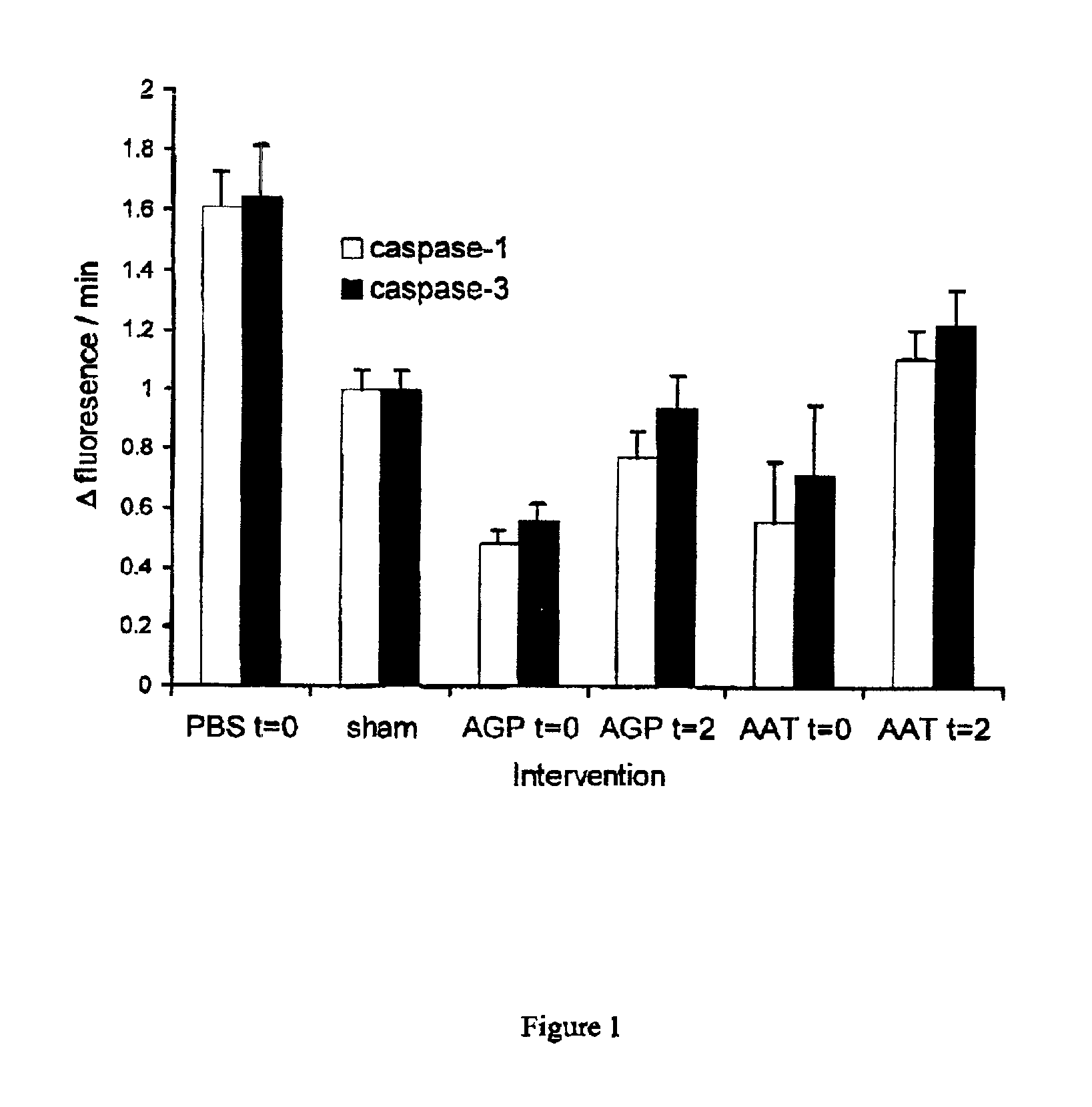
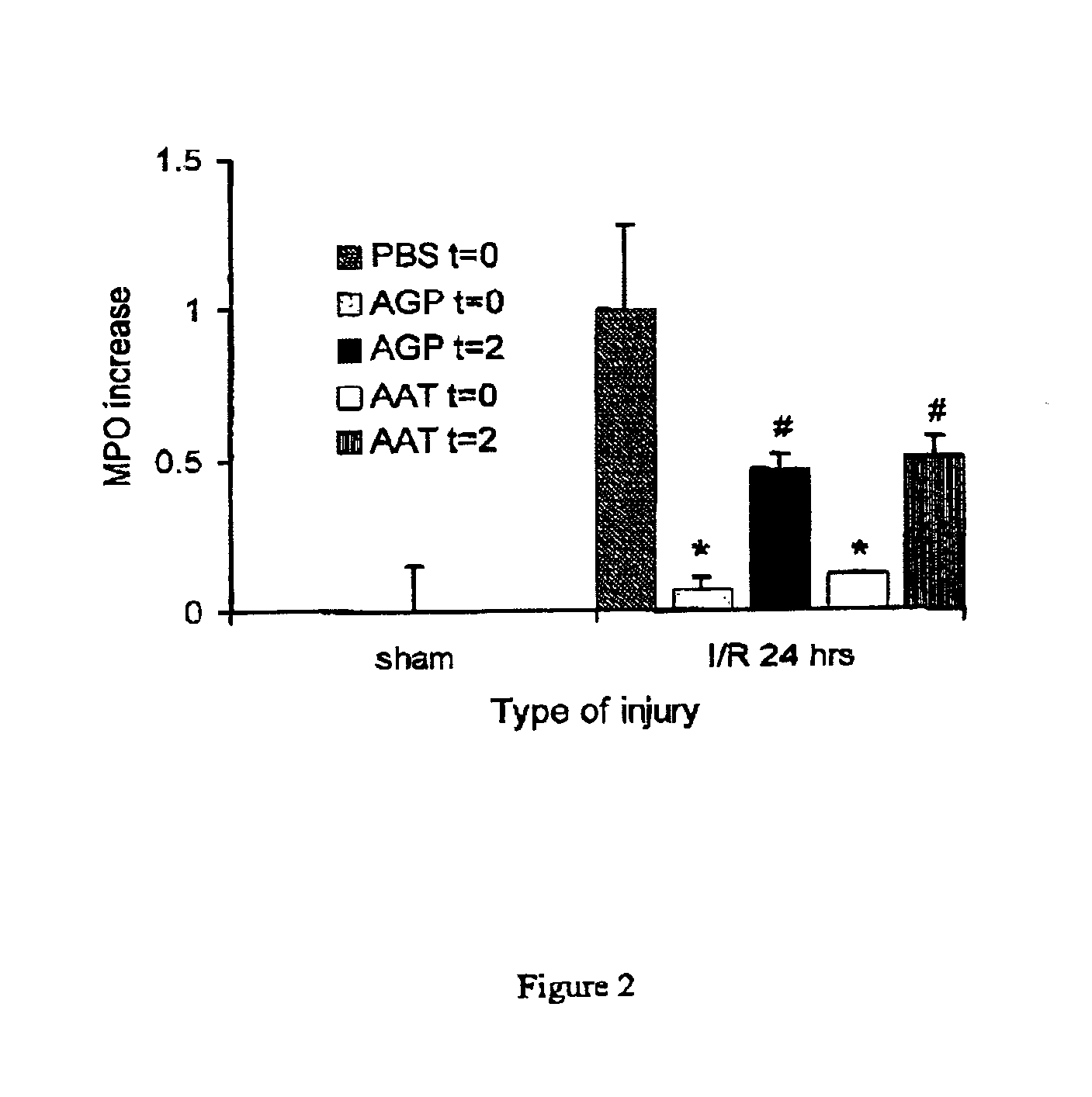
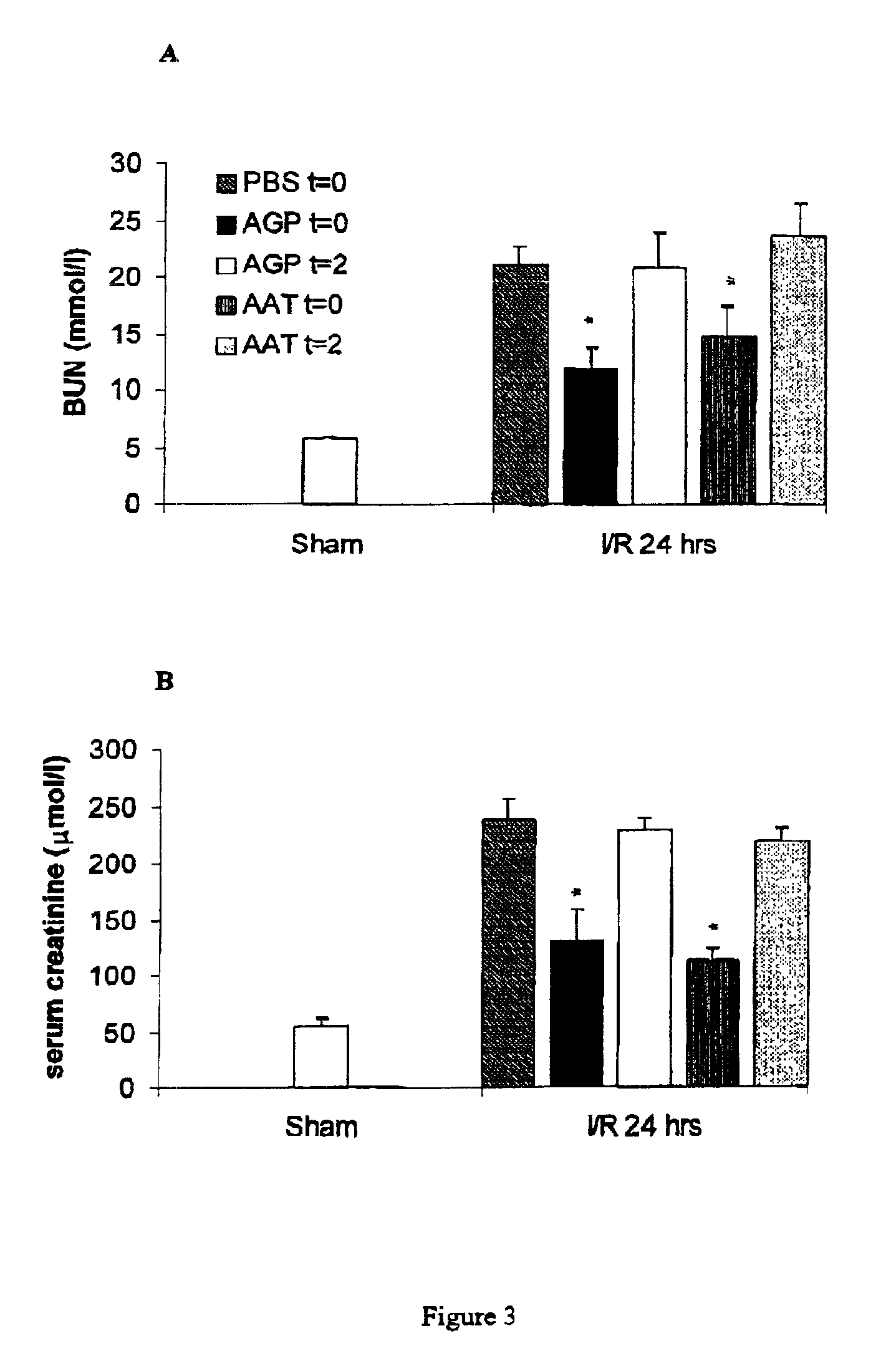
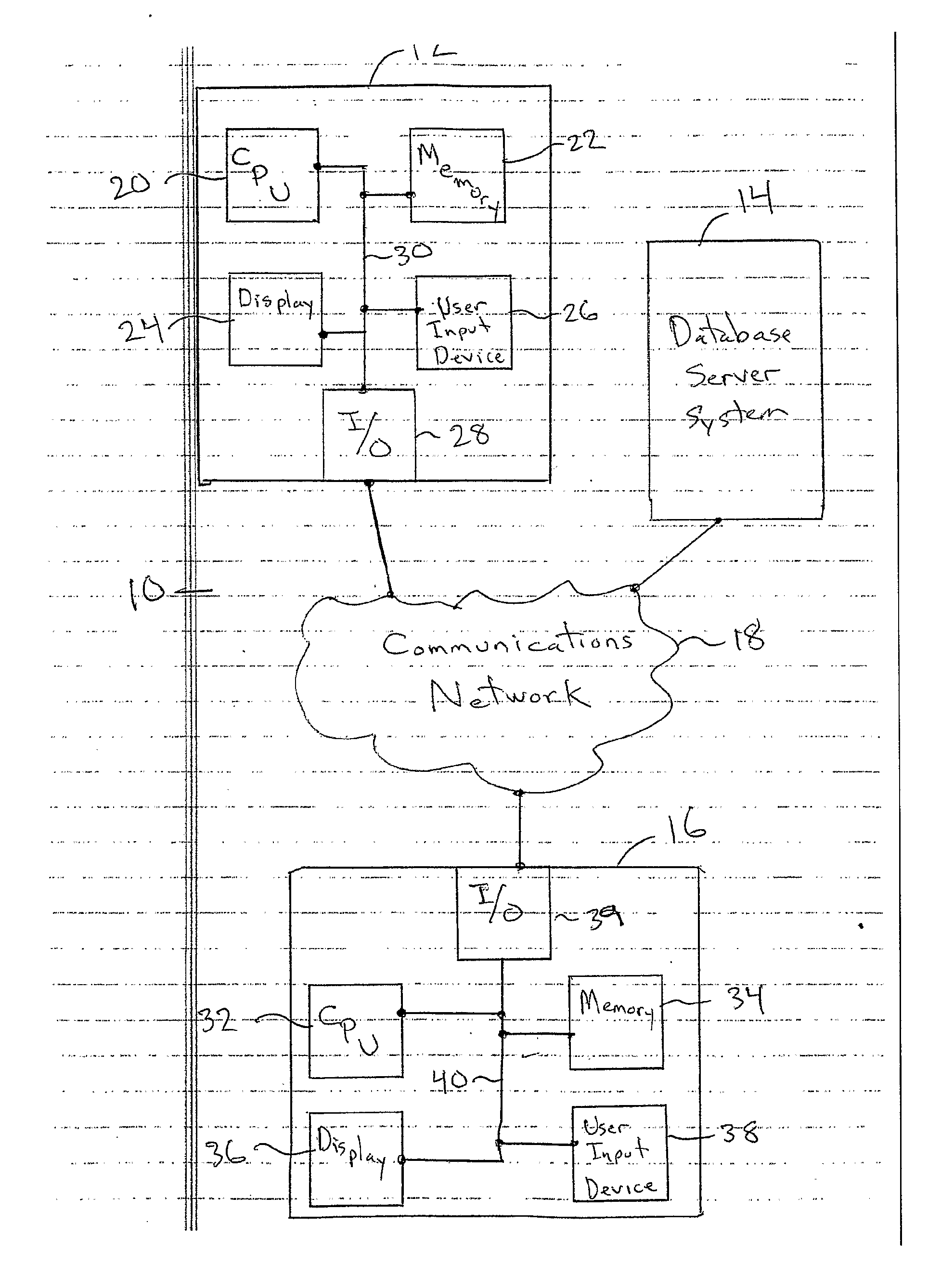
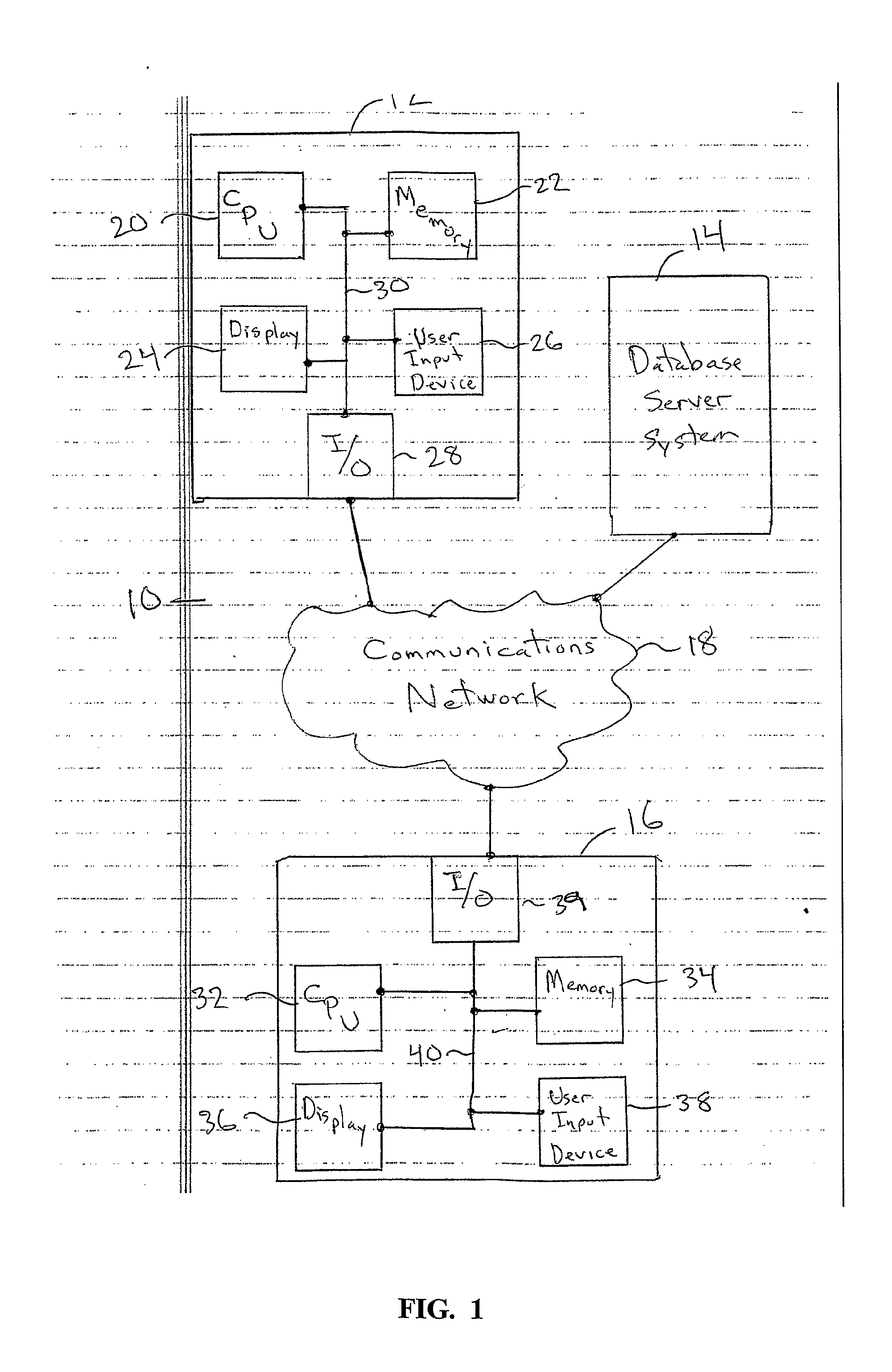
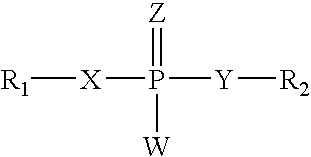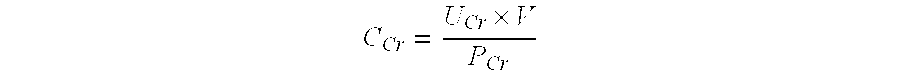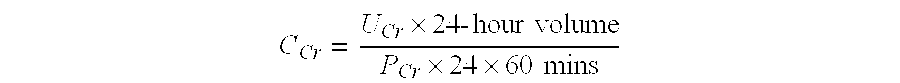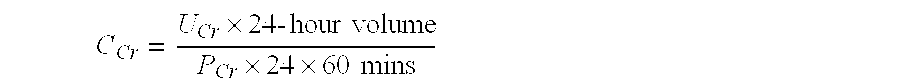Patents
Literature
83 results about "Alpha-1-Proteinase Inhibitor (Human)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This medication is used to treat lung problems (emphysema) caused by a certain inherited disease (alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor deficiency). In people with this condition, lung damage is caused by elastase, a natural substance that the body needs to kill bacteria in the lungs.
