Patents
Literature
78results about How to "Suppressed dislocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
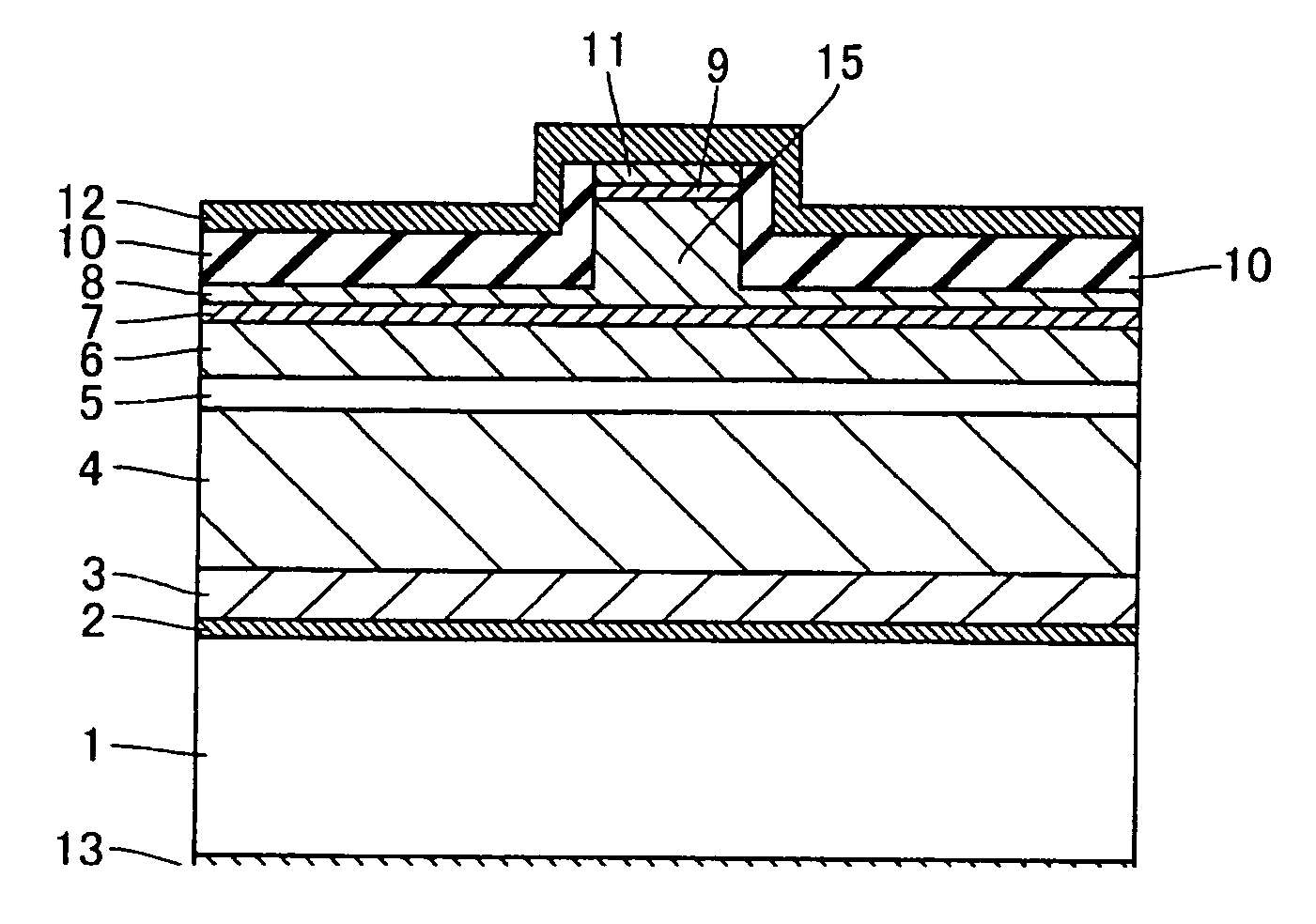
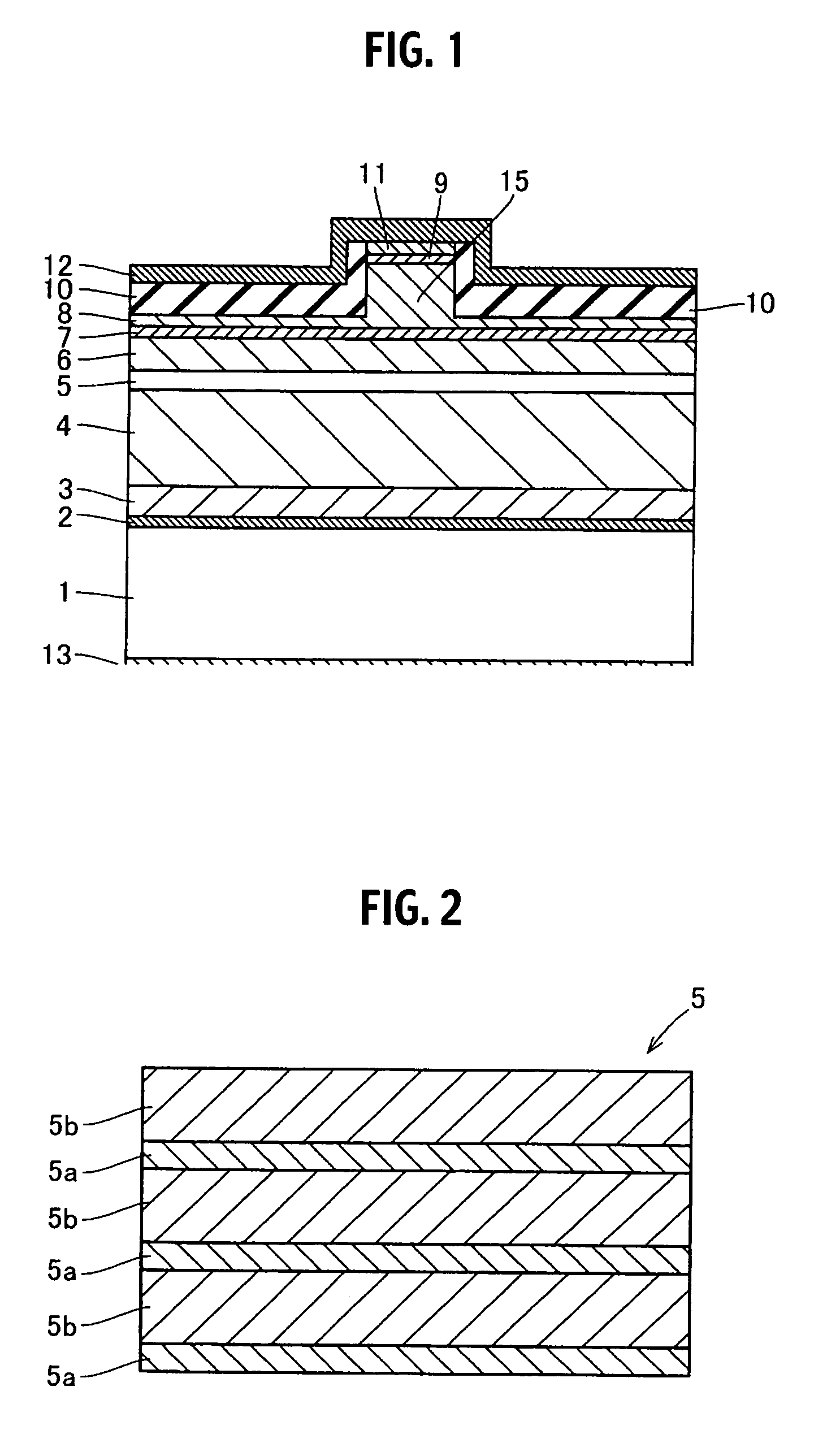
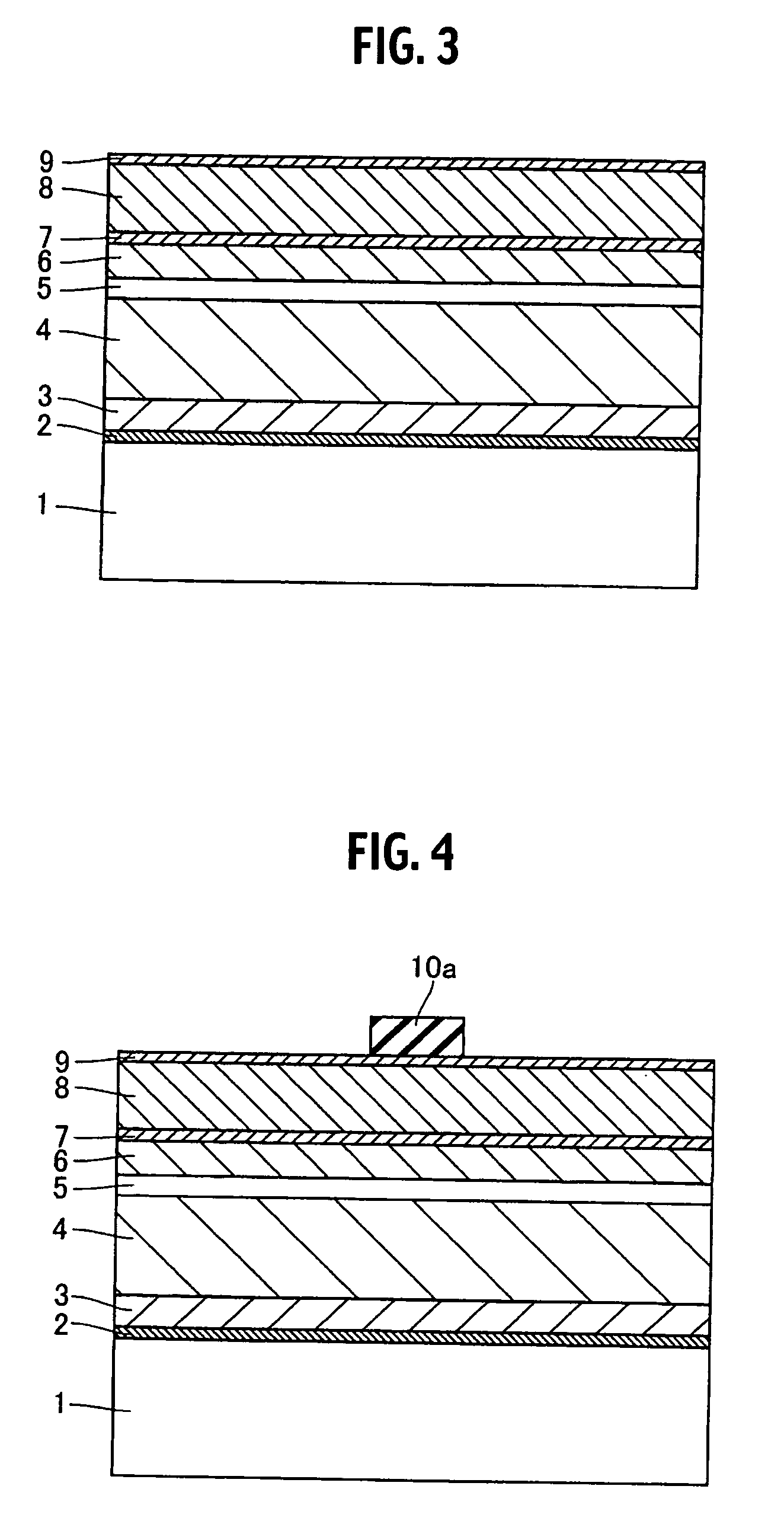
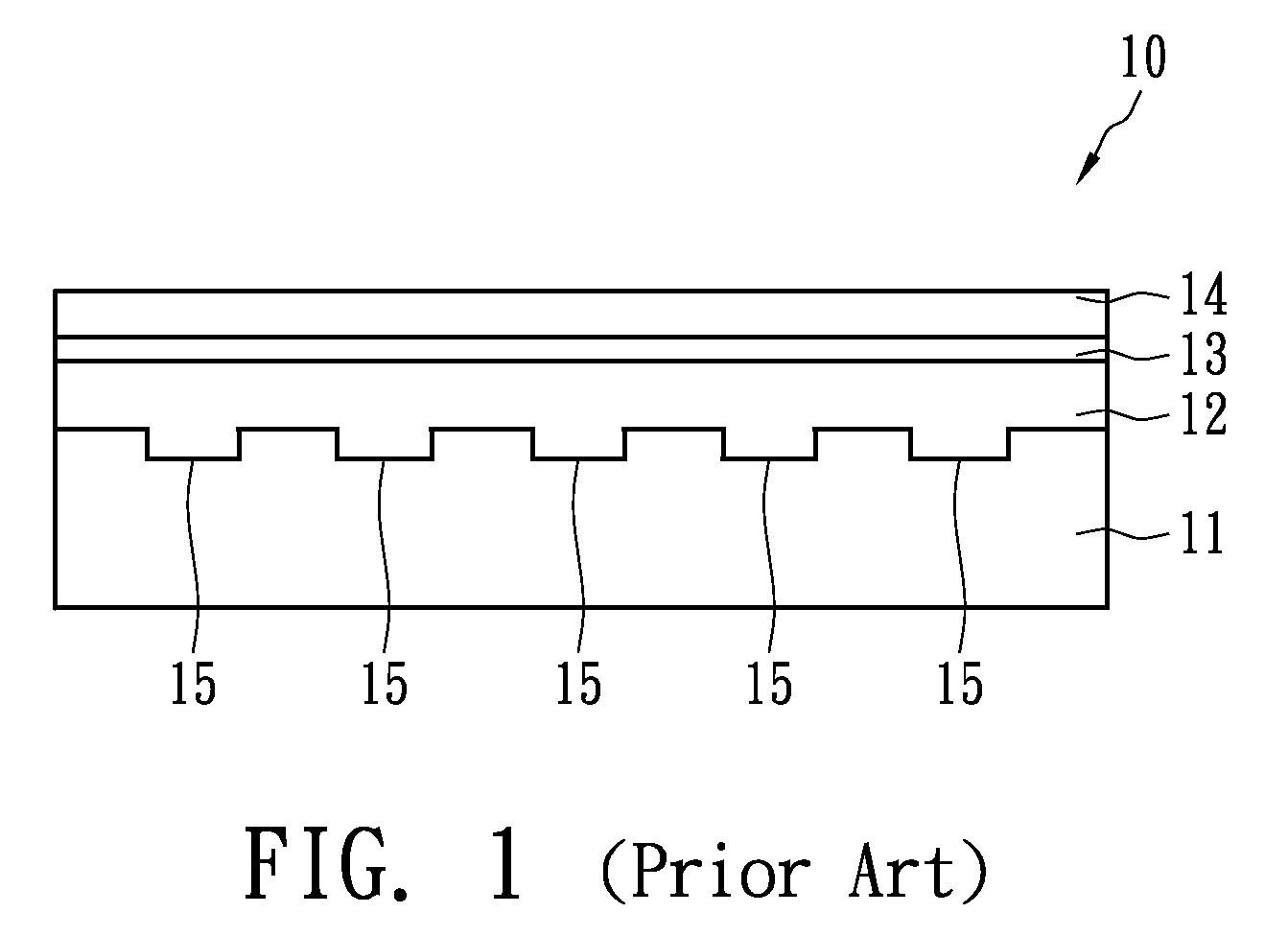
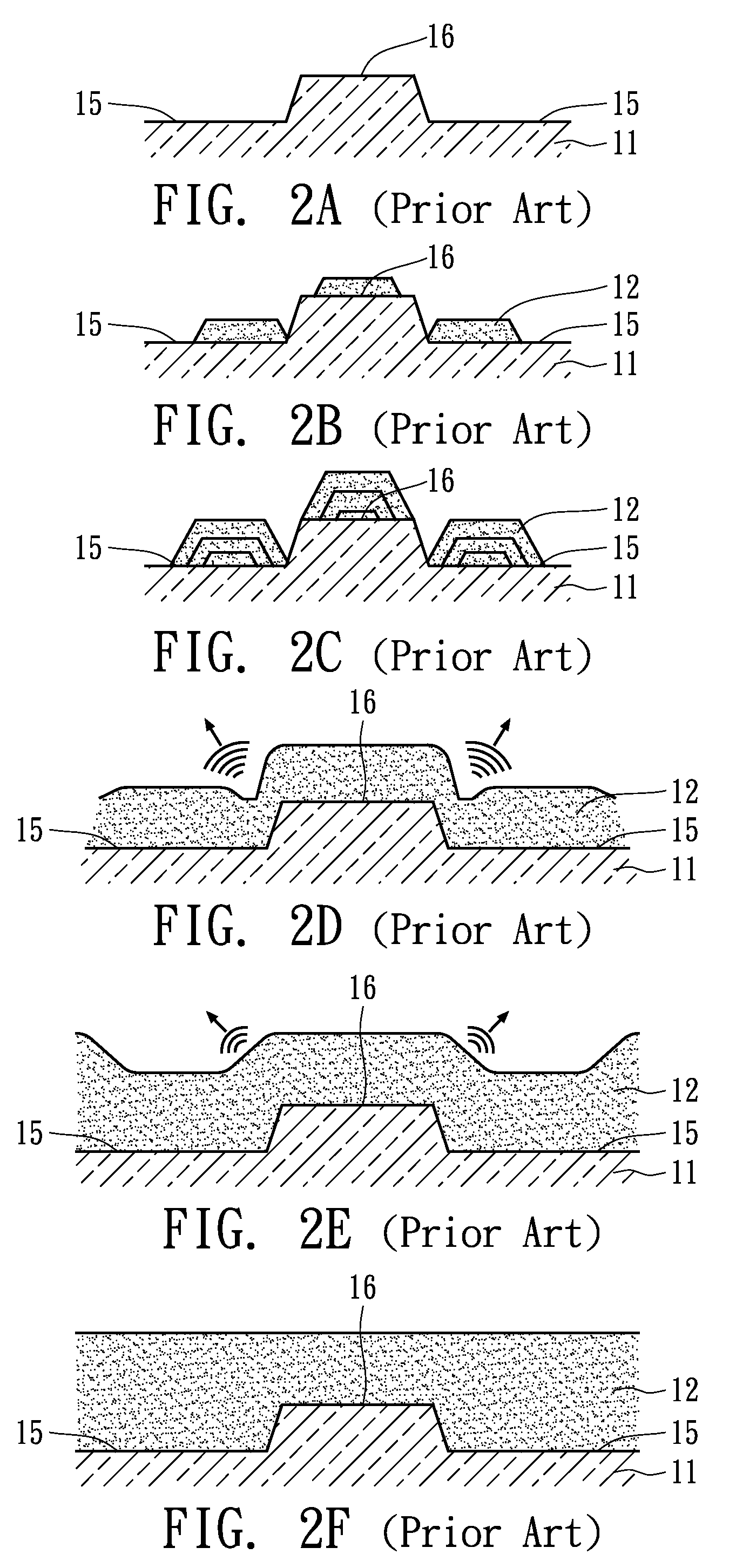
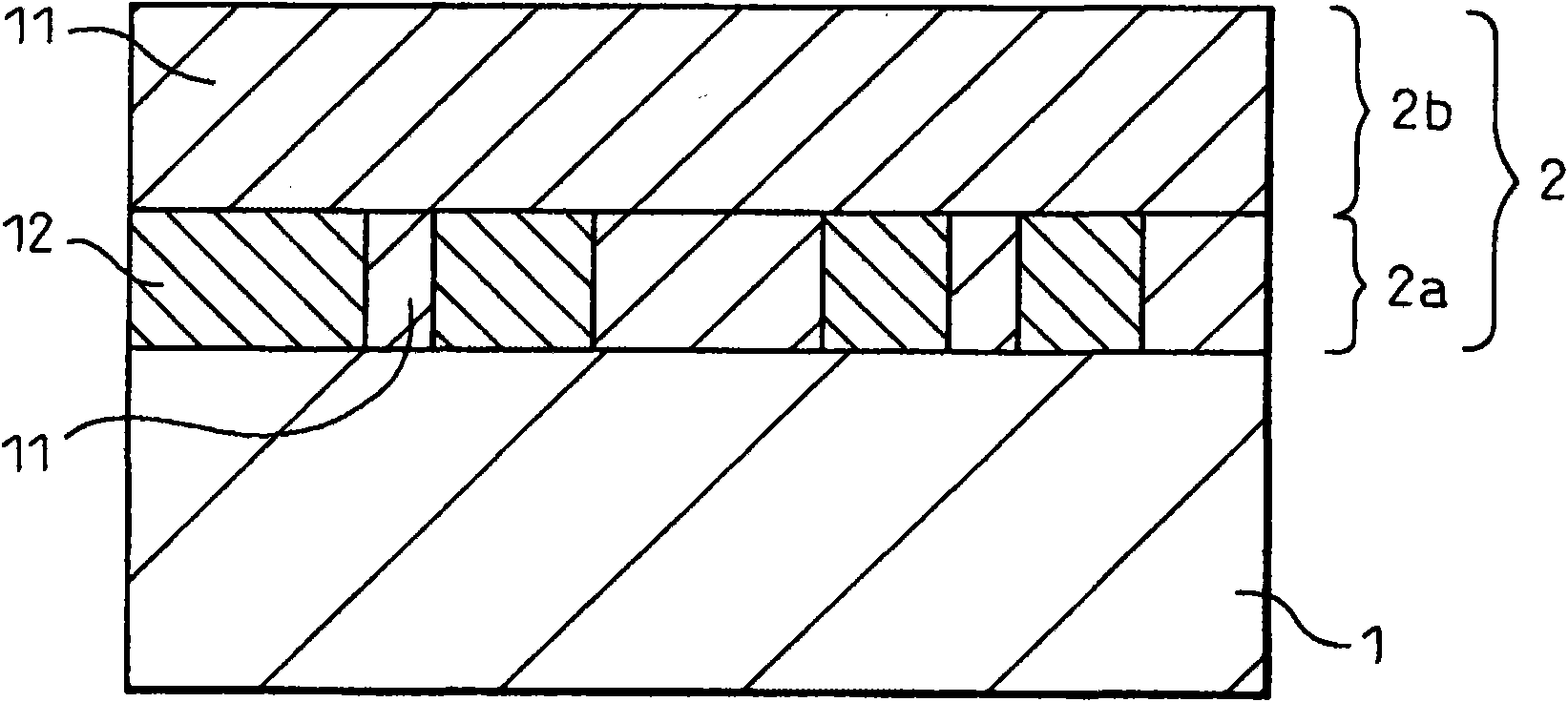
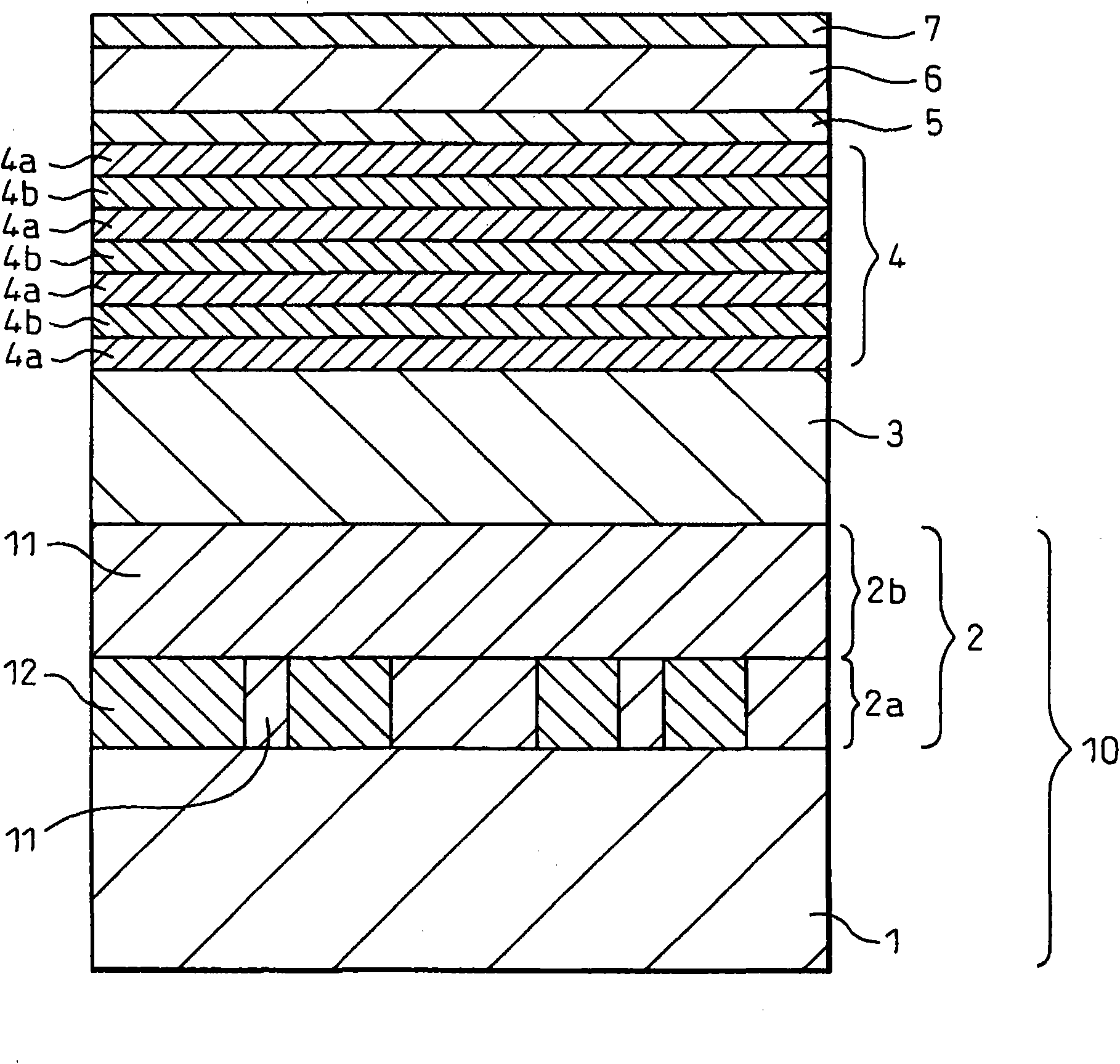
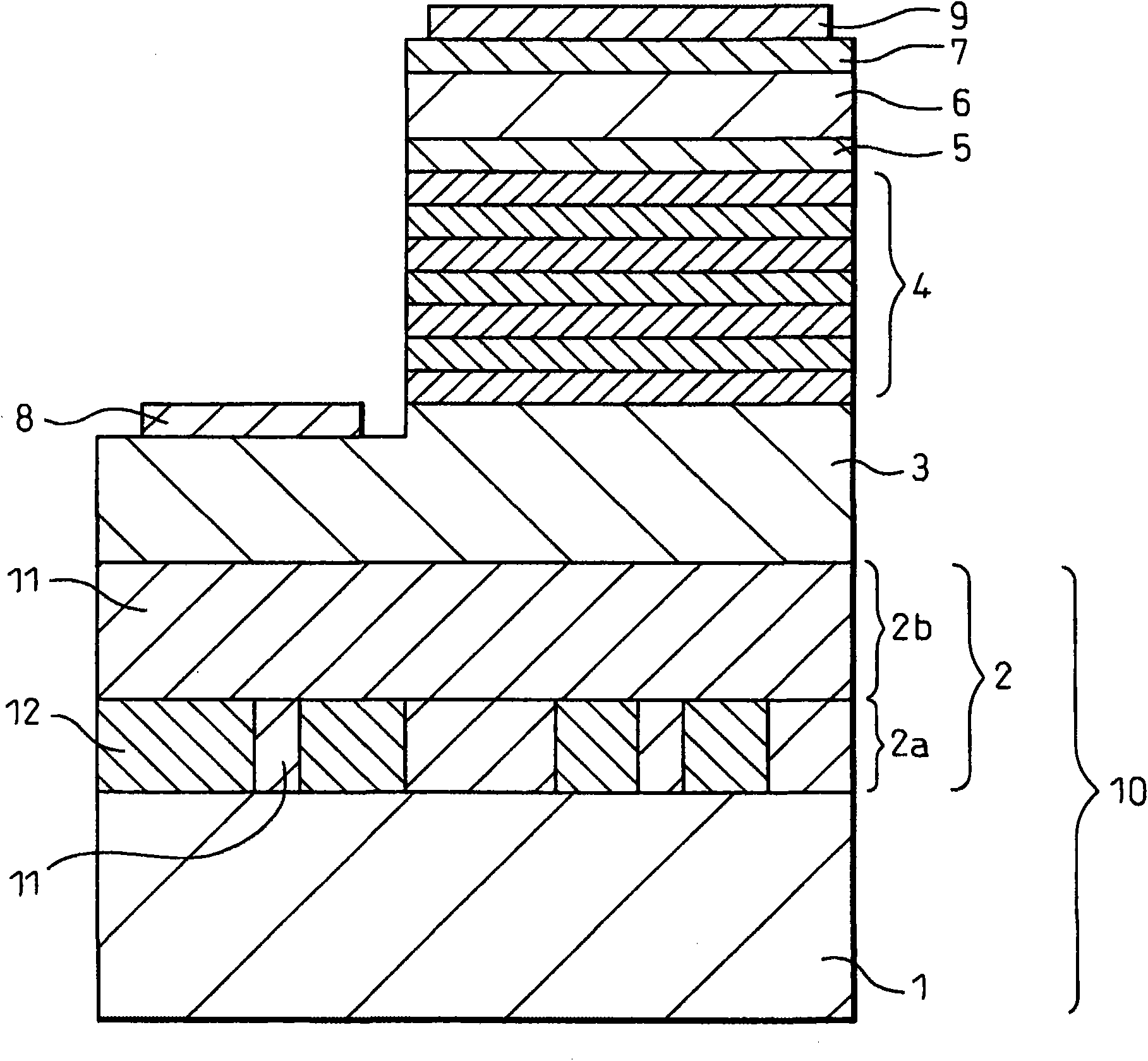
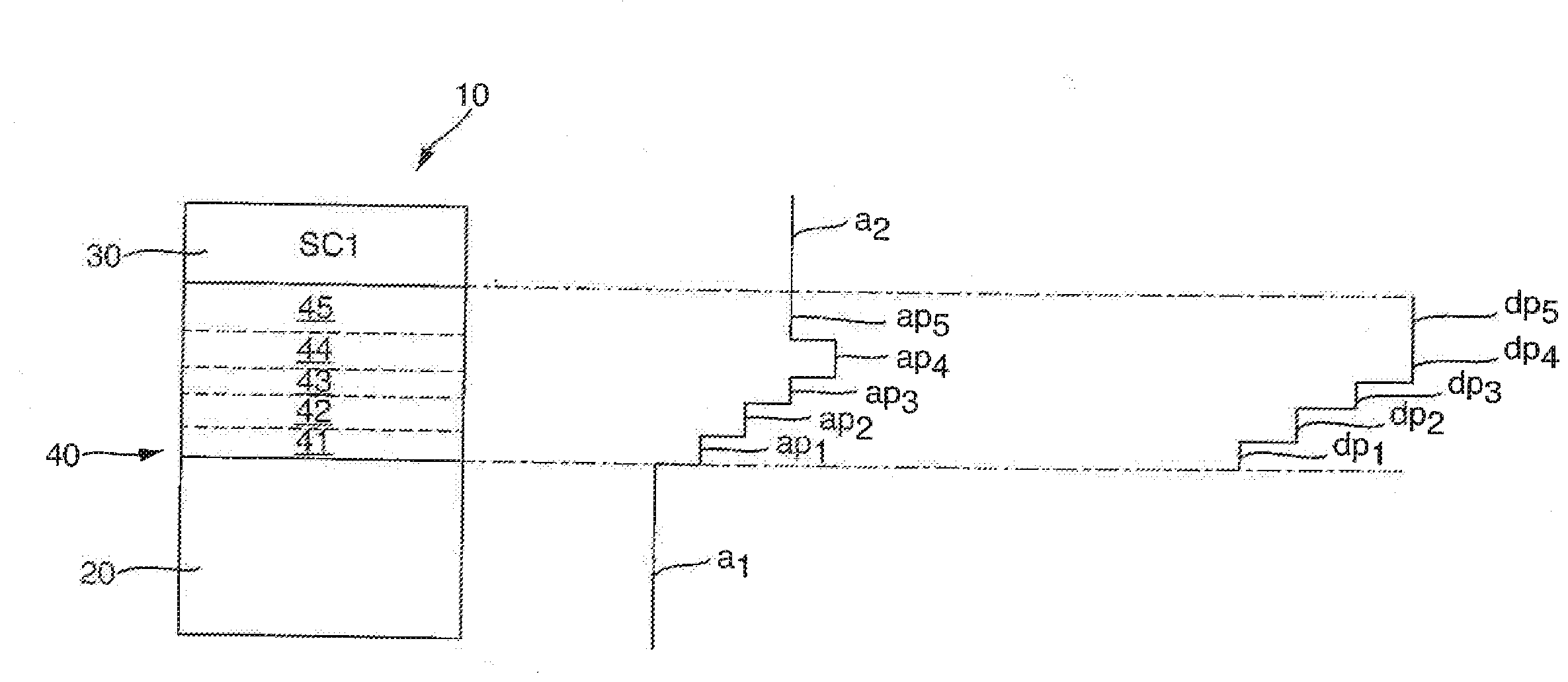
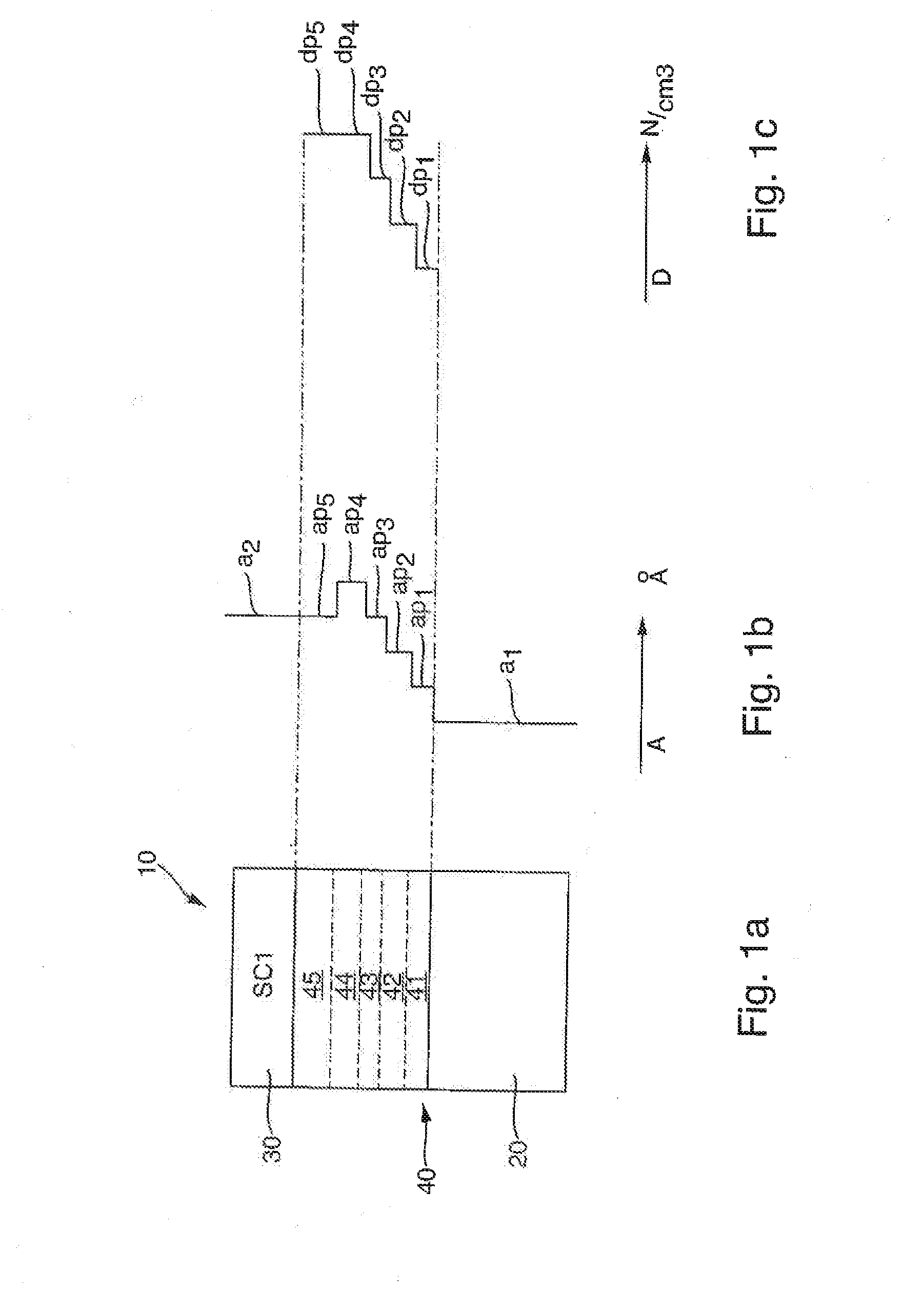
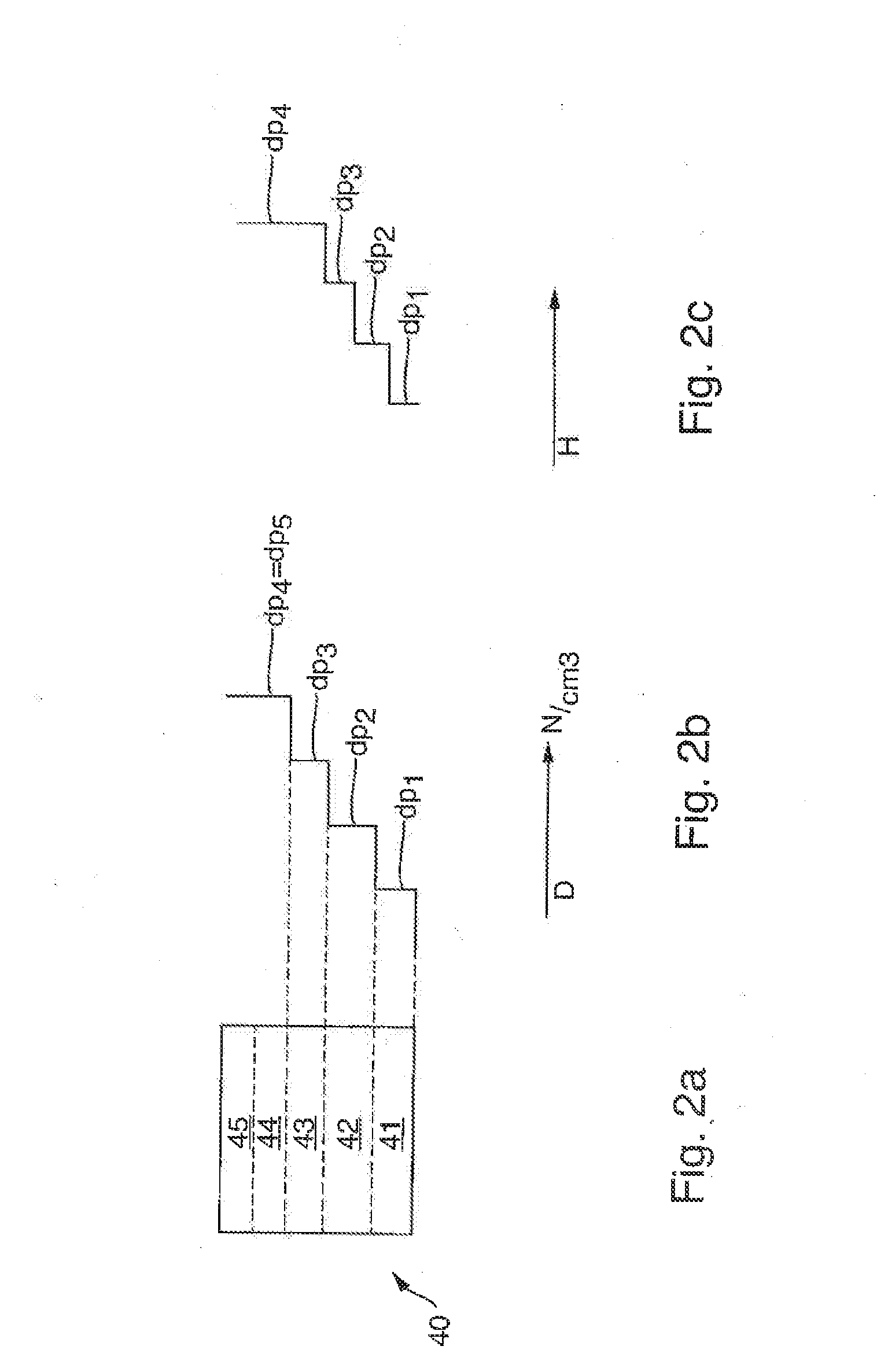
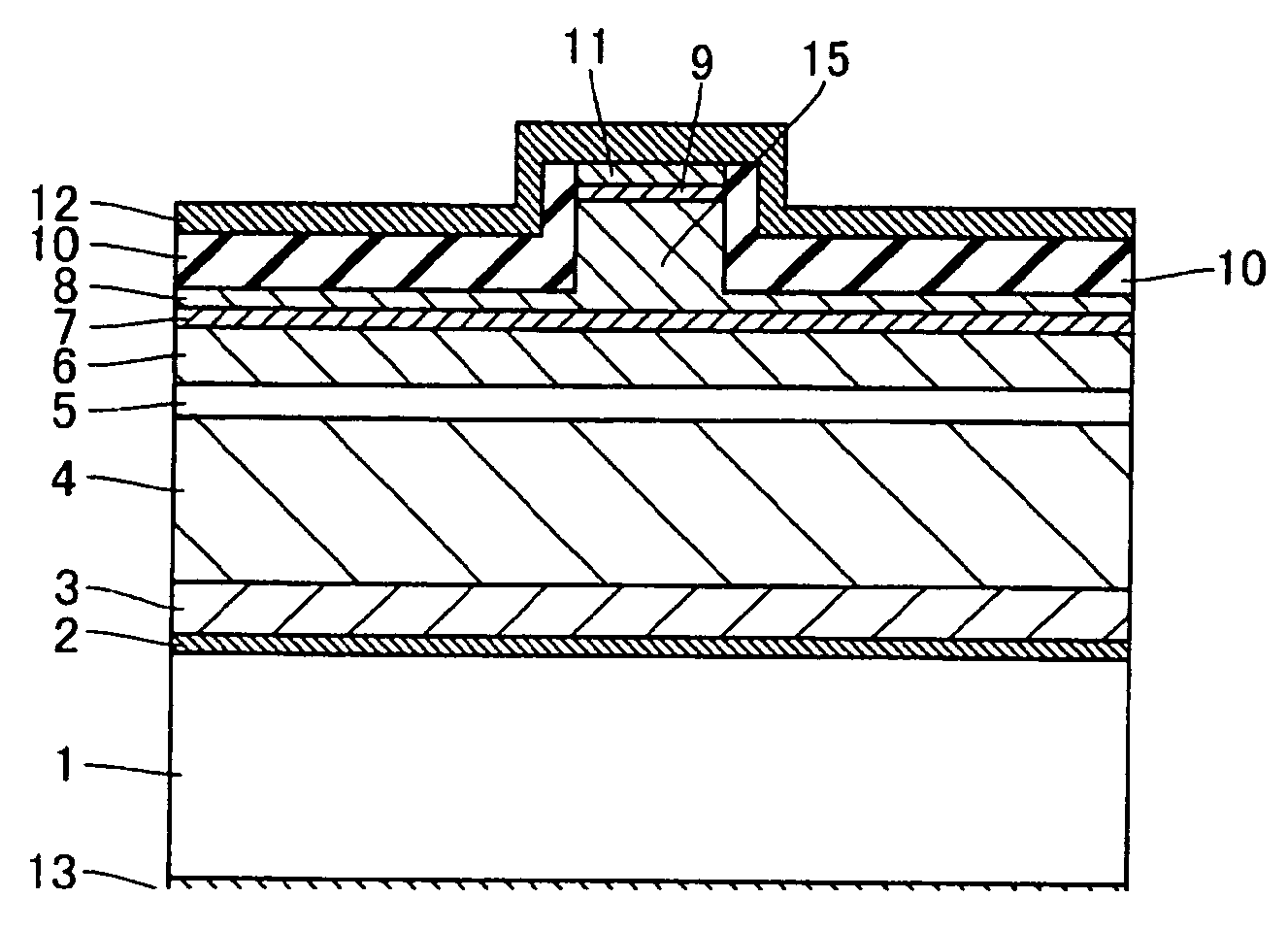
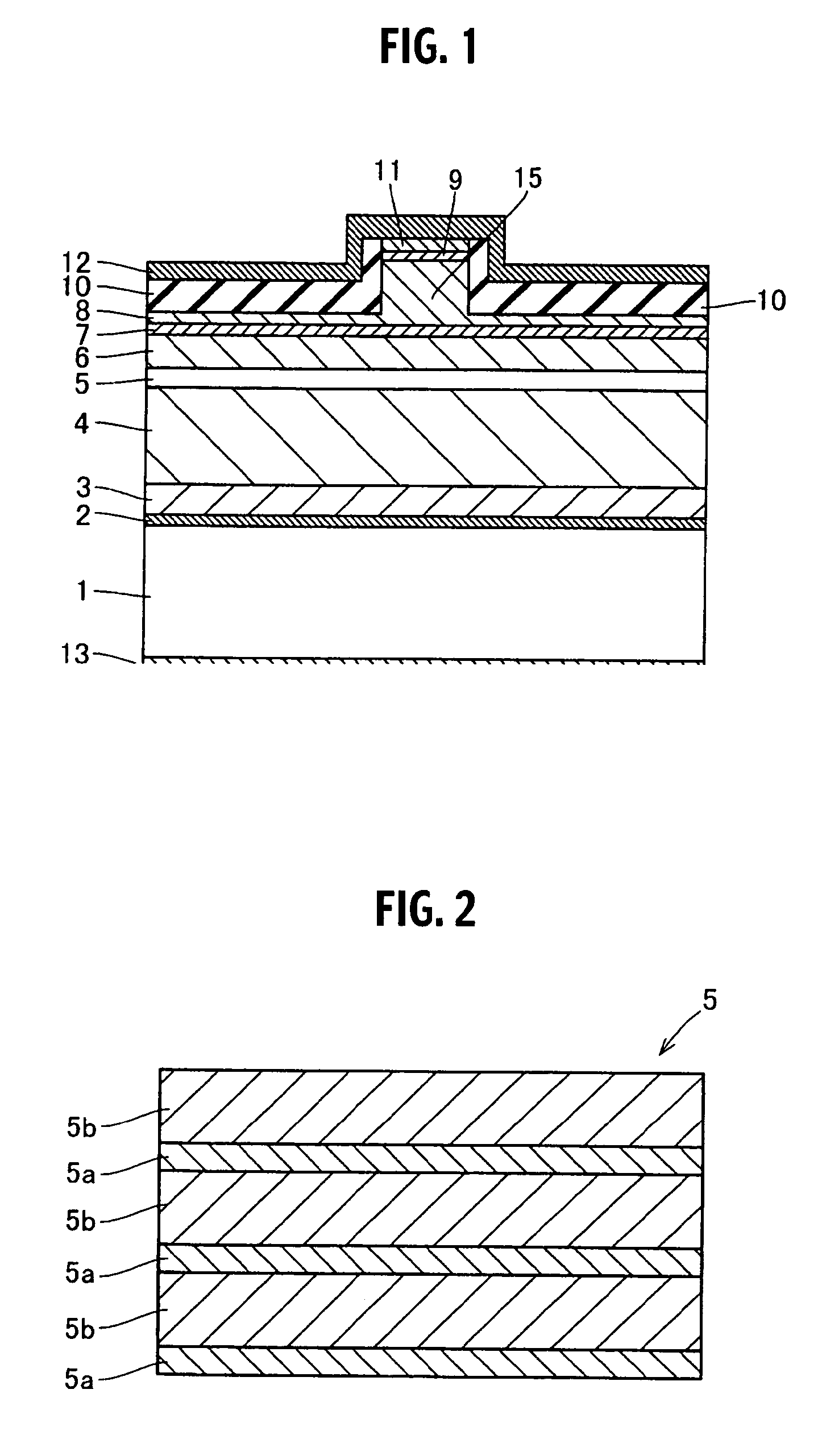
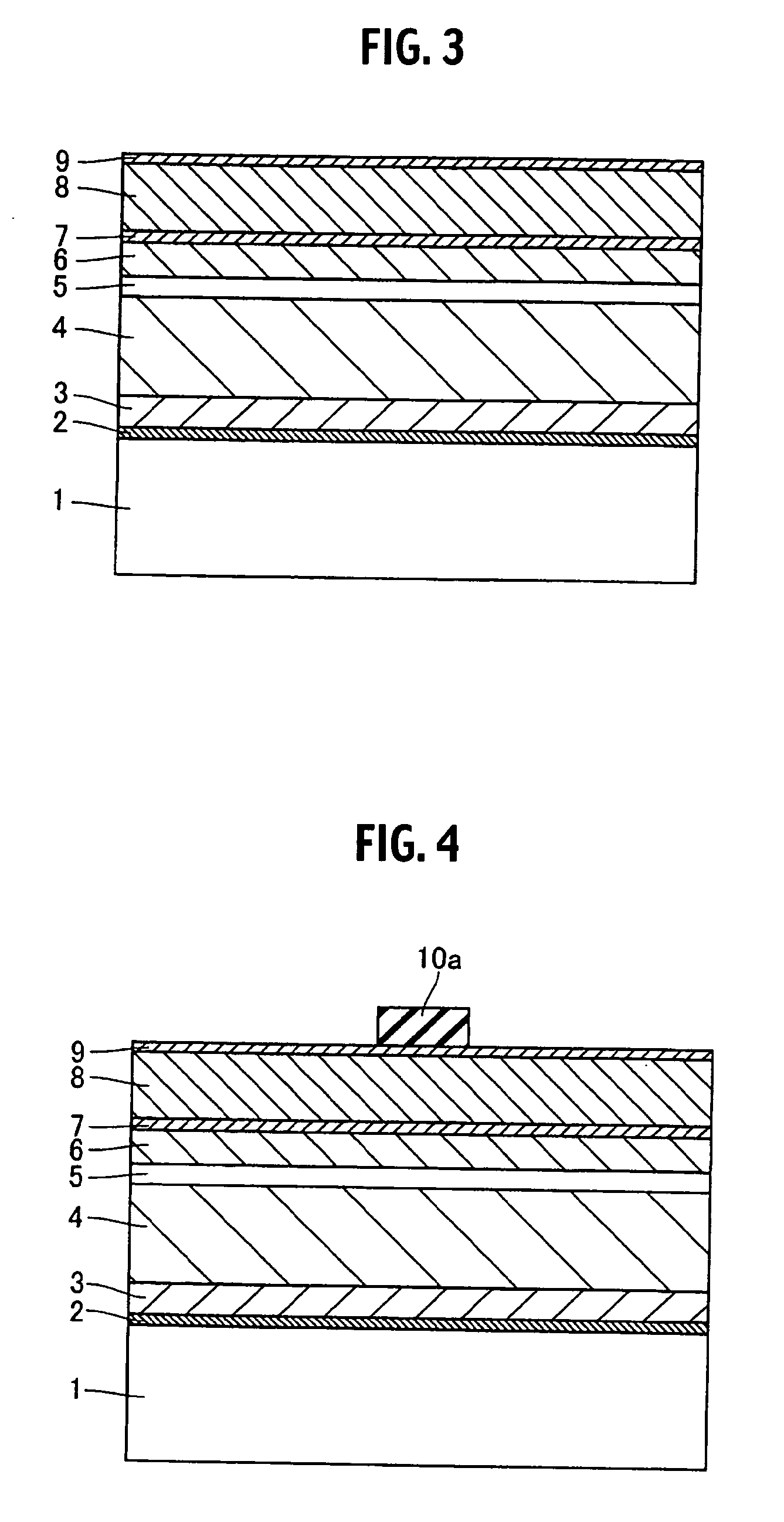
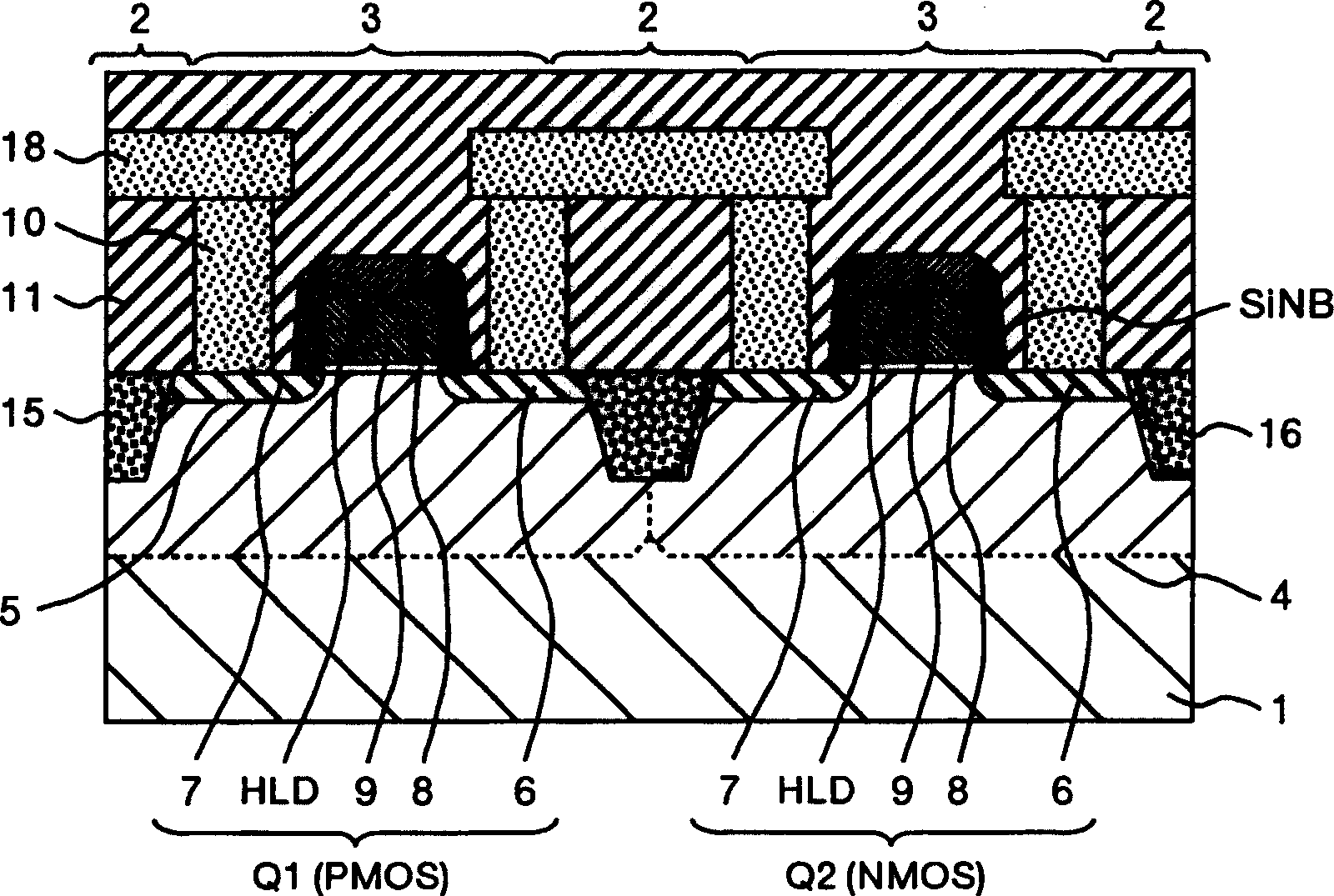
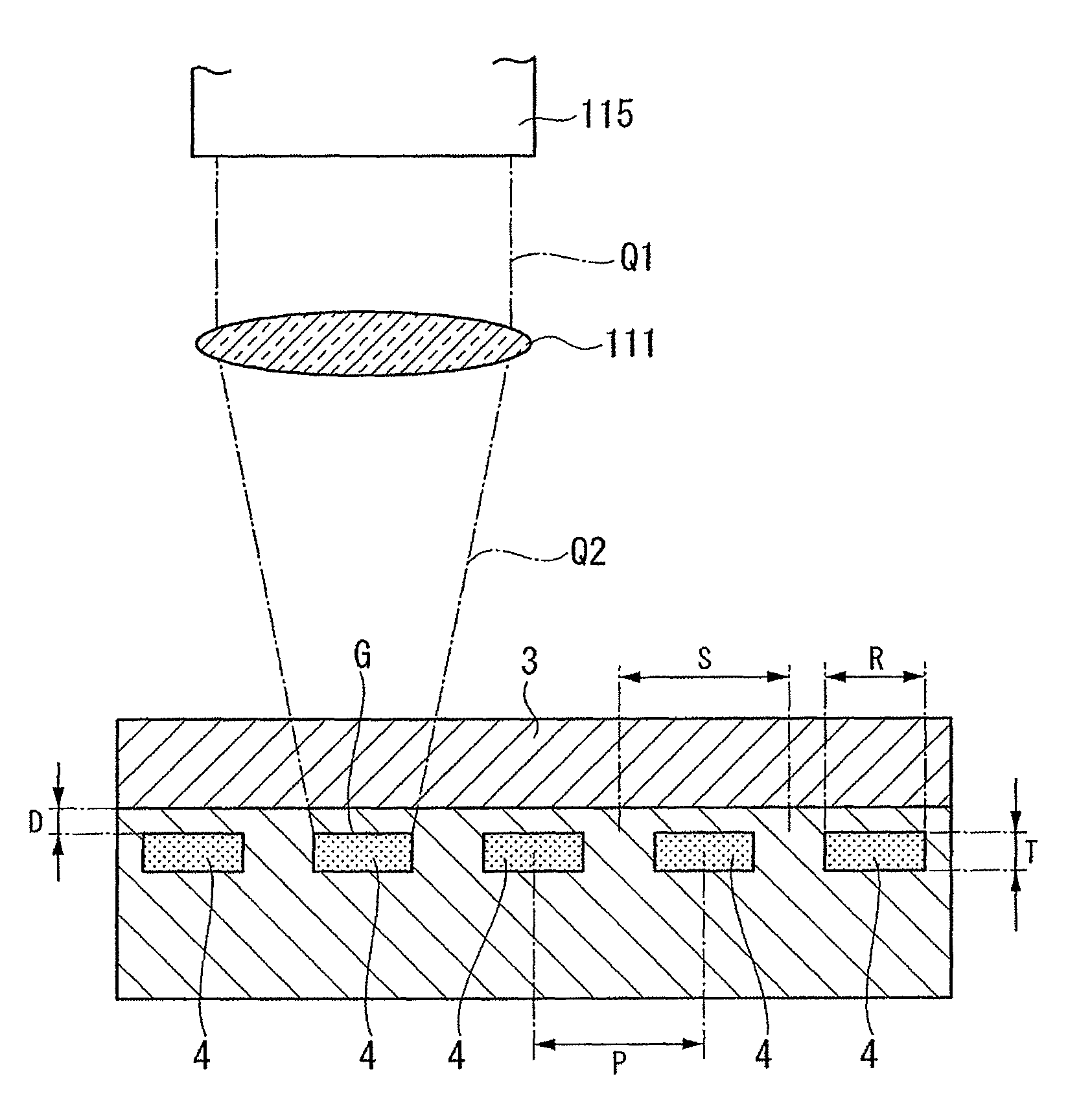
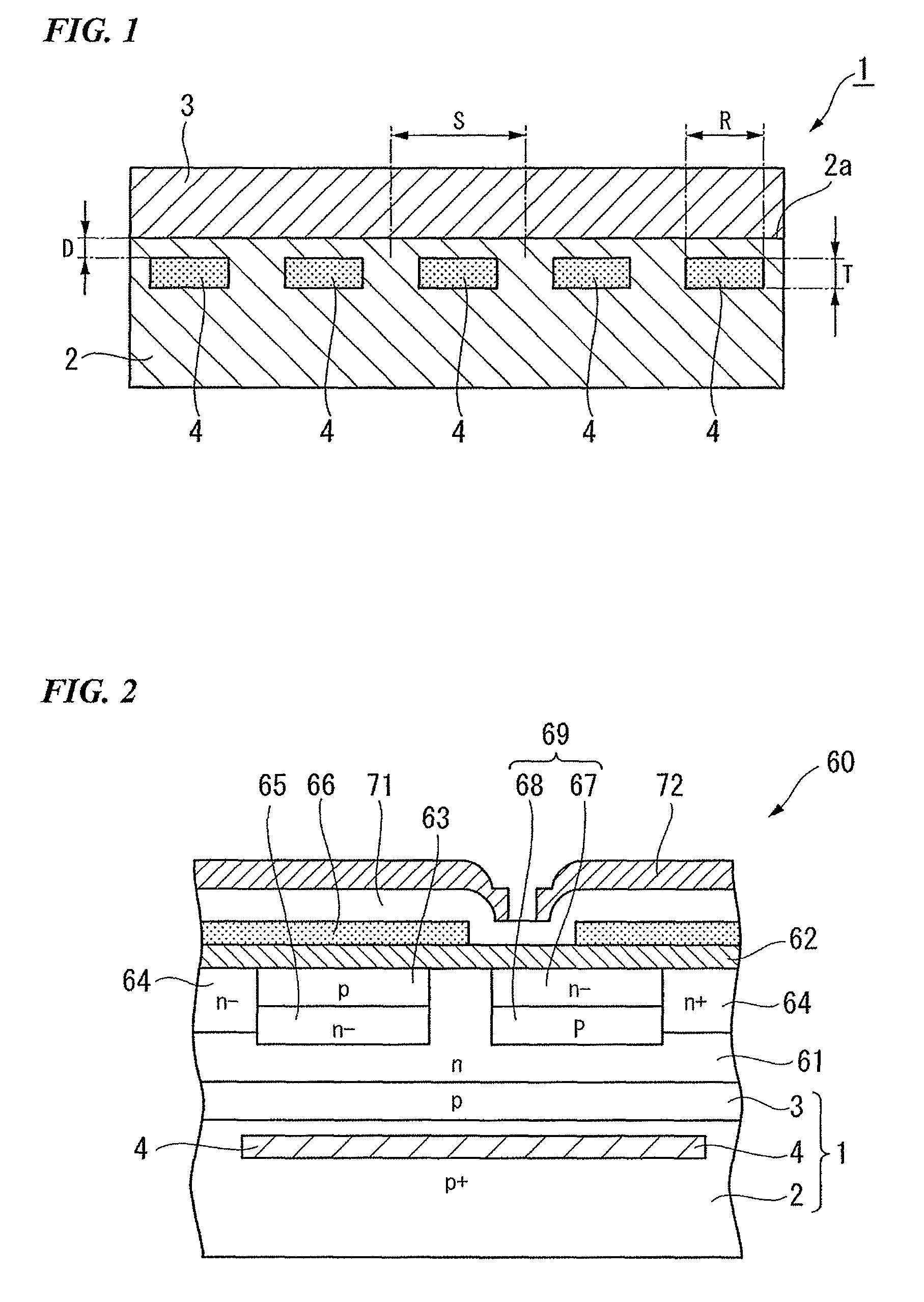
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070057337A1Suppressed dislocationReduce layeringLaser detailsSolid-state devicesNitrogenSemiconductor device
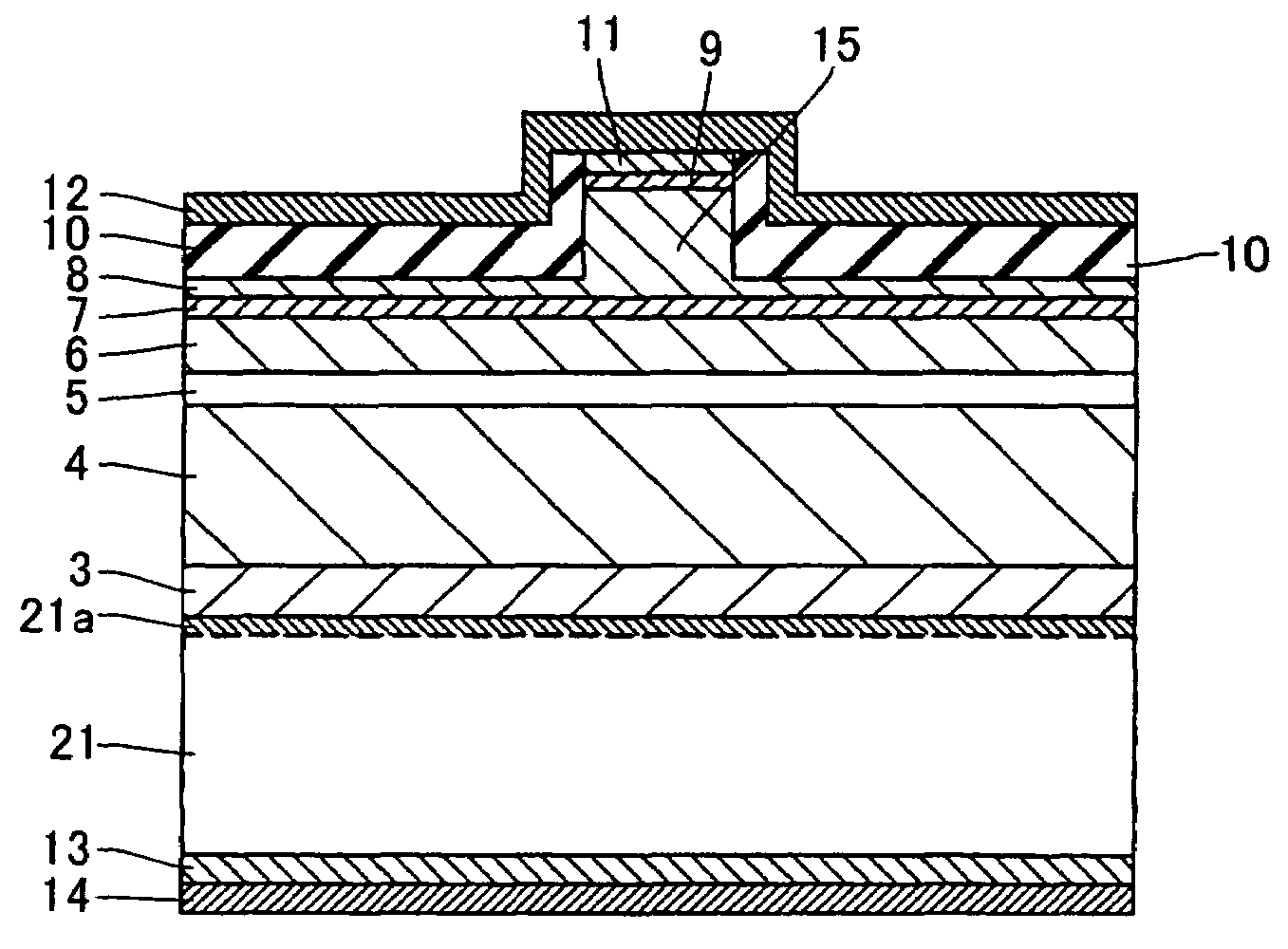
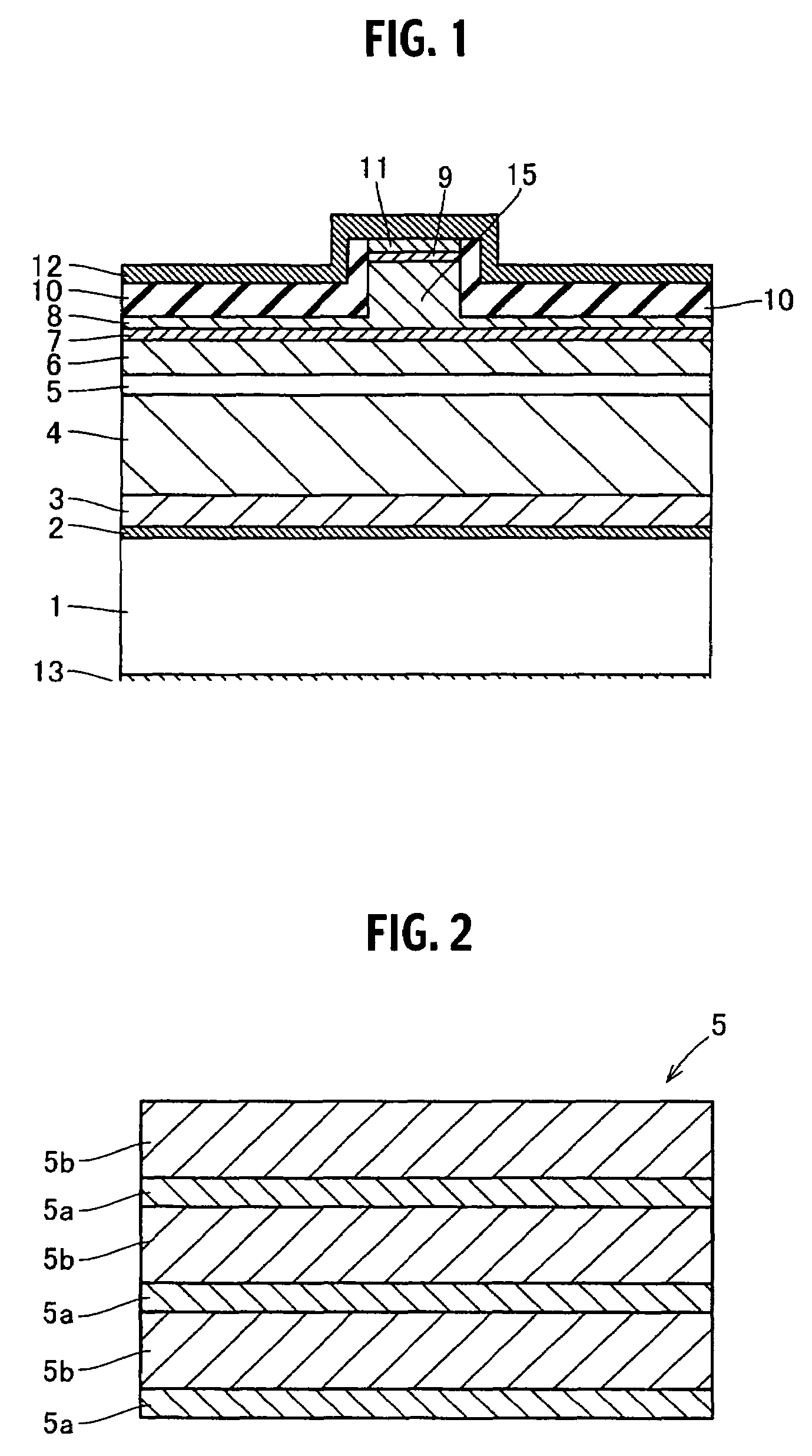
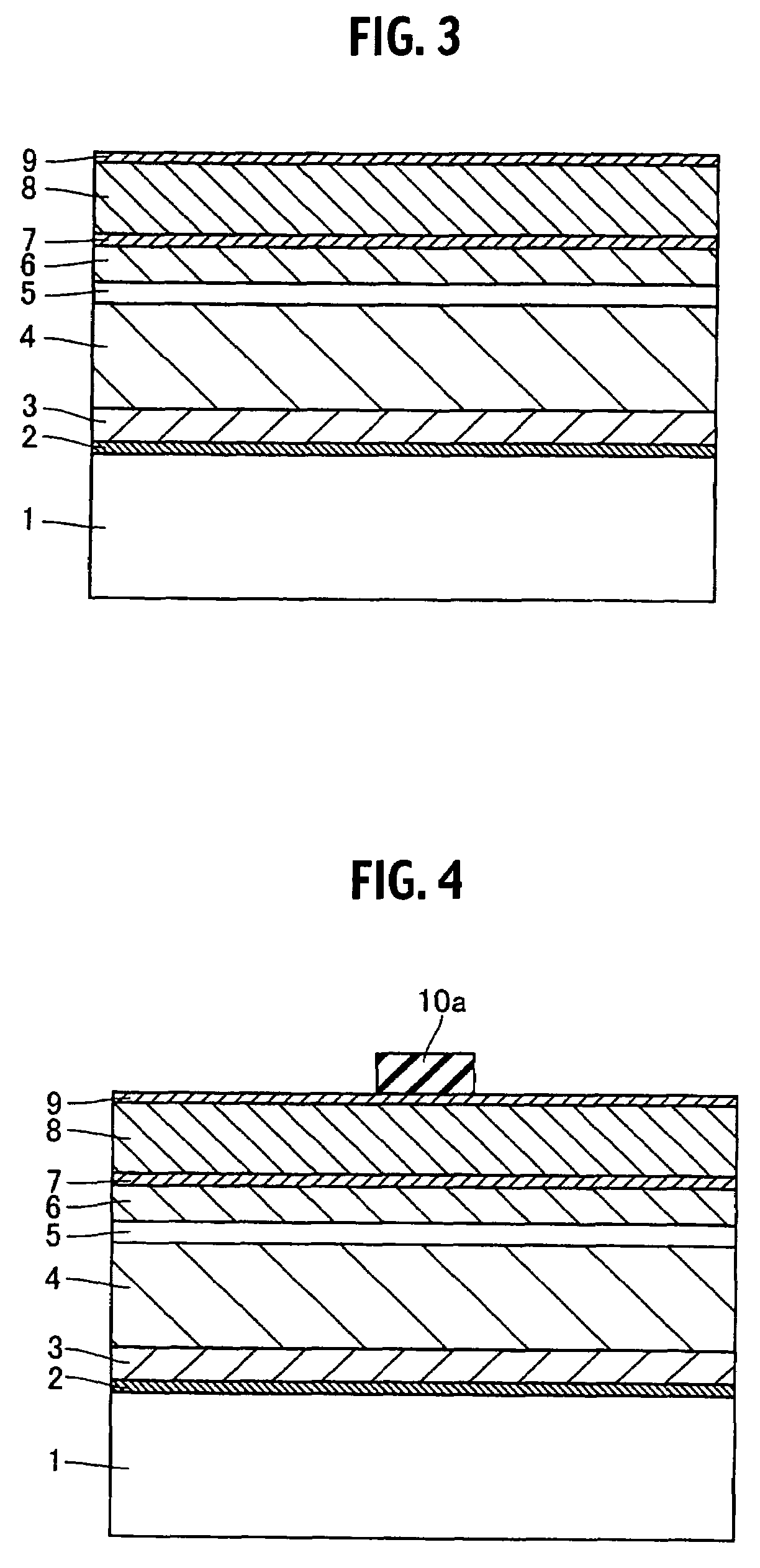
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate formed of at least two kinds of group III elements and nitrogen, an active layer formed on the semiconductor substrate, and a nitride semiconductor layer formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate and formed between the semiconductor substrate and the active layer. The nitride semiconductor layer is formed of the same constituent