Patents
Literature
78results about How to "Significant heating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
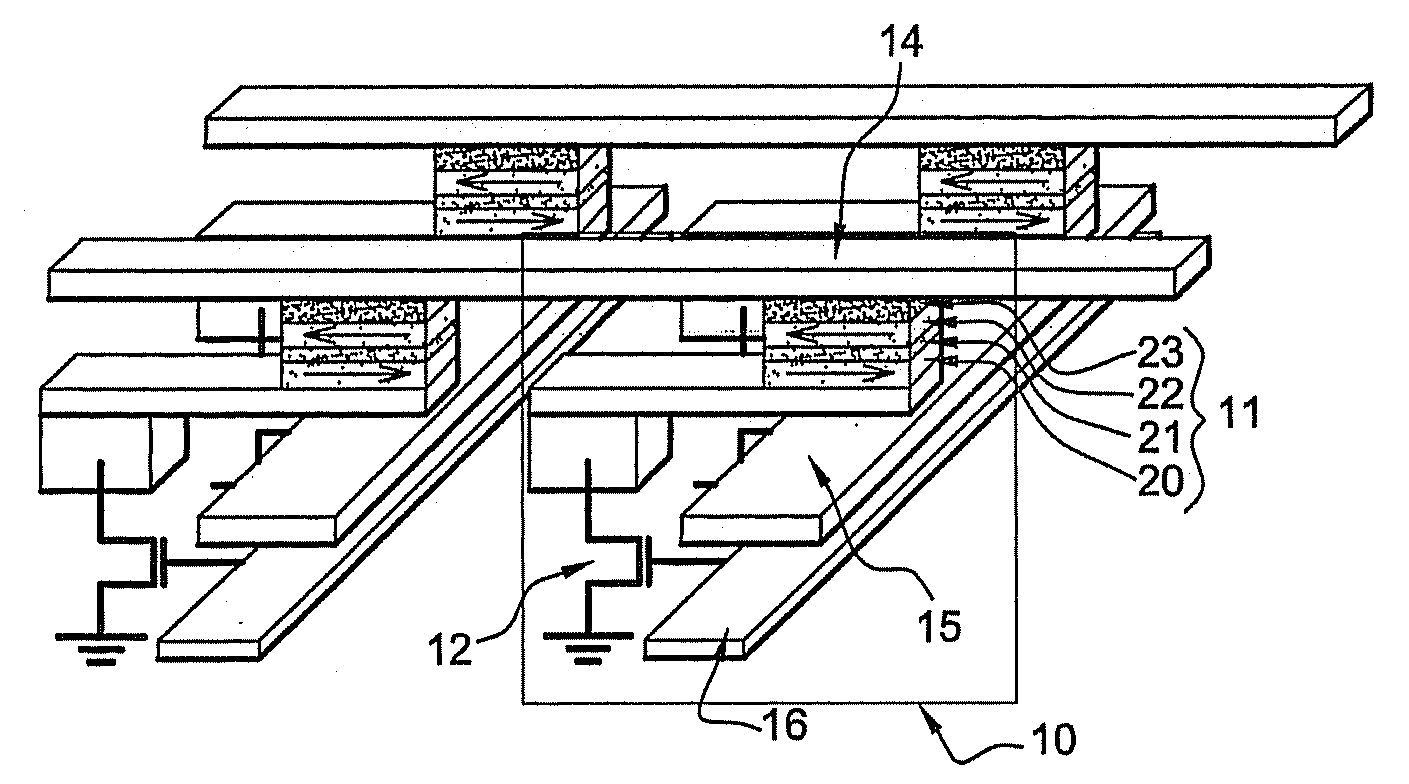
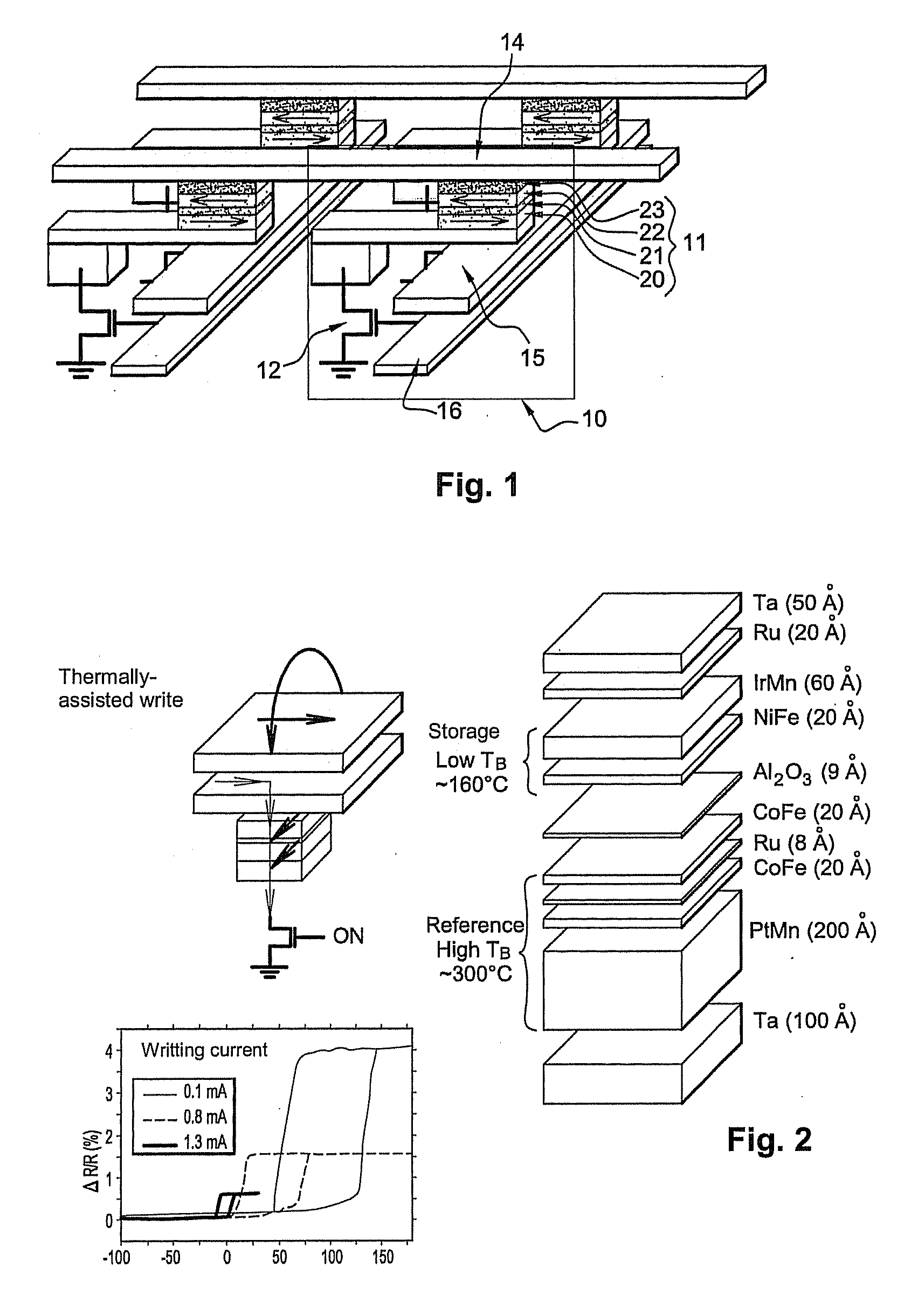
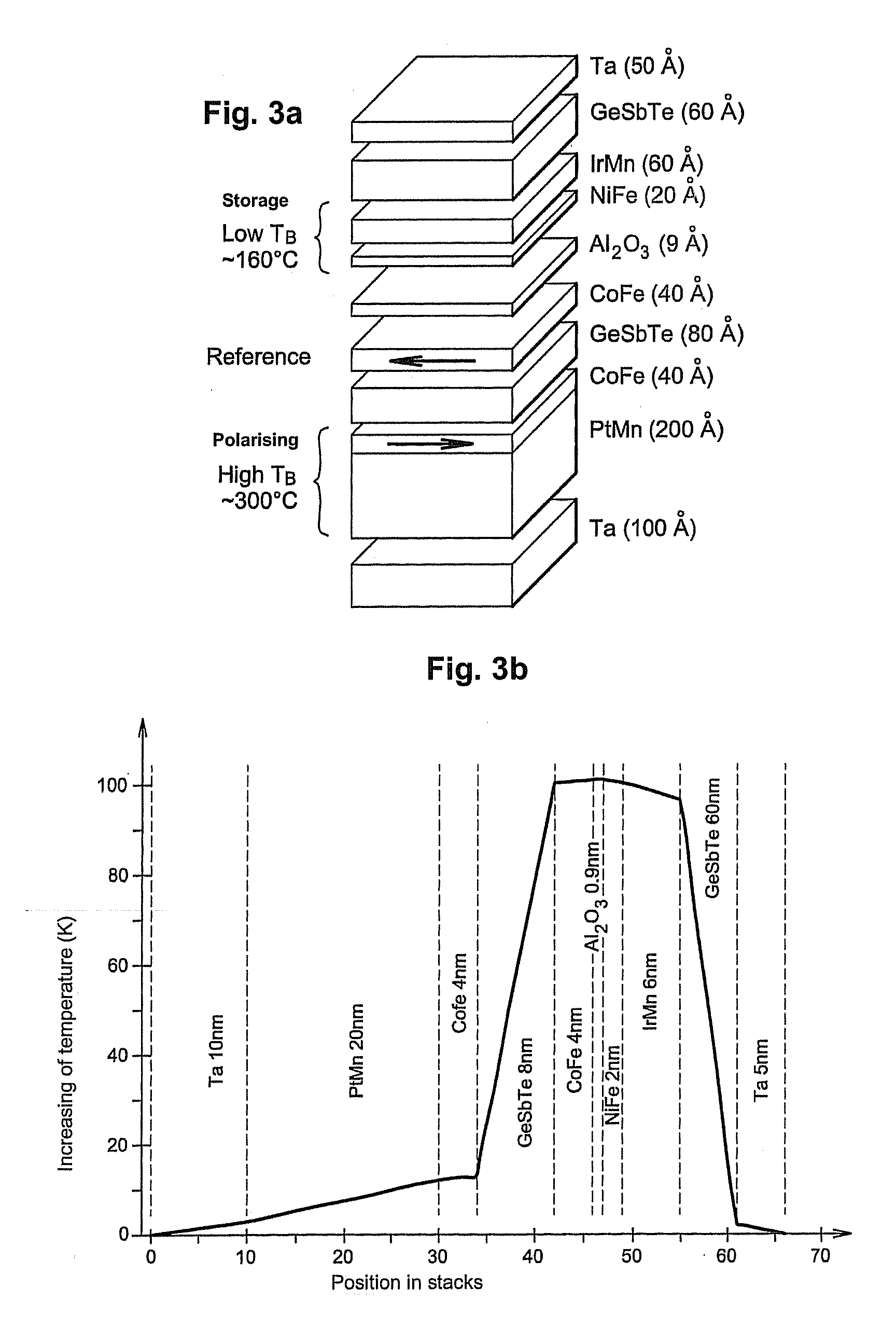
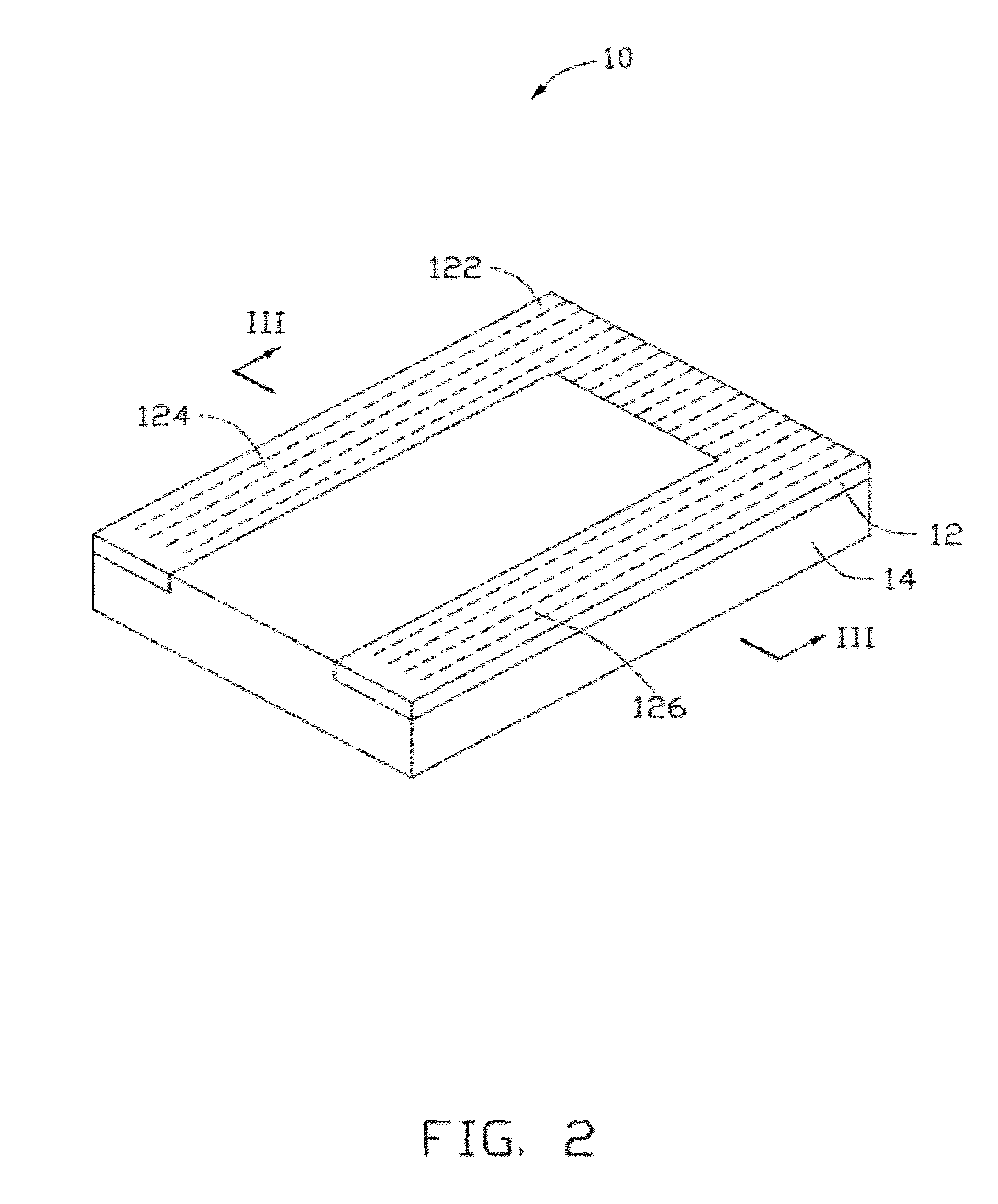
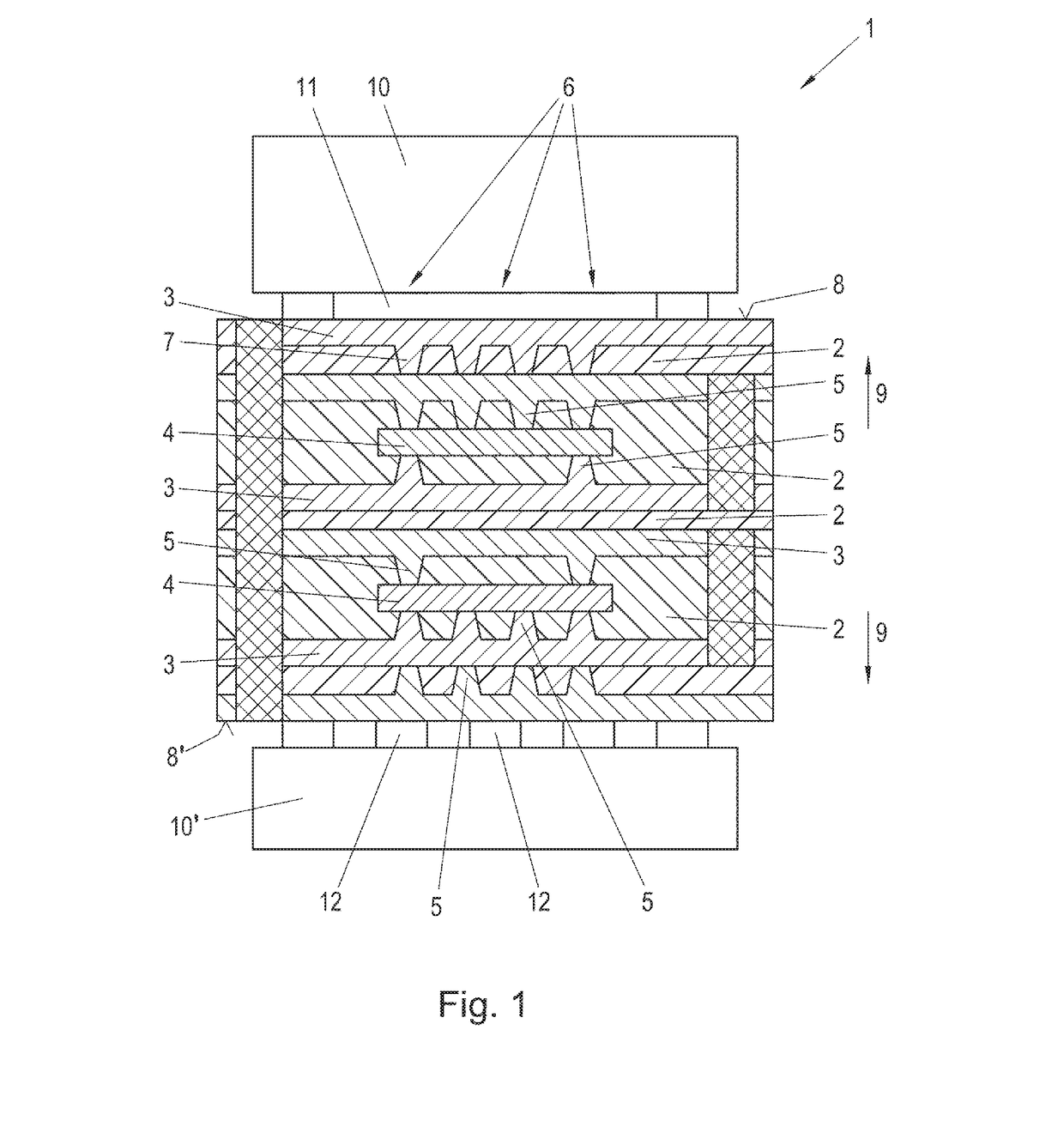
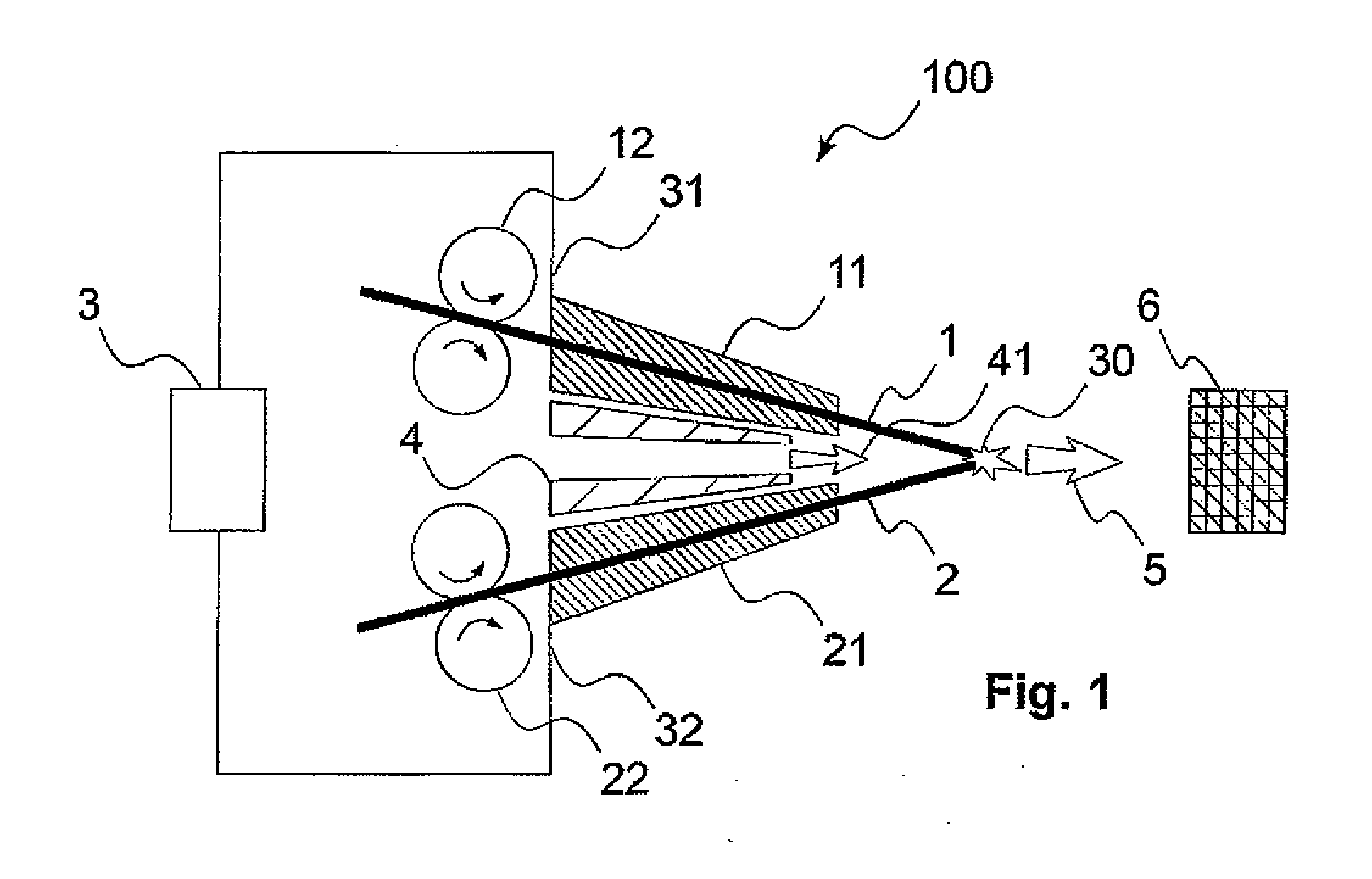
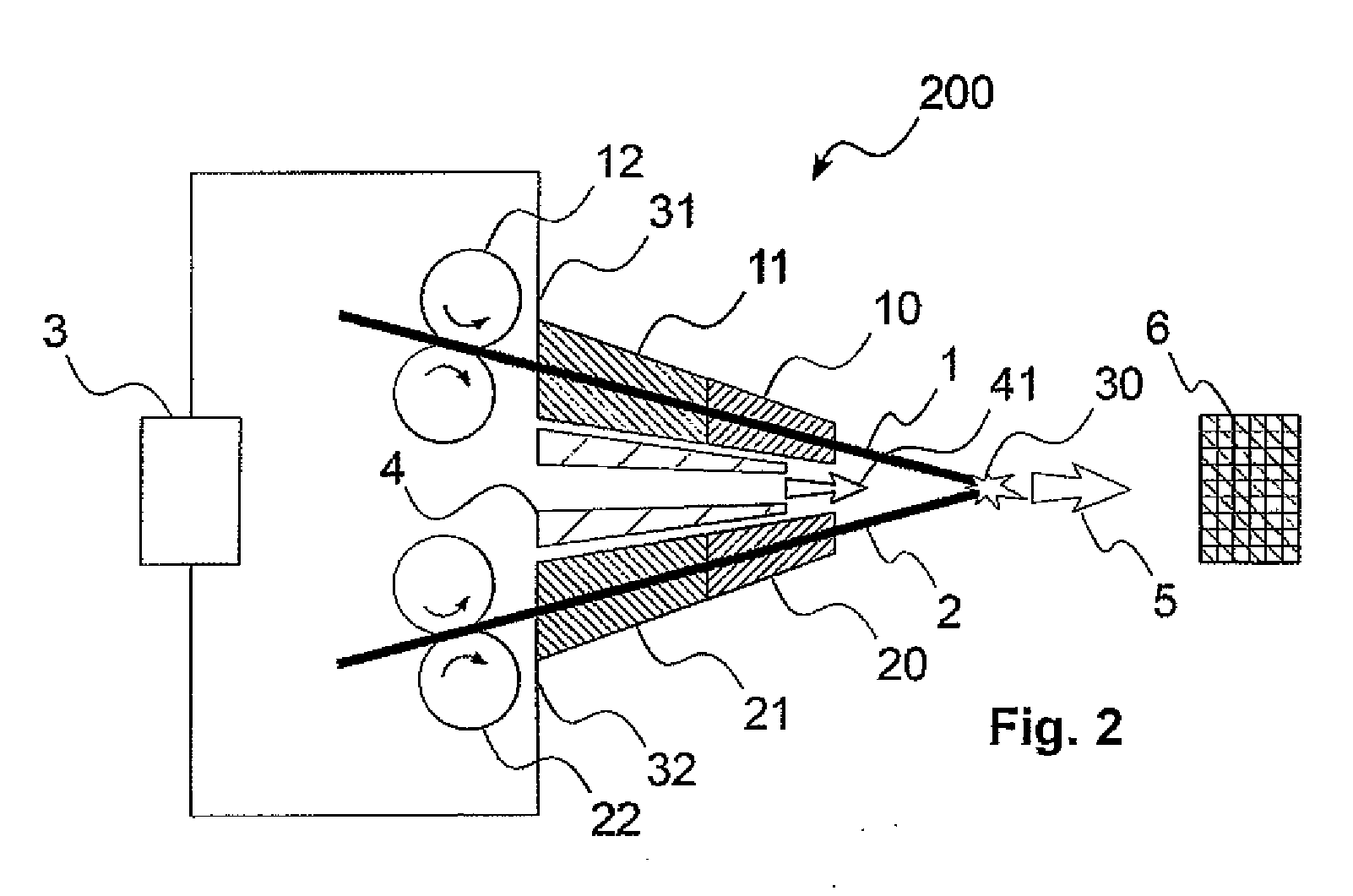
Magnetic tunnel junction magnetic memory
This magnetic memory with a thermally-assisted write, every storage cell of which consists of at least one magnetic tunnel junction, said tunnel junction comprising at least:one magnetic reference layer, the magnetization of which is always oriented in the same direction at the time of the read of the storage cell;one so-called “free” magnetic storage layer, the magnetization direction of which is variable;one insulating layer sandwiched between the reference layer and the storage layer.The magnetization direction of the reference layer is polarized in a direction that is substantially always the same at the time of a read due to magnetostatic interaction with another fixed-magnetization layer called the “polarizing layer”.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
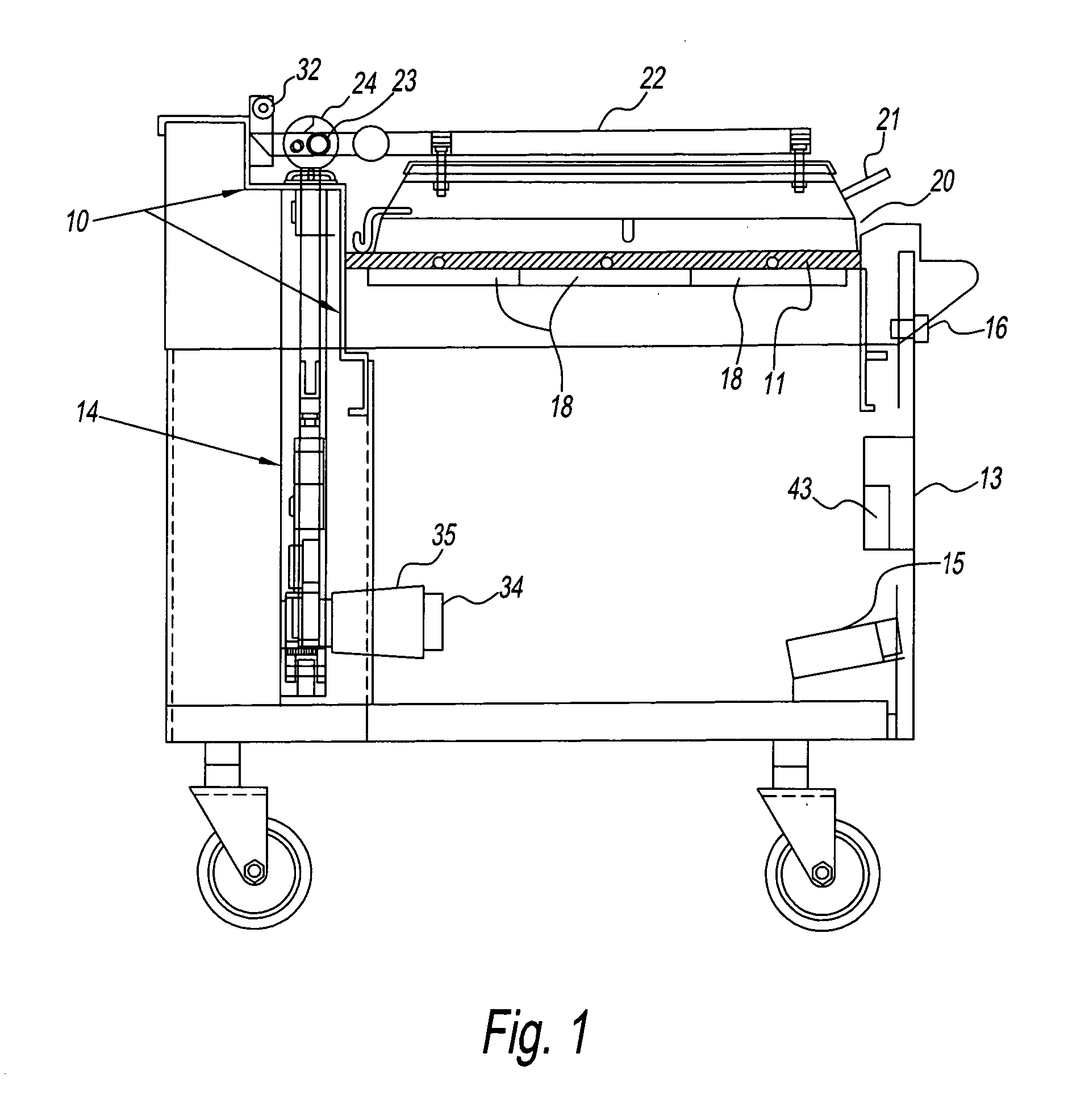
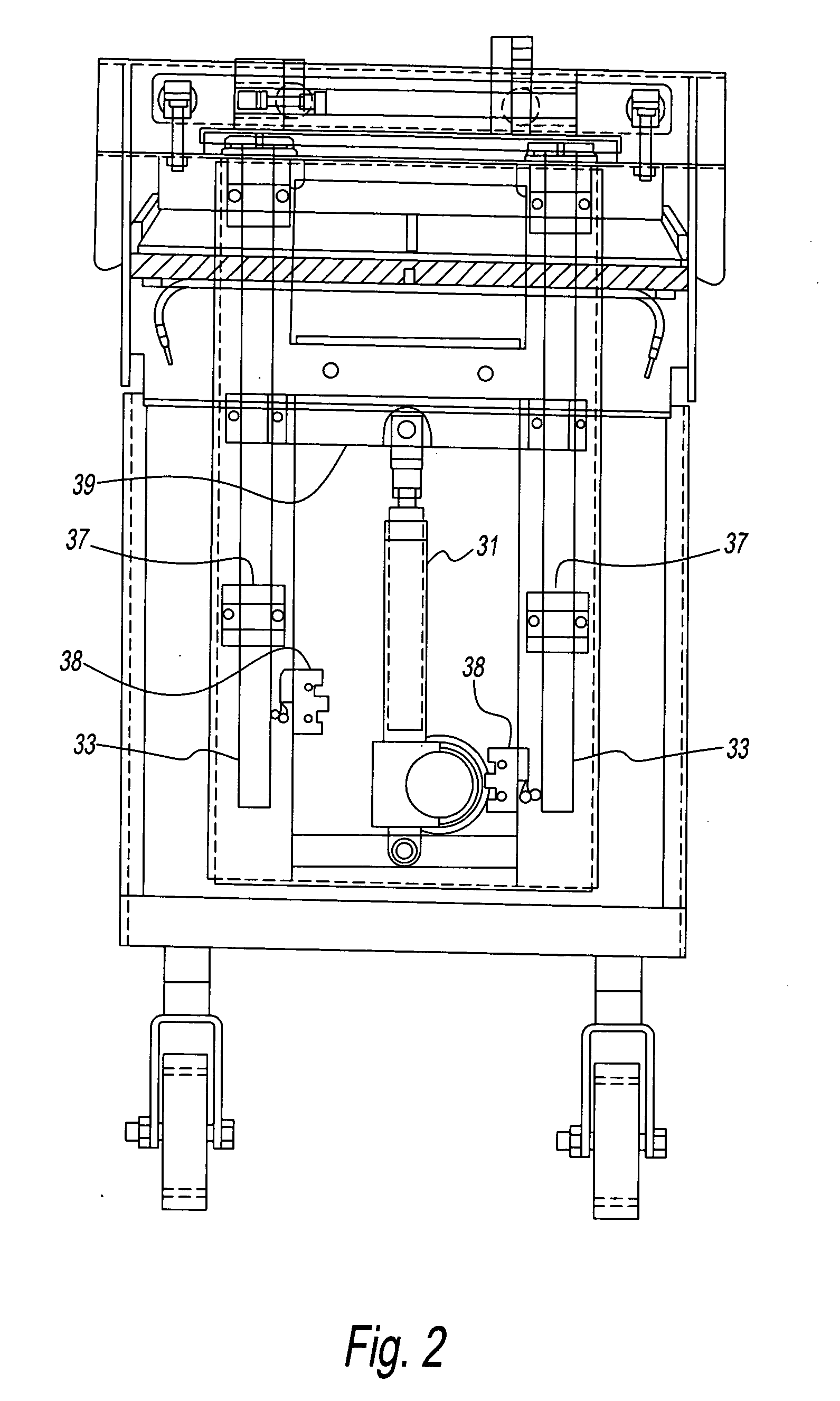
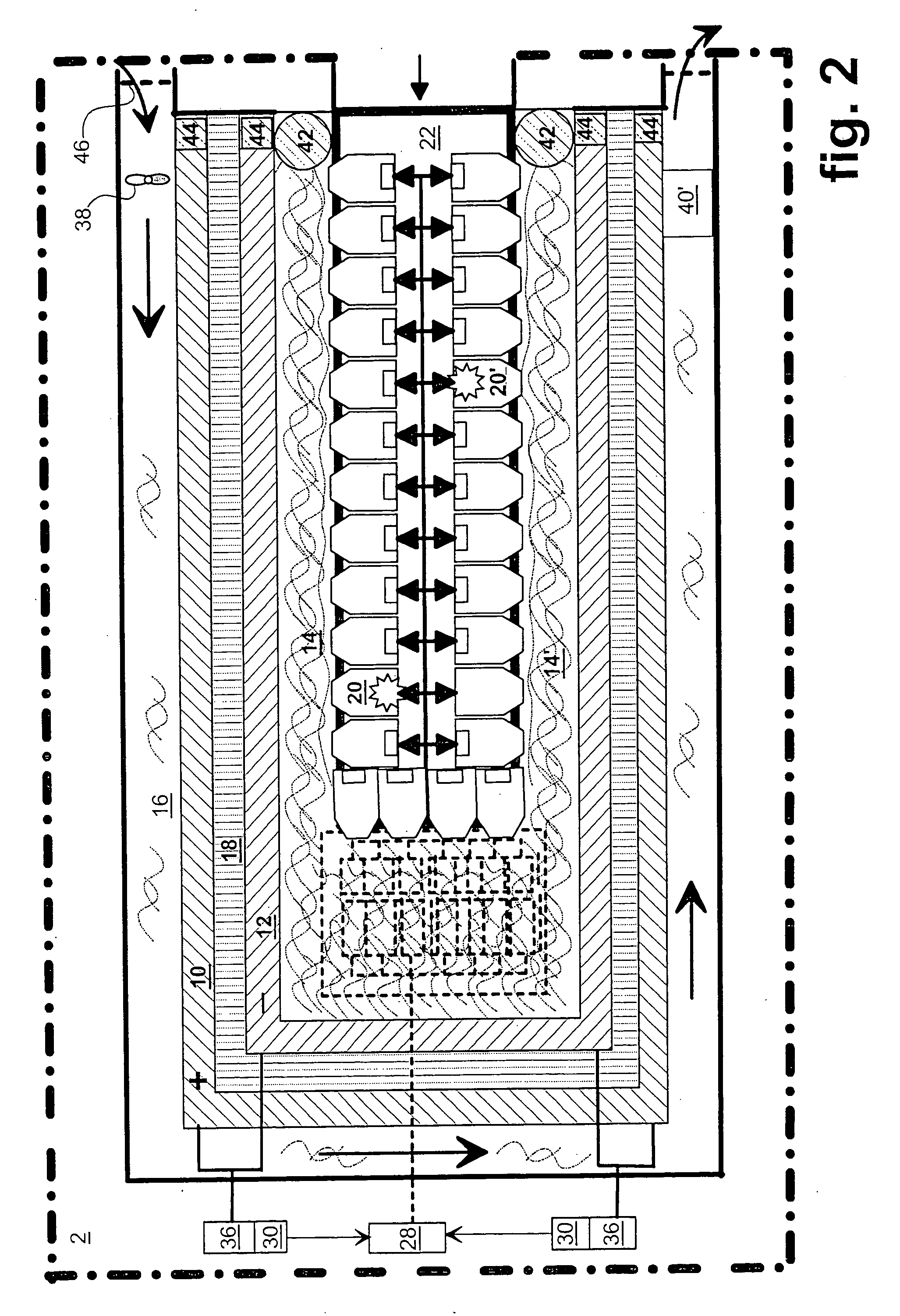
Grill with independent heating zones