RNA interference mediated inhibition of alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050137153A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityCompounds screening/testingSugar derivativesDouble strandCellular process
The present invention concerns compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases and conditions associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) allelic variants that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity. The present invention also concerns compounds, compositions, and methods relating to diseases and conditions associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) allelic variants that respond to the modulation of expression and / or activity of genes involved in alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) gene expression pathways or other cellular processes that mediate the maintenance or development of alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) diseases and conditions such as liver disease, lung disease, and any other diseases or conditions that are related to or will respond to the levels of an alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) variant protein in a cell or tissue, alone or in combination with other therapies. Specifically, the invention relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (mRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against the expression disease related genes or alleles having alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) sequences.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
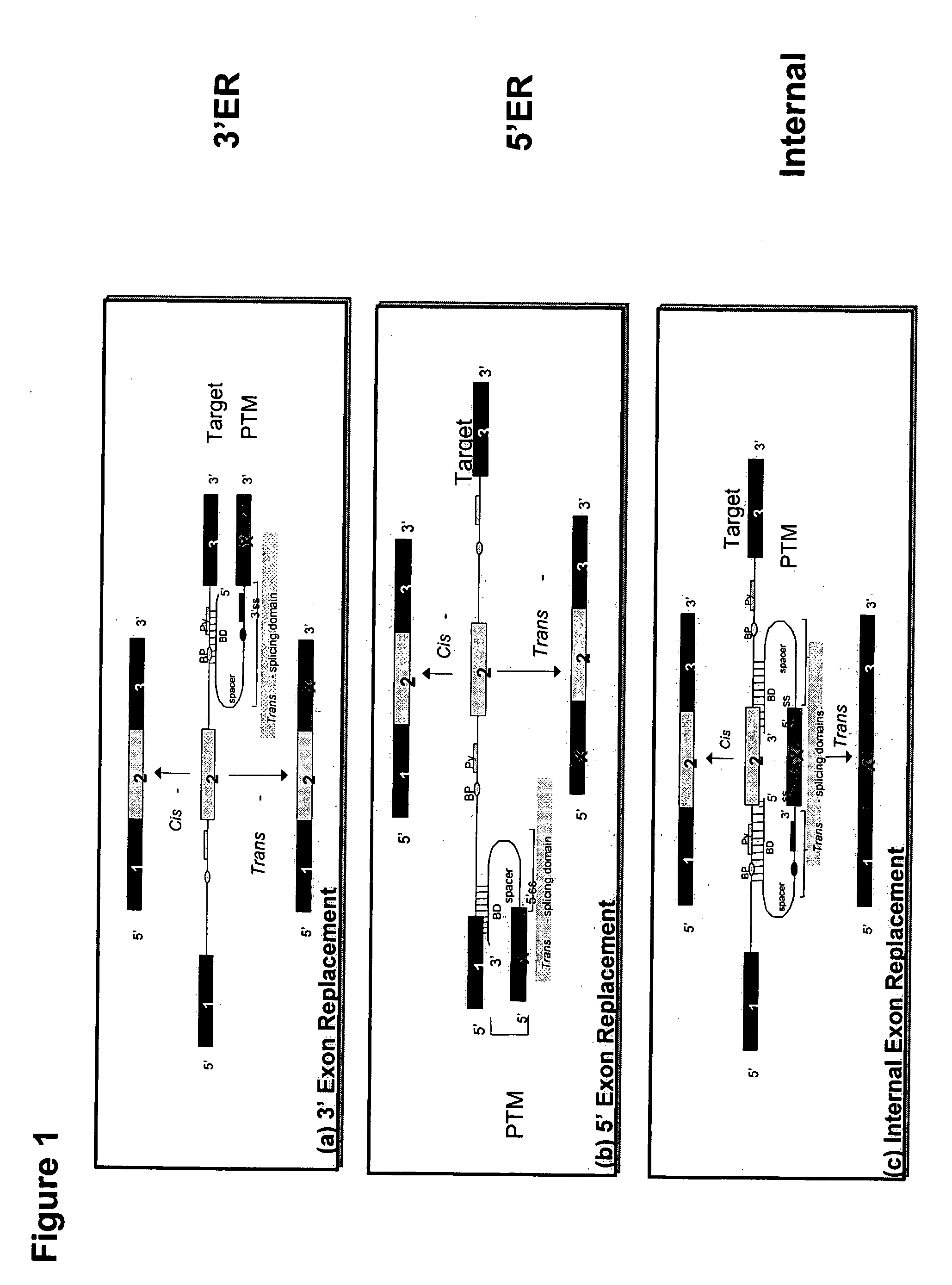
Correction of alpha-1-antitrypsin genetic defects using spliceosome mediated RNA trans splicing
InactiveUS20060234247A1Reduce lungReduce liver pathologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseRNA Trans-Splicing
The present invention provides methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosomal mediated RNA trans-splicing. The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a SERPINA1 target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA). In particular, the PTMs of the present invention include those genetically engineered to interact with SERPINA1 target pre-mRNA so as to result in correction of SERPINA1 genetic defects responsible for AAT deficiency. The PTMs of the invention may also comprise sequences that are processed out of the PTM to yield duplex siRNA molecules directed specifically to mutant SERPIN A1 mRNAs. Such duplexed siRNAs are designed to reduce the accumulation of toxic AAT protein in liver cells. The methods and compositions of the present invention can be used in gene therapy for correction of SERPINA1 disorders such as AAT deficiency.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Optimised coding sequence and promoter
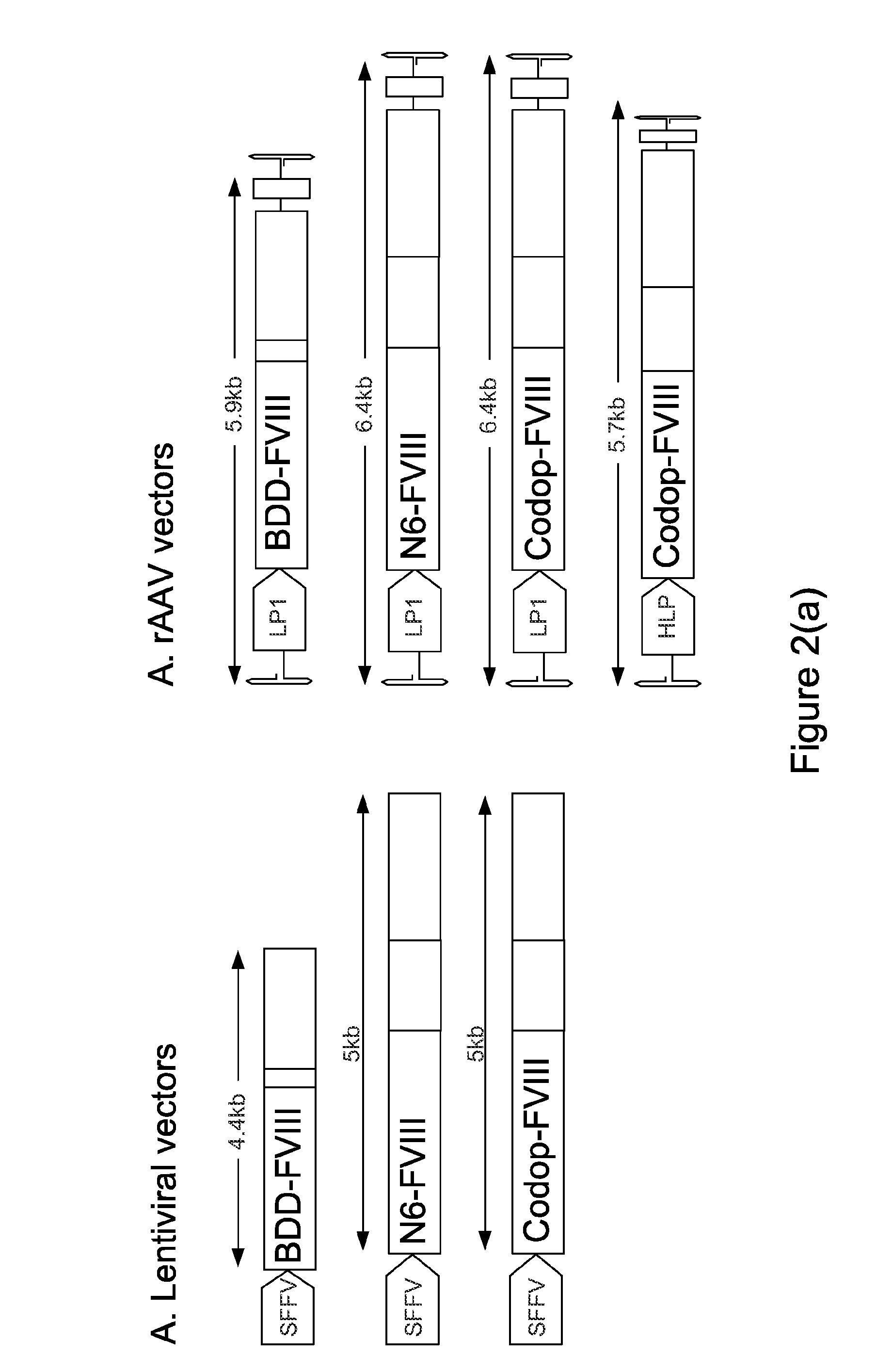
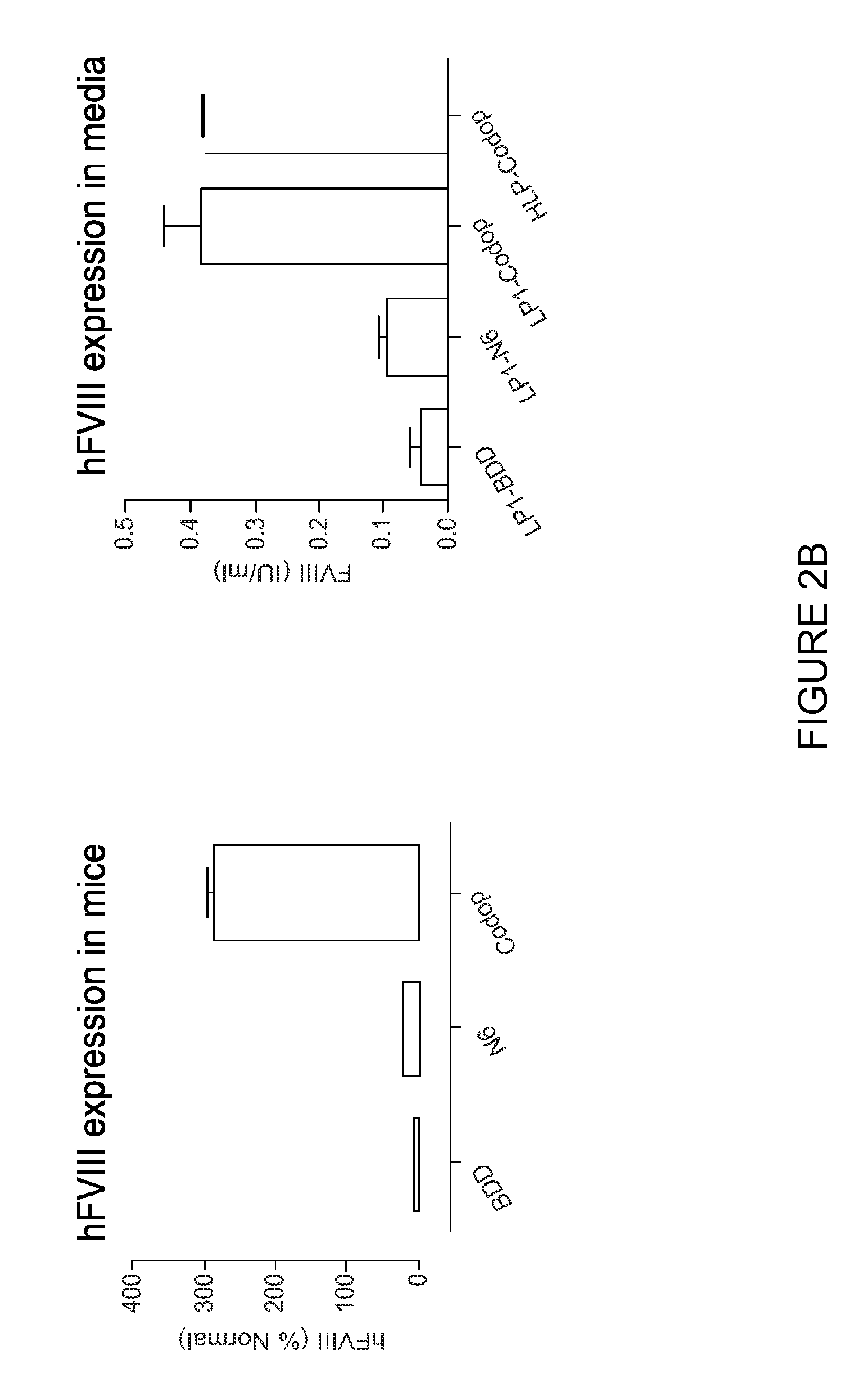
ActiveUS20130024960A1Shorten the timeImprove the level ofFactor VIIOrganic active ingredientsLipid storageLipid storage disease
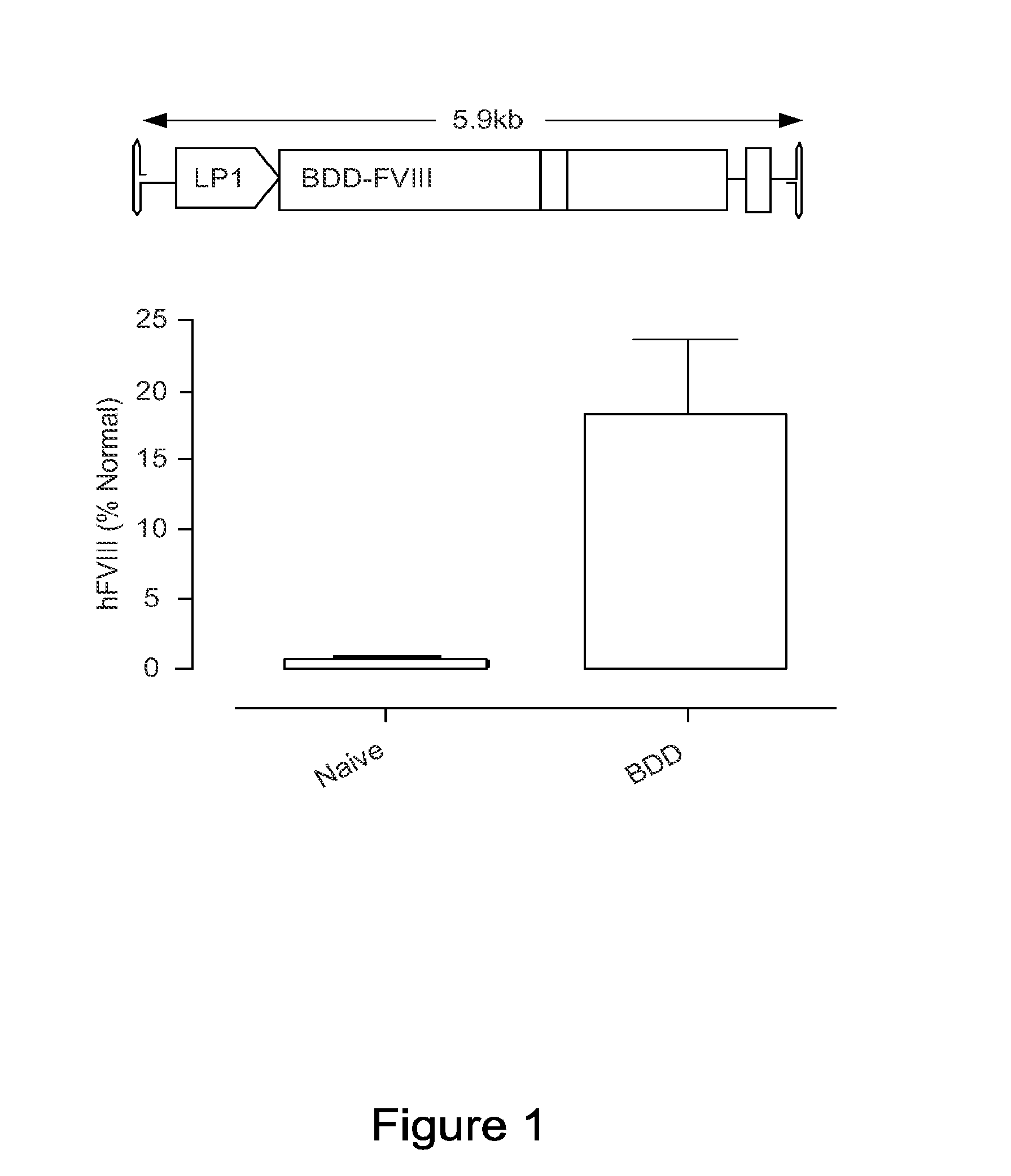
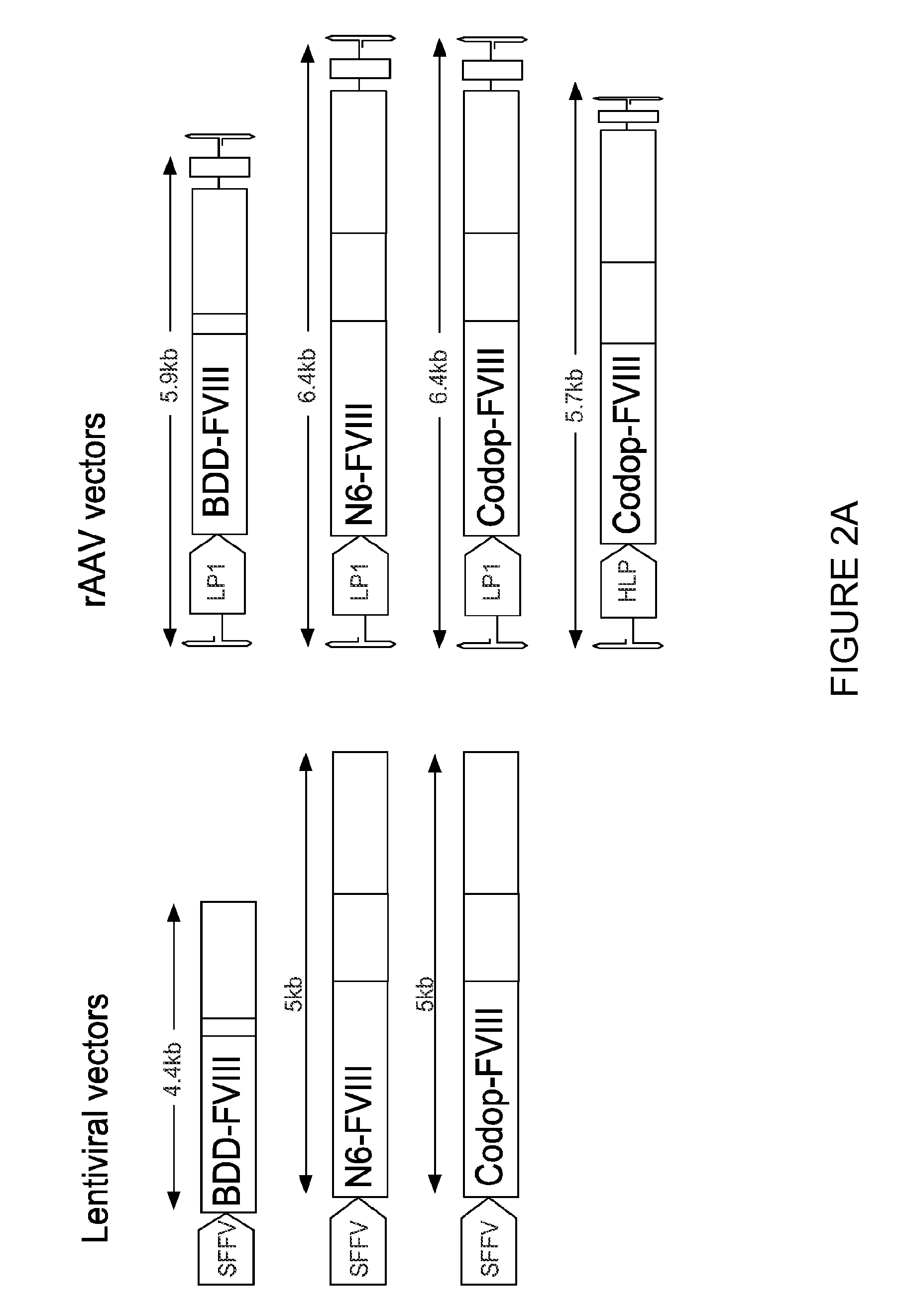
An optimized coding sequence of human blood clotting factor eight (VIII) and a promoter may be used in vectors, such as rAAV, for introduction of factor VIII, and / or other blood clotting factors and transgenes. Exemplary of these factors and transgenes are alpha-1-antitrypsin, as well as those involved in the coagulation cascade, hepatocye biology, lysosomal storage, urea cycle disorders, and lipid storage diseases. Cells, vectors, proteins, and glycoproteins produced by cells transformed by the vectors and sequence, may be used in treatment.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC +2
Compositions and methods of use for alpha-1 antitrypsin having no significant serine protease inhibitor activity
InactiveUS20090203580A1Reduce riskReduce symptom associated with diabetesMetabolism disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsDiabetes mellitusMedical disorder
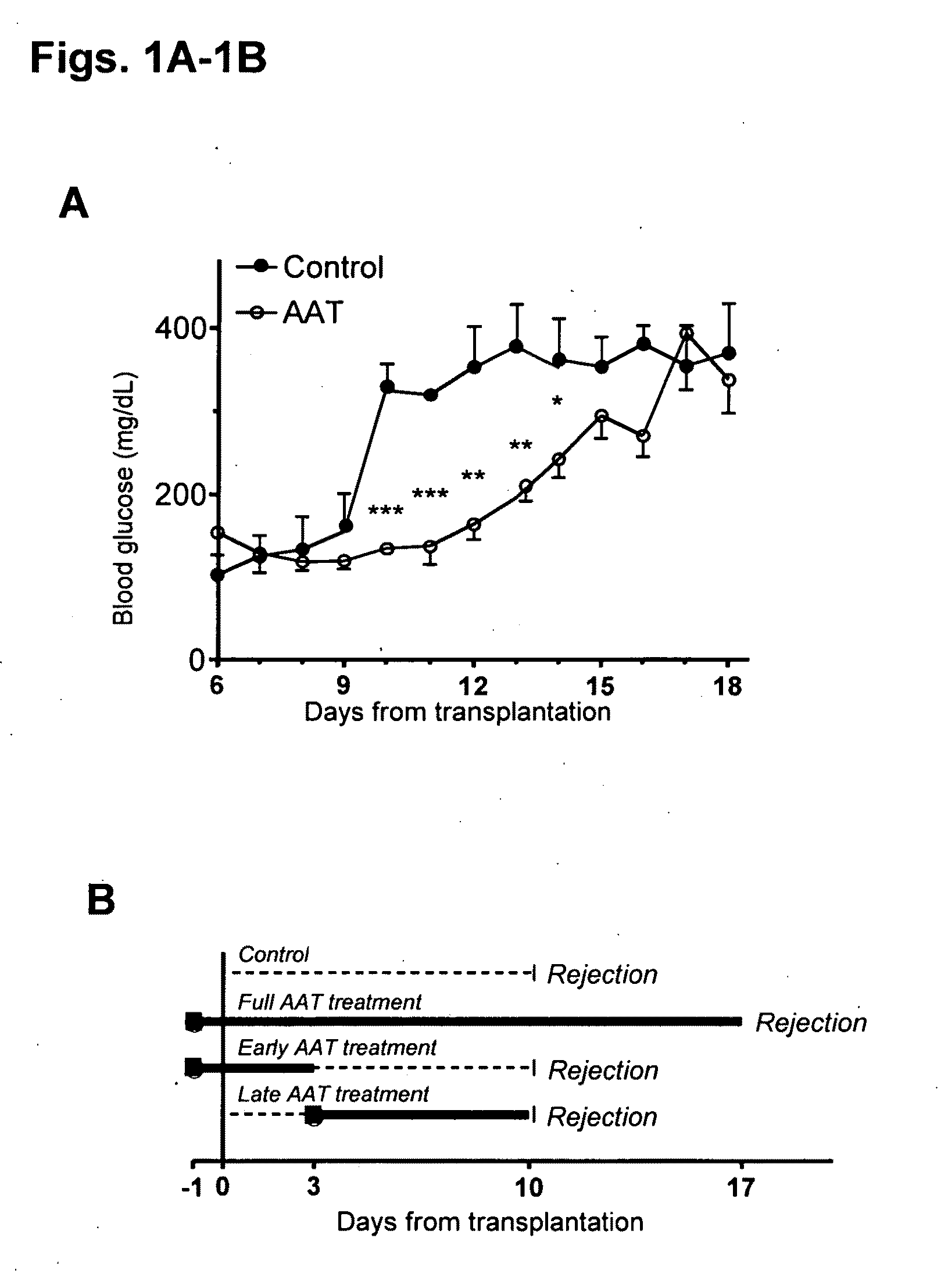
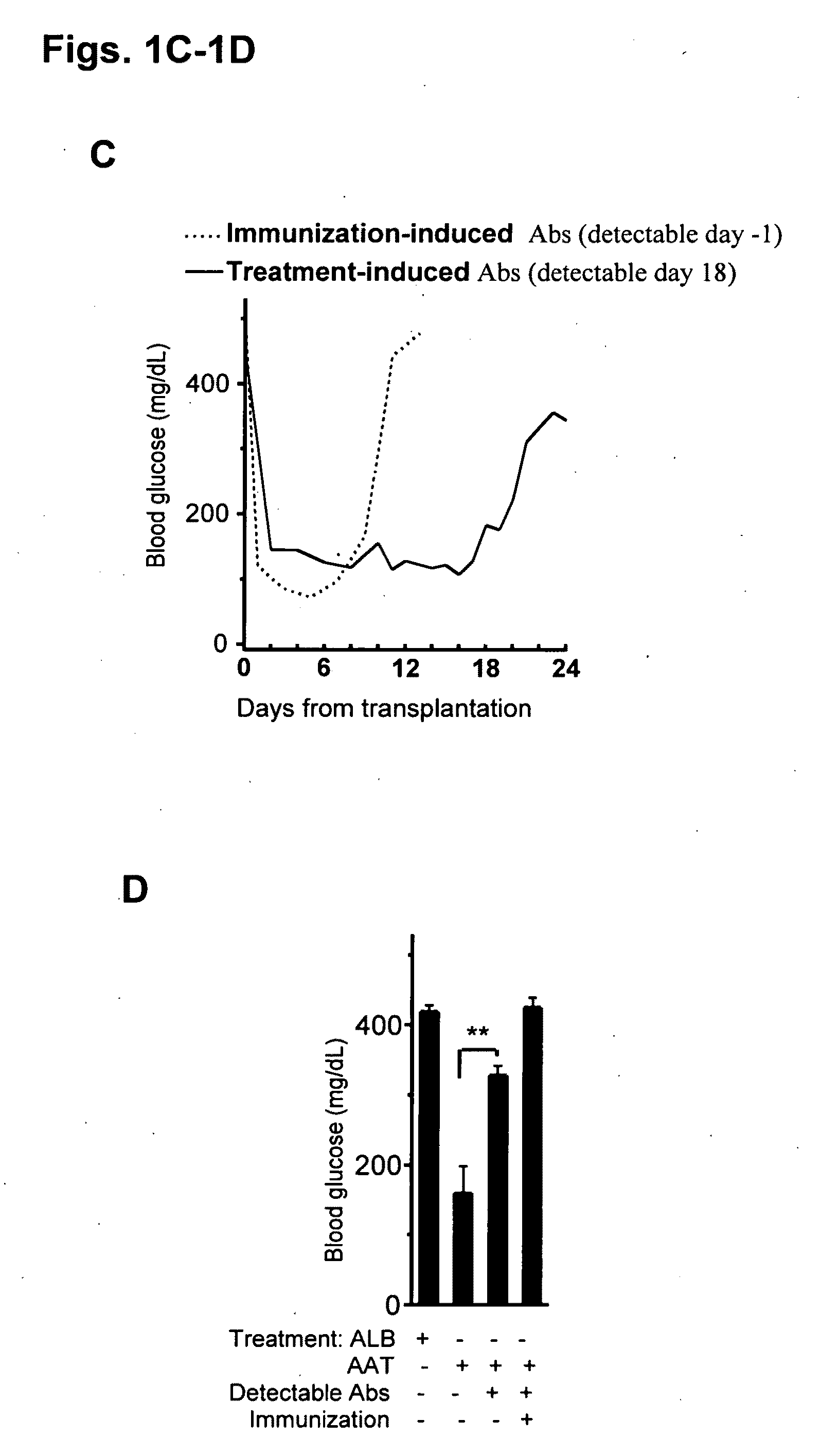
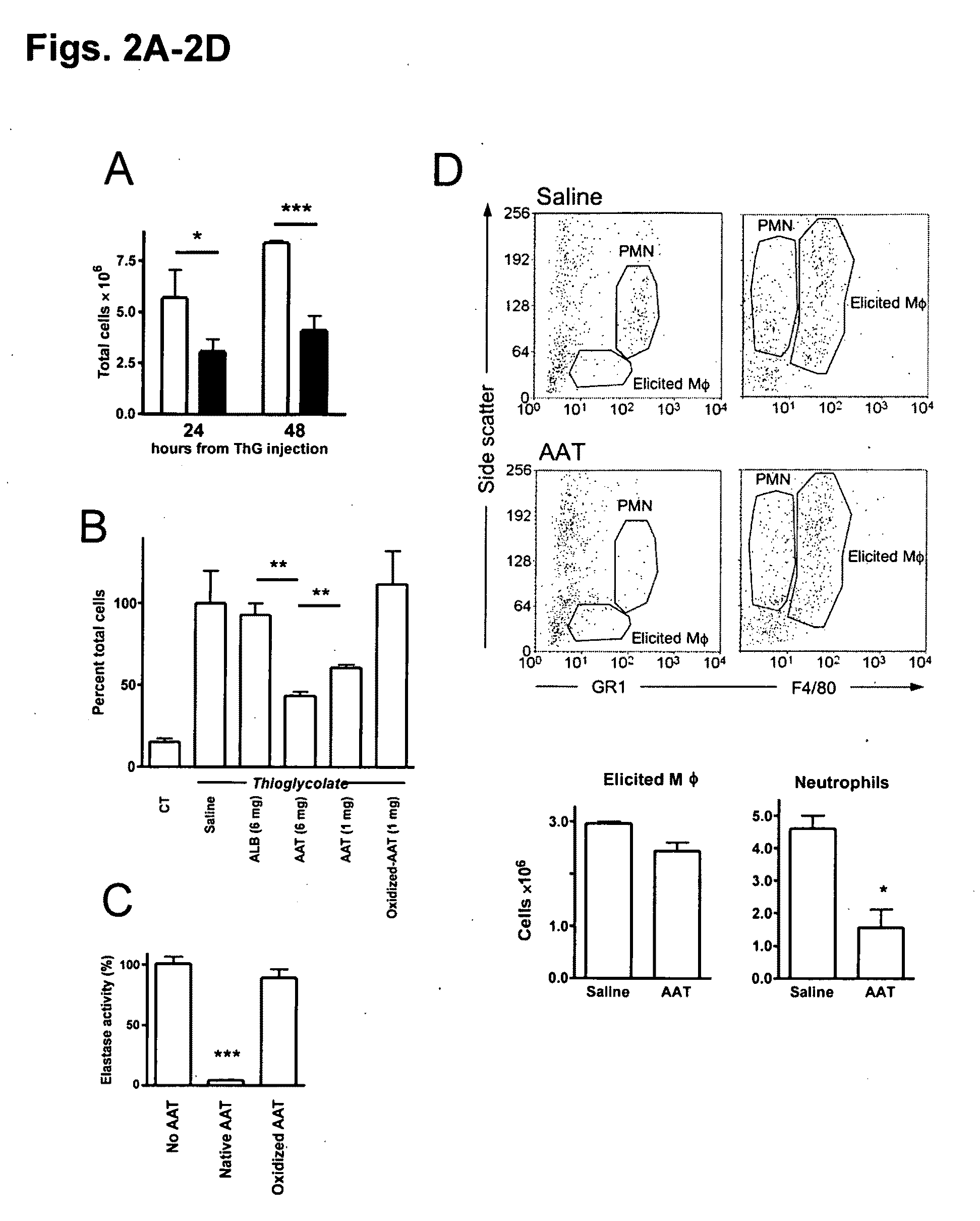