elements of the semiconductor substrate. A composition ratio of the lightest element among the group III elements of the nitride semiconductor layer is higher than a composition ratio of the corresponding element of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method
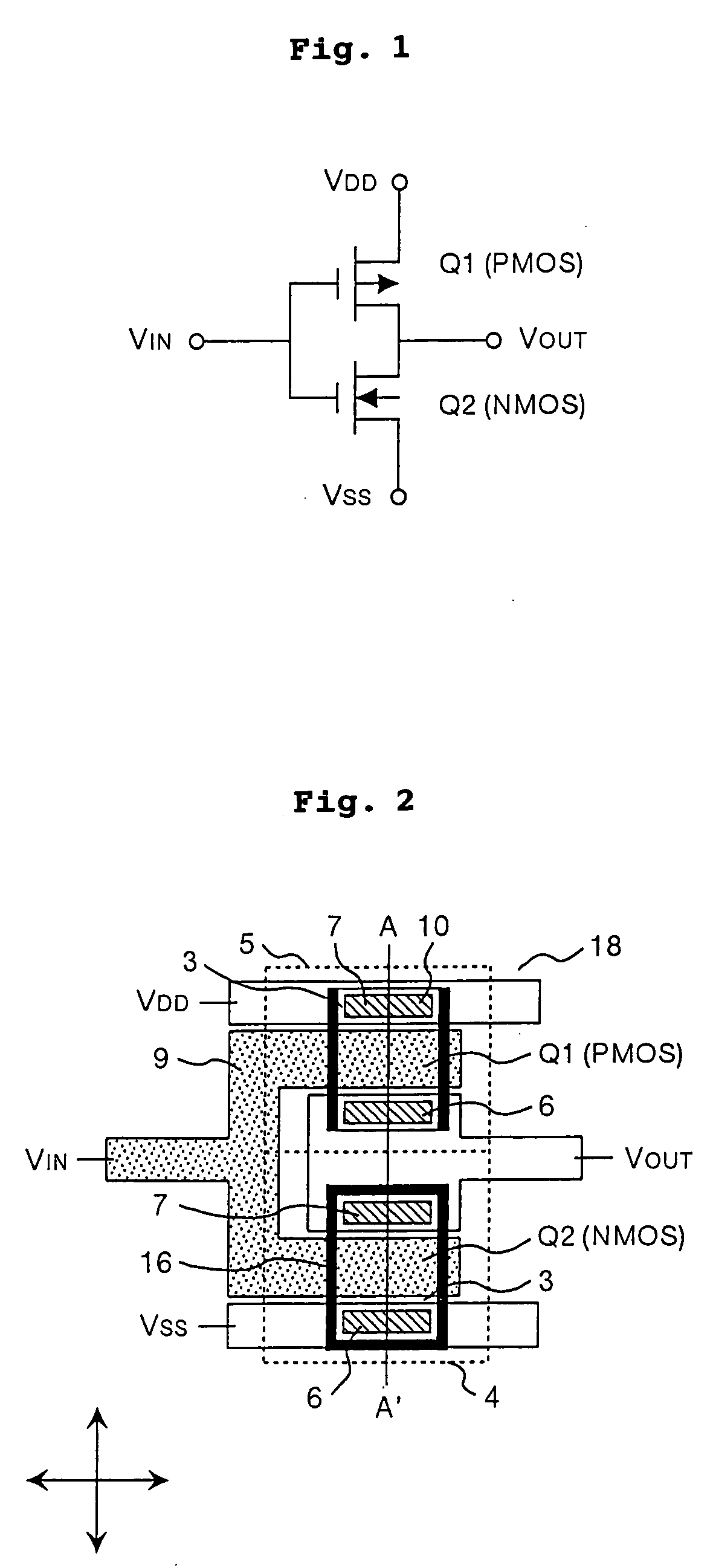
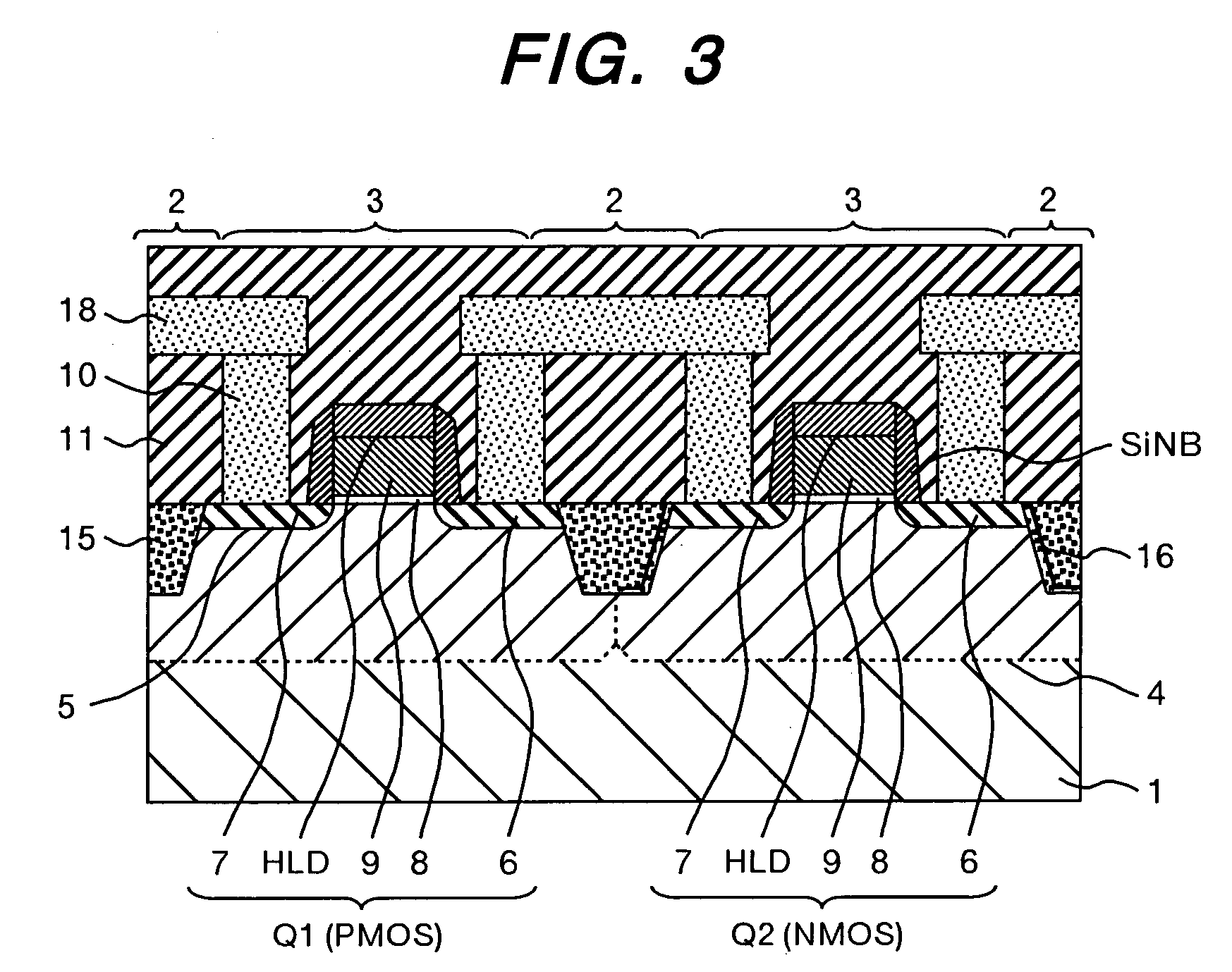
InactiveUS20050121727A1Excellent in drain current characteristicImprove mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialDrain current
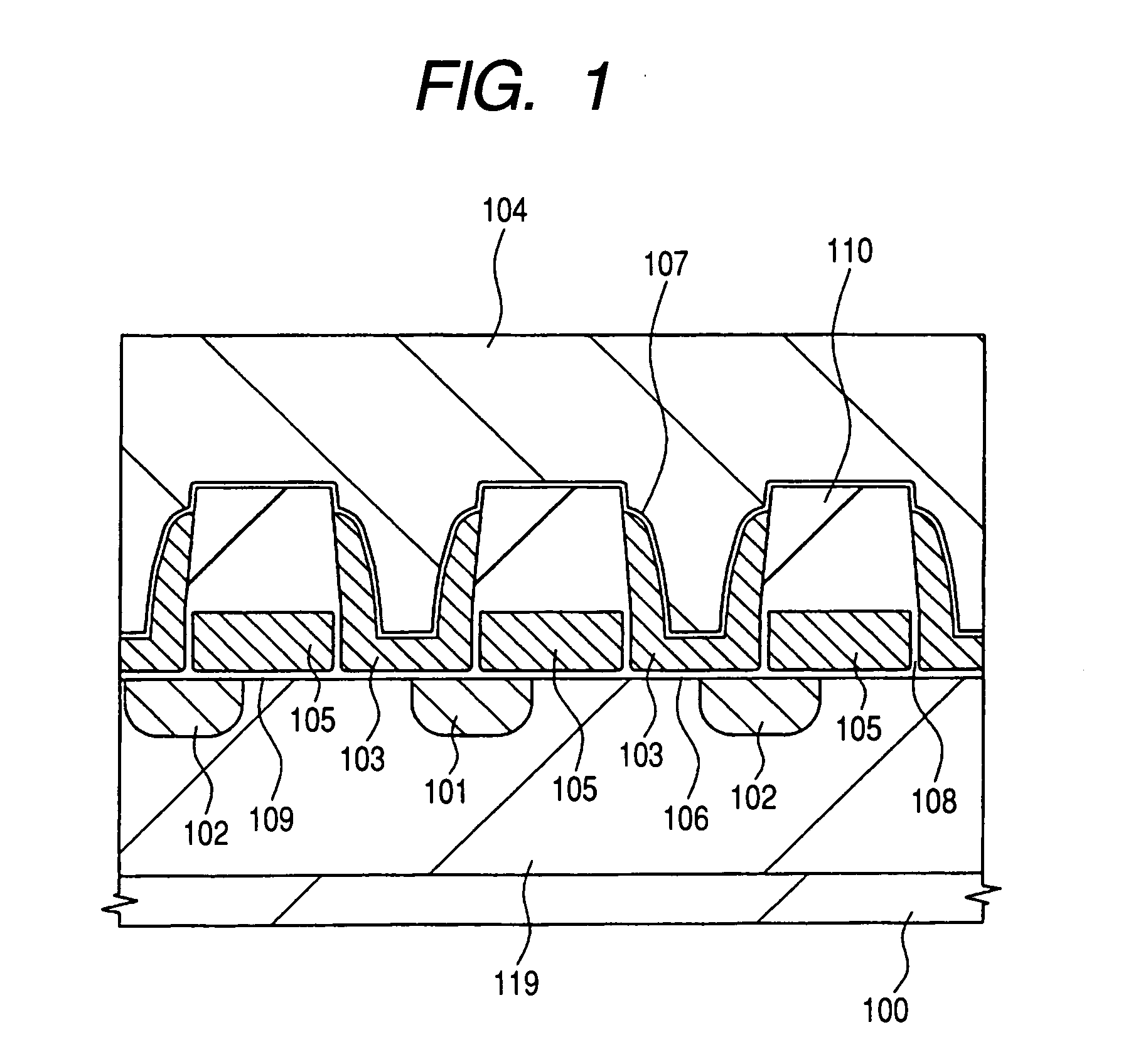
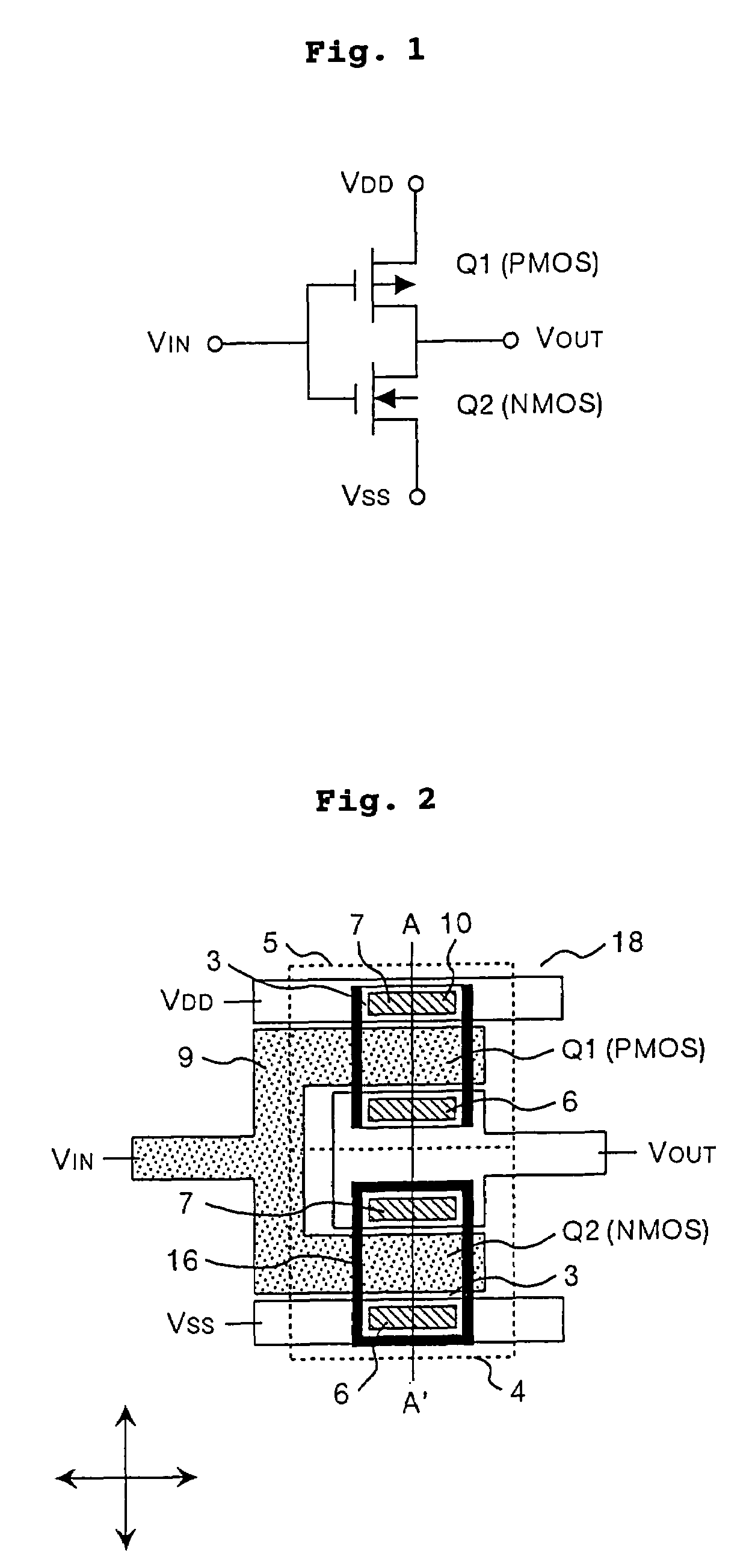
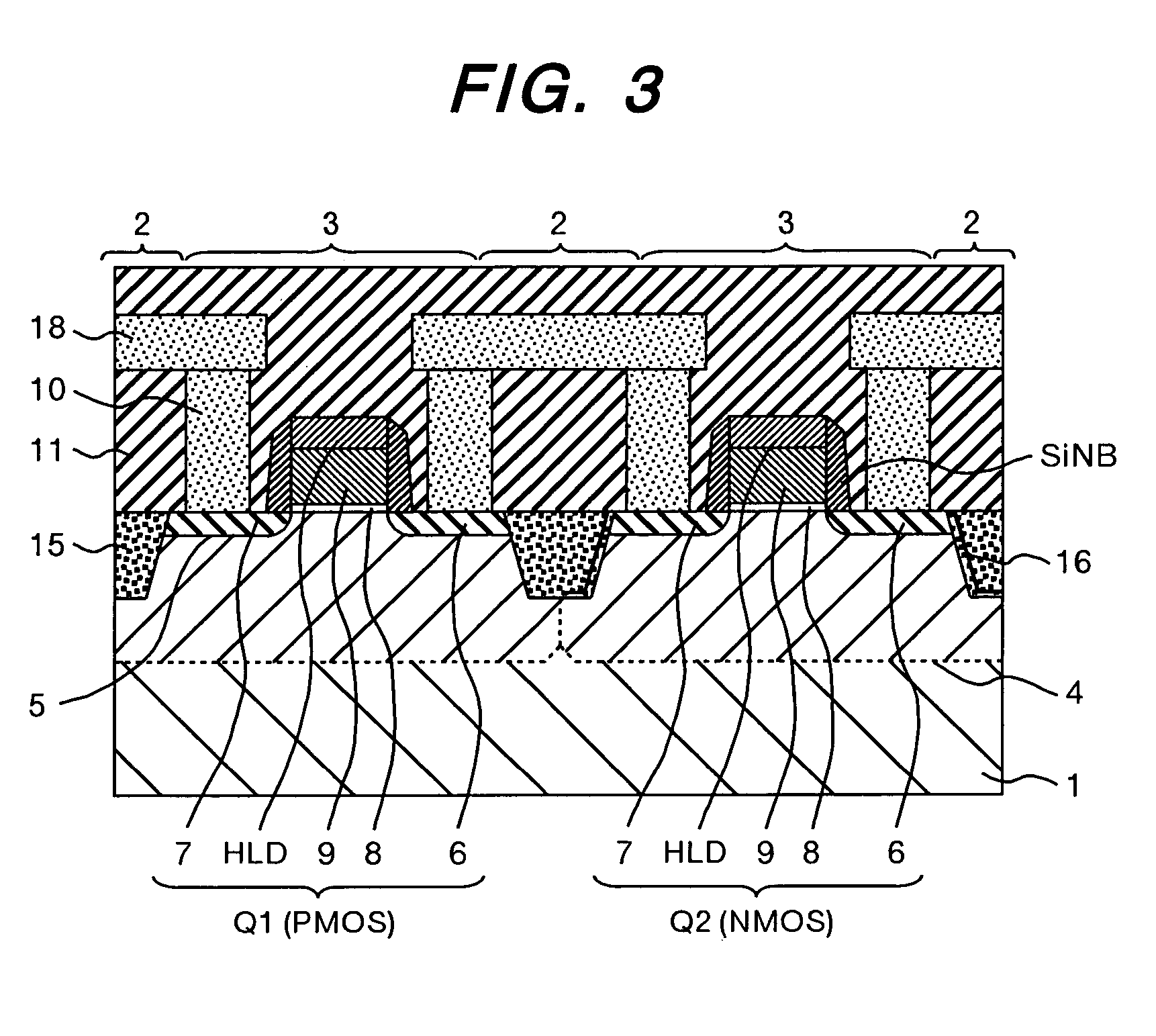
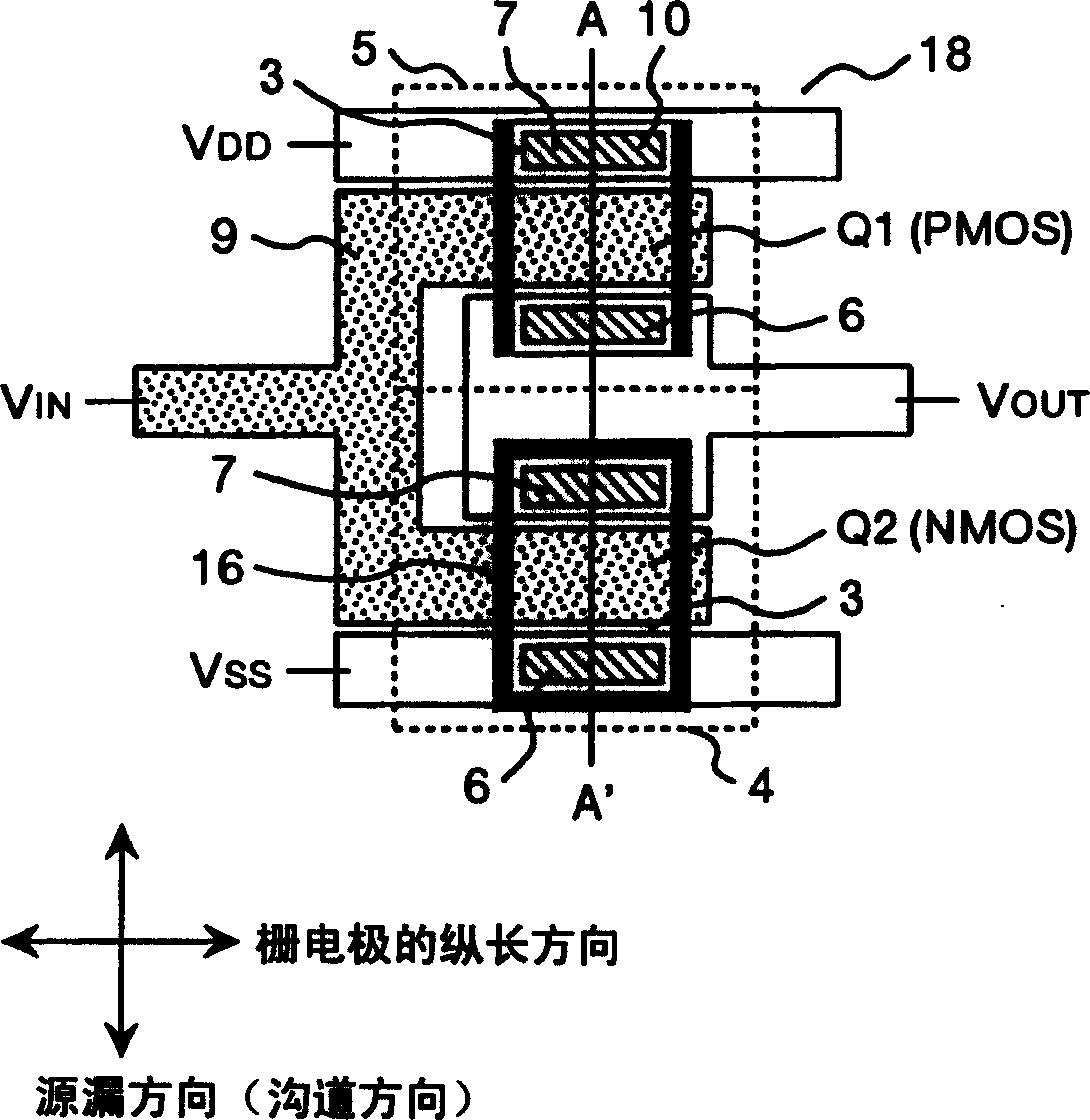
The object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device comprising an n-type channel field effect transistor and a p-type channel field effect transistor, which has a high degree of reliability and excellent drain current characteristics. The gist of the invention for attaining the object resides in disposing a silicon nitride film to the side wall of a trench for an active region in which the n-type channel field effect transistor is formed and disposing the silicon nitride film only in the direction perpendicular to the channel direction to the sidewall of the trench for the active region of the p-type channel field effect transistor. According to the present invention, a semiconductor device comprising an n-type channel field effect transistor and a p-type channel field effect transistor of excellent current characteristics can be provided.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
