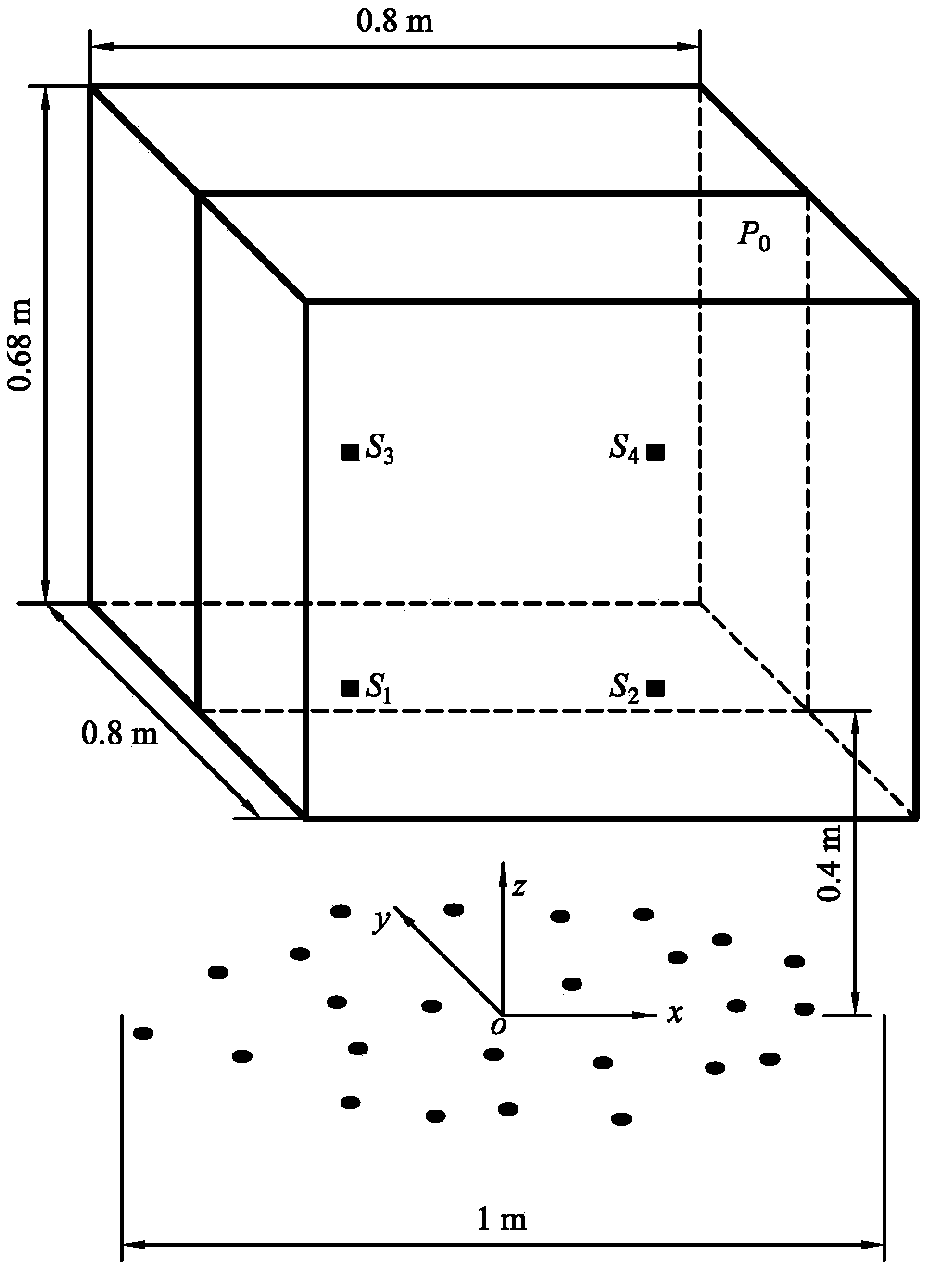
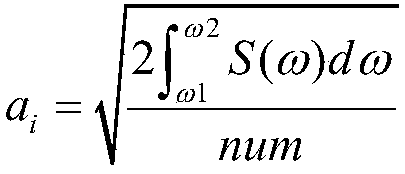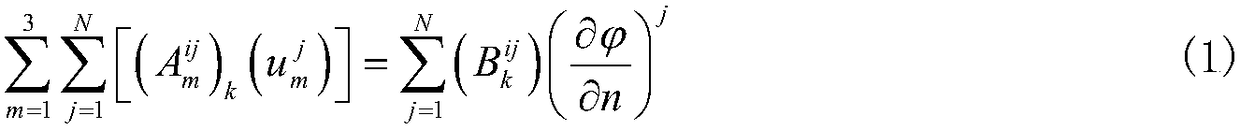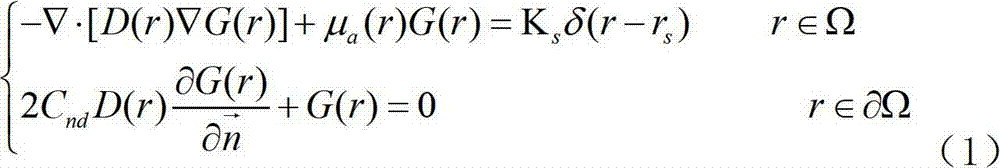Patents
Literature
184 results about "Green's function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, a Green's function of an inhomogeneous linear differential operator defined on a domain with specified initial conditions or boundary conditions is its impulse response.
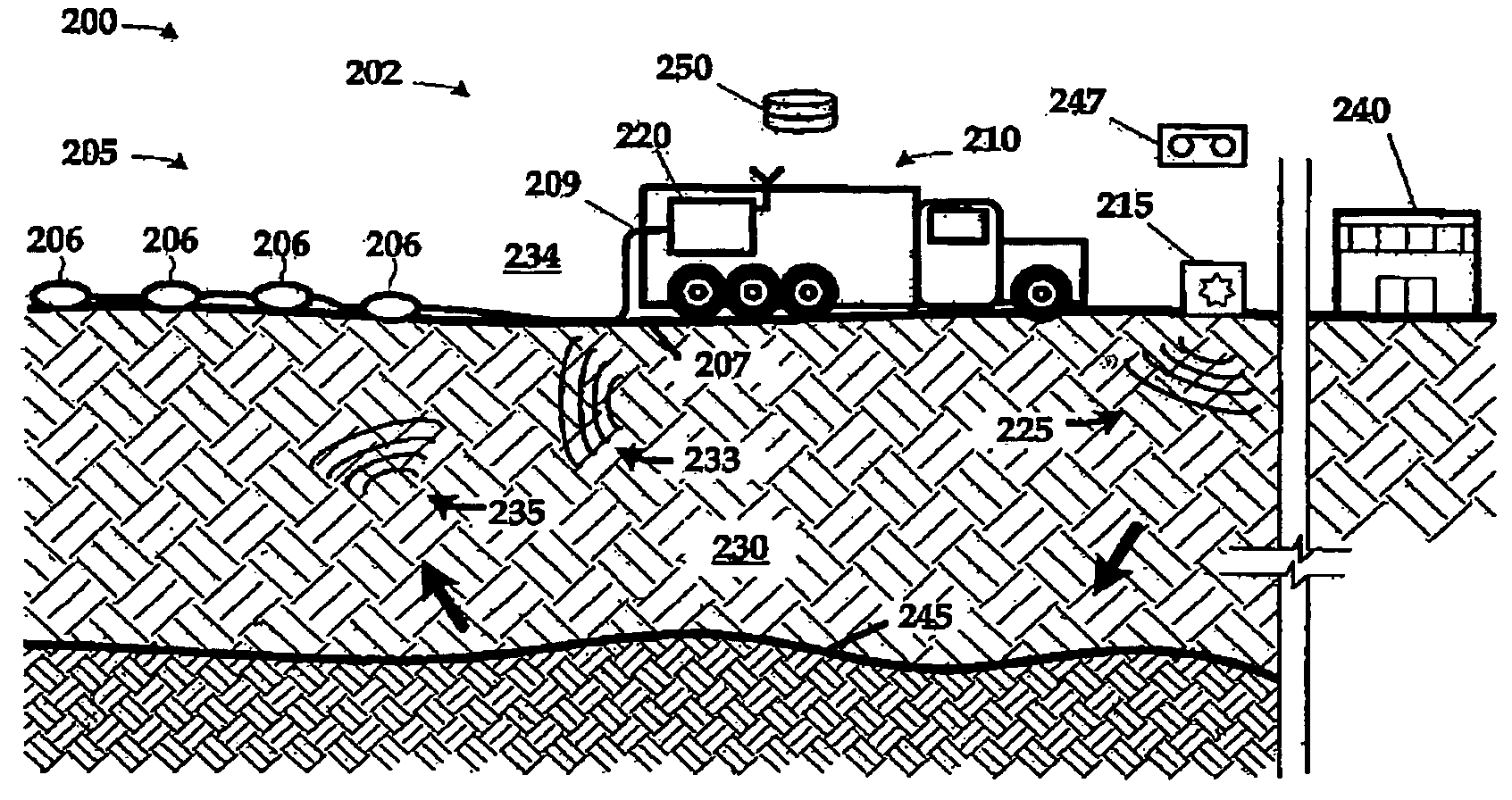
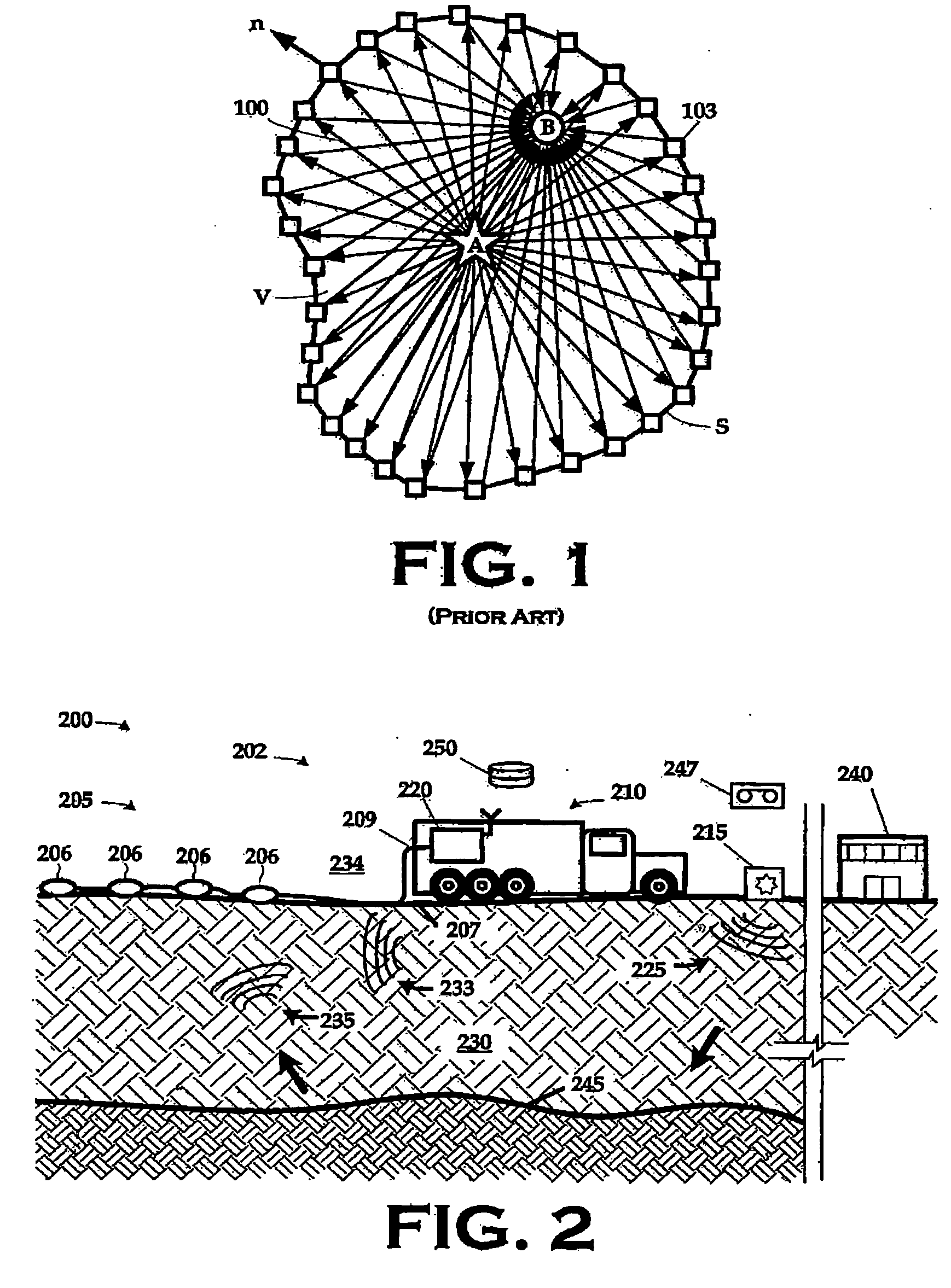
Construction and removal of scattered ground roll using interferometric methods
InactiveUS20070104028A1Interface is in effectSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingData setWave field
A data set can be corrected for the effects of interface waves by interferometrically measuring an interface wavefield between each of a plurality of planned locations within a survey area; and correcting survey data acquired in the survey area for the interface waves. The interface wavefield may be interferometrically measured by receiving a wavefield including interface waves propagating within a survey area, the survey area including a plurality of planned survey locations therein; generating interface wave data representative of the received interface wavefield; and constructing a Green's function between each of the planned survey positions from the interface wave data. Other aspects include an apparatus by which the interface wavefield may be interferometrically measured and a computer apparatus programmed to correct the seismic data using the interferometrically measured interface wave data.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
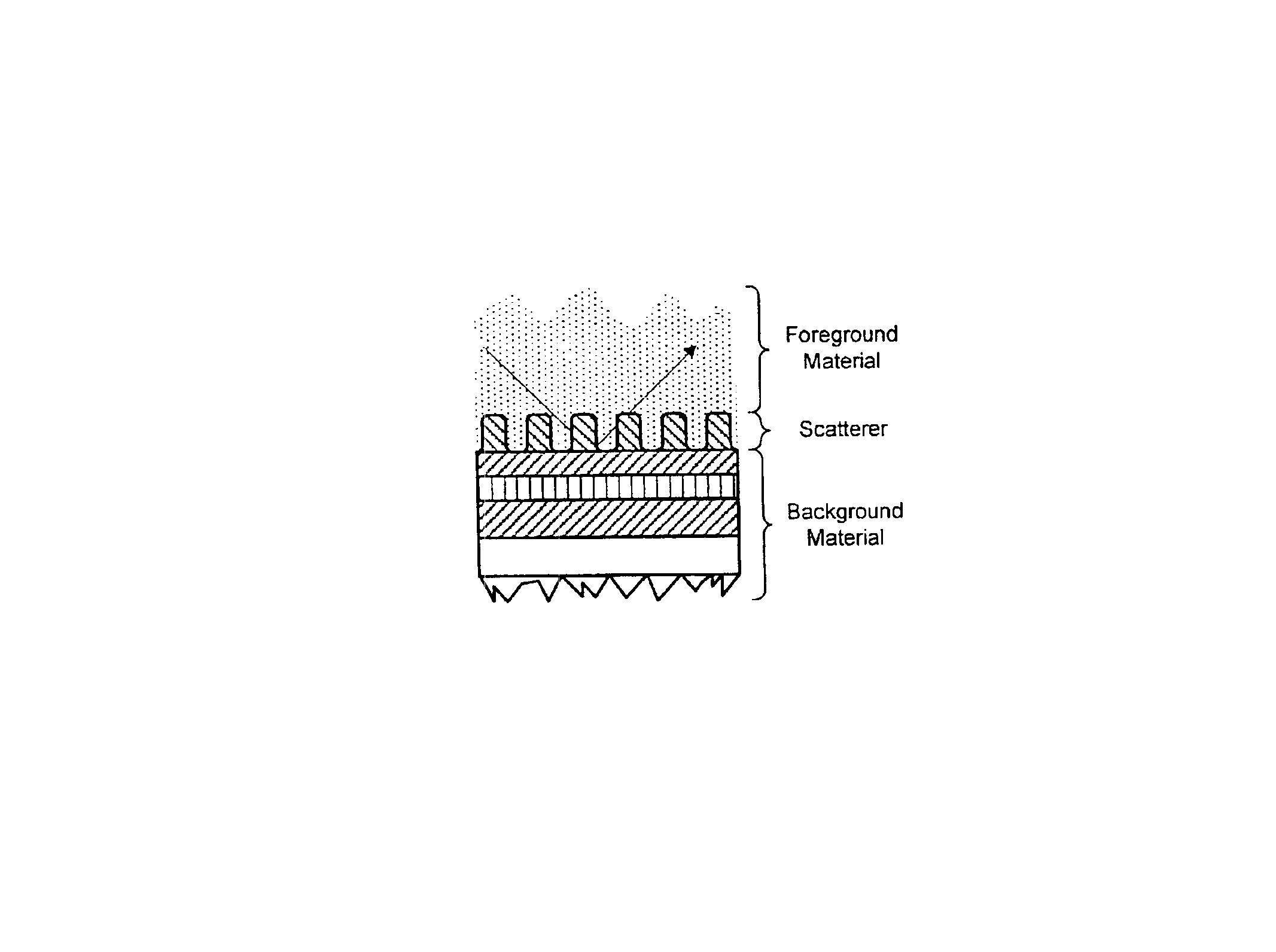
CD metrology analysis using green's function
InactiveUS6867866B1Efficient methodImprove efficiencyScattering properties measurementsDigital computer detailsMetrologyRigorous coupled-wave analysis
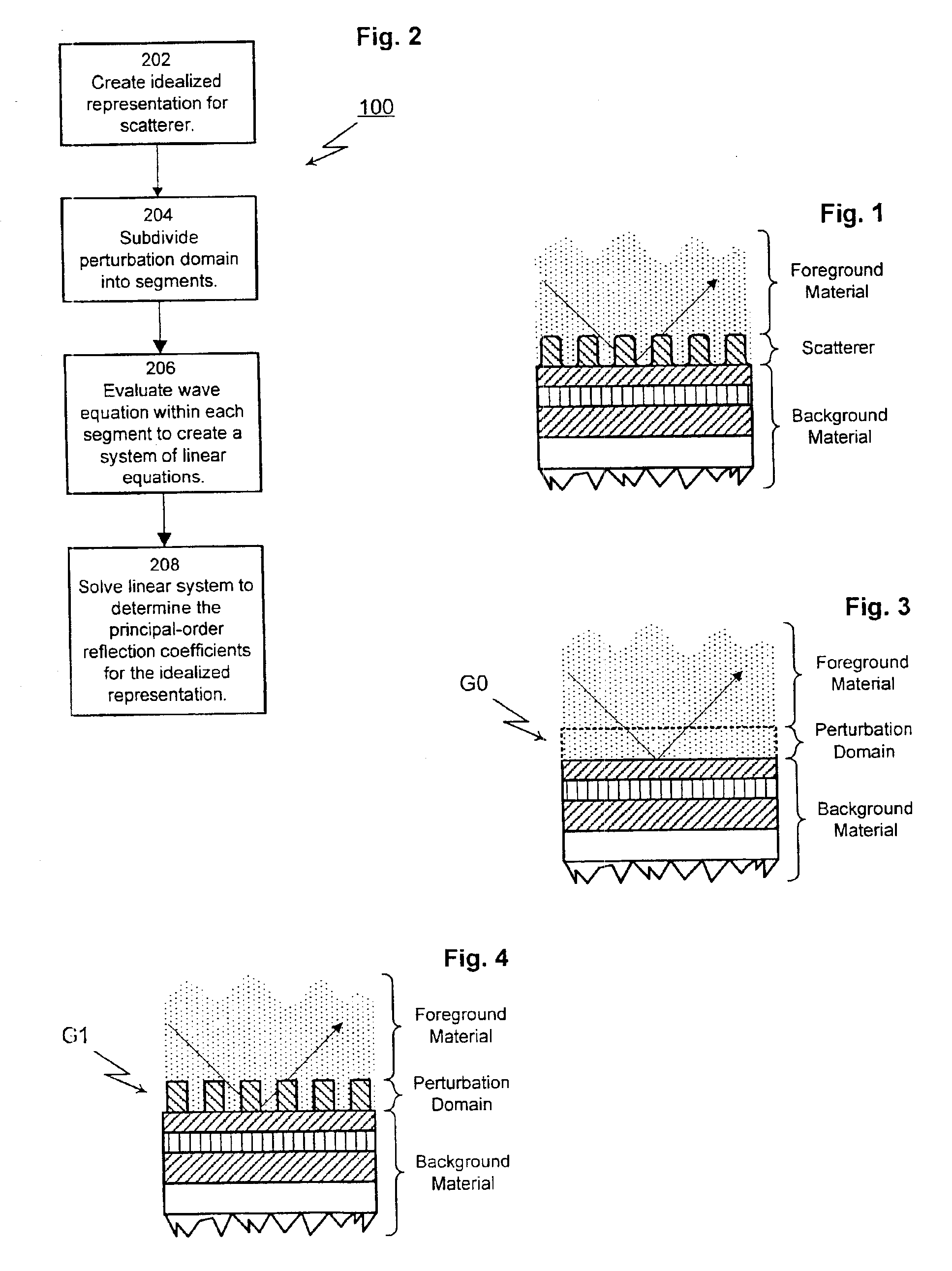
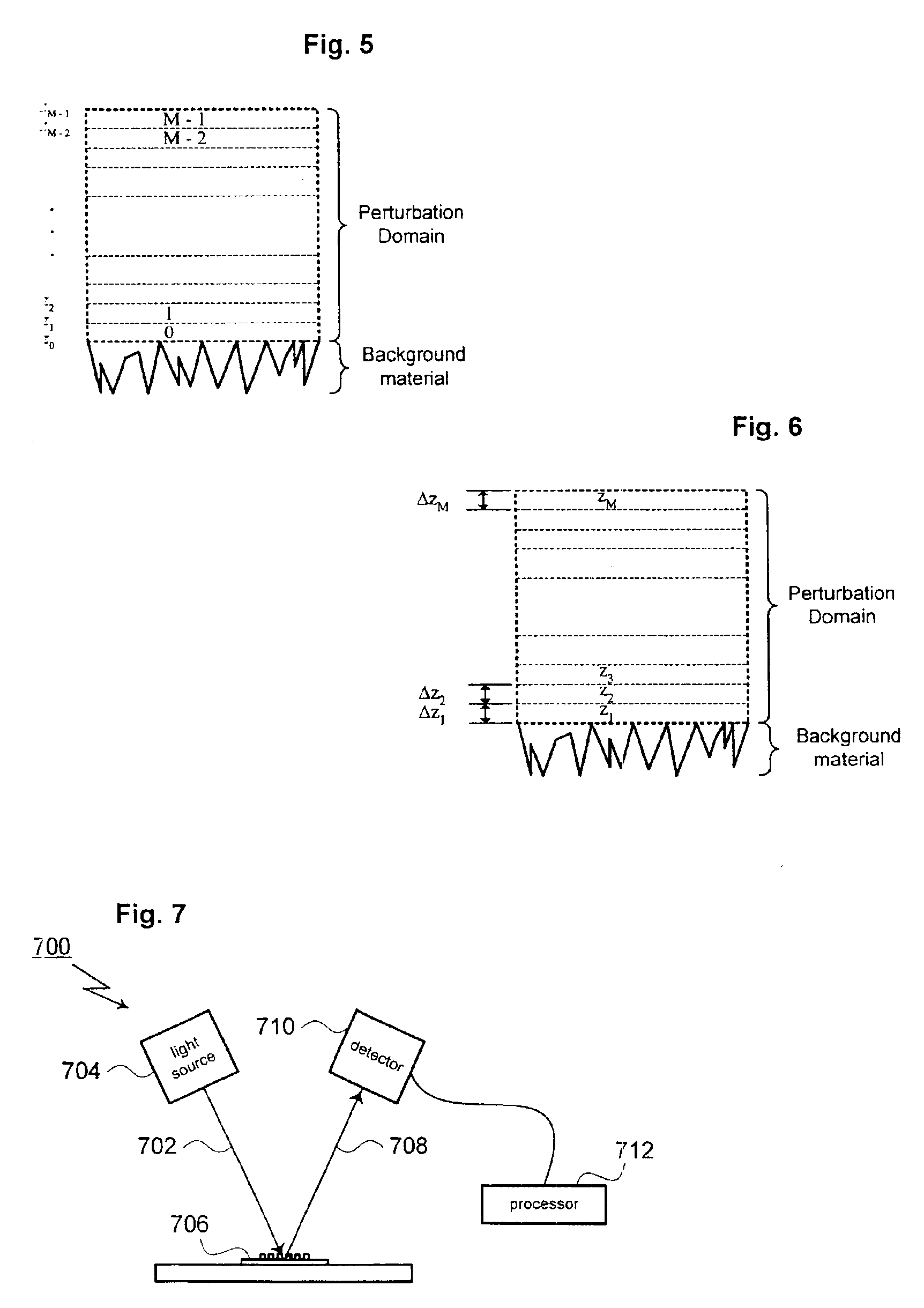
A method for modeling optical scattering includes an initial step of defining a zero-th order structure (an idealized representation) for a subject including a perturbation domain and a background material. A Green's function and a zero-th order wave function are obtained for the zero-th order structure using rigorous coupled wave analysis (RCWA). A Lippmann-Schwinger equation is constructed including the Green's function, zero-th order wave function and a perturbation function. The Lippmann-Schwinger equation is then evaluated over a selected set of mesh points within the perturbation domain. The resulting linear equations are solved to compute one or more reflection coefficients for the subject.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Method of evaluating the interaction between a wavefield and a solid body
InactiveUS7715985B2Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputer scienceGreen's function
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Seismic imaging with natural green's functions derived from vsp data
