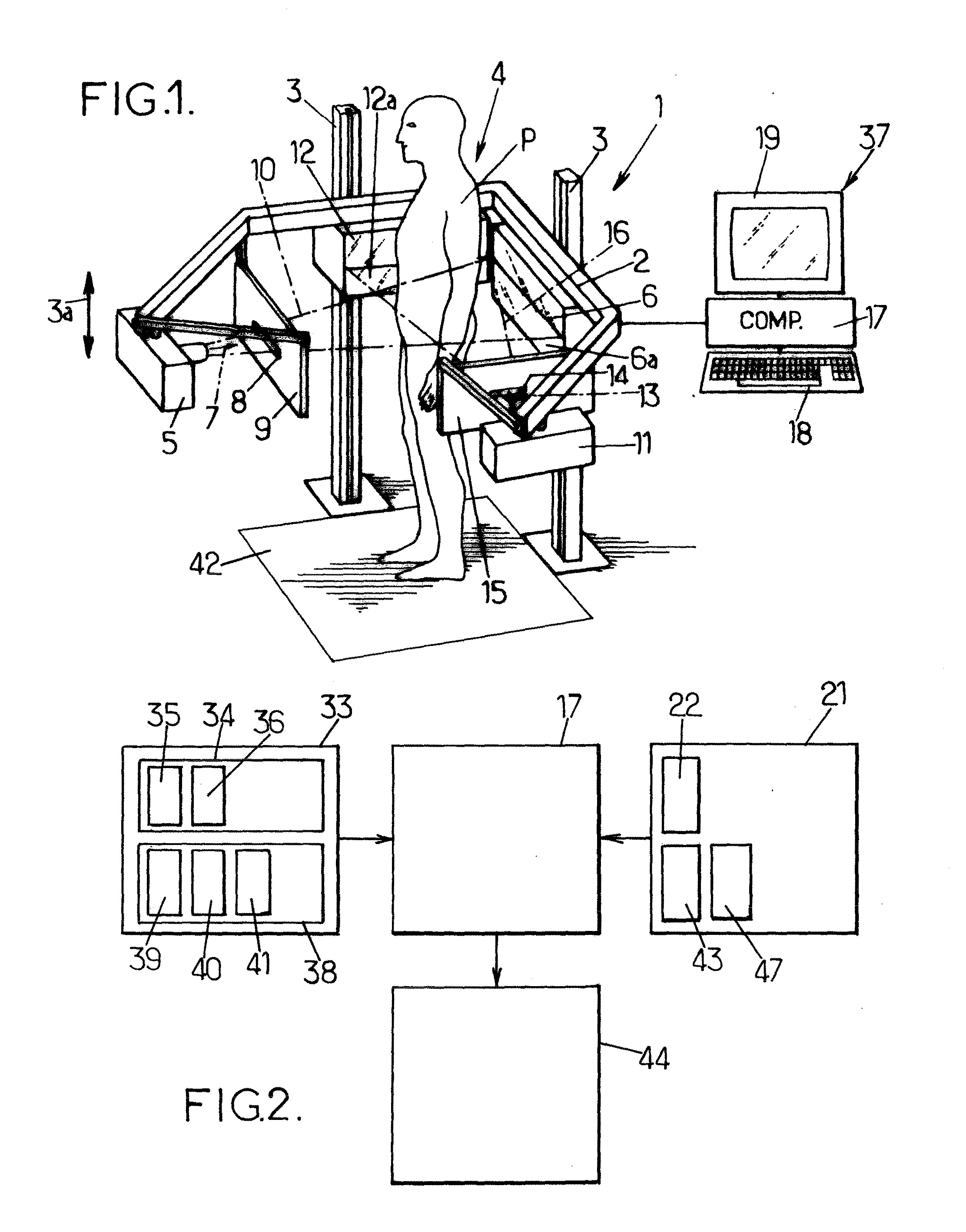
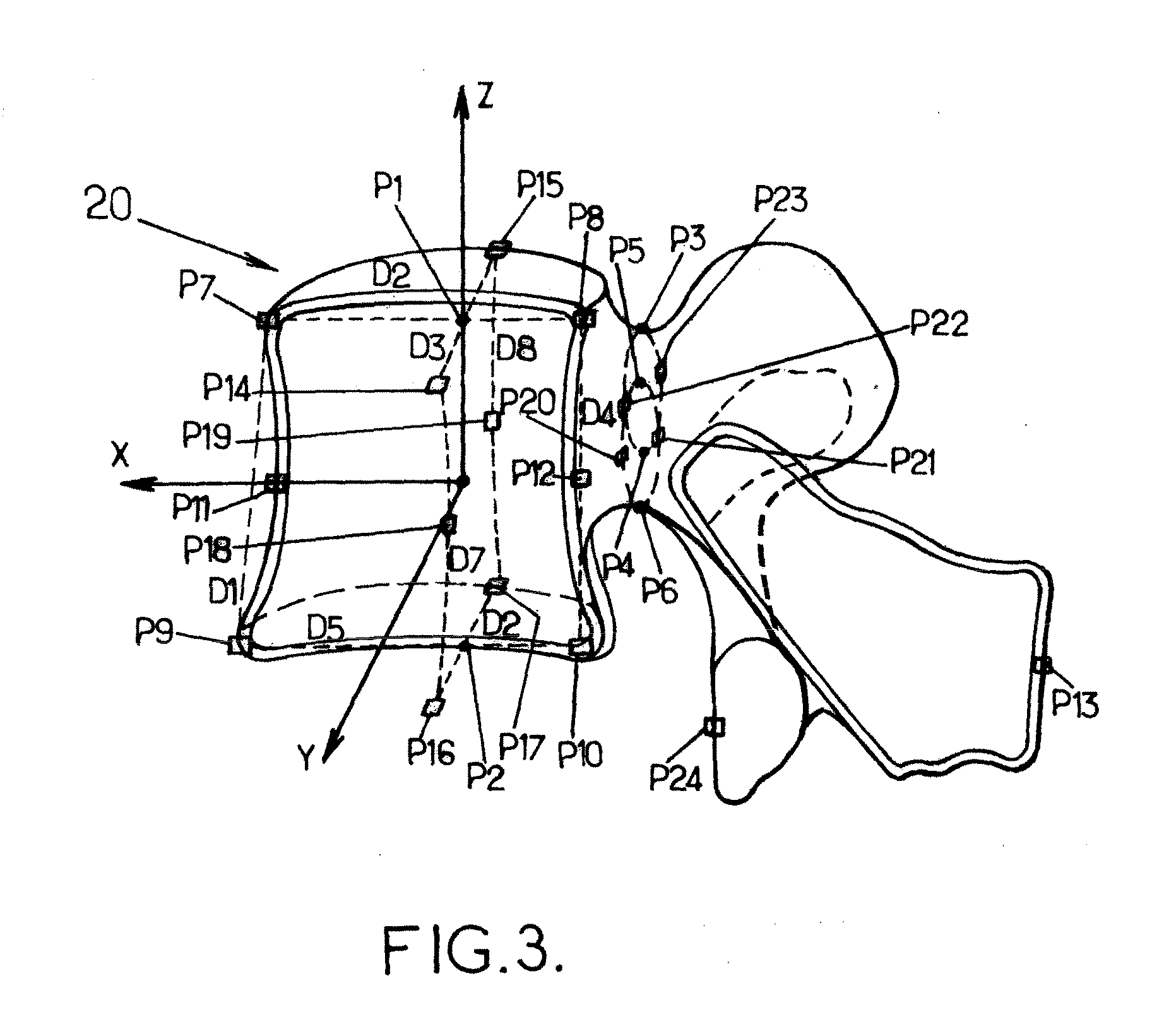
Method for constructing vertebral three-dimensional geometry and finite element mixture model
The invention provides a method for constructing a vertebral three-dimensional geometry and finite element mixture model, which belongs to the technical field of processing of medical images. The method comprises the following construction processes of: inputting a vertebral computer tomography (CT) image; performing three-dimensional reconstruction and three-dimensional cutting on the CT image to acquire a vertebral three-dimensional image set; establishing a three-dimensional geometric statistical model, namely defining and manually calibrating vertebral characteristic points, aligning and registering vertebral images, and training a sample set to acquire the statistical model; and generating a finite element model, importing the statistical model, generating a surface mesh model, and generating a volume mesh model, wherein the model can be directly imported into finite element