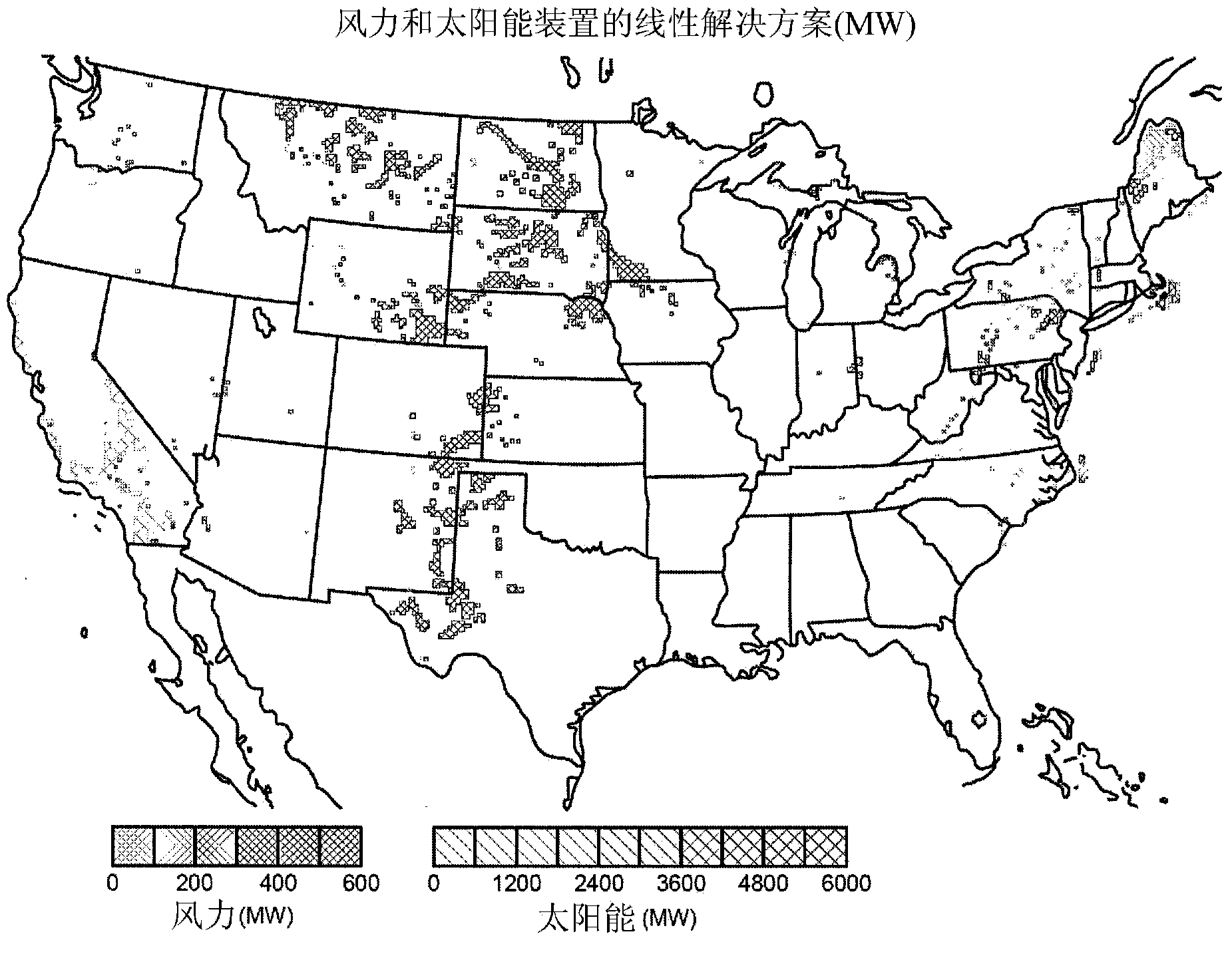
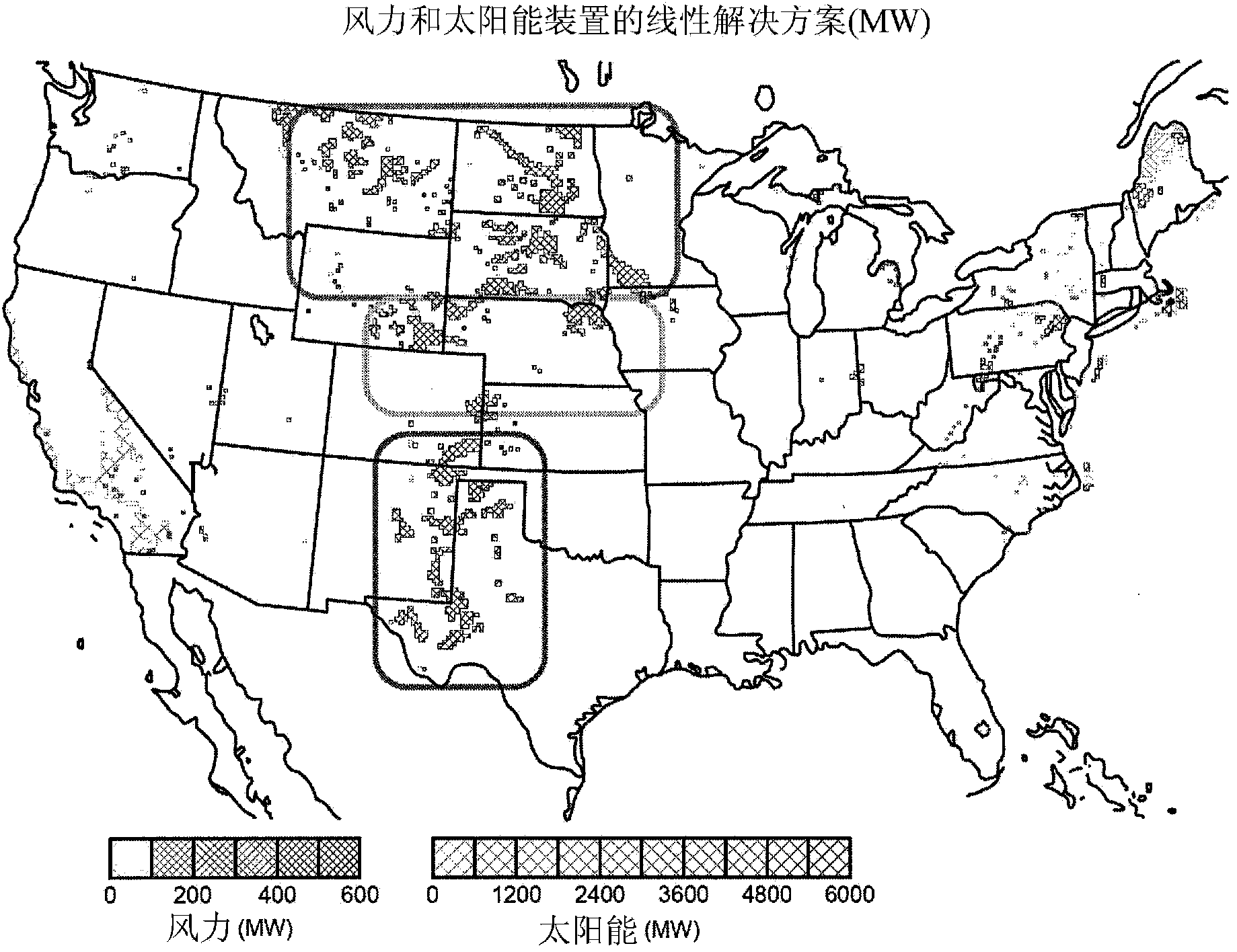
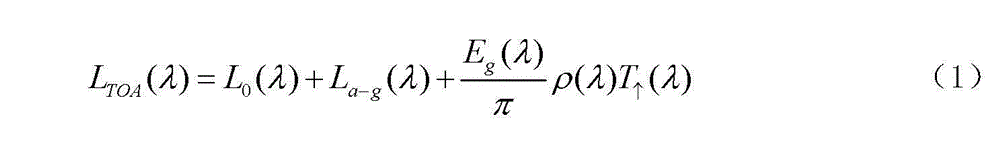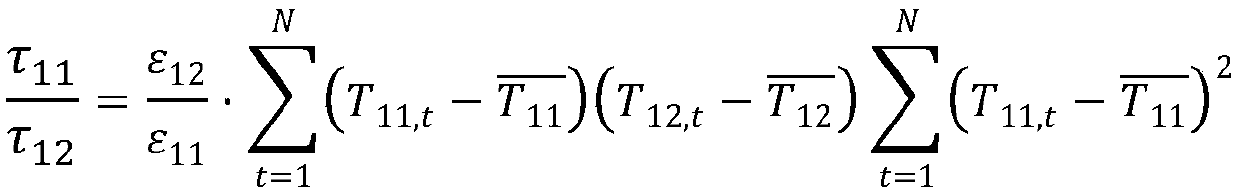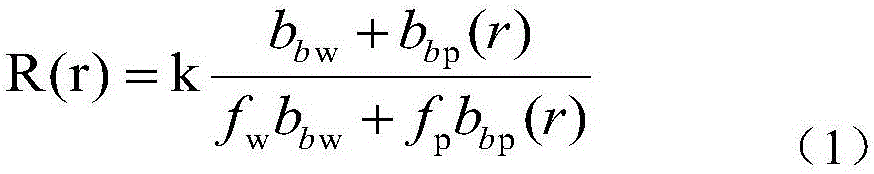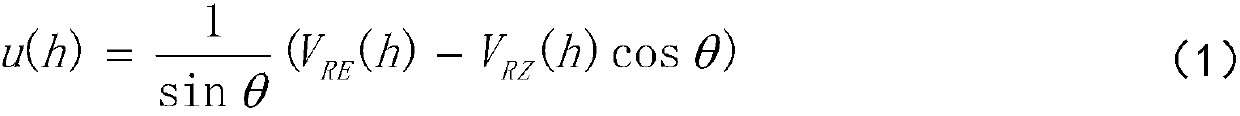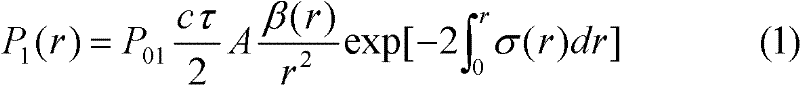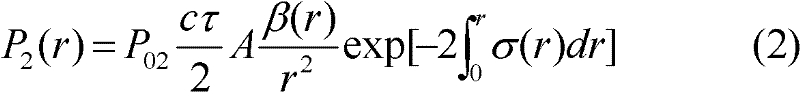Patents
Literature
48 results about "Radio atmospheric" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
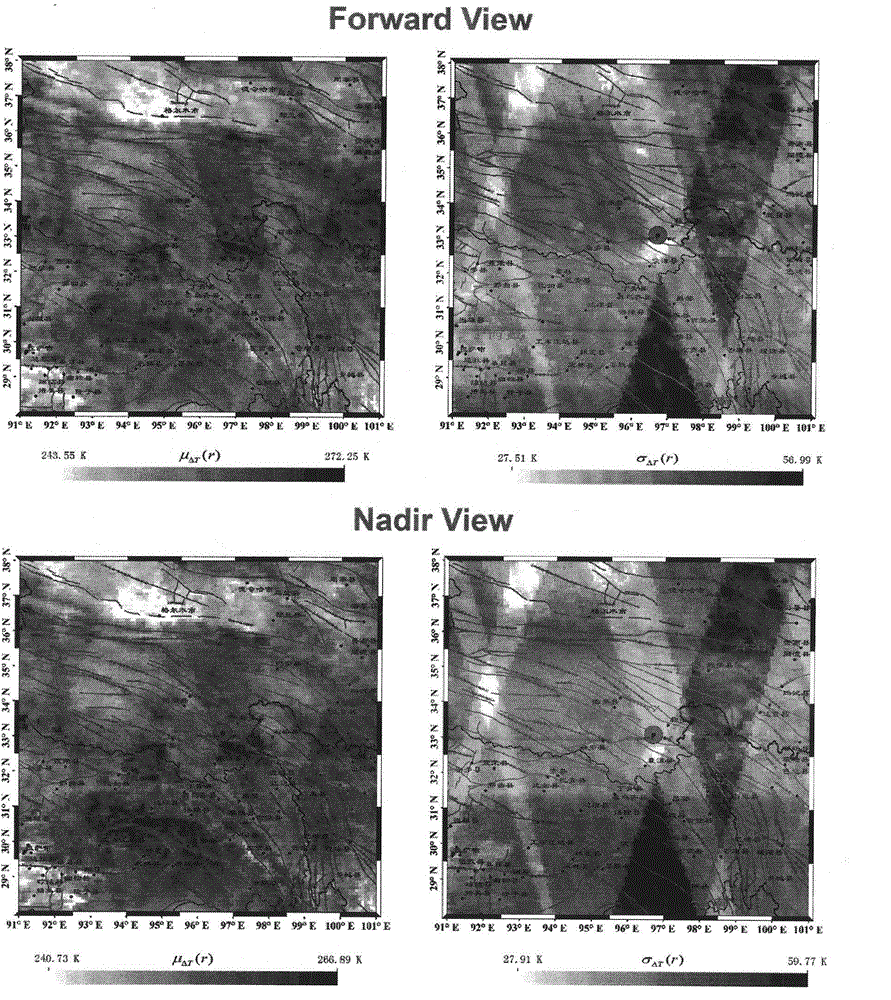
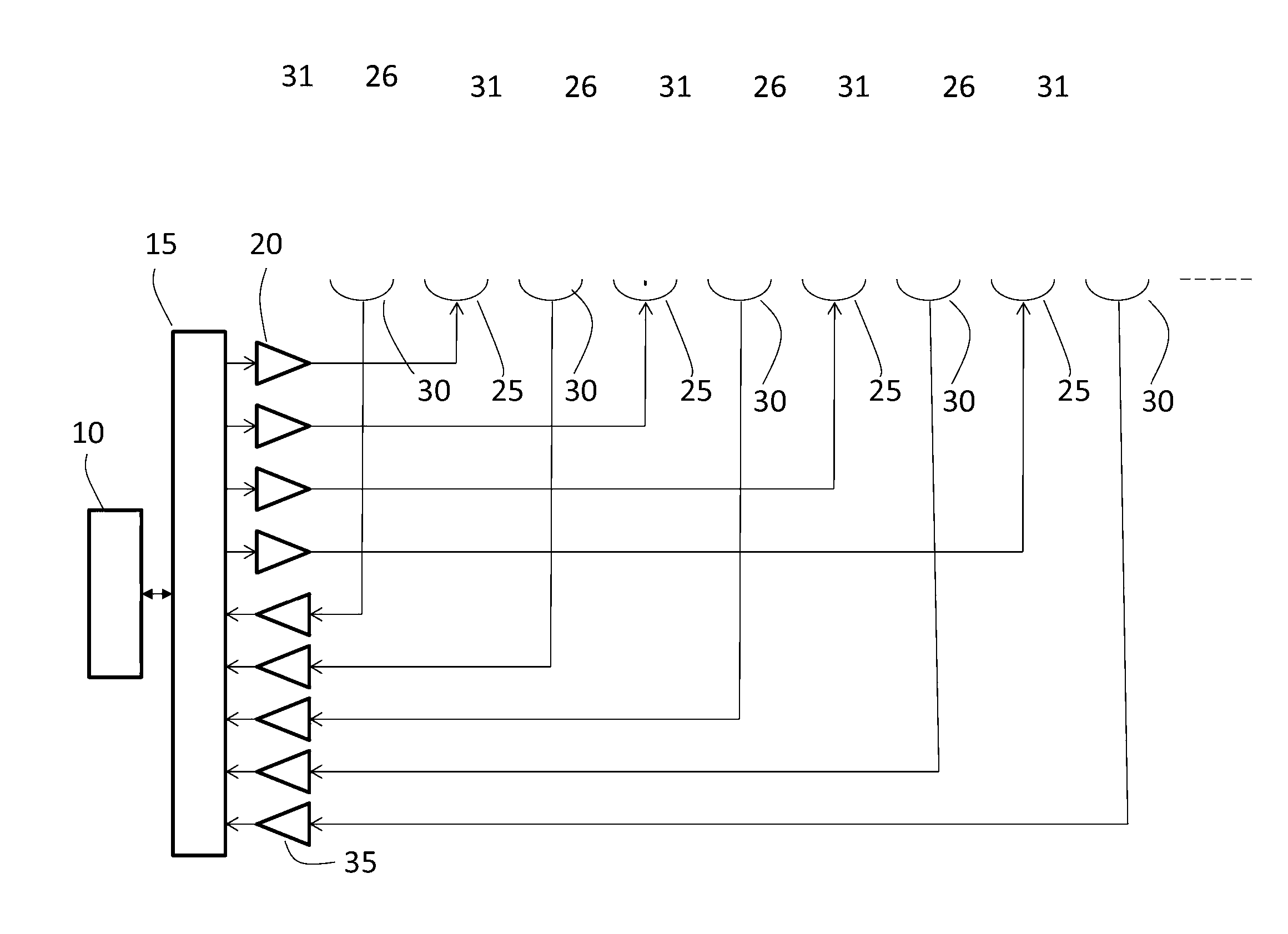
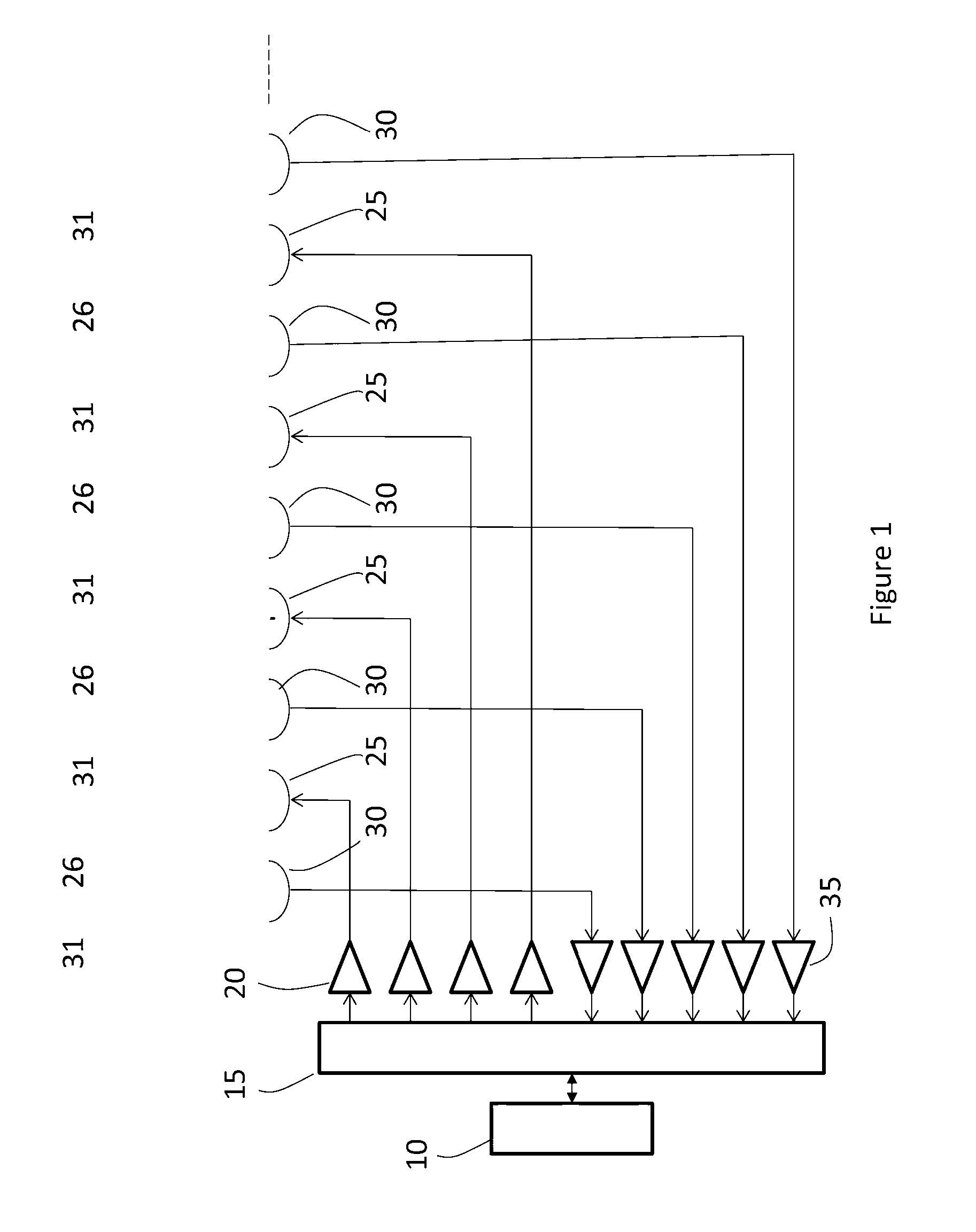
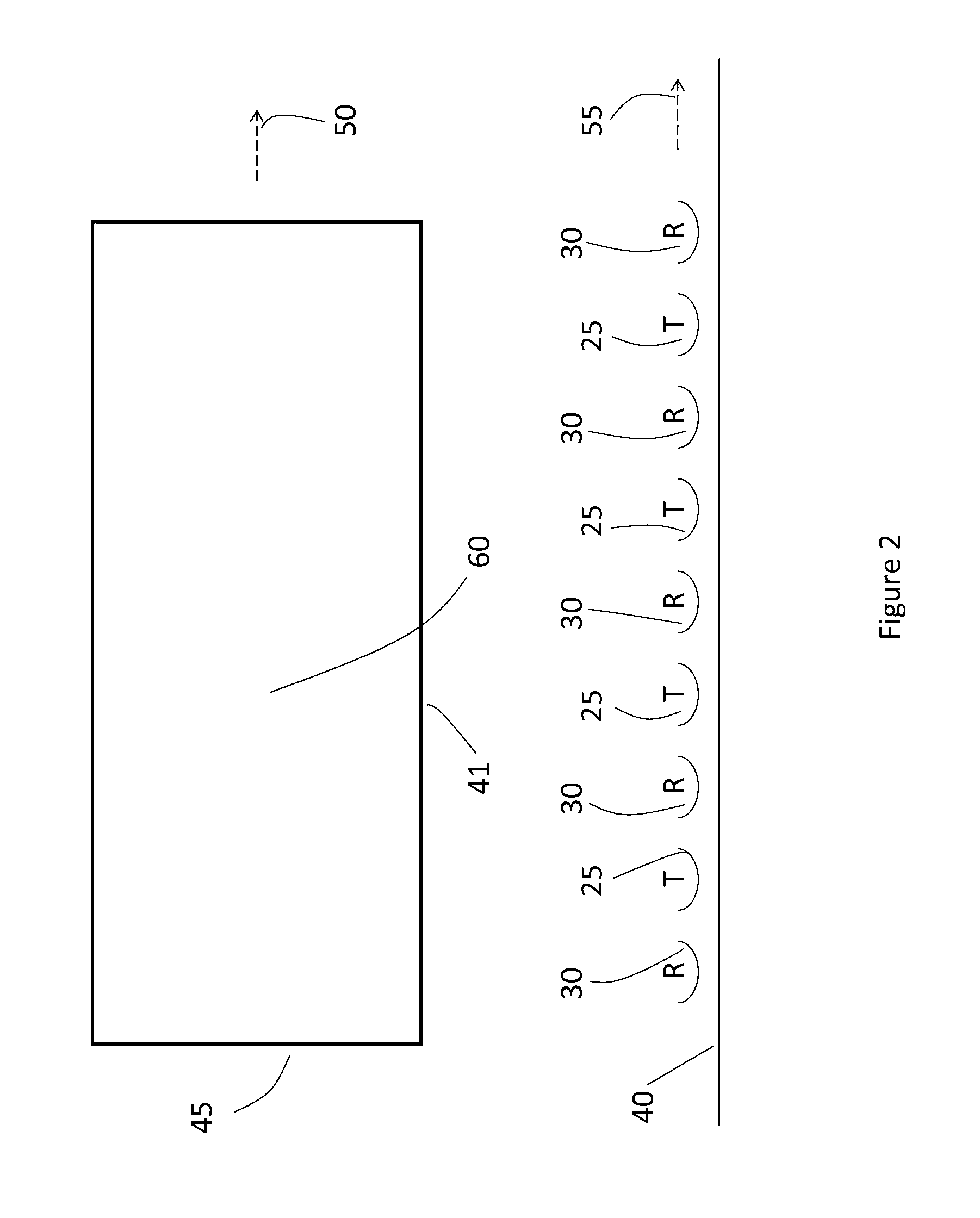
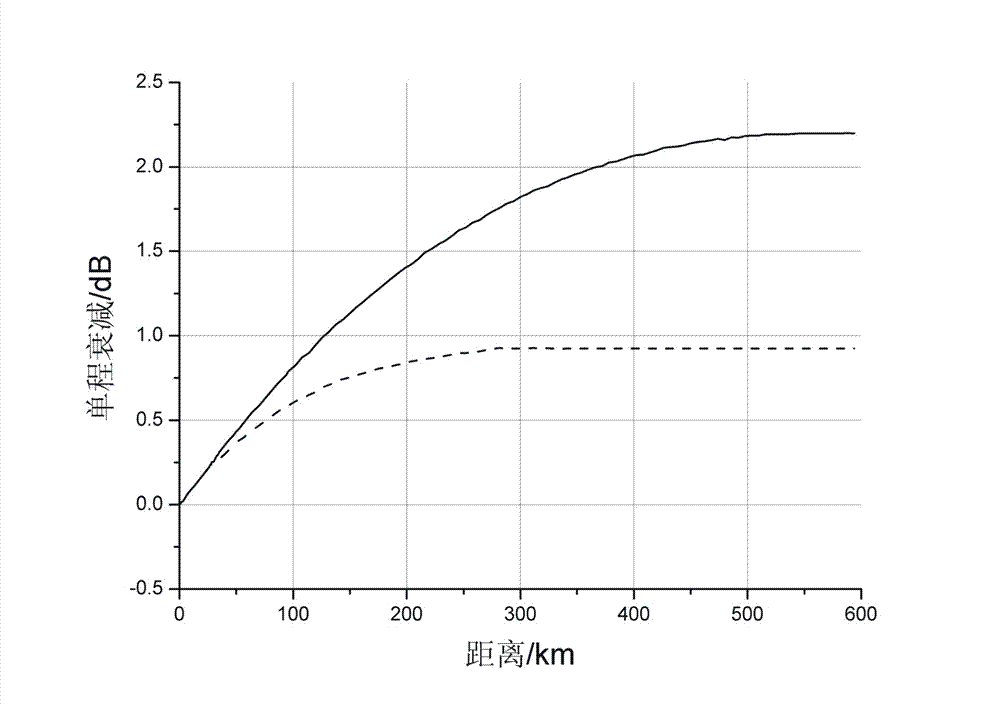
A radio atmospheric signal or sferic (sometimes also spelled "spheric") is a broadband electromagnetic impulse that occurs as a result of natural atmospheric lightning discharges. Sferics may propagate from their lightning source without major attenuation in the Earth–ionosphere waveguide, and can be received thousands of kilometres from their source. On a time-domain plot, a sferic may appear as a single high-amplitude spike in the time-domain data. On a spectrogram, a sferic appears as a vertical stripe (reflecting its broadband and impulsive nature) that may extend from a few kHz to several tens of kHz, depending on atmospheric conditions.
Mobile terawatt femtosecond laser system (MTFLS) for long range spectral sensing and identification of bioaerosols and chemical agents in the atmosphere
InactiveUS7391557B1Reduce probabilitySimultaneous measurementRadiation pyrometryLaser detailsFilamentationUltraviolet
The present invention relates to a system for detection and identification of airborne biological, chemical and / or nuclear threats such as toxins, spores, bacteria, and viruses in real time at distances from a few meters to several kilometers. Compact femtosecond terawatt laser technology is combined with spectroscopic and mathematical methods for spectral sensing of airborne warfare agents such as bio-aerosols. Trigger sensors and standoff devices based on mobile terawatt femtosecond laser systems are provided that may be placed at strategic monitoring locations. Furthermore, the invention relates to the propagation of airborne ultra-short, ultra-intense laser pulses giving rise to plasma channels (filamentation) producing white light supercontinuum ranging from the ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS), near infra-red (NE) and middle infra-red (MIR). According to this invention, the supercontinuum can be directly produced in a particle cloud and hence is uniquely suitable for multi-spectral long-range atmospheric agent and radioactive isotope detection.
