Patents
Literature
55 results about "Stain tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrophoretic in situ tissue staining
InactiveUS20050074890A1Easy to moveReduce background stainingElectrotherapyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsDiffusionTissue staining
The present invention introduces a radically different way of accelerating biomolecule conjugates into tissue, and hence towards their targets for purposes of tissue staining. The invention provides for an order of magnitude improvement over the prior art diffusion process used to stain tissue. The invention comprises a method of tissue staining by applying an electric field to a tissue sample in the presence of an electrolyte and biomolecular conjugates of interest suspended in the electrolyte. Typical staining times are reduced to seconds as opposed to 30-120 minutes common in the prior art. The invention is also directed to devices for performing the method.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
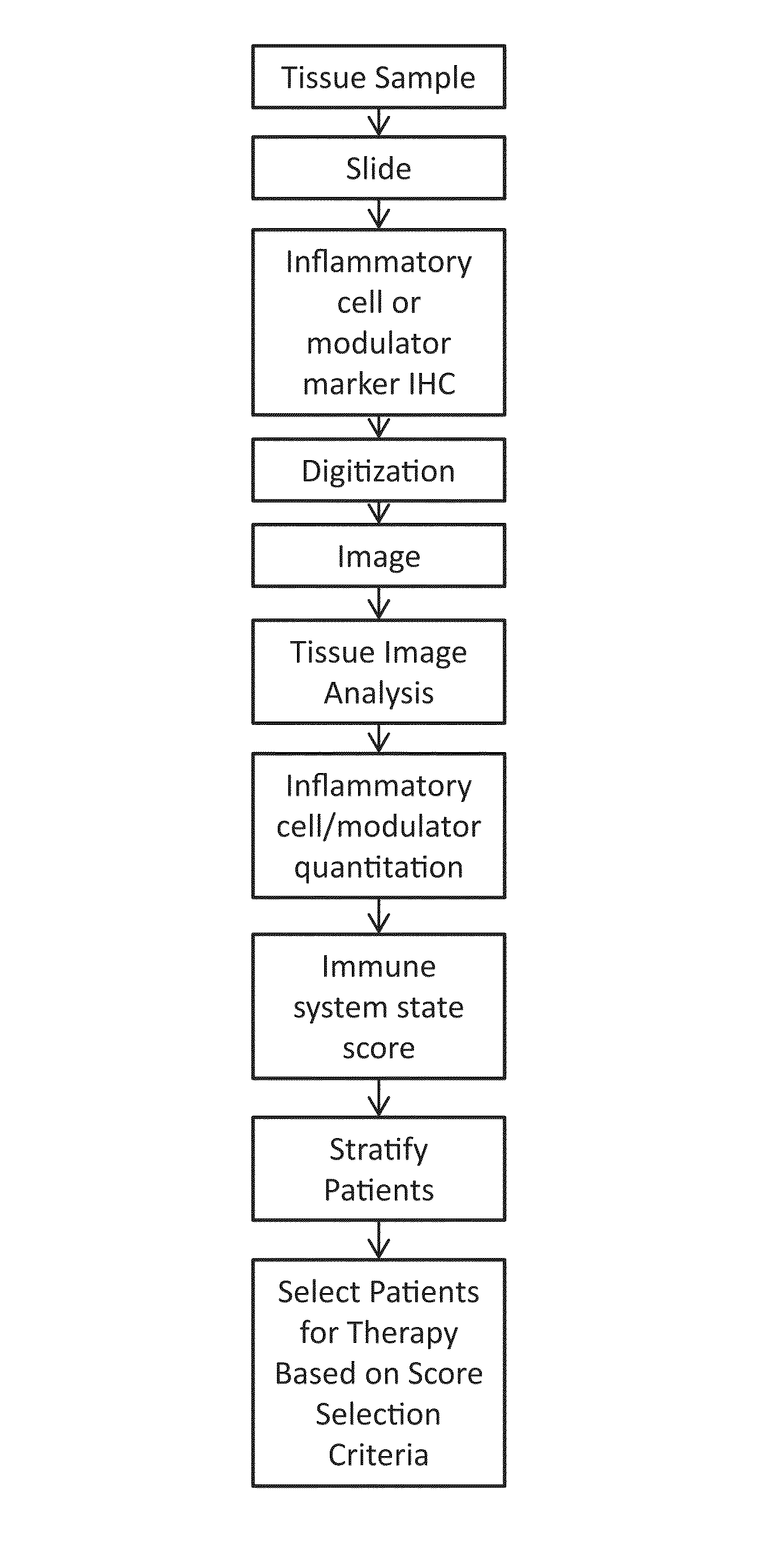
Digital image analysis of inflammatory cells and mediators of inflammation
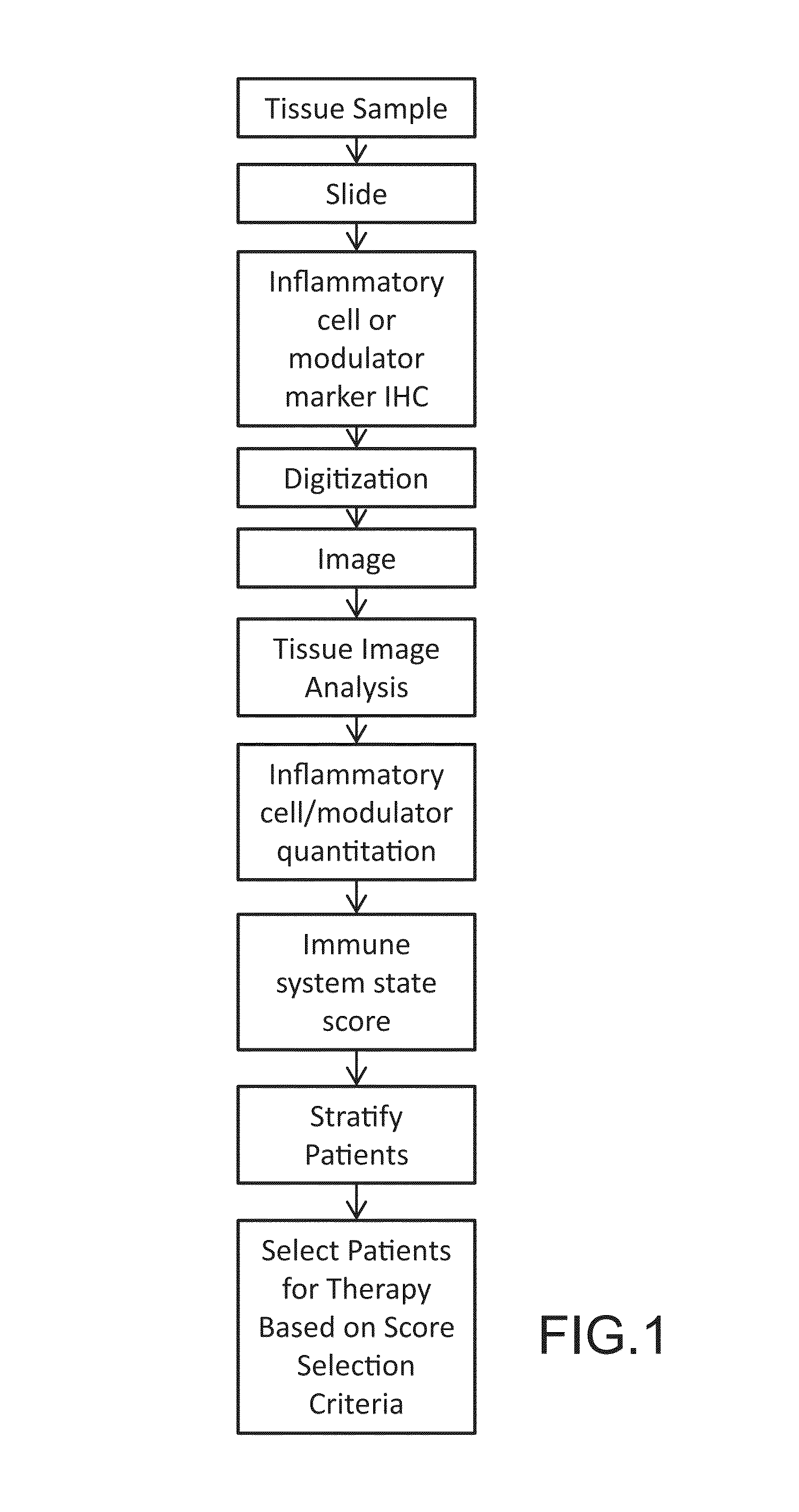
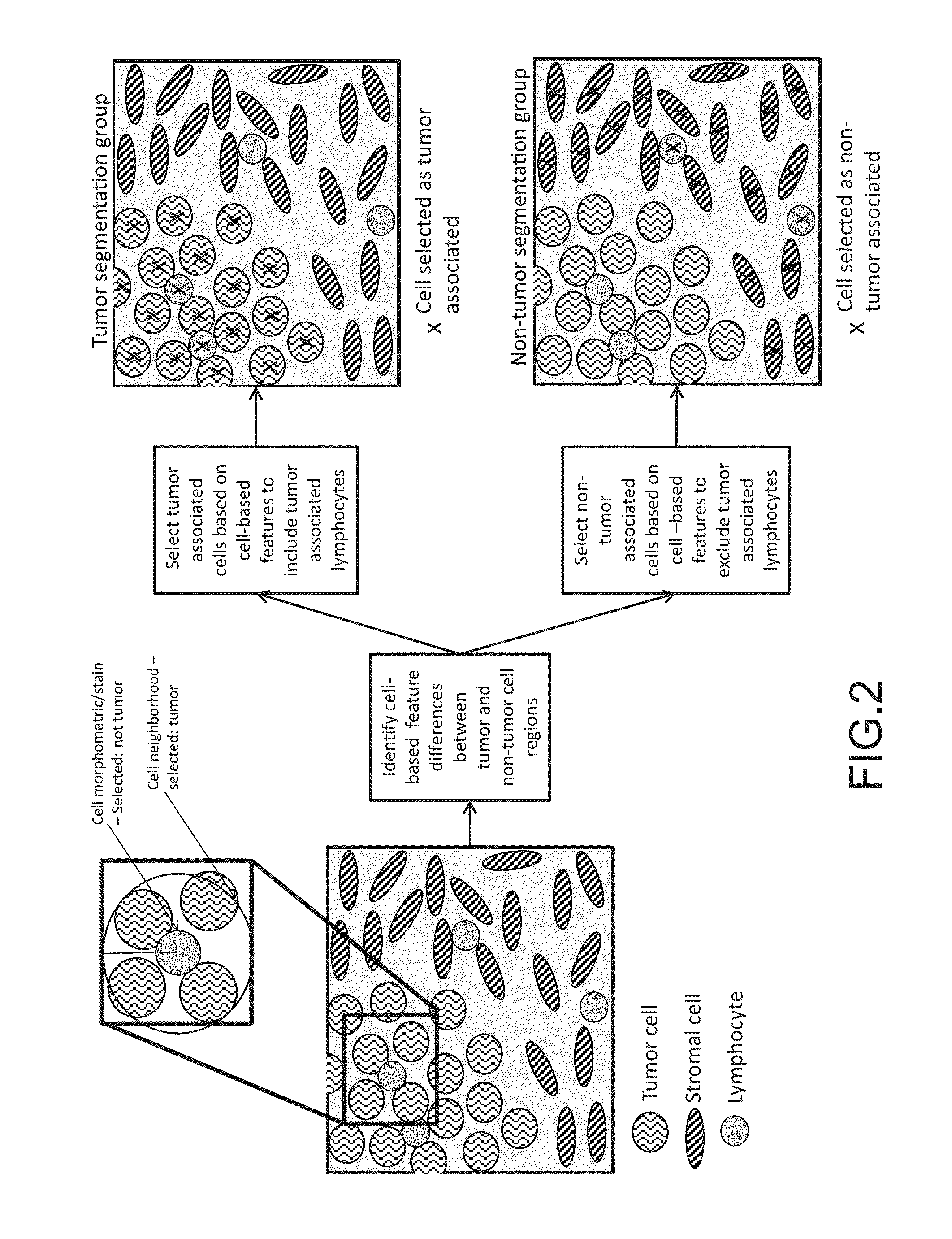
This disclosure concerns methods for evaluating inflammatory cells and modulators of the inflammatory response in tumor tissue and other relevant tissue types. The methods entail: obtaining a tissue sample and processing said tissue sample to produce histologic slides of tissue sections; staining of the tissue sections to identify inflammatory cells and modulators of the inflammatory response; digitizing slides to produce an image of the stained tissue sections; digitally stratifying the tissue sample into tumor and other relevant tissue compartments; and using digital image analysis to quantify cell-based and cell population-based features. The quantification of cell-based and cell population-based features within a tissue compartment of interest is used to develop a summary score of the immune system-tissue compartment of interest interaction. Patient stratification and selection as candidates for a therapeutic approach is ultimately based on the summary score value.
Owner:FLAGSHIP BIOSCI
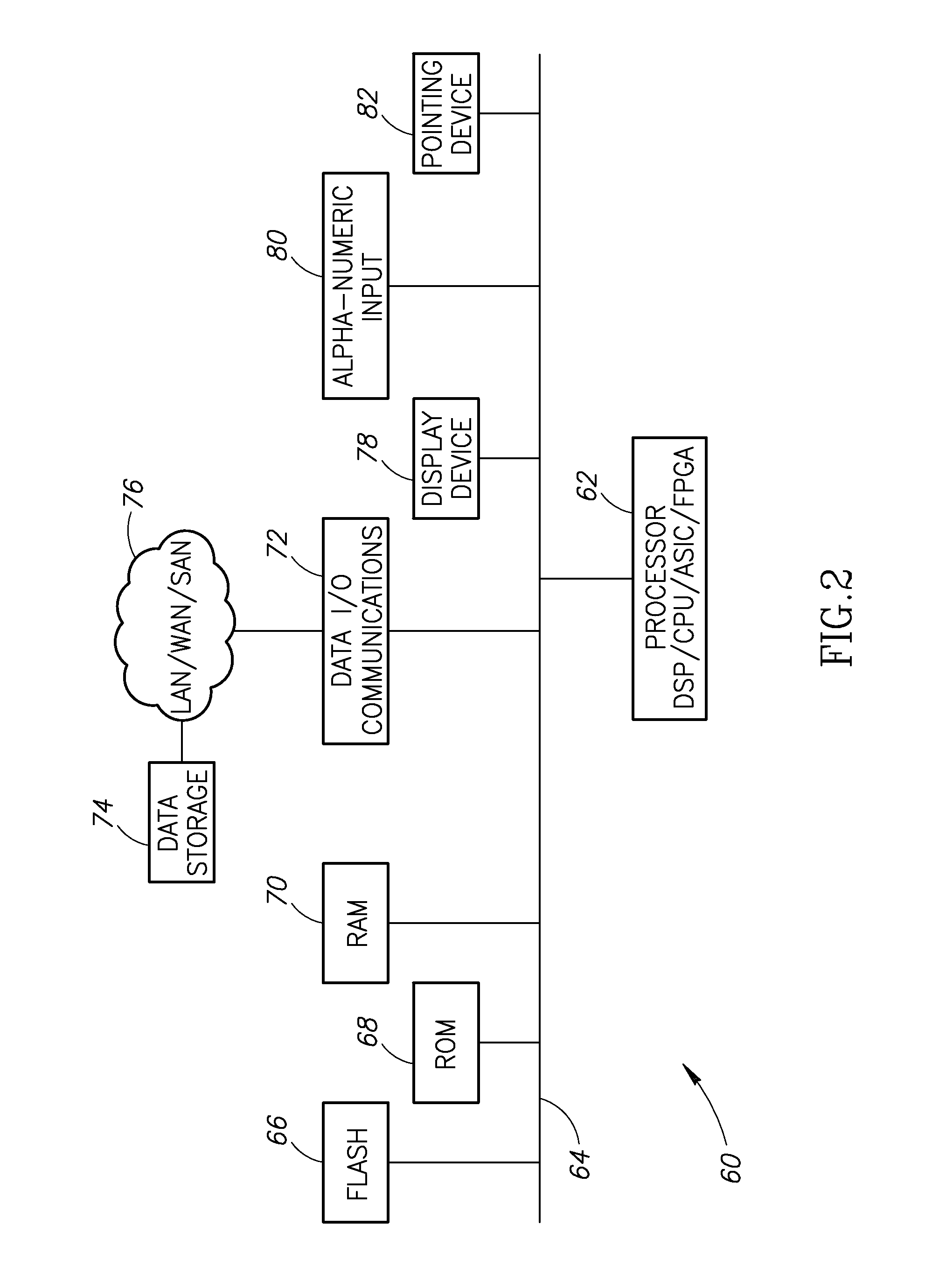
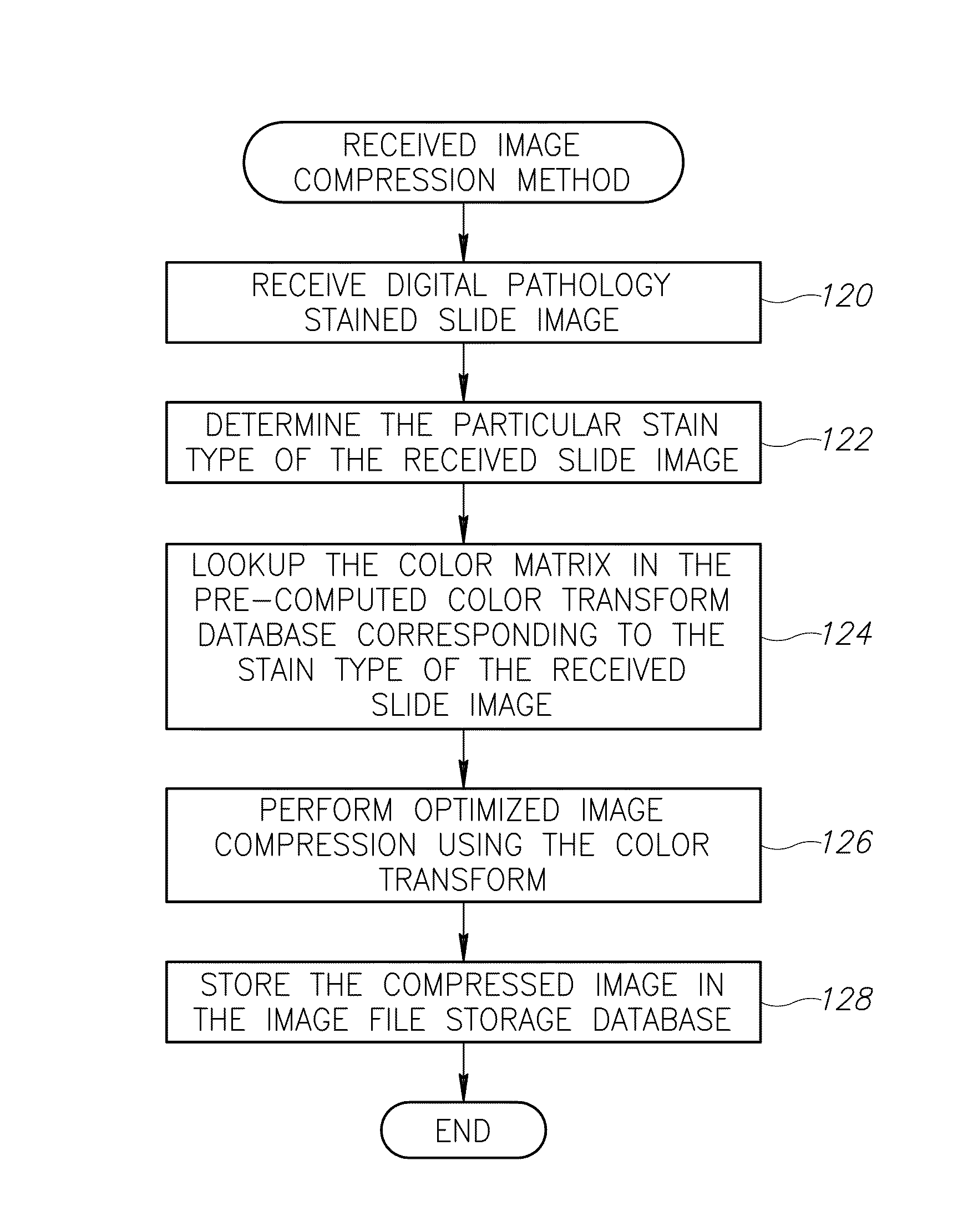
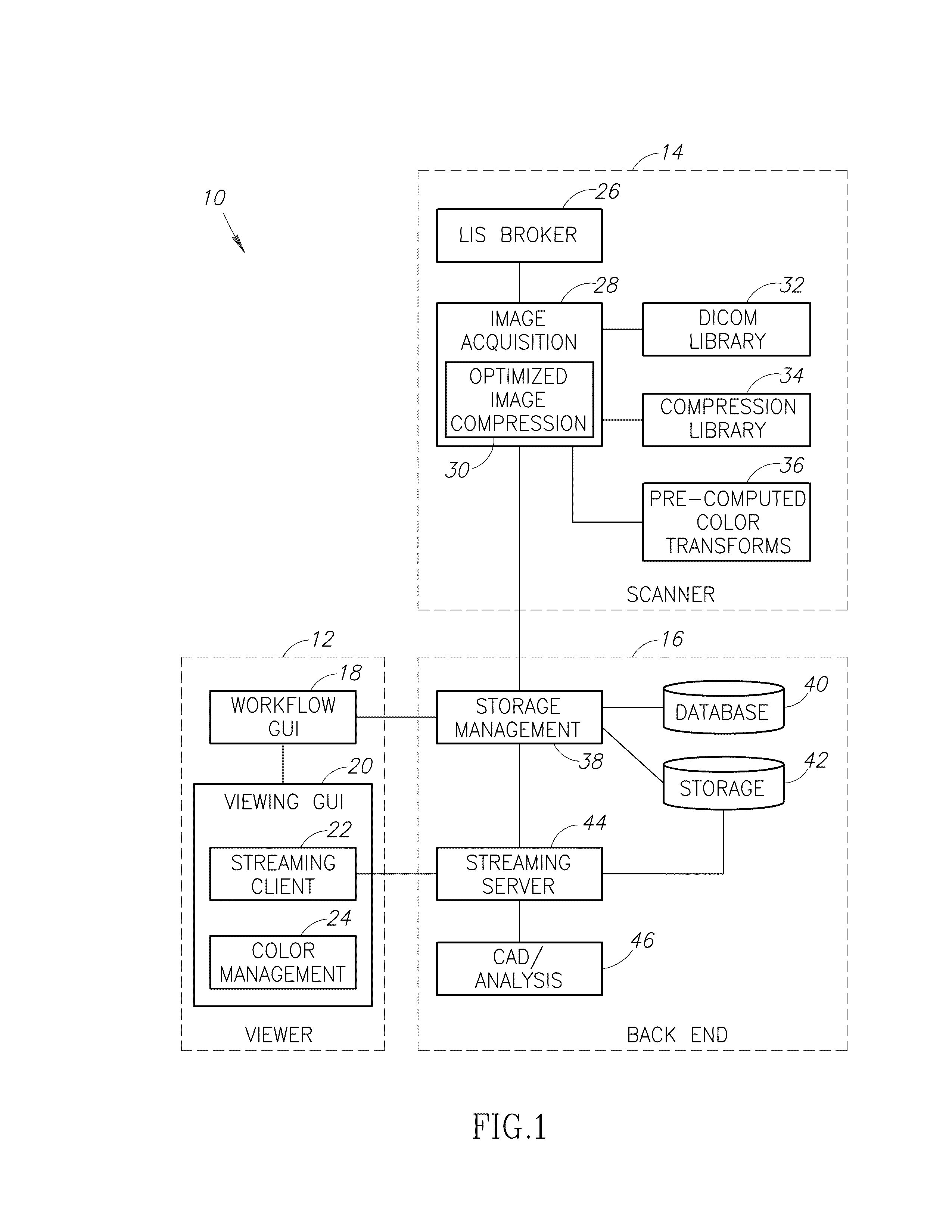
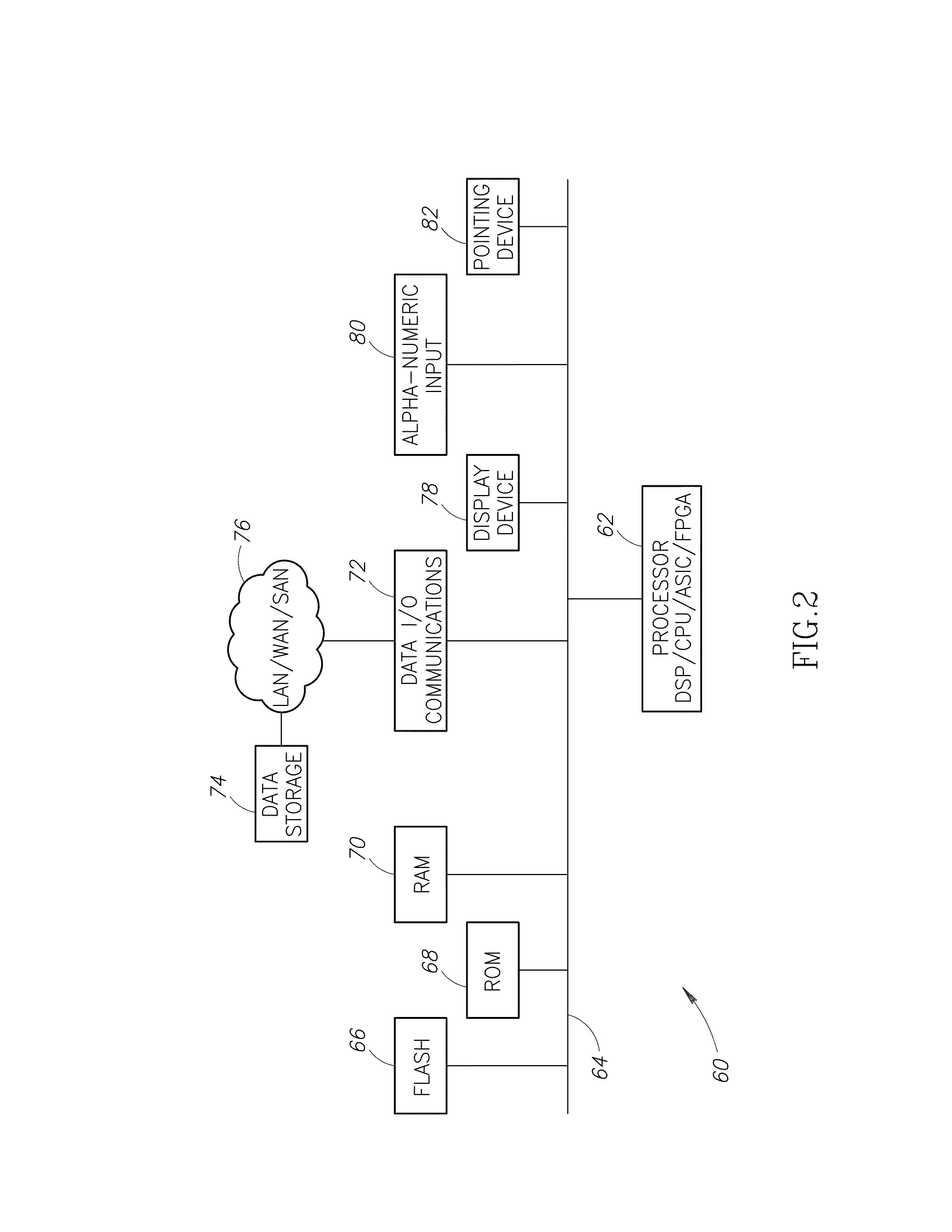
Stain-based optimized compression of digital pathology slides
ActiveUS20110075897A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationColor transformationRate distortion
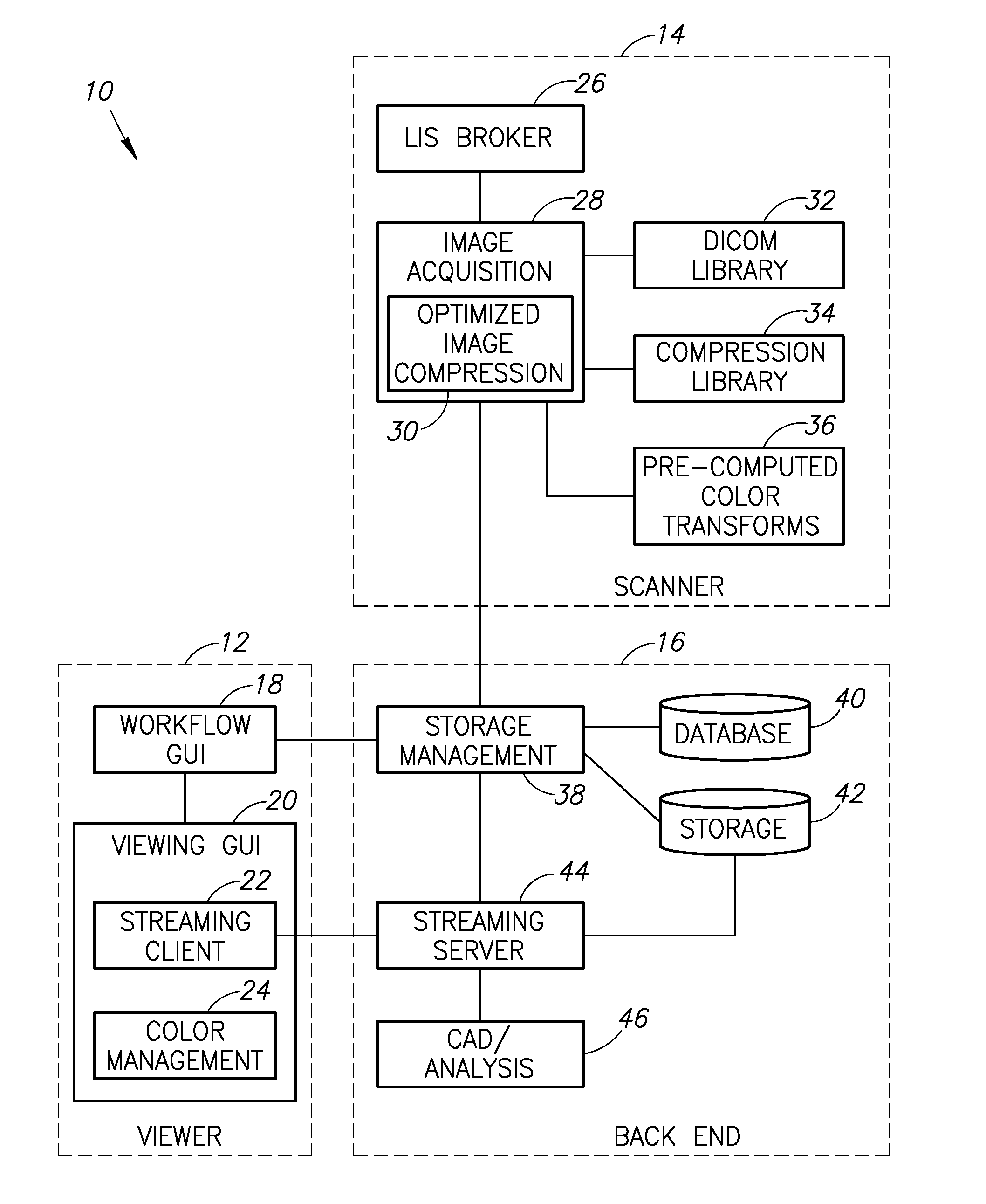
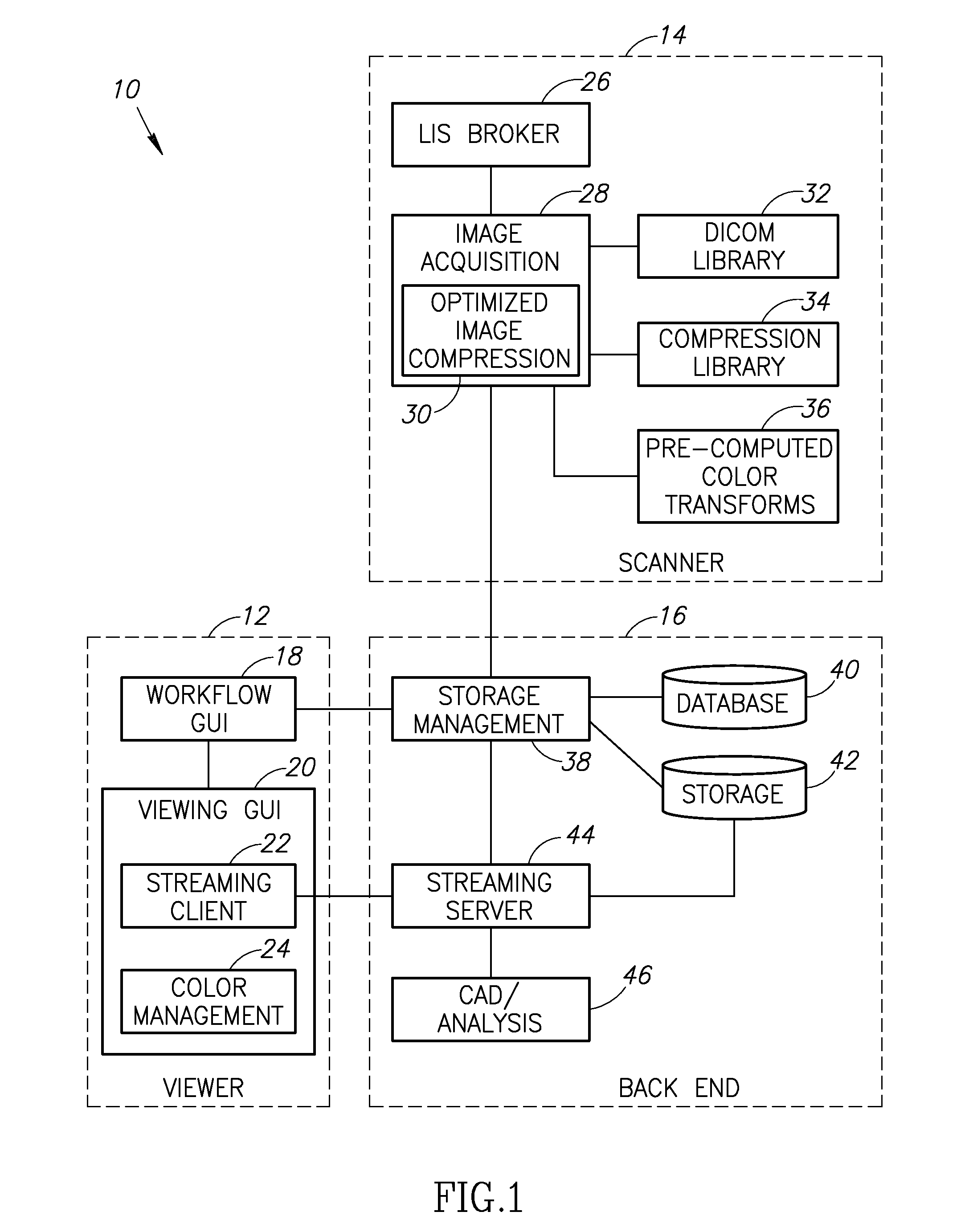
A novel and useful method and system of optimized image compression of digital pathology slide images. The optimized image compression mechanism exploits the special color properties of the stained tissue represented by the digital pathology slides and provides an image compression algorithm having improved rate-distortion performance. Optimized color transforms are pre-computed using training sets of pathology slide image scan data for each stain type. The optimized color transforms are used to compress input slide image scans resulting in more efficient image streaming enabling users to review extremely large digital slide scans from any connected location, such as in a hospital, satellite center, home or on a mobile telephone.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Antimicrobial photo-stable coating composition