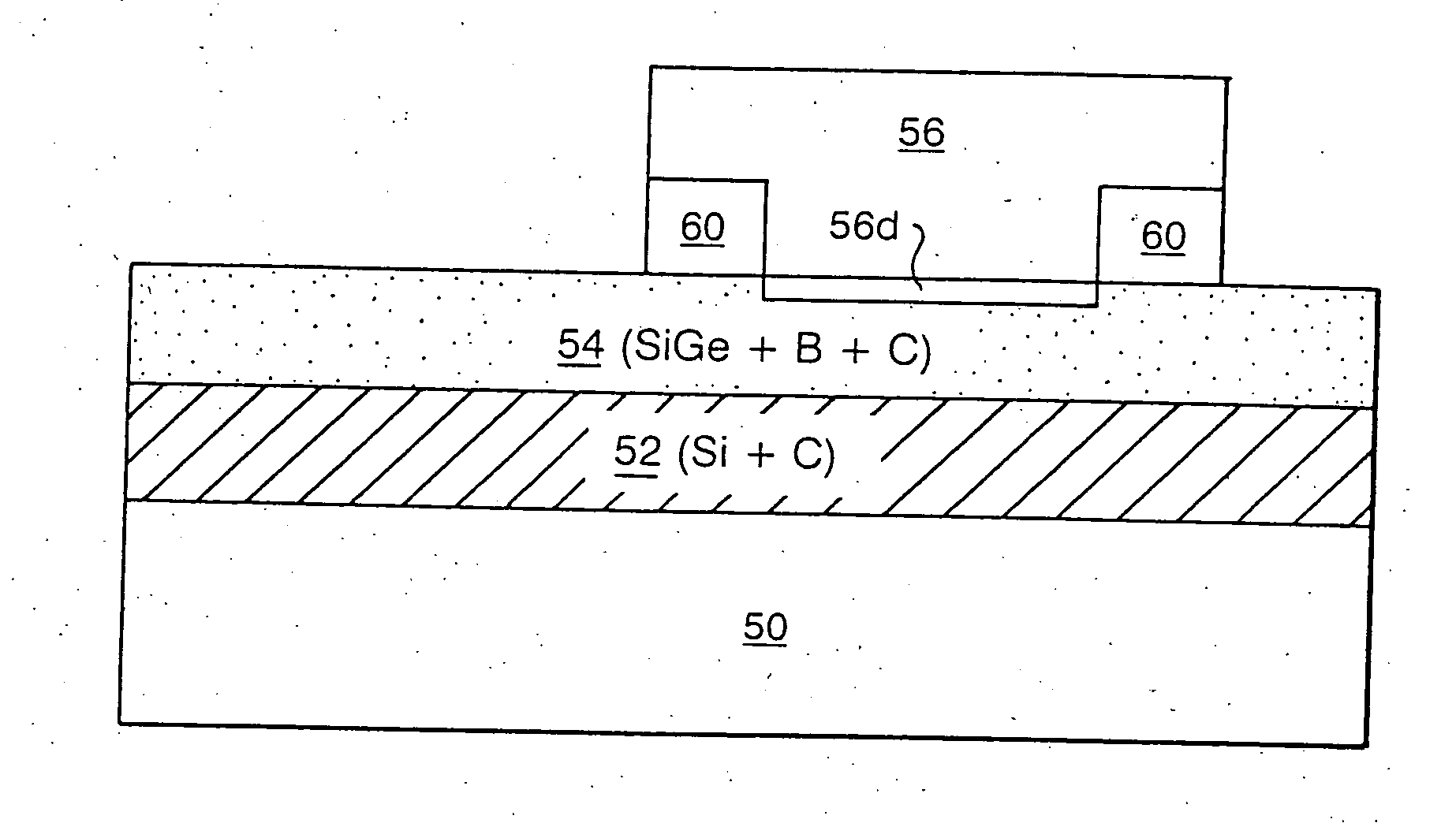
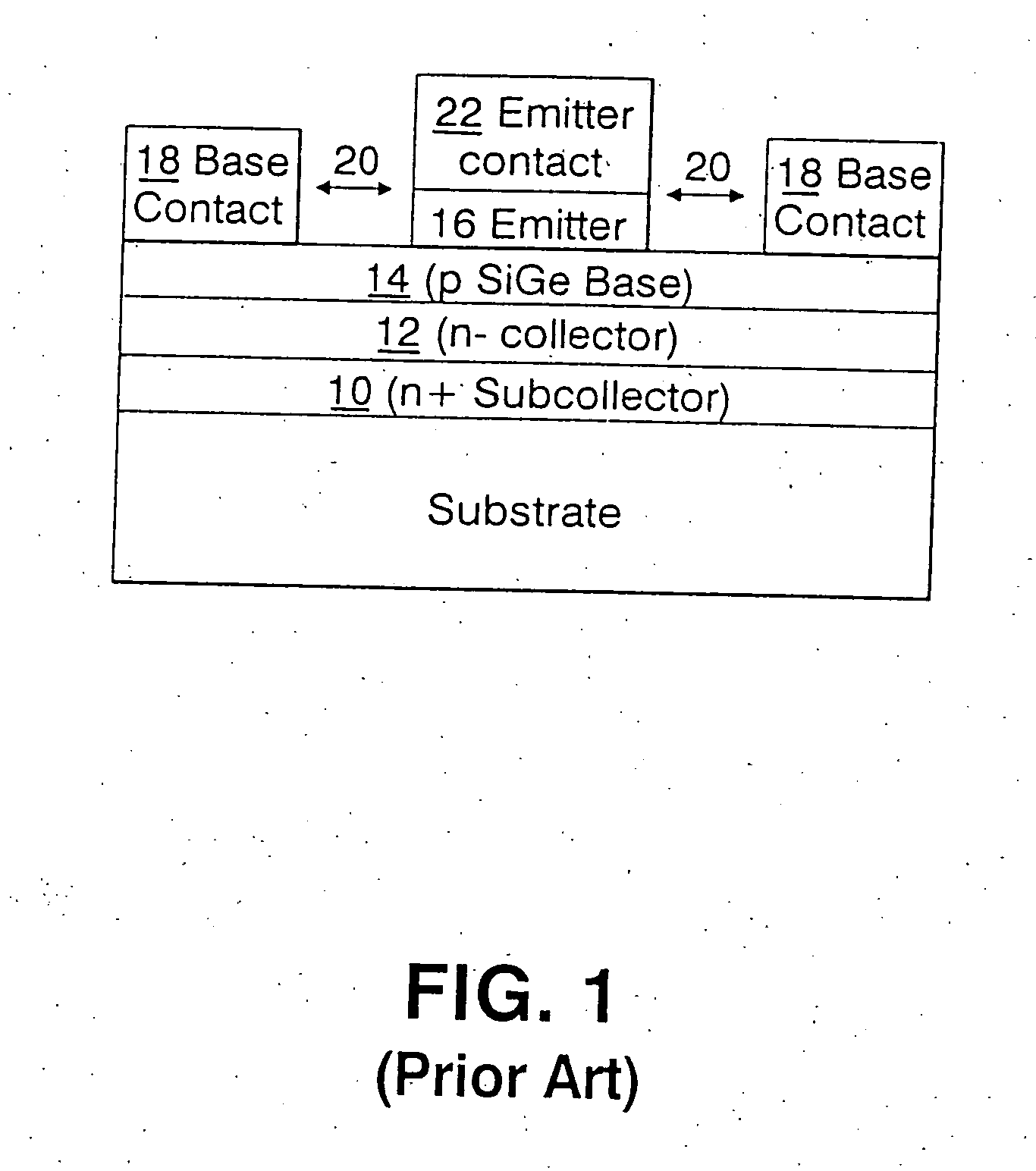
Incorporation of carbon in silicon/silicon germanium epitaxial layer to enhance yield for Si-Ge bipolar technology
InactiveUS20050054171A1Suppressed dislocationAvoid problemsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringBoron
A SiGe bipolar transistor containing substantially no dislocation defects present between the emitter and collector region and a method of forming the same are provided. The SiGe bipolar transistor includes a collector region of a first conductivity type; a SiGe base region formed on a portion of said collector region; and an emitter region of said first conductivity type formed over a portion of said base region, wherein said collector region and said base region include carbon continuously therein. The SiGe base region is further doped with boron.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20070090370A1Fine surfaceForward voltage can be preventedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDopantDevice material
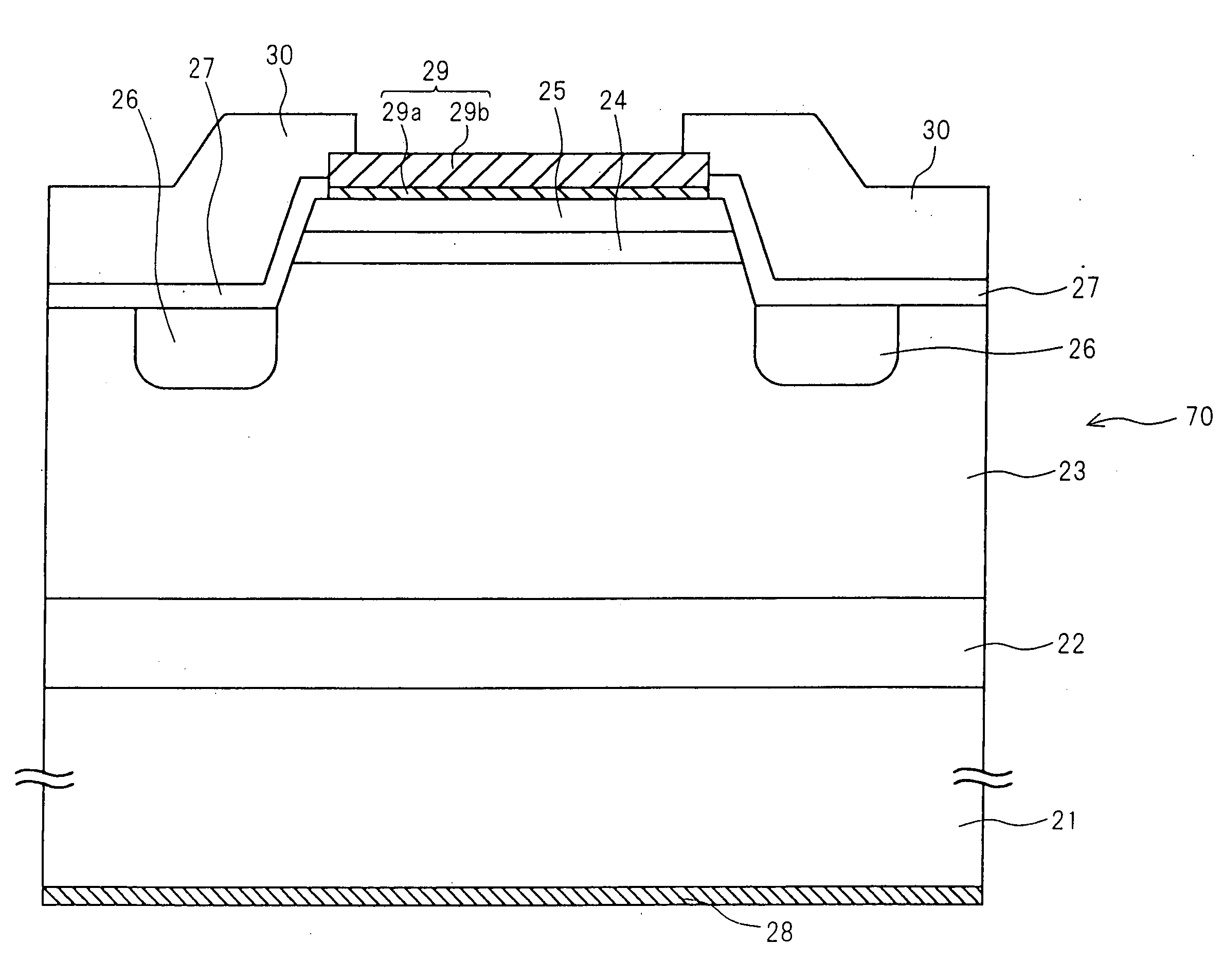
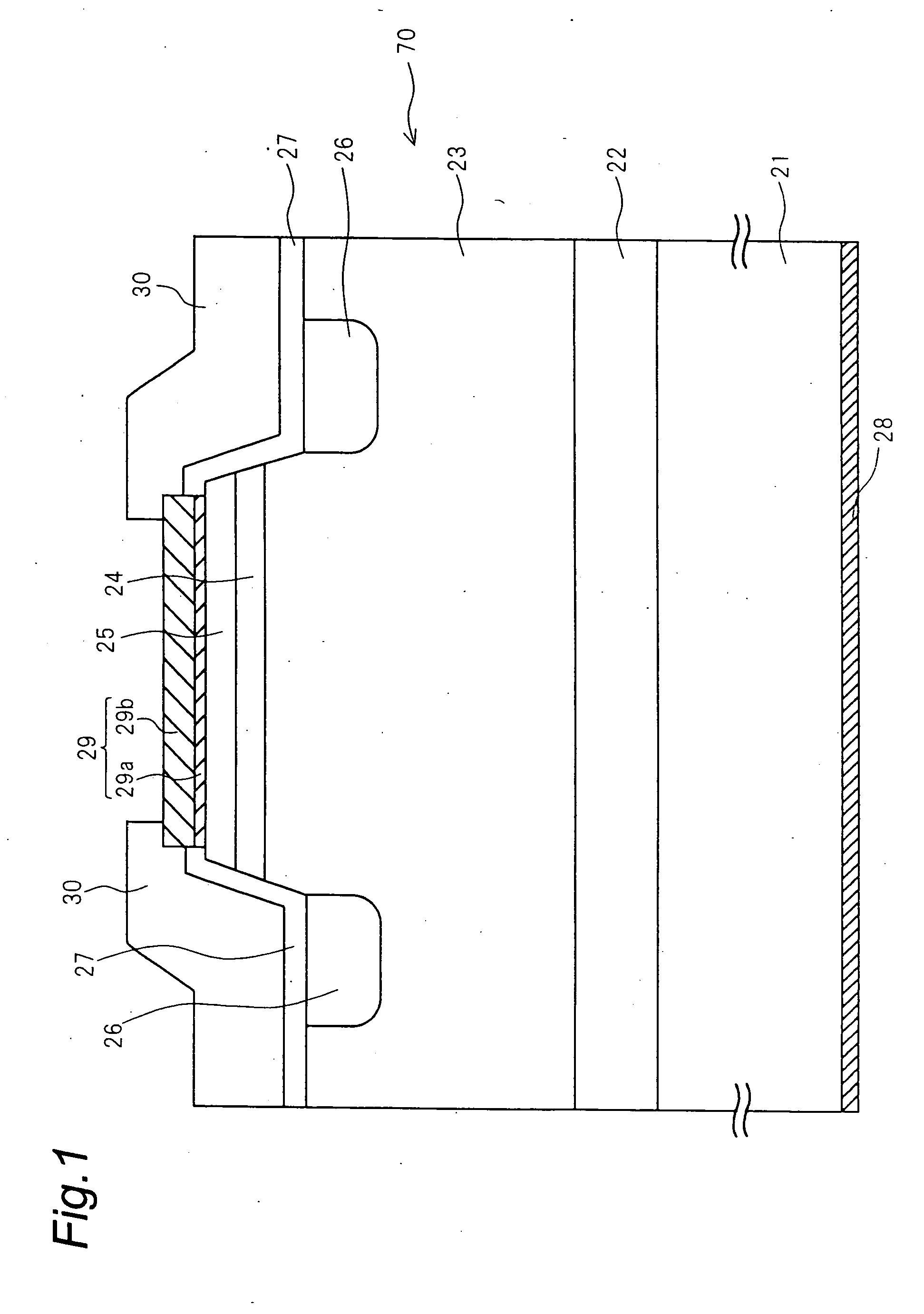
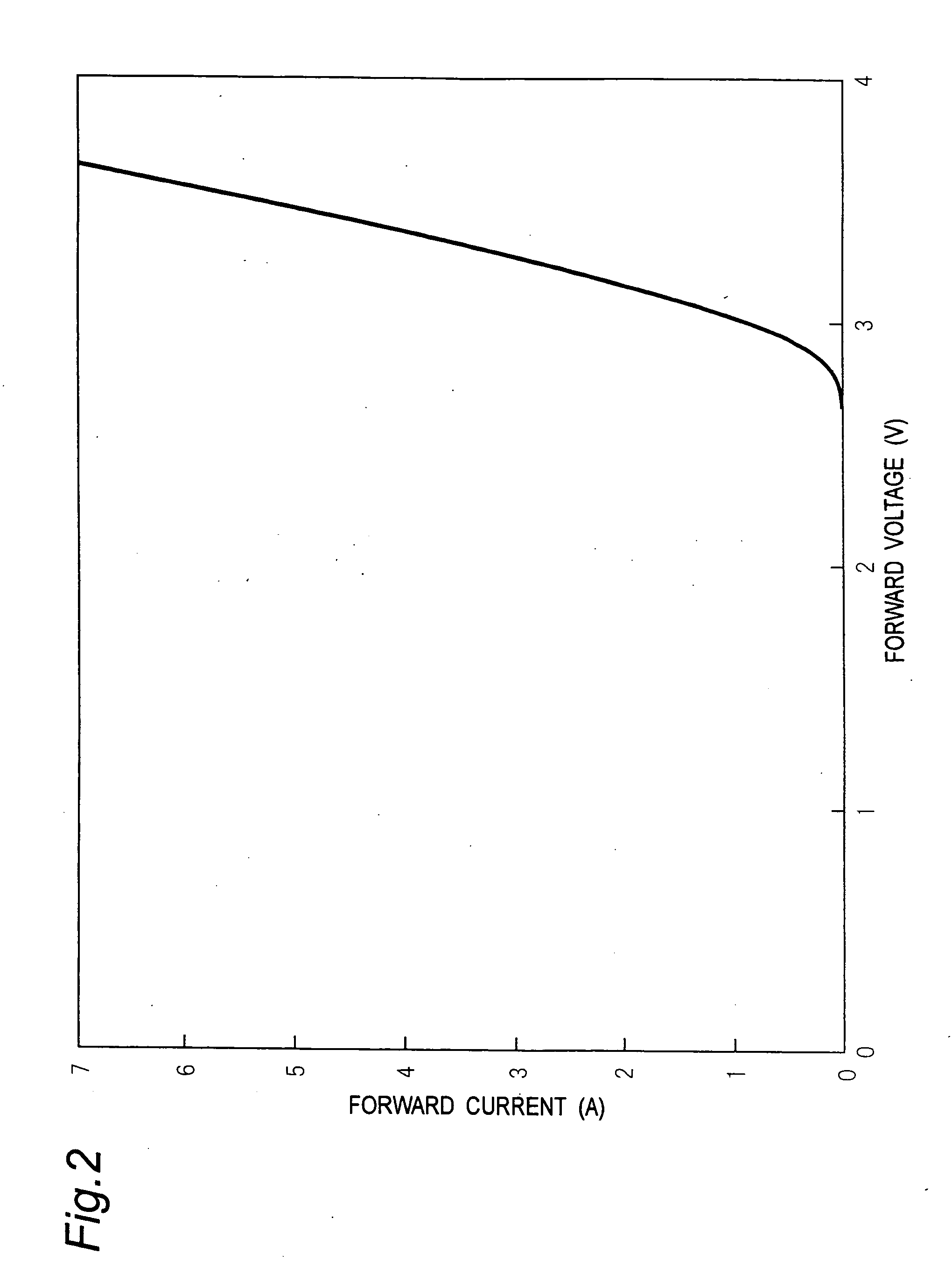
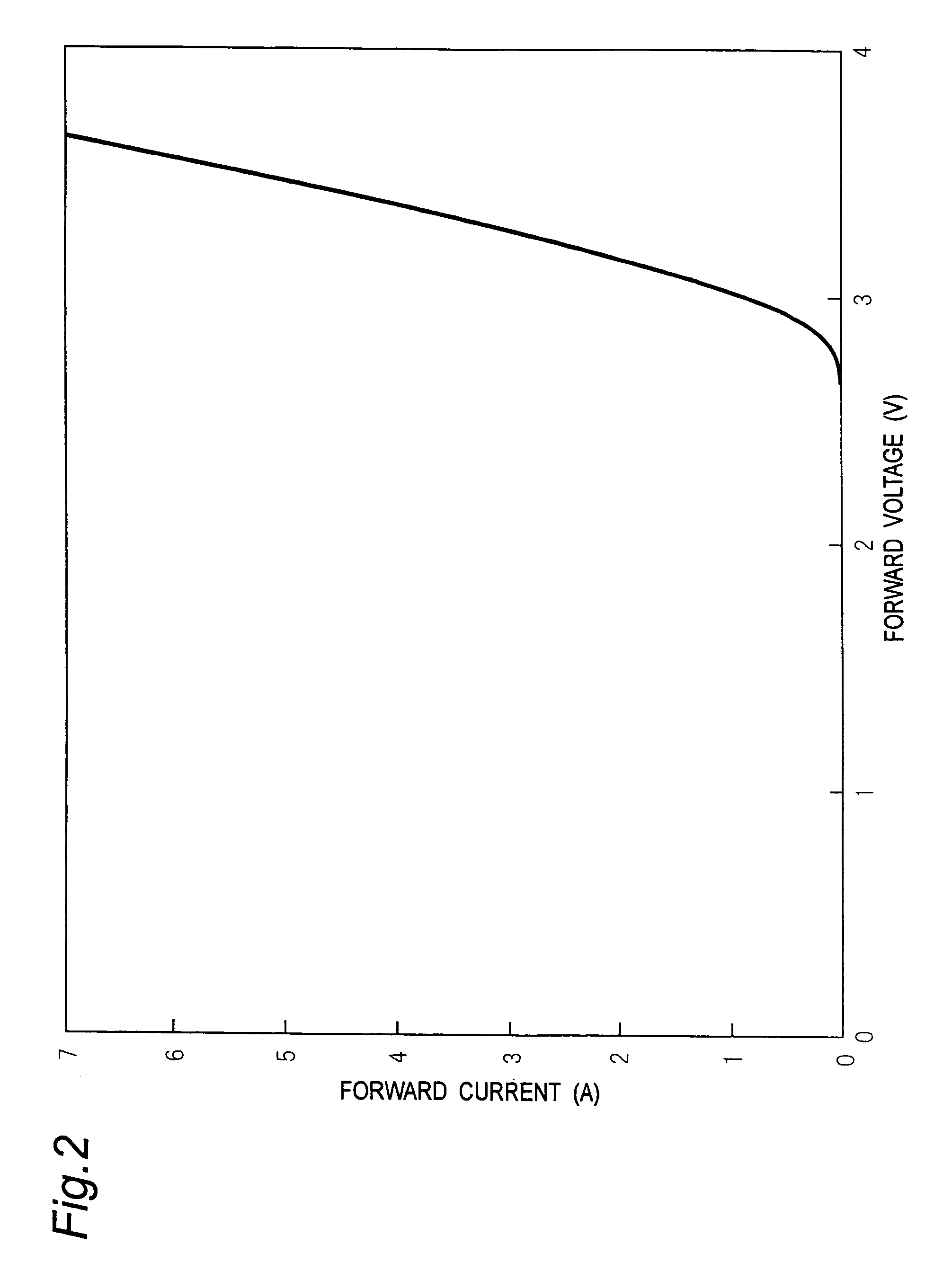
