Patents
Literature
40 results about "Spore forming bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
What are Spore Forming Bacteria. Spore-forming bacteria are a group of bacteria that can produce spores in response to unfavorable conditions such as extreme temperatures, desiccation, high UV irradiation, and enzymatic destruction. Some genera of Bacillus, Clostridium and Sporolactobacillus form spores.
Antimicrobial cidality formulations with residual efficacy, uses thereof, and the preparation thereof
InactiveUS20090074881A1Easy to manufactureEasy to prepareBiocidePeroxide active ingredientsMicroorganismDistilled water
The present invention is a quick-kill formulation that is able to kill organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, mold, spore-forming bacteria and combinations thereof. In addition, the formulation contains a residual kill component that is effective for at least one day. The unique formulation is effective without being corrosive. This is an advantage that allows it to be used in a wide range of applications, one application being in the medical field for sterilizing instruments. Another improvement of this formulation over the prior art is that it is stabilized such that, unlike prior art formulations, tap water, as opposed to distilled water, may be used in its manufacture.
Owner:YCLEAN ENTERPRISES LLC
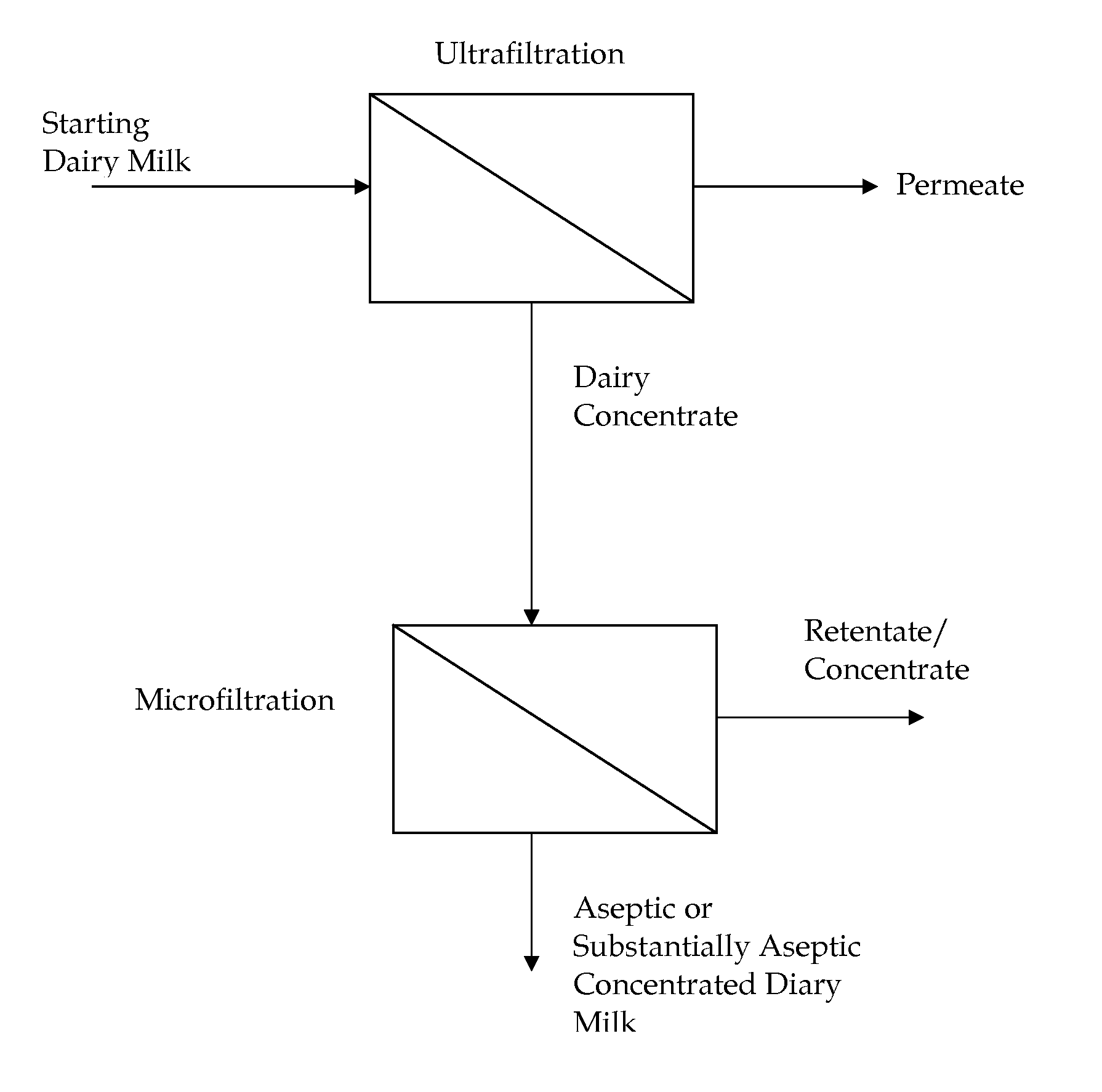
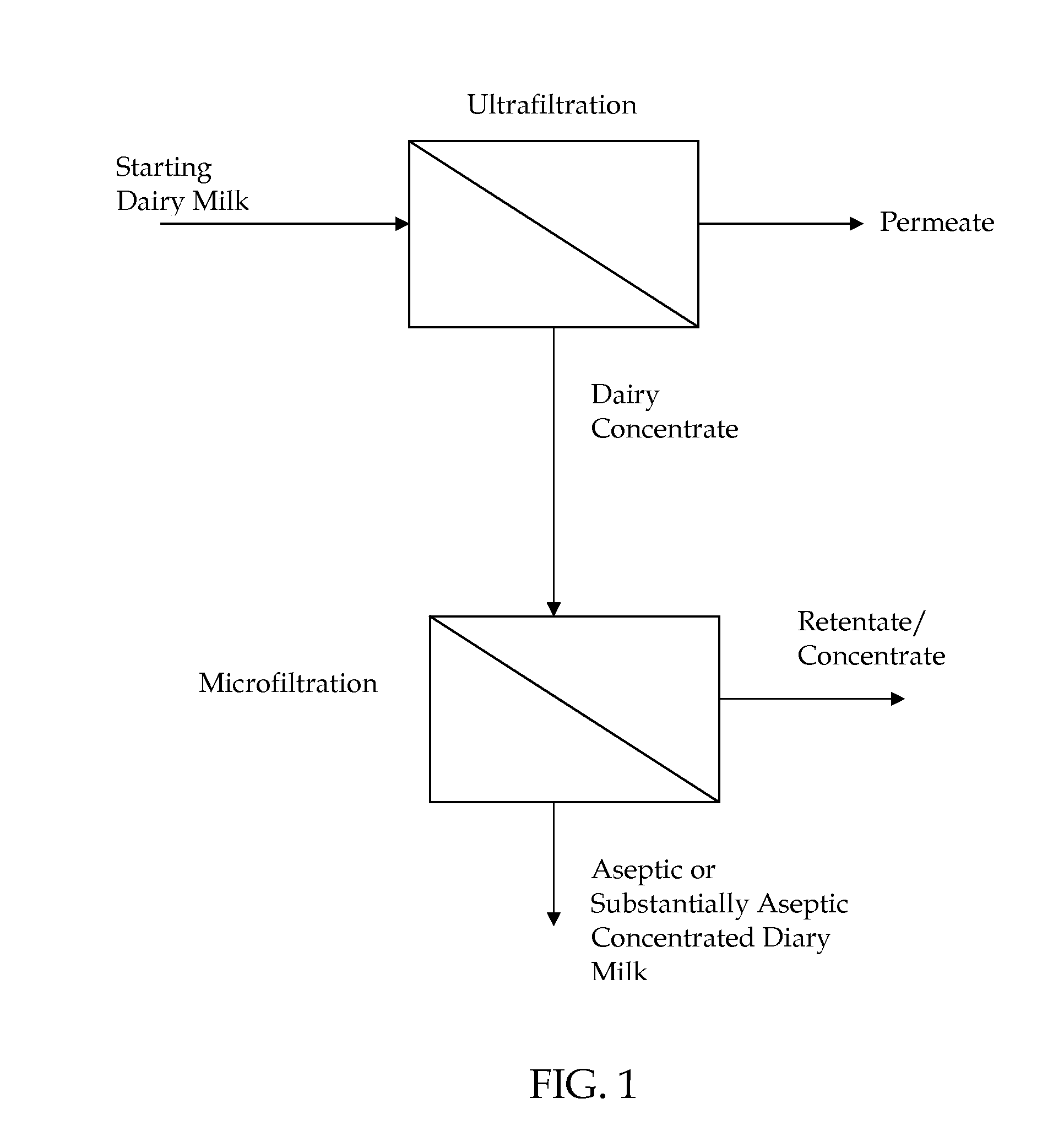
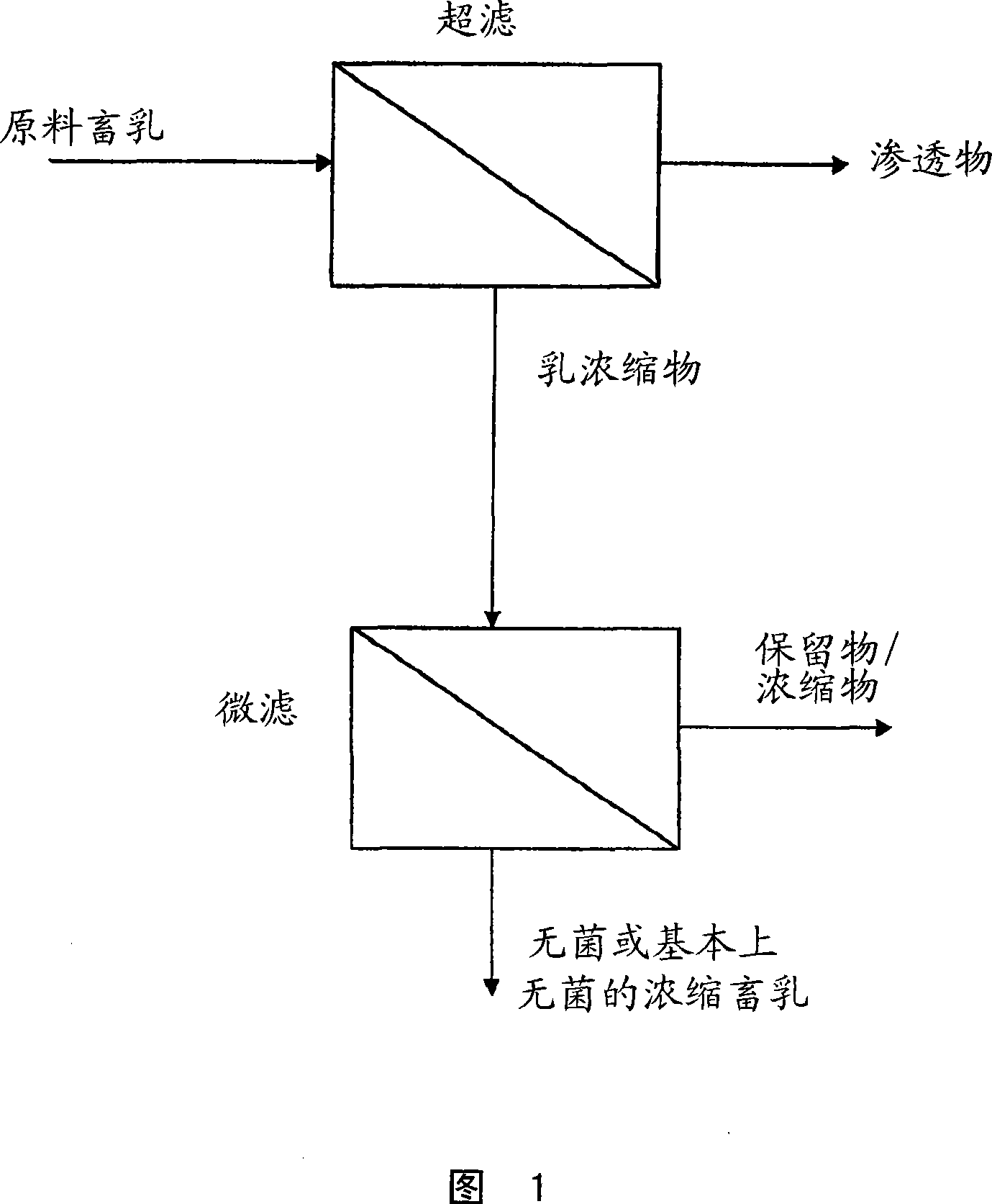
Method Of Producing Concentrated Liquid Dairy Products
InactiveUS20080160134A1Add flavorGreat tasteMilk preparationMilk preservationUltrafiltrationMicrofiltration membrane
A method is provided for forming aseptic or substantially aseptic concentrated dairy liquid, such as dairy milk, without significant heat treatment. In one form, the method first concentrates a starting dairy milk to about 2× to about 7× concentration using an ultrafiltration membrane to form a dairy concentrate. Thereafter, the dairy concentrate is filtered using a microfiltration membrane to provide the aseptic or substantially aseptic concentrated dairy milk. The resultant concentrated dairy milk has less than about 0.5 percent total bacteria and less than about 5 colony forming units of spore forming bacteria per gram. The substantially aseptic concentrated dairy milk is not subjected to significant heat treatment during processing.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS LLC
Biological soil remediation agent and method for remediating soil
InactiveCN105618478AImprove the growing environmentEffective passivationContaminated soil reclamationSoil remediationBiology
The invention discloses a biological soil remediation agent which is prepared by mixing a solid passivator and a microbic solution according to the volume-weight ratio of 1:(15-30) (L / kg). The solid passivator comprises the following ingredients in percent by mass: 50-60 percent of clay carrier, 15-30 percent of diatomite, 10-15 percent of humic acid and 10-20 percent of charcoal. The microbic solution comprises a non-spore forming bacterium and streptomyces microflavus. The biological soil remediation agent can be used for remediating a soil ecosystem, improving the crop growth environment, effectively passivating heavy metal pollutants, such as lead, and reducing the availability for plants.