analysis software for biomechanics analysis. By the method, a vertebral geometrical shape can be precisely described, the accuracy of finite element analysis results can be ensured, and the precision of vertebral models can be improved. The method is convenient to use, facilitates the scientific measurement of the shapes and the stress of vertebras and can be used for researches related to vertebral columns and the vertebras in the field of surgical medicine.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
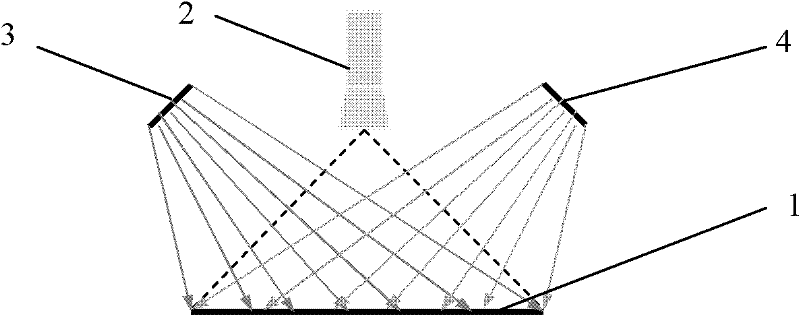
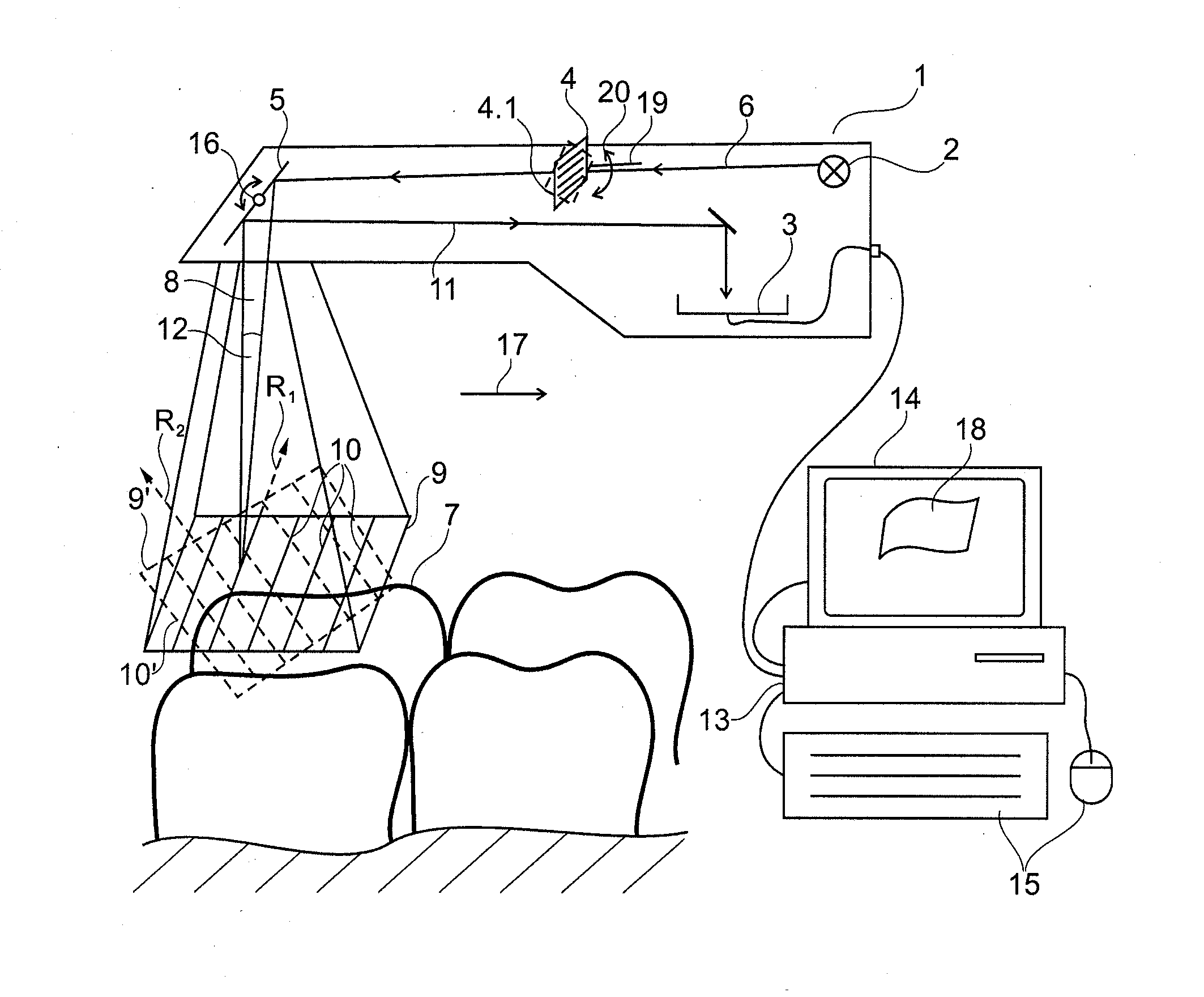
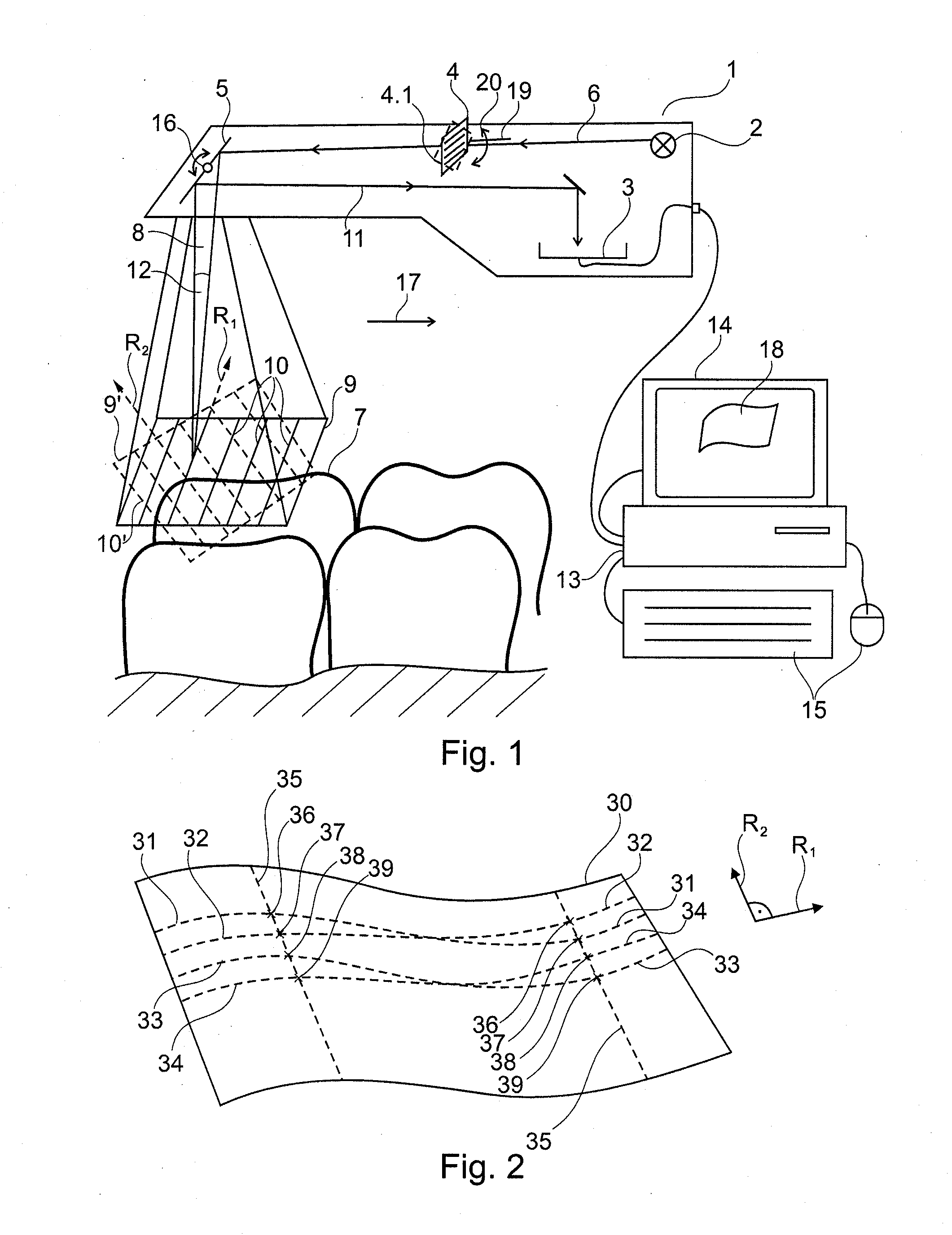
Method for optical measurement of the three dimensional geometry of objects
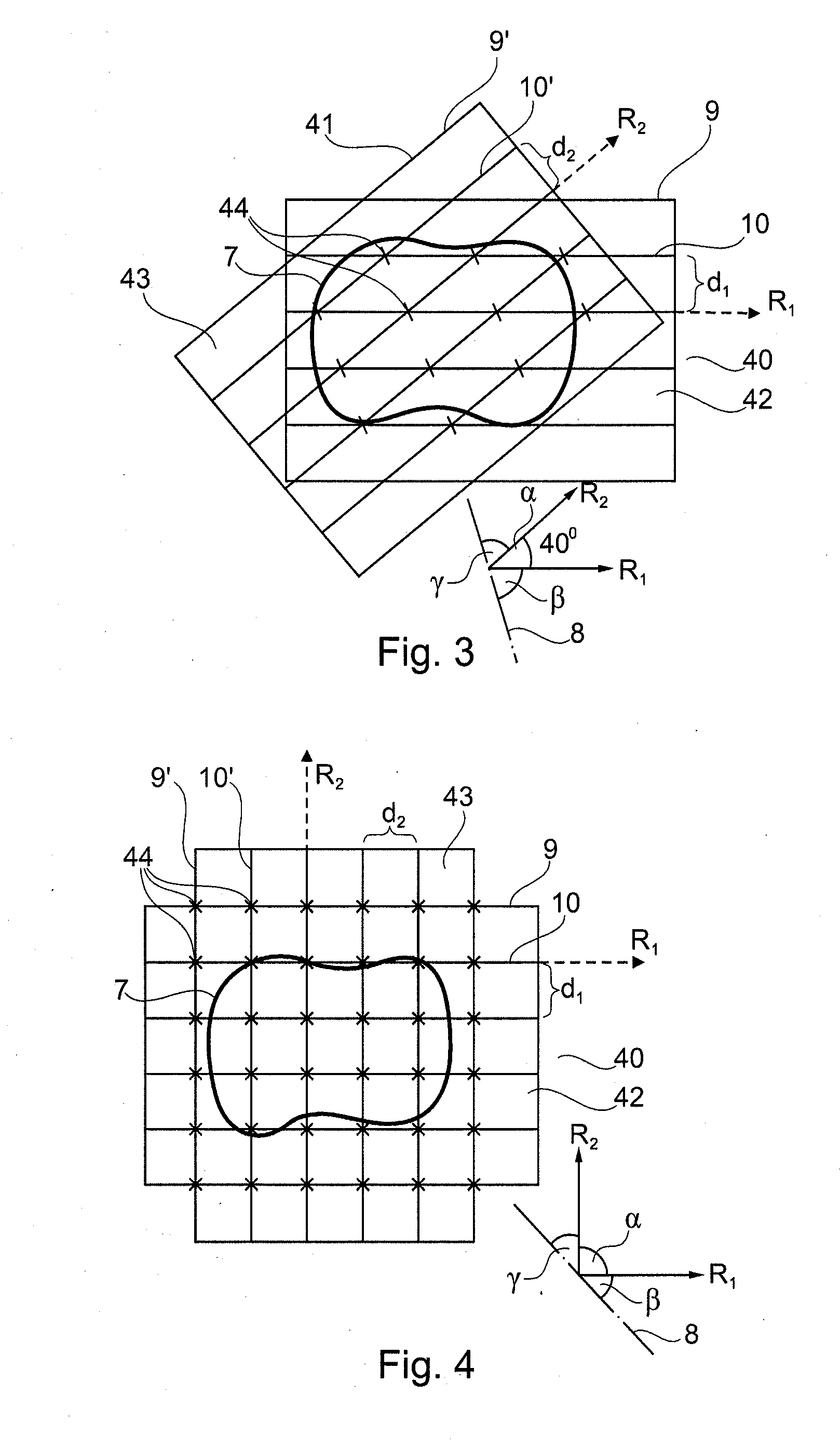
ActiveUS20100209002A1Possible to measureSmooth movementCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringData setTriangulation
The invention relates to a method for optically scanning the three-dimensional geometry of an object by means of triangulation, in which a pattern (9, 9′) is projected