With a view to preventing increases in forward voltage due to a change with the lapse of time of a bipolar semiconductor device using a silicon carbide semiconductor, a buffer layer, a drift layer and other p-type and n-type semiconductor layers are formed on a growth surface, which is given by a surface of a crystal of a silicon carbide semiconductor having an off-angle θ of 8 degrees from a (000-1) carbon surface of the crystal, at a film growth rate having a film-thickness increasing rate per hour h of 10 μm / h, which is three times or more higher than conventional counterparts. The flow rate of silane and propane material gases and dopant gases is largely increased to enhance the film growth rate.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Epitaxial wafer and method of manufacturing the same
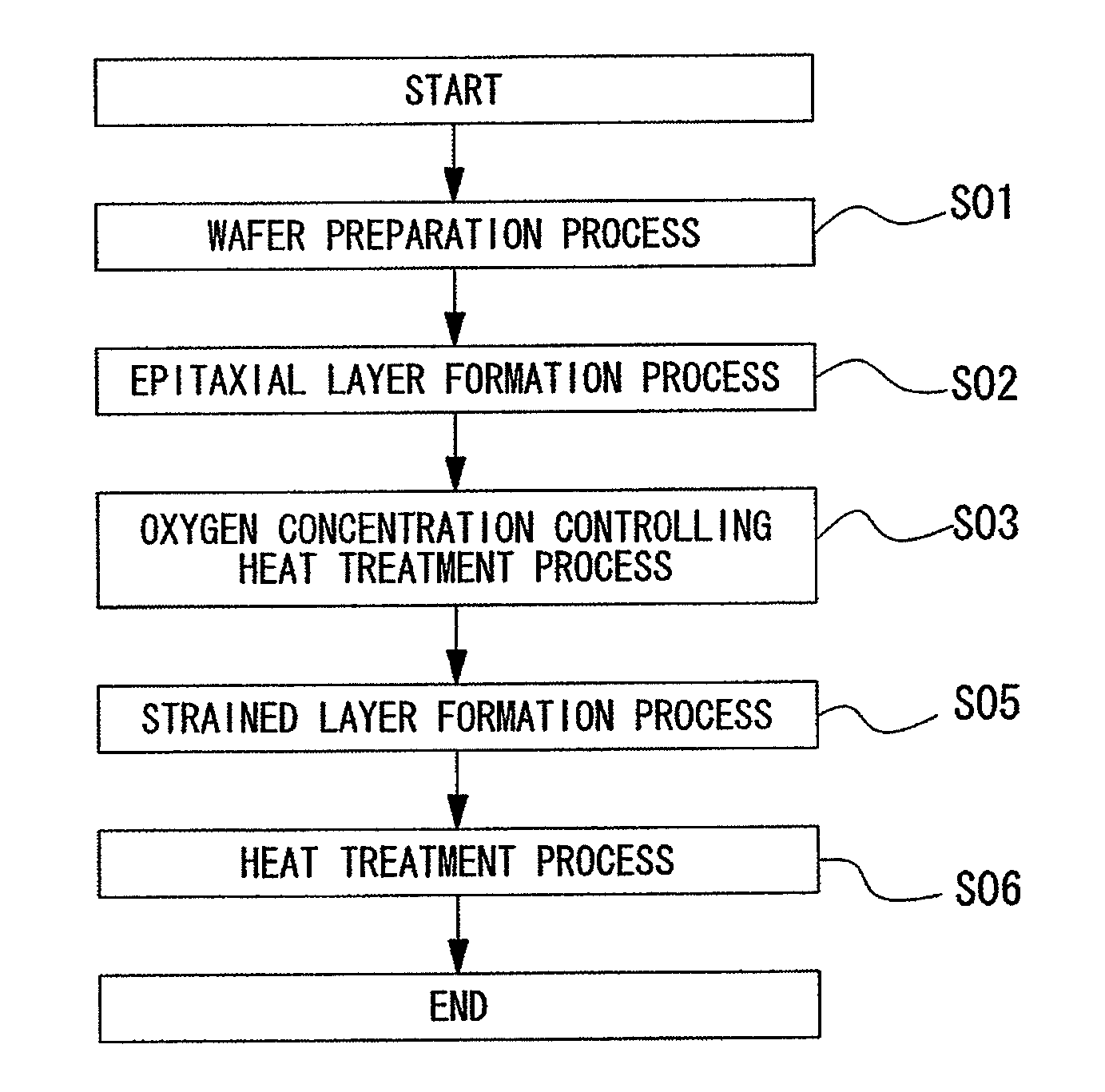
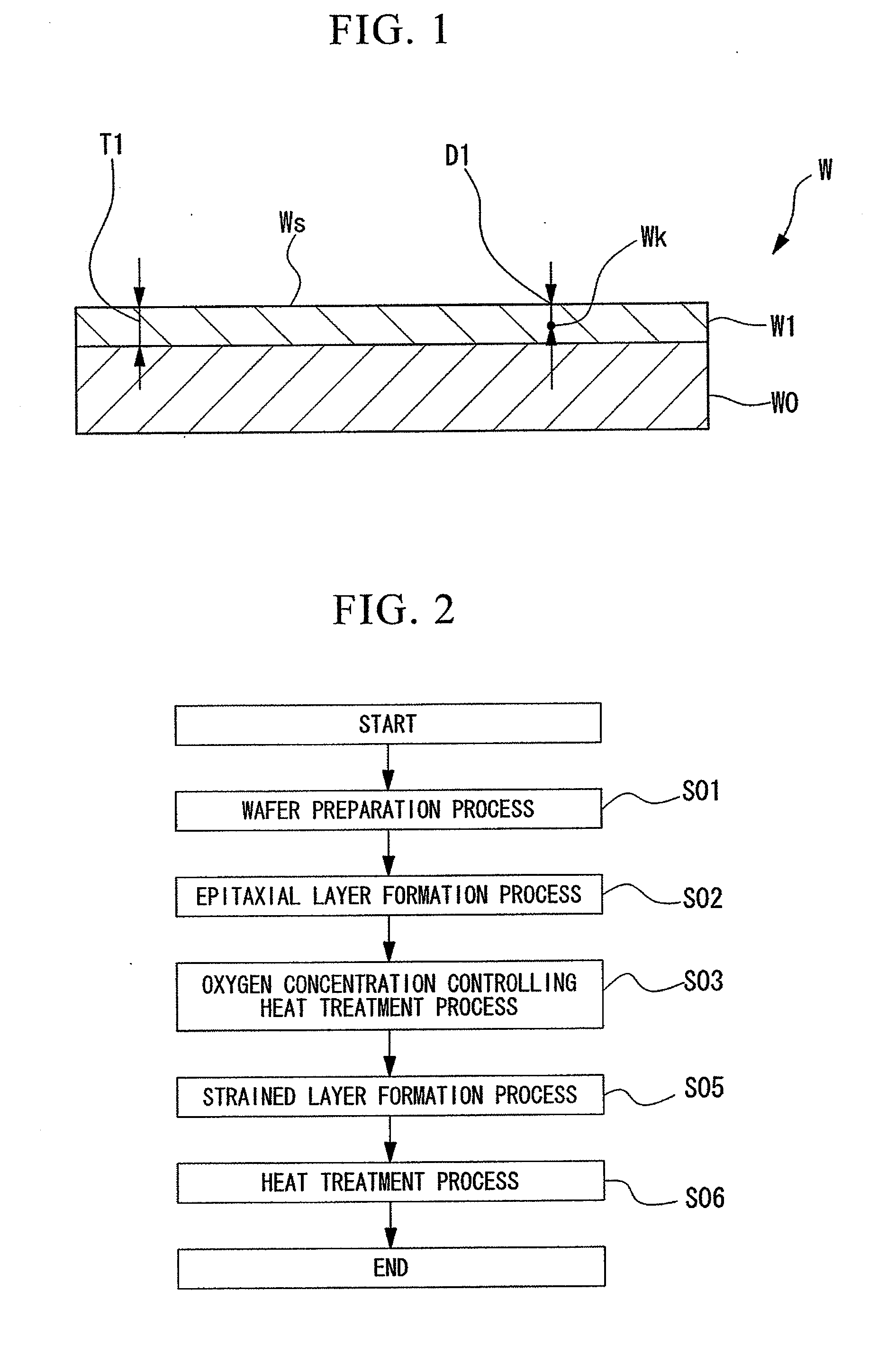
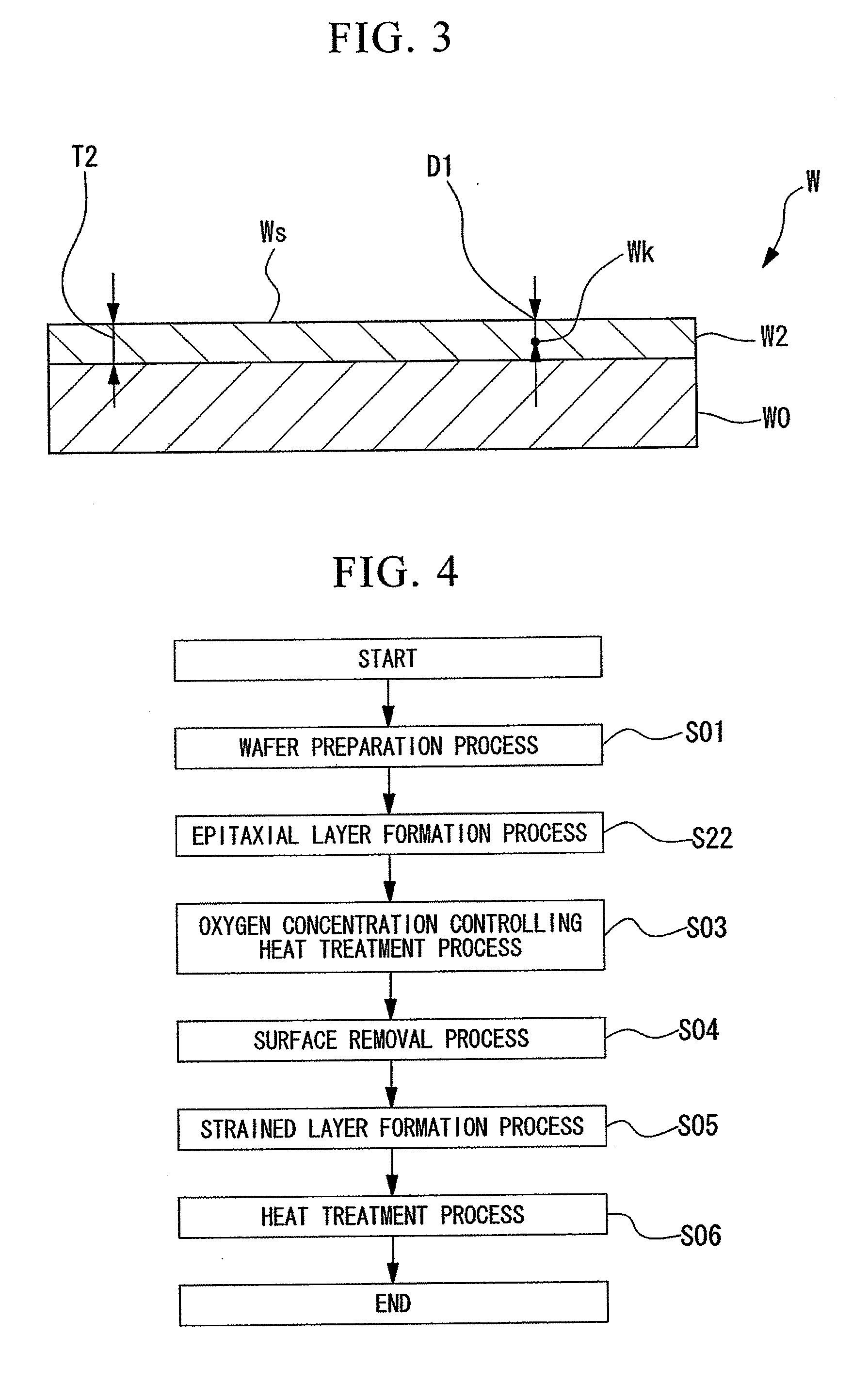
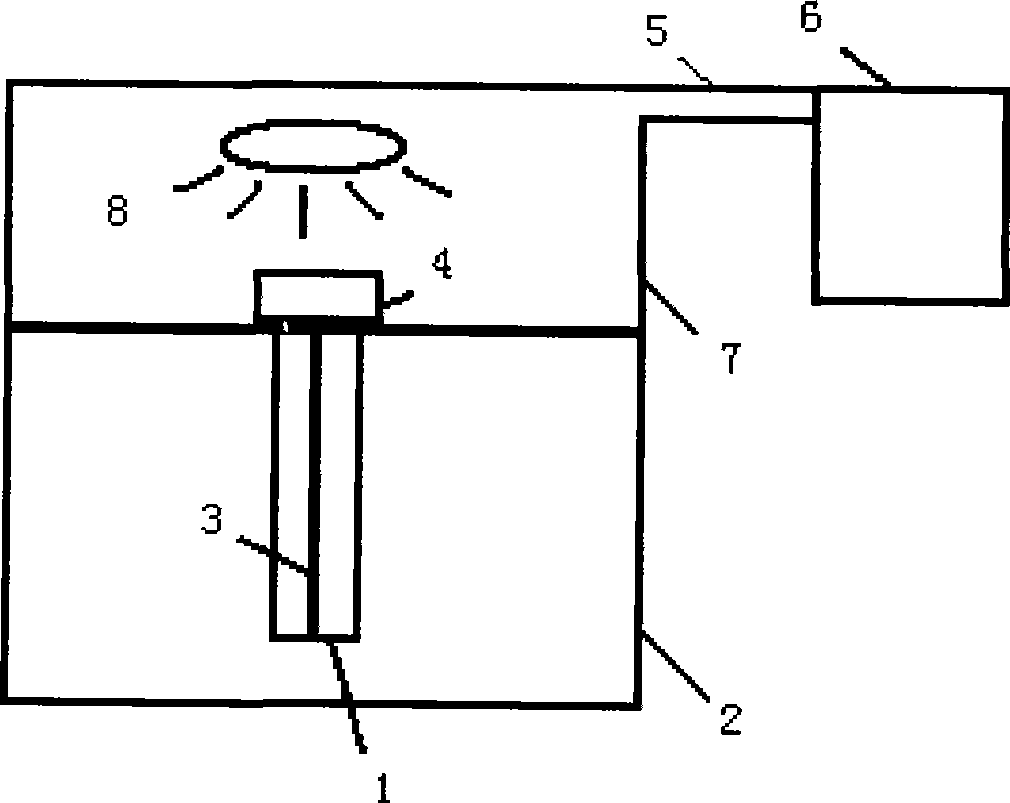
ActiveUS20100151692A1Suppressed dislocationGood conditionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMonocrystalline siliconCrystalline silicon
A method of manufacturing an epitaxial wafer, including a silicon substrate having a surface sliced from single-crystalline silicon and a silicon epitaxial layer deposited on the surface of the silicon substrate, includes an oxygen concentration controlling heat treatment process in which a heat treatment of the epitaxial layer is performed under a non-oxidizing atmosphere after the epitaxial growth such that an oxygen concentration of the surface of the silicon epitaxial layer is set to 1.0×1017 to 12×1017 atoms / cm3 (ASTM F-121, 1979).