Owner:NANJING GAIA BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
Lactobacillus buchneri strain LN1326 and its use to improve aerobic stability of silage
InactiveUS20090028993A1Improving animal performanceImprove performanceMilk preparationBacteriaBacteroidesMicroorganism
A method for treating silage to enhance aerobic stability by inhibiting growth of microorganisms selected from yeasts, molds and spore-forming bacteria is disclosed. The method comprises treating silage or feed with a composition comprising Lactobacillus buchneri, LN 1326, or the antimicrobial components produced thereby. The strain of Lactobacillus buchneri disclosed in the invention has been purified and isolated and has been found to be nontoxic, safe and able to improve aerobic stability of silage.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
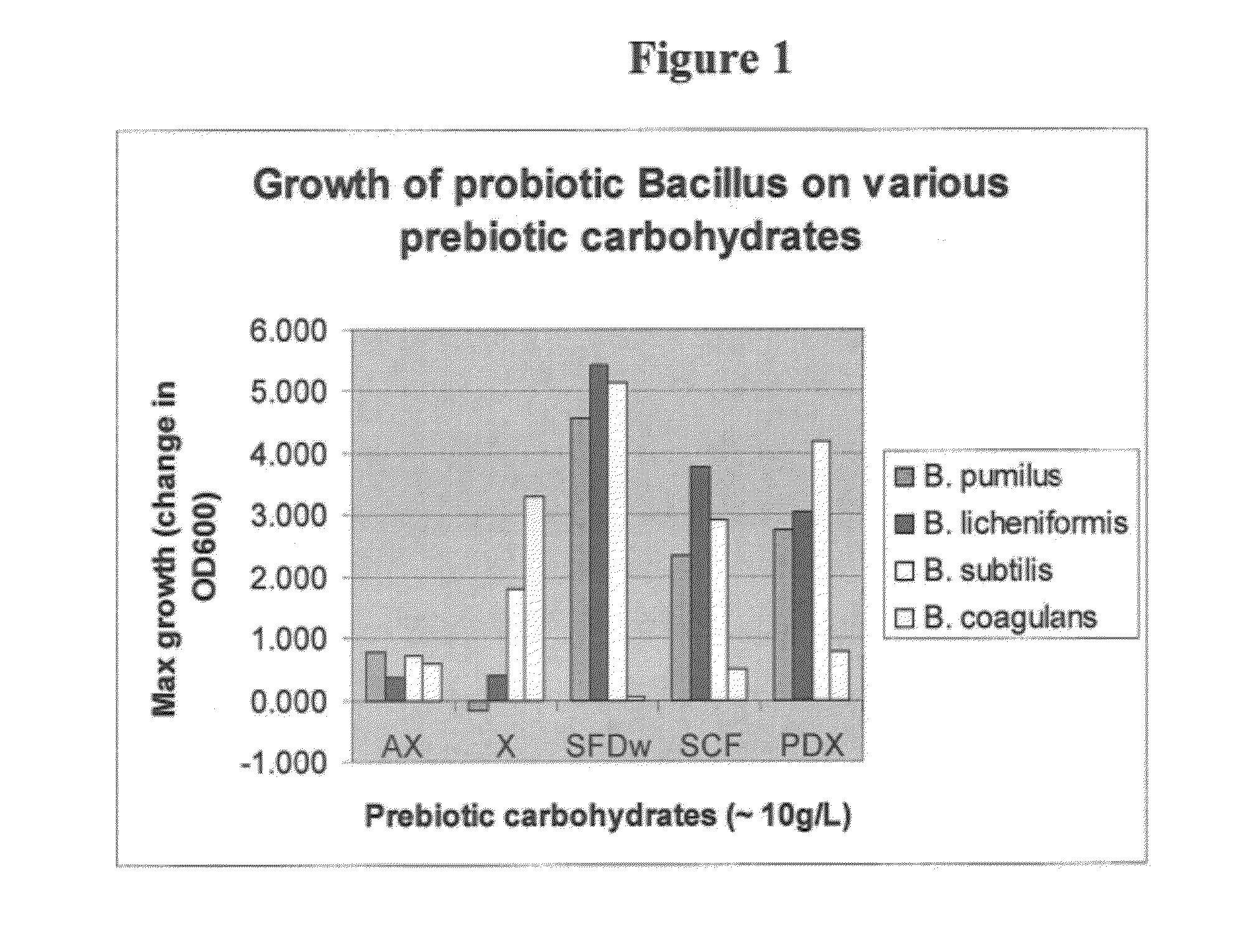
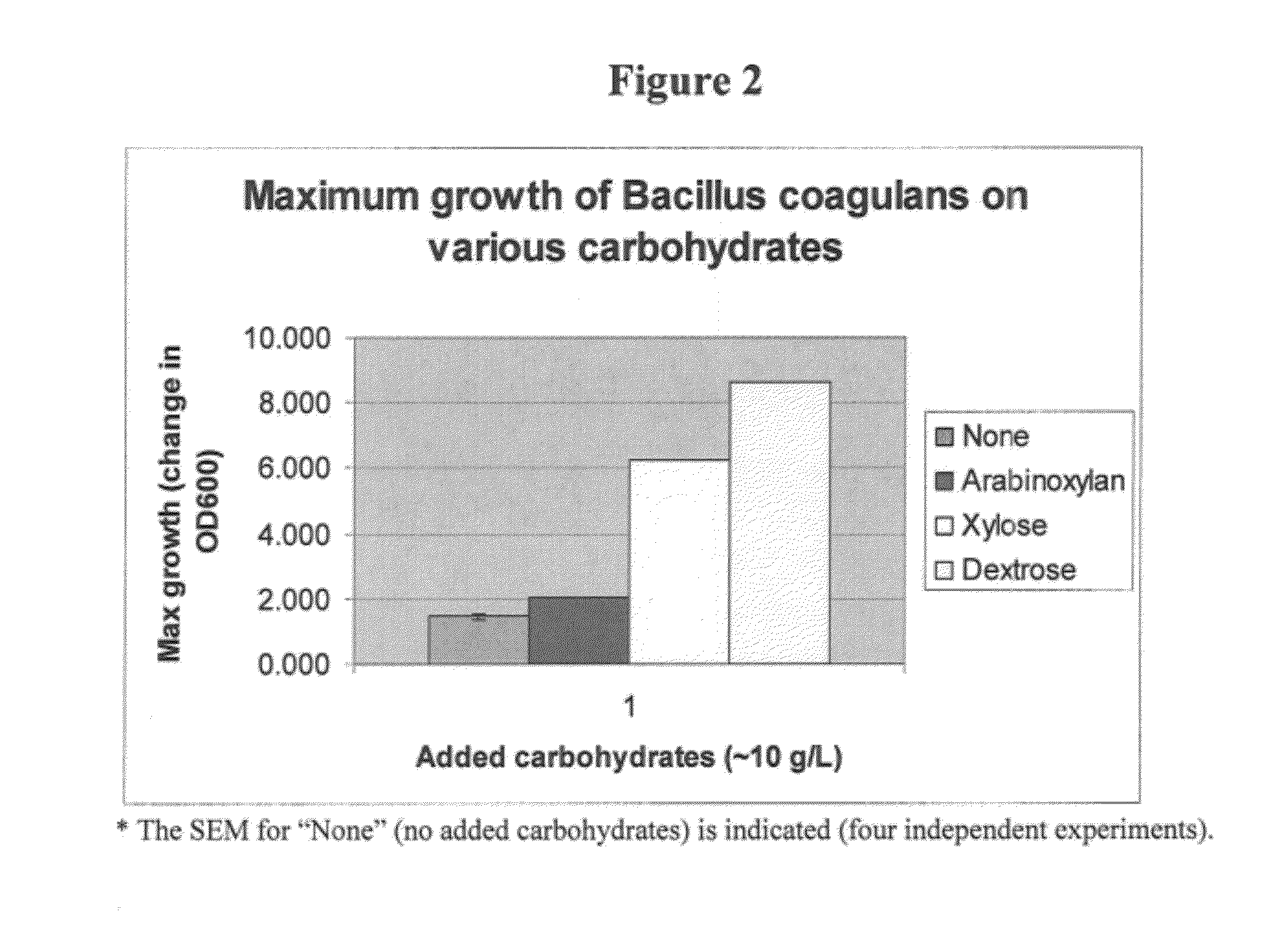
Synbiotic Product
ActiveUS20120052152A1High potencyProvide health benefitAntibacterial agentsMilk preparationBacteroidesMammal
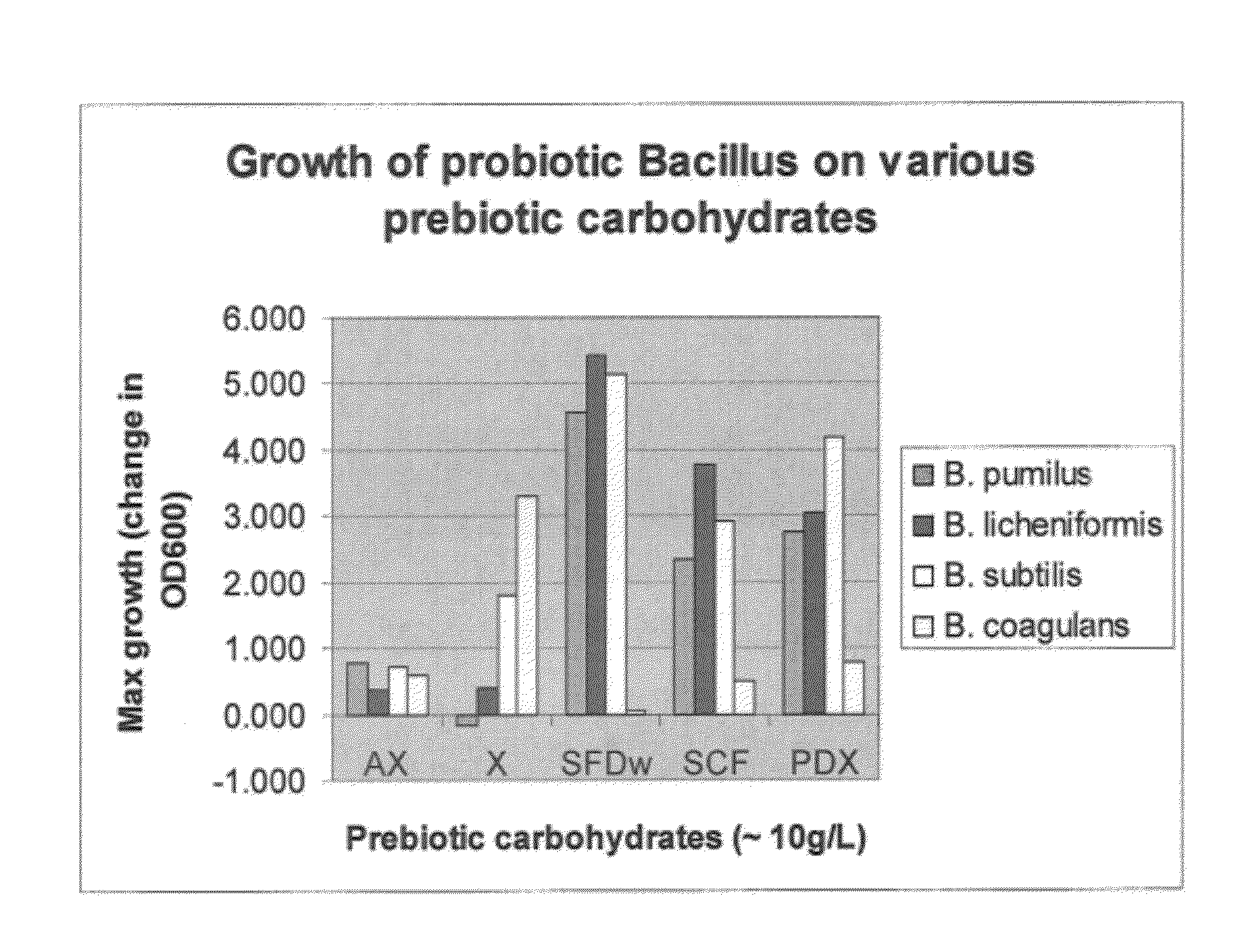
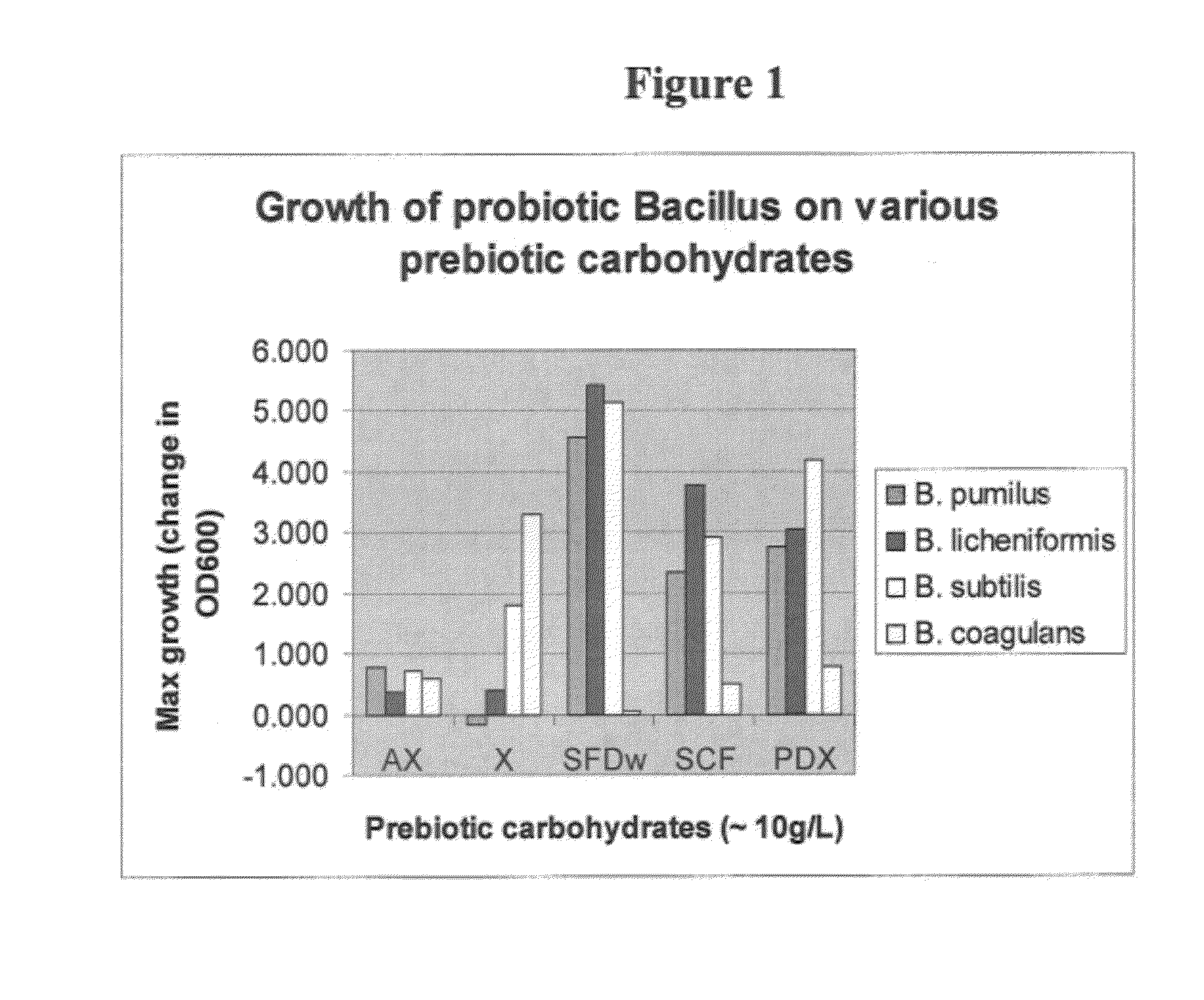
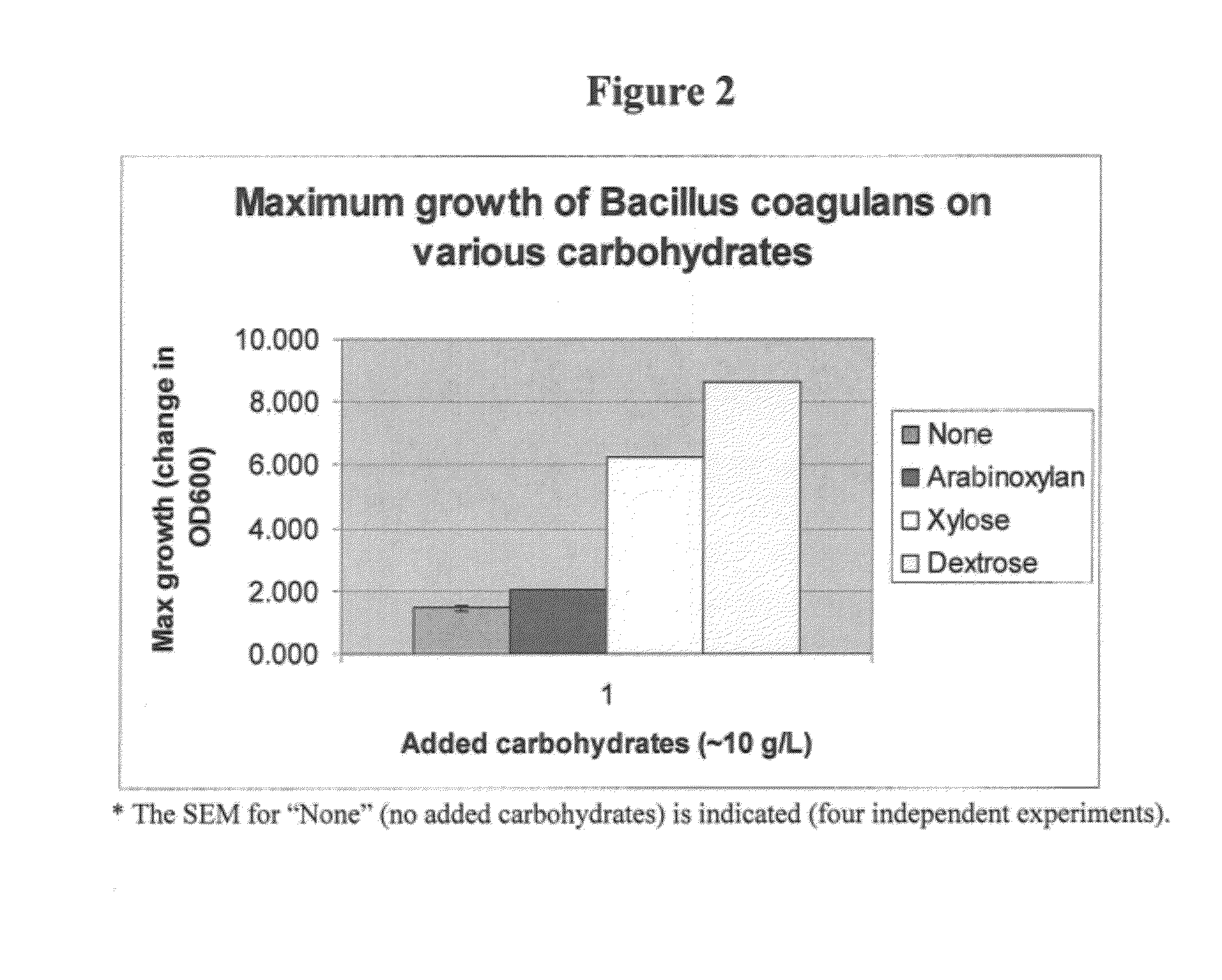
The present invention relates to a synbiotic product composition comprising a blend or mixture of a prebiotic carbohydrate and a probiotic spore-forming Bacillus bacteria. Examples of prebiotic carbohydrates useful in synbiotic product include arabinoxylan, arabinoxylan oligosaccharides, xylose, soluble fiber dextrin, soluble corn fiber, and polydextrose. The present invention also relates to human foodstuffs and animal feed comprising such synbiotic products and methods of increasing the titer of spore-forming bacteria in the intestinal tracts of mammals by administration of symbiotic products.