ActiveUS20050000957A1Minimal heatSignificant heatingBoiling over preventionHot plates heating arrangementsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A grill having a platen with a plurality of heating zones. Each heating zone has a heating unit. Thermal transfer between adjacent heat zones is limited by air gaps and insulation. The heater unit of each zone has a heater that is disposed to attain substantially uniform temperature of the platen for that zone before a temperature sensor senses a set temperature during either pre-heat or recovery modes.
Owner:GARLAND COMML IND
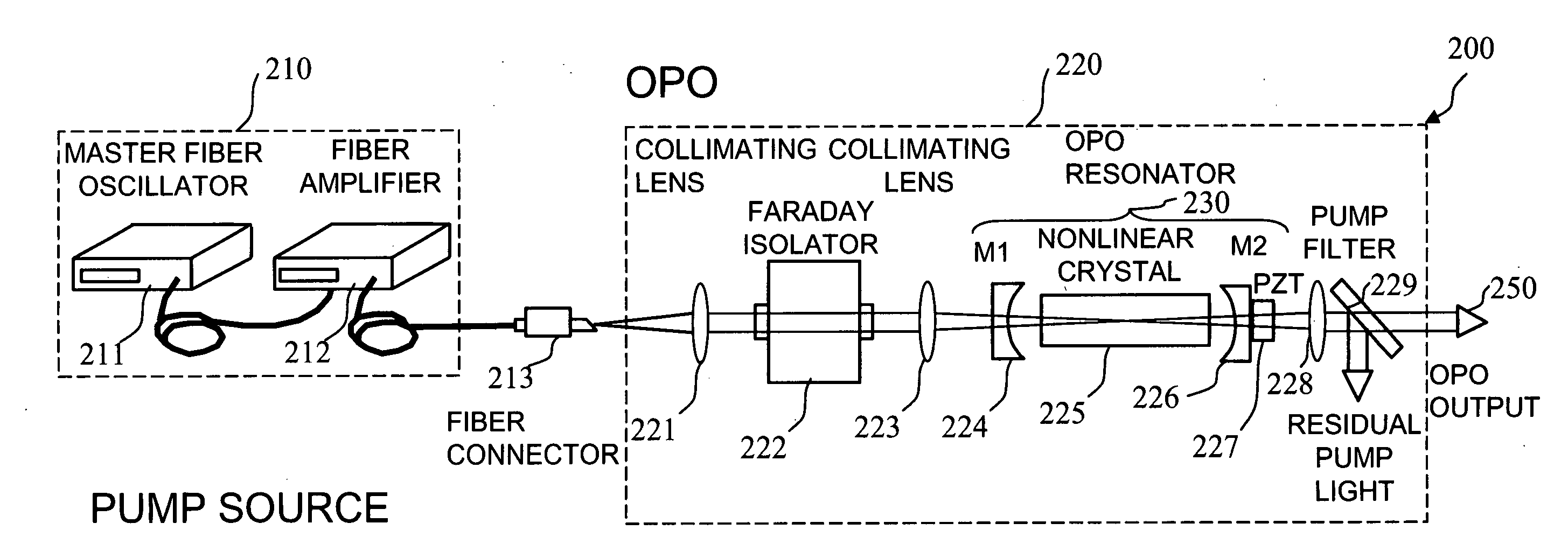
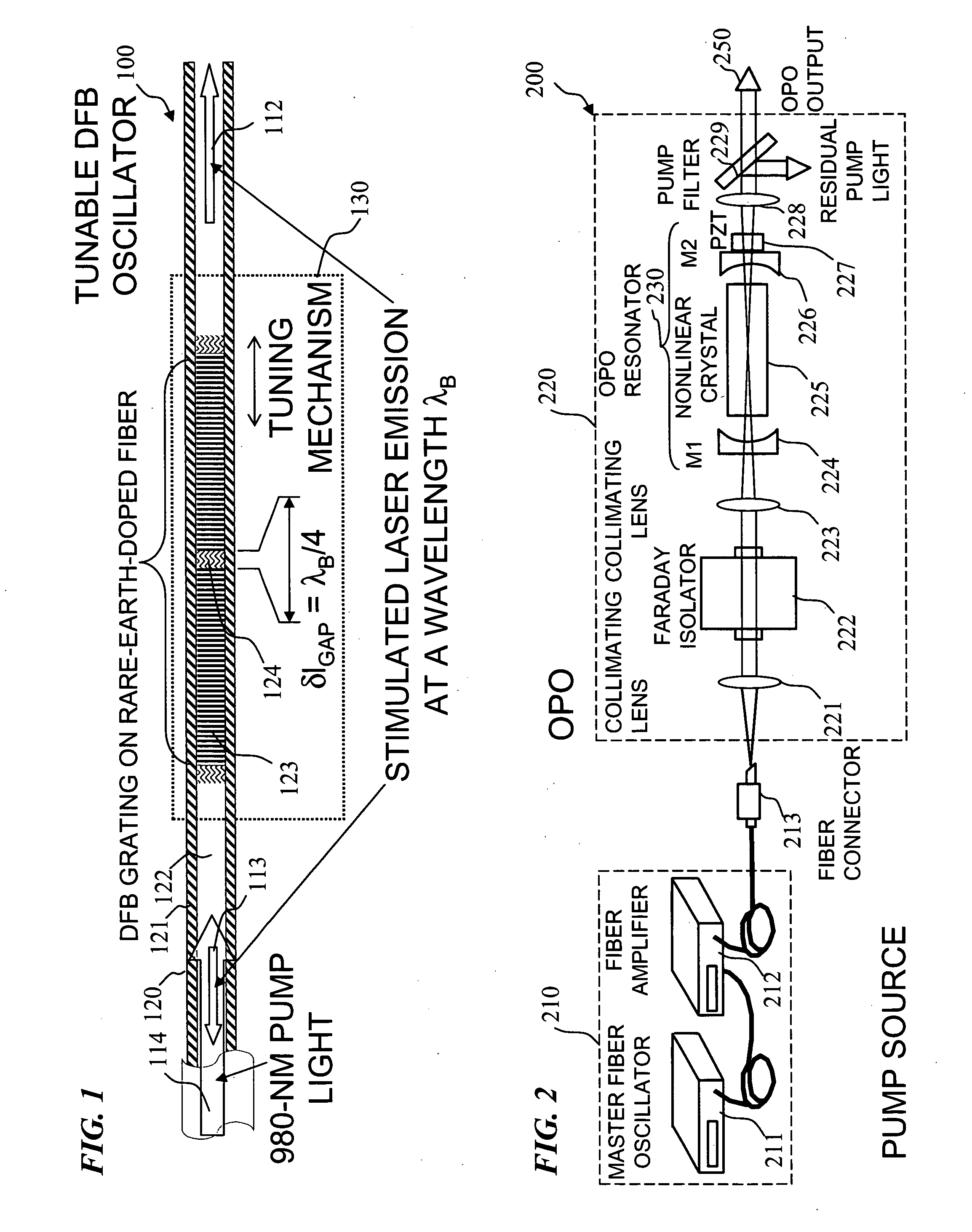
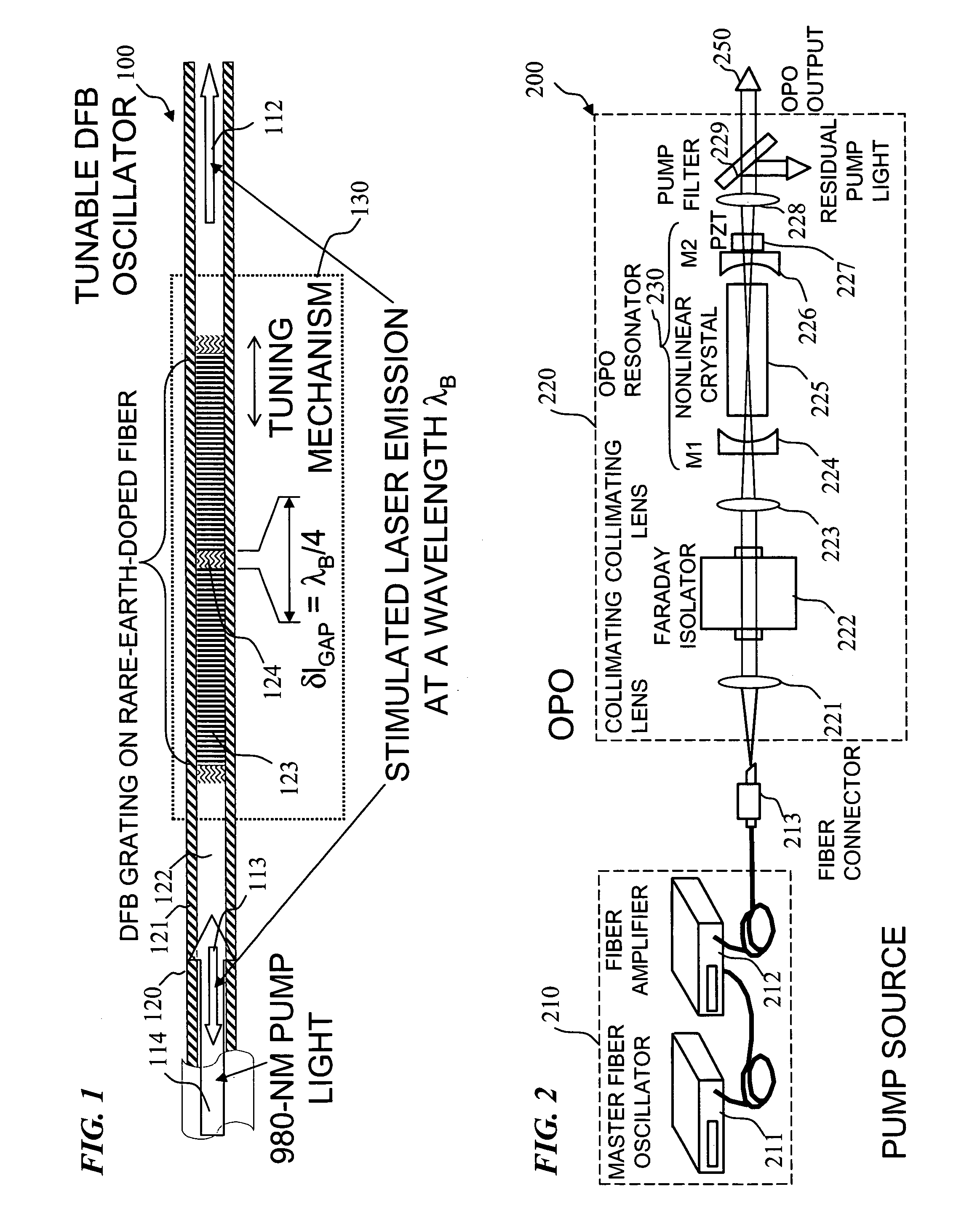
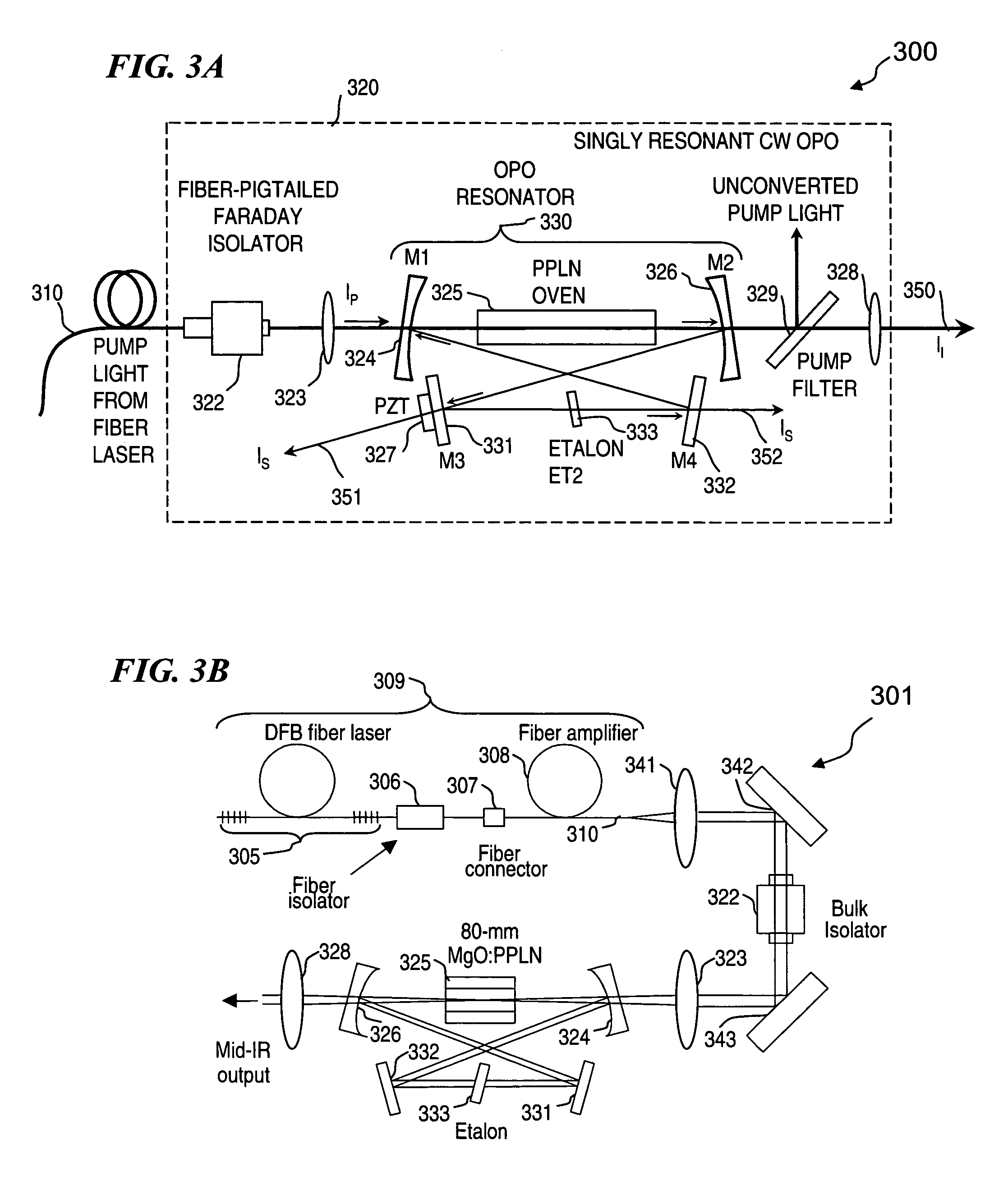
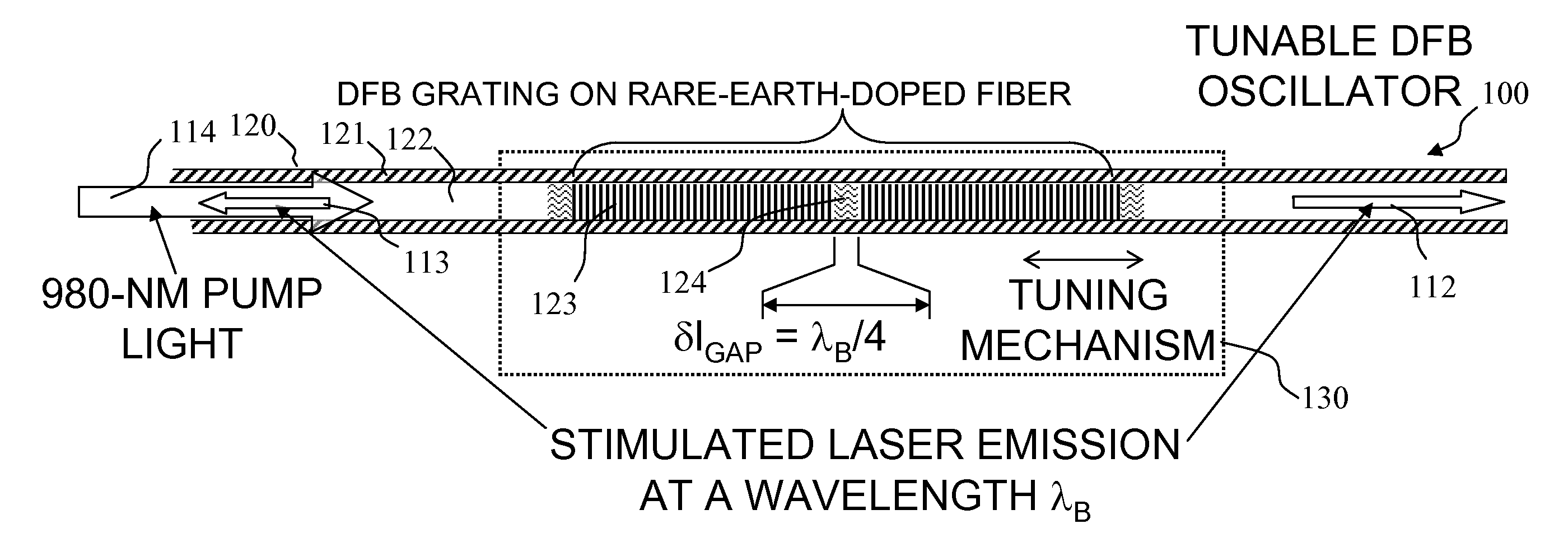
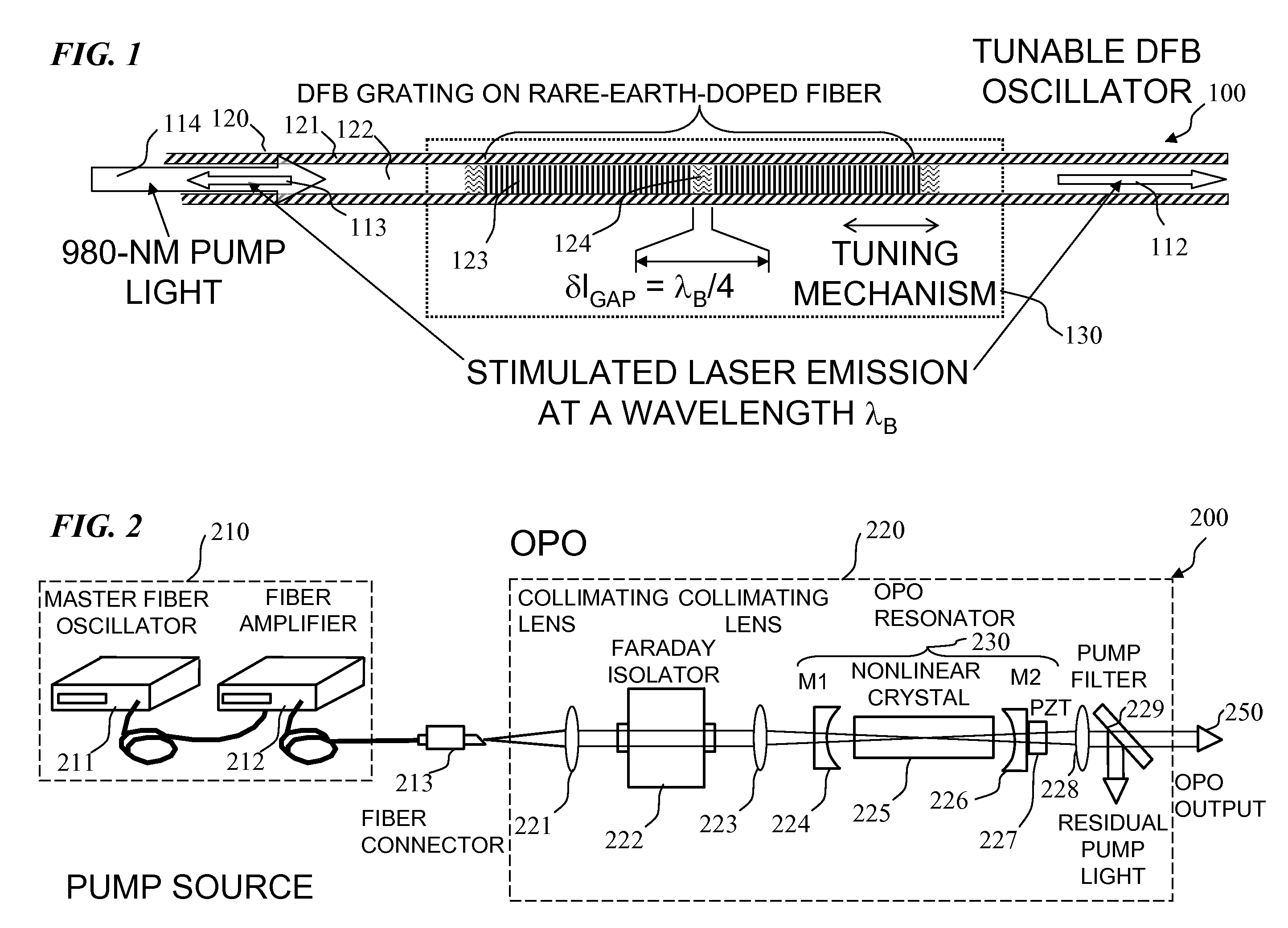
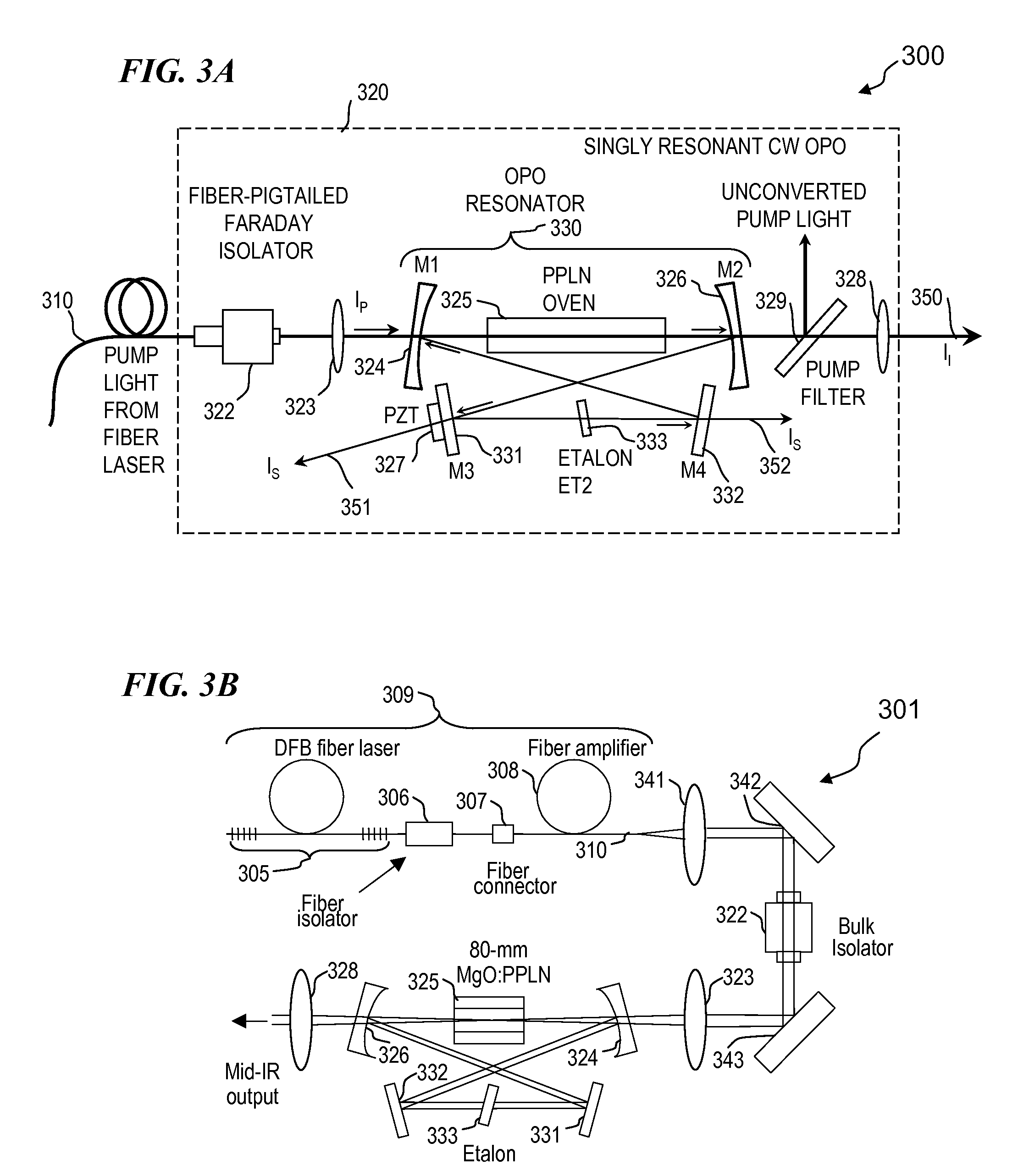
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS20070035810A1Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
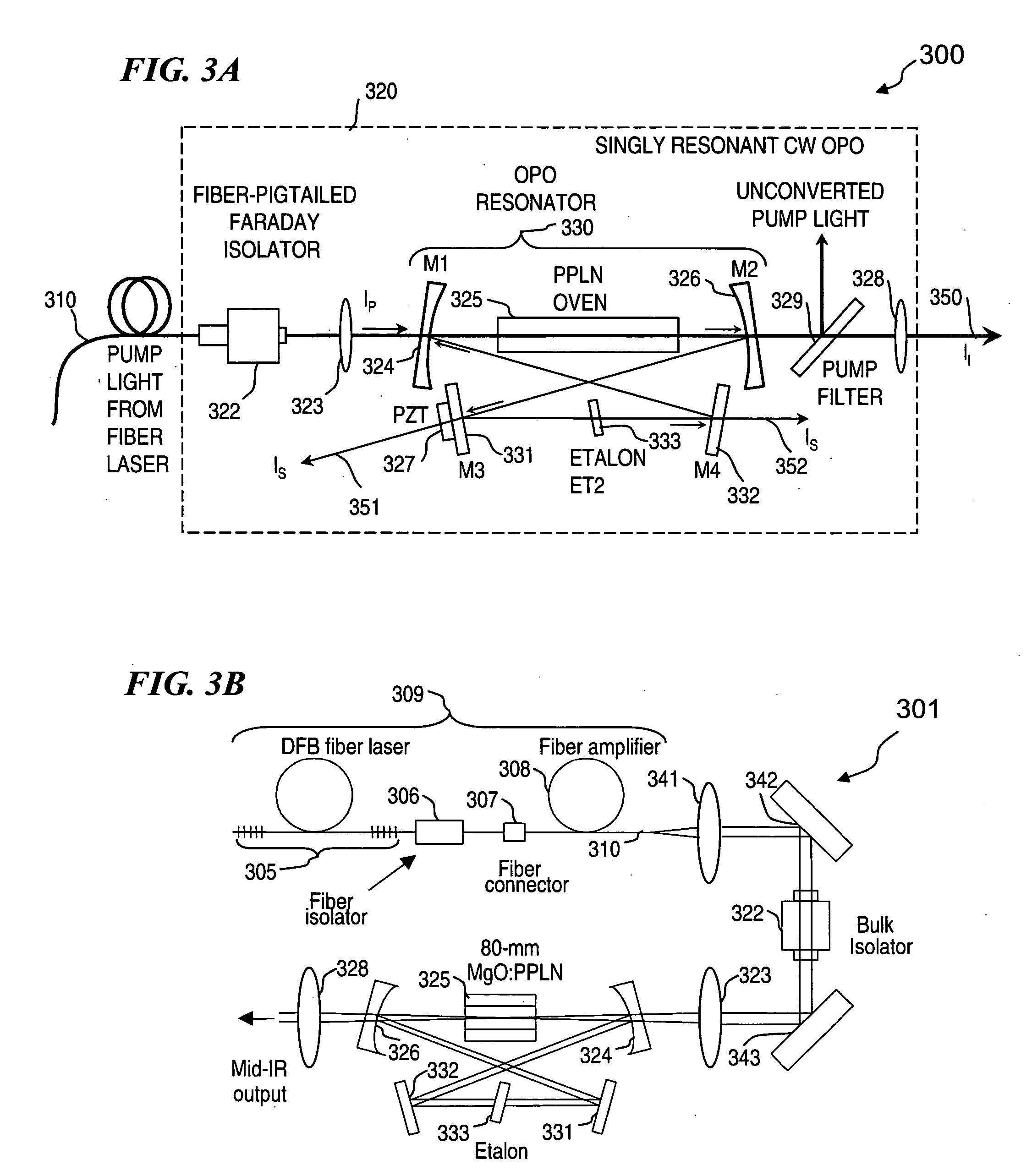
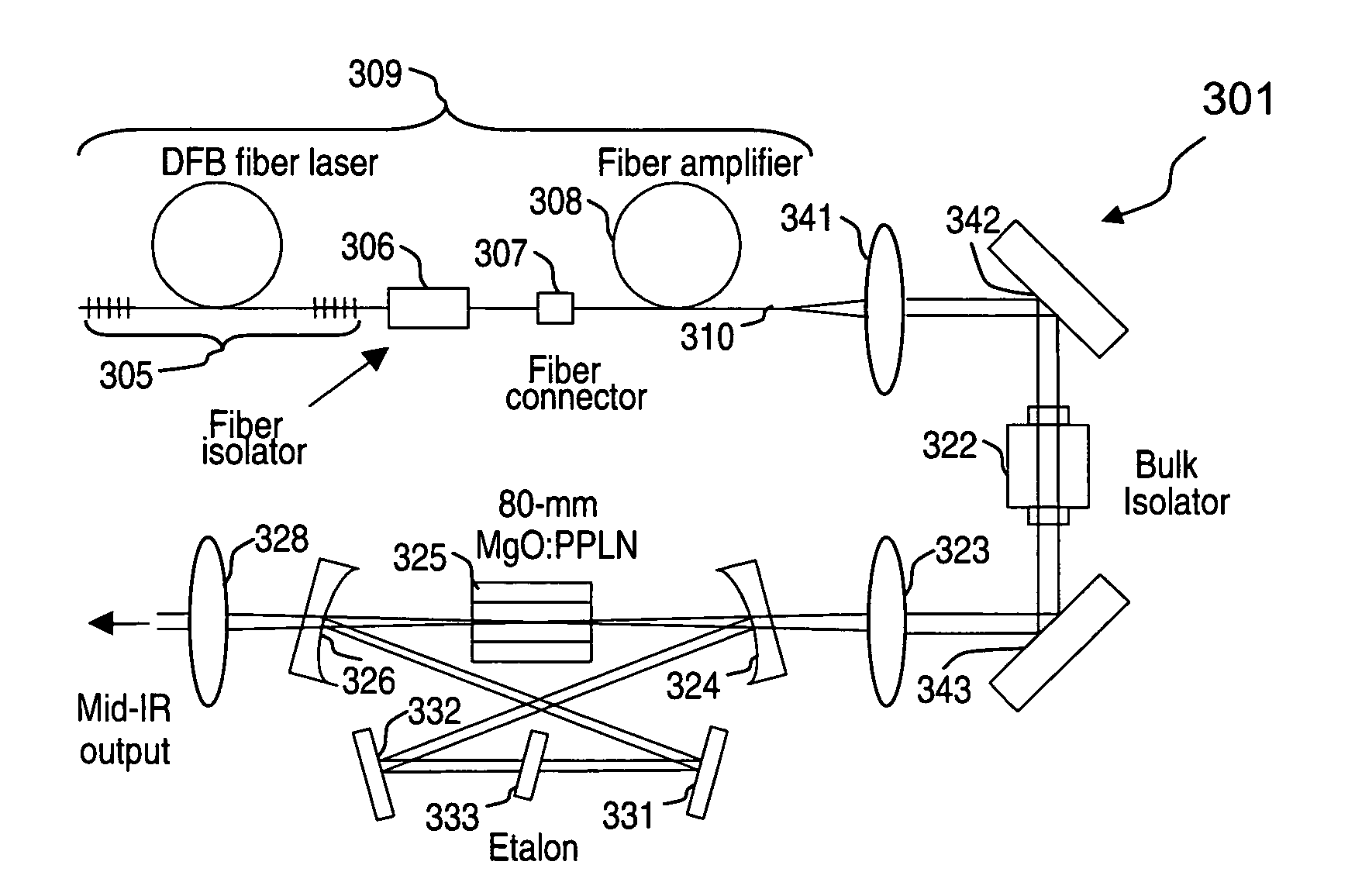
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is described that efficiently converts a near-infrared laser beam to tunable mid-infrared wavelength output. In some embodiments, the OPO includes an optical resonator containing a nonlinear crystal, such as periodically-poled lithium niobate. The OPO is pumped by a continuous-wave fiber-laser source having a low-power oscillator and a high-power amplifier, or using just a power oscillator). The fiber oscillator produces a single-frequency output defined by a distributed-feedback (DFB) structure