Patents
Literature
85results about How to "Constant precision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
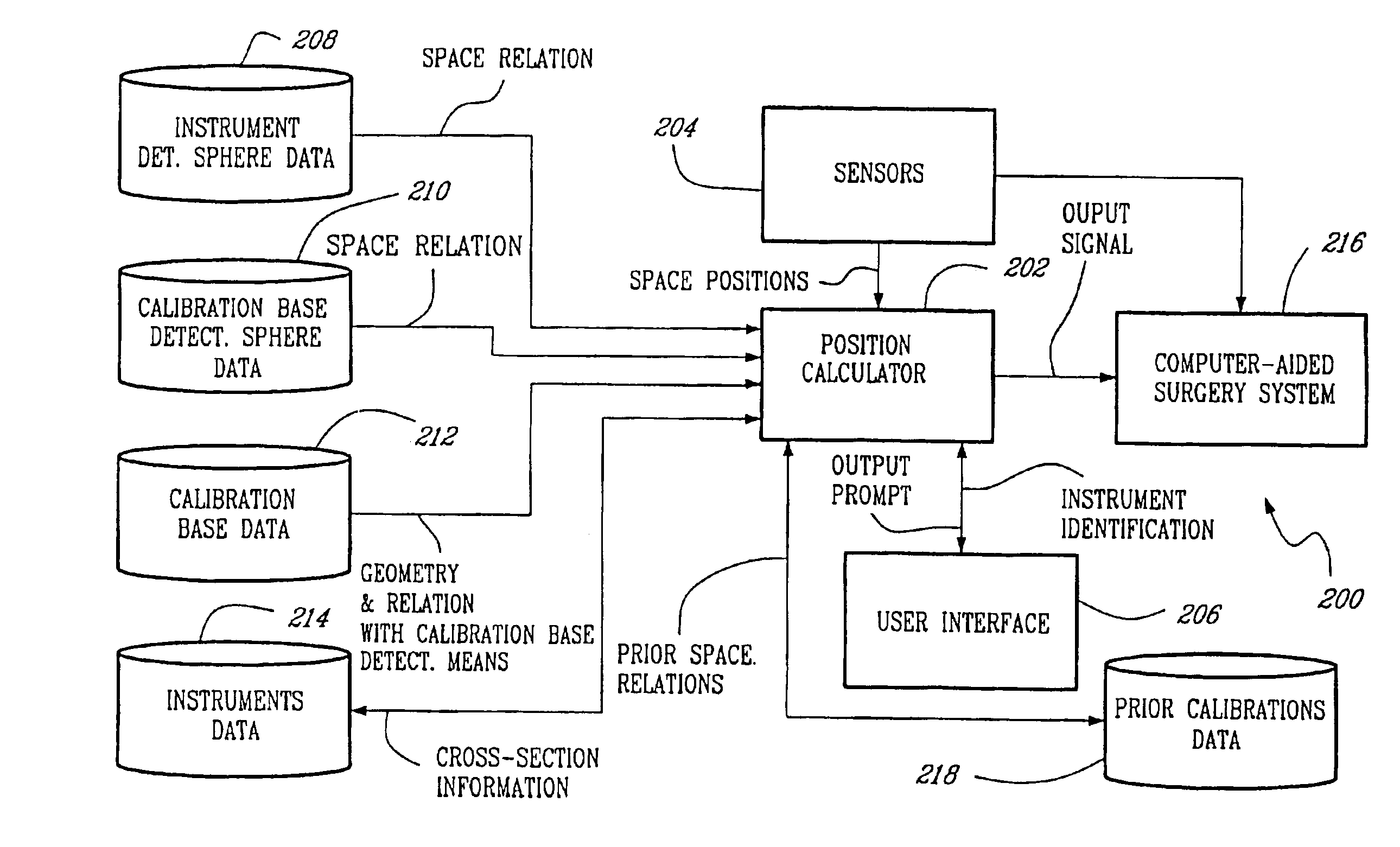
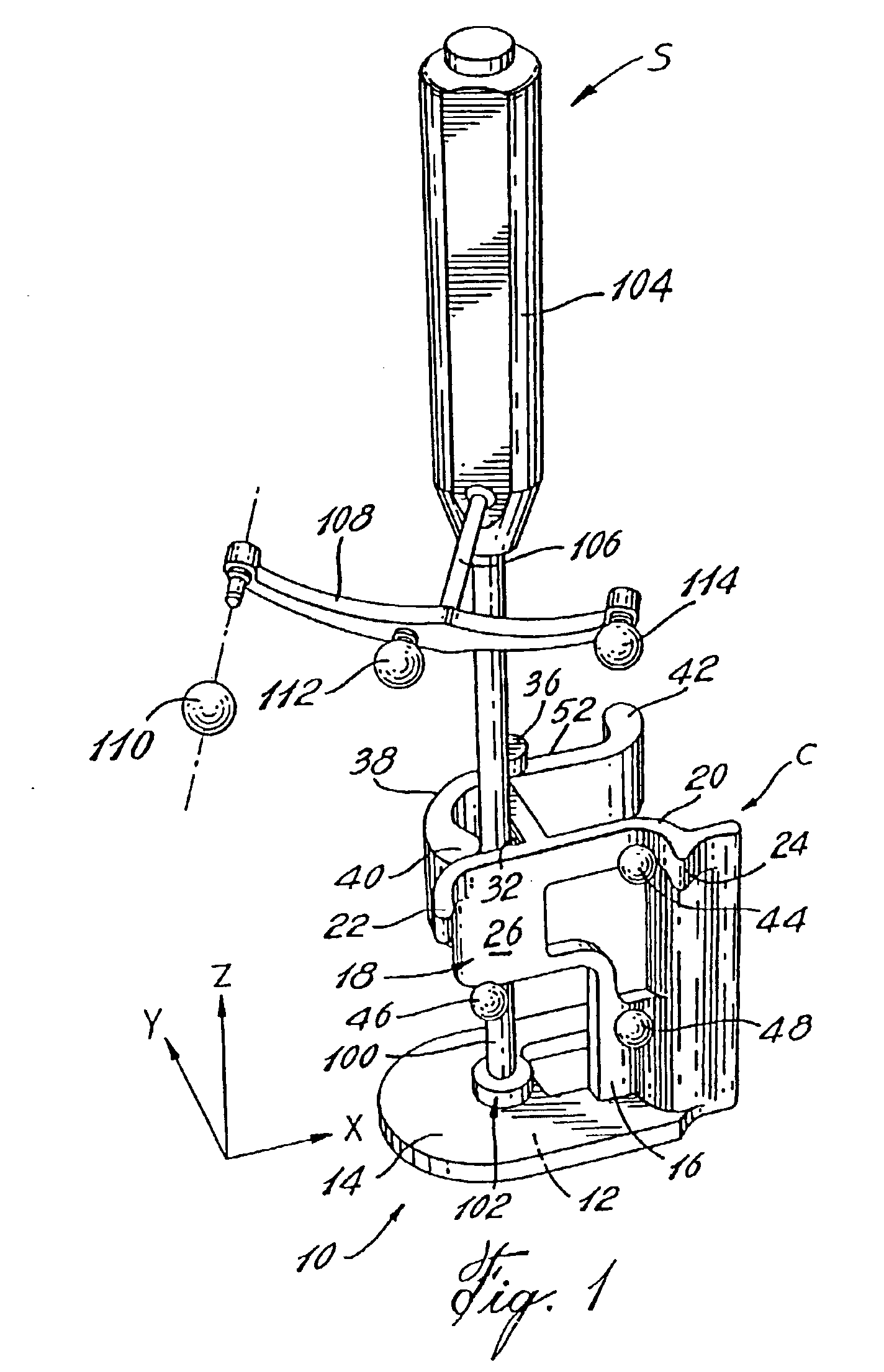
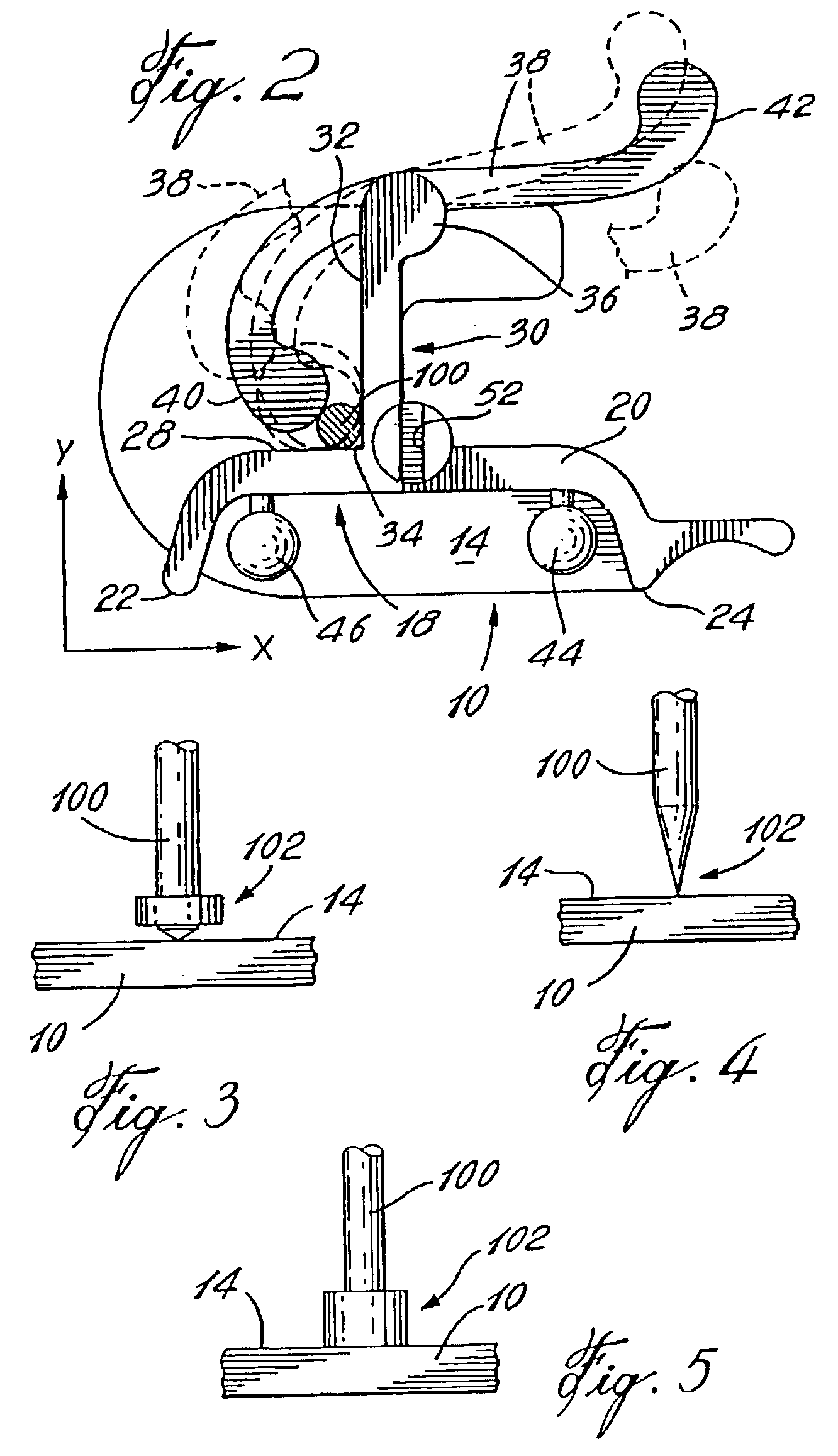
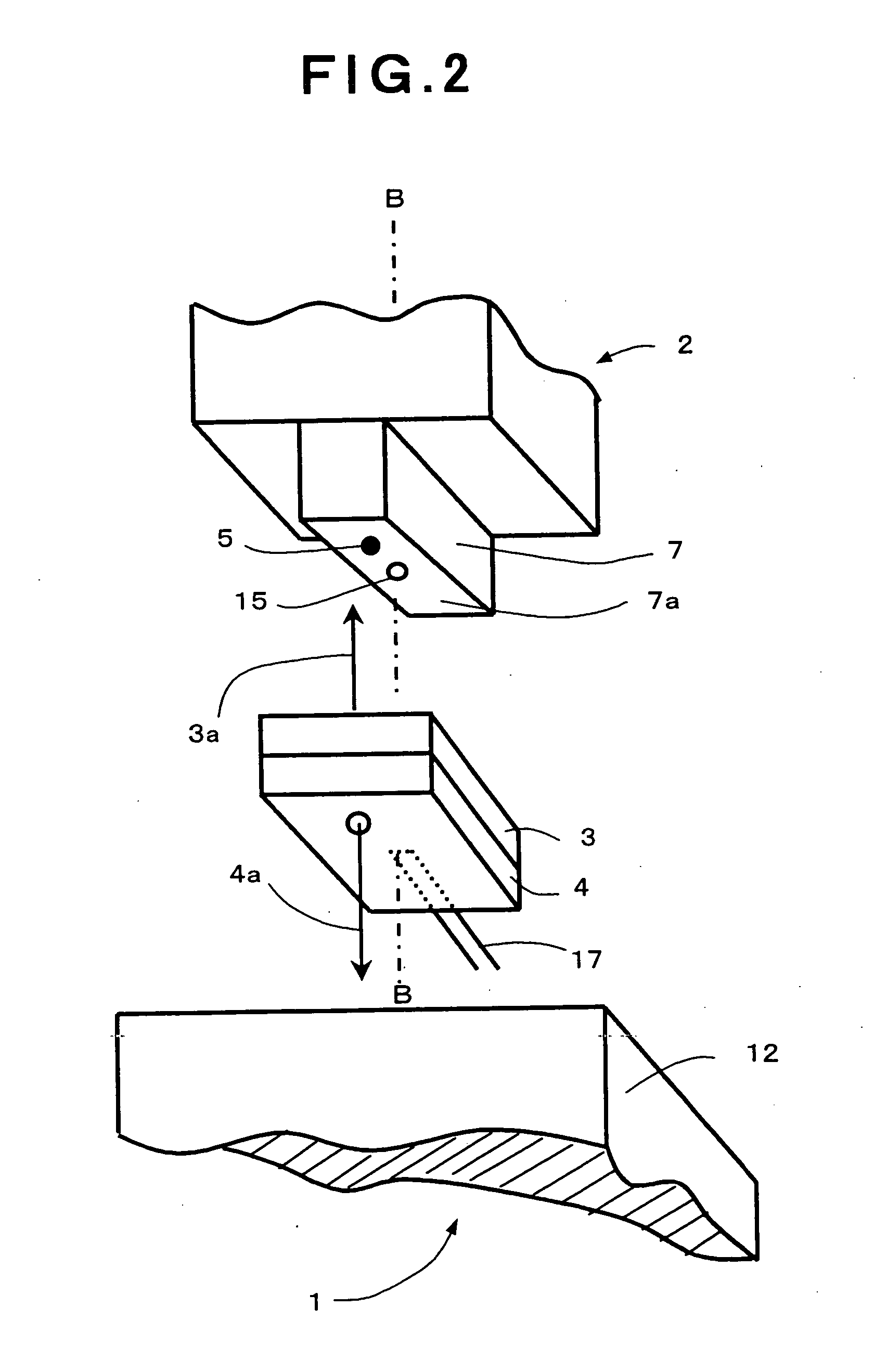
Automatic calibration system for computer-aided surgical instruments
InactiveUS6996487B2Simple and rapid in useEasy CalibrationSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer-assisted surgeryEngineering
A system for automatic calibration of instruments (S) having varying cross-sectional dimensions within a predetermined range and having detectable elements (110, 112, 113, 114) thereon for computer-aided surgery, comprising a calibration base (C) having detectable elements (43, 44, 46, 48) secured thereto for detecting a position and an orientation thereof in space by sensors (204) connected to a position calculator (202). The calibration base is adapted to receive and to releasably secure a working shaft (100) of any of the instruments (S) and provides an abutting surface (14) for a tip (102) thereof in such a way that a position and orientation of the tip (102) of the instrument (S) secured therein is calculable when working shaft cross-section dimensions thereof are known. The position calculator (202) receives instrument data (214) and calibration data (218) from an operator through a user interface (206) and stores the instrument data (214) and calibration data (218) for subsequent calibrations.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
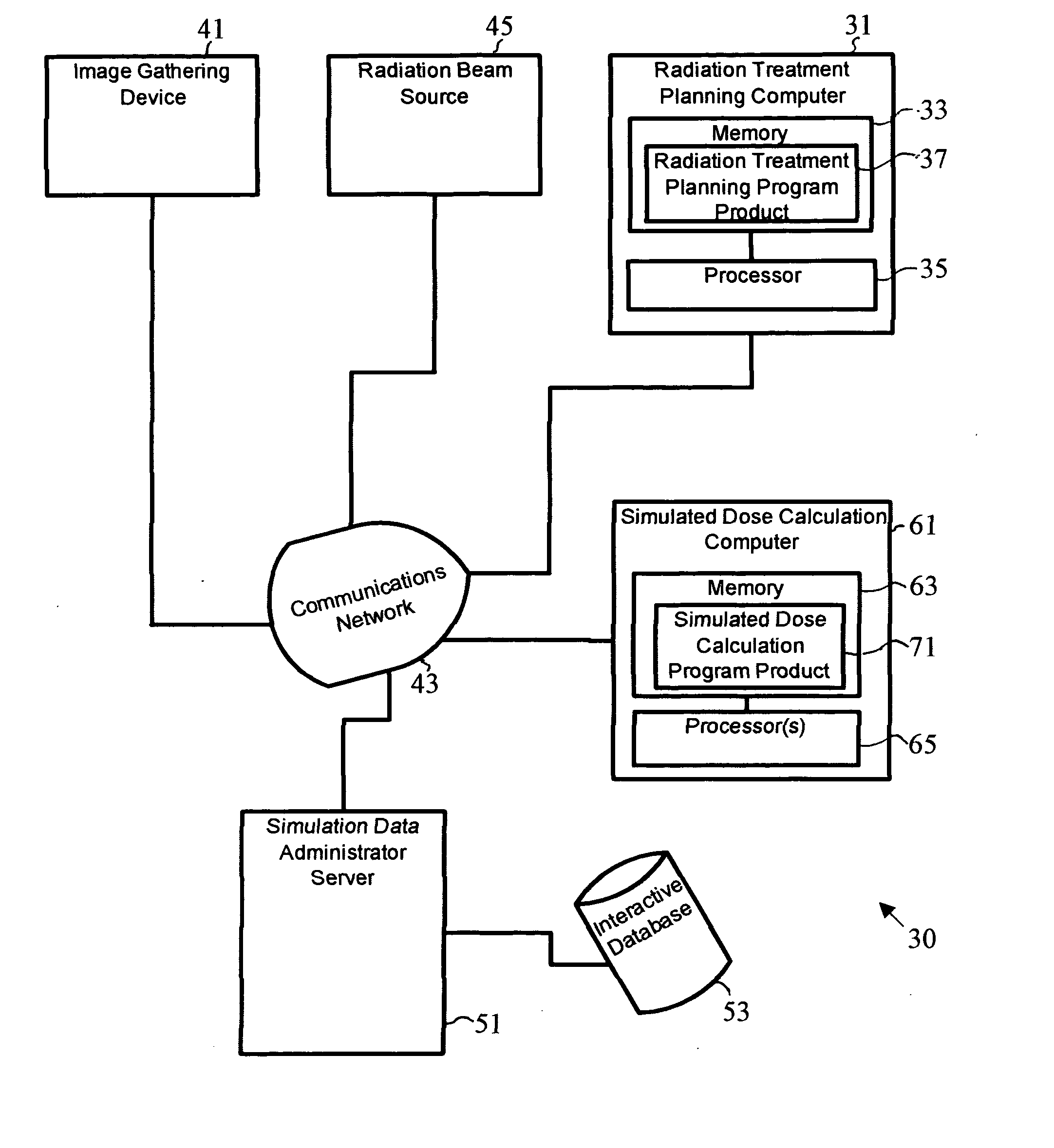
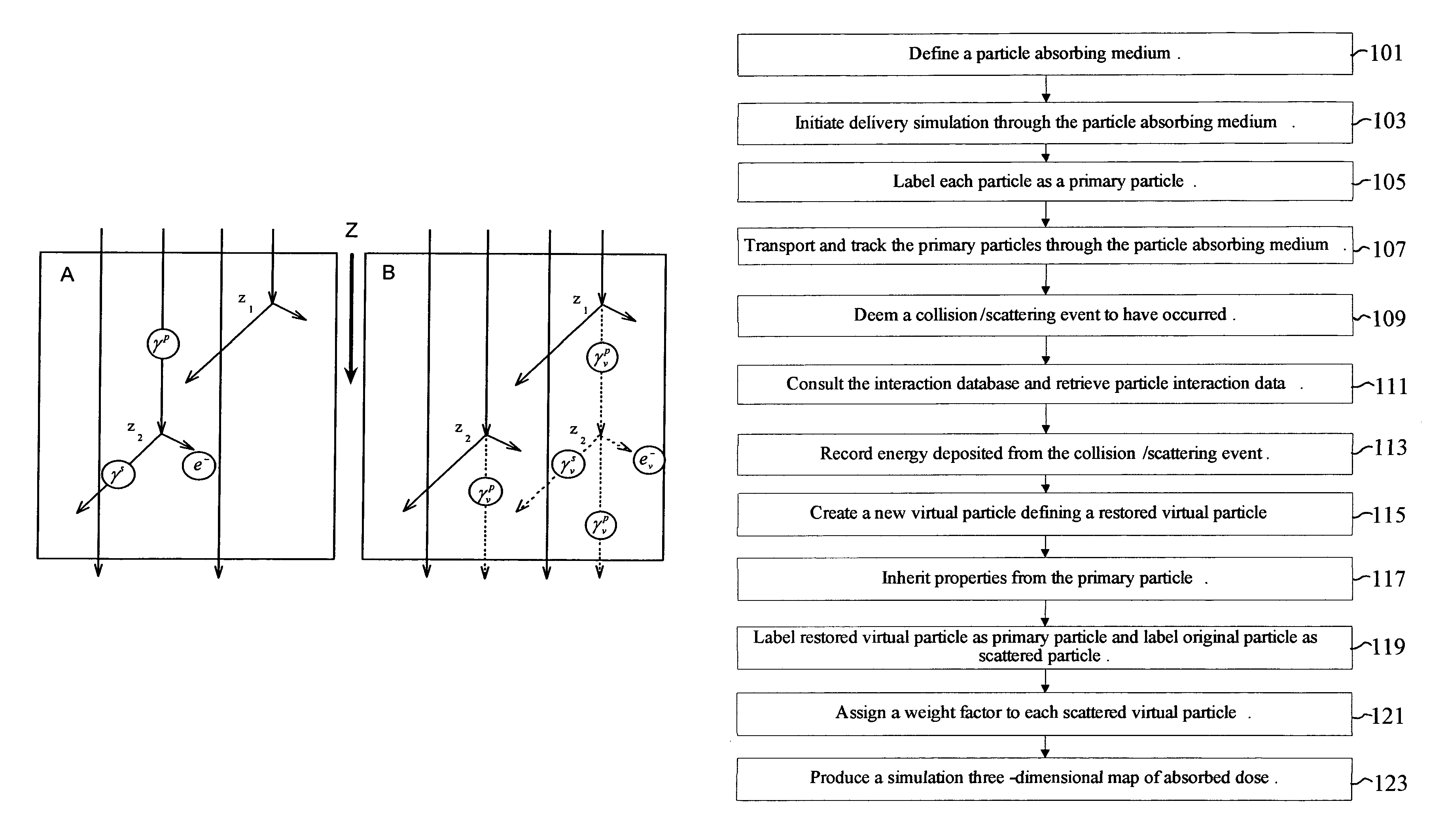
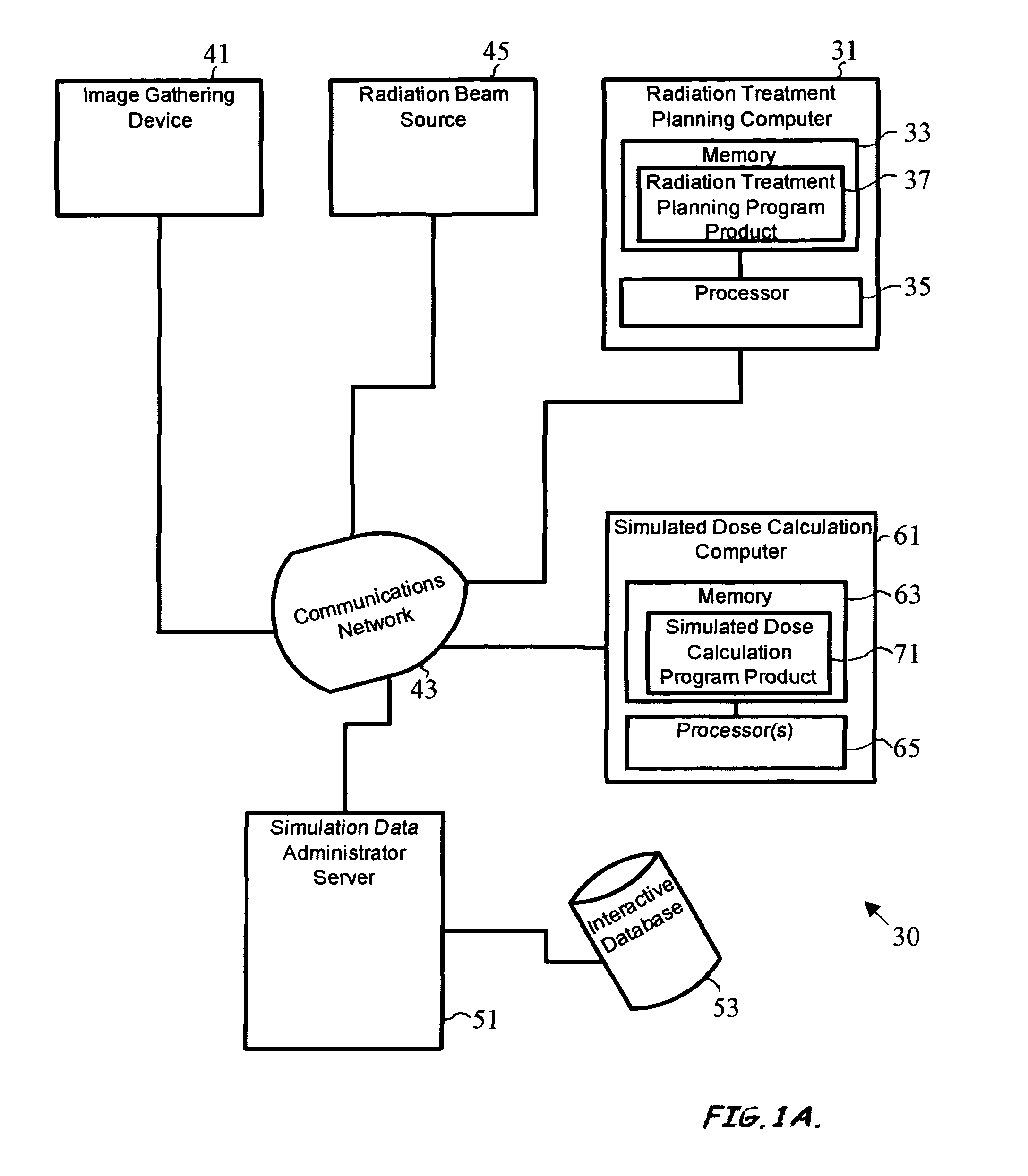
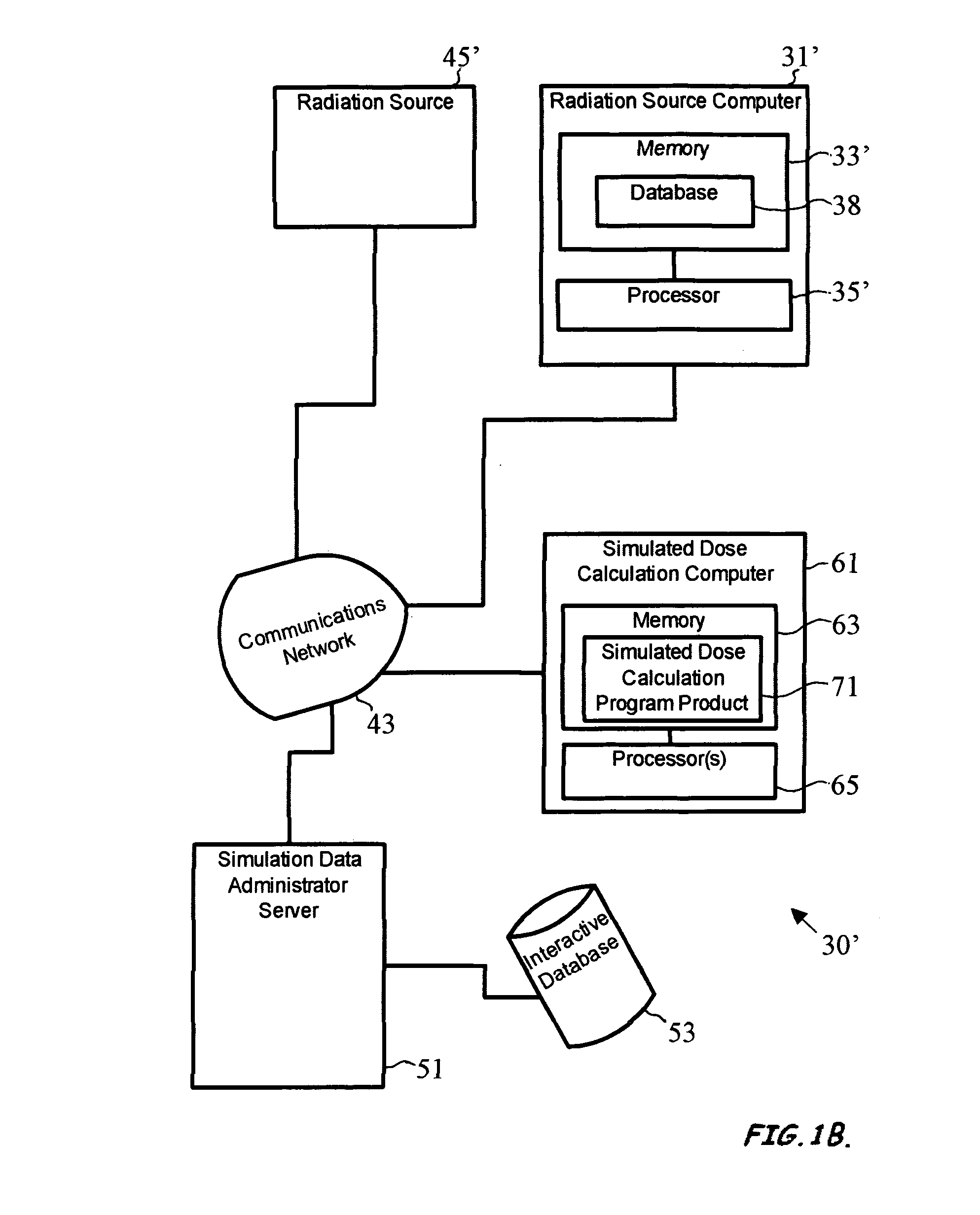
Variance reduction simulation system, program product, and related methods
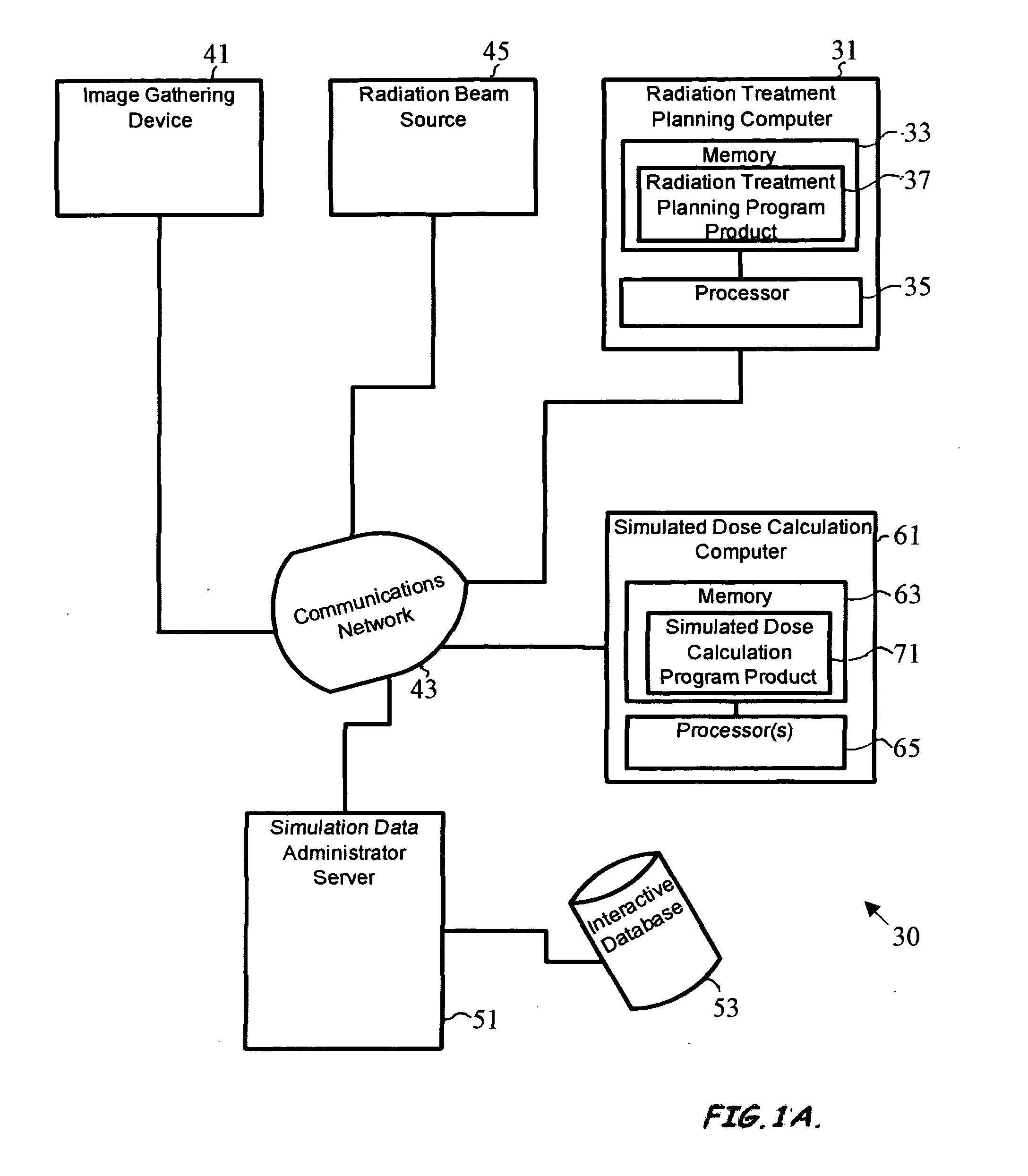
ActiveUS20060285640A1Constant varianceIncrease efficiencyDigital storageProbabilistic CADDose calculationParticle source
A system to provide enhanced computational efficiency in a simulation of particle transport through a medium, program product, and related methods are provided. The system can include a simulation data administrator server having access to an interaction database including records related to parameters describing interactions of particles in an absorbing medium to provide particle interaction parameters, and a simulated dose calculation computer in communication with the simulation data administrator server through a communications network. The system can also included simulated dose calculation program product stored in memory of the simulated dose calculation computer and including instructions that when executed by a processor causes the processor to perform for each of a plurality of particles deliverable from a particle source the operations of providing parameters for a medium to perform a Monte Carlo simulation to develop a map of simulated absorbed dose in the medium, and artificially adjusting simulation particle fluxes to achieve a substantially constant variance throughout a depth of the medium.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
Auto-focus apparatus, image-capture apparatus, and auto-focus method
