Patents
Literature
52 results about "Laser pulse duration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
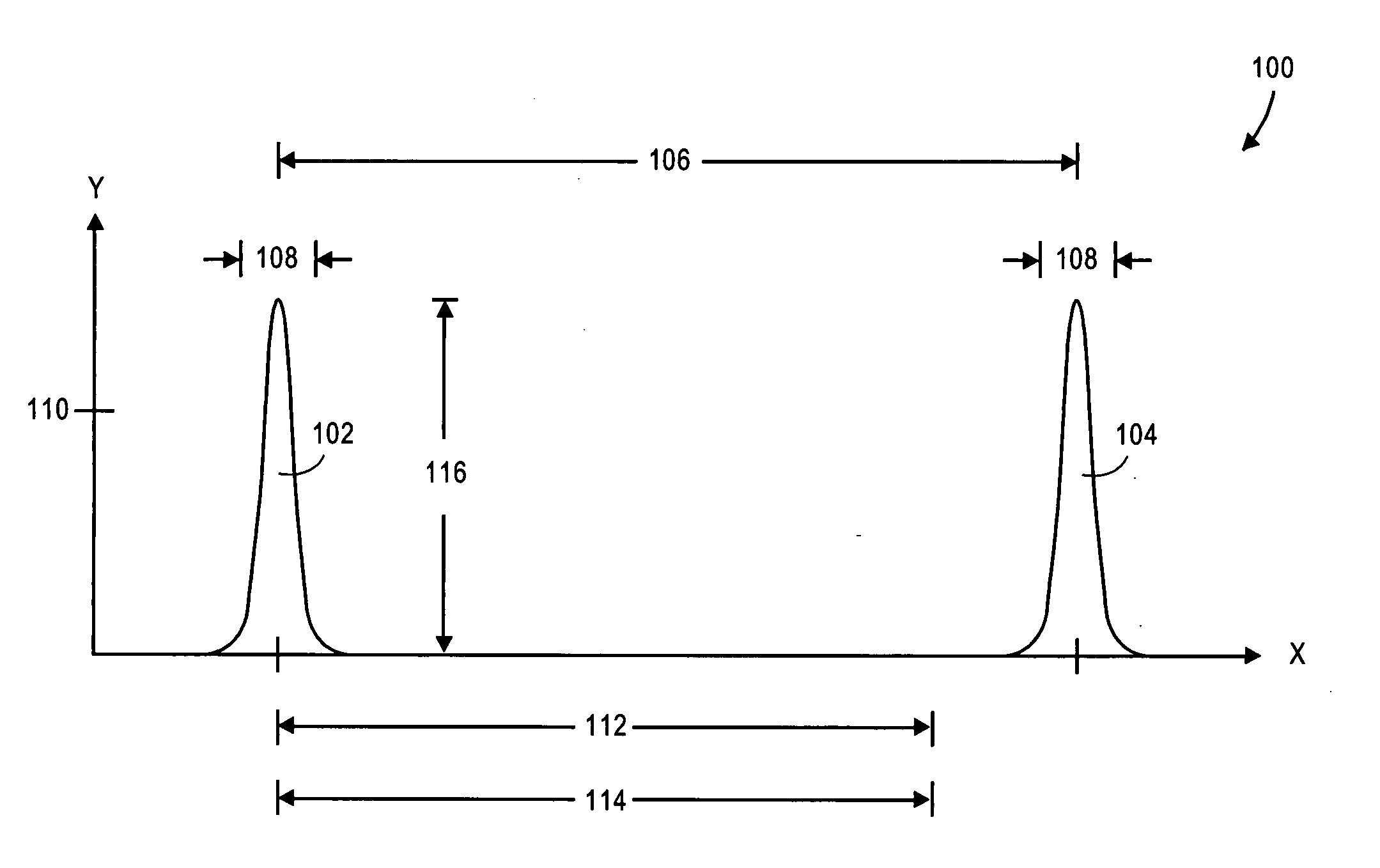
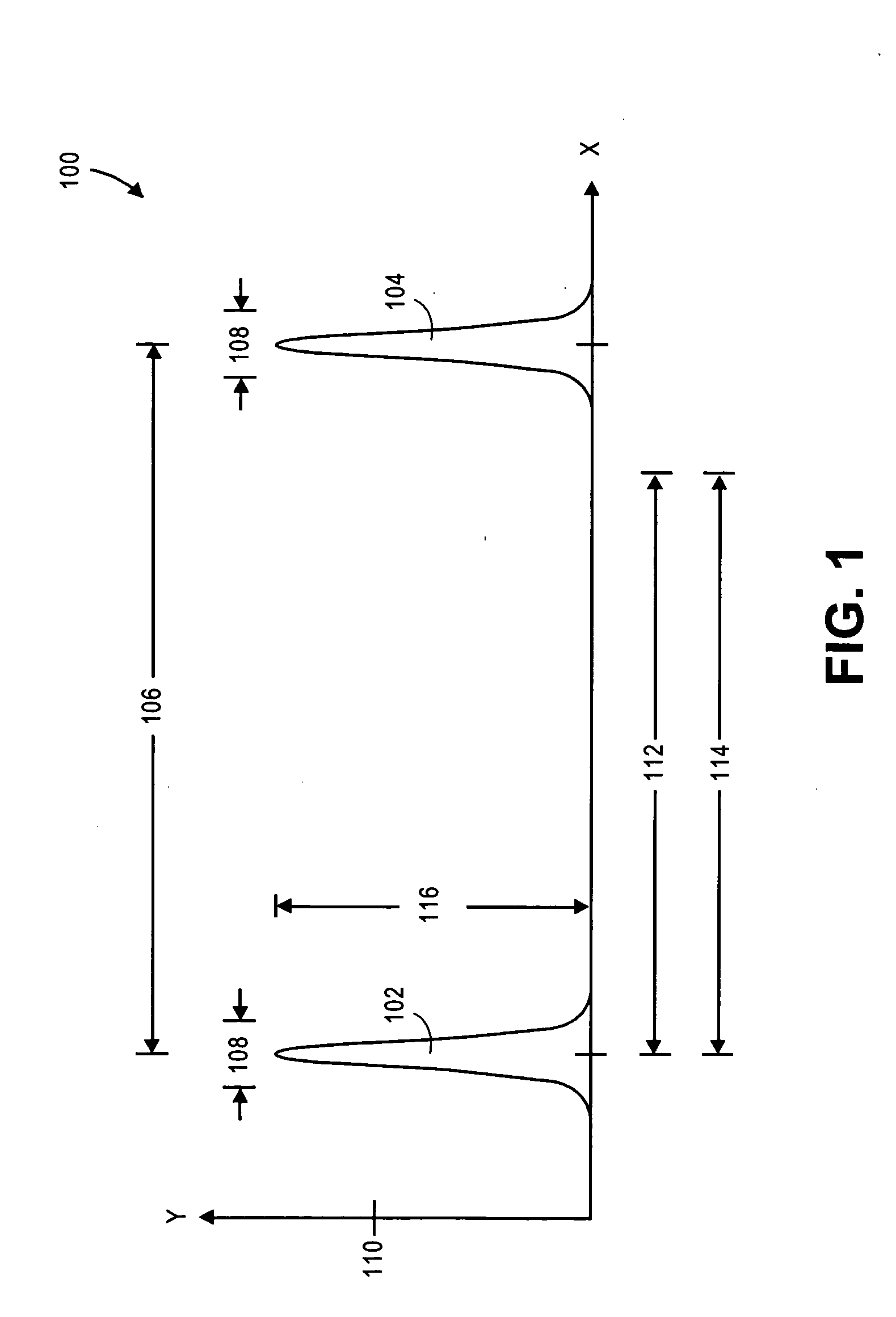
A pulsed laser emits light in a series of short pulses, each having a duration of 25.0 ms. The average power of each pulse is 5.00 mW, and the wavelength of the light is 633 nm.
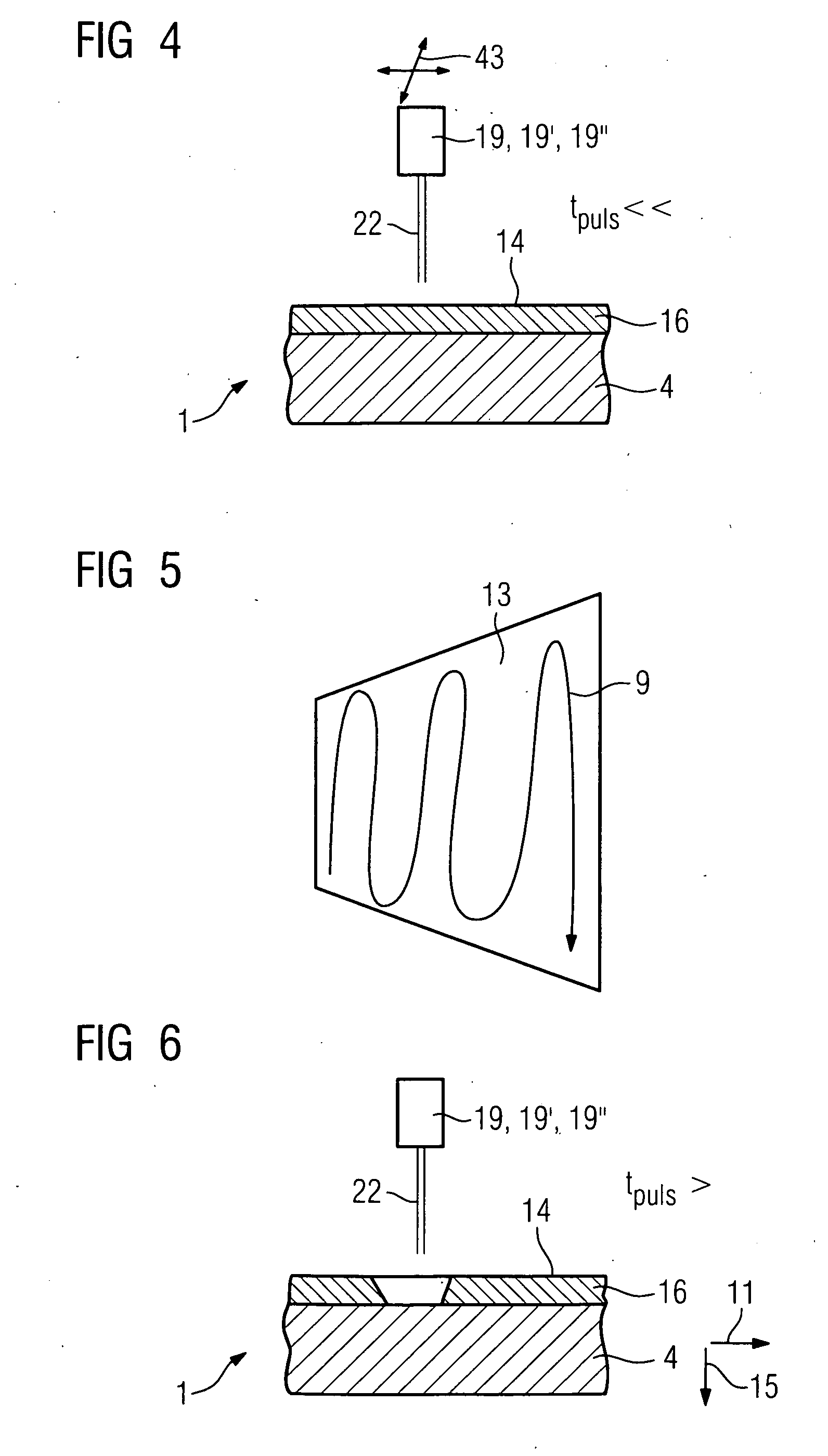
Laser ablation method
InactiveUS20060088984A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusLaser scribingLaser pulse duration
A combination of specific laser pulse durations and repetition rates are incorporated into a semiconductor wafer laser scribing / dicing process. The disclosed combination can reduce factors that contribute to thermal effects, explosive melting and evaporation, and laser / plasma interactions, thereby reducing problems with microcracks, delamination, and particles that can affect semiconductor die yields and reliability.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Tissue treatment device and method
InactiveUS7041094B2High peak powerReduce peak powerSurgical instruments for heatingLight therapyHair removalLaser light
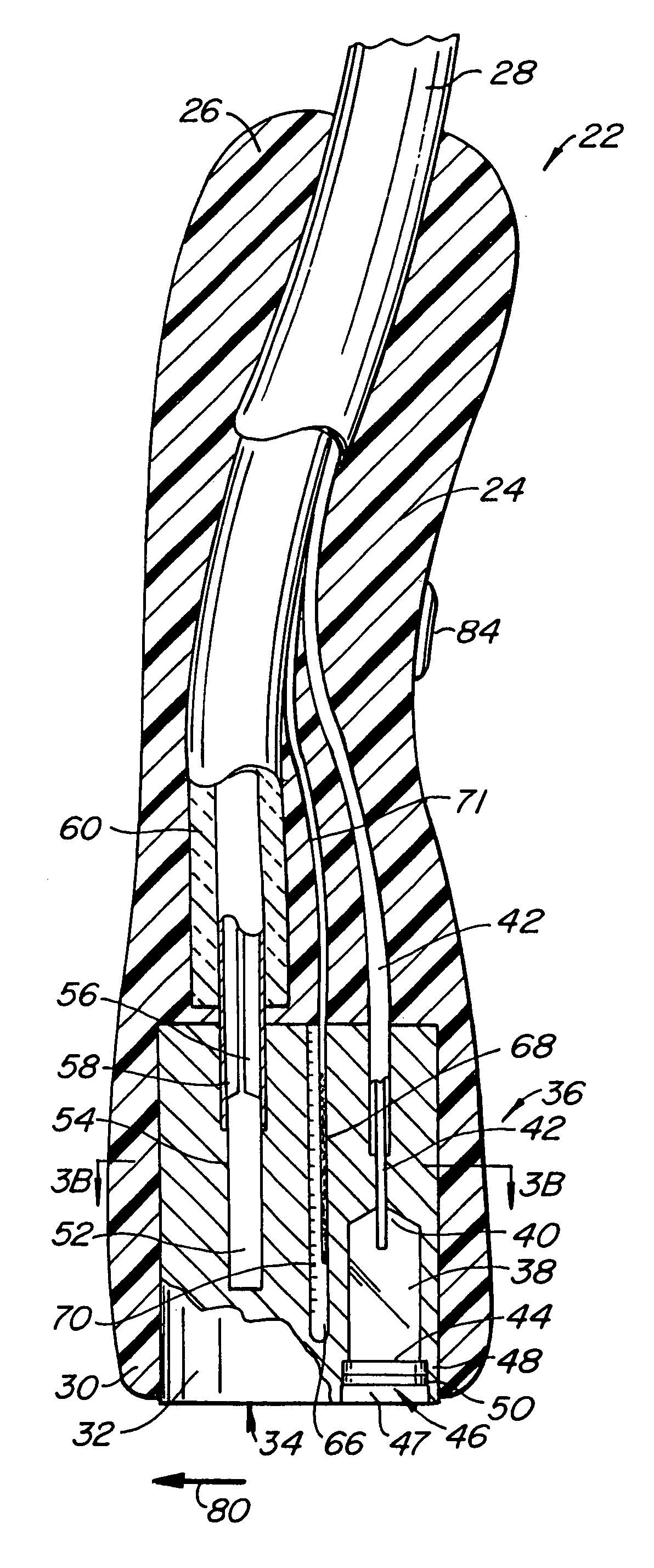
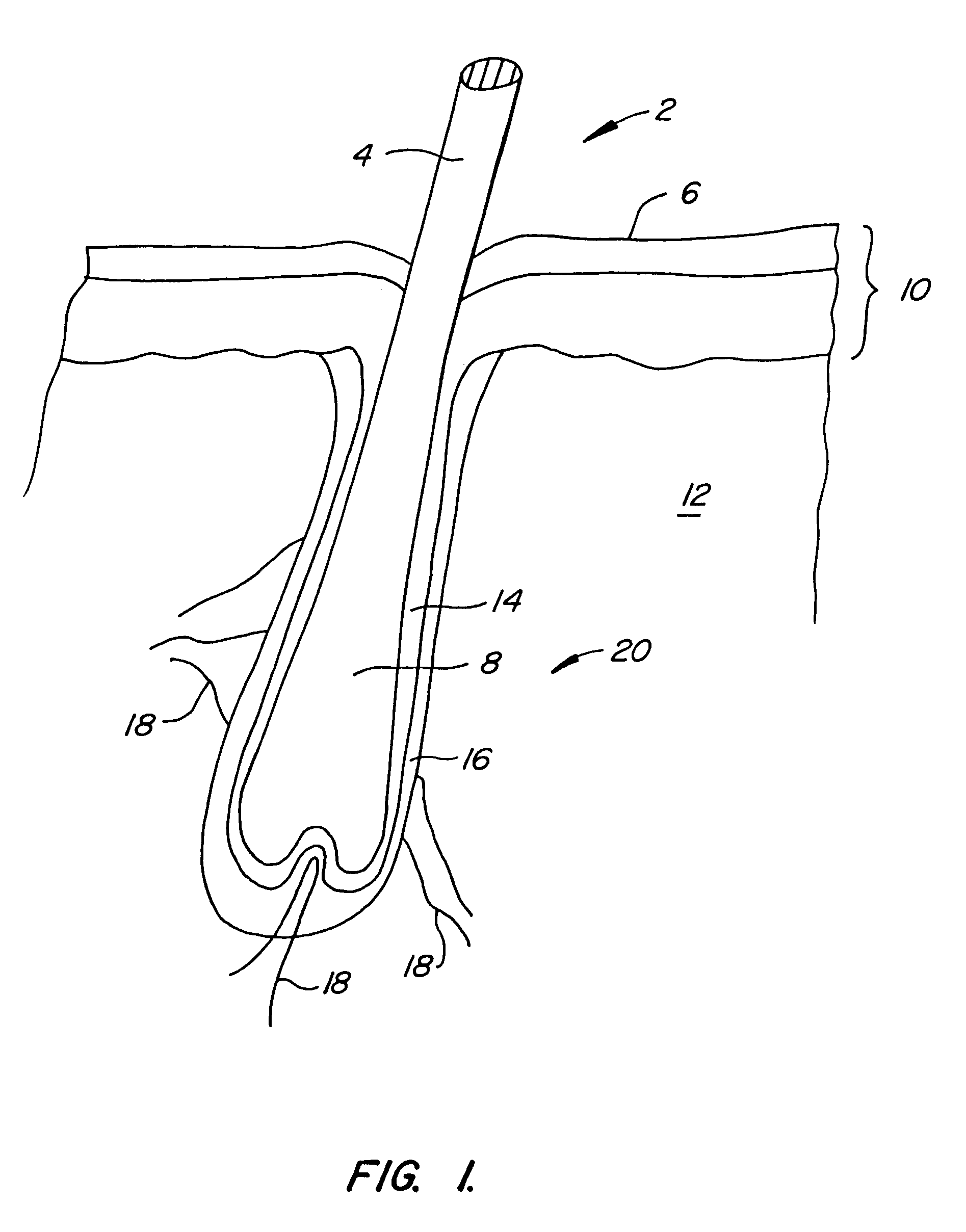
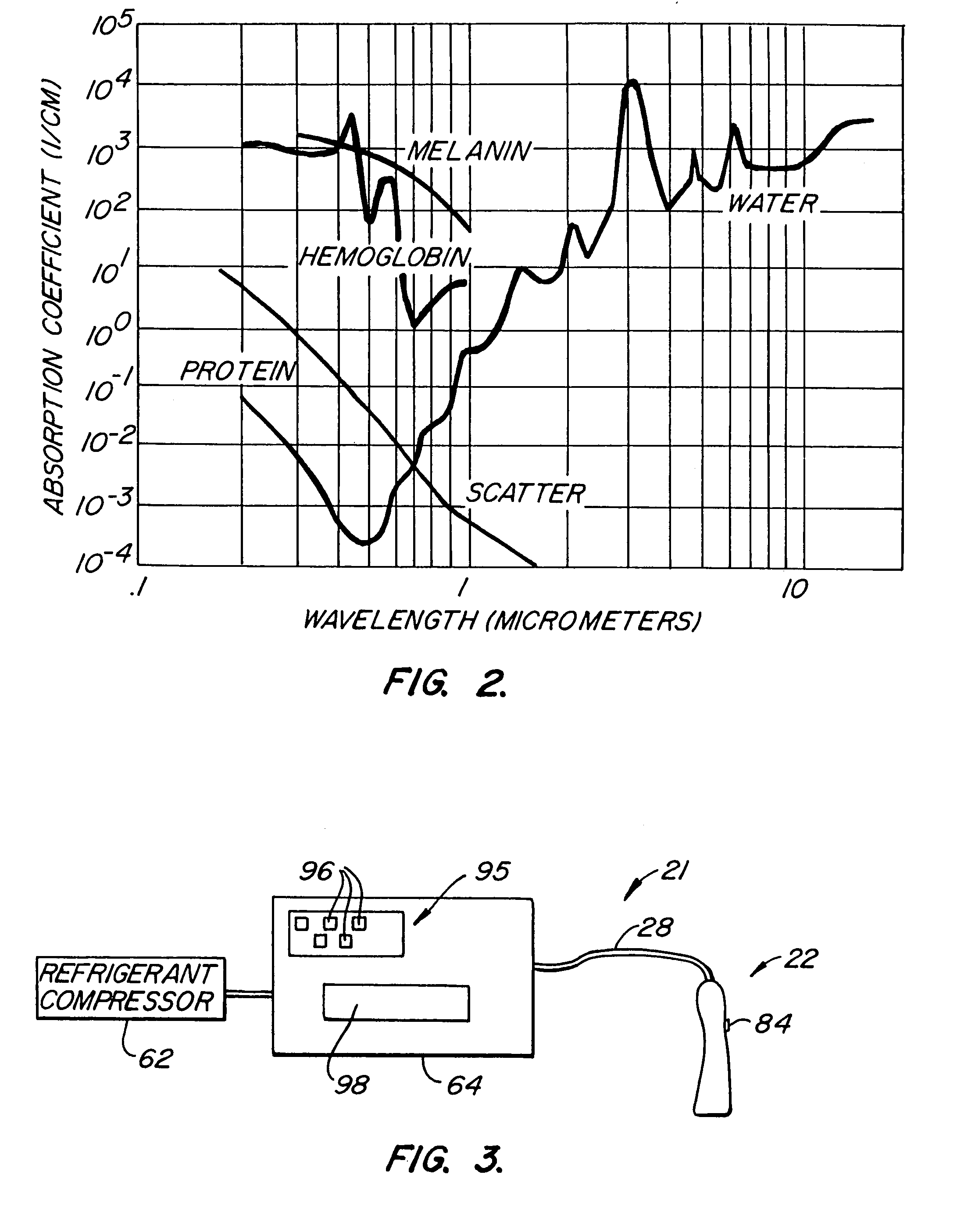
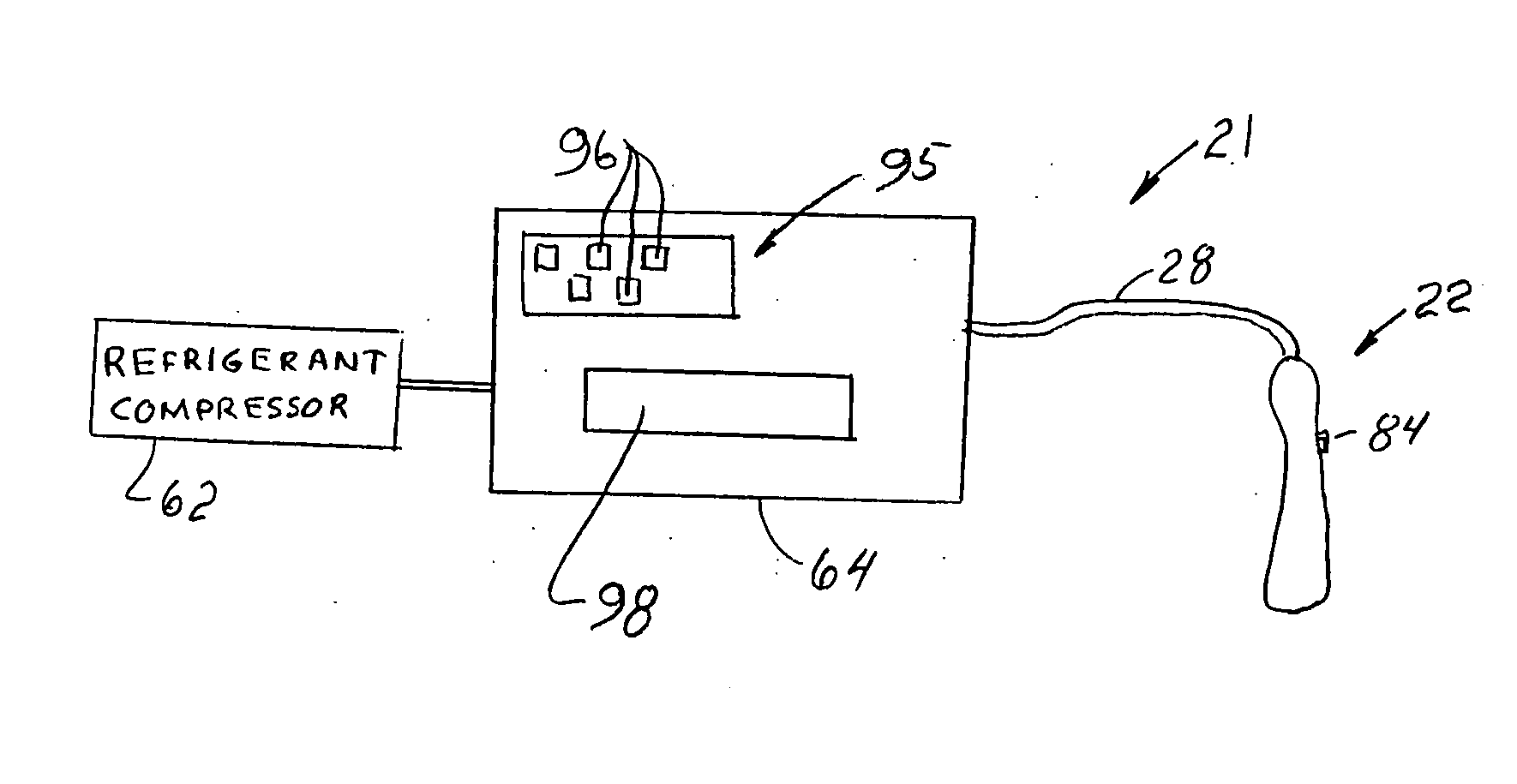
A hair removal device (22) includes a cooling surface (34) which is used to contact the skin (6) prior to exposure to hair tissue-damaging laser light (74) passing from a radiation source (36) through a recessed window (46). The window is laterally offset from the cooling surface and is spaced apart from the cooling surface in a direction away from the patient's skin to create a gap between the window and the skin. The window preferably includes both an inner window (46) and an outer, user-replaceable window (48). The laser-pulse duration is preferably selected according to the general diameter of the hair.