The invention is an antimicrobial photo-stable coating composition that deters photo-induced discoloration, does not stain tissue and can be applied to the surface of a variety of medical materials. The composition comprises in an aspect silver-PCA complex and dye.
Owner:COVALON TECH LTD
Stain-based optimized compression of digital pathology slides
ActiveUS8077959B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationColor transformationRate distortion
A novel and useful method and system of optimized image compression of digital pathology slide images. The optimized image compression mechanism exploits the special color properties of the stained tissue represented by the digital pathology slides and provides an image compression algorithm having improved rate-distortion performance. Optimized color transforms are pre-computed using training sets of pathology slide image scan data for each stain type. The optimized color transforms are used to compress input slide image scans resulting in more efficient image streaming enabling users to review extremely large digital slide scans from any connected location, such as in a hospital, satellite center, home or on a mobile telephone.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Histochemical labeling stain for myelin in brain tissue
InactiveUS6372451B1Eliminating the drawbacks associated therewithShort timePhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesFiberSodium phosphates
A novel aurophosphate stain for staining a slide-mounted brain tissue slice or section to label myelin therein, the method of staining, and the method of making the stain. The stain is potassium aurophosphate or sodium aurophosphate produced as the reaction product of an aurochloride and a dibasic potassium or sodium phosphate. Slide-mounted brain tissue slices are stained by immersing the slice in a warn solution of the aurophosphate. The stained slice may be intensified by immersing the slide-mounted stained tissue slice in a potassium tetrachloroaureate solution. The stained or intensified slice can be fixed by immersion in a sodium thiosulfate solution. Large bundles of stained myelin appear deep red-brown, while smaller bundles and individual fibers appear black.
Owner:SCHMUED LAURENCE C
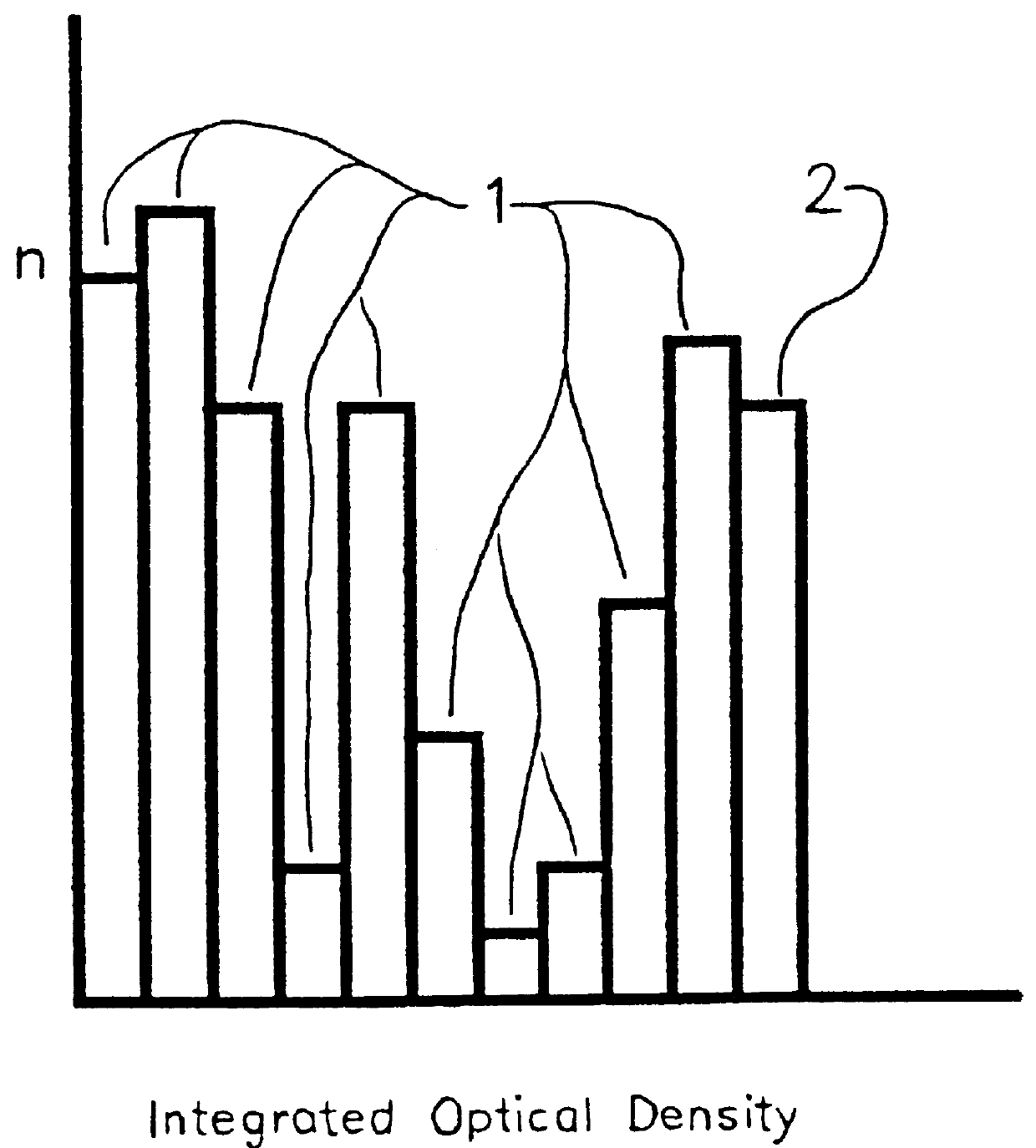
Method for correction of quantitative DNA measurements in a tissue section
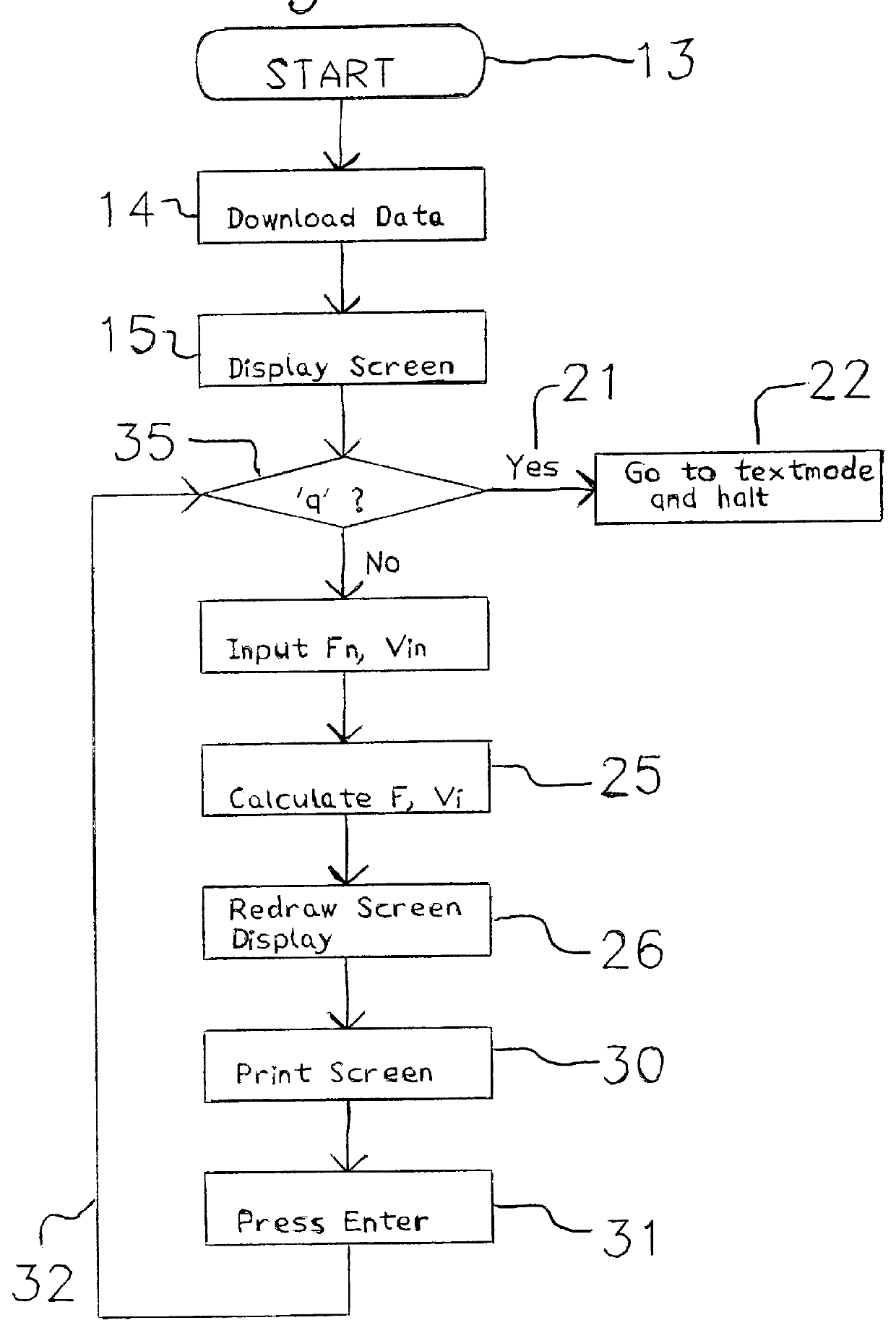
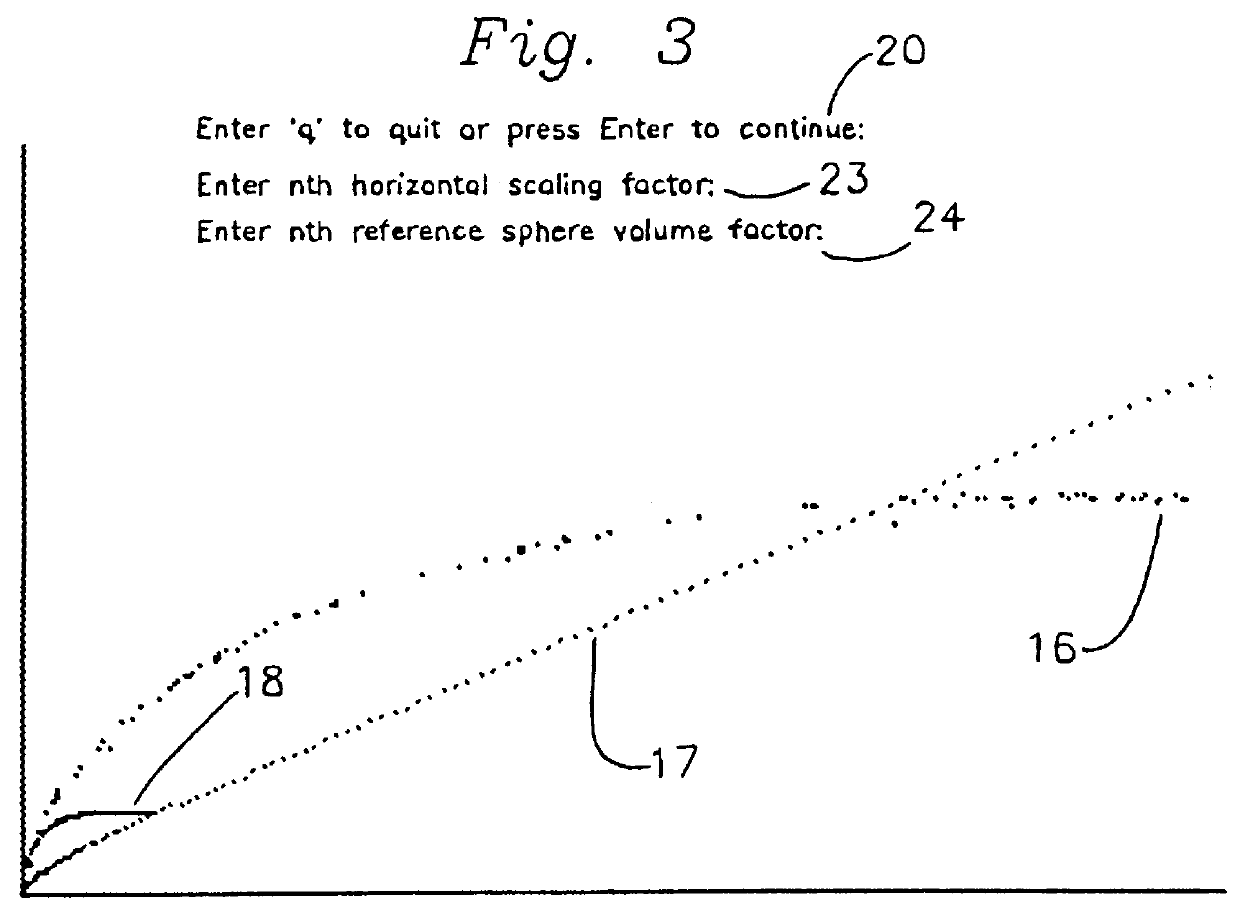
InactiveUS6035258AAnalogue computers for chemical processesColor/spectral properties measurementsRandom access memoryFeulgen stain
The operator downloads, from a data file into the random access memory of a personal computer, integrated optical density and profile area data for a plurality of nuclei and partial nuclei in a Feulgen-stained histologic tissue section; the thickness of the section; and the integrated optical density of an intact diploid nucleus. The operator then operates a computer program which plots the data curve together with a reference line and a reference curve. The data curve is scaled and the reference curve is recalculated and redrawn through a number of iterations until the operator is satisfied that the scaled data curve terminates on the reference line, and the scaled data curve is as nearly congruent as possible with the latest reference curve. The program calculates and displays the corrected DNA index on a video screen, the contents of which the operator may print on a printer.