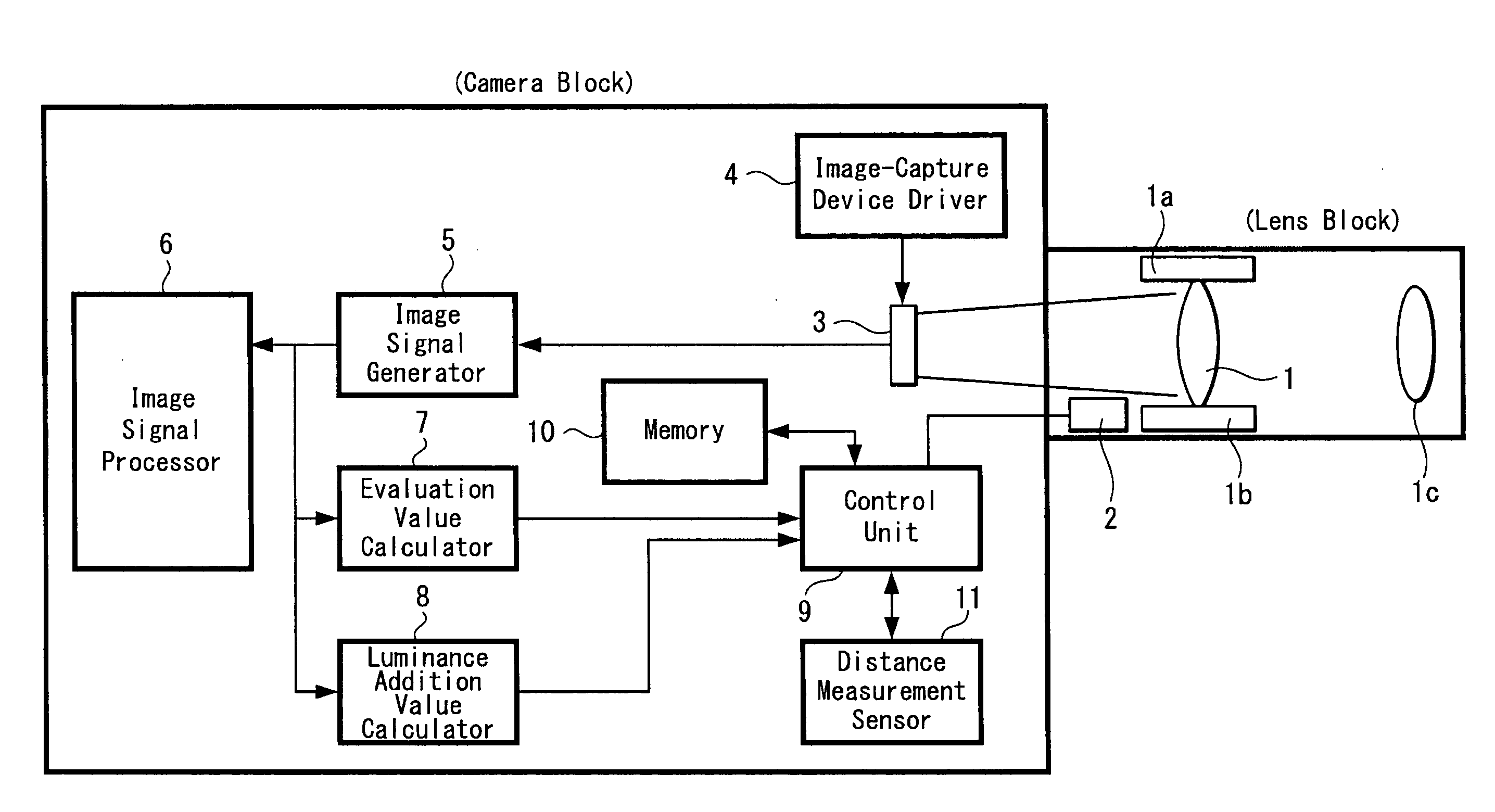
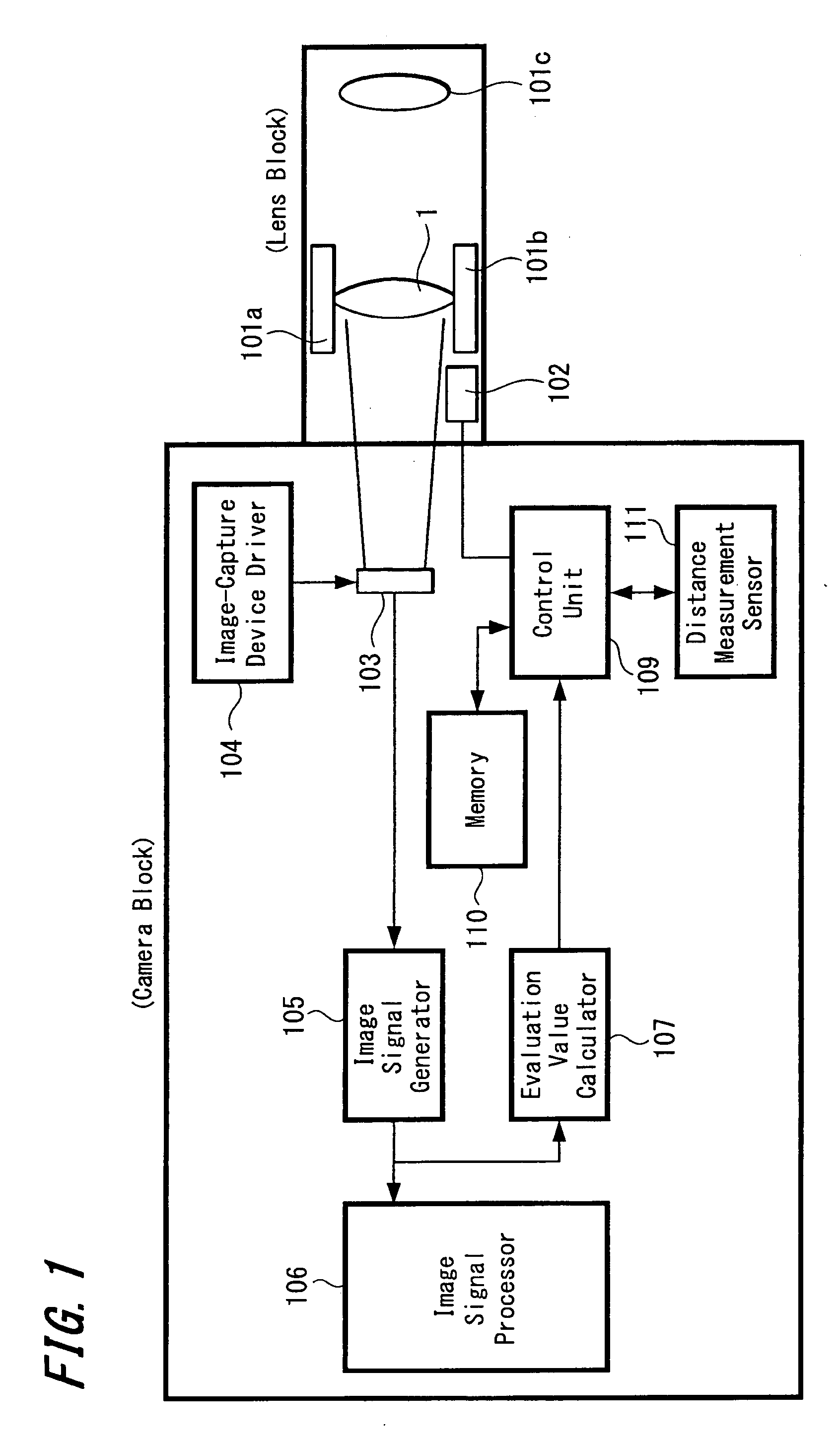
InactiveUS20080002960A1Maintain precisionSecuring searching accuracyTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementRelative maximumPeak value
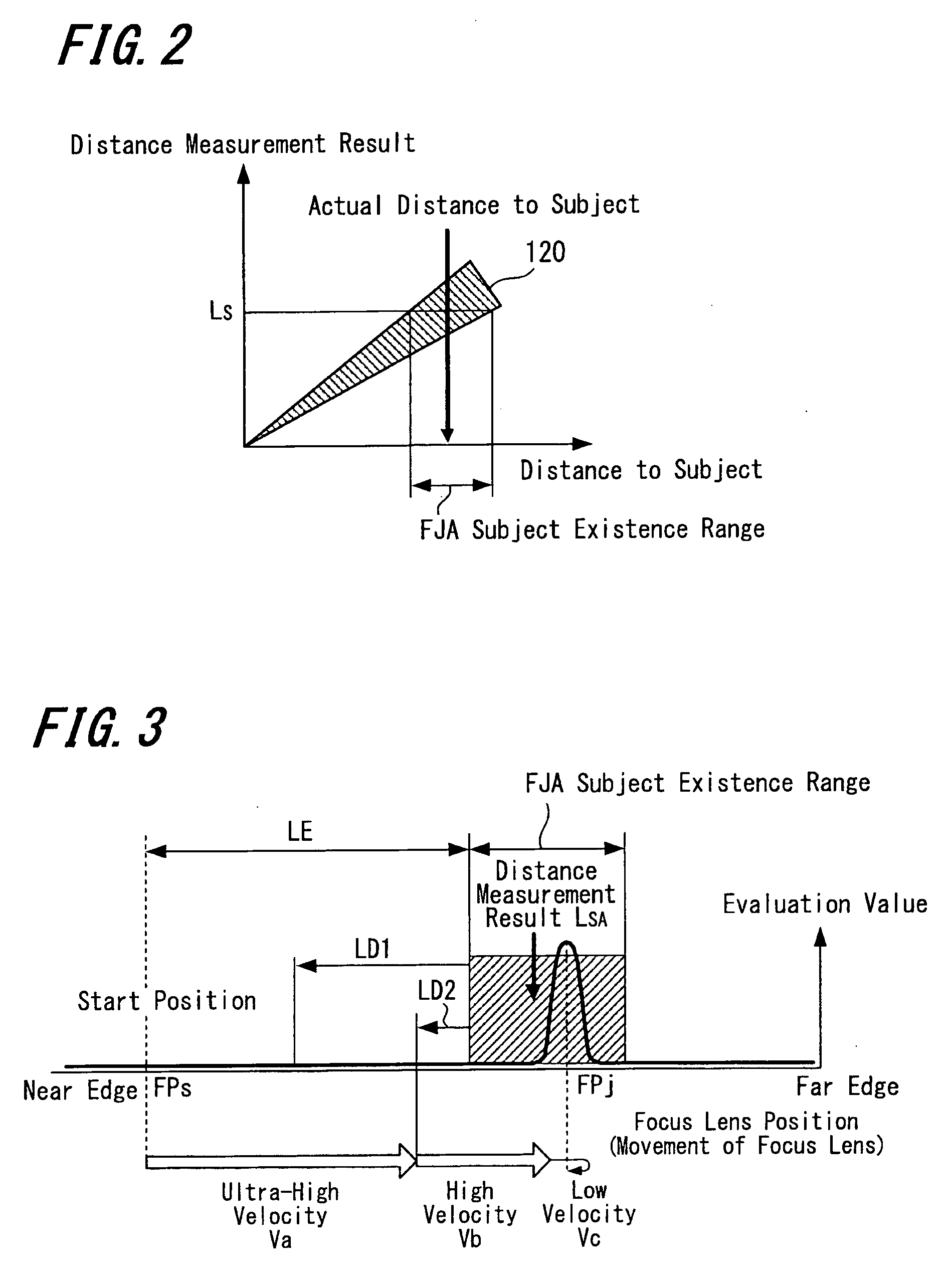
Disclosed is an auto-focus apparatus including an evaluation value calculator periodically calculating evaluation values using high frequency components of image signals in a specific region of a subject image, a distance measurement unit measuring a distance to a subject and output a distance measurement result, a control unit outputting instruction values based on the evaluation values and determines whether a subject image is in-focus or out-of-focus, and a storage storing the distance measurement results and lens positions. In the apparatus, after searching the peak of the evaluation values, the control unit returns the lens to the position at which the relative maximum has been detected, obtains evaluation values, stores lens positions and distance measurement results when the evaluation values satisfy a prescribed condition, and retrieves distance measurement results and lens positions when the number of times that results are stored reaches a prescribed number, and computes a correction amount.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and method for the measurement of electrical conductivity and dielectric constant of high impedance fluids
ActiveUS20100188111A1Low costLow component requirementsFluid resistance measurementsMaterial impedanceMicrocontrollerElectron
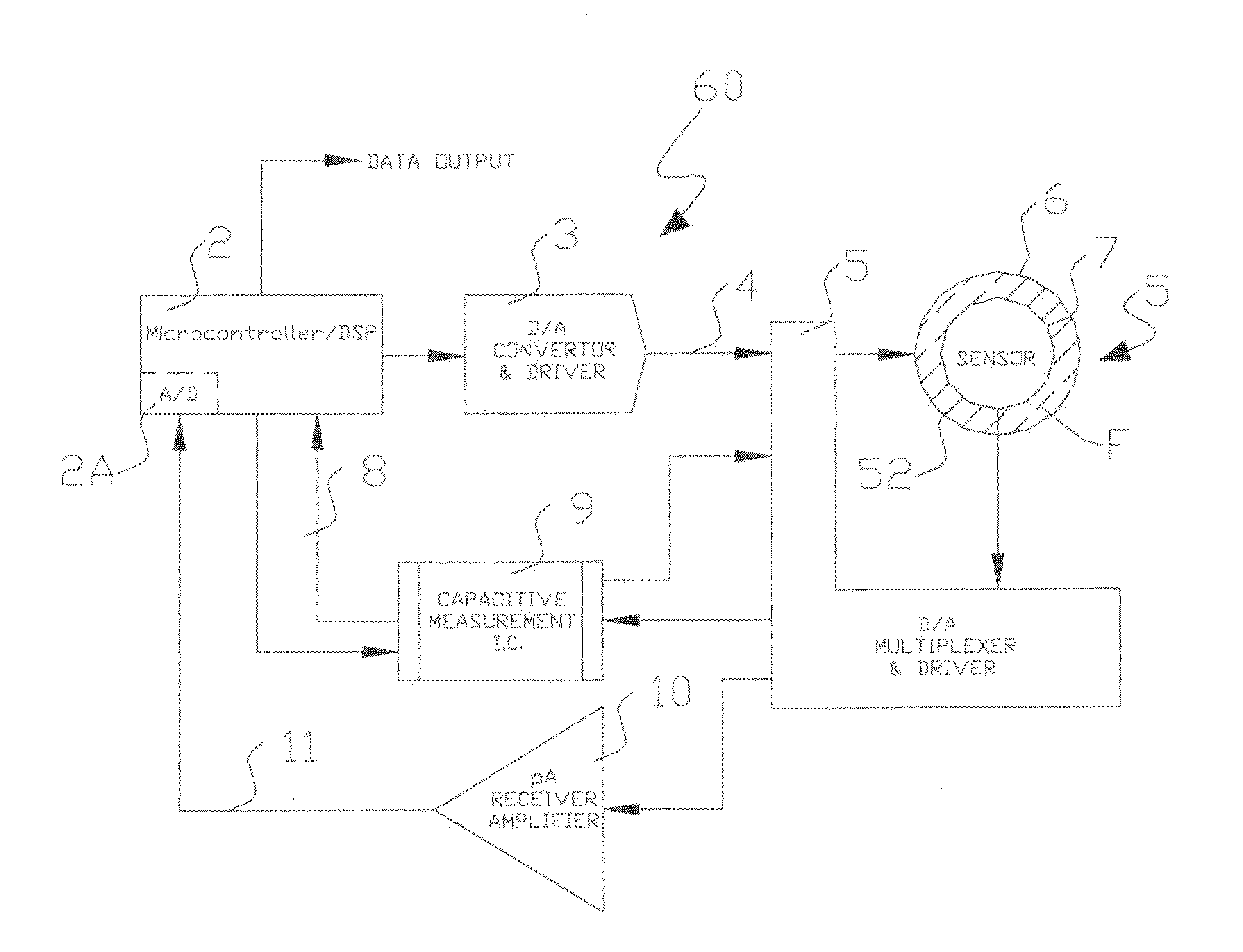
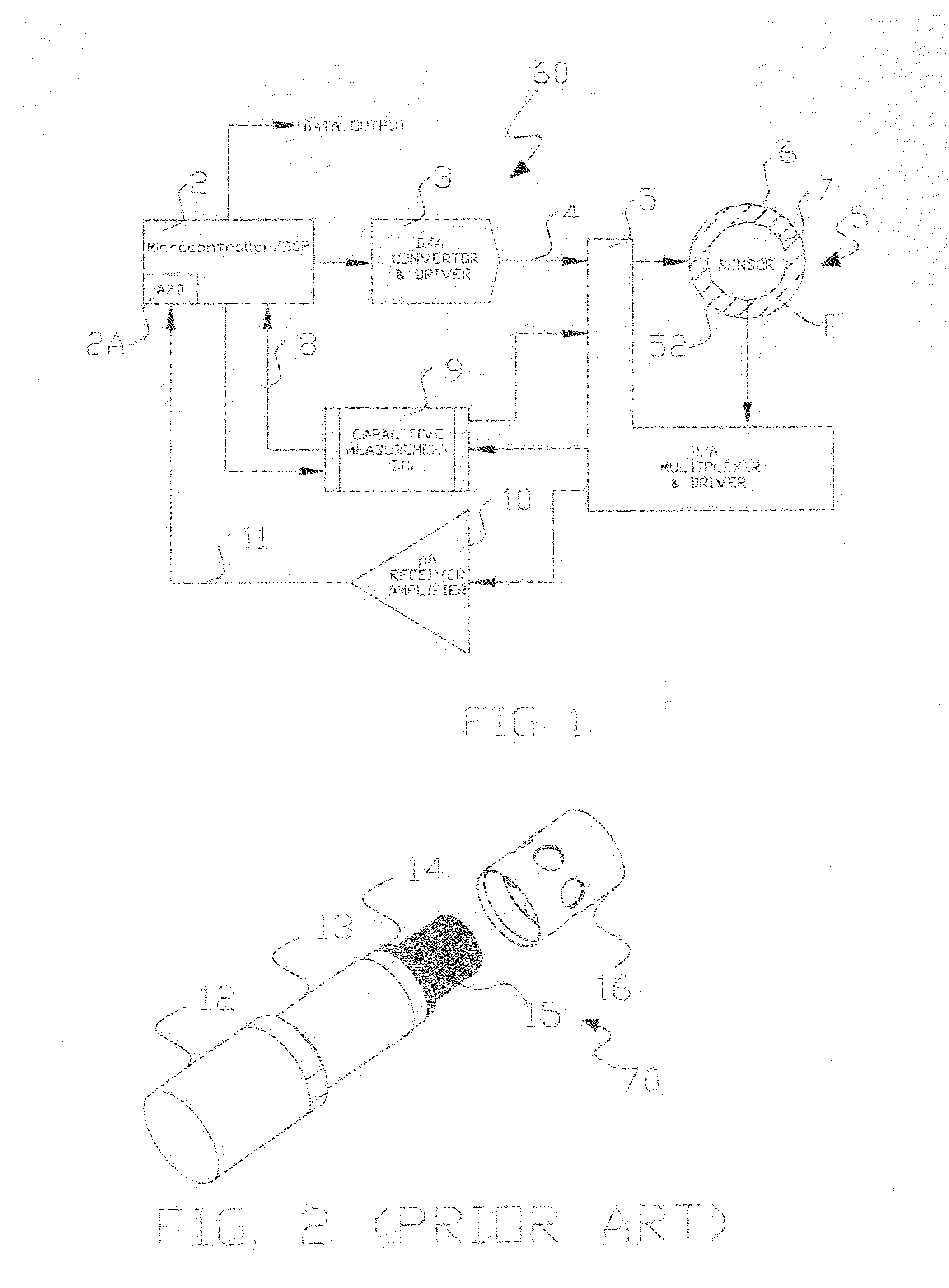
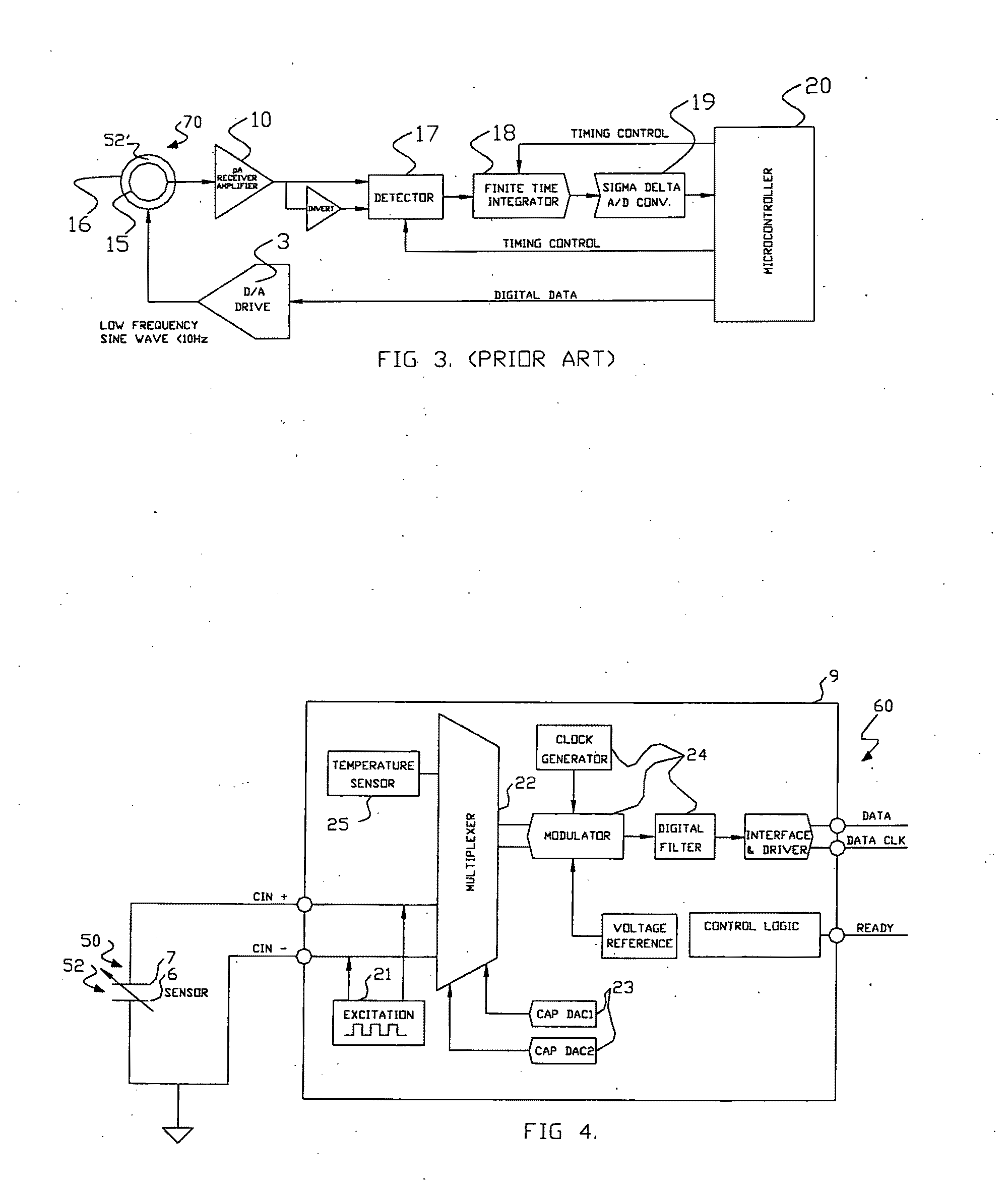
A sensor, a system of direct measurement using that sensor, and a method of direct and simultaneous measurement of conductivity and dielectric constant of a fluid, particularly high impedance, hydrocarbon-based fluids. The sensor has a cell that holds the fluids to be measured between a single pair of coaxial, bare metal electrodes connected through interface circuitry to measurement circuitry preferably implemented in one or several IC's. The sensor has a mutually compatible electrode geometry that provides both the correct cell constant for measurement of conductivity of hydrocarbons fluids (typical range 0-100,000 pS / cm), and a bulk capacitance (for use in dielectric constant measurement) in the range of measure of readily available low cost commercial IC's (having a typical capacitance measurement span of <10 pF, with a total bulk capacitance at the chip of <20 pF). The cell conductivity constant for use with hydrocarbon-based oils having a conductivity in the range of 1 to 500,000 pS / M is preferably less than or equal to about 0.1. The cell bulk capacitance with hydrocarbon fluids inside the sensor results in a bulk capacitance of at least about 4 pF. In one embodiment, the electronic circuitry is a Microcontroller / DSP that both generates synchronous drive signals at various frequencies, for both conductivity and dielectric constant measurements while directly digitizing and numerically processing the sensor output.
