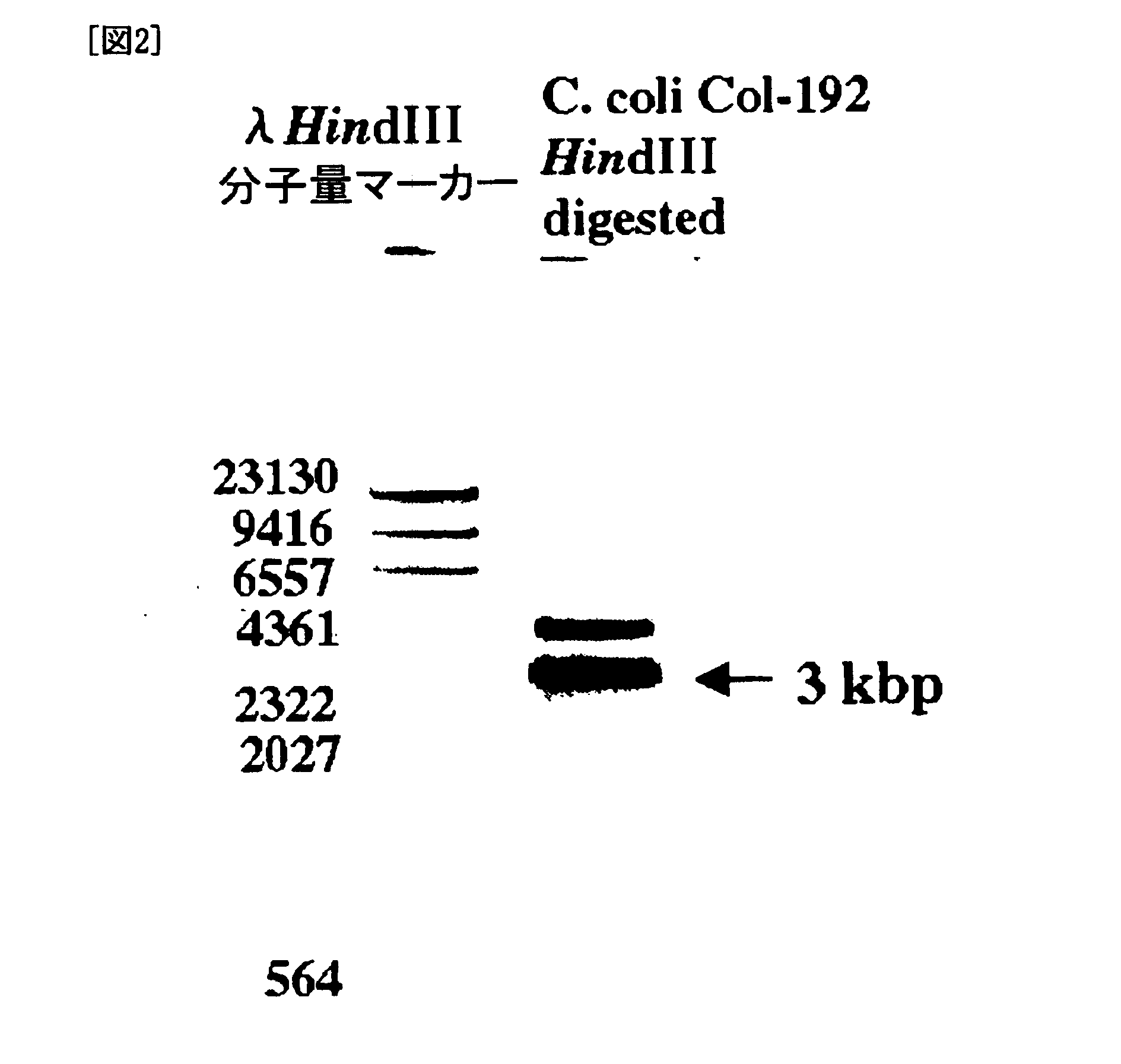
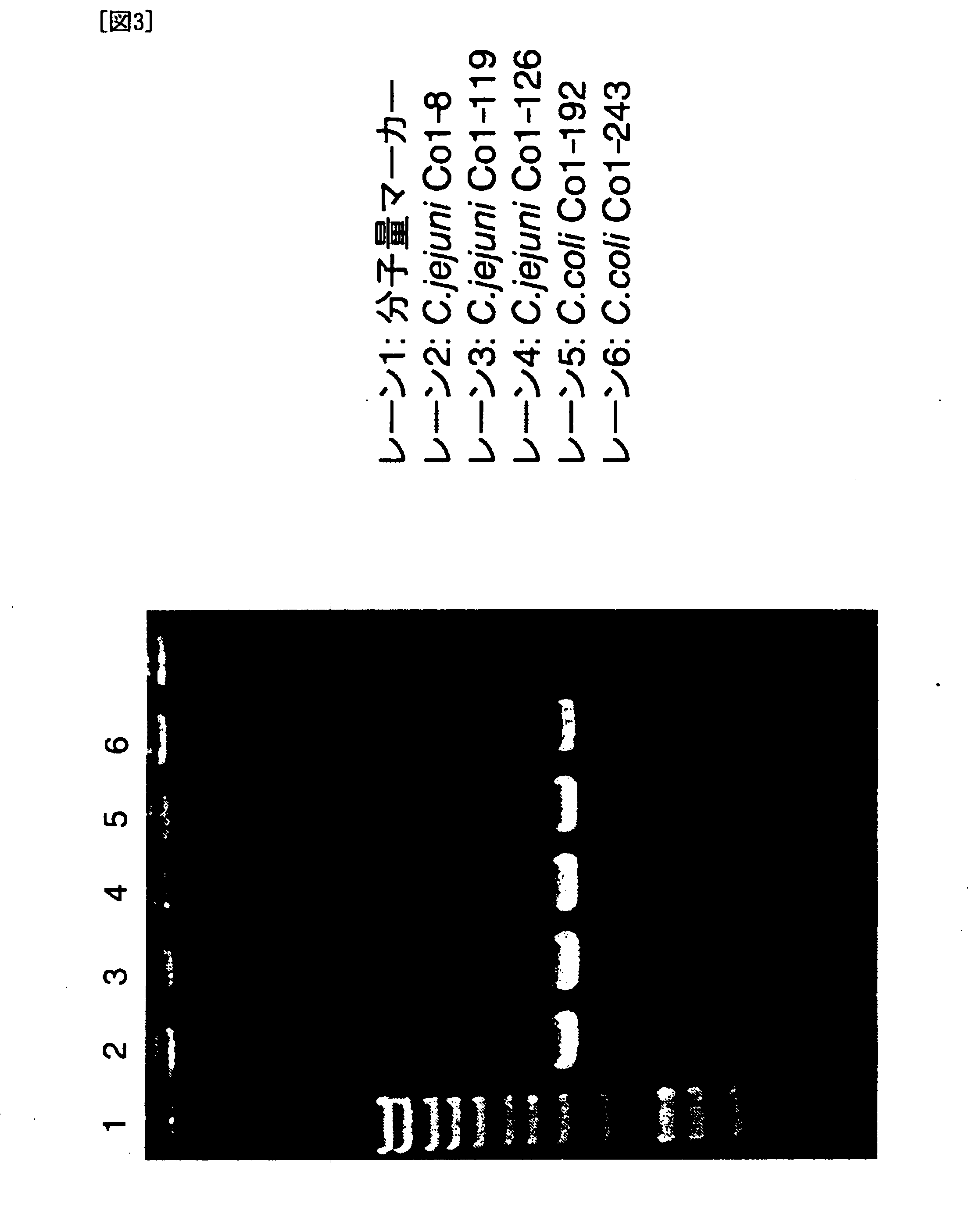
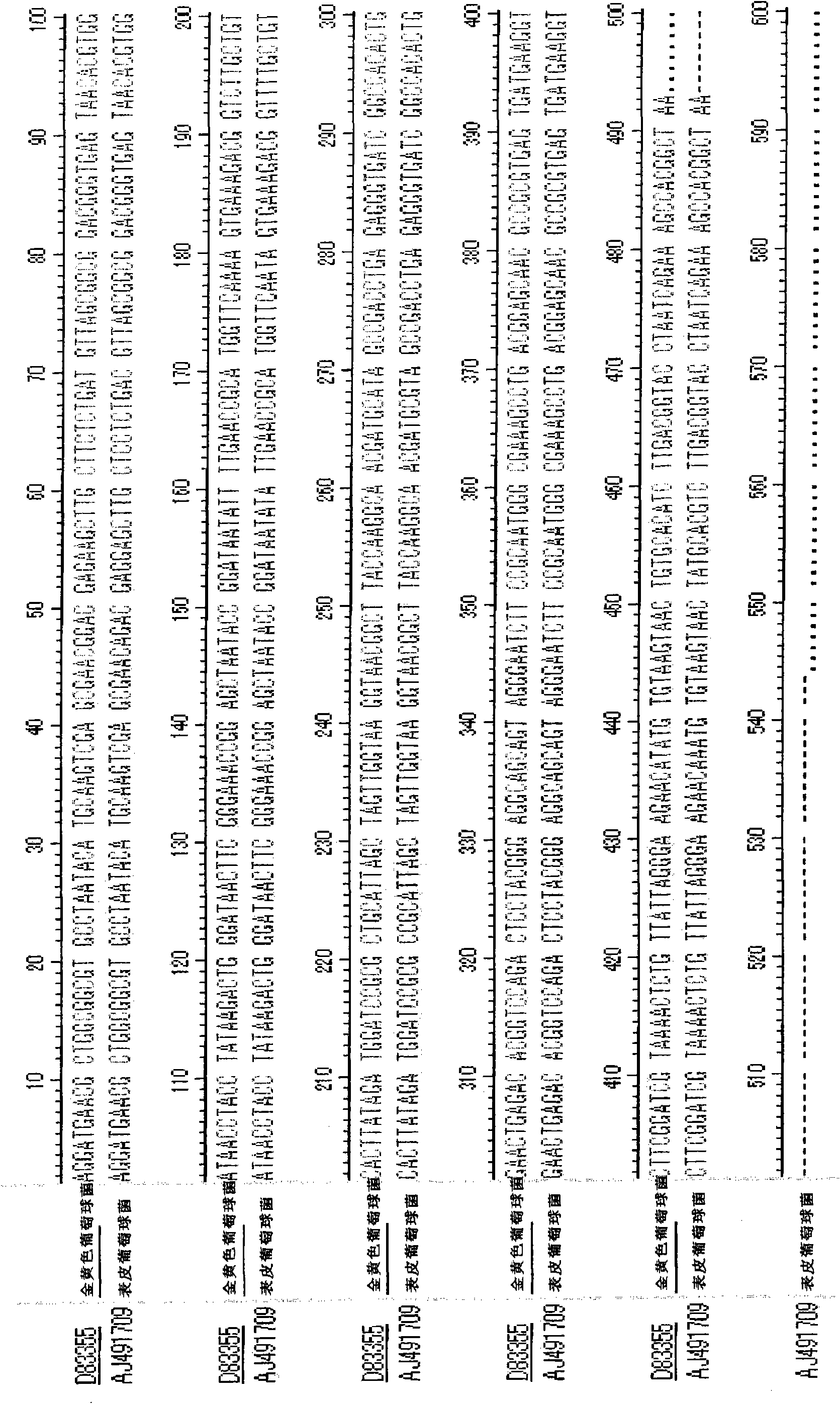
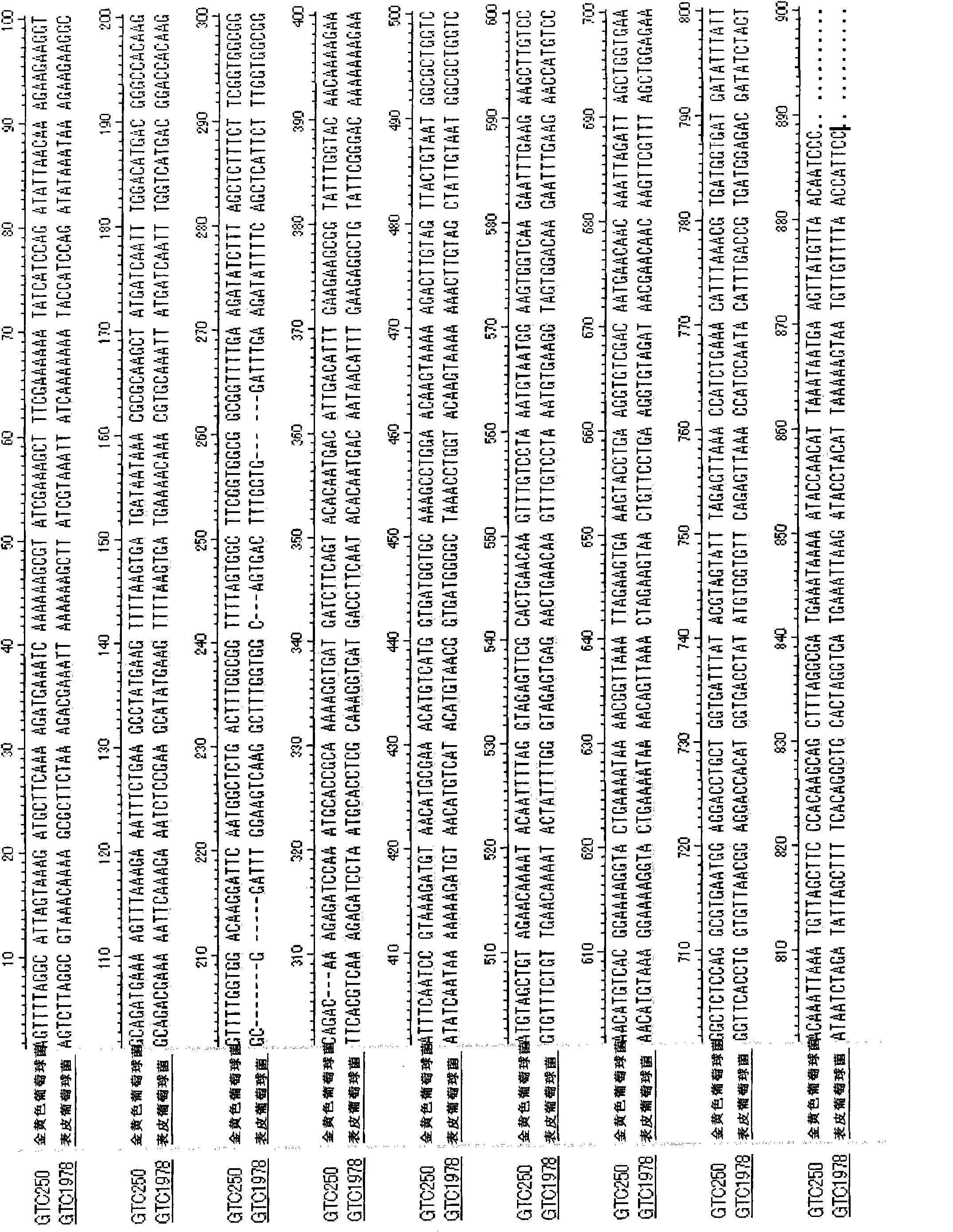
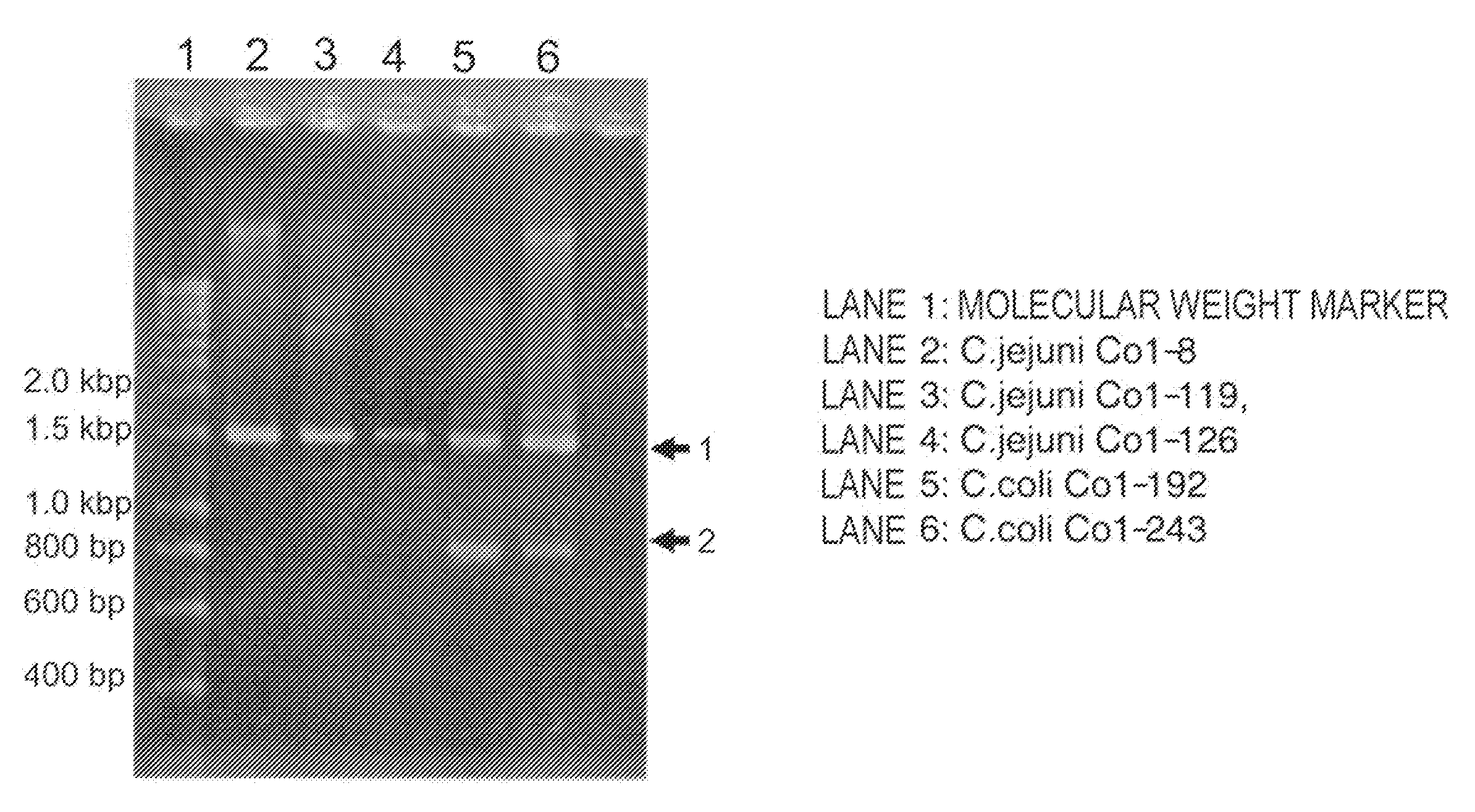
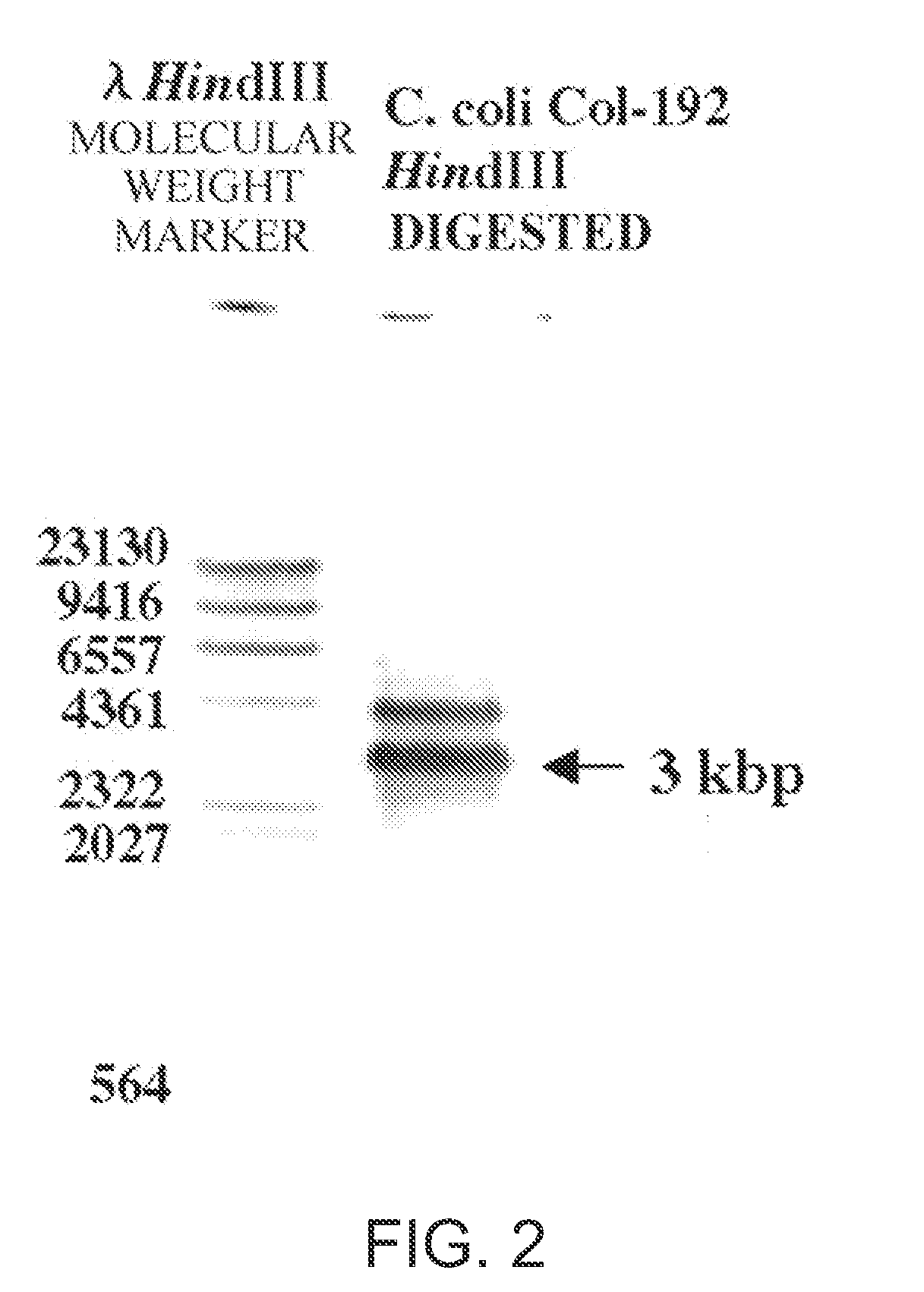
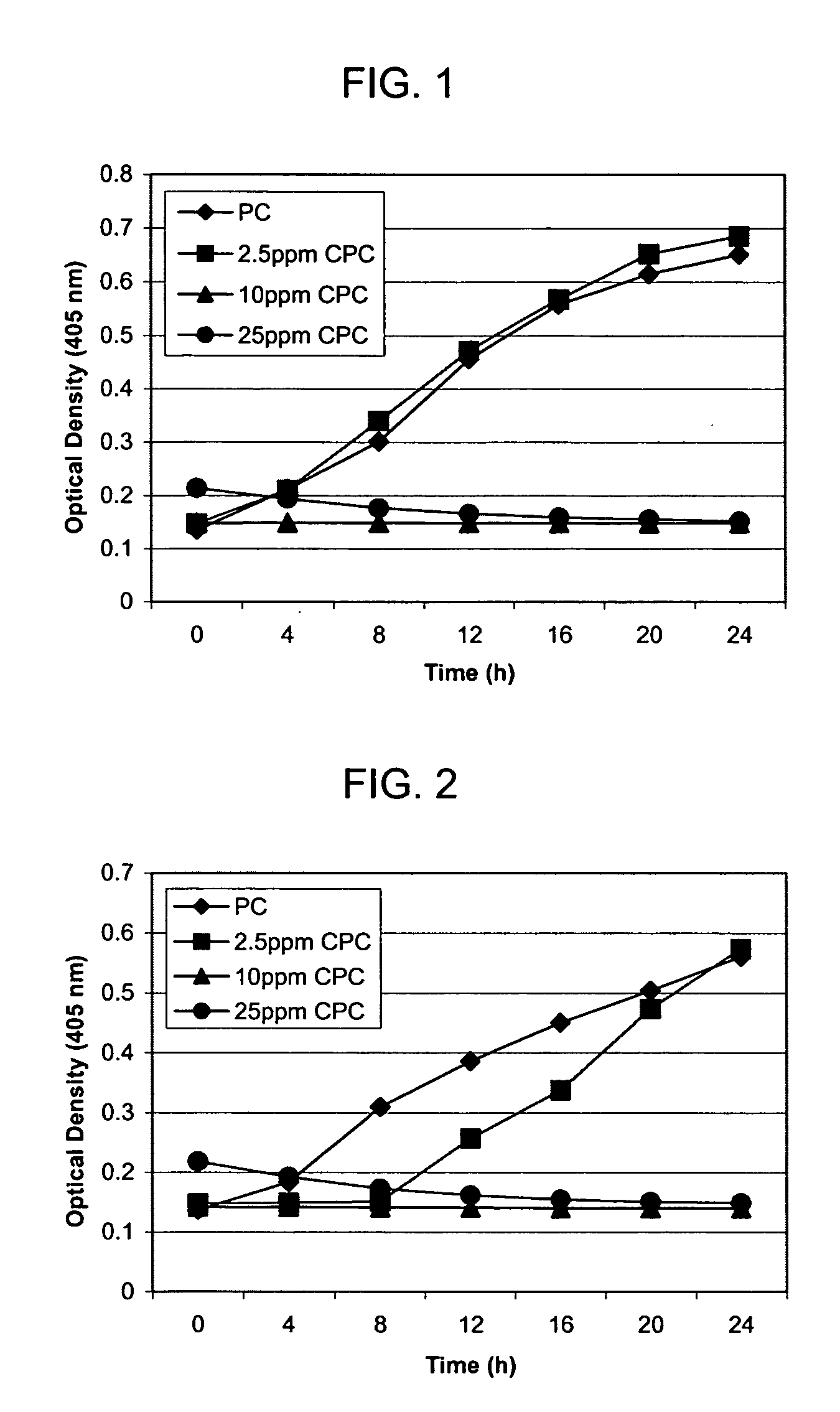
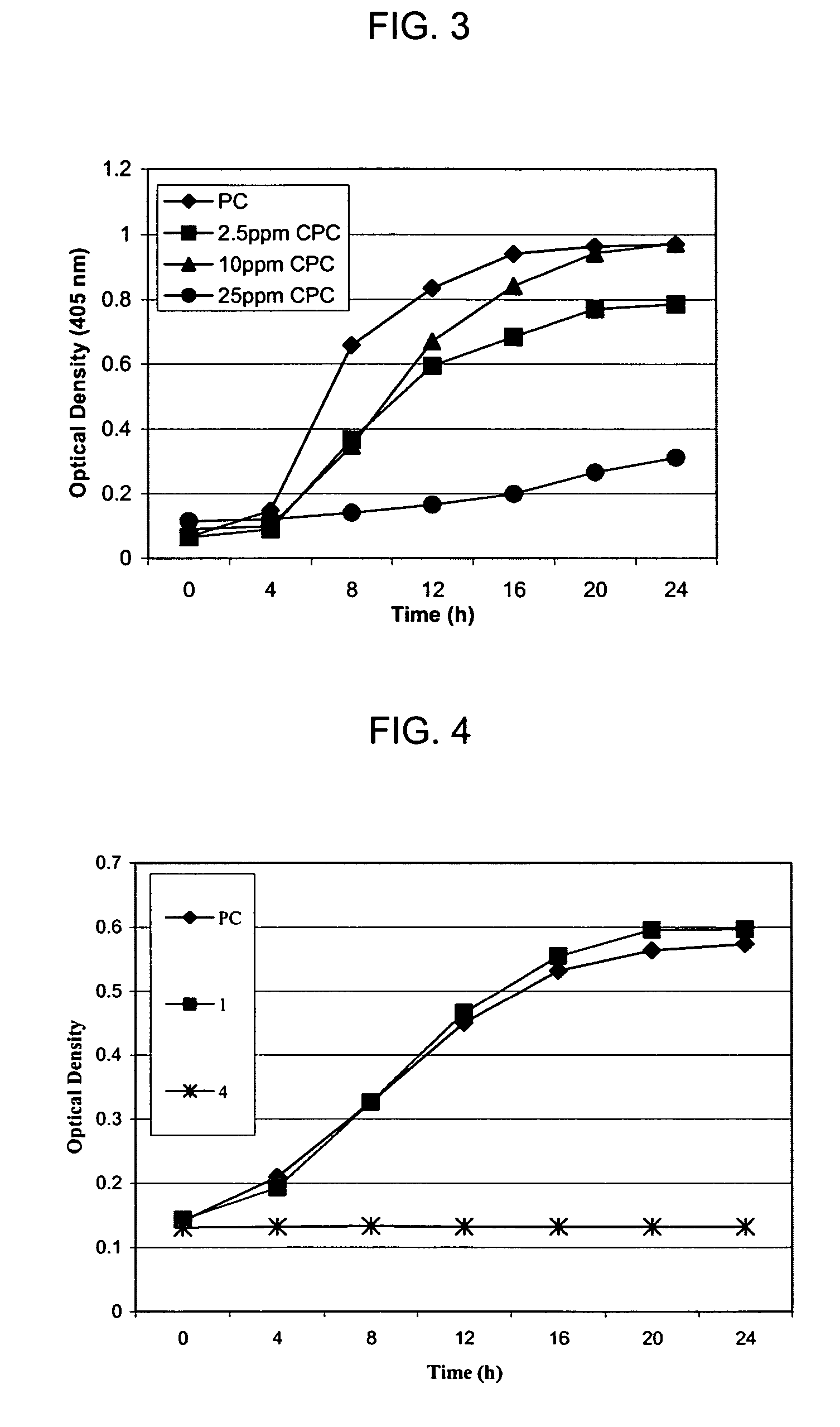
