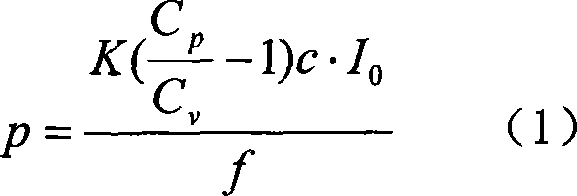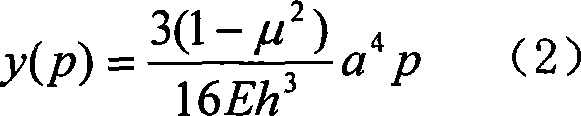Patents
Literature
225 results about "Fabry–Pérot interferometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
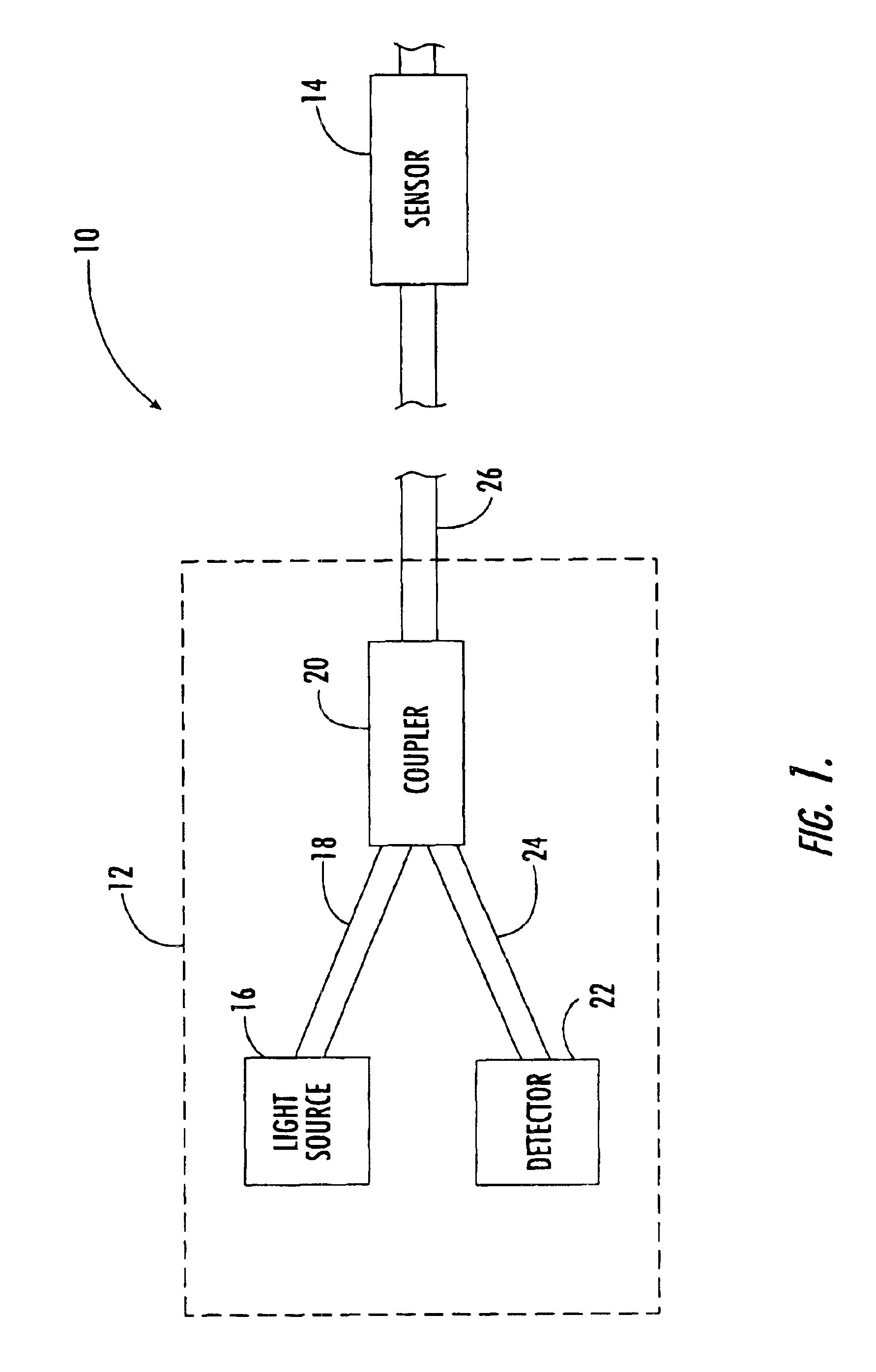
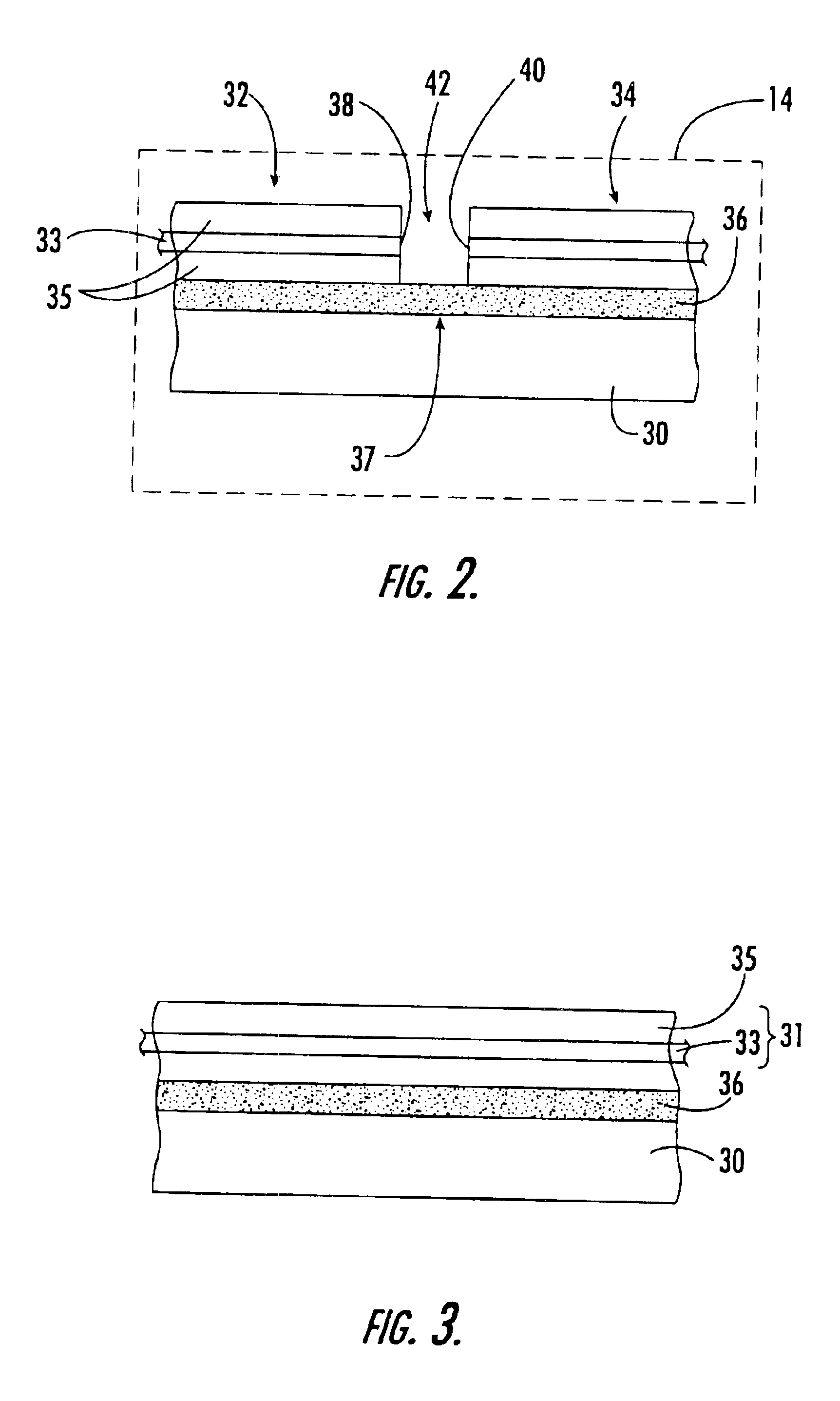
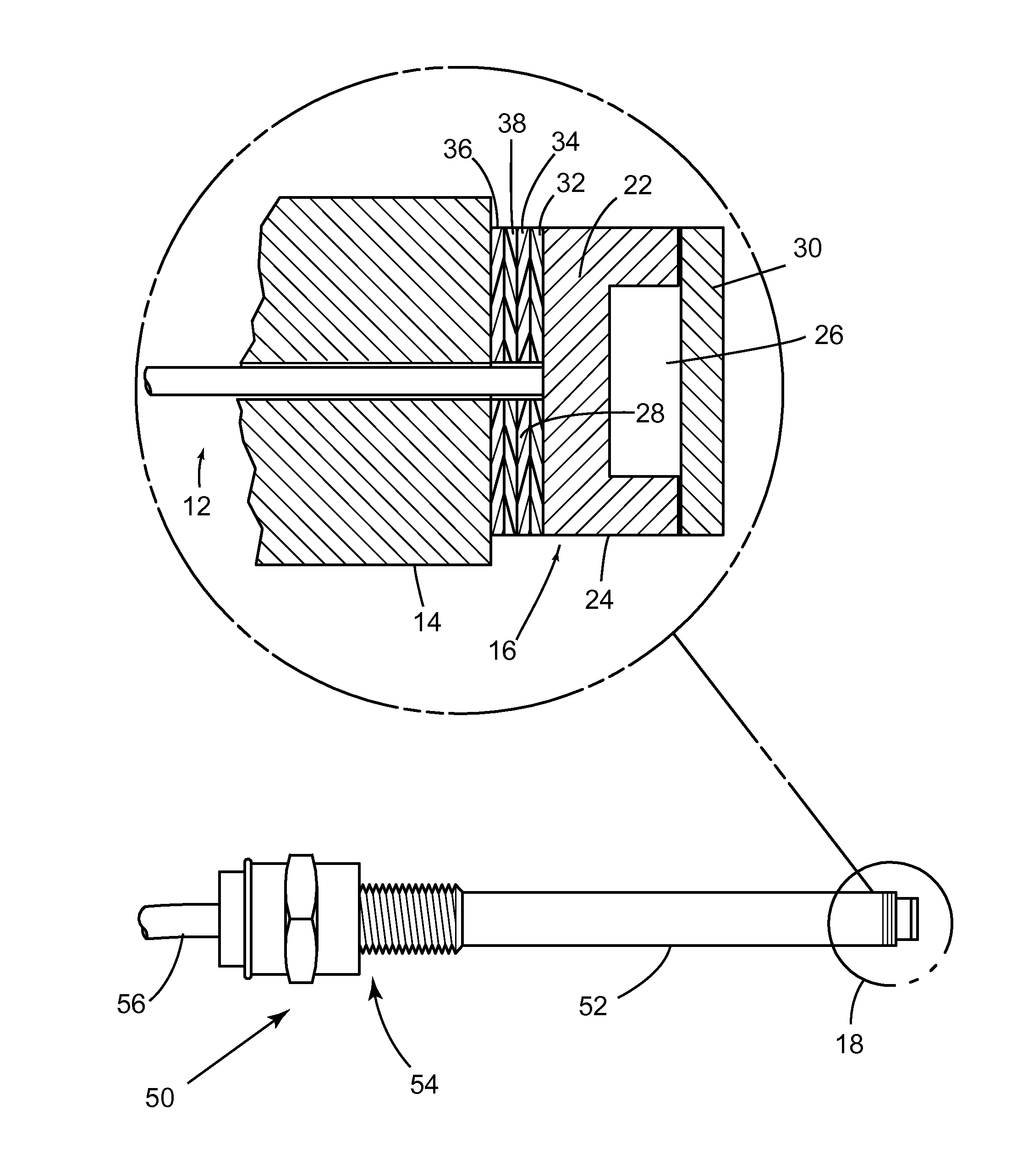
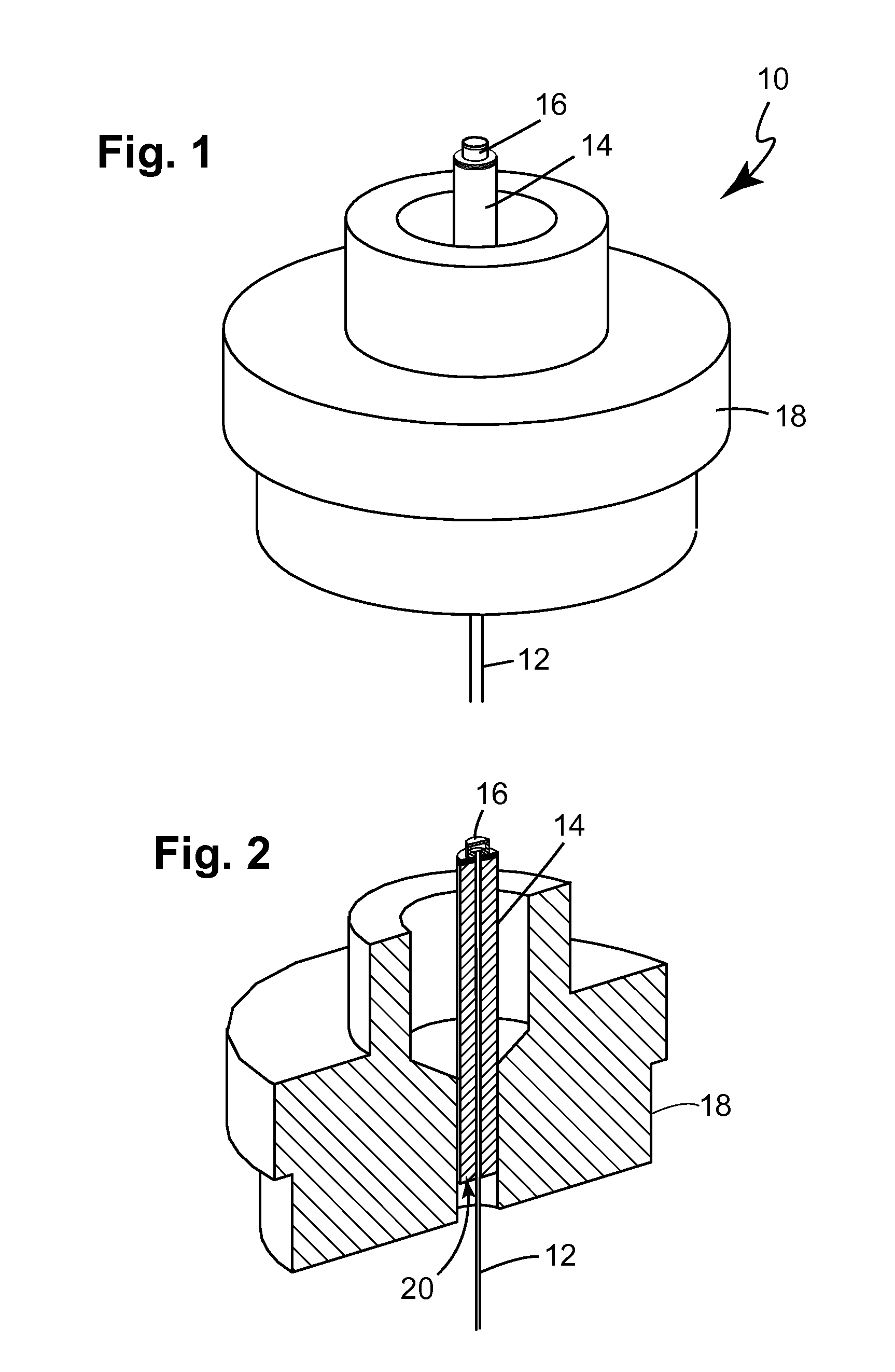
In optics, a Fabry–Pérot interferometer (FPI) or etalon is an optical cavity made from two parallel reflecting surfaces (i.e: thin mirrors). Optical waves can pass through the optical cavity only when they are in resonance with it. It is named after Charles Fabry and Alfred Perot, who developed the instrument in 1899. Etalon is from the French étalon, meaning "measuring gauge" or "standard".
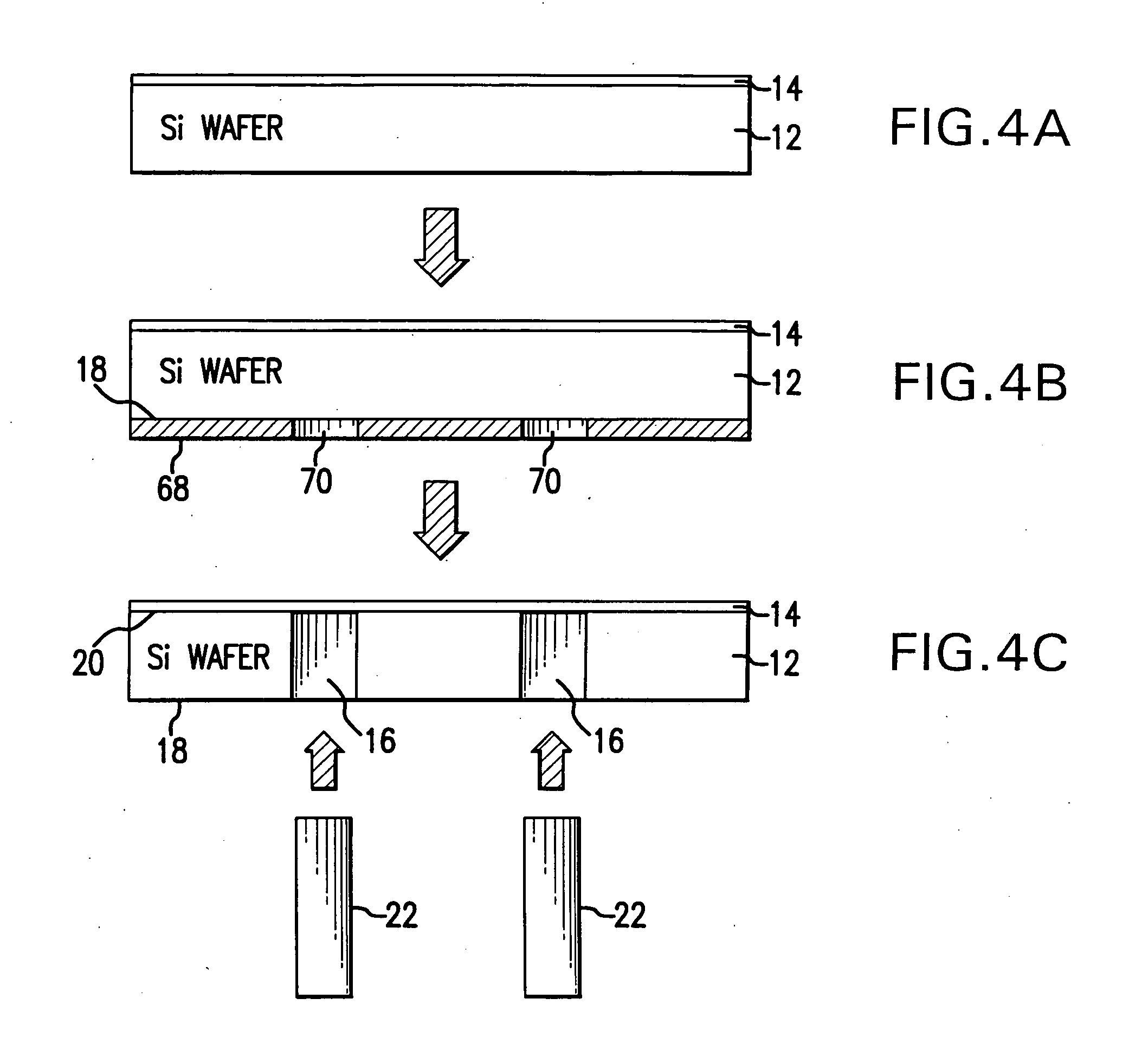
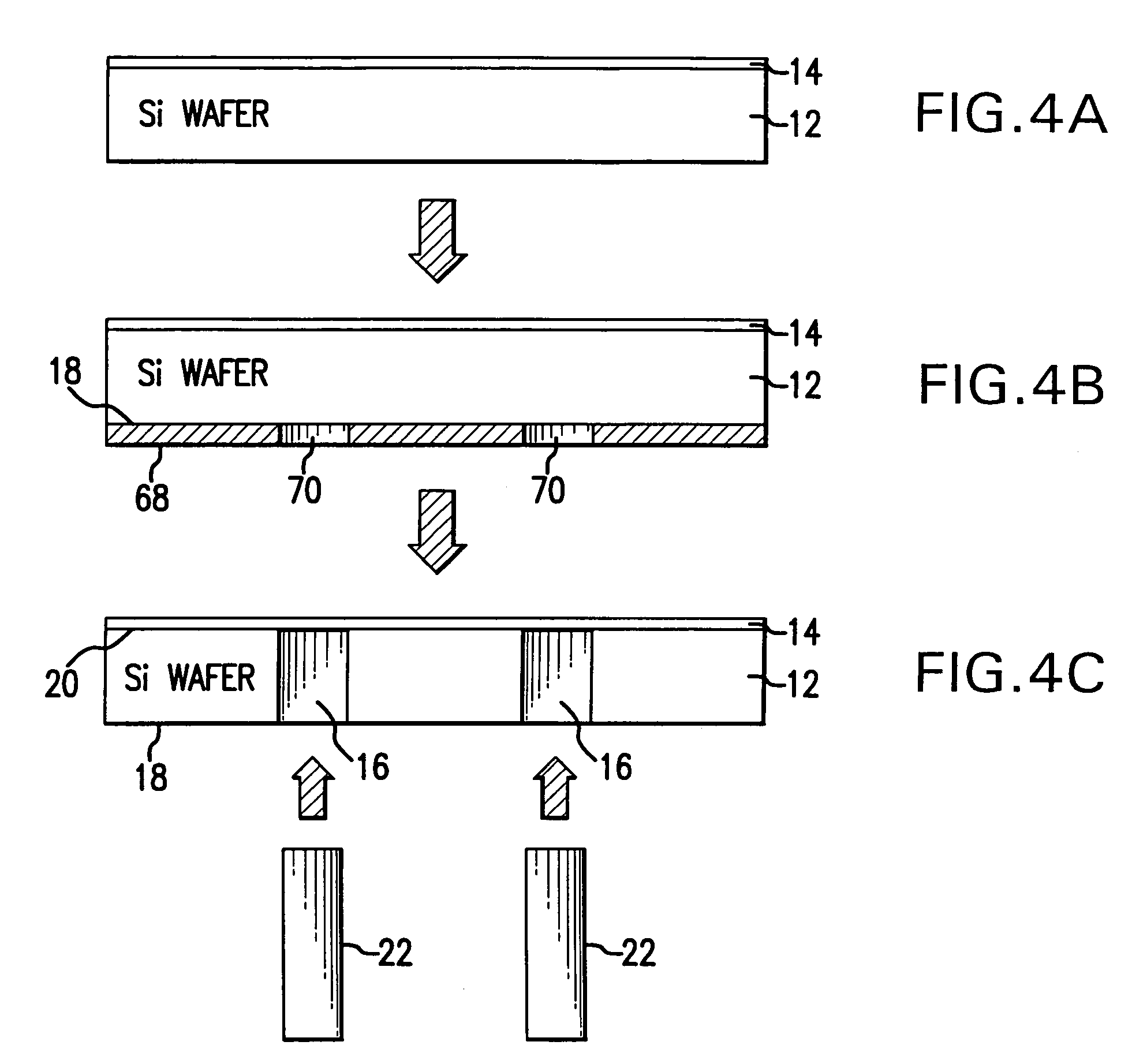
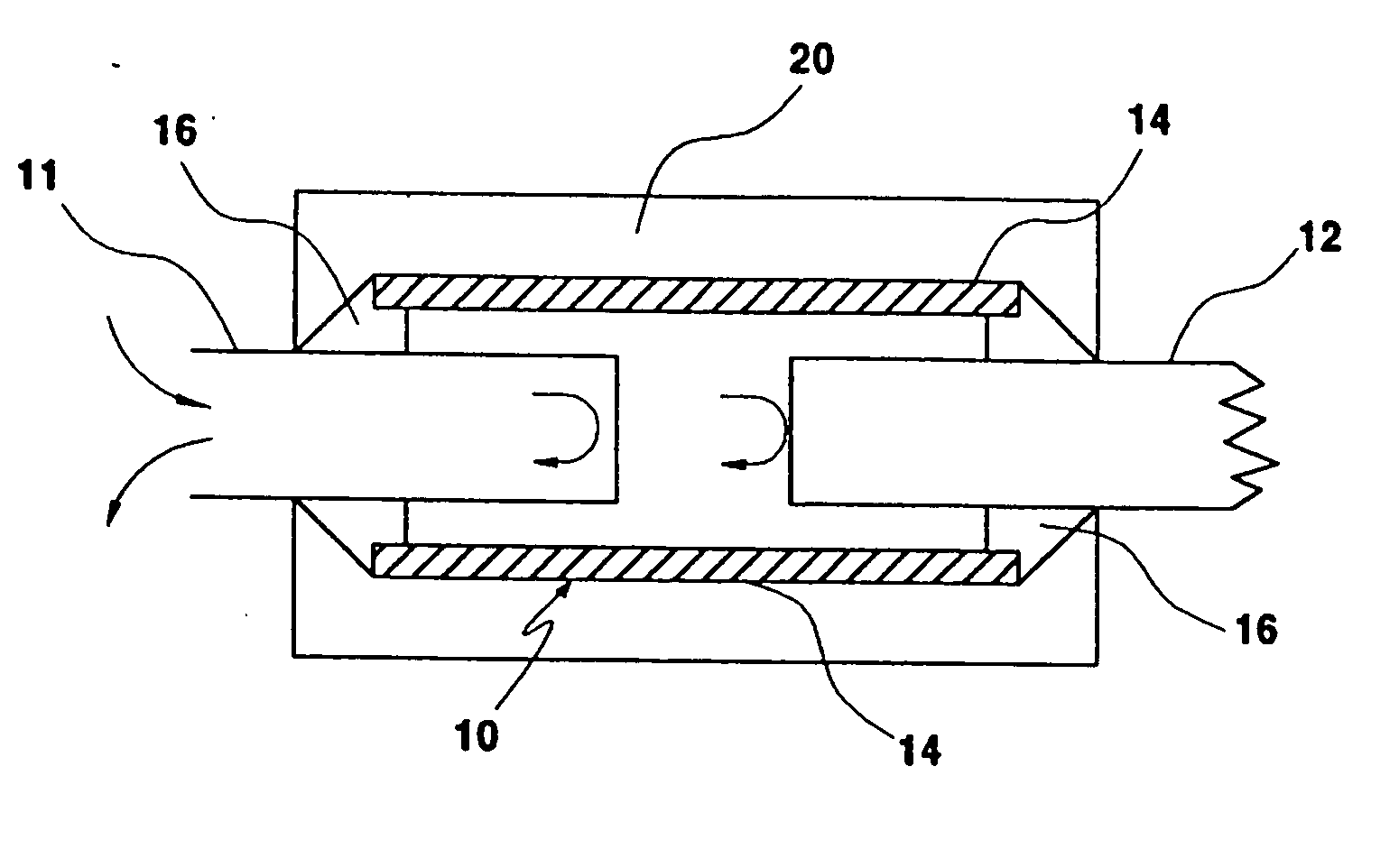
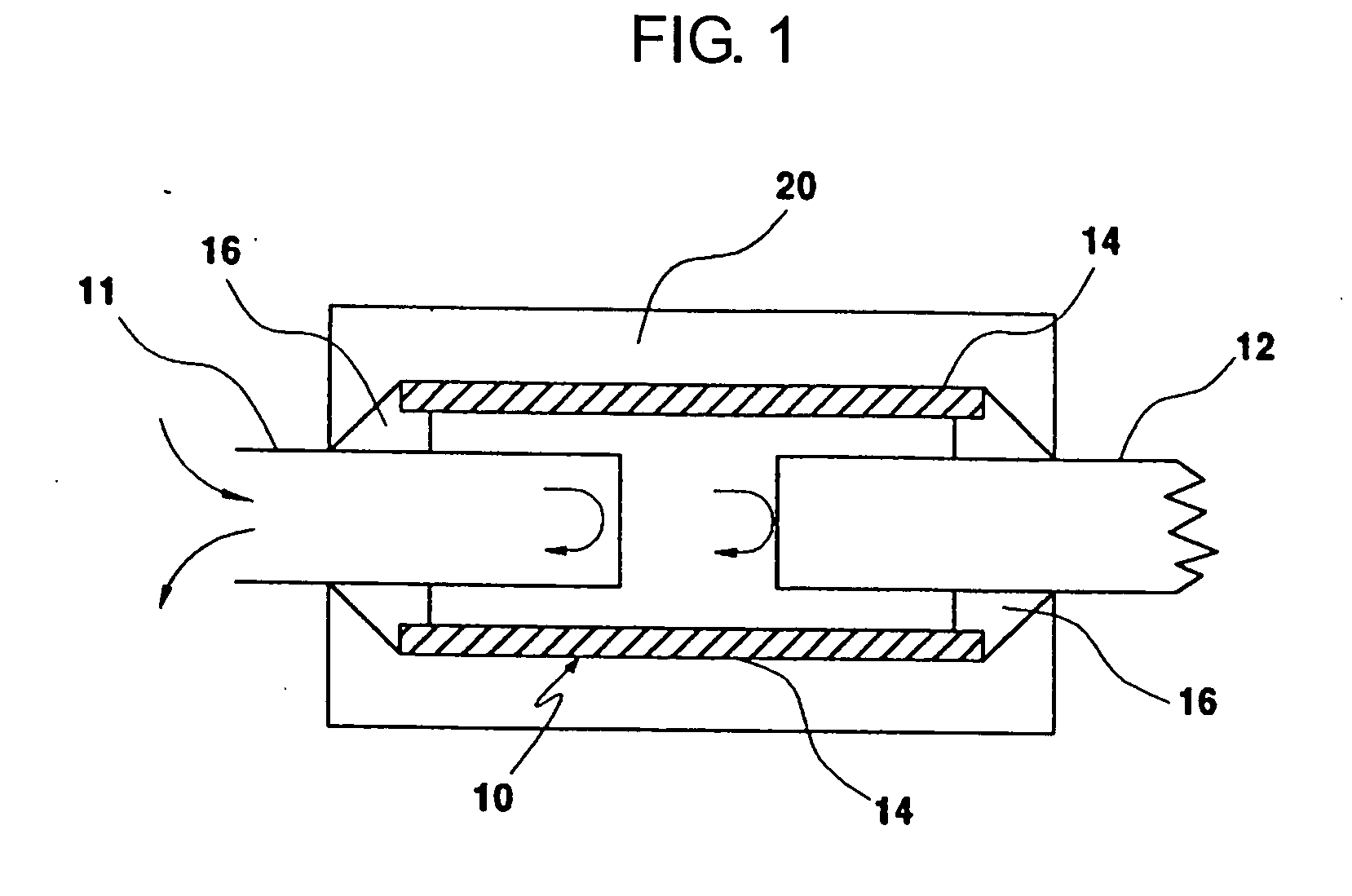
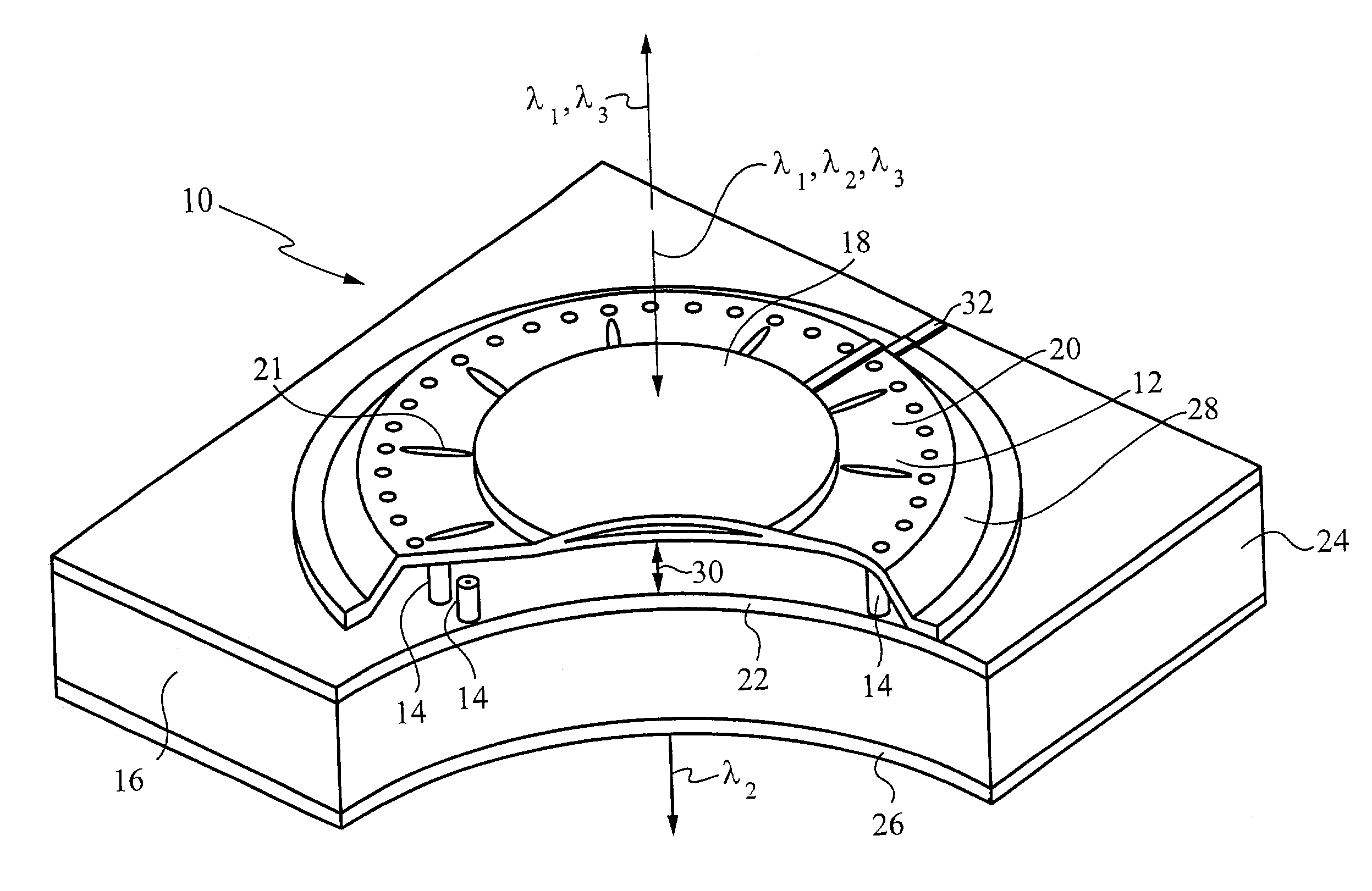
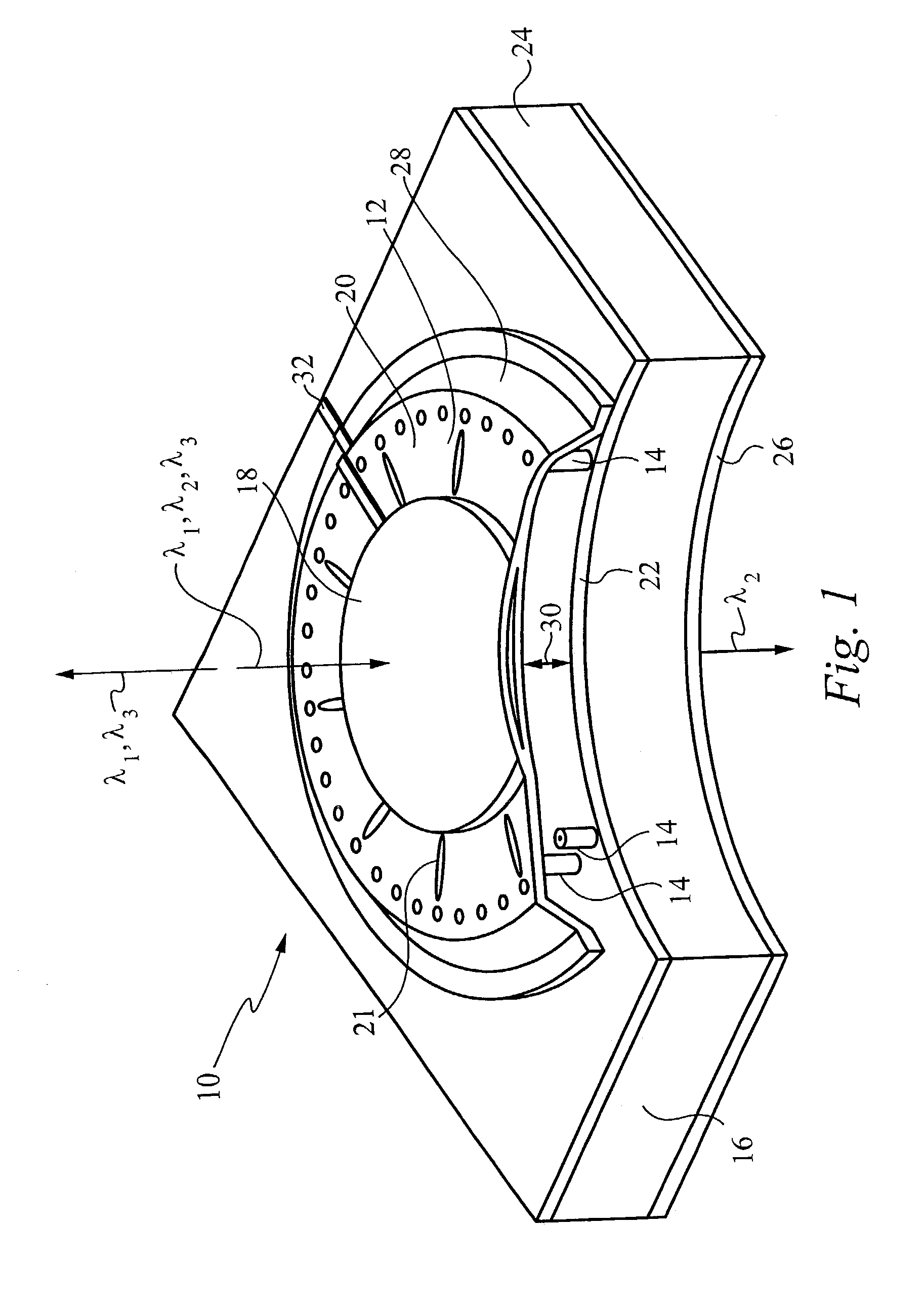
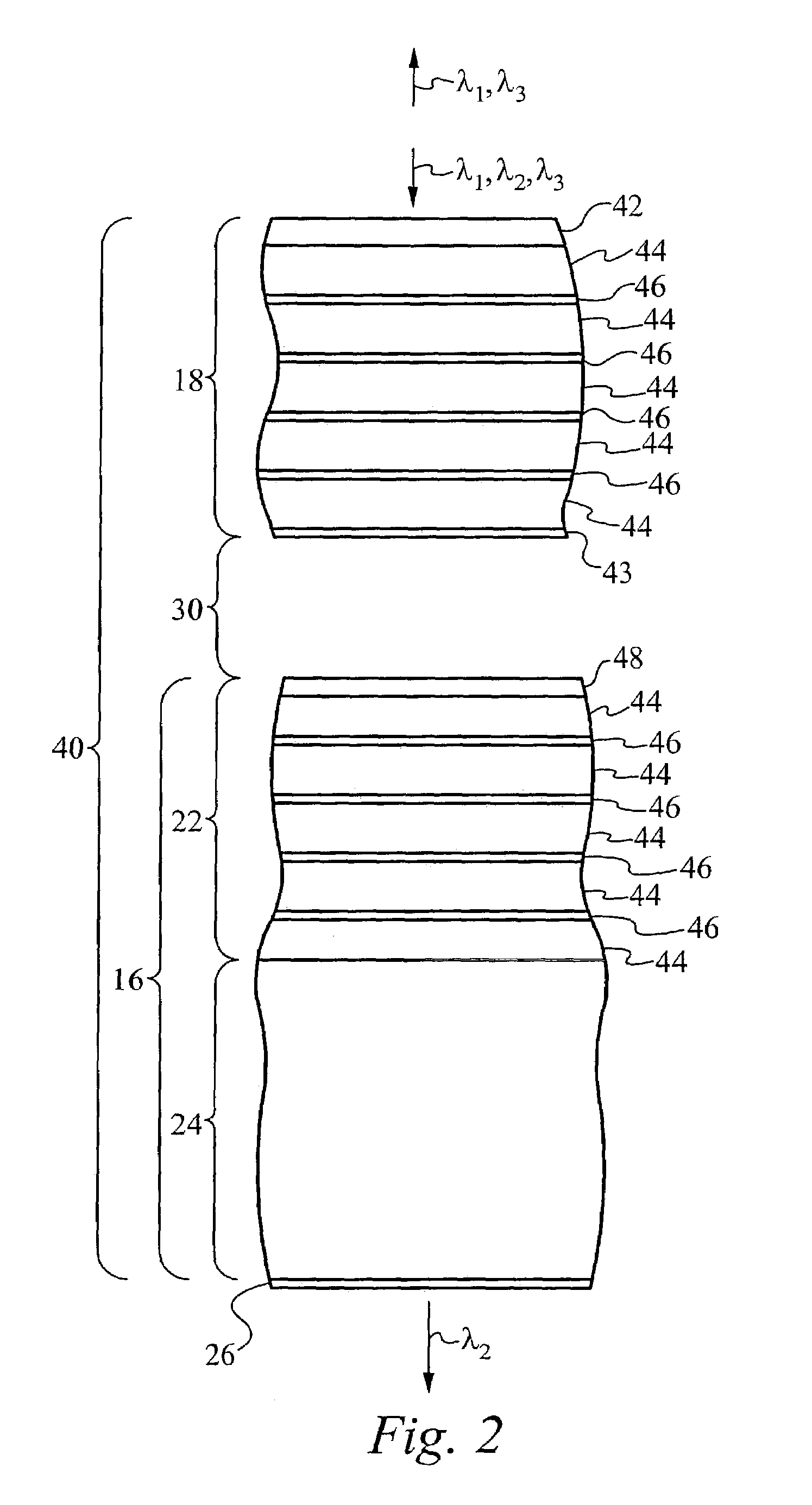