onto the object (7) to be scanned in order to obtain a 3D data set, and the projected pattern (9, 9′) is recorded in an image (40, 41). In a first step for the production of at least one first image (40), a first pattern (9) is projected and in a second step for the creation of at least one further image (40), a further pattern (9′) deviating from the first as regards position or shape is projected onto the object (7) to be scanned and the image (41) is created. The first image (40) and the further image (41) comprise at least one common point (44). The 3D data acquired from the images (40, 41) are merged in a subsequent step on the basis of the 3D data of the at least one common point (44) such that the 3D data acquired from said images (40, 41) agree at least with reference to the 3D data of the common point (44) in the 3D data set.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for presenting two and three-dimensional computer applications within a 3D meta-visualization
InactiveUS20010040571A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsData set
A method and apparatus for organizing two and / or three-dimensional computer applications on a display in a three-dimensional viewing perspective. A two-dimensional bitmap is created for each respective computer application and applied to a three-dimensional geometry (i.e., primitive). In one embodiment, the three-dimensional geometry is a cube and each respective computer application is mapped onto a respective surface of the cube. The computer user has the ability to manipulate the orientation of the cube, via a computer mouse, for example, to view the different surfaces, and, thus, different computer applications mapped thereon. The user is further given the capability to manipulate or interact with each computer application on each respective surface of the cube. In another embodiment, two or more cubes could be employed for displaying the various computer applications running on the computer's processor. The user could also allocate a particular group or category of applications to each respective cube to accomplish different tasks.