Owner:CUTERA
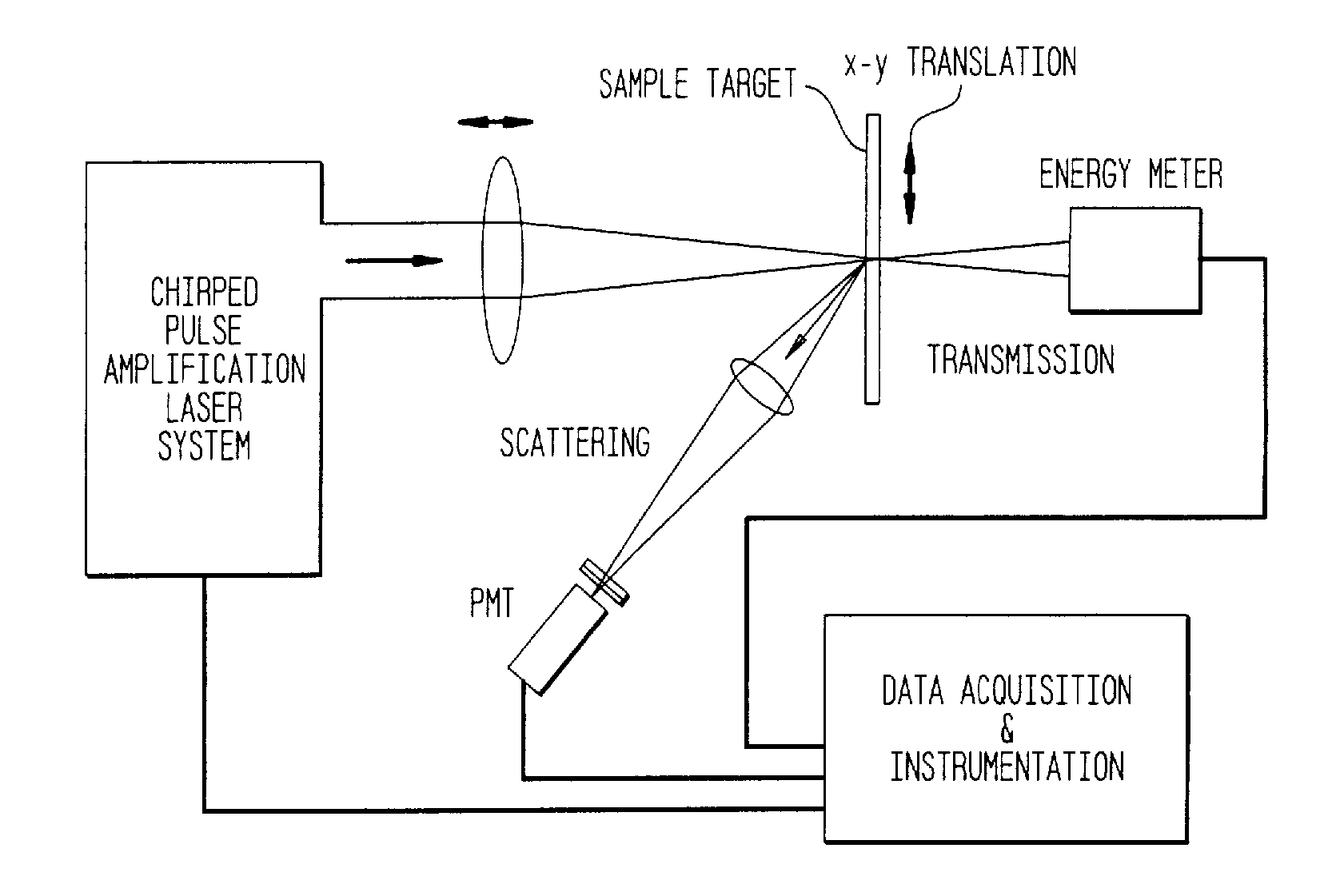
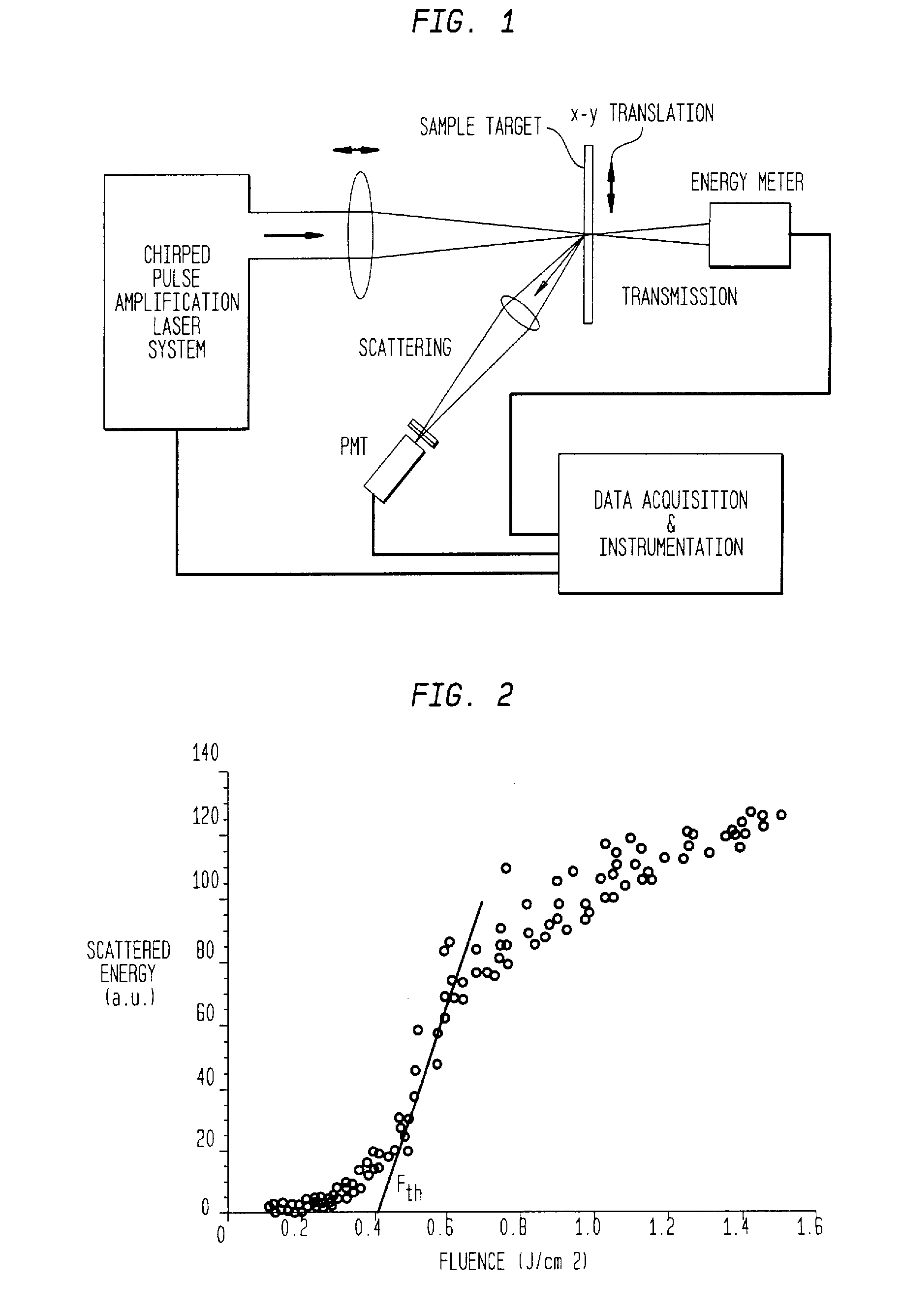
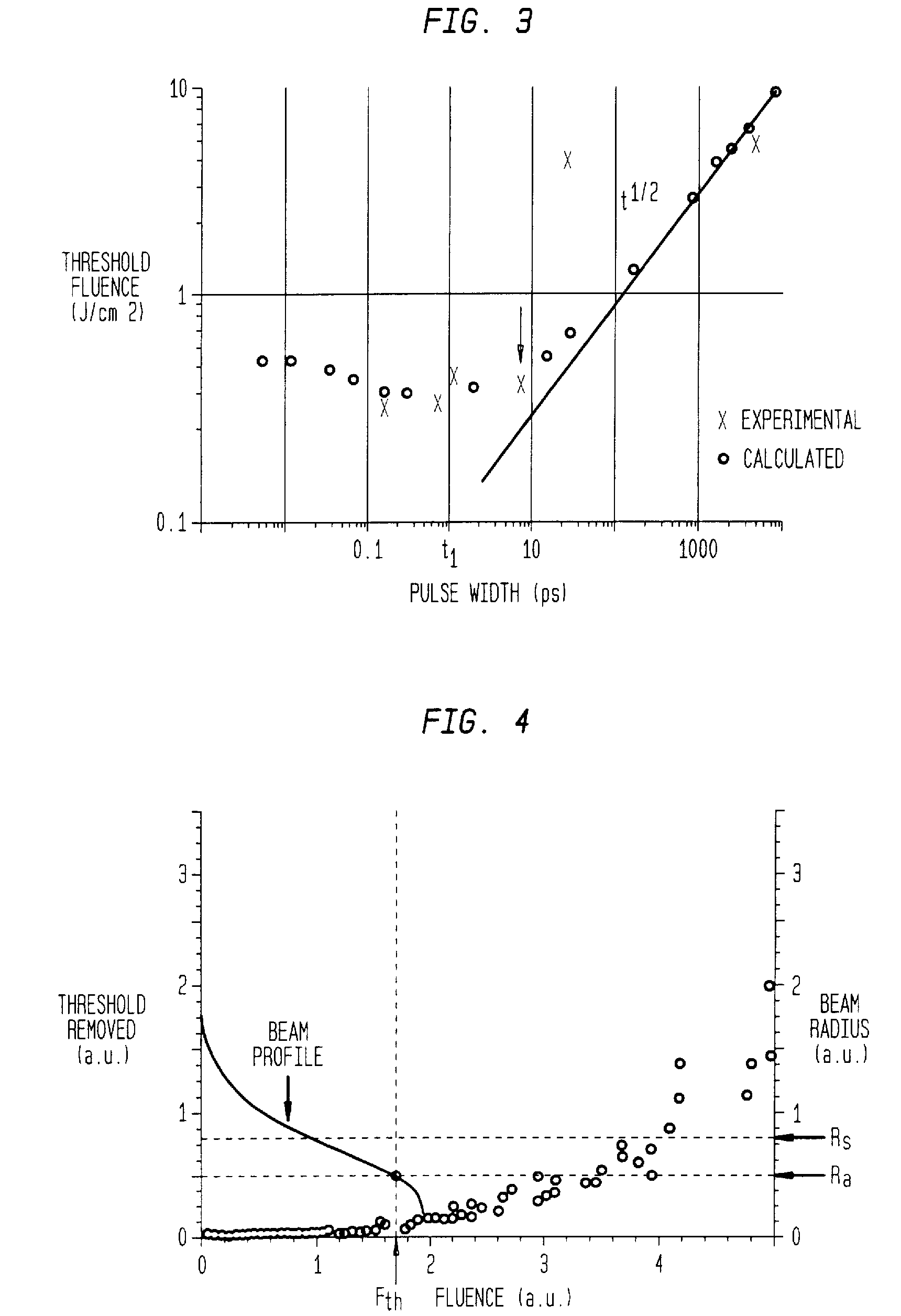
Method for minimizing sample damage during the ablation of material using a focused ultrashort pulsed laser beam
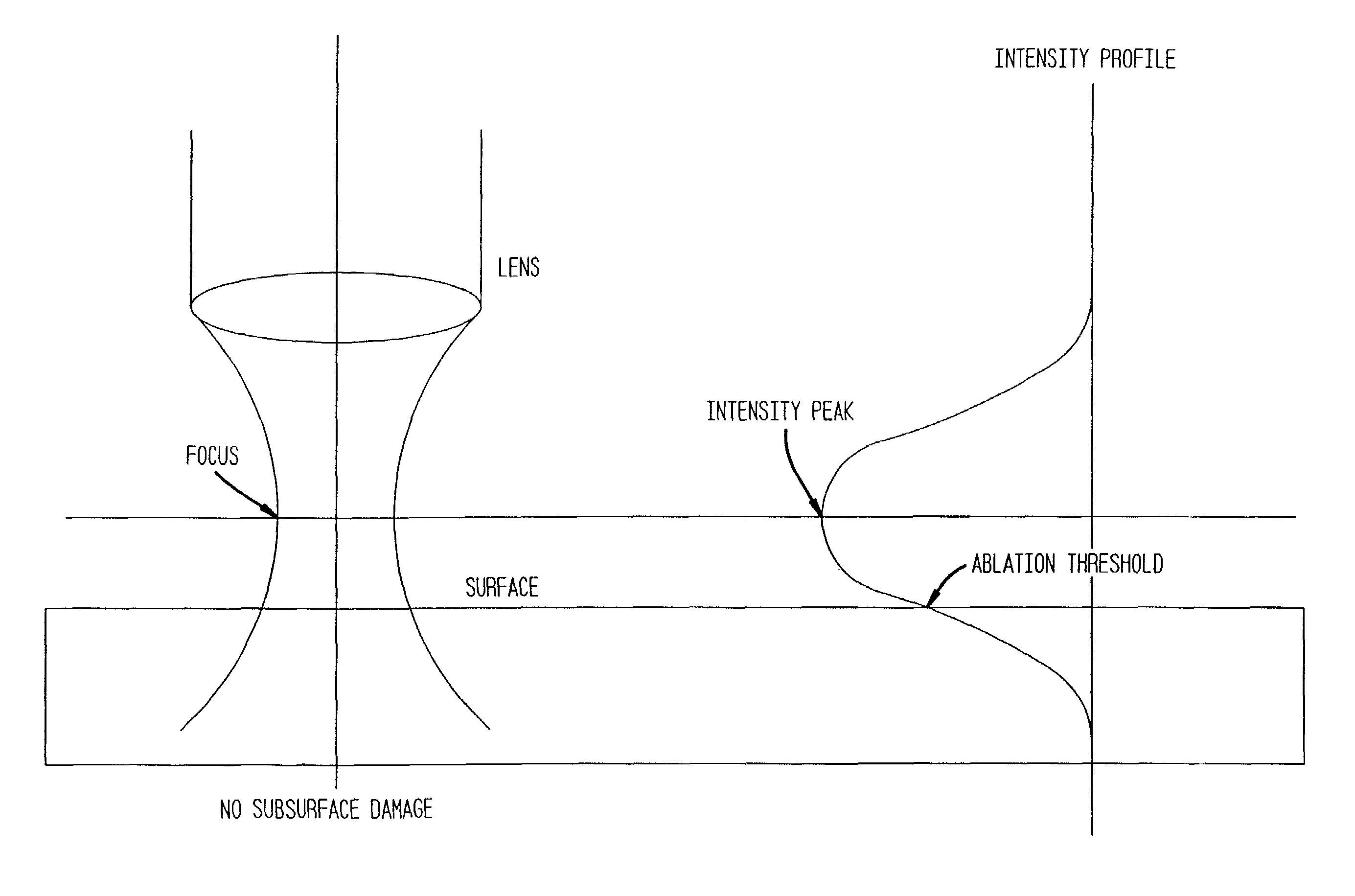
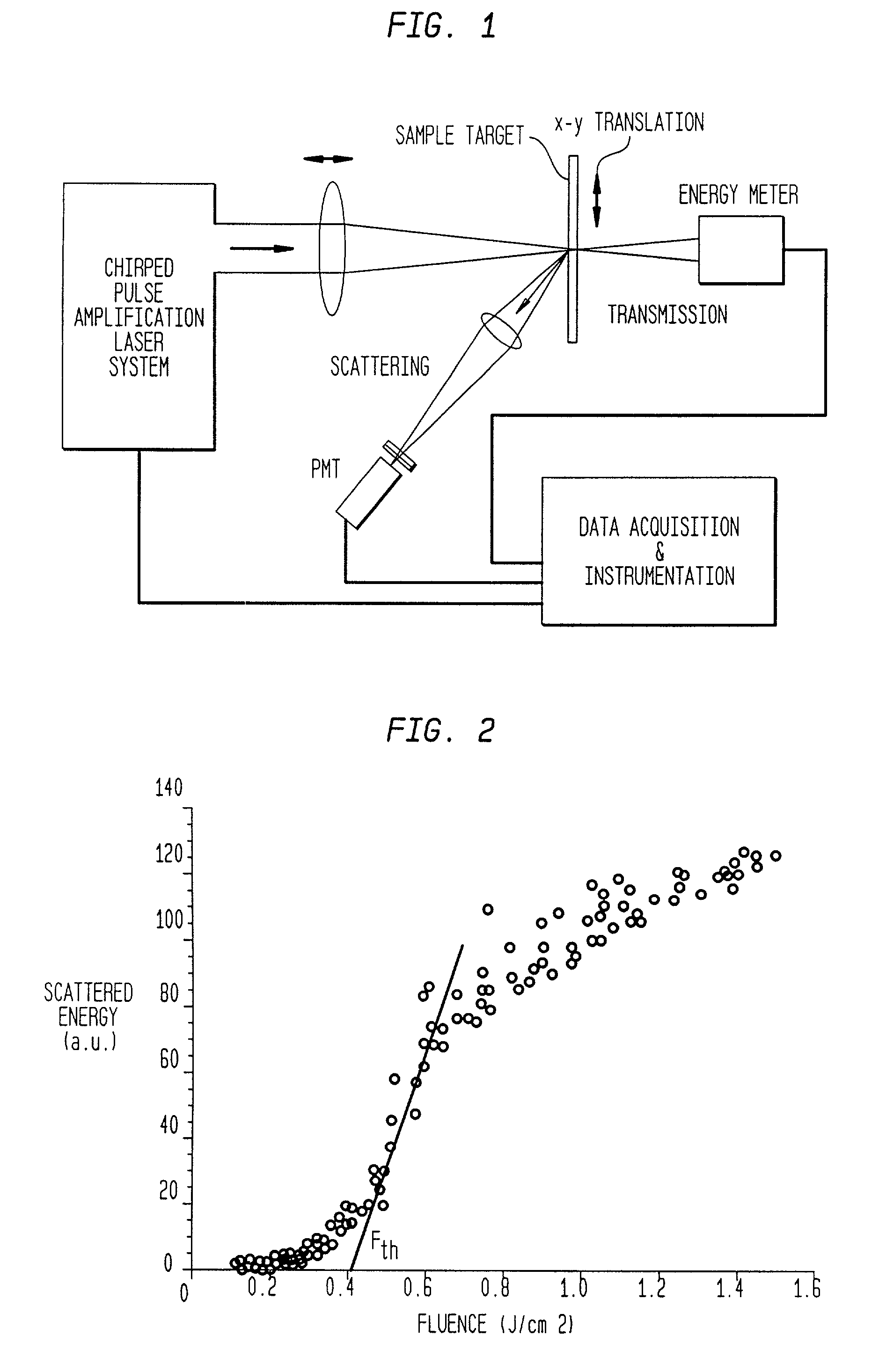
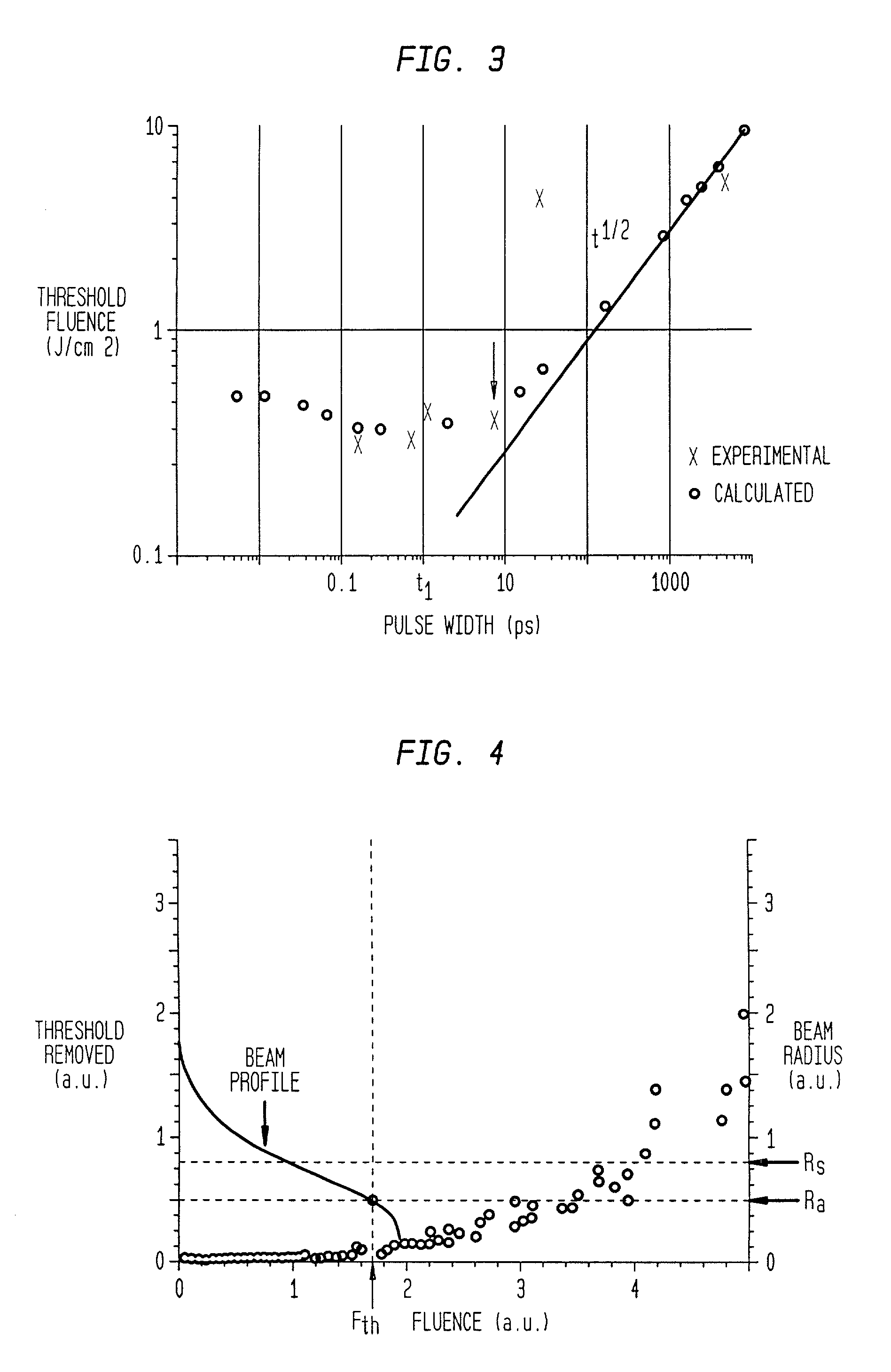
In one aspect the invention provides a method for laser induced breakdown of a material with a pulsed laser beam where the material is characterized by a relationship of fluence breakdown threshold (Fth) versus laser beam pulse width (T) that exhibits an abrupt, rapid, and distinct change or at least a clearly detectable and distinct change in slope at a predetermined laser pulse width value. The method comprises generating a beam of laser pulses in which each pulse has a pulse width equal to or less than the predetermined laser pulse width value. The beam is focused above the surface of a material where laser induced breakdown is desired. The region of least confusion (minimum beam waist or average spot size) is above the surface of the material in which laser induced breakdown is desired since the intensity of the beam falls off in the forward direction, preferably the region of the beam at or within the surface is between the region of least confusion and sufficient to remove material and the minimum intensity necessary for laser induced breakdown of the material to be removed, most preferably the region of minimum intensity is disposed at the surface of the material to be removed. The beam may be used in combination with a mask in the beam path. The beam or mask may be moved in the x, y, and Z directions to produce desired features. The technique can produce features smaller than the spot size and Rayleigh range due to enhanced damage threshold accuracy in the short pulse regime.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
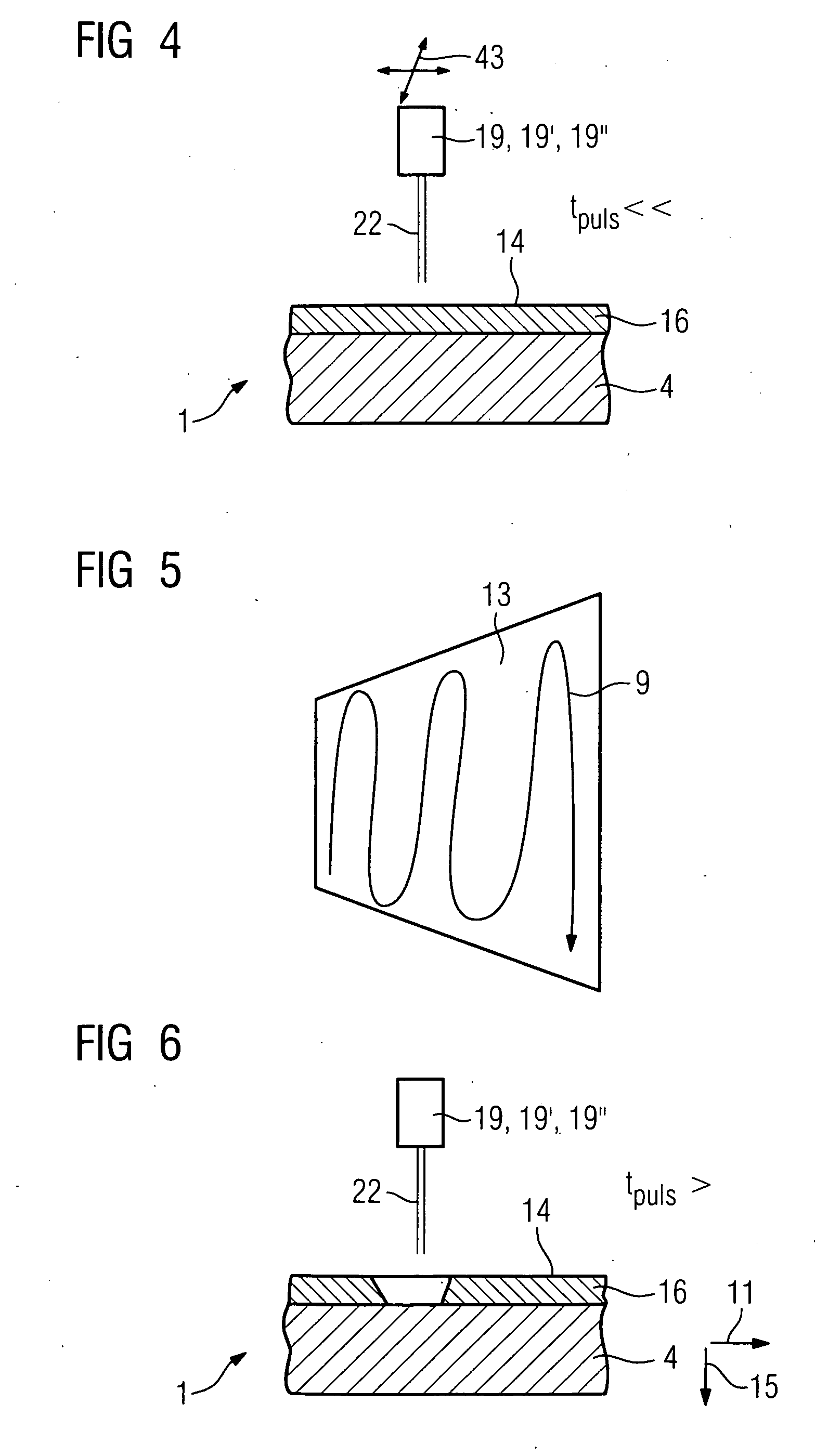
Method For Producing A Hole
InactiveUS20100147812A1Maintain good propertiesLaser beam welding apparatusOptoelectronicsLaser pulse duration
There is described a method for producing a hole using e.g. a lasers, wherein short laser pulse durations are used. The laser pulse durations are varied, short laser pulse durations being utilized only in the area to be removed in which an influence on the penetration behavior and discharge behavior is noticeable while longer pulse durations of >0.4 ms are used. This is the case for the inner surface of a diffuser of a hole, for example, which can be produced very accurately by means of short laser pulse durations.
