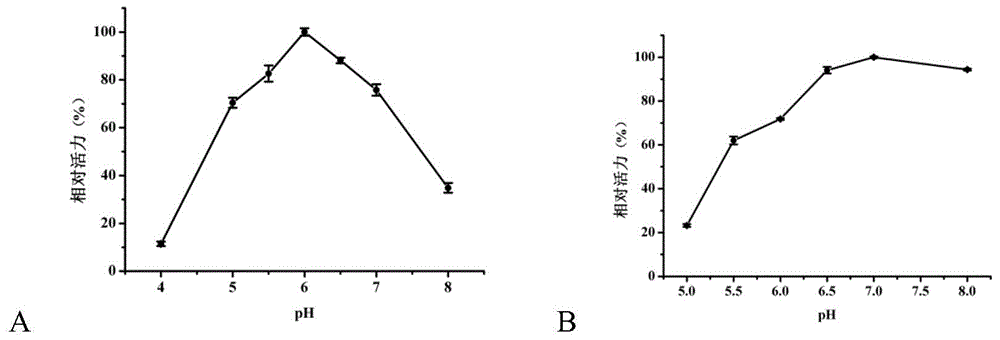
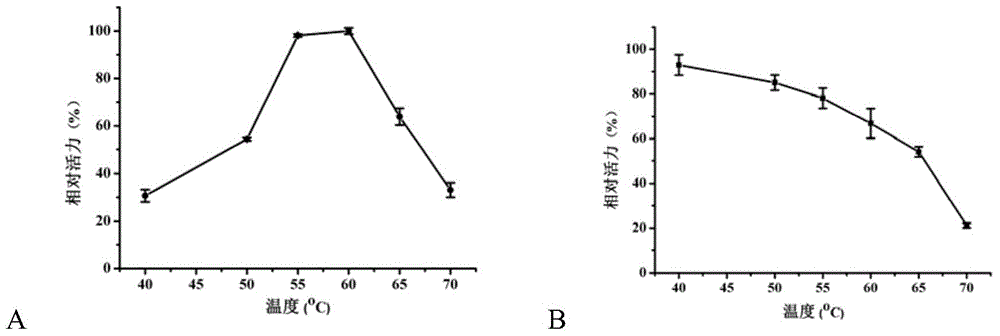
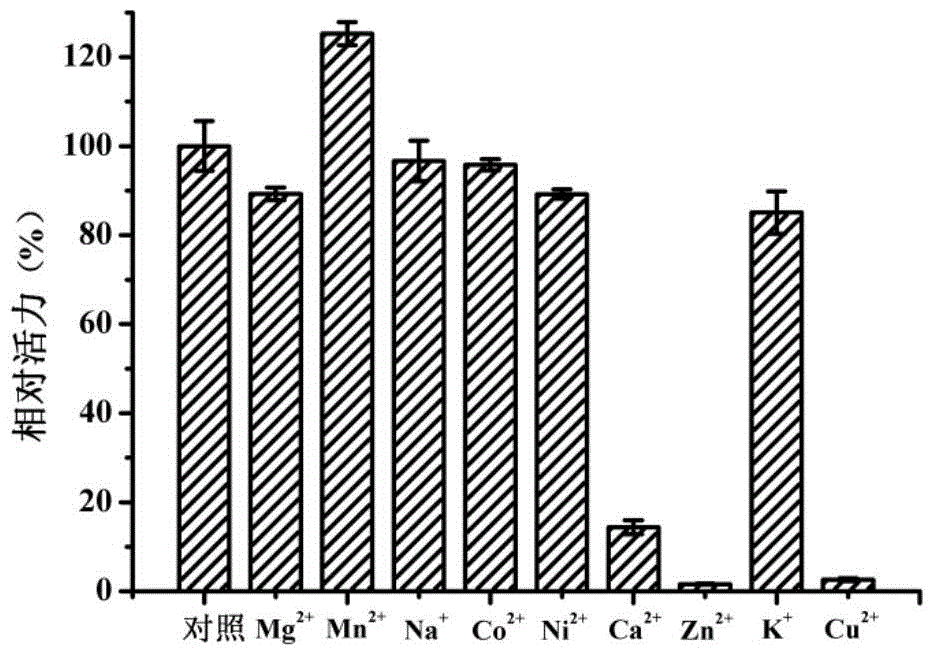
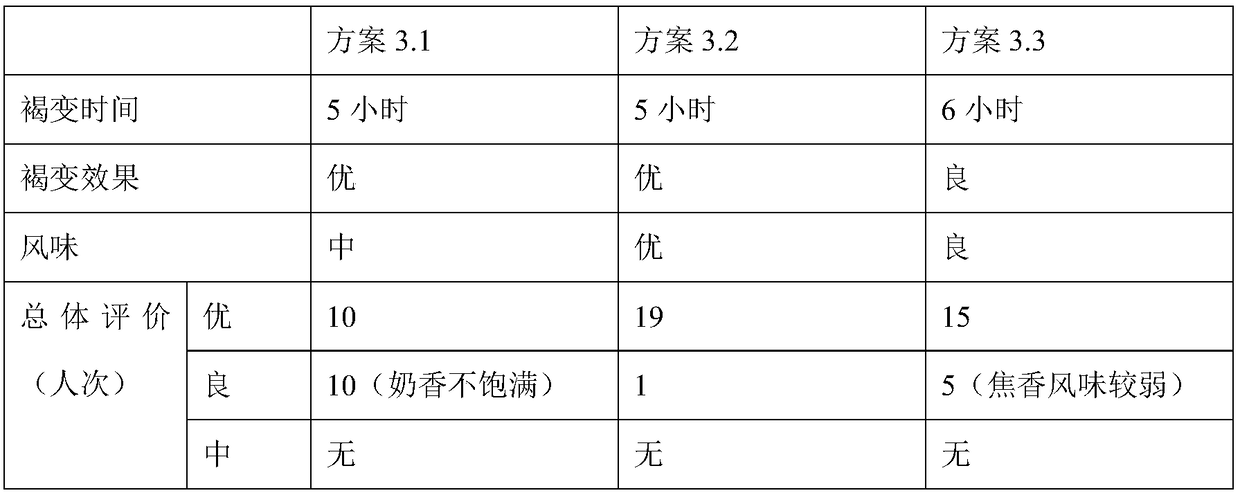
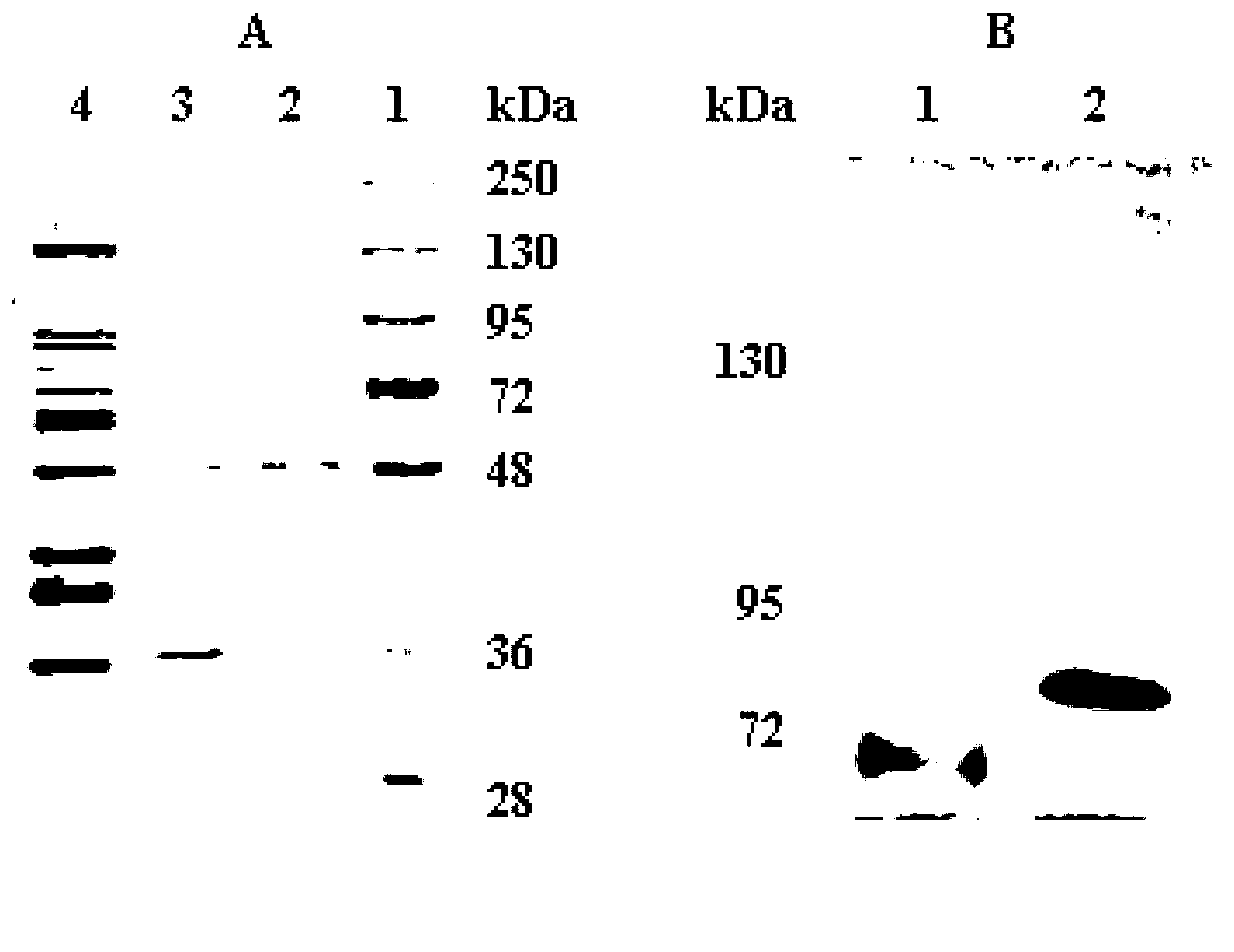
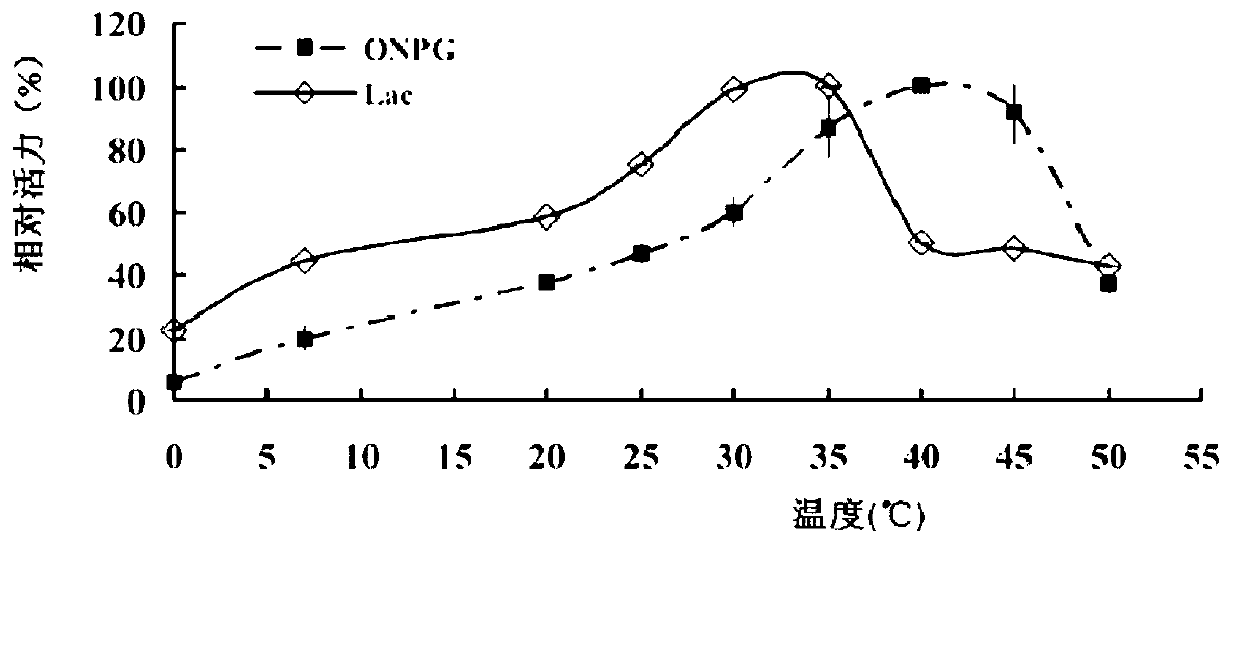
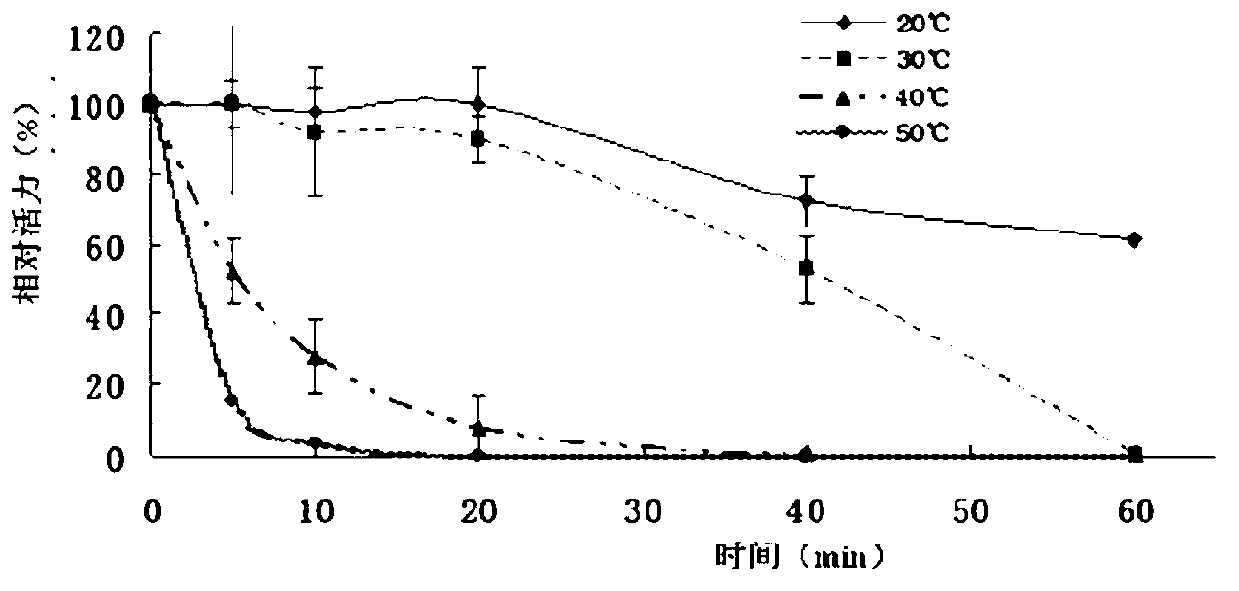
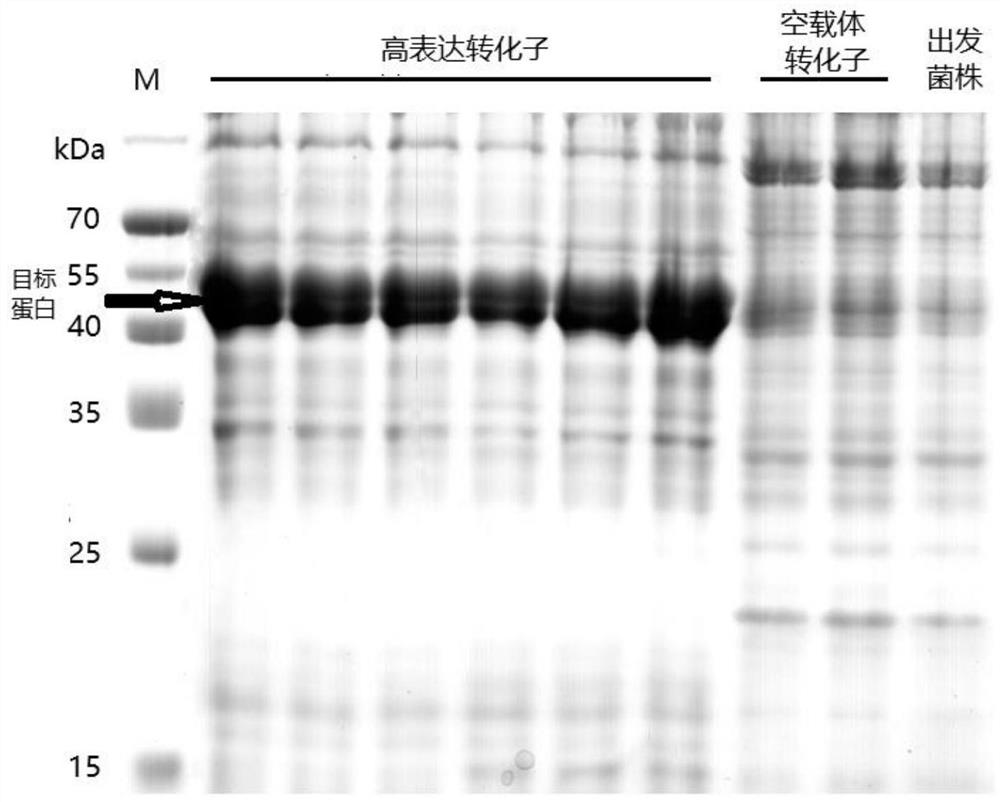
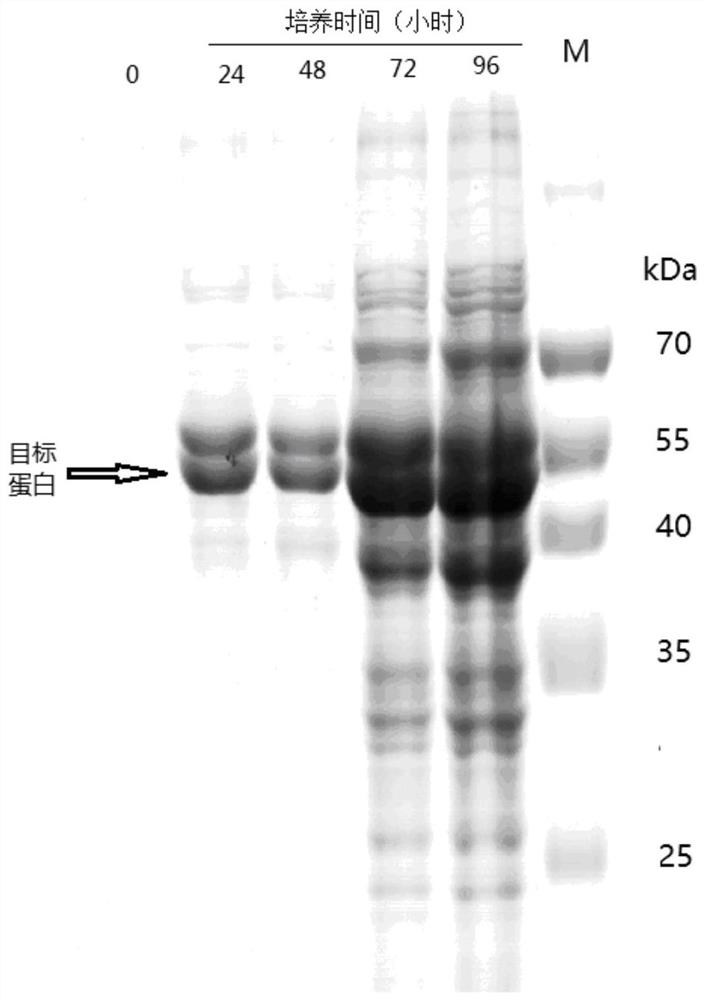