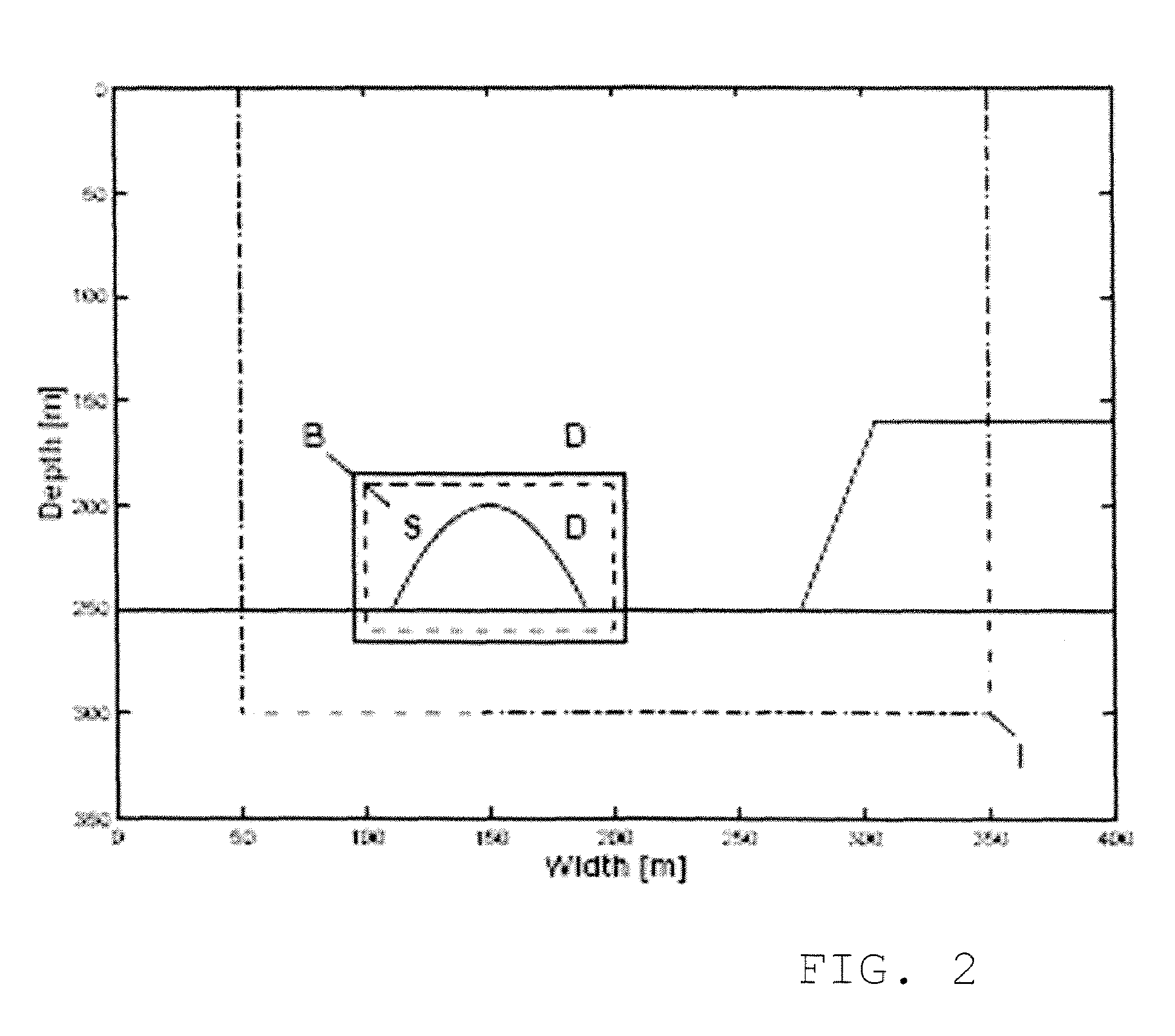
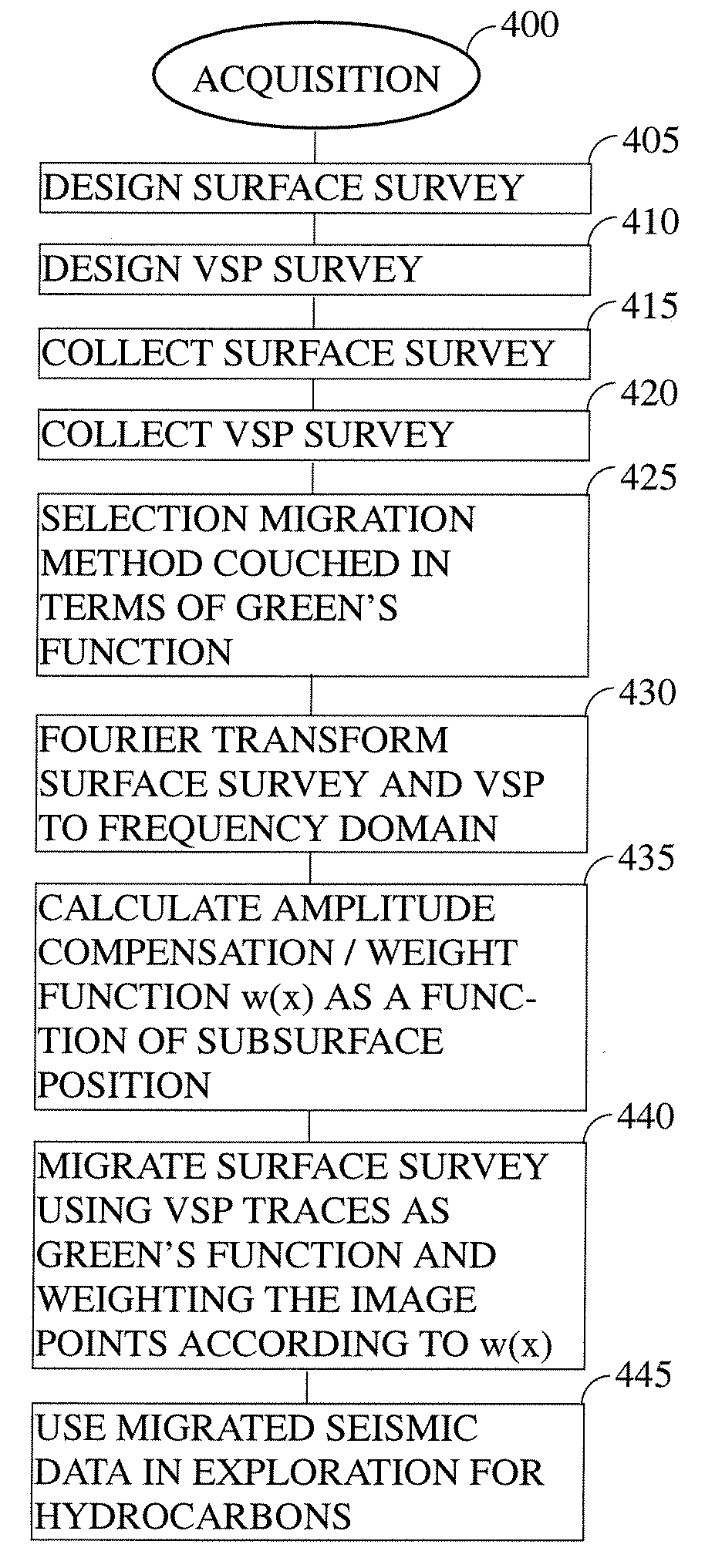
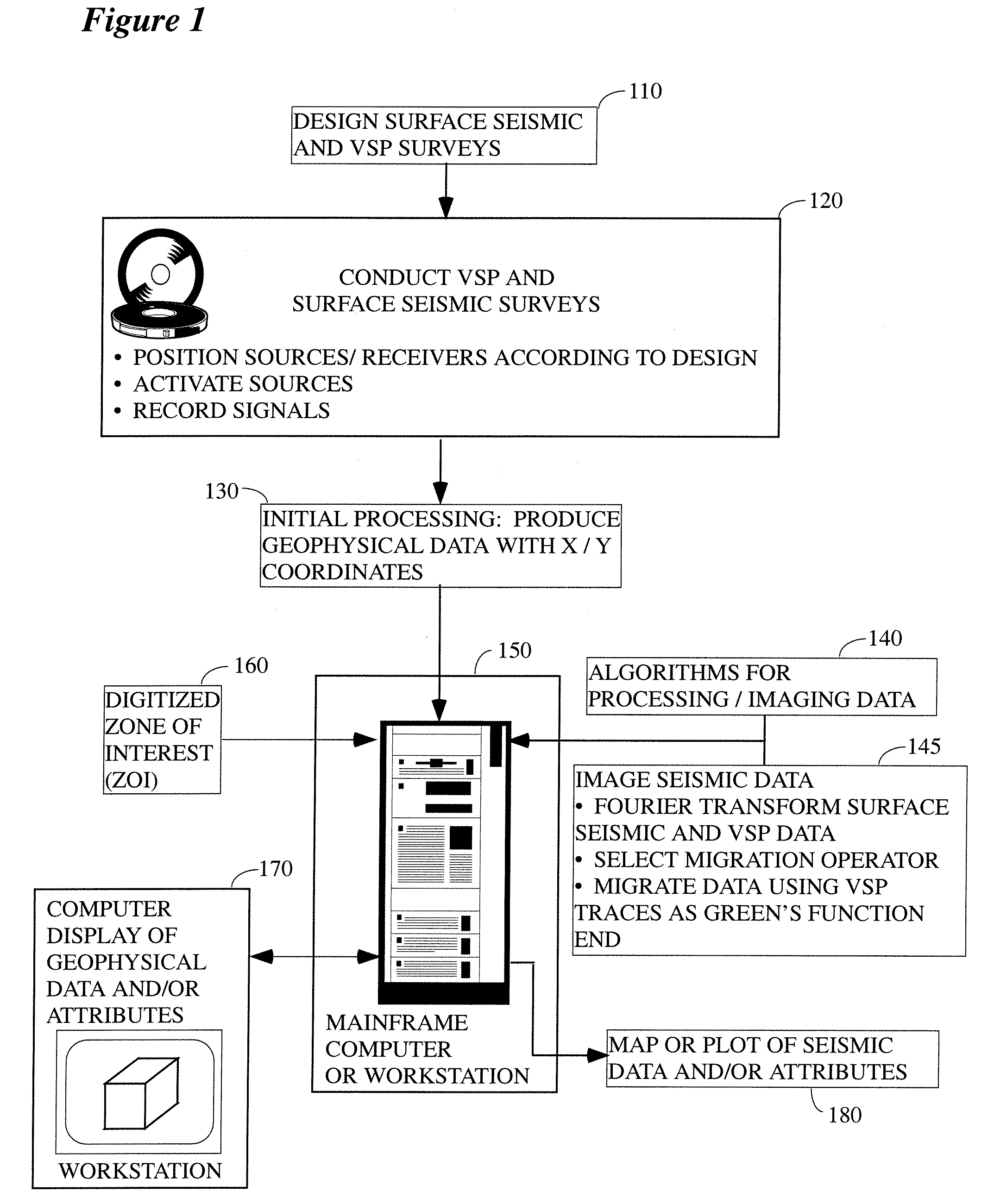
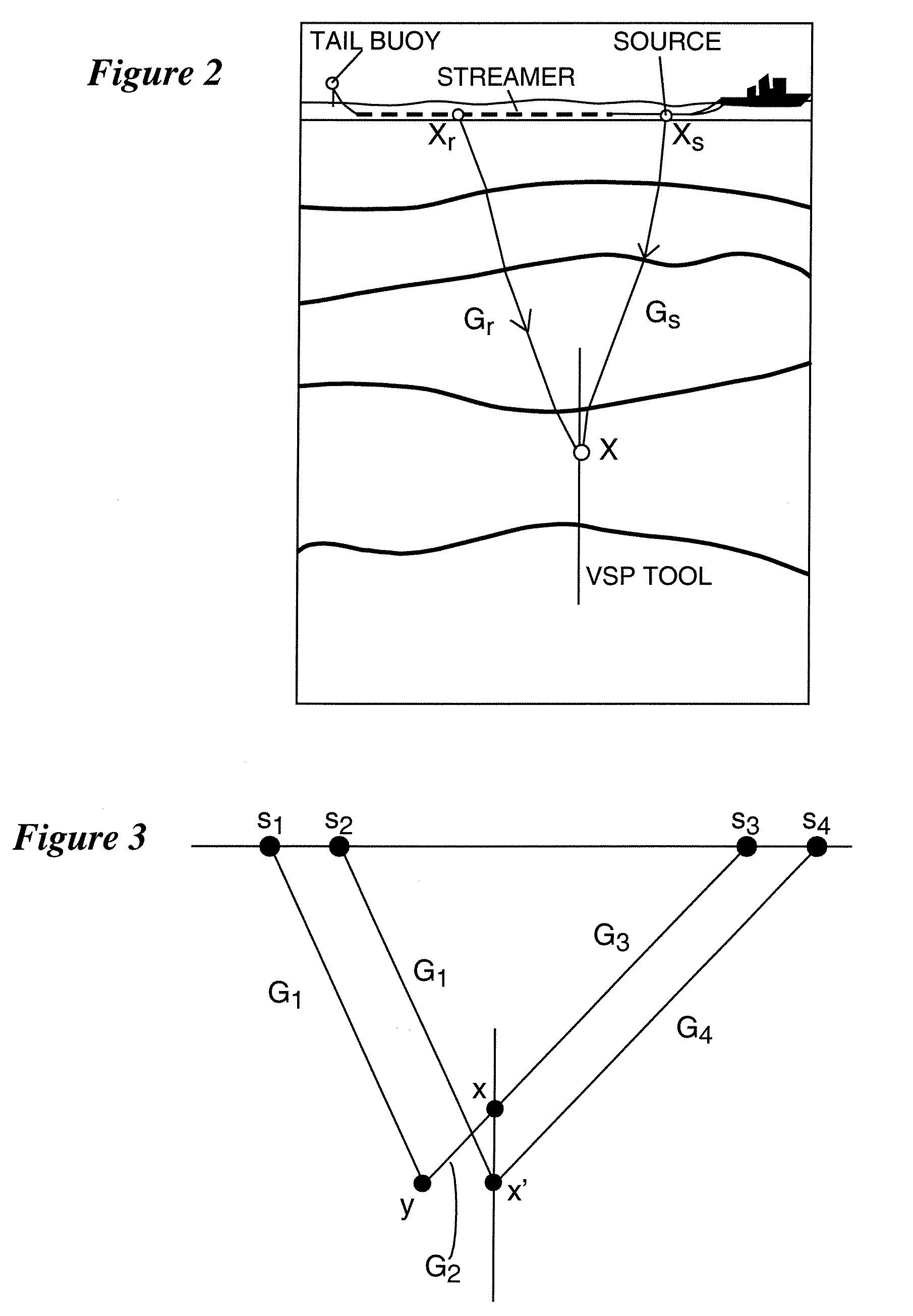
The methods described herein are conceptually similar to classical migration / imaging for surface seismic data. However, instead of using computed (estimated) Green's functions in the imaging process, the instant invention utilizes measured (near-exact) Green's functions from VSP data to image the surface seismic data. Although the instant invention is best utilized where the velocity profile is approximately 1D (i.e., v(z)), the methods disclosed herein can also be extended to instances where there are some lateral velocity variations. Under these conditions, the instant invention allows for imaging surface seismic data and ‘self-imaging’ VSP data without first having to estimate a velocity model. The measurements obtained from the VSP data can also be used as a tool for calibrating computed Green's functions and migration operators.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
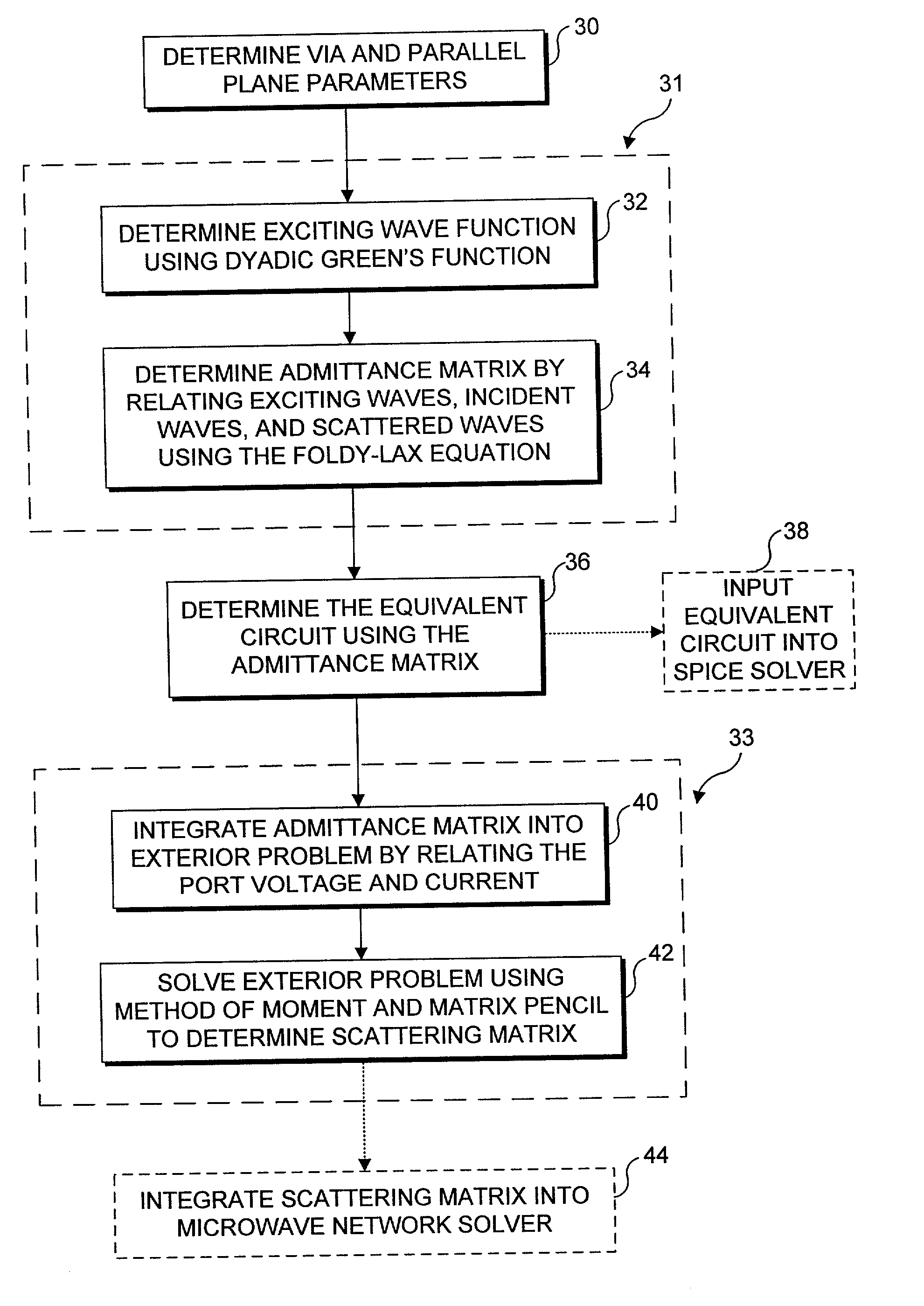
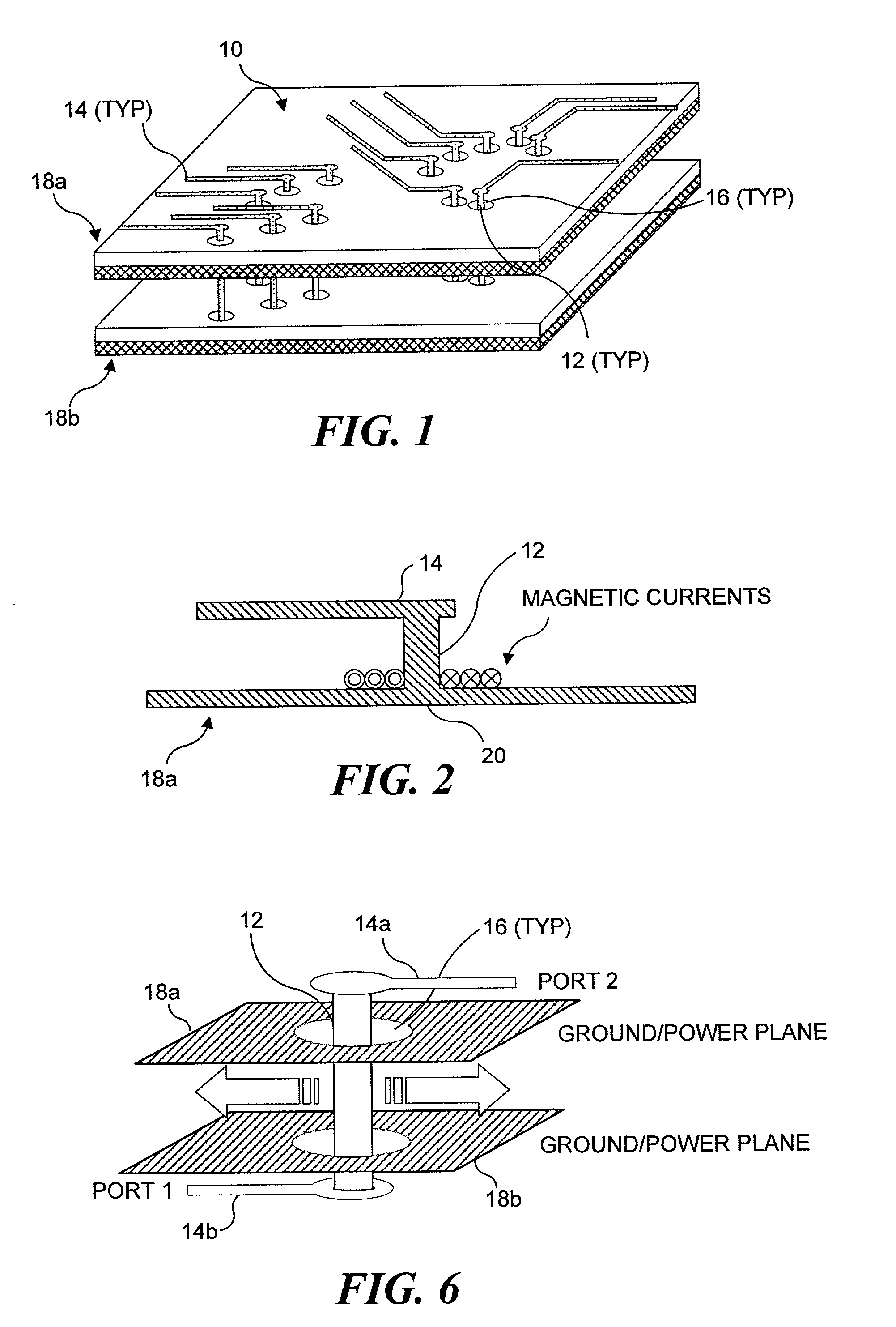
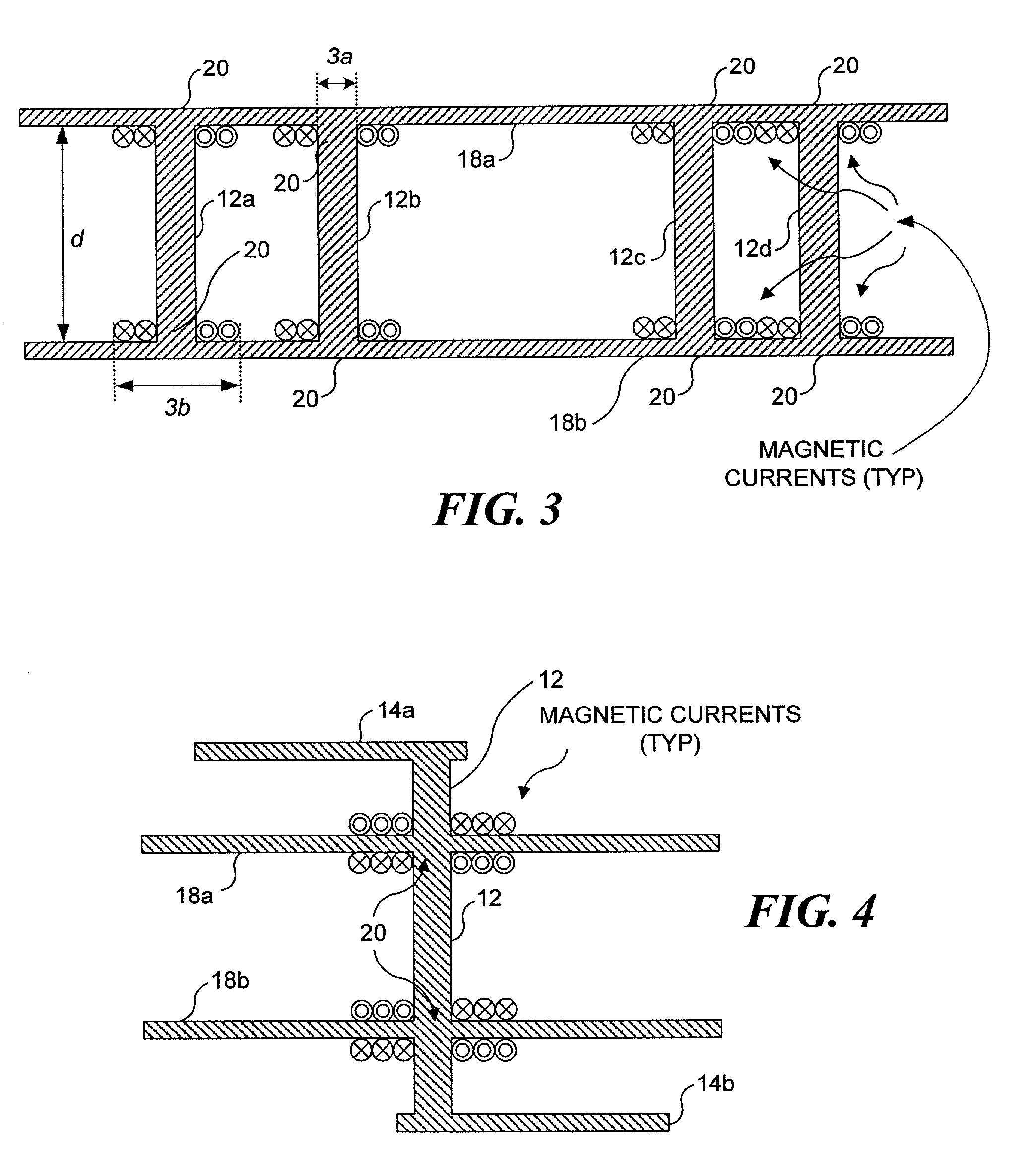
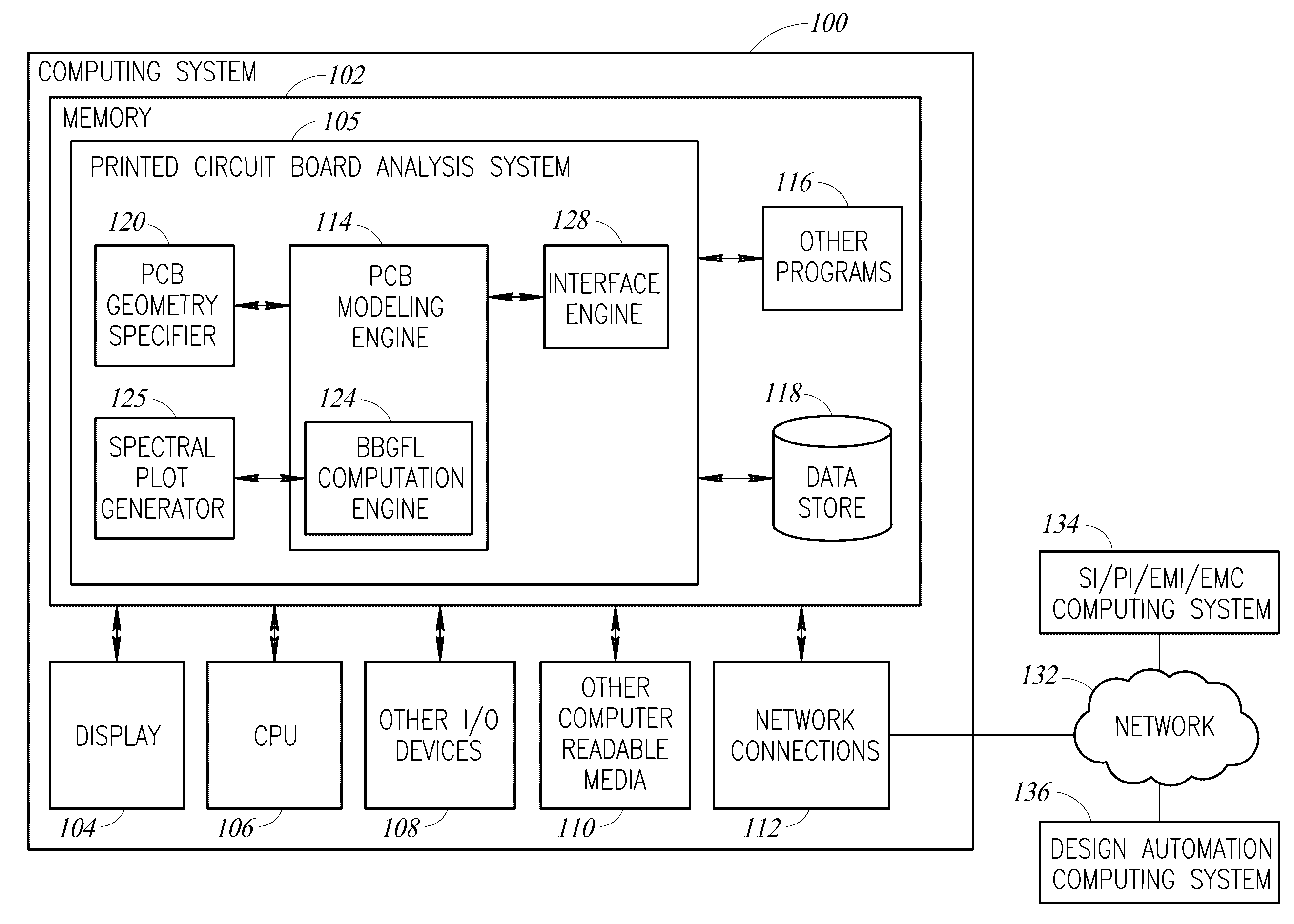
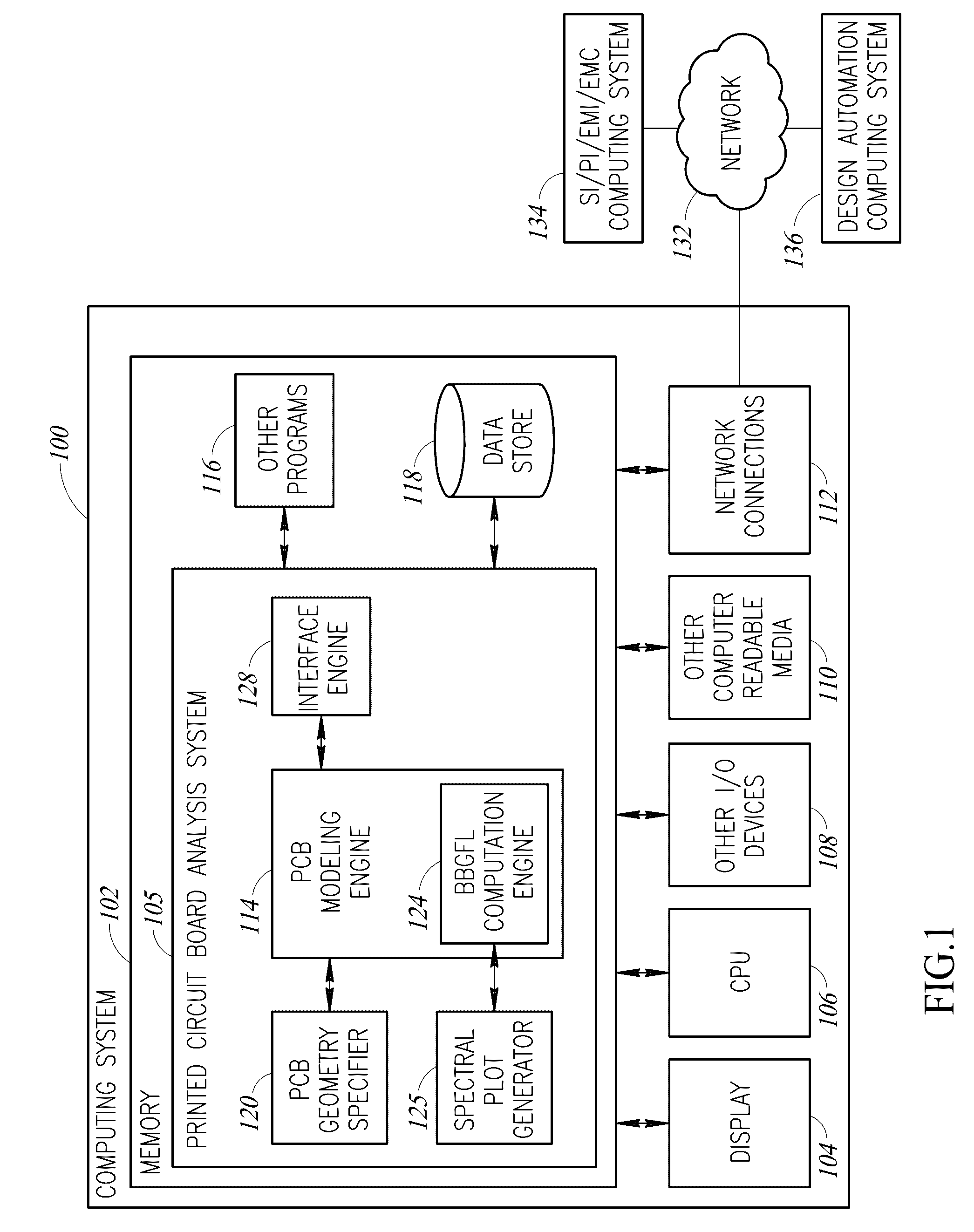
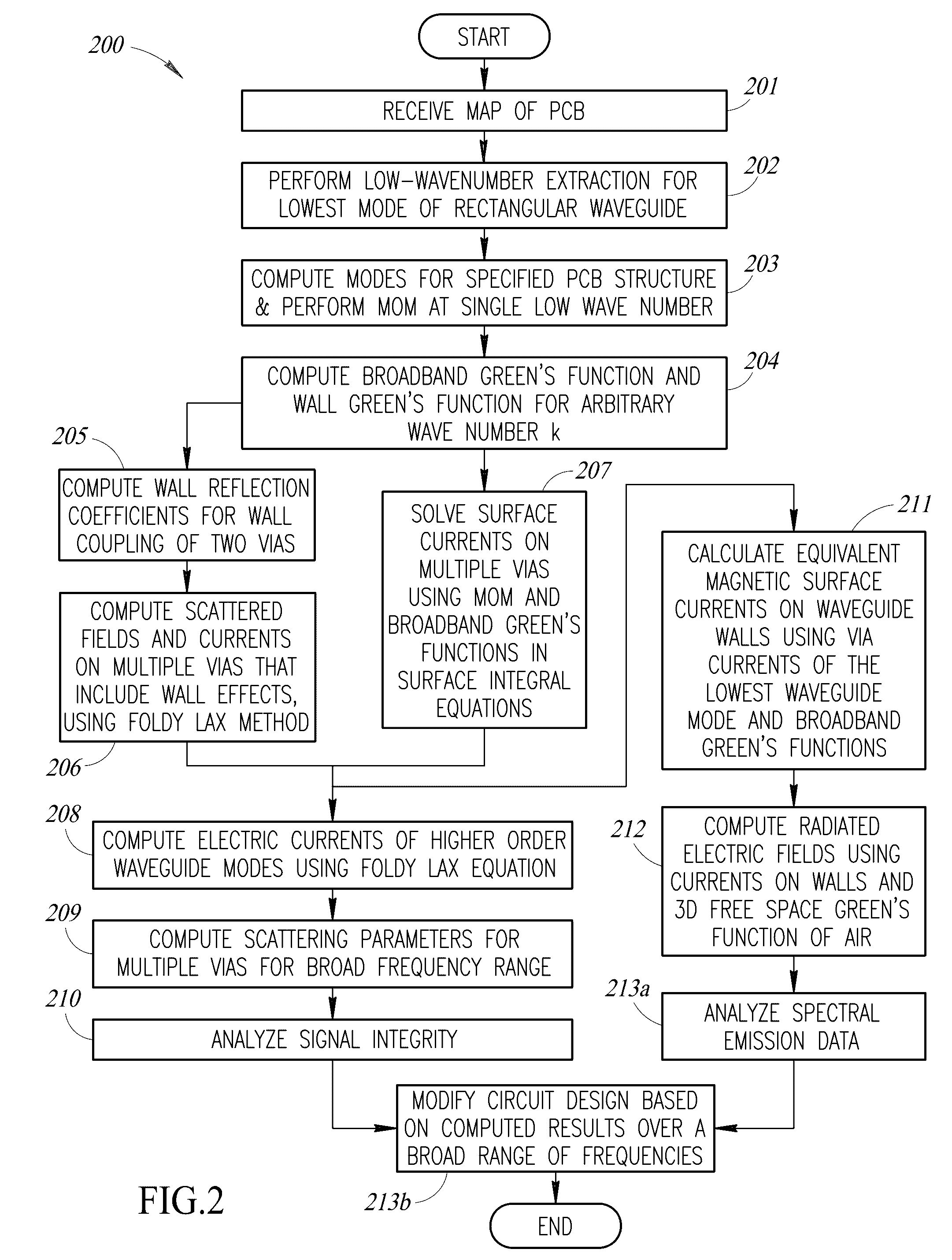
Methods for modeling interactions between massively coupled multiple vias in multilayered electronic packaging structures
ActiveUS7149666B2Rapidly and accurately coupling effectThe result is accurateAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDetecting faulty computer hardwareFull waveWaveguide mode
Analyzing interactions between vias in multilayered electronic packages that include at least two spaced-apart conducting planes, and multiple vias that connect signal traces on different layers. Voltages at active via ports are represented as magnetic ring current sources, which generate electromagnetic modes inside the plane structure. Substantial electromagnetic coupling between vias occurs. A full-wave solution of multiple scattering among cylindrical vias in planar waveguides is derived using Foldy-Lax equations. By using the equivalence principle, the coupling is decomposed into interior and exterior problems. For the interior problem, the dyadic Green's function is expressed in terms of vector cylindrical waves and waveguide modes. The Foldy-Lax equations for multiple scattering among the cylindrical vias are applied, and waveguide modes are decoupled in the Foldy-Lax equations. The scattering matrix of coupling among vias is then calculated for use in determining signal reflection, transmission, and / or coupling in the electronics package.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Migration Velocity Analysis of Seismic Data Using Common Image Cube and Green's Functions
InactiveUS20110320180A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis dataData set
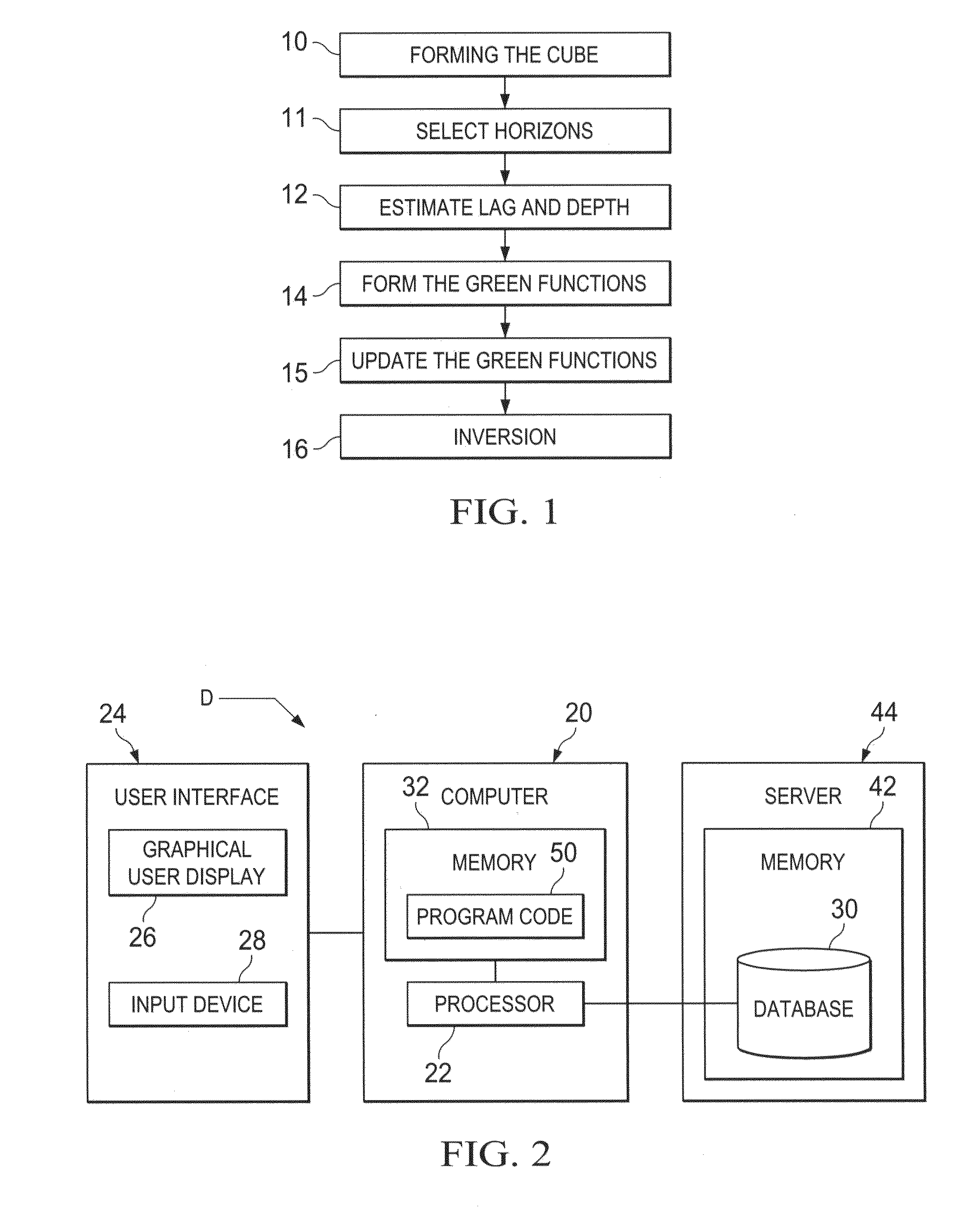