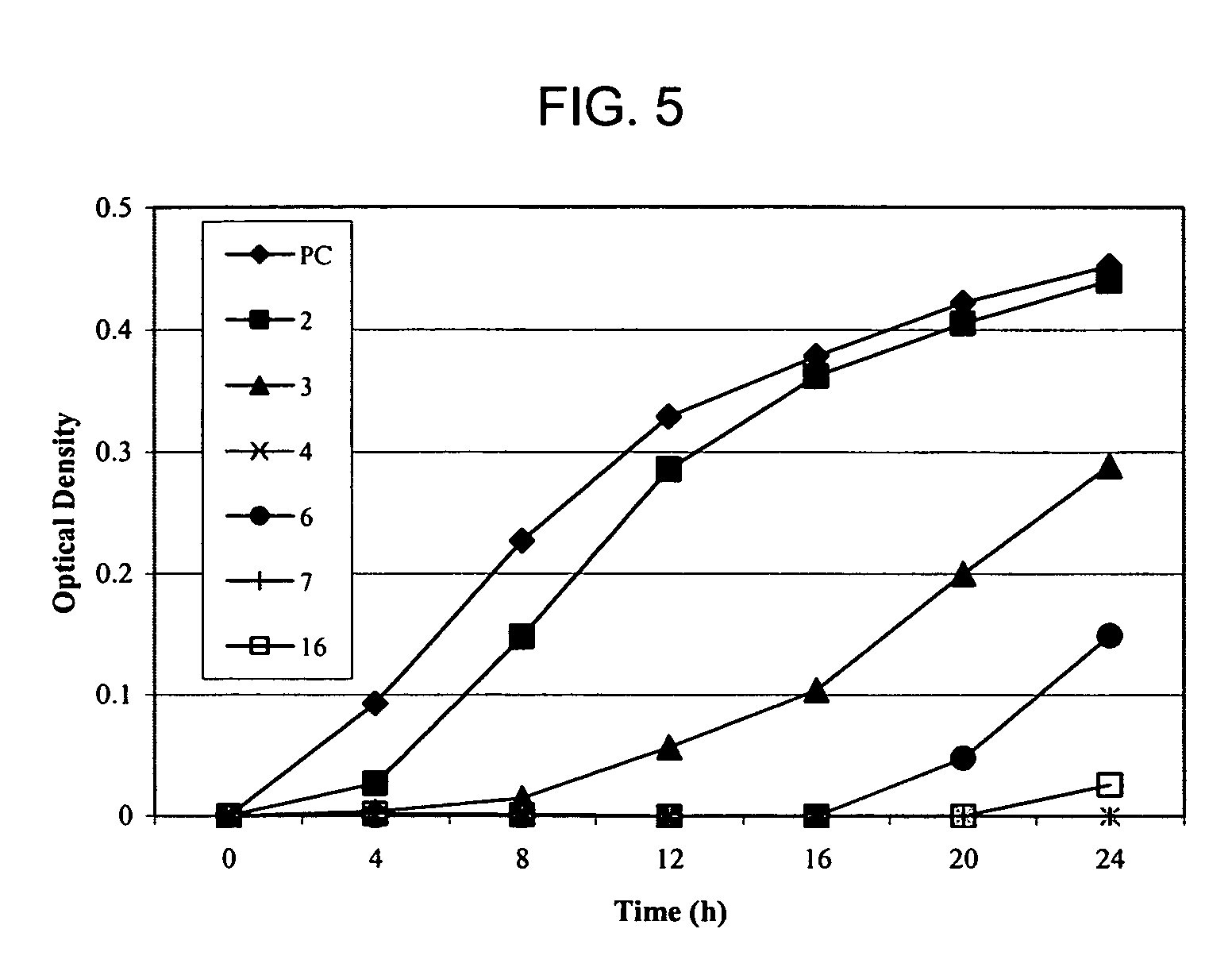
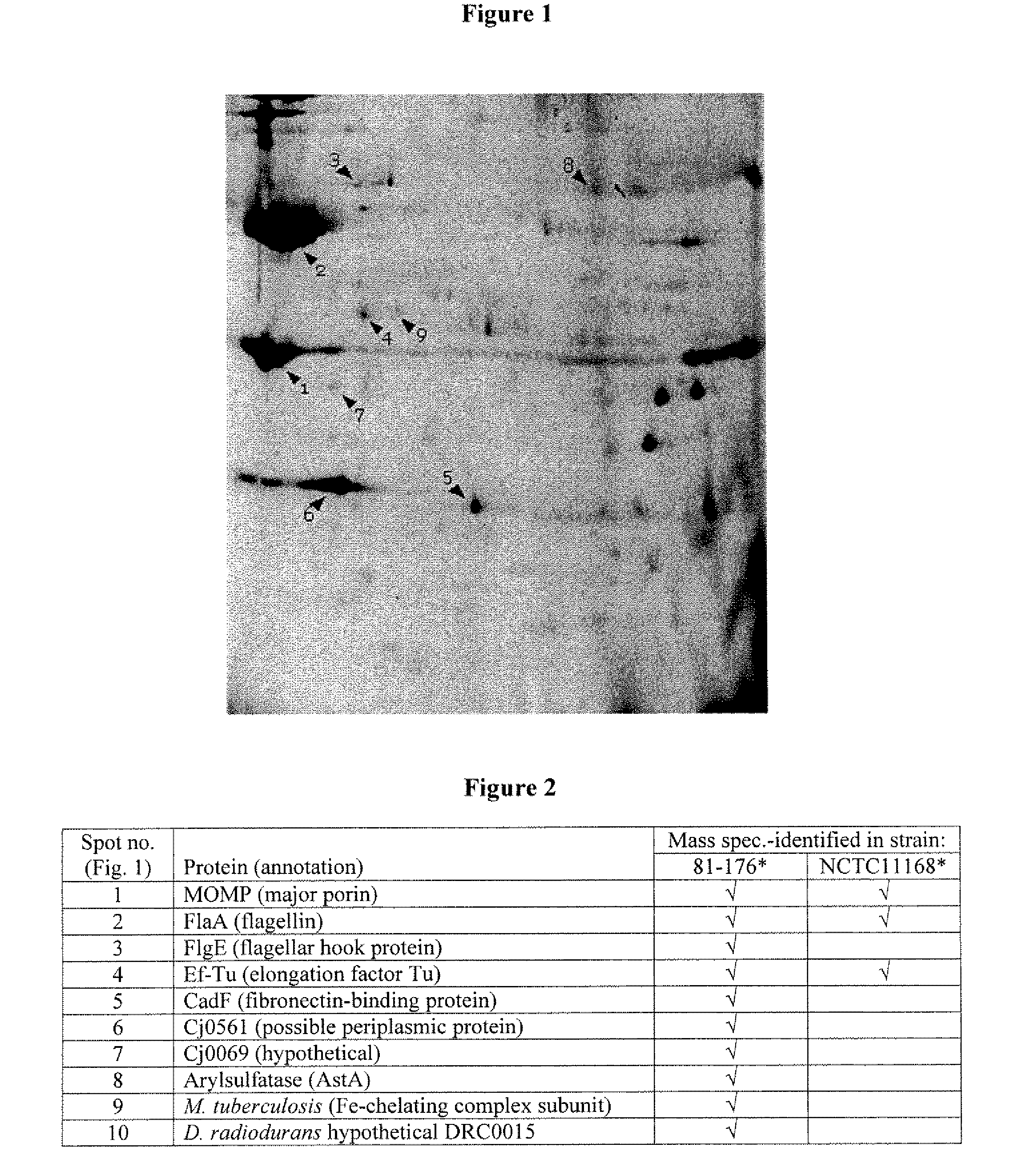
Patents
Literature
100 results about "Genus Campylobacter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Campylobacter (meaning "curved bacteria") is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. Campylobacter typically appear comma or s-shaped and motile.