of the fiber. The DFB-fiber-laser output is amplified to a pump level consistent with exceeding an oscillation threshold in the OPO in which only one of two generated waves (“signal” and “idler”) is resonant within the optical cavity. This pump source provides the capability to tune the DFB fiber laser by straining the fiber (using an attached piezoelectric element or by other means) that allows the OPO to be continuously tuned over substantial ranges, enabling rapid, wide continuous tuning of the OPO output frequency or frequencies.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
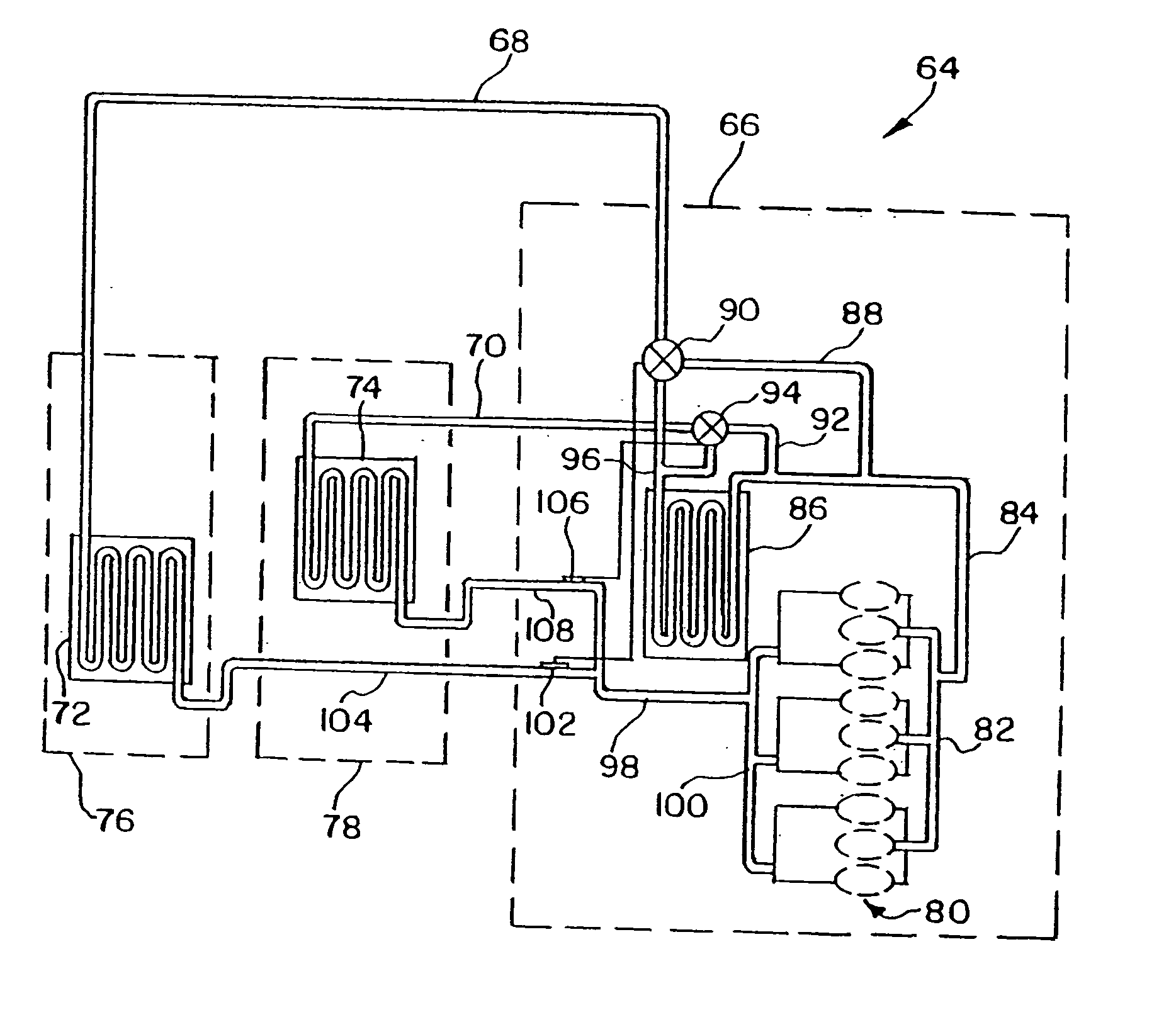
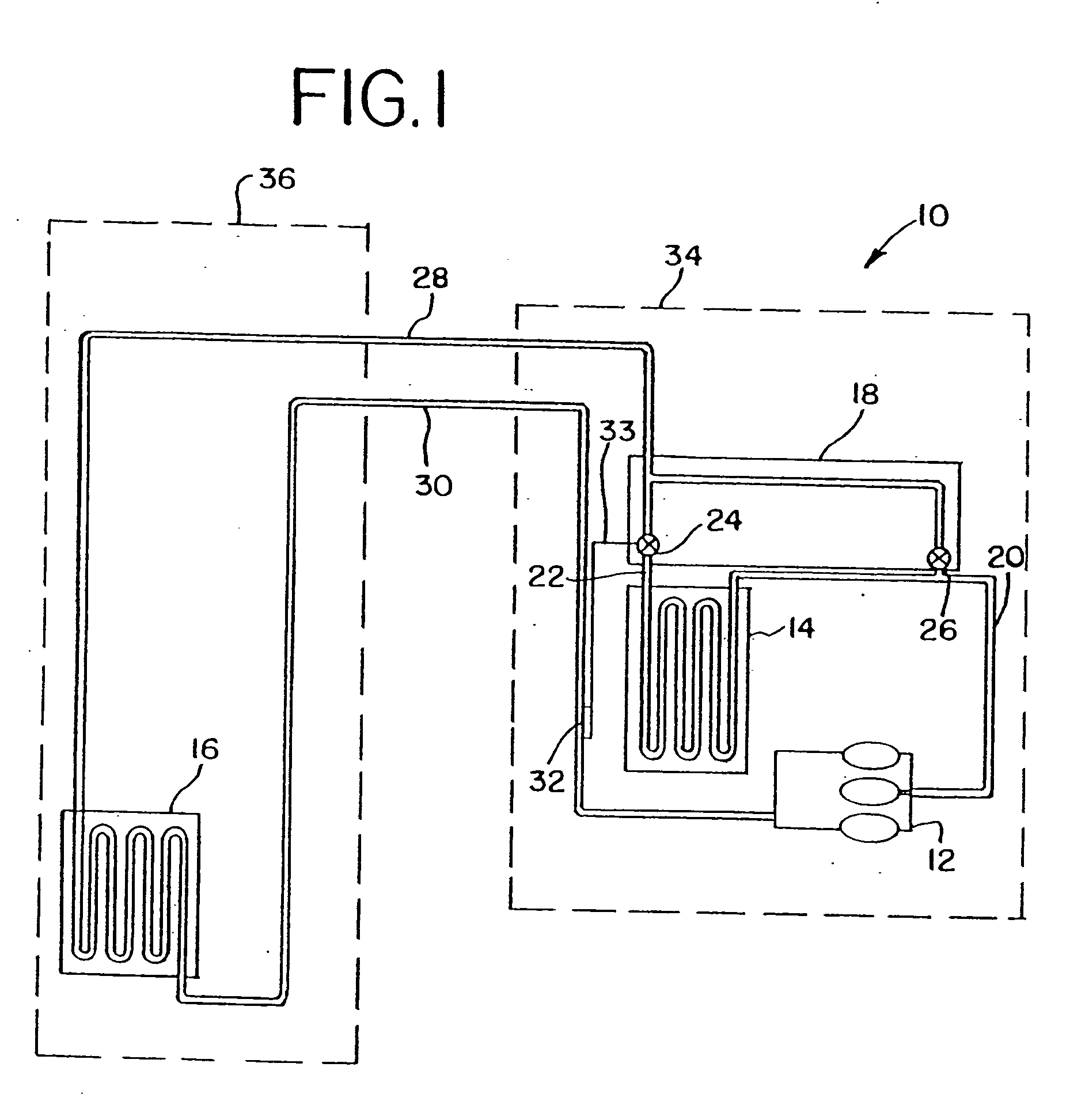
Vapor compression system
InactiveUS6393851B1Operation efficiency is highEasy to operateTemperature control without auxillary powerMechanical apparatusEngineeringHeat transfer fluid
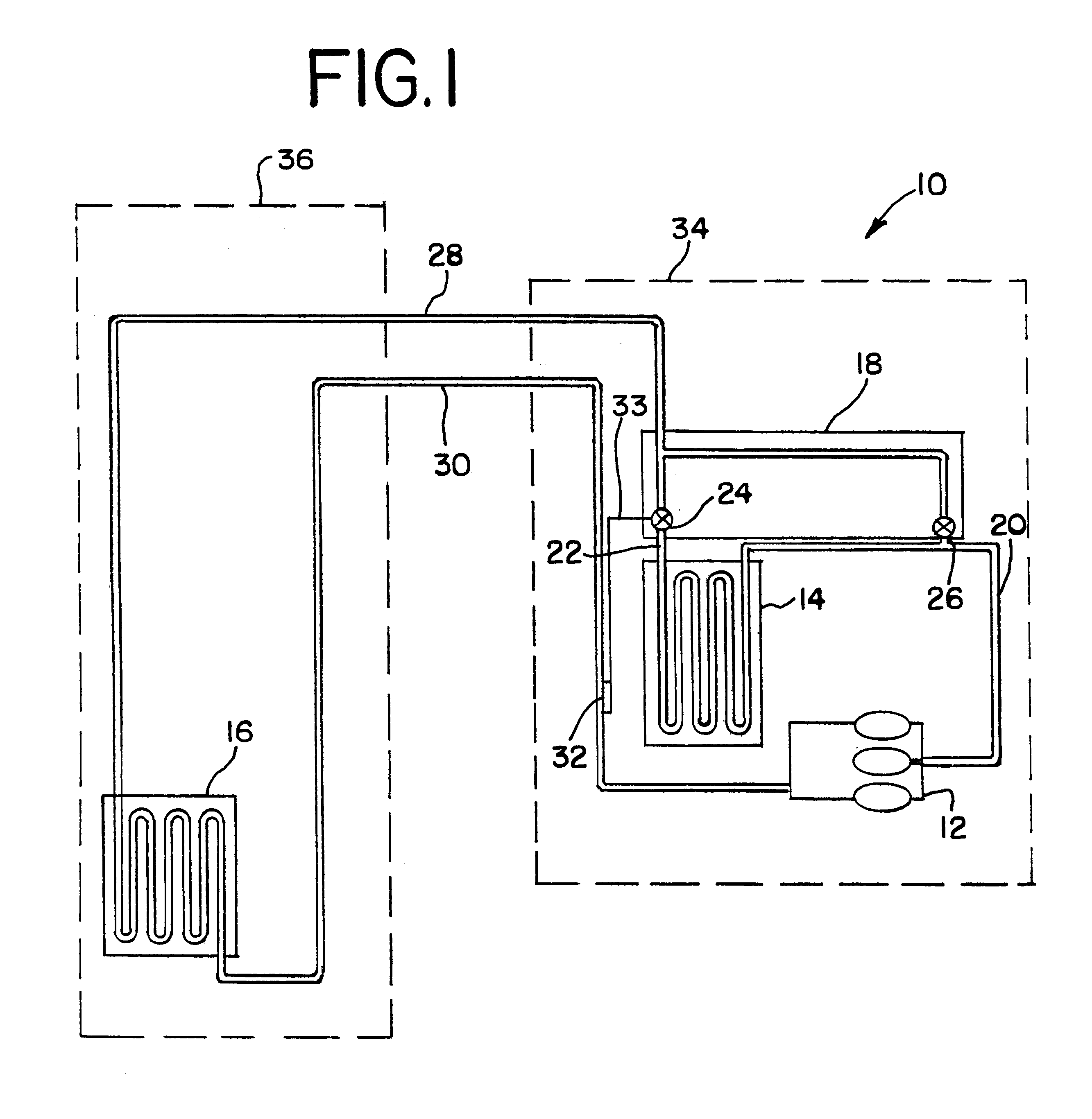
A vapor compression system including a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve, and an evaporator. The compressor increases the pressure and temperature of a heat transfer fluid. The condenser is connected with the compressor for liquefying the heat transfer fluid. The expansion valve is connected with the condenser and includes an expansion device for expanding the heat transfer fluid, and an internal sensor for detecting conditions within the heat transfer fluid. The evaporator is connected with the expansion valve for transferring heat from ambient surroundings to the heat transfer fluid.