Seismic data are assembled and stored for a set of cross-correlation lag times to form an array of common image gathers over depth levels of interest. The two dimensional gathers assembled over different lag times form a three-dimensional cube of common image data. The data are analyzed to determine the travel time shift required to equalize upgoing and downgoing wavefields. Events in the common image gathers are then modeled using Green's functions to generate a data set representing the data resulting from processing had a precise velocity model been obtainable from the seismic data. The generated data are then processed with inversion techniques to form a velocity model for seismic data analysis.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Processing Data Representing Energy Propagating Through A Medium
InactiveUS20090043545A1Efficiency and flexibilityImprove computing efficiencySeismic data acquisitionGeomodellingWave equationCombined use
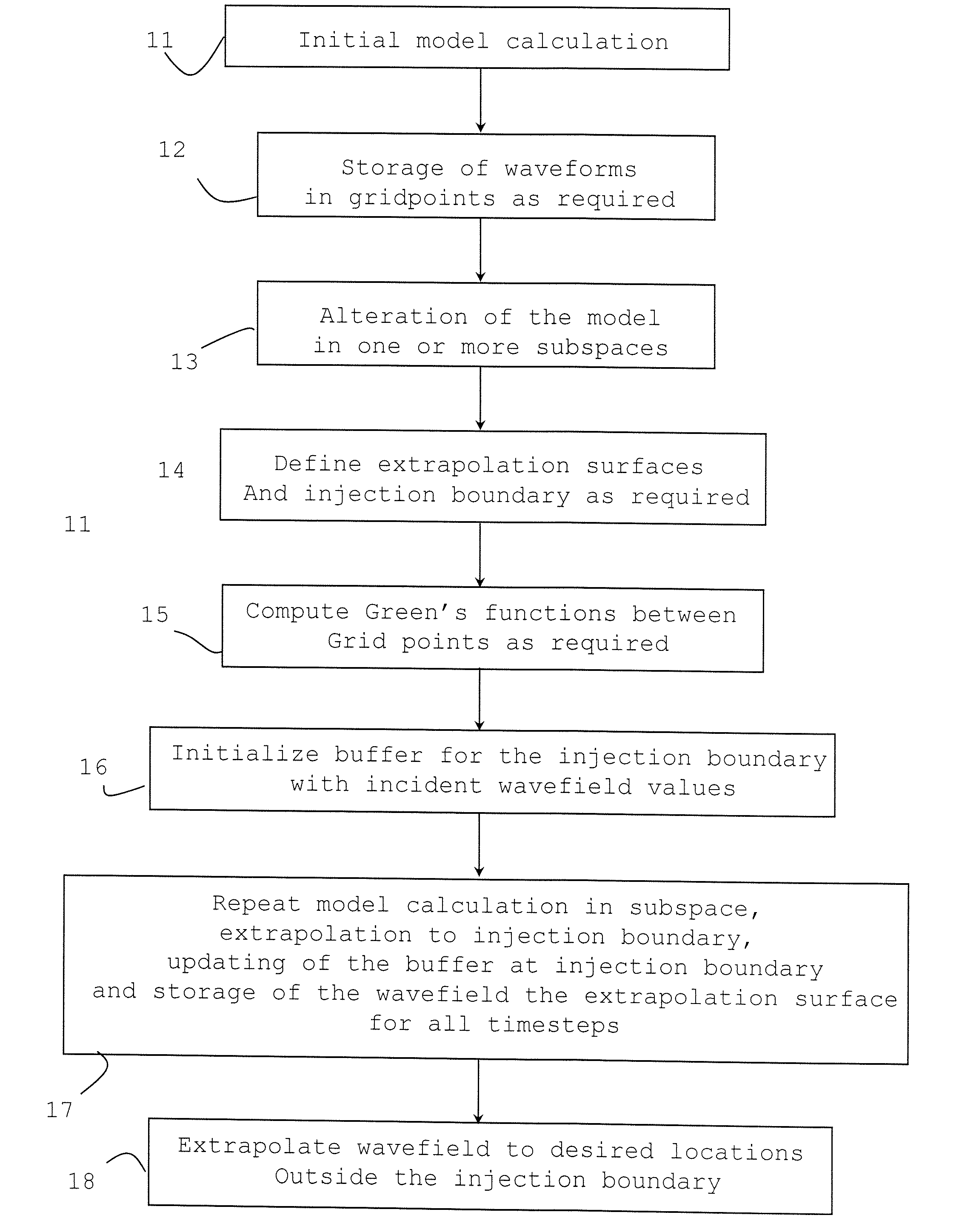
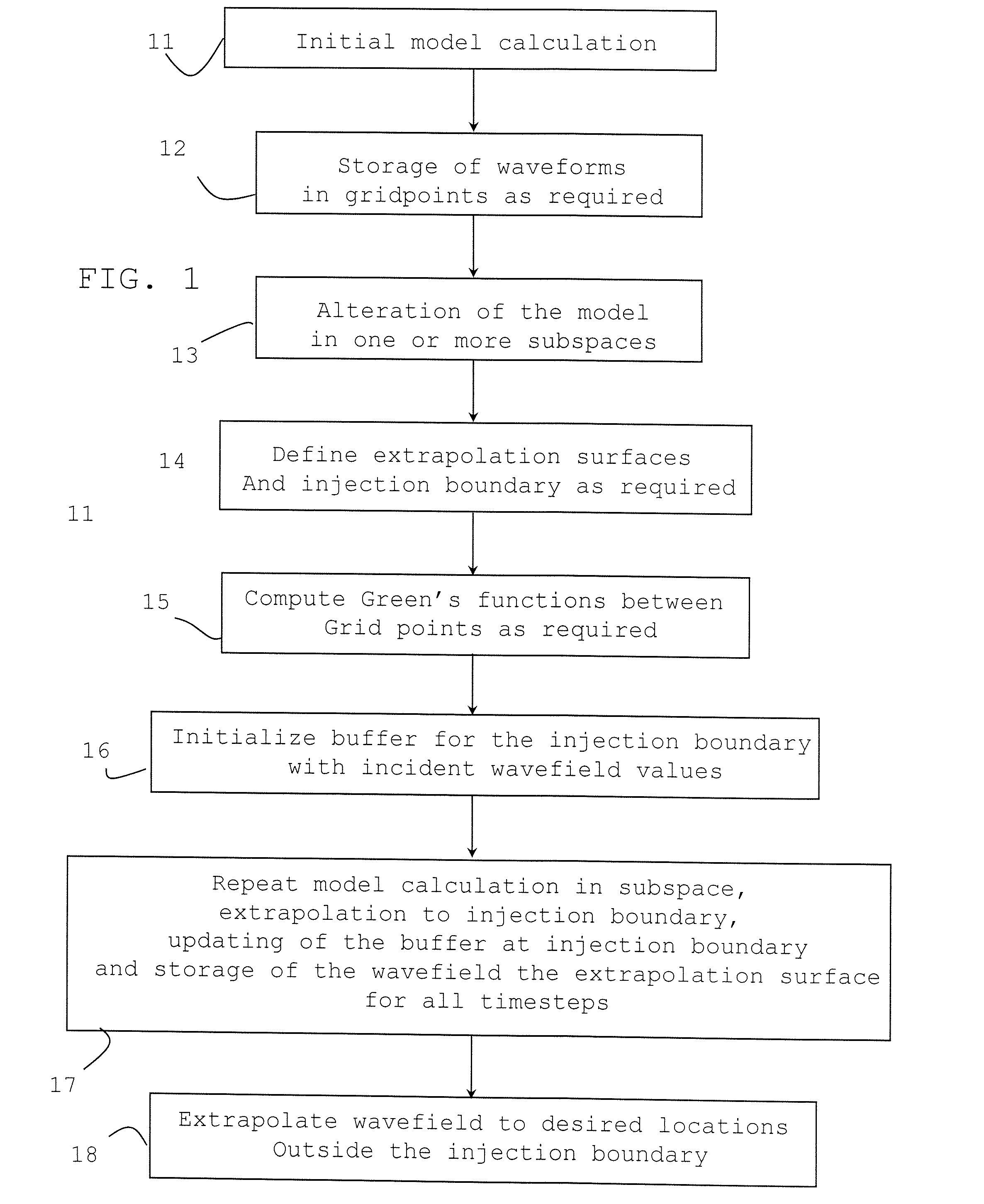
The present invention relates to a method of processing data representing energy propagating through a medium (e.g., acoustic, elastic or electromagnetic energy) and describes an efficient and flexible e approach to forward modeling and inversion of such energy for a given medium. The representation theorem for the wave-equation is used, in combination with time-reversal invariance and reciprocity, to express the Green's function between two points in the interior of the model as an integral over the response in those points due to sources regularly distributed on a surface surrounding the medium and the points.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Electromagnetic scattering analyzing method for superspeed flight targets
ActiveCN103198227ALittle unknownFast solutionSpecial data processing applicationsInternal memorySelf adaptive
The invention discloses an electromagnetic scattering analyzing method for superspeed flight targets. For non-uniform characteristics of plasmas around the superspeed flight targets, a part of equivalent relative dielectric constant, approximate to one, of the plasmas is used as the air to be processed by analyzing through a volume-surface integer equation, and areas with larger equivalent relative dielectric constant are encrypted by the adaptive network so as to achieve required solving accuracy. By adopting conventional method of uniform grid subdivision plasma casing, the electromagnetic scattering analyzing method can greatly save computing resources, green function adopted in the volume-surface integer equation is green function in vacuum, multilayer speedy multi-step ion technology is used for accelerating solving, so that fewer internal memory and shorter computing time are required for solving the problem of scattering of the superspeed flight targets.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
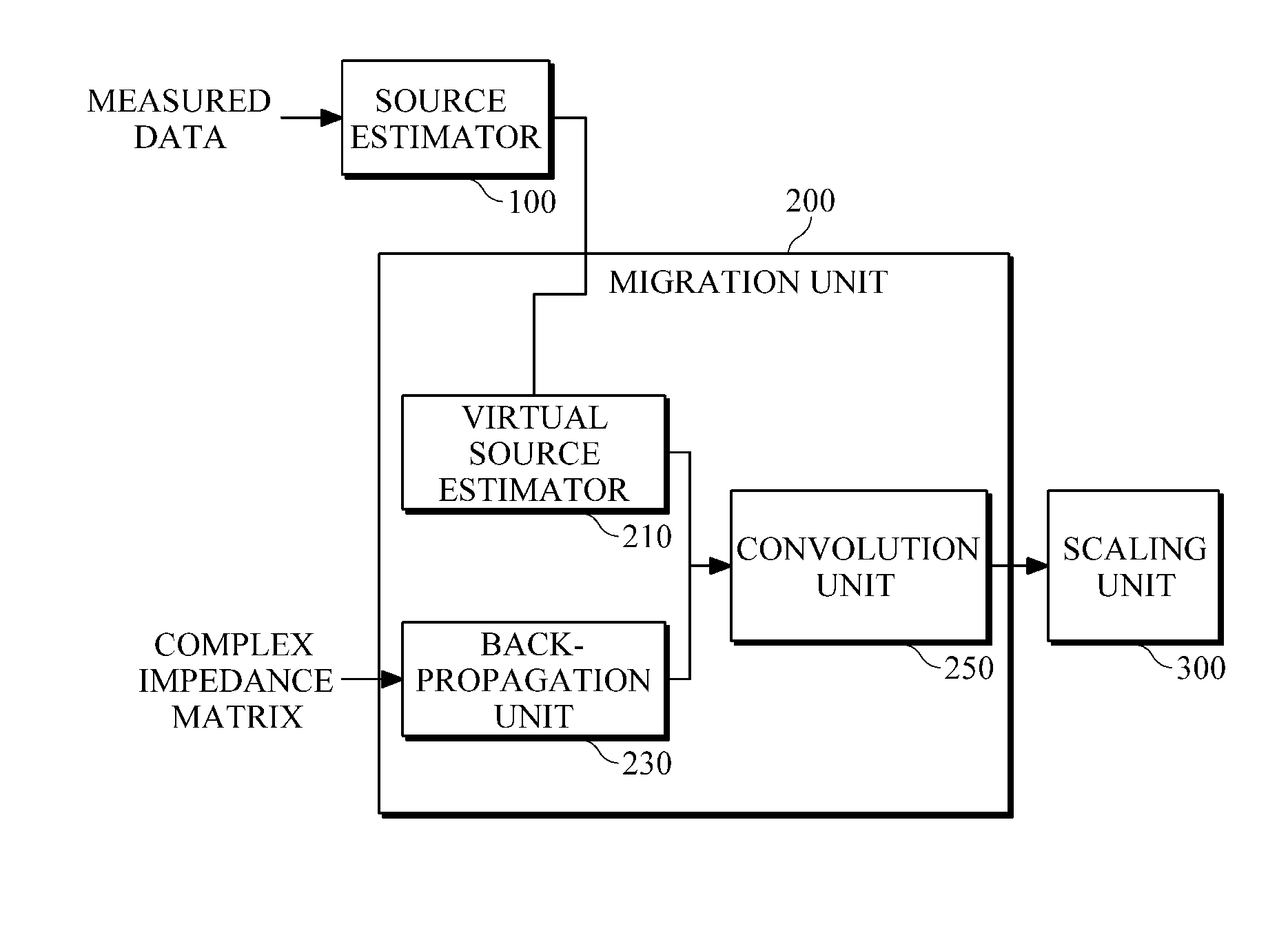
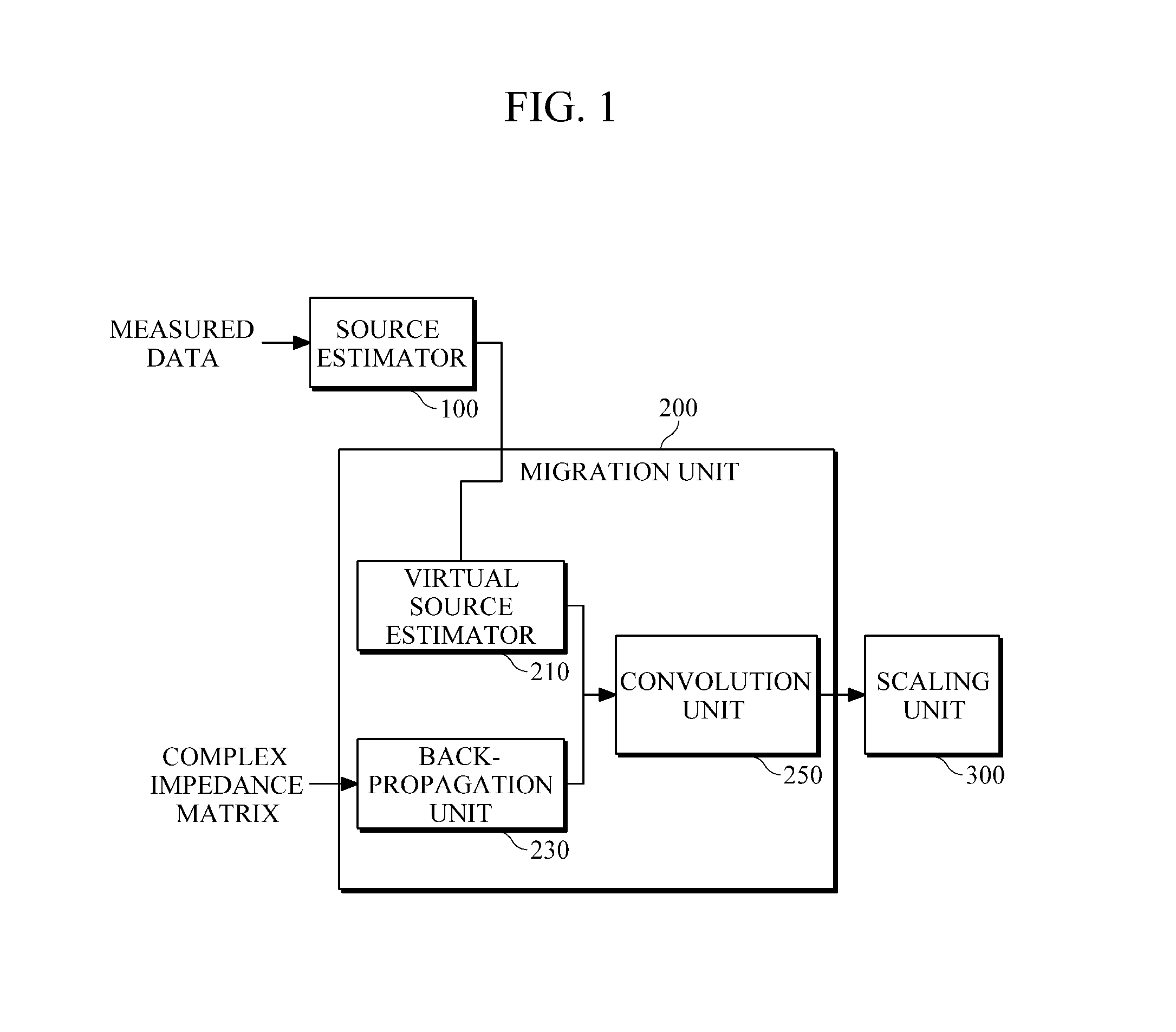
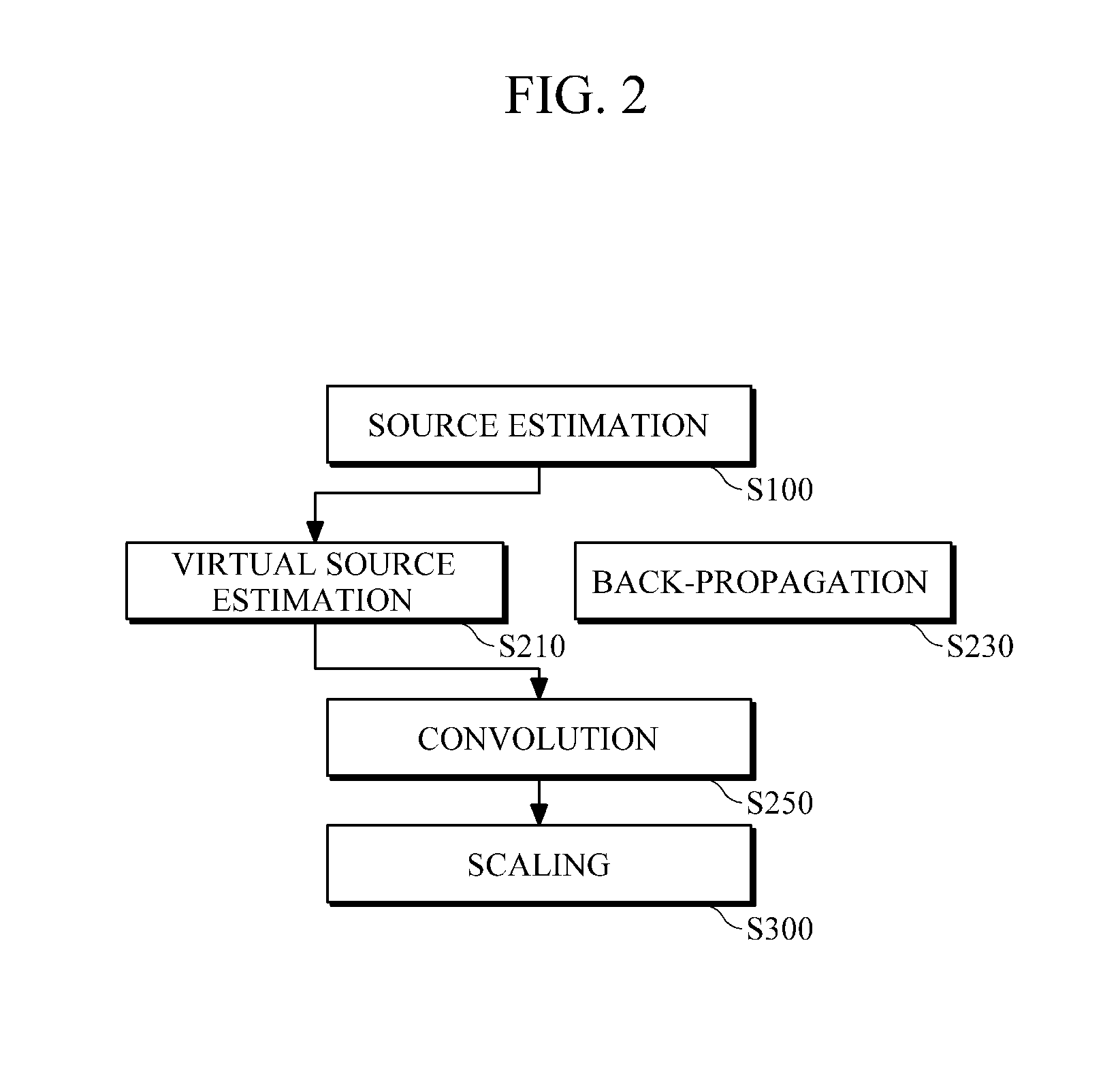
Method and apparatus for time-domain reverse-time migration with source estimation