Owner:CHROMALLOY GAS TURBINE +1
Method and apparatus for holographic recording of fast phenomena
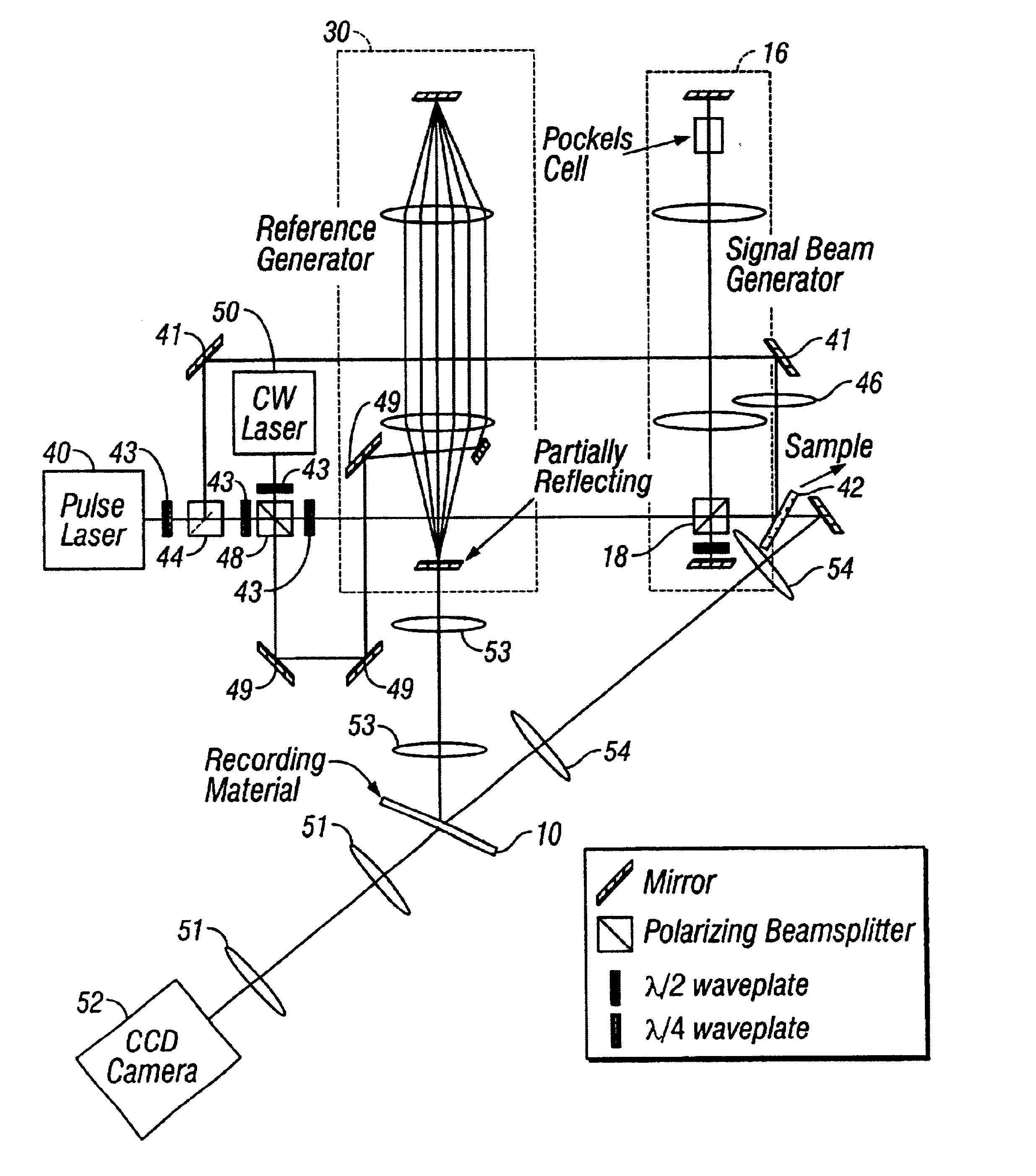
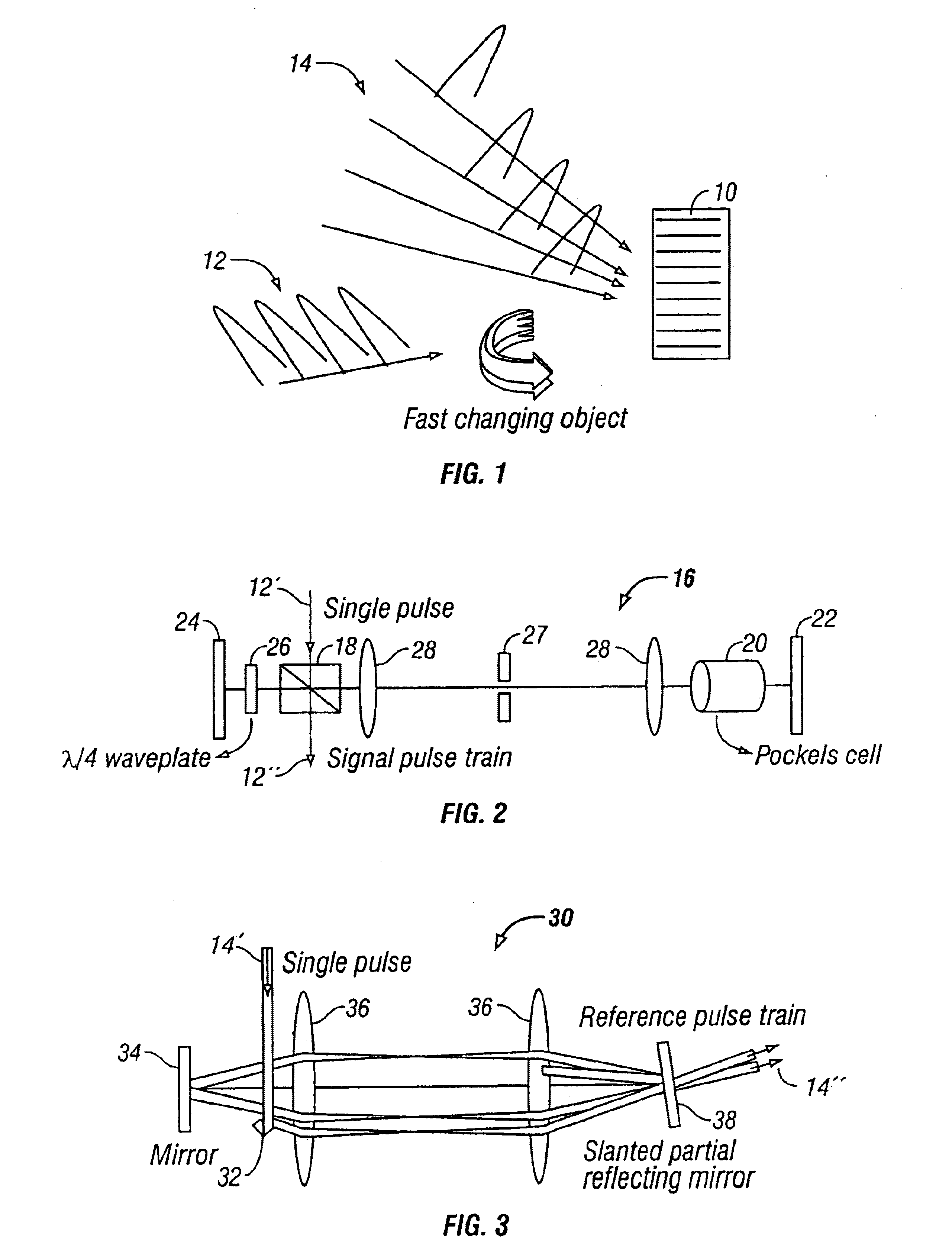
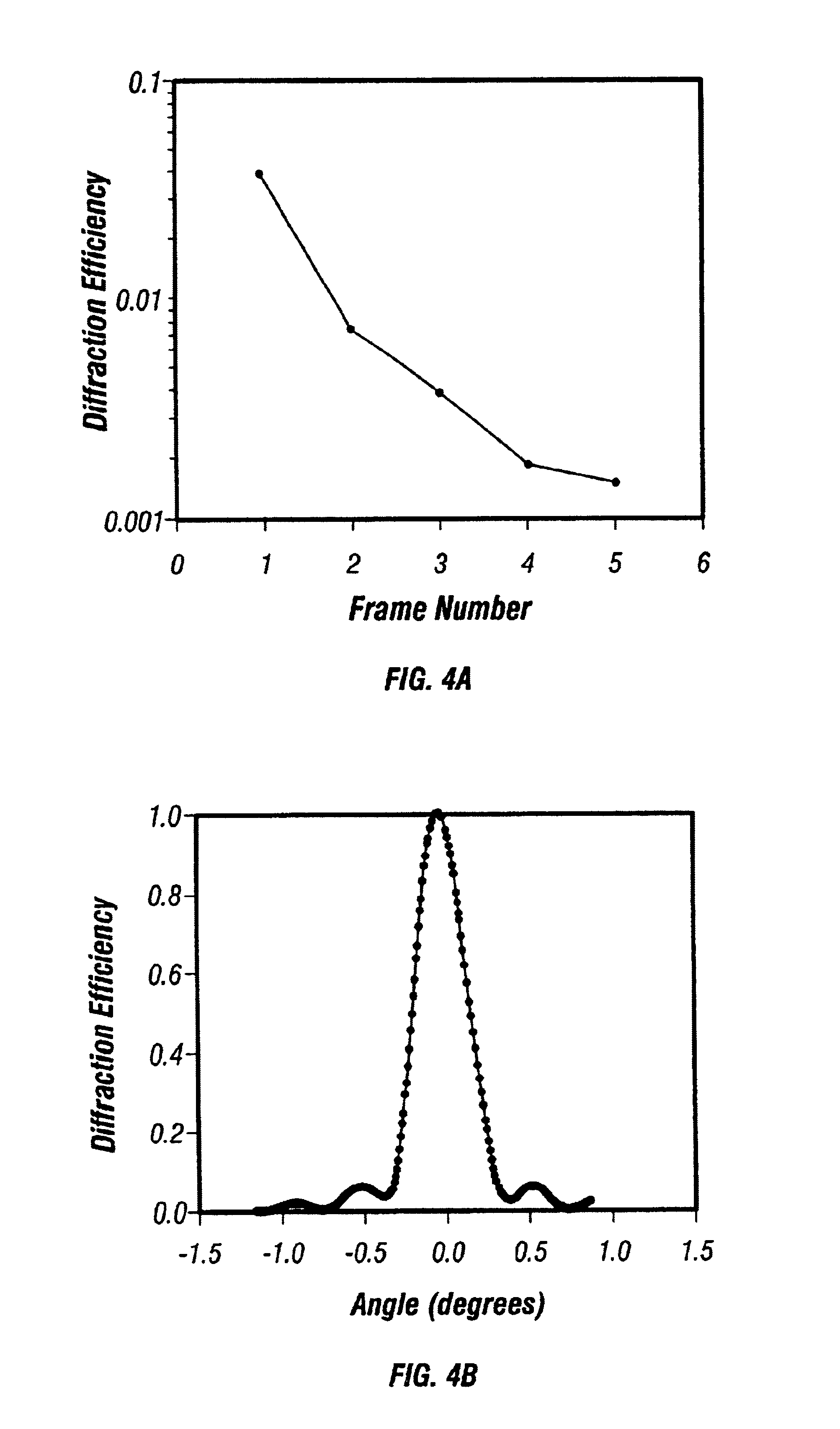
InactiveUS6862121B2Television system detailsHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesShock waveMultiplexing
Holographic methods for recording fast movies whose speed is limited by the laser pulse duration if the recording material has sufficient sensitivity to reliably record a frame of the fast event with a single pulse. The method we describe uses the selectivity of multiplexed holograms to resolve frames that are recorded with adjacent pulses. Specially designed pulse generators are used to generate the signal and reference pulse trains. We experimentally demonstrate the system by making movies of laser induced shock waves with a temporal resolution of 5.9 ns, limited by the pulse width of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser used in the experiments.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
A method of making at least one hole in a transparent body and devices made by this method
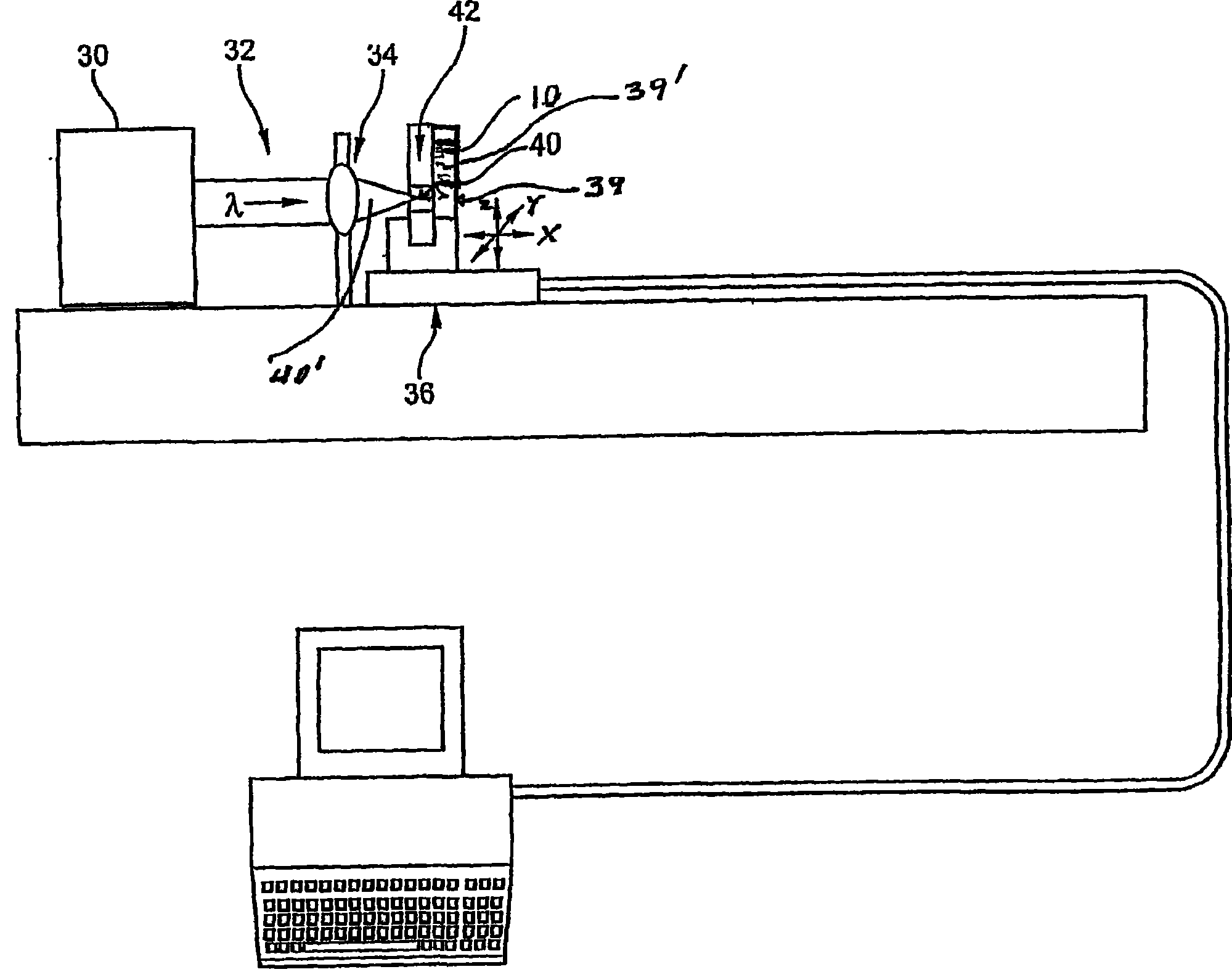
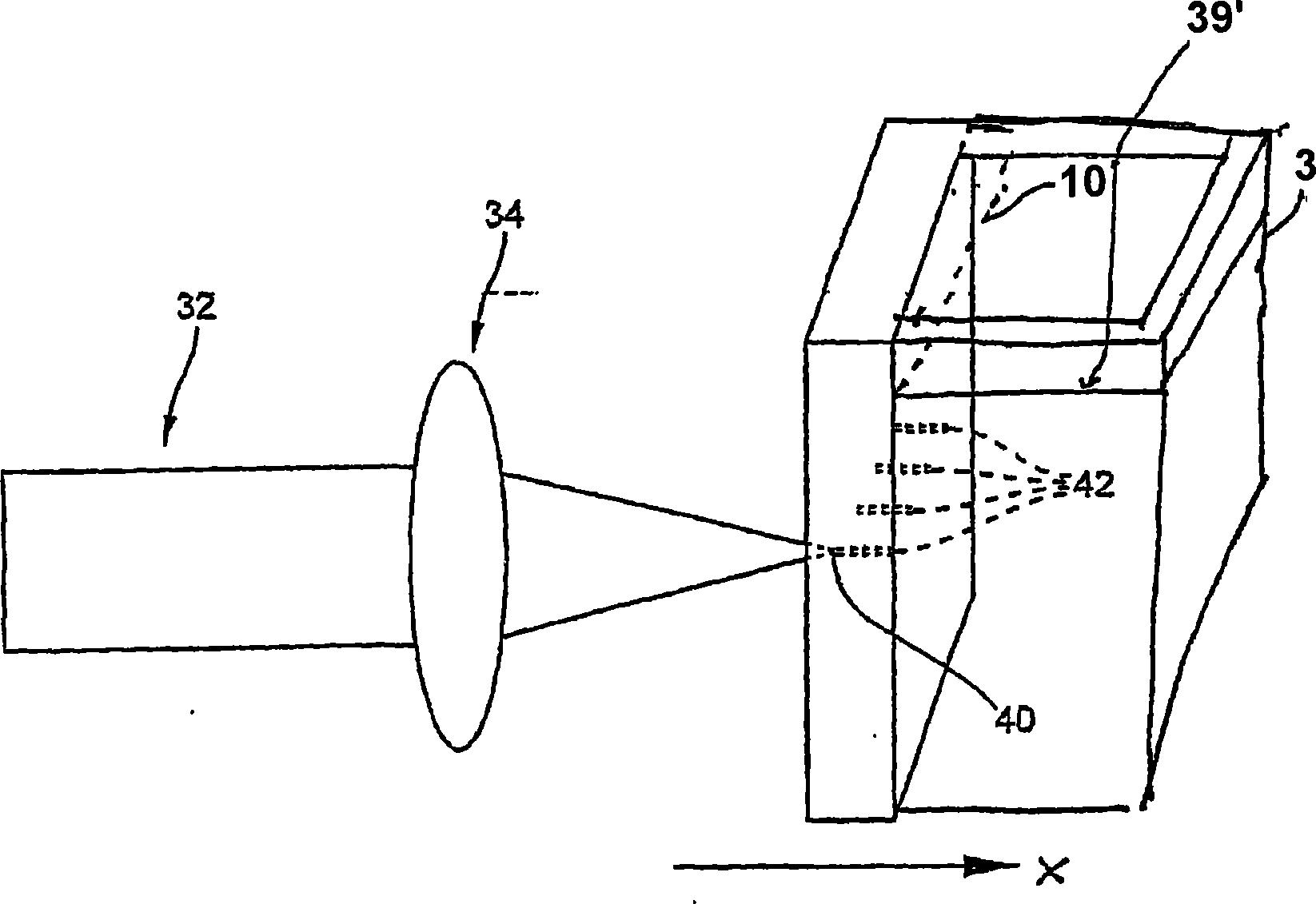
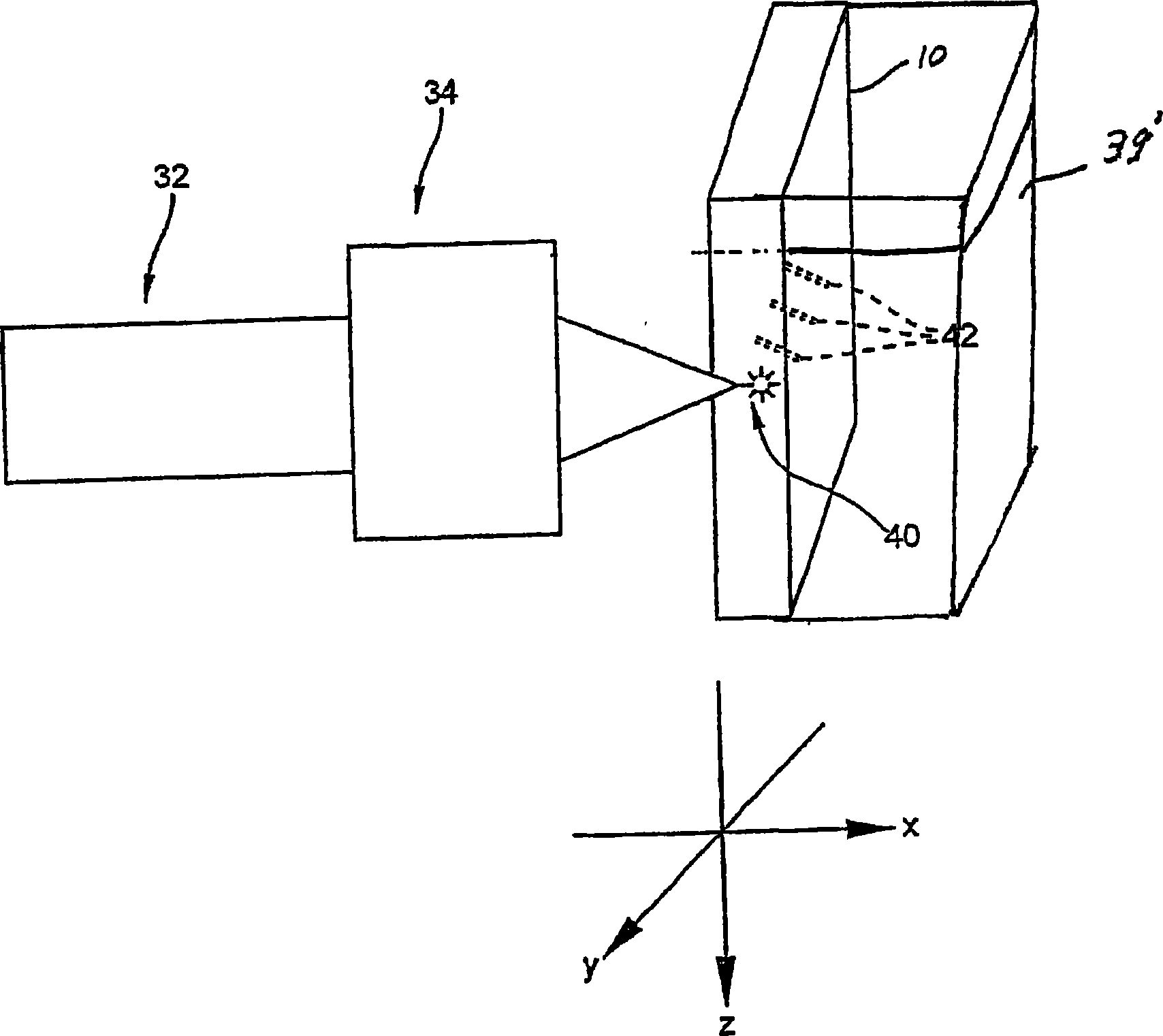
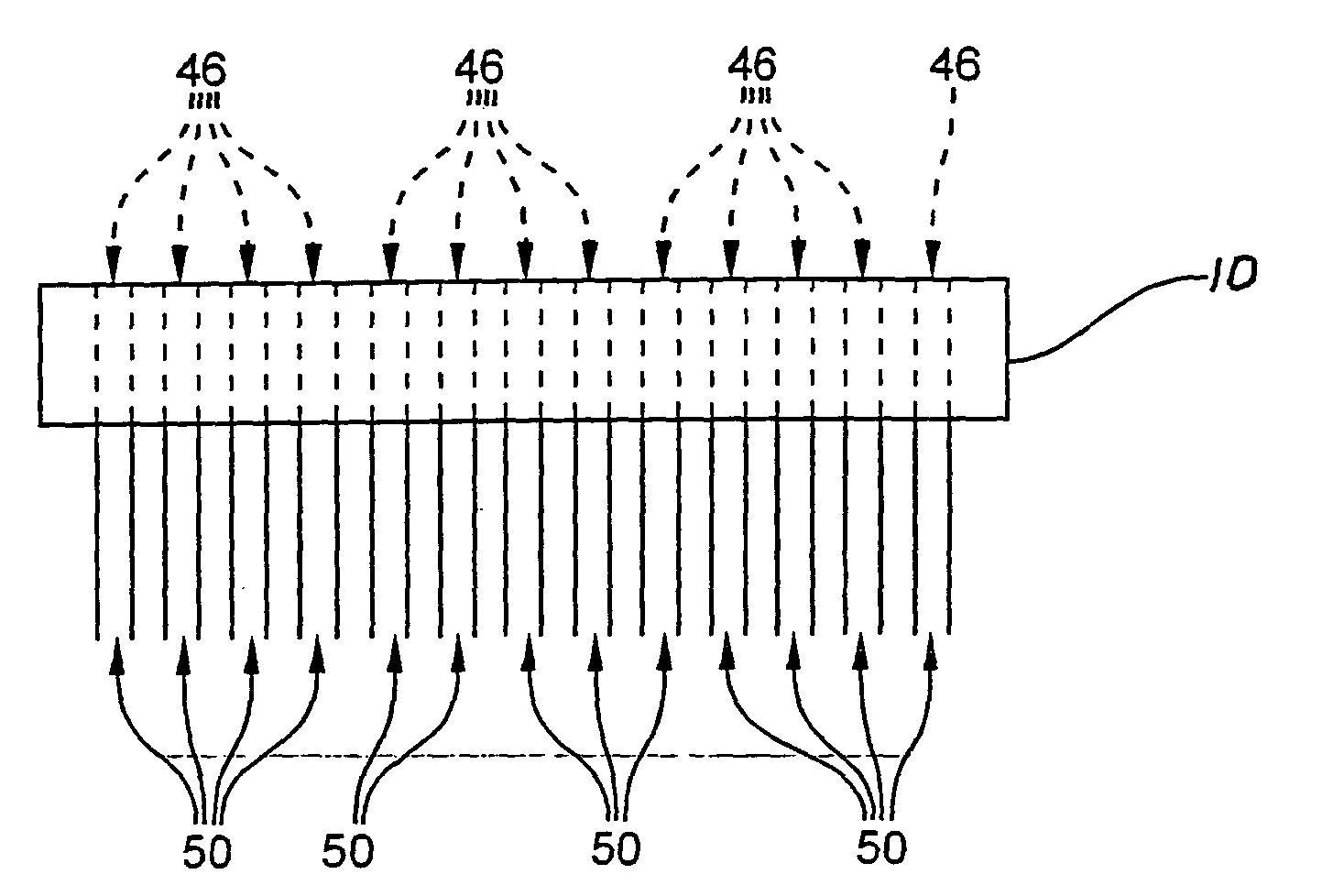
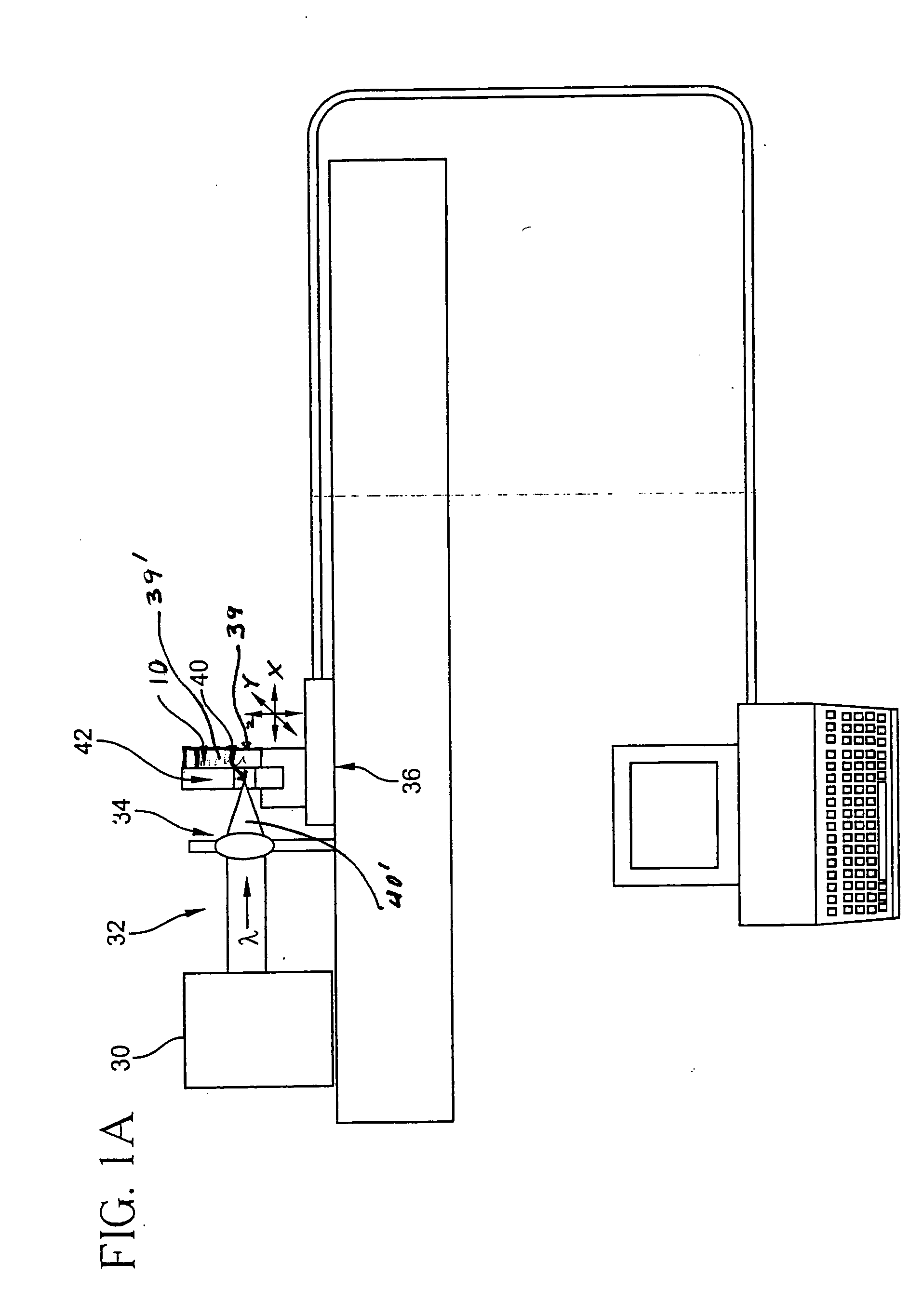
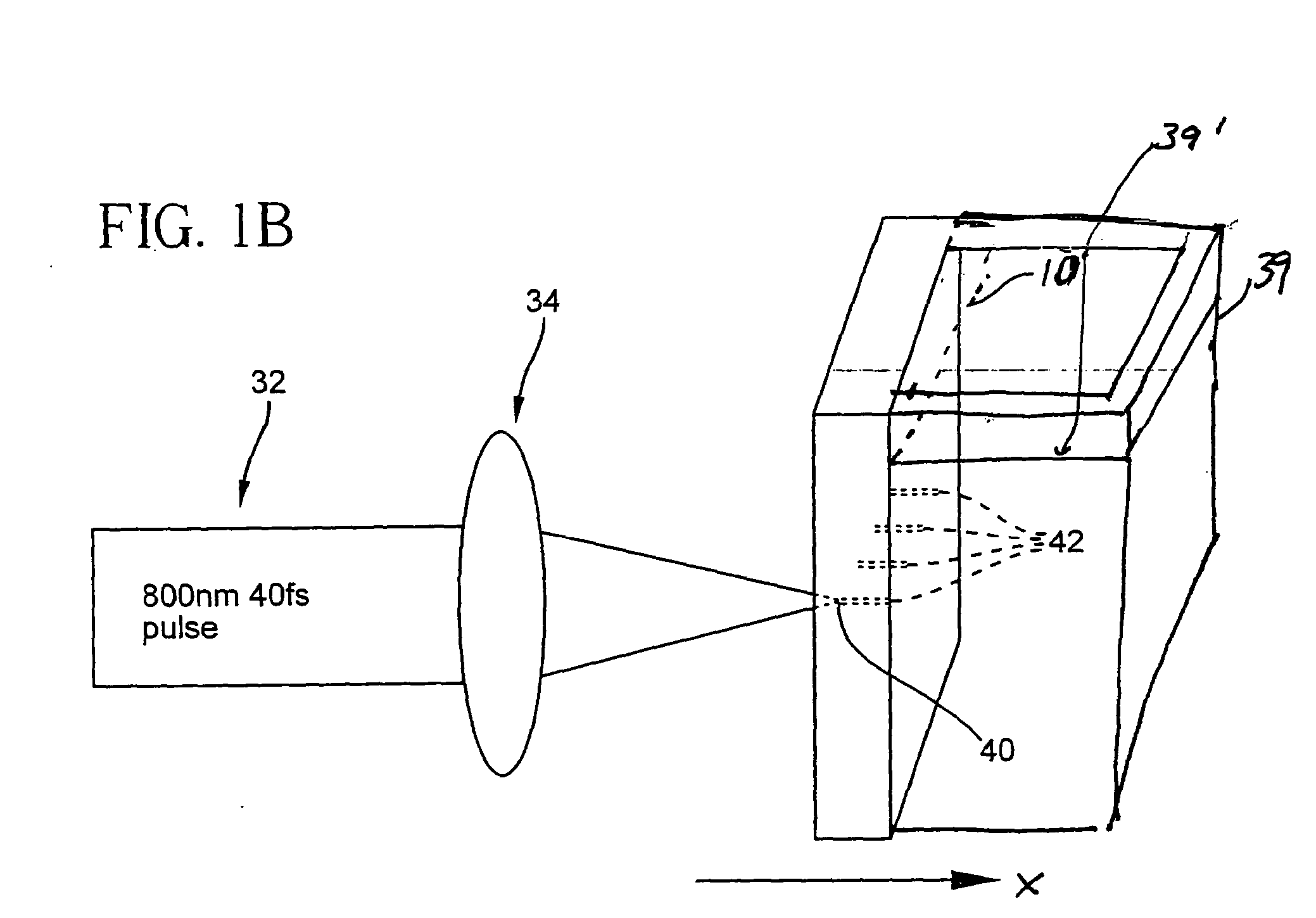
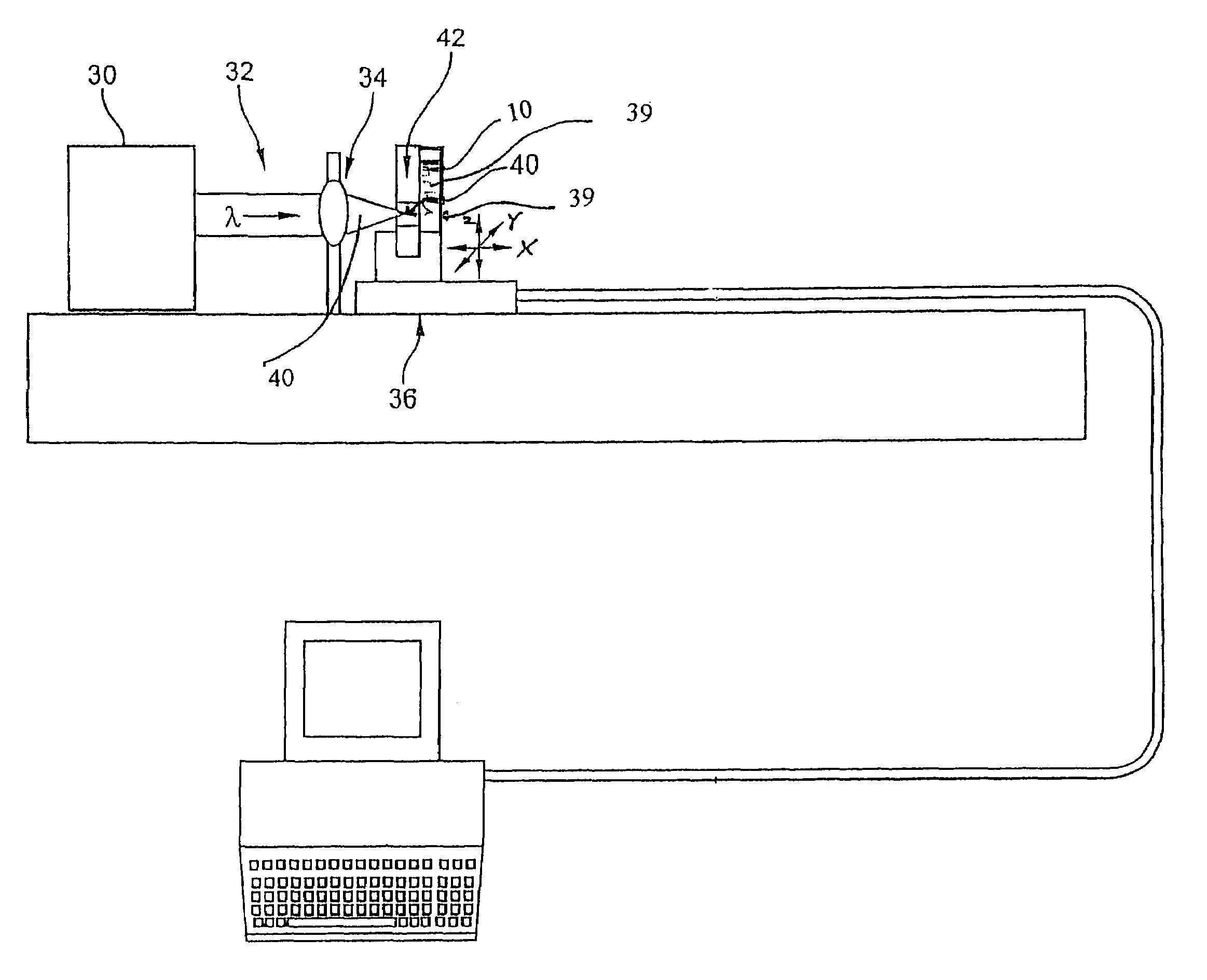