Owner:FALMOUTH SCI +1
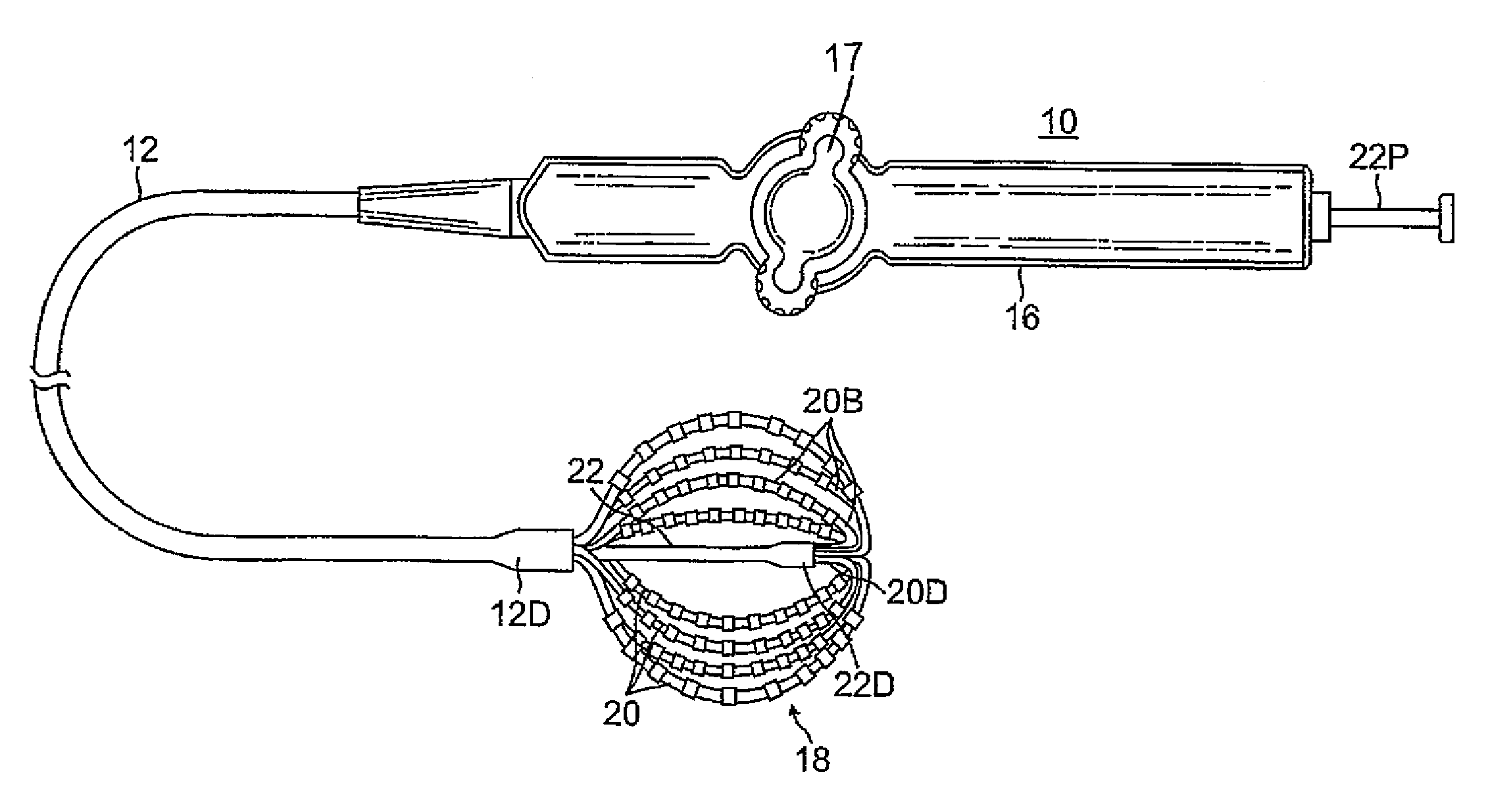
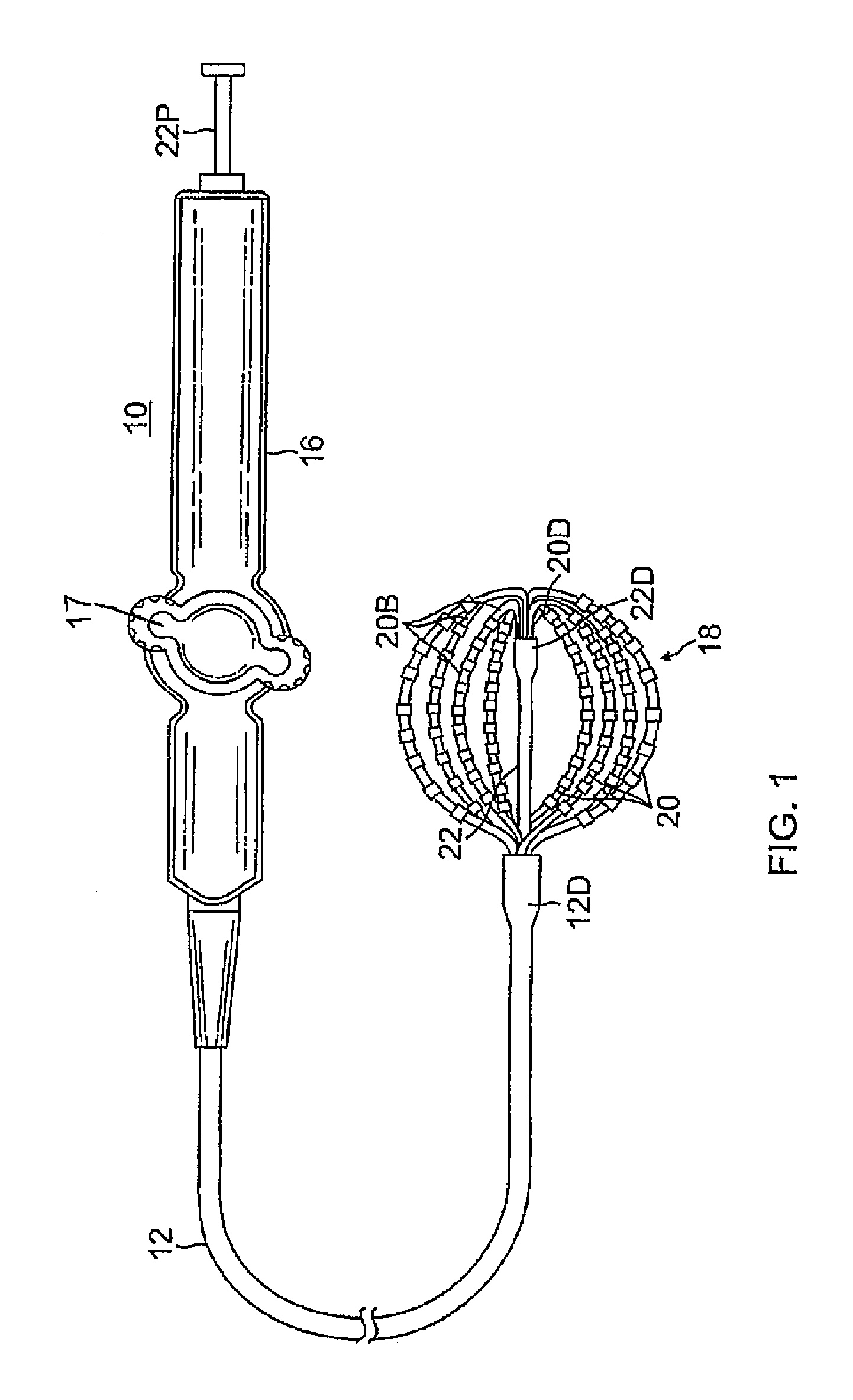
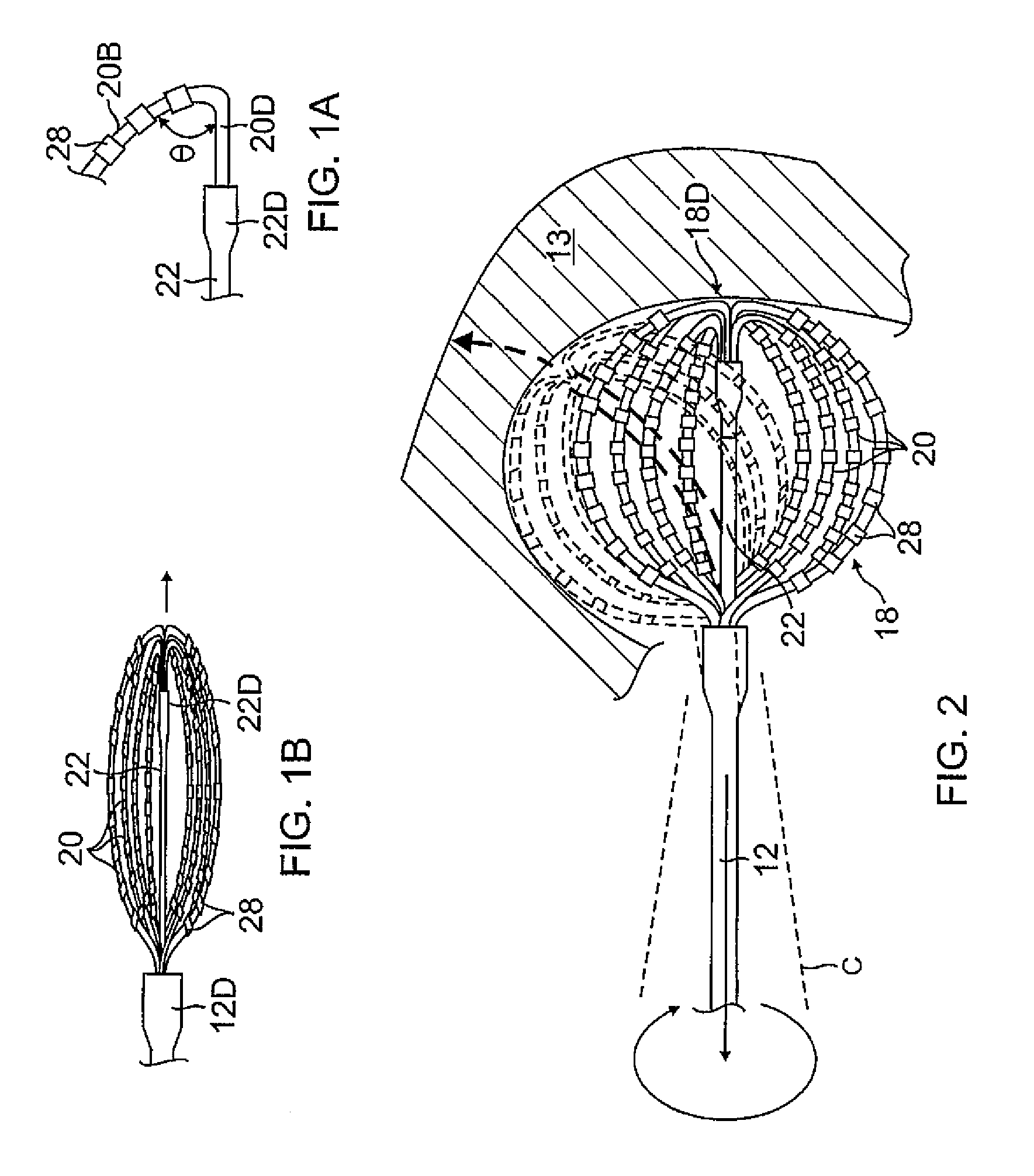
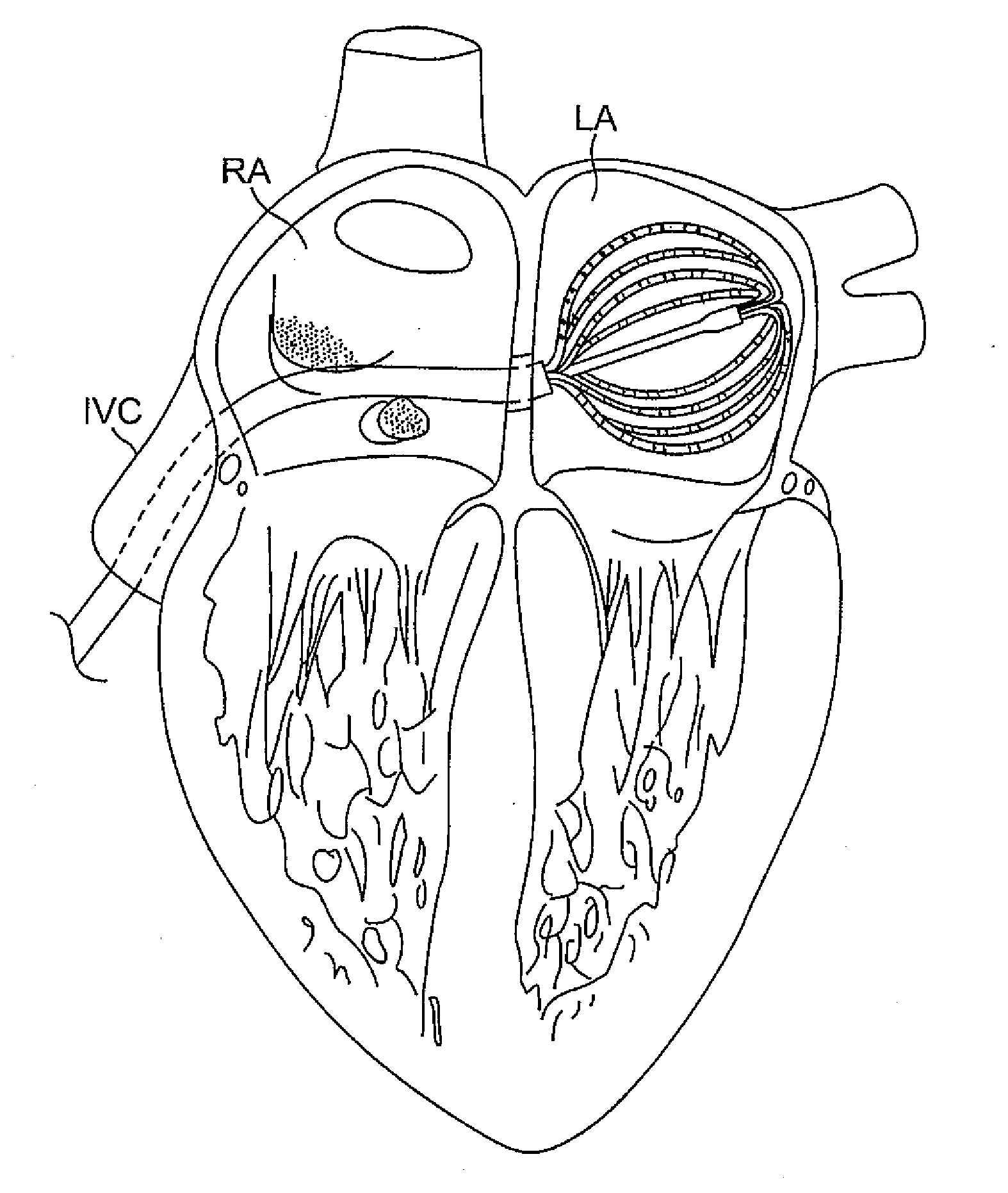
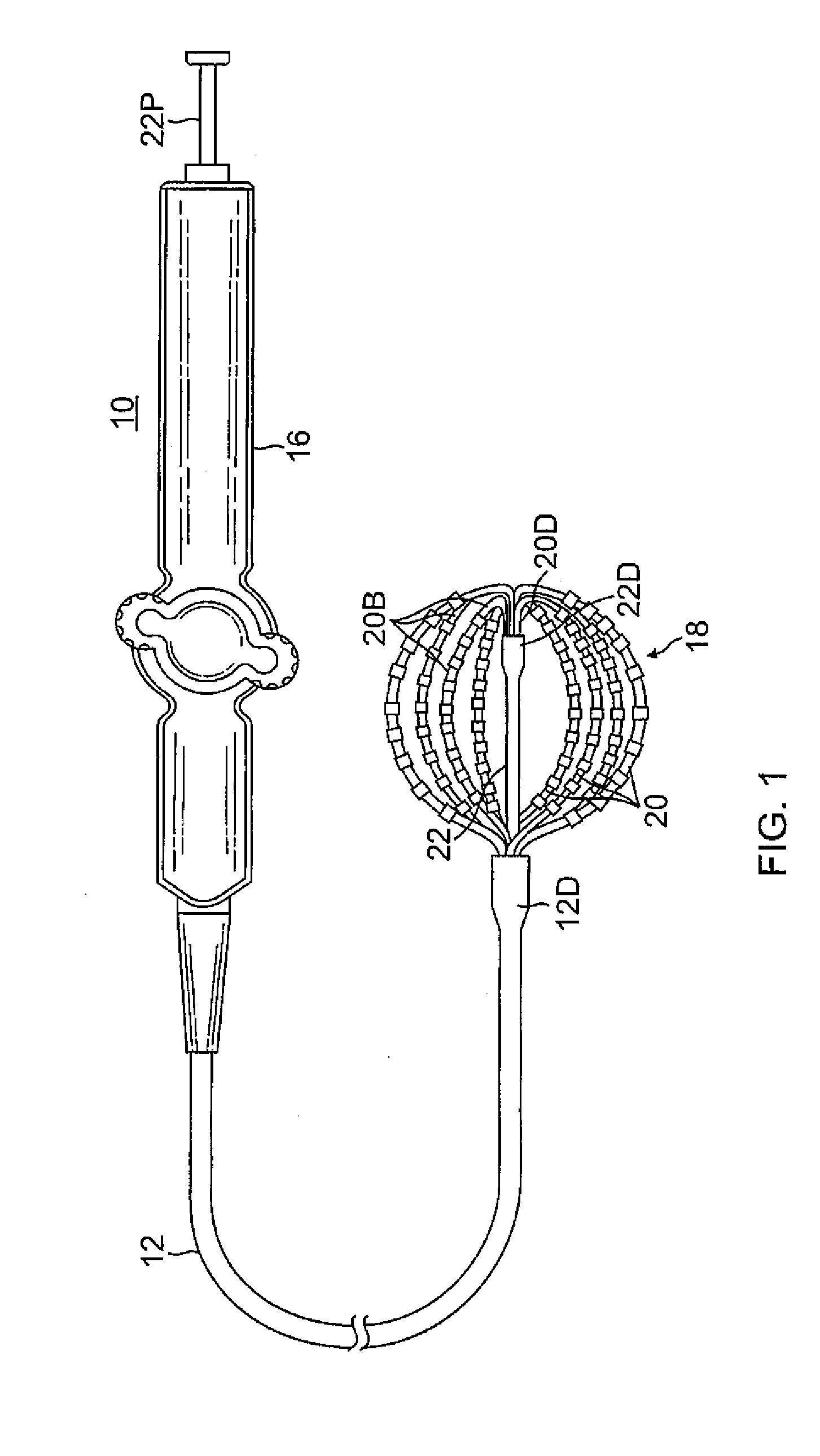
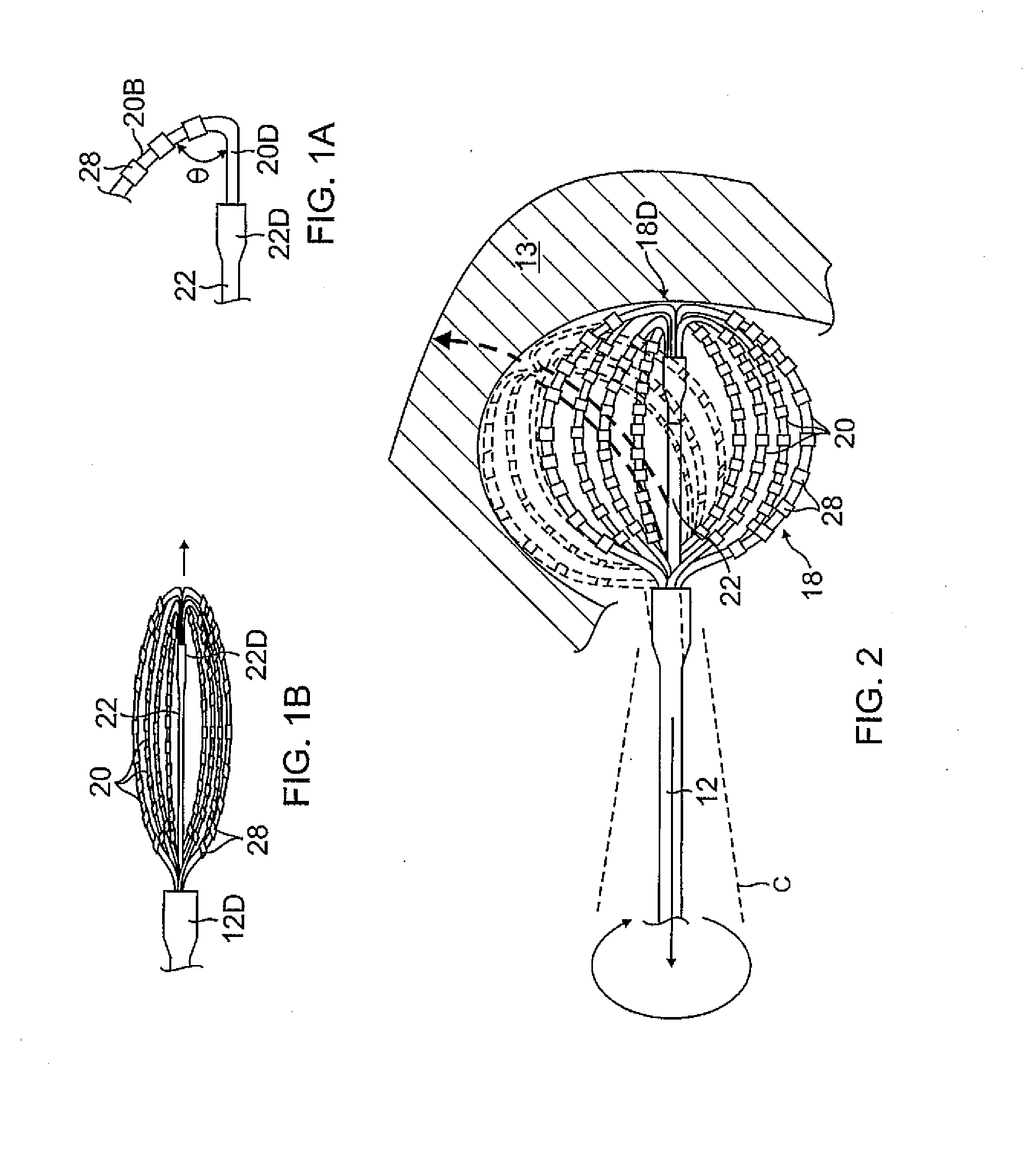
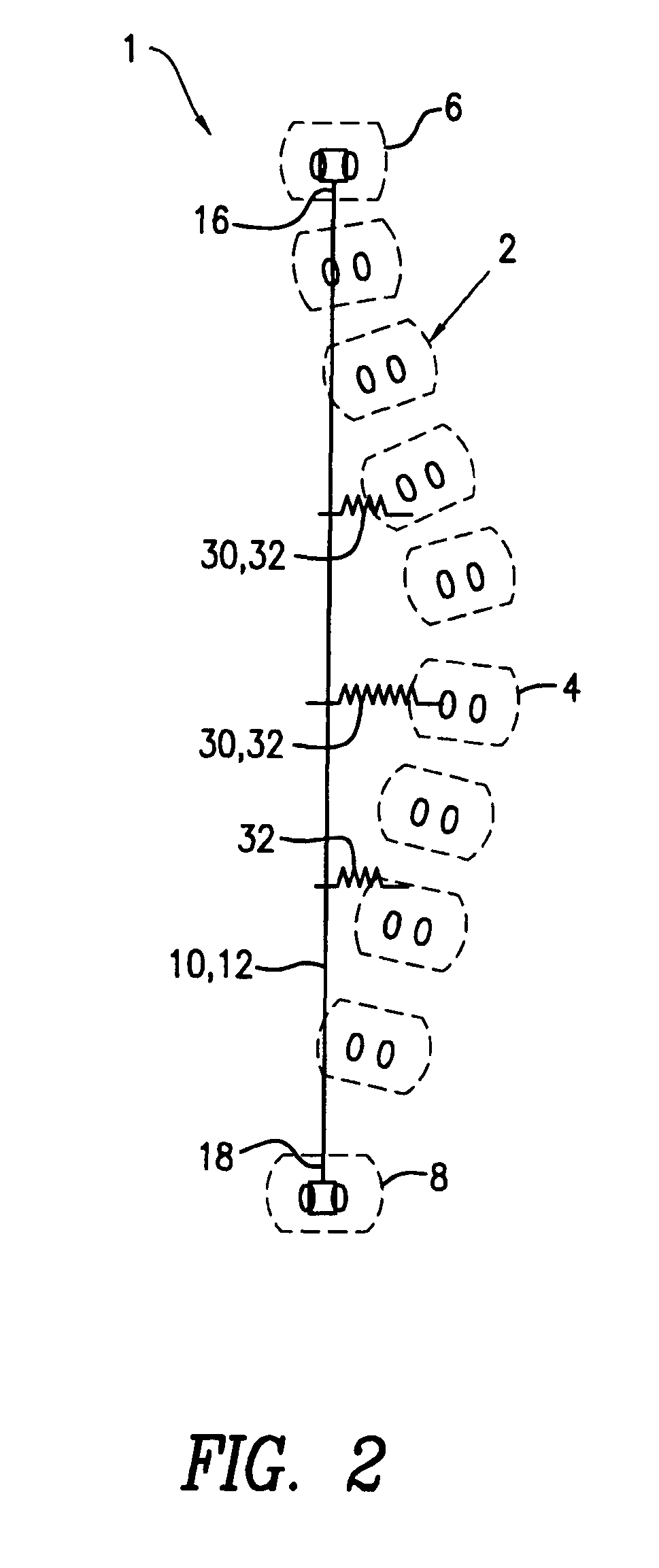
Basket catheter with deflectable spine
ActiveUS9204929B2Improved control and placementConstant precisionElectrocardiographyCatheterDilatorActuator
A catheter adapted for mapping and / or ablation in the atria has a basket-shaped electrode array with two or more location sensors with a deflectable expander. The catheter has comprises a catheter body, a basket electrode assembly at a distal end of the catheter body, and a control handle at a proximal end of the catheter body. The basket electrode assembly has a plurality of electrode-carrying spines and an expander that is adapted for longitudinal movement relative to the catheter body for expanding and collapsing the assembly via a proximal end portion extending past the control handle that can be pushed or pulled by a user. The expander is also adapted for deflection in responsive to an actuator on the control handle that allows a user to control at least one puller wire extending through the catheter body and the expander.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Basket catheter with deflectable spine
ActiveUS20150080693A1Improved control and placementConstant precisionElectrocardiographyCatheterSpinal columnDilator
A catheter adapted for mapping and / or ablation in the atria has a basket-shaped electrode array with two or more location sensors with a deflectable expander. The catheter has comprises a catheter body, a basket electrode assembly at a distal end of the catheter body, and a control handle at a proximal end of the catheter body. The basket electrode assembly has a plurality of electrode-carrying spines and an expander that is adapted for longitudinal movement relative to the catheter body for expanding and collapsing the assembly via a proximal end portion extending past the control handle that can be pushed or pulled by a user. The expander is also adapted for deflection in responsive to an actuator on the control handle that allows a user to control at least one puller wire extending through the catheter body and the expander.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Chip mounting device and callibration method therein
InactiveUS20040026006A1Reduce calibration timeReduce the number of timesLamination ancillary operationsControlling laminationPattern recognitionIdentification device
A chip mounting device comprising a first recognition means (3) for recognizing a first recognition mark (5) on the upper chip-retainable head (2) side, a second recognition means (4) for recognizing a second recognition mark (6) on the lower substrate-retainable stage (1) side, a third recognition means (18) for recognizing the recognition marks (5, 6) concurrently when the first recognition mark (5) is brought close to or into contact with the second recognition mark (6), and a temperature detection means (17) attached to the first recognition means (3) or the second recognition means (4), wherein calibration is carried out based on the recognition of the recognition marks when the temperature detection means (17) detects a beyond-allowance temperature change, whereby permitting a high-accuracy, efficient calibration independently of mechanical deformation and temperature change in environmental atmosphere.
Owner:TORAY ENG CO LTD
Variance reduction simulation system, program product, and related methods
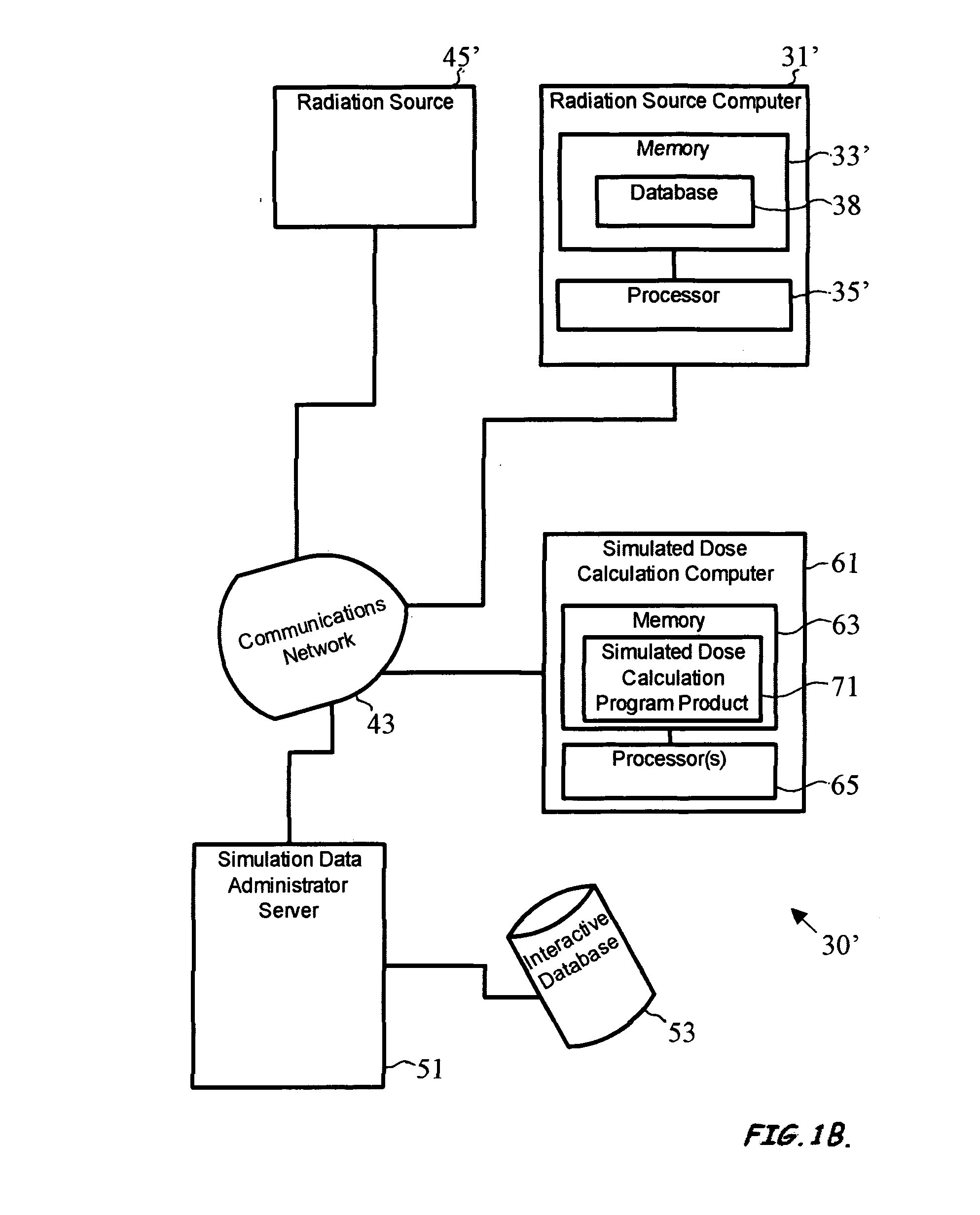
ActiveUS8125813B2Improve computing efficiencyCost efficientDigital storageProbabilistic CADParticle interactionComputer science
A system to provide enhanced computational efficiency in a simulation of particle transport through a medium, program product, and related methods are provided. The system can include a simulation data administrator server having access to an interaction database including records related to parameters describing interactions of particles in an absorbing medium to provide particle interaction parameters, and a simulated dose calculation computer in communication with the simulation data administrator server through a communications network. The system can also included simulated dose calculation program product stored in memory of the simulated dose calculation computer and including instructions that when executed by a processor causes the processor to perform for each of a plurality of particles deliverable from a particle source the operations of providing parameters for a medium to perform a Monte Carlo simulation to develop a map of simulated absorbed dose in the medium, and artificially adjusting simulation particle fluxes to achieve a substantially constant variance throughout a depth of the medium.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