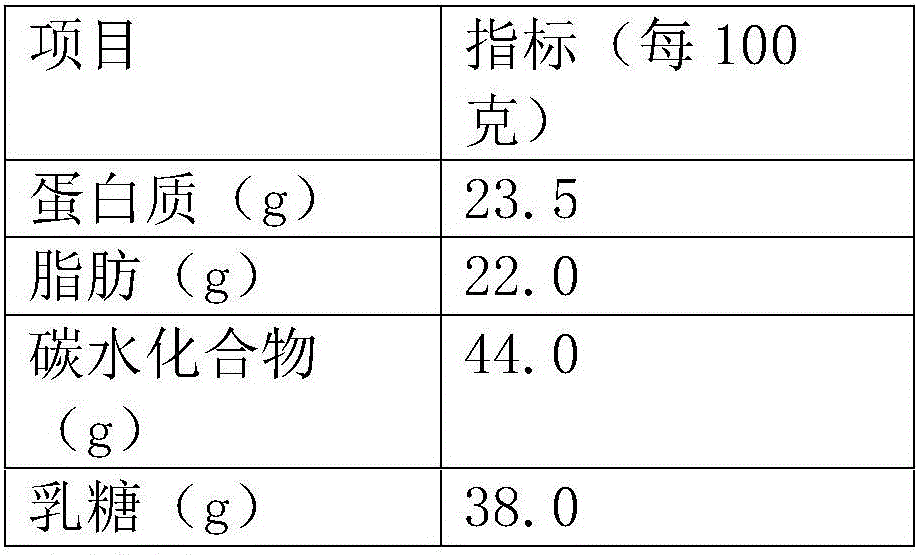
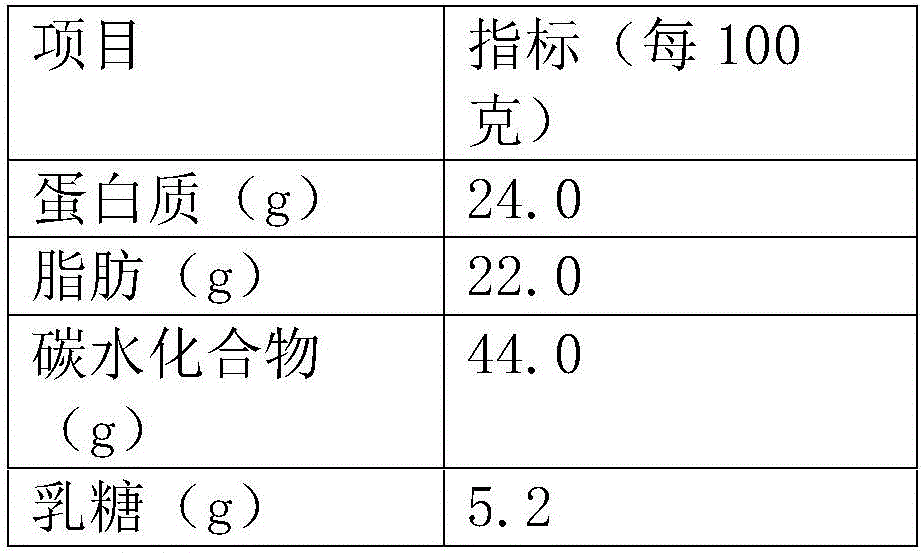
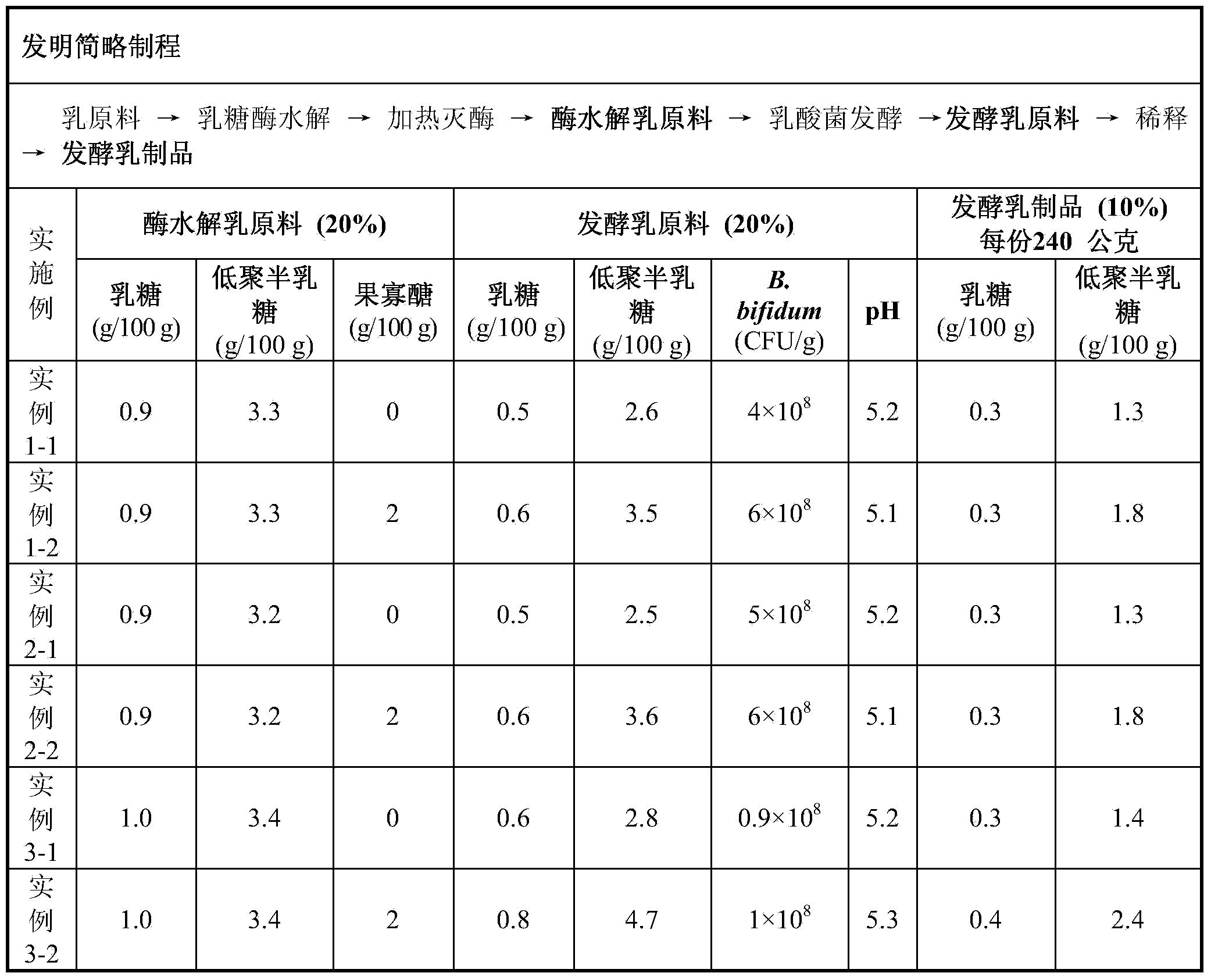
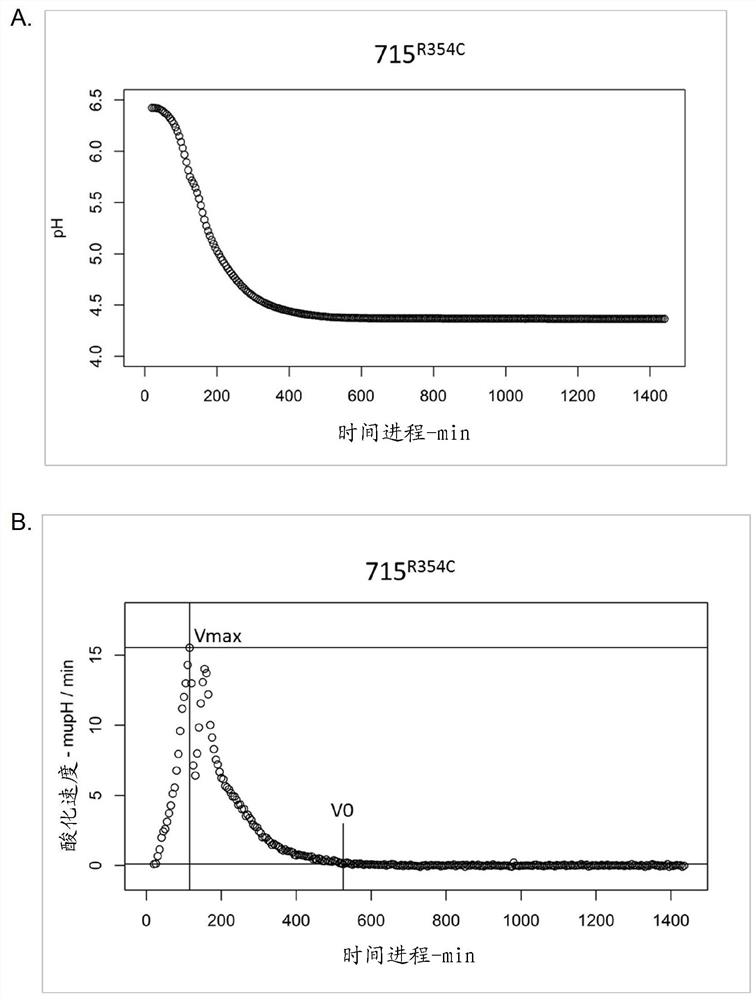
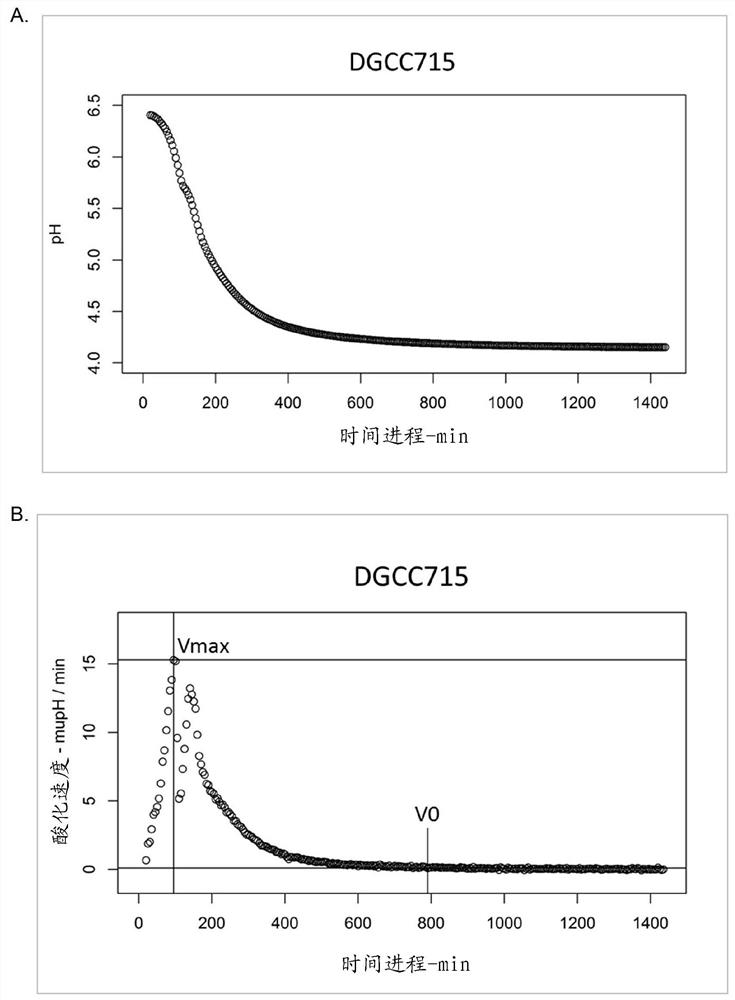
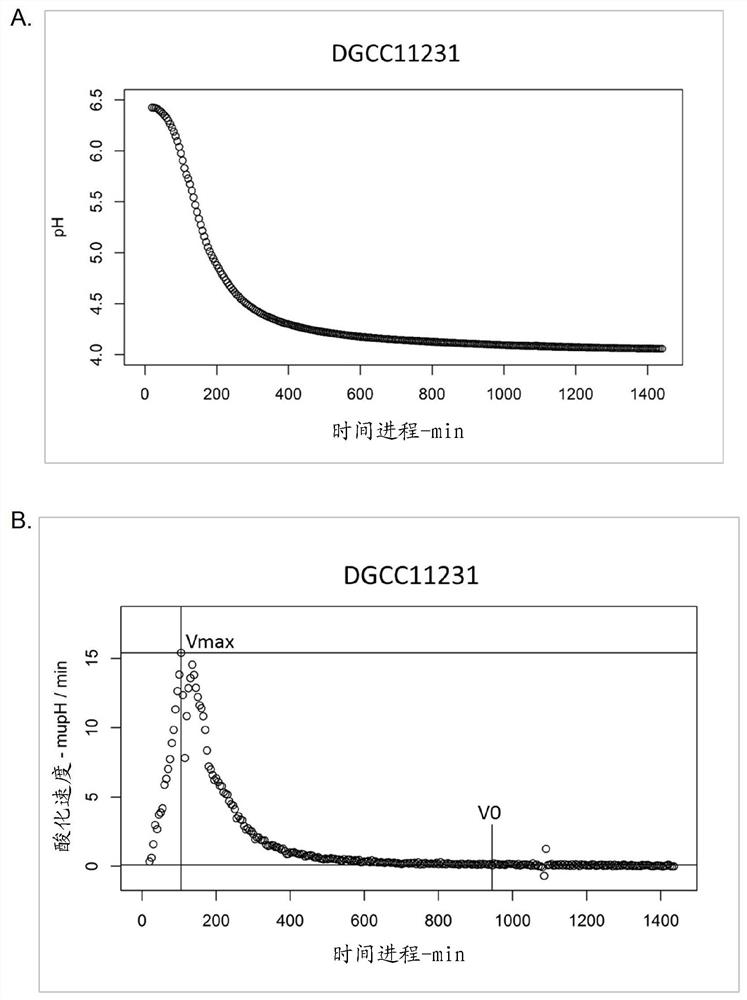
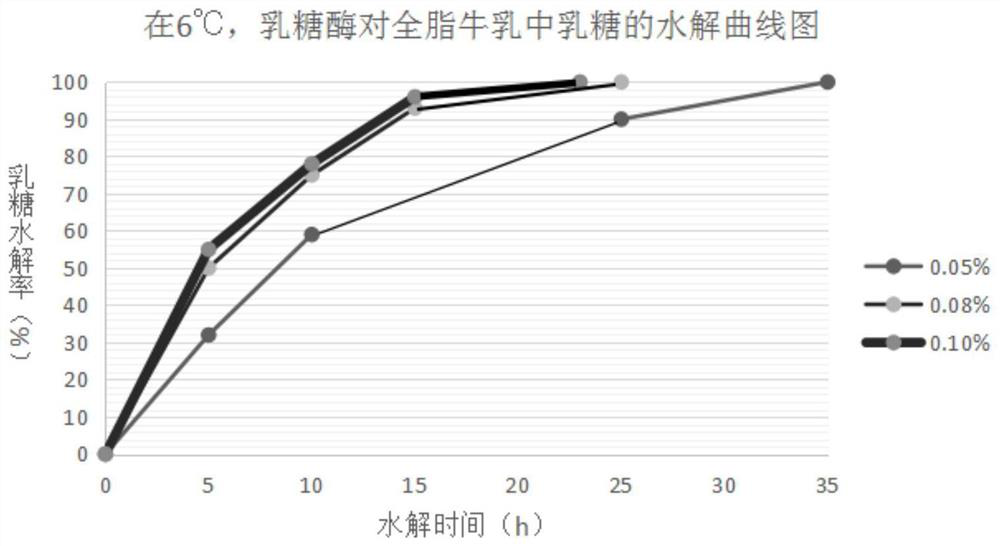
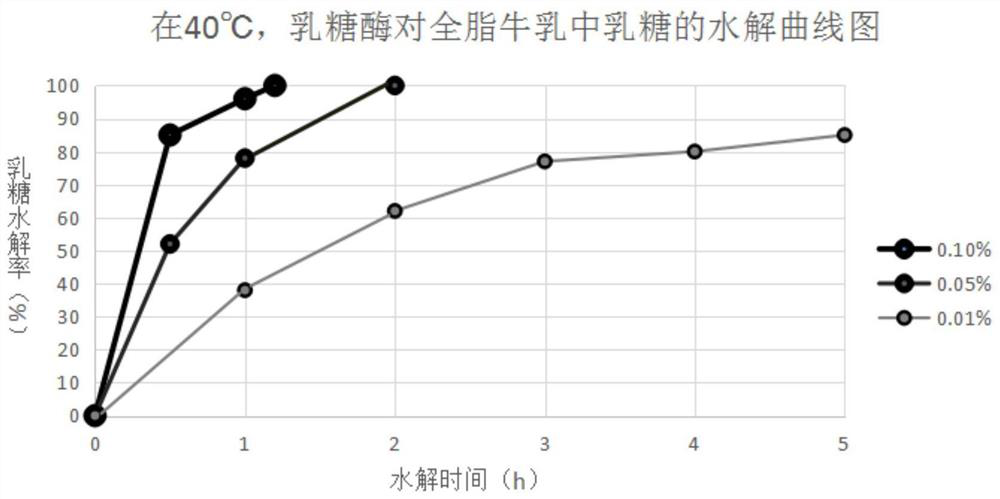
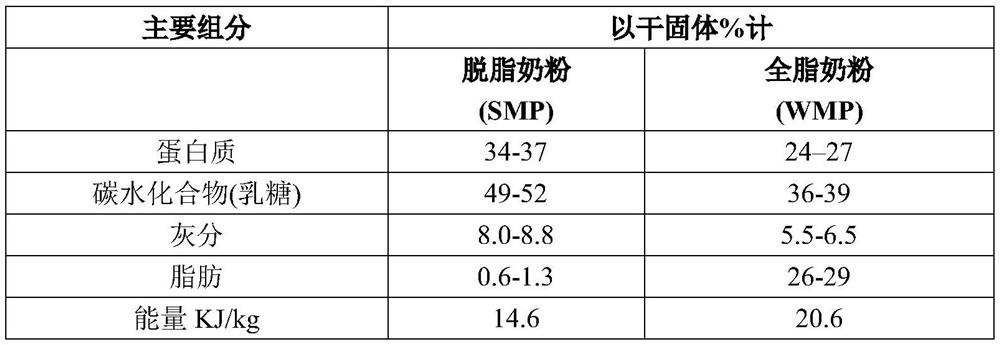
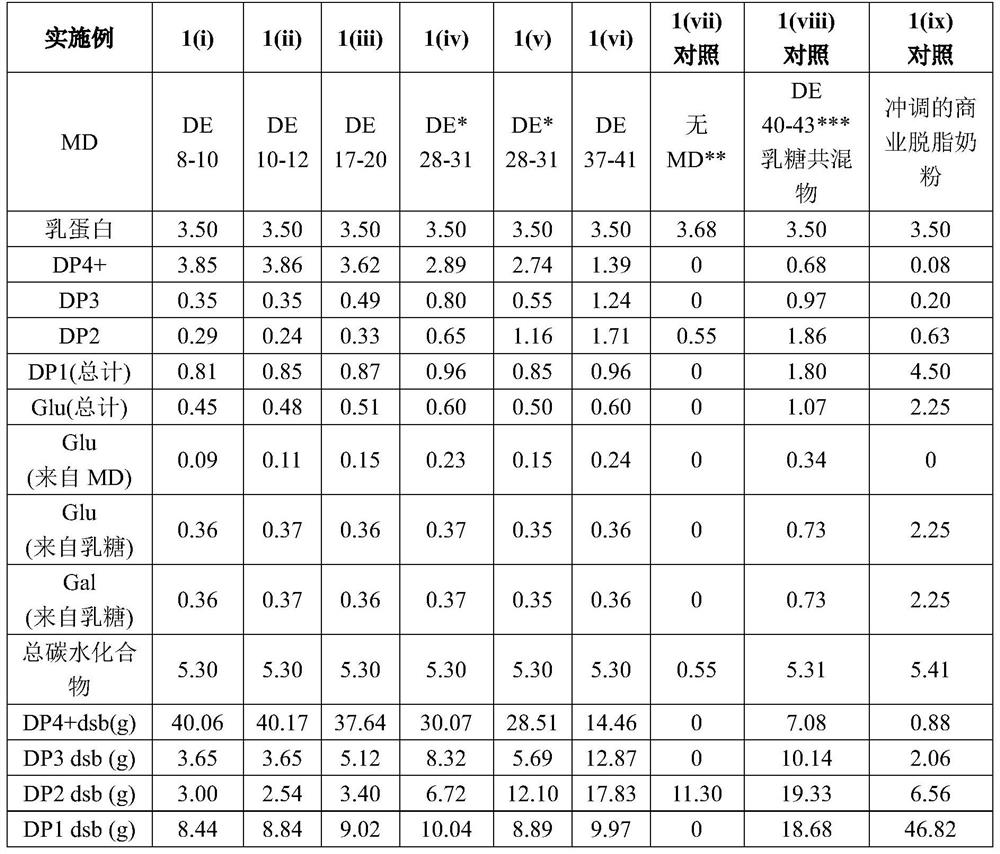