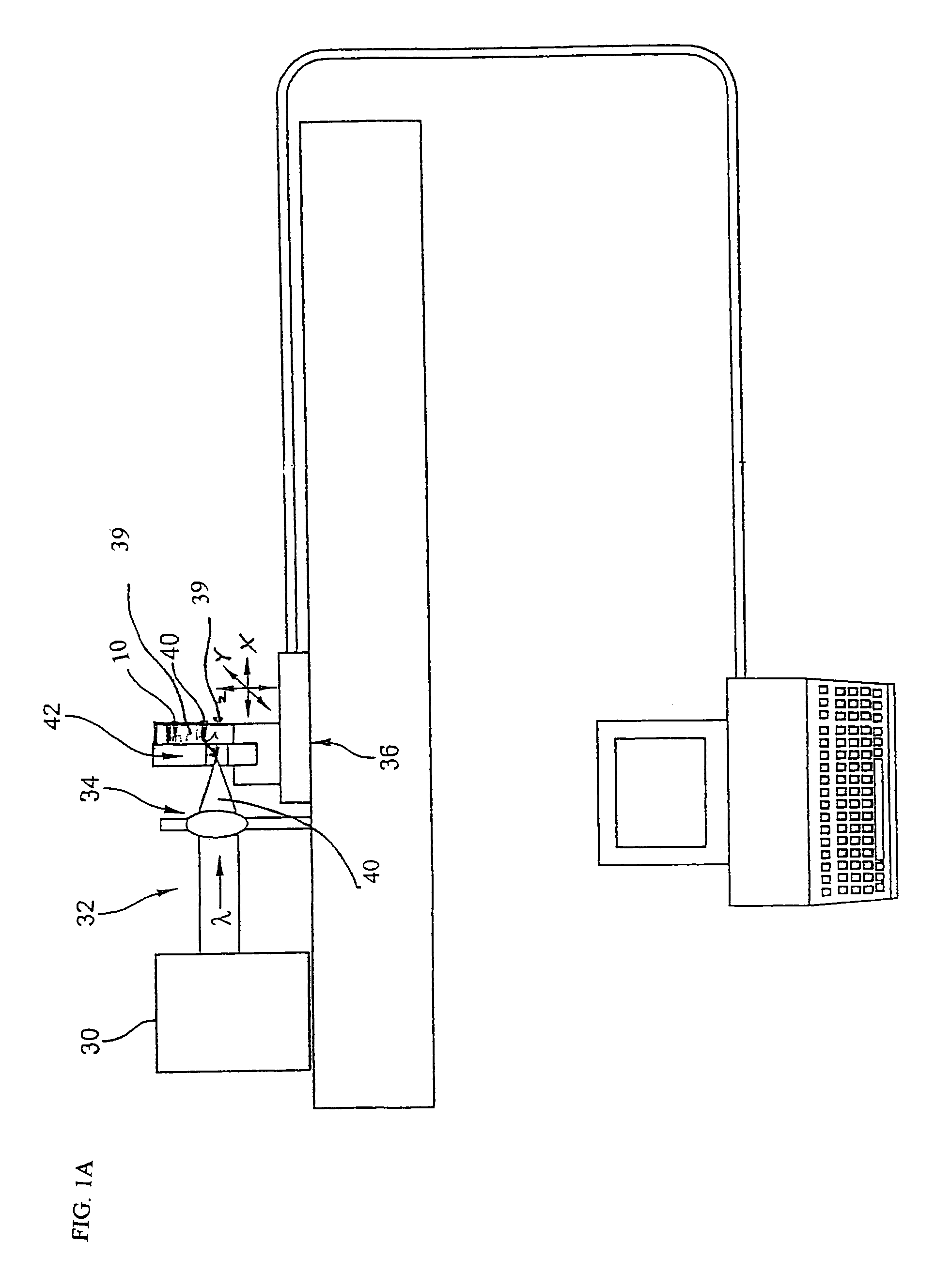
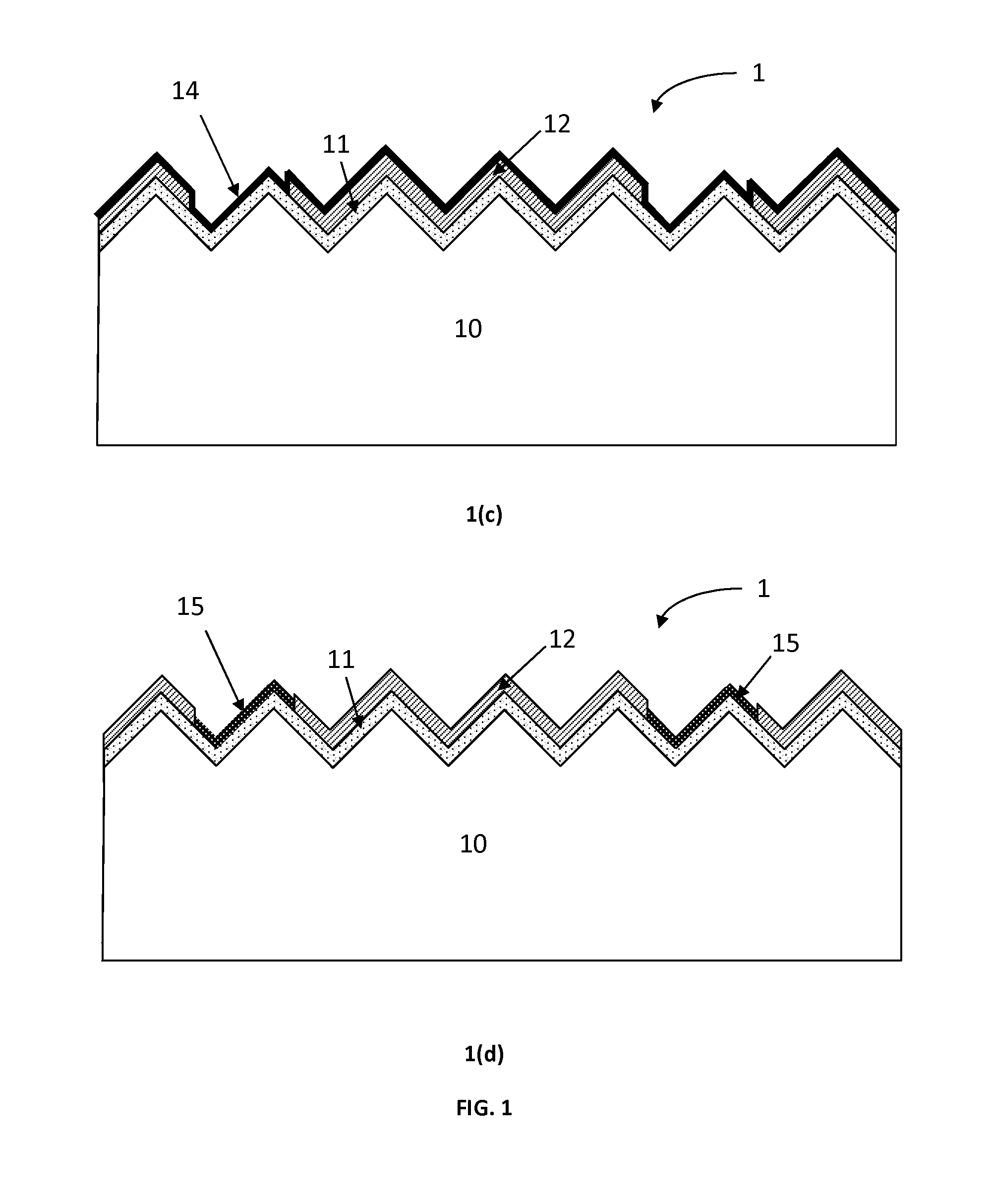
A method of making an at least one hole in an optically transparent body (10) comprises the following steps: (i) providing an ultrashort pulse laser for producing a laser output with a wavelength , the laser output having a subpicosecond laser pulse duration; (ii) providing a laser output focusing lens (34) for focusing the laser output, the focusing lens (34) having a numerical aperture NA; (iii) providing an optically transparent body (10), the optically transparent body (10) having a transparency at of at least 90% / cm; (iv) providing a liquid (39') filled container (39) situated proximate to the optically transparent body (10), such that the optically transparent body (10) is in direct contact with the liquid (39'); and (v) directing the laser output through the focusing lens (34) to produce a focused laser output with a subpicosecond laser pulse duration proximate the optically transparent body (10), wherein the focused laser output traces at least one hole track pattern through the transparent glass body while the optically transparent body (10) and said focused laser output move relative to one another in X-Y-Z directions . The at least one hole track pattern is in contact with the liquid and the focused laser output, in conjunction with the liquid (39'), creates at least one hole in the optically transparent body (10).