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
Lactobacillus buchneri strain LN1297 and its use to improve aerobic stability of silage
InactiveUS20080138461A1Improving animal performanceImprove performanceMilk preparationBacteriaBacteroidesMicroorganism
A method for treating silage to enhance aerobic stability by inhibiting growth of microorganisms selected from yeasts, molds and spore-forming bacteria is disclosed. The method comprises treating silage or feed with a composition comprising Lactobacillus buchneri, LN1297, or the antimicrobial components produced thereby. The strain of Lactobacillus buchneri disclosed in the invention has been purified and isolated and has been found to be nontoxic, safe and able to improve aerobic stability of silage.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
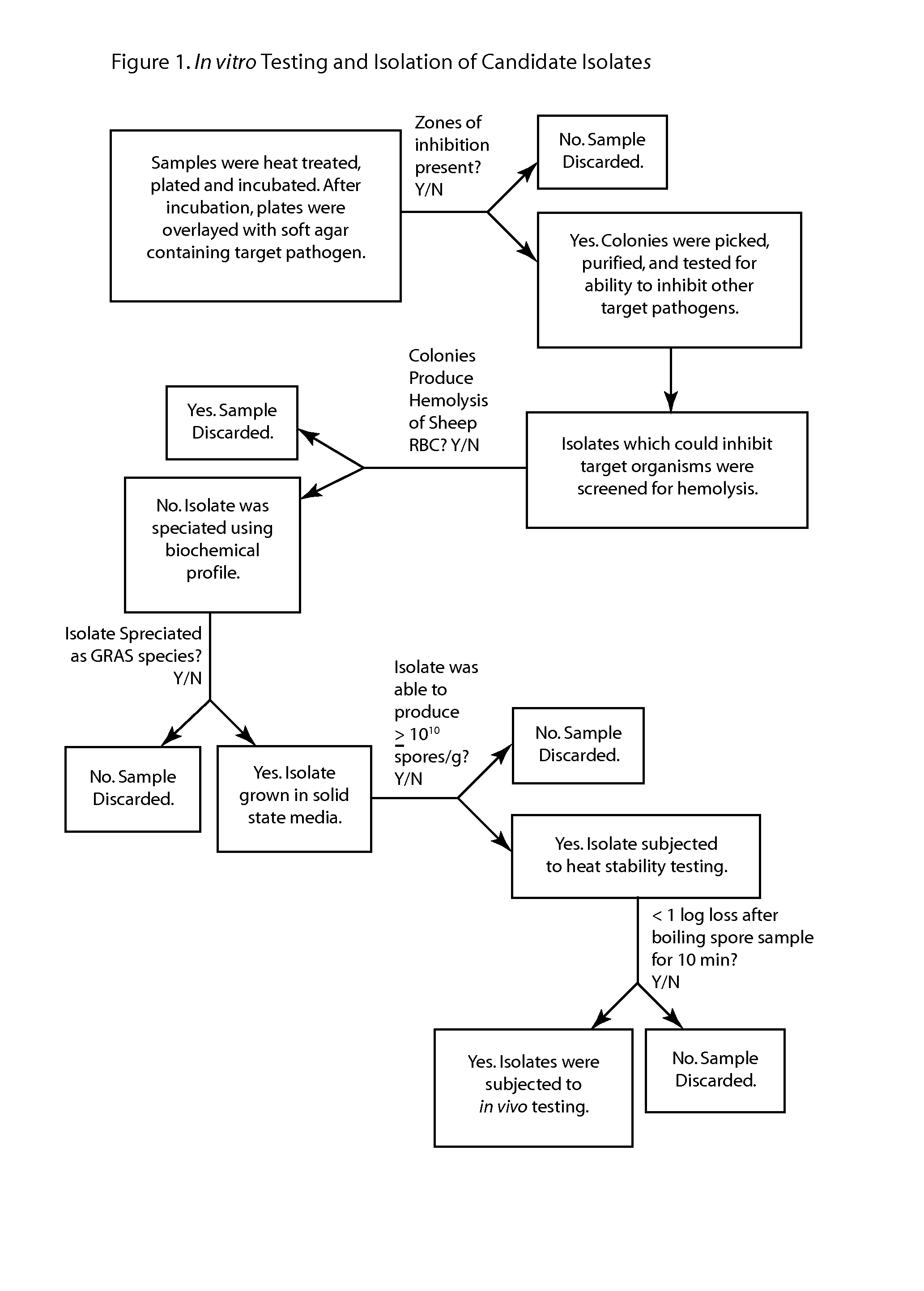
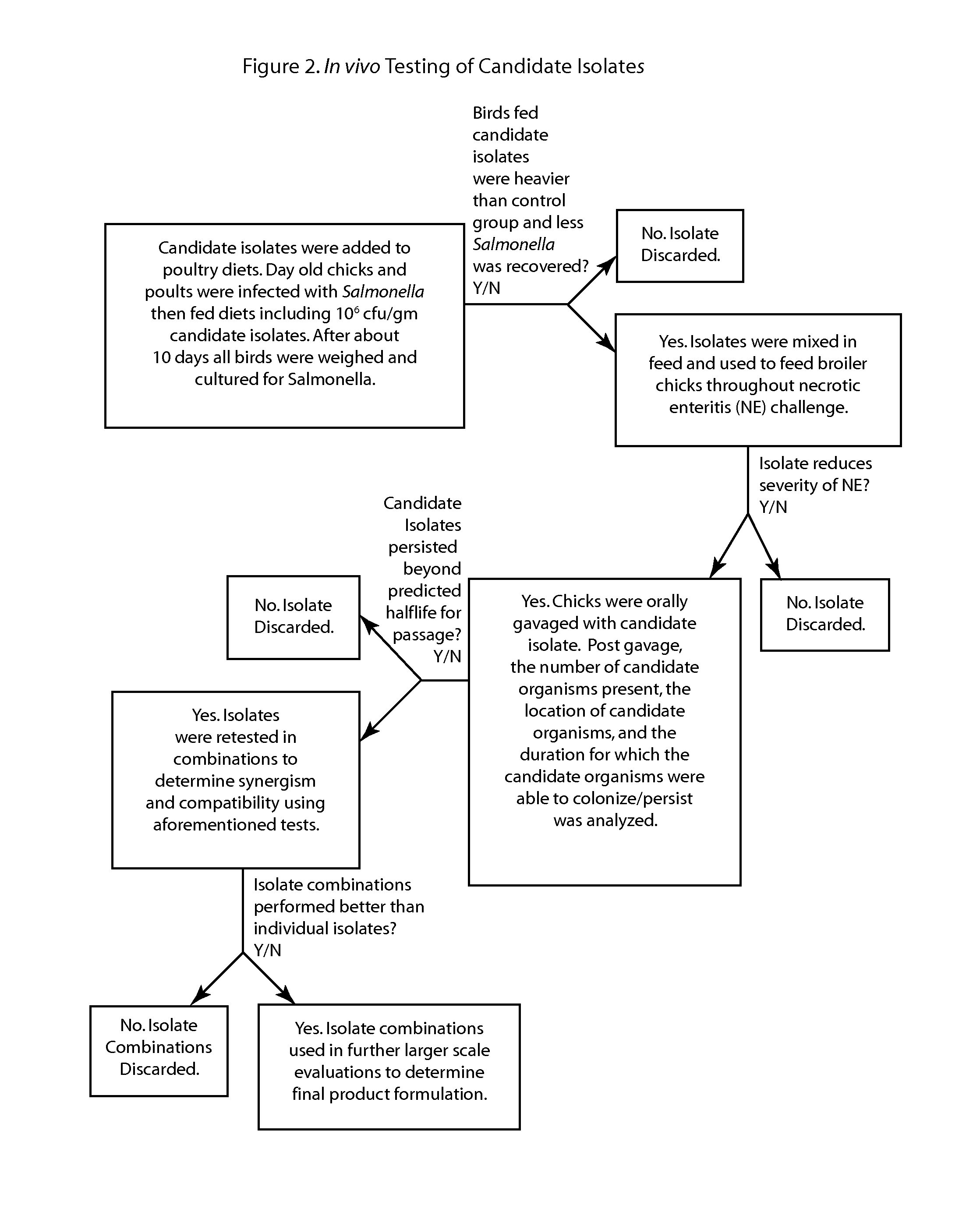
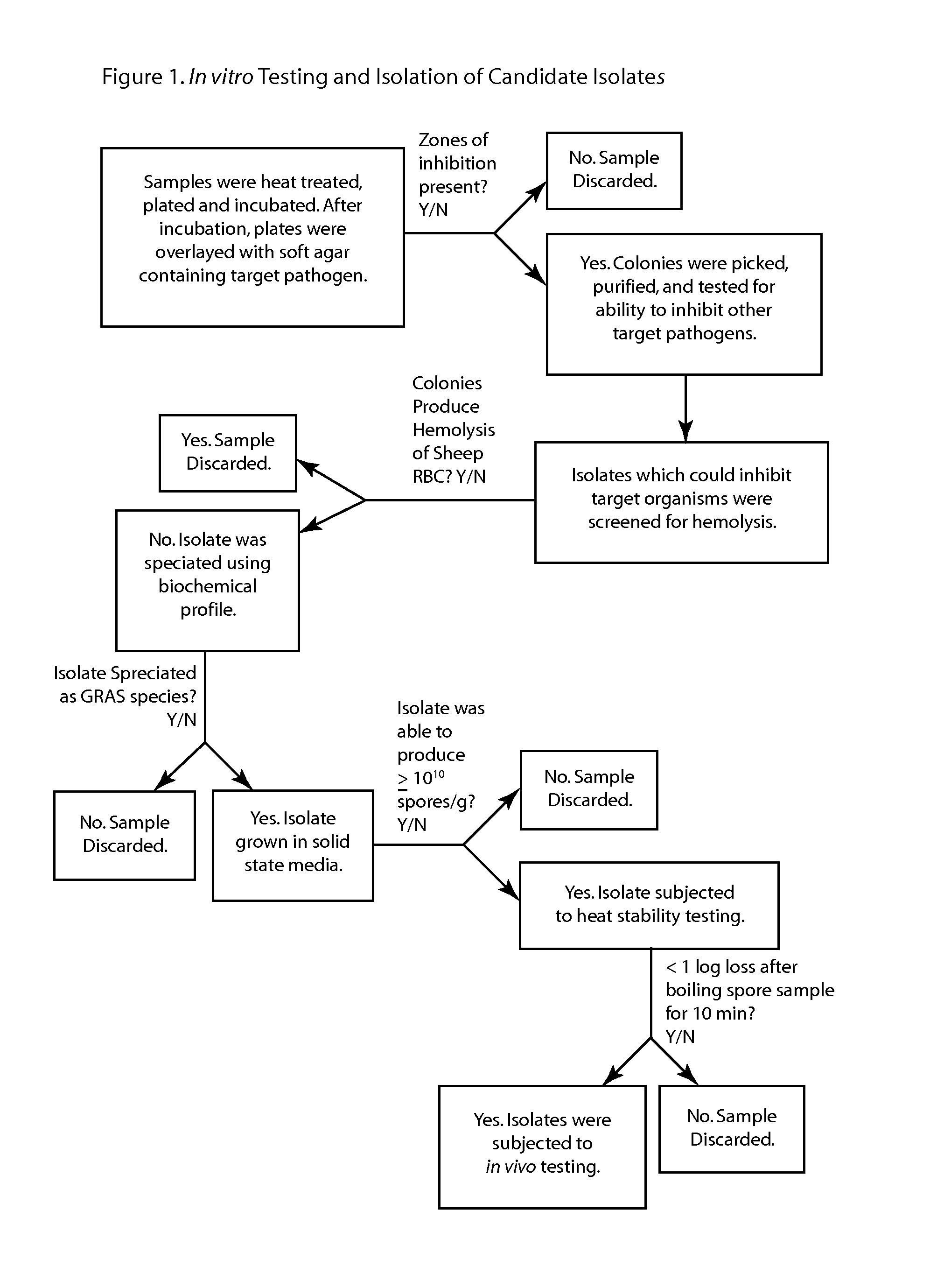
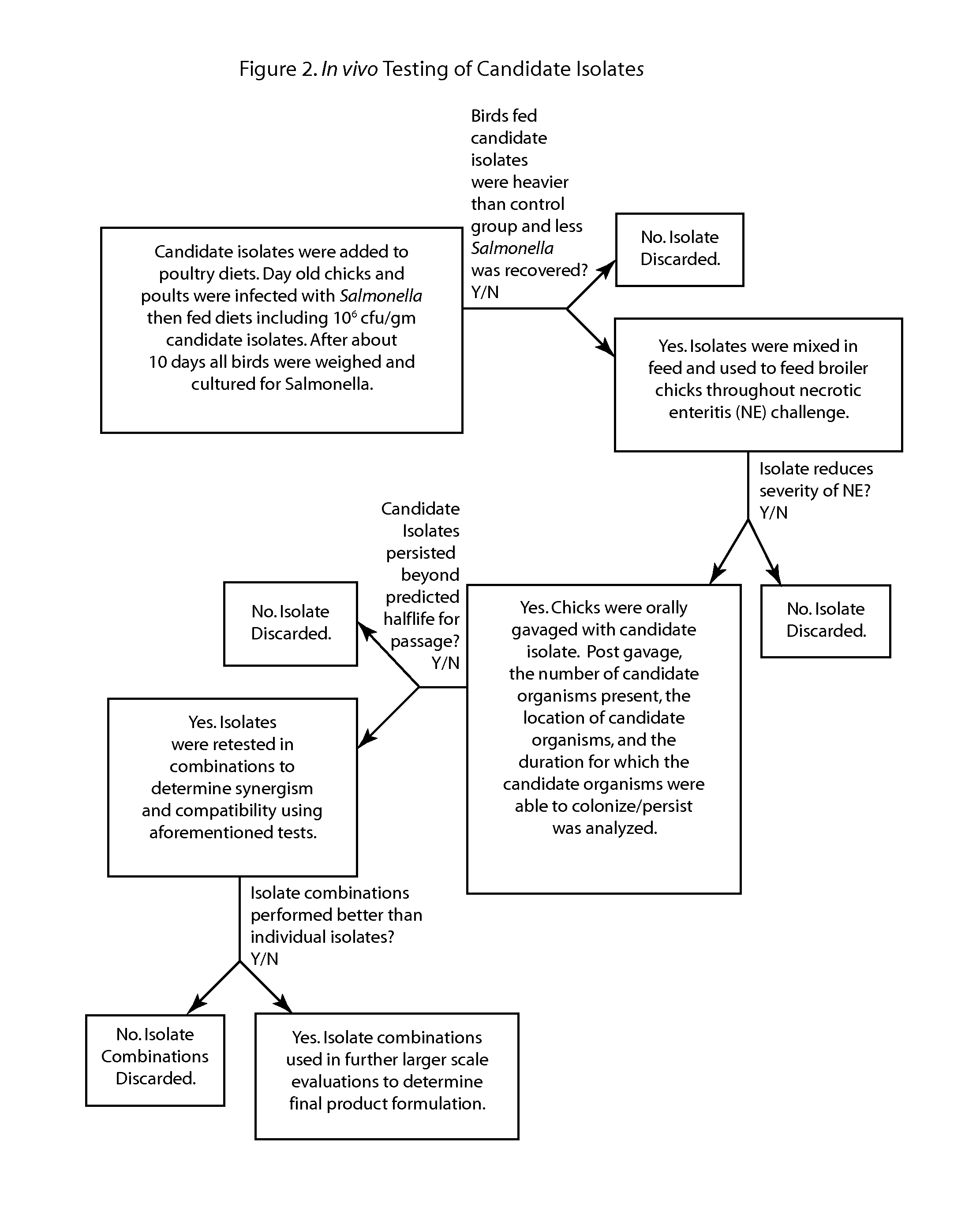
Methods and compositions including spore-forming bacteria for increasing the health of animals
ActiveUS20130136695A1Good for healthIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesBiology
Methods, compositions and bacterial isolates for improving the gastrointestinal health of animals and in particular of poultry are provided herein. The methods include administering an endospore-forming bacteria to an animal. The bacteria are selected for the ability to reduce the growth and presence of bacterial pathogens, such as Salmonella, Clostridium, and Campylobacter, in the gastrointestinal tract of the animal. The bacteria are also selected for the ability to improve at least one production parameter in the animal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
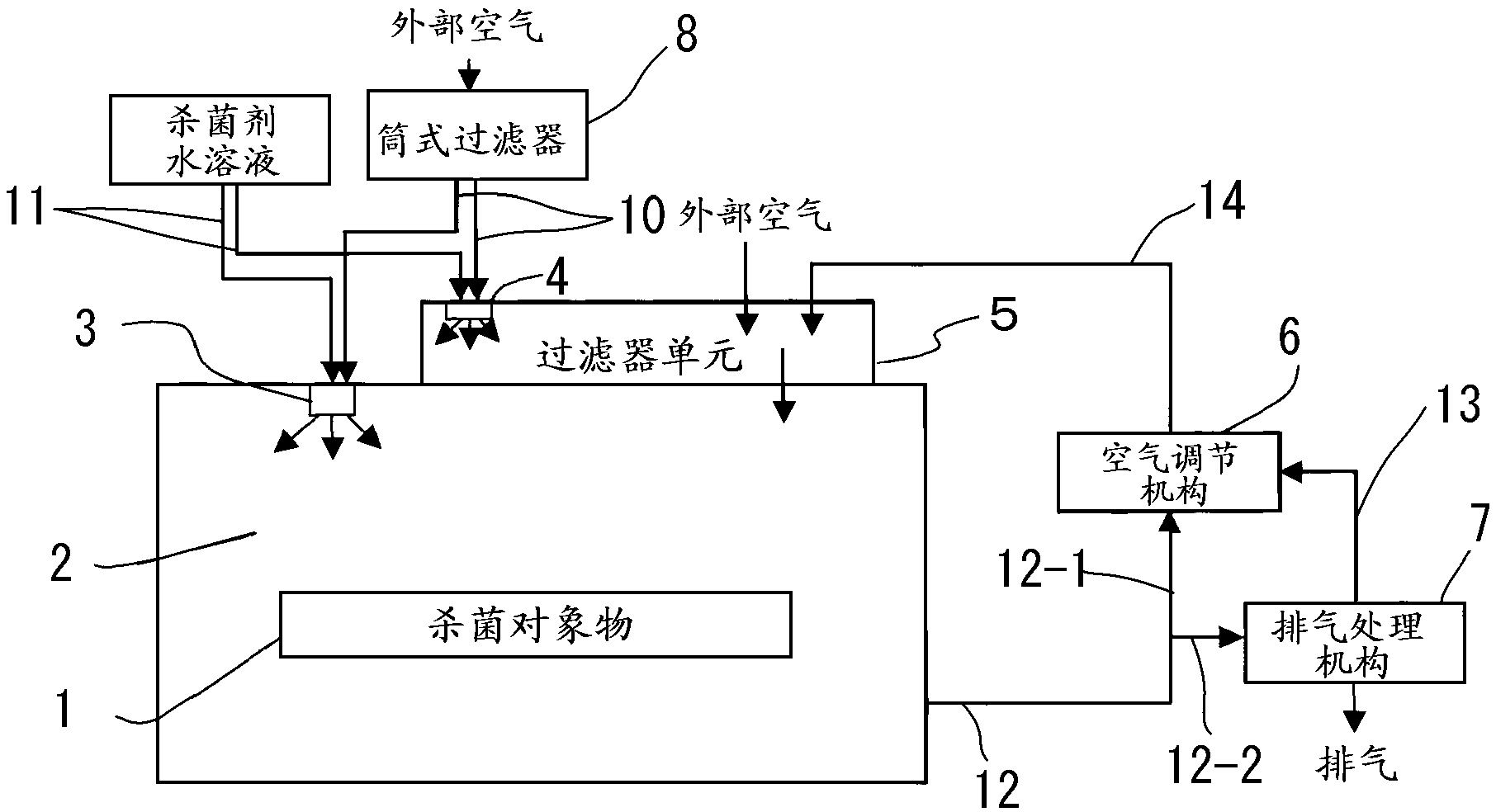
Method for sterilizing surface of space and sterilization system
ActiveCN102711845AReduce the impactLow costPackage sterilisationLavatory sanitoryAcetic acidAqueous solution
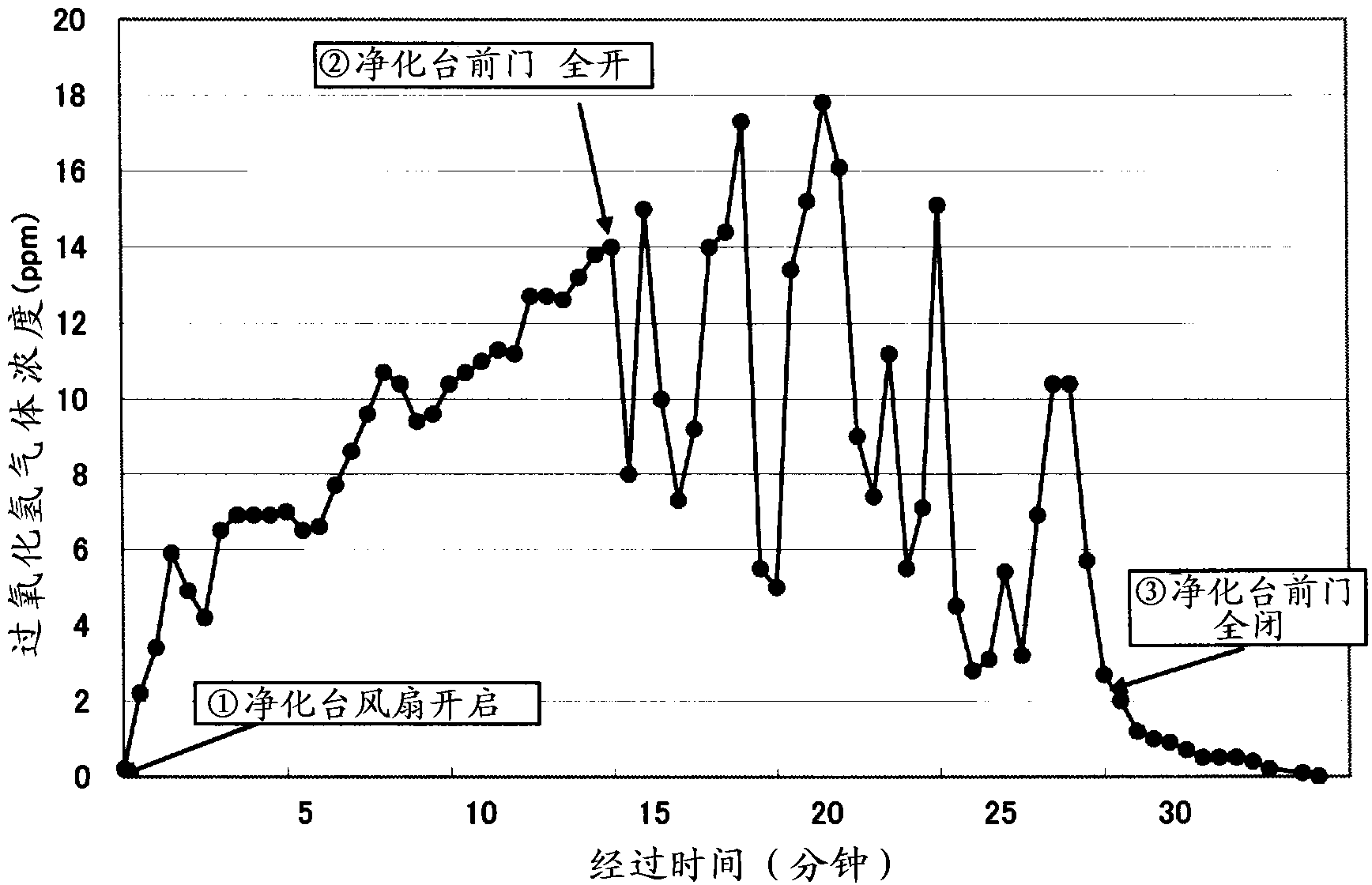
Provided are a method and a device for sterilizing the surface of a space-to-be-sterilized which are safe to the human body, which are effective even for sterilizing spore-forming bacteria, which do not require the space-to-be-sterilized to be highly shielded, and which can sterilize the surface of the space efficiently with inexpensive equipment. The disclosed method involves: spraying a low-concentration sterilizing agent in the form of fine particles into the space-to-be-sterilized and making the sterilizing agent adhere to the surface thereof, the low-concentration sterilizing agent being any one of a 1-10 wt% aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide, a 0.1-1 wt% aqueous solution of peracetic acid, or a 0.01-0.1 wt% aqueous solution of hypochlorous acid; adjusting the humidity in the space-to-be-sterilized; and air-drying the sterilizing agent. Thus, a high level of sterilization can be achieved in a short time and at low cost.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN KAISHA LTD
Lactobacillus buchneri strain LN5665 and its use to improve aerobic stability of silage
InactiveUS20080138462A1Improving animal performanceImprove performanceBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologySporeling
