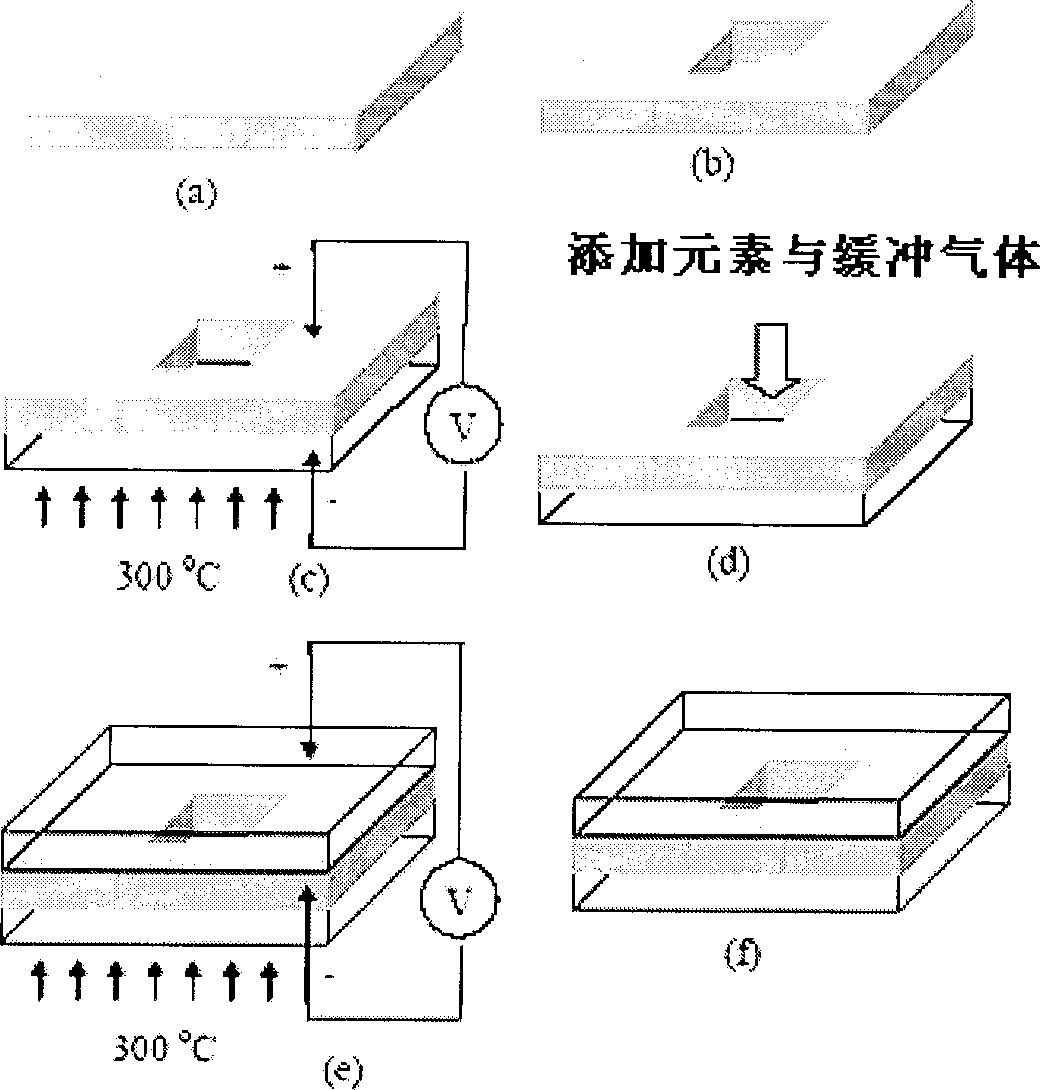
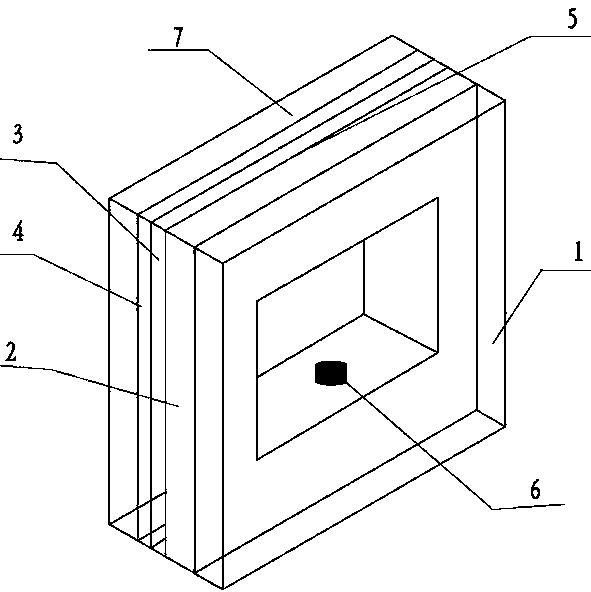
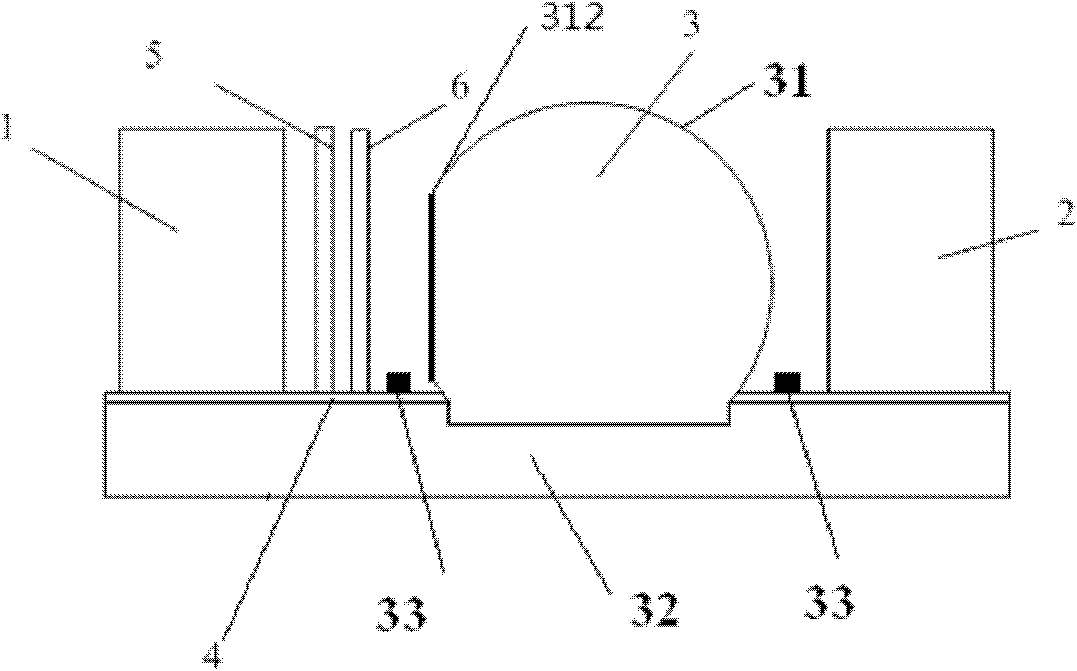
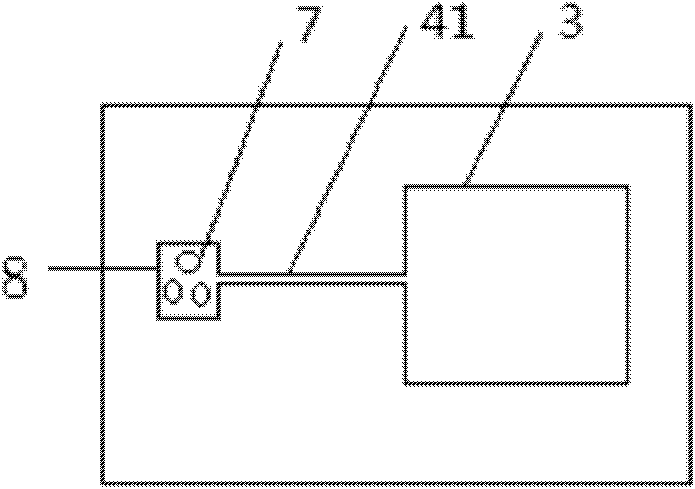
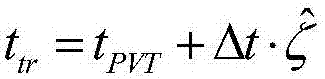Patents
Literature
39 results about "Chip-scale atomic clock" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A chip scale atomic clock (CSAC) is a compact, low-power atomic clock fabricated using techniques of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and incorporating a low-power semiconductor laser as the light source. The first CSAC physics package was demonstrated at NIST in 2003 , based on an invention made in 2001 . The work was funded by the US Department of Defense's Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) with the goal of developing a microchip-sized atomic clock for use in portable equipment. In military equipment it is expected to provide improved location and battlespace situational awareness for dismounted soldiers when the global positioning system is not available, but many civilian applications are also envisioned. Commercial manufacturing of these atomic clocks began in 2011. The CSAC, the world's smallest atomic clock, is 4 x 3.5 x 1 cm (1.5 x 1.4 x 0.4 inches) in size, weighs 35 grams, consumes only 115 mW of power, and can keep time to within 100 microseconds per day after several years of operation.
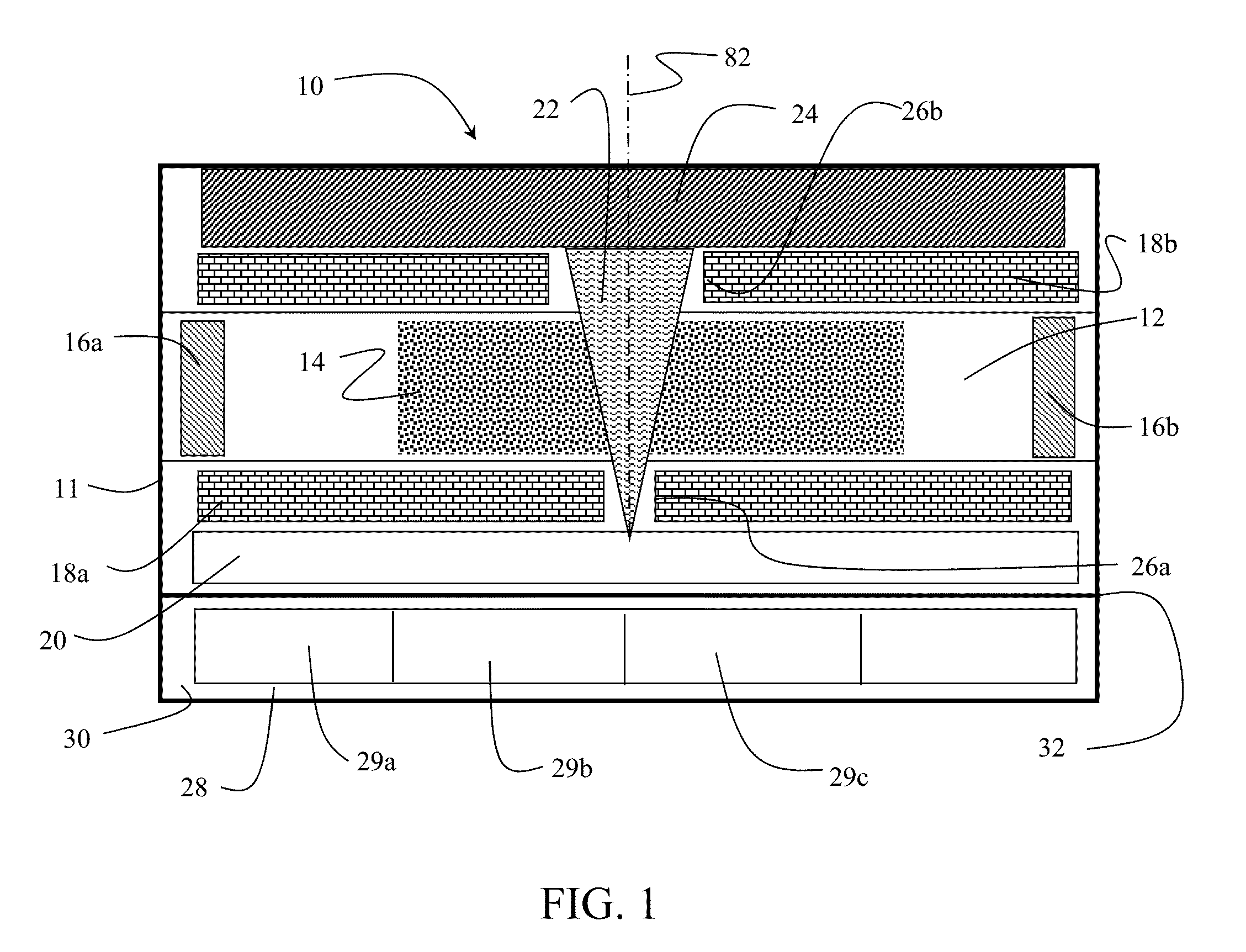
Chip-scale atomic clock (CSAC) and method for making same
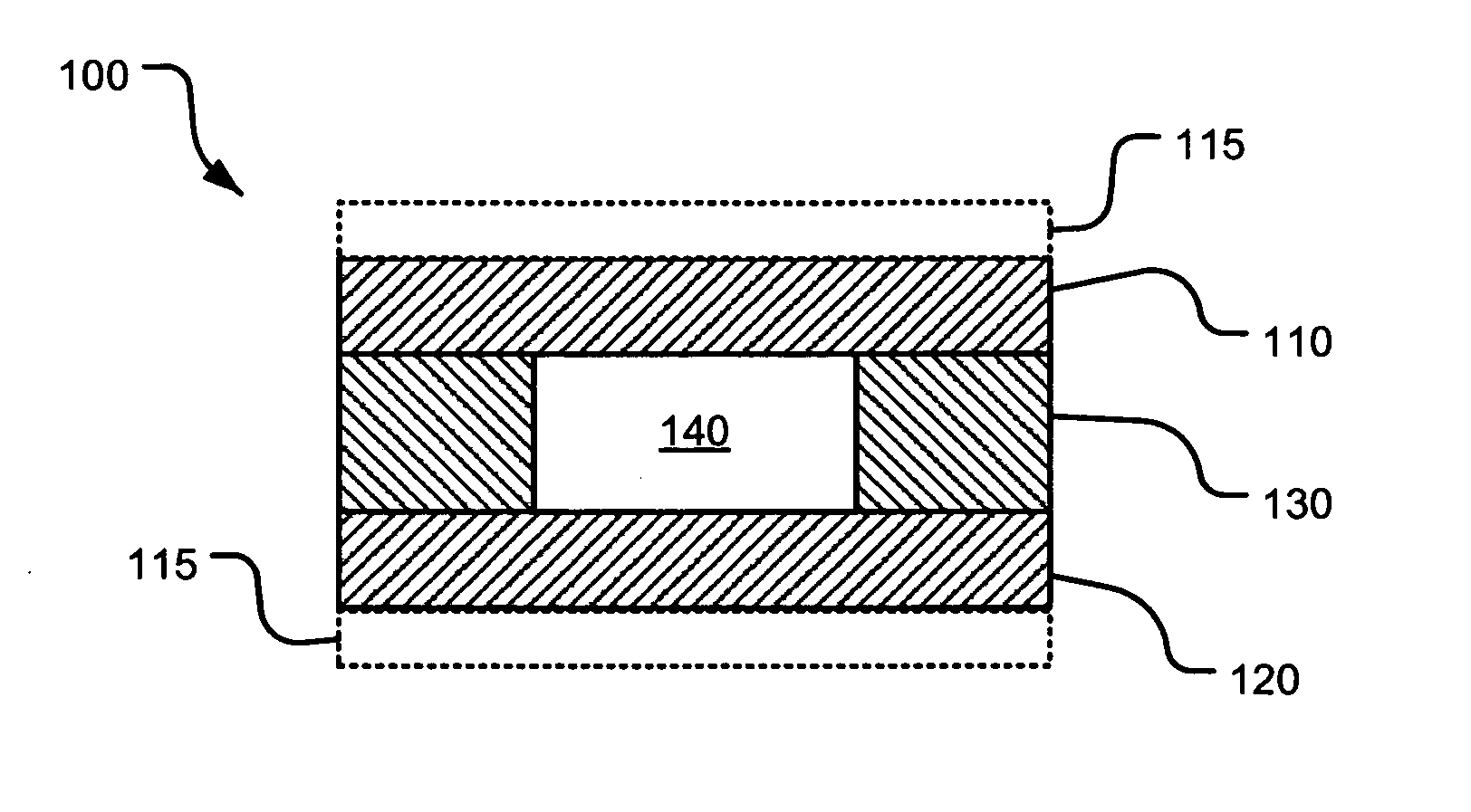
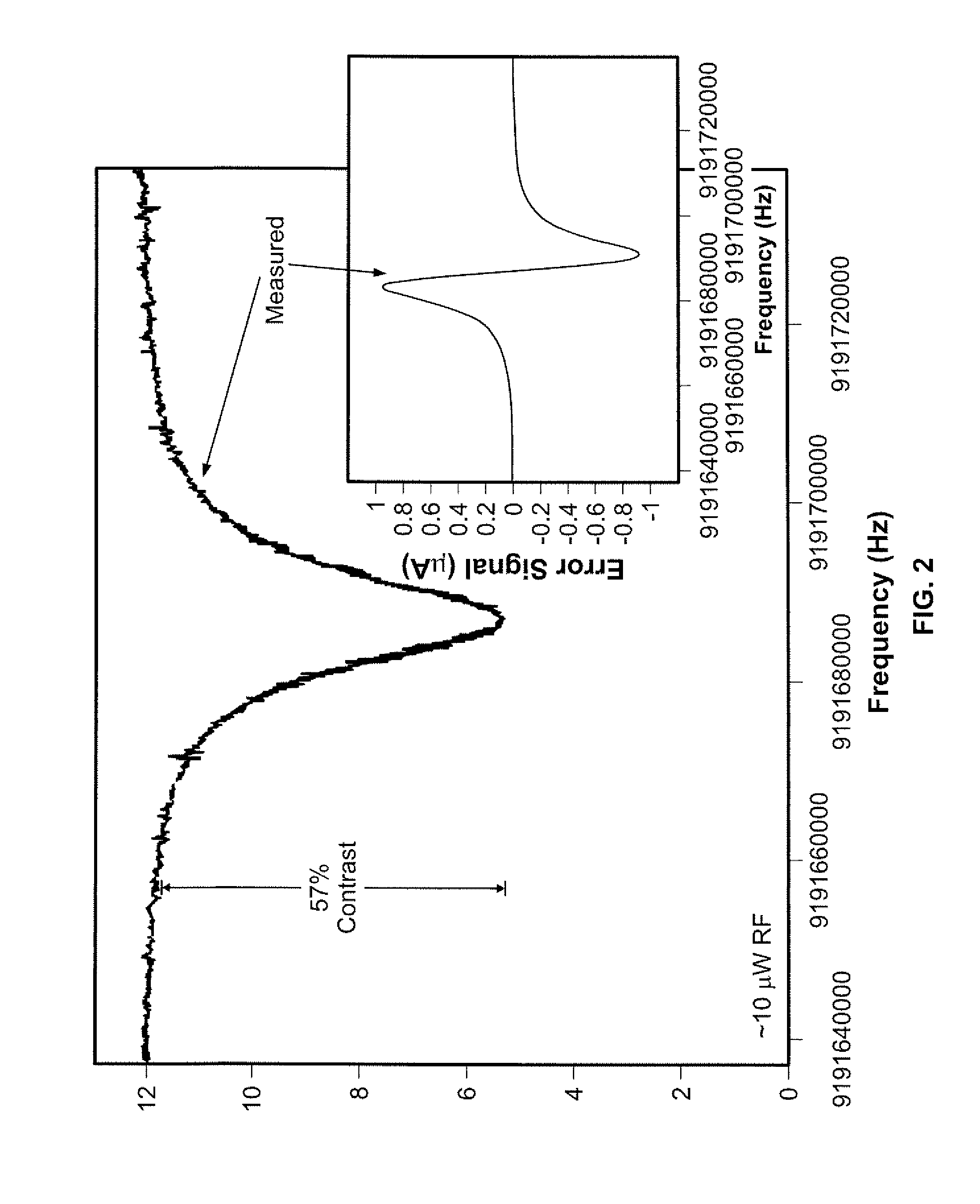
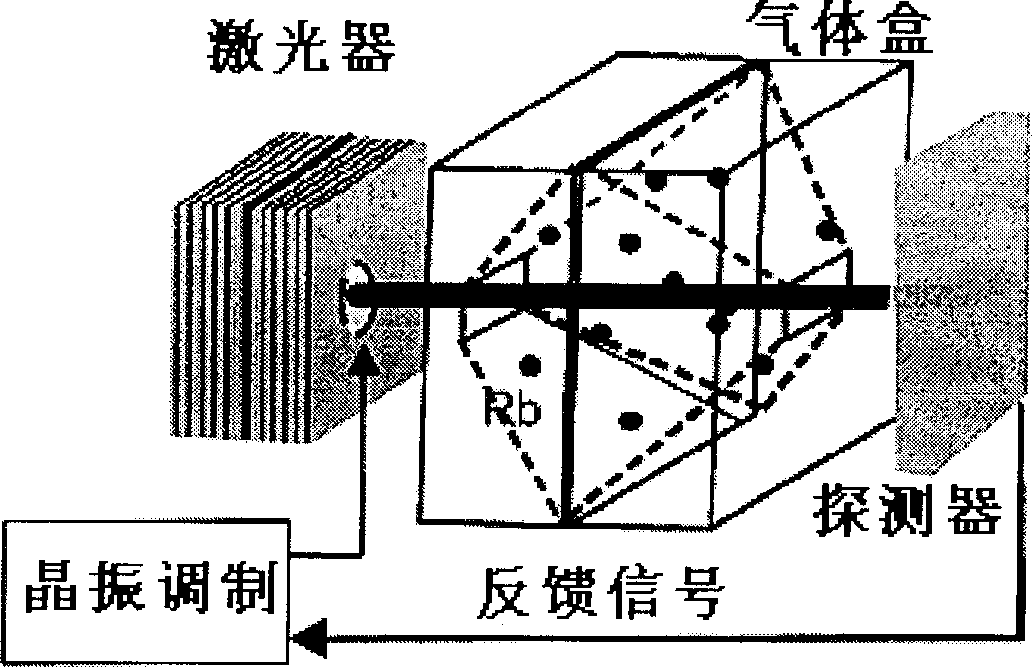
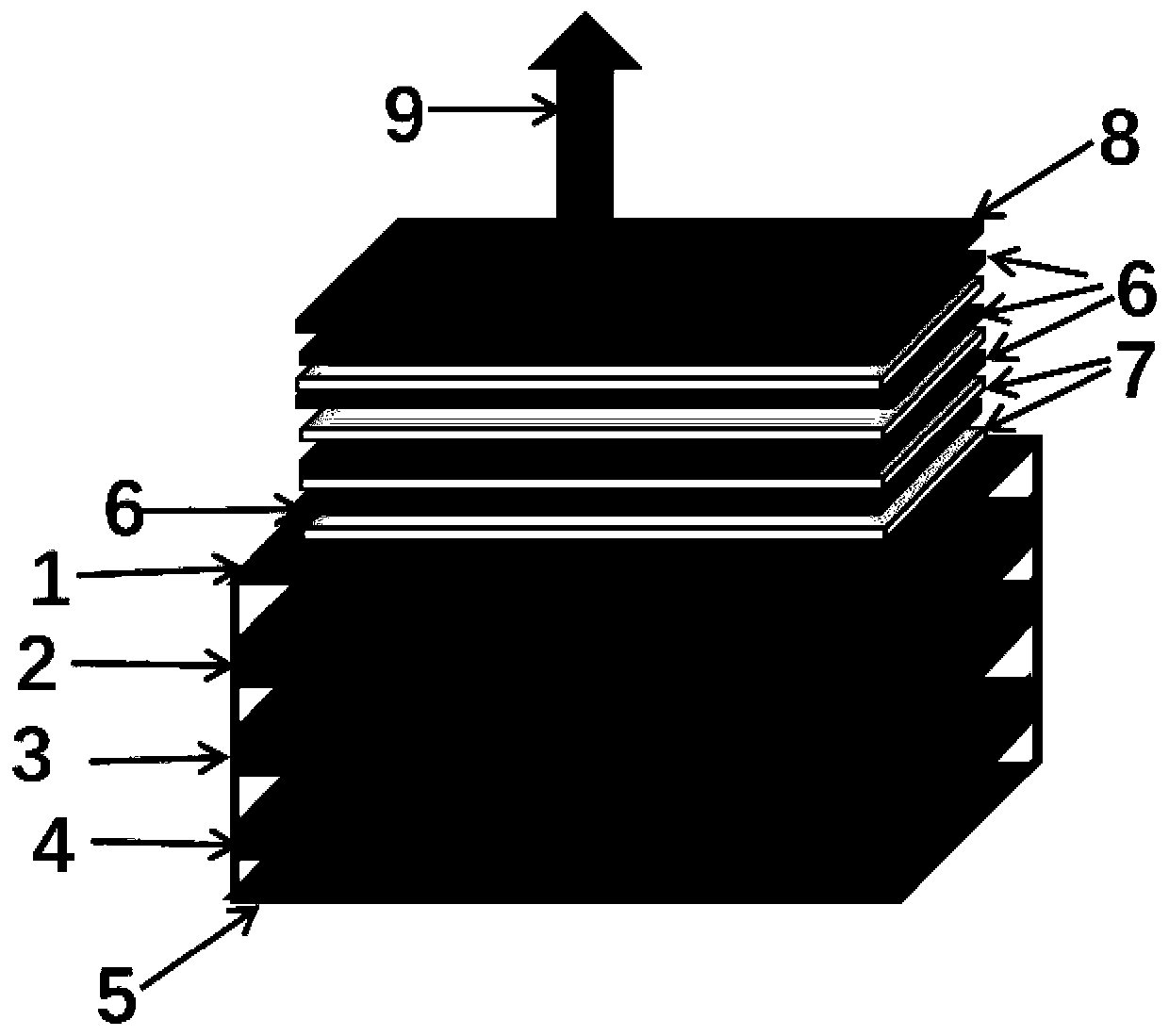
A clock including: a portable, at least partially evacuated housing; a cell being positioned within the housing and including an internal cavity having interior dimensions each less than about 1 millimeter, an intra-cavity pressure of at least about 760 Torr, and containing a metal atomic vapor; an electrical to optical energy converter being positioned within the housing to emit light through the metal atomic vapor; an optical energy intensity detector being positioned within the housing to receive the light emitted by the converter through the metal atomic vapor; at least one conductive winding around the cavity to stabilize the magnetic field experienced in the cavity dependently upon the detector; and, an output to provide a signal from the housing dependently upon the detector detecting the light emitted by the converter through the metal atomic vapor.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
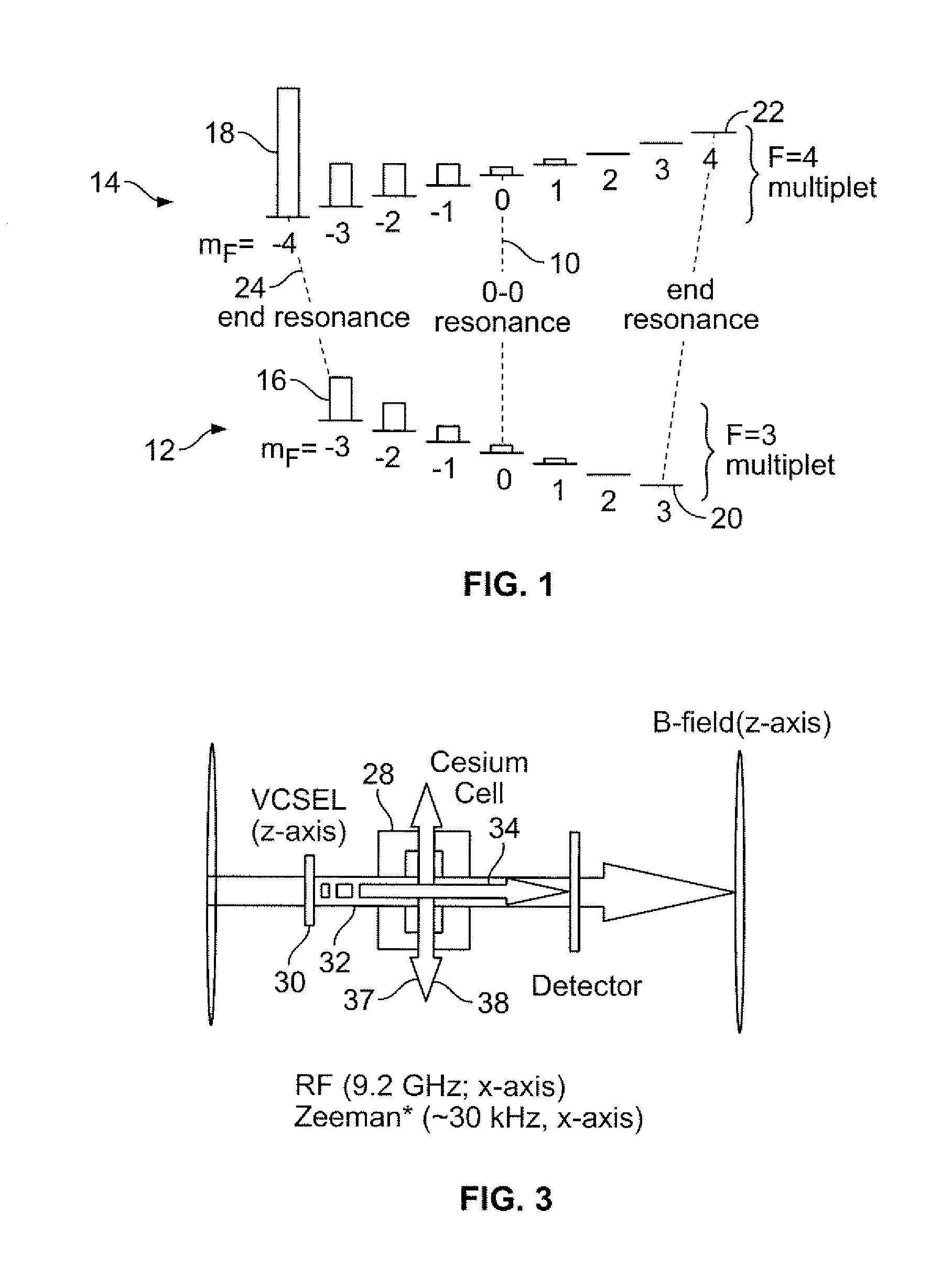
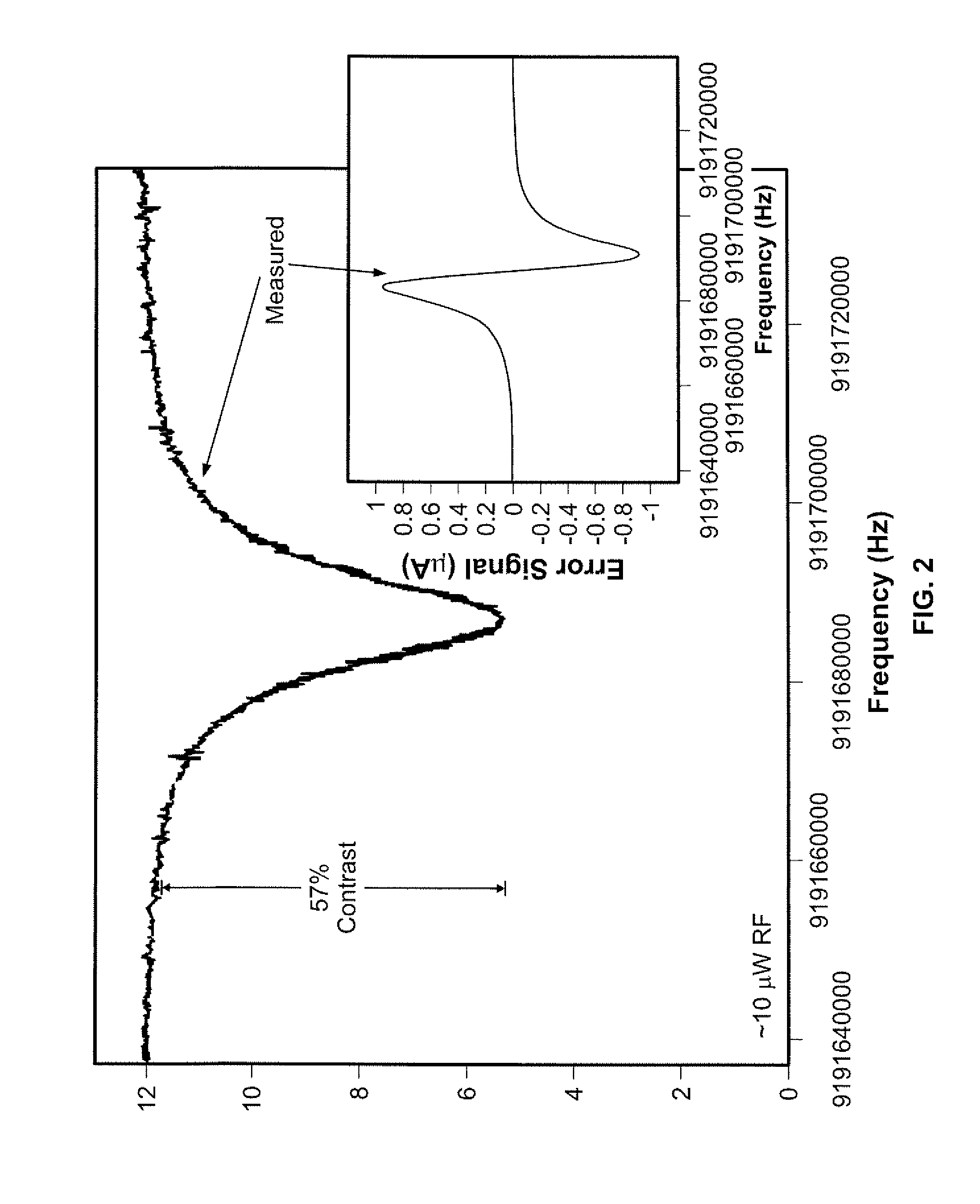
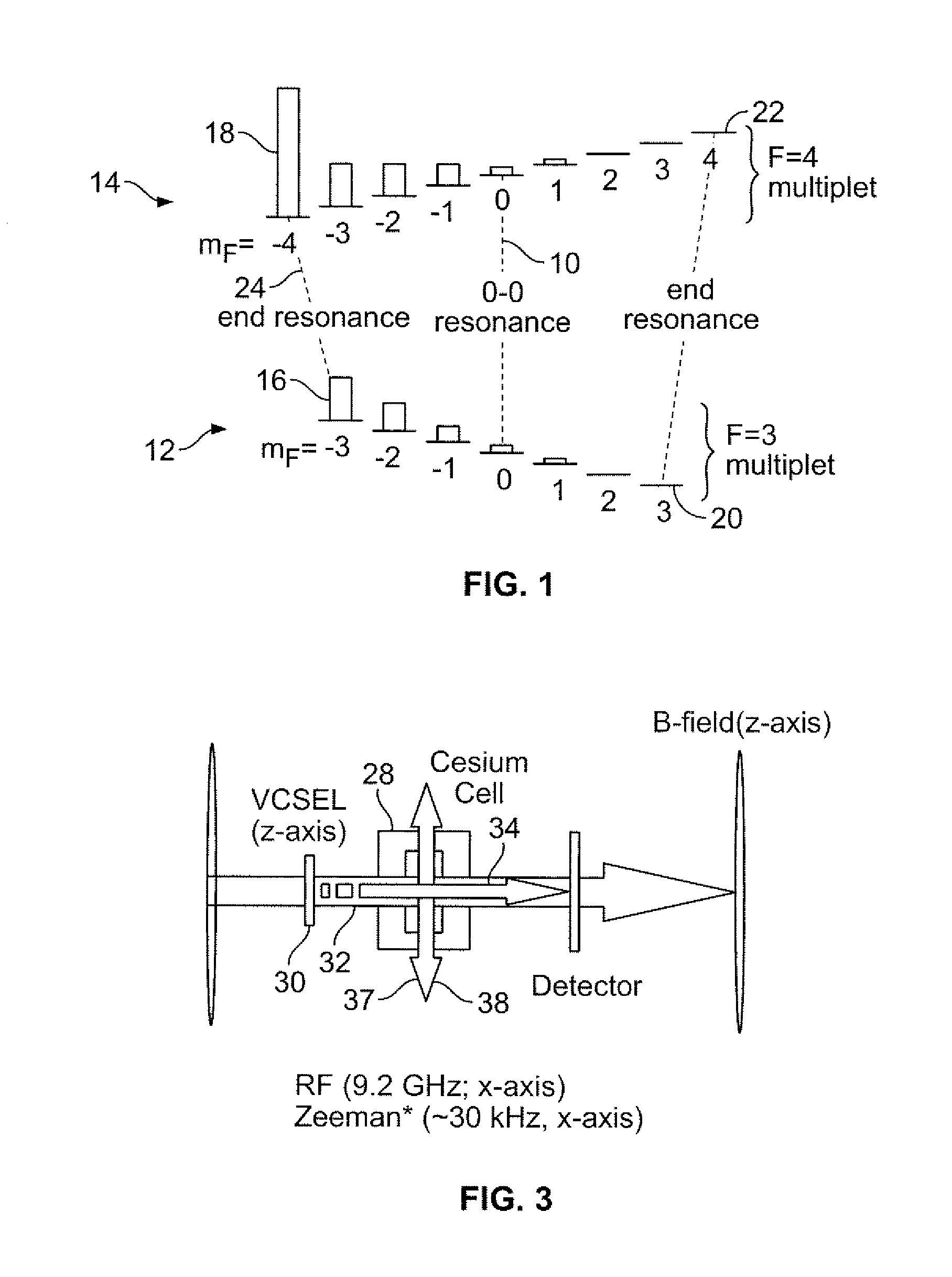
Batch-fabricated, rf-interrogated, end transition, chip-scale atomic clock
InactiveUS20070247241A1Increased signal noiseApparatus using atomic clocksPulse automatic controlThermal isolationVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
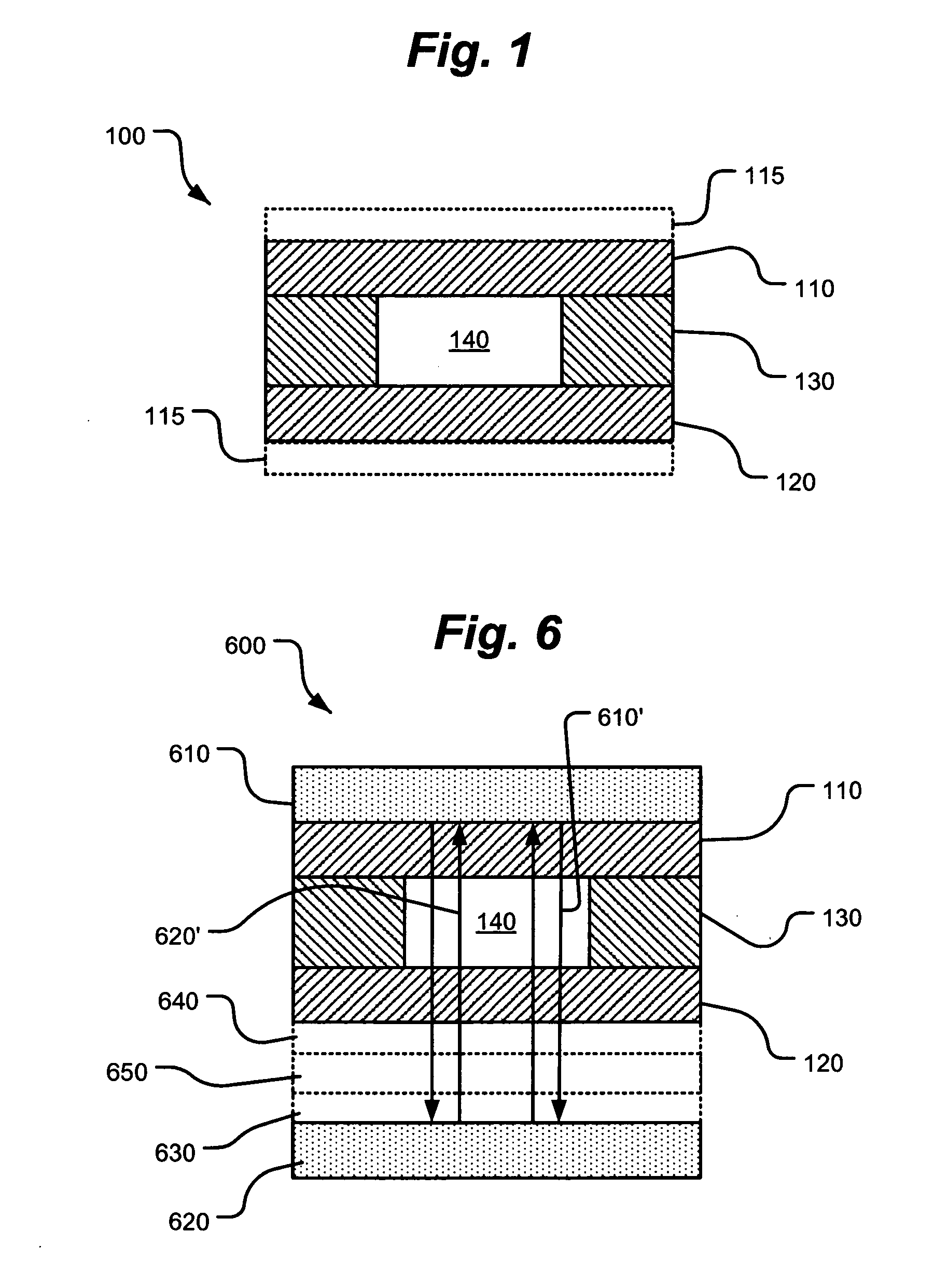
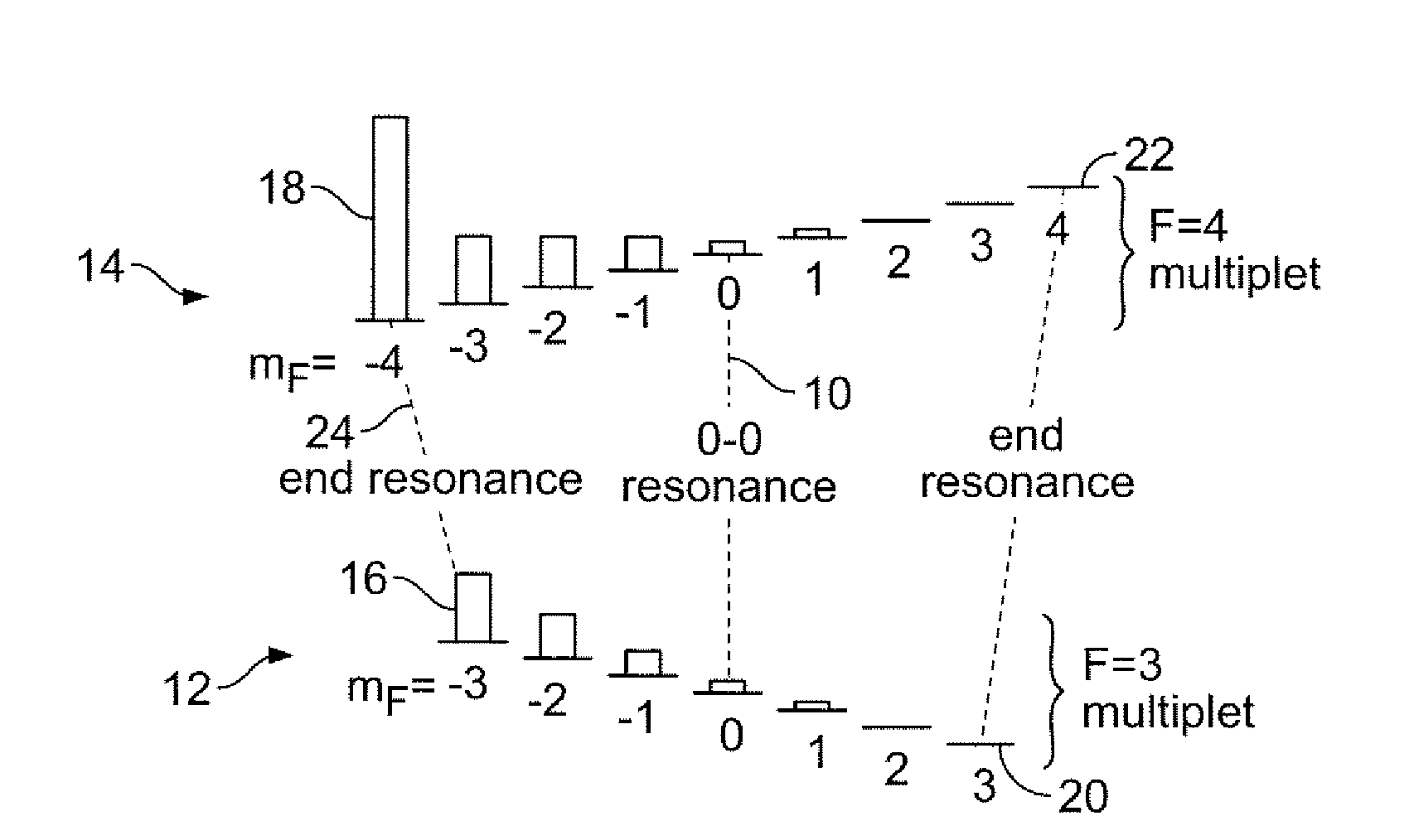
A chip scale atomic clock is disclosed that provides a low power atomic time / frequency reference that employs direct RF-interrogation on an end-state transition. The atomic time / frequency reference includes an alkali vapor cell containing alkali atoms, preferably cesium atoms, flex circuits for physically supporting, heating, and thermally isolating the alkali vapor cell, a laser source for pumping alkali atoms within the alkali vapor cell into an end resonance state by applying an optical signal along a first axis, a photodetector for detecting a second optical signal emanating from the alkali vapor cell along the first axis, a pair of RF excitation coils for applying an RF-interrogation signal to the alkali atoms along a second axis perpendicular to the first axis, a pair of bias coils for applying a uniform DC magnetic field along the first axis, and a pair of Zeeman coils for applying a Zeeman interrogation signal to the alkali atoms and oriented and configured to apply a time-varying magnetic field along the second axis through the alkali vapor cell. Another flex circuit is used for physically supporting the laser source, for heating the laser source, and for providing thermal isolation of the laser source. The laser source can be a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VSCEL). The bias coils can be Helmholtz coils.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Batch-fabricated, RF-interrogated, end transition, chip-scale atomic clock
InactiveUS7468637B2Increased signal noiseApparatus using atomic clocksPulse automatic controlVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserThermal isolation