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of making at least one hole in a transparent body and devices made by this method
InactiveUS20050025445A1Improved micromachining speedCoupling light guidesGlass reforming apparatusPicosecond laser pulseErbium lasers
A method of making an at least one hole in an optically transparent body comprises the following steps: (i) providing an ultrashort pulse laser for producing a laser output with a wavelength λ, the laser output having a subpicosecond laser pulse duration; (ii) providing a laser output focusing lens for focusing the laser output, the focusing lens having a numerical aperture NA; (iii) providing an optically transparent body, the optically transparent body having a transparency at λ of at least 90% / cm; (iv) providing a liquid filled container situated proximate to the optically transparent body, such that the optically transparent body is in direct contact with the liquid; and (v) directing the laser output through the focusing lens to produce a focused laser output with a subpicosecond laser pulse duration proximate the optically transparent body, wherein the focused laser output traces at least one hole track pattern through the transparent glass body while the optically transparent body and said focused laser output move relative to one another in X-Y-Z directions. The at least one hole track pattern is in contact with the liquid and the focused laser output, in conjunction with the liquid, creates at least one hole in the optically transparent body.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of making at least one hole in a transparent body and devices made by this method
InactiveUS6990285B2Improved micromachining speedCoupling light guidesGlass reforming apparatusPicosecond laser pulseErbium lasers
A method of making an at least one hole in an optically transparent body comprises the following steps: (i) providing an ultrashort pulse laser for producing a laser output with a wavelength λ, the laser output having a subpicosecond laser pulse duration; (ii) providing a laser output focusing lens for focusing the laser output, the focusing lens having a numerical aperture NA; (iii) providing an optically transparent body, the optically transparent body having a transparency at λ of at least 90% / cm; (iv) providing a liquid filled container situated proximate to the optically transparent body, such that the optically transparent body is in direct contact with the liquid; and (v) directing the laser output through the focusing lens to produce a focused laser output with a subpicosecond laser pulse duration proximate the optically transparent body, wherein the focused laser output traces at least one hole track pattern through the transparent glass body while the optically transparent body and said focused laser output move relative to one another in X-Y-Z directions. The at least one hole track pattern is in contact with the liquid and the focused laser output, in conjunction with the liquid, creates at least one hole in the optically transparent body.
Owner:CORNING INC
Tissue treatment system
InactiveUS20060122585A1Avoid condensationEasy to replaceSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyHair removalLaser light
A hair removal device (22) includes a cooling surface (34) which is used to contact the skin (6) prior to exposure to hair tissue-damaging laser light (74) passing from a radiation source (36) through a recessed window (46). The window is laterally offset from the cooling surface and is spaced apart from the cooling surface in a direction away from the patient's skin to create a gap between the window and the skin. The window preferably includes both an inner window (46) and an outer, user-replaceable window (48). The laser-pulse duration is preferably selected according to the general diameter of the hair.
Owner:CUTERA
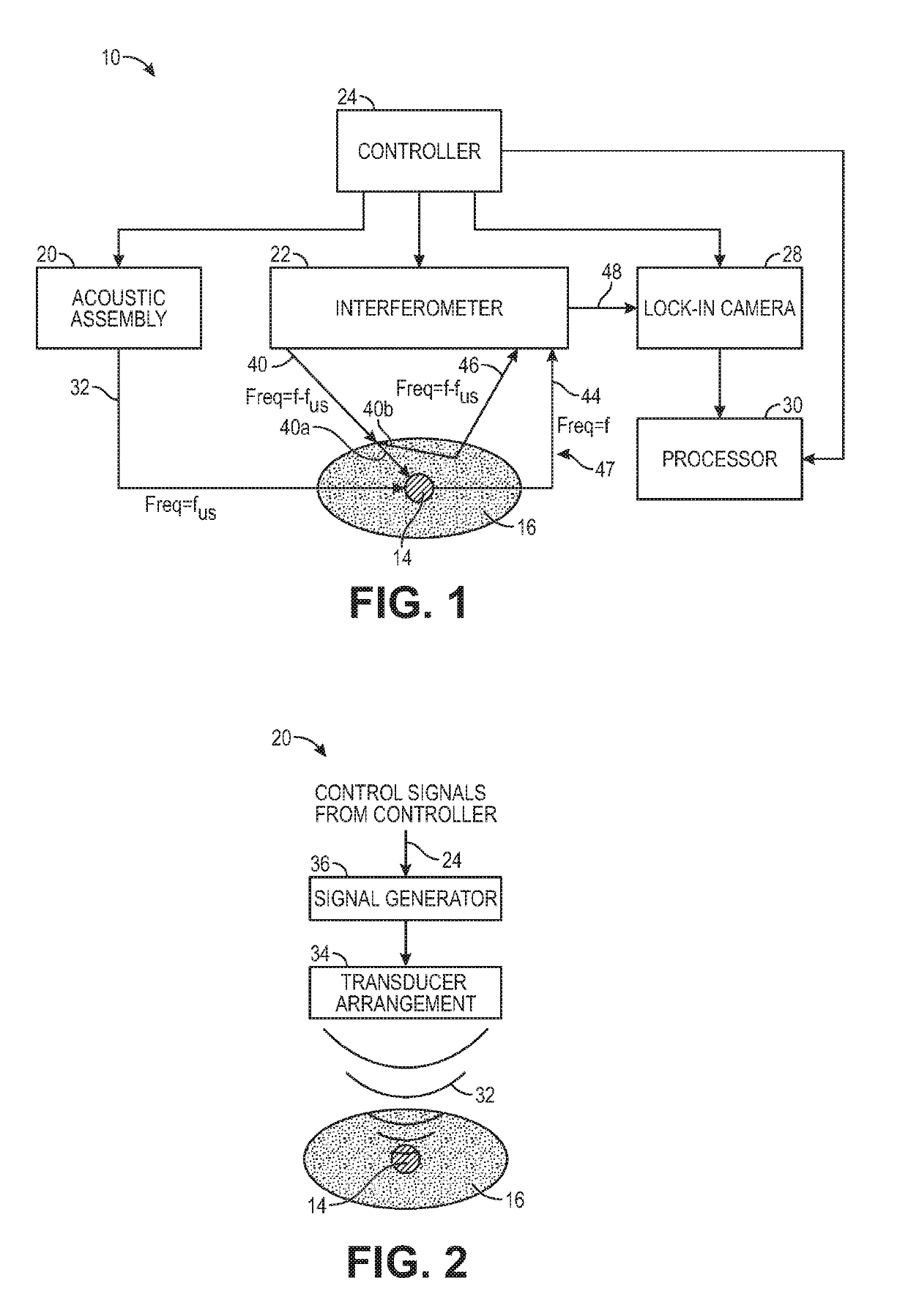
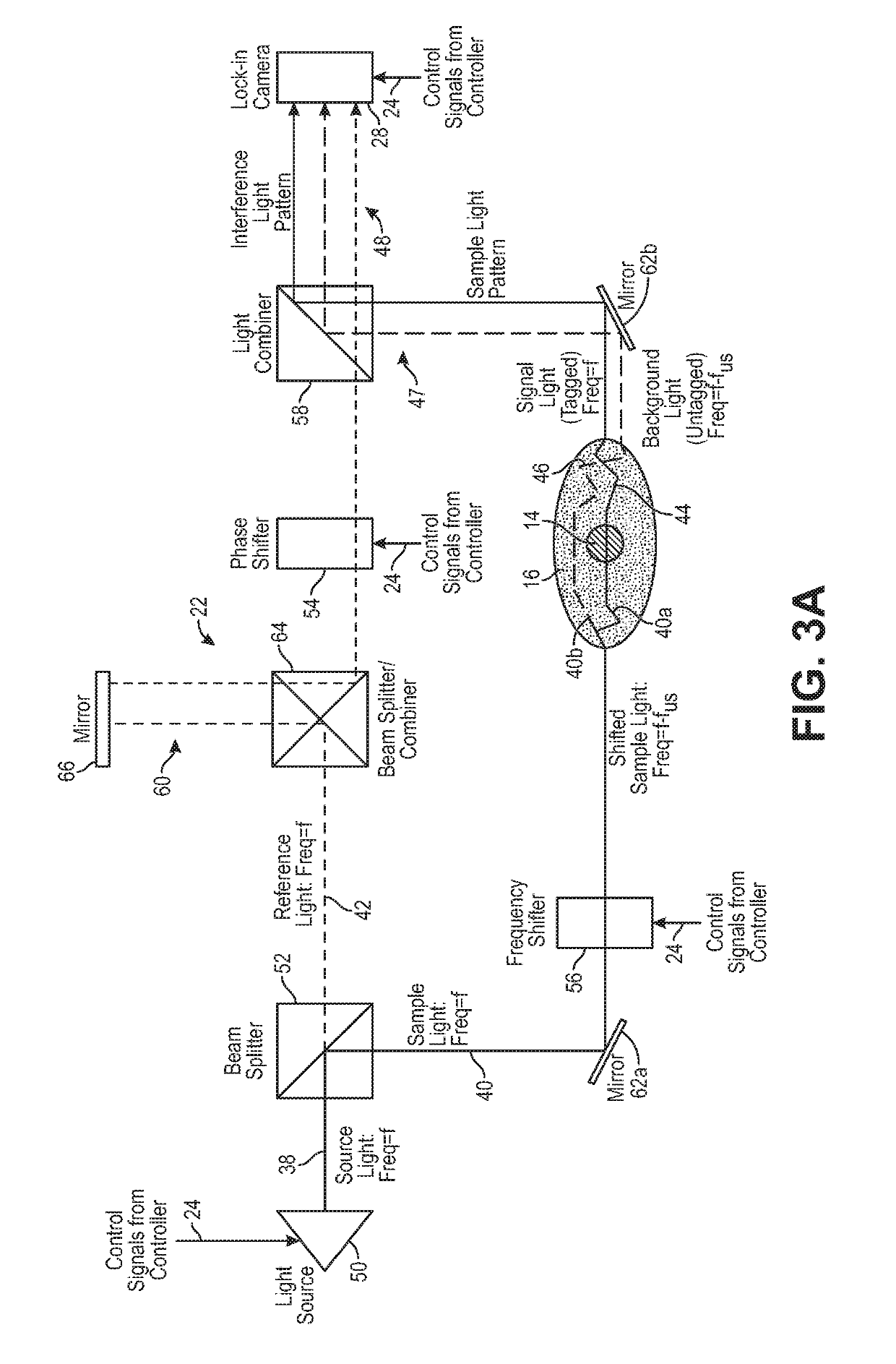
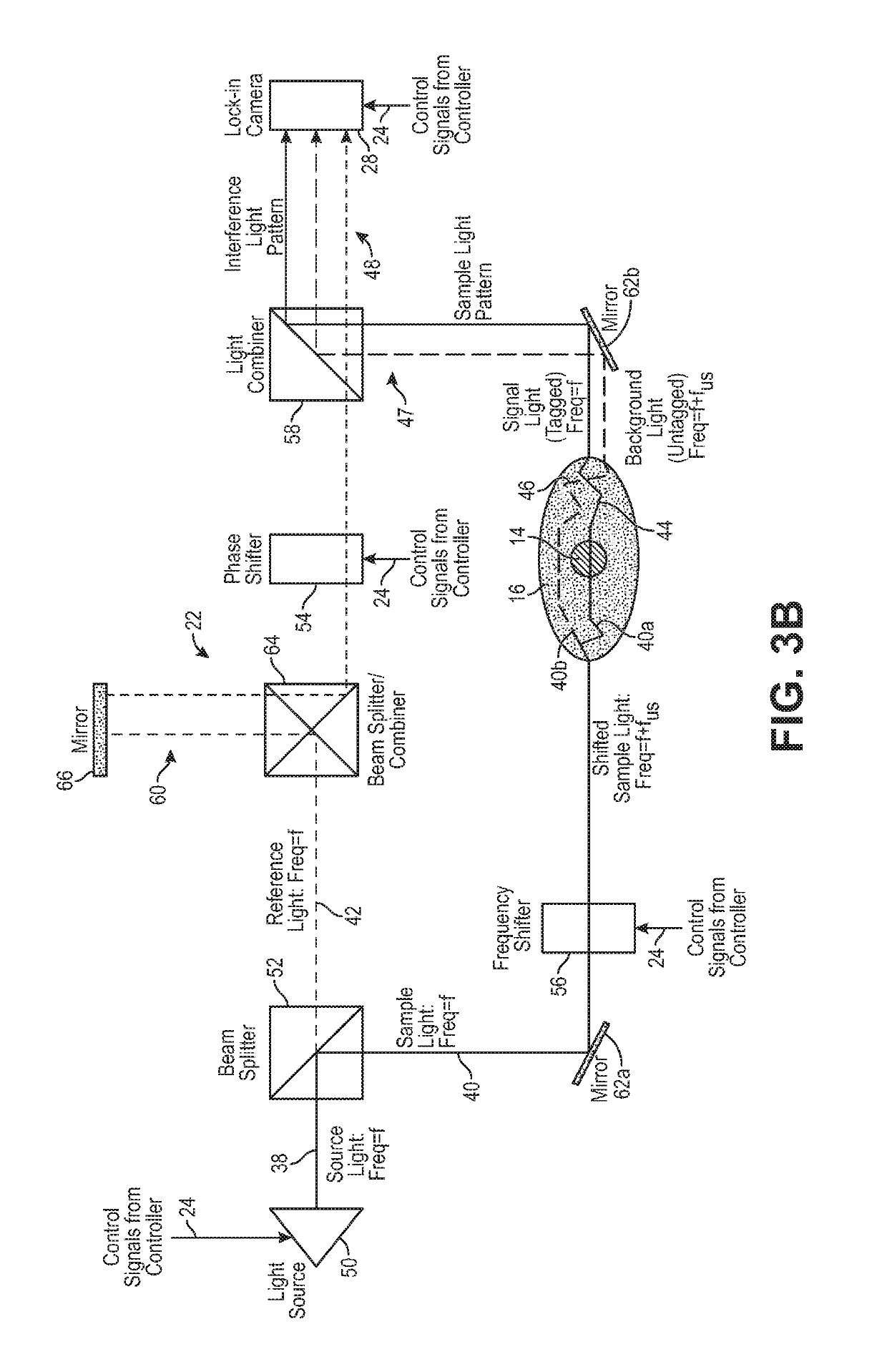
Ultrasound modulating optical tomography using reduced laser pulse duration
InactiveUS20190269331A1Maximize width of optical pulseIncrease costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomical structuresOptical tomography
Sample light is delivered into the anatomical structure having a target voxel, whereby a portion of the sample light passing through the target voxel is scattered by the anatomical structure as signal light, and another portion of the sample light not passing through the target voxel is scattered by the anatomical structure as background light that is combined with the signal light to create a sample light pattern. Reference light is combined with the sample light pattern to generate an interference light pattern, such that the signal light and the reference light are combined in a heterodyne manner. Ultrasound is delivered into the target voxel, such that the signal light is frequency shifted by the ultrasound. The ultrasound and the sample light are pulsed in synchrony at the target voxel, such that at least one pulse of the sample light has a combined duration less than a pulse width of the ultrasound.
Owner:HI LLC
Laser etching method of transparent conductive thin film
ActiveCN104475979ANo need to damageNo need to worry about damageLaser beam welding apparatusLaser etchingLength wave
The invention discloses a laser etching method of a transparent conductive thin film. The method comprises the following steps of (1) outputting pulse laser beams with an output wavelength of 1.4-3.0 mu m through a short-wave long-infrared pulse laser device at a pulse width of 0.1-800 ns, and performing collimation treatment, wherein the short-wave long-infrared pulse laser device is an optical fiber laser device and has a single-pulse laser power capacity of 1-2000 microjoules and a pulse frequency of 1 KHz-1 MHz; (2) enabling the laser beams to illuminate a film substrate on a two-dimensional moving table, controlling the relative movement of the laser beams and the two-dimensional moving table to enable the focus point of the laser beams to move on the transparent conductive thin film according to a set path to perform etching, and controlling the laser beams and the transparent conductive thin film to move relatively as a speed of 50-9000 mm / s and to have a spot overlapping degree of 10-90%. The laser etching method of the transparent conductive thin film can overcome the problems of high laser focusing precision requirements and implementing complexity in the prior art.