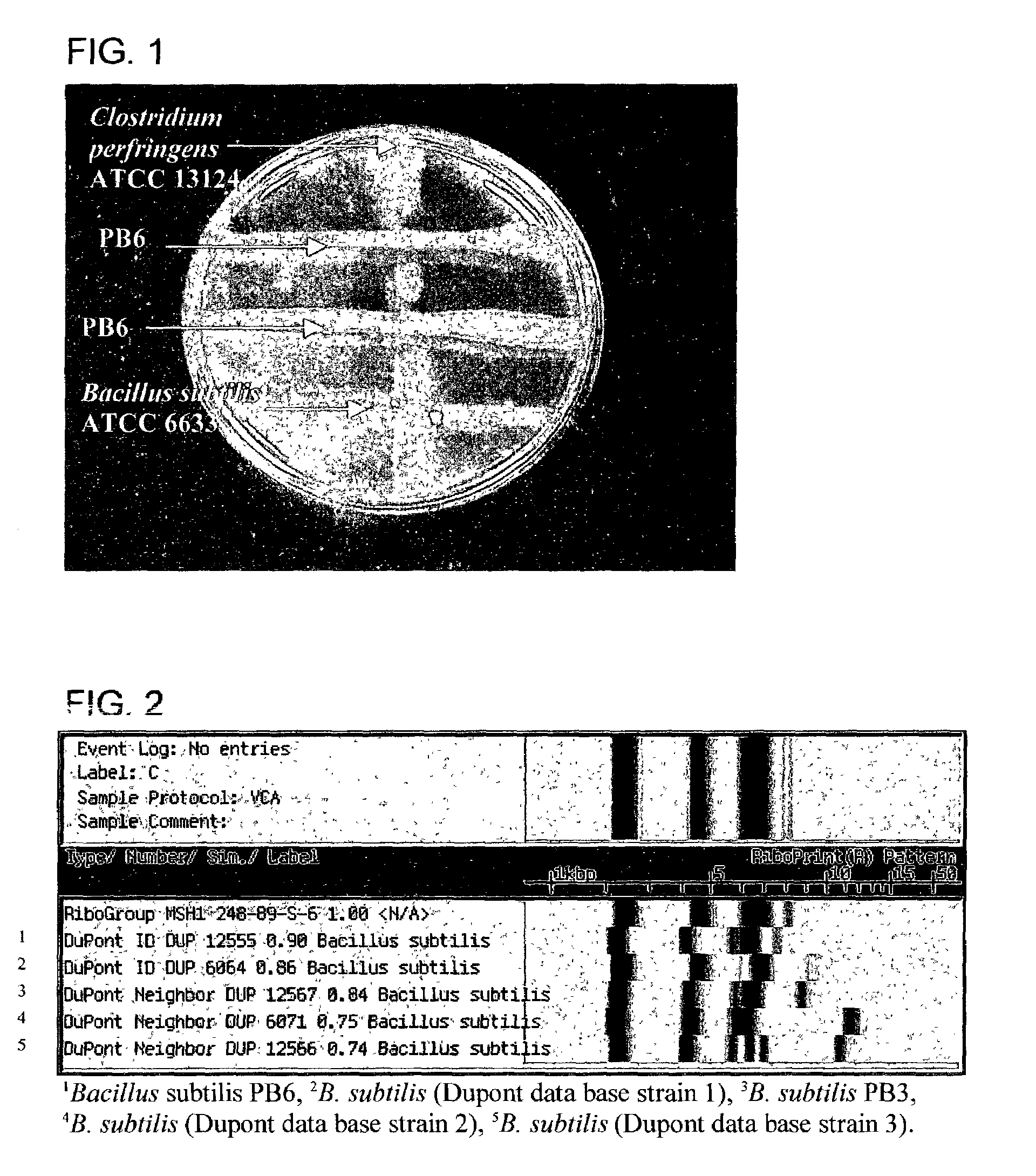
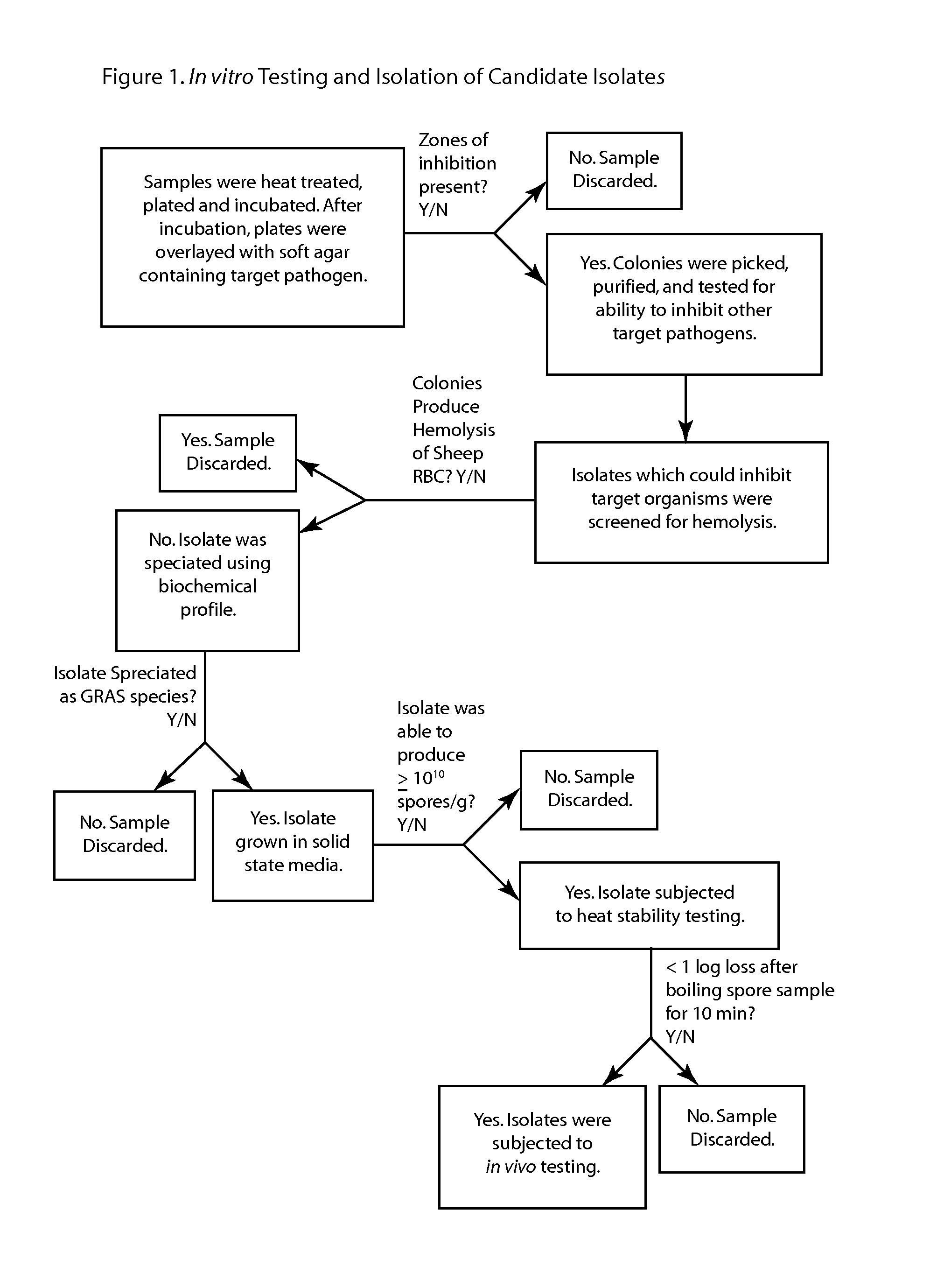
Antimicrobial compounds from Bacillus subtilis for use against animal and human pathogens
ActiveUS7247299B2Enhanced inhibitory effectRetain viabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacillus perfringensClostridium difficile (bacteria)
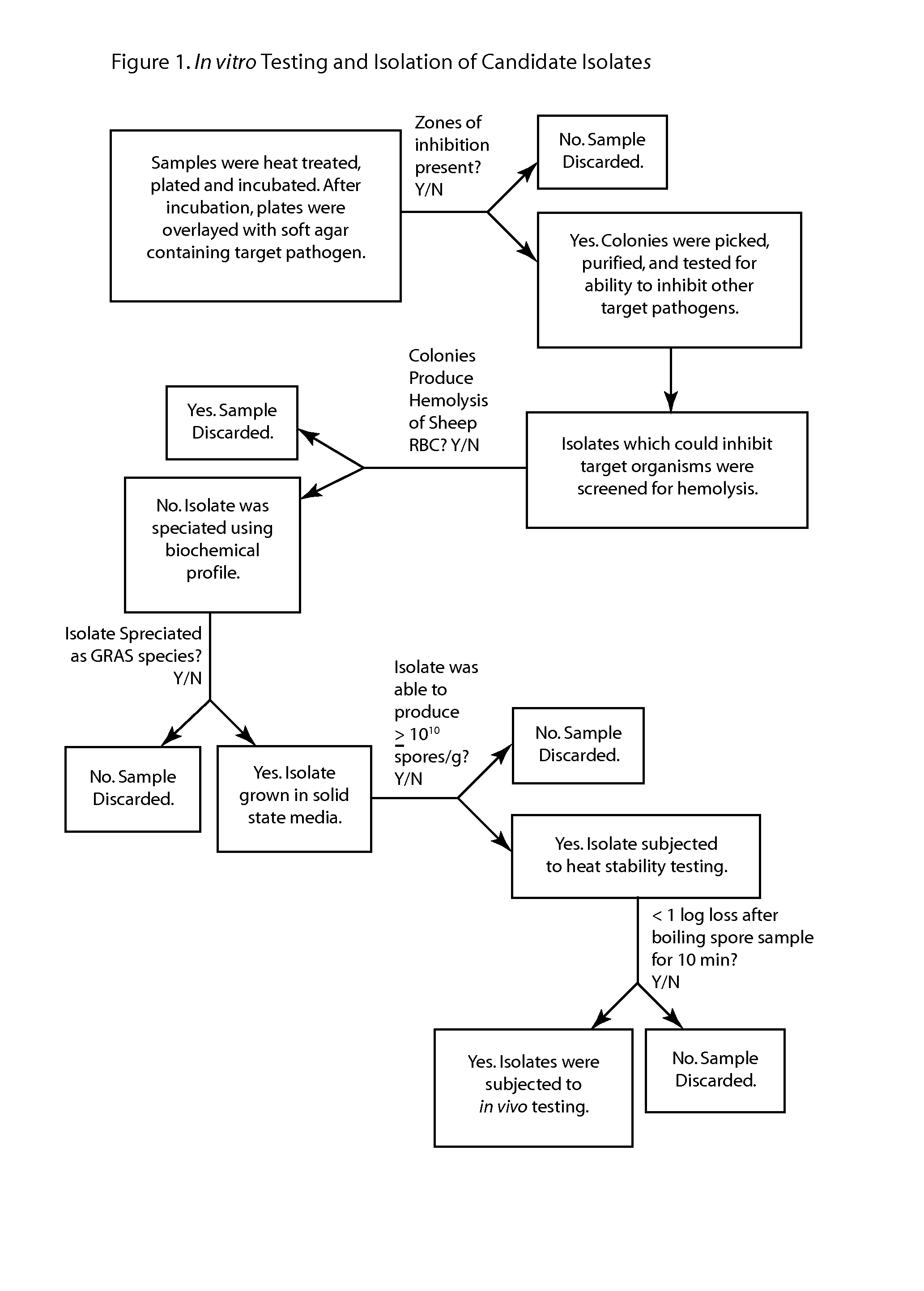
Antimicrobial compounds from Bacillus subtilis for use against animal and human pathogens. A novel strain of Bacillus subtilis was isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of poultry and was found to produce a factor or factors that have excellent inhibitory effects on Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium difficile, Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. The factor(s) retain full viability and antimicrobial activity after heat treatment. The invention provides a method of treatment of pathogenic microorganisms including C. perfringens.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Mammalian animal composition
InactiveUS7427398B2Avoid loweringReduces and prevents riskBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismGenus Campylobacter
The present invention relates to the use of probiotic microorganism in the manufacture of a composition for the prevention or reduction of gastrointestinal Campylobacter infection in a mammalian animal. It also relates to a method for the prevention or reduction of gastrointestinal Campylobacter infection in a mammalian animal, the method comprising administering to said animal, a probiotic microorganism. The invention also relates to a probiotic microorganism, for use in preventing or reducing gastrointestinal Campylobacter infection in a mammalian animal.
Owner:MARS INC
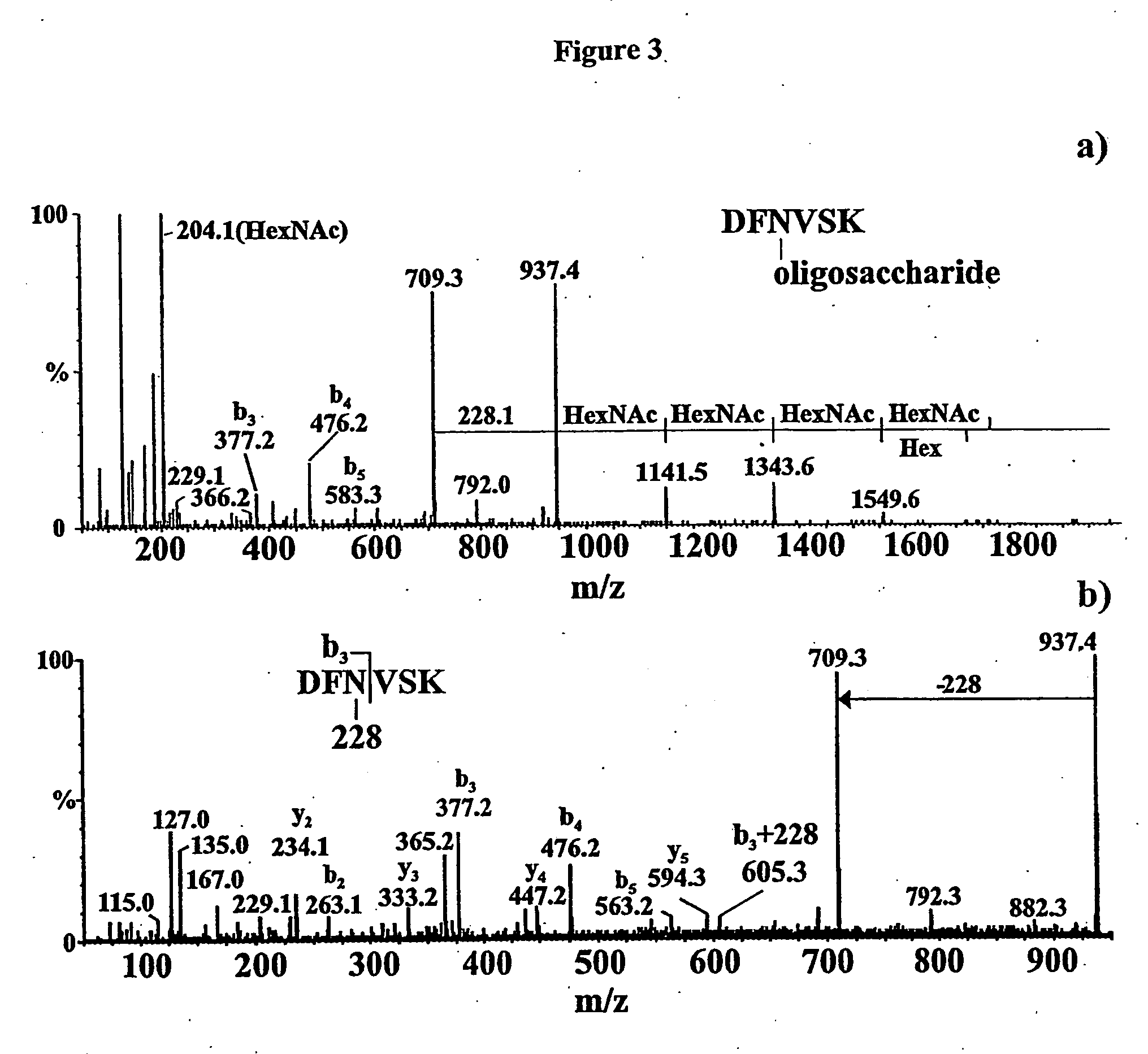
Campylobacter glycans and glycopeptides
ActiveUS20060165728A1Prevent groundwater pollutionEliminating and reducing presenceAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMagic angle spinningGlycopeptide
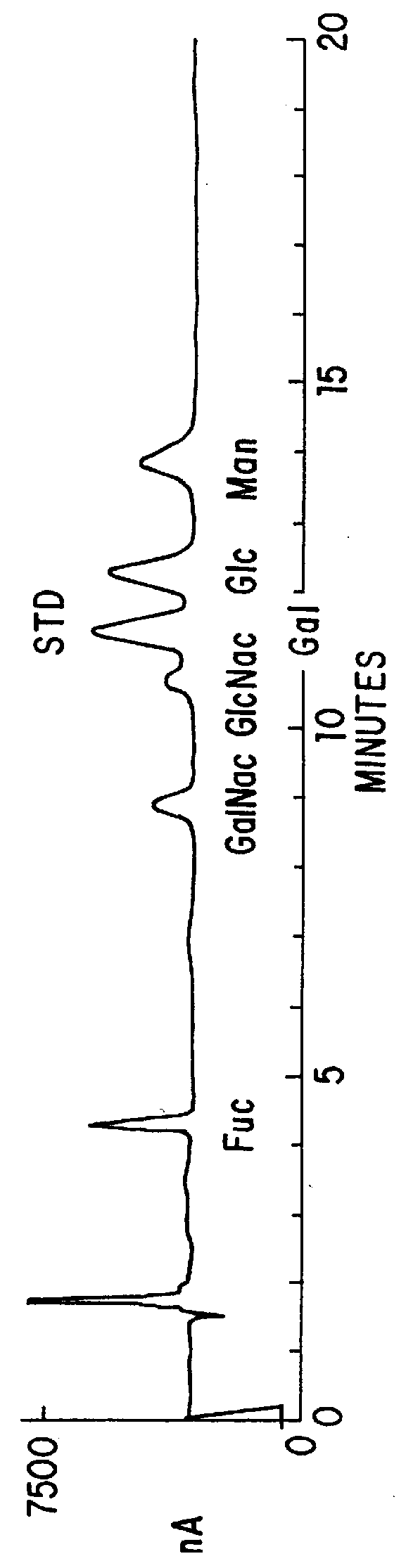
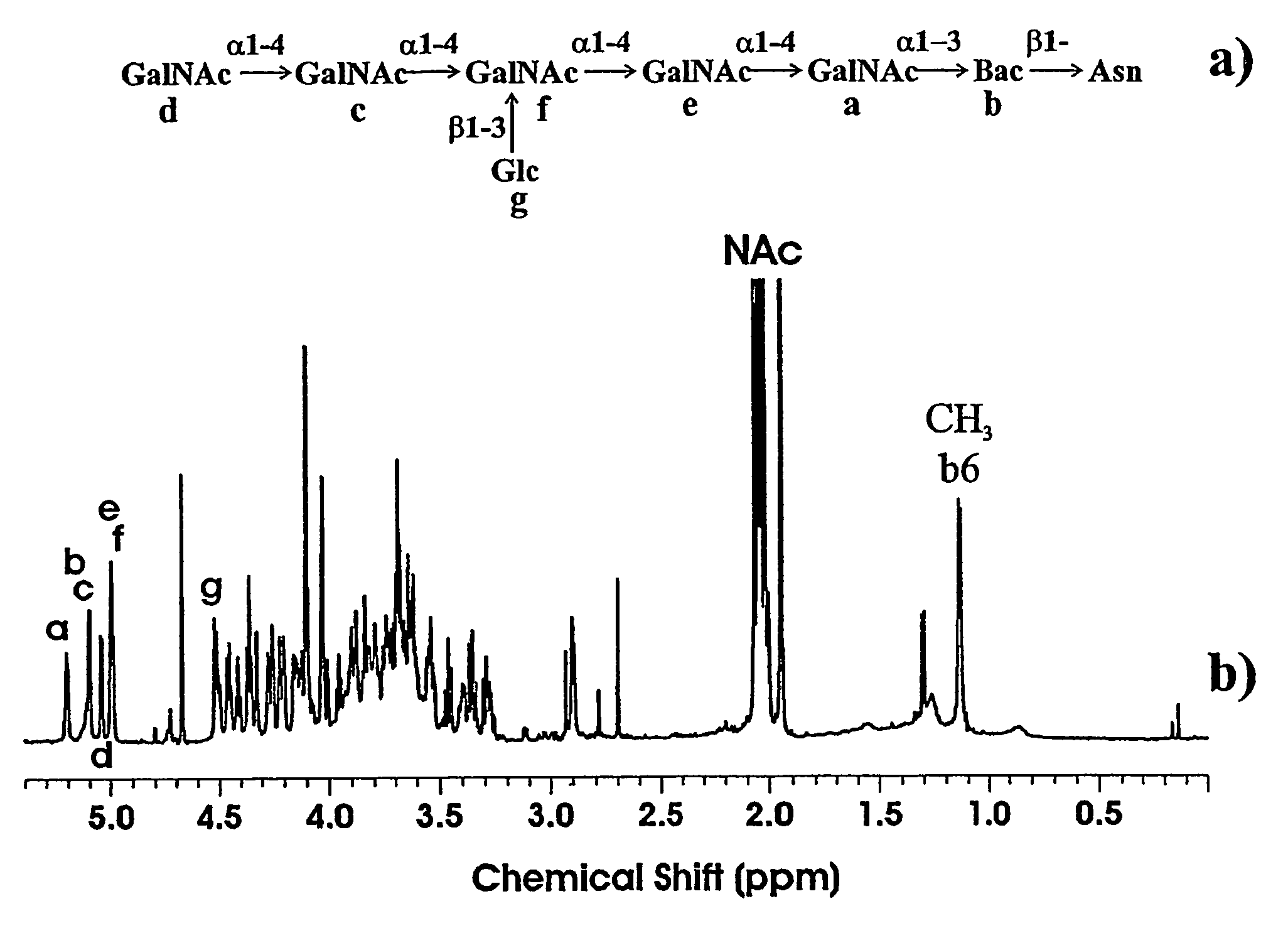
Multiple strains and species of Campylobacter were found to share a common glycan moitie which is present in a plurality of surface-exposed glycoproteins. This glycan has the formula: GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,4-[Glc-β1,3]GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,3-Bac, wherein Bac is 2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-D-glucopyranose. This glycan and immunologically active fragments of it have use as vaccines against campylobacter infection in humans and animals. As well, antibodies which specifically bind these compounds may be provided. Such antibodies and vaccines may be used to prevent or neutralize campylobacter infections in livestock thereby preventing this pathogen from entering the human food chain. The glycan may be linked to one or more amino acids to form a glycopeptide. As well, a method for determining the glycan structure of an intact glycoprotein consists of subjecting a sample to high resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS-NMR) spectroscopy.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Oligonucleotide probe kit for detecting common intestine trac kpathogenic bacteria and its use
InactiveCN1683565AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesAntigenBio engineering
The present invention belongs to the field of microbe detecting technology. The oligonucleotide probe for detecting common intestinal tract pathogenic bacteria is designed on 16S rRNA and 23S rRNA of bacteria, ipaH of dysentery bacillus giant plasmid, VipR of Salmonella typhi and other gene sequence, has length of 25-50 bp, and relatively high sensitivity and specificity. The oligonucleotide probe is suitable for detection based on nucleic acid hybridization principle, especially detection based on gene chip principle. Under certain use condition, it can detect Listeria, parahemolutic vibrio, Campylobacter, etc. It may be used in many aspects, such as disease diagnosis, environment detection, food poisoning detection, etc.