Owner:XDX GLOBAL LLC
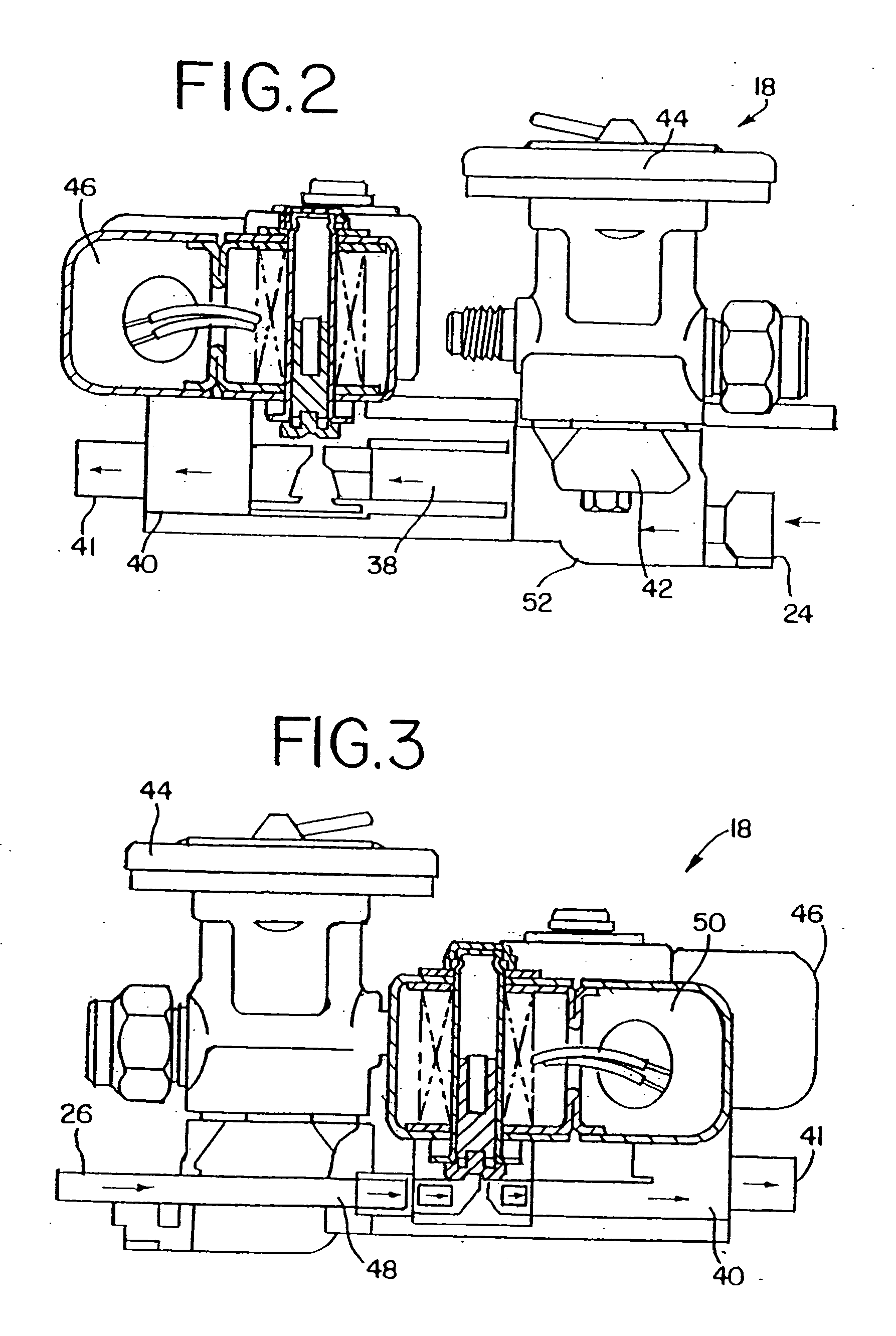
Method and circuit arrangement for reducing noise produced by electromagnetically actuated devices
InactiveUS6560088B1Minimizes excess energyGeneration can be minimizedOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectric switchesEngineeringElectromagnet
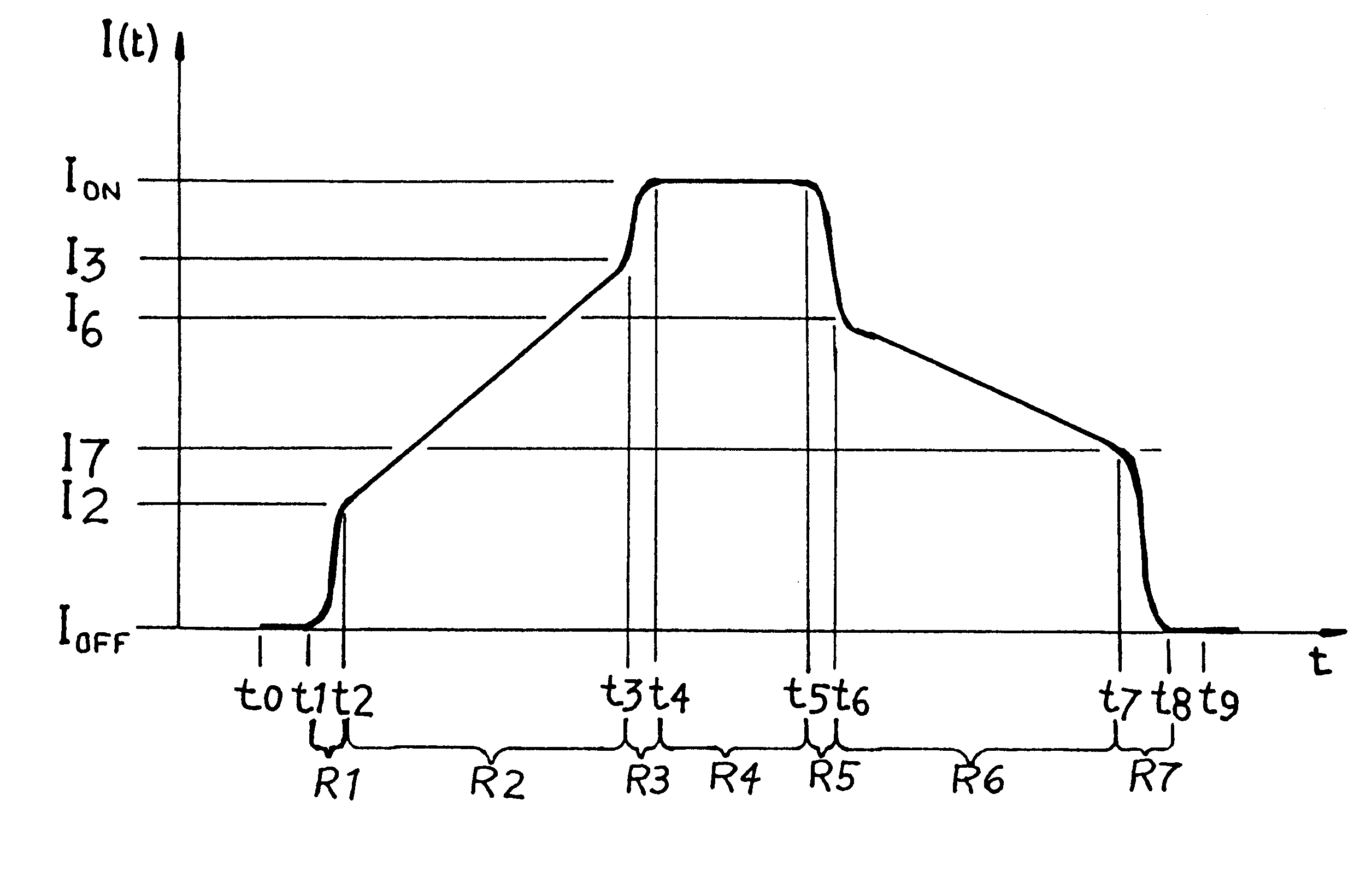
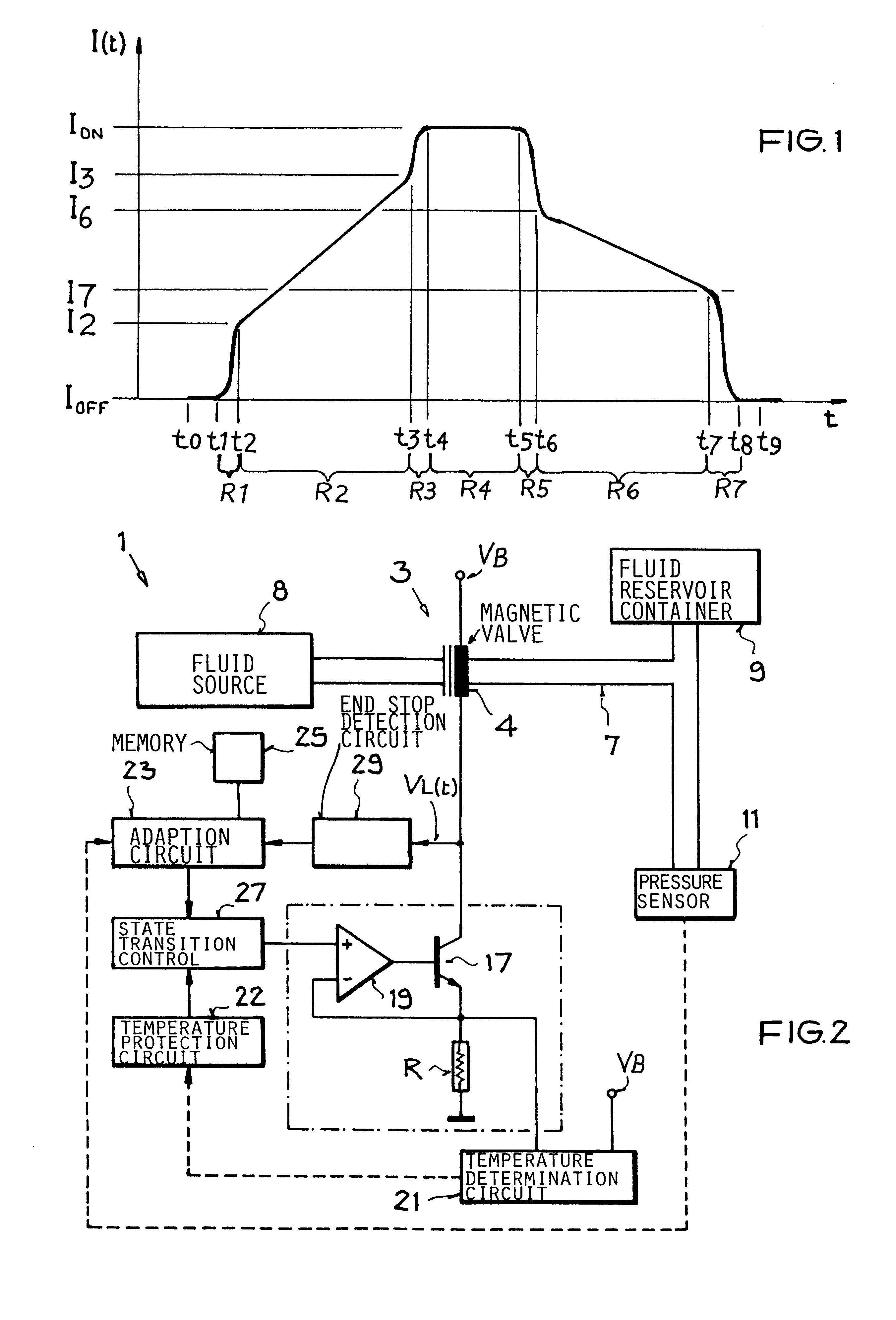
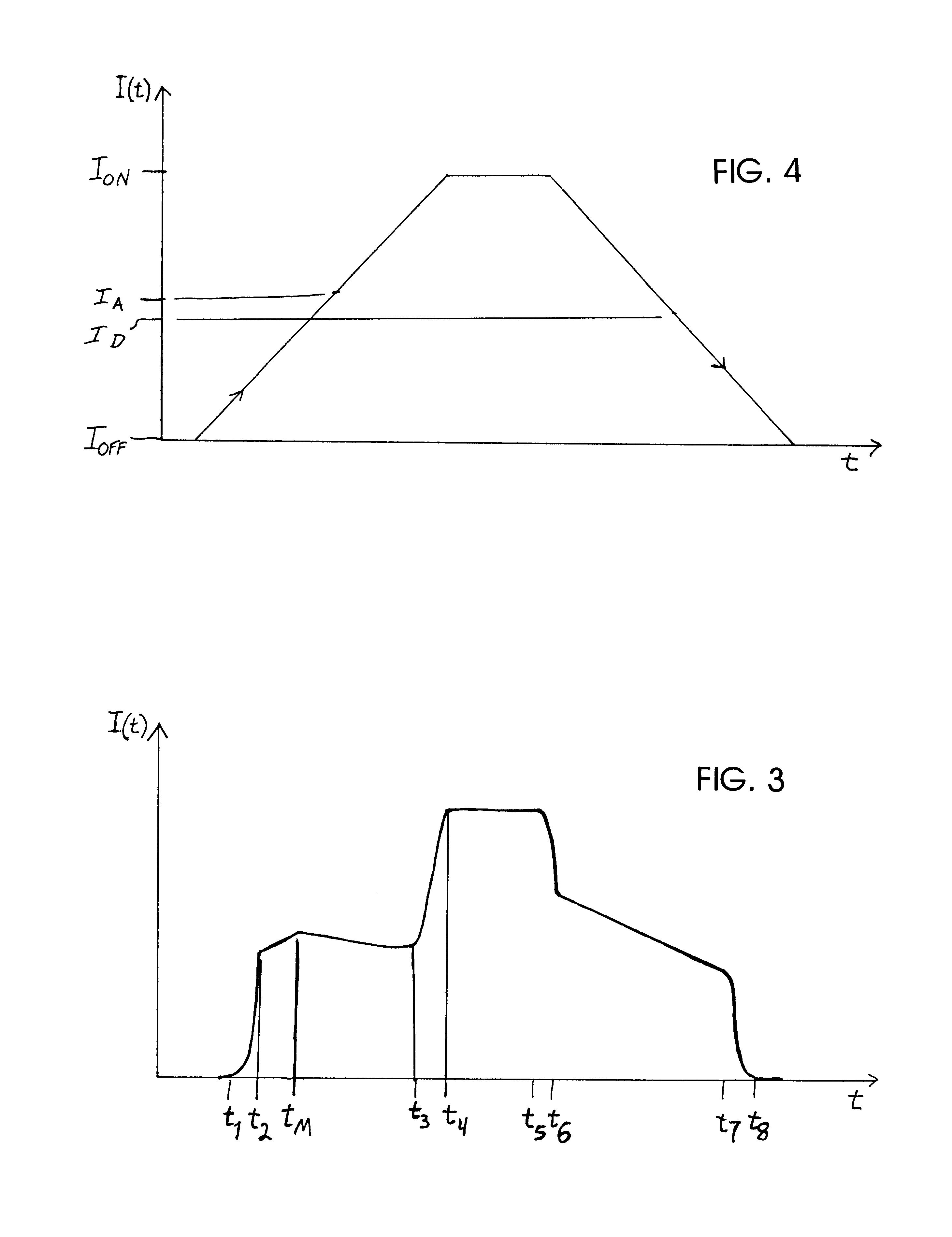
In an electromagnetically actuatable device, an electromagnet is driven with a controlled current progression so that the armature of the electromagnet can be actuated at the lowest possible current level while still achieving the most rapid overall increase of the actuating current from zero to maximum amperage. A first portion or range of the current increase is carried out with a steep or jump-like current increasing characteristic. A second portion or range of the current increase is carried out with a more gradual variation of the current. The current levels at the end points of the respective ranges are selected to ensure that the electromagnet is actuated during the second range in which the current varies more gradually. Preferably, two steep or jump-like current increase ranges are respectively provided before and after the second range having the gradual current increase. The armature of the electromagnet is thereby actuated with the lowest possible energy, and the lowest possible acceleration, so that noise and wear are reduced.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS7620077B2Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Heating system to alleviate hypothermia
ActiveUS20070049997A1Aggressive treatmentFacilitates patient insertionTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingCold exposureBody area
A medical, electrically powered thermal cover for fitting predominantly the trunk and head of a person experiencing or potentially experiencing traumatic or cold-exposure hypothermia. The thermal cover encases all of the torso and neck, and portions of other body areas. Heating may be distinctly non-uniform, being applied to the body surface only in special regions where the body's capacity for heat uptake may be relatively high. In sum, the system may monitor deep body core temperature, direct heat to the body core where it may be most needed, and controls therapy over time to restore normothermia.
Owner:GRI ALLESET INC
Traction stud mount and method of manufacturing and mounting
A one-piece stud mount for mounting a traction stud on a reinforcing rod adapted to be embedded in a yieldable drive track. The stud mount includes an elongated, stud receiving receptacle having a threaded opening therein for threadedly receiving a traction stud and a transversely disposed head defining an aperture which has a shape complemental to the shape of the rod for slidably receiving the rod prior to the molding of the track. The invention contemplates a method of manufacturing the stud mount and mounting the stud mount on a track reinforcing bar. The invention also contemplates a method of manufacturing a track in which the stud mount is embedded after being mounted on a reinforcing rod which is also embedded in the track.
Owner:INT ENG & MFG
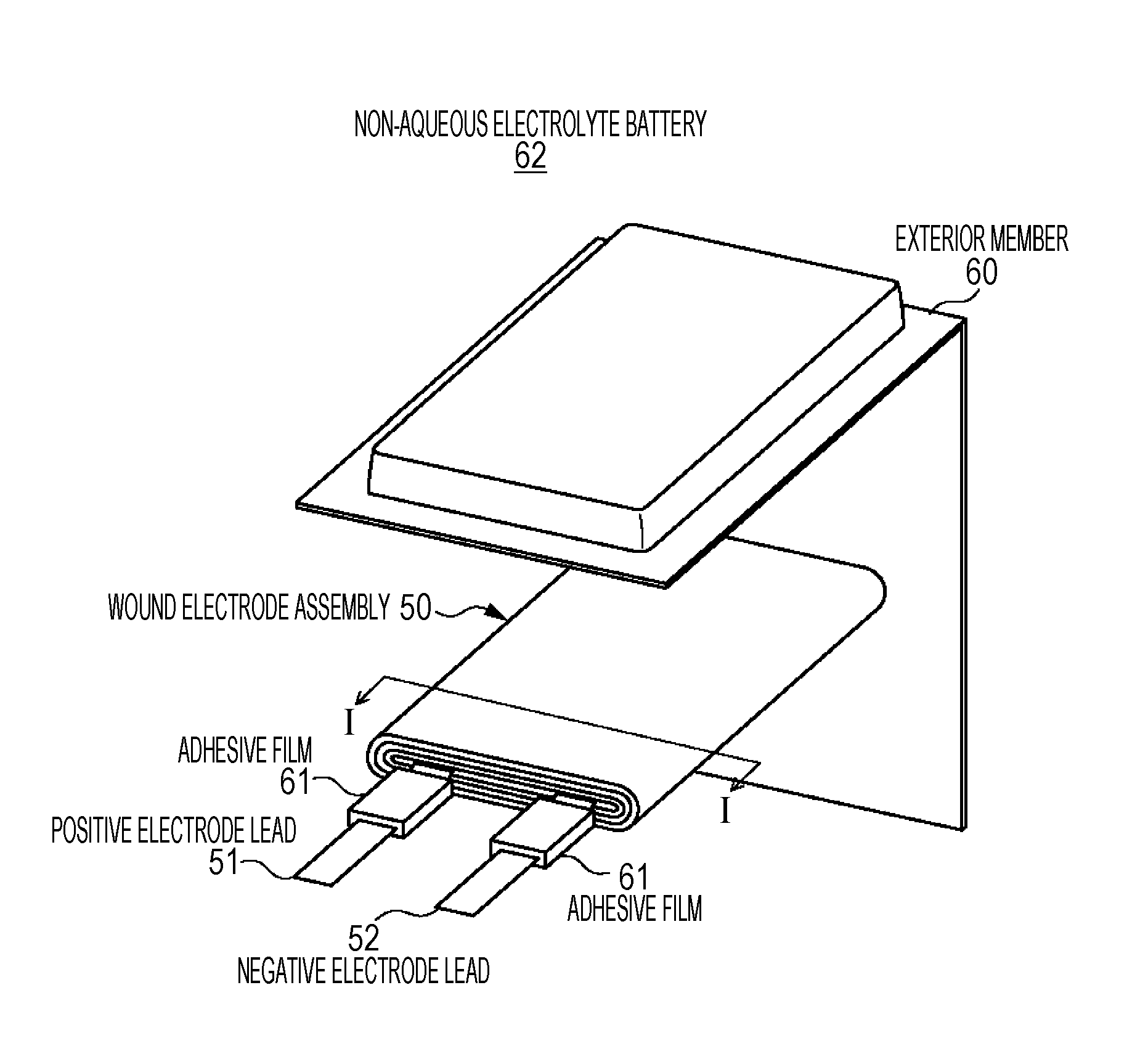
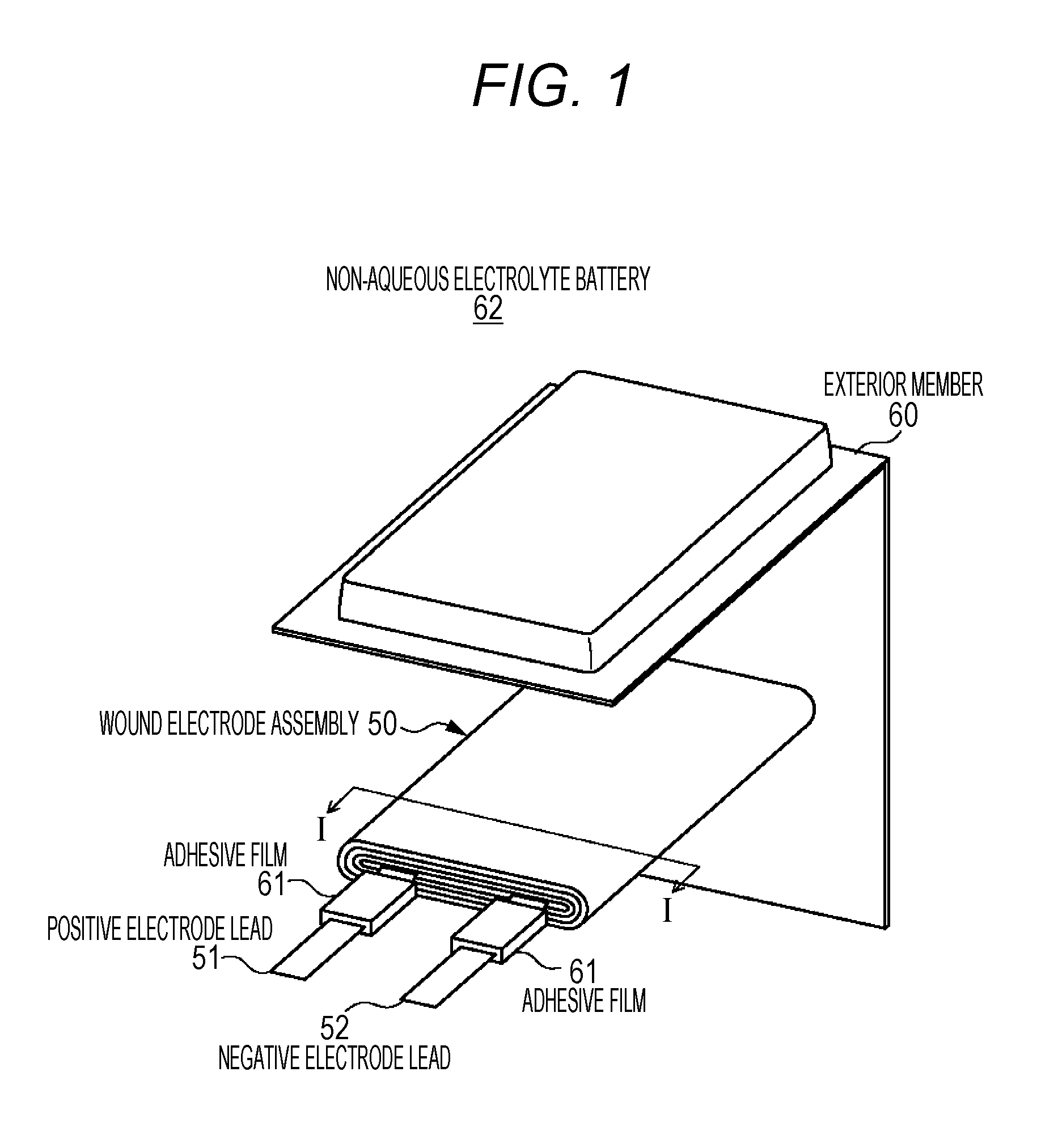
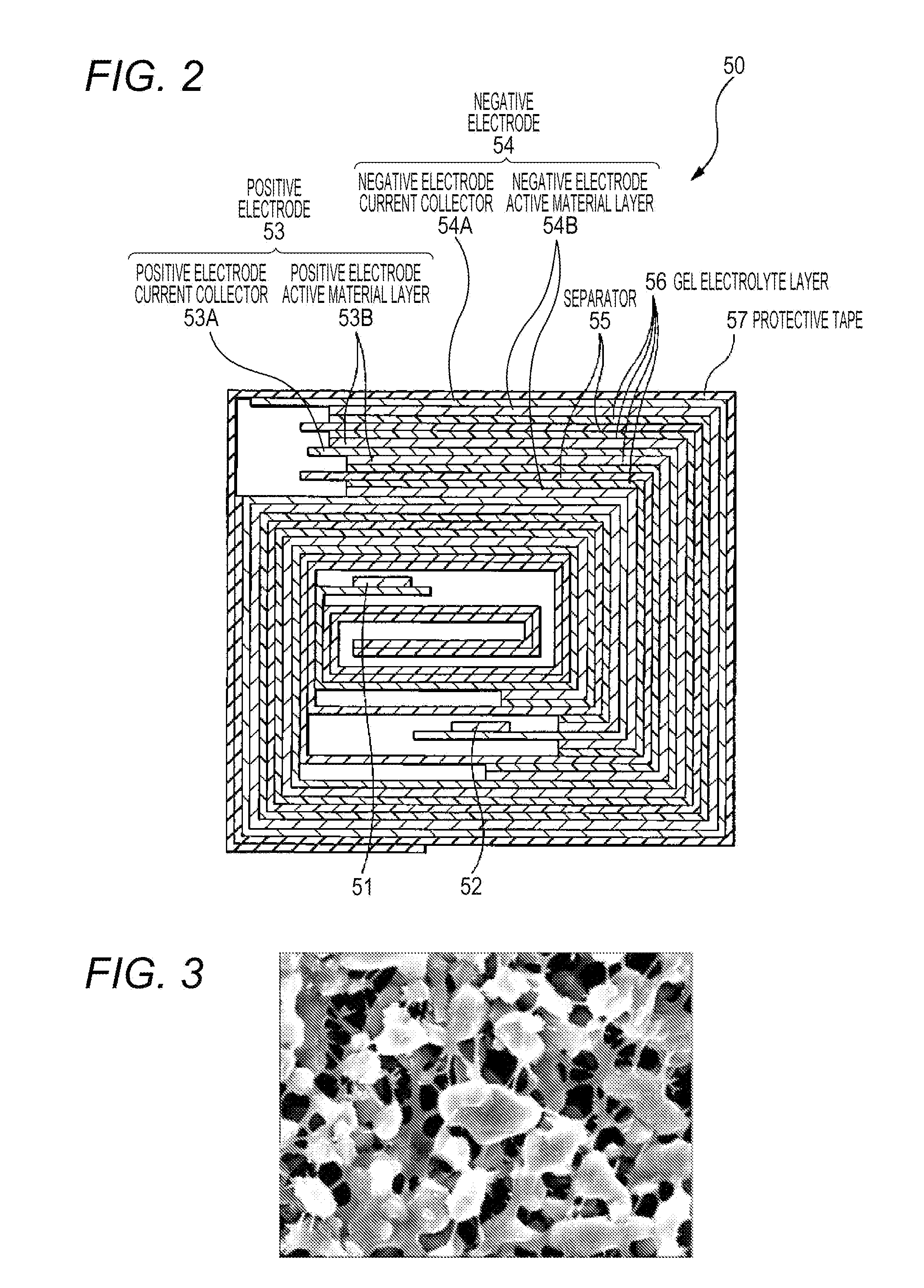
Battery, electrolyte layer, battery pack, electronic apparatus, electric vehicle, power storage device, and electric power system
ActiveUS20160043429A1Significant heatingThermal decomposition reaction of the positive electrode, can be suppressedDigital data processing detailsSolid electrolyte cellsElectrical batteryElectric power system
A gel electrolyte layer is provided between a positive electrode and a second electrode. The gel electrolyte layer is a layer containing particles, a resin material, and a polymer compound for retaining the resin material, and having a heat capacity per unit area of 0.0001 J / Kcm2 or more and a heat capacity per unit volume of 3.0 J / Kcm3 or less.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
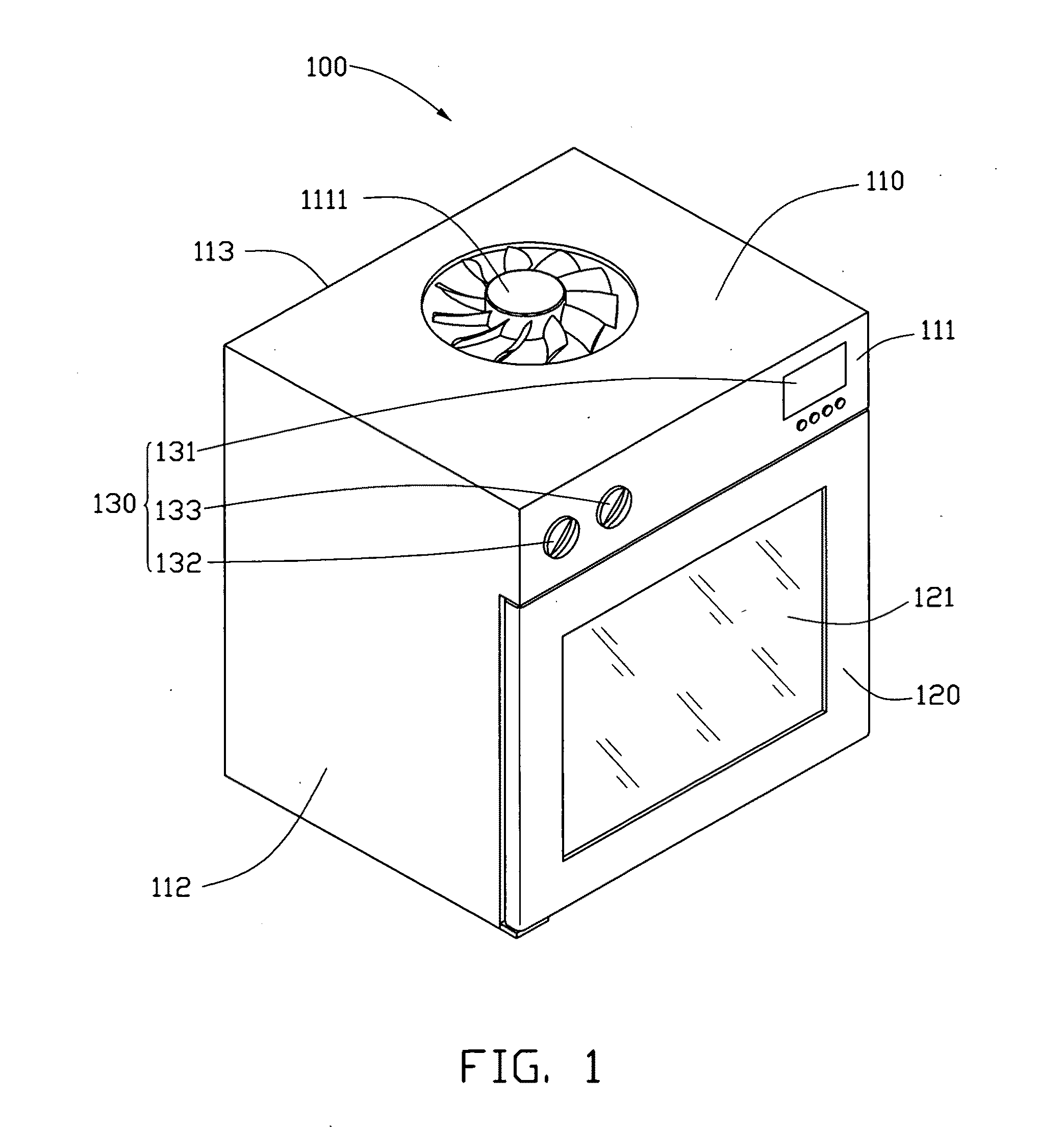
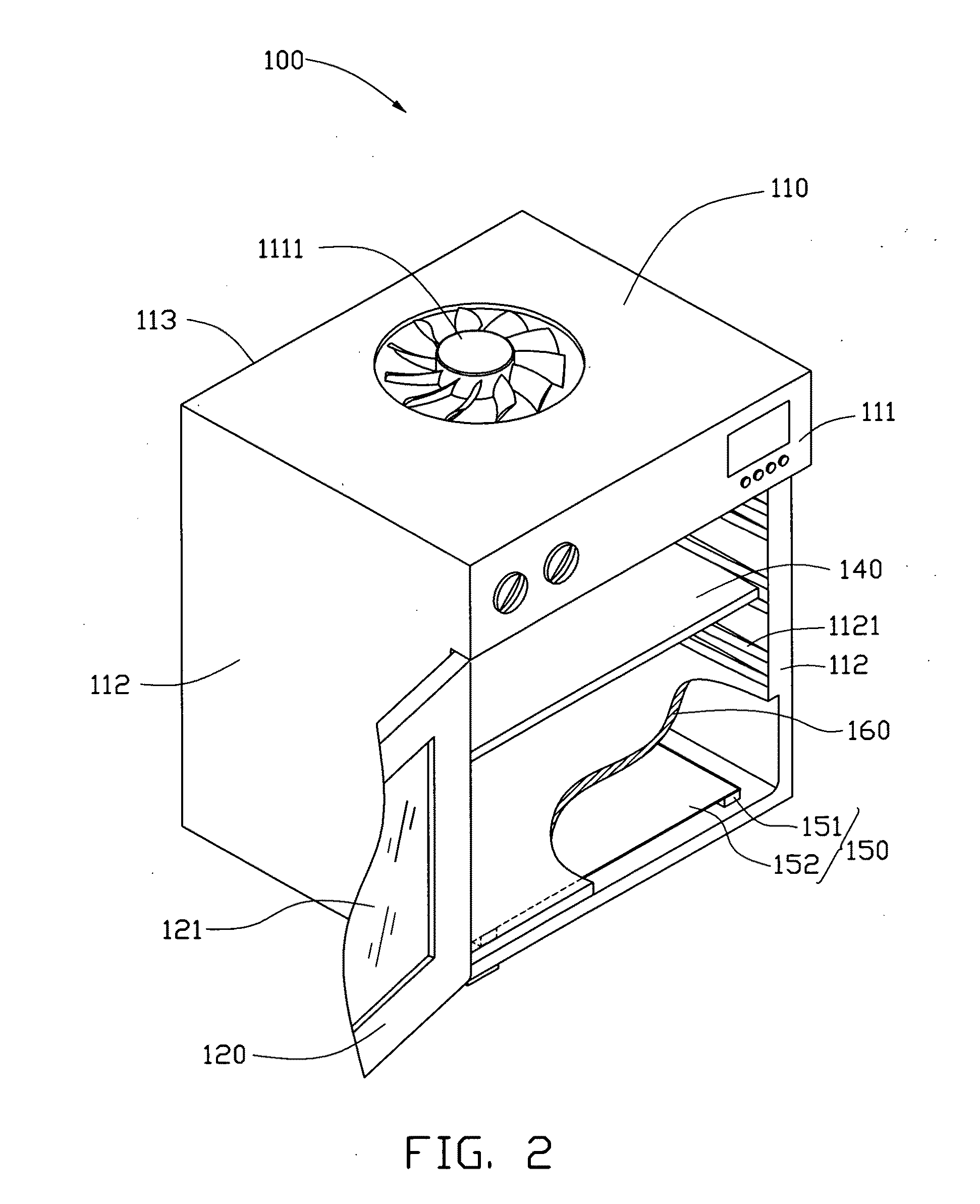
Carbon nanotube heater-equipped electric oven