A method for treating silage to enhance aerobic stability by inhibiting growth of microorganisms selected from yeasts, molds and spore-forming bacteria is disclosed. The method comprises treating silage or feed with a composition comprising Lactobacillus buchneri, LN5665, or the antimicrobial components produced thereby. The strain of Lactobacillus buchneri disclosed in the invention has been purified and isolated and has been found to be nontoxic, safe and able to improve aerobic stability of silage.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Lactobacillus buchneri strain LN5689 and its use to improve aerobic stability of silage
InactiveUS20080138463A1Improving animal performanceImprove performanceMilk preparationBacteriaBacteroidesMicroorganism
A method for treating silage to enhance aerobic stability by inhibiting growth of microorganisms selected from yeasts, molds and spore-forming bacteria is disclosed. The method comprises treating silage or feed with a composition comprising Lactobacillus buchneri, LN5689, or the antimicrobial components produced thereby. The strain of Lactobacillus buchneri disclosed in the invention has been purified and isolated and has been found to be nontoxic, safe and able to improve aerobic stability of silage.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Lactobacillus buchneri strain LN1284 and its use to improve aerobic stability of silage
InactiveUS20090028991A1Improving animal performanceImprove performanceMilk preparationBacteriaBacteroidesMicroorganism
A method for treating silage to enhance aerobic stability by inhibiting growth of microorganisms selected from yeasts, molds and spore-forming bacteria is disclosed. The method comprises treating silage or feed with a composition comprising Lactobacillus buchneri, LN1284, or the antimicrobial components produced thereby. The strain of Lactobacillus buchneri disclosed in the invention has been purified and isolated and has been found to be nontoxic, safe and able to improve aerobic stability of silage.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Methods and compositions including spore-forming bacteria for increasing the health of animals
Methods, compositions and bacterial isolates for improving the gastrointestinal health of animals and in particular of poultry are provided herein. The methods include administering an endospore-forming bacteria to an animal. The bacteria are selected for the ability to reduce the growth and presence of bacterial pathogens, such as Salmonella, Clostridium, and Campylobacter, in the gastrointestinal tract of the animal. The bacteria are also selected for the ability to improve at least one production parameter in the animal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Soil-based compositions and methods for removal of toxins from mammals
Humans and other mammals are continually exposed to toxins in the environment, toxins in ingested food and water, and toxins formed in the body through metabolism or breakdown of complex material. Such toxins impair health and contribute to disease in mammals but are difficult to avoid given the conditions of modern life. The present invention provides compositions for promoting removal of toxins from a subject which include an alkalizing agent, spore-forming bacteria, clay, at least one type of humic acid and / or at least one type of fulvic acid. Methods for use of compositions for promoting removal of toxins from a subject are described.