Owner:RADIOLOGY INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE SCI PLA
Cytolethal Distending Toxins and Detection of Campylobacter Bacteria Using the Same as a Target
ActiveUS20070212691A1Quick checkRapid and convenient determinationBacteriaImmunoglobulins against bacteriaTypingCytolethal distending toxin
The present inventors succeeded in cloning the CDT genes of C. coli and C. fetus, which were previously unknown, and in determining their sequences. In addition, the inventors also developed specific primers and primers common to the two species by comparing the CDTs of C. jejuni and C. fetus. Furthermore, the inventors demonstrated that these primers were applicable to multiplex PCR that simultaneously allows for the rapid and convenient determination of the presence of Campylobacter CDT and identification of species, and that they can also be used in PCR-RFLP-based typing.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
Detection of bacterium by utilizing dnaj gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101558168AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyBacteroidesStaphylococcus species
Disclosed is a method for detecting the species of a bacterium in a simple manner. Specifically disclosed is a method for detecting the species of a bacterium, which can detect at least one bacterial species selected from Staphylococcus species, Streptococcus species, Klebsiella species, Escherichia species, Mycobacterium species, Legionella species, Vibrio species, Bacillus species, Neisseria species, Campylobacter species, Chlamydia species, Chlamydophila species, Mycoplasma species, Listeria species, Salmonella species and Yersinia species, and which comprises the steps of: a) contacting a sample suspected to contain a nucleic acid derived from the bacterium species to be detected with a nucleic acid molecule capable of hybridizing with at least a part of a DnaJ gene derived from the bacterial species; and b) detecting the presence or absence of the hybridization between the nucleic acid molecule and the nucleic acid contained in the sample.
Owner:GIFU UNIVERSITY +1
Methods and compositions including spore-forming bacteria for increasing the health of animals
ActiveUS20130136695A1Good for healthIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesBiology
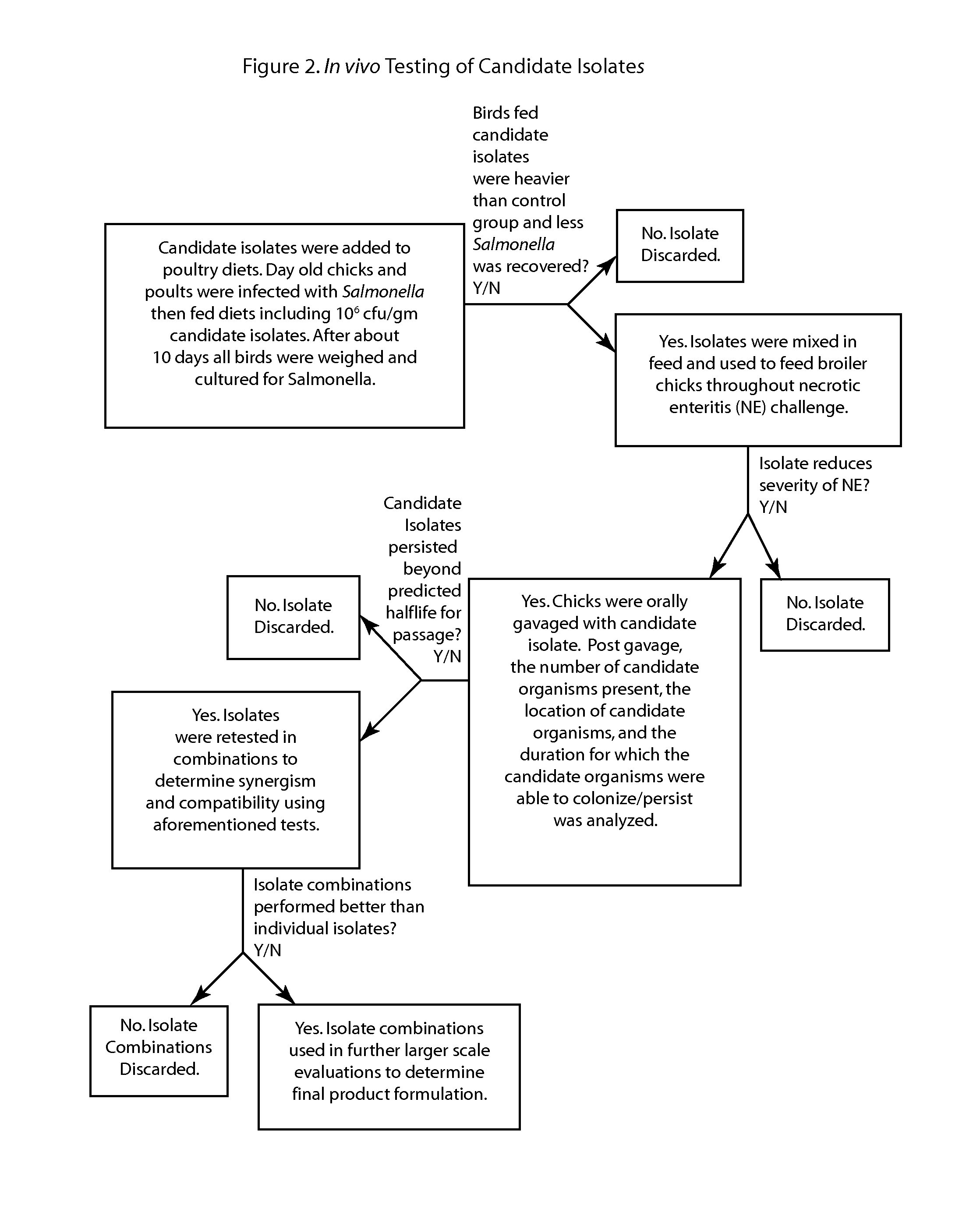
Methods, compositions and bacterial isolates for improving the gastrointestinal health of animals and in particular of poultry are provided herein. The methods include administering an endospore-forming bacteria to an animal. The bacteria are selected for the ability to reduce the growth and presence of bacterial pathogens, such as Salmonella, Clostridium, and Campylobacter, in the gastrointestinal tract of the animal. The bacteria are also selected for the ability to improve at least one production parameter in the animal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Antibodies against flagellin and uses thereof
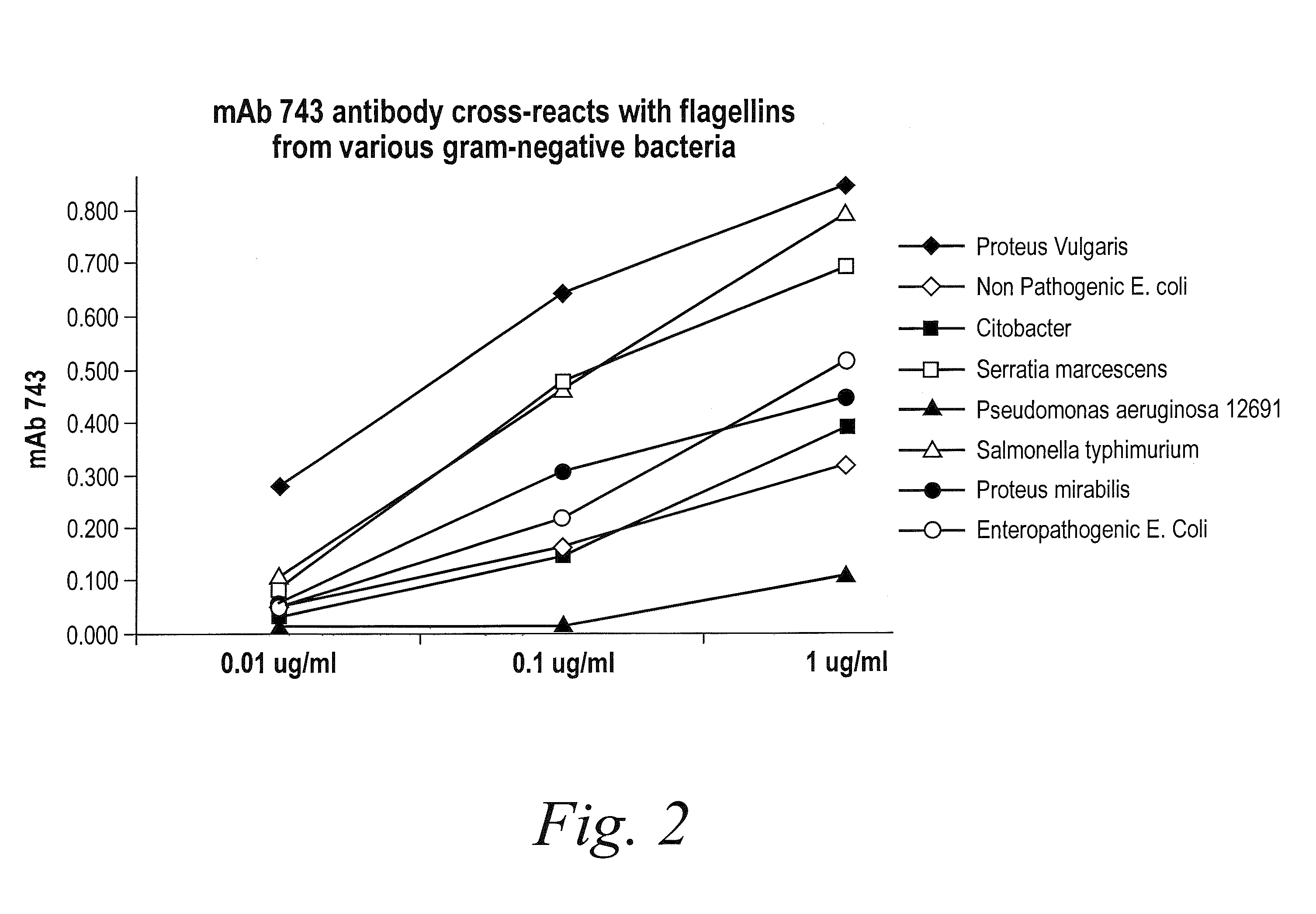
The present invention provides a novel class of monoclonal antibodies which have a high affinity, broad spectrum neutralizing reactivity to flagellin from various Gram-negative bacteria including, but not limited to, E. coli, Salmonella, Serratia, Proteus, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Campylobacter and Pseudomonas. The present invention further provides methods of treating infections and diseases using anti-flagellin antibodies in humans, other animals and birds.
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
Combinant polypeptide for use in the manufacture of vaccines against Campylobacter induced diarrhea and to reduce colonization
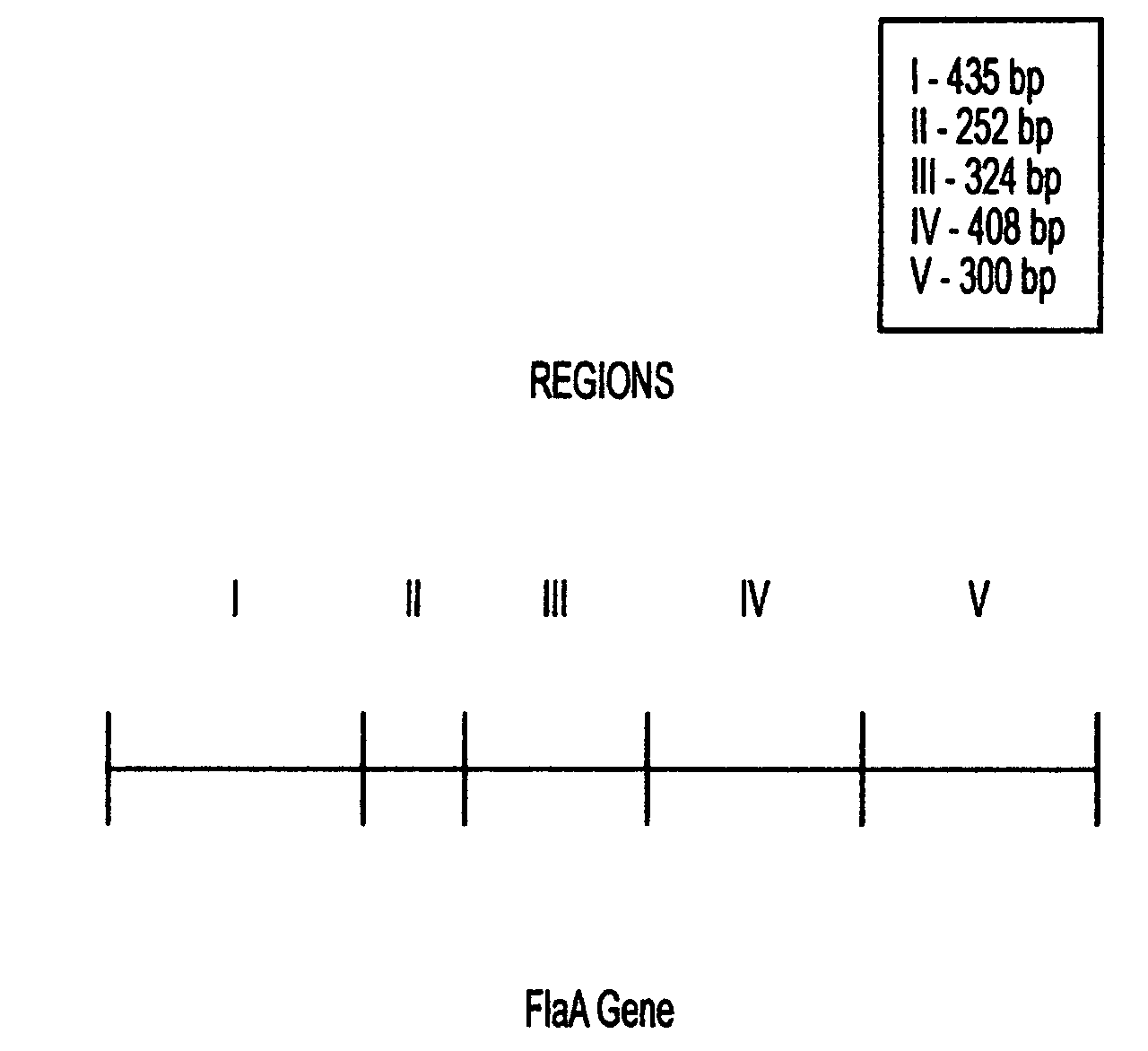
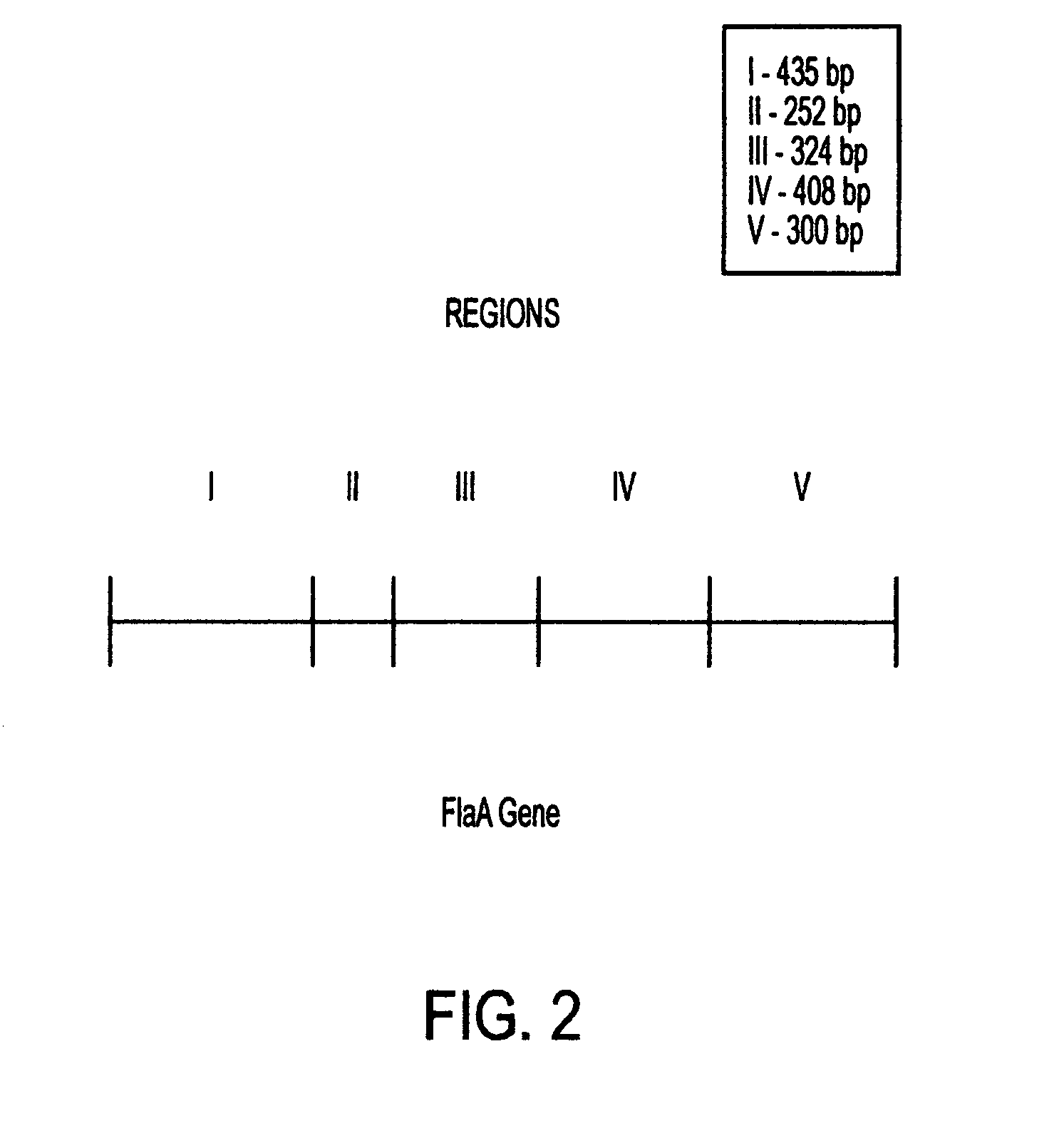
This invention comprises a recombinant protein comprising the maltose binding protein (MBP) of Escherichia coli fused to amino acids 5–337 of the FlaA flagellin of Campylobacter coli VC167 which has provided evidence of immunogenicity and protective efficacy against challenge by a heterologous strain of campylobacter, Campylobacter jejuni 81–176 in mammals. The invention further comprises a recombinant DNA construct encoding the immunodominant region (region I through III) of flagellin from Campylobacter spp. for use as a component of a vaccine against Campylobacter diarrhea. The invention therefore represents an effective treatment against Campylobacter but avoids inducing the autoimmune Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS), a post-infection polyneuropathy caused by Campylobacter molecular mimicry of human gangliosides which has hampered the development of vaccines heretofore.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Methods for specific rapid detection of pathogenic food-relevant bacteria
InactiveUS20050123946A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention relates to a method for the detection of pathogenic food-relevant bacteria, particularly to a method for the simultaneous specific detection of bacteria of the genus Listeria and the species Listeria monocytogenes by in situ-hybridization as well as to a method for the specific detection of bacteria of the species Staphylococcus aureus by in situ-hybridization as well as to a method for the specific detection of bacteria of the genus Campylobacter and the species C. coli and C. jejuni by in situ-hybridization as well as the corresponding oligonucleotide probes and kits, with which the inventive methods may be carried out.