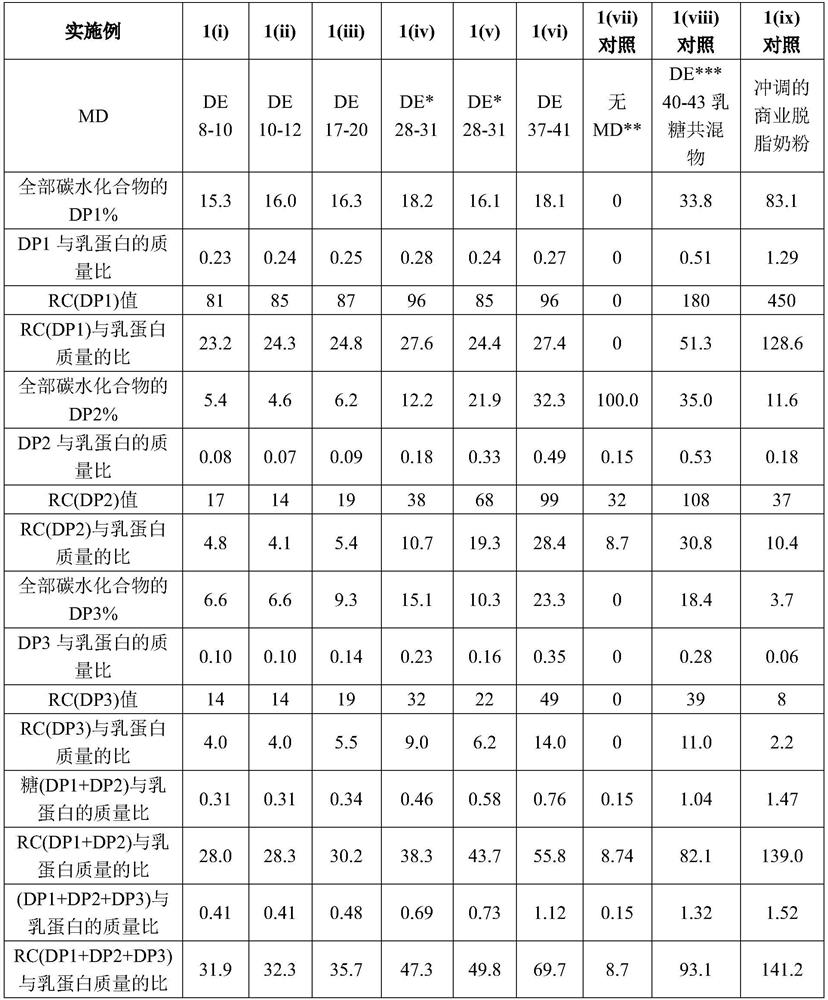
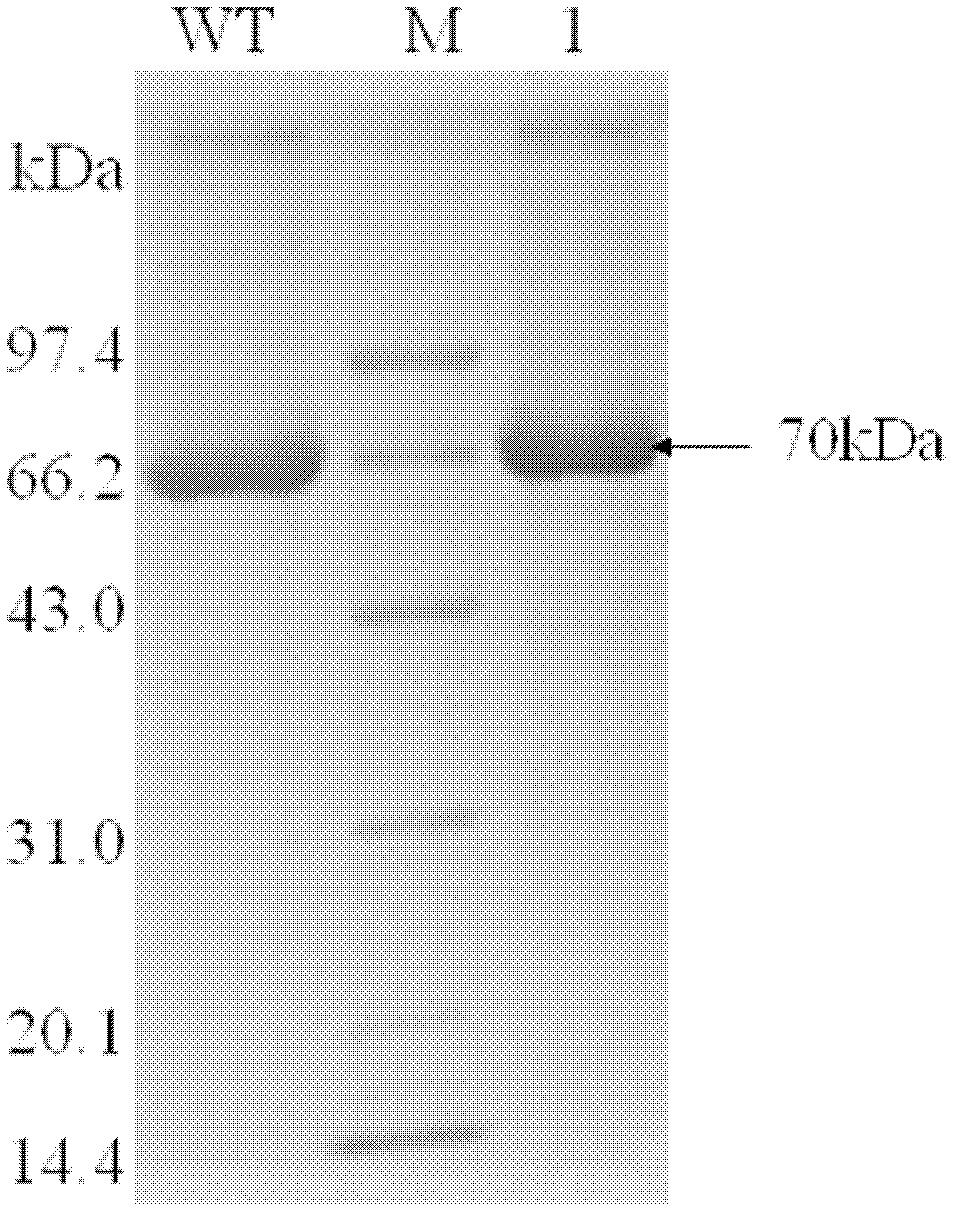Patents
Literature
58 results about "Lactose hydrolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lactose hydrolysis occurs for lactase-persistent individuals and the people who have a lactase deficiency. Lactose hydrolysis is found in dairy products and also to the various milk products.
