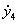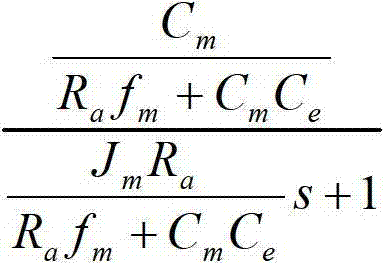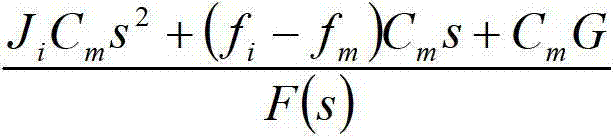Patents
Literature
41 results about "First order system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
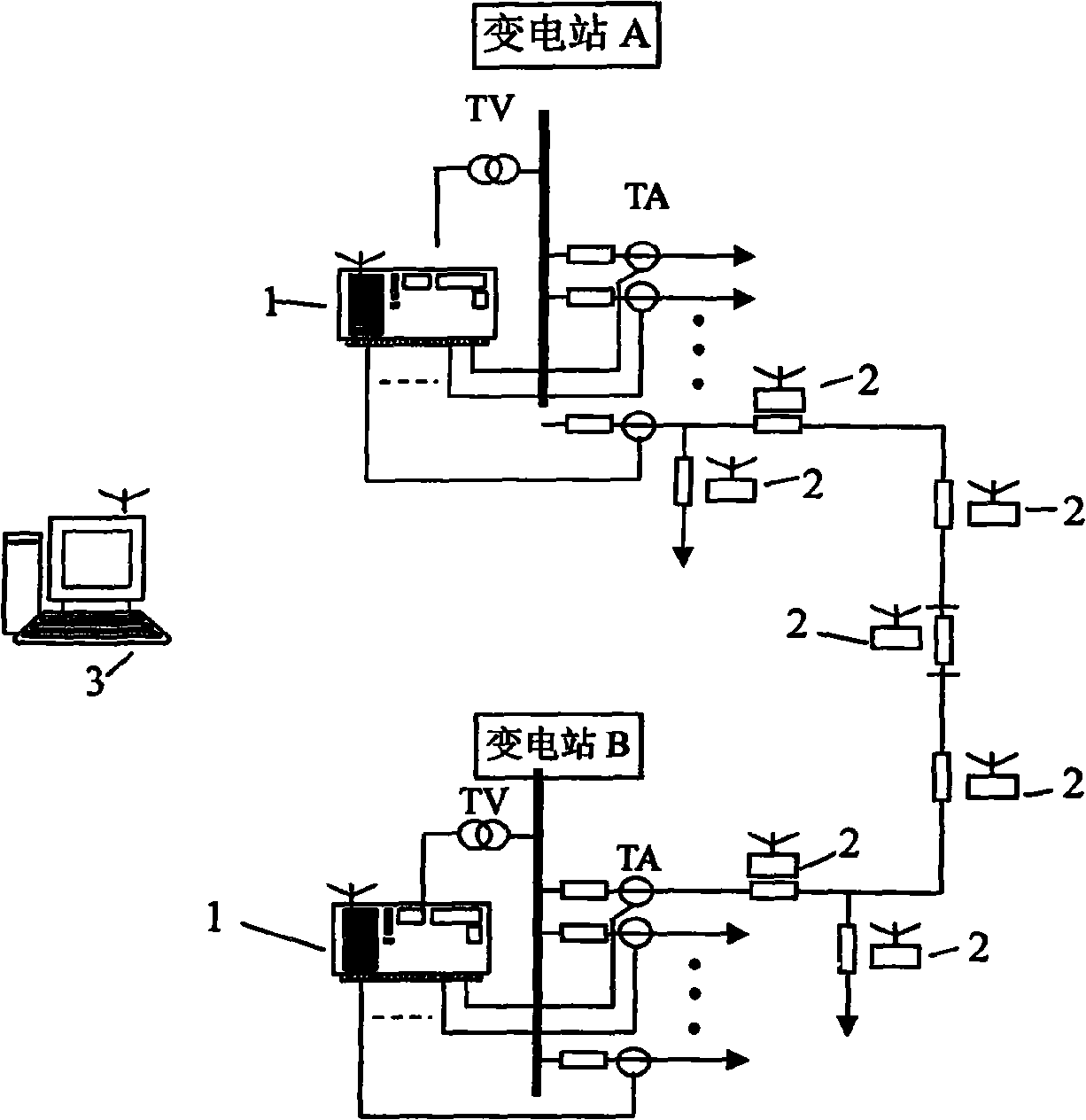
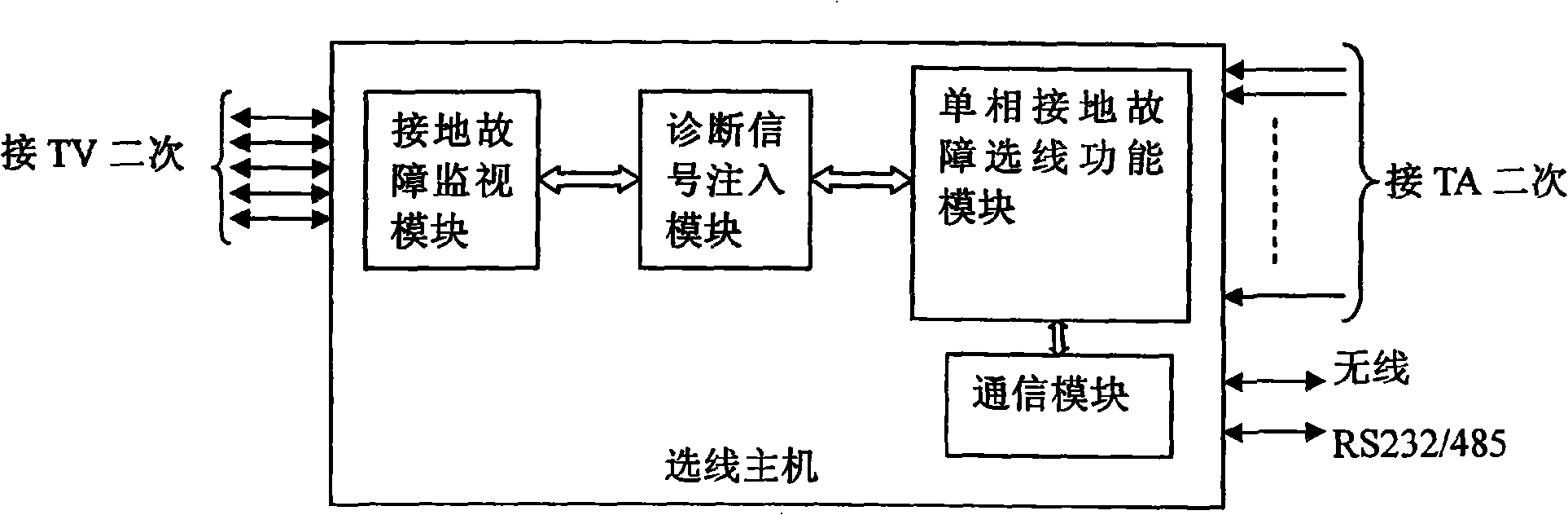
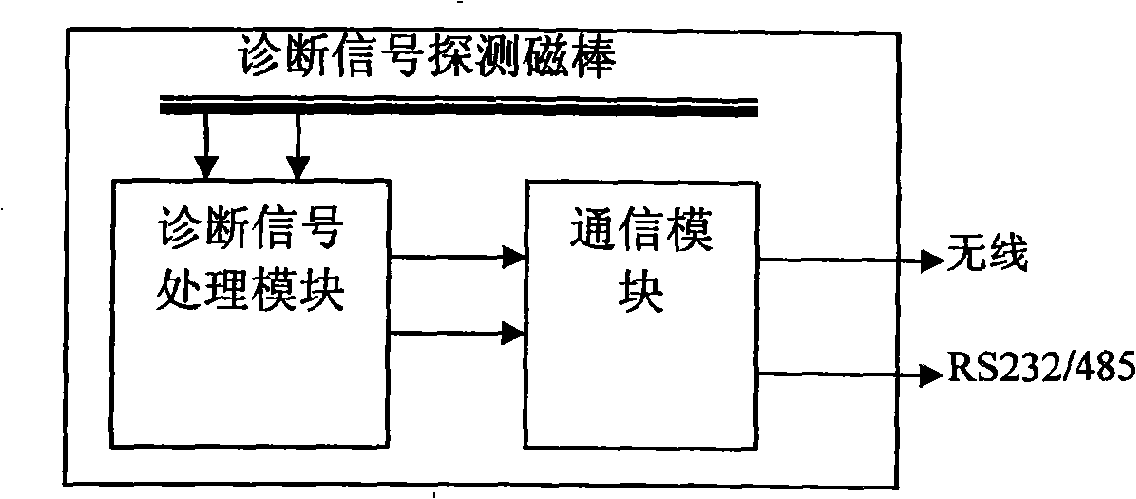
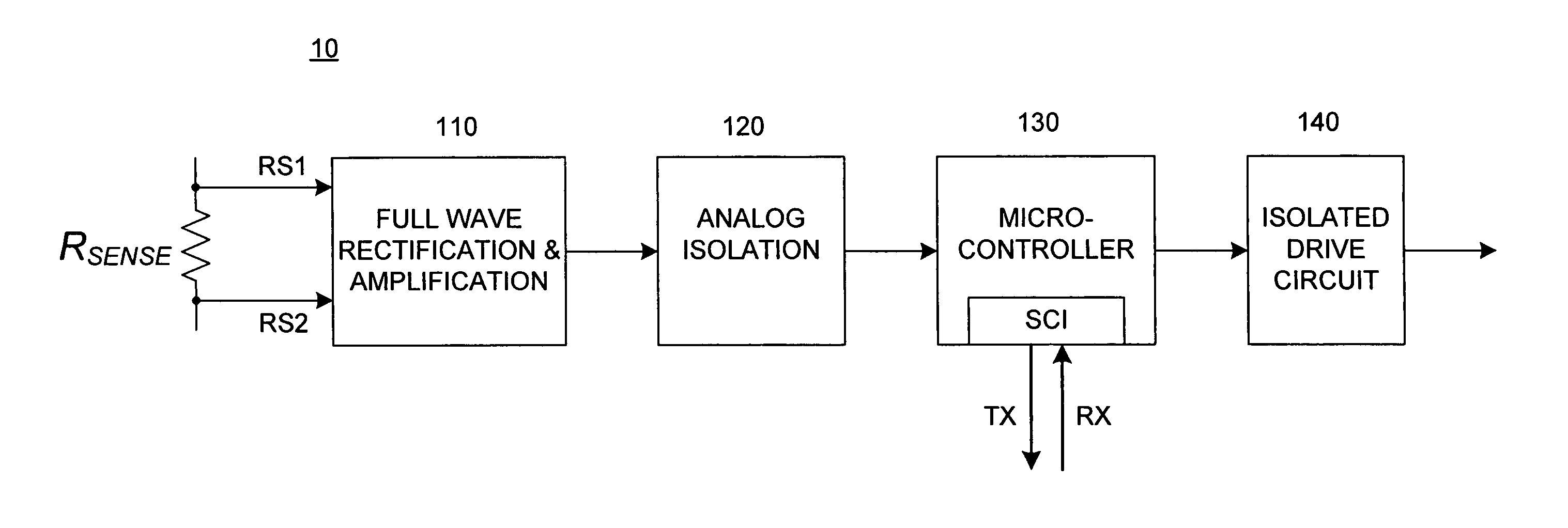
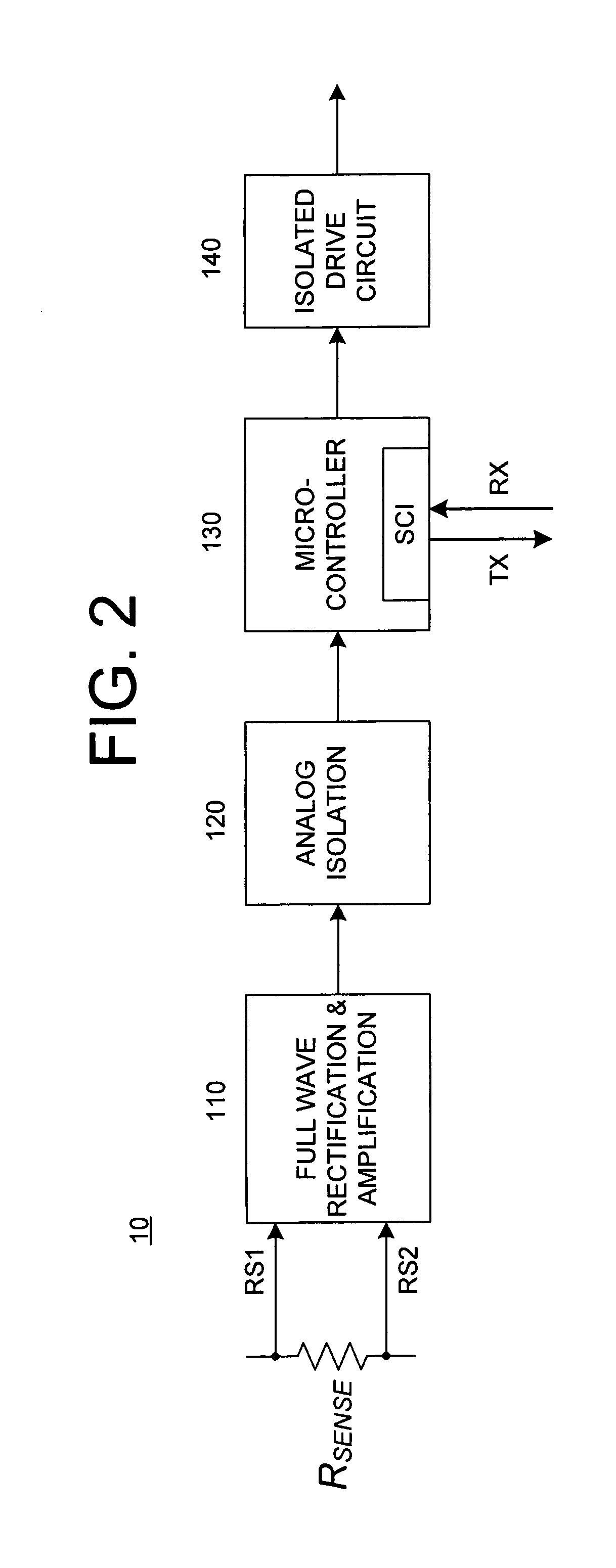
Low current grounding system distribution circuit single-phase earth fault automatic position setting method
InactiveCN101261304AReduce the impactImprove positioning efficiencyFault locationInformation technology support systemEngineeringSignal detector
The invention relates to a distribution circuit single-phase earth fault automatic locating method, which comprises: (1) by allocating a route selection core which includes the monitoring of earth fault, the instilling of diagnosis signals, the detection of diagnosis signals and a communicating module in a distribution substation, the system is judged whether a single-phase earth fault happens; the diagnosis signals are instilled to the system automatically in the fault condition; the biggest feeder line of the diagnosis signals is detected to be an earth circuit line; the route selecting result is transmitted to an error locating computer by a communicating network. (2) A signal detector is arranged along the distribution circuit line to detect whether a diagnosis signal exists in a first order system and the detecting result is sent to the error locating computer by the communicating networks. (3) The error locating computer is installed in a dispatching center to communicate with the signal detectors on feeder lines and each route selection core in the jurisdiction, and determine automatically the sections of a single-phase earth fault by using error locating software. The distribution circuit single-phase earth fault automatic locating method has the advantages of high degree of automation, short location time and high location accuracy, etc.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
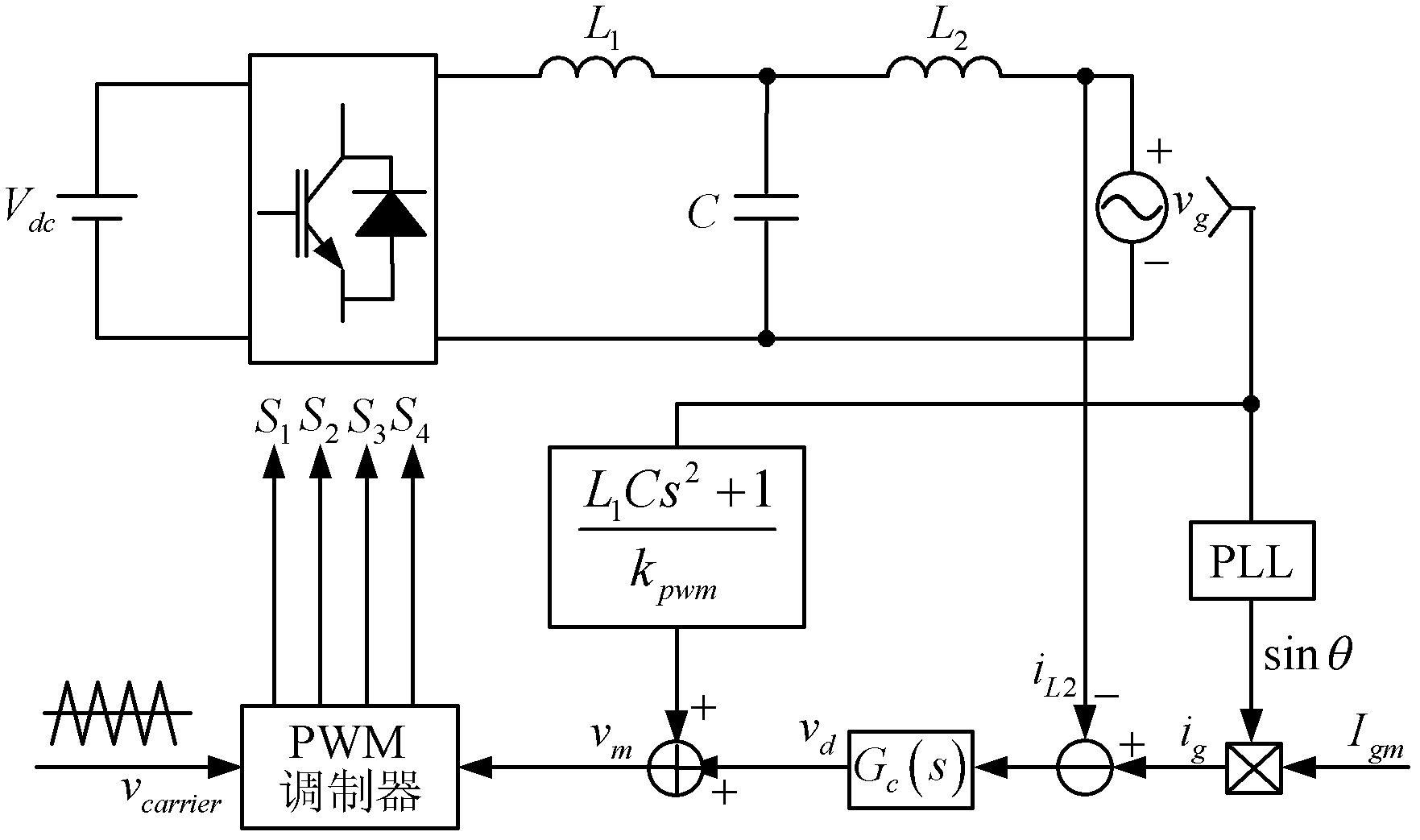
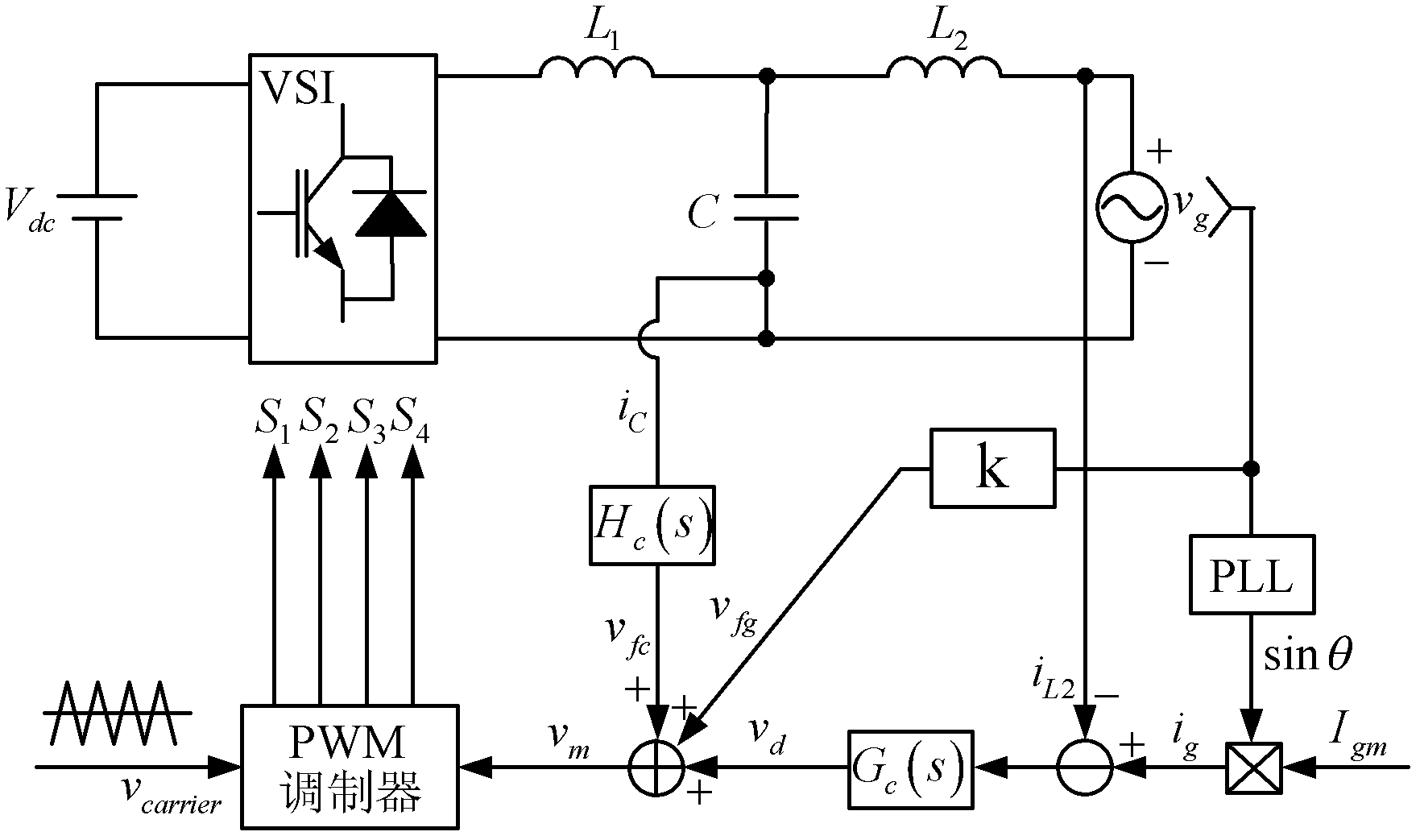
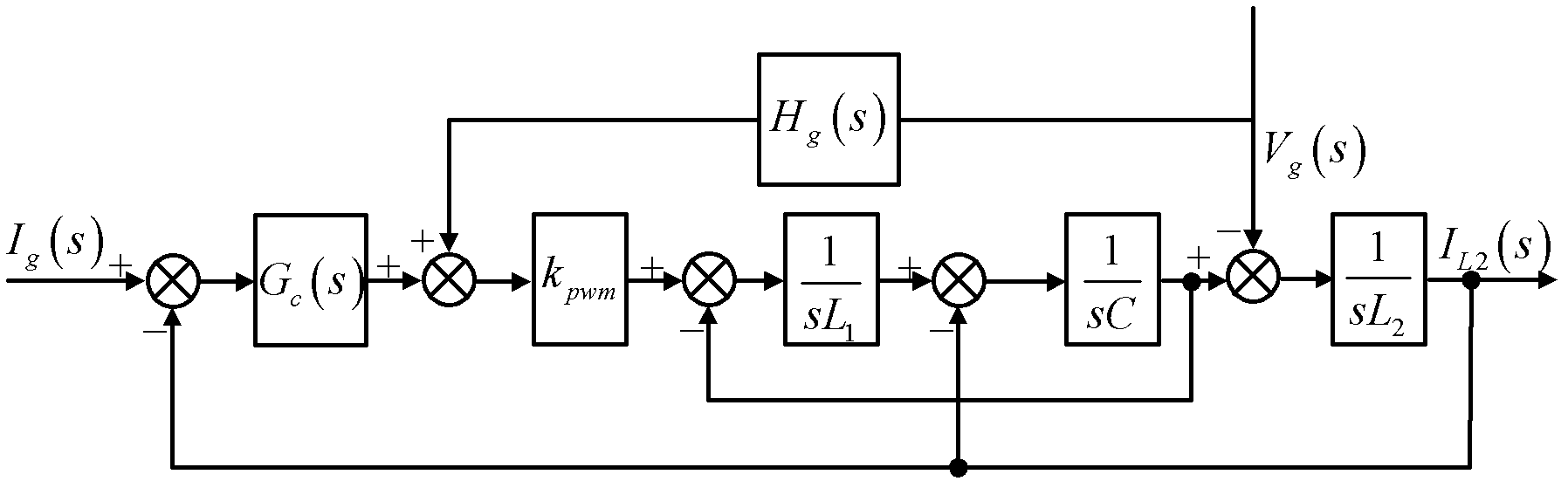
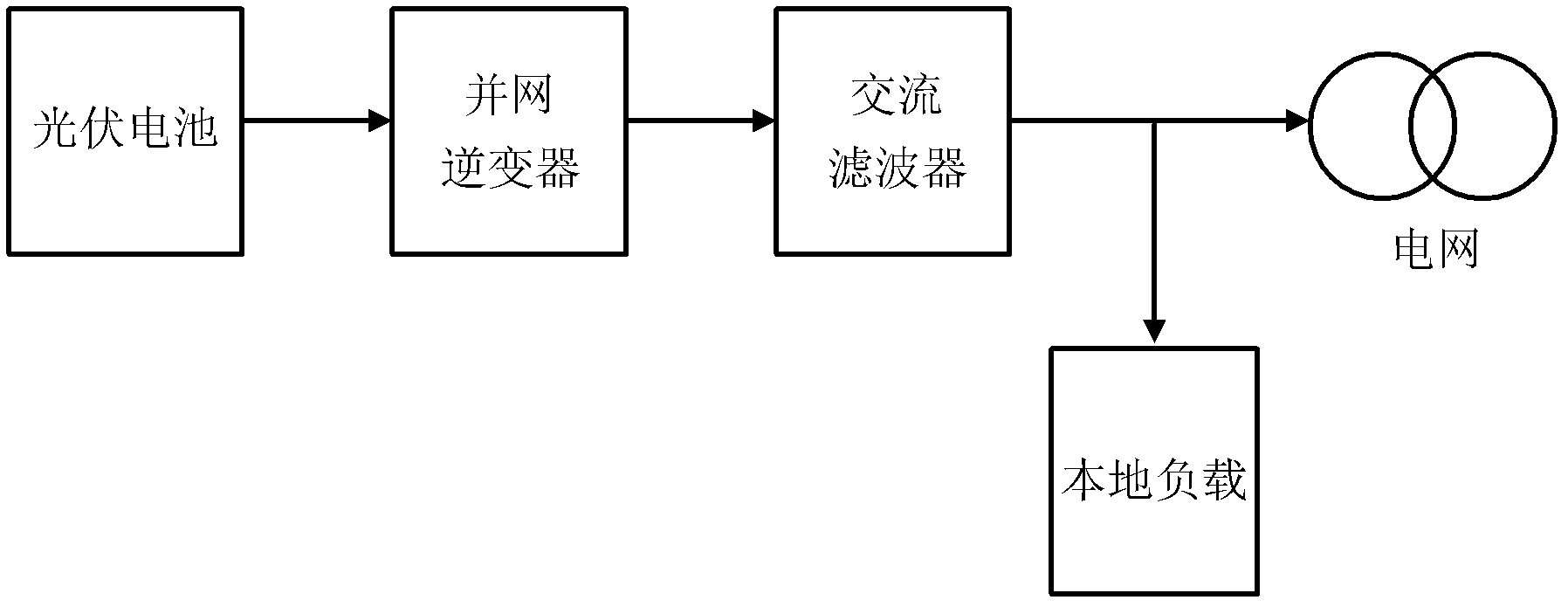
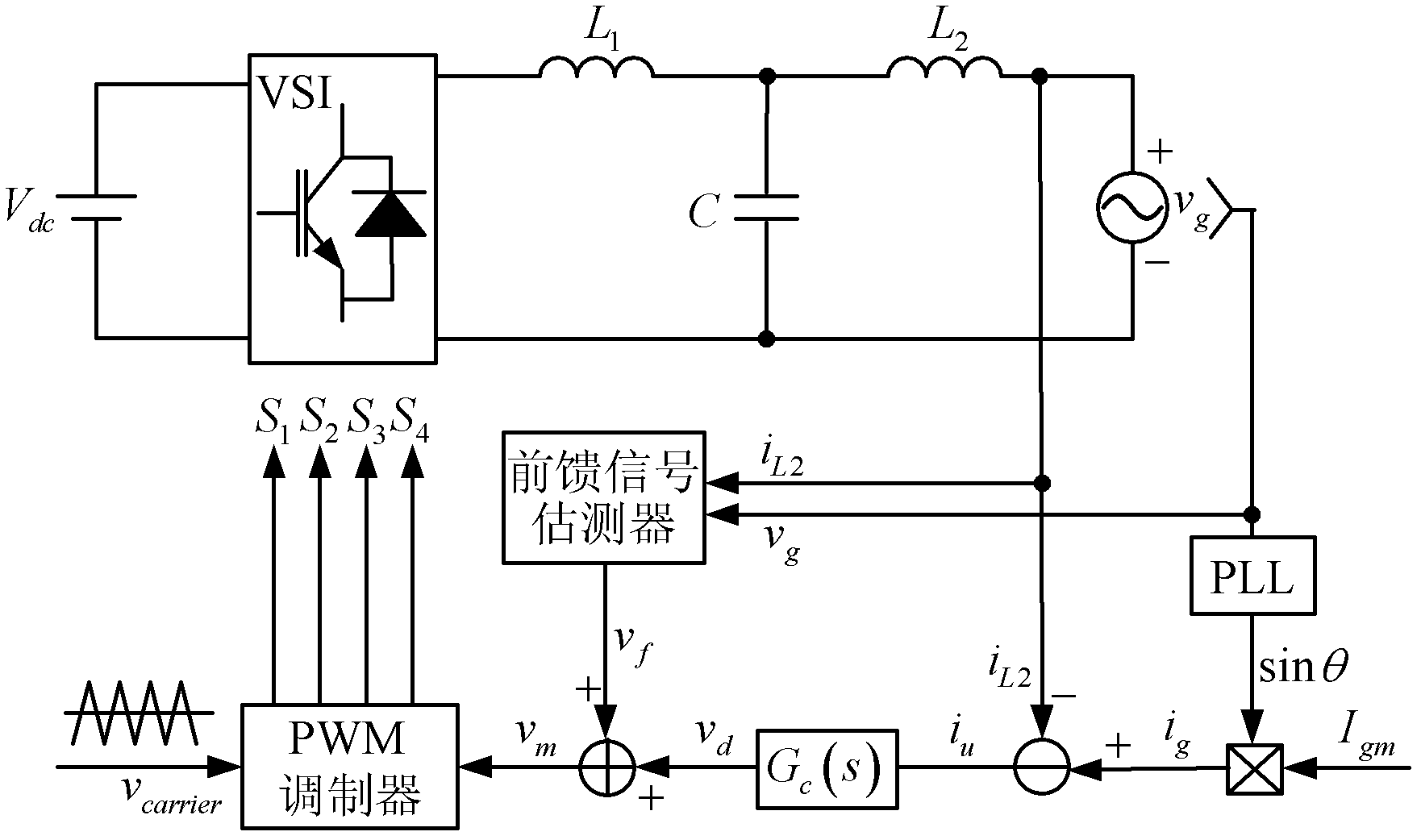
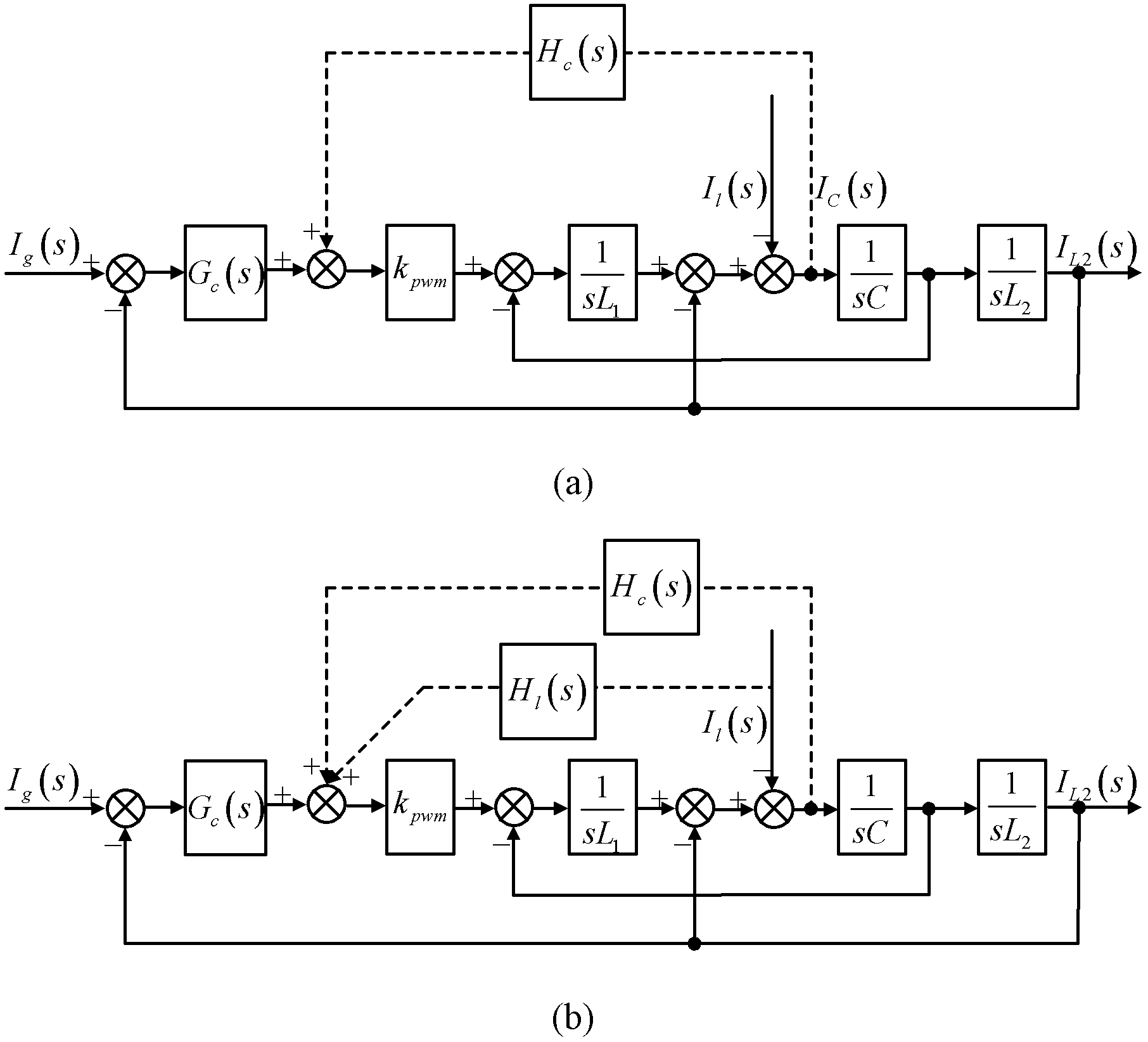
Method for controlling grid-connected inverter based on feed-forward compensation
InactiveCN102545266ANot affected by disturbanceEliminate Amplitude Gain SpikesSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceGrid connected inverter
The invention discloses a method for controlling a grid-connected inverter based on feed-forward compensation. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a grid voltage, a grid side current and a capacitance current; (2) according to the grid side current, generating an instruction signal; (3) according to the grid voltage and the capacitance current, acquiring a current feed-forward signal and a voltage feed-forward signal; and (4) superposing the instruction signal, the current feed-forward signal and the voltage feed-forward signal to obtain a modulation signal, and generating a switching signal for controlling the grid-connected inverter according to the modulation signal. The method has the advantages that: a second-order differential feed-forward item of the grid voltage is compensated by a first-order differential feed-forward link of the capacitance current, so that a third-order system is reduced to a first-order system, the stability margin of the system is improved, the design process of a current regulator is simplified, and the grid side current cannot be influenced by grid voltage harmonic waves.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compensation method for automatic temperature detection and automatic temperature detection system
InactiveCN103234662AGood approximation effectImprove accuracyThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansWater bathsLiquid temperature