A chip scale atomic clock is disclosed that provides a low power atomic time / frequency reference that employs direct RF-interrogation on an end-state transition. The atomic time / frequency reference includes an alkali vapor cell containing alkali atoms, preferably cesium atoms, flex circuits for physically supporting, heating, and thermally isolating the alkali vapor cell, a laser source for pumping alkali atoms within the alkali vapor cell into an end resonance state by applying an optical signal along a first axis, a photodetector for detecting a second optical signal emanating from the alkali vapor cell along the first axis, a pair of RF excitation coils for applying an RF-interrogation signal to the alkali atoms along a second axis perpendicular to the first axis, a pair of bias coils for applying a uniform DC magnetic field along the first axis, and a pair of Zeeman coils for applying a Zeeman interrogation signal to the alkali atoms and oriented and configured to apply a time-varying magnetic field along the second axis through the alkali vapor cell. Another flex circuit is used for physically supporting the laser source, for heating the laser source, and for providing thermal isolation of the laser source. The laser source can be a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VSCEL). The bias coils can be Helmholtz coils.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Alkali metal-wax micropackets for alkali metal handling
ActiveUS7666485B2Inexpensive and flexible manufacturingEasy to operateEnvelopes/bags making machineryApparatus using atomic clocksWaxPhysical chemistry
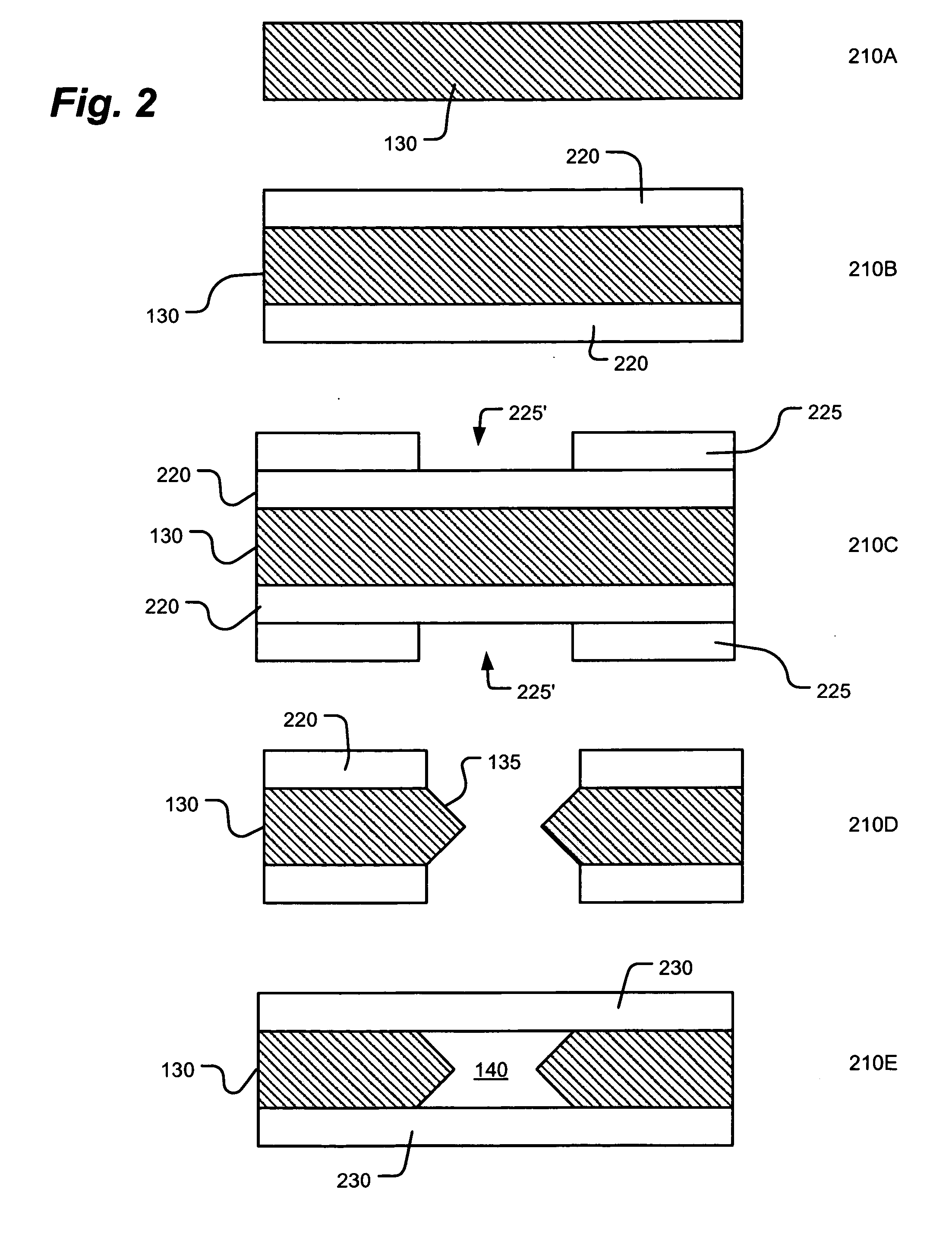
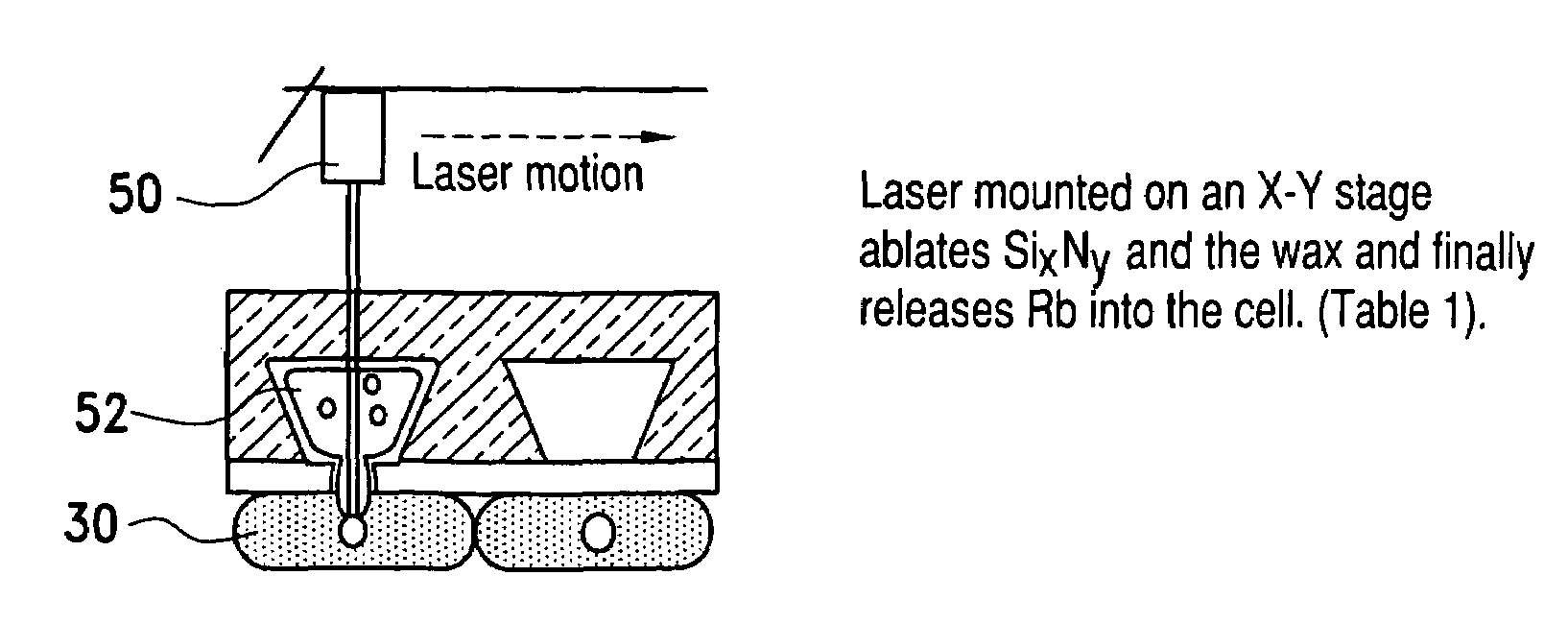
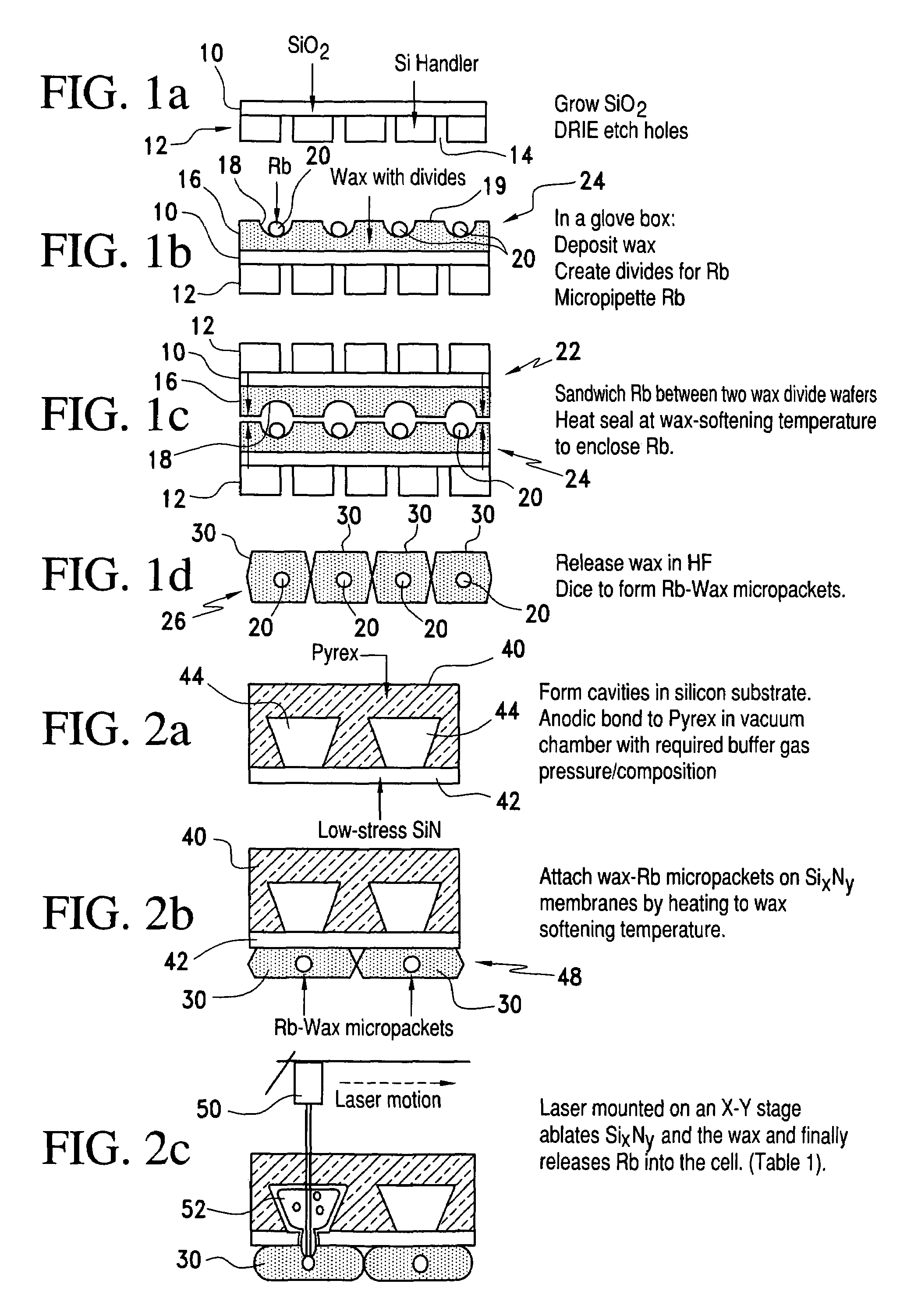
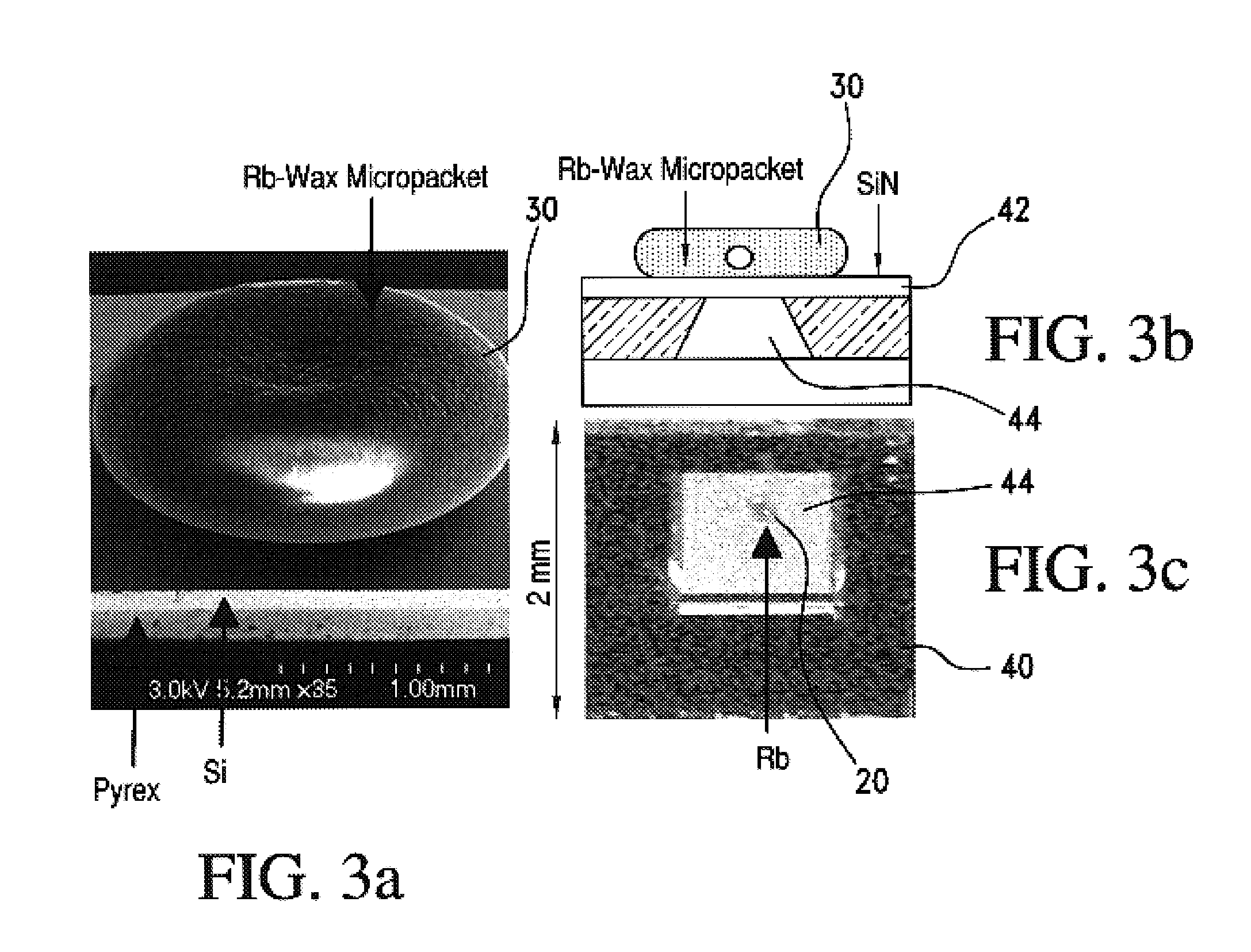
A method of making alkali-metal vapor cells by first forming microscale-wax micropackets with alkali metals inside allows fabrication of vapor cells at low cost and in a batch fabricated manner. Alkali metals are enclosed in a chemically inert wax to preform alkali metal-wax micropackets, keeping the alkali metals from reacting with the ambient surroundings during the vapor cell fabrication. This enables the deposition of precise amounts of pure alkali metal inside the vapor cells. Laser ablation of the alkali metal-wax micropackets provides a simple and effective way of releasing the enclosed metal. The method reduces the cost of making chip-scale atomic clocks and allows shipping of alkali vapor packets without contamination issues, thereby creating a technology for alkali-metal vendors to provide small packets of alkali metals.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
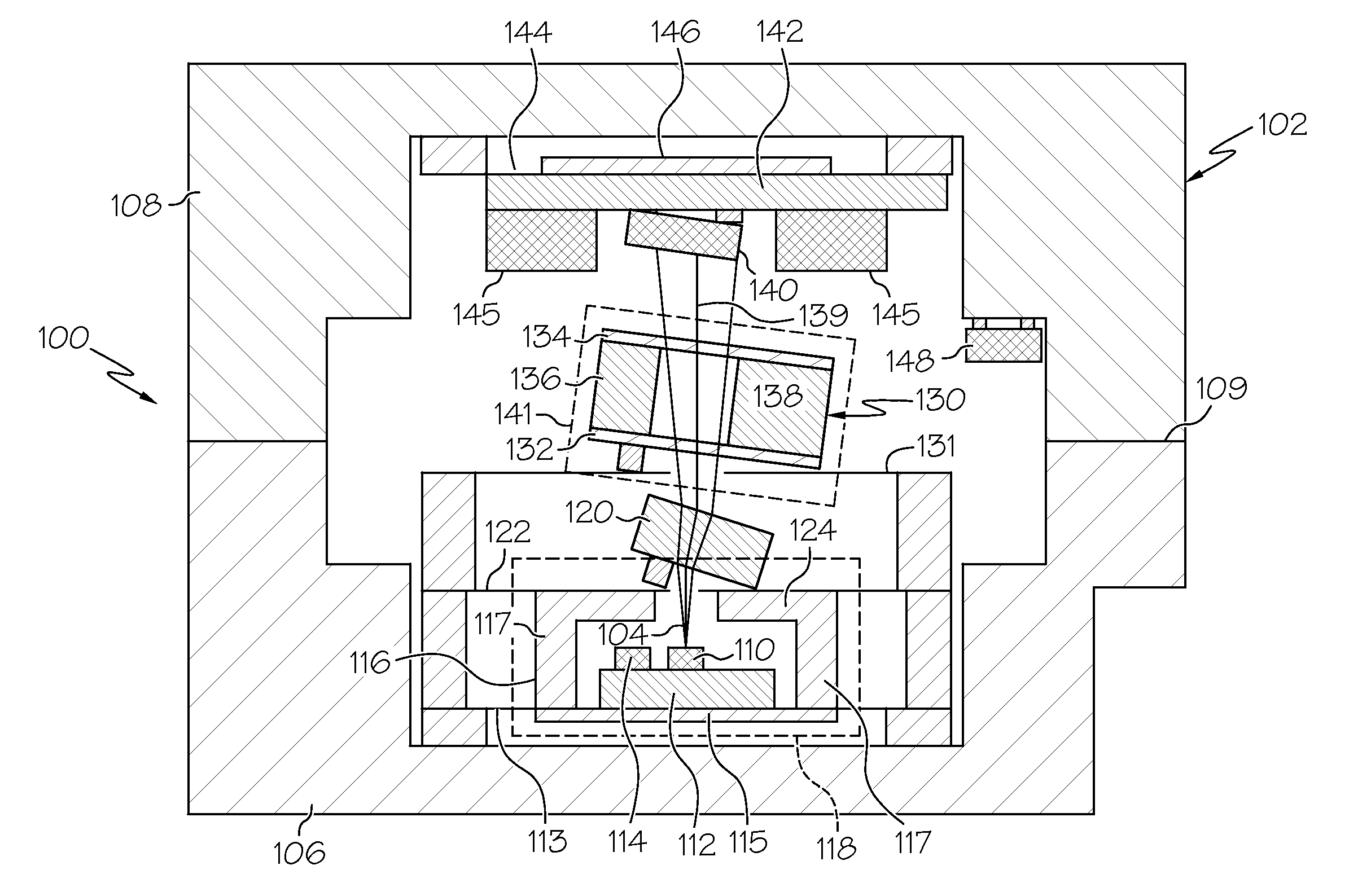
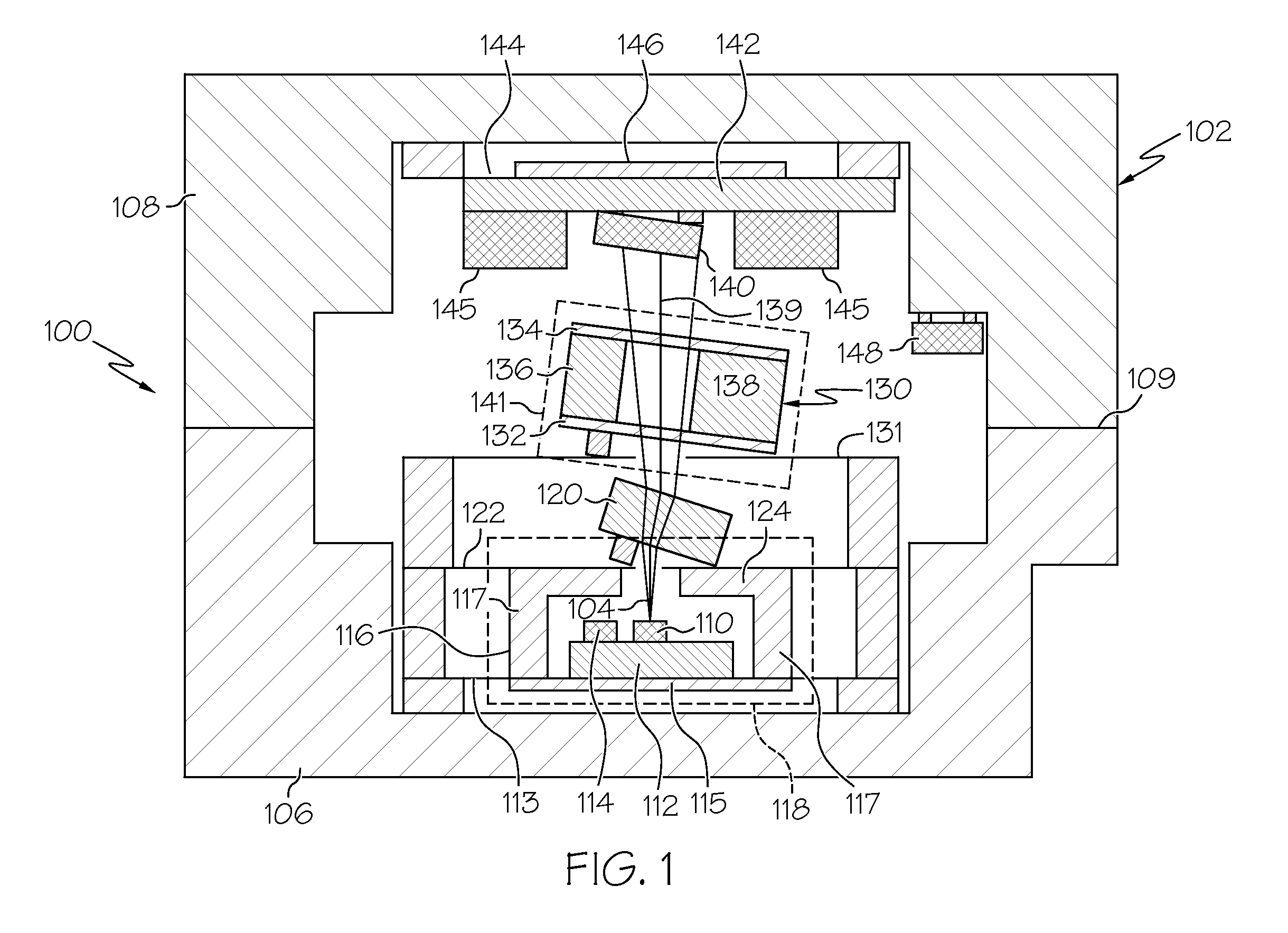
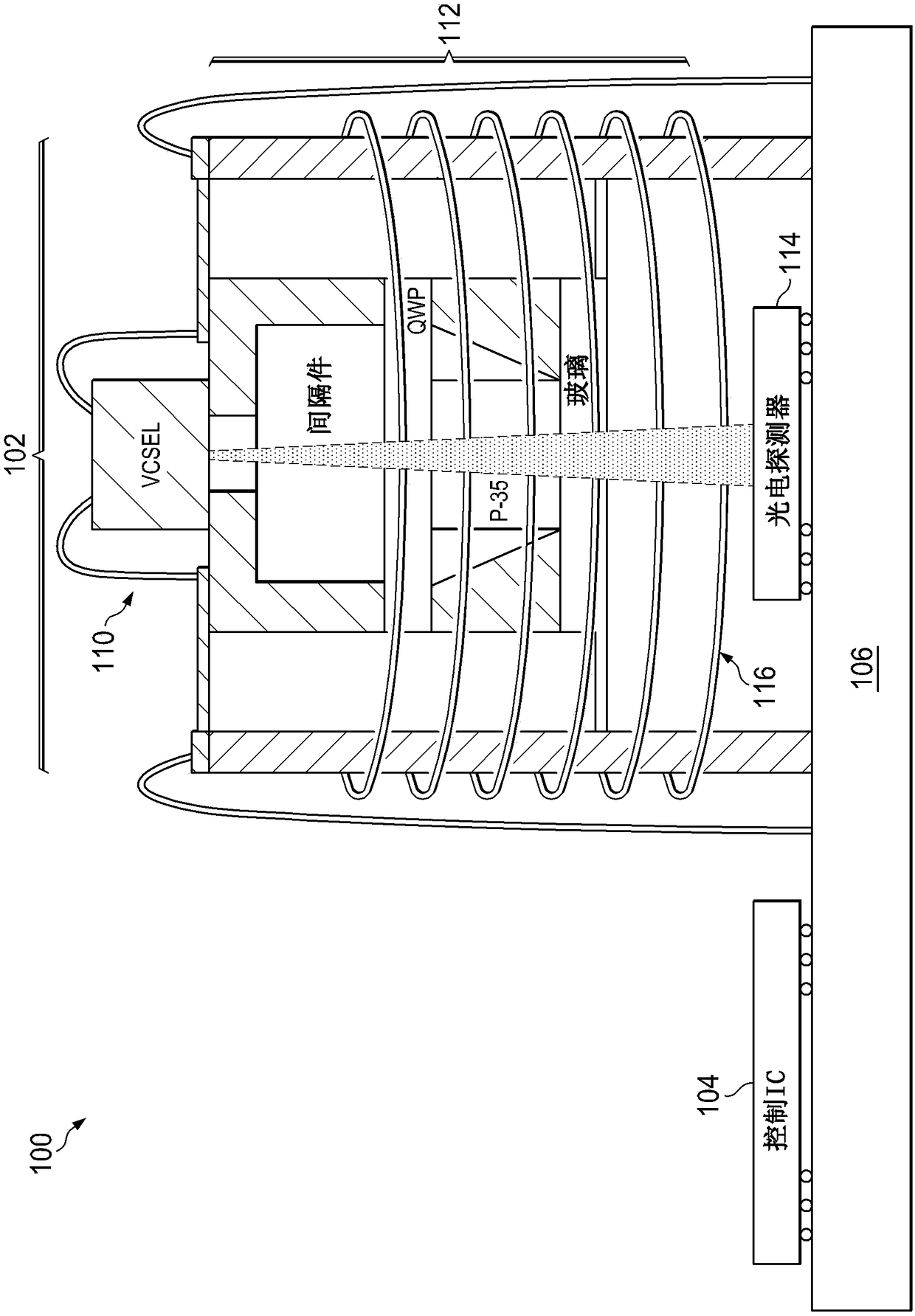
Chip-scale atomic clock with two thermal zones
ActiveUS20110187466A1Semiconductor laser structural detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceThermodynamicsOptical communication
A chip-scale atomic clock comprises a physics package and a laser die located in a first thermal zone of the physics package. A quarter wave plate is mounted in the physics package and is in optical communication with the laser die. A vapor cell is mounted in the physics package and is in optical communication with the quarter wave plate. The vapor cell is located in a second thermal zone that is independent from the first thermal zone. An optical detector is mounted in the physics package and is in optical communication with the vapor cell. The first thermal zone provides a first operation temperature at a first stability point associated with the laser die, and the second thermal zone provides a second operation temperature at a second stability point associated with the vapor cell.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
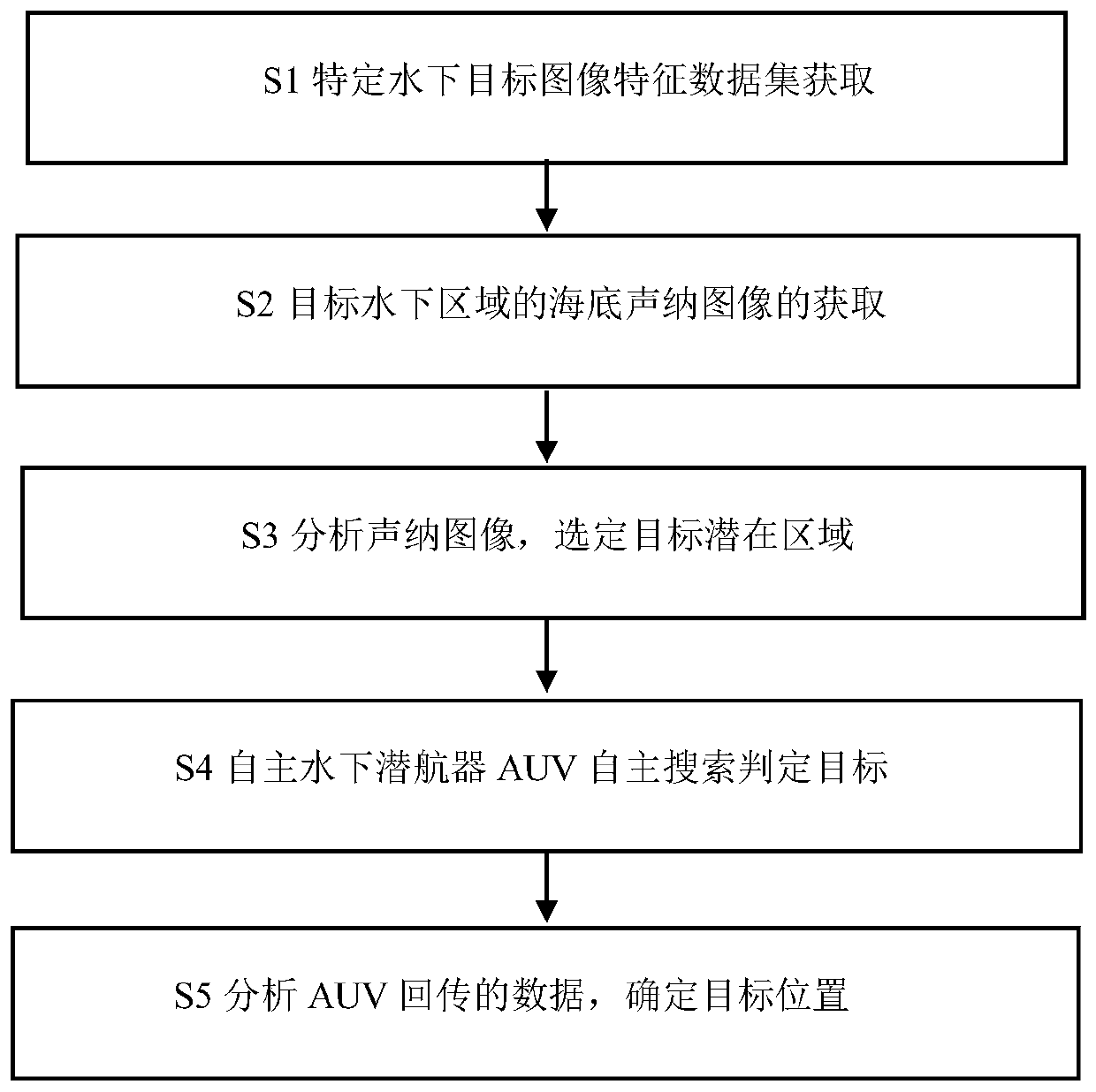
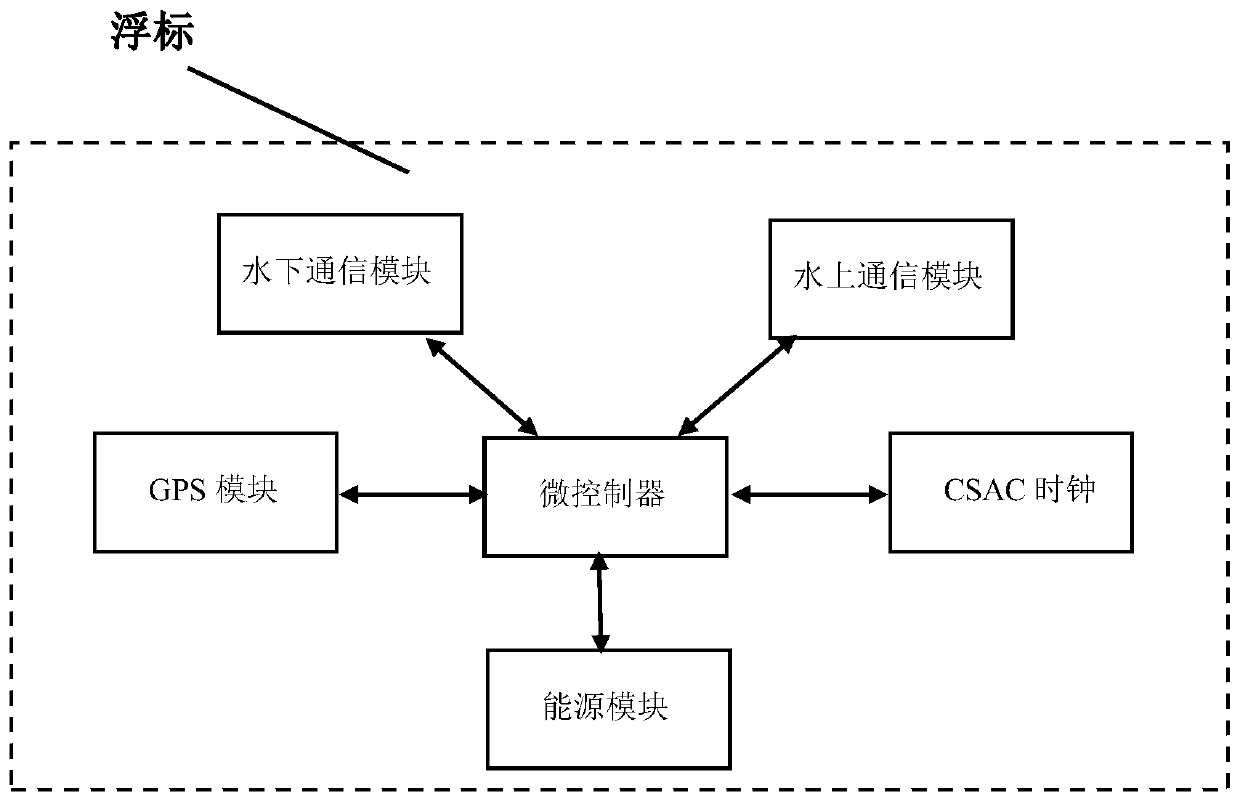
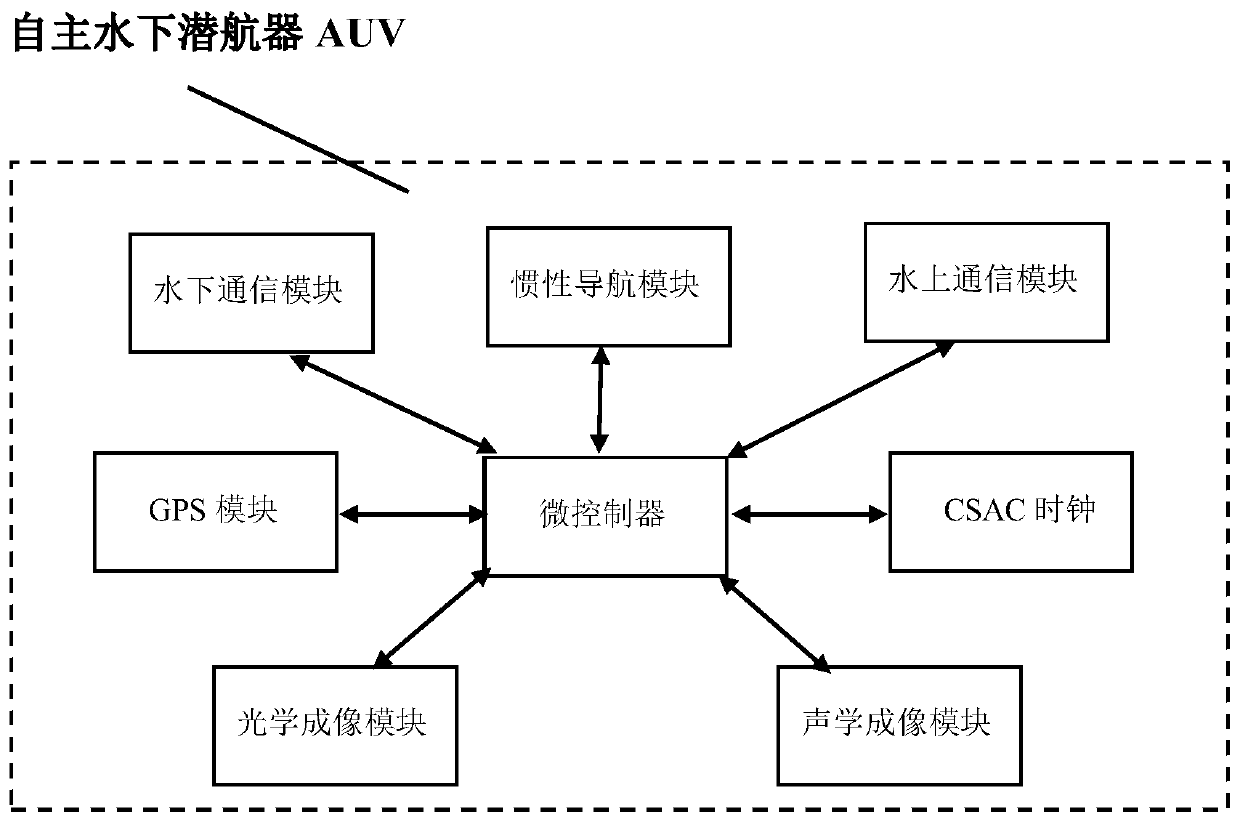
Method for automatically searching and positioning specific underwater target
ActiveCN109856638AHigh positioning accuracyConvenient, efficient and comprehensive collectionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature setComputer science
The invention discloses a method for automatically searching and positioning a specific underwater target. An autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) serves as a movable sonar signal receiving transducerarray, thus underwater sonar images are collected more conveniently, more efficiently and more comprehensively, the positioning precision of the AUV is improved through an EKF-SLAM algorithm and a chip-scale atomic clock (CSAC), an optical and acoustic image data feature set of the specific underwater target is formed by applying machine learning, possible target data are transmitted back to a mother ship for manual secondary judgment after the AUV is subjected to feature identification, and the target searching efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
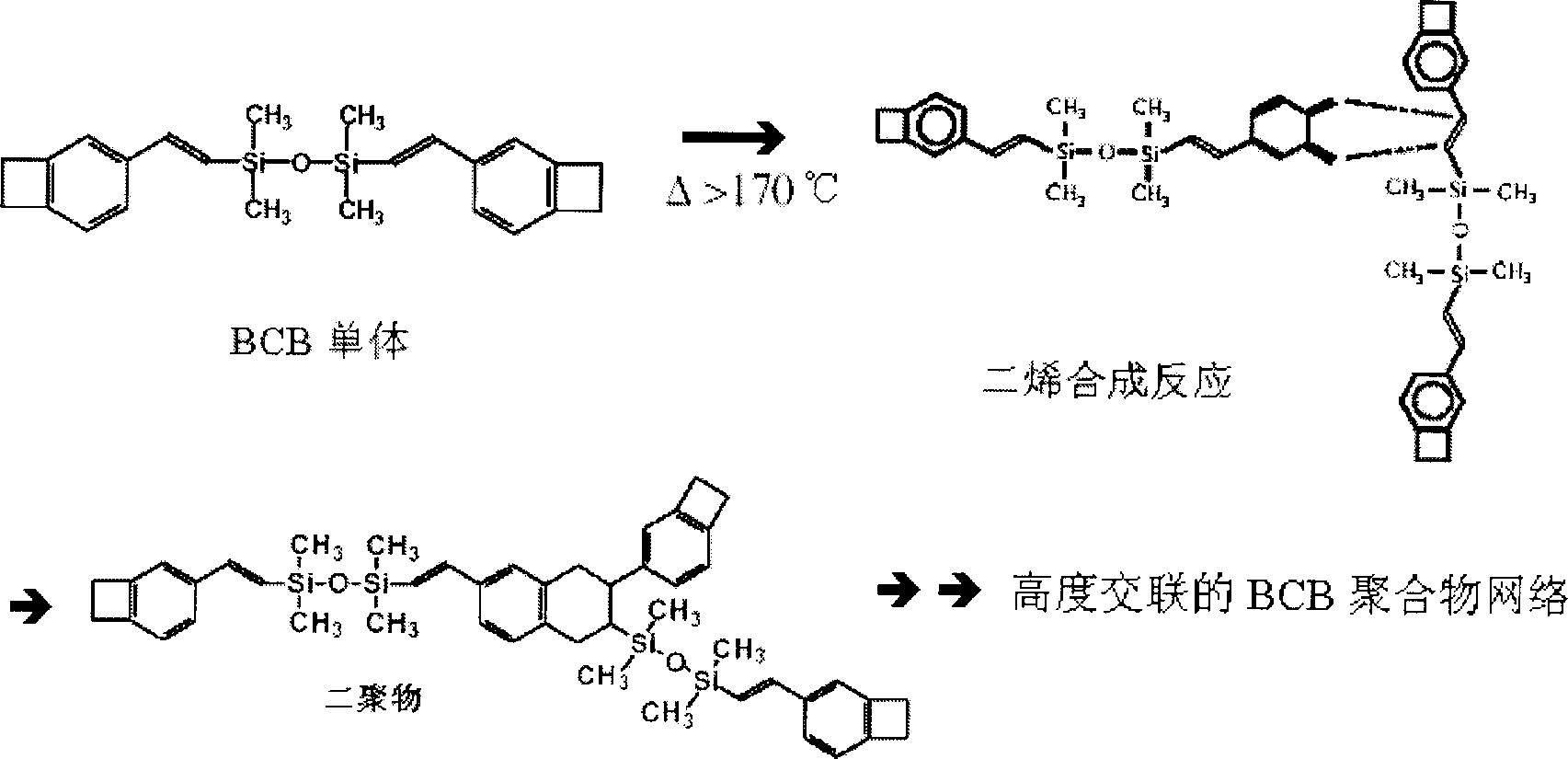
Process for preparing low-temperature wafer-level mini-sized gas container
InactiveCN1827522AMeet packaging requirementsAvoid lostNanostructure manufactureSemiconductor materialsAir tightness