Owner:杭州银湖激光科技有限公司
Pulse coding distribution-type fiber Raman and Brillouin scattering sensor
InactiveCN102322883AHigh-resolutionIncrease the number of emitted photonsThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFrequency shiftFiber amplifier
The invention discloses a pulse coding distribution-type fiber Raman and Brillouin scattering sensor which comprises a waveform generator, a semiconductor F-P (Fabry-Perot) cavity broadband fiber laser, a semiconductor outer cavity narrow-band pulse fiber laser, a fiber wave separator, a pulse coding photomodulator, an one-way device, an Er-doped fiber amplifier, a bidirectional coupler, a sensing fiber, an integrated wavelength division multiplexer, two photoelectric receiving and amplifying modules, a direct detection system, a narrow-band transmission fiber bragg grating, a circulator, a coherent detection system and an industrial personal computer. The sensor adopts tow laser sources, wherein the semiconductor F-P cavity broadband fiber laser measures temperature by use of a spontaneous fiber Raman scattering intensity ratio; and the other one semiconductor outer cavity narrow-band pulse fiber laser measures strain of frequency shift by use of the spontaneous fiber Brillouin scattering ray. A time sequence codes laser pulse, the spatial resolution is improved by lowering laser pulse width while the transmission photon number is improved, the signal to noise ratio of the systemis improved, and the measurement precision is measured and improved while on-line temperature and strain are realized in space.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
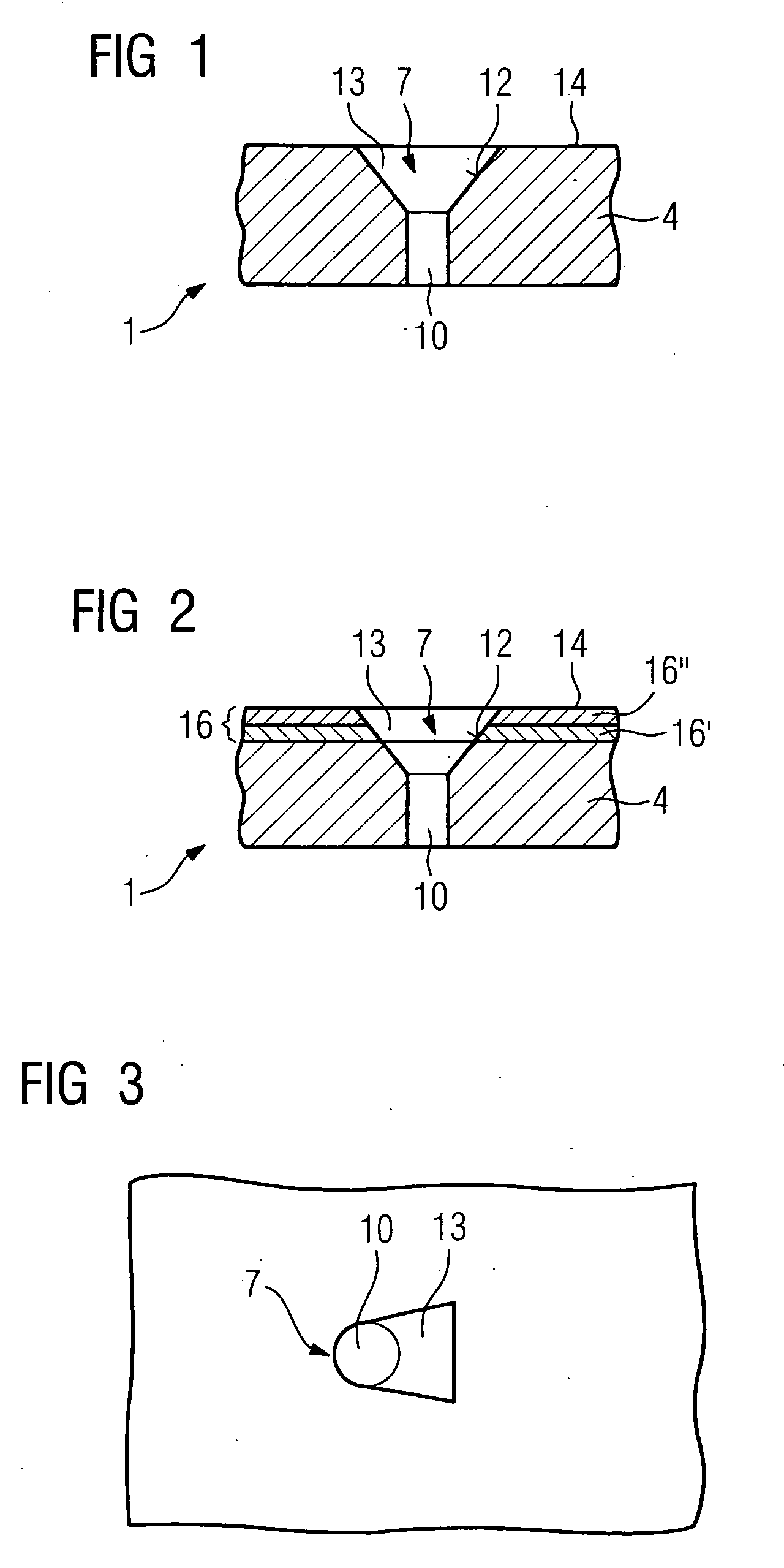
Process for the fabrication of a hole
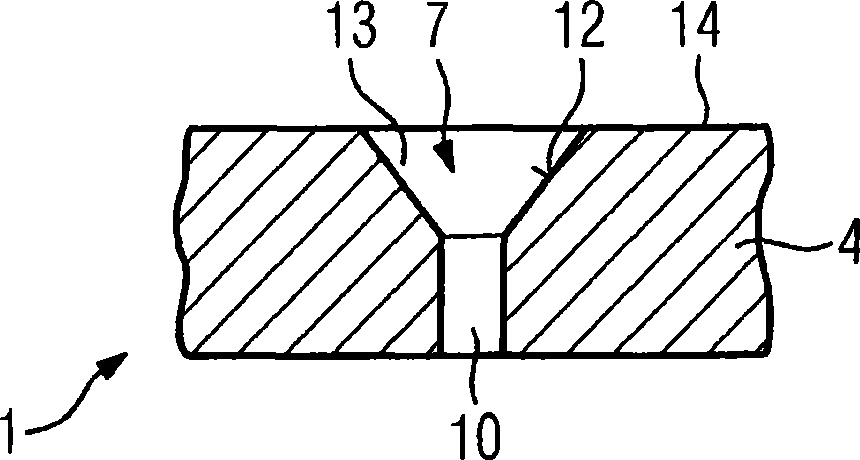
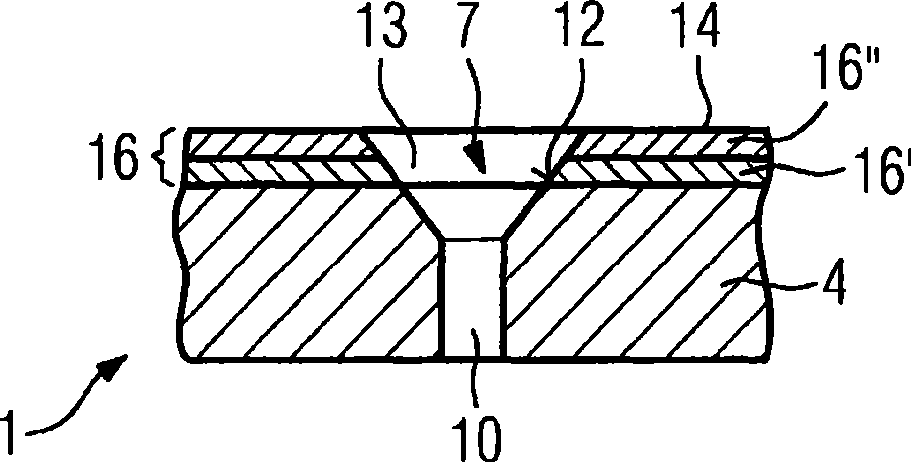
Conventional methods for producing a hole in a component are time-consuming and costly as special lasers featuring short laser pulse durations are used. In the inventive method, the laser pulse durations are varied, short laser pulse durations being utilized only in the area to be removed in which an influence on the penetration behavior and discharge behavior is noticeable while longer pulse durations of >0.4ms are used. This is the case for the inner surface (12) of a diffuser (13) of a hole (7), for example, which can be produced very accurately by means of short laser pulse durations.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for minimizing sample damage during the ablation of material using a focused ultrashort pulsed laser beam wherein the slope of fluence breakdown is a function of the pulse width
InactiveUS20100006550A1Avoid damageSmall featureLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLight beamCombined use
In one aspect the invention provides a method for laser induced breakdown of a material with a pulsed laser beam where the material is characterized by a relationship of fluence breakdown threshold (Fth) versus laser beam pulse width (T) that exhibits an abrupt, rapid, and distinct change or at least a clearly detectable and distinct change in slope at a predetermined laser pulse width value. The method comprises generating a beam of laser pulses in which each pulse has a pulse width equal to or less than the predetermined laser pulse width value. The beam is focused above the surface of a material where laser induced breakdown is desired. The region of least confusion (minimum beam waist or average spot size) is above the surface of the material in which laser induced breakdown is desired since the intensity of the beam falls off in the forward direction, preferably the region of the beam at or within the surface is between the region of least confusion and sufficient to remove material and the minimum intensity necessary for laser induced breakdown of the material to be removed, most preferably the region of minimum intensity is disposed at the surface of the material to be removed. The beam may be used in combination with a mask in the beam path. The beam or mask may be moved in the x, y, and Z directions to produce desired features. The technique can produce features smaller than the spot size and Rayleigh range due to enhanced damage threshold accuracy in the short pulse regime.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
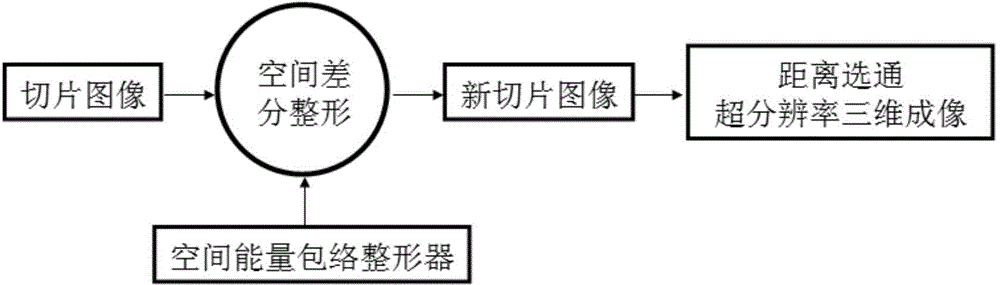
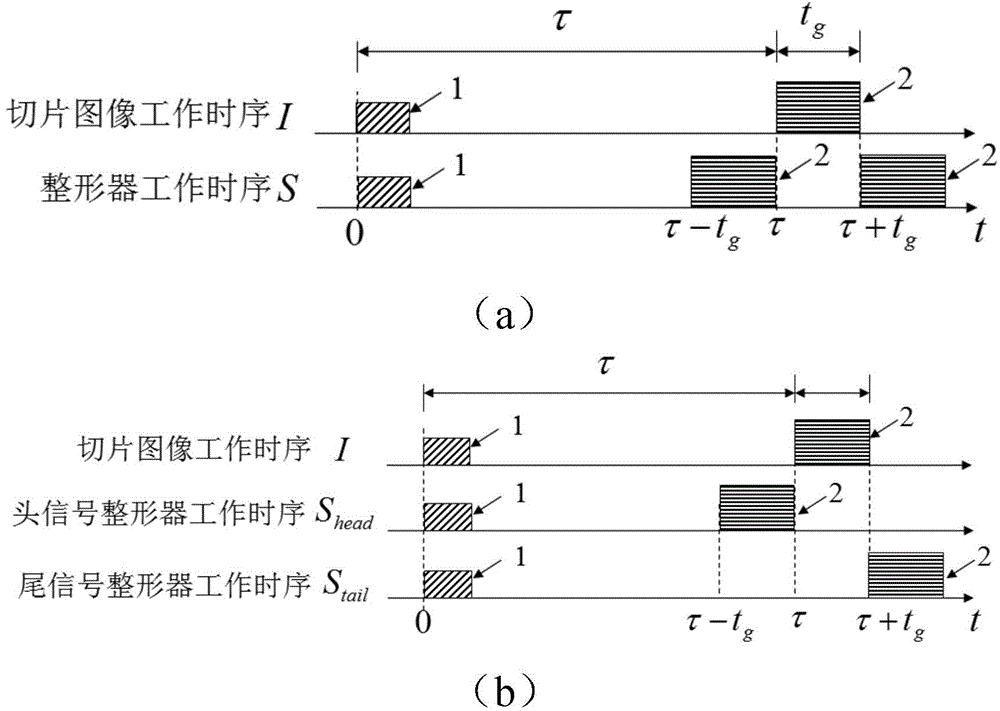
Range gating super-resolution three-dimensional imaging method based on spatial differencing shaping
ActiveCN104101330AHigh distance resolutionReduce the requirements of pulse width time domain characteristicsPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryImage resolutionRange gate
The invention discloses a range gating super-resolution three-dimensional imaging method based on spatial differencing shaping. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a first slice image used for three-dimensional reconstruction; building a first space energy envelope shaper in space overlapping with the first slice image; adopting the first space energy envelope shaper to carry out space difference shaping treatment to the first slice image, so as to obtain a first new slice image; obtaining two new slice images with overlapped spaces by adopting gating delayed stepping treatment according to the former step, and carrying out range gating super-resolution three-dimensional reconstruction on the basis of the new slice images. The equivalent narrowing laser pulse durations of the new slice images are half of that of the original laser pulse duration, so that the purposes of narrowing laser pulse duration and improving range resolution are achieved. According to the method provided by the invention, the limitation of the minimal pulse duration of an impulse laser is broken, three-dimensional imaging in higher range resolution is achieved, and the application of range gating super-resolution three-dimensional imaging is developed.
Owner:北京中科盛视科技有限责任公司
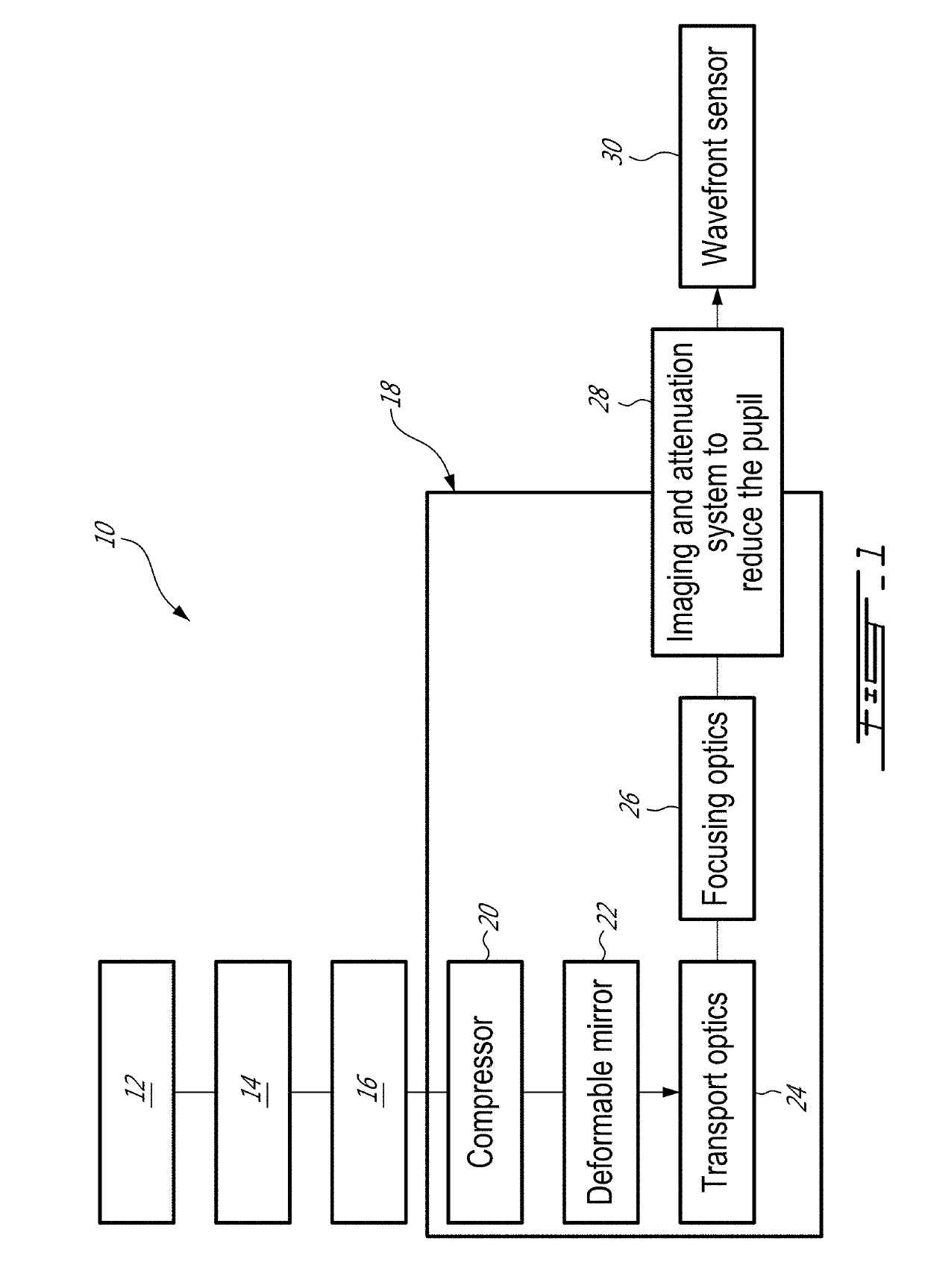
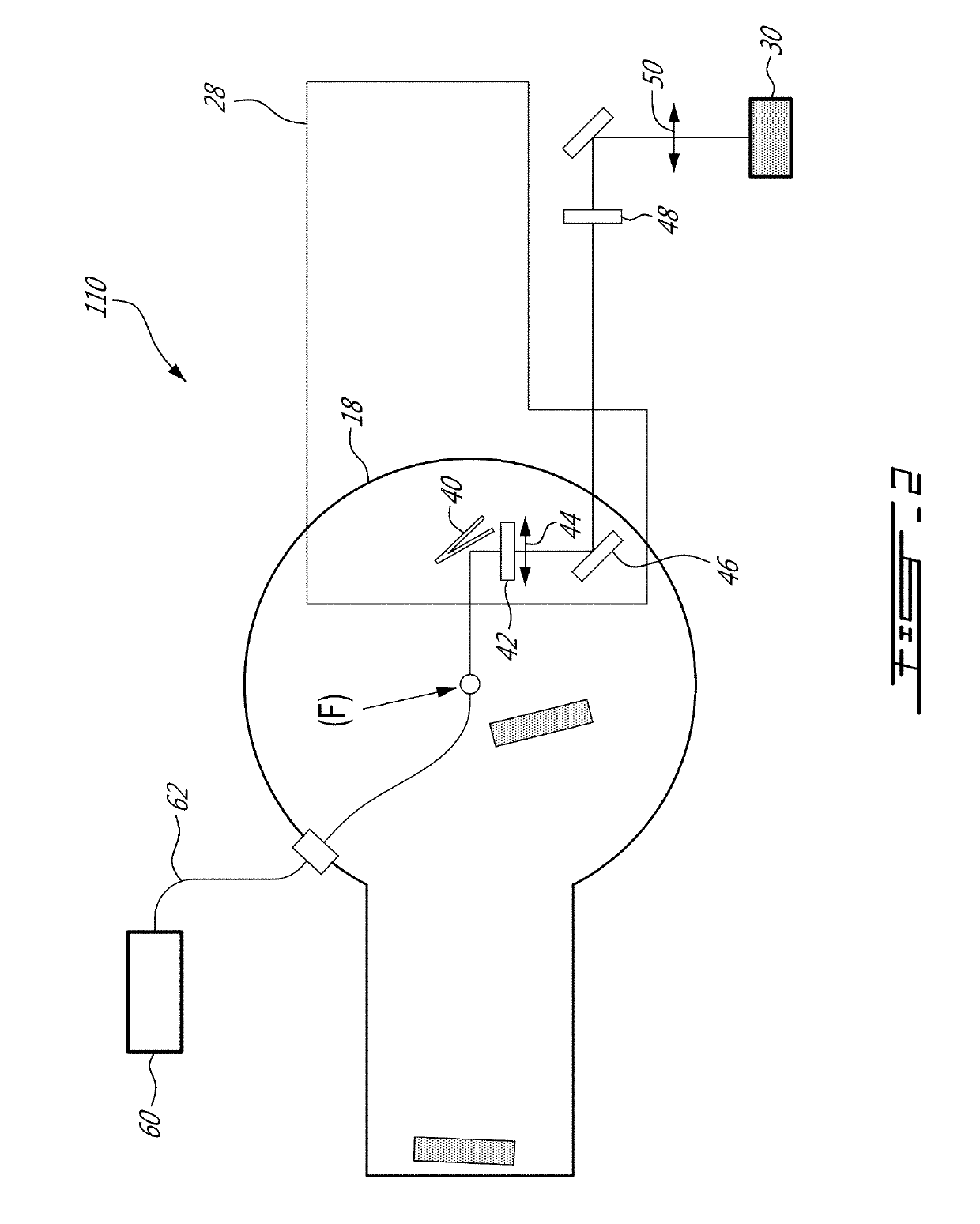
System and method for correcting laser beam wavefront of high power laser systems
ActiveUS20190165538A1Active medium shape and constructionOptical elementsHigh power lasersWavefront sensor
A method and a system for laser pulse wavefront correction and focusing optimization for laser Wakefield interaction to accelerate electrons to high energy, and more generally for laser matter interaction where both far field and intermediate field optimization are important, allowing a robust wavefront correction and focusing optimization with a high-power laser system at its nominal laser pulse energy and laser pulse duration. The method comprises, after laser beam focusing by focusing optics, coupling an imaging unit to a wavefront sensor, thereby measuring the laser beam wavefront, and adjusting the measured laser beam wavefront to converge to a reference wavefront of the imaging unit using a spatial phase-modifying device.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
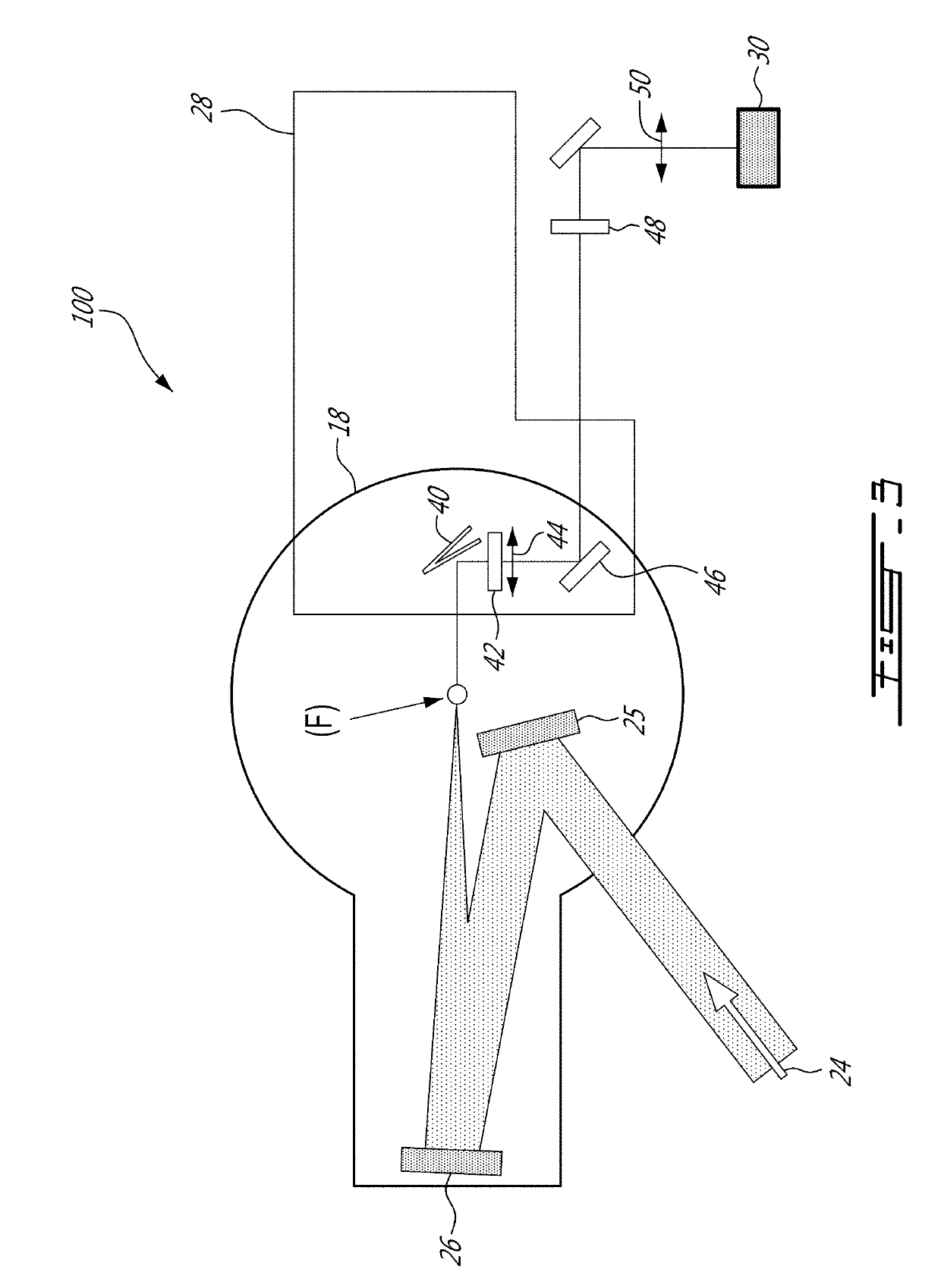
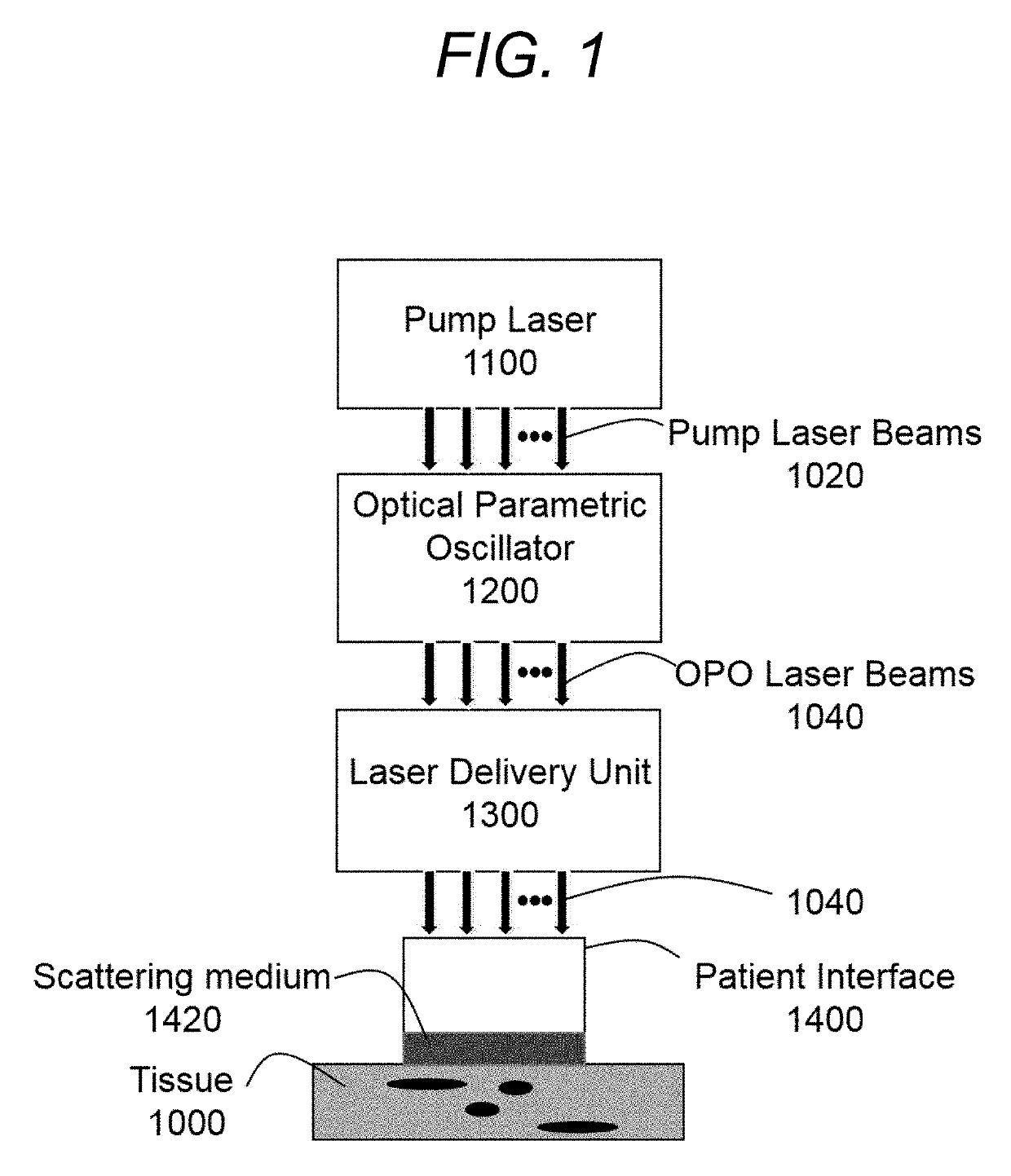
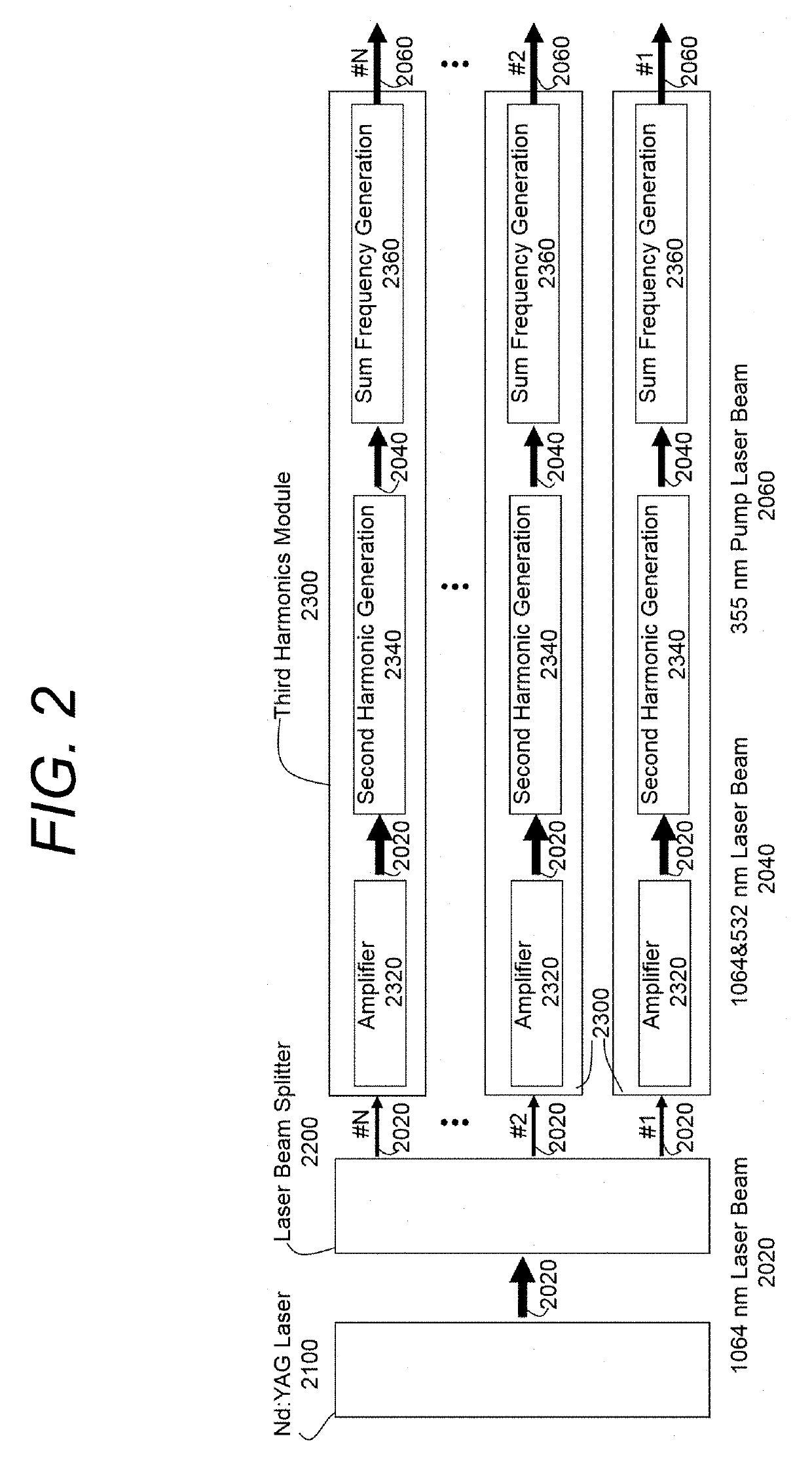
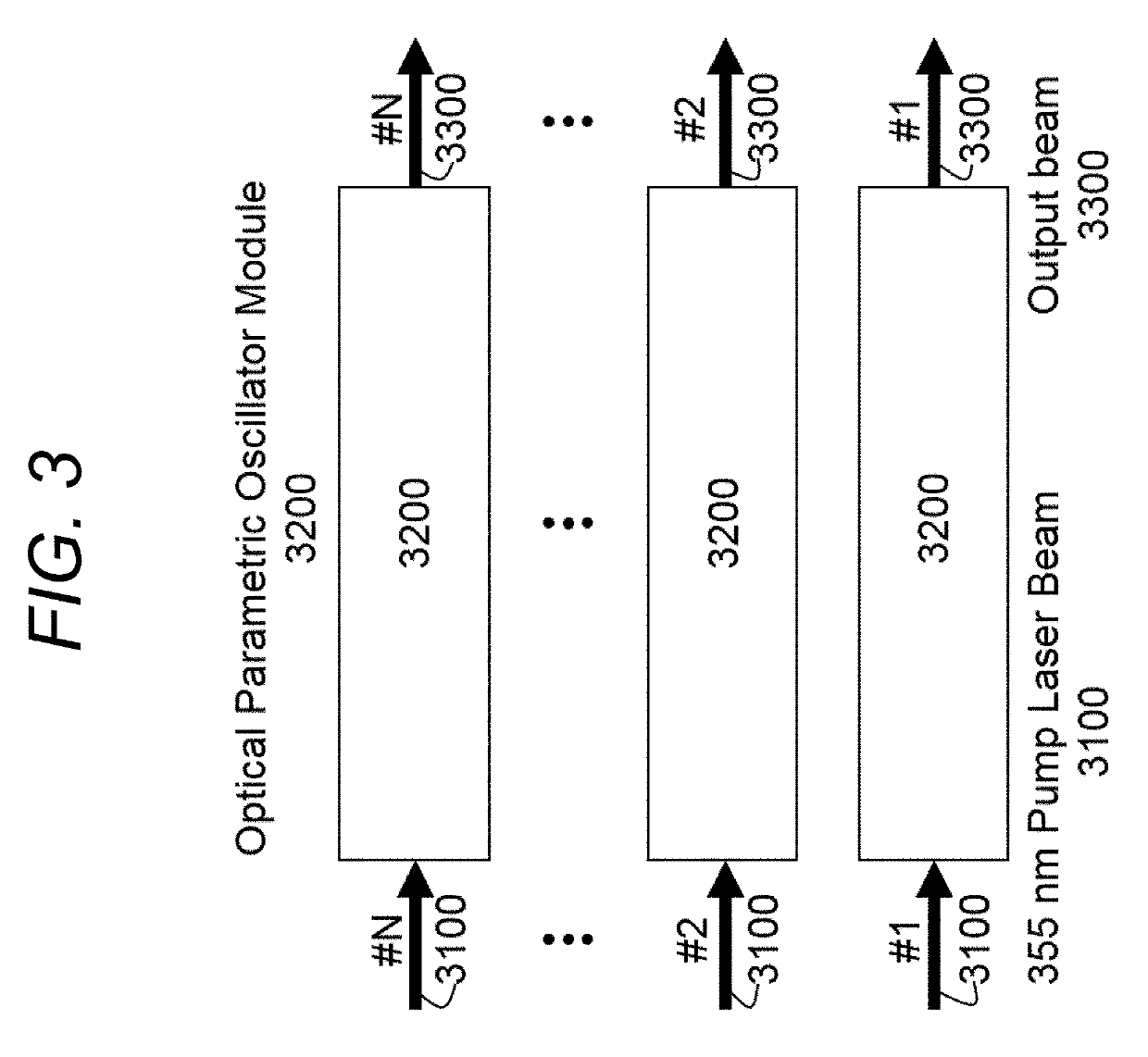
High power tunable optical parametric oscillator for selective photothermolysis laser surgeries
ActiveUS20190336213A1Improve transmittanceEfficient combinationSurgical instrument detailsLaser arrangementsPulse sequenceLaser pulse duration
A laser with a wide continuous wavelength tuning range is desirable for optimized selective photothermolysis (SP) laser surgeries that treat light-absorptive lesions and unwanted pigments in human tissue with minimal collateral damages. However, current SP laser surgical systems are limited to a few lasing lines including 1024 nm by Nd:YAG, 755 nm by Alexandrite, 694 nm by Ruby, and 532 nm by second harmonic generation of 1064 nm. This invention discloses techniques to implement a high power, tunable optical parametric oscillator (OPO) system for demanding SP applications such as laser tattoo removal. In addition to wavelength tuning, the OPO laser system's output pulse energy, pulse duration, and pulse-train duration are also adjustable by tuning the pump laser pulse energy, pump laser pulse duration, and pump laser pulse-train duration for optimizing SP laser surgical outcomes.
Owner:RAO BIN
Short pulse fiber laser for LTPS crystallization
ActiveCN104956466ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesAmorphous siliconLight beam
Laser pulses from pulsed fiber lasers are directed to an amorphous silicon layer to produce a polysilicon layer comprising a disordered arrangement of crystalline regions by repeated melting and recrystallization. Laser pulse durations of about 0.5 to 5 ns at wavelength range between about 500 nm and 1000 nm, at repetition rates of 10 kHz to 10 MHz can be used. Line beam intensity uniformity can be improved by spectrally broadening the laser pulses by Raman scattering in a multimode fiber or by applying varying phase delays to different portions of a beam formed with the laser pulses to reduce beam coherence.
Owner:NLIGHT INC
Ultrafast laser cutting method and device for transparent material
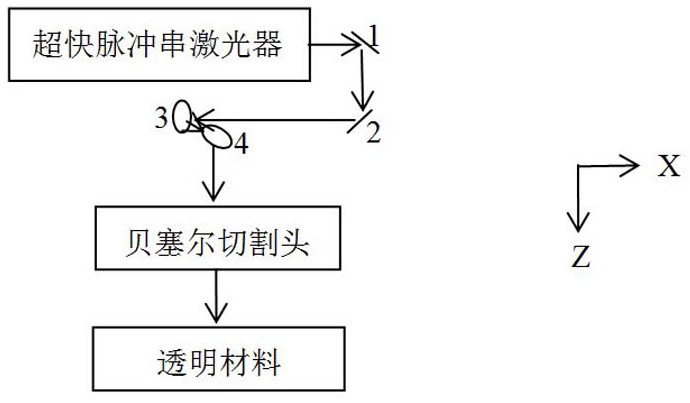
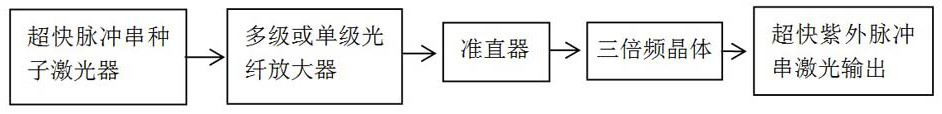
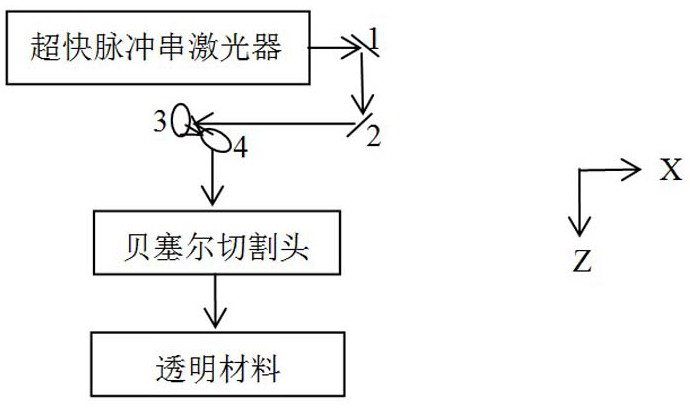
PendingCN111618452AGuaranteed reliabilityQuality assuranceWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamLaser cutting
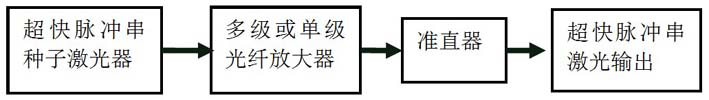
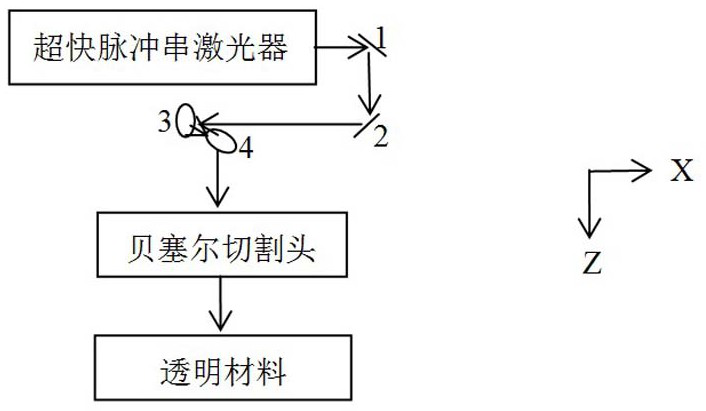