Owner:FREED JEFFREY A
Method, Processor and Carrier for Processing Frozen Slices of Tissue of Biospecimens
InactiveUS20120276583A1Quality improvementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStainingAnatomy
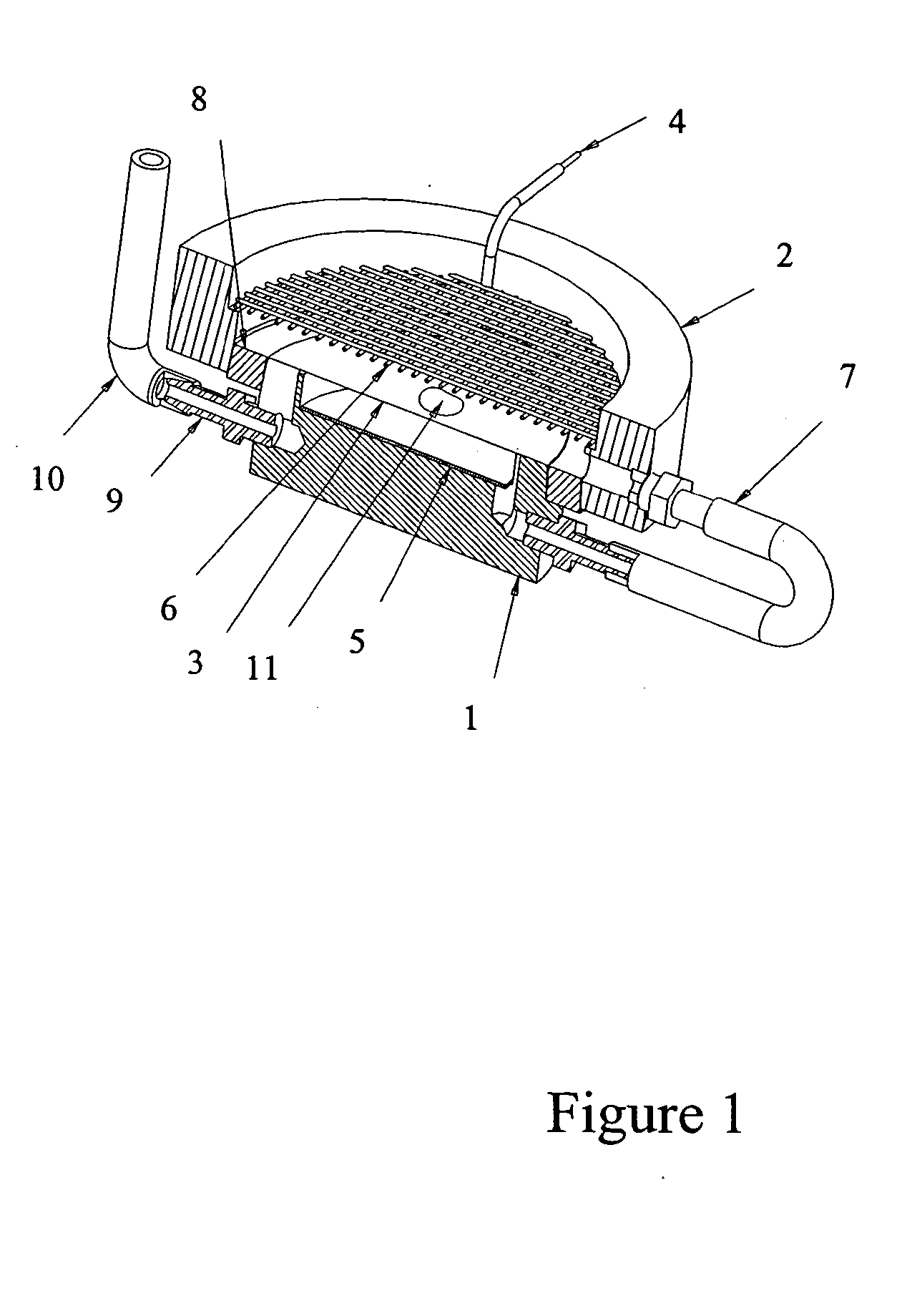
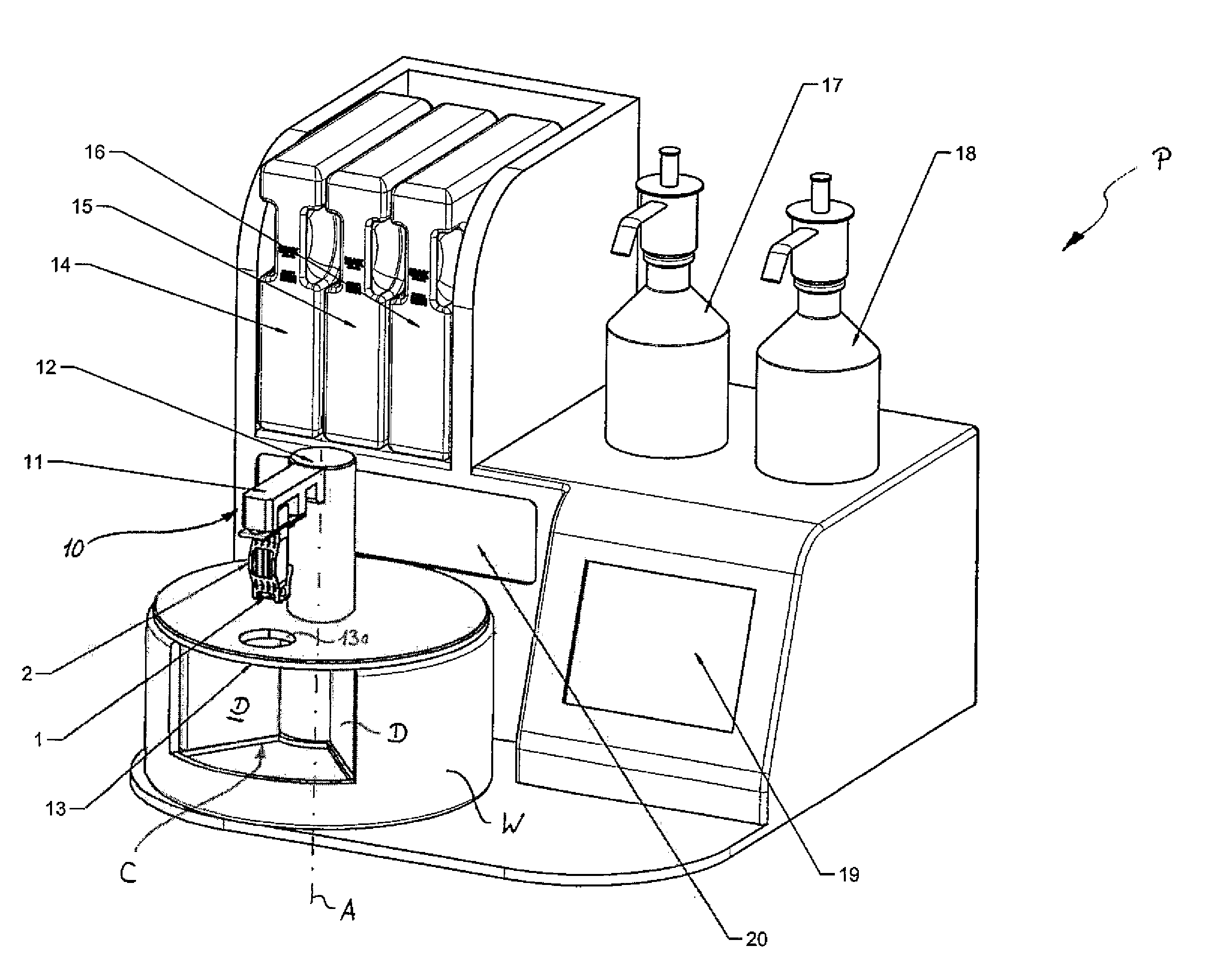
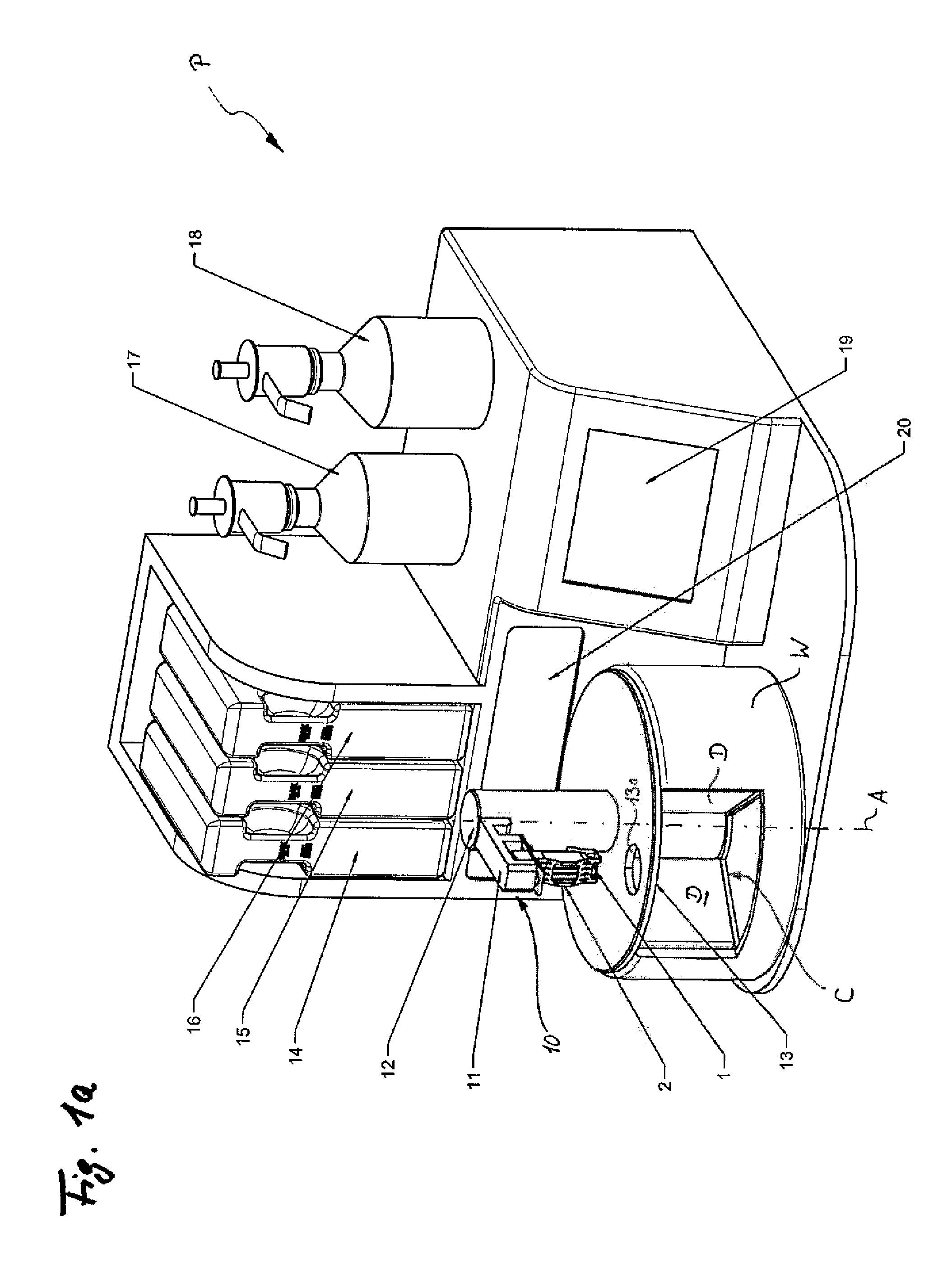
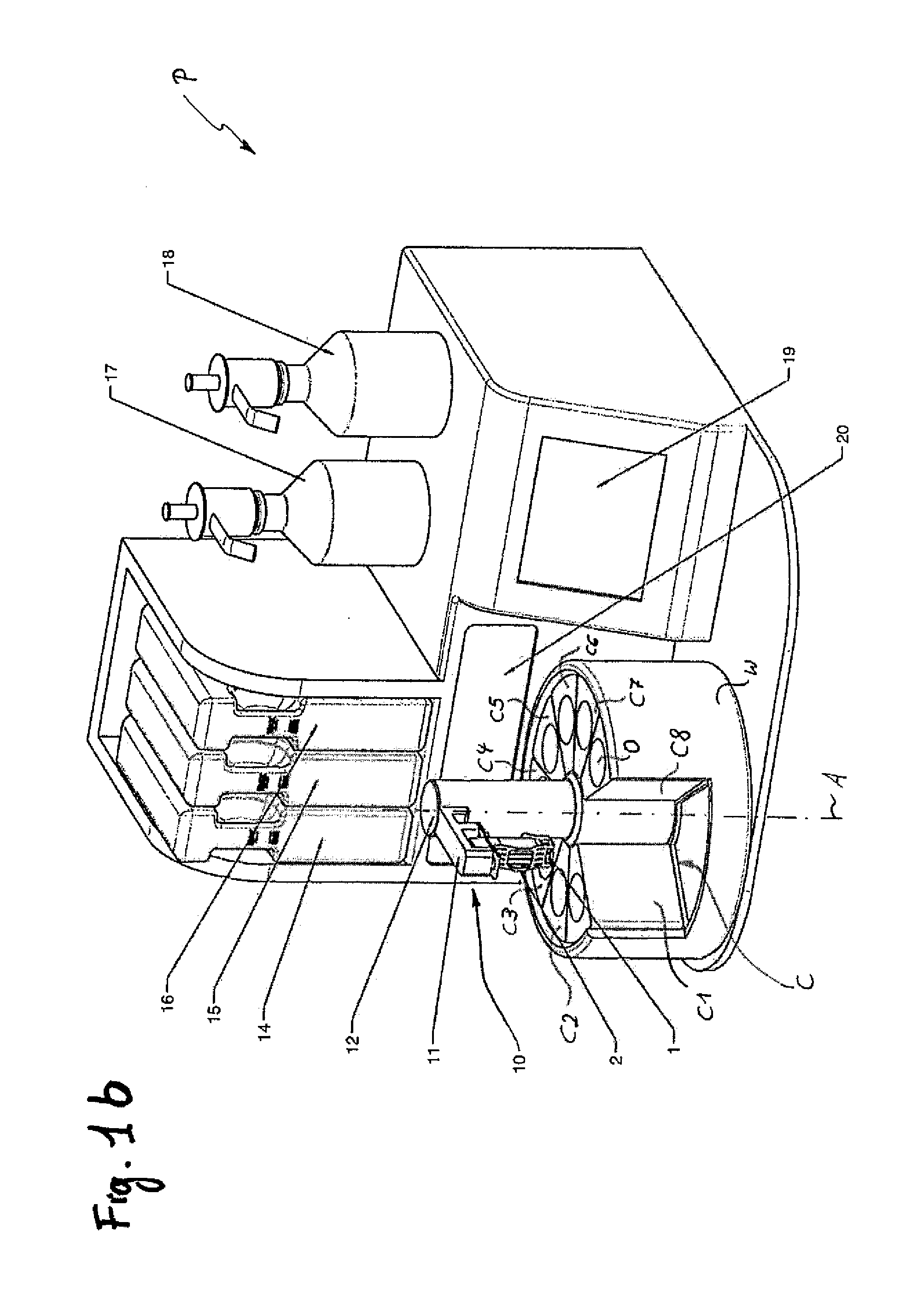
A method for processing frozen slices of tissue of biospecimens mounted on or adhered to glass slides, i.e. forming a frozen section (2), and arranged on a carrier (1), has the following steps: a.) immersing the frozen tissue slices in a fixative, b.) staining the tissue slice, c.) dehydrating the tissue slice, and d.) optionally clearing the tissue slice. Steps a.) to d.) are performed by automatically transferring the frozen sections (2) on the carrier (1) between and into and out of at least a container (C1) holding a fixative, at least one or optionally more, preferably two containers (C3, C5) holding a staining solution, a container (C6, C7) holding a dehydrating solution, and optionally a container (C8) holding a clearing solution. The transfer and the time duration during which the tissue slices are in said containers (C) are controlled by a control unit controlling an actuator (10).
Owner:MILESTONE SRL
Color x-ray histology for multi-stained biologic sample
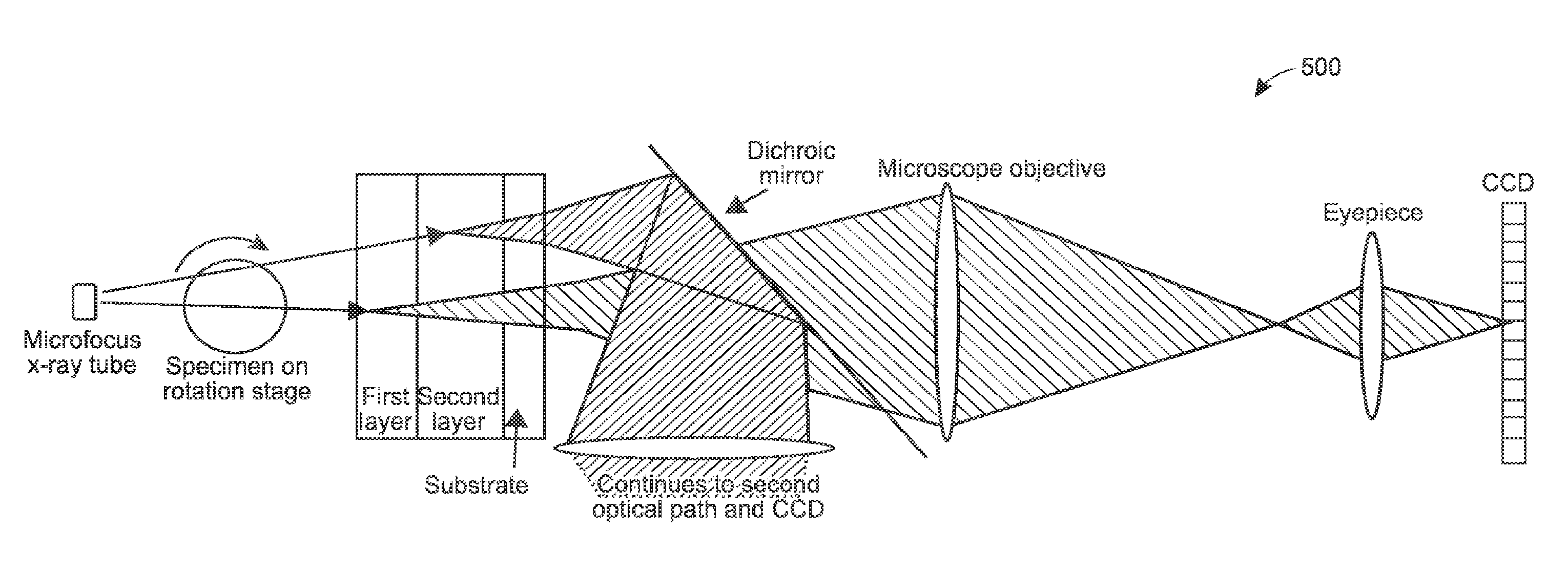
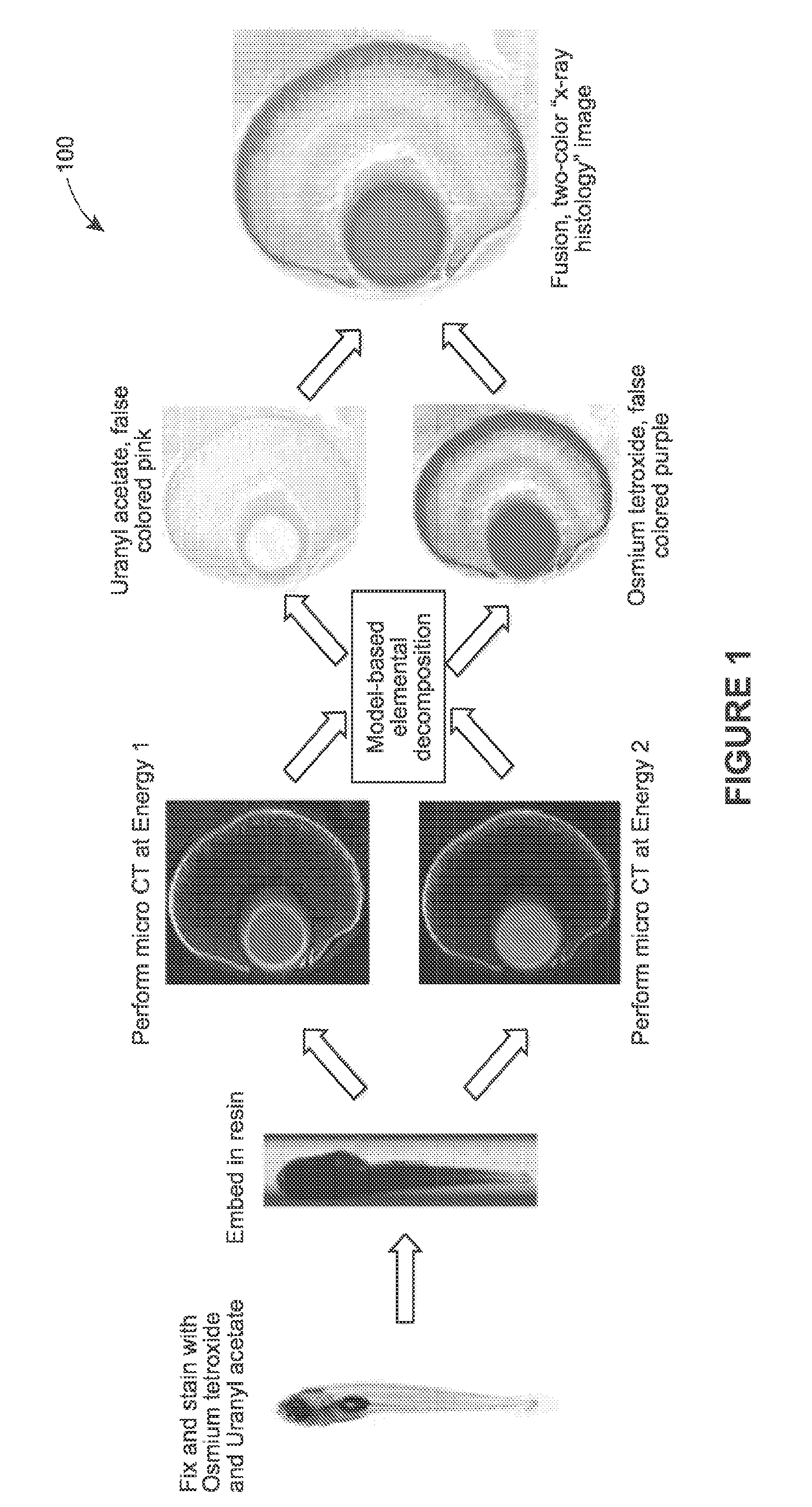
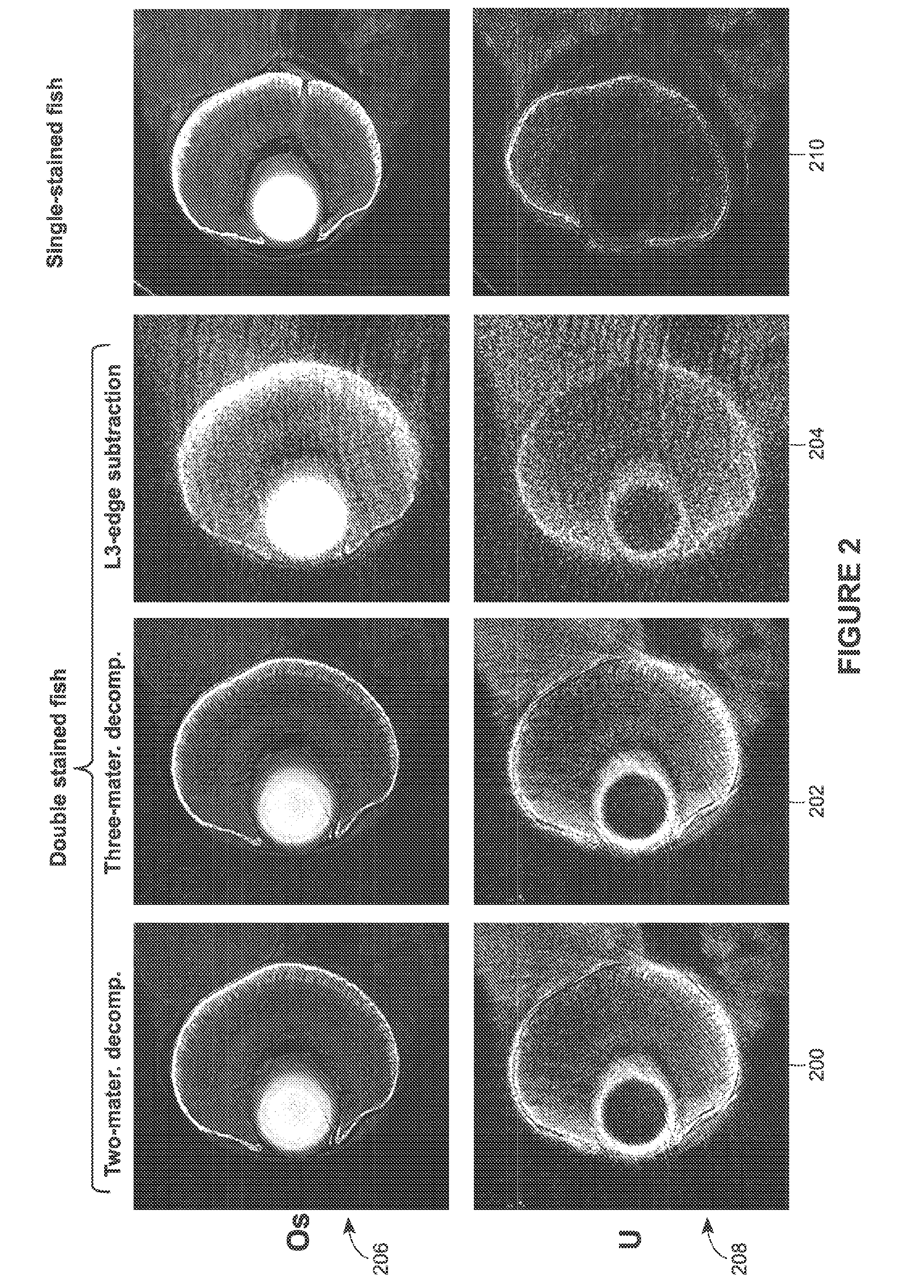
Systems and methods are provided for staining tissue with multiple biologically specific heavy metal stains and then performing X-ray imaging, either in projection or tomography modes, using either a plurality of illumination energies or an energy sensitive detection scheme. The resulting energy-weighted measurements can then be used to decompose the resulting images into quantitative images of the distribution of stains. The decomposed images may be false-colored and recombined to make virtual X-ray histology images. The techniques thereby allow for effective differentiation between two or more X-ray dyes, which had previously been unattainable in 3D imaging, particularly 3D imaging of features at the micron resolution scale. While techniques are described in certain example implementations, such as with microtomography, the techniques are scalable to larger fields of view, allowing for use in 3D color, X-ray virtual histology of pathology specimens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +2
Method of Marking Biological Tissues for Enhanced Destruction by Applied Radiant Energy
InactiveUS20060282133A1Promote absorptionIncreased and accelerated destructionSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyMedicineLength wave
Methods for staining a selected tissue with a dye, stain or pigment that is attuned to absorb the energy from a radiant energy source are disclosed. The radiant energy source can be sufficient to destroy or combust radiated tissues. The dye or stain can enhance absorption of incoming radiant energy, which results in increased destruction of stained tissues and decreased destruction of underlying tissues. This method provides clinicians with the ability to selectively mark a tissue for destruction, while leaving wanted tissues generally intact. A clinician may dispense the stain with a pen and directly stain selected biological tissues, similar to the current practice of drawing current incision guides, followed by radiating the stained area with a laser that produces a wavelength that the stain readily absorbs. Optionally, a radiant energy opaque substance that can be applied adjacent the stained treatment area to protect against accidental or incidental exposure to wanted tissue. Also optionally, an oxidizing substance may be applied with the stain to further enhance the effect of this method.
Owner:CAO GROUP
Antimicrobial photo-stable coating composition
The invention is an antimicrobial photo-stable coating composition that deters photo-induced discoloration, does not stain tissue and can be applied to the surface of a variety of medical materials. The composition comprises in an aspect silver-PCA complex and dye.