The invention relates to a compensation method for automatic temperature detection and an automatic temperature detection system. According to the method, the temperature is risen for detection by using a water bath constant temperature heating method, a static characteristic value of a temperature sensor is calibrated by using a liquid thermometer, and the time constant and the compensation function of each heat transfer characteristic are determined by using a three-order system formed by connecting three first-order systems in series and a first-order inertial system with pure lag respectively. The system is formed by connecting a constant current source, a temperature sensor, a signal conditioning amplifier, an A / D (Analog / Digital) converter, a single-chip microprocessor and a computer. The automatic temperature detection system has the characteristics that the dynamic characteristic of the automatic temperature detection system approaches the liquid thermometer, and the calibration of the detection instrument parameters can be finished by only performing experimental calibration once according to the characteristic that the automatic temperature detection system with the temperature sensor of the same type has the same transfer function in a relatively stable experimental environment, so that the accuracy and the convenience of the system are improved.
Owner:DALIAN SCI TEST & CONTROL TECH INST
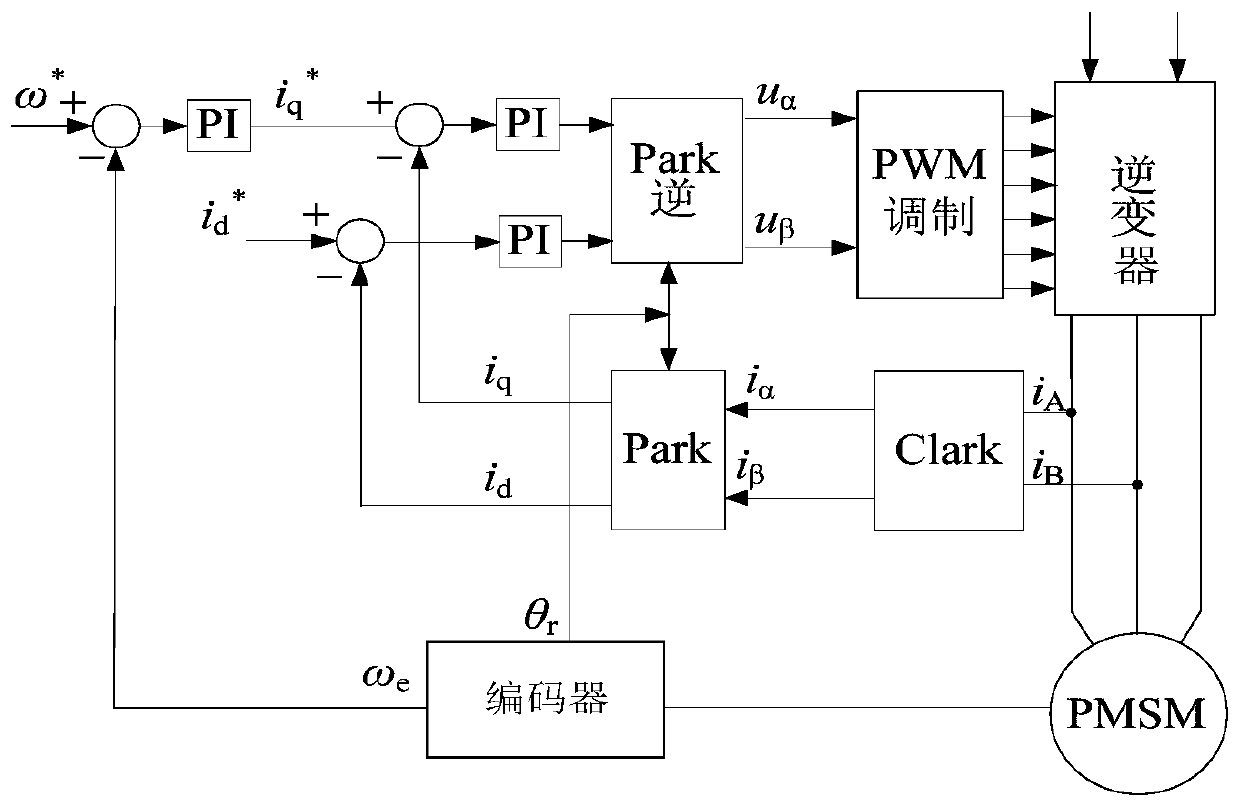
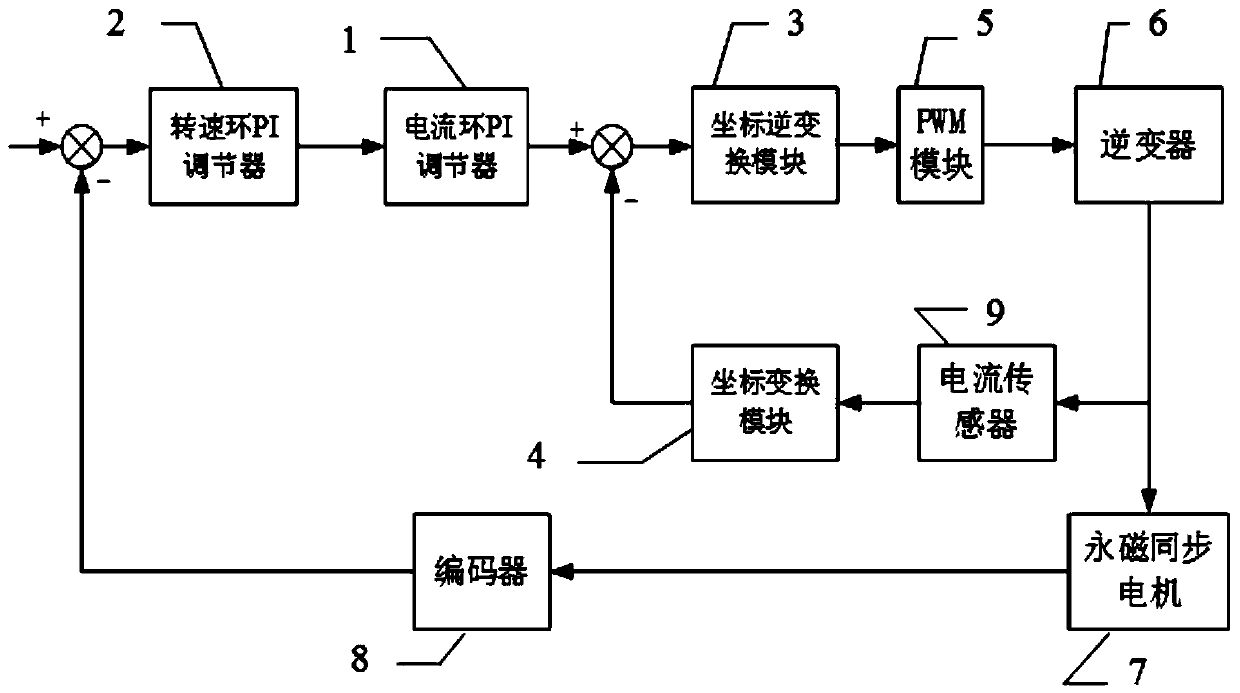
Parameter setting method for double-closed-loop vector control PI regulator of permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN109756166AFlexible settingsAccurate settingElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsDamping factorAutomatic control
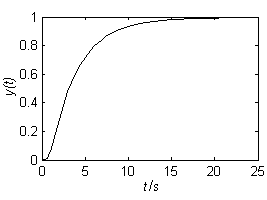
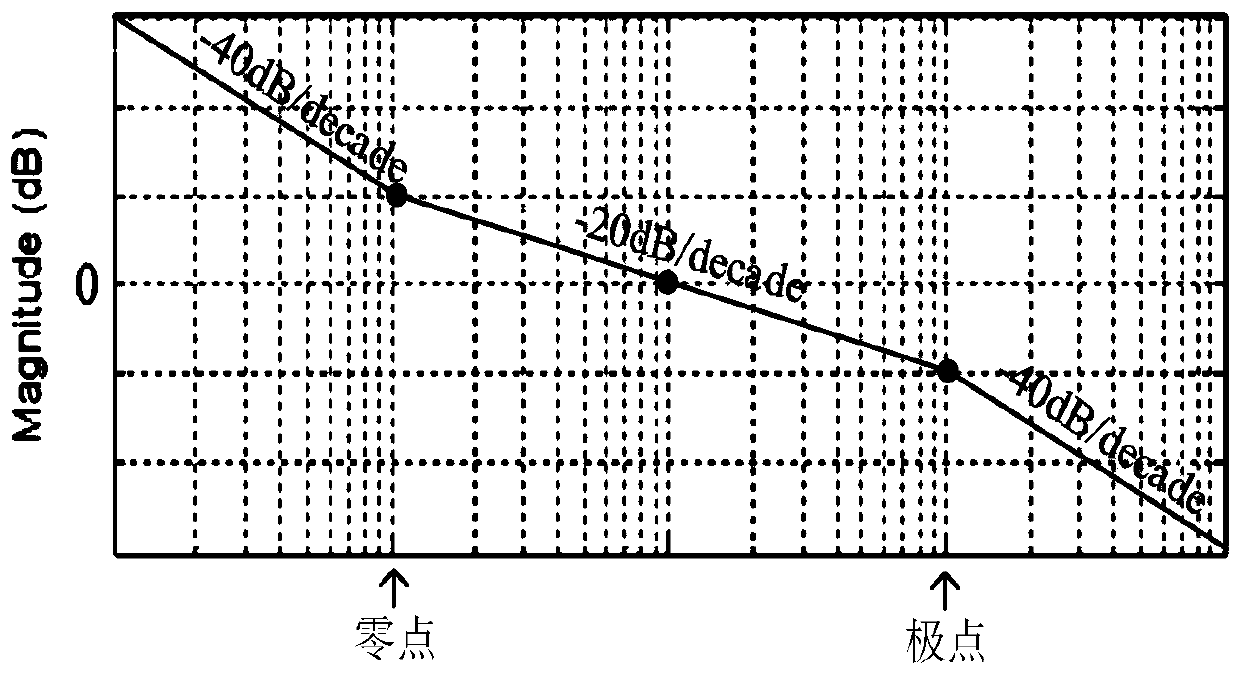
The invention discloses a parameter setting method for a double-closed-loop vector control PI regulator of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. A current inner loop system is corrected into a first-order system by utilizing a pole-zero cancellation principle in a current loop closed-loop transfer function; a proportional coefficient and an integral coefficient of a current loop PI regulator are obtained through the current loop closed-loop transfer function; when two constraint conditions of enabling the slope at a cut-off frequency of a speed loop open-loop transfer function to be -20 dB / decand obtaining the maximum phase angle margin are met, a proportional coefficient and an integral coefficient of a speed loop PI regulator are determined; and parameters of the speed loop PI regulatorare obtained. An automatic control related theory is combined, and a theoretical basis is provided for setting the PI parameters; change relations between the PI parameters, and a motor parameter-current loop bandwidth and a system performance index-damping factor are revealed; the PI parameters can be set for different motor systems more flexibly and accurately; and therefore, the universality is high.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
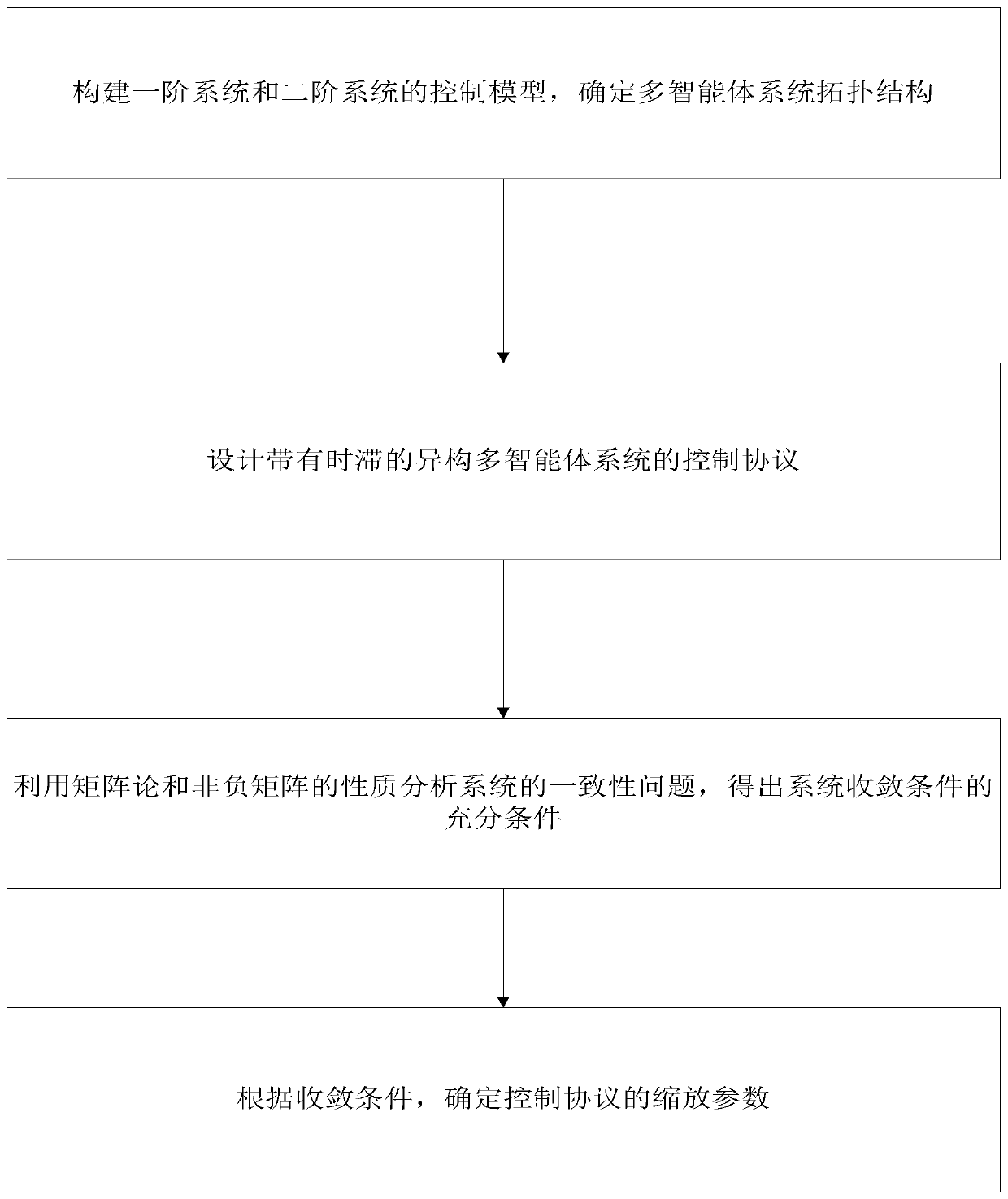
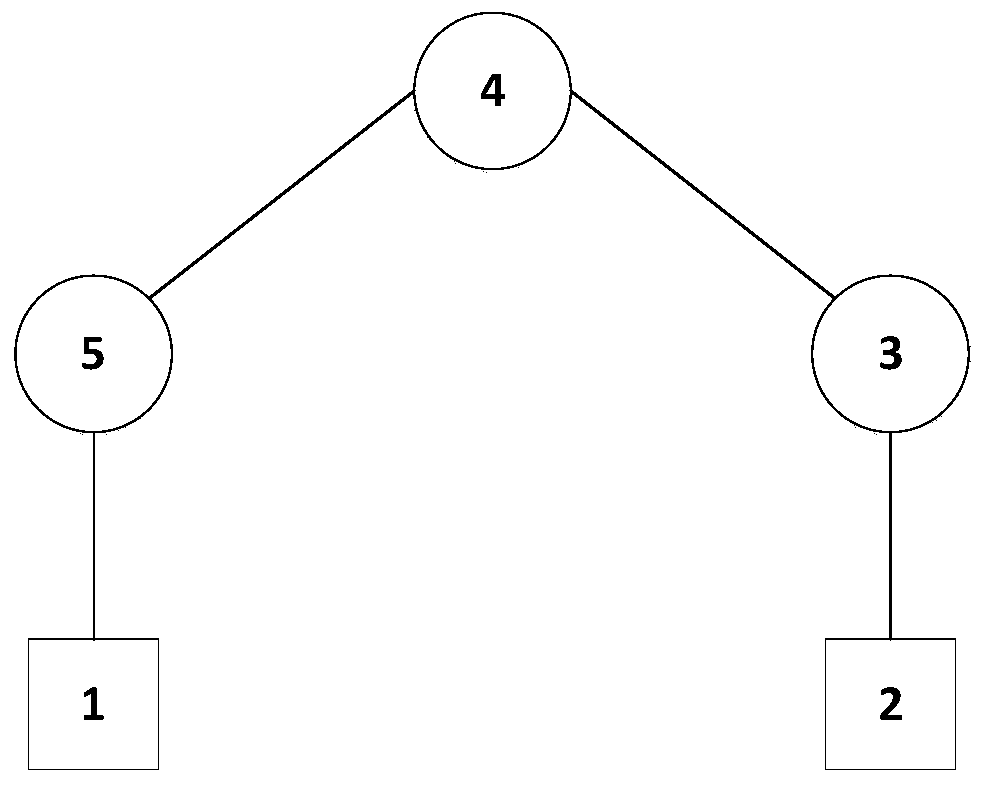
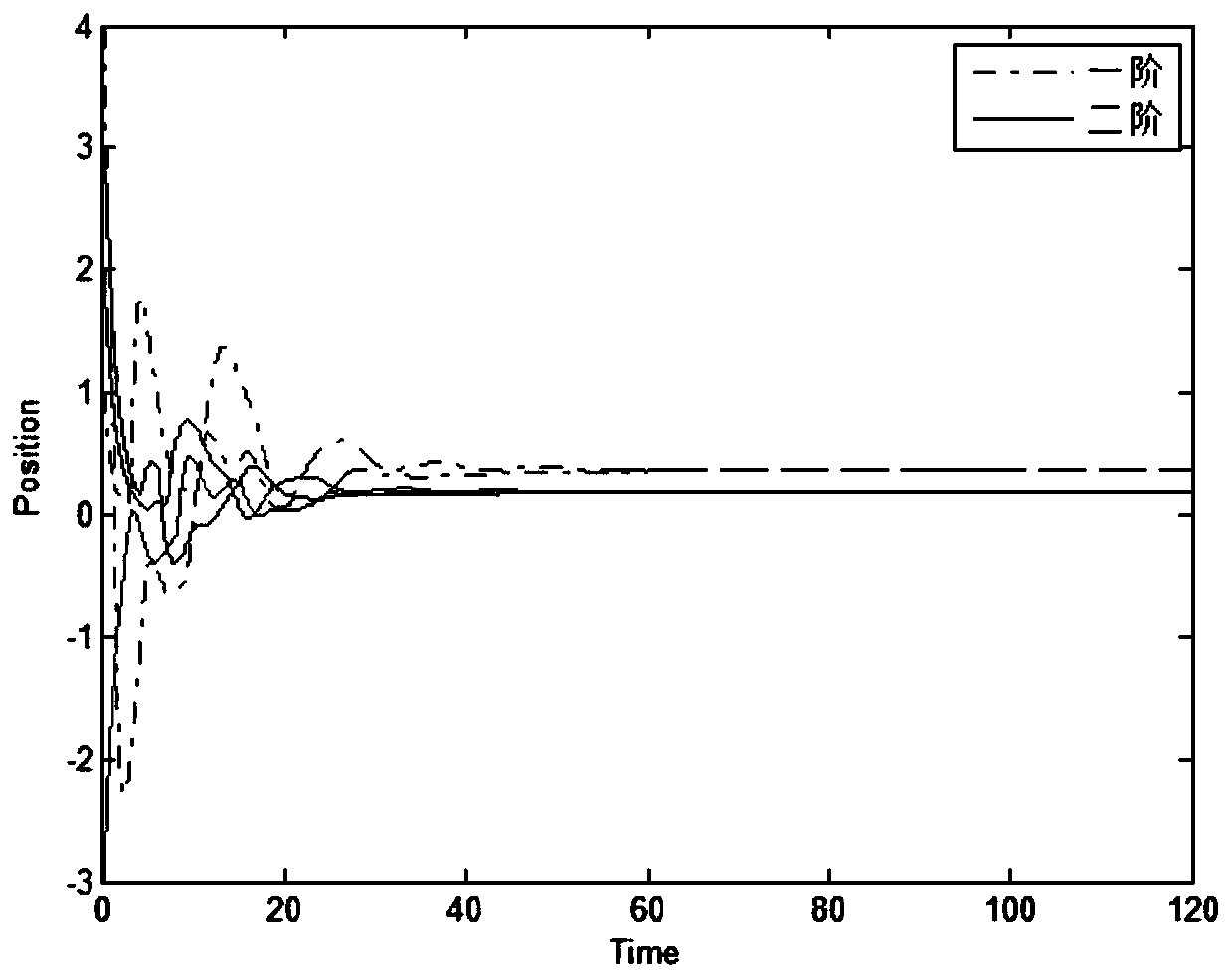
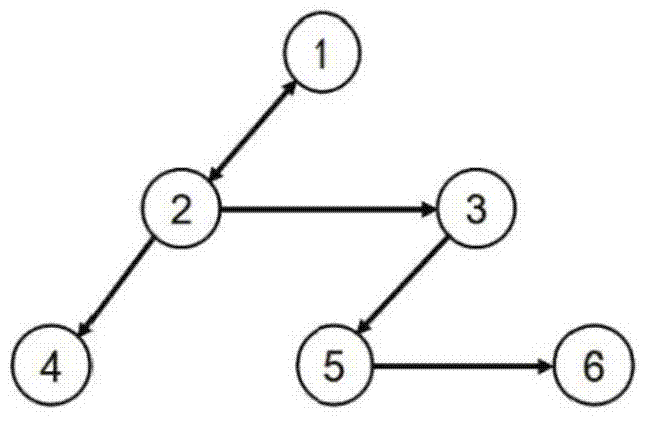
Group consistency control method for heterogeneous multi-agent system with time delay
ActiveCN110442022AAddressing Convergence EffectsTotal factory controlAdaptive controlAlgorithmTime delays
The invention discloses a group consistency control method for a heterogeneous multi-agent system with arbitrary bounded time delay, and the method comprises the following steps of constructing mathematical models of a first-order system and a second-order system, determining a topology of the multi-agent system, and describing its topological relationship by using graph theory knowledge; designing a control protocol of heterogeneous multi-agent system with time delay; analyzing the consistency problem of the system by using the properties of matrix theory and non-negative matrix to obtain a system convergence condition; determining a control protocol scaling parameter that meets the system convergence condition, and substituting the parameter into the system control protocol to implementthe group consistency control of the system. The invention provides the group consistency control method for the heterogeneous multi-agent system with arbitrary bounded time delay, and the method solves the global control problem by a distributed control method with no need of global information of the system, and only requires joint connection of topological graphs of the system at the same timewithout requiring their sub-graphs to be connected, thereby improving the robustness of the system and being suitable for group consistency control of heterogeneous multi-agent systems with arbitrarybounded delays.
Owner:COMP APPL RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Five-DOF (freedom of degree) bearingless synchronous reluctance motor decoupling controller and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102136822ALearnedAchieving the Curse of DimensionalityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlHysteresisSynchronous reluctance motor