Owner:INTEL CORP
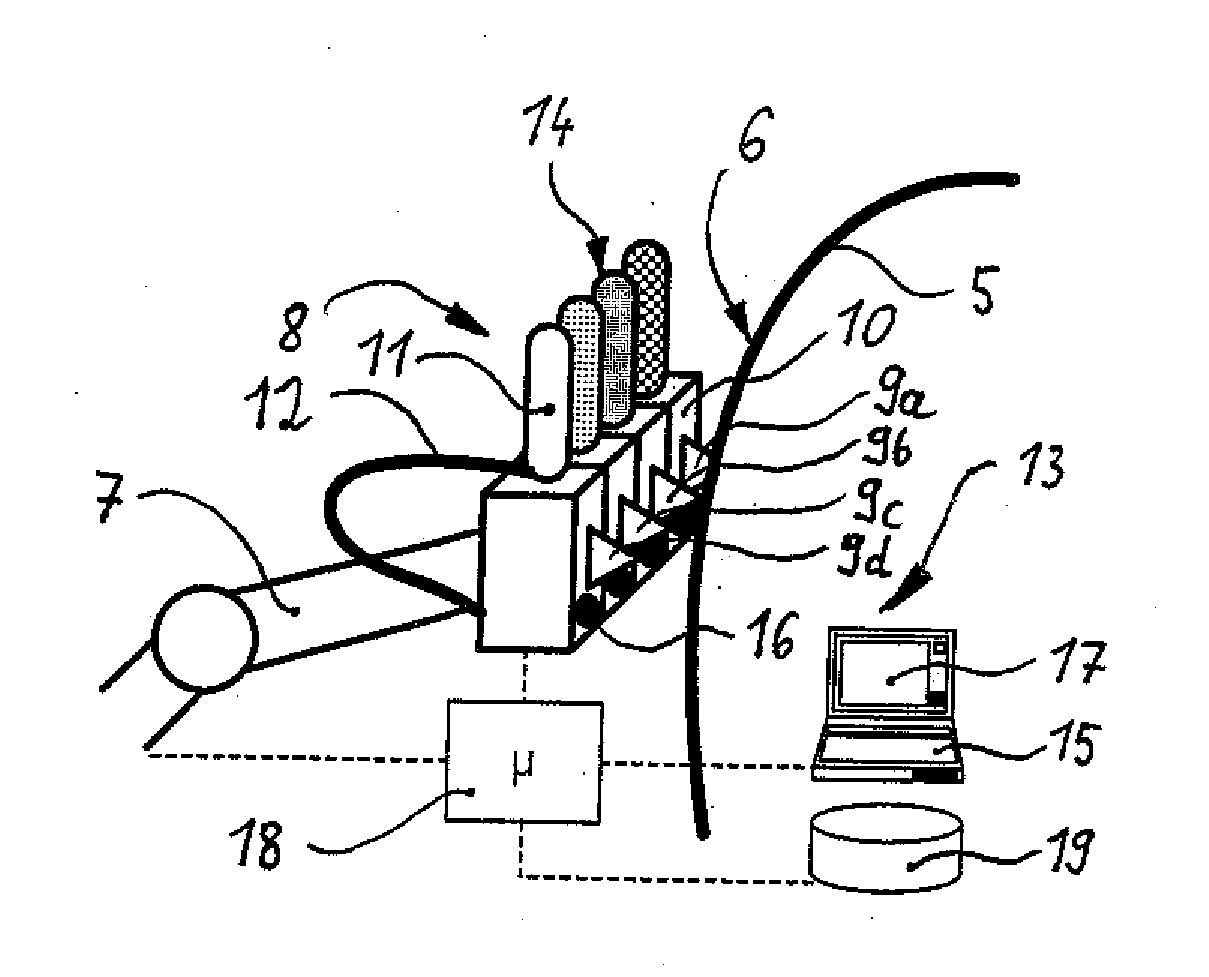
Device and method for painting curved outer surfaces of an aircraft
ActiveUS20100304009A1Durably applyShort production timeProgramme controlLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringAirplane
A device for painting a curved outer surface of an aircraft includes a paint applicator having a plurality of spray painting heads each assigned to one of a plurality of different base color supply units containing one of polyurethane aircraft paint and ink. The device further includes a spatially adjustable positioning device configured to move the paint applicator relative to the curved outer surface and at least one sensor device configured to determine a three-dimensional geometry of the curved outer surface. The device also includes a control unit configured to coordinate a movement of the positioning device with a paint output of the paint applicator, wherein the control unit is configured to alternately activate each of the plurality of spray painting heads so as to produce a picture motif so as to derive a two-dimensional driving geometry based on the three-dimensional geometry.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Nanoparticle-sized magnetic absorption enhancers having three-dimensional geometries adapted for improved diagnostics and hyperthermic treatment
InactiveUS20110105825A1Limiting collateral damageOvercome limitationsAntibacterial agentsBiocideThermal energyNanoparticle
Nanoparticle-sized magnetic absorption enhancers (MAEs) that exhibit a controlled response to a magnetic field, including a controlled mechanical response and inductive thermal response. The MAEs have a magnetic material that exhibits the inductive thermal response to the magnetic field and is embedded in a coating, such that the MAE conforms to a particular shape, e.g., a hemisphere, a dome or a shell, that is chosen to produce the desired controlled mechanical response of the entire MAE to the magnetic field. A targeting moiety for specifically binding the MAE to a pathogen target is also provided. The MAEs are preferably bound by a flexible linker to promote the desired mechanical response, which includes interactions between MAEs that are not bound to their pathogen target for the purpose of forming spheres, spherical shells, or generally spherical dimers. Such forms contain the thermal energy produced by the thermal inductive response of the magnetic material and thus reduce collateral healthy tissue damage during hyperthermic treatment. The inventing extends to appropriate apparatus and methods for diagnostics and hyperthermic treatments employing the MAEs.