The invention discloses an ultrafast laser cutting method and device for a transparent material. Pulse string seed lasers are provided through semiconductor laser modulation, third harmonic generationis carried out after the lasers are amplified through an optical fiber amplifier, and laser pulse strings are focused on a to-be-processed position of the transparent material through a Bethel cutting head. Three or more focusing points are formed in the processed material, and the transparent material is cut by moving the focusing positions. Each laser pulse string comprises at least four laserpulses, the pulse width is smaller than 60 ps, the peak power is larger than 1 MW, and the time between the adjacent laser pulses is shorter than 30 ns; the interval time between the adjacent pulse strings is longer than 100 ns; and the widening amount and compression amount of the laser pulse width both do not exceed 40% of the laser pulse width. According to the ultrafast laser cutting method and device, the reliability of light beam cutting is guaranteed, the waste heat of the former pulse is effectively utilized, the quality of cutting machining is guaranteed, and the linear and various special-shaped appearances of the material are cut.
Owner:SUZHOU TUSEN LASER
Gradient-index (GRIN) lens fabrication employing laser pulse width duration control, and related components, systems, and methods
ActiveUS20140116995A1Prevent and reduce heat accumulationEasy to cleanWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusLaser pulse widthSpherical aberration
Gradient-index (GRIN) lens fabrication employing laser pulse width duration control, and related components, systems, and methods are disclosed. GRIN lenses can be fabricated from GRIN rods by controlling the pulse width emission duration of a laser beam emitted by a laser to laser cut the GRIN rod, as the GRIN rod is disposed in rotational relation to the laser beam. Controlling laser pulse width emission duration can prevent or reduce heat accumulation in the GRIN rod during GRIN lens fabrication. It is desired that the end faces of GRIN lenses are planar to facilitate light collimation, easy bonding or fusing of the GRIN lens to optical fibers to reduce optical losses, polishing to avoid spherical aberrations, and / or cleaning the end faces when disposed in a fiber optic connector, as non-limiting examples.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Method for Forming Metal Silicide Layers
ActiveUS20140335646A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUv laserMetal silicide
The present invention is related to a method for forming a metal silicide layer on a textured silicon substrate surface. The method includes providing a metal layer on a textured silicon substrate and performing a pulsed laser annealing step providing at least one UV laser pulse with a laser fluence in the range between 0.1 J / cm2 and 1.5 J / cm2 and with a laser pulse duration in the range between 1 ns and 10 ms. Then, the method includes converting at least part of the metal layer into a metal silicide layer. In addition, the present invention is related to the use of such a method in a process for fabricating a photovoltaic cell, wherein the dielectric layer is a surface passivation layer, or wherein the dielectric layer is an antireflection coating.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +2
Ultrafast laser cutting method and device for transparent materials
PendingCN111618454AGuaranteed reliabilityQuality assuranceWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamEngineering
The invention discloses an ultrafast laser cutting method and device for transparent materials. Pulse train seed laser is provided by semiconductor laser modulation, after being amplified by an optical fiber amplifier, a laser pulse train is focused to the to-be-processed position of the transparent materials through a Bezier cutting head, three or more focus points are formed in the processed materials, and cutting of the transparent materials is realized by moving the focusing position; At least four laser pulses are included in each laser pulse train, the pulse width is less than 60 ps, thepeak power is greater than 1 mW, and the time between adjacent laser pulses is less than 30 ns; the interval time between adjacent pulse trains is greater than 100 ns; and the laser pulse width broadening amount and the compression amount do not exceed 20% of the seed laser pulse width. The reliability of a cutting light beam is ensured, the waste heat of previous pulse is effectively utilized, the cutting machining quality is ensured, and outline cutting in a straight line shape and various special shapes of the materials is realized.
Owner:SUZHOU TUSEN LASER
Method For Producing A Hole
InactiveUS20120091106A9Maintain good propertiesLaser beam welding apparatusOptoelectronicsLaser pulse duration
There is described a method for producing a hole using e.g. a lasers, wherein short laser pulse durations are used. The laser pulse durations are varied, short laser pulse durations being utilized only in the area to be removed in which an influence on the penetration behavior and discharge behavior is noticeable while longer pulse durations of >0.4 ms are used. This is the case for the inner surface of a diffuser of a hole, for example, which can be produced very accurately by means of short laser pulse durations.
Owner:CHROMALLOY GAS TURBINE +1
Pulse coding fiber Brillouin optical time domain analyzer
InactiveCN102322885AHigh gainHigh precisionThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansGratingGain
The invention discloses a pulse coding fiber Brillouin optical time domain analyzer which comprises a pulse coding waveform generator, a narrow-band single-frequency fiber laser, a fiber shunt, an optical pulse coding modulator, two fiber circulators, an heterodyne receiver, a digital signal processor, a fiber bragg grating filter, a sensing fiber, a fiber Raman pump sensor and an industrial personal computer. The sensor adopts a time sequence to code laser pulse to improve the spatial resolution by reducing laser width while the transmission photon number is improved; a continuously operated fiber Raman pump laser serves as a pump light source to overcome the difficulty that the Brillouin optical time domain analyzer needs to strictly lock the frequency of a detection laser and a pump laser; and strong laser generated by the continuously operated fiber Raman pump laser is amplified by stimulated Raman scattering light in a sensing fiber instead of being amplified by the narrow-band Brillouin, the gain of the back coherent amplification stimulated Brillouin scattering can be increased, the signal to noise ratio is improved, the measurement precision is improved, and the measurement length is increased.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
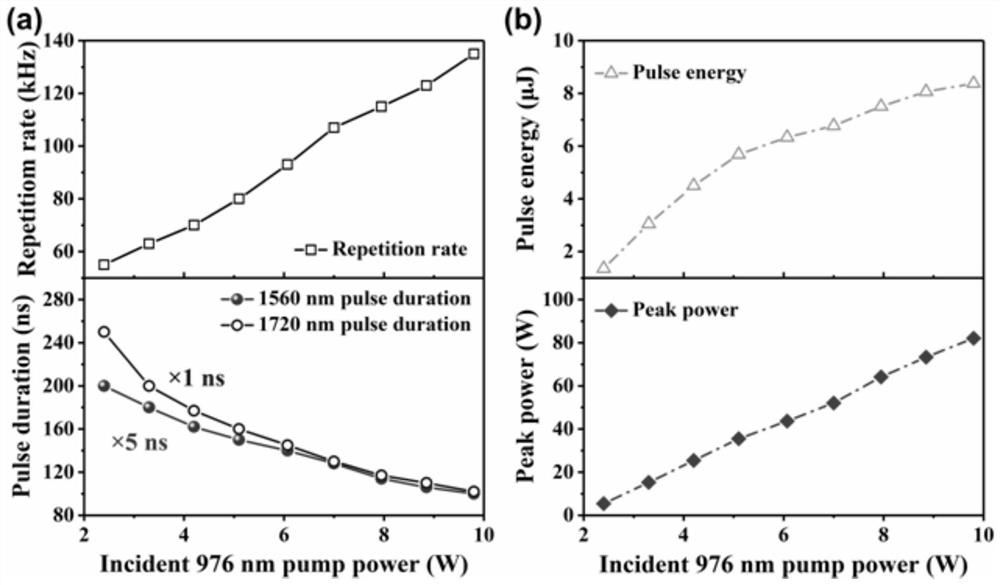
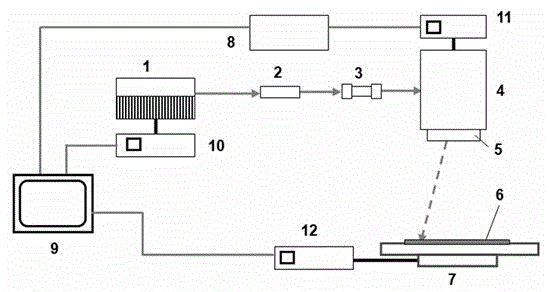
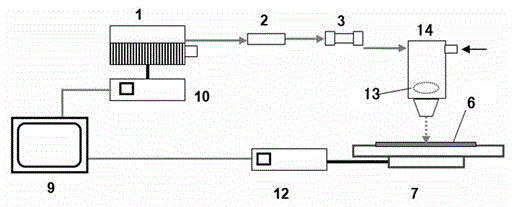
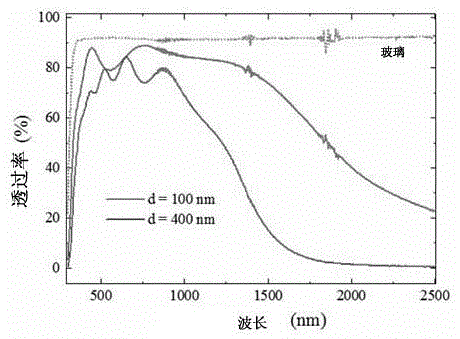
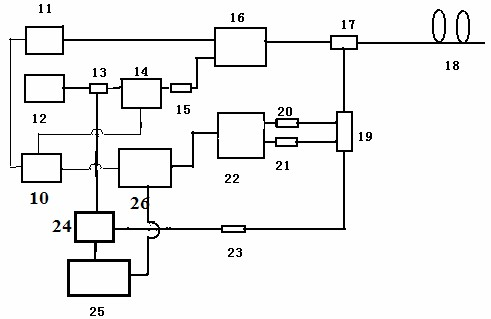
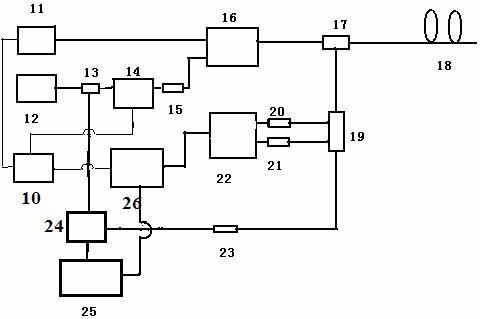
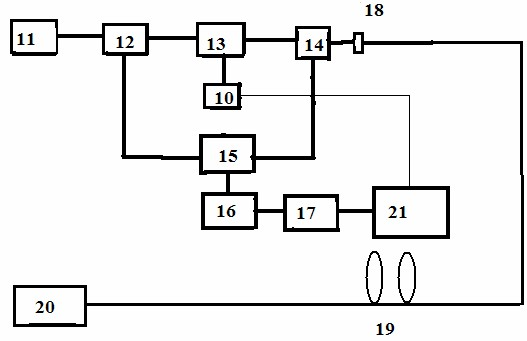
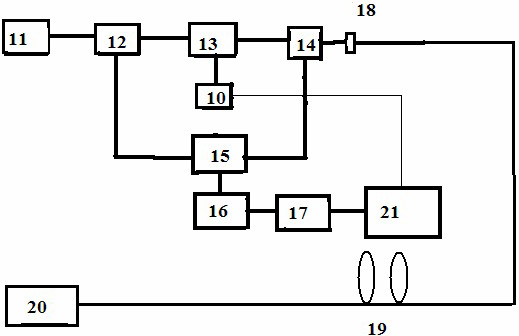
High-energy 1.0[mu]m single-frequency laser amplification system with 100ns pulse width
ActiveCN111129922AGuaranteed single frequencyGuaranteed stabilityActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionLaser lightErbium lasers
The invention discloses a high-energy 1.0[mu]m laser amplification system with 100ns pulse width. The system employs a 1.0[mu]m DFB semiconductor laser as a seed source so as to obtain high-stabilitysingle-frequency laser output. The system utilizes an optical fiber amplification module for chopping, the continuous seed source is chopped into pulse laser with a Lorentz waveform rising edge through an acoustic optical modulator, and finally the width of laser pulse is continuously widened through the amplification effect of a rear-stage solid amplification module, so that 1.0[mu]m pulse laserwith the pulse width greater than 100ns is obtained. According to the invention, the single frequency and stability of 1.0[mu]m laser are ensured, and a new technical route is provided for coherent detection radar to adopt a 1.0[mu]m laser light source through the characteristic that the laser pulse width is gradually broadened through the laser amplification effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultrafast laser cutting method and device for transparent material
PendingCN111618453AGuaranteed reliabilityQuality assuranceWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamLaser cutting
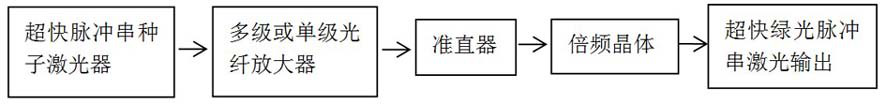
The invention discloses an ultrafast laser cutting method and device for a transparent material. Pulse string seed lasers are provided through semiconductor laser modulation and are converted into green light through a frequency doubling crystal after being amplified by an optical fiber amplifier, and laser pulse strings are focused on a to-be-processed position of the transparent material througha Bethel cutting head. Three or more focusing points are formed in the processed material, and the transparent material is cut by moving the focusing positions. Each laser pulse string comprises at least four laser pulses, the pulse width ranges from 50 ps to 60 ps, the peak power is larger than 1 MW, and the time between the adjacent laser pulses ranges from 10 ns to 20 ns; the interval time between the adjacent pulse strings is longer than 100 ns; and the widening amount and compression amount of the laser pulse width both do not exceed 20% of the laser pulse width. According to the ultrafast laser cutting method and device, the reliability of light beam cutting is guaranteed, the waste heat of the former pulse is effectively utilized, the quality of cutting machining is guaranteed, andthe linear and various special-shaped appearances of the material are cut.