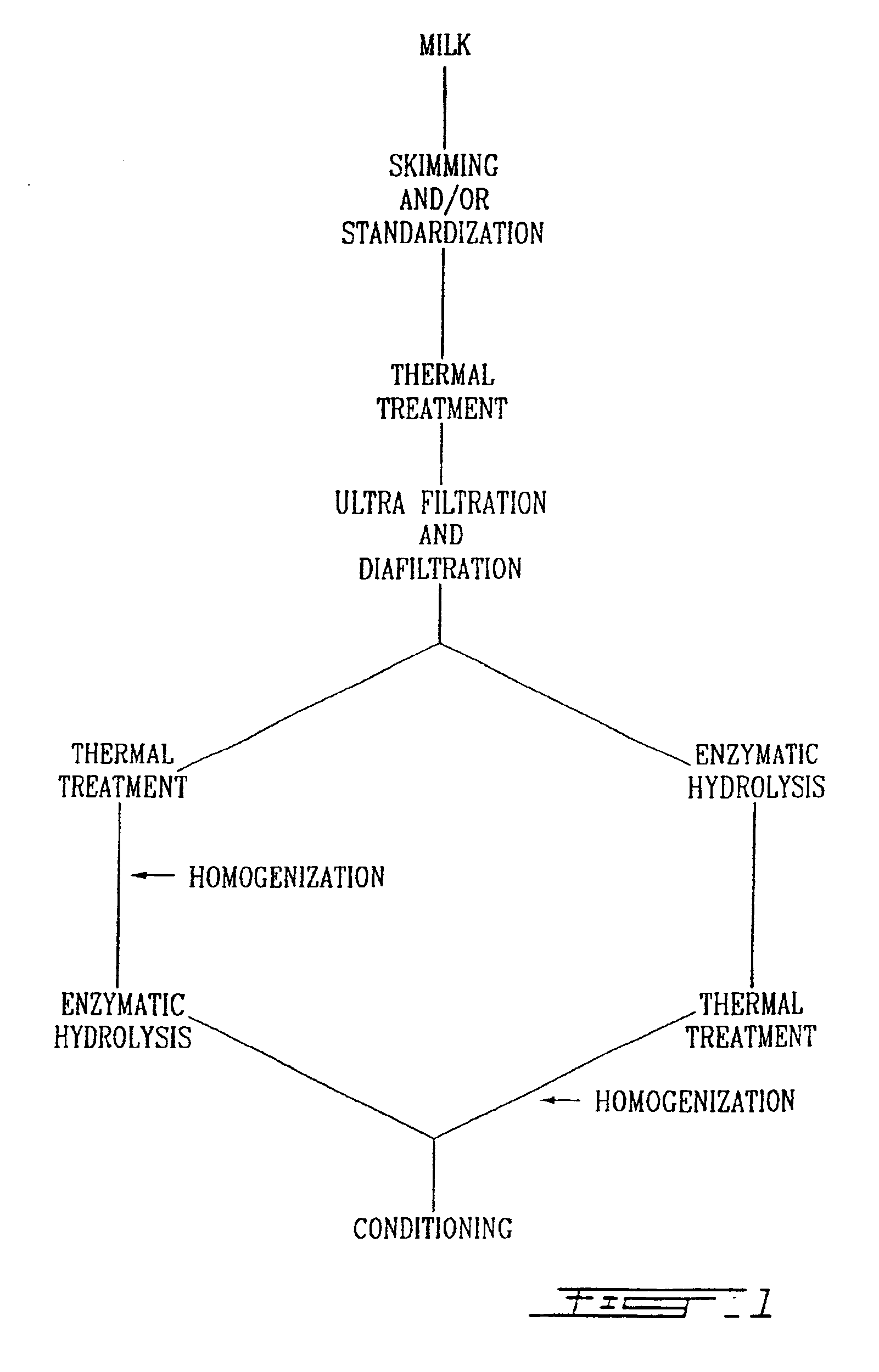
Process for making a lactose-free milk and milk so processed
InactiveUS6881428B2Affecting tasteLactose is reduced or substantially eliminated from milkMilk preparationWort preparationBiotechnologyLactose free milk
This invention relates to a process for producing a lactose-free milk which does not confer a sweet taste to the milk normally resulting from the hydrolysis of lactose into monosaccharides. The process comprises the step of reducing the lactose content of the milk to about 3% prior to hydrolysis with lactase. When the milk is skimmed milk, the protein content may be increased to about 3.8-4.0% or greater, which further improves the organoleptic properties of the milk. Milk so processed and dairy products derived therefrom are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:AGROPUR COOP
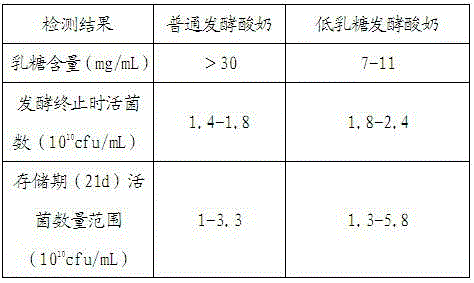
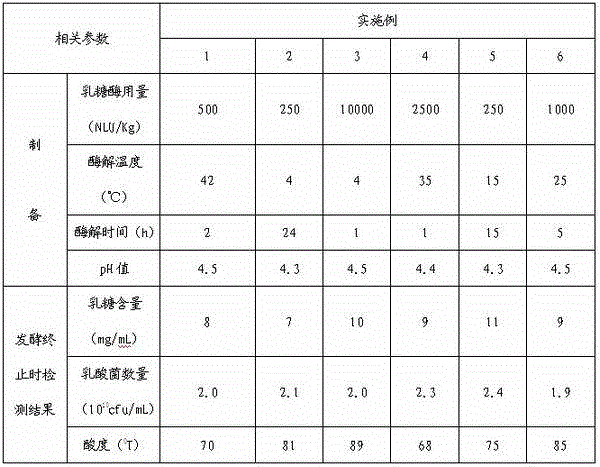
Preparation method for low-lactose fermented dairy product
The invention discloses a preparation method for a low-lactose fermented dairy product. The preparation method has two modes; in one of the modes, lactase is added into milk and ferment is inoculated at the same time, so that the low-lactose fermented dairy product is prepared; in the other mode, lactase is first added into fresh milk, so that lactose is hydrolyzed into glucose and galactose, and ferment is then inoculated, so that the fermented dairy product is prepared. The low-lactose fermented dairy product prepared by the preparation method not only has the characteristics of low lactose content and high viable count, but also has the specific flavor and taste of fermented milk, the change of acidity is little in the process of later storage, and the taste is good. The preparation method is applicable to the preparation of low-lactose fermented dairy products.
Owner:JUNLEBAO DAIRY GRP CO LTD
Low-lactose milk powder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101779703AReduce and improve intolerance symptomsReduce contentMilk preparationFiltrationEvaporation
The invention relates to a low-lactose milk powder and a preparation method thereof. The lactose content of the low-lactose milk powder of the invention is 4.5-10%; the preparation method of the low-lactose milk powder includes that lactose enzyme is added into crude milk for hydrolysis after pasteurization on crude milk and before production burdening on the basis of the conventional production process. The invention adopts advanced biological enzymolysis technology, through researches on technological conditions of the steps of burdening, filtration, homogenizing, preheating and sterilization, evaporation concentration, spray drying, cooling, sieving, packaging and the like, a low lactose milk power is developed, the milk powder is full of nutriments, lactose hydrolysis rate can be above 70%, not only intolerance symptom of lactose intolerant people to lactose can be relived, but also the requirement of the lactose intolerant people on flavour and taste can be met.
Owner:WANDASHAN MILK IND HEILONGJIANG
Construction of heat-resistant beta-galactosidase mutant
InactiveCN102250856AMaintain heat resistanceSuitable for hydrolysisMilk preparationMicroorganism based processesLactasePasteurization
The invention relates to construction of a heat-resistant beta-galactosidase mutant. When the heat-resistant beta-galactosidase (BgaB) mutant (BgaB-F341T) provided by the invention is used for a lactose hydrolysis process to produce low-lactose products, the inhibition action of the hydrolysis products to the hydrolytic activity of the enzyme can be effectively removed, so that the hydrolysis reaction is thoroughly carried out and the hydrolysis efficiency is improved; and when the heat-resistant beta-galactosidase (BgaB) mutant (BgaB-F341T) is used to replace medium-temperature lactase, the low-temperature hydrolysis process of low-lactose milk can be innovated. The hydrolysis temperature can be set at 55-60 DEG C, at the temperature, not only is the hydrolysis reaction speed high, but also common impure bacteria in the milk has stopped growing, therefore the product hygiene and quality problems caused by impure bacterial contamination can be effectively controlled; and in addition, by the high-temperature hydrolysis process using the heat-resistant lactase, the lactose hydrolysis and pasteurization processes can be combined, not only is the production cycle shortened, but also the energy consumption is reduced by taking full use of the waste heat from the pasteurization process, thus significantly saving production cost.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method of preparing low lactose milk
ActiveCN101223912AIncrease hydrolysis rateDecompose fullyMilk preparationFood preparationLactose intoleranceDietary fiber
The invention relates to a low-lactose milk preparation method which comprises the following steps: (1) mechanical impurities of raw milk are removed by milk purification technique; (2) raw milk after purification is sterilized at ultra-temperature or pasteurized and then cooled to temperature below 8 DEG C; (3) milk compound is prepared; (4) the prepared milk compound is sterilized at ultra-temperature or pasteurized and cooled; (5) lactase preparation is added under aseptic condition; (6) the milk is bottled sterilely. The milk compound in step (3) also comprises: 0.1-10 wt parts of dietary fiber for increasing the health care function of the milk and further comprises essence less than 2 parts by wt. The method of the invention overcomes the shortcoming of low lactose hydrolysis rate of the prior technique. The product prepared by the method of the invention has good stability, and is particularly suitable for people with severe lactose intolerance symptom. The invention is also added with dietary fiber in the formula.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Beta-galactosidase and application thereof
InactiveCN104130990AImprove stabilityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBeta-Galactosidases
The invention discloses beta-galactosidase and application thereof. The application method comprises the following steps: cloning beta-galactosidase genes bgl from bacillus coagulans into an expression vector pETDuet-1, transforming the beta-galactosidase genes into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), thus obtaining the beta-galactosidase with the expression quantity of 2031U / mg. The expressed beta-galactosidase has the optimal pH value of 6.0 and the optimal temperature of 60 DEG C. The recombinant beta-galactosidase can be used for lactose hydrolysis.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Simplified preparation method of low-lactose milk powder
The invention provides a simplified preparation method of low-lactose milk powder, and belongs to the technical field of dairy product production. According to the invention, a pasteurizing process and a lactose degradation process of the milk are carried out synchronically. In the initial stage of the pasteurizing process of the milk, lactase is added into the milk, and the enzyme hydrolysis process and the pasteurizing process are carried out simultaneously. The equipment used for common milk production processes is not increased, such that equipment investment is relatively reduced. Also, the chance for secondary pollution is reduced. Because the enzyme has a characteristic of high activity, the lactose hydrolysis process is achieved simultaneously during the pasteurizing process. Therefore, the production period of the low-lactose milk is shortened, and the production efficiency is improved. With the enzyme, during the lactose hydrolysis process, galactooligosaccharide with relatively high yield is obtained, such that the nutritive value of the milk is improved.
Owner:山东东兴生物科技股份有限公司
Recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing 2'-fucosyllactose and construction method thereof
ActiveCN112625990AEfficient Genome Editing SolutionFermentation does not affectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneColanic acid
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing 2'-fucosyllactose and construction method thereof, and the recombinant Escherichia coli is obtained by knocking out a beta-galactosidase gene in the genome of Escherichia coli, synthesizing a key enzyme gene of colanic acid from guanosine diphosphate fucose, enhancing expression key enzyme genes of lactose permease genes and a guanylate diphosphate fucose denovo synthesis route and expressing exogenous fucosyltransferase genes. According to the scheme, lactose hydrolysis can be reduced, and the rate of transferring exogenous lactose into cells is increased, so that the concentration of lactose in the cells is effectively increased; meanwhile, the consumption of the guanosine diphosphate fucose is reduced, and the concentration of the guanosine diphosphate fucose in cells is effectively improved; through codon optimization, the expression of an exogenous fucosyltransferase gene is improved, and synthesizing of the 2'-fucosyllactose is effectively promoted.
Owner:量子高科(广东)生物有限公司
Synbiotic product and it's application as a carrier of natural bioactive substances in functional food additives
InactiveUS20070166433A1Long storageFast shippingMilk preparationSugar food ingredientsBacteroidesLactobacillus acidophilus
It used as carrier of bioactive substances of natural origin like dry herb extracts or combinations thereof, other vegetable products as essential oils, fruit concentrates, animal products as bee products, added to vitamins combinations, said product ensuring bacteria proliferation and growth when stored and after intake. The bioactive products can be stored for period 2 to 3 years without the probiotic losing its activity. In the gastroinitestinal tract they can colonize supplying the body with useful substances resulting from their metabolism ensuring fast transportation of bioactive substances to body's cells. It contains low-lactose sour-milk product, low-lactose hydrolyzate with more than 95% degraded milk casein, saccharose, pectin, full-cream or skimmed low-lactose cow's milk fermented using selected strains of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, and additionally lyophilized monoculture of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus or lyophilized mixture of monocultures of Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactobacillus lactis and dextrose.
Owner:PENEVA DANIELA PETROVA +1
Lactase and recombinant expression engineering bacterium thereof
InactiveCN103031289AIncrease hydrolysis rateFungiMicroorganism based processesLactaseAspergillus oryzae
The invention relates to lactase and a recombinant expression engineering strain thereof. The conservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO:M2012482. The trichoderma reesei strain disclosed by the invention can efficiently express the lactase of aspergillus oryzae, and the enzyme activity can reach 251U / ml. The optimum acting pH value of the lactase is 5.0 and the optimum acting temperature is 50 DEG C, and the lactase can effectively hydrolyze lactose in the milk by a hydrolysis rate of 70%, so that the lactase has a potential application value for industrial production of low-lactose milk.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Brown concocted concentrated milk and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses brown concocted concentrated milk and a preparation method thereof. The brown concentrated milk is composed of the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 42-46% of white granulated sugar, 1.5-2.5% of cream, 0.0001-0.0003% of lactose, 0.05-0.1% of lactase, and the balance of raw milk, wherein the raw milk is raw milk and / or a dairy product. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses the preparation method of the brown concocted concentrated milk. The method comprises the following steps: 1) milk powder dissolution; 2) lactose hydrolysis; 3) warming for browning; 4)cream adding; 5) homogenization and sterilization; 6) sugar liquid disinfection; 7) concentration; 8) homogenization; and 9) cooling crystallization. The brown concentrated milk prepared by the methoddoes not need extra glucose, has moderate viscosity and good product texture and flavor stability, and can meet the demand of consumers and market for scorch-aroma dairy products.