Owner:MANKOVITZ ROY J
Genetically Modified Seed Combined with Spore Forming Bacterium and Optional Insect Control Agents and Methods for Treating Plants
Products are provided that improve overall plant vigor and yield by combining agriculturally effective amounts of at least one spore-forming bacterium and at least one optional insect control agent to a genetically modified plant, plant part, or seed. This product is particularly effective in the presence of plant parasitic nematode and fungal species. Use of the product leads to an overall reduction in crop losses caused by either plant parasitic nematodes or fungi and this reduction is much greater than using genetically modified seed with just an insect control agent. According to some embodiments, the use of the product results in about a 2%-10% increase in soybean bushel yield, 3%-6.5% increase in cotton yield, and 3%-8% in corn bushel yield. Methods for utilizing and manufacturing the combination are also provided.
Owner:BASF CORP
Esterified Catechins, Processes for Producing the Same, and Foods and Beverages as well as Cosmetics Containing Such Esterified Catechins
InactiveUS20080058409A1Extended shelf lifePreventing putrefaction or deterioration of cosmetic creamAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntibacterial activityMedium chain fatty acid
The present invention provides substances having sufficiently antibacterial activity against heat-resistant spore-forming bacteria that they can be used to improve the shelf life of beverages and processed foods, as well as to control the growth of microorganisms in cosmetics. The present invention provides a catechin ester in which at least one of the hydroxyl groups of a catechin is esterified with a medium-chain fatty acid. This medium-chain fatty acid ester of a catechin, which may be used either alone or as a composition, shows a strong growth suppressing effect on heat-resistant spore-forming bacteria and, if added to foods or beverages, can prevent them from rotting or deterioration and, if added to cosmetics, can prevent their rotting or deterioration.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Method of producing concentrated liquid dairy products
InactiveCN101209068AUnlimited processingMilk preparationMilk preservationMicrofiltration membraneUltrafiltration
A method is provided for forming aseptic or substantially aseptic concentrated dairy liquid, such as dairy milk, without significant heat treatment. In one form, the method first concentrates a starting dairy milk to about 2X to about 7X concentration using an ultrafiltration membrane to form a dairy concentrate. Thereafter, the dairy concentrate is filtered using a microfiltration membrane to provide the aseptic or substantially aseptic concentrated dairy milk. The resultant concentrated dairy milk has less than about 0.5 percent total bacteria and less than about 5 colony forming units of spore forming bacteria per gram. The substantially aseptic concentrated dairy milk is not subjected to significant heat treatment during processing.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS LLC
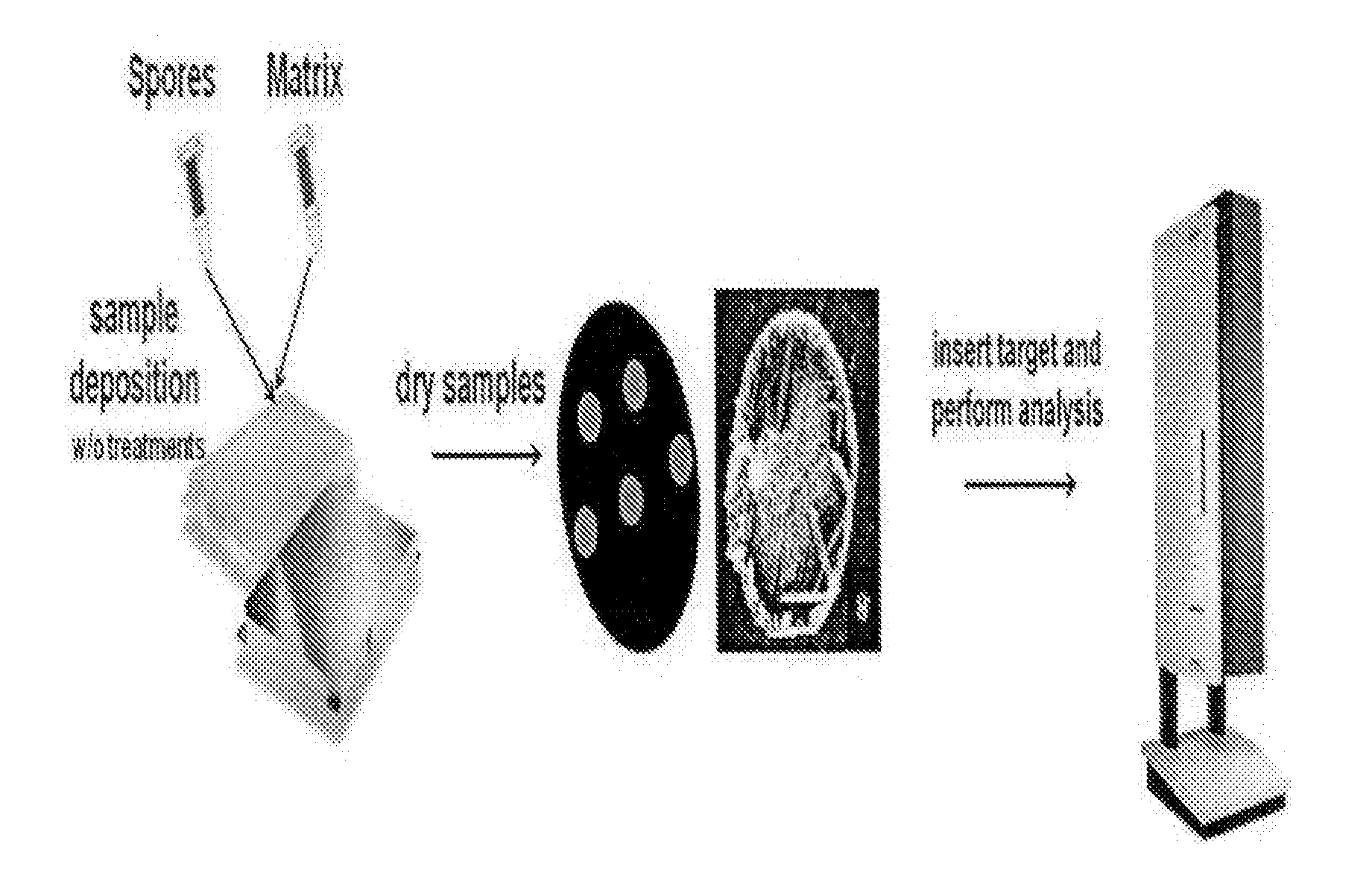
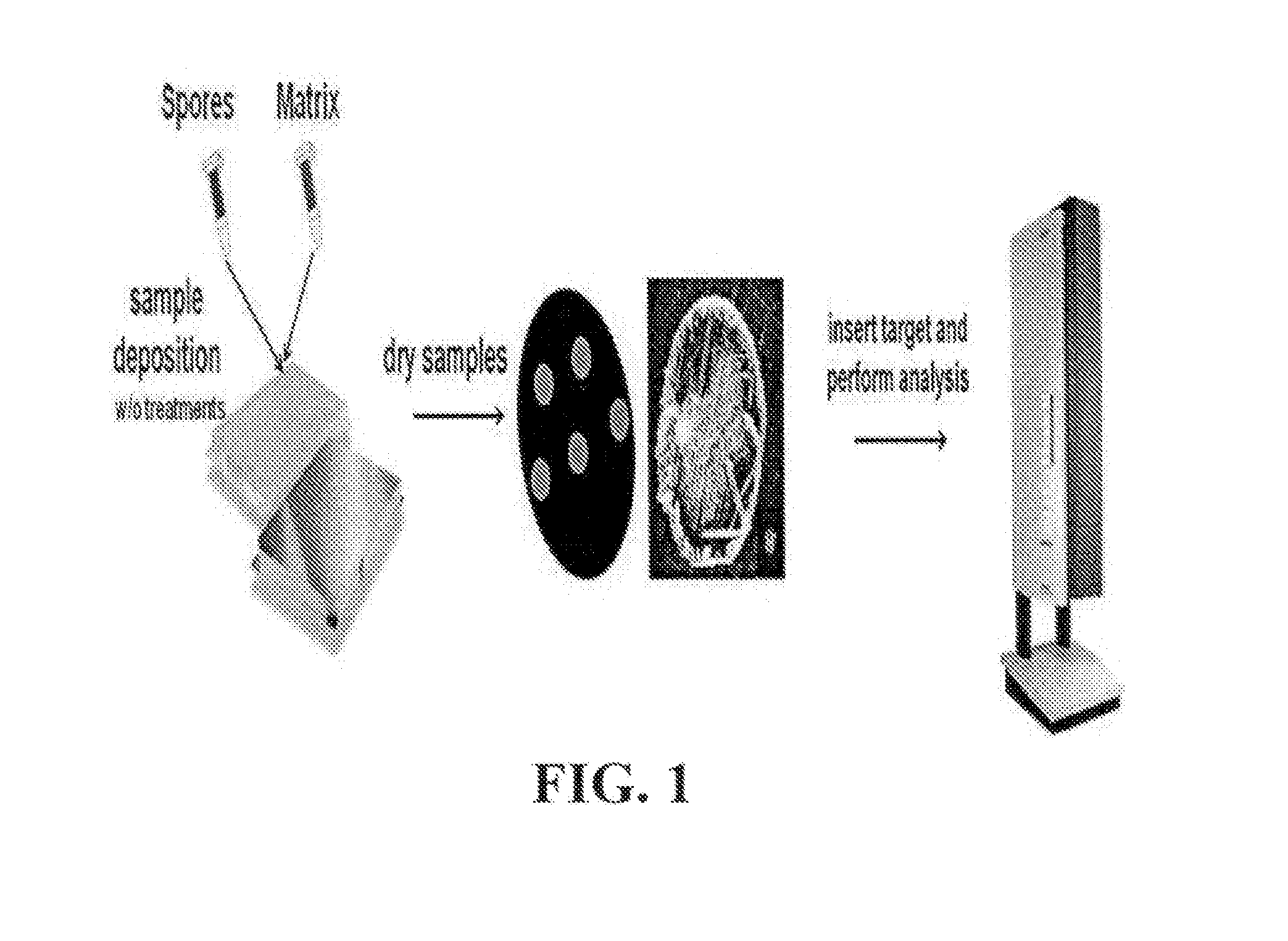
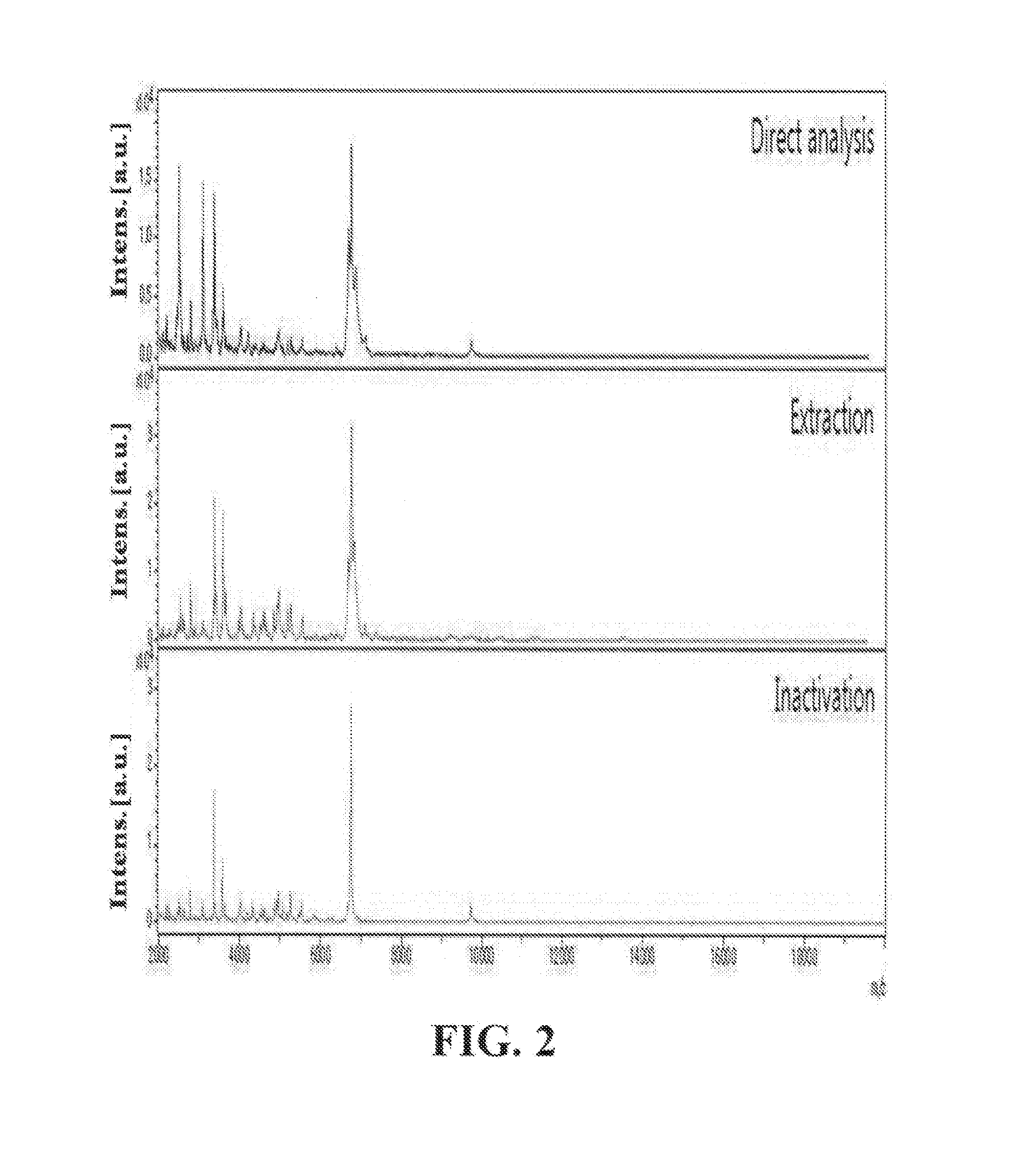
METHOD OF IDENTIFICATION OF SPORE-FORMING Bacillus spp. BY DIRECT In-situ ANALYSIS OF MALDI-TOF MASS SPECTROMETRY, AND ANALYSIS SYSTEM
InactiveUS20150024428A1High-precision detectionEasily and rapidlyTime-of-flight spectrometersMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyTime of flight
A method of the identification of Bacillus species by direct in-situ analysis of MALDI-TOF MS (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption / Ionization Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectometry) in which spore-forming bacteria are applied intact without any pretreatment, and an analysis system of distinctive biomarkers which allow Bacillus spores to be distinguished. Rapid and accurate detection and identification of Bacillus species can be achieved by the method and analysis system.
Owner:AGENCY FOR DEFENSE DEV
Process for producing plant-origin antibacterial substance
InactiveUS20020192311A1Promote decompositionPrevent proliferationBiocideFood preservationPlant tissueAdditive ingredient
A process for producing an antibacterial substance which comprises disintegrating at least a part of a plant tissue and releasing the antibacterial substance therefrom; and antibacterial or bacteriostatic compositions containing the antibacterial substance thus obtained as the active ingredient. By using the above process and compositions, the proliferation of spore-forming bacteria can be efficiently inhibited.