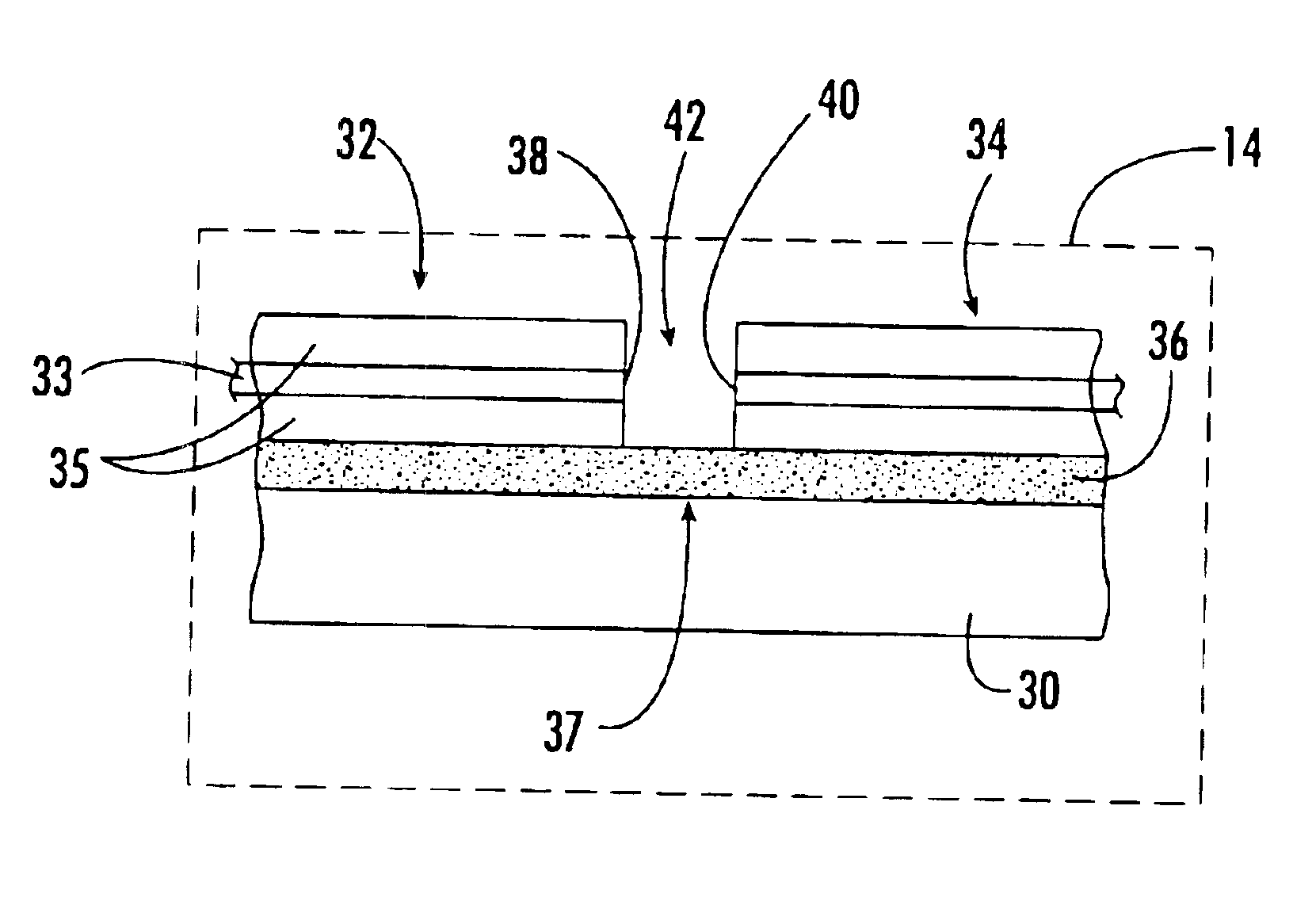
Electrically controlled variable thickness plate
InactiveUS6950227B2Easy and economical to manufactureNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectricityVariable thickness
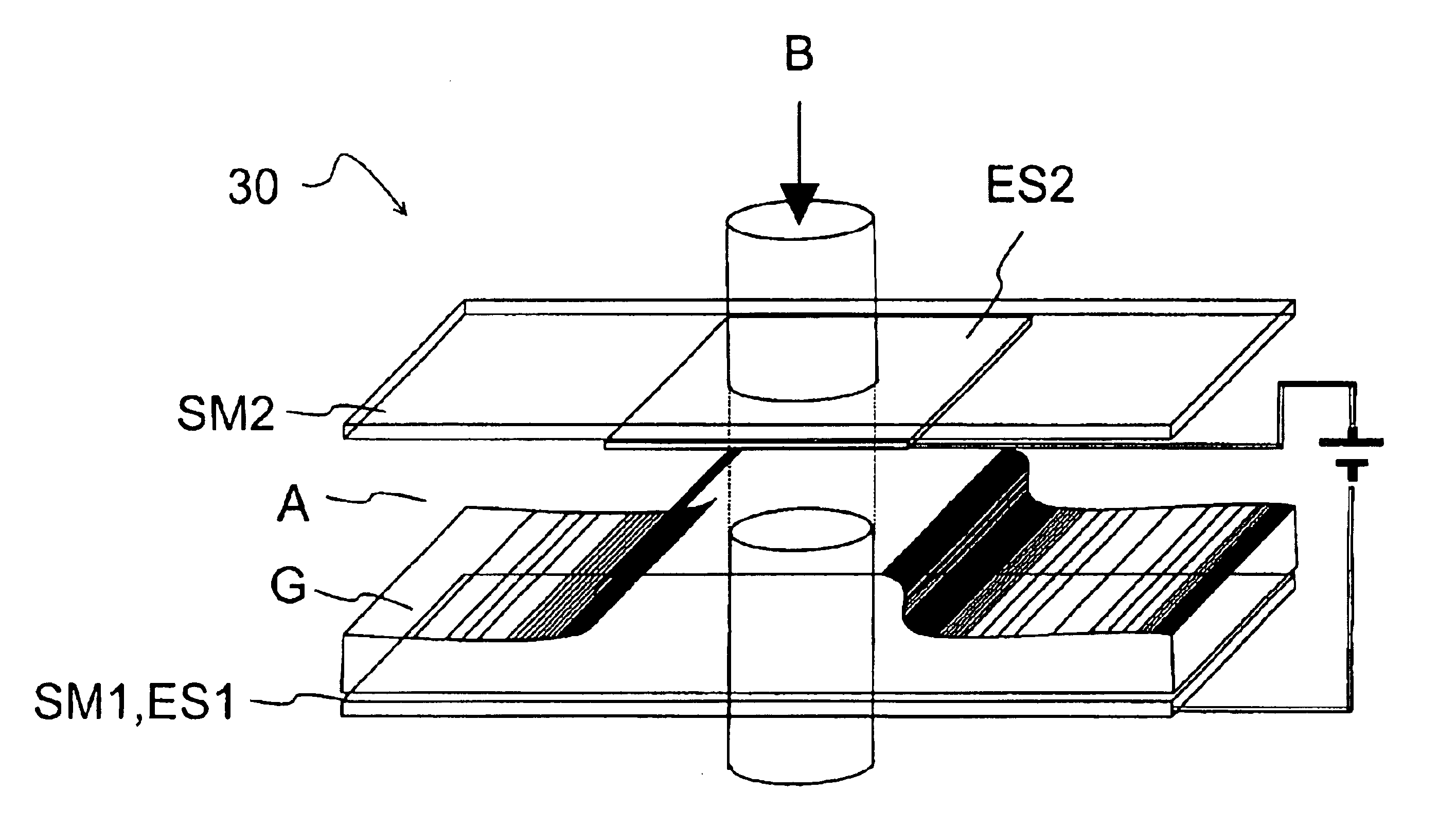
The invention refers to electrically controlled optical switching devices which are based on the use of a layer of dielectric and transparent viscoelastic material (G) located between transparent first (ES1) and transparent second (ES2) electrode structures. According to the invention, the first (ES1) and second (ES2) electrode structures are arranged in a manner that the thickness of the layer of the viscoelastic material (G) can be electrically altered maintaining the thickness of said layer substantially equal. This makes it possible to realize a generic, electrically controlled variable thickness plate (30). The generic variable thickness plate (30) can be further used to create optical switching devices based on a Fabry Perot Interferometer or a Mach-Zehnder Interferometer.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