Owner:广州风行乳业股份有限公司
Marine-microbe-sourced low-temperature beta-galactosidase, and coding gene thereof and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of marine biotechnology, and provides a marine-microbe-sourced low-temperature beta-galactosidase, which is obtained by fermentation culturing and purification of a marine halomonas sp. strain P6009-1 obtained by the applicant previously. The marine halomonas sp. strain P6009-1 is cultured and separated from seawater in East China Sea areas, and has a collection number of CCTCC No: M2011001. Under a temperature of 0 DEG C, a capacity of the enzyme in catalyzing lactose hydrolysis is 20% of a maximal activity, such that good low-temperature performance is shown. The invention further provides a coding gene of beta-galactosidase, and an application of beta-galactosidase in decomposing milk lactose.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Controllable post-acidification fermented milk product and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108684816ASolve the problem of post-acidificationMilk preparationLactobacillusLactaseFermentation starter
The invention discloses a controllable post-acidification fermented milk product. The controllable post-acidification fermented milk product is prepared through the following steps that at the temperature of 44-45 DEG C, lactase is used for performing enzymolysis on raw milk after normalization treatment and setting constant volume until the lactose hydrolysis rate is 40-50%, and a fermenting agent is inoculated for fermentation until the pH is 4.5-4.6, wherein the fermenting agent is selected from one kind of lactobacillus casei and Switzerland bacterium lacticum or is formed by mixing lactobacillus casei with Switzerland bacterium lacticum. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the fermented milk product. According to the method, the problems that the fermented milk product is easy to be subjected to post-acidification within the storage period, so that the mouth feel is sour and the quality is poor, are solved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA DAIRY TECH RES INST CO LTD
Method for testing lactose hydrolysis ratio in low lactose milk
ActiveCN101034066AHigh speedLow costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSpecial data processing applicationsPhysical chemistryCow milk
This application discloses a glucose oxidase - spectrophotometric method of measuring low lactose creamery's lactose hydrolization rate. this method includes (1) determine lactose concentration after creamery hydrolization; (2) determine lactose concentration before creamery hydrolization;(3) calculate lactose hydrolization rate, hydrolyze rate =( lactose concentration after hydrolization / lactose concentration before hydrolization)X100%. This test method has feature of fast velocity, low cost, high accuracy.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
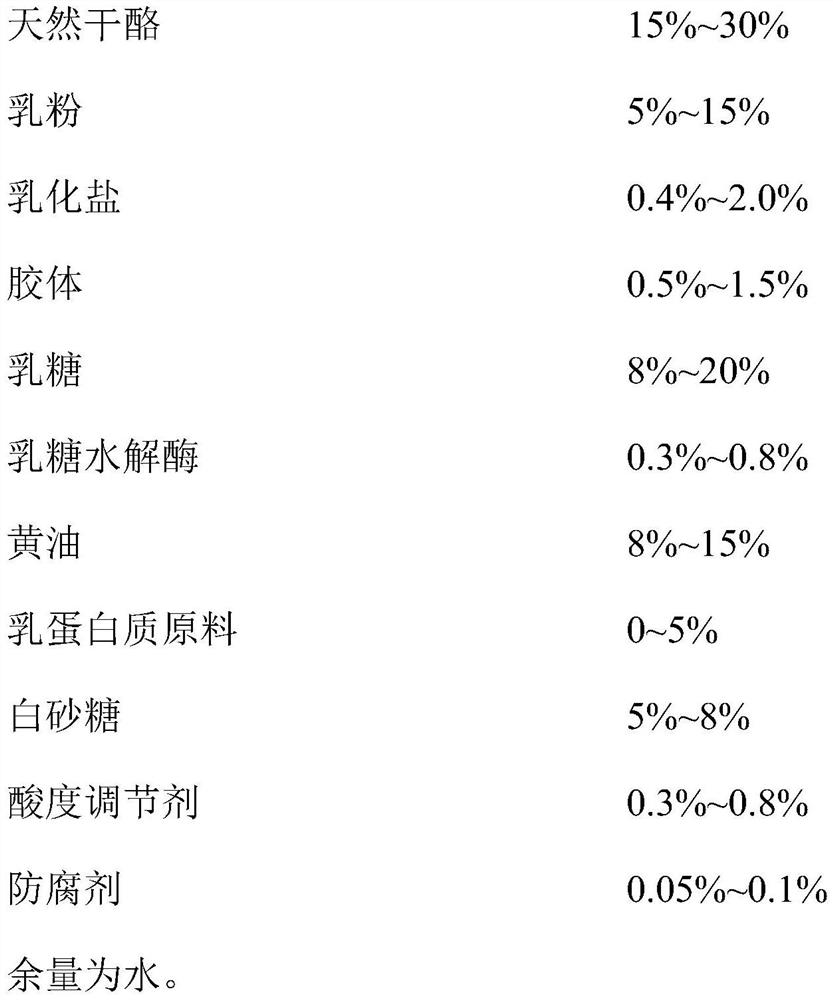
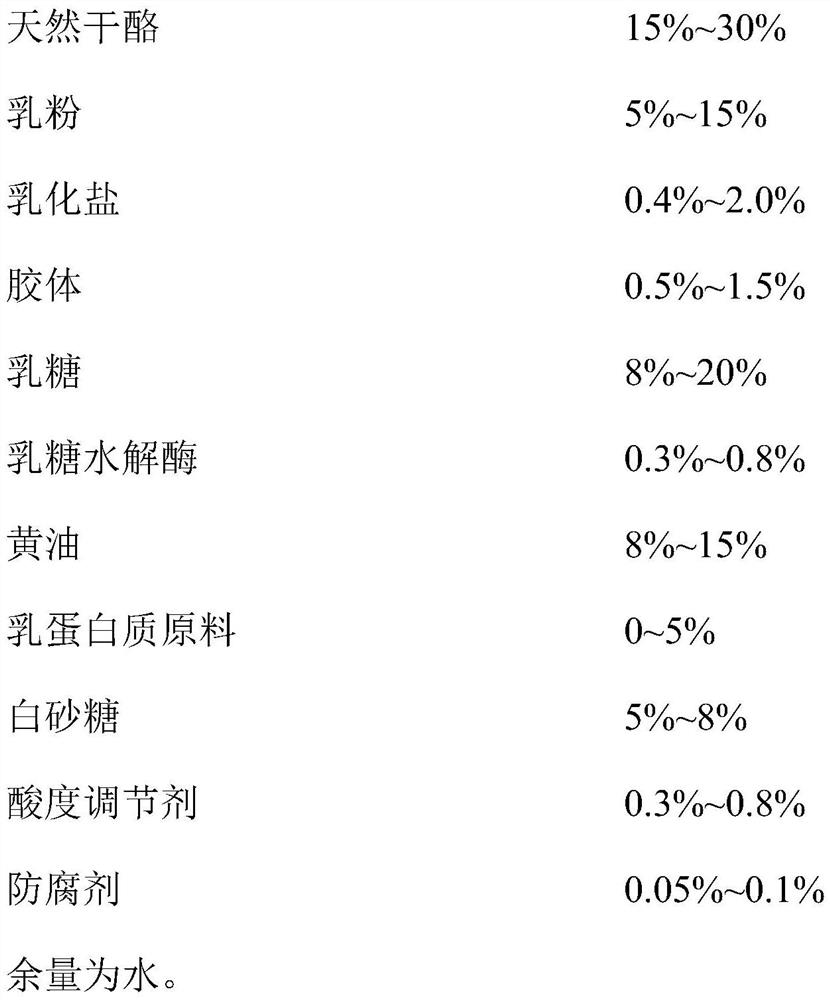
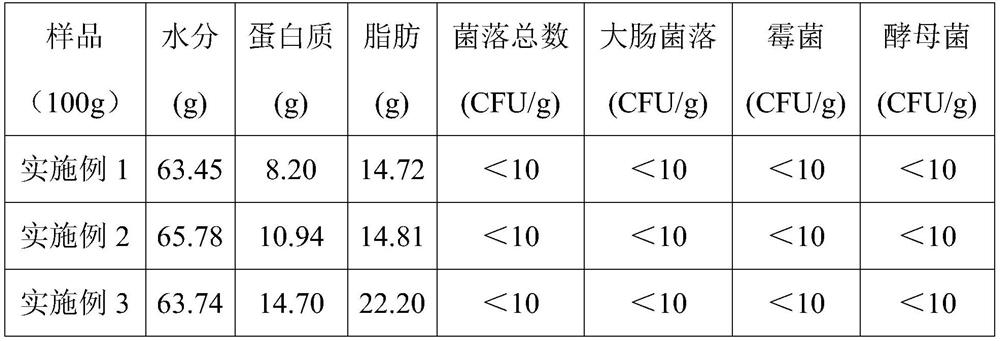
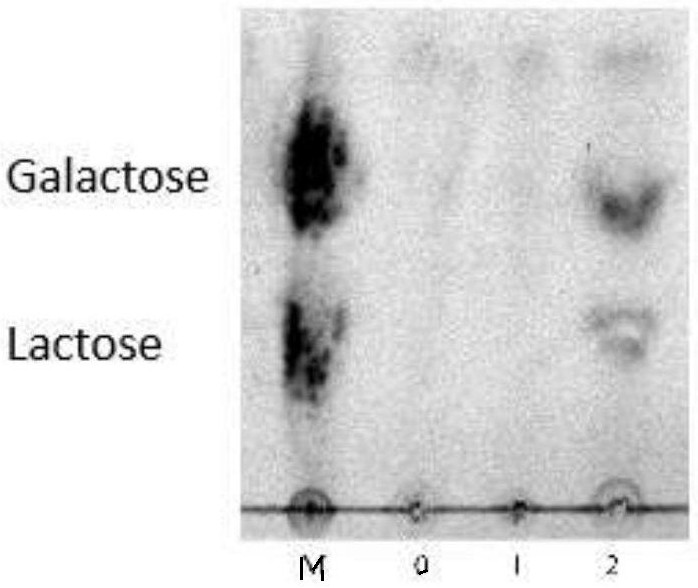
Processed cheese and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111955555AStrong aromaUnique Charcoal FlavorCheese manufactureBiotechnologyMaillard reaction
The invention provides processed cheese and a preparation method thereof. The processed cheese comprises natural cheese, milk powder, emulsifying salt, colloid, lactose, lactose hydrolase and water. The preparation method of the processed cheese comprises the following steps: adding water into natural cheese, butter, milk powder and milk protein raw materials, chopping and mixing to obtain a chopped mixture, adding lactose, white granulated sugar, emulsifying salt and colloid into the chopped mixture, heating and mixing, adding lactose hydrolase, and stirring and mixing, raising the temperature to carry out Maillard reaction, dynamically sterilizing the Maillard reaction product, and filling the sterilized product to obtain the processed cheese. According to the invention, the Maillard reaction is introduced into the preparation of the processed cheese, the charcoal-roasted flavor processed cheese and the preparation method thereof are provided, and the processed cheese prepared according to the invention is rich in nutrition, strong in stability, attractive in color and excellent in flavor and taste.