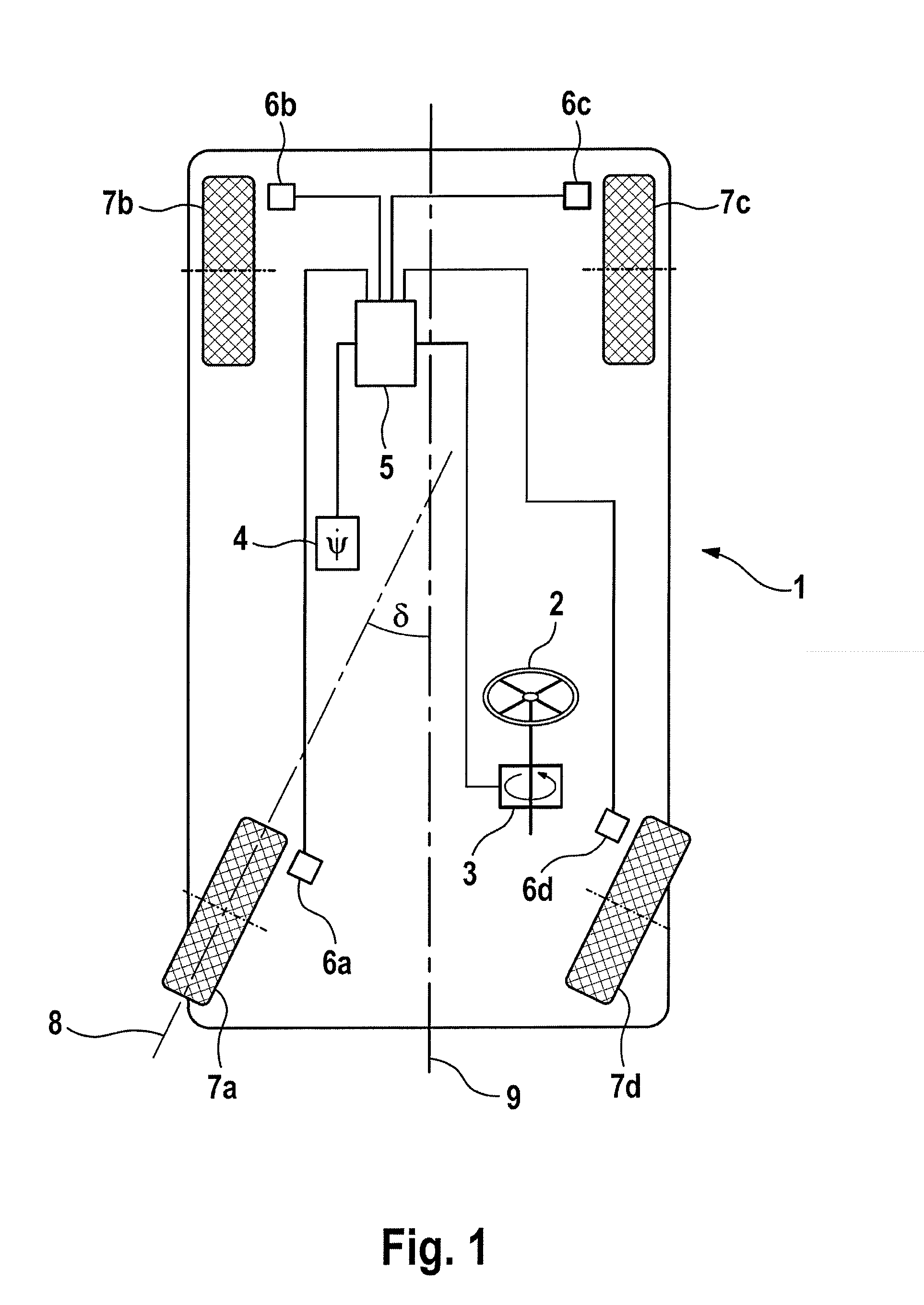
Determination of steering angle for a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20130151066A1Constant precisionEasy to carryVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesContinuous measurementMobile vehicle
Method and control device for determining a steering angle of a motor vehicle, wherein a theoretical steering angle is calculated by a vehicle model and a measured steering angle is determined with a steering angle sensor, and the difference between the measured and theoretical steering angles is determined, wherein at least one data record including a number of successive measured values is acquired, and a correction constant for the measured steering angle is determined from the mean value of the differences between the theoretical steering angle and the measured steering angle. According to the invention, a confidence level, which changes incrementally between successive data records, is calculated by travel conditions present during the acquisition of the data record and / or an analysis of the data record.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
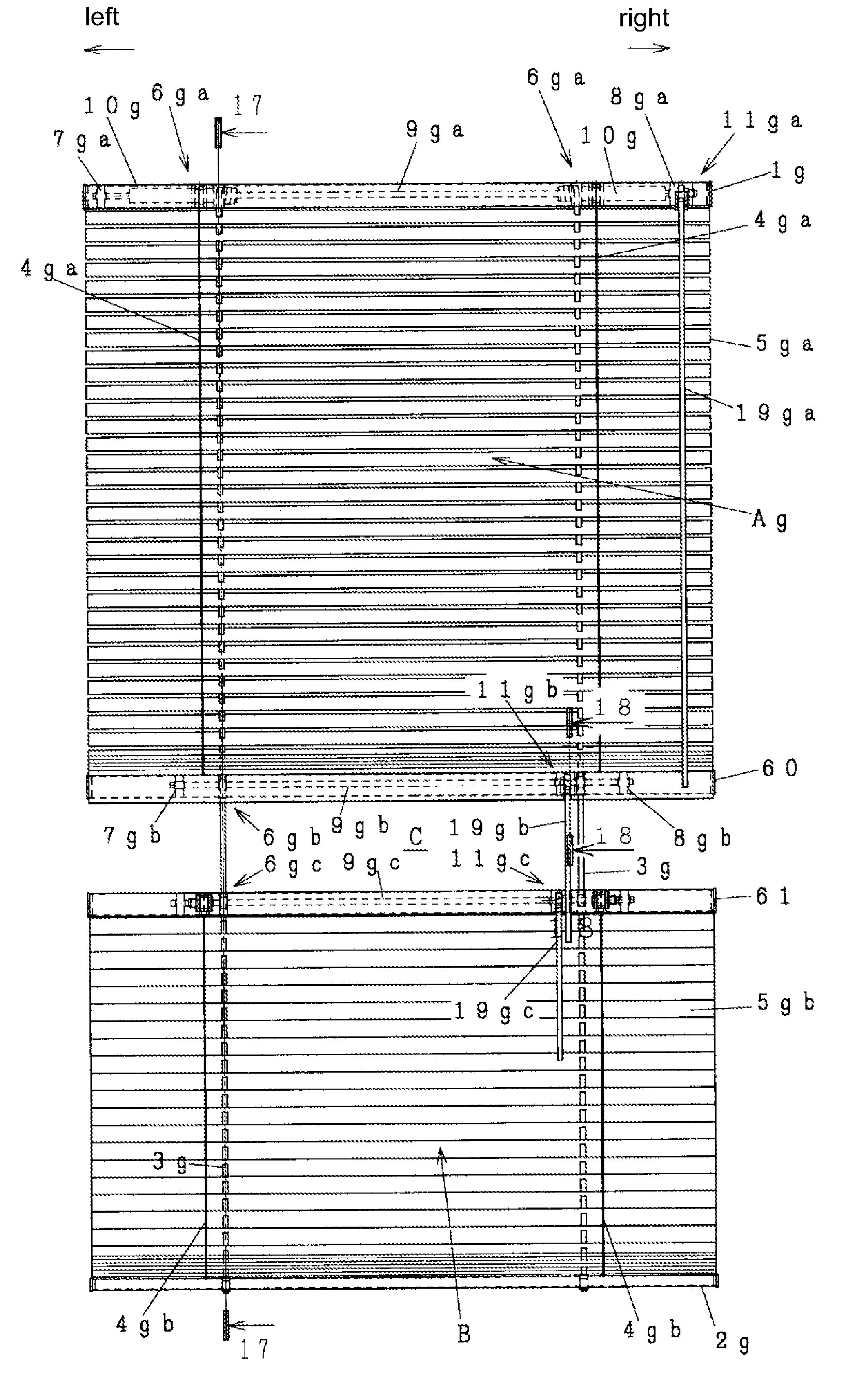
Blind
InactiveUS8079398B2Increase elasticityIncrease flexibilityExtensible doors/windowsCurtain accessoriesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:TSUKAMOTO TATUSABU
Thin film transistor array inspection device
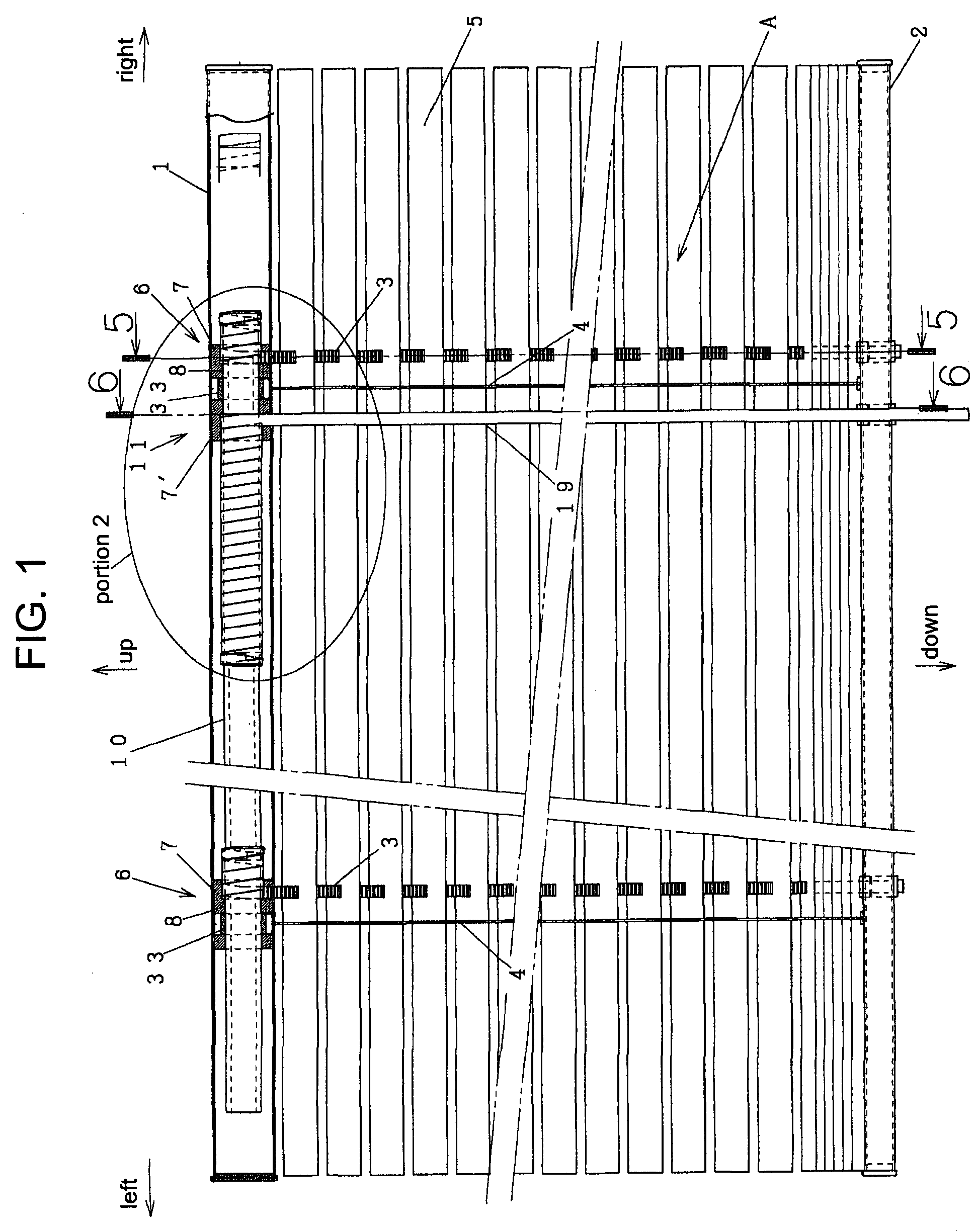
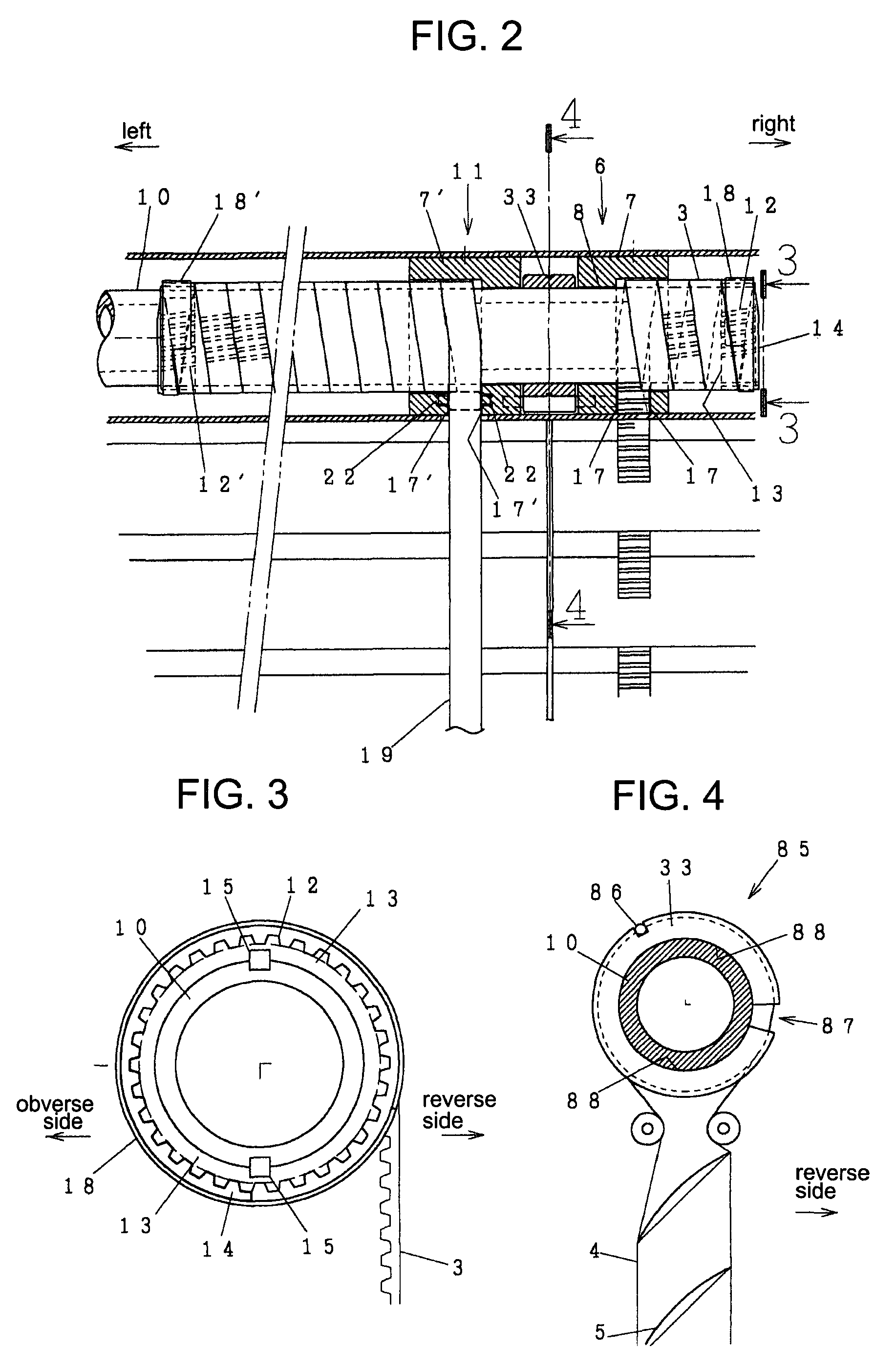
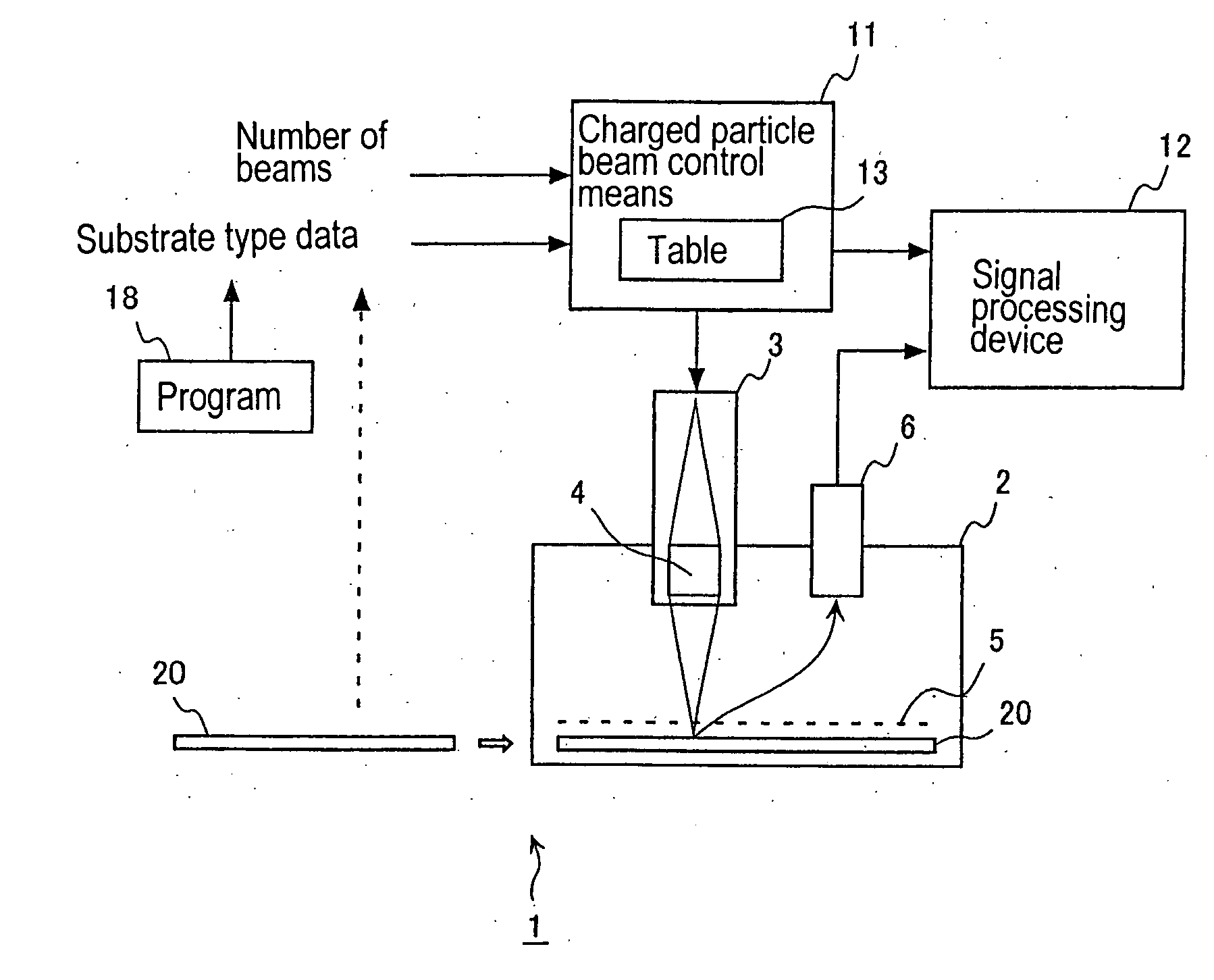
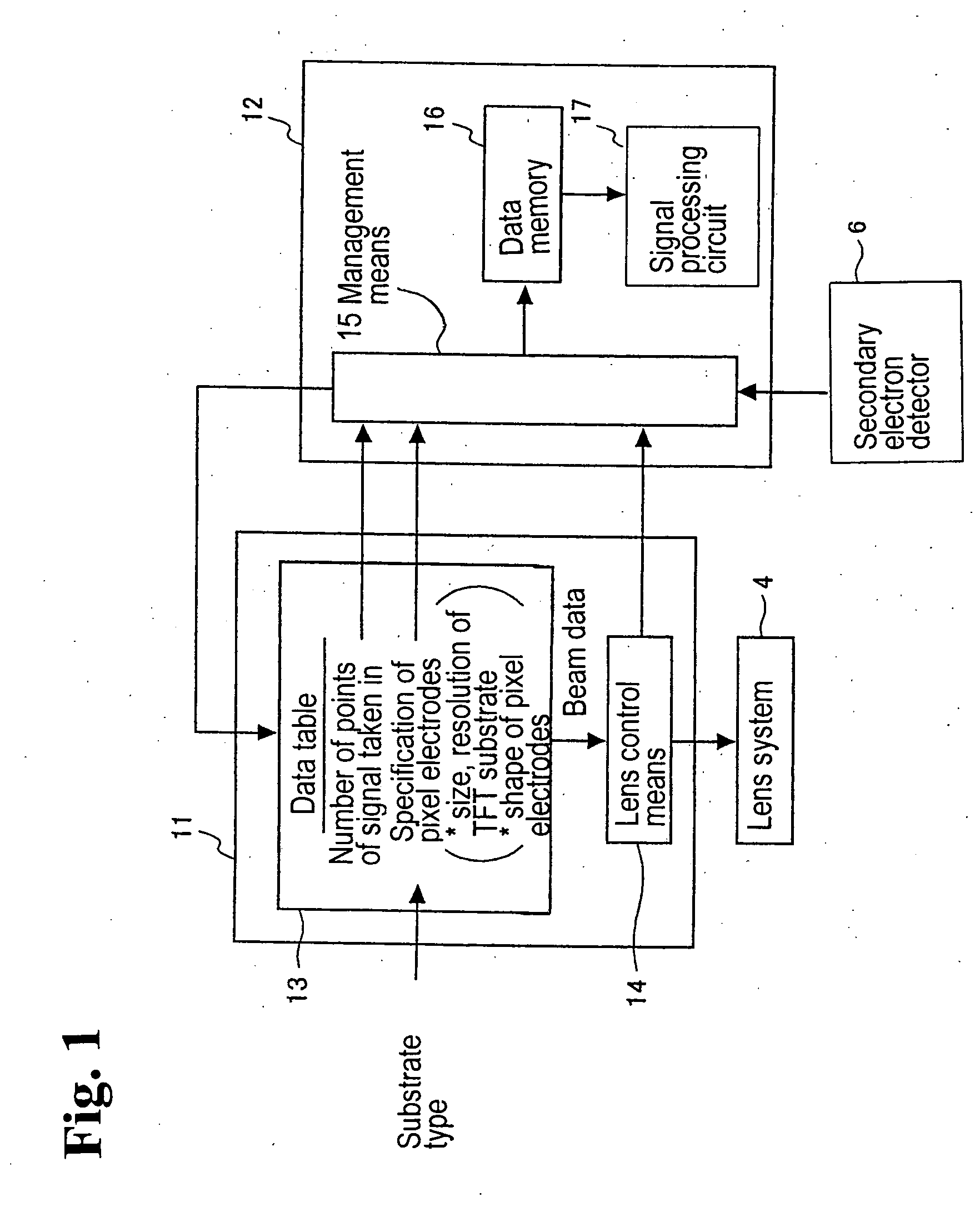
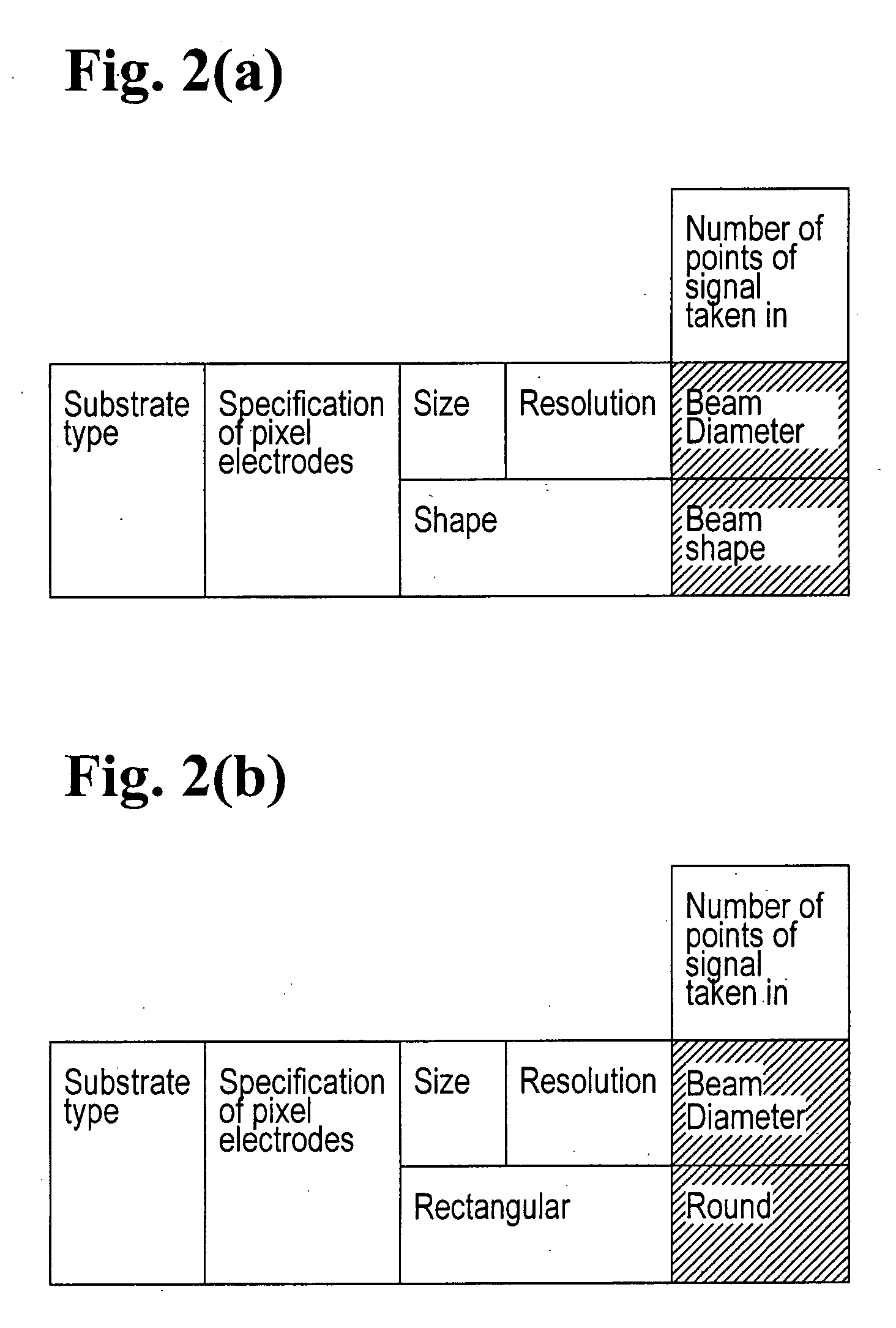
InactiveUS20050174140A1Constant precisionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSecondary electronsIrradiation
A TFT array inspection device inspects a TFT array by irradiating a TFT substrate with a charged particle beam and detecting secondary electrons produced from a pixel electrode of the TFT substrate by irradiation of the charged particle beam. The TFT array inspection device includes a charged particle beam control device for changing at least one of a size and a shape of the charged particle beam in accordance with at least one of a specification of the pixel electrode and a number of detection points on the pixel electrode.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Radiation emission control method, apparatus and program
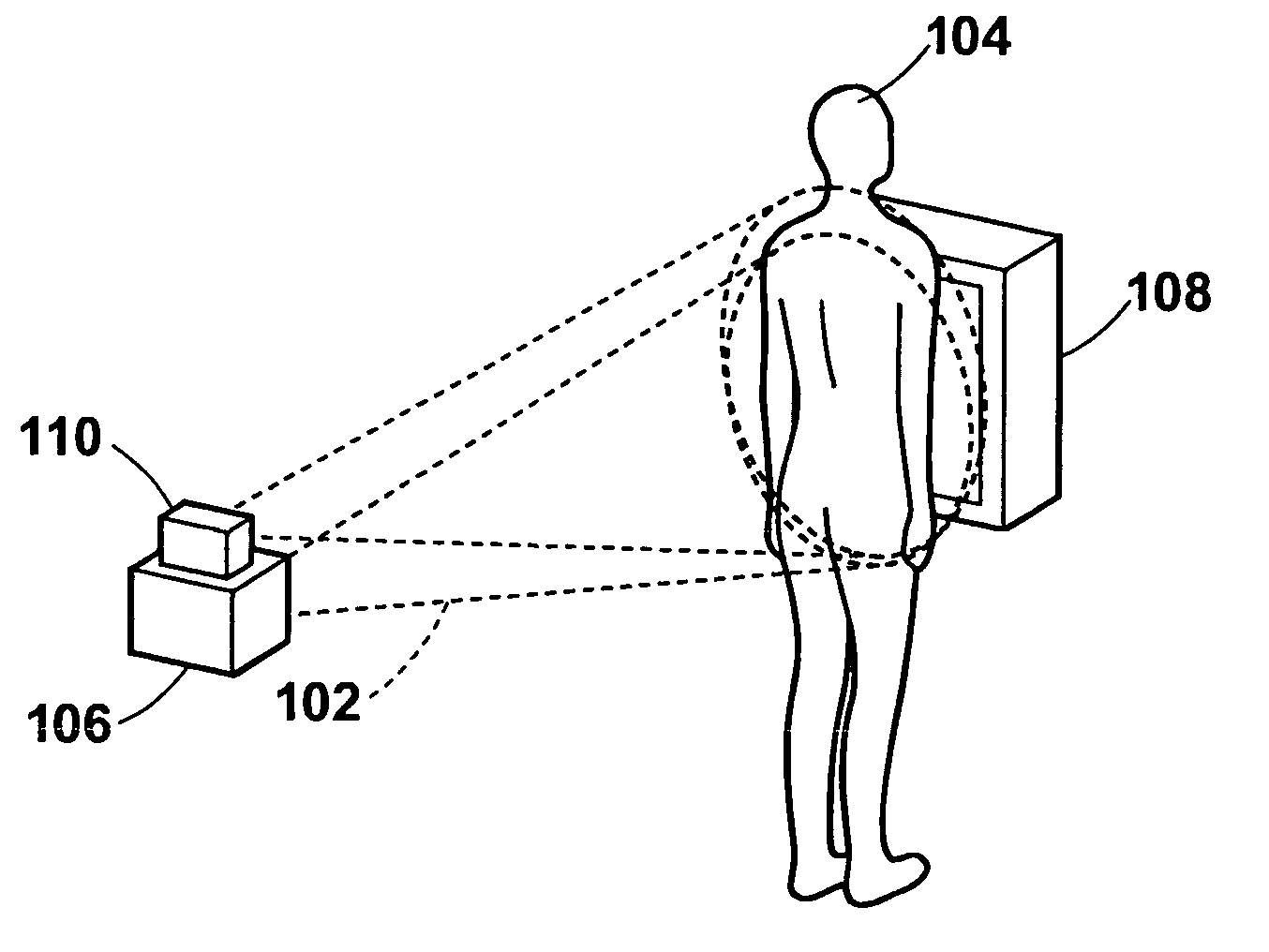
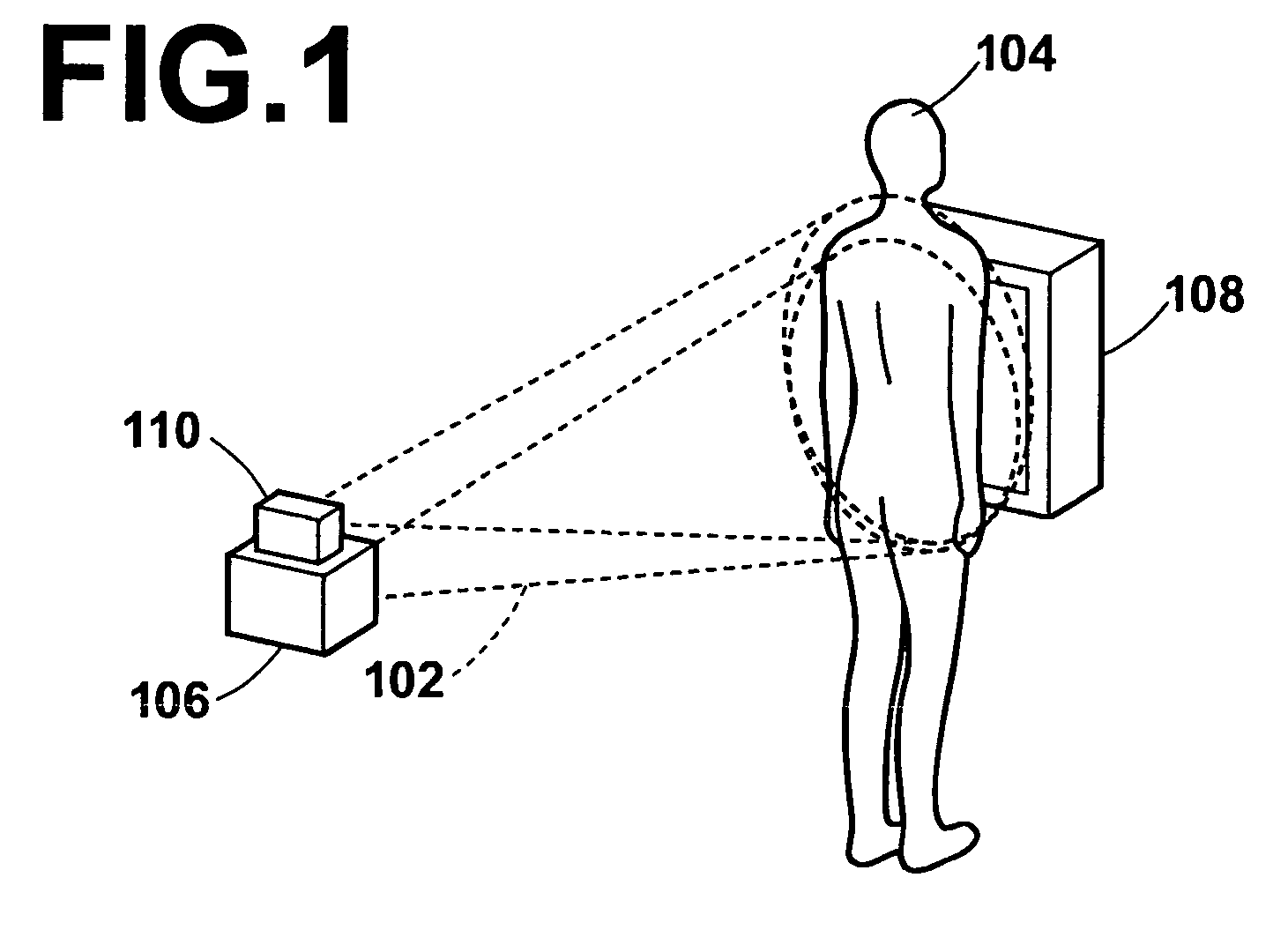
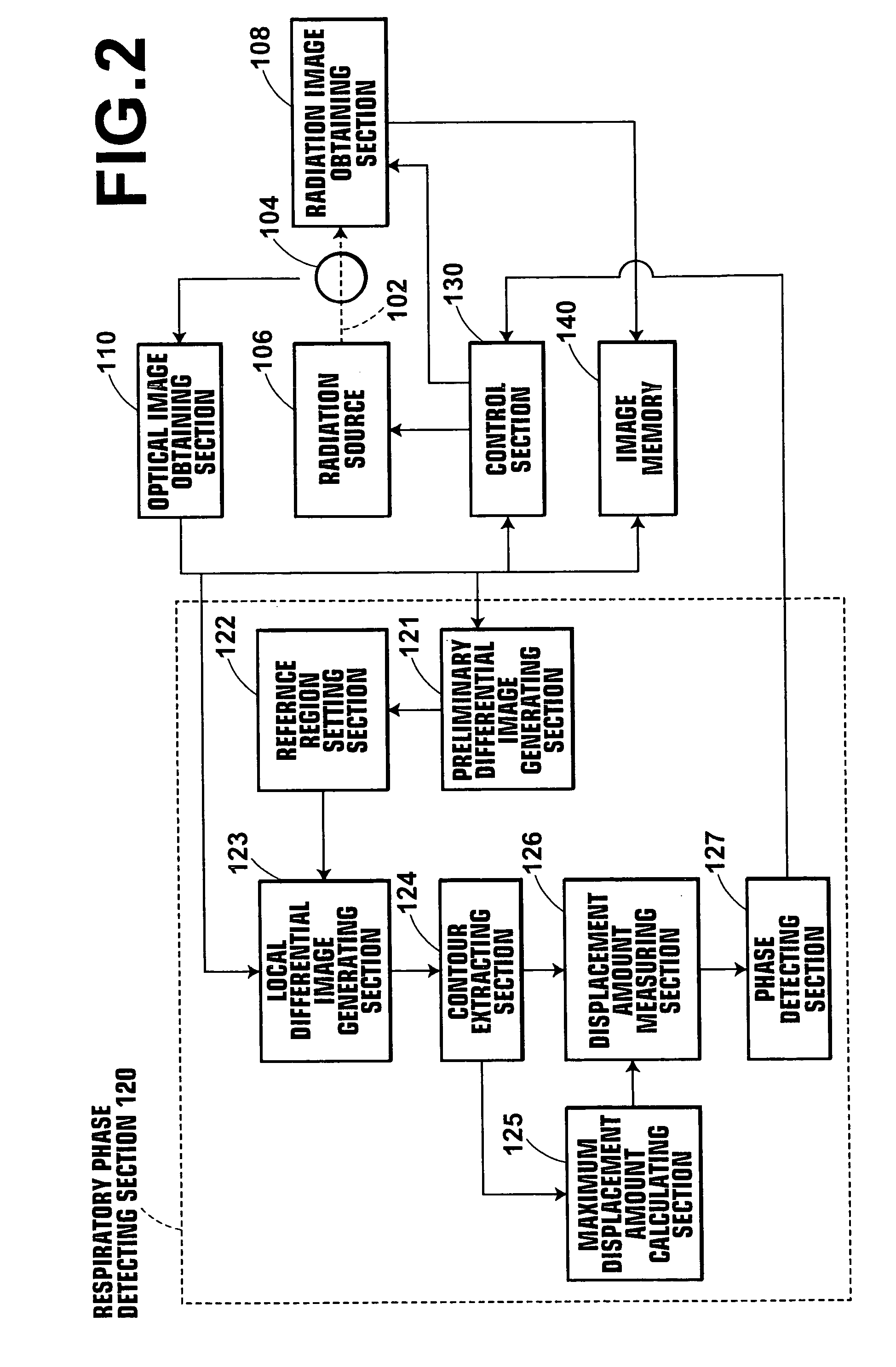
InactiveUS20060025672A1Minimize exposureConstant precisionRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsRespiratory phaseRadiation rays
A radiation emission control method, apparatus and the program capable of detecting respiratory phases of a test subject with constant accuracy and emitting radiation rays to the test subject in synchronization with an intended respiratory phase, while minimizing the radiation exposure to the subject. A test subject having a contour that varies with the respiration is optically imaged continuously by the optical image obtaining section to sequentially obtain optical images of the subject, and respiratory phases of the subject are detected simultaneously with the optical imaging by the respiratory phase detecting section based on the contour of the subject on the optical images. During the optical imaging, a radiation source is controlled by the control section such that radiation rays are emitted to the test subject when the detected respiratory phase corresponds to an intended respiratory phase of the subject.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
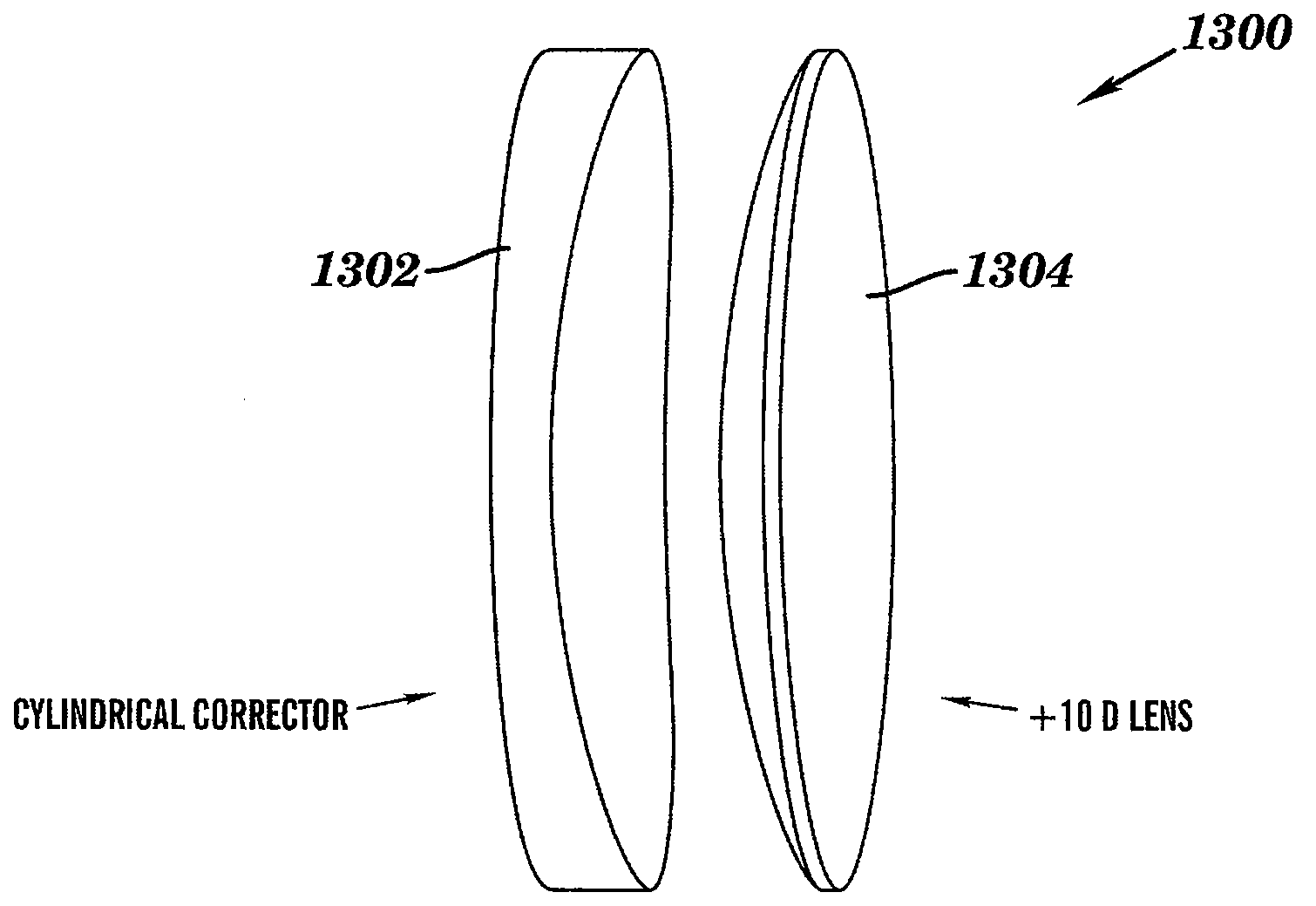
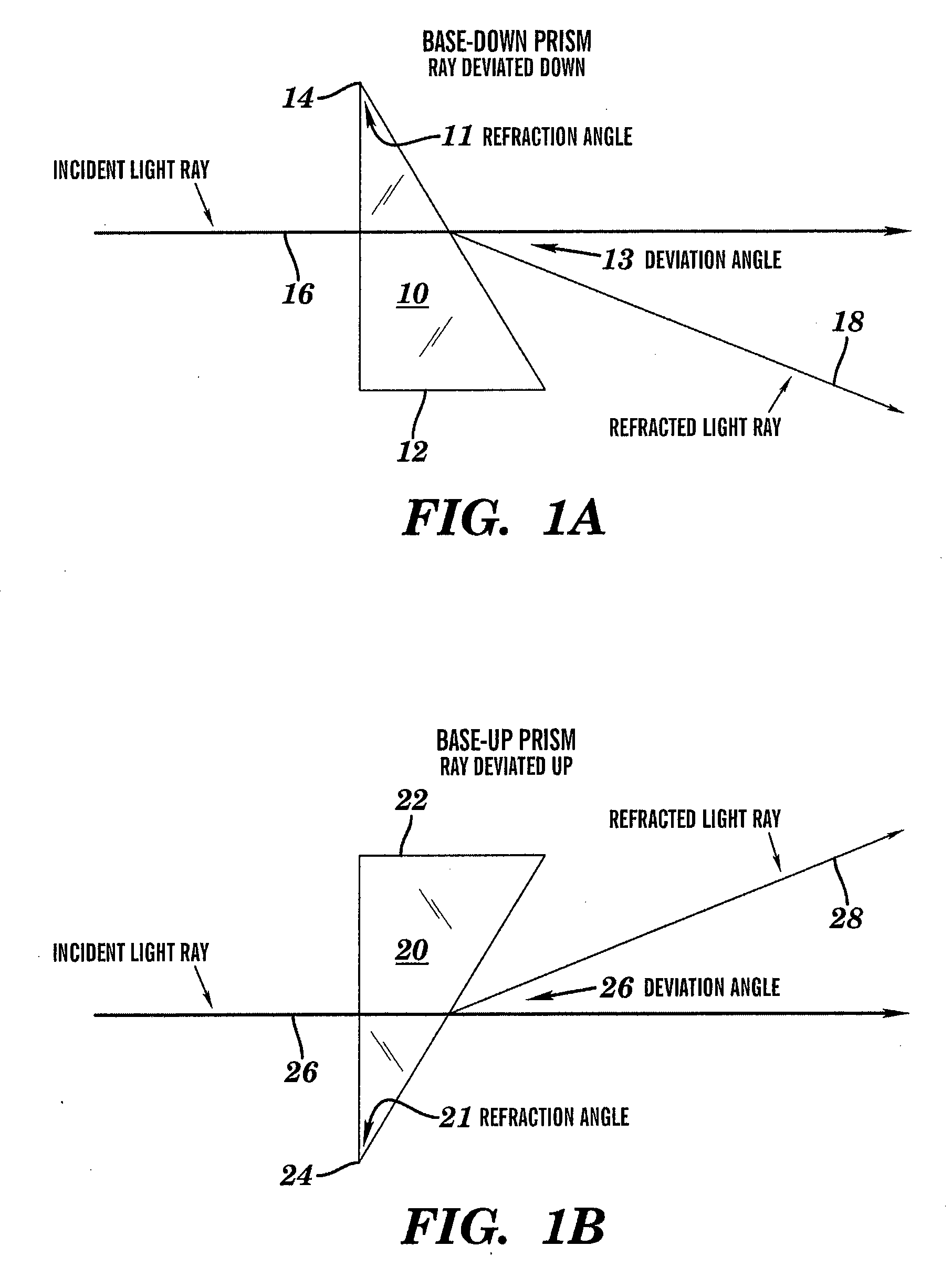
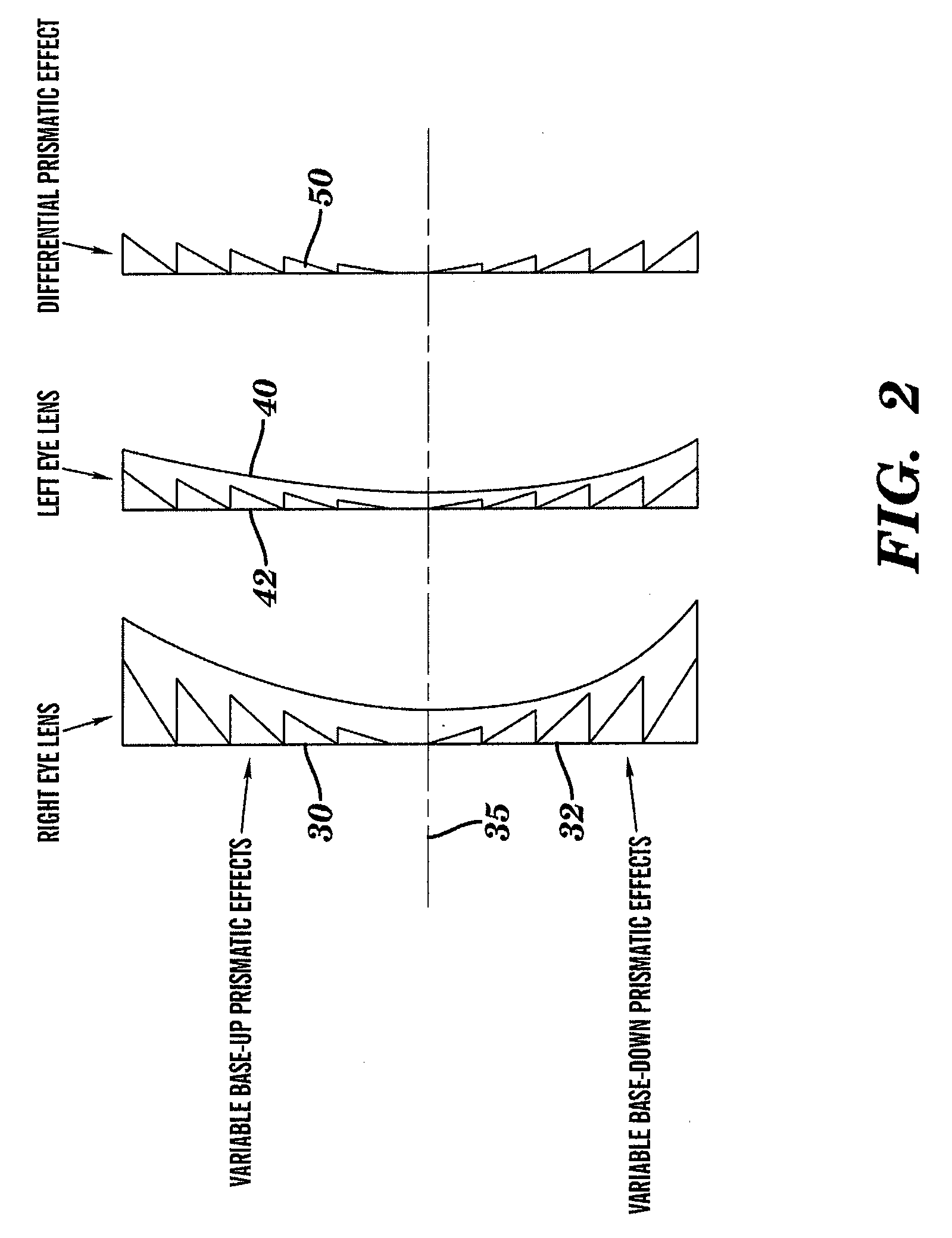
Optical elements having variable power prisms