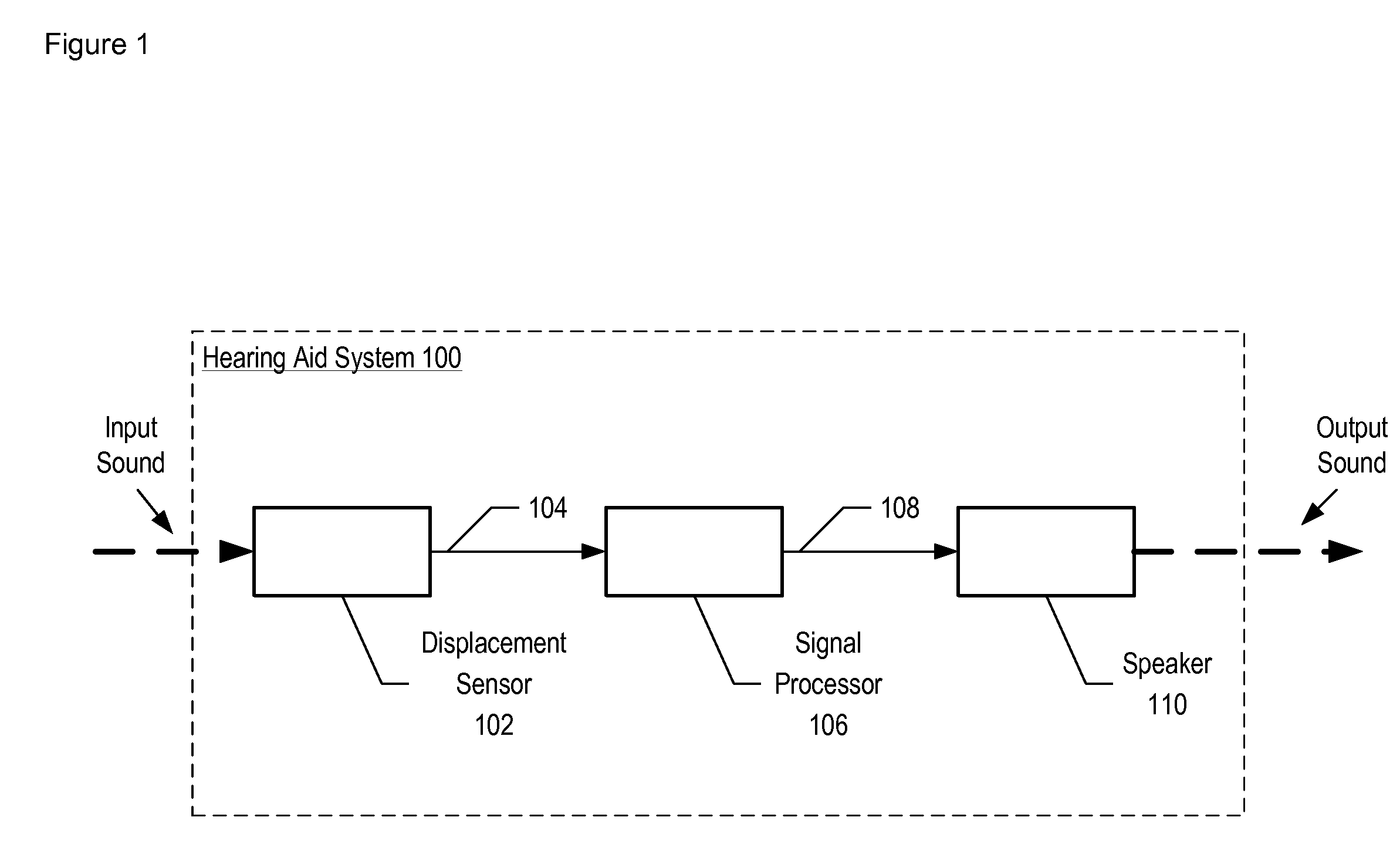
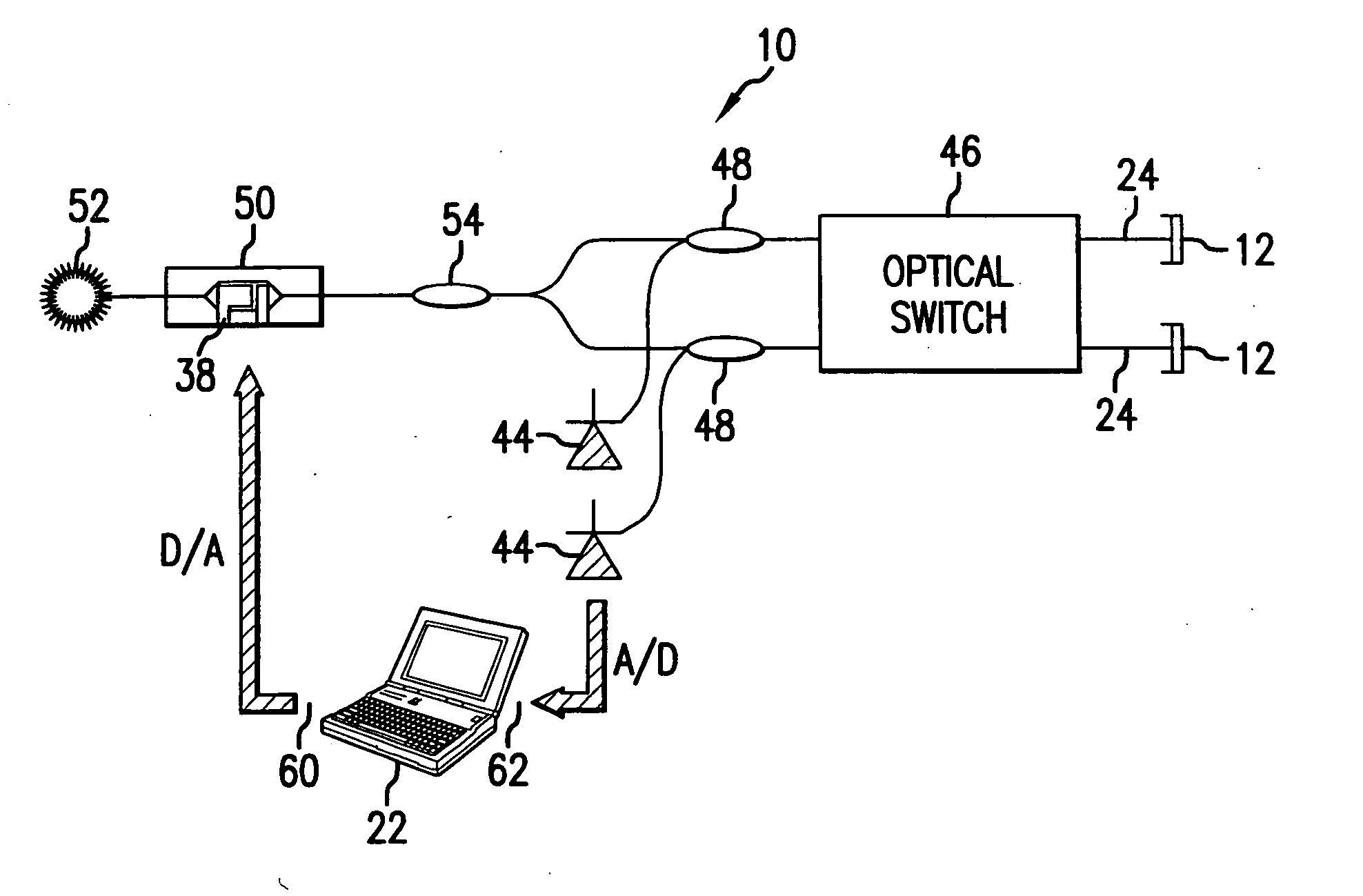
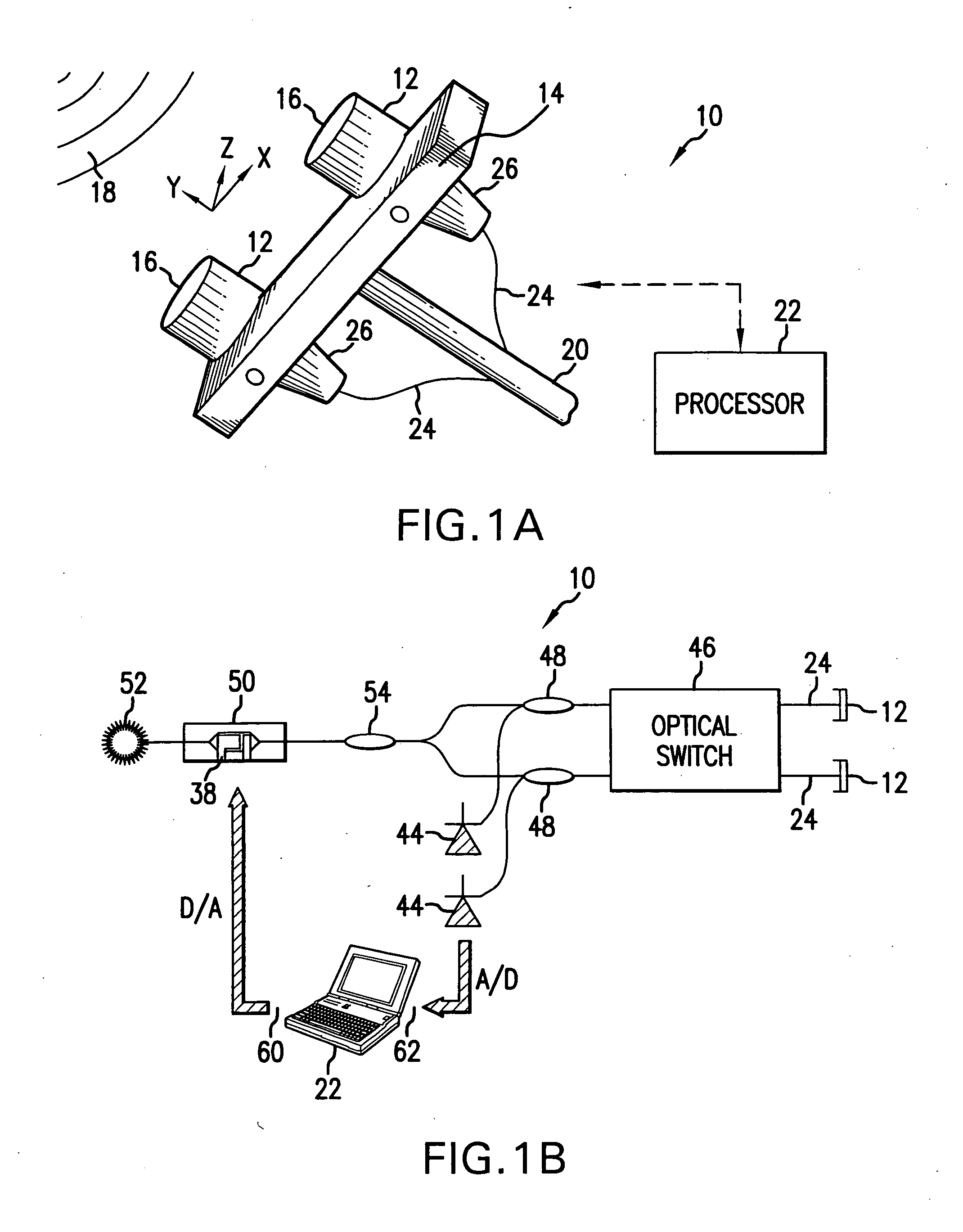
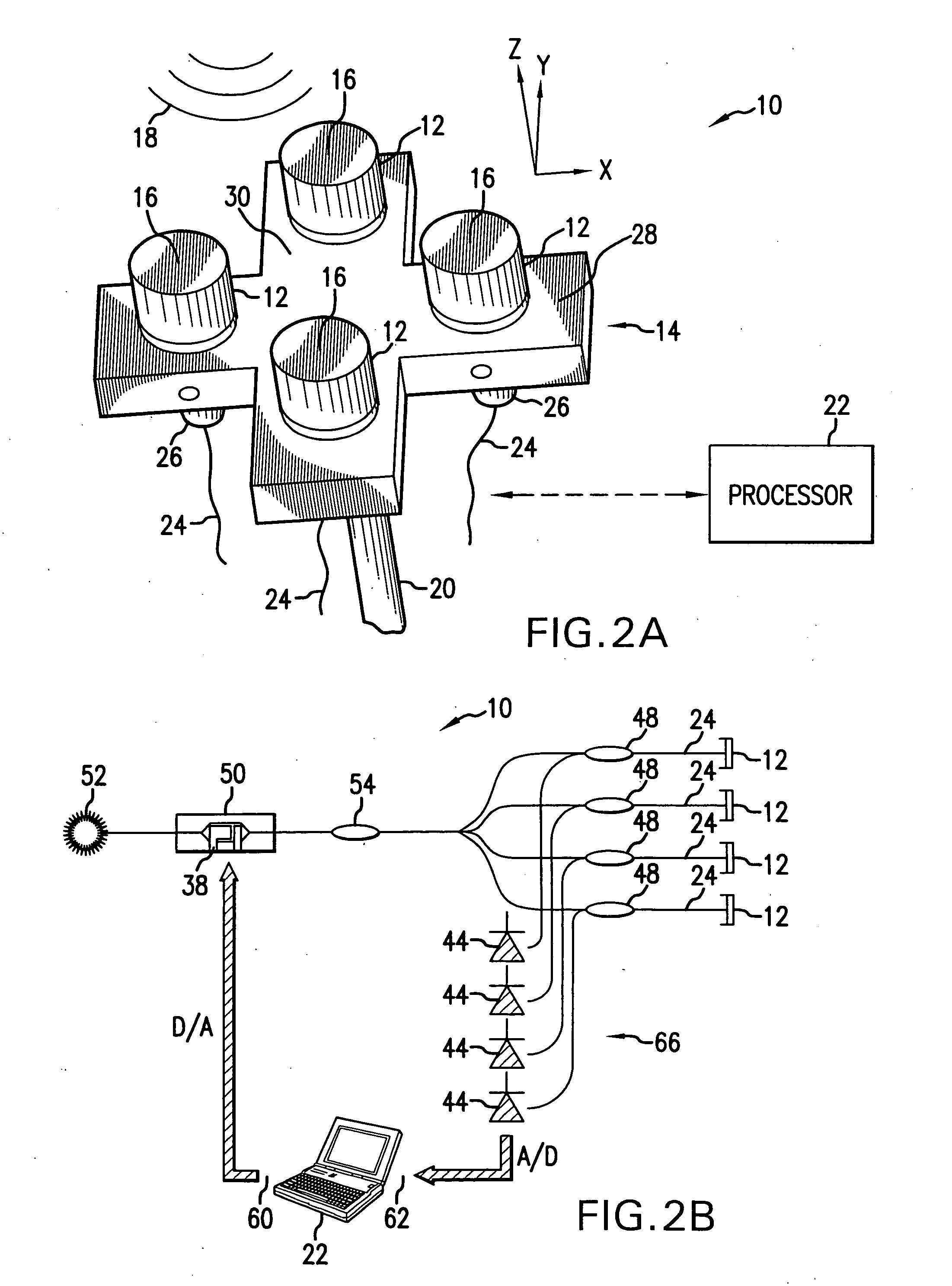
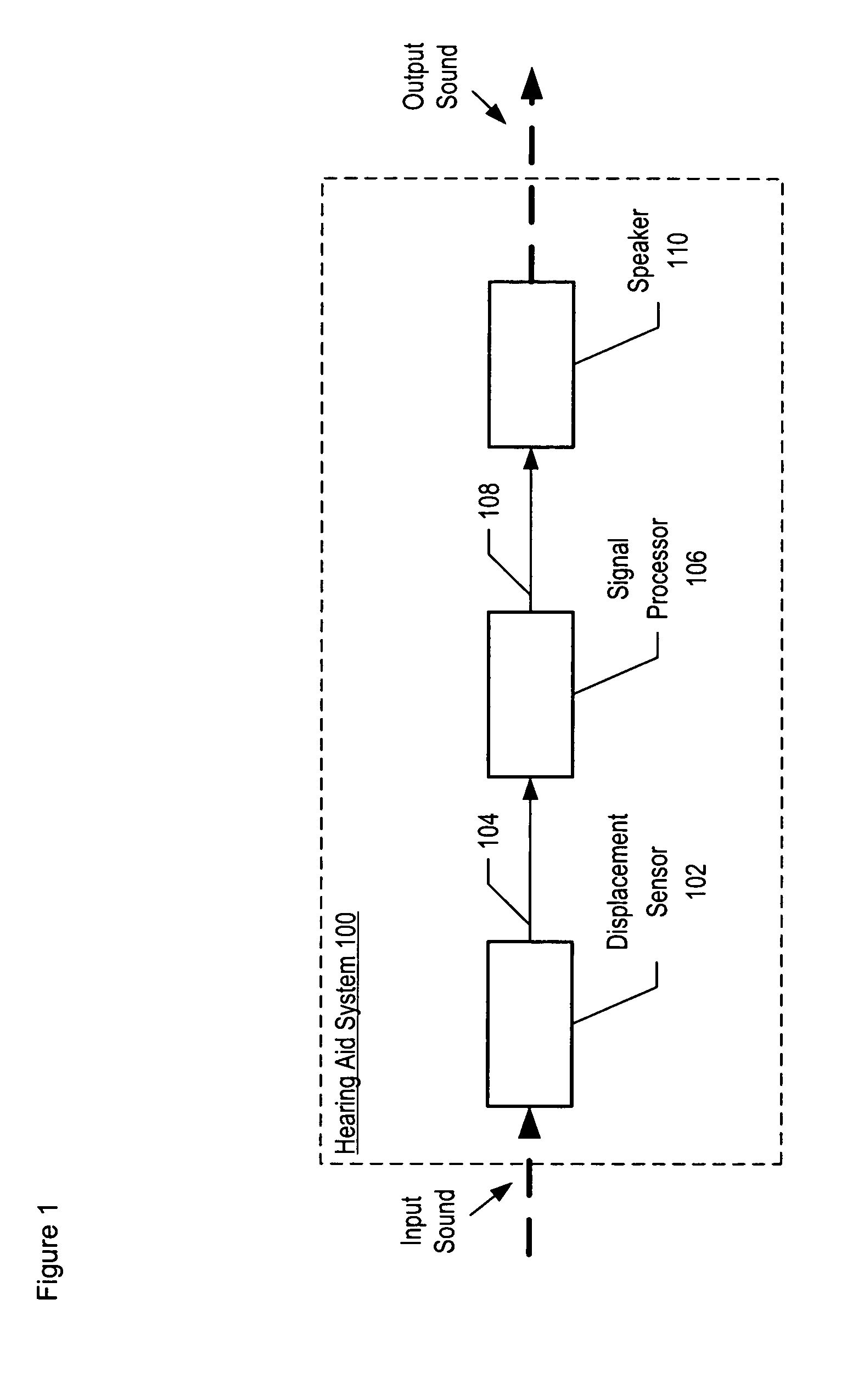
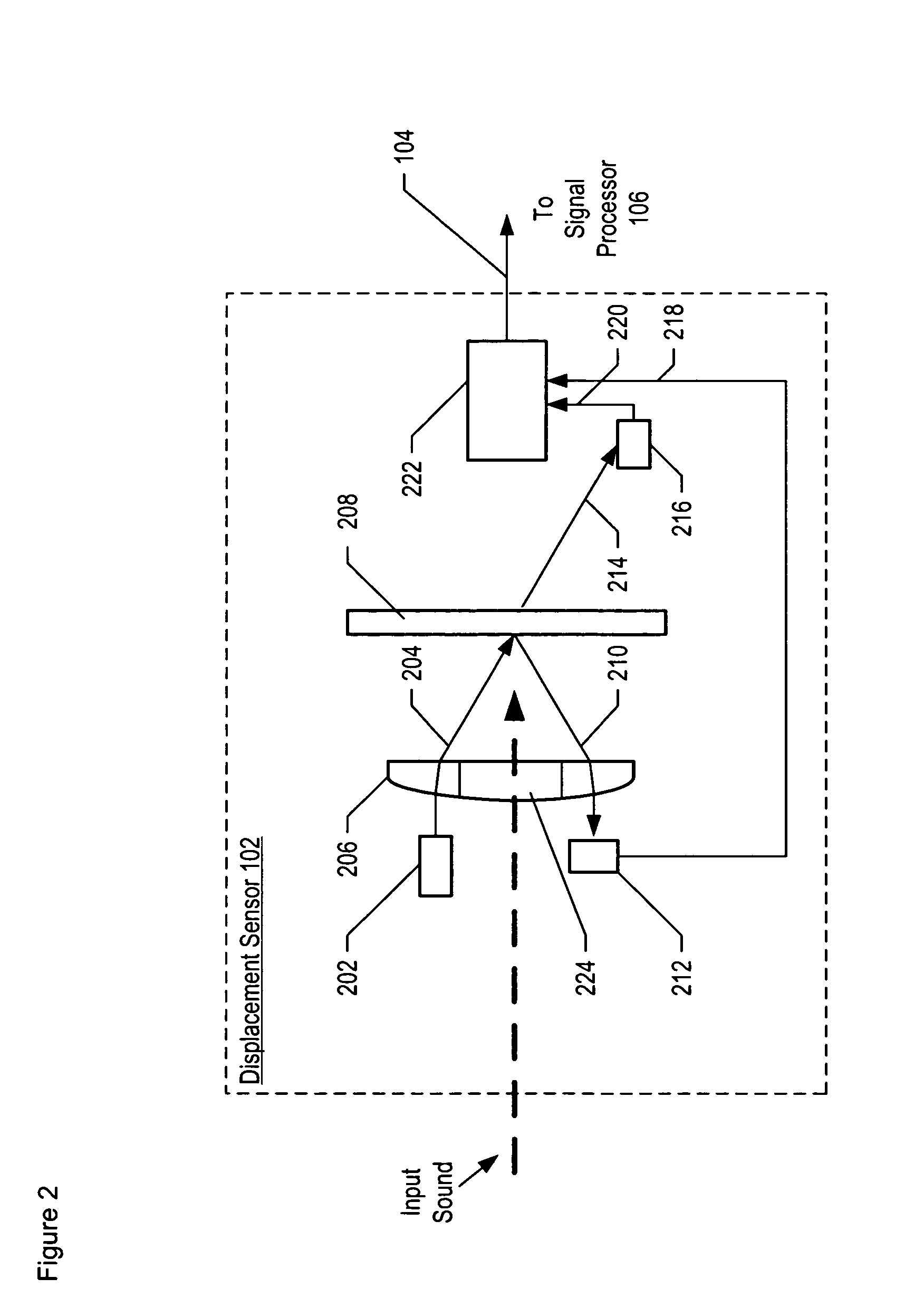
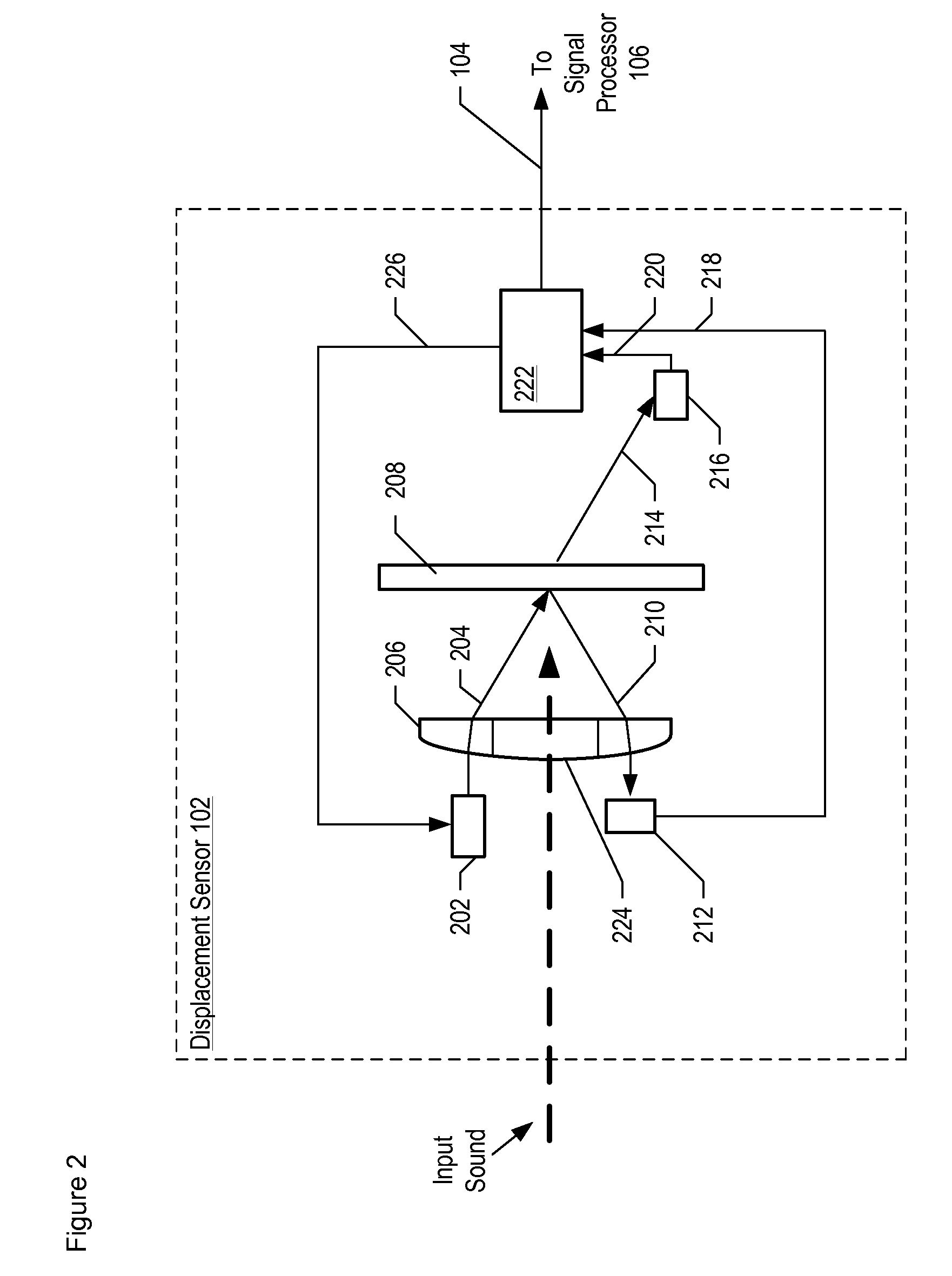
Optical Displacement Sensor Comprising a Wavelength-tunable Optical Source
InactiveUS20070236704A1Optical signal transducersFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsResonant cavityOptical cavity
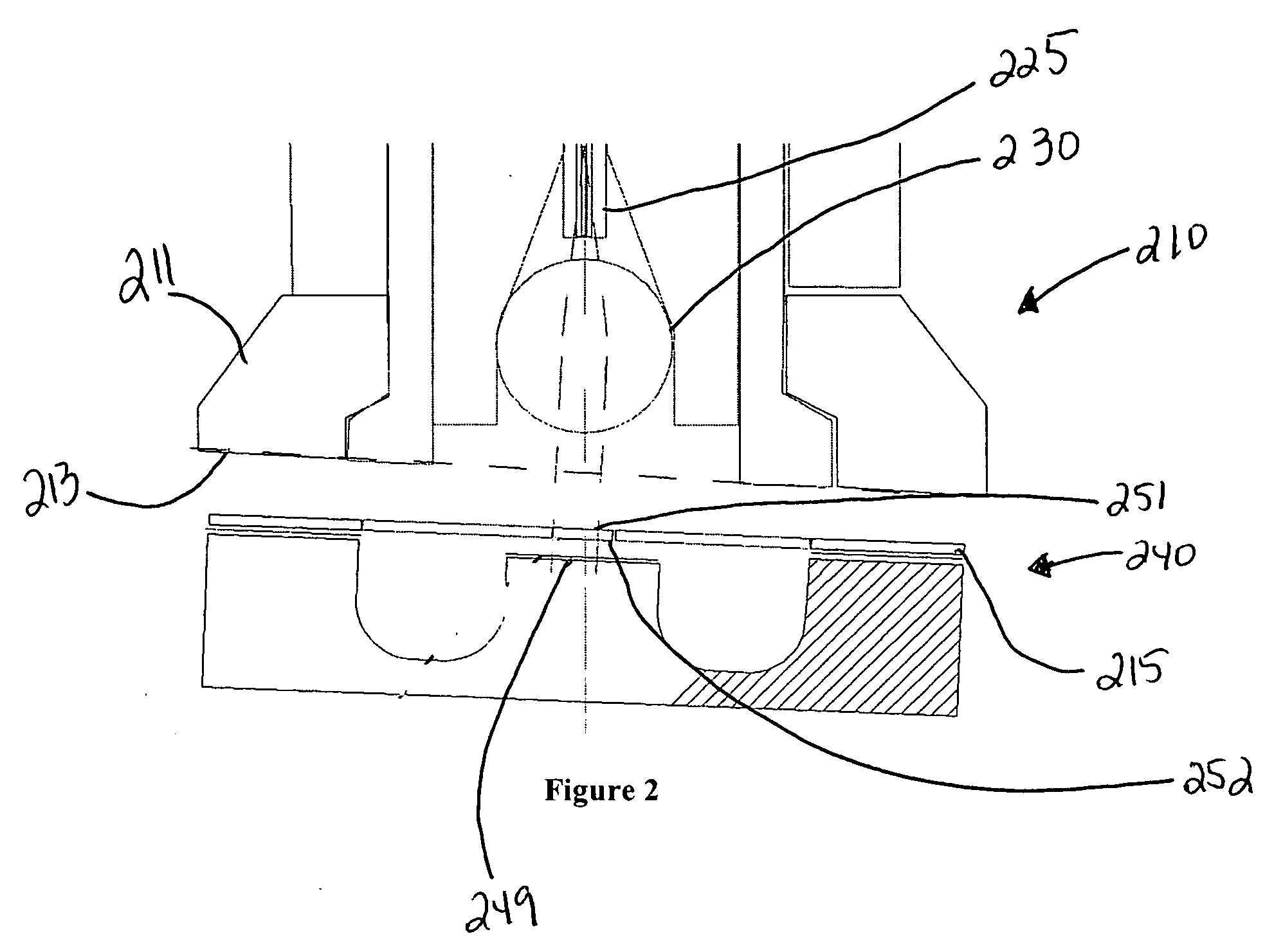
An optical displacement sensor is disclosed that provides a optical displacement sensor that includes a optically-resonant cavity tuned to an operating wavelength without some of the disadvantages for doing so in the prior art. An embodiment of the present invention tunes an operating wavelength used with a Fabry-Perot interferometer to develop a desired relationship between the wavelength and the Fabry-Perot interferometer's initial cavity length.