Owner:COVALON TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Method for fluorescently staining tissue
InactiveUS20070172912A1Clear and accurate stained imageGood fluorescence propertiesPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingFluorescent stainingMedicine
It is intended to provide a method for fluorescently staining a tissue accurately and clearly by convenient procedures and a staining agent used in this method. The present invention provides a method for fluorescently staining a tissue, comprising treating a tissue with a solution comprising fluorescein or a salt thereof and then fluorescently observing the treated portion under an acidic condition of lower than pH 7.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
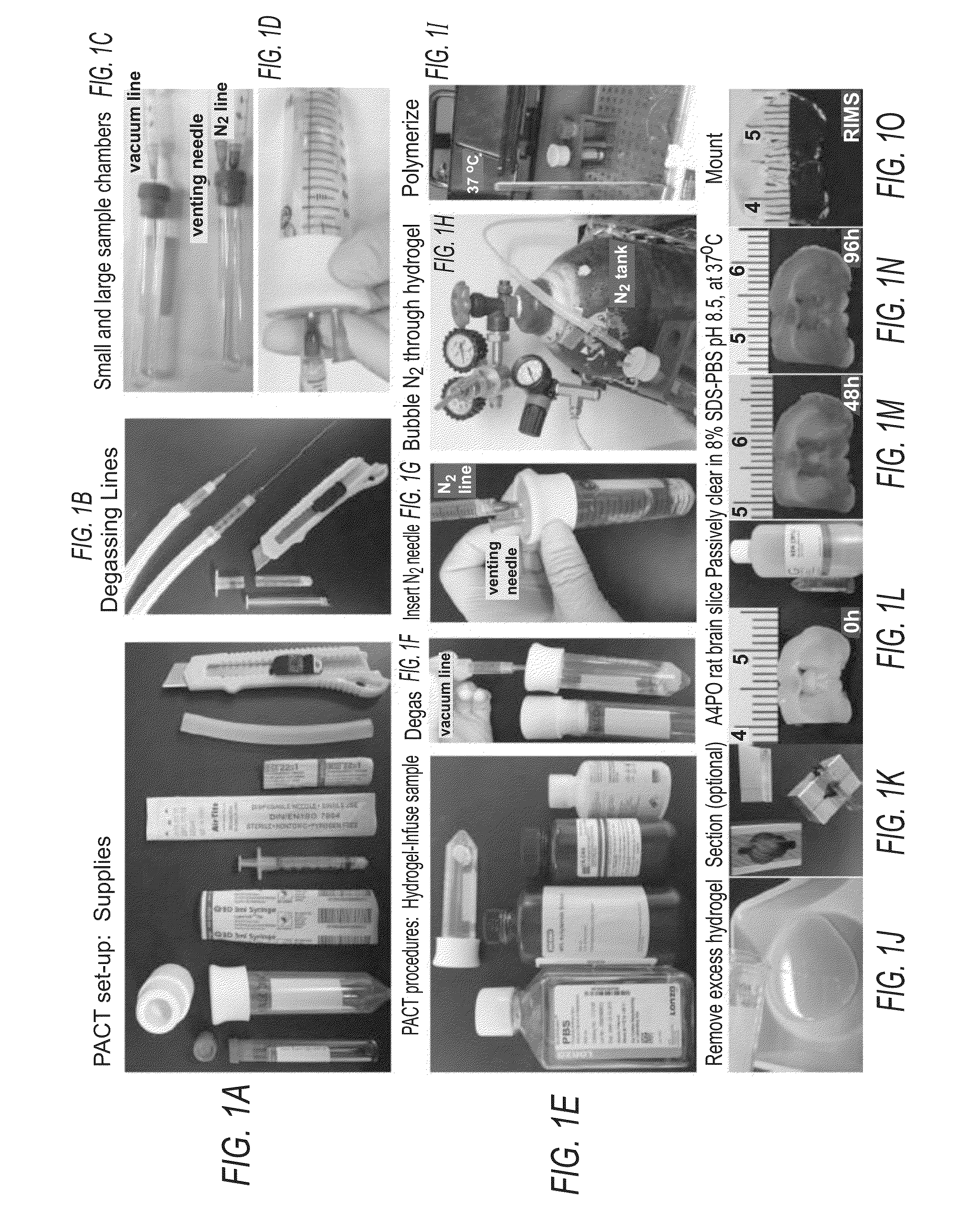
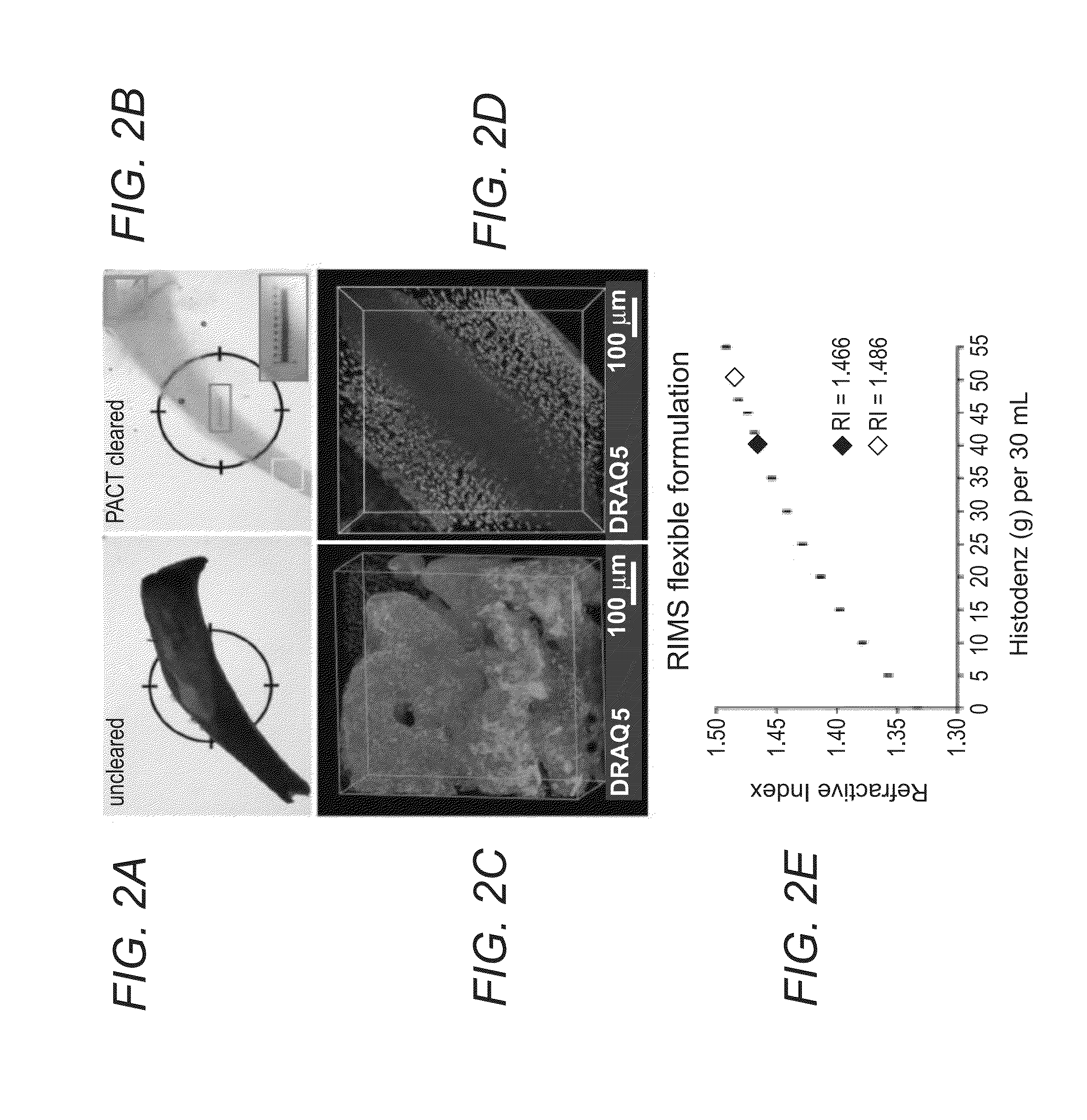
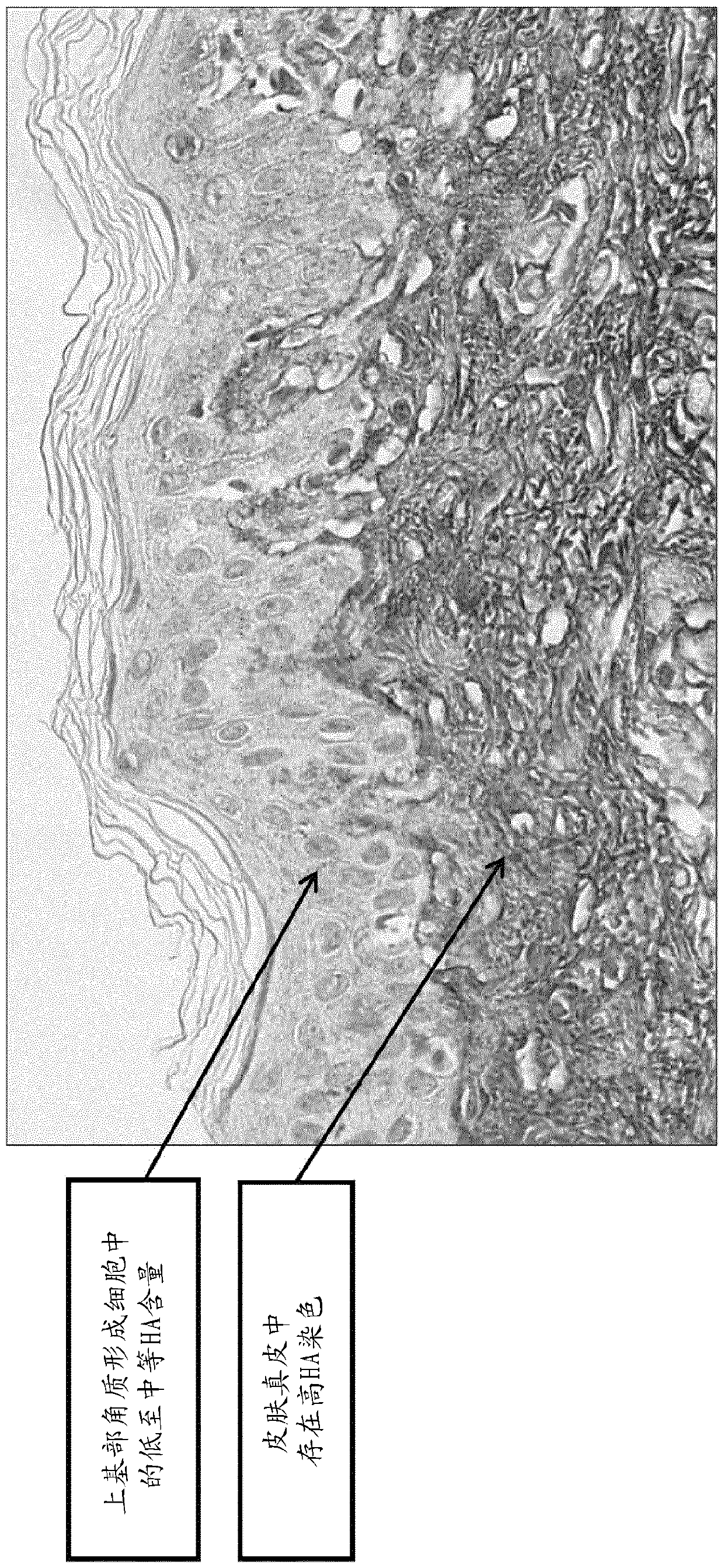
Methods for phenotyping of intact bones by tissue clearing and staining
InactiveUS20160131560A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationStainingTissue clearing
In various embodiments, the present application teaches methods and kits for clearing and optionally subsequently visualizing tissue containing bone. In some embodiments, the method includes serially incubating cleared bone in refractive index matching solutions with progressively higher refractive indexes. In some embodiments, the methods teach immunolabeling and / or staining tissue containing bone and optionally visualizing the immunolabeled and / or stained tissue containing bone.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Kit for pathologic diagnosis of tumors and method for staining tissue sections
ActiveCN103245789AQuick checkSimple and fast operationPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingNanoparticleClick chemistry
The invention relates to a kit for the pathologic diagnosis of tumors. The kit comprises a probe for the pathologic diagnosis of the tumors, wherein the probe comprises a gold nanoparticle cluster, an antibody of a tumor specific marker and CBB (Coomassie brilliant blue) in the molar ratio of (1-10):(1-100):(1-100); the gold nanoparticle cluster and the antibody of the tumor specific marker are connected in the manner of click chemistry; and the CBB and the gold nanoparticle cluster connected with the antibody of the tumor specific marker are combined in a static manner. The kit has high accuracy on the pathologic diagnosis of the tumors. In addition, the invention also provides a method for staining tissue sections.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
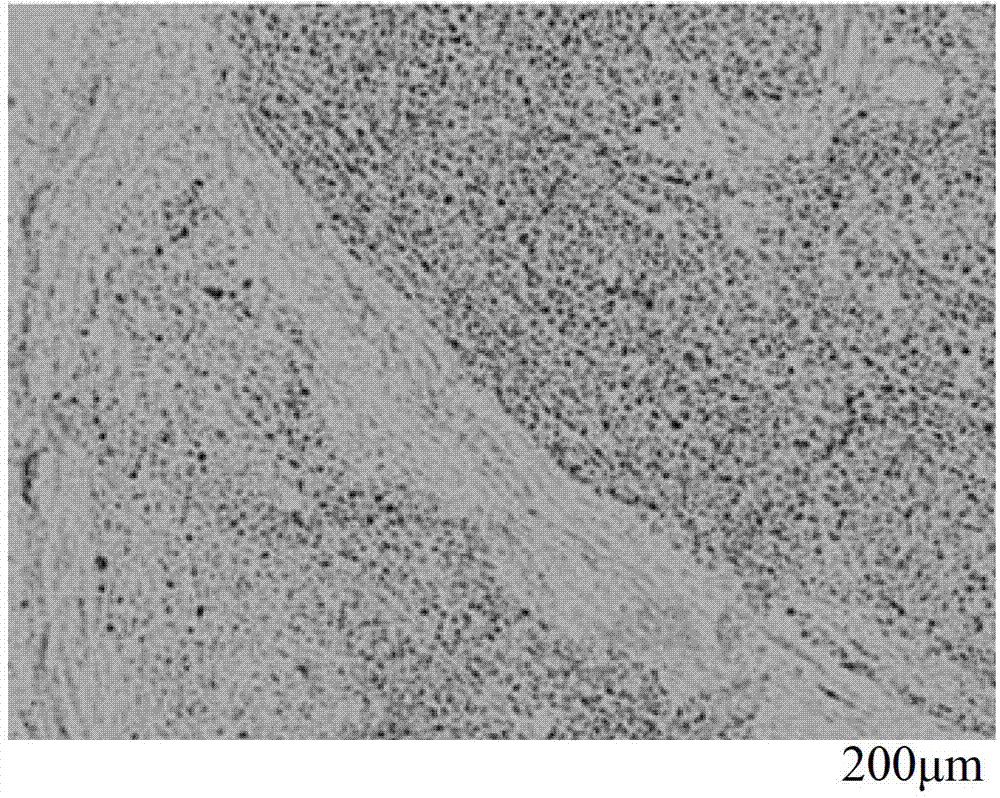
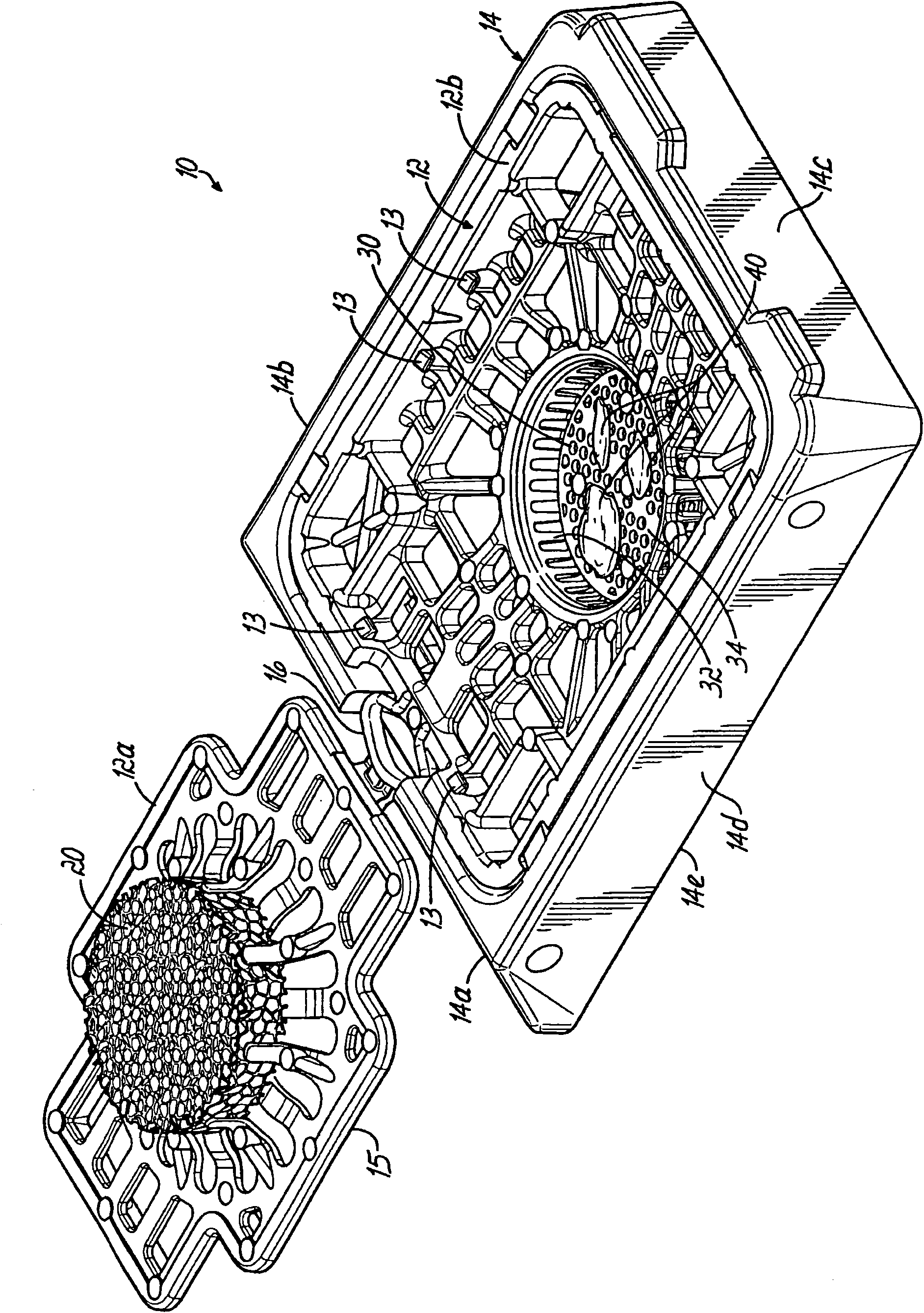
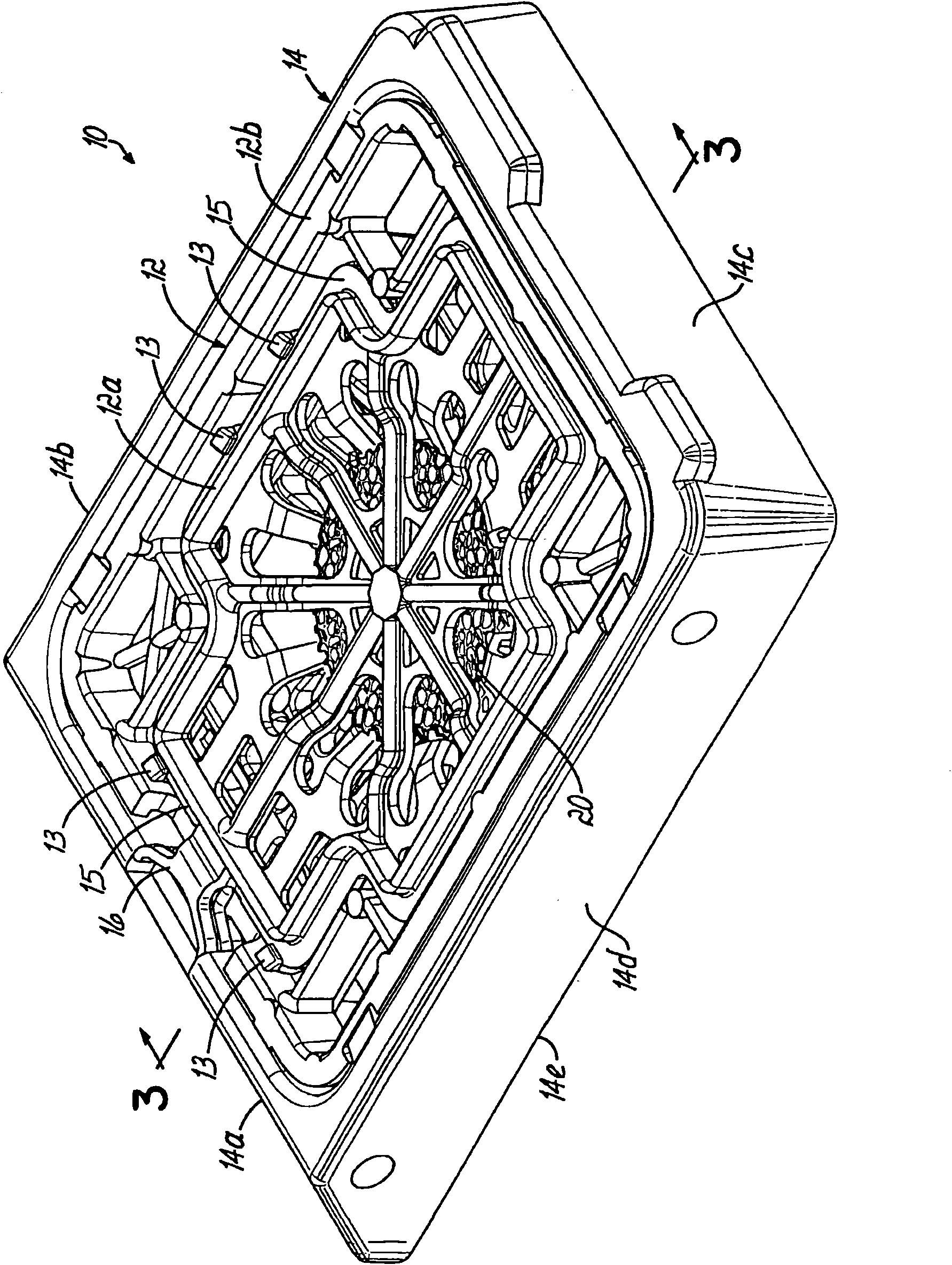
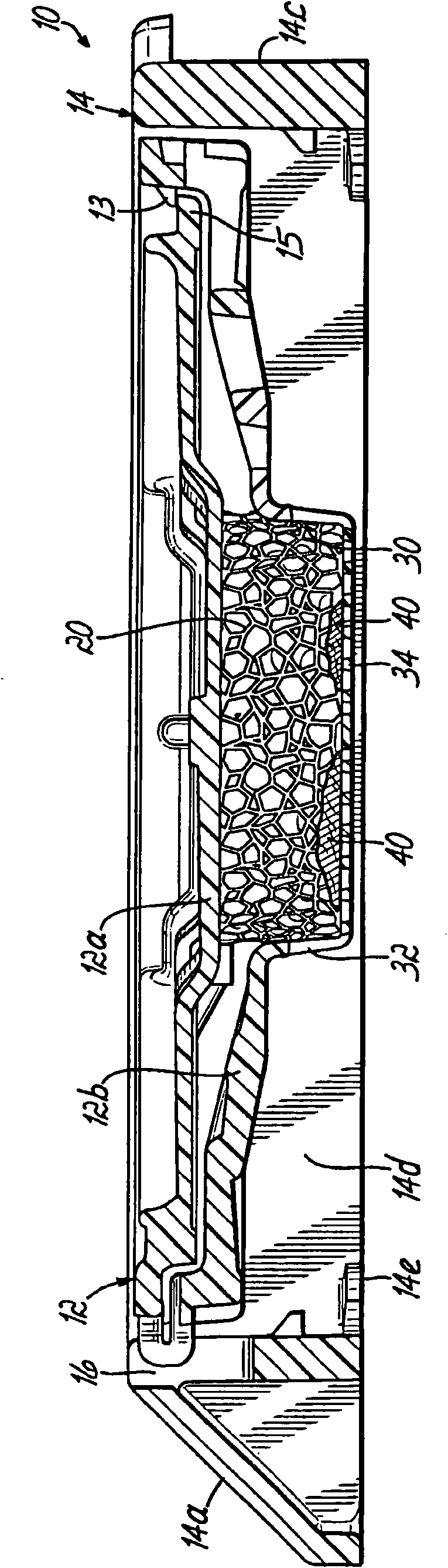
Biopsy support with sectionable resilient cellular material
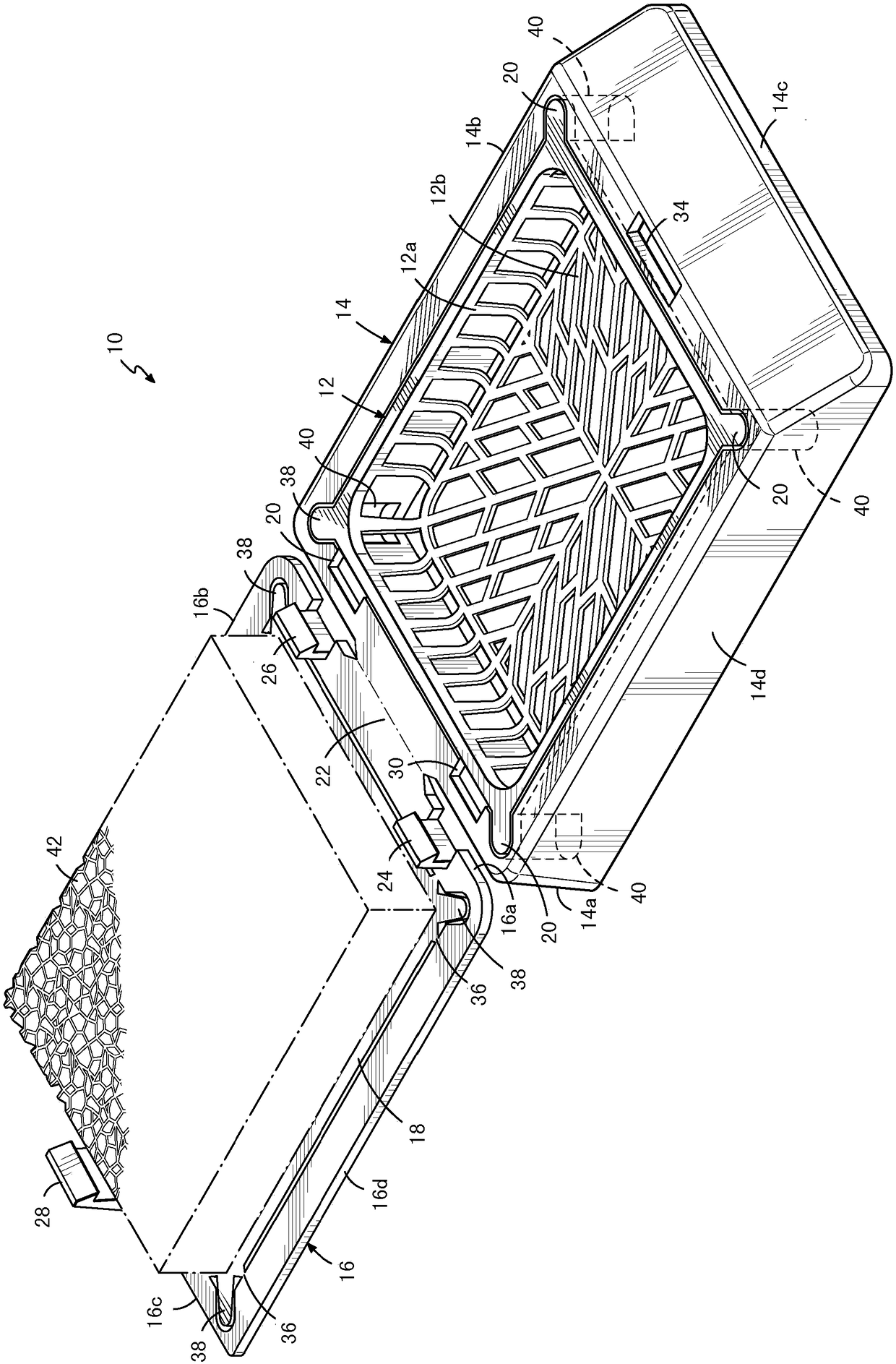
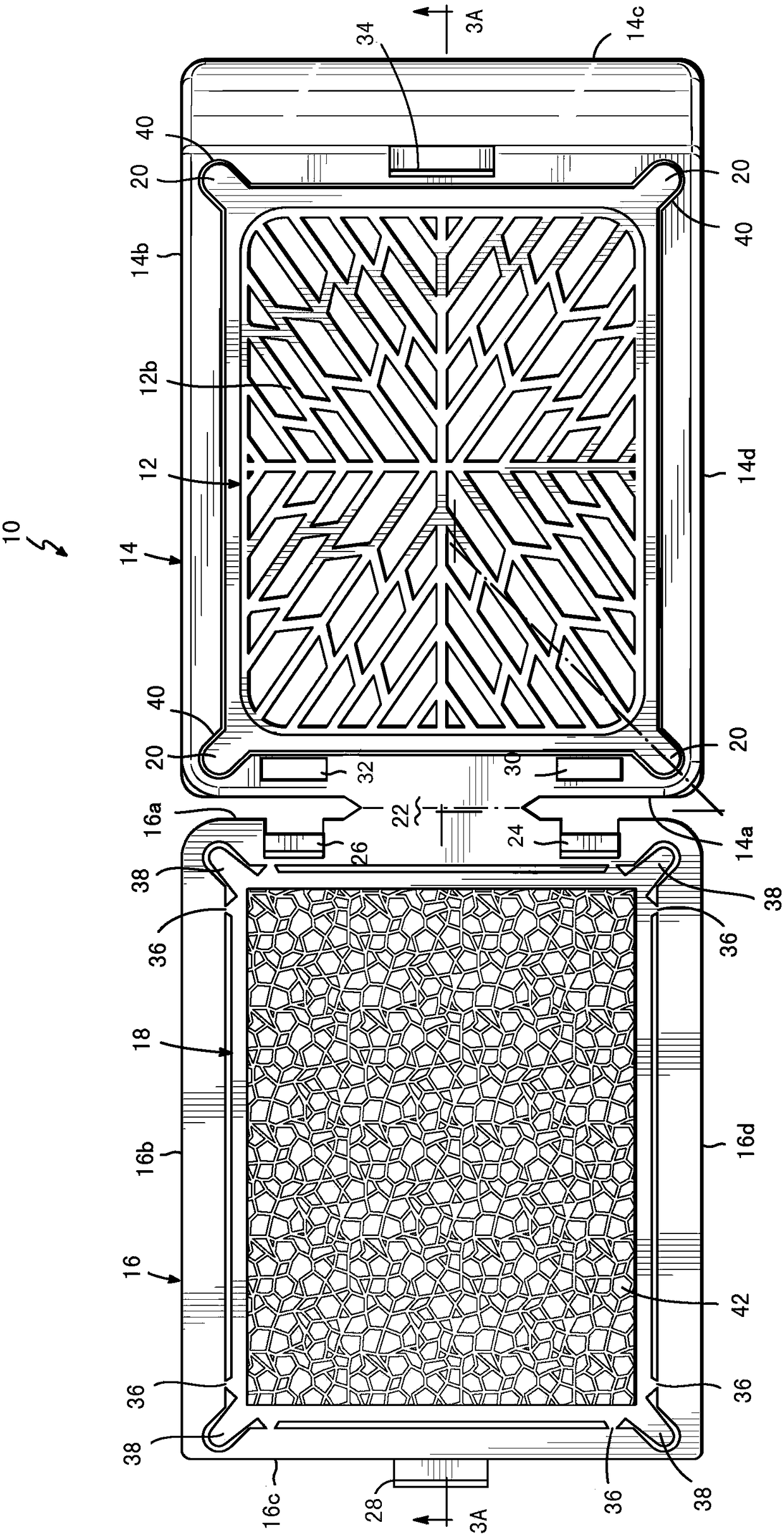
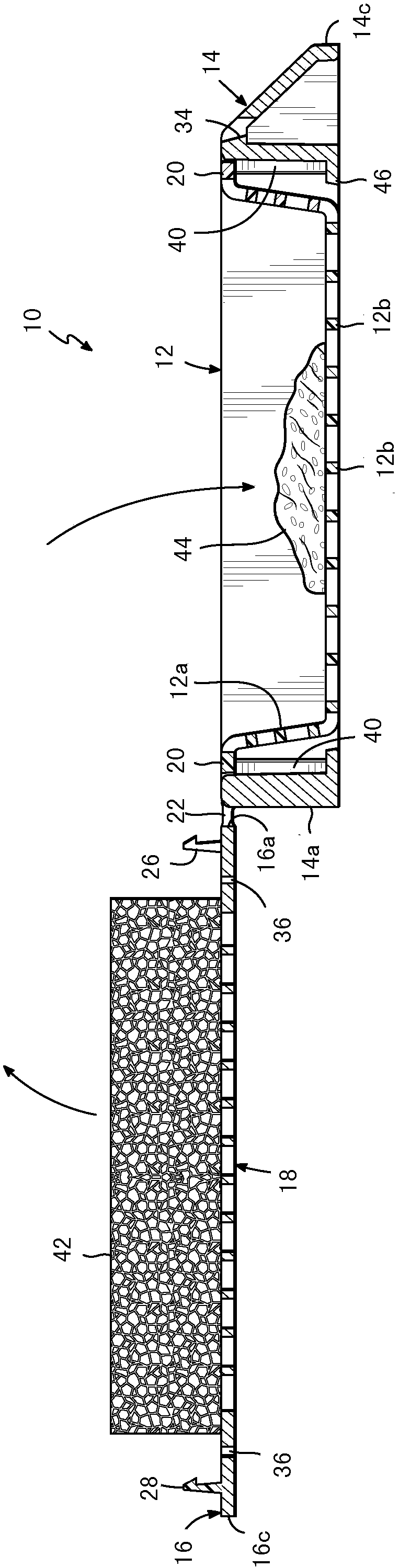
A histologic tissue sample support device includes a tissue support (12) formed of material that can be successfully sectioned in a microtome and is resistant to degradation from solvents and chemicals used to fix, process and stain tissue (40). A resilient cellular material (20) is coupled to the tissue support (12) and is configured to engage and retain tissue (40) in place during processing and embedding. The resilient cellular material (20) is also capable of successful sectioning in the microtome and porous to allow infiltration of the solvents and chemicals used to fix, process and stain tissue, and of embedding material (50) used to embed the tissue (40) while the tissue (40) is retained by the resilient cellular material (20).