Optical elements having a plurality of integral prism facets having varying prismatic power are provided. These optical elements address the disadvantages of conventional therapeutic optical prisms by addressing the undesirable variation in prismatic effect that results when conventional prisms are combined with optical lenses in binocular vision. Specifically, the present invention can equalize differential prismatic effects of right and left eye lenses over their entire aperture. The optical elements may include a plurality of prism facets having base-down and base-up prismatic power. The elements may include individual elements having variable prismatic elements, individual elements combining both conventional prisms and variable prism, or separate elements having conventional prisms and variable prism. The plurality of integral facets or a substantially continuous smooth surface may be provided, for, example, a cylindrical surface having a circular or non-circular profile. Methods of correcting binocular vision are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
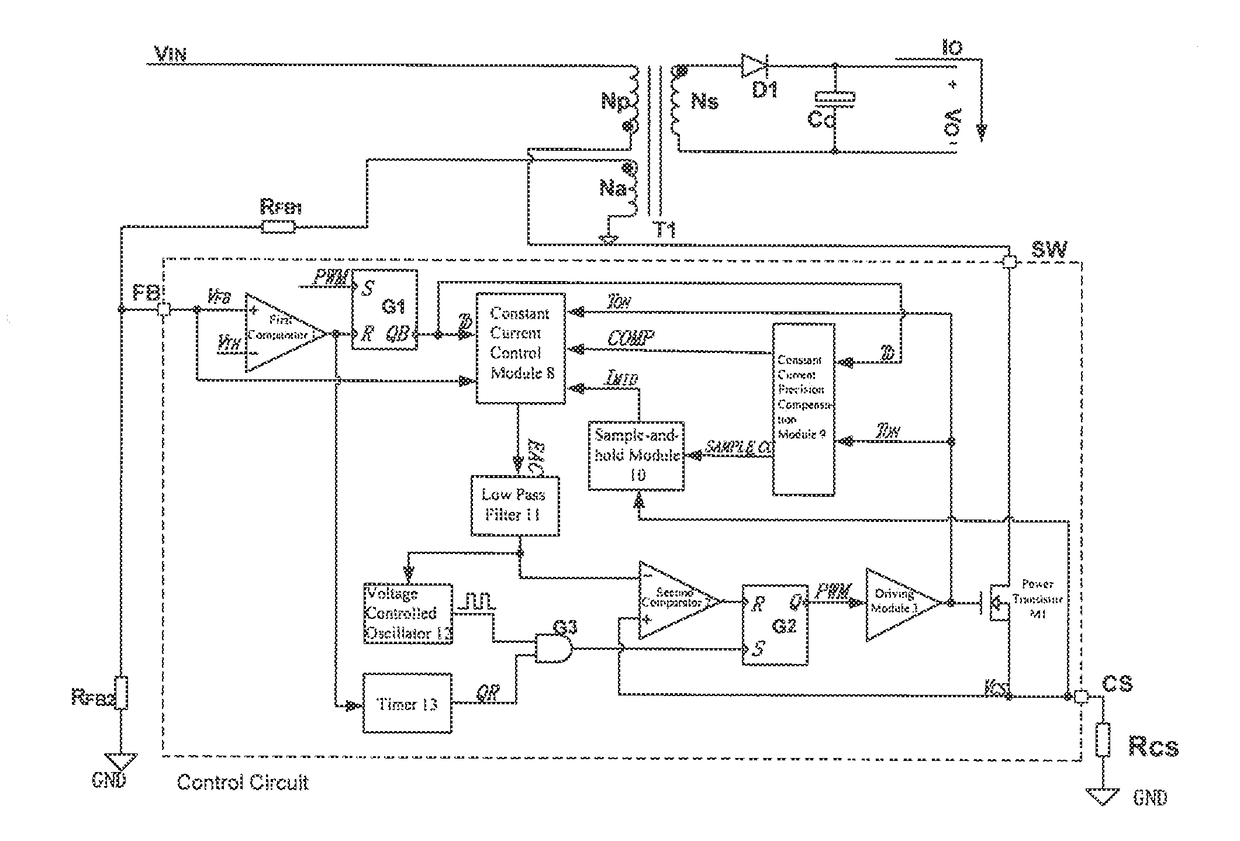
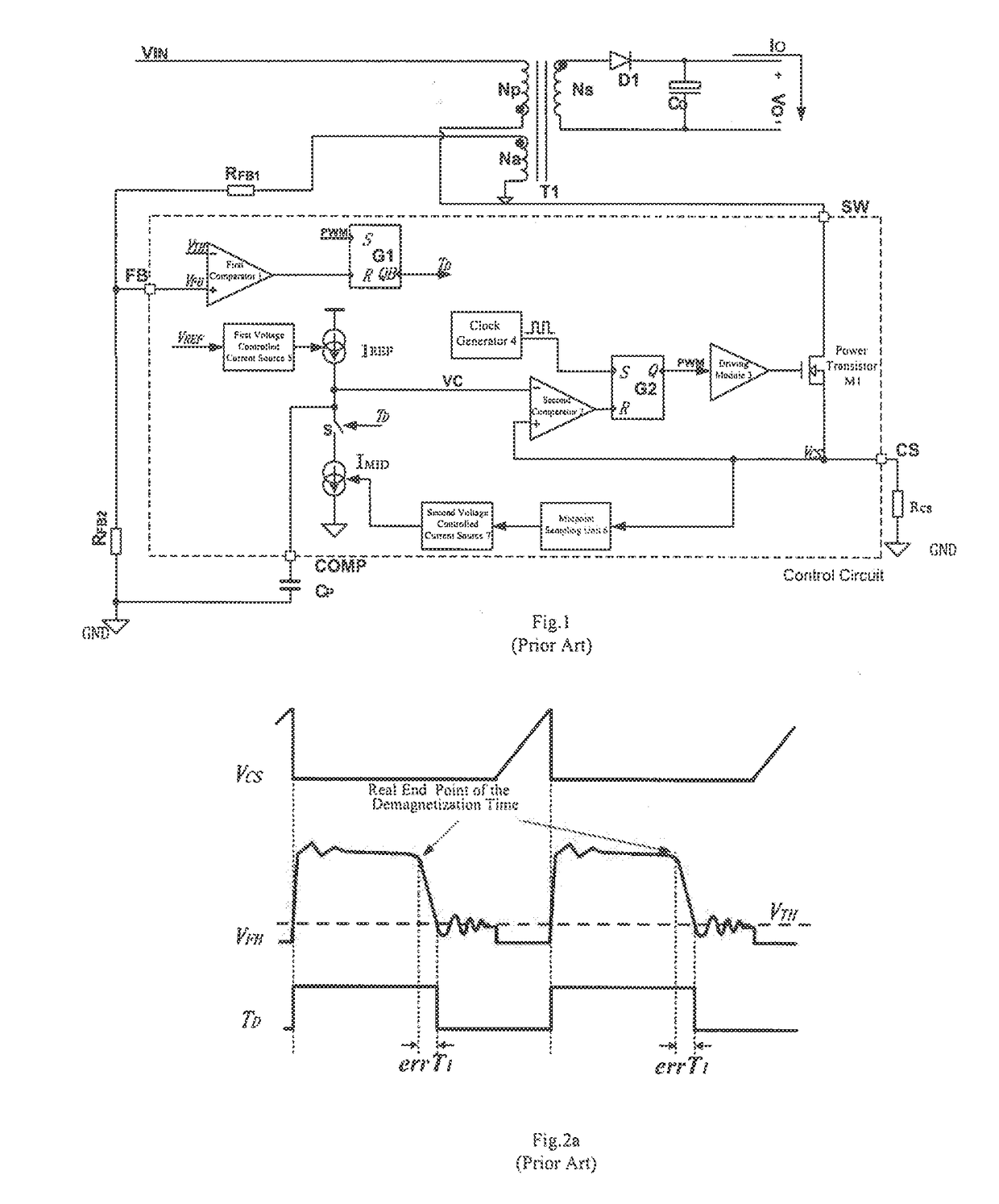
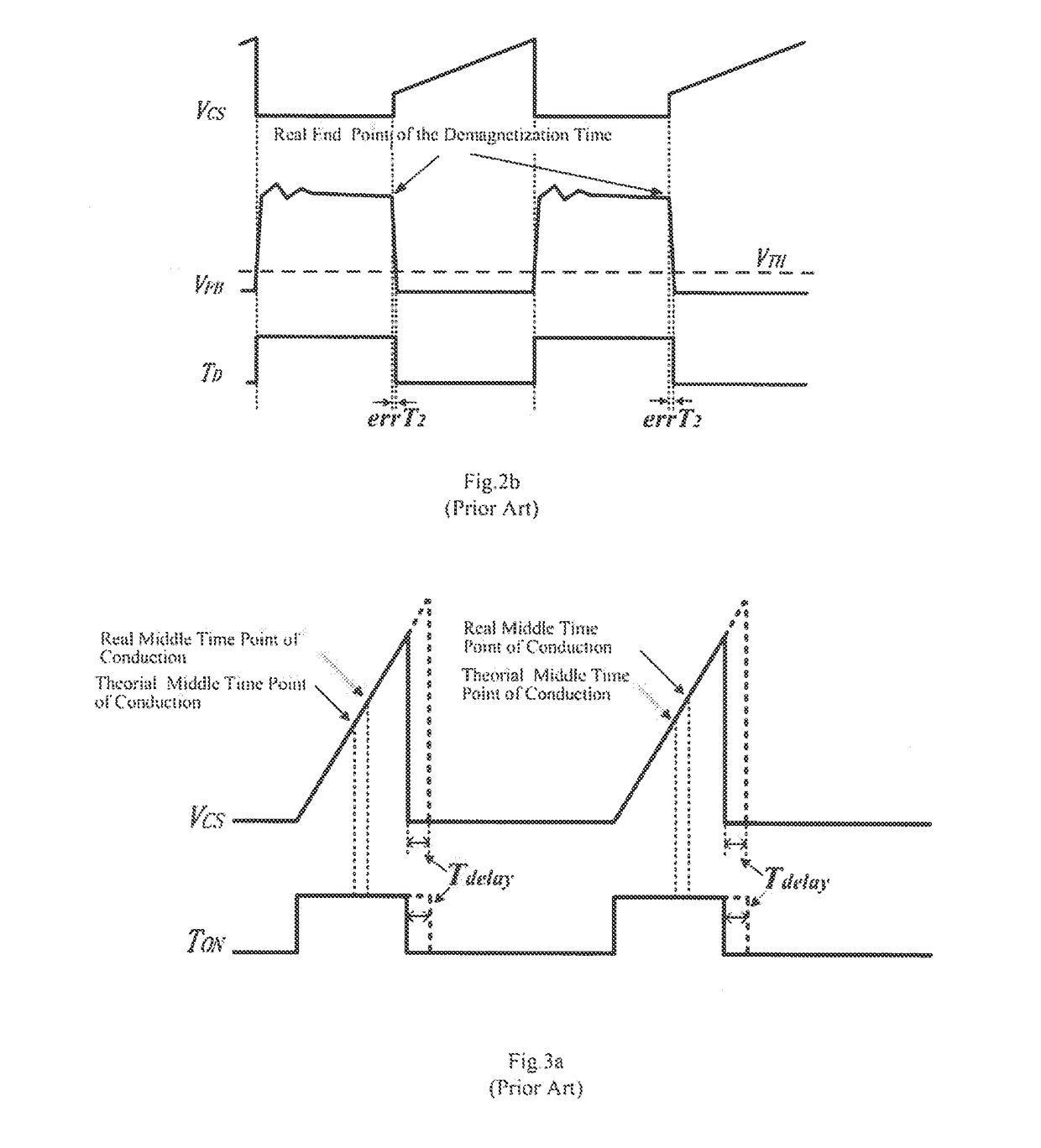
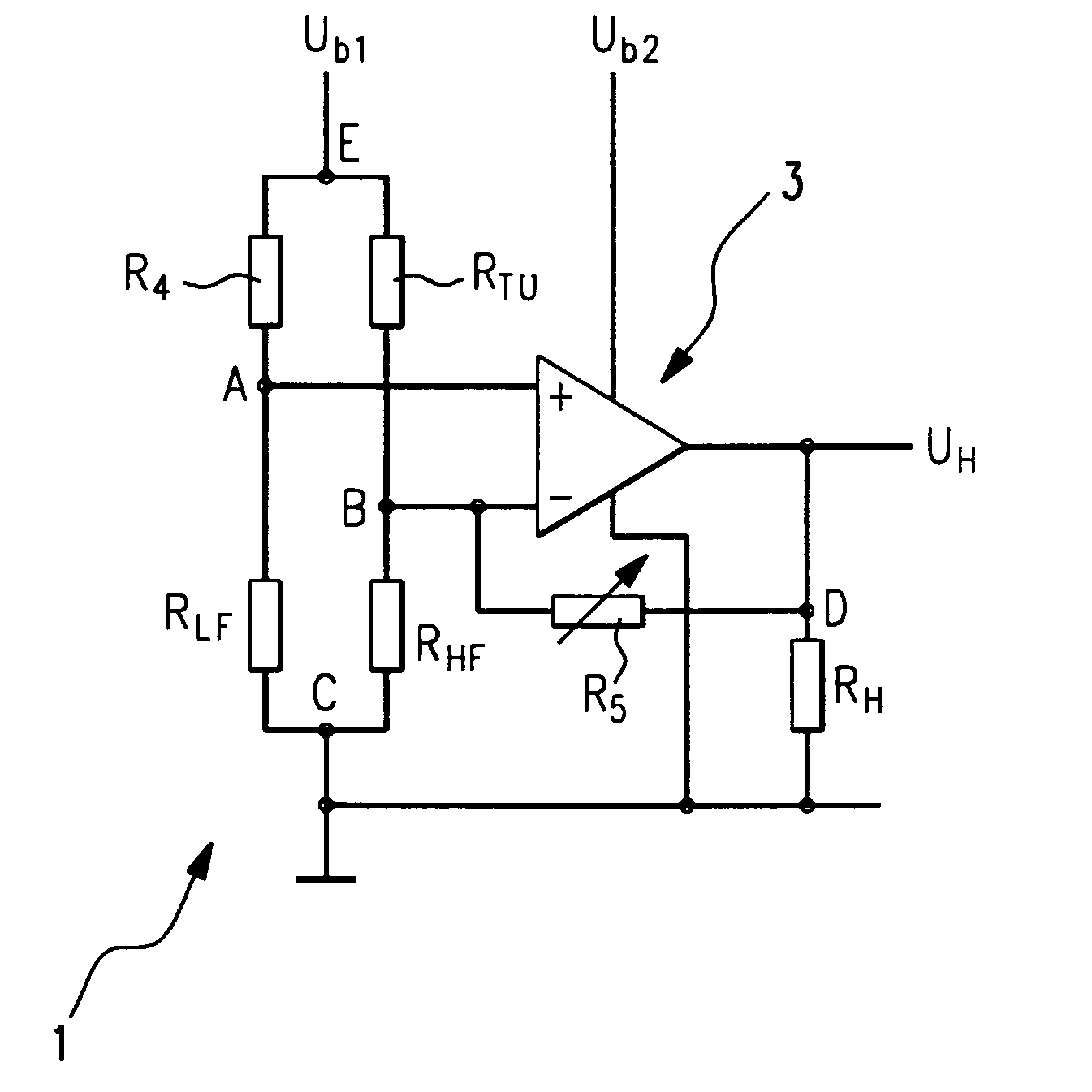
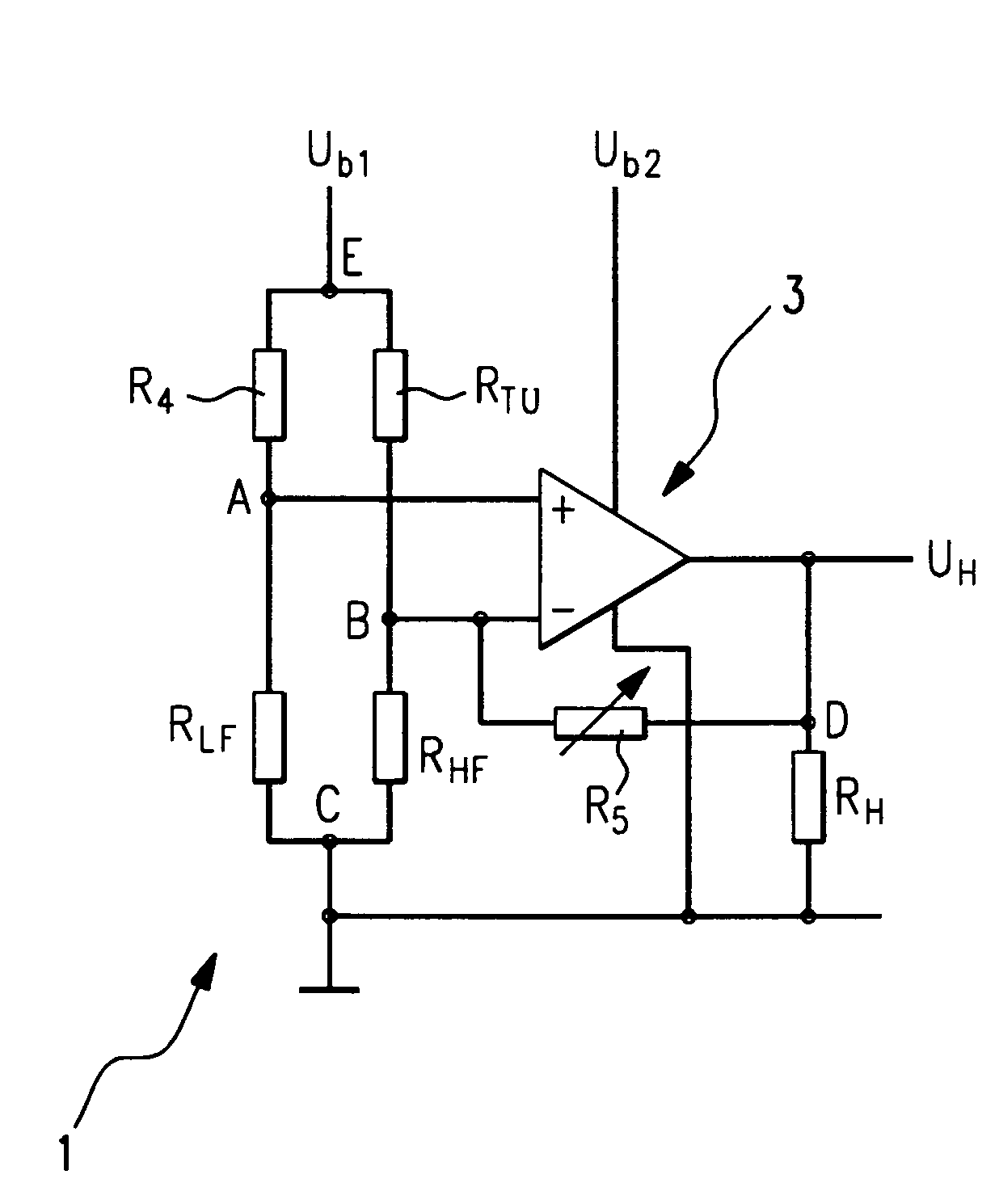
Control Circuit and Control Method of Switching Power Supply
ActiveUS20180287479A1Switch power supplyHigh precisionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSignal onSelf adaptive
What disclosed are a control circuit and a control method of a switching power supply, according to feedback signals on a pin FB and a pin CS, a constant current control module generates and outputs a control signal to control an output current of the switching power supply, thereby regulating duty cycle of a first transistor adaptively and controlling an output current Io of a power supply system to be constant; according to the feedback signals on the pin FB and on the pin CS, a constant current precision compensation module adaptively regulates circuit parameters of the constant current control module and a sample-and-hold module, preventing precision of constant current output from being influenced by change of a working mode and / or by variation of input conditions; when an output voltage changes, QR mode keeps unchanged or depth of a CCM keeps approximately constant.
Owner:WUXI CHIPOWN MICROELECTRONICS
Device for correcting spinal deformities
ActiveUS7976568B2Accurate forceCorrection of spinal deformityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsKyphoscoliosisPost operative
The present invention relates generally to a device of and a method for correcting spinal deformities, such as scoliosis and kyphosis. The invention employs the superelasticity or pseudoelasticity, such as found in a nickel-titanium alloy, to provide a continuous, predictable, and controllable correction force and to achieve a gradual and full correction. The correction force can be exerted on the deformed spine either at the time of the spine surgery or after the surgery or both, to afford a full or substantially full correction. The continuous and controllable correction force of the present invention is safer than an instantaneous and large correction force applied only at the time of surgery. Additionally, the continuous and controllable correction force is capable of gradually and fully correcting the spinal deformities without any post-operative manipulation of the correction device or re-operation.
Owner:HONG KONG UNIV OF +1
Flow sensor having improved operational performance
InactiveUS20050000281A1Reduce impactConstant precisionElectrical controlVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsElectrical resistance and conductanceFlow transducer
A flow sensor in which all bridge resistor elements of a bridge circuit are arranged on a chip together with a heating resistor element, so that the drift of the bridge resistor elements will then have only a very slight effect on the output signal of the bridge circuit, which may be picked off at the electrical connections.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Apparatus and method for supporting and shaping a photo-stimulable phosphor plate
InactiveUS20050029475A1Optimization mechanismConstant precisionX-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhosphorLight beam
Apparatus and method for supporting and shaping a photo-stimulable phosphor plate (PSP) during scanning in a CR reader, the apparatus including elements for shaping at least part of a PSP to an arc which is a part cylinder, and which provides a substantially unitary radial distance from a beam deflecting device to a target point of scanning.