Provided is seismic imaging, particularly, a time-domain reverse-time migration technique for generating a real subsurface image from modeling parameters calculated through waveform inversion, etc. A reverse-time migration apparatus according to an example includes a source estimator configured to estimate sources by obtaining transmission waveforms from data measured by a plurality of receivers, through waveform inversion, and a migration unit configured to receive information about the estimated sources, and to perform reverse-time migration in the time domain. The source estimator estimates sources, by solving first-order matrix equation including a Toeplitz matrix composed of autocorrelation values of the Green's function, and a cross-correlation matrix of measured data and the Green's function, through Levinson Recursion. In more detail, the migration unit includes a back-propagation unit configured to back-propagate the measured data; a virtual source estimator configured to estimate virtual sources from the sources estimated by the source estimator; and a convolution unit that configured to convolve the back-propagated data with the virtual sources and output the results of the convolution.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
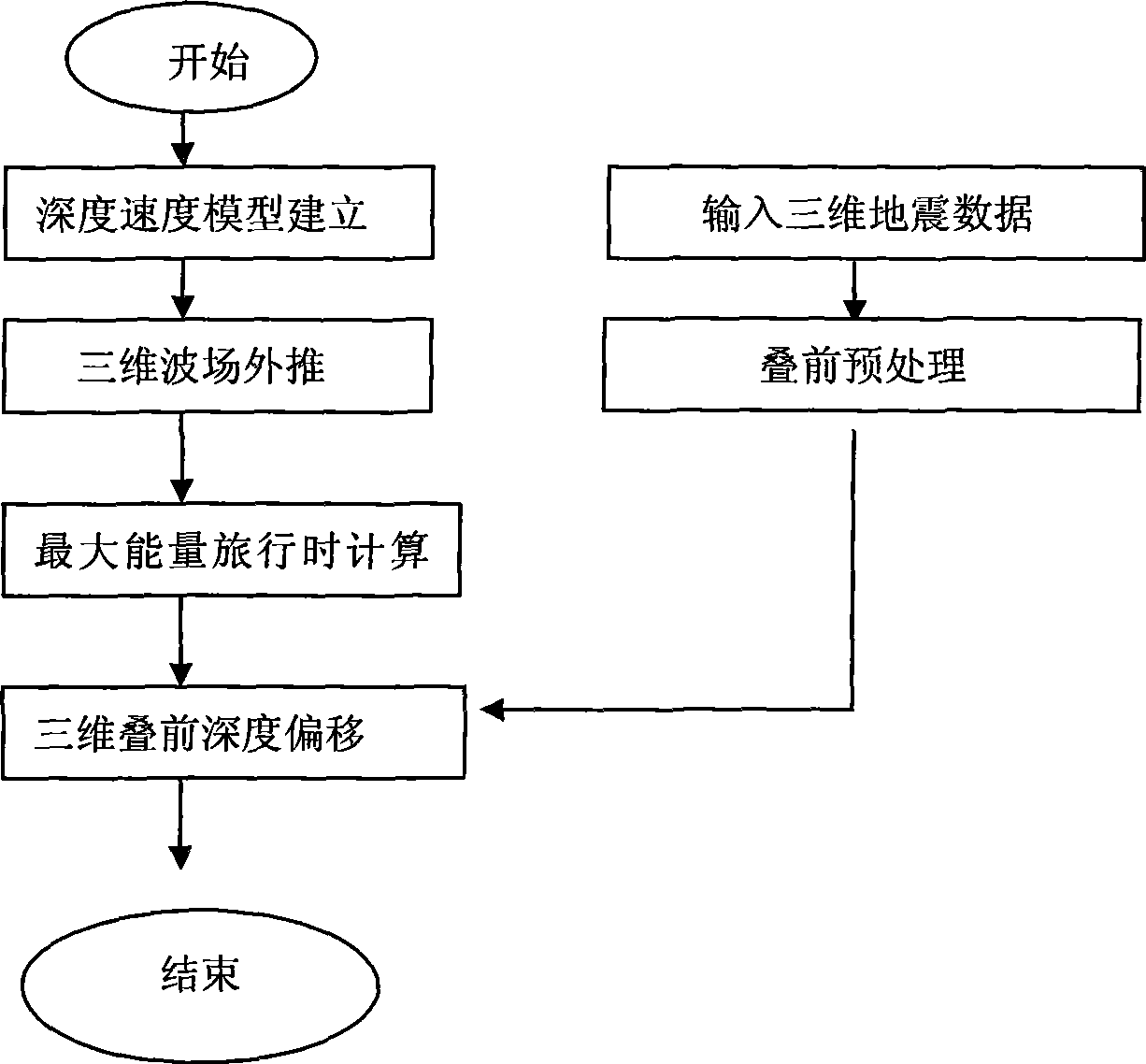
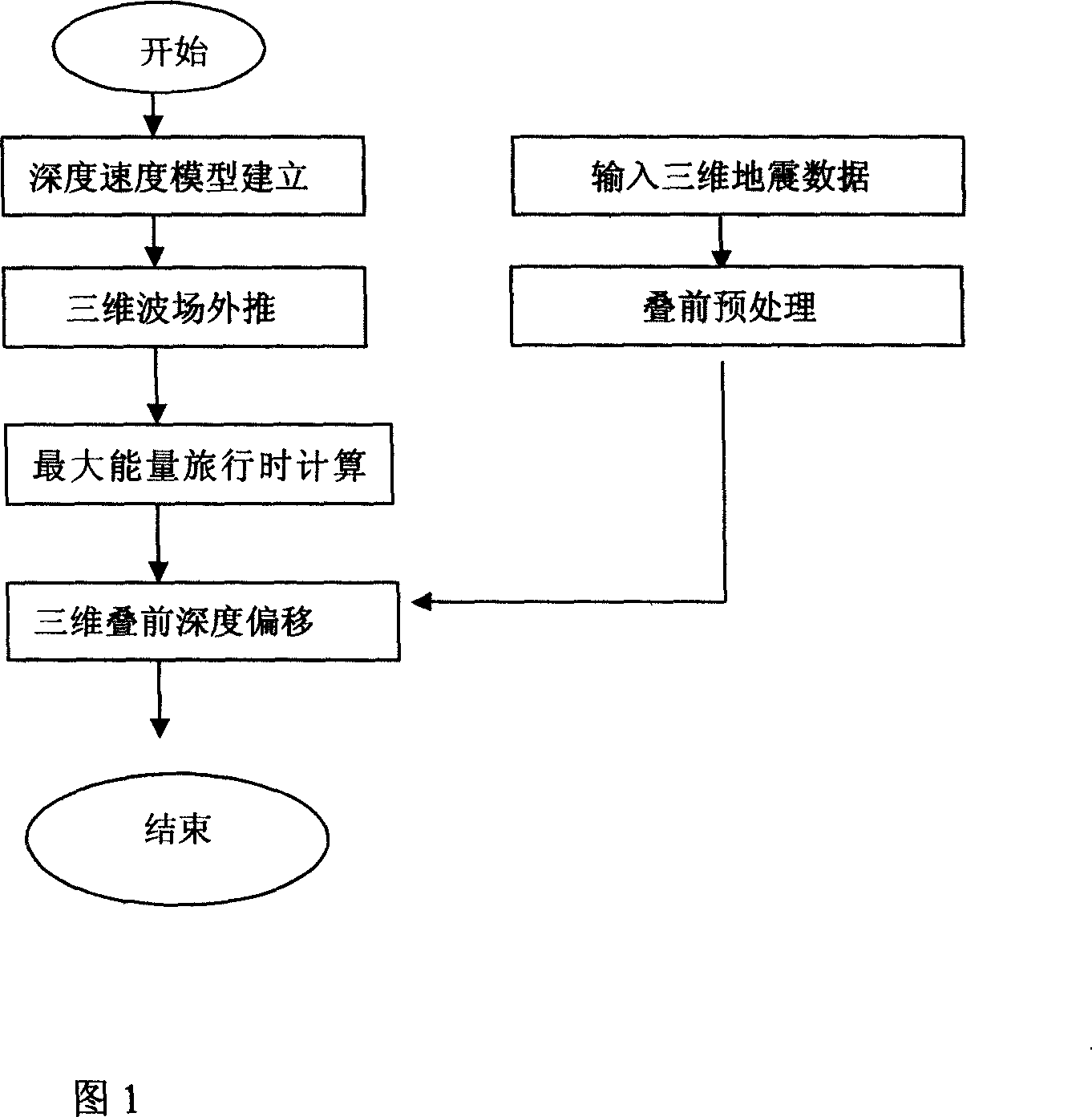
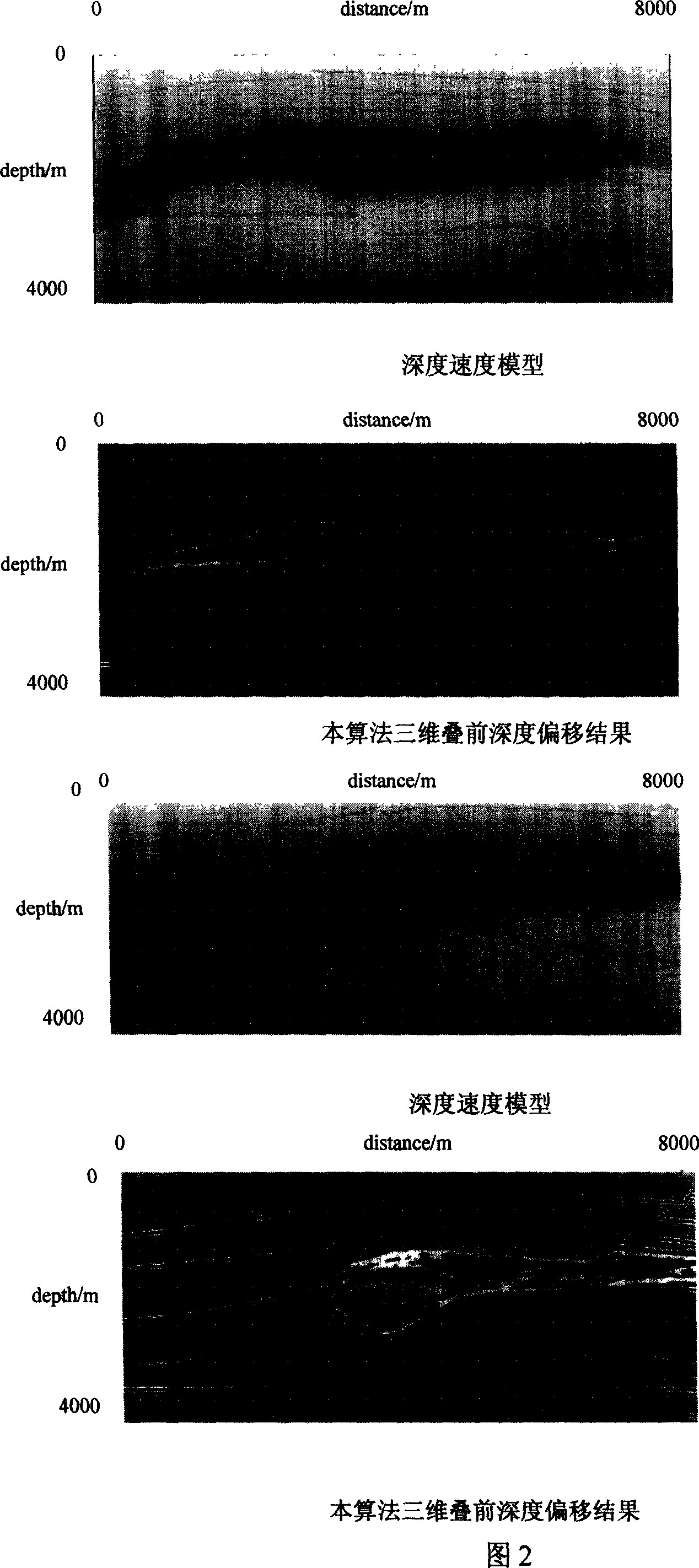
Tridimensional integral prestack depth migration method based on maximum energy travel calculation
InactiveCN101545986ASmall amount of calculationFlexible imagingSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingVibration amplitudeRectangular coordinates
The invention relates to the prestack depth migration technique during the data processing of petroleum seismic prospecting, including the following concrete steps: establishing depth rate pattern of prestack seismic data; well designing observation grids, and solving wave equation in sphere coordinate system to simulate the communication process of seismic waves; changing and converting the calculated seismic wave field of a frequency domain into a time domain, and fitting the Green function energy spectrum of the seismic wave field in the time domain to detect the arriving time and the vibration amplitude when the maximum energy arrives; transferring the travel time and the vibration amplitude field calculated in the sphere coordinate system to a rectangular coordinate system; accomplishing the maximum energy integral prestack depth migration according to the well calculated travel time and the vibration amplitude; analyzing the operation of speed to the imaging gather of the prestack depth migration to modify the depth rate pattern; and modifying the depth rate pattern by iteration, and outputting the ultimate result until the migration result meets the precision requirement. The invention provides the self-adapting variation difference grid calculation technique so as to achieve the purpose that the difference grids are automatically and gradually thinned along with radius increase, thereby guaranteeing the finite difference calculation precision.