Owner:BIOPATH AUTOMATION
Method for studying on prostate cancer reoccurrence and metastasis
InactiveCN105861692AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisLymphatic SpreadProstate cancer
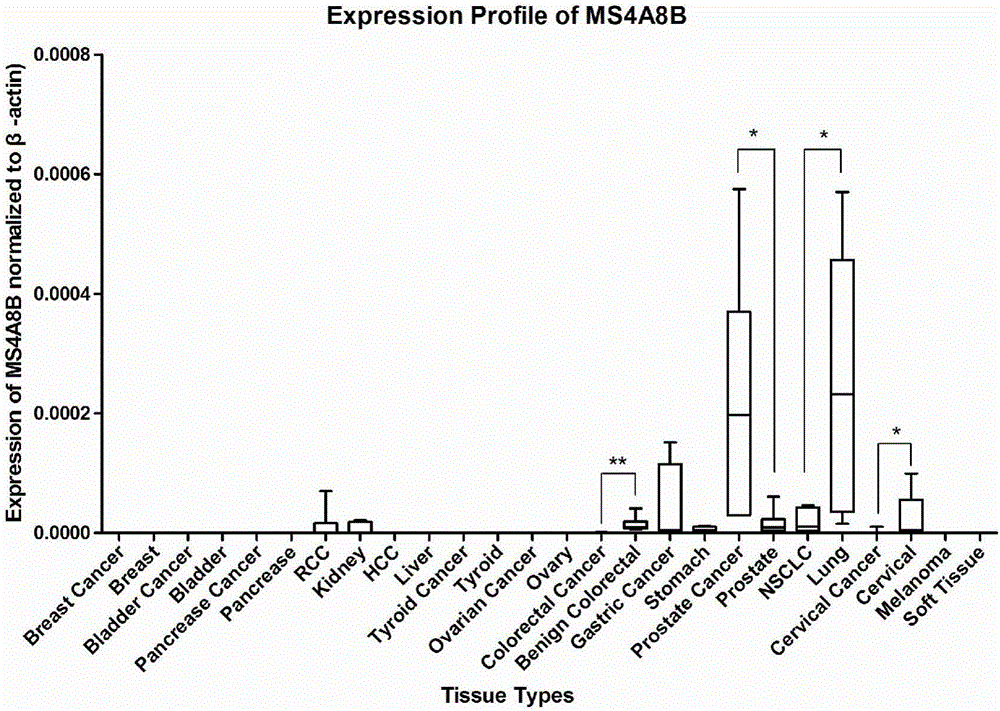
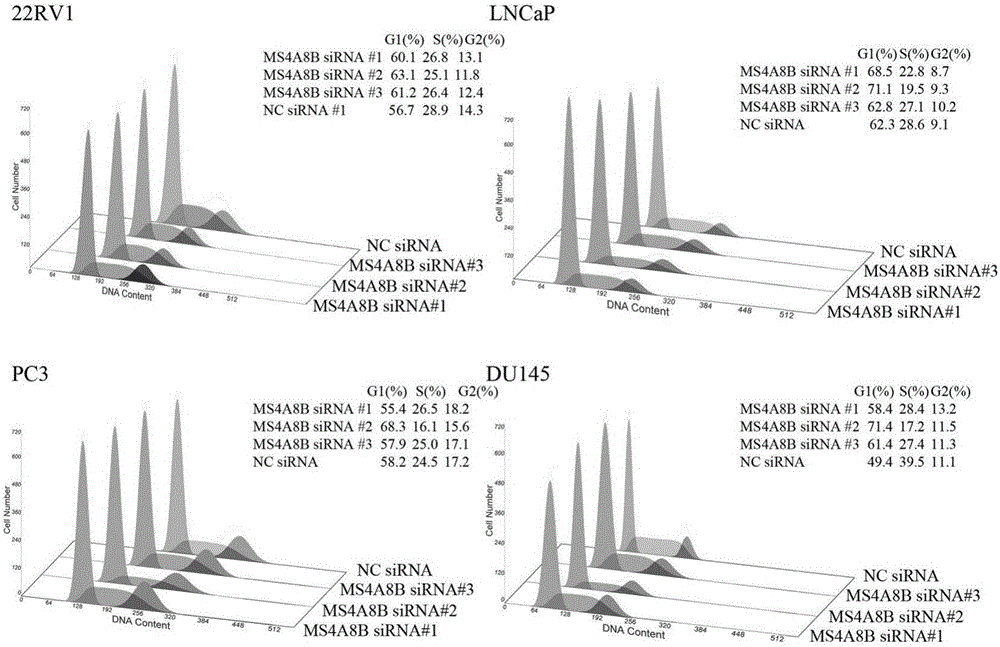
The invention discloses a method for studying on prostate cancer reoccurrence and metastasis, not useful in diagnosing and treating diseases. The method is characterized by including: using paraffin-embedded tissue samples containing prostate tissues, making the samples into HE (hematoxylin and eosin) stained tissue slices, making the tissue slices into microarray tissue chips, subjecting the microarray tissue chips to immunohistochemical staining, observing under a microscope, acquiring stained cell scores according to stained cell percentage ranges of the samples, acquiring a positive staining strength coefficient according to staining strength, multiplying the stained cell scores by the positive staining strength coefficient to obtain protein expression level of MS4A8B gene, and determining prostate cancer reoccurrence rate and metastasis rate according to the protein expression level of MS4A8B gene or by subjecting the protein expression level of MSA8B gene and a proliferation index of MS4A8B gene to correlation analysis. Prostate cancer reoccurrence and metastasis are studied herein by detecting the protein expression level and proliferation index of prostate cancer gene in the tissue samples to be detected.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
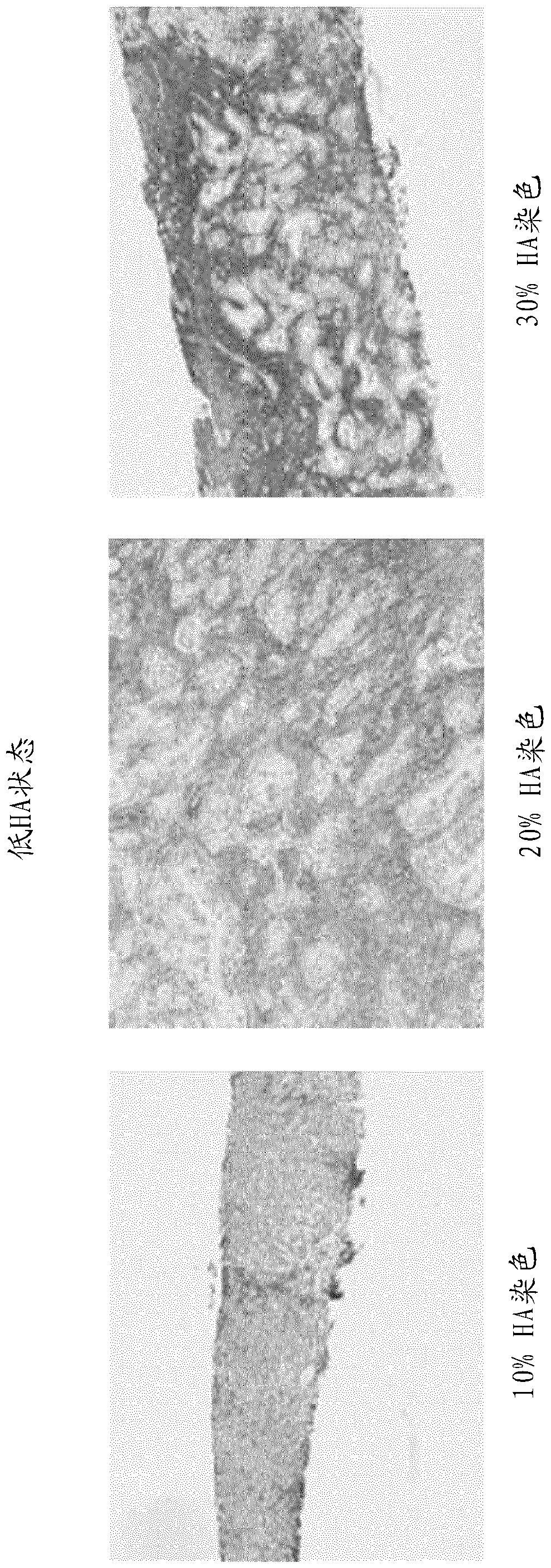
Methods and systems for scoring extracellular matrix biomarkers in tumor samples
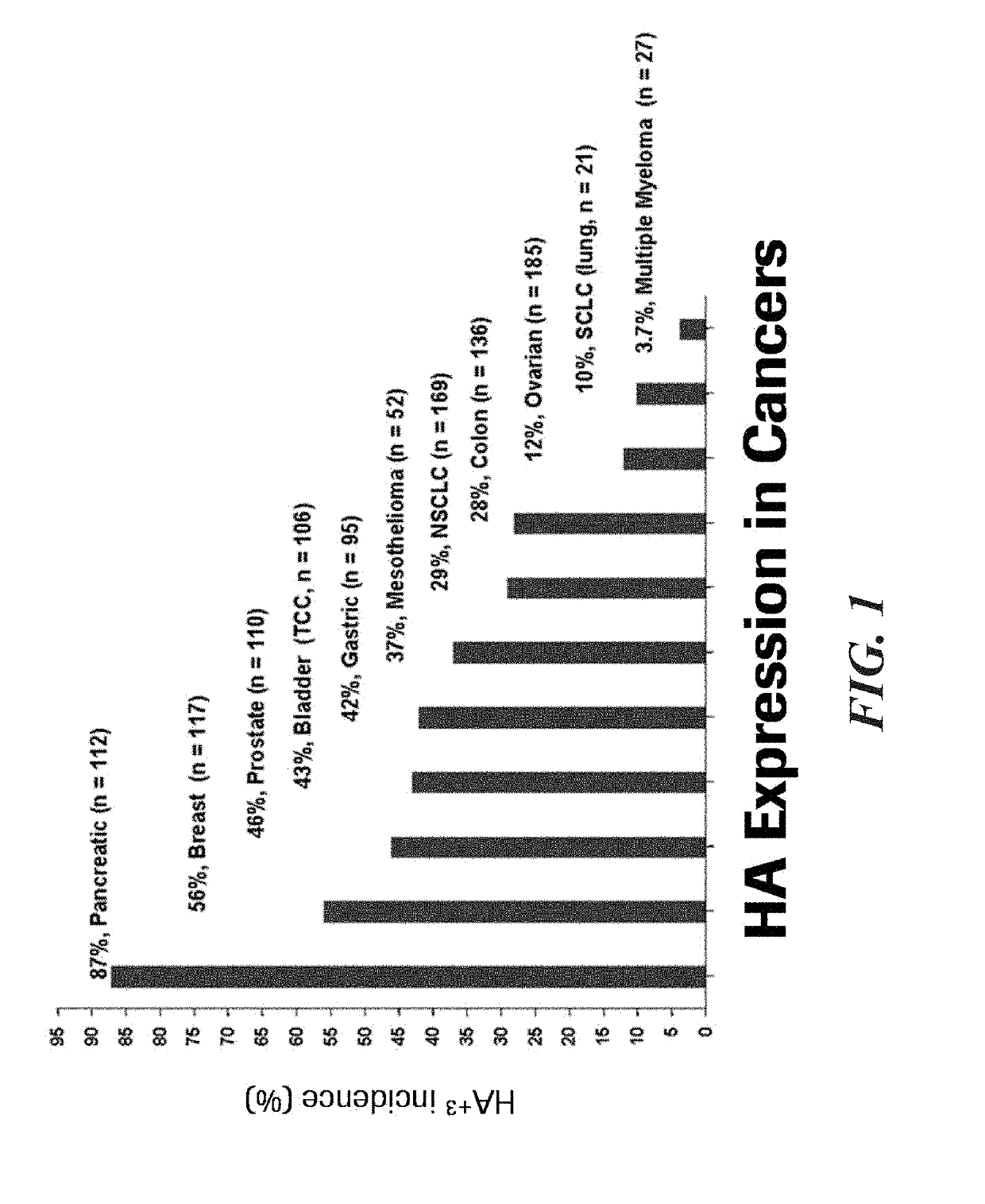
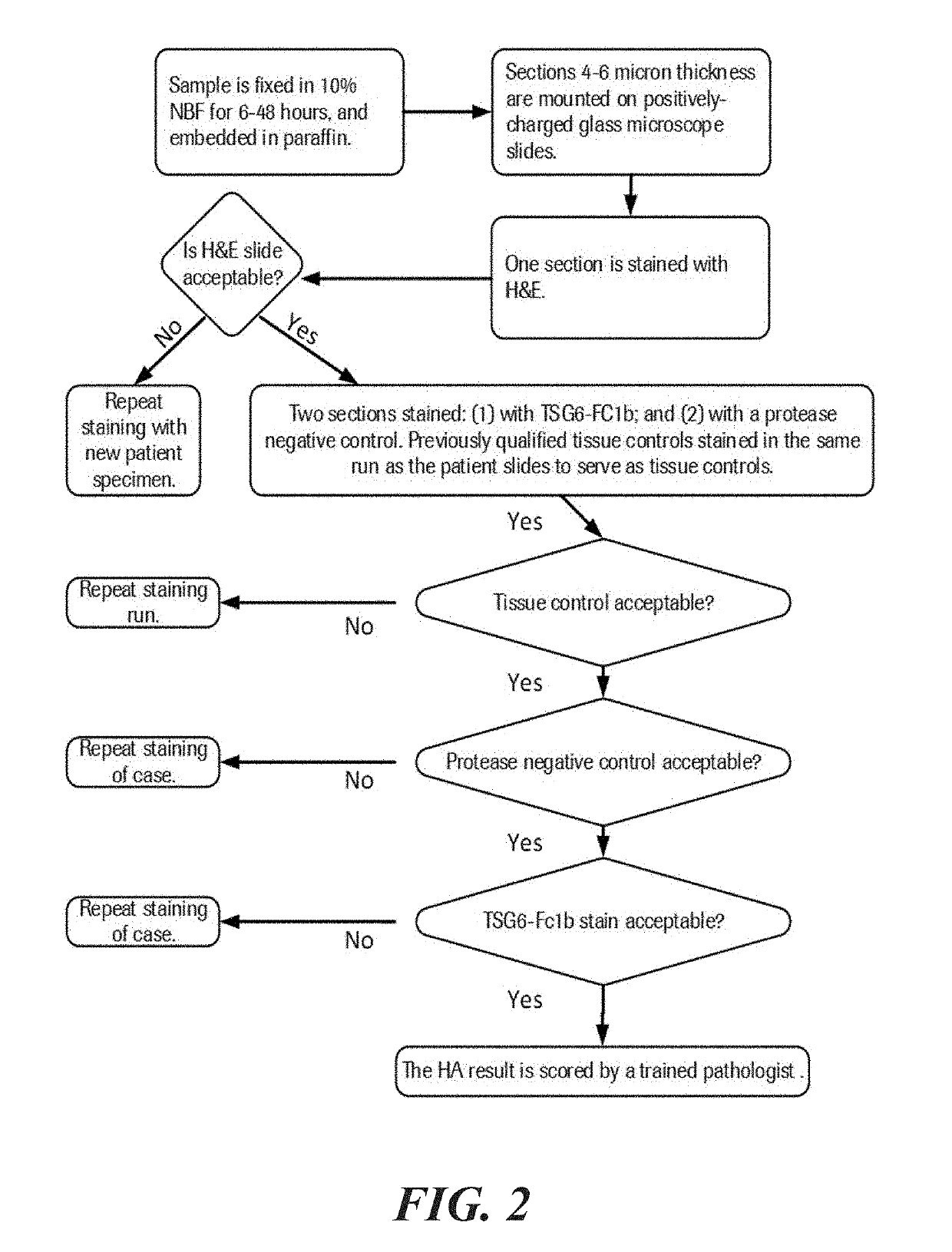
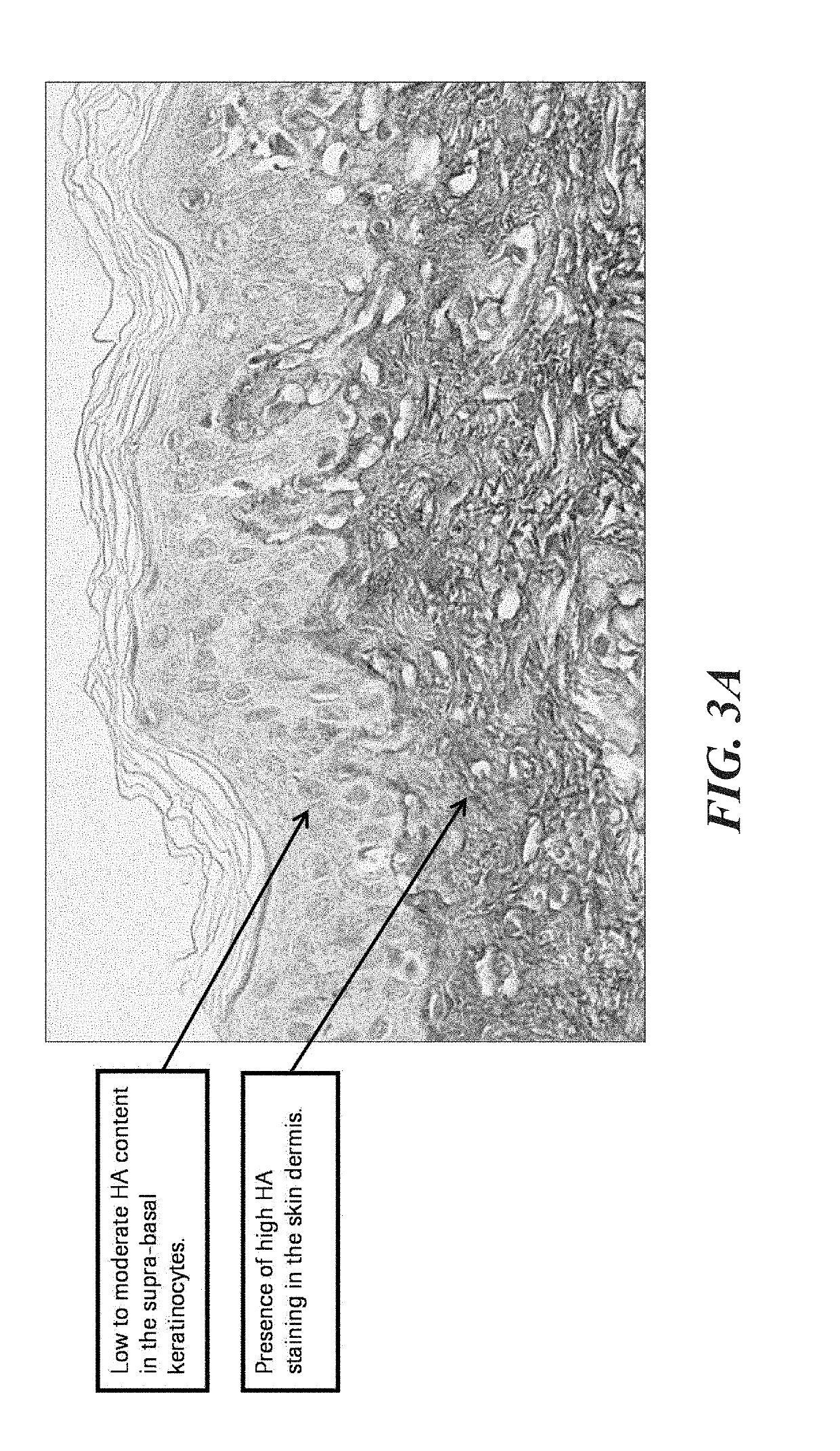
Methods and systems for scoring hyaluronan-stained tissue samples by assessing the area of tumor-associated extracellular matrix (ECM) with hyaluronan staining compared to the entire surface area of the relevant portion of the sample. The methods and systems of the present disclosure may be used to, for example, to select patients for receipt of specific treatments.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Simultaneous dehydration and staining of tissue for deep imaging
A biopsy-sized tissue sample is stained for quick imaging. A significant amount of permeation enhancer is included in a mixed solution of permeant enhancer, fixative or dehydrant, and one or two fluorescent dyes to simultaneously dehydrate and dye the tissue sample. The permeation enhancer, e.g., 10% to 50% in the mixed solution, achieves an image of dyed tissue in the contacted tissue sample at a depth of at least 200 um within no more than 1.5 hours. One of the fluorescent dyes is a fluorescent nuclear dye such as DAPI, SYTOX green, acridine orange, propidium iodide, or a Hoechst dye. The other fluorescent dye is a fluorescent protein dye such as eosin or rhodamine B. The tissue sample is cleared with a clearing agent having a refractive index of at least 1.4[R2], e.g., using BABB. The mixed solution may further include Chloroform or other morphology preservative.