Owner:SUZHOU TUSEN LASER
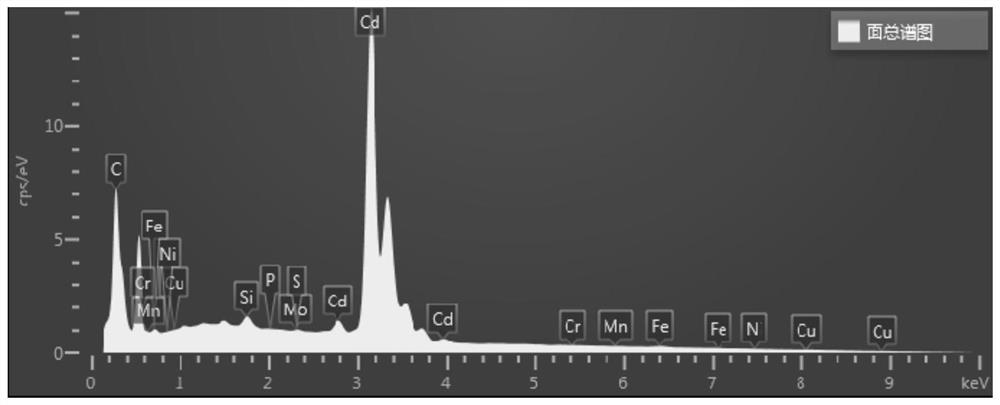
Method for cleaning cadmium coating on surface of workpiece through laser and laser cleaning device
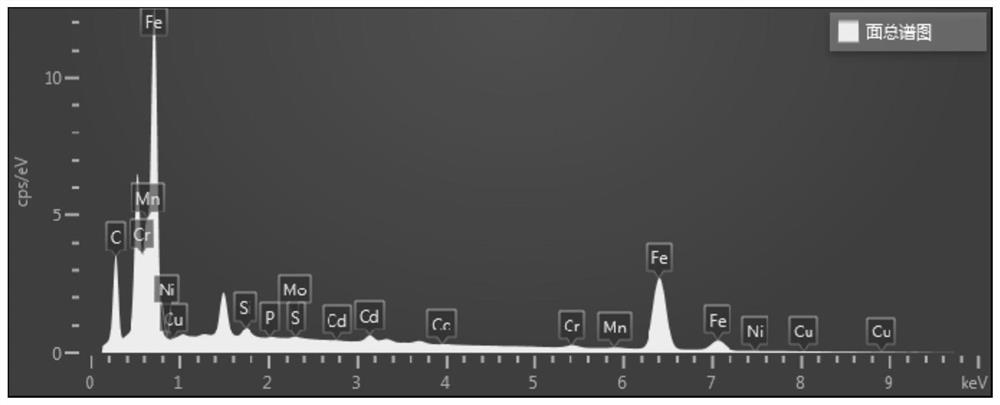
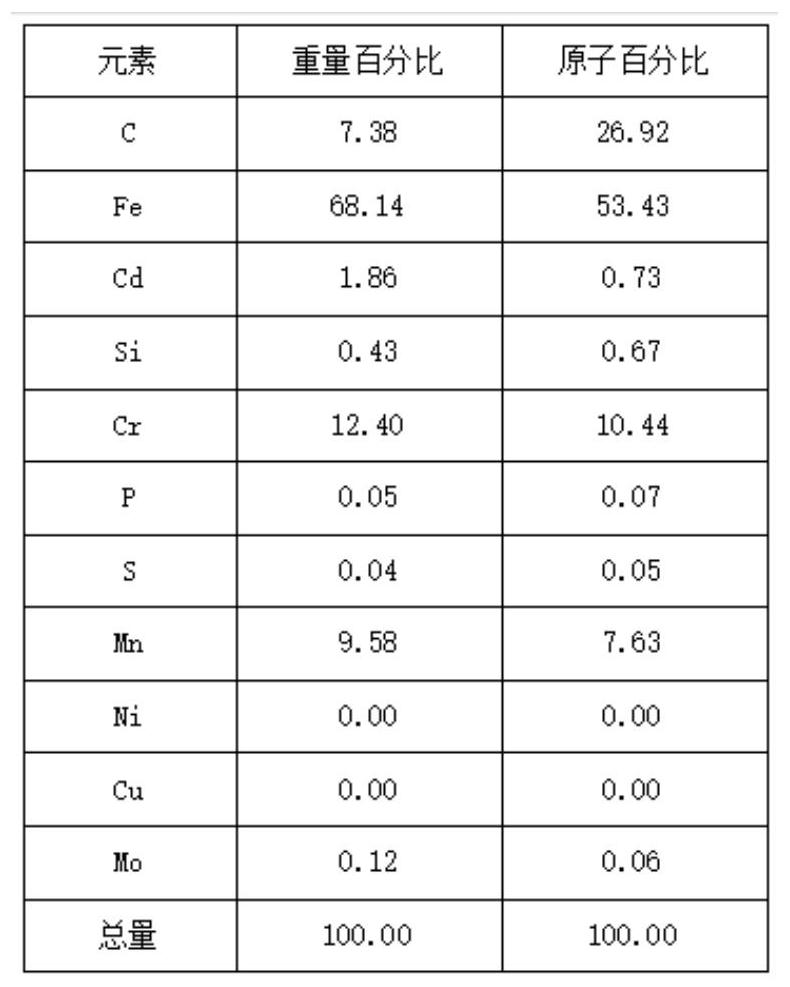
InactiveCN113877893AEasy to cleanImprove cleaning efficiencyCleaning processes and apparatusPhysical chemistryPulse energy
The invention discloses a method for cleaning a cadmium coating on the surface of a workpiece through laser and a laser cleaning device. The cadmium coating on the surface of the workpiece is cleaned through the laser with the laser output power smaller than or equal to 100 W, the laser output repetition frequency ranging from 100 kHz to 1000 kHz, the laser pulse width ranging from 12 ns to 500 ns, the laser spot overlap rate smaller than or equal to 50% and the laser single pulse energy smaller than or equal to 0.5 mJ, and the number of laser cleaning times is larger than or equal to 8. The method can be used for fully cleaning the cadmium coating on the surface layer of the workpiece without causing an overburning phenomenon on the workpiece.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT IND GROUP
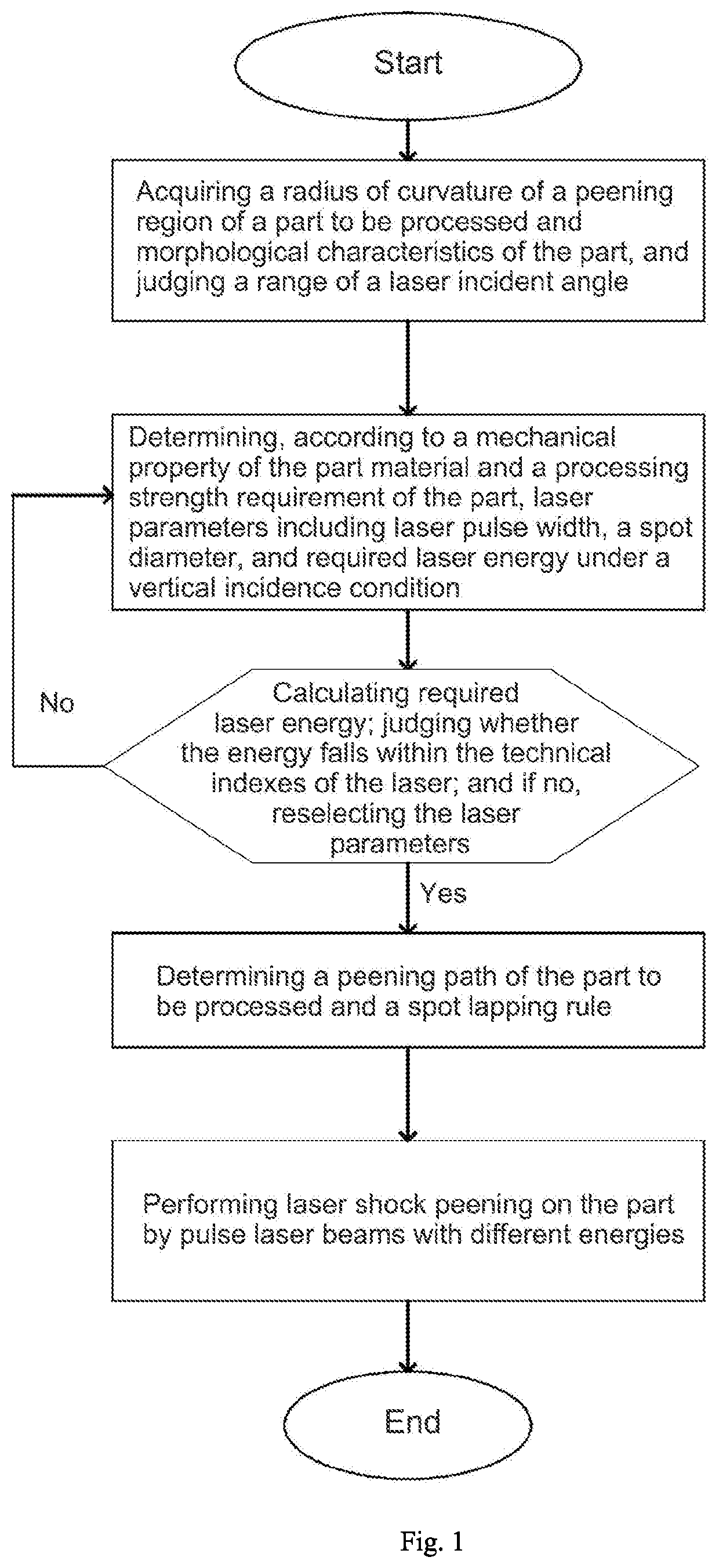
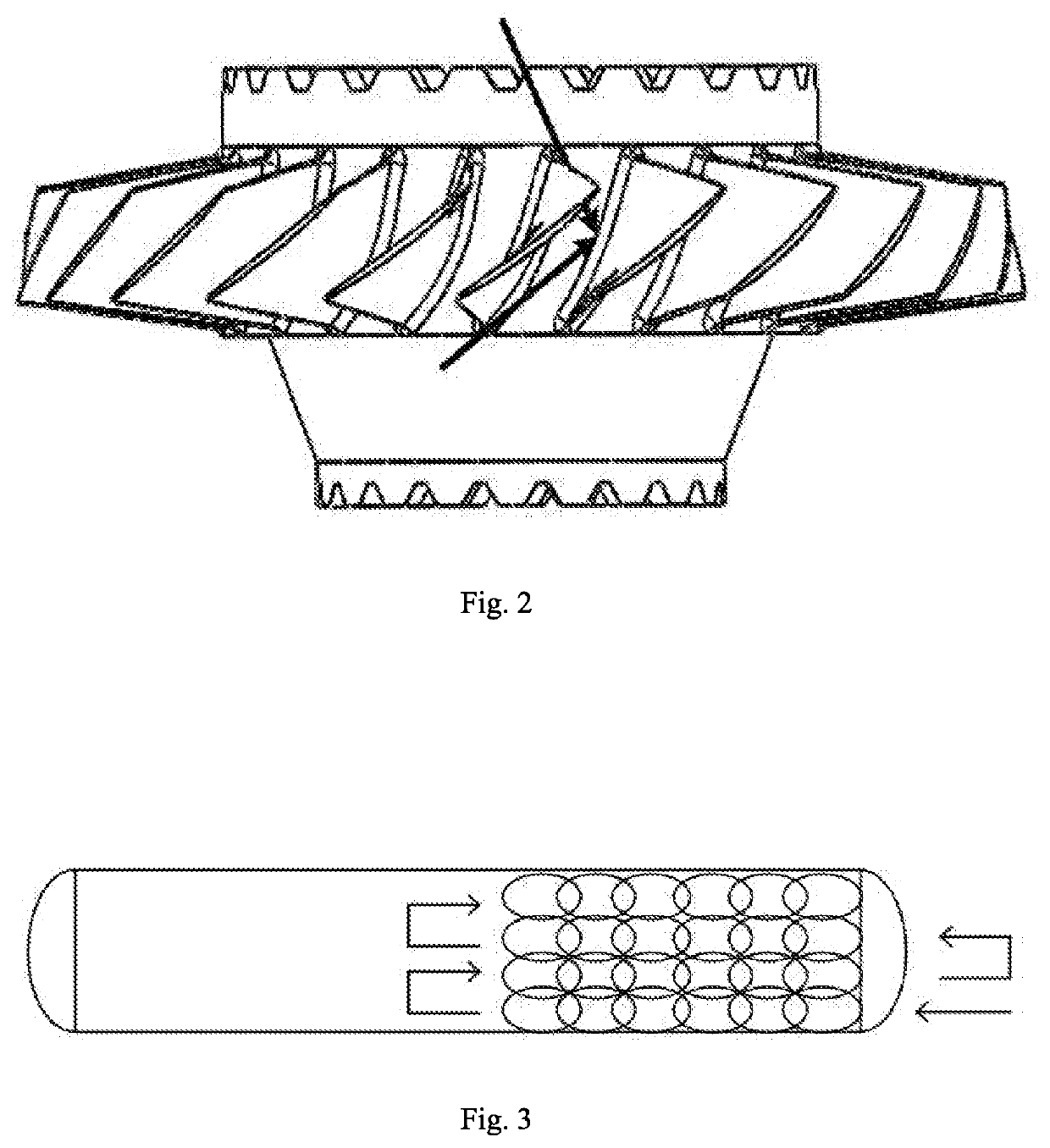
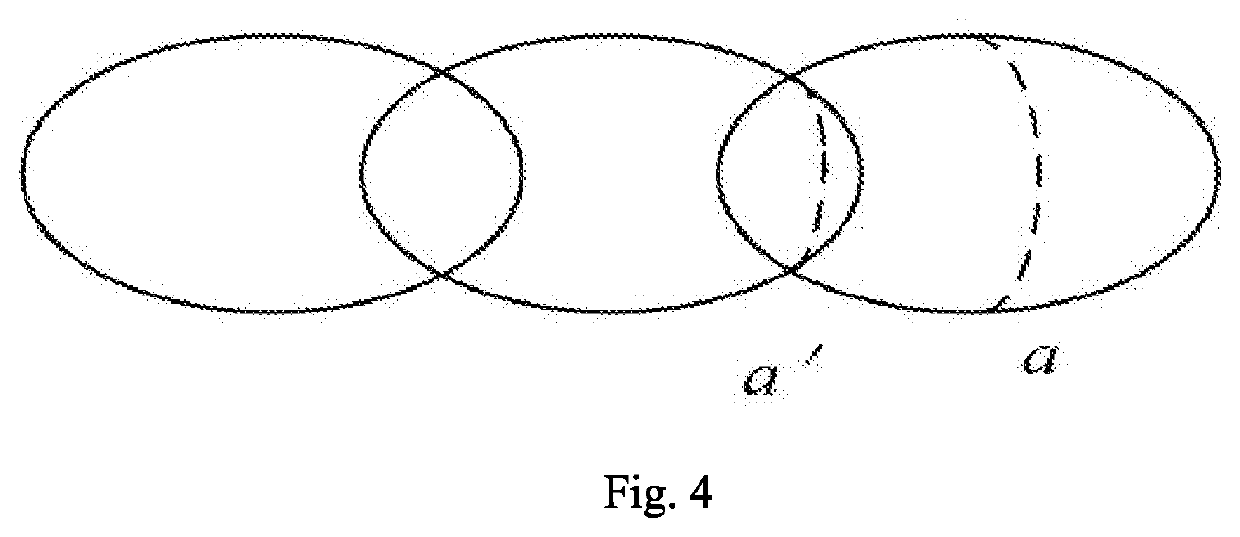
Energy compensated equipower density oblique laser shock method
ActiveUS20200407819A1Improve uniformityReduce roughnessLaser beam welding apparatusAngle of incidenceErbium lasers
The present invention relates to the technical field of material surface peening, and more particularly to an energy compensated equipower density oblique laser shock method. The method includes: acquiring a radius of curvature of a peening region of a part to be processed, and judging a range of a laser incident angle; determining laser parameters, such as laser pulse width, a spot diameter, and required laser energy under a vertical incidence condition; calculating the required laser energy at the minimum incident angle, and judging whether the energy falls within the technical indexes of a laser; and performing laser shock peening on the part by pulse laser beams with different energies. According to the present invention, the laser power or energy is compensated according to changes in the incident angle and the radius of curvature of the part to be processed.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Pulse thulium-doped fiber laser device
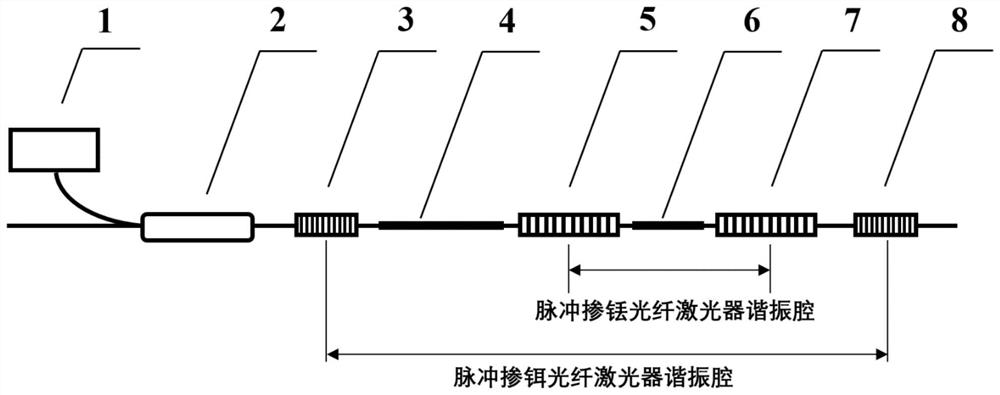
PendingCN113675715ASimple structureLow costOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionGainLaser pulse duration
The invention discloses a pulse thulium-doped fiber laser device, which is characterized in that a thulium-doped active optical fiber is arranged in a resonant cavity of a 1.5 [mu]m band erbium-doped (Er<3+>) optical fiber laser device, the 1.5 [mu]m band erbium-doped (Er<3+>) fiber laser device can operate in a passive Q-switched pulse mode due to the fact that the thulium-doped active optical fiber has a saturable absorption effect on 1.5 [mu]m band laser emitted by the erbium-doped optical fiber, and the process that the thulium-doped optical fiber absorbs laser in the 1.5 [mu]m wave band so as to make the erbium-doped optical fiber laser device operate in a pulse mode is the process that the thulium-doped optical fiber absorbs pump light to generate 1.7-2 [mu]m laser gain based on transition from 3F4 to 3H6; and the 1.5 [mu]m wave band laser runs in a passive Q-switched nanosecond (ns) pulse form, so that the thulium-doped fiber laser device works in a gain switch mode, and 1.7-2 [mu]m wave band pulse laser output which is narrower than the 1.5 [mu]m laser pulse width and higher in peak power can be generated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
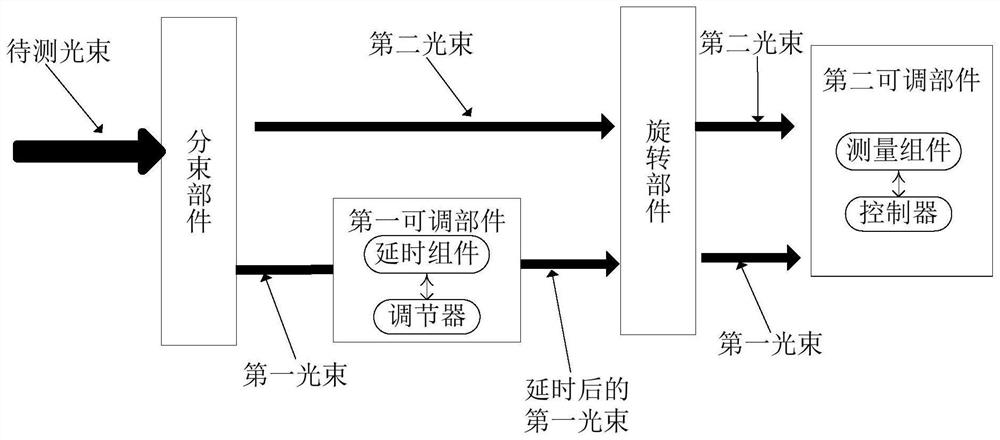
Ultrafast laser pulse width measuring device and control method thereof
InactiveCN111693156AHigh precision outputLow structural costPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsBeam splittingFirst light
The invention discloses an ultrafast laser pulse width measuring device and a control method thereof. The device comprises a beam splitting part, a first adjustable part, a rotating part and a secondadjustable part, the first adjustable part comprises a time delay assembly and an adjuster, the time delay assembly is connected with the adjuster, the second adjustable part comprises a measuring assembly and a controller, and the measuring assembly is connected with the controller; a to-be-measured light beam is divided into a first light beam and a second light beam by a beam splitting part; the reliability of pulse width measurement is ensured; based on the first adjustable part, the accurate adjustment of the optical path of the first light beam can be quickly realized. Based on the rotating part and the second adjustable part, beam pulse detection of any angle polarization state and measurement of autocorrelation signals of the beam pulse detection are achieved, so that the pulse width of a to-be-detected beam is output accurately with high precision, the device is low in structure cost and easy and convenient to operate, operation of professionals is not needed, and the detectable work efficiency is improved.
Owner:广州市固润光电科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
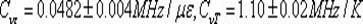


![High-energy 1.0[mu]m single-frequency laser amplification system with 100ns pulse width High-energy 1.0[mu]m single-frequency laser amplification system with 100ns pulse width](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/af1416e8-f4b4-42eb-8170-c434257ccdd2/HDA0002308190780000011.png)
![High-energy 1.0[mu]m single-frequency laser amplification system with 100ns pulse width High-energy 1.0[mu]m single-frequency laser amplification system with 100ns pulse width](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/af1416e8-f4b4-42eb-8170-c434257ccdd2/201911247865.png)