ActiveUS20110036826A1Add considerable weightImprove thermal conductivityDomestic stoves or rangesElectrical heating fuelCarbon nanotubeNanotechnology
An electric oven includes an oven body defining a chamber. The heater is located in the chamber of the oven body. The heater includes a carbon nanotube structure. The carbon nanotube structure includes a plurality of carbon nanotubes joined end to end by van der Waals attractive force.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
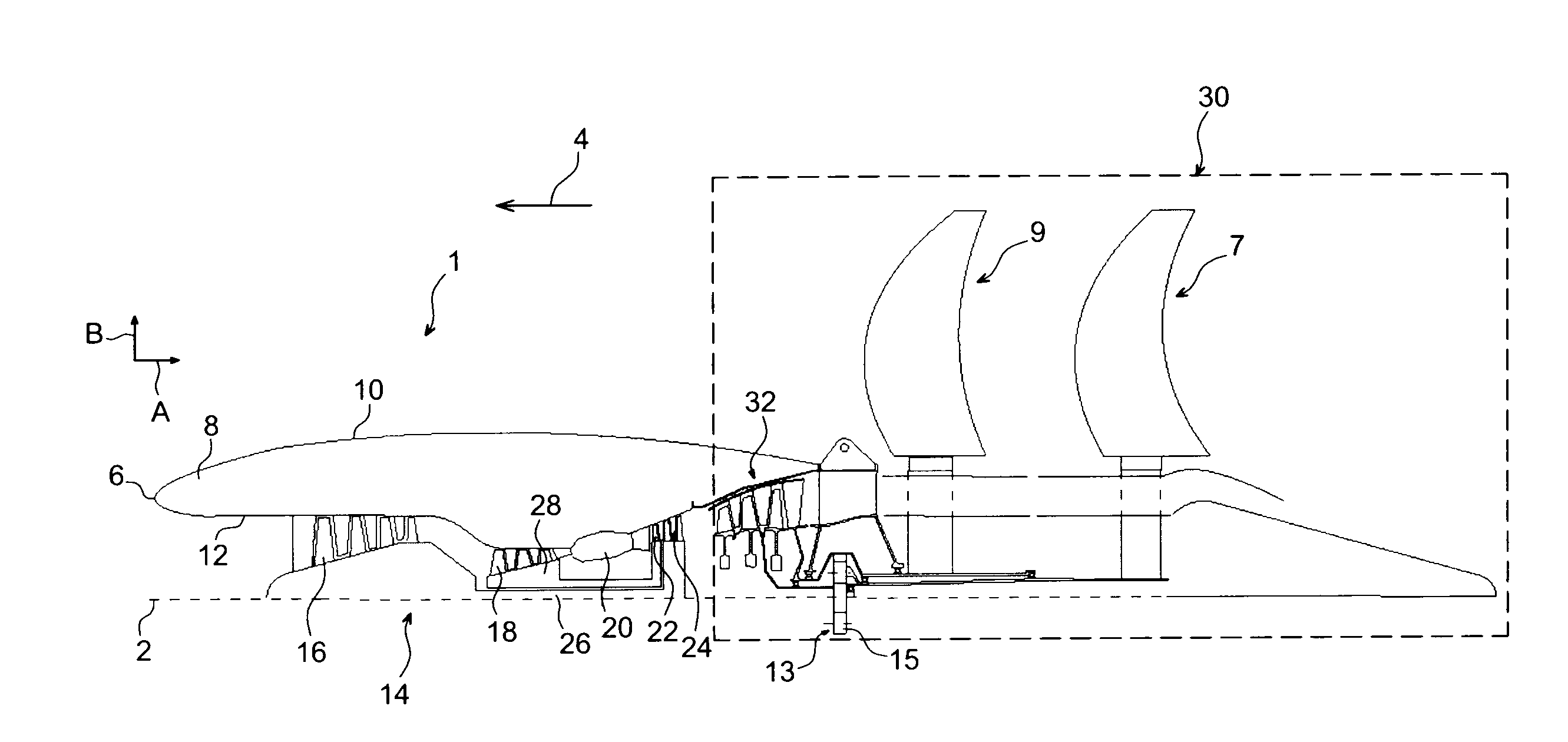
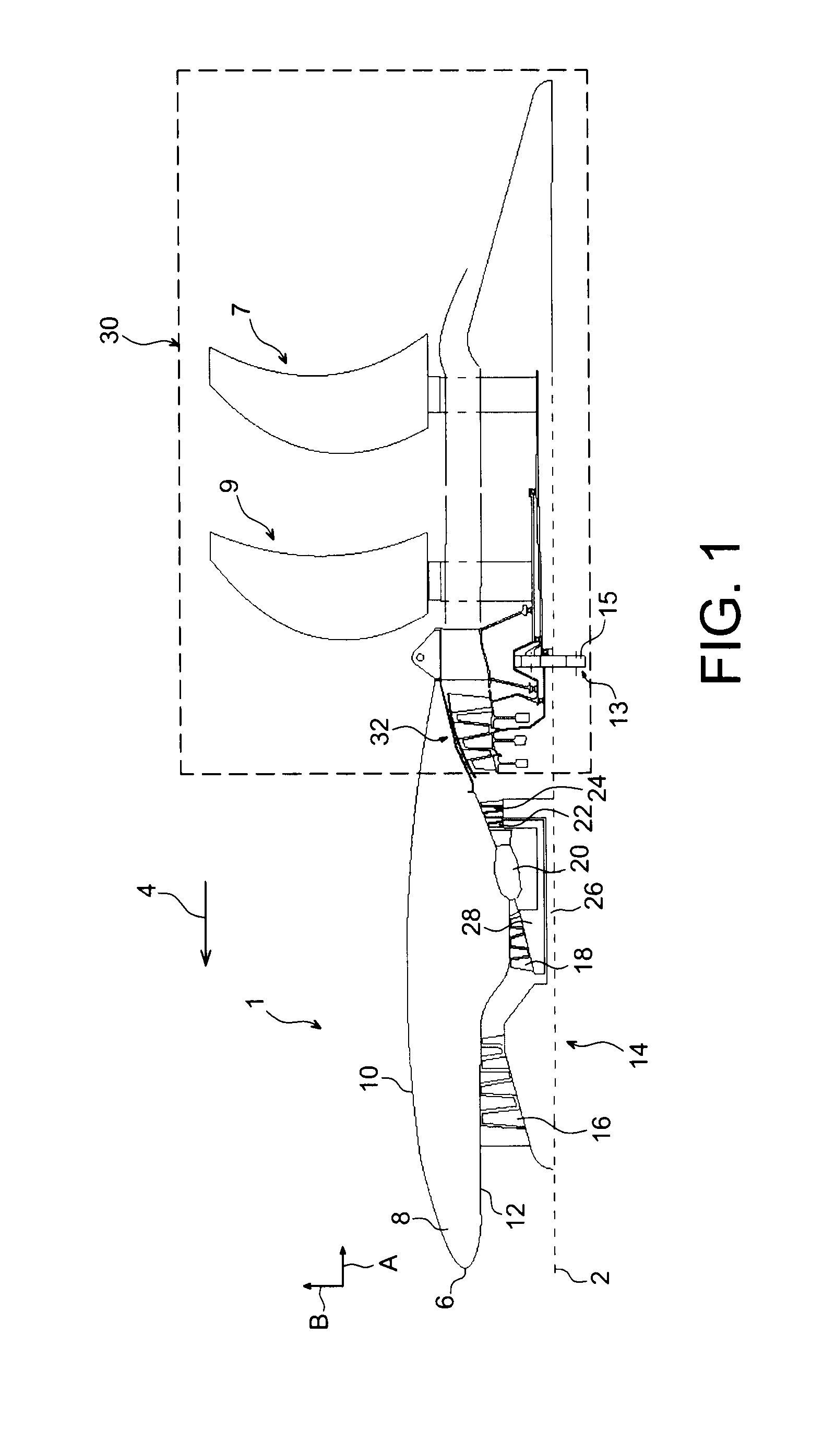
System of contra-rotating propellers driven by a planetary gear train providing a balanced distribution of torque between the two propellers
ActiveUS20110243735A1Improve efficiencyReduce sound levelPropellersPump componentsGear drivePropeller
A system of contra-rotating propellers for an aircraft turbomachine, including: a free power turbine including a first rotor; first and second propellers; and a mechanical transmission system including a planetary gear train fitted with a sun gear driven by the rotor, at least one planet gear driving the first propeller, and a ring driving the second propeller. The free power turbine also includes a second rotor that is contra-rotating relative to the first rotor, and rotating the ring.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
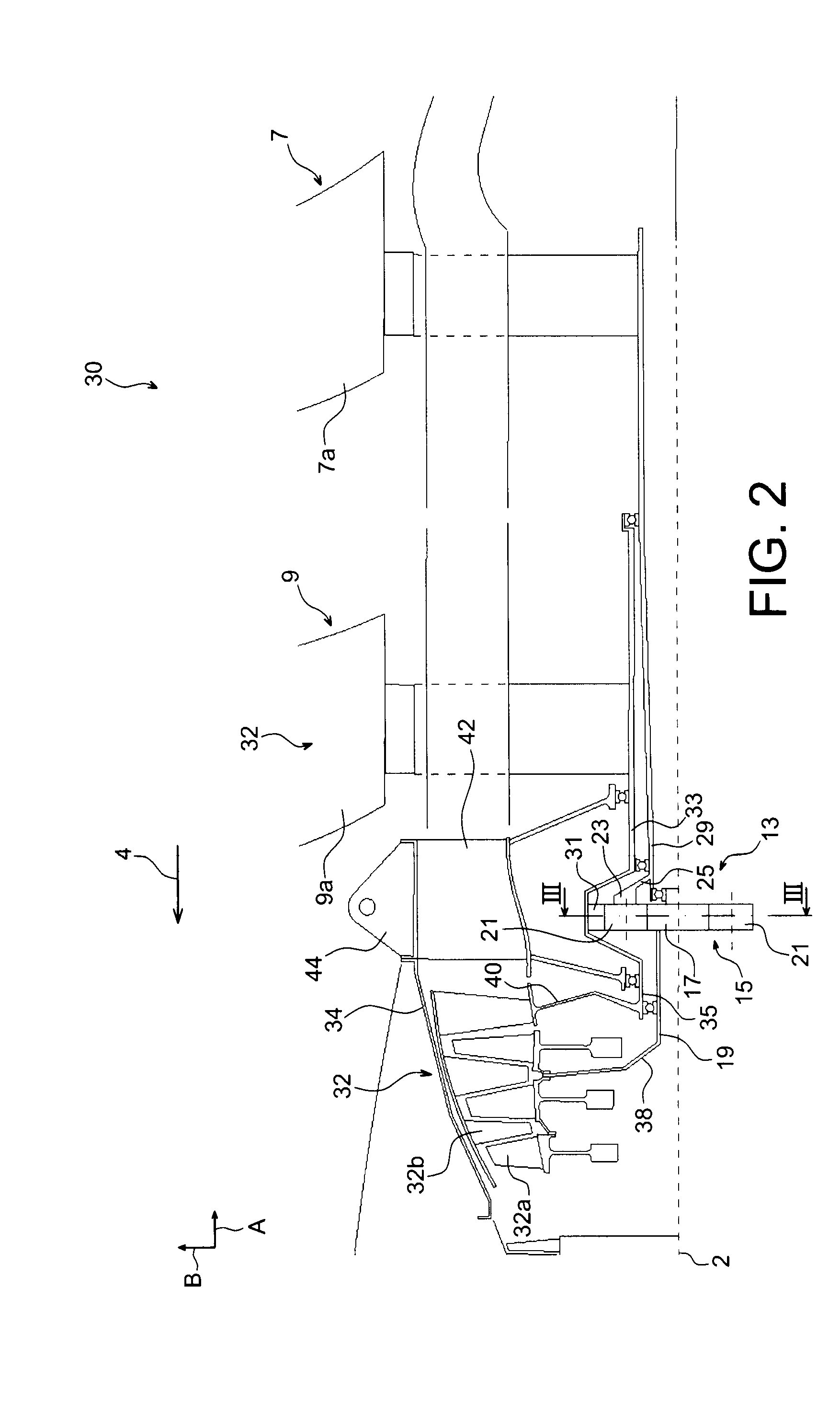
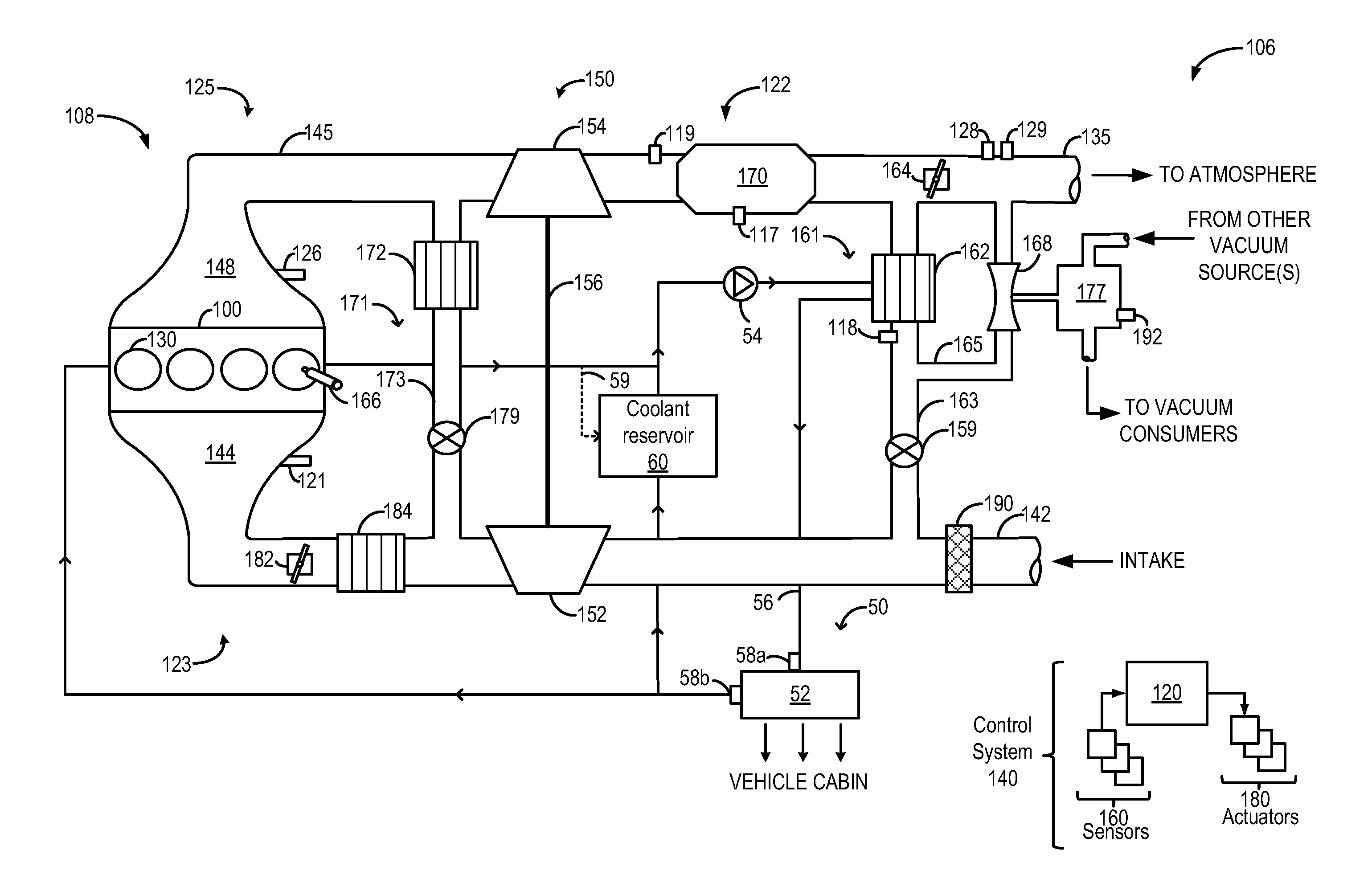
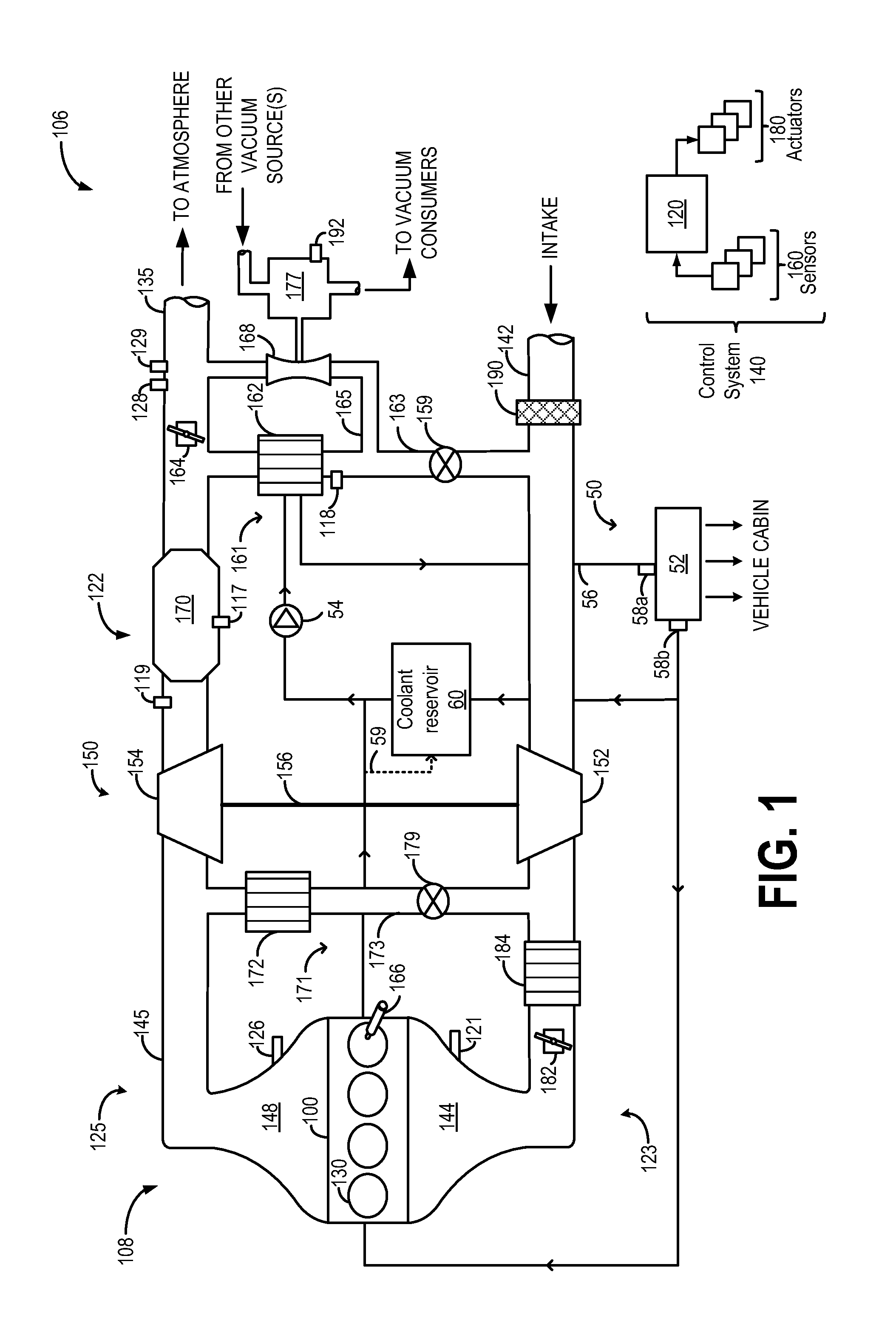
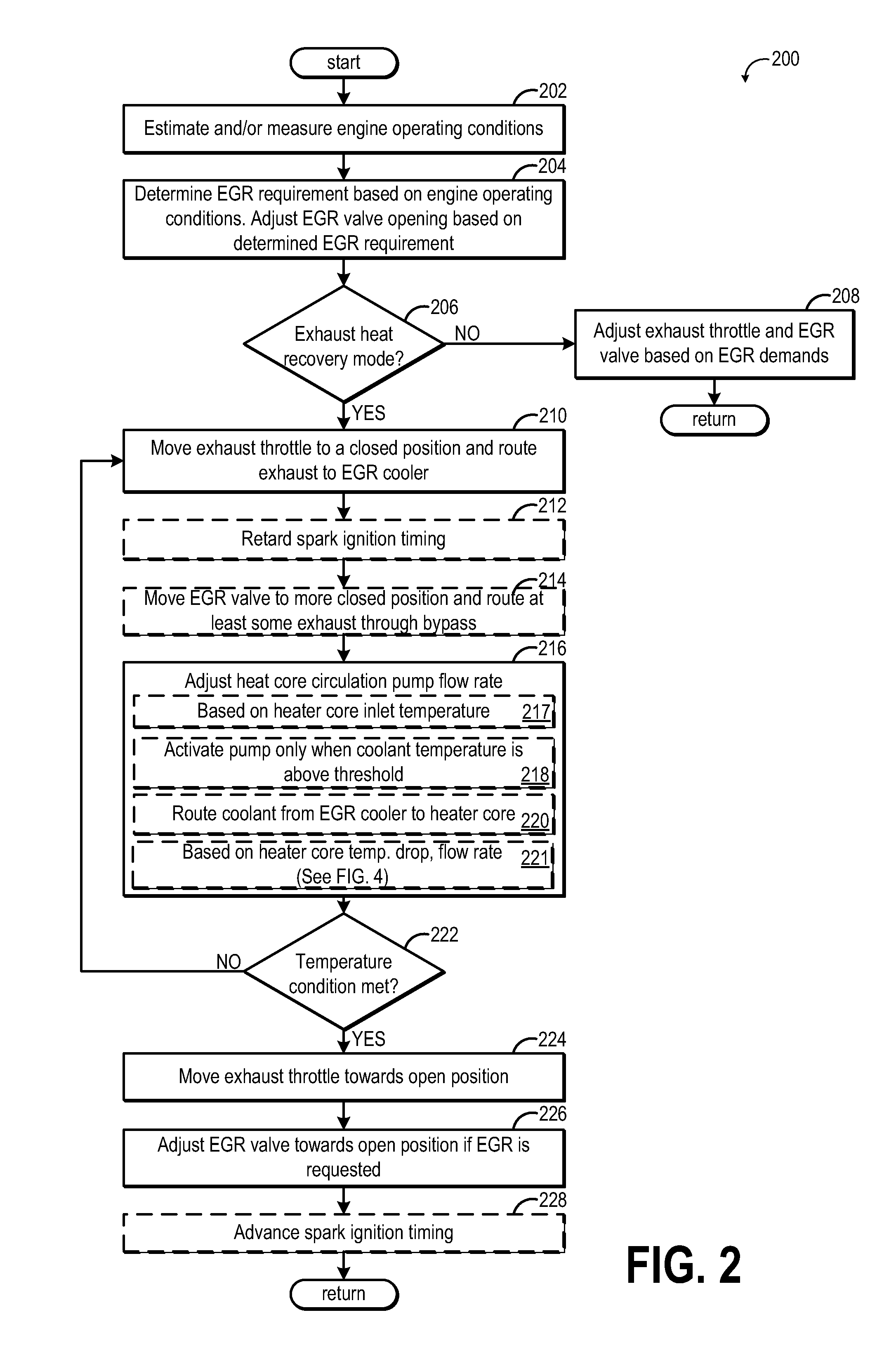
Exhaust throttling for cabin heating
ActiveUS20150121848A1Maximize heat transferConvenient amountInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHeater coreHeat transfer
Embodiments for heating a vehicle cabin are disclosed. In one example, a method for an engine comprises pumping coolant from a coolant reservoir to an exhaust component and then to a heater core, the coolant heated by the exhaust component, and during engine warm-up conditions, adjusting a flow rate of coolant into a heater core to maximize heat transfer to a vehicle cabin.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using dfb fiber lasers
ActiveUS20100085632A1Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is described that efficiently converts a near-infrared laser beam to tunable mid-infrared wavelength output. In some embodiments, the OPO includes an optical resonator containing a nonlinear crystal, such as periodically-poled lithium niobate. The OPO is pumped by a continuous-wave fiber-laser source having a low-power oscillator and a high-power amplifier, or using just a power oscillator. The fiber oscillator produces a single-frequency output defined by a distributed-feedback (DFB) structure of the fiber. The DFB-fiber-laser output is amplified to a pump level consistent with exceeding an oscillation threshold in the OPO in which only one of two generated waves (“signal” and “idler”) is resonant within the optical cavity. This pump source provides the capability to tune the DFB fiber laser by straining the fiber (using an attached piezoelectric element or by other means) that allows the OPO to be continuously tuned over substantial ranges, enabling rapid, wide continuous tuning of the OPO output frequency or frequencies.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ACULIGHT CORP
Indexable cutting insert with coolant delivery
InactiveUS20150063926A1Facilitate enhanced deliveryReduce heatTransportation and packagingCutting insertsEngineeringCoolant
An indexable cutting insert includes a rake face, a flank surface, a bottom surface, and a central aperture defined by an aperture side wall. The indexable cutting insert further has a mouth defined by a mouth surface. There is a primary coolant trough that has an aperture section in the side wall contained in the aperture side wall, a mouth section contained in the mouth surface, and a rake face section contained in the rake face. There is a radial angular coolant trough, which has an entrance end opening into a selected one of the primary coolant trough and the mouth. The radial angular coolant trough has an orientation wherein the central longitudinal axis thereof is generally perpendicular to a corresponding discrete cutting edge whereby during operation a coolant stream is directed toward the corresponding discrete cutting edge.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Metal powder composition for use in selective laser sintering