Owner:APPLIKATE TECH INC
Method for analyzing tissue specimens
ActiveUS20200388031A1Improve performanceReliable diagnostic reportImage enhancementImage analysisFluoProbesDisease
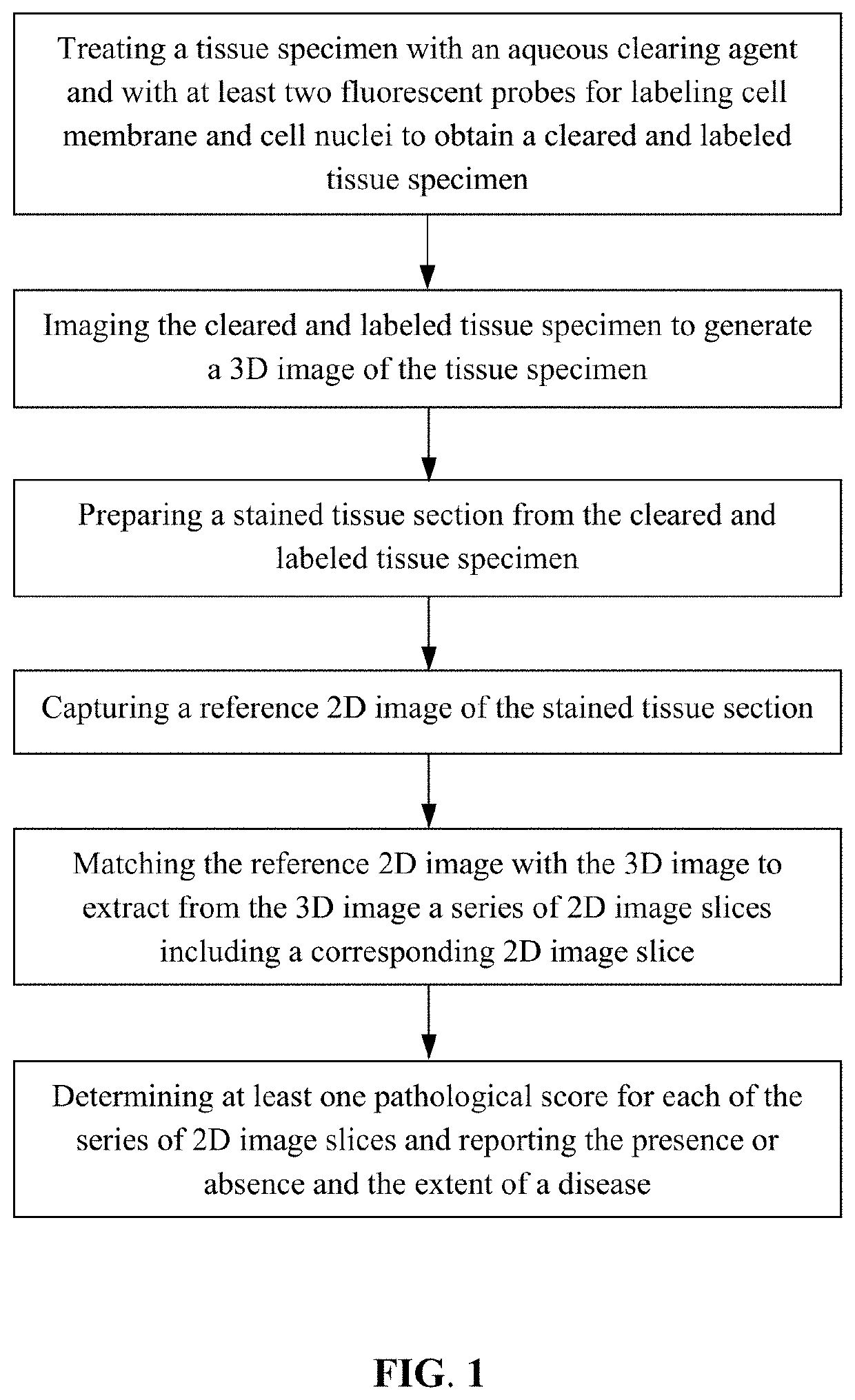
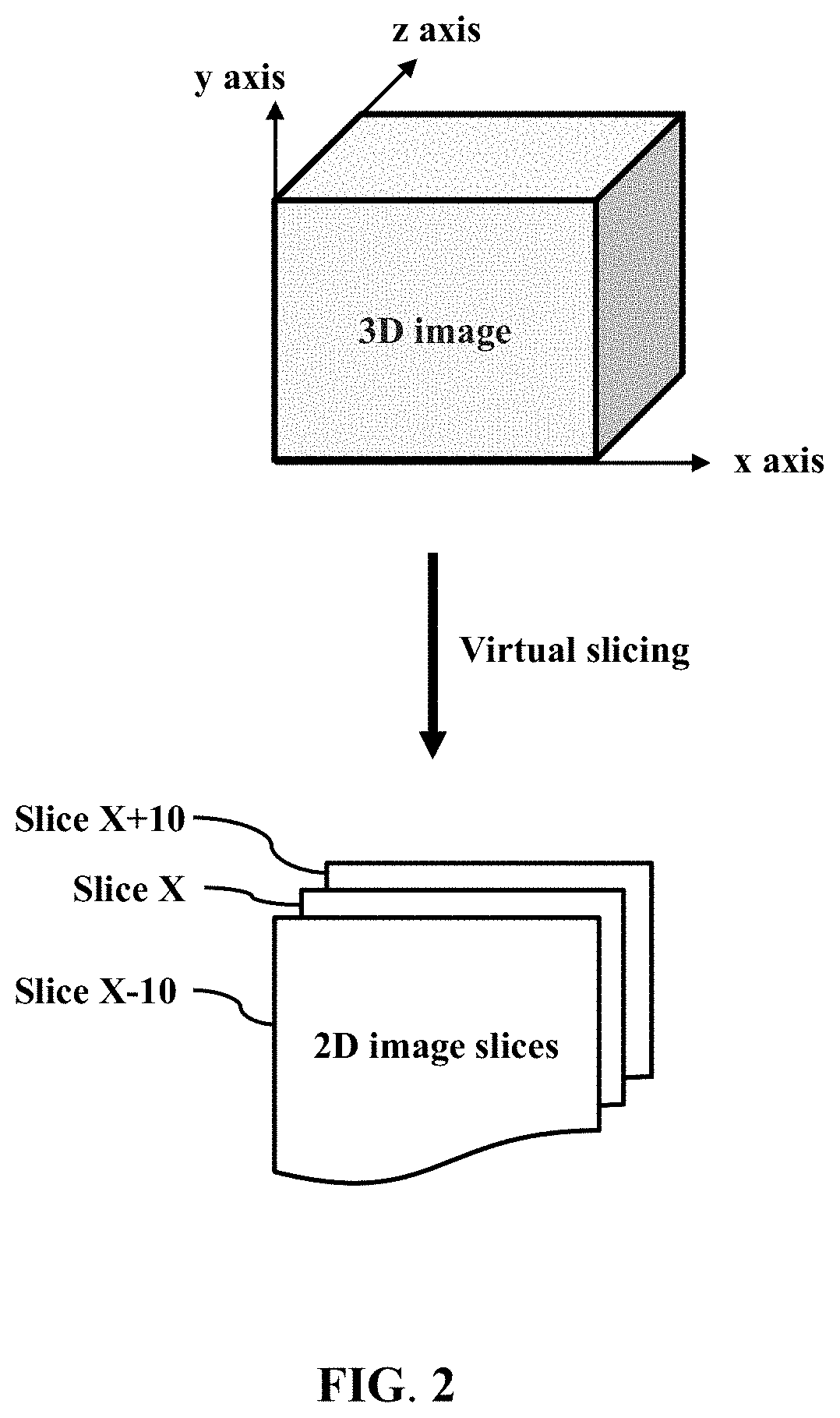
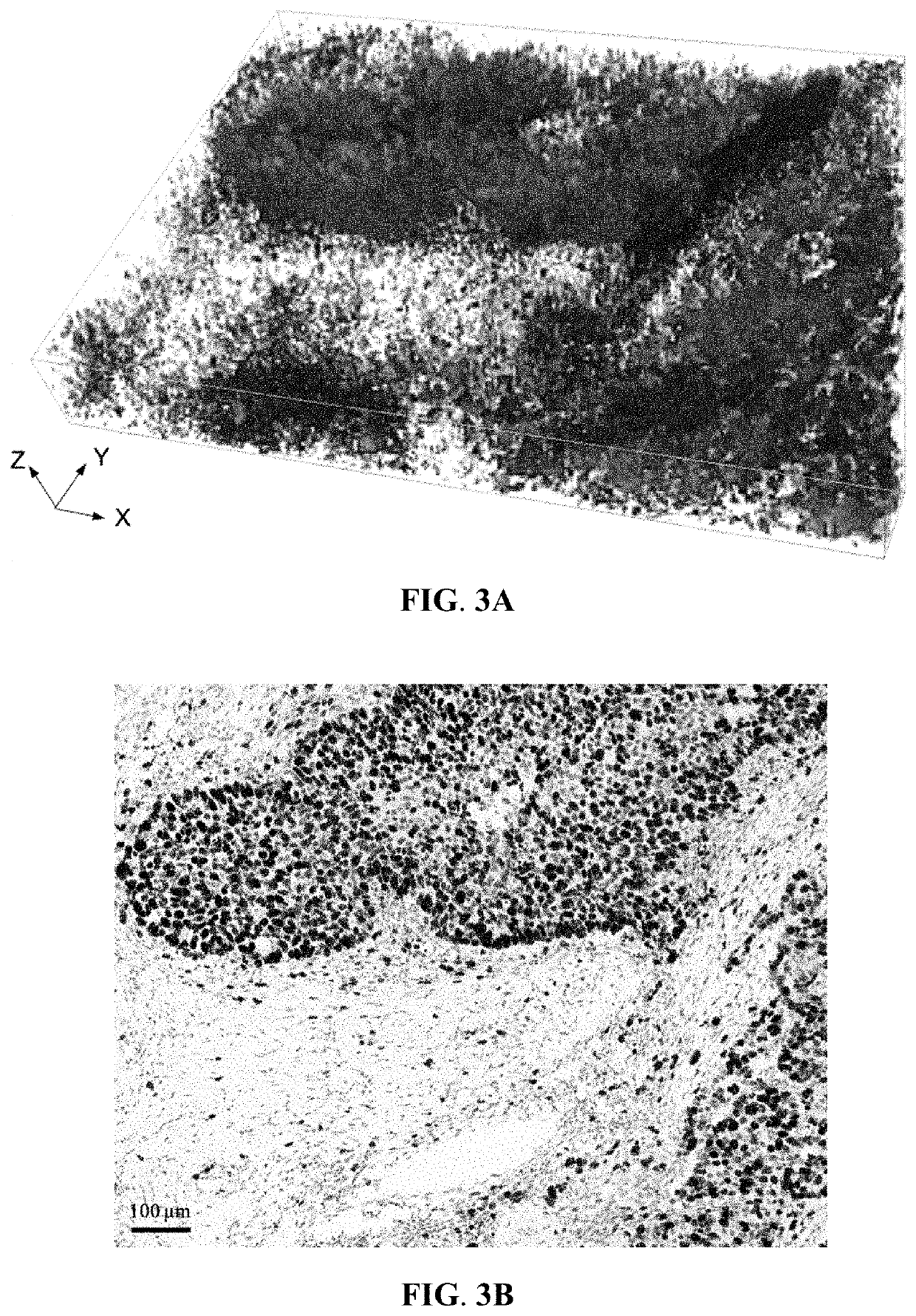
Provided is a method for analyzing a tissue specimen, including treating a tissue specimen with an aqueous clearing agent and with at least two fluorescent probes to obtain a cleared and labeled tissue specimen; imaging the cleared and labeled tissue specimen to generate a three-dimensional (3D) image of the tissue specimen; preparing a stained tissue section from the cleared and labeled tissue specimen; capturing a reference two-dimensional (2D) image of the stained tissue section; matching the reference 2D image with the 3D image to extract from the 3D image a series of 2D image slices including a corresponding 2D image slice that corresponds to the reference 2D image; and determining at least one pathological score for each of the series of 2D image slices and reporting the presence or absence and the extent of the disease based on the pathological scores. The method can improve the accuracy of histopathologic diagnosis.
Owner:JELLOX BIOTECH INC
Analysis method and system for early hepatocellular carcinoma postoperative recurrence prognosis based on artificial intelligence (AI)
ActiveCN113591919AImprove accuracyImprove forecast accuracyImage enhancementMedical data miningEarly Hepatocellular CarcinomaEosin
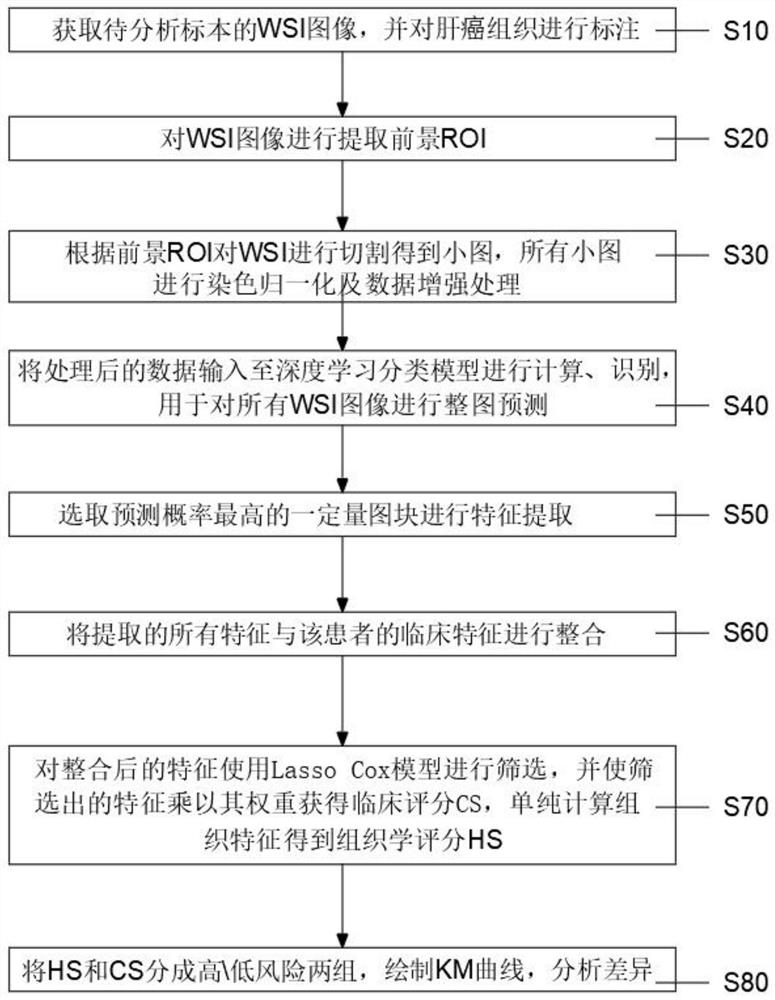
The invention relates to the technical field of prognosis intelligent algorithms, in particular to an analysis method and system for early hepatocellular carcinoma postoperative recurrence prognosis based on artificial intelligence (AI). The early hepatocellular carcinoma postoperative recurrence risk and prognosis are predicted through a complete digital hematoxylin-eosin staining (HE) staining tissue pathological section, and the method comprises the specific steps that a full-view digital section (WS I) image of a specimen to be analyzed is obtained; a foreground region of interest (ROI) is extracted from the WS I image; according to the invention, different areas of the digital pathological image are identified through deep learning. The early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma postoperative recurrence risk and prognosis are effectively analyzed directly according to the HE staining section, the accuracy is very high while multiple different cell regions are identified, and the invention has great guiding significance for patient recurrence.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
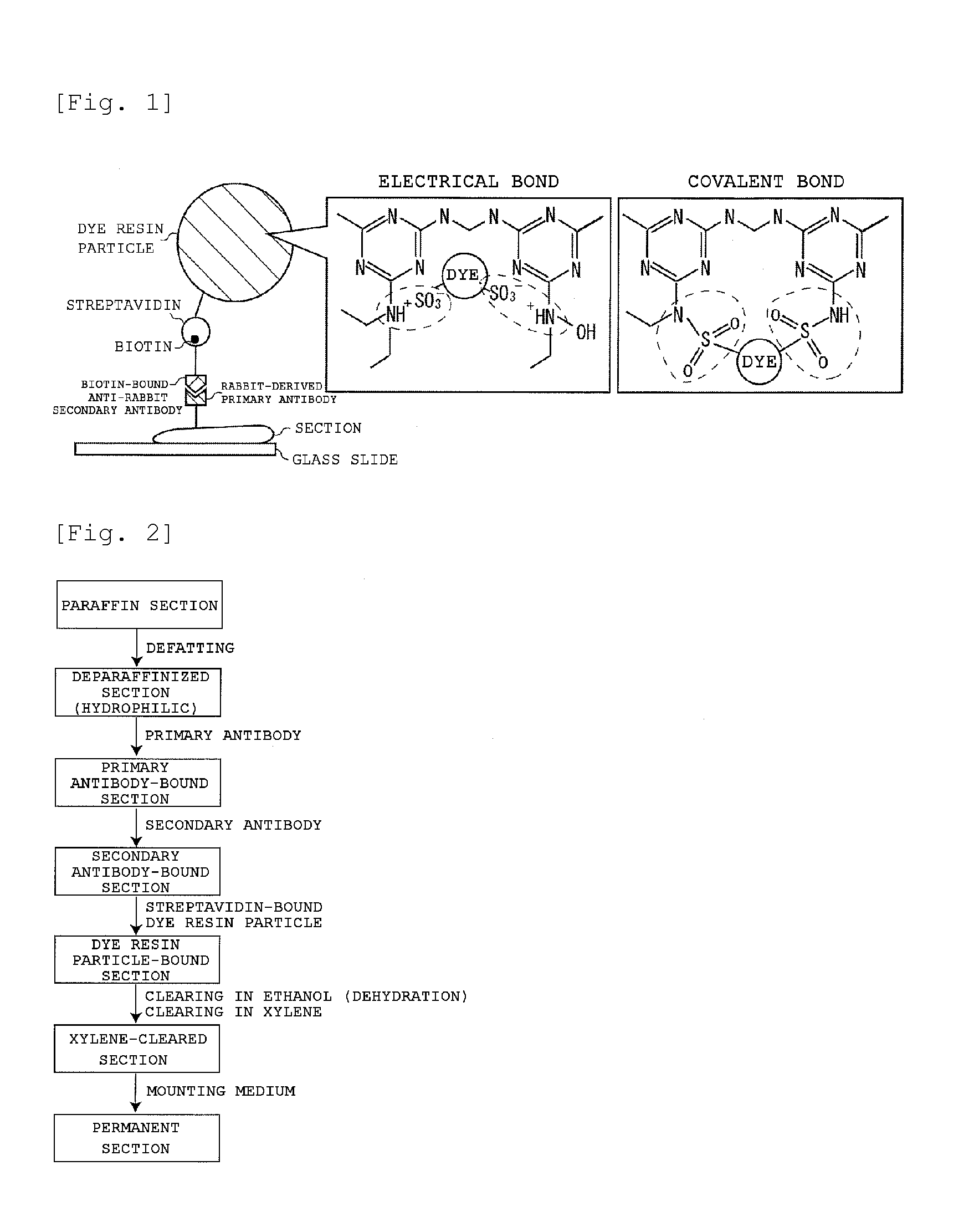
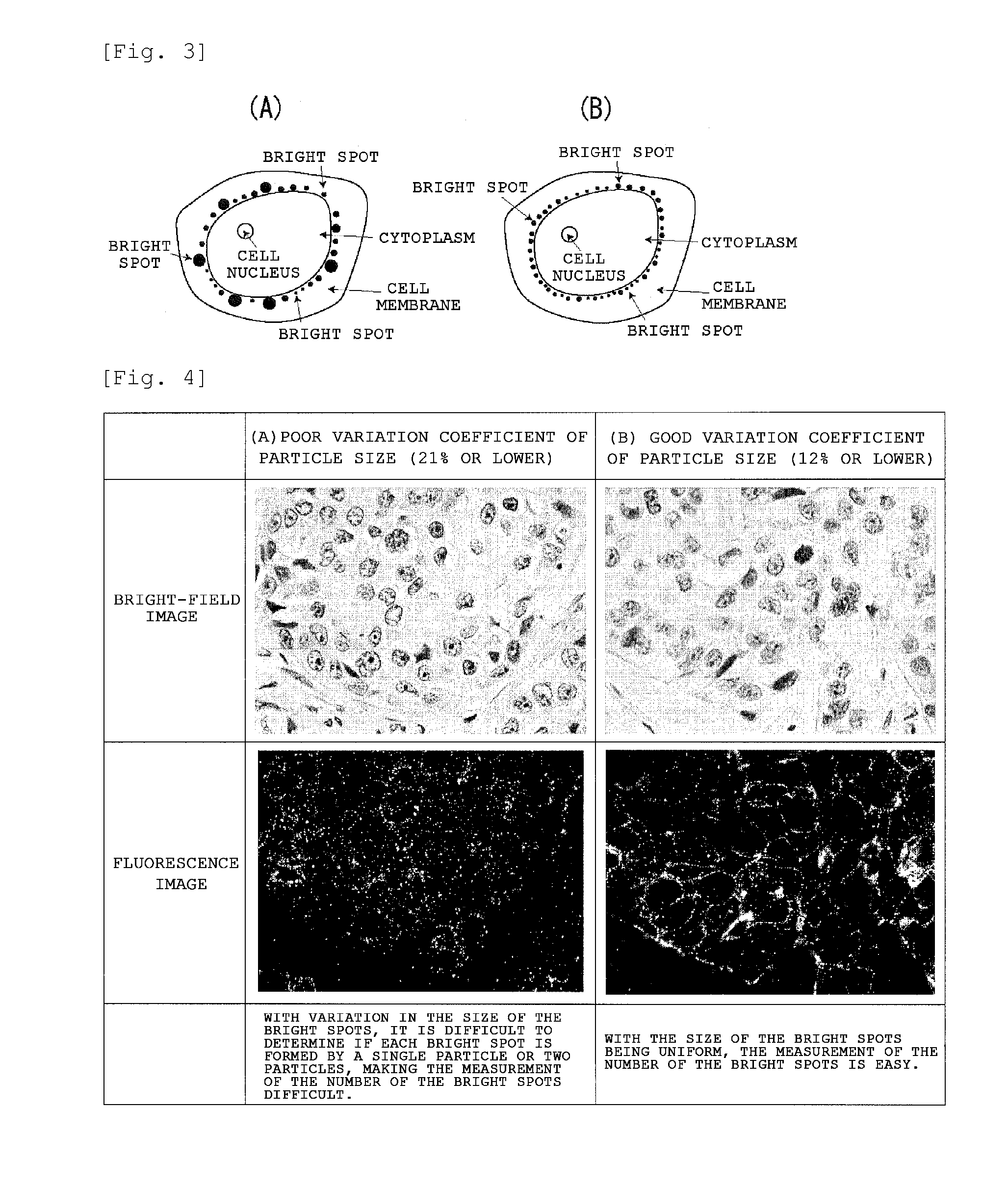
Staining agent for staining tissue, production method for staining agent for staining tissue and tissue staining kit including staining agent for staining tissue
ActiveUS20160018300A1Fluorescent signal enhancementAvoid bleedingPreparing sample for investigationOrganic dyesTissue stainingFluorescence
An object of the present invention is to provide: a staining agent for tissue staining which has an improved fluorescence signal evaluation accuracy; and a tissue staining kit comprising the staining agent. The staining agent for tissue staining contains, as a staining component, dye-resin particles comprising thermosetting resin particles and a fluorescent dye immobilized on the resin particles, wherein the resin particles contains a substituent having an electric charge opposite to that of the fluorescent dye and forms an ionic bond or a covalent bond with the fluorescent dye, and the dye-resin particles have a particle size variation coefficient of 15% or less.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Methods for quantitative assessment of mononuclear cells in muscle tissue sections
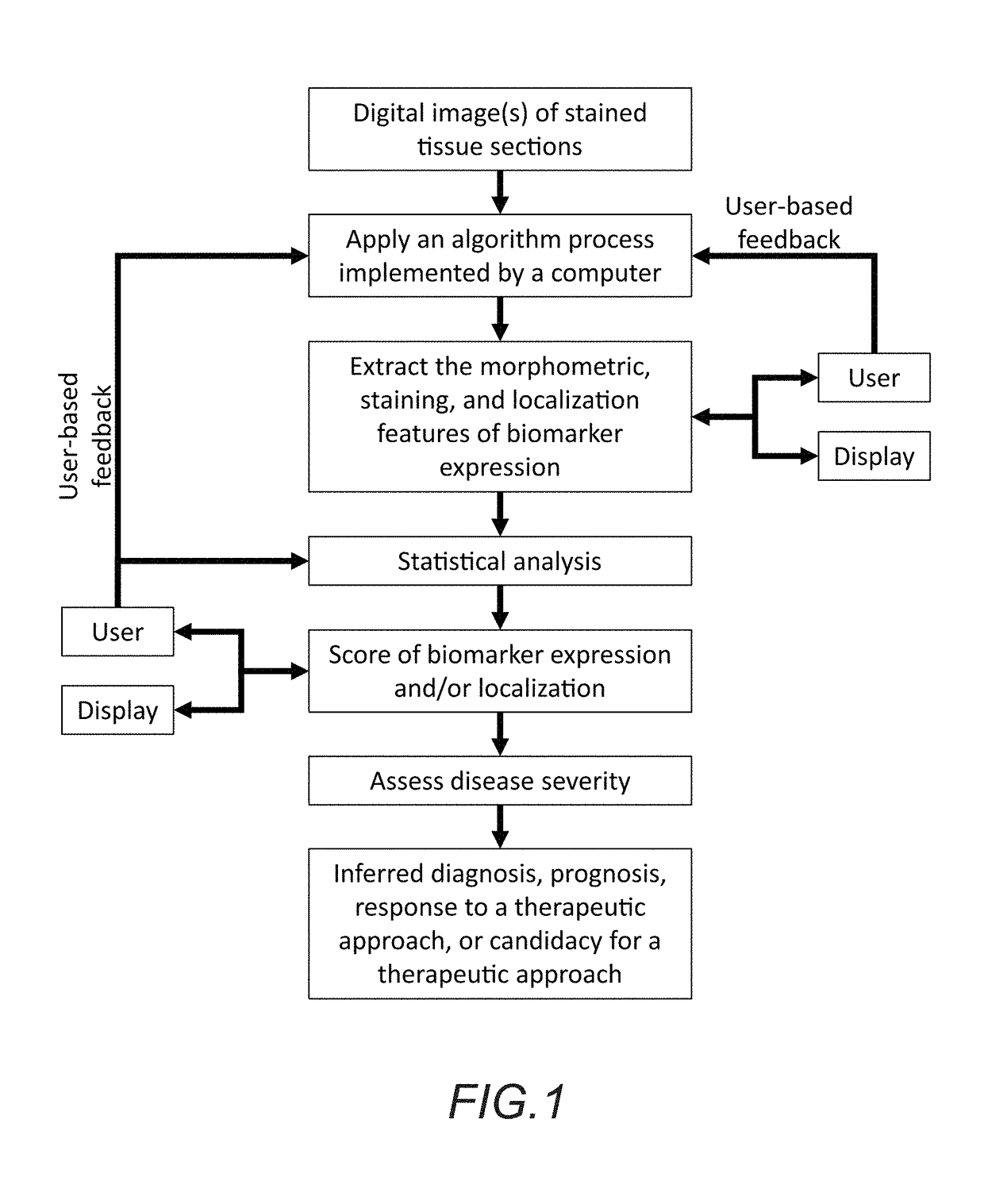
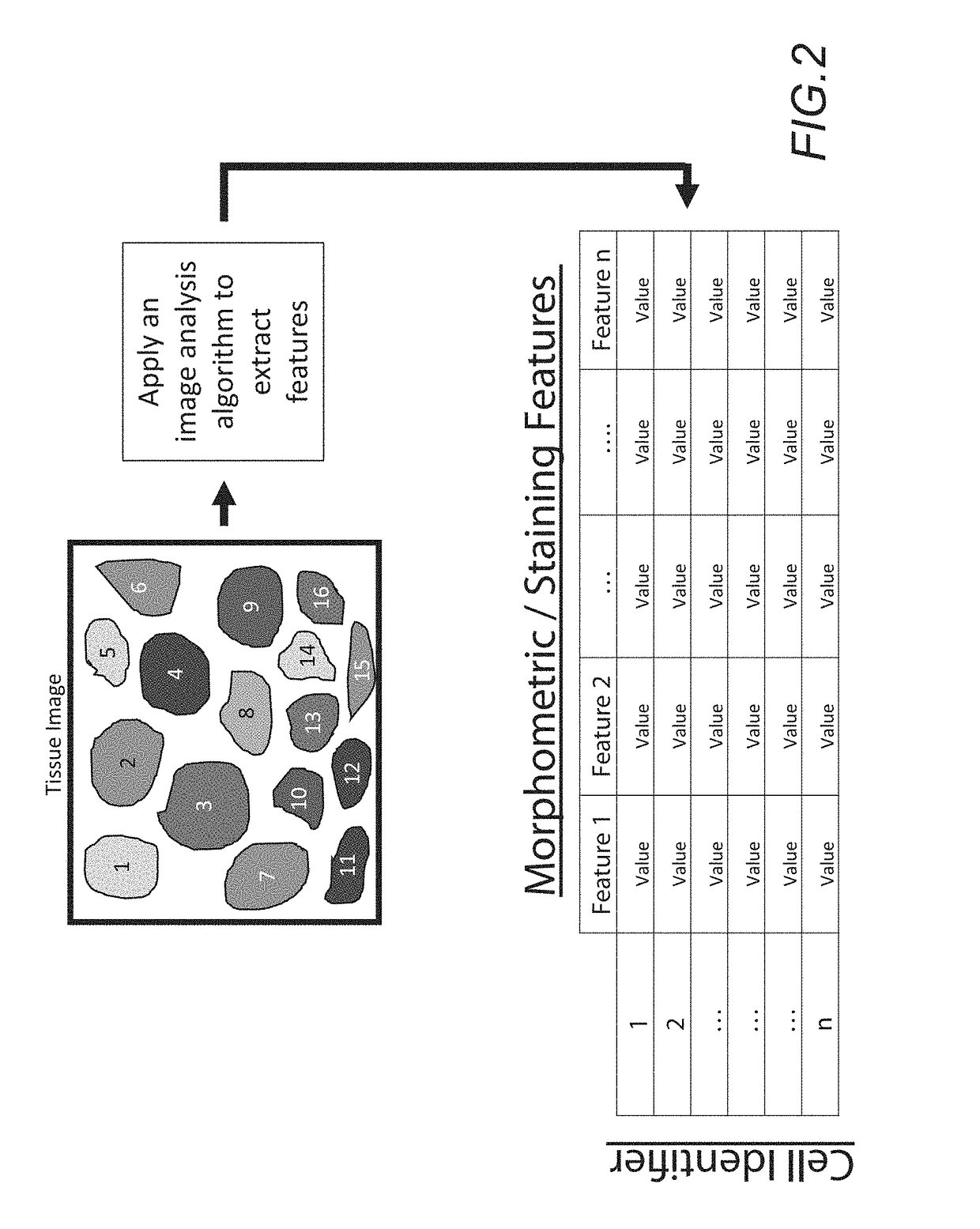
