Patents
Literature
91 results about "64-bit computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits (8 octets) wide. Also, 64-bit CPU and ALU architectures are those that are based on registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. 64-bit microcomputers are computers in which 64-bit microprocessors are the norm. From the software perspective, 64-bit computing means the use of code with 64-bit virtual memory addresses. However, not all 64-bit instruction sets support full 64-bit virtual memory addresses; x86-64 and ARMv8, for example, support only 48 bits of virtual address, with the remaining 16 bits of the virtual address required to be all 0's or all 1's, and several 64-bit instruction sets support fewer than 64 bits of physical memory address.
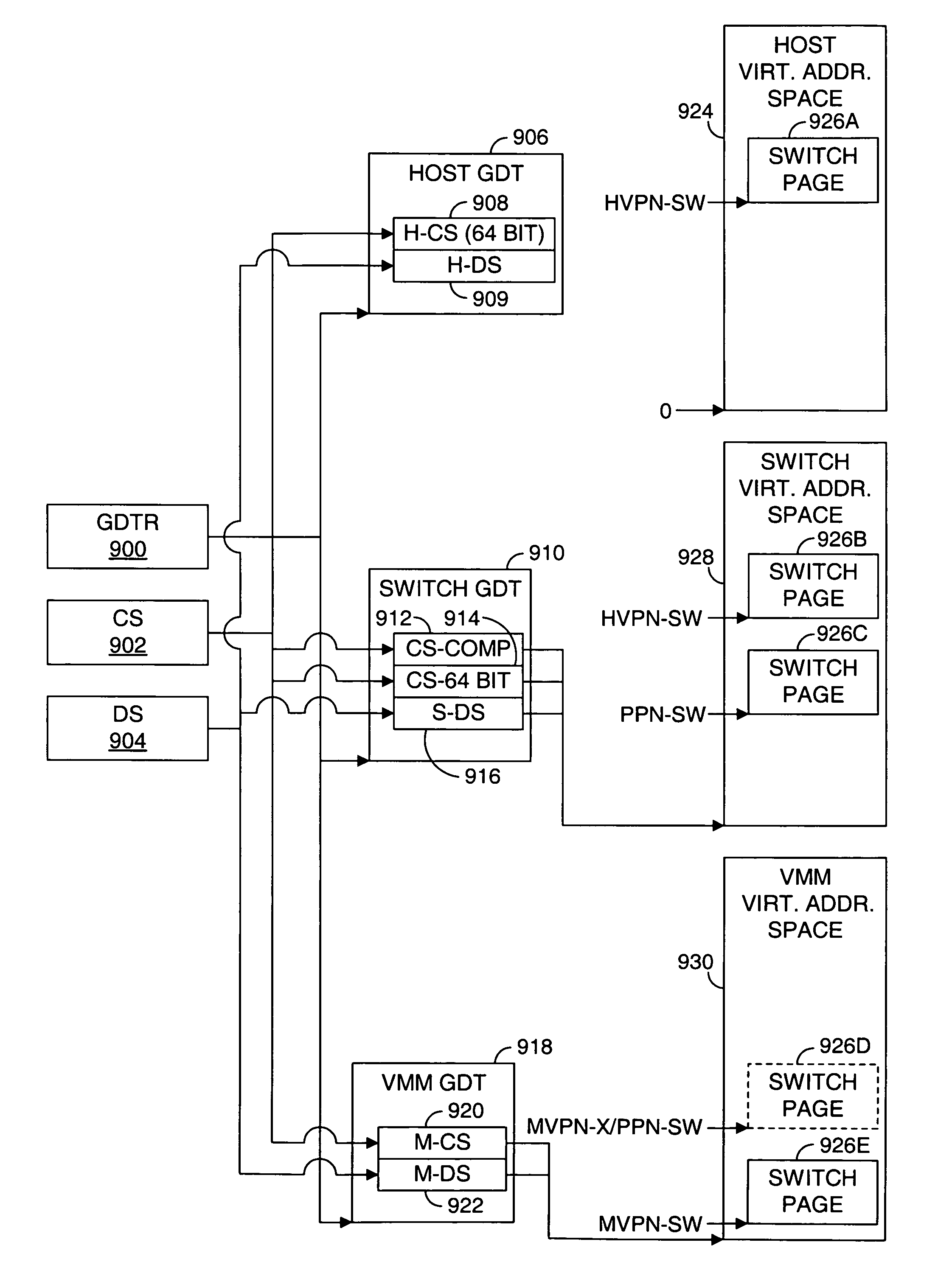
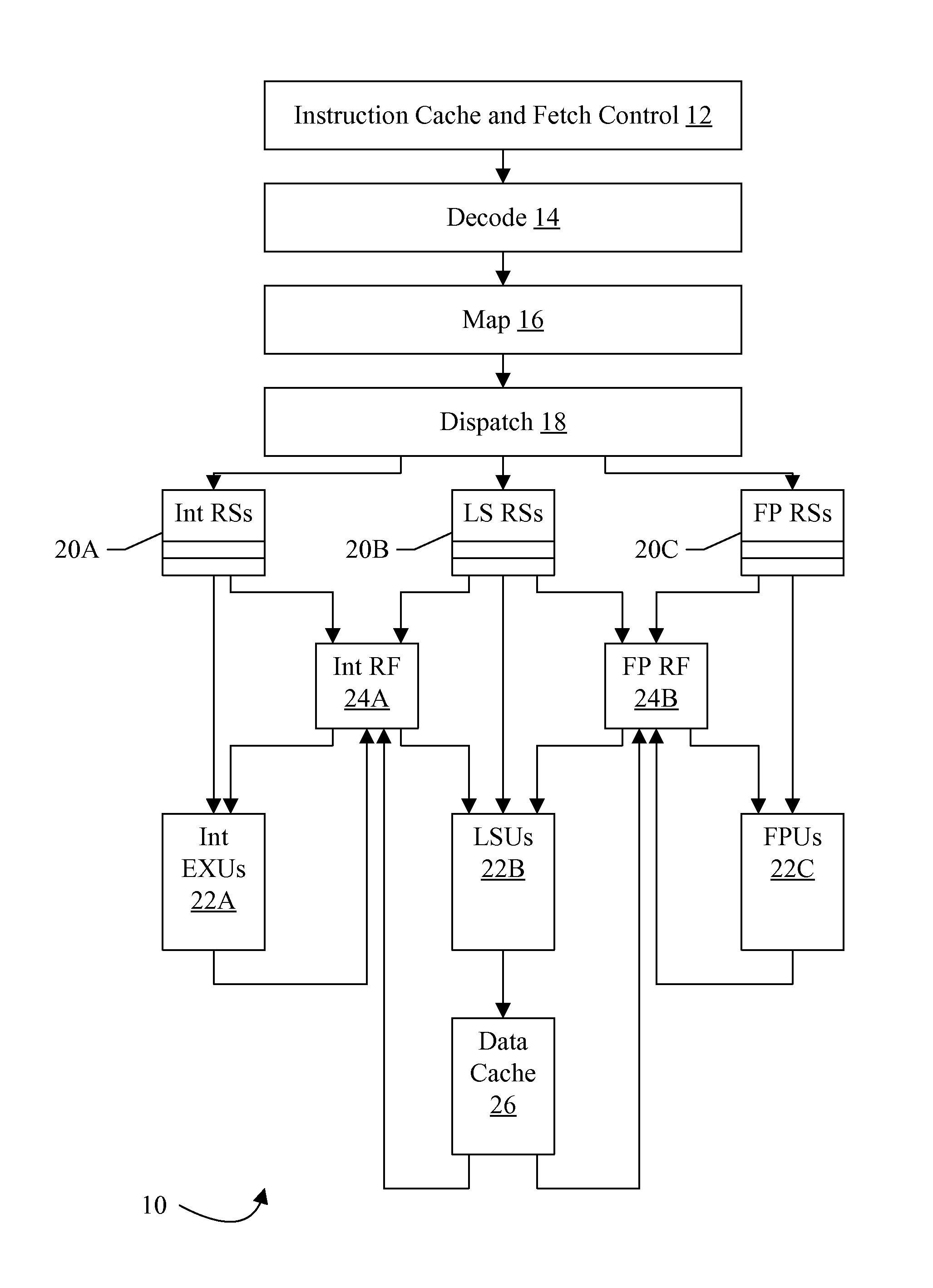
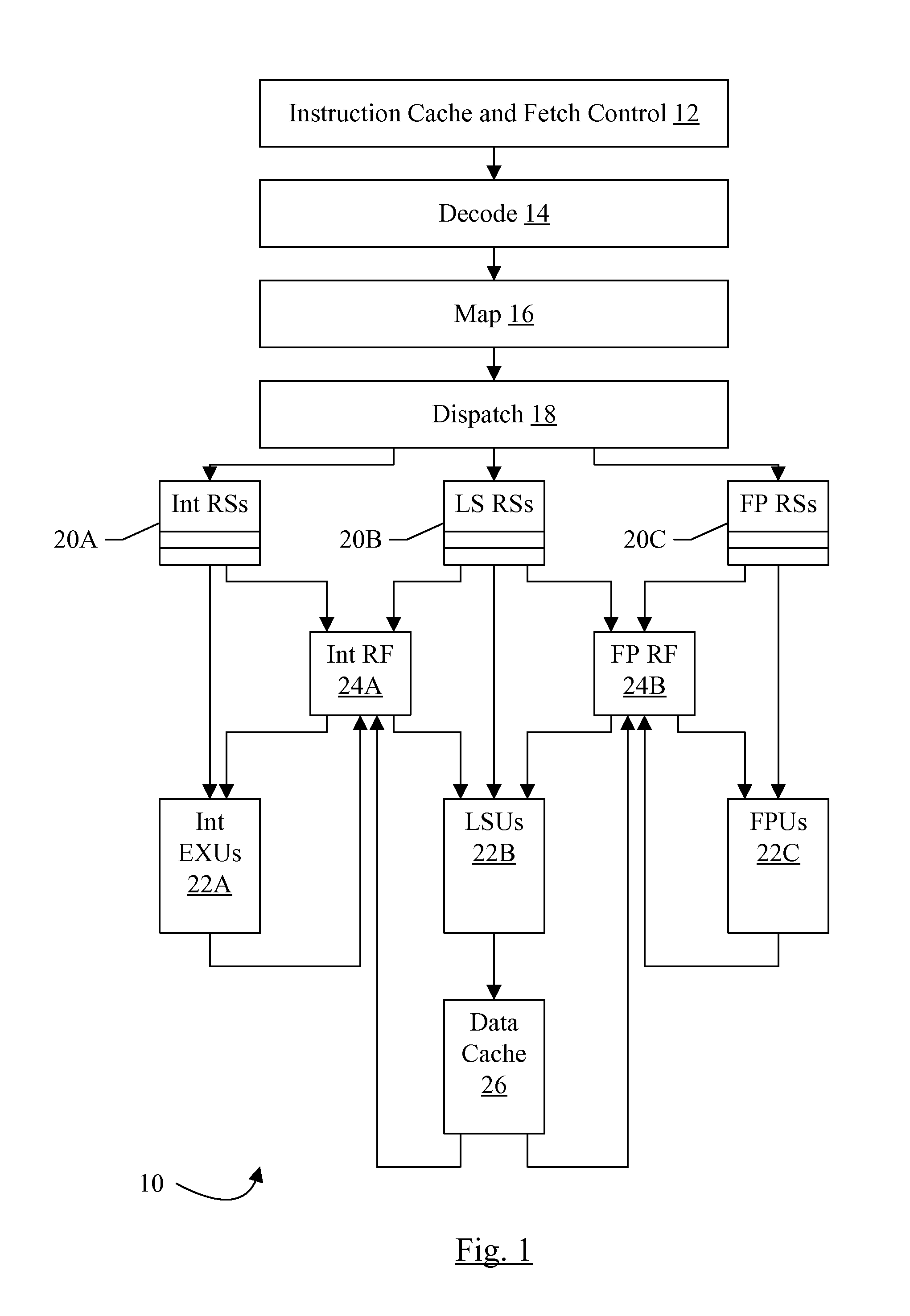
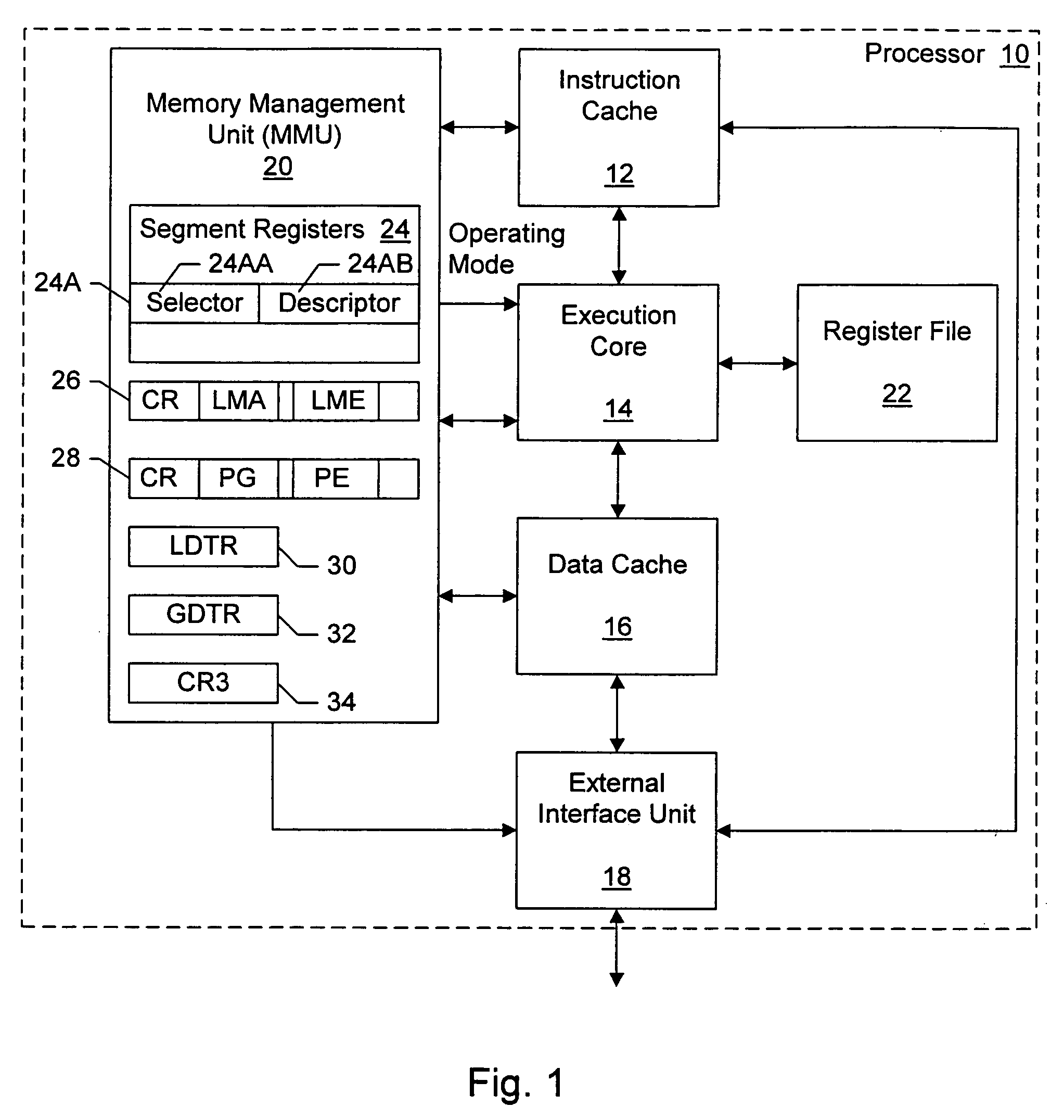
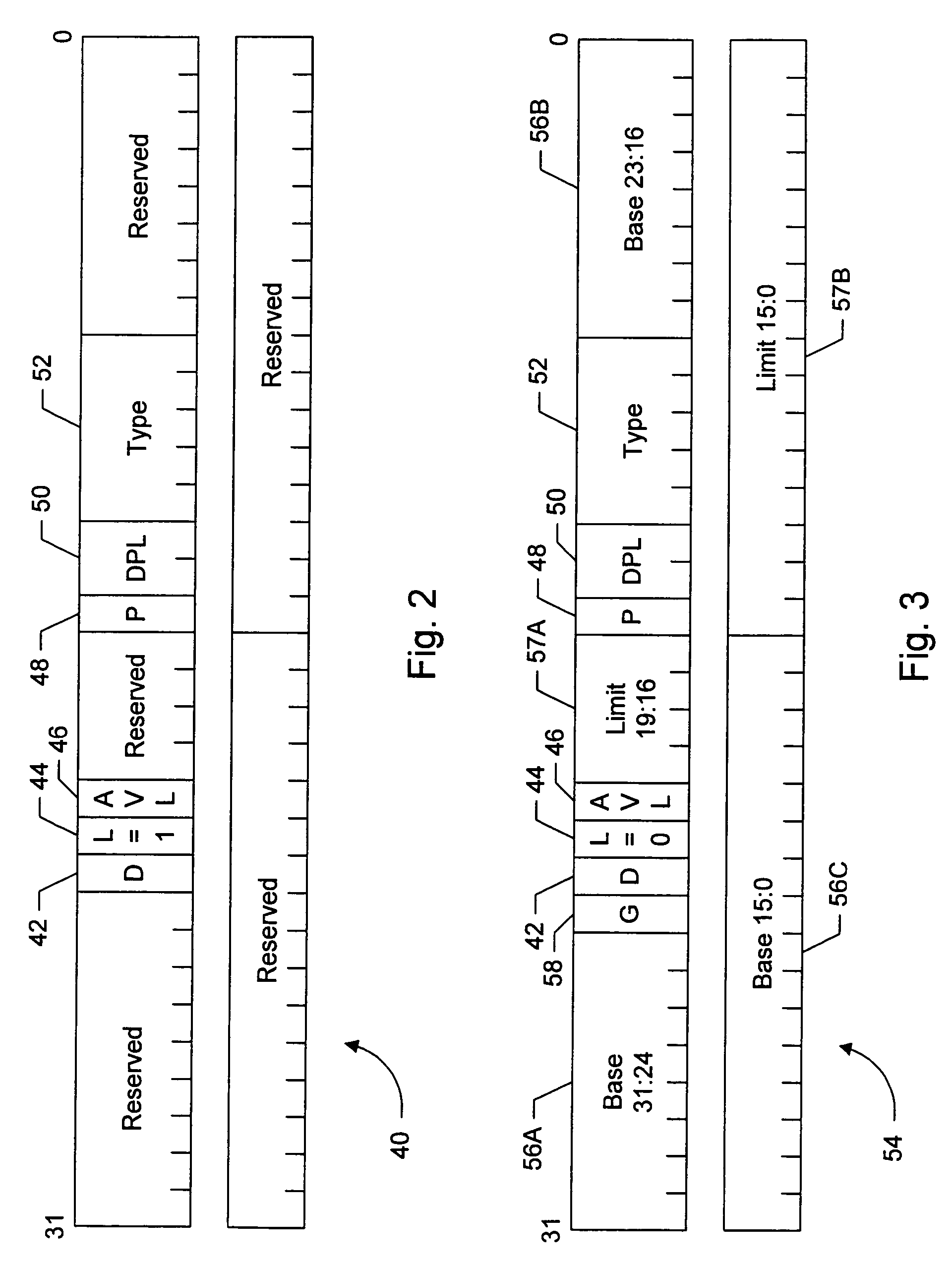
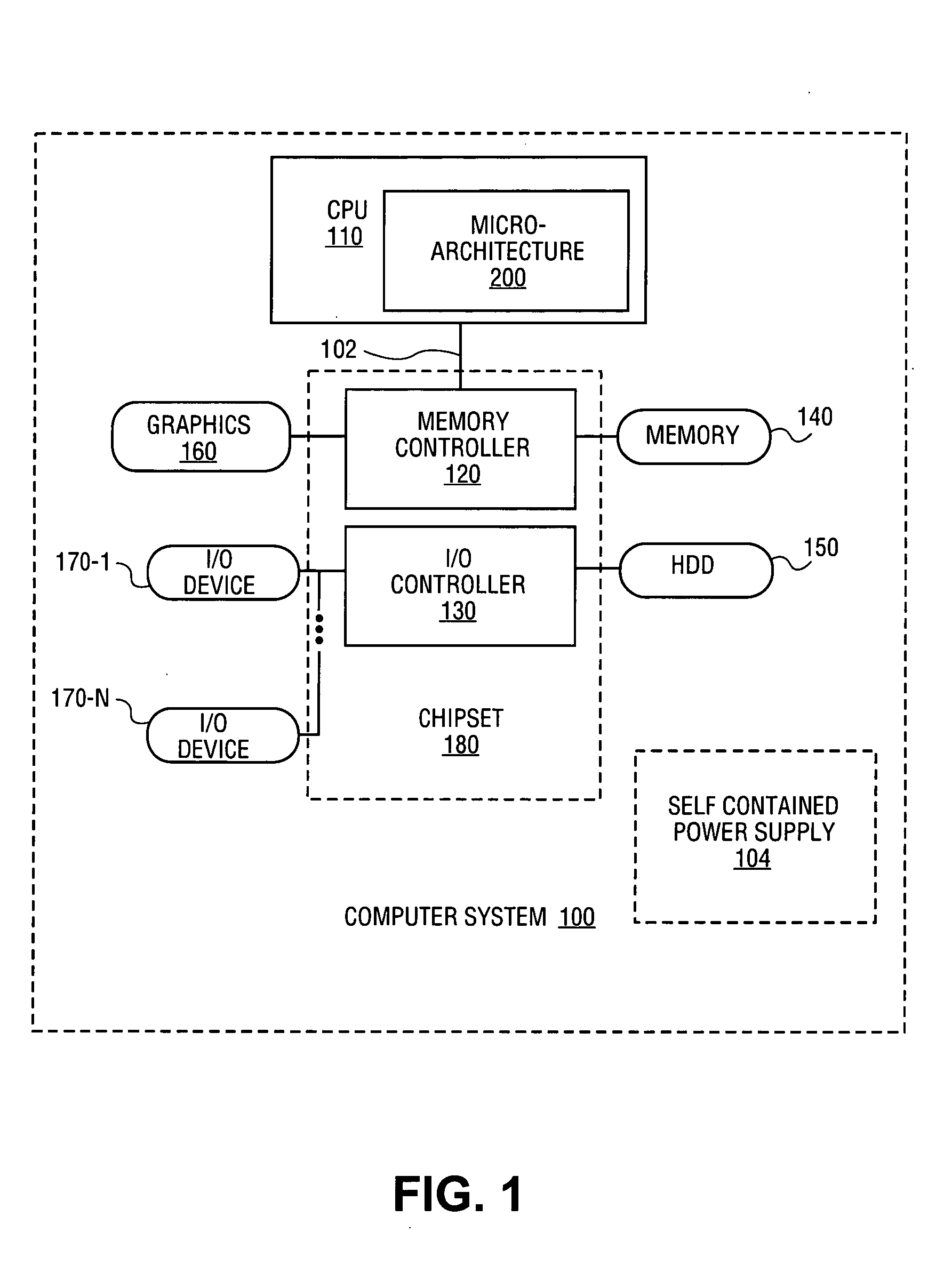
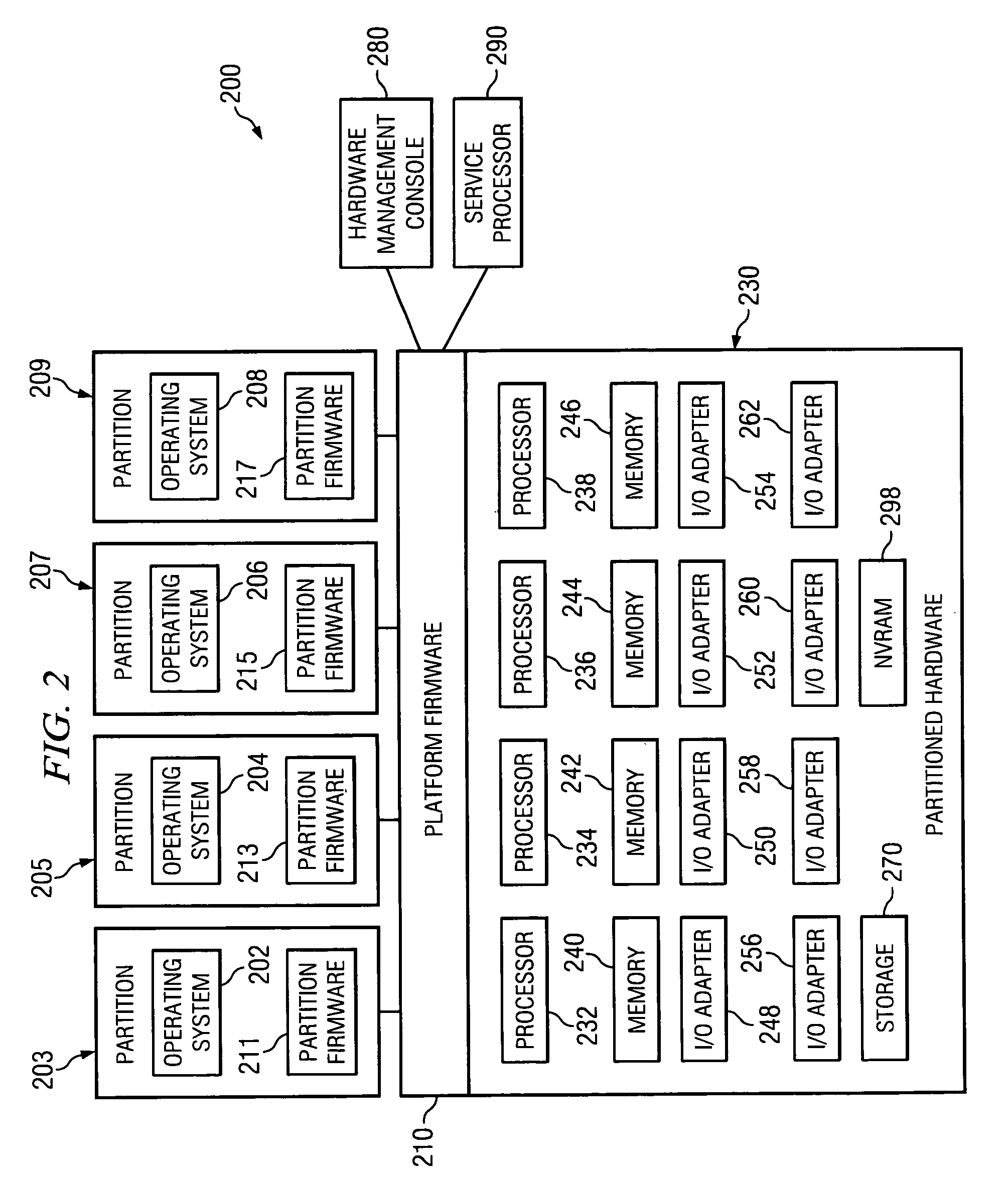
Switching between multiple software entities using different operating modes of a processor in a computer system
ActiveUS7478388B1Restoring contextSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsLong modeOperational system
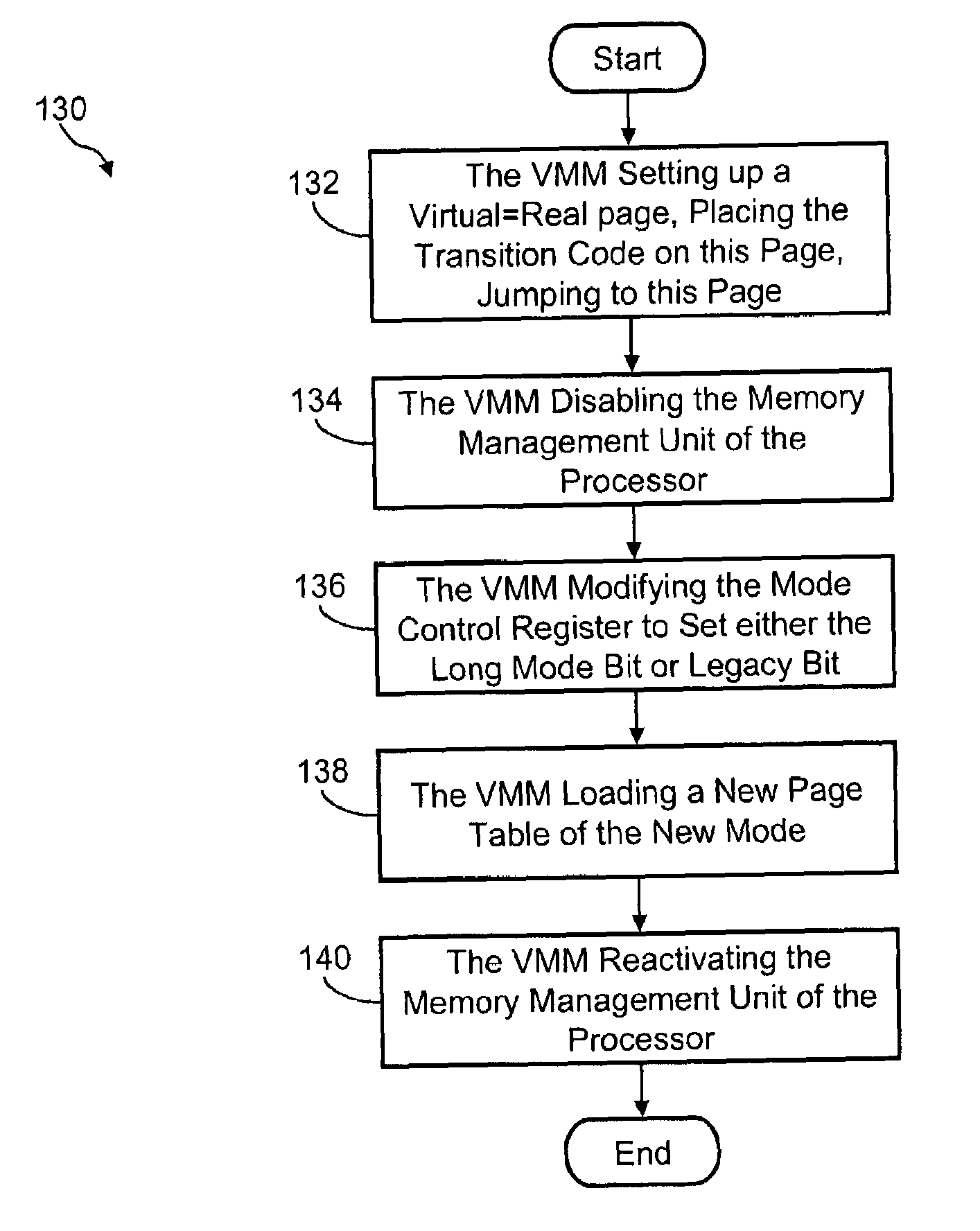
A processor has multiple operating modes, such as the long / compatibility mode, the long / 64-bit mode and the legacy modes of the x86-64 microprocessor. Different software entities execute in different ones of these operating modes. A switching routine is implemented to switch from one operating mode to another and to transfer control from one software entity to another. The software entities may be, for example, a host operating system and a virtual machine monitor. Thus, for example, a virtual computer system may comprise a 64-bit host operating system and a 32-bit virtual machine monitor, executing on an x86-64 microprocessor in long mode and legacy mode, respectively, with the virtual machine monitor supporting an x86 virtual machine. The switching routine may be implemented partially or completely in an identity-mapped memory page. Execution of the switching routine may be initiated by a driver that is installed in the host operating system of a virtual computer system.