Owner:SAKAI TAKUO
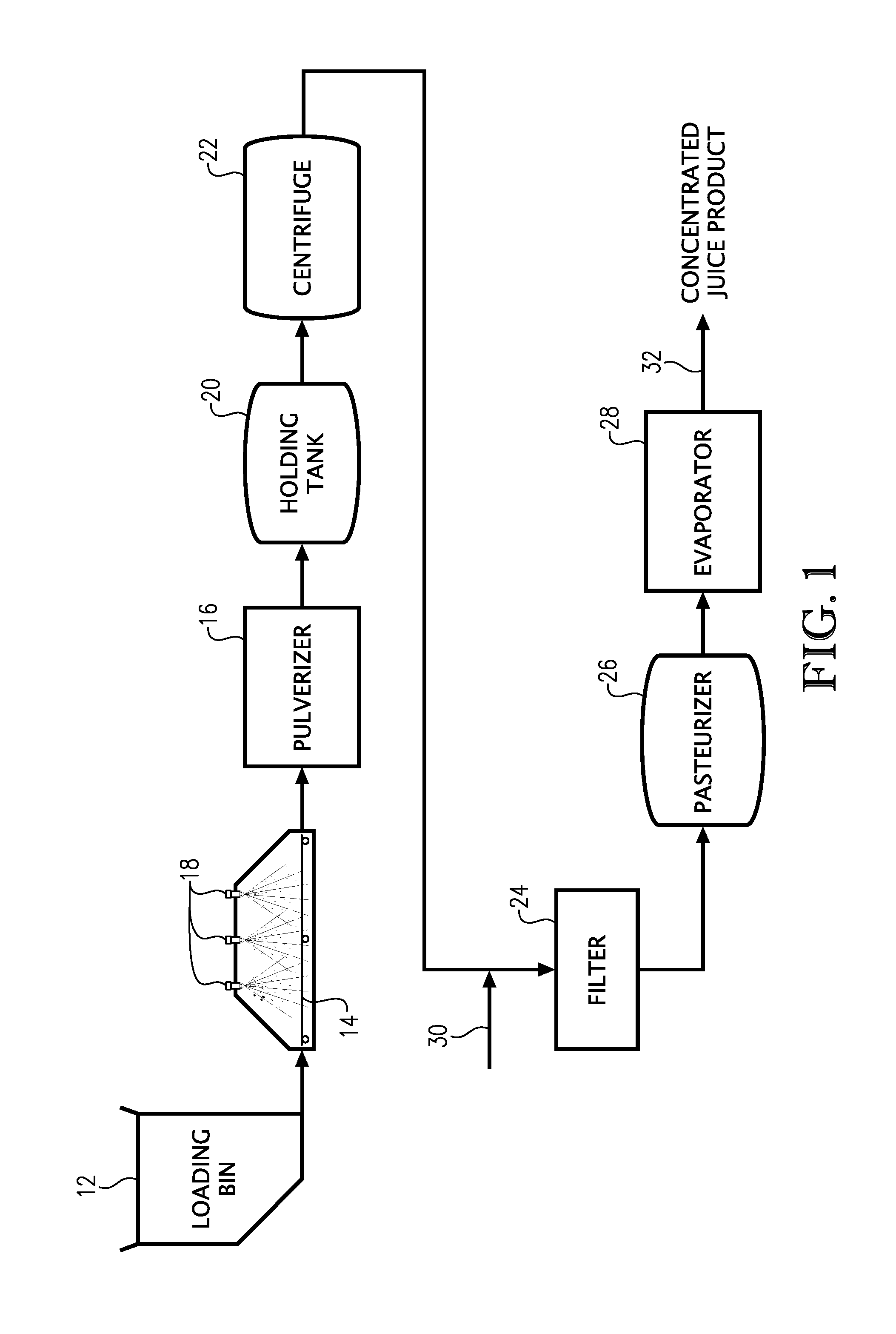
Process for controlling microorganisms in beverage products
InactiveUS20130280392A1Adversely impacting tasteAdversely impacting colorBiocidePeroxide active ingredientsMicroorganismFiltration
Methods for reducing thermophilic spore-forming bacteria that can lead to off-odors and tastes in beverage products, especially fruit or vegetable juice products, are provided. The methods employ one or more peroxy acids that are added to the beverage handling system prior to pasteurization and concentration of the beverage product. Particularly, the peroxy acid is added prior to final filtration of the beverage product upstream of the pasteurizer and concentrator.
Owner:DELAVAL HLDG AB
Detection of spore forming bacteria
Disclosed are methods, probes, and nucleic acid sequences for the systematic identification of sporulation genes in spore forming bacteria. A probe comprises a nucleic acid sequence able to form a detectable hybrid with highly conserved regions of the spoOA gene of certain spore forming bacteria Bacillus and Clostridium bacteria species, said nucleic acid sequence being unable to form a detectable hybrid with genetic material of non-spore forming bacteria. Amplification of a portion of the spoOA gene from the cellular DNA of a spore forming bacteria by a polymerase chain reaction using such probe, primer or nucleic acid sequence as one member of a primer set results in the generation of a detectable 346-365 nucleotide long DNA product. One disclosed method comprises a) combining a tagged or labeled probe with a sample, b) hybridizing the probe to the target spore forming bacteria spoOA gene; and c) detecting the hybridized product.
Owner:HERCULES INC
Method For Sterilization Of Food
InactiveUS20120082772A1Improve pressure resistanceDifficult to sterilizePre-baking dough/flour preservationSeed preservation by pressure variationBiotechnologyHigh pressure
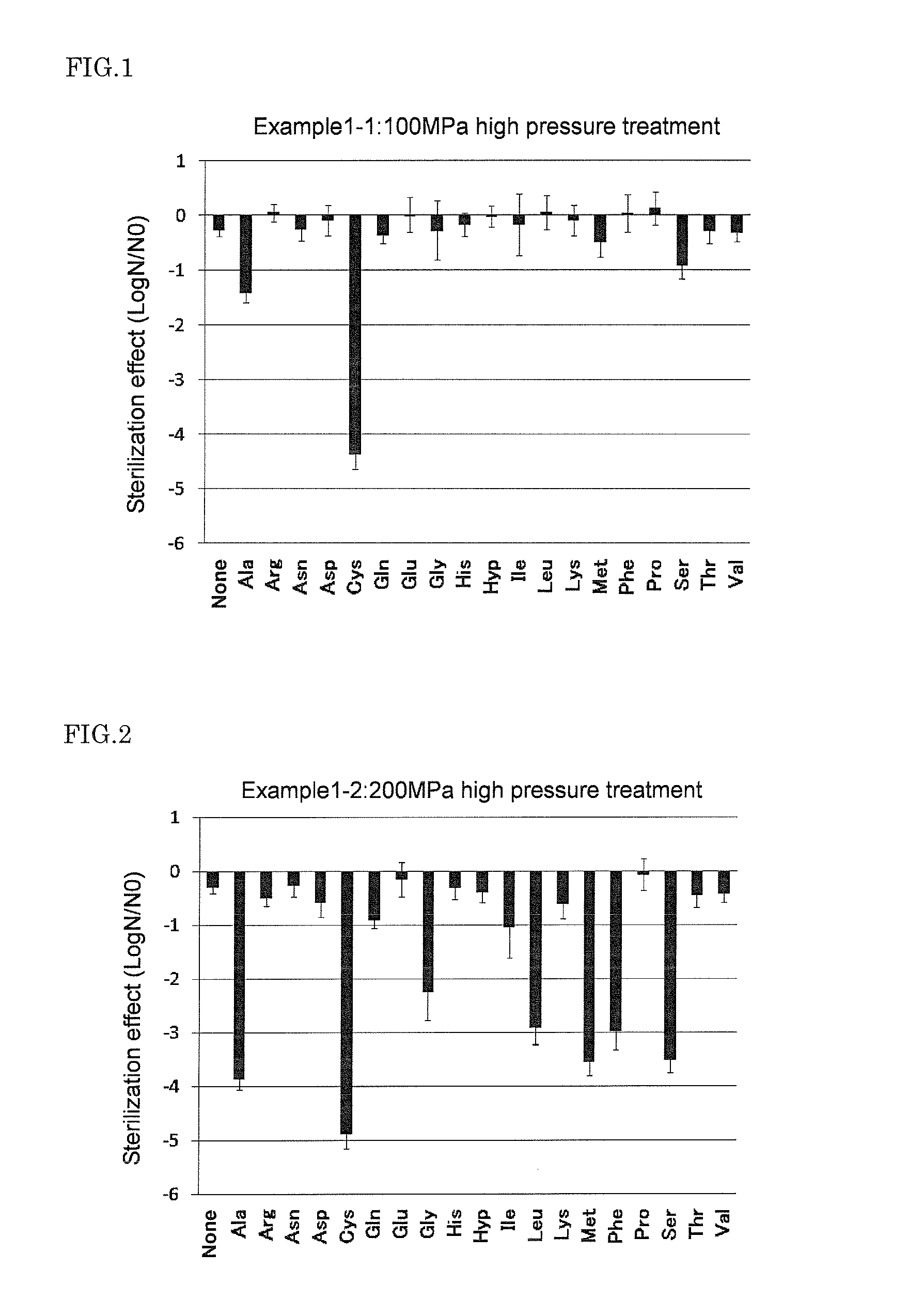
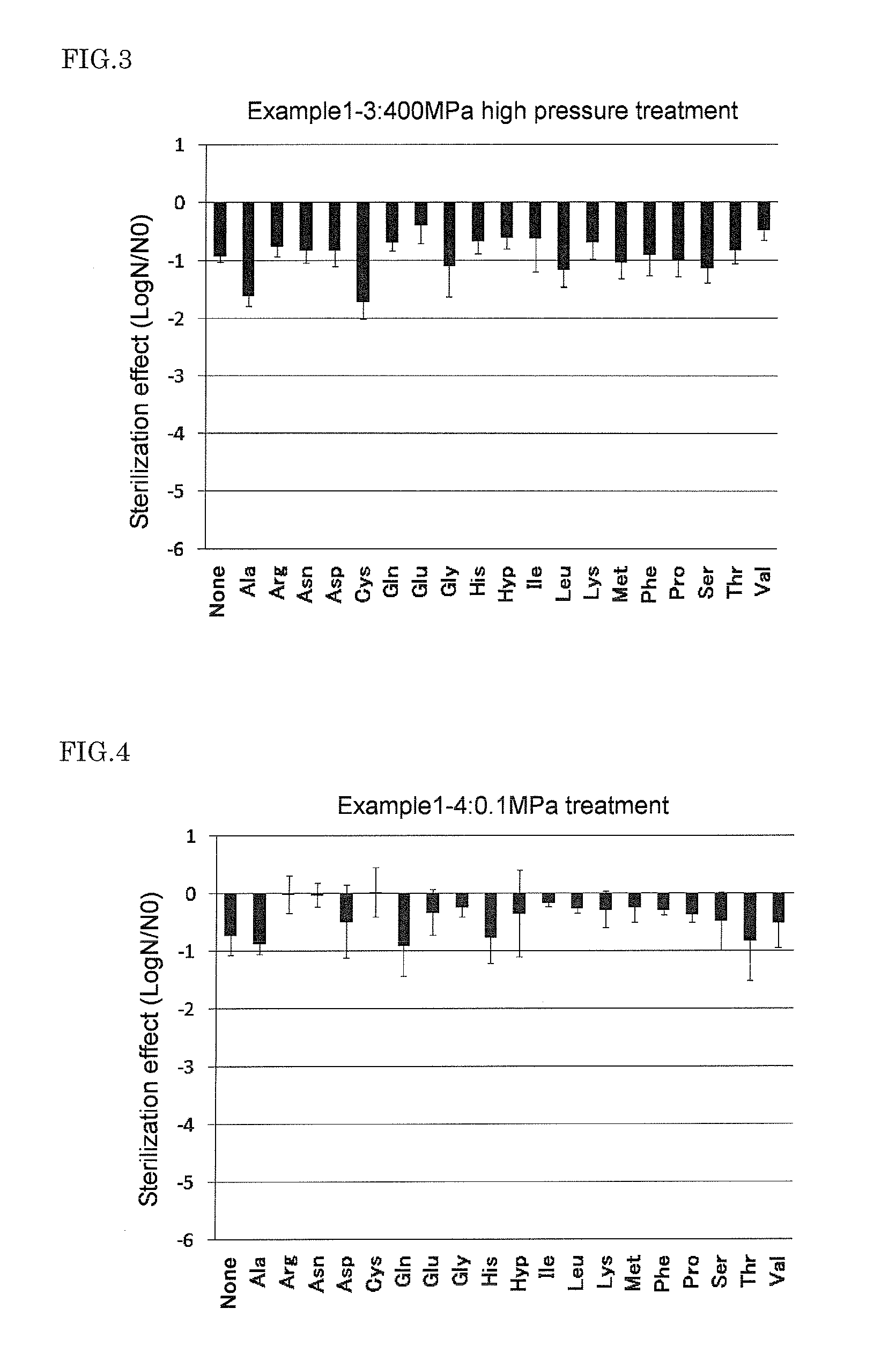
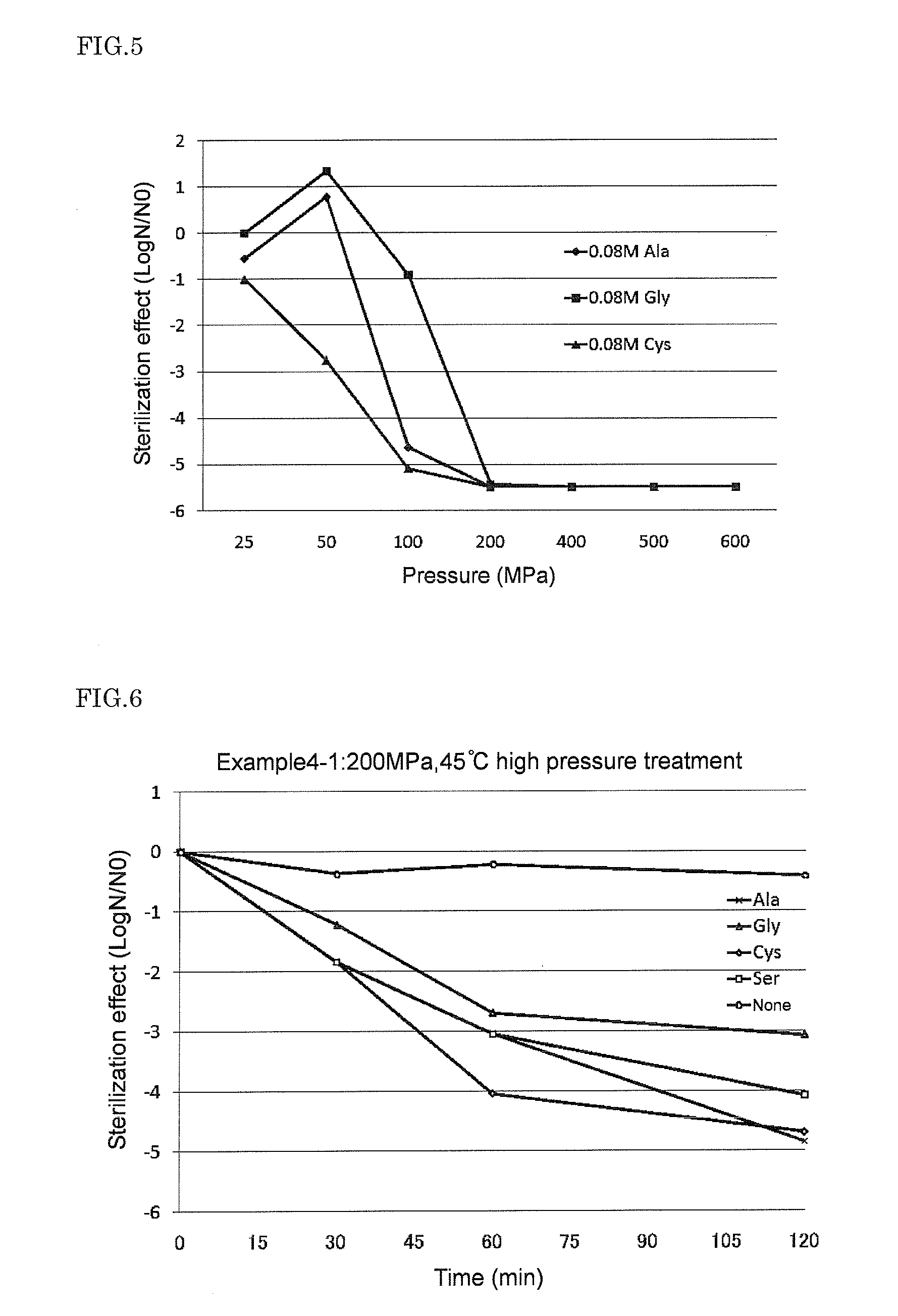
The present invention provides a food sterilization method by which the effective sterilization of the spore-forming bacteria having high heat resistance and high pressure resistance is possible without impairing the taste, flavor, and texture of food. A method for sterilization of food comprising: high-pressure treatment step in which one or more amino acids selected from the group consisting of cysteine, alanine, methionine, phenylalanine, serine, leucine, and glycine is added to a sterilization target food, and then the sterilization target food including the amino acid is treated at 50 to 600 MPa for 1 to 120 minutes; and low-temperature heating step in which the sterilization target food is heated at 60 to 100° C. for 5 minutes or more after the high-pressure treatment step.