Owner:KATZ NOA
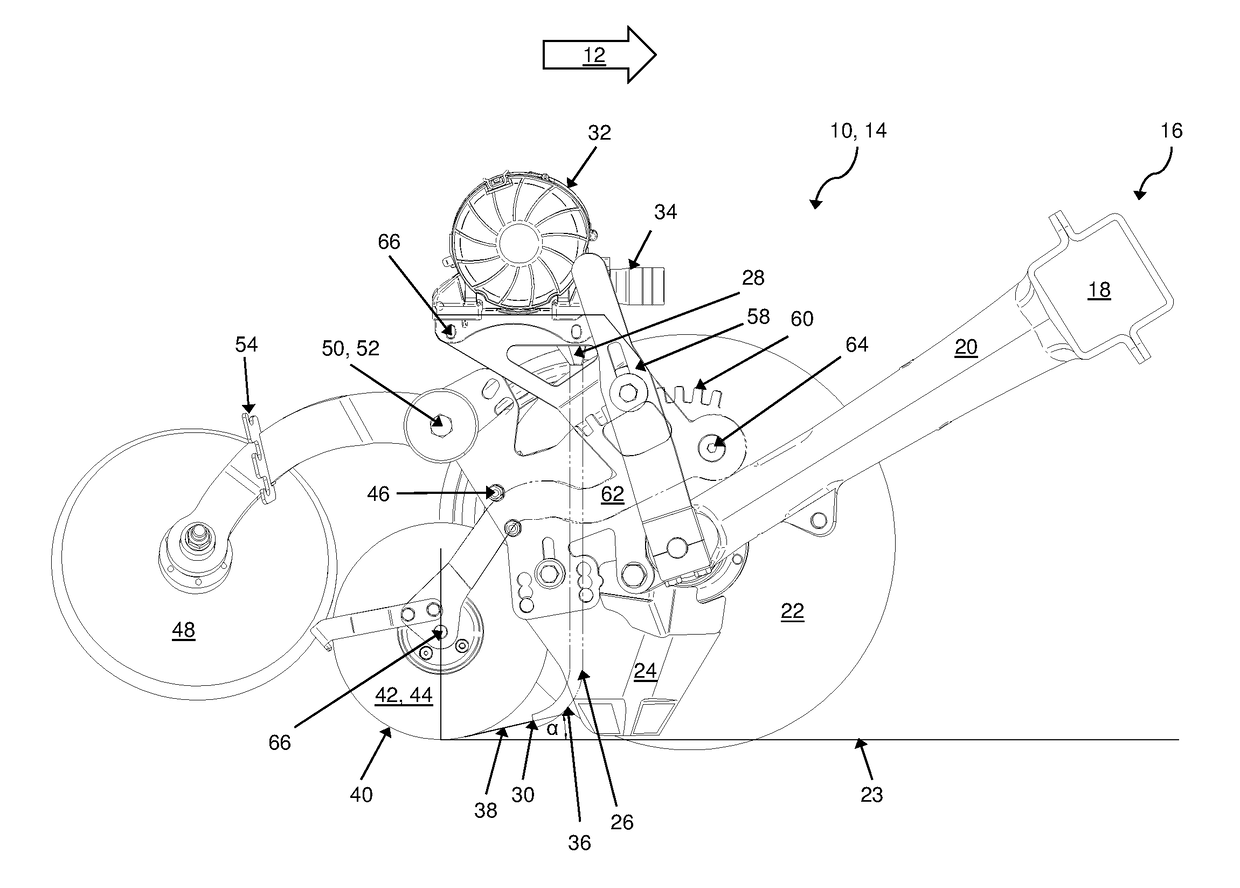
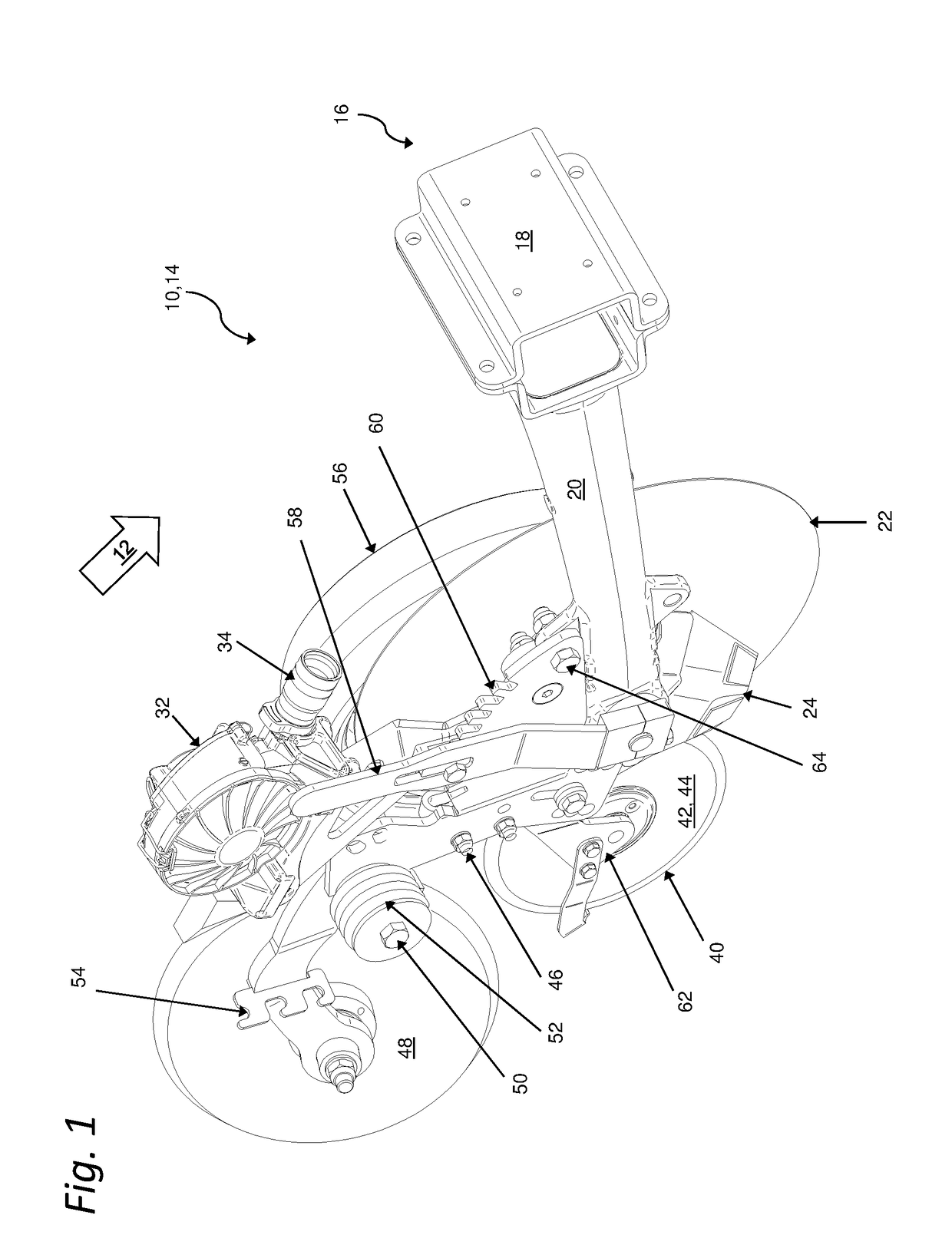
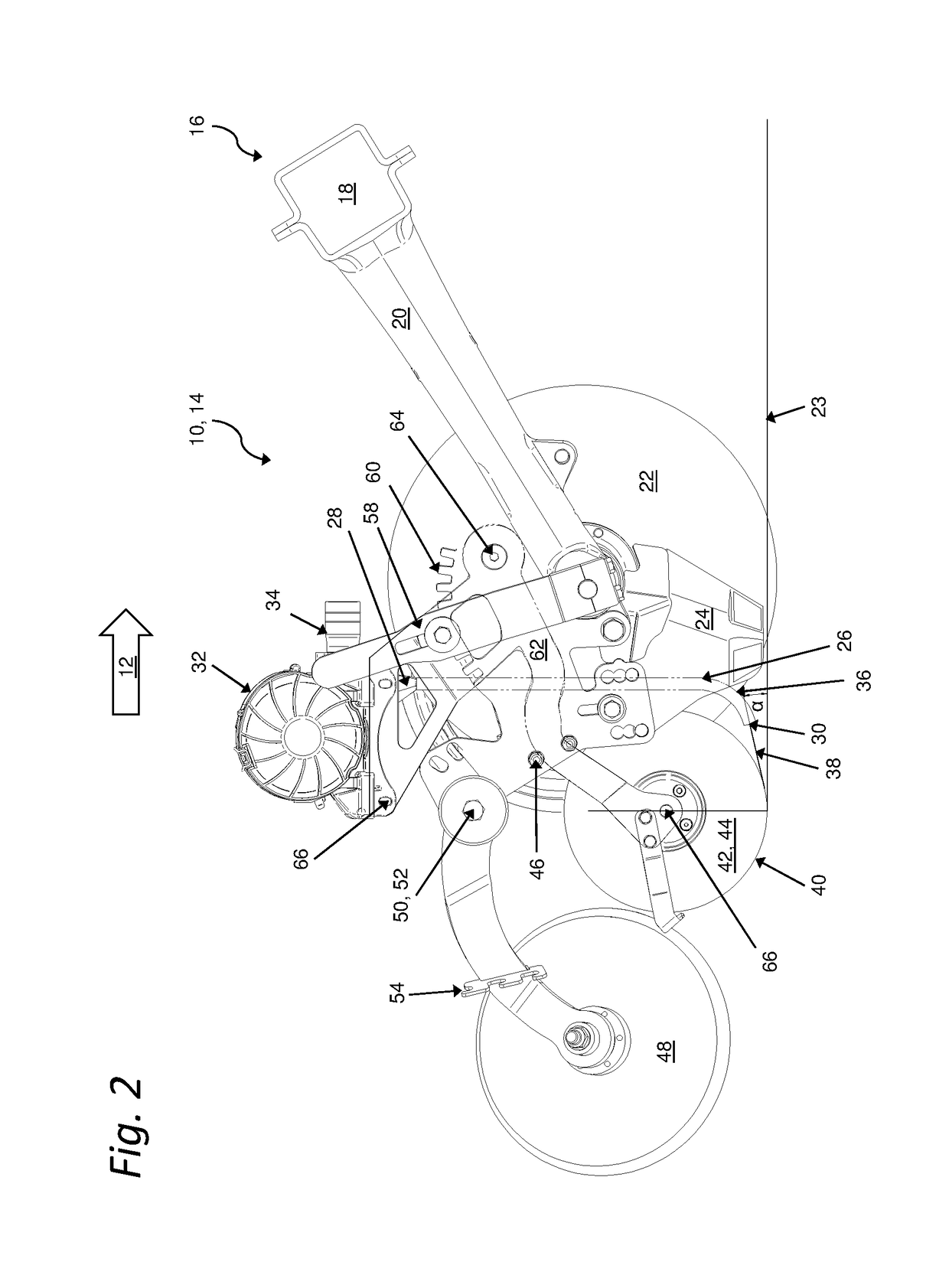
Sowing coulter arrangement of an agricultural machine
ActiveUS20180249621A1Constant precisionSuitable for useSpadesAgricultural machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Disclosed is a sowing coulter arrangement comprising a suspension device for mounting the sowing coulter arrangement on a machine frame; a coulter frame connected to the suspension device for mounting components of the sowing coulter arrangement thereon; and a coulter disk. The arrangement further comprises a furrow closer pivotally mounted on the coulter frame; a metering device for dispensing the material to be distributed; a seed tube for transporting the material to be distributed from the metering device to a seed furrow; and a catching element for catching the material disposed downstream of the outlet of the seed tube. The metering device, the seed tube, and the catching element form a unit and are mounted on a carrier that is pivotably affixed to the coulter frame, whereby an arrangement of an outlet of a seed tube in relation to a catching element is at all times kept largely constant.
Owner:HORSCH MASCHEN
Polymer-based platform for microfluidic systems
InactiveUS7601286B2Many timesFeeding a sample fluid efficientlyCeramic shaping apparatusDomestic articlesMicrofluidicsMechanical engineering
A method of forming a polymer-based microfluidic system platform using network building blocks selected from a set of interconnectable network building blocks, such as wire, pins, blocks, and interconnects. The selected building blocks are interconnectably assembled and fixedly positioned in precise positions in a mold cavity of a mold frame to construct a three-dimensional model construction of a microfluidic flow path network preferably having meso-scale dimensions. A hardenable liquid, such as poly (dimethylsiloxane) is then introduced into the mold cavity and hardened to form a platform structure as well as to mold the microfluidic flow path network having channels, reservoirs and ports. Pre-fabricated elbows, T's and other joints are used to interconnect various building block elements together. After hardening the liquid the building blocks are removed from the platform structure to make available the channels, cavities and ports within the platform structure. Microdevices may be embedded within the cast polymer-based platform, or bonded to the platform structure subsequent to molding, to create an integrated microfluidic system. In this manner, the new microfluidic platform is versatile and capable of quickly generating prototype systems, and could easily be adapted to a manufacturing setting.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Game tower
ActiveUS20110115157A1Enhance board game playEfficient and robustBoard gamesColor television detailsLow distortionEngineering
A game apparatus and a method using a light source, a convex mirror and an optical sensor, all disposed within a housing, are described. The housing is transparent to the range of wavelengths from the light source and is composed of a low distortion scratch-resistant material. A game board is also used along with retro-reflective elements, such as moveable playing markers or game tokens, cards or regions affixed to and integrated into the game board. A data store stores the locations of the reflective elements and other game-related data, such as data needed to measure a player's score or position in a game or data to provide guided play. The convex mirror is disposed inside the housing such that light reflects from the light source, off the convex mirror, through the housing, and onto the game board. The one or more retro-reflective elements, when placed on the game board, receive light emanated from the light source. The light received by the one or more retro-reflective elements reflects off of the convex mirror and along substantially the same path from which the light was received. The optical sensor receives light reflected from the one or more retro-reflective elements, senses increases and decreases in the intensity of the reflected light, and signals changes in the intensity of the reflected light greater than or equal to a predefined level. A processor, or computer, is responsive to signals from the sensor and the data in the data store.
Owner:HASBRO INC
Proximity effect correction in a charged particle lithography system
InactiveUS9184026B2Reduce negative impactConstant precisionElectric discharge tubesIrradiation devicesLithographic artistDirac delta function
The invention relates to a method for performing charged particle beam proximity effect correction, comprising the steps of: receiving a digital layout pattern to be patterned onto a target using one or more charged particle beams; selecting a base proximity function comprising a sum of an alpha and a beta proximity function, wherein said alpha proximity function models a short range proximity effect and said beta proximity function models a long range proximity effect, wherein a constant η is defined as a ratio between the beta proximity function and the alpha proximity function in said sum, with 0<η<1;determining a modified proximity function which corresponds to said base proximity effect function wherein the alpha proximity function has been replaced by a Dirac delta function, andusing an electronic processor, performing a deconvolution of the digital layout pattern with the modified proximity function to produce a corrected layout pattern.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
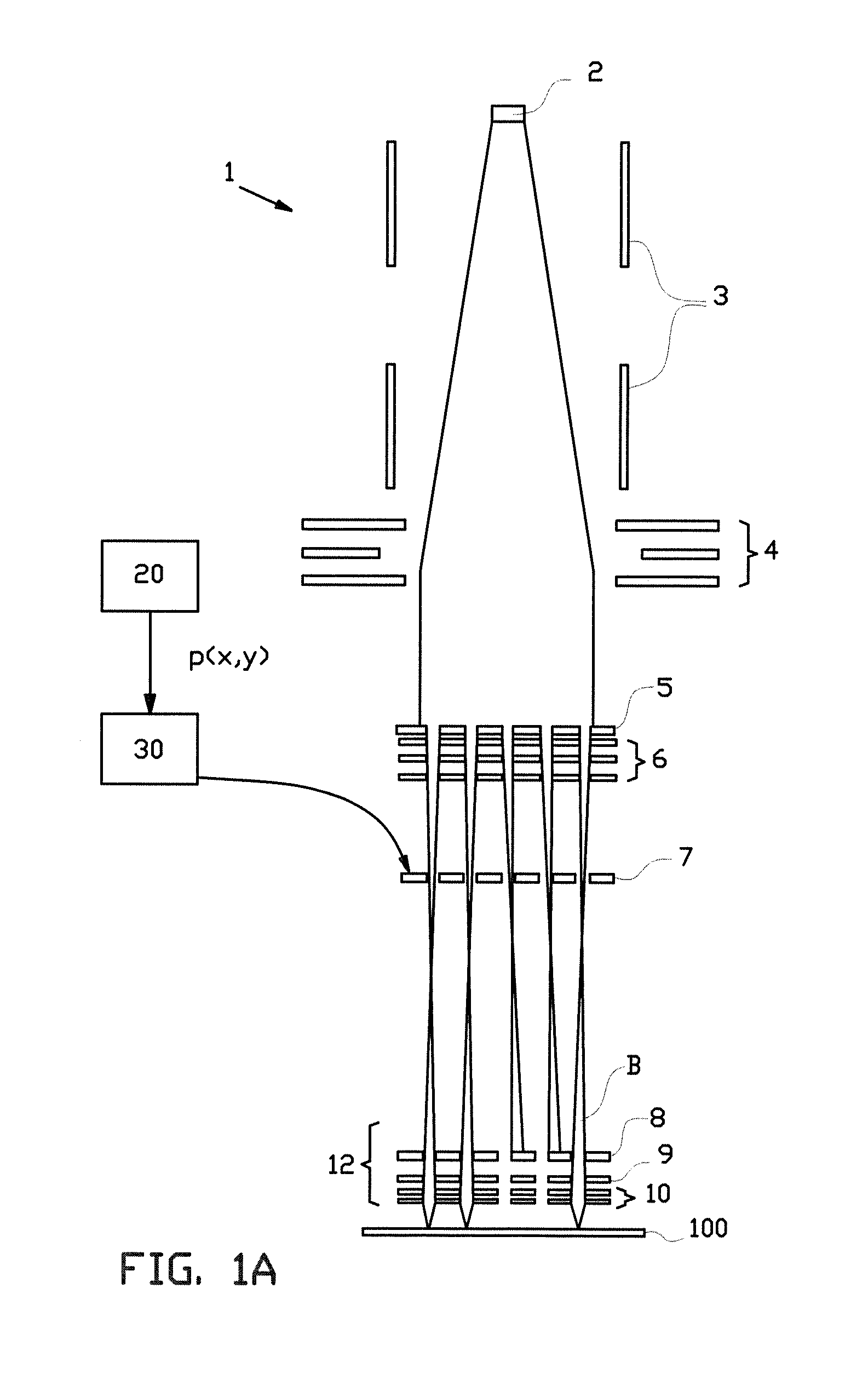
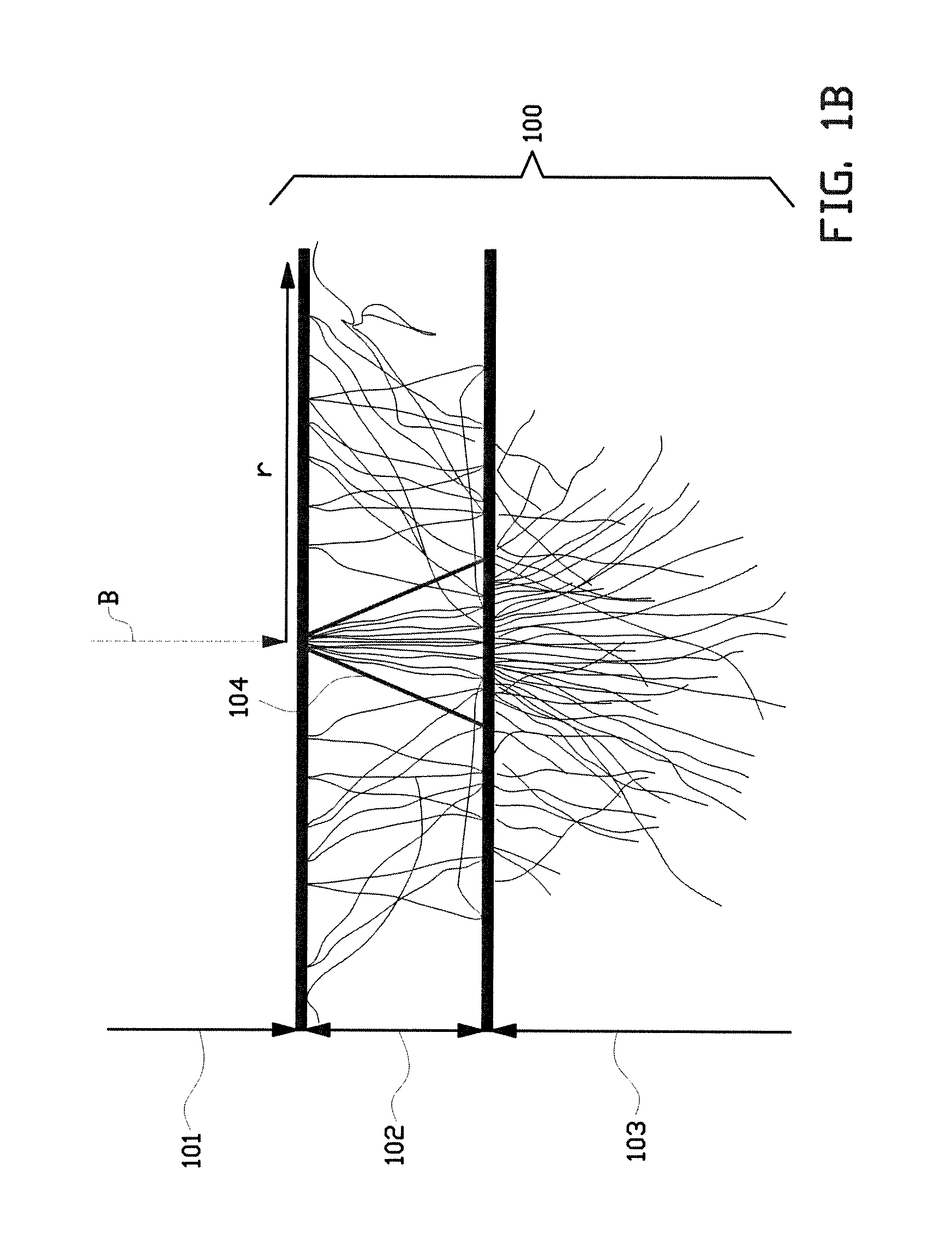
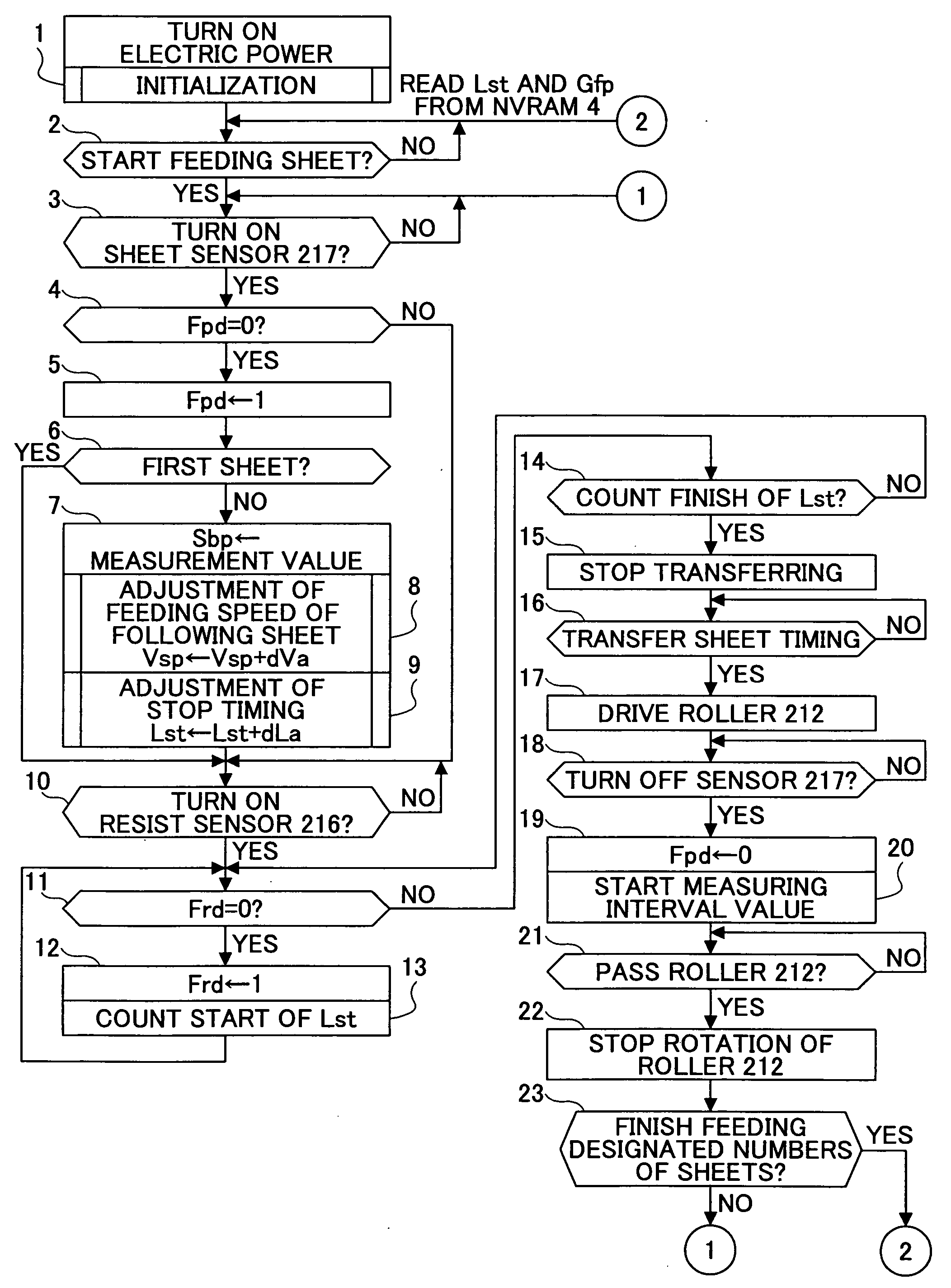
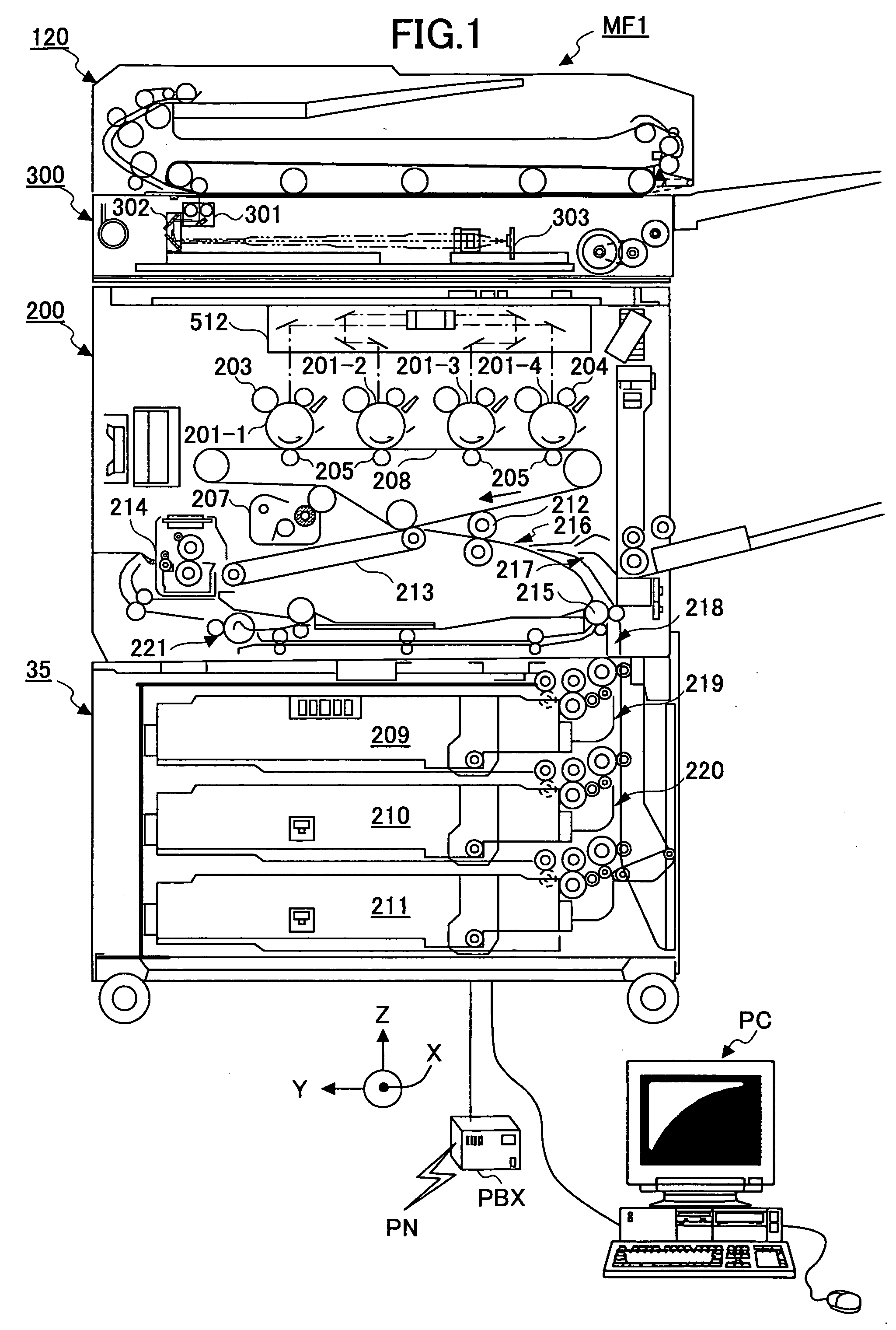
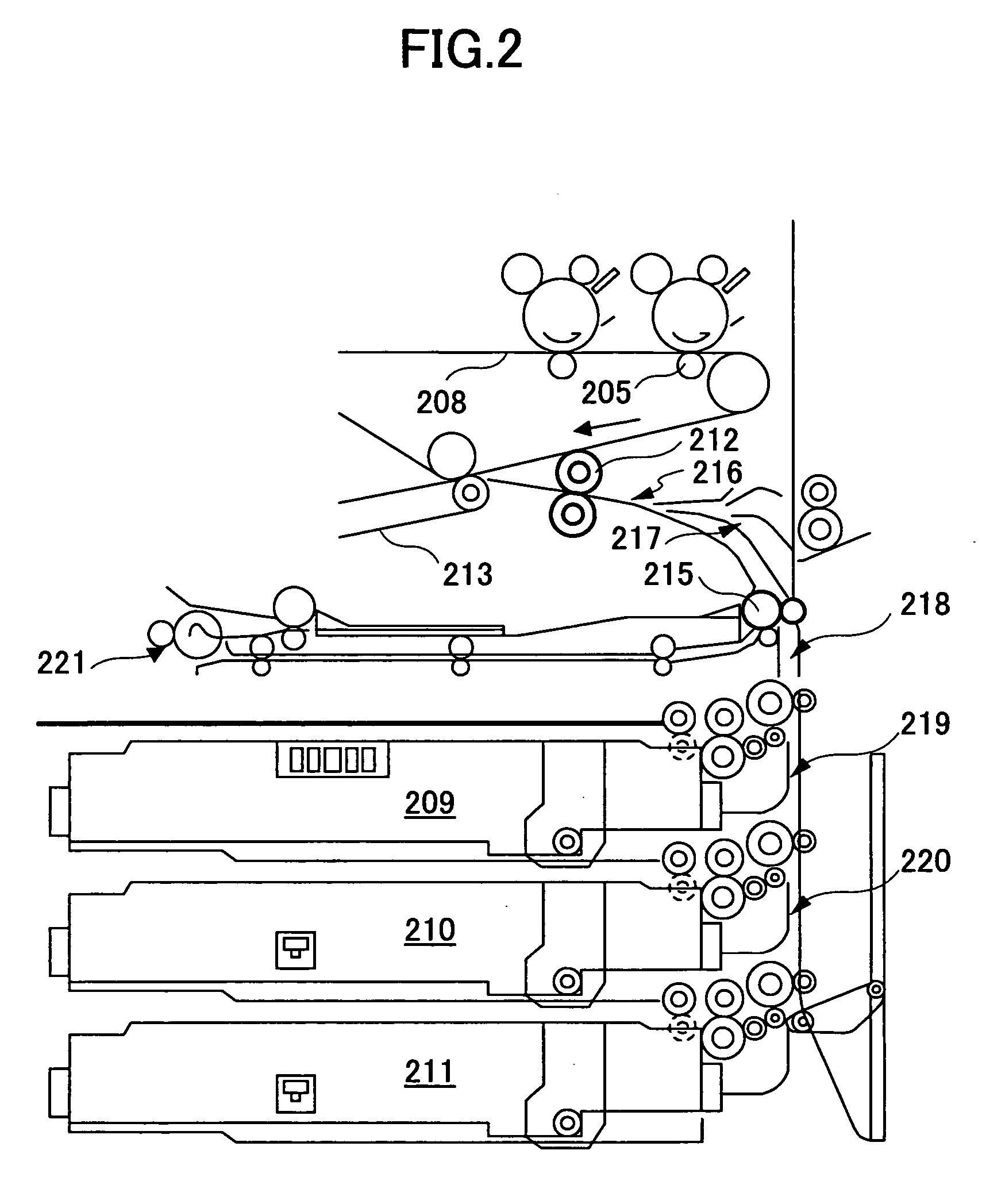
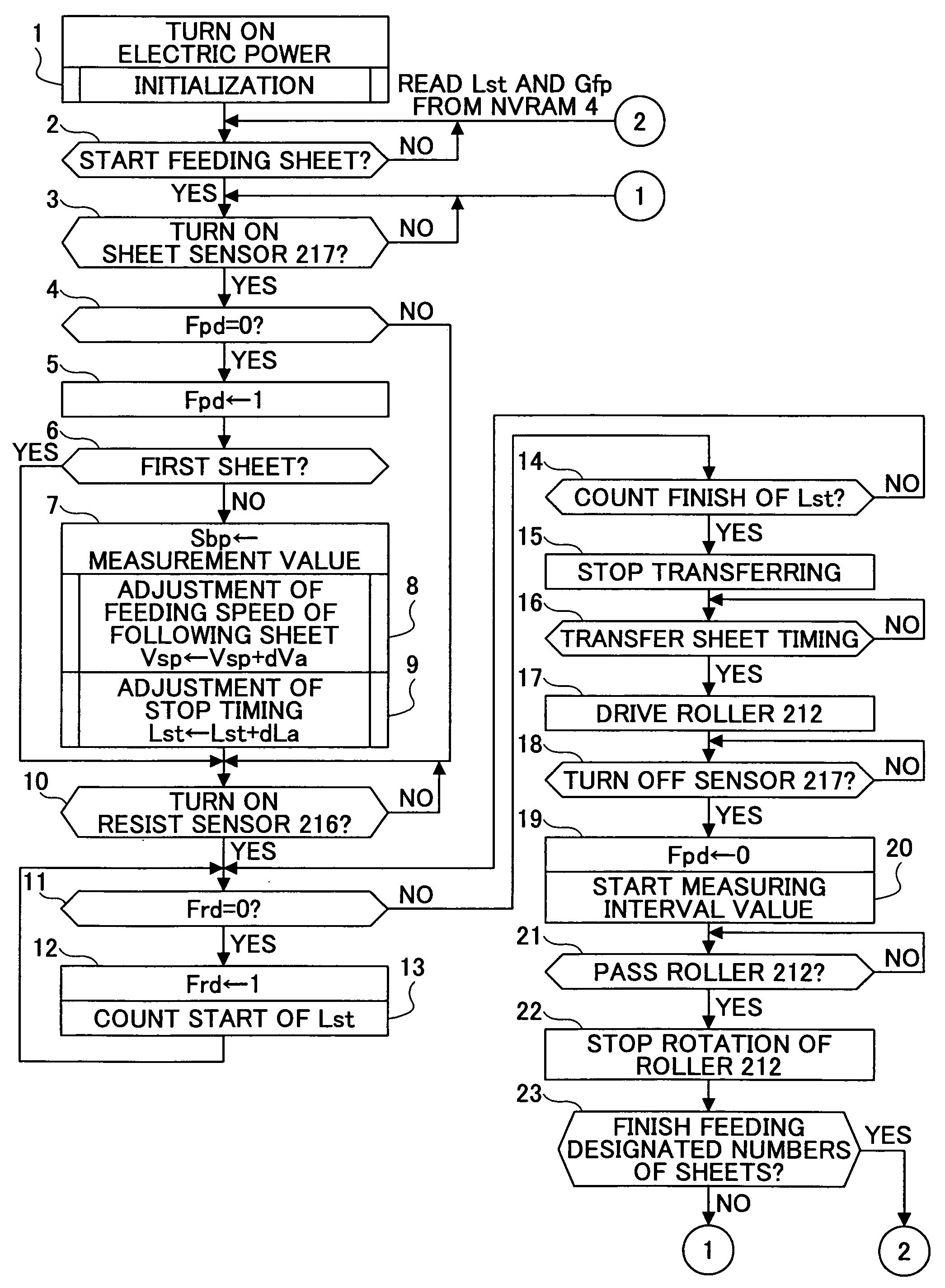
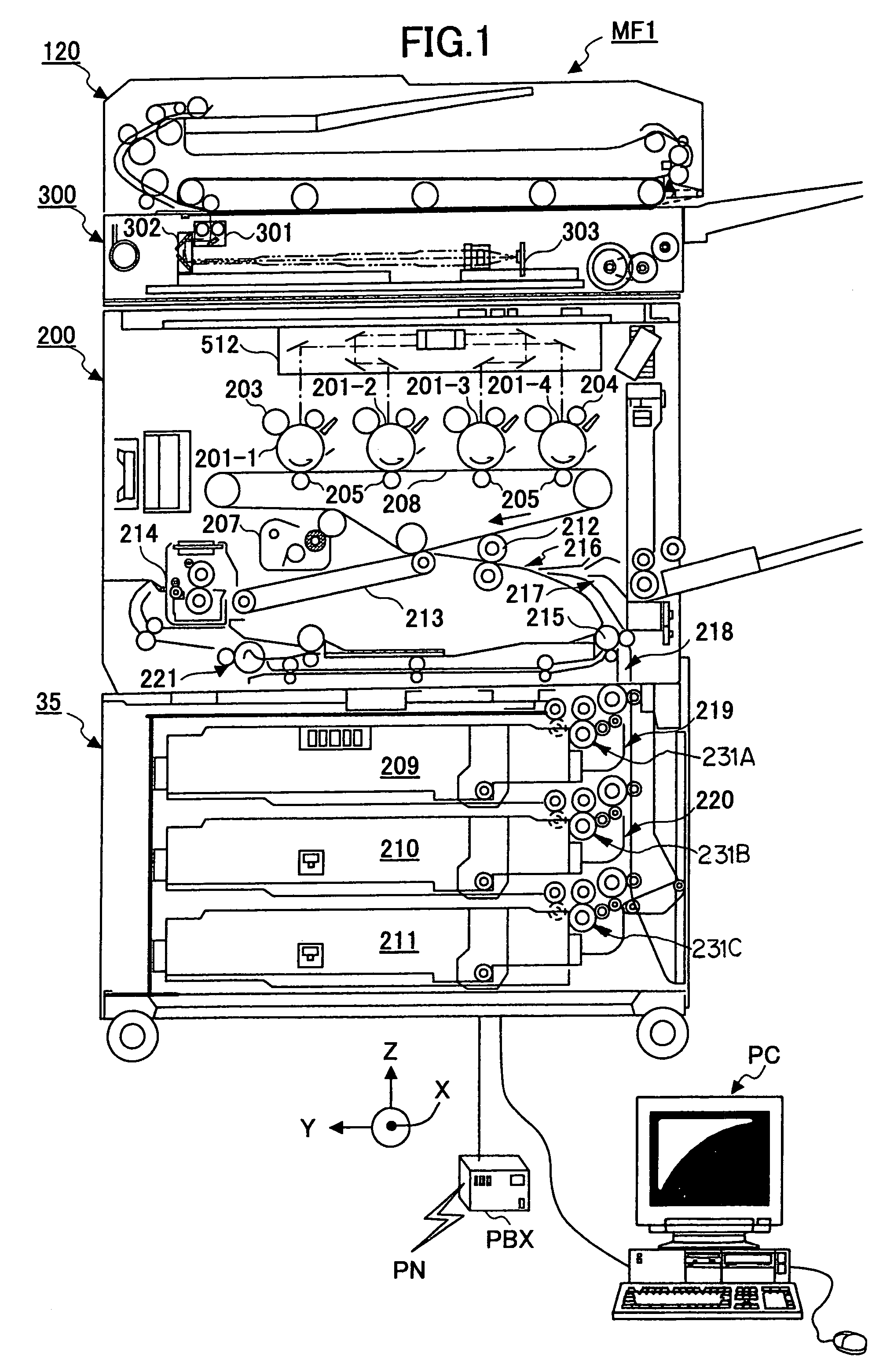
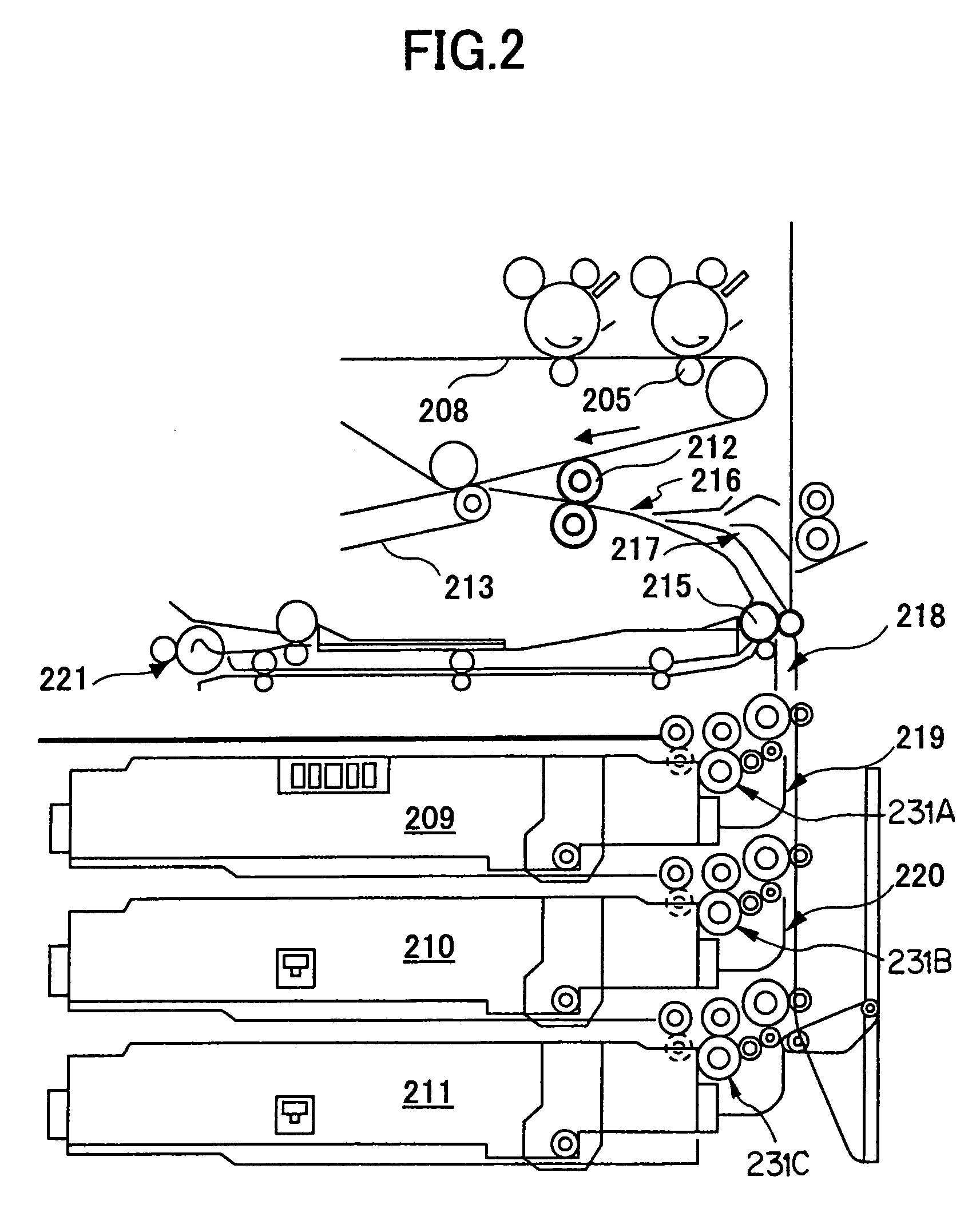
Sheet transferring device and image forming device
InactiveUS20060251452A1Uniform transferring gapImprove accuracyElectrographic process apparatusArticle feedersImage formationEngineering
A sheet transferring device includes a feeding roller configured to feed a sheet; a transferring roller configured to transfer the sheet to the feeding roller; a sheet sensor configured to detect the sheet at a sheet transferring part from the transferring roller to the feeding roller; a measuring part configured to measure an interval of a rear end of a prior sheet and a head end of a following sheet based on a sheet detection signal of the sheet sensor; and a transferring control part configured to adjust a sheet transferring speed of the transferring roller so that the interval between the prior sheet and the following sheet is adjusted to a set value as corresponding to the interval measured by the measuring unit.