The invention discloses a five-DOF (freedom of degree) bearingless synchronous reluctance motor decoupling controller and a construction method thereof. Three expanded current hysteresis loop PWM (pulse width modulation) inverters, a switch power amplifier and a five-DOF bearingless synchronous reluctance motor form a compound controlled object; five support vector machine second-order systems, one support vector machine first-order system and eleven integrators are utilized to construct a support vector machine alpha-order inverse system and offline training is carried out, the support vector machine alpha-order inverse system is placed in front of the compound controlled object to form a pseudo linear system, and the pseudo linear system is equivalent to five position second-order integration subsystems and one position first-order integration subsystem; and five position controllers and one rotating speed controller are respectively designed for the six integration subsystems, thus a linear closed-loop controller is formed. In the invention, a least square support vector machine is adopted to approach an alpha-order inverse model of a nonlinear system, the dynamic decoupling control among all the controlled variables is realized, and the control performance of the overall system is effectively improved.
Owner:江阴智产汇知识产权运营有限公司
Method for controlling grid-connected inverter with anti-load disturbance function
InactiveCN102545265AUnaffected by load disturbancesSimple designSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceGrid-tie inverter
The invention discloses a method for controlling a grid-connected inverter with an anti-load disturbance function. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a grid voltage and a grid side current; (2) according to the grid side current, generating an instruction signal; (3) according to the grid voltage and the grid side current, acquiring a feed-forward signal; and (4) superposing the instruction signal and the feed-forward signal to obtain a modulation signal, and generating a switching signal for controlling the grid-connected inverter according to the modulation signal. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that: feed-forward quantity is calculated by using a feed-forward signal estimator according to the grid voltage and the grid side current, a sensor which is required for detecting a capacitance current of a filter is eliminated, and system cost is saved; and under the condition that the grid-connected inverter has a local load, the grid side current cannot be influenced by load disturbance, so that a third-order system is reduced to a first-order system, a damping effect on the system is achieved, and the design process of a current regulator is simplified.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
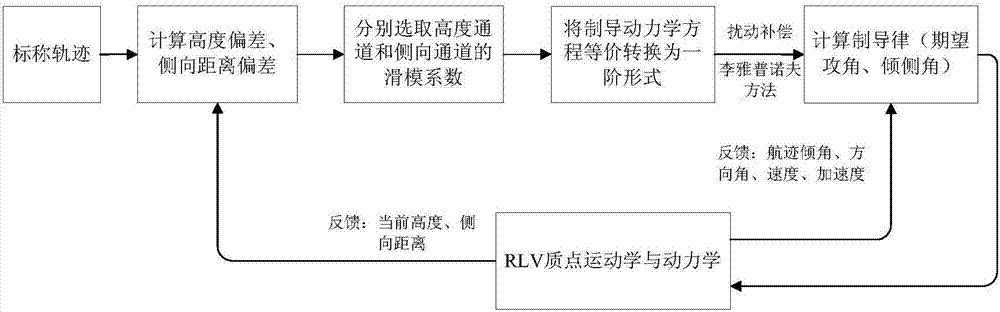
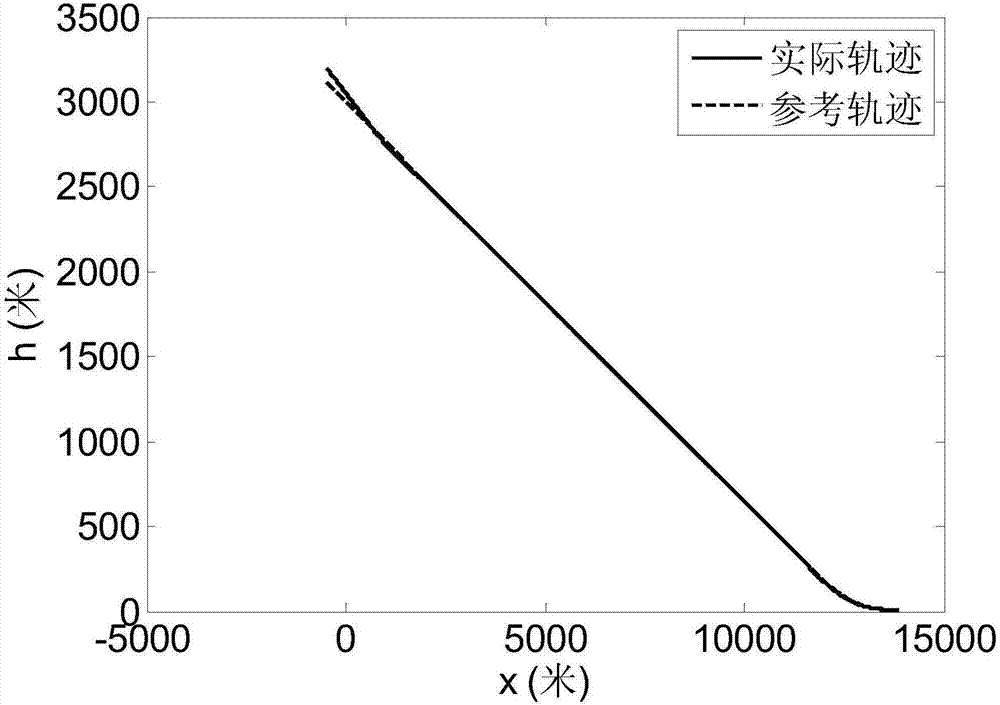
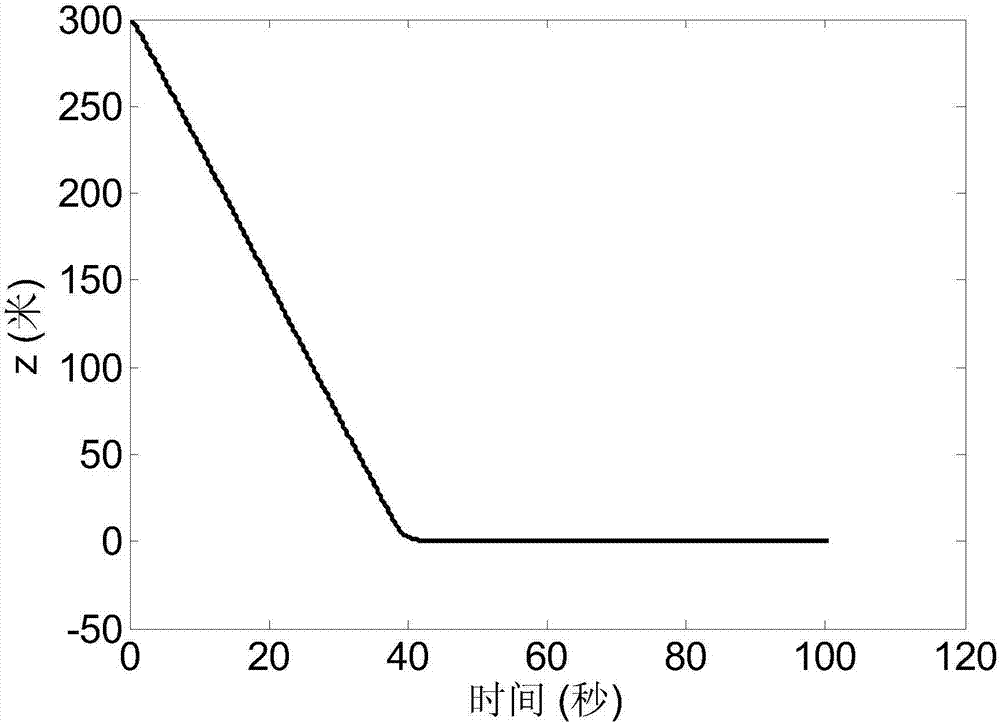
RLV landing section guidance law acquiring method based on sliding-mode control theory
ActiveCN107102547AImplement trackingSimplify the design processAdaptive controlGuidance systemThree degrees of freedom
A RLV landing section guidance law acquiring method based on a sliding-mode control theory comprises steps of: calculating a height deviation and a lateral distance deviation according to an RLV landing section nominal trajectory; then, selecting an appropriate sliding-mode surface according to the tracking deviation of the nominal trajectory, and equivalently converting a RLV three-degree-of-freedom kinetic equation into a form described by the sliding-mode surface; and finally, designing the guidance law by using a Lyapunov method. In the design process, by analyzing aerodynamic data, the uncertainty upper bound of a guidance circuit is obtained and a compensation term is introduced to suppress the uncertainty so that the guidance system has asymptotic stability to the uncertainties such as disturbance. The method can overcome the influence of the uncertainty of the RLV guidance system so as to improve guidance precision, converts an original second-order system into a first-order system by introducing the sliding-mode control method, thereby achieving a visual design process.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Method and apparatus applying virtual Deltat trip criterion in power distribution