Embodiments herein illustrate methods and compositions for treating medical disorders. In certain embodiments, compositions and methods relate to reducing, inhibiting or treating graft rejection, transplant rejection or diabetes in a subject. Other embodiments herein relate to compounds including naturally occurring and synthetic mutant compositions of alpha-1 antitrypsin, wherein the alpha-1 antitrypsin has no significant serine protease inhibitor activity.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Methods and active substances for protecting organs
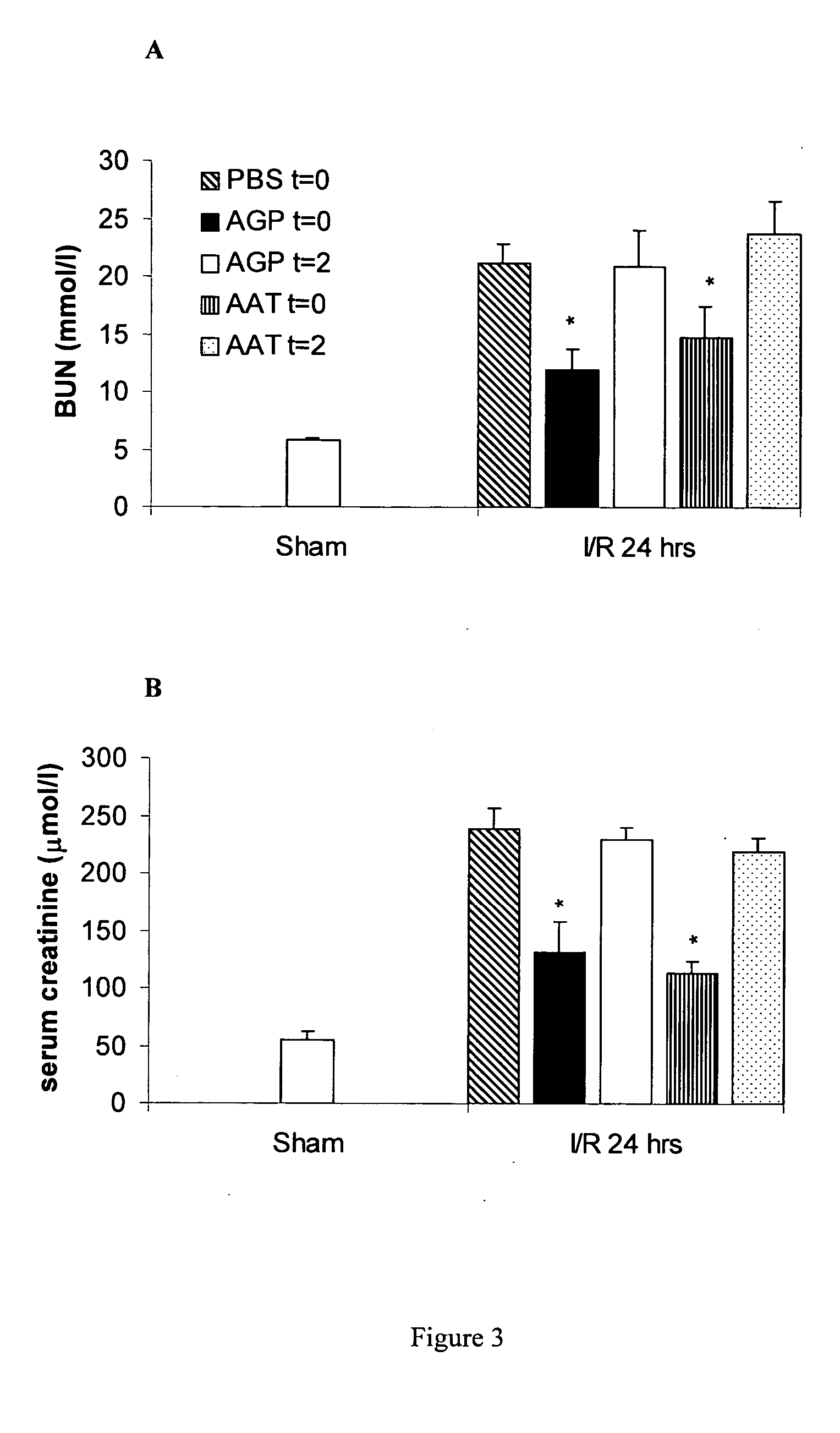
InactiveUS6924267B2Avoid problemsAvoid dysfunctionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsMedicineTissue transplant
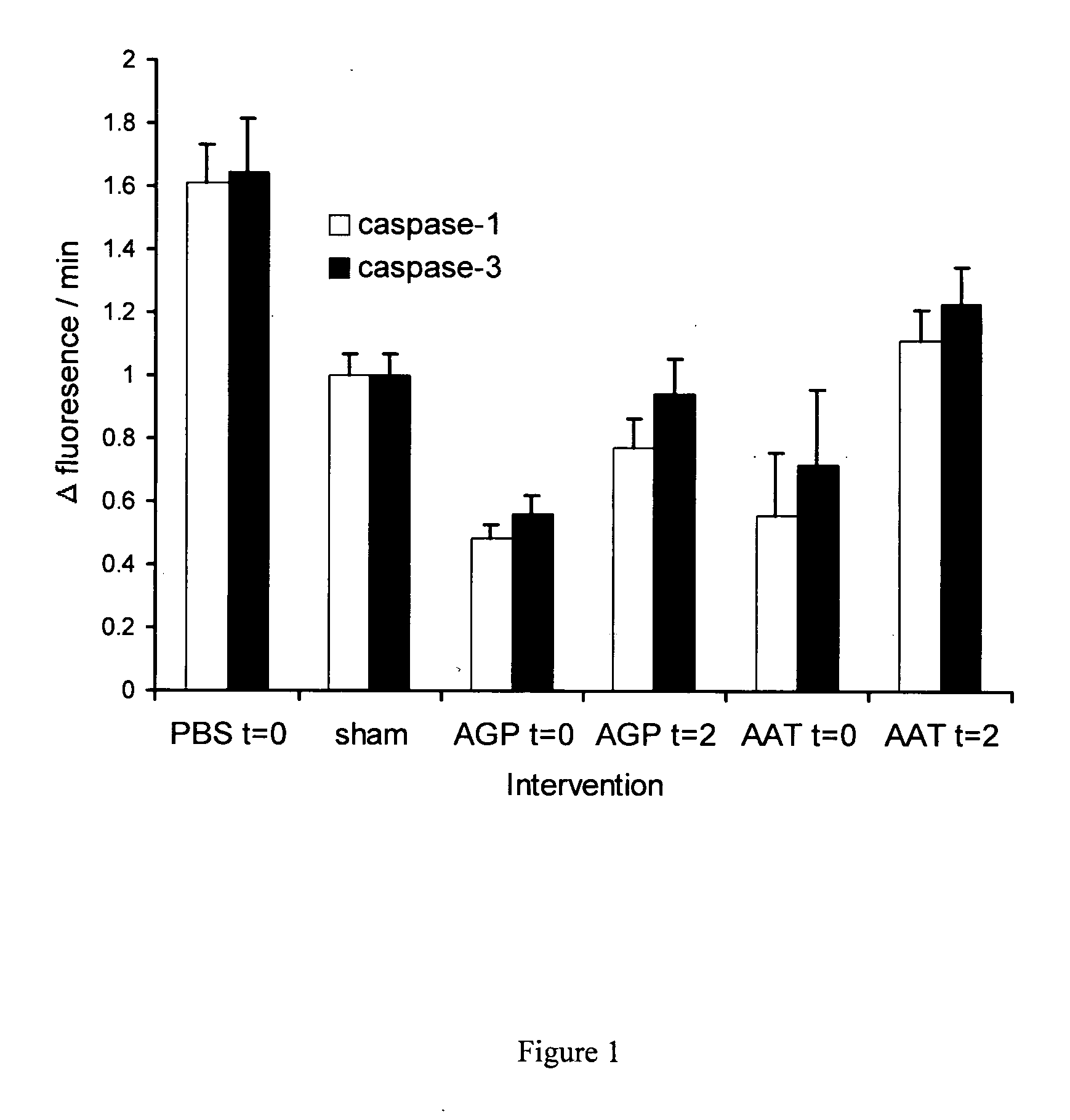
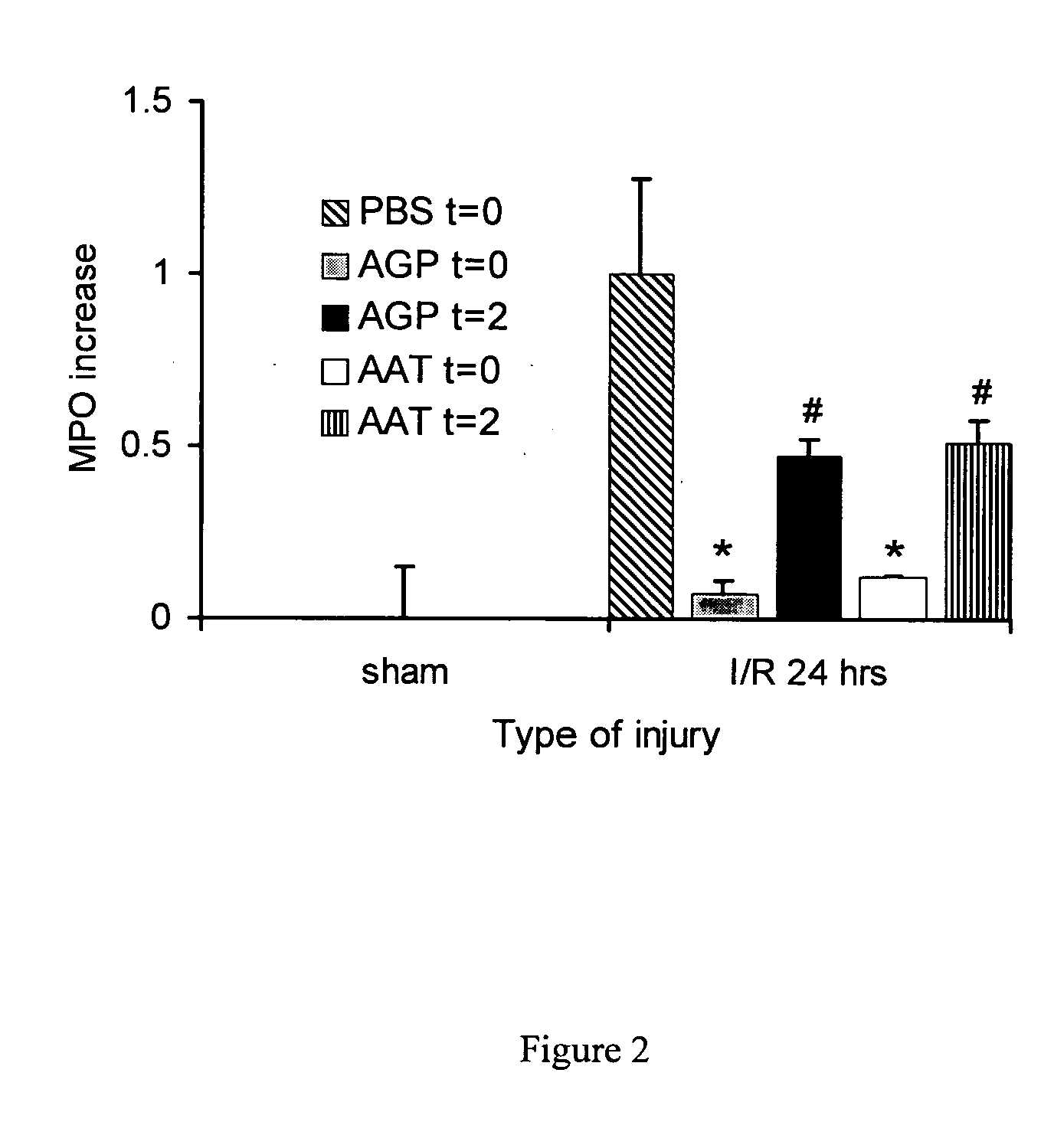
The present invention comprises a method of protecting organs or tissue susceptible to reperfusion-induced dysfunction after ischemia. The method comprises parenterally administering to a patient a therapeutical composition containing natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or a mixture thereof. Alternatively, organ or tissue transplants can be contacted with natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-antitrypsin or mixtures by perfusing or flushing them with a solution containing natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or mixtures thereof in a concentration of 0.1 to 5 g / l.
Owner:SUOMEN PUNAINEN RISTI VERIPALVELU
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
ActiveUS20110195429A1Eliminate needEasy to adaptDisease diagnosisBiological testingSoluble P-SelectinFactor ii
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using assays that detect one or more markers selected from the group consisting of soluble p-selectin, protein NOV homolog, soluble epidermal growth factor receptor, netrin-4, haptoglobin, heat shock protein beta-1, alpha-1-antitrypsin, leukocyte elastase, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6, soluble tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 6, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 2, active caspase-3, and soluble platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
ActiveUS20120283128A1Eliminate needEasy to adaptBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMatrilysinInterleukin-1beta
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using a plurality of assays, one or more of which is configured to detect a kidney injury marker selected from the group consisting of Hyaluronic acid, Immunoglobulin A, Immunoglobulin G1, Immunoglobulin G2, Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7, Alpha-1 antitrypsin, Serum amyloid P component, Metalloproteinase inhibitor 2, Hepatocyte growth factor, Intercellular adhesion molecule 1, Beta-2-glycoprotein 1, Interleukin-1 beta, Neutrophil Elastase, Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B, Interleukin-11, Cathepsin D, C—C motif chemokine 24, C—X—C motif chemokine 6, C—C motif chemokine 13, C—X—C motif chemokines -1, -2, and -3, Matrilysin, Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain, Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3, and Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
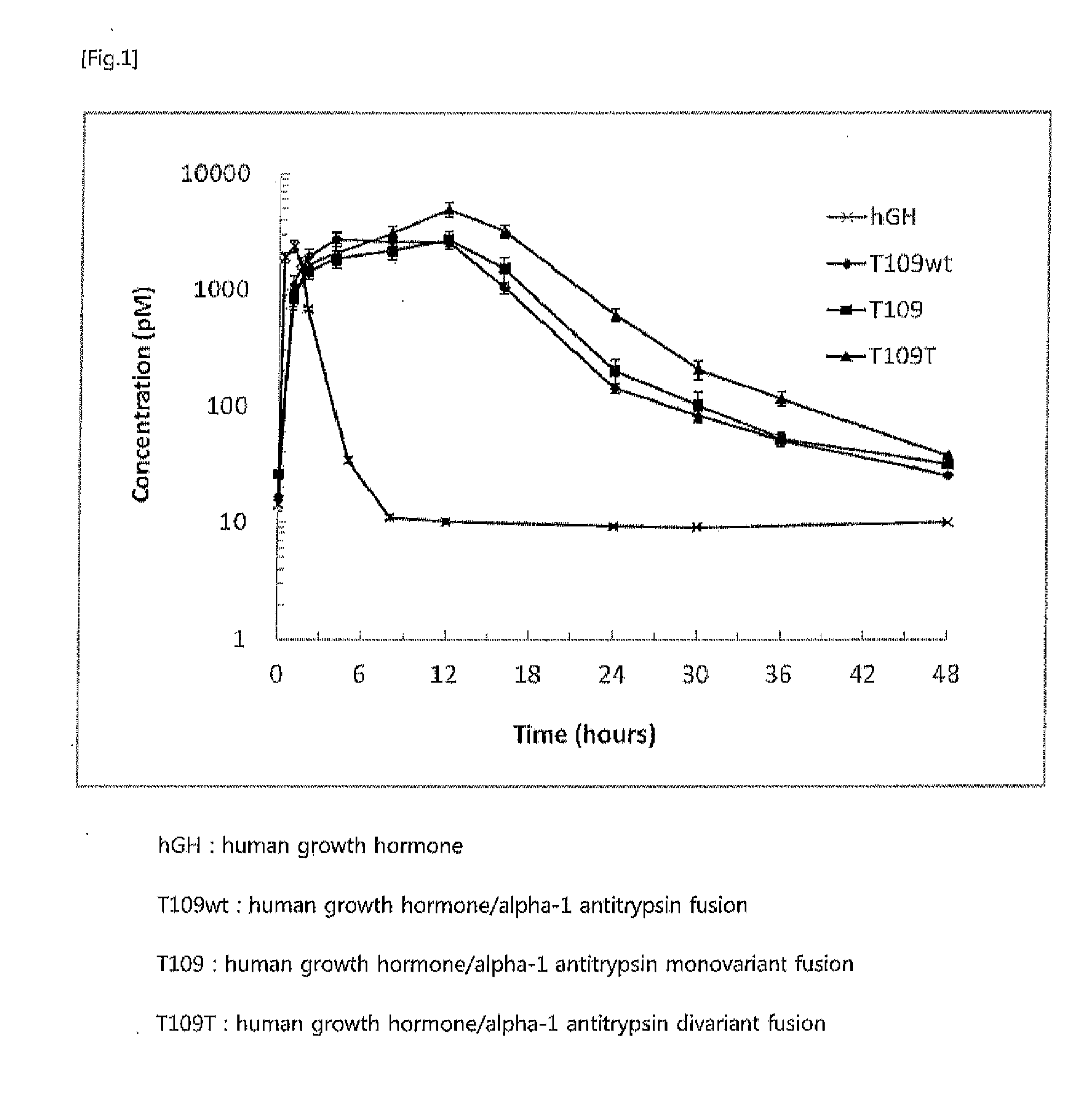
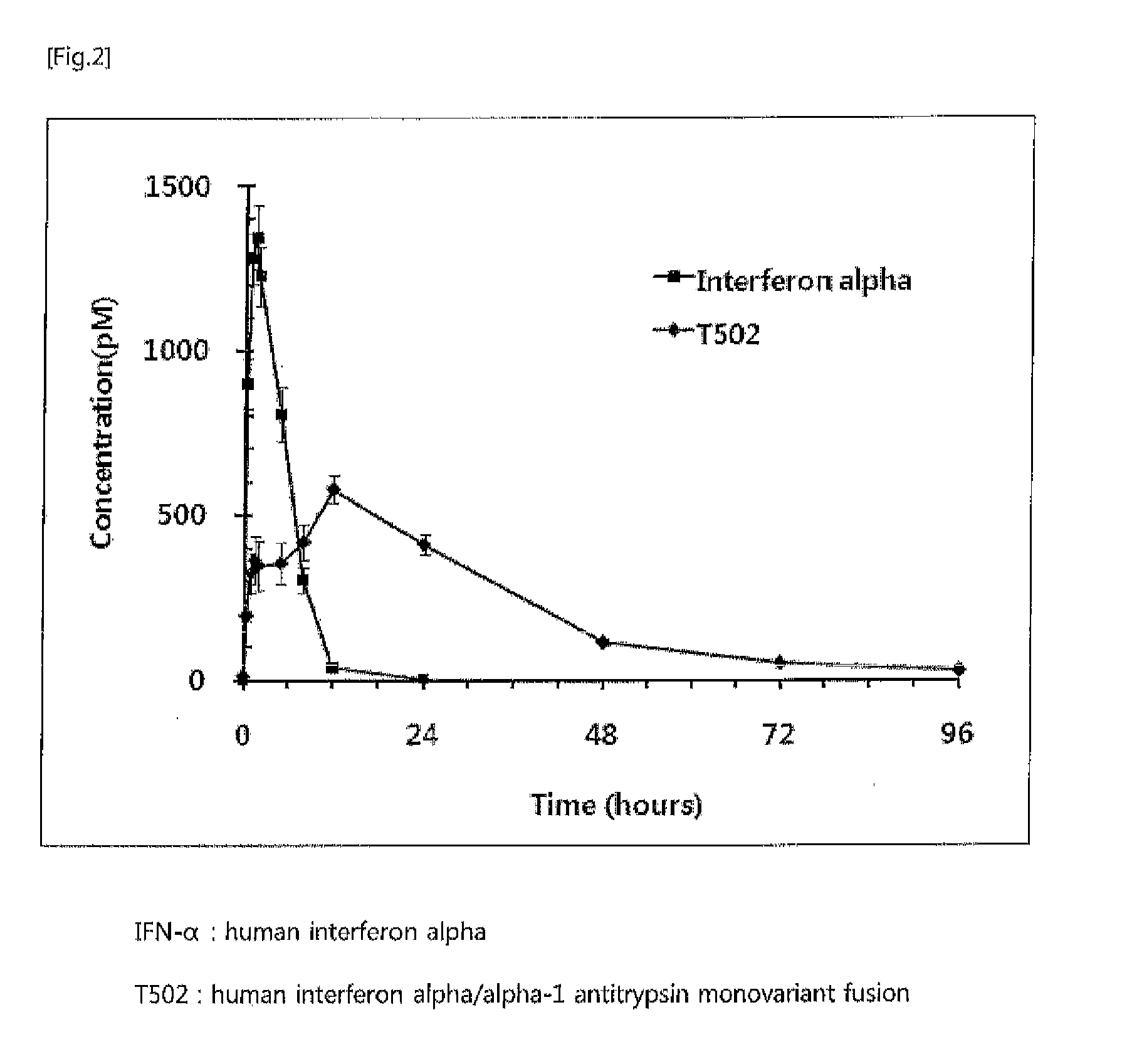
In vivo half life increased fusion protein or peptide maintained by sustained in vivo release, and method for increasng in vivo half-life using same
ActiveUS20120094356A1Prolong half-life in vivoLoss minimizationPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsPeptide drugHalf-life
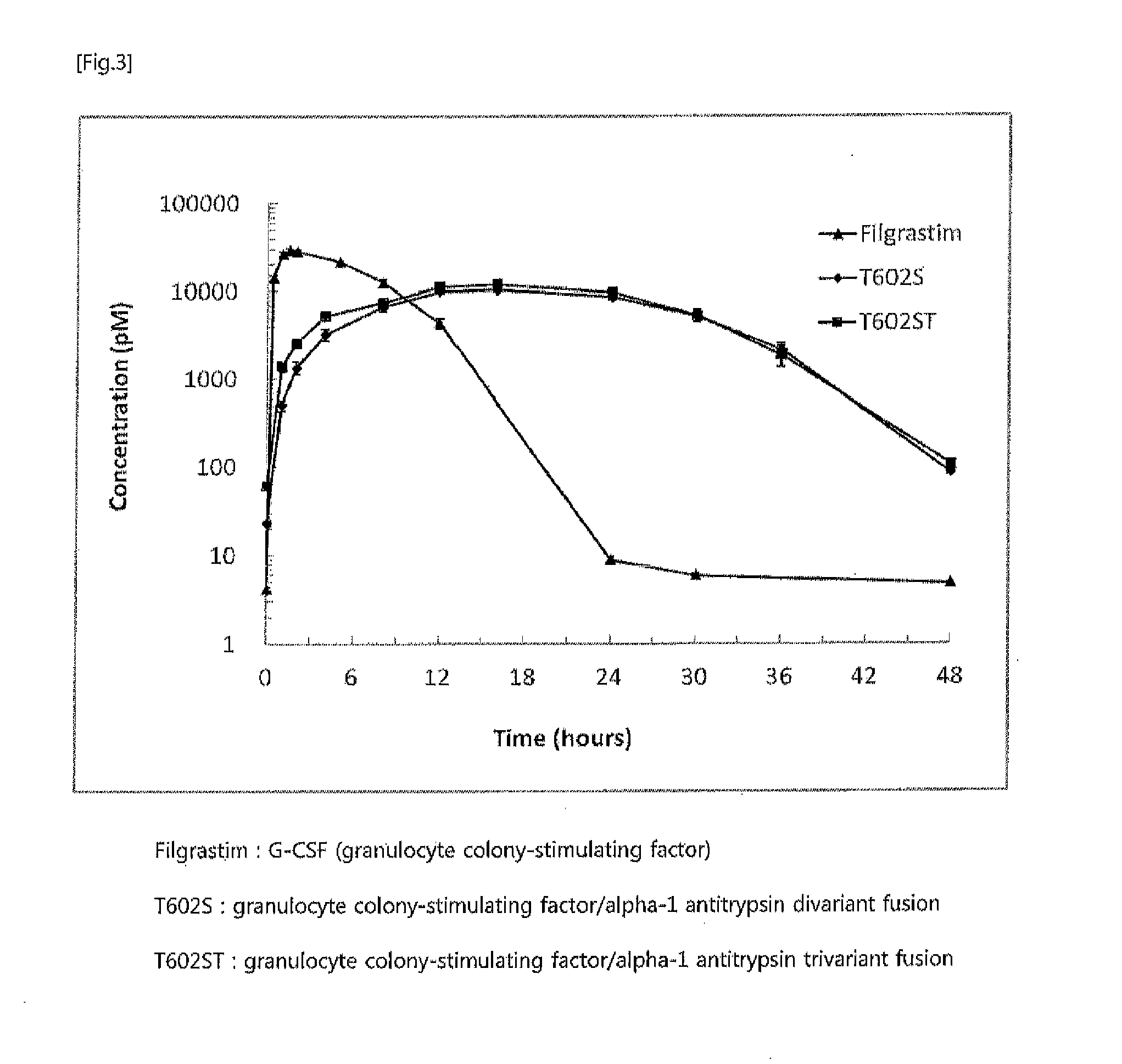
The present invention relates to a fusion protein or peptide, the in vivo half-life of which is increased by maintaining in vivo sustained release, and to a method for increasing in vivo half-life using same. A fusion protein or peptide according to the present invention has excellent in vivo stability by binding a physiologically active protein or physiologically active peptide to an alpha-1 antitrypsin or alpha-1 antitrypsin mutant with one or more amino acids mutated to maintain the in vivo sustained release and to significantly increase the half-life thereof in blood (T1 / 2) compared to an inherent physiologically active protein or physiologically active peptide. Thus, a fusion protein or peptide according to the present invention can be useful in developing a sustained-release preparation of a protein or peptide drug.