Owner:DAIWA CAN +1
Synbiotic product
The present invention relates to a synbiotic product composition comprising a blend or mixture of a prebiotic carbohydrate and a probiotic spore-forming Bacillus bacteria. Examples of prebiotic carbohydrates useful in synbiotic product include arabinoxylan, arabinoxylan oligosaccharides, xylose, soluble fiber dextrin, soluble corn fiber, and polydextrose. The present invention also relates to human foodstuffs and animal feed comprising such synbiotic products and methods of increasing the titer of spore-forming bacteria in the intestinal tracts of mammals by administration of symbiotic products.
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
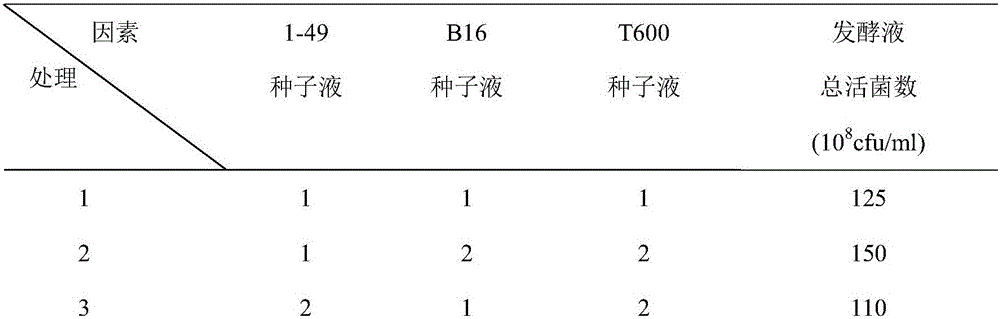
Composite microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107177525ANitrogen saving effect is remarkableClear market advantageBacteriaAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserBacillus megateriumMicrobial agent
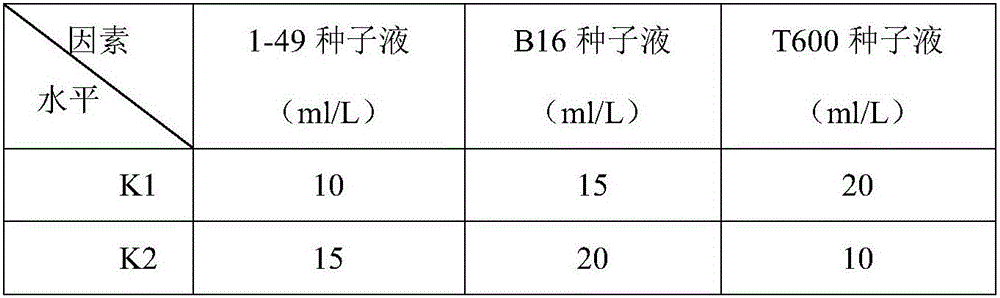
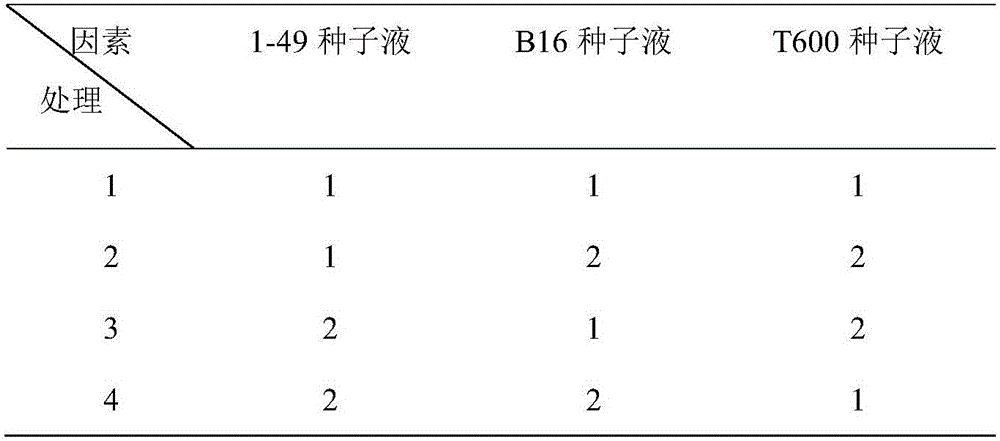
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial inoculations, in particular to a composite microbial inoculation and its preparation method and application. The compound microbial agent includes Paenibacillus nitrogen-fixing 1-49, Bacillus megaterium B16 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens T600; the preparation method of the compound microbial agent includes seed culture, fermentation culture, and the optimal combination of different bacterial liquid additions in the fermentation culture is passed through positive The cross-test confirmed; the compound microbial agent is applied to promote the growth of sugarcane and improve the agricultural nitrogen-saving effect. The composite microbial bacterial agent of the present invention has a remarkable nitrogen-saving effect and has a huge market advantage; the present invention optimizes the addition amount of different bacterial solutions for liquid fermentation through orthogonal experiments, improves the spore production of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, and greatly improves the quality of production , can effectively reduce production costs; the three strains of the present invention are spores, which have the advantages of long storage time and long shelf life, and will have good application prospects in future agricultural production.
Owner:DONGGUAN BAODE BIOLOGICAL ENG
Meat extract and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20050255225A1Conducive to preservationAdd flavorSolid waste disposalFood preparationMuscle tissueMicroorganism
A meat extract is provided such that it contains no detectable microorganisms other than spore-forming bacteria and includes 60 mmol / l or more of phosphate ion, preferably 60 to 500 mmol / l, more preferably 70 to 500 mmol / l, and even more preferably 70 to 200 mmol / l. Also a process for producing a meat extract is provided. The process includes obtaining a liquid extract from a material containing muscle tissues or bone tissues of livestock; adjusting the phosphate ion concentration of the liquid extract to 60 mmol / I or more; and then sterilizing at ultra-high temperature (UHT sterilization).
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO FOOD SPECIALTIES
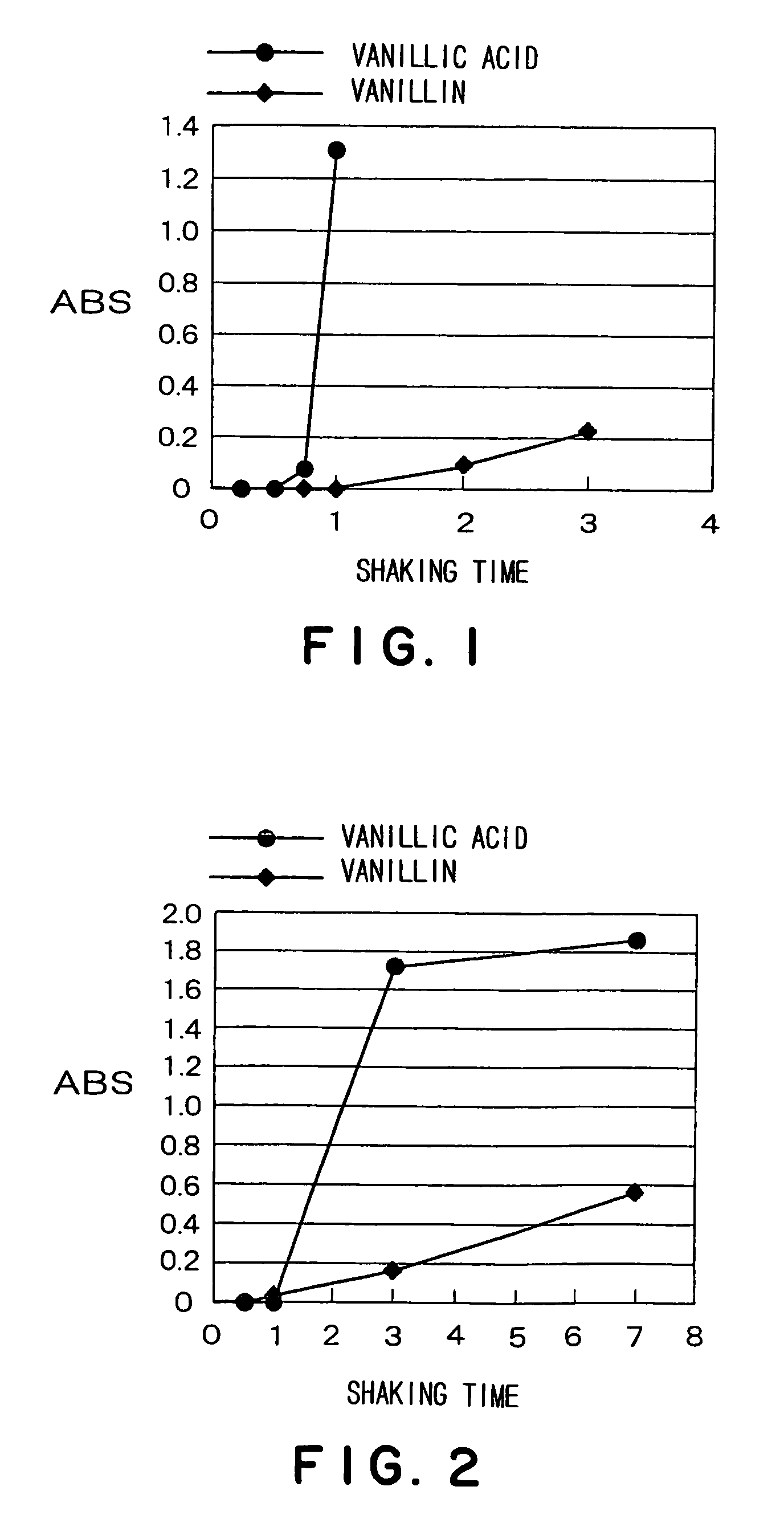
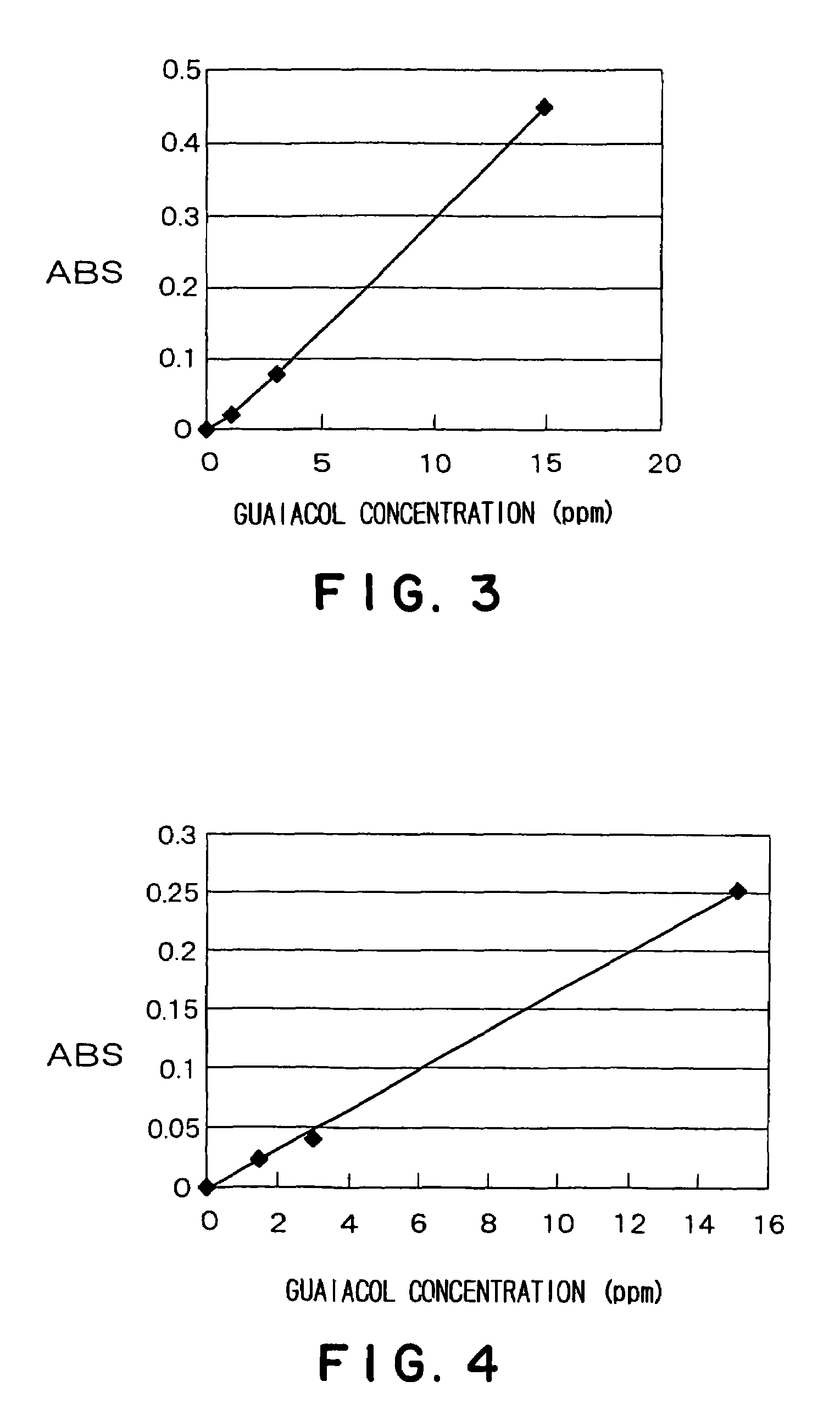
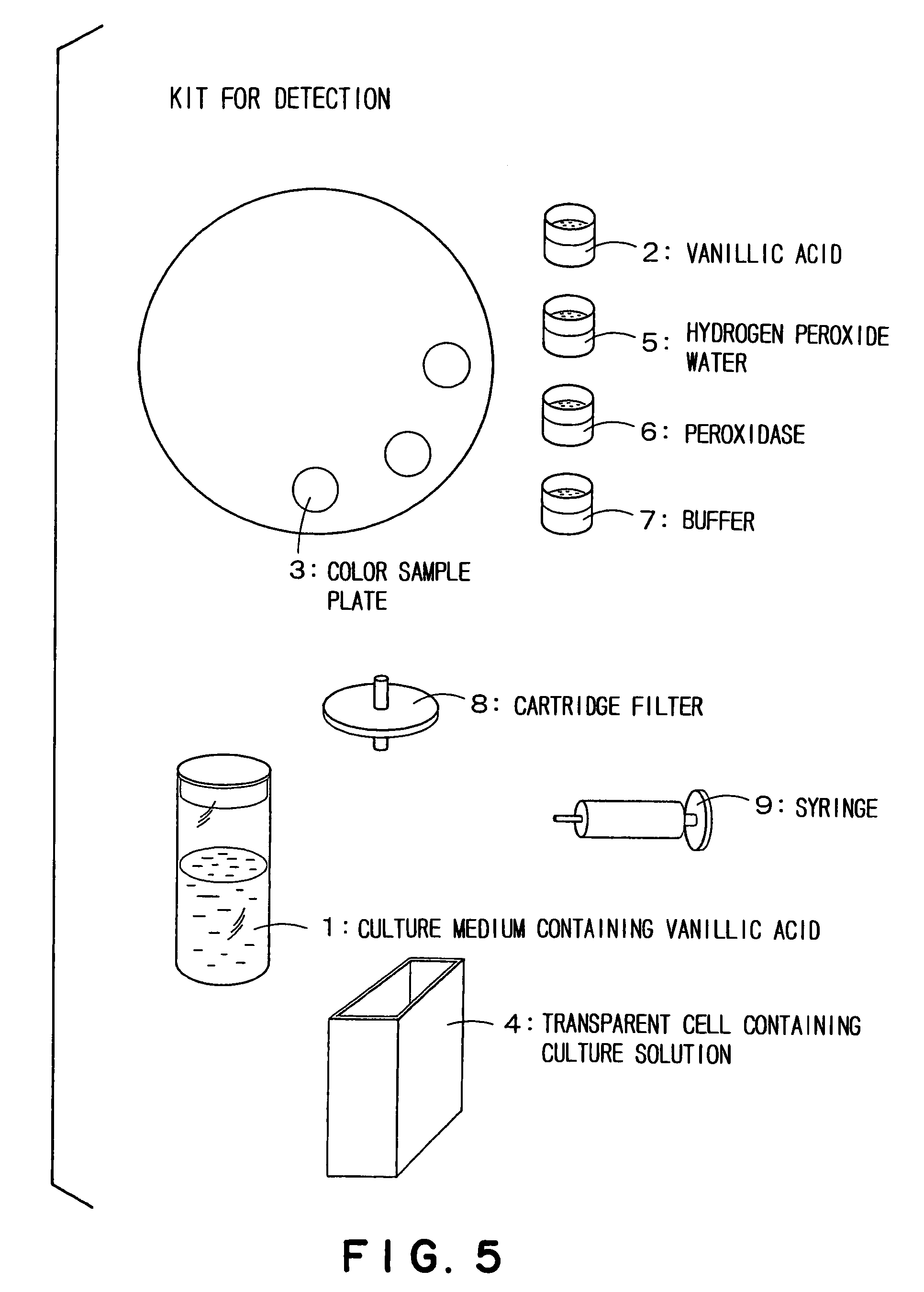
Method for detecting guaiacol producing bacteria
ActiveUS7432073B2Easy to measureRapid determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesVanillic acidCulture fluid
Owner:KIRIN BEVERAGE CO LTD
Rapid acting lactobacillus strains and their use to improve aerobic stability of silage