Owner:APPLIED PHOTONICS WORLDWIDE
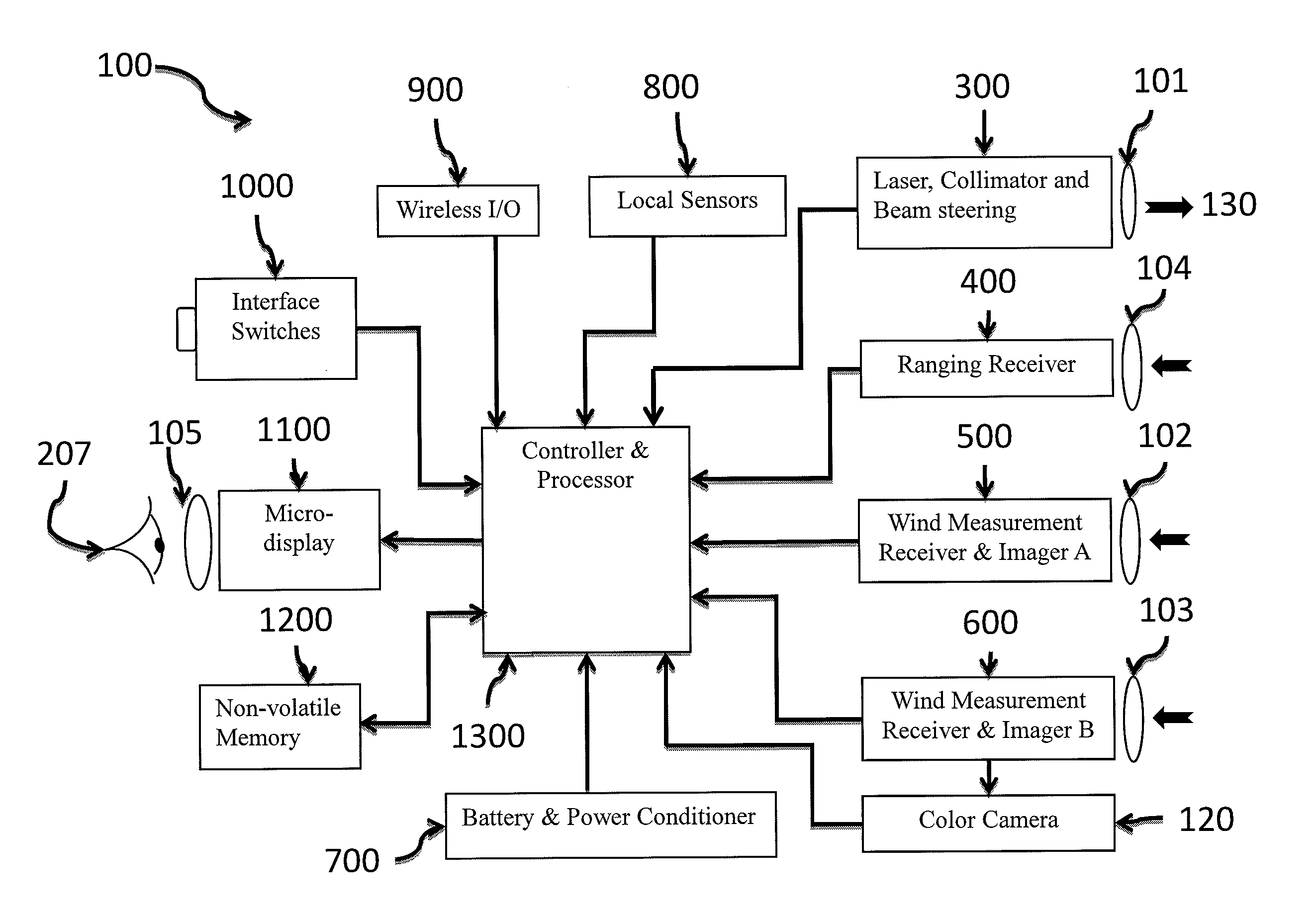
Electro-optic system for crosswind measurement
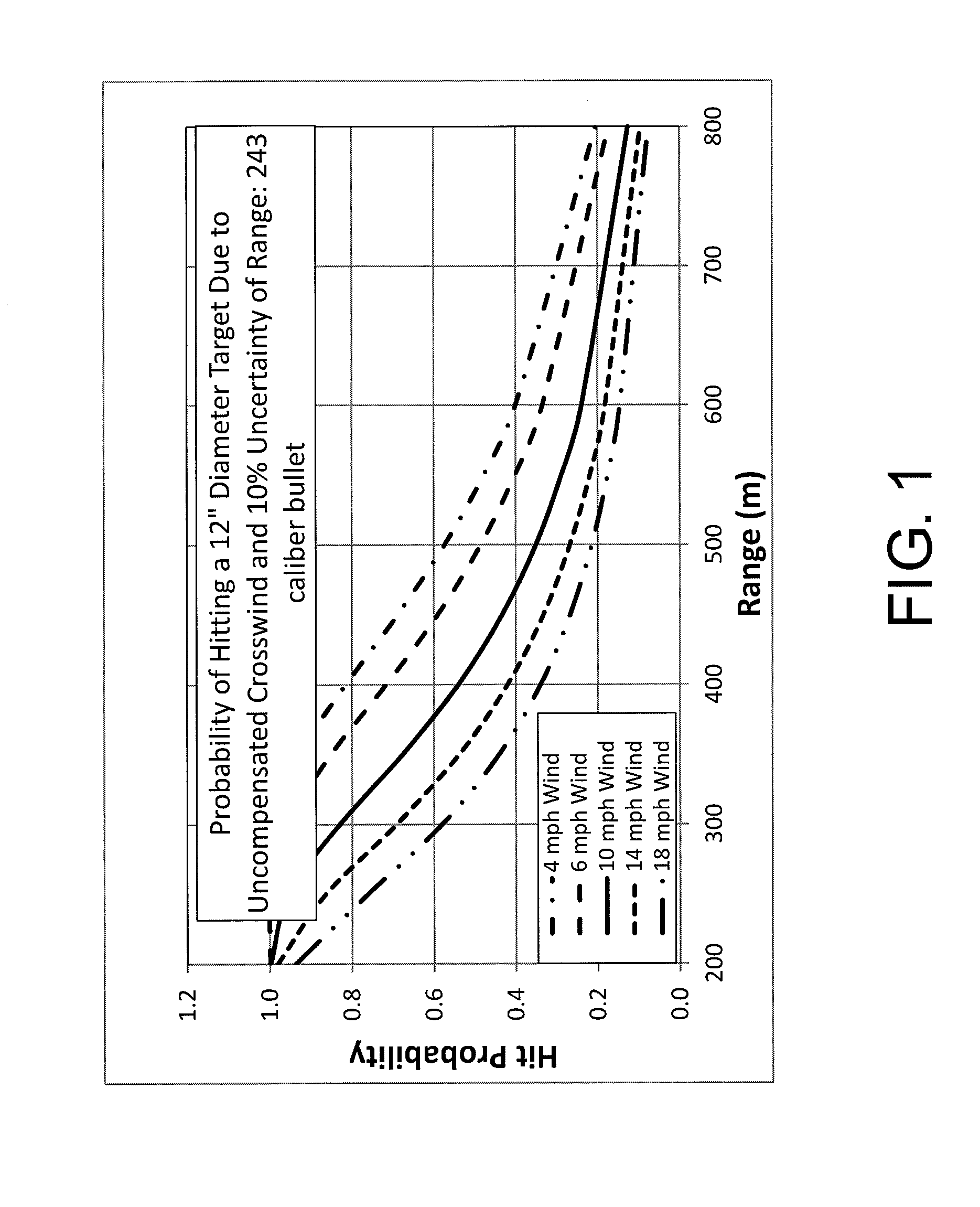
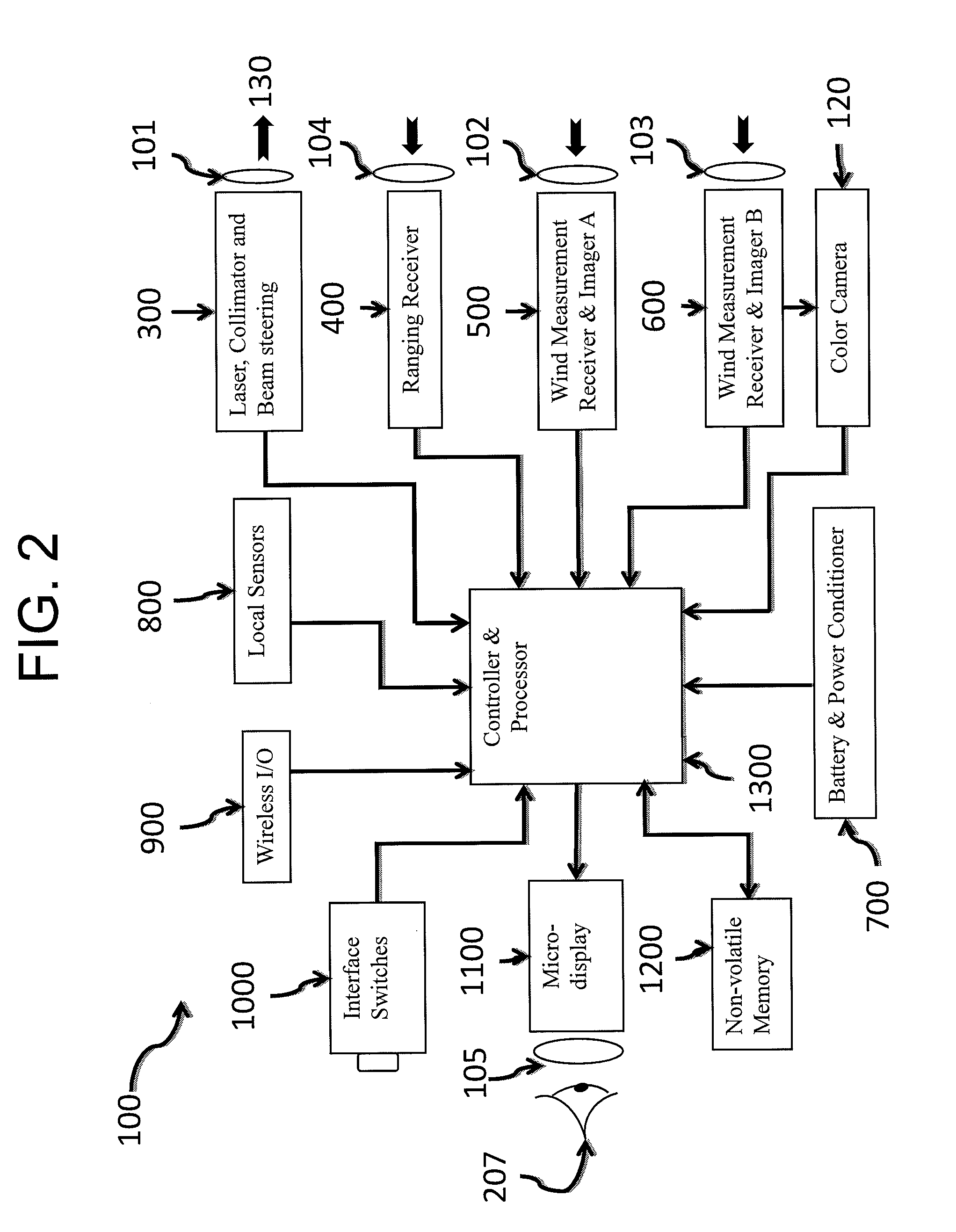
An electro-optic system, e.g., mounted to a weapon, measures down range winds and a range-to-target for compensating the ballistic hit point. The system may include an optical light source, collimated to generate a laser spot on the target. The system may include a wind measurement receiver that captures laser light scattered from the target. The captured light may be modulated by atmospheric scintillation eddies, producing optical patterns which change in time and move with the crosswind. These patterns may be analyzed by a processor using covariance techniques to determine path-integrated crosswinds and associated errors. Ranging is done by measuring the time of flight of the laser pulse to the target collecting the scattered signal from the target. Compensated ballistic hit point, measurement errors and other data may be displayed on a micro-display digital eyepiece, overlaid on the real-time image of the target.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY DEFENSE ADVANCED RES PROJECTS AGENCY +1
Laser radar system for measuring Raman spectra of atmospheric water and fluorescence spectra of aerosols
ActiveCN105675576AGuaranteed normal transmissionRealize simultaneous measurementRaman/scattering spectroscopyLaser detailsRadar systemsFluorescence spectra
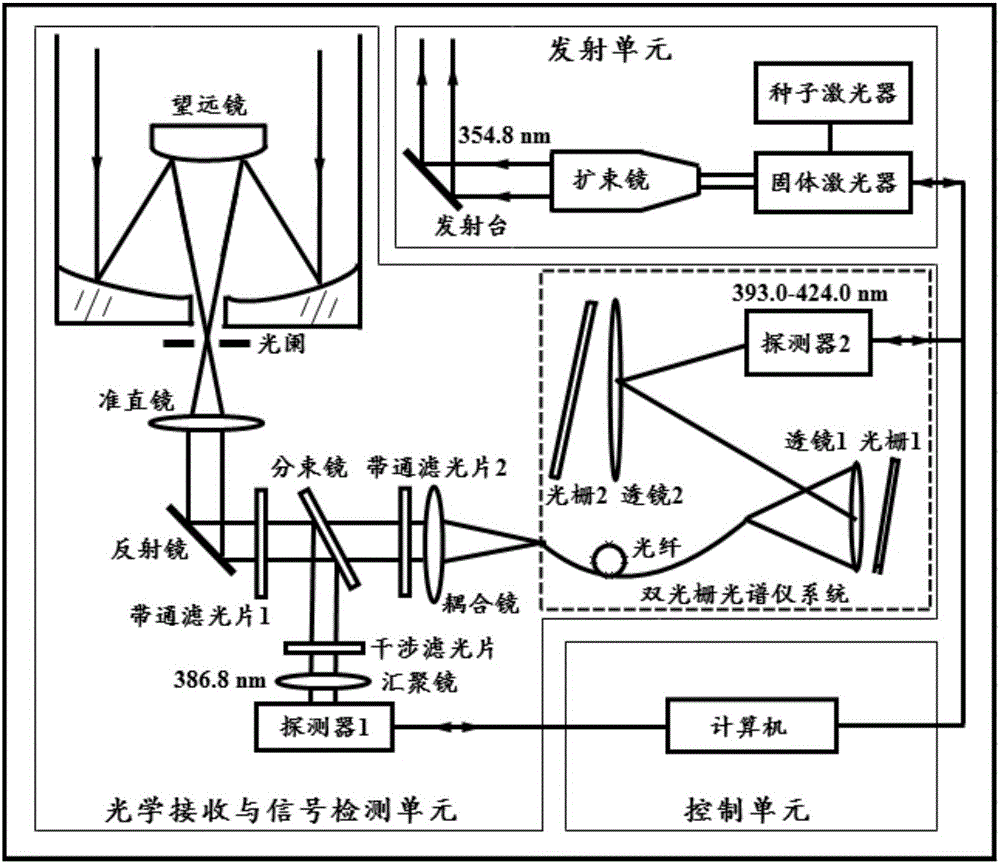
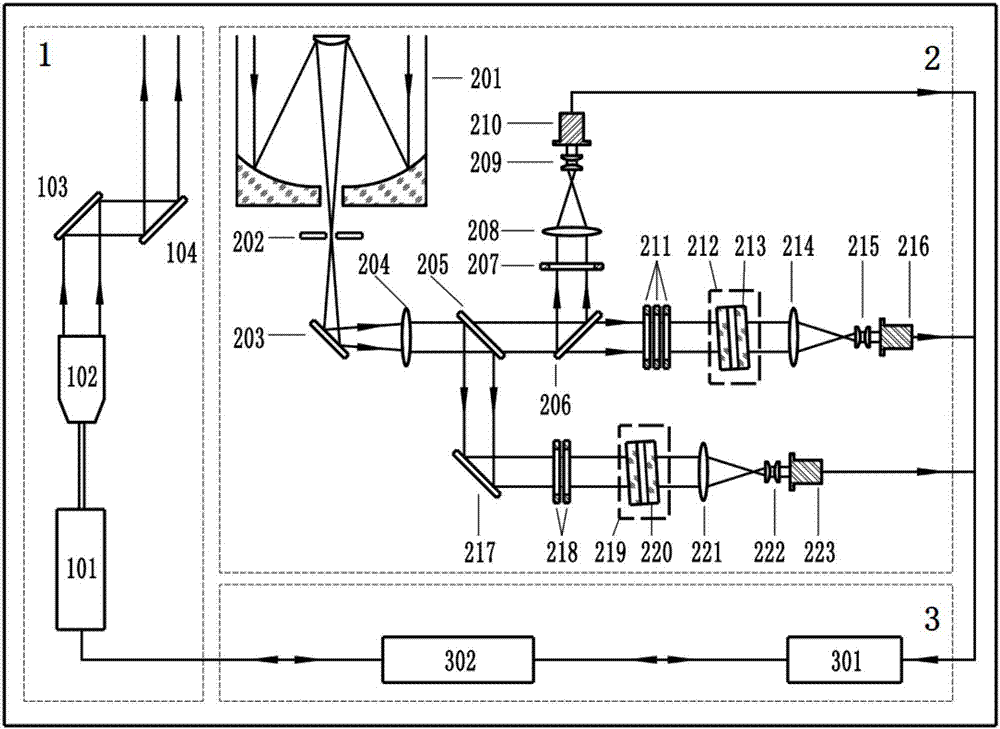
The invention discloses a laser radar system for measuring Raman spectra of atmospheric water and fluorescence spectra of aerosols.The system consists of a transmitting unit, an optical receiving and signal detection unit and a control unit.The transmitting unit adopts a seed injected solid laser to output ultraviolet laser with the narrow linewidth of 354.8 nm and guide the ultraviolet laser to the zenith.The optical receiving and signal detection unit collects backward scattering light from atmospheric substances, produces inhabitation superior to 15 orders of magnitude to nearby light of 354.8 nm and distinguishes and records signal light in the spectrum band range of 393.0-424.0 nm at the spectral precision of 0.8 nm.The control unit guarantees the orderly work of the whole radar system.Under the radiation of ultraviolet laser with the wave length of 354.8 nm, the vibrational-rotational Raman spectrum regions of gas-state, liquid-state and solid-state water sequentially correspond to the ranges of 395-409 nm, 396-410 nm and 401-418 nm.The laser radar system can simultaneously record the Raman spectra produced by the three states of water and fluorescence spectra of produced by aerosol particles and achieve simultaneous detection of the atmospheric water, aerosols and other substances.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