A virtual ΔT trip criterion is implemented in an electrical power distribution system to provide current-based tripping for a solid state power switching device. A first-order system model is implemented either by hardware or software to represent a rise in temperature of the electrical wire through which power is supplied. When the simulated temperature exceeds a threshold, the solid state power switching device may be tripped.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
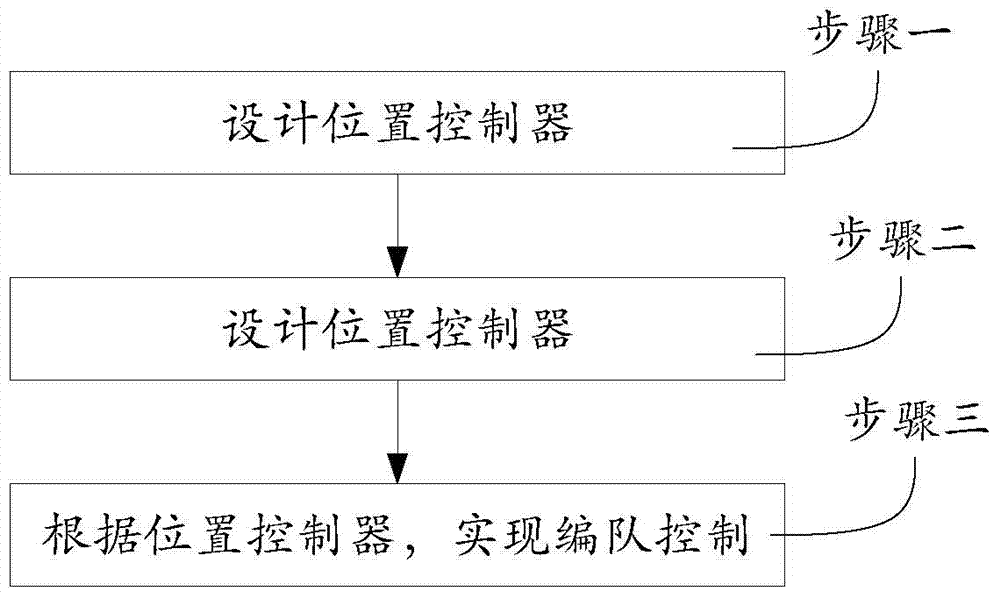
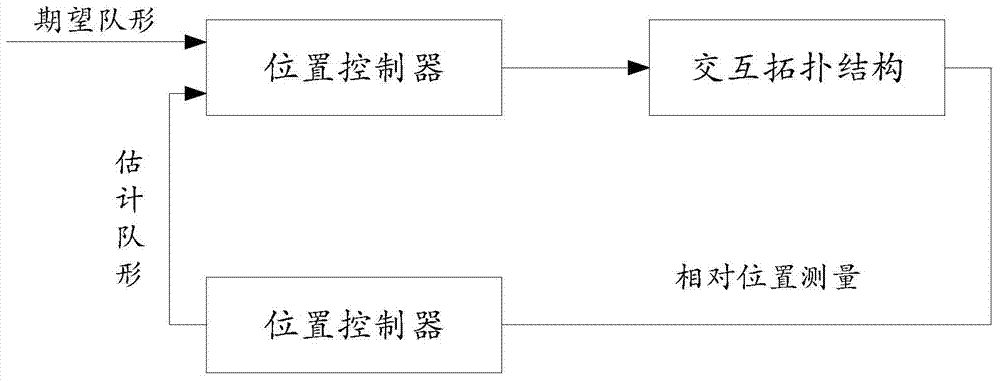
Robot team formation control method based on position estimation
InactiveCN104850131AAvoid absolute positionEffective formation movementPosition/course control in three dimensionsRobotic systemsFirst order system
The present invention provides a robot team formation control method based on position estimation. The method concretely comprises the process of first designing corresponding position estimators to different robot systems; secondary, designing first-order system position controllers based on the position estimator of a first-order system; and then realizing control of robot team formation according to the first-order system position controllers. In combination with the position estimators which act in different system models formed by multiple robots, effectively formation motion may be realized, desired formation configurations can be achieved, and when a formation process starts, desired formation effects can be formed even when positions of the robots may be arbitrary.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
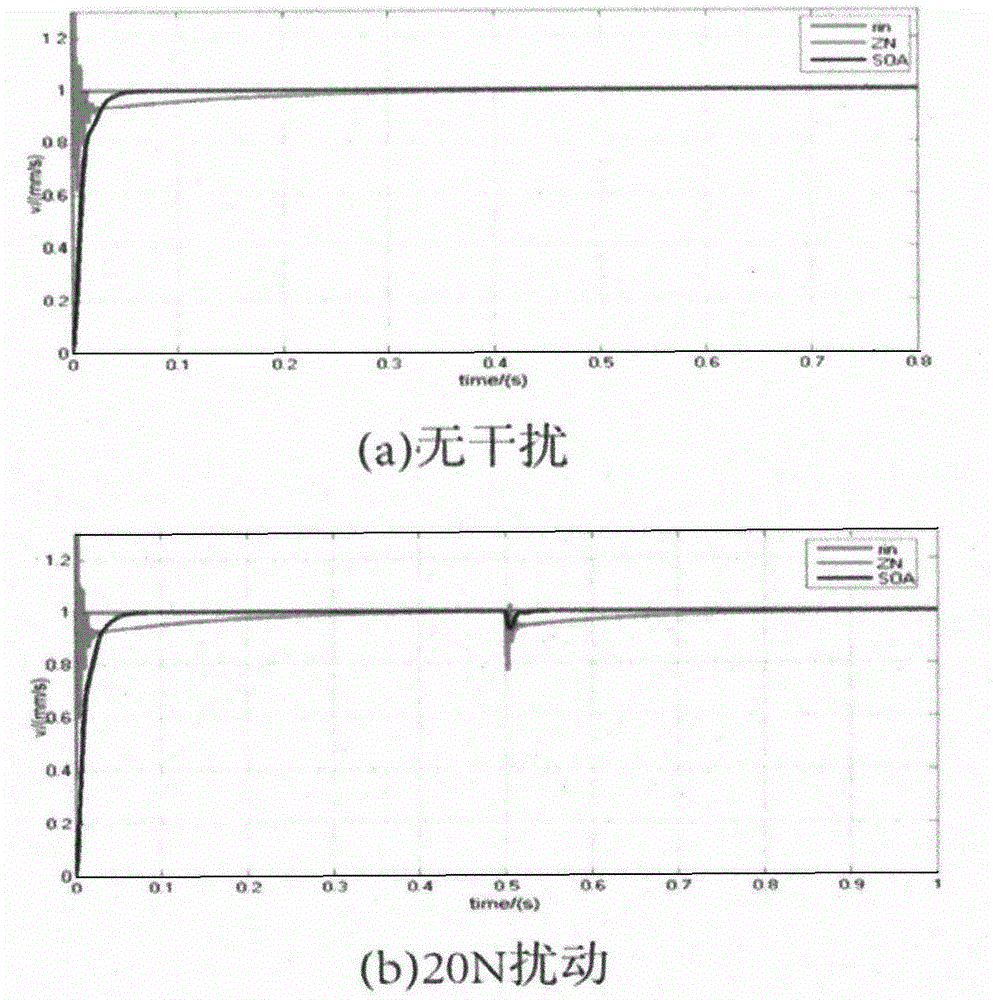
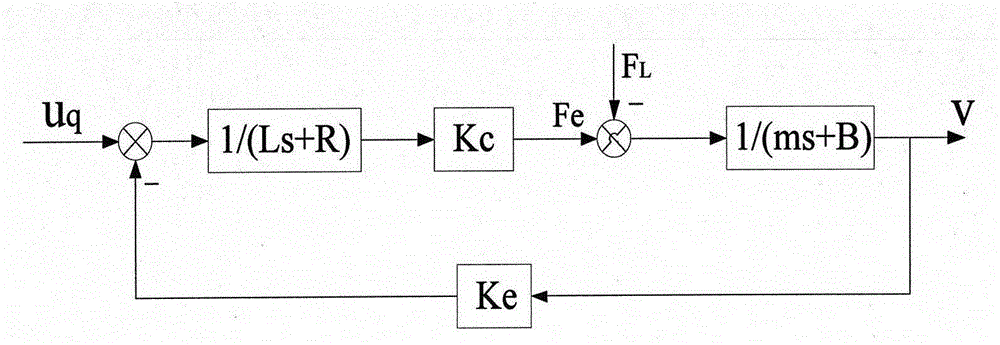
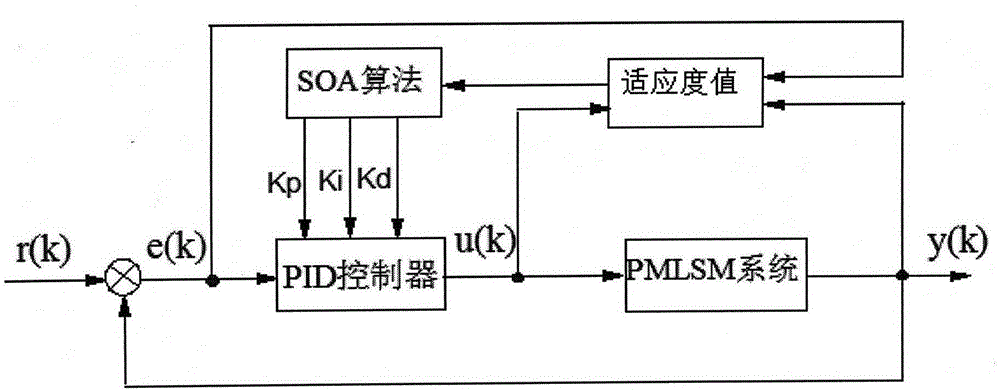
SOA-based PMLSM feed system PID parameter optimization method
The invention provides an SOA-based PMLSM feed system PID parameter optimization method and belongs to the numerical control technical field and swarm intelligent algorithm field. According to the method of the invention, as for defects existing in application of a traditional PID controller to a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor PMLSM feed system, a seeker optimization algorithm (SOA) and a traditional PID algorithm are combined together so as to be applied to a PMLSM feed system; a penalty controlled fitness function is introduced into the SOA to evaluate a solution, so that the response of an original second-order system is similar to the response of a first-order system, namely, overshoot will not occur on the system. The method has the advantages of simplicity, fast convergence speed, high robustness and flexible and adjustable fitness function. With the SOA-based PMLSM feed system PID parameter optimization method adopted, a new idea can be provided for the optimal design of the control parameters of the PMLSM feed system.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF IND TECH
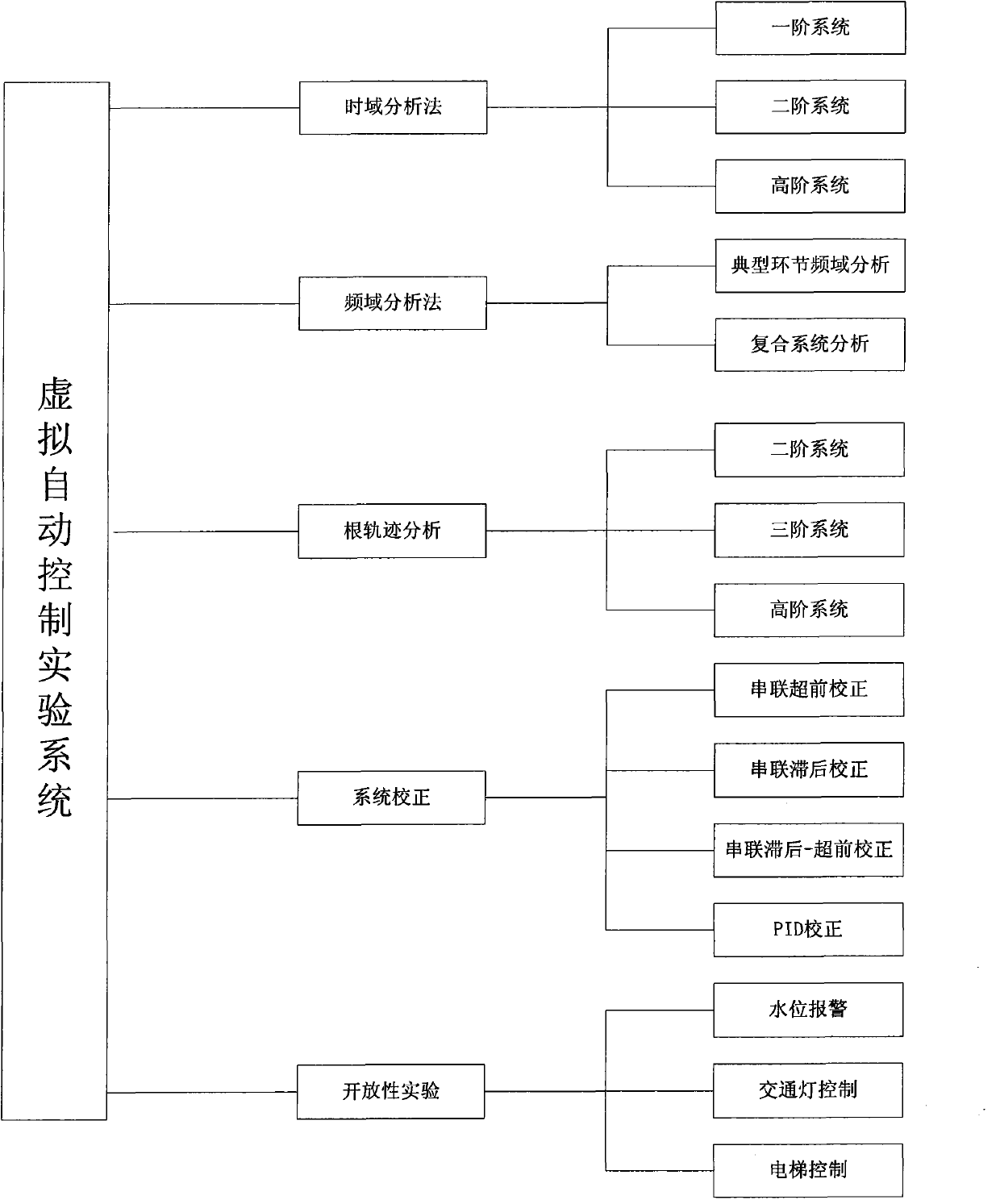
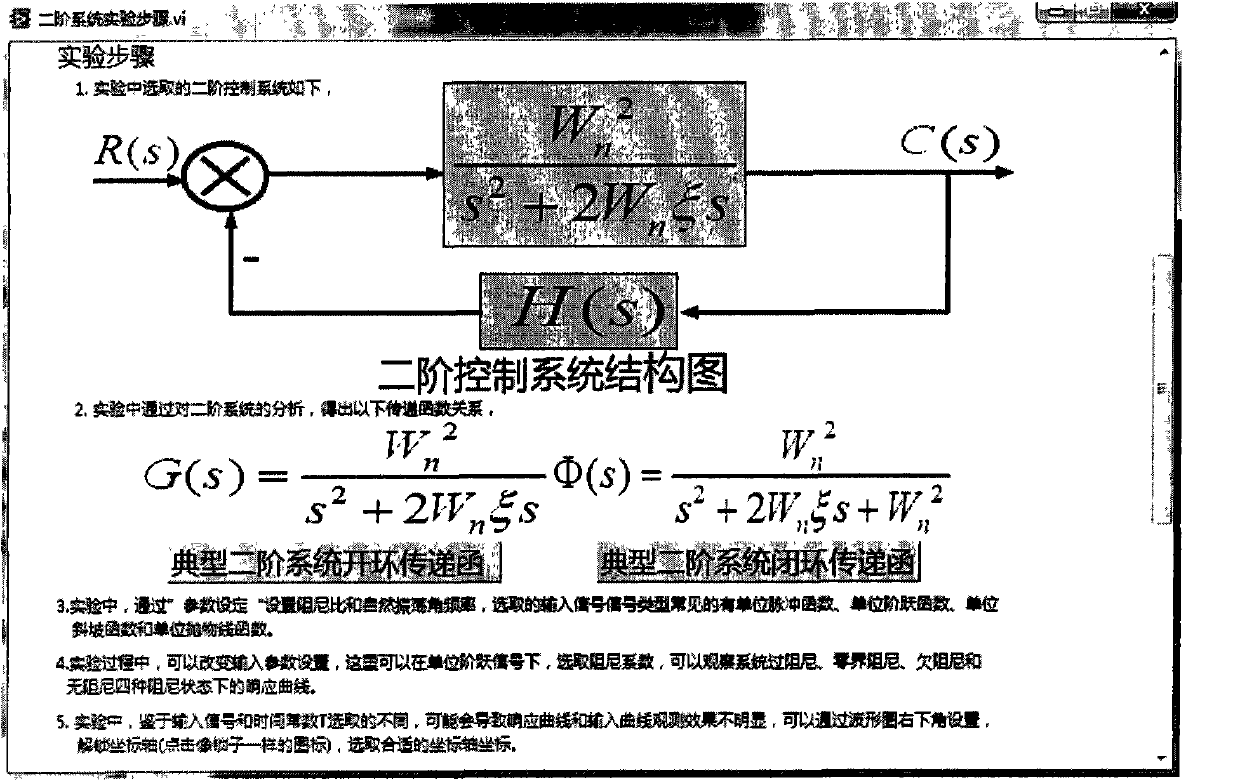
Virtual automatic control experimental system and design method of virtual automatic control experimental system
InactiveCN103995474AExperiment content is flexibleEasy to operateSimulator controlAutomatic controlSimulation
The invention discloses a virtual automatic control experimental system and a design method of the virtual automatic control experimental system. The virtual automatic control experimental system comprises a time domain analysis method experiment module, a root-locus method experiment module, a frequency domain analysis method experiment module, a system correction experiment module and an open experiment module, wherein the time domain analysis method experiment module comprises a first-order system time domain analysis module, a second-order system time domain analysis module and a high-order system time domain analysis module; the root-locus method experiment module comprises a second-order system root-locus analysis module, a third-order system root-locus analysis module and a high-order system root-locus analysis module; the frequency domain analysis method experiment module comprises a typical link frequency response characteristic analysis module and a composite system frequency response analysis module; the system correction experiment module comprises a series connection lead correction module, a series connection lag correction module, a series connection lag-lead correction module and a PID correction module; the open experiment module comprises a water level control module, an elevator control module and a traffic lamp control module. By means of the virtual automatic control experimental system and the design method, a user can design and simulate an automatic control experiment, the efficiency of the automatic control experiment is improved, limitation of hardware equipment is avoided, an experimenter can conveniently have a study, and shortcomings in a traditional experiment are overcome.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