Owner:SYMPHONY ACOUSTICS
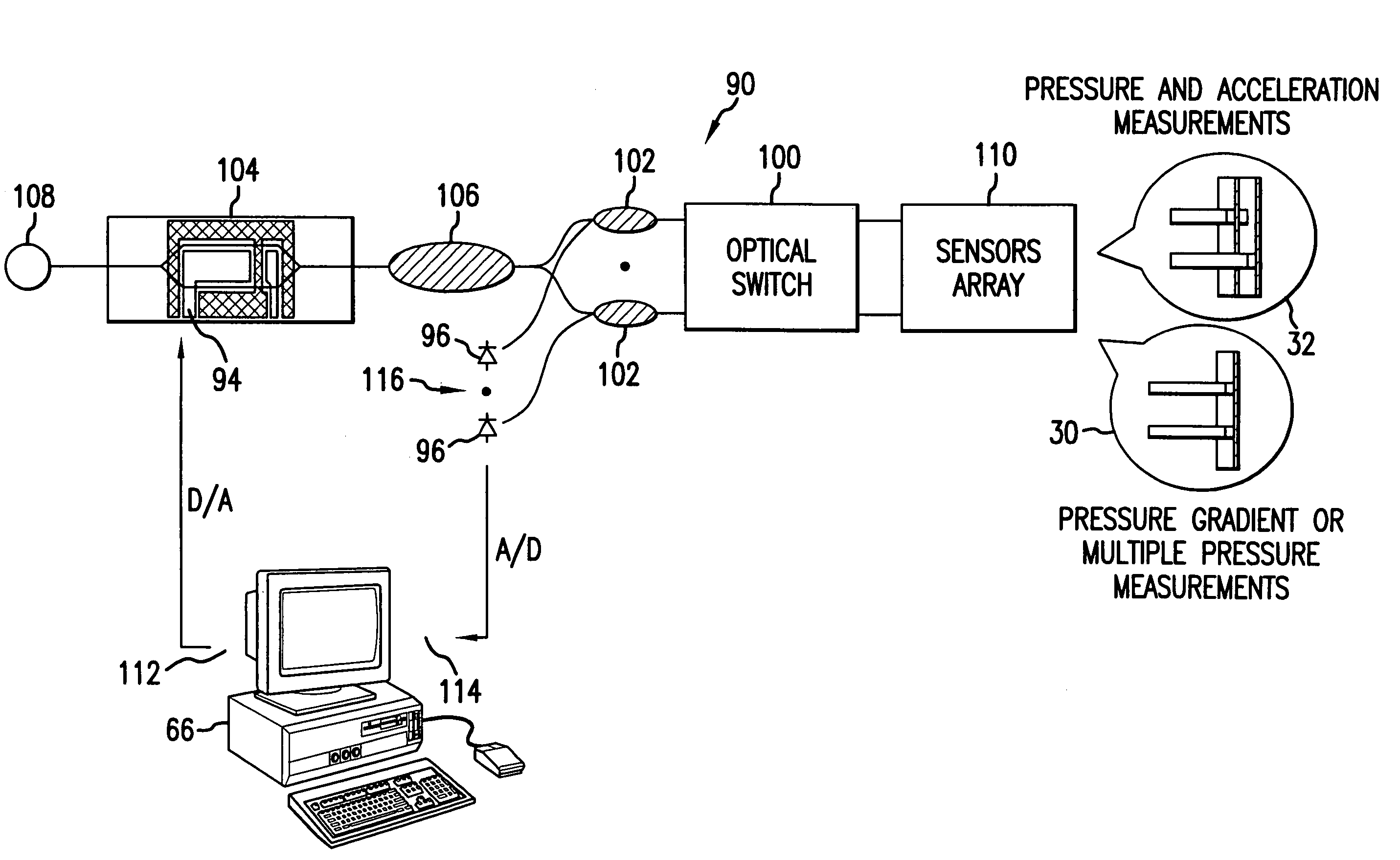
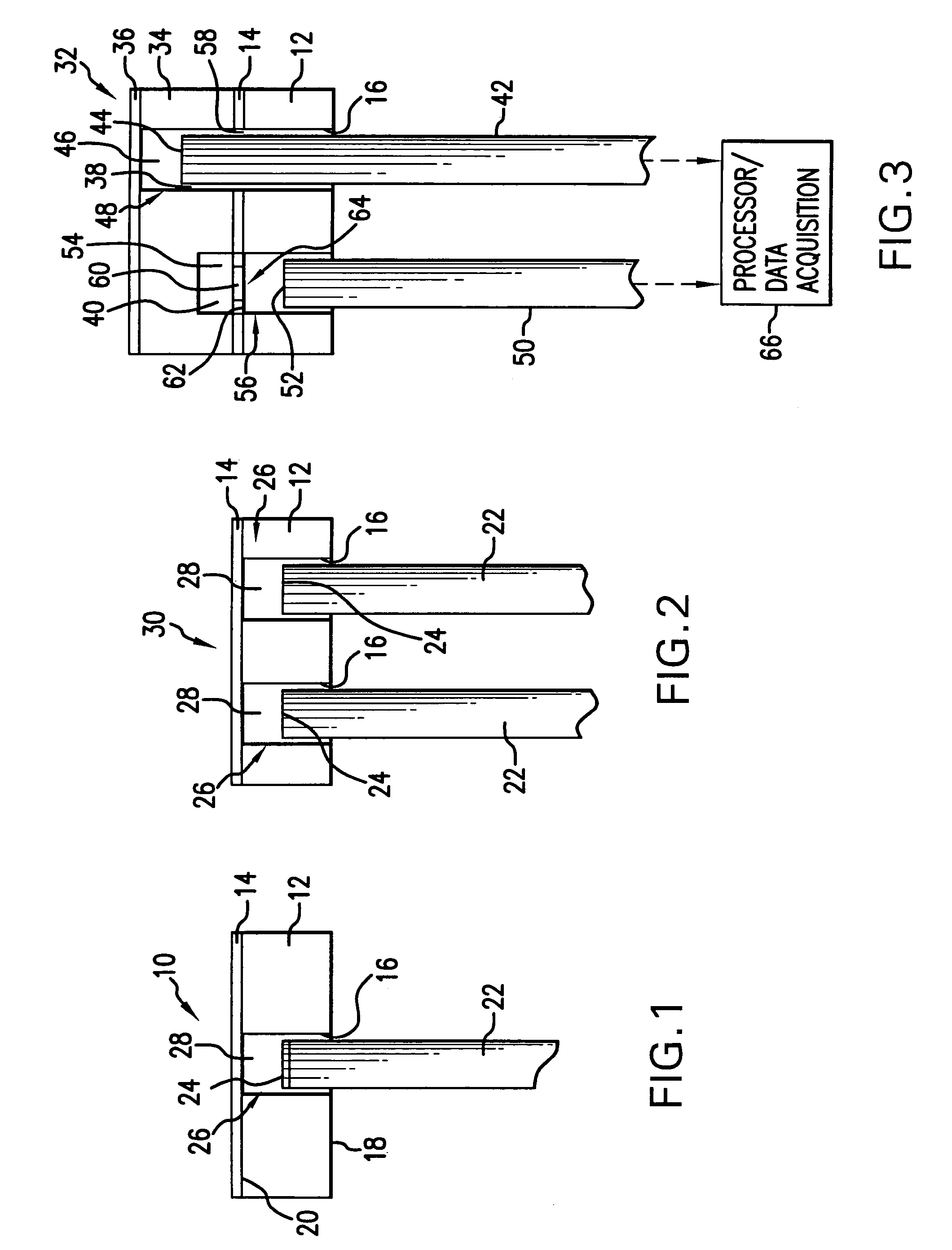
Micro-optical sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements
InactiveUS20050157305A1Good flexibilitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansFiberPhase step
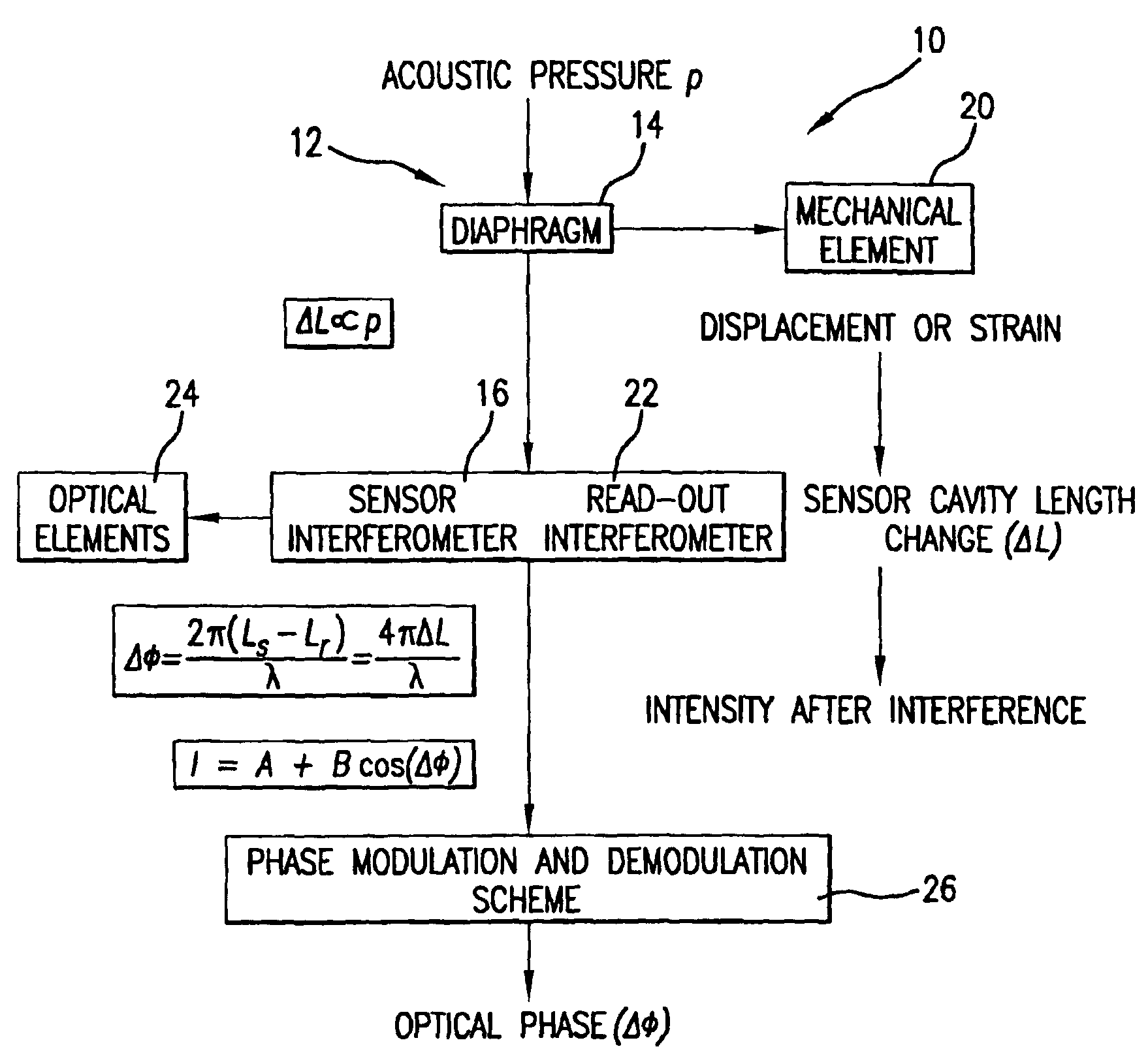
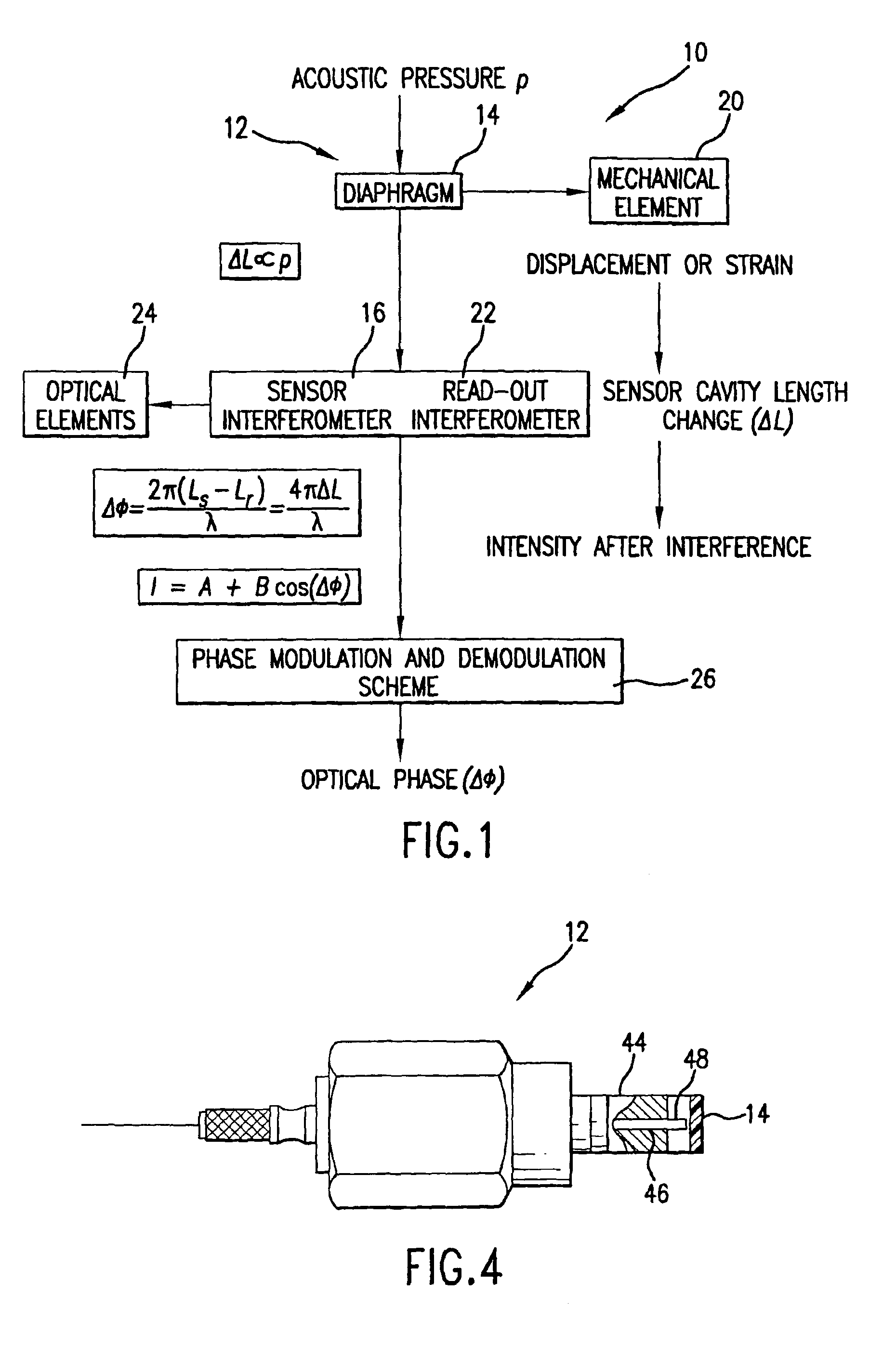
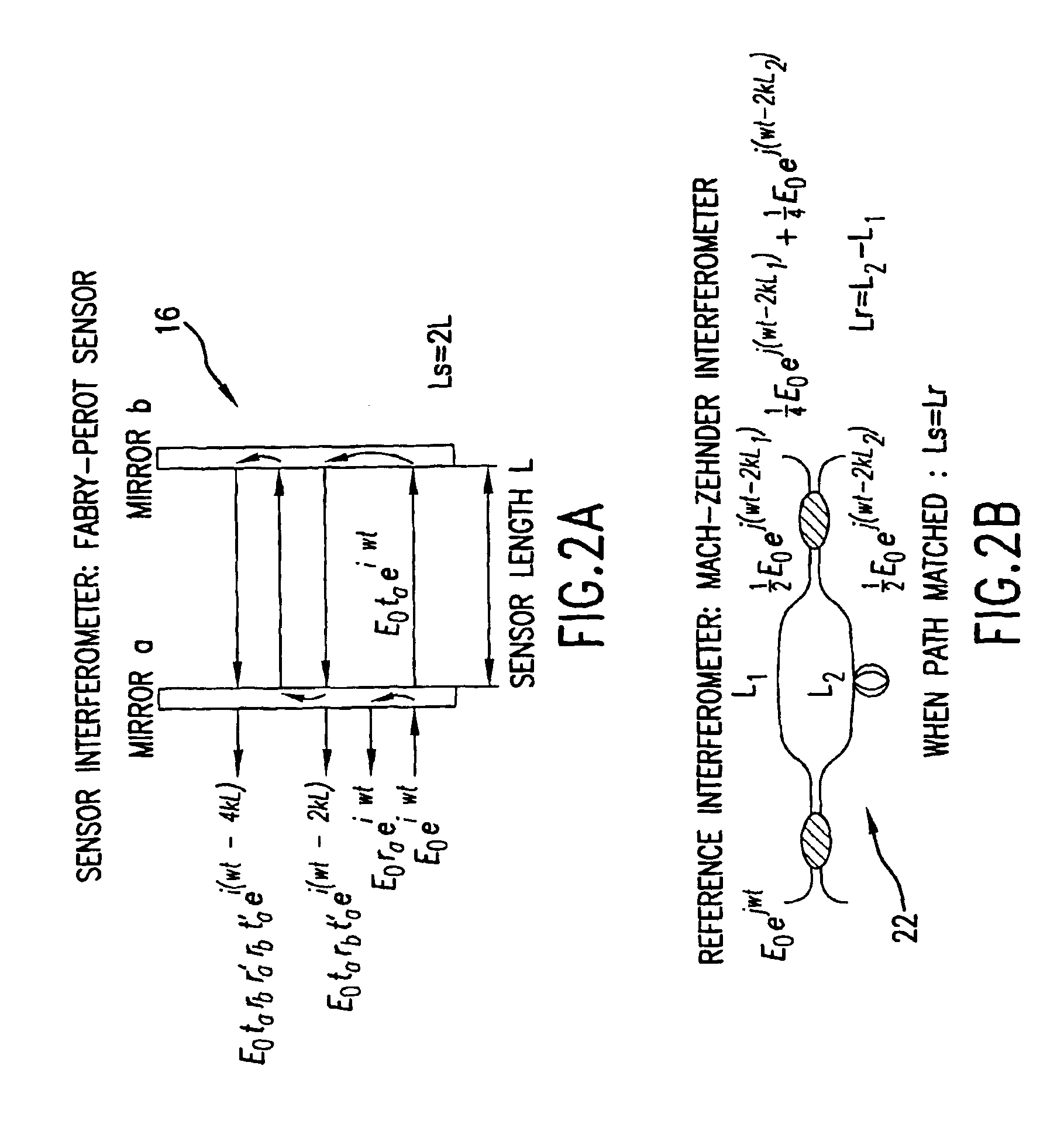
A micro-optical fiber tip based sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements in a wide bandwidth, the design of which allows for multiplexity of the input side of the system is based on micro-electromechanical fabrication techniques. The optical portion of the system is based on low coherence fiber-optic interferometry techniques which has a sensor Fabry-Perot interferometer and a read-out interferometer combination that allows a high dynamic range and low sensitivity to the wavelength fluctuation of the light source. A phase modulation and demodulation scheme takes advantage of the Integrated Optical Circuit phase modulator and multi-step phase-stepping algorithm for providing high frequency and real time phase signal demodulation. The system includes fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors each of which has a diaphragm that is used as a transducer.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Fiber tip based sensor system for measurements of pressure gradient, air particle velocity and acoustic intensity
InactiveUS20050146726A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansLight sourceFiber optic sensor
A fiber optic sensor system for pressure measurements where the design permits multiplexity on the input side of the system and the optical part of the system, which has a sensor Fabry-Perot interferometer and a read-out interferometer, is based on low coherence fiber-optic interferometry techniques. This permits a high dynamic range and low sensitivity to the wavelength fluctuation of the light source as well as to the optical intensity fluctuations. The system includes fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors, where each sensor includes a diaphragm as the transducer. A combined pressure gradient sensor, air particle velocity sensor, as well as acoustic intensity sensor is built based on the fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
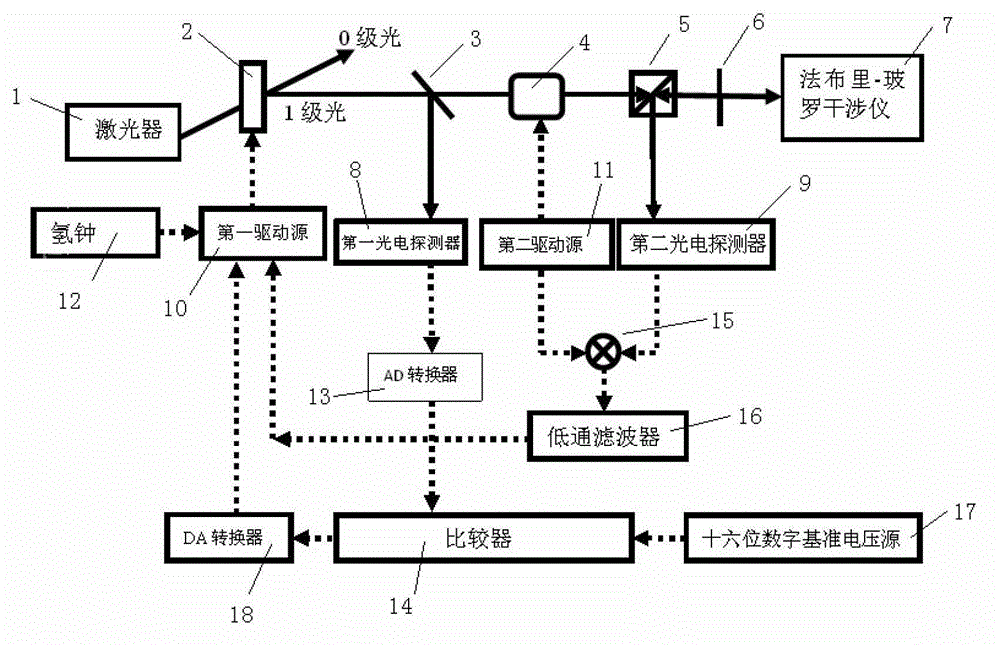
Method and device for measuring and stabilization using signals from a Fabry-Perot
InactiveUS6178002B1Simple and low-cost and compact structureEasy to implementOptical measurementsLaser detailsPhase shiftedPath length
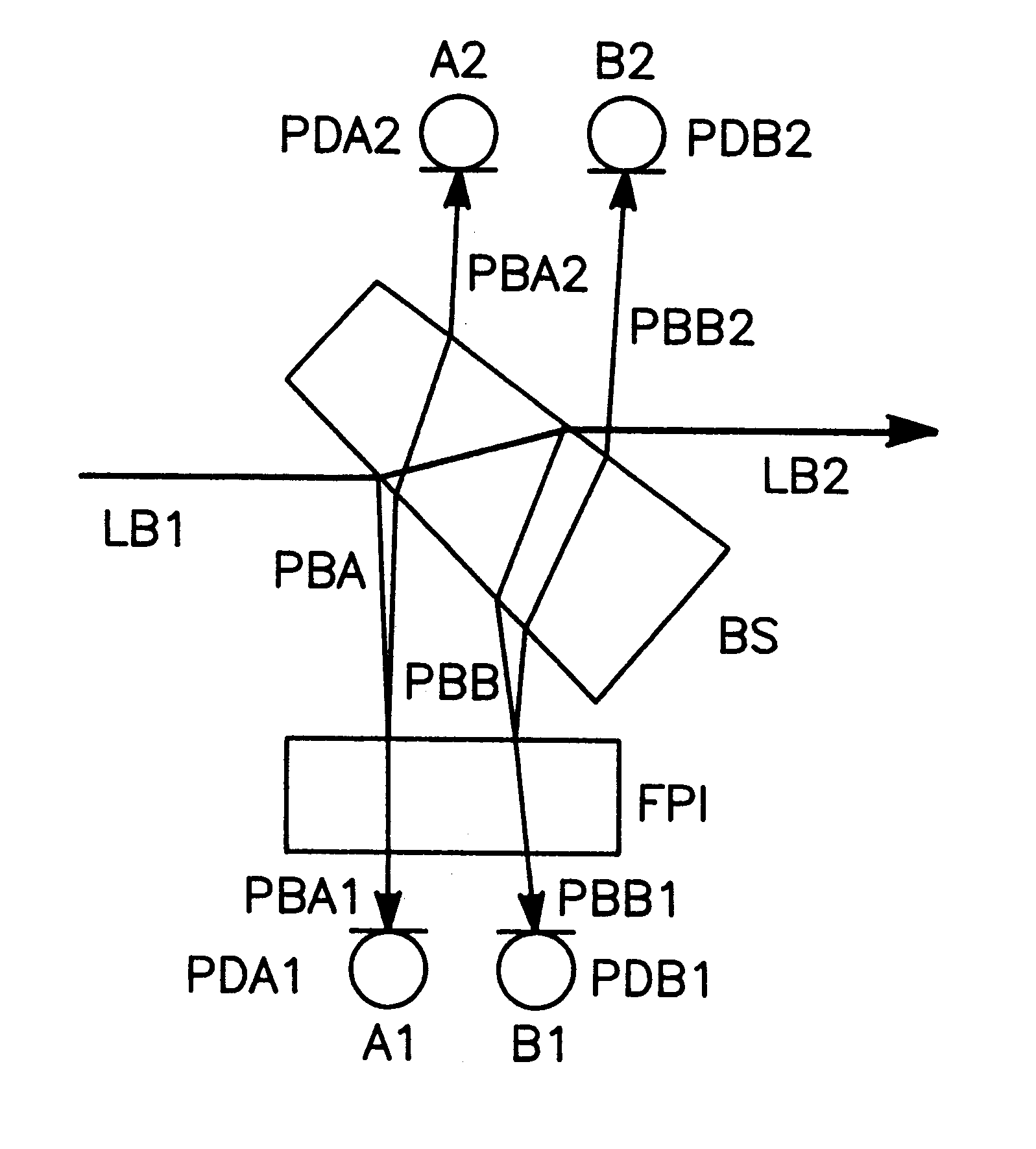
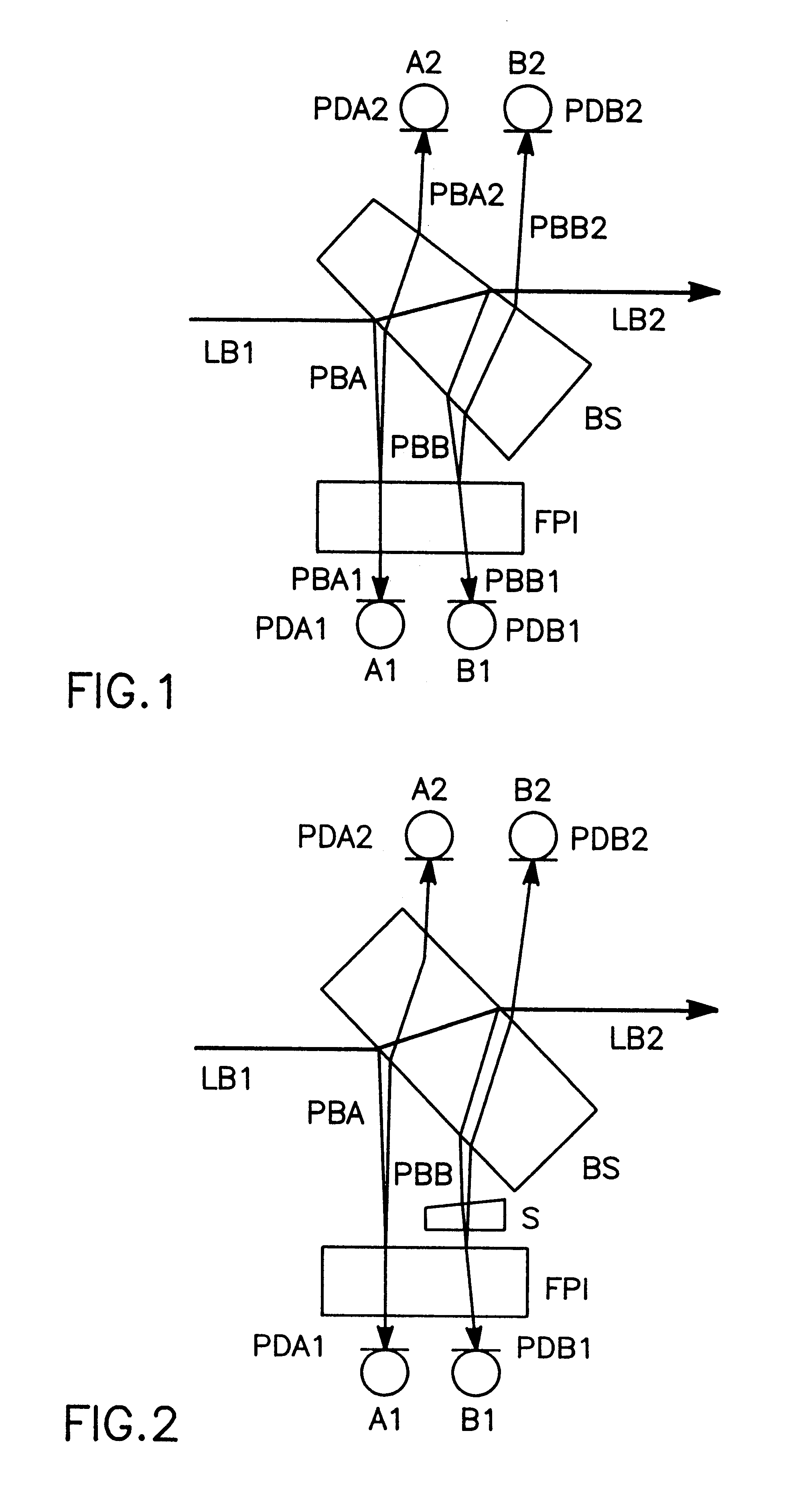
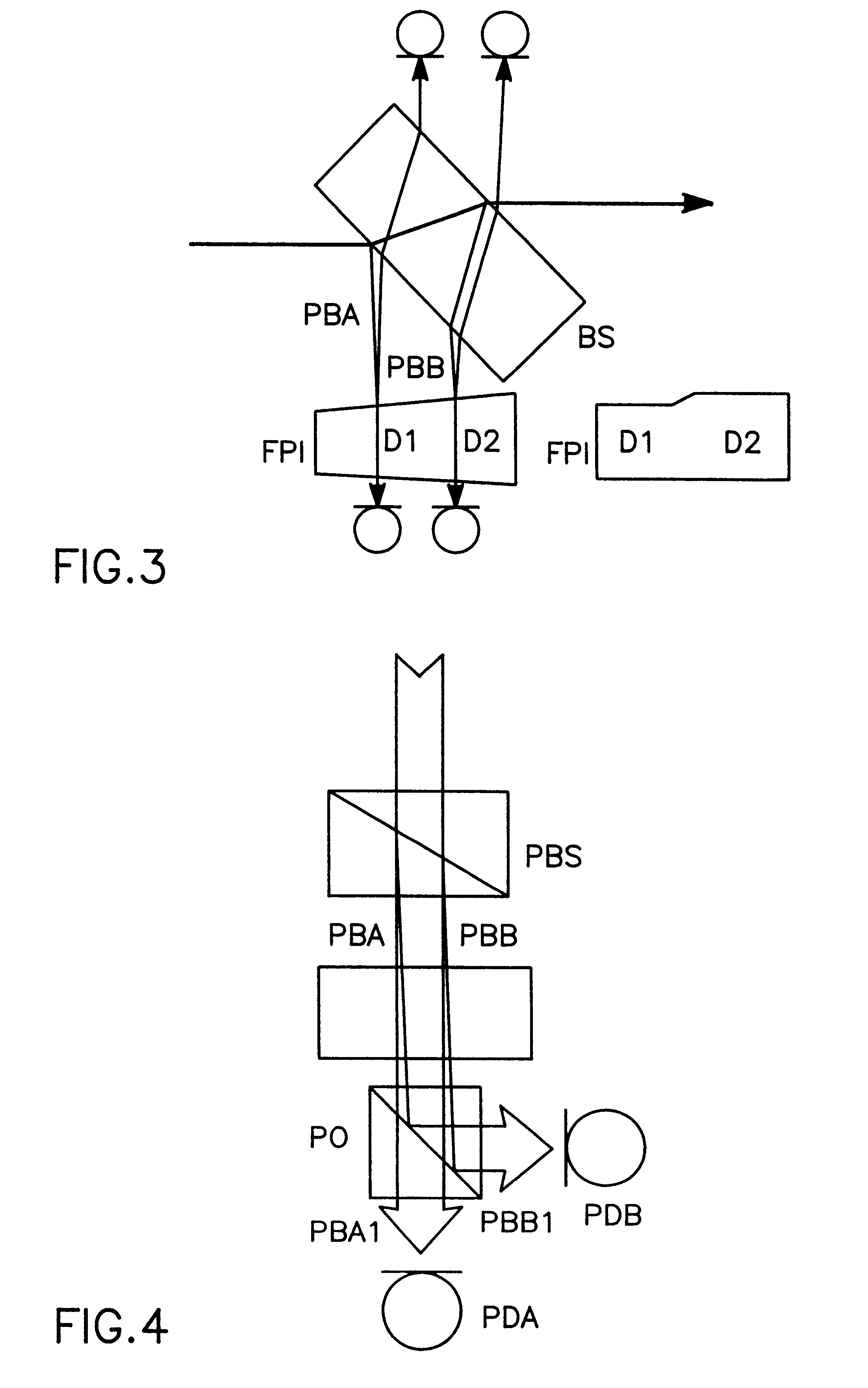
For measuring a laser frequency electronic signals can be generated by means of optical interferometers, especially Michelson, Mach-Zehnder and Fabry-Perot interferometers. These signals present profiles with a variation of the laser frequency which are practically identical but shifted in phase by 90°. It is common to generate such phase-shifted signals for frequency measurement in various systems, e.g. by means of a sigmameter, which present, however, disadvantages on account of the great number of the necessary high-quality optical components. The inventive method is based on the analysis of transmission and reflection signals of a Fabry-Perot interferometer (FPI) wherein the signals are obtained from two component beams (PBA and PBB) which are passed through slightly different path lengths within the interferometer. These differences in the length of the optical paths are so selected by different angles of incidence of the component beams into the Fabry-Perot interferometer or by an appropriate shape of the interferometer that the required 90° phase shift is adjusted between the detected intensity signals. From these signals electronic signals can be obtained for detection and also for a rapid correction of the laser frequency.
Owner:MUELLER WIRTS THOMAS
Fiber tip based sensor system for measurements of pressure gradient, air particle velocity and acoustic intensity
InactiveUS7224465B2Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansTransducerLength wave
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Novel Fabry-Perot interference MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) sound wave sensor
InactiveCN103528665AImplement detectionImprove anti-interference abilitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFiberInterference resistance
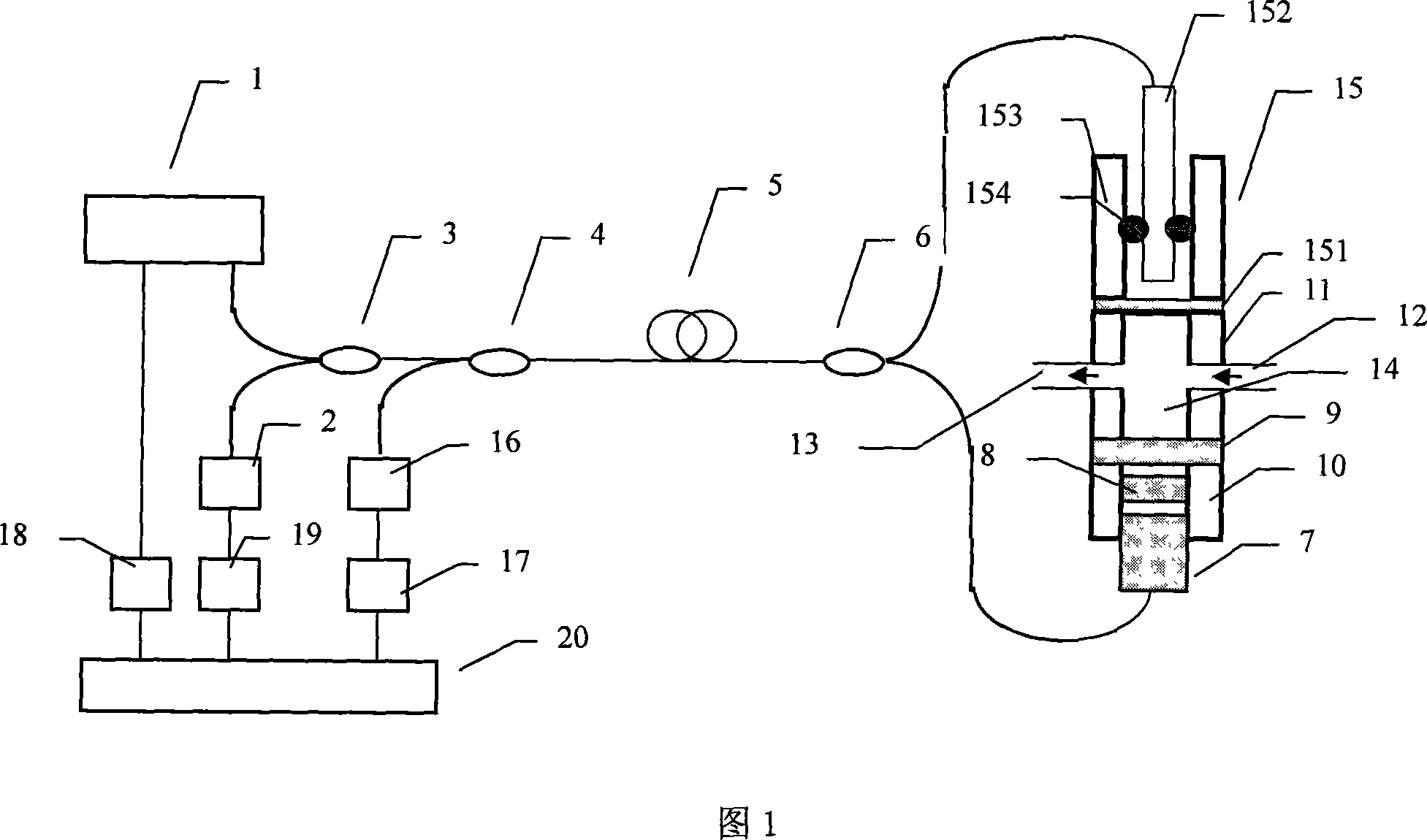
The invention discloses a novel Fabry-Perot interference MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) sound wave sensor, which comprises a collimator, an SOI (Silicon on Insulator) wafer and a bushing, wherein the bushing is arranged below the SOI wafer and is used for supporting the SOI wafer and fixing the collimator; the SOI wafer is provided with a sound-sensitive film; the central axis of the bushing is coincided with the central normal of a circular silicon film on the SOI wafer; the end face of the optical fiber collimator inserted into the bushing is 100-300 microns away from the sound-sensitive film. According to the novel Fabry-Perot interference MEMS sound wave sensor, the end face of the optical fiber collimator provided with a tail fiber and the inner surface of a silicon micro film construct two parallel surfaces of a Fabry-Perot interferometer, and the film is deformed when pressure generated by external sound waves is applied to the film, so that the cavity length of an Fabry-Perot interference cavity is changed. The detection of sound wave signals is realized by modulating the length variation of the F-P cavity, so that a micro microphone with high interference resistance and high sensitivity is provided for use in an environment with strong electromagnetic interference.