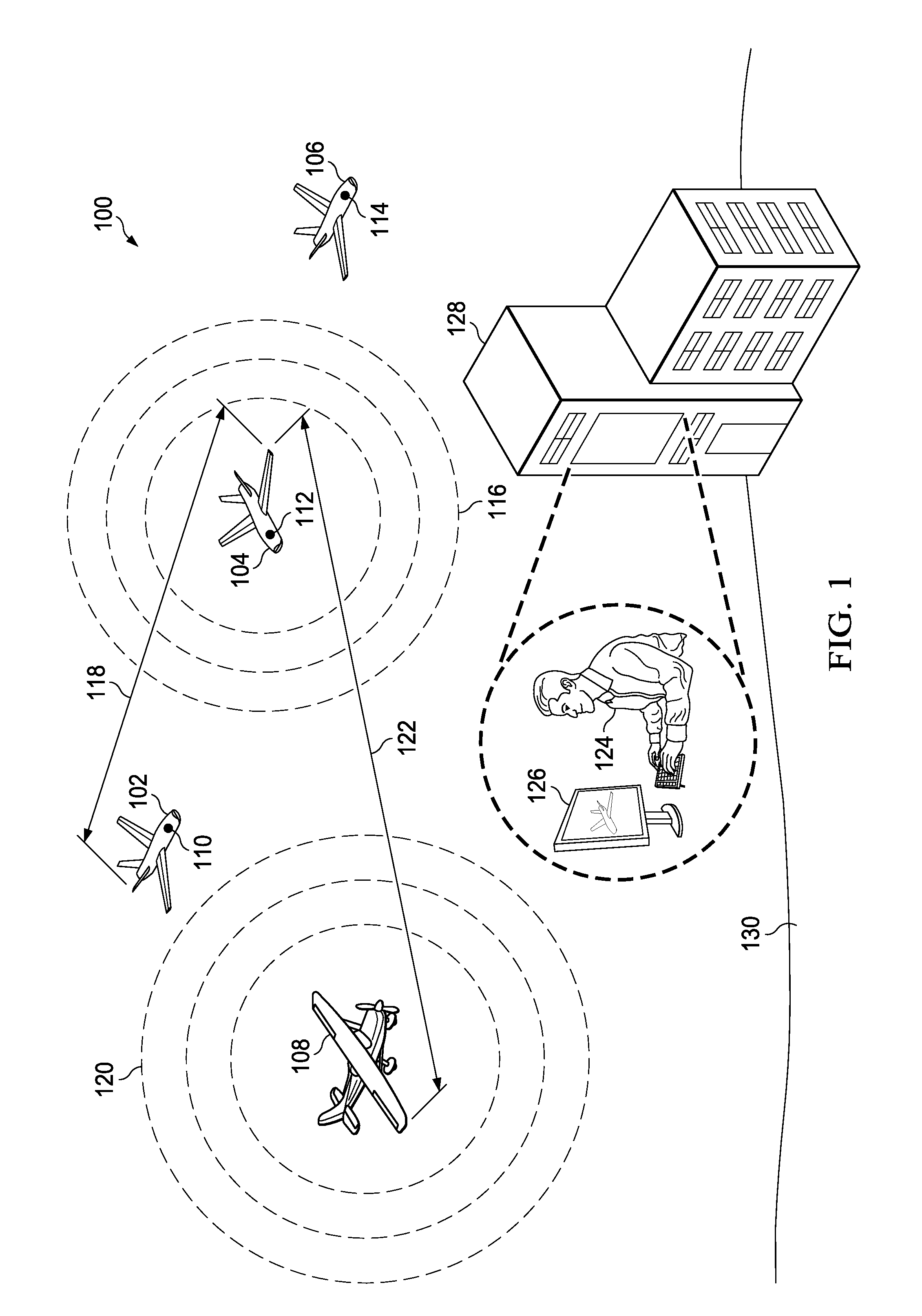
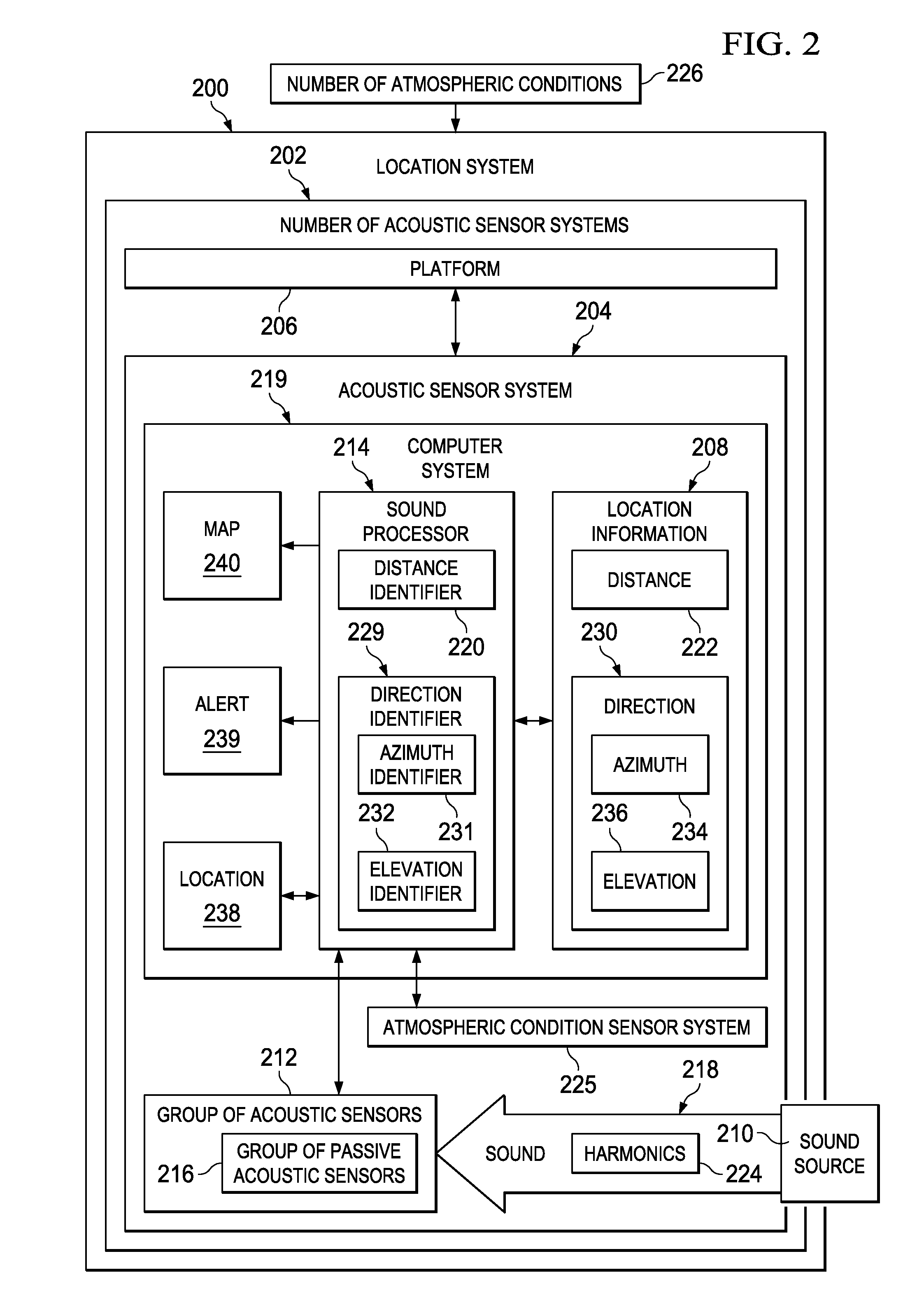
Acoustic Ranging System Using Atmospheric Dispersion
ActiveUS20130317669A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesDigital data processing detailsSound sourcesHarmonic
A method and apparatus for processing sound from a sound source. The sound from the sound source is detected. Harmonics in the sound from the sound source are identified. A distance to the sound source is identified using the harmonics and a number of atmospheric conditions.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
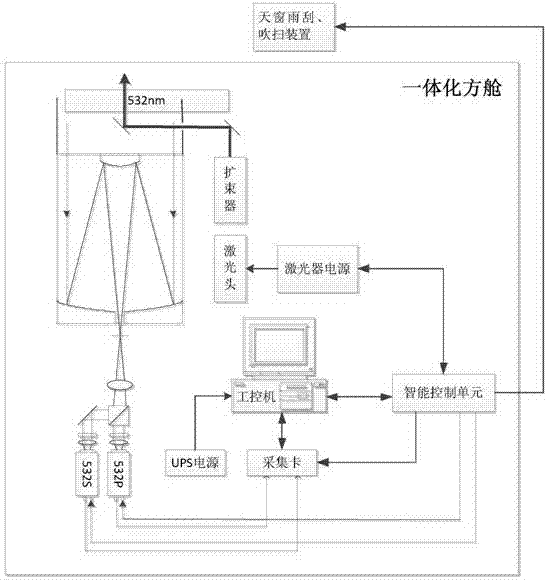
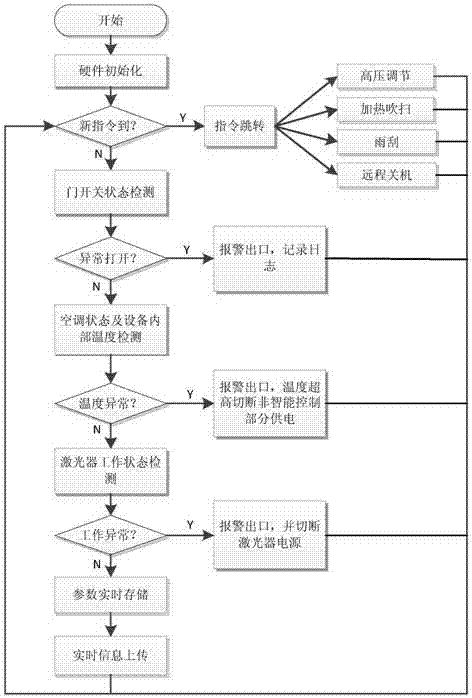
Outdoor all-weather and all-time atmospheric aerosol particle laser radar device
PendingCN107037447AGuaranteed cleanlinessImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationPrismHigh pressure
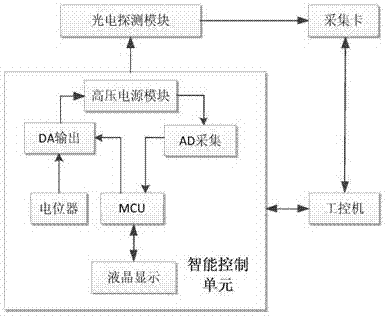
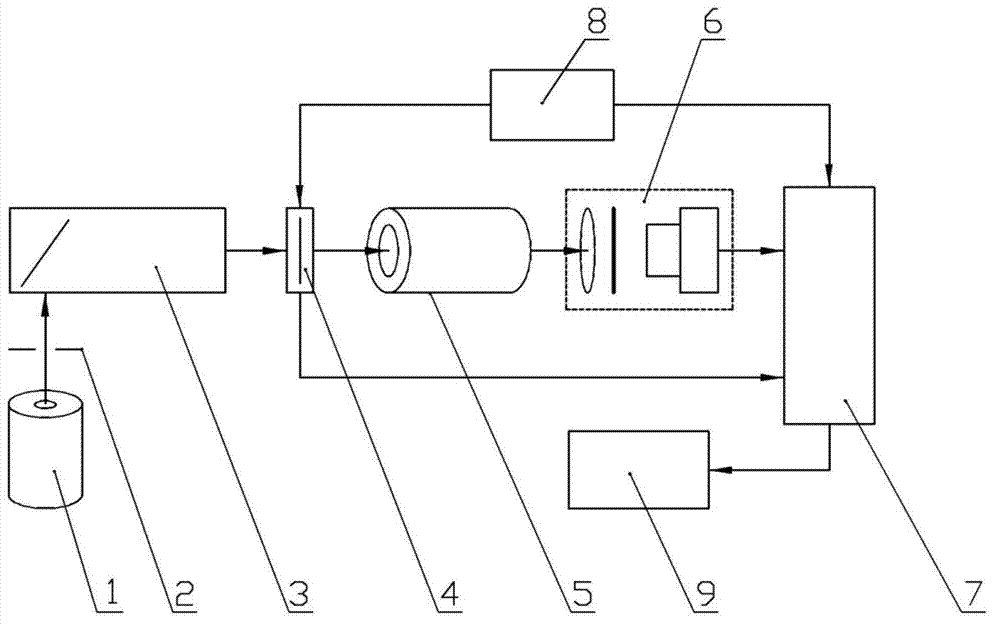
The invention discloses an outdoor all-weather and all-time atmospheric aerosol particle laser radar device which comprises an integrated square cabin, a laser, an intelligent control unit, an optical unit, a signal acquisition and analysis unit, an electric wiper, and a blowing device. The intelligent control unit controls the operation of the machine equipment. The laser emits pulse laser, which is incident on the atmosphere after beam expansion. An optical receiving unit receives back scattered light of atmospheric aerosol particles. A polarization detection prism of a receiving channel separates vertical polarization components from parallel polarization components. A photoelectric detection module converts the light into electrical signals. The signal acquisition and analysis unit acquires, analyzes and displays the electrical signals. Thus, vertical distribution information of the atmospheric aerosol particles is obtained. The device improves the signal-to-noise ratio of detection signals, and has such functions as lightning protection design, photoelectric detection module high-voltage online program-controlled adjustment, instrument internal temperature monitoring and automatic skylight cleaning. The device has a protection grade up to IP65, and meets the requirement for outdoor all-weather and all-time operation.