Owner:VMWARE INC
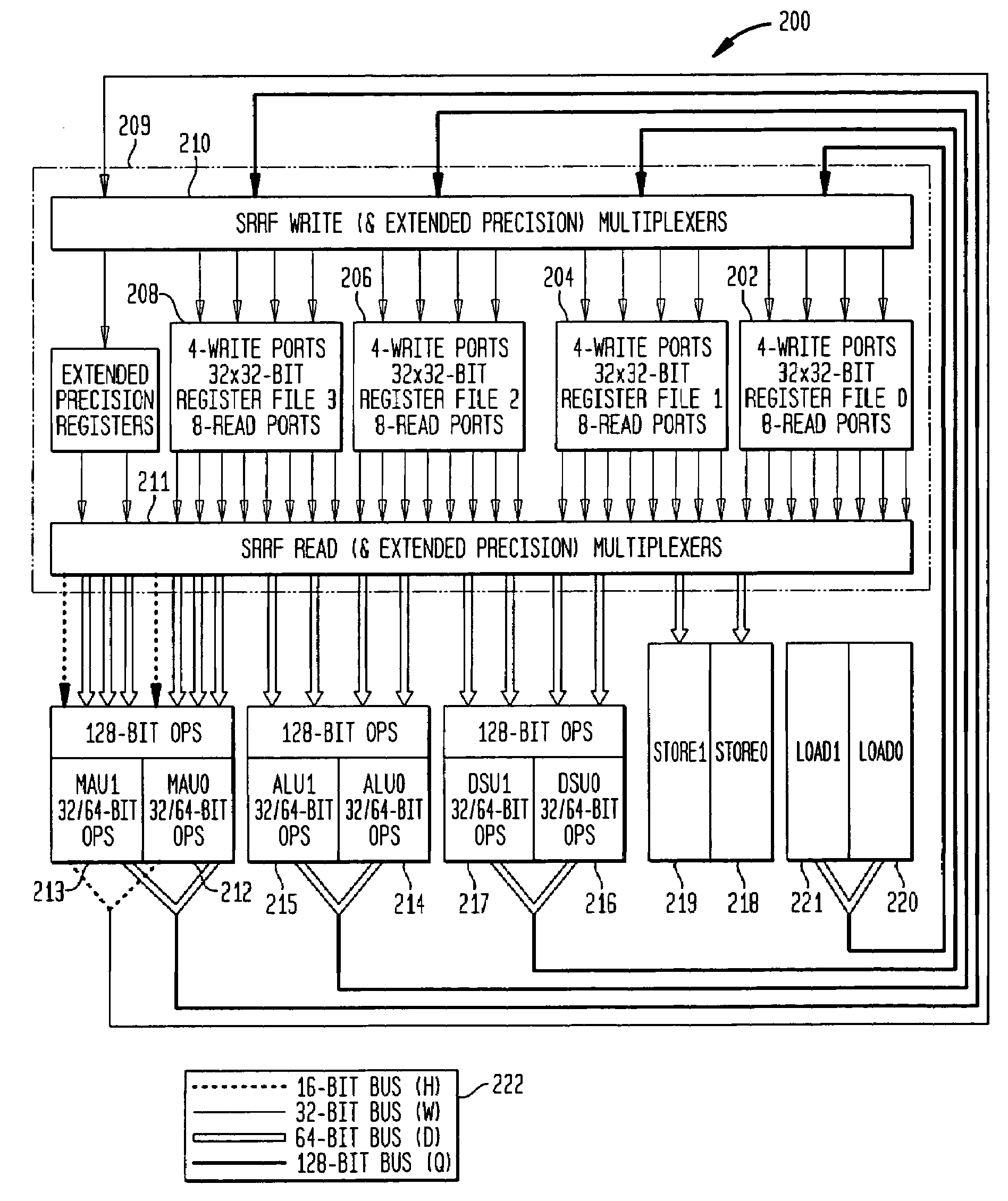
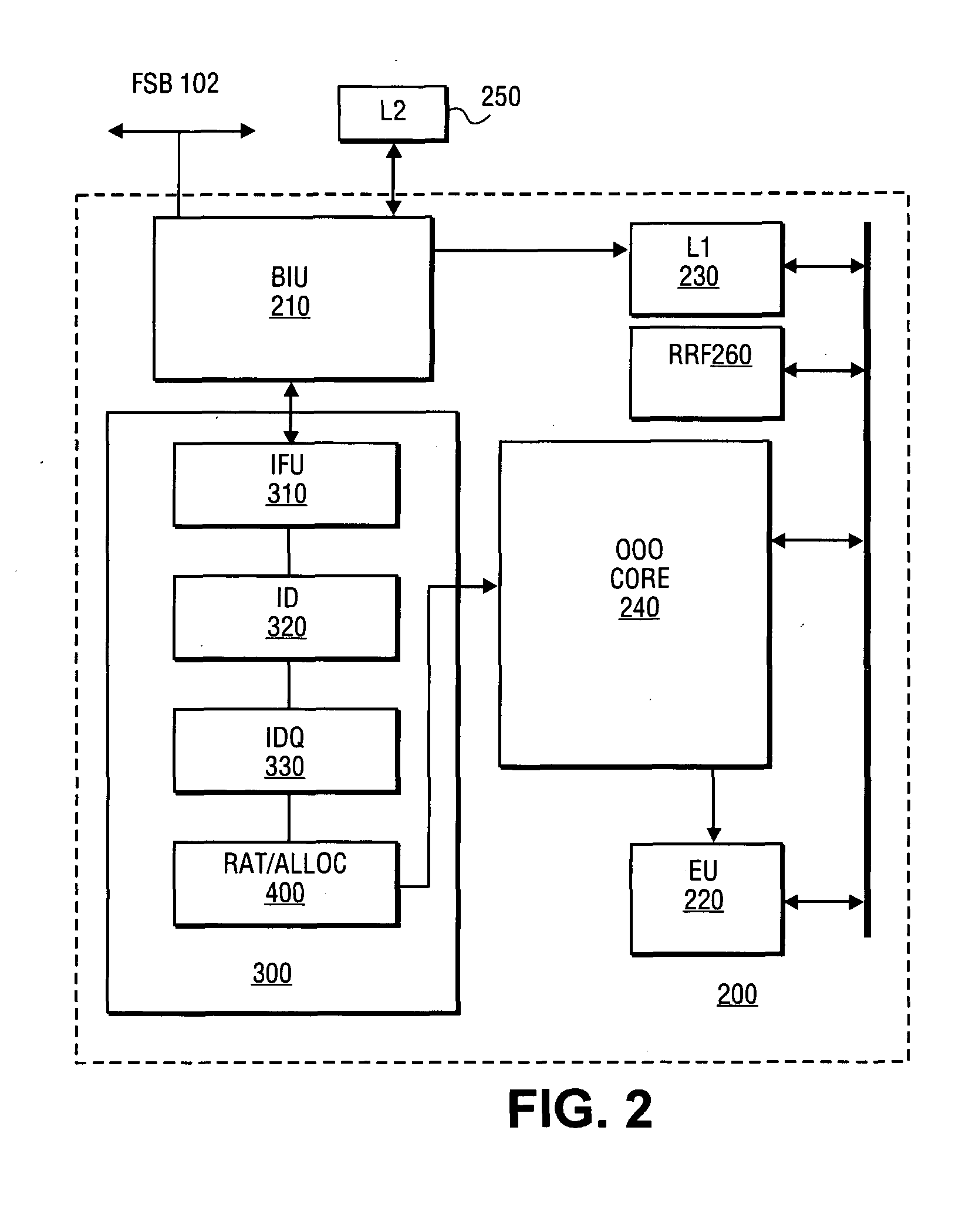
Methods and apparatus for dynamic instruction controlled reconfigurable register file
InactiveUS7398347B1Instruction analysisMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcessor registerMultiplexer
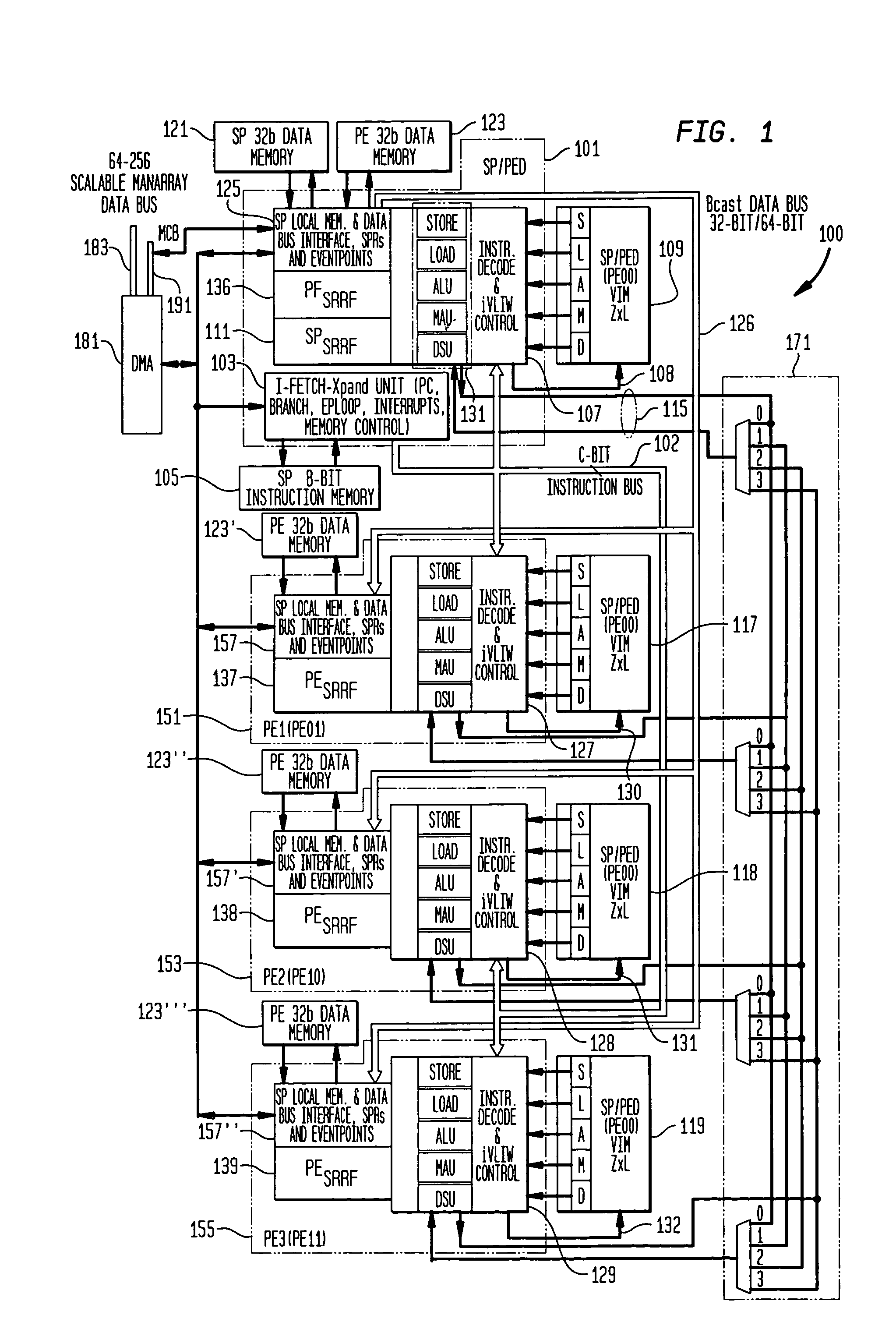
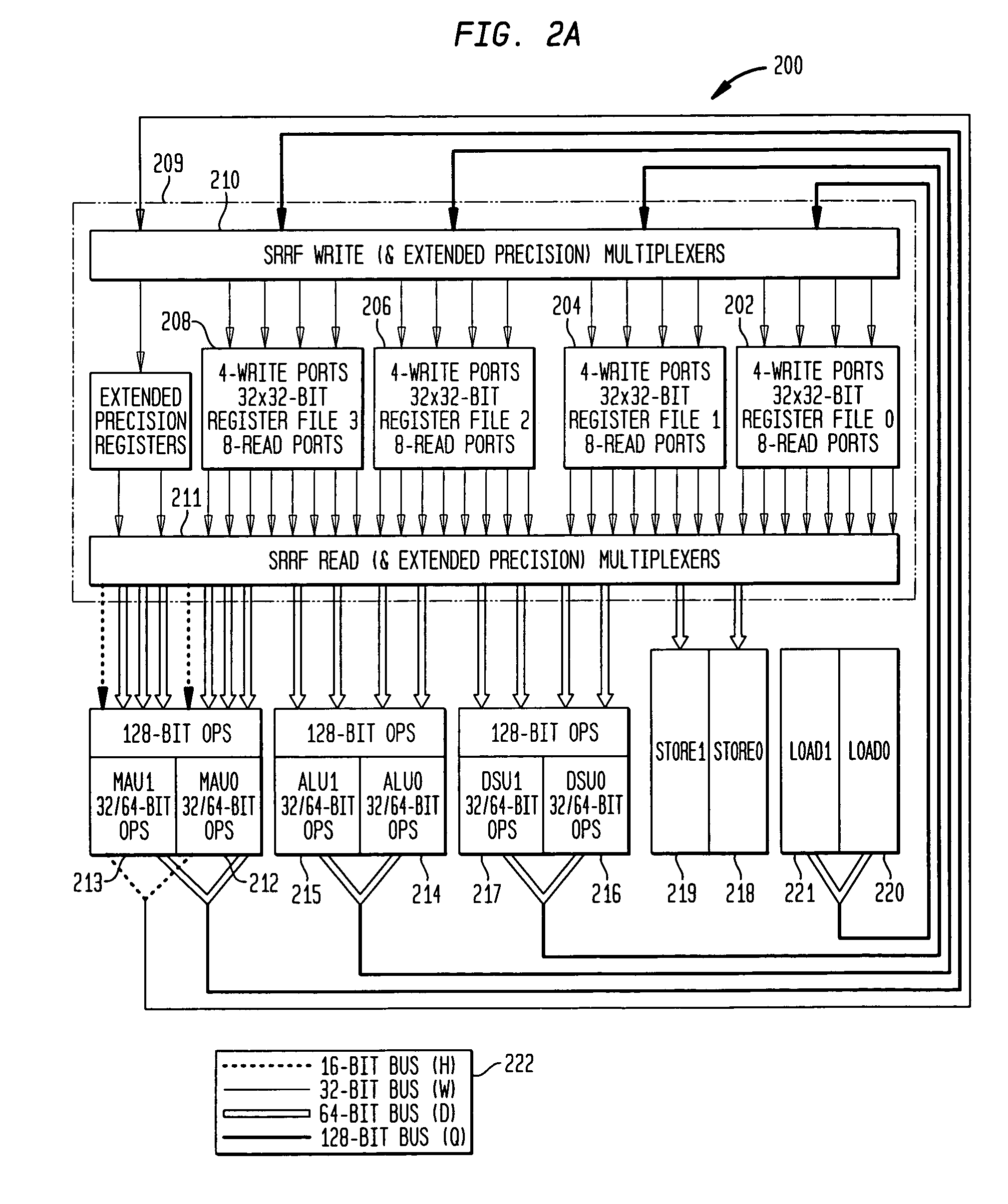
A scalable reconfigurable register file (SRRF) containing multiple register files, read and write multiplexer complexes, and a control unit operating in response to instructions is described. Multiple address configurations of the register files are supported by each instruction and different configurations are operable simultaneously during a single instruction execution. For example, with separate files of the size 32×32 supported configurations of 128×32 bit s, 64×64 bit s and 32×128 bit s can be in operation each cycle. Single width, double width, quad width operands are optimally supported without increasing the register file size and without increasing the number of register file read or write ports.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
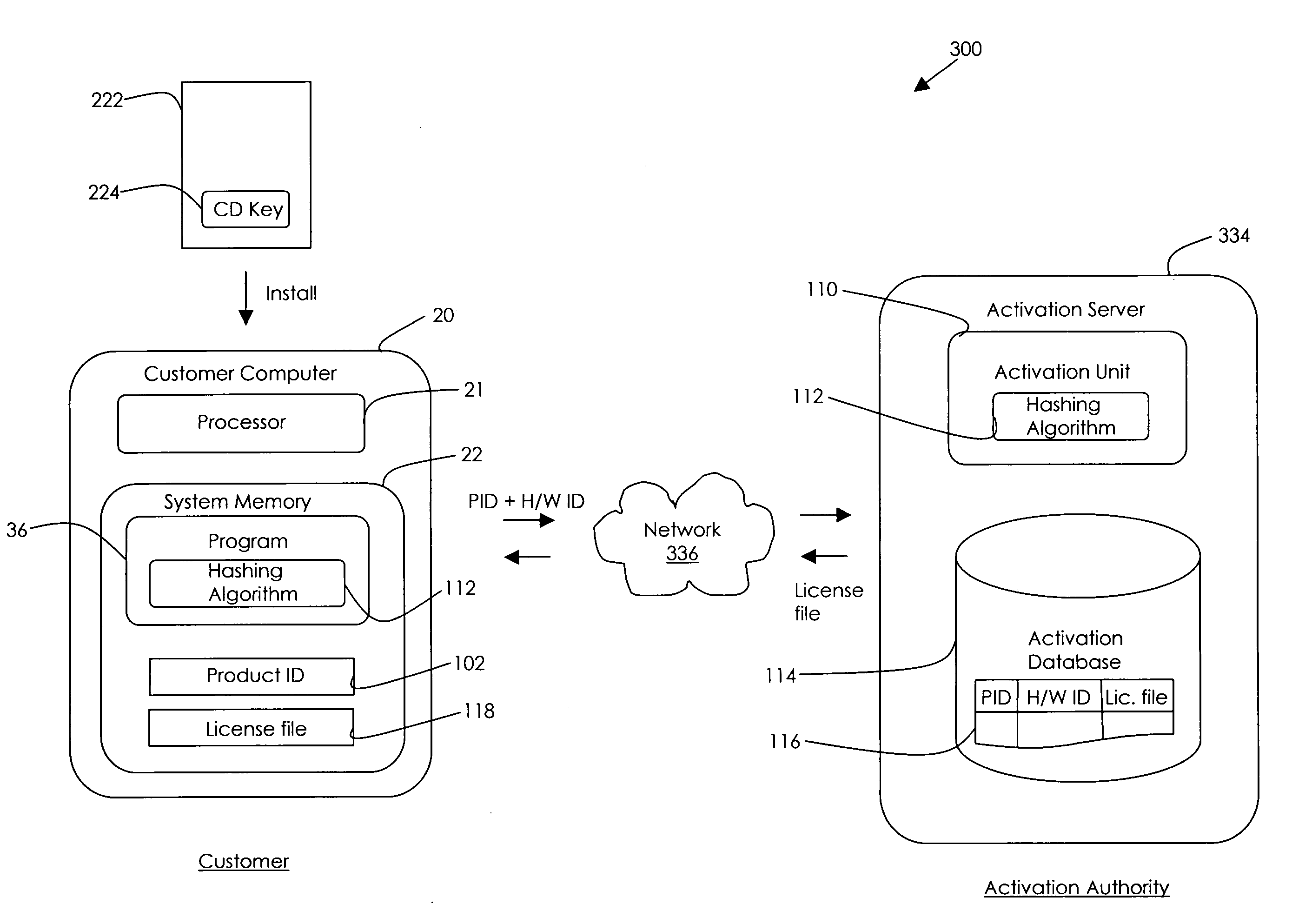
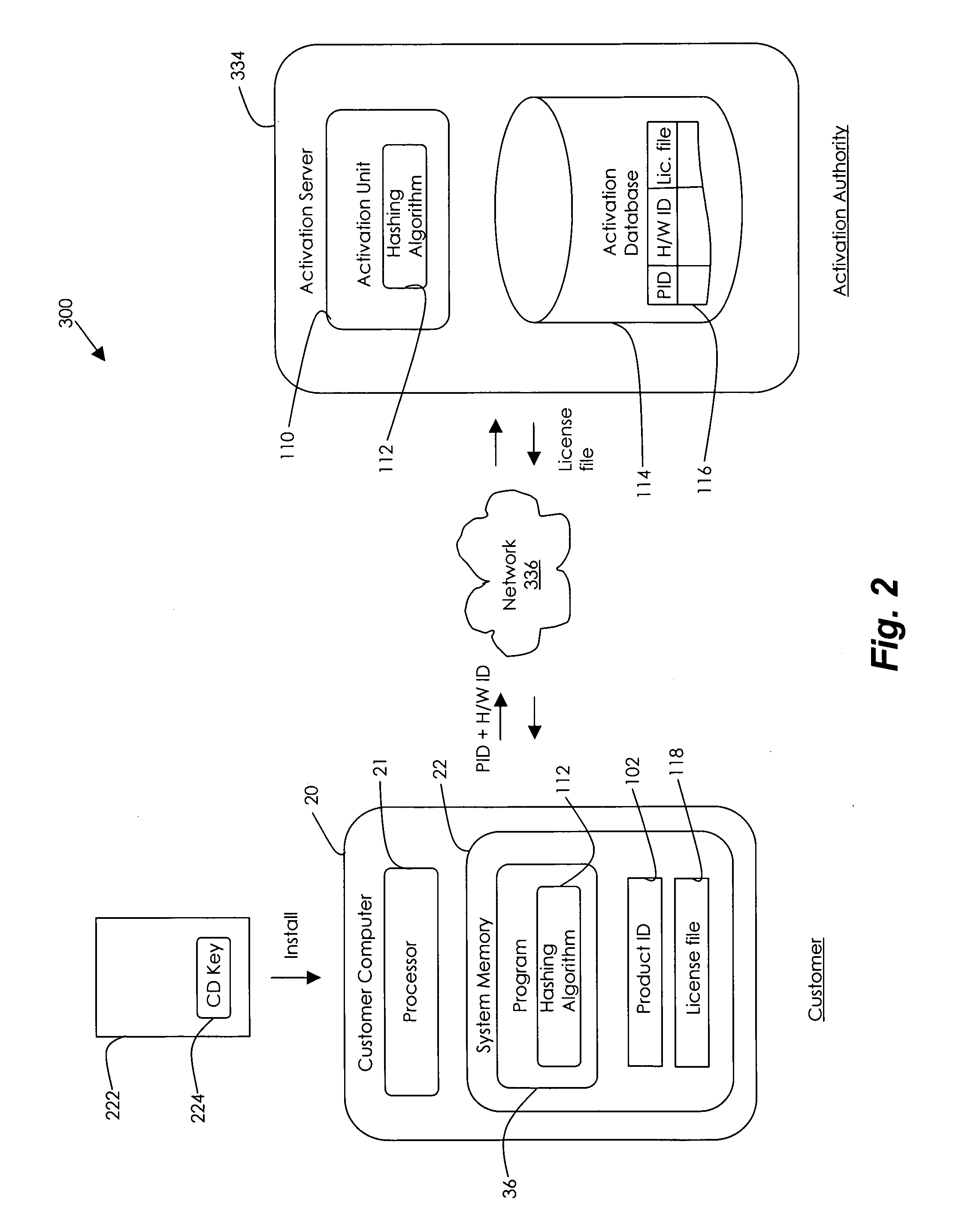
Hardware ID to prevent software piracy
In one embodiment, the invention is a 64 bit hardware ID (H / W ID) for tying a software product to a particular computer to prevent software piracy. The 64 bit hardware ID represents ten different components of the user's computer: the CD-ROM device, the disk adapter, the disk device, the display adapter, the first drive serial number, the MAC address, the processor serial number, the processor type, the RAM size in Mb, and the SCSI adapter. Each time the software product is opened, the expanded H / W ID is compared to the hardware on the computer to determine whether a predetermined minimum number of components match. In one embodiment, the expanded H / W ID allows for expansion of the user's computer because so long as the component originally listed in the expanded H / W ID can be found on the computer, then that component matches the expanded H / W ID. Typically, seven out of ten components in the expanded H / W ID must match the computer before the software product will fully operate.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP
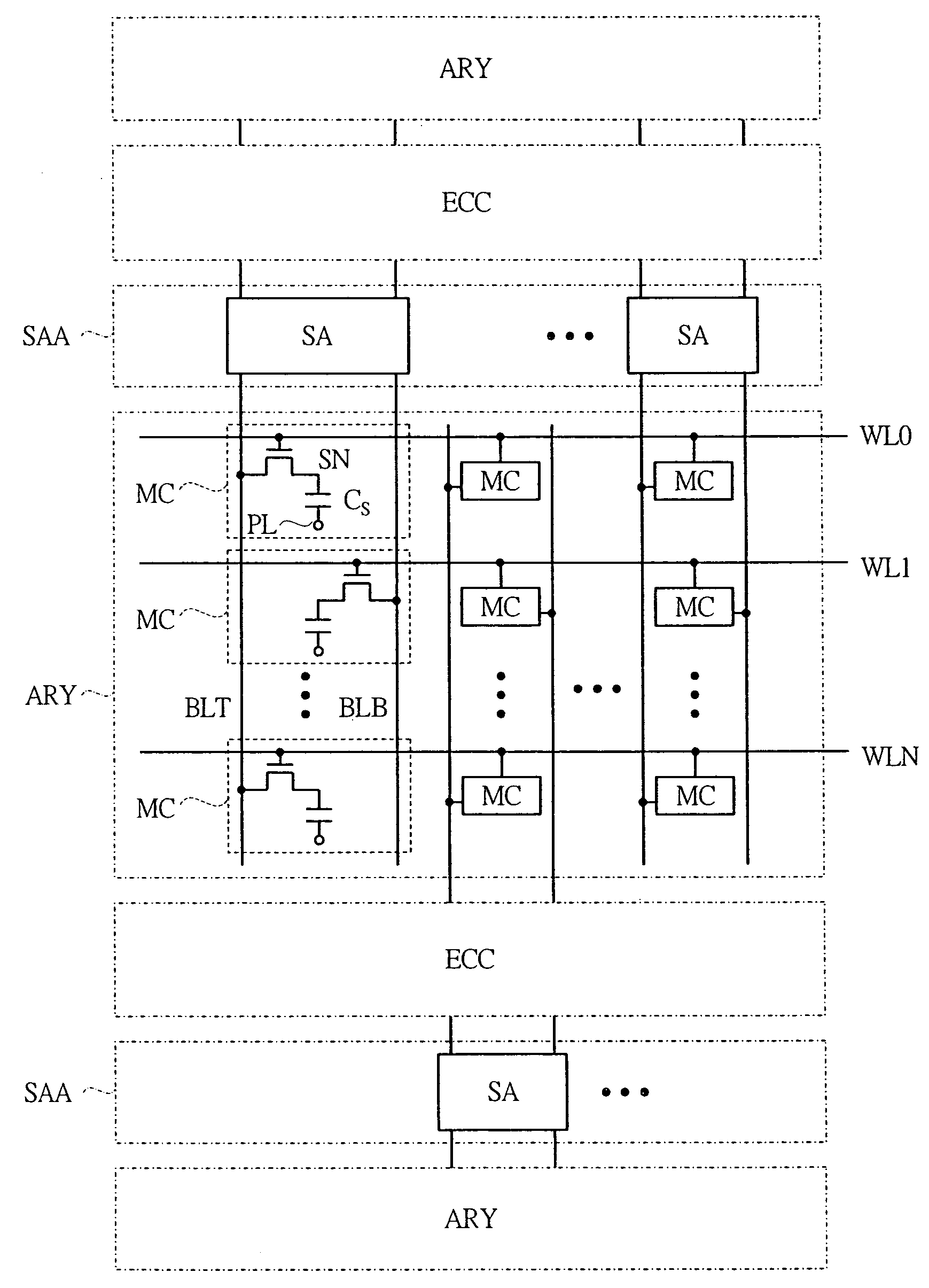
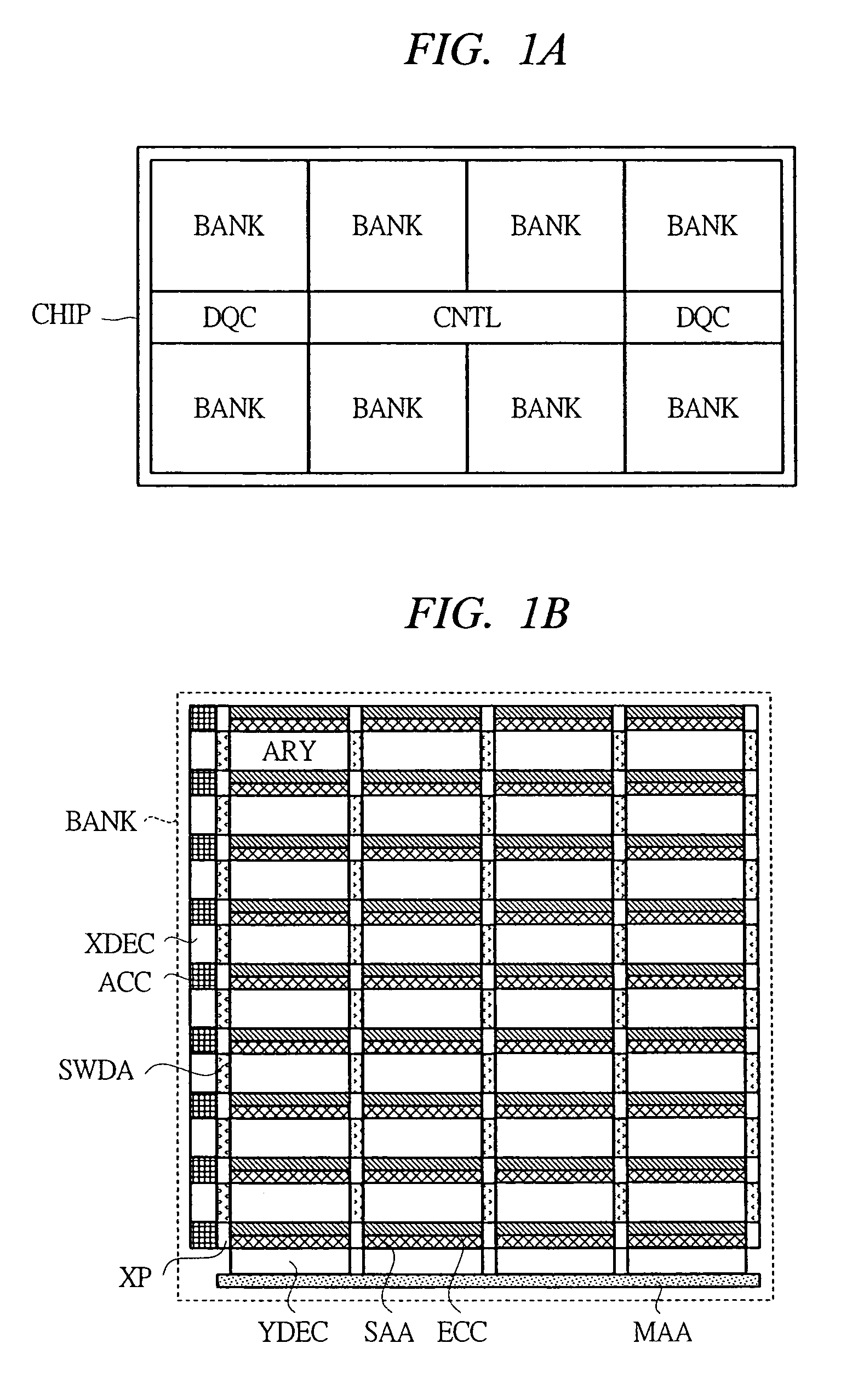
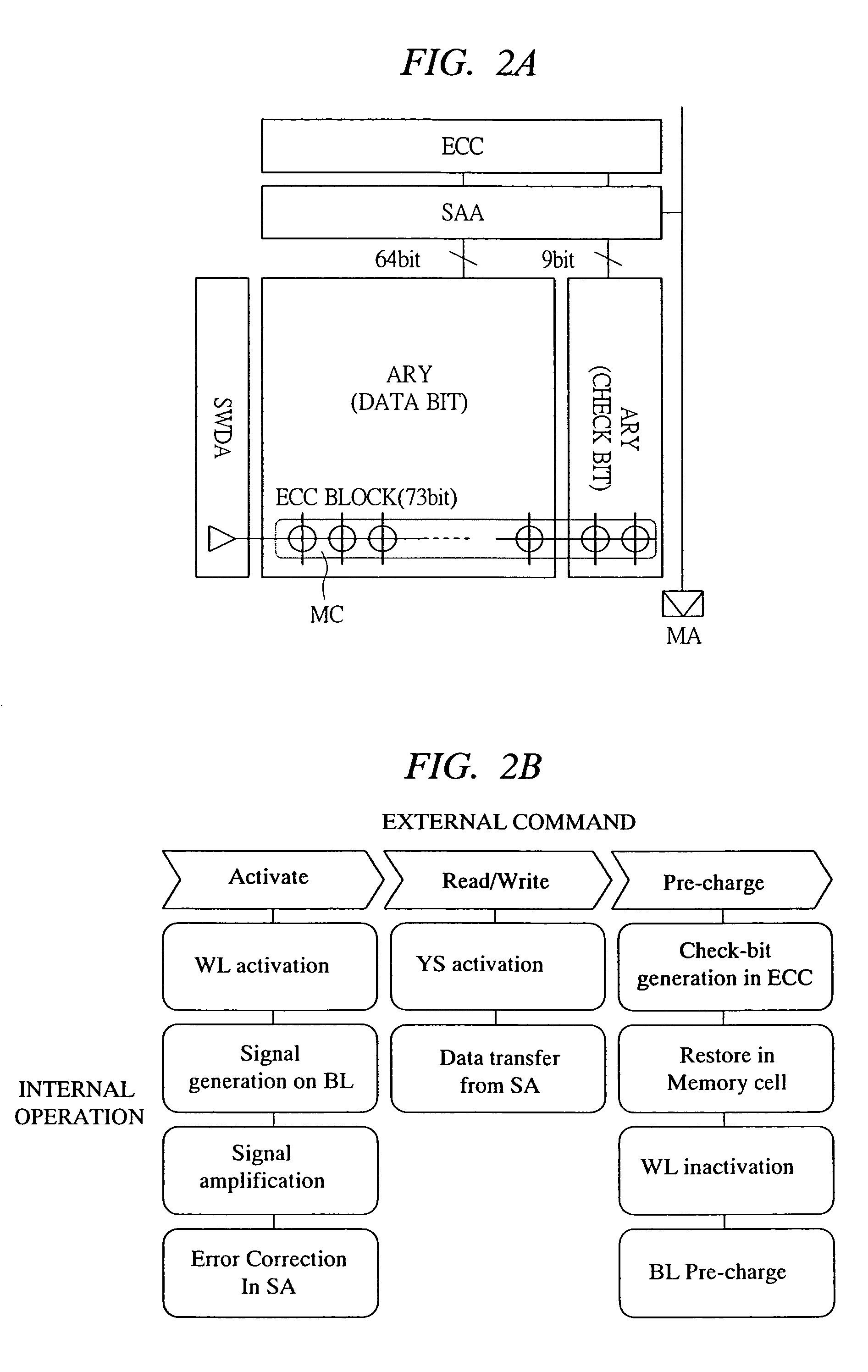
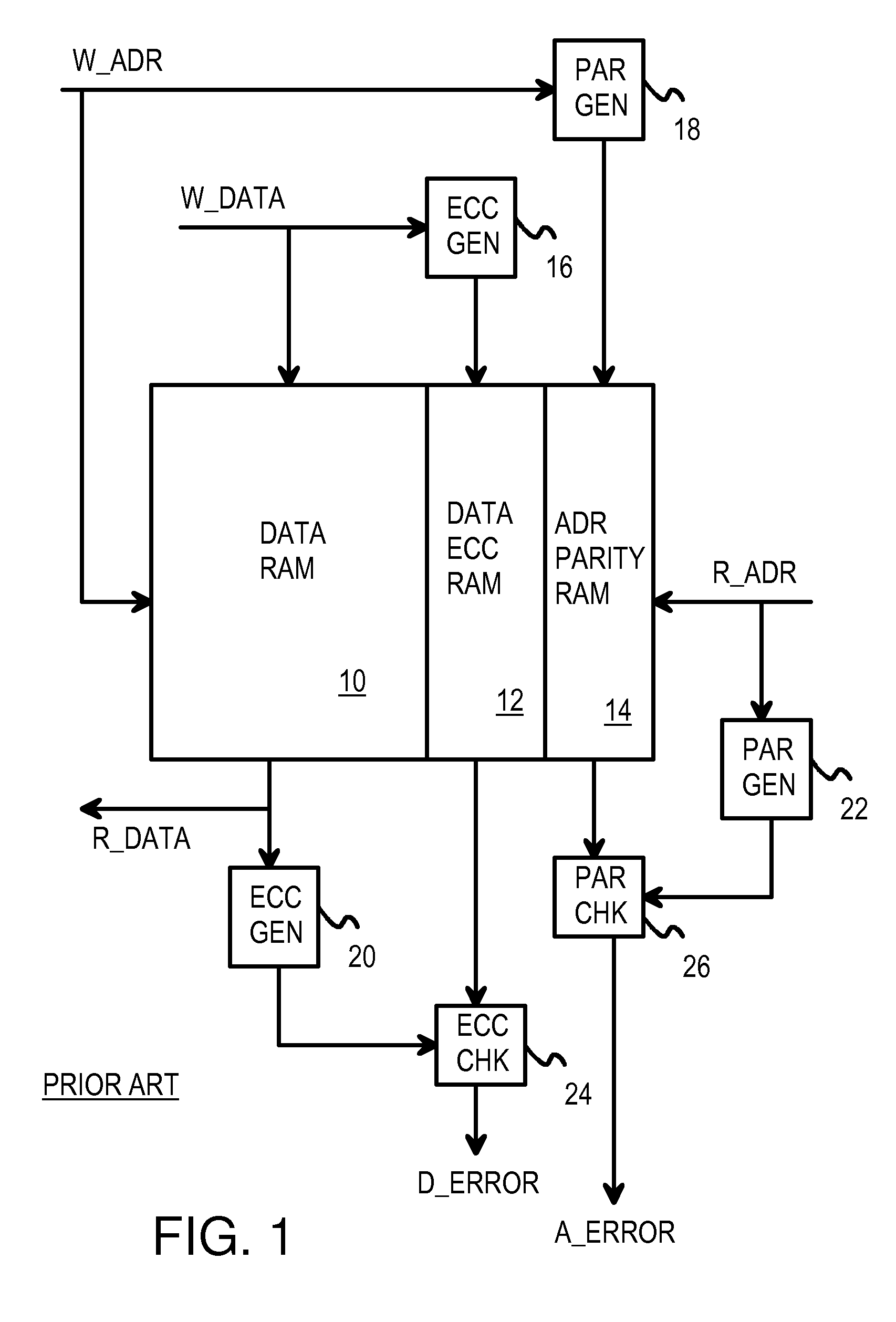
Semiconductor device having a sense amplifier array with adjacent ECC
ActiveUS7603592B2Improve the mismatchImprove leakage currentError detection/correctionCode conversionAudio power amplifierPre-charge
A semiconductor memory device capable of achieving a sufficient operating margin without increasing an area penalty even in the case of miniaturization is provided. An error correction system composed of a data bit of 64 bits and a check bit of 9 bits is introduced to a memory array such as DRAM, and an error correction code circuit required therein is disposed near a sense amplifier array. In addition to normal memory arrays composed of such memory arrays, a redundant memory array having a sense amplifier array and an error correction code circuit adjacent thereto is provided in a chip. By this means, the error which occurs in the manufacture can be replaced. Also, the error correction code circuit corrects the error at the time of an activate command and stores the check bit at the time of a pre-charge command.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
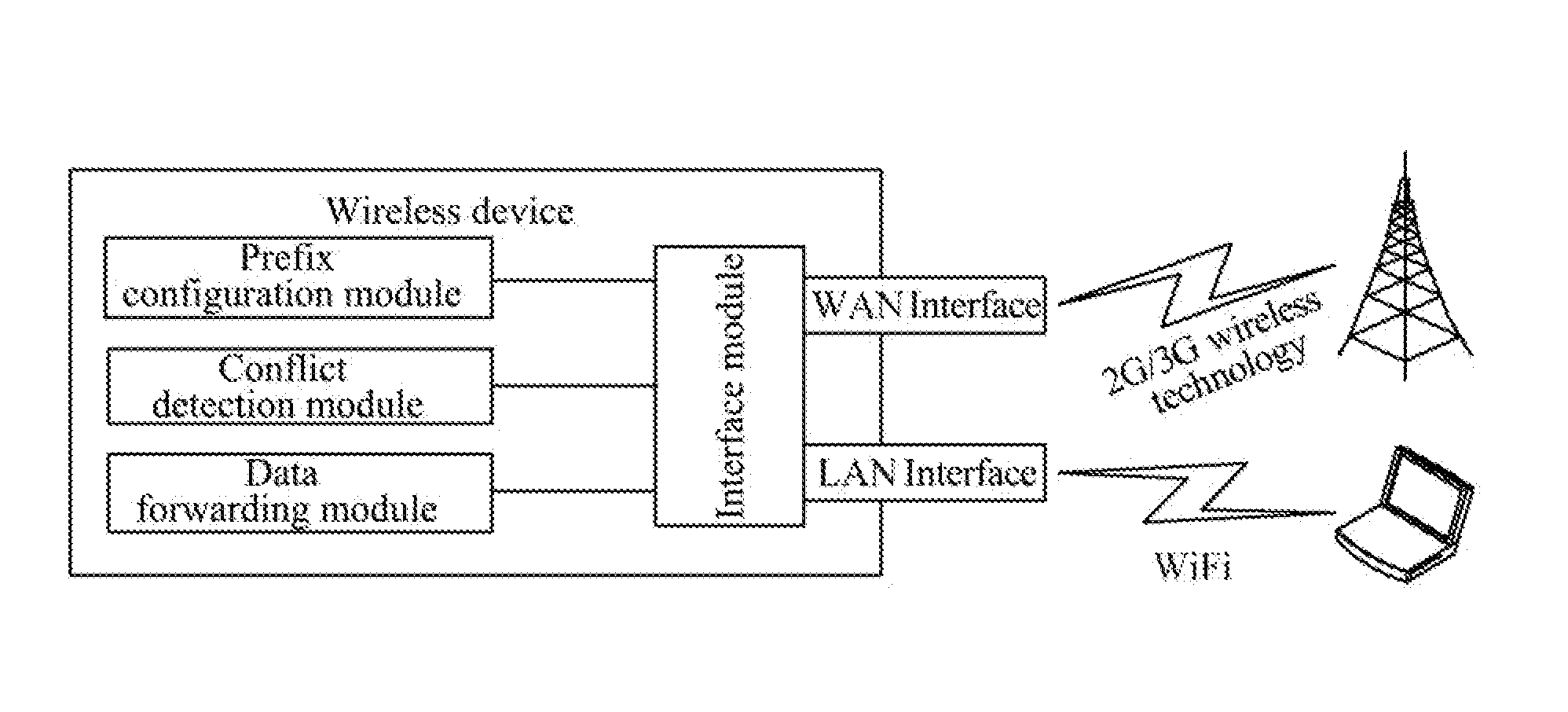
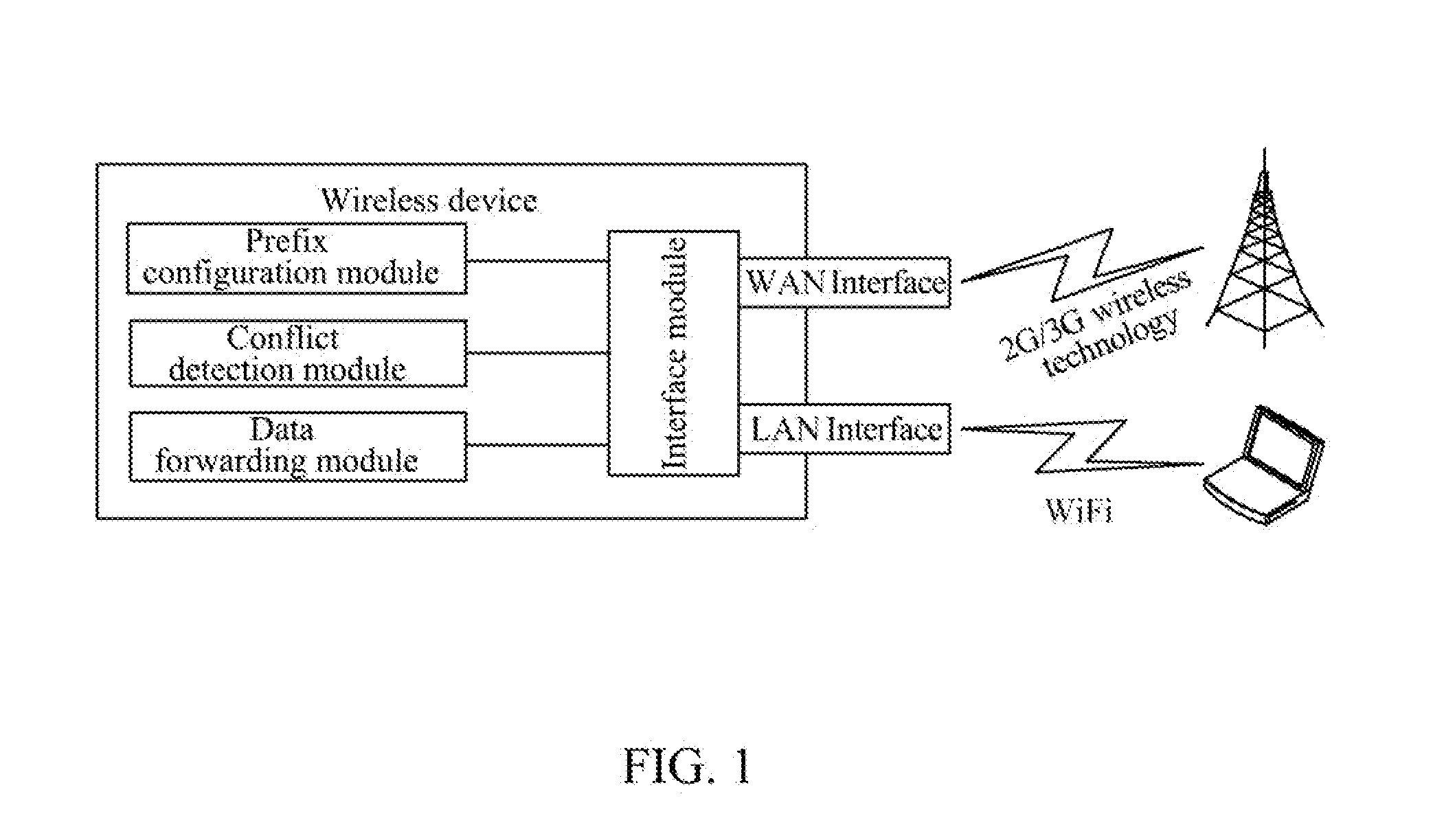
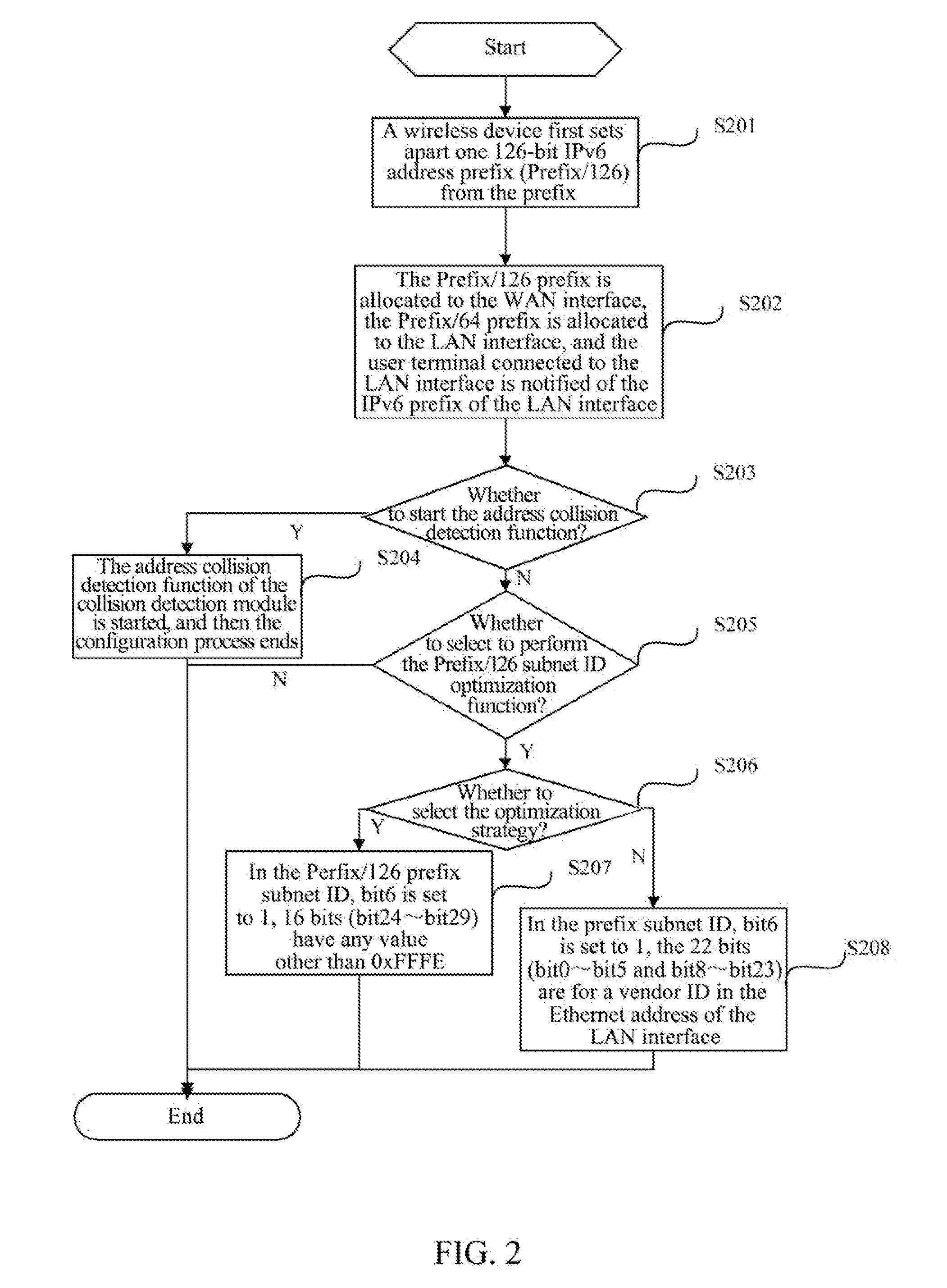
Method for Route Transmission Based on Single IPv6 Address Prefix, and Wireless Device
ActiveUS20140215087A1Reduce resource consumptionNetwork topologiesMultiple digital computer combinationsAuto-configurationComputer terminal
The present document provides a method and wireless device for implementing route transmission based on a single IPv6 address prefix. The method includes: when a wireless device succeeds in IPv6-based dialing and obtains one 64-bit-long IPv6 address prefix from a network side, the wireless device first setting apart a 126-bit IPv6 address prefix from the prefix, and then allocating the 126-bit IPv6 address prefix to a WAN interface, allocating the 64-bit-long IPv6 address prefix to a LAN interface, and notifying a user terminal connected to the LAN interface of the IPv6 prefix of the LAN interface, so that the user terminal connected to the LAN interface generates its own IPv6 address through a stateless address auto-configuration mechanism for communication. With the technical solutions of the present document, in an IPv4 / IPv6 dual stack mode, IPv4 and IPv6 protocol stacks operate normally, and the radio resource consumption is reduced.
Owner:DRNC HLDG INC