Owner:匡斌
Redatuming Seismic Data with Correct Internal Multiples
ActiveUS20130301387A1Convenient lightingGood partitionSeismic signal processingSource fieldComputer science
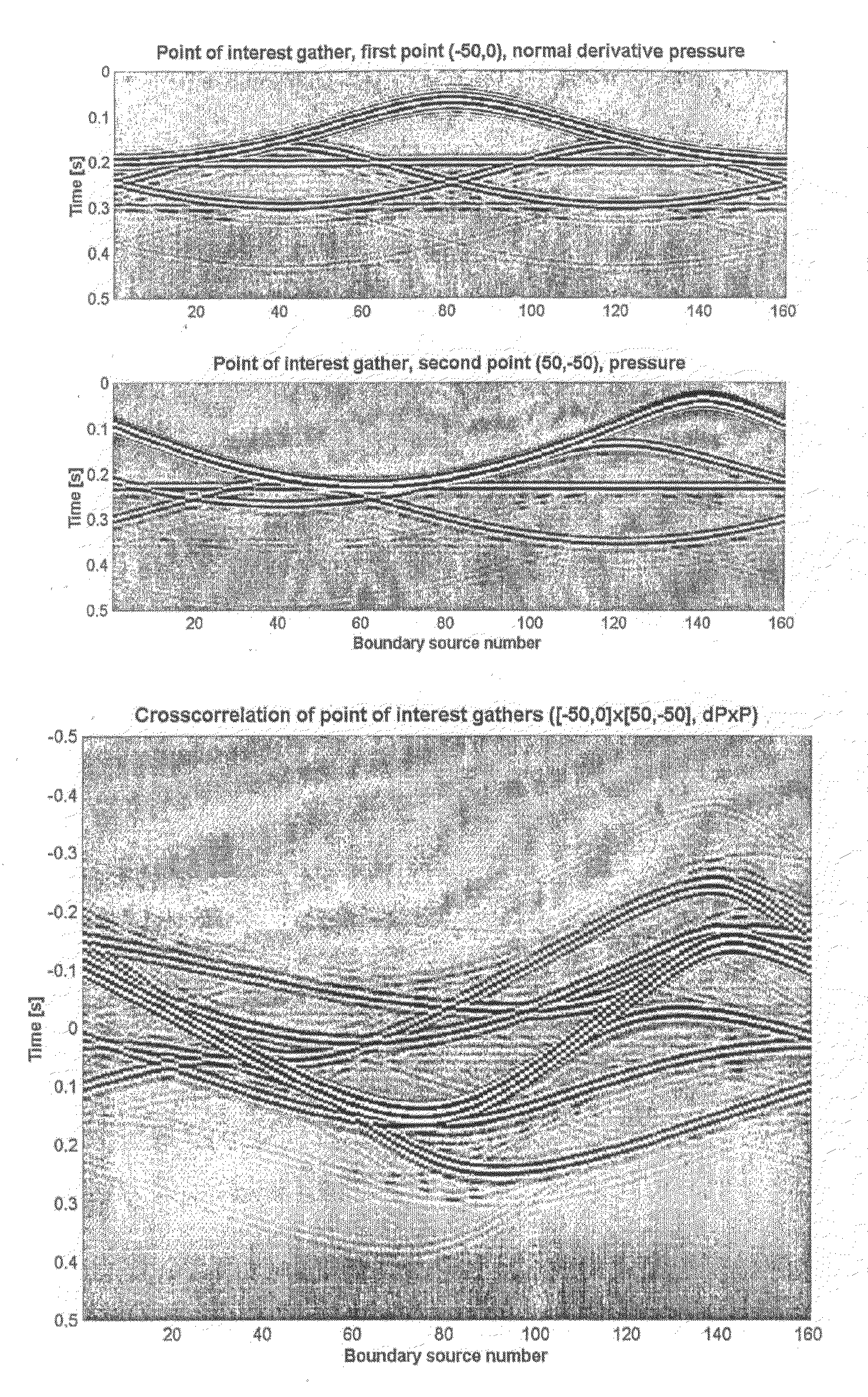
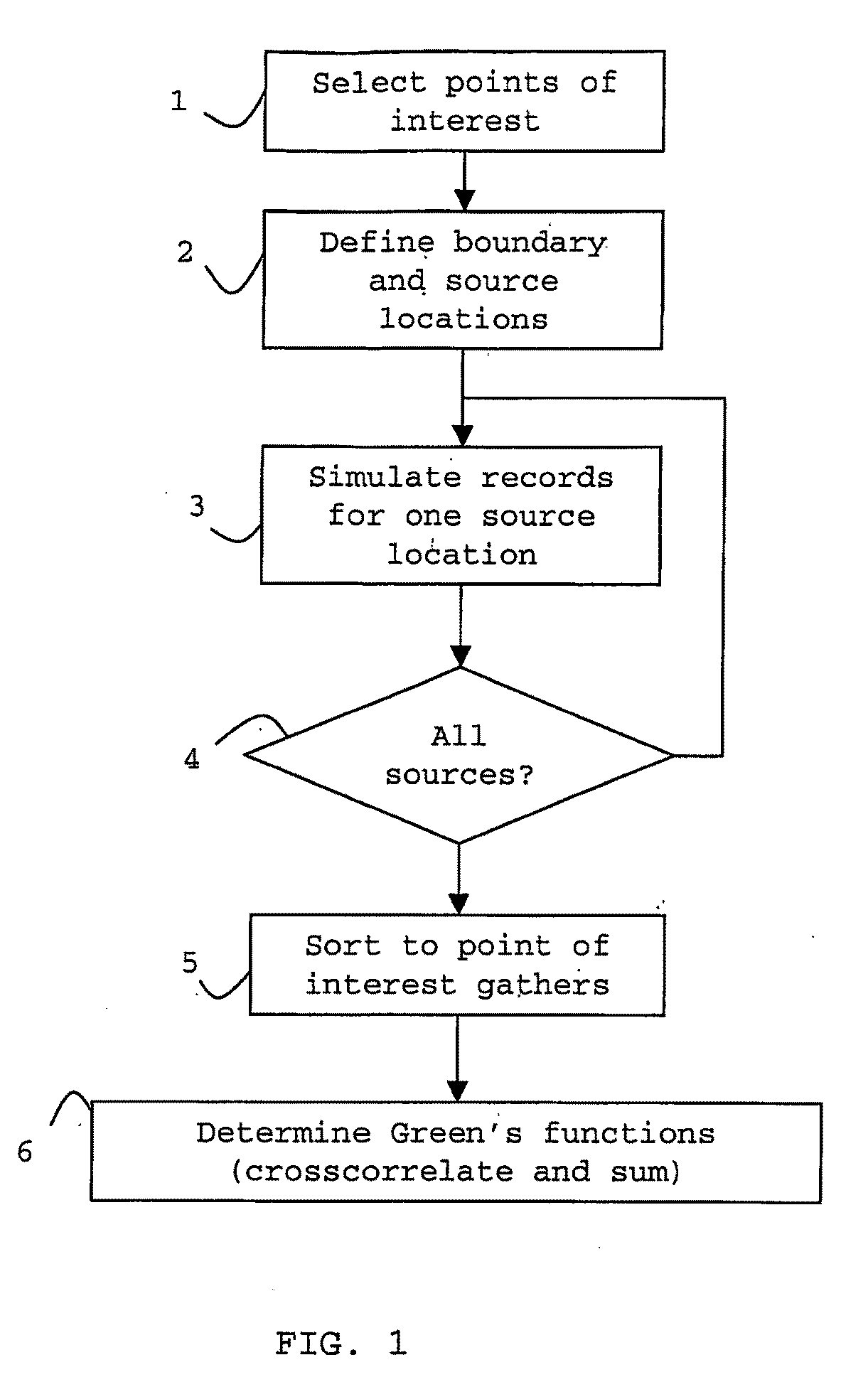
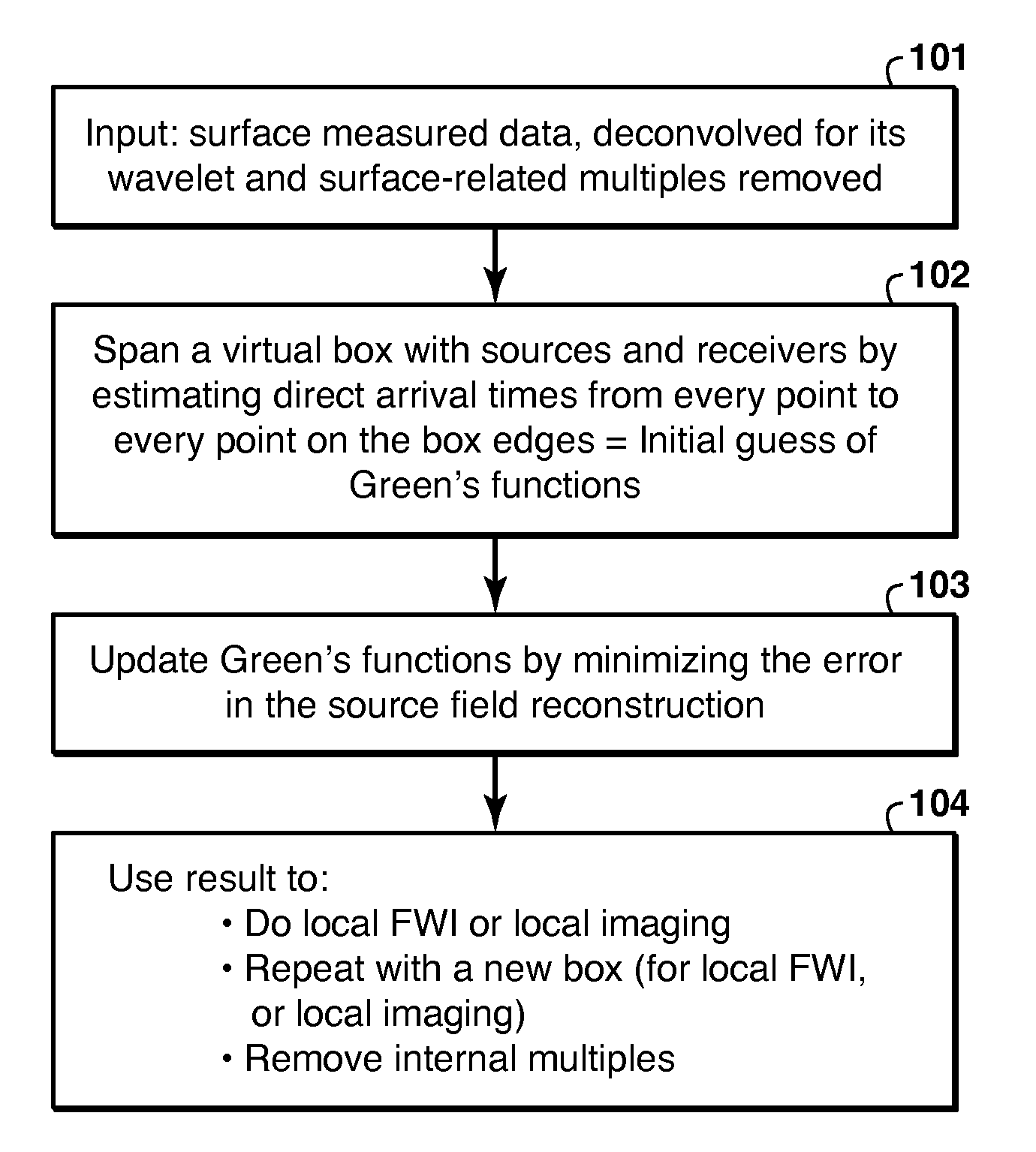
Method for redatuming seismic data to any arbitrary location in the subsurface in a way that is consistent with the internal scattering in the subsurface. Direct arrival times are estimated from every point to every point on the edges of a virtual box in the subsurface (102). Green's functions are estimated by iterative optimization (103), using the direct arrival times as initial guesses (102), to minimize error in the source field reconstruction, which consists of the multidimensional auto-correlation of the Green's functions. The estimated Green's functions are the used to determine simulated internal multiple reflections (104). The measured data may be corrected by subtracting the simulated internal multiple reflections, or the Green's function may be used to do local imaging or local velocity model building, particularly advantageous in full wavefield inversion (104).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
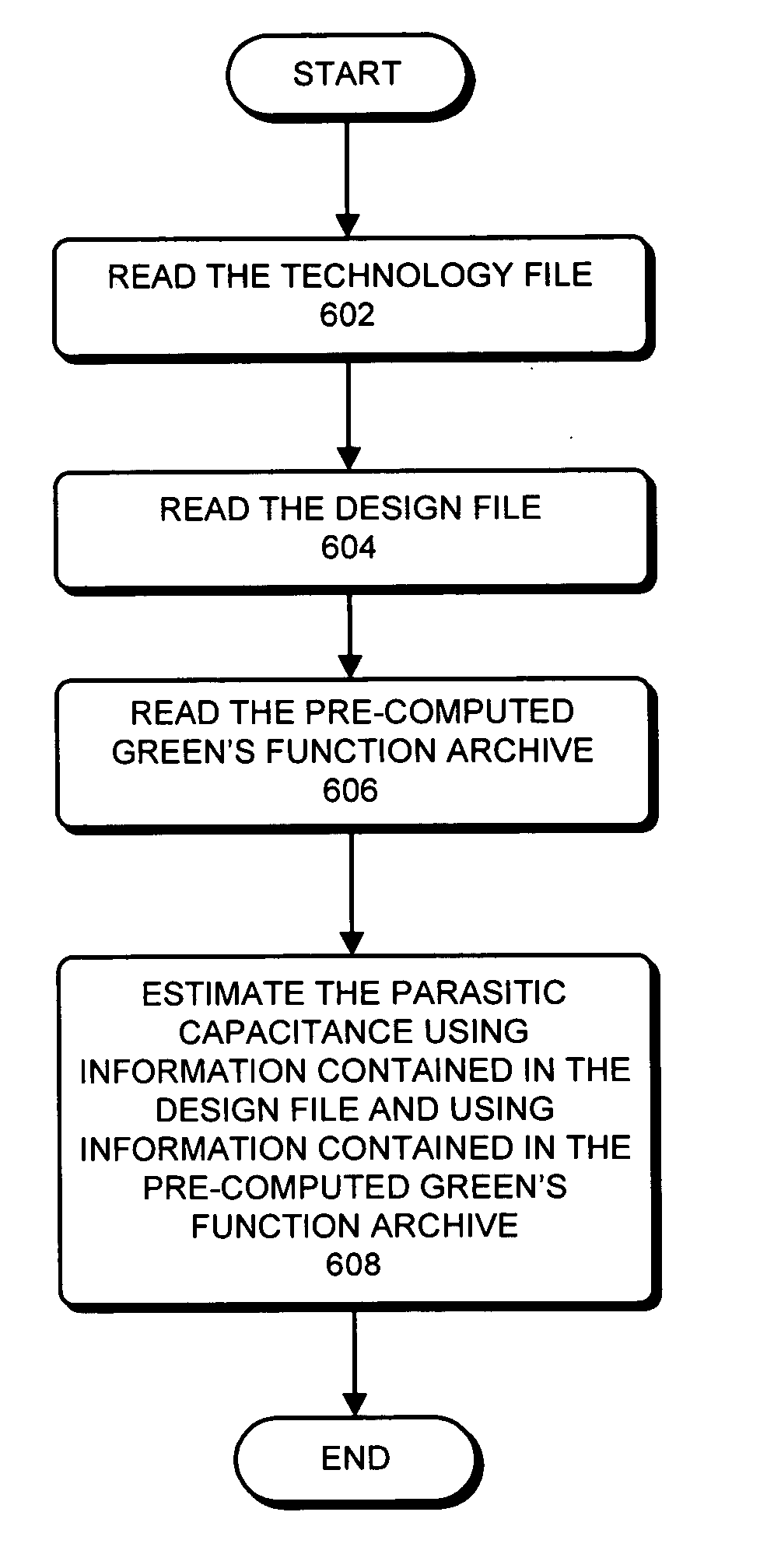
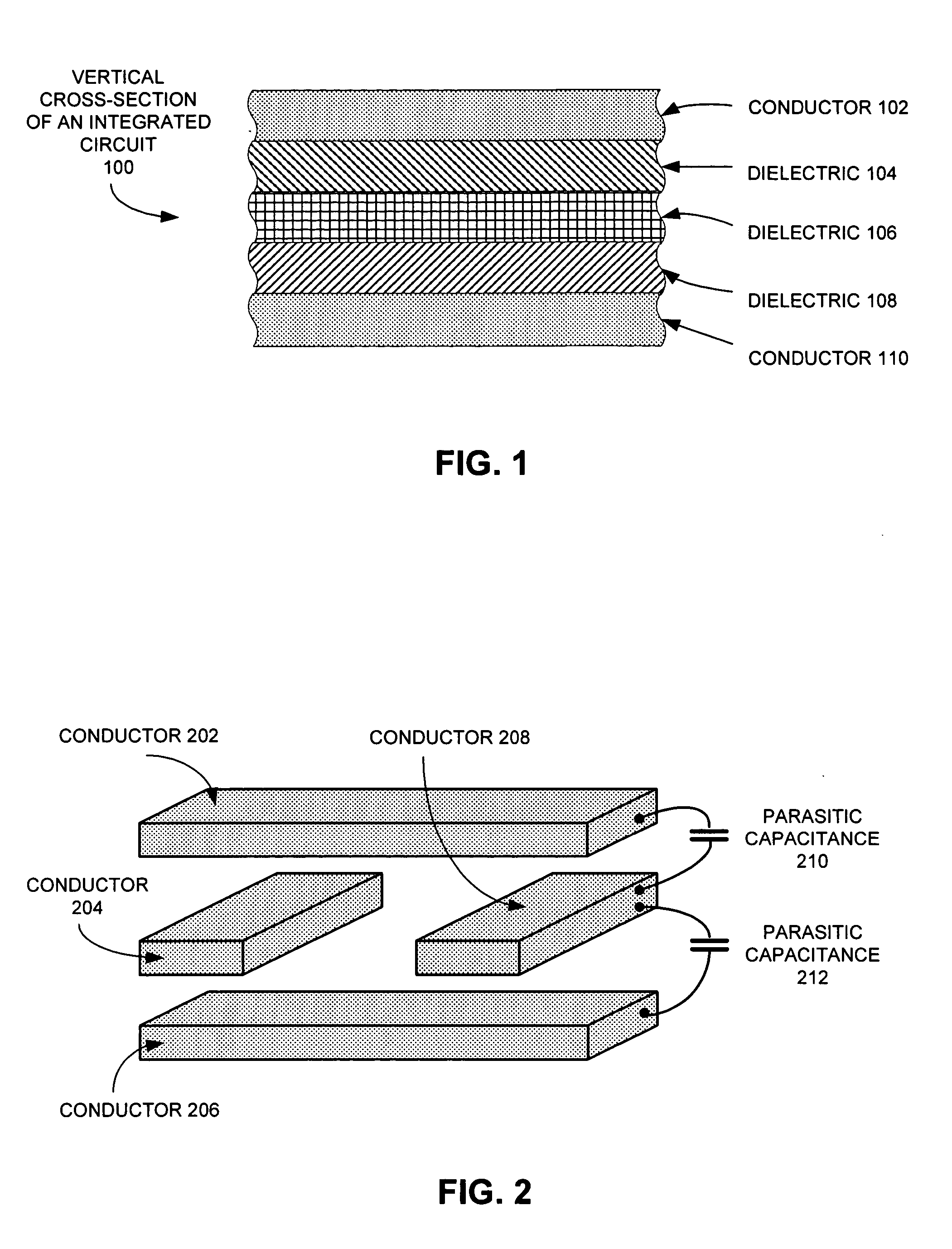
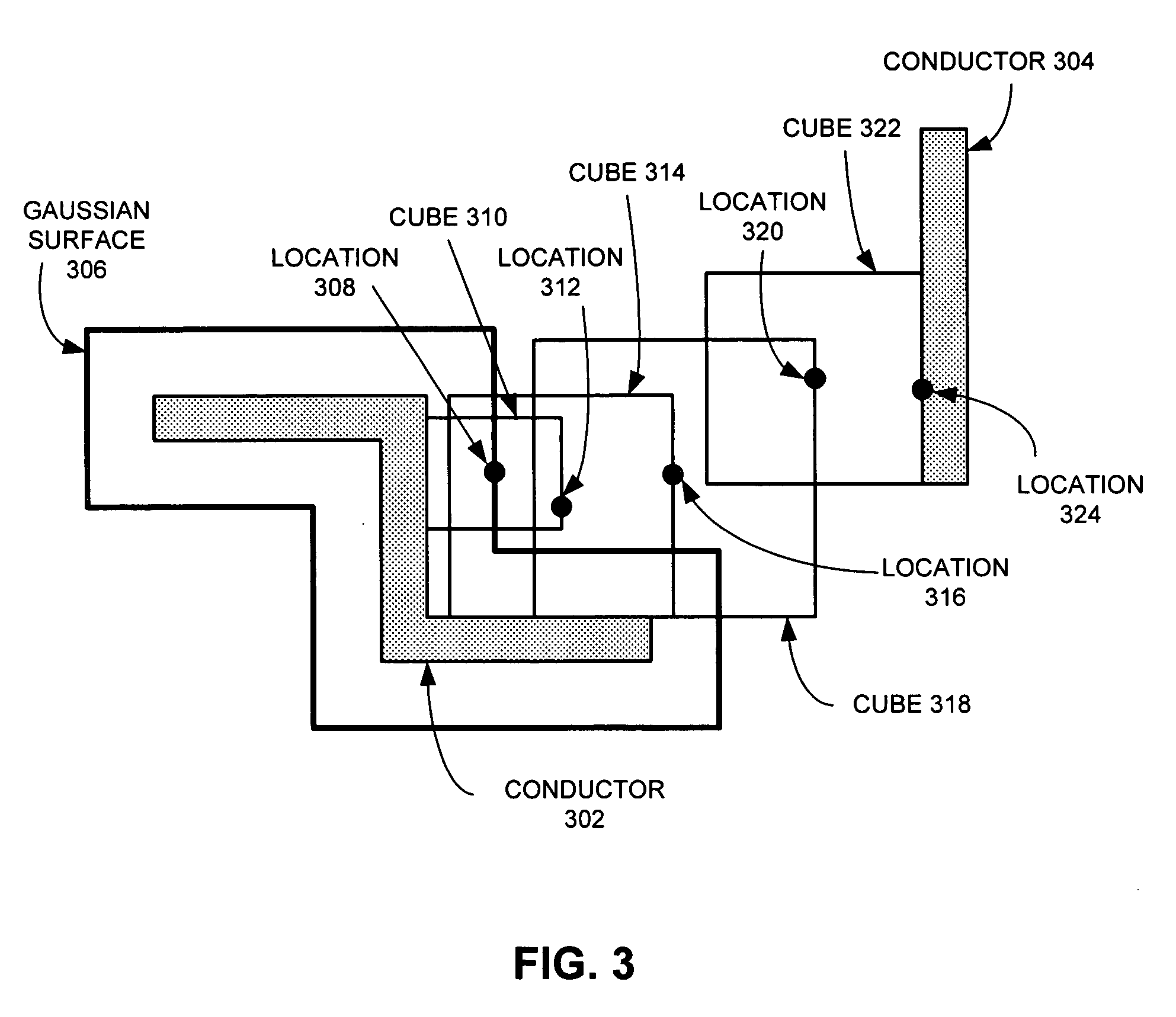
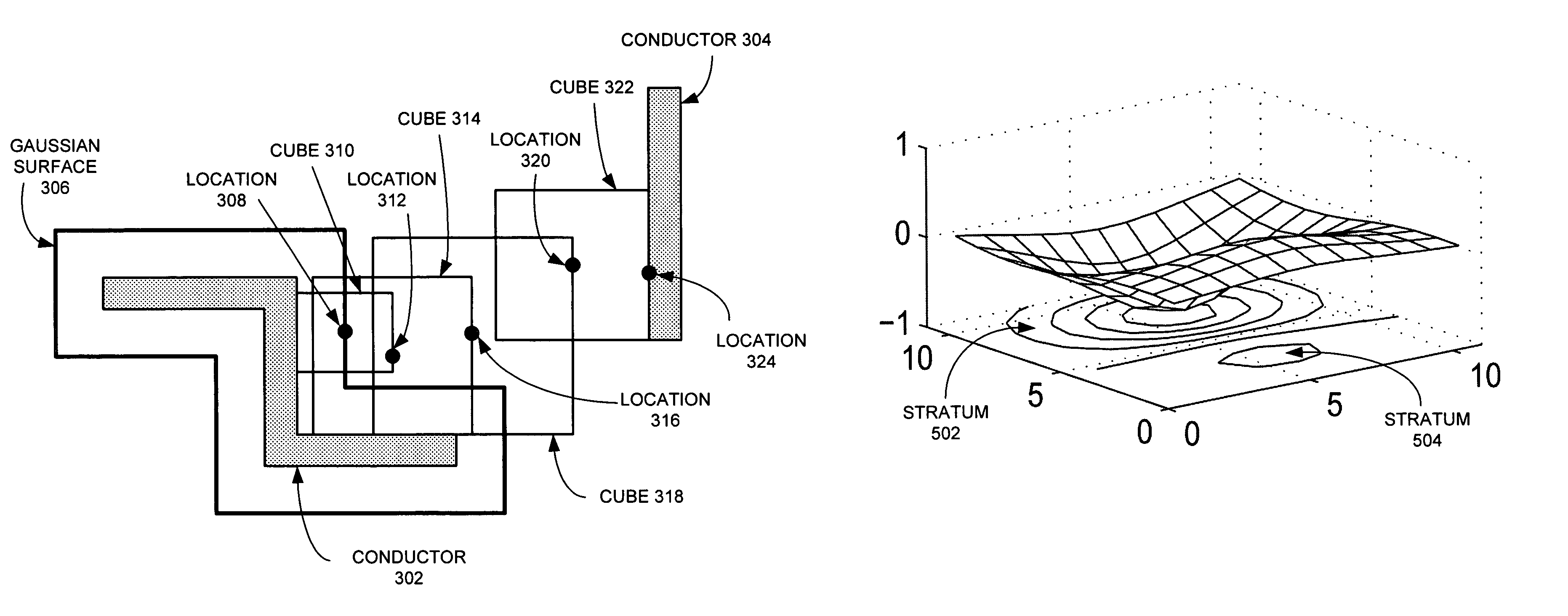
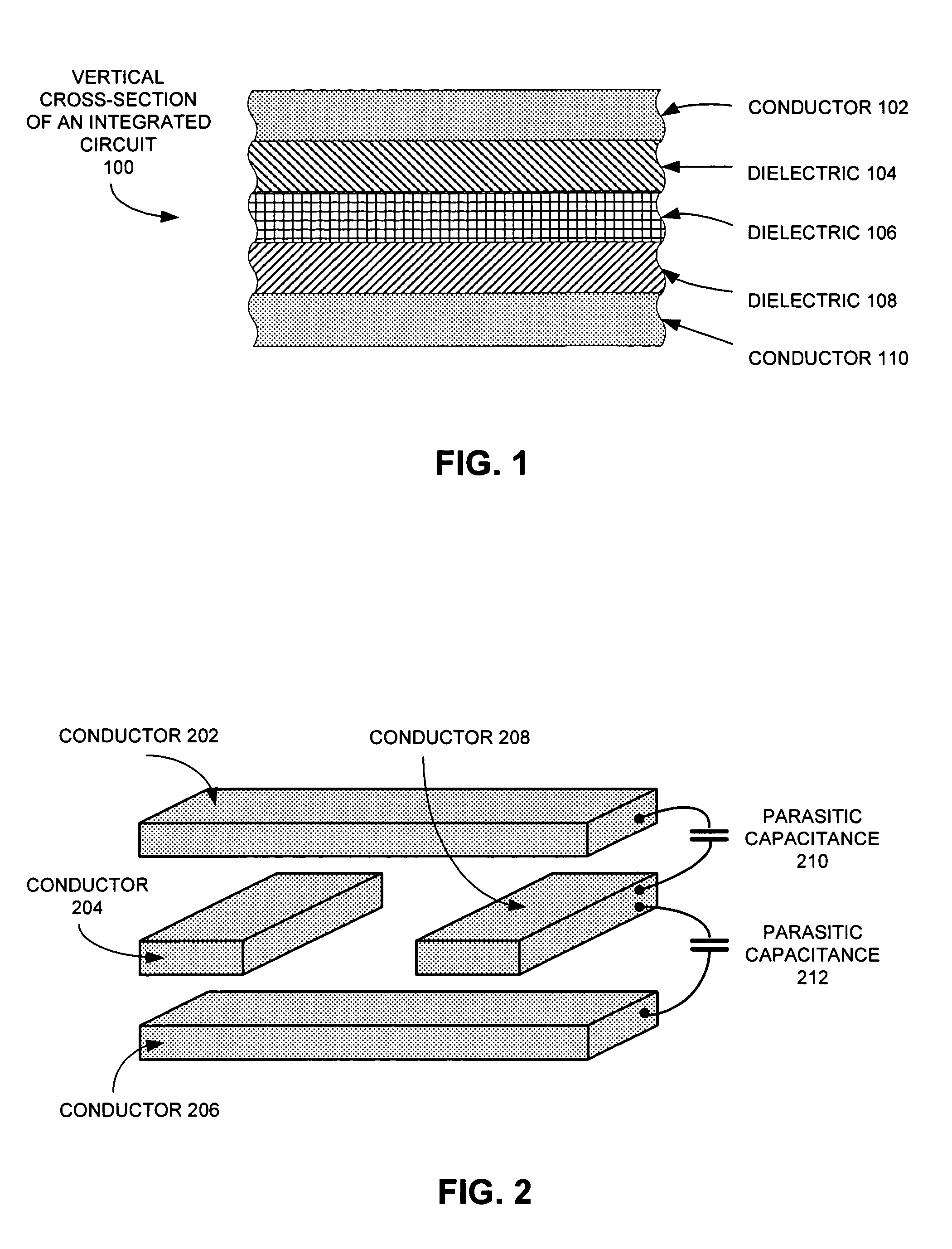
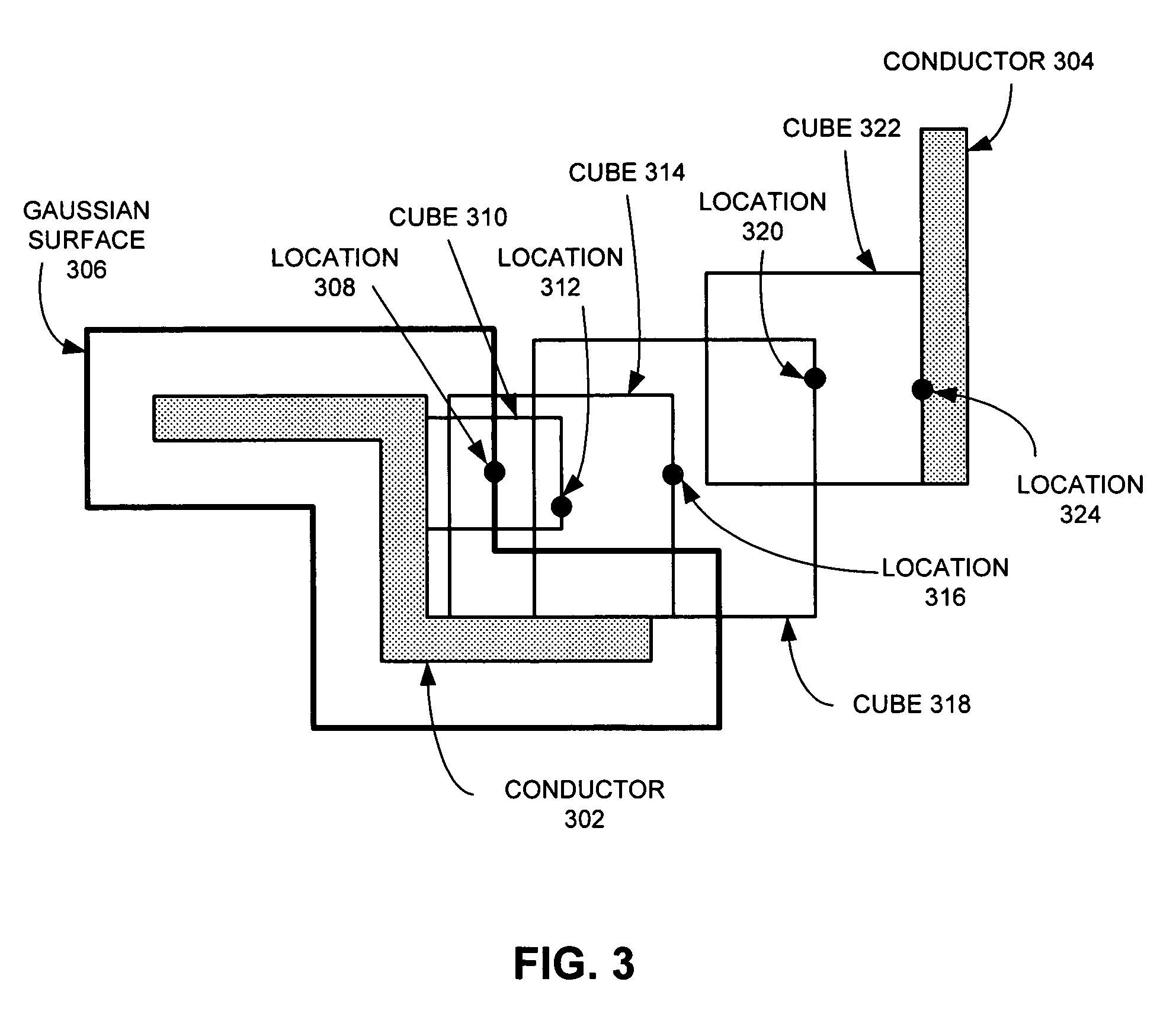
Method and apparatus for estimating parasitic capacitance
ActiveUS20060053394A1Lookup is very fastGuaranteed execution efficiencyComputation using non-denominational number representationProgram controlElectricityParasitic capacitance
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for estimating parasitic capacitance for an integrated circuit. During operation, the system reads a technology file, which describes the composition of a vertical cross-section of the integrated circuit. Next, the system reads a design file, which specifies the layout of the integrated circuit. The system then identifies a set of dielectric configurations based on information contained in the technology file. It then computes Green's function for each of these configurations. Next, the system estimates a parasitic capacitance using information contained in the design file and using the set of Green's functions.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
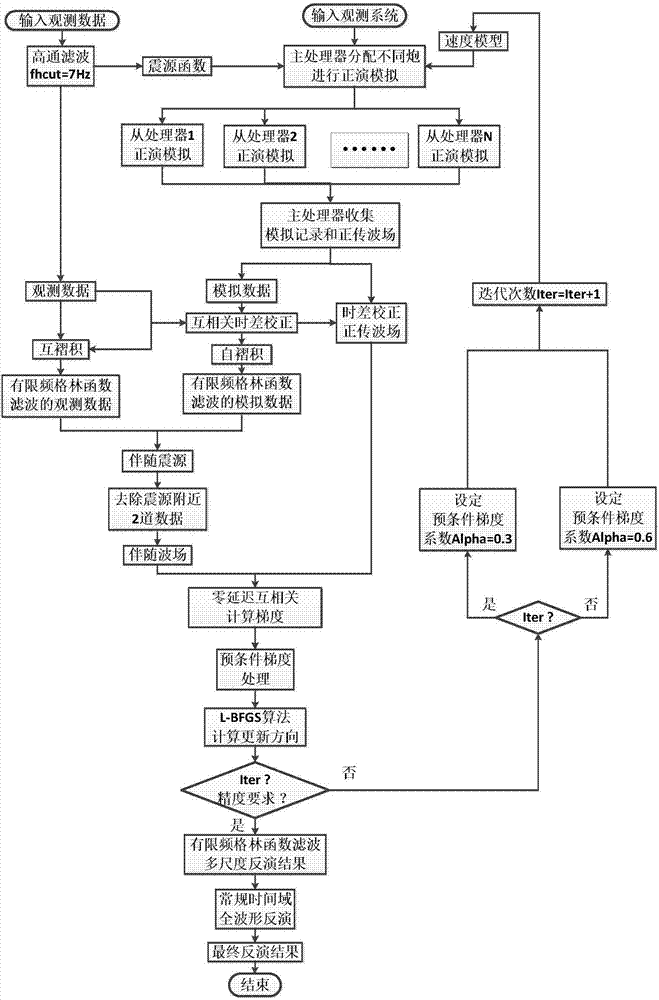
Band-limit Green function filtering multi-scale full-waveform inversion method
InactiveCN106908835AShorten the timeReduce non-linearitySeismic signal processingFull waveformComputer science
The invention relates to a band-limit Green function filtering multi-scale full-waveform inversion method, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the filtering of seismic data through the Green function of an initial speed model; processing solved gradient through a precondition gradient method, and enabling the method provided by the invention to be able to obtain the macroscopic information of the model at the initial stage of inversion; adjusting a precondition gradient coefficient when the speed model gradually approaches a real speed model, and enabling the method provided by the invention to be able to gradually depict the detail information of the speed model; finally combining with a minute gun parallel inversion strategy, making the most of advantages of computer multi-thread parallelism, and speeding up the full-waveform inversion. From the point of a testing result of the method, the method can effectively alleviate the cycle wave jump of full-waveform inversion under the condition that an initial model is not good when the low-frequency part of seismic data is lost.