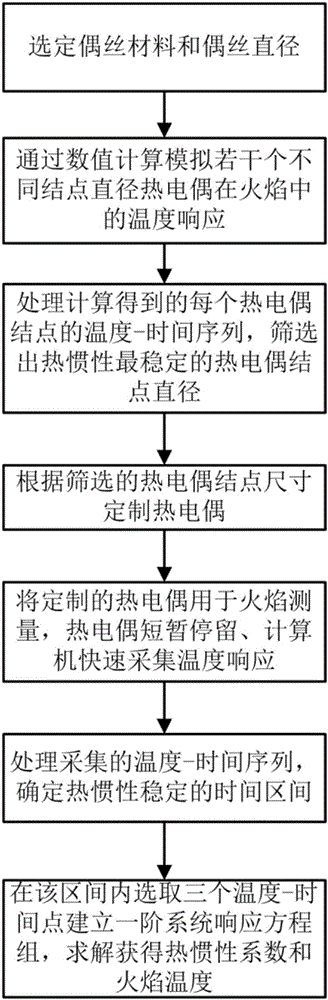
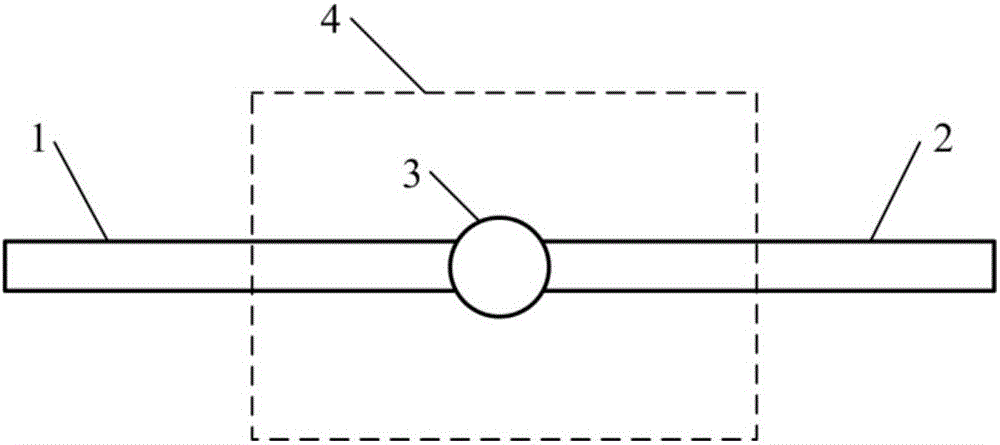
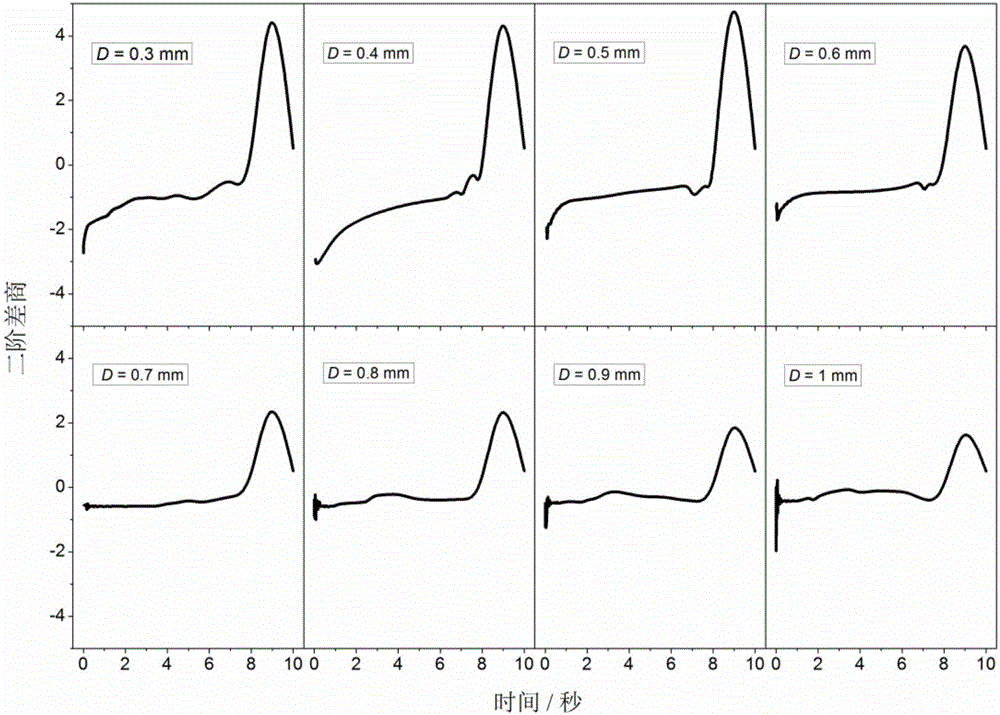
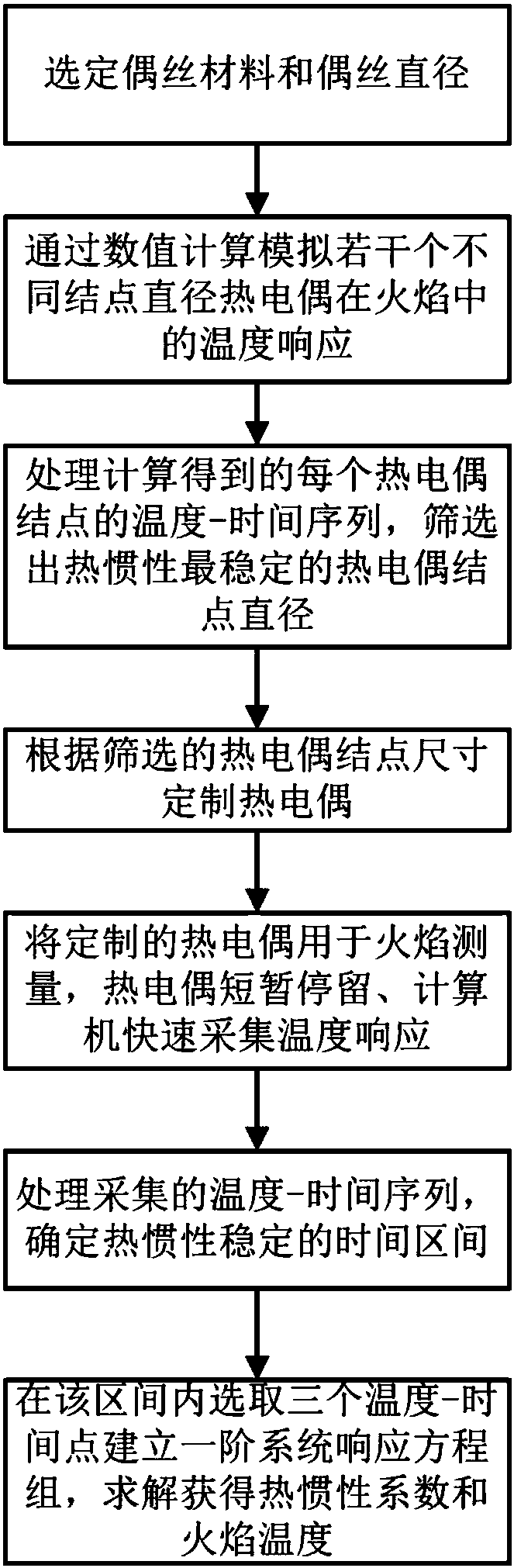
Dynamic temperature measuring method for correcting thermal inertia drift of system thermocouple
ActiveCN106248259AIncrease temperatureThermal inertial stabilityThermometer testing/calibrationTemperature responseMeasurement point
The invention relates to a dynamic temperature measuring method for correcting the thermal inertia drift of a system thermocouple. According to the method, thermocouples of different thermocouple wire / node diameters are simulated and analyzed in the numerical calculation mode. During the temperature response process in the flame, a thermocouple wire / node accouplement optimal in thermal inertia stability is screened out. According to the requirement of the above accouplement, a thermocouple is customized, so that the purpose of correcting the thermal inertia drift is achieved. During measurement, a thermocouple node is quickly moved into a specified measurement point in the flame. The temperature / time data of the thermocouple are recorded and analyzed by a data acquisition module and a computer. Based on the second-order difference quotient characteristics of a thermocouple temperature and time sequence, a time interval that is stable in thermal inertia is screened out. After that, the data treatment of a first-order system response equation is conducted in the above time interval, so that a thermal inertia coefficient and a flame temperature are obtained. The above method is wider in applicability and higher in accuracy compared with the traditional thermocouple temperature measuring method.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
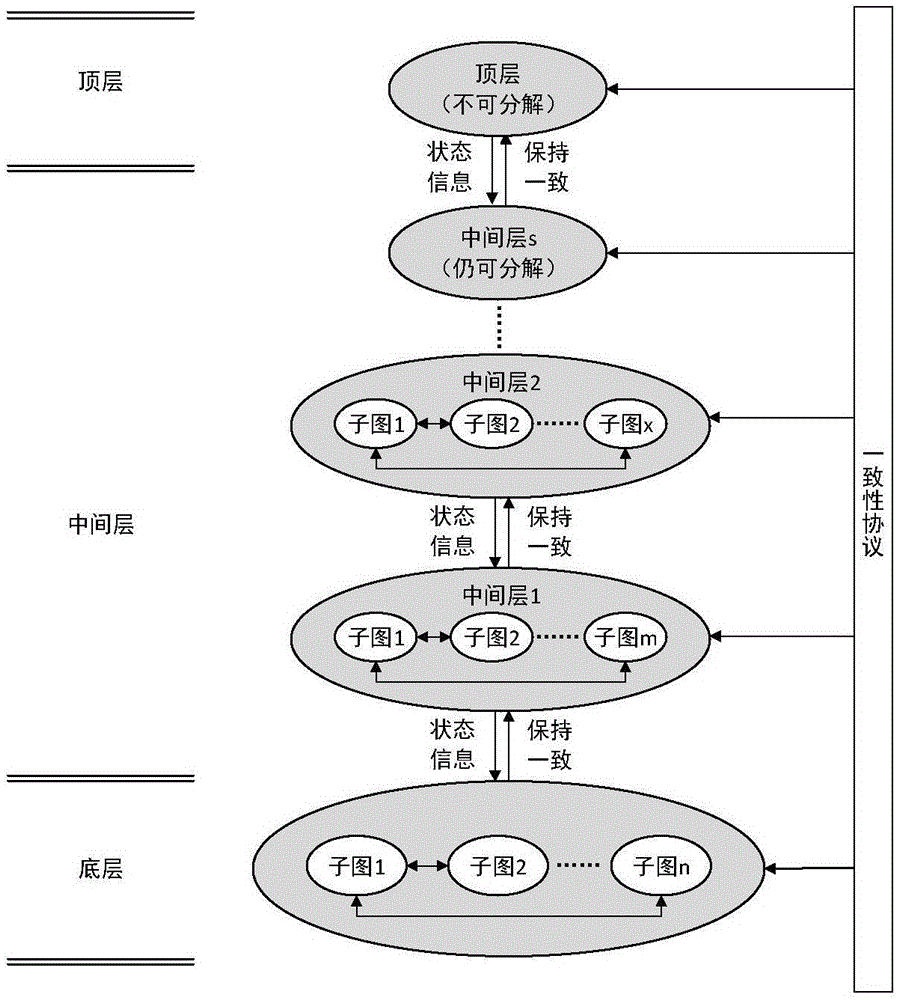
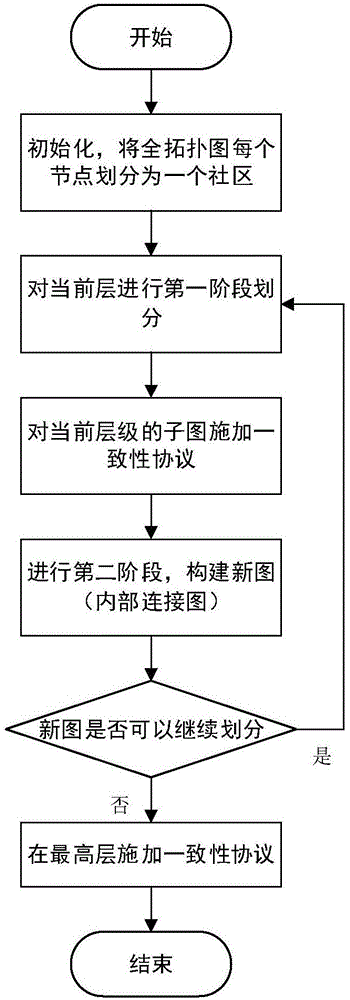
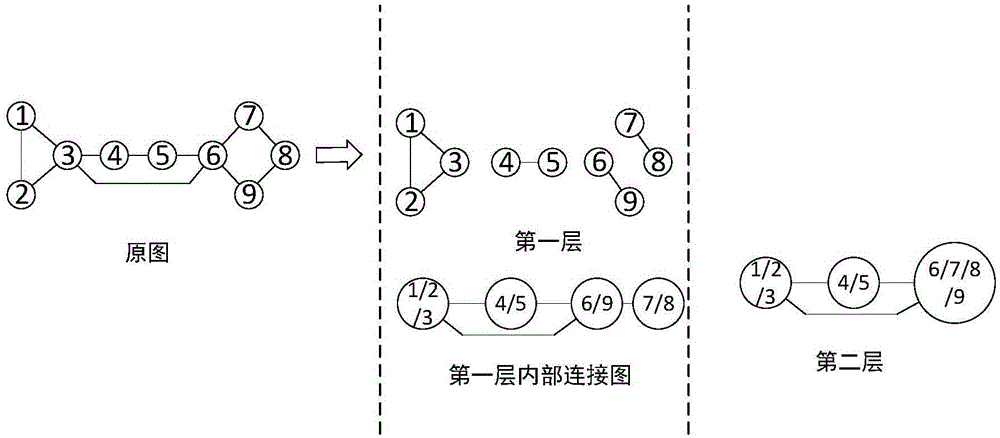
Multi-agent system consistency achieving method based on cell decomposition
InactiveCN105138768ADo not change topologyDoes not change connection weightsSpecial data processing applicationsCommunity basedDecomposition
The invention discloses a multi-agent system consistency achieving method based on cell decomposition, and belongs to the technical field of multi-agent systems. By means of the multi-agent system consistency achieving method based on cell decomposition, the multi-agent system consistency convergence speed is increased, the problem that a consistency convergence speed increasing method is difficult to implement in actual application is solved, and the problem of a single-layer topology is converted to the problem on a multi-layer topology to be solved on the premise of neither changing a multi-agent topology relation nor changing connecting weight. Meanwhile, the method has the good improvement effect on a first-order system and a second-order system. The multi-agent system consistency achieving method is applied in wide-range engineering application based on a ground unmanned trolley system, an unmanned aerial vehicle system, a self-organization underwater fleet, a satellite group and the like, and has the practical significant in better application.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
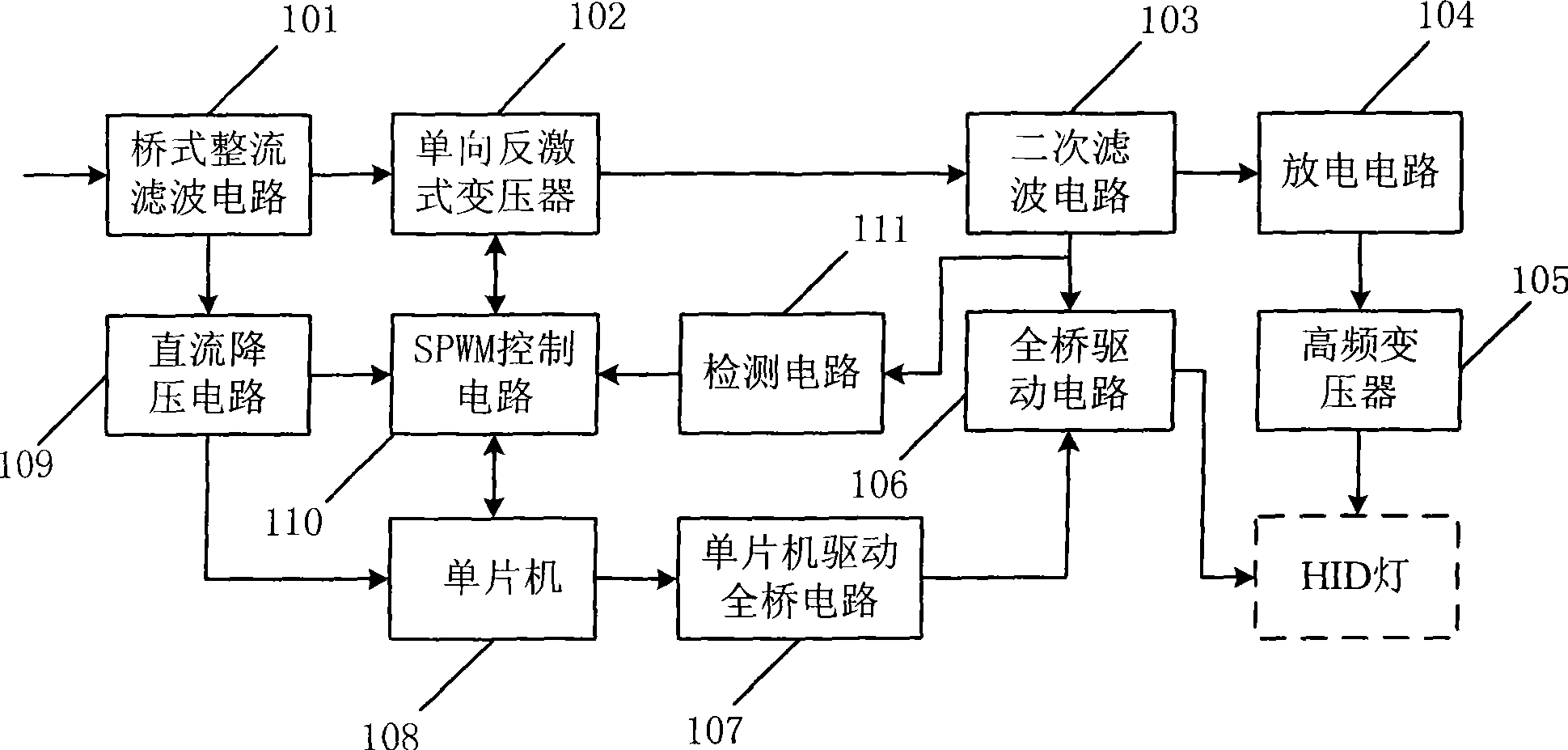
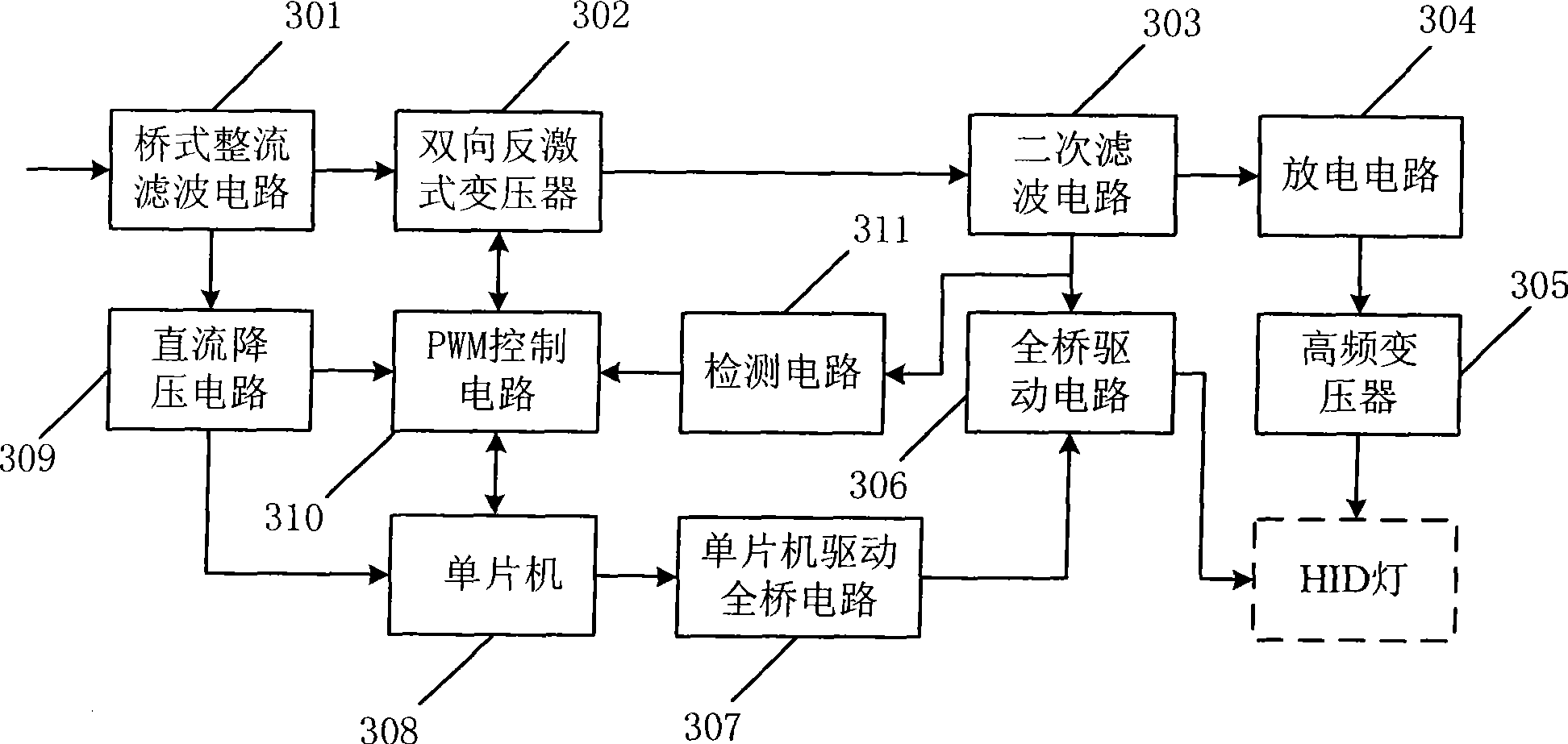
Electronic ballast of HID lamps
ActiveCN101448354AExtended service lifeImprove power factorElectrical apparatusElectric lighting sourcesPower factorEngineering
The invention provides an electronic ballast of HID lamps. The electronic ballast of the HID lamps employs a two-way flyback transformer capable of generating negative voltage based on the existing electronic ballast of the HID lamps to replace the one-way flyback transformer of the existing electronic ballast of HID lamps, and employs a PWM control circuit with high power factor, good first-order system steadiness and quick loading response speed to replace the SPWM control circuit of the existing electronic ballast of the HID lamps, thereby being capable of prolonging the service life of the HID lamps; moreover, the electronic ballast of the HID lamp has the advantages of high power factor, good first-order system steadiness and quick loading response speed.