Owner:上海芝然乳品科技有限公司
Beta-galactosidase and application thereof in lactose degradation
PendingCN113493777ANovel structureNovel functionFermentationGlycosylasesReaction temperatureHydrolase
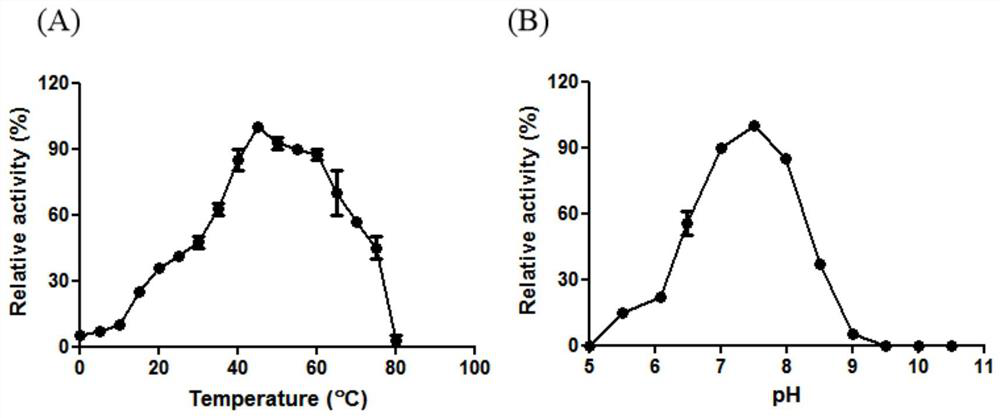
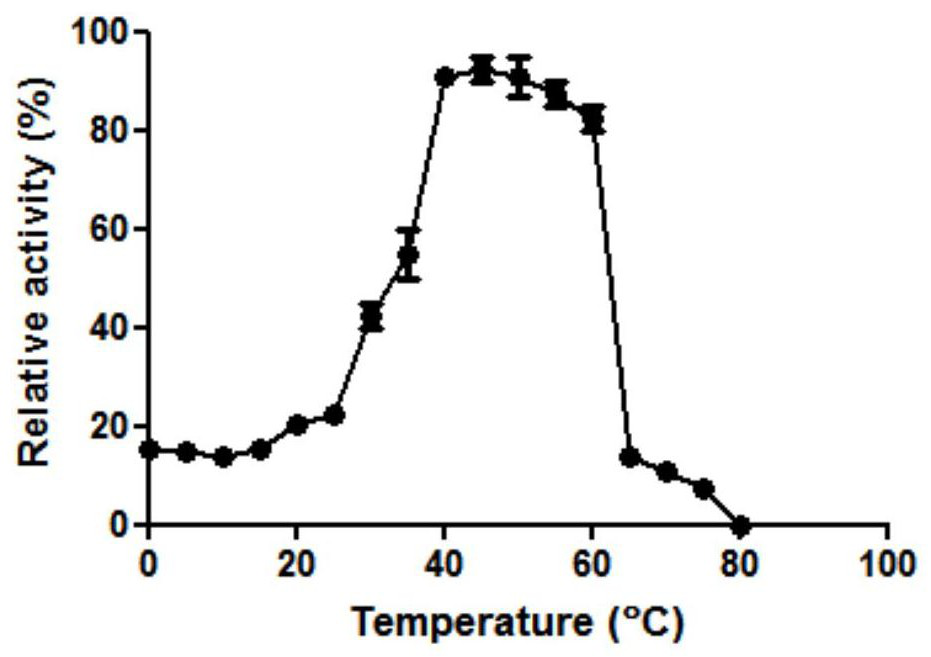
The invention relates to beta-galactosidase and an application thereof in lactose degradation. The amino acid sequence of the beta-galactosidase is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The beta-galactosidase Gal39 is a lactose hydrolase with a novel structure and functions, the similarity between the amino acid sequence of the beta-galactosidase Gal39 and the reported beta-galactosidase sequence is only 79.28%, and the beta-galactosidase Gal39 is a new enzyme. The yield of the beta-galactosidase can reach 366.2 U / mL, the optimum reaction temperature is 40 DEG C, and the optimum reaction PH is 7.5. The beta-galactosidase disclosed by the invention has heat resistance, and can still keep 56.2% of enzymatic activity after being incubated at 60 DEG C for 1 hour. The beta-galactosidase disclosed by the invention is high in yield and good in stability, and has excellent industrial application potential.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Artificially modified beta-galactosidase GaLT1 and application thereof in lactose hydrolysis
PendingCN114149987AImprove degradation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPeptide sequenceAmino acid
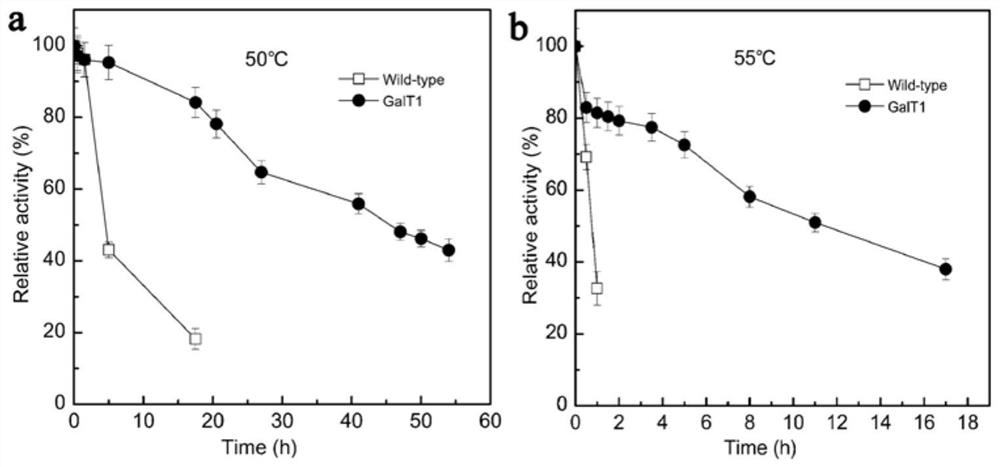
The invention discloses an artificially modified beta-galactosidase GaLT1 and an application of the artificially modified beta-galactosidase GaLT1 in hydrolysis of lactose, the beta-galactosidase GaLT1 is formed by connecting an artificially modified amphiphilic oligopeptide sequence to an N-terminal amino acid sequence of wild type beta-galactosidase GaLT0 derived from T.cotoductus, and the amino acid sequence of the beta-galactosidase GaLT1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. Compared with wild type beta-galactosidase GaLT0, the beta-galactosidase GaLT1 disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the temperature stability is obviously improved, and the half-life period at 55 DEG C is prolonged by 10 times; besides, the milk lactose degradation rate of the beta-galactosidase GaLT1 is also obviously improved, 95% of lactose in milk can be degraded within 2 hours at 55 DEG C, and the national standard of lactose-free milk products is met.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Heat-resistant beta-galactosidase and application thereof to lactose degradation
ActiveCN113564146ANovel structureNovel functionFermentationGenetic engineeringReaction temperatureHydrolase
The invention relates to heat-resistant beta-galactosidase and an application thereof to lactose degradation. The amino acid sequence of the beta-galactosidase is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The beta-galactosidase Gal-T is a lactose hydrolase with a novel structure and functions, the similarity between the amino acid sequence of the beta-galactosidase Gal-T and the reported beta-galactosidase sequence is only 75.75%, and the beta-galactosidase Gal-T is a new enzyme. The yield of the beta-galactosidase can reach 460.4 U / mL, the optimum reaction temperature is 45 DEG C, and the optimum reaction PH is 7.5. The beta-galactosidase disclosed by the invention has heat resistance, and shows wide temperature stability in a temperature range of 40 DEG C to 60 DEG C. The beta-galactosidase disclosed by the invention is high in yield and good in thermal stability, and has excellent industrial application potential.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
A kind of cold tolerance lactase gene and its expression vector and protein
ActiveCN110628792BMaintain biological activityStrong lactose hydrolysis activityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionLactaseNucleotide
The present invention relates to an artificially synthesized gene encoding cold tolerance lactase, the gene at least contains a DNA piece of one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence table; 2) the nucleotide sequence with The nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 has more than 90% homology and encodes a nucleotide sequence of the same biological function protein; or 3) hybridizes with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and encodes Nucleotide sequences of proteins with the same biological function. According to the gene sequence of the present invention, the recombinant vector is further constructed and transformed into yeast, which can realize the constitutive secretory expression of the recombinant lactase under high-density fermentation conditions, and can obtain a purity higher than 95% through simple nickel affinity purification. And active protein with high protein concentration, the active protein has a strong activity of hydrolyzing lactose at low temperature, and will provide efficient enzyme products for converting lactose in dairy products.
Owner:HUAIHUA UNIV
Low-lactose milk powder and preparation method thereof
PendingCN107432323AQuality assuranceGuaranteed microbial indicatorsMilk preparationLactaseFluidized bed
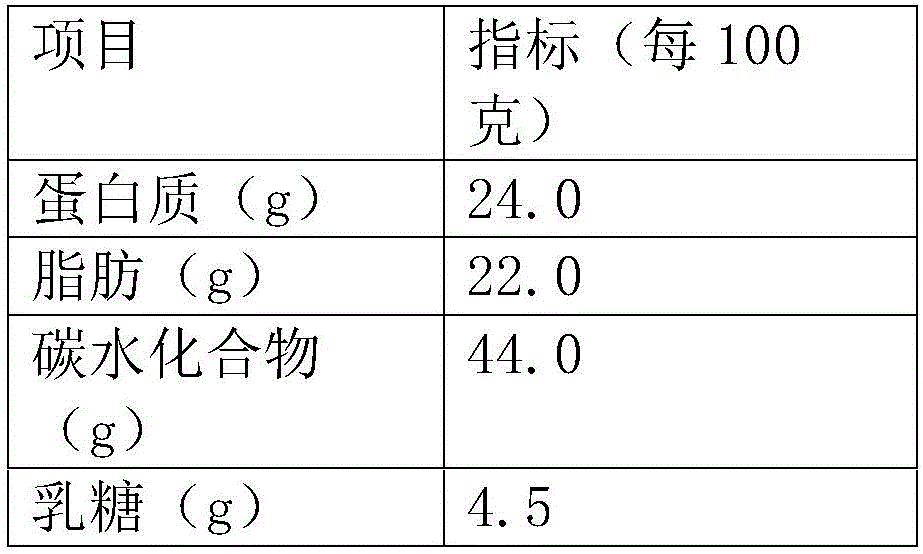
The title of the invention is low-lactose milk powder and a preparation method thereof. The invention discloses low-lactose milk powder, which contains (by weight): 22-25% of fat, 20-23% of protein and 5.5% and below of lactose. The invention discloses a preparation method of the low-lactose milk powder, comprising the following steps: (1) acceptance inspection of raw milk; (2) separation for milk purification; (3) pre-sterilization; (4) primary burdening; (5) secondary burdening; (6) homogenizing and pre-sterilization; (7) lactase enzymolysis; (8) enzyme deactivation treatment; (9) milk heating-up and preheat sterilization; (10) evaporation and concentration; (11) high pressure atomizing; (12) drying and fluidized bed redrying; (13) powder discharge and powder screening; and (14) packaging. By controlling physical and chemical indexes of a material before hydrolysis and by the utilization of a high-temperature lactose enzyme hydrolysis technology, the low-lactose milk powder is produced, and lactose hydrolysis rate reaches 80% and above.
Owner:YUNNAN XINXIWANG DENGCHUAN DIEQUAN DAIRY +1
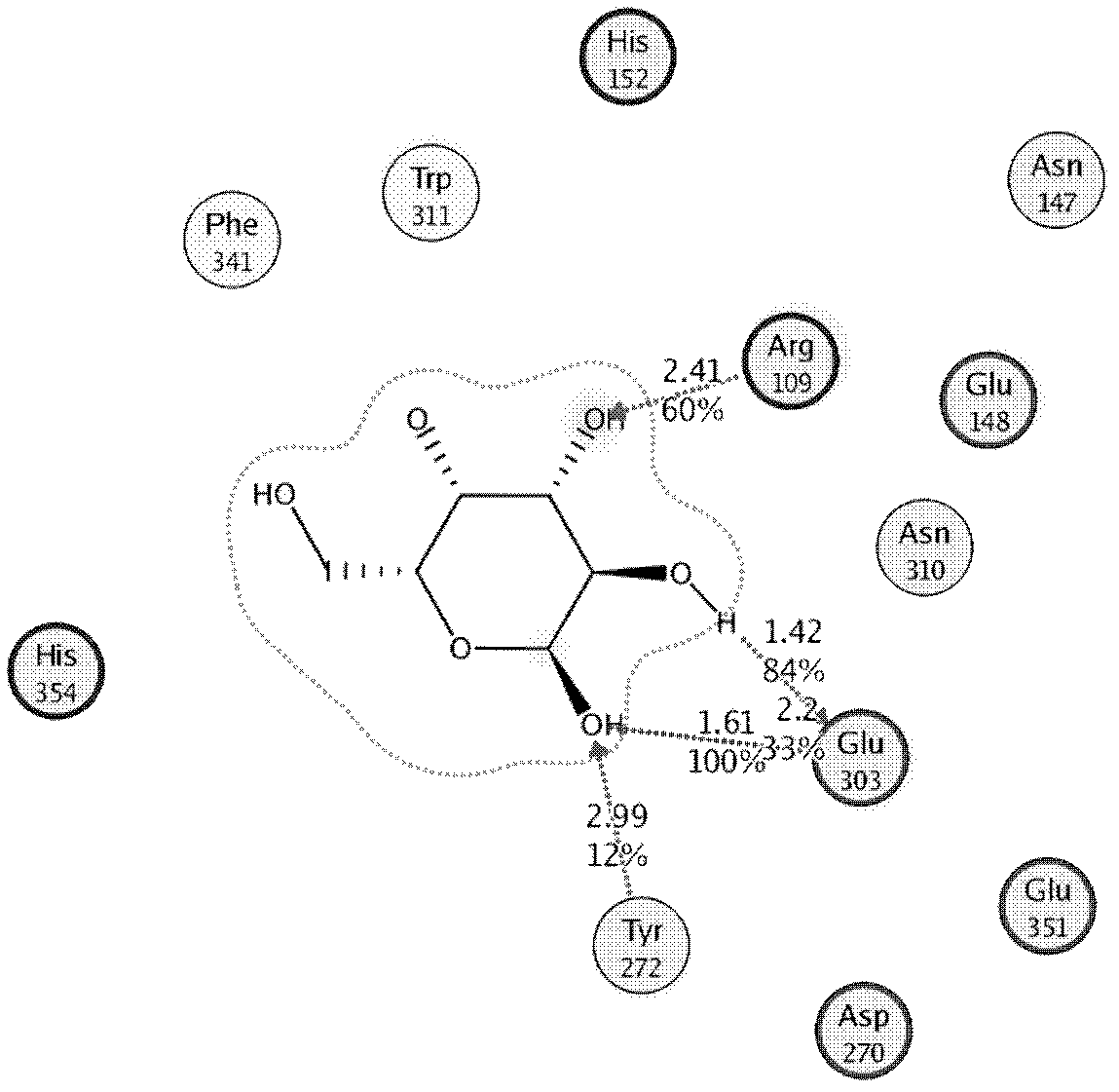
Beta-galactosidase two-site mutant with high transglycosylation and low hydrolytic activity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105950588AReduce degradationLow hydrolytic activityNucleic acid vectorFermentationGalactooligosaccharideBeta-Galactosidases
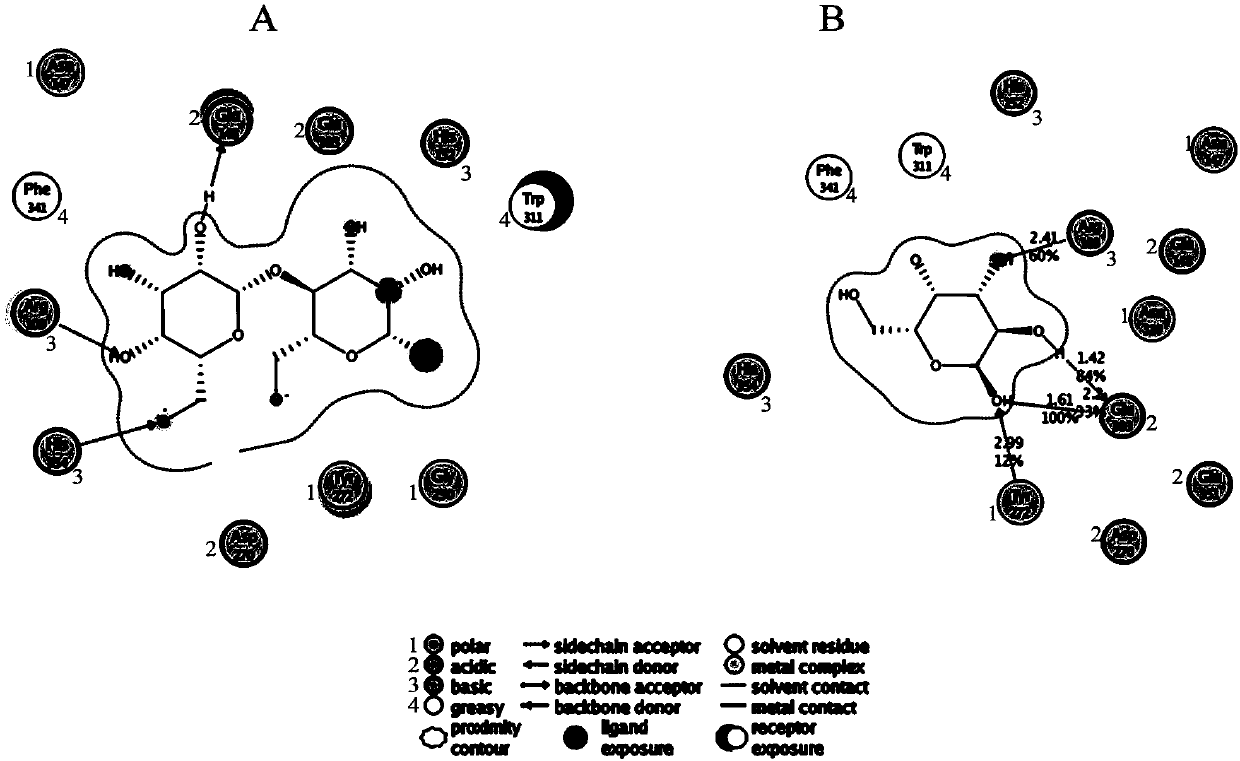
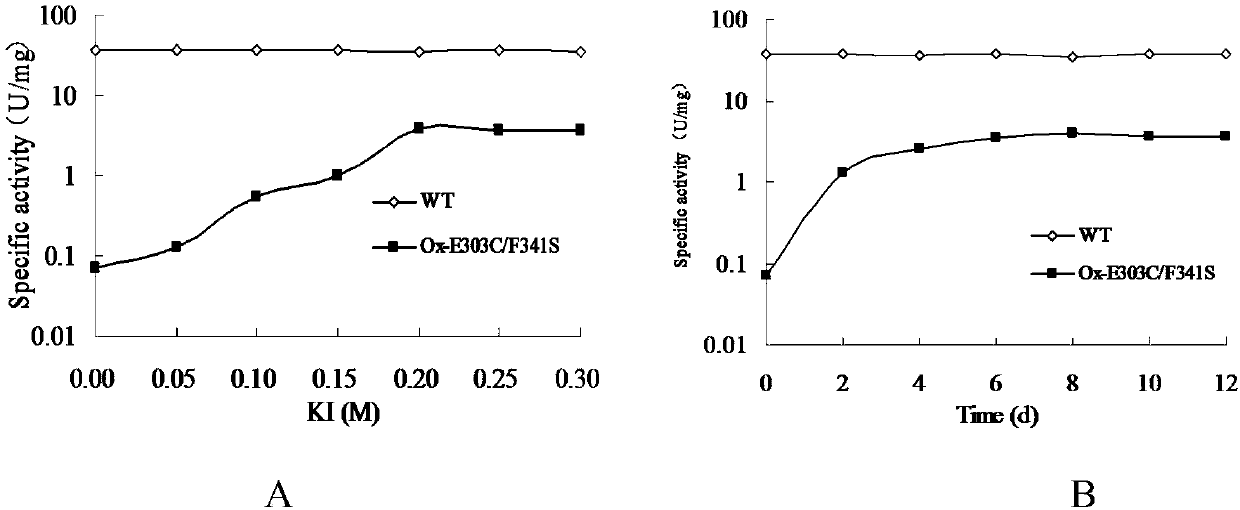
The invention provides a beta-galactosidase two-site mutant with the high transglycosylation and the low hydrolytic activity. The mutant is obtained through the steps that site-specific mutagenesis on an E303 site and an F341 site of beta-galactosidase, wherein the E303 site is mutagenized into cysteine (Cys) from original glutamic acid (Glu), and the F341 site is mutagenized into serin (Ser) from original phenylalanine (Phe); a two-site mutant is subjected to KI oxidation treatment. The invention further relates to a construction method and application of the two-site mutant. According to the beta-galactosidase two-site mutant, a bacillus stearothermophilus source beta-galactosidase (BgaB) is taken as a function renovation objective, a mixture of oligosaccharides larger than a disaccharide can be obtained by catalyzing substrate lactose through the obtained two-site mutant, the synthetic amount reaches 9.5%, and the degradation capacity of the two-site mutant to the synthetic product is reduced. In addition, the mutant is suitable for catalyzing lactose hydrolysis and galactooligosaccharide synthesis under the neutral and high-temperature conditions.