Owner:RICOH KK
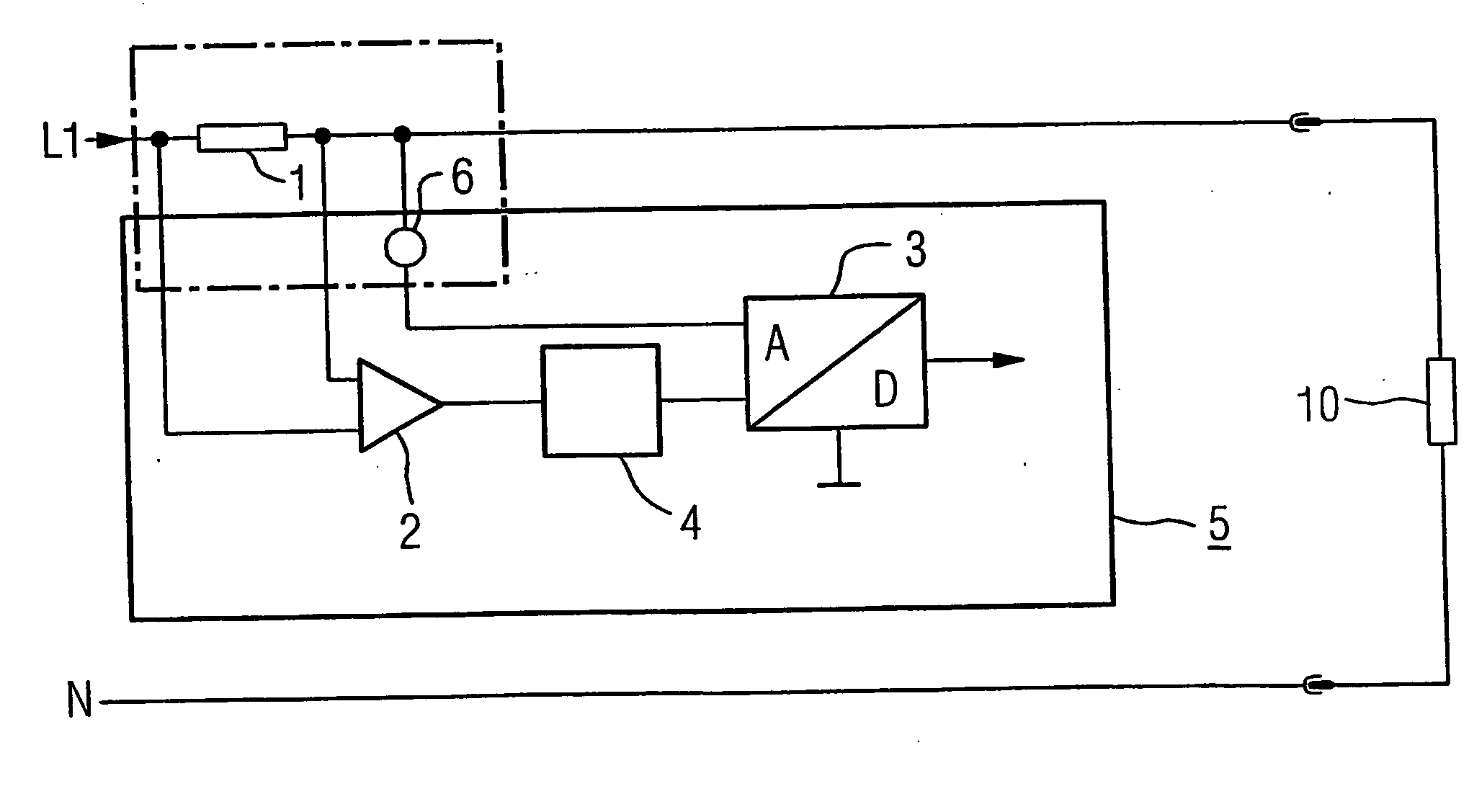
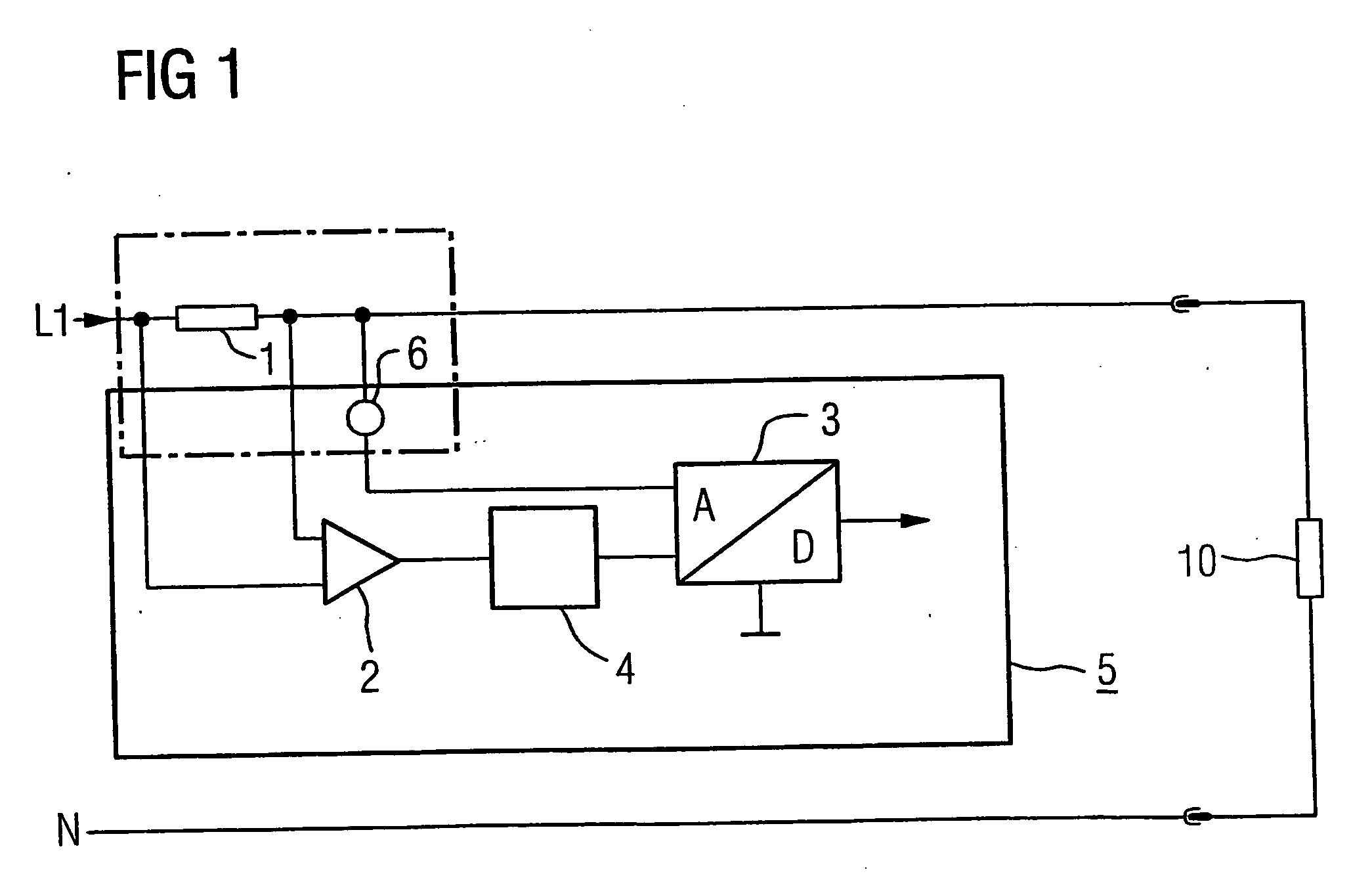
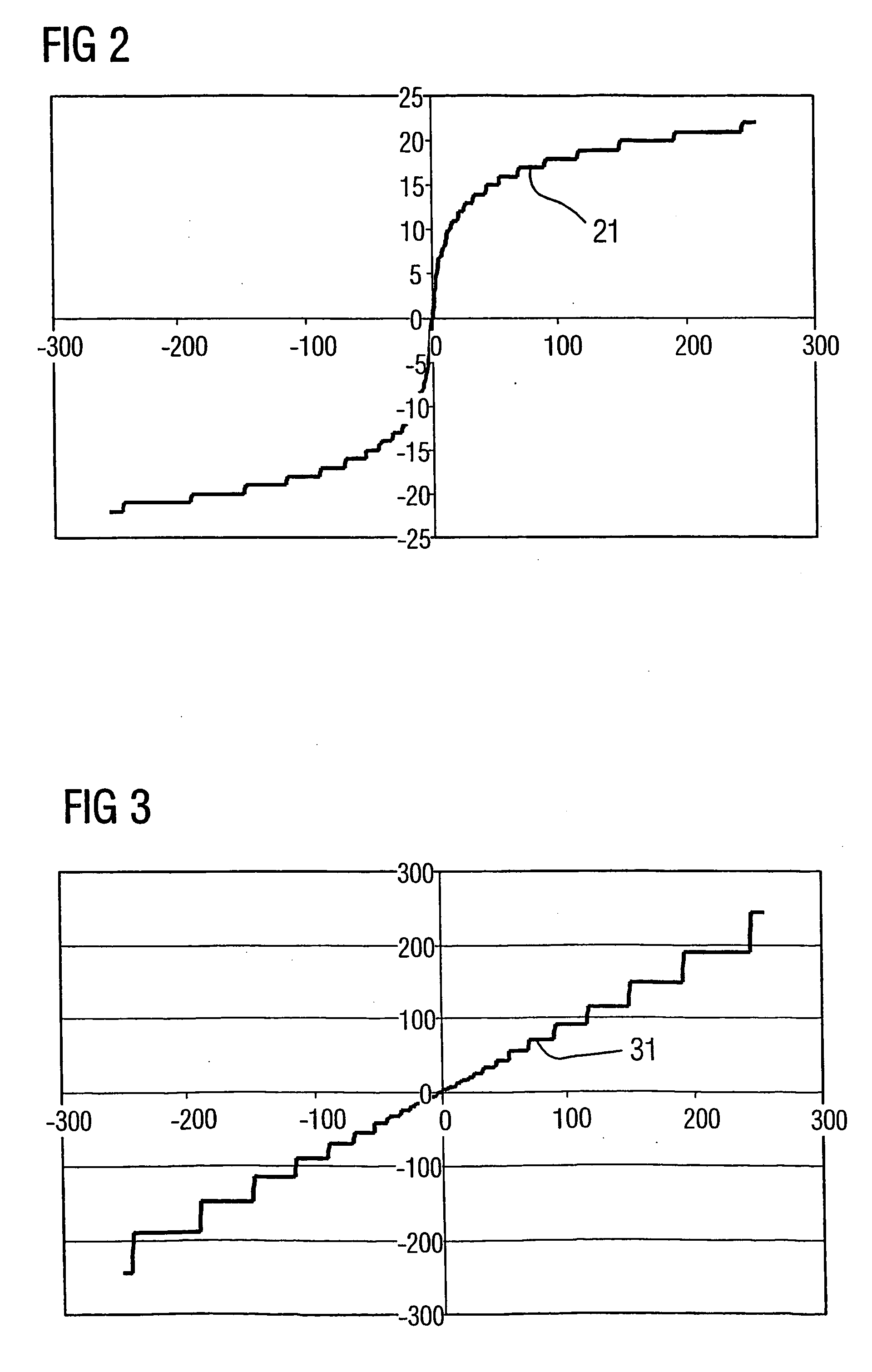
Method and circuit arrangement for current measurement
InactiveUS20060164069A1Cost-effectiveConstant precisionMeasurement using dc-ac conversionBase element modificationsMeasurement deviceTHD analyzer
A method with corresponding circuit arrangement is disclosed, whereby for evaluation of a measured signal arising as an analogue value with a potential greater than zero potential in a measuring device requiring a supply current, the measured information therefrom is transmitted as a digital signal to an analytical unit lying at earth potential after an A / D conversion. The generated digital signal thus provides the clock signal for a modulation of the supply current and thus also carries out the function of the carrier for the information content of the measured signal. Curved characteristic lines for compression / decompression of the signals are used. Suitable devices for temperature compensation may be similarly provided.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Sheet transferring device and image forming device
InactiveUS7548721B2Improve accuracyConstant precisionElectrographic process apparatusArticle feedersEngineeringSheet material
A sheet transferring device includes a feeding roller configured to feed a sheet; a transferring roller configured to transfer the sheet to the feeding roller; a sheet sensor configured to detect the sheet at a sheet transferring part from the transferring roller to the feeding roller; a measuring part configured to measure an interval of a rear end of a prior sheet and a head end of a following sheet based on a sheet detection signal of the sheet sensor; and a transferring control part configured to adjust a sheet transferring speed of the transferring roller so that the interval between the prior sheet and the following sheet is adjusted to a set value as corresponding to the interval measured by the measuring unit.
Owner:RICOH KK
Machine tool having onboard measuring device
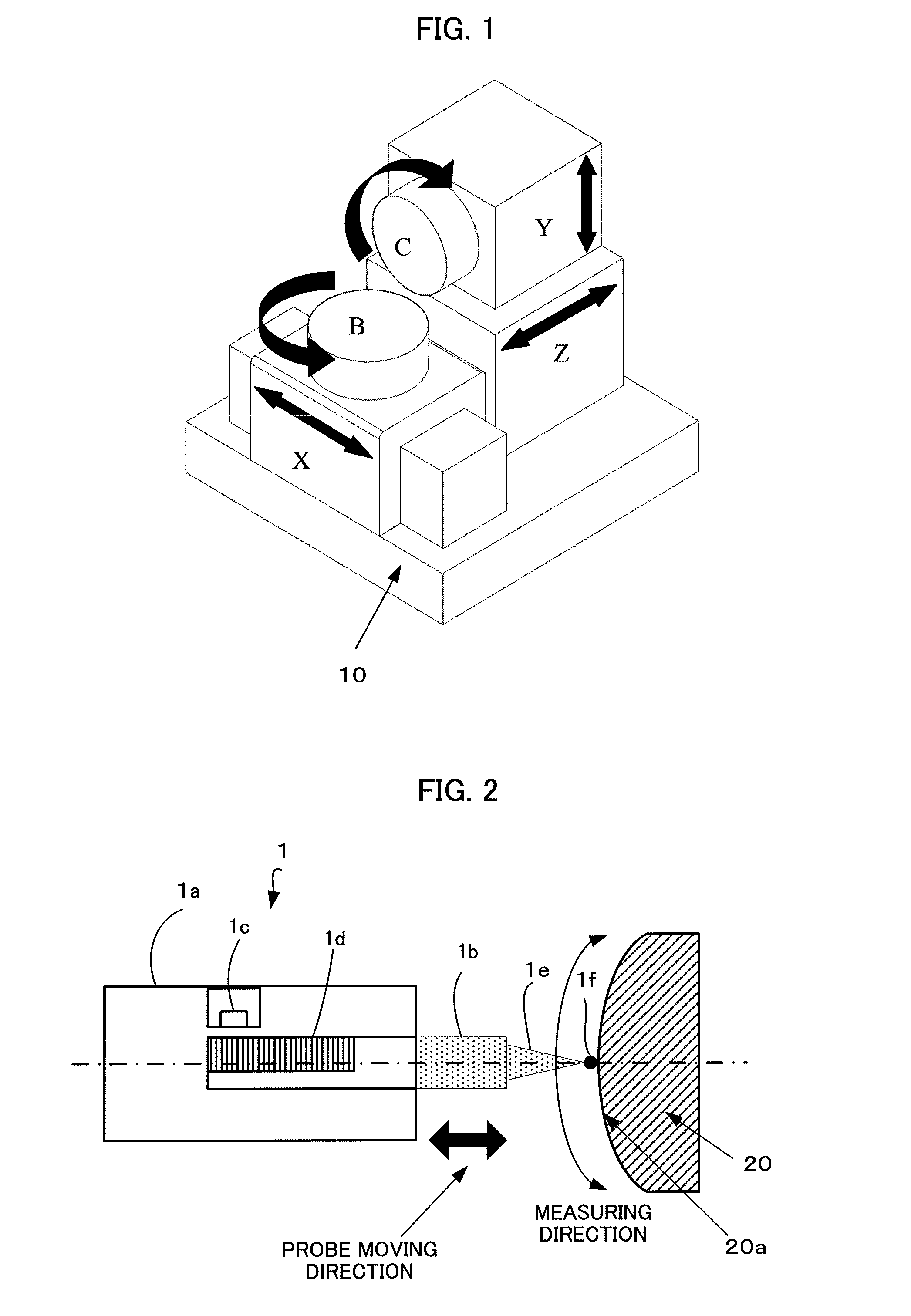
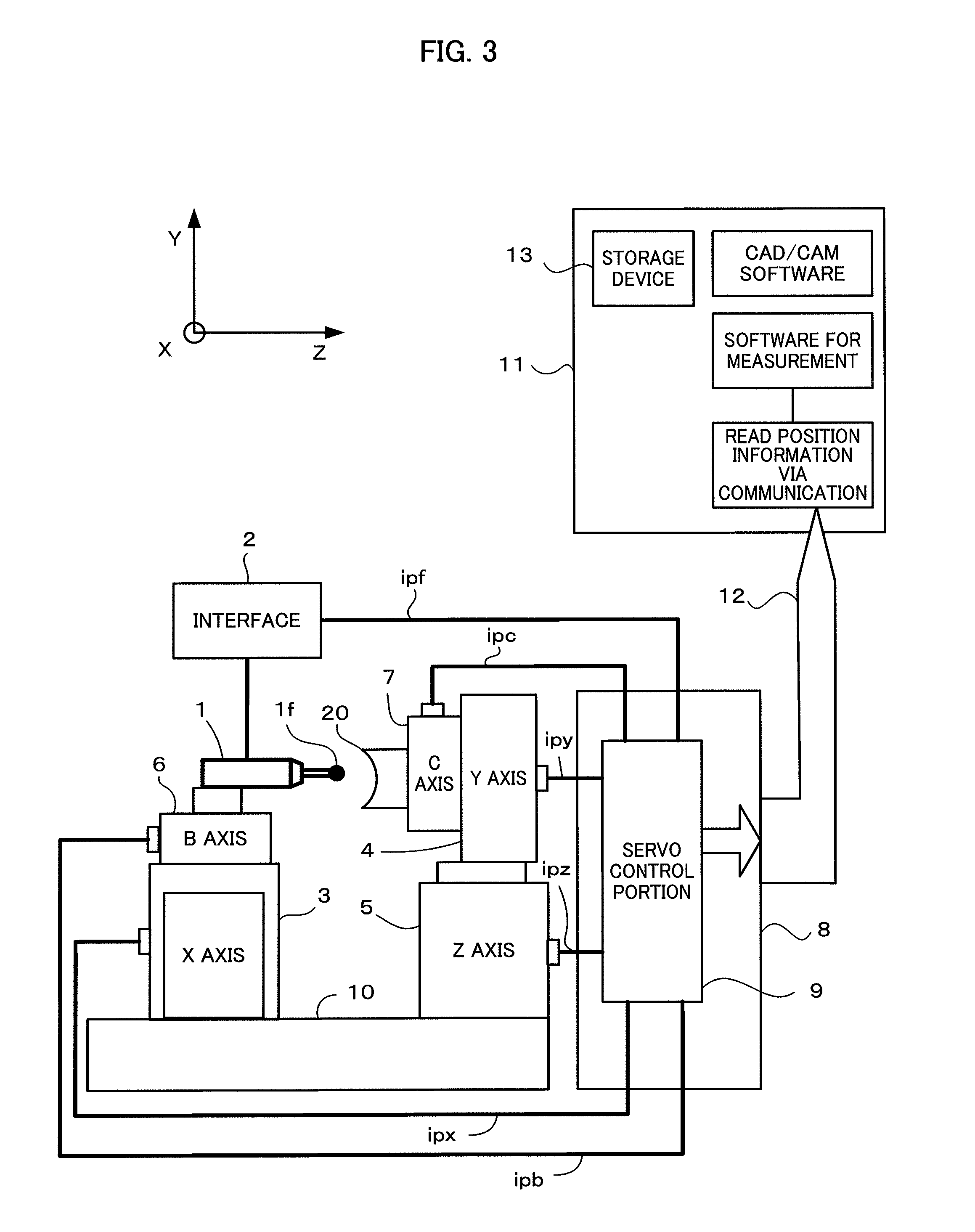
ActiveUS20130166044A1High shape accuracyStable production of a machined productComputer controlSimulator controlMeasurement deviceMachine tool
A machine tool having an onboard measuring device automatically carries out various works which include ultra precision machining, washing and onboard measuring, by a numerical controller, without any interposition of a worker. For achieving this, an operation region of drive axes of the machine tool is previously divided into a machining region, a washing region and a measuring region. Positions of the drive axes are always monitored by the numerical controller, and when the drive axes enter each of the regions, a work allocated to each of the regions is automatically started and the work is continuously carried out until drives axes exit the region.
Owner:FANUC CORP
Device for measuring volume change of at least one textile fiber band
ActiveCN101566469ADirect and precise access toEasy to installMeasurement devicesCombing machinesTextile fiberMeasurement device
The invention relates to a device for measuring volume change of one or a plurality of textile fiber bands, which comprises a first movable wheel and a second fixed wheel, wherein the wheel shafts of the first movable wheel and the second fixed wheel are parallel, and the wheel center distance between the first movable wheel and the second fixed wheel can be changed. At least one textile fiber band is pulled between the first movable wheel and the second fixed wheel in a sliding mode. A circumferential ring of the first movable wheel is matched in an annular groove, wherein the annular groove is arranged at the outer rim of the second fixed wheel, and the shape of the annular groove corresponds to that of the circumferential ring. The first movable wheel and the second fixed wheel are pressed together by an elastic device to enable the first movable wheel to move away from or move to the second fixed wheel according to the instant section of at least one band. The band is pressed in the groove of the second fixed wheel by the circumferential ring of the first movable wheel, and the first movable wheel is connected to a measuring device, wherein the second fixed wheel is pivoted on a supporting member which is integrated with an equipment stand of an installation device; the first movable wheel is supported by an eccentric element and is pivoted to the eccentric element; the eccentric element is pivoted on the supporting member; and a rotating shaft line of the eccentric element is parallel but not coincident with a shaft line of the first movable wheel.