Owner:ALTEOGEN
Methods for purification of alpha-1-antitrypsin andapolipoprotein a-1
ActiveUS20110087008A1Minimize deamidationMinimize denaturationApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsPurification methodsApolipoproteins E
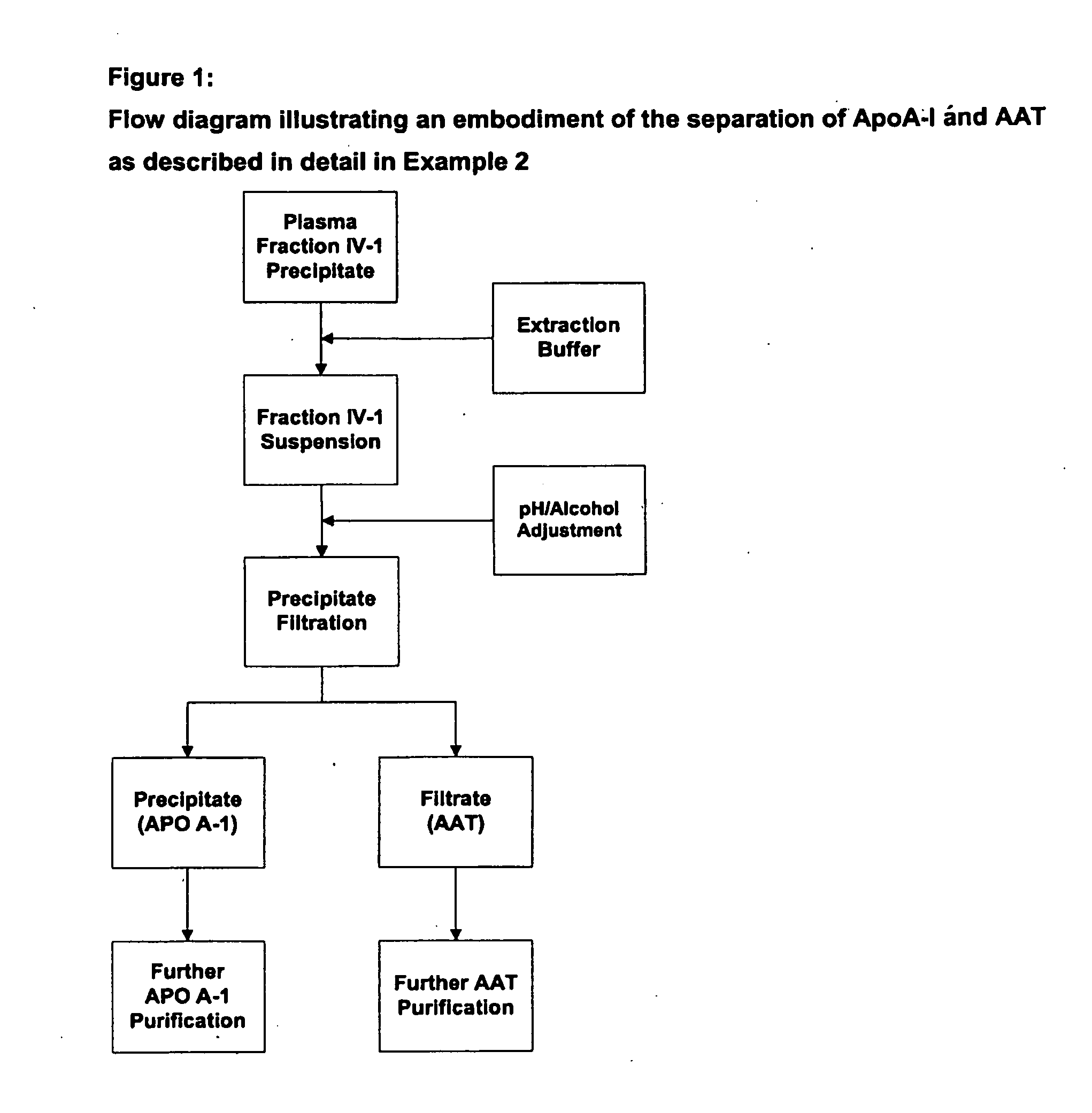
This invention relates to protein separation and purification methods for both alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT, also known as alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor, API, and A1-PI) and Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-1) from, for example, a fraction of human blood plasma. In certain embodiments, the invention provides methods for separating AAT from ApoA-1 at the initial stage of purification, so that the same starting material can be used as a source for both proteins. The methods further pertain to providing compositions of AAT and of ApoA-1 suitable for pharmaceutical use and are suitable for large-scale purification.
Owner:CSL BEHRING GMBH
Methods and active substances for protecting organs
InactiveUS20050277106A1Avoid dysfunctionPreventing transplantPeptide/protein ingredientsDead animal preservationMedicineTissue transplant
The present invention comprises a method of protecting organs or tissue susceptible to reperfusion-induced dysfunction after ischemia. The method comprises parenterally administering to a patient a therapeutical composition containing natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or a mixture thereof. Alternatively, organ or tissue transplants can be contacted with natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or mixtures by perfusing or flushing them with a solution containing natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or mixtures thereof in a concentration of 0.1 to 5 g / l.
Owner:SUOMEN PUNAINEN RISTI VERIPALVELU
Separation of plasma components
InactiveUS6402913B1Improve methodWithout adversely altering propertyElectrolysis componentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPlasma compositionBlood plasma
A method for separating components from plasma, the method comprising (I) separating the plasma into a first and second component, the first component comprising an albumin / alpha-1-antitrypsin pool and the second component comprising plasma containing components having a molecular mass greater than albumin; (II) treating the second component to form an immunoglobulins concentrate containing immunoglobulins substantially free from components having a molecular mass less than immunoglobulins; (III) treating the immunoglobulins concentrate to remove components having a molecular mass greater than immunoglobulins; and (IV) separating albumin and alpha-1-antitrypsin from the albumin / alpha-1-antitrypsin pool.
Owner:GRADIPORE
Multiplexed biomarkers for monitoring the alzheimer's disease state of a subject
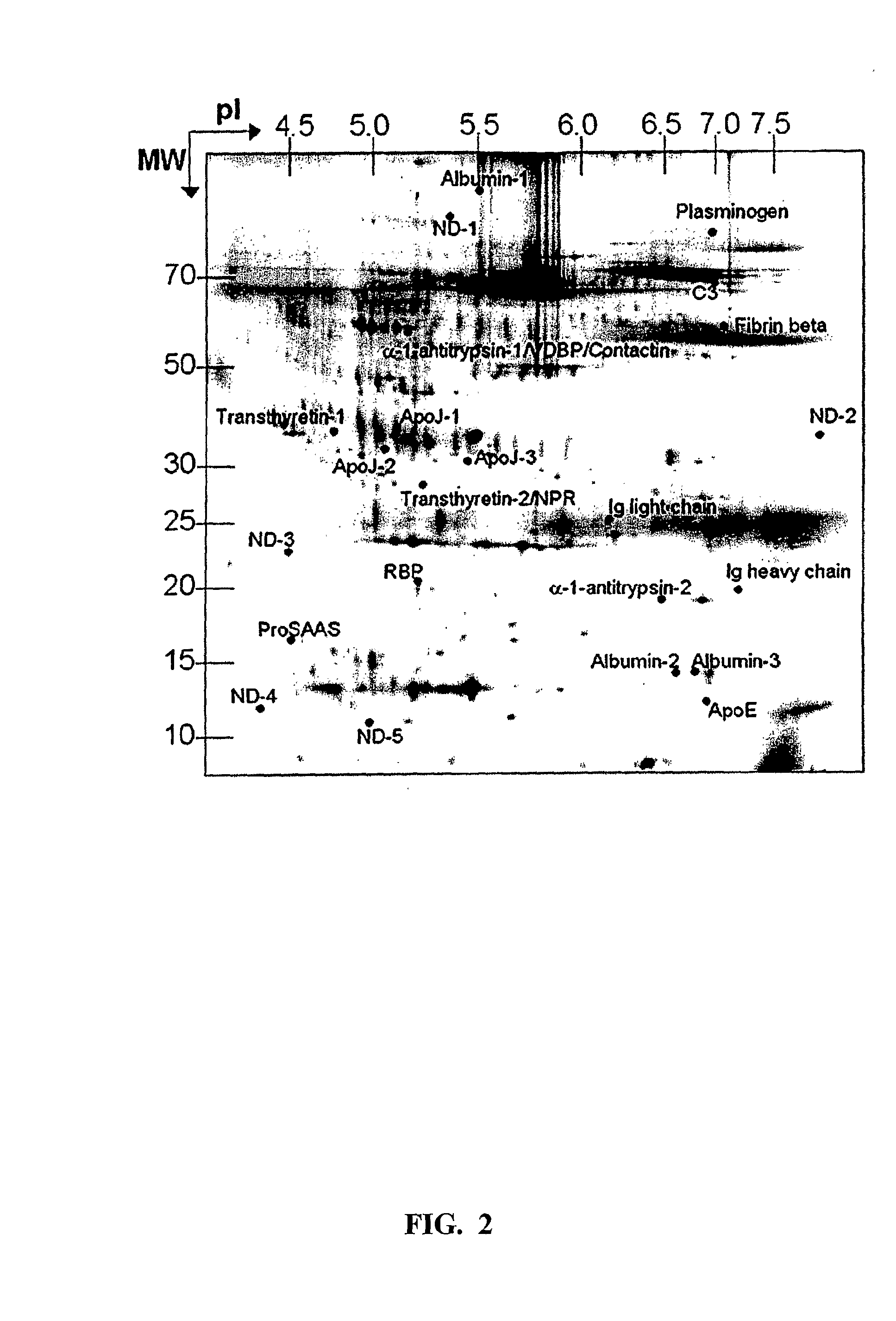
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing a subject's Alzheimer's disease state. The method involves providing a database containing information relating to protein expression levels associated and not associated with Alzheimer's disease. The database includes information relating to at least a majority of the following proteins: albumin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, apolipoprotin E, apolipoprotein J, complement component 3, contactin, fibrin beta, Ig heavy chain, Ig light chain, neuronal pentraxin receptor, plasminogen, proSAAS, retinol-binding protein, transthyretin, and vitamin D binding protein. Information relating to proteins found in one or more cerebrospinal fluid samples from a subject is also provided and a database is used to analyze the information from the subject to diagnose the subject's Alzheimer's disease state. Also disclosed is a computer readable medium and a system, both useful in carrying out the present invention.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Diagnosis Of Neurodegenerative Diseases
InactiveUS20080286263A1Improve trustNervous disorderElectrolysis componentsHemoglobin Beta ChainApolipoprotein C-II
The invention relates to a method of diagnosis of Huntington's Disease in a diagnostic sample of a valid body tissue taken from a human subject, which comprises detecting an altered concentration of a protein in the diagnostic sample, compared with a sample of a control human subject, the protein being selected from: Swiss Prot accession number: Protein name; P10909: Clusterin precursor; P00738: Haptoglobin precursor; P01009: Alpha-1-antitrypsin precursor; P01024: Complement C3 precursor; P01620: 1 g kappa chain V-III region; P01834: 1 g kappa chain C region P01842: 1 g lambda chain C regions; P01857: 1 g gamma-1 chain C region; P01859: Ig gamma-2 chain C region; P01876: 1 g alpha-1 chain C region P02647: Apolipoprotein A-I precursor; P02649: Apolipoprotein E precursor; P02652: Apolipoprotein A-II precursor; P02655: Apolipoprotein C-II precursor; P02656: Apolipoprotein C-II precursor P02671: Fibrinogen alpha / alpha-E chain precursor; P02763: Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 precursor; P02766: Transthyretin precursor; P02768: Serum albumin precursor; P02787: Serotransferrin precursor; P04196: Histidine-rich glycoprotein precursor; P06727: Apolipoprotein A-IV precursor; P19652: Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 precursor; P68871 / P02042: Hemoglobin beta chain / Hemoglobin delta chain; P60709: Beta actin.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
Optimised coding sequence and promoter