InactiveUS7258720B2Significant heatingEasy to separateAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingSelective laser sinteringGraphite
A three-dimensional object of a desired shape is made by irradiating an optical beam on a metal powder layer to form a sintered layer and by laminating such sintered layer one above another. A metal powder composition for use in making such a three-dimensional object includes an iron-based powder material, a nickel and / or nickel alloy powder material, a copper and / or copper alloy powder material, and a graphite powder material. The graphite powder material acts to enhance the wettability during melting and to reduce microcracks during solidification.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Gripper with carbon nanotube film structure
ActiveUS8585109B2No position control capabilitySignificant heatingMicromanipulatorPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPower flowCarbon nanotube
A gripper includes a support and a plurality of gripping arms fixed on the support. One of the plurality of gripping arms includes a base and a carbon nanotube film structure to define a conductive circuit. The conductive circuit receives current to heat the base and the carbon nanotube film structure to actuate the gripper for gripping an object.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
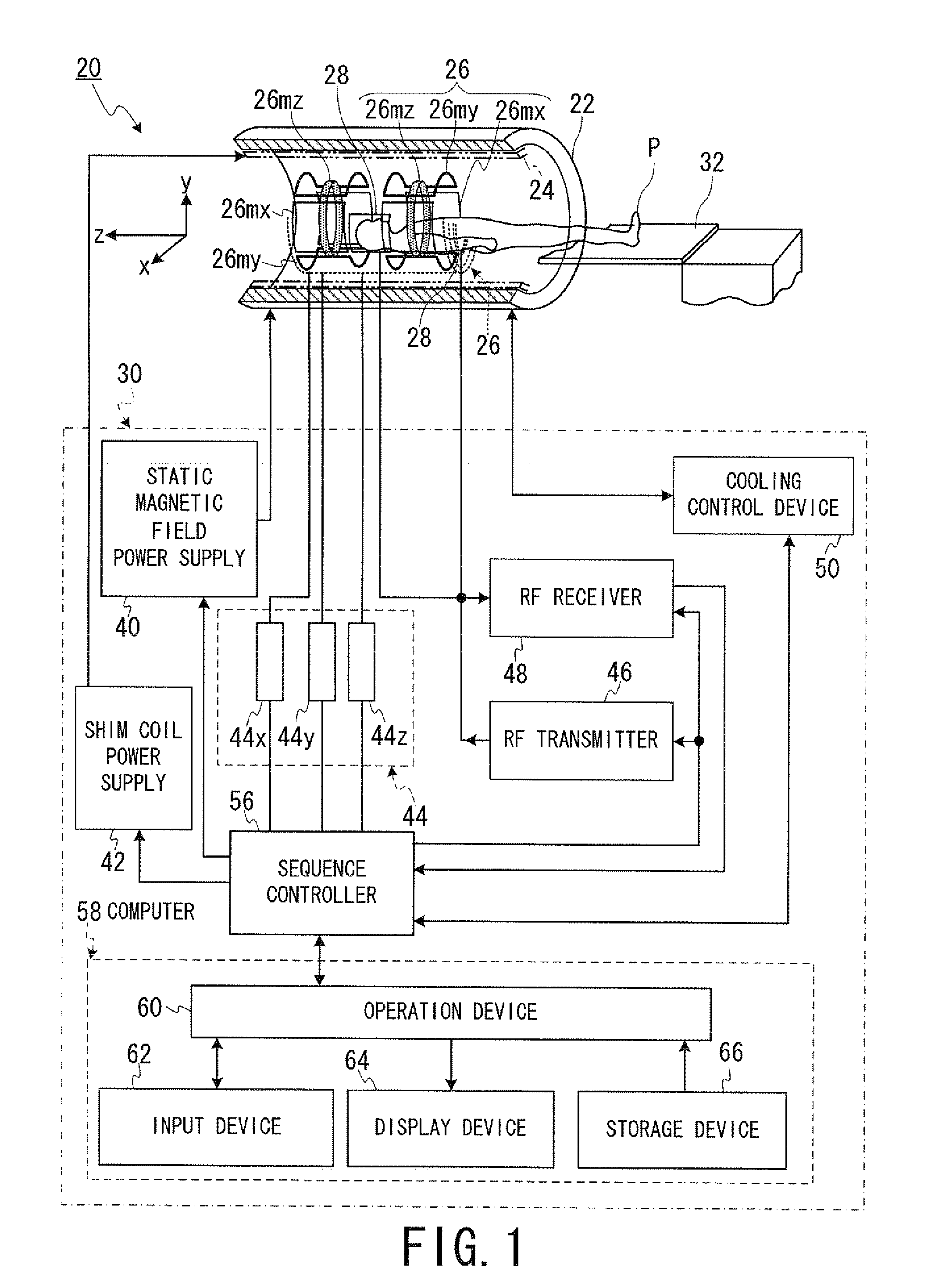
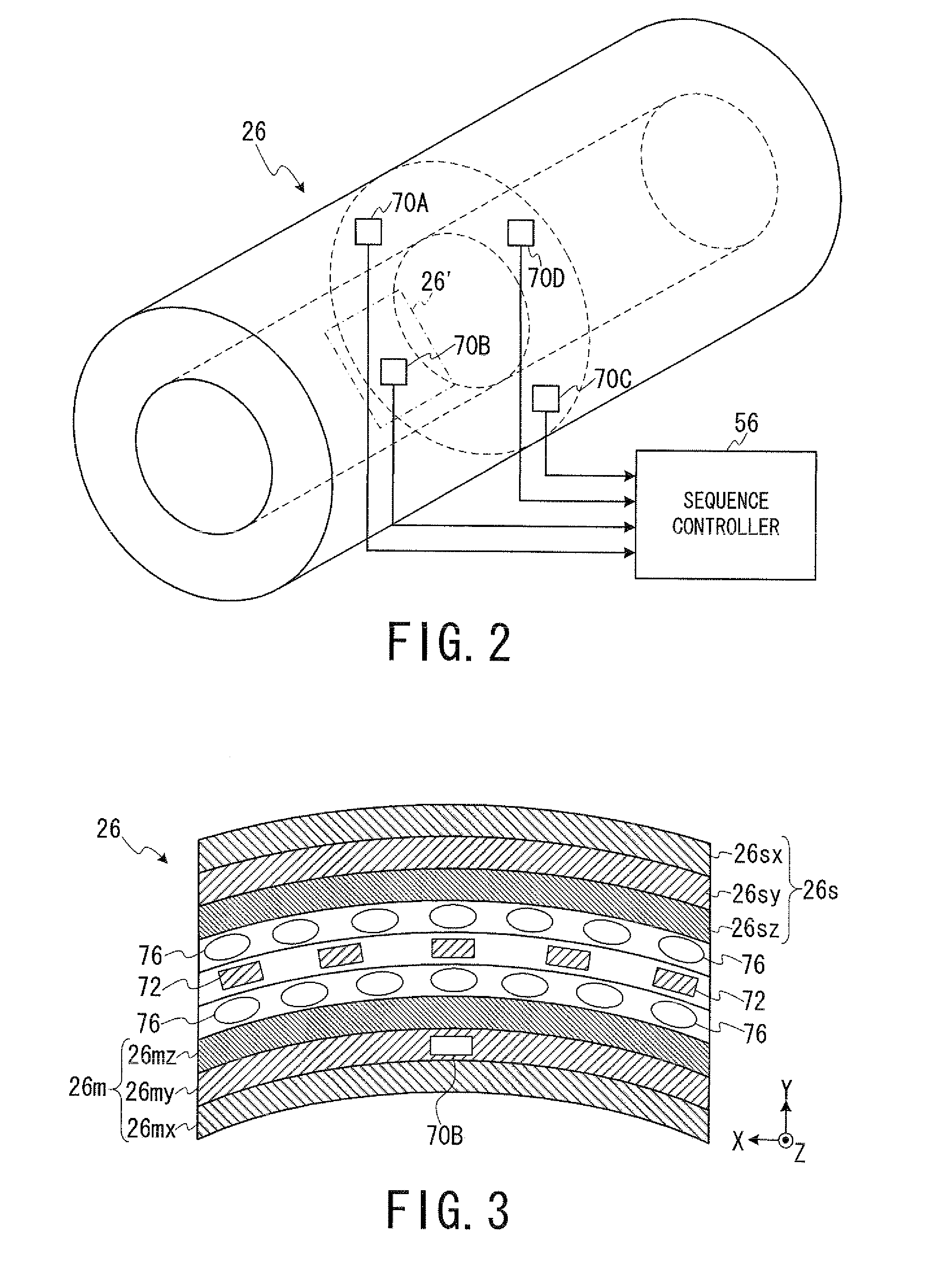
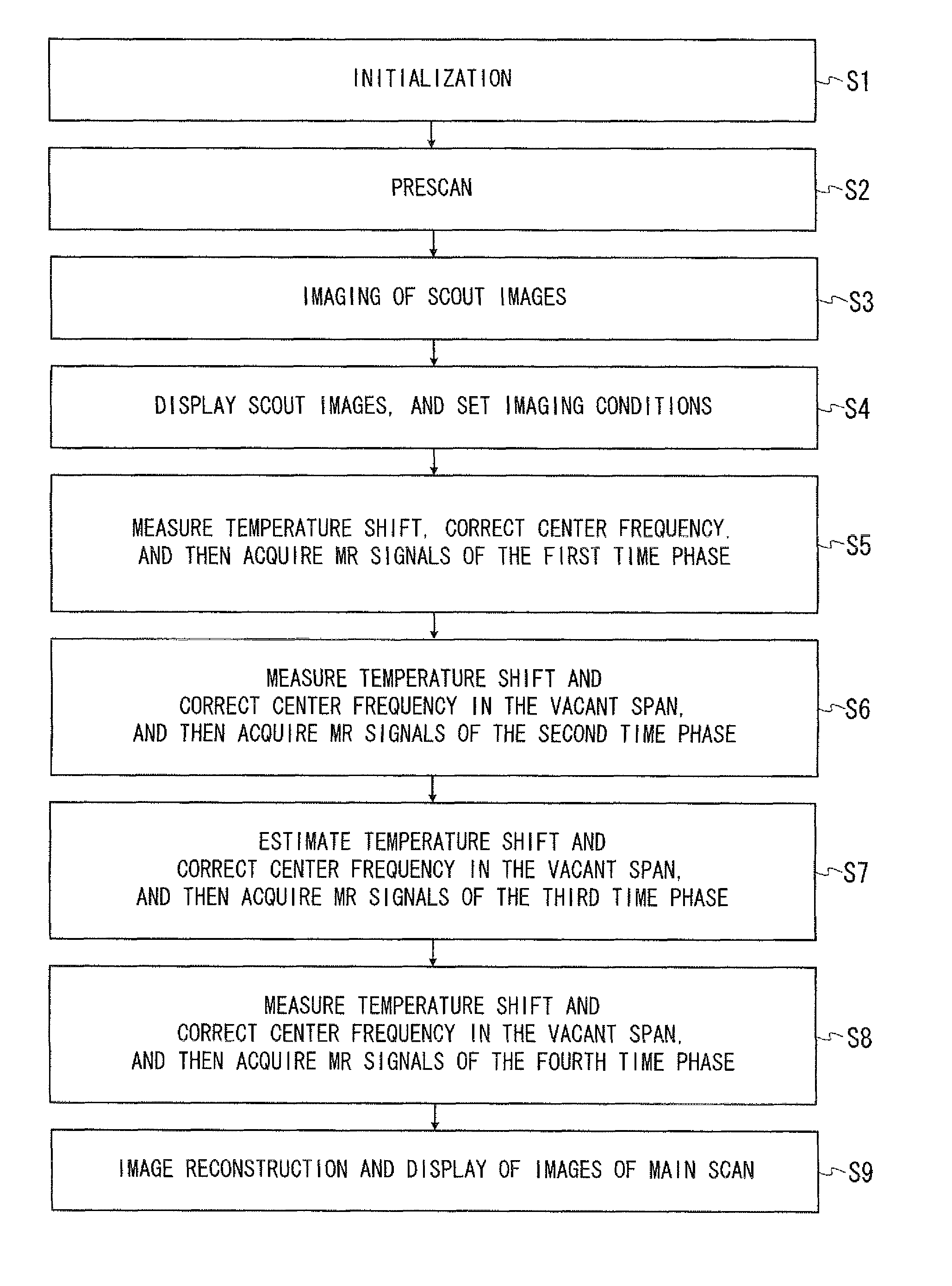
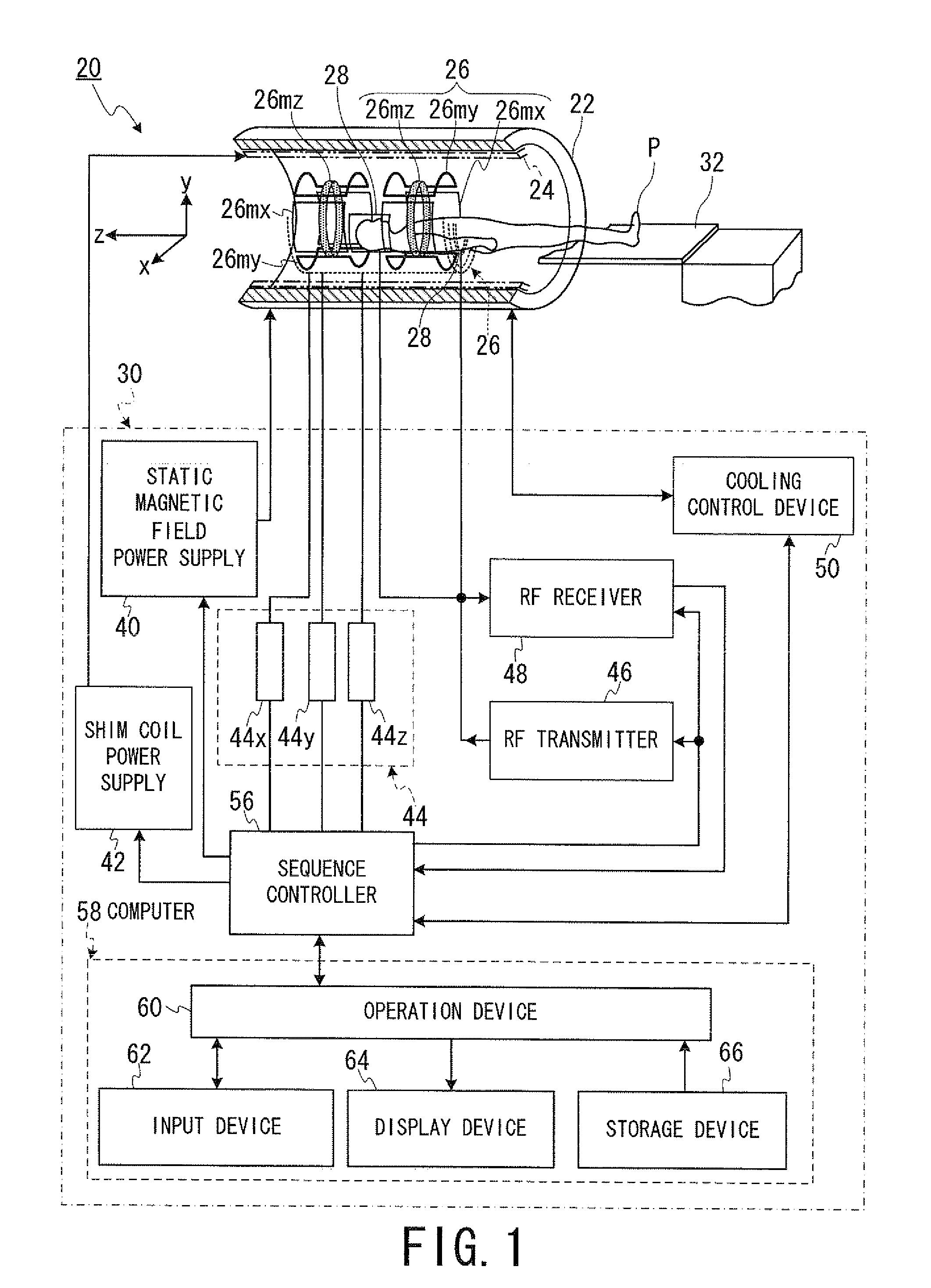
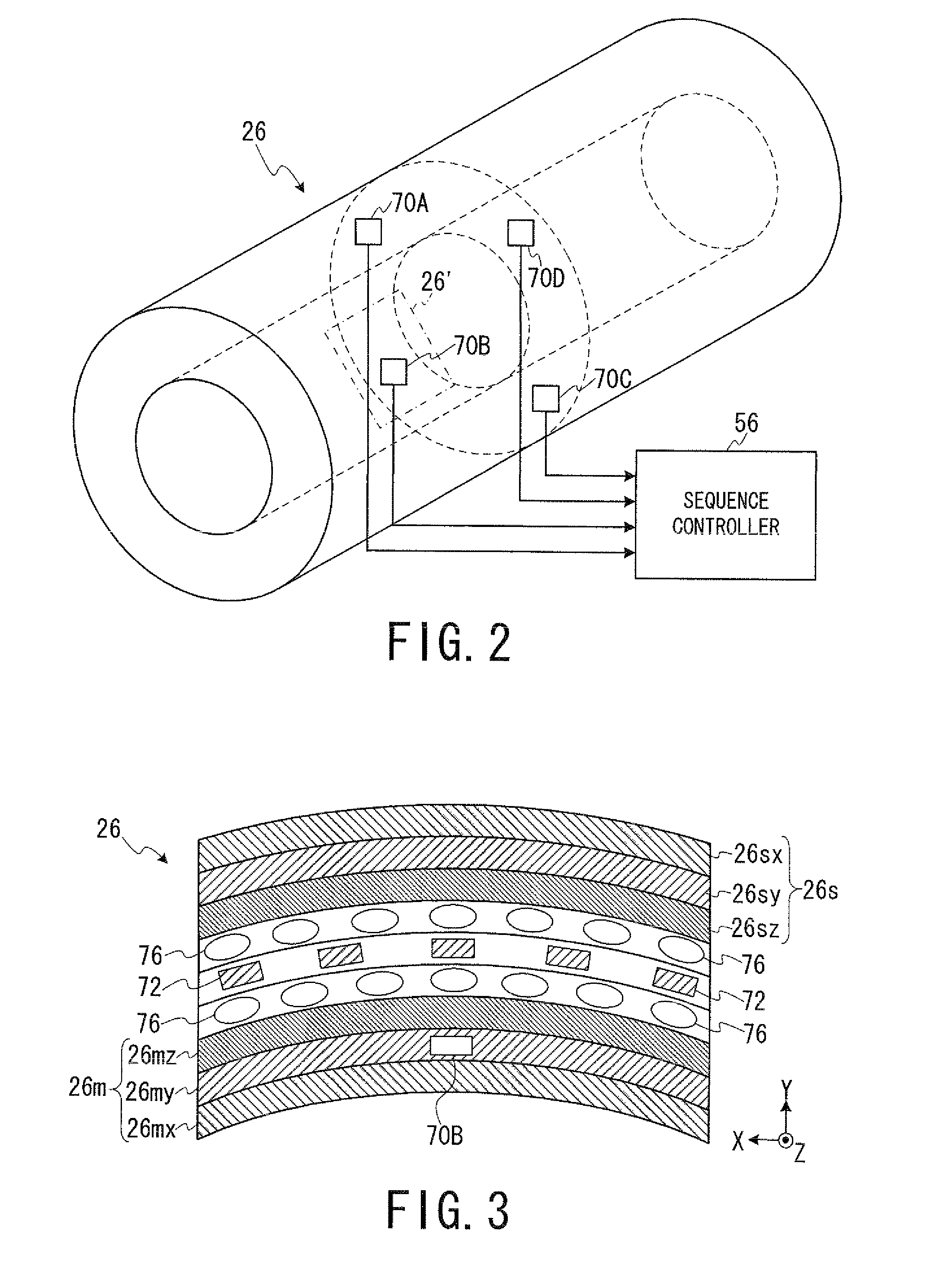
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20130154642A1Significant heatingProvide informationElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceHydrogenHydrogen atom
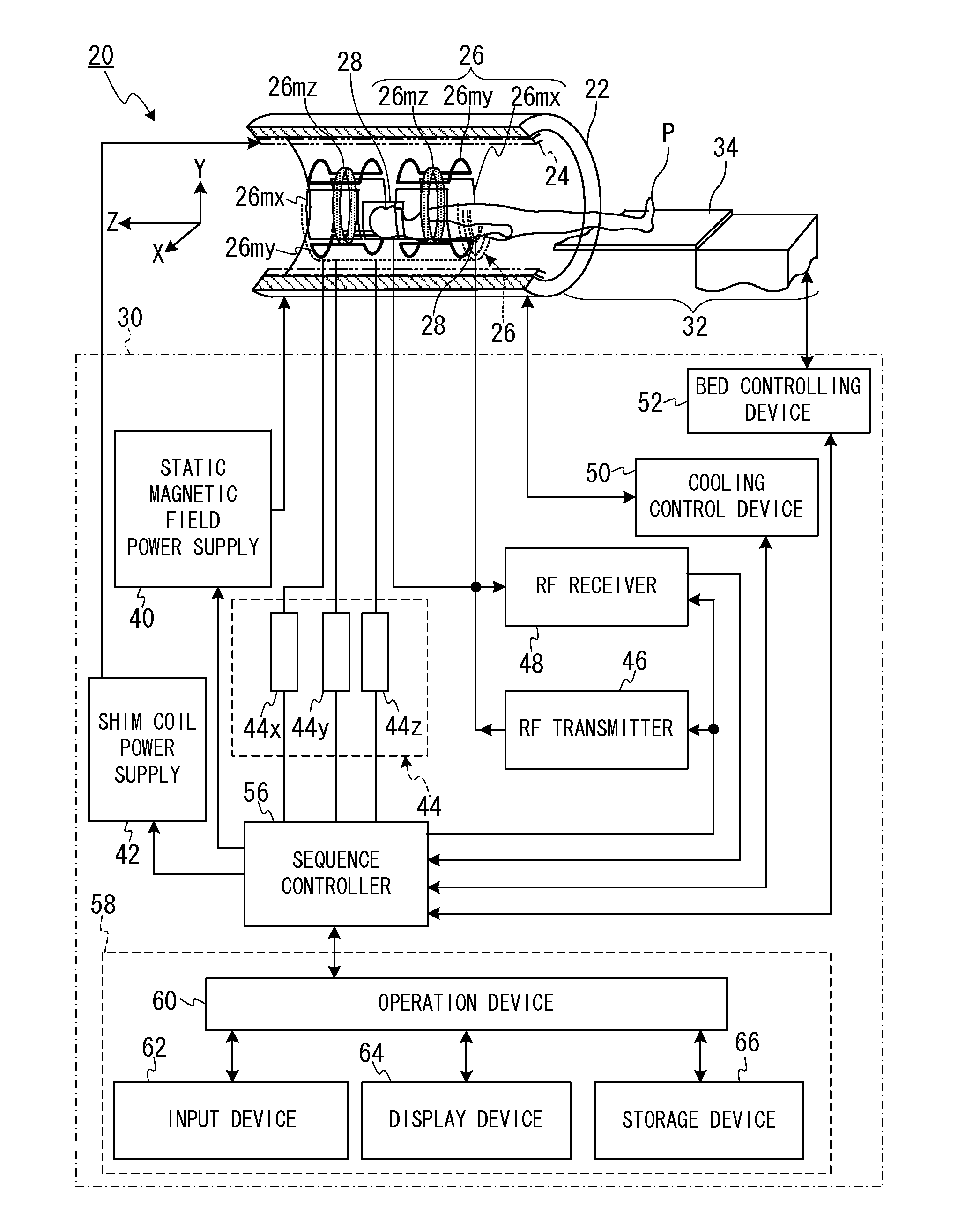
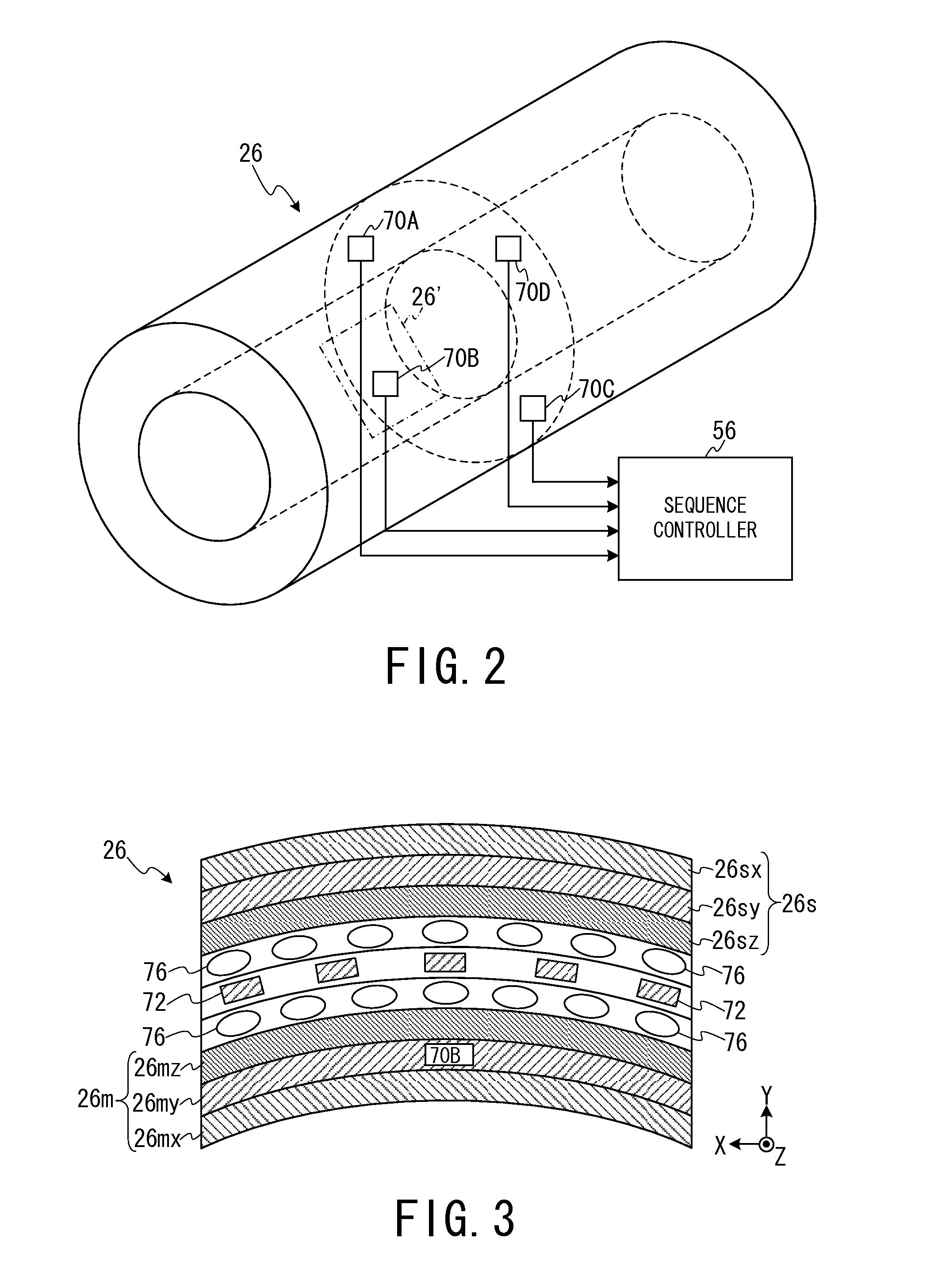
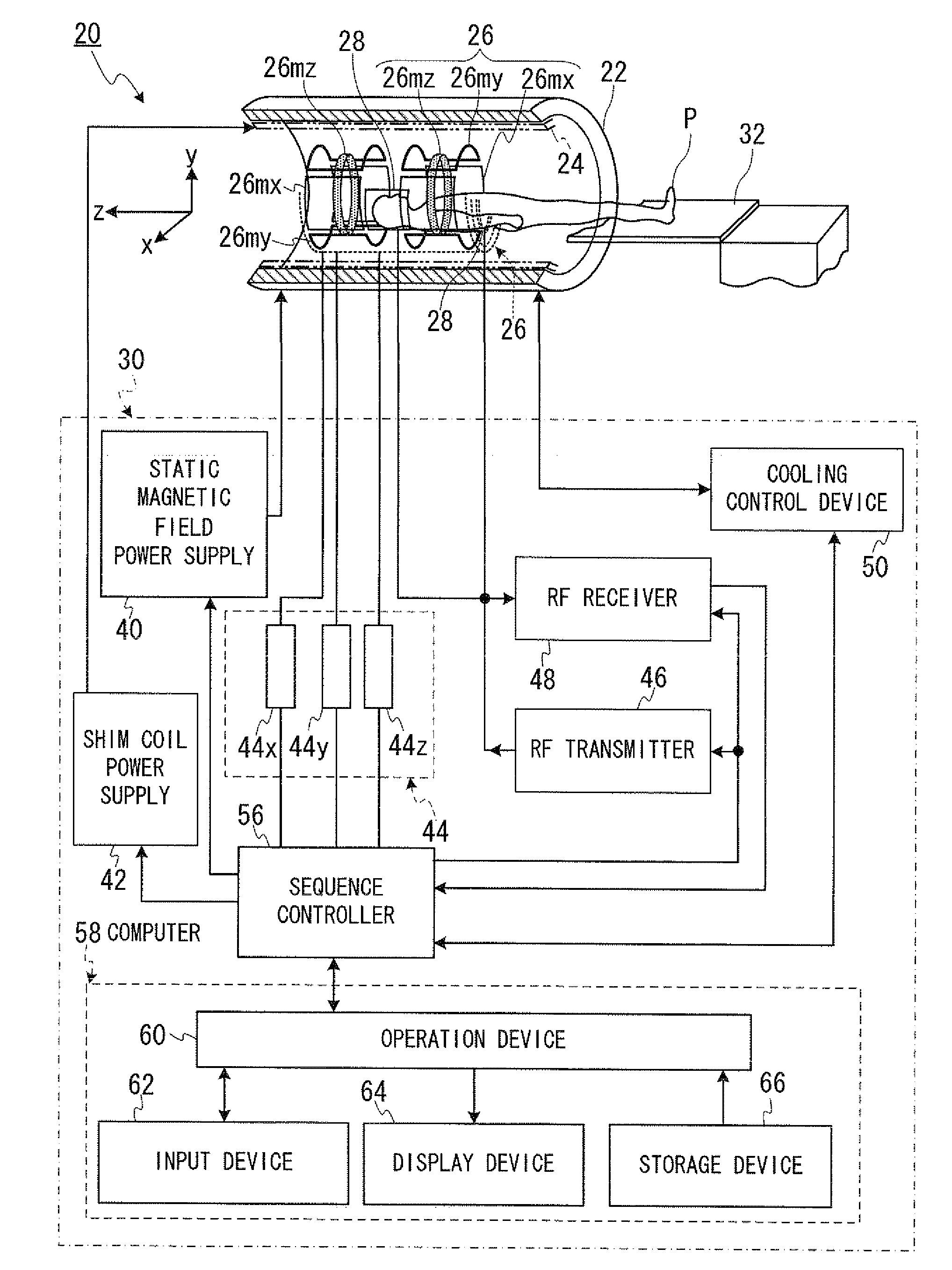
In one embodiment, an MRI apparatus (20) includes “a temperature measuring unit (70A to 70D) performing temperature measurement of a gradient magnetic field coil unit (26)”, a data storing unit (100), a pulse setting unit (102), and an imaging unit. The data storing unit stores the first and second data indicating a shift of a center frequency of magnetic resonance of hydrogen atoms. The first data corresponds to a case of temperature rise of the gradient magnetic field coil unit, and the second data corresponds to a case of temperature fall of that. The pulse setting unit corrects a center frequency of an RF pulse by calculating an estimated shift of the center frequency based on data corresponding to result of the temperature measurement out of the first and second data. The imaging unit performs magnetic resonance imaging based on the corrected RF pulse.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20120001635A1Significant heatingProvide informationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHydrogen atomResonance
In one embodiment, an MRI apparatus includes a temperature measuring unit, a data storing unit, a pulse setting unit and an imaging unit.The temperature measuring unit measures a temperature of a gradient magnetic field coil unit at least two times.The data storing unit stores “shift data indicating a shift of a center frequency of magnetic resonance of a hydrogen atom in response to a variation of the temperature of the gradient magnetic field coil unit”, in advance.The pulse setting unit determines an estimated shift of the center frequency of the magnetic resonance according to “the variation of the temperature of the gradient magnetic field coil unit based on the measurement result” and “the shift data”, and corrects a center frequency of an RF pulse based on the estimated shift.The imaging unit performs imaging with the RF pulse whose center frequency is corrected.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Fuel cell for powering electronic appliances, in particular portable objects