The invention relates to a method for producing low-temperature circle sheet micro gas box, which is characterized in that: the benzocyclobutene is used to process material linkage with humid etching or dry etching technique of semi-conductor in 250Deg. C, to realize the circle sheet air-tightness sealing linkage of chip-level gas box. The invention comprises a atom gas box containing a chip-level atom clock gas box, a high-precision magnetic field sensor gas box, a atom feedback glimmer frequency stabilizer; a atom gas box containing a atom light filter, with glimmer Fabry-Perot chamber. The linked BCB glue is in 0.2ª–m thickness, the air-tightness of sealed He gas can reach 2.1-5.9X10-4Pa cm3 / s, and the linkage strength is higher than 4.65MPa, while the thermal cycle reliability can fully reach the packing standard of micro electric device.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chip-level atomic clock air chamber and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103885325AImprove stabilityImprove yieldApparatus using atomic clocksSilicon chipChip-scale atomic clock
The invention discloses a chip-level atomic clock air chamber and a manufacturing method thereof. An SOI silicon chip is used, a cavity is manufactured on a silicon layer used as a substrate and is used for placing of alkali metal and inflating of inert gas, glass is used for sealing the cavity, finally supporting materials are arranged on one side of a silicon layer used as a device layer to protect a device, and accordingly manufacturing of the high-stability chip-level atomic clock air chamber is completed. Only by one-time key static bonding, manufacturing of the atomic clock air chamber can be completed, the problem of bad stability due to poor static bonding quality is avoided, and finished product rate is improved. The air chamber is simple and reasonable in structure, so that the manufactured air chamber is small in size, easy to use, low in manufacturing cost and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Microfluidic atom cavity, on-chip atomic clock chip and preparation method
InactiveCN102515084AAvoid enteringReduce performanceApparatus using atomic clocksDecorative surface effectsChemical physicsMicrofluidics
The invention discloses a microfluidic atom cavity, an on-chip atomic clock chip and a preparation method. The method includes steps: a silicon substrate with a microfluidic channel and a borosilicate glass assembly wafer with a glass microcavity structure corresponding to the microfluidic channel are bonded to form a closed system, the closed system comprises a glass atom cavity, a reactant partition microfluidic channel and a reactant microcavity, reactant particles of materials necessarily required by atomic clock generation are arranged in the reactant microcavity, the glass atom cavity is communicated with the reactant microcavity through the reactant partition microfluidic channel, the aperture of the reactant microcavity on a bonding surface is smaller than that of the glass atom cavity, the minimum width of the reactant partition microfluidic channel is no larger than the minimum particle diameter of the reactant particles, and the glass micro cavity is provided with a light incidence plane. The smaller microcavity containing the reactant powder is connected with the larger microcavity required by forming of the spherical glass microcavity, forming of a spherical rubidium steam cavity and sealing of gas can be completed at one step, fine sealing performance is achieved, no impurities can be led in, performance of an atomic clock can be improved, the spherical rubidium steam cavity can be integrated into a microchip-level atomic clock system, planar packaging of the atomic clock can be realized, and size of the atomic clock is reduced effectively.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
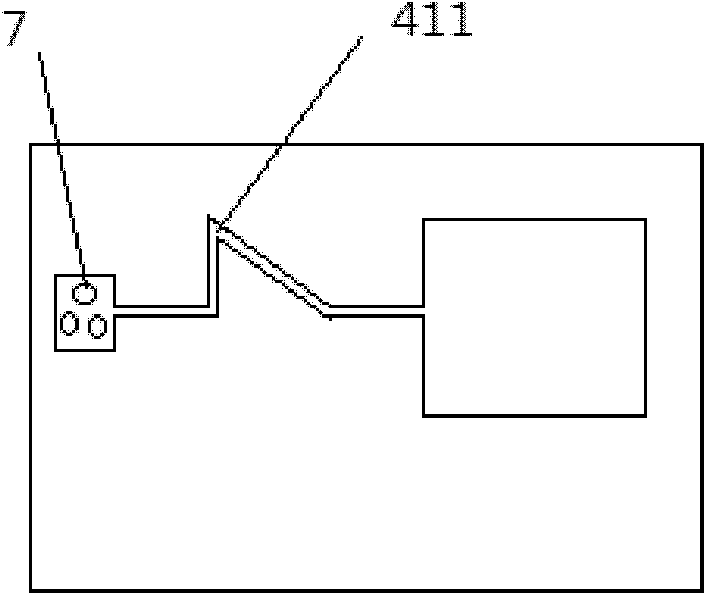
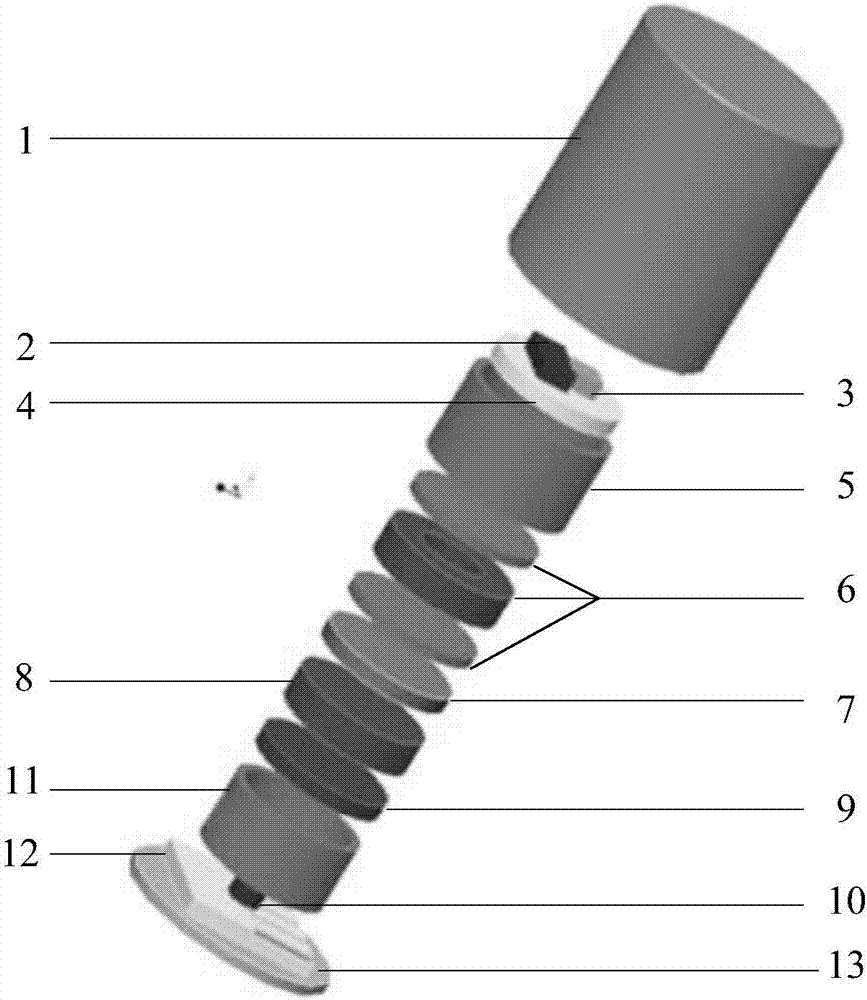
Low-power-consumption chip level atomic clock physical packaging device
InactiveCN103856215AReduce power consumptionEasy to processPulse automatic controlPhotovoltaic detectorsEngineering
The invention discloses a low-power-consumption chip level atomic clock physical packaging device which comprises an external package, an upper support, a lower support, a frame space device and an internal element. The external package is composed of a ceramic package body and a base. The internal element comprises a laser, a photoelectric detector, an alkaline atom bubble air chamber, a 1 / 4 wave plate and a C-field bias module. The C-field bias module comprises a permanent magnet assembly which generates a magnetic field in the physical packaging axial direction. The magnetic field generated by a permanent magnet can totally or partially replace a magnetic field generated by a coil in original chip level atomic clock physical packaging, currents flowing through the coil can be minimum, and therefore energy consumption of chip level atomic clock packaging can be greatly reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Chip scale atomic clock (CSAC)-based high-high sensitivity global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver and recapture realization method thereof