ActiveUS20150273082A1Shorten the timeImprove the level ofFactor VIIBacteriaLipid storageLipid storage disease
An optimized coding sequence of human blood clotting factor eight (VIII) and a promoter may be used in vectors, such as rAAV, for introduction of factor VIII, and / or other blood clotting factors and transgenes. Exemplary of these factors and transgenes are alpha-1-antitrypsin, as well as those involved in the coagulation cascade, hepatocyte biology, lysosomal storage, urea cycle disorders, and lipid storage diseases. Cells, vectors, proteins, and glycoproteins produced by cells transformed by the vectors and sequence, may be used in treatment.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC +2
Alpha-1 antitrypsin for treating exacerbation episodes of pulmonary diseases
ActiveUS20090131305A1Suitable for useImprove dose accuracyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseInhalation
The present invention relates to methods for the treatment of exacerbation periods of pulmonary diseases, particularly chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, by administering alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) to a subject in need thereof. Particularly, the present invention discloses the efficient treatment of exacerbation periods of pulmonary diseases by administering AAT via inhalation.
Owner:KAMADA
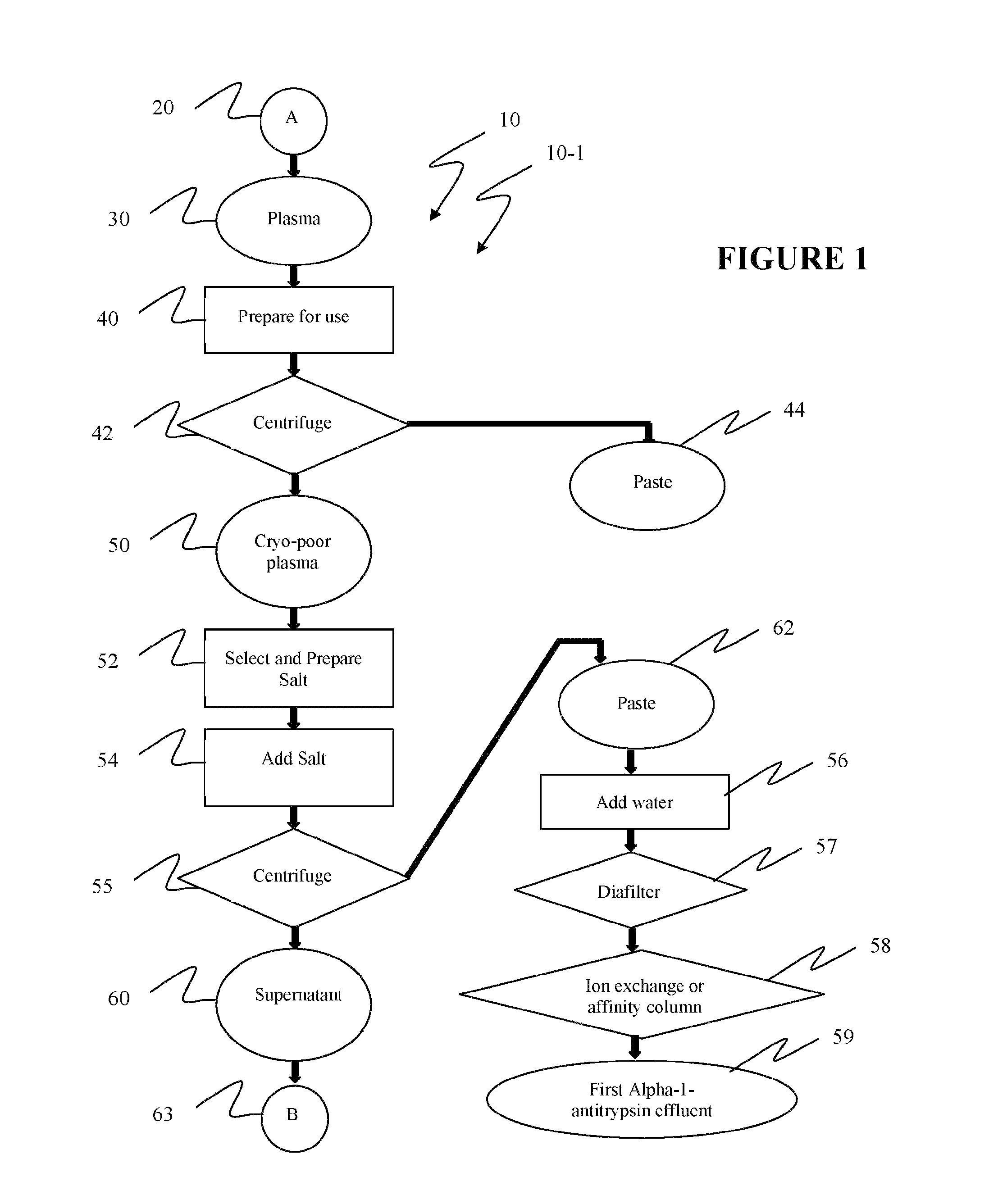
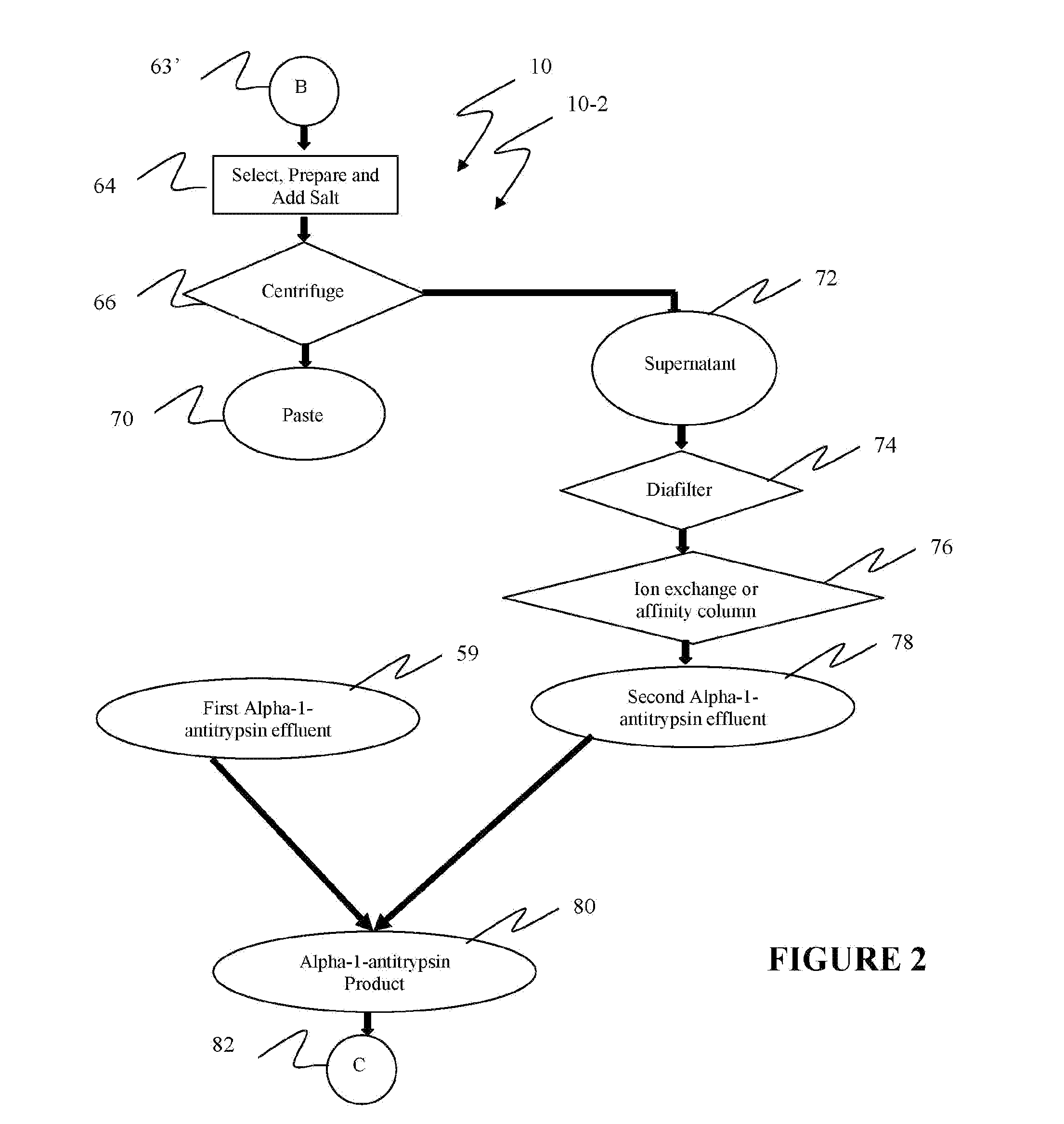
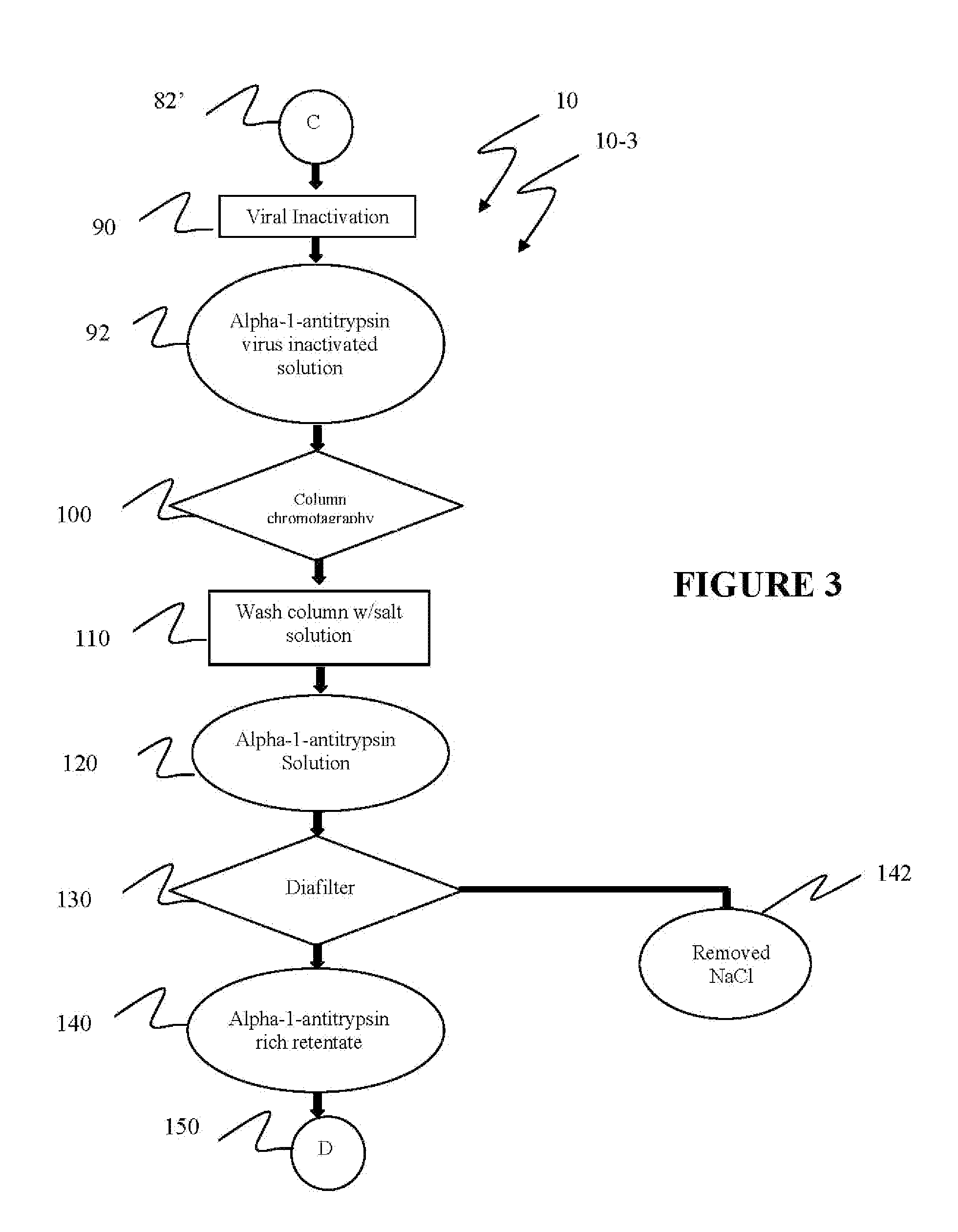
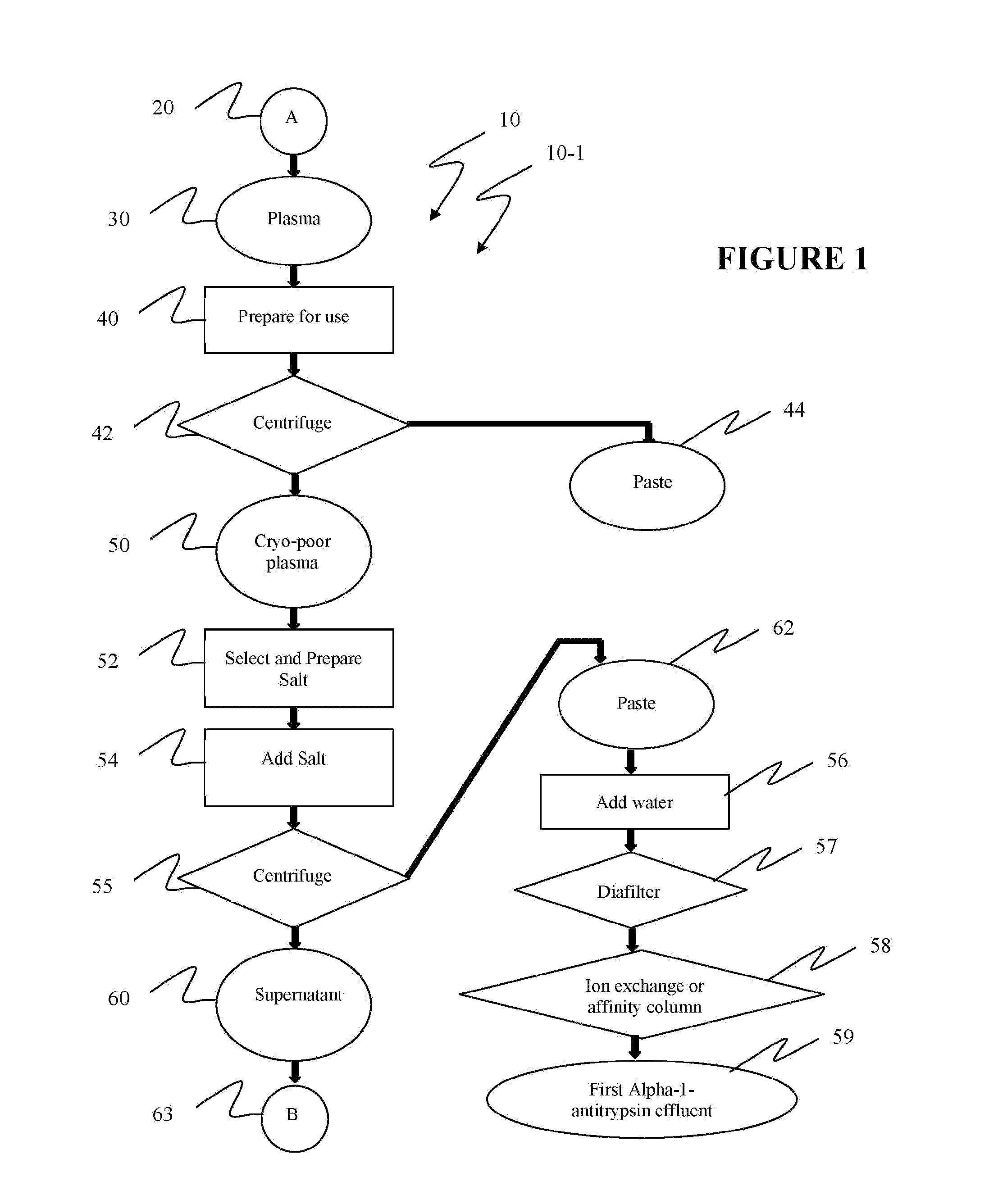
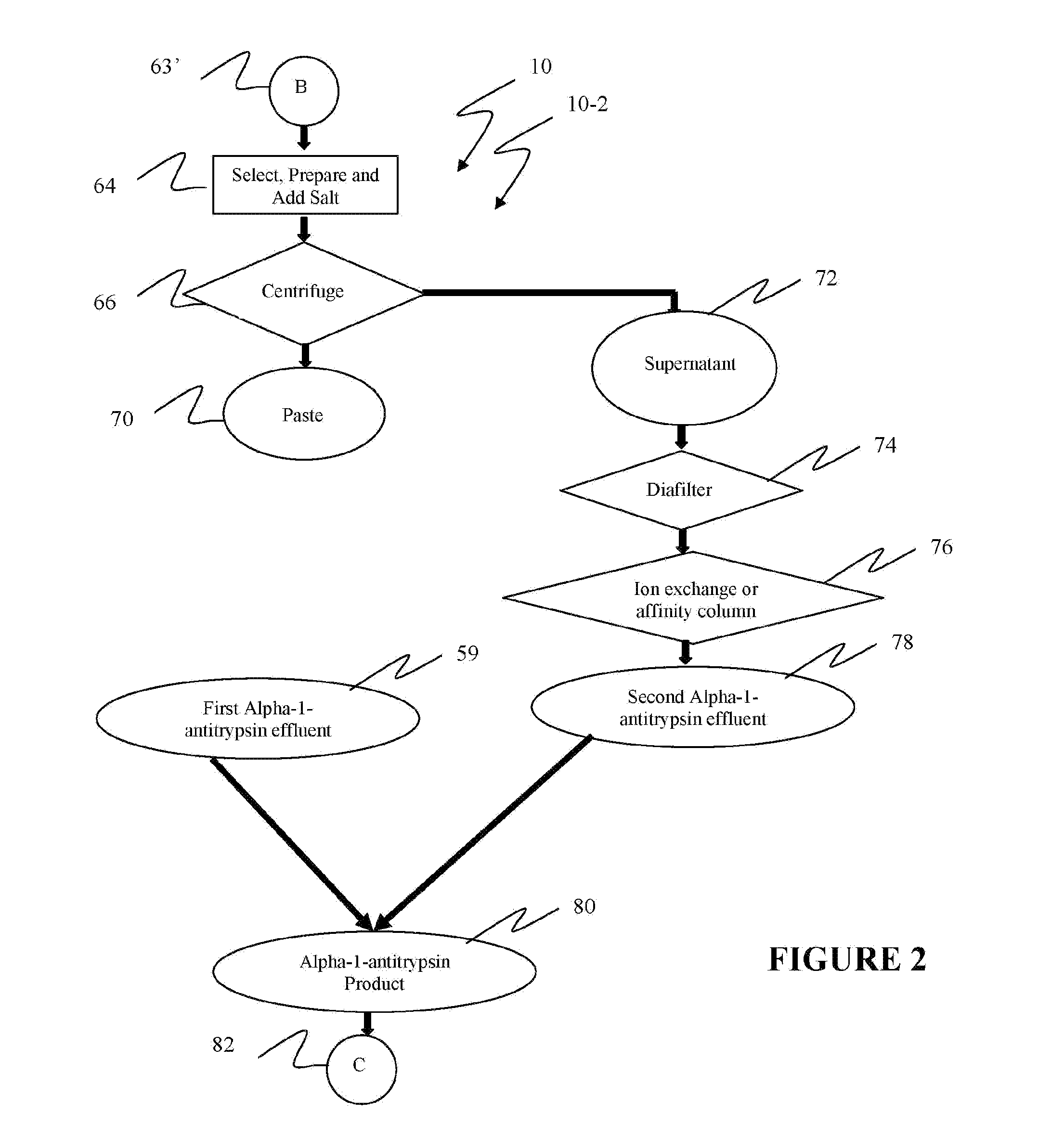
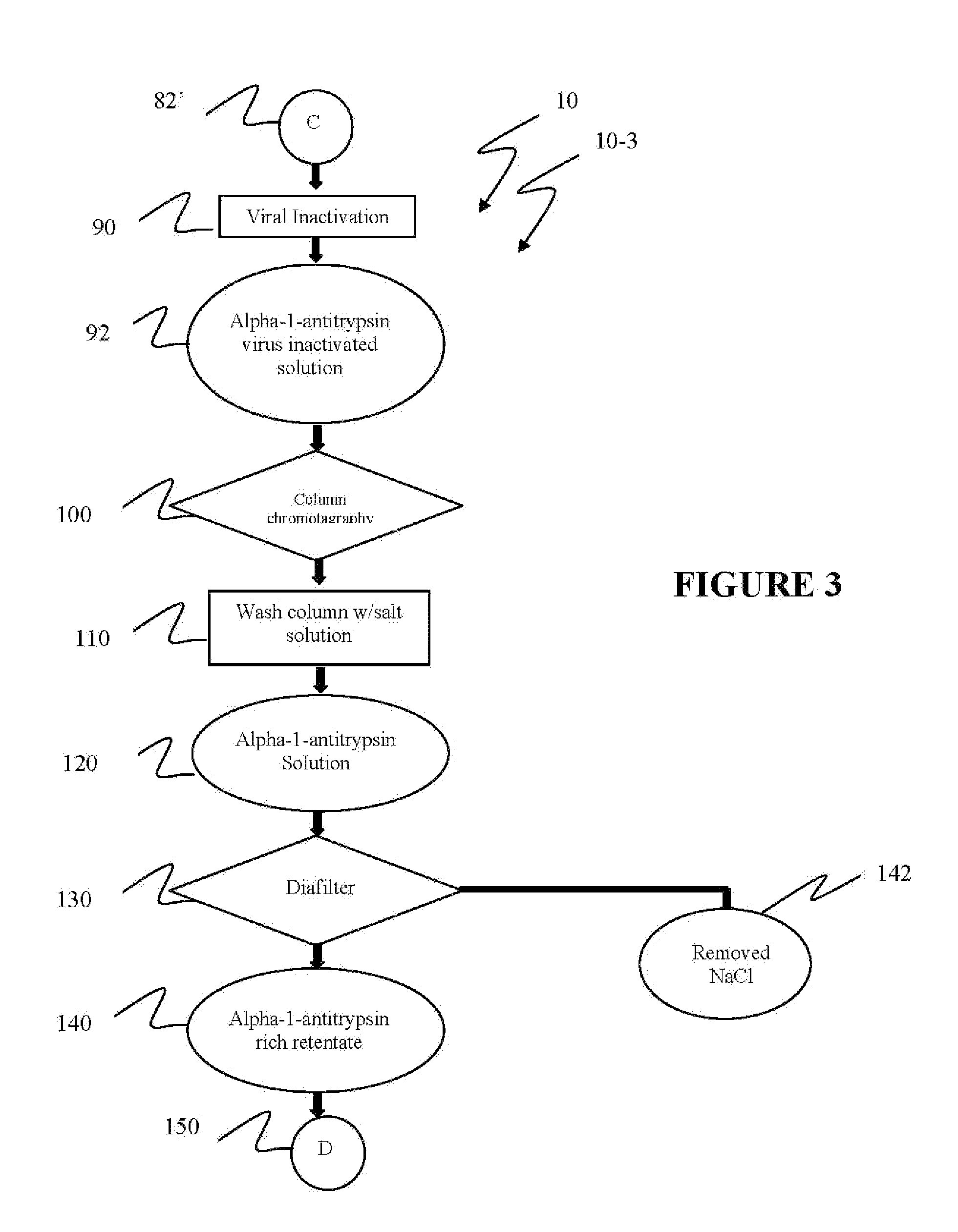
Ultra-high yield of alpha-1-anti-trypsin
ActiveUS8293242B2Quick restoration of the internal water moleculeHigh yieldBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSodium acetateFractionation
The instant invention provides novel and effective methods of isolating alpha-1-antitrypsin from cryo-poor plasma and formulating it into therapeutic products. This invention achieves higher yields and a superior quality of alpha-1-antitrypsin. Alpha-1-antitrypsin is isolated from cryo-poor plasma, using one or more salts selected from a group comprising sodium citrate, sodium acetate, sodium gluconate, ammonium sulfate, sodium chloride, sodium sulfate and ammonium chloride in two fractionation steps, followed by diafiltration to remove those salts employed.
Owner:PLASMA TECH LLC
Ultra-high Yield Of Alpha-1-Antitrypsin
ActiveUS20110152503A1High alpha-1-antitrypsin yieldReduce energy costsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSodium acetateFractionation
The instant invention provides novel and effective methods of isolating alpha-1-antitrypsin from cryo-poor plasma and formulating it into therapeutic products. This invention achieves higher yields and a superior quality of alpha-1-antitrypsin. Alpha-1-antitrypsin is isolated from cryo-poor plasma, using one or more salts selected from a group comprising sodium citrate, sodium acetate, sodium gluconate, ammonium sulfate, sodium chloride, sodium sulfate and ammonium chloride in two fractionation steps, followed by diafiltration to remove those salts employed.
Owner:PLASMA TECH LLC
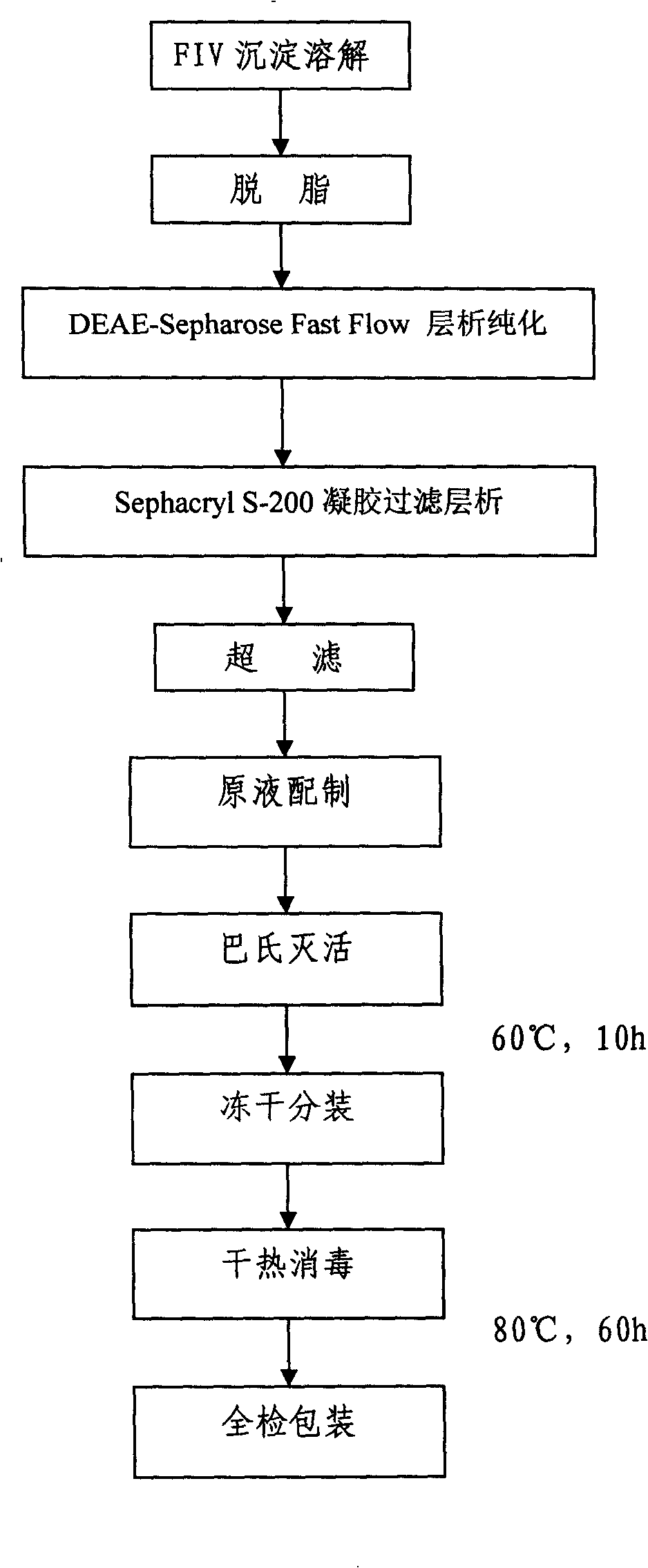
Method for separating and purifying alpha 1-antitrypsin from human blood plasma component FIV precipitation
ActiveCN101274956AHigh purityHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsProtease inhibitorsFiltrationBlood plasma
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying alpha1-antitryptase from the FIV component precipitation of human plasma, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of (A) pretreatment of plasma precipitation; (B) anion gel chromatography; (C) gel-filtration chromatography; (D) ultrafiltration desalting concentration; (E) Baculovirus inactivation; (F) lyophilization and subpackaging; (G) dry heat sterilization. The method takes the FIV component precipitation which is waste material produced from human plasma during the production process of human serum albumin as raw material and adopts chromatography technique to separate and purify a protease inhibitor, namely, alpha 1- antitryptase (alpha 1-AT) and builds the production technique of alpha 1-AT concentrate. Products prepared by the method has good pureness, high yield and simple and easy operation as well as few occupied equipment, little labor intensity, low energy consumption and low production cost due to taking the waste material generated by albumin as raw material.
Owner:广东双林生物制药有限公司
Method for purification of alpha-1-antitrypsin
ActiveUS7777006B2Reduce suspensionLess timePeptide/protein ingredientsIon-exchanger regenerationSorbentCohn fraction IV
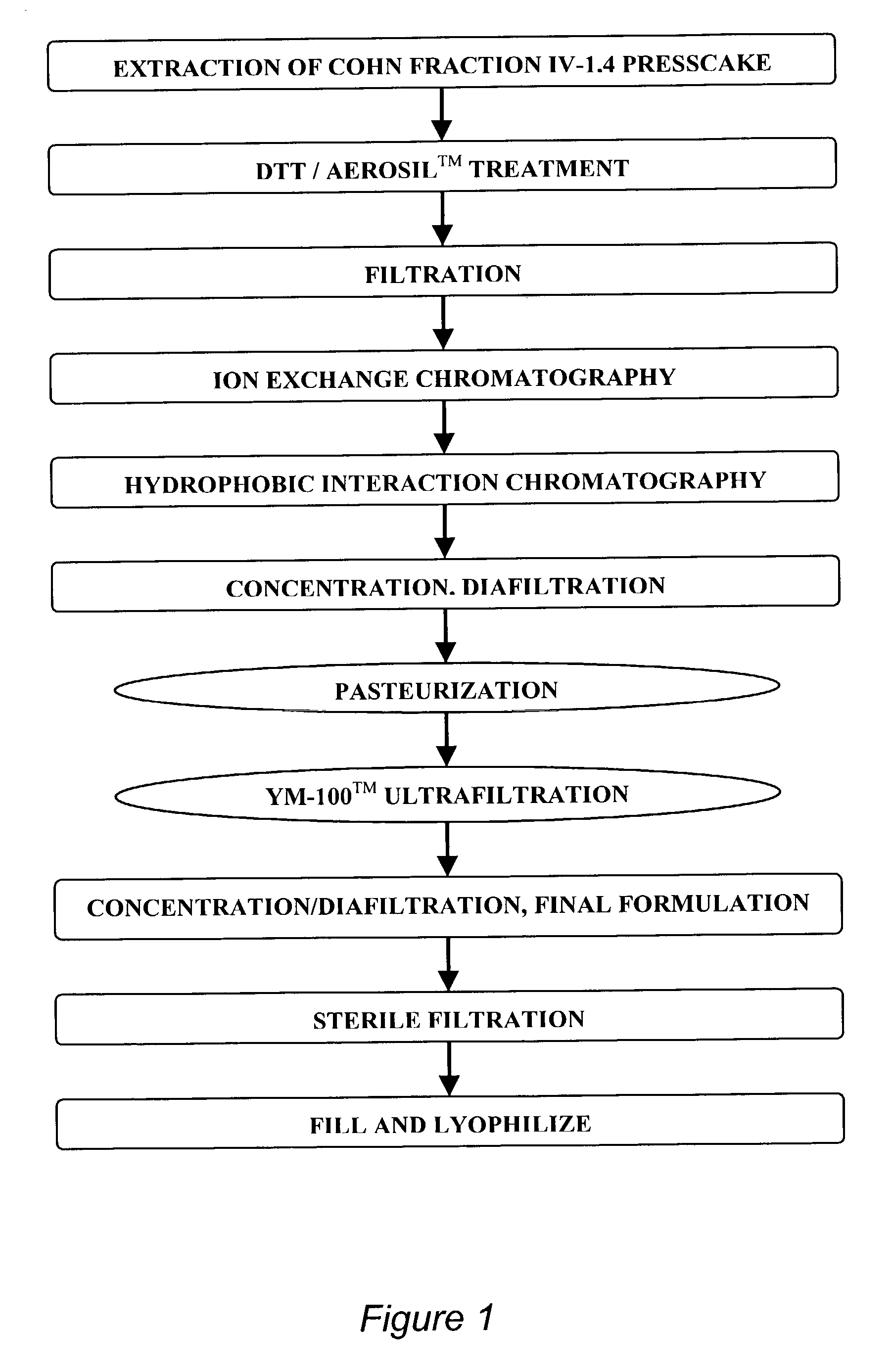
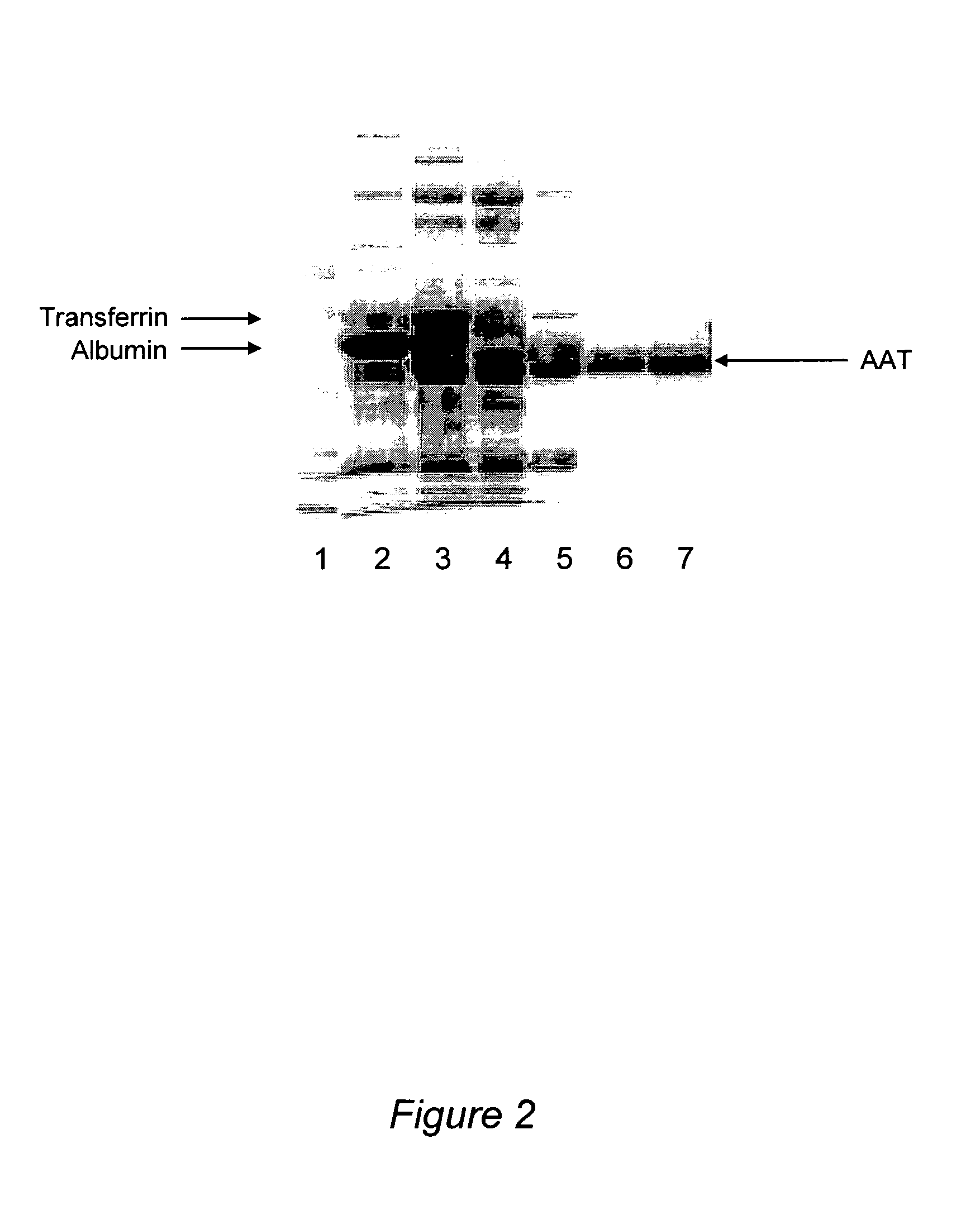
A streamlined method for purifying alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT) from an AAT-containing protein mixture, such as a Cohn fraction IV precipitate, is provided. In the method of the invention, contaminating proteins are destabilized by cleavage of disulfide bonds with a reducing reagent, such as a dithiol, which does not affect AAT. The destabilized proteins are then preferentially adsorbed on a solid protein-adsorbing material, without the addition of a salt as a precipitant. Separation of the solid adsorbent from the solution leaves a purified AAT solution that is directly suitable for chromatographic purification, without the need for extensive desalting as in prior art processes. A process incorporating this method, which provides pharmaceutical grade AAT in high yield on a commercial scale, is also described.