Owner:NO 27 RES INST CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
All-fiber direct detection anemometric laser radar system and closed-loop control method thereof
InactiveCN103499820AReduce volumeReduce weightFluid speed measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsClosed loop
The invention discloses an all-fiber direct detection anemometric laser radar system and a closed-loop control method thereof. The system comprises an optical emission part, a frequency locking part, an emission part and a receiving part, wherein the optical emission part is used for emitting a modulated and amplified laser pulse; the frequency locking part is used for detecting the laser frequency variation, feeding back to the laser emission part, adjusting the laser wavelength and further realizing the function of locking the laser wavelength according to the deviation; the emission part is used for enabling the laser beam to point to the detection zone of the atmosphere, coupling the atmospheric back scattered light to a receiver through an optical telescope and modulating the near field signal strength; the receiving part is used for filtering out sun background from a signal and dividing the signal into two paths, one path of signal passes through a Fabry-Perot interferometer, the other path of signal is used as energy reference, the transmittance is obtained through the ratio of the signal intensities of the two paths of signal, and the wind velocity is obtained through inversion according to Doppler frequency shift. The laser radar adopts an all-fiber structure and has the advantages of small size and light weight, the manufacturing cost of the radar is low, the laser radar is controlled through a 3-level closed-loop, and the environmental adaptability and working stability of the laser radar are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fiber tip based sensor system for acoustic measurements
InactiveUS6901176B2Easy to measureSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansAccelerometerPhase step
A fiber optic sensor system for acoustic measurements over a 6 kHz bandwidth, the design of which allows for multiplexity of the input side of the system, and where the optical part of the system is based on low coherence fiber-optic interferometry techniques which has a sensor Fabry-Perot interferometer and a read-out interferometer as well, that allows a high dynamic range and low sensitivity to the wavelength fluctuation of the light source, as well as the optical intensity fluctuations. A phase modulation and demodulation scheme takes advantage of the Integrated Optical Circuit phase modulator and multi-step phase-stepping algorithm for providing for high frequency and real time phase signal demodulation. The system includes fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors which have a diaphragm, which is used as the transducer. Pressure microphone, velocity sensor, as well as accelerometer, are built based on the fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Optical fiber gas sensing method and sensor
InactiveCN101055243AReduce noiseNo polarization effectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationMaterial analysis by optical meansLight energyBand-pass filter
A optical fiber gas sensor employs a optical fiber Fabry-Perot interferometer constituting a low reflection cavity lens and a measurement optical fiber to detect sound pressure wave signal generated by gas after absorbing light energy, and a realization method for optical acoustic gas sense technique is provided. Pulse modulated excited light is emitted by an excitation light source, passes through a band-pass filter and enters a gas cavity from a gas cavity window; the excited light emitted into the gas cavity generates a sound pressure wave which strength corresponds to measured gas concentration in the gas cavity after absorbing by the measured gas; the sound pressure wave is transmitted to vibration of a vibrating film sheet by the vibrating film sheet which is equipped at other end of the gas cavity; a measuring light signal emitted by measuring light source driven by a first drive power supply passes through a optical fiber wave combination equipment, a transmission optical fiber and a optical fiber wave separation equipment and enters a measuring optical fiber of the Fabry-Perot interferometer; concentration value of the measured gas is obtained by optical path difference of the return light beam and the light beam directly reflected by an optical end face.
Owner:NANJING XUFEI PHOTOELECTRIC
Fabry-perot interferometer and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20110019202A1Broaden a spectroscopy bandOptical articlesSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionOptoelectronicsVoltage
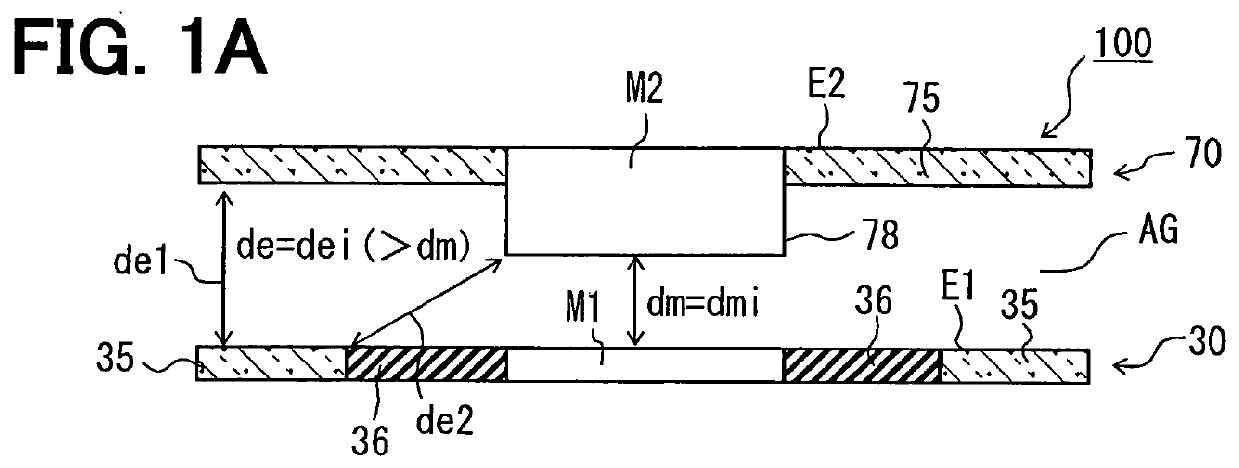
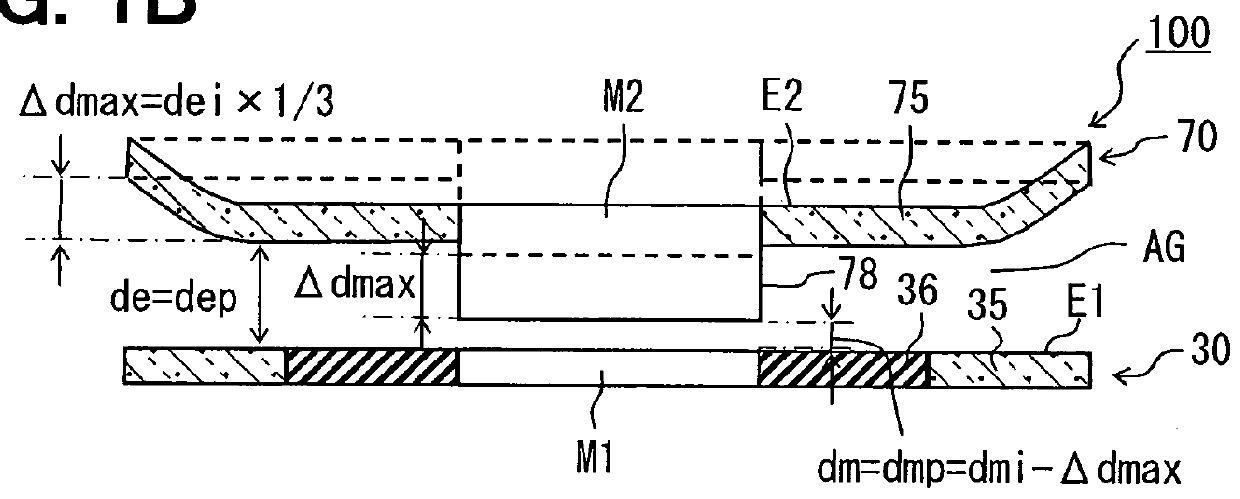
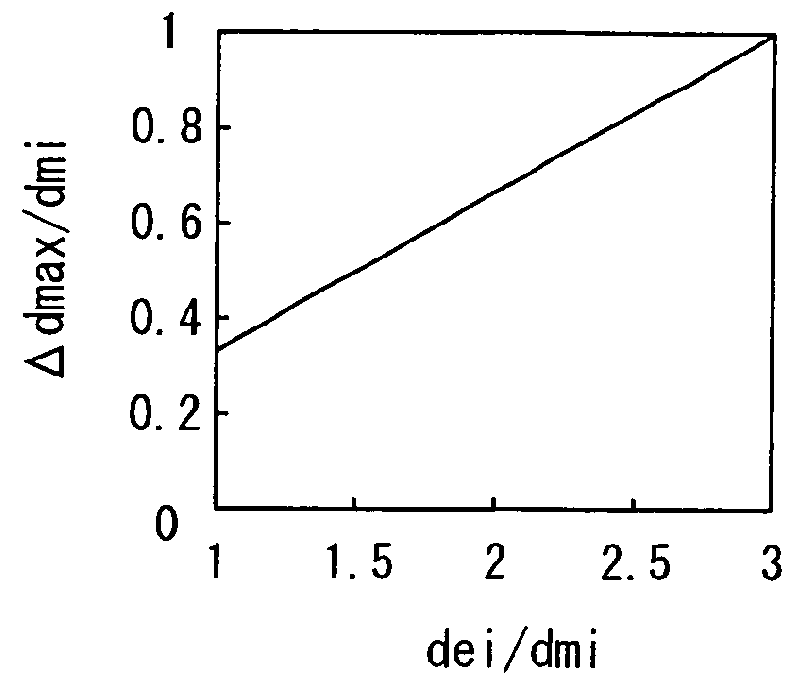
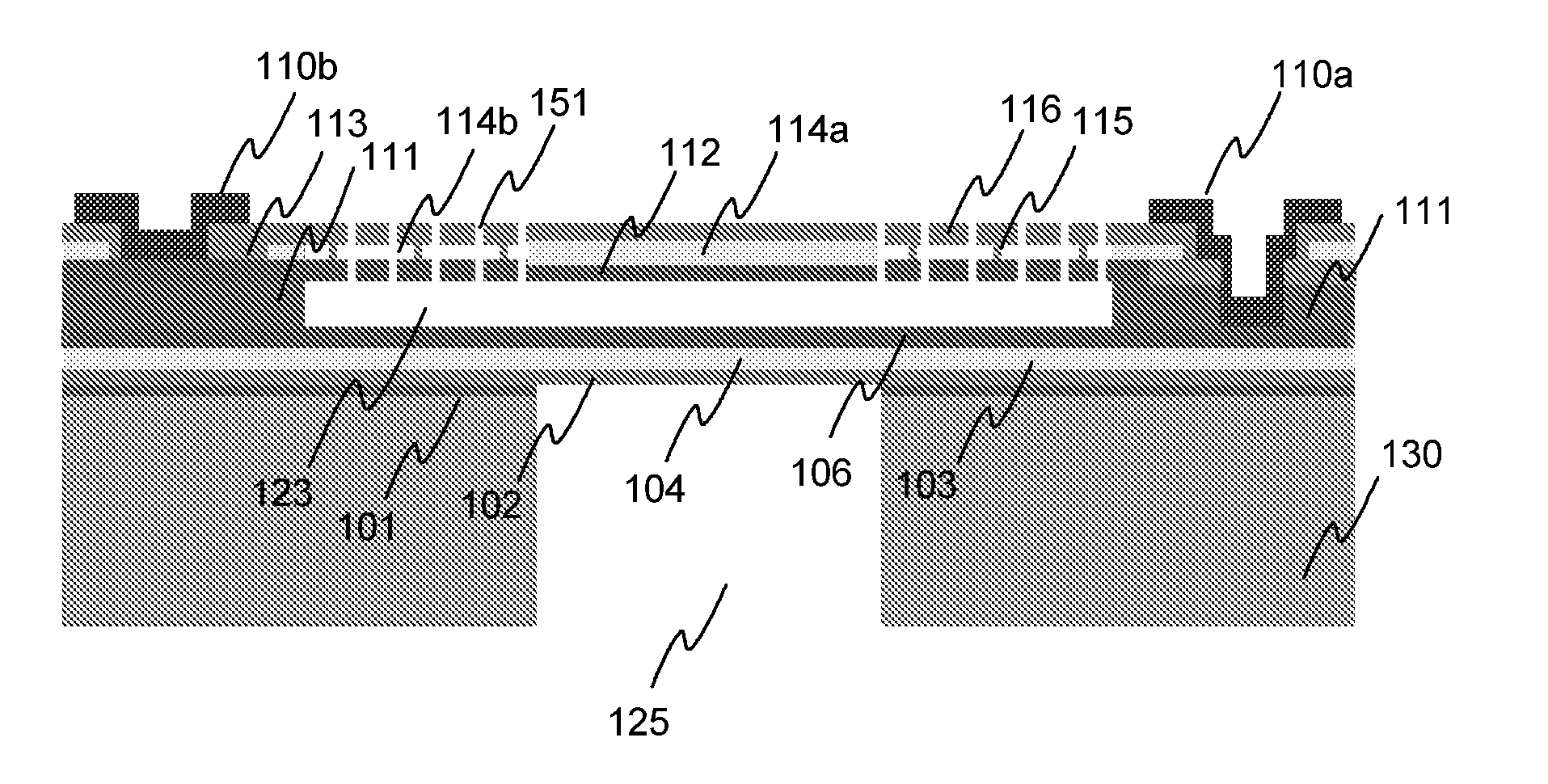
A Fabry-Perot interferometer and a manufacturing method of the same are disclosed. The Fabry-Perot interferometer includes a first mirror structure and a second mirror structure opposed to each other with a gap therebetween. A first mirror and a first electrode of the first mirror structure are electrically insulated from each other, or, a second mirror and a second electrode of the second mirror structure are electrically insulated from each other. In a state of voltage application between the first and second electrode, a distance “dmi” between the first mirror and the second mirror is shorter than a distance “dei” between a first-electrode-inclusive-portion and a second-electrode-inclusive-portion.
Owner:DENSO CORP
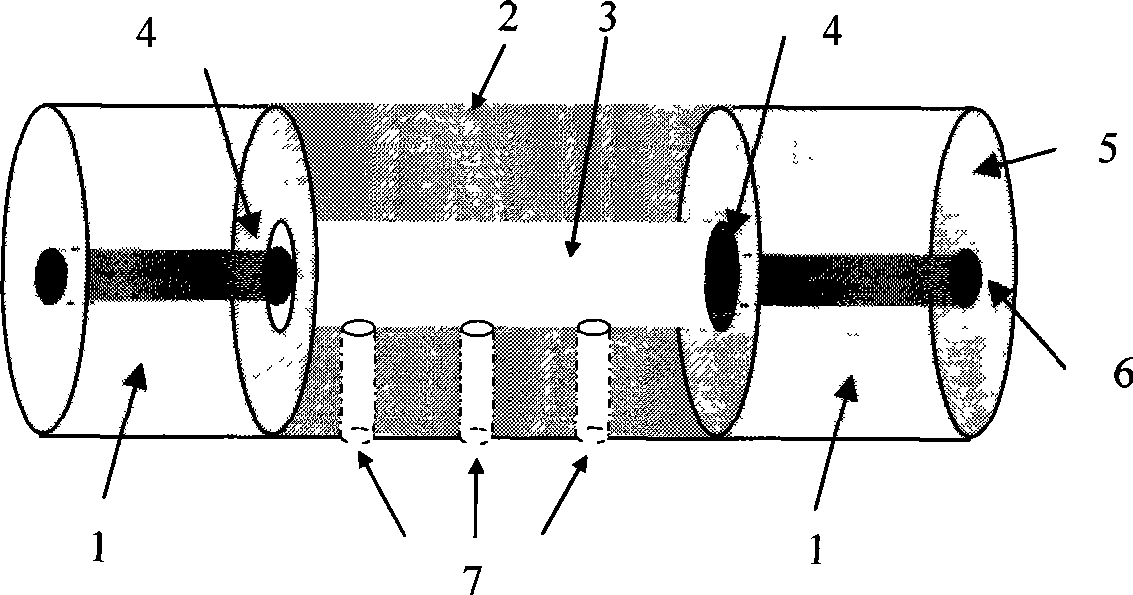
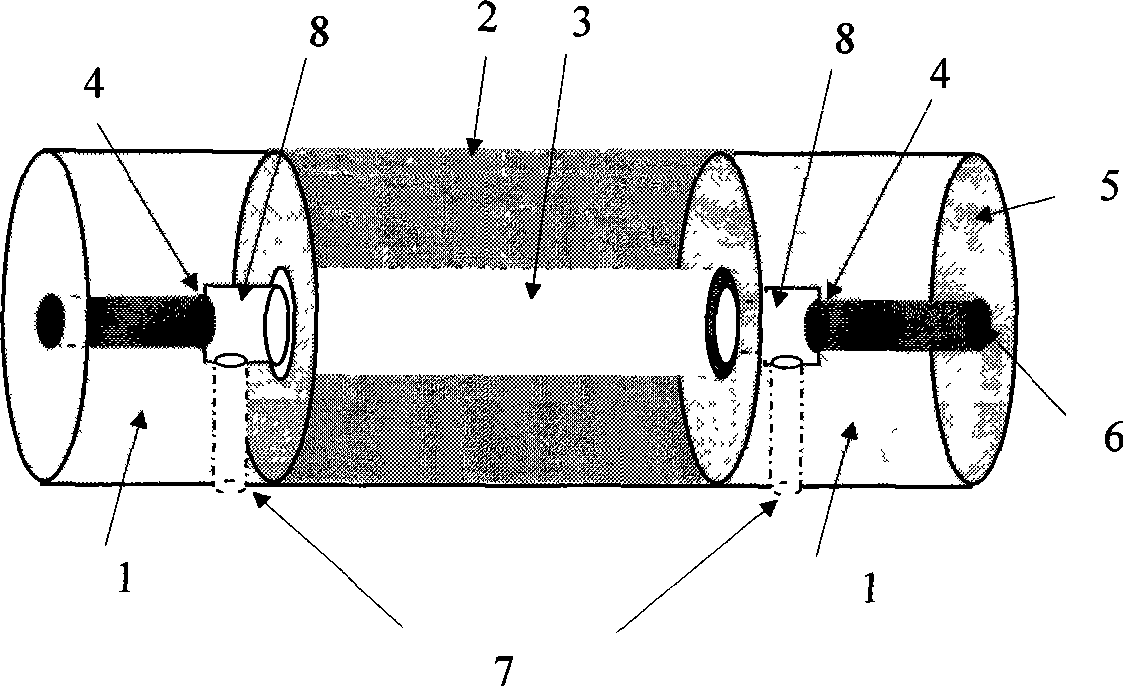
Hollow photon crystal optical fiber based Fabry-perot interferometer sensor and its production method
ActiveCN101055196ASmall coefficient of temperature variationHigh fringe contrastCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideIntrinsicsMillimeter
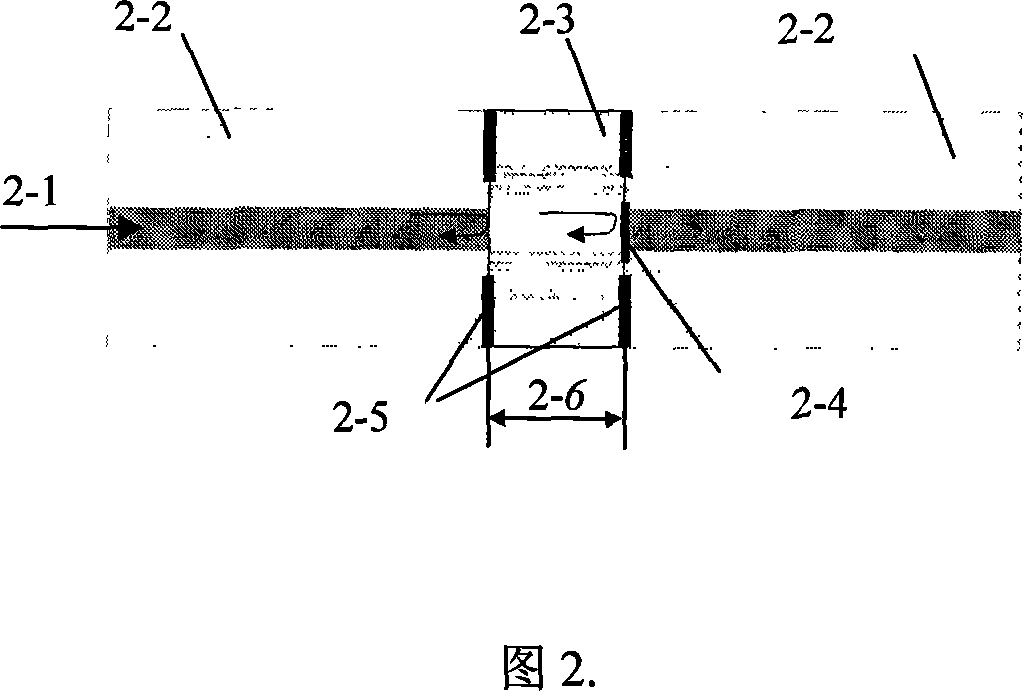