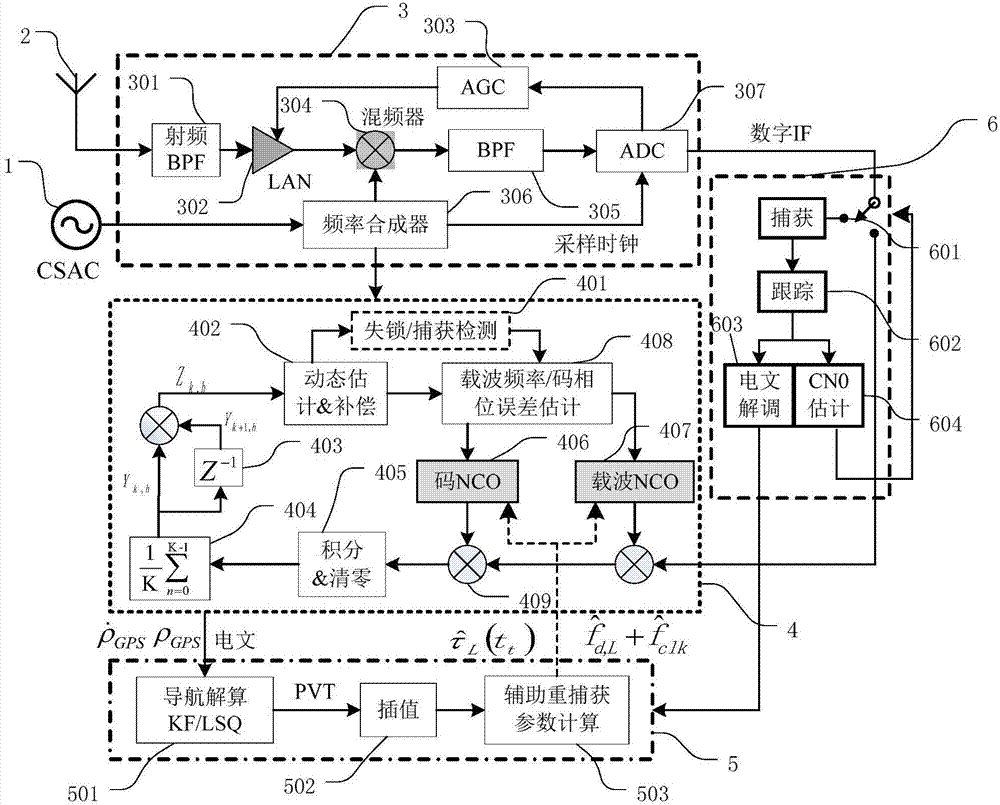
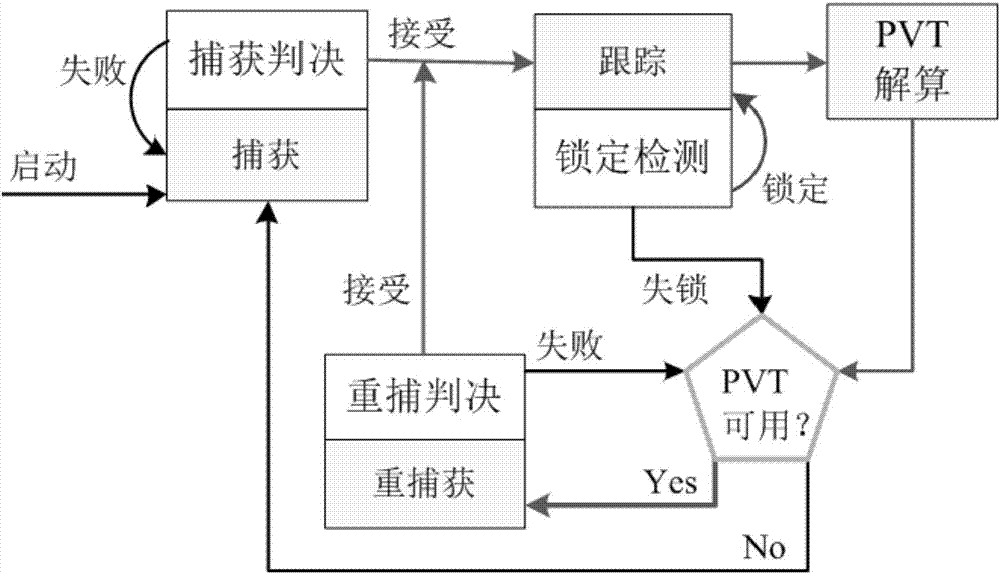
ActiveCN107450084AGood phase noise characteristicsAvoid cumulative decaySatellite radio beaconingRadio frequency signalMarine navigation
The present invention provides a CSAC-based high-high sensitivity GNSS receiver and a recapture realization method thereof. The CSAC-based high-high sensitivity GNSS receiver comprises a CSAC module for providing a reference signal; an antenna for receiving a radio frequency signal; a radio frequency front end for processing the radio frequency signal based on the reference signal and outputting a digital IF signal; a conventional baseband processing module used for capturing and tracking the digital IF signal, demodulating the message of digital IF signal and estimating the carrier-to-noise ratio of the digital IF signal, wherein when the result of the carrier-to-noise ratio estimation is greater than a predetermined threshold value, the conventional baseband processing module captures and tacks, otherwise, in a high-sensitivity work mode, a high-sensitivity tracking and capturing module captures and tracks; a high-sensitivity tracking and recapturing module used for processing the digital IF information outputted by the radio frequency front end to realize the high-sensitivity capture and tracking; and a navigation calculation and auxiliary parameter calculation module used for providing a needed local code phase estimated value and a carrier frequency estimated value for the high-sensitivity capture and tracking. The sensitivity and dynamic performance of the GNSS receiver of the present invention can be improved substantially.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Micro atomic and inertial measurement unit on a chip system
A chip scale atomic clock (CSAC) accelerometer incorporates a case in which a cesium vapor resonance cell is carried. An optical laser is mounted in the case and emits a laser beam through the resonance cell. The laser is modulated by a microwave signal generator. A photon detector mounted in the case receives photons emitted by cesium atoms in the resonance cell and provides a frequency output representative of interference of energy levels of the emitted photons including momentum changes due to acceleration.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
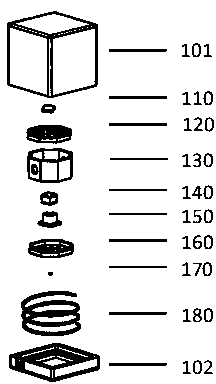
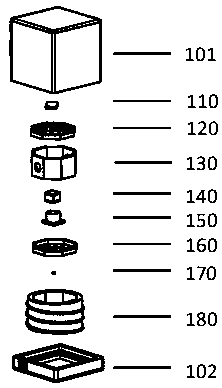
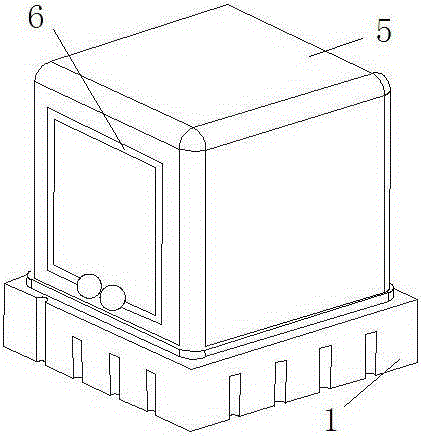
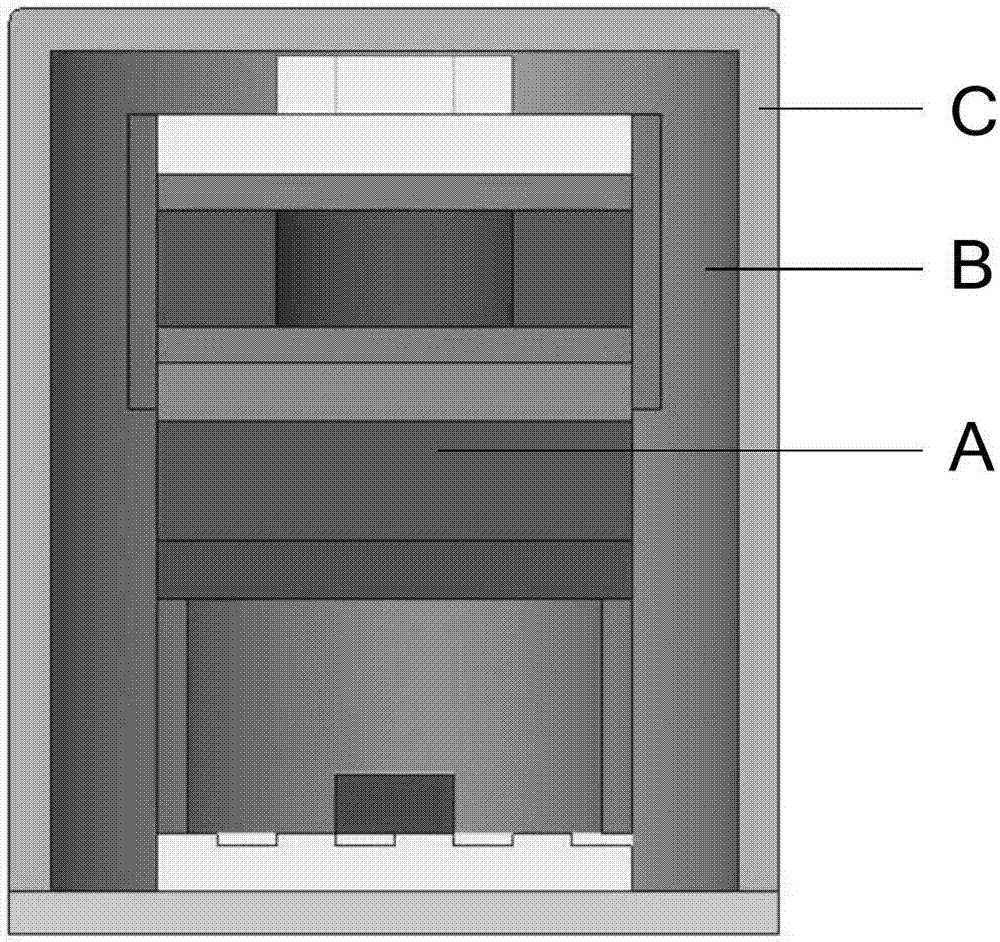
Physical system of ultra-thin chip-level atomic clock
The invention discloses a physical system of an ultra-thin chip-level atomic clock for the purpose of solving the problem of a conventional chip-level atomic clock is high in cost and energy consumption in structure duplication. The physical system of the ultra-thin chip-level atomic clock comprises an LCC base, a physical support frame fixed to the LCC base, a VCSEL system, a photocell and a ceramic sealing cap matching the LCC base for vacuum seal of all parts. The VCSEL system and the photocell are arranged on two opposite sides of the physical support frame. A slide system and an absorbing foam system are arranged between the VCSEL system and the photocell. The slide system draws close to the VCSEL system. The absorbing foam system draws close to the photocell. An electrode and a welding disc used for adapting leading wires are arranged on the physical support frame. A signal of the physical support frame is adapted to a leading wire electrode of the LCC base. The physical system of the ultra-thin chip-level atomic clock is simple in structure and low in cost and lays a solid foundation for large-area promotion and application.
Owner:CHENGDUSCEON ELECTRONICS
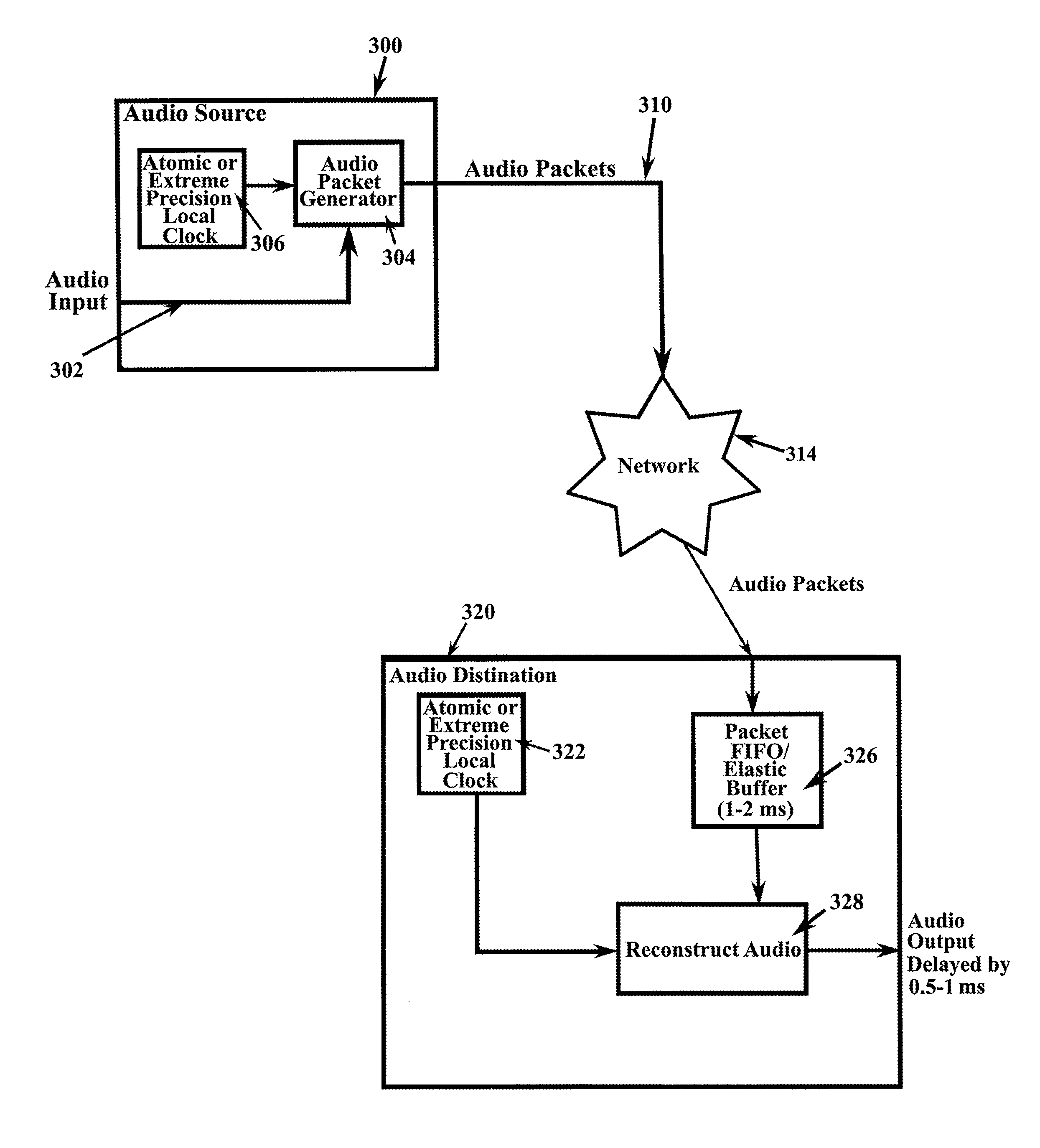
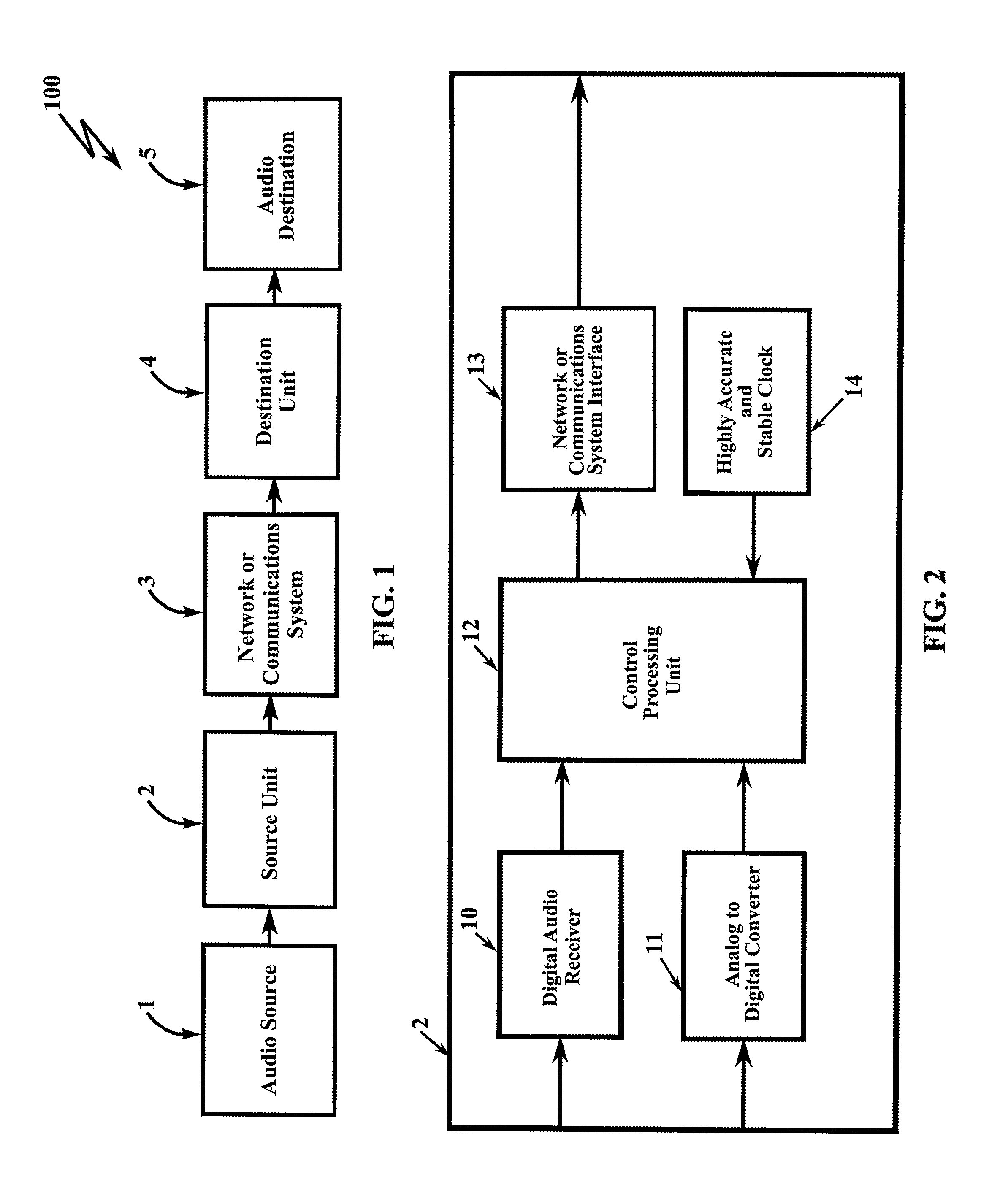
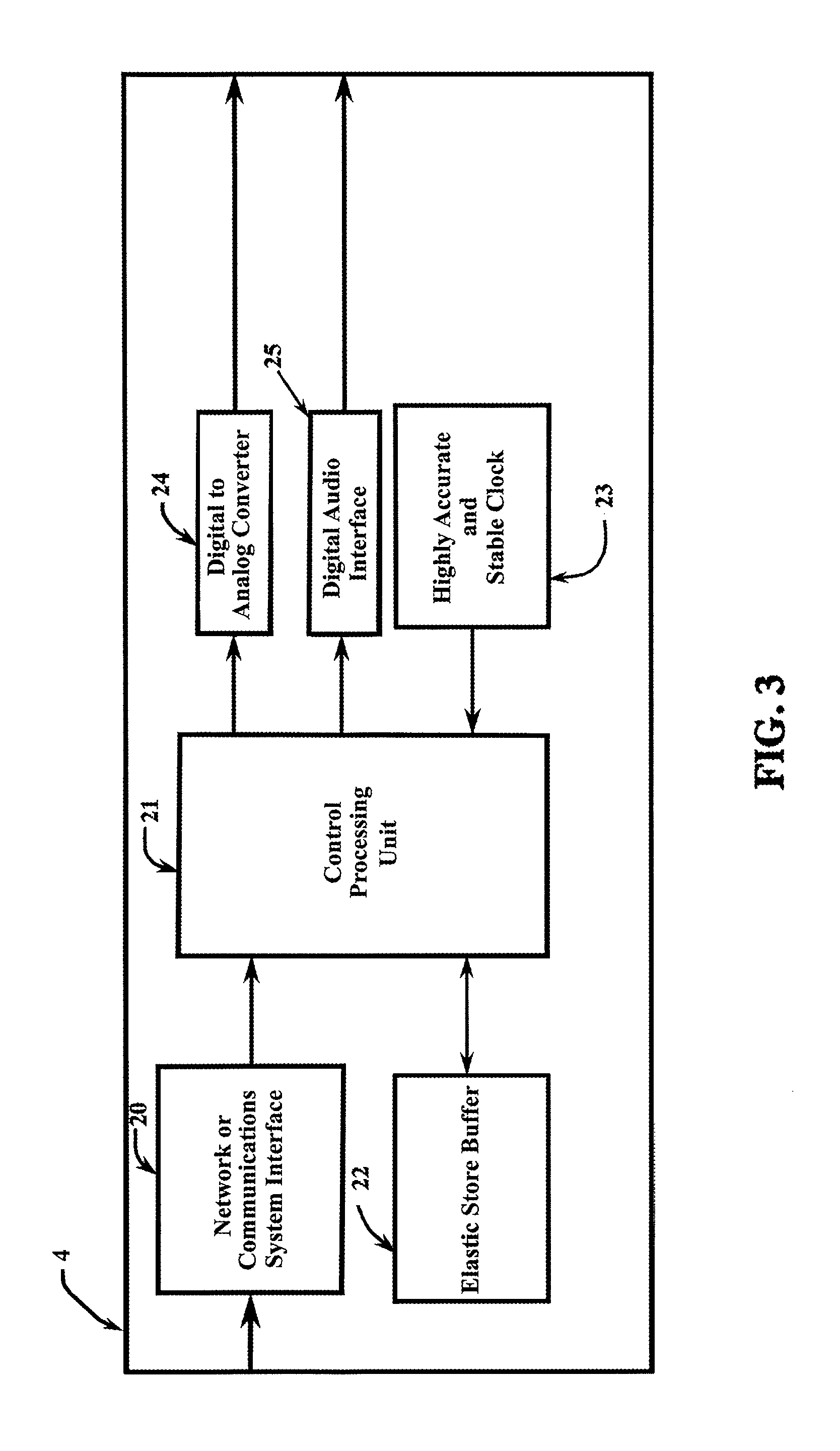
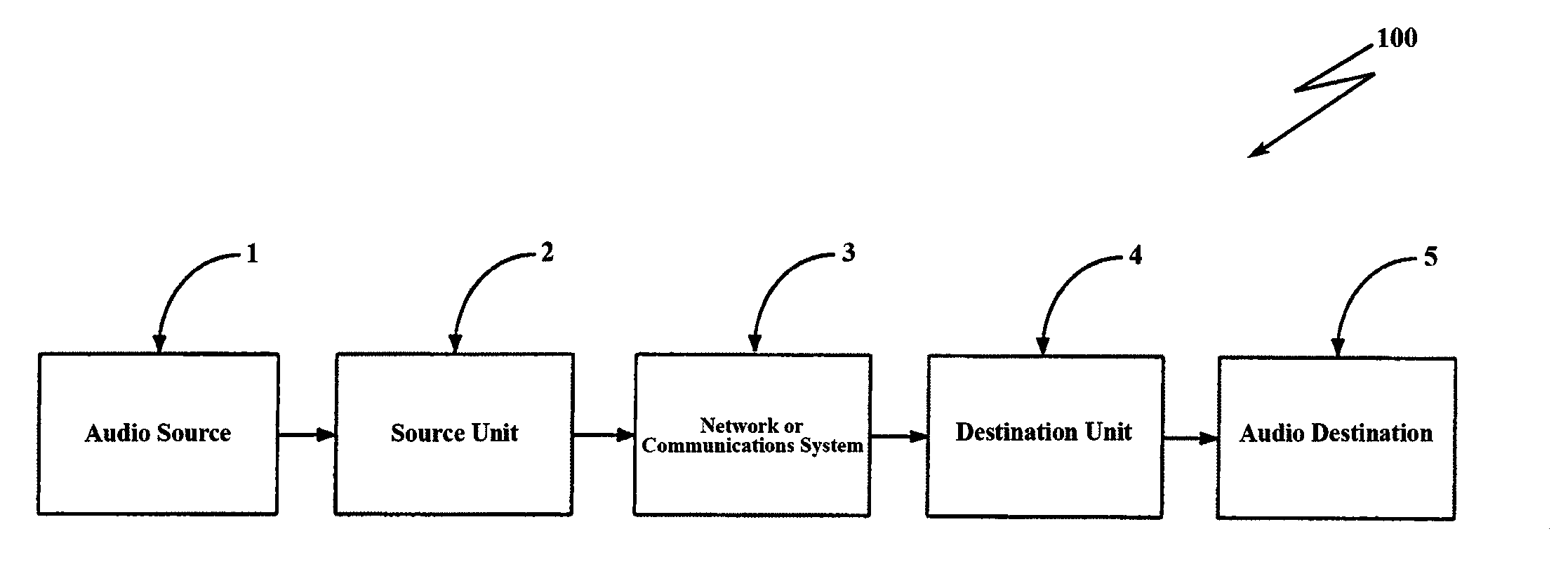
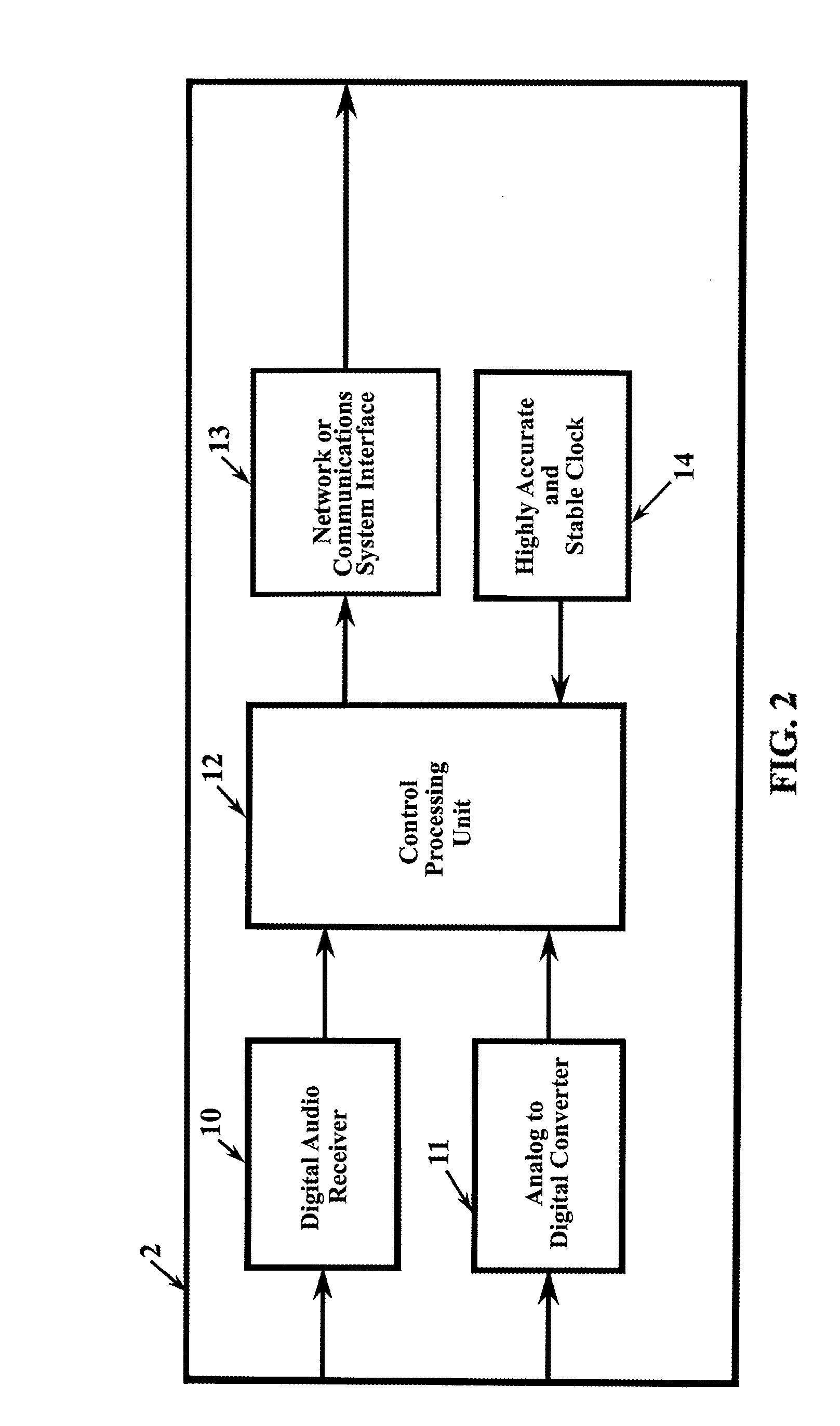
System and method for routing digital audio data using highly stable clocks
ActiveUS9219938B2Quality improvementEliminate buffer overflow or underflowSelective content distributionSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
A system and method for routing digital audio data synchronized where the source and destination units are synchronized to individual, local chip-scale atomic clocks. A source unit receives audio data and digitizes the data in synchronization to a local atomic clock. The data is transmitted via a communications network to at least one destination unit that receives the network transmitted data, decodes and reconstructs the data in synchronization with its own local atomic clock, and outputs the data to an audio destination.