Owner:合肥中科光博量子科技有限公司
Laboratory testing method for atmospheric transmissivity of multi-band light radiation
The invention relates to a laboratory testing method for atmospheric transmissivity of multi-band light radiation. The laboratory testing method comprises the following steps that radiation light is generated by a radiation light source device, and converted into parallel sine radiation light; the sine radiation light radiates into the front of a simulated atmosphere column transmission attenuation device and radiates out from the back of the simulated atmosphere column transmission attenuation device; the simulated atmosphere column transmission attenuation device comprises a seal pot filled with at least one kind of compressed gas to be tested; optical windows are arranged at the front and the back of the seal pot; the compressed gas to be tested is a certain gas in the atmosphere, which is compressed into the seal pot, has the same sectional area as that of the seal pot, and is within a certain length range; and data collection and analytical processing are conducted on the sine radiation light attenuated by the simulated atmosphere column transmission attenuation device. Under a laboratory environment, the laboratory testing method for the atmospheric transmissivity of the multi-band light radiation can simulate the testing of attenuation coefficients of ultraviolet light radiation, visible light radiation and infrared light radiation in the atmospheric transmission through a compressed air column, and is simple and convenient.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spectrum calibration method based on sun and atmosphere characteristic spectrum in hyperspectral remote sensor flight
ActiveCN102749138AReduce the impact of radiometric calibration uncertaintyImprove execution efficiencyAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyRadiometerLength wave
The invention discloses a spectrum calibration method in hyperspectral remote sensor flight. The spectrum calibration method includes that a sun fraunhofer line and an atmosphere characteristic absorbing line are used as a standard reference spectrum under the normal working condition in the hyperspectral remote sensor flight, and determination of center wavelength offset and spectral bandwidth is achieved through matching of equivalent spectrum reflection rate rho*(lambda) and equivalent spectrum reflection rate of lowpass filtering. The spectrum calibration process does not depend on measurement of surface feature spectrum reflection rate, and effects of indeterminacy of radiation calibration of a remote sensor are reduced. The spectrum calibration method is achieved through a look-up table method and improves executive efficiency of a program. The spectrum calibration method can achieve spectrum calibration during onboard or satellite-borne hyperspectral remote sensor flight and spectrum calibration of a field surface feature spectrum radiometer smaller than 0.2 nm and has significant meaning in hyperspectral remote sensing.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
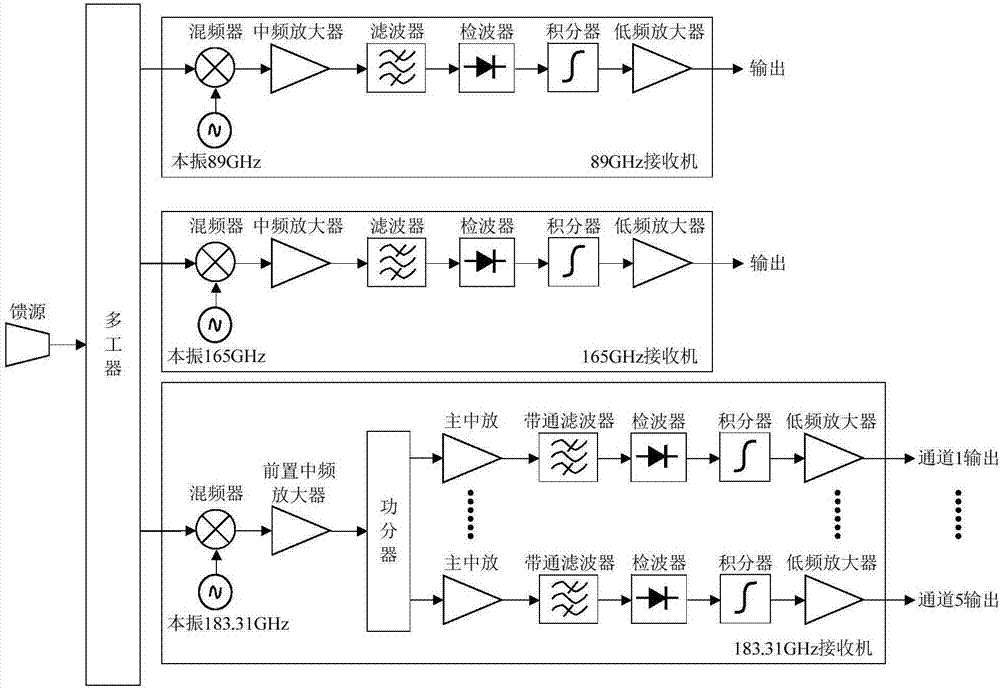
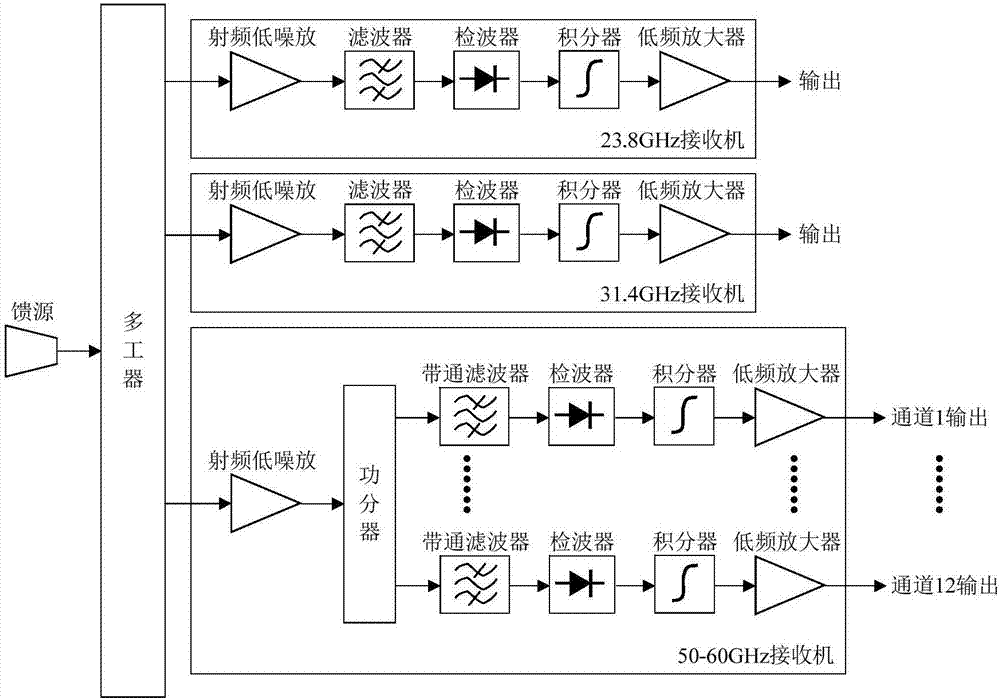
Space-borne microwave atmospheric sounding instrument
InactiveCN107450074AAvoid output fluctuationsEliminate interference errorsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationMicrowaveMultiplexer
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Double-wavelength single receiving channel-based rotation Raman temperature measurement laser radar
ActiveCN105182365AReduce the difficulty of adjustmentAvoid job performance varianceElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationAtmospheric temperatureRaman lidar
The invention discloses a double-wavelength single receiving channel-based rotation Raman temperature measurement laser radar. The laser radar is based on two working wavelengths and a single receiving channel. The two working wavelengths of the laser radar are respectively composed of odd number pulses and even number pulses. The low-quantum-number rotation Raman signals of one working wavelength and the high-quantum-number rotation Raman signals of the other working wavelength are extracted by the receiving channel of the laser radar. The laser radar is operated alternately at the two working wavelengths in the time division multiplexing manner. The atmospheric temperature is calculated based on the ratio of high-quantum-number rotation Raman signals to low-quantum-number rotation Raman signals. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the rotation Raman temperature measurement is realized only by means of a single filter, a single detector and a single acquisition card. Compared with a single-wavelength double receiving channel-based rotation Raman temperature measurement laser radar, the above laser radar is compact in structure, wherein the difficulty of optical path adjustment and the difficulty of system parameter calibration are lowered. Meanwhile, the double-wavelength single receiving channel-based rotation Raman temperature measurement laser radar is low in cost. The working performance difference between the filter and the detector caused by the inconsistence of working environments can be avoided. Moreover, the detection accuracy, the system stability and the environmental adaptability are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
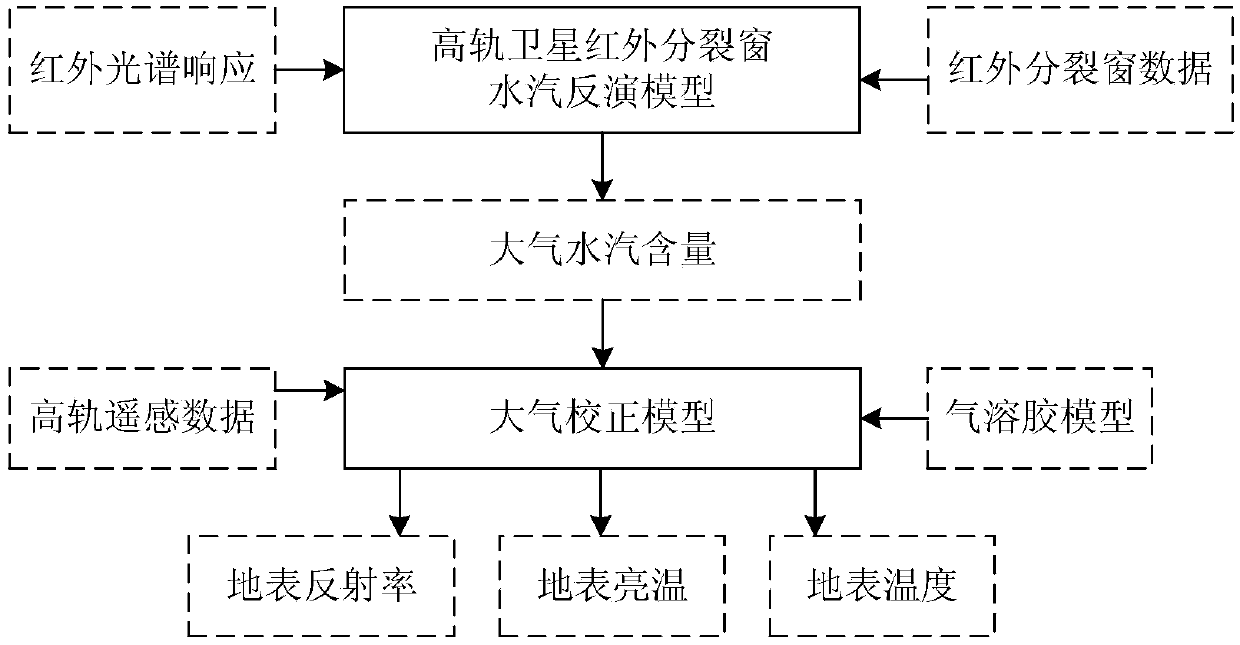
Atmospheric correction method for infrared channel of common-caliber high-rail remote sensing satellite
ActiveCN108896188AAchieving real-time atmospheric correctionImprove imaging effectRadiation pyrometryImaging conditionSplit window
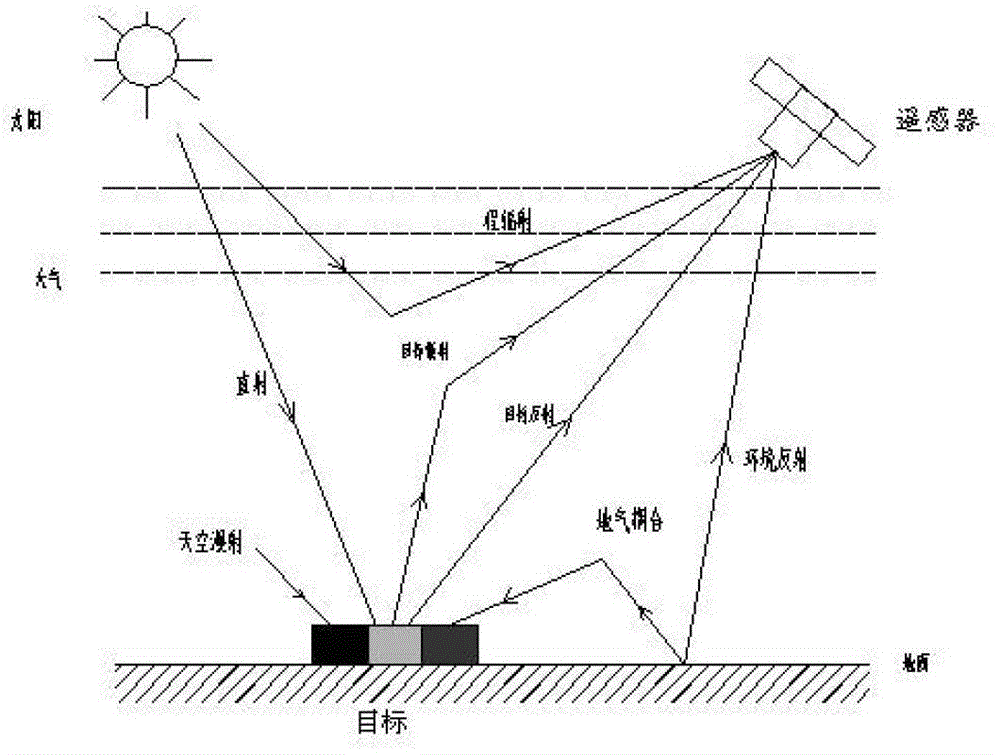
The invention discloses an atmospheric correction method for an infrared channel of a common-caliber high-rail remote sensing satellite. The method comprises: step one, constructing an atmospheric vapor inversion model of a high-rail thermal-infrared split window and carrying out calculation to obtain an atmospheric column vapor content W of an image coverage area at a satellite imaging time; steptwo, according to atmospheric correction coefficients of all visible-near-infrared channels of a high-rail remote sensing satellite under different imaging conditions and atmospheric conditions, forming an atmospheric correction coefficient look-up table; step three, retrieving the atmospheric correction coefficient look-up table to obtain an atmospheric correction coefficient and calculating surface reflectances of all visible-near-infrared channels of the satellite to complete atmospheric correction of a visible-near-infrared band; step four, calculating atmospheric transmissivity values tau 11 and tau 12 of a thermal infrared absorption channel B11 and a transmission channel B12; and step five, completing surface temperature inversion by using an thermal infrared split window surface temperature inversion model, thereby obtaining a surface temperature. With the method disclosed by the invention, the satellite image quality as well as the remote sensing observation accuracy of the surface radiation amount and the reflection amount is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Ultraviolet quasi-single pure-rotation Raman spectrum extraction-based all-day temperature measurement laser radar