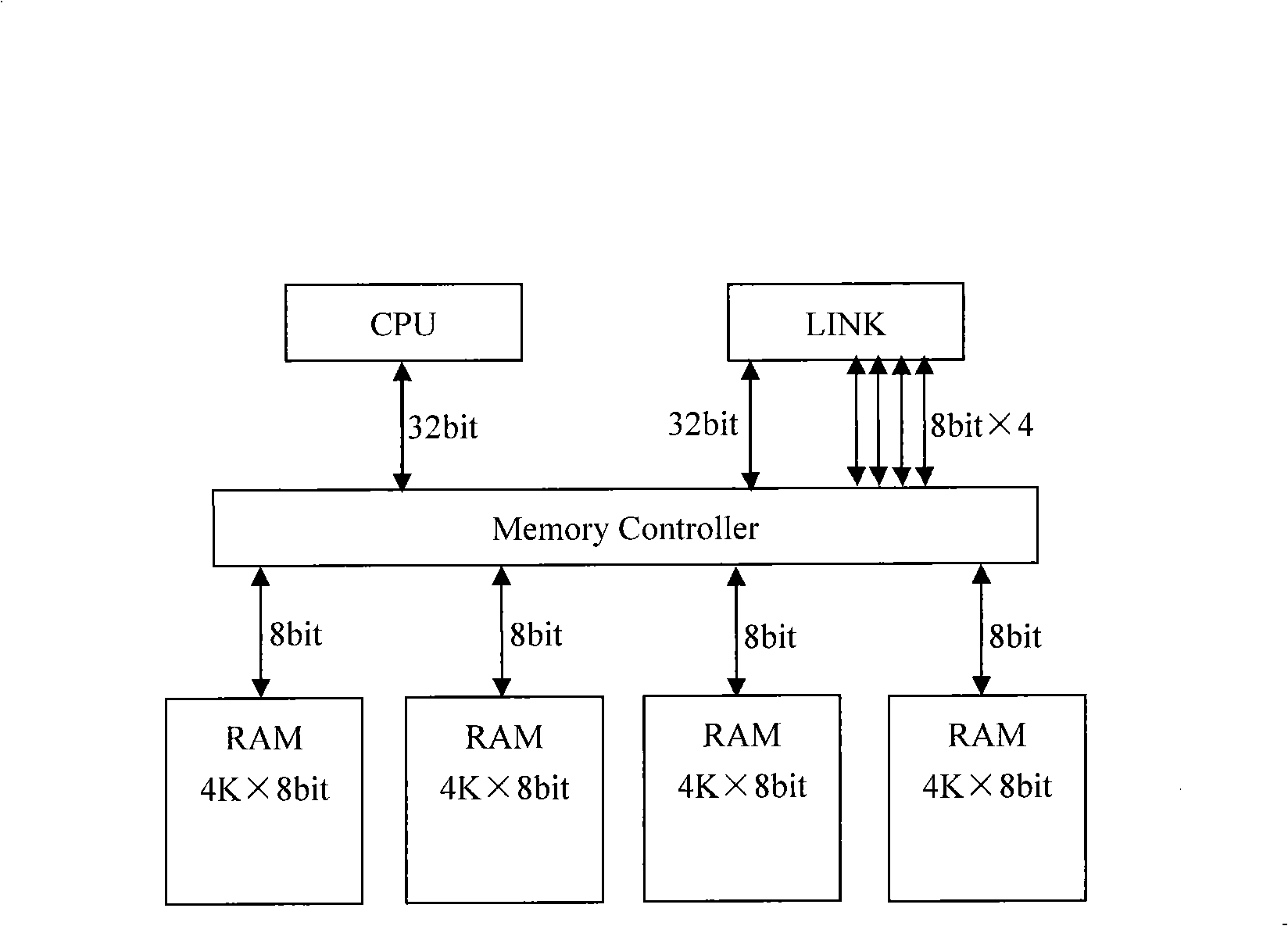
Paralleling microprocessor and its realization method
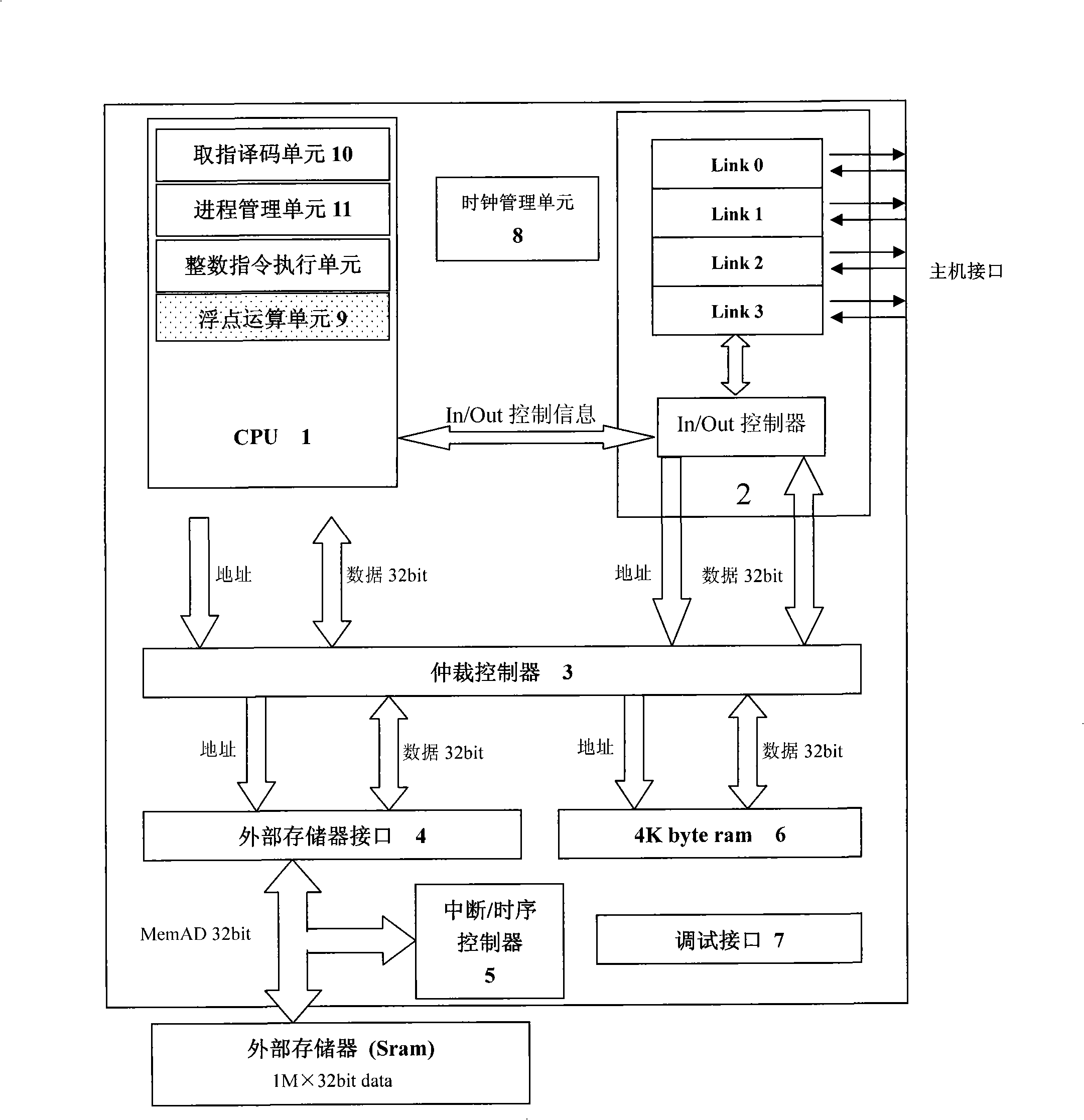
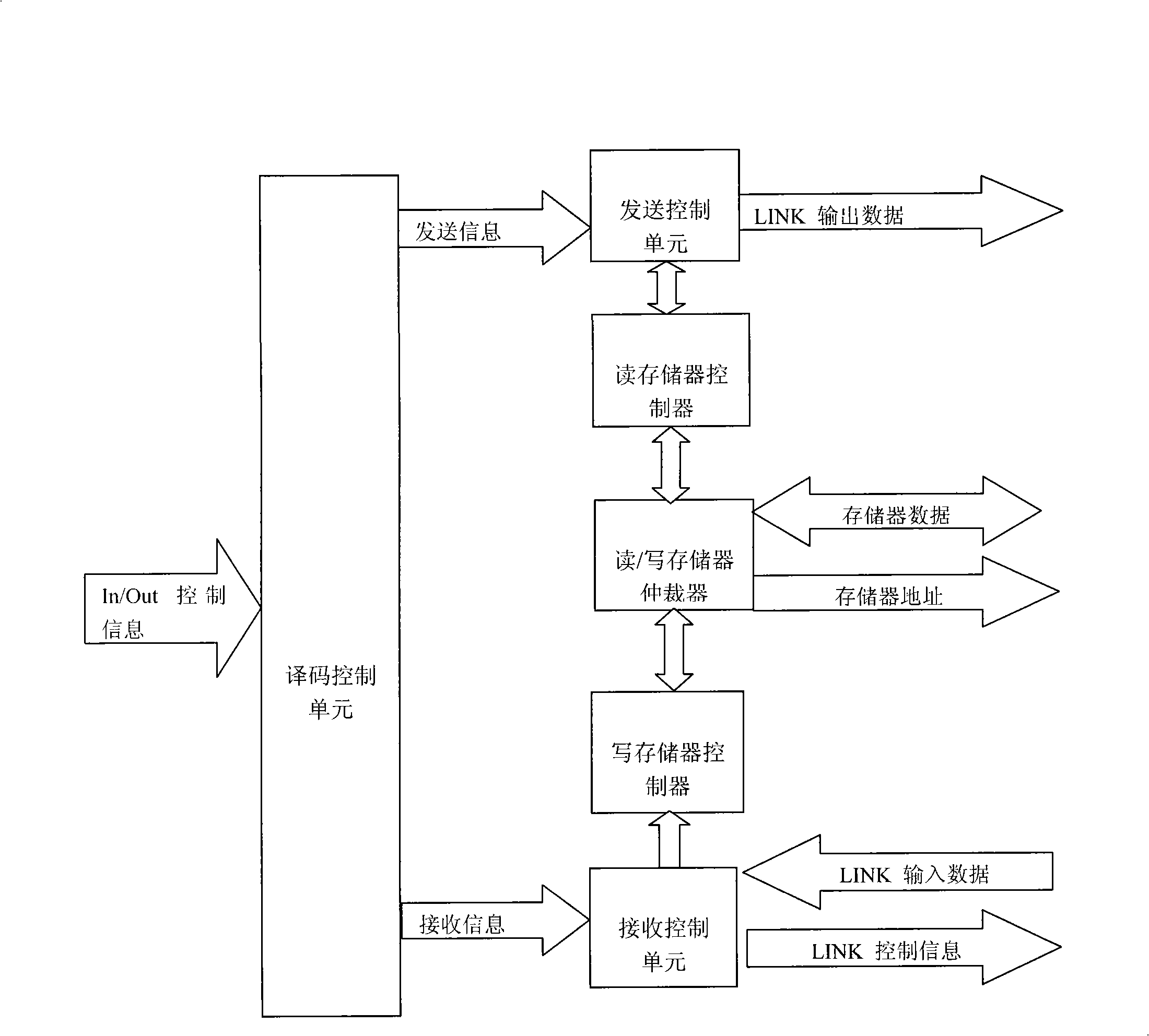
ActiveCN101334766ALow costEasy to modifyProgram initiation/switchingDigital data processing detailsInternal memoryParallel computing
The invention relates to a parallel microprocessor and a corresponding realization method which are based on FPGA development. The parallel microprocessor comprises a CPU which is a 32-bit fixed-point CPU formed by a fetch decoding unit, a process management unit and an integer instruction execution unit; a communication module formed by a plurality of units of LINK channels and In / Out controllers; an arbitration controller used for arbitrating internal and external address buses and a data bus of the CPU; an external memory interface used for providing reading / writing time-sequence logic for an external memory; an interruption / time-sequence controller used for providing timing and interruption for the CPU; an internal memory used for providing the instructions of the CPU and quickly accessing data. The CPU is also provided with a floating point unit (FPU) combining the 32-bit fixed-point CPU to form a 64-bit floating point CPU. The 32-bit fixed-point parallel microprocessor and the 64-bit floating point parallel microprocessor provided by the invention work stably, bring convenience for system modification and debugging, accelerate verification speed and provide a low-cost operation platform for programs written in OccamII language.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
Method and apparatus for managing shared virtual storage in an information handling system
ActiveUS6981125B2Easy to trackAvoid overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationThree levelOperational system
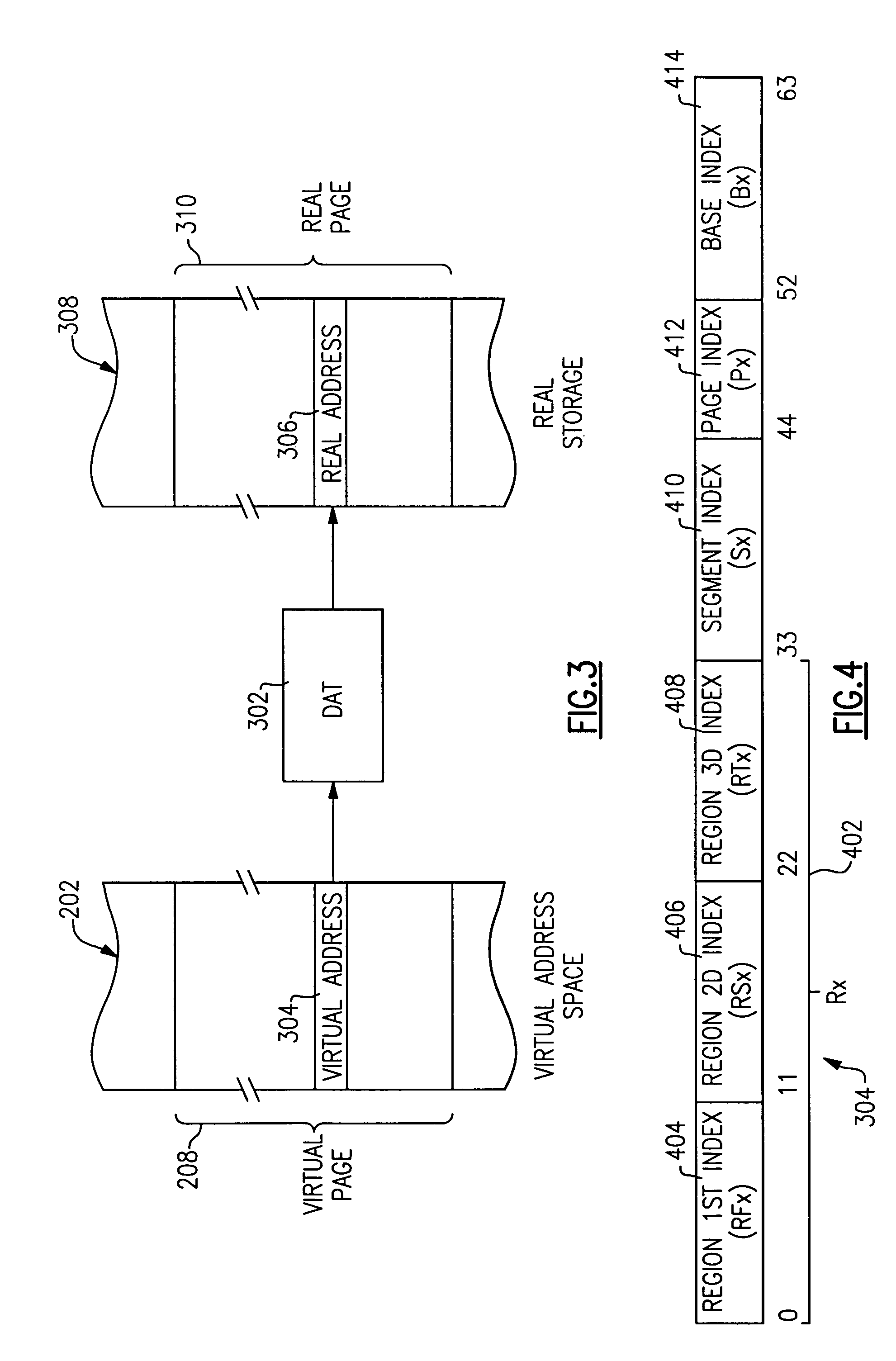
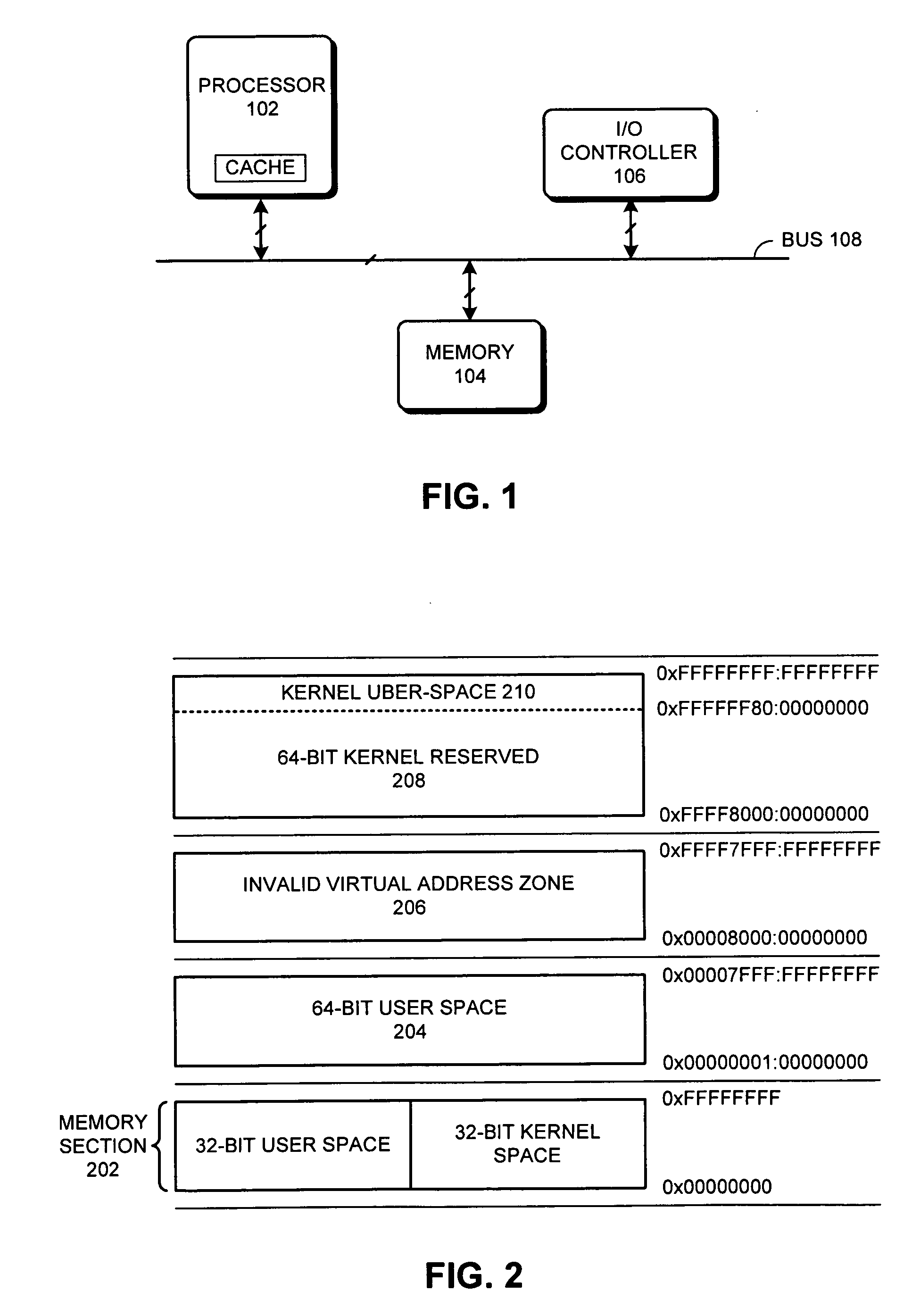
A method and apparatus for managing shared virtual storage in an information handling system in which each of a plurality of processes managed by an operating system has a virtual address space comprising a range of virtual addresses that are mapped to a corresponding set of real addresses representing addresses in real storage. The virtual address spaces are 64-bit address spaces requiring up to five levels of dynamic address translation (DAT) tables to map their virtual addresses to real addresses. One or more shared ranges of virtual addresses are defined that are mapped for each of a plurality of virtual address spaces to a common set of real addresses. The operating system manages these shared ranges using a system-level DAT table that reference a shared set of DAT tables used by the sharing address spaces for address translation, but is not attached to the hardware address translation facilities or used for address translation. The shared range of virtual addresses straddles the 242-byte boundary between ranges served by different third-level DAT tables and is situated between a lower private range and an upper private range so that an individual address space can map both a lower private range and a shared range using only three levels of DAT tables. Each shared address range may be shared with either global access rights, in which each participating process has the same access rights, or local access rights in which each participant may have different access rights to the given range. Access rights for each participant may be changed over the lifetime of the process.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for running a legacy 32-bit x86 virtual machine on a 64-bit x86 processor
ActiveUS7260702B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMode controlPage table
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
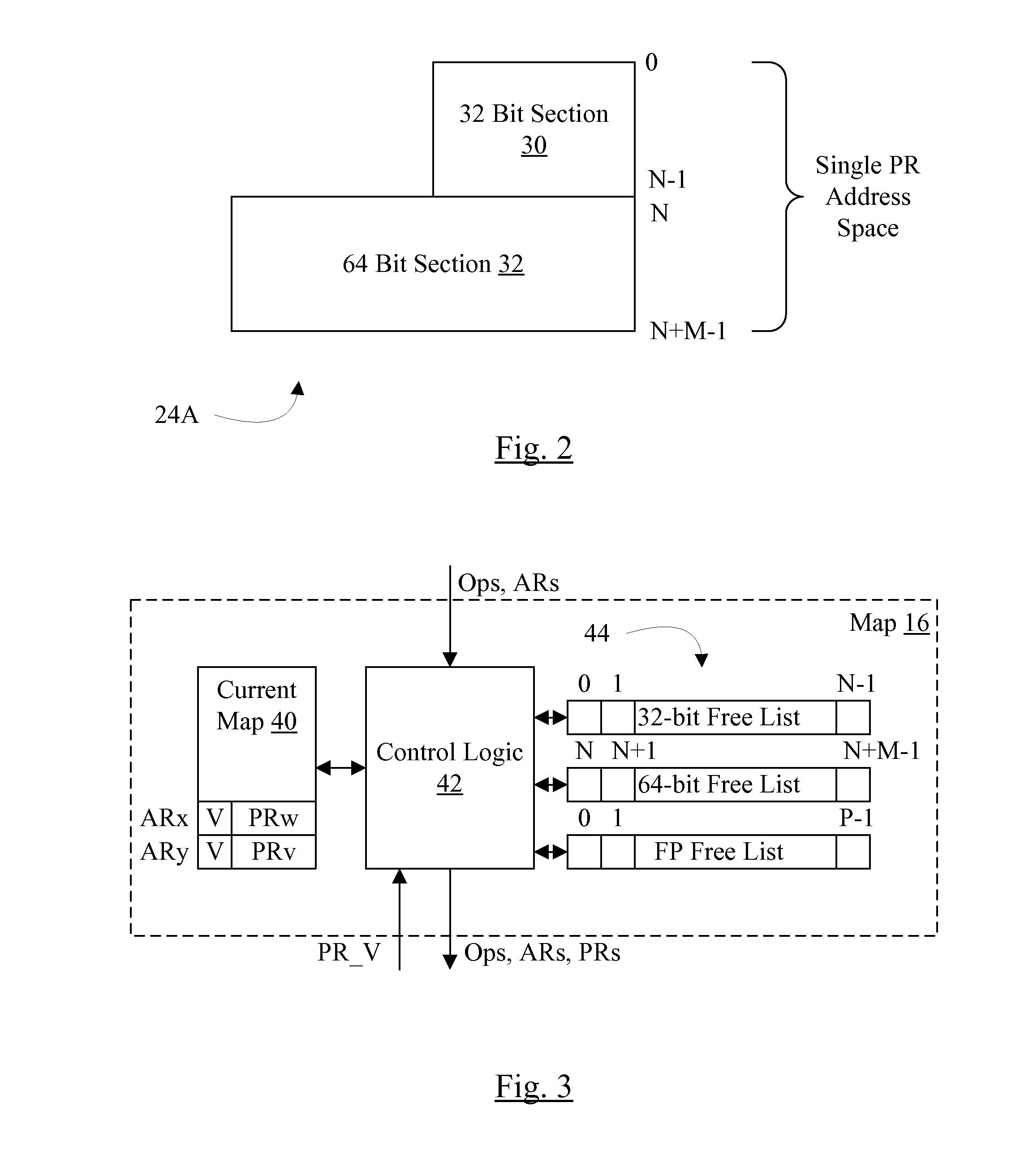
Split Register File for Operands of Different Sizes
ActiveUS20150134935A1Consume integrated circuit areaDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsProcessor registerOperand
In an embodiment, a processor includes a register file having multiple widths corresponding to different operands sizes of a given data type implemented by the processor. For example, the integer register file may have 32 bit and 64 bit widths for 32 and 64 bit operand sizes. The register file may have a section of registers for each operand size, and the map unit may allocate registers from the appropriate section for each instruction operation based on the operand size of that instruction operation. The register file may consume less integrated circuit area than another register file having the same number of registers, all of which are implemented at the largest operand size. In some embodiments, only the register file and the map unit (specifically the free list management logic in the map unit) are changed to implement the multiple-width register file.