Owner:中诺生物科技发展江苏有限公司
Process for preparing a functional fermented milk product and functional fermented milk product prepared therewith
Owner:V PRODS CORP
Recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing 3-fucosyllactose and construction method thereof
PendingCN112662604AOvercome the cycleOvercoming success rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneColanic acid
The invention provides recombinant Escherichia coli for synthesizing 3-fucosyllactose and a construction method of the recombinant Escherichia coli, and the recombinant Escherichia coli is prepared by knocking out a beta- galactosidase gene in the genome of Escherichia coli, synthesizing a key enzyme gene of Colanic acid from guanosine diphosphate fucose, enhancing expression of lactose permease genes and key enzyme genes of a guanylate diphosphate fucose de novo synthesis route and expressing exogenous fucosyltransferase genes. According to the scheme, lactose hydrolysis can be reduced, and the rate of transferring exogenous lactose into cells is increased, so that the concentration of lactose in the cells is effectively increased; meanwhile, the consumption of the guanosine diphosphate fucose is reduced, and the concentration of the guanosine diphosphate fucose in cells is effectively improved; and through codon optimization, the expression of an exogenous fucosyltransferase gene is improved, and the synthesis of 3-fucosyllactose is effectively promoted.
Owner:量子高科(广东)生物有限公司
Method of preparing low lactose milk
ActiveCN100566578CIncrease hydrolysis rateDecompose fullyMilk preparationFood preparationDietary fiberLactose intolerance
The invention relates to a low-lactose milk preparation method which comprises the following steps: (1) mechanical impurities of raw milk are removed by milk purification technique; (2) raw milk after purification is sterilized at ultra-temperature or pasteurized and then cooled to temperature below 8 DEG C; (3) milk compound is prepared; (4) the prepared milk compound is sterilized at ultra-temperature or pasteurized and cooled; (5) lactase preparation is added under aseptic condition; (6) the milk is bottled sterilely. The milk compound in step (3) also comprises: 0.1-10 wt parts of dietary fiber for increasing the health care function of the milk and further comprises essence less than 2 parts by wt. The method of the invention overcomes the shortcoming of low lactose hydrolysis rate of the prior technique. The product prepared by the method of the invention has good stability, and is particularly suitable for people with severe lactose intolerance symptom. The invention is also added with dietary fiber in the formula.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
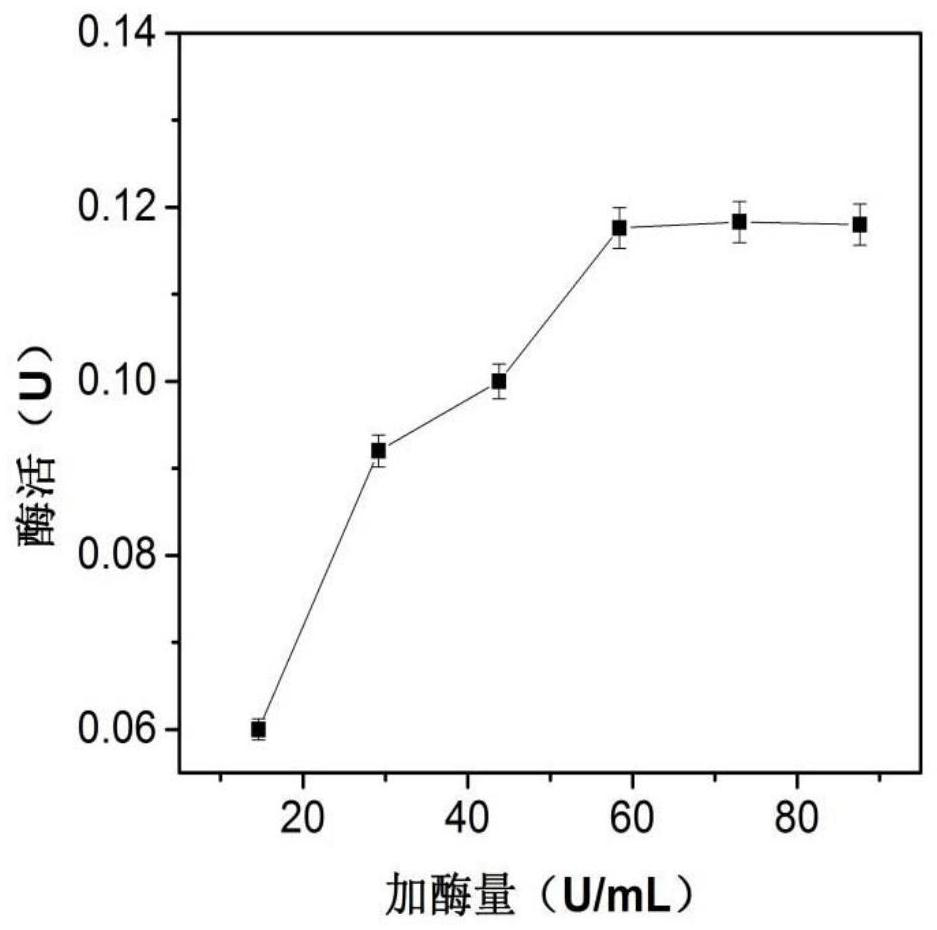
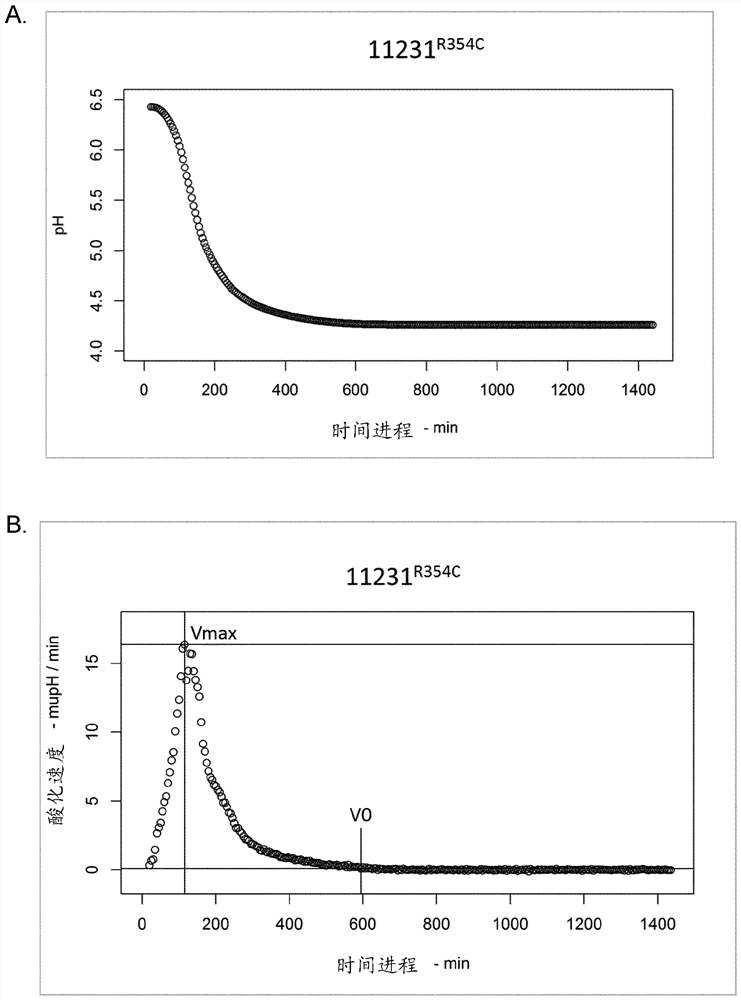
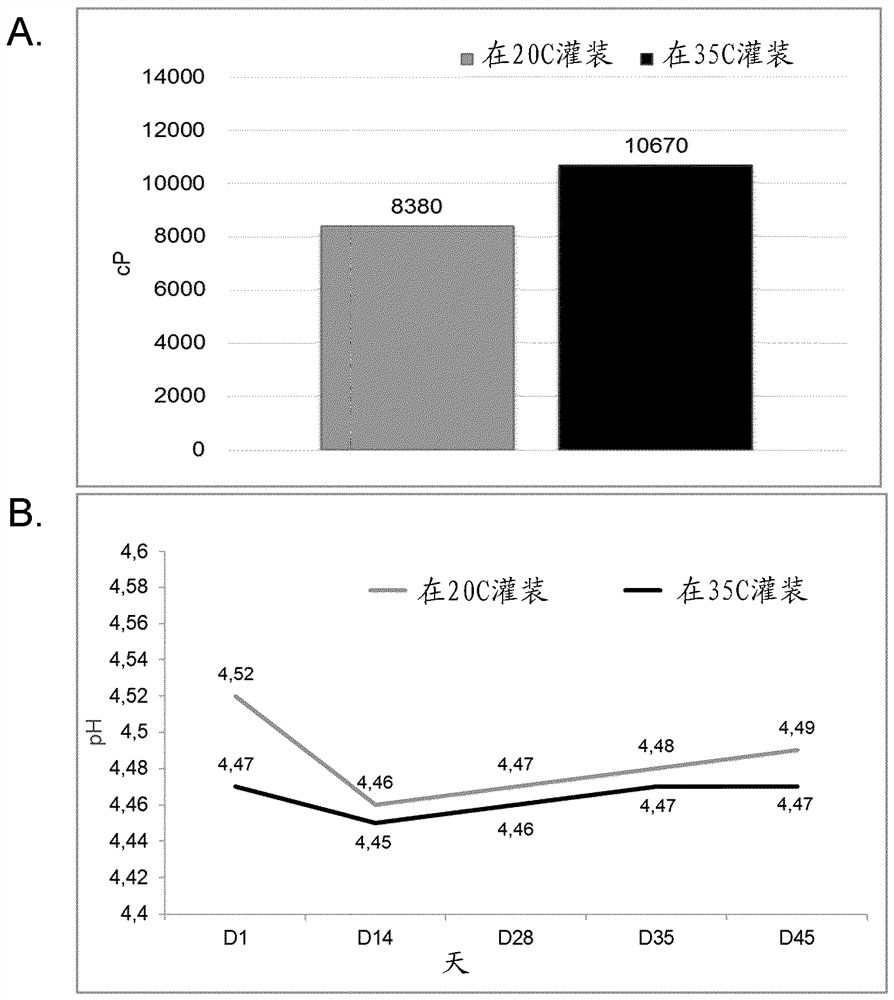
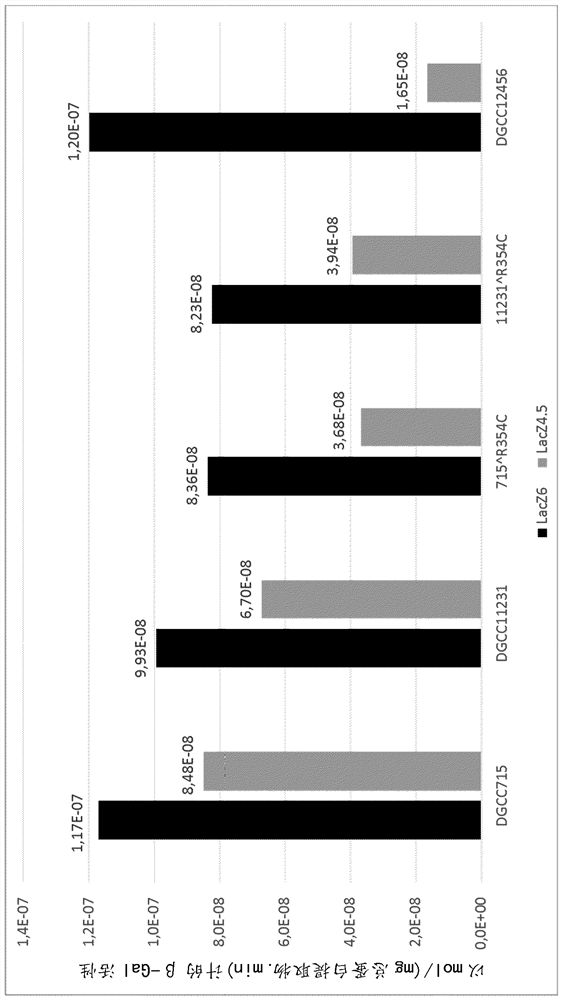
New lactic acid bacteria
The invention relates to a polynucleotide comprising a lacZ gene (lacZFS) encoding a [beta]-galactosidase characterized by a particular profile regarding its efficiency of hydrolysis of lactose. The invention is also directed to a Streptococcus thermophilus strain comprising a lacZFS allele and bacterial composition thereof, and their use to obtain fermented milk not undergoing post-acidification.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Zero-lactose full milk powder and preparation method thereof
The invention provides zero-lactose full milk powder and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding raw milk, which is qualified through inspection and has the temperature of 4 DEG C to 8 DEG C, and lactase, of which the weight is 0.05%-0.1% the total weight of the raw milk, in a mixing process, carrying out uniform stirring, and carrying out hydrolyzing for 24-48 hours at the temperature of 4 DEG C to 8 DEG C; or performing pasteurization on the raw milk, which is qualified through inspection and has the temperature of 4 DEG C to 8 DEG C, for 15 seconds at the temperature of 65 DEG C to 85 DEG C in the mixing process, cooling the temperature of the raw milk to 38 DEG C to 42 DEG C, adding the lactase, of which the weight is 0.05%-0.1% the total weight of the raw milk, carrying out uniform stirring, and carrying out hydrolyzing for 2-4 hours at the temperature of 38 DEG C to 42 DEG C; and carrying out sampling and detecting again to obtain zero-lactose full milk when the hydrolysis rate of the lactose is more than 98% or more and the residual quantity of the lactose is 0.06% or less. According to the zero-lactose full milk powder and the preparation method thereof, the lactose is thoroughly hydrolyzed before concentration and spray drying, the condition that the concentration, the spray drying and filling are performed after the product reaches a zero-lactose level is guaranteed, the hydrolysis rate of the lactose can be more than 98%, the zero lactose level is achieved, and the condition that the lactose content required by national standards is 0.5% or below is met.