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Three-dimensional integral prestack depth migration method
InactiveCN101021568ASmall amount of calculationFlexible imagingSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGratingOrthogonal coordinates
The invention relates to pre-fold depth excursion technology in the data processing of the oil and earthquake exploration. It includes: setting up the depth speed module for the pro-fold earthquake data; designing the observation grating to solve the wave equation which modulates the propagating process of the earthquake wave in the ball coordinate system; the earthquake wave field switch with computed the frequency field is changed to the time field, then to fit the earthquake wave field Green function energy spectrum and get the reaching time and the swing of the max energy; transforming the travel time and the swing field computed in the ball coordinate system to the orthogonal coordinate system; according to the travel time and the swing to get the max energy integral pro-fold depth excursion; analyzing the speed of the image path collection to modify the depth speed module; by iteration to modify the module until the excursion result fit for the precision. The invention provides the self adaptive switch difference grating computing technology to make the difference grating change thin along with the radius, so the limit difference computing precision can be assured.
Owner:匡斌
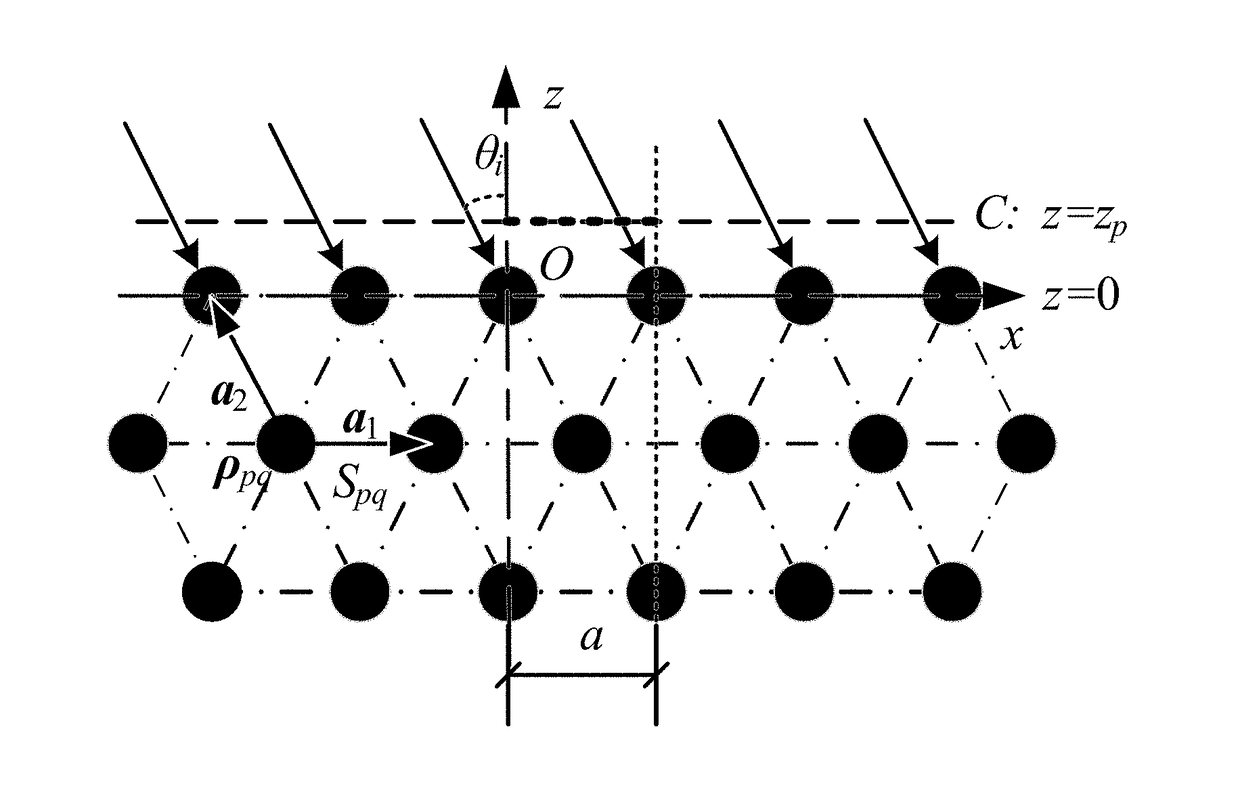
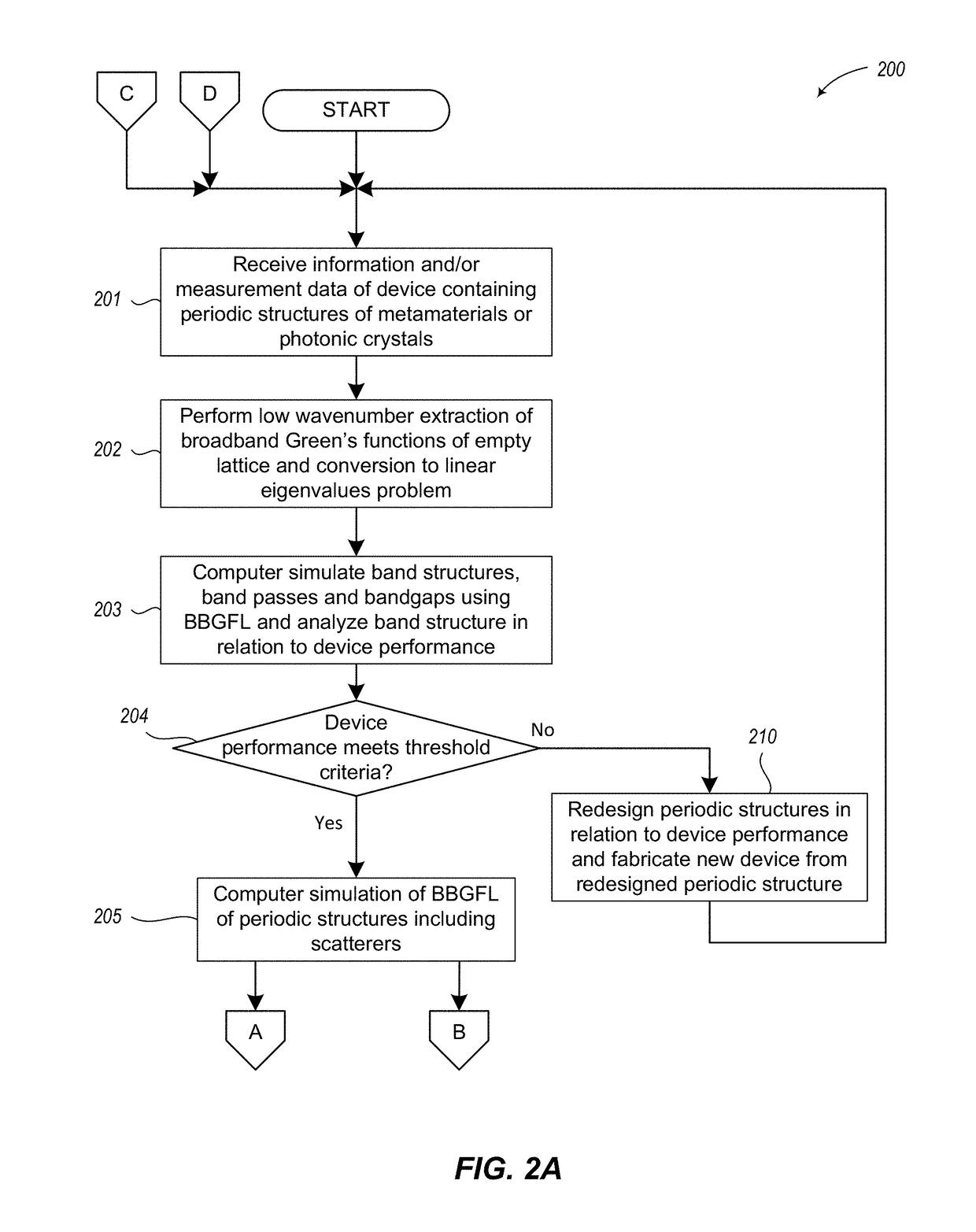
Full wave simulations of photonic crystals and metamaterials using the broadband green's functions
ActiveUS20180121580A1Efficiently obtainedFast convergenceDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingFull wavePhotonics
Broadband Green's function computing technique that employs low wavenumber extraction, obtains fast frequency independent modal band solutions and achieves fast convergence of modal expansions, is used to model and design electromagnetic wave behavior of signals in artificial materials with periodic structures, including metamaterials, photonic crystals, and phononic crystals, which are used for smart microwave devices, photonic devices, and acoustic devices. The Broadband Green's function is a general response function for artificial materials and is used to model bandgaps, bandpasses, impurities, defects, displacements of scatterers, and to formulate integral equations for periodic scatters in a finite volume. Designs of metamaterials, photonic crystals, and phononic crystals enable controlling the waves through bandpasses, bandgaps, surface states, polarizations, defects, absorption, enhancement, refraction, substrates, and guidance. The Broadband Green's function technique is used in computer simulations to analyze wave behavior over a broad frequency range, which improves design optimization of smart microwave and photonic devices.