In accordance with the embodiment described herein, we describe a method for evaluating muscle fiber nuclei and non-muscle fiber mononuclear cells, and biomarkers expressed within these and muscle fibers, within the context of muscle tissue using digital tissue image analysis. An algorithm process is applied to histologically stained tissue sections to extract the morphometric, staining, and localization features of a plurality of tissue objects. These features can be further analyzed to describe relationships between tissue objects or tissue object image analysis features. One or more of these image analysis features or relationships between objects and features are summarized to derive a patient-specific score. Patient stratification criteria are applied to the patient-specific score and patient strata membership is evaluated to infer presence of disease, natural course of disease, disease severity, treatment efficacy, or response to a therapy and eligibility for said therapy.
Owner:FLAGSHIP BIOSCI
Method for staining tissue
ActiveUS20150064717A1High quantitativityImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansTissue stainingFluorescence
Provided is a method for staining a tissue enabling highly precise staining, by which the expression amount and / or the location of a biological substance in a tissue sample can be detected with a high quantitativity together with detailed information that can be obtained by bright field observation.The tissue staining method of the present invention is a method for staining a tissue, in which both staining that allows bright field observation and fluorescence staining are carried out for the same specific biological substance.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Systems and methods for multiplexed biomarker quantitation using single cell segmentation on sequentially stained tissue
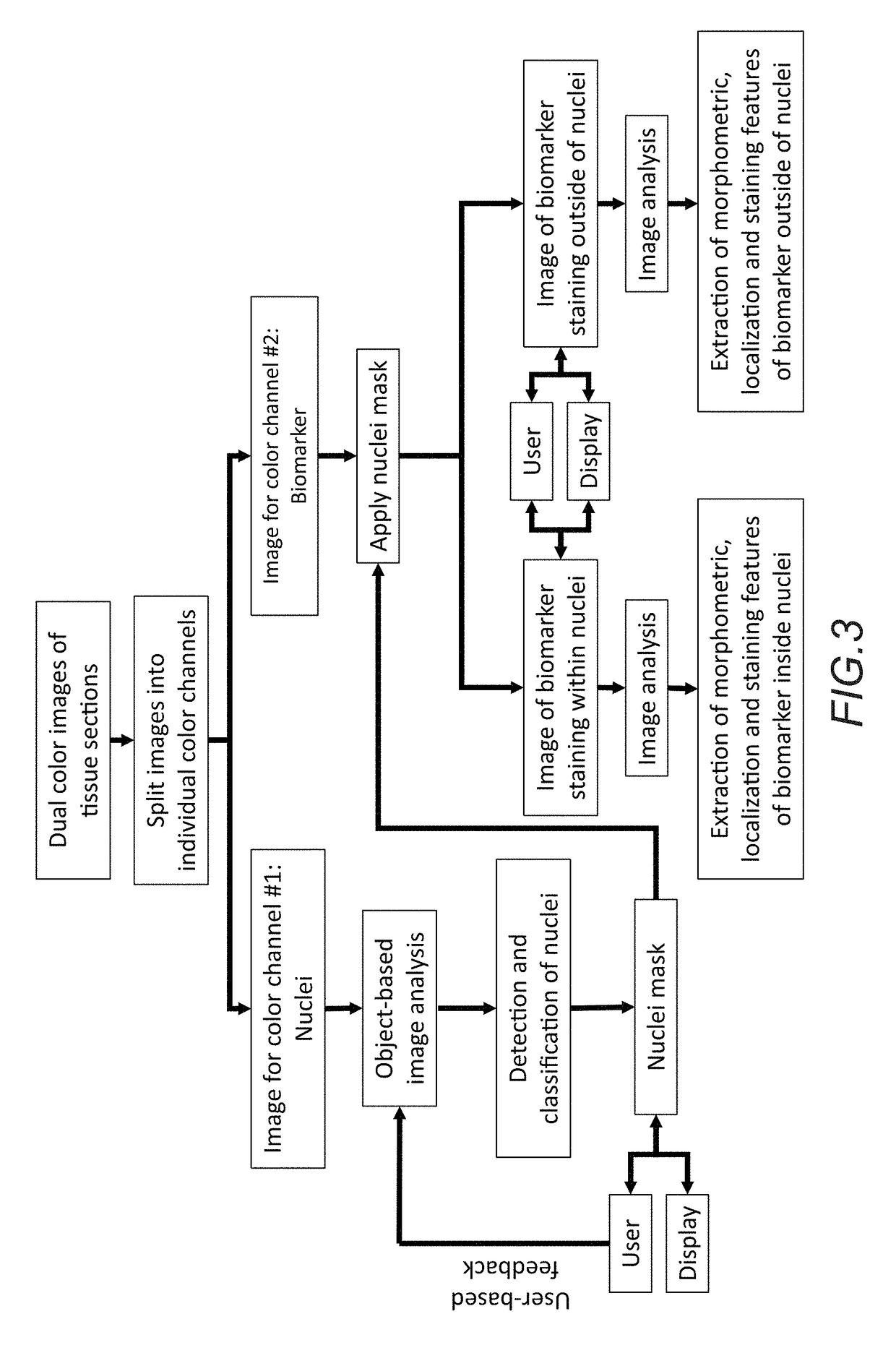
Improved systems and methods for the analysis of digital images are provided. More particularly, the present disclosure provides for improved systems and methods for the analysis of digital images of biological tissue samples. Exemplary embodiments provide for: i) segmenting, ii) grouping, and iii) quantifying molecular protein profiles of individual cells in terms of sub cellular compartments (nuclei, membrane, and cytoplasm). The systems and methods of the present disclosure advantageously perform tissue segmentation at the sub-cellular level to facilitate analyzing, grouping and quantifying protein expression profiles of tissue in tissue sections globally and / or locally. Performing local-global tissue analysis and protein quantification advantageously enables correlation of spatial and molecular configuration of cells with molecular information of different types of cancer.
Owner:莱卡微系统 CMS +1
Method for stratifying and selecting candidates for receiving a specific therapeutic approach
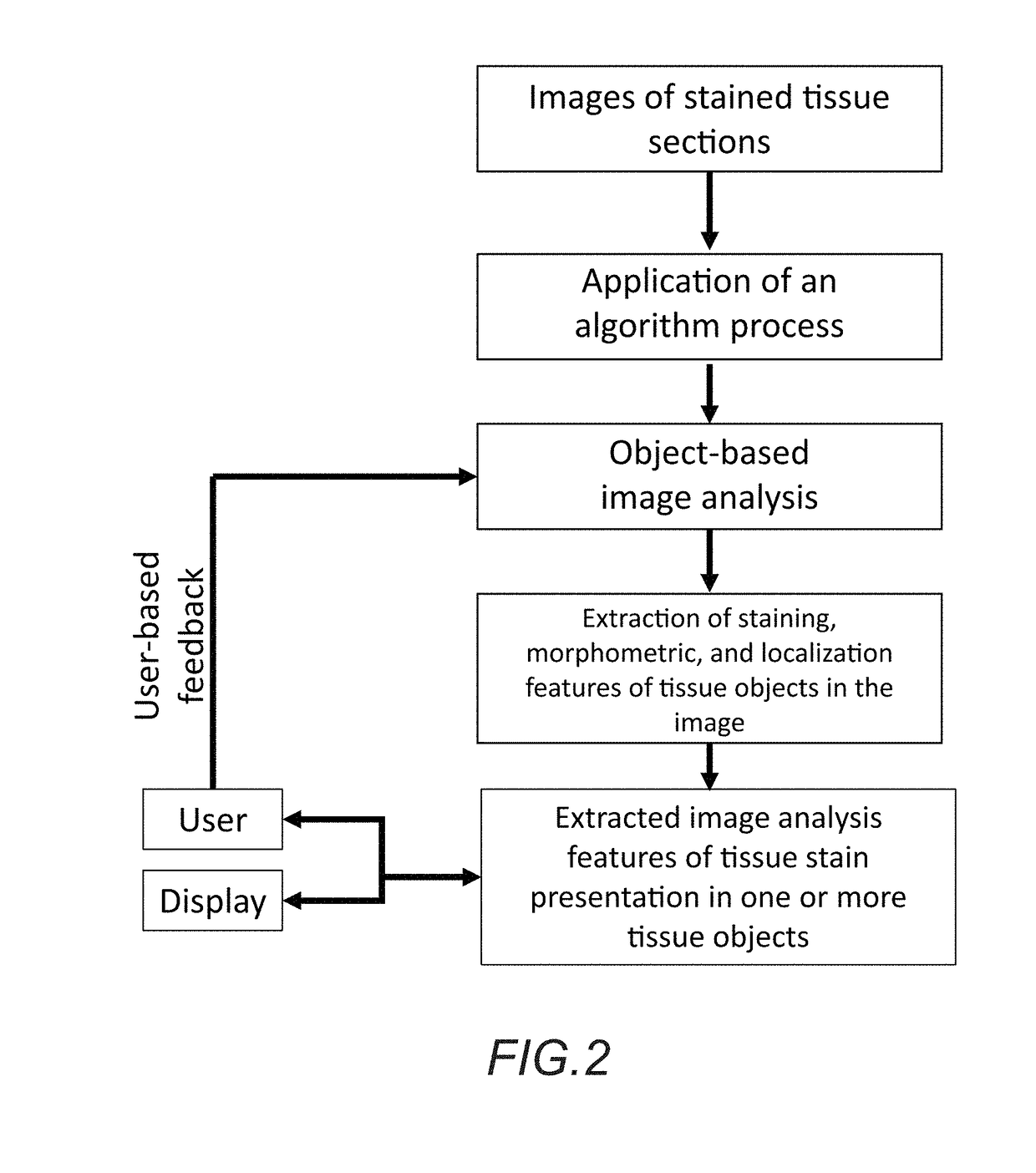
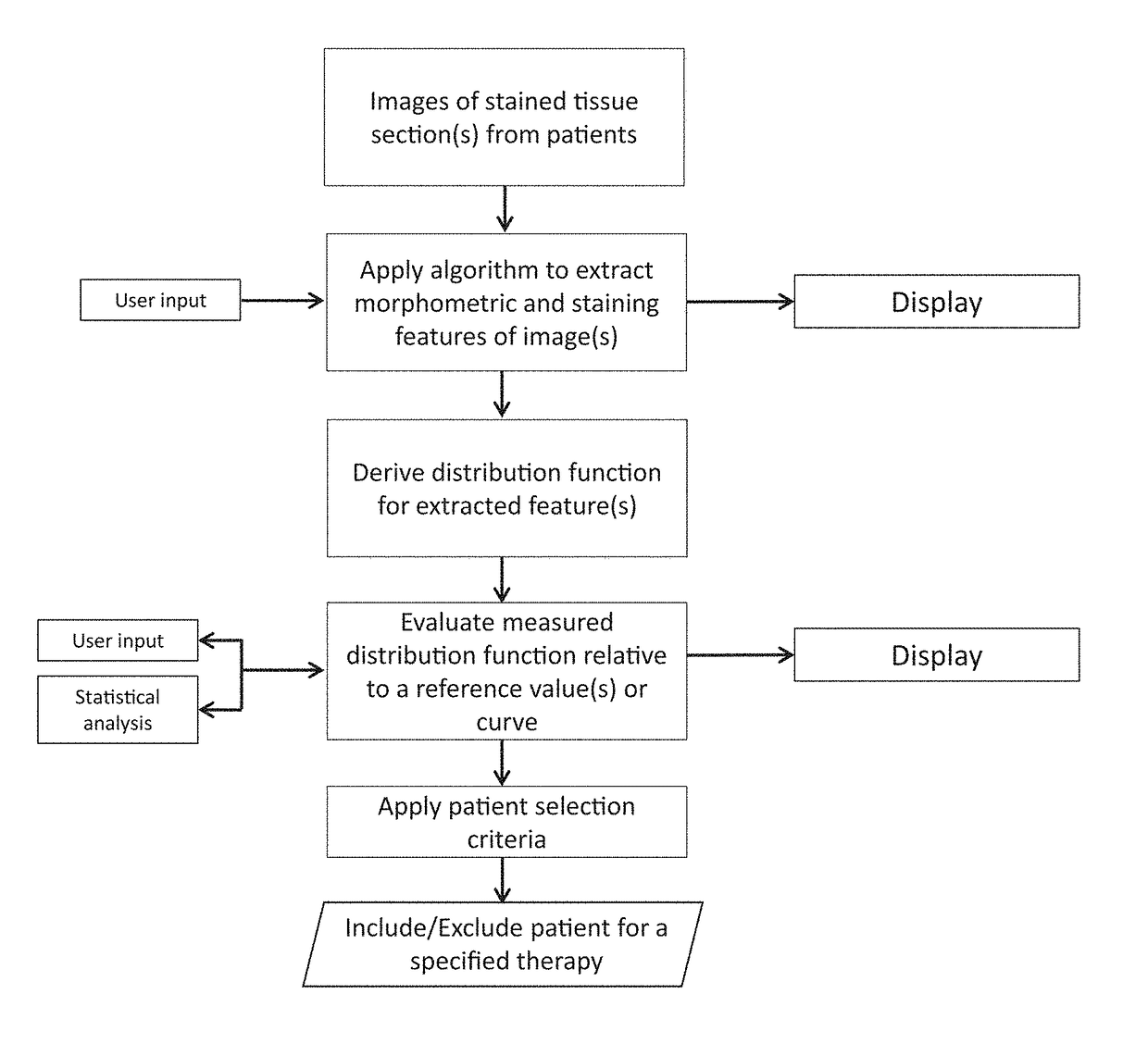
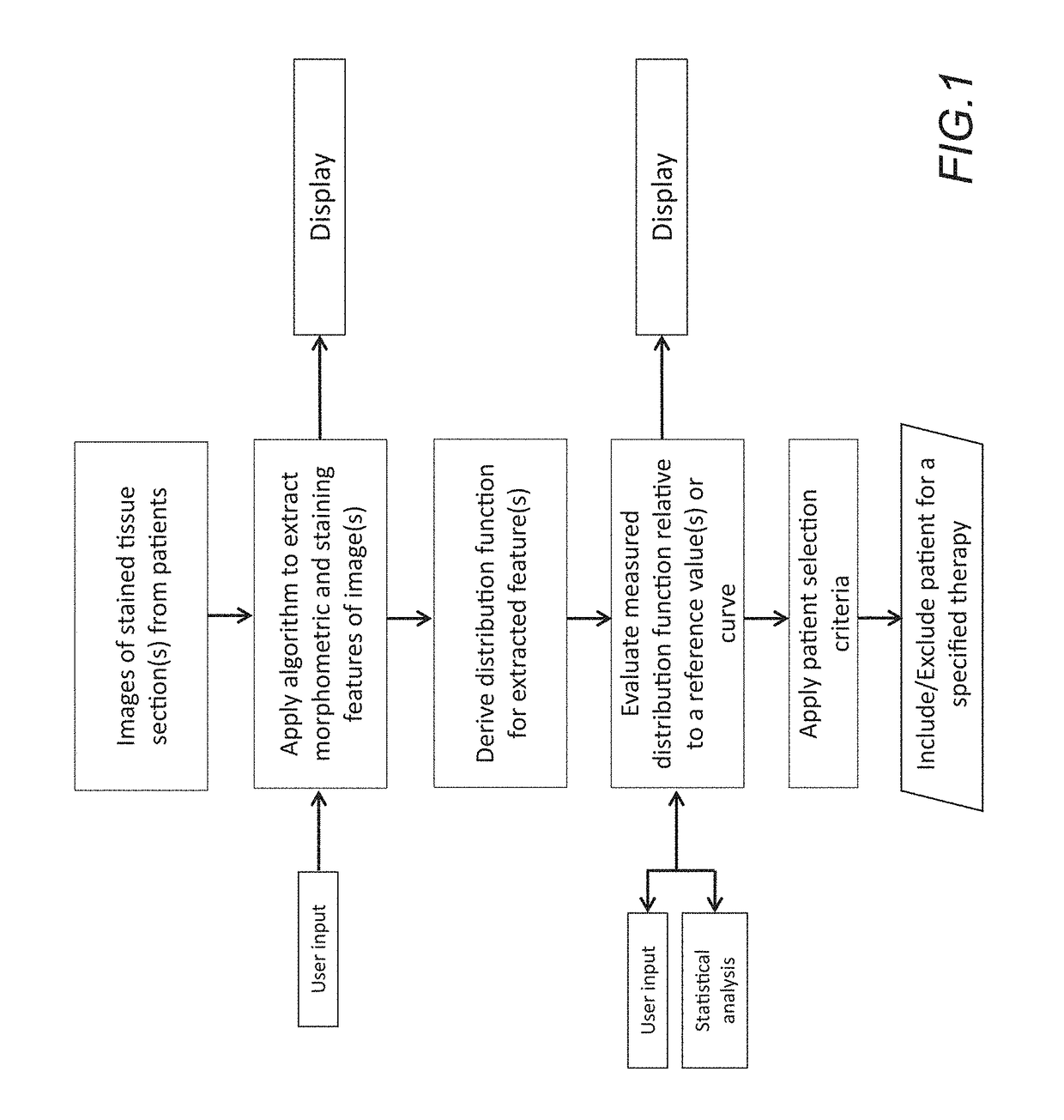
The disclosure concerns a method for patient stratification and selection of patients who are candidates for a specific therapy is described which is based on quantifying one or more digital image analysis feature distributions from stained tissue. The method extends beyond the abilities of a manual observer and a microscope, and generally comprises: acquiring digital images of stained tissue sections from patients submitted for evaluation, applying an algorithm process to said images with a computer to extract the morphometric and staining features of image pixels and tissue objects, deriving one or more distribution function for one or more image analysis features, calculating a summary statistic of the one or more distribution functions, and using said summary statistic along with an associated predefined patient stratification paradigm to separate a patient cohort into distinct strata which correspond to a decision to include or exclude a patient for a specific therapy.