Owner:河北德玉泉乳业有限公司
Lactose free milk products
Described herein are liquid, concentrated or dried lactose-free skim milk products or lactose- free, fat containing milk products that exhibit stability during thermal processing and storage as a result of the reductive carbohydrate to milk protein ratio of the milk products. The osmolality of the lactose-free milk products described herein also enable improved nutritional availability when compared to commercially available lactose hydrolysed milk products.
Owner:AGROTEKNIK +1
On-Line System, Method of its Calibration and Simultaneous Detection of Antibiotic Residues and Their Concentration in Milk
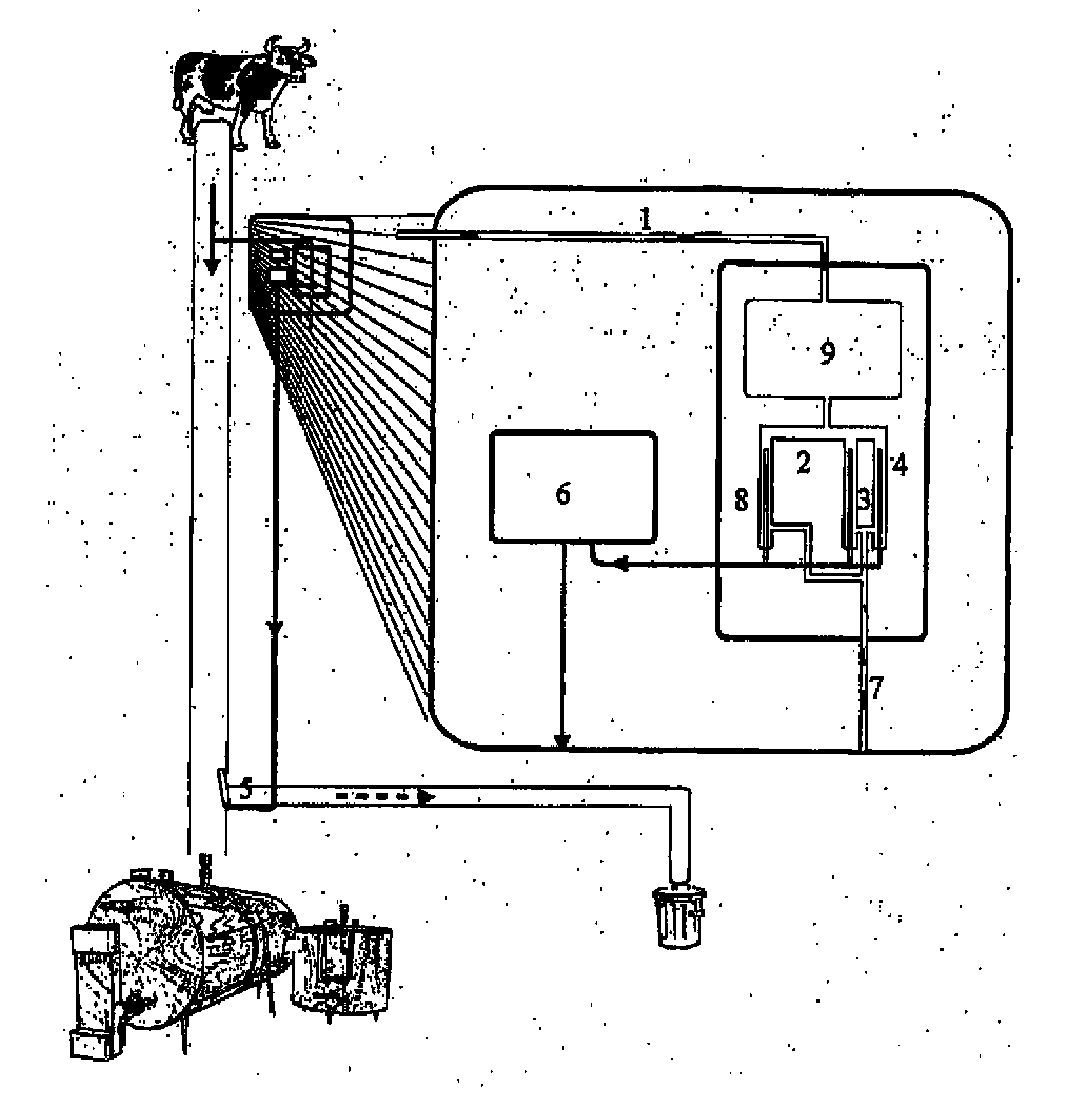
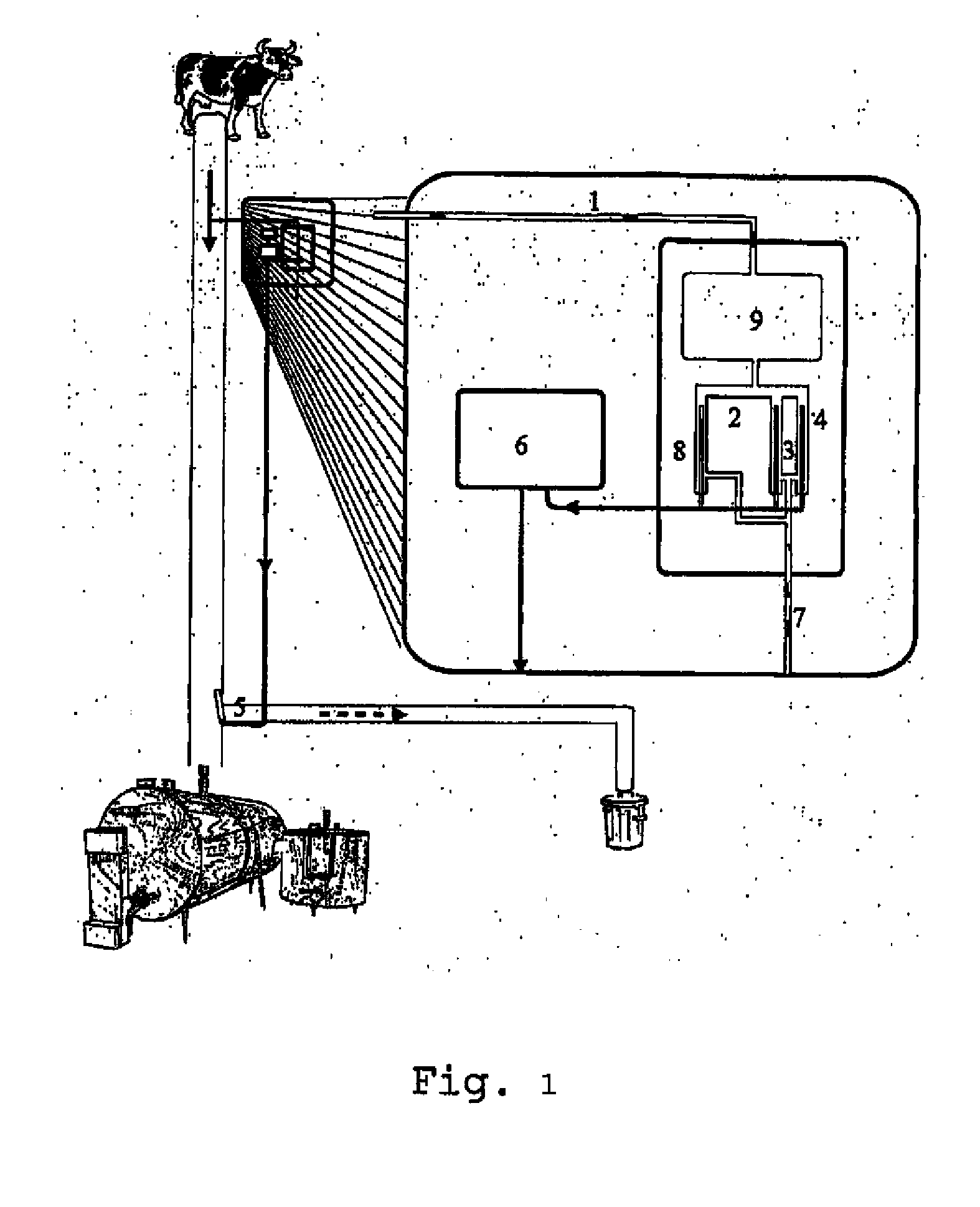
InactiveUS20130011528A1Avoid pollutionIncrease ionic strengthMilk preparationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMilk sampleAntibiotic Y
The present invention discloses an on-line system, a method for its calibration and simultaneous detection of antibiotic residues and their concentrations in milk. The system comprises a device for lactose hydrolysis to increase the concentrations of glucose and galactose in milk samples at least 10 times to obtain their equal concentrations in all investigated samples and a biosensor array to measure the transient phase decrease of dissolved oxygen concentration caused by the enzymatic oxidation of glucose and galactose. Parameters, characterising the oxidation of glucose and galactose, are calculated for each biosensor on the basis of the transient phase decrease of dissolved oxygen concentration and initial oxygen concentration in milk sample. The combination of different parameters of different biosensors forms a pattern of milk sample and in the presence of antibiotics this combination forms the fingerprints of particular antibiotics.
Owner:UNIV OF TARTU
Immobilization method of beta-galactosidase and application of beta-galactosidase in preparation of low-lactose milk
PendingCN111763666AIncrease hydrolysis rateSimple processMilk preparationOn/in organic carrierBiotechnologyGalactosidases
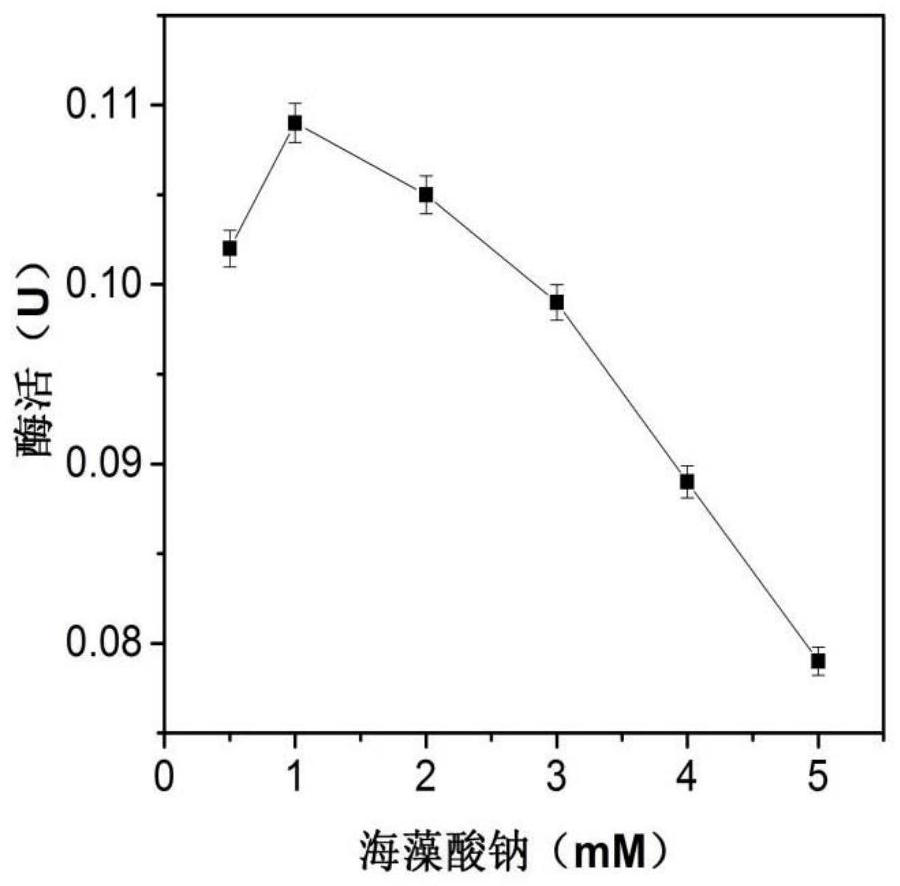
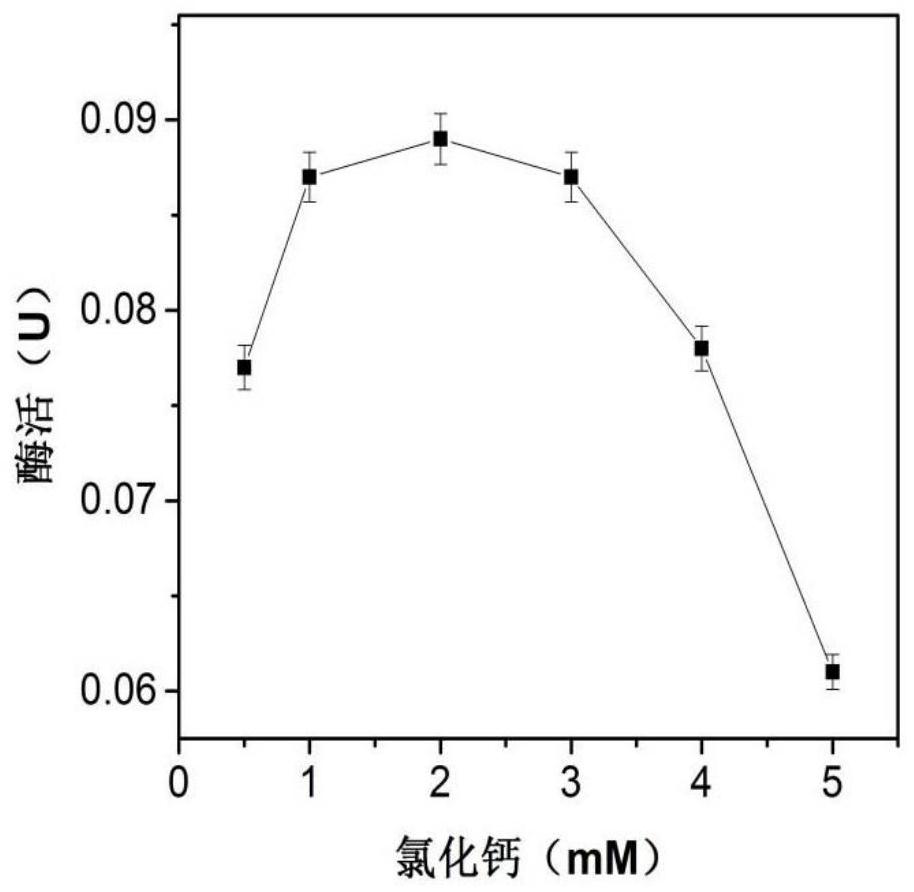
The invention discloses an immobilization method of beta-galactosidase and an application of the beta-galactosidase in preparation of low-lactose milk, and the immobilized beta-galactosidase is prepared by taking sodium alginate as an immobilization carrier. The enzyme activity of the obtained immobilized beta-galactosidase is up to 438 U / mg; when the immobilized beta-galactosidase is used for hydrolyzing lactose in milk, 64% of lactose can be hydrolyzed only in 40 min, and after the immobilized beta-galactosidase is recycled four times, the lactose hydrolysis rate can still be kept 60% or above. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, high speed, high hydrolysis rate and good industrial application value.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
New lactic acid bacteria
The invention relates to a polynucleotide comprising a lacZ gene (lacZ FS ) encoding a [beta]-galactosidase characterized by a particular profile regarding its efficiency of hydrolysis of lactose. The invention is also directed to a Streptococcus thermophilus strain comprising a lacZ FS allele and bacterial composition thereof, and their use to obtain fermented milk not undergoing post-acidification.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com