InactiveUS20170208836A1Improves aerobic stabilityIncreasing fermentation and stabilizationBacteriaLactobacillusBacteroidesMicrobiome
A method for treating silage to enhance the aerobic stability by increasing the fermentation and stabilization of silage by inhibiting growth of microorganisms selected from yeasts, molds and spore-forming bacteria and permitting earlier aerobic exposure is disclosed. The method comprises treating silage or feed with a composition comprising Lactobacillus buchneri strain LN7125, or Lactobacillus brevis strain LB5328, or Lactobacillus brevis strain LB7123, and mixtures or a mutant thereof which retains the silage preservative activity of LN7125, LB5328, or LB7123, or the antimicrobial components produced thereby. The strains of Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus brevis disclosed in the invention have been purified and isolated and have been found to improve aerobic stability of silage allowing earlier aerobic exposure post ensiling than is presently practiced
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Methods and compositions for generating sporulation deficient bacteria
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for engineering sporulating bacterial cells, particularly a cell of the class Clostridia. In particular, the present invention relates to the generation of sporulation deficient bacteria for the generation of industrial superior phenotypes.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
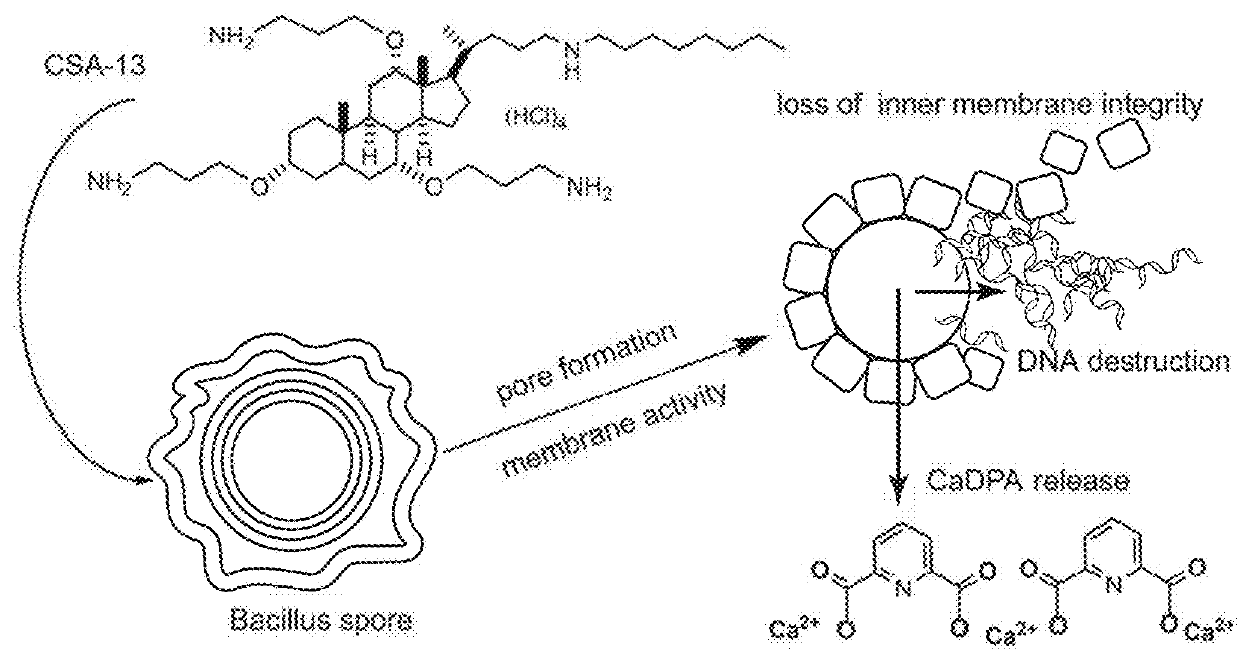
Use of cationic steroidal antimicrobials for sporicidal activity
ActiveUS20180271100A1Reduce generationReduce spoilage of the food productAntibacterial agentsBiocideIndustrial equipmentFood processing
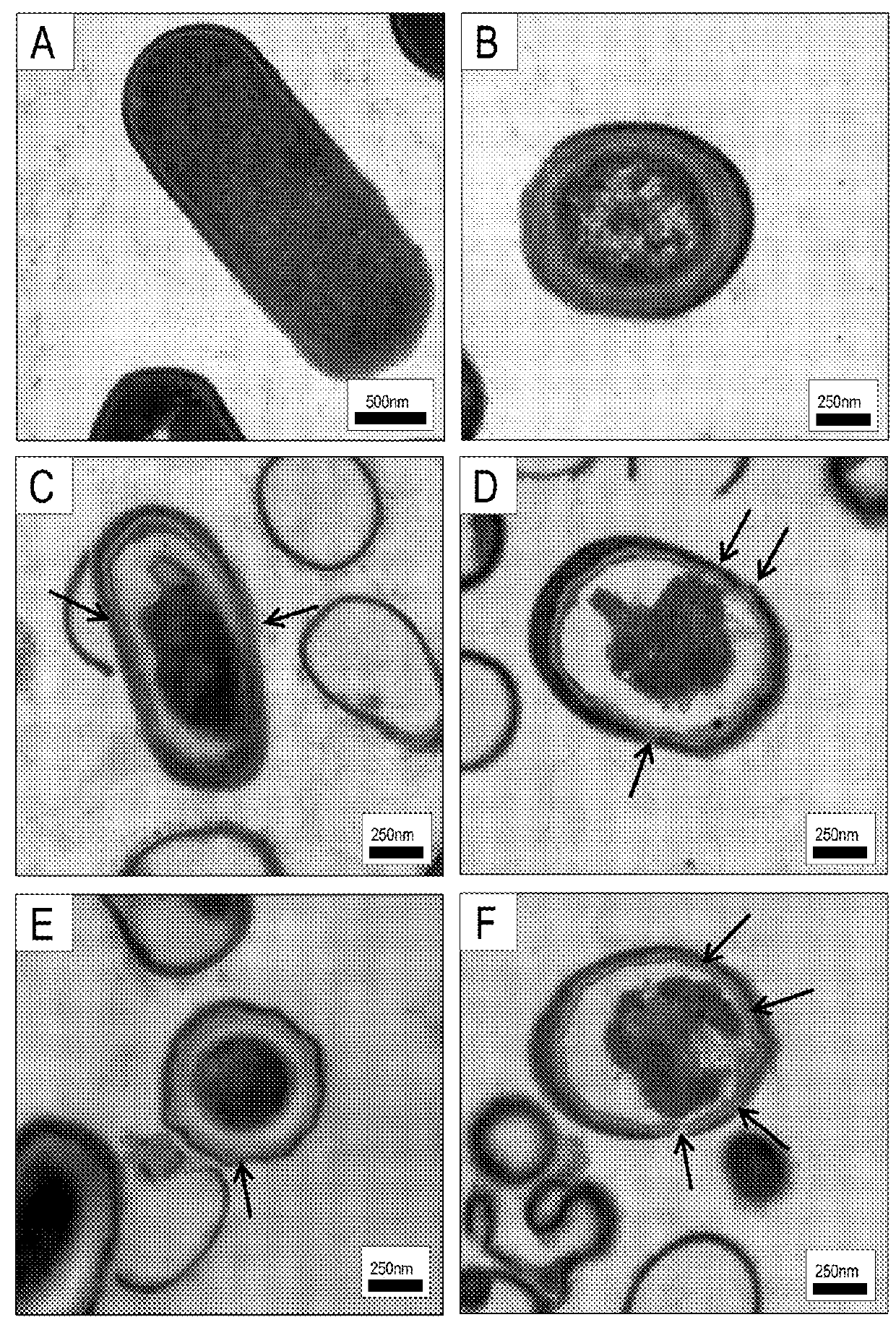
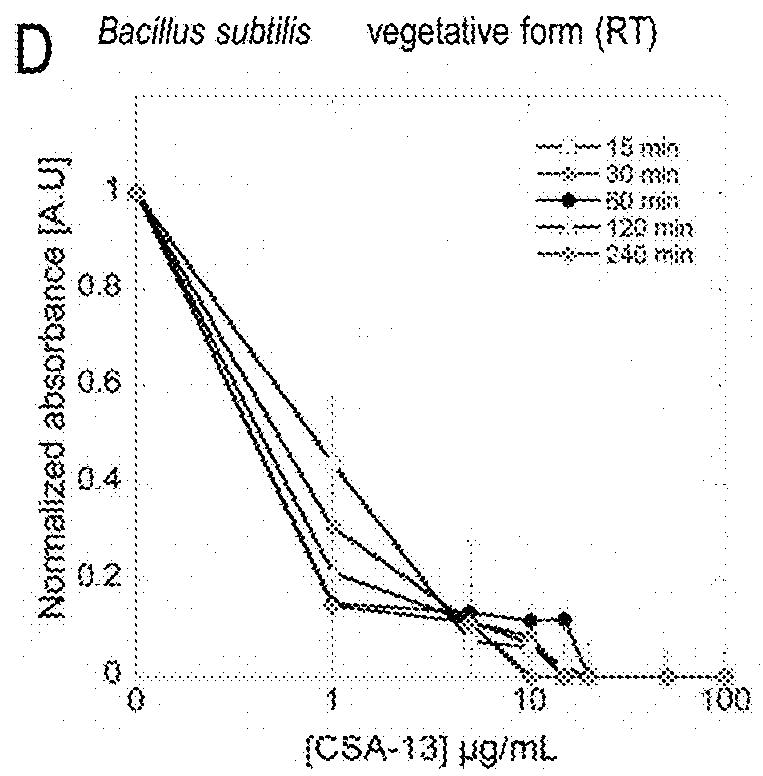
This disclosure relates to sporicidal compositions and uses thereof. The sporicidal compositions include one or more cationic steroidal antimicrobials (CSAs). The sporicidal compositions may be applied to an object to kill or deactivate bacterial spores contacting the sporicidal composition. The object may be a food product, food processing equipment, industrial equipment, or healthcare facility objects. The sporicidal composition may be administered to a subject that has, is suspected to have, or is at risk for an infection associated with spore-forming bacteria.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Meat extract and process for producing the same
The present invention provides a meat extract and a production method thereof. The meat extract contains no detectable microorganisms other than spore-forming bacteria and includes 60 mmol / l or more of phosphate ion, wherein the spore-forming bacteria are microorganisms selected from bacillus, sporolactobacillus, clostridium, and sporosarcina. The meat extract is obtained from a material containing muscle tissues or bone tissues of livestock. The production method includes: obtaining the liquid extract from a material containing muscle tissues or bone tissues of livestock; and adjusting the phosphate ion concentration of the liquid extract to 60 mmol / I or more to inhibiting proliferation of the spore-forming bacterium in the meat extract.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO FOOD SPECIALTIES
New Compositions
ActiveUS20140234441A1Reduce and eliminate adhesionIncreasing their resistance to oxidation attackBiocideAnimal repellantsChlorine dioxideSURFACTANT BLEND
Acidic aqueous compositions for elimination of spores of spore forming bacteria comprise from about 100 to about 2000 ppm dissolved chlorine dioxide and a surfactant system having both a wetting effect and a spore solubilising effect.
Owner:LIFECLEAN INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com