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Method for self-assembly growth of three-dimensional ordered polyporous material
ActiveCN101429049AOvercoming the disadvantage of not being able to self-assemble large-size colloidal spheres synergisticallyWill not affect the flowCeramicwareEvaporationSolvent
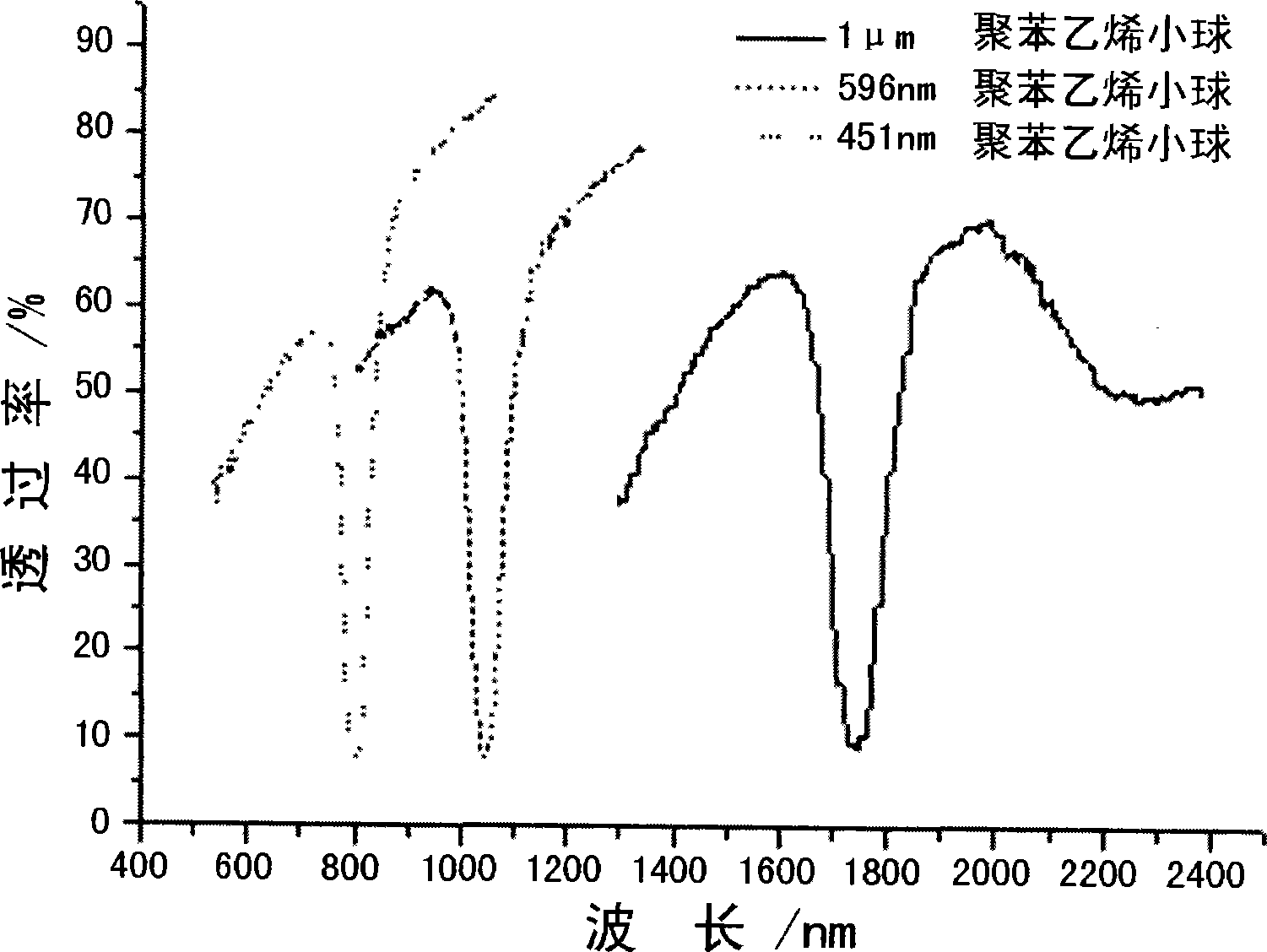
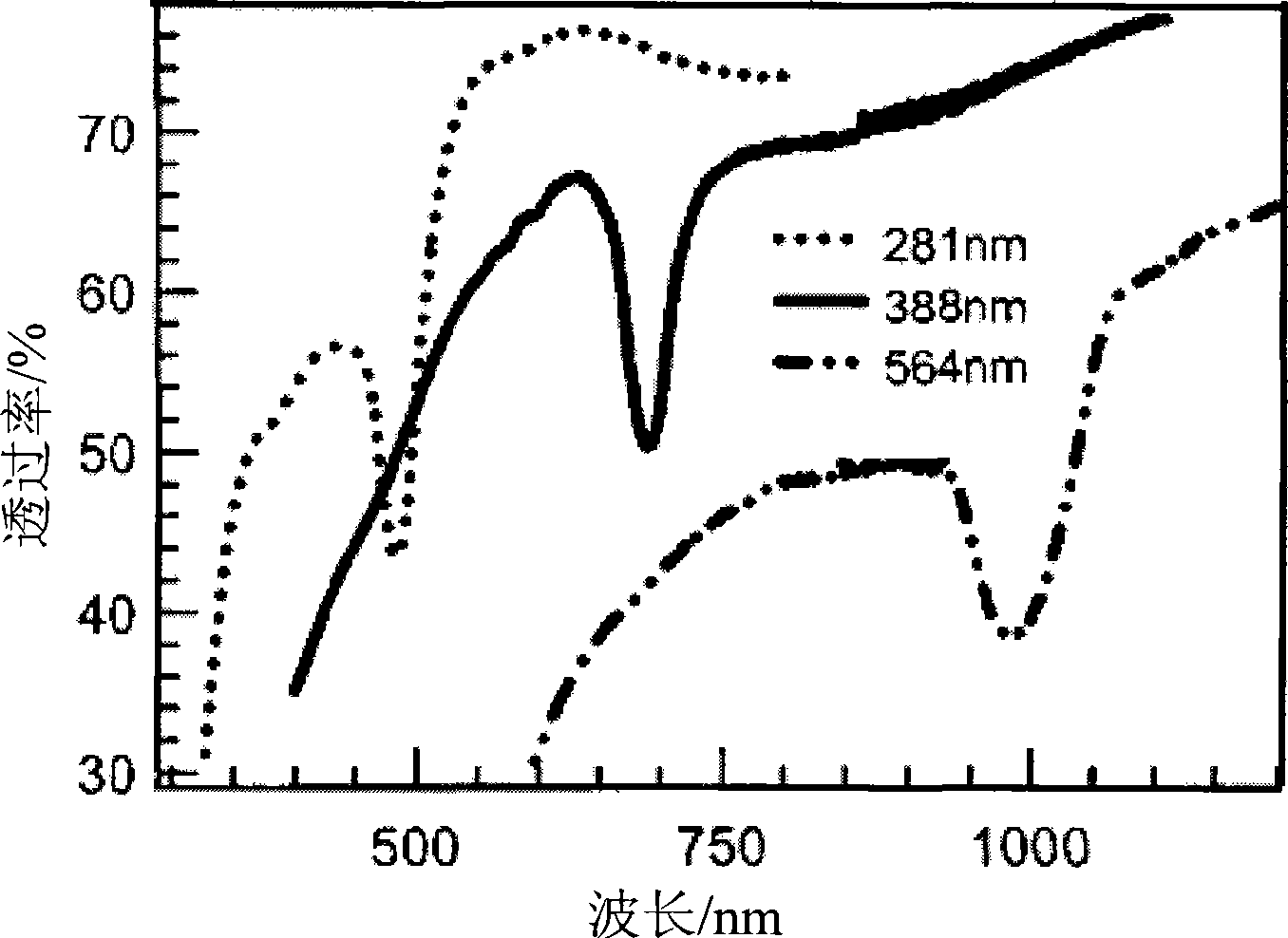
The invention relates to a method for self-assembly growth of three-dimensional orderly porous materials, which is a method for self-assembly growth of multi-component material colloid crystals with single structures or composite structures and three-dimensional orderly porous membranes by combining assistant acceleration of evaporation through characteristic infrared light and the control of the boiling temperature of a solvent by decompression. The method basically overcomes the defect that the prior method is not suitable for the situations of overlarge colloid particles, overhigh boiling point of the solvent in a colloidal solution system, no high temperature resistance of the colloid particles, incapability of completing crystal growth and so on when the prior method is applied to cooperated self-assembly growth of the multi-component colloid crystals and three-dimensional orderly porous materials of the multi-component colloid crystals. The method has the characteristics of high efficiency, easy control, simple operation and good repeatability, can grow the high-quality multi-component colloid crystals and the three-dimensional orderly porous membranes, and is suitable for self-assembly and cooperated self-assembly of multi-component colloid particle mixed systems with various particle diameters and various varieties.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Light-emitting device of group iii nitride-based semiconductor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20090166650A1Suppressed dislocationImprove light extractionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceNitride
A light-emitting device of Group III nitride-based semiconductor comprises a substrate, a first Group III nitride layer and a second Group III nitride layer. The substrate comprises a first surface and a plurality of convex portions protruding from the first surface. Each convex portion is surrounded by a part of the first surface. The first Group III nitride layer is jointly formed by lateral growth starting at top surfaces of the convex portions. The second Group III nitride layer is formed on the first surface, wherein a thickness of the second Group III nitride layer is less than a height of the convex portion. Moreover, the first Group III nitride layer and the second Group III nitride layer are made of a same material.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Group iii nitride semiconductor epitaxial substrate
InactiveCN101778967AImprove qualityCrack suppressionPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emitting deviceDislocation
Disclosed is a group III nitride semiconductor epitaxial substrate, specifically an AlxGa1-xN epitaxial substrate (0 = x = 1), which is improved in crystal quality by suppressing generation of cracks and dislocations. More specifically disclosed is an AlxGa1-xN epitaxial substrate (0 < x = 1), which is useful for a light-emitting device of ultraviolet or deep ultraviolet region. The group III nitride semiconductor epitaxial substrate is composed of a base and an AlxGa1-xN (0 = x = 1) layer arranged on the base. This group III nitride semiconductor epitaxial substrate is characterized in that a layer, wherein crystals having -C polarity and crystals having +C polarity are mixed, is arranged on the base side of the AlxGa1-xN layer.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Solar cell stack
ActiveUS20160133775A1Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationDopantSolar cell
A solar cell stack, having a first semiconductor solar cell having a p-n junction made of a first material with a first lattice constant, and a second semiconductor solar cell having a p-n junction made of a second material with a second lattice constant, and the first lattice constant being at least 0.008 Å smaller than the second lattice constant, and a metamorphic buffer, the metamorphic buffer being formed between the first semiconductor solar cell and the second semiconductor solar cell, and the metamorphic buffer including a series of three layers, and the lattice constant increasing in a series in the direction of the semiconductor solar cell, and the lattice constants of the layers of the metamorphic buffer being bigger than the first lattice constant, two layers of the buffer having a doping, and the difference in the dopant concentration between the two layers being greater than 4E17 cm−3.
Owner:AZUR SPACE SOLAR POWER
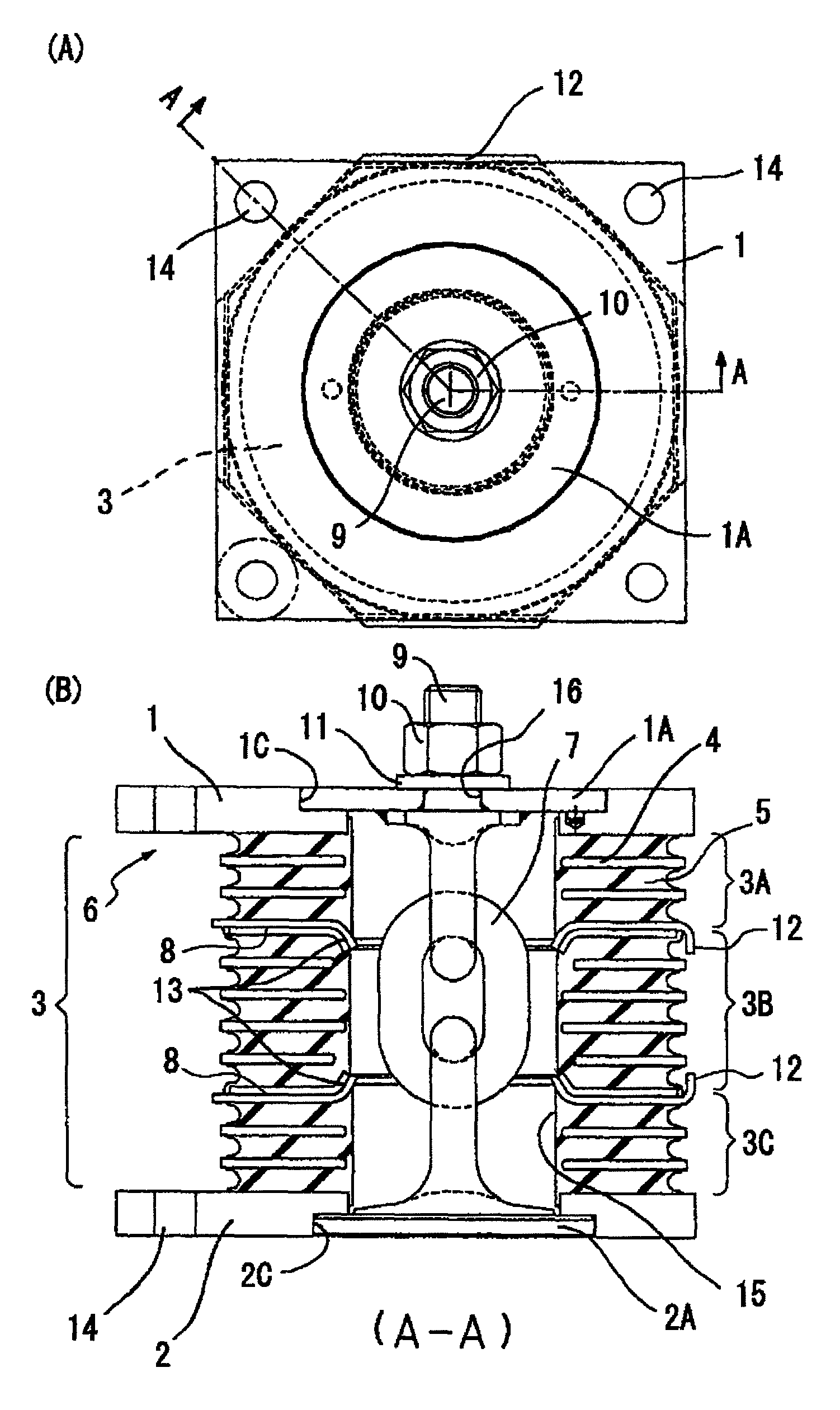
Vibration damping system
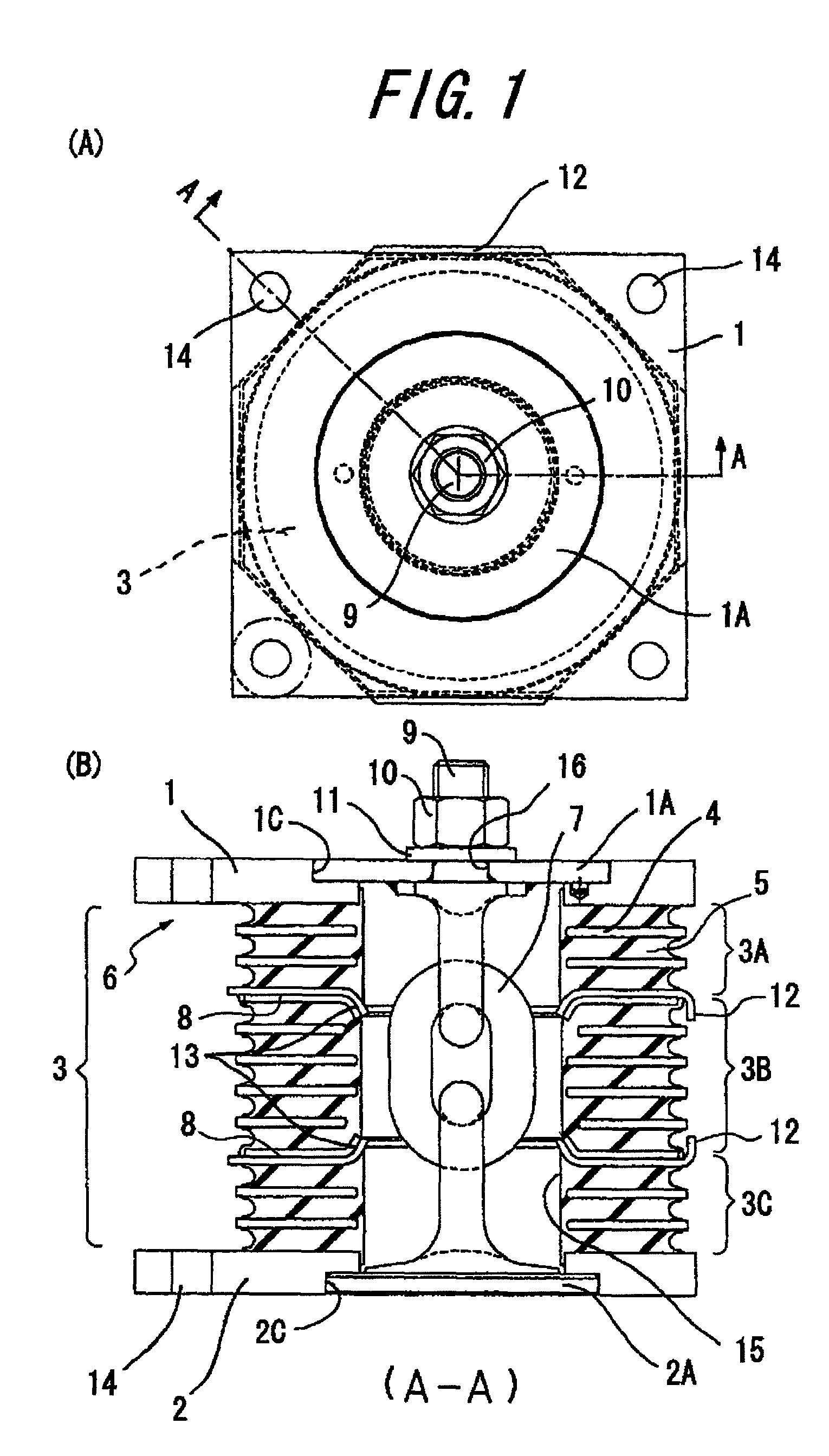
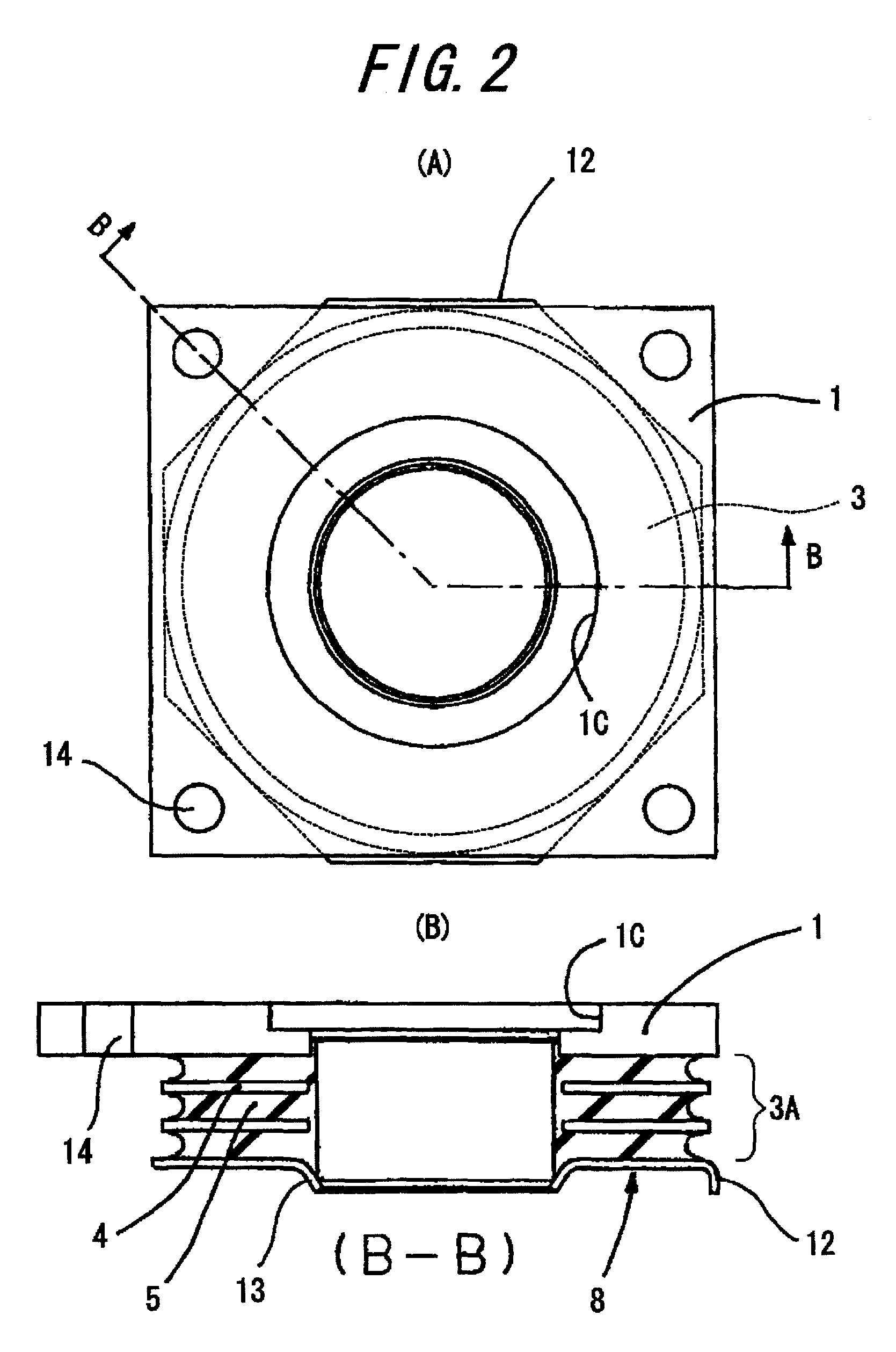
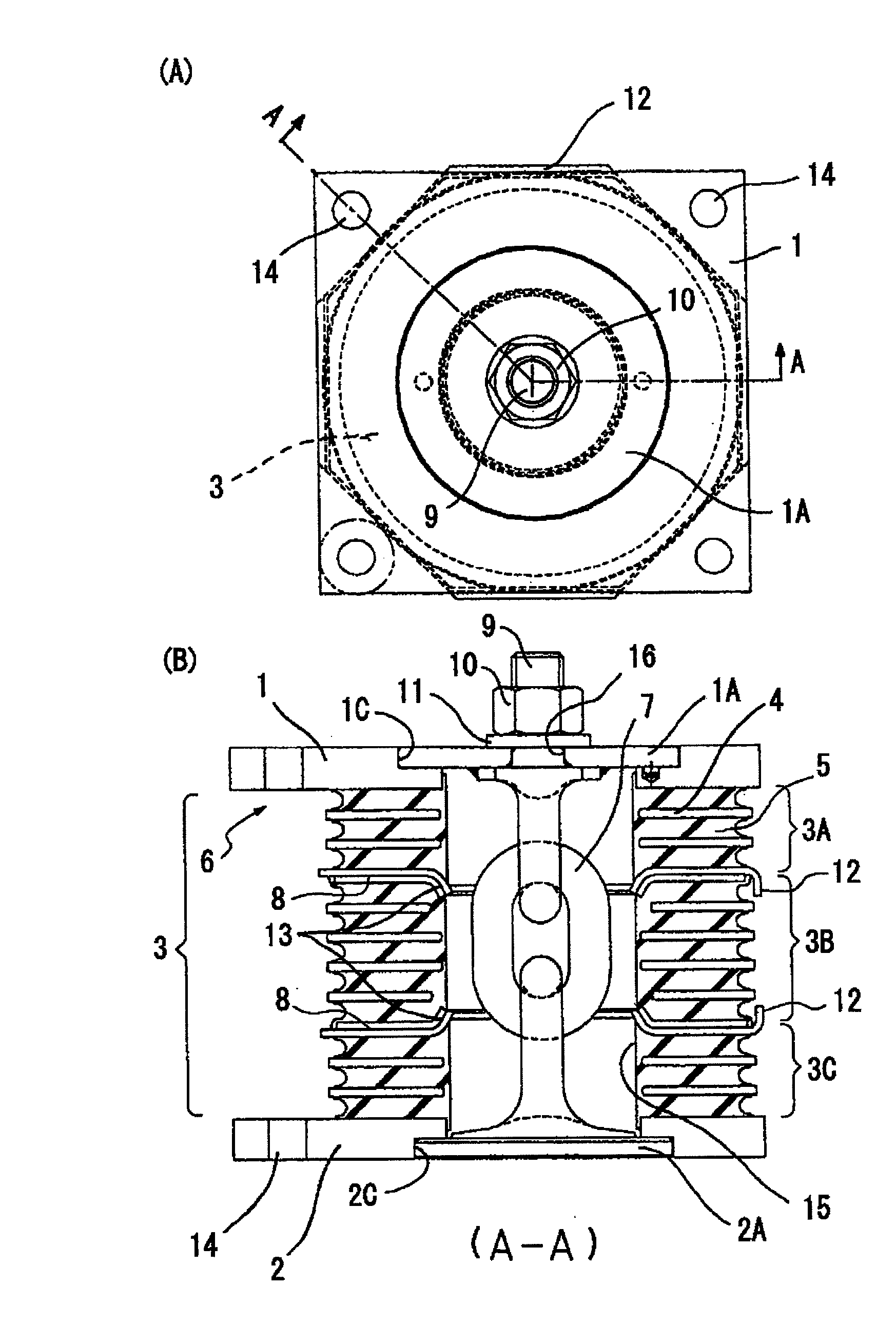
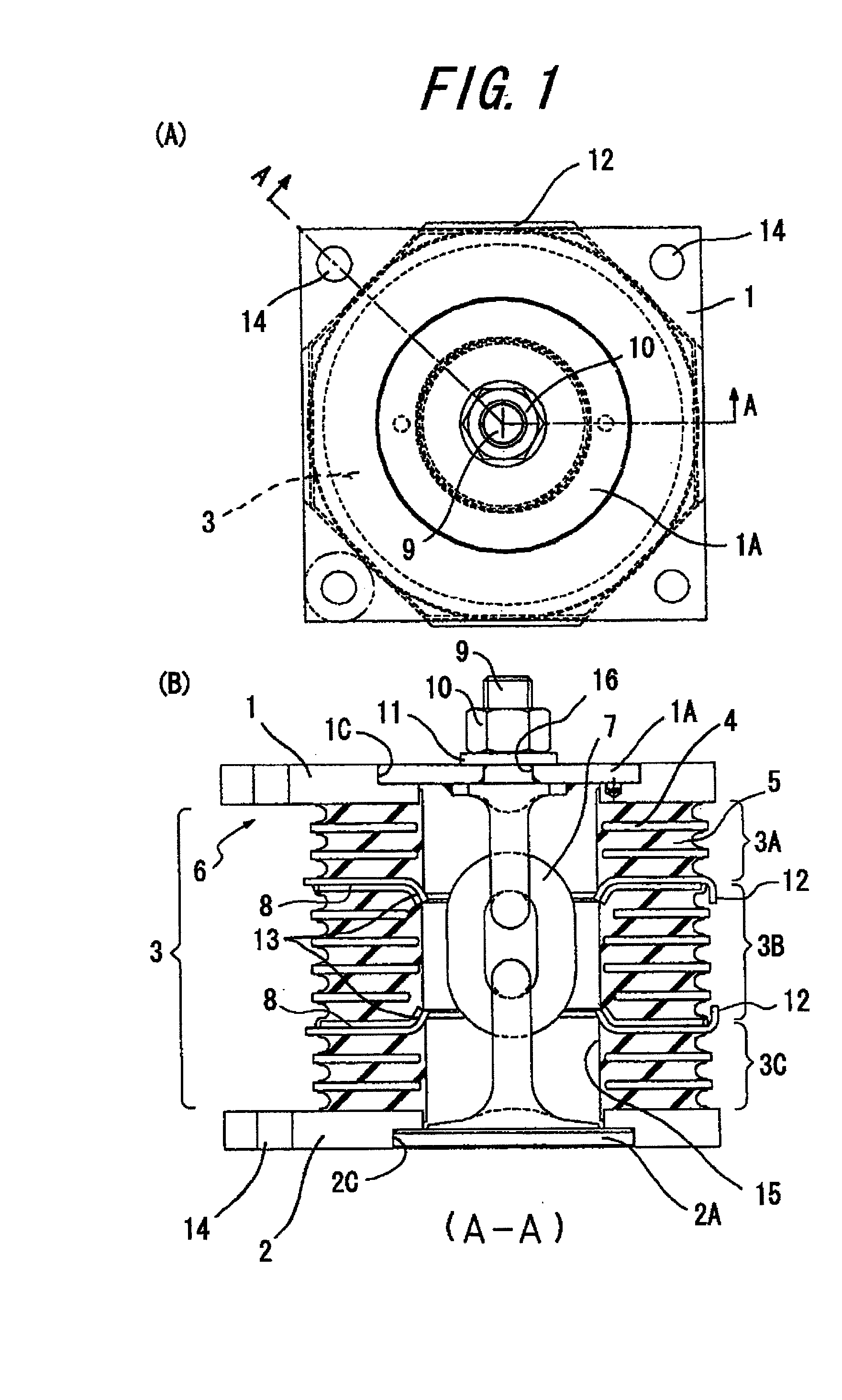
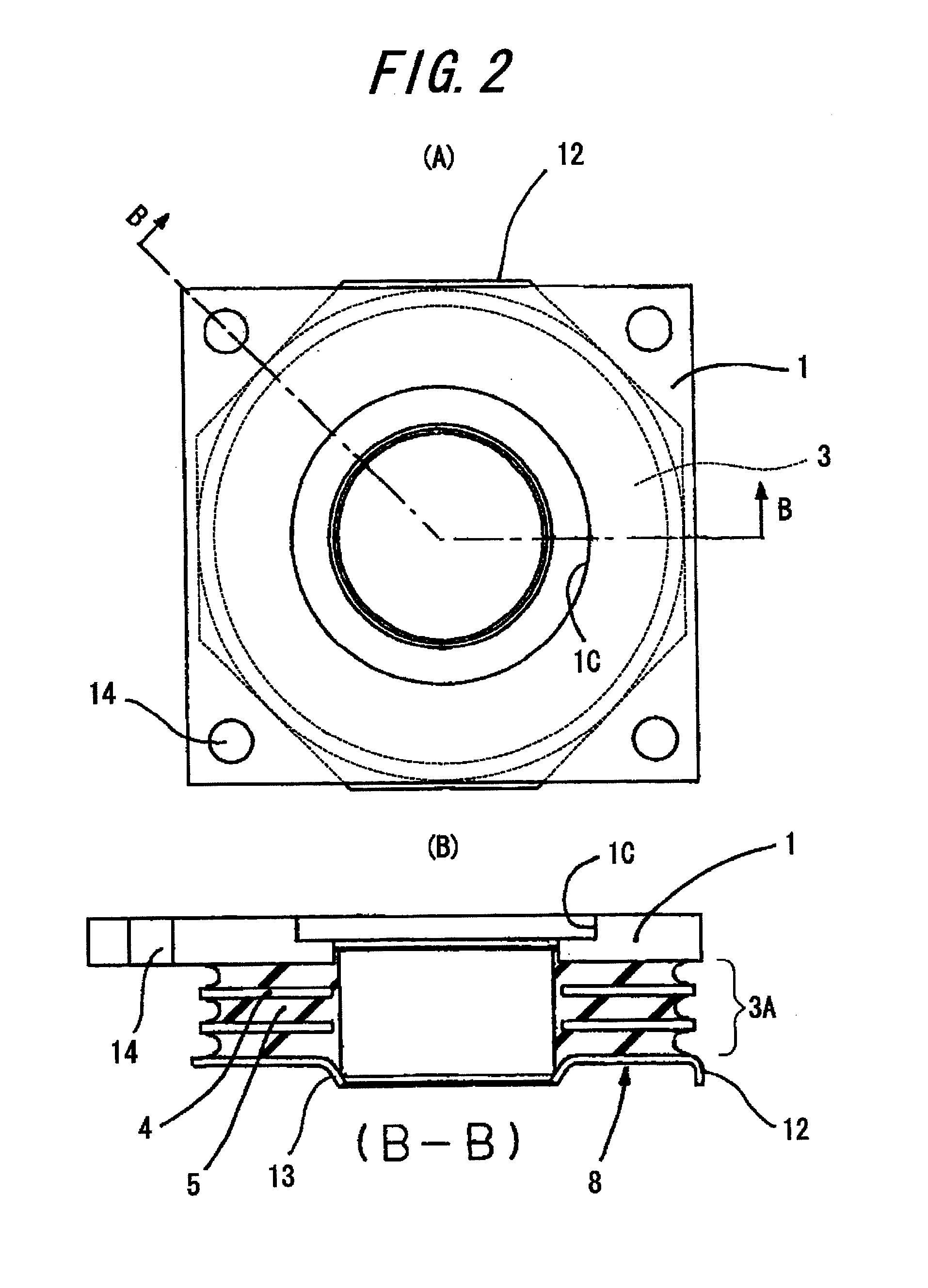
InactiveUS8317173B2Avoid damageSuppressed dislocationPortable framesStands/trestlesPre compressionEngineering
A vibration damping system includes a laminated body (3) formed by alternately laminating rigid hard plates (4) and viscoelastic soft plates (5), and pair of shoe plates (1, 2) at both ends in the laminating direction of the laminated body (3), to form a vibration damping body (6). The show plates (1, 2) are connected to each other by a displacement restriction member (7), so as to applying a pre-compression to the laminated body. The vibration damping body (6) is divided into a plurality of segments (3A, 3B, 3C) in the laminating direction, for allowing the vibration-proof main body (6) to be separated and displaced at the parting faces (8), without causing an excessive tensile force in the vibration damping system, even if the displacement restriction member (7) has worn to degrade the pre-compression function and a tensile force is applied due to a prying deformation. Thus, the soft members (5) of the laminated body (3) are effectively protected from isostatic fracture, to provide a significantly improved durability of the vibration damping system.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS7768017B2Less liableEasy to useTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDopantSilanes
With a view to preventing increases in forward voltage due to a change with the lapse of time of a bipolar semiconductor device using a silicon carbide semiconductor, a buffer layer, a drift layer and other p-type and n-type semiconductor layers are formed on a growth surface, which is given by a surface of a crystal of a silicon carbide semiconductor having an off-angle θ of 8 degrees from a (000-1) carbon surface of the crystal, at a film growth rate having a film-thickness increasing rate per hour h of 10 μm / h, which is three times or more higher than conventional counterparts. The flow rate of silane and propane material gases and dopant gases is largely increased to enhance the film growth rate.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Method for Producing Silicon Wafer
InactiveUS20090197396A1Sufficient amountQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenNitrogen gas
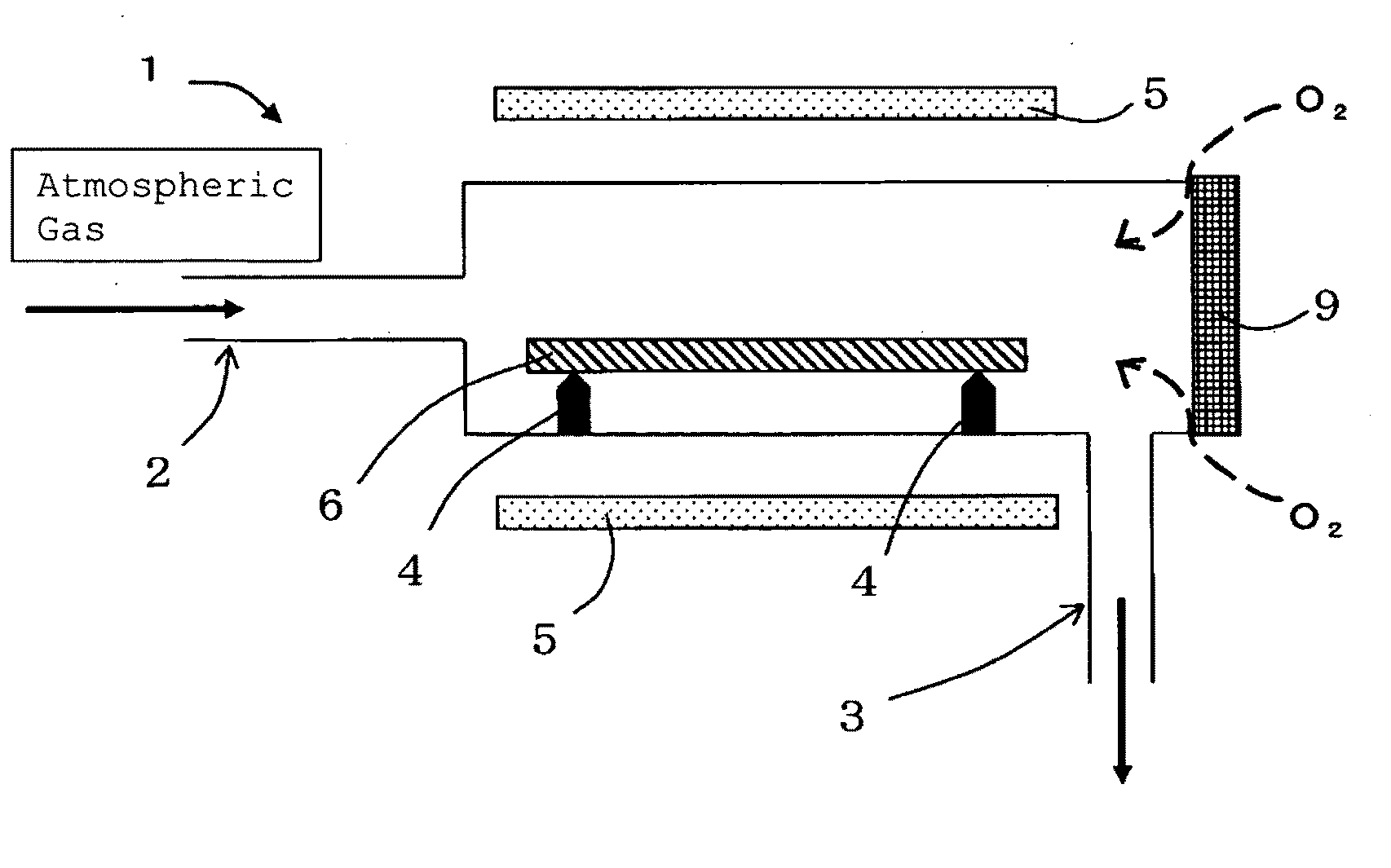
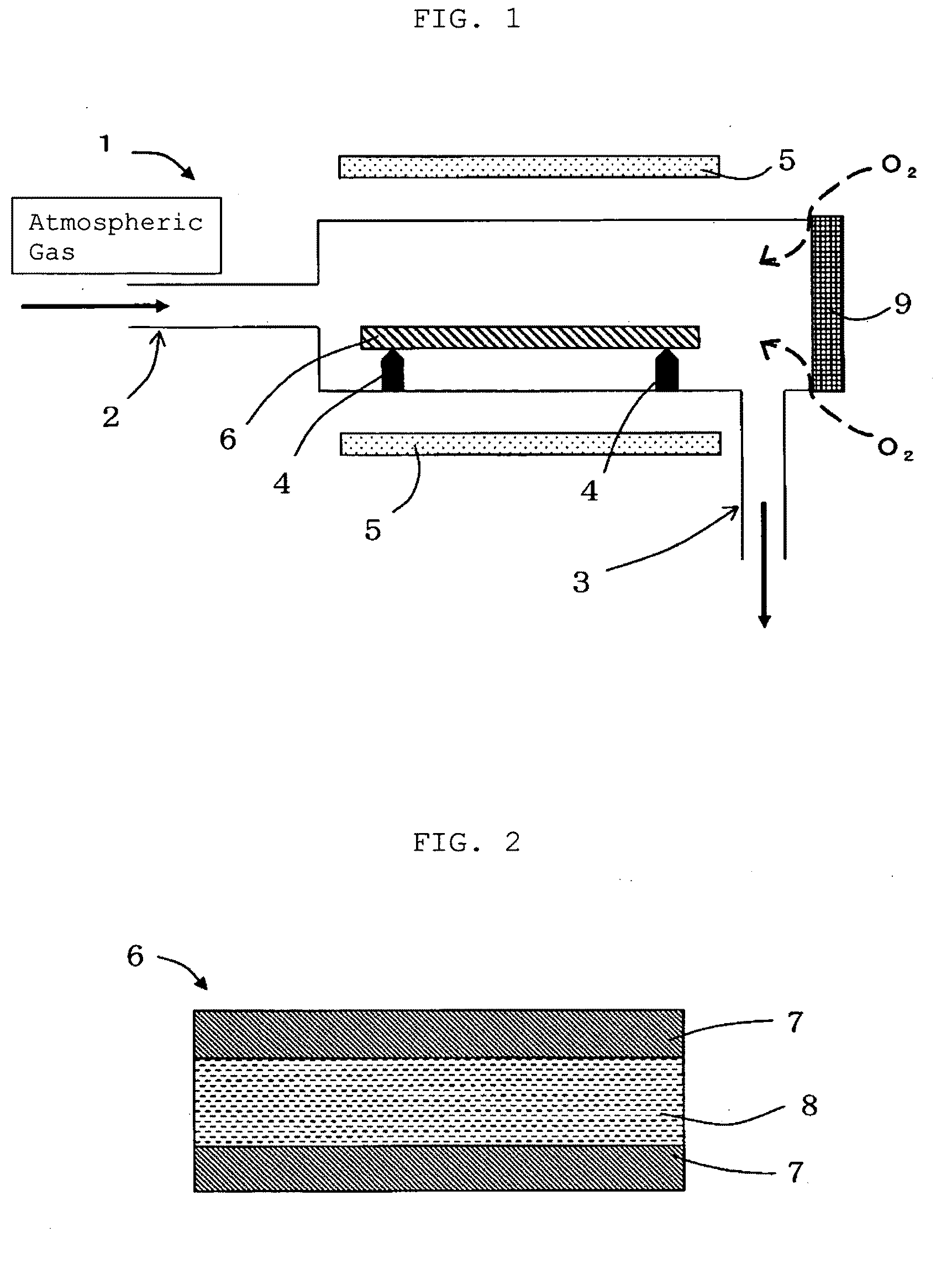
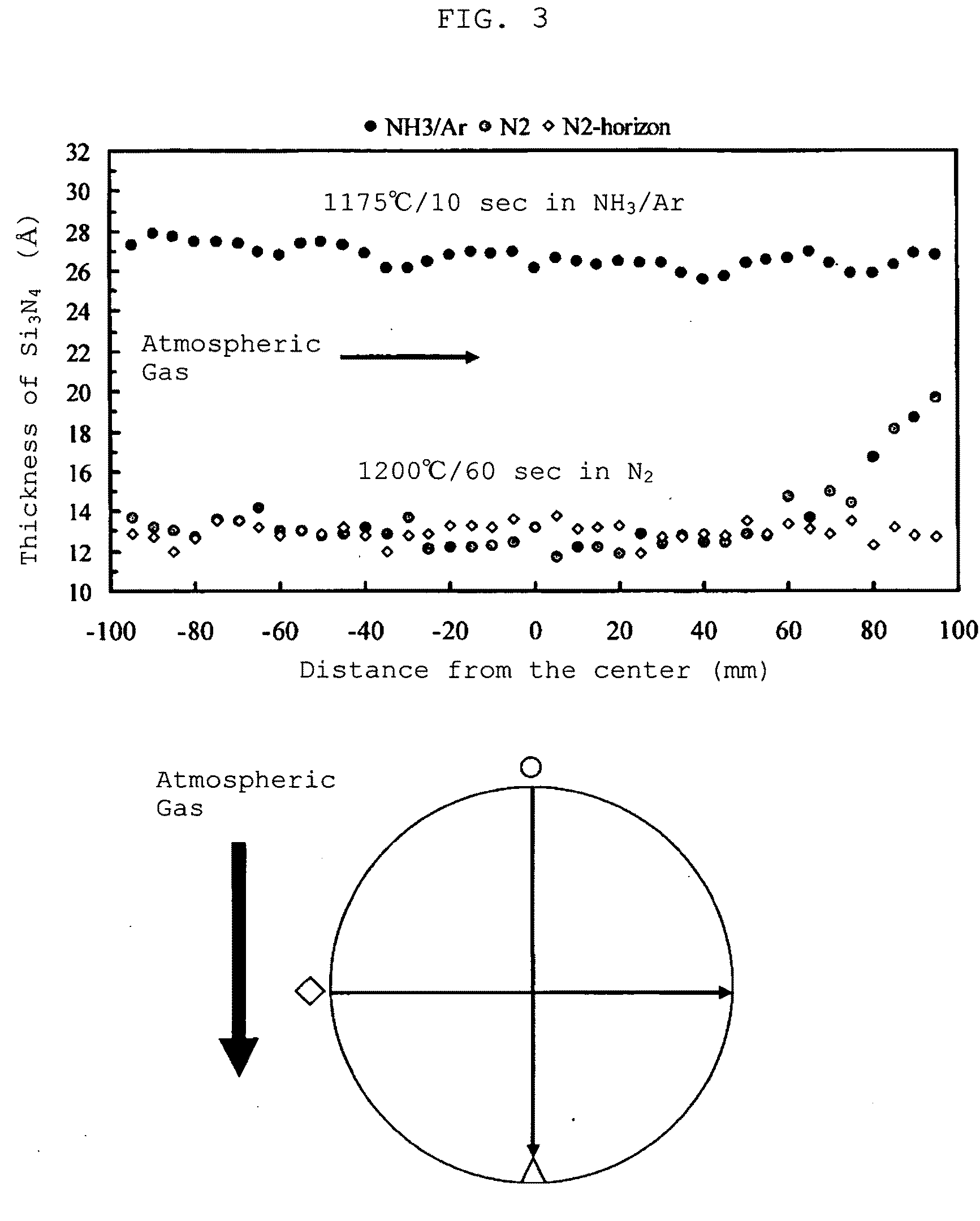