Owner:VERMICON
One-step multiplex pcr for the identifiation and differentiation of campylobacter species
InactiveUS20060051752A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assayBacterial isolate
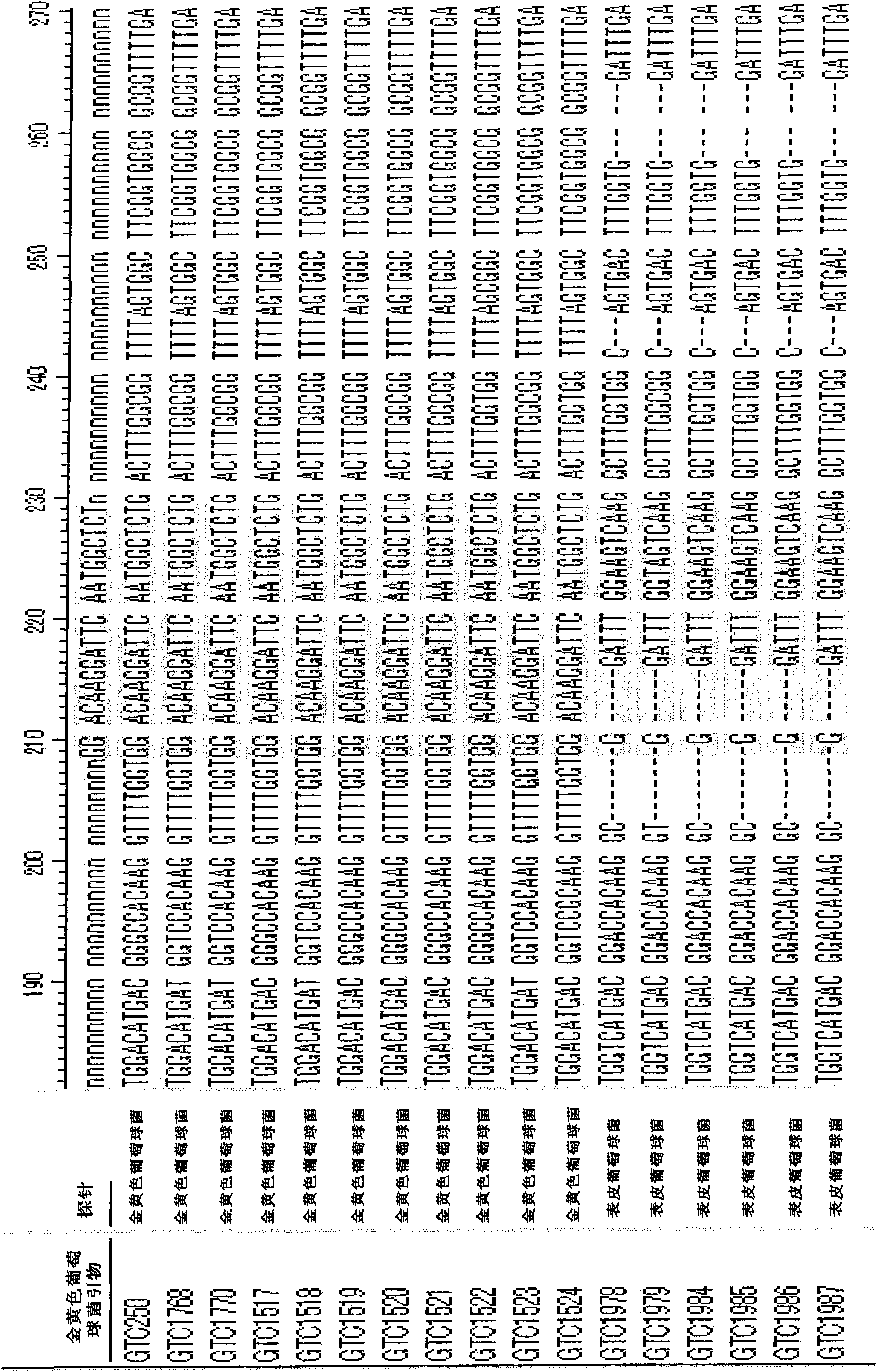
Described herein are a plurality of primers which may be used in a multiplex PCR assay in a fast, accurate, reliable and specific fashion for detecting the presence of specific Campylobacter strains within a sample. These kits can be used on bacterial isolates and has the potential for use directly on foods and environmental samples.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF HEALTH
Antibodies against flagellin and uses thereof
The present invention provides a novel class of monoclonal antibodies which have a high affinity, broad spectrum neutralizing reactivity to flagellin from various Gram-negative bacteria including, but not limited to, E. coli, Salmonella, Serratia, Proteus, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Campylobacter and Pseudomonas. The present invention further provides methods of treating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and methods of treating enterobacterial infections using anti-flagellin antibodies in humans, other animals and birds.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD +1
Methods and compositions including spore-forming bacteria for increasing the health of animals
Methods, compositions and bacterial isolates for improving the gastrointestinal health of animals and in particular of poultry are provided herein. The methods include administering an endospore-forming bacteria to an animal. The bacteria are selected for the ability to reduce the growth and presence of bacterial pathogens, such as Salmonella, Clostridium, and Campylobacter, in the gastrointestinal tract of the animal. The bacteria are also selected for the ability to improve at least one production parameter in the animal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Cytolethal distending toxins and detection of Campylobacter bacteria using the same as a target
ActiveUS7563594B2Quick checkRapid and convenient determinationBacteriaTissue cultureEscherichia coliTyping
The present inventors succeeded in cloning the CDT genes of C. coli and C. fetus, which were previously unknown, and in determining their sequences. In addition, the inventors also developed specific primers and primers common to the two species by comparing the CDTs of C. jejuni and C. fetus. Furthermore, the inventors demonstrated that these primers were applicable to multiplex PCR that simultaneously allows for the rapid and convenient determination of the presence of Campylobacter CDT and identification of species, and that they can also be used in PCR-RFLP-based typing.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
Methods for detecting Campylobacter bacteria or antibodies to Campylobacter bacteria with an immunoassay
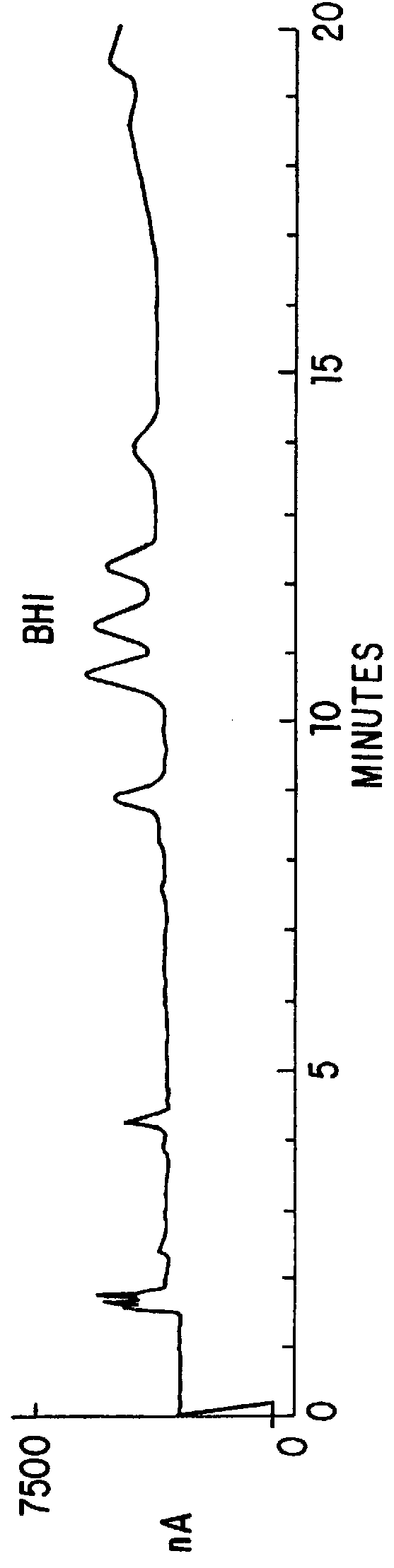
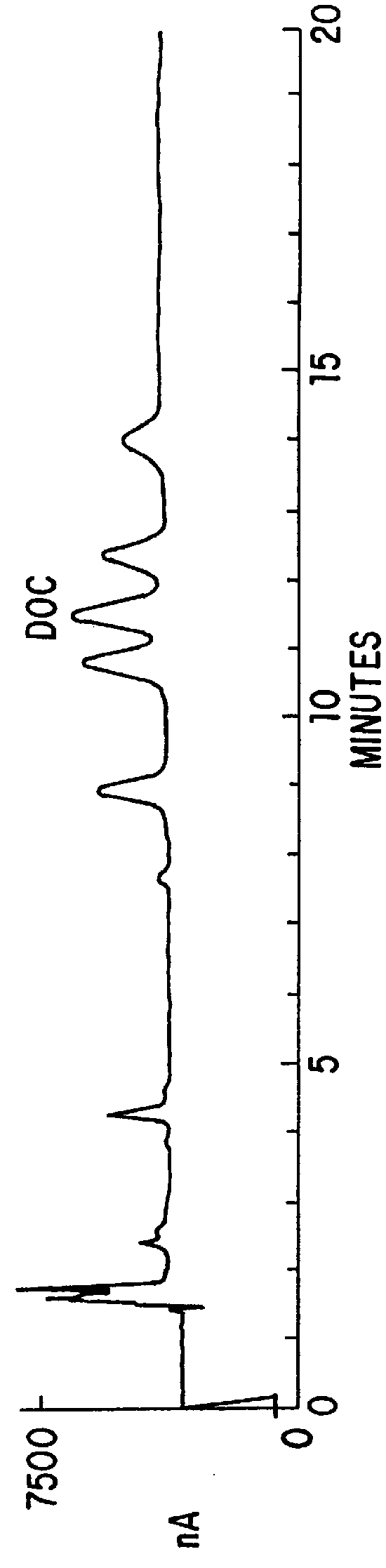
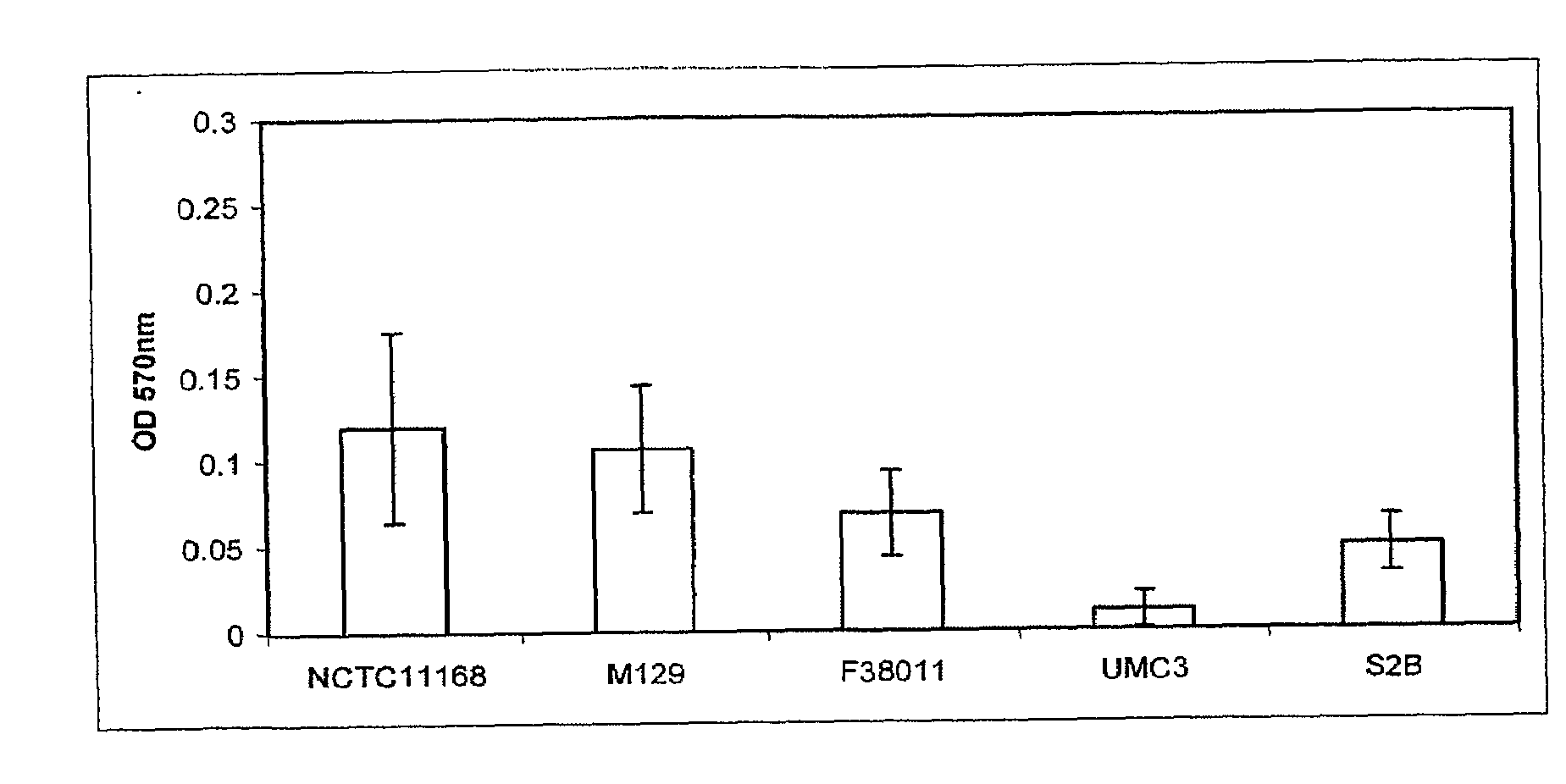
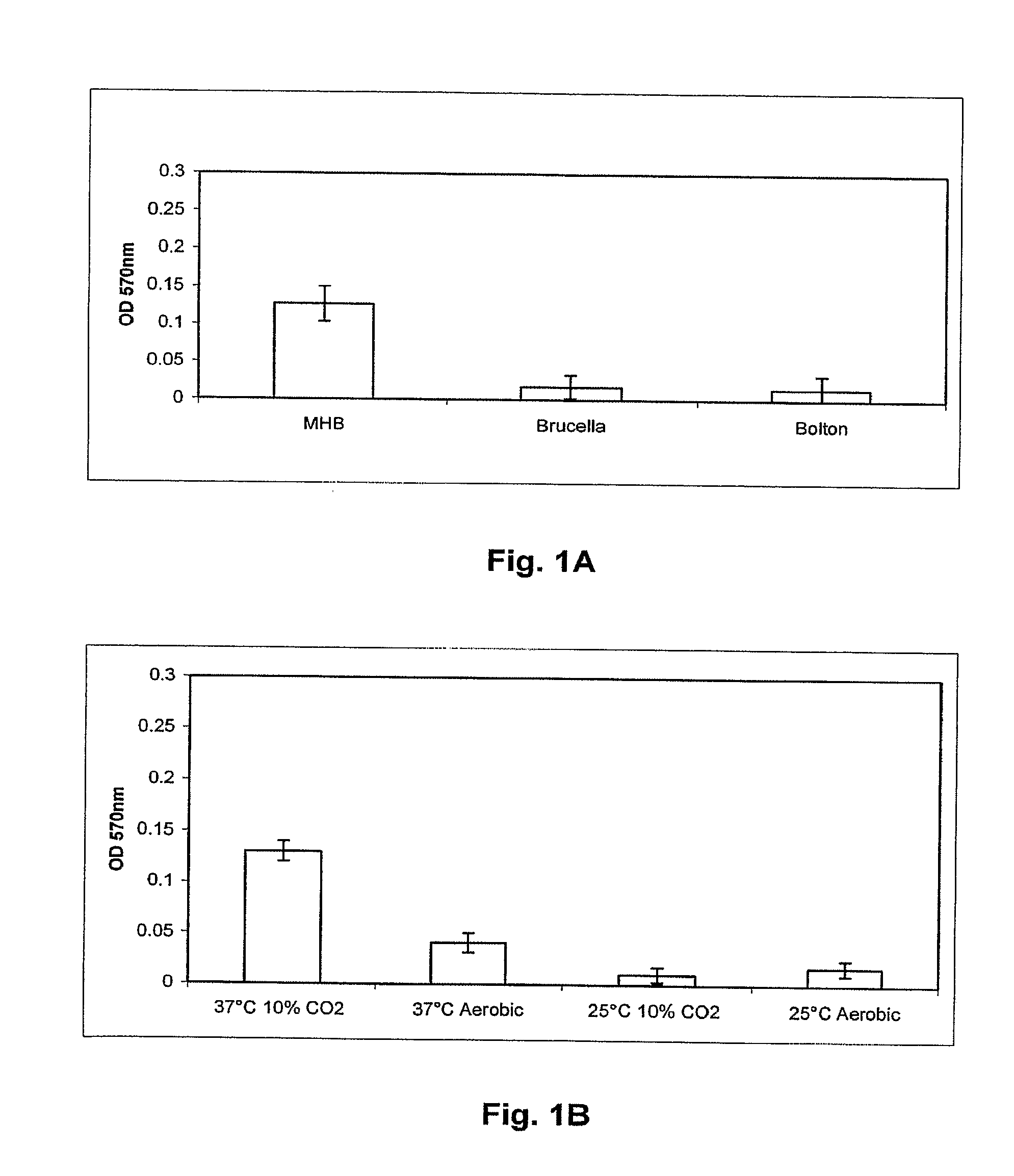
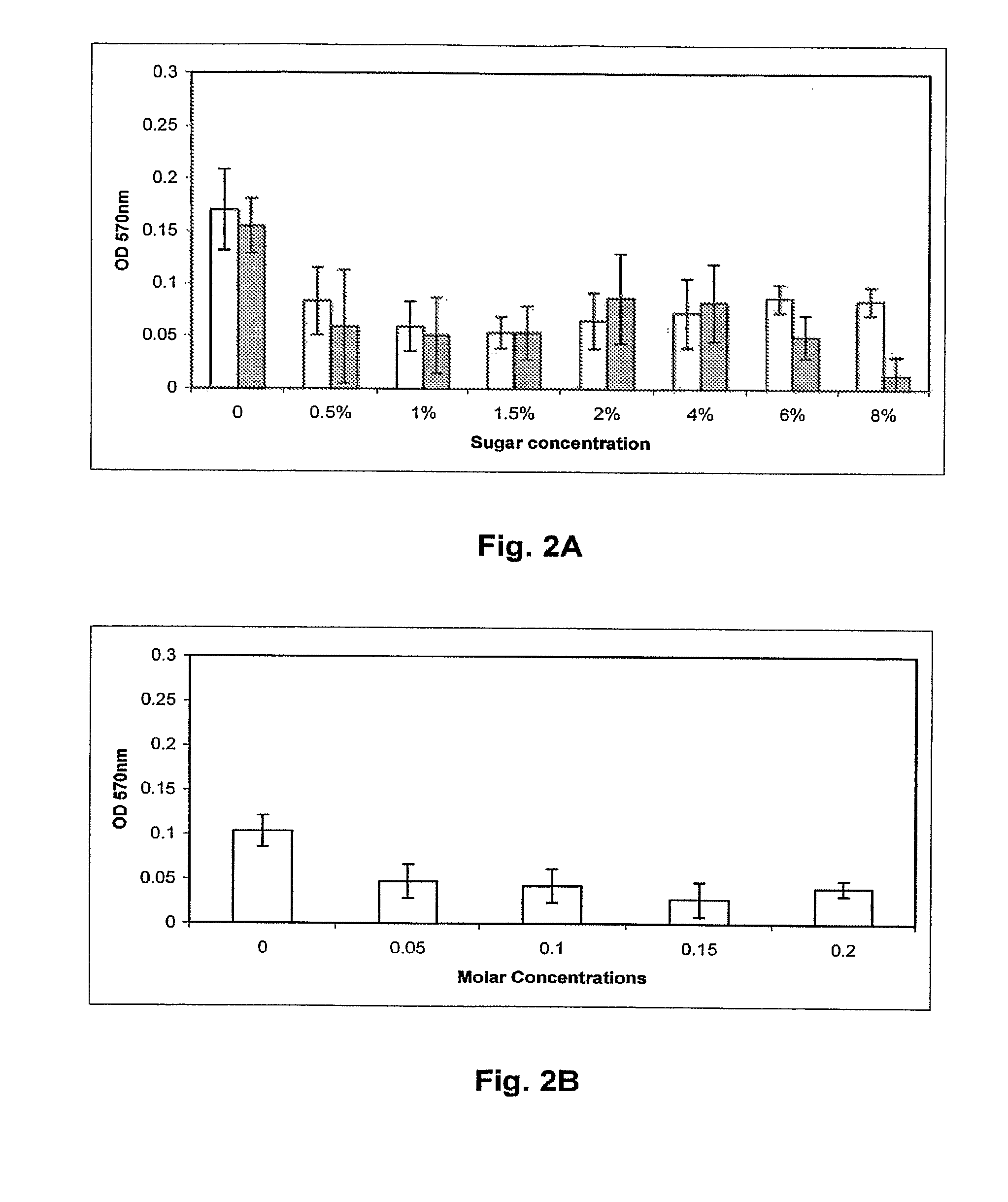
This invention relates generally to in vitro methods for inducing or enhancing expression of enteric bacterial antigens and / or virulence factors thereby producing antigenically enhanced enteric bacteria, to methods for using antigenically enhanced enteric bacteria and to vaccines comprising antigenically enhanced enteric bacteria. A Campylobacter bacterium having enhanced antigenic property is disclosed. A culture medium useful for culturing the Campylobacteria comprises 0.05% to 3% bile or 0.025% to 0.6% of one or more bile acids or salts. In addition a divalent cation chelator can also be included in the culture medium. The bacteria culture is in a growth phase at early log phase and between early log phase and stationary phase. The enhanced antigenic property is a higher level of an immunogenic antigen when compared to the antigenic property of the same bacteria grown on brain heart infusion broth. Also, antibodies to Campylobacter bacteria or Campylobacteria in samples are detected by immunoassays.