The invention discloses a hallow photonic crystal fiber based non-intrinsic fiber FP interference sensor composed two ordinary communication single-mode optical fibers 2-2 and a hallow photonic crystal fiber 2-3, the two ends of which are welded with one end of two ordinary communication single-mode optical fibers 2-2, otherwise, one end of one ordinary communication single-mode optical fiber 2-2 is coated with Ti203 film with diameter of 20um-30 um. The invention also discloses the production method of the sensor. The available technical effects of the invention are: (1) the temperature coefficient of EFPI sensor of the invention is small, and capable of working under temperature of 600 deg; (2) when the cavity length of the FP sensor is extended to several centimeter (the cavity length of traditional FP sensor is several hundred microns to millimeter in order), the stripe contrast is high, thereby establishing the foundation in the application of high capacity, quasi-distributed sensing system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
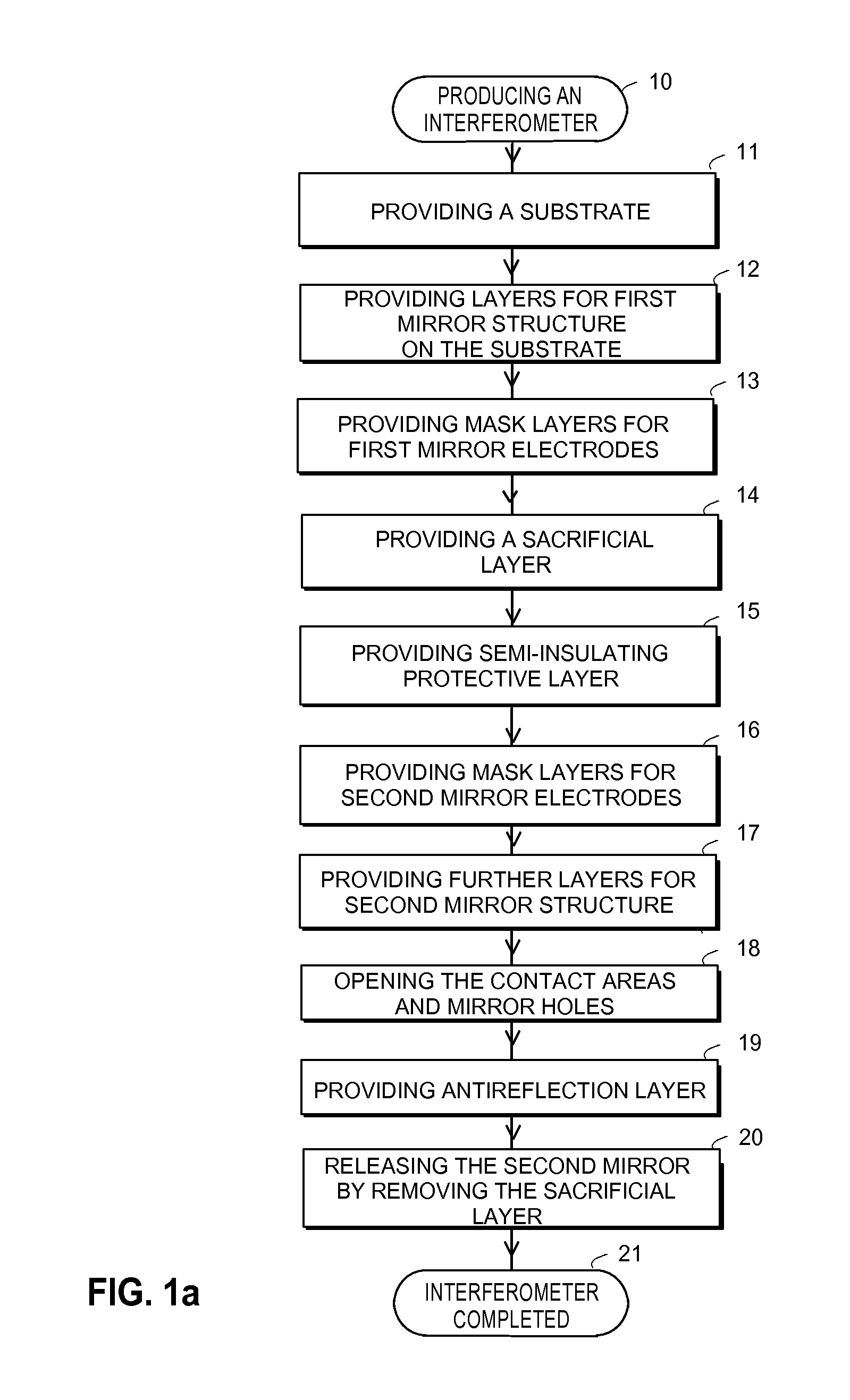
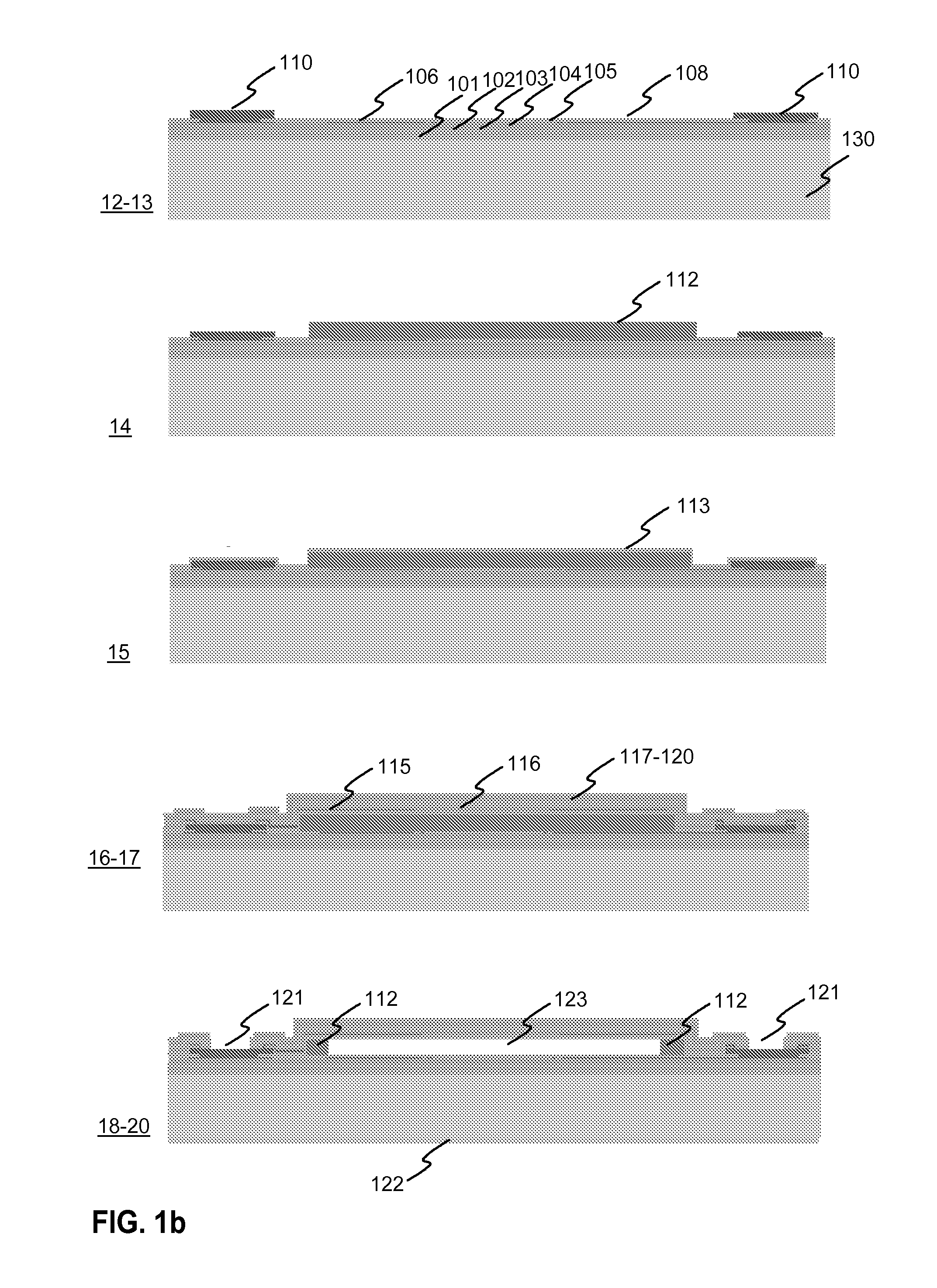
Electrically tunable fabry-perot interferometer, an intermediate product an electrode arrangement and a method for producing an electrically tunable fabry-perot interferometer
InactiveUS20110279824A1Prevents electrical short circuitPrevent electric chargeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringEvaporation
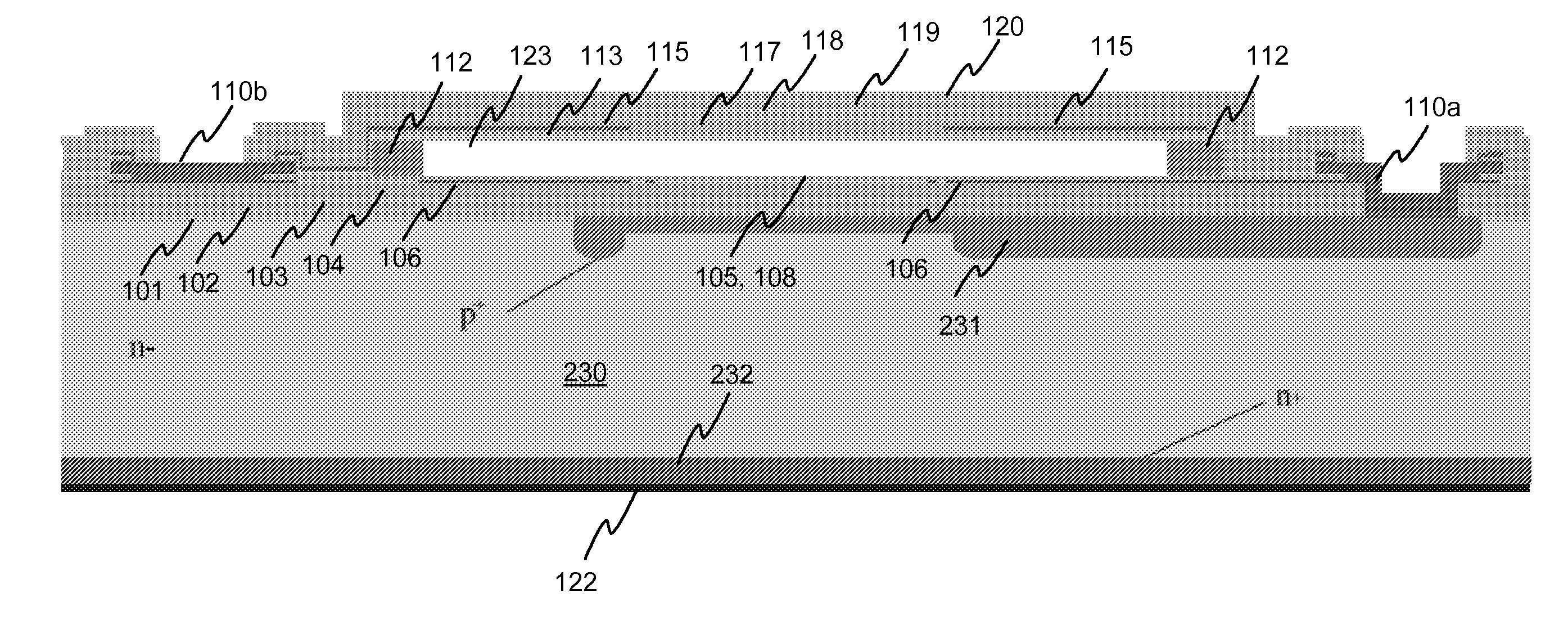
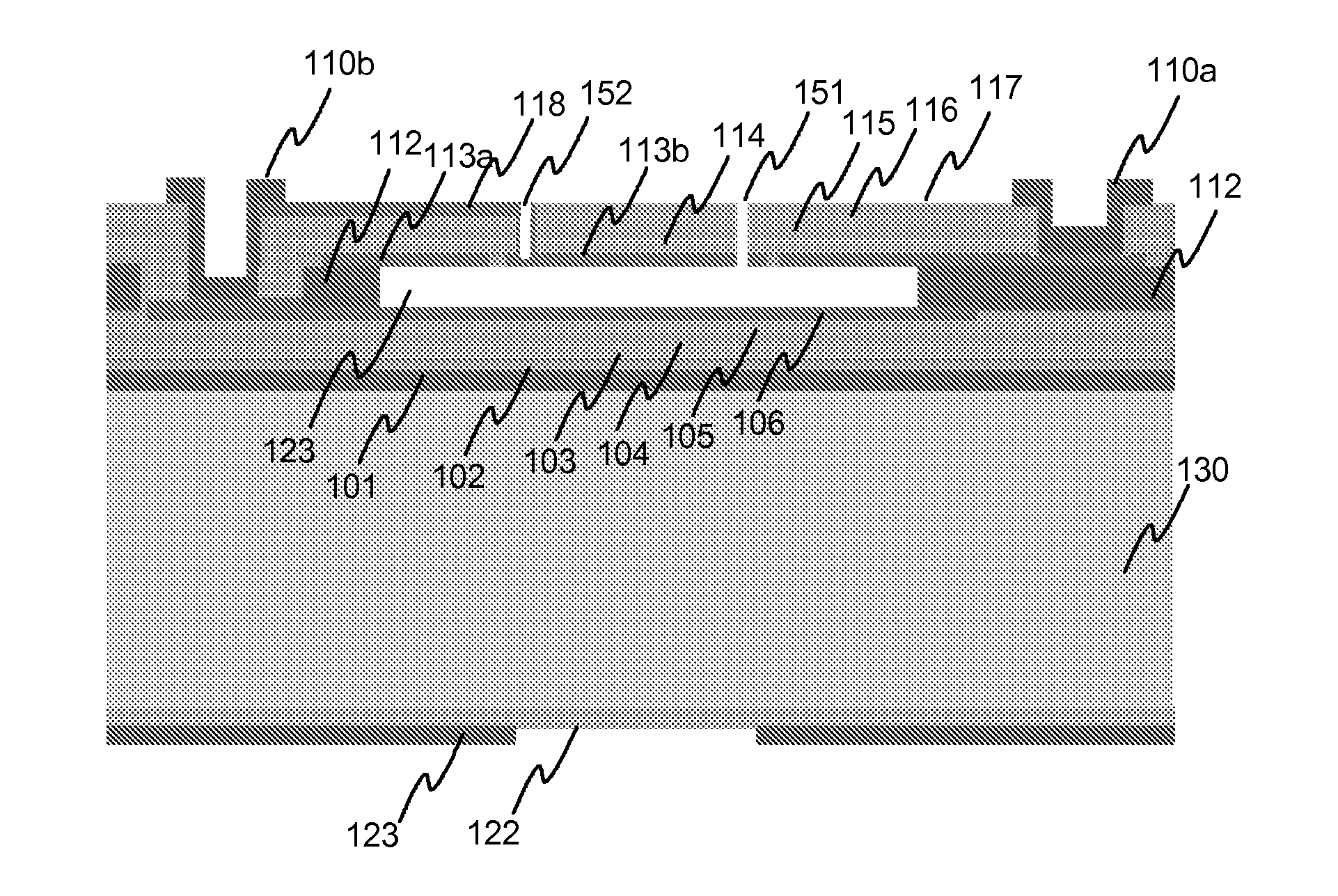
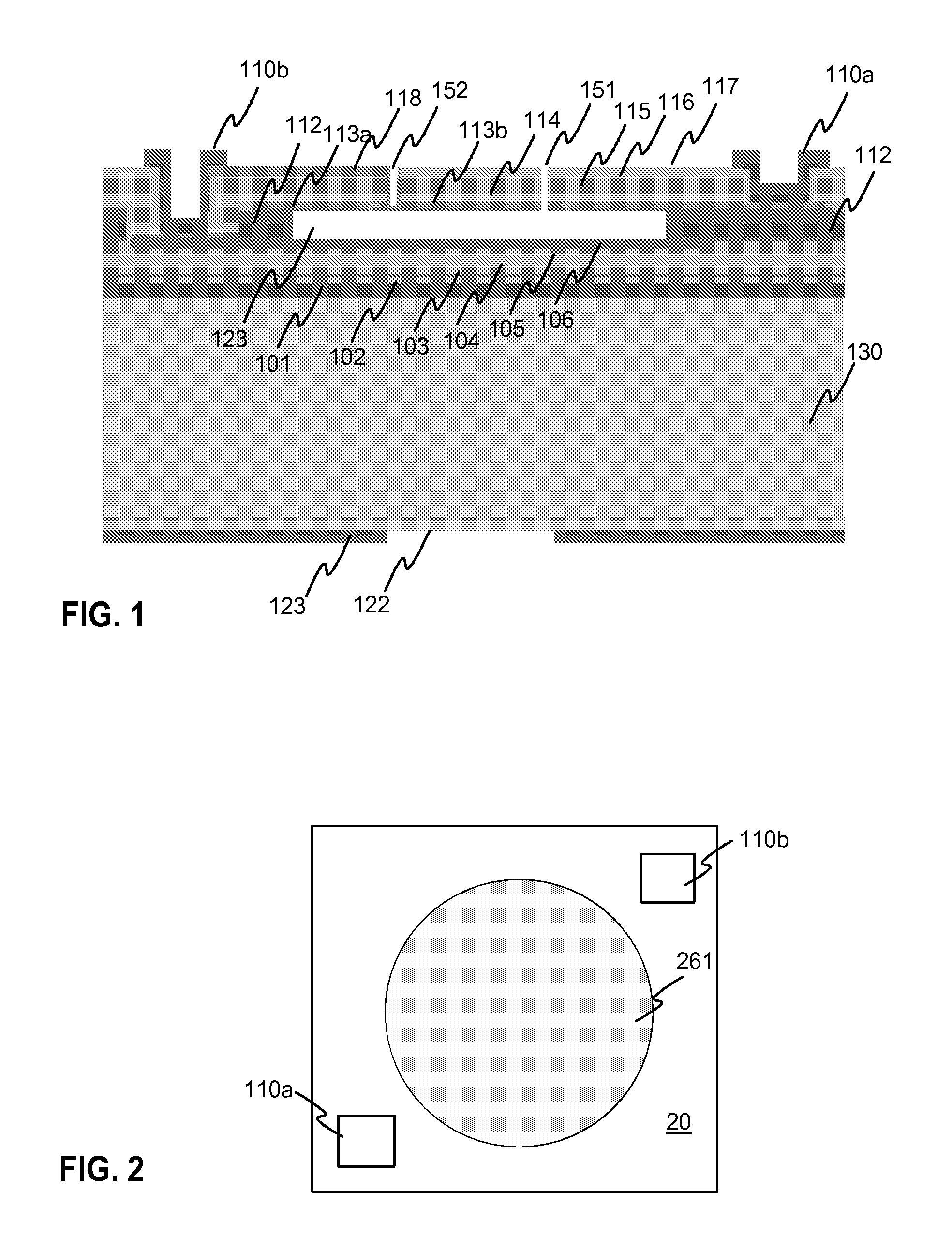
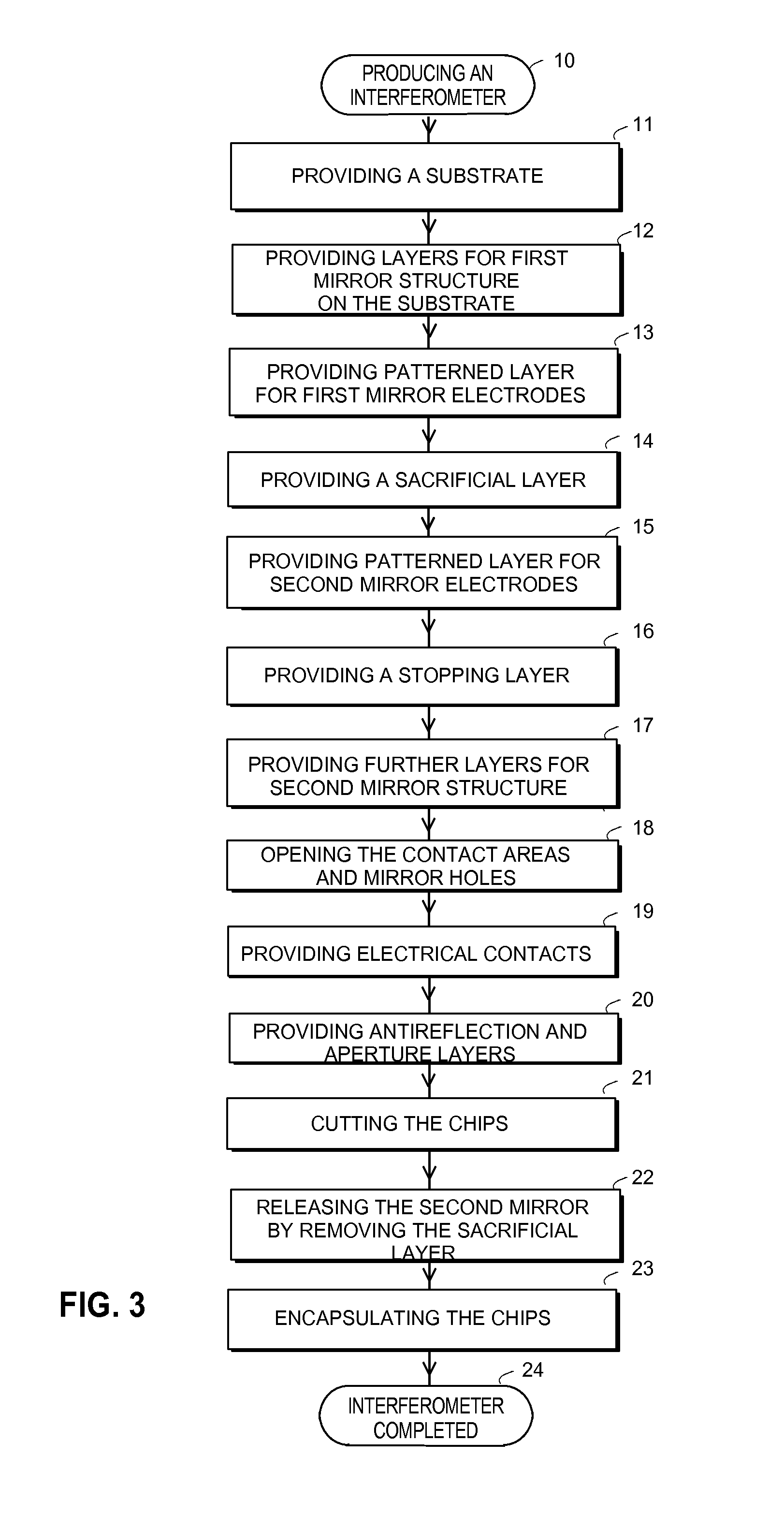
Electrically tunable Fabry-Perot interferometers which are produced with micromechanical (MEMS) technology. Producing interferometers with prior art processes includes costly and complicated production phases. Therefore, it has not been possible to apply interferometers in consumer mass products. According to the present solution, the Fabry-Perot cavity is made by removing a sacrificial layer (112) which has been polymer material. A mirror layer (113, 117-120) which is produced above the sacrificial layer can be made with atomic layer deposition technology, for example. According to a preferable embodiment, electrodes (106b, 115b) of the mirror structures are formed by using sputtering or evaporation. With the present solution it is possible to avoid the above mentioned problems related with prior art.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
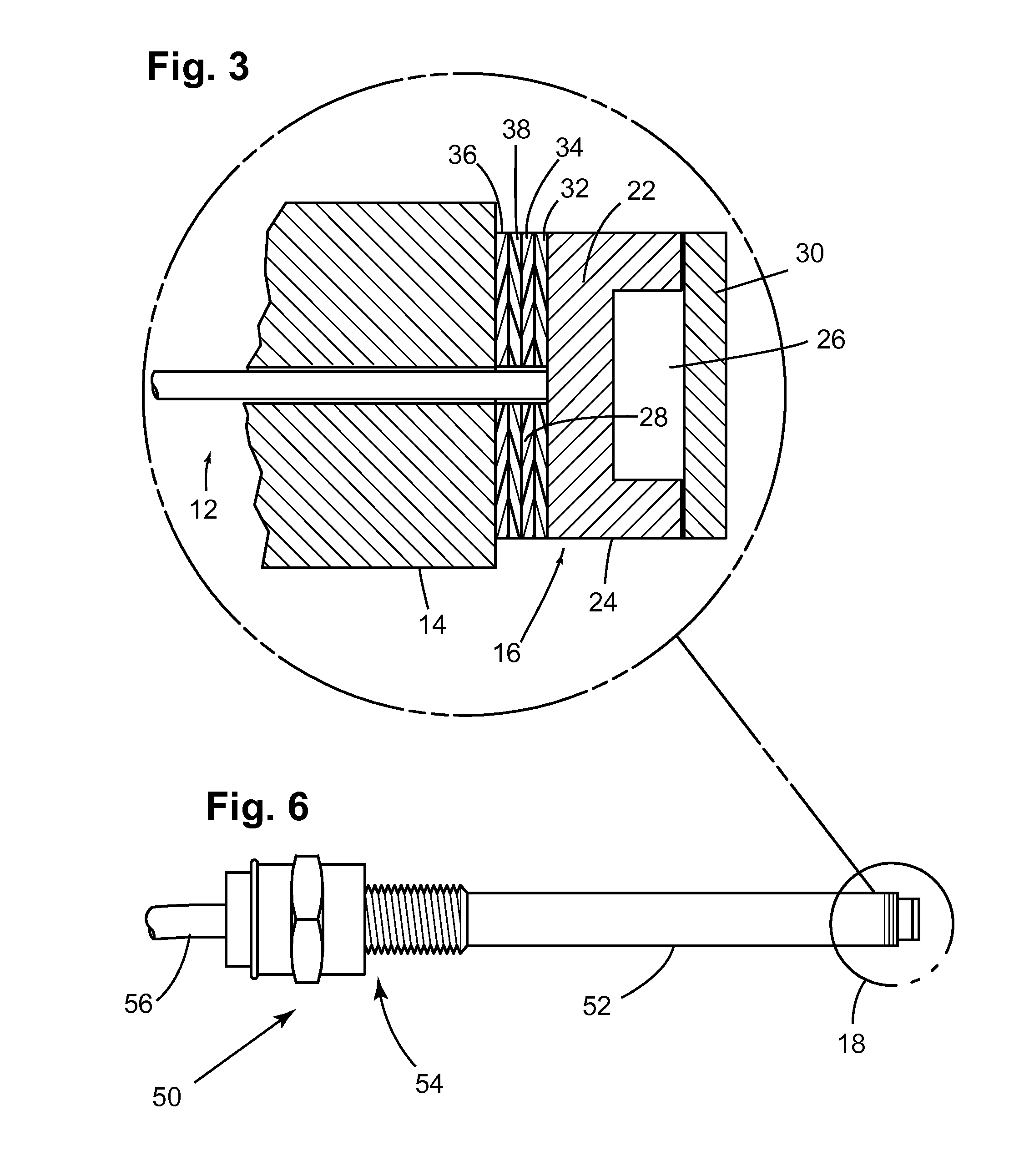
High-temperature pressure sensor and method of assembly
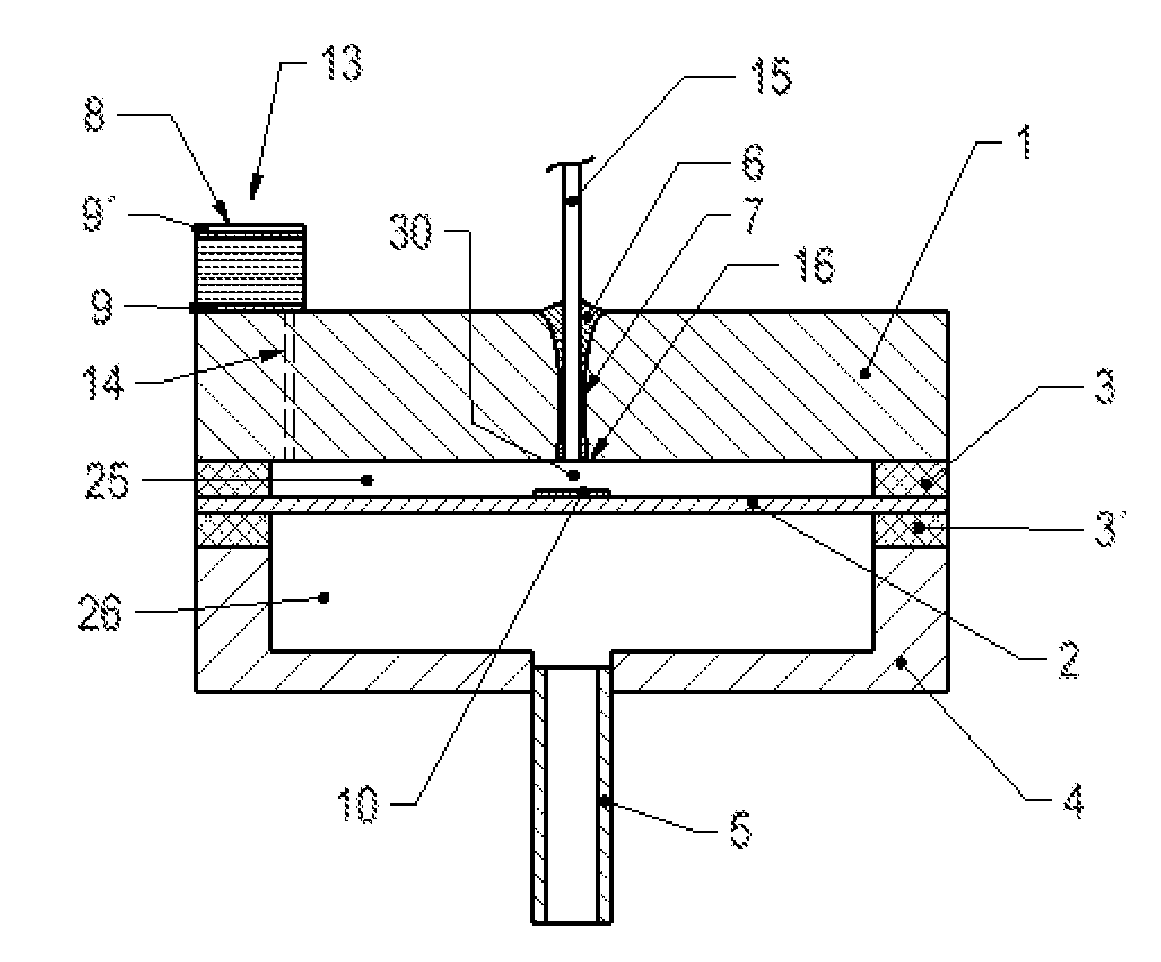
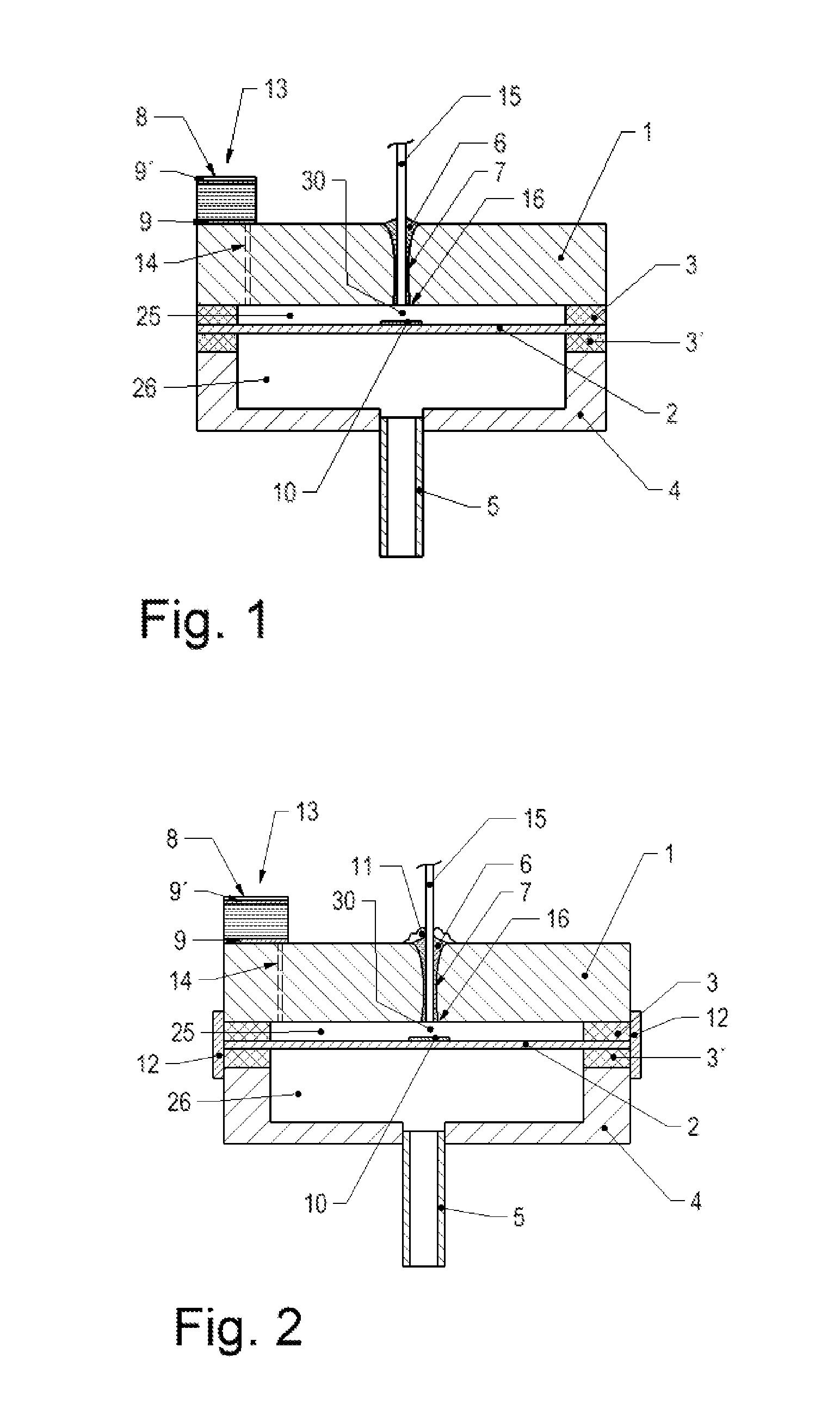
ActiveUS20080232745A1Easy to useQuick fixInterferometric spectrometryTubular articlesForce sensorSilicon
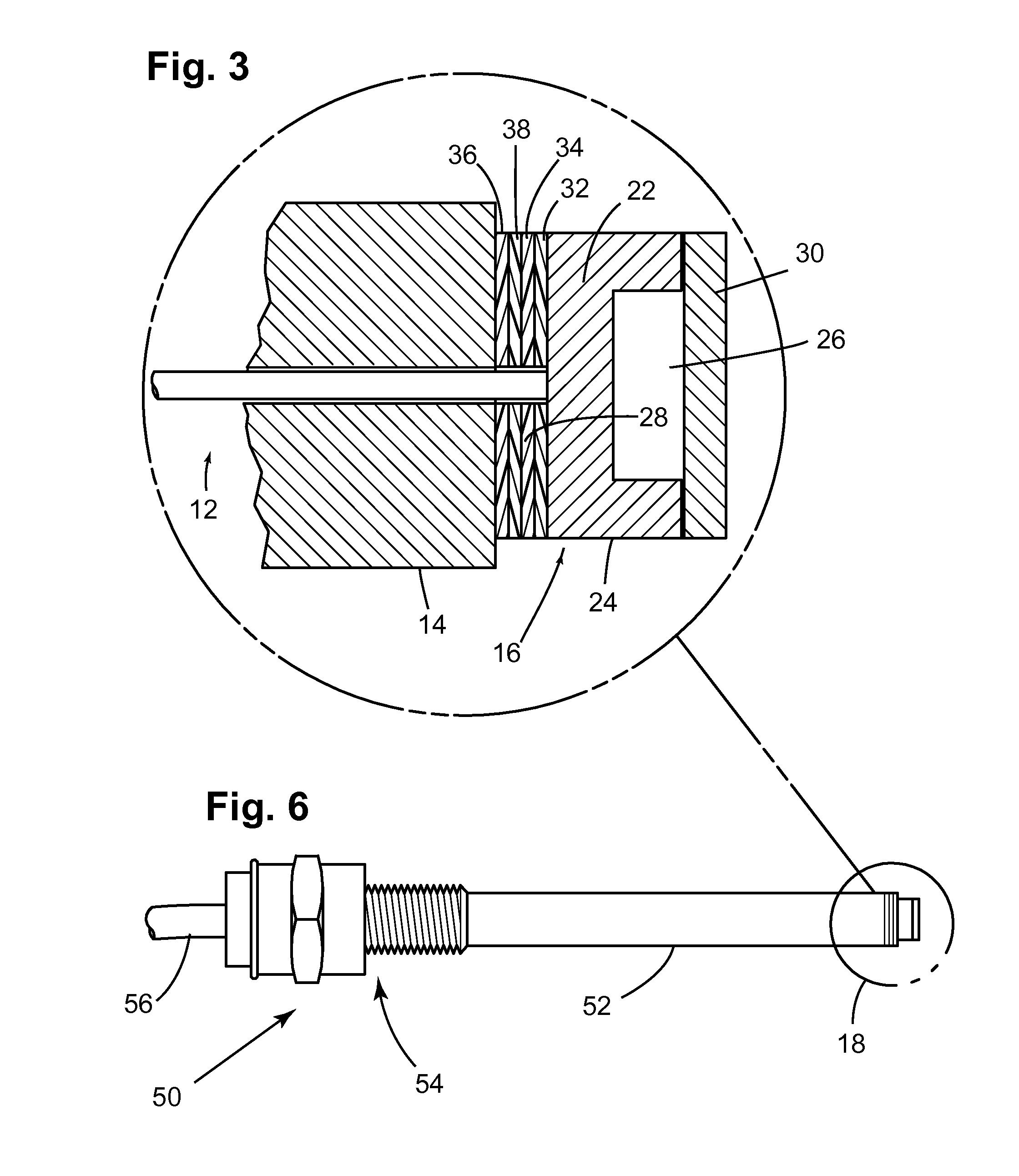
A method for assembling a Fabry-Perot interferometer includes depositing a first metal layer on an end portion of a ferrule, depositing a second metal layer on a back portion of a die, placing the first metal layer and the second metal layer in contact with each other with respective first and second orifices aligned with respect to each other, and bonding the ferrule to the die by thermo compression. The resulting interferometer includes a glass die with a cavity, a silicon diaphragm disposed over the opening of the cavity and bonded to the glass die, a ferrule bonded to the glass die by thermo compression with the first and second orifices being aligned to each other, and an optical fiber inserted through the other end of the ferrule in direct contact to a back portion of the die and aligned with the first orifice.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Micromechanical tunable fabry-perot interferometer, an intermediate product, and a method for producing the same
ActiveUS20120050751A1Reduce and avoid useHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionEtchingSilicon oxide
The invention relates to controllable Fabry-Perot interferometers which are produced with micromechanical (MEMS) technology. Producing prior art interferometers includes a risk of deterioration of mirrors during the etching of the sacrificial layer (123). According to the solution according to the invention at least one layer (103, 105, 114, 116) of the mirrors is made of silicon-rich silicon nitride. In the inventive Fabry-Perot interferometer it is possible to avoid or reduce using silicon oxide in the mirror layers whereby the risk of deterioration of the mirrors is reduced. It is also possible to use mirror surfaces with higher roughness, whereby the risk of the mirrors sticking to each other is reduced.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Method and device for stabilizing laser frequency and power
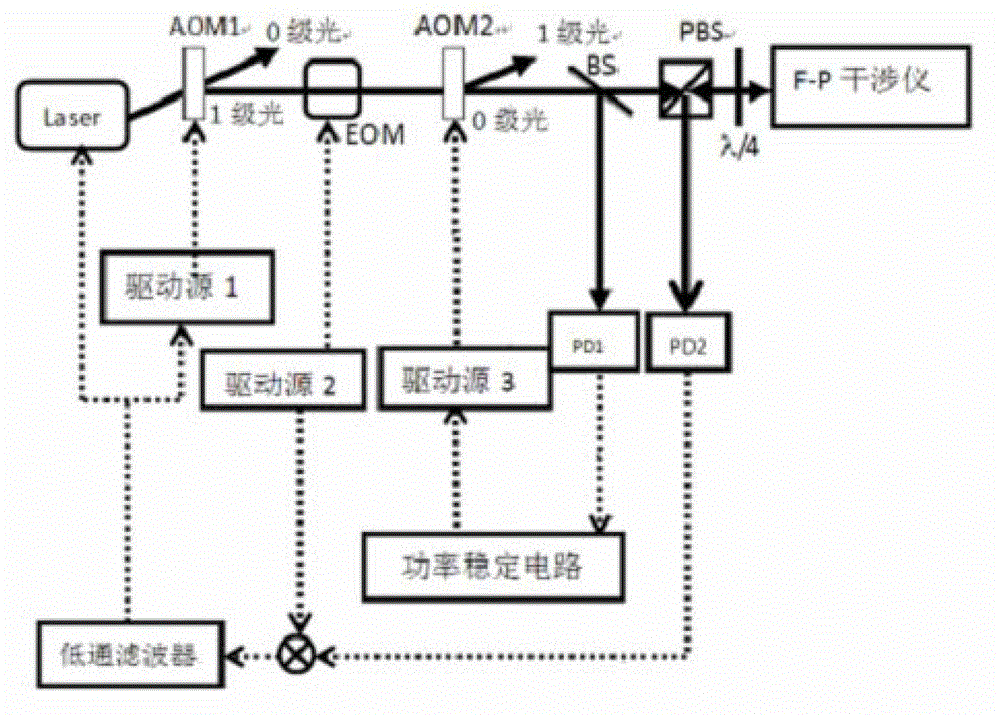
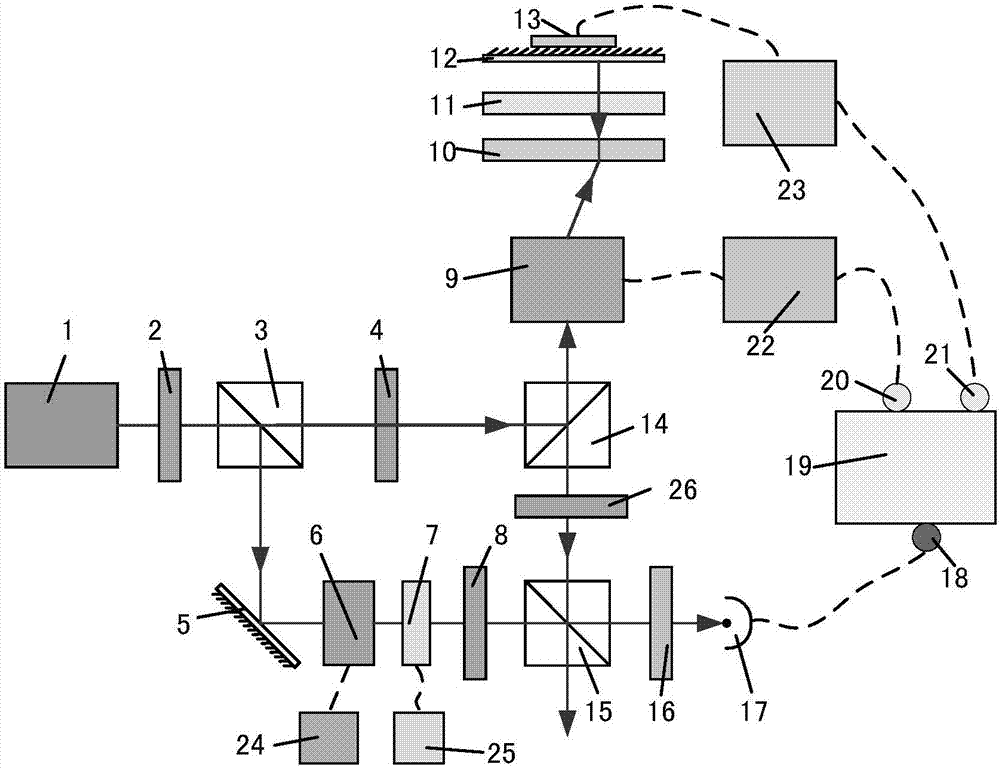
InactiveCN103151696AFrequency stabilityStable powerLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFrequency stabilizationPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a method and a device for stabilizing laser frequency and power. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining primary diffracted light, and radiating the primary diffracted light into a photoelectric detector; detecting the intensity of the primary diffracted light; processing a detected signal; sending the processed signal to a driving source; and enabling an output signal of the driving source to act on an acoustic optical modulator. The device comprises a laser, the acoustic optical modulator, an electrooptical modulator, a polarization splitting prism, a quarter-wave plate and a Fabry-Perot interferometer. The method and the device have the advantages that reference precision and stability are greatly improved, better power stabilizing effect is realized, and frequency stabilizing effect is improved.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Micro-optical sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements
InactiveUS7428054B2Good flexibilitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansFiberPhase step
A micro-optical fiber tip based sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements in a wide bandwidth, the design of which allows for multiplexity of the input side of the system is based on micro-electromechanical fabrication techniques. The optical portion of the system is based on low coherence fiber-optic interferometry techniques which has a sensor Fabry-Perot interferometer and a read-out interferometer combination that allows a high dynamic range and low sensitivity to the wavelength fluctuation of the light source. A phase modulation and demodulation scheme takes advantage of the Integrated Optical Circuit phase modulator and multi-step phase-stepping algorithm for providing high frequency and real time phase signal demodulation. The system includes fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors each of which has a diaphragm that is used as a transducer.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Ultralong Fabry-Parot interferent gas sensor and gas tester based on the sensor