The present invention provides a method for producing a silicon wafer at least including a step of performing RTA heat treatment with respect to a silicon wafer in an atmospheric gas, wherein nitrogen gas is used as the atmospheric gas, which is mixed with oxygen at a concentration of less than 100 ppm so as to perform the heat treatment. Hereby a method for producing a high-quality wafer can be provided, where the RTA heat treatment subject to the silicon wafer can be performed at a low temperature or over a short period of time, so that generation of slip dislocation of the silicon wafer can be suppressed, and at the same time vacancies can be implanted inside the silicon wafer without using NH3.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Construction machine
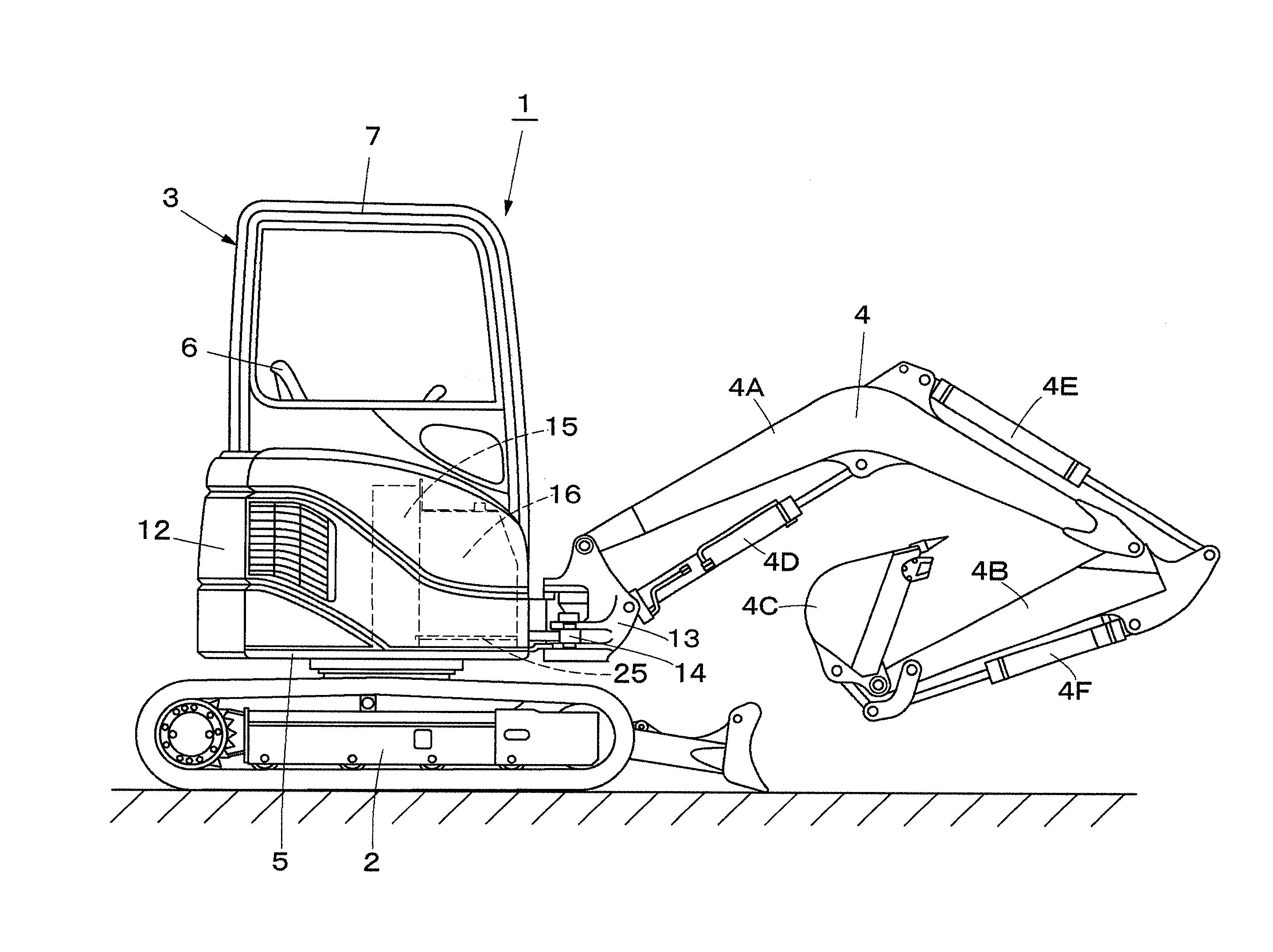
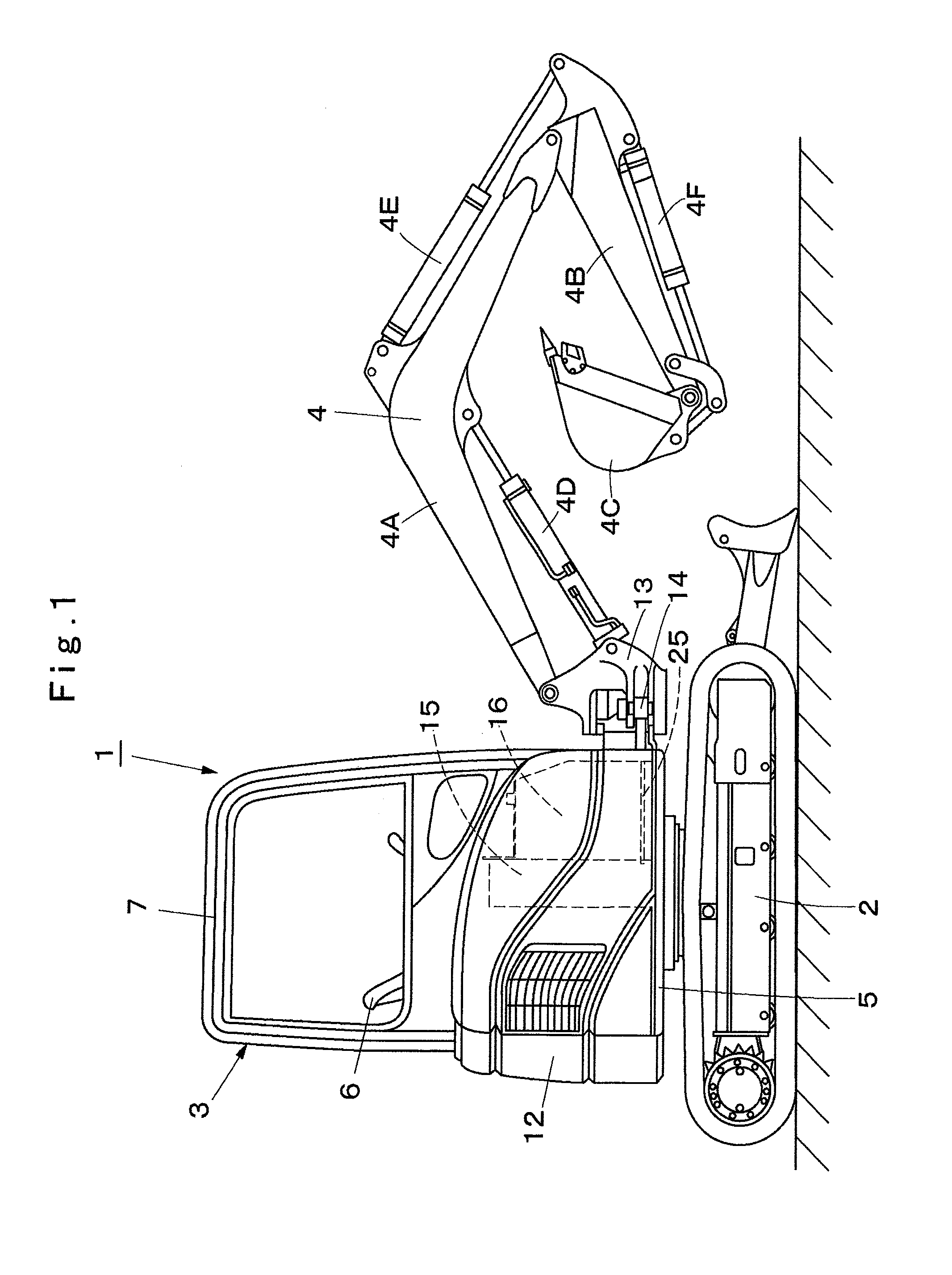
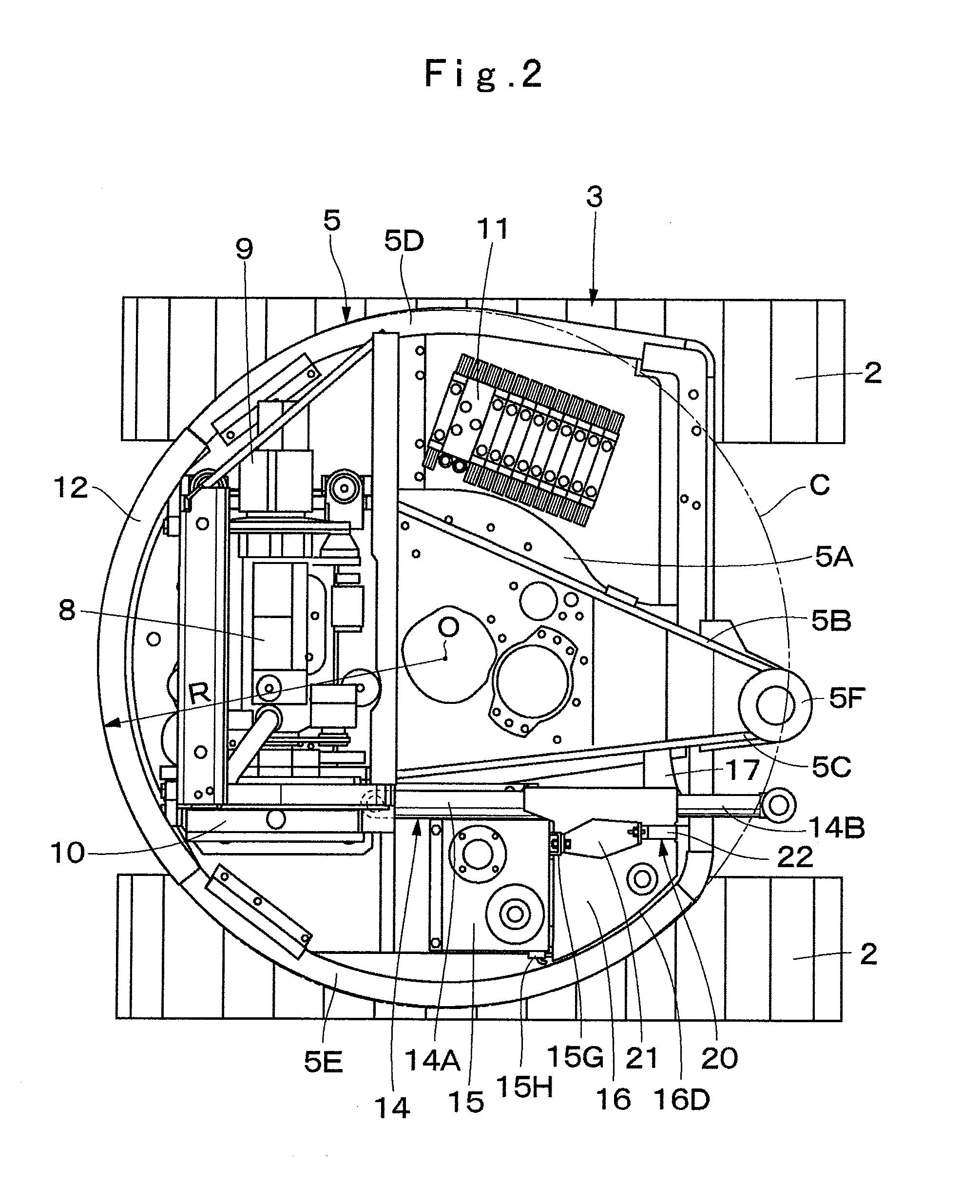
ActiveUS20140017054A1Increase capacity of fuel tankReduce component countMechanical machines/dredgersLifting devicesFuel tankBuilding construction
On a revolving frame (5), an operating oil tank (15) located on the front side of an engine (8) is provided, and a fuel tank (16) located on the front side of the operating oil tank (15) is arranged. A mounting member (17) is provided on the lower side of the fuel tank (16) across a part of a swing cylinder (14). Between the operating oil tank (15) and the mounting member (17), a vertical restraining element (20) for restraining the fuel tank (16) in a front-rear direction and a vertical direction and a lateral restraining element (25) for restraining the fuel tank (16) in a left-right direction are detachably provided. Therefore, the fuel tank (16) can be restrained in two directions, that is, in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
Silicon wafer and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060016385A1High mechanical strengthAvoid spreadingPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsIngotSingle crystal
A method for manufacturing a silicon wafer includes a step of annealing a silicon wafer which is sliced from a silicon single crystal ingot, thereby forming a DZ layer in a first surface and in a second surface of the silicon wafer and a step of removing either a portion of the DZ layer in the first surface or a portion of the DZ layer in the second surface.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
Method for producing silicon single crystals and silicon single crystal produced thereby
ActiveCN101175872ASuppressed dislocationIncrease production capacityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltHydrogen atomHydrogen
The growth method of the silicon single crystal is to cool at least a part of the silicon single crystal with a cooling member which surrounds the silicon single crystal being grown and whose inner peripheral surface is coaxial with the pulling axis, and uses the Ceclaus The silicon single crystal is grown by the basic method, and the medium gas for growing the above single crystal includes a gas containing hydrogen atom substances.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Method for producing silicon single crystal
InactiveUS20020129759A1Avoid misalignmentIncrease airflowPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltField conditionsCzochralski method
A method for producing a silicon single crystal, the method being capable of suppressing the dislocation of a single crystal. When a silicon single crystal is produced by a Czochralski method in which a horizontal magnetic field or a cusp magnetic field is applied and the single crystal during growth is dislocated, the single crystal with dislocations is dissolved in a nonmagnetic field condition and thereafter a magnetic field is applied again to pull up the silicon single crystal. The flow rate of argon gas is designed to be 100 L / min or more and the pressure in a furnace is designed to be 6700 pa or less when the single crystal with dislocations is dissolved.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
Method for growing silicon single crystal
ActiveCN101203634ASuppressed dislocationPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystal growthMonocrystalline silicon
The invention relates to a method for growing single crystal silicon. Single crystal silicon is grown by the Czochralski method under the condition that the side of the growing single crystal silicon is subjected to thermal stress. The atmosphere gas for growing the single crystal is a mixed gas of an inert gas and a substance gas containing hydrogen atoms.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Semiconductor assembly with built-in stiffener and integrated dual routing circuitries and method of making the same
InactiveUS20160293514A1Serious problemAvoid connection failureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor assembly with built-in stiffener and integrated dual routing circuitries is characterized in that a semiconductor device and a first routing circuitry are positioned within a through opening of a stiffener whereas a second routing circuitry extends to an area outside of the through opening of the stiffener. The mechanical robustness of the stiffener can prevent the assembly from warping. The first routing circuitry can enlarge the pad size and pitch of the semiconductor device, whereas the second routing circuitry not only provides further fan-out wiring structure, but also mechanically binds the first routing circuitry with the stiffener.
Owner:BRIDGE SEMICON
Device for preparing precipitation strengthened type high-strength and high-conductivity CuZr alloy
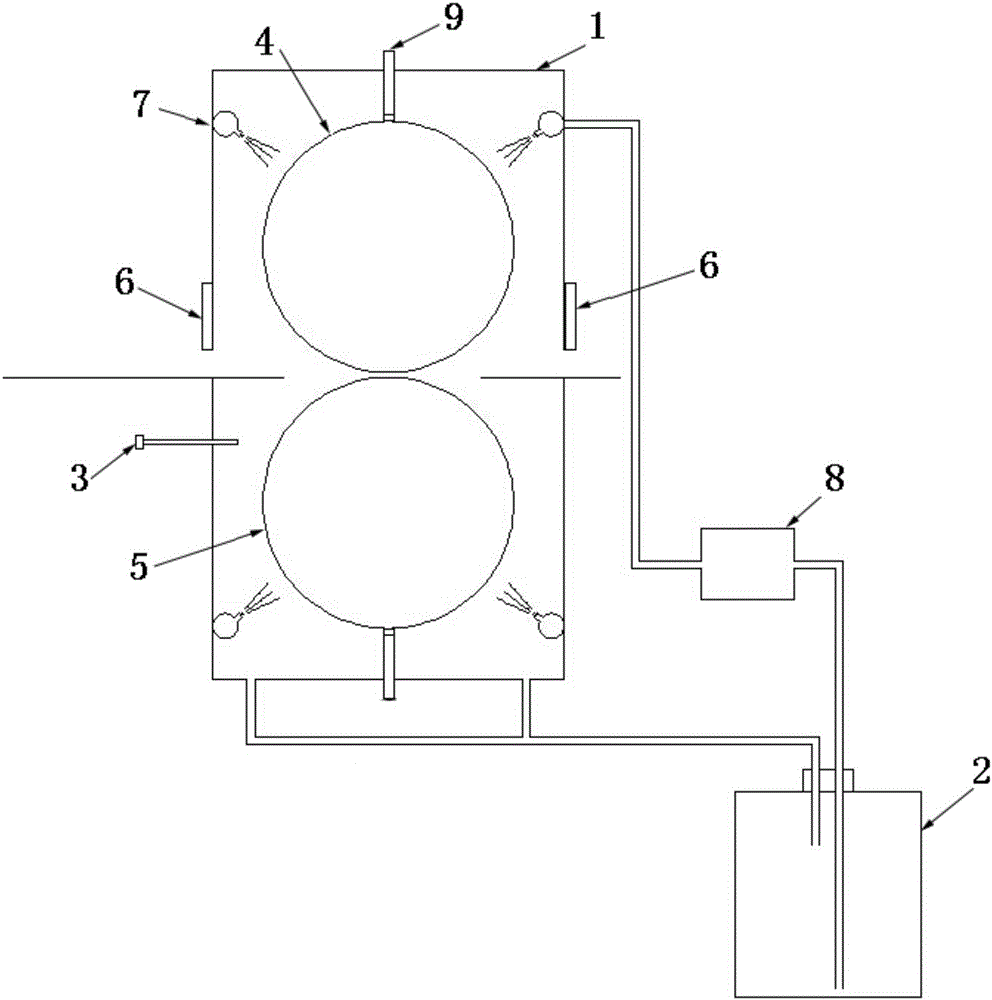
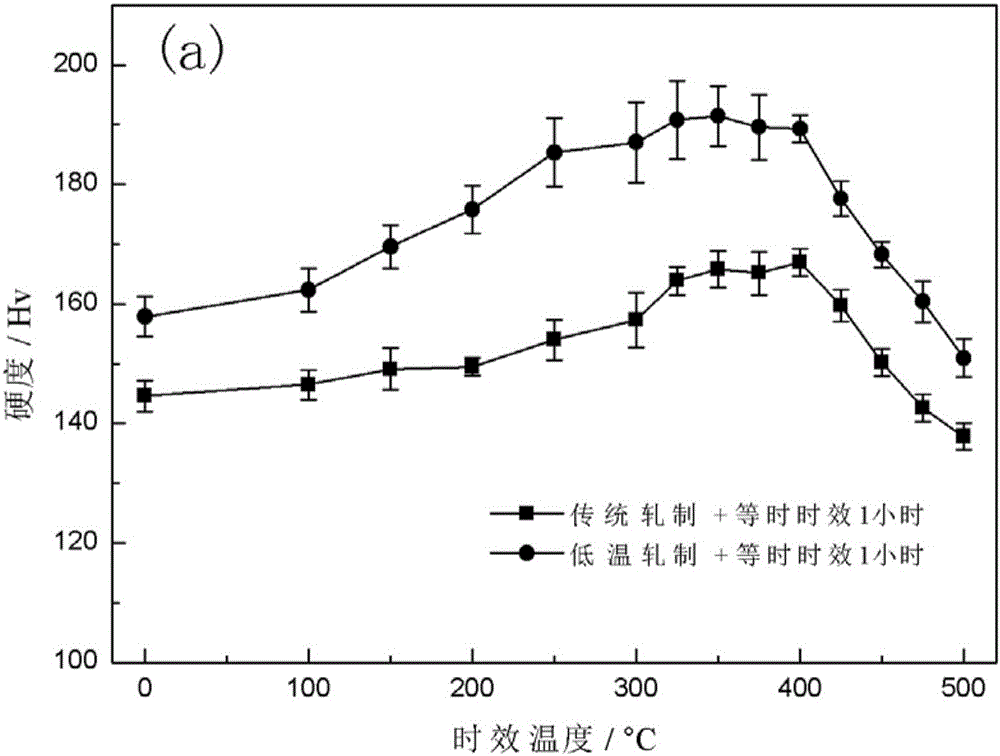
The invention provides a device for preparing a precipitation strengthened type high-strength and high-conductivity CuZr alloy. The device comprises a lower-temperature rolling box body, a liquid nitrogen tank and a temperature sensor. An upper roller and a lower roller are arranged in the low-temperature rolling box body in a matched manner. A material inlet and a material outlet which are matched with the upper roller and the lower roller respectively are formed in the side wall of the low-temperature rolling box body. The material inlet and the material outlet are each provided with a sliding baffle. The material inlet and the material outlet can be opened and closed by sliding the sliding baffles. A plurality of spray nozzles are arranged on the inner wall of the low-temperature rolling box body and are communicated with the liquid nitrogen tank through a pipeline. A peristaltic pump is arranged on the pipeline between the spray nozzles and the liquid nitrogen tank. The temperature sensor is arranged on the side wall of the low-temperature rolling box body. The precipitation strengthened type high-strength and high-conductivity CuZr alloy prepared through the device has an excellent mechanical property and excellent conductivity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor Device
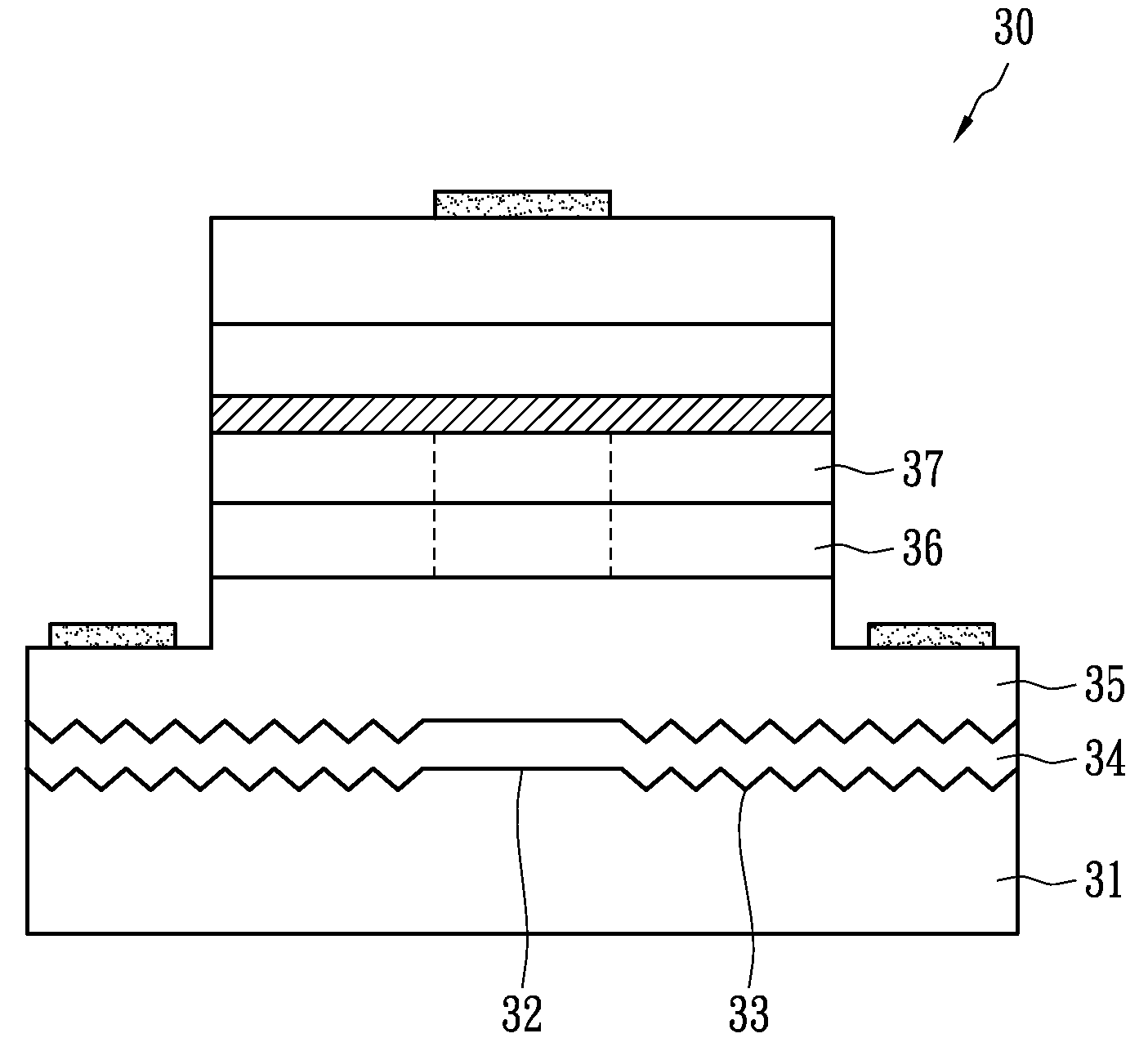
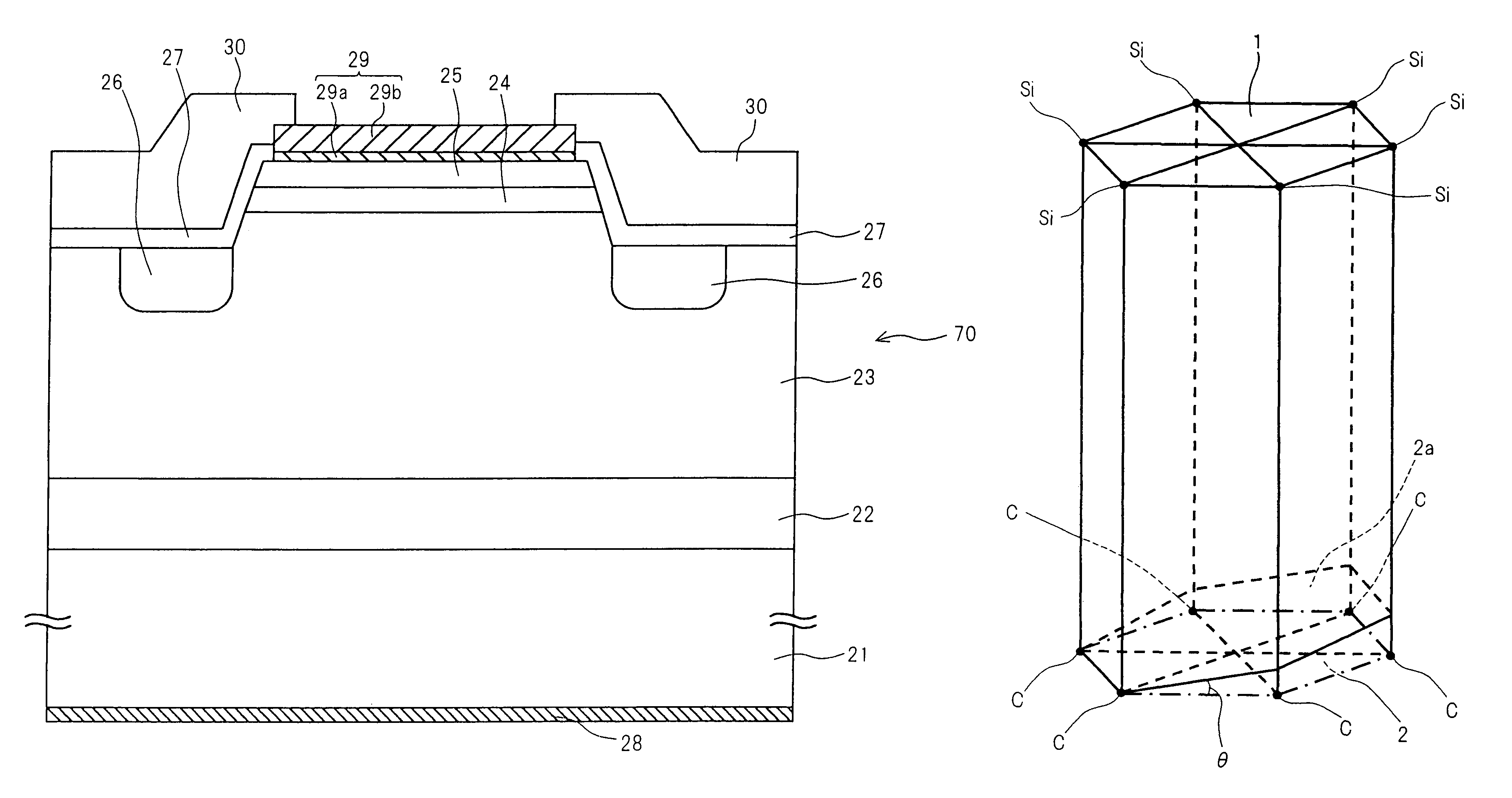
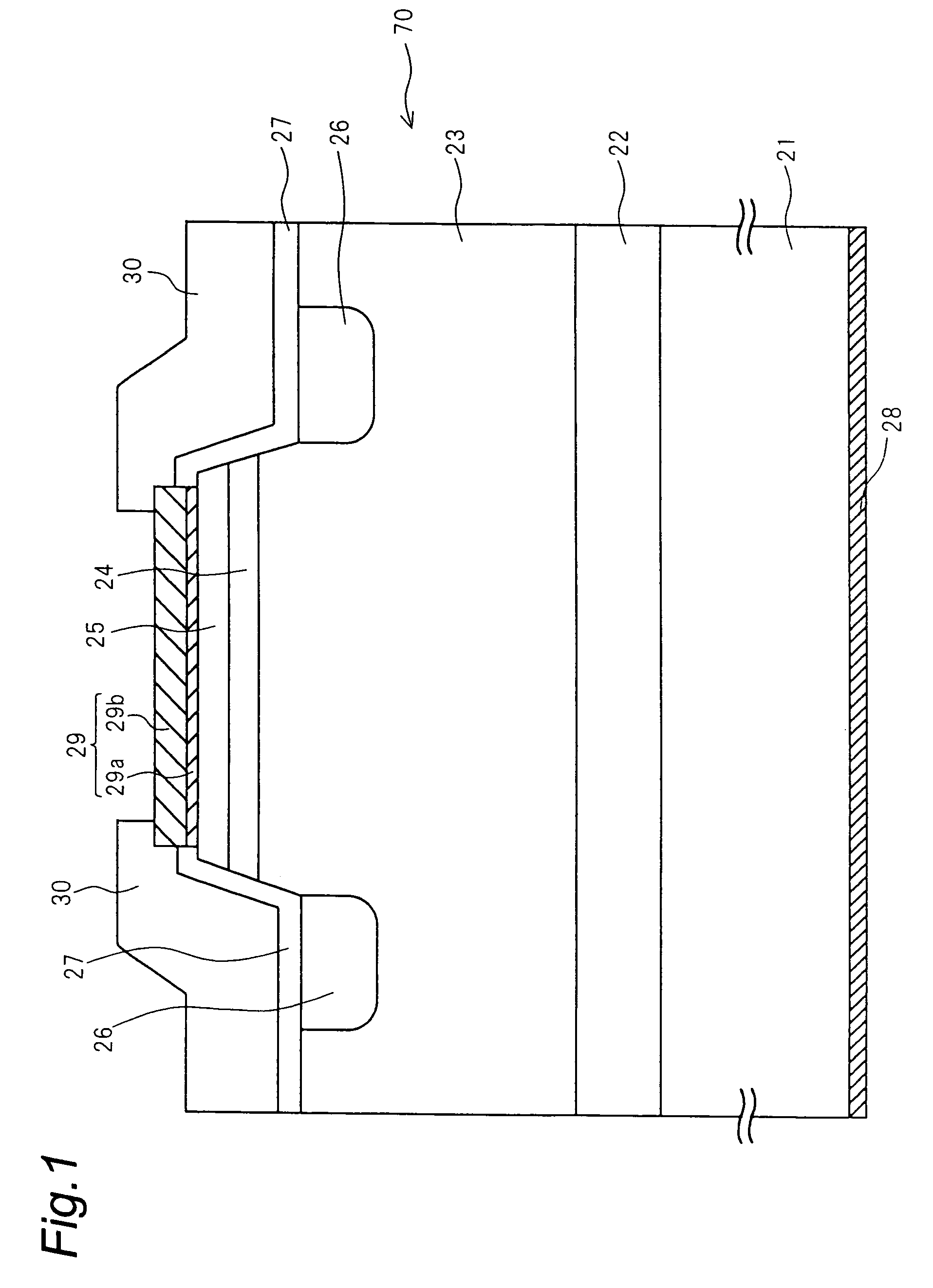
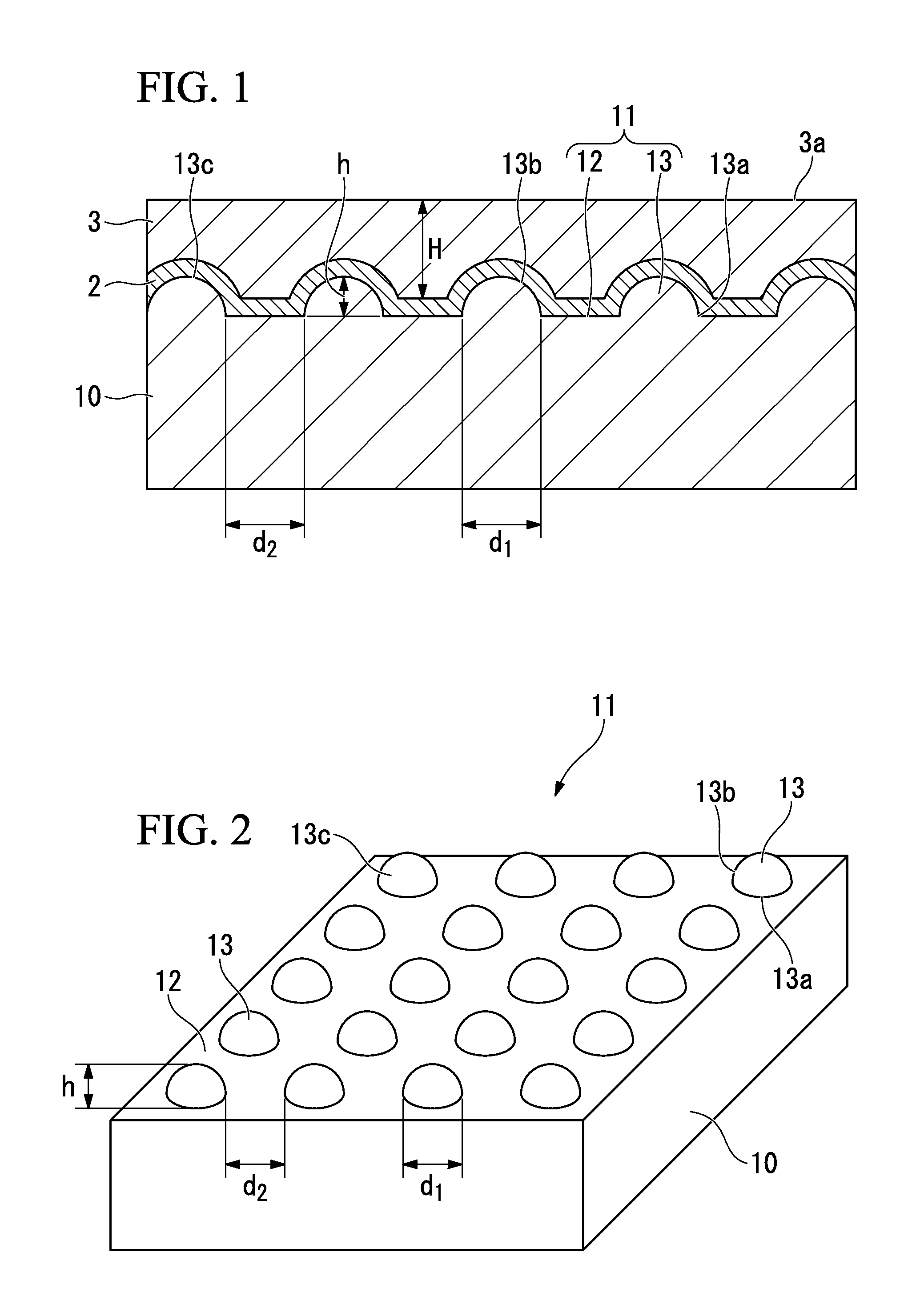
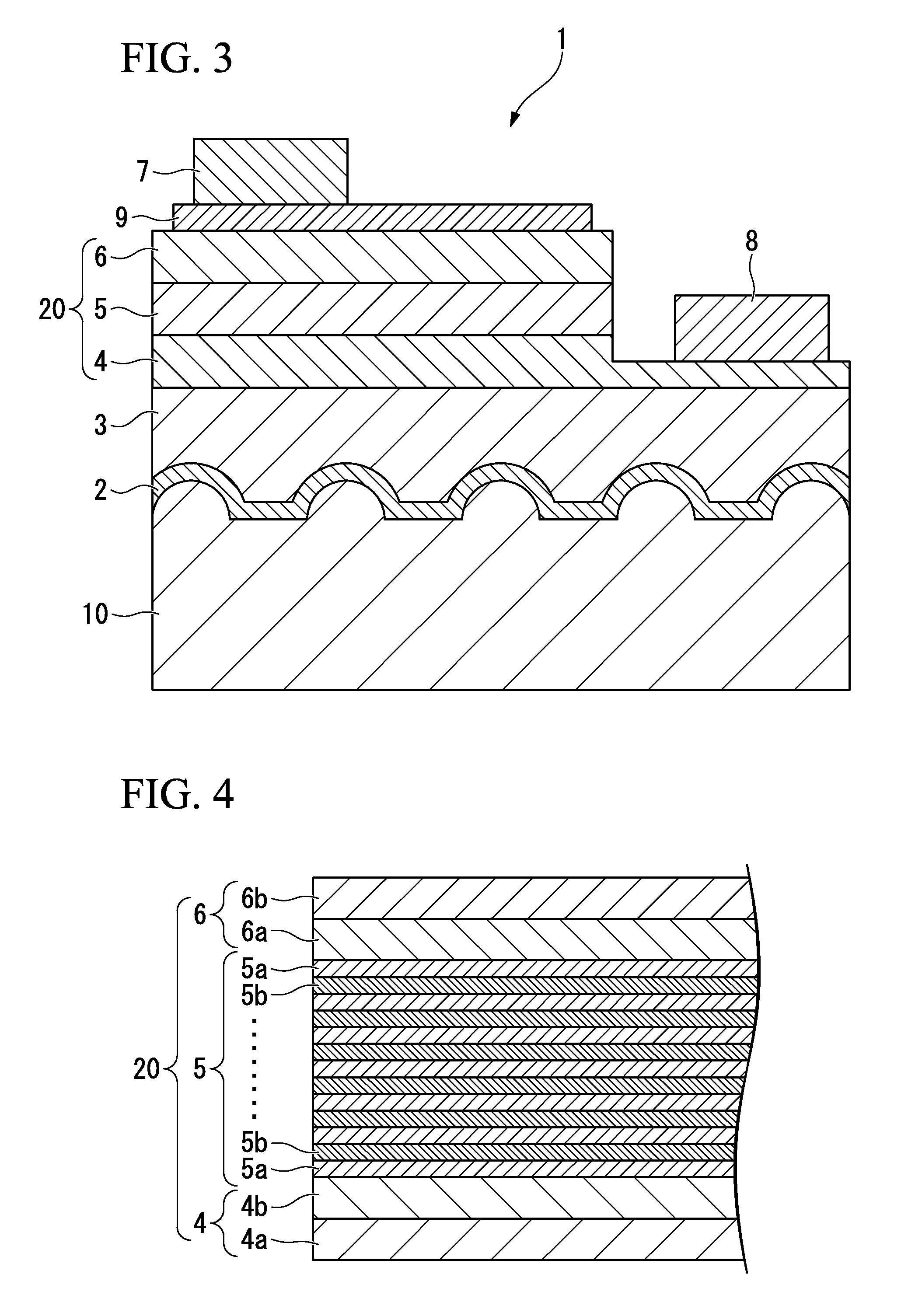
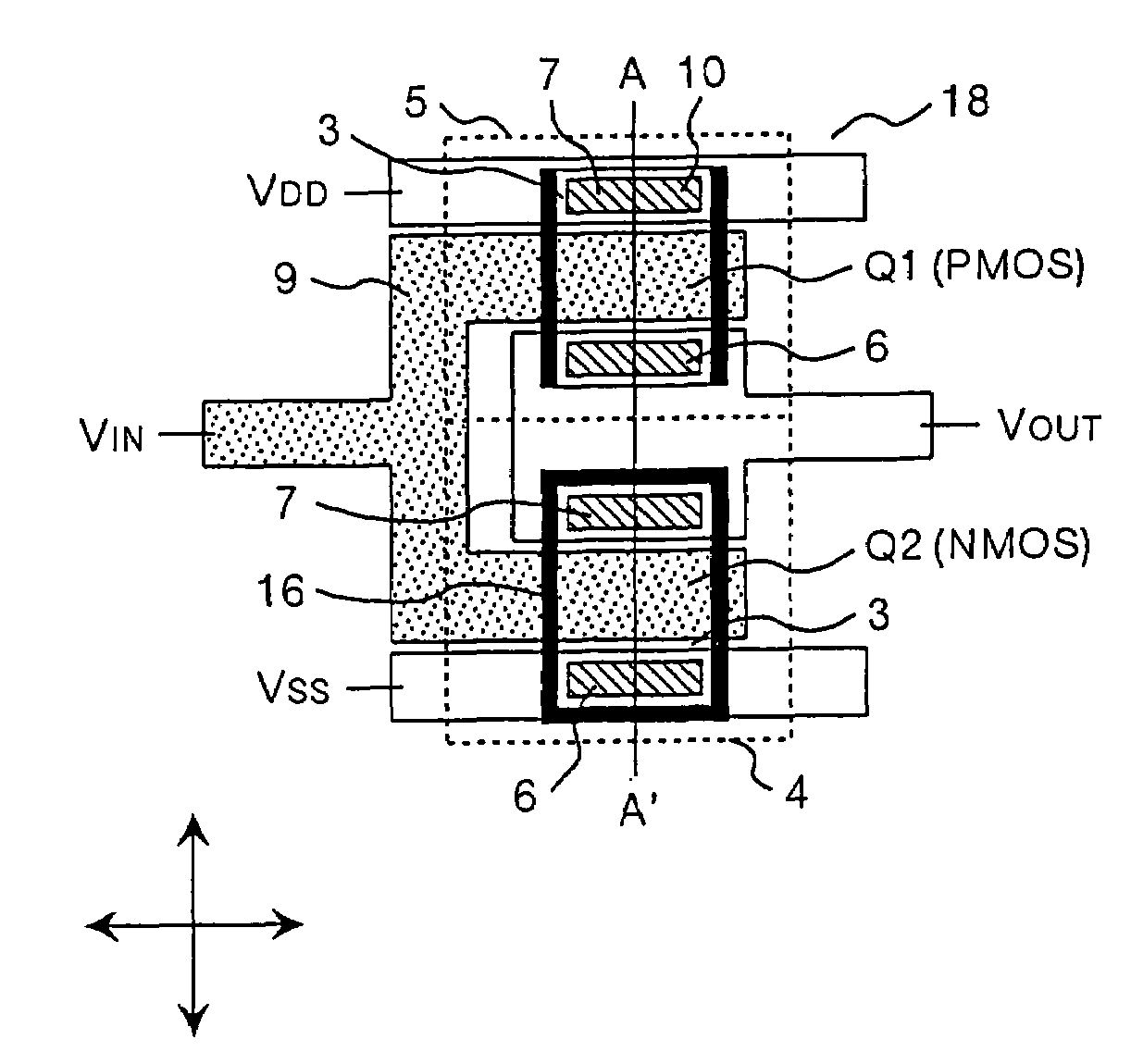
ActiveUS20090174035A1Improve adhesionInhibit deteriorationLaser detailsSolid-state devicesNitrogenActive layer
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate formed of at least two kinds of group III elements and nitrogen, an active layer formed on the semiconductor substrate, and a nitride semiconductor layer formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate and formed between the semiconductor substrate and the active layer. The nitride semiconductor layer is formed of the same constituent elements of the semiconductor substrate. A composition ratio of the lightest element among the group III elements of the nitride semiconductor layer is higher than a composition ratio of the corresponding element of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Method for manufacturing group iii nitride semiconductor light-emitting element, group iii nitride semiconductor light-emitting element, lamp, and reticle