Owner:BIOPORT R&D
Campylobacteria sixtuple PCR detection kit
InactiveCN105695585AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesTrue positive rateMicrobiology
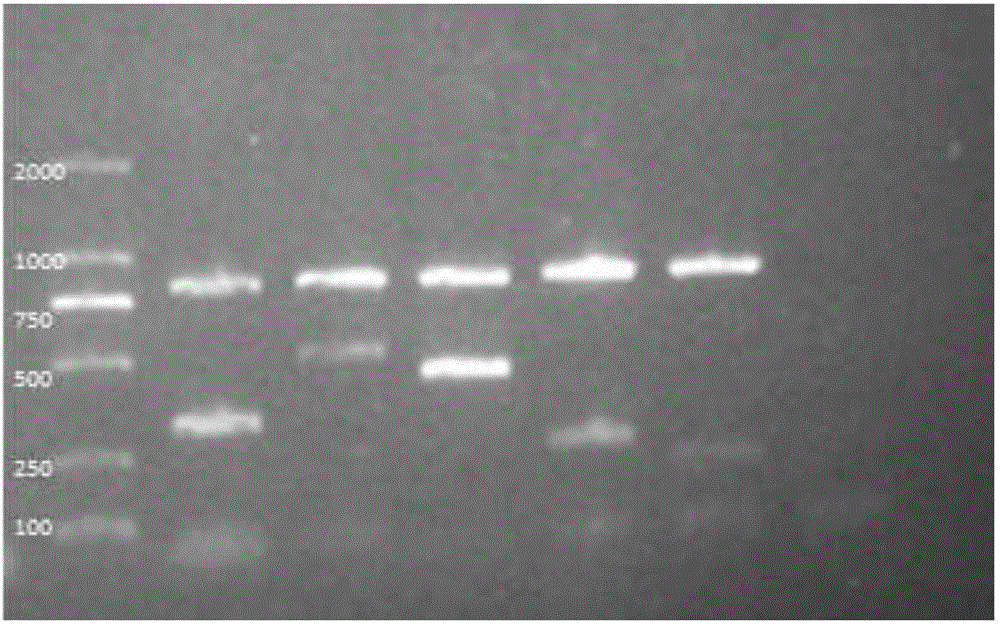
The invention provides a campylobacteria sixtuple PCR detection kit, and belongs to the technical field of bacterium PCR detection. The kit contains six pairs of primers which have nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.12. The kit can authenticate whether a to-be-detected strain is campylobacteria or not and authenticate the five frequently-seen strains of campylobacteria including campylobacter jejuni, campylobacter coli, campylobacter fitus, campylobacter loridis and campylobacter liensis. The kit has sensitivity and specificity of 100% on detecting the five strains of campylobacteria, is easy to operate, greatly reduces detection cost and operation difficulty, and has good clinical application value.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Cytolethal distending toxins and detection of campylobacter bacteria using the same as a target
ActiveUS20100047797A1Quick checkRapid and convenient determinationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliTyping
The present inventors succeeded in cloning the CDT genes of C. coli and C. fetus, which were previously unknown, and in determining their sequences. In addition, the inventors also developed specific primers and primers common to the two species by comparing the CDTs of C. jejuni and C. fetus. Furthermore, the inventors demonstrated that these primers were applicable to multiplex PCR that simultaneously allows for the rapid and convenient determination of the presence of Campylobacter CDT and identification of species, and that they can also be used in PCR-RFLP-based typing.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
Use of an enzyme for the manufacture of an agent for controlling bacterial infection
InactiveUS20060083731A1Advantage for human healthLess harmful to the environmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacillus perfringensEconomic benefits
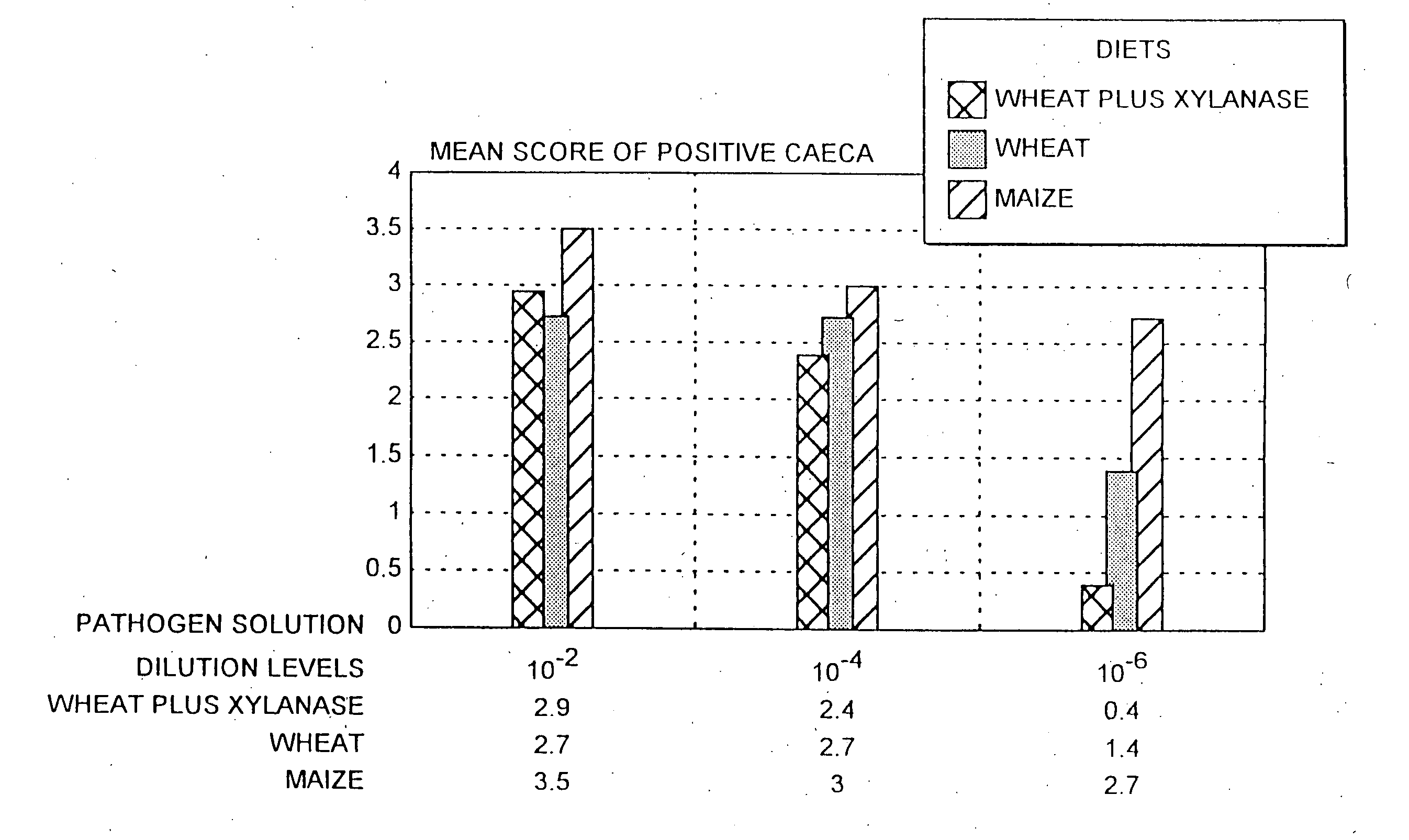
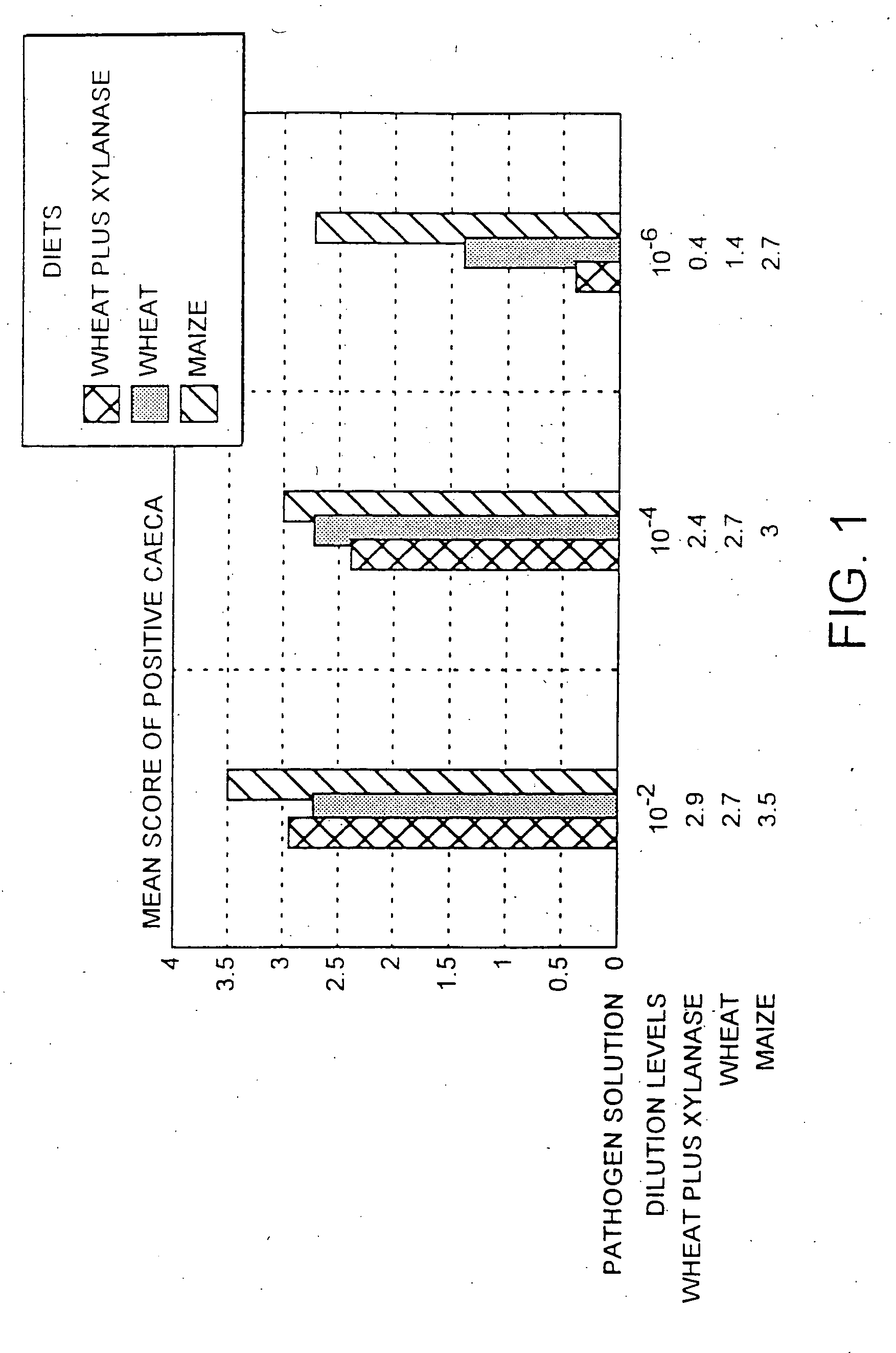
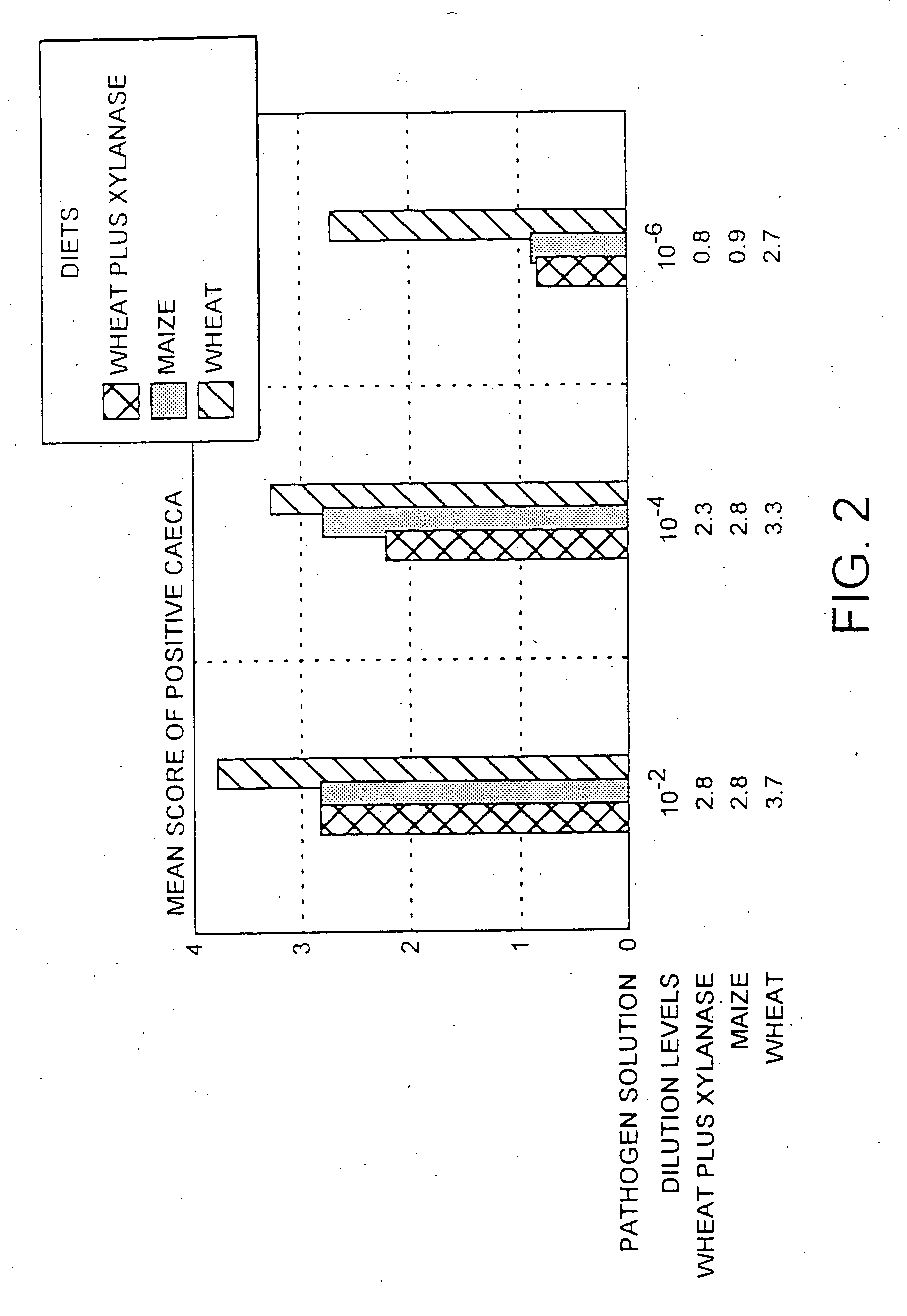
Xylanase or a cellulase for the manufacture of an agent for the treatment and / or prophylaxis of bacterial infection in an animal caused by Salmonella, Campylobacter or Clostridium perfringens. It is preferred that xylanase is used in combination with wheat to form an animal feed. Such a diet is particularly effective in controlling Campylobacter and Salmonella in chickens. The use provided by the present invention affords an alternative to antibiotics when controlling bacterial infection in animals. This leads to considerable health, environmental and economic benefits.
Owner:FINNFEEDS INT
Antibodies against flagellin and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090191208A1Avoid loweringIncrease intakeSnake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEscherichia coliCitrobacter
The present invention provides a novel class of monoclonal antibodies which have a high affinity, broad spectrum neutralizing reactivity to flagellin from various Gram-negative bacteria including, but not limited to, E. coli, Salmonella, Serratia, Proteus, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Campylobacter and Pseudomonas. The present invention further provides methods of treating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and methods of treating enterobacterial infections using anti-flagellin antibodies in humans, other animals and birds.
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
Quaternary ammonium compounds in the treatment of water and as antimicrobial wash
InactiveUS20050250821A1Growth inhibitionLow costBiocideWater/sewage treatment by substance additionEscherichia coliAmmonium compounds
Low levels of quaternary ammonium compounds are effective antimicrobial agents in drinking water and potentiate the antimicrobial power of organic acids used as antimicrobials for such purposes. The method is effective against both Gram (−) and Gram (+) bacteria, including but not limited to, Salmonella sp., E. coli, Campylobacter sp. as Staphylococcus sp. and Listeria sp. The combination of quaternary ammonium compounds and one or more organic acids can also be effectively used as antimicrobial washes for fruits, vegetables, meat, and animal carcasses.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Campylobacter Jejuni Outer Membrane Protein Immunogenic Composition
InactiveUS20080131453A1Reduce probabilityBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEpitopeMicrobiology
The field of this invention is the development of therapeutic agents having immunogenic efficacy against Campylobacter. The present invention is directed to a method of producing monoclonal antibodies that are highly specific for epitopes of Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane proteins; to specific monoclonal antibodies made by using the epitopes; and to uses thereof. The invention is drawn further to immunogens comprising certain outer membrane proteins or portions thereof from C. jejuni.
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF GEORGIA RES INST
Mammalian animal compositon
InactiveUS20060134082A1Reduce and prevent Campylobacter infectionReduces and prevents zoonotic riskBiocideBacteria material medical ingredientsMicroorganismMicrobiology
The present invention relates to the use of probiotic microorganism in the manufacture of a composition for the prevention or reduction of gastrointestinal Camplylobacter infection in a mammalian animal. It also relates to a method for the prevention or reduction of gastrointestinal Campylobacter infection in a mammalian animal, the method comprising administering to said animal, a probiotic microorganism. The invention also relates to a probiotic microorganism, for use in preventing or reducing gastrointestinal Campylobacter infection in a mammalian animal.