Owner:SHANDONG HUADING WEIYE ENERGY TECH
Order reduction method for LCL-T module of photovoltaic power generation system
ActiveCN110266045AReduced simulation timeImprove simulation accuracySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationMathematical modelEngineering
The invention relates to an order reduction method for an LCL-T module of a photovoltaic power generation system, which comprises the steps of in the case that an isolation transformer is unsaturated, building a mathematical model based on the LCL-T module of the photovoltaic power generation system, acquiring transfer functions between input voltage of a filter and output current of the filter and between the input voltage of the filter and primary side current of the transformer, and introducing weighted feedback current so as to realize zero and pole cancellation and achieve the purpose of simplification; and in the case that the isolation transformer is saturated, solving a transfer function between the input voltage of the filter and primary side output current of the transformer in consideration of primary and secondary side resistance and excitation resistance of the isolation transformer, and reducing the high-order LCL-T module into a first-order system with series connection of an equivalent resistor and an equivalent inductor by adopting a Routh approximation method of a high-order system based on the Routh stability rule; and carrying out Bode diagram verification through PSCAD / EMTDC modeling and simulation and MATLAB data processing, and comparing the detailed model with the equivalent model result, thereby being capable of effectively reducing the simulation time and improving the simulation accuracy.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY +2
Uncertain parameter interference suppression method for LCL filter grid-connected inverter
InactiveCN110365199AImplementing a Robust Current Control MethodPower conversion systemsEquation of stateError feedback
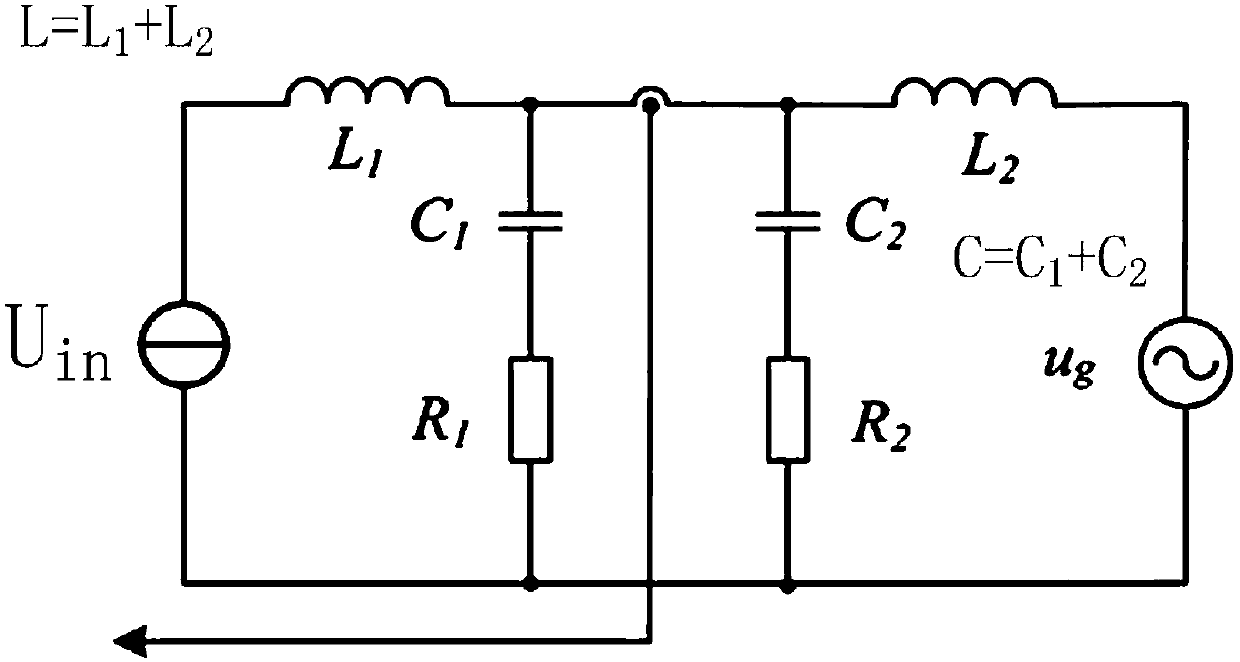
The invention is an uncertain parameter interference suppression method for an LCL filter grid-connected inverter. The LCL filter parameters are set, the third-order LCL filter is simplified to a first-order system, and a transfer function of a control system based on the traditional time-delay control is established; a state equation corresponding to the expected reference model is obtained, andaccording to the state equation corresponding to the expected reference model, a preliminary input expression is obtained; a filter for estimating uncertainty and interference is introduced to obtainan interference function in a frequency domain; Laplace transform is carried out on the preliminary input expression, a completed filter and an error feedback gain are independently designed in the frequency domain, a functional expression between control system output and input and errors is obtained, and the controller can thus suppress the interference. According to the LCL filter inverter uncertain parameter control method applicable to the power grid with various disturbances, suppression on external disturbances and parameter changes can be realized in a relatively simple manner.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
Variable gain-based supercoiled sliding mode control method
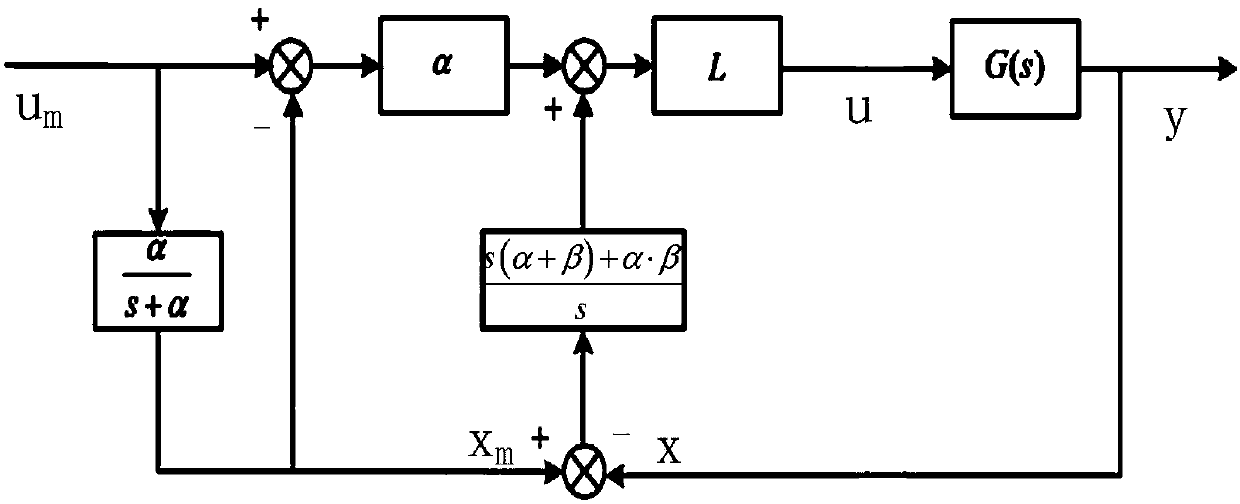
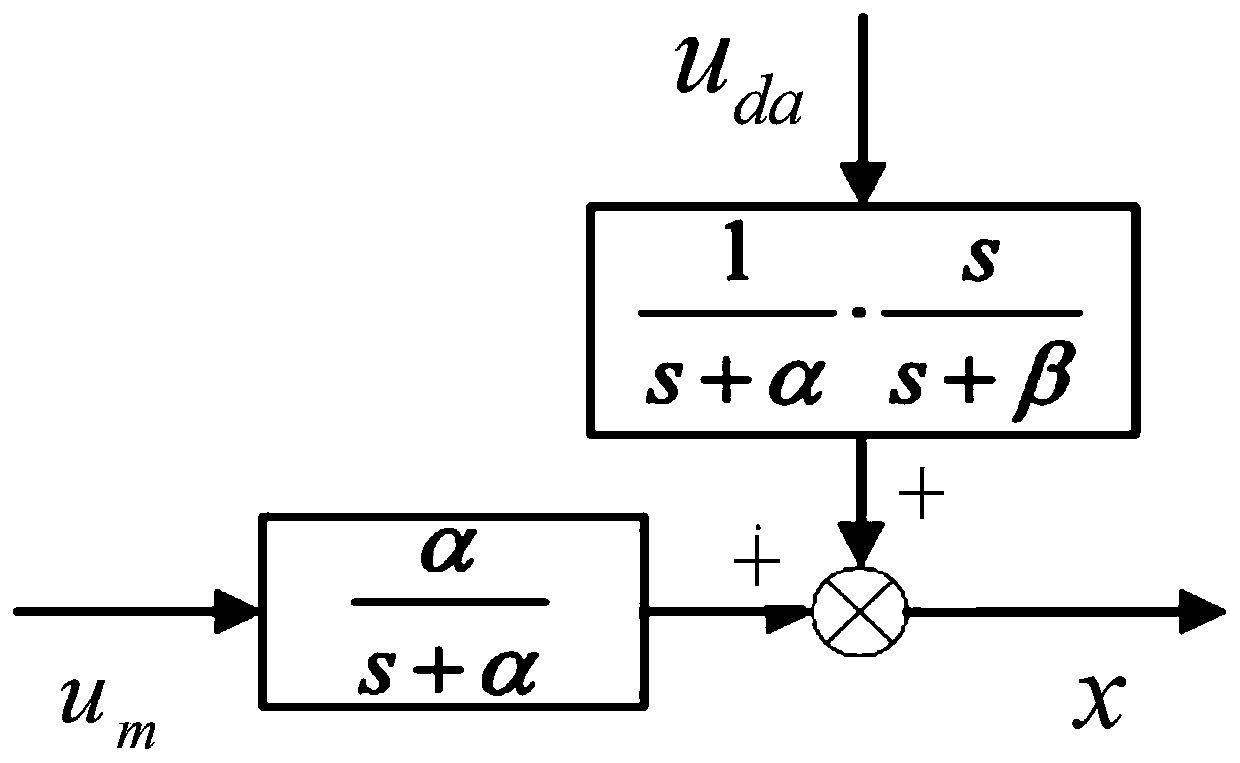
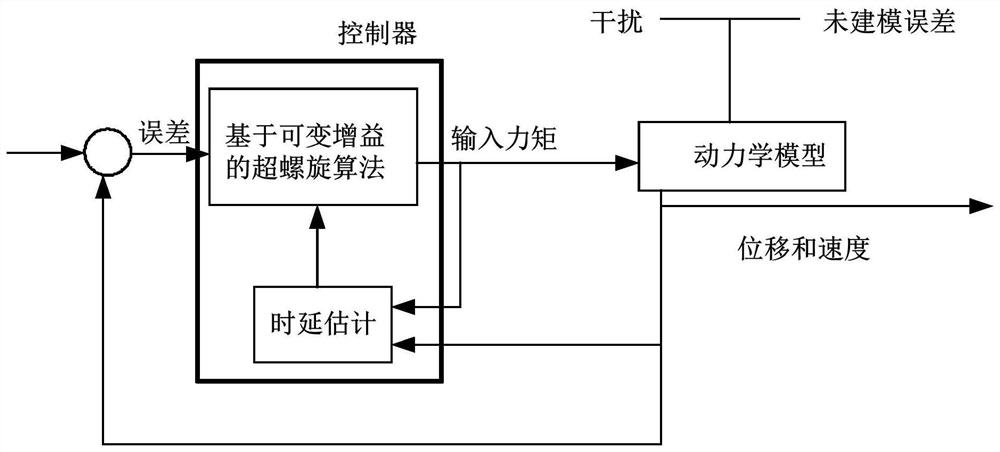
ActiveCN112356034AChatter suppressionChatter suppression needsProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl engineeringFirst order system
The invention discloses a variable gain-based supercoiled sliding mode control method, and the variable gain-based supercoiled sliding mode control method is mainly applied to control of multi-axis systems such as a mechanical arm. The power item gain in a general supercoiled algorithm is redesigned to be variable gain, the newly increased gain is used as output of a first-order system, an absolute value of a sliding mode function is increased in proportion, the function after amplitude limiting is used as an input signal of the first-order system, and the violent change degree of the input signal is smoothed by using the low-pass filtering characteristic. The newly increased gain has the following advantages that when the system state track is farthest from a sliding mode switching surface, the variable gain is increased to a maximum value, so that a controller accelerates the system state track to approach the sliding mode switching surface with the maximum force; and when the systemstate is in a quasi-sliding mode, the variable gain is attenuated to a minimum value, so that the controller fully inhibits the motion amplitude of the system state track by taking the sliding mode switching surface as the center so as to inhibit control input jitter of the system.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Model-free prediction current control method based on super-local model
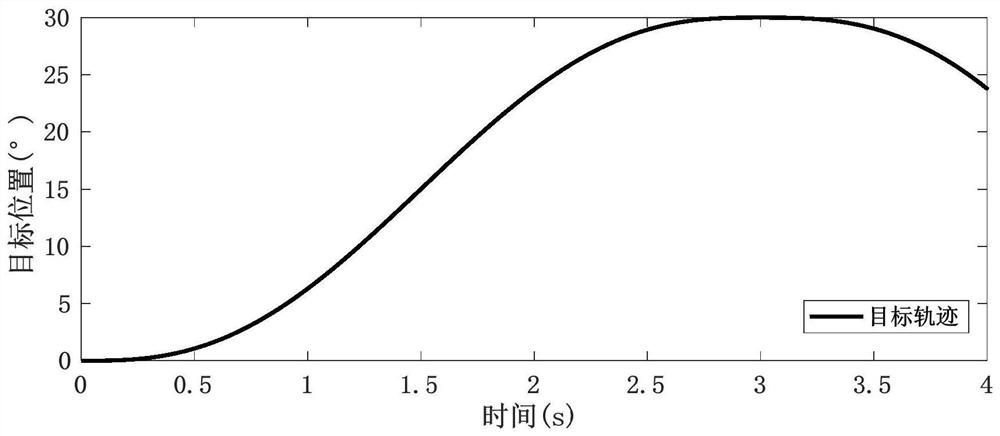
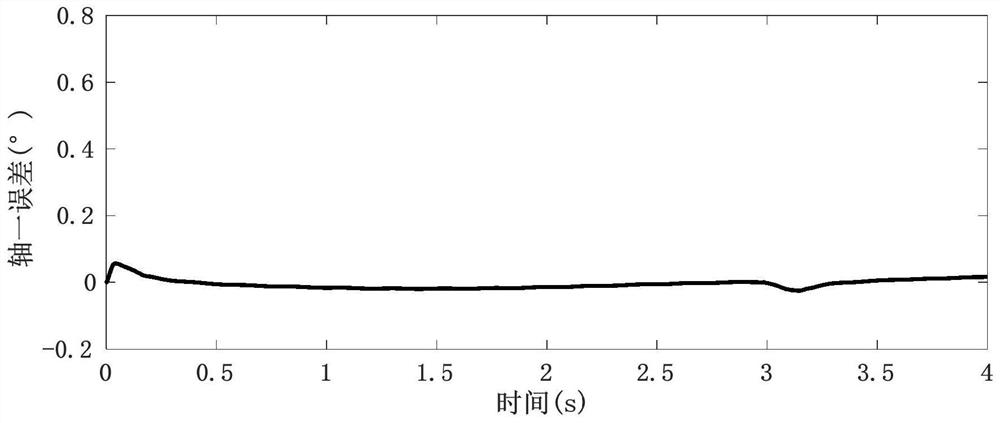
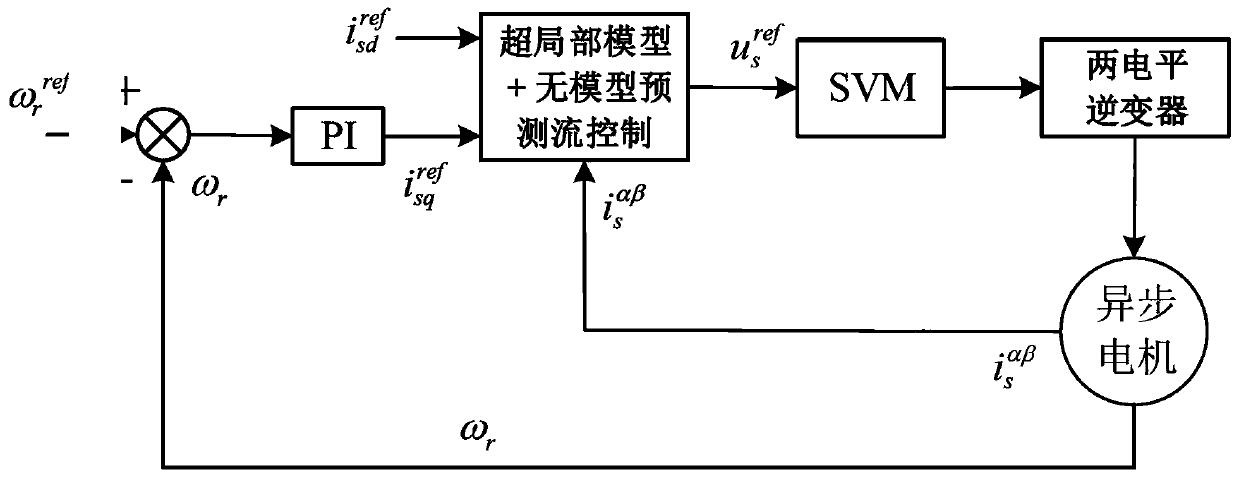
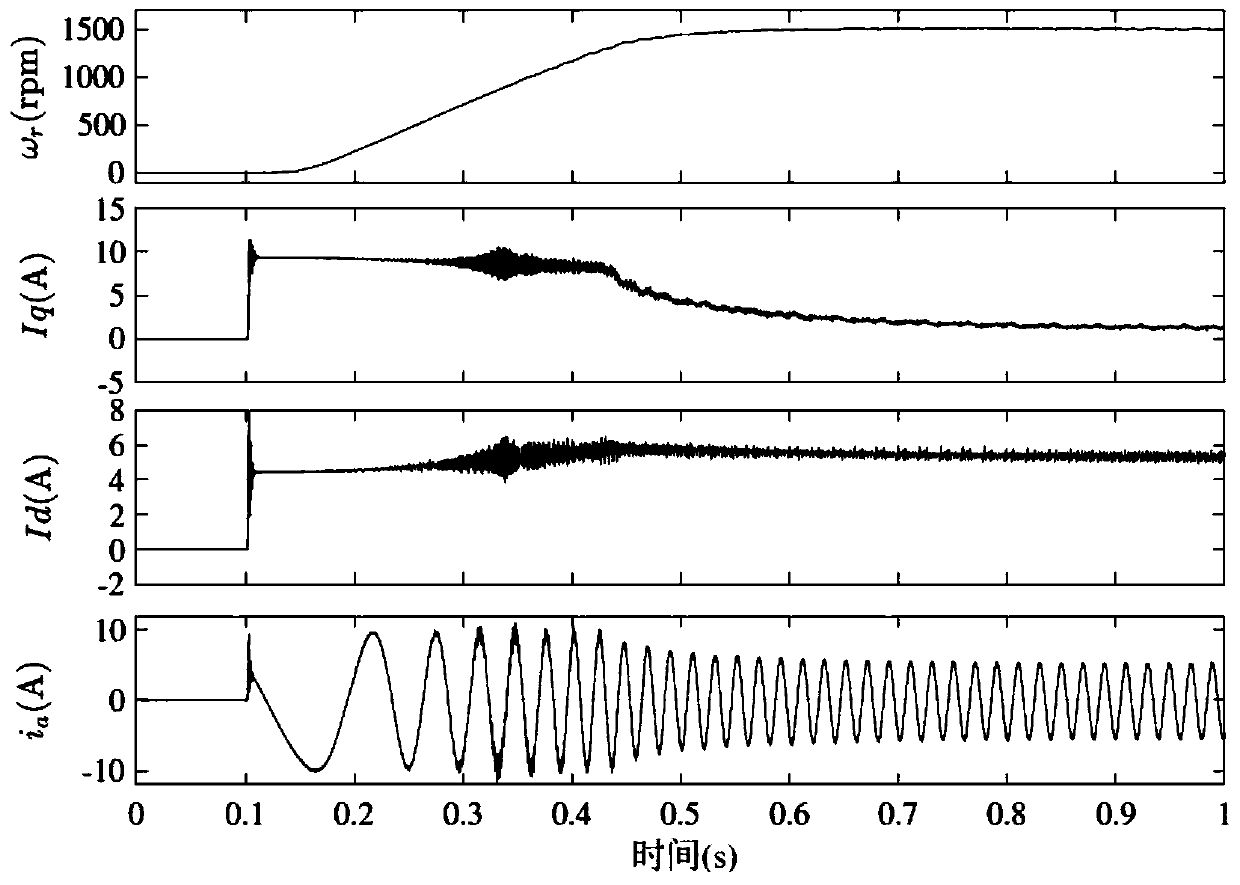
InactiveCN111313781AImprove robustnessImprove control effectElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsAlgorithmMathematical model
The invention provides a model-free prediction current control method based on a hyper-local model, and the method comprises the steps: A, employing indirect magnetic field directional control according to the hyper-local model of an asynchronous motor, and simplifying current control of a hyper-local model of the asynchronous motor into a first-order system through complex vector description; B,according to the simplified first-order system in the step A, combining the first-order system with the intelligent PI to obtain the input of a closed-loop system; C, estimating F in a short time by adopting a differential algebraic method, wherein F is a variable containing structural information of the system, an unknown part of the system and interference; and D, combining super-local model-free control with asynchronous motor indirect magnetic field directional prediction current control, and solving an estimated value of F according to the complex vector mathematical model and the super-local model under the two-phase static coordinate system of the asynchronous motor. According to the method, the robustness of model predictive control (MPC) to motor parameters is greatly improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for controlling grid-connected inverter based on feed-forward compensation
InactiveCN102545266BNot affected by disturbanceEliminate Amplitude Gain SpikesAc-dc conversionCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a method for controlling a grid-connected inverter based on feed-forward compensation. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a grid voltage, a grid side current and a capacitance current; (2) according to the grid side current, generating an instruction signal; (3) according to the grid voltage and the capacitance current, acquiring a current feed-forward signal and a voltage feed-forward signal; and (4) superposing the instruction signal, the current feed-forward signal and the voltage feed-forward signal to obtain a modulation signal, and generating a switching signal for controlling the grid-connected inverter according to the modulation signal. The method has the advantages that: a second-order differential feed-forward item of the grid voltage is compensated by a first-order differential feed-forward link of the capacitance current, so that a third-order system is reduced to a first-order system, the stability margin of the system is improved, the design process of a current regulator is simplified, and the grid side current cannot be influenced by grid voltage harmonic waves.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