ActiveCN107024699AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove working environmentThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsAtmospheric temperature
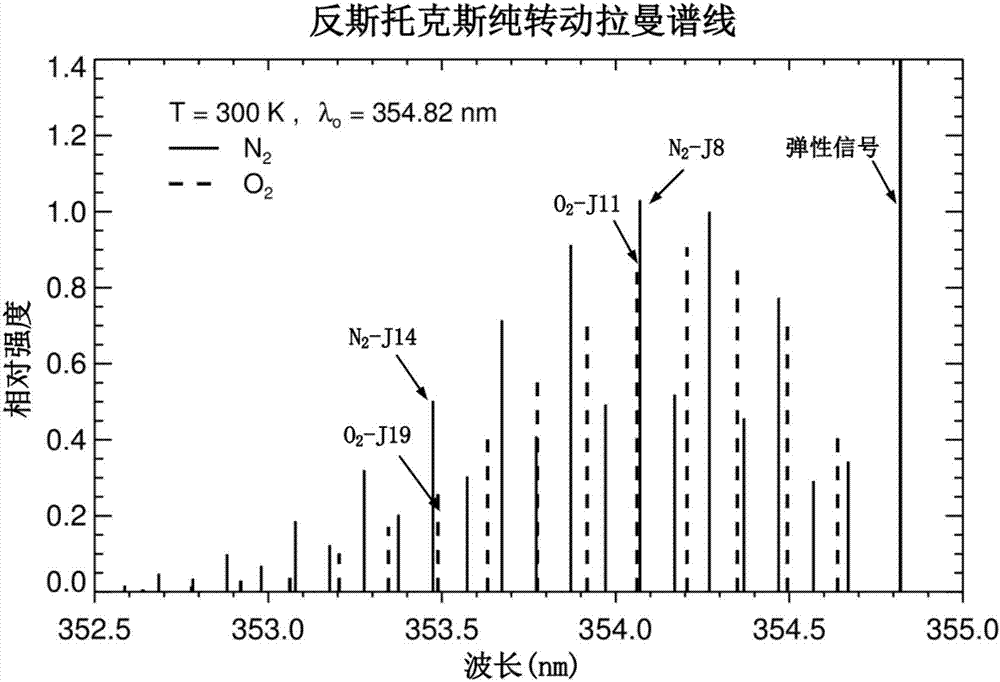
The present invention discloses an ultraviolet quasi-single pure-rotation Raman spectrum extraction-based all-day temperature measurement laser radar. The laser radar comprises a laser emitting unit, an optical receiving unit and a signal acquisition and control unit. The laser emitting unit emits the ultraviolet laser of 354. 82 nm in wavelength and the ultraviolet laser is adopted as a detection light source. The laser emitting unit sends a pulse laser beam to the atmosphere. The pulse laser beam and atmospheric particles interact to generate a series of discrete spectrum line scattering signals. The optical receiving unit receives the scattering signals through a telescope and then respectively and simultaneously extracts elastic scattering signals and quasi-single-branched anti-stoke pure-rotation Raman spectral line signals through three channels. The signal acquisition and control unit realizes the real-time acquisition and the inversion of signals, so that the normal and orderly operation of the entire laser radar system is ensured. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the signal-to-noise ratio of the system is enhanced, and the light-receiving path is optimized. The system stability is improved. The all-day detection of the atmospheric temperature, the aerosol space distribution and time evolution parameters is implemented.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Optical pulse signal simulation generation method influenced by atmospheric turbulence
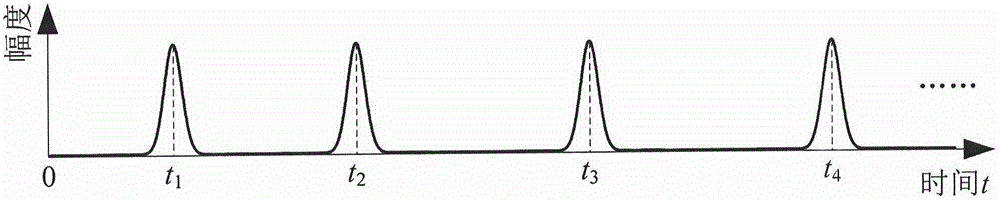
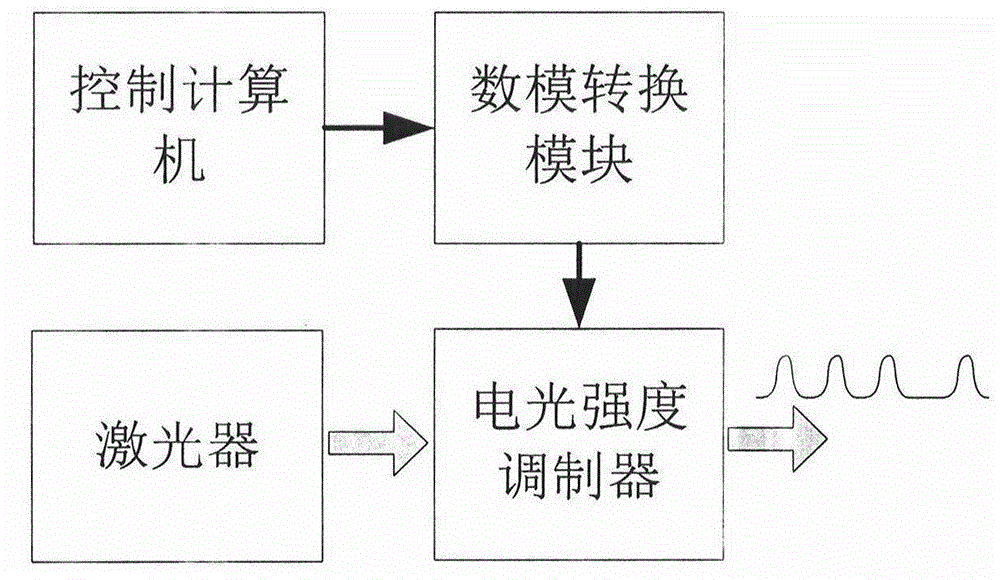
ActiveCN104486000AAchieve modulationModulation implementation of the modulatorElectromagnetic transmissionTime domainControl signal
The invention discloses an optical pulse signal simulation generation method influenced by atmospheric turbulence and belongs to the technical field of wireless optical communication of atmospheric channels. The optical pulse signal simulation generation method comprises the following steps: firstly calculating a series of optical pulse discrete time domain waveform data arriving at a receiver by using a multi-random-phase-screen-based optical pulse atmospheric turbulence transmission value simulation method and saving the series of optical pulse discrete time domain waveform data in a computer file; then generating modulation control signals of an electro-optic intensity modulator by a control computer according to the discrete time domain waveform data in the computer file and modulating laser signal intensity so as to simulate and generate the optical pulse signals. Compared with the existing semi-object simulation method, the method is not limited by the physical conditions of transmission distance and atmospheric turbulence parameters; the method is relatively high in flexibility and applicability.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Satellite remote sensing atmospheric ozone profile inversion algorithm
InactiveCN108760662AIncreased signal degrees of freedomIncrease vertical resolutionColor/spectral properties measurementsAtmospheric ozoneEarth surface
The invention discloses a satellite remote sensing atmospheric ozone profile inversion algorithm, which comprises: 1, carrying out radiation calibration and wavelength calibration by using an ozone monitoring instrument OMI; 2, carrying out radiation transmission model and weighting function calculation; and 3, inverting atmospheric ozone profile information based on an optimal estimation technology algorithm by using the radiation spectrum simulation value and the weighting function parameter calculated in the step 2 after the radiation calibration and the wavelength calibration of the ozonemonitoring instrument OMI are completed. According to the present invention, the algorithm is established by using the OMI ultraviolet radiation spectrum data and selecting the fitting wave bands UV-1and UV-2, and can invert the atmospheric ozone profile information from the earth surface to the 60 km atmosphere based on the optimal estimation technology, wherein the atmospheric ozone profile information comprises the total ozone column concentration, the troposphere ozone column concentration and the stratosphere ozone column concentration, such that the troposphere atmosphere ozone profileis accurately inverted; and the method can be used for analyzing the relationship between atmospheric ozone convective motion, exchange processes, biomass burning and human pollution, and tracking thetemporal and spatial transport of ozone.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
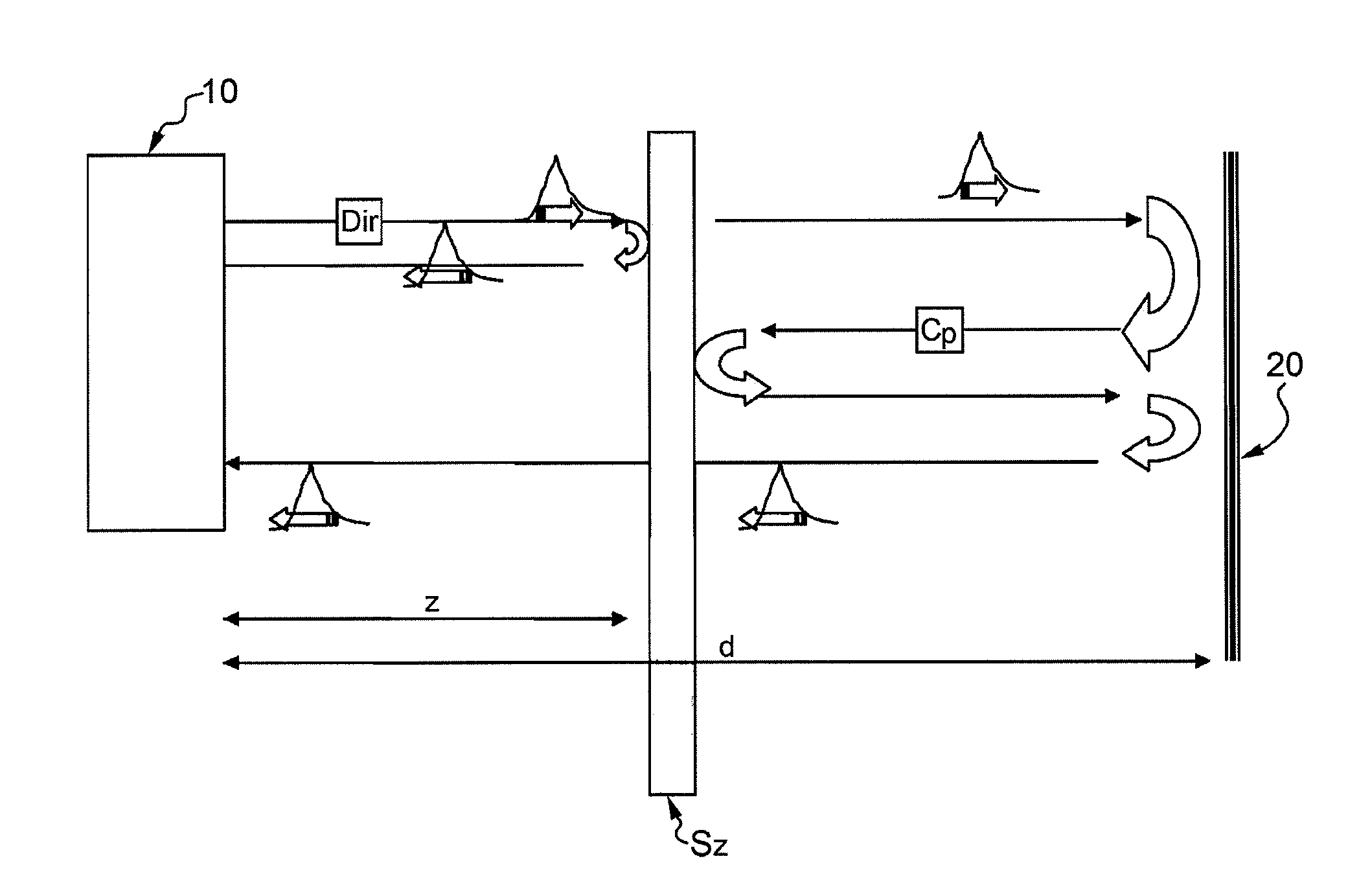
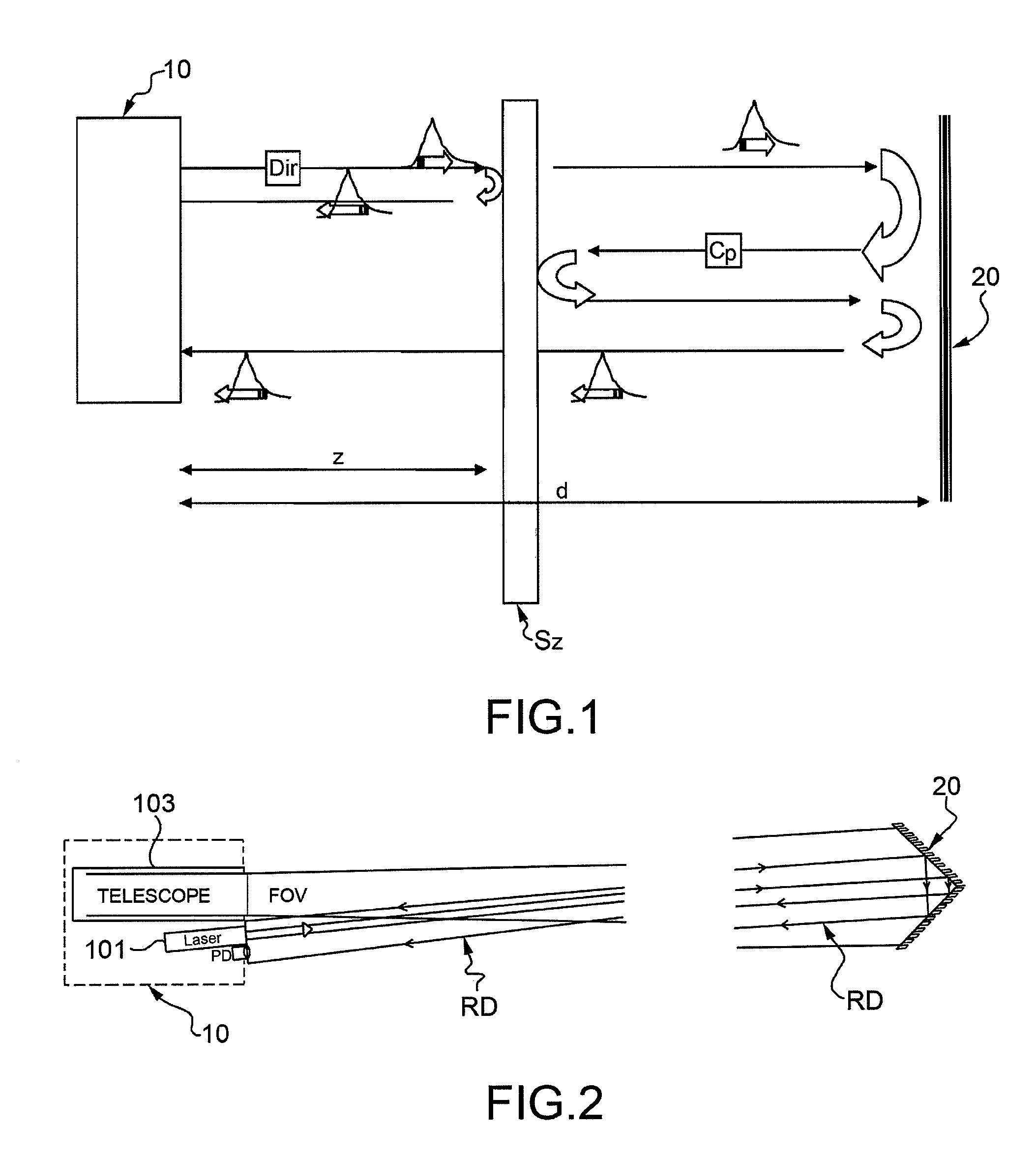
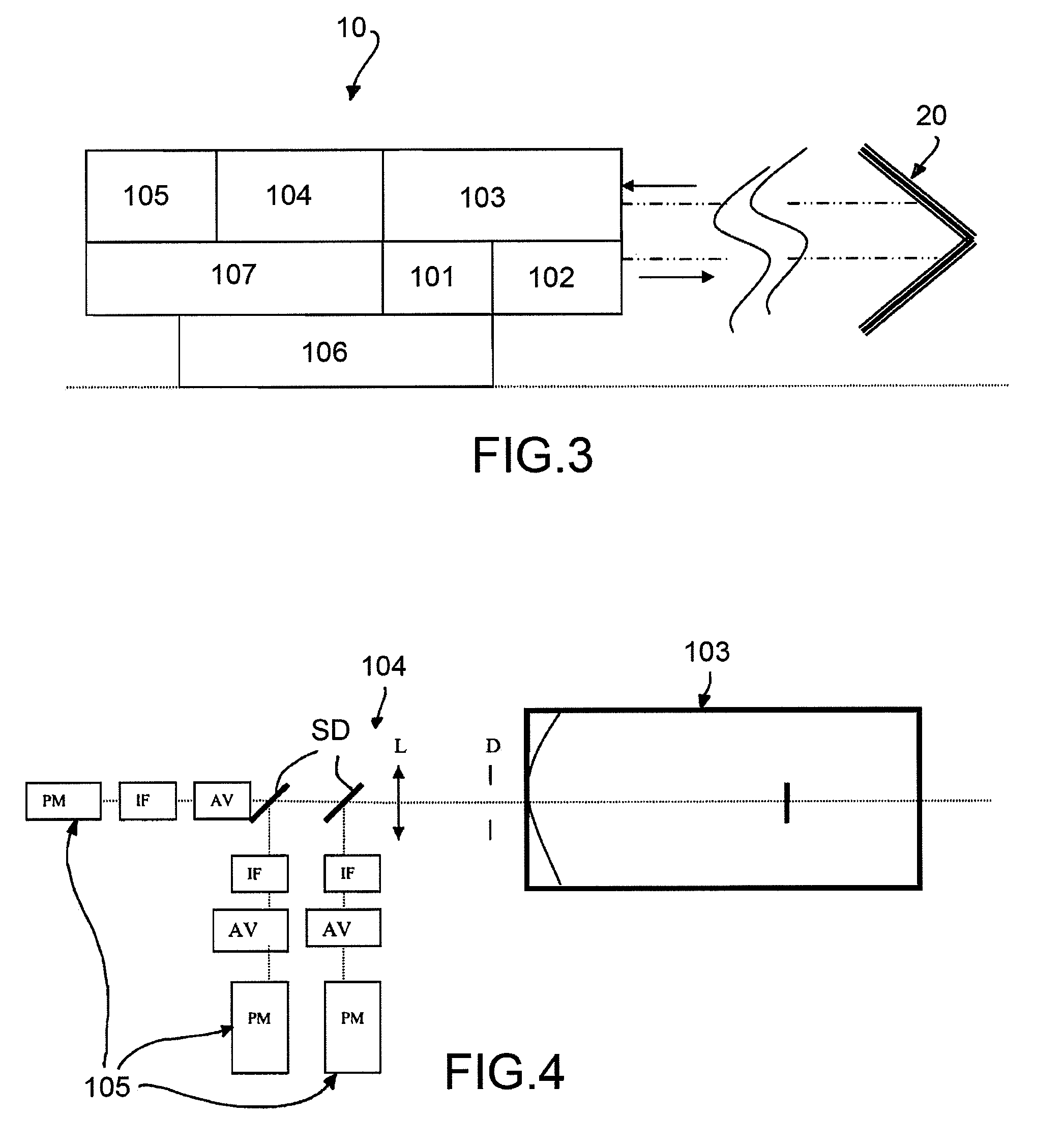
Elastic backscattering and backreflection lidar device for the characterization of atmospheric particles
InactiveUS8269950B2Accurate measurementAvoid disadvantagesOptical rangefindersMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyRadar
A method is described for the characterization of atmospheric particles by means of a lidar device. The method provides to send a laser pulse in the atmosphere, a part of which is directly backscattered by the particles in the atmosphere. A reflecting optical device is provided, that is positioned at a predetermined distance d from the lidar device, whereby a part of the laser pulse that directly reaches the reflecting device is backreflected and is later backscattered by the particles in the atmosphere thus generating a counterpropagating backscattering signal directed towards the reflecting device, which signal reaches the reflecting device and is backreflected towards the lidar device. The lidar device detects the direct backscattering and counterpropagating signals. The optical characteristics of the particles are determined on the basis of the direct backscattering signal and the counterpropagating backscattering signal.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE +1
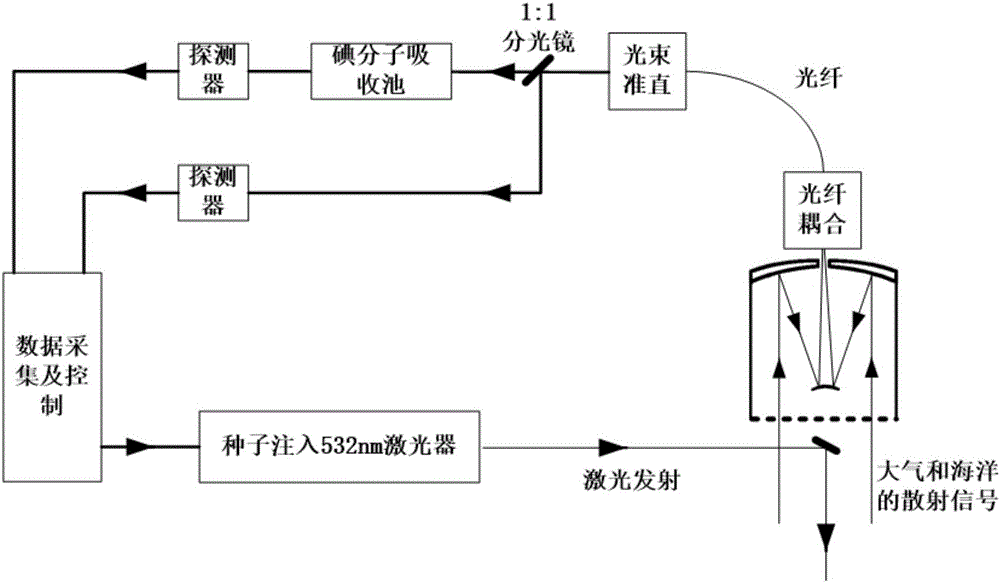
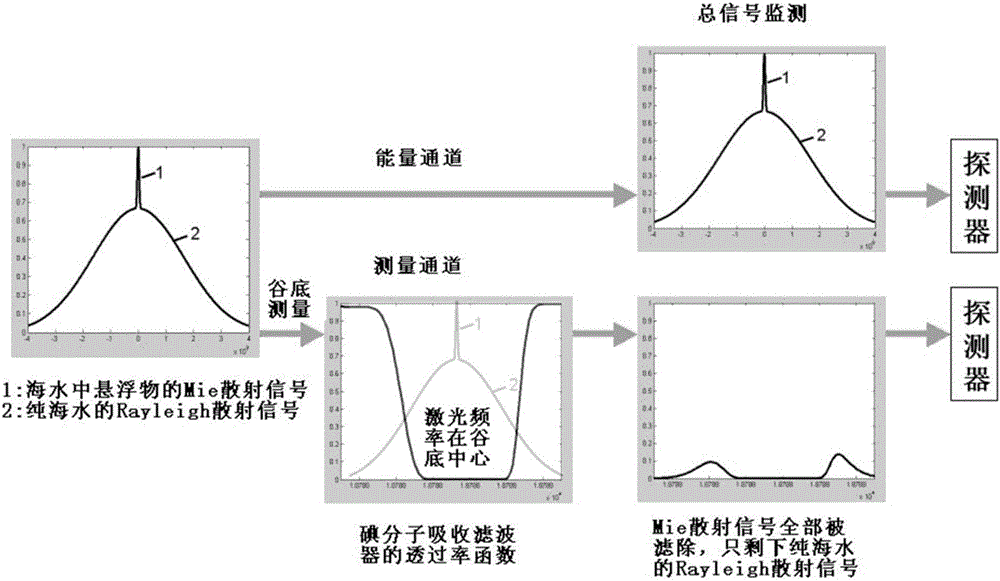
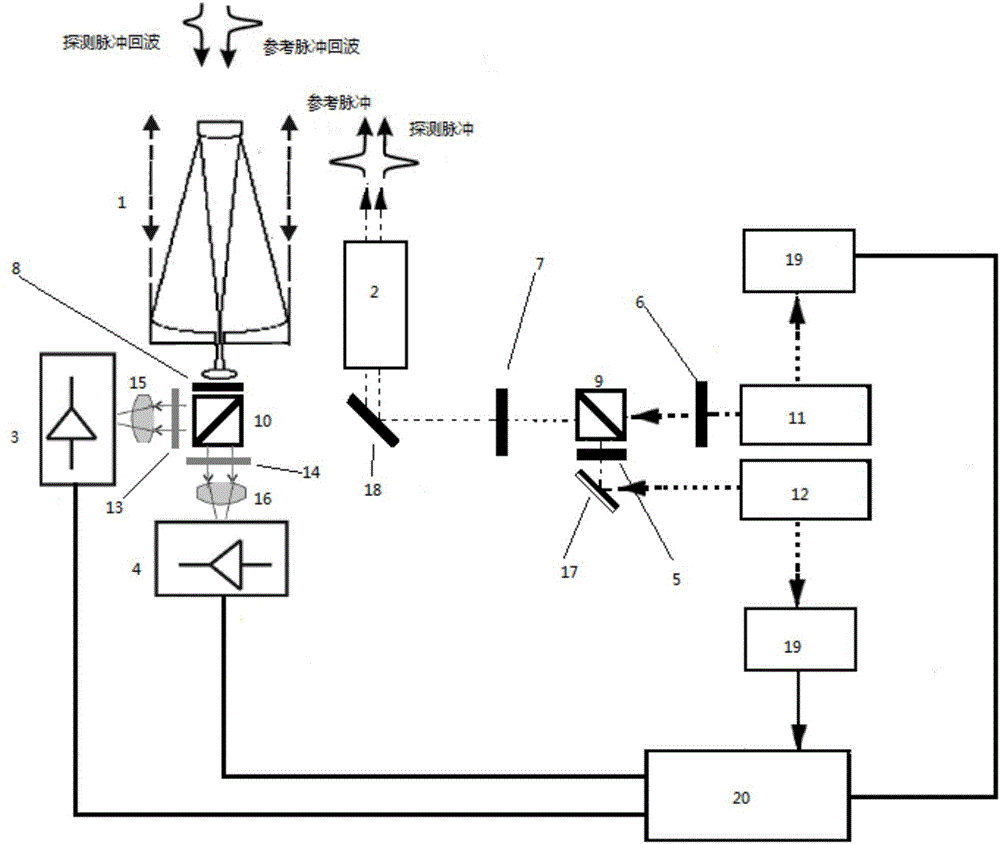
Method for measuring ocean inherent optical parameter by using laser radar system
InactiveCN106526611AEnables separate measurementsHyperspectral resolution characteristicsColor/spectral properties measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsAbsorption filter