Owner:MARS INC
Antibacterial Peptide and Method of Treatment Using the Antibacterial Peptide
ActiveUS20170246240A1Treat and prevent bacterial infectionPreventing and delaying onsetPeptide/protein ingredientsFood processingStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
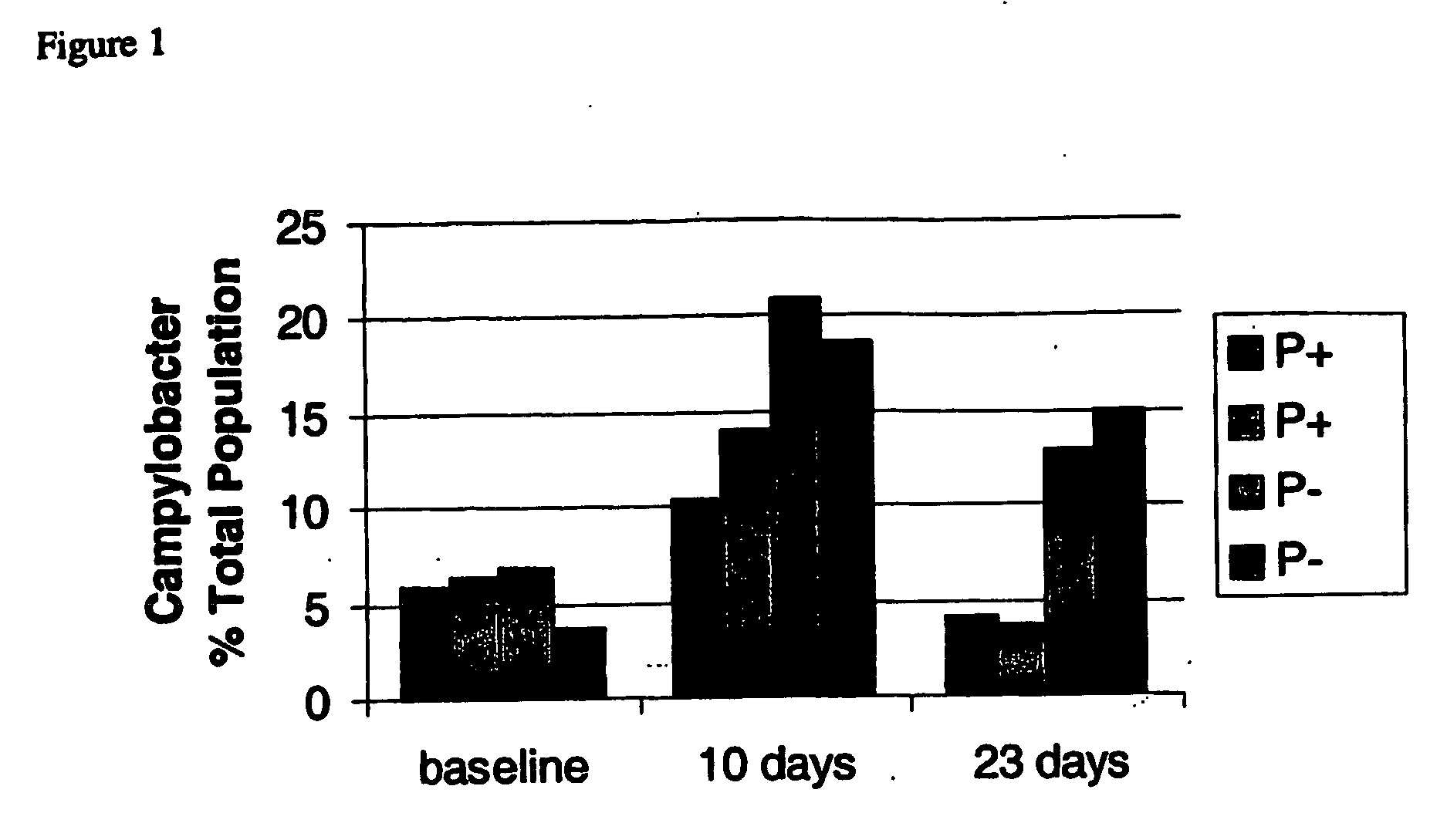
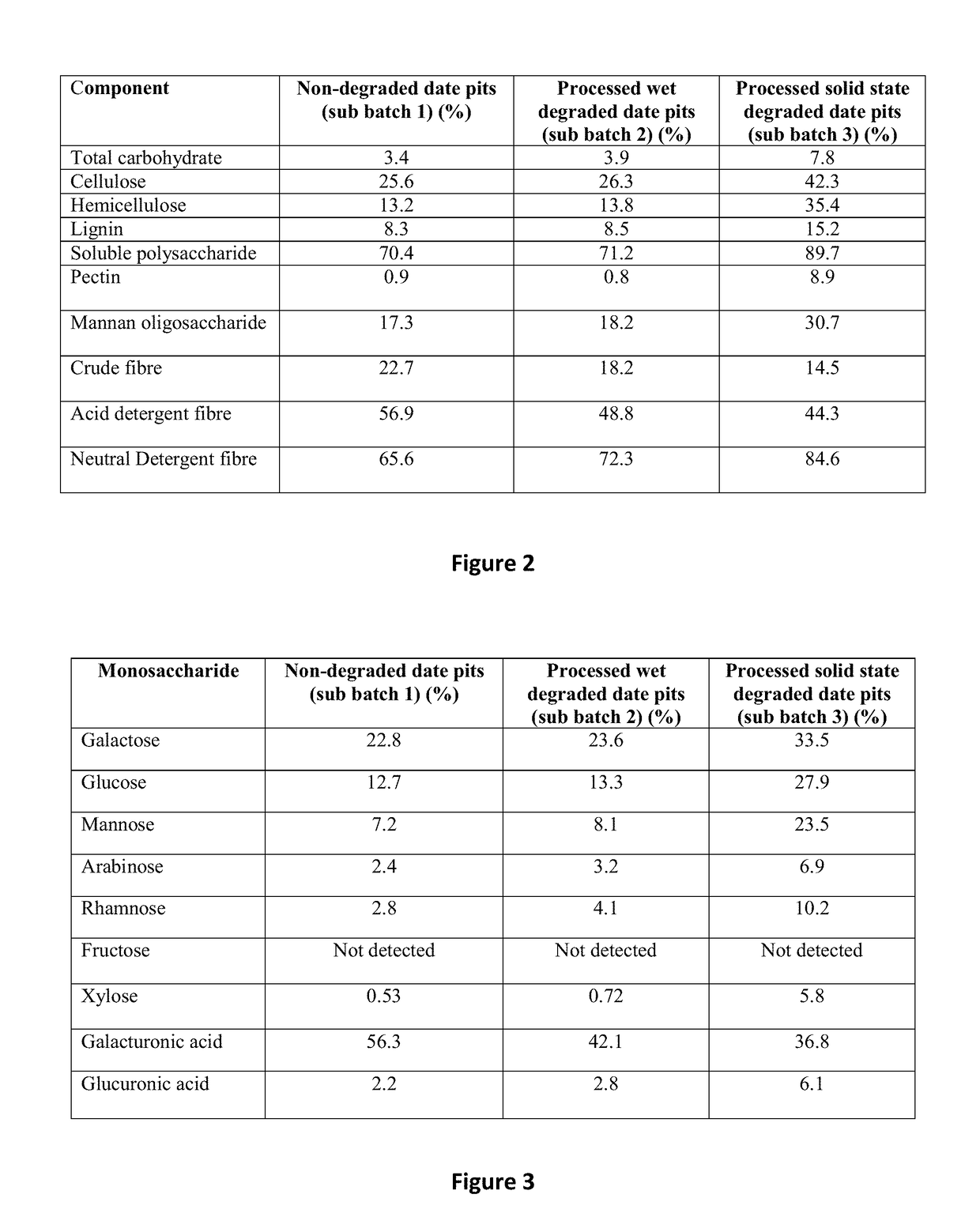
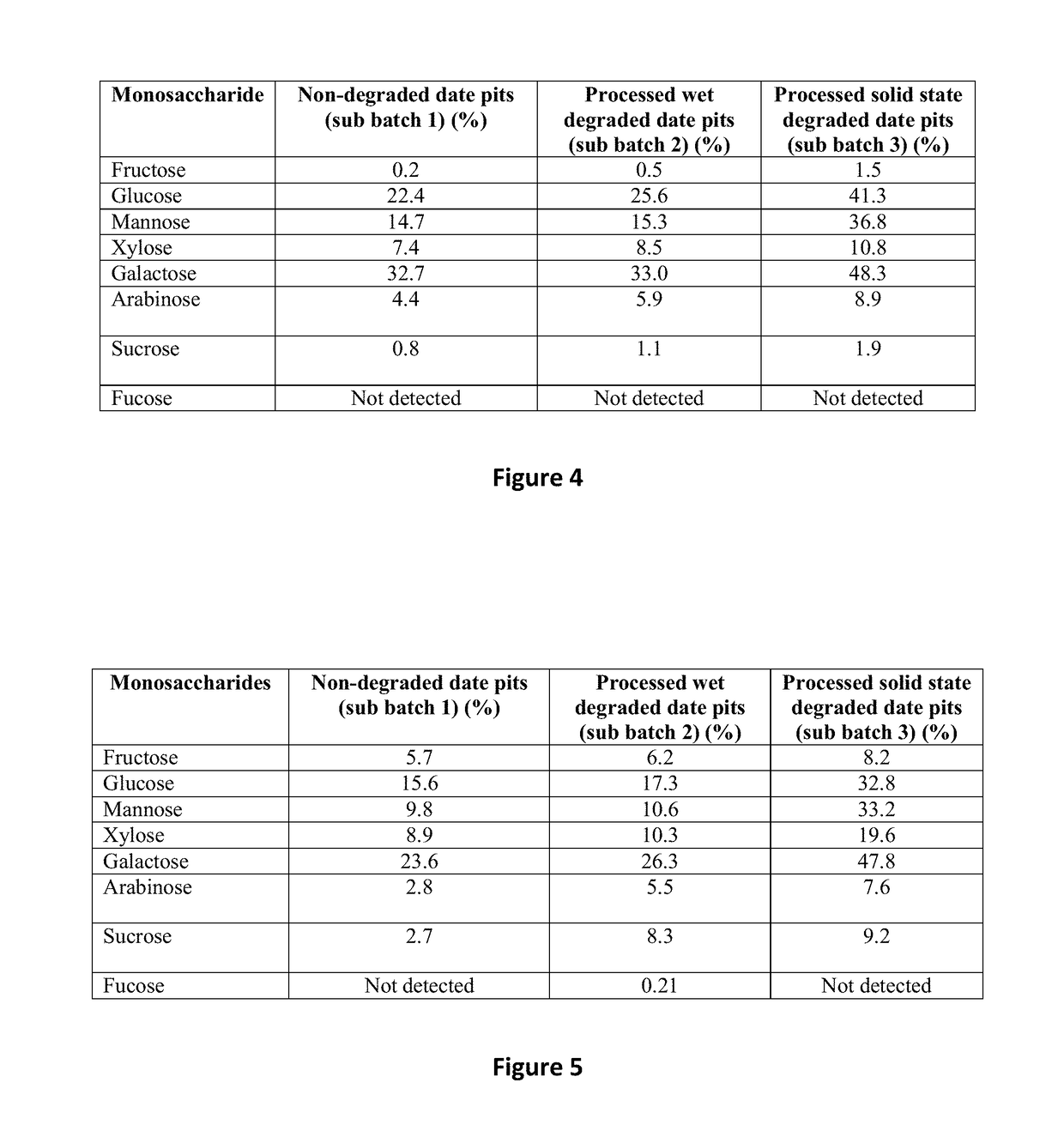
A method of treating or preventing a bacterial infection in an animal comprises administering to the animal an effective amount of an antibacterial peptide, the antibacterial peptide being derived from degraded date pits which are degraded by solid state degradation by a fungus, Trichoderma reesei. The antibacterial peptide has a molecular mass of less than 10 kDa and an amino acid sequence including (a) SEQ ID NO:4 or (b) SEQ ID NO:6. The bacterial infection is caused by a Gram-positive bacteria or a Gram-negative bacteria, for example, a Salmonella species, a Campylobacter species, a Shigella species, an Escherichia species, a Pseudomonas species, and a Staphylococcus species.
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
Campylobacter Pilus Protein, Compositions and Methods
InactiveUS20090285821A1Reduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunogenicityOrganism
The present disclosure provides coding and amino acid sequences for a Campylobacter jejuni pilus protein (and from other species as well). This protein, when administered to a human or animal, elicits the expression of an immune response to Campylobacter jejuni, with the result that colonization and / or infection by this organism is reduced. Recombinant protein or biofilm material comprising the pilus protein is formulated into immunogenic compositions, especially for mucosal administration. Thus, the present invention provides methods for improvement of the microbial quality of food products including poultry, eggs, meat and dairy products, and indirectly of plant foods that may come in contact with agricultural waste, either from fertilization or from irrigation water.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Campylobacter Immunogenic Compositions and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20150030624A1Stimulate immune responseReduce decreaseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunogenicityGenus Campylobacter
The present invention provides immunogenic compositions against Campylobacter and methods for using the immunogenic composition to generate an immune response against Campylobacter and / or reduce intestinal colonization by Campylobacter.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Food-poisoning bacteria detection carrier, and method for detecting food-poisoning bacteria
InactiveCN102844447ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStaphylococcus cohniiFood poisoning
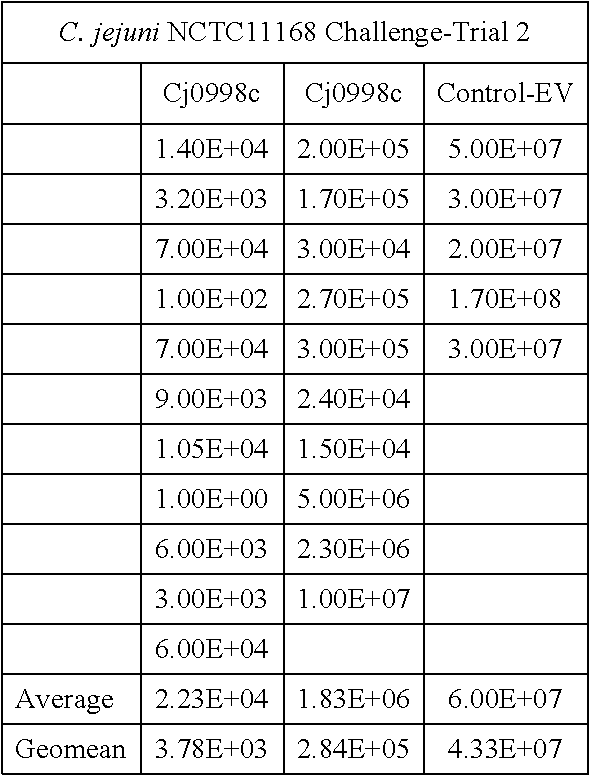
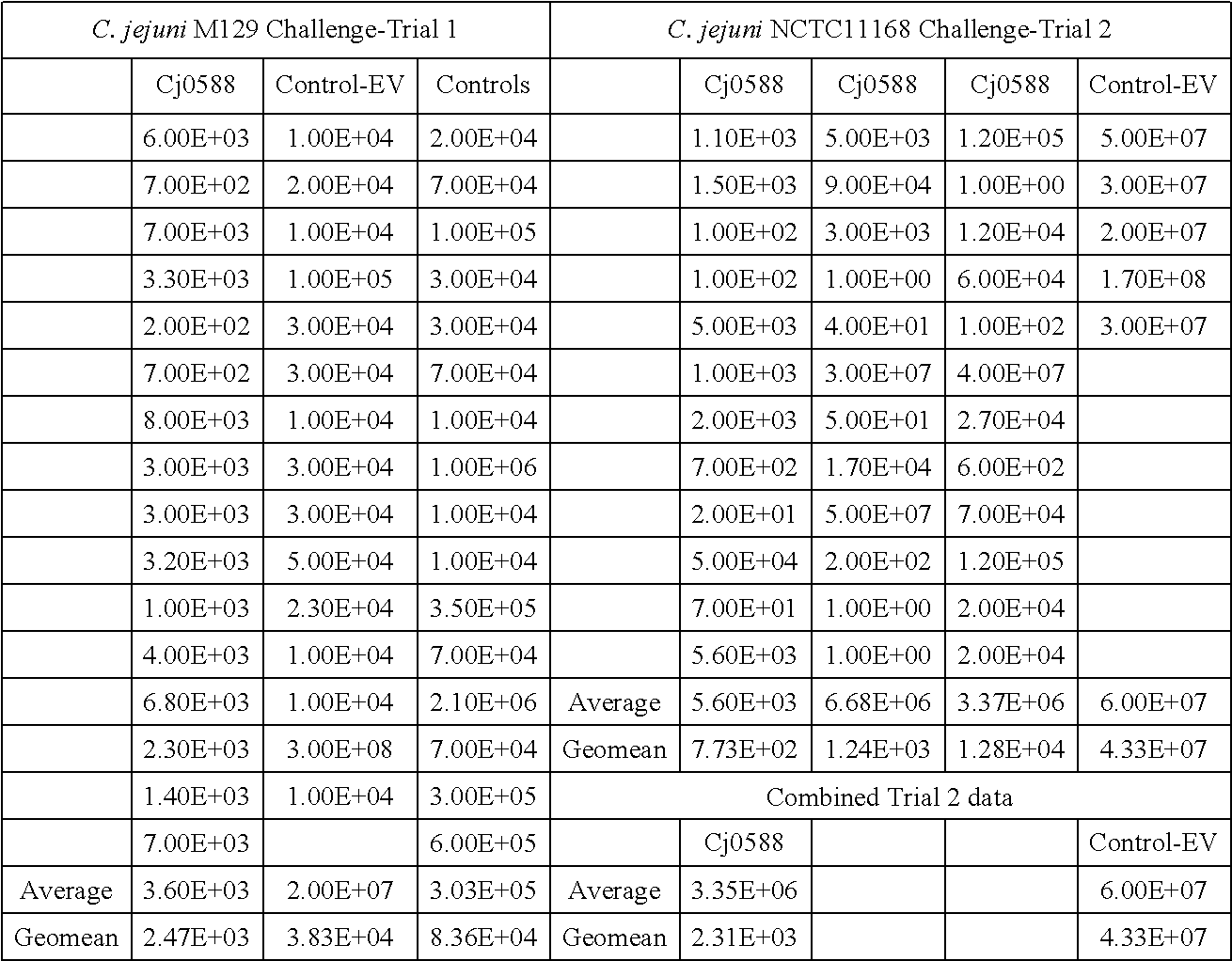
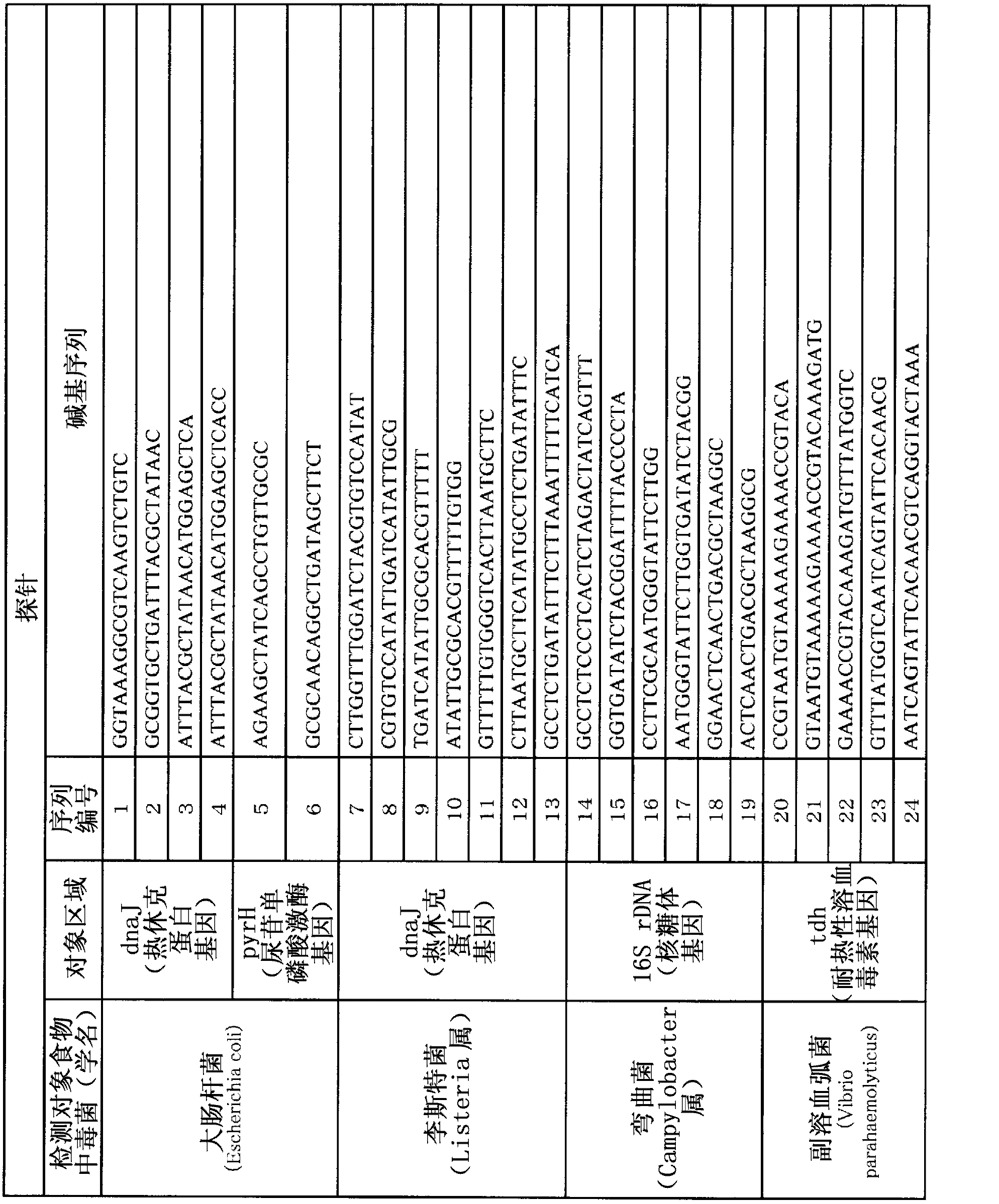
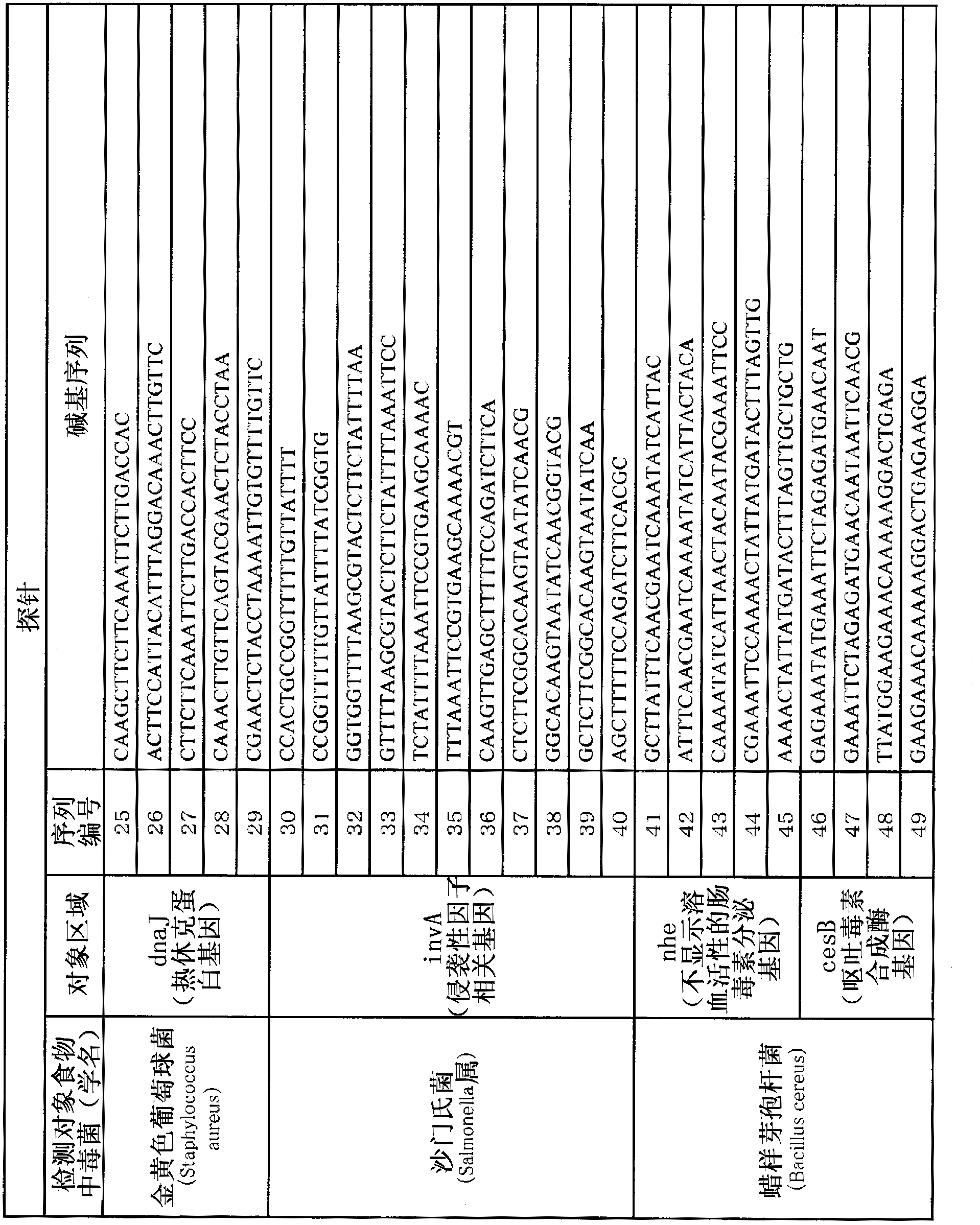
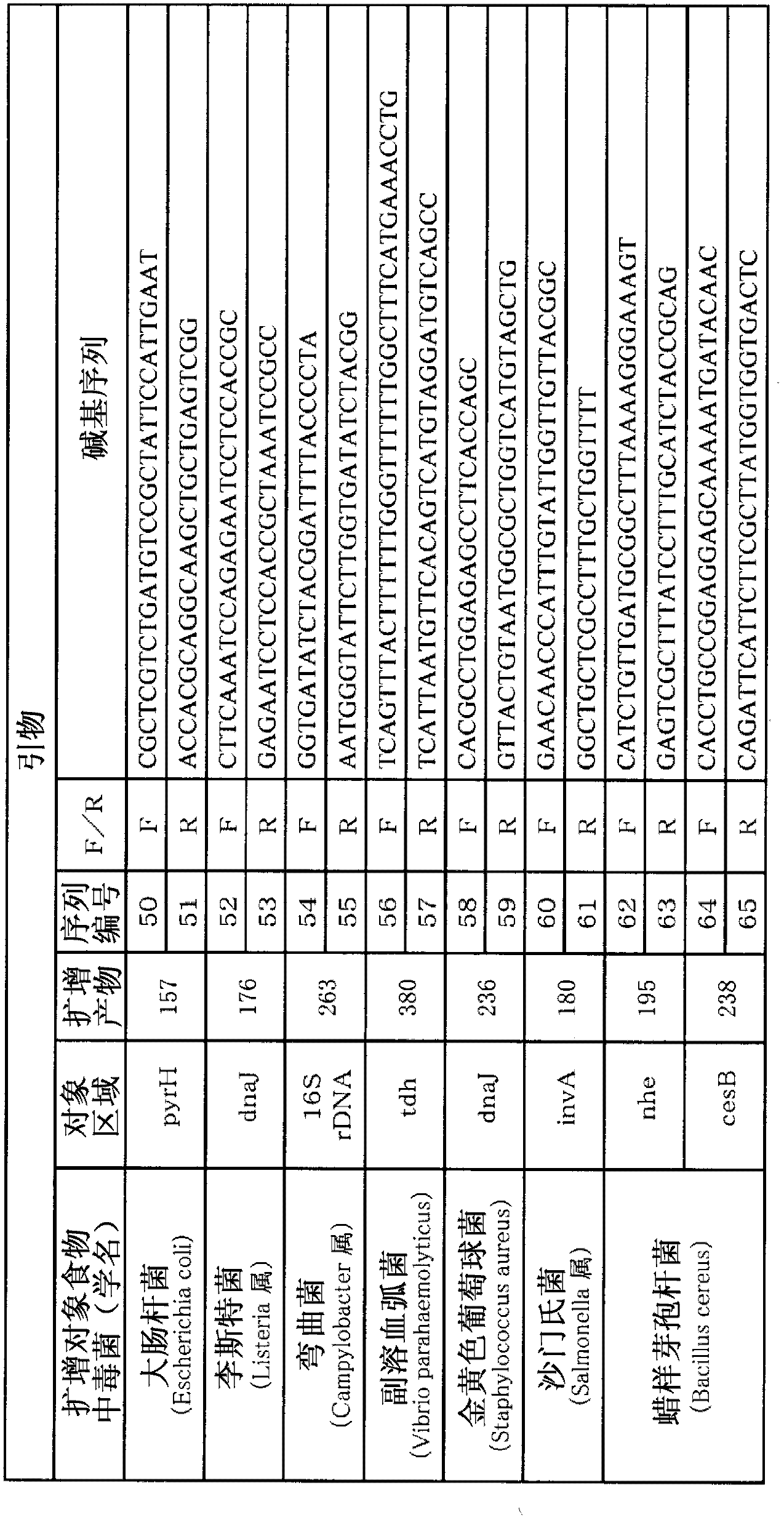
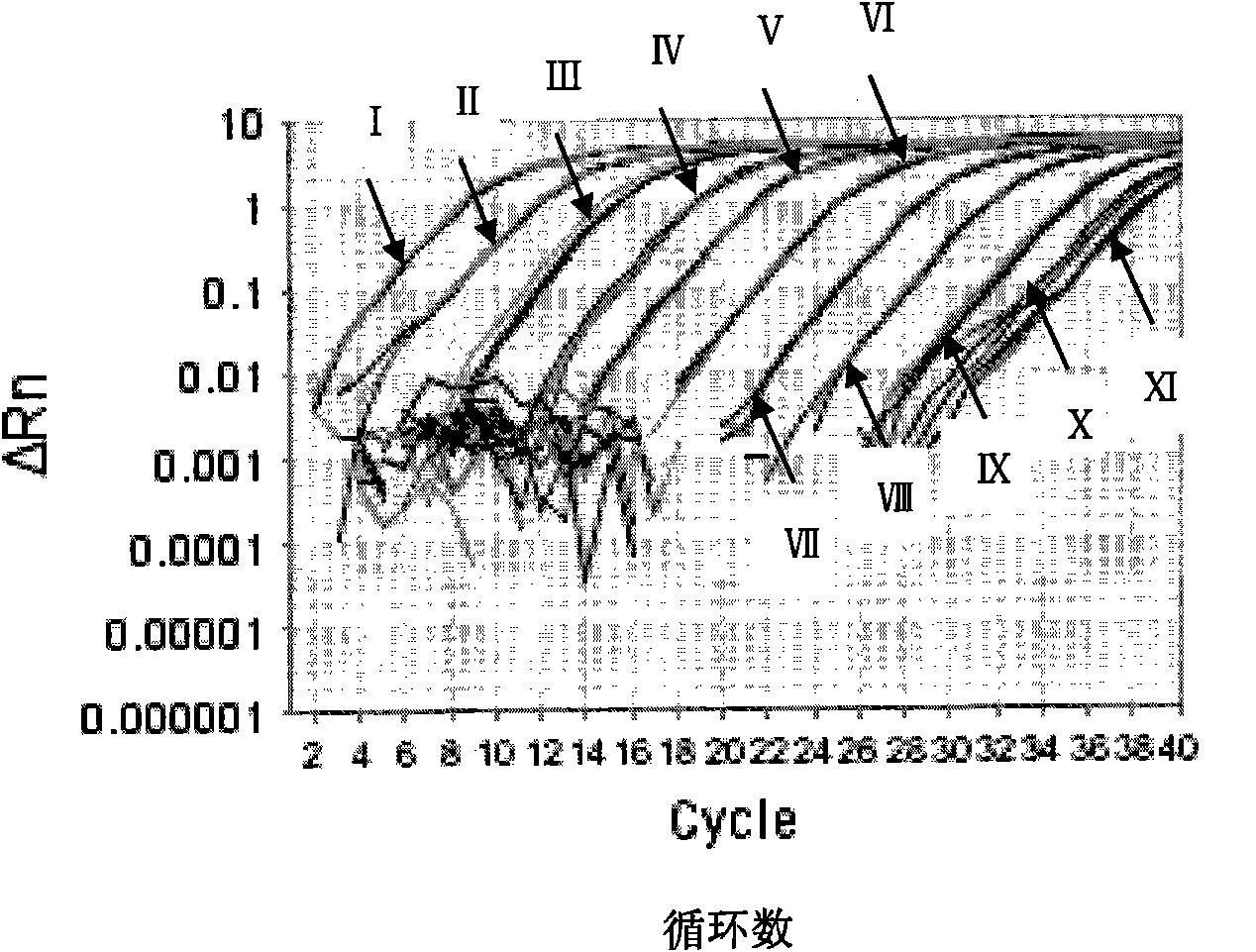
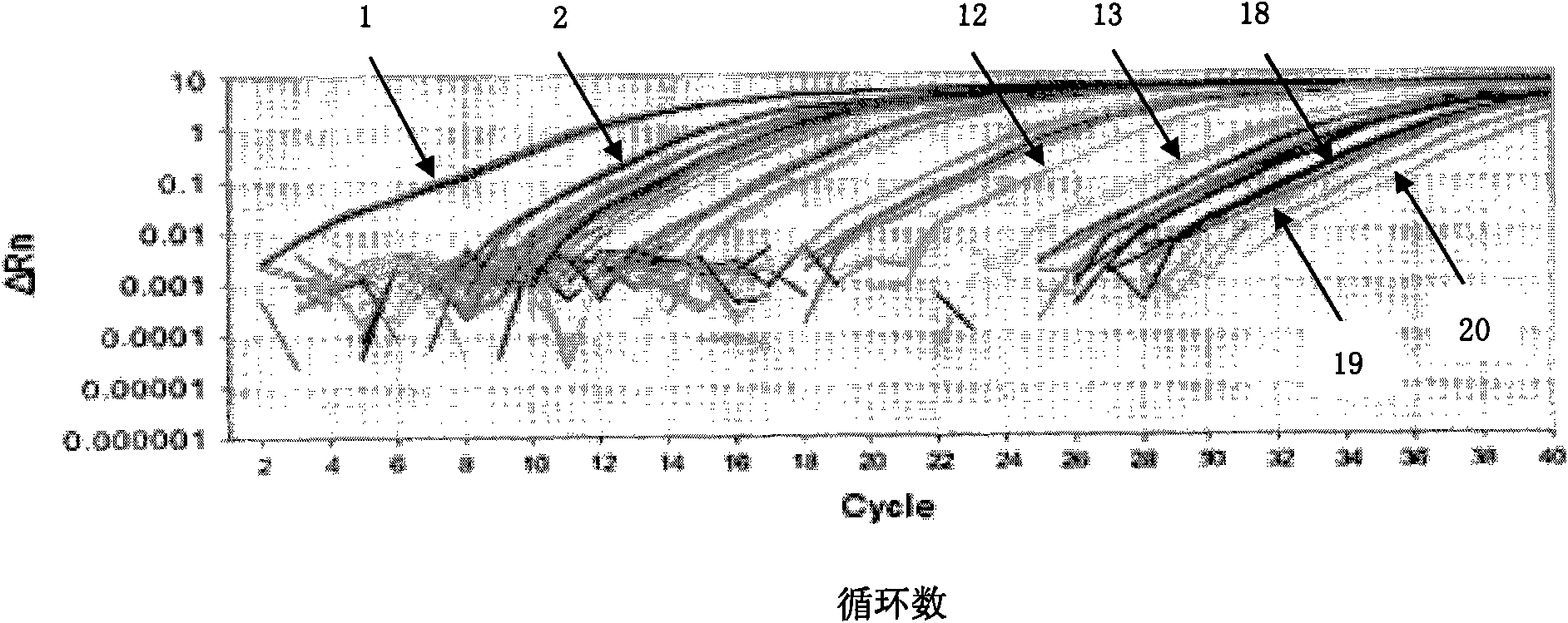
The disclosed method simultaneously and specifically detects at least two types of food-poisoning bacteria from among Escherichia coli, Listeria, Campylobacter, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, and Bacillus cereus. The food-poisoning bacteria detection carrier immobilizes one or at least two probes selected from each of at least two groups from among: an E. coli-detecting first probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 1-6 and probes (hereinafter written as "and the like") that are complementary thereto; a Listeria-detecting second probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 7-13, and the like; a Campylobacter-detecting third probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 14-19, and the like; a Vibrio parahaemolyticus-detecting fourth probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 20-24, and the like; a Staphylococcus aureus-detecting fifth probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 25-29, and the like; a Salmonella-detecting sixth probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 30-40, and the like; and a Bacillus cereus-detecting seventh probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 41-49.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN KAISHA LTD +1
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method of campylobacter jejuni and kit