Owner:APPLE INC
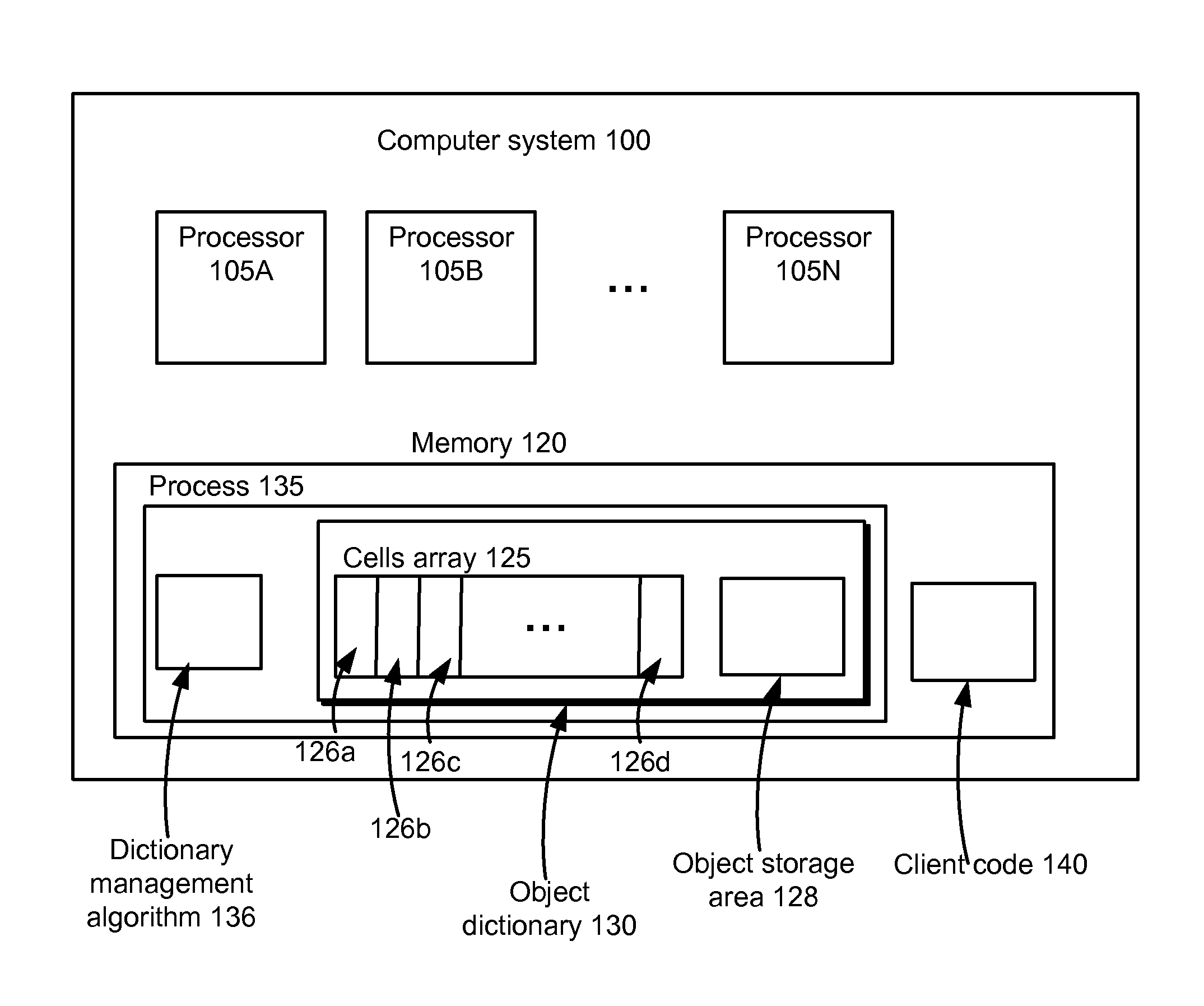
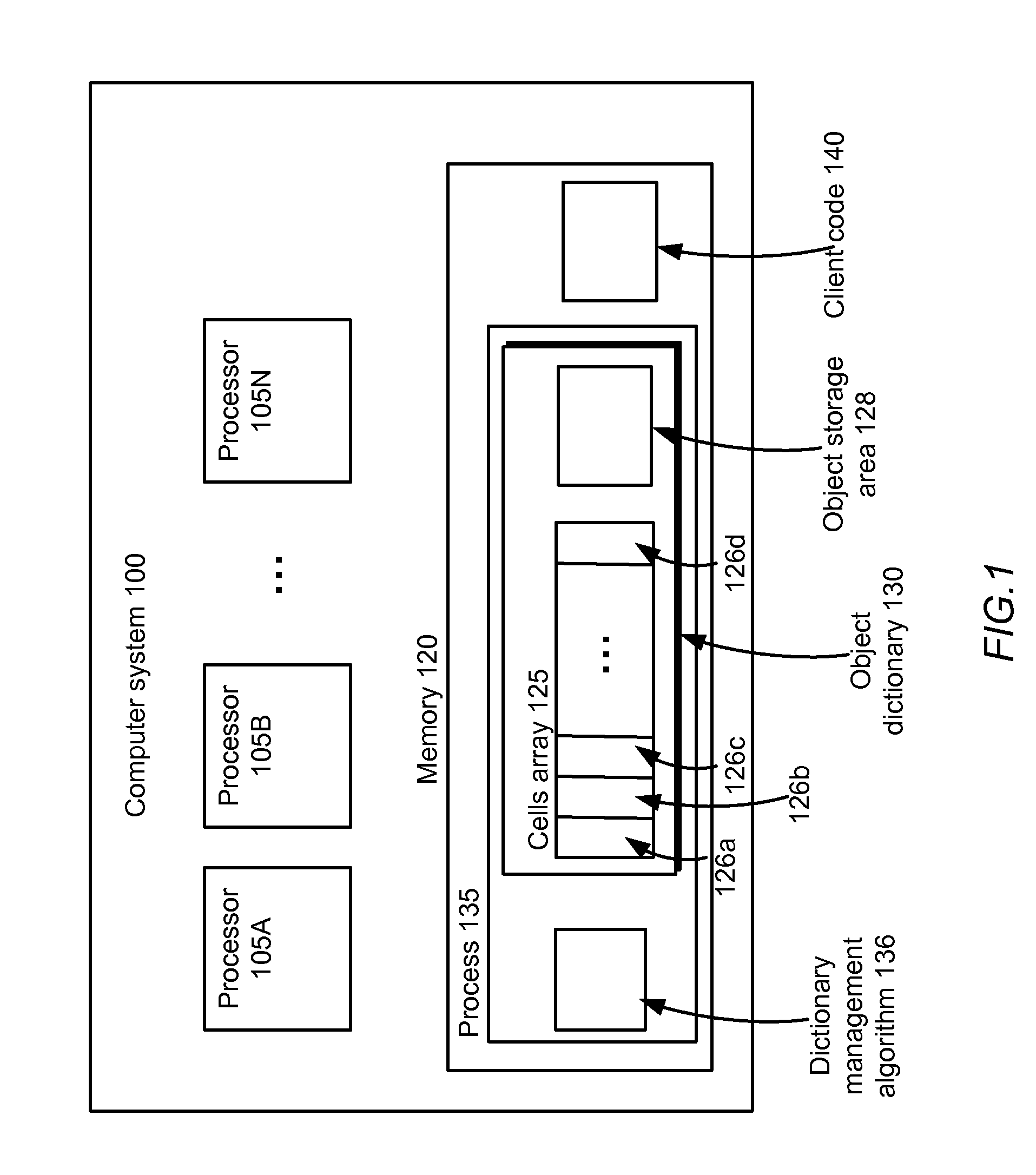
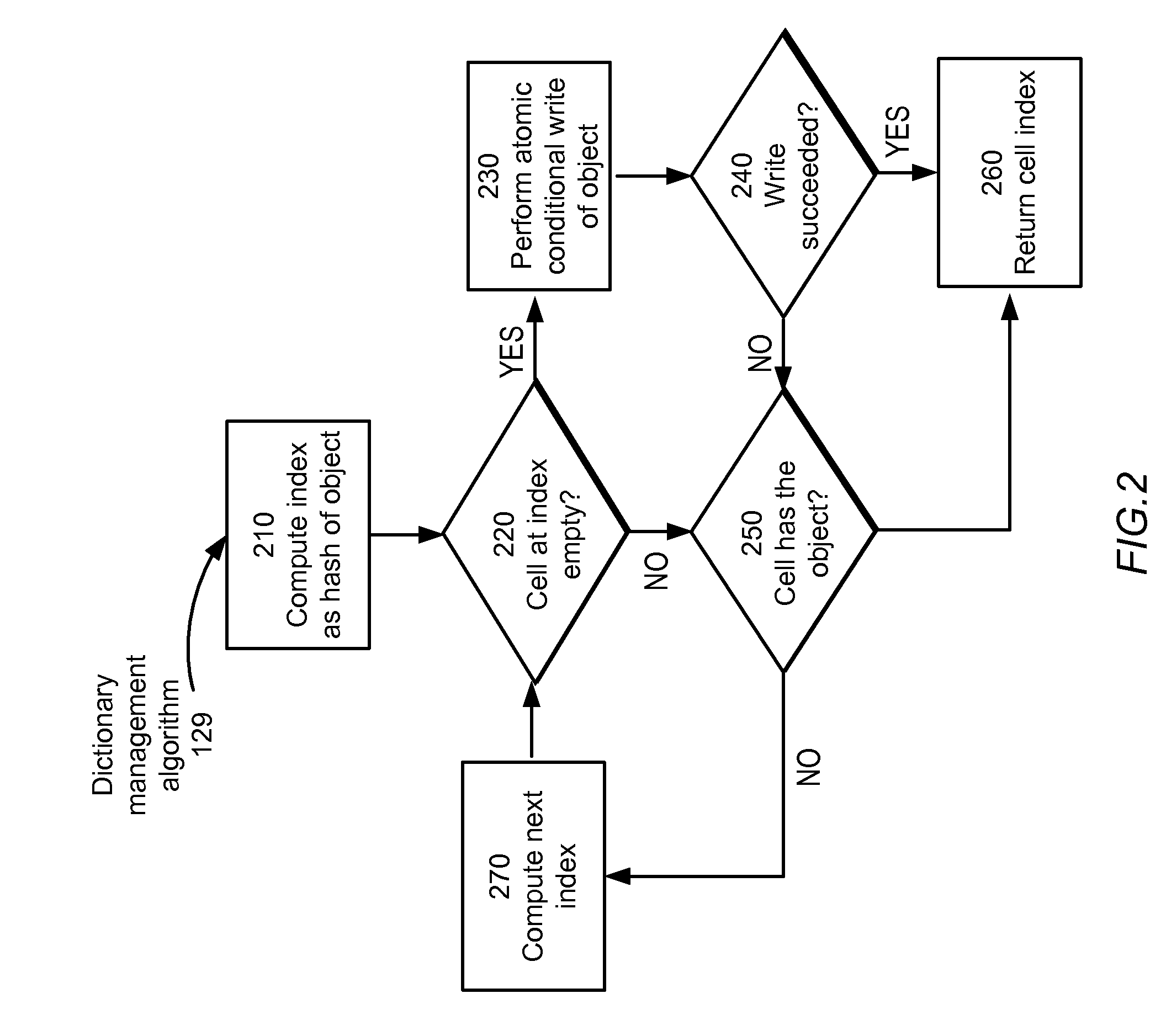
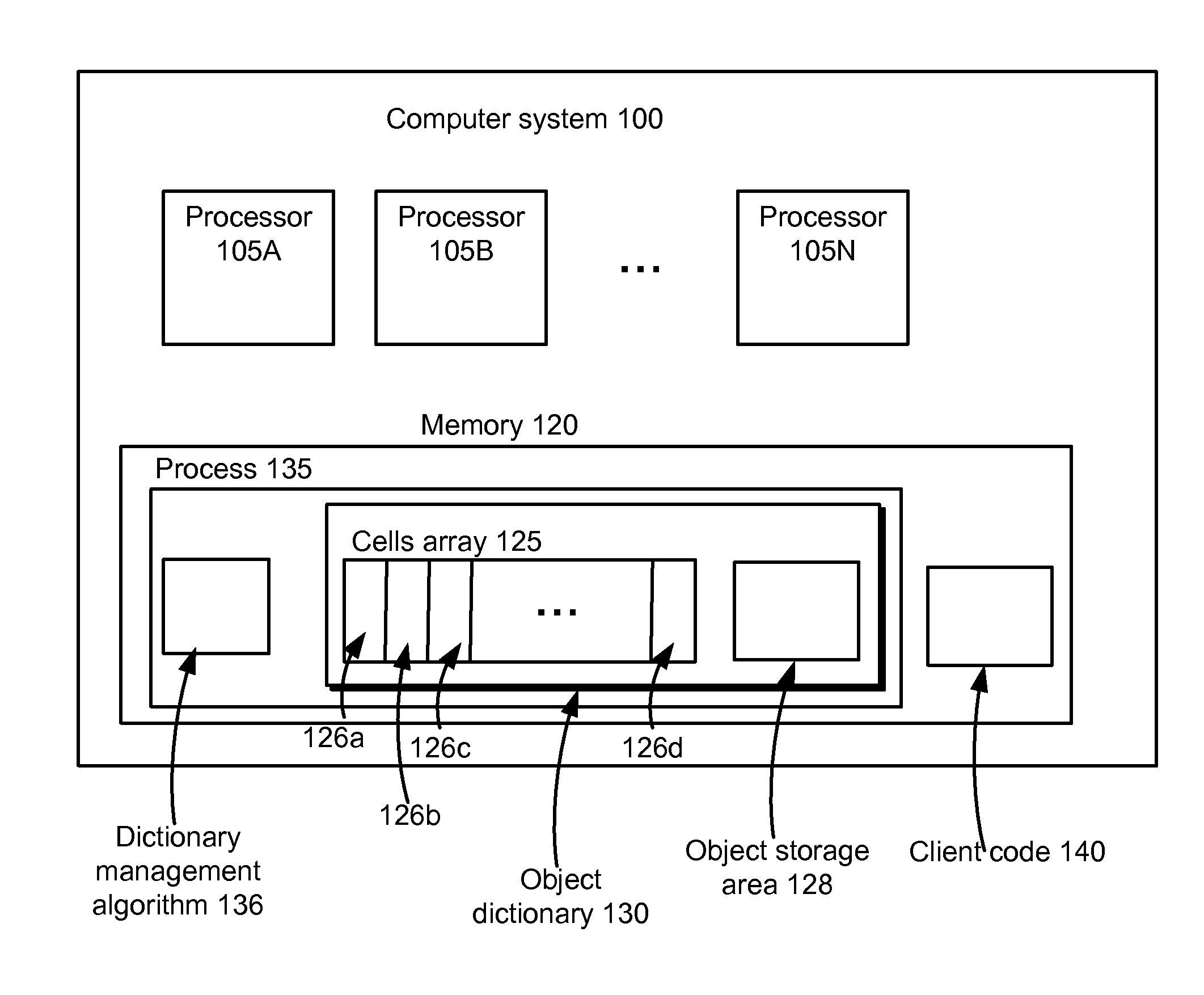
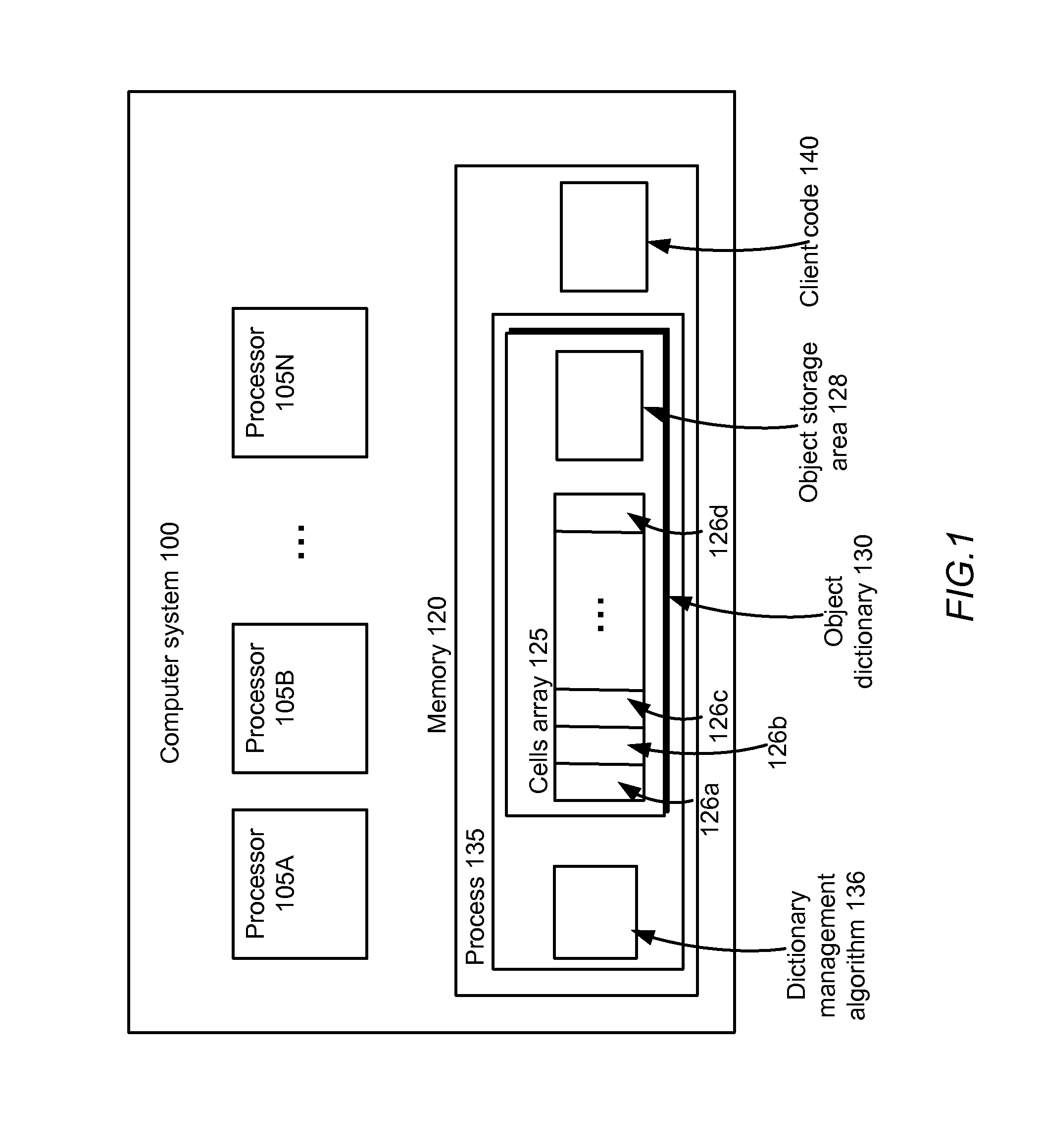
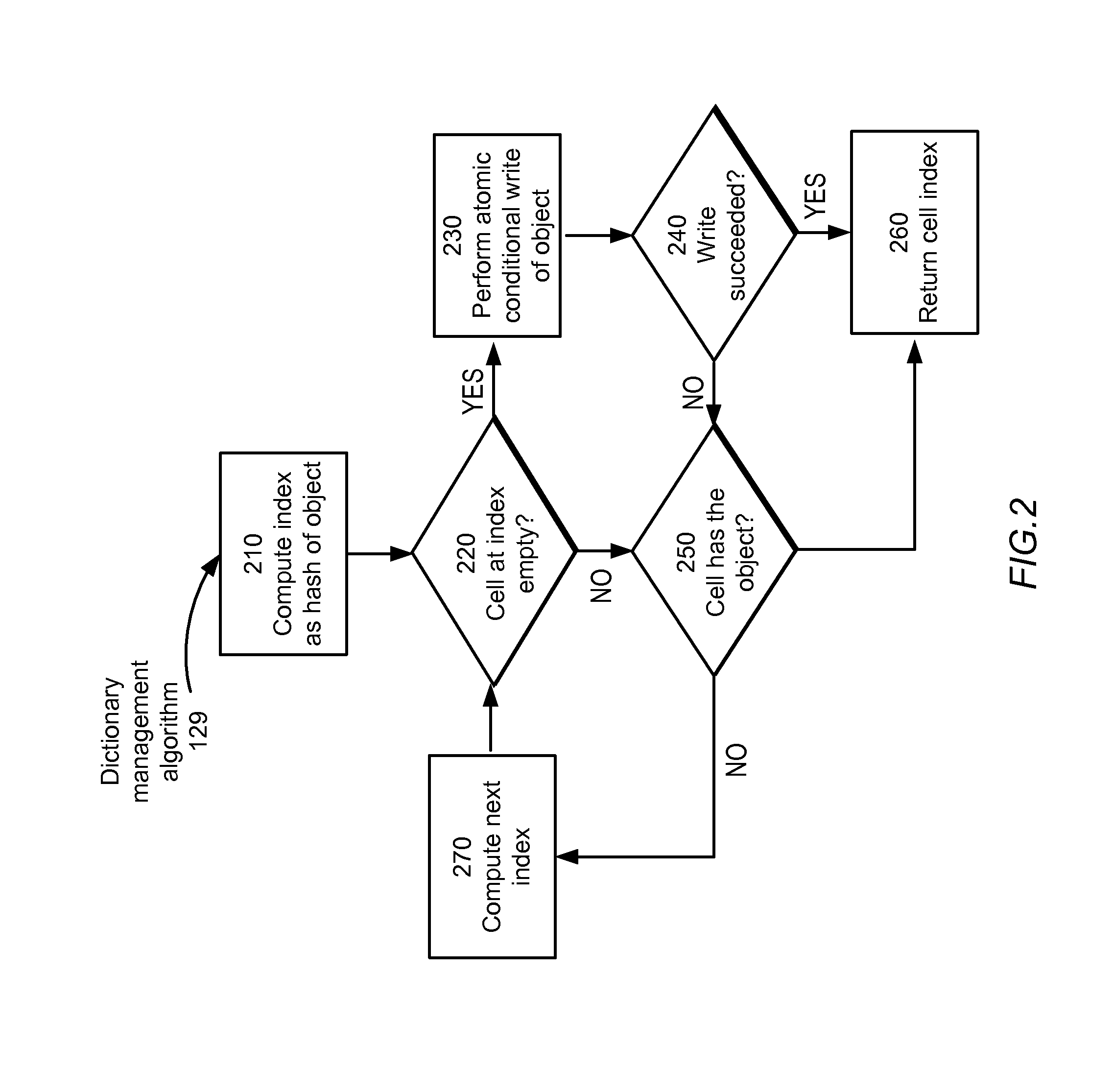
Lock-free concurrent object dictionary
ActiveUS20110161602A1Reduce memory requirementsSave memoryMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProgram controlObject storage64-bit computing
An object storage system comprises one or more computer processors or threads that can concurrently access a shared memory, the shared memory comprising an array of equally-sized cells. In one embodiment, each cell is of the size used by the processors to represent a pointer, e.g., 64 bits. Using an algorithm performing only one memory write, and using a hardware-provided transactional operation, such as a compare-and-swap instruction, to implement the memory write, concurrent access is safely accommodated in a lock-free manner.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
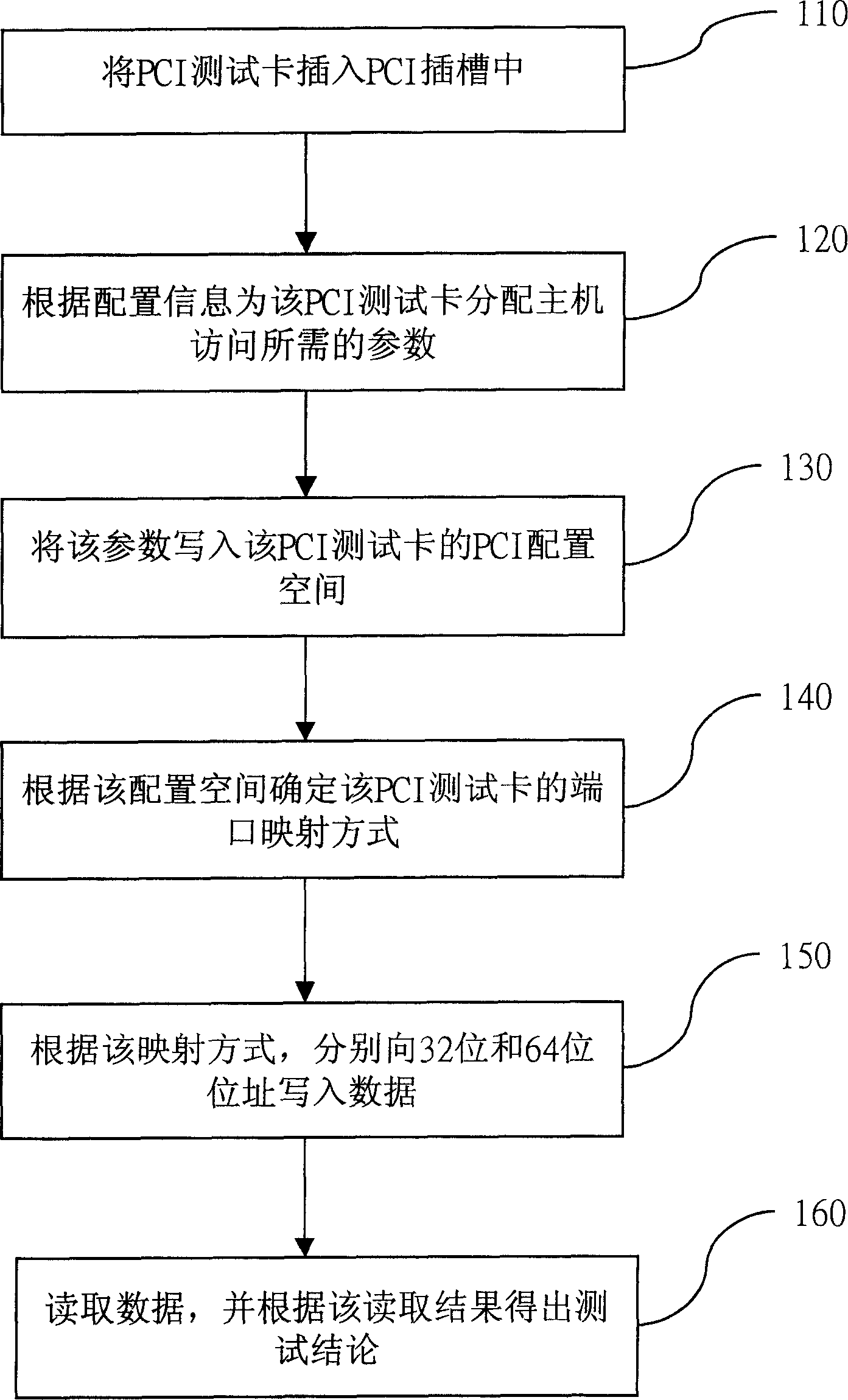
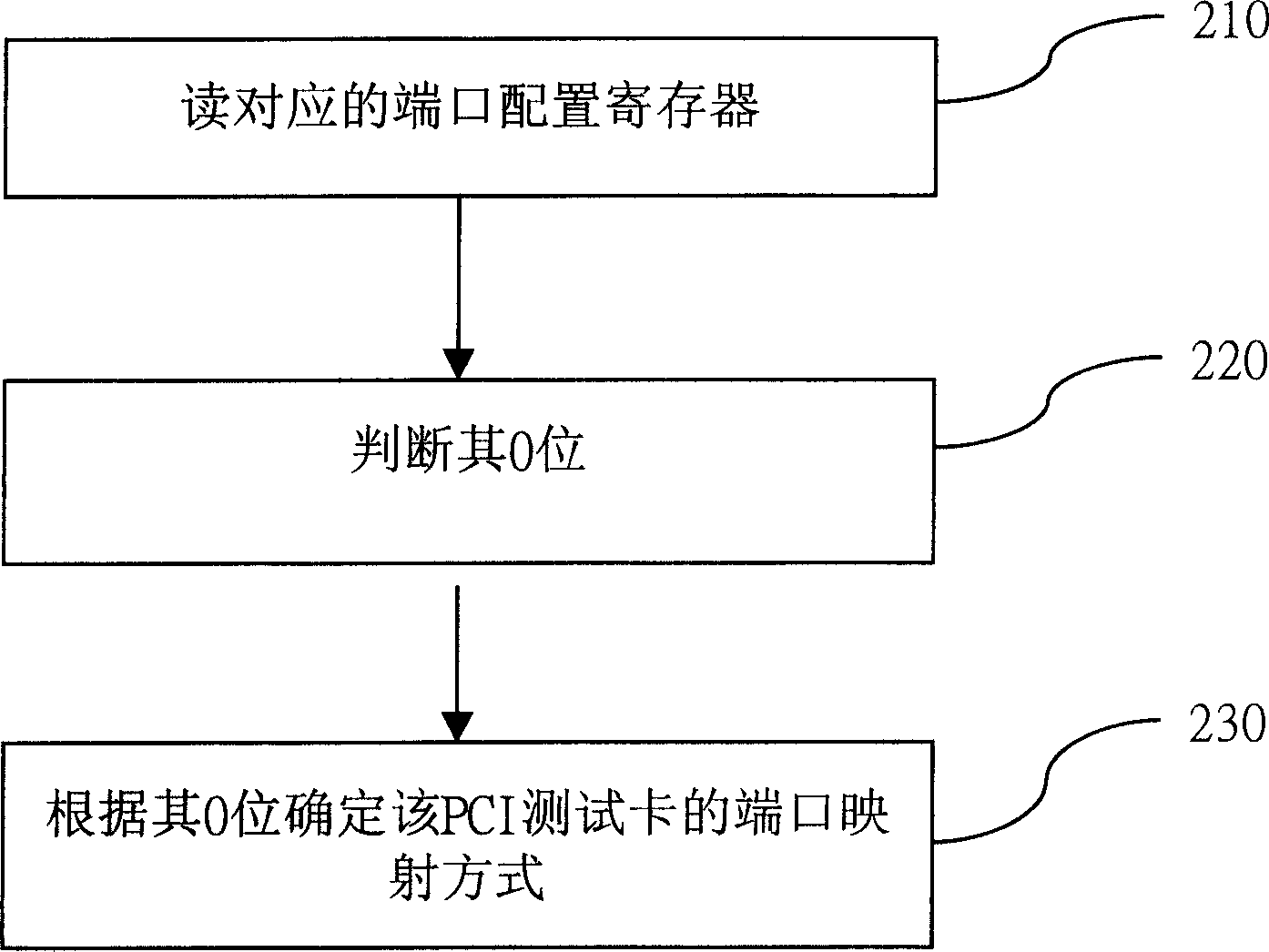
Method for testing interconnected bus of external components
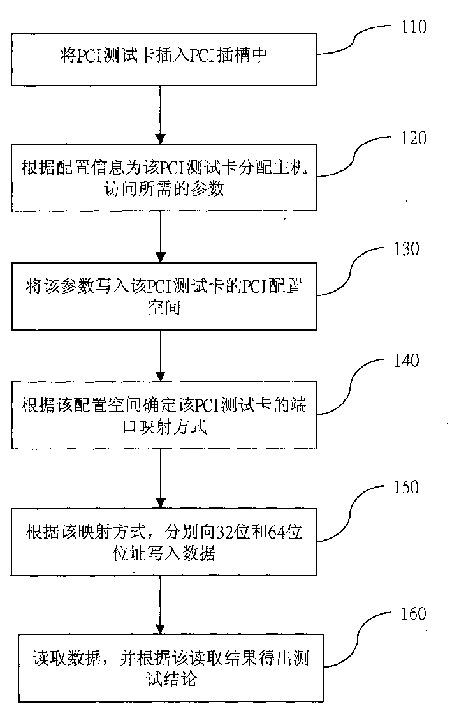
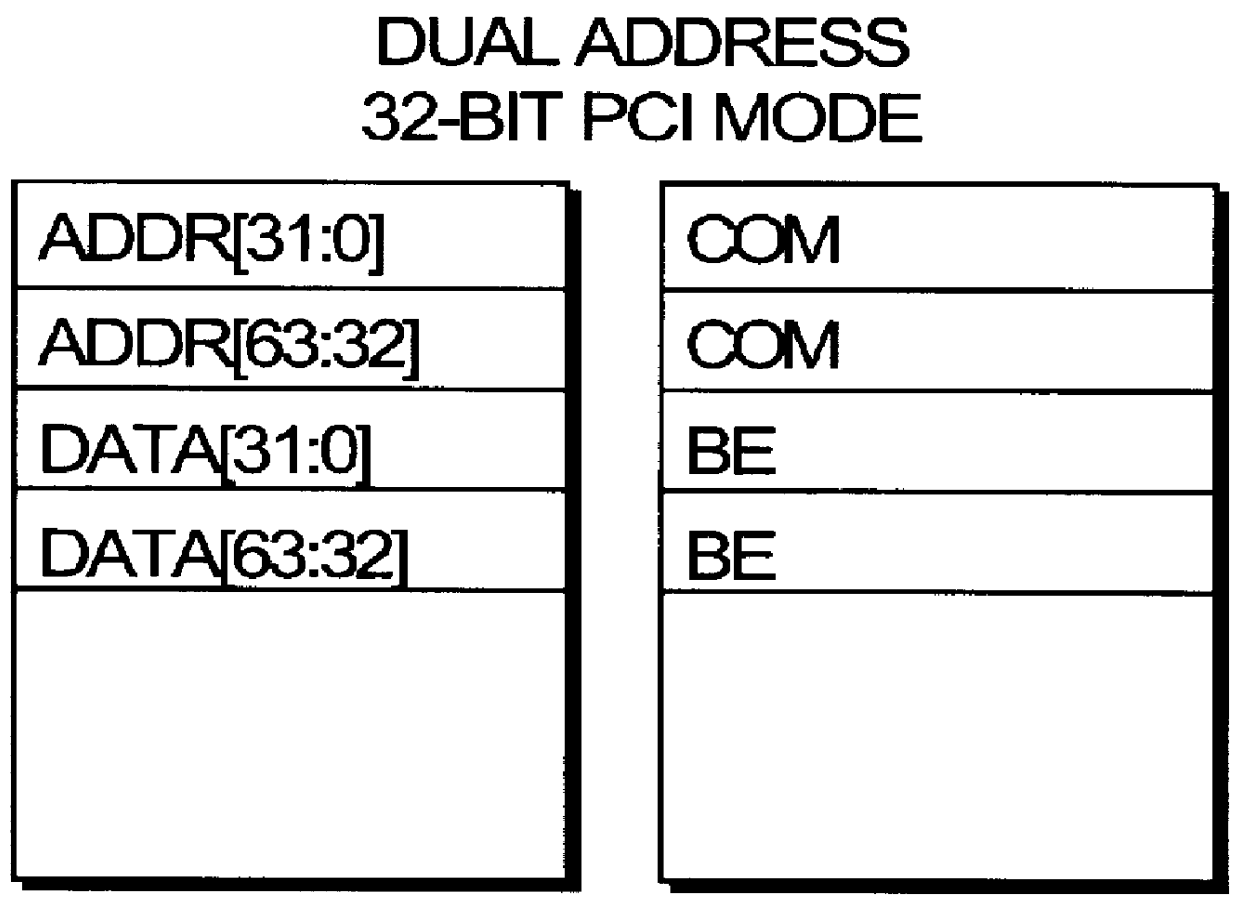
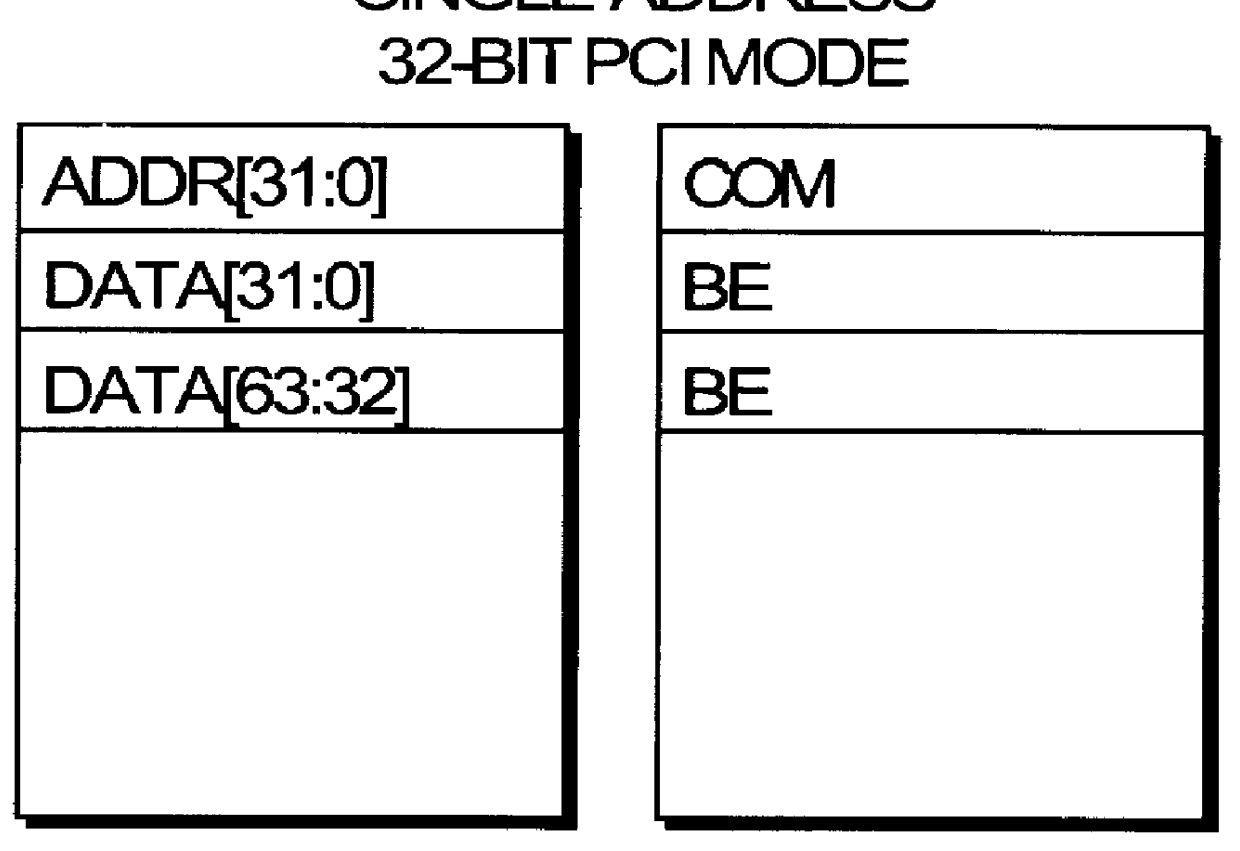
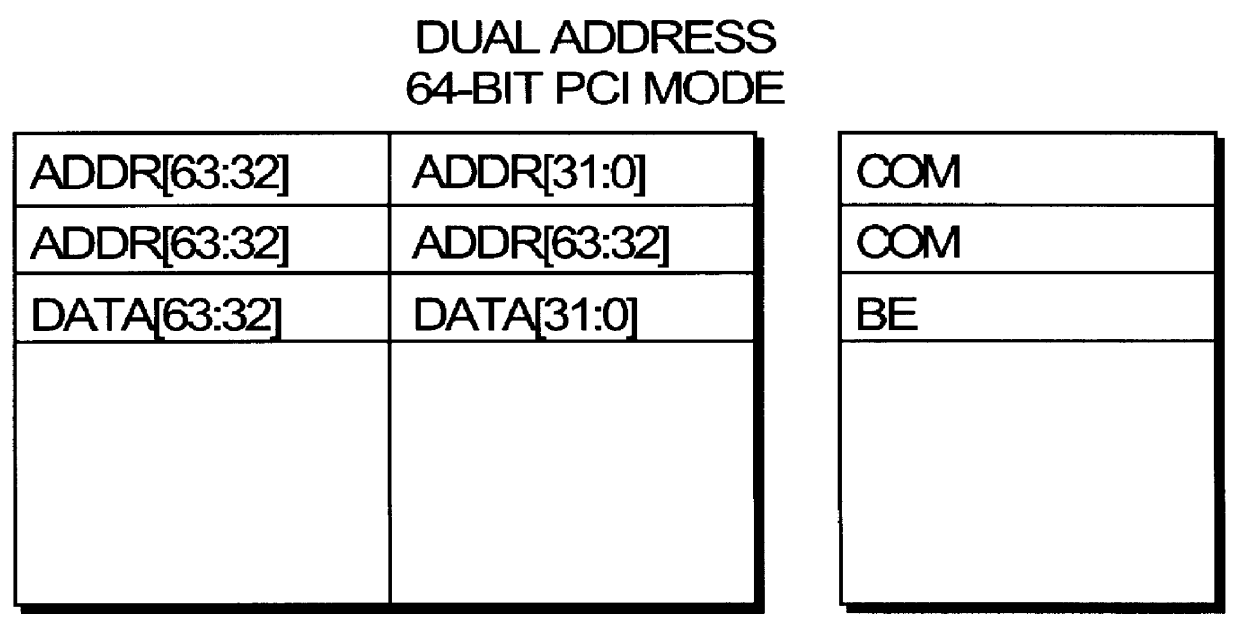
InactiveCN1516014ALarge memory spaceVerify performanceDetecting faulty computer hardwareInternal memoryTest card
The present invention relates to a testing method of interconnection buss for peripheral components. It utilizes PCI test card to directly operate I / O and internal memory space of PCI bus map, firstly, the PCI test card is inserted into PCI slot, then according to the configuration information the parameters required for host access can be distributed for said PCI test card, then the parameters can be written into the PCI configuration space of PCI test card, according to said configuration space the port mapping mode of said PCI test card can be defined, the data can be written into 32-bit and 64-bit address respectively, finally, according to fetch result the test conclusion can be obtained.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
Dual mode bus bridge for interfacing a host bus and a personal computer interface bus
InactiveUS6047120AConcurrent instruction executionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDual modeEngineering
The dual mode bus bridge accommodates either two 64-bit personal computer interface (PCI) buses or four 32-bit PCI buses. In either case, only a single load is applied to the host bus. The dual mode bridge includes a bridge controller unit connected to a pair of expansion bridge units by respective internal buses. Each expansion bridge unit includes two sets of 64-bit wide queues and buffers. For 32-bit PCI operation, the two sets of queues and buffers are operated in parallel. For 64-bit PCI operation, the two sets of queues and buffers are linked together so as to appear in series to provide a single queue structure having twice the depth of the separate queue structures for a 32-bit mode operation. As such, undue duplication of queue and buffer resources is avoided. Method and apparatus embodiments of the invention are described.