Owner:AVENTIS BEHRING
Multifunctional protease inhibitors and their use in treatment of disease
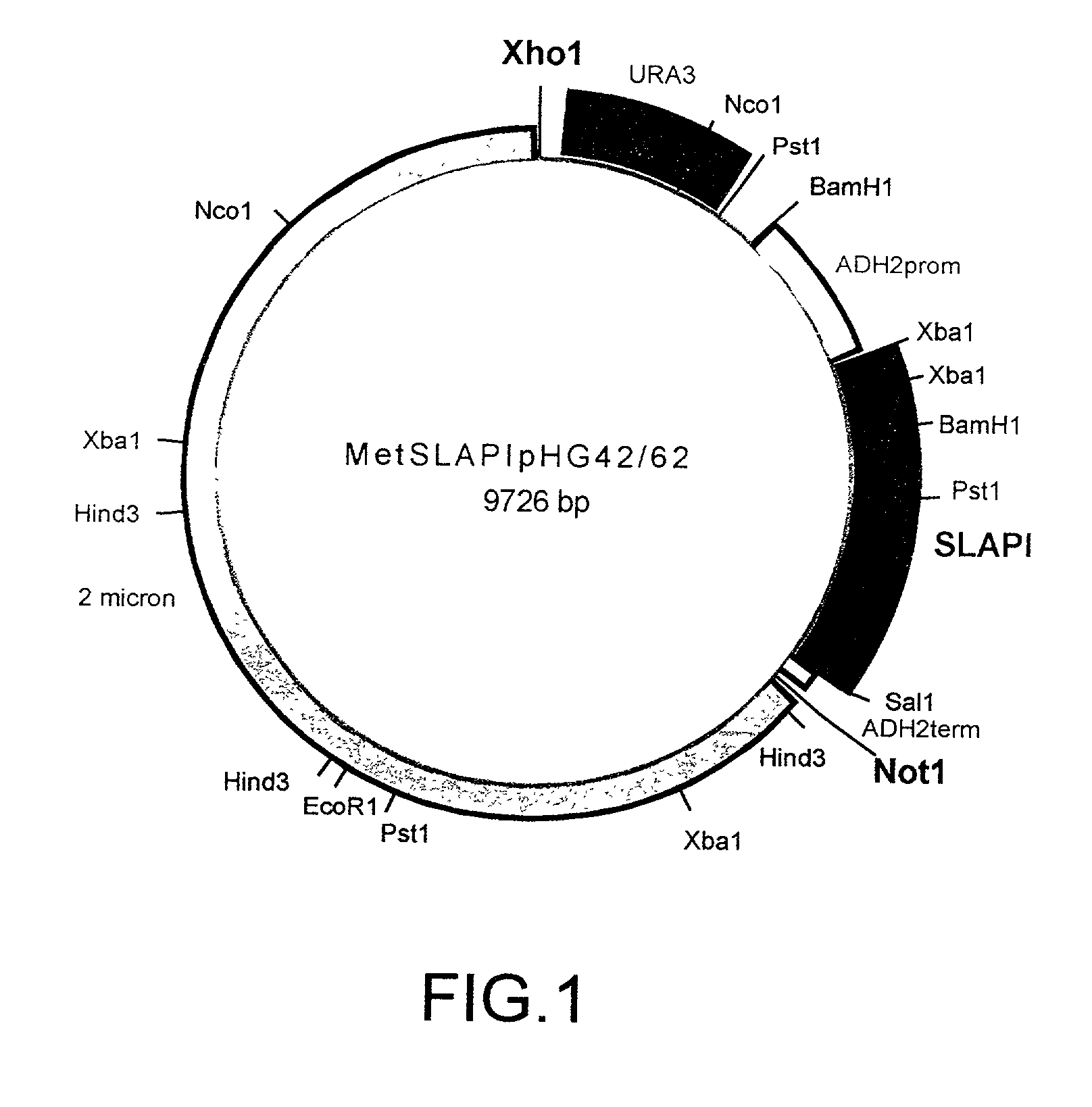
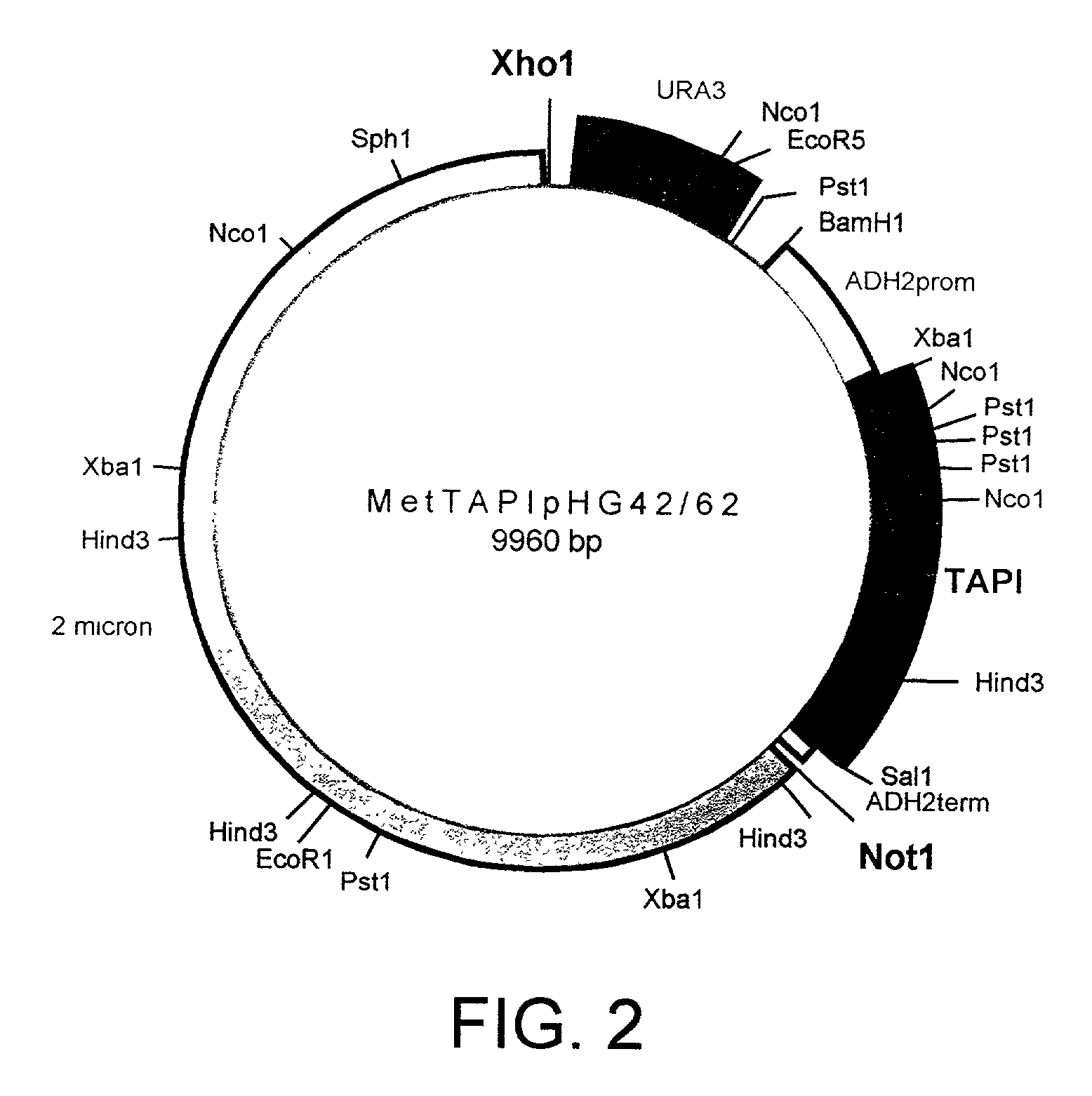
Fusion proteins of protease inhibitors are provided, in particular fusion proteins of alpha 1-antitrypsin (AAT) and a second protease inhibitor, such as secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) or tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases (TIMP). Polynucleotides encoding the fusion proteins, vectors comprising such polynucleotides, and host cells containing such vectors are also provided. Methods of making the fusion proteins of the invention are also provide, as well as methods of using the fusion proteins, for example to inhibit protease activity in a biological sample or in the treatment of an individual suffering from, or at risk for, a disease or disorder involving unwanted protease activity.
Owner:ARRIVA PHARMA
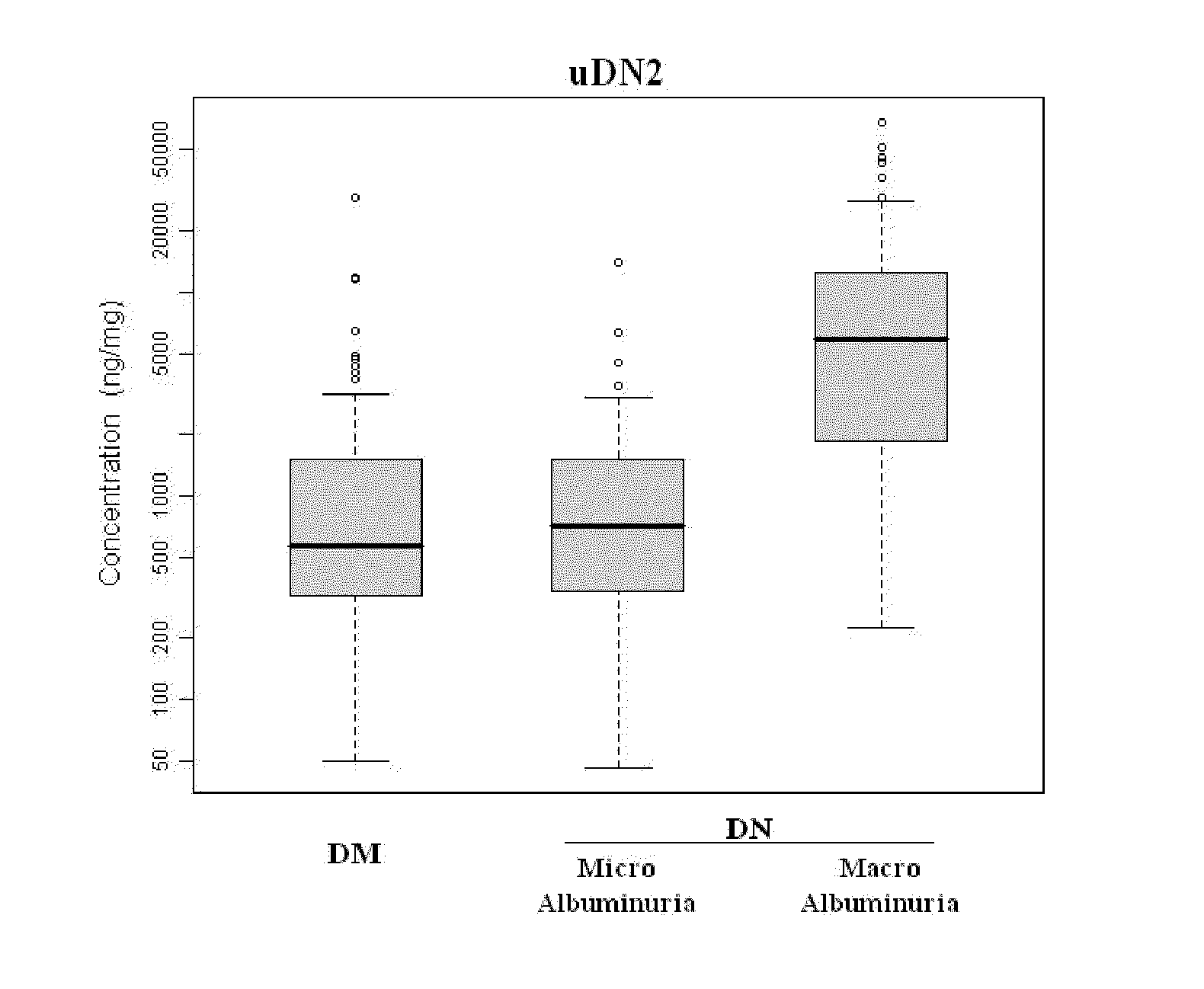
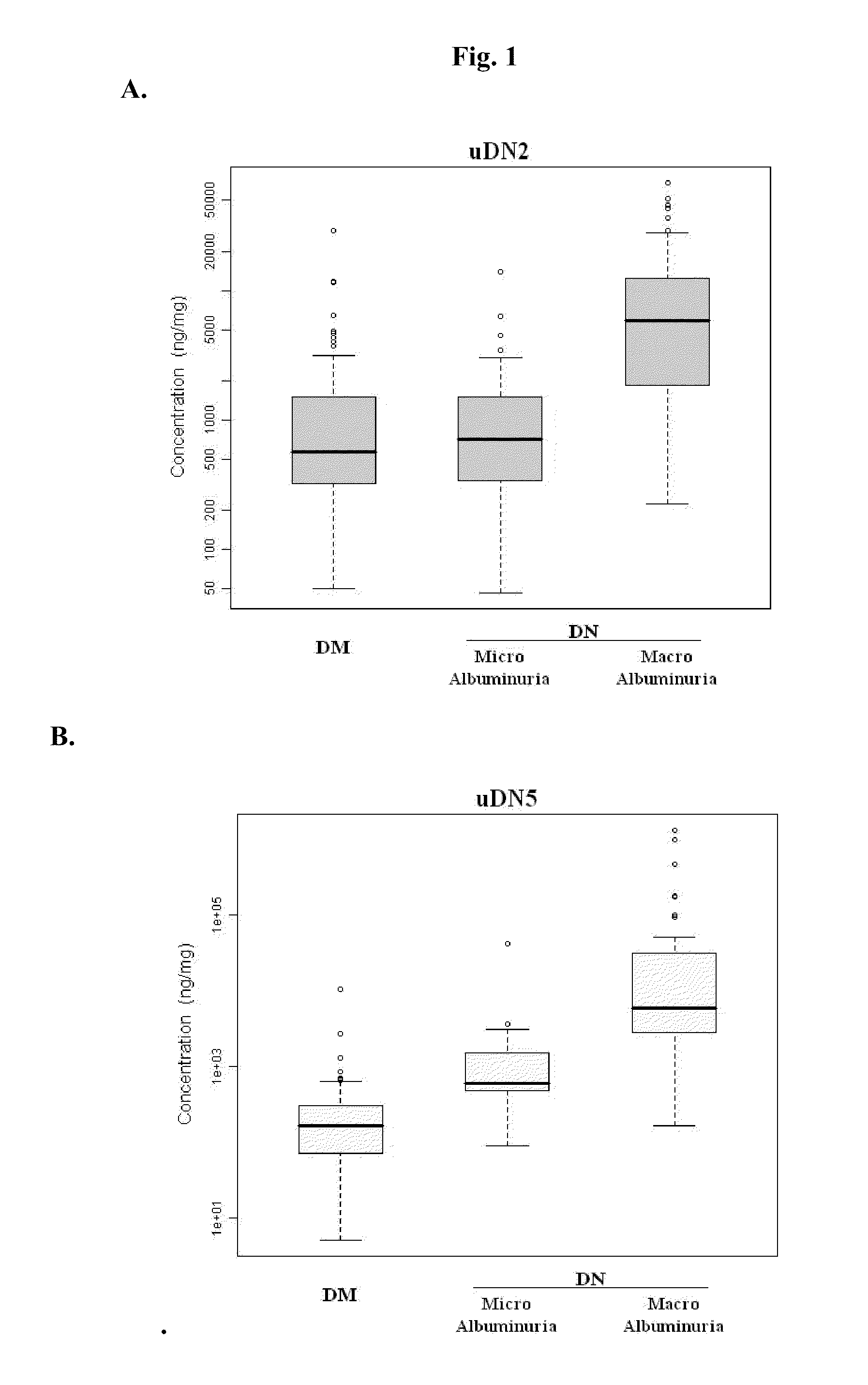
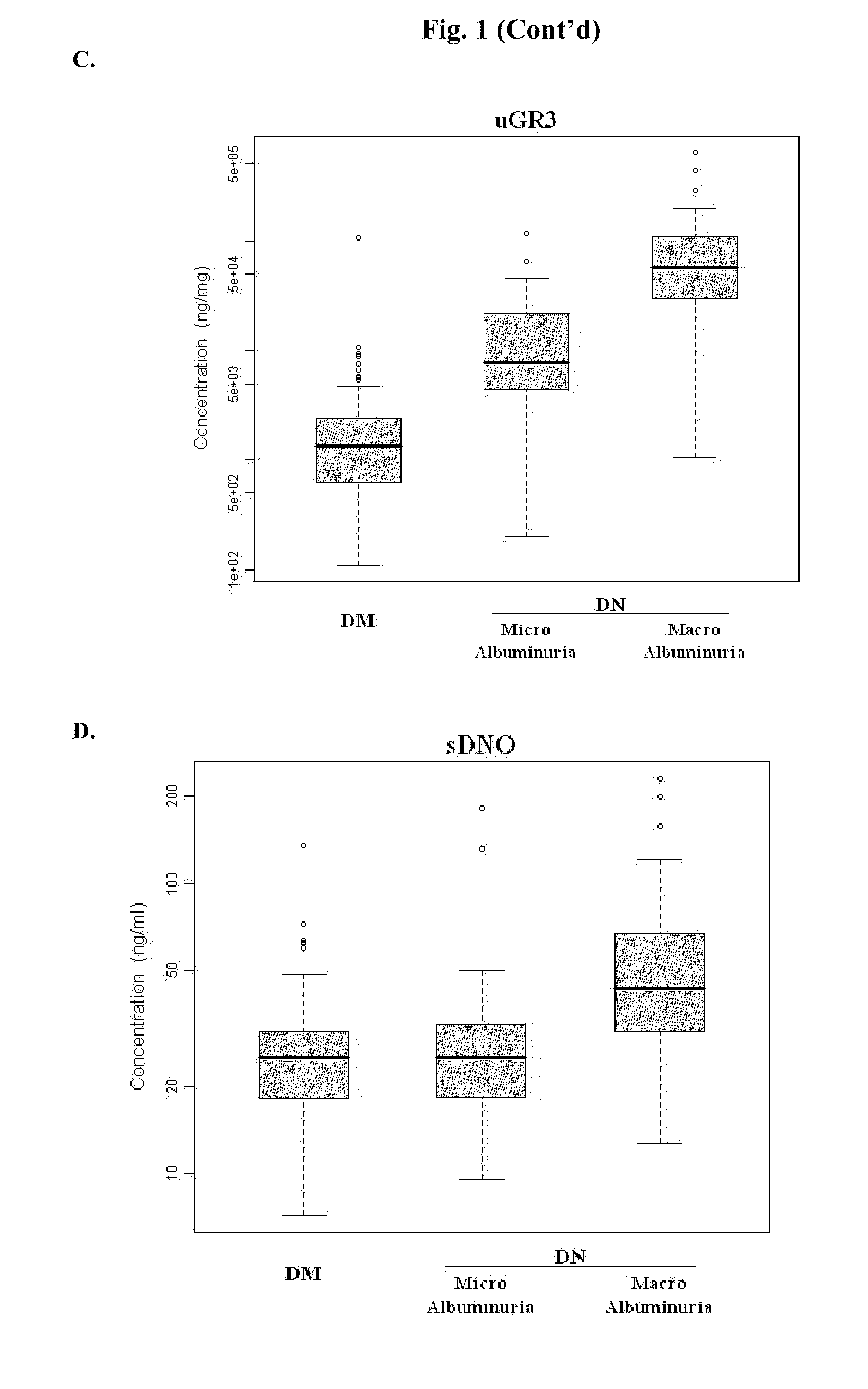
Urine and Serum Biomarkers Associated with Diabetic Nephropathy
Use of urine and serum biomarkers in diagnosing diabetic nephropathy, staging diabetic nephropathy, monitoring diabetic nephropathy progress, and assessing efficacy of diabetic nephropathy treatments. These biomarkers include urine precursor alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein, urine alpha-1 antitrypsin, urine alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, urine osteopontin, serum osteopontin, their fragments, and combinations thereof.
Owner:BIO PREVENTIVE MEDICINE CORP
Alpha 1-Antitrypsin Compositions and Treatment Methods Using Such Compositions
Alpha 1-antitrypsin compositions and treatment methods using such compositions for treating a variety of pulmonary diseases are provided. The compositions generally contain AAT, a stabilizing carbohydrate such as trehalose, a surfactant such as Polysorbate 80 and an antioxidant to stabilize AAT for use as a therapeutic. The formulations can be prepared as both liquids and solids and administered by nebulization of the liquid formulation or by conversion of dry powder formulation into an aerosol.
Owner:ARRIVA PHARMA +2
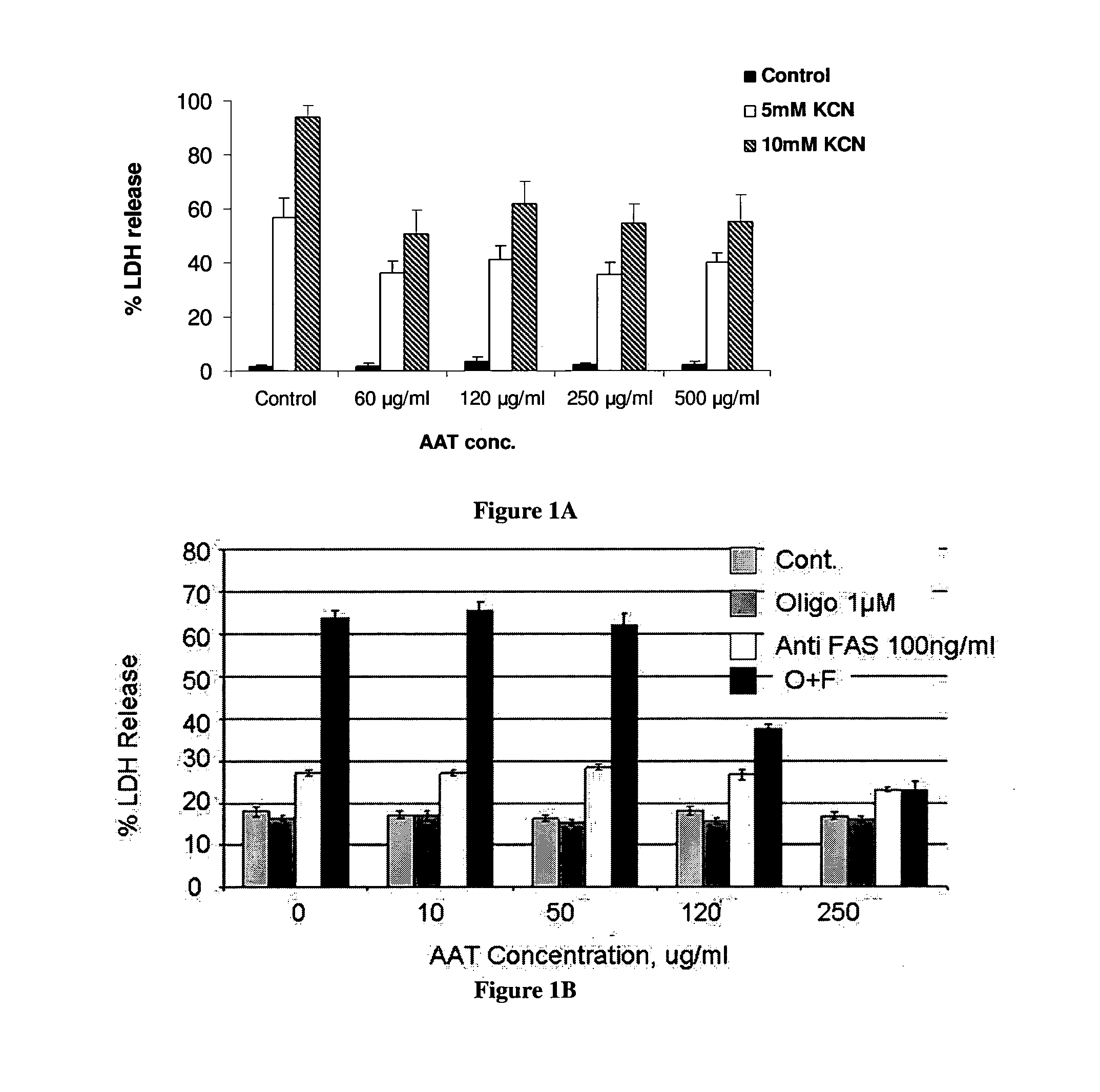
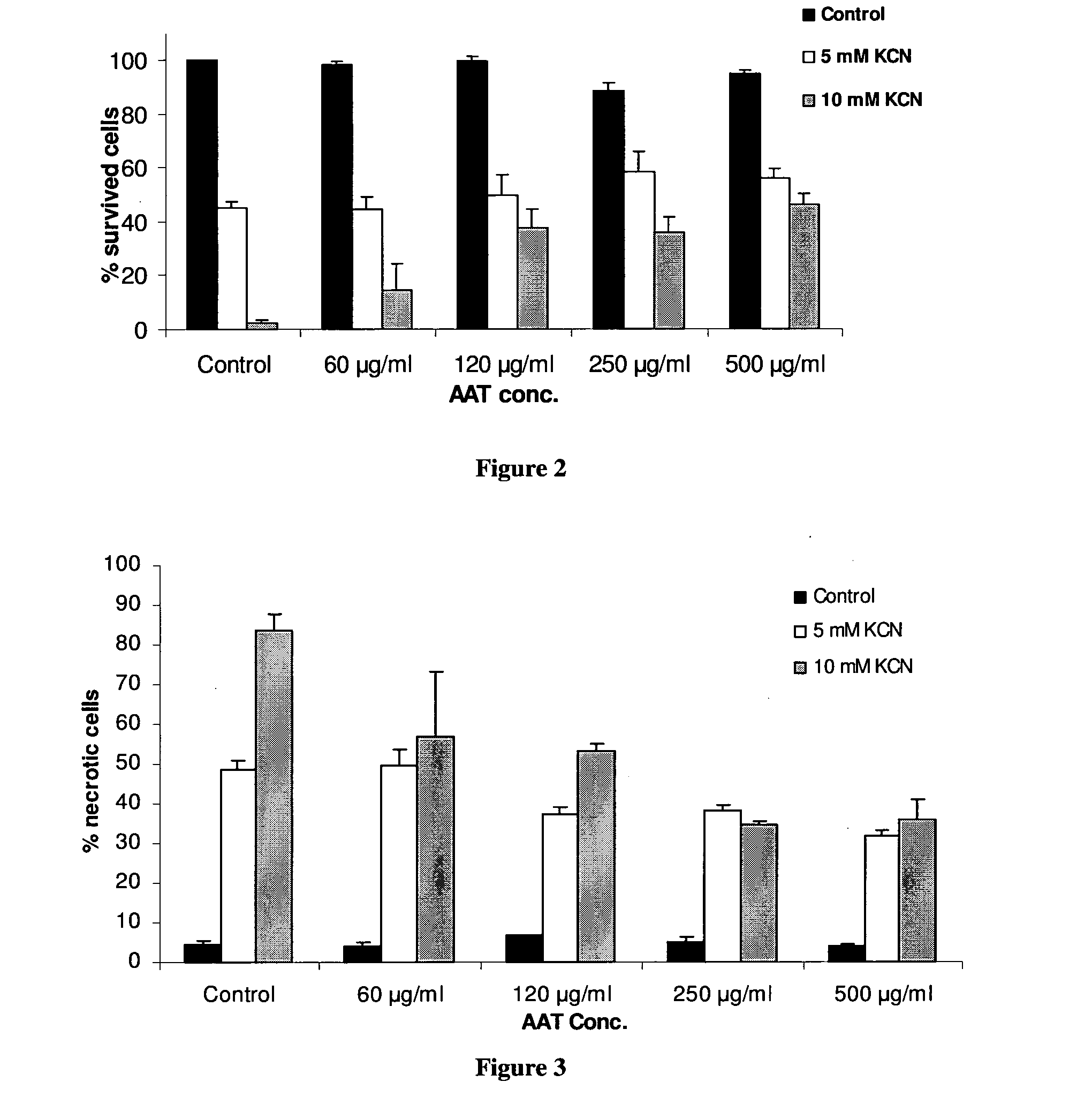
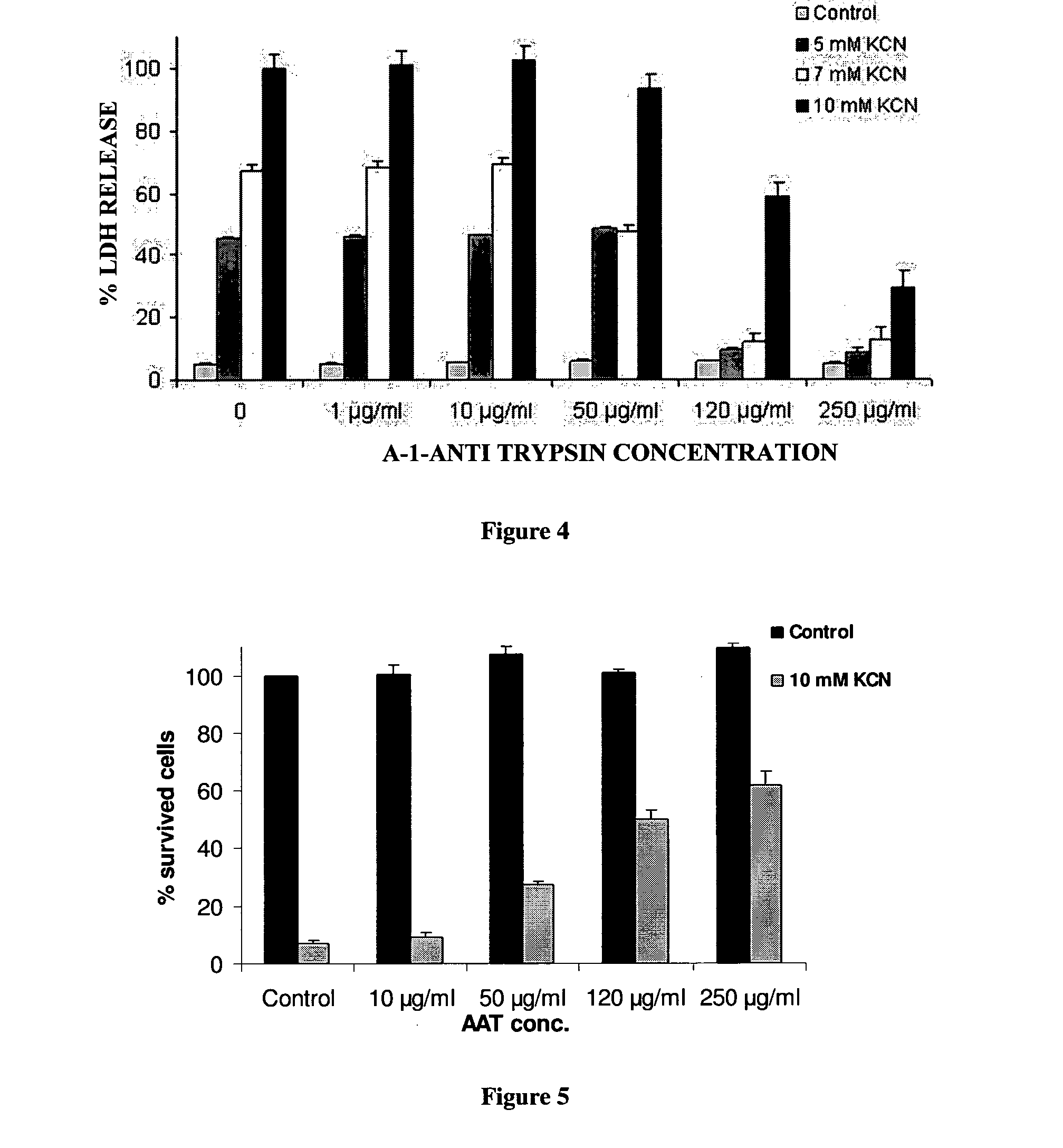
Antinecrotic activity of alpha 1-antitrypsin
InactiveUS20110237496A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsProphylactic treatmentAlpha 1-antitrypsin Pittsburgh
The present invention is related to the use of alpha-1-antitrypsin as an anti-necrotic agent. This invention provides a method for the treatment of tissue necrosis by administration of alpha-1-antitrypsin. This invention further provides methods for prophylactic treatment of tissue necrosis and for inhibition of tissue necrosis in culture by addition of alpha-1-antitrypsin.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV +1
Amniotic fluid formulation for treatment of lung disorders
InactiveUS20170354692A1Improving exercise enduranceIncreasing baseline blood oxygen saturationDispersion deliveryAntipyreticInterstitial lung diseaseDisease
Formulations of human amniotic fluid and methods of use thereof for treatment of lung disorders, and / or injuries have been developed. The formulations are suitable for topical delivery to the lung for treatment of lung disorders including chronic obstructive pulmonary disorders (COPD), asthma, emphysema, bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis, interstitial lung disease, alpha-1 antitrypsin emphysema, as well as for treatment of acute lung injuries. Methods including administering specifically formulated, diluted sterile de-cellularized human amniotic fluids topically to the lungs, preferably as aerosol droplets, are described. In particular, the methods involving administration of the amniotic fluid formulation in the form of aerosol droplets with size between about 1.5 μm to about 5 μm, preferably from about 2.5 μm to about 3.5 μm, inclusive, using apparatus such as high-efficiency vibrating mesh nebulizers, are described. Formulations described can treat, or prevent one or more symptoms of a chronic lung disorder.