The invention discloses a method for measuring an ocean inherent optical parameter by using a laser radar system. 532nm wavelength output is employed by the laser emitting system in the laser radar system, a receiving system is used to carry out signal receiving, received atmosphere and ocean scattering signals are divided into two paths according to 1:1 in a receiving system, one path is used as a reference channel, the other path goes through an iodine molecule absorption filter as a measurement channel. The photoelectric conversion of two paths of optical signals is realized through a photoelectric detector, and the signals are inputted to a processing system for processing computing via a signal collection system. According to the method, the iodine molecule absorption filter is used, the back scattering signal spectrum of a laser sea water body is considered, the separate measurement of the narrow linewidth suspended matter scattering and broadband water molecule scattering is realized, the spectral resolution characteristic is high, and the detection range of ocean information by the laser radar system is expanded.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Difference absorption lidar system for composite light beam transmission and reception
ActiveCN106019311AEliminate errorsElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationEarth observationPlane mirror
The present invention discloses a difference absorption lidar system for composite light beam transmission and reception. The system consists of two pulsed lasers, two half-wave plates, two reflectors, two polarization beam splitters, two quarter-wave plates, two plane mirrors, a beam expander, a telescope, two filters, two photo detectors, a pulse energy monitor and a data processing unit. The invention is characterized in that two laser pulses, a detection pulse and a reference pulse are simultaneously transmitted and received, and the wavelengths are close to each other, so that they travel the same atmospheric path, and their landing footprints coincide in earth observation. An advantage of the present invention is that influences of other interfering atmospheric factors are eliminated with the difference in the received echoes only caused by differences in the absorption of the two laser pulses by the atmosphere along the travel path.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Energy detection system and energy detection method for atmosphere turbulence of wind profile radar
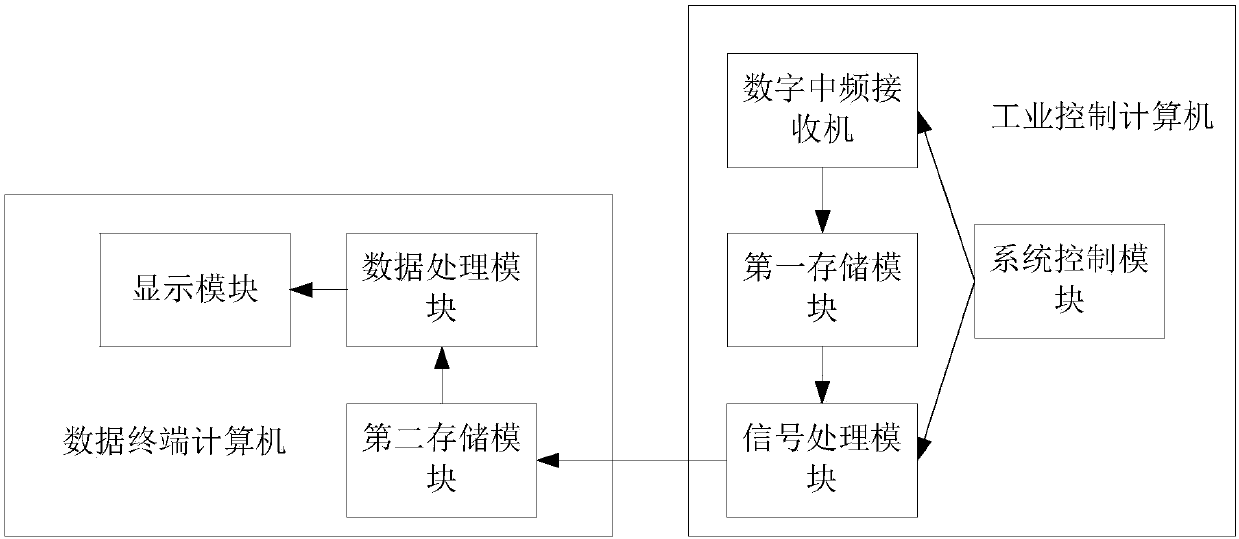
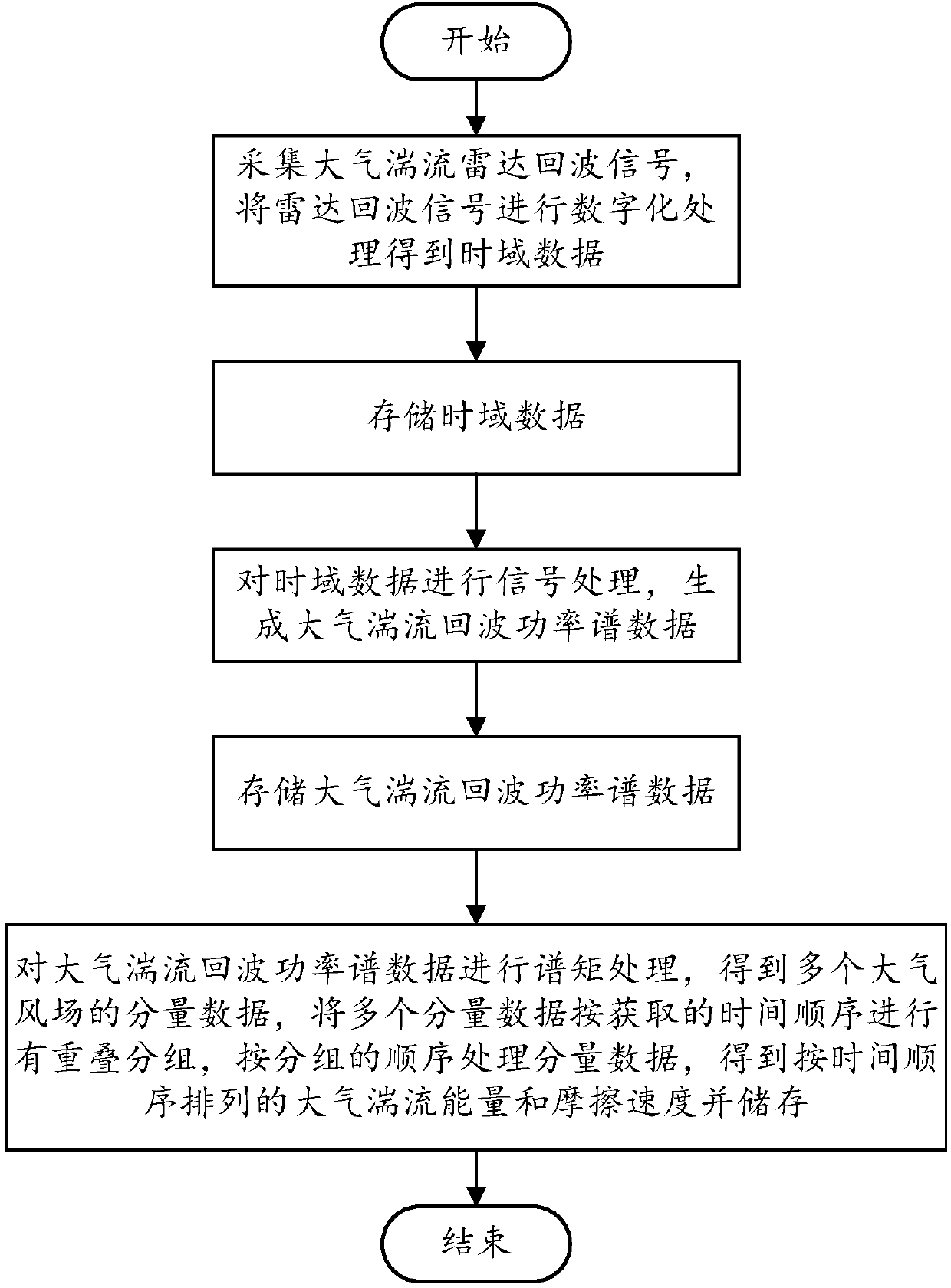
ActiveCN107870332ATrue restorationConvenient queryICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainWind profiler
The invention relates to the field of atmospheric turbulence energy detection, and particularly relates to an energy detection system and an energy detection method for the atmosphere turbulence of awind profile radar. The system comprises a digital intermediate-frequency receiver used for acquiring an atmospheric turbulence radar echo signal, carrying out digital processing on the radar echo signal to obtain time-domain data, and sending the time-domain data to a first storage module; the first storage module used for storing the time-domain data sent by the digital intermediate-frequency receiver; and a signal processing module used for carrying out signal processing on the time-domain data in the first storage module, generating atmospheric turbulence echo power spectrum data and sending the atmospheric turbulence echo power spectrum data to a second storage module. According to the invention, based on the system and the method, the energy and the friction speed of the atmosphericturbulence can be observed, detected and processed, and data can be obtained in real time. Meanwhile, obtained data are accurate and high in precision. The atmospheric turbulence can be truly restored. Therefore, the system and the method can be applied to the fields of scientific research, atmospheric observation, agricultural application and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO MEASUREMENT
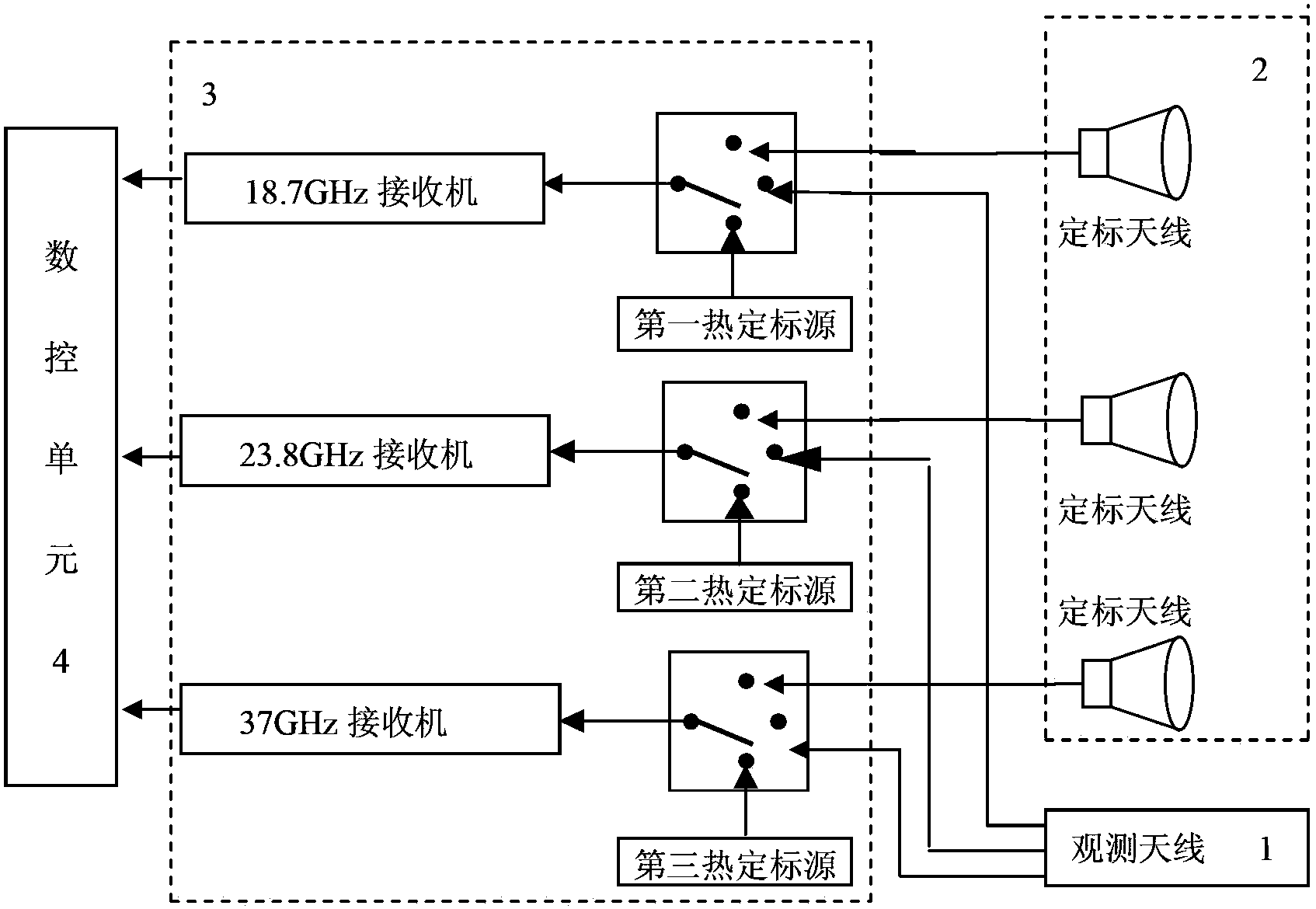
Spaceborne microwave radiometer system for measuring atmosphere path time-delay
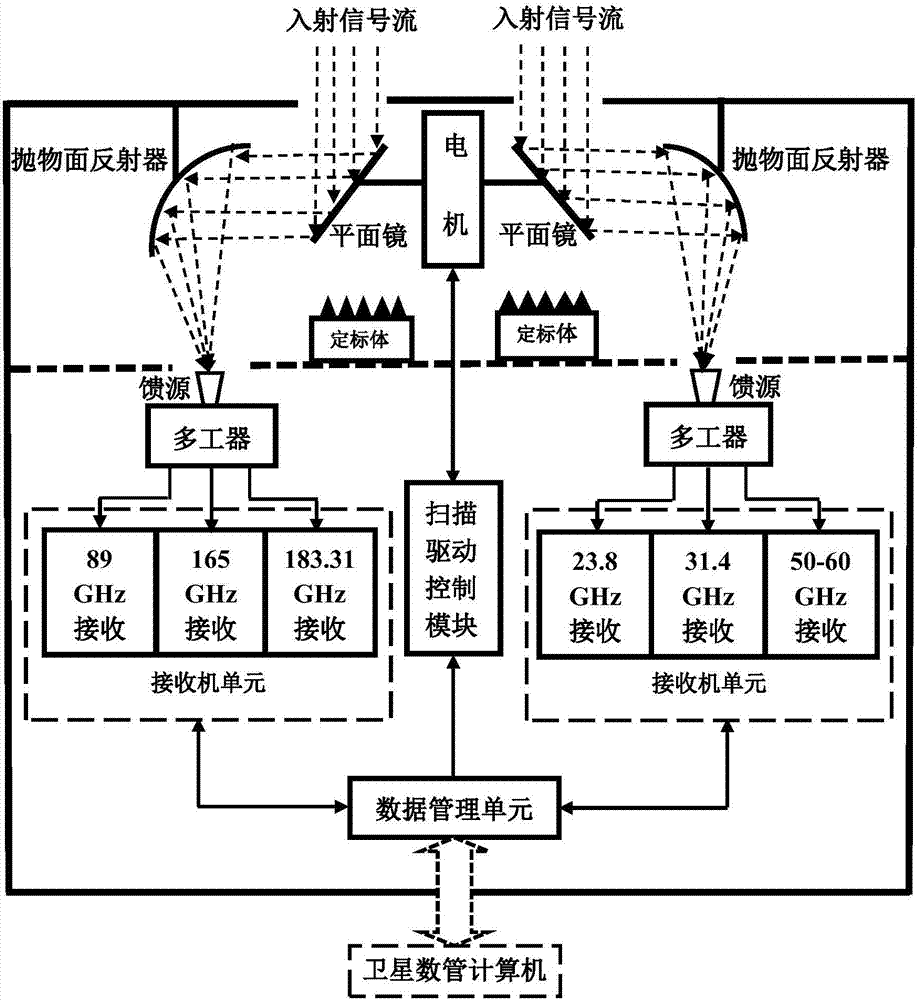
The invention discloses a spaceborne microwave radiometer system for measuring atmosphere path time-delay. The system comprises an observation antenna unit, a scaling antenna unit, a receiving unit, and a control and data processing unit. The observation antenna unit and the scaling antenna unit respectively transmit received signals to the receiving unit, and the receiving unit transmits the received signals to the control and data processing unit; the observation unit is used for receiving microwave radiation from sea surface or atmosphere and comprises three feed sources and a paraboloid; the three feed sources respectively cover a 18.7 GHz frequency range, a 23.8 GHz frequency range and a 37 GHz frequency range; the three feed sources are arranged along the flying direction of a satellite, the feed source with the 37 GHz frequency range is arranged in the middle during arrangement and has a wave beam direction which is oriented towards a nadir point, the feed sources with the 23.8 GHz frequency range and the 18.7 GHz frequency range are arranged at the two sides of the feed source with the 37 GHz frequency range and have wave beam directions which are respectively oriented within negative and positive 2.5 degrees at the two sides of the wave beam oriented towards the nadir point.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
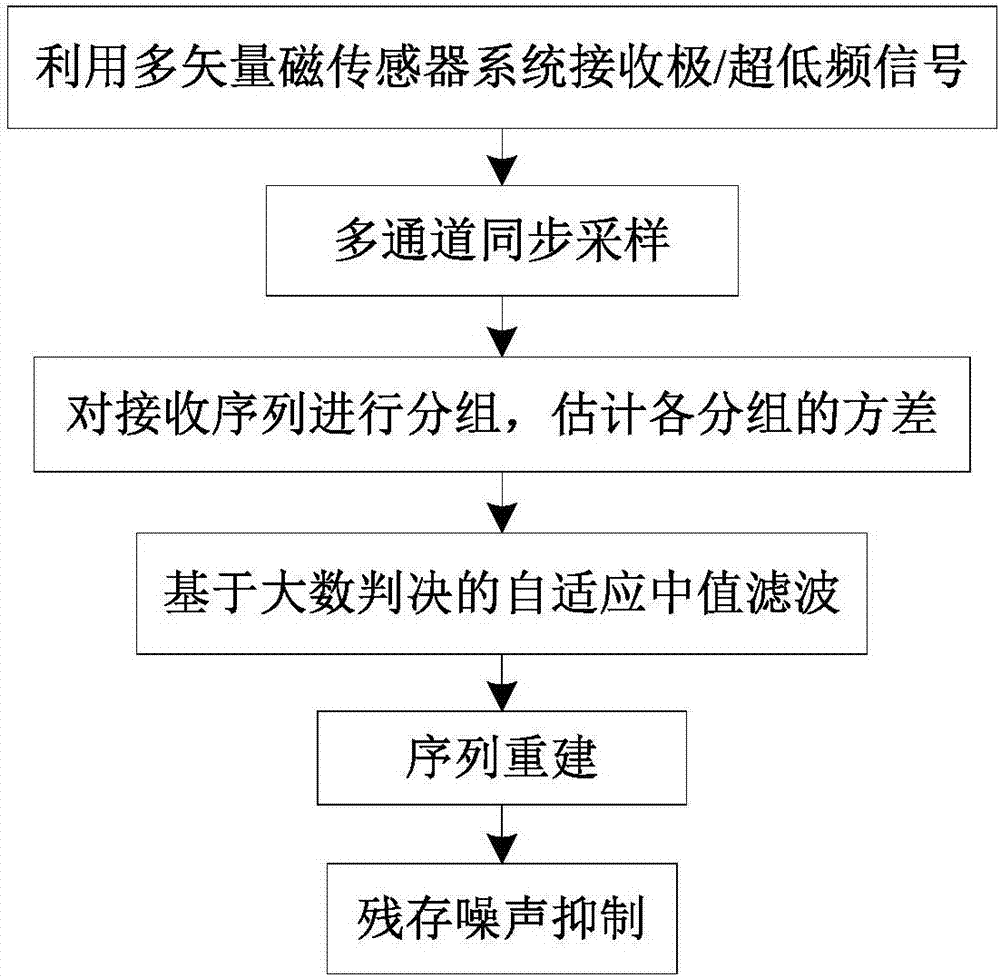
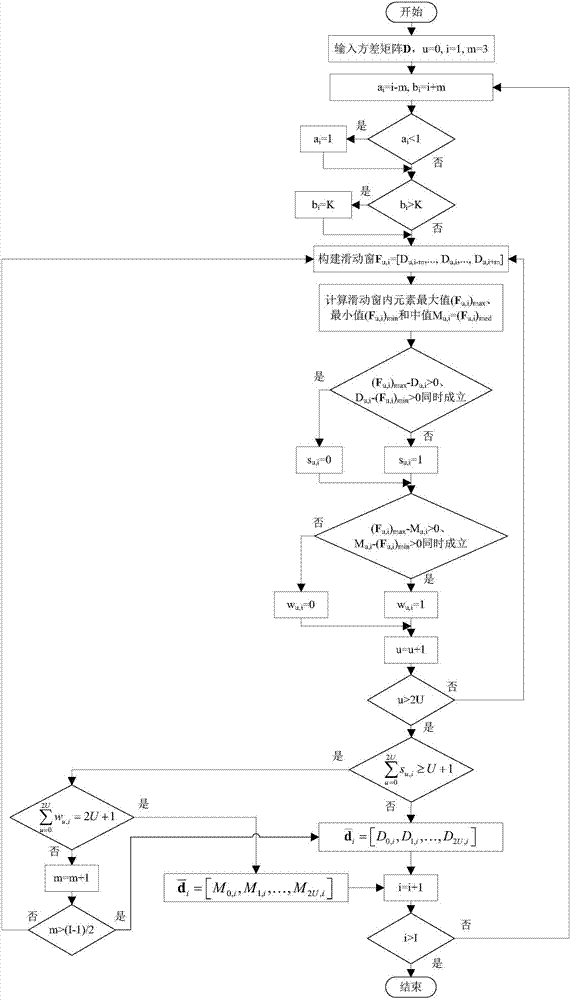
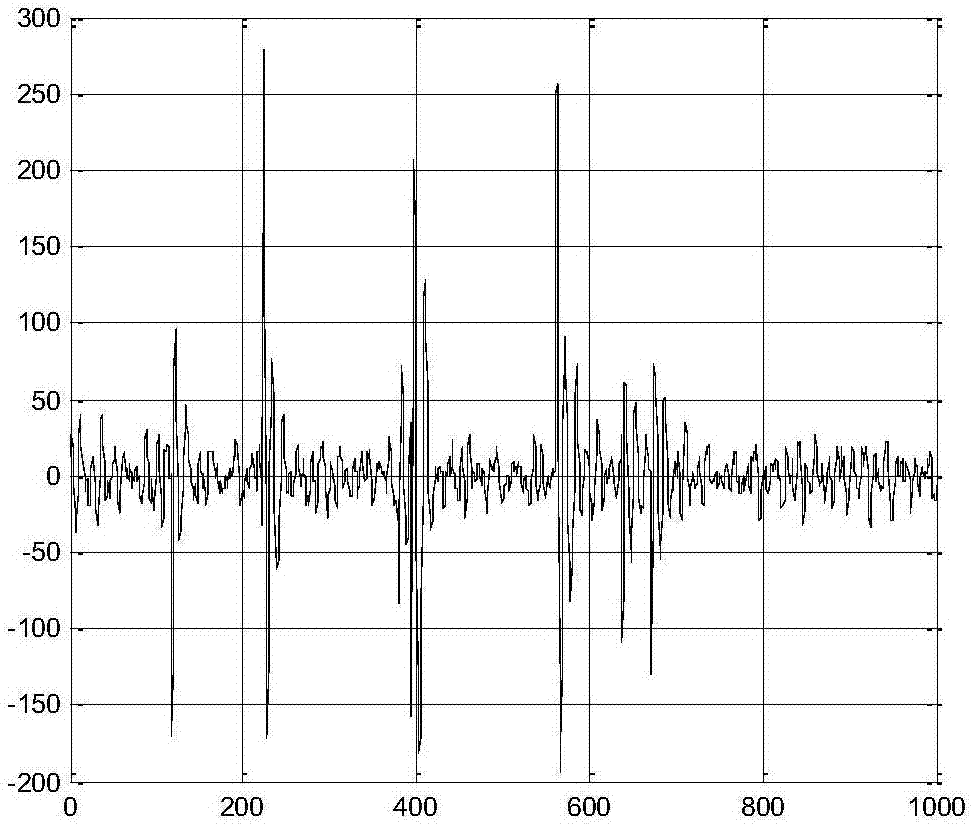
Extremely-ultra low frequency channel atmosphere noise suppression method based on variance median filtering
InactiveCN107040269ALightning pulse suppressionEasy to operateTransmissionEngineeringHarmonic interference
The invention relates to the technical field of radio long wave communication technology, and specifically relates to an extremely-ultra low frequency channel atmosphere noise suppression method based on variance median filtering. The extremely-ultra low frequency channel atmosphere noise suppression method based on variance median filtering includes the steps: constructing a multi-reference magnetic vector sensing system, synchronously receiving extremely-ultra low frequency signals through multi channels, and obtaining a magnetic induction output sampling point matrix X; according to the channel sampling point sequence, grouping X, estimating the variance of each group, and obtaining the variance matrix D; based on a large number decision criterion, performing pulse detection and two-stage adaptive median filtering on D; according to output of the second stage median filtering and input of the first stage median filtering, performing sequence reconstruction, and obtaining an output matrix Y; and performing power frequency harmonic interference and remaining atmosphere noise suppression on Y. As the extremely-ultra low frequency channel atmosphere noise suppression method based on variance median filtering taking the variance of the sampling point group as input of the adaptive median filter, the impulsiveness is improved. As the extremely-ultra low frequency channel atmosphere noise suppression method based on variance median filtering determines the pulse state of each element of the variance matrix based on the large number decision criterion, the pulse detection accuracy is improved and the defect that the performance is low when the median filtering is in the local high density pulse noise condition in the traditional method.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Methodology for Short-term and Impending Earthquake Prediction