InactiveCN101387608ALow costReduce volumePhase-affecting property measurementsSignal processing circuitsOptical coupler
The invention discloses a super-long fabry-perot interferometer gas sensor, which is characterized in that two ends of a hollow-core photonic crystal fiber are fused and jointed with single mode fibers, the core of the hollow-core photonic crystal fiber and the external condition are communicated by the permeable microporous on the optical fiber. The invention further discloses a gas tester adopting the super-long fabry-perot interferometer gas sensor, comprising a frequency sweeping laser, an optical coupler, an induction interferometer cavity adopting a super-long fabry-perot interferometer gas sensor, an interference interferometer cavity, a photoelectric detector, a data receiving and signal processing circuit and a monitoring computer. The invention has the advantages of low cost, small volume, simple system, safety, reliability, high stability, batch production, easy networking, and the application for the component recognition of various mixed gases and high-sensitivity density detection and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Acoustic wave acquiring apparatus
InactiveUS20130160557A1Resolve changeResolution imaging areaVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage resolutionBeam diameter
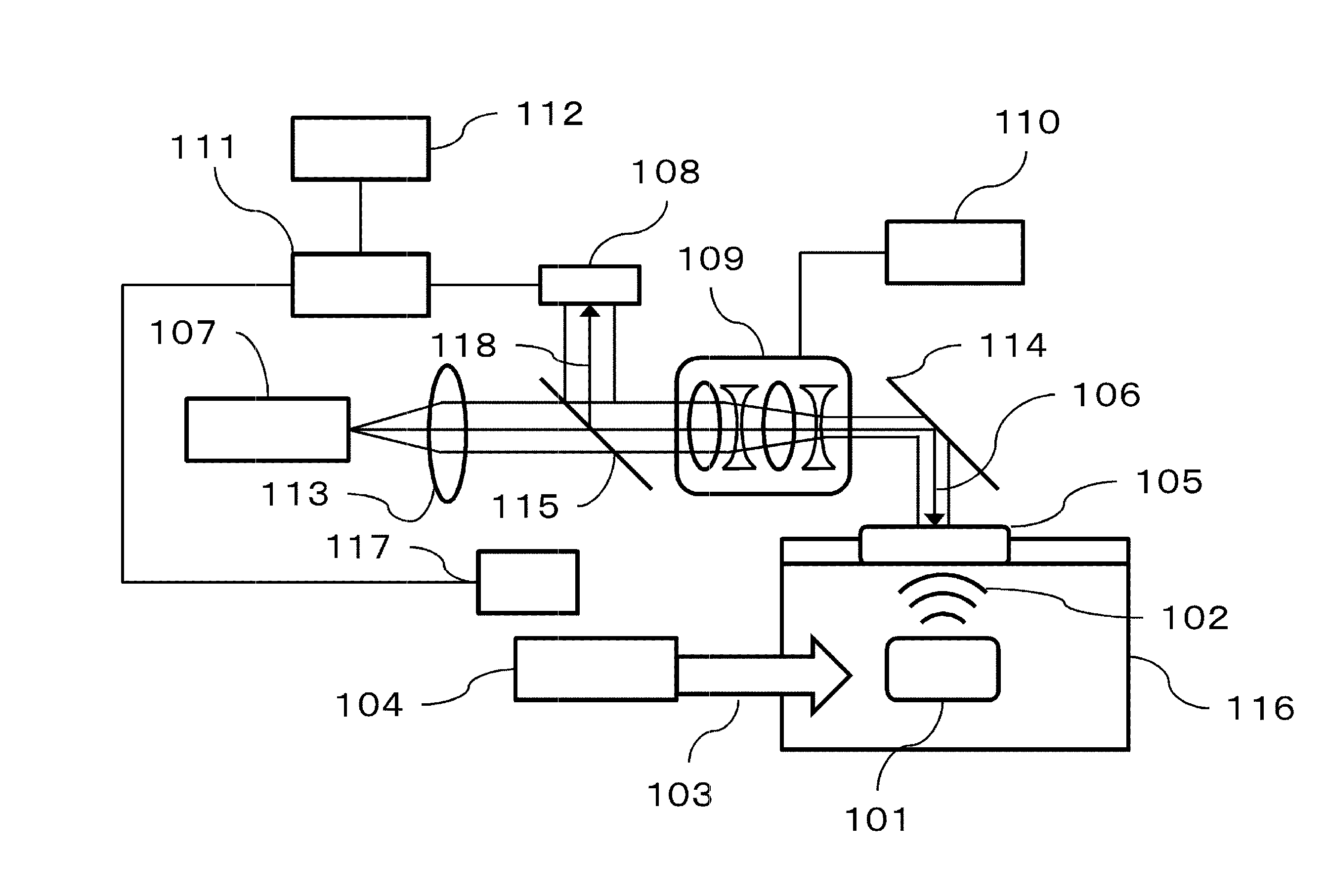
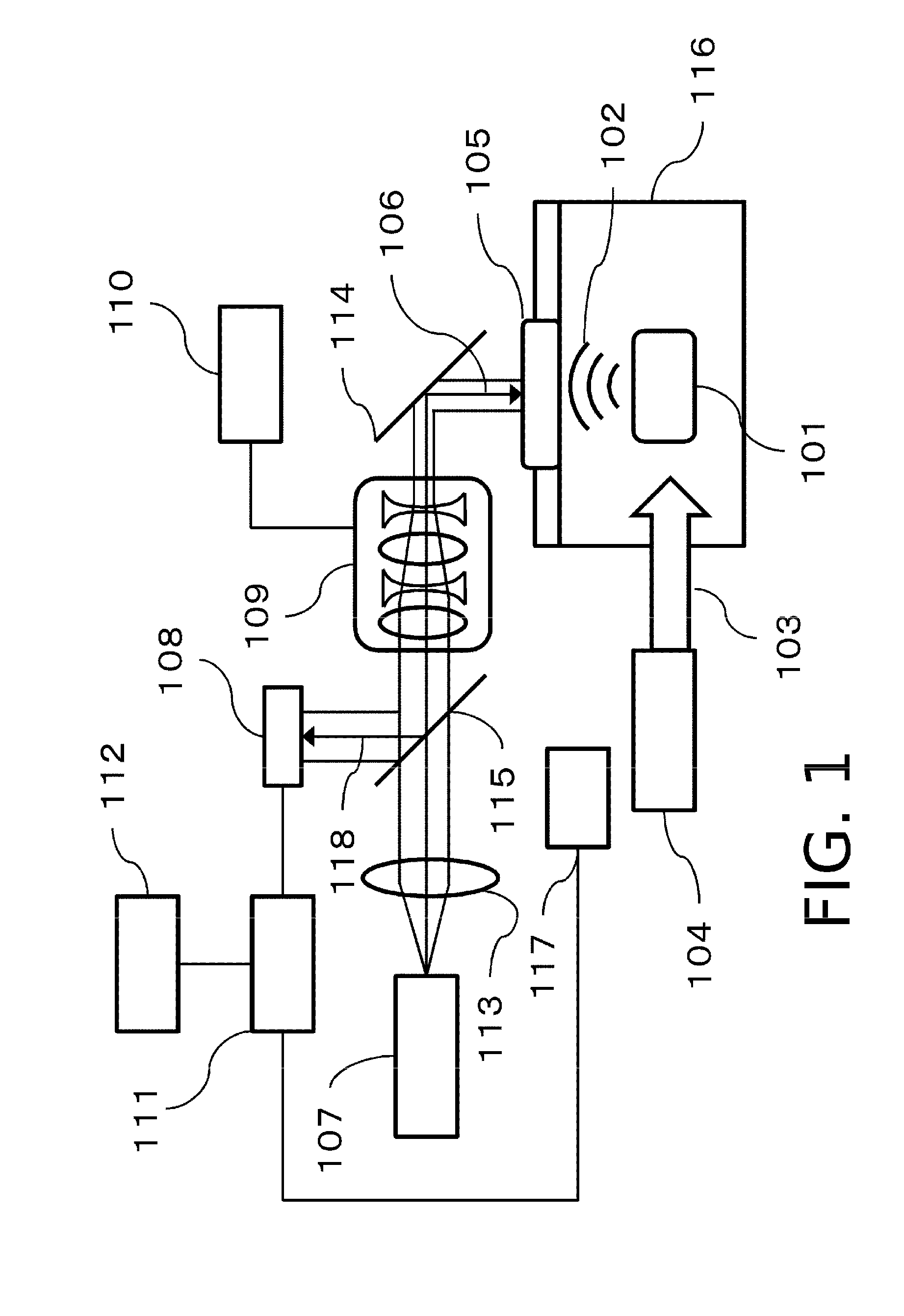
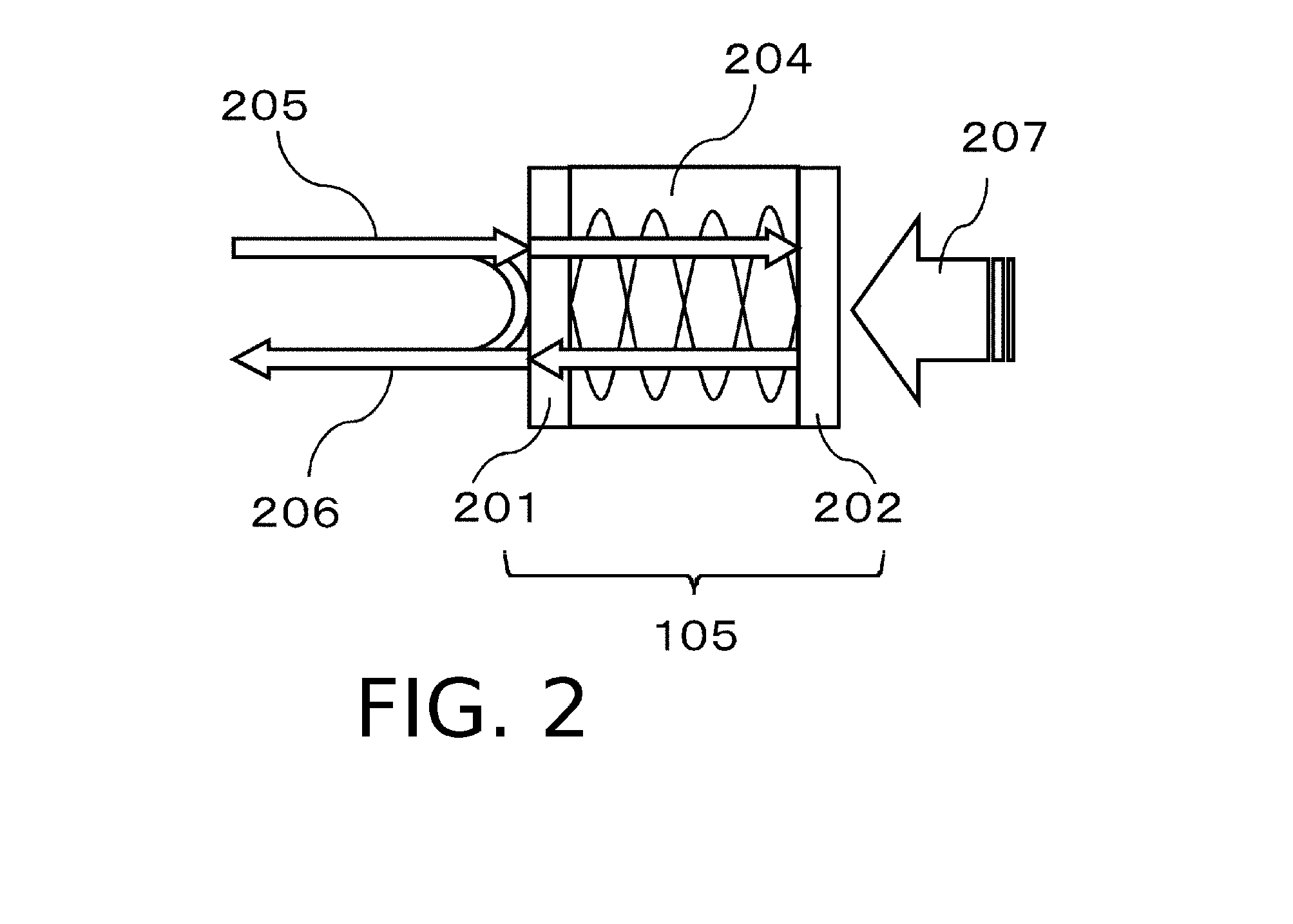
Provided is a technique capable of changing resolution or an imaging area during imaging, in an acoustic wave acquiring apparatus using a Fabry-Perot probe. An acoustic wave acquiring apparatus includes a measurement light source emitting measurement light, a probe having a Fabry-Perot interferometer including a first mirror, upon the side of which the measurement light is incident, and a second mirror, upon the side of which an elastic wave from an object is incident, an optical system changing a beam diameter of the measurement light, a controller controlling change in the beam diameter performed by the optical system, a photosensor measuring a light intensity of the measurement light reflected on the Fabry-Perot interferometer, and a processor acquiring intensity of the elastic wave on the basis of change in the light intensity measured by the photosensor due to incidence of the elastic wave.
Owner:CANON KK
Micromechanical tunable fabry-perot interferometer and a method for producing the same
ActiveUS20140111811A1Improve performanceReduce decreaseLine/current collector detailsSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionOptoelectronicsVoltage
Electrically tunable Fabry-Perot interferometers produced with micro-optical electromechanical (MOEMS) technology. Micromechanical interferometers of the prior art require high control voltage, their production includes complicated production phases, and the forms of the movable mirrors are restricted to circular geometries. In the inventive solution, there is a gap in the movable mirror, whereby mirror layers opposite to the gap are connected with anchoring. The anchoring is such that the stiffness of the mirror is higher at the optical area than at the surrounding area. This way it is possible keep the optical area of the mirror flat even if the control electrodes extend to the optical area. Due to large electrodes, lower control voltages are required.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
High intensity fabry-perot sensor
InactiveUS20060274323A1Maximize reflected light signalInterferometersUsing optical meansFiberOptical axis
In a Fabry-Perot interferometer based sensor if insufficient light reflected from the sensor re-enters the fiber, the results from the Fabry-Perot interferometer-based sensor are compromised. Accordingly, a sensor assembly is provided that comprises an optical fiber having an optical axis, a lens in optical communication with the optical fiber, the lens having an optical axis and the lens capable of transmitting a beam of light, a reflective surface, the reflective surface spaced from the lens such that the beam of light transmitted from the lens is capable of reflecting from the reflective surface back to the lens, and an alignment device capable of aligning the beam of light transmitted from the lens substantially perpendicular with the reflective surface.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Optical Interferometric Pressure Sensor
ActiveUS20090320605A1Improve reflectivityStable mechanical propertiesWave amplification devicesFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsFiberOptical reflection
A pressure measuring cell has a first housing body and a membrane arranged proximate the housing body, both of ceramic. The membrane has a peripheral edge joined to the first housing body to create a reference pressure chamber. A second housing body made of ceramic material is opposite the membrane and is joined to the peripheral edge of the membrane, the second housing body together with the membrane forming a measurement pressure chamber. The second housing body has a port for connecting the pressure measuring cell to a medium to be measured. The first housing body, the second housing body and the membrane are tightly connected along the peripheral edge of the membrane in a central area of the first housing body a hole is formed, reaching through the first housing body and at least in the central region of the membrane and opposite the hole a surface of the membrane is formed as a first optically reflective area. An optical fiber is arranged and tightly fixed within the hole for feeding light onto the surface of the membrane. The end of the fiber reaches at least the surface of the first housing body and is formed as a second reflective optical area linking the surface so that between the fiber end and the reflection area an optical cavity is present which forms a measuring section for determining the level of deflection of the membrane and which is part of a Fabry-Perot Interferometer.