Owner:QTERIS
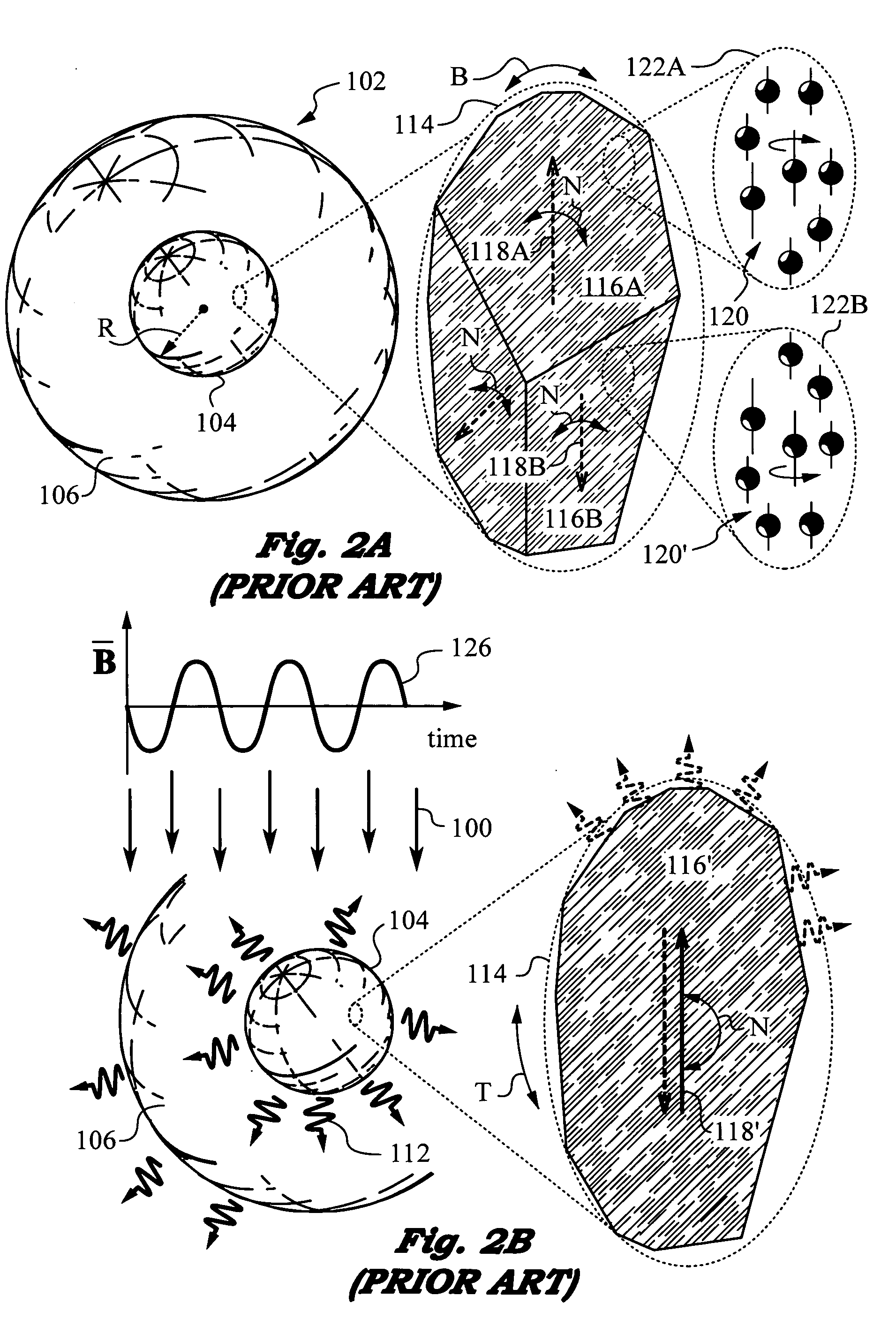
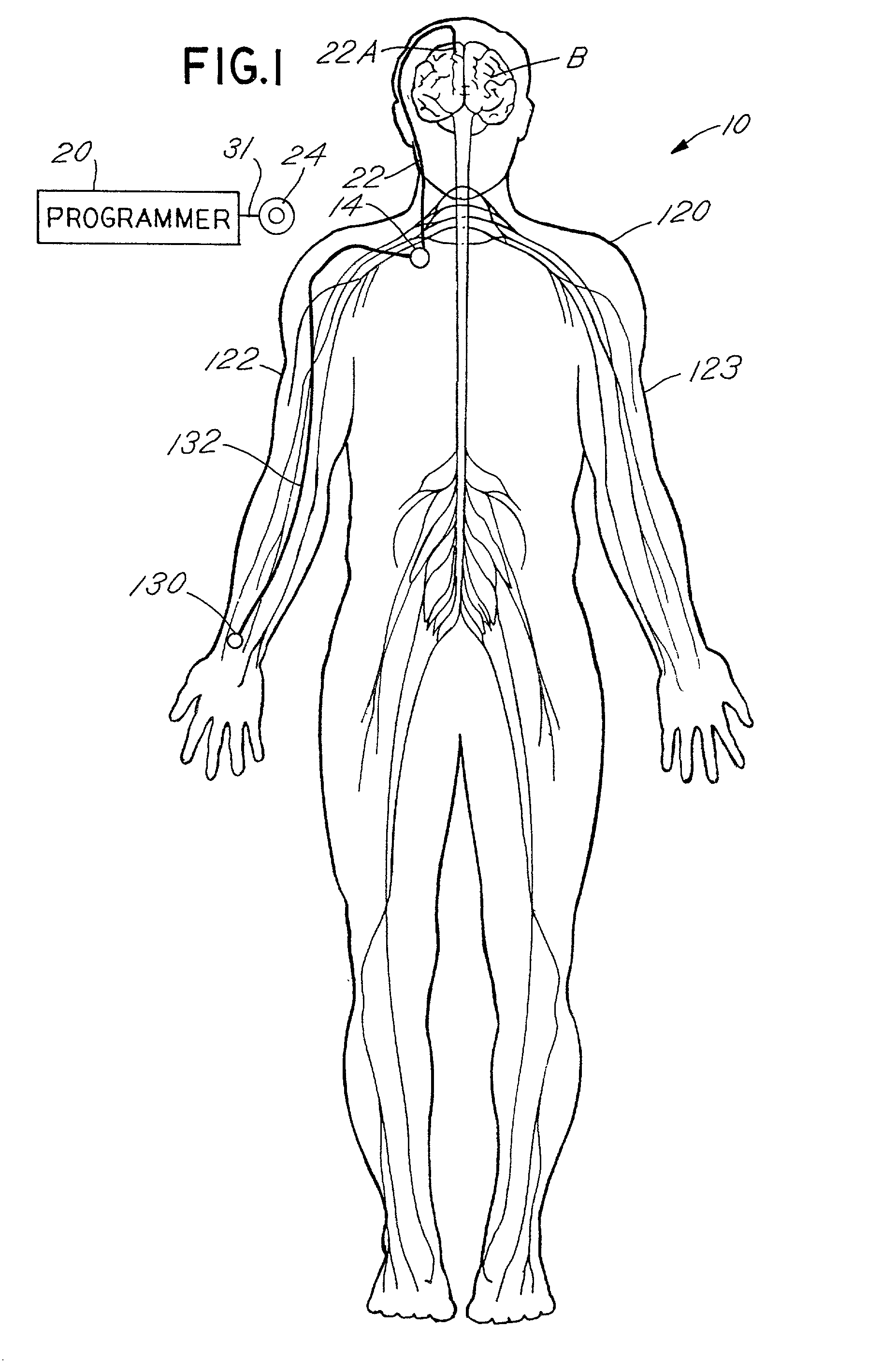
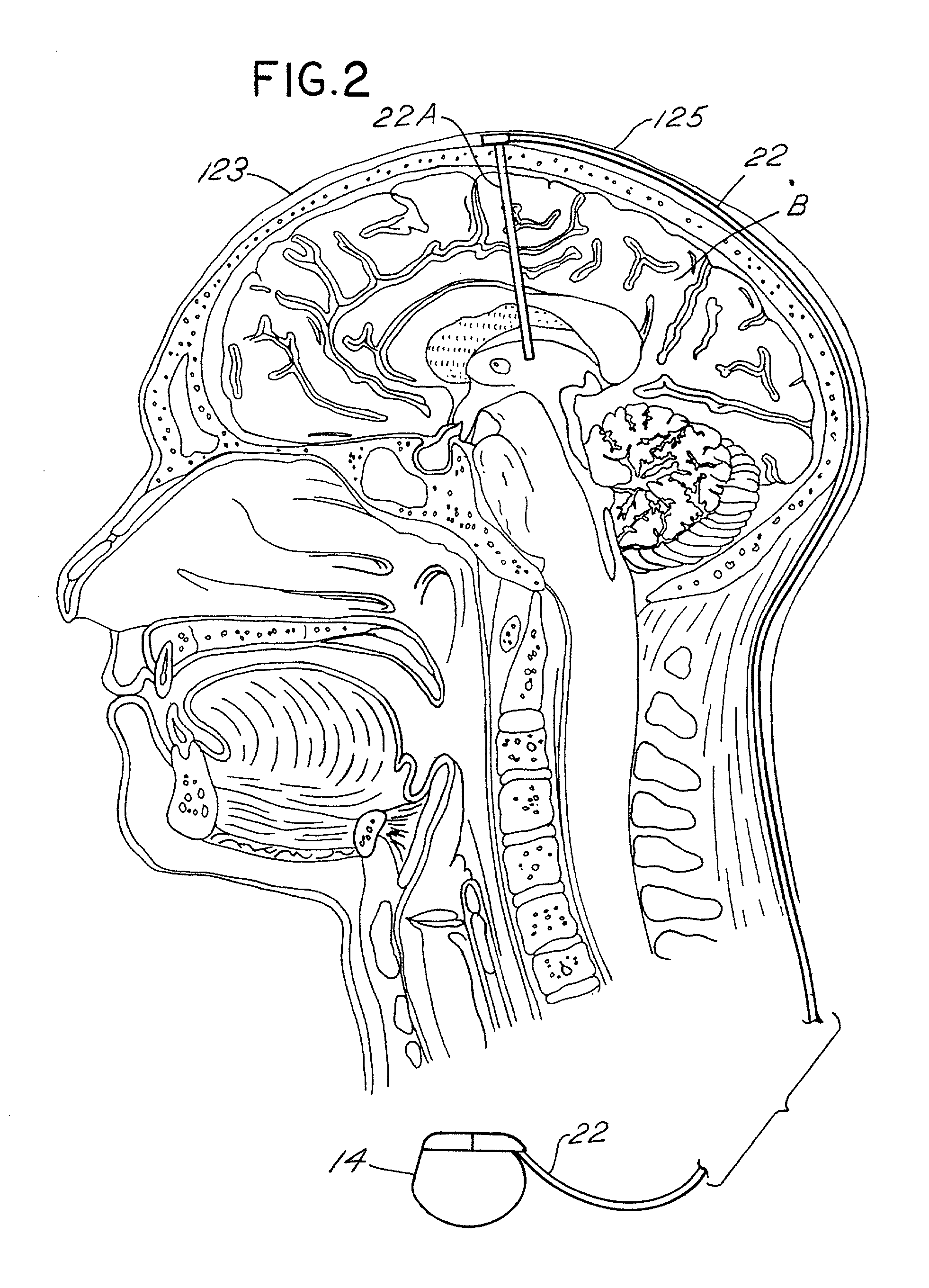
Techniques for selective activation of neurons in the brain, spinal cord parenchyma or peripheral nerve
Techniques capable of selectively affecting and adjusting a volume of neural tissue in the brain, parenchyma of the spinal cord, or a peripheral nerve are disclosed. A lumen having at least one opening at its distal end that is capable of directing a lead outwardly along a predetermined trajectory is preferred. The lumen is capable of accepting a plurality of leads that can project outward in different directions from the distal end of the lumen. The leads have one or more electrodes at its ends and are thereby configured by the lumen in accordance with a predetermined two- or three-dimensional geometry. Anode / cathode relationships may be established between the electrodes by the operator to stimulate the neural tissue surrounding these electrodes. The operator may also adjust the stimulation to selectively stimulate the desired portion of the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerve. Sensor feedback may be implemented to adjust the treatment therapy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Medical imaging method and system for providing a finite-element model
InactiveUS20110015514A1Reduce radiation doseMedical simulationDiagnostic recording/measuringElement modelBone structure
A method comprising: -providing acquisition data (34,38) of a patient, comprising acquisition data of a bone structure of the patient in a given position, providing a knowledge base (22,43,47), comprising data related to such bone structures, -determining a patient-specific position-specific finite-element model of the bone structure comprising: patient-specific three-dimensional geometry, patient-specific mechanical characteristics of the bone structure, and patient-specific position-specific mechanical load applied to the bone structure in the position.