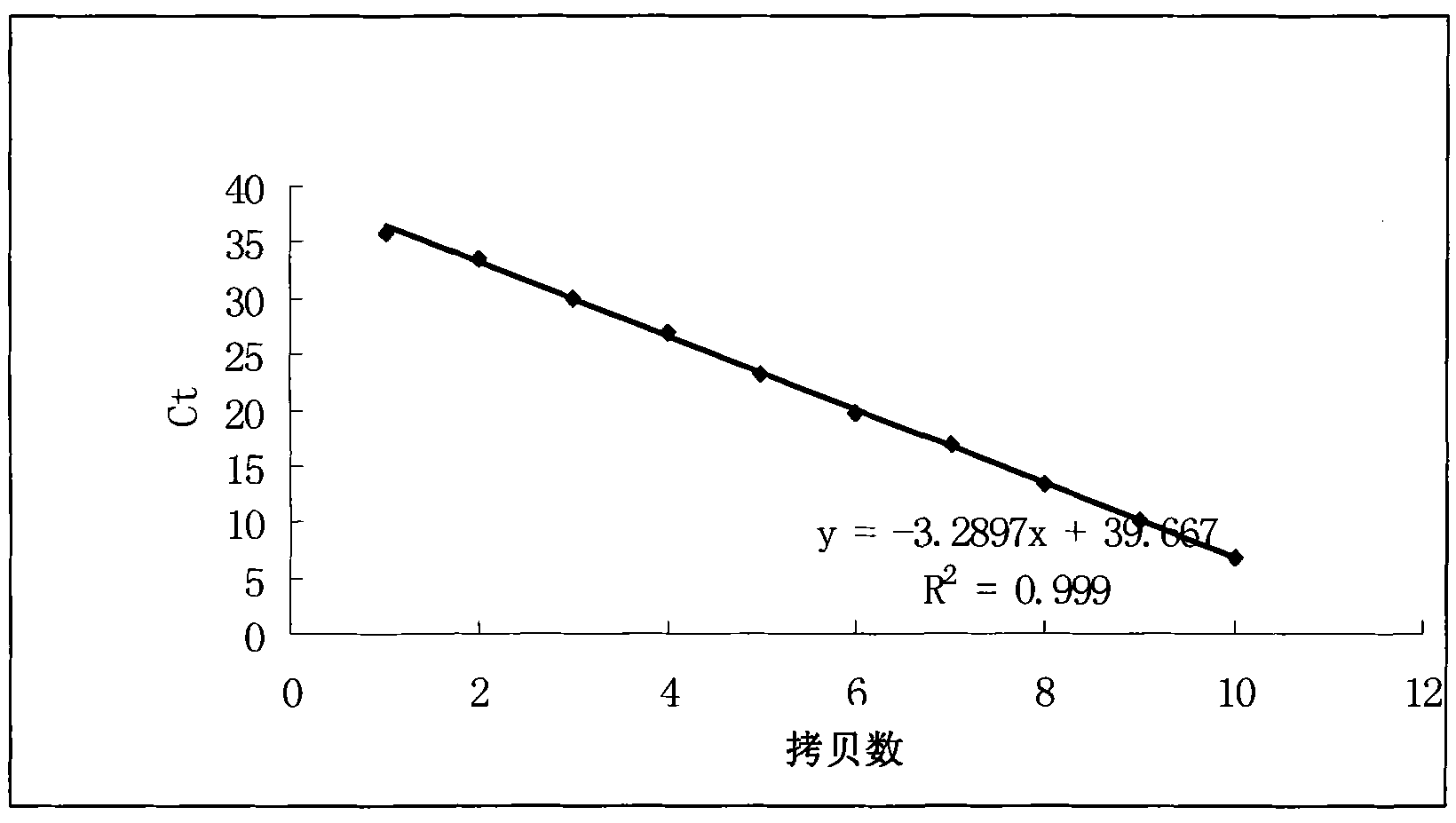
ActiveCN101886133AImprove accuracyGood precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseaseFeces
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method of campylobacter jejuni and a kit. In the invention, a primer and a Taqman probe are designed according to a conserved region of a campylobacter jejuni flagellin A (flaA) gene for qualitatively detecting the copy number of nucleic acid of the campylobacter jejuni in a fecal sample of a clinical patient, the fecal samples of a monkey and a dog, and the sample of ileocecal contents of a miniature swine, an upstream primer sequence SEQ ID NO:1, a downstream primer sequence SEQ ID NO:2 and a Taqman probe sequence SEQ ID NO:3. The invention has a great practical significance on quality control of relevant people and animal derived biological products and the inspection and quarantine field of import and export animals, and can ensure the quality of the relevant biological products. The detection method and the kit of the invention can be applied to diagnosis of campylobacter diseases and verification of the campylobacter jejuni in the biological products, thus having wide application prospect.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Campylobacter glycans and glycopeptides
ActiveUS7598354B2Avoid pollutionEliminating and reducing presenceAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMagic angle spinningGlycopeptide
Multiple strains and species of Campylobacter share a common glycan moiety which is present in a plurality of surface-exposed glycoproteins. This glycan has the formula: GalNAc-a1, 4-GalNAc-a1,4-[Glc-β1,3]GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,3-Bac, wherein Bac is 2, 4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-D-glucopyranose. This glycan and immunologically active fragments of it have use as vaccines against campylobacter infection in humans and animals. As well, antibodies which specifically bind these compounds may be provided. Such antibodies and vaccines may be used to prevent or neutralize campylobacter infections in livestock thereby preventing this pathogen from entering the human food chain. The glycan may be linked to one or more amino acids to form a glycopeptide. As well, a method for determining the glycan structure of an intact glycoprotein consists of subjecting a sample to high resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS-NMR) spectroscopy.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Loop-mediated isothermal amplication technology-based quick campylobacter jejunii detection kit and using method thereof
InactiveCN102121049AHigh sensitivityNot easy to polluteMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesManganeseBiology
The invention discloses a loop-mediated isothermal amplication technology-based quick campylobacter jejunii detection kit and a using method thereof. The kit consists of (1) reaction solution, (2) a primer group, (3) sample pretreatment solution and (4) positive contrast solution, wherein the primer group is one of the following eight primer groups, and each primer group comprises a pair of primers, namely an internal primer and an external primer; and a calcein manganese complex is added in advance in the reaction, the manganese is combined with pyrophosphate radical ions separated by dNTP to release the calcein, the released calcein can be observed and identified by naked eyes, the positive result is yellow green, and the negative result is light yellow. The kit has the advantages of strong specificity, short reaction time, high sensitivity and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI +2
Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane protein immunogenic composition
InactiveUS20050106159A1Reduce probabilityGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEpitopeCell Membrane Proteins
The field of this invention is the development of therapeutic agents having immunogenic efficacy against Campylobacter. The present invention is directed to a method of producing monoclonal antibodies that are highly specific for epitopes of Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane proteins; to specific monoclonal antibodies made by using the epitopes; and to uses thereof. The invention is drawn further to immunogens comprising certain outer membrane proteins or portions thereof from C. jejuni.
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF GEORGIA RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com