ActiveUS20130221388A1Good lookingHigh crystallinitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentOptoelectronicsLead structure
A method for manufacturing a Group III nitride semiconductor light-emitting element of the invention includes a substrate-processing process of forming a main surface including a flat surface and a convex portion 13 on the substrate 10, an epitaxial process of epitaxially growing an underlying layer on the main surface of the substrate 10 so as to cover the flat surface and the convex portion 13, and an LED lamination process of forming an LED structure by epitaxially growing a Group III nitride semiconductor. In the substrate-processing process, mask patterns 15 are sequentially formed in respective regions R1 and R2 of the flat surface using a polygonal reticle 51 having two pairs of parallel opposing ends in a plan view, by a stepper exposure method, and then the flat surface is etched to dispose and form three arbitrary convex portions 13, which are arranged to be adjacent to each other, in an isosceles triangular shape in a plan view.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
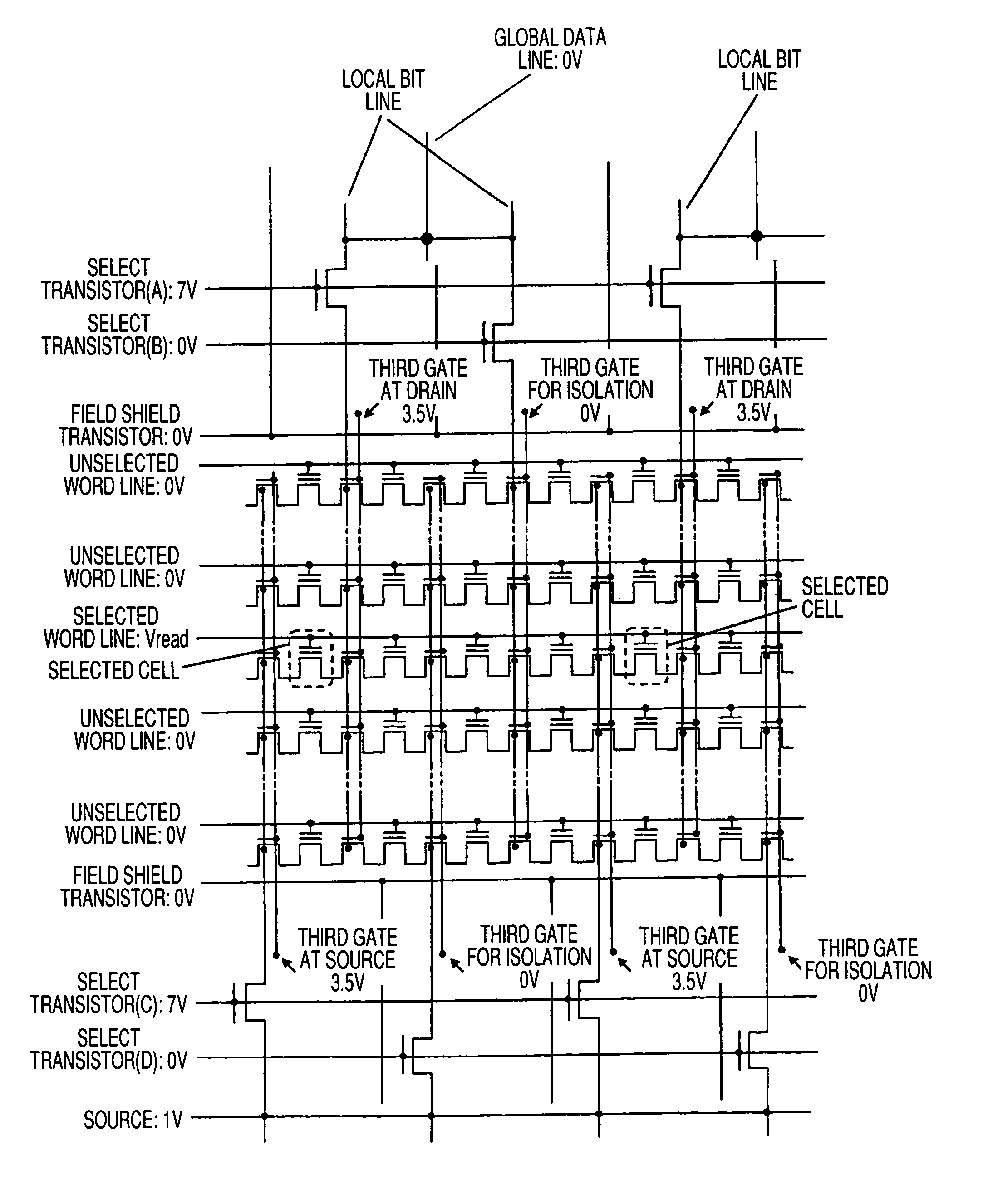
InactiveUS20050195630A1Reduce productionLower Reliability RequirementsTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineEngineering
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device to be manufactured at a high production yield has memory cells disposed in a highly integrated manner by suppressing the occurrence of dislocation typically caused by such highly integrated disposition of the memory cells. In order to achieve is result, each field shielding transistor is formed in a select transistor region having a small isolation width, and 0 V is applied to a gate of the field shielding transistor to isolate each local bit line from the others. The gate of each field shielding transistor is connected to another one with a gate member, so that the layout area is reduced more than when a contact hole is provided directly at the gate of each field shielding transistor.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Sic epitaxial wafer
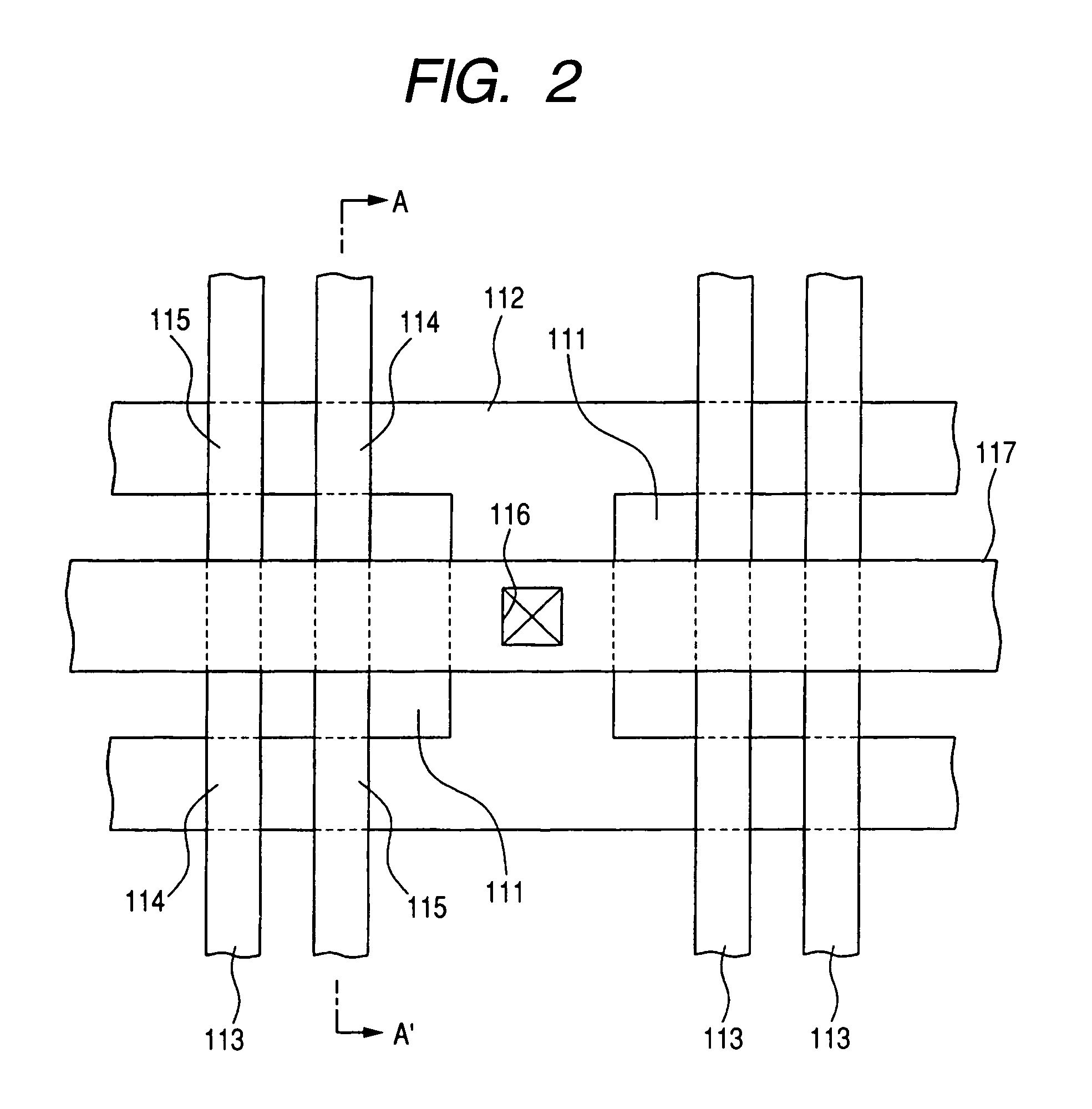
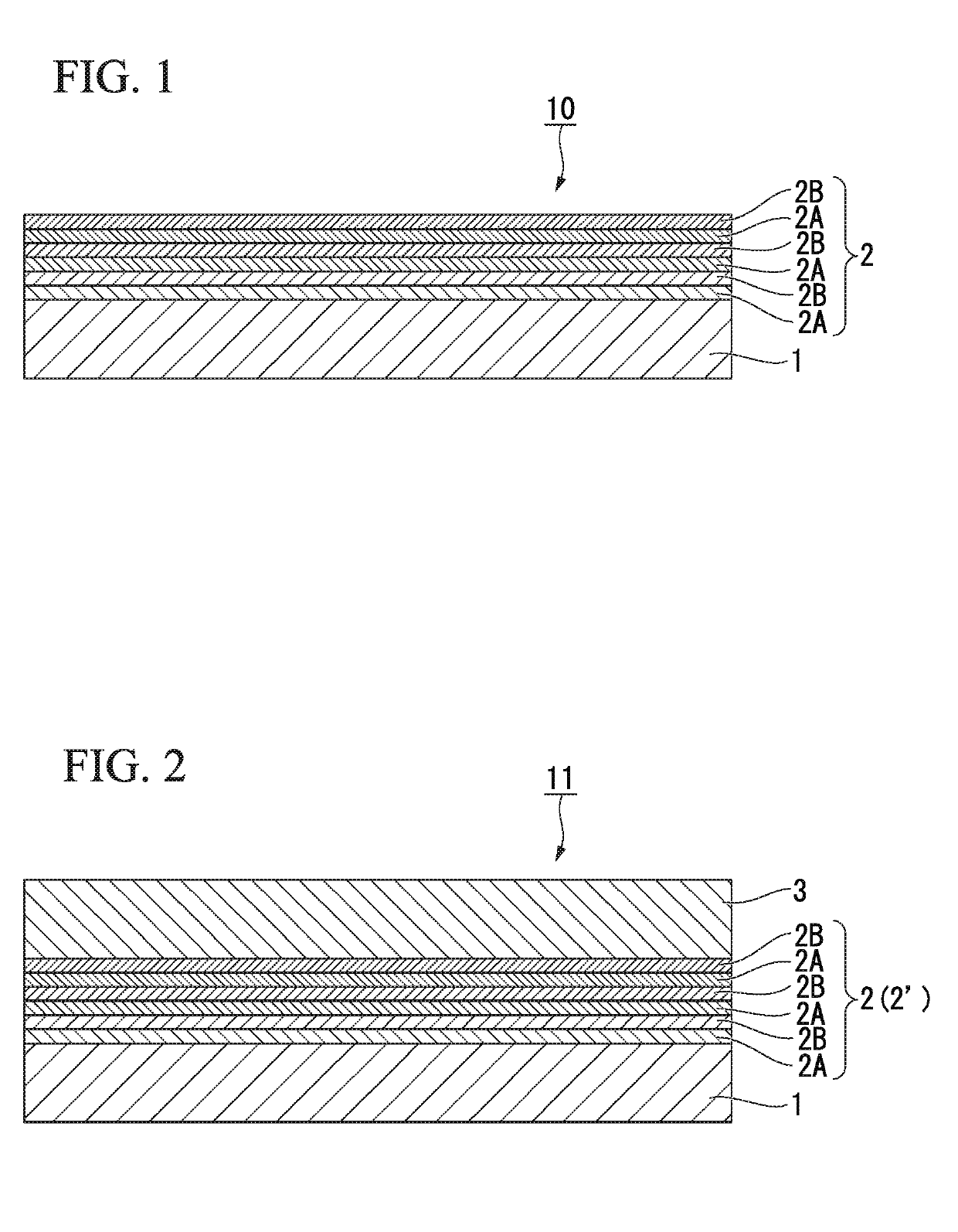
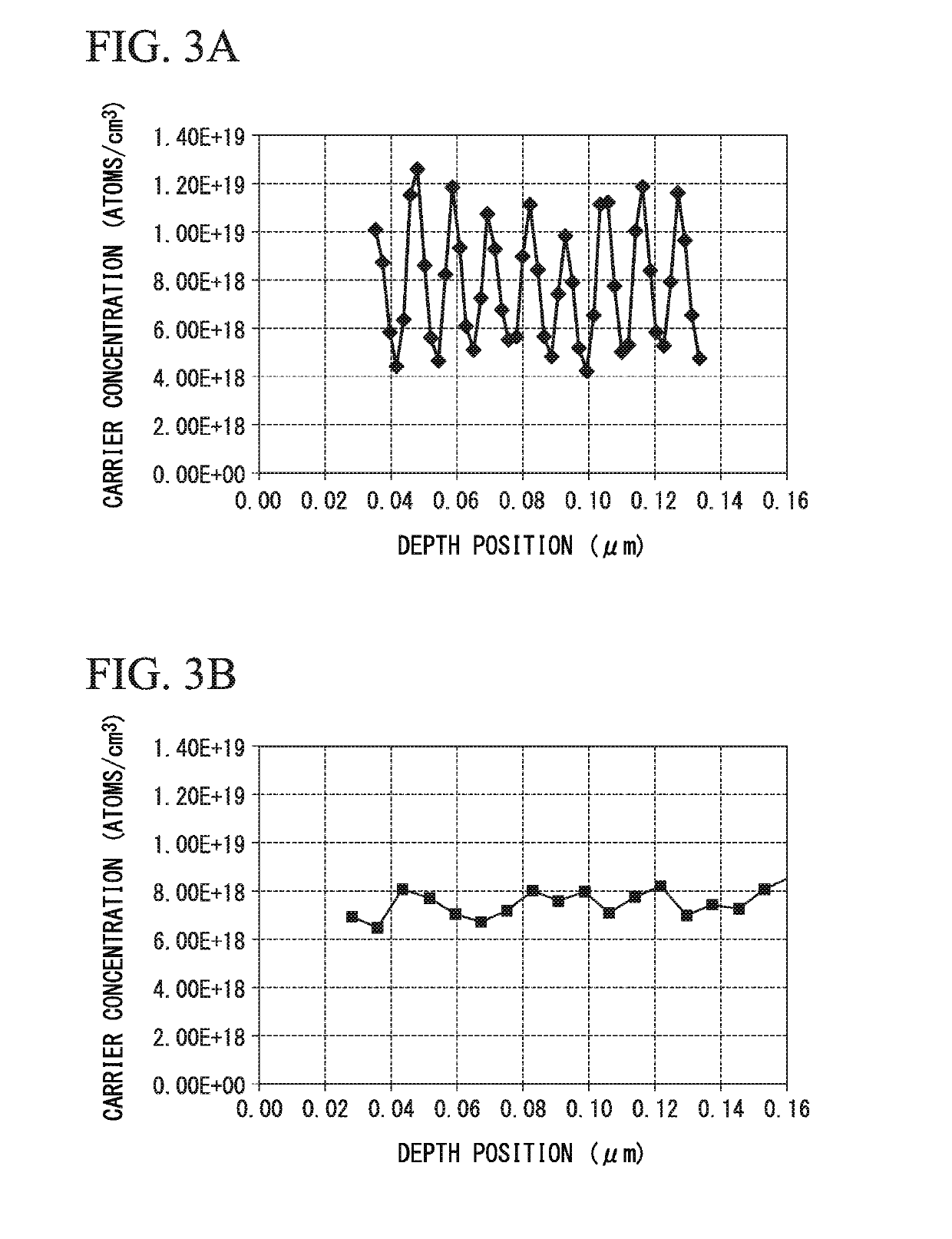
InactiveUS20190148496A1Suppress basal plane dislocationSuppressed dislocationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationCharge carrier
An SiC epitaxial wafer according to the present invention includes: an SiC single crystal substrate; and a carrier concentration variation layer disposed on one face side of the SiC single crystal substrate, wherein the carrier concentration variation layer includes: high concentration layers in which carrier concentrations thereof are higher than carrier concentrations of adjacent layers; and low concentration layers in which carrier concentrations are lower than in adjacent layers, and the high concentration layers and the low concentration layers are laminated alternately.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Vibration damping system
InactiveUS20100084797A1Avoid using forceFlexible functionsPortable framesStands/trestlesPre compressionEngineering
A vibration damping system includes a laminated body (3) formed by alternately laminating rigid hard plates (4) and viscoelastic soft plates (5), and pair of shoe plates (1, 2) at both ends in the laminating direction of the laminated body (3), to form a vibration damping body (6). The show plates (1, 2) are connected to each other by a displacement restriction member (7), so as to applying a pre-compression to the laminated body. The vibration damping body (6) is divided into a plurality of segments (3A, 3B, 3C) in the laminating direction, for allowing the vibration-proof main body (6) to be separated and displaced at the parting faces (8), without causing an excessive tensile force in the vibration damping system, even if the displacement restriction member (7) has worn to degrade the pre-compression function and a tensile force is applied due to a prying deformation. Thus, the soft members (5) of the laminated body (3) are effectively protected from isostatic fracture, to provide a significantly improved durability of the vibration damping system.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7244643B2Improve mobilityIncrease currentTransistorSolid-state devicesDrain currentField-effect transistor
The object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device comprising an n-type channel field effect transistor and a p-type channel field effect transistor, which has a high degree of reliability and excellent drain current characteristics. The gist of the invention for attaining the object resides in disposing a silicon nitride film to the side wall of a trench for an active region in which the n-type channel field effect transistor is formed and disposing the silicon nitride film only in the direction perpendicular to the channel direction to the sidewall of the trench for the active region of the p-type channel field effect transistor. According to the present invention, a semiconductor device comprising an n-type channel field effect transistor and a p-type channel field effect transistor of excellent current characteristics can be provided.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method
InactiveCN1592969ASuppressed dislocationImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDrain currentSemiconductor
The object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device comprising an n-type channel field effect transistor and a p-type channel field effect transistor, which has a high degree of reliability and excellent drain current characteristics. The gist of the invention for attaining the object resides in disposing a silicon nitride film to the side wall of a trench for an active region in which the n-type channel field effect transistor is formed and disposing the silicon nitride film only in the direction perpendicular to the channel direction to the sidewall of the trench for the active region of the p-type channel field effect transistor. According to the present invention, a semiconductor device comprising an n-type channel field effect transistor and a p-type channel field effect transistor of excellent current characteristics can be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
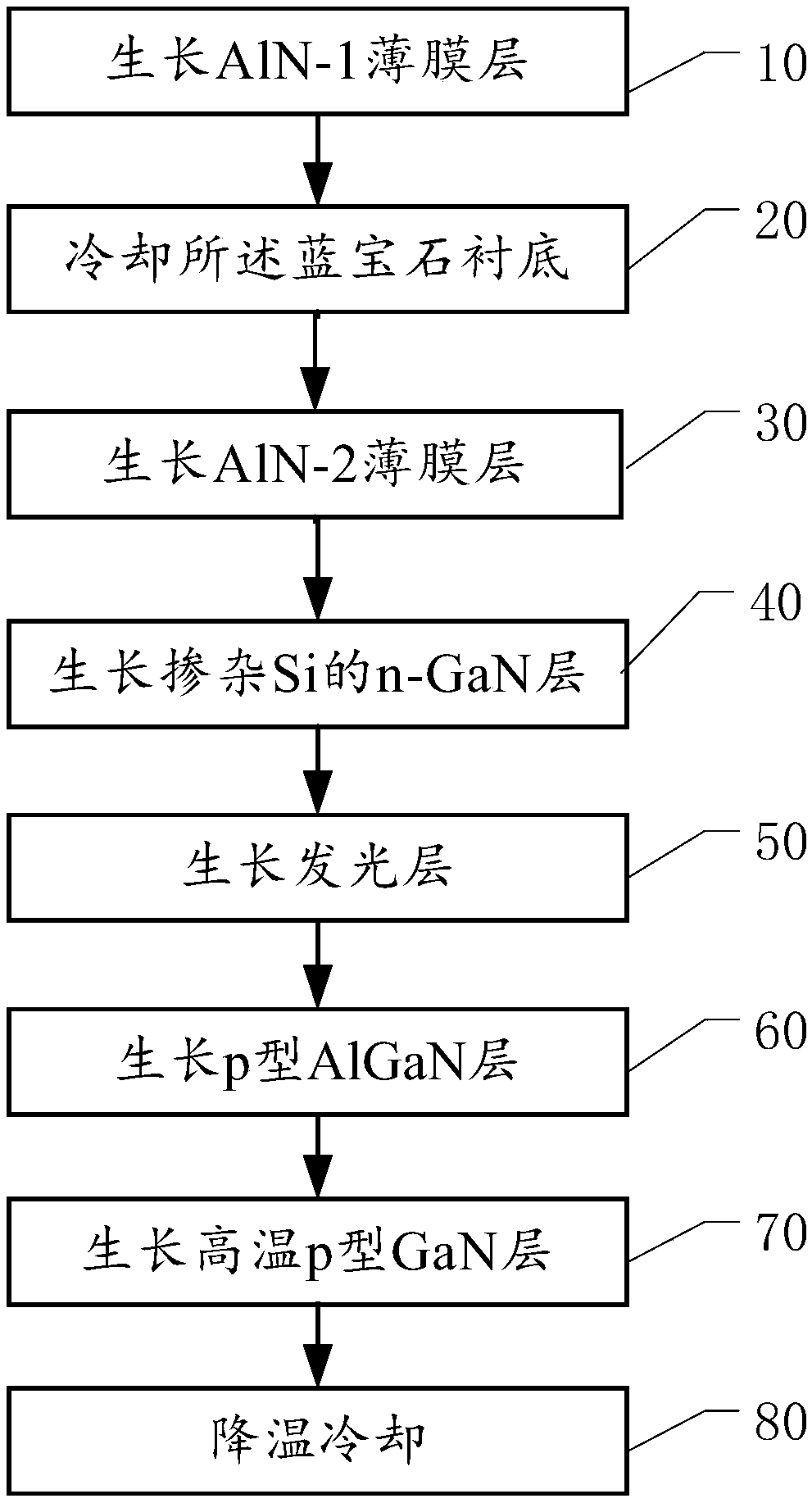
AlN buffer layer of LED and epitaxial growth method of buffer layer
The invention discloses an AlN buffer layer of an LED and an epitaxial growth method of the buffer layer. The method comprises the steps of performing growing of an AlN-1 thin film layer, cooling a sapphire substrate, and performing growing of an AlN-2 thin film layer, a Si-doped n-GaN layer, a light-emitting layer, a p-type AlGaN layer and a high-temperature p type GaN layer, and carrying out cooling, wherein the step of performing growing of the AlN-1 thin film layer comprises the steps of putting the sapphire substrate into a magnetron sputtering reaction device to be heated to 650 DEG C, and introducing Ar, N2 and O2, wherein the sputtering bias voltage is controlled to be reduced from 3000V to 2200V, and the target-substrate distance is set to be 3-4cm, and the sputtering thickness ofthe AlN-1 thin film layer is 15-20nm; and the step of performing growing of the AlN-2 thin film layer comprises the steps of putting the sapphire substrate with the AlN-1 thin film layer in an MOCVDreaction cavity, wherein the temperature is controlled to be gradually increased to 950 DEG C from 850 DEG C, the pressure of the reaction chamber is kept to be 250 mbar, and H2, NH3 and a TMAl sourceare pumped, and the AlN-2 thin film layer with the growth thickness of 15-20 nm is grown Compared with the prior art, the brightness of the LED is higher.