Owner:WHEATSTONE CORP
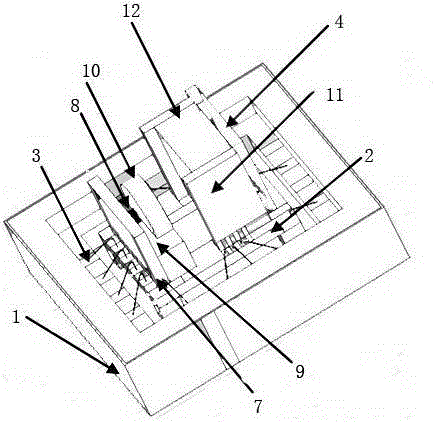
Micro-physical system of chip-scale atomic clock
InactiveCN107193204AReliable mechanical structureMeet anti-vibrationApparatus using atomic clocksCore componentPhysical system
The invention discloses a micro-physical system of a chip-scale atomic clock. The system comprises a magnetic shield shell, a core component and a buffer gas cavity which is enclosed by the magnetic shield shell and the core component, wherein the magnetic shield shell comprises a magnetic shield cylinder and a magnetic shield base which is used for sealing the magnetic shield cylinder; the core component is arranged in the magnetic shield shell and comprises a light source unit, a light path unit and an atom cavity unit which are arranged in sequence, wherein the atom cavity unit comprises an MEMS atom cavity, and the MEMS atom cavity is filled with rubidium atoms and buffer gas; the buffer gas cavity is filled with the buffer gas of which the pressure intensity is equal to that in the MEMS atom cavity. The micro-physical system of the chip-scale atomic clock has the advantages that the system is convenient to install, stable in performance, compact in structure, small in size, low in power dissipation and long in service life.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
System and method for routing digital audio data using highly stable clocks
ActiveUS20140121795A1Quality improvementEliminate buffer overflow or underflowSelective content distributionSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
A system and method for routing digital audio data synchronized where the source and destination units are synchronized to individual, local chip-scale atomic clocks. A source unit receives audio data and digitizes the data in synchronization to a local atomic clock. The data is transmitted via a communications network to at least one destination unit that receives the network transmitted data, decodes and reconstructs the data in synchronization with its own local atomic clock, and outputs the data to an audio destination.
Owner:WHEATSTONE CORP
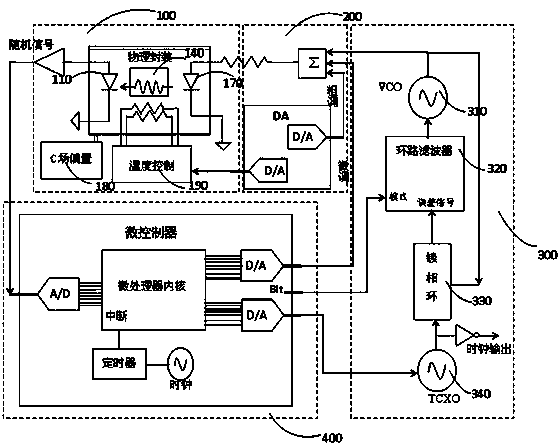
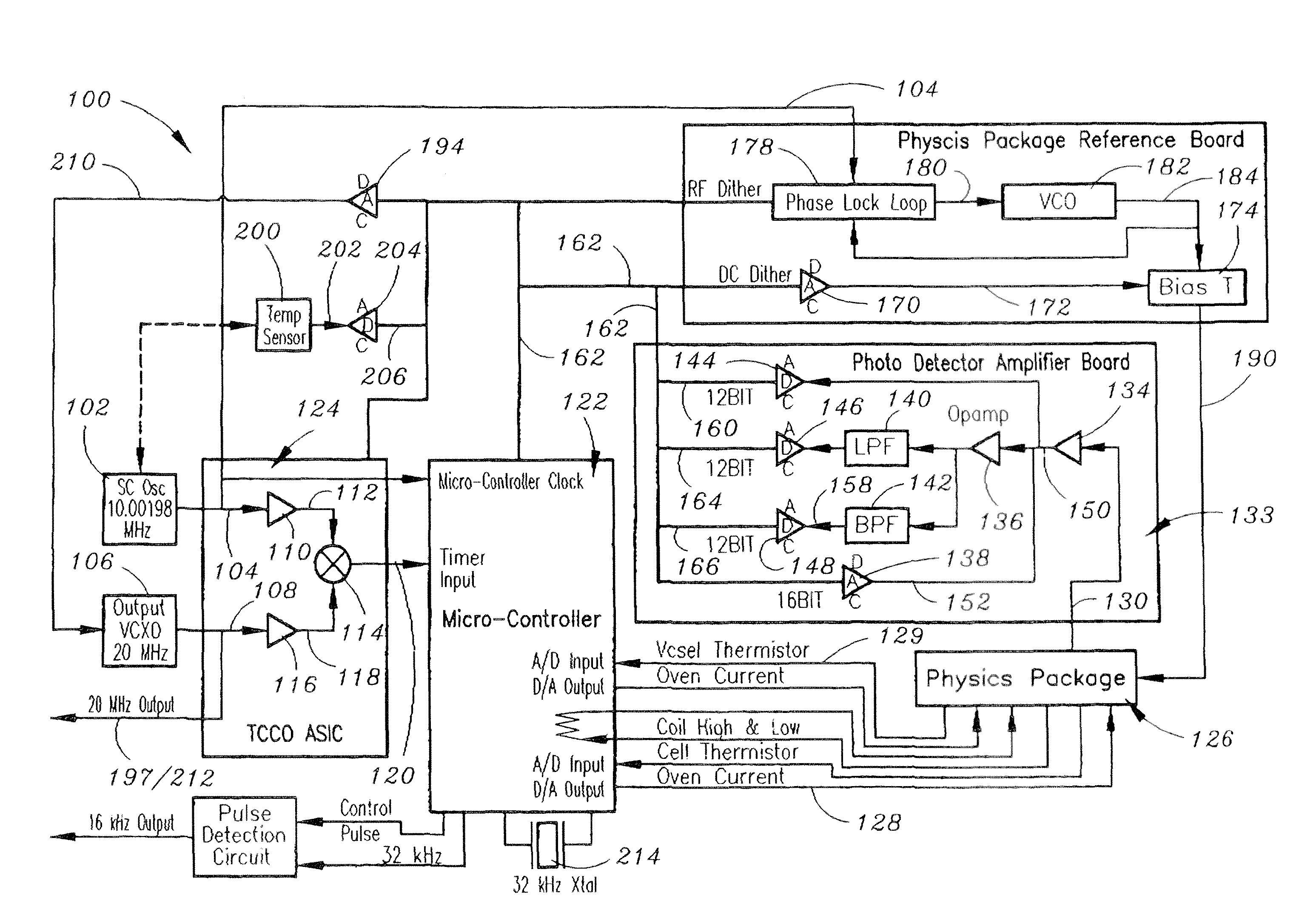
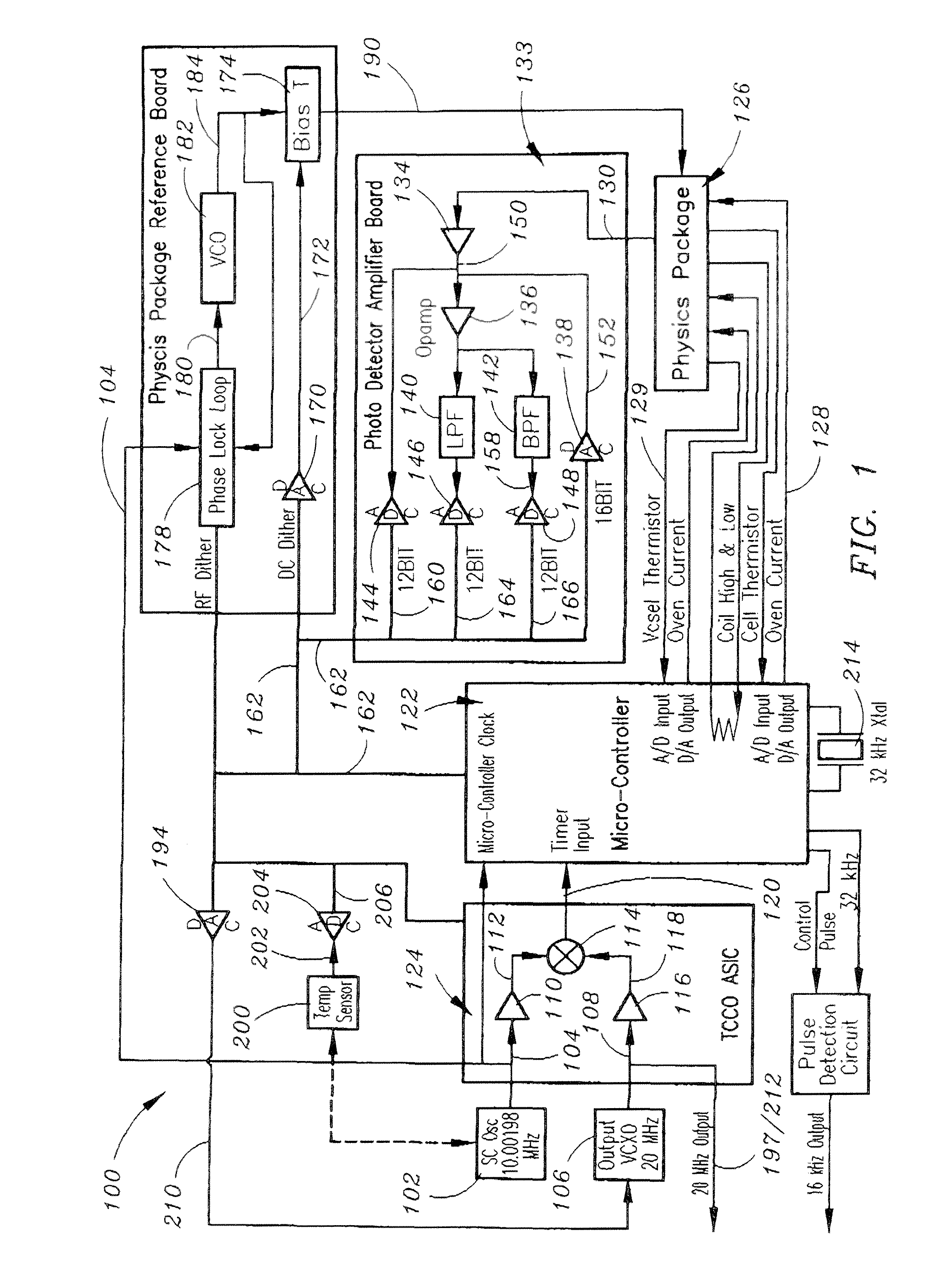
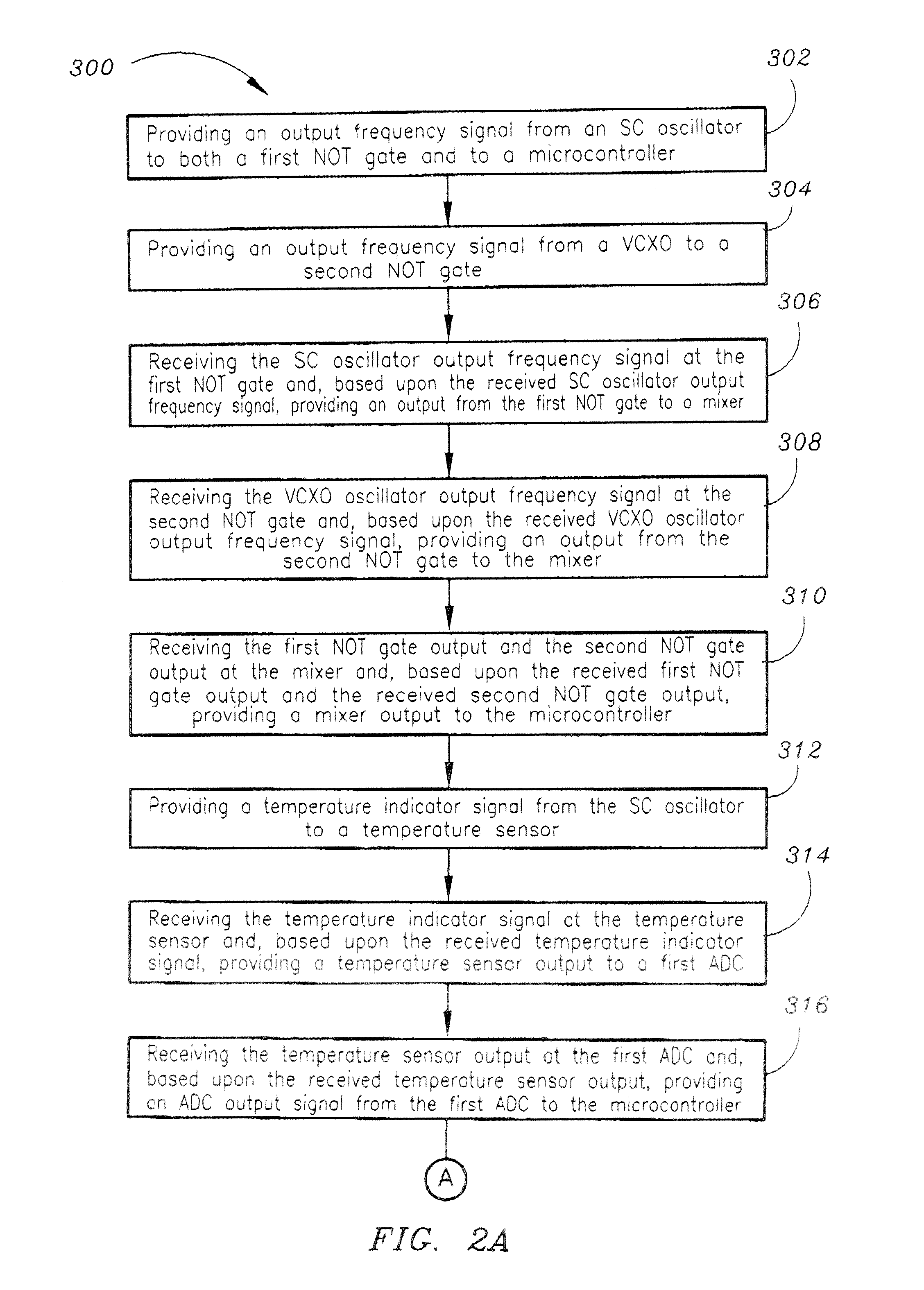
Ruggedized chip scale atomic clock
The present invention is a Chip Scale Atomic Clock (CSAC)-enabled Time and Frequency Standard (CTFS) architecture. The CTFS architecture includes a microcontroller, a Time Compensated Crystal Oscillator (TCCO) circuit which is connected to the microcontroller, and a Chip Scale Atomic Clock (CSAC) which is connected to the microcontroller. The microcontroller is configured for selectively causing the CTFS to provide a TCCO circuit-based output frequency when the CTFS has not locked to a predetermined atomic resonance, and is further configured for causing the CTFS to provide a CSAC-based output frequency when the CTFS has locked to a predetermined atomic resonance.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
System for positioning, navigation, and time (PNT)
ActiveUS10620296B1Accurate measurementImprove performancePosition fixationDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsRadio frequencyRemote sensing
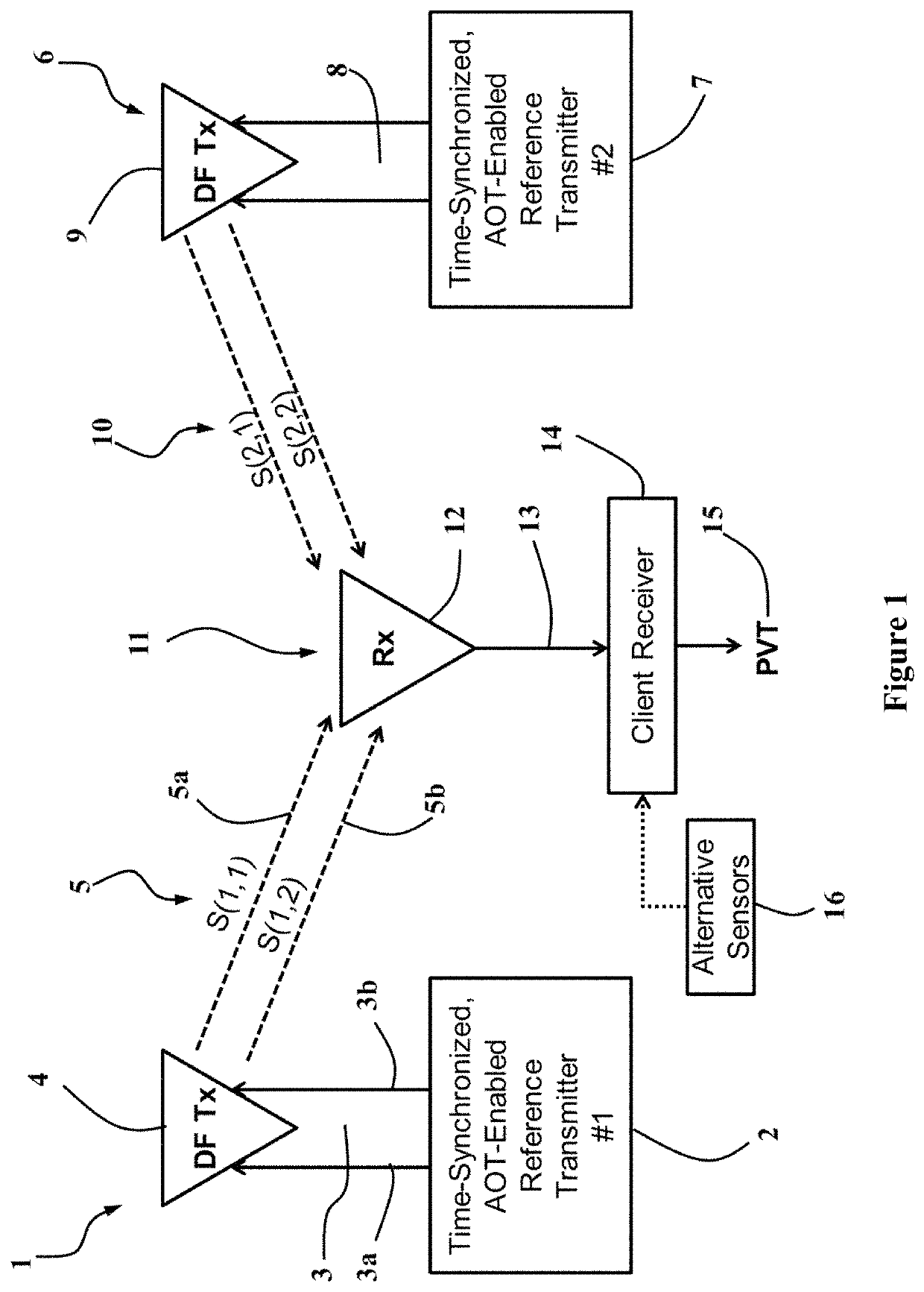
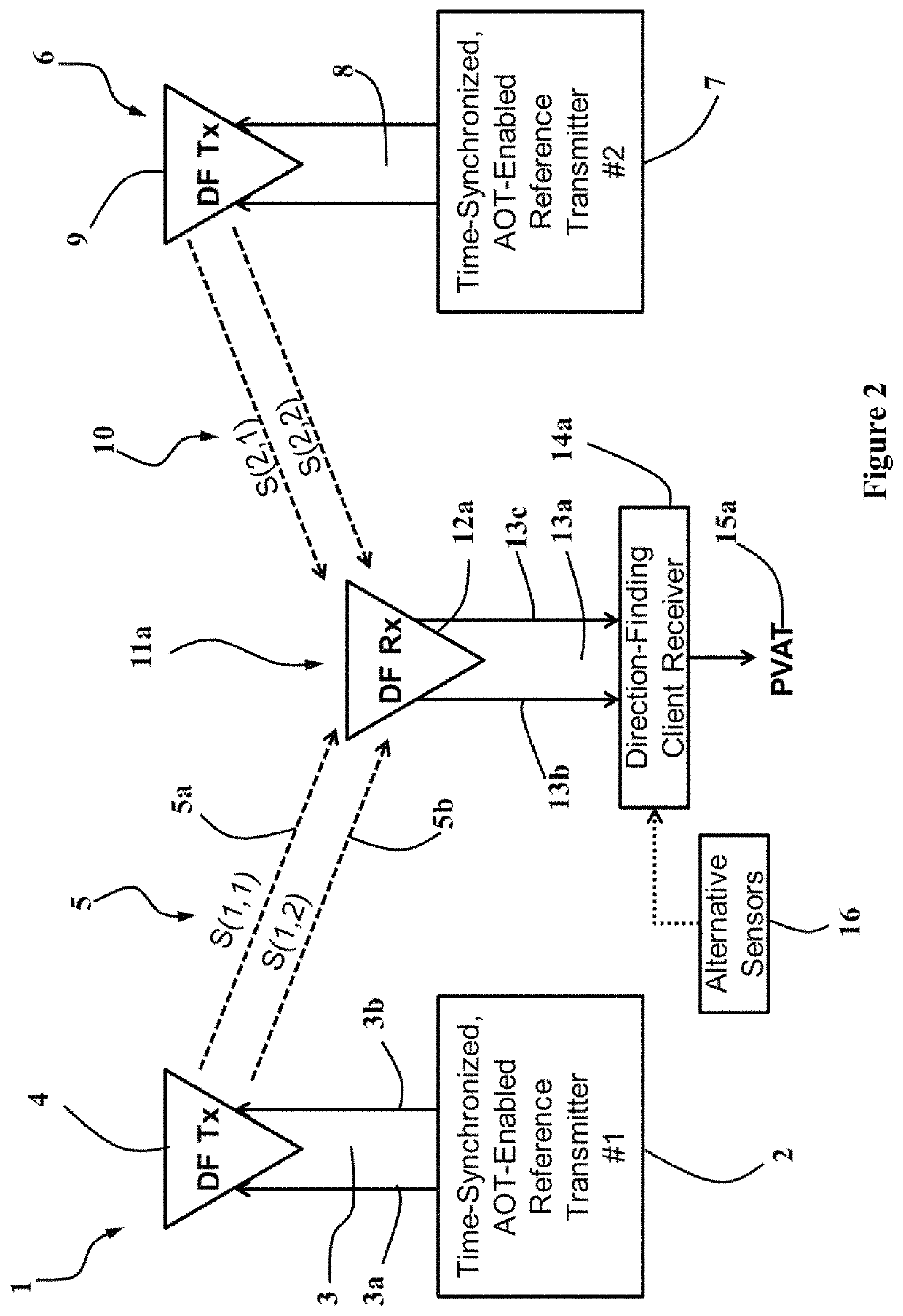
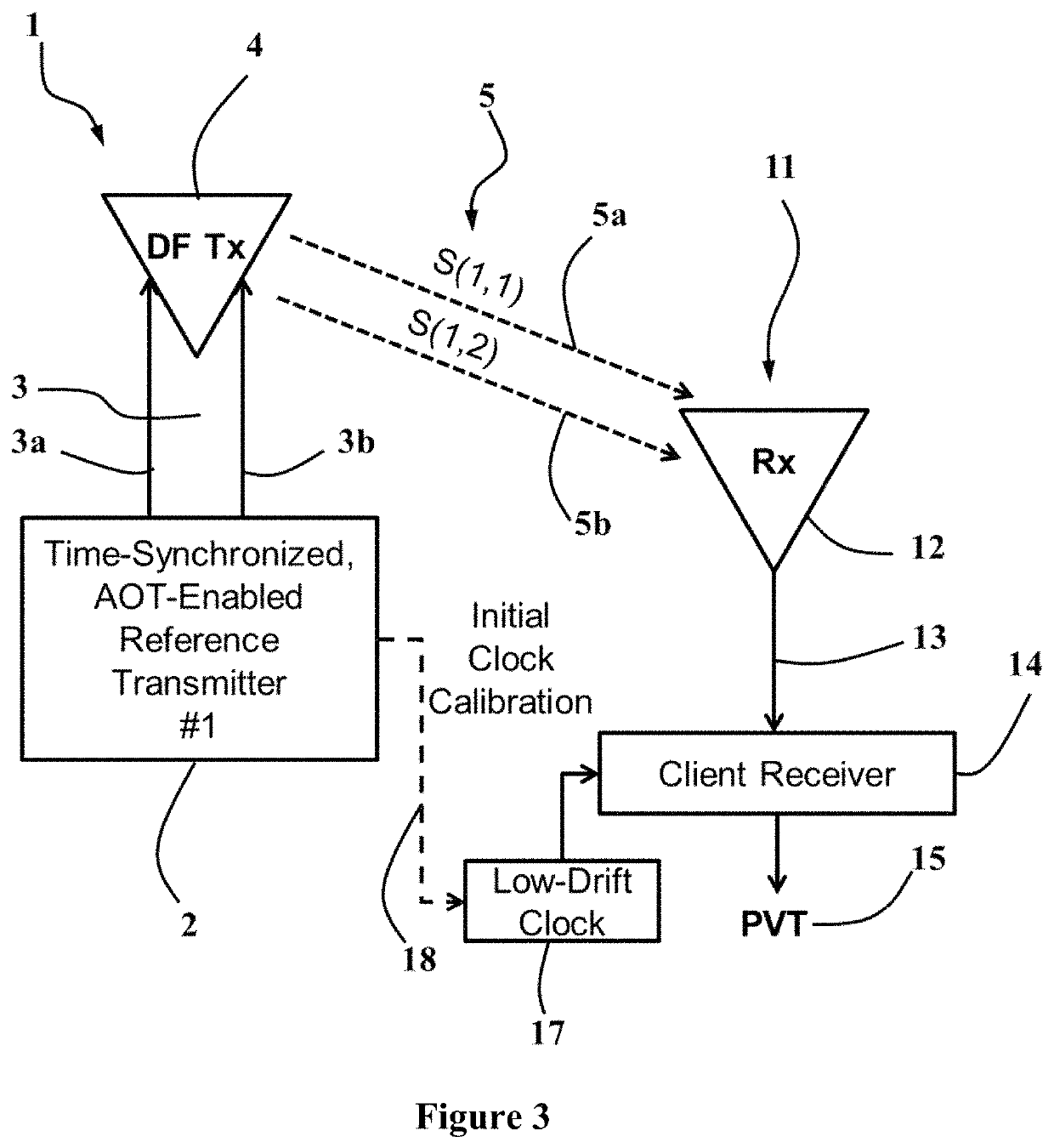
An exemplary radio-frequency (RF)-based navigation reference system uses one or more non-collocated and time-synchronized direction-finding transmitters to enable a client receiver to estimate its own 3-D position, velocity and time (PVT) using direction-finding (DF) waveforms obtained from said reference transmitters. At least one reference transmitter is sufficient for obtaining a 3-D PVT solution provided the client receiver is equipped with an accurate (low-drift) local clock such as a chip-scale atomic clock (CSAC). All other client receivers require at least two reference transmitters to estimate their 3-D PVT.