Owner:TSANG LEUNG W
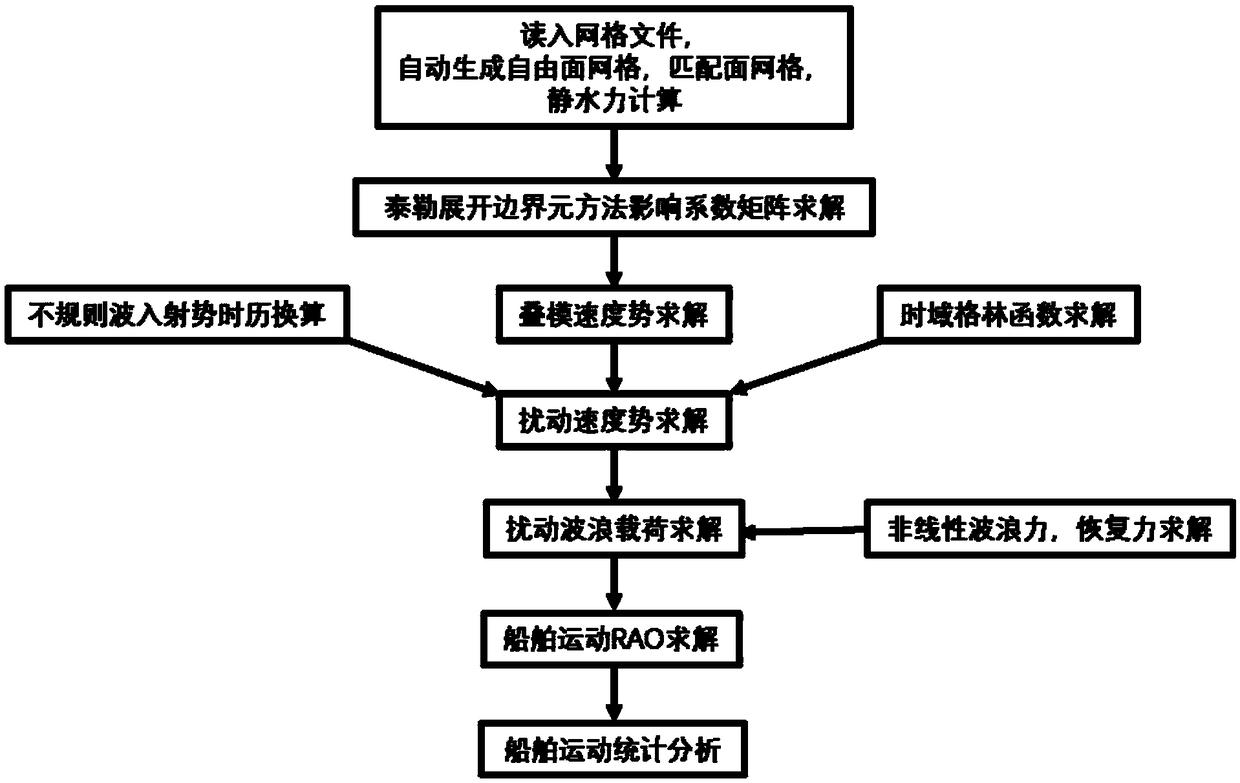
A three-dimensional numerical simulation method for ship large-scale rolling motion
The invention provides a three-dimensional numerical simulation method for ship large-scale rolling motion, which comprises the following steps of reading a grid file to carry out ship hydrostatic calculation; calculating an influence coefficient matrix of boundary integral equation for Taylor expansion boundary element method; solving velocity potential of laminated modes and its spatial first and second derivatives and mj terms; carrying out the green's function in time domain and its spatial derivative solution; calculating a roll damping coefficient; carrying out the irregular wave decomposition, linear superposition into incident wave time calendar; carrying out the direct time-domain disturbance wave force calculation by taylor expansion boundary element method; calculating incidentwave force and hydrostatic recovery force; modeling a large-scale motion forecasting equation; using the fourth-order runge-kutta method to solve the motion equation step by step to evaluate the nonlinear motion of the ship in the top wave or oblique wave; and carrying out the numerical simulation and characteristic statistics of ship large amplitude motion in irregular waves. The method of the invention can predict the large amplitude motion of a container ship in regular waves and irregular waves, and can be used for numerical simulation and characteristic statistics of the large amplitude motion of a ship in irregular waves.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for synthesizing seismic records based on three-dimensional Gaussian beam ray tracing and frequency domain
InactiveCN103675894AEasy to calculateHigh precisionSeismic signal recordingUltrasound attenuationKinematics
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing seismic records based on three-dimensional Gaussian beam ray tracing and a frequency domain. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) performing kinematics tracking by utilizing a common ray tracing way to obtain a ray path and kinematics characteristics; 2) performing dynamics tracking by utilizing a Gaussian ray beam to calculate dynamics characteristics; 3) synthesizing the seismic records in the frequency domain. As a Futyterman equation based attenuation algorithm, a frequency based green function and a weak anisotropic model of a coupling ray theory can be considered for the synthesis of the seismic records in the frequency domain, the dynamics characteristics of a seismic wave field can be described more delicately in comparison with a conventional method, and the seismic records synthesized by utilizing the ray theory is close to the precision of the wave theory. The method for synthesizing the seismic records based on the three-dimensional Gaussian beam ray tracing and the frequency domain can calculate information such as ray amplitude and phase shift conveniently, can be applied to the fields such as manufacturing of synthesized records, prestack depth migration and waveform tomography inversion.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
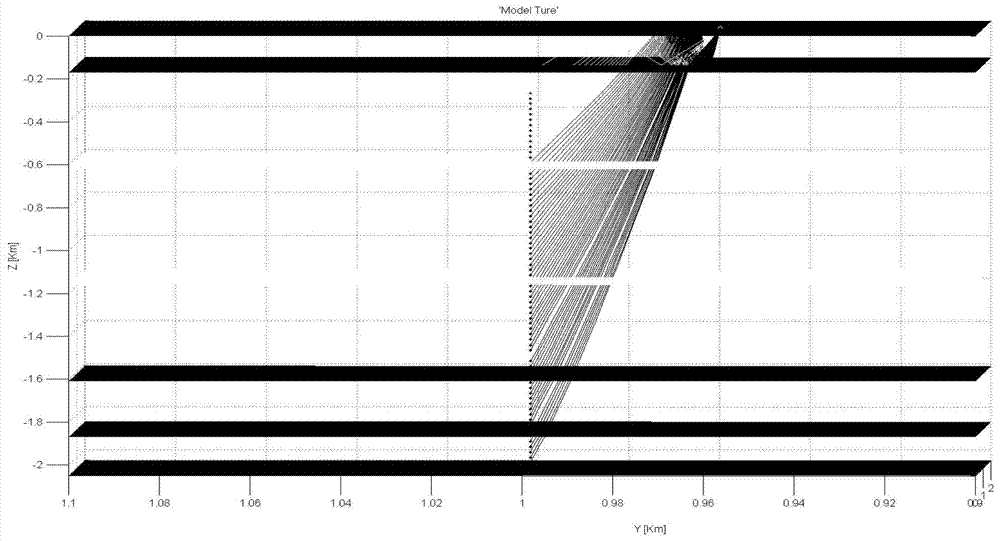
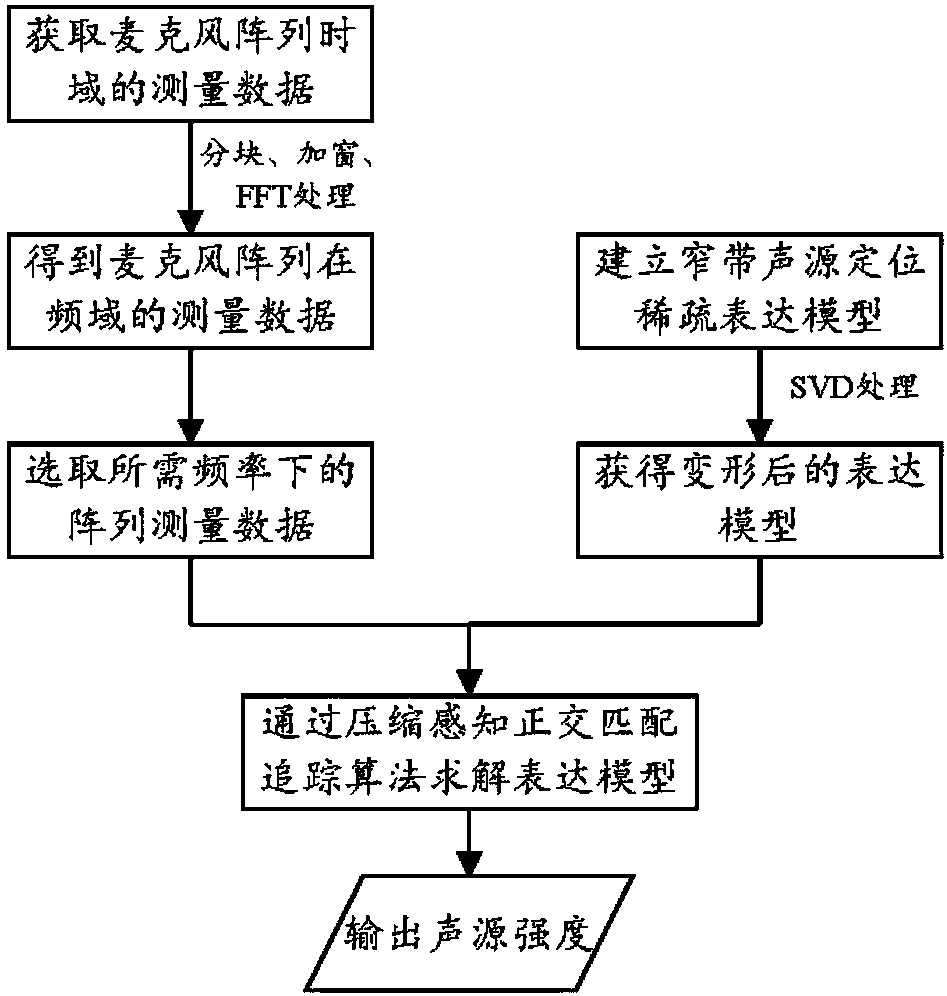
Three-dimensional sound source localization method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN107247251AImprove noise immunityPosition fixationSound source locationSingular value decomposition
The invention discloses a three-dimensional sound source localization method based on compressed sensing, so as to solve the technical problem of poor anti-noise performance of the existing three-dimensional sound source localization method. In the technical scheme, the measurement value of sound source signals is acquired through a microphone array, a selected three-dimensional sound source area is subjected to uniform mesh generation, and each mesh node is used as a hidden sound source position; according to a Helmholtz equation of a free field Green's function, a measurement matrix between the mesh node and the microphone array is built, and a three-dimensional narrowband sound source localization sparse representation model between the measurement value of the microphone array and unknown sound source signals is acquired; through carrying out singular value decomposition on the measurement value of the microphone array in the sparse representation model, a sound source localization sparse representation model after deformation is acquired; and finally, a compressed sensing OMP (orthogonal matching pursuit) algorithm is adopted to carry out iterative solution on the representation model after deformation, the sound source strength of each mesh node in the sound source area is acquired, and the sound source is localized. The anti-noise performance of sound source localization is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
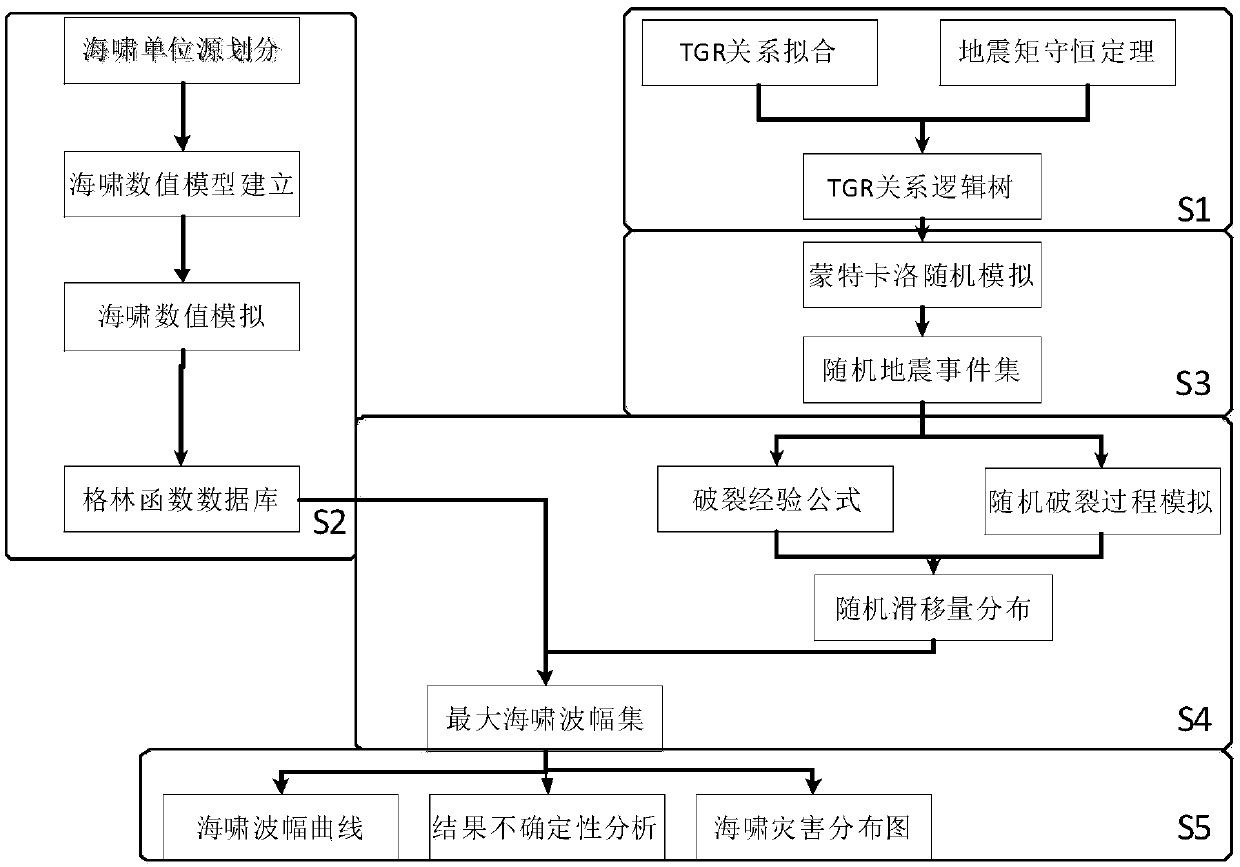
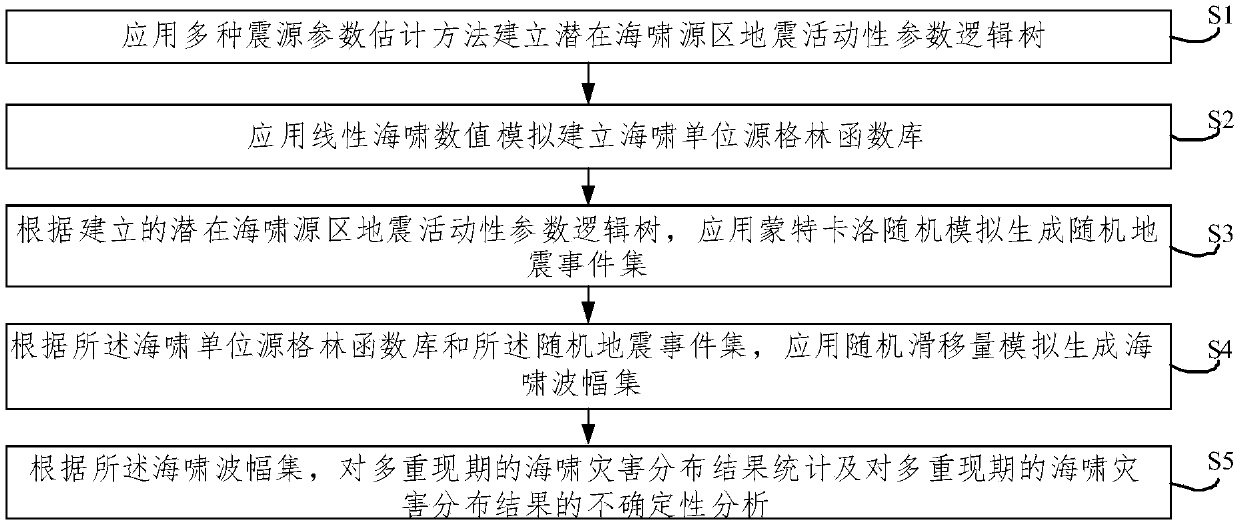
Multi-return-period tsunami disaster evaluation method based on Monte Carlo stochastic simulation
ActiveCN108492236AThe assessment results are accurateImprove accuracyData processing applicationsICT adaptationSource areaReturn period
The invention discloses a multi-return-period tsunami disaster evaluation method based on Monte Carlo stochastic simulation. The method comprises: S1, applying multiple source parameter estimation methods to establish a seismic activity parameter logic tree of potential tsunami source areas; S2, applying linear tsunami numerical simulation to establish a tsunami unit source Green's-function library; S3, applying a Monte Carlo stochastic simulation to generate a stochastic seismic event set according to the above logic tree; S4, applying stochastic slippage simulation to generate a tsunami waveamplitude set according to the tsunami unit source Green's-function library and a stochastic seismic event set; and S5, carrying out counting and uncertainty analysis on multi-return-period tsunami disaster distribution results according to the tsunami wave amplitude set. According to the above method, problems that in the prior art, risk evaluation results are higher, and corresponding occurrence probability thereof cannot be given can be solved, multiple types of uncertainty are fused into a final evaluation result, credibility of the result is increased, running efficiency is improved at the same time, and targeted disaster prevention and mitigation deployment and urban construction planning of decision makers are facilitated.
Owner:国家海洋环境预报中心
Method and apparatus for estimating parasitic capacitance
ActiveUS7260797B2Guaranteed execution efficiencyLookup is very fastComputation using non-denominational number representationProgram controlParasitic capacitanceEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for estimating parasitic capacitance for an integrated circuit. During operation, the system reads a technology file, which describes the composition of a vertical cross-section of the integrated circuit. Next, the system reads a design file, which specifies the layout of the integrated circuit. The system then identifies a set of dielectric configurations based on information contained in the technology file. It then computes Green's function for each of these configurations. Next, the system estimates a parasitic capacitance using information contained in the design file and using the set of Green's functions.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Control method for acquiring offset speeds of longitudinal and transverse waves based on Gaussian beam
ActiveCN102914796AImprove computing efficiencyGood directionSeismic signal processingGaussian beamLongitudinal wave
The invention relates to a control method for acquiring the offset speeds of longitudinal and transverse waves based on a Gaussian beam. The control method comprises the following steps of: constructing a Green function in a Gaussian beam manner according to a record of earthquake wave shapes, and carrying out wave field prolongation imaging by decomposing a seismic record in a range close to a beam central point into local plane waves in different emitting directions through local slanting stacking according to the constructed Green function; respectively extracting common imaging point gathers of the longitudinal wave and the transverse wave from an obtained image by offsetting the pre-stack depth of the Gaussian beam; and updating the offset speeds of the longitudinal wave and the transverse wave in the extracted common imaging point gathers of the longitudinal wave and the transverse wave according to a common imaging point gather leveling rule, and finishing the acquiring of the offset speeds of the longitudinal wave and the transverse wave. According to the control method for acquiring the offset speeds of the longitudinal and transverse waves based on the Gaussian beam, the problem that the computing efficiency is low or the accuracy of a speed analyzing result is relative poor in the exiting method is solved.
Owner:北京多分量地震技术研究院
Matrix decomposition and novel singular value decomposition combined method for complex layered medium structures
InactiveCN102708229ADiscrete Fit ExactGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsSingular value decompositionInternal memory
The invention discloses a method capable of implementing quick electromagnetic simulation of complex layered medium structures, wherein the method is used for efficient simulation of the complex layered medium structures on basis of combination of matrix decomposition and novel singular value decomposition. The method includes: using triangular meshes to precisely simulate a model, and subjecting far-field groups to low-order compact according to the principle of fine low-order characteristics of far-field groups in tree structures to obtain a sparse matrix representation form. The method which is a pure mathematic analytical method is independent of an expansion form of the green function, internal memory and computing time are reduced by the novel singular value compact method based on MDA (matrix decomposition algorithm), the computing complexity can be lowered to O (NlogN), and memory consumption can be lowered to O (NlogN). The method is especially suitable for electromagnetic simulation analysis of complex layered medium structures and can be also used for providing effective means for layered medium structure simulation with the complex green function.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fast directional multilevel simulation method for planar microstrip circuit