InactiveUS20110238314A1Accurately determineFast transferEarthquake measurementSeismic signal processingNatural satelliteMeasuring instrument
Short-term and impending earthquake prediction using orbiting satellites equipped with infrared wave scanners, receivers and image processors. The color densities of infrared images are categorized and applied to different seasons and latitudes to obtain an atmospheric model. The scanners detect the grayness value, from which the actual temperature can be obtained after modification of the atmospheric model. A ring of temperature decrease might appear above the cloud layer where the earthquake is breeding. Strange-shaped clouds might occur over the area. When the earthquake occurs in an inland highland area, thermal stress lines can be observed and the area where these stress lines converge is the future epicenter for an earthquake. A network of infrasonic sound measuring instruments detects infrasonic sound anomalies to improve the accuracy of predicting the time and epicenter of an earthquake. The invention can increase the rate of successful earthquake forecasting by 50%.
Owner:QIANG ZUJI +6
Device for remotely detecting hazardous gas on basis of TeraHertz wave
ActiveCN105784625AReduce riskAvoid Absorbing EffectsMaterial analysis by optical meansAtmospheric airImage resolution
The invention relates to a device for remotely detecting hazardous gases on the basis of TeraHertz waves. The device comprises a TeraHertz emission source, a TeraHertz signal receiver, a high-speed time delay module, a sealed gas box, a vacuum pump and a gas valve, wherein TeraHertz waves received by the TeraHertz signal receiver in a vacuum environment is taken as a reference signal; TeraHertz waves received by the TeraHertz signal receiver in an environment that remote hazardous gases are introduced into the sealed gas box from a long-distance vacuum pipeline; the two groups of TeraHertz waves are compared, and then the components and the concentration content ratios of hazardous gases in the sealed gas box can be obtained. The remote hazardous gases can be detected by using the TeraHertz waves; the influence that in a common method, light waves can be absorbed by moisture in the atmosphere when probe laser is remotely transmitted in the atmosphere can be avoided; the hazardous gases can be absorbed into the sealed gas box for detection through the long-distance vacuum pipeline, then possible danger of the hazardous gases in the detection process can be reduced, and the device is high in resolution ratio, simple in structure, easy to operate and wide in application range.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Atmosphere laser remote sensing method based on polarization modulation and polarization laser radar
ActiveCN108614278AAccurate measurementSimple structureElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationCarrier signalOptoelectronics
The invention discloses an atmosphere laser remote sensing method based on polarization modulation and polarization laser radar. According to the invention, by use of specially designed polarization modulation light signals as detection light, back scattering light of a to-be-detected target includes two paths of orthogonal polarization echo signals and respectively carries carriers and positive first-order sideband signals. Thus, a receiving end detects reflection echoes only by use of a detector. By measuring frequency and power of beat frequency electrical signals in the echo signals, real-time measurement can be performed on wind speed information and depolarization ratio information in the atmosphere simultaneously. The invention discloses a polarization laser radar. Compared with theprior art, by ingeniously designing detection of optical signals, it can be achieved that real-time accurate measurement can be performed on wind speed and depolarization effects of to-be-detected atmosphere; only one set of detectors can be required; and the system structure is quite simple and the achieving cost is quite low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Earthquake infrared radiation anomaly characteristic multi-angle remote sensing extraction method based on robustness satellite data analysis technology
The invention provides an earthquake infrared radiation anomaly characteristic multi-angle remote sensing extraction method based on a robustness satellite data analysis technology. The method comprises the steps that 1, observation areas, affected by cloud, on a remote sensing image are removed; 2, atmospheric correction is carried out on atmosphere layer top signals received by a satellite sensor; 3, infrared multi-angle remote sensing images of land and oceans are processed through land and water separation masks, and the pixel difference of a single infrared image is calculated; 4, an infrared background reference field is built as a reference background for earthquake infrared radiation anomaly characteristic multi-angle remote sensing extraction; 5, an earthquake infrared radiation anomaly characteristic multi-angle remote sensing anomaly robustness evaluation index is provided for single-angle infrared data and is used for extraction of single-angle earthquake infrared radiation characteristics; 6, on the basis of the infrared multi-angle remote sensing data, a multi-angle brightness and temperature synthesis earthquake infrared radiation analysis method is provided and used for synthesis and analysis of earthquake infrared radiation characteristic multi-angle remote sensing.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
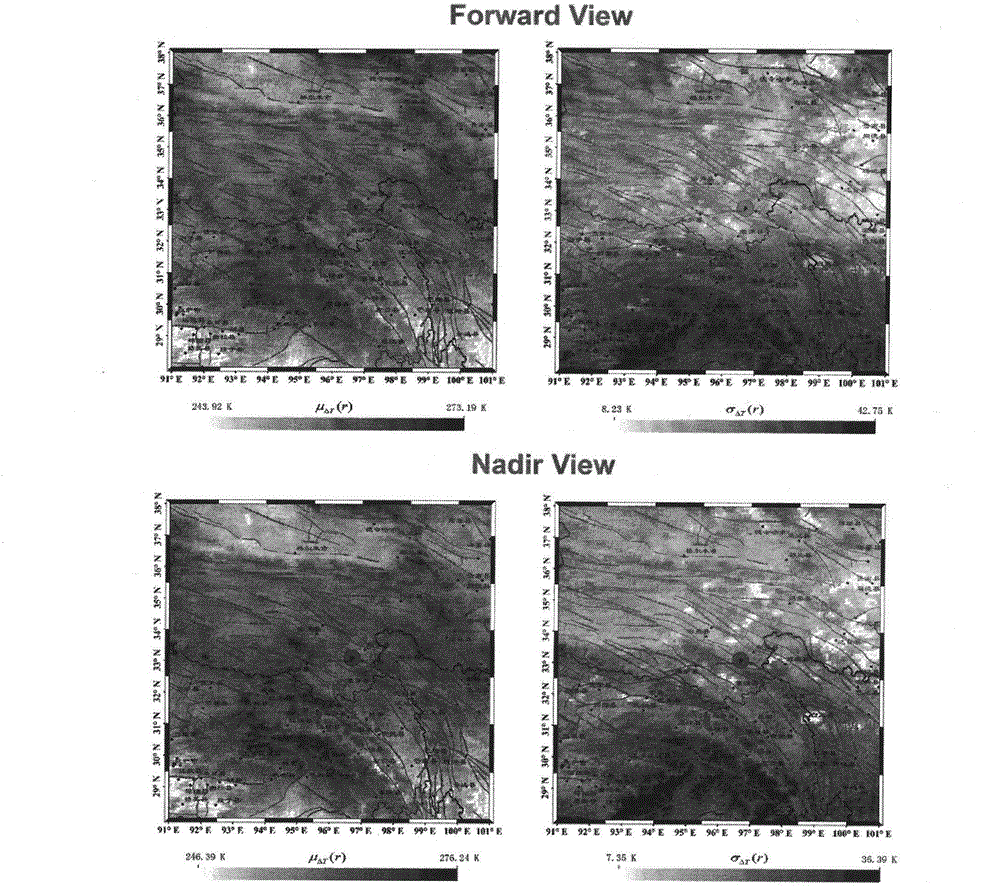
Method for detecting atmospheric influence of satellite-to-ground bidirectional high-speed laser communication based on thermal imager
ActiveCN105657342AFeature monitoring implementationImplement detectionRadiation pyrometryClosed circuit television systemsImage transferImaging data