Owner:ECOLE NAT SUPERIEURE DARTS & METIERSENSAM
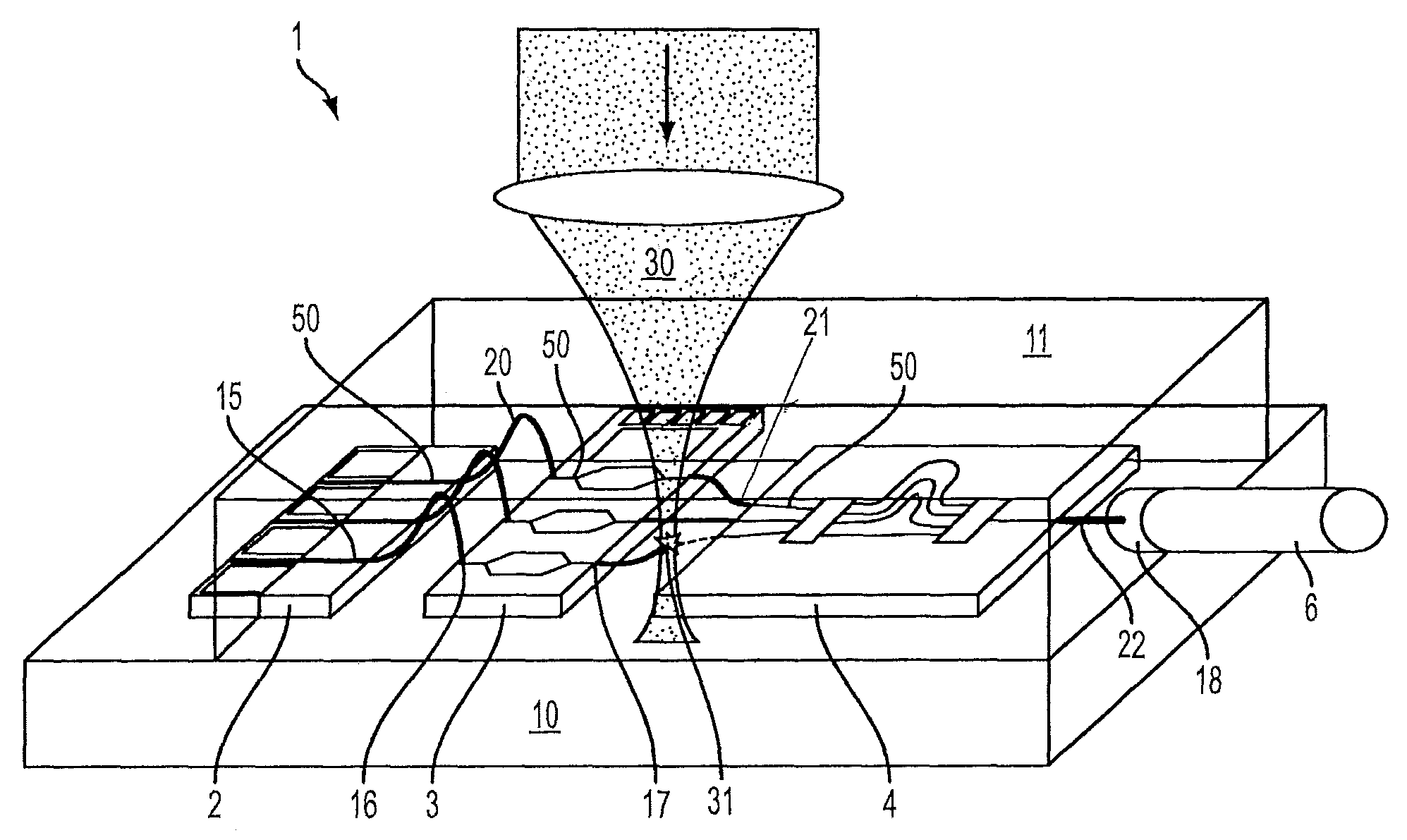
Method for producing photonic wire bonds
ActiveUS9034222B2Highly integratedIncrease the number ofOptical articlesCoupling light guidesResistLithographic artist
A method for making optical connections with optical waveguides includes mounting the optical waveguides or a device comprising the optical waveguides, on a component carrier. A partial region of the optical waveguides is embedded in a volume of resist material. Positions of the optical waveguides to be connected are detected with reference to a coordinate system using a measuring system. Favorable, three-dimensional geometries are determined for optical waveguide structures for connecting the optical waveguides to each other at predetermined connecting locations and the optical waveguide structure geometries are converted to a machine-readable dataset. The optical waveguide geometries in the volume of the resist material are three-dimensionally structured using a direct-writing lithography device operating on the basis of the machine-readable dataset. The structured resist material is treated using physical or chemical methods to form at least one optical waveguide structure having ends connected to predetermined connecting locations of the optical waveguides.
Owner:KARLSRUHER INST FUR TECH
Decompression of three-dimensional geometry data representing a regularly tiled surface portion of a graphical object
Methods and systems for compressing and decompressing 3-D geometry data which includes regularly tiled surface portions. One compression method includes representing a surface portion as a "vertex raster" by specifying an extent value and encoding the vertex parameter values of vertices within the surface portion. The extent value specifies the arrangement of vertices within the surface portion and allows the vertices to be properly assembled into drawing primitives during decompression. The encoded vertex parameter values (such as position, color, normals, z-displacement values, texture map coordinates, and surface material properties) may be encoded globally (by setting initial values and corresponding delta values), locally (on a per-vertex basis), or using a combination of these techniques. Absolute, delta, or delta-delta encoding may be utilized for these parameter values. Connectivity information may also be encoded using this compression method by specifying quad split bits and half-resolution edges. For graphical objects which include a plurality of adjacent surface portions, a step command may be used to allow reuse of data for more than one surface.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Optimum design method of non-bearing frame structure of light vehicle
InactiveCN104112050AIncreased bending stiffnessIncrease stiffnessSpecial data processing applicationsVehicle frameData file
The invention provides an optimum design method of a non-bearing frame structure of a light vehicle. The optimum design method comprises the steps of establishing a three-dimensional geometrical model of the original frame structure of the light vehicle by use of SolidWorks software and outputting the model in the IGES (Initial Graphics Exchange Specification) data file format, thereby obtaining the IGES model of the frame structure, next, reading the IGES model of the frame structure in Hypermesh software, performing geometrical processing and dividing finite element meshes by use of the Hypermesh software, and performing topological optimization on the cross beam structure of the frame by use of the structure optimization function of the Hypermesh software without changing the structural forms of the longitudinal beam and the attached seats of the frame, thereby realizing the optimum design of the arrangement position and the structural form of the cross beam structure. The optimum design method of the non-bearing frame structure of the light vehicle is capable of improving the bending rigidity and torsional rigidity of the frame of the light vehicle and the inherent frequency of the frame structure without increasing the weight of the frame structure, thereby ensuring that the frame has relatively high overall rigidity and improving the reliability, security, operation stability and vibration property of the vehicle.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com