Owner:FLAGSHIP BIOSCI
Sectionable cassette and embedding frame with tissue immobilizing separable lid, and methods for preparing biopsy tissue samples
A histologic tissue sample support device (200) includes a tissue cassette (112), a frame (14), and a lid (118"). The tissue cassette (112) has a recess (112b) including a body (112a) with at least one side wall and a bottom wall (112c) and is formed of material that can be successfully sectioned in a microtome and is resistant to degradation from solvents and chemicals used to fix, process and stain tissue. The tissue cassette (112) is movably coupled to the frame (14). The lid (118") is separably coupled to a peripheral portion (16) of the frame (14). When the lid (118") is separated from the peripheral portion (16), the lid (118") and the tissue cassette (112) are capable of moving from a first position to a second position with respect to the frame (14), and in the second position thebottom wall (112c) and at least a portion of the side wall extend beyond a bottom edge of the frame (14) for sectioning in the microtome.
Owner:BIOPATH AUTOMATION
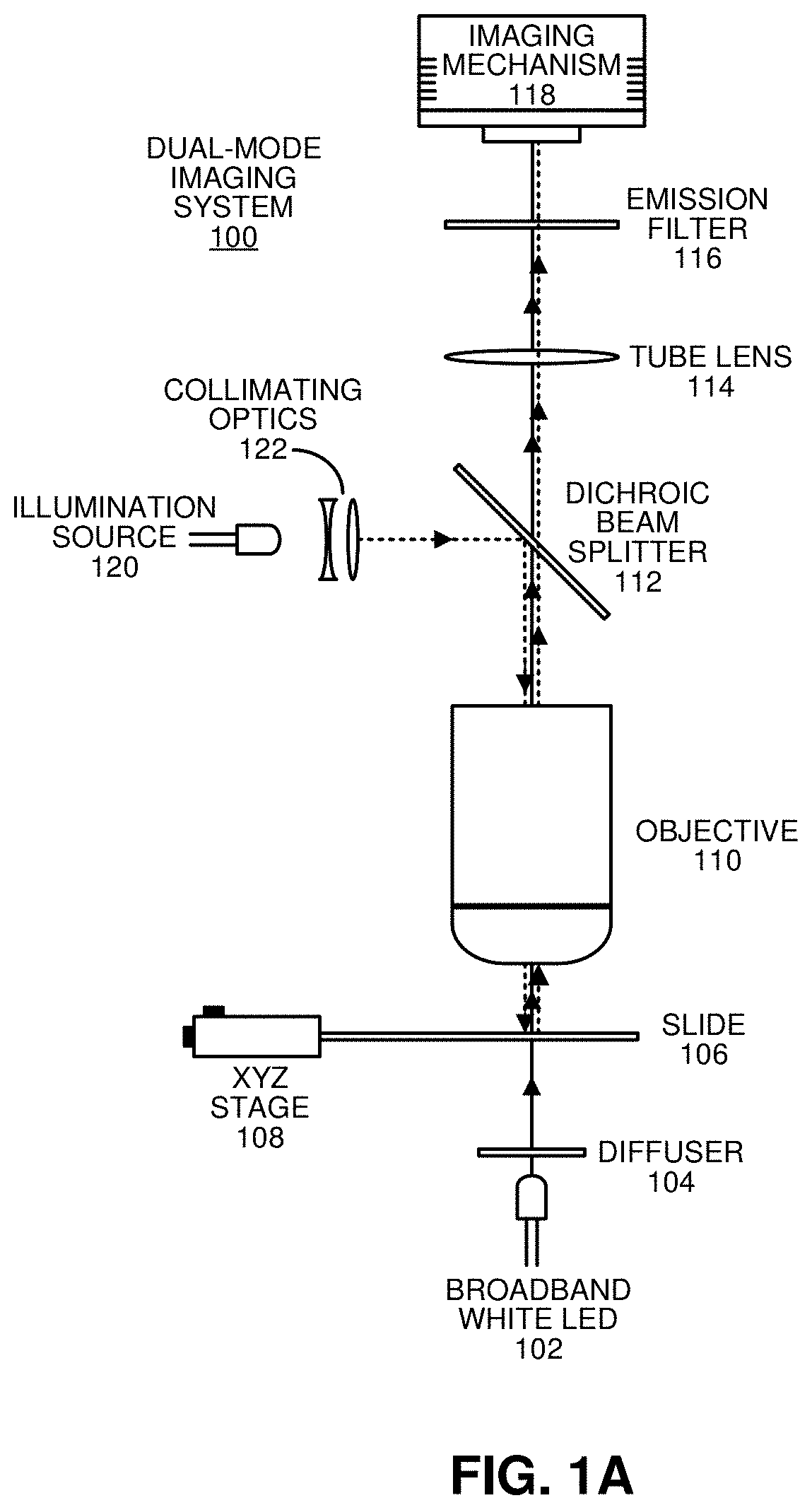
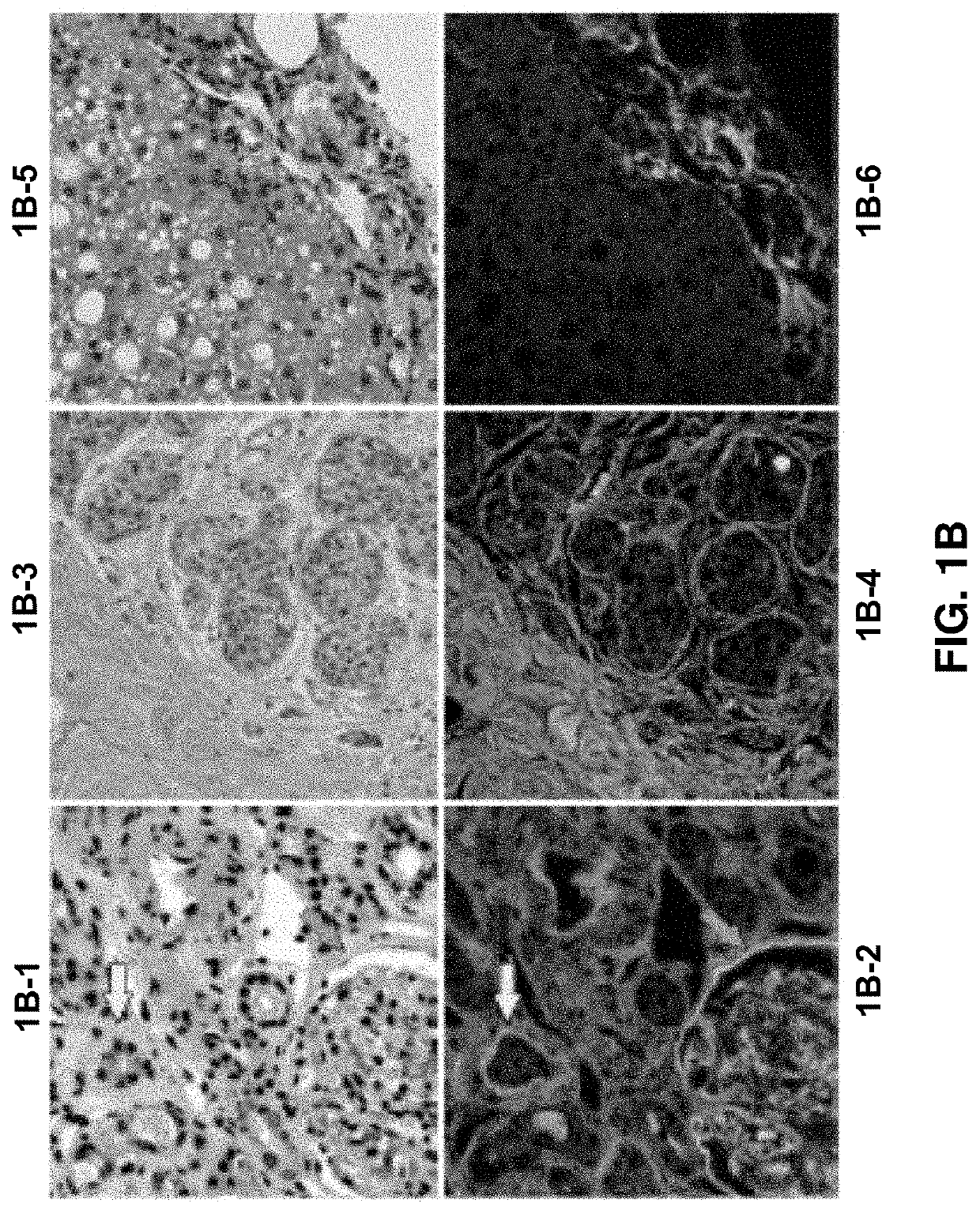
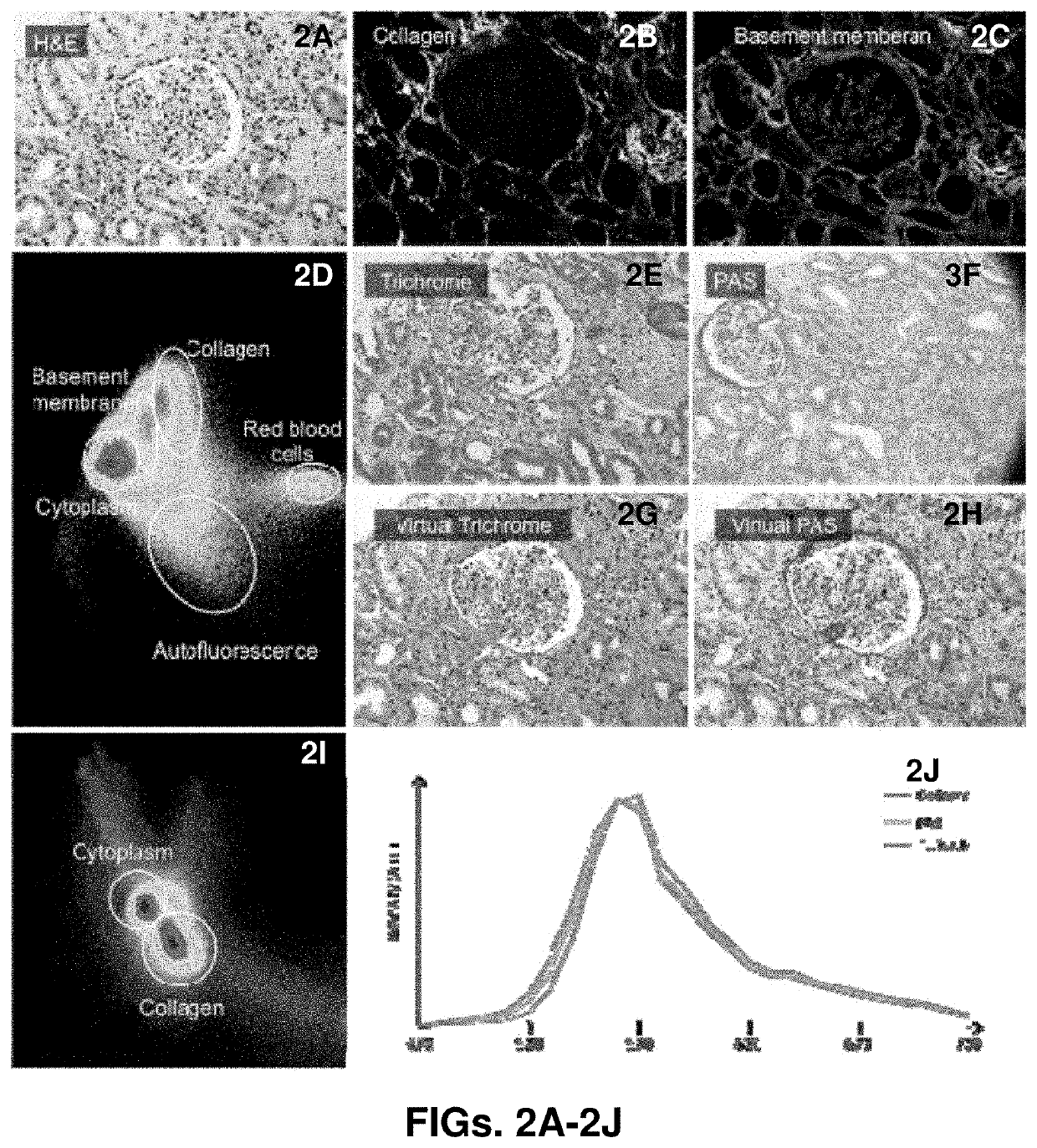
Producing a composite image of a stained tissue sample by combining image data obtained through brightfield and fluorescence imaging modes
PendingUS20210199582A1Improve image qualityMore informationRaman/scattering spectroscopyPreparing sample for investigationStainingRadiology
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system that produces a composite image of a stained tissue sample by combining image data obtained through brightfield and fluorescence imaging modes. While operating in a brightfield imaging mode, the system illuminates the stained tissue sample with broadband light, and collects image data comprising a brightfield histology image using a multispectral imaging system. While operating in a fluorescence imaging mode, the system illuminates the stained tissue sample with one or more bands of excitation light, and collects image data associated with resulting fluorescence emissions using the multispectral imaging system. Next, the system processes the image data collected during the brightfield and / or fluorescence imaging modes. Finally, the system combines the image data collected during the brightfield and fluorescence imaging modes to produce the composite image.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
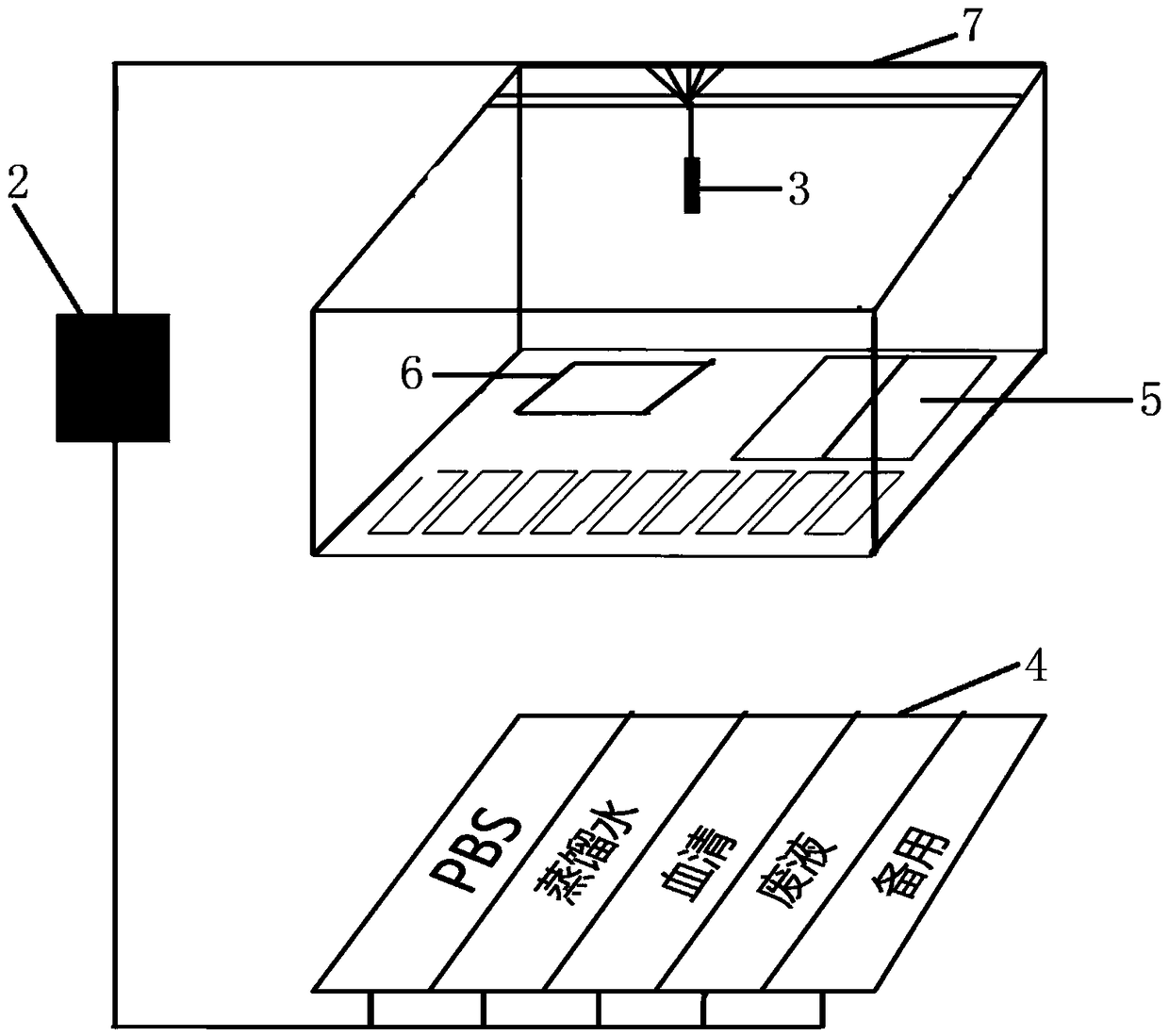
Frozen section immunohistochemical automatic stainer
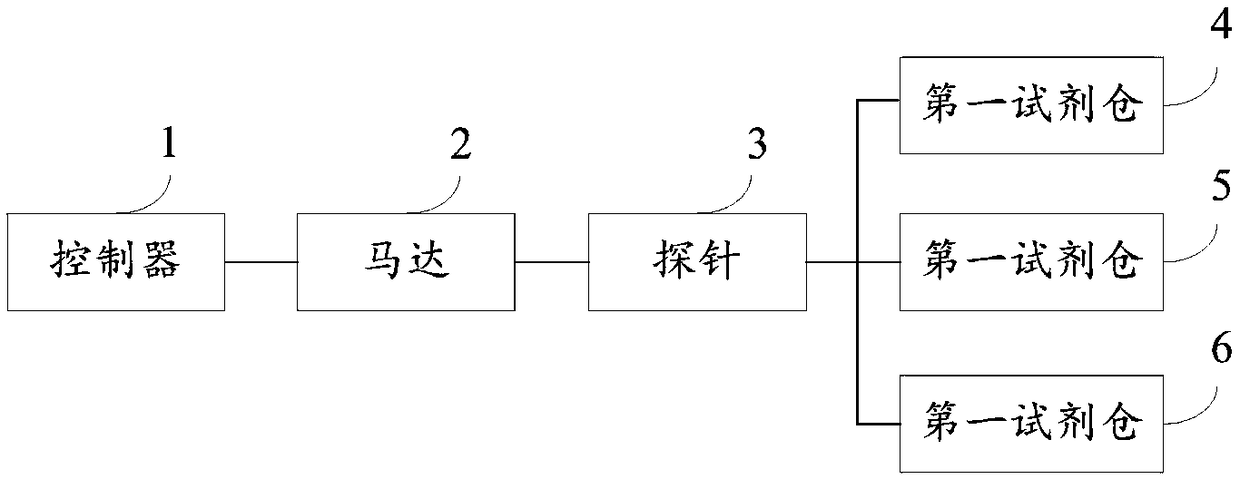
PendingCN109283032AReduce volumeSmall footprintPreparing sample for investigationStainingEngineering
The invention discloses a frozen section immunohistochemical automatic stainer. The stainer comprises a controller, a motor, a probe, a pipeline, a first reagent bin, a second reagent bin, a third reagent bin, and a mechanical shaft; the controller is used for controlling the probe to move along the mechanical shaft; the controller is further used for controlling the motor to rotate, thereby feeding the liquid in the first reagent bin, the second reagent bin and the third reagent bin into the probe along the pipeline; and the probe is used for spraying the liquid to a to-be-stained tissue section. The timeliness and the stability of the staining technology can be well improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
Methods and systems for scoring extracellular matrix biomarkers in tumor samples
Methods and systems for scoring hyaluronan-stained tissue samples by assessing the area of tumor-associated extracellular matrix (ECM) with hyaluronan staining compared to the entire surface area of the relevant portion of the sample. The methods and systems of the present disclosure may be used to, for example, to select patients for receipt of specific treatments.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
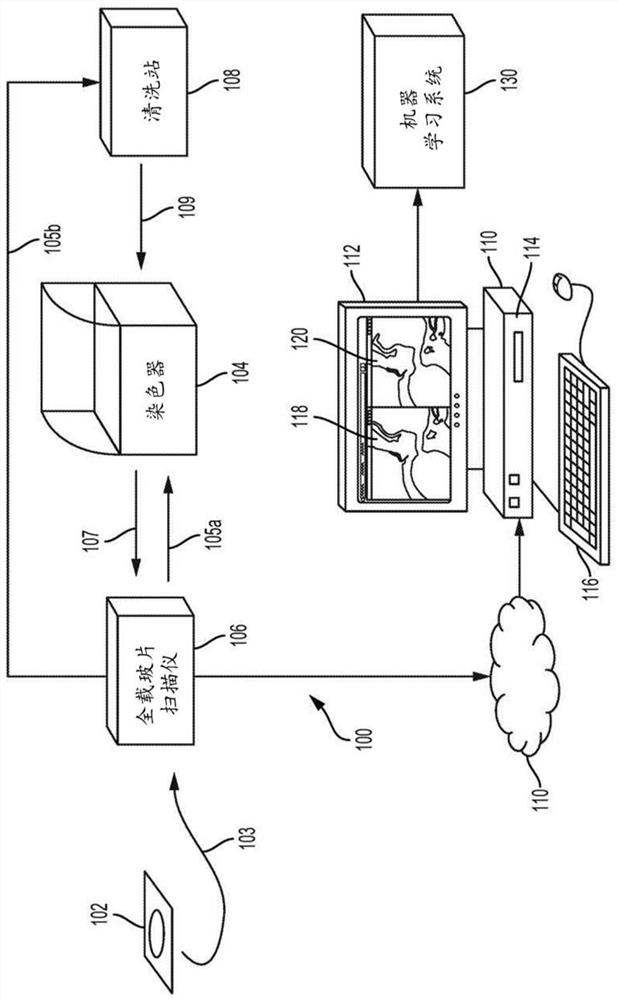
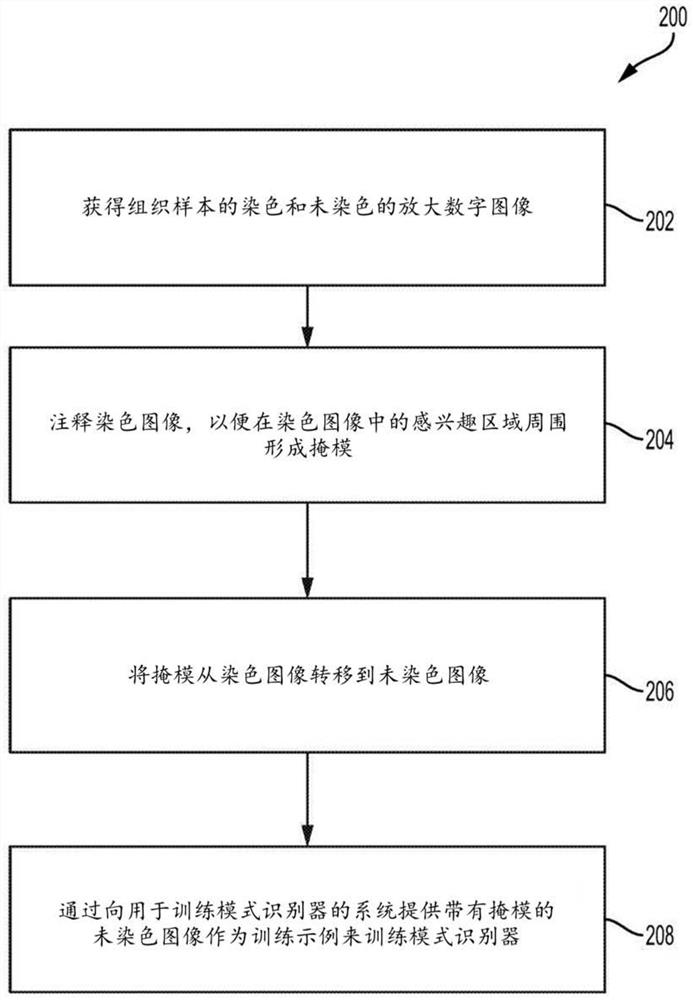
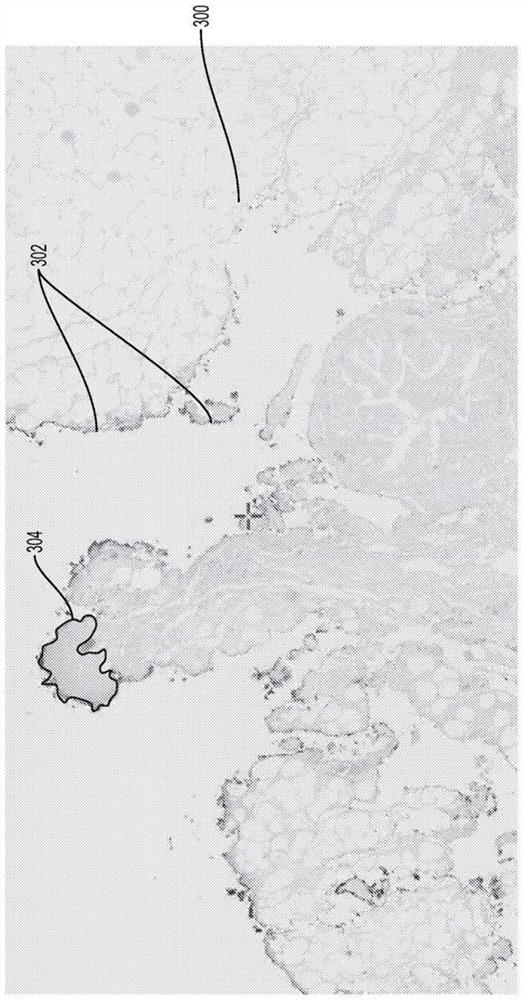
Pathology predictions on unstained tissue
A method for training a pattern recognizer to identify regions of interest in unstained images of tissue samples is provided. Pairs of images of tissue samples are obtained, each pair including an unstained image of a given tissue sample and a stained image of the given tissue sample. An annotation (e.g., drawing operation) is then performed on the stained image to indicate a region of interest. The annotation information, in the form of a mask surrounding the region of interest, is then applied to the corresponding unstained image. The unstained image and mask are then supplied to train a pattern recognizer. The trained pattern recognizer can then be used to identify regions of interest within novel unstained images.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com