Owner:TOYON RES CORP
Atomic clock, micro-inertia measurement combination and navigation system coupling method and system
ActiveCN105549058AImprove accuracyImprove usabilitySatellite radio beaconingUsabilityNavigation system
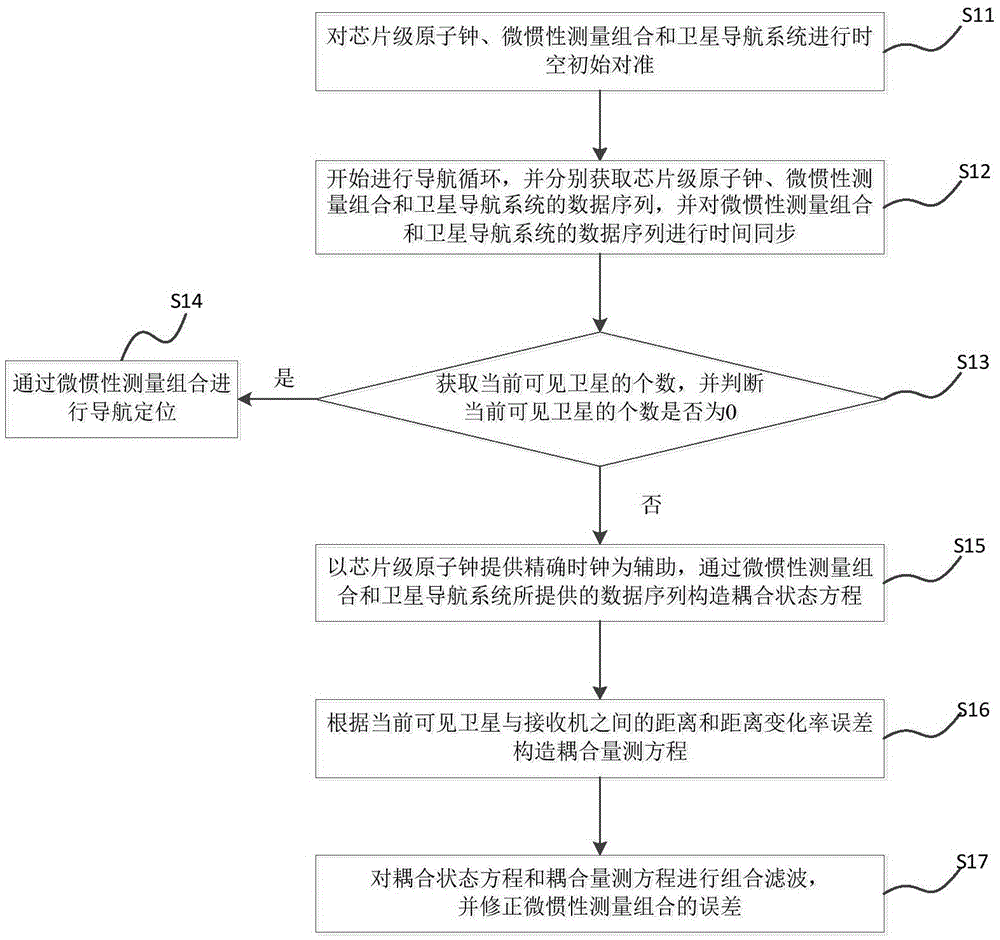
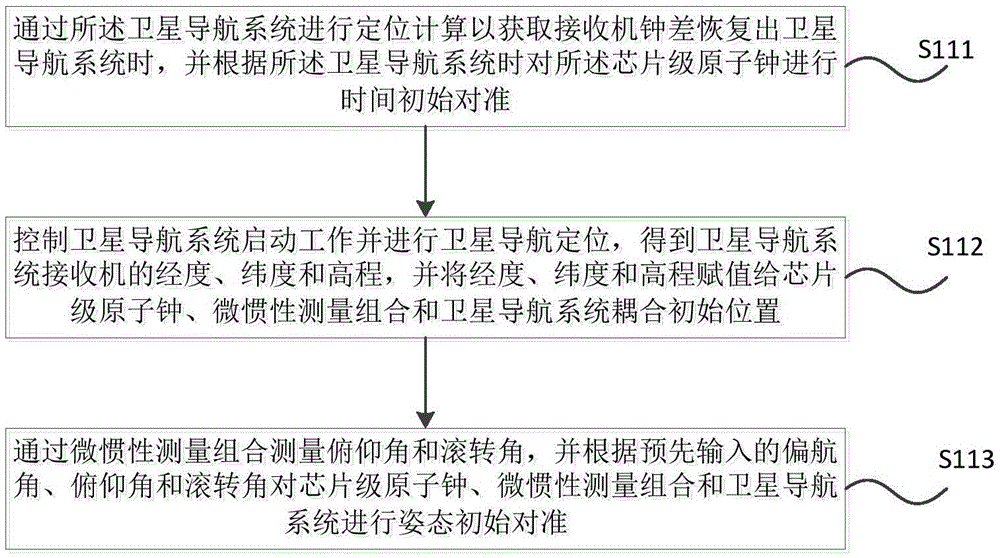
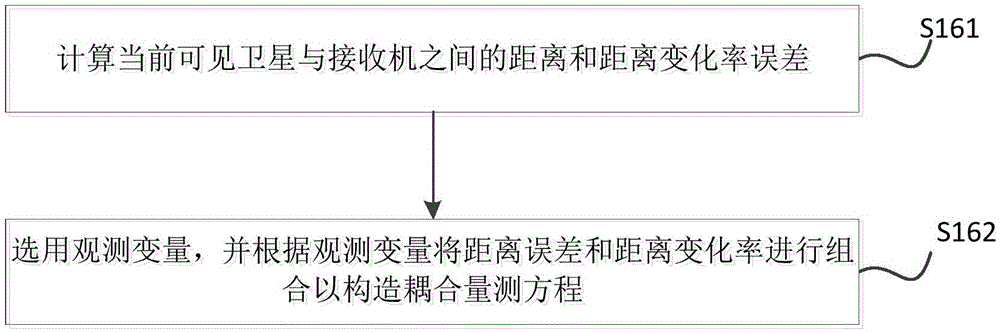
The invention discloses a chip-level atomic clock, micro-inertia measurement combination and satellite navigation system coupling method and system. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the initial temporal and space alignment of a chip-level atomic clock, a micro-inertia measurement combination and a satellite navigation system; starting the navigation cycle, respectively obtaining the data sequences of the chip-level atomic clock, the micro-inertia measurement combination and the satellite navigation system, and carrying out the time synchronization of the data sequences of the micro-inertia measurement combination and the satellite navigation system; taking a precise clock provided by the chip-level atomic clock as the assistance when the number of currently obtained satellites is judged to be greater than zero, constructing a coupling state equation and a coupling measurement equation, carrying out the combined filtering of the coupling state equation and the coupling measurement equation, and correcting the error of the micro-inertia measurement combination. The method can improve the usability of the information of the satellite navigation system, and further improves the precision of the navigation system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
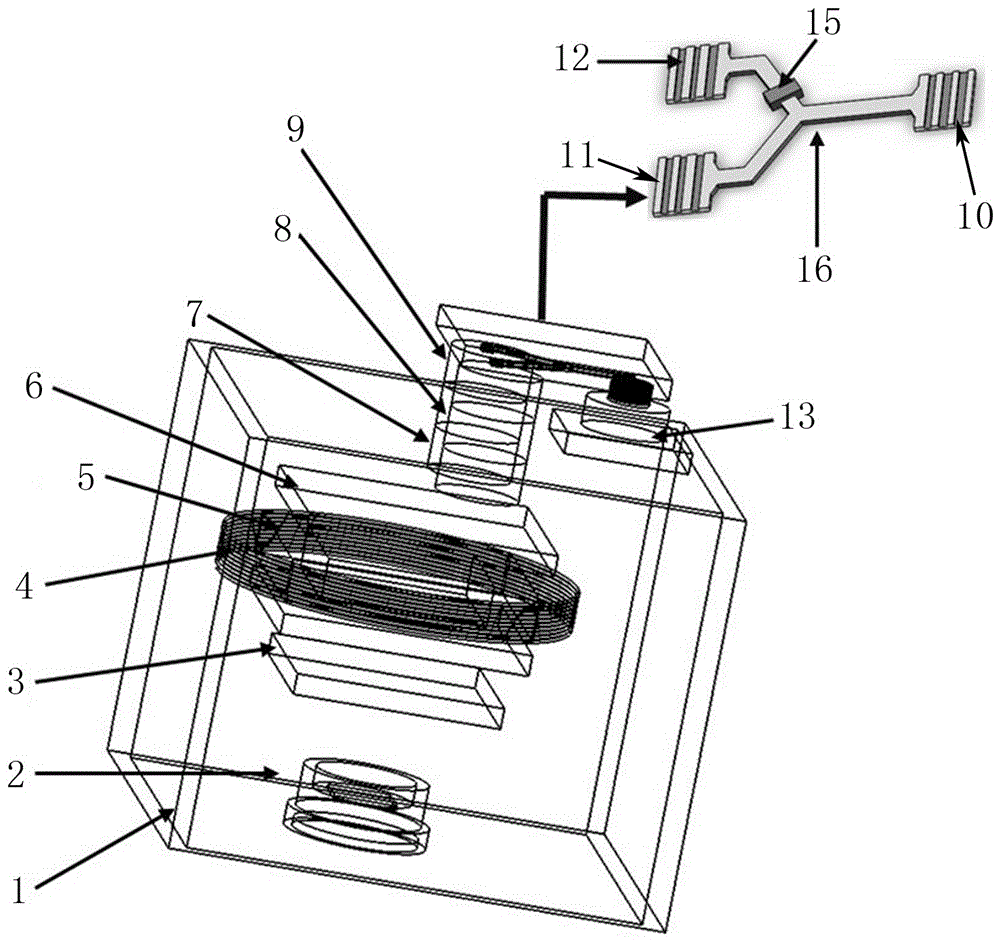
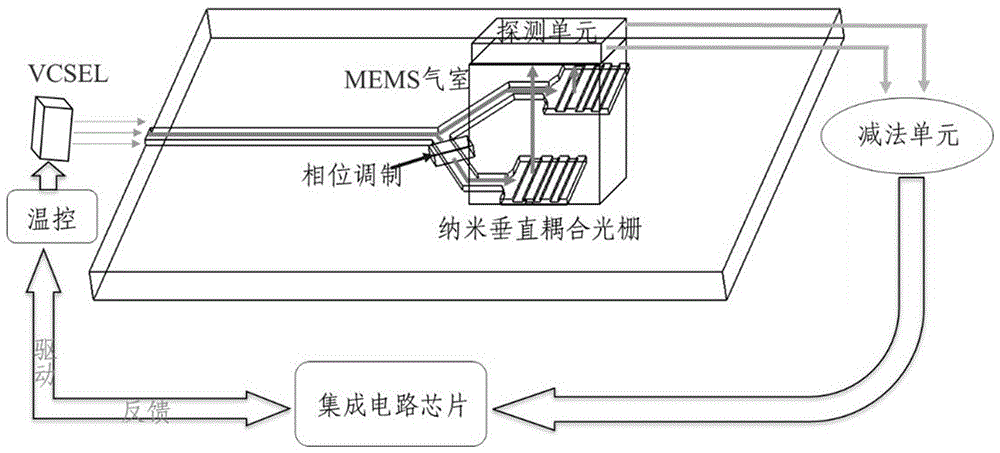
Perpendicular coupling nanometer optical waveguide dual-optical-path chip atomic clock
InactiveCN106406074AImprove stabilityImprove short-term stabilityApparatus using atomic clocksGratingBeam splitter
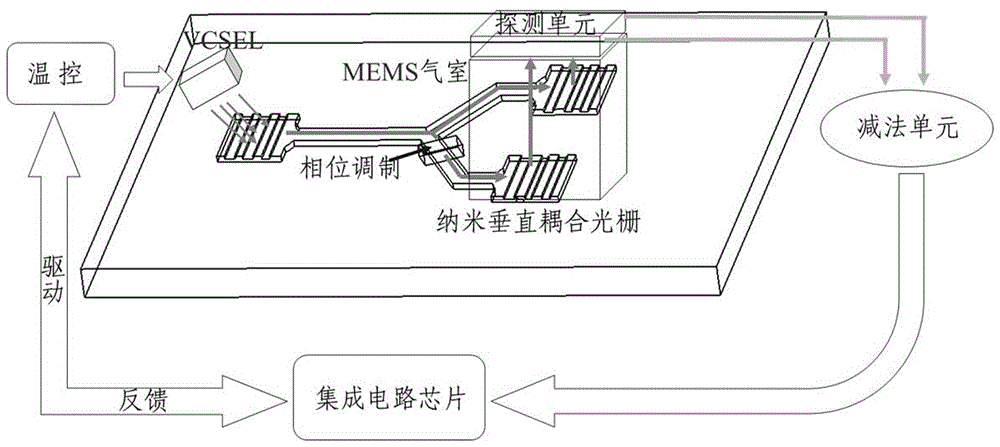
The invention discloses a perpendicular coupling nanometer optical waveguide dual-optical-path chip atomic clock which comprises a laser, light beams emitted by the laser enter a Y waveguide beam splitter through coupling of a perpendicular coupling optical grating I, one beam of light is output after passing by a phase modulation unit, another beam of light is output after regulation compensation, the two beams of light are output after passing by the perpendicular coupling optical grating I and a perpendicular coupling optical grating II respectively, enter a rubidium atom air chamber after passing by a polarizing film, an attenuation plate and a wave plate and after collimation and focussing and are input into an integrated circuit chip by a subtracter after emitted and converted into electrical signals by a detection unit, and the integrated circuit chip controls the laser and the phase modulation unit. According to the scheme, luminous power fluctuation and frequency fluctuation noise influences can be reduced greatly through dual-optical-path common-mode rejection, the signal-to-noise ratio of a CPT atomic clock is effectively improved, and accordingly, the short period stability of a chip level atomic clock can be improved greatly.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
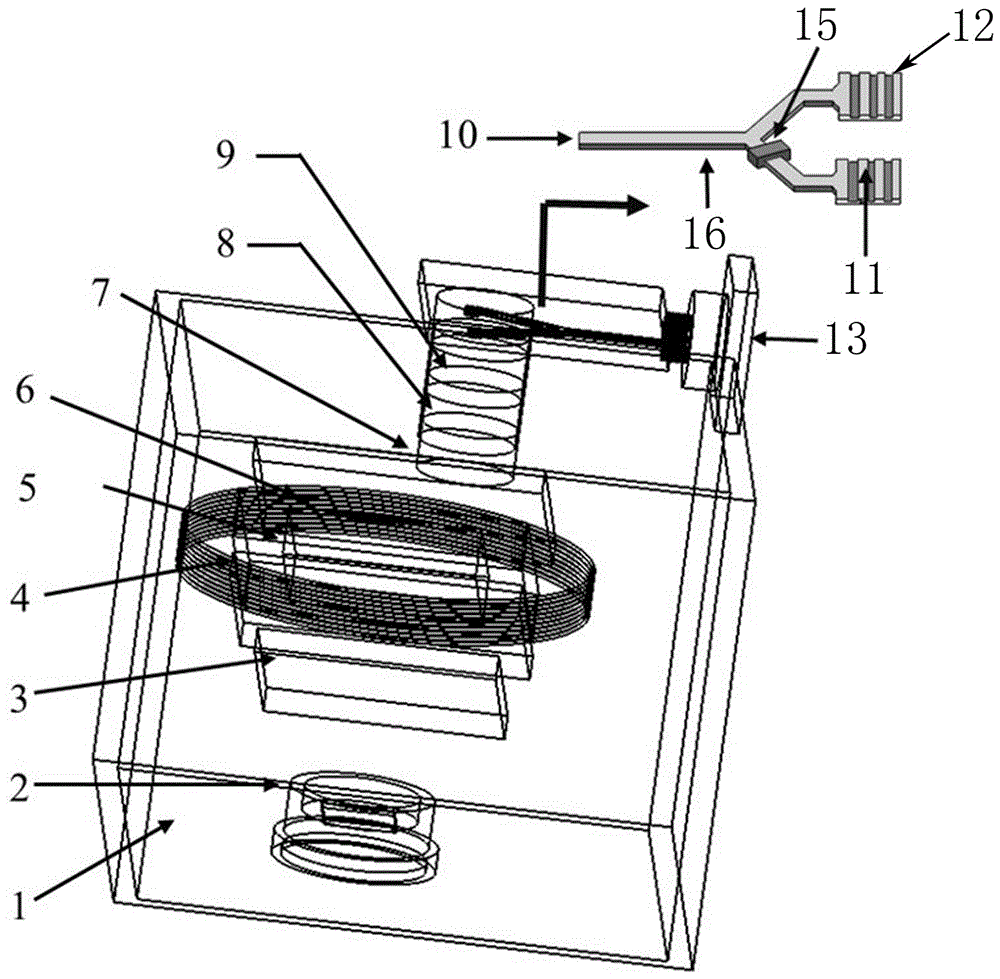
End-coupling nano optical waveguide type dual-optical-path chip-scale atomic clock
InactiveCN106325049AImprove stabilityImprove short-term stabilityApparatus using atomic clocksGratingBeam splitter
The invention discloses an end-coupling nano optical waveguide type dual-optical-path chip-scale atomic clock comprising a laser device. An emergent light beam of the laser device enters a Y-waveguide beam splitter through coupling of the end-coupling input end, wherein one light beam is outputted after passing through a phase modulation unit while the other light beam is outputted after adjust compensation, and the two light beams are outputted after passing through a vertical coupling grating II and a vertical coupling grating III respectively and sequentially pass through a polaroid, attenuation slices, a wave plate, collimation and focusing prior to entering an air chamber. After being emergent, the two light beams are converted into electrical signals through a detection unit, the electrical signals are inputted into an integrated circuit chip through a subtracter, and the integrated circuit chip is used for regulating and controlling the laser device and the phase modulation unit. The end-coupling nano optical waveguide type dual-optical-path chip-scale atomic clock has the advantages that the effect of optical power fluctuation and frequency fluctuation noise can be greatly weakened and the signal-to-noise ratio of the CPT atomic clock can be effectively improved through dual-optical-path common-mode rejection, so that short-term stability of the chip-scale atomic clock can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Interference type VCSEL laser device applied to chip level atomic clock and atomic magnetometer
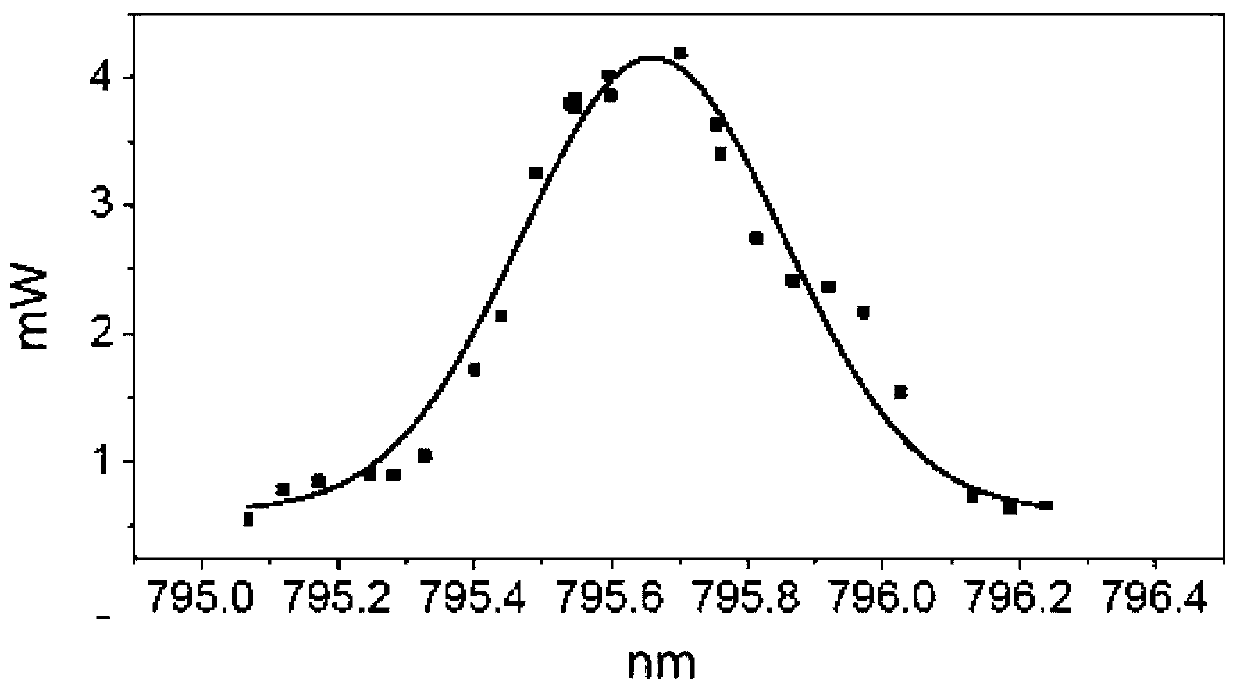
InactiveCN110265873ASimple structureLow costLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionLine widthRefractive index