Owner:MAM HLDG OF WEST FLORIDA L L C
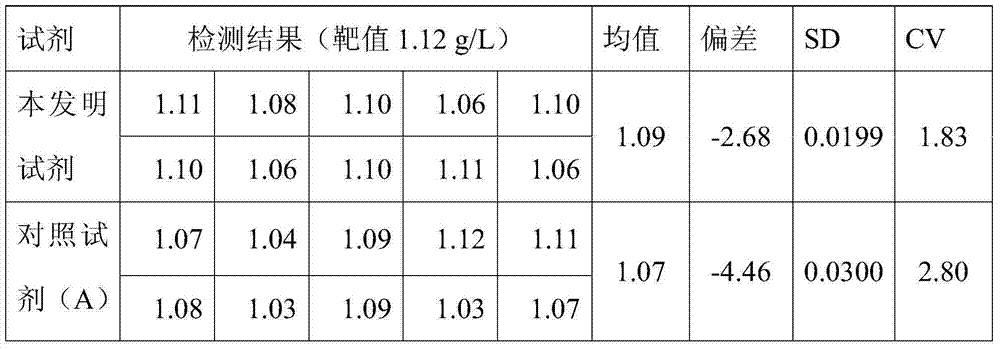
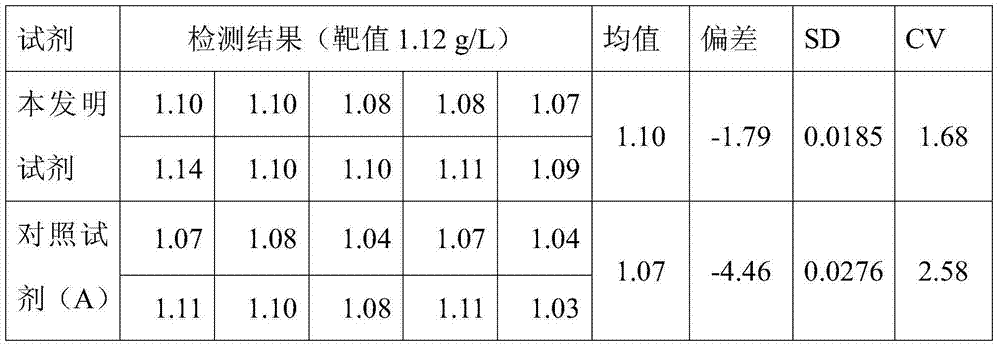
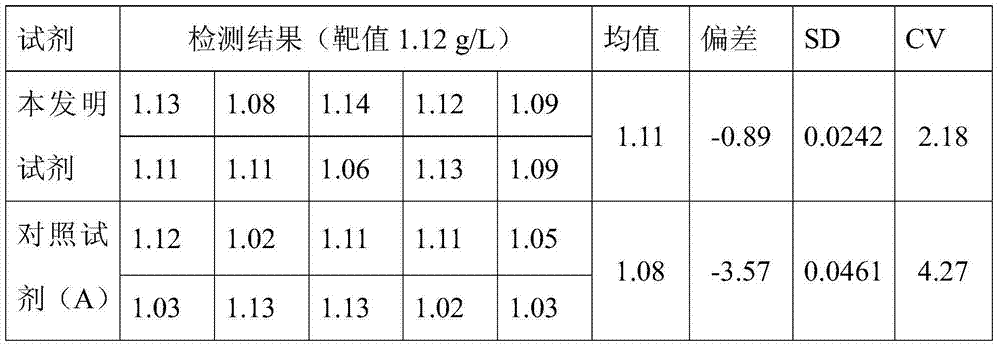
Reagent for quantitative detection of serum alpha 1-antitrypsin
ActiveCN103760360AImprove accuracyQuick checkMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological material analysisSerum igeTryptase
The invention discloses a reagent for quantitative detection of serum alpha 1-antitrypsin. The reagent comprises a reagent R1, a reagent R2 and a calibrator. The reagent R1 comprises a buffer, a surfactant, a reaction promoter, an electrolyte, a stabilizing agent and an antibacterial agent. The reagent R2 comprises a buffer 2, an anti-human alpha 1-antitrypsin antibody, an electrolyte, a stabilizing agent and an antibacterial agent. The calibrator comprises a buffer, a human alpha 1-antitrypsin, an electrolyte, a stabilizing agent and an antibacterial agent. The reagent has the advantages of fast detection, high detection sensitivity, linearity range of 4.00g / L, high accuracy and good stability.
Owner:PUREBIO LAB NINGBO
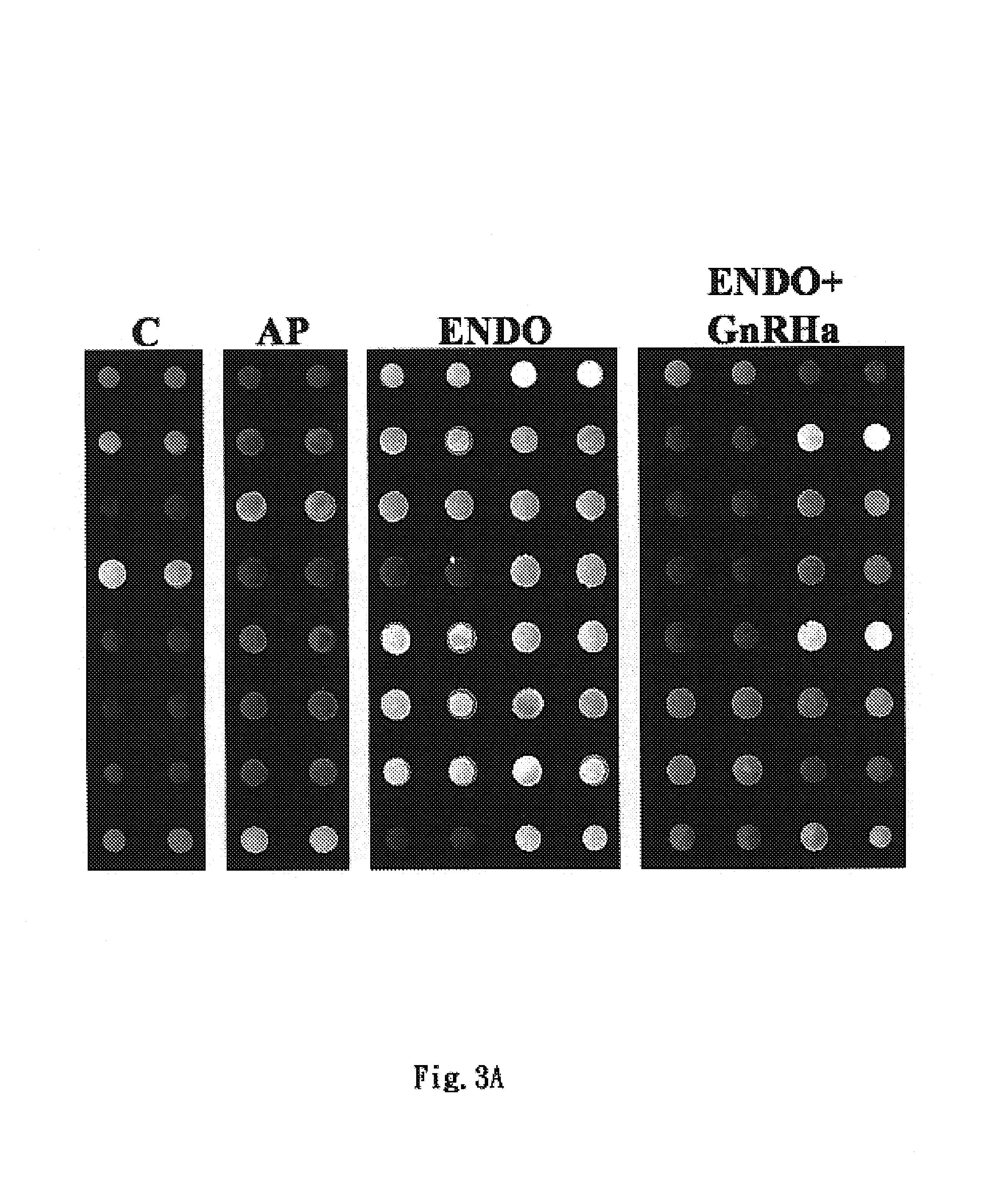
Diagnosis method of endometriosis by detecting biochemical markers and usage of these biochemical markers
ActiveUS7399598B2Fast expressionFast quantitiesDisease diagnosisBiological testingGuidelinePeritoneal fluid
The present invention relates to a non-invasive diagnosis method of endometriosis by detecting biochemical marker in serum or peritoneal fluid, in particular alpha 1-antitrypsin, fragments of alpha 1-antitrypsin, or a combination of both. The diagnosis of endometriosis is performed with observing in serum specimens of a patient the concentration and change of the biochemical marker, in particular molecules related to alpha 1-antitrypsin, and comparing with a predetermined baseline level of the biochemical marker contained in serum. Statistical analysis can be performed to evaluate the baseline level indicating the occurrence of endometriosis. Therefore, the present invention can provide an auxiliary guideline for the diagnosis of endometriosis. The present invention also relates to usage of the biochemical marker.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
Process for preparing alpha-1-antitrypsin
ActiveCN1900107AImprove utilizationImprove efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsProtease inhibitorsEconomic benefitsBlood plasma
The present invention discloses safe and effective process of preparing alpha-1-antitrypsin through purifying human plasma component IV-1. The present invention extracts alpha-1-antitrypsin with high treating value from the waste human plasma component IV-1, and can raise the utilization rate of valuable human plasma, lower cost and raise economic benefit.
Owner:博晖生物制药(河北)有限公司
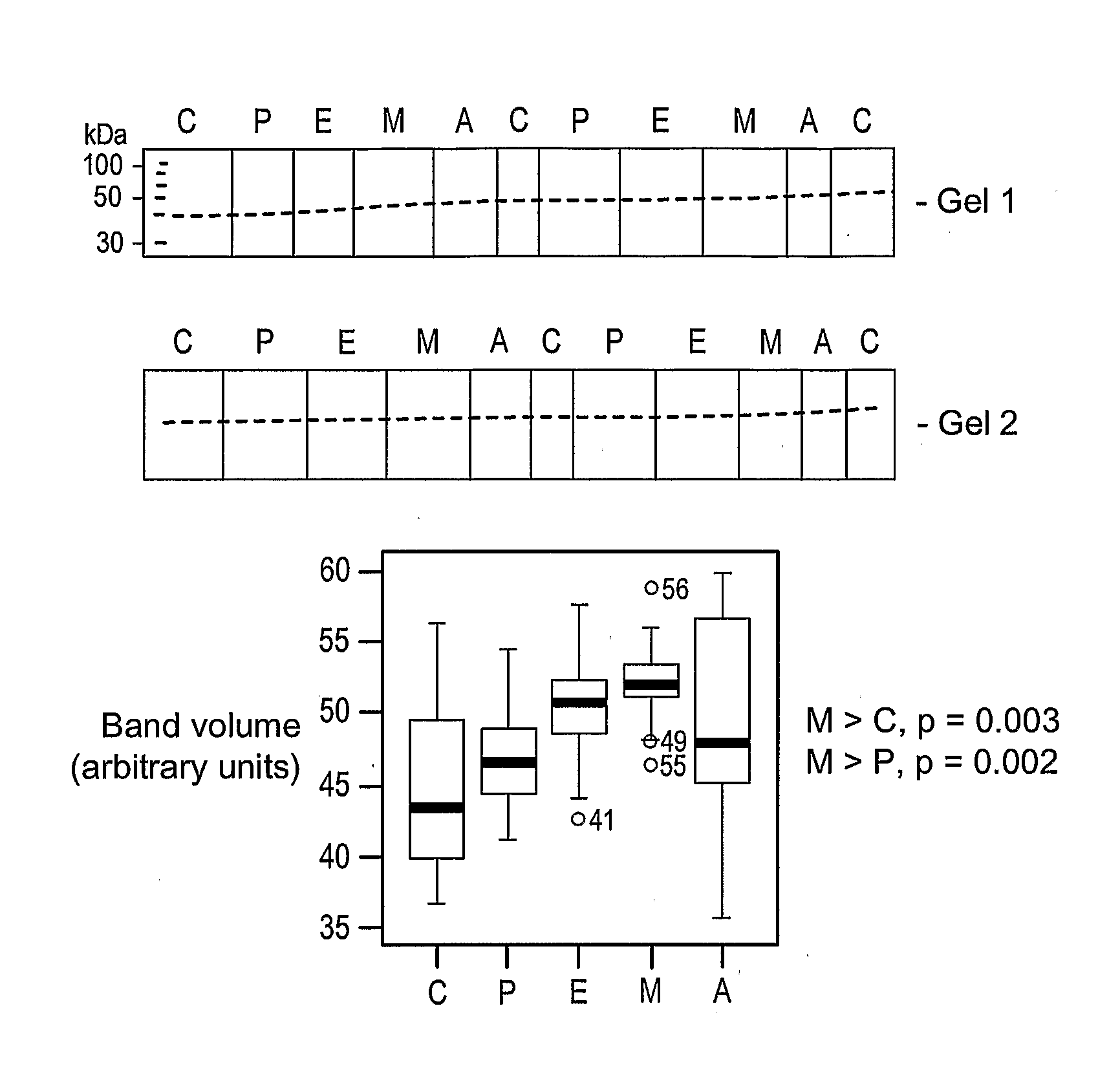
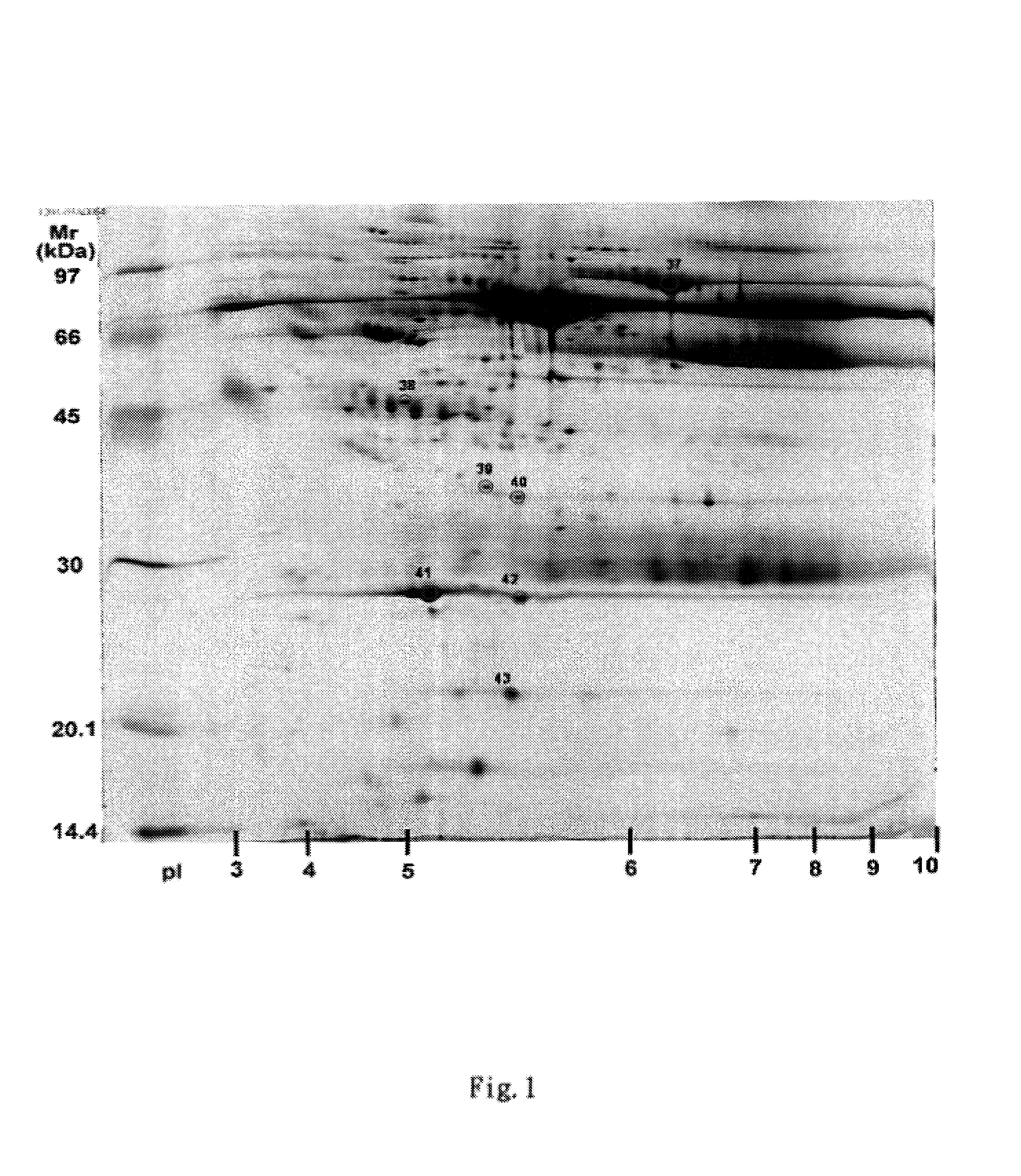
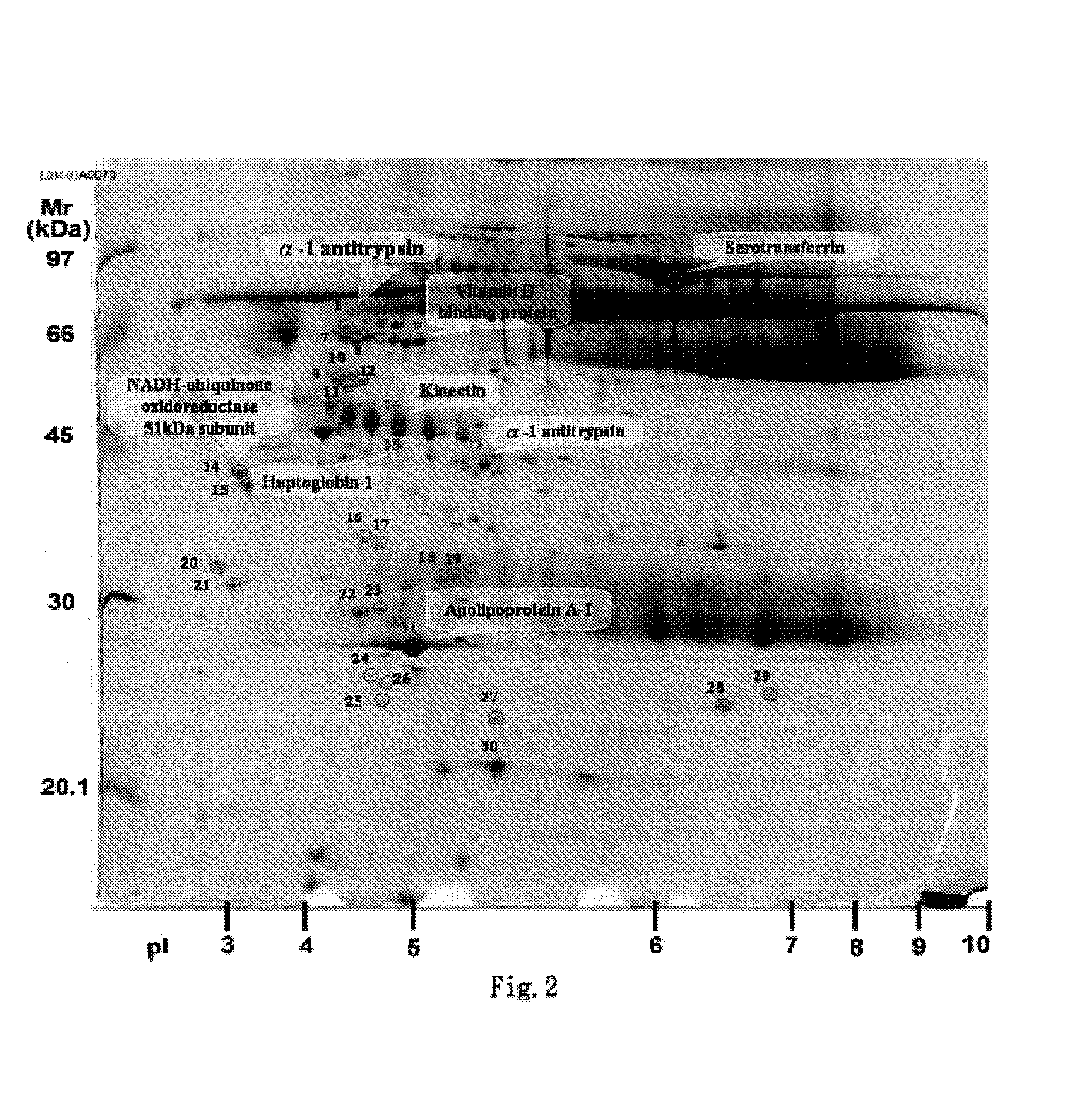
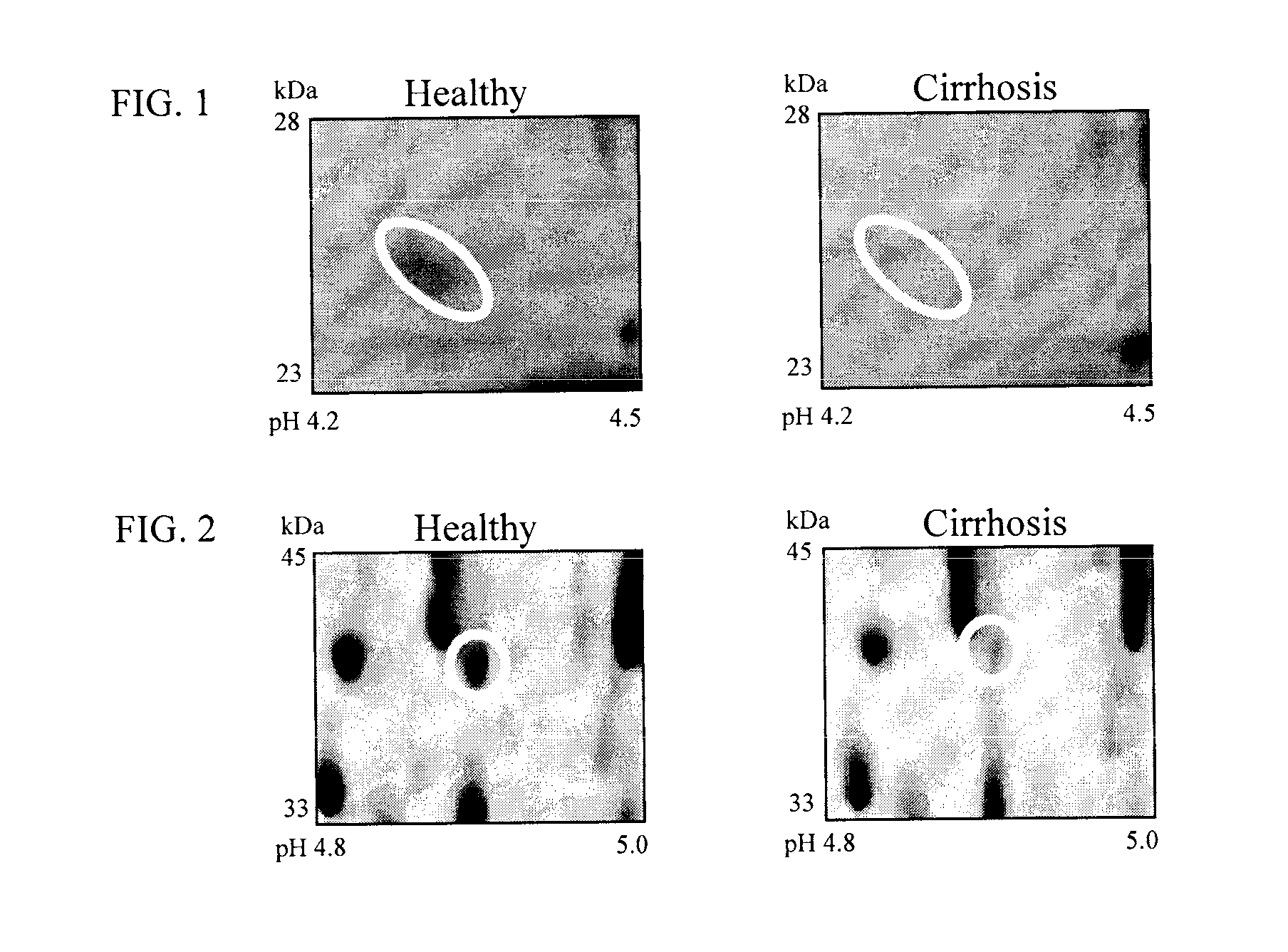
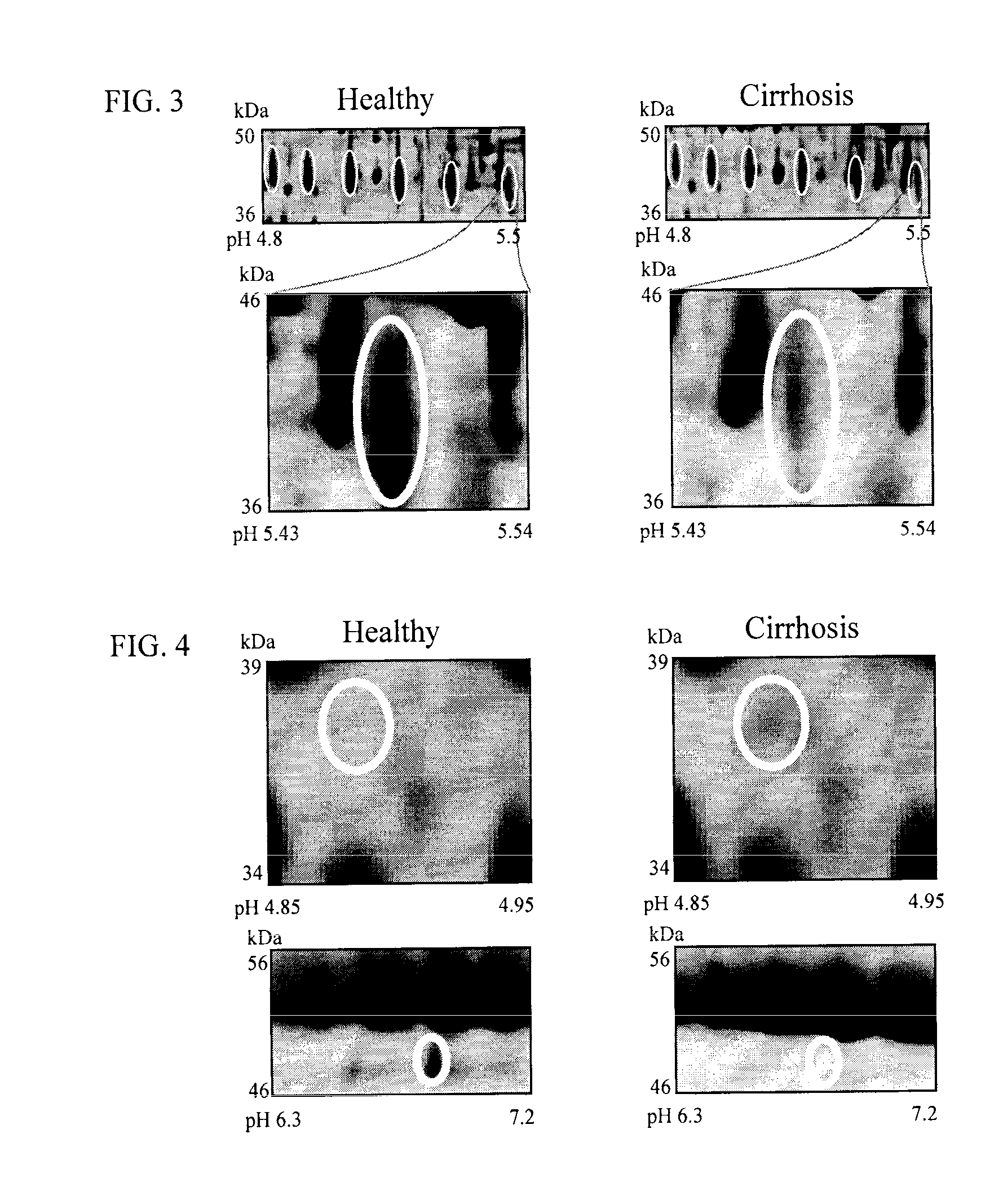
Clinical diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis using a novel panel of low abundant human plasma protein biomarkers