Owner:INTEL CORP
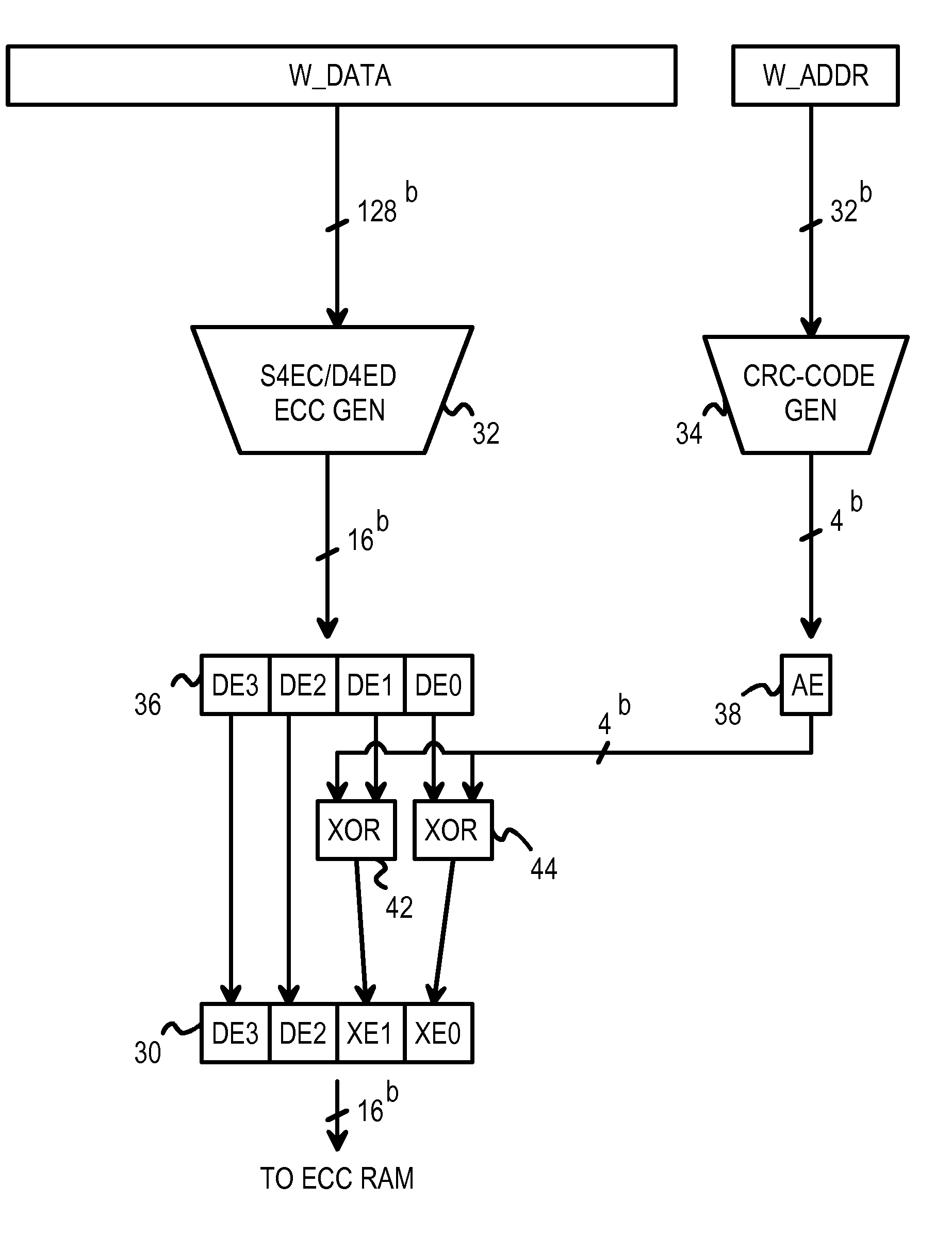
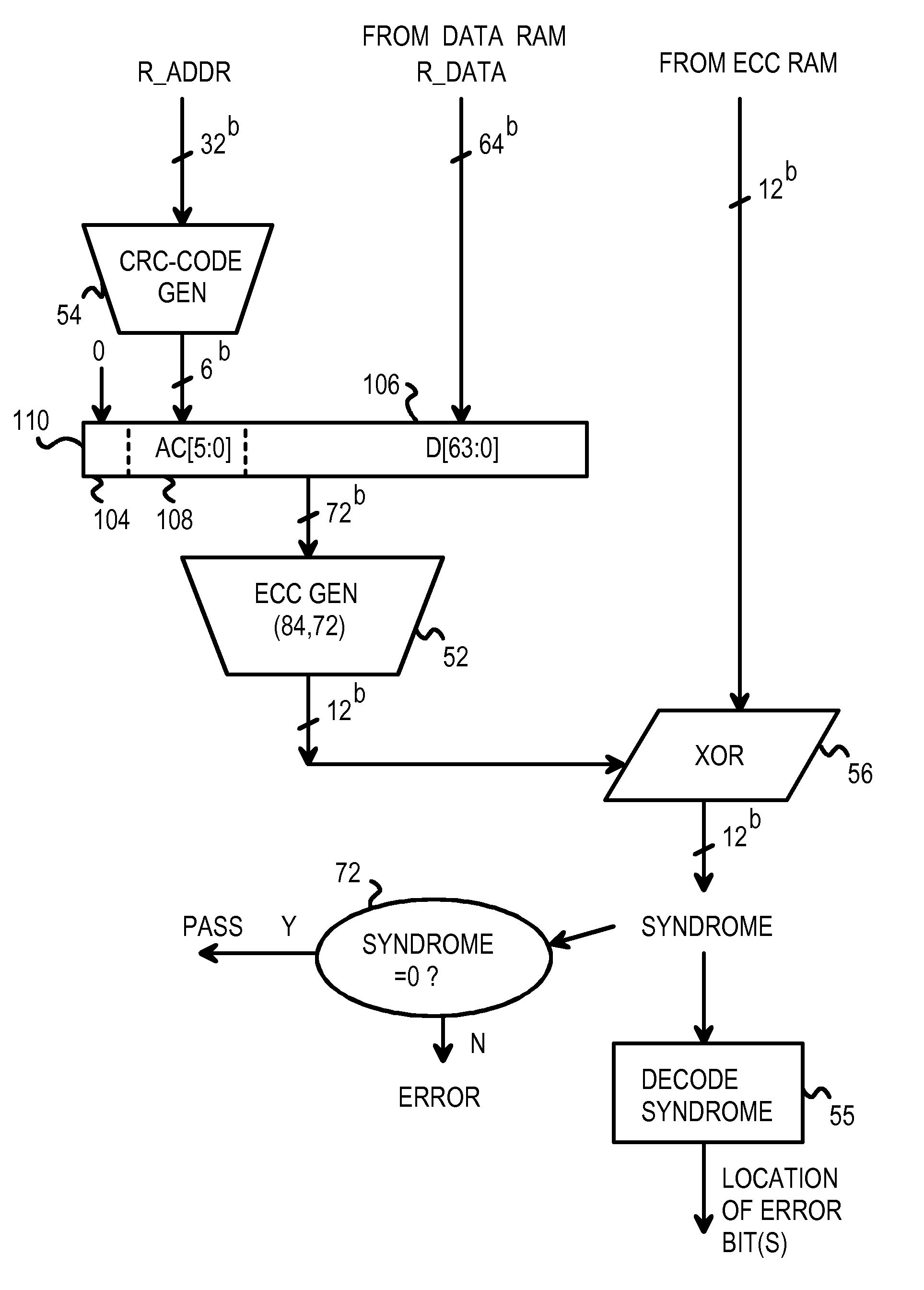
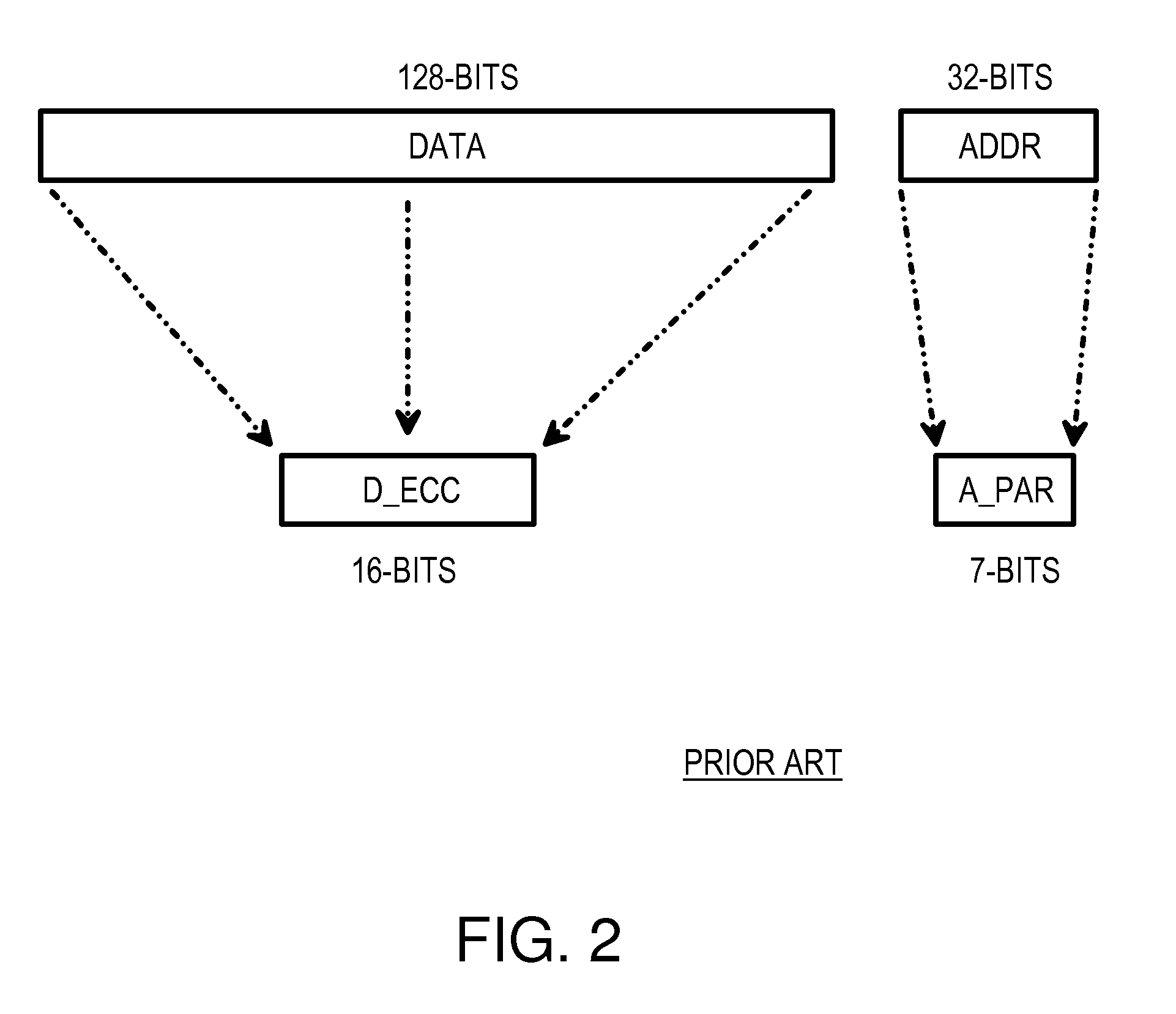
Subsystem and Method for Encoding 64-bit Data Nibble Error Correct and Cyclic-Redundancy Code (CRC) Address Error Detect for Use in a 76-bit Memory Module
A memory system provides data error detection and correction and address error detection. A cyclical-redundancy-check (CRC) code generates address check bits. A 32-bit address is compressed to 6 address check bits using the CRC code. The 6 address check bits are concatenated with 64 data bits and 2 flag bits to generate a 72-bit check word. The 72-bit check word is input to an error-correction code (ECC) generator that generates 12 check bits that are stored in memory with the 64 data bits. A 76-bit memory module can store the 64 data and 12 check bits. Nibble errors can be corrected, and all nibble+1 bit errors can be detected. Also, a 6-bit error in a sequence of bits can be detected. This allows all errors in the 6-bit CRC of the address to be detected. The CRC code and ECC are ideal for detecting double-bit errors common with multiplexed-address DRAMs.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
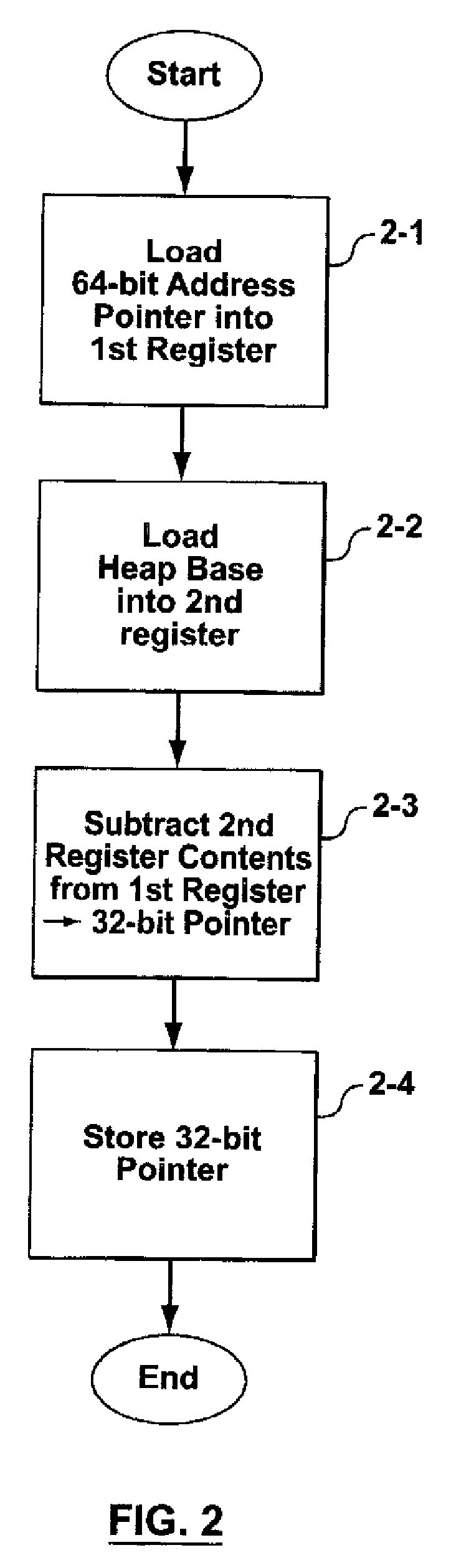
Methods and computer program products for implementing low-cost pointer compression and decompression
InactiveUS20090119321A1Program controlSpecial data processing applications64-bit computingProgram transformation
Prior art attempts to provide 32-bit addressing within a 64-bit computing environment lead to other complications. Hardware solutions result in more complicated hardware which, in turn, increases costs and may reduce the functionality of 64-bit computing and significant changes to commercially available 64-bit processors. Alternatively, previous software solutions are computationally expensive, requiring add and subtract routines convert between 32-bit addresses and 64-bit addresses. An additional problem, specific to IBM™ zSeries hardware, is that the only way to provide a heap size larger than 2 GB, even if less than 4 GB, is to employ the 64-bit addressing in combination with a computationally expensive software patch to emulate 32-bit addressing. By contrast, provided by aspects of the present invention there are systems, methods and computer program products for implementing low-cost pointer compression and decompression. In accordance with more specific aspects of the invention, the systems, methods and computer program products for implementing low-cost point compression and decompression can be specifically adapted to compress 64-bit pointers to 32-bit pointers, and conversely convert 32-bit pointers to 64-bit pointers.