The invention provides an interference type VCSEL laser device applied to a chip level atomic clock and an atomic magnetometer. Filtering / feedback film groups and a partial reflection film are arranged on an output light end face, the filtering / feedback film groups comprise a plurality of high refraction index material and low refraction index material film layers, a single wave length light beam is obtained through frequency selection of the filtering / feedback film groups for a coherent light beam output by a VCSEL laser chip and then is reflected by the partial reflection film, and reflected light is oscillated inside a resonant cavity composed of the output light end face and the filtering / feedback film groups and amplified to exceed an oscillation threshold value. The VCSEL laser chip and the multiple layers of filtering / feedback film groups with filtering and outer cavity feedback functions integrally are integrated into one body, a small and integrated laser device with narrow line width is obtained, and the interference type VCSEL laser device has the characteristics of simple structure, low production cost, high interference immunity and narrow line width, so that the device is applicable for chip level atomic optical devices and realizes batch production.
Owner:WENZHOU COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION CENT OF LASER & OPTOELECTRONICS
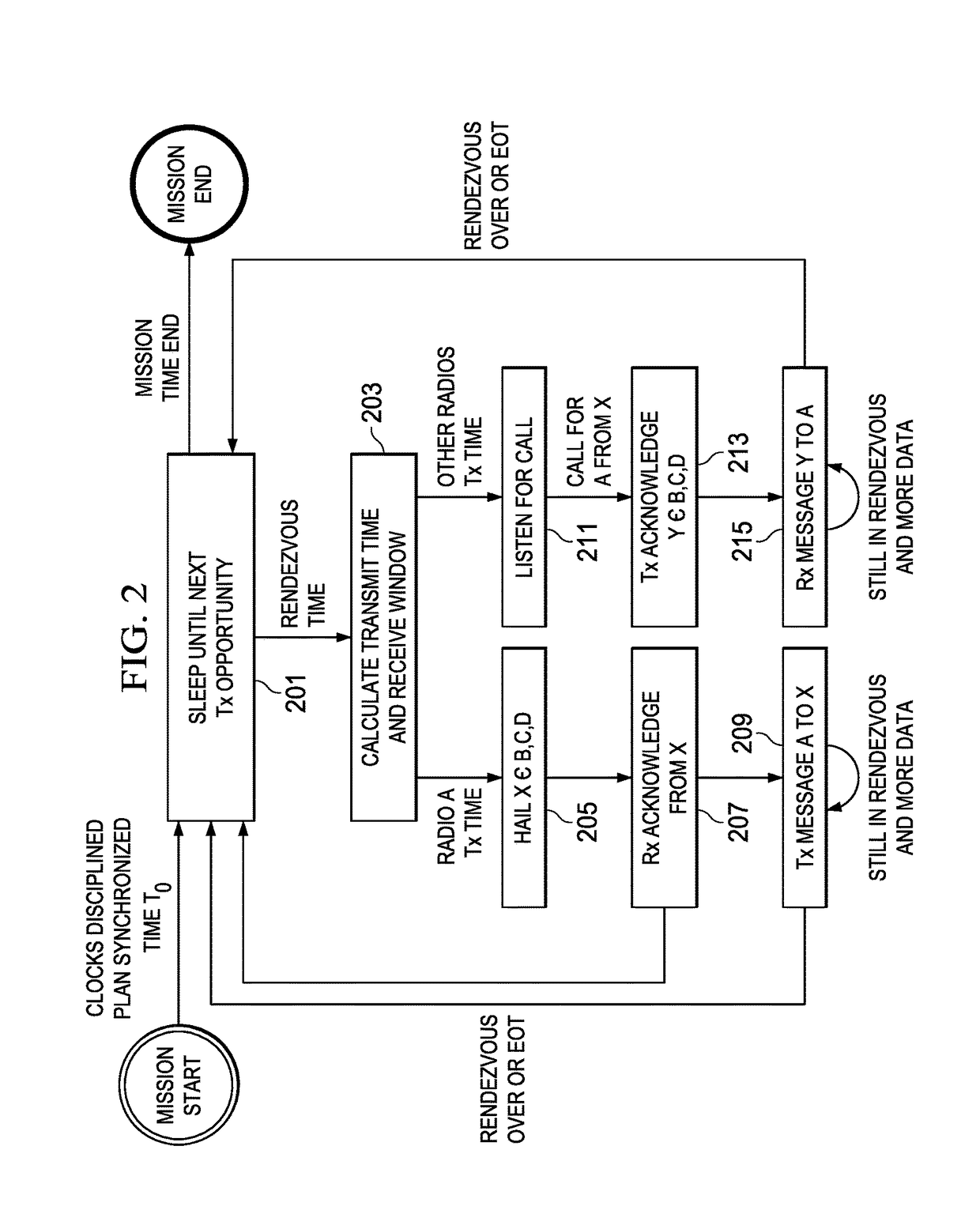
Media access control method with time-coherence and deterministic scheduling for wireless communications network
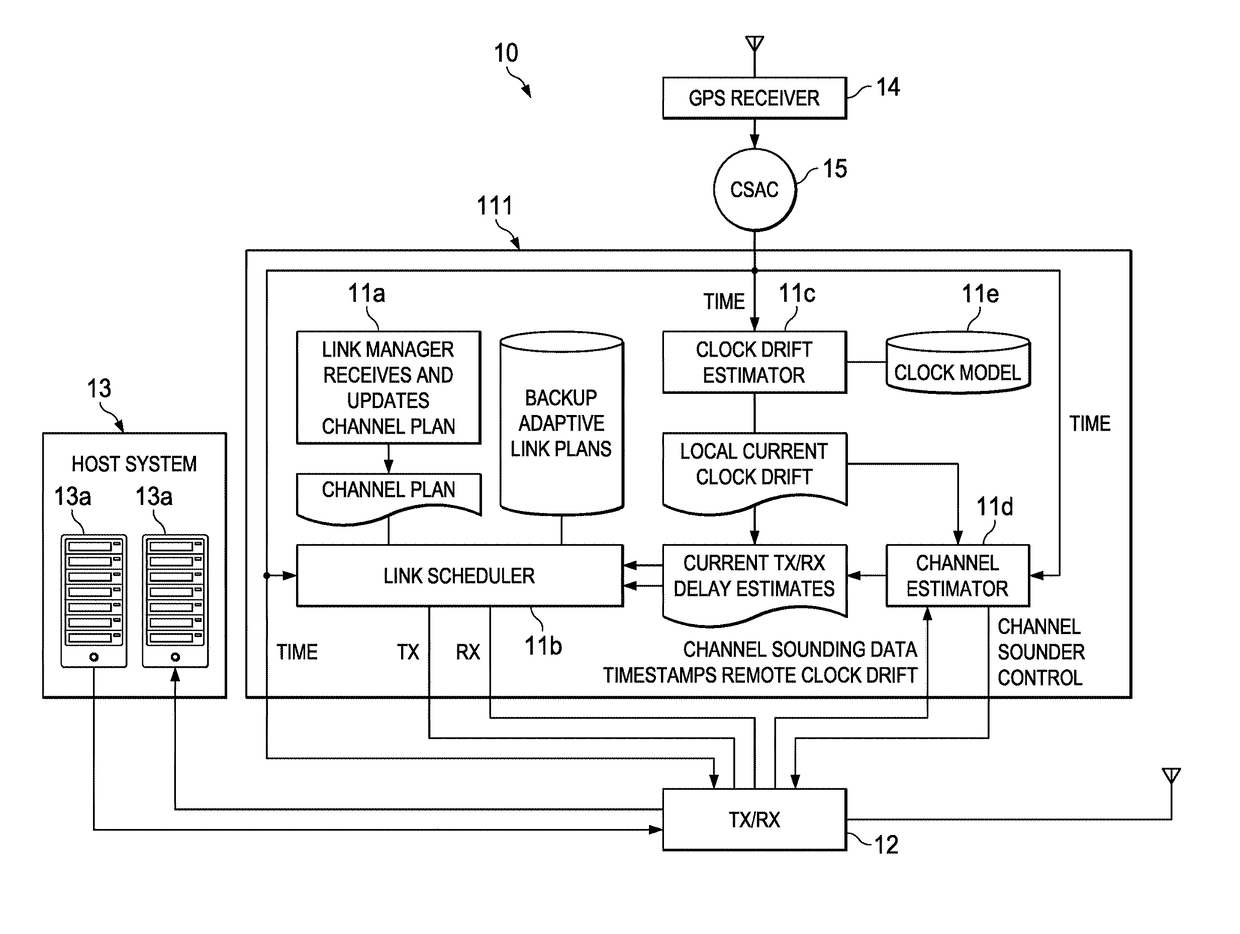
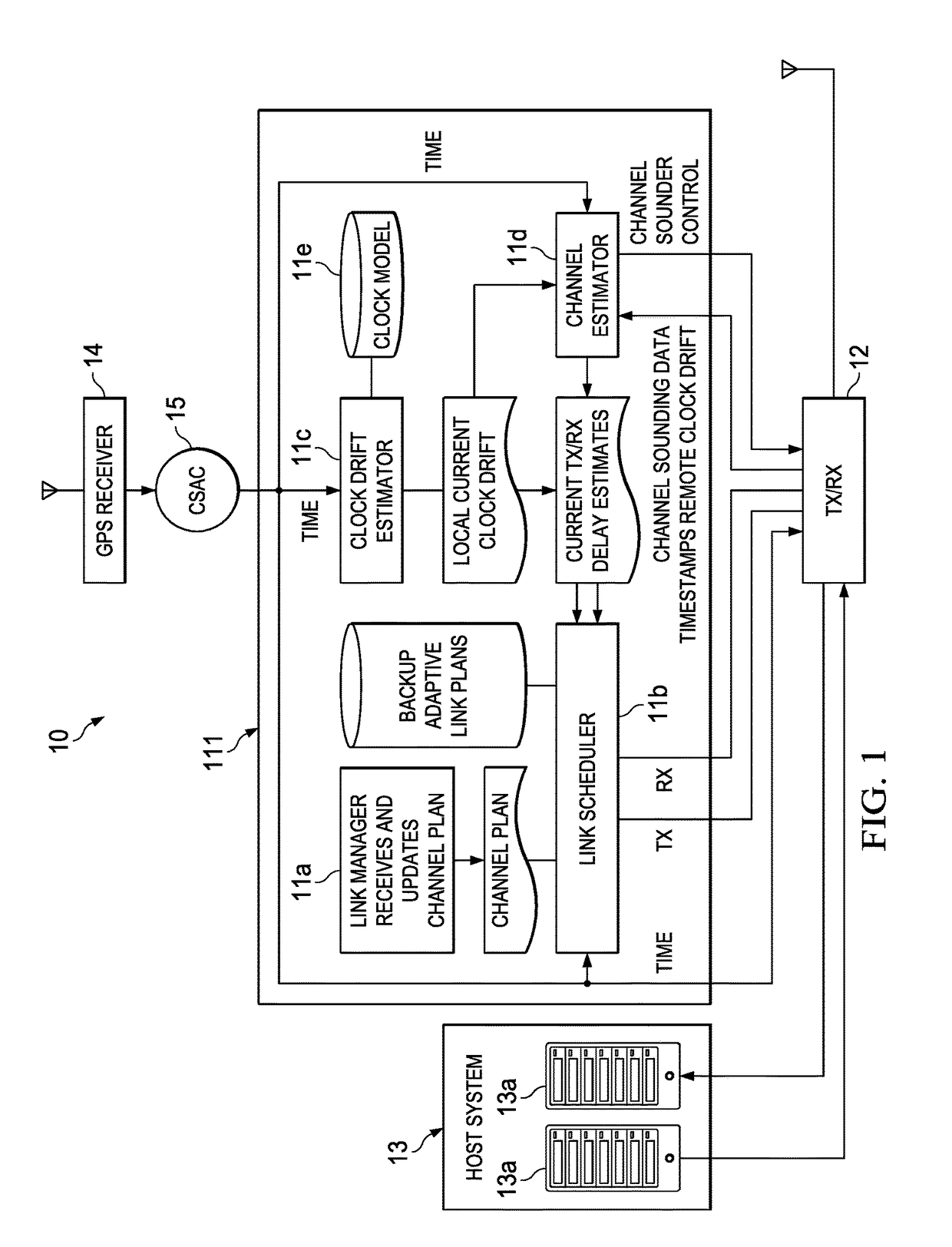
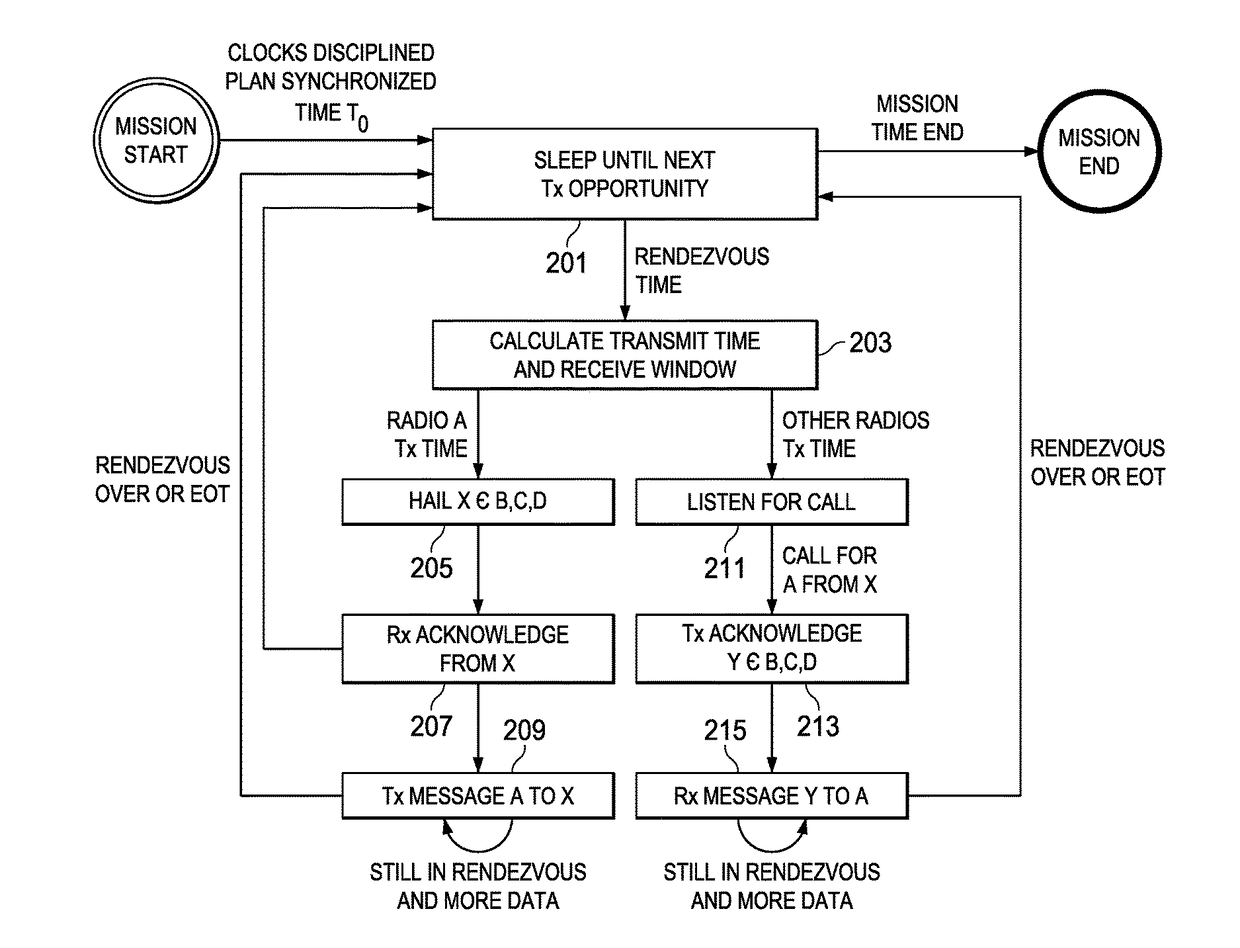
ActiveUS10123294B2Reduce power consumptionReduce the amount requiredSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexPropagation delayRadio equipment
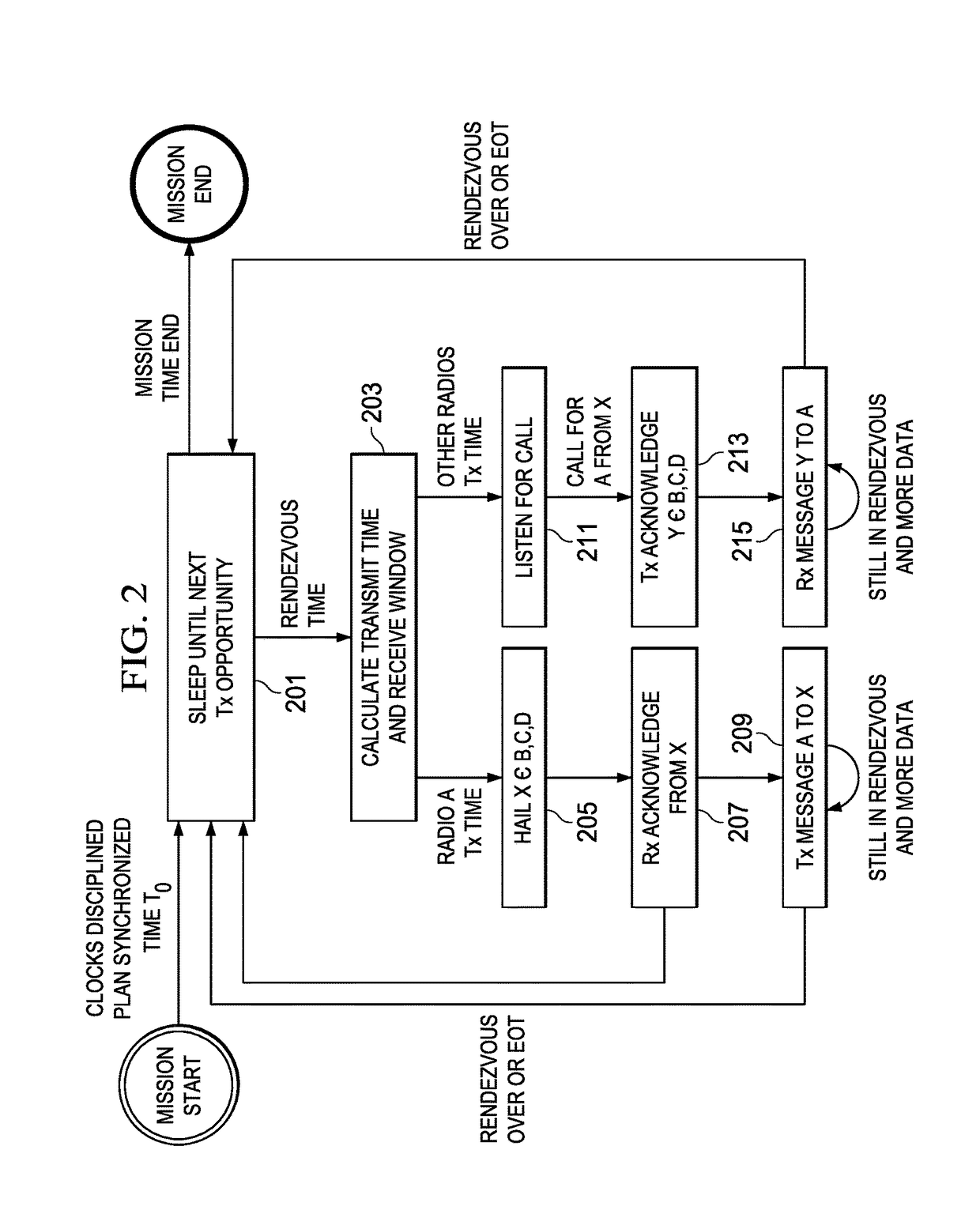
A method of synchronizing the transmission and receipt of messages by radios within a wireless communications network. It is assumed that the radios have chip scale atomic clocks, which are externally synchronized, such as by GPS, but only at the beginning of a mission. Each radio defaults to a sleep mode, in which its receive and transmit circuitry is inactive. Each radio stores a channel plan of pre-determined base transmit times, and calculates a worst case time drift between clocks and a propagation delay value between combinations of radios. At each base transmit time, if a radio has an outgoing message to transmit, it subtracts propagation delay from the base transmit time, and transmits only at that time. Also, for each base transmit time, each radio subtracts time drift, thereby determining a receive time window during which it listens for messages from other radios.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Chip level atomic clock based long code signal receiver processing method of navigation satellite
ActiveCN109425877AImprove performanceShorten positioning timeSatellite radio beaconingNoise bandwidthCoherent integration
The invention relates to a chip level atomic clock based long code signal receiver processing method of a navigation satellite, and belongs to data processing methods. The method comprises the steps that 1) a satellite signal is captured from one selected from cold-start, hot-start and unlocked relocation states; 2) the satellite signal is tracked by (2.1) a tracking loop equivalent noise bandwidth is reduced, a chip level atomic clock is used, errors are reduced and the precision is improved; and (2.2) coherent integration time of the tracking loop is prolonged, the chip level atomic clock isused, and the integration time is increased from 1ms to 1s; and 3) navigational positioning is carried out. The method has the advantages that the chip level atomic clock is used instead of a traditional crystal oscillator, as a temperature compensating or temperature-constant crystal oscillator in design of the satellite receiver, the chip level atomic clock is characterized by small size and low power consumption, and the chip level atomic clock can serve as the high-precision board-level clock for portable equipment.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
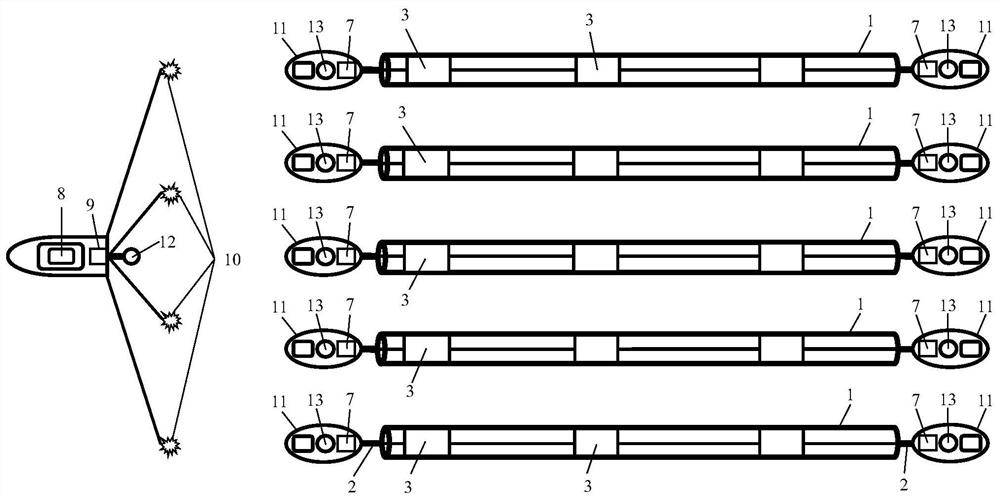
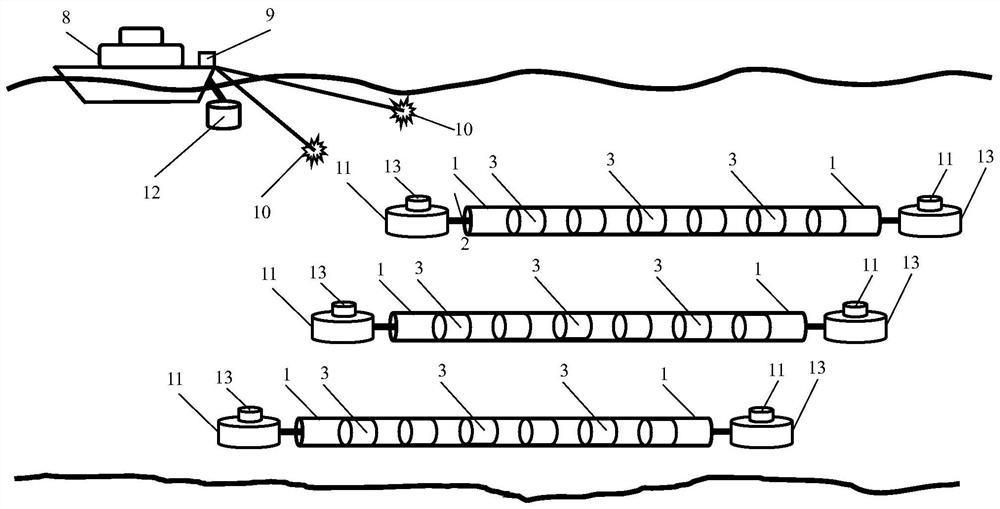
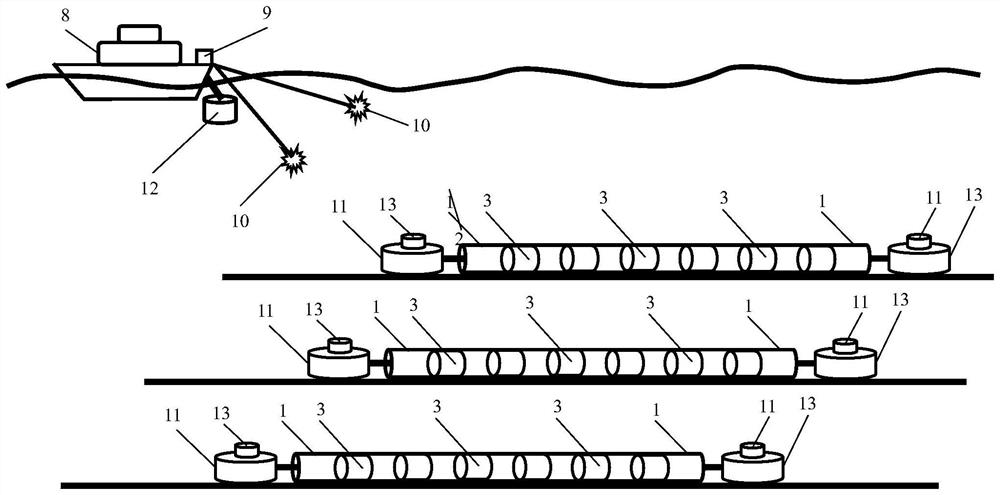
Deep-sea seismic data acquisition towing cable based on deep-sea robot and acquisition method
PendingCN112817048AHigh sensitivityBandwidthSeismic signal receiversSeismic signal transmissionData acquisitionEngineering
The invention provides a deep-sea seismic data acquisition towing cable based on a deep-sea robot and an acquisition method. The deep-sea robot is used for towing the array type marine seismic data acquisition towing cable in the deep sea, and single-component or multi-component marine seismic data can be directly acquired in the deep sea. The pull-type or bottom-sinking array type marine seismic data acquisition cable is composed of three-component wave detectors or sensors, piezoelectric crystals or optical fiber sound pressure hydrophones and electronic or optical fiber three-component attitude sensors, wherein the three-component wave detectors or sensors, the piezoelectric crystals or the optical fiber sound pressure hydrophones and the electronic or optical fiber three-component attitude sensors are evenly distributed in the cable. The head end and the tail end of each seismic data acquisition towing cable are respectively towed by a deep-sea robot; the cable is connected with a seismic data acquisition and storage instrument or a modulation and demodulation instrument on the deep-sea robot; and a high-precision chip-level atomic clock in the seismic data acquisition and storage instrument or the modulation and demodulation instrument is used for timing the acquired marine seismic data and carrying out time synchronization and data processing on excitation signals of an underwater controllable air gun seismic source in the later period.