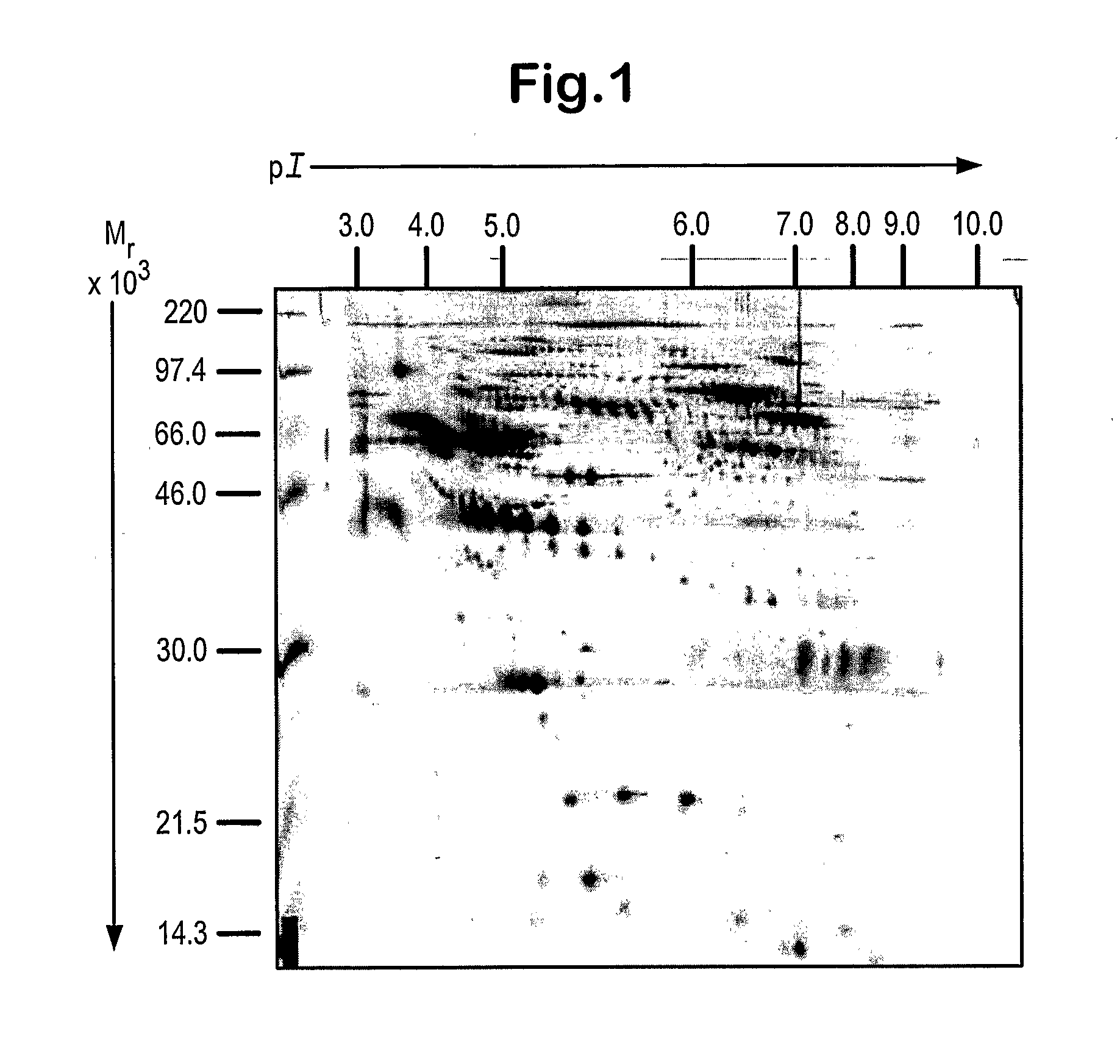
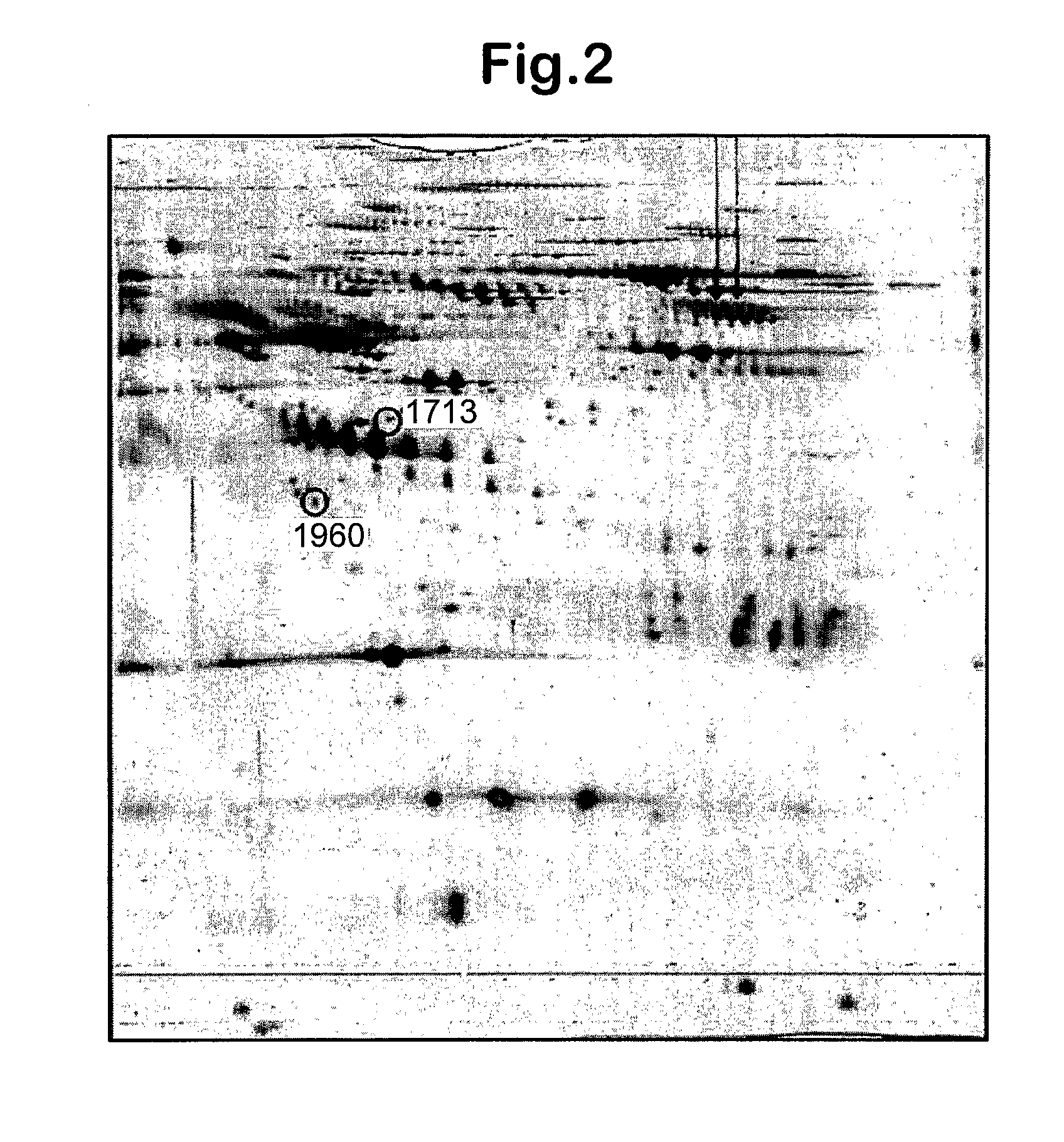
The inventors have proposed a novel panel of human plasma protein biomarkers for diagnosing hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Presently there is no reliable non-invasive way of assessing liver fibrosis. A 2D-PAGE based proteomics study was used to identify potential fibrosis biomarkers. Plasma from patients with hepatic cirrhosis induced by infection with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) were analysed. Several proteins associated with liver scarring and potentially also related to viral infection were identified. These proteins include 14-3-3 protein zeta / delta, adiponectin, afamin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein, apolipoprotein C-III, apolipoprotein E, C4b-binding protein beta chain, intact / cleaved complement C3dg, corticosteroid-binding globulin, fibrinogen gamma chain, beta haptoglobin at pH 5.46-5.49, haptoglobin-related protein, hemopexin, immunoglobulin J chain, leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein, lipid transfer inhibitor protein, retinol-binding protein 4, serum paraoxonase / arylesterase 1, sex hormone-binding globulin and zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein. These biomarkers can be used in conjunction with polypeptides in WO / 2008 / 031051. The concentrations of these novel biomarkers can be determined using an immunoassay where the concentrations would reflect the extent of fibrosis. A fibrosis scoring scale for each of the novel biomarkers is proposed. The additive result from the scores of all the novel biomarkers would give a more reliable indication of the degree of fibrosis rather than examining individual biomarkers.
Owner:UNIV OF OXFORD
Alpha 1-Antitrypsin Compositions and Treatment Methods Using Such Compositions
Alpha 1-antitrypsin compositions and treatment methods using such compositions for treating a variety of pulmonary diseases are provided. The compositions generally contain AAT, a stabilizing carbohydrate such as trehalose, a surfactant such as Polysorbate 80 and an antioxidant to stabilize AAT for use as a therapeutic. The formulations can be prepared as both liquids and solids and administered by nebulization of the liquid formulation or by conversion of dry powder formulation into an aerosol.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +2
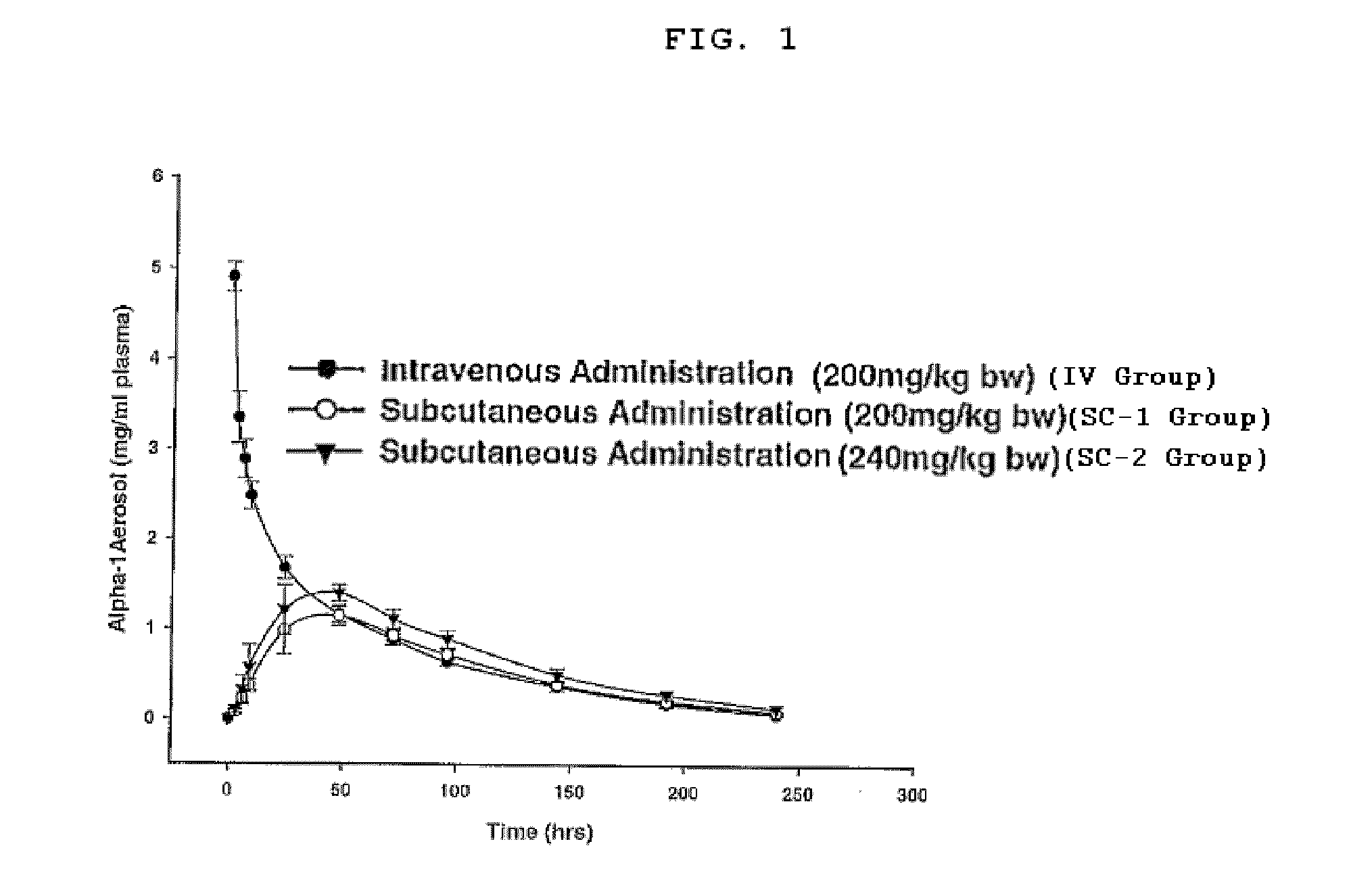
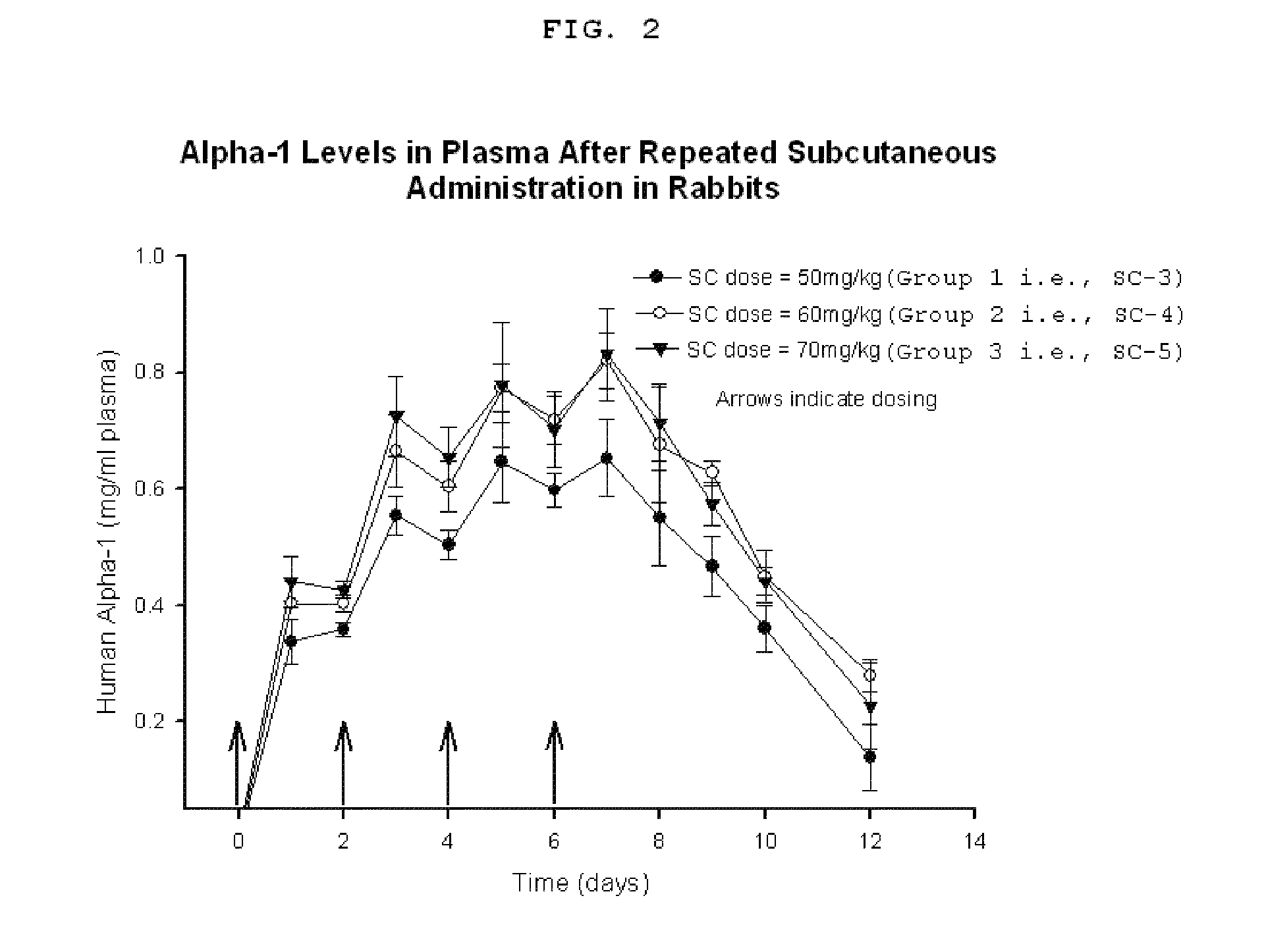
Method, composition, and article of manufacture for providing alpha-1 antitrypsin
The present invention provides a method for providing alpha-1 antitrypsin (α1-AT) to a subject, in particular a method for treating or preventing a disorder or disease associated with α1-AT deficiency in the subject, wherein the method comprises providing, subcutaneously, a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of α1-AT to the subject. Also provided is a composition and article of manufacture comprising α1-AT, in particular a formulation suitable for subcutaneous administration of α1-AT.
Owner:GRIFOLS THERAPEUTICS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com