Owner:IBM CORP
Subsystem and method for encoding 64-bit data nibble error correct and cyclic-redundancy code (CRC) address error detect for use in a 76-bit memory module
A memory system provides data error detection and correction and address error detection. A cyclical-redundancy-check (CRC) code generates address check bits. A 32-bit address is compressed to 6 address check bits using the CRC code. The 6 address check bits are concatenated with 64 data bits and 2 flag bits to generate a 72-bit check word. The 72-bit check word is input to an error-correction code (ECC) generator that generates 12 check bits that are stored in memory with the 64 data bits. A 76-bit memory module can store the 64 data and 12 check bits. Nibble errors can be corrected, and all nibble+1 bit errors can be detected. Also, a 6-bit error in a sequence of bits can be detected. This allows all errors in the 6-bit CRC of the address to be detected. The CRC code and ECC are ideal for detecting double-bit errors common with multiplexed-address DRAMs.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
Dynamic bank mode addressing for memory access
ActiveUS20130268715A1Avoid bank conflictsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationConcurrent instruction executionParallel computing64-bit computing
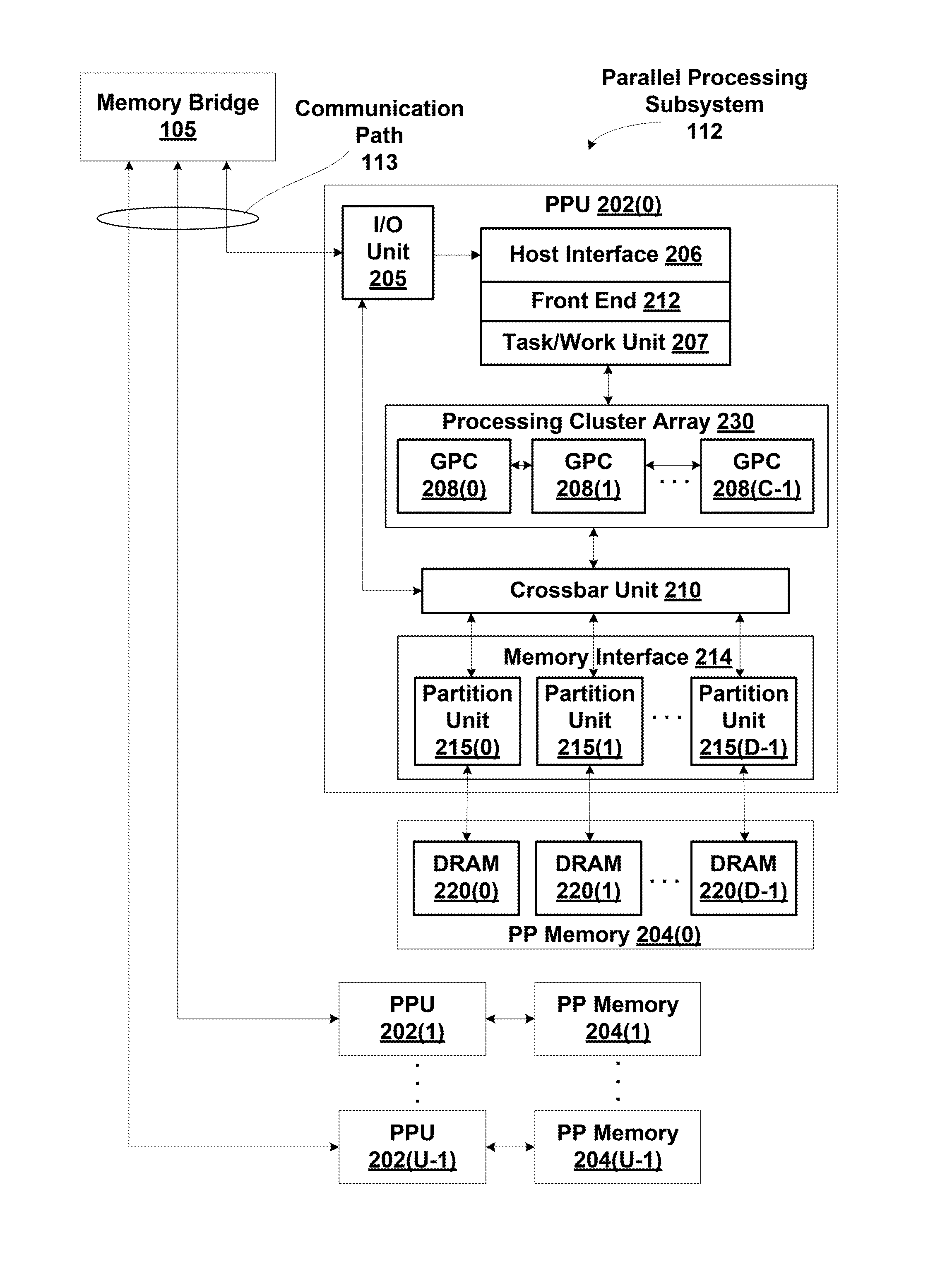
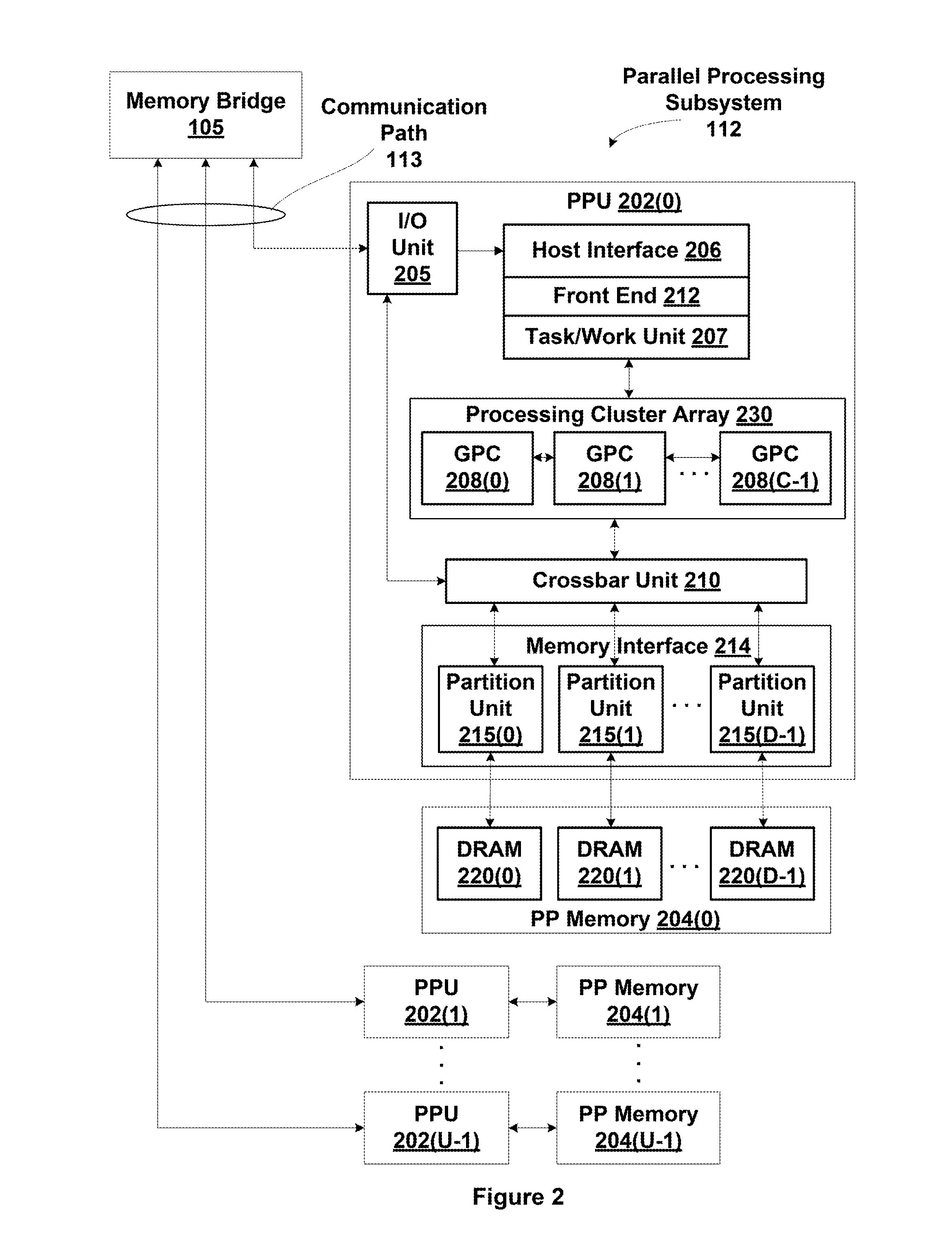
One embodiment sets forth a technique for dynamically mapping addresses to banks of a multi-bank memory based on a bank mode. Application programs may be configured to perform read and write a memory accessing different numbers of bits per bank, e.g., 32-bits per bank, 64-bits per bank, or 128-bits per bank. On each clock cycle an access request may be received from one of the application programs and per processing thread addresses of the access request are dynamically mapped based on the bank mode to produce a set of bank addresses. The bank addresses are then used to access the multi-bank memory. Allowing different bank mappings enables each application program to avoid bank conflicts when the memory is accesses compared with using a single bank mapping for all accesses.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
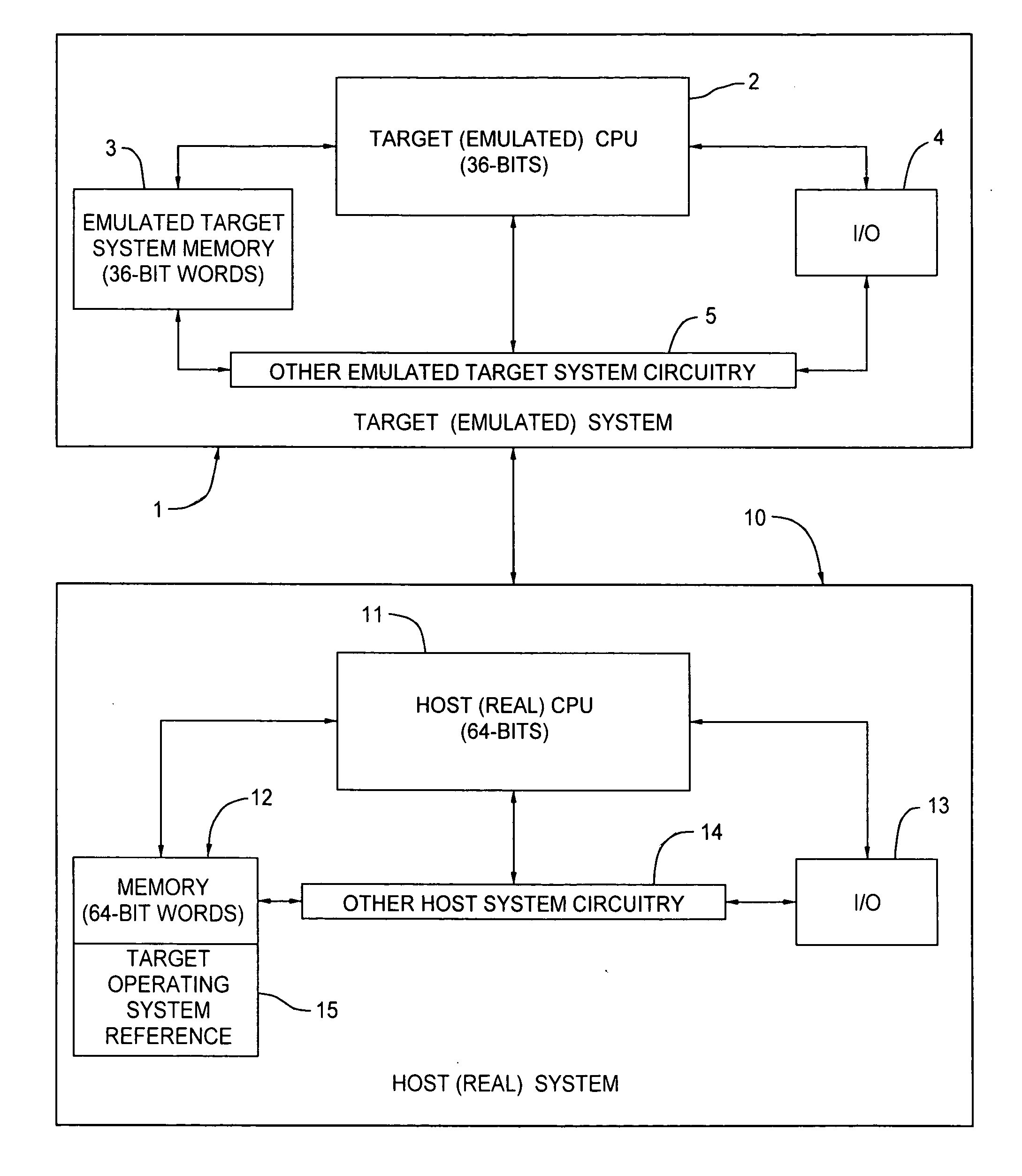
Host computer system emulating target system lagacy software and providing for incorporating more powerful application program elements into the flow of the legacy software
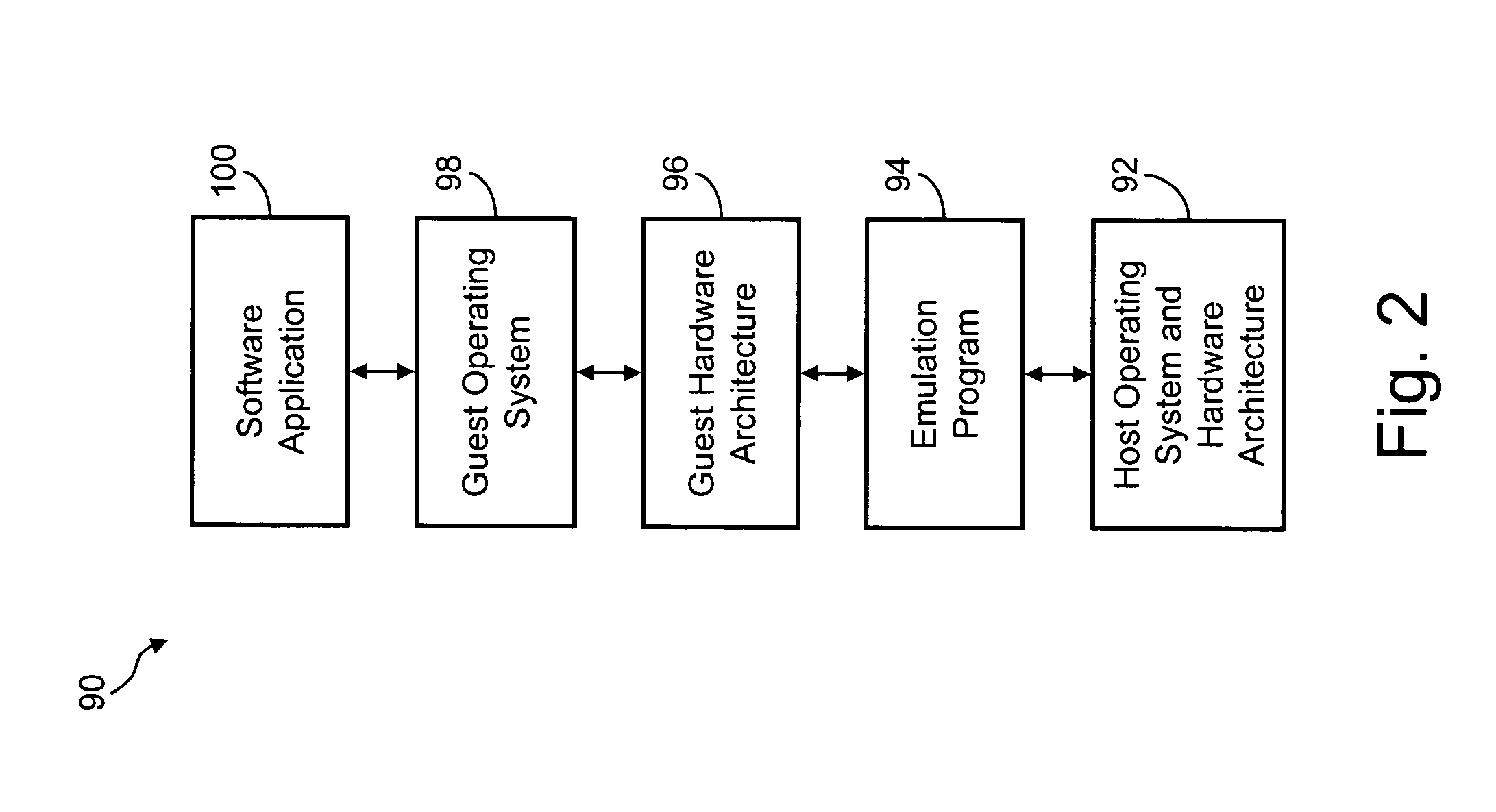
ActiveUS20070156391A1Faster and more versatile operationImprove abilitiesDigital computer detailsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProprietary hardwareSoftware emulation
As manufacturers of very fast and powerful commodity processors continue to improve the capabilities of their products, it has become practical to emulate the proprietary hardware and operating systems of powerful older computers on platforms built using commodity processors such that the manufacturers of the older computers can provide new systems which allow their customers to continue to use their highly-regarded proprietary legacy software on state-of-the-art new computer systems by emulating the older computer in software that runs on the new systems. In an example of the subject invention, a 64-bit Cobol Virtual Machine instruction provides the capability of adding to or improving the performance of legacy 36-bit Cobol code. Legacy Cobol instructions can be selectively diverted, in the host CPU, to a 64 bit Virtual Machine Implementation. The output legacy and new Cobol code is compiled in a dedicated implementation of the Cobol compiler, and the output of the special purpose compiler is emulated in a special purpose software emulator, separate from the main software emulator that handles the normal 36-bit stream of legacy code.
Owner:BULL HN INFORMATION SYST INC
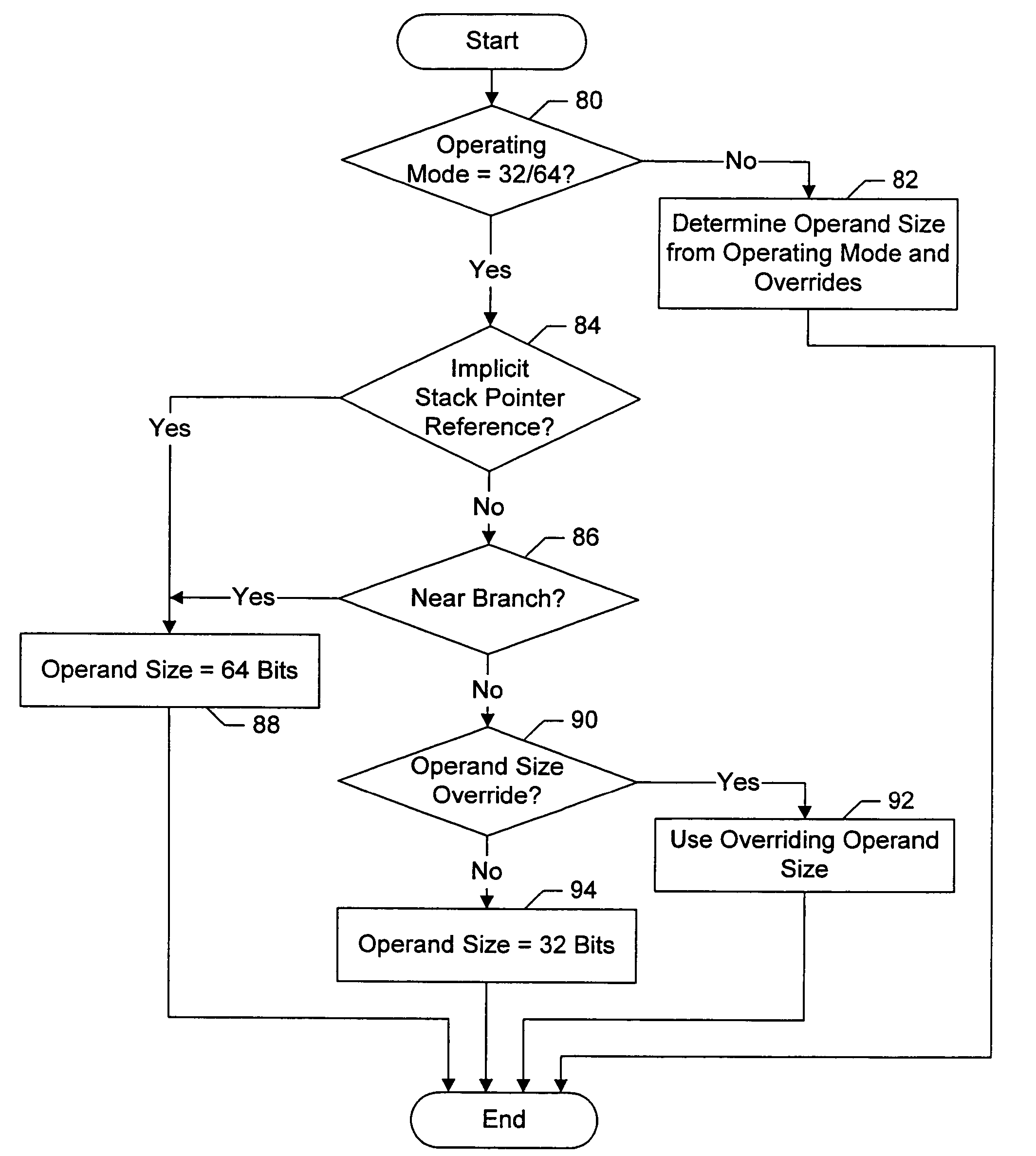
Processor which overrides default operand size for implicit stack pointer references and near branches
A processor supports a mode in which the default operand size is 32 bits, but which supports operand size overrides to 64 bits. Furthermore, the default operand size may automatically be overridden to 64 bits for instructions having an implicit stack pointer reference and for near branch instructions. The overriding of the default operand size may occur without requiring an operand size override encoding in these instructions. In one embodiment, the instruction set specifying the instructions may be a variable byte length instruction set (e.g. x86), and the operand size override encoding may be a prefix byte which increases the instruction length.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Lock-free concurrent object dictionary
ActiveUS8443155B2Reduce memory requirementsSave memoryProgram controlMemory systemsObject storage64-bit computing
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
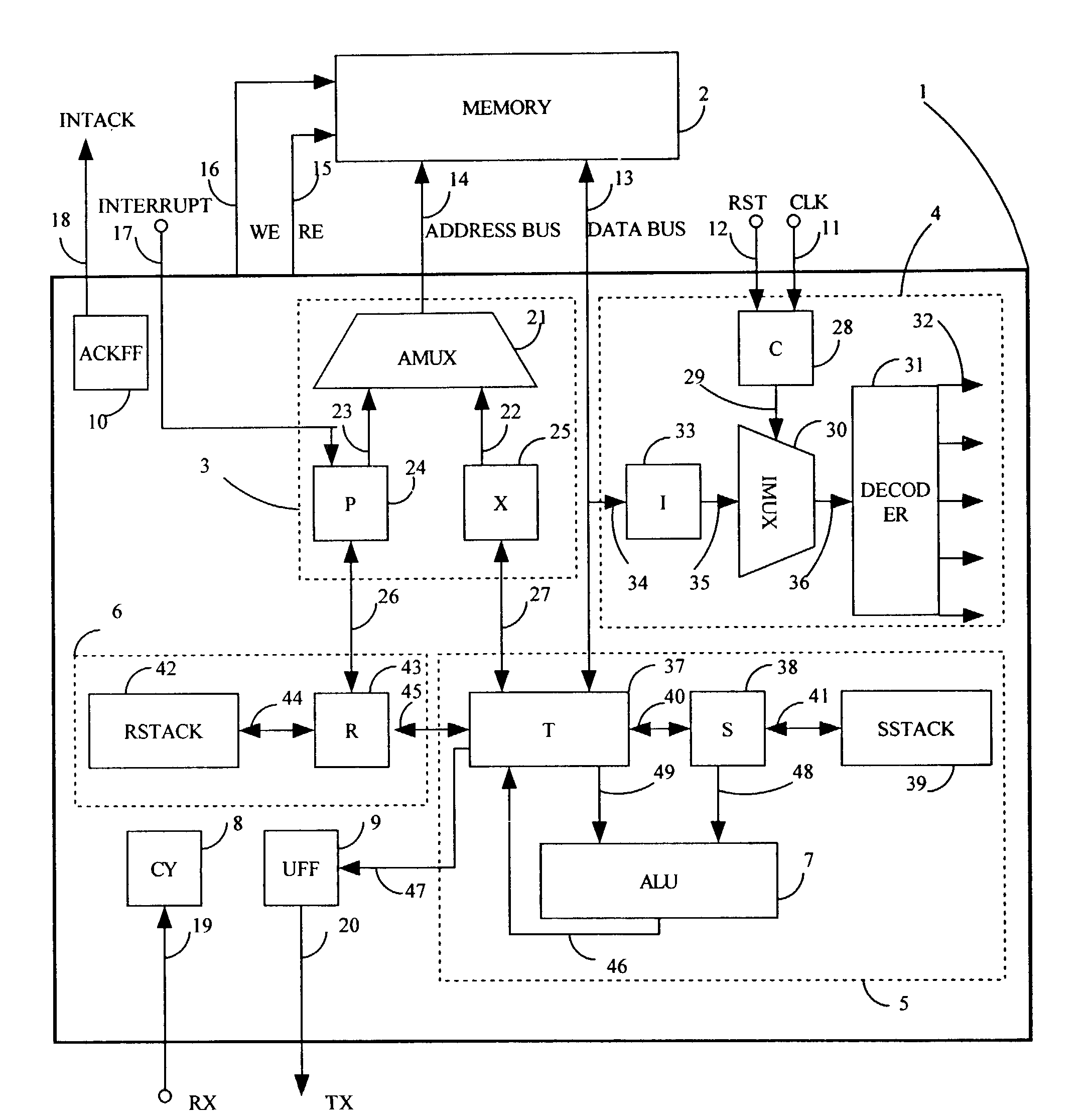
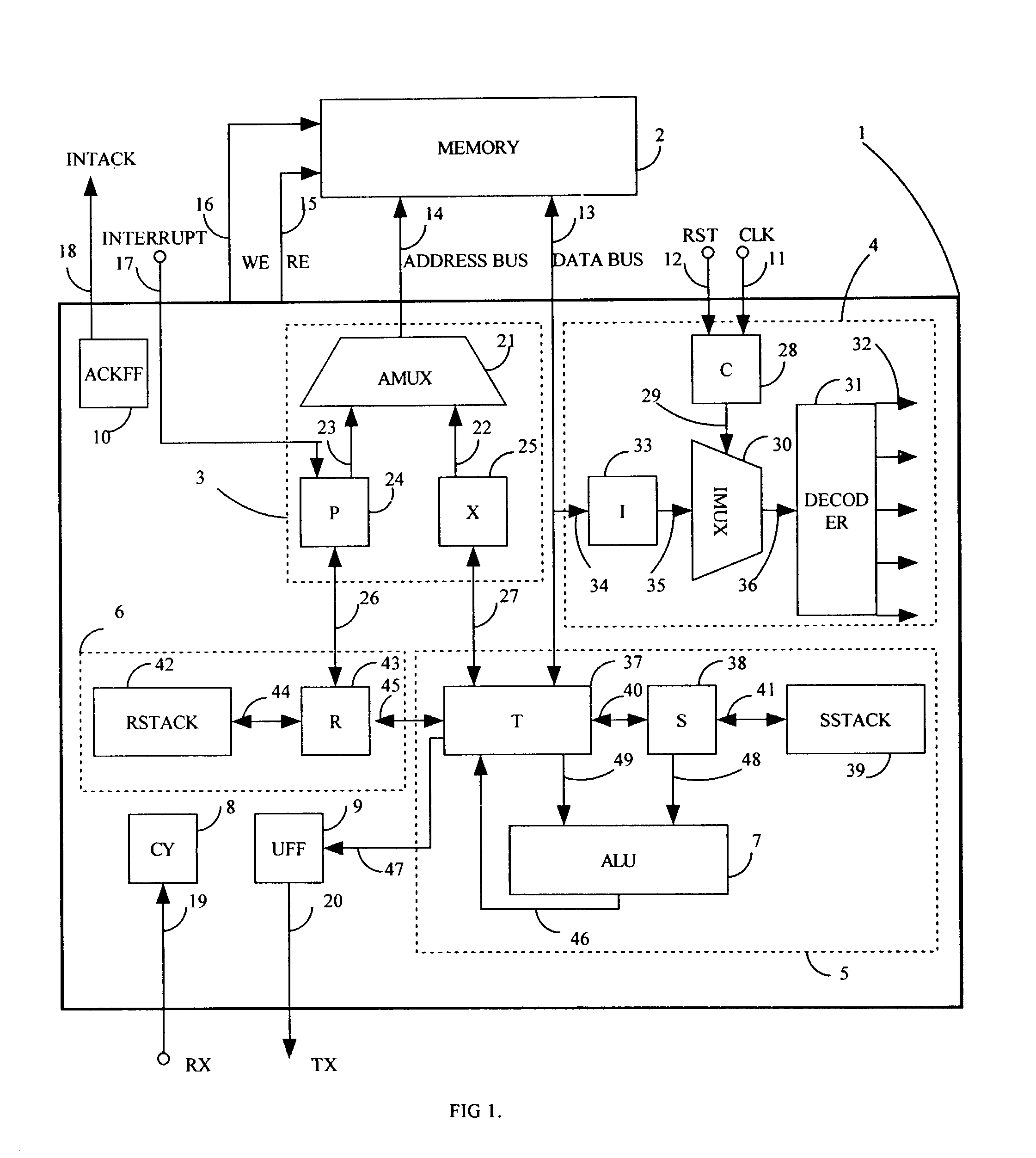
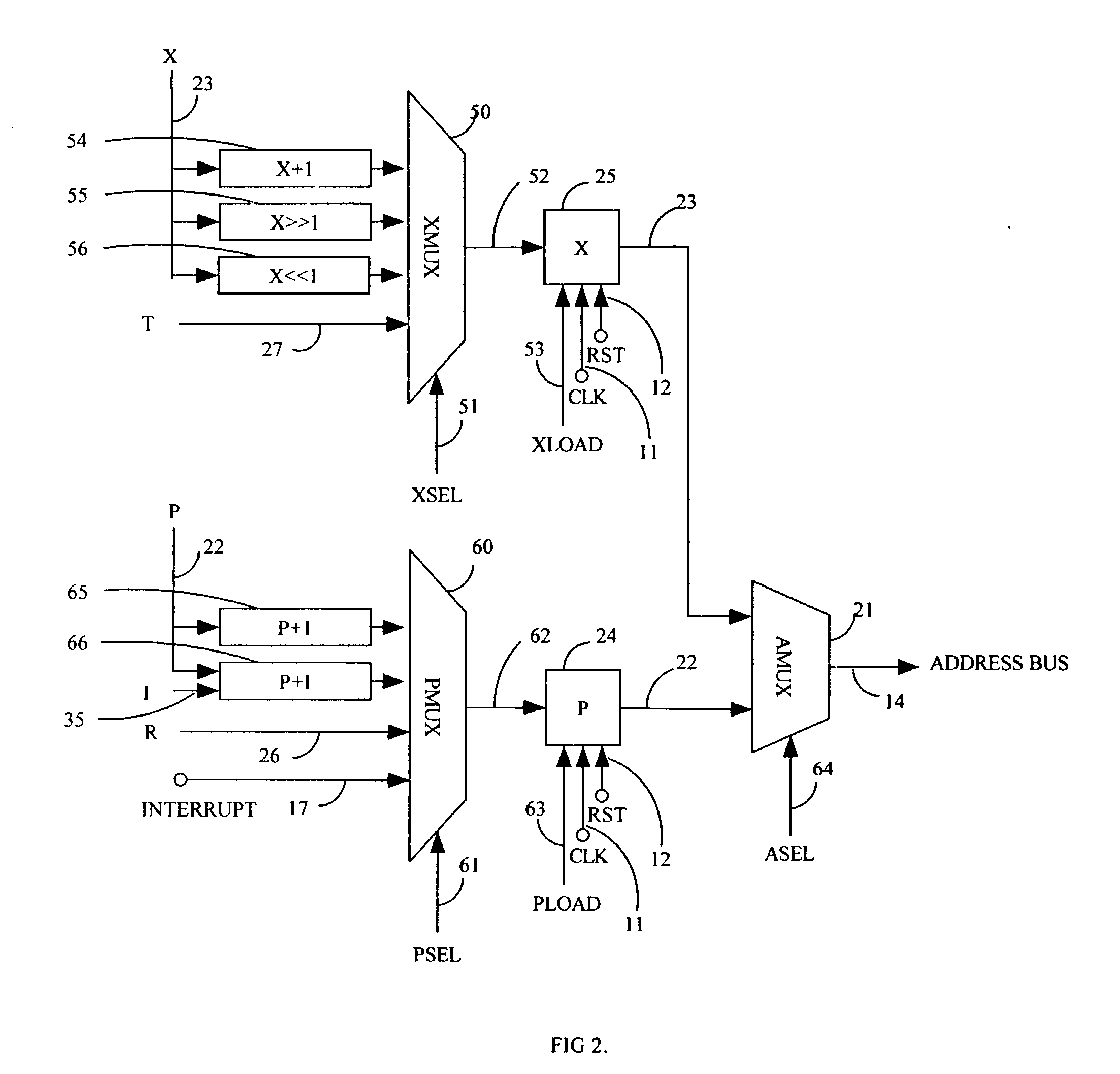
64 bit floating-point integer amalgamated arithmetic group capable of supporting local register and conditional execution
InactiveCN101021832AExtended Data WidthWide data widthArchitecture with multiple processing unitsInstruction memoryFloating point
The invention discloses a 64-bit floating-point integer-fusion operation group which support partial deposit and conditional execution. It includes one or more 64-bit floating point / integer-fusion arithmetic unit, conditional execution unit, component interconnect structure and control unit. The computing unit is connected with conditional execution unit by interconnect structure which also is used to transfer data among units. The storage address of operation group is made up of several independent address spaces, and the local operations can indirectly visiting each address space by unified controller. There are specialized instruction register to storage compiled order. The controller send the compiled instruction to each function unit of the corresponded computing group at the same time when the program running, then each group receive instructions and run it by SIMD and storage the result in the same LRF or output.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
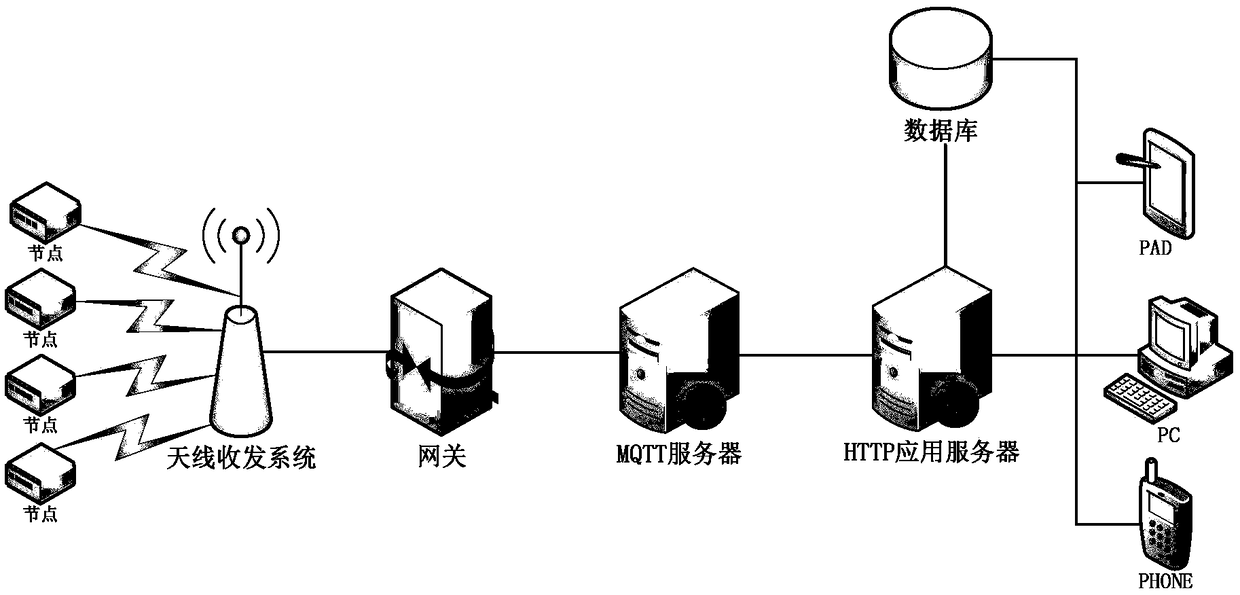
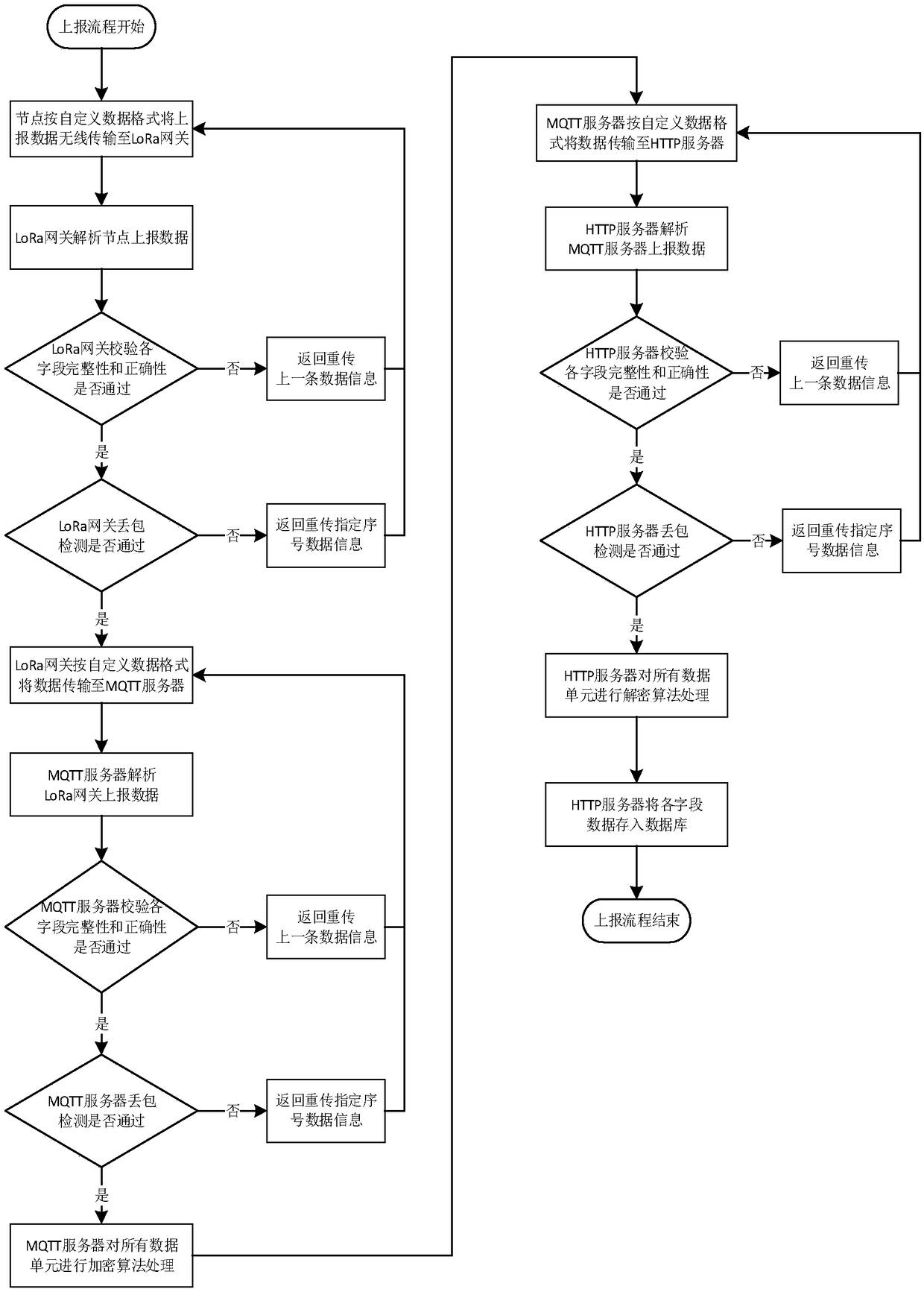
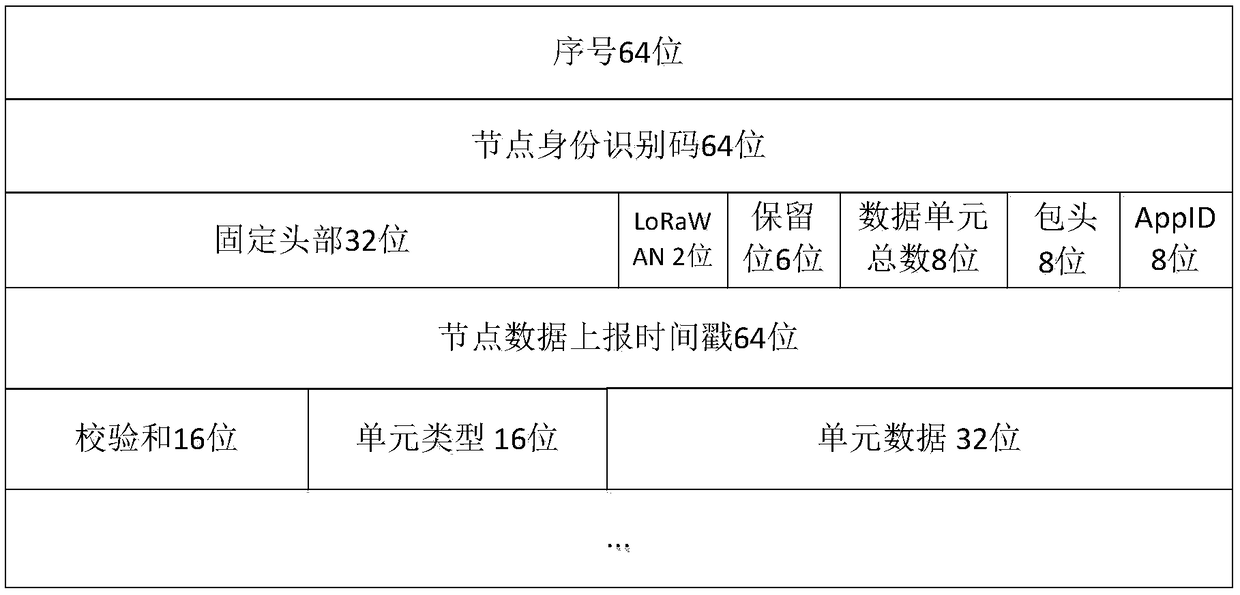
A data reporting and instruction sending method based on LoRa Internet of Things
InactiveCN108989455ASolve the errorResolve integrityTransmission systemsData switching networksPacket lossOriginal data
A method for node data reporting and instruction issuing based on LoRa Internet of Things comprises the following steps: step S1-1) the LoRa network node reports the data packet to the LoRa gateway according to the self-defined data format; Step S1-2) the LoRa gateway analyzes the data packet according to the self-defined data format, carries out integrity and correctness verification of each field and packet loss detection, and after the checksum detection is passed, a 64-bit LoRa gateway identification code is added into the data packet and sent to the MQTT server through the MQTT protocol;Step S1-3) the MQTT serv parses the data packet according to the self-defined data format, after passing the check and packet loss detection, encrypts all data units of the data packets, and then sends the data packets to the HTTP server through the MQTT protocol; Step S1-4) the HTTP server parses the data packet according to the self-defined data format, after the checksum packet loss detection is passed, decrypts all data units of the data packet, obtains the original data units, and then stores the data of each field of the data packet into the database.