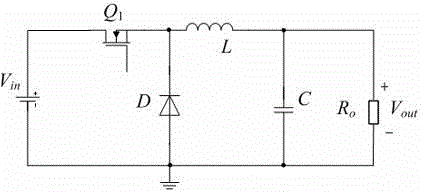
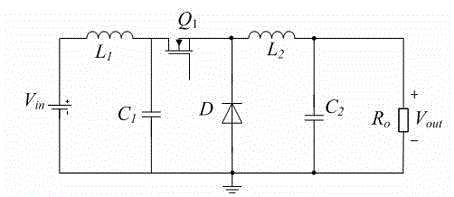
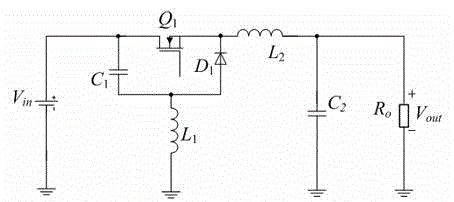
Improved Buck converter
InactiveCN104821719ASimple topologyImprove reliabilityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl systemBuck converter
The invention discloses an improved Buck converter comprising an input filter circuit, a power conversion circuit, and an output filter circuit. The converter evolves from a Buck topology provided with an input filter, and the position of an input filter inductor is moved to a power loop line. The converter is simple in structure and high in conversion efficiency, and high-frequency response manifests as a first-order system. For a converter controlled by a PWM transconductance error amplifier, the stability of a closed-loop control system is further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPACE POWER SOURCES
A dynamic temperature measurement method for systematically correcting thermocouple thermal inertia drift
ActiveCN106248259BIncrease temperatureThermal inertial stabilityThermometer testing/calibrationTemperature responseMeasurement point
The invention relates to a dynamic temperature measuring method for correcting the thermal inertia drift of a system thermocouple. According to the method, thermocouples of different thermocouple wire / node diameters are simulated and analyzed in the numerical calculation mode. During the temperature response process in the flame, a thermocouple wire / node accouplement optimal in thermal inertia stability is screened out. According to the requirement of the above accouplement, a thermocouple is customized, so that the purpose of correcting the thermal inertia drift is achieved. During measurement, a thermocouple node is quickly moved into a specified measurement point in the flame. The temperature / time data of the thermocouple are recorded and analyzed by a data acquisition module and a computer. Based on the second-order difference quotient characteristics of a thermocouple temperature and time sequence, a time interval that is stable in thermal inertia is screened out. After that, the data treatment of a first-order system response equation is conducted in the above time interval, so that a thermal inertia coefficient and a flame temperature are obtained. The above method is wider in applicability and higher in accuracy compared with the traditional thermocouple temperature measuring method.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
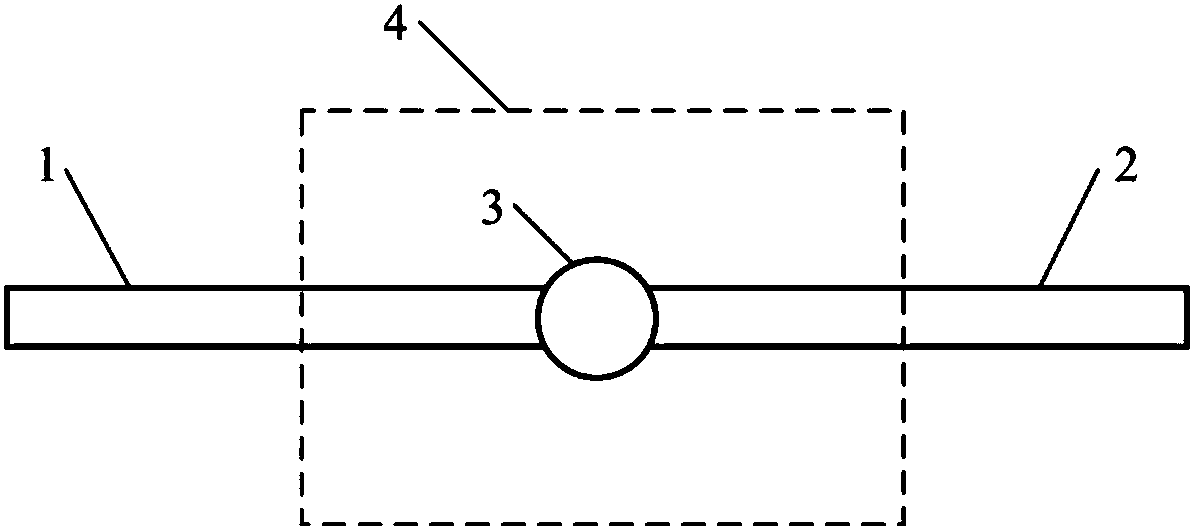
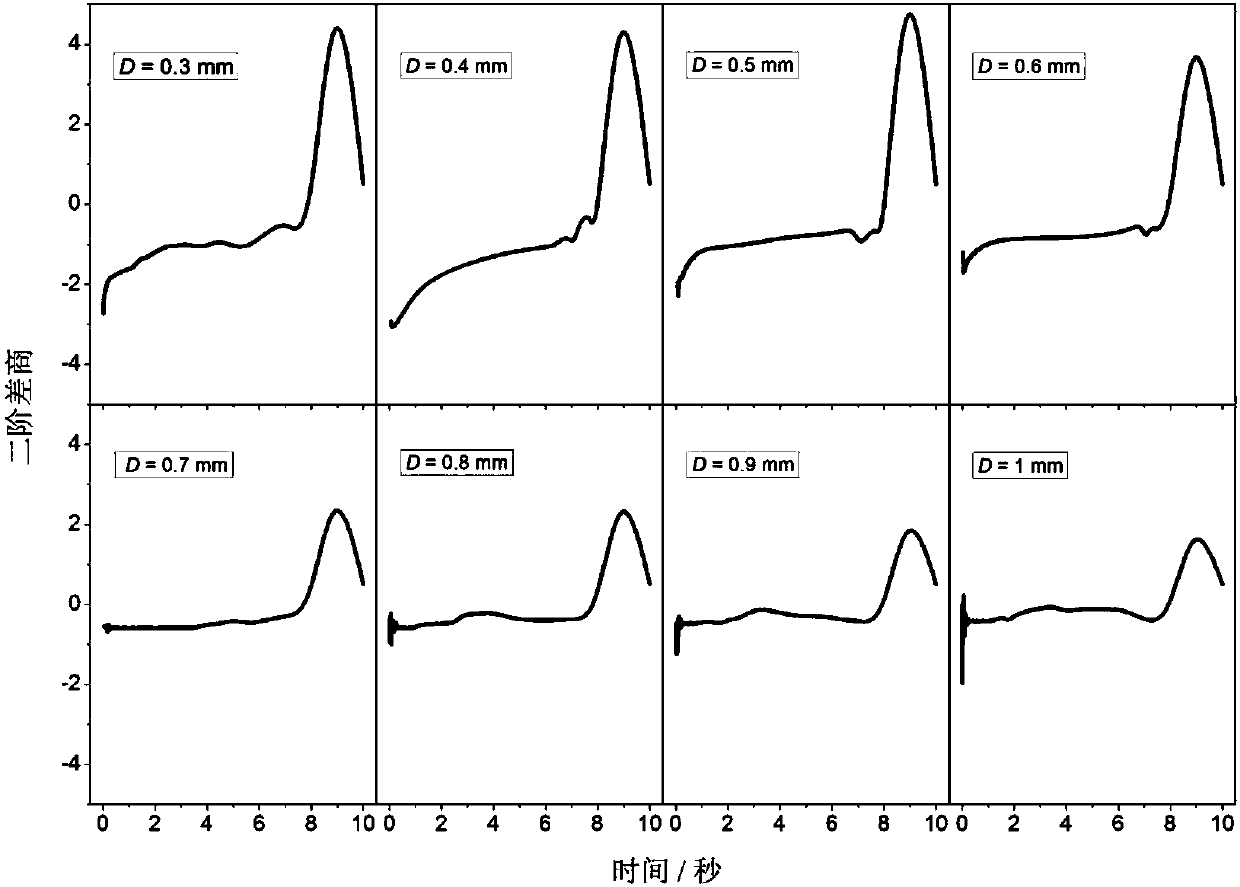
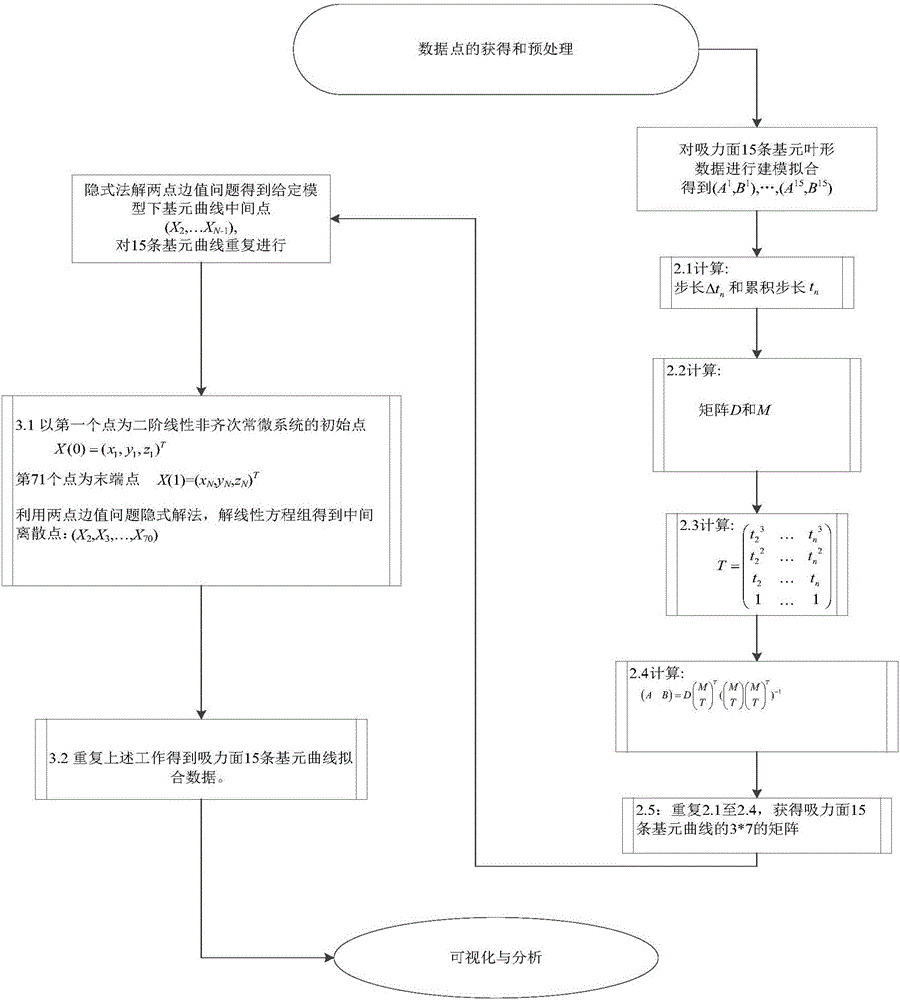
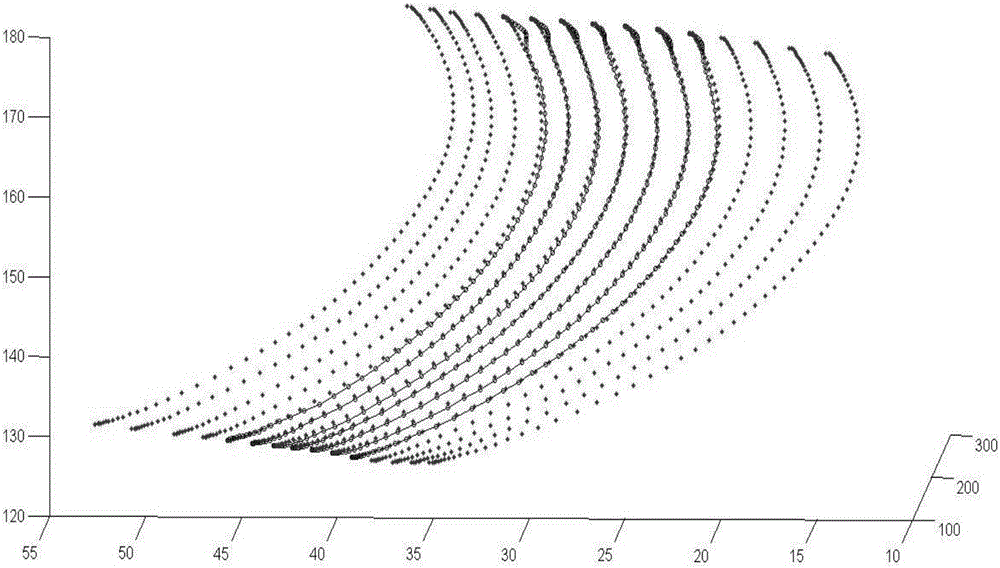
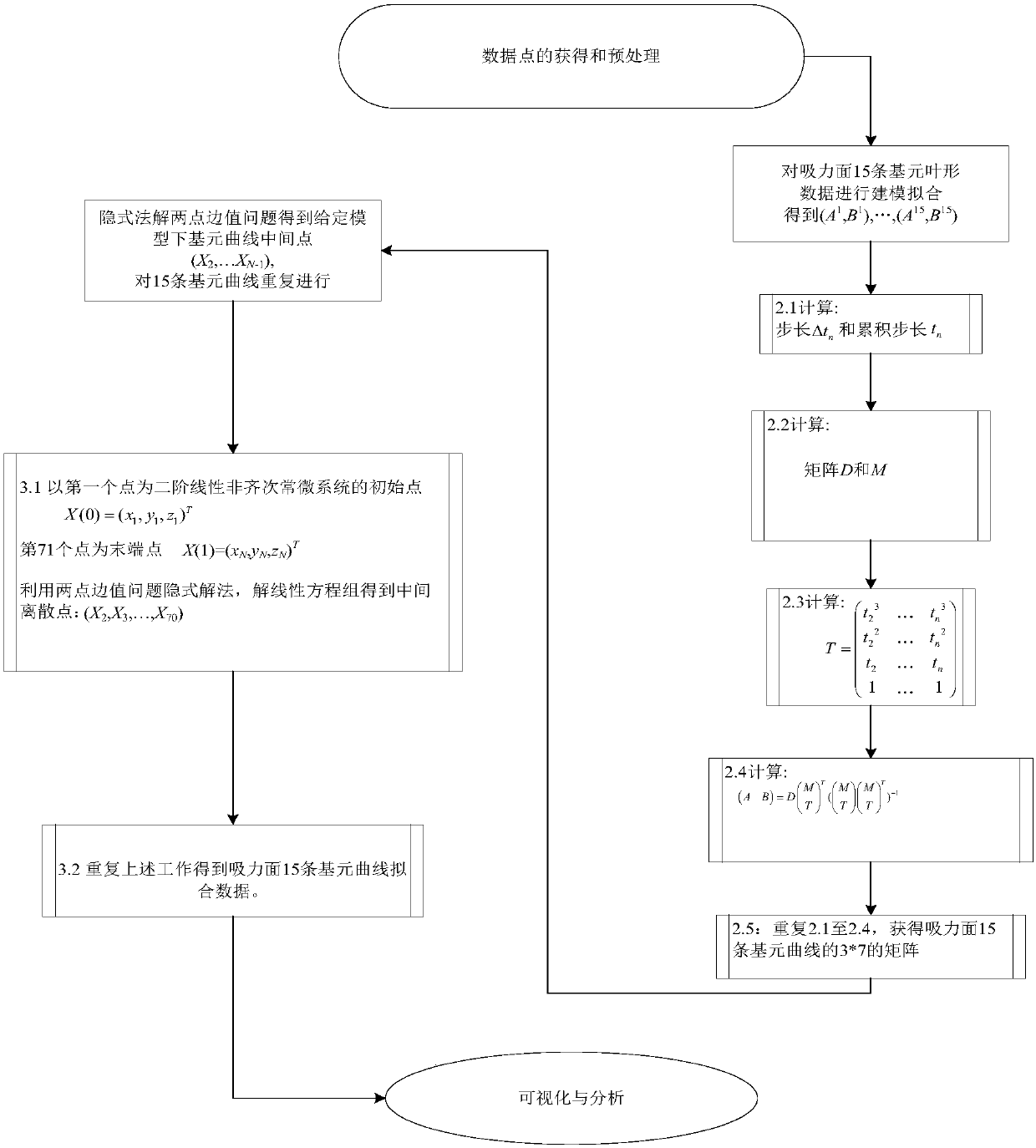
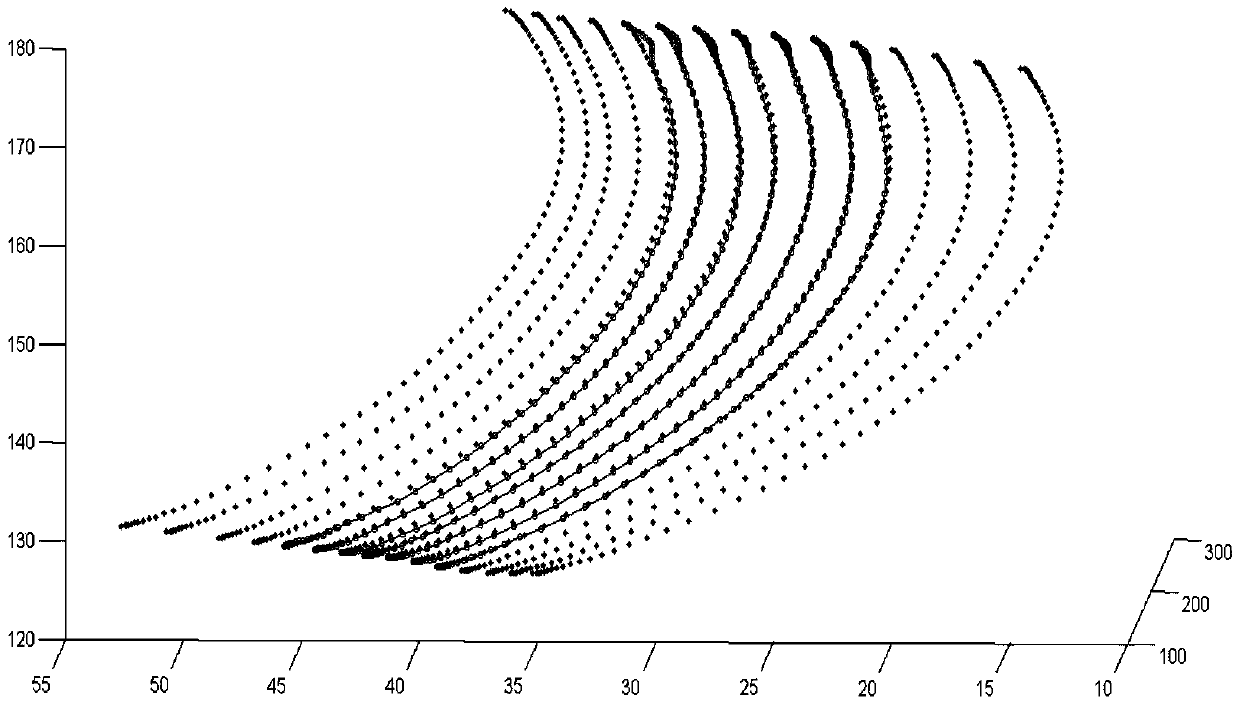
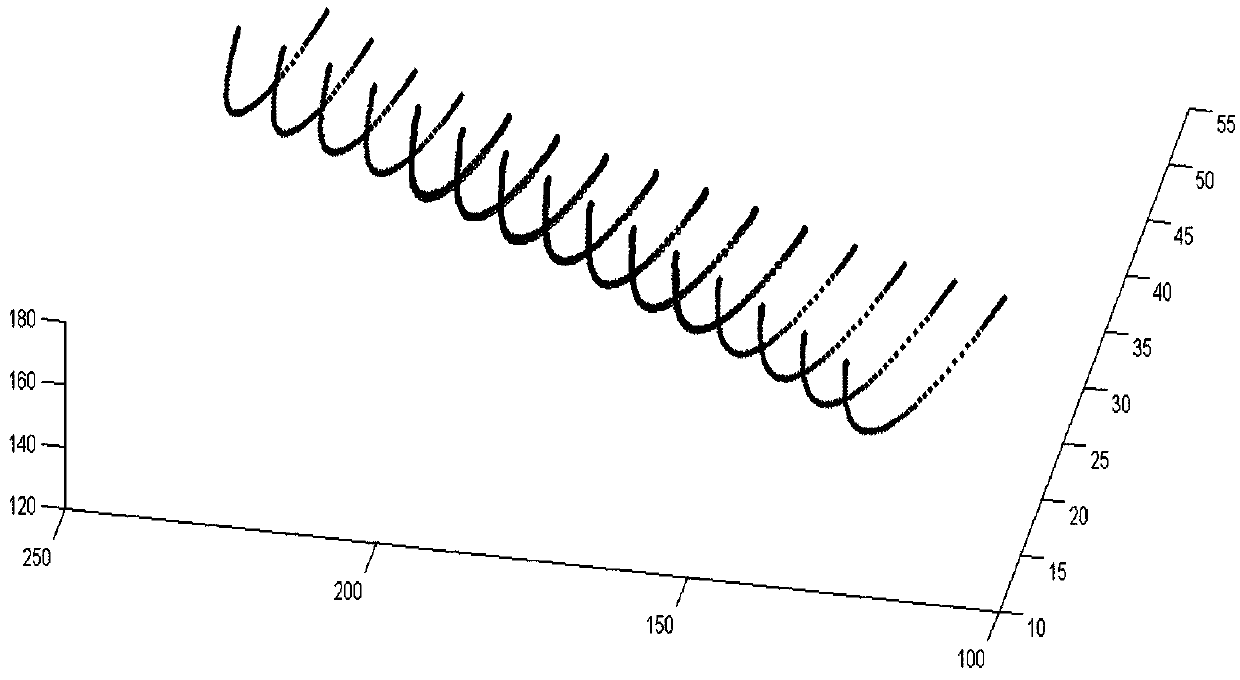
Compressor blade suction surface primitive curve modeling method based on second order ordinary differential equation
ActiveCN106227978AReduce sensitivityPromote reductionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSecond order ordinary differential equationPoint boundary
The invention provides a compressor blade suction surface primitive curve modeling method based on a second order ordinary differential equation, and the method comprises the steps of pre-treating compressor blade primitive curve data; and selecting a second order ordinary coefficient linear non-homogeneous ordinary differential system for fitting to obtain an expression of a primitive curve. According to the boundary condition requirement, a second-order curve problem coinciding with the first and last points of the given data is transformed into a two-point boundary value problem; an Implicit Euler method is selected for solving an intermediate point of a primitive curve. In this way, the primitive curve is reconstructed. According to the invention, the problem that a first order system can't guarantee interpolation conditions at the first and last points at the same time is solved; a larger optimization operation space is obtained; and sensitive degree to a parameter matrix is reduced. Interpolation in the first and last points of data scatter is accurate, which has a great advantage in connecting data scatter that is fitted in sheets or segments; and the shape of a compressor blade can be restored in high precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
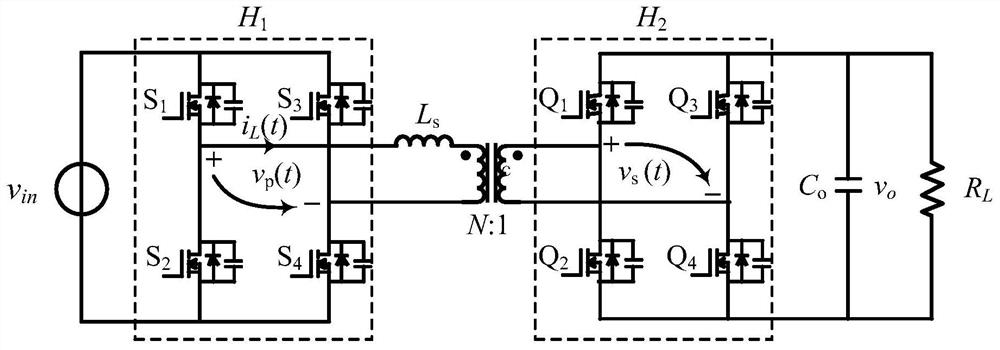
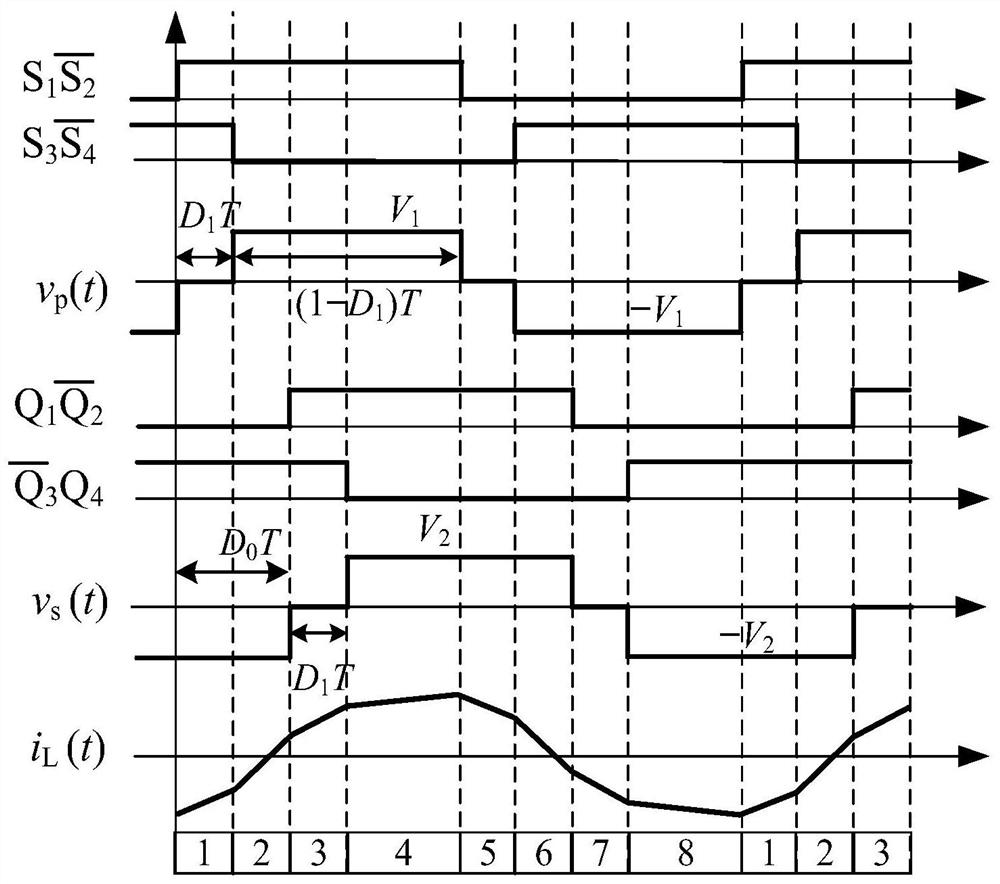
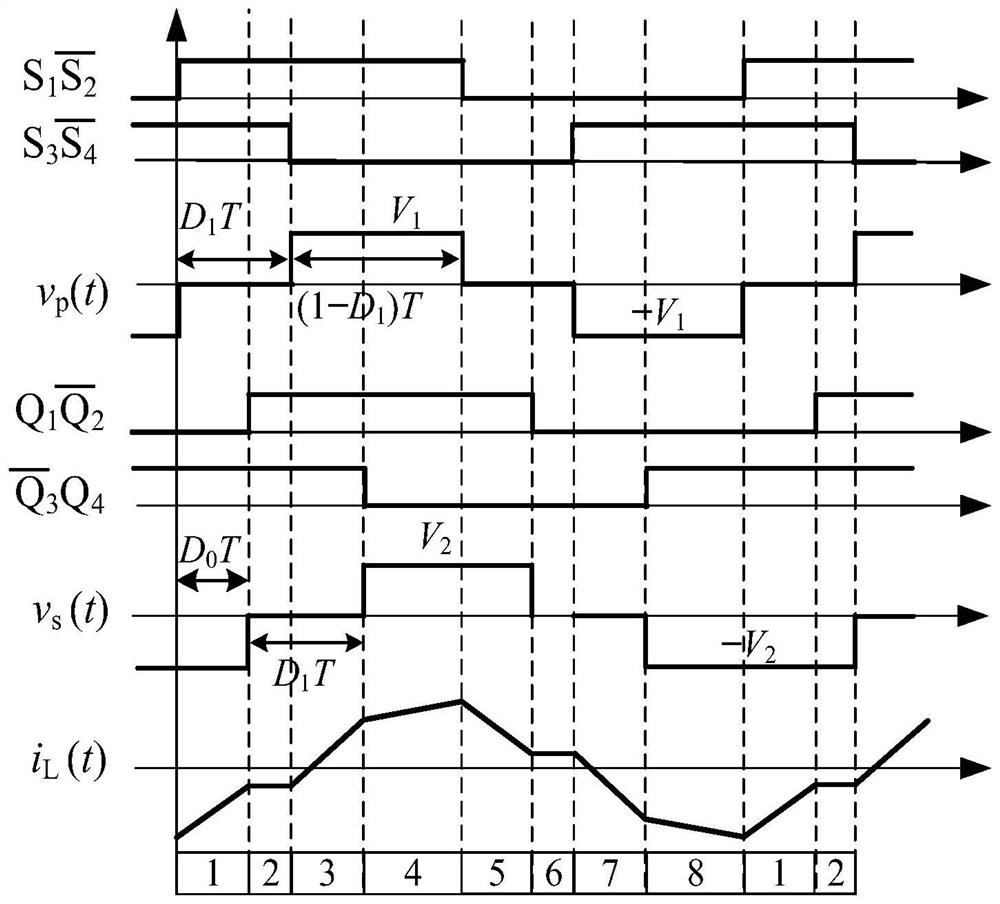
A small-signal modeling method for dual active full-bridge converters under dual phase-shift modulation
The invention discloses a dual-active full-bridge converter small signal modeling method under dual phase shift modulation, linearization is performed on an established large signal equivalent circuit, and a small signal model is established in combination with a mathematical model so that control-output small signal models corresponding to different control variables under different working modesof a converter can be obtained. The invention further discloses a method for further simplifying the model according to the characteristics of the equivalent circuit, and further discloses a circuitmodel for equivalently controlling the output characteristics of the dual-active full-bridge converter by using a first-order system. According to the method, the equivalent circuit is linearized, themathematical model is combined to discuss small signal characteristics of the equivalent circuit, and control-output small signal models of different control variables can be obtained. A first-ordersystem can be used for approximation, and the control-output characteristics of the dual-active full-bridge converter can be approximately described by the first-order system. Therefore, a new thoughtis provided for related research work such as control and stability analysis of the dual-active full-bridge converter.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Dynamic modal-split transfer function model for helicopter
InactiveCN101950158AReflect dynamic propertiesImprove flight qualitySimulator controlTransfer function modelDynamic models