Owner:INFICON HLDG AG
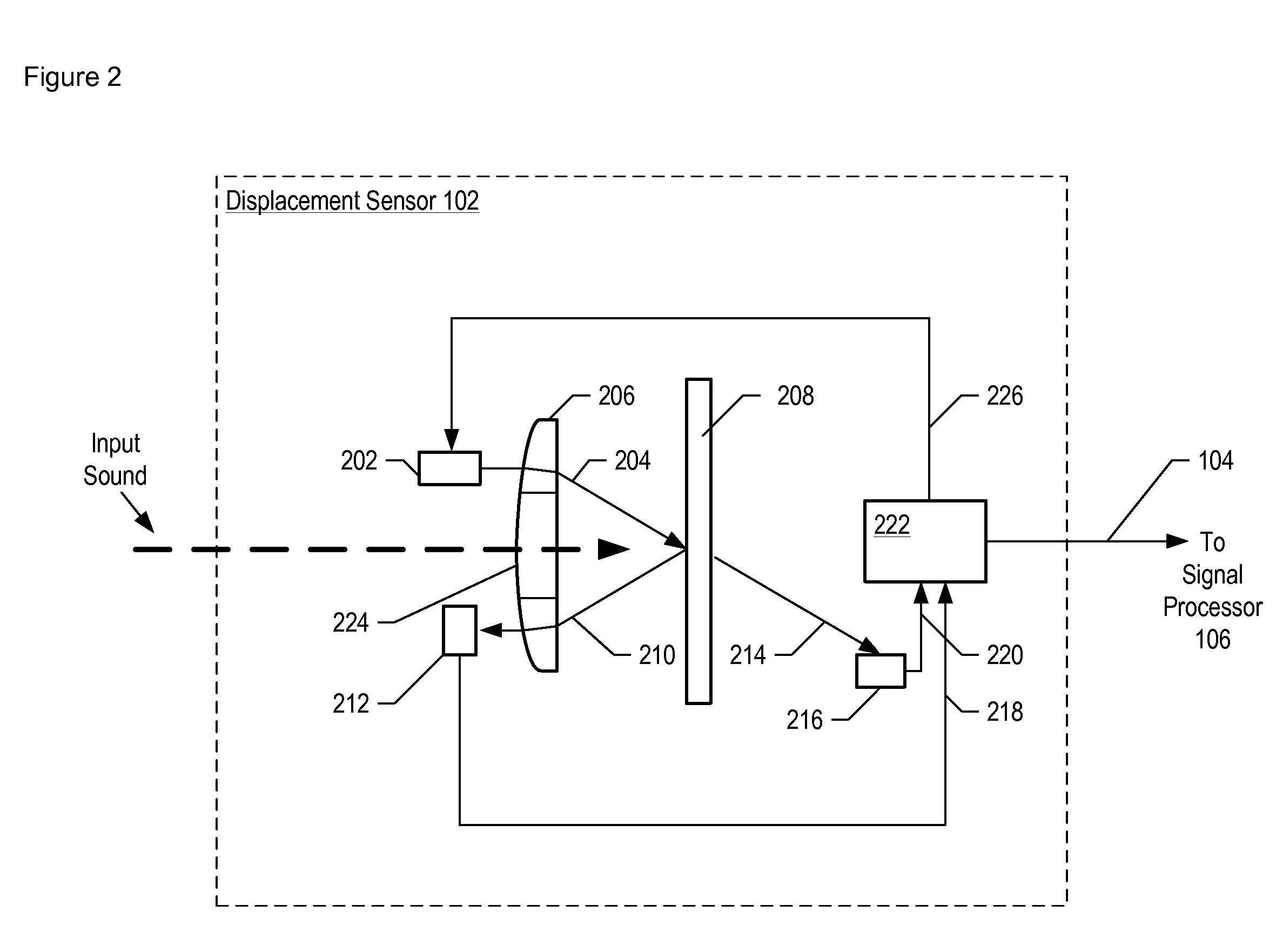
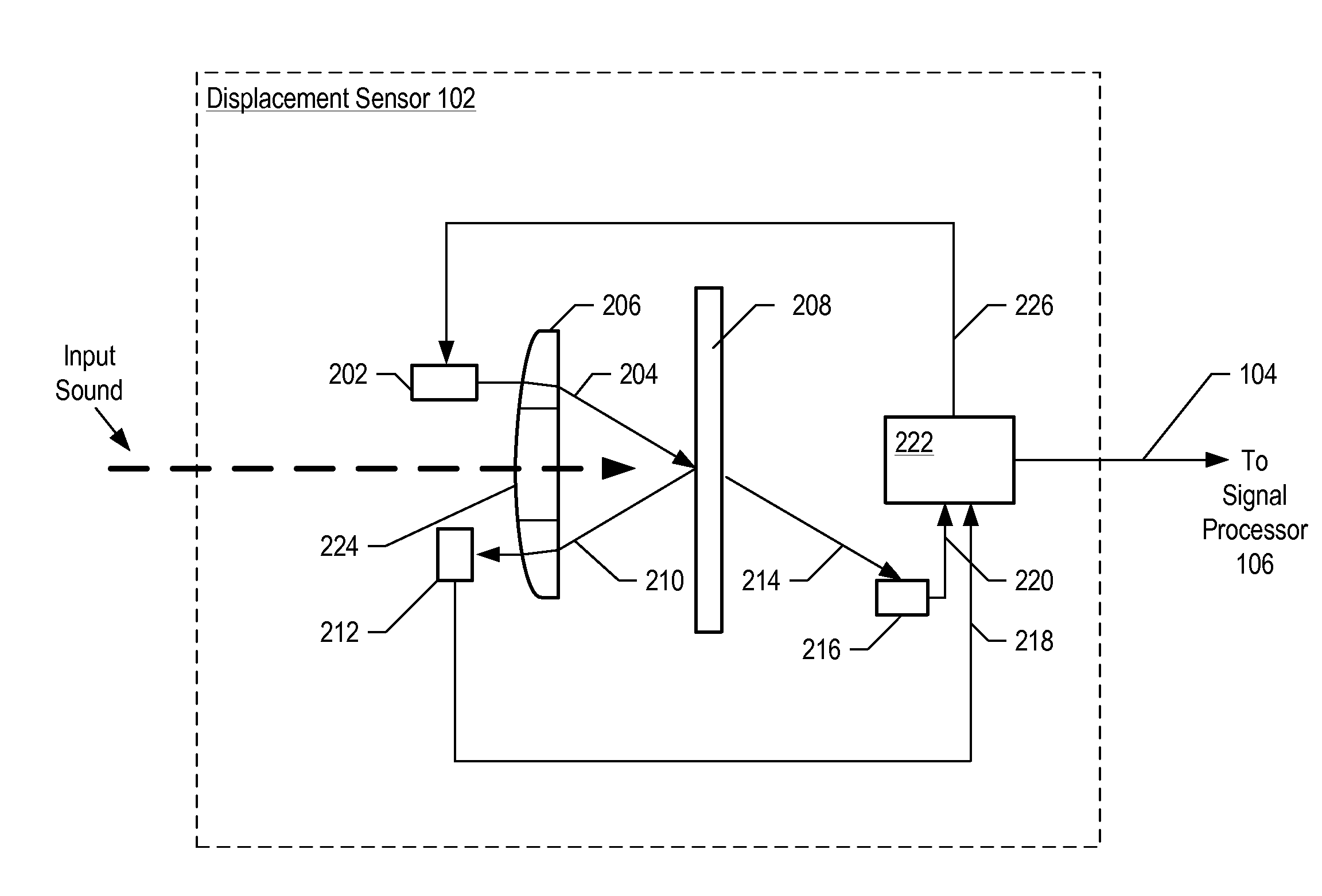
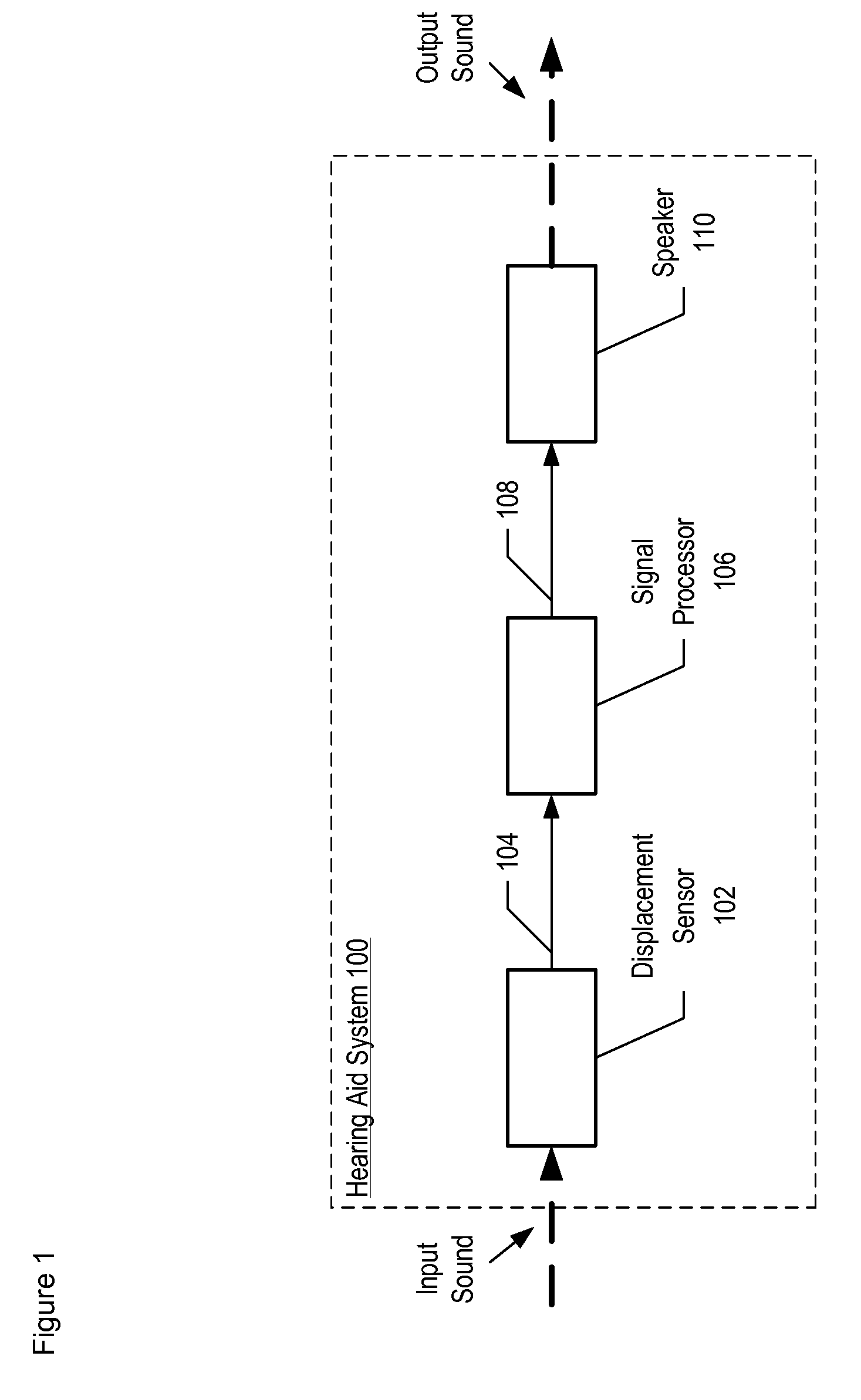
Apparatus comprising a high-signal-to-noise displacement sensor and method therefore
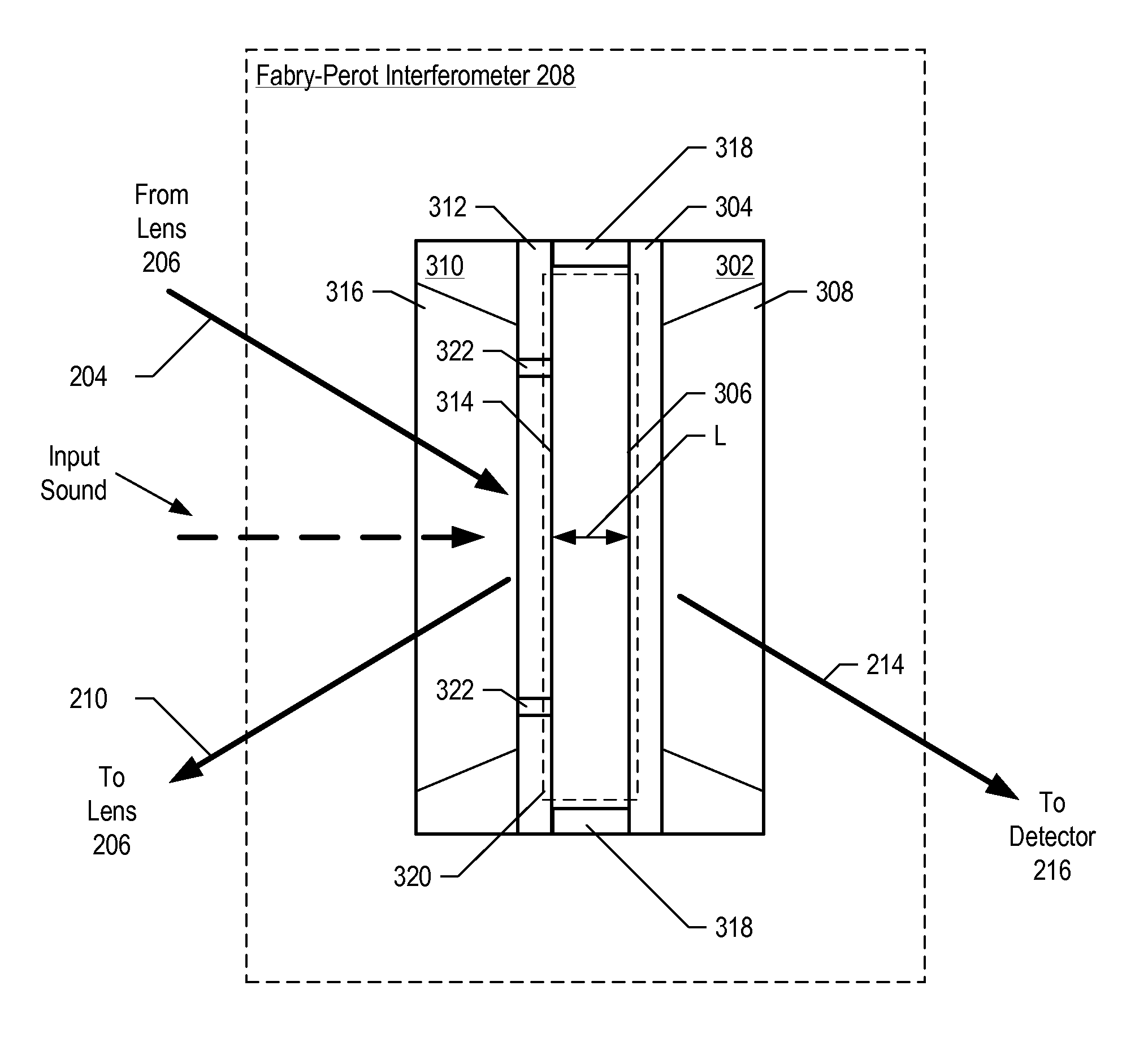
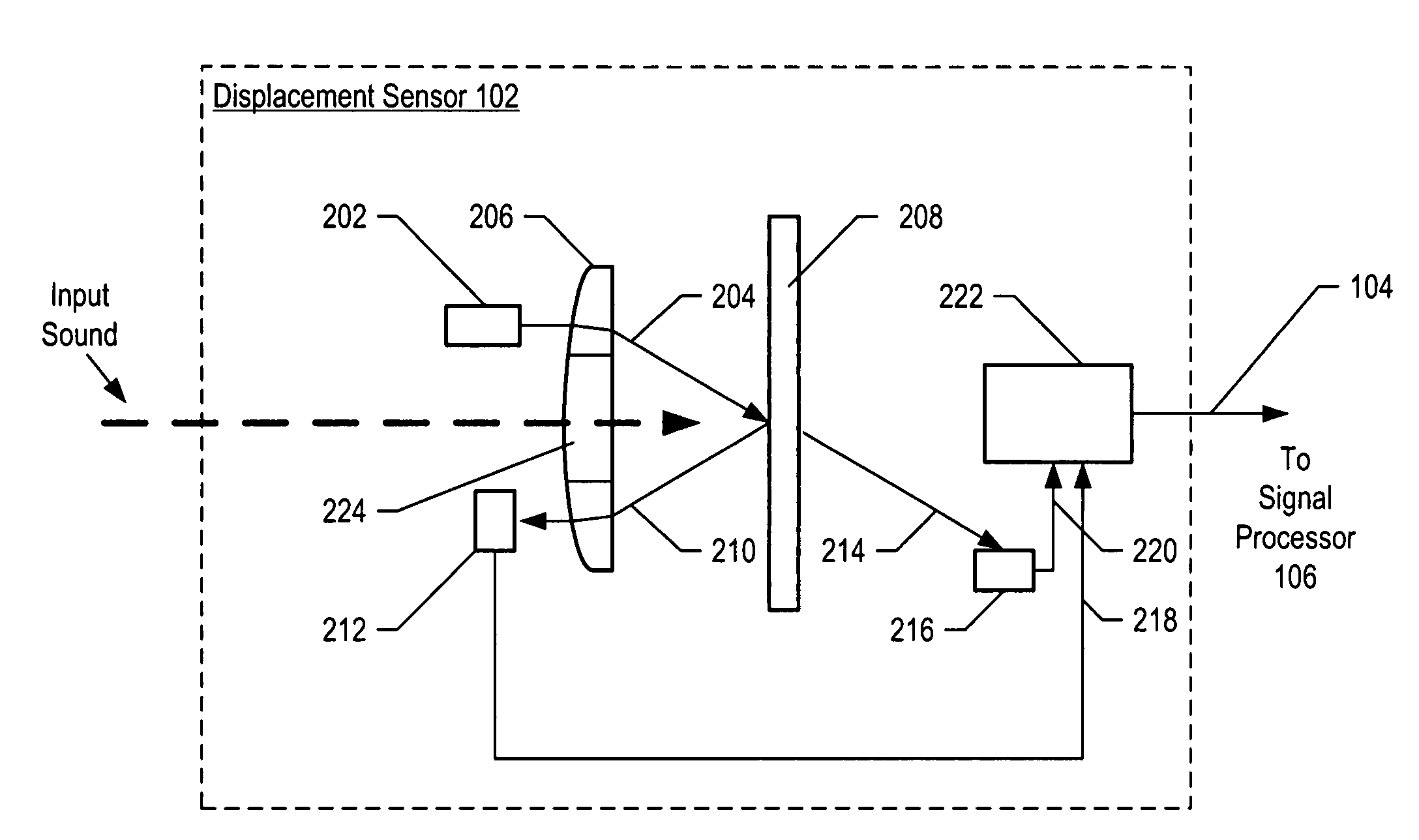
InactiveUS7355723B2Increase signal strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioOptical signal transducersSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Light beam
An optical displacement sensor is disclosed that provides a high signal-to-noise ratio output signal without some of the disadvantages for doing so in the prior art. An embodiment of the present invention directs a light beam toward a Fabry-Perot interferometer and detects both the reflected and transmitted optical beams that result from interaction with the Fabry-Perot interferometer. Signal processing techniques are applied to signals based on both the reflected and transmitted beams, resulting in higher signal strength and / or reduced noise in the resulting output signal.
Owner:SYMPHONY ACOUSTICS
Patch-type extrinsic fabry-perot interferometric fiber optic sensor and real-time structural vibration monitoring method using the same
InactiveUS20050013526A1Stable and reliableSimple system constructionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySelf sensingDirection information
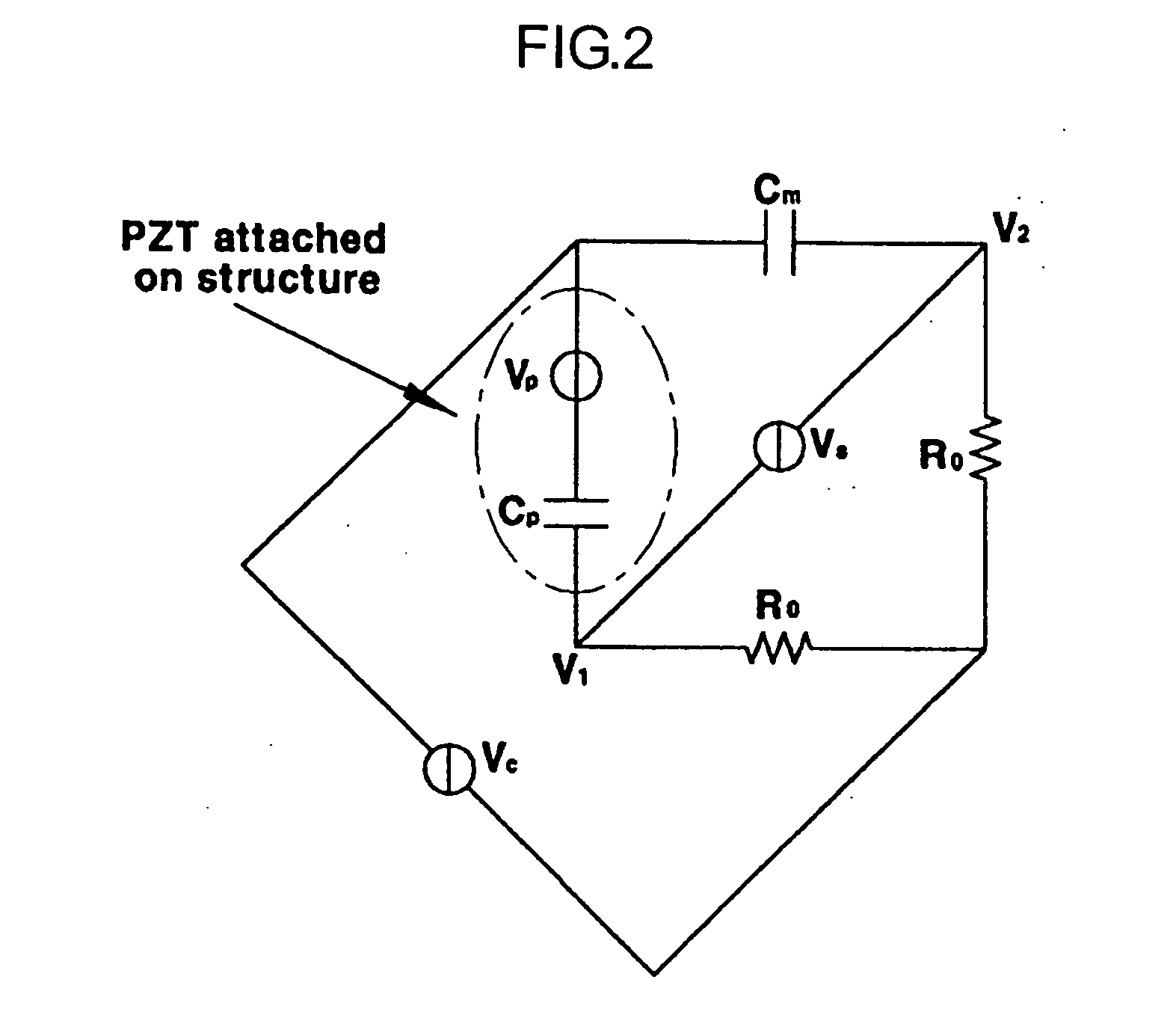
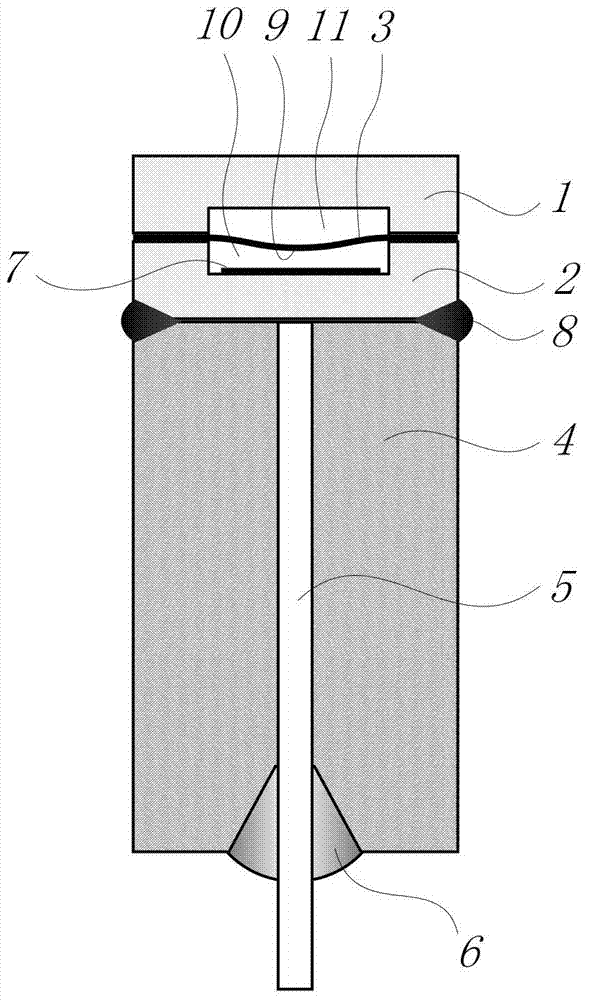
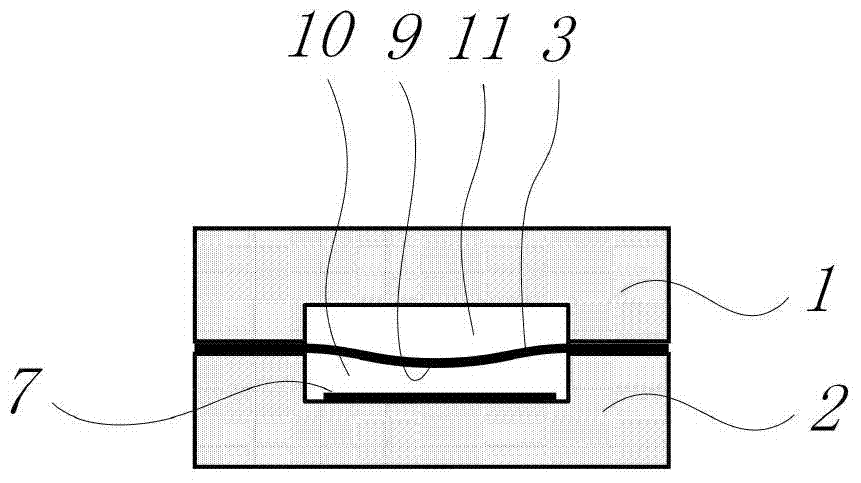
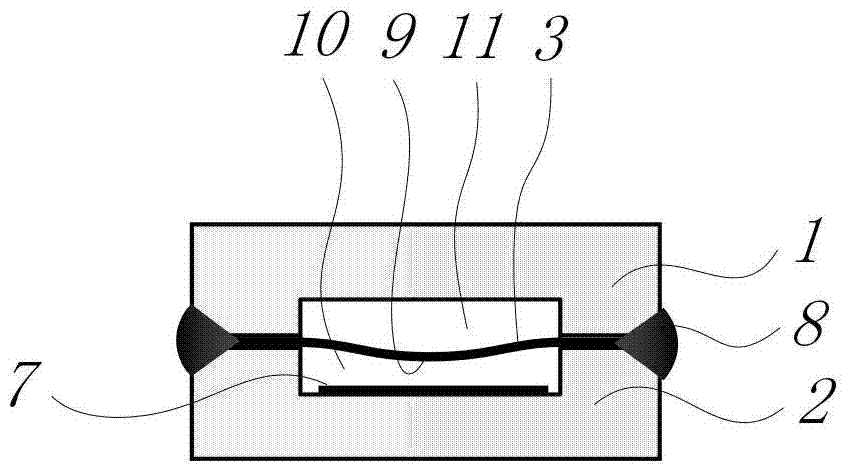
A patch-type extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric fiber optic sensor and a real-time structural vibration monitoring method using the same are disclosed. The patch-type extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric fiber optic sensor is provided by combining the existing EFPI (Extrinsic Fabry-Perot Interferometer) fiber optic sensor with a direction-detecting sensor which can acquire direction information of a strain of a structure, which can solve a signal distortion problem occurring in the existing EFPI fiber optic sensor through a simple signal process. The patch-type extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric fiber optic sensor includes a piezoelectric material which can apply a control force to the existing EFPI fiber optic sensor, and a self-sensing bridge circuit for extracting the direction information when the piezoelectric material is used as an actuator, so that the sensible range of strain can be extended and the piezoelectric material can directly be used as the actuator based on the sensed signal.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Fiber optic temperature sensor based on sealed micro cavity gas thermal effect and manufacturing method of fiber optic temperature sensor
ActiveCN104515621AImprove consistencyWith mass productionThermometers using physical/chemical changesIdeal gas lawMaterials science
The invention discloses a fiber optic temperature sensor based on a sealed micro cavity gas thermal effect and a manufacturing method of the fiber optic temperature sensor. A sensor structure comprises a Fabry-Perot micro cavity and an air micro cavity, and the two micro cavities are partitioned through a thin silicon membrane. The atmospheric pressure environments of the two micro cavities are respectively controlled in the sensor manufacturing process, so that the two micro cavities have pressure difference. When the temperature changes, according to an ideal gas state equation, the atmospheric pressure inside the two micro cavities is changed, so that a silicon wafer in the middle of the two micro cavities is deformed because of the change of the pressure difference. At the same time the inner surface of the silicon wafer and the reflection surface inside the Fabry-Perot micro cavity form a low-fineness Fabry-Perot interferometer, the deformation of the membrane is just the length change of the Fabry-Perot micro cavity, and temperature measurement is achieved by demodulating the length change of the cavity. Compared with the prior art, the temperature sensitivity of the sensor disclosed by the invention can be flexibly controlled by designing the diameter, the temperature and the pressure difference of the silicon wafer, and expected temperature sensitivity is achieved. In addition, the in-batch production of the senor is beneficial to cost reduction, and commercialization can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Fabry-Perot interferometer including membrane supported reflector
ActiveUS6958818B1Spectrum generation using multiple reflectionUsing optical meansOptoelectronicsMembrane configuration
Owner:SILICON LIGHT MACHINES CORP
Fiber optic Fabry-Perot interferometer and associated methods
InactiveUS6886365B2Less-expensive to produceImprove automationGlass making apparatusRadiation pyrometryAdhesiveSingle fiber
The method for making the fiber optic Fabry-Perot sensor includes securing an optical fiber to a substrate, and forming at least one gap in the optical fiber after the optical fiber is secured to the substrate to define at least one pair of self-aligned opposing spaced apart optical fiber end faces for the Fabry-Perot sensor. Preferably, an adhesive directly secures the at least one pair of optical fiber portions to the substrate. The opposing spaced apart optical fiber end faces are self-aligned because the pair of optical fiber end portions are formed from a single fiber which has been directly secured to the substrate. Also, each of the self-aligned spaced apart optical fiber end faces may be substantially rounded due to an electrical discharge used to form the gap. This results in integral lenses being formed as the end faces of the fiber portions.
Owner:HARRIS CORP +1
High-temperature pressure sensor and method of assembly
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
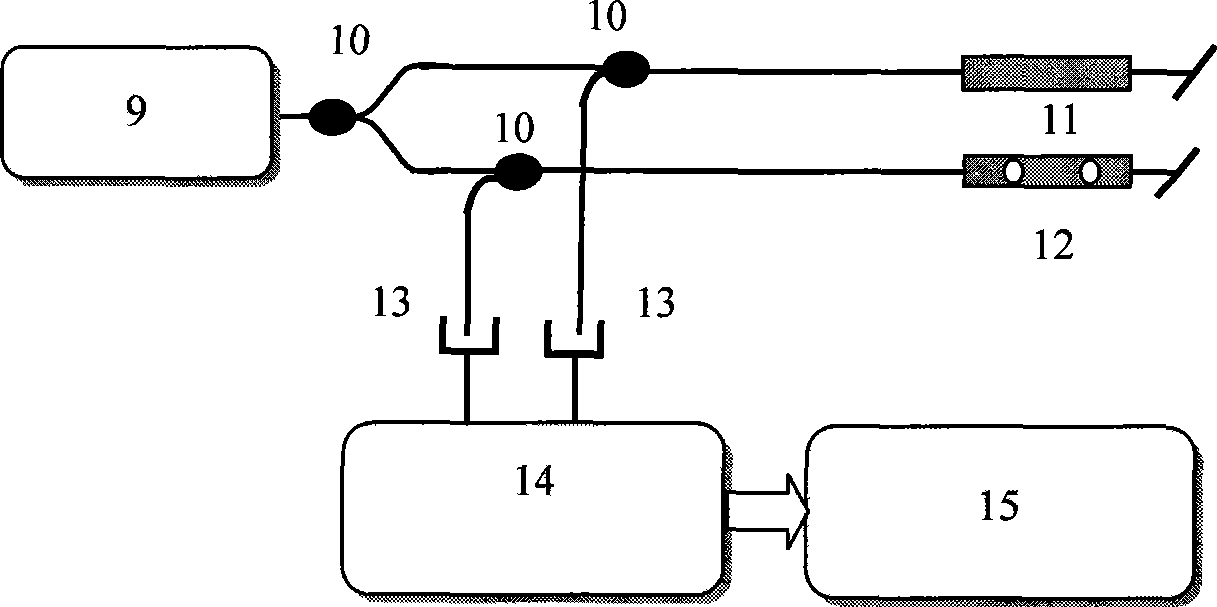
Two-channel phase jitter inhibiting device and method for Raman laser system
ActiveCN107463007AAchieve independent controlPhase Noise SuppressionLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsPrismPolarizer
The invention provides a two-channel phase jitter inhibiting device and a method for a Raman laser system. The device comprises a frequency stabilized laser, a 1 / 2 wave piece, a polarization splitting prism, a 45 degrees reflecting mirror, an electrooptical modulator, a Fabry-Perot interferometer, an acousto-optic modulator, a plano-convex lens, a 1 / 4 wave piece, a 0 degree reflecting mirror, a PZT, a polarizer, a pretreatment circuit, a control circuit based on FPGA, a D / A converter, a acousto-optic modulator driver, a PZT driver, an electrooptical modulator driver and a Fabry-Perot interferometer controller. The two-channel phase jitter inhibiting device and the method can realize the independent control of power and frequency of two lasers; a high-frequency feedback and a low-frequency feedback are utilized to inhibit the phase jitter of the Raman laser; compared with a single-channel phase feedback system, the requirement on the circuit system is reduced, and the stability of the phase feedback system is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com