Owner:NANHAI RES STATION OF INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
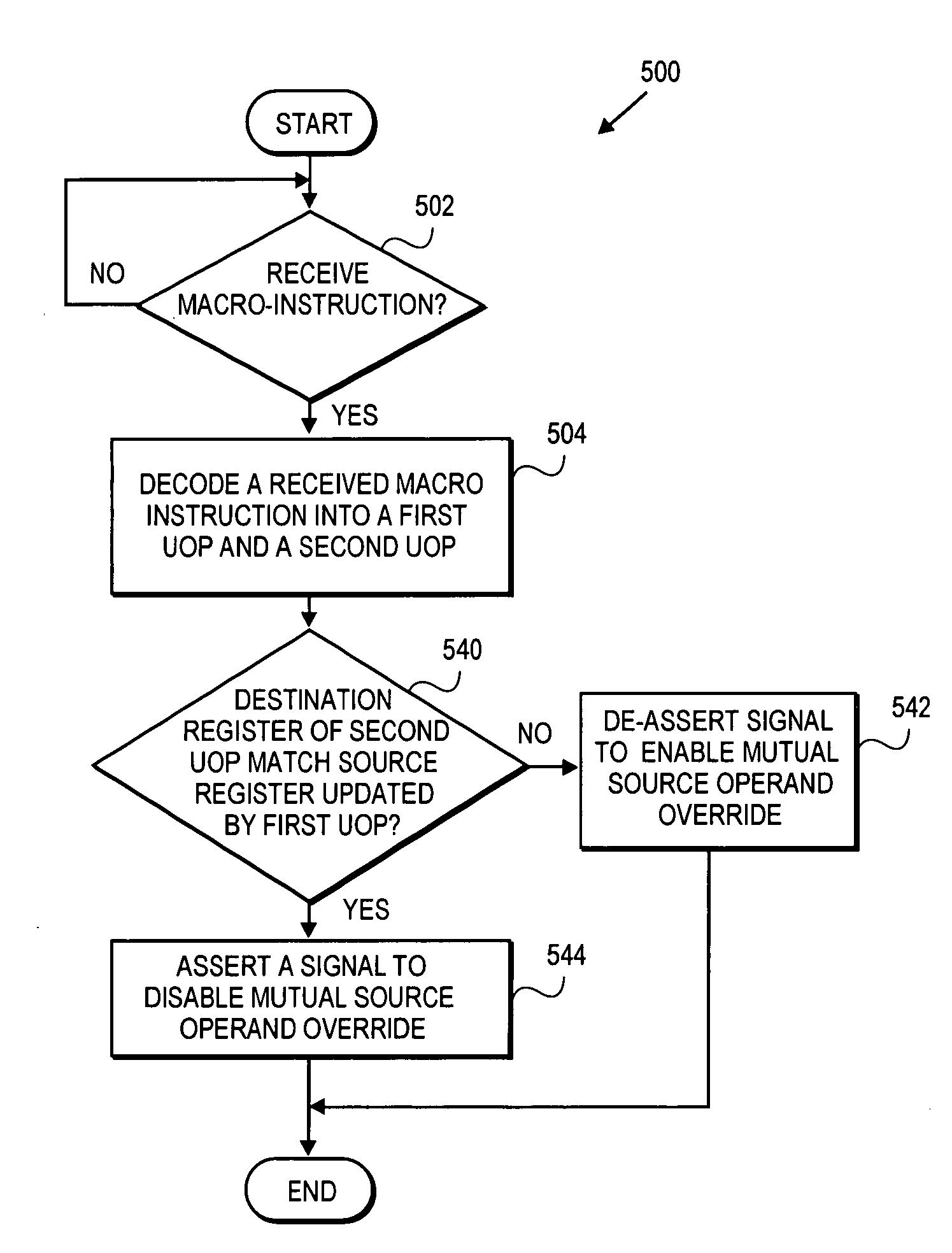
Apparatus and method for two micro-operation flow using source override
InactiveUS20050027967A1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyInstruction analysisRuntime instruction translationProgramming languageMicro-operation
A method and apparatus for a two micro-operation flow using source override. In one embodiment, the method includes the identification of a macro-instruction having one or more streaming single instruction multiple data extension type operands. Once received, the macro-instruction is decoded into a first micro-operation (uOP) and a second uOP. Once decoded, a signal is asserted to disable source operand override logic if the first micro-operation updates a logical destination register that matches a logical source register of the micro-operation. Otherwise, the mutual source override is active and executed by a register alias table (RAT) when uOP with matching logic source and destination register are detected in a same clock cycle. In doing so, macro-instructions having 128-bit operands may be processed using, for example, two uOPs (one for the lower half and one for the upper half) in a 64-bit implementation, while preserving the atomicity of the original instruction.
Owner:INTEL CORP
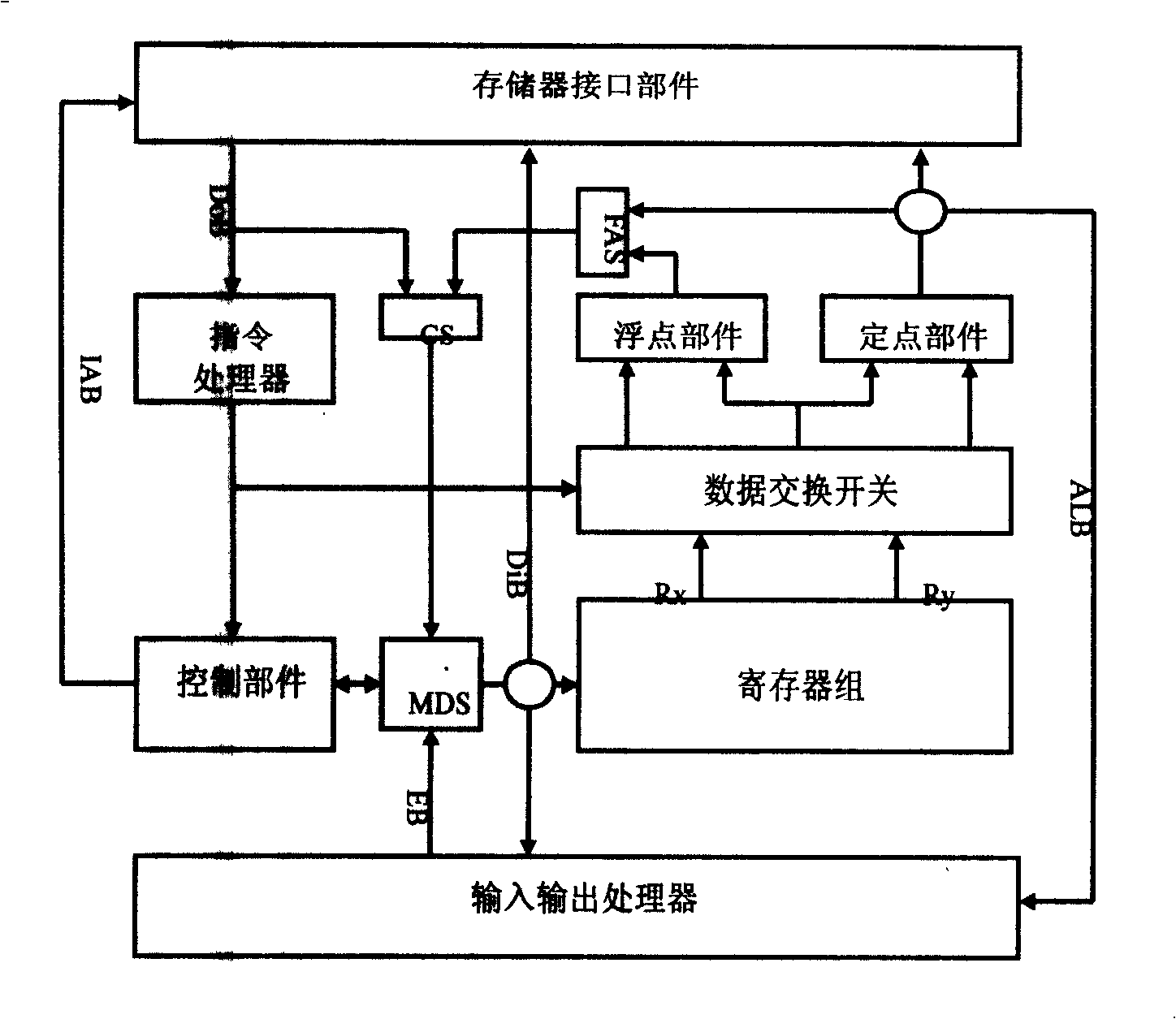
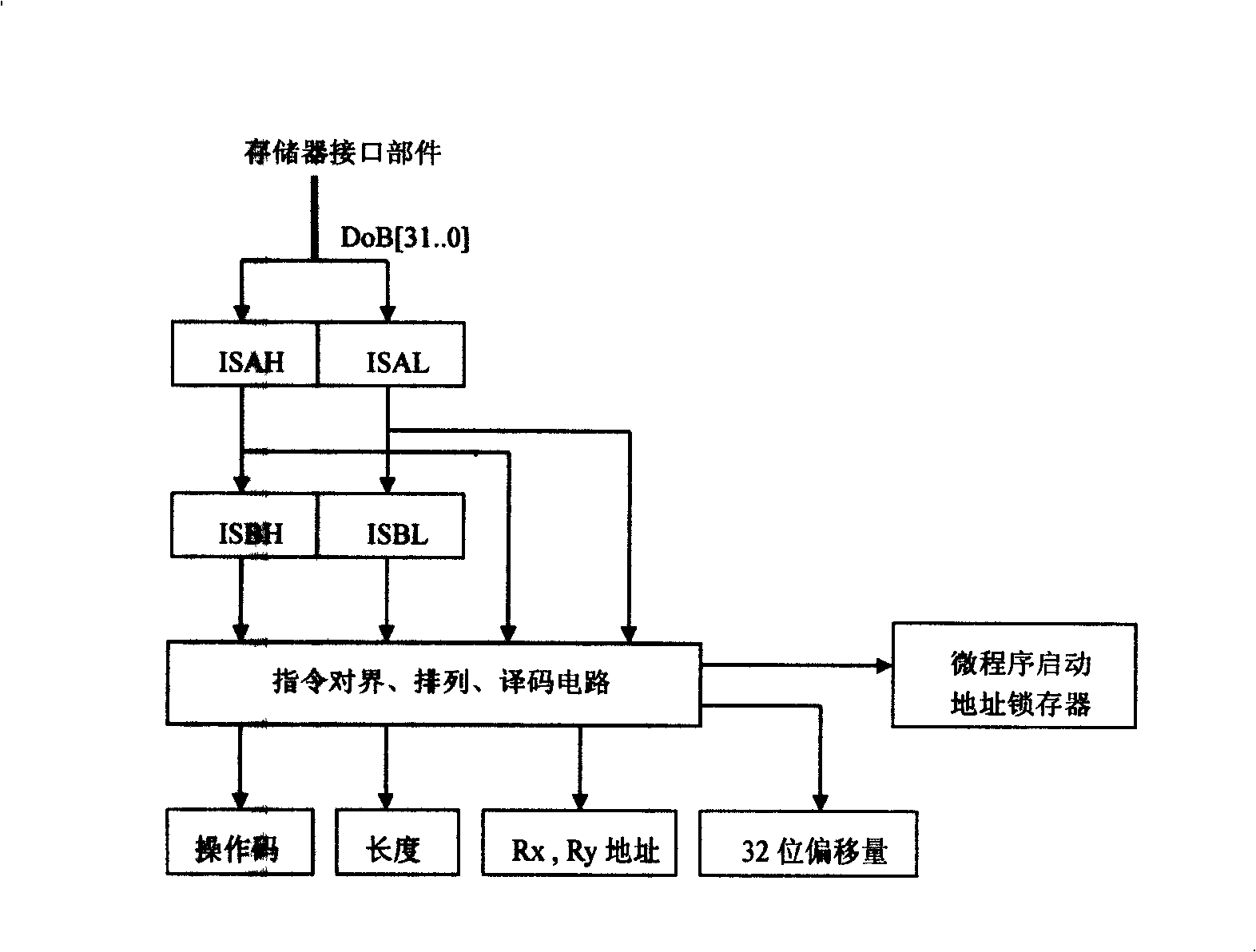
32 bits micro-processor
InactiveCN101256546AConcurrent instruction executionArchitecture with single central processing unitMemory interfaceInstruction cycle
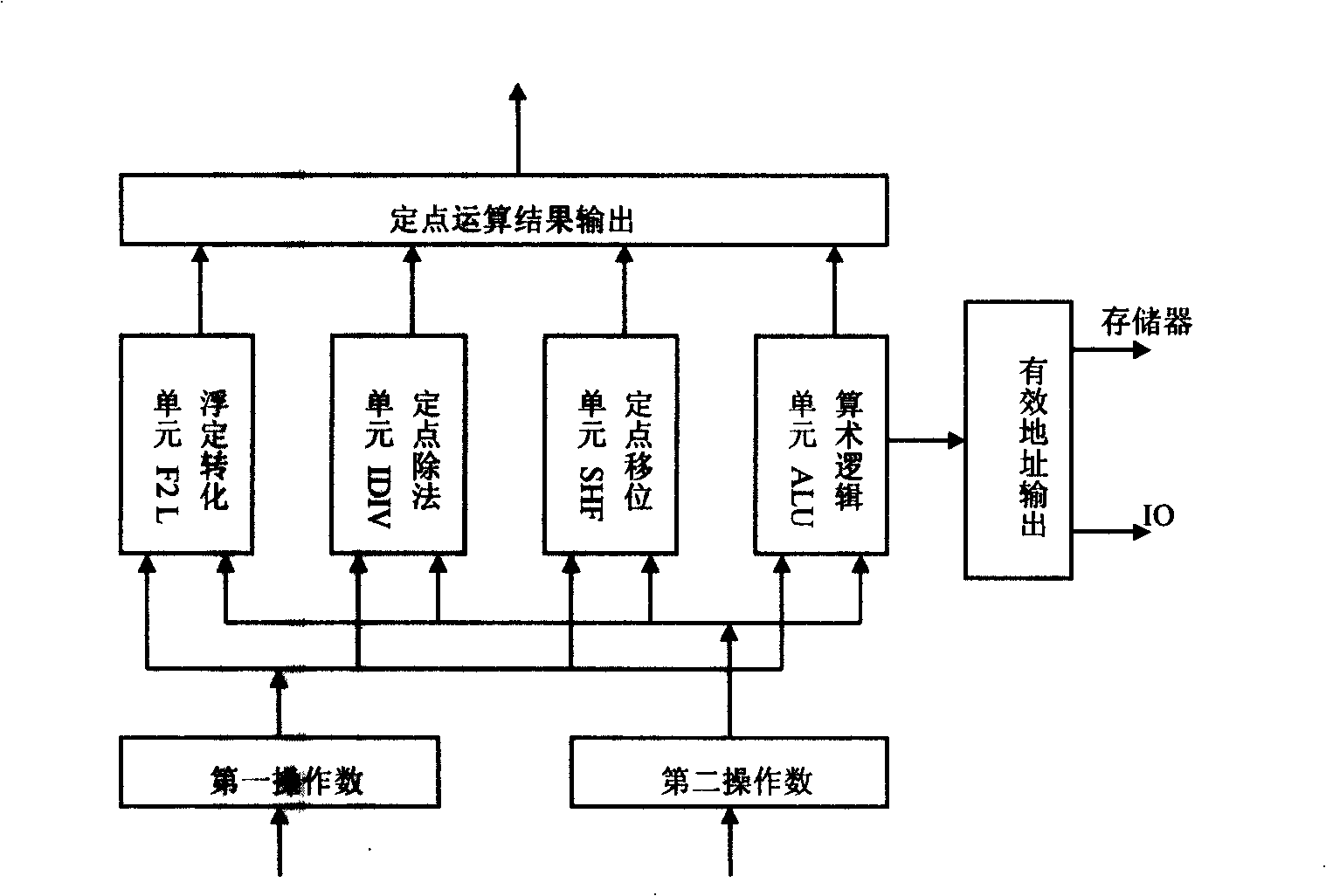
The invention relates to a 32 bits microprocessor and its instruction set. The microprocessor system comprises an instruction processor, a control component, a fixing point operation a floating-point operation, a register group, a storage interface component and an I / O processor. The entire instruction cycle adapts two state pipelining and is simple in structure. The system is provided with 16 32 bits general registers which hold 4GB storage address space and input output address space. The storage, the I / O processor and the central processor are connected with 64 bits data path. The speed of the processor can be up to 32 bits instruction flow and 32 bits data flow in each clock cycle. The microprocessor system supports 16 bits, 32 bits and 48 bits three instruction formats which are nine kinds and 50 instructions, wherein, the floating-point add, subtract, multiply and divide, fixing-point divide, fixing-point modulus, the conversion between floating-point and fixing-point are all realized by instructions. The instruction is simplified in number but is strong in function, and also has advantages of RISC and CISC.
Owner:黄新亚 +1
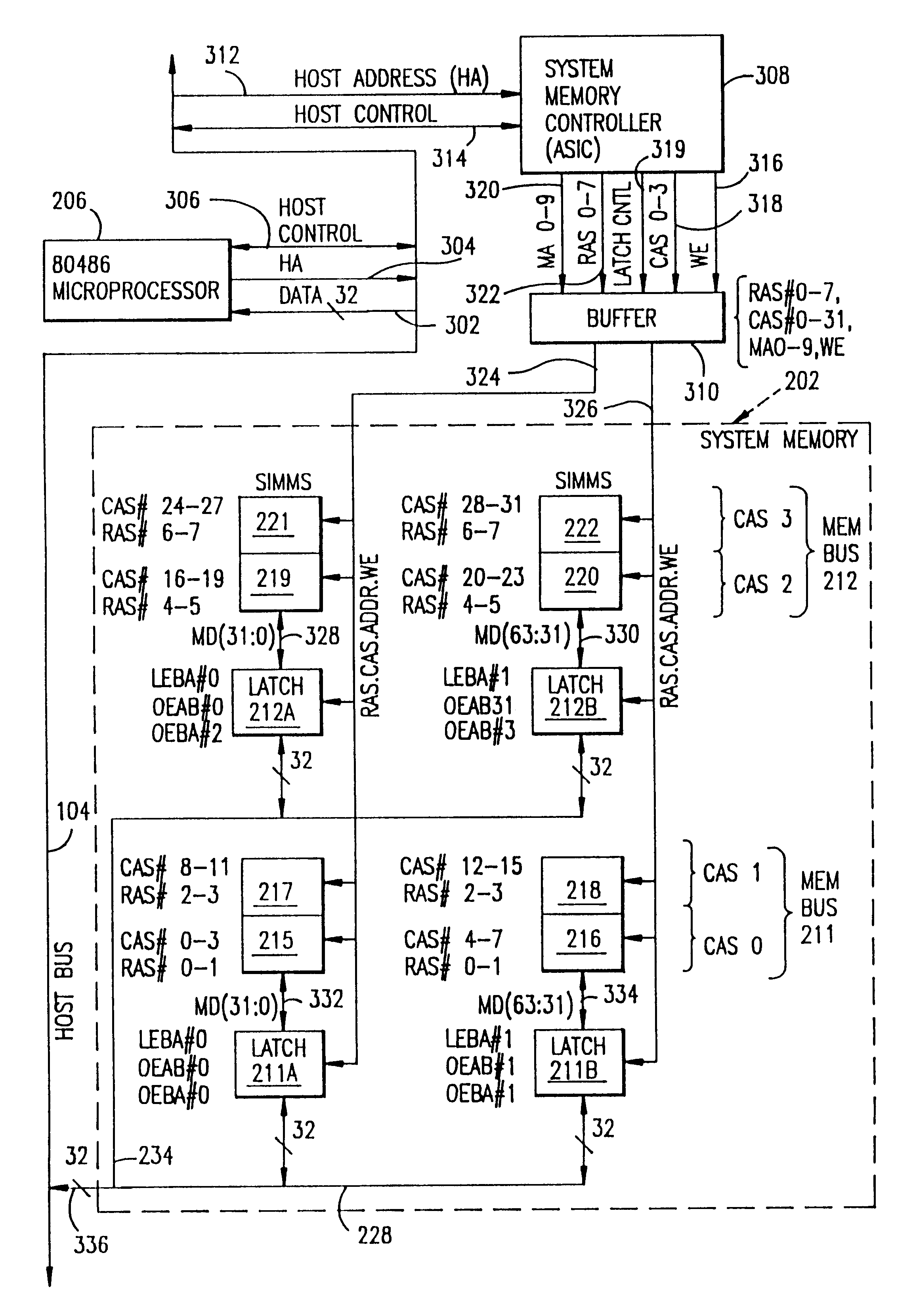
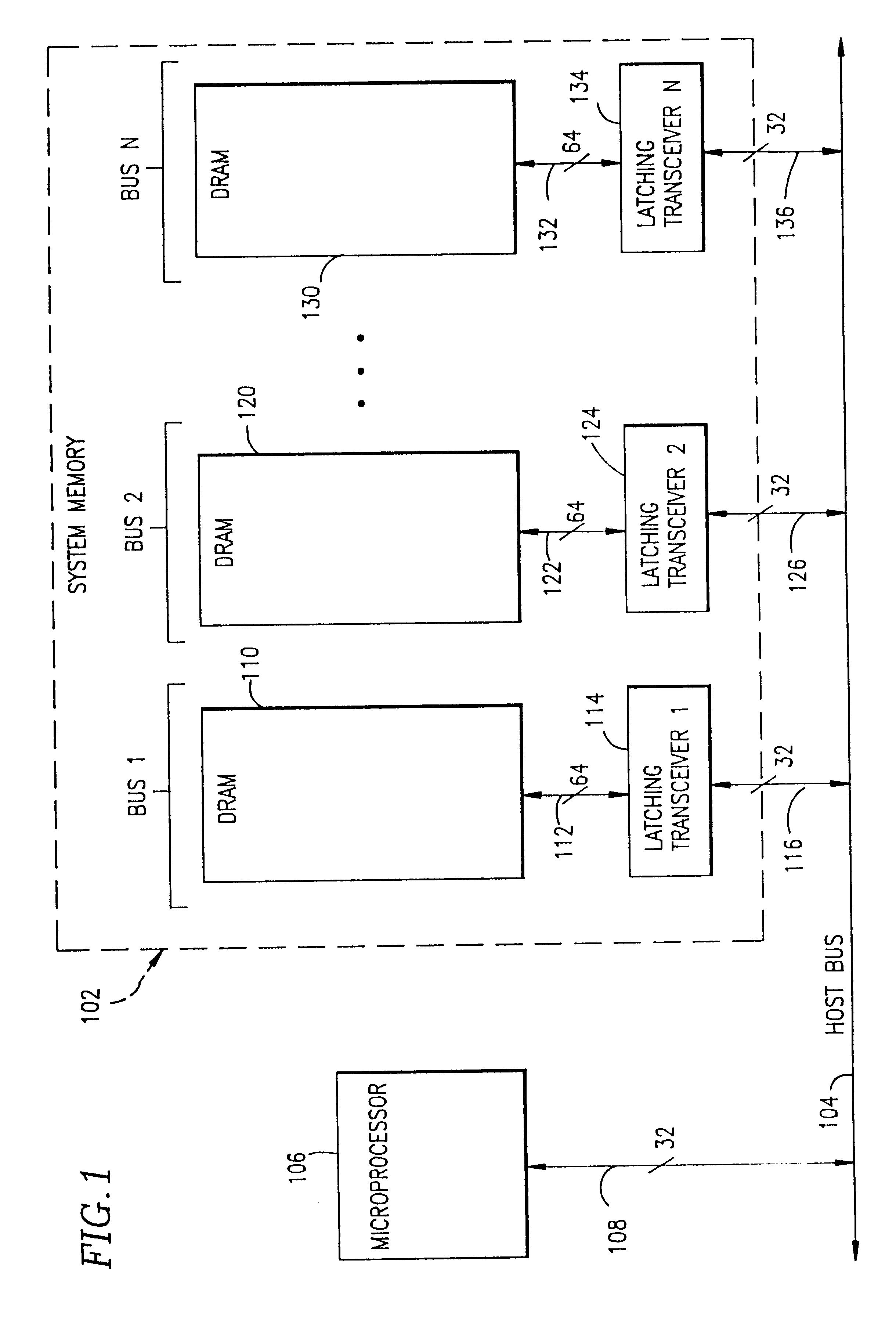
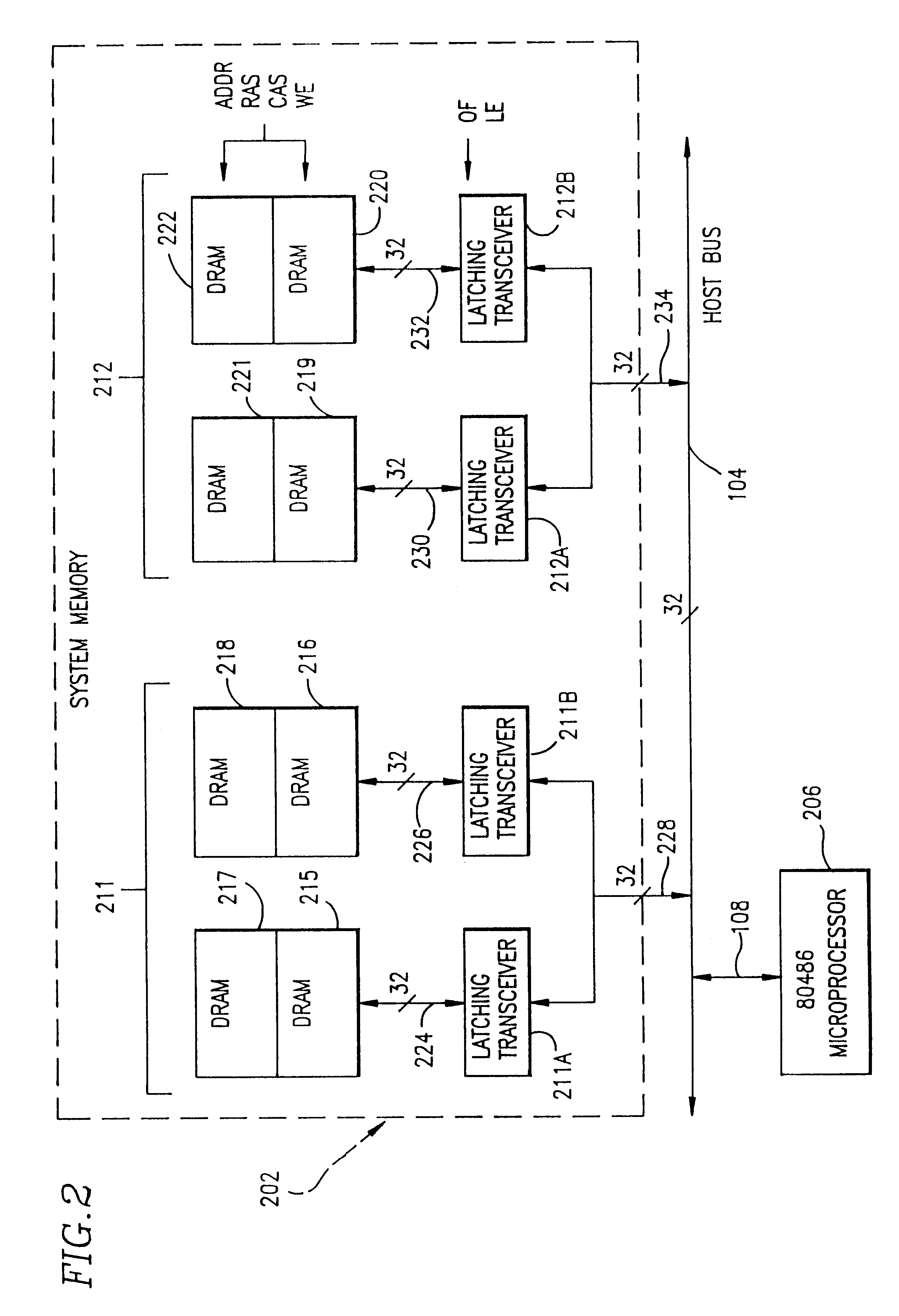
System and method for accessing data between a host bus and a system memory bus where the system memory bus has a data path that is twice the width of the data path for the host bus
A microcomputer system memory architecture and method allows the system memory to provide data access at high speeds in a burst mode. The architecture and method utilizes a system memory controller capable of performing the addressing of the system memory. The microprocessor and the system memory communicate via a high speed host bus. The system memory is comprised of multiple 64-bit system memory buses to permit high speed data transfer to the microprocessor in a burst mode without the need for an external cache.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO
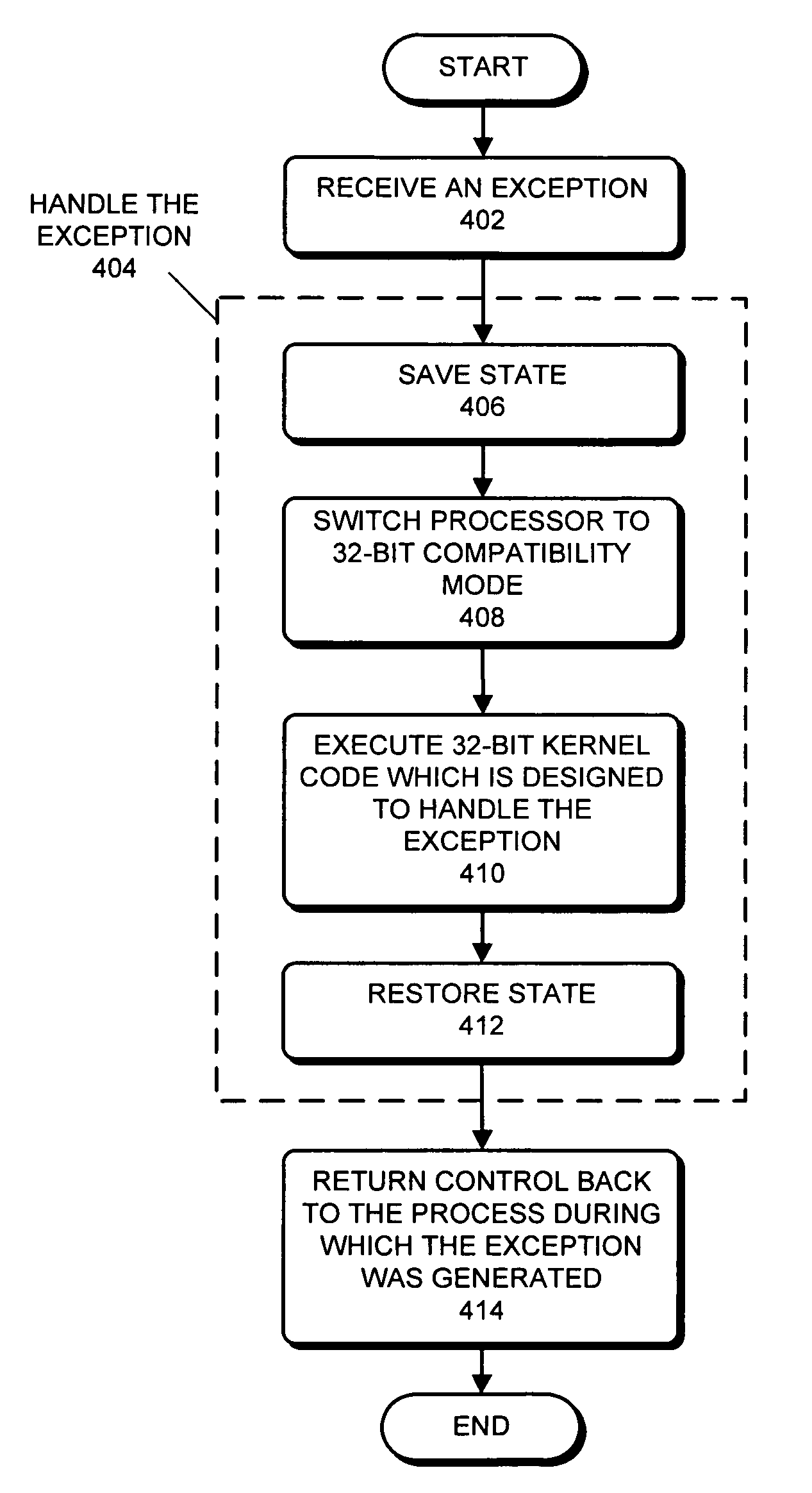
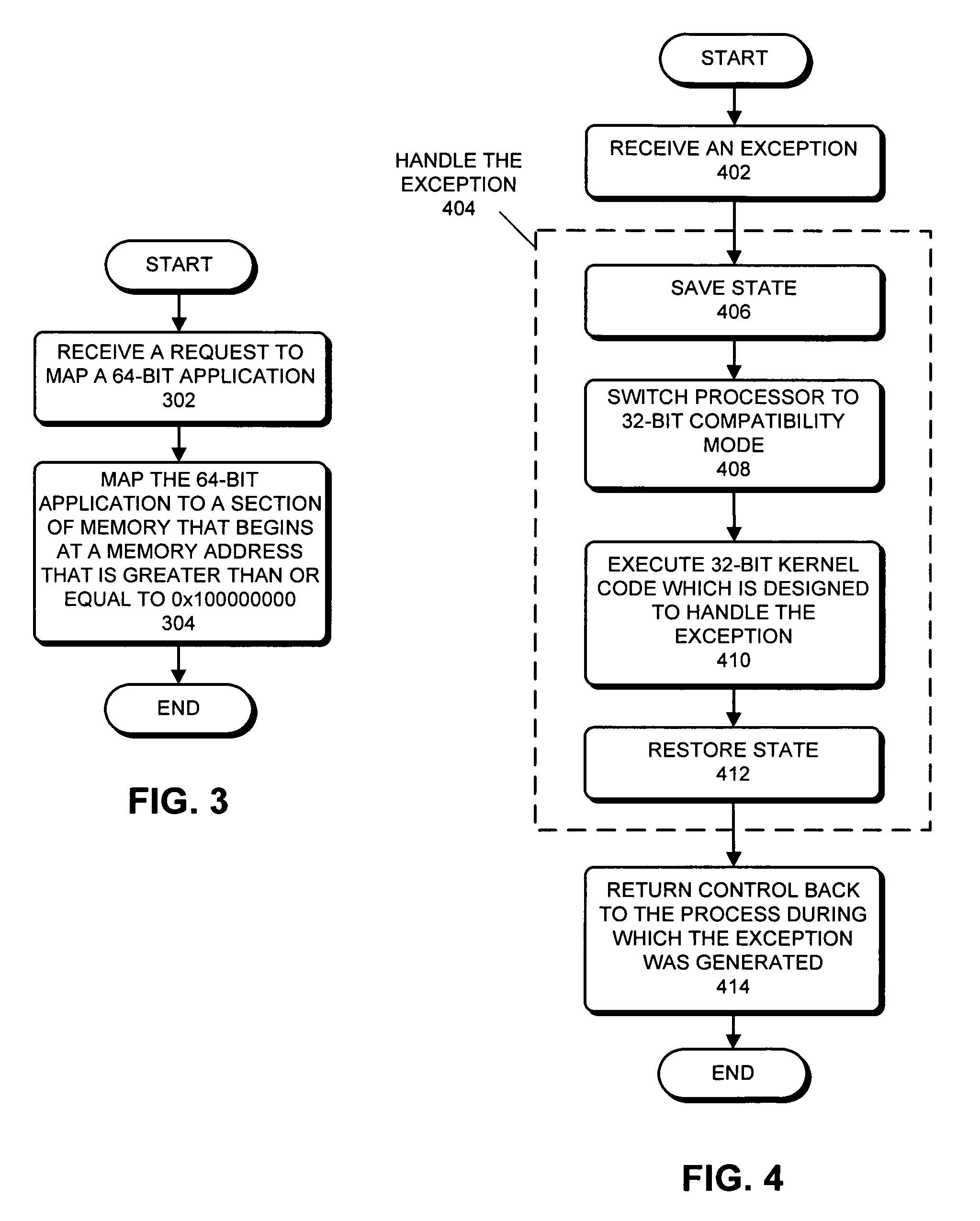
Method and apparatus for using a 32-bit operating system kernel to support 64-bit applications
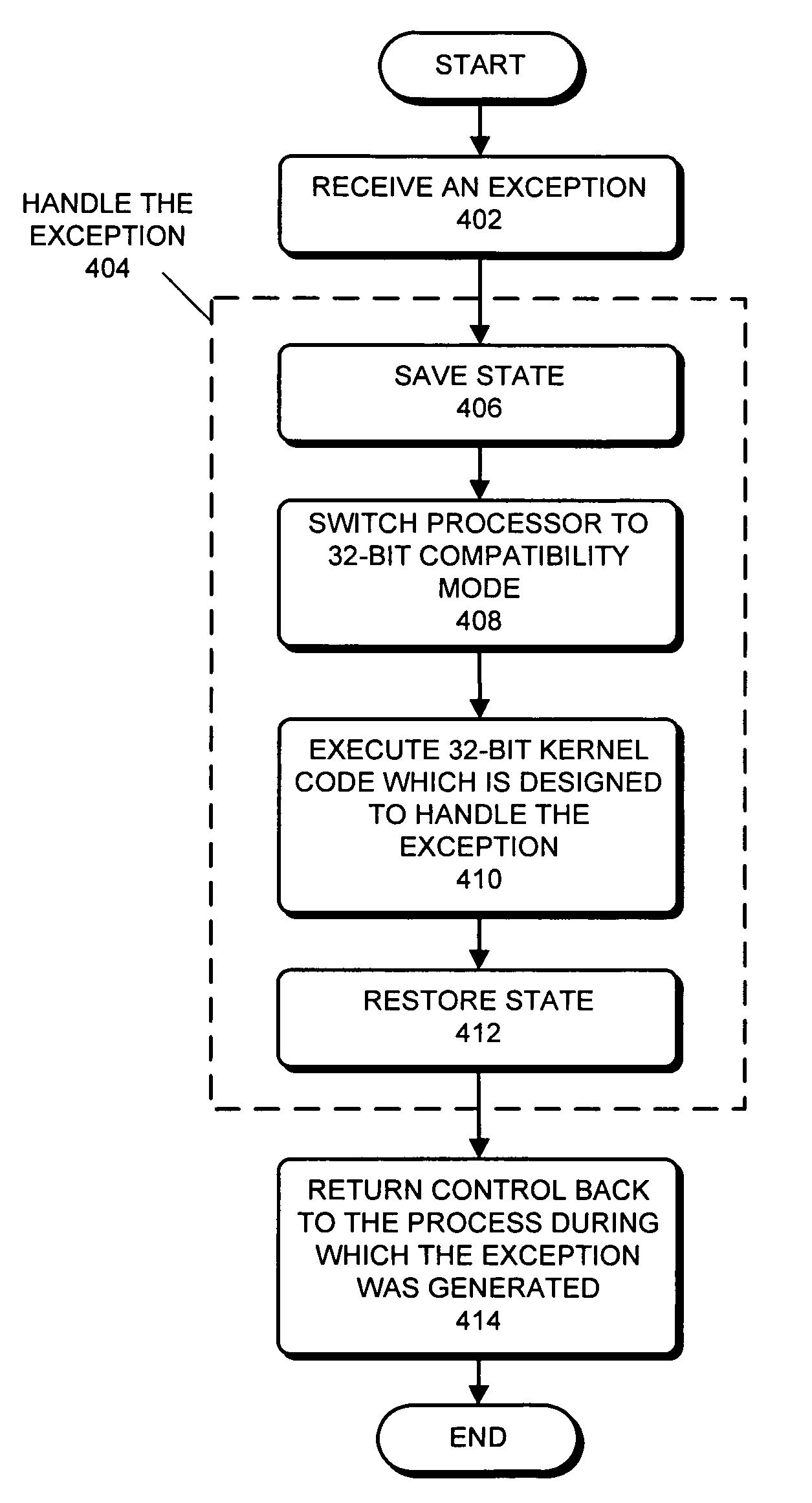
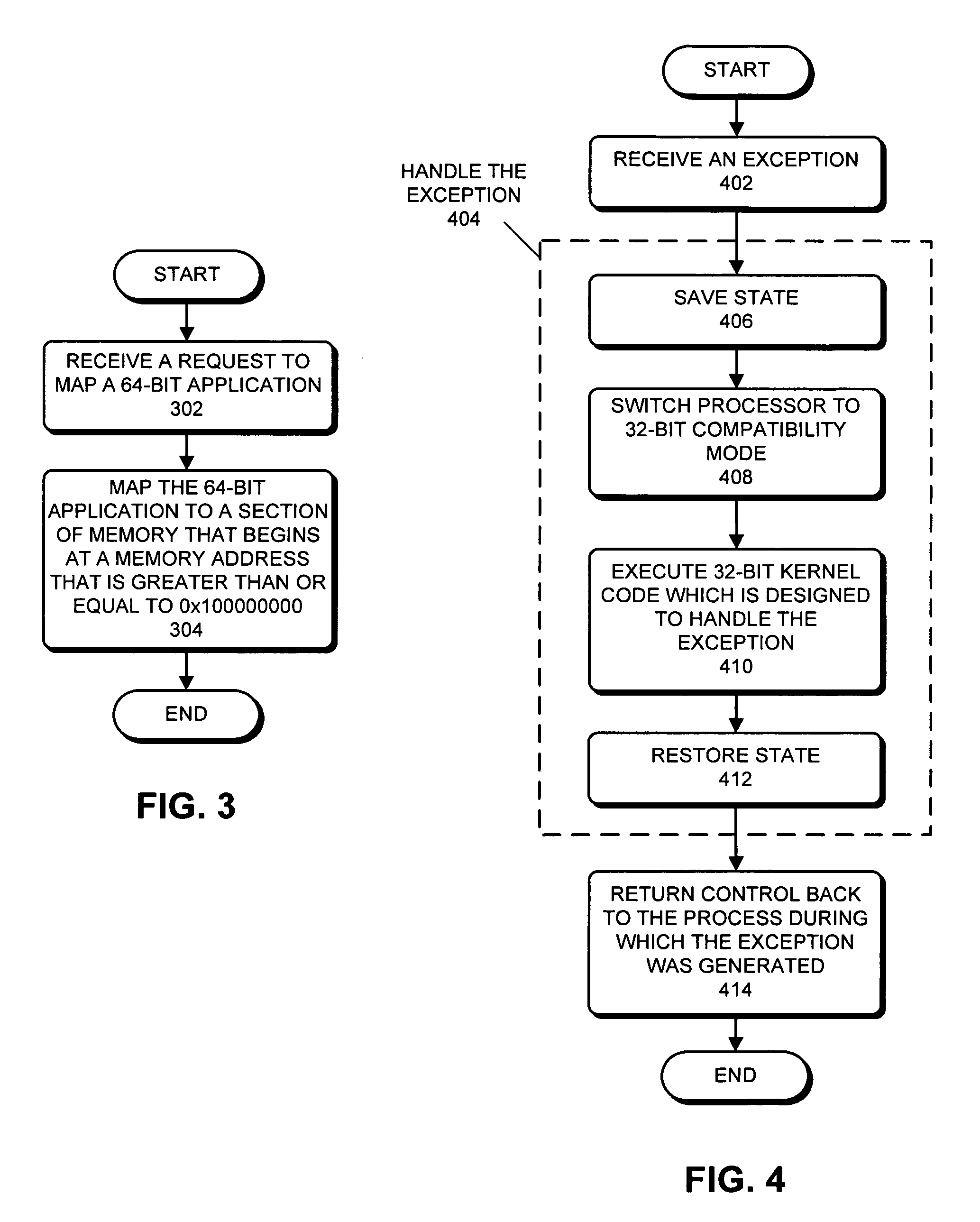
ActiveUS20080034194A1Easy to findDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsOperational systemSystem call
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that uses an M-bit operating system (OS) kernel to support N-bit user processes. During operation, the system receives an exception. Note that the exception can be any event that needs to be handled by executing OS kernel code. Specifically, the exception can be a hardware interrupt, a software interrupt, an asynchronous interrupt, a synchronous interrupt, a signal, a trap, or a system call. Next, the system handles the exception by first switching the processor to the M-bit mode, and then executing M-bit OS kernel code which is designed to handle the exception. Note that the processor may primarily be designed to operate in the N-bit mode; the M-bit mode may primarily be provided for backward compatibility reasons.
Owner:APPLE INC
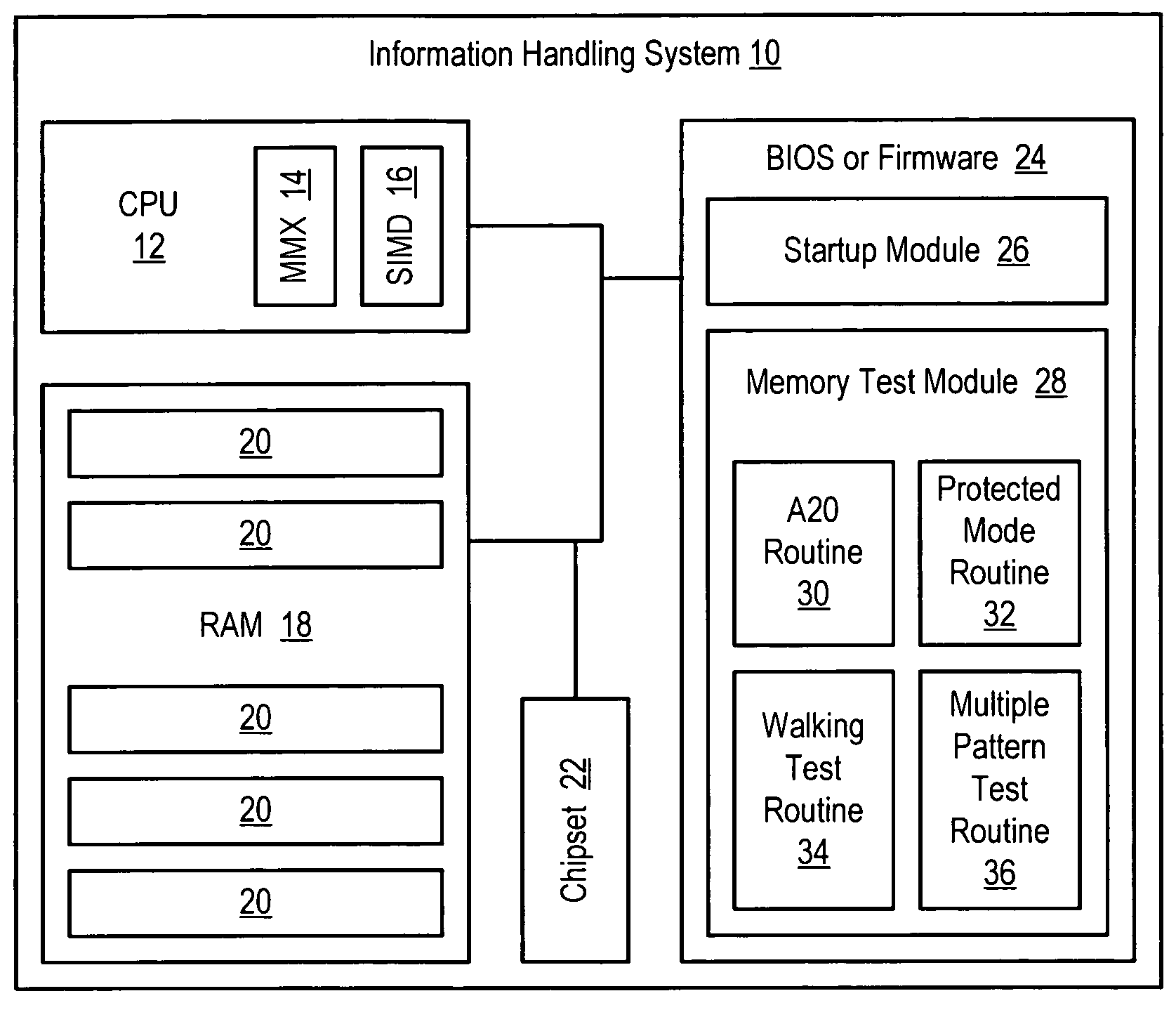
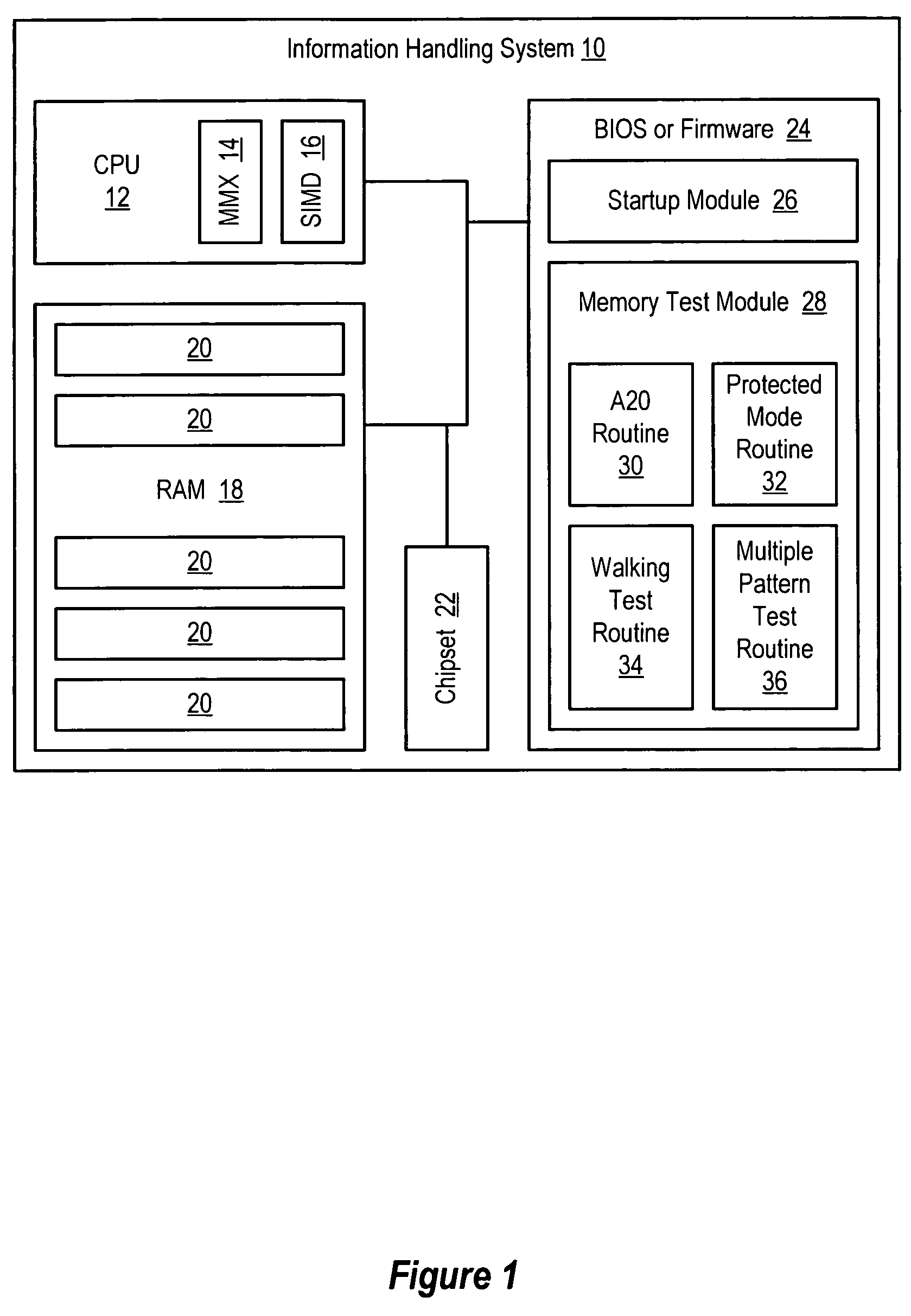
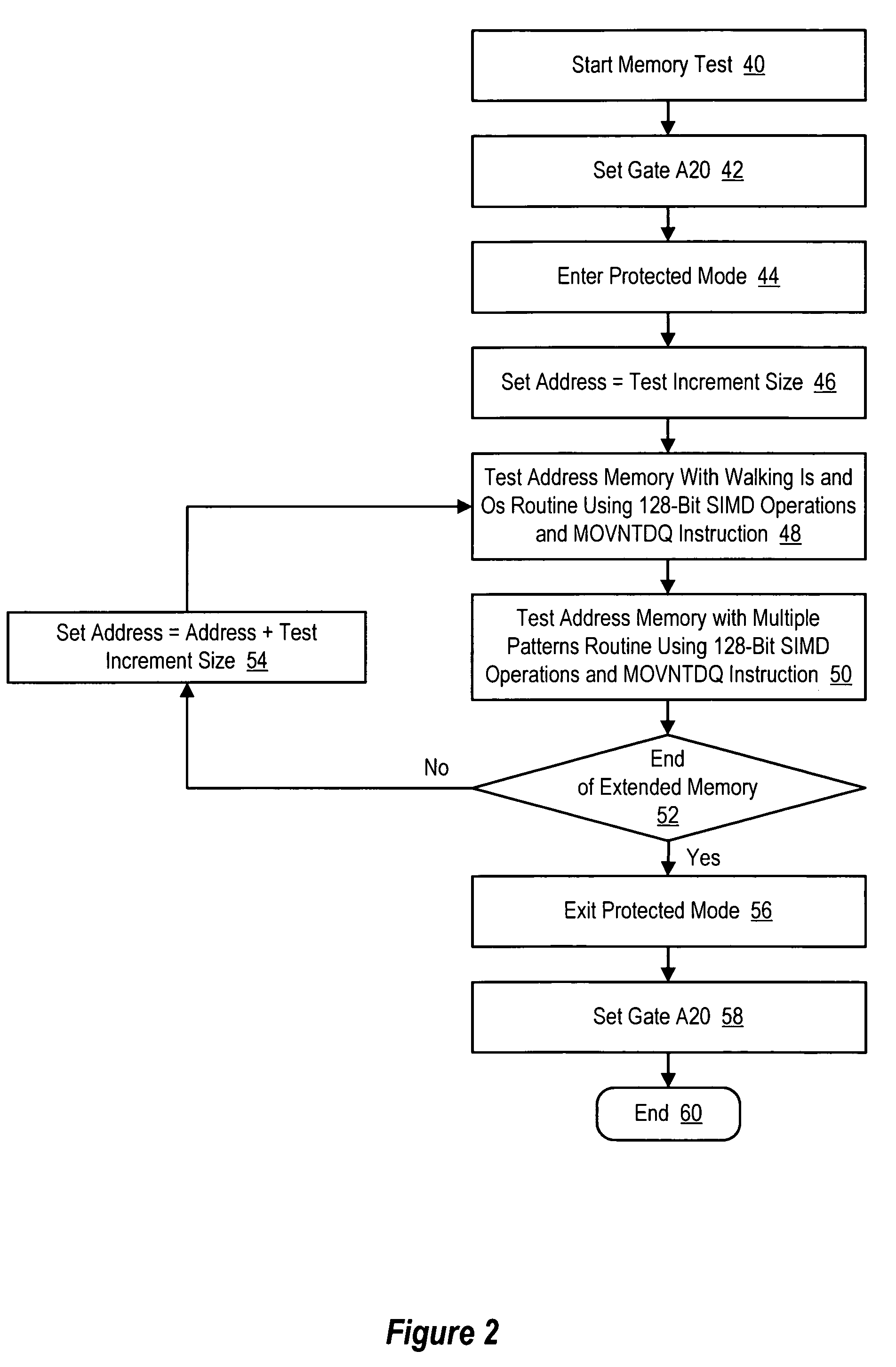
System and method for accelerated information handling system memory testing
ActiveUS7325176B2Easy to testReduce disadvantagesError detection/correctionDigital storageCpu architectureProtected mode