InactiveCN102054094AReduce complexityGood low-rank propertiesSpecial data processing applicationsInternal memoryComputation complexity
The invention discloses a fast directional multilevel algorithm for analyzing a planar microstrip circuit. The planar microstrip circuit structure is analyzed based on the fast directional multilevel algorithm. In the algorithm, a complex circuit is divided by a planar triangular surface element, and the fast directional multilevel algorithm is combined with a Rao-Wilton-Glisson (RWG) function to be applied to an electric field integral equation to ensure the calculating accuracy of a model; and by utilizing a principle that an impedance matrix formed by a moment method when the field-to-source point distance is long enough has good low-rank characteristic, fast directional multilevel calculation is adopted for a far field area, a Green function is unfolded by a low-rank expression, the expansion is only related to calculation of a kernel function so as to greatly reduce the calculating complexity of the multilayer microstrip circuit, and the calculating complicity and internal memory demand are reduced to O(NlogN) magnitude. A quadtree form is also adopted for grouping analysis of the planar microstrip multilayer circuit, the consumption of the internal memory is effectively reduced, the calculation result is accurate, the testing cost is low, and the fast directional multilevel algorithm can be widely applied to simulation analysis of complex circuits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three-dimensional frequency domain controllable source numerical simulation method
ActiveCN108509693ASmall scaleThe number of unknowns to be solved is smallDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMixed finite element methodFinite element equation
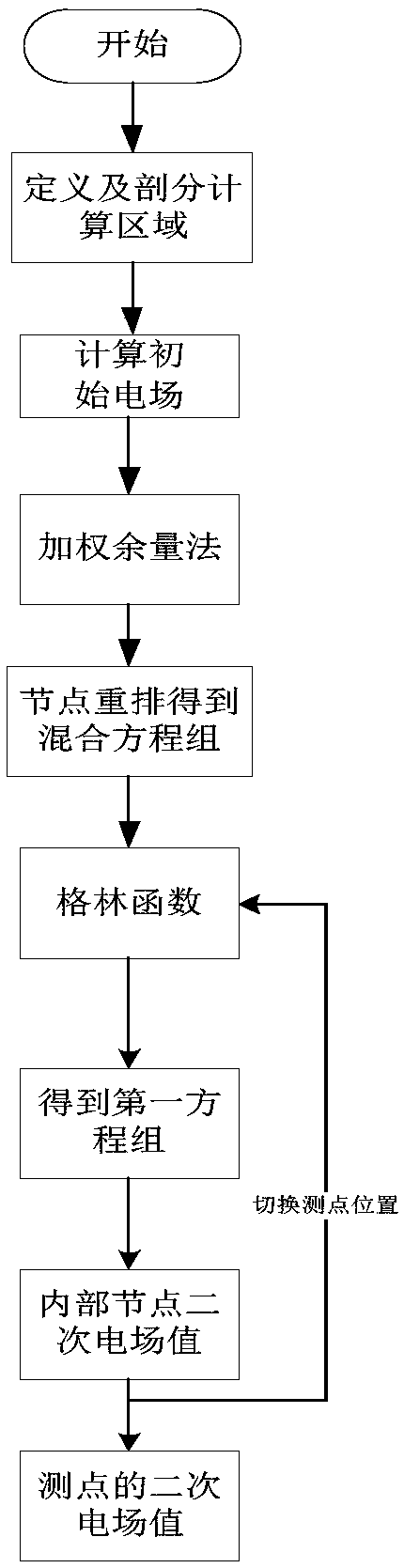
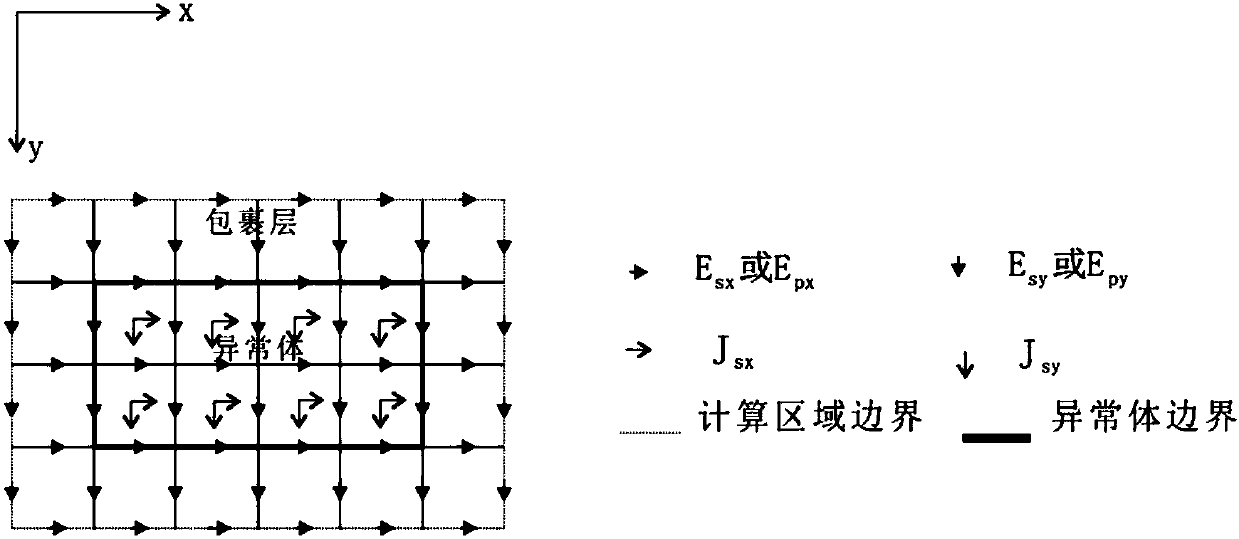
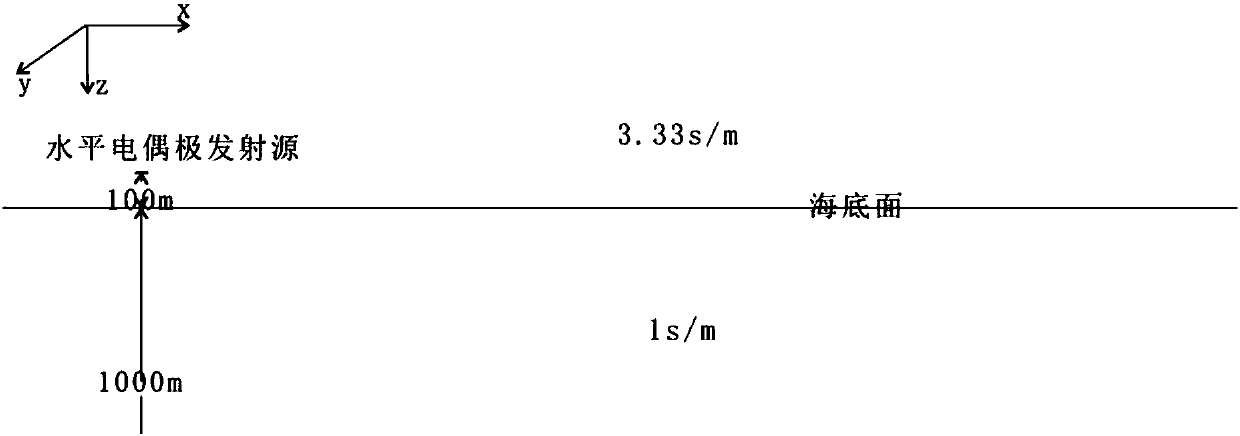
The invention provides a three-dimensional frequency domain controllable source numerical simulation method. The method comprises the steps of S100: defining a calculation region in a resistivity anomaly body and an adjacent wrapping layer, and dividing the calculation region into multiple regular unit bodies; S200: calculating an initial electric field under an artificial source excitation condition, and by adopting a weighted residual method, establishing a finite element equation set of edge midpoints of the unit bodies in the calculation region; S300: defining an observation point as a boundary node by using a Green function, and enabling a secondary electric field of an internal node to express a secondary electric field of the boundary node; S400: substituting a Green function expression into a mixed equation set to obtain a first equation set only about the secondary electric field of the internal node; and S500: solving the first equation set to obtain secondary electric fieldvalues of nodes comprised in the unit bodies. According to the method, a vector finite element method and a volume integral equation method are applied; the calculation region is reduced; the calculation amount is reduced; the calculation precision is improved; formed equations are sparse in coefficient matrix and good in condition number; and a calculation result is accurate.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
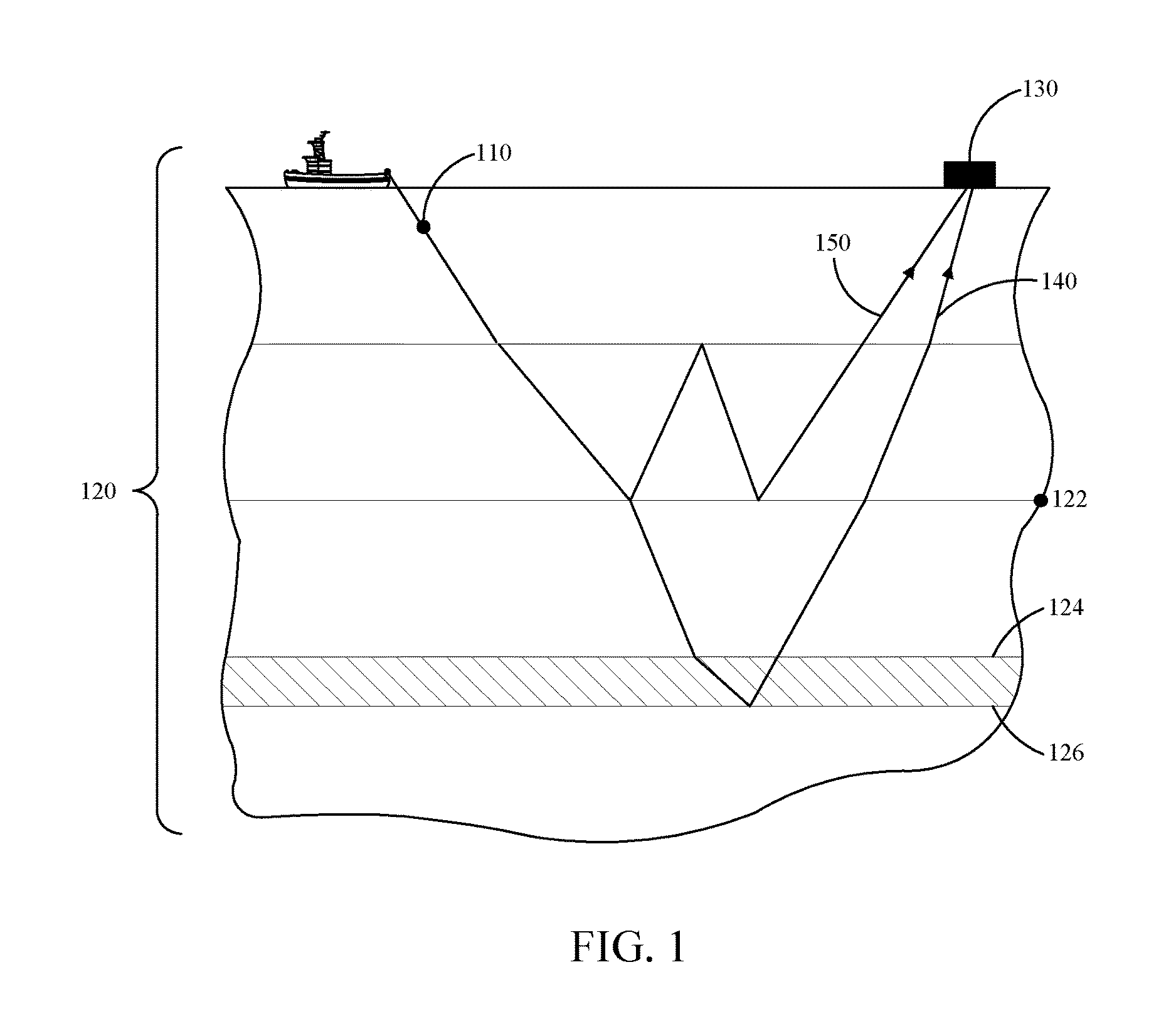
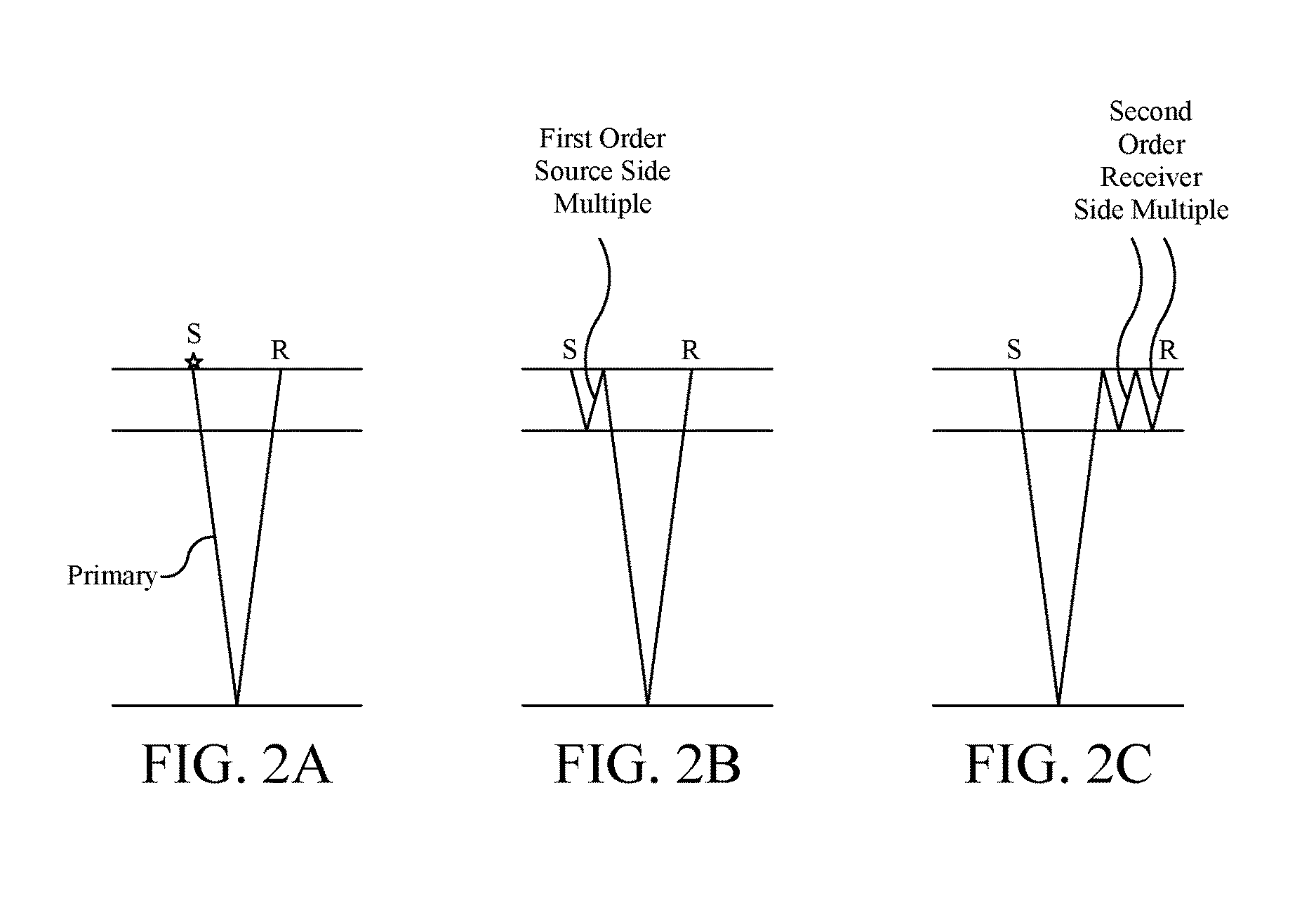
Method and apparatus for modeling and separation of primaries and multiples using multi-order green's function
Data is recorded by sensors while an underground formation is explored, e.g., using a seismic acquisition system that emits and receives waves. A model, which is indicative of primary waves contained in the received data, is derived using a multi-order Green's function. Using the model, an image of the underground formation is generated.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
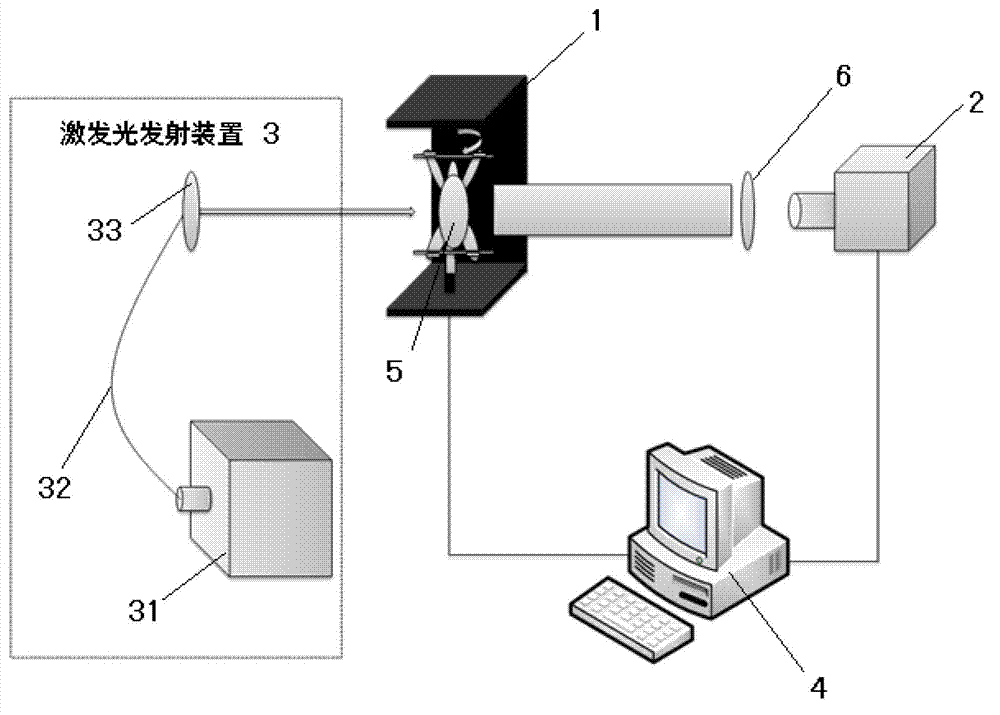
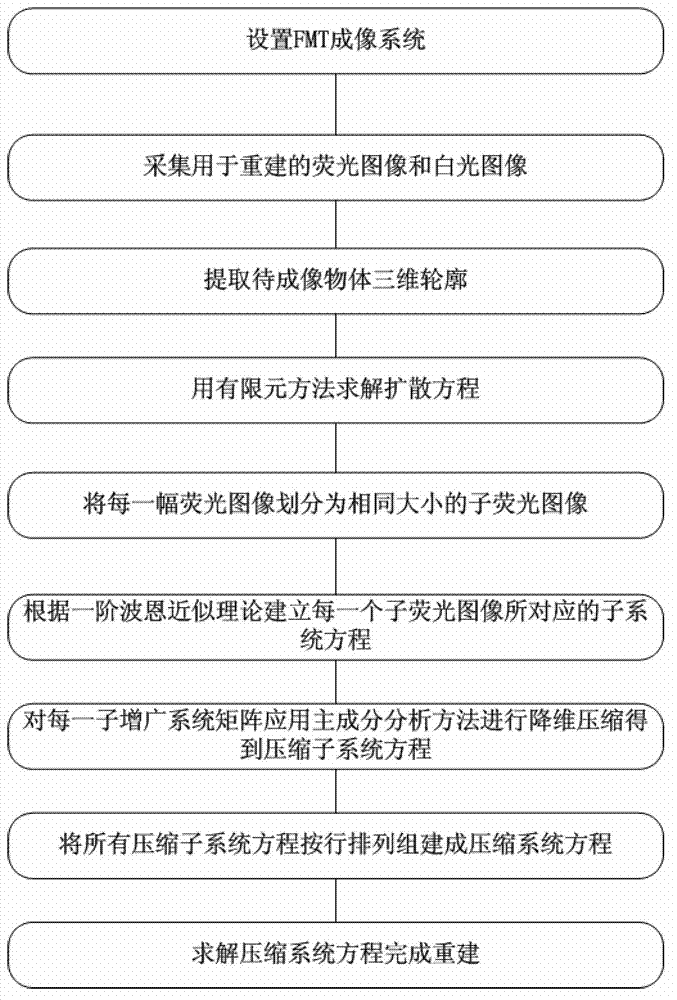
Large-data-size fluorescent molecule tomography reconstruction method
InactiveCN102871646AReduce the reconstruction effectReduce computing timeImage codingDiagnostic recording/measuringFluorescenceReconstruction method
The invention relates to a large-data-size fluorescent molecule tomography reconstruction method which comprises the following steps: acquiring a fluorescence picture and a white light picture of a to-be-imaged object by a full-angle free space FMT imaging system; extracting a borderline outline of the to-be-imaged object in each white light picture through an edge detection method, so as to obtain a projection outline picture; conducting back projection on protection outline pictures through a filter back reflection method in sequence to obtain a three-dimensional outline picture of the to-be-imaged object; solving the green function of a diffusion equation through a finite element method; dividing each fluorescence picture into a plurality of equal sub fluorescence picture; building a sub system equation corresponding to each sub fluorescence picture with the solved green function; compressing the corresponding sub system equation of each sub fluorescence picture divided from each fluorescence picture, then sequentially arranging the sub system equations to obtain a compression system equation; and solving the compression system equation to obtain the distribution of fluorescence markers in the to-be-imaged object. The large-data-size fluorescence molecule tomography reconstruction method is widely applied to the large-data-size fluorescent molecule tomography reconstruction.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Microseismic source location estimation method with high resolution using green's functions
InactiveUS20120116680A1Improve accuracyReliable functionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingHydraulic fracturingComputer science
The sources of microseismic hydraulic fracture events (“hydro-fracs”) are located for image mapping by the calculation of Green's functions G(x,z,t|x′,z′,0) which is estimated using, e.g., RVSP, VSP, SWD and / or surface data, with the Green's functions used as migration kernels with greater accuracy than the prior art techniques, e.g. the diffraction limit, because all of the natural arrivals in the data are utilized.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method of Evaluating the Interaction Between a Wavefield and a Solid Body
InactiveUS20070233437A1Computationally efficientComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputer scienceGreen's function
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Full wave modeling and simulations of the waveguide behavior of printed circuit boards using a broadband green's function technique
ActiveUS20160314231A1Fast simulationReduce extractionCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsPresent methodFull wave
A broadband Green's function computation technique that employs low wavenumber extraction on a modal summation is used to model the waveguide behavior of electronic components, systems, and interconnects on a printed circuit board. Use of the broadband technique permits discretizing the surface of the printed circuit board across a wide range of frequencies all at once. The broadband Green's function is also extended to via waveguides on circuit boards and power / ground plane waveguides of arbitrary shape. Such a method can analyze a given circuit board geometry over a broad frequency range several hundred times faster than is otherwise possible with existing commercial analysis tools. The present method is useful in electronic design automation for analyzing signal integrity and power integrity, reducing electromagnetic interference and ensuring electromagnetic compatibility.
Owner:TSANG LEUNG W +1
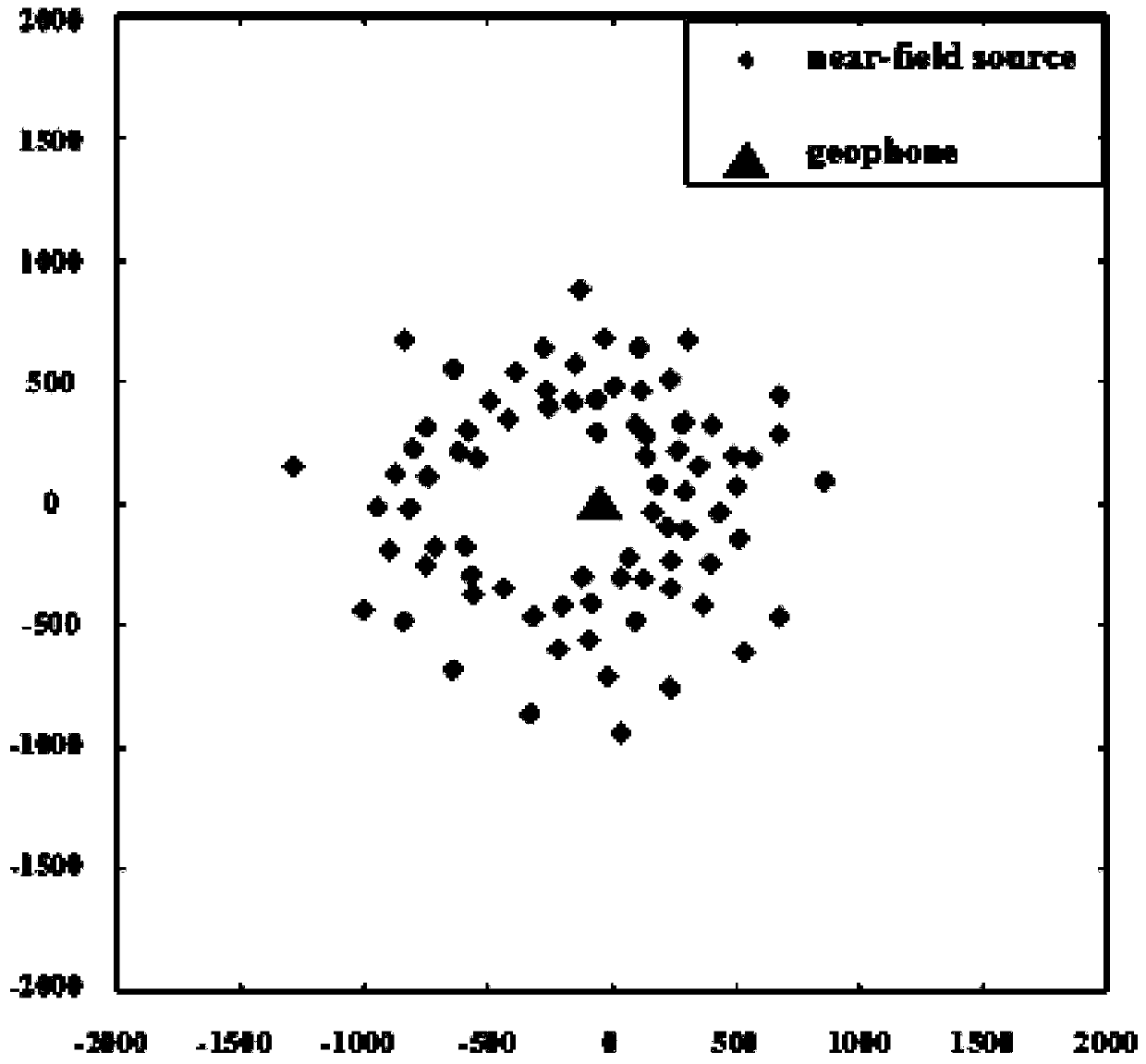
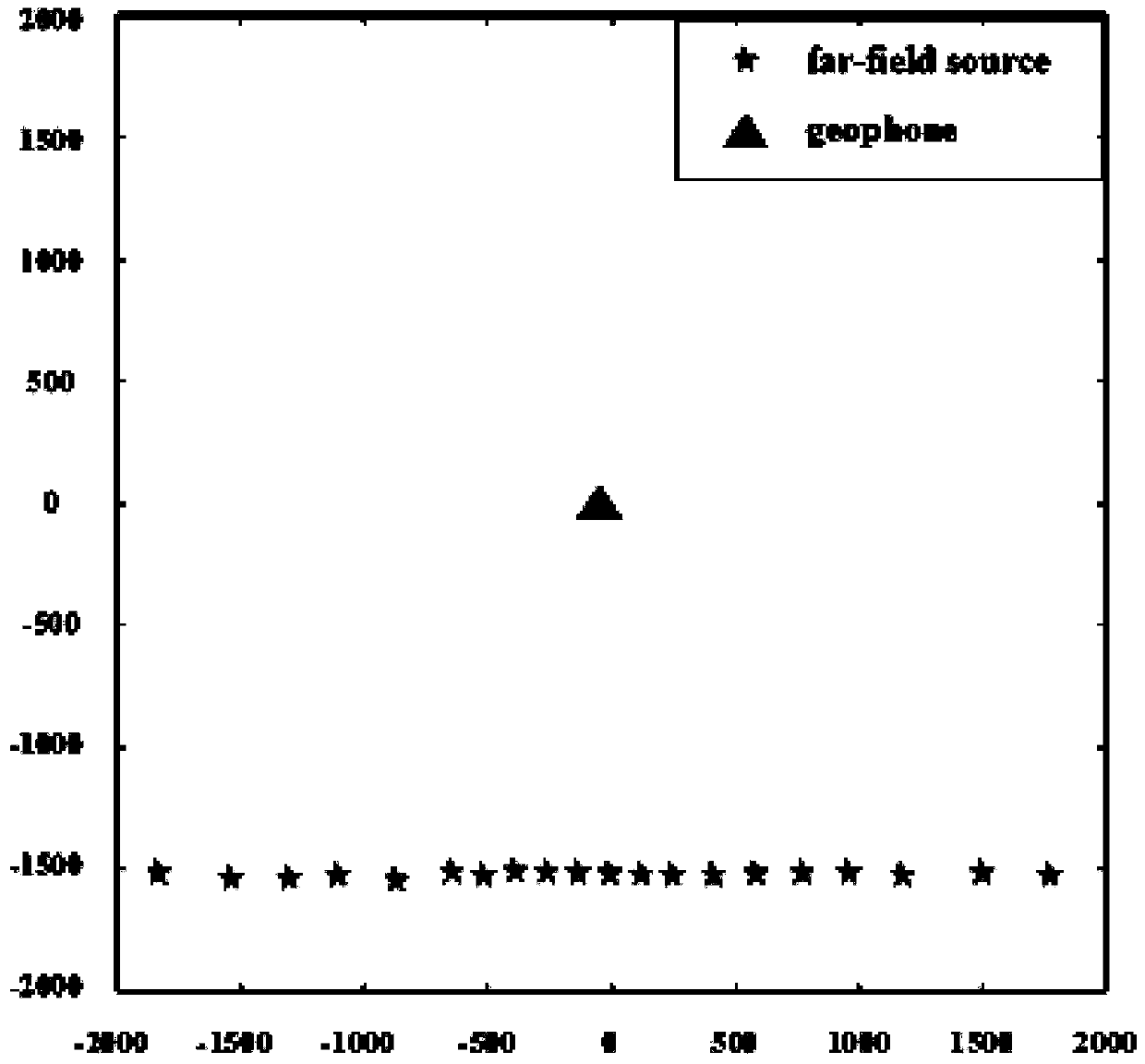
Desert seismic exploration random noise eliminating method based on noise modeling analysis
InactiveCN109991664AAccurate and reliable prior knowledgeFit closelySeismic signal processingPattern recognitionNoise field
The invention relates to a desert seismic exploration random noise eliminating method based on noise modeling analysis, and belongs to the technical field of physical geography. The desert seismic exploration random noise eliminating method comprises the following steps: building a noise-containing synthetic record; building desert seismic exploration random noise model; taking a natural noise function, a near-field human noise function, and a far-field human noise function as excitation functions of the wave function; solving a wave equation with a green function to obtain a noise field of the natural noise, a noise field of a near-field human noise and a noise field of a far-field human noise; overlapping the noise field of the natural noise, the noise field of the near-field human noiseand the noise field of the far-field human noise to obtain a desert area random noise model; and determining a proper filtering method for filtering and denoising by using the random noise model. Through adoption of the desert seismic exploration random noise eliminating method, a shearlet variable threshold denoising method finally determined based on the noise modeling is suitable for eliminating the desert seismic exploration noise; the signal-to-noise ratio of the seismic exploration data is improved; the effective signal can be recovered accurately; and the interpretation of subsequent seismic data is effectively facilitated.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com