The invention relates to a method for detecting the atmospheric influence of satellite-to-ground bidirectional high-speed laser communication based on a thermal imager, belonging to the technical field of atmosphere detection of communication systems. The method disclosed by the invention aims to solve the problem that the judgement reliability of atmospheric cloud layer characteristics is low at night due to the fact that the traditional imaging system used for monitoring the atmospheric cloud layer characteristics is only sensitive to a visible light wave band and not sensitive to an infrared wave band. A thermal imager control unit sends a communication instruction to the thermal imager according to a promised data packet format, such that the thermal imager is controlled to execute the communication instruction and acquire a current atmospheric cloud layer image; when receiving a state inquiry communication instruction, the thermal imager feeds back currently acquired atmospheric cloud layer image data to the thermal imager control unit according to the promised data packet format; the atmospheric cloud layer image acquired by the thermal imager is transmitted to an image processing unit to be subjected to video compression and image processing, such that a current atmospheric cloud layer characteristic image is obtained; and then, detection on the atmospheric cloud layer characteristics is realized. The method disclosed by the invention is used for detecting the atmospheric cloud layer characteristics.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
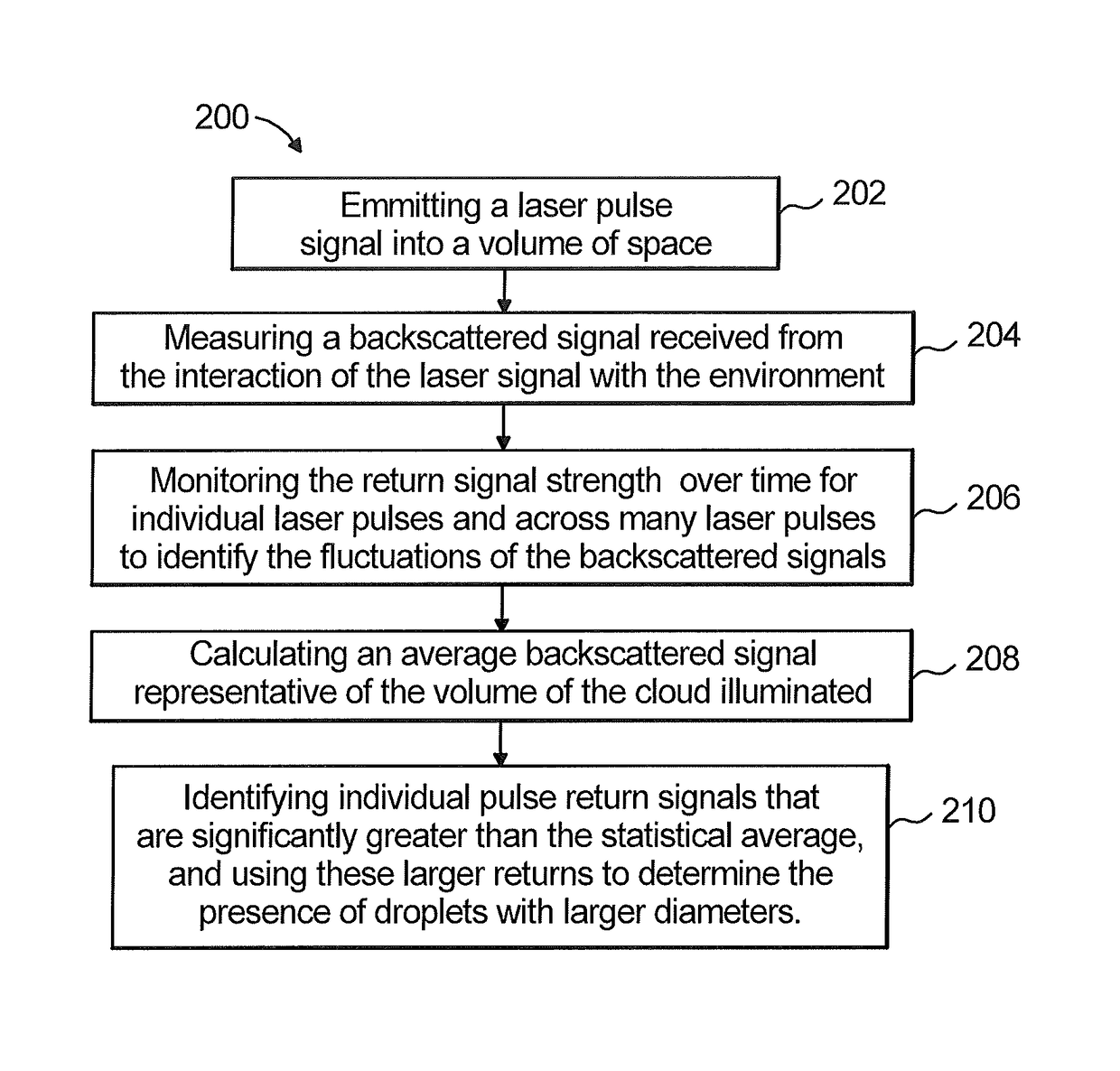
Large droplet detection by statistical fluctuations in lidar backscatter
A method of optically detecting the presence of a bimodal droplet size distribution in the atmosphere. The method comprising monitoring statistical fluctuations in a backscattered signal received from a series of pulsed laser light beams directed into a cloud and analyzing the statistics of the fluctuations of the backscattered signals to identify the presence of larger diameter droplets.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
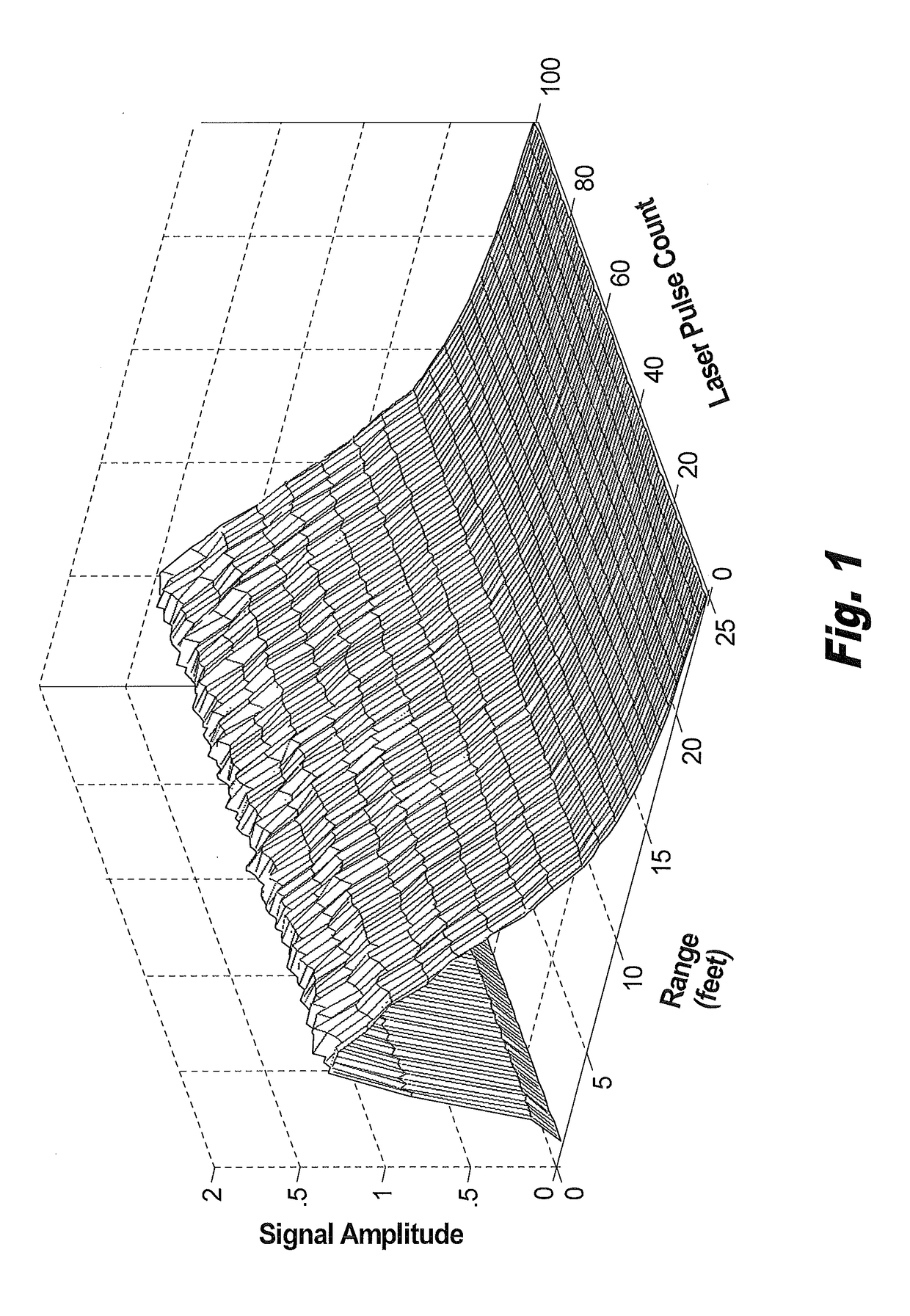
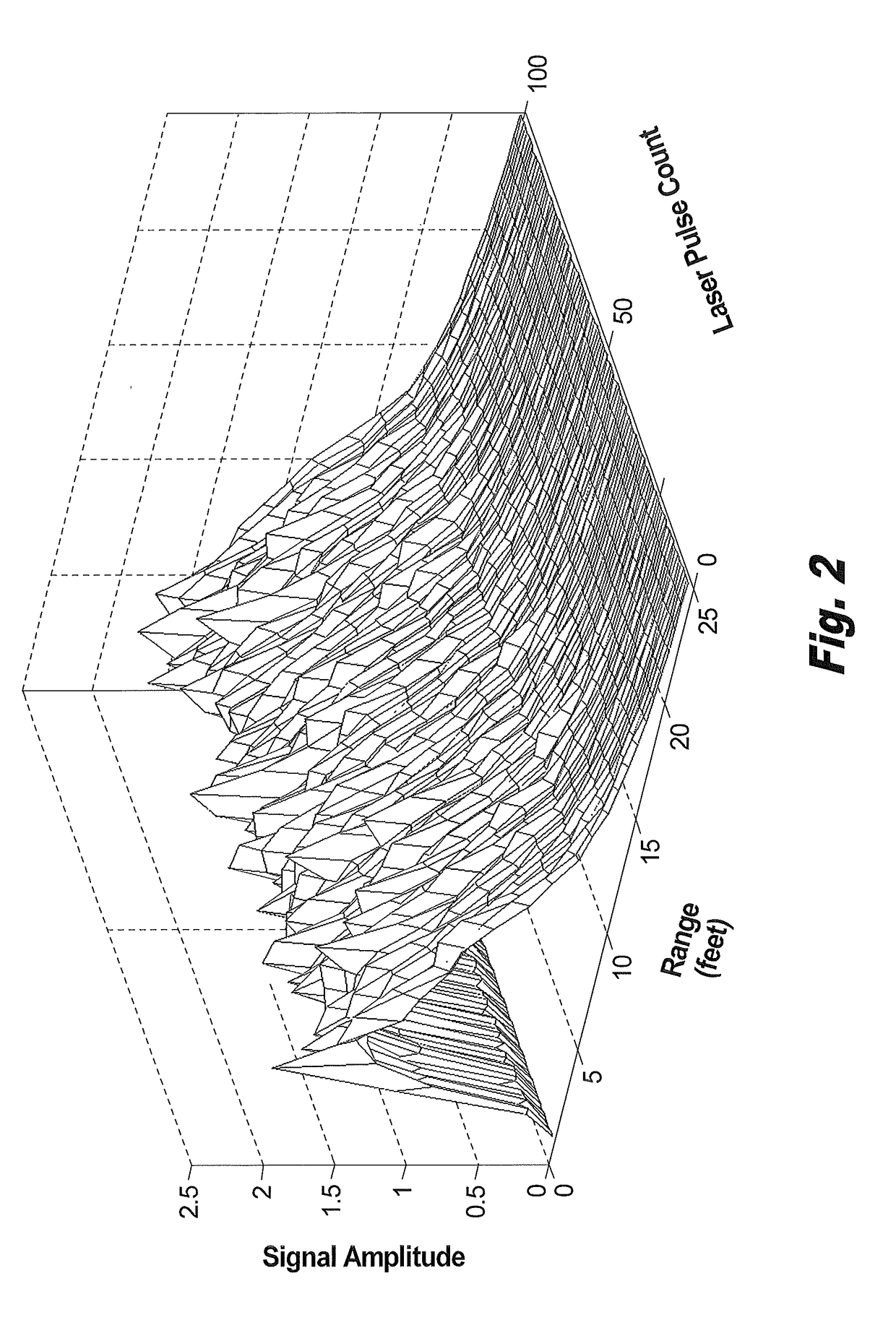
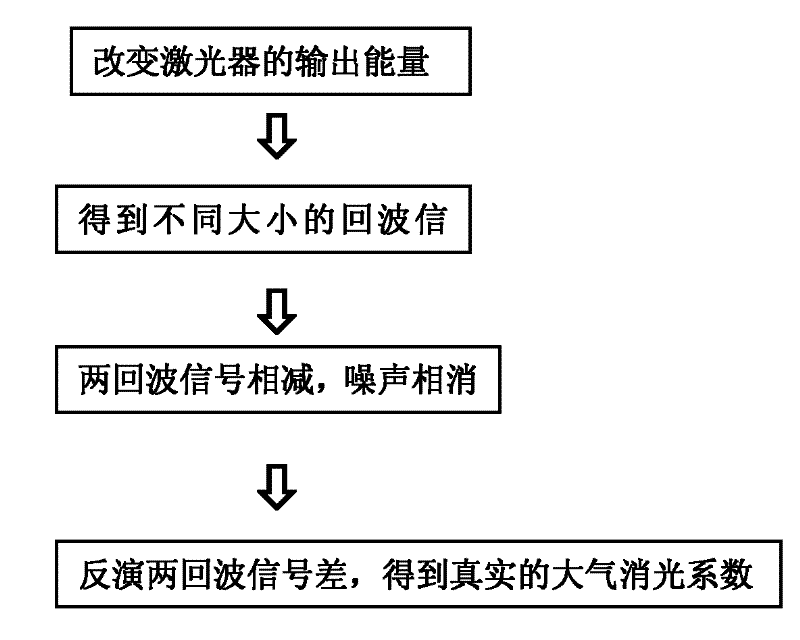
Method for eliminating influence of background light and thermal noise on measurement accuracy of atmospheric extinction coefficient
InactiveCN102200508AEliminate the effects of probing accuracyAccurate and reliable atmospheric optical parametersScattering properties measurementsExtinctionLight beam
The invention discloses a method for eliminating influence of background light and thermal noise on measurement accuracy of an atmospheric extinction coefficient. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, output energy of a laser is reduced and scattering echo signals of laser beams with different energies are measured; because background light signals and thermal noise signals in two echo signals are equal in a short interval, the background light signals and the thermal noise signals are mutually offset through a subtraction of the two echo signals; lastly, a equation of the subtraction of the two echo signals is inversed to obtain a real atmospheric extinction coefficient. According to the present invention, a new experiment and a new inversion method are provided for effective eliminating the influence of the background light and the thermal noise on the measurement accuracy so as to obtain an exact and reliable atmospheric extinction coefficient.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Technique to mitigate storms using arrays of wind turbines
This invention describes a system whose operation can change the track and intensity of atmospheric storms. The invention uses arrays of wind turbines which are being built for power generation. Using existing atmospheric and storm tracking models, calculations of a storm track may be determined to establish a baseline track calculation. The storm track may then be calculated for a number of permutations where various groups or individual wind turbines are curtailed (e.g., feathered). The optimal storm track may be determined based on damage estimate calculations. Signals may be sent to individual or groups of wind turbines to curtail the turbines to alter the track of the tropical storm.
Owner:THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY
Method and system for detecting aircraft induced wake turbulence
ActiveUS20170045615A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesClear air turbulence detection/forecastingWind shearEngineering
A method is disclosed for detecting atmospheric turbulence including aircraft induced wake turbulence and / or wind shear within an aperture associated with an aircraft approach or departure corridor around an airport. The method comprises transmitting into the aperture acoustic signals having a waveform suitable for pulse compression and receiving backscattered acoustic echoes of the acoustic signals from the atmospheric turbulence and / or wind shear. The method further includes processing the acoustic echoes in a matched filter receiver to provide a measure of the atmospheric turbulence and discriminating the aircraft induced demise time, being a time taken for the aircraft induced wake turbulence and / or wind shear to fall below a set threshold at least in the aperture. A system for detecting atmospheric turbulence including aircraft induced wake turbulence and / or wind shear associated with an aircraft approach or departure corridor around an airport is also disclosed.
Owner:WINDBIDCO
Full-frequency-range RCS (Radar Cross-Section) value pre-estimating and correcting method based on atmospheric absorption loss
InactiveCN102759729AWave based measurement systemsElectromagnetic wave transmissionAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to a full-frequency-range RCS (Radar Cross-Section) value pre-estimating and correcting method based on an atmospheric absorption loss, which can utilize a loss caused by oxygen absorption and steam absorption under an atmospheric environment in an electromagnetic wave transmission process to correct a target RCS. In order to grasp scattering properties of each target under the atmospheric environment, the method can provide reference evidences for accurate remote sensing and detection.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
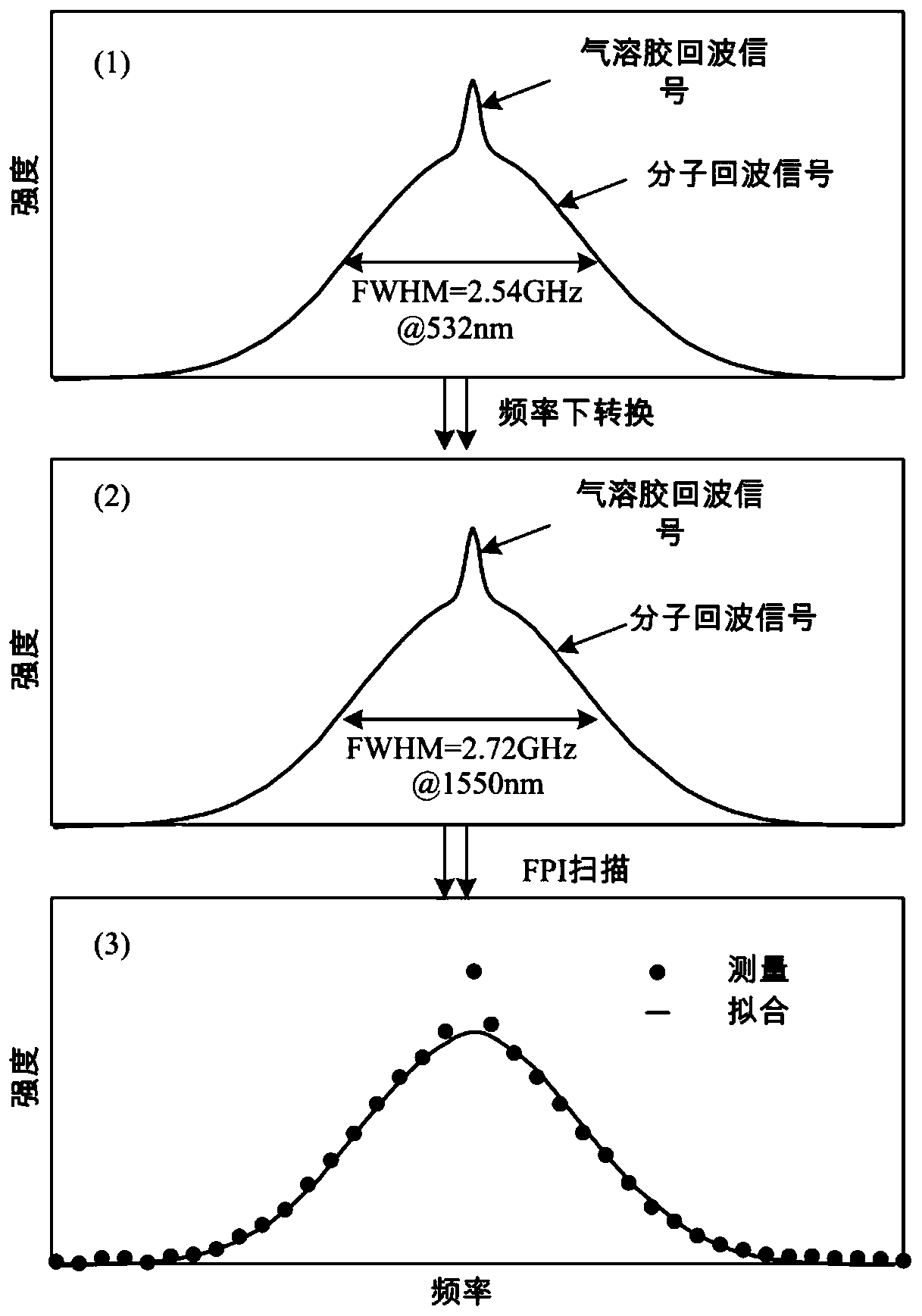
Atmospheric temperature measurement laser radar based on frequency down-conversion and atmospheric temperature measurement method
PendingCN110018497AHigh strengthIncrease the backscatter coefficientThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectromagnetic wave reradiationRayleigh scatteringAtmospheric temperature
The invention discloses an atmospheric temperature measurement laser radar based on frequency down-conversion and an atmospheric temperature measurement method. The technical scheme employs short-wavelaser so as to improve the backward scattering coefficients of Rayleigh scattering and rotational Raman scattering; and at a laser radar receiving end, a frequency down conversion technology is adopted to convert the wavelength of the detection light to an optical communication wave band, and a filter and a detector in the optical communication wave band are employed to process and detect the atmospheric echo signals related to the temperature so as to invert the atmospheric temperature information. The difficulty that near-infrared laser Rayleigh and rotational Raman backscattering signals are weak is overcome, and the problems that on the short wavelength, a space optical filter is large in bandwidth, high in price and poor in stability are solved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com