The fuel cell (2) is of the kind comprising an anode (12) and a cathode (10) between which an electrolyte (18) is interposed. Solid bodies (20) storing a hydrogen mass, able to be decomposed by combustion, are associated to pyrotechnic means (24,26) to release the hydrogen and bring it into contact with the anode (12). Means (38) tap the ambient air to bring it into contact with the cathode (10). Firing of the pyrotechnic means (24,26) is placed under the control of addressing means (28) embedded in the appliance (2). The surplus water produced by the exchange between the hydrogen and the oxygen is resorbed by the temperature increase induced by combustion of the bodies (20). The solid bodies (20) are supported by an interchangeable card (22).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Vapor compression system and method for controlling conditions in ambient surroundings
InactiveUS20050257564A1Operation efficiency is highEasy to operateMechanical apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleClosed loopEngineering
A vapor compression system including an evaporator, a compressor, and a condenser interconnected in a closed-loop system and a method of operating such a system. The method includes the conversion of expanded liquid heat transfer fluid from a liquid form to a high quality liquid vapor mixture before delivery to the evaporator. In one embodiment, the heat transfer surface of the evaporator coil is smaller than that required to obtain an equivalent evaporator capacity when the expanded liquid heat transfer fluid is not converted from a liquid form to a high quality liquid vapor mixture
Owner:XDX GLOBAL LLC
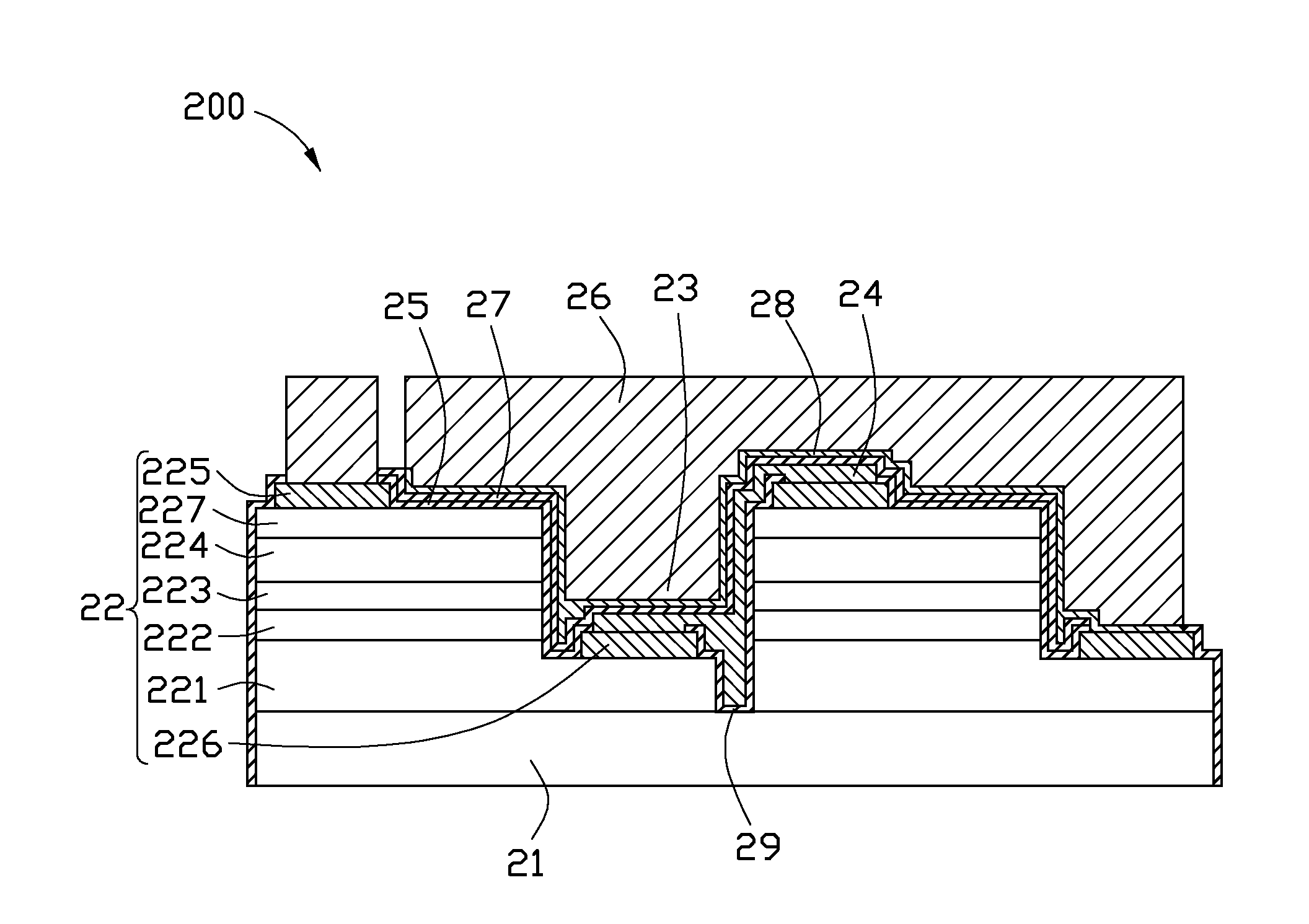
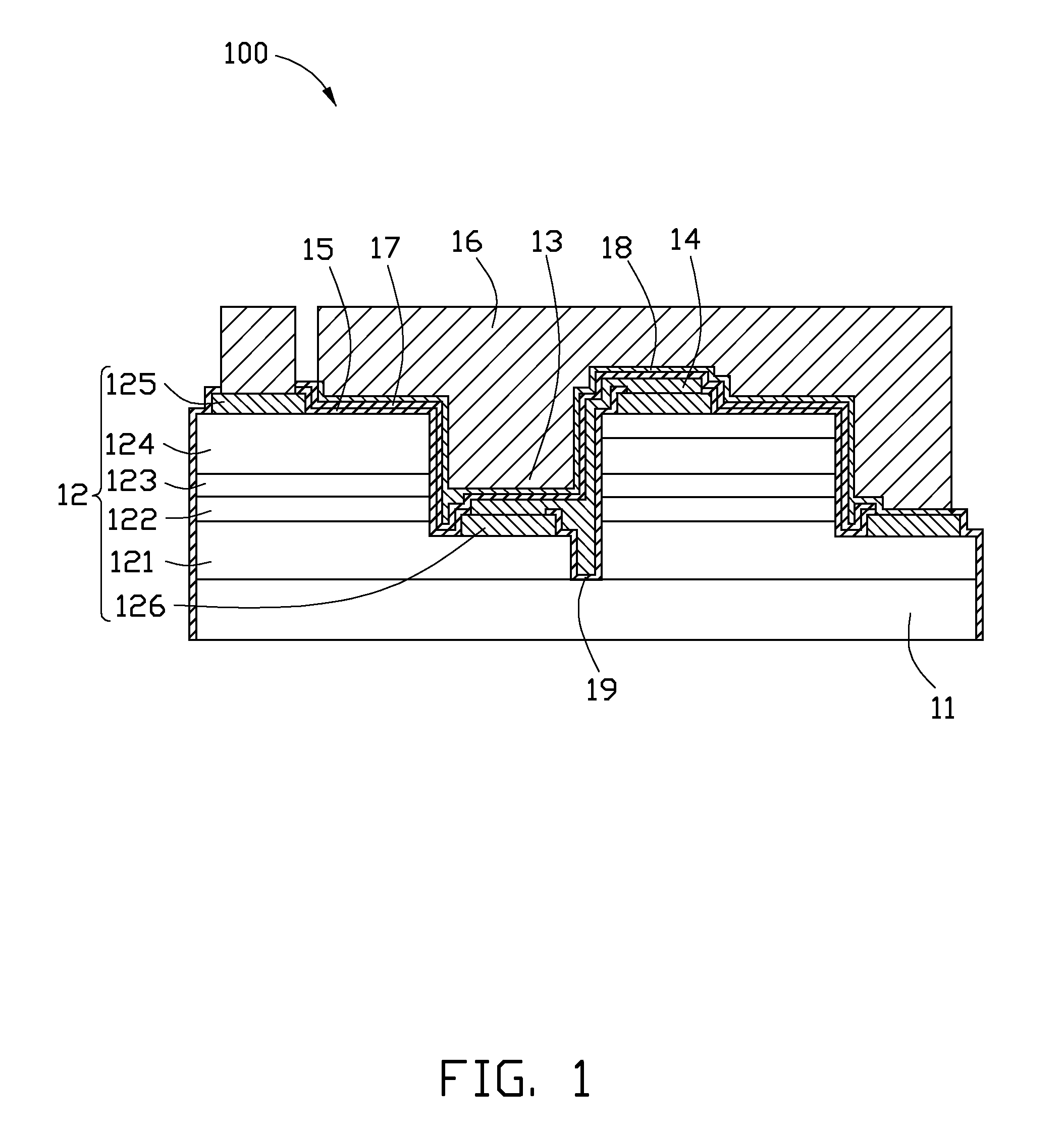
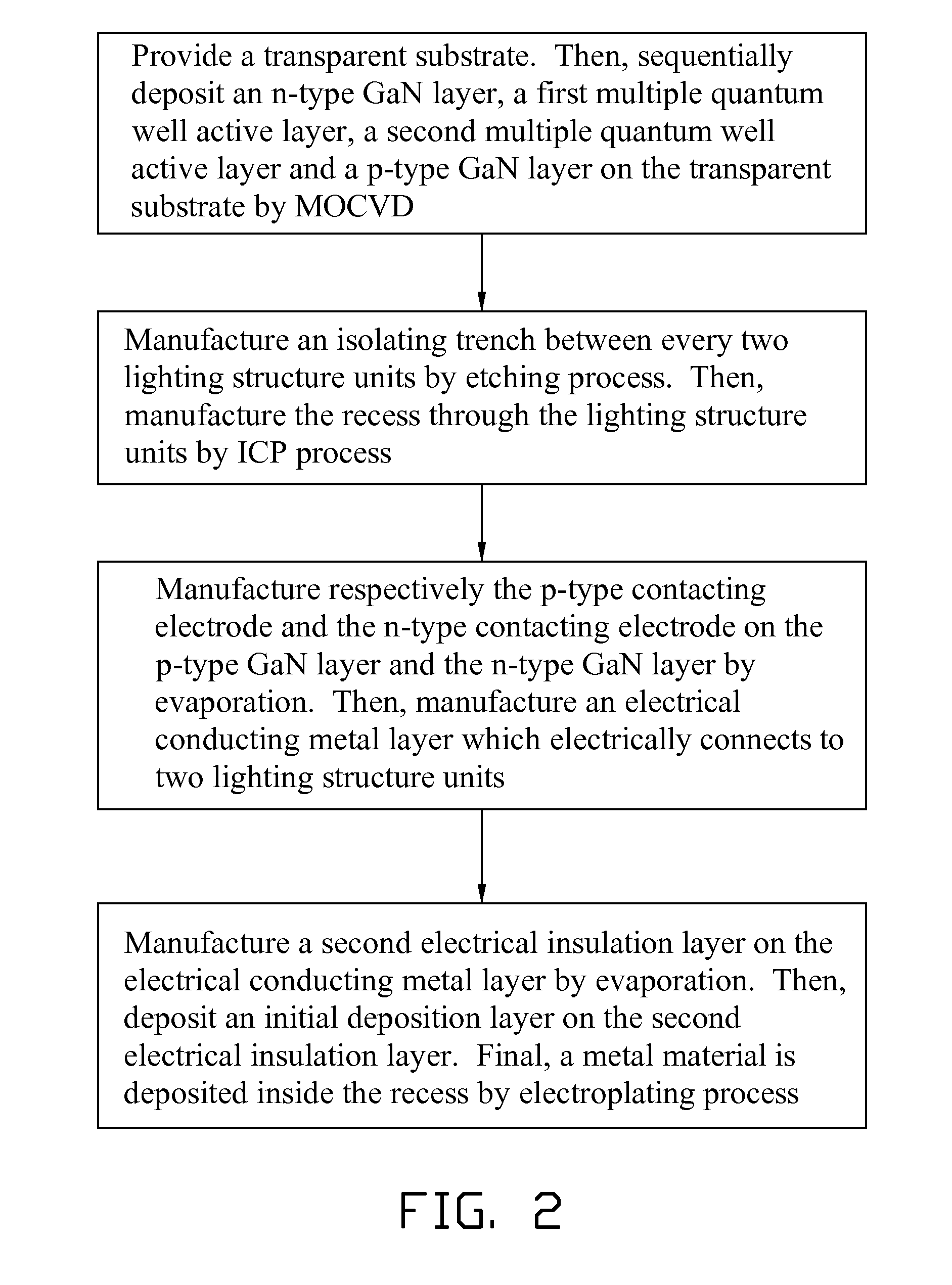
Light emitting diode chip and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110233564A1Significant heatingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic materialsEngineering
An LED chip includes a transparent substrate and a number of lighting structure units each including a p-type semiconductor and an n-type semiconductor and a recess extending from the p-type semiconductor to the n-type semiconductor. The recess is filled with metal material which covers the surface of the lighting structure units. By filling the recess with metal material, the heat generated by the lighting structure units can rapidly transfer to the metal material. A method for manufacturing the light emitting diode chip is also provided.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Solid fuel
ActiveUS8721746B2A large amountEasy to useSolid waste disposalBiofuelsSolid fuelPulp and paper industry
Owner:CREATIVE CO LTD
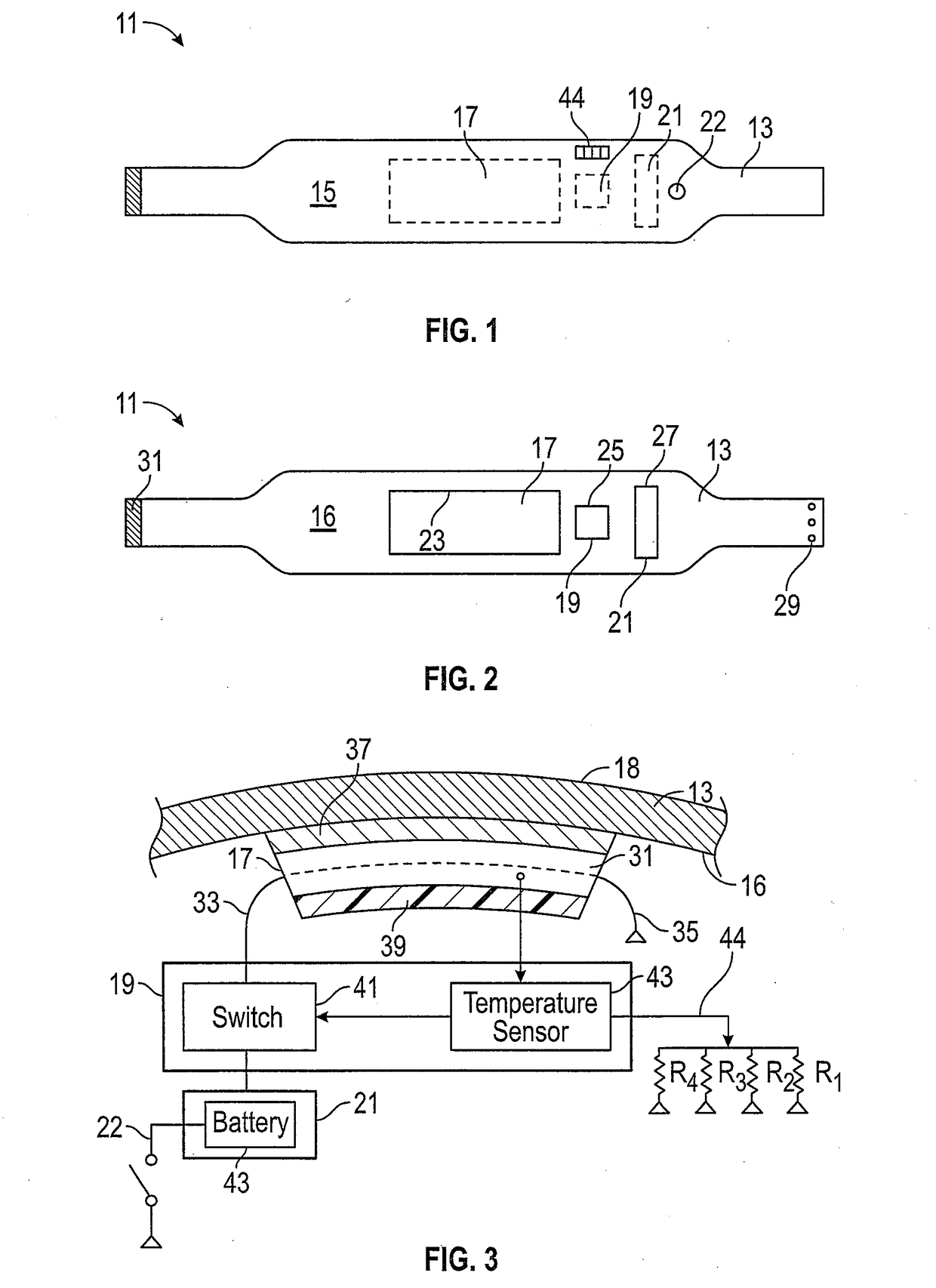
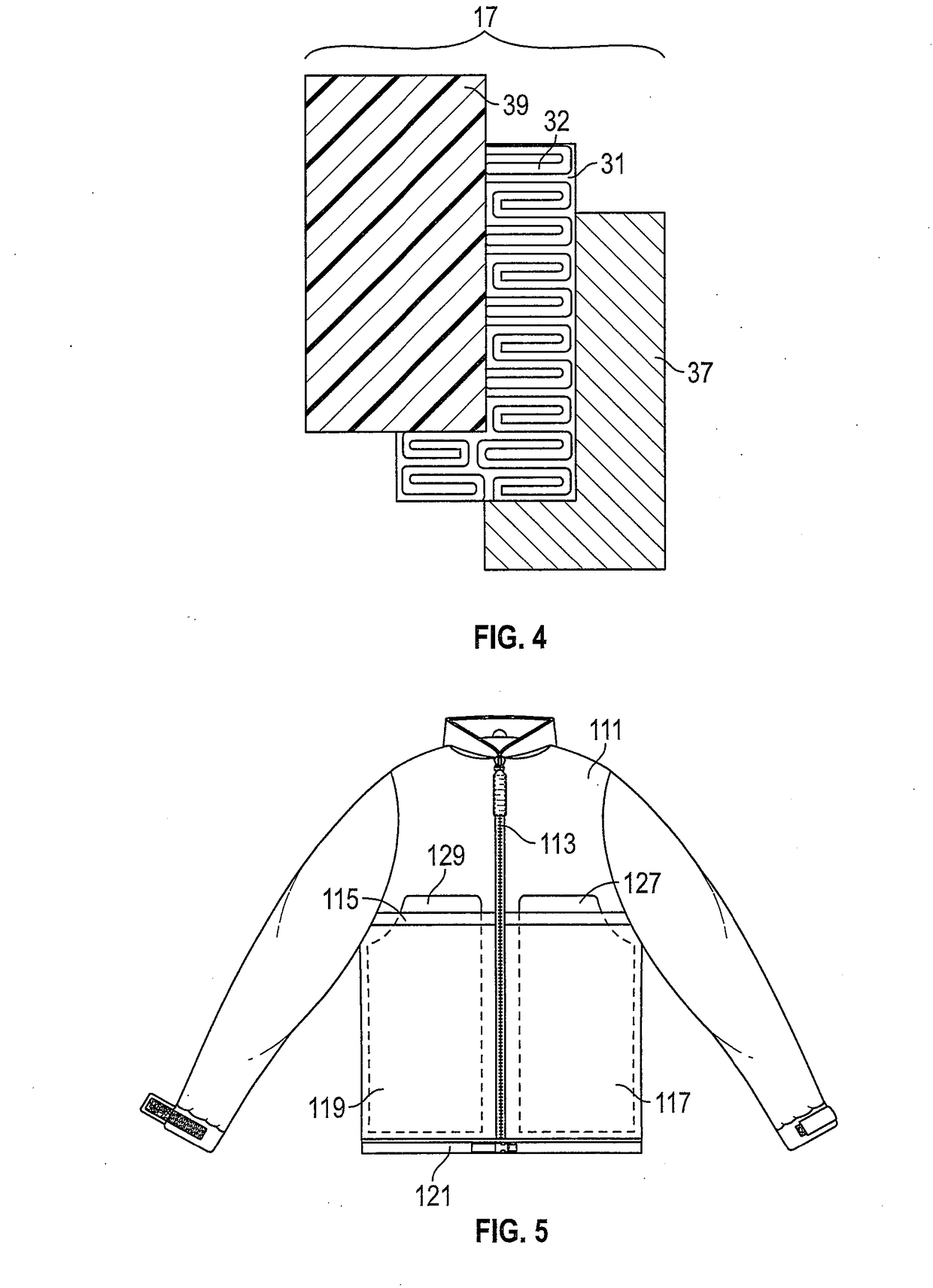
Tri-modal localized heating garment
InactiveUS20180280190A1Significant heatingIncrease heatOvergarmentsTherapeutic coolingOptical radiationElectricity
A garment that heats a portion of a human body during warm-up prior to athletic endeavor having a heater pad member with a size between the size of a common index card and an ordinary sheet of paper for localized penetrating heating of tissue and muscles. Heating is achieved by electrical heating of a heater pad member having a reflective metal foil on one side of the heater pad and thermally conductive PVF sheets on the opposite side. On the one hand, the metal foil reflects optical radiation toward a human body, while on the other hand, the PVF sheets direct infrared radiation into the human body. Control electronics, a battery and the heater pad are contained in separate pockets of the garment that are electrically connected together.
Owner:BETKOWSKI MAXIMILLIAN
Gripper with carbon nanotube film structure
ActiveUS20120049552A1No position control capabilitySignificant heatingMicromanipulatorPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPower flowCarbon nanotube
A gripper includes a support and a plurality of gripping arms fixed on the support. One of the plurality of gripping arms includes a base and a carbon nanotube film structure to define a conductive circuit. The conductive circuit receives current to heat the base and the carbon nanotube film structure to actuate the gripper for gripping an object.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Solid fuel
ActiveUS20110078947A1A large amountEasy to useSolid waste disposalBiofuelsSolid fuelPulp and paper industry