Owner:XIANGNENG HUALEI OPTOELECTRONICS
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7518204B2Improve adhesionInhibit deteriorationLaser detailsSolid-state devicesNitrogenActive layer
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate formed of at least two kinds of group III elements and nitrogen, an active layer formed on the semiconductor substrate, and a nitride semiconductor layer formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate and formed between the semiconductor substrate and the active layer. The nitride semiconductor layer is formed of the same constituent elements of the semiconductor substrate. A composition ratio of the lightest element among the group III elements of the nitride semiconductor layer is higher than a composition ratio of the corresponding element of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
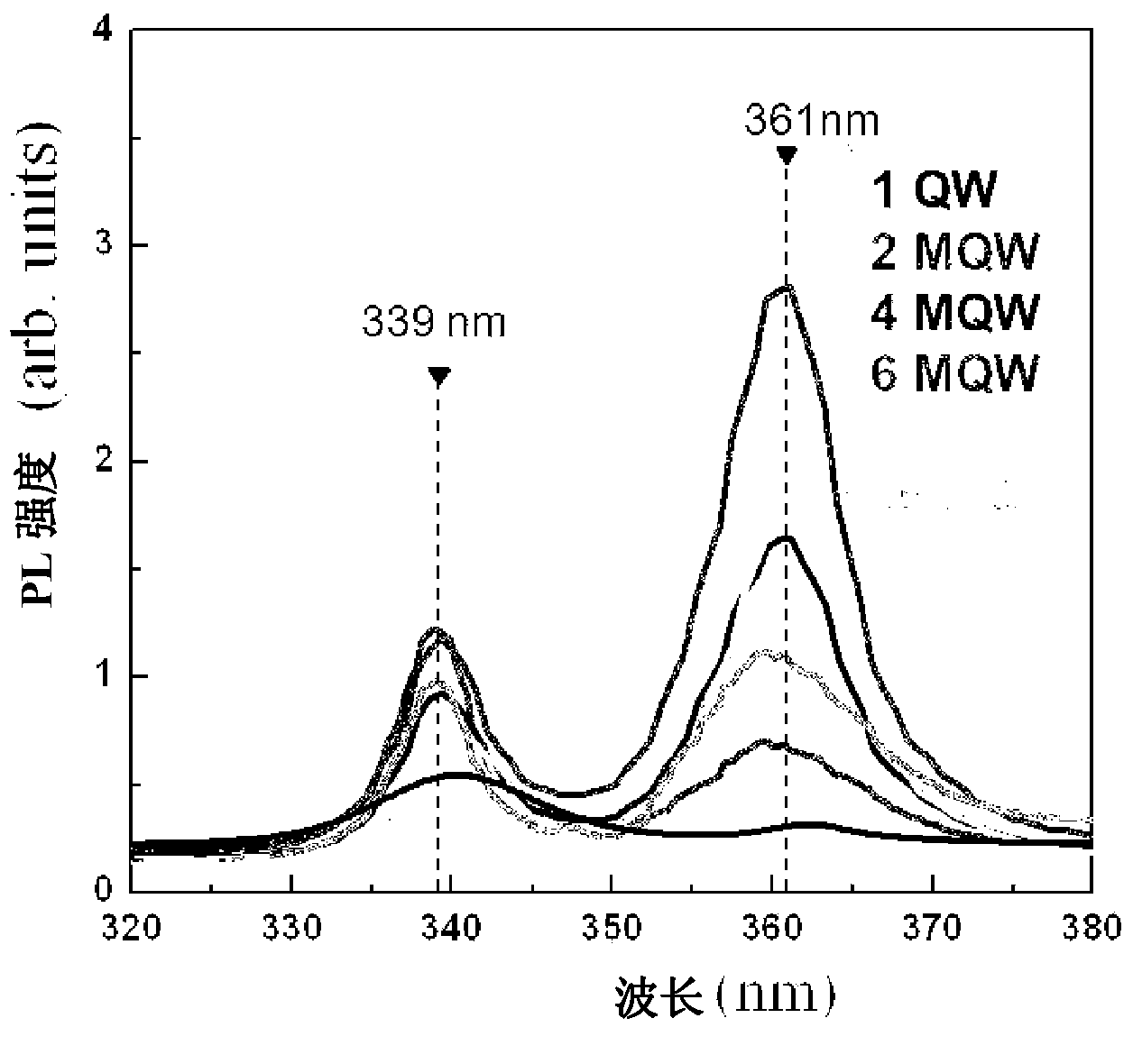
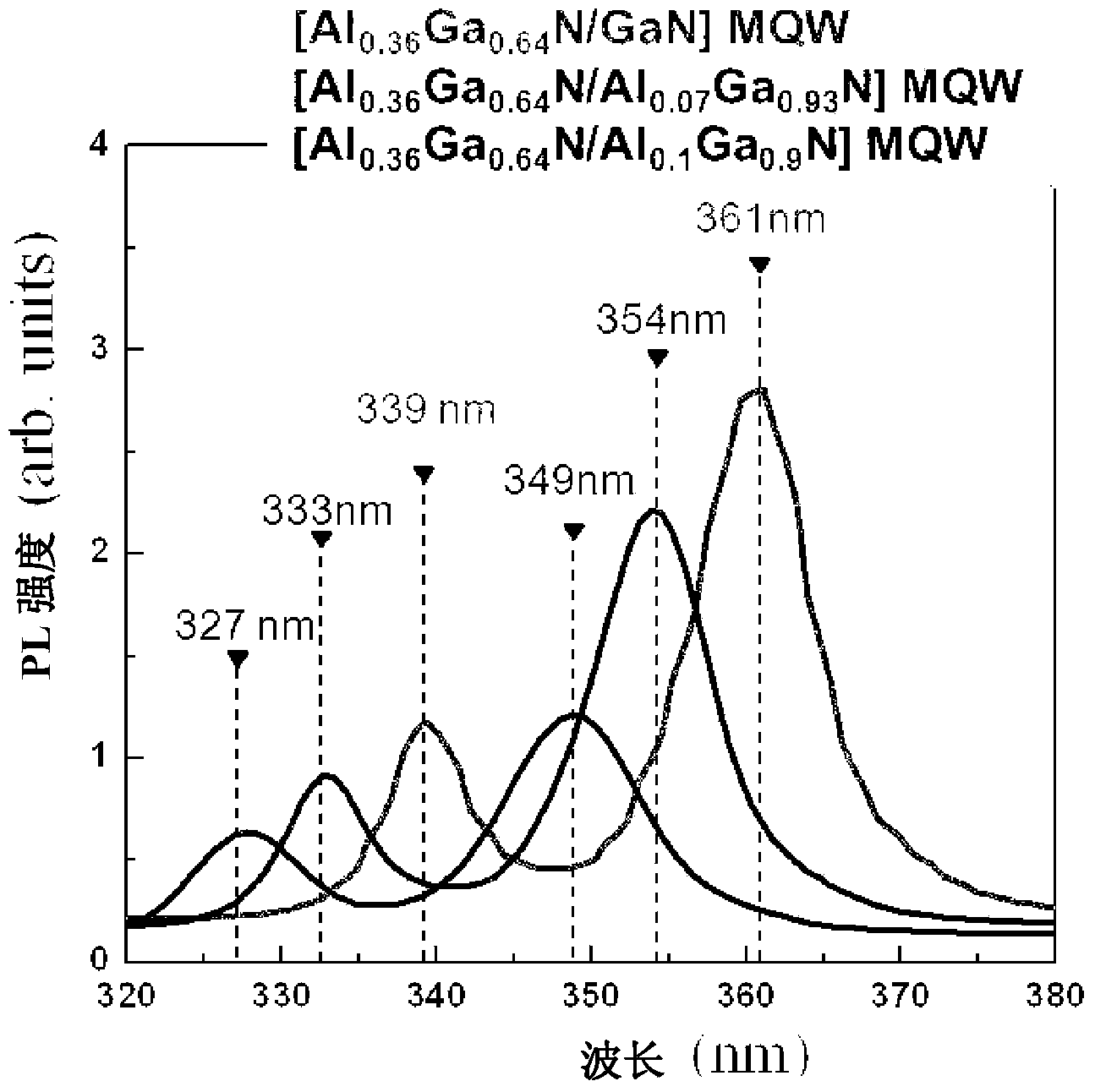
Multiple quantum well for ultraviolet light emitting diode and a production method therefor
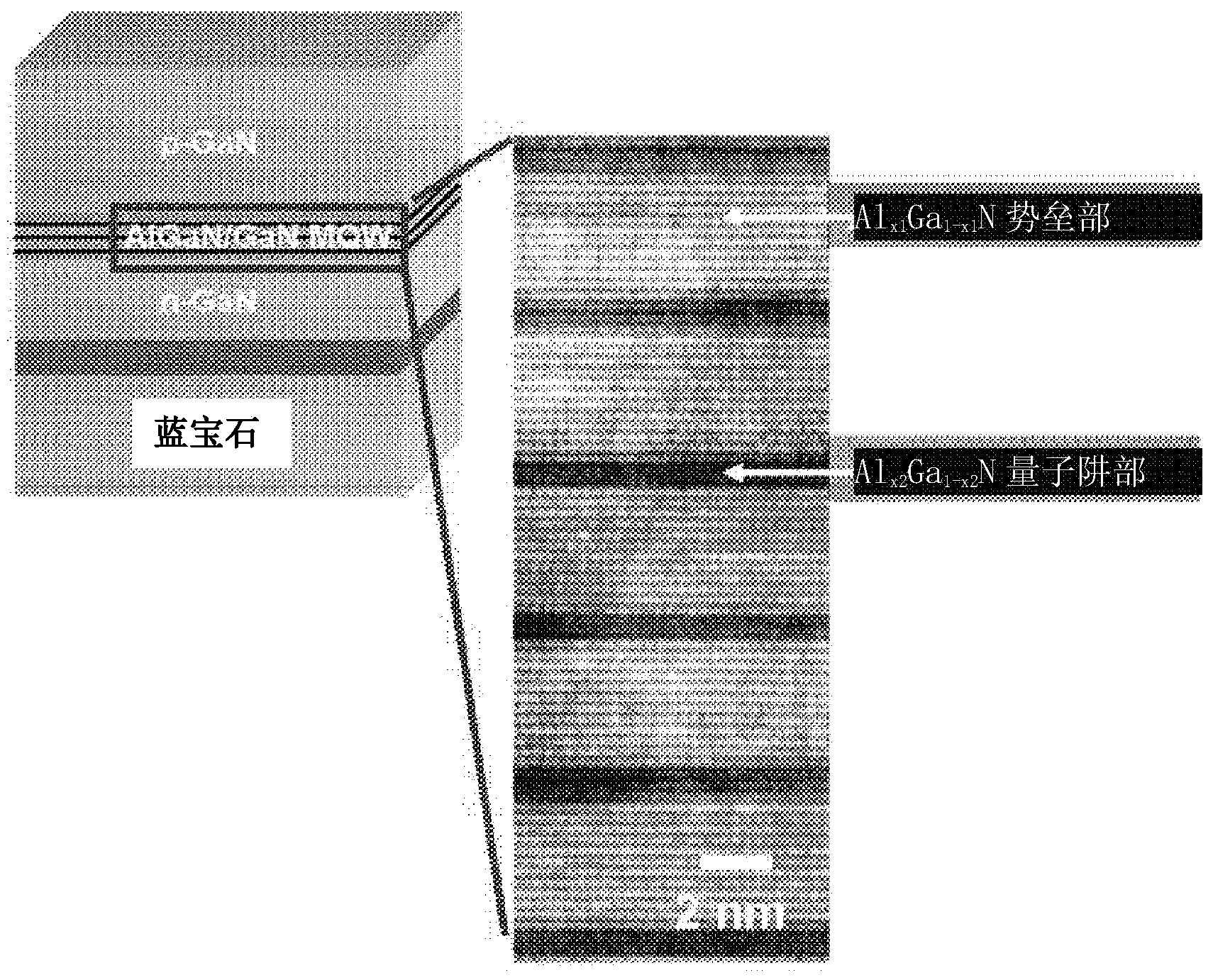
PendingCN103703576ASuppressed dislocationEasy to manufactureSemiconductor devicesUltraviolet light emitting diodesMultiple quantum
Provided is a multiple quantum well for an ultraviolet light emitting diode, comprising: an Alx1Ga1-x1N barrier unit in which are alternately disposed an AlN barrier atomic layer and a GaN barrier atomic layer on the AlN barrier atomic layer; and an Alx2Ga1-x2N quantum well unit in which are alternately disposed an AlN well atomic layer formed on the Alx1Ga1-x1N barrier unit and a GaN well atomic layer formed on the AlN well atomic layer. The Al compositional ratio (x1) in the Alx1Ga1-x1N barrier unit is between 0 and 0.7; the Al compositional ratio (x2) in the Alx2Ga1-x2N quantum well unit is between 0 and 0.7; the Al compositional ratio (x1) in the Alx1Ga1-x1N barrier unit is larger than the Al compositional ratio (x2) in the Alx2Ga1-x2N quantum well unit; and the Alx1Ga1-x1N barrier unit and the Alx2Ga1-x2N quantum well unit are alternately laminated at least twice.
Owner:CHIP TECH
Method and apparatus for manufacturing semiconductor substrate dedicated to semiconductor device, and method and apparatus for manufacturing semiconductor device
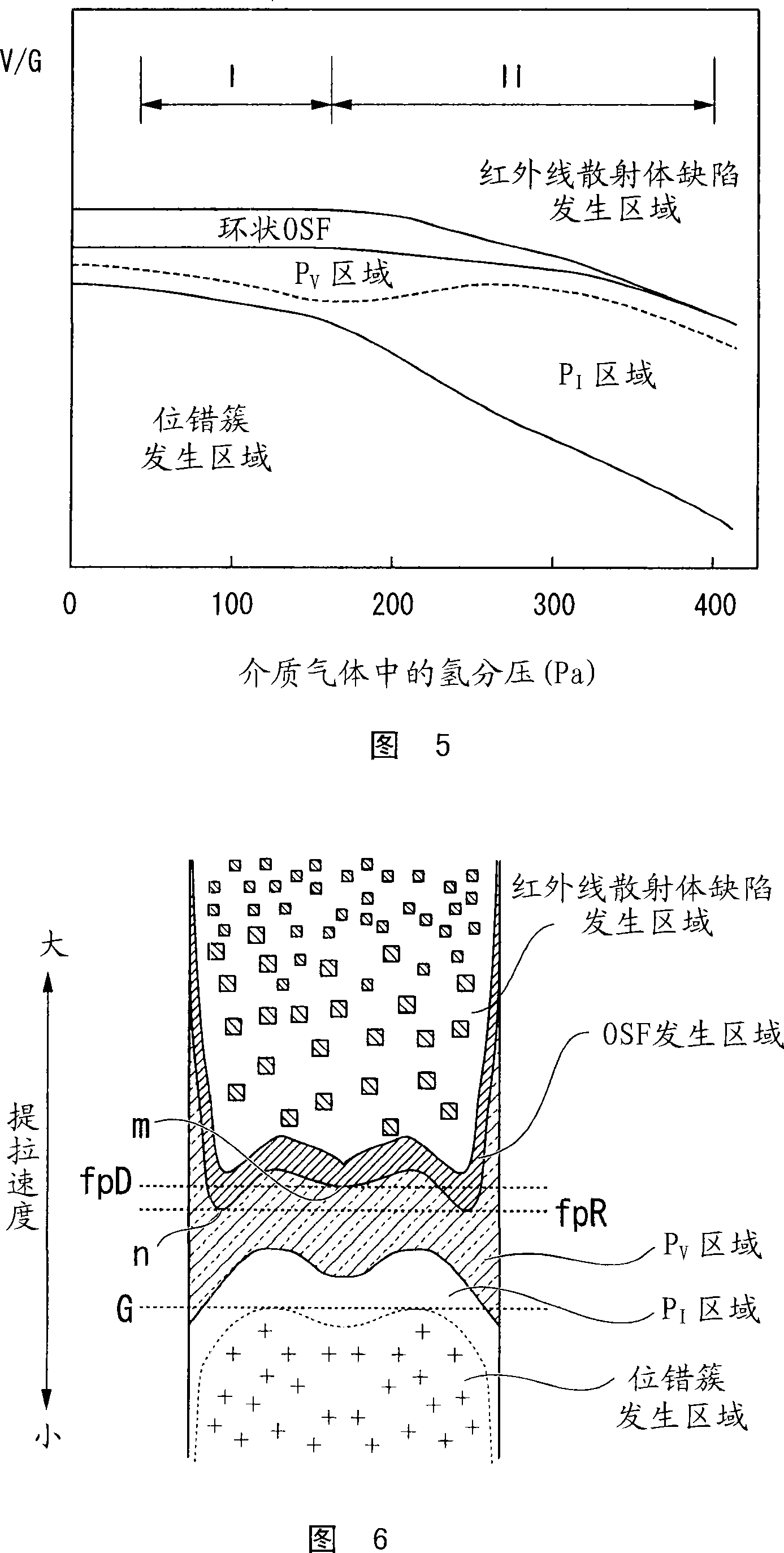
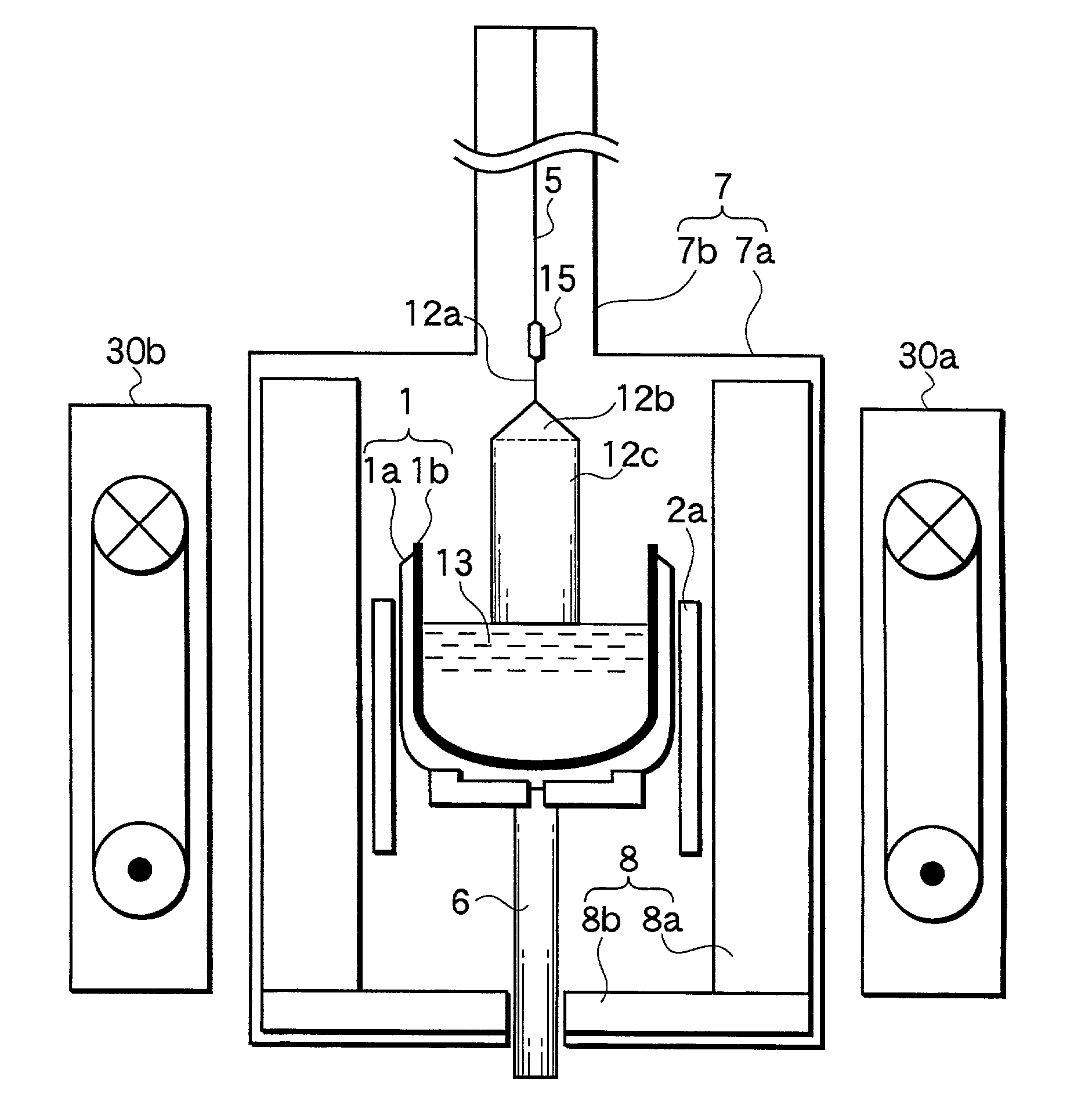
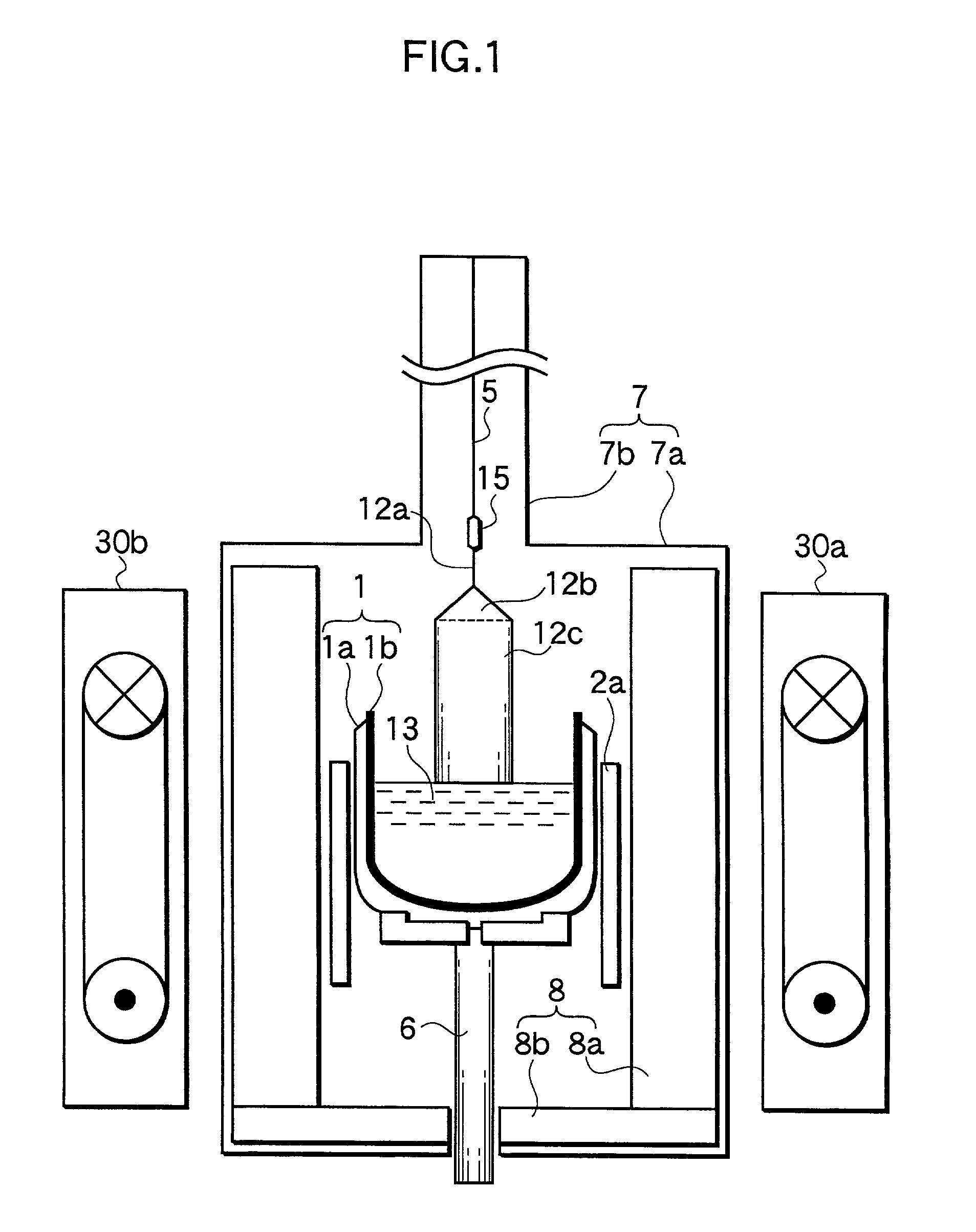
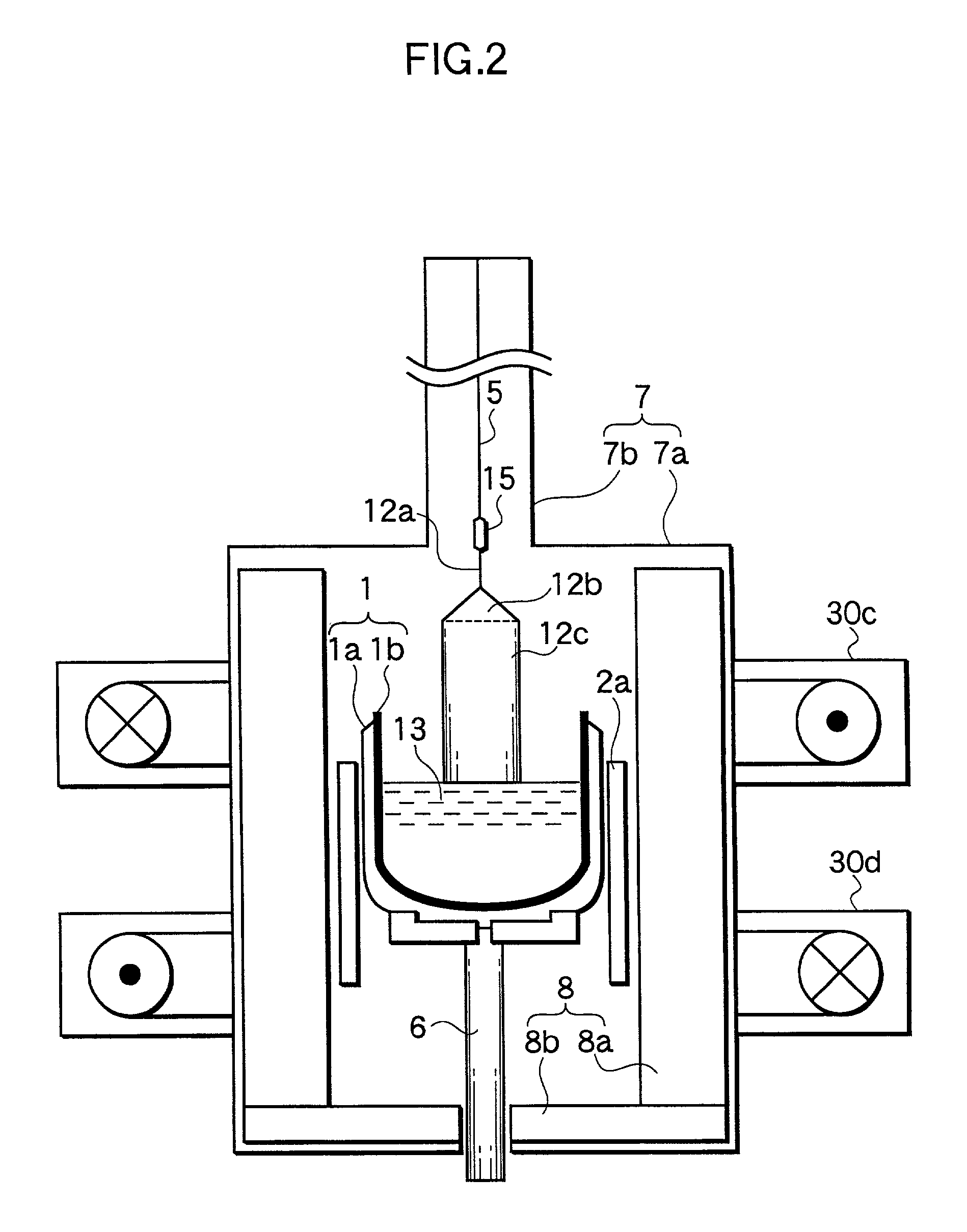
ActiveUS8357592B2Well formedSuppressed dislocationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCrystal structureEngineering
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com