Owner:OPTICAL SCI & TECH (CHENGDU) LTD
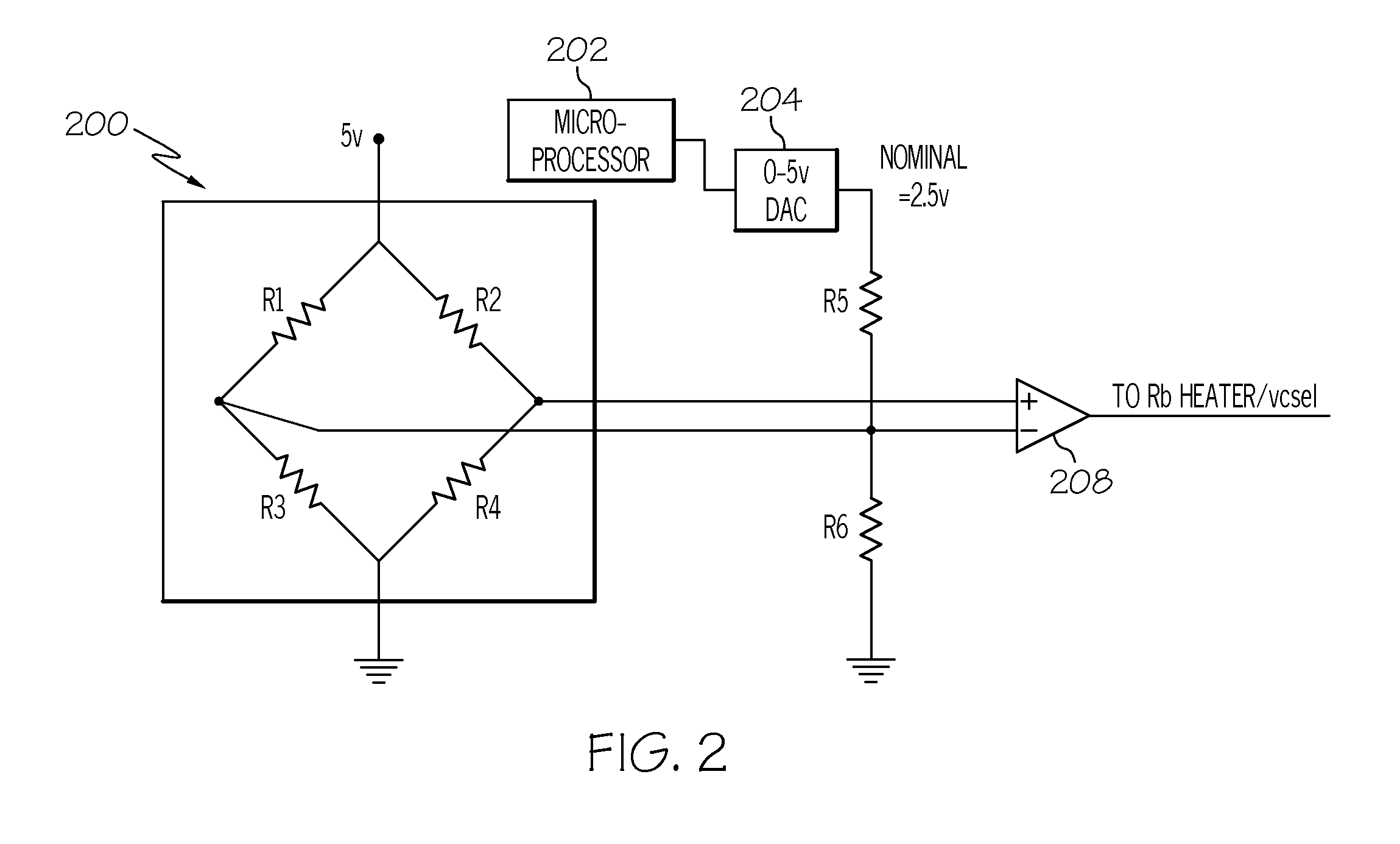
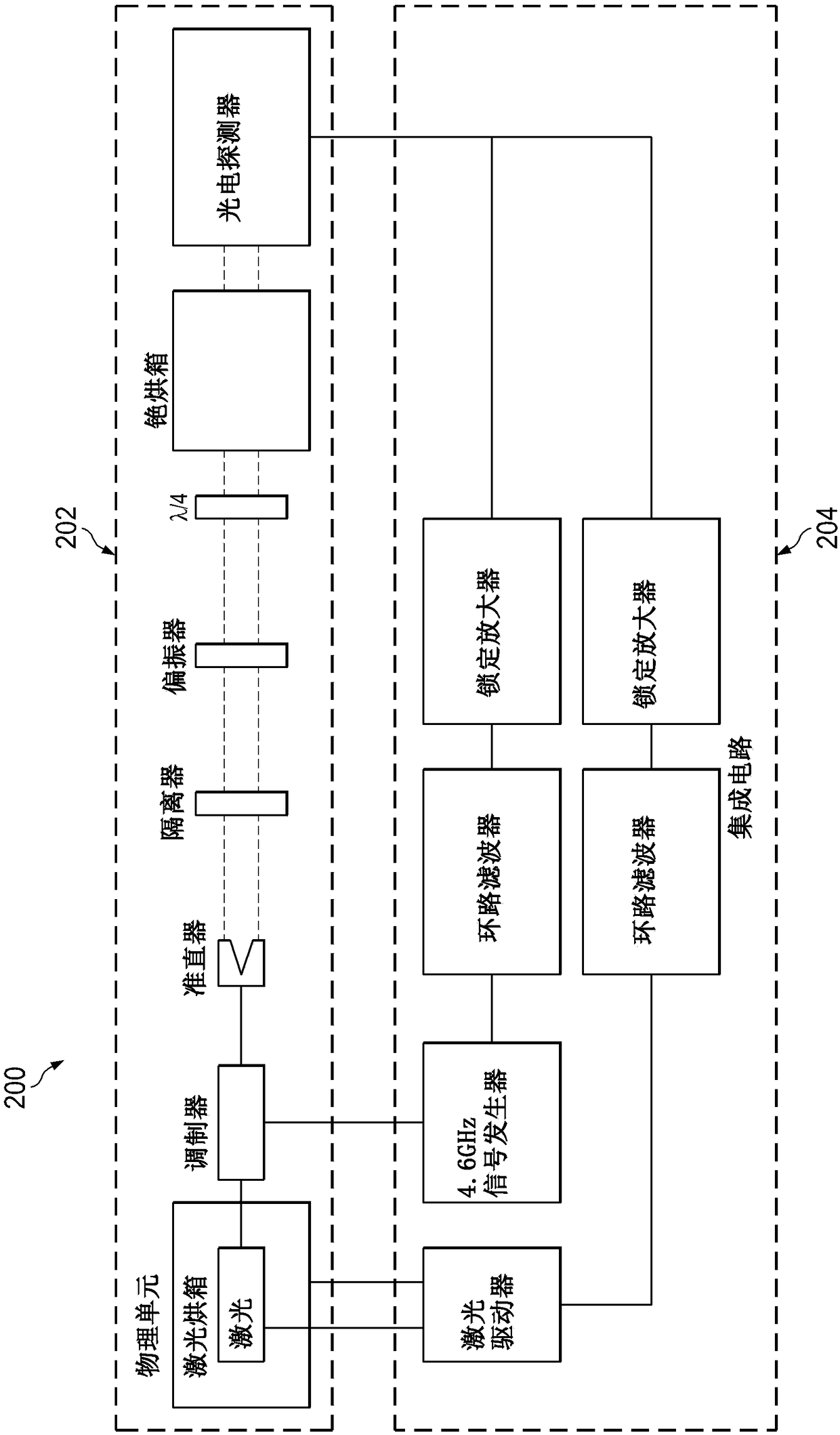
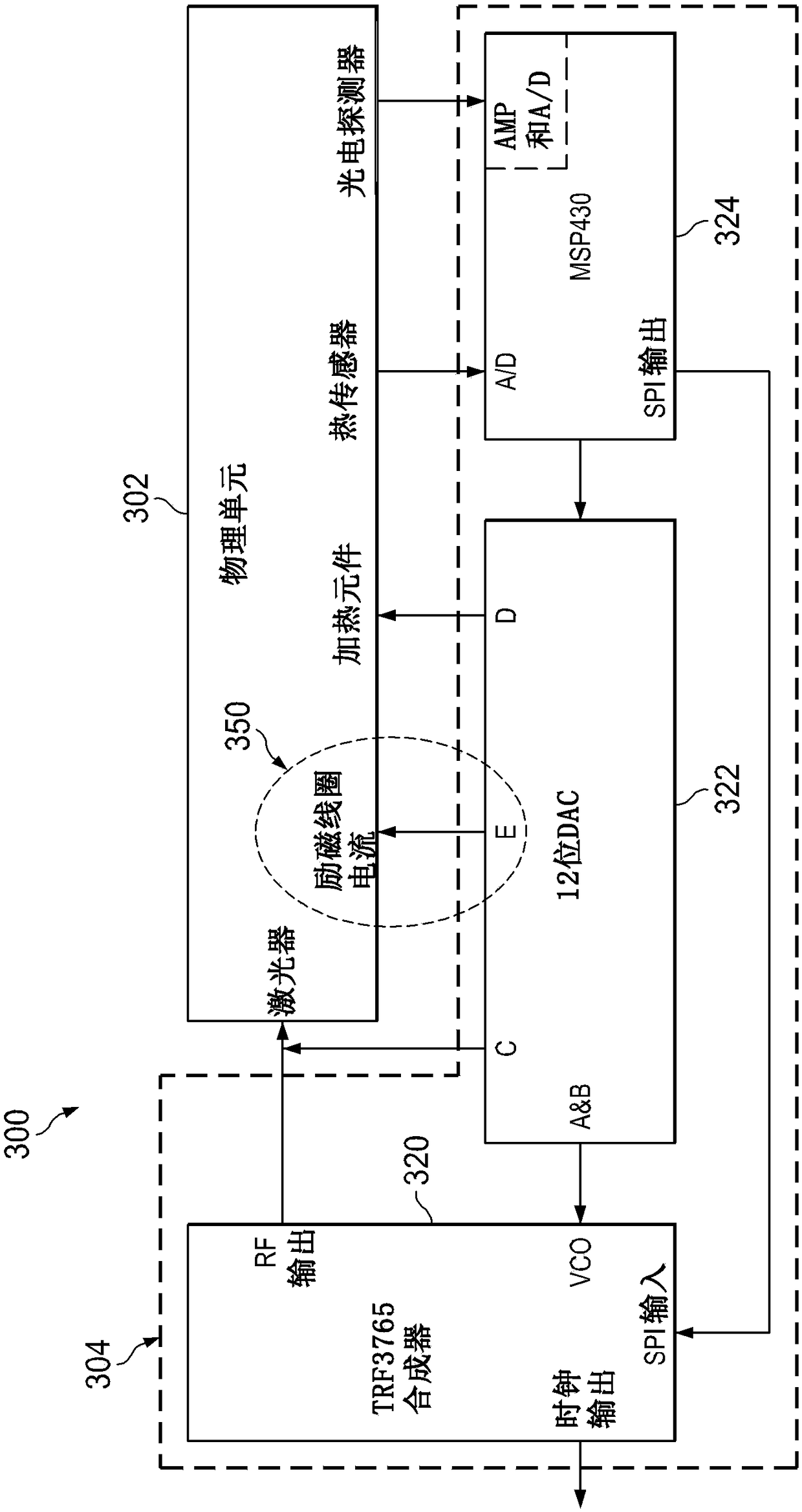
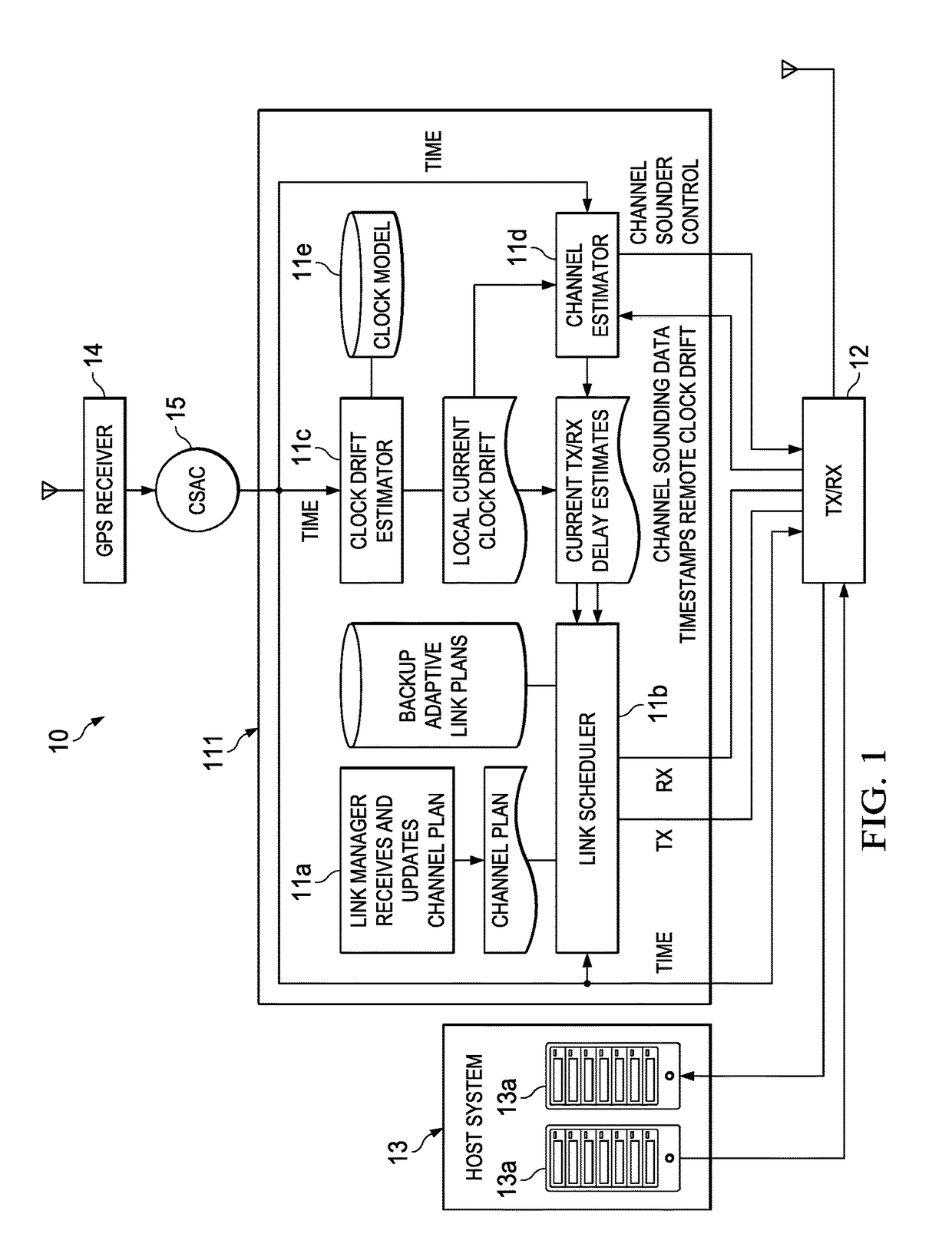
Methods and apparatus for magnetically compensated chip scale atomic clock
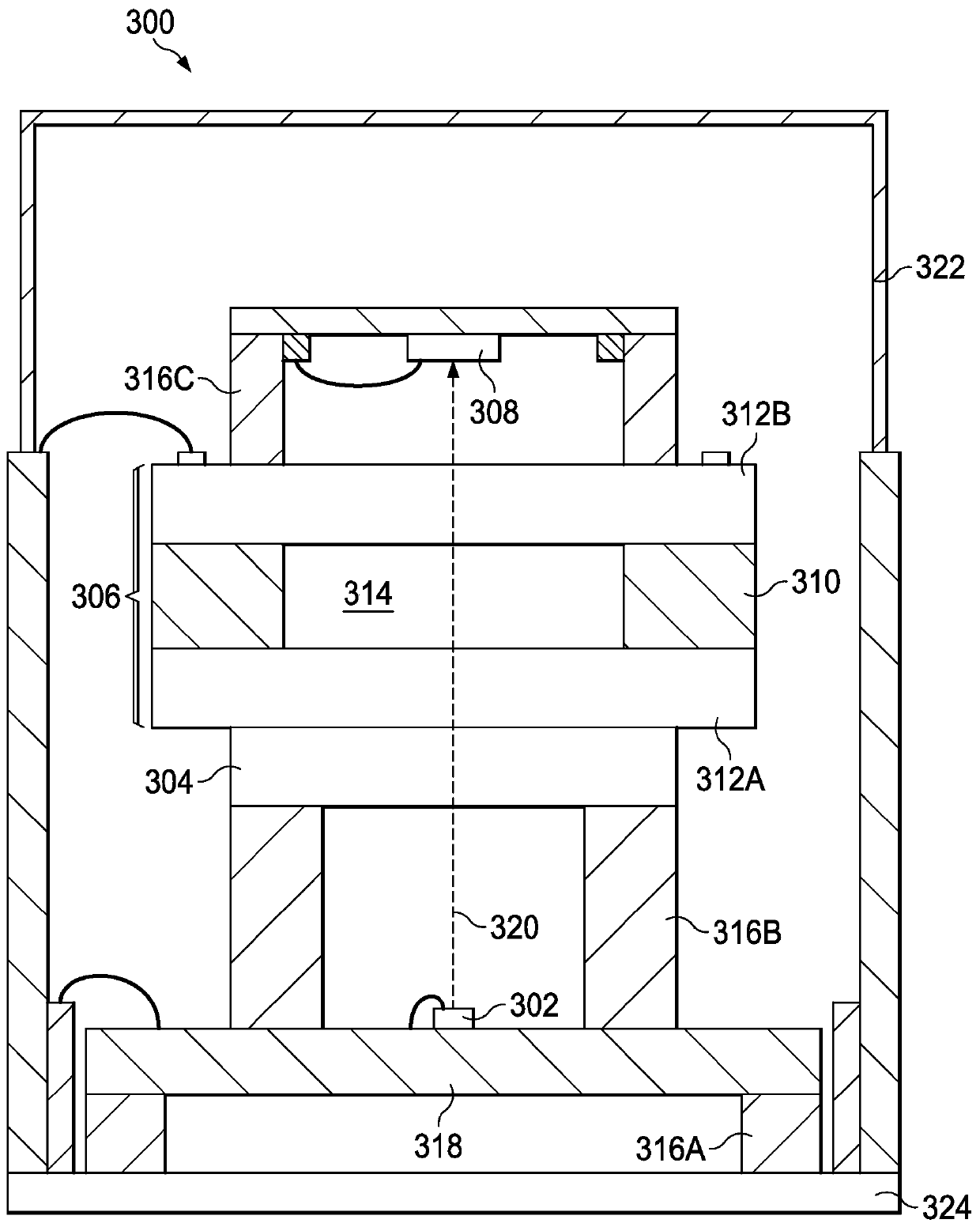
The application relates to methods and apparatus for magnetically compensated chip scale atomic clock. In described examples, an apparatus includes: a physics cell(302) including: a laser source configured to emit light towards an atomic chamber containing an atomic gas; a photodetector configured to receive emissions from the atomic chamber; and a coil for generating a magnetic field in the atomic chamber; and an electronics circuit(304), including: a controller circuit(324) coupled to the photodetector output and having control outputs to a digital to analog converter circuit(322); the digital to analog converter circuit having a coil current output(E) to adjust the magnetic field, a modulation control output to control a modulation of the light(C), and having an output(A&B) to control avoltage controlled oscillator; and a radio-frequency output circuit(320) having a voltage controlled oscillator coupled to the output of the digital to analog converter circuit and outputting a radiofrequency signal to the laser(LASER) source in the physics cell(302).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
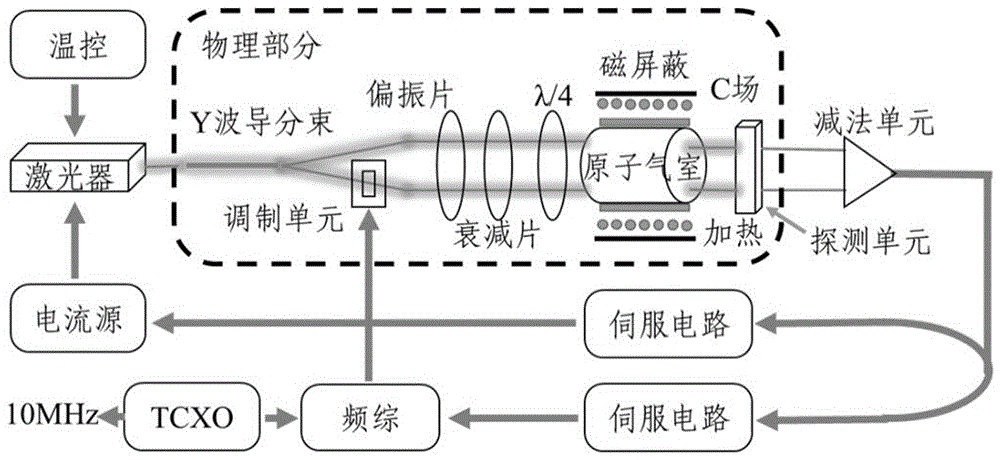
Apparatus and method for vapor cell atomic frequency reference having improved frequency stability
ActiveCN110361959APulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksFrequency stabilizationElectricity
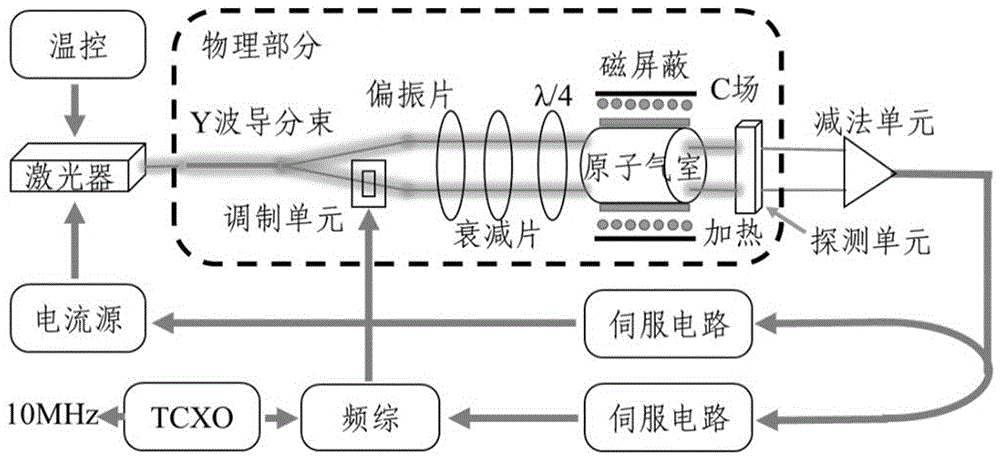
The invention provides an apparatus and method for a vapor cell atomic frequency reference having improved frequency stability. A chip scale atomic clock (CSAC) is provided. The CSAC comprises a temperature stabilized physics system, comprising a vapor cell and a magnetic field coil, and which is enclosed in a magnetic shield; and a temperature stabilized electronics circuitry electrically coupledto the temperature stabilized physics system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Media Access Control Method With Time-Coherence and Deterministic Scheduling for Wireless Communications Network
ActiveUS20170303223A1Reduce power consumptionReduce the amount requiredSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexPropagation delayRadio equipment
A method of synchronizing the transmission and receipt of messages by radios within a wireless communications network. It is assumed that the radios have chip scale atomic clocks, which are externally synchronized, such as by GPS, but only at the beginning of a mission. Each radio defaults to a sleep mode, in which its receive and transmit circuitry is inactive. Each radio stores a channel plan of pre-determined base transmit times, and calculates a worst case time drift between clocks and a propagation delay value between combinations of radios. At each base transmit time, if a radio has an outgoing message to transmit, it subtracts propagation delay from the base transmit time, and transmits only at that time. Also, for each base transmit time, each radio subtracts time drift, thereby determining a receive time window during which it listens for messages from other radios.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
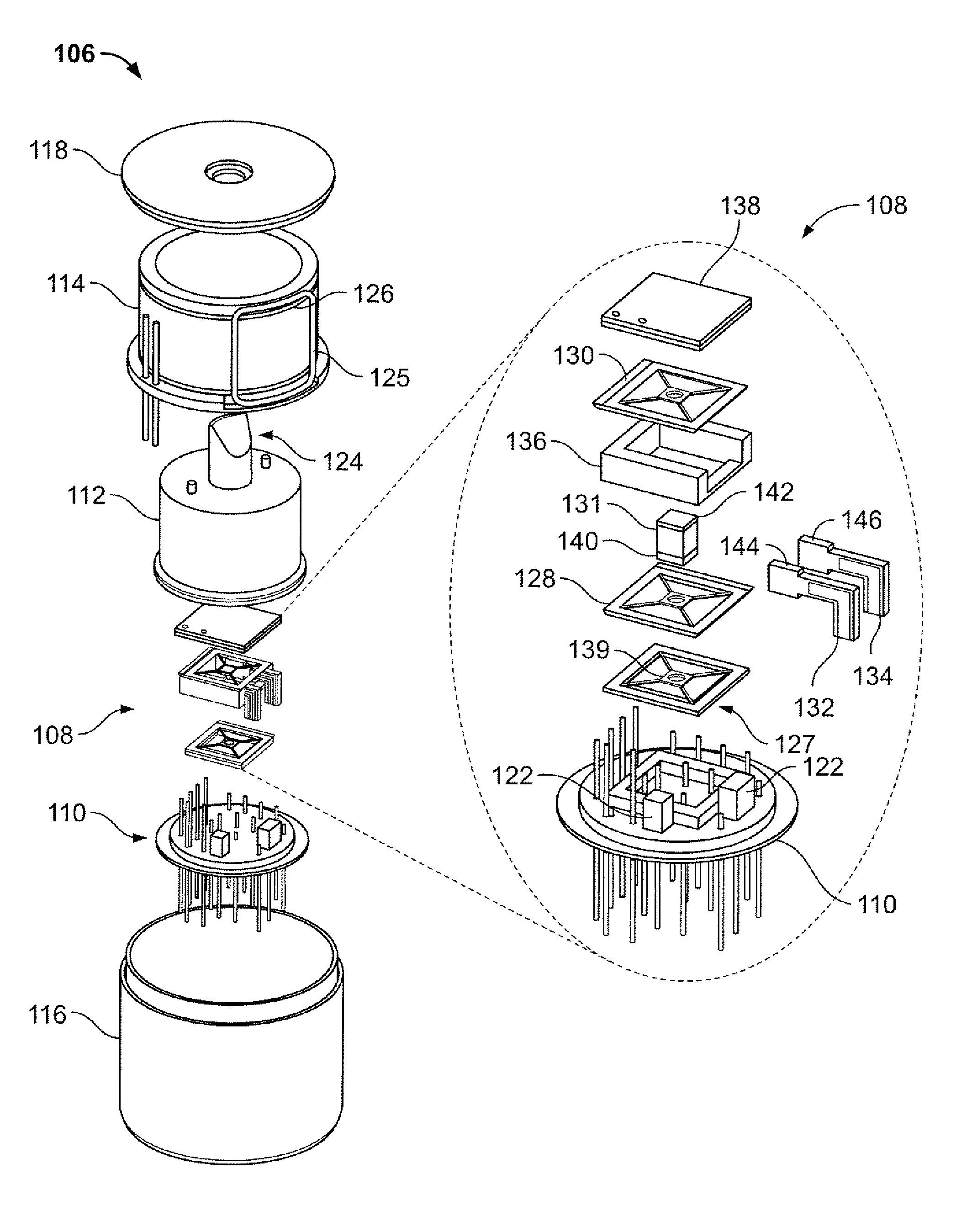
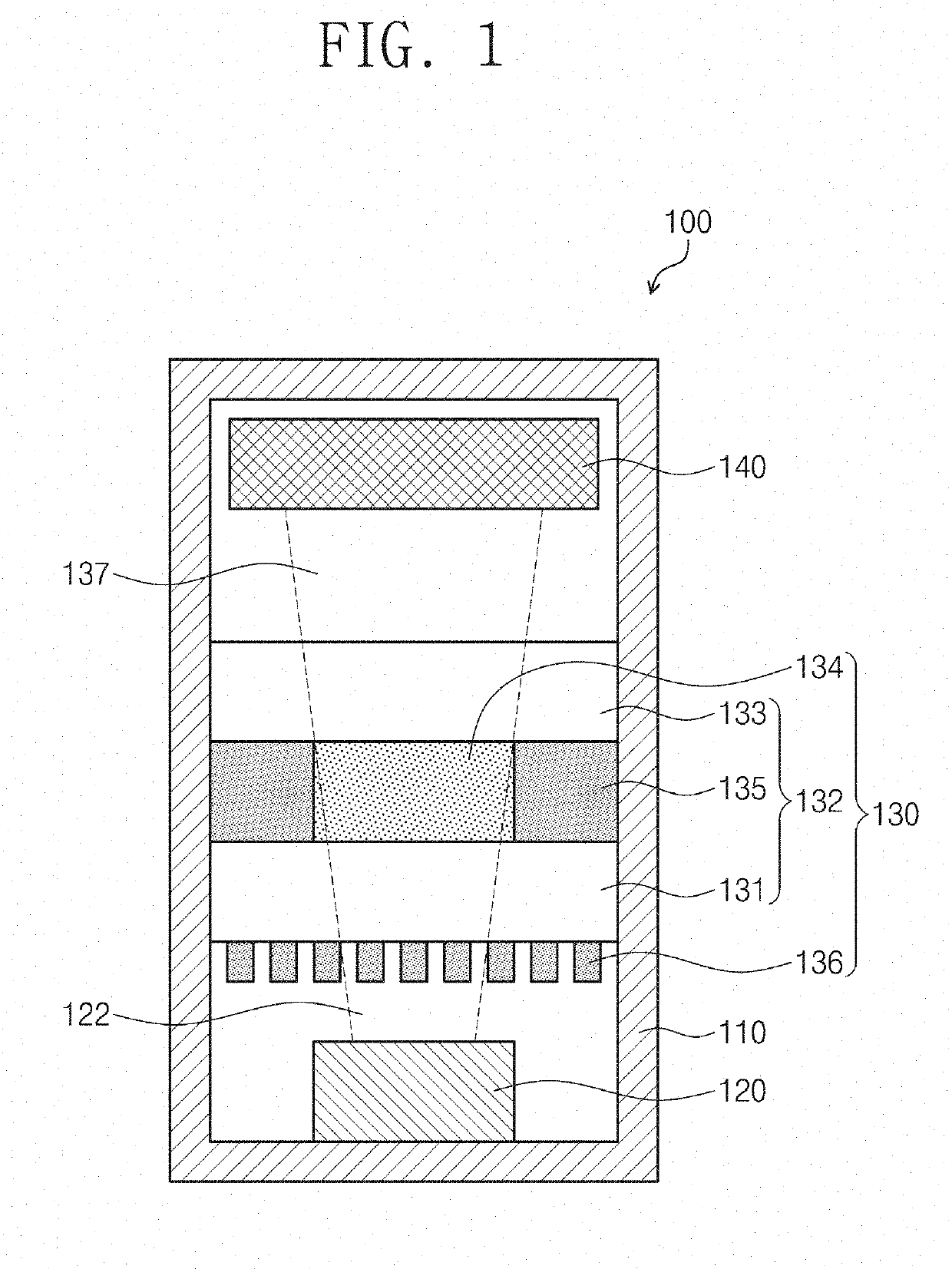
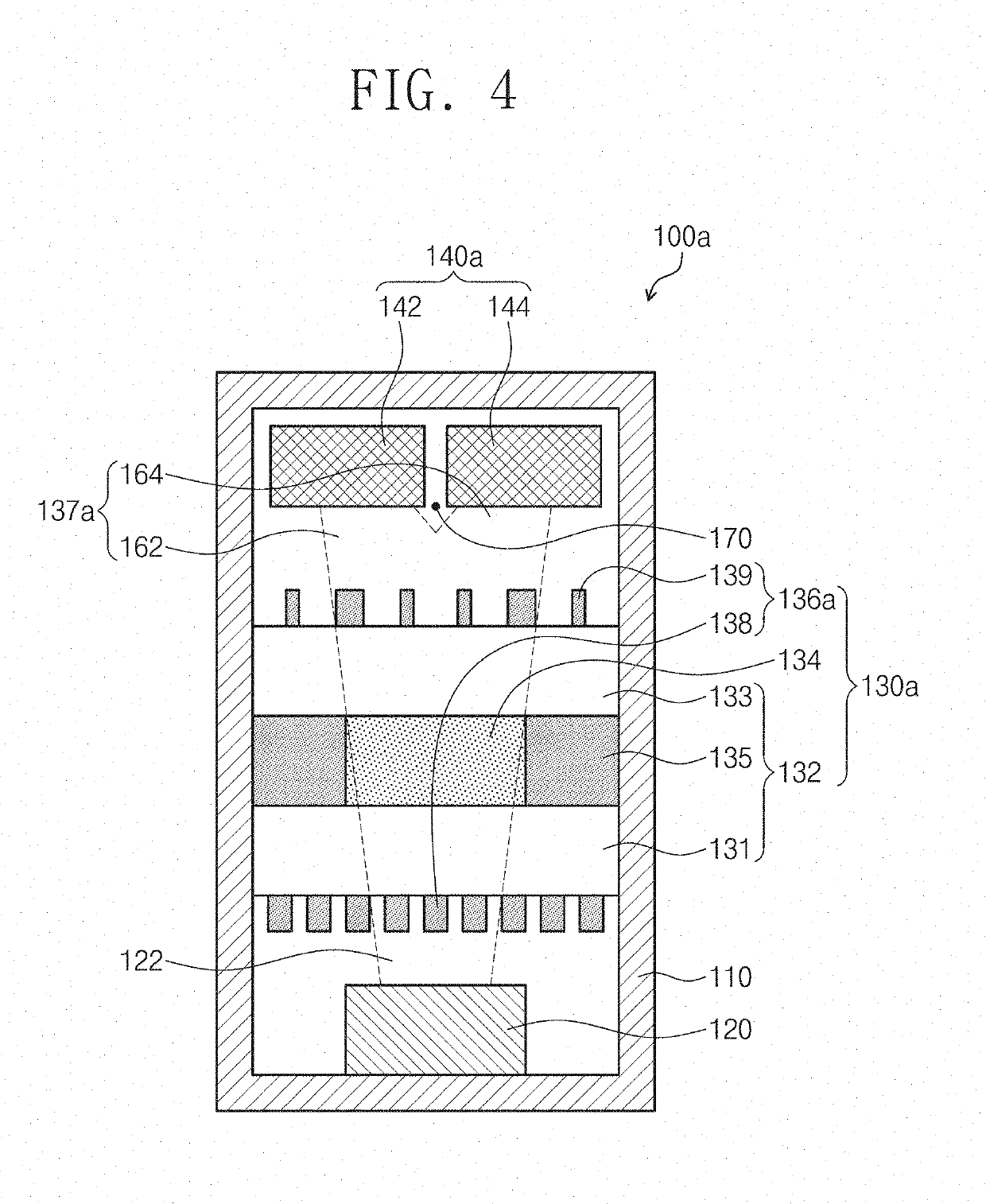
Physics module of chip-scale atomic clock
ActiveUS20190346815A1Reduce power consumptionReduce volume consumptionApparatus using atomic clocksPulse automatic controlLaser sourceChip-scale atomic clock
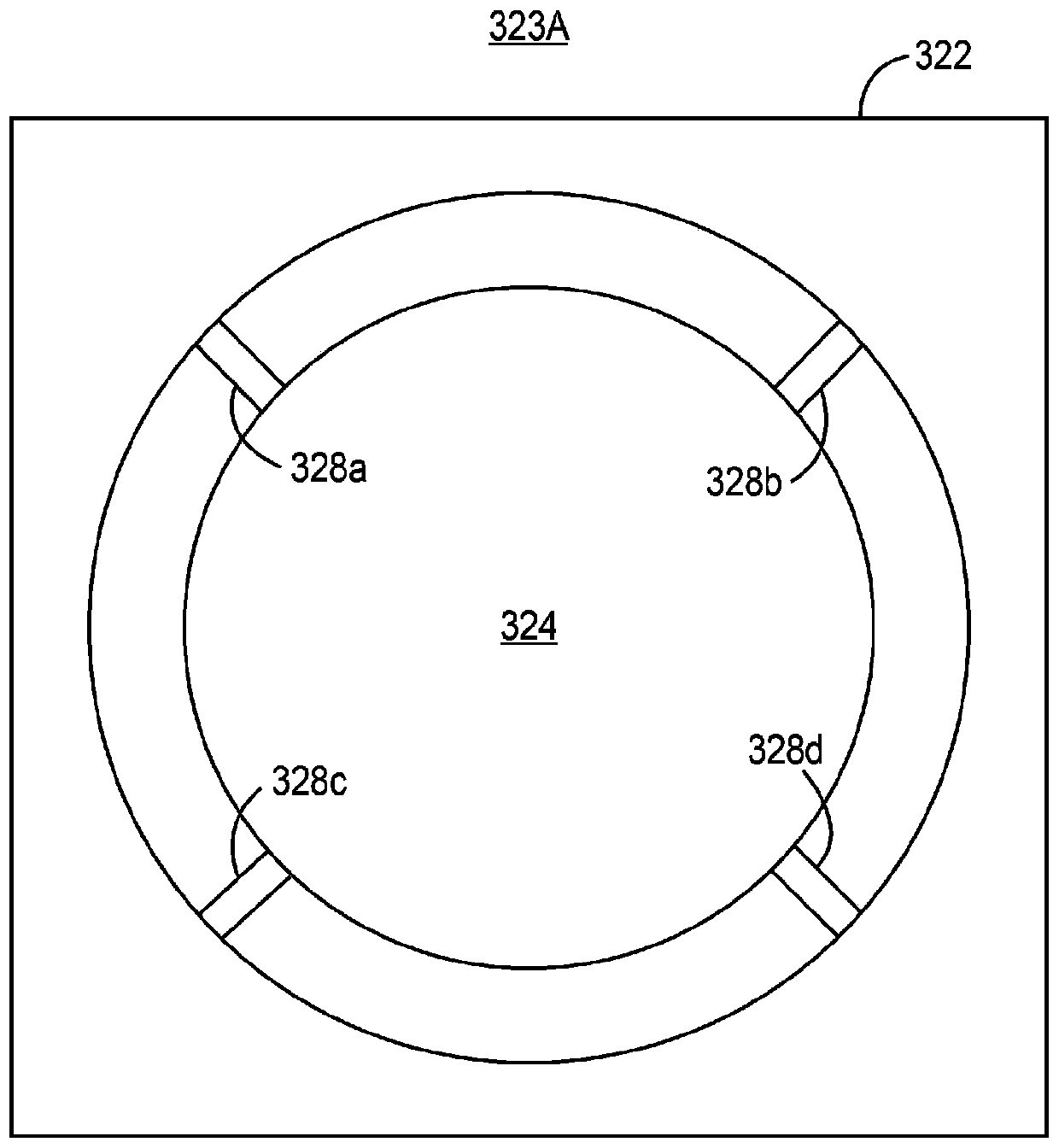
An embodiment of the inventive concept provides a physics module of a chip-scale atomic clock. The physics module includes: a housing; a laser source disposed in the housing and generating a laser beam; a vapor cell disposed above the laser source to generate a transmitted beam from the laser beam; and a detector disposed above the vapor cell to detect the transmitted beam. Here, the vapor cell may include a plurality of optical patterns configured to polarize the laser beam.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
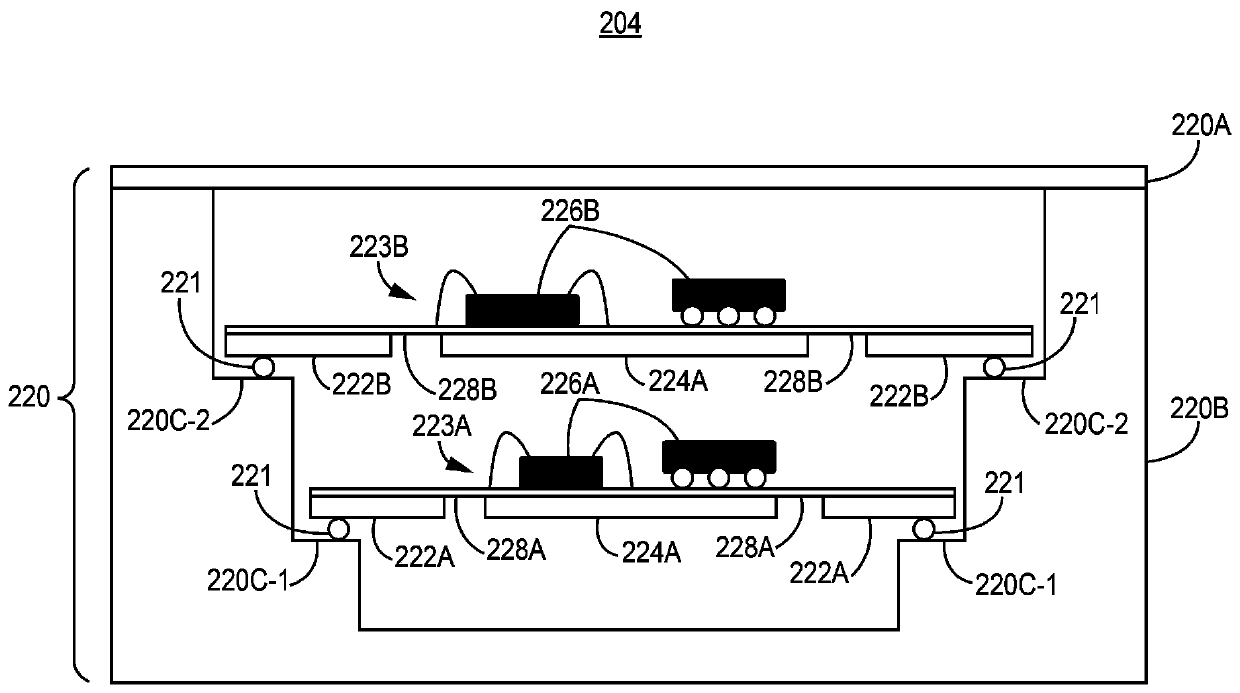
Package for chip scale magnetometer or atomic clock
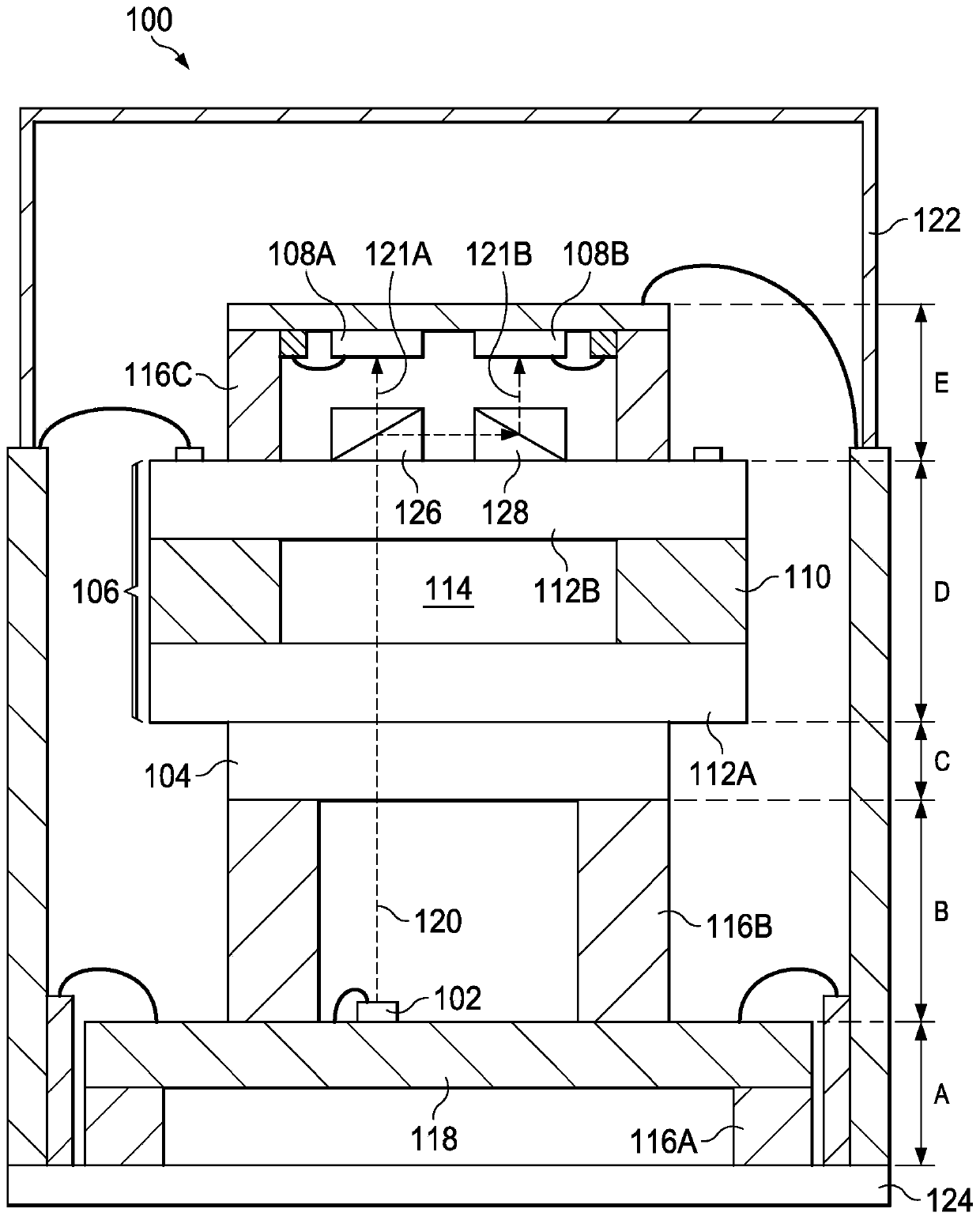
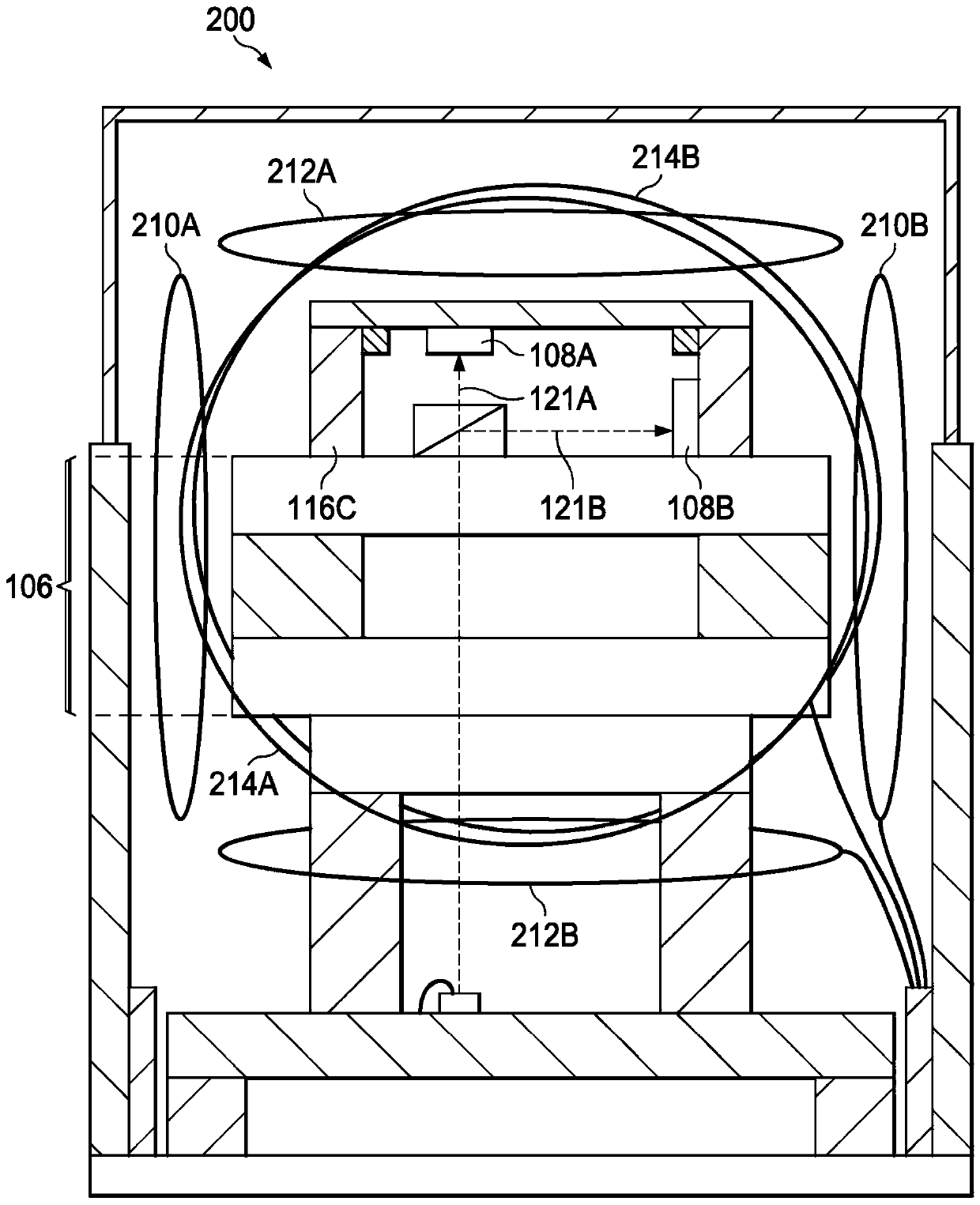
In described examples of a package (200) for a chip scale atomic clock or magnetometer, the package (200) includes a vapor cell using an alkali metal vapor, first and second photodetectors (108A, 108B), and a laser operable at a frequency that excites an electron transition in the alkali metal vapor. The laser is positioned to provide an optical signal directed through the vapor cell and towards the first photodetector (108A). The package (200) further contains a polarizing beam splitter, which is positioned between the vapor cell and the first photodetector (108A) to receive the optical signal and to split the optical signal into a first signal (121A) directed toward the first photodetector (108A) and a second signal (121B) directed toward the second photodetector (108B). The first signal(121A) is orthogonal to the second signal (121B).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com