A solid fuel molded out of a mixture of wood pieces having a size of 1 to 25 mm, paper pieces having a size of 1 to 25 mm and thermoplastic resin, wherein the mixture contains 80 to 95 parts by weight of the total of the wood pieces and the paper pieces and 5 to 15 parts by weight of the thermoplastic resin, and the weight ratio of the wood pieces to the paper pieces is 20:80 to 90:10.The solid fuel which generates a stable amount of heat is manufactured by using waste wood, waste paper and waste thermoplastic resin in a well-balanced ratio.
Owner:CREATIVE CO LTD
Thermally-armored radio-frequency identification device and method of producing same
InactiveUS20140015643A1Sufficient protectionImprove abilitiesSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesExtreme temperatureRadio frequency
A thermally-armored RFID tag is configured to withstand extreme temperatures associated with certain product fabrication, including, but not limited to, the temperatures of molten metal and plastic. The thermal protection allows the RFID tag to be inserted into products during their fabrication, molding, casting, or extrusion, instead of being applied to the surface or inserted into the surface of the products after their fabrication
Owner:AITA
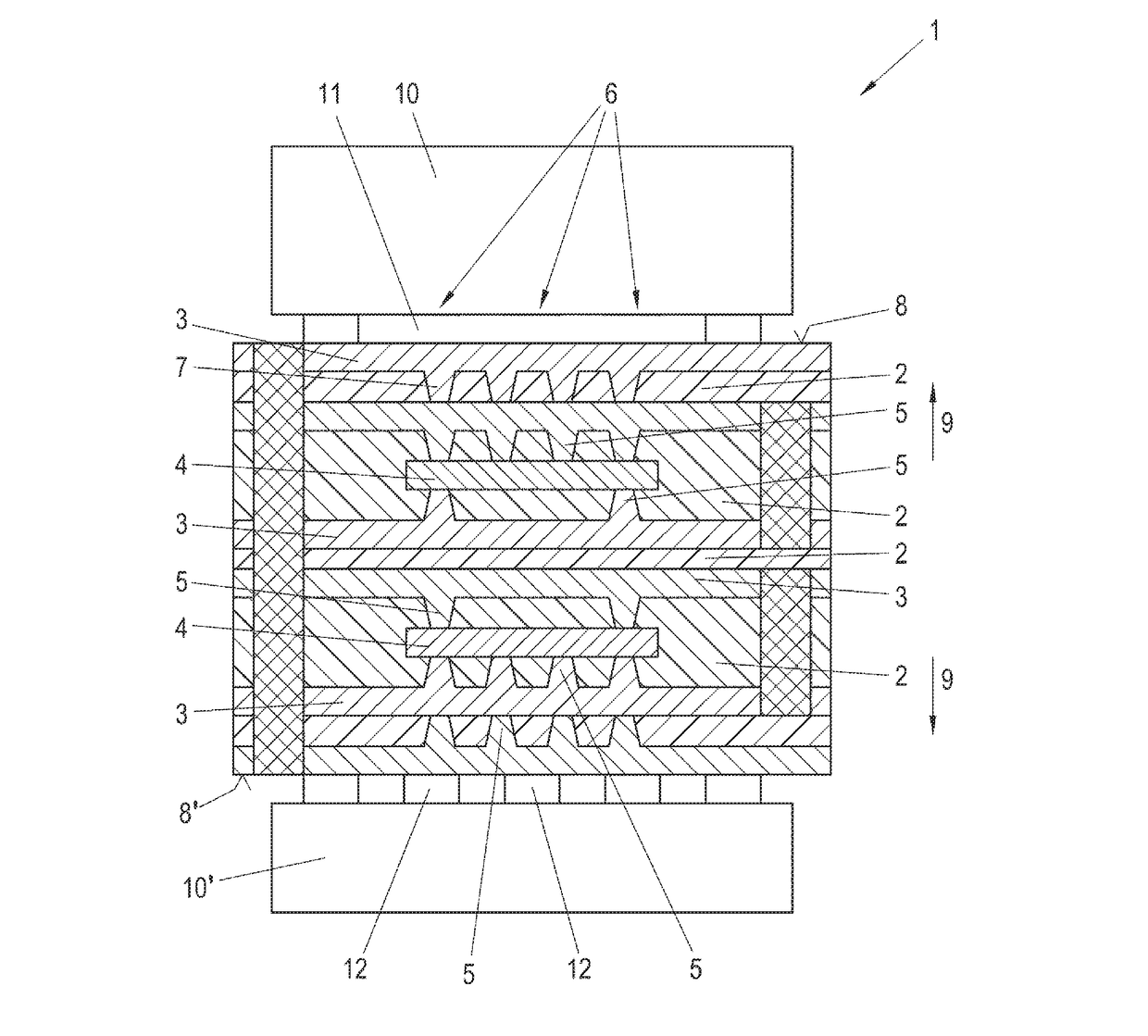
Connection system for electronic components
ActiveUS20170092630A1Accelerated dissipationImprove cooling effectFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface mountingEngineering
In a connection system for electronic components (1) comprising a plurality of insulating layers (2) and conductive layers (3) and further comprising at least one embedded electronic component (4) embedded within at least one of the plurality of insulating layers (2) and conductive layers (3) the at least one embedded electronic component (4) is at least one first transistor having a bulk terminal thereof in thermal contact with a thermal duct (6) comprised of a plurality of vias (7) reaching through at least one of an insulating layer (2) and a conductive layer (3) of the connection system for electronic components (1) and emerging on a first outer surface (8) of the connection system for electronic components (1) under a first surface-mounted component (10).
Owner:AT & S AUSTRIA TECH & SYSTTECHN AG
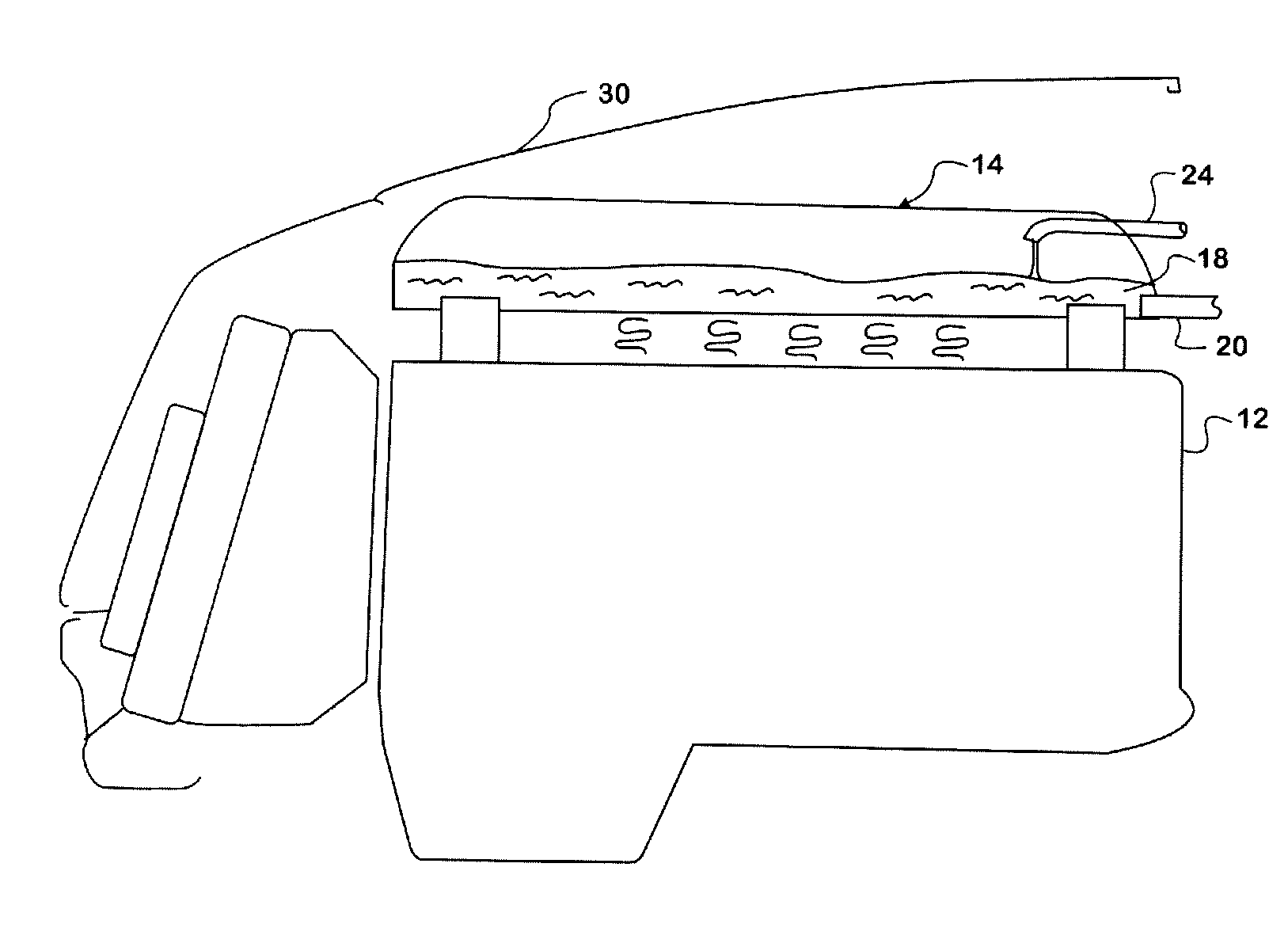
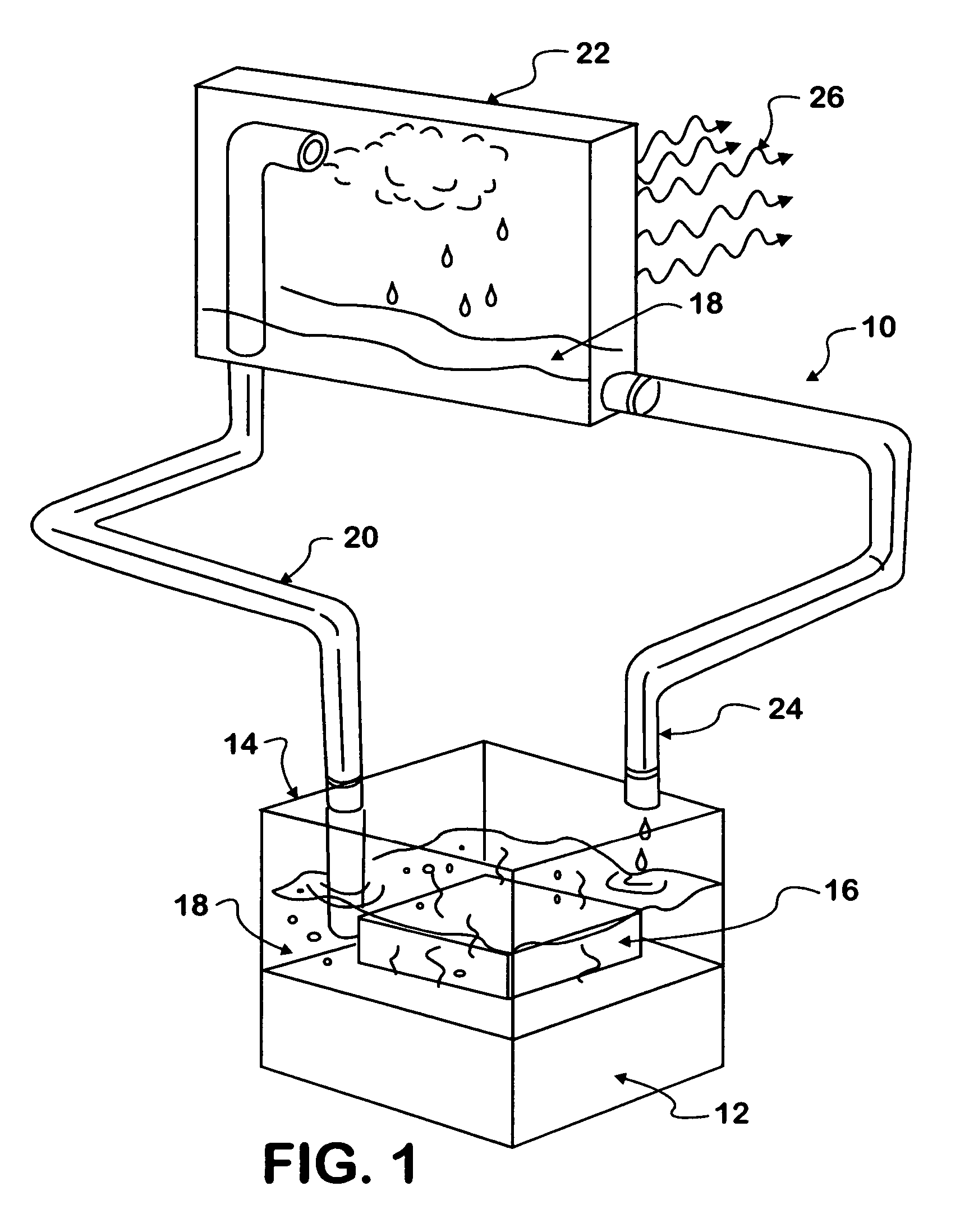
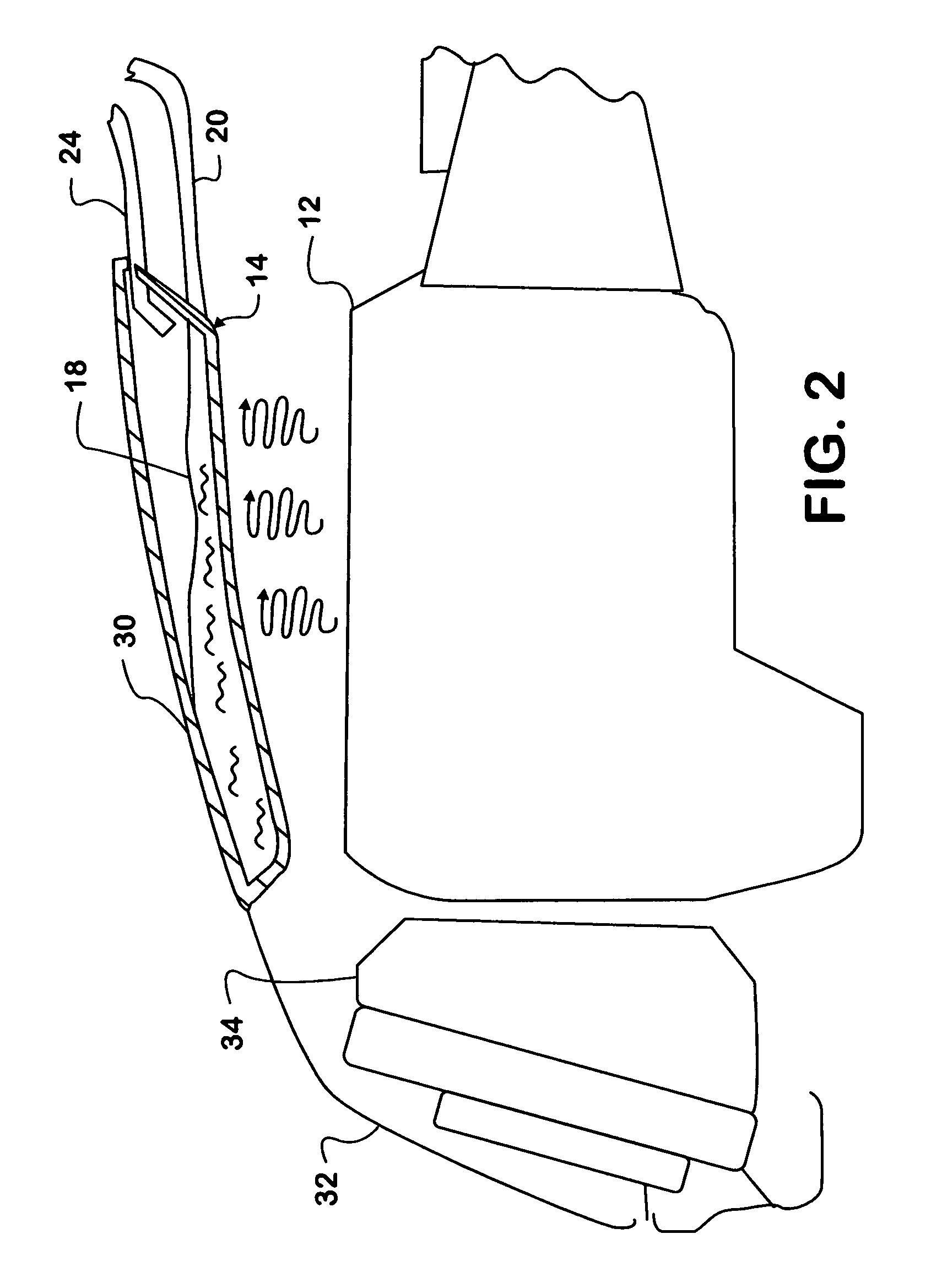
Thermosyphon heat reduction system for a motor vehicle engine compartment
A system (10) and method for removing heat from an engine compartment in a motor vehicle where heat generated by operation of a heat engine (12) that propels the vehicle tends to collect. Engine heat is collected in a thermofluid in a reservoir forming an evaporator (14) where the thermofluid absorbs heat sufficient to evaporate it. The vapor naturally migrates to a condenser (22) that is cooled sufficiently to condense the vapor back to liquid phase. The liquid falls by gravity back to the condenser.
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS8797032B2Significant heatingProvide informationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringCenter frequencyField coil
The temperature of an MRI gradient magnetic field coil unit is measured at least two times. Shift data indicating a center magnetic resonance frequency of a hydrogen atom in response to variation of the gradient coil temperature is stored in advance. Estimated shift of the center frequency based on the measurement result is determined and the center frequency of an RF NMR excitation pulse is corrected based on the estimated shift.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and device for arc spraying
InactiveUS20130011569A1Increase melting rateIncrease diversitySpark gapsLiquid surface applicatorsFilling materialsArc melting
A method for arc spraying in which at least one wire-shaped spray filler material is melted in an arc by means of electric current and atomised by means of an atomising gas flow and applied in the form of a particle stream onto a workpiece, at least one wire-shaped spray filler material being preheated before the melting in the arc.
Owner:LINDE AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com