The invention discloses a dynamic modal-split transfer function model for a helicopter, which belongs to the field of modeling and control of unmanned aerial vehicles. The dynamic modal-split transfer function model for the helicopter is characterized by comprising first-order subsystems, second-order subsystems, system gain and equivalent delay. Real zero poles and complex conjugate zero poles of a transfer function are divided into the first-order subsystems and the second-order subsystems by a modal-splitting method; and during the division, the complex conjugate zero poles are first divided into the second-order subsystems, and redundant real zero poles are combined into the second-order subsystems in pairs, so that the whole system consists of not more than two first-order subsystems and a few second-order subsystems, and the dynamic model for the unmanned helicopter can be determined by specifying real roots of the first-order subsystems, the natural frequency and damping ratio of the second-order subsystems, the system gain and the equivalent delay. In the invention, a complex dynamic model for the helicopter is converted into the combination of low-order subsystems dominated by second-order systems and supplemented by first-order systems, and model parameters can be classified and defined into a plurality of relatively more compact and order-irrelative ranges, so that the model parameters can be searched in a concentrated range and the dynamic model for the helicopter can be easily identified by an identification algorithm.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
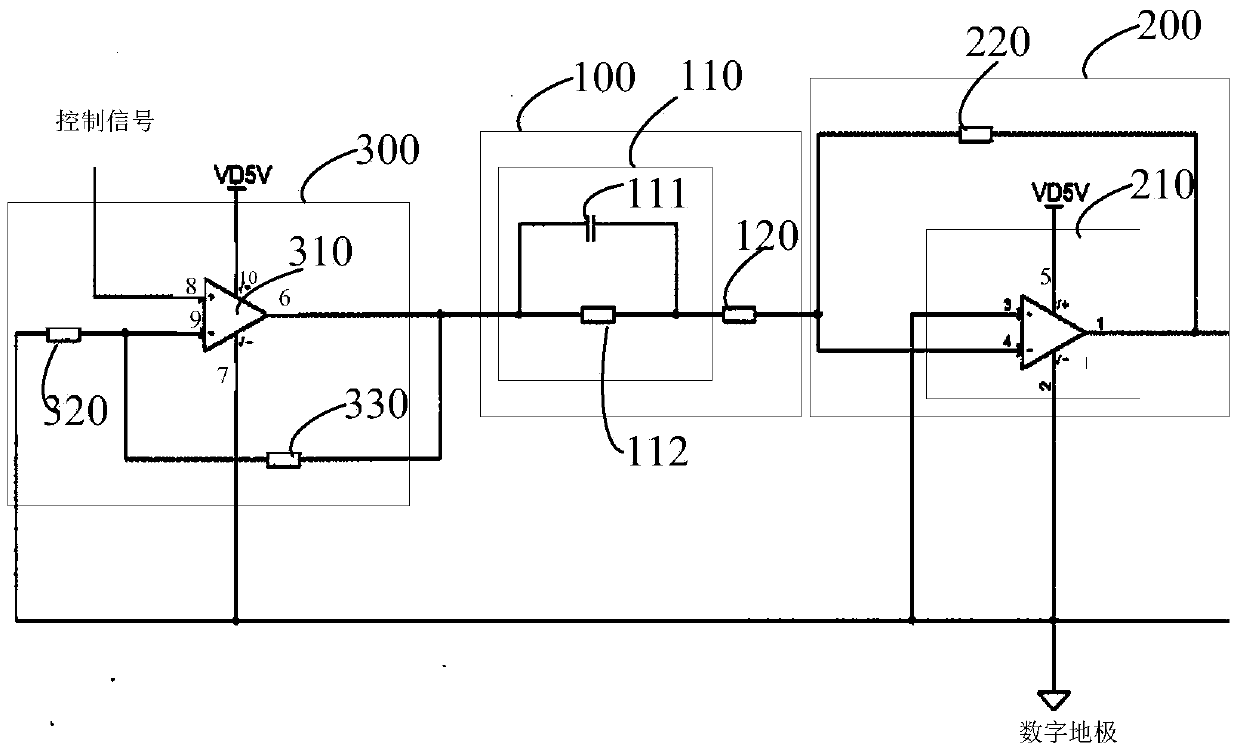
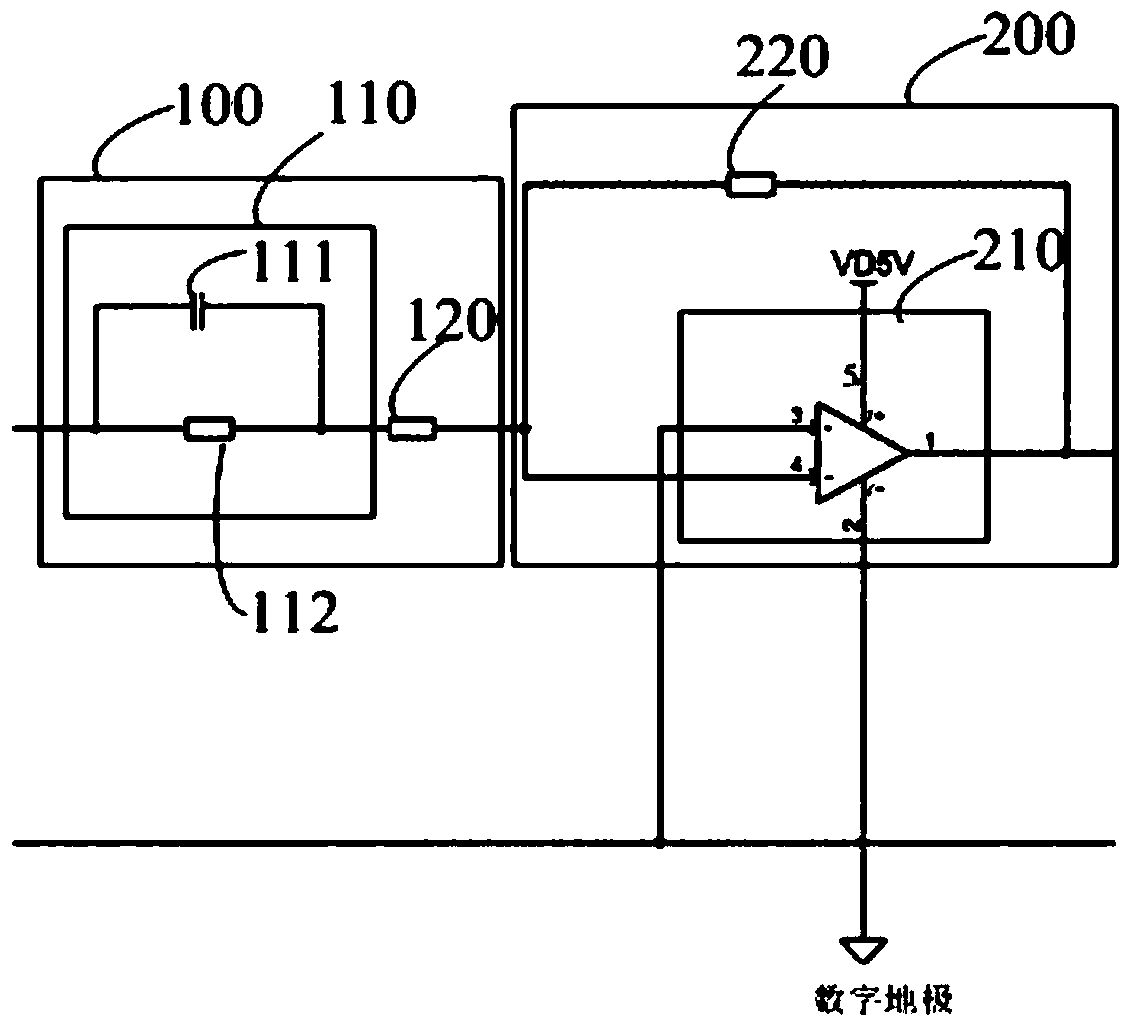
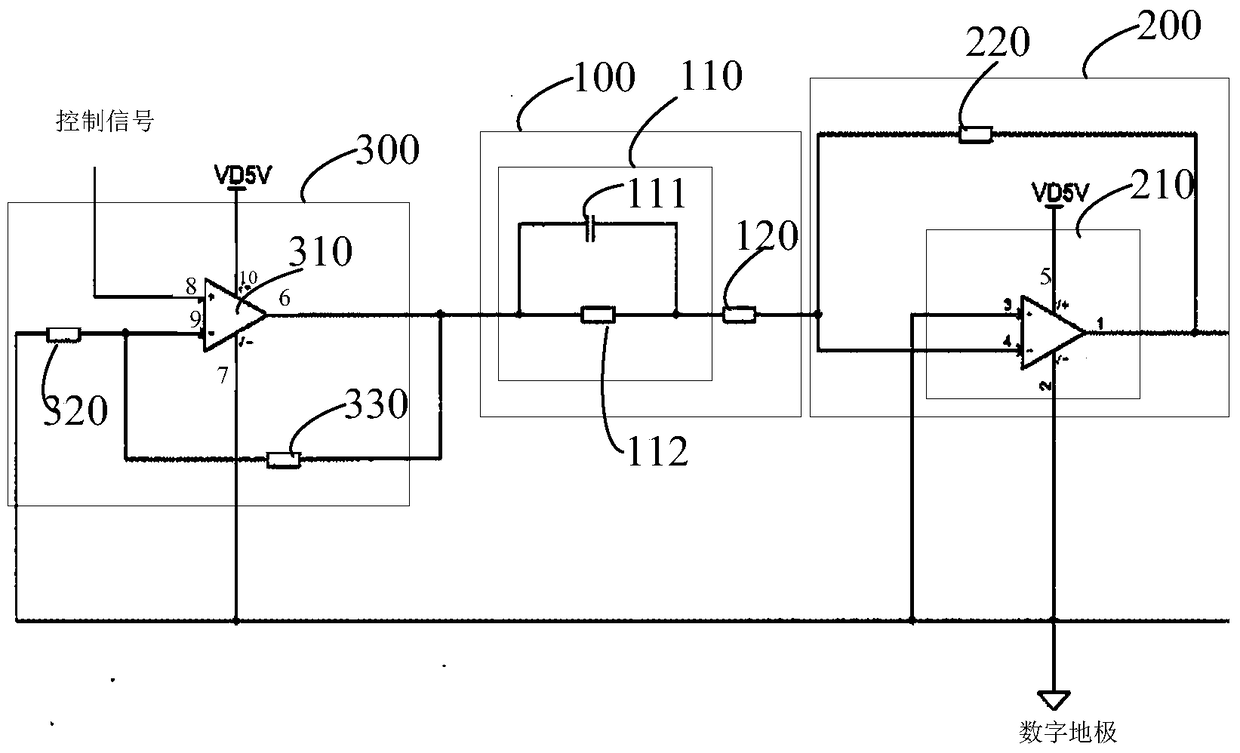
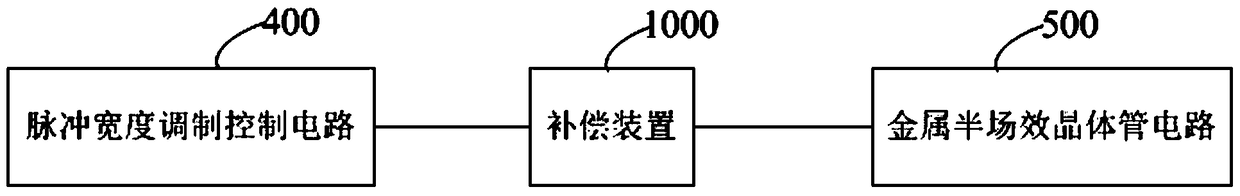
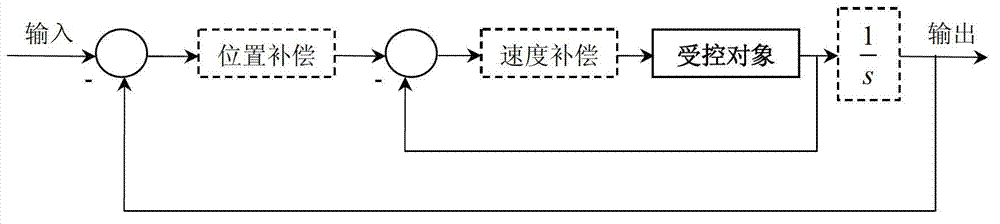
Compensation device and drive device
The invention discloses a compensation device and a drive device. The compensation device comprises a voltage stabilizing unit and a zero point regulating unit; the zero point regulating unit is used for counteracting first-order system poles of a metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor. The zero point regulating unit comprises a phase shift circuit and a divider resistor connected with each other in series. The phase shift circuit comprises a phase shift capacitor and a phase shift resistor connected in parallel. The voltage stabilizing unit comprises an operational amplifying unit and a feedback resistor. The feedback resistor is connected between the output end of the operational amplifying unit and an inverted phase input end thereof. The same-phase input end of the operational amplifying unit is grounded. The divider resistor is connected between the phase shift circuit and the inverted phase input end of the operational amplifying unit. The compensation device and the drive device have the advantages that first-order system poles of the MOSFET (metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor) circuit can be counteracted, poles of the compensation device turn into compensated first-order system poles of the MOSFET circuit, a constant o the MOSFET circuit is regulated, rising time of output current of the MOSFET is shortened, and rising speed of the output current is increased.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTRON TECH CO LTD
Compensation device and drive device
The invention discloses a compensating device and a driving device. The compensating device includes a voltage stabilizing unit and a zero point adjusting unit for canceling the first-order system pole of a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor. The zero point adjusting unit includes a series phase shifting unit. circuit and a voltage dividing resistor, the phase-shifting circuit includes a parallel phase-shifting capacitor and a phase-shifting resistor, the voltage stabilizing unit includes an operational amplifier unit and a feedback resistor, and the feedback resistor is connected to the output terminal of the operational amplifier unit and Between the inverting input terminals, the non-inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier unit is grounded, and the voltage dividing resistor is connected between the phase shifting circuit and the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier unit. Implement the device of the present invention, can offset the pole of the first-order system of MOSFET circuit, make the pole of compensation device become the pole of the first-order system of MOSFET circuit after compensation, adjust the constant of its circuit, shorten the output current rise time of MOSFET, accelerate output current rise rate.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTRON TECH CO LTD
Primitive Curve Modeling Method of Compressor Blade Suction Surface Based on Second-order Ordinary Differential Equation
ActiveCN106227978BReduce sensitivityPromote reductionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSecond order ordinary differential equationEngineering
The invention provides a compressor blade suction surface primitive curve modeling method based on a second order ordinary differential equation, and the method comprises the steps of pre-treating compressor blade primitive curve data; and selecting a second order ordinary coefficient linear non-homogeneous ordinary differential system for fitting to obtain an expression of a primitive curve. According to the boundary condition requirement, a second-order curve problem coinciding with the first and last points of the given data is transformed into a two-point boundary value problem; an Implicit Euler method is selected for solving an intermediate point of a primitive curve. In this way, the primitive curve is reconstructed. According to the invention, the problem that a first order system can't guarantee interpolation conditions at the first and last points at the same time is solved; a larger optimization operation space is obtained; and sensitive degree to a parameter matrix is reduced. Interpolation in the first and last points of data scatter is accurate, which has a great advantage in connecting data scatter that is fitted in sheets or segments; and the shape of a compressor blade can be restored in high precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Control loop design method capable of reflecting vibration attenuation system performance
ActiveCN102866636ARealize simulationImplement hardware-in-the-loop simulationSimulator controlVibration attenuationRadar systems
The invention discloses a control loop design method capable of reflecting vibration attenuation system performance, which is suitable for simulation or semi-physical simulation of a control system of a photoelectric tracking system or a radar system which is arranged on a vibration attenuation system. Aiming at the situations that the vibration attenuation system and the control system are established relatively independently during simulation and the photoelectric tracking system is required to be fixed on a physical platform during testing, a three-order system is used as a controlled object in a control loop, and the influence of the vibration attenuation system on the control loop of the photoelectric tracking system is reflected. An implement method comprises the following steps of: substituting the original one-order system by the three-order system containing the vibration attenuation system to serve as the controlled object so as to design the control loop. The design can be realized in the control loop of a simulation or actual system.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
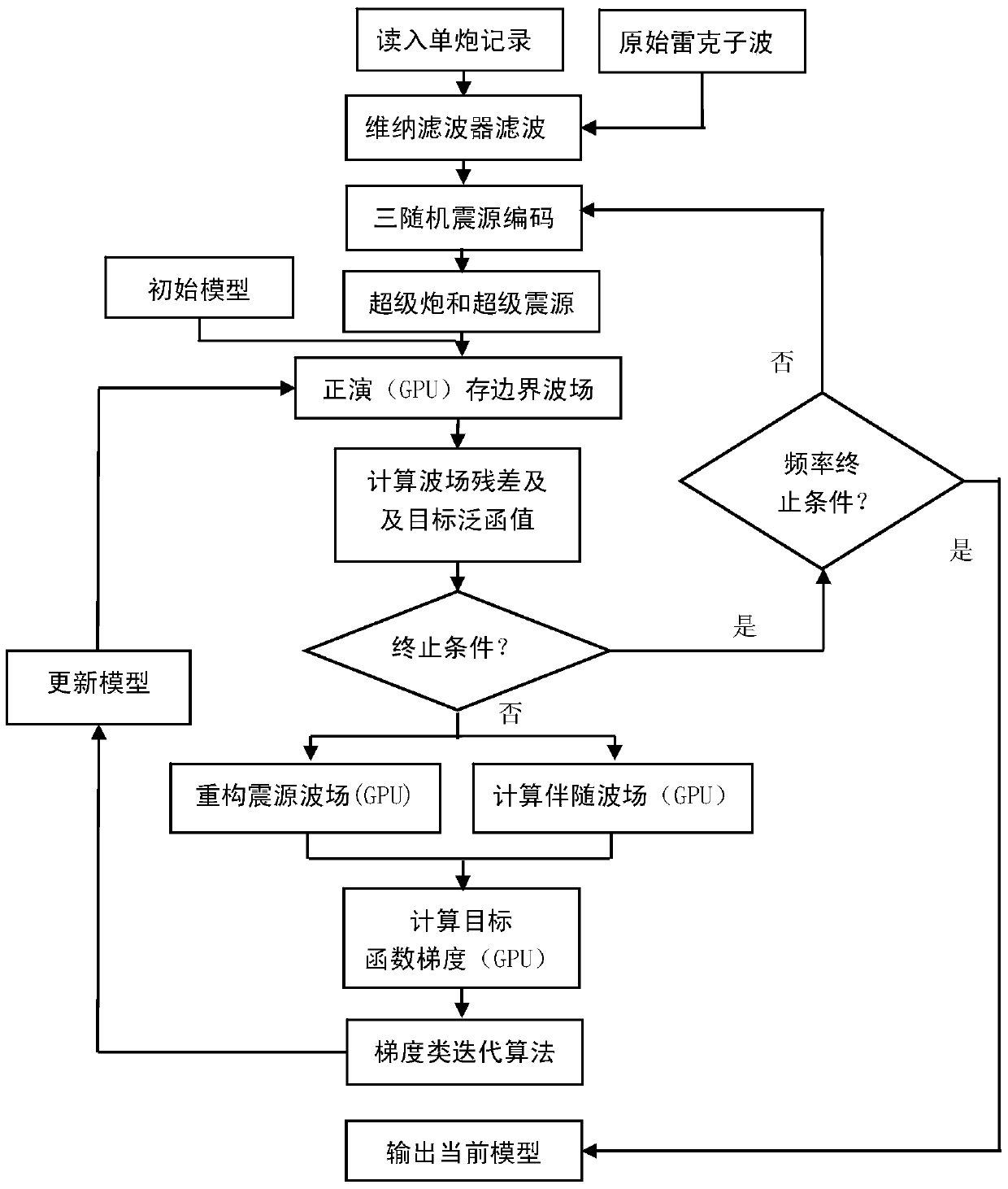
An Efficient Time Domain Full Waveform Inversion Method
ActiveCN105319581BReduce the number of simulationsReduce input and outputSeismic signal processingWave equationFull waveform
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com