Owner:DELL PROD LP
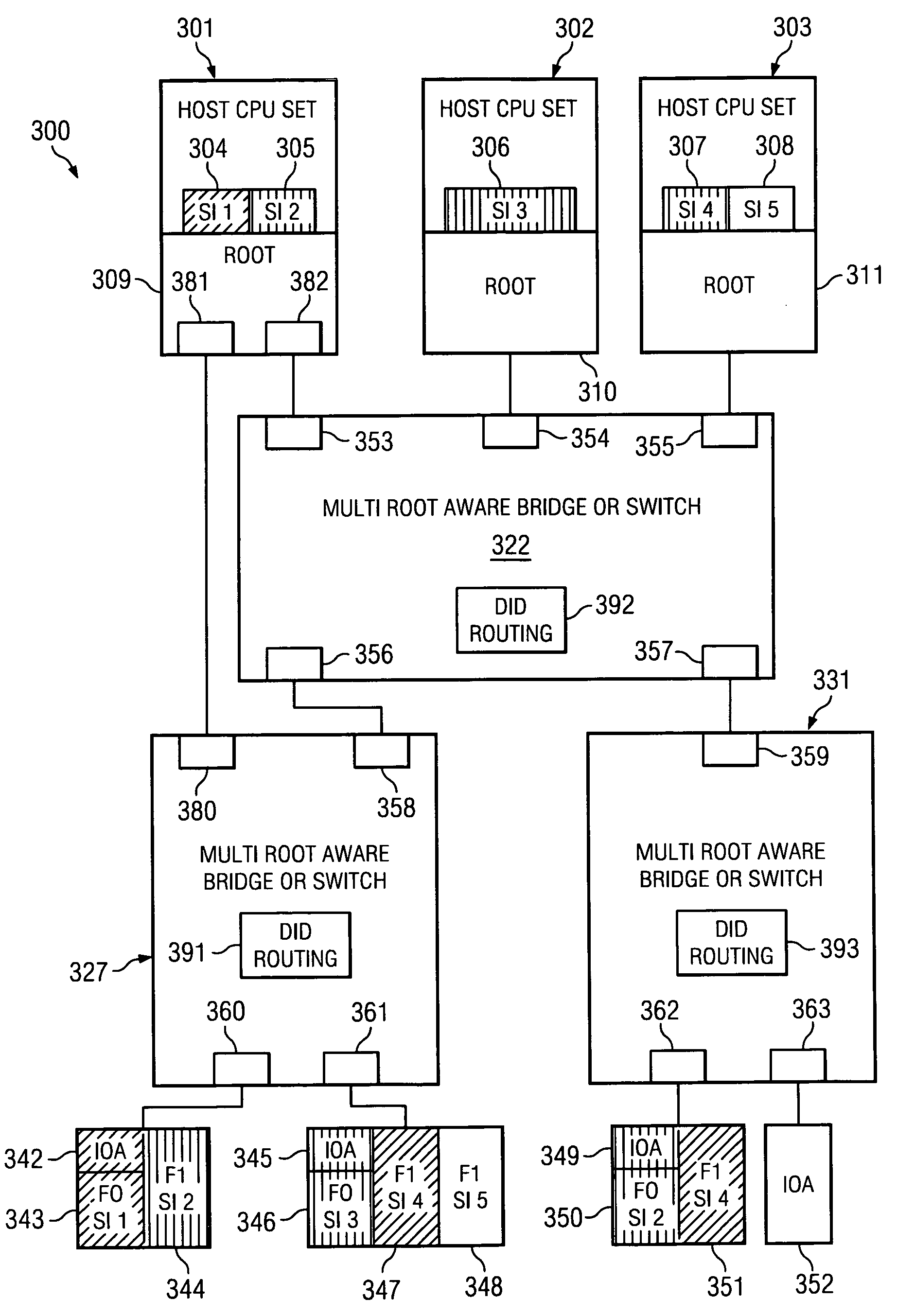
Routing mechanism in PCI multi-host topologies using destination ID field
InactiveUS7430630B2Data switching by path configurationElectric digital data processingField methodsPCI Express
Method and system for address routing in a distributed computing system, such as a distributed computing system that uses PCI Express protocol to communicate over an I / O fabric. A destination identifier is provided to identify a physical or virtual host or end point. When a physical or virtual host or end point receives a PCI data packet it compares a list of source identifiers with destination identifiers to determine if a source identifier included in the transaction packet is associated with a destination identifier included in the transaction packet to determine if the transaction packet has a valid association. If the transaction packet has a valid association, it is routed to the target device. The present invention enables each host that attaches to PCI bridges or switches and shares a set of common PCI devices to have its own PCI 64-bit address space and enables the routing of PCI transaction packets between multiple hosts and adapters, through a PCI switched-fabric bus using a destination identifier.
Owner:IBM CORP
Scaleable microprocessor architecture
InactiveUS20030212878A1Executed quickly and reliablyGeneral purpose stored program computerNext instruction address formationArray data structureCode density
A scaleable microprocessor architecture has an efficient and orthogonal instruction set of 20 basic instructions, and a scaleable program word size from 15 bits up, including but not limited to 16, 24, 32, and 64 bits. As many instructions are packed into a single program word as allowed by the size of a program word. An integral return stack is used for nested subroutine calls and returns. An integral data stack is also used to pass parameters among nested subroutines. The simplified instruction set and the dual stack architecture make it possible to execute all instructions in a single clock cycle from a single phase master clock. Additional instructions can be added to facilitate accessing arrays in memory, for multiplication and division of integers, for real time interrupts, and to support an UART I / O device. This scaleable microprocessor architecture greatly increases code density and processing speed while decreasing significantly silicon area and power consumption. It is most suitable to serve as microprocessor cores in System-on-a-Chip (SOC) integrated circuits.
Owner:TING CHEN HANSON
DMA (Direct Memory Access) controller access implementation method for Loongson blade large-memory address devices
InactiveCN102331978AResolution supportElectric digital data processingMemory addressDirect memory access
The invention provides a DMA controller access implementation method for Loongson blade large-memory address devices. A management control module applies for a 256M address space in a memory; when a DMA controller and an address space lower than 32 bits carry out data transmission, data are transmitted according to the conventional DMA transmission mode; when the DMA controller and an address space higher than 32 bits carry out data transmission, the DMA controller sends an access address to an address-parsing module, the address-parsing module parses and then sends the address to an address conversion module, the address conversion module converts the address, and a mapping module carries out memory mapping according to the address converted by the address conversion module to map the address higher than 32 bits into the memory for which the management control module applies in advance. The method effectively solves the problem that a 32-bit Loongson CPU (central processing unit) cannot support memories exceeding the 32-bit address, and thereby the Loongson CPU can use a 64-bit address space at most.
Owner:SUGON INFORMATION IND
Processing exceptions from 64-bit application program executing in 64-bit processor with 32-bit OS kernel by switching to 32-bit processor mode
ActiveUS7451298B2Easy to findDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsOperational systemSystem call
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that uses an M-bit operating system (OS) kernel to support N-bit user processes. During operation, the system receives an exception. Note that the exception can be any event that needs to be handled by executing OS kernel code. Specifically, the exception can be a hardware interrupt, a software interrupt, an asynchronous interrupt, a synchronous interrupt, a signal, a trap, or a system call. Next, the system handles the exception by first switching the processor to the M-bit mode, and then executing M-bit OS kernel code which is designed to handle the exception. Note that the processor may primarily be designed to operate in the N-bit mode; the M-bit mode may primarily be provided for backward compatibility reasons.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com