Owner:托姆希克有限公司
Separation device and separation method
ActiveUS20160136543A1Quality improvementLittle difference in qualityIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationStationary phaseSeparation column
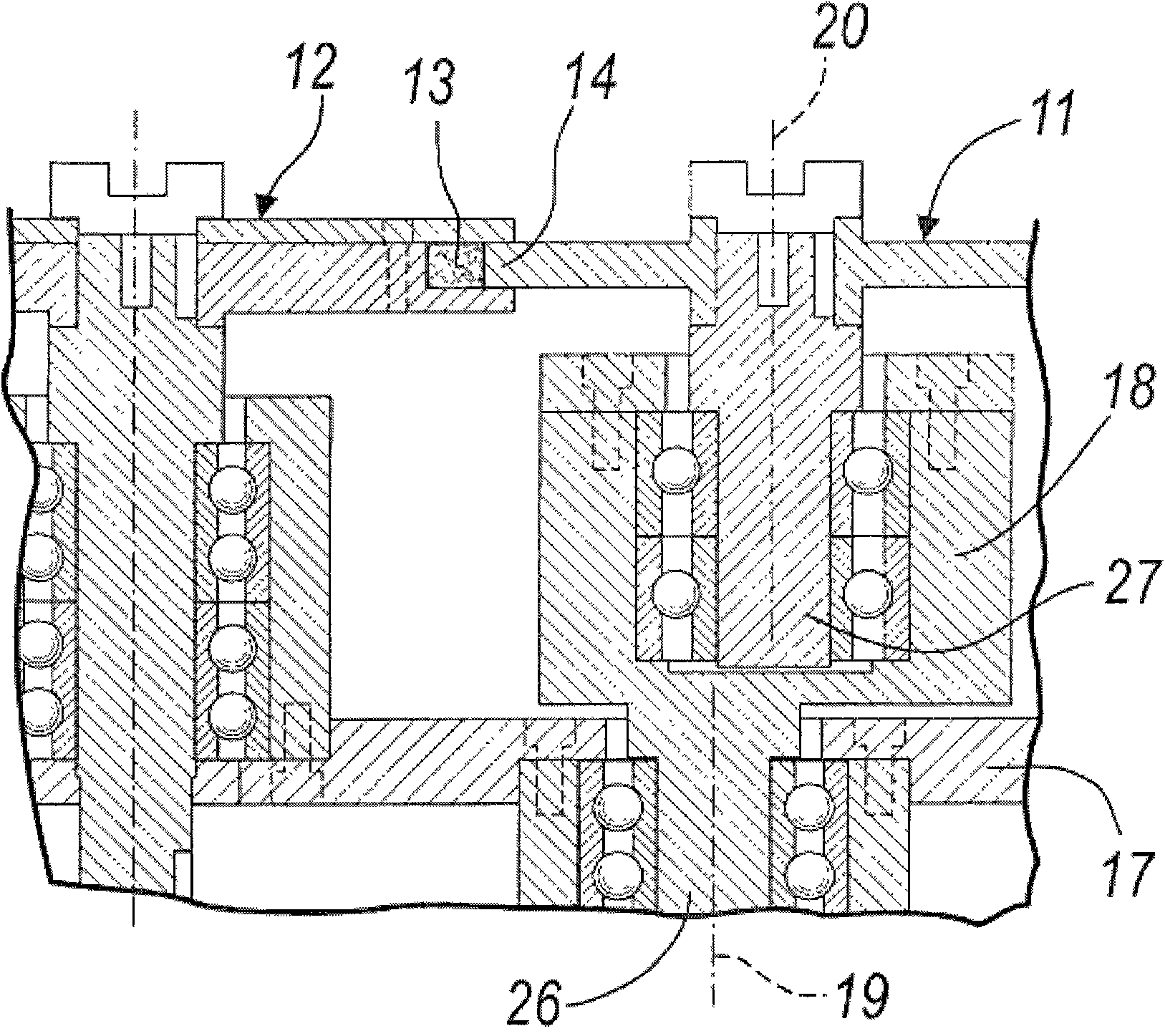
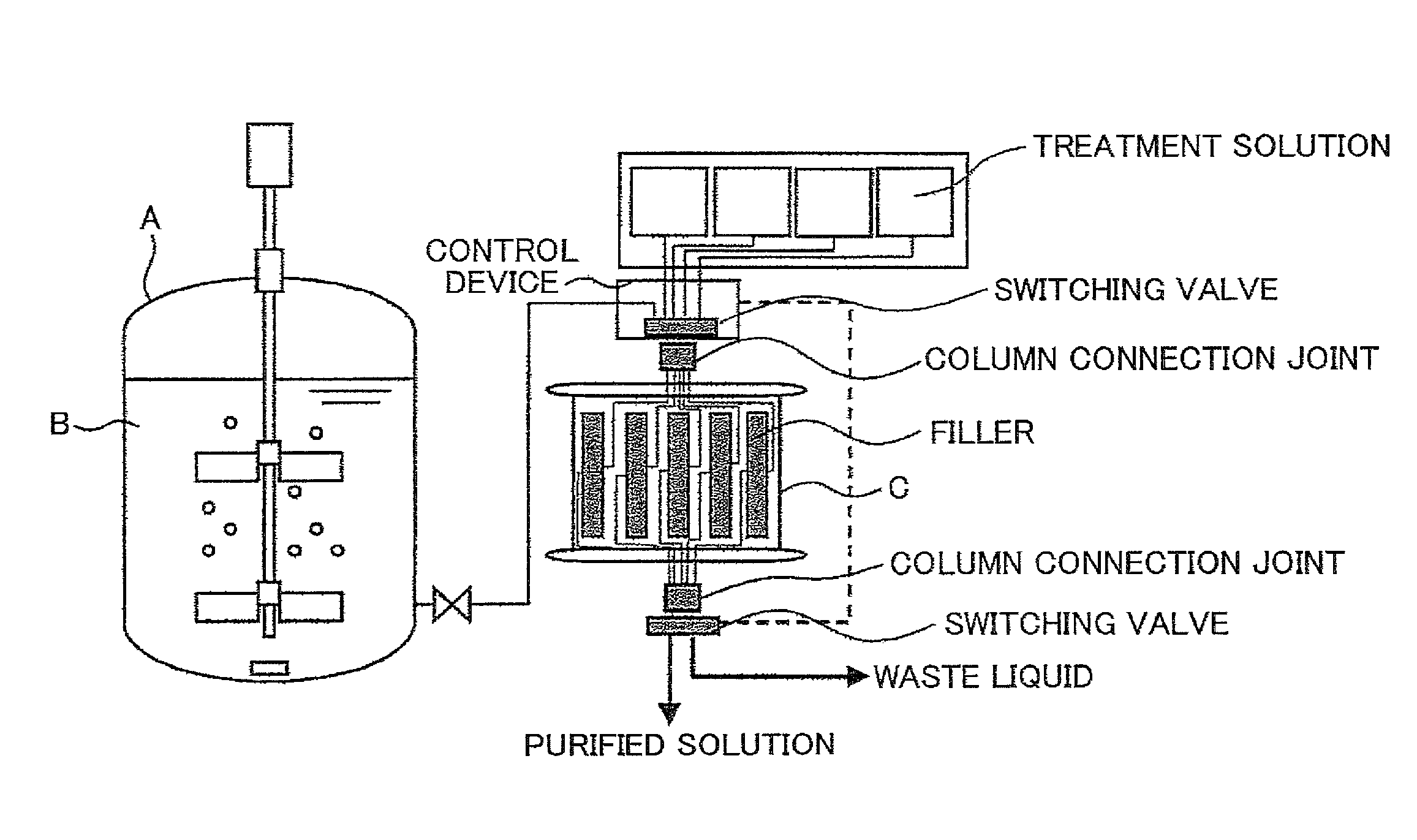
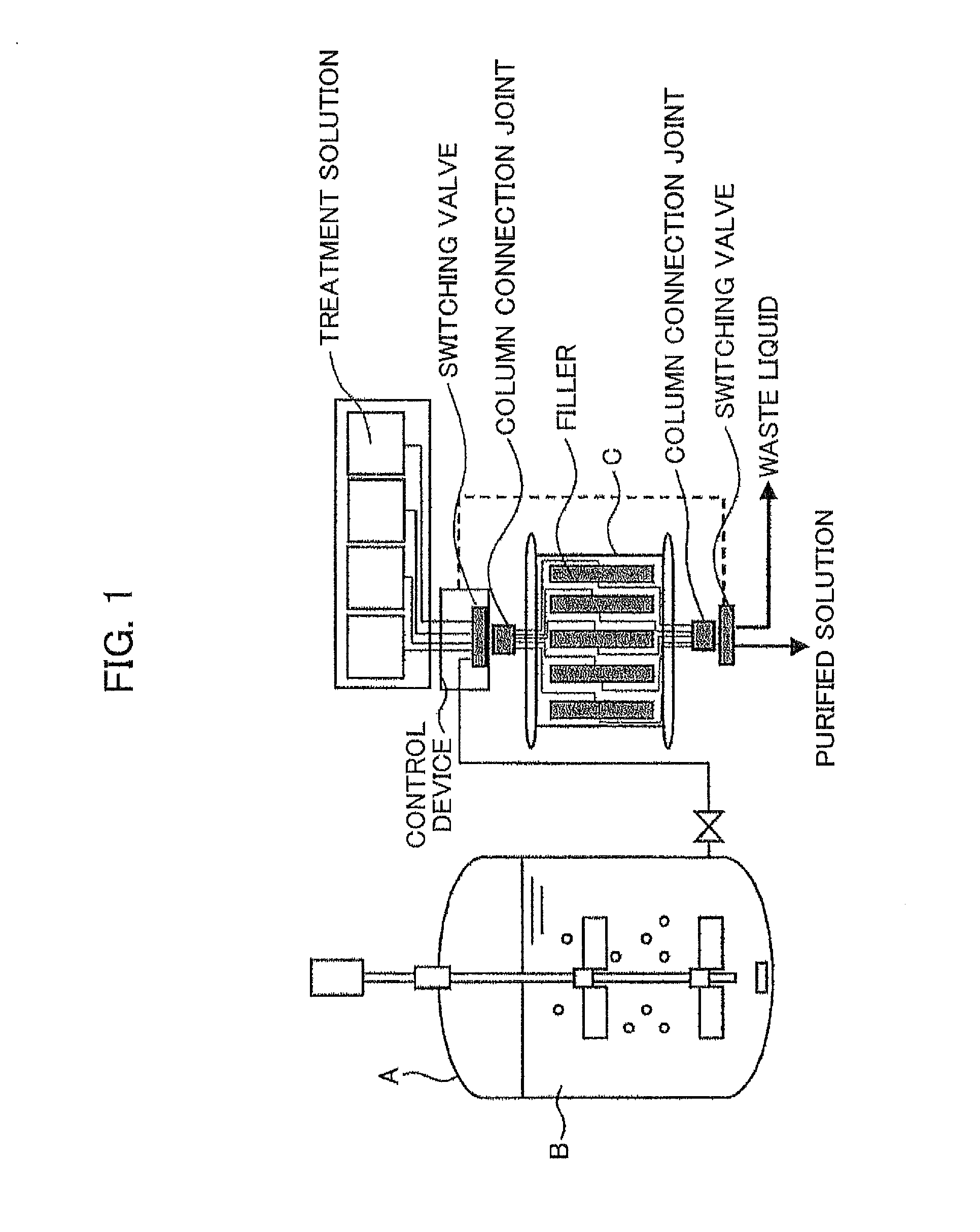
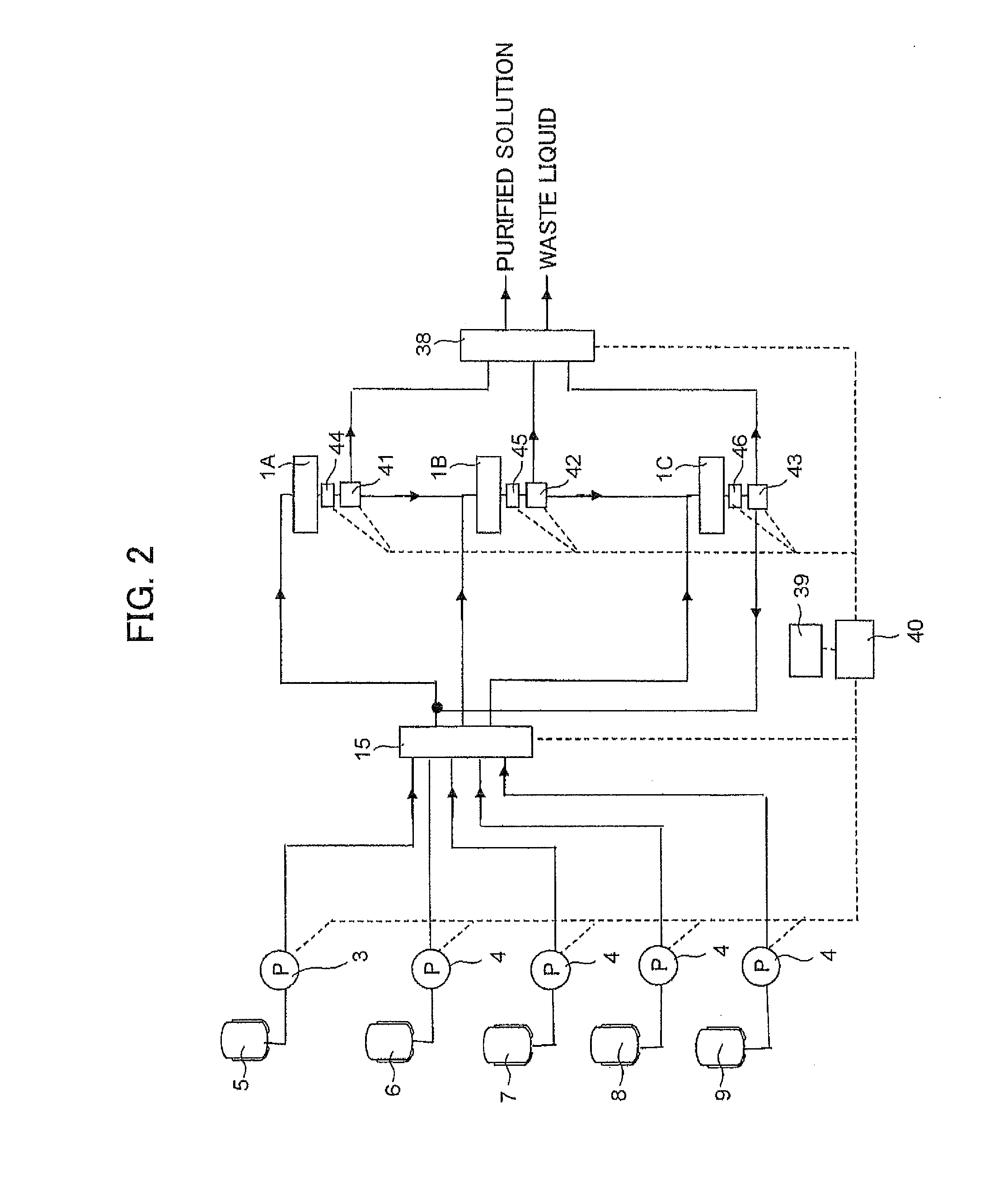
An object of the present invention is to separate a material to be separated at a low cost and constant accuracy when the material to be separated is separated from a mobile phase containing the material to be separated through the passing of the mobile phase through a stationary phase, even if the mobile phase has a large volume. A separation device characterized in that a separation column provided with a stationary phase having a volume capable of processing the entire volume of a mobile phase containing a material to be separated is provided, the separation column is replaceable, and the usage count of the stationary phase reaches a lifetime count through the processing of one batch.
Owner:HITACHI PLANT SERVICES
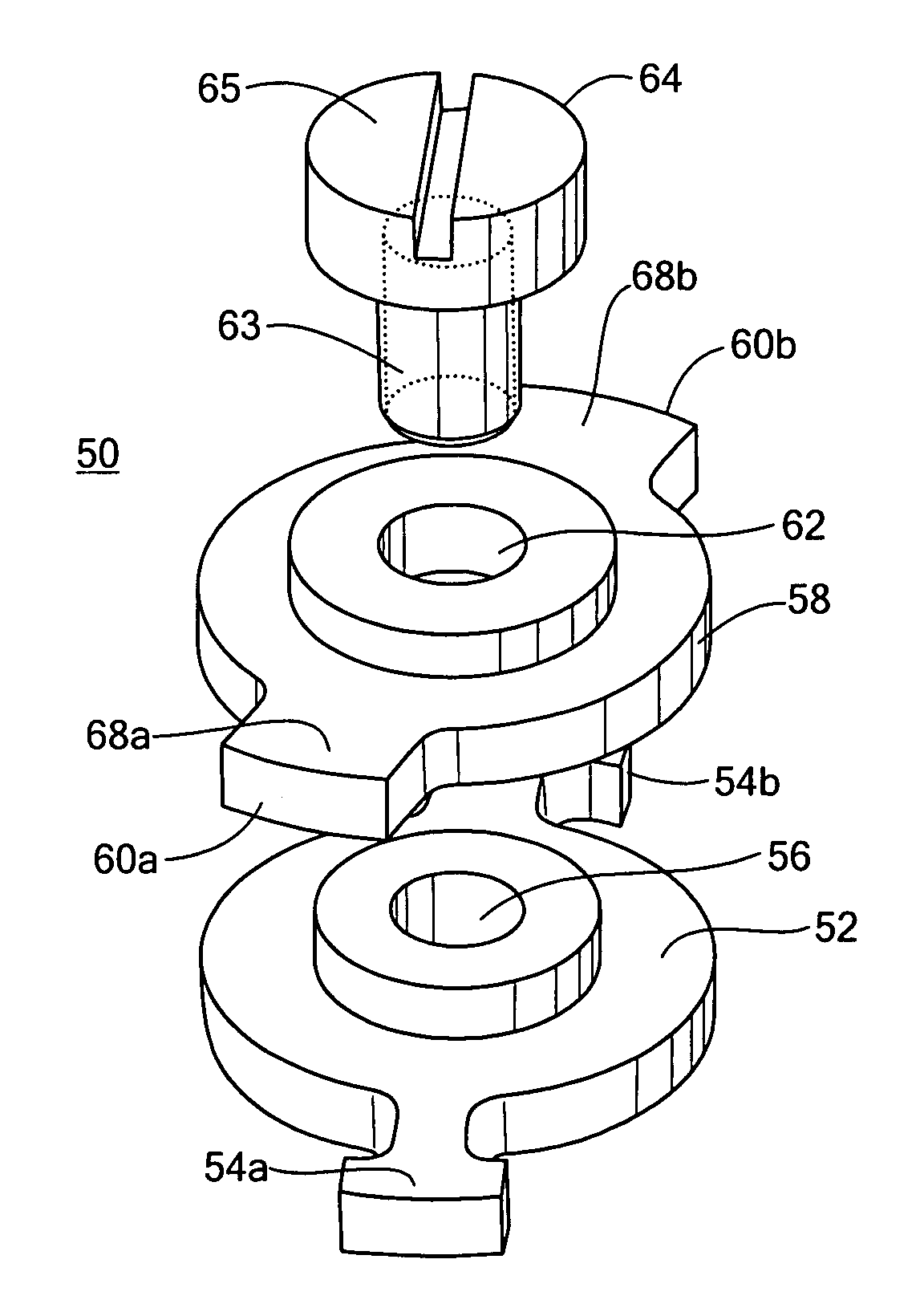
Musical instrument piston valve
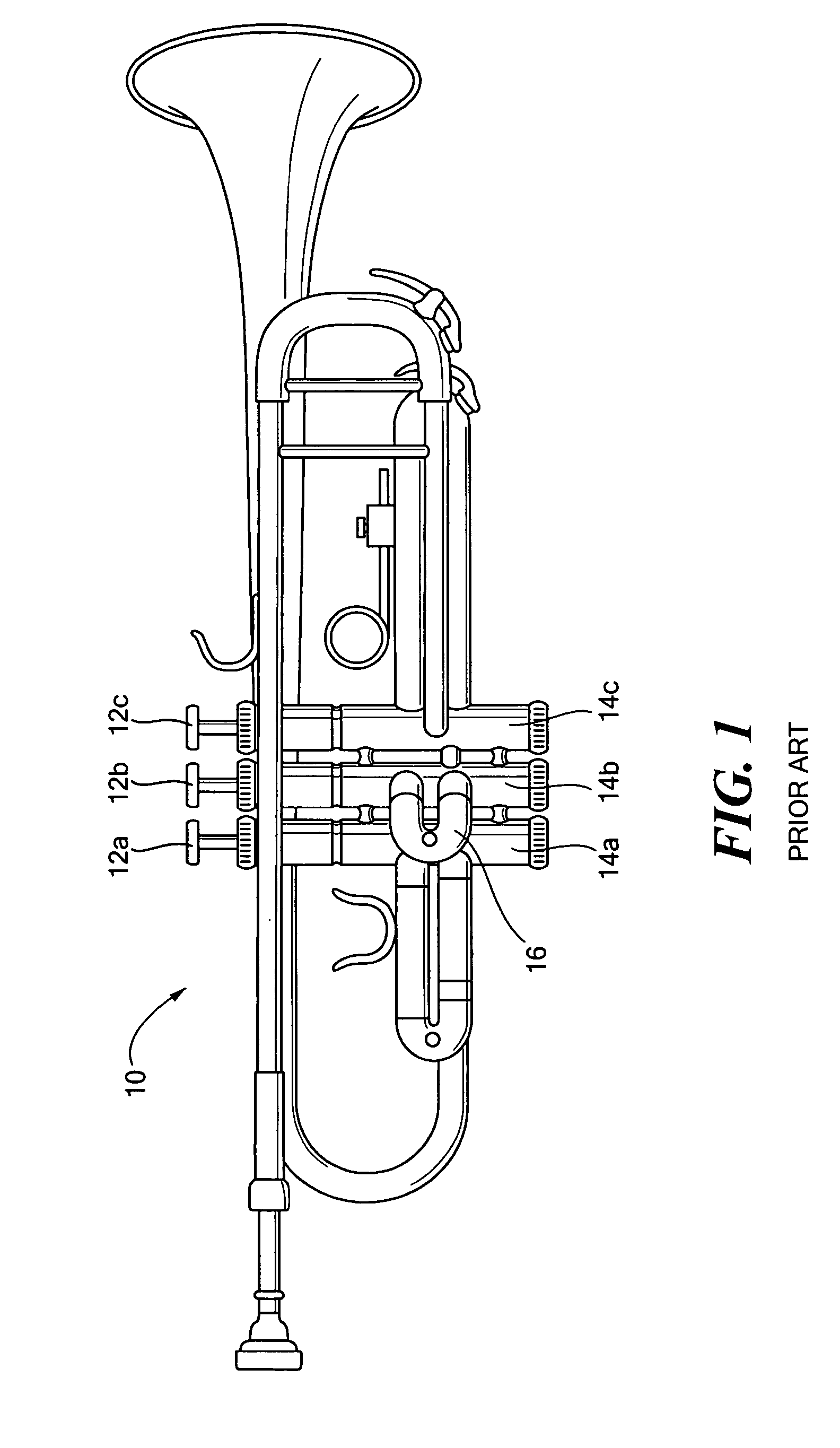
InactiveUS7667117B2Low costMinimize operationAutomatic musical instrumentsWind musical instrumentsAngular orientationValve stem
A musical instrument piston valve receivable in a valve casing. The valve includes a valve stem, a valve barrel connected to the valve stem, and a valve guide slidably disposed with respect to the valve barrel. A spring is disposed in the valve barrel extending between the valve stem and the valve guide. A piston extends from the valve barrel and includes one or more ports. There are also various ways of adjusting the angular orientation of the piston in the valve casing. It is preferred that the piston and the valve barrel are monolithic in construction and the piston valve includes an adjustable valve guide.
Owner:WASSER STEVEN A
Musical instrument piston valve
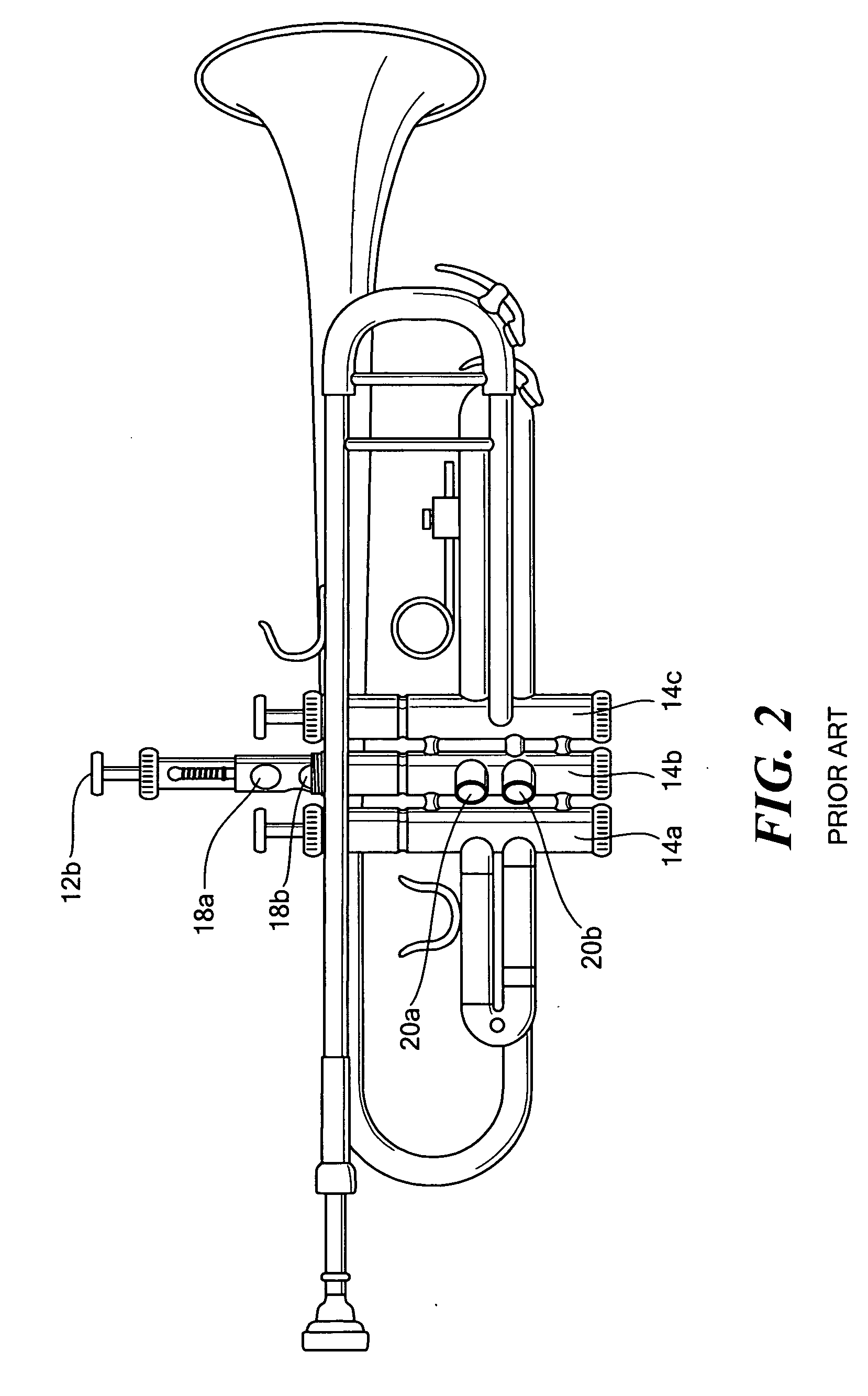
InactiveUS20060219083A1Low costMinimize assembly requirementAutomatic musical instrumentsWind musical instrumentsPistonValve stem
Owner:WASSER STEVEN A
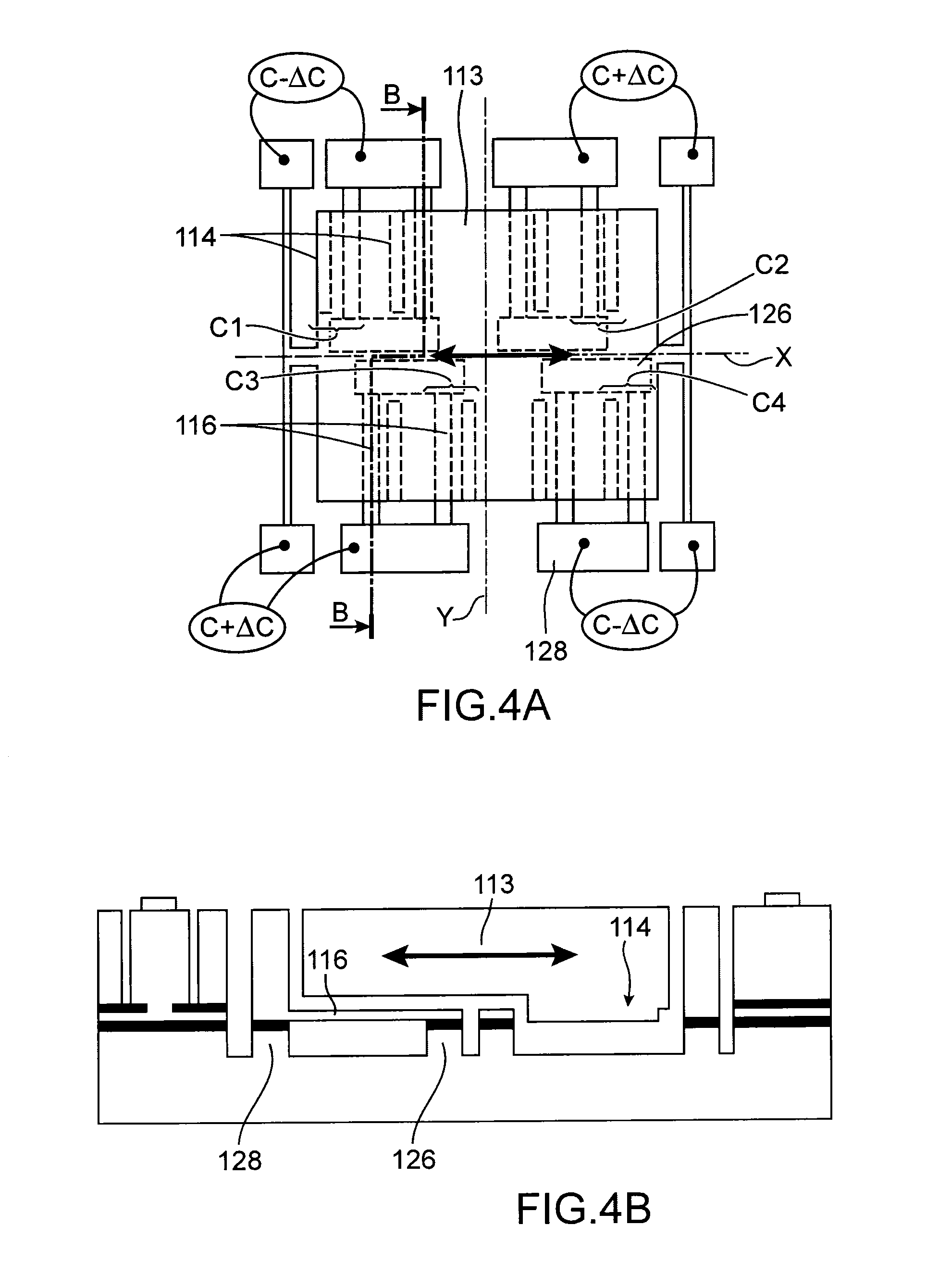
Capacitive microelectronic and/or nanoelectronic device with increased compactness
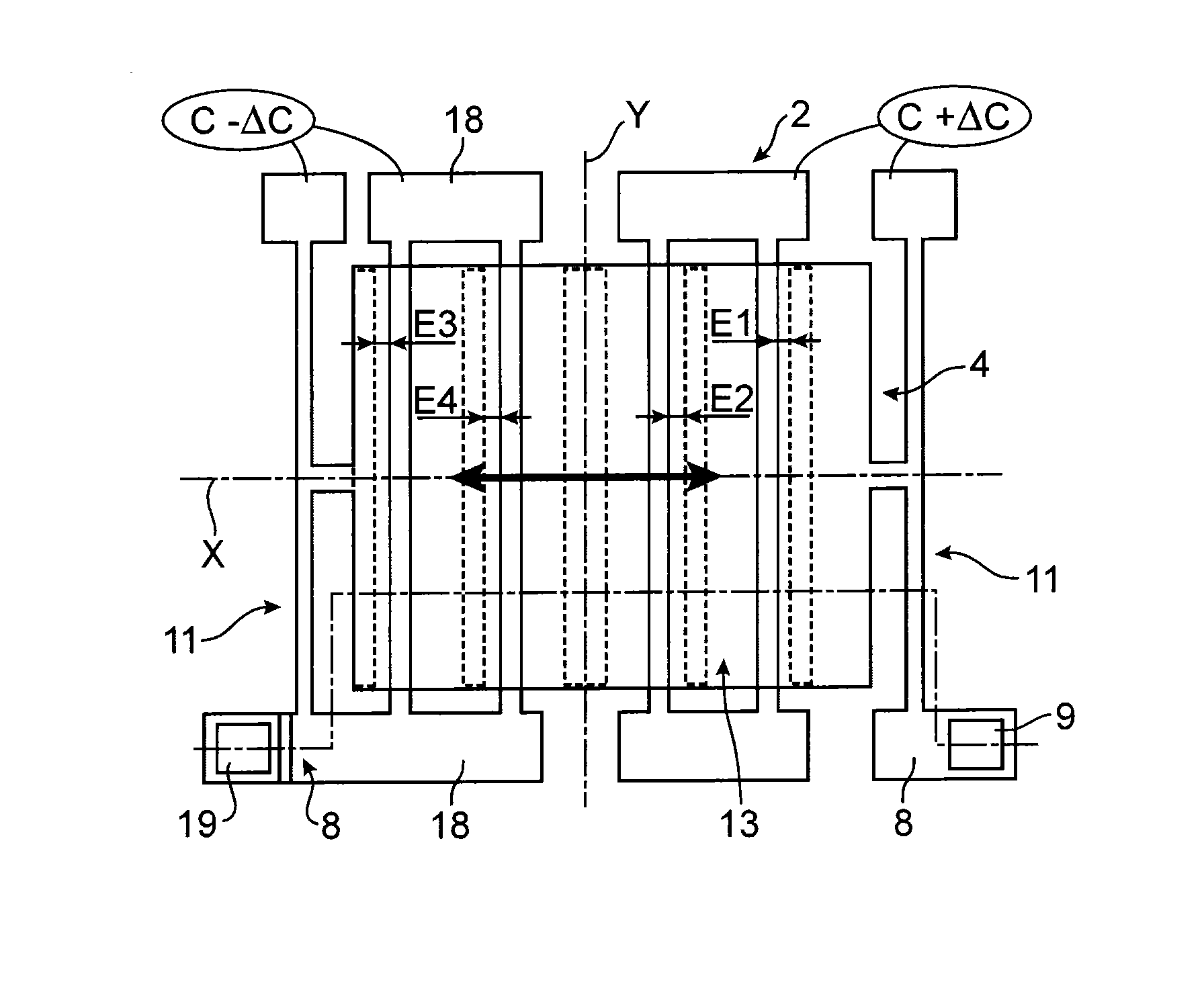
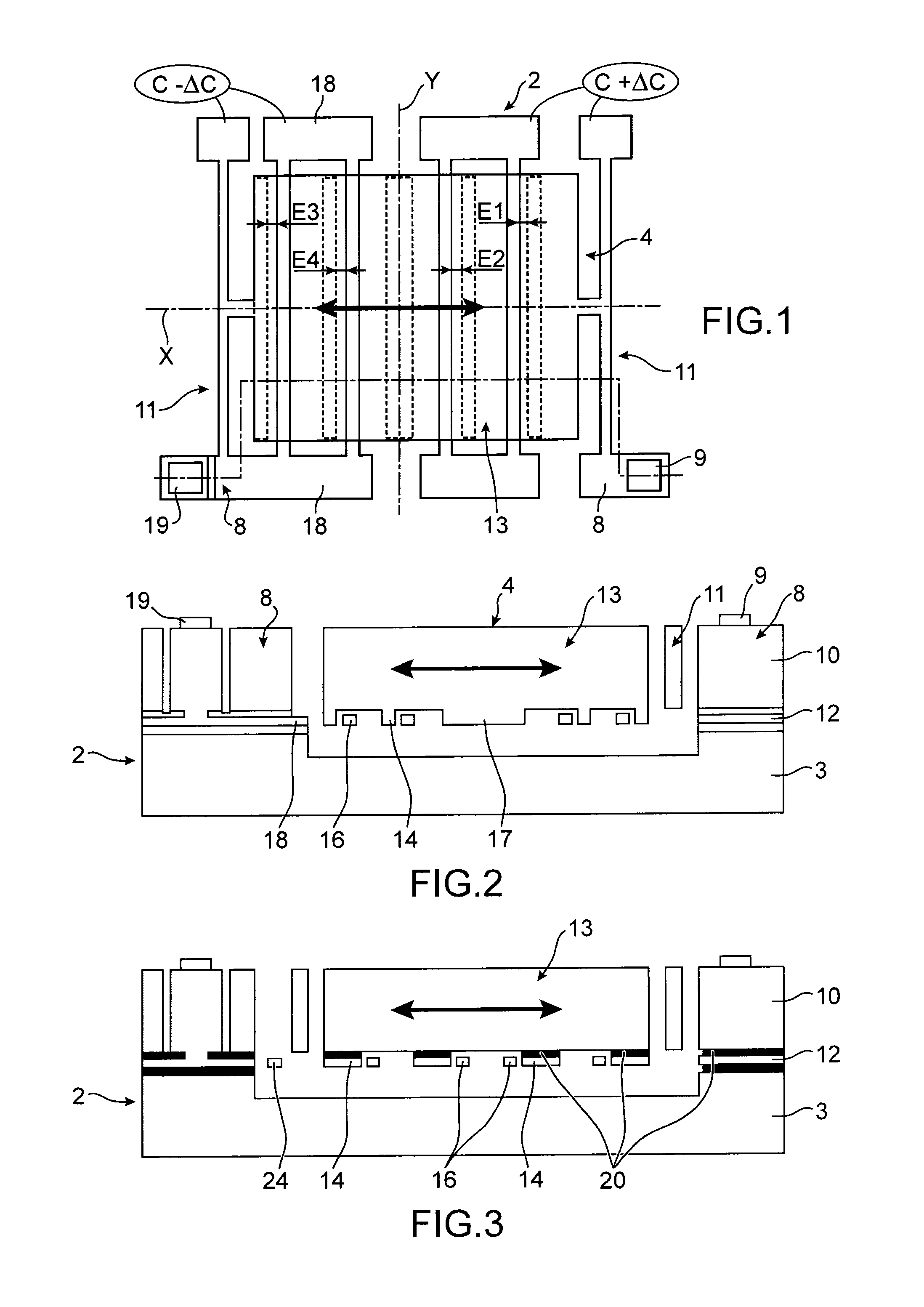
ActiveUS20150338246A1Improve compactnessReduced footprintResistance/reactance/impedenceDecorative surface effectsIn planeCapacitance
A device with a mobile element extending along a given plane comprising at least one first, one second and one third layers extending in planes parallel to the given plane, with the first layer forming a support, the second layer comprising all or a portion of the mobile element and means for suspending the mobile element with respect to the support and the third layer comprising all or a portion of the capacitive means of which the capacitance varies according to the relative position of the mobile element with respect to the support, said capacitive means comprising at least one mobile electrode integral with one of the faces of the mobile element parallel to the given plane, and at least one fixed electrode with respect to the support, with the fixed and mobile electrodes being arranged at least partially in the same plane parallel to the given plane and